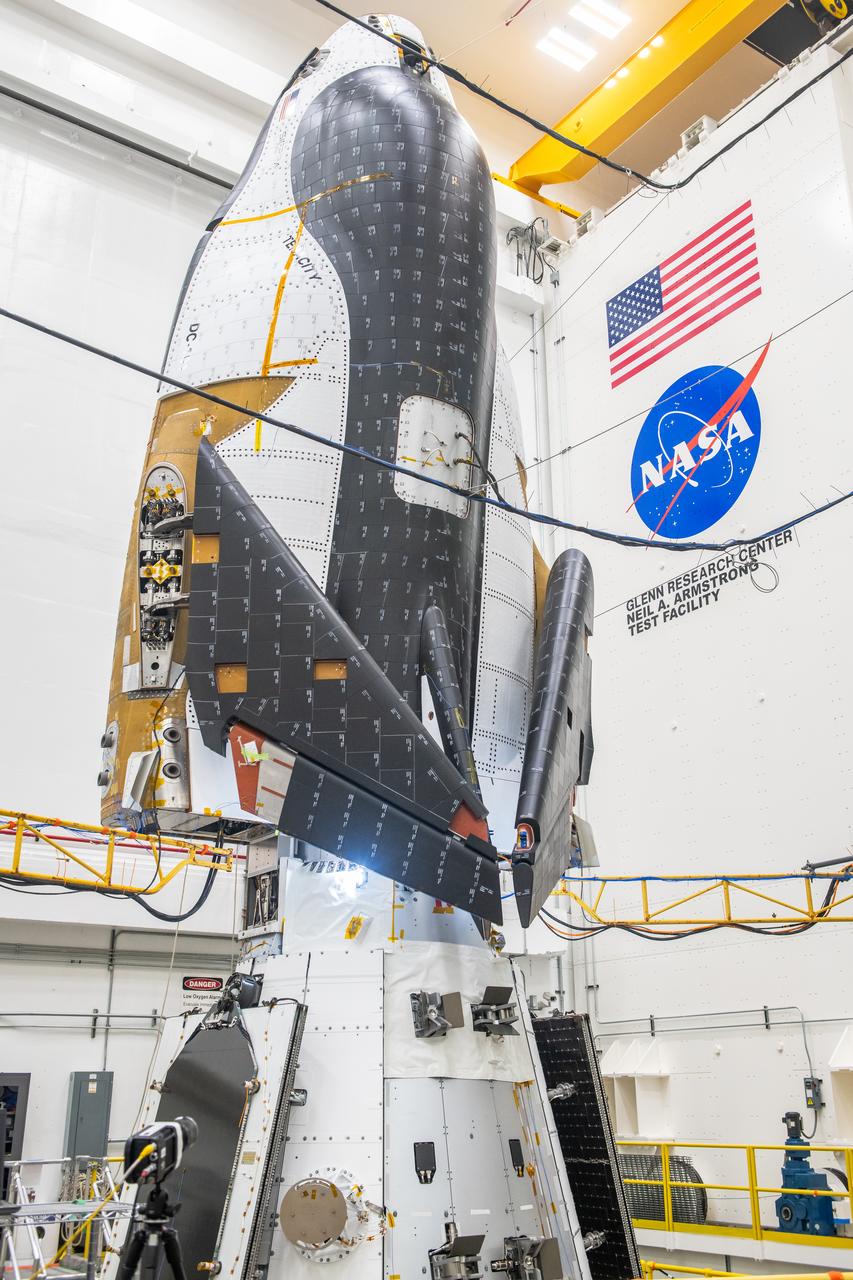

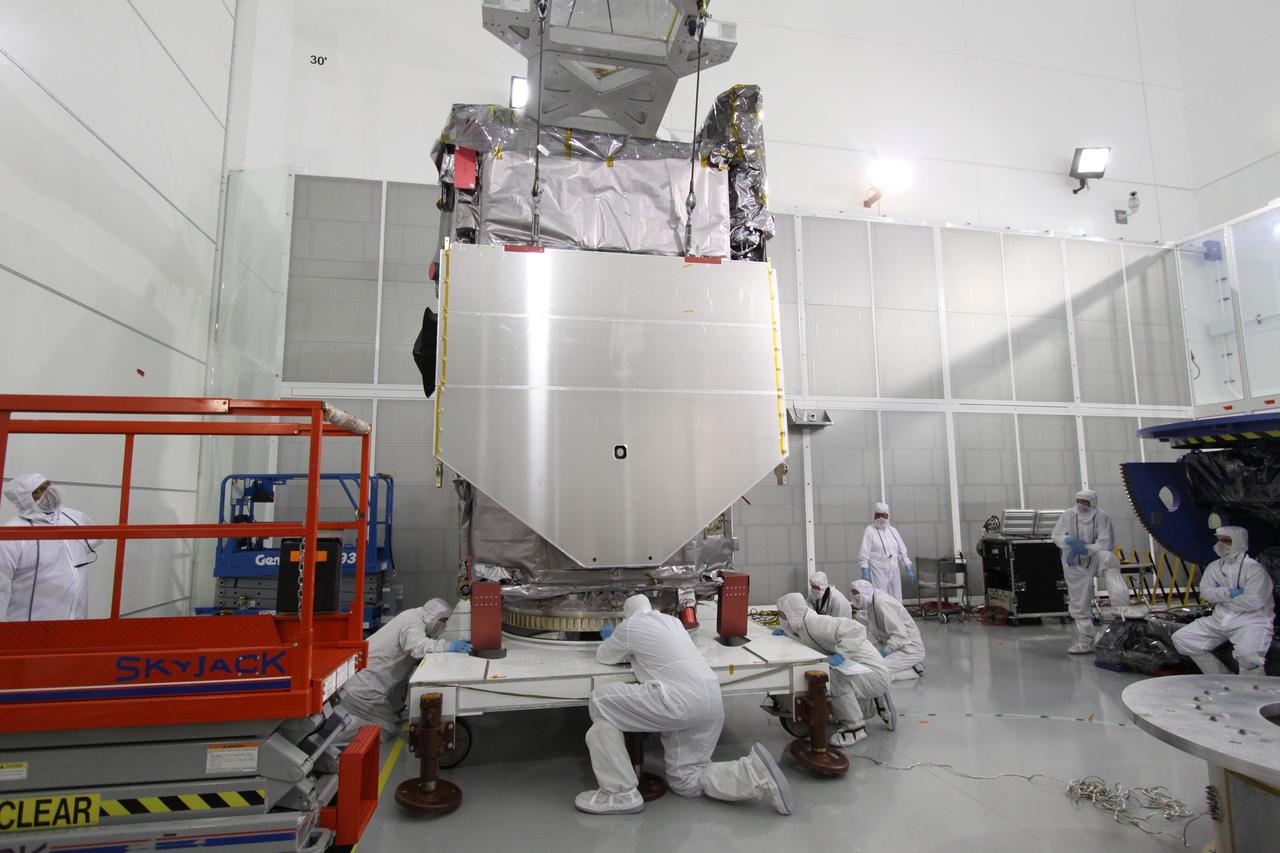
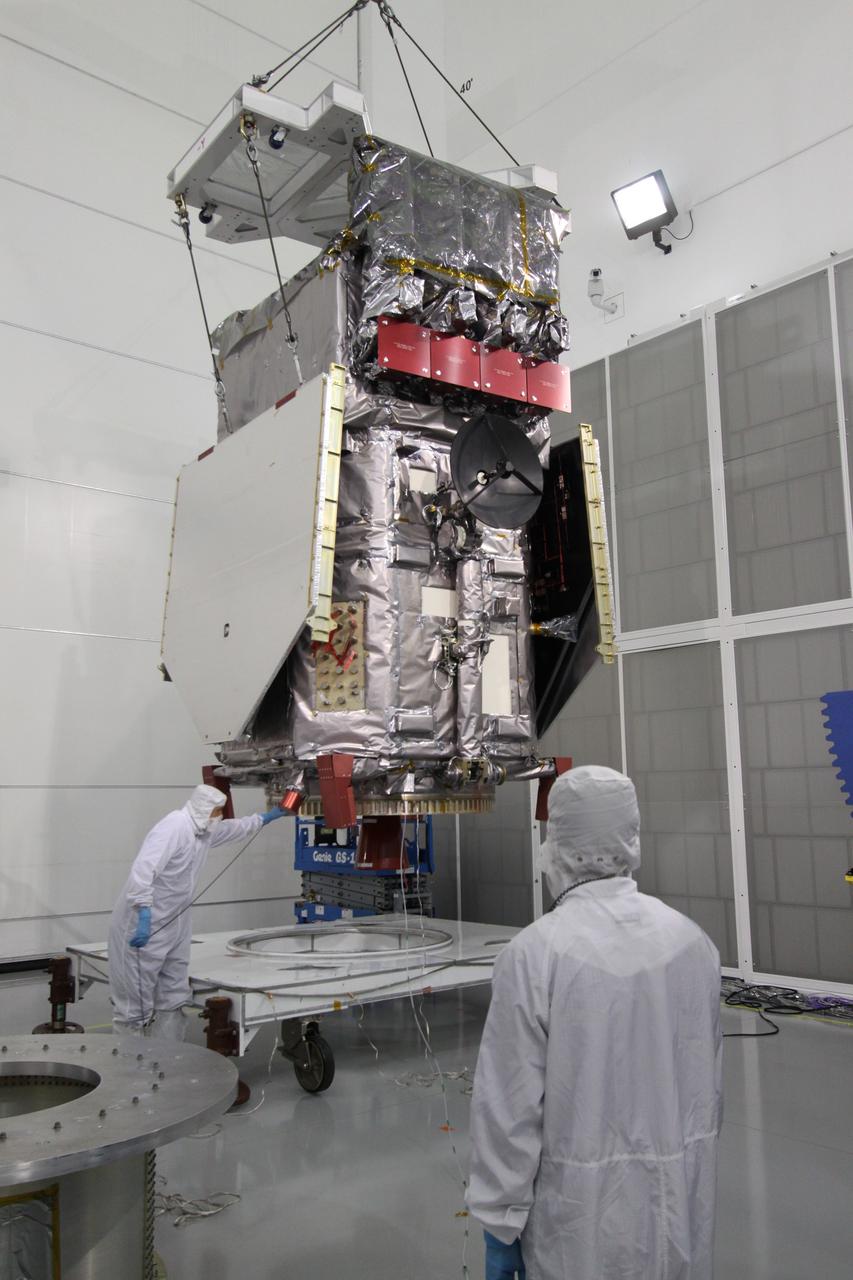
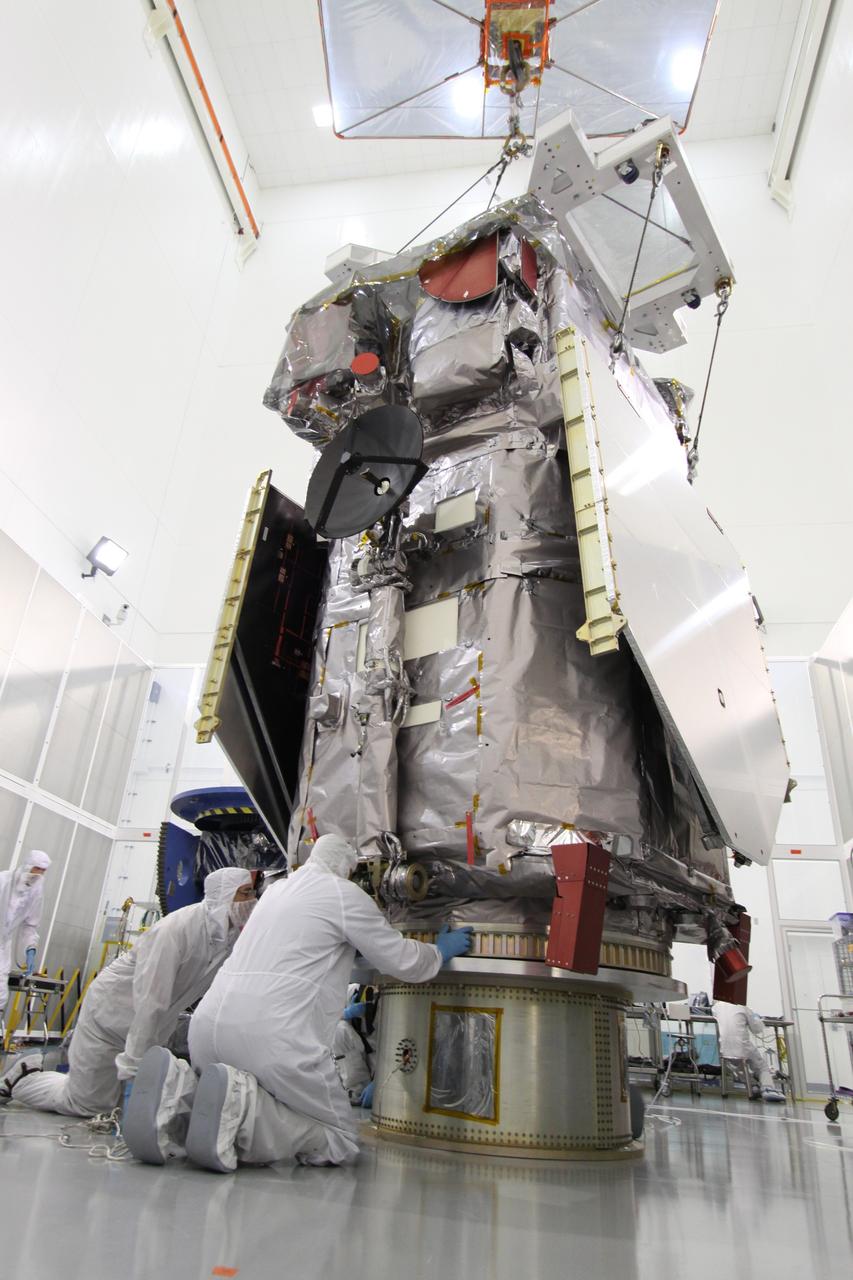
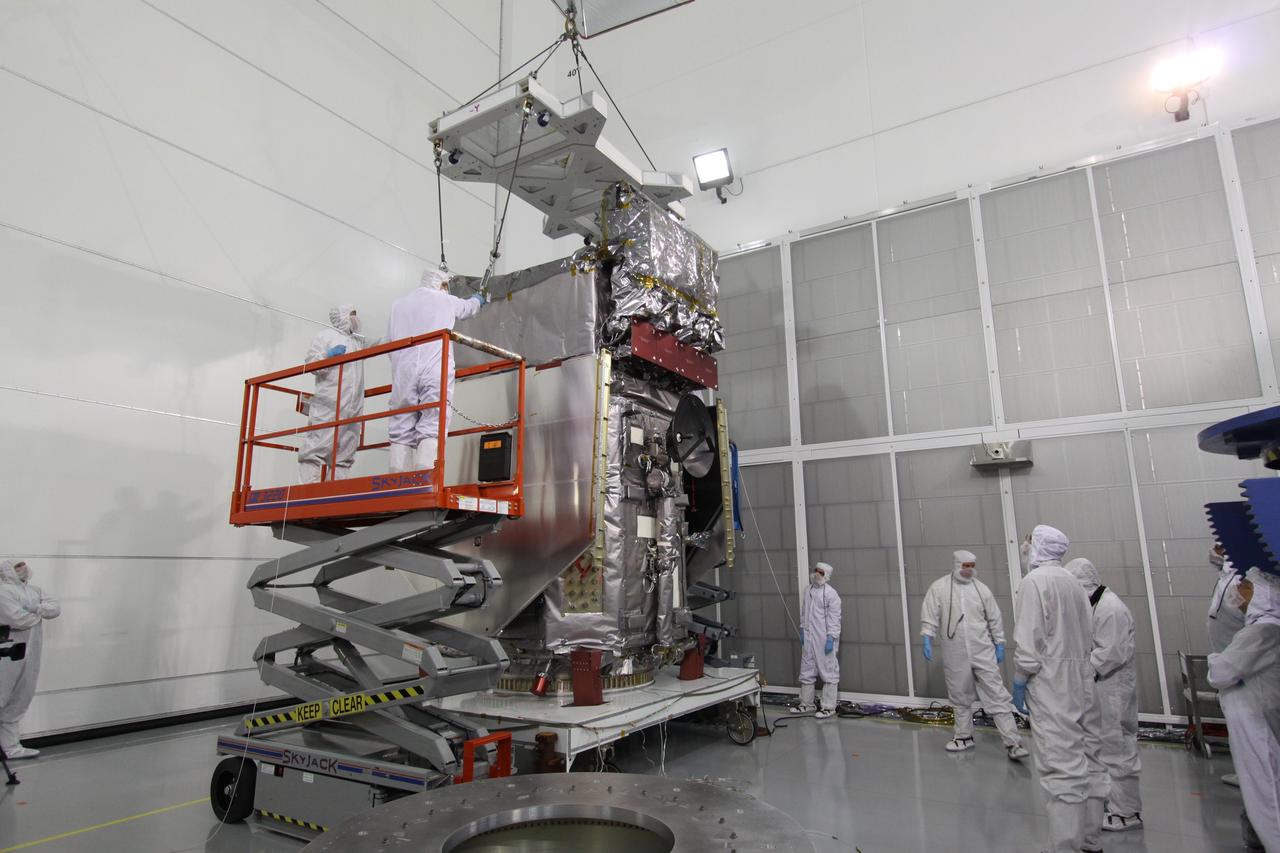
The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.
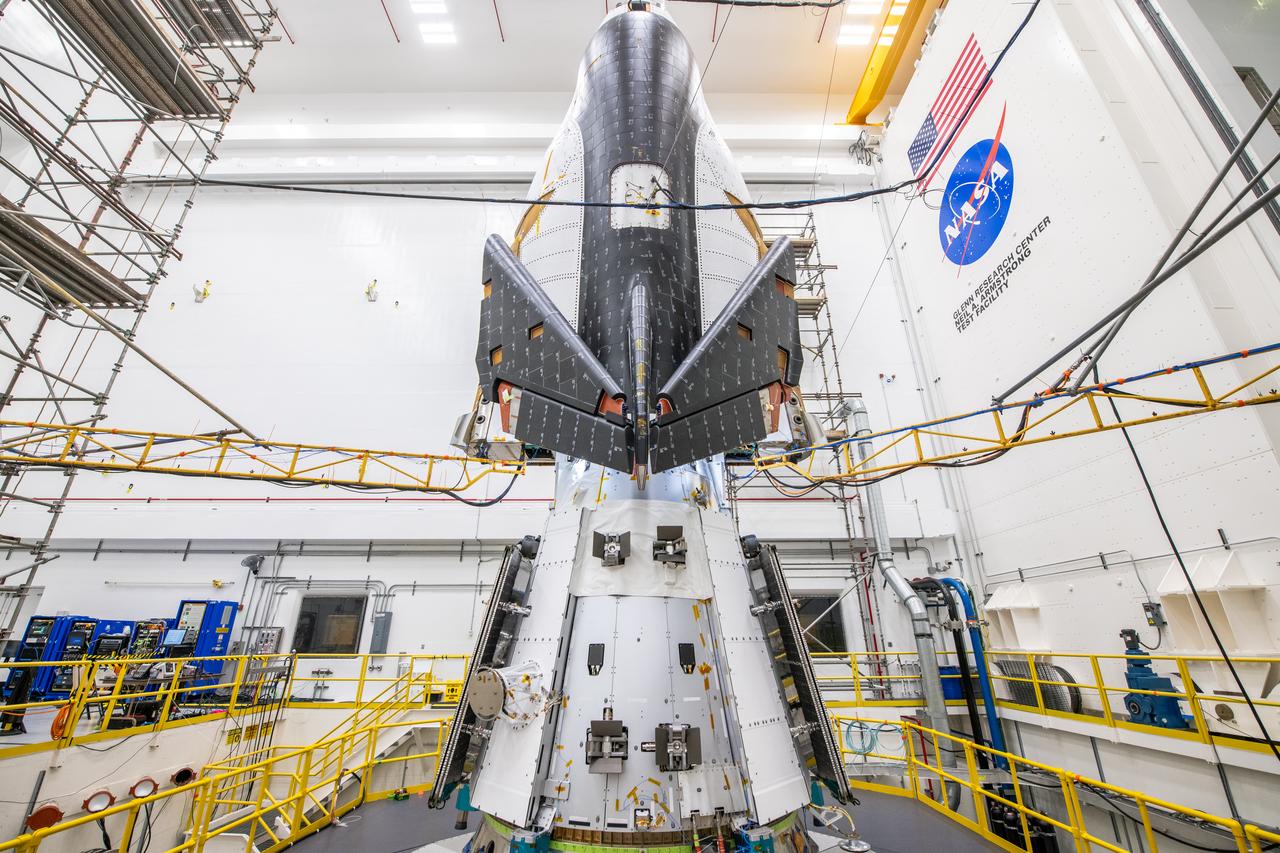

The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.
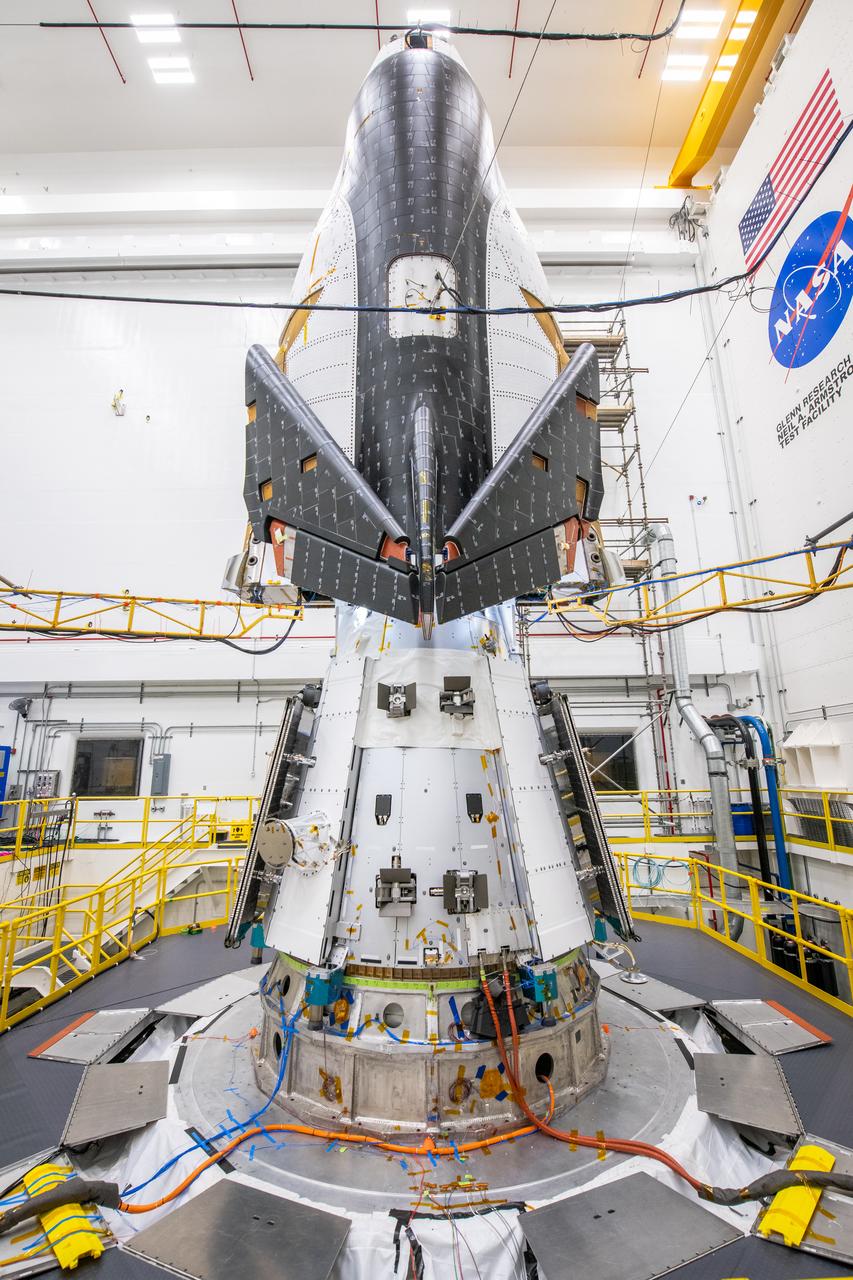

The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.

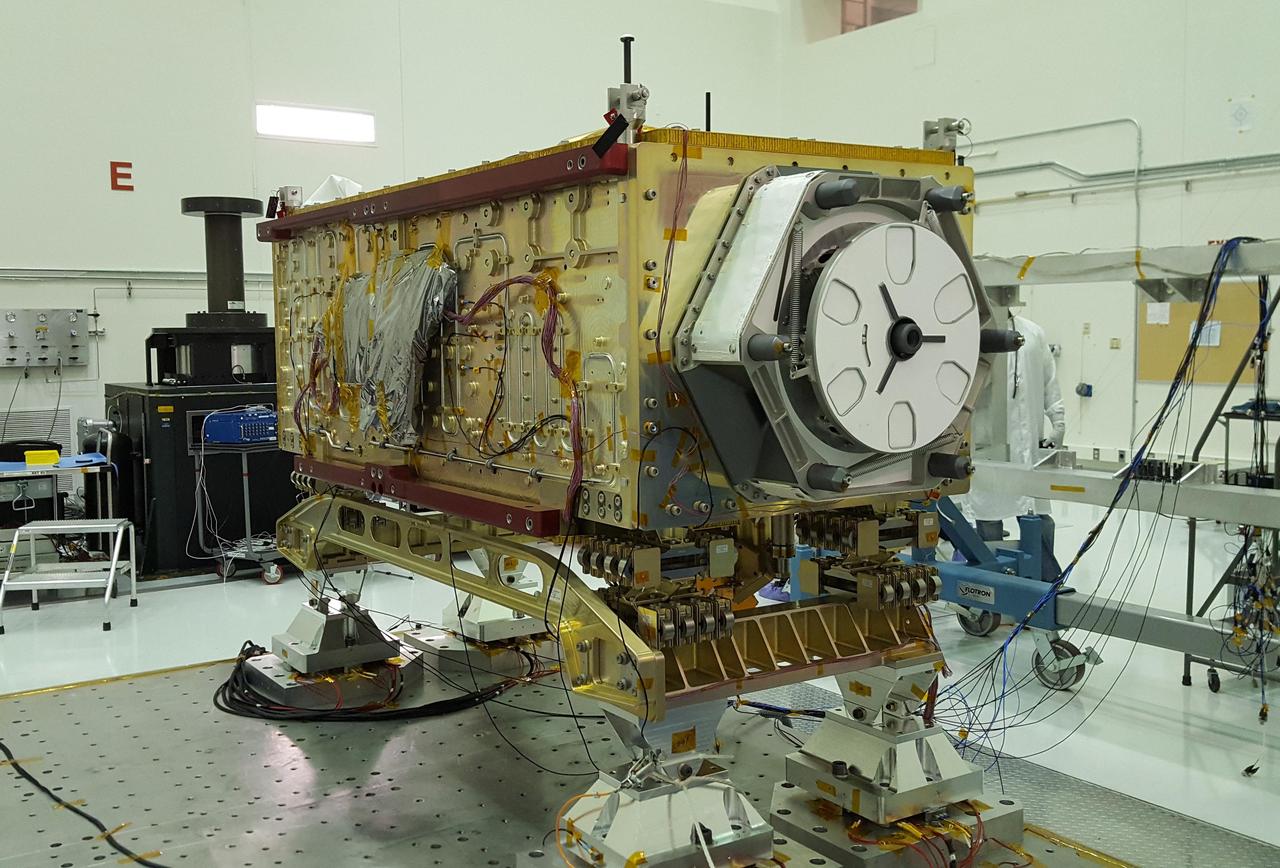
Mechanical technicians, Thomas Huber and John Poulsen, don safety harnesses and carefully guide the crane lifted Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) from the vibration table after successful testing. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.

OCO-3 sits on the large vibration table (known as the "shaker") in the Environmental Test Lab at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The exposed wires lead to sensors used during dynamics and thermal-vacuum testing. Thermal blankets will be added to the instrument at Kennedy Space Center, where a Space-X Dragon capsule carrying OCO-3 will launch in on a Falcon 9 rocket to the space station on May 1, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23211

Arrival and Unloading of the Mechanical Vibration Facility Table Hardware at Space Power Facility, SPF
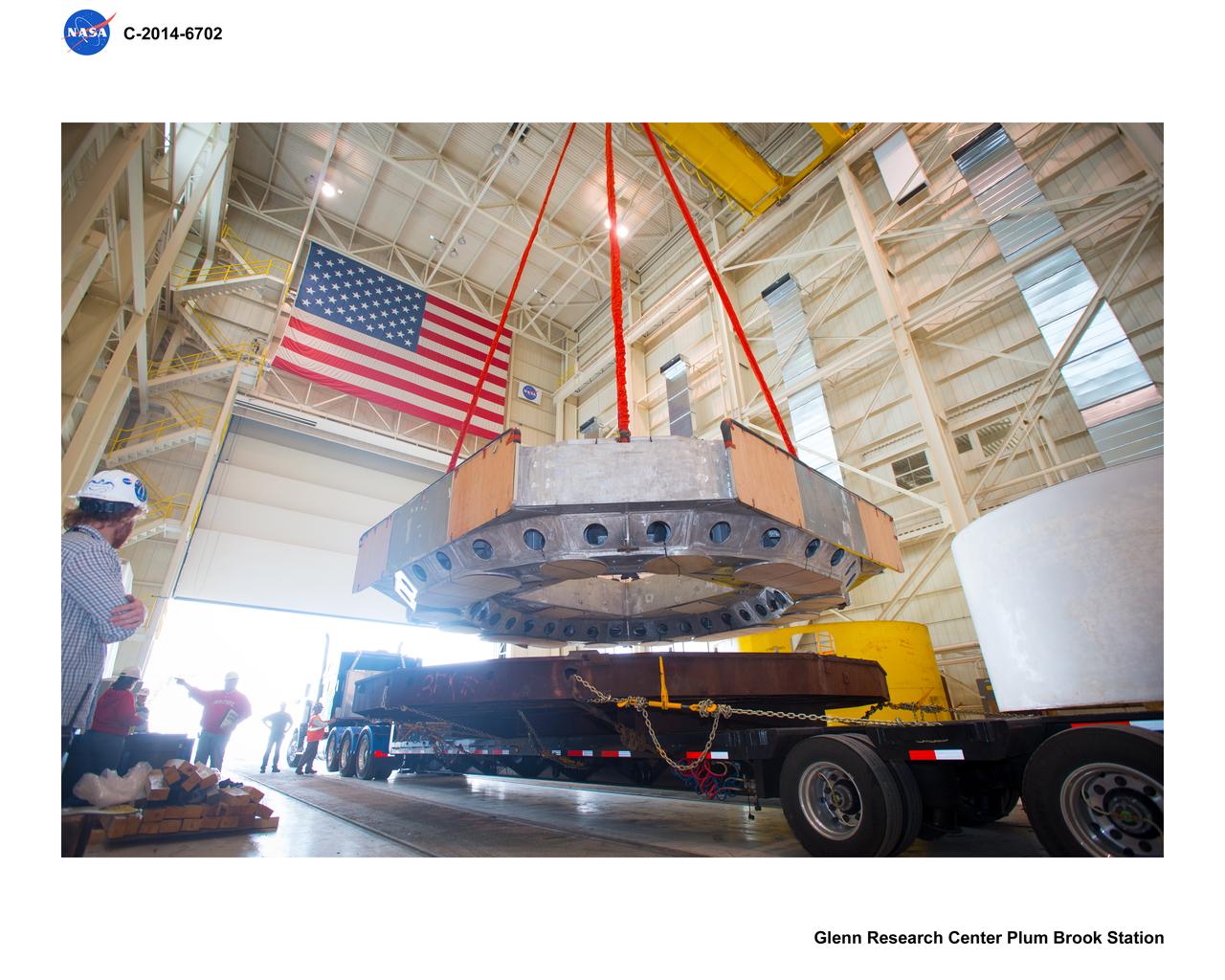

Arrival and Unloading of the Mechanical Vibration Facility Table Hardware at Space Power Facility, SPF

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
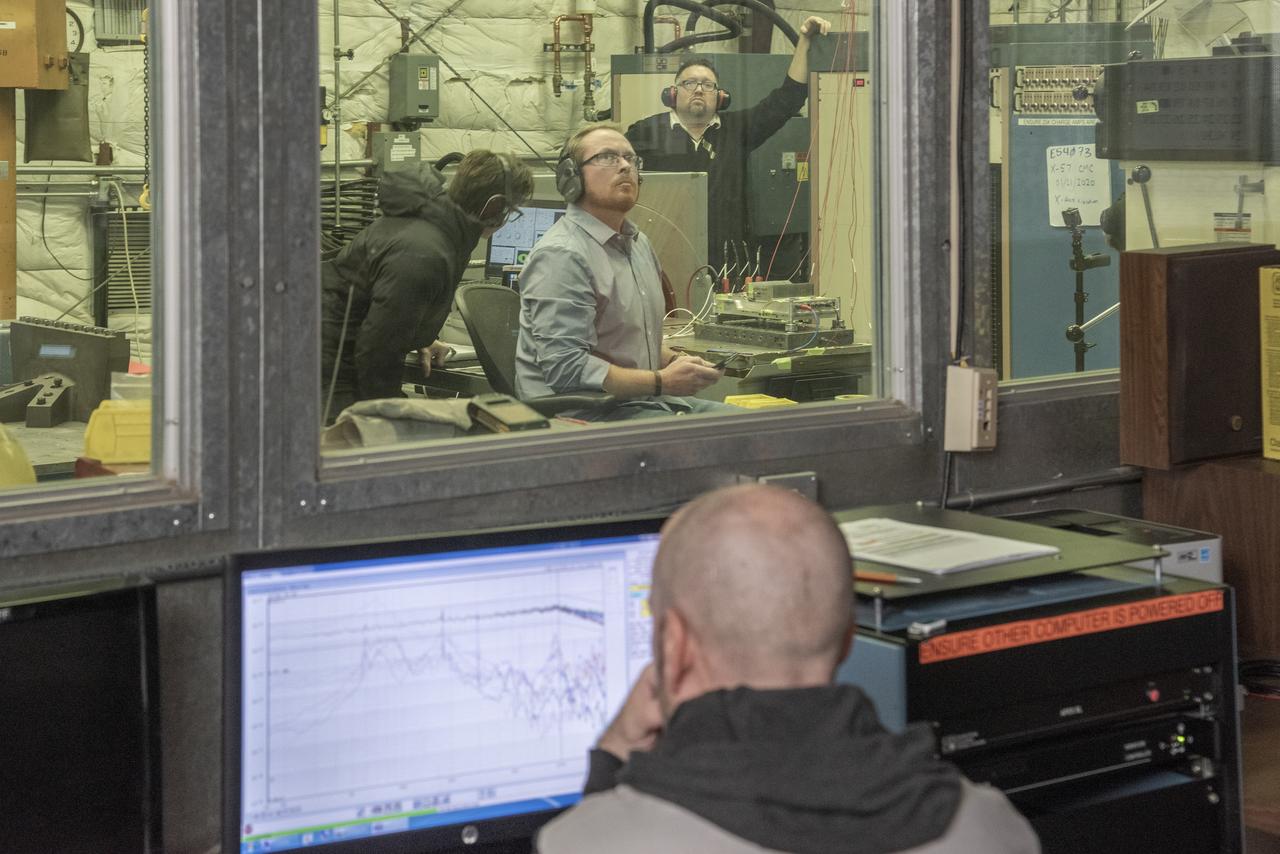

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

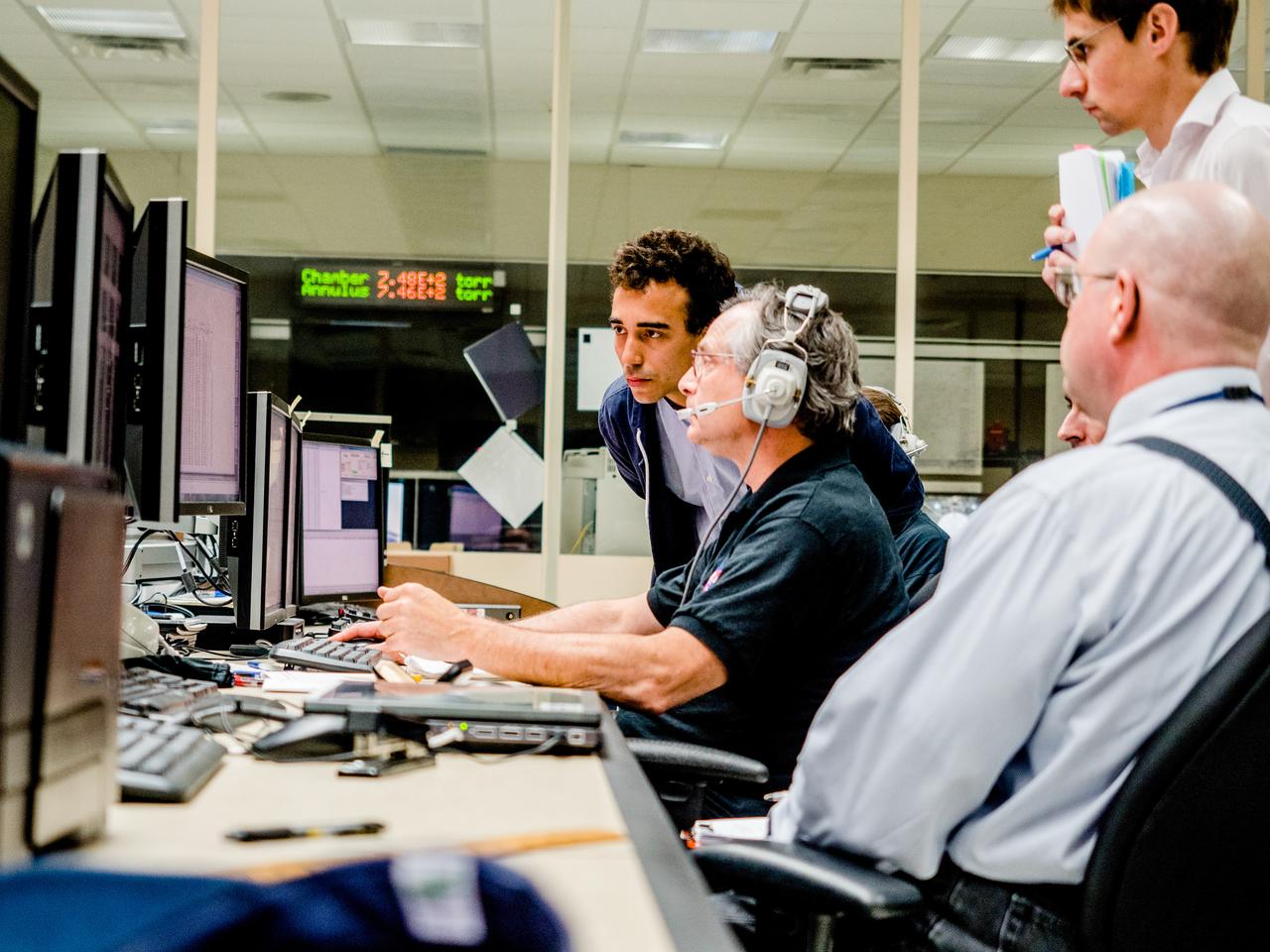
A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.
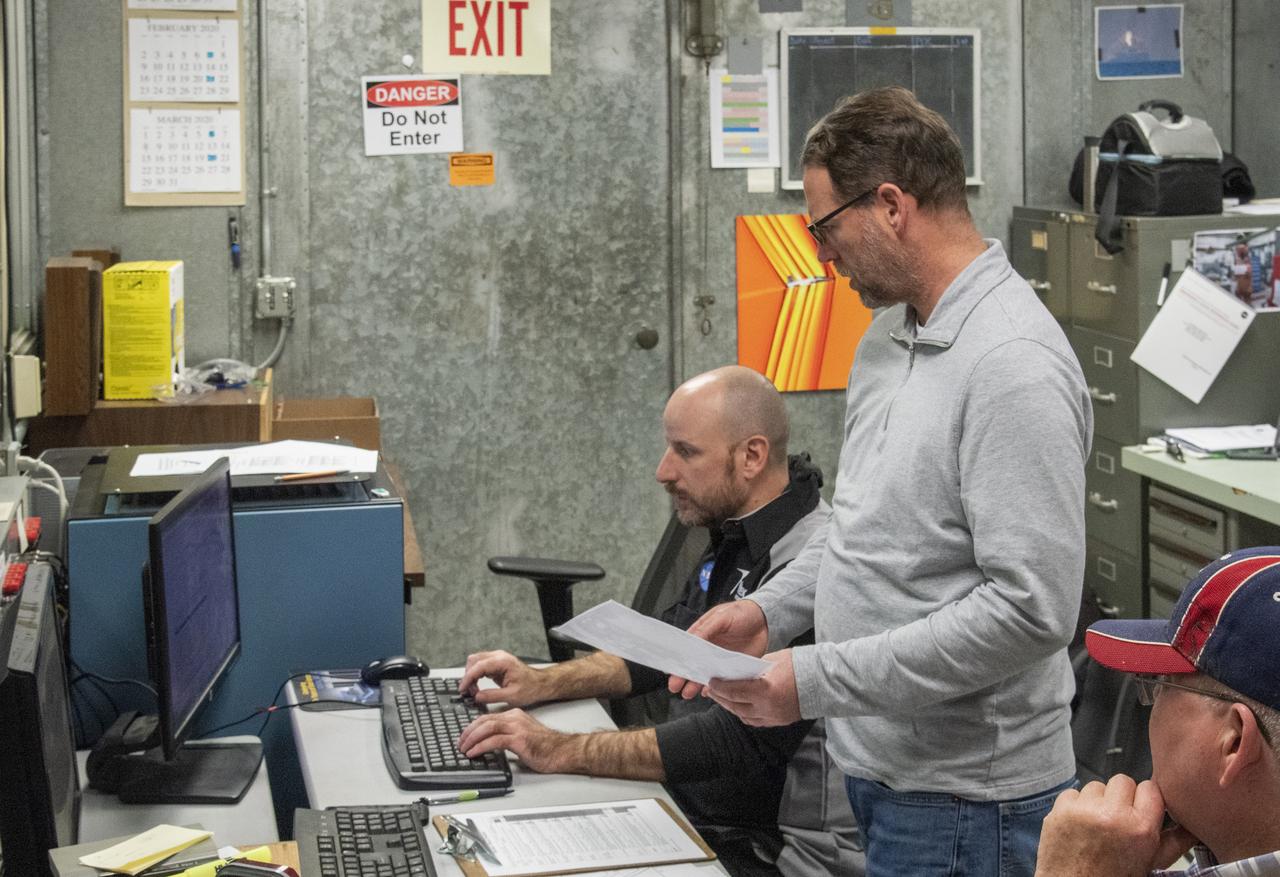

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
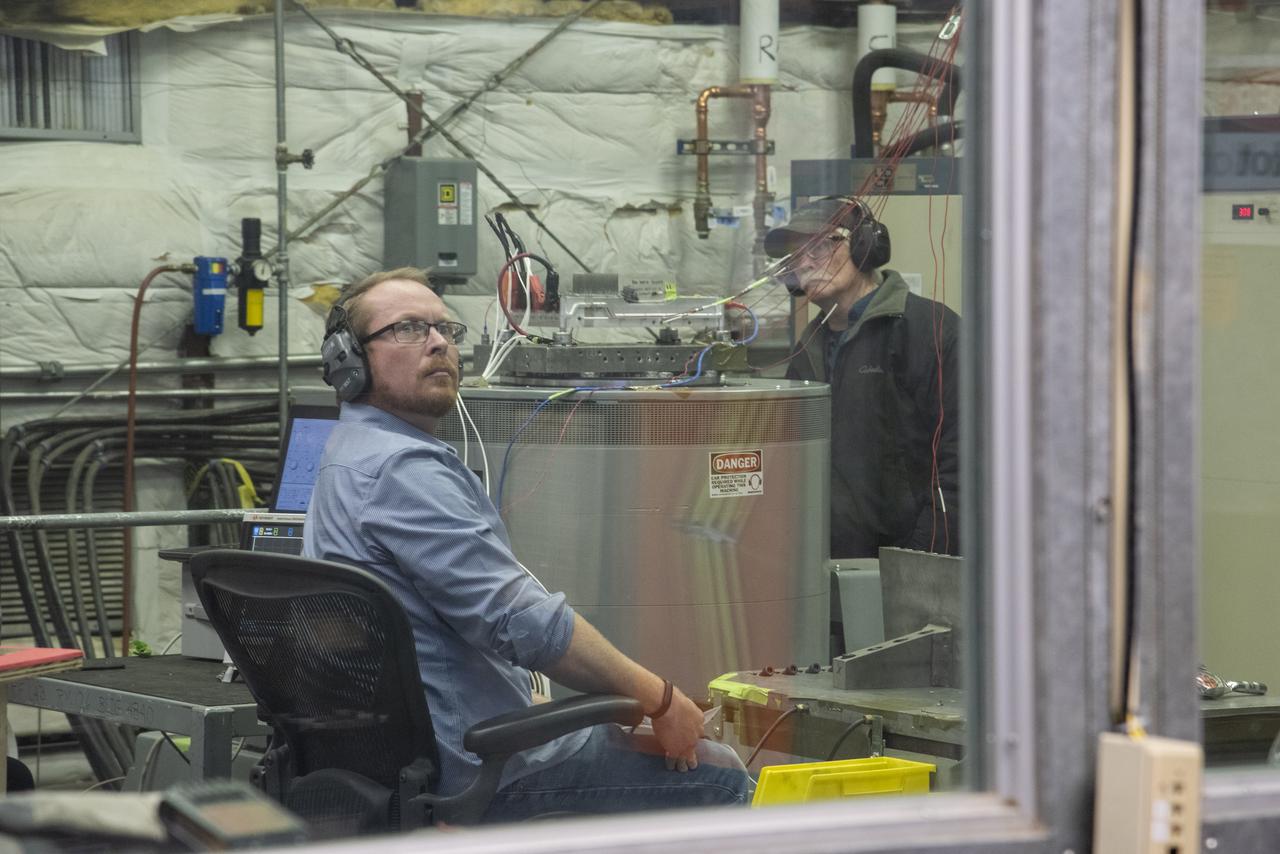

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

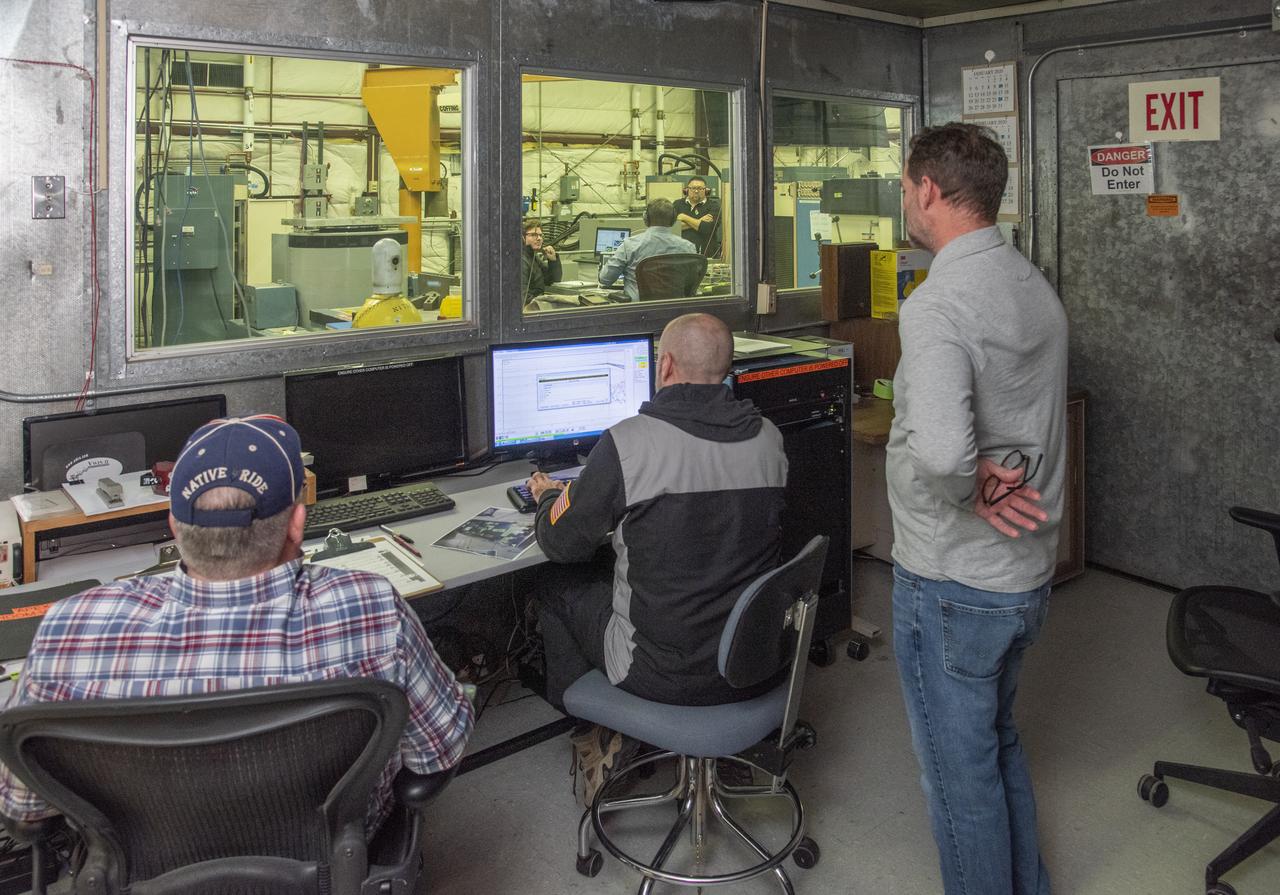
A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

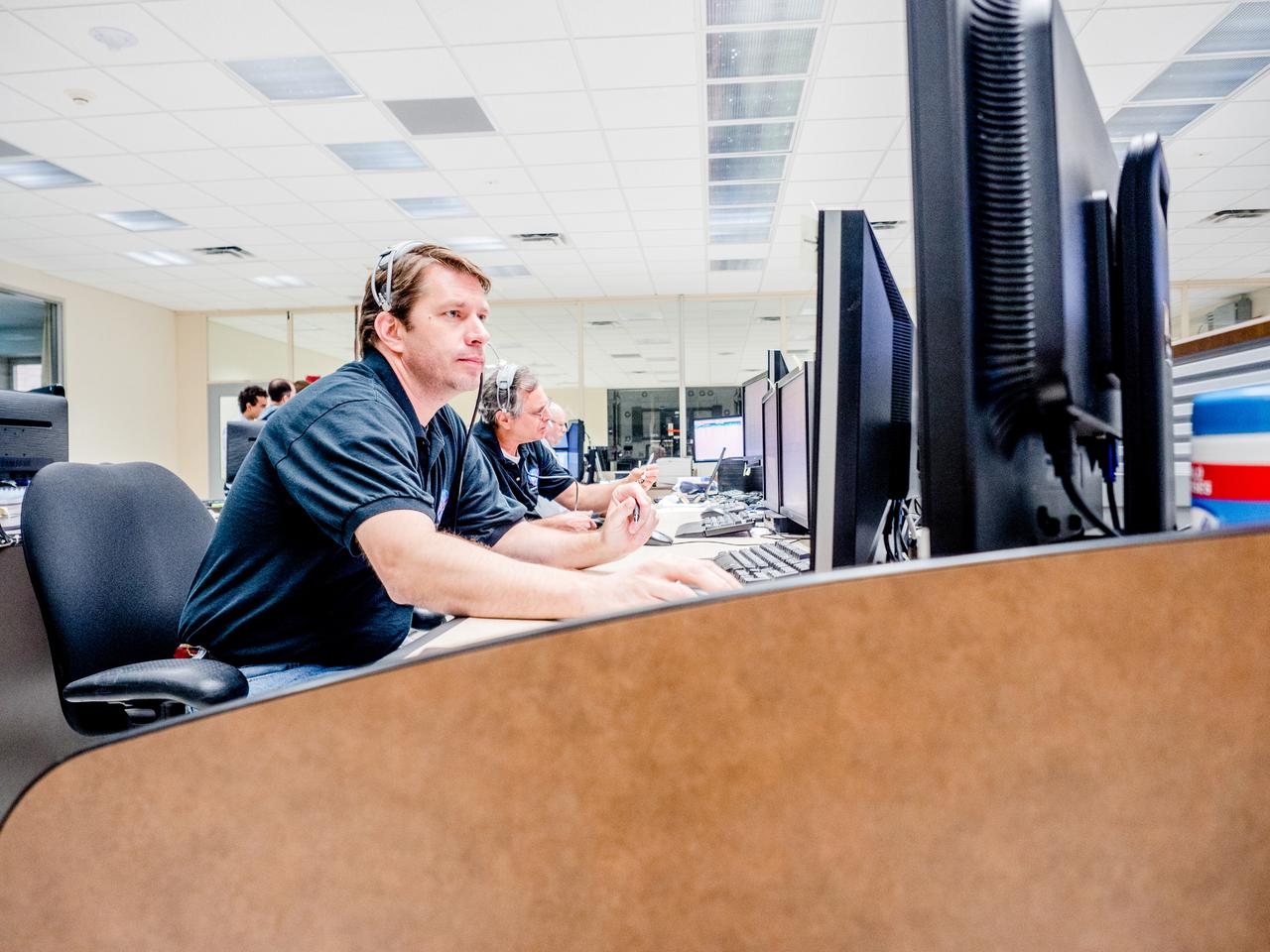
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
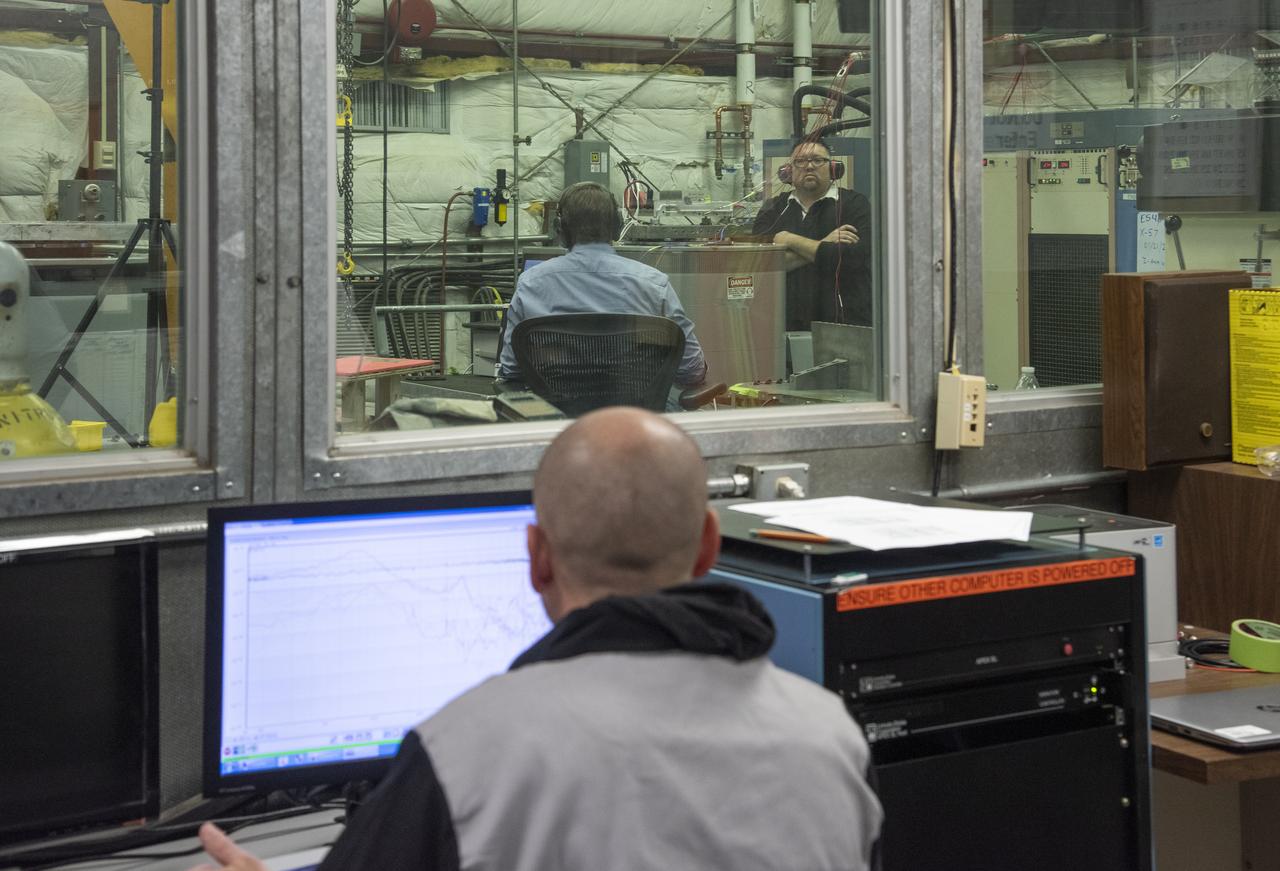

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
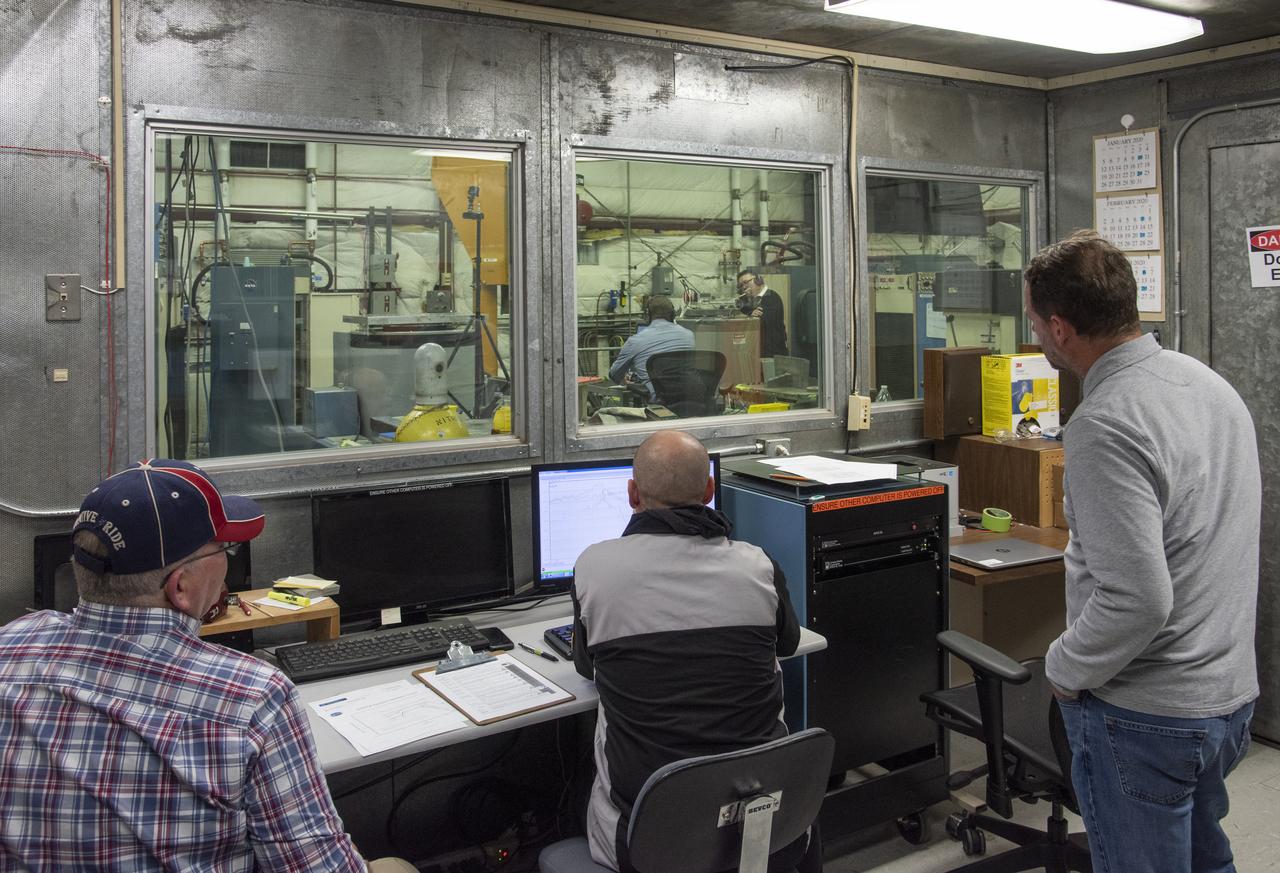

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
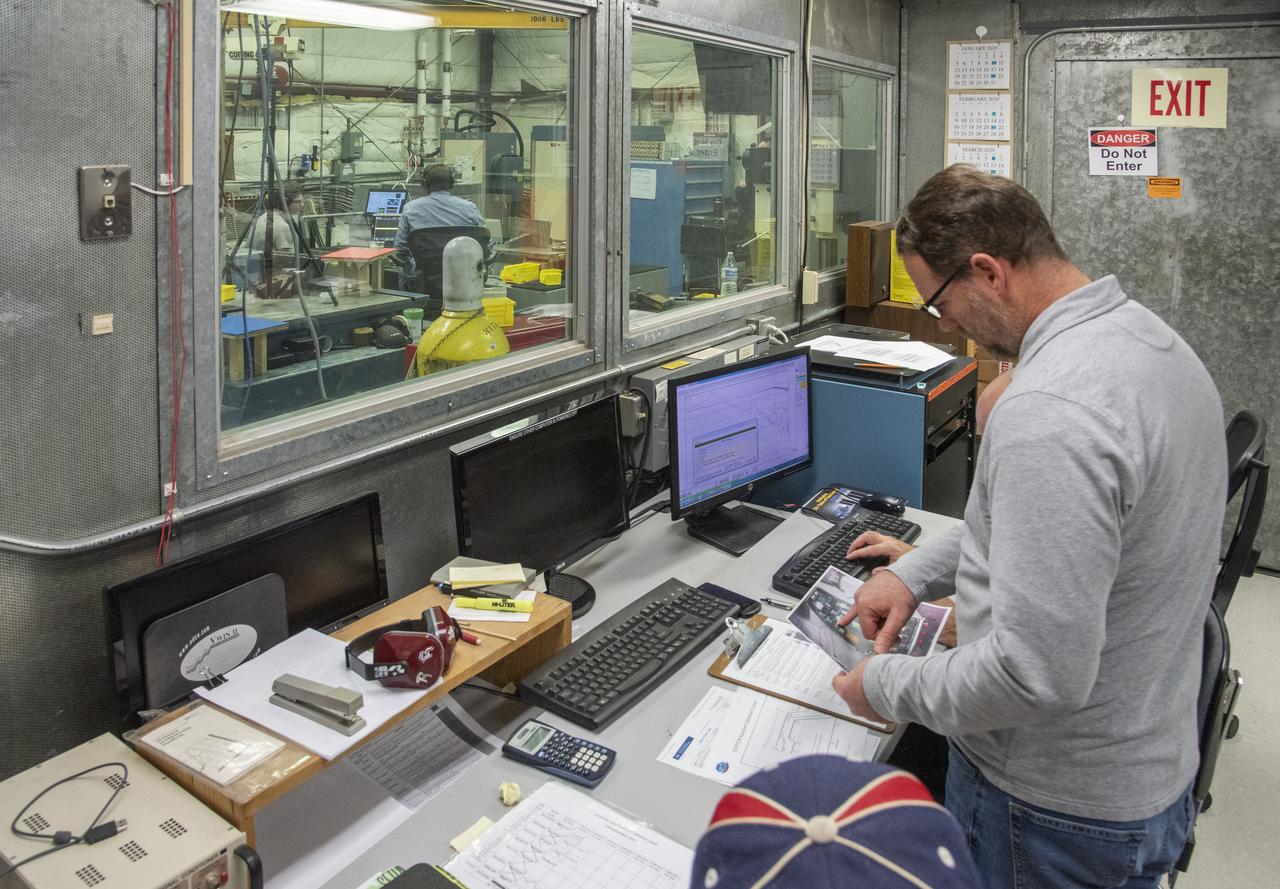

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
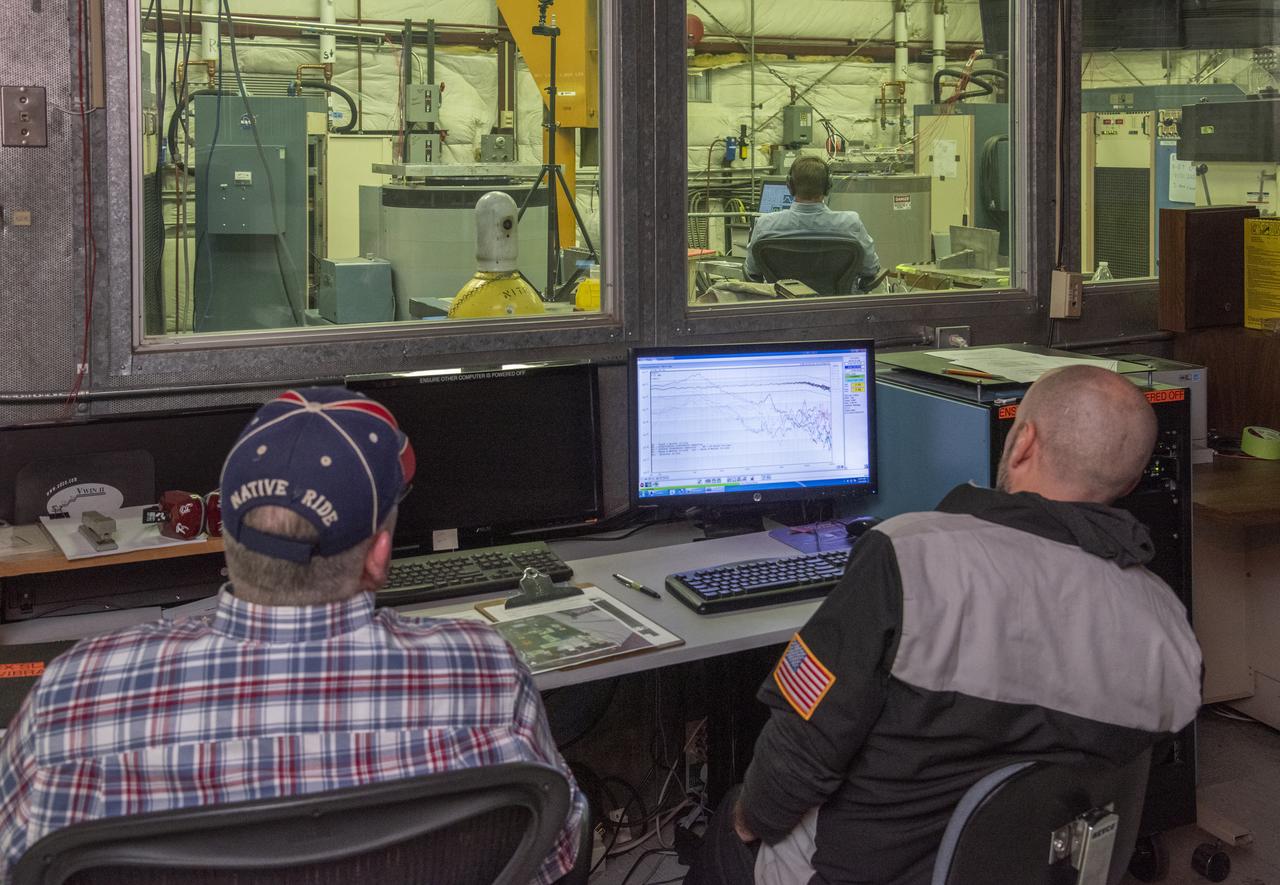

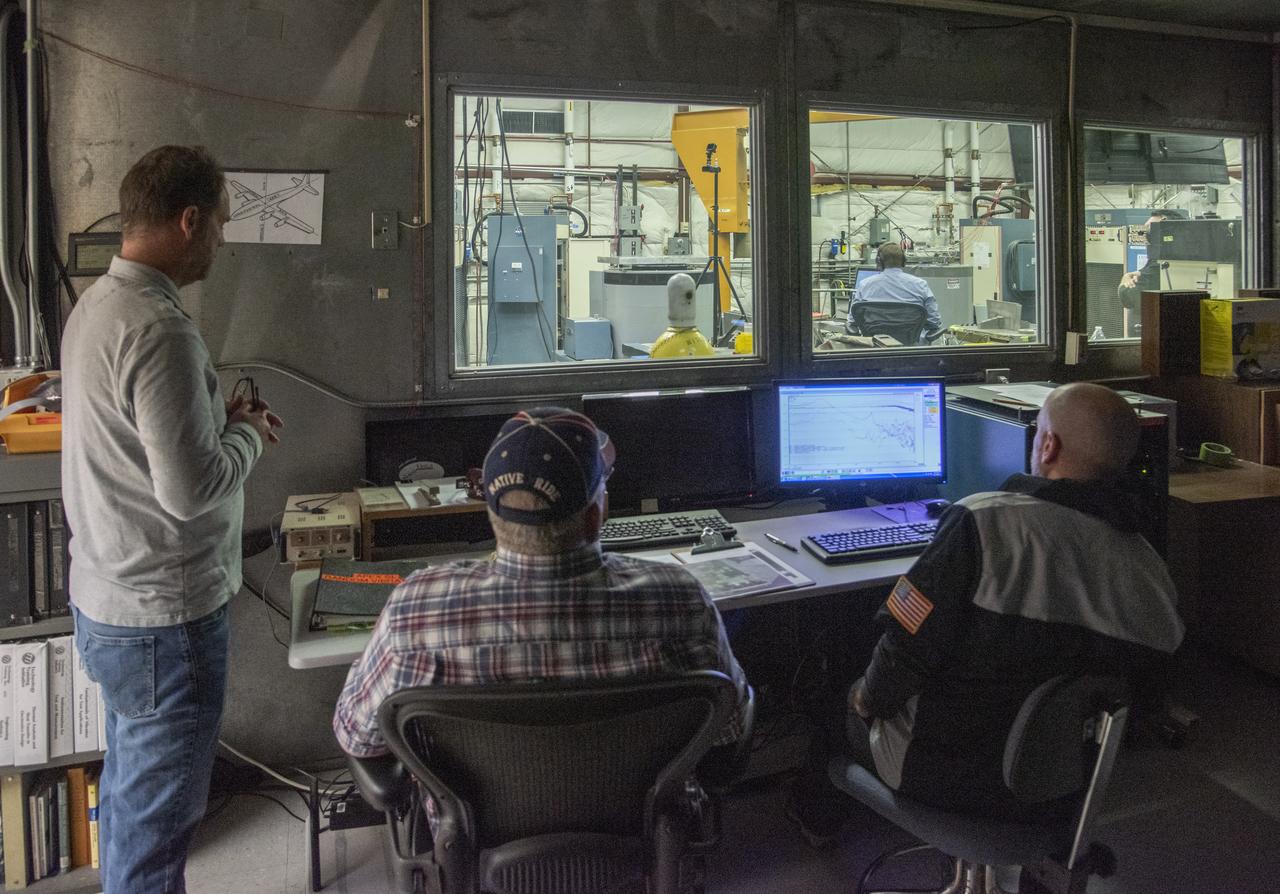
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 . Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

A successful test is completed of the European Structural Test Article (E-STA) partial tank vibration test (Y- axis at 80% power) performed on the Mechanical Vibration Facility (MVF) table at NASA Glenn’s Space Power Facility at Plum Brook Station, Sandusky, Ohio on Sept. 7, 2016 .Part of Batch images transfer from Flickr.

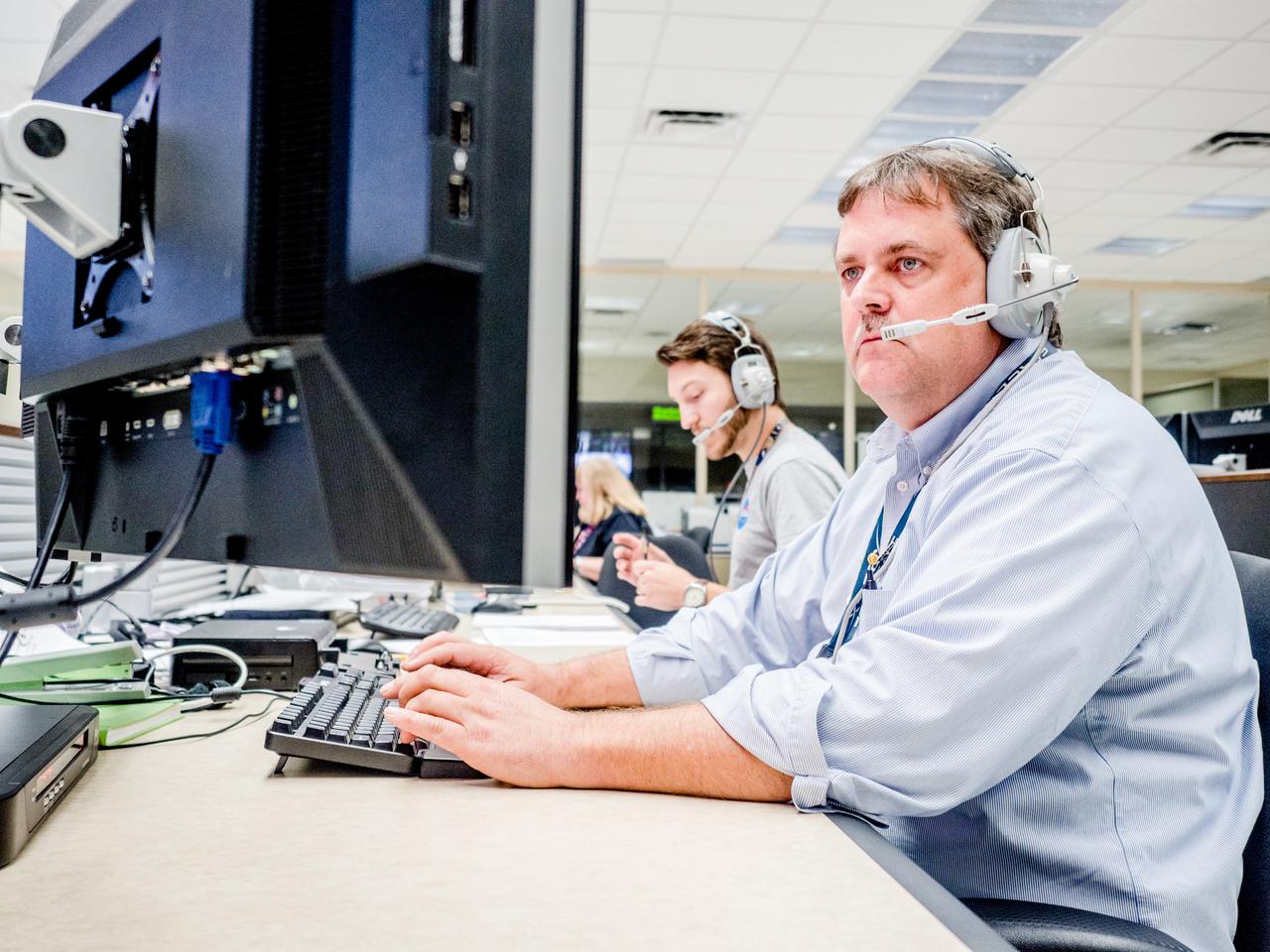
Engineers monitor data during vibration testing of a cruise motor controller for the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane. Attached to a table at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center's environmental lab, the cruise motor controller is exposed to specific levels of vibration, allowing NASA to examine the structural integrity of the hardware. Engineers, meanwhile, monitored data, including waveforms of electrical current, and recorded readings.
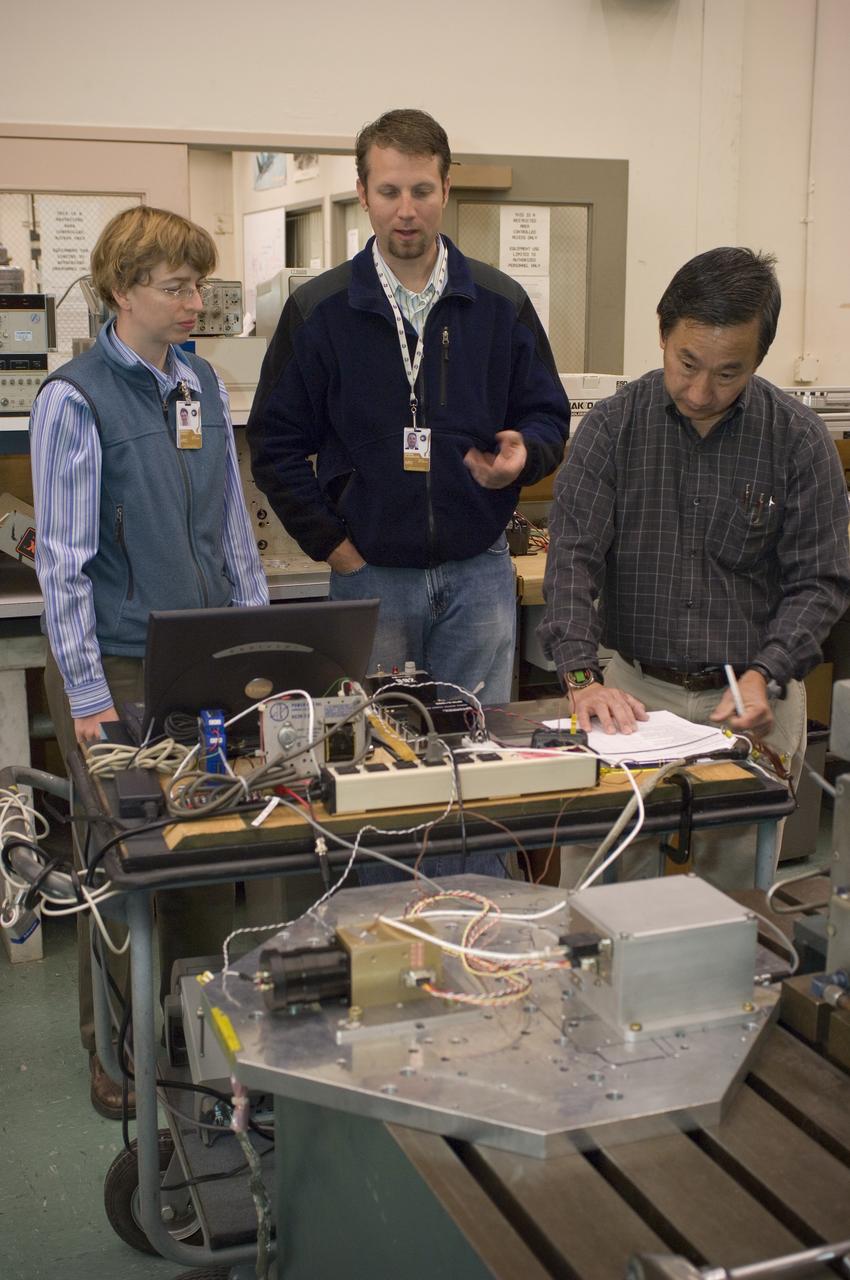

Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) and P.I. at NASA Ames Research Center - (l to r) Kim Ennico, Damon Flansburg and Gi Kojima check out the LCROSS Total Luminance Photometer lens and electronics attached to a metal plate in preparation for a vibe (vibration) test on the shake table in N-2444 EEL Laboratory
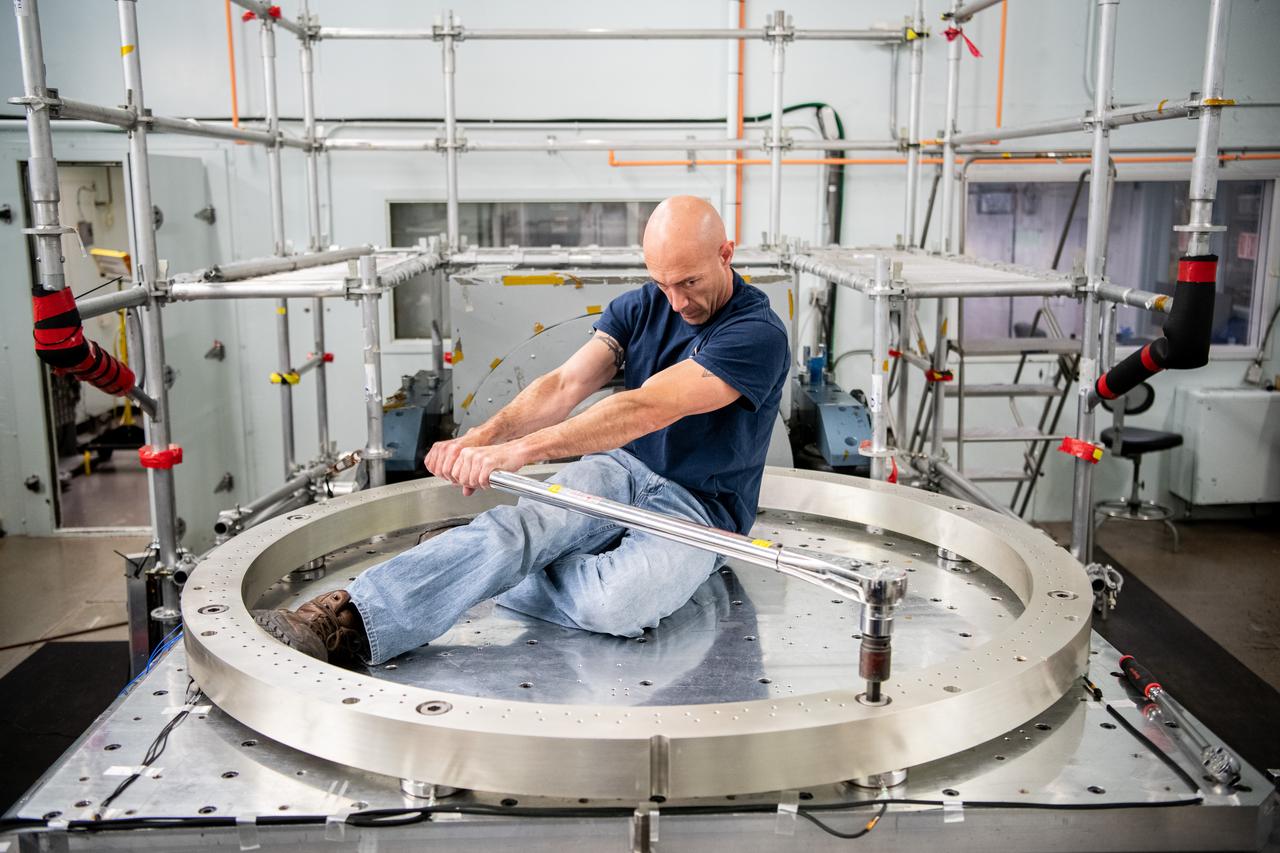

Engineering Technician Ryan Fischer torques the Force Gauge Ring on to the vibe table in preparation for vibration testing of the PACE spacecraft bus at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on June 16th, 2021. Photographer: Denny Henry – Goddard Space Flight Center
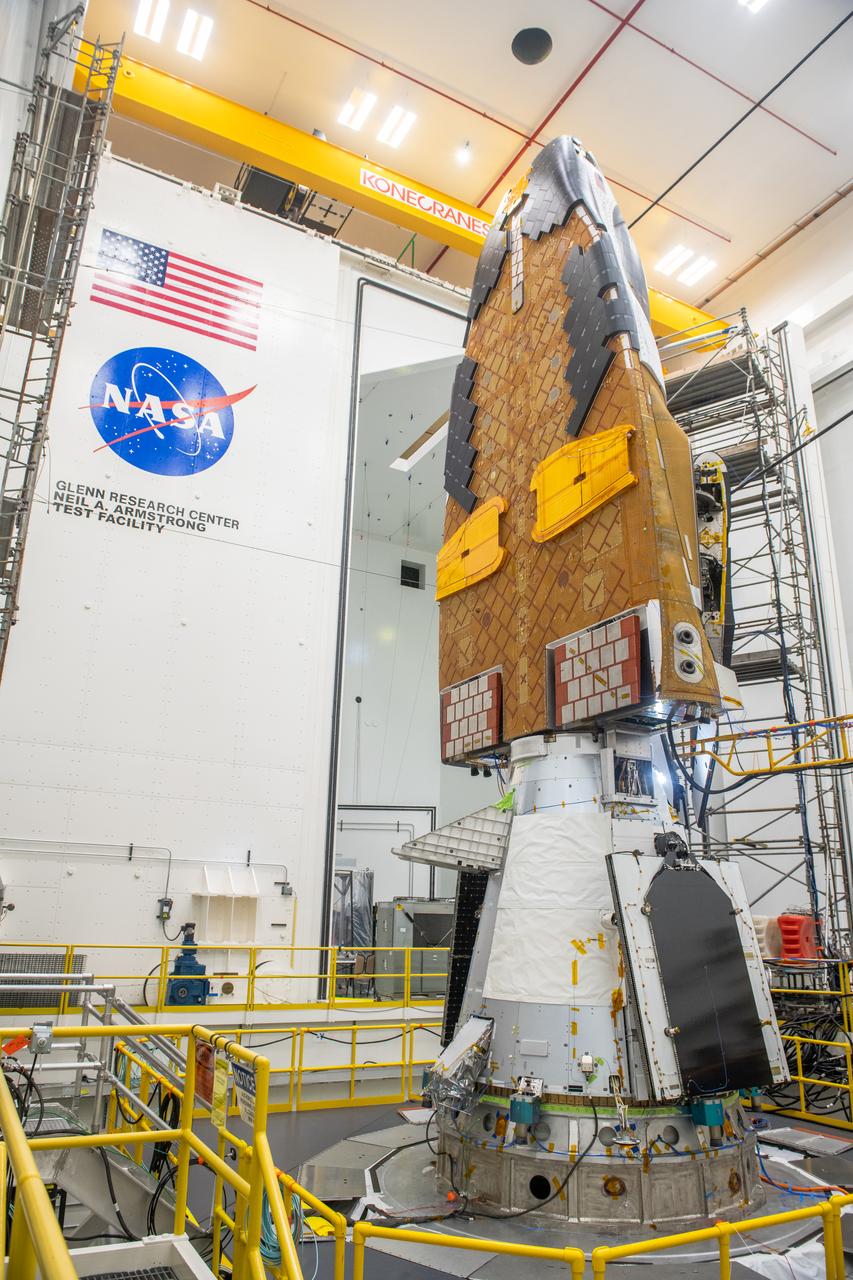

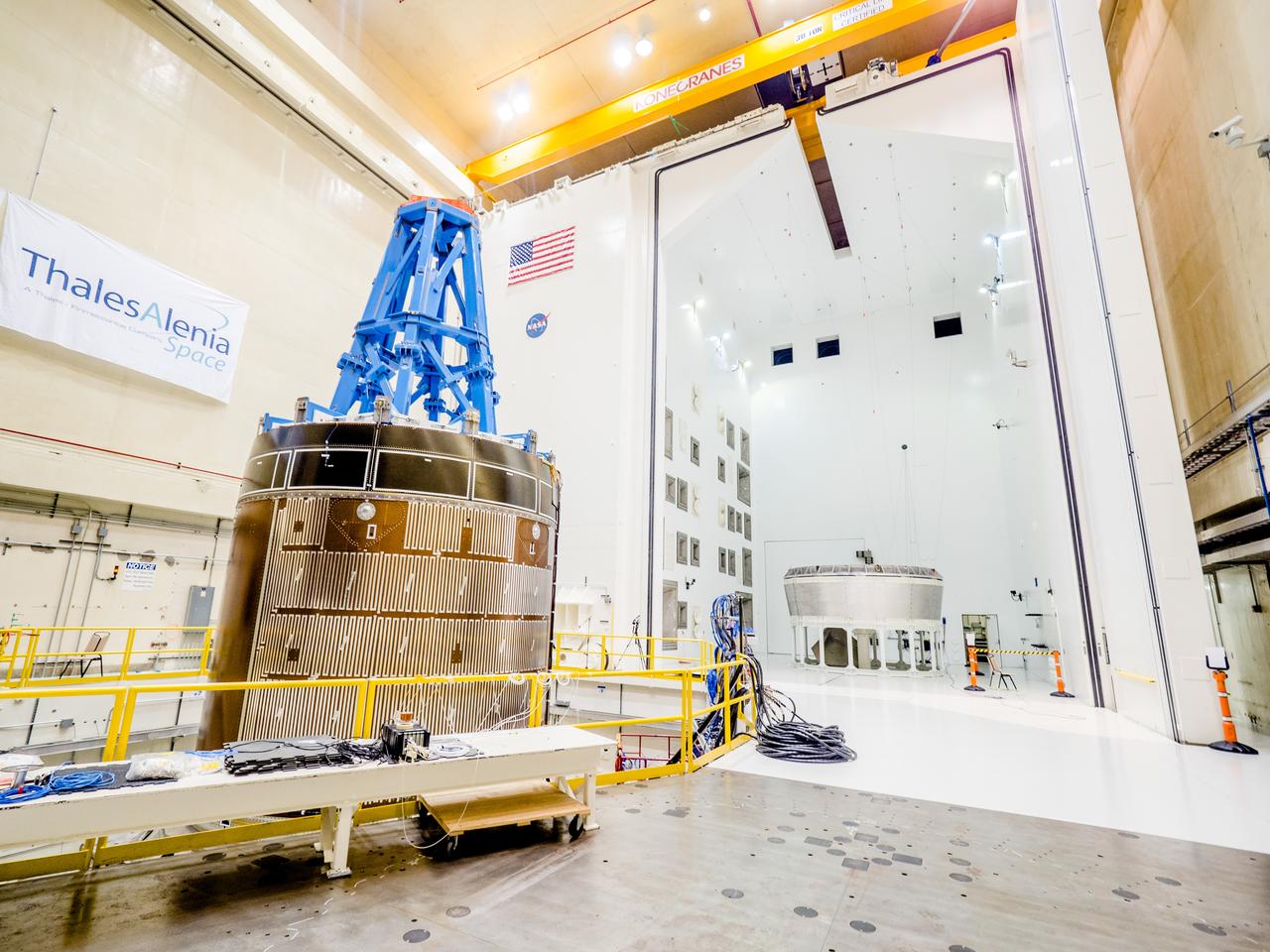
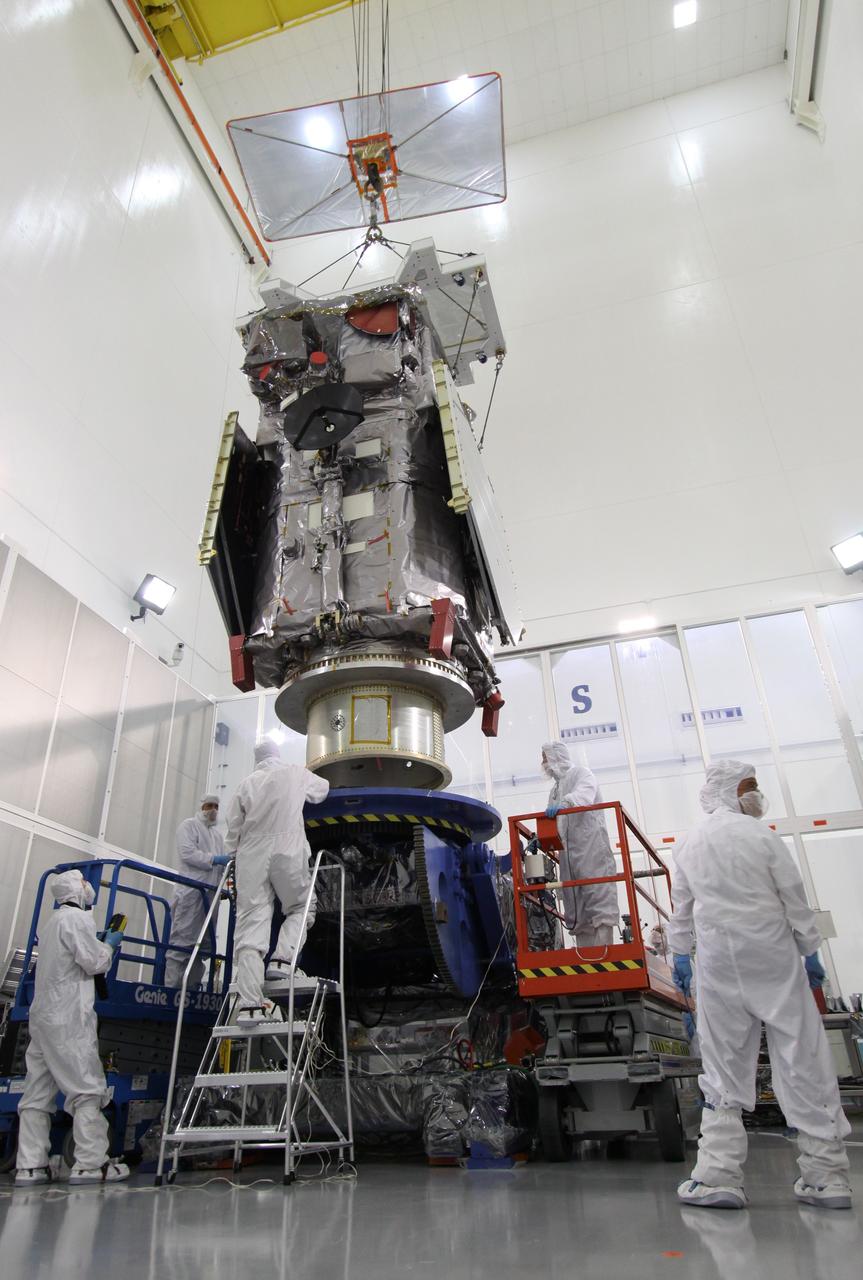
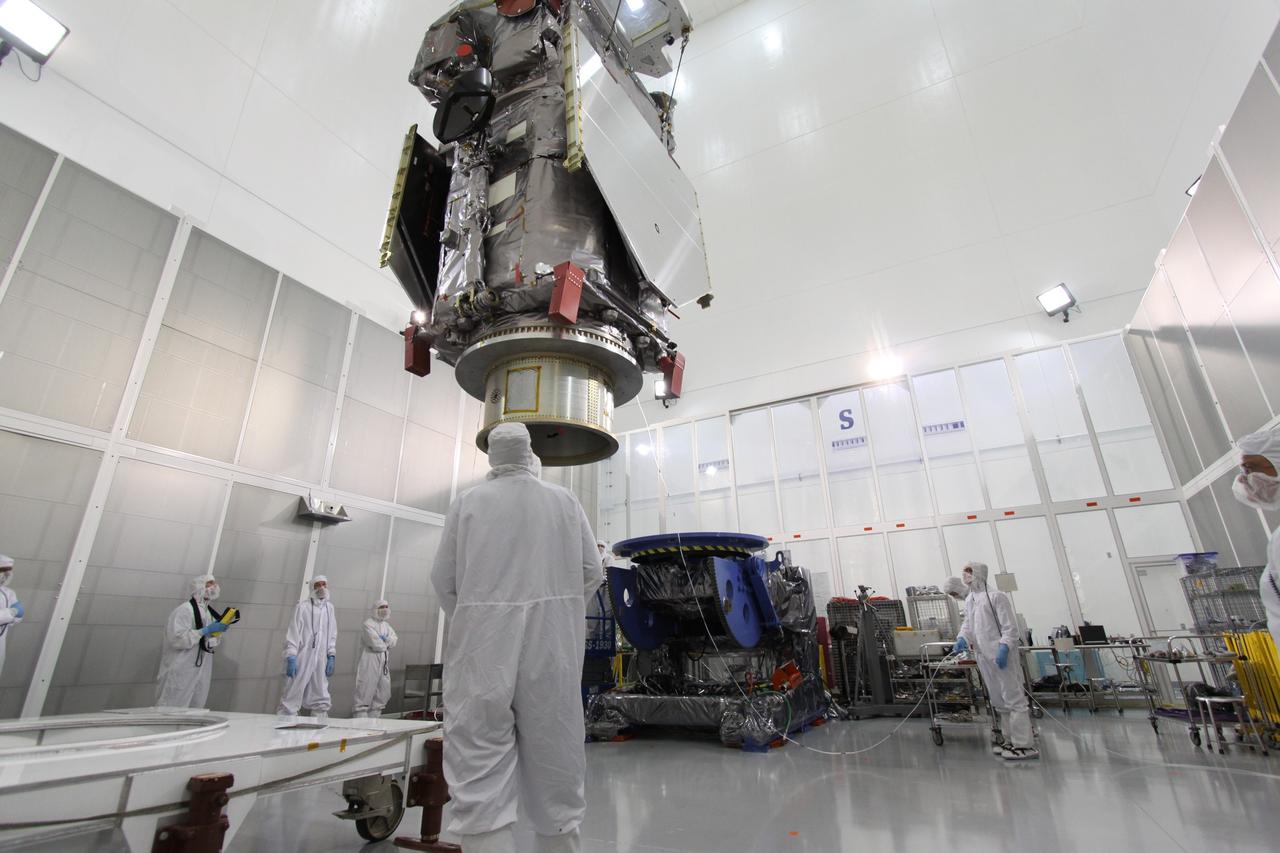
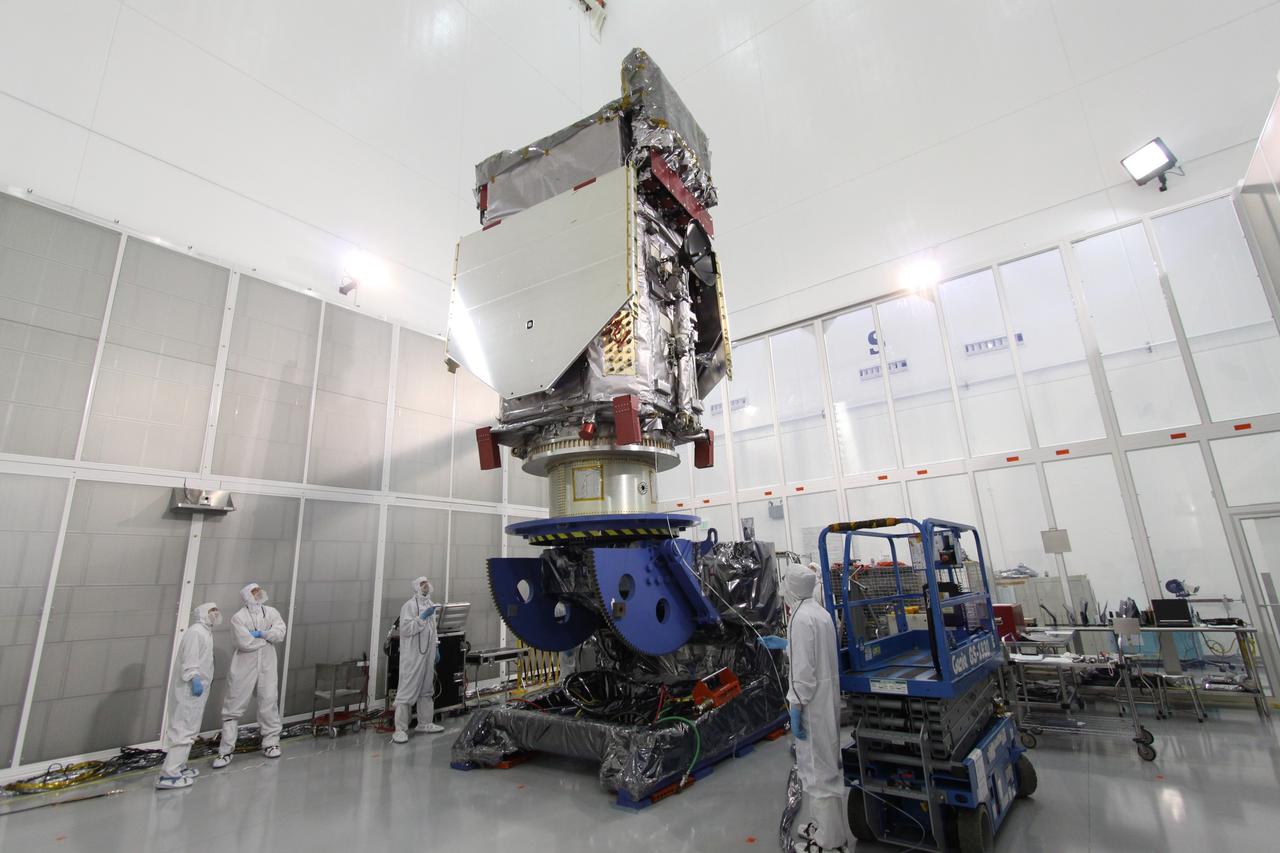
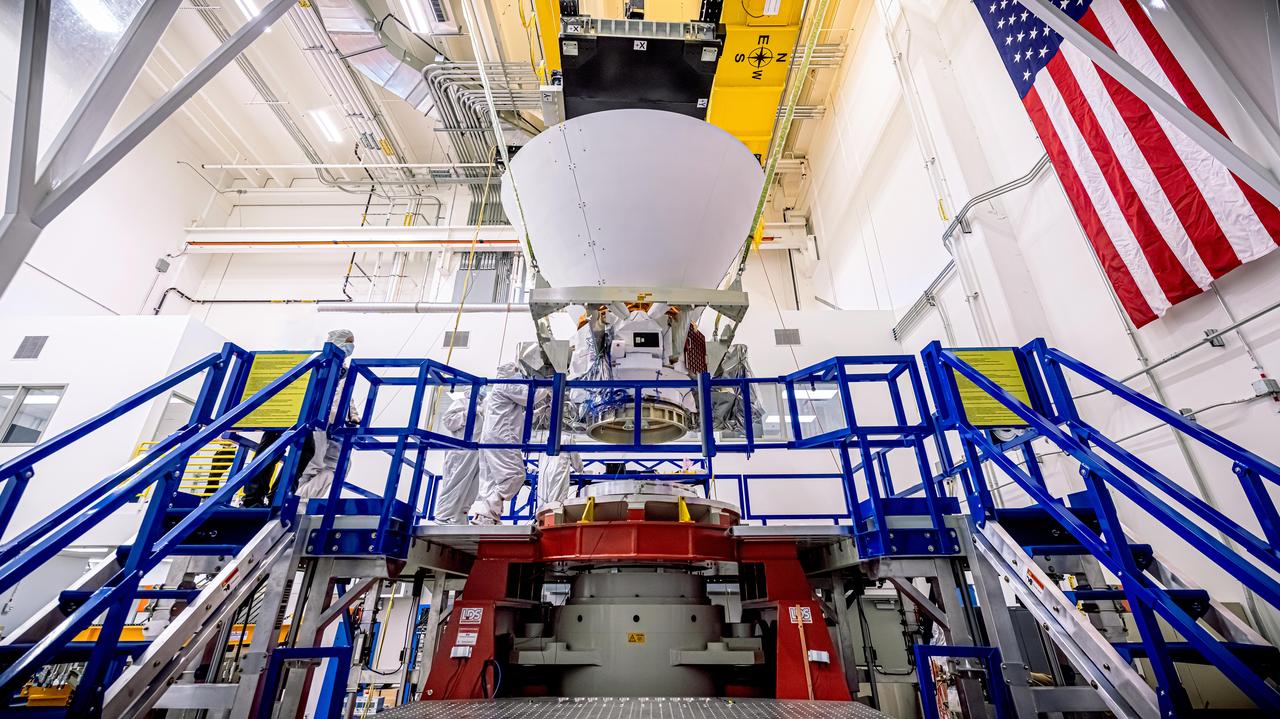
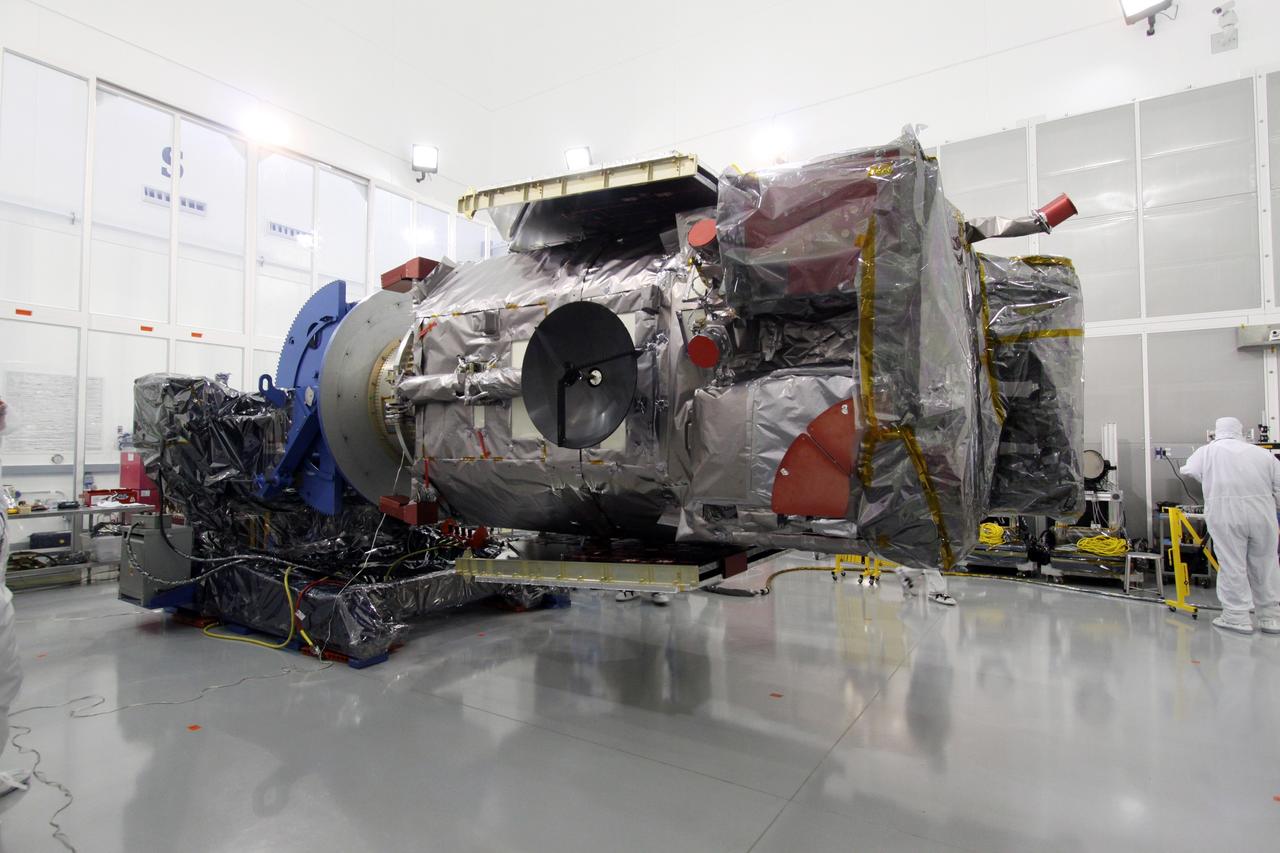
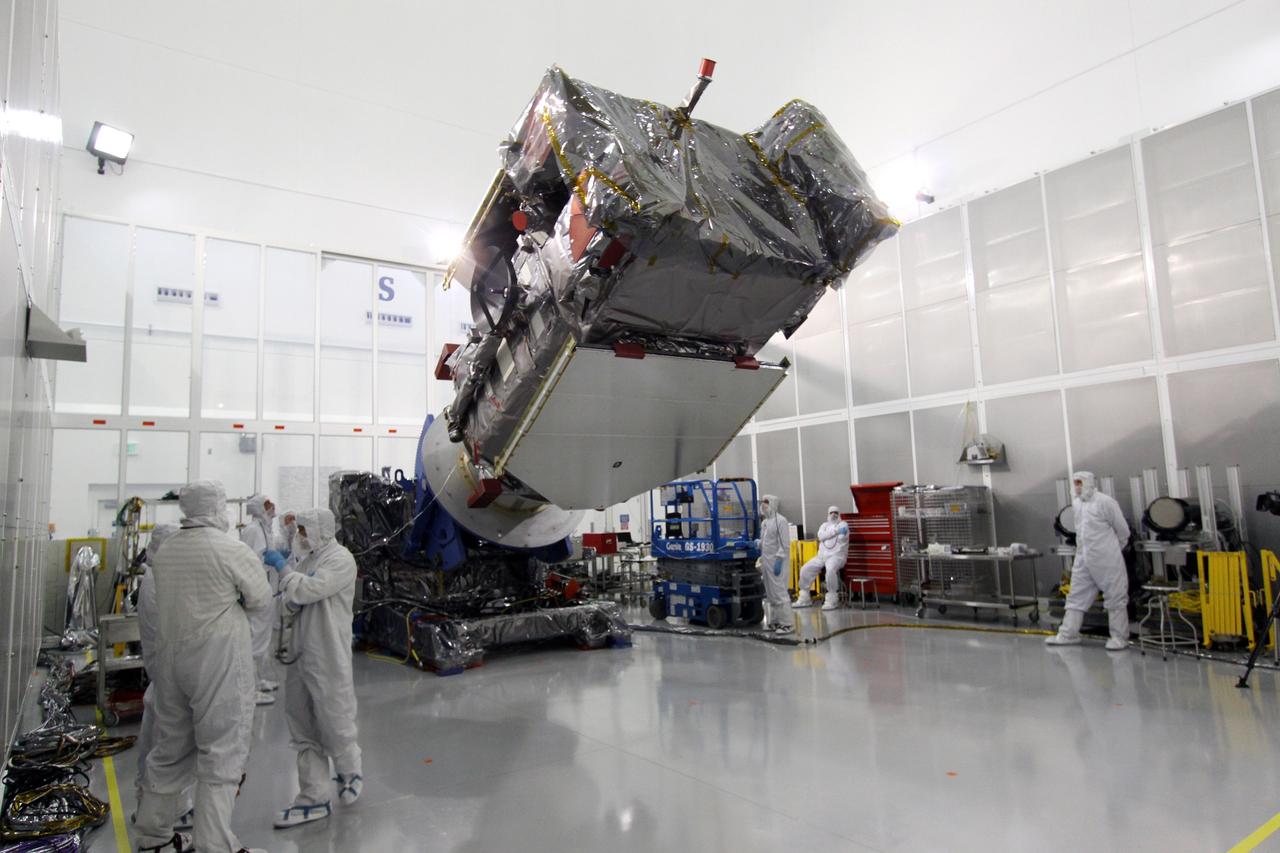
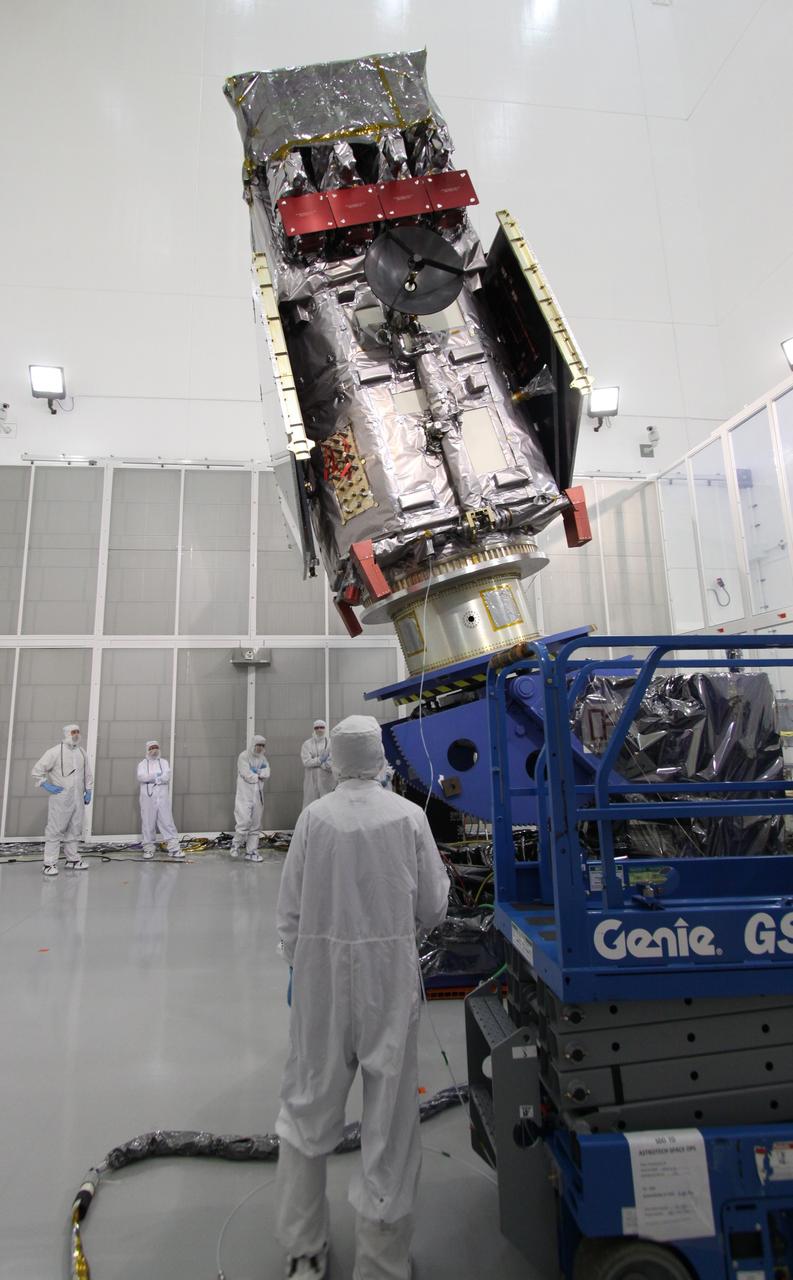
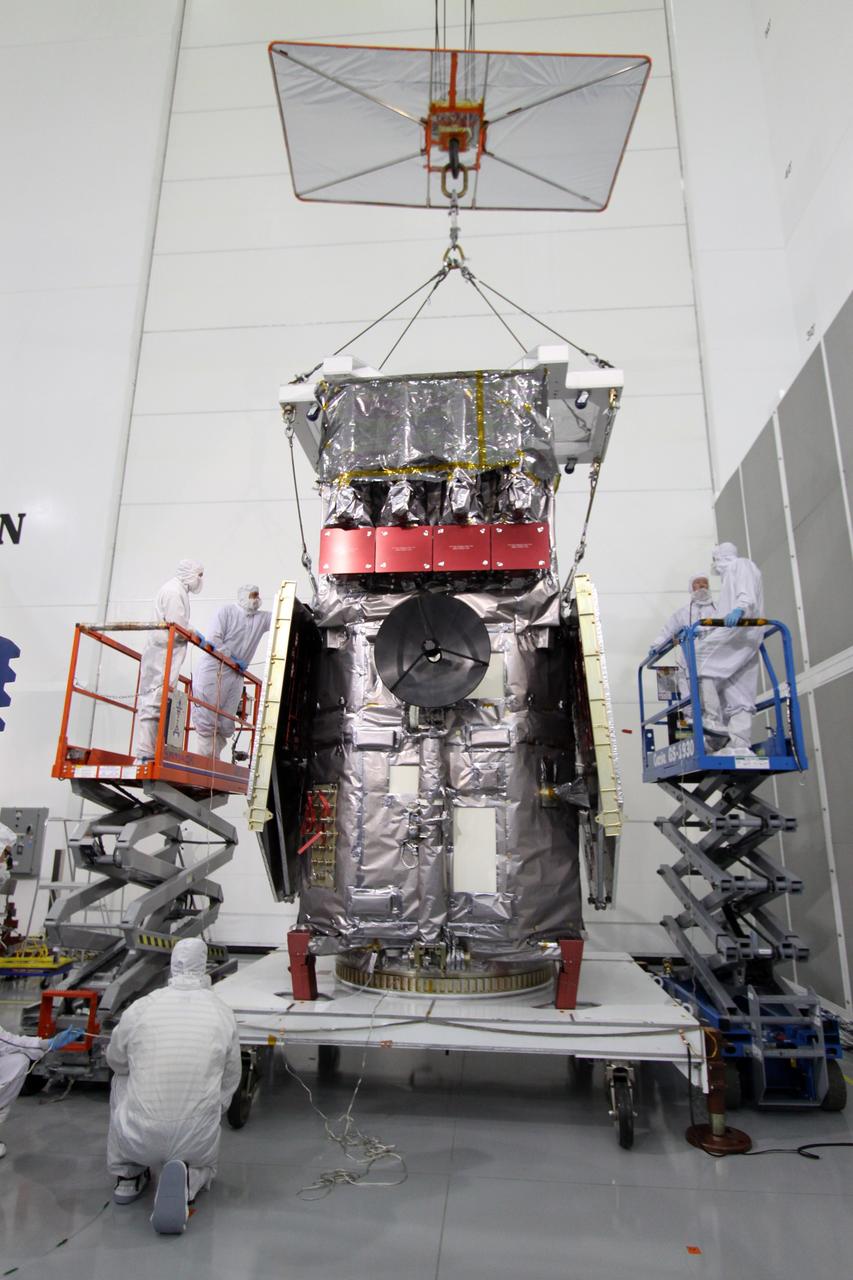
Sierra Space Dream Chaser Spaceplane Documentation Photographs
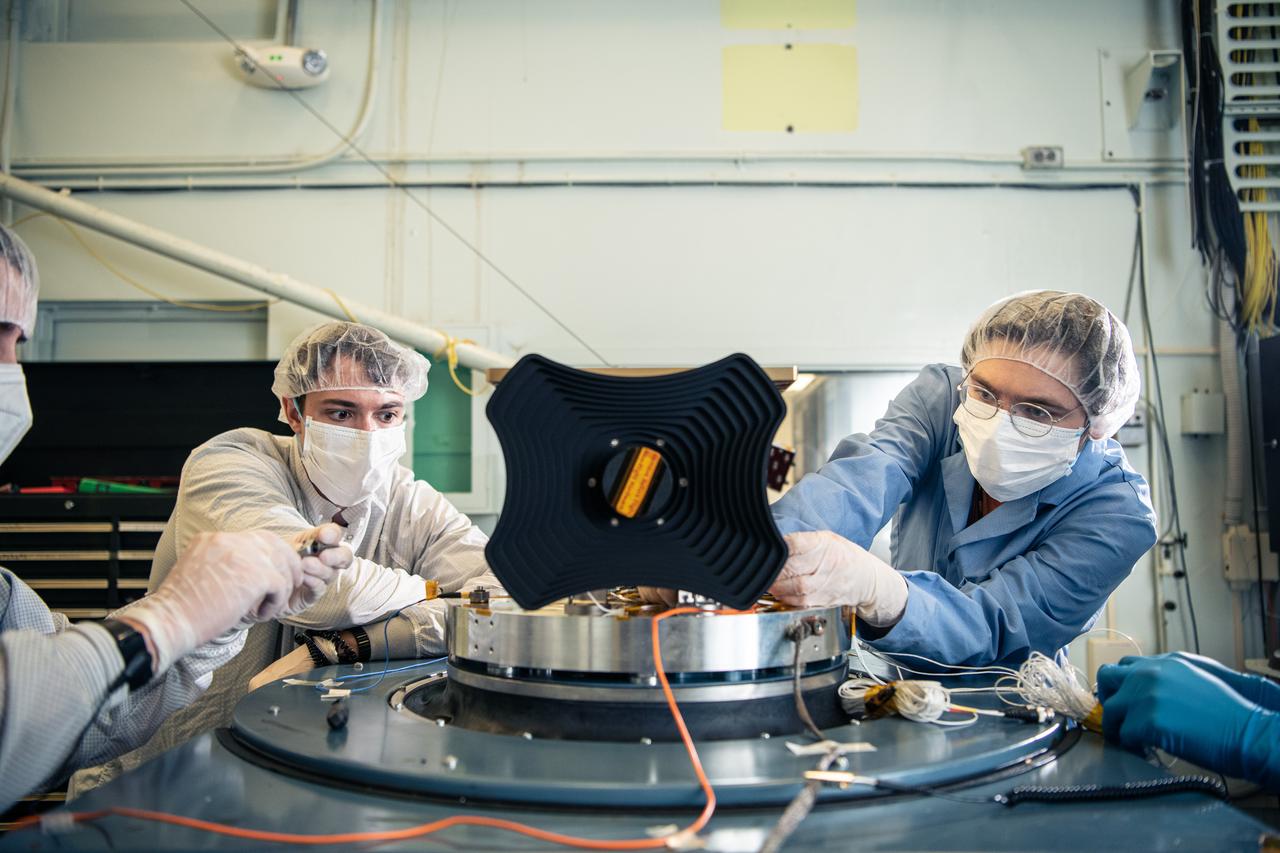
UMBC Earth and Space Institute engineers Ian Decker (left) and Danny Nelson (right) attach the Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument to the shaker table for vibration testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on August 8th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.
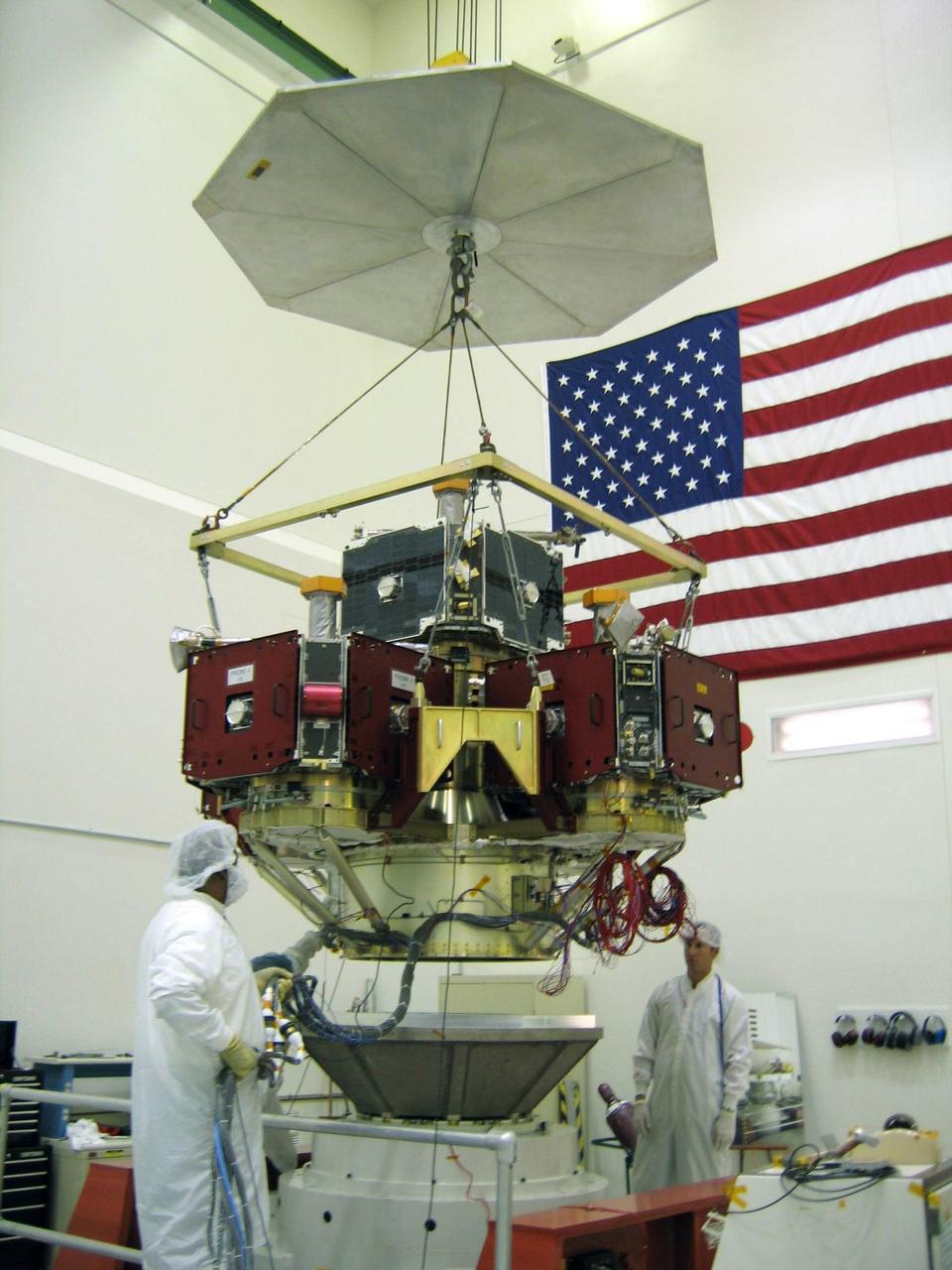

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. -- An overhead crane hoists the probe carrier assembly on the THEMIS spacecraft to the vibration table (Z-axis). THEMIS, which stands for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, comprises five identical probes that will study the dynamic and colorful eruptions of auroras. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Oct. 19 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is lowered onto the Ransome table. The table will be used to rotate the spacecraft in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is moved across the floor toward the Ransome table in the background. The table will be used to rotate the spacecraft in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is lowered onto the Ransome table. The table will be used to rotate the spacecraft in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

NASA's SPHEREx observatory is lifted and installed onto a vibration table in the Z-axis configuration at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in August 2024. In this test, the spacecraft is subjected to vibrations in all three axes separately. The test was successfully completed Aug. 16, 2024. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26539

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is rotated on a Ransome table to a horizontal position. The rotation will allow access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is rotated on a Ransome table. The rotation will allow access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is rotated on a Ransome table. The rotation will allow access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
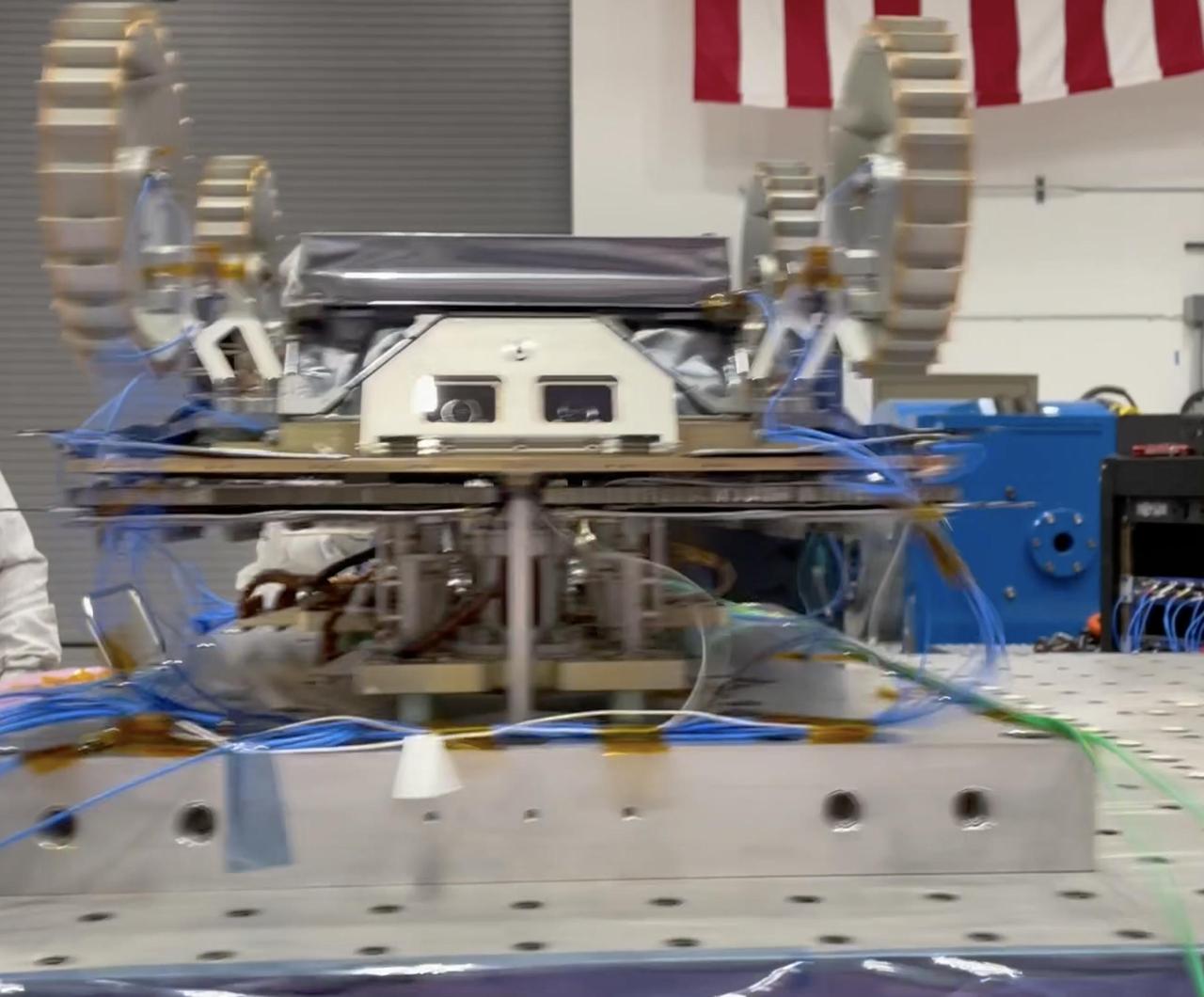
A small Moon-bound rover is clamped to a special "shaker table" that vibrates intensely to make sure the hardware will survive the jarring rocket ride out of Earth's atmosphere. This is one of three rovers – each about the size of a carry-on suitcase – that are part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration. This vibration testing took place in November 2023 at a National Technical Systems test facility in Santa Clarita, California. In the video, the rover is shaken in two directions – first along the "z" axis and then the "x" axis. Another test, not shown, subjected the rover to a "y" axis vibration test. CADRE is designed to show that a group of robotic spacecraft can work together as a team to accomplish tasks and record data autonomously &ndash without explicit commands from mission controllers on Earth. The three small rovers will ride aboard a lunar lander that will carry the project's base station and camera assembly. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26167

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians secure an overhead crane on the Solar Dynamics Observatory . The crane will lift the spacecraft from the work stand and move it onto a Ransome table that will allow it to be rotated in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians check the clearance as the Solar Dynamics Observatory is lifted from the stand. The spacecraft is being moved onto a Ransome table that will allow it to be rotated in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is lifted from the work stand under the guidance of technicians. The spacecraft is being moved onto a Ransome table that will allow it to be rotated in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians check the Solar Dynamics Observatory after it was lifted from its work stand. The spacecraft is being moved onto a Ransome table that will allow it to be rotated in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Payload Processing Facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory is fitted with a crane to lift it from the work stand. The spacecraft will be moved onto a Ransome table that will allow it to be rotated in various directions for access to different areas of the spacecraft. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
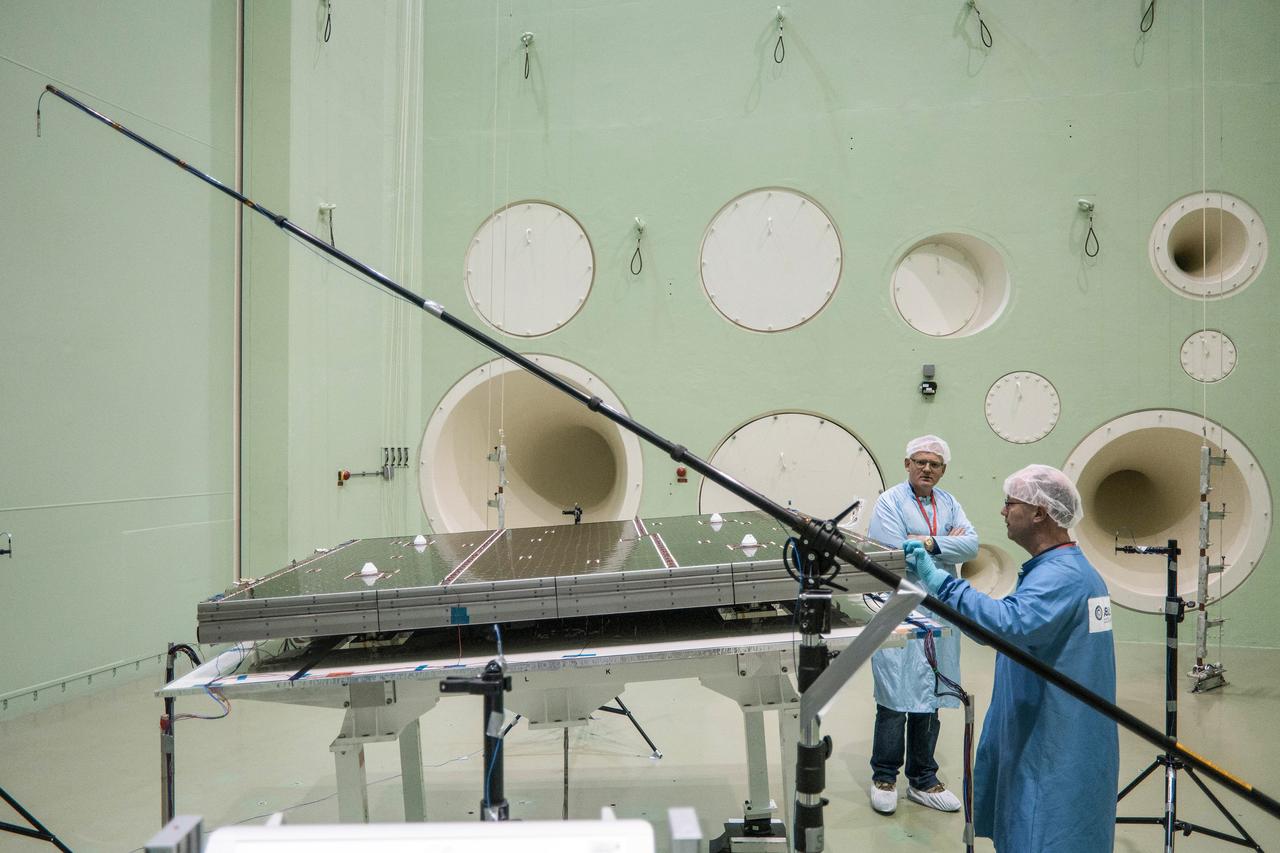

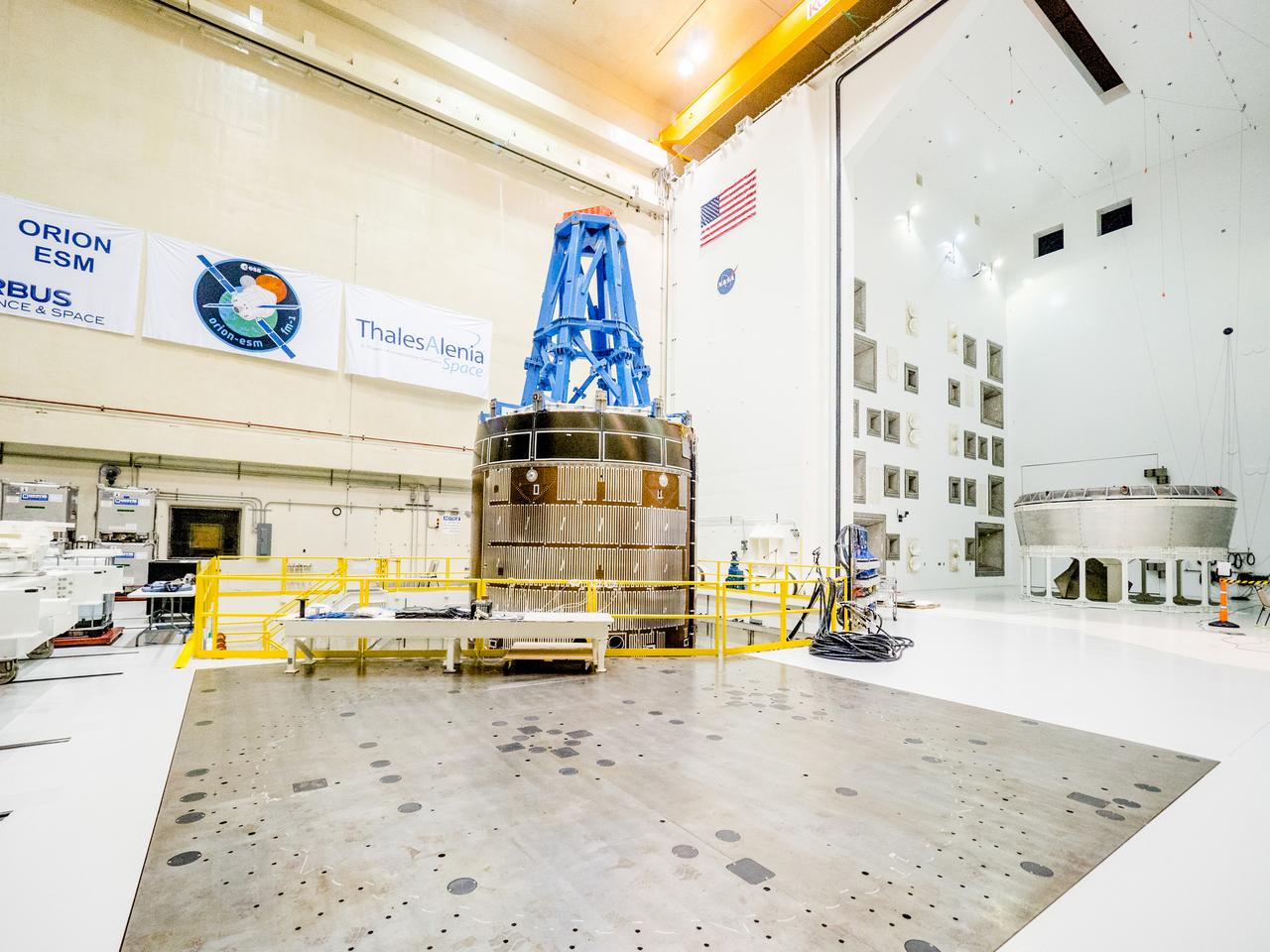
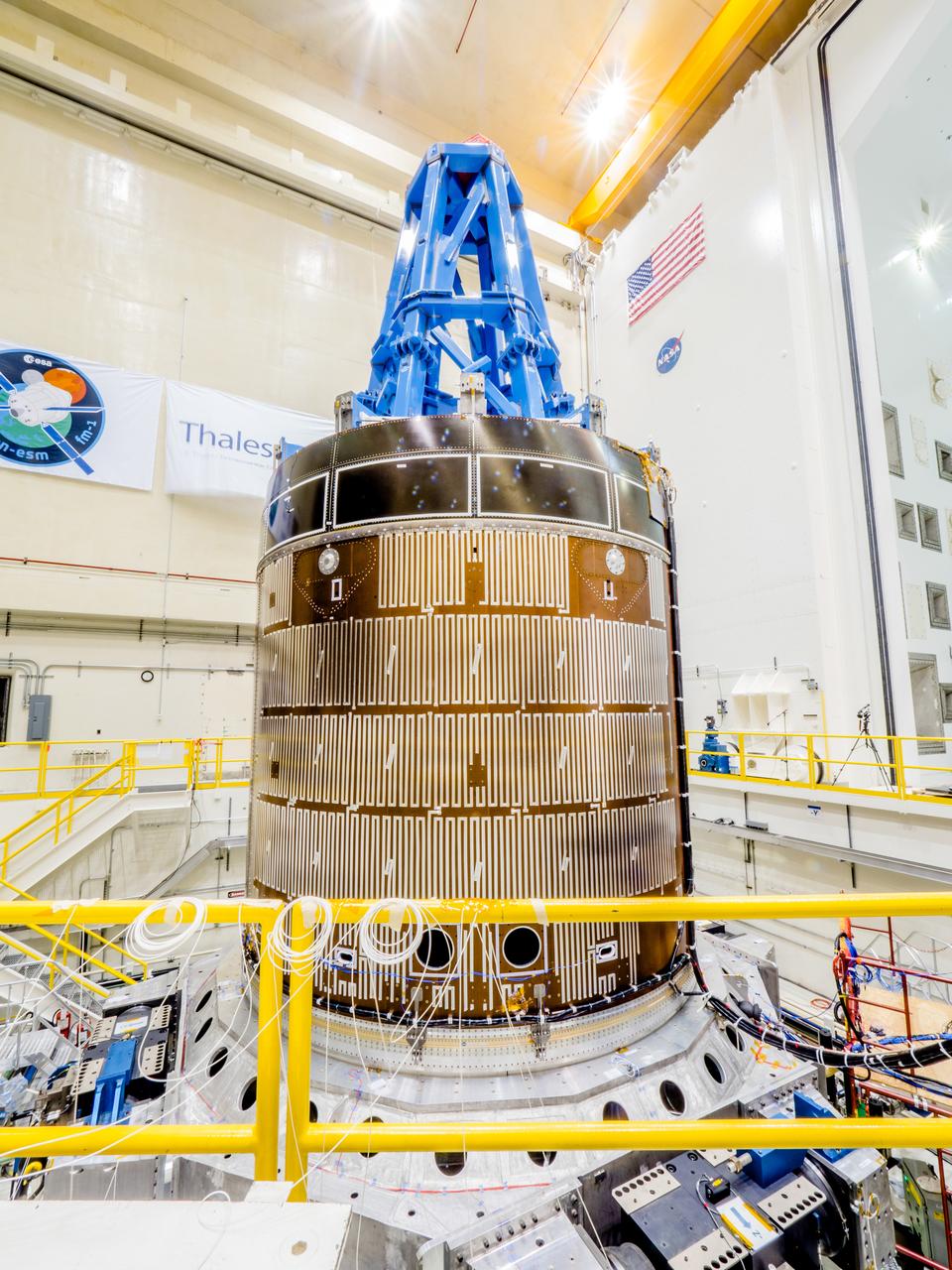
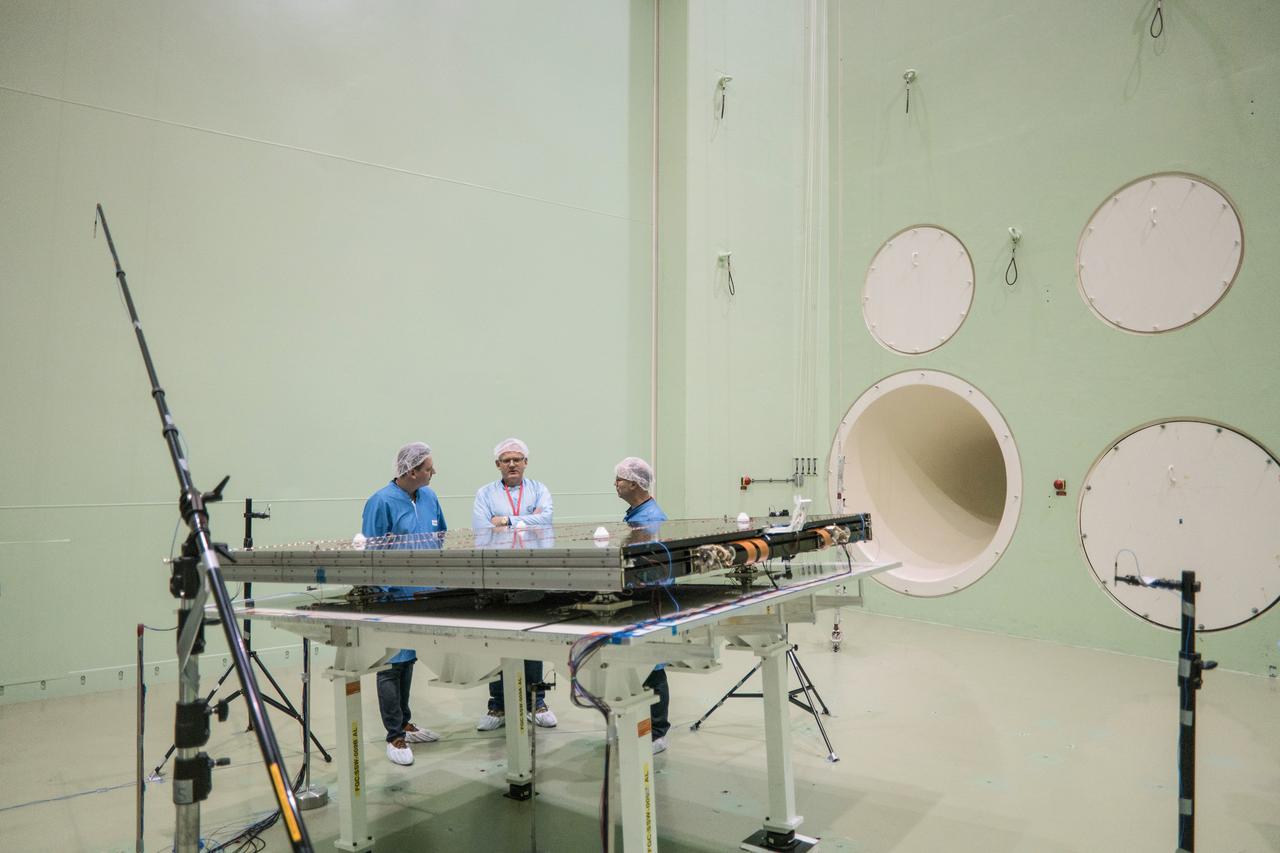
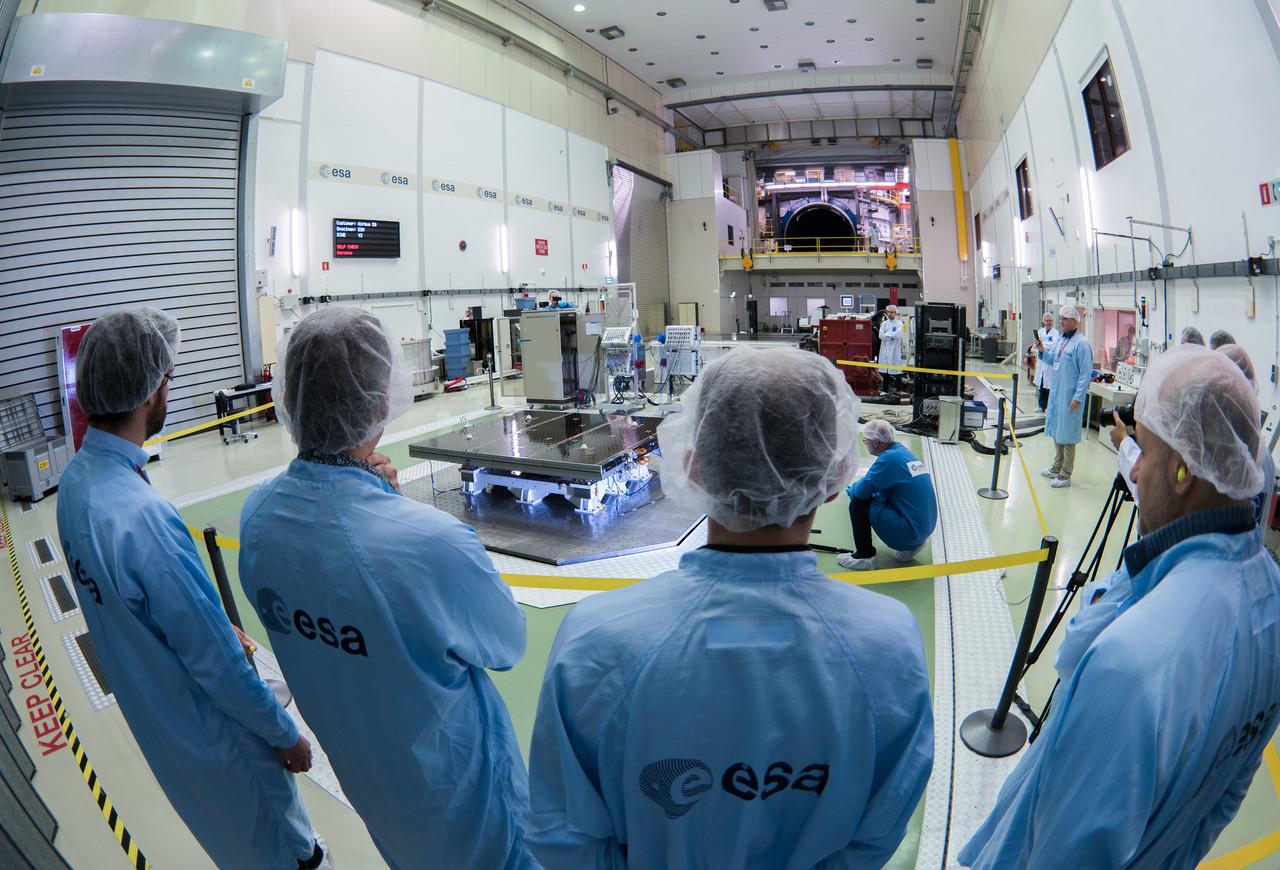
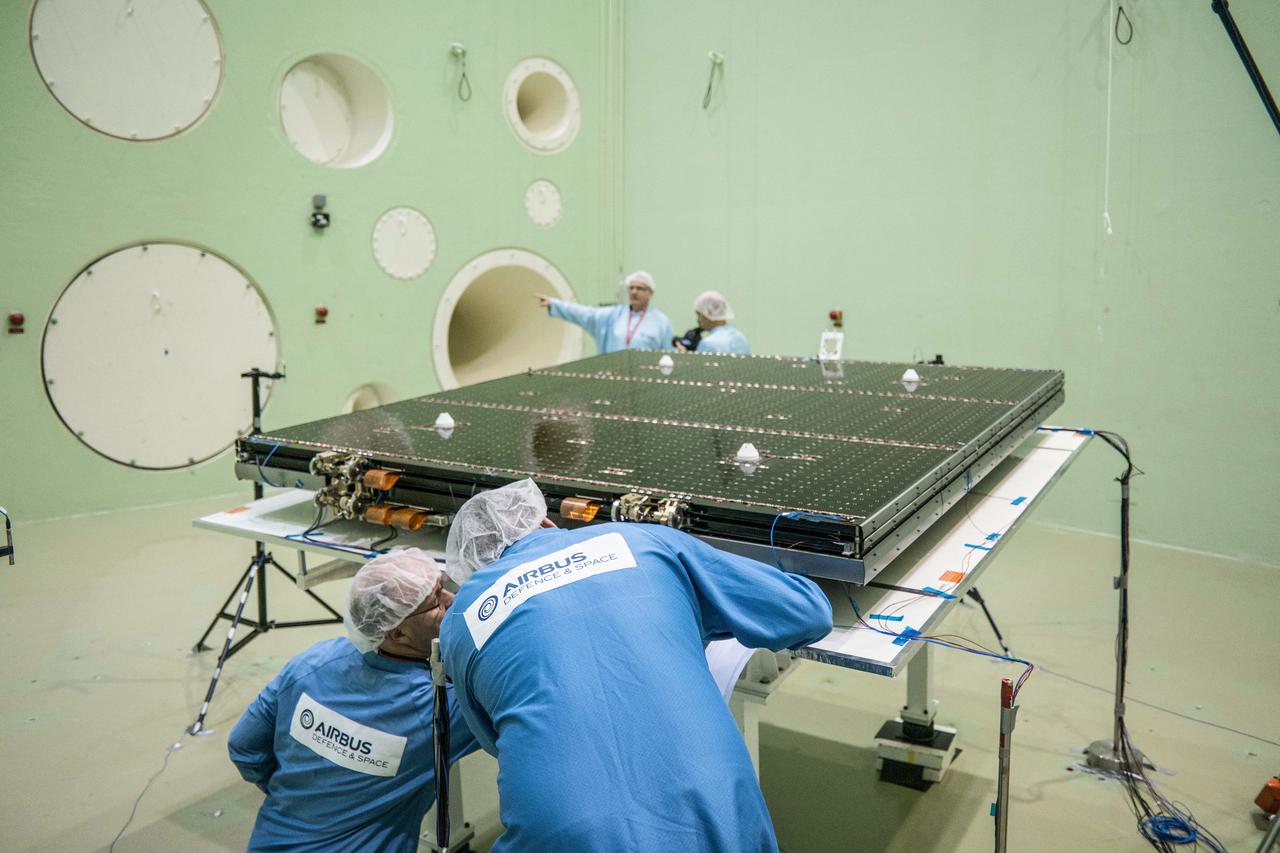
The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
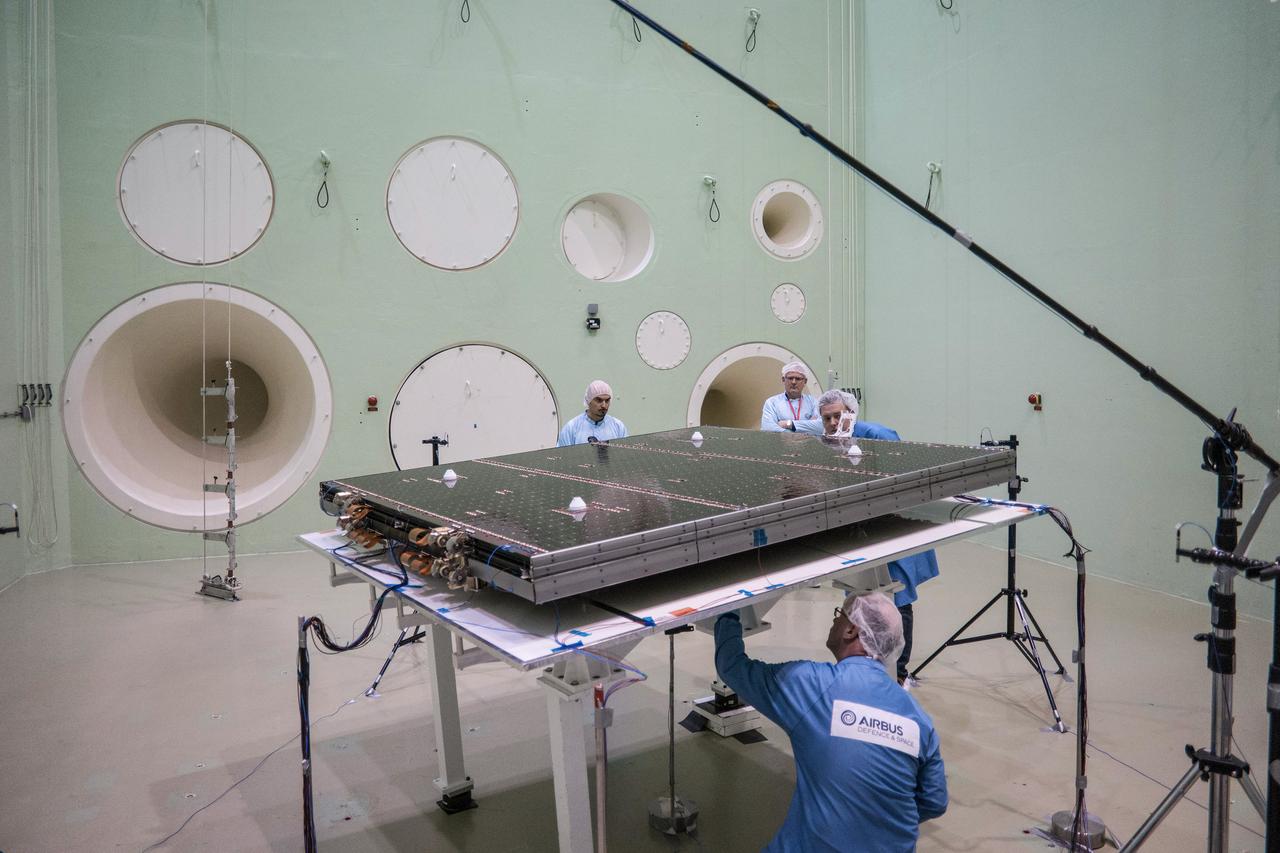

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.
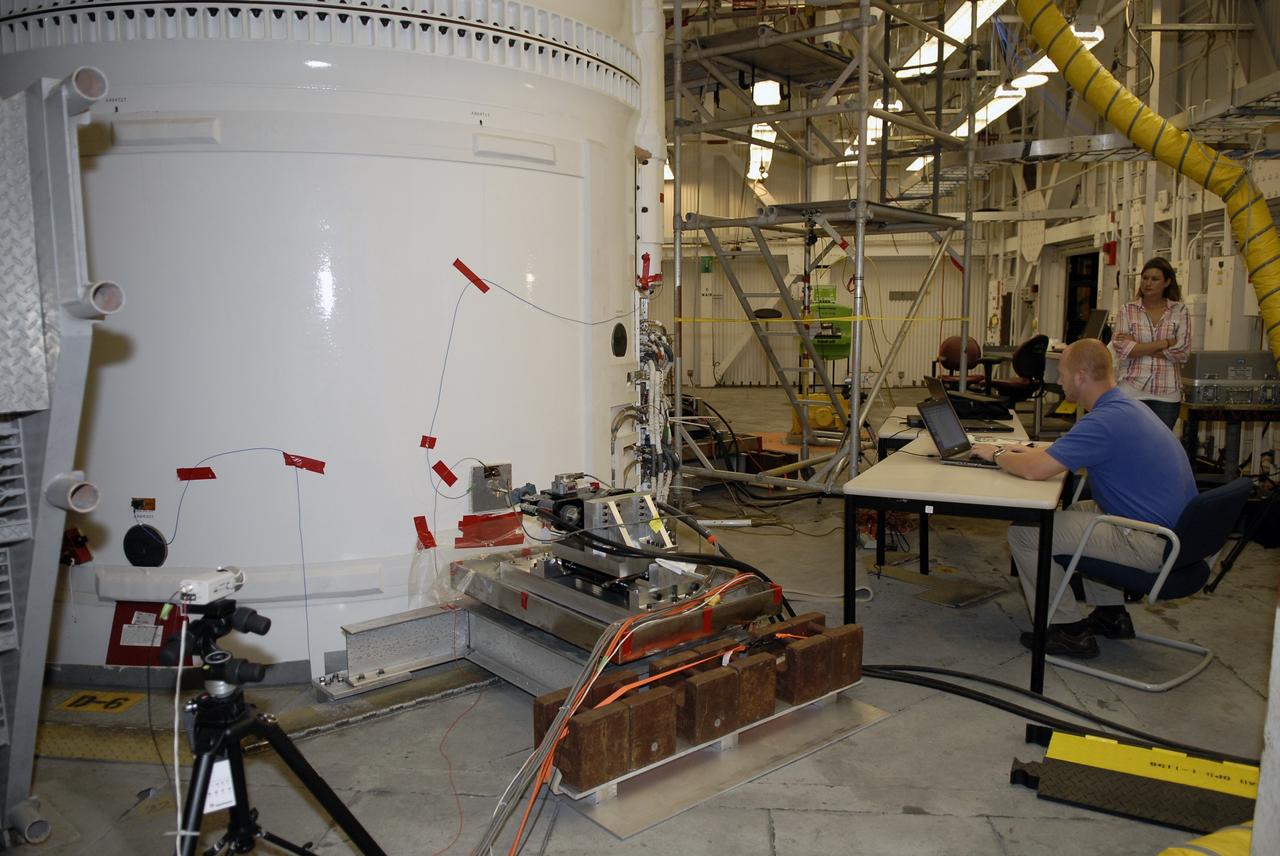

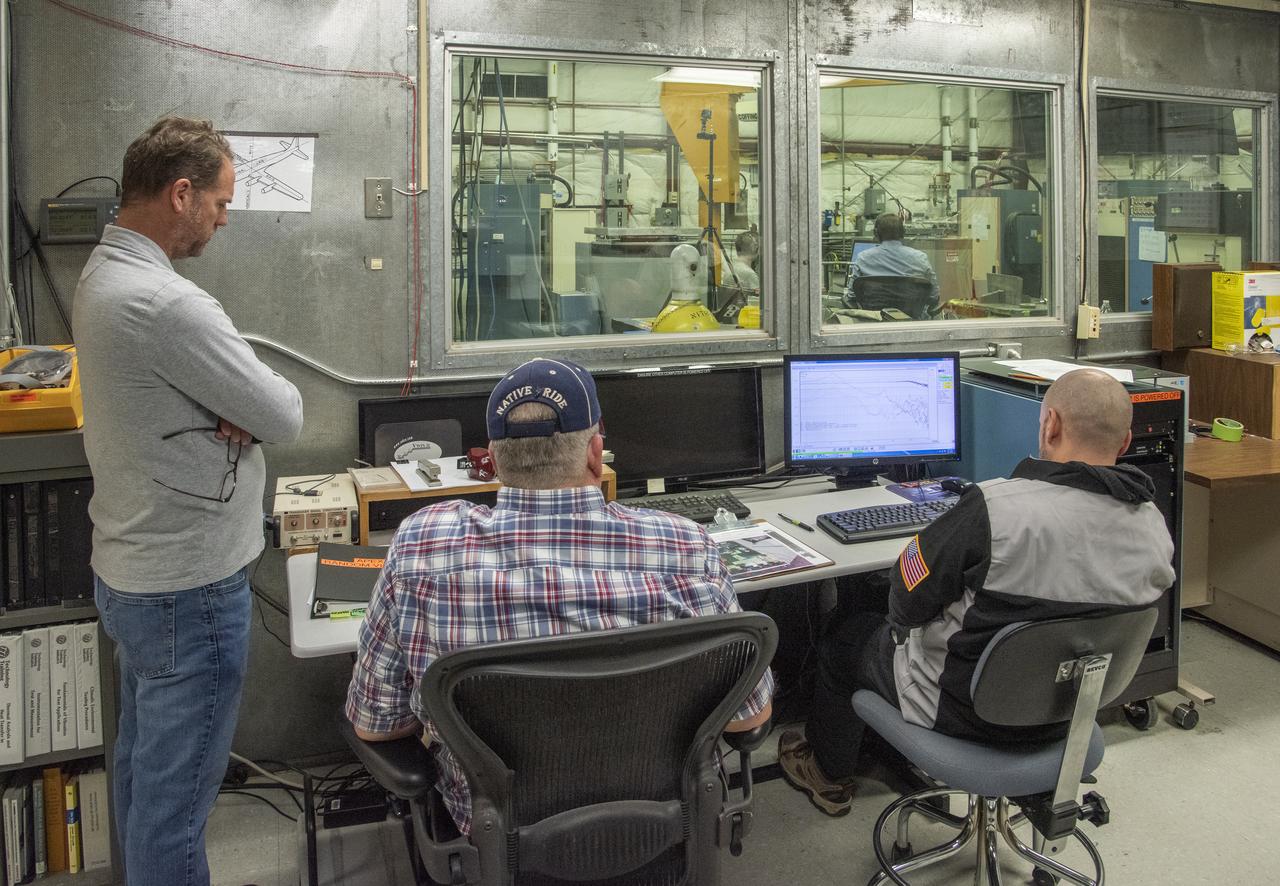
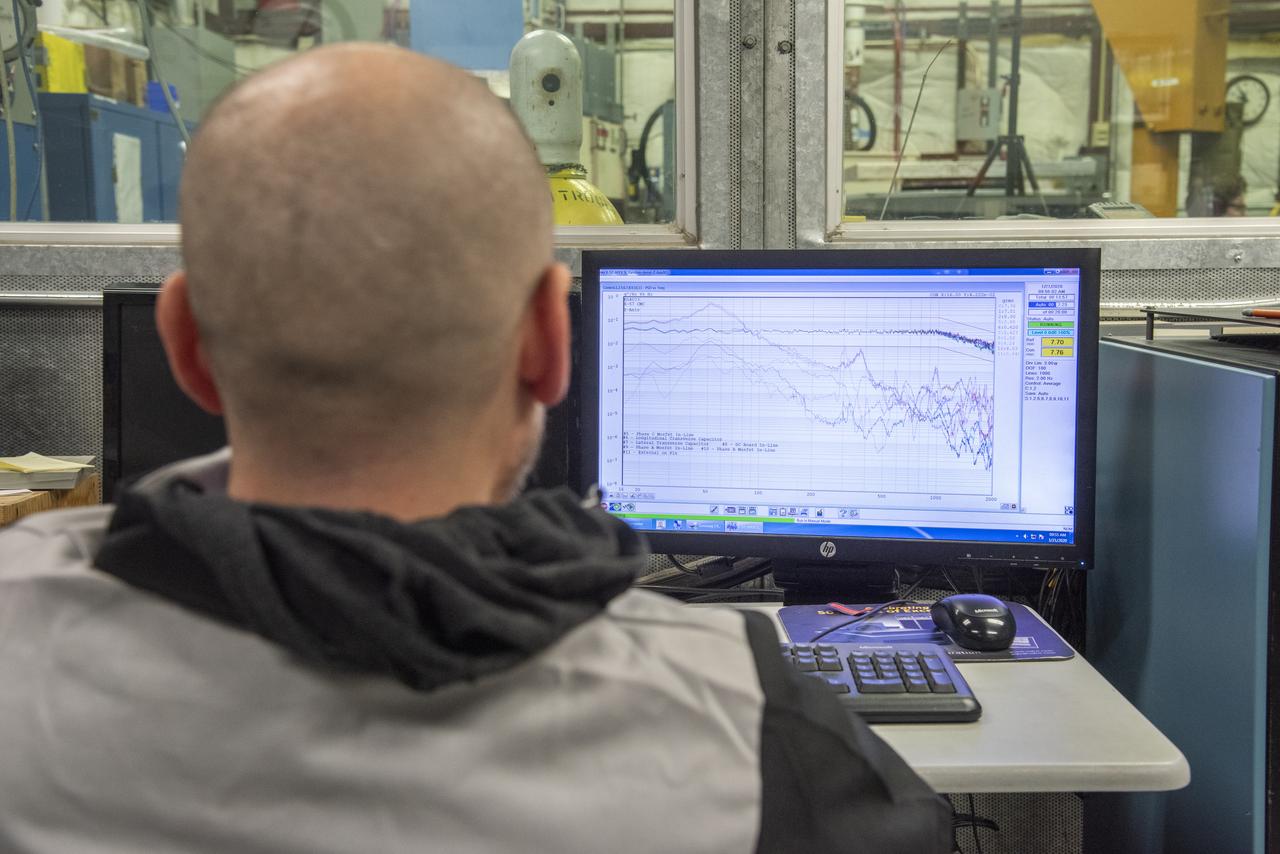
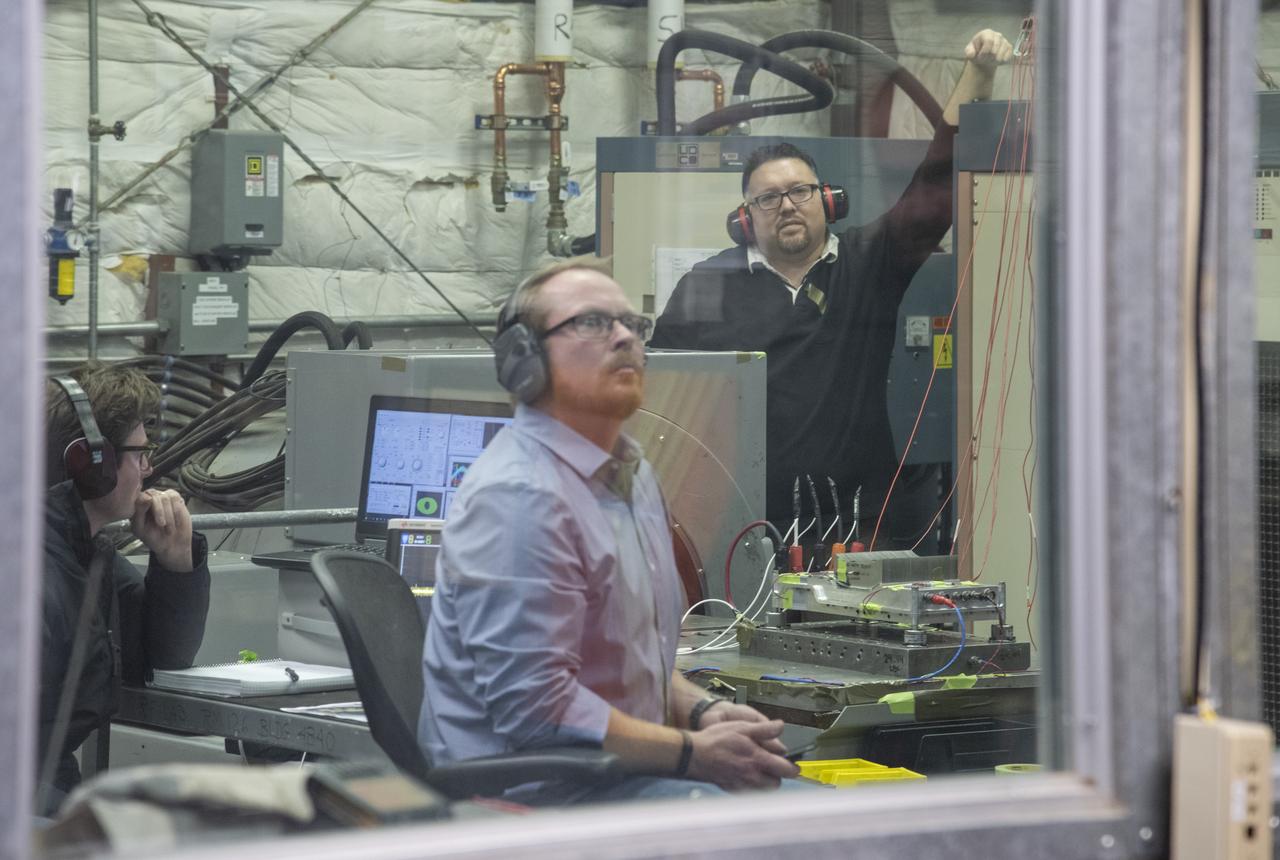
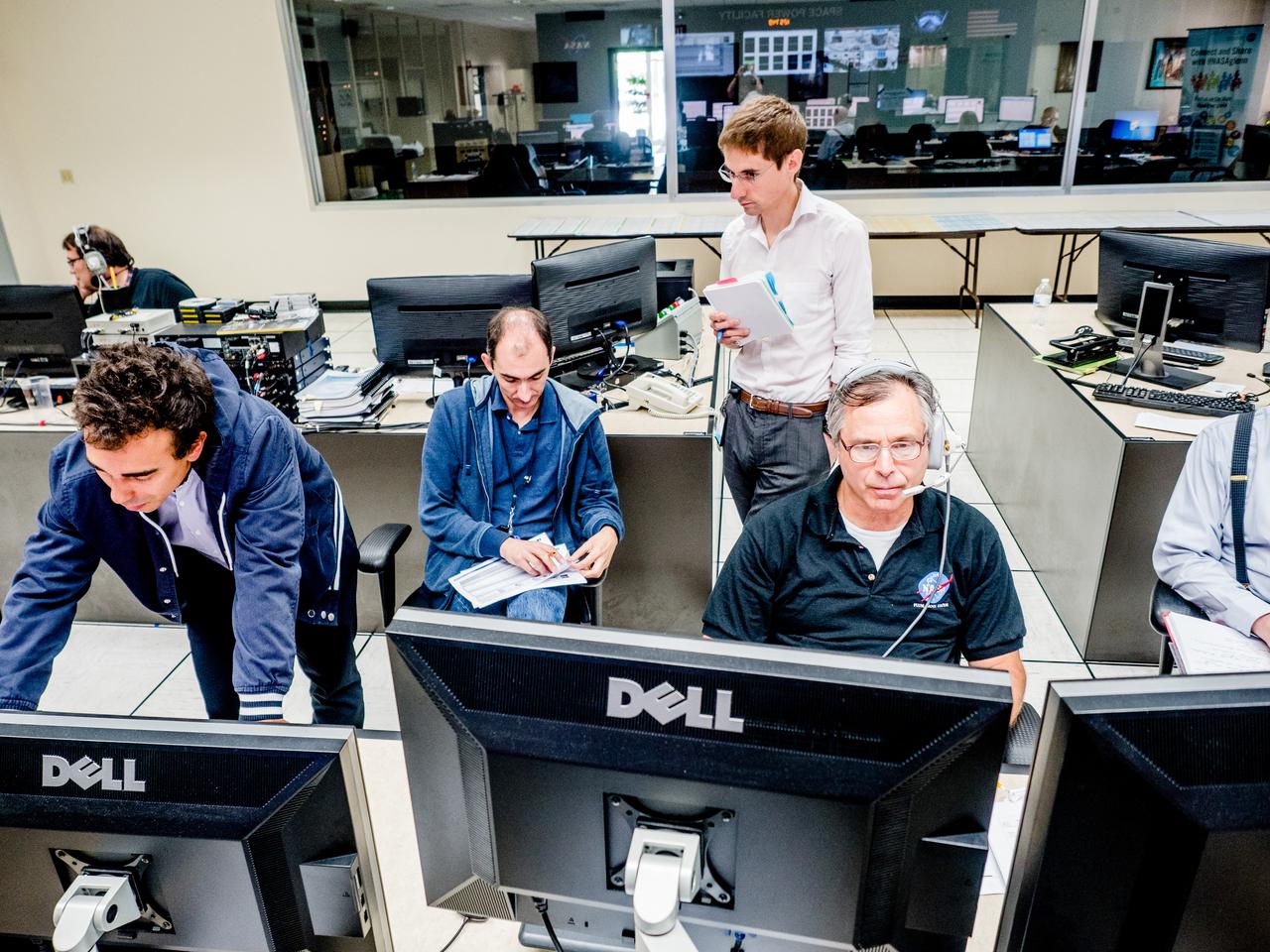
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker seated at the table monitors data collected during a sway test on the Ares I-X launch vehicle. The test is simulating conditions the rocket could experience during rollout to Launch Pad 39B, wind conditions at the pad and first-stage ignition. During the test, vibrations are mechanically induced into the rocket by four hydraulic shakers and a sway is manually introduced for lateral motion to measure the vehicle's response. A total of 44 accelerometers are installed on the flight test vehicle that required more than 27,000 feet of cable. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
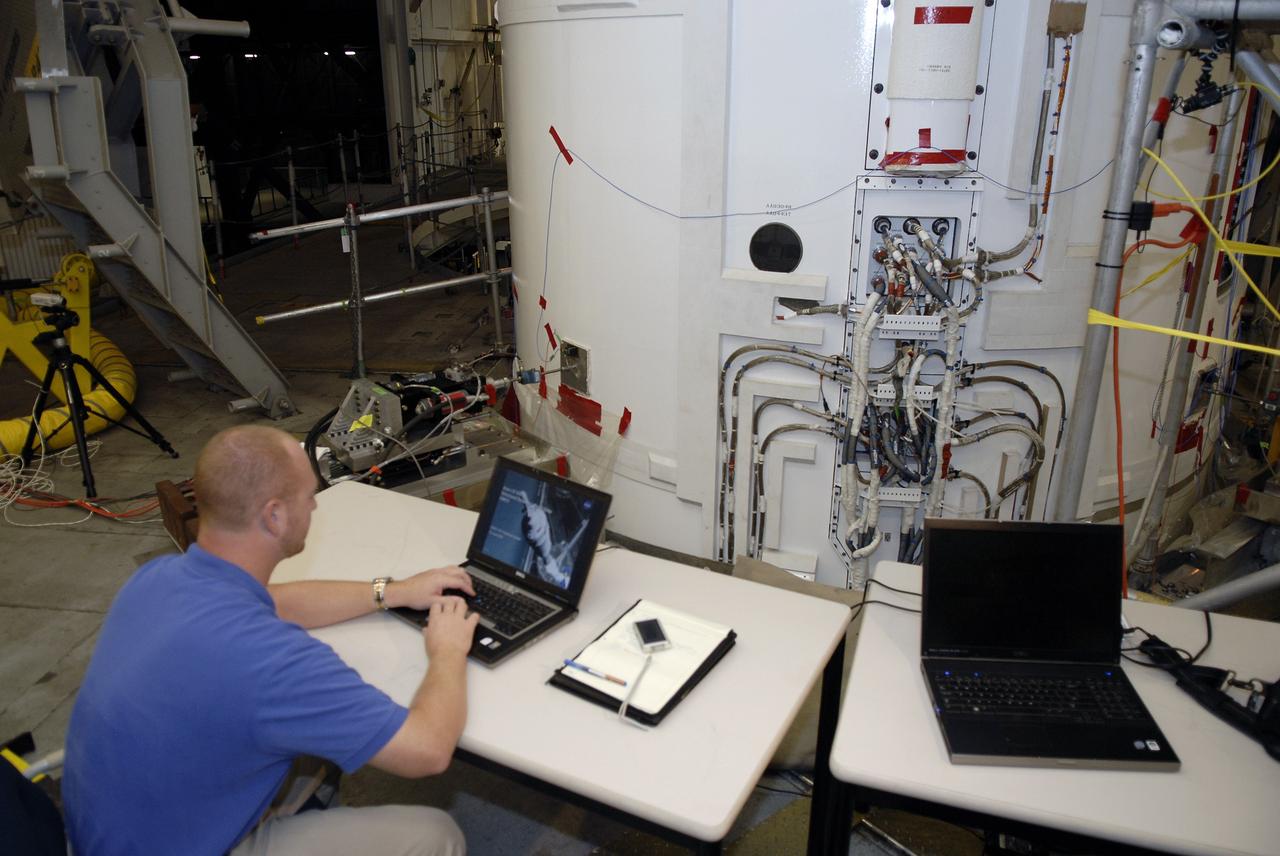

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker seated at the table monitors data collected during a sway test on the Ares I-X launch vehicle. The test is simulating conditions the rocket could experience during rollout to Launch Pad 39B, wind conditions at the pad and first-stage ignition. During the test, vibrations are mechanically induced into the rocket by four hydraulic shakers and a sway is manually introduced for lateral motion to measure the vehicle's response. A total of 44 accelerometers are installed on the flight test vehicle that required more than 27,000 feet of cable. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
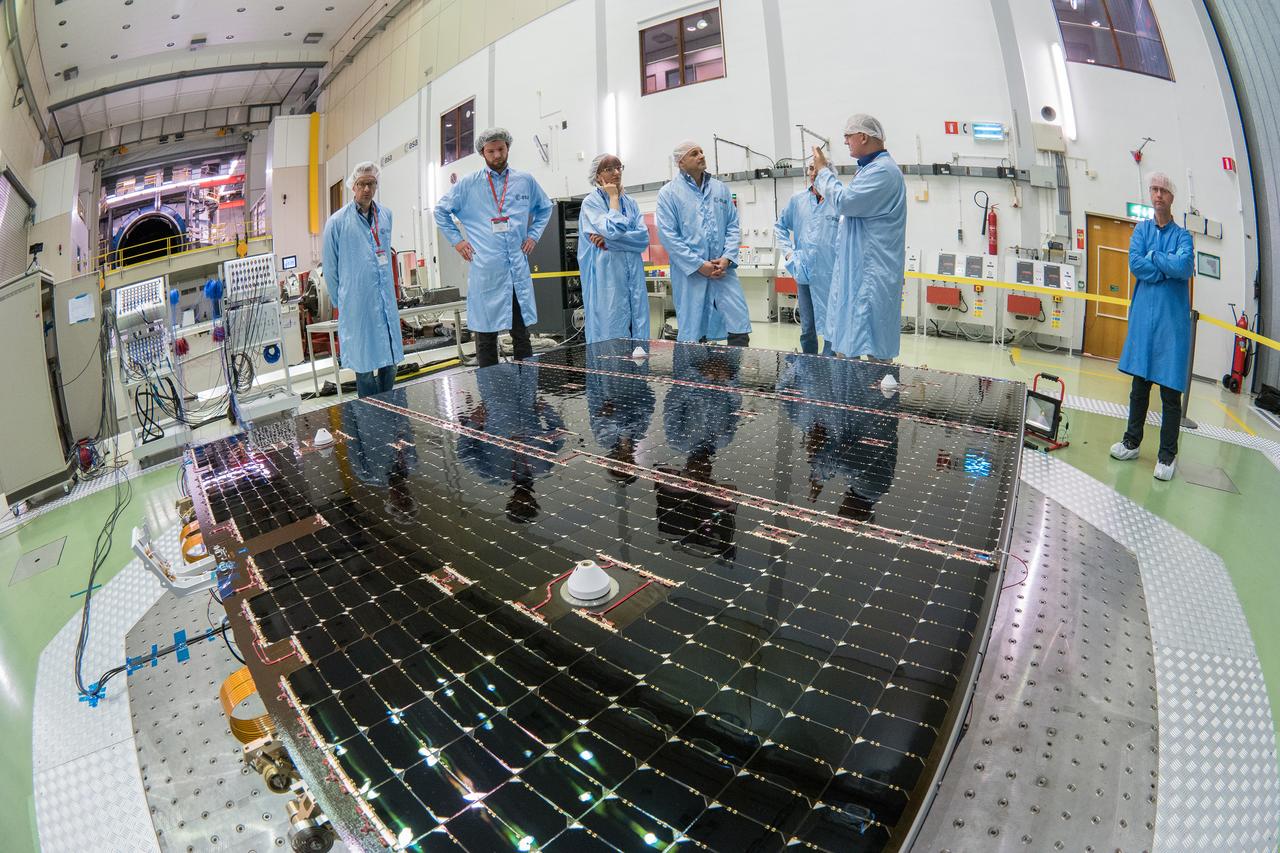

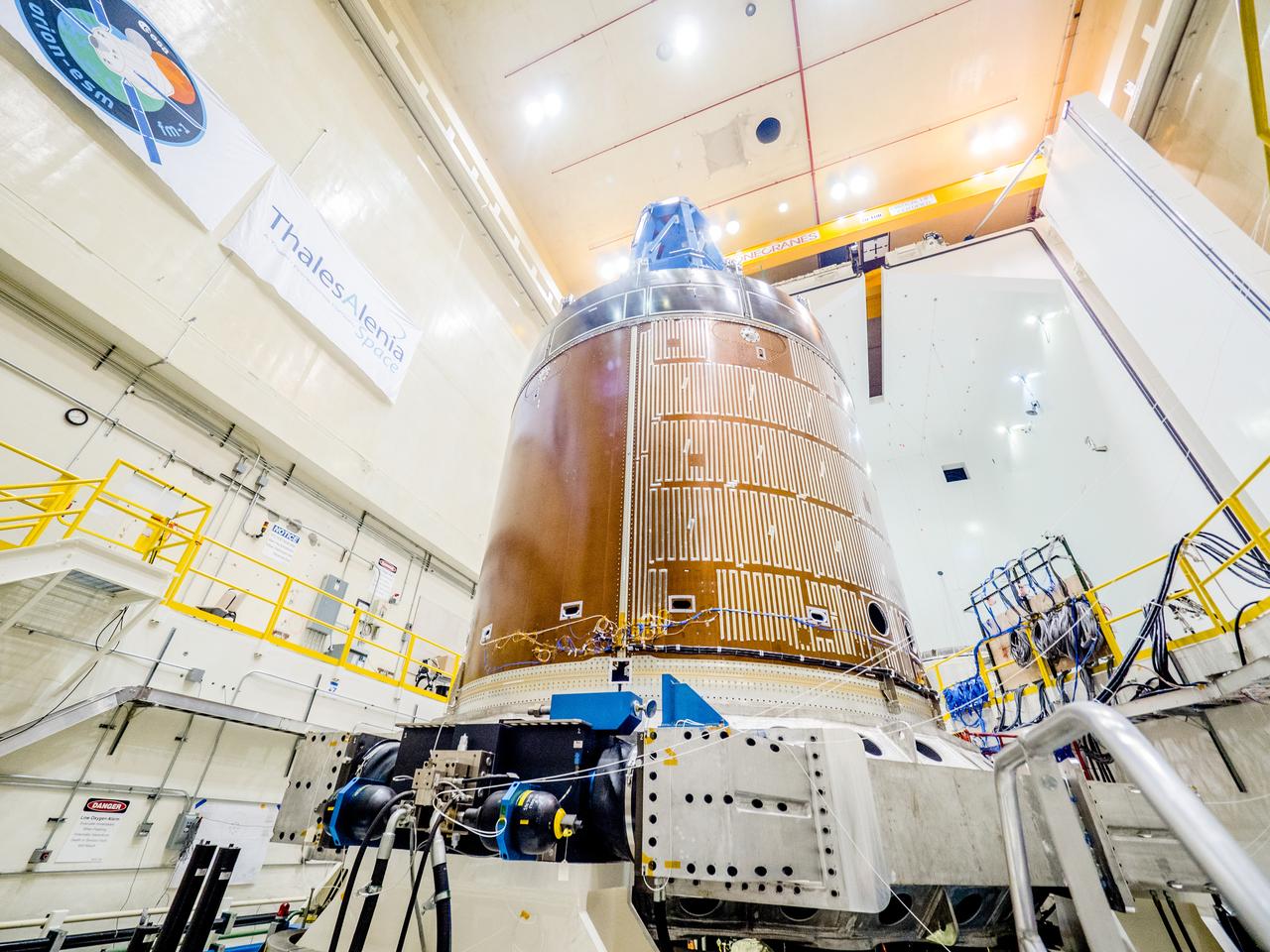
The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.

The solar arrays that will provide electricity to the Orion spacecraft were put through launch-day paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands to verify that they can handle the rigours of the trip around the Moon... .The wings are seen here on April 11, 2018, on the shaking table that vibrates with the full force of a rumbling rocket. They were also placed in front of enormous speakers that recreate the harsh conditions they can expect on launch day. The solar arrays passed with flying colours... .The wings will be tested on how they deploy before shipping to Bremen, Germany, for integration with the European service module. ESA’s contribution to the Orion mission will provide power, propulsion, water, and air... .The first mission will take Orion around the Moon without astronauts. The solar panels will be folded inside the rocket fairing, once released from NASA’s Space Launch System rocket they will unfold and rotate towards the Sun to start delivering power... .With solar wings tested and fuel tanks installed, Orion is one step closer to its maiden voyage.