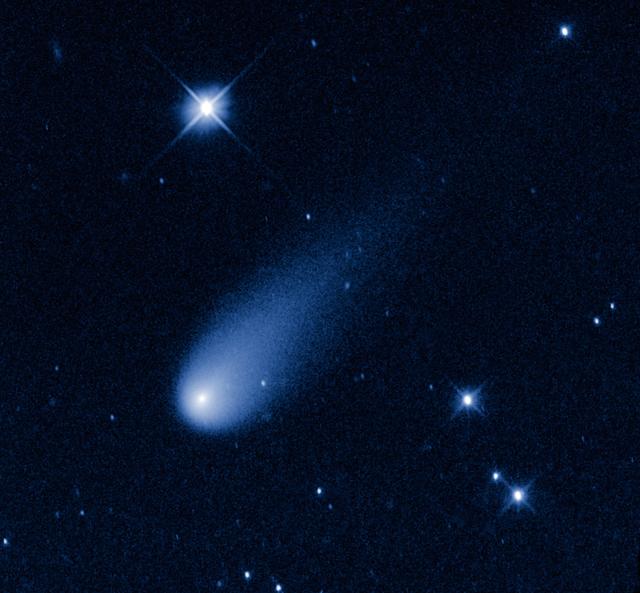

Superficially resembling a skyrocket, Comet ISON is hurtling toward the Sun at a whopping 48,000 miles per hour. Its swift motion is captured in this image taken May 8, 2013, by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. At the time the image was taken, the comet was 403 million miles from Earth, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Unlike a firework, the comet is not combusting, but in fact is pretty cold. Its skyrocket-looking tail is really a streamer of gas and dust bleeding off the icy nucleus, which is surrounded by a bright, star-like-looking coma. The pressure of the solar wind sweeps the material into a tail, like a breeze blowing a windsock. As the comet warms as it moves closer to the Sun, its rate of sublimation will increase. The comet will get brighter and the tail grows longer. The comet is predicted to reach naked-eye visibility in November. The comet is named after the organization that discovered it, the Russia-based International Scientific Optical Network. This false-color, visible-light image was taken with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scienti
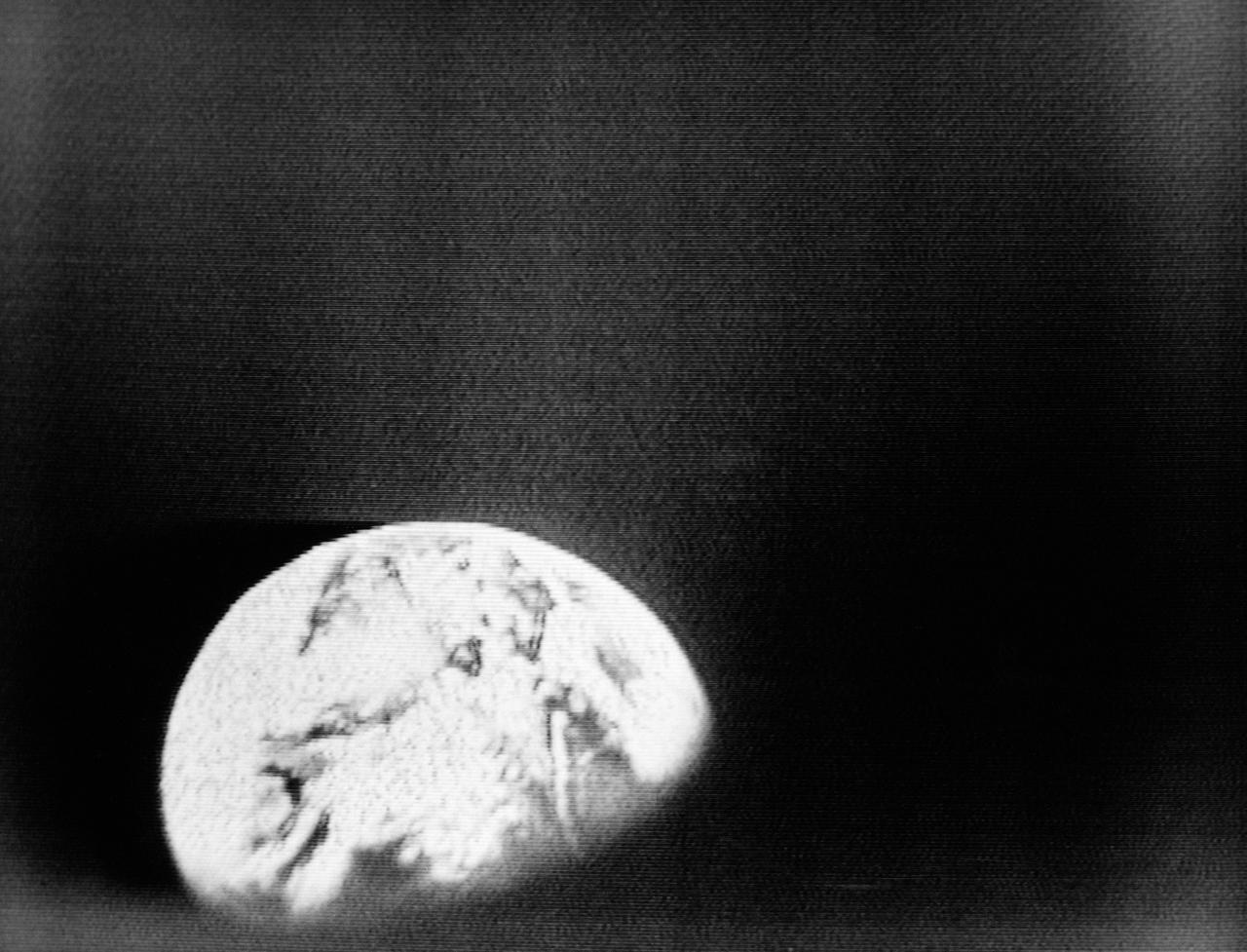

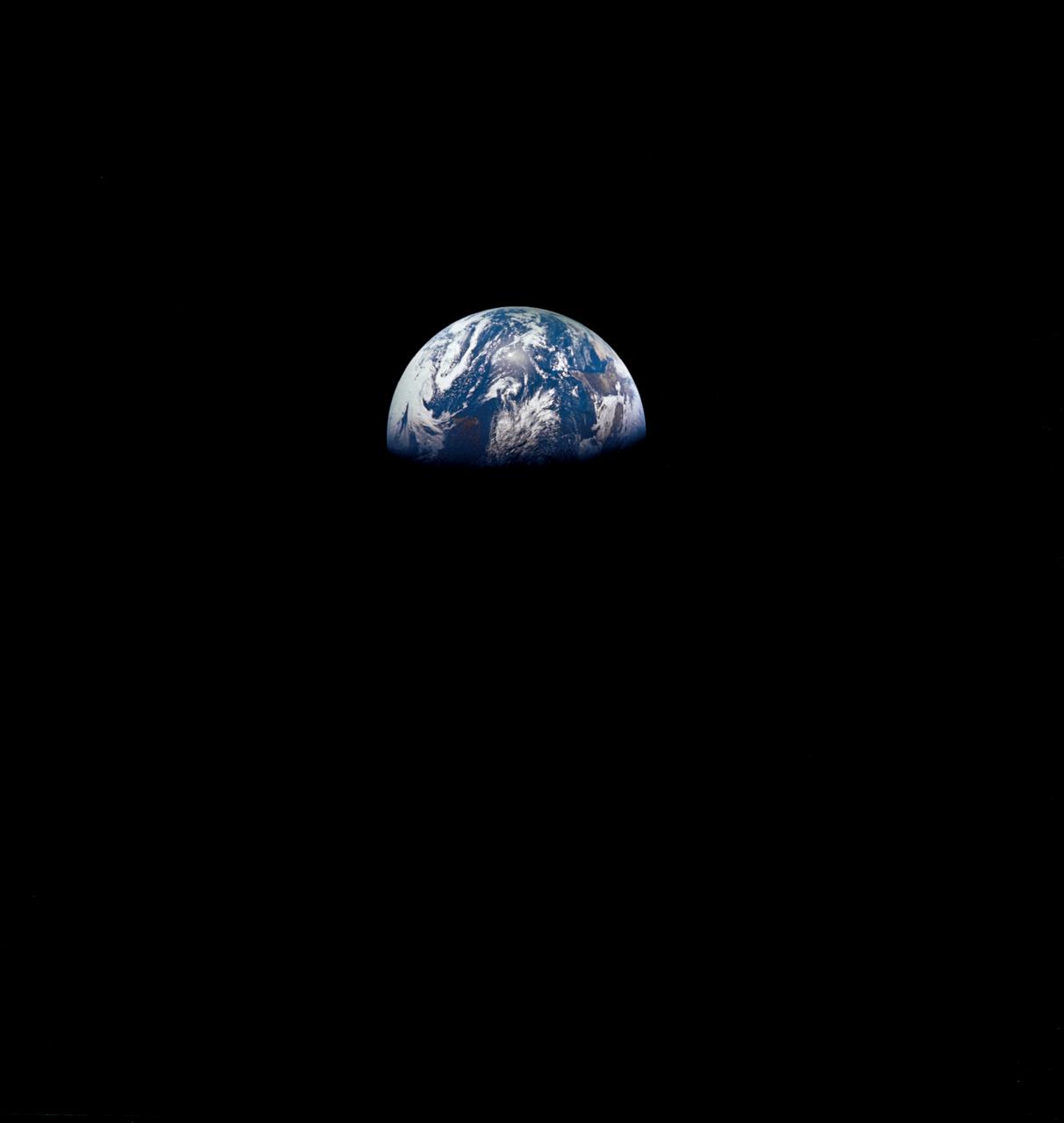
S68-55808 (23 Dec. 1968) --- This spectacular view of Earth was transmitted back from space during the second live television transmission from the Apollo 8 spacecraft on the third day of its journey toward the moon. This view is looking through a spacecraft window. At the time of this TV transmission (at 2 p.m. CST), Apollo 8 was traveling on its trans-lunar course at about 3,254 feet per second, and was some 176,533 miles from Earth.
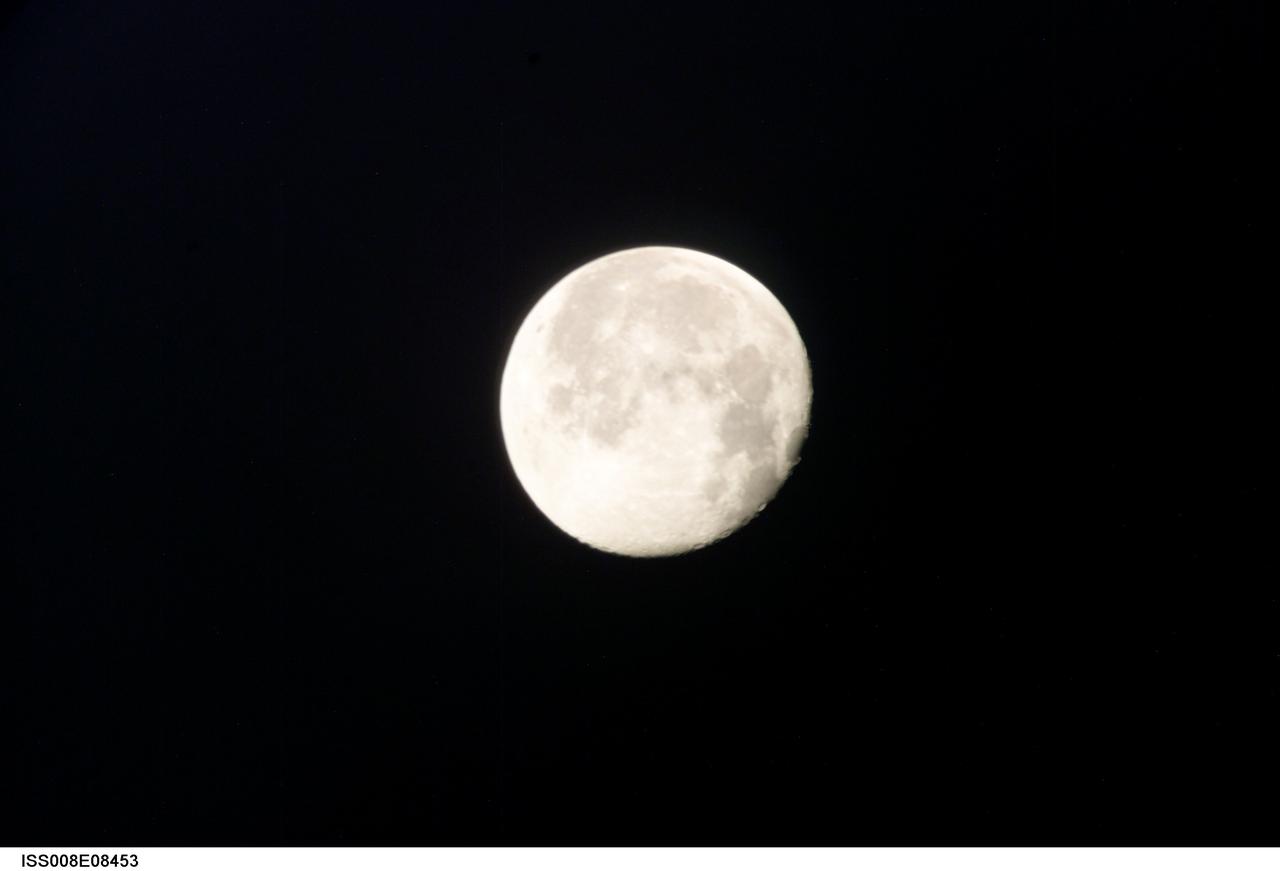

ISS008-E-08453 (10 December 2003) --- This view of a full moon was photographed by one of the Expedition 8 crewmembers aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
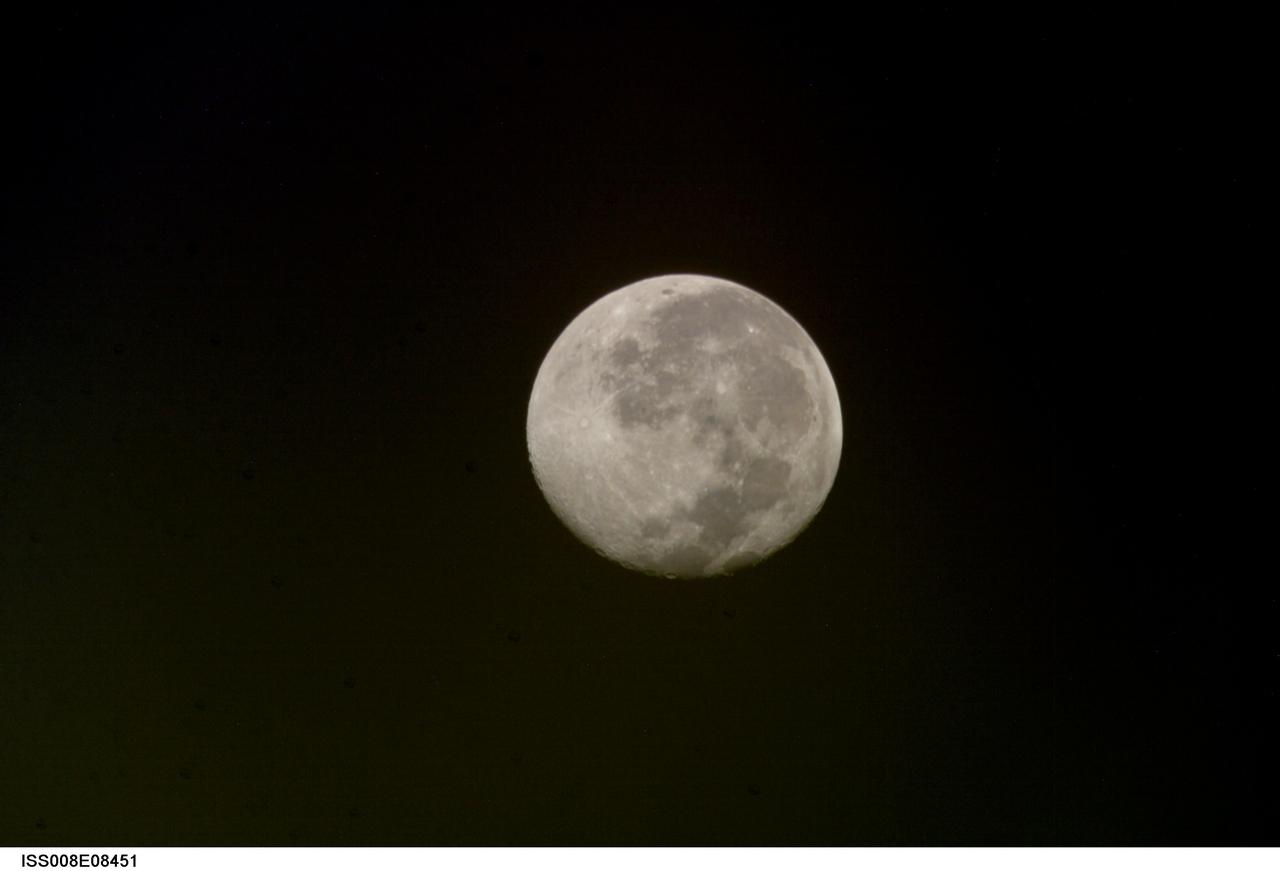

ISS008-E-08451 (10 December 2003) --- This view of a full moon was photographed by one of the Expedition 8 crewmembers aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
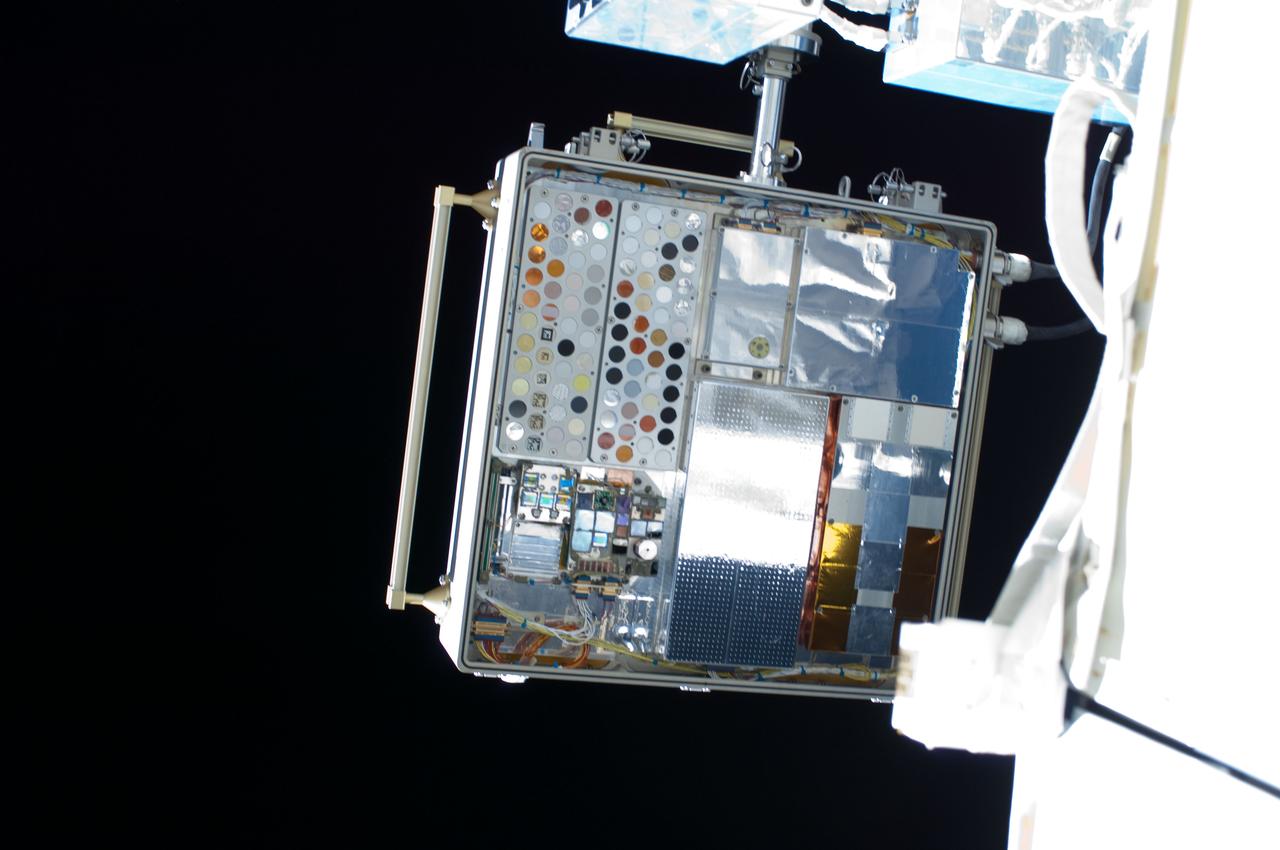

iss028e016106 (7/12/2011) --- View of a Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8) installed on the starboard truss. The Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8) tests various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. The payload container is mounted so one side faces the Earth and the other faces space.
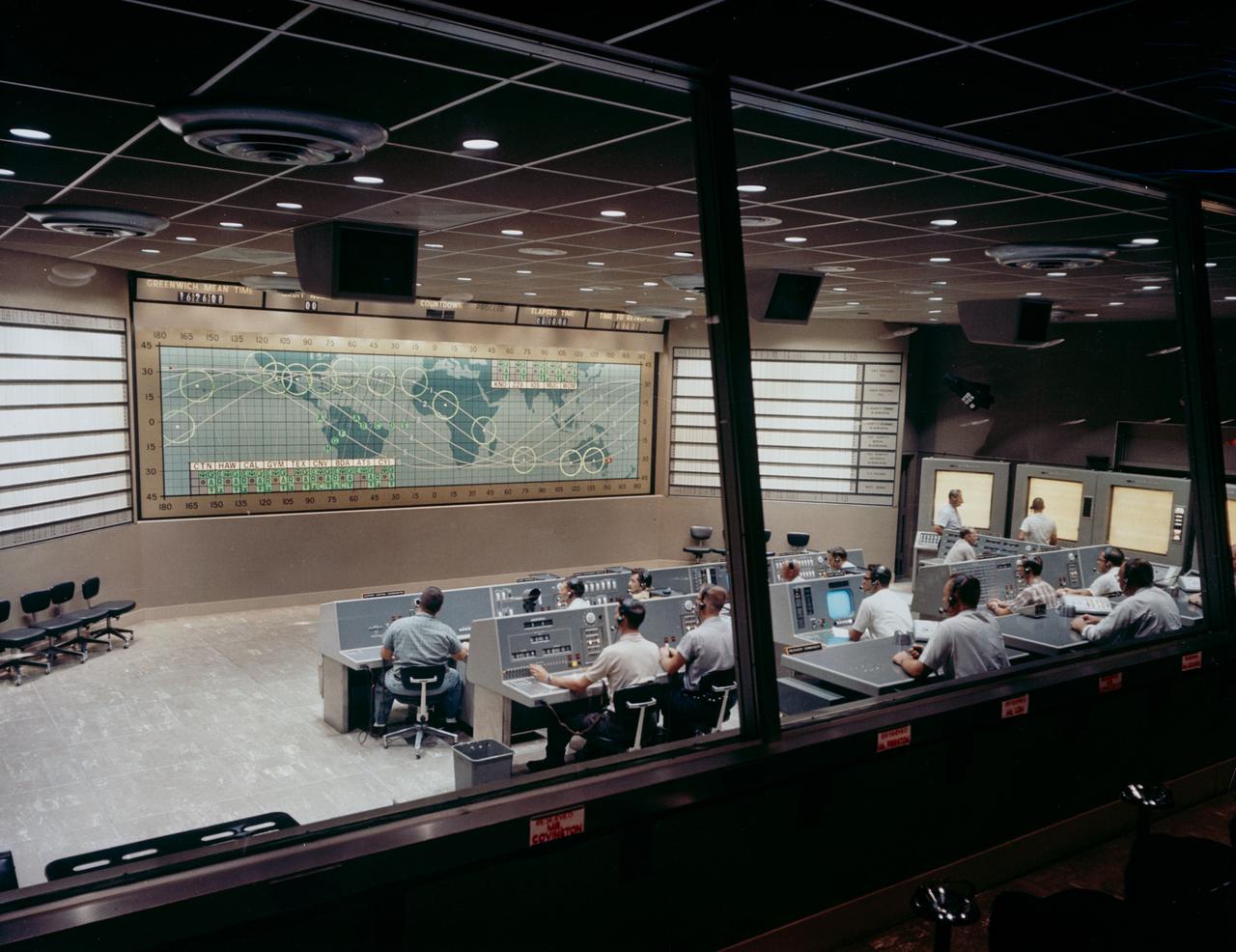

S62-05139 (1962) --- View of Mercury Control Center prior to the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) flight of the Sigma 7. Photo credit: NASA
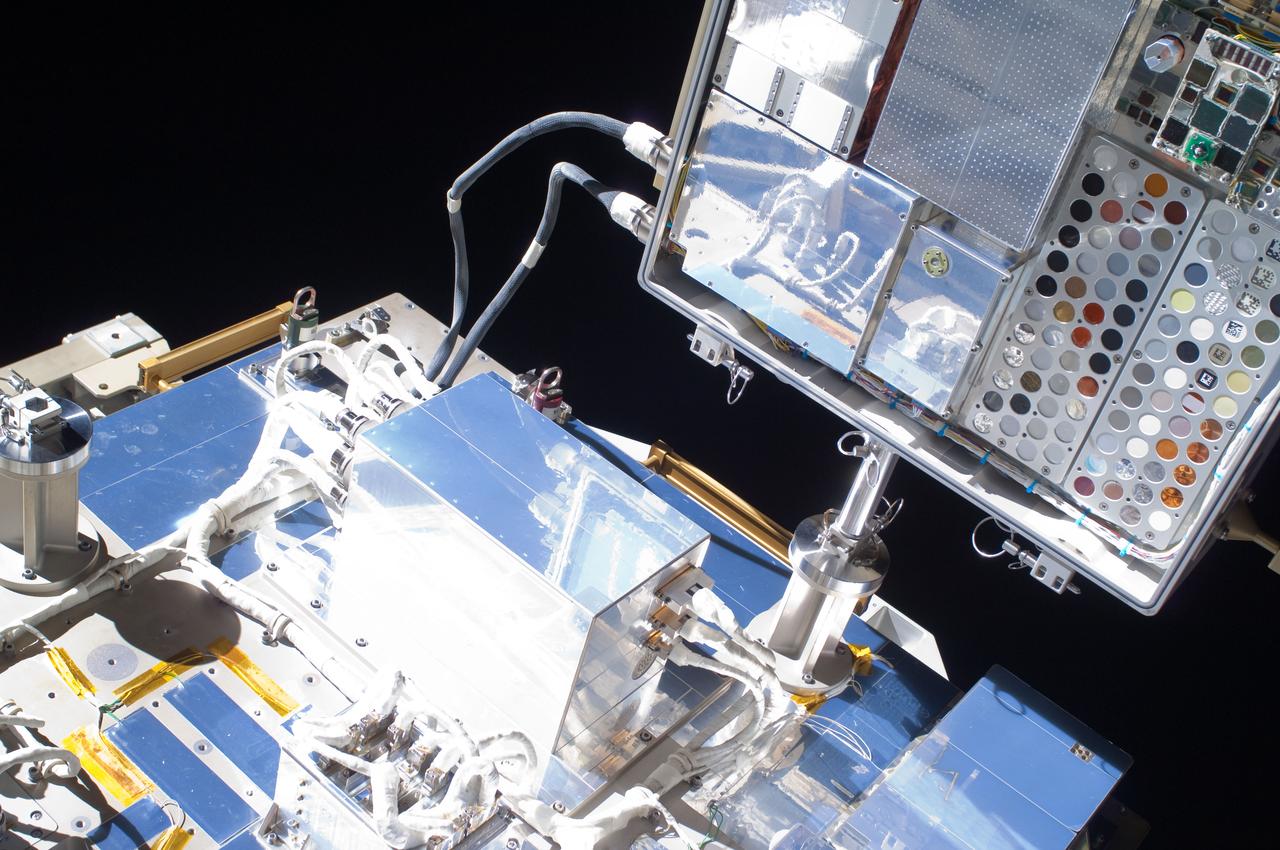

iss027e034948 (5/20/2011) --- Close-up view of Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) 8 and ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier-2 (ELC-2) taken during MISSE 8 installation. Image was taken by Extravehicular crewmember 1 (EV1) during Expedition 27 / STS-134 Extravehicular Activity 1 (EVA 1).
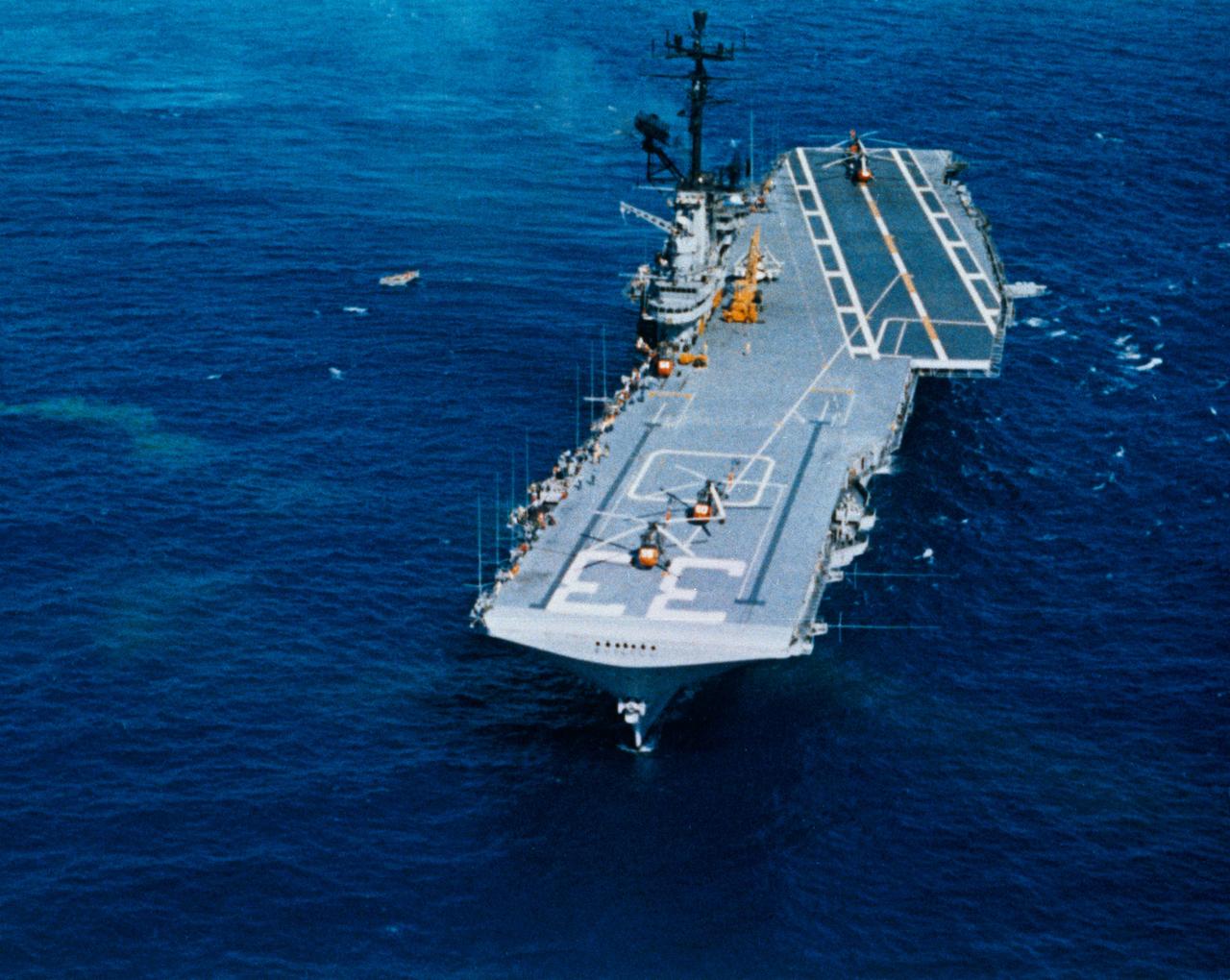

S62-09048 (3 Oct. 1962) --- Aerial view of the USS Kearsarge, recovery ship for the Mercury-Atlas 8 mission. Photo credit: NASA
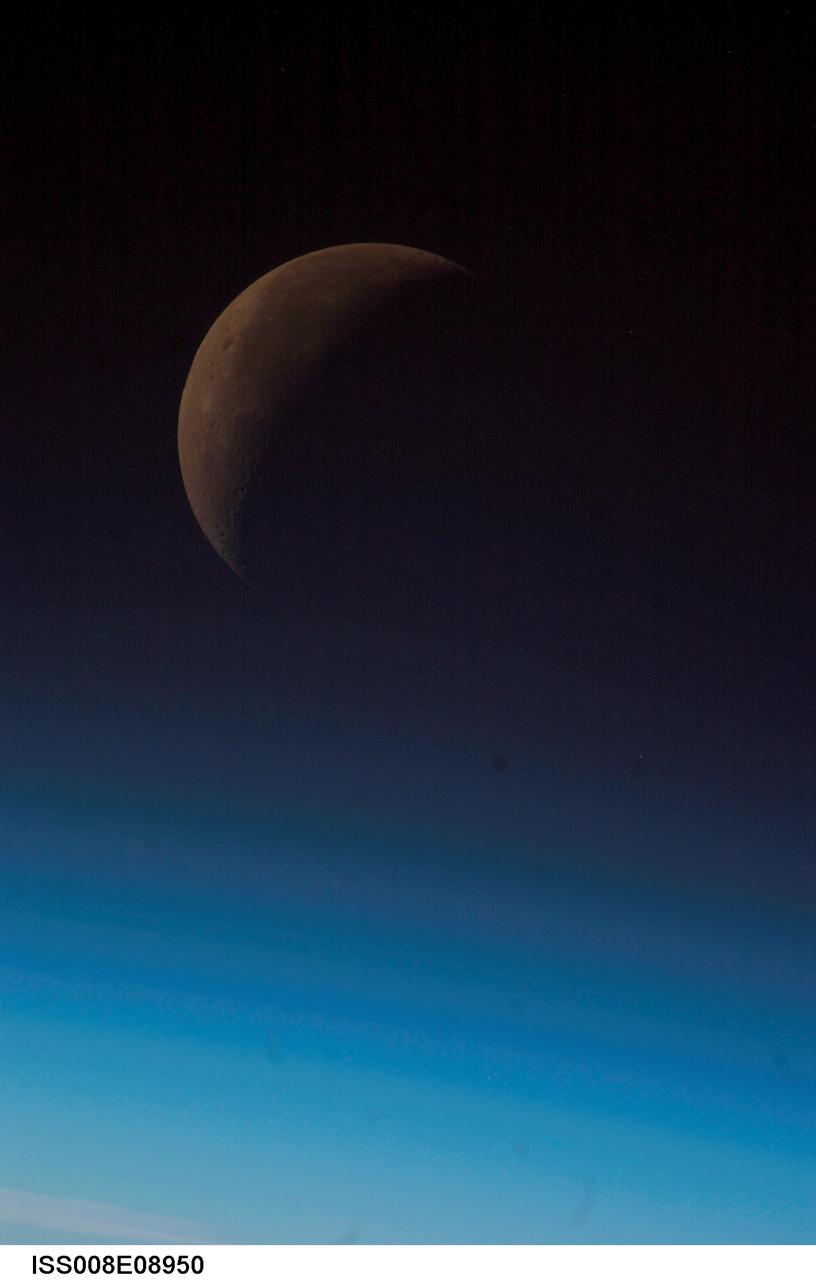

ISS008-E-08950 (December 2003) --- A partial moon is visible in this view of Earth’s horizon and airglow, photographed by an Expedition 8 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS).
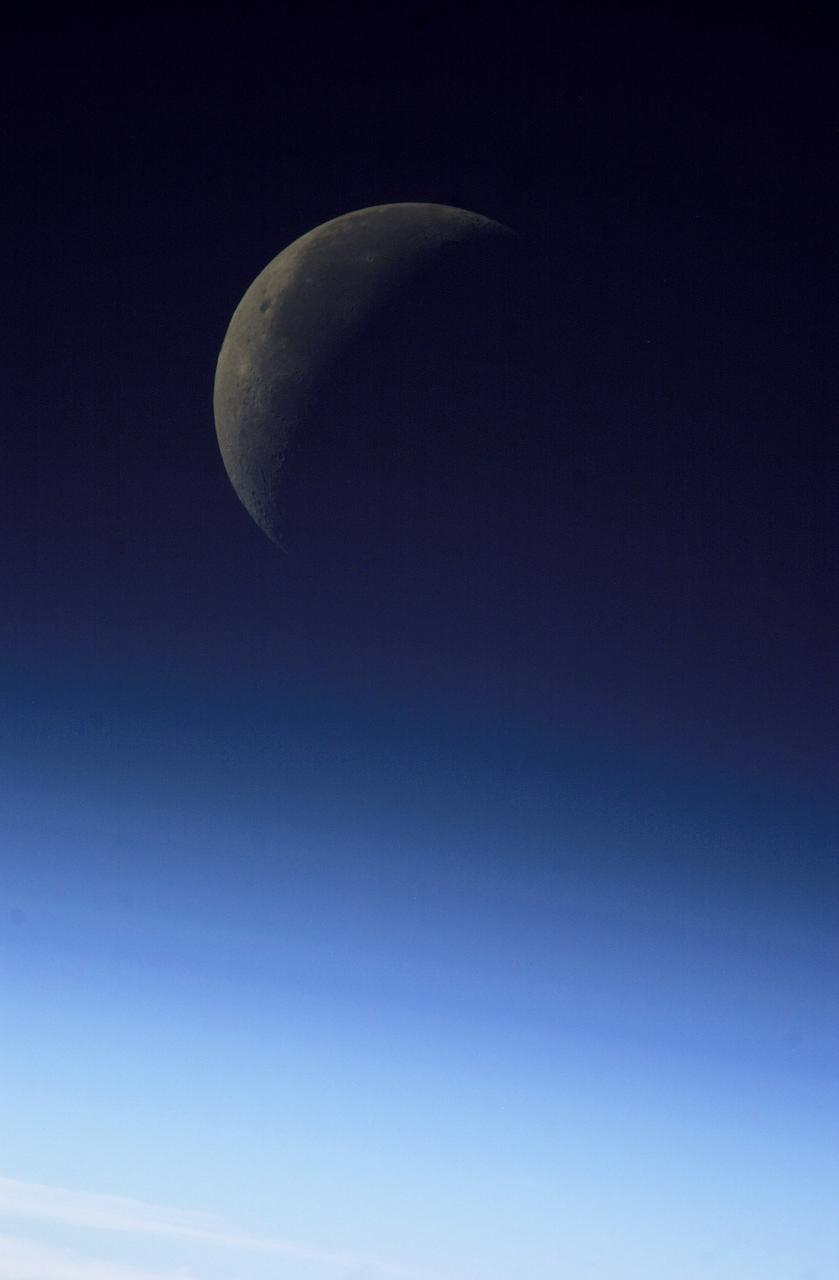

ISS008-E-08949 (December 2003) --- A partial moon is visible in this view of Earth’s horizon and airglow, photographed by an Expedition 8 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS).

<b>Join NASA's Google+ Hangout on Friday, December 20th 2:00 - 3:00 PM (EST) at <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/18S2TbC" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/18S2TbC</a> </b> It was 45 years ago, on December 24, 1968 when Apollo 8 astronauts captured 'Earthrise' – the first color photograph of Earth taken by a person in lunar orbit. NASA announces a new simulation of the events leading to the creation of 'Earthrise,' one of the iconic photographs of the 20th Century – Earth seen from the moon captured by the crew of Apollo 8. This new simulation allows anyone to virtually ride with the astronauts and experience the awe they felt at the vista in front of them. Apollo 8 Commander Frank Borman and crew members William A. Anders and James A. Lovell photographed the stunning scene as their spacecraft orbited the moon on December 24, 1968. The new computer simulation was created using data from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, spacecraft and includes details not seen in the previous visualization released last year. Participants in this Hangout include: * John Keller, project scientist for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter project * Ernie Wright, project lead with the Scientific Visualization Studio at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center * Andrew Chaikin, space historian, author of the book A Man on the Moon "This will also be the first time we've released a video that's synchronized with the onboard audio recording of the astronauts,", says Ernie Wright. "The new visualization tells us not only what time the photos were taken, but also exactly which way the spacecraft was pointing and therefore which window each photo was taken from." Earthrise is the cover photo of TIME's Great Images of the 20th Century and is among photos on the cover of LIFE's 100 Photographs That Changed the World. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
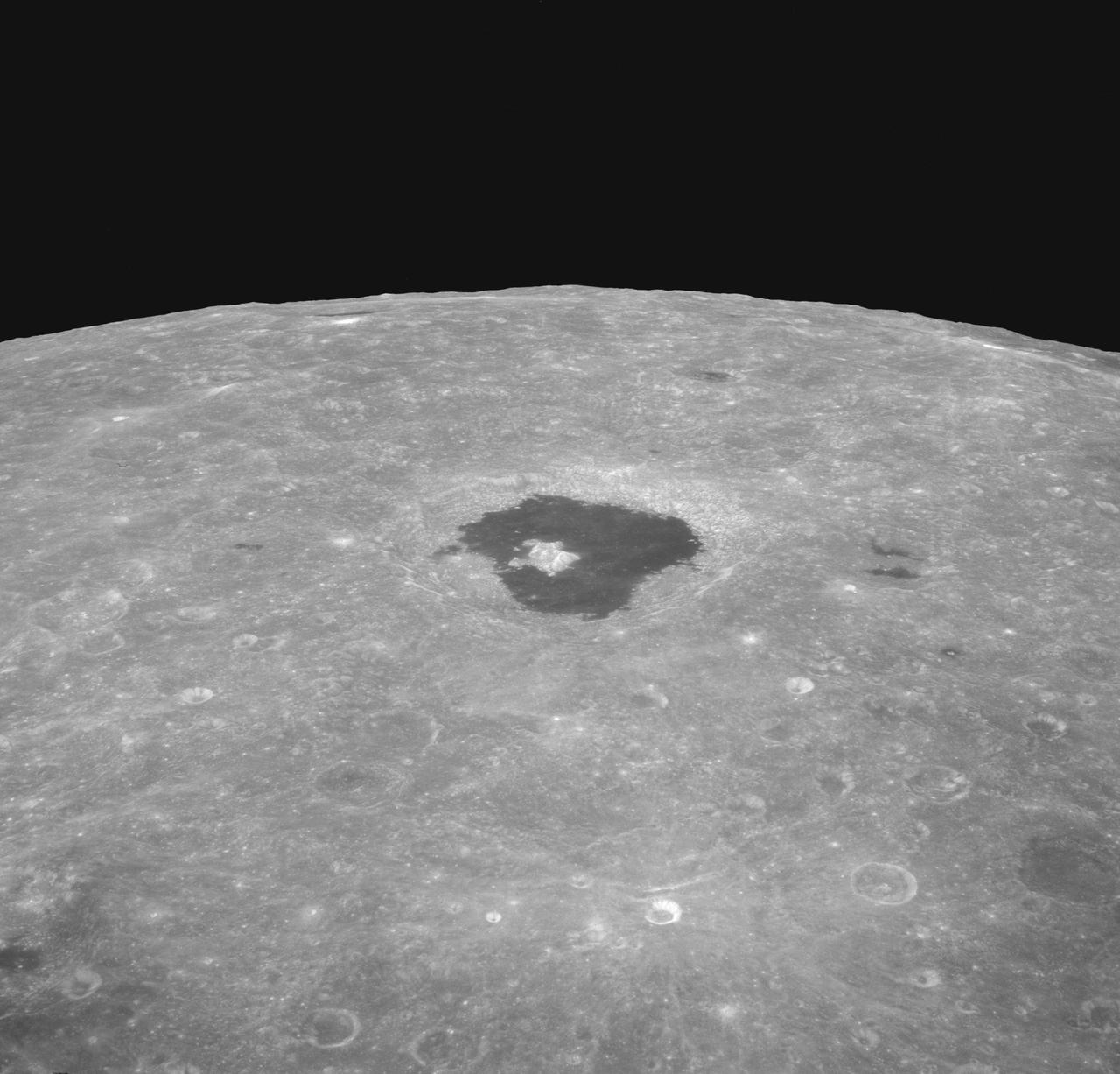

AS08-12-2196 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- An oblique view from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking eastward across the lunar surface from about 115 degrees east longitude to the horizon near 180 degrees east longitude. The crater Tsiolkovsky in the center of the picture is 150 kilometers wide and is located at 129 degrees east longitude and 21 degrees south latitude. While in lunar orbit, Apollo 8 moved toward the camera position over the terrain along the left (north) side of this photograph.
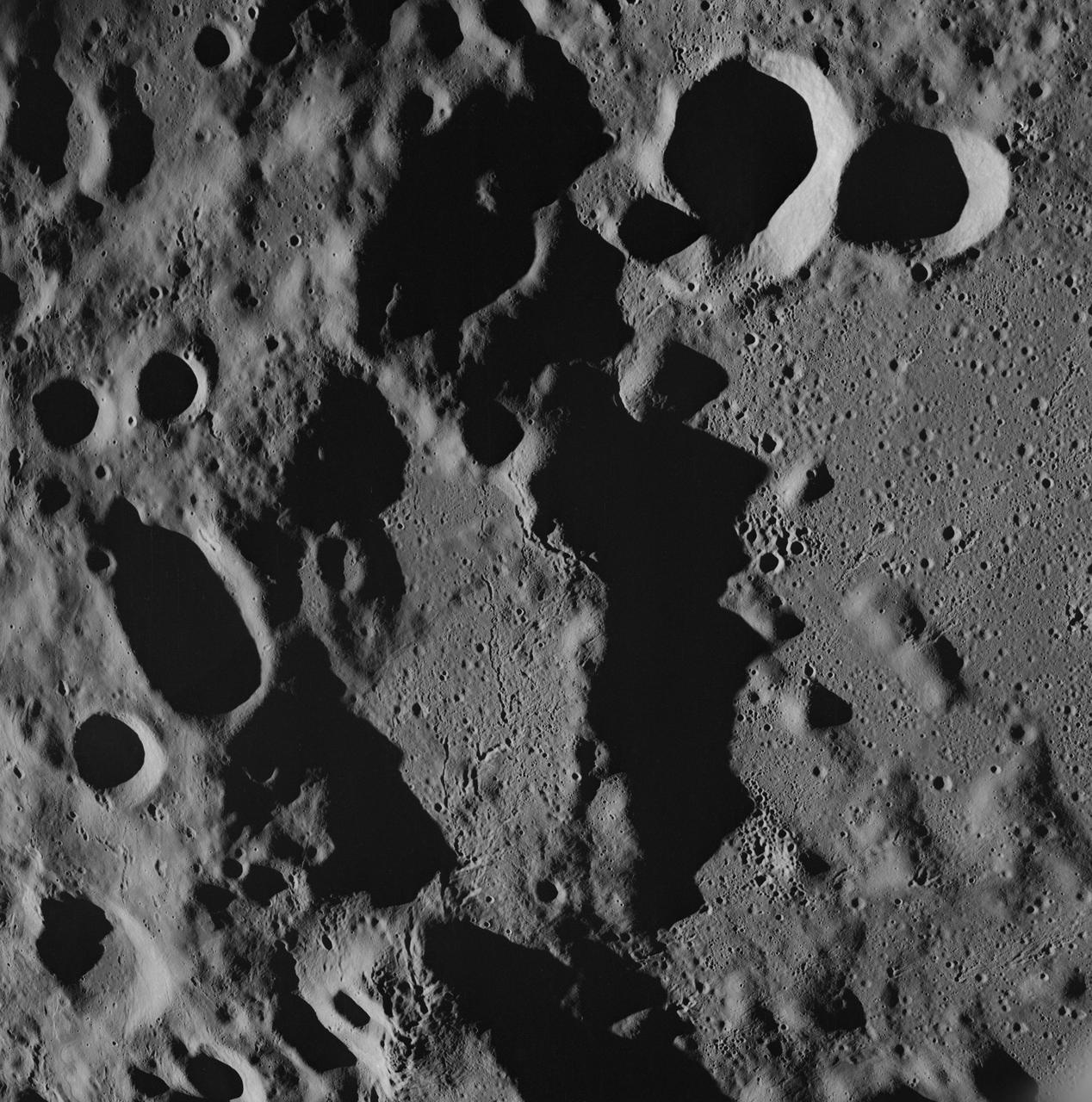

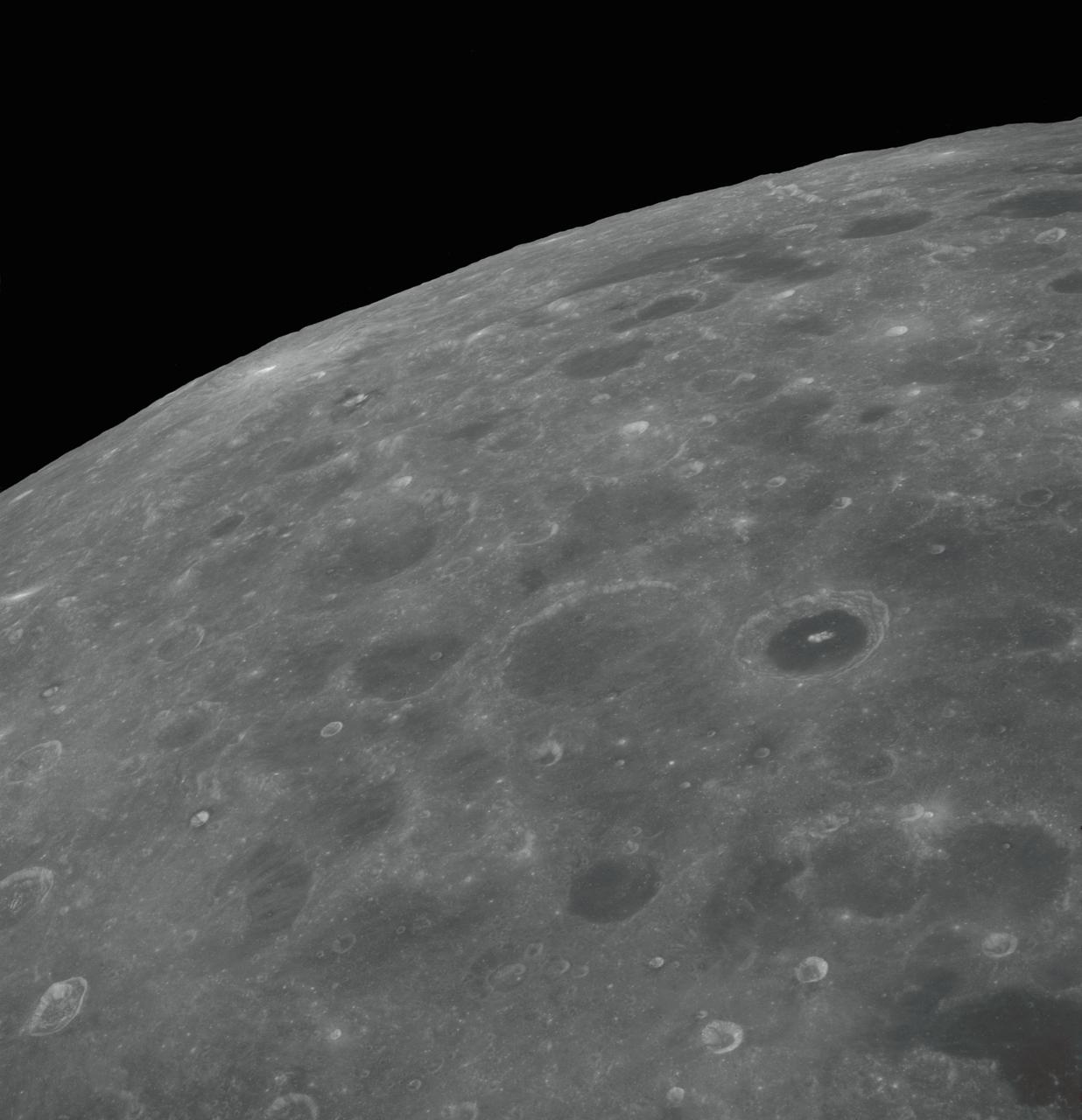
AS08-17-2670 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Near vertical view of the lunar farside as photographed from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. The center of the picture is located approximately at 162 degrees west longitude and 6 degrees south latitude.
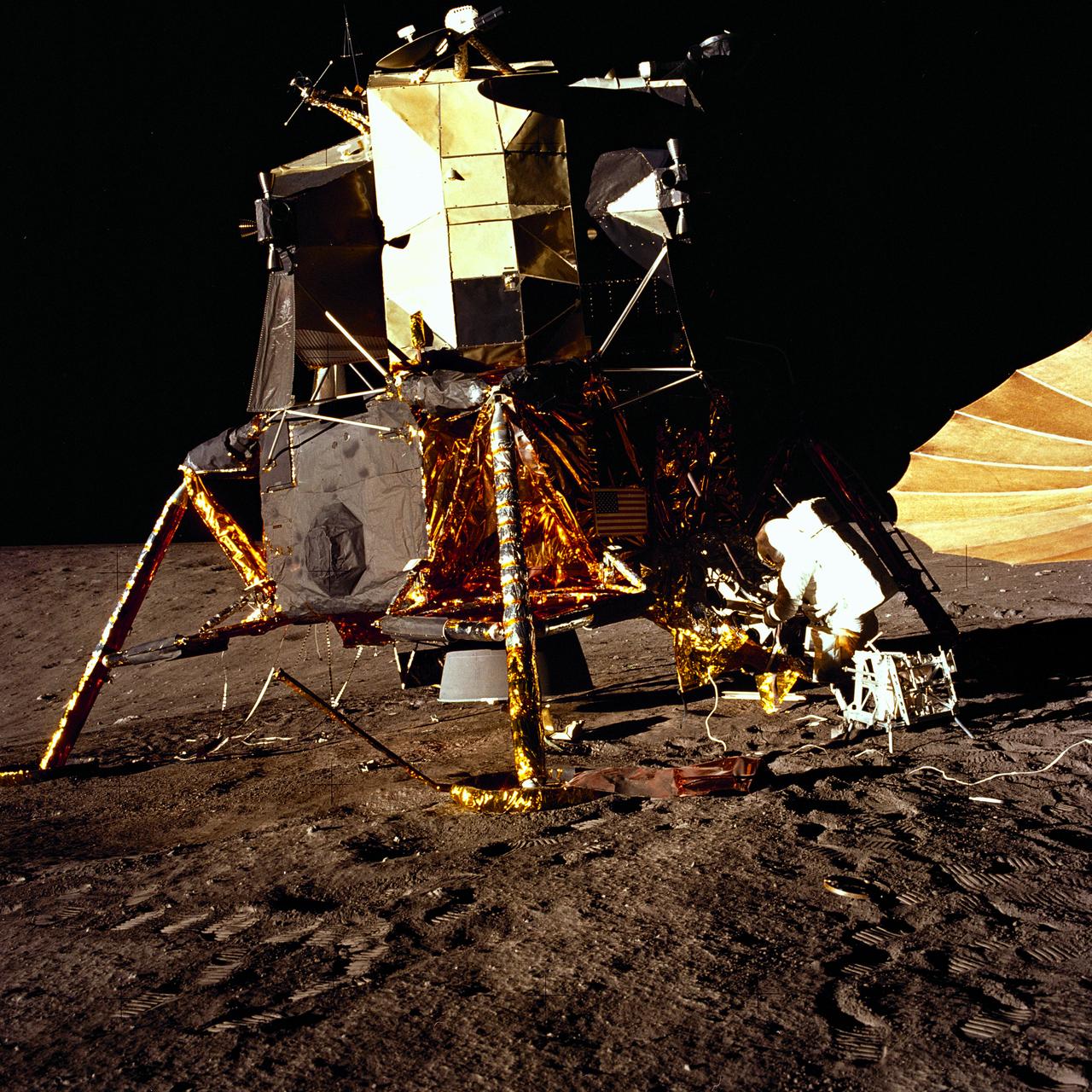

The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12, launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard Apollo 12 was a crew of three astronauts: Alan L. Bean, pilot of the Lunar Module (LM), Intrepid; Richard Gordon, pilot of the Command Module (CM), Yankee Clipper; and Spacecraft Commander Charles Conrad. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms while astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples. This is the eighth of 25 images captured by the crew in attempt to provide a 360 degree Lunar surface scene. Apollo 12 safely returned to Earth on November 24, 1969.
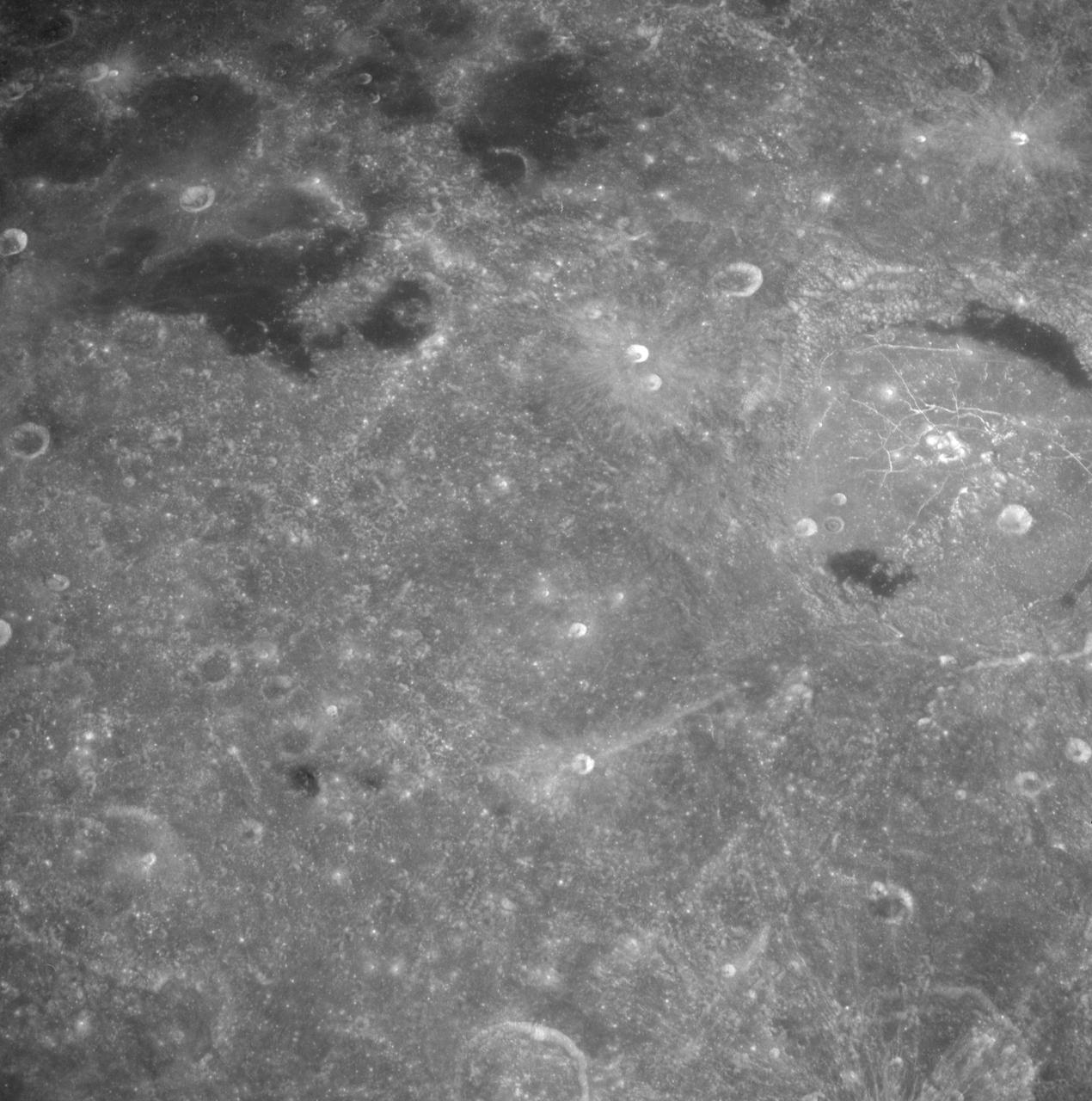

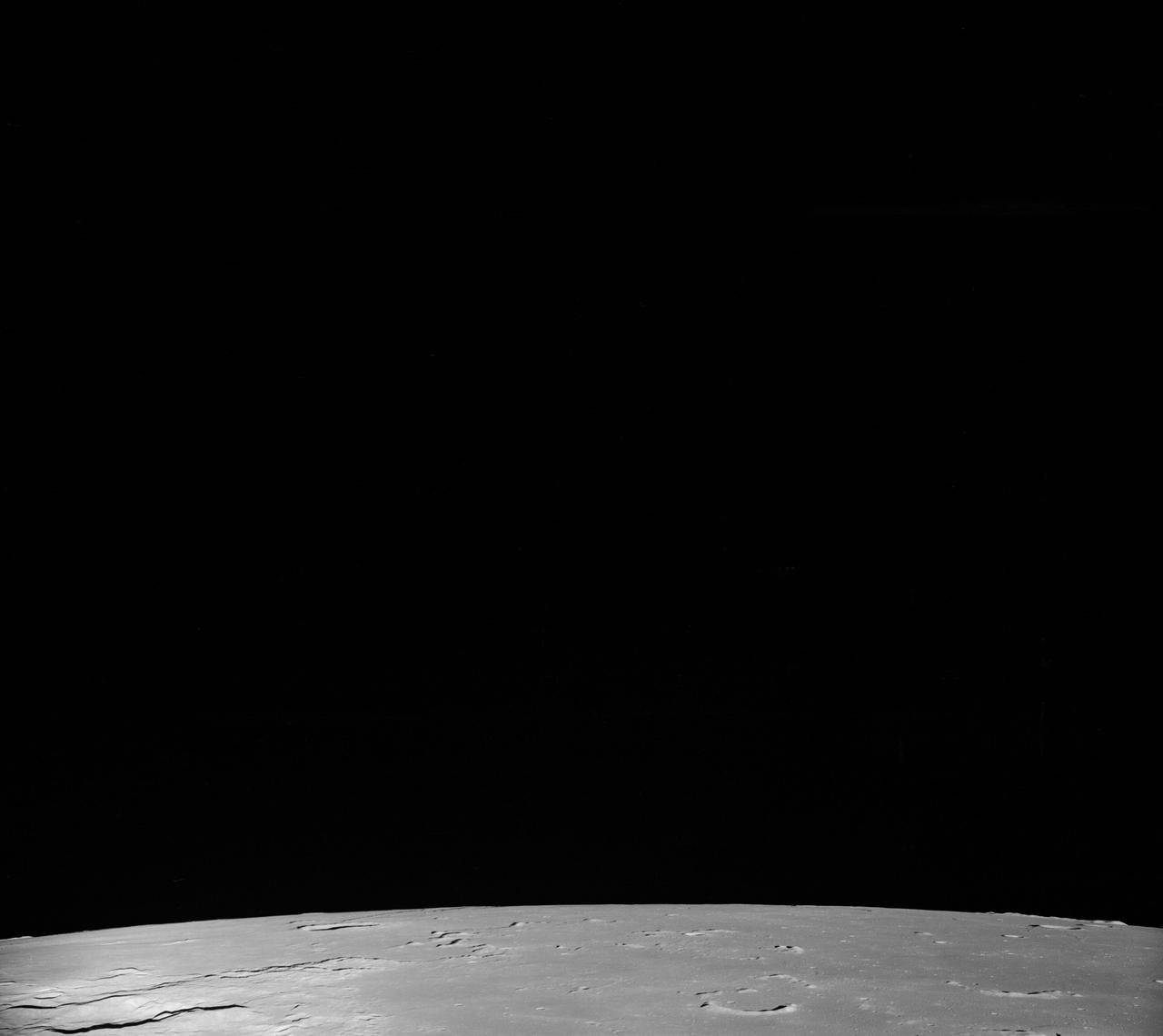
AS08-12-2193 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking southward from high altitude across the Southern Sea. (Hold picture with AS8 number in upper right corner). The bright-rayed crater near the horizon is located near 130 degrees east longitude and 70 degrees south latitude. The dark-floored crater near the middle of the right side of the photograph is about 70 kilometers (45 statute miles) in diameter. Both features are beyond the eastern limb of the moon as viewed from Earth; neither has a name.

AS08-12-2192 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking southward from high altitude across the Southern Sea. (Hold picture with AS8 number in upper right corner). The bright-rayed crater near the horizon is located near 130 degrees east longitude and 70 degrees south latitude. The dark-floored crater near the middle of the right side of the photograph is about 70 kilometers (45 statute miles) in diameter. Both features are beyond the eastern limb of the moon as viewed from Earth; neither has a name.
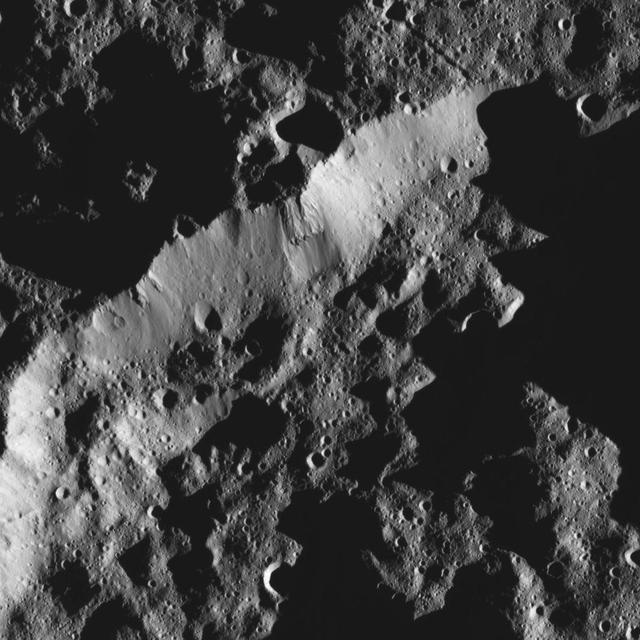

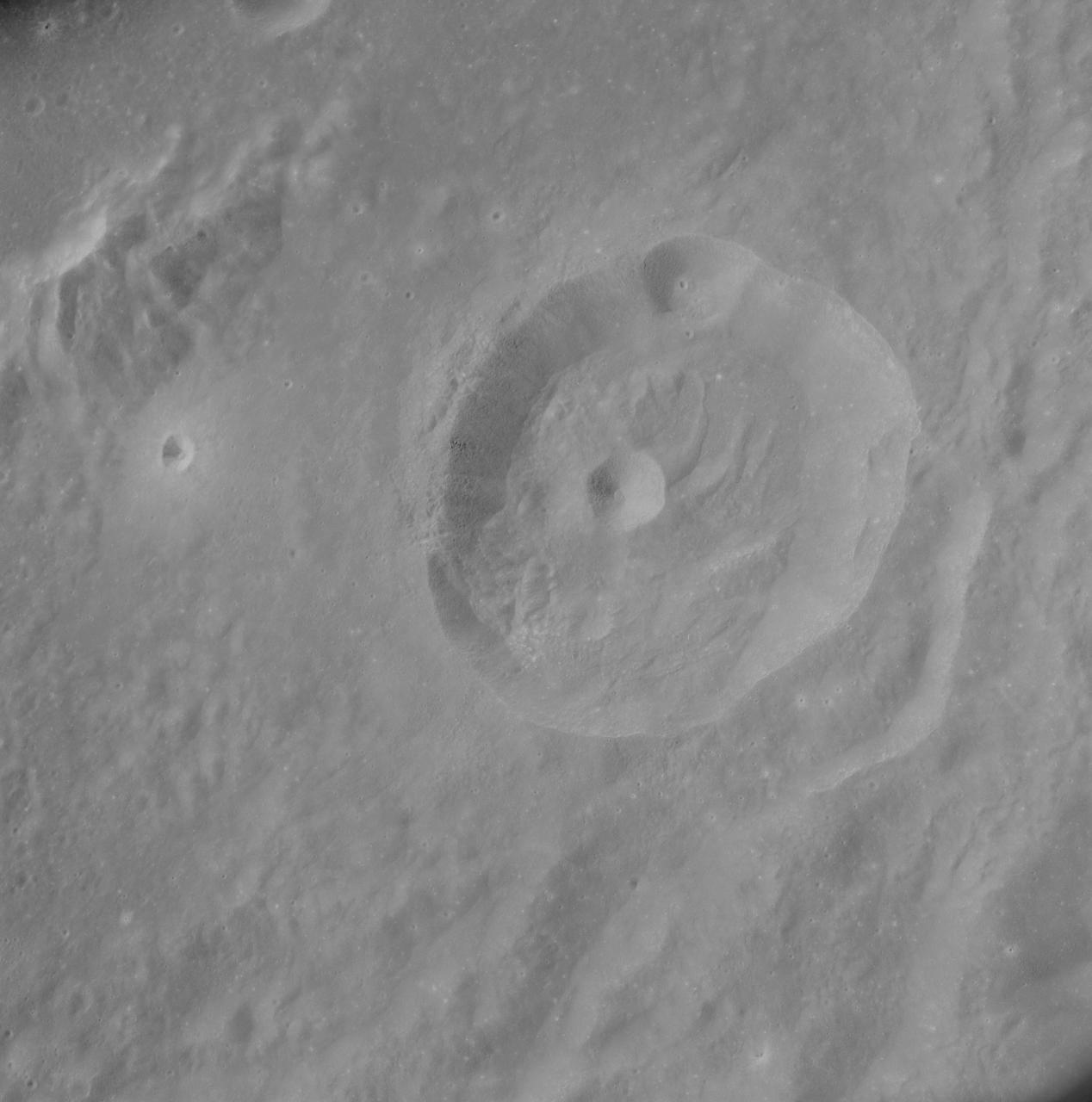
This view from NASA Dawn spacecraft shows the rim of a crater near the south pole of Ceres, taken on Feb. 8, 2016.
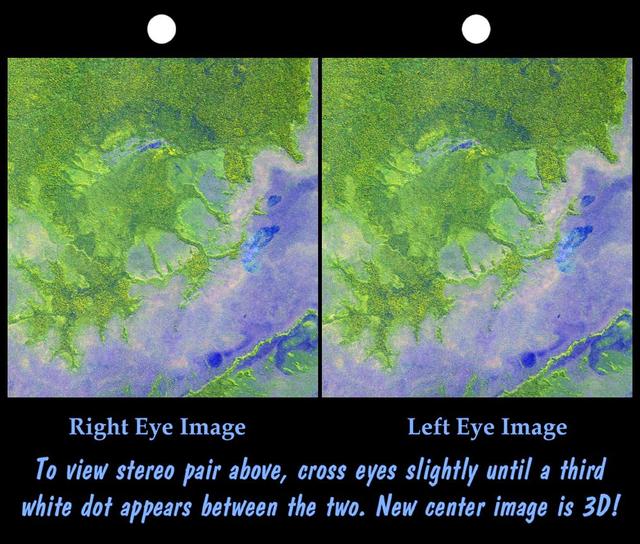
An 8-kilometer 5-mile wide crater of possible impact origin is shown in this stereoscopic view of an isolated part of the Bolivian Amazon.
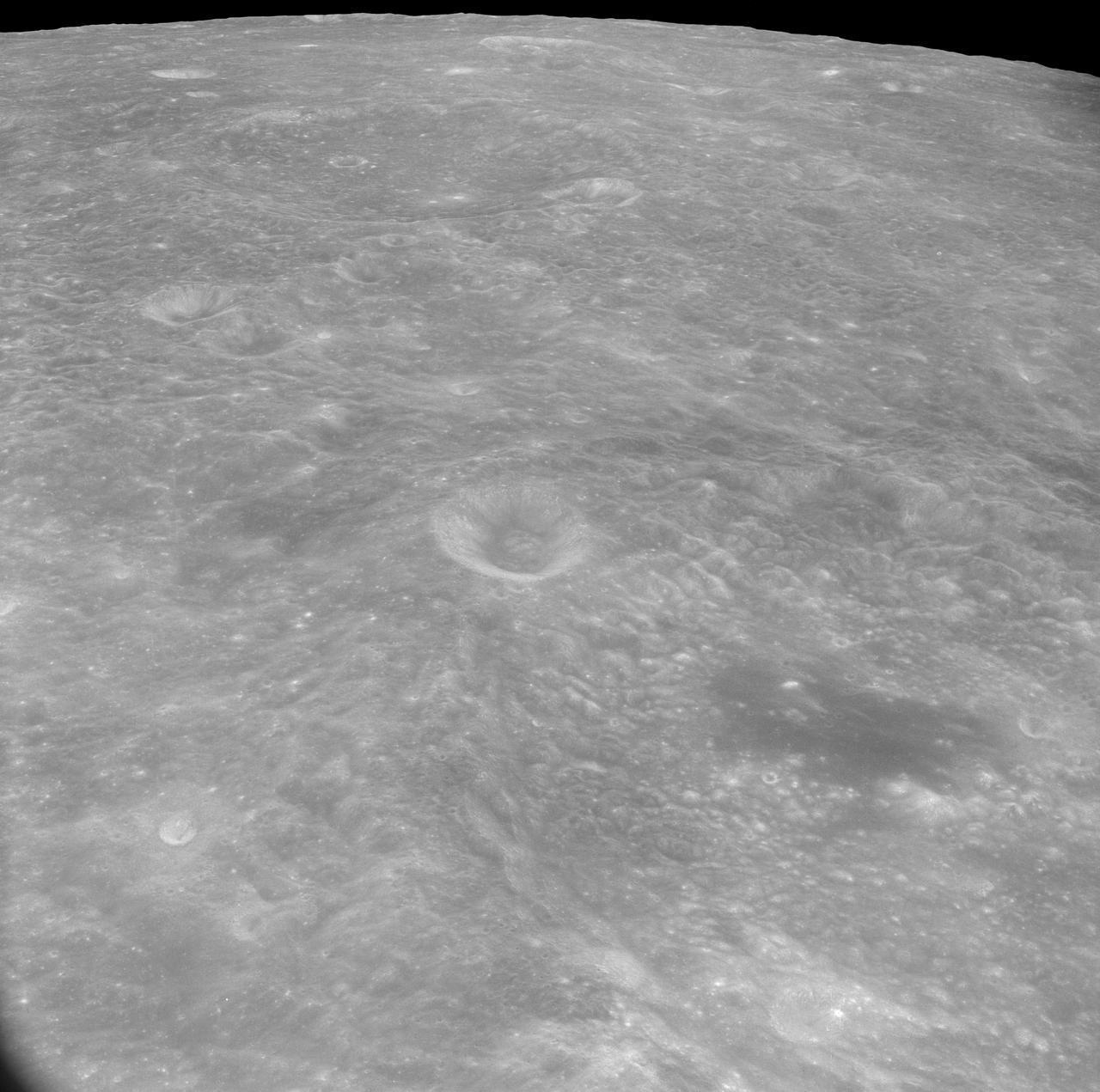

AS8-17-2744 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward showing typical lunar farside terrain. (HOLD PICTURE SO THAT DARK IRREGULAR AREA SURROUNDED BY LIGHT SPOTS IS IN THE LOWER RIGHT QUARTER). The sharp crater near the center of then scene is near 117 degrees east longitude and 5 degrees south latitude; and it is 25 kilometers (15 statute miles) in diameter. That crater is on the rim of a large crater that occupies the lower right quarter of the photograph.

AS08-17-2821 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward across the Sea of Tranquility shows Apollo Landing Site East 2 illuminated by a sun that is six to eight degrees above the eastern horizon. The landing site is on the dark gray, smooth surface of the Sea of Tranquility and north (to the right) of the bright highland terrain at the lower left corner of the photograph. The landing site is about four tenths of the distance from the left to right margin of the photograph.

AS08-17-2814 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward across the Sea of Fertility into the Sea of Tranquility shows the terrain the astronauts will see as the approach Apollo Landing Site East 2. The landing site is at the horizon about one-third of the distance from the left to the right photograph margin. The prominent crater in the highlands near the center of the picture is Secchi, about 25 kilometers (15 statute miles) in diameter.

AS08-12-2148 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of the lunar surface as photographed from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. Zero-phase bright spot. With near-vertical sun illumination, topographical detail is washed out and differences in surface brightness are accentuated. The numerous small bright-halo craters become conspicuous. A few larger craters have extremely bright inner walls that are commonly streaked by darker material. The bright glow near the conspicuous bright-walled crater is a halo that surrounds the position of the spacecraft shadow.
AS8-17-2704 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Near vertical view of the lunar farside as photographed from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. This crater, which is about 22 statute miles in diameter, is located at 167 degrees east longitude and 11 degrees south latitude. This crater is located on the eastern edge of a much larger unnamed crater which is about 90 statute miles in diameter.
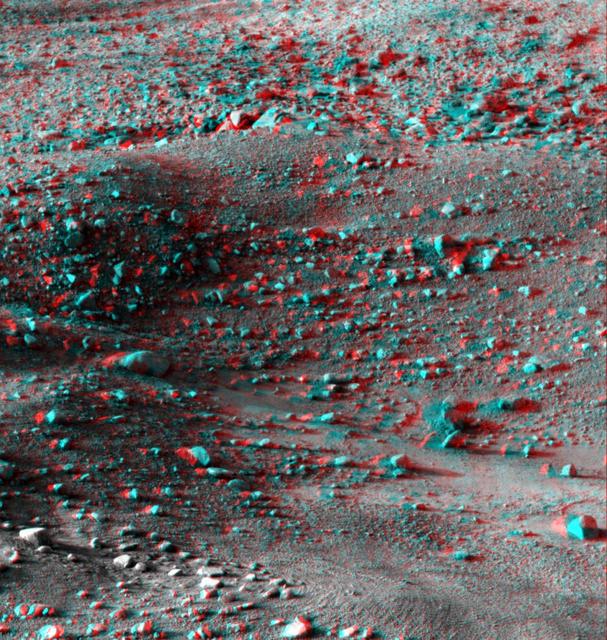

This anaglyph, acquired by NASA Phoenix Lander on Jun. 8, 2008, shows a stereoscopic 3D view of the Martian surface near the lander. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

AS8-15-2561 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of Earth as photographed by the Apollo 8 astronauts on their return trip from the moon. Note that the terminator is straighter than on the outbound pictures. The terminator crosses Australia. India is visible. The sun reflection is within the Indian Ocean.
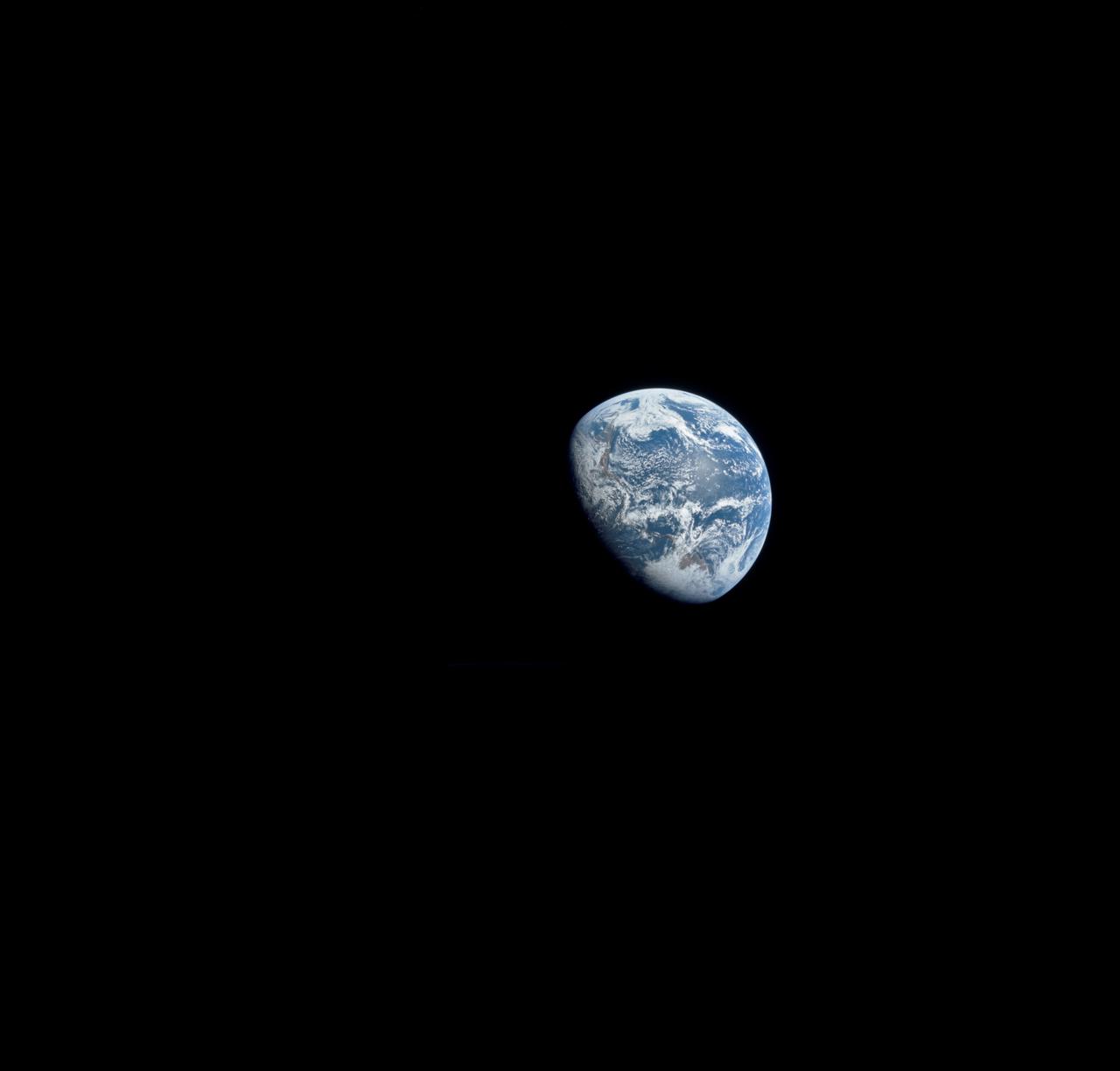

AS08-16-2596 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of Earth as photographed by the Apollo 8 astronauts during their lunar orbit mission. North is about five percent to the right of vertical. The sunset terminator crosses North and South America. Clouds cover most of the United States. Only the desert southwest and Florida are clear.
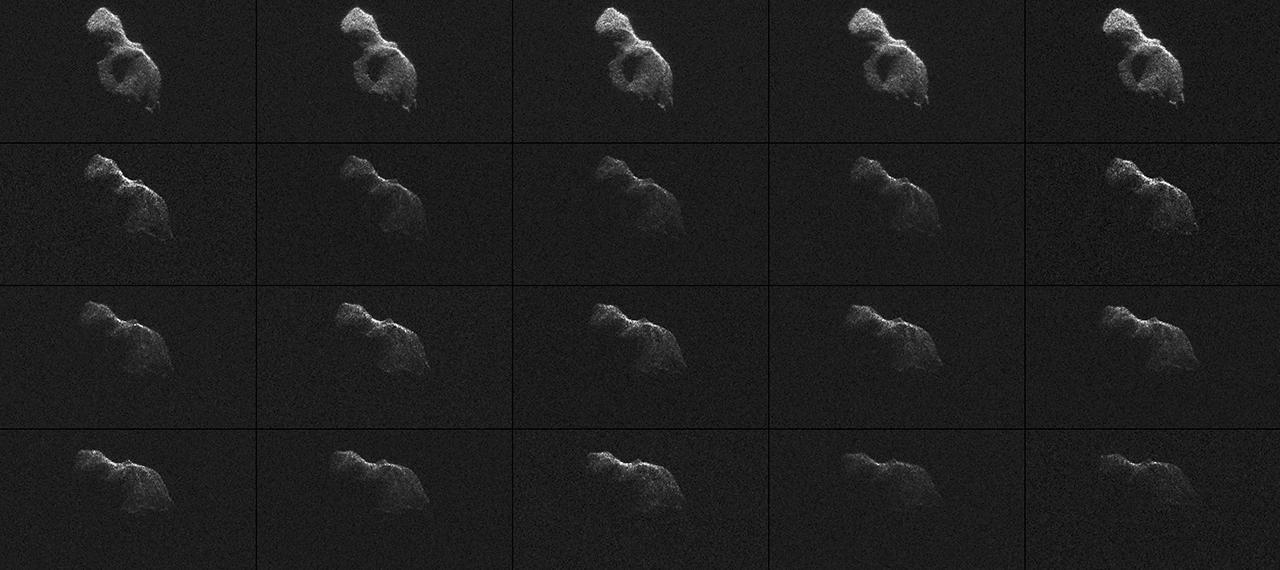

NASA scientists used Earth-based radar to produce these sharp views -- an image montage and a movie sequence -- of the asteroid designated 2014 HQ124 on June 8, 2014.

This view of the north polar region of the Moon was obtained by NASA's Galileo camera during the spacecraft flyby of the Earth-Moon system on December 7 and 8, 1992. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00126
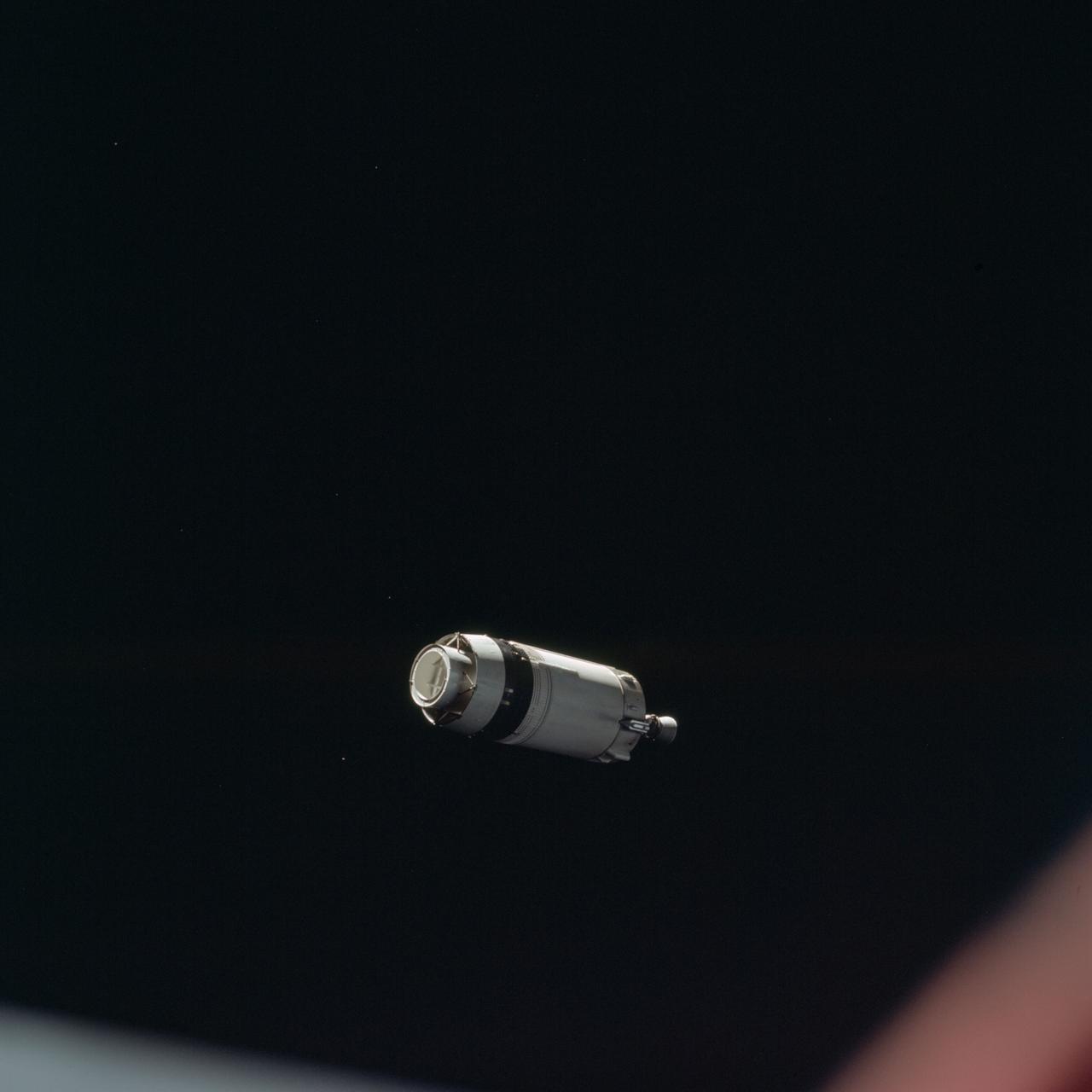

AS08-16-2584 (21 Dec. 1968) --- This is a photograph taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking back at the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage from which the spacecraft had just separated following trans-lunar injection. Attached to the S-IVB is the Lunar Module Test Article (LTA) which simulated the mass of a Lunar Module (LM) on the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. The 29-feet panels of the Spacecraft LM Adapter which enclosed the LTA during launch have already been jettisoned and are out of view. Sunlight reflected from small particles shows the "firefly" phenomenon which was reported by astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. during the first Earth-orbital flight, Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) of the Mercury Program.
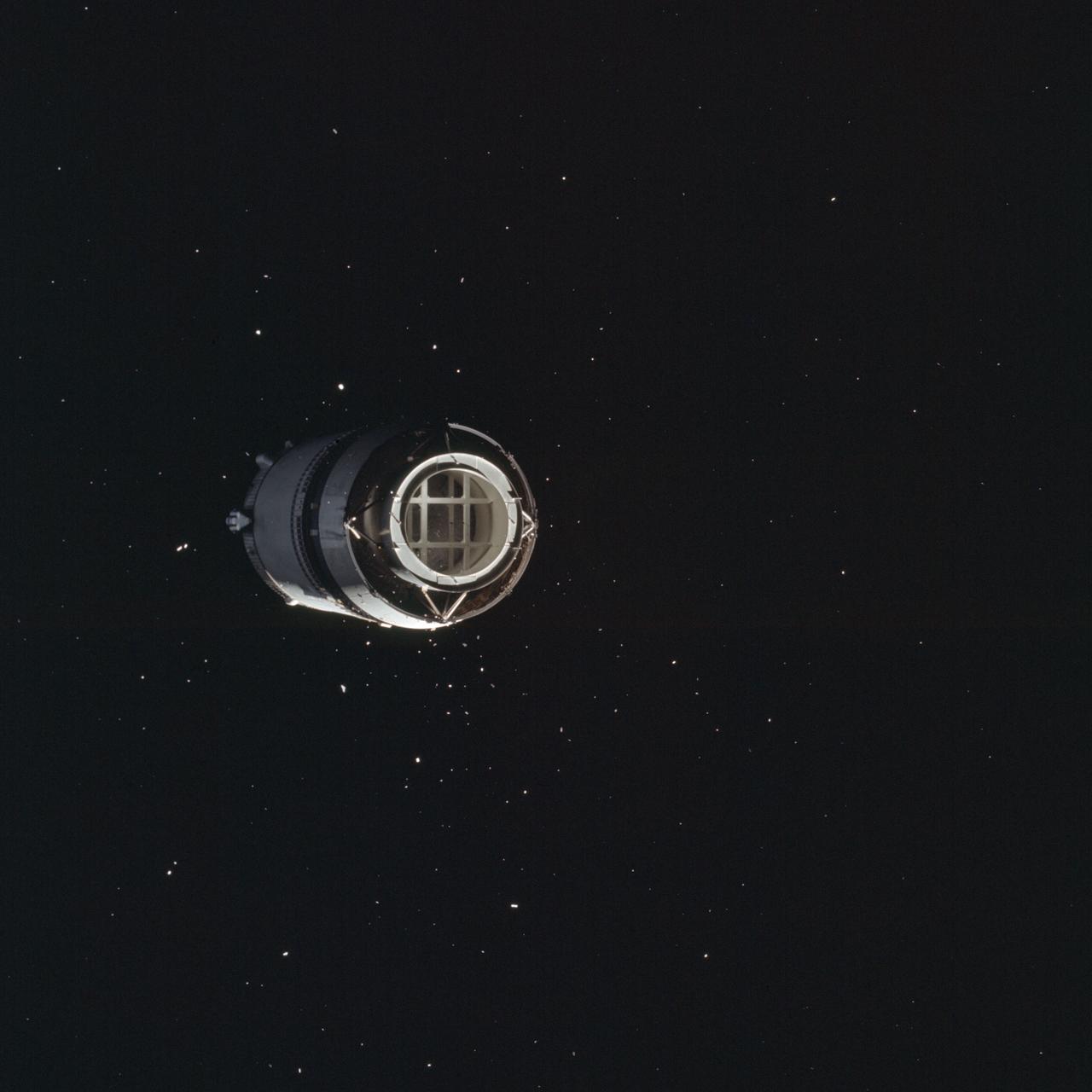

AS08-16-2583 (21 Dec. 1968) --- This is a photograph taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking back at the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage from which the spacecraft had just separated following trans-lunar injection. Attached to the S-IVB is the Lunar Module Test Article (LTA) which simulated the mass of a Lunar Module (LM) on the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. The 29-feet panels of the Spacecraft LM Adapter which enclosed the LTA during launch have already been jettisoned and are out of view. Sunlight reflected from small particles shows the "firefly" phenomenon which was reported by astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. during the first Earth-orbital flight, Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) of the Mercury Program.
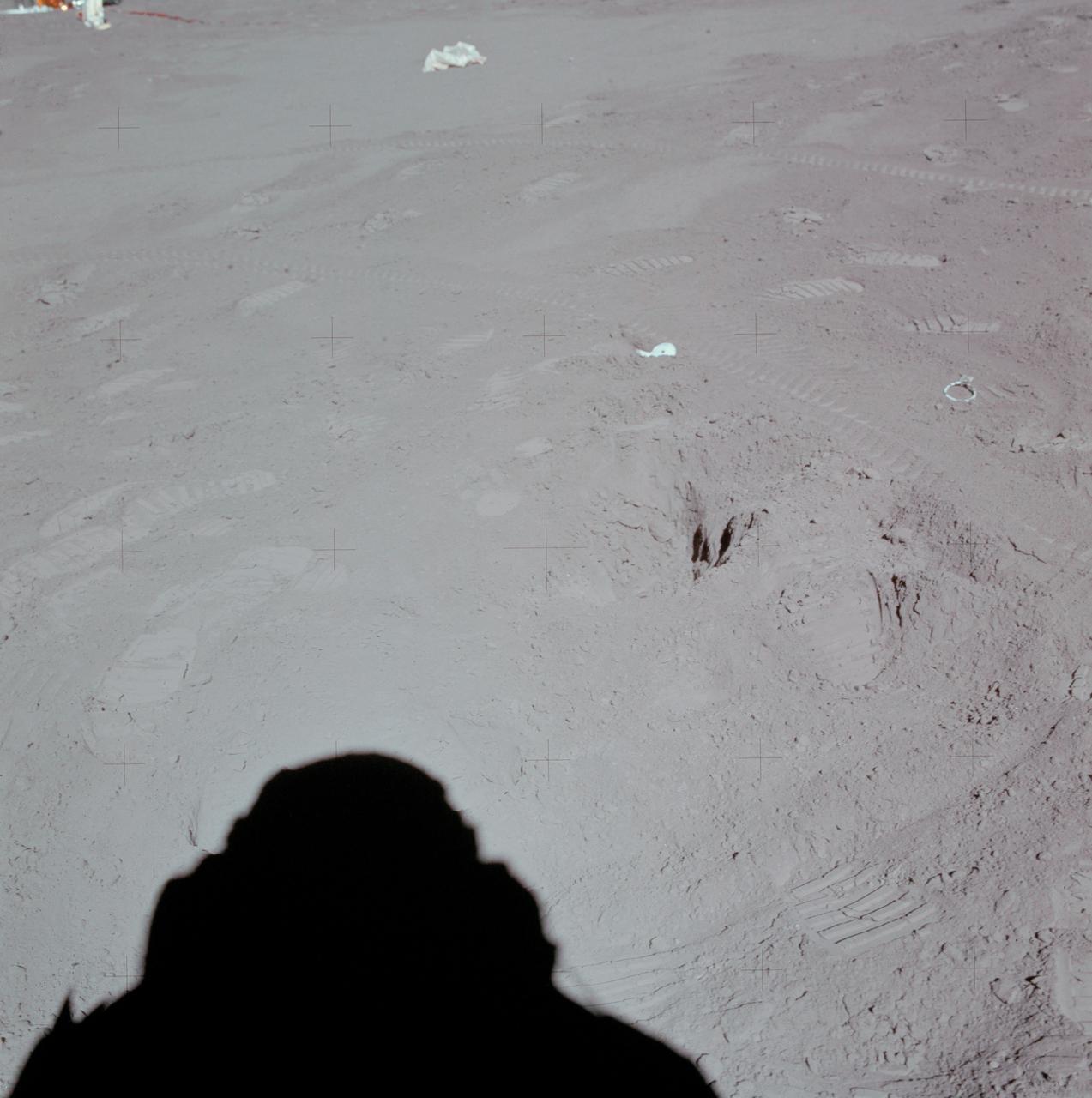

AS15-88-11872 (31 July 1971) --- This north-looking view at Station 8 near the Hadley-Apennine landing site was photographed by one of the missions two moon explorer's (see shadow, foreground) during the third Apollo 15 extravehicular activity (EVA). Prints from the boots of astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, as well as tire tracks from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) are scattered throughout the view. A small part of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) is in the upper left corner. Lunar samples 15252 and 15253 were removed from this area and returned to Earth for analysis by scientists. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
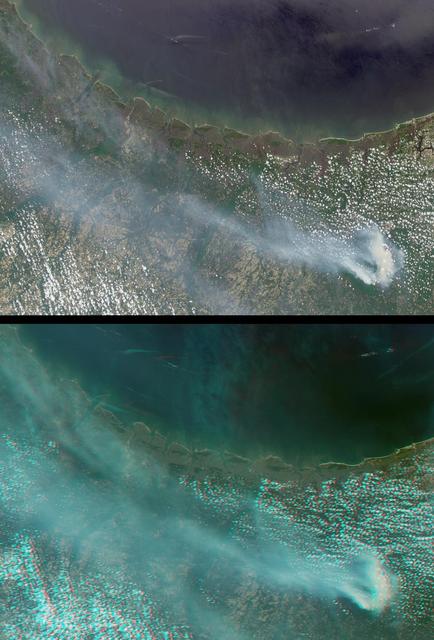

Large smoke plumes were produced by the Blackjack complex fire in southeastern Georgia Okefenokee Swamp as seen by the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft May 8, 2002. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
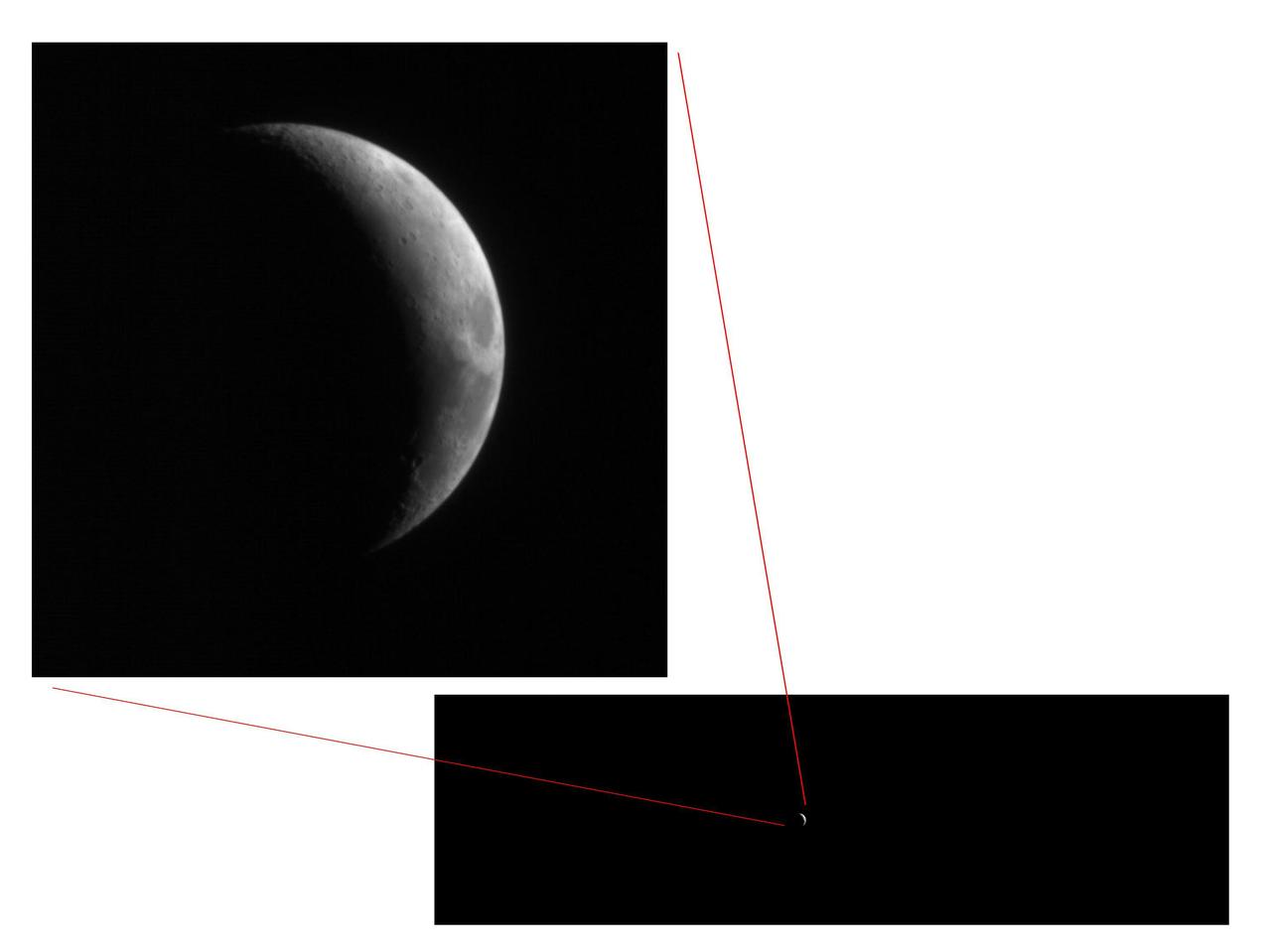

This pair of views shows how little of the full image frame was taken up by the Moon in test images taken Sept. 8, 2005, by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
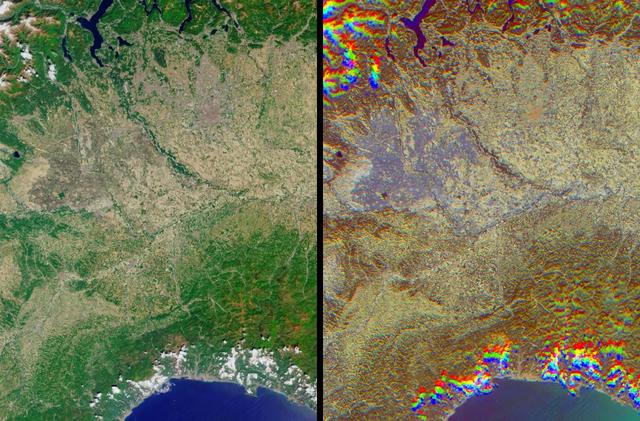

The lowlands of Lombardy and Piedmont in northwest Italy are some of the most highly developed irrigation areas in the world. These views of the region were acquired on May 8, 2005, by NASA Terra spacecraft.
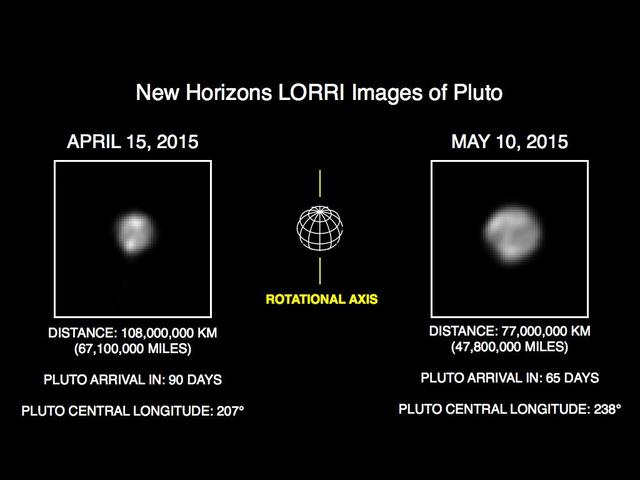
This image of Pluto is part of series of New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI photos taken May 8-12, 2015; the image at left shows LORRI view of Pluto just one month earlier.

What does Earth look like when viewed from Mars? At 13:00 GMT on 8 May 2003, NASA Mars Global Surveyor MGS Mars Orbiter Camera MOC had an opportunity to find out.
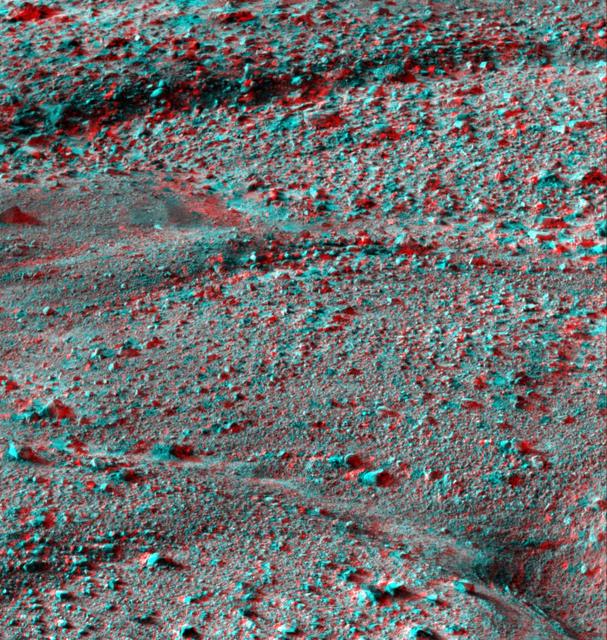
This anaglyph, acquired by NASA Phoenix Lander Surface Stereo Imager on June 8, 2008, shows a stereoscopic 3D view of the Martian surface near the lander. 3D glasses are necessary.
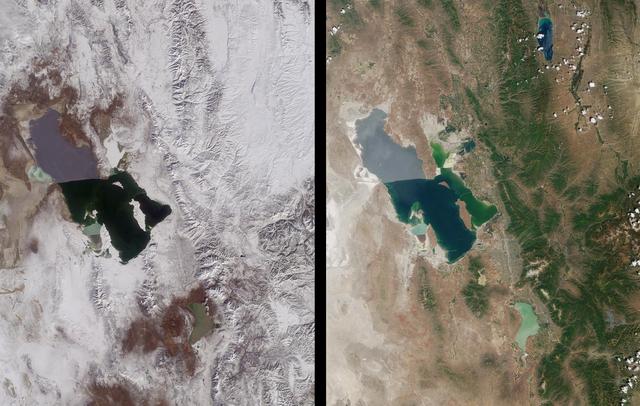

Magnificent views of the region surrounding Salt Lake City, Utah are captured in these winter and summer images from NASA Terra satellite imaged on February 8, 2001 and June 16, 2001.
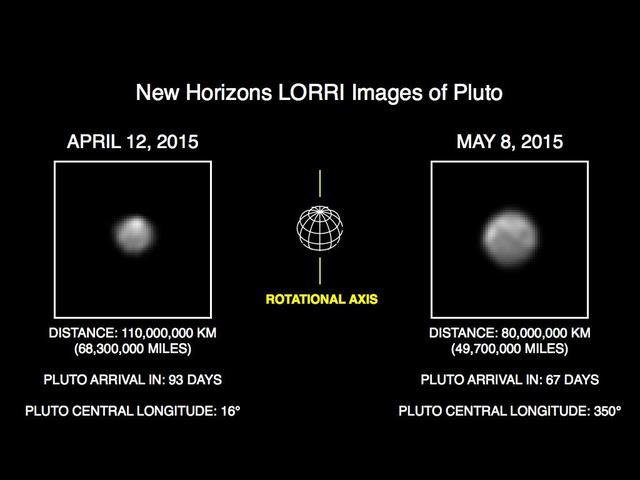
This image of Pluto is part of series of New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI photos taken May 8-12, 2015; the image at left shows LORRI view of Pluto just one month earlier.
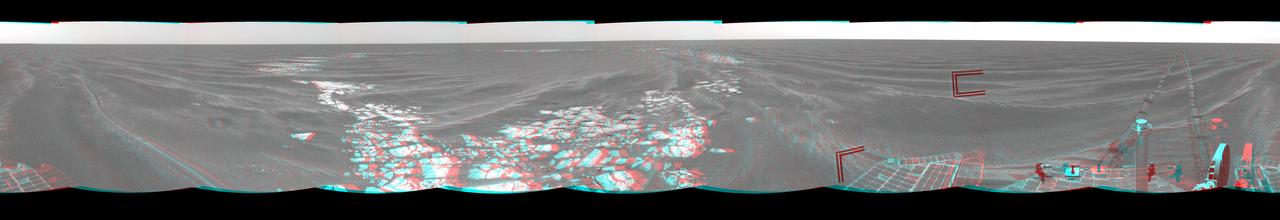
On Mar. 8, 2005, NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity drove 95 meters 312 feet toward Vostok Crater that sol before taking images. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

This image of Pluto is part of series of New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI photos taken May 8-12, 2015; the image at left shows LORRI view of Pluto just one month earlier.
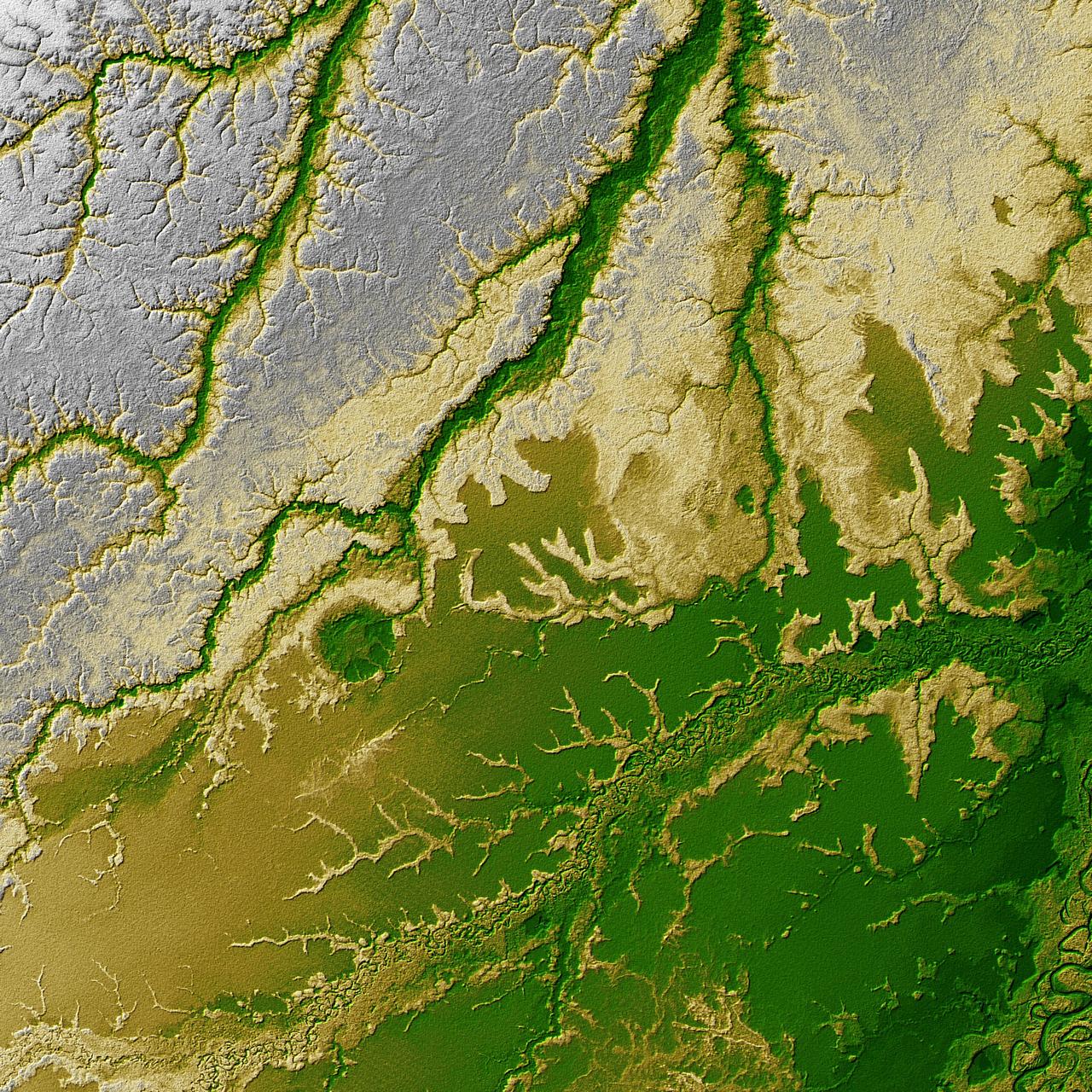

An 8-kilometer 5-mile wide crater of possible impact origin is shown in this view of an isolated part of the Bolivian Amazon from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission.
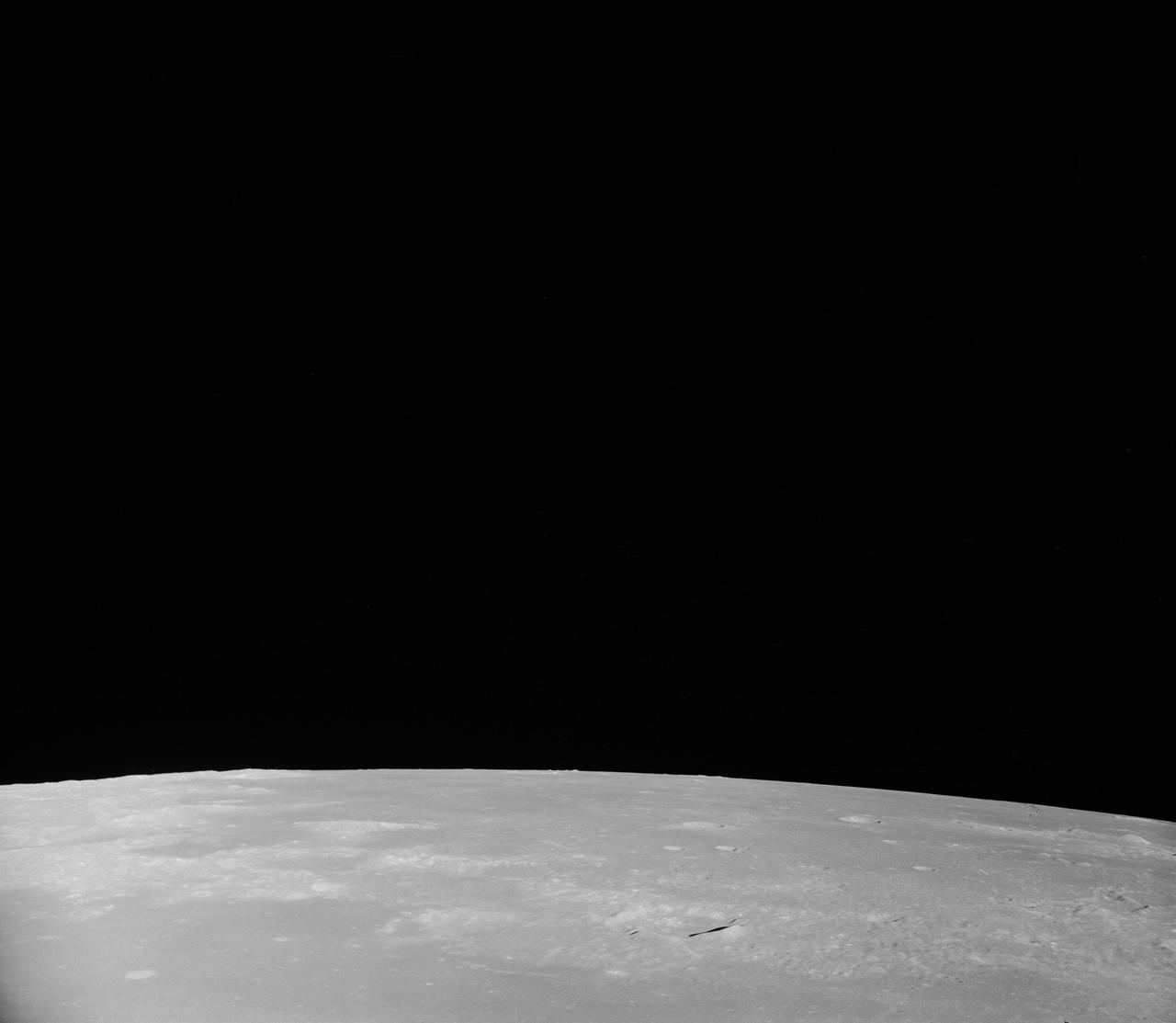
AS08-12-2209 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- High altitude oblique view of the lunar surface, looking northeastward, as seen from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. The crater Joliot-Curie, about 175 kilometers in diameter and centered near 94 degrees east longitude and 27 degrees north latitude, is near the center of the left side of this photograph. The bright rayed crater near the horizon is probably located near 105 degrees east longitude and 45 degrees north latitude. Long, narrow rays that have been reported in the polar region of Earth facing hemisphere may radiate from this crater.
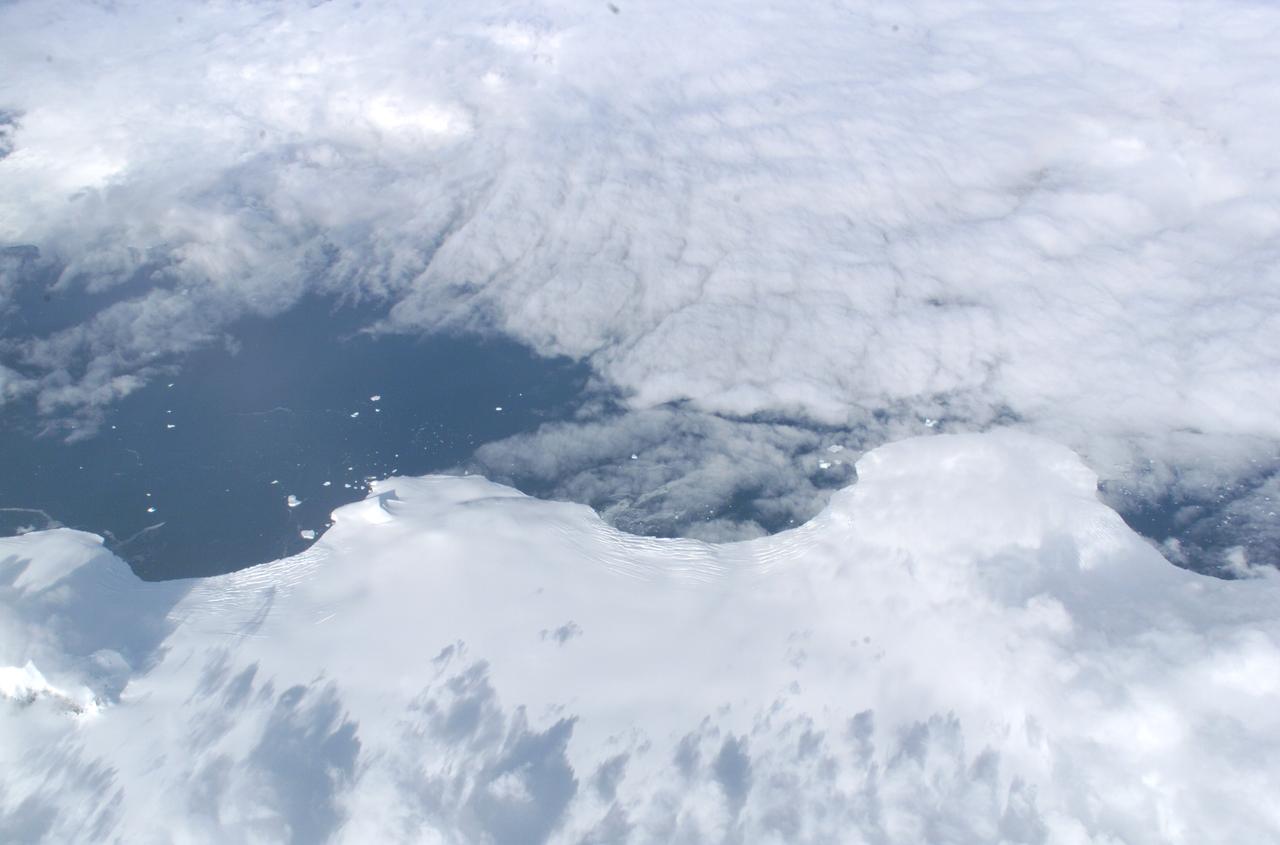

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
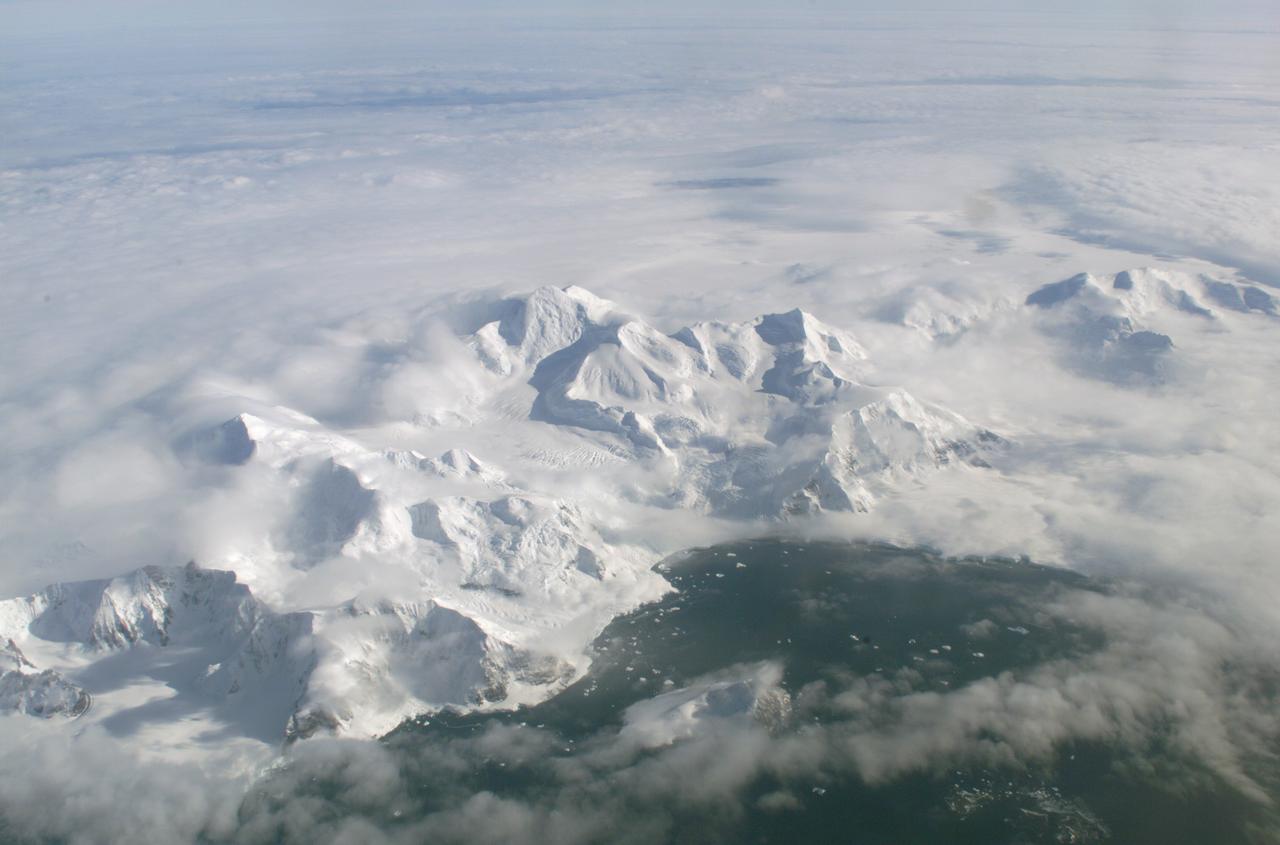

An AirSAR 2004 view from the DC-8 as it approaches the Larsen Ice Shelf, which is part of the Antarctic Peninsula. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
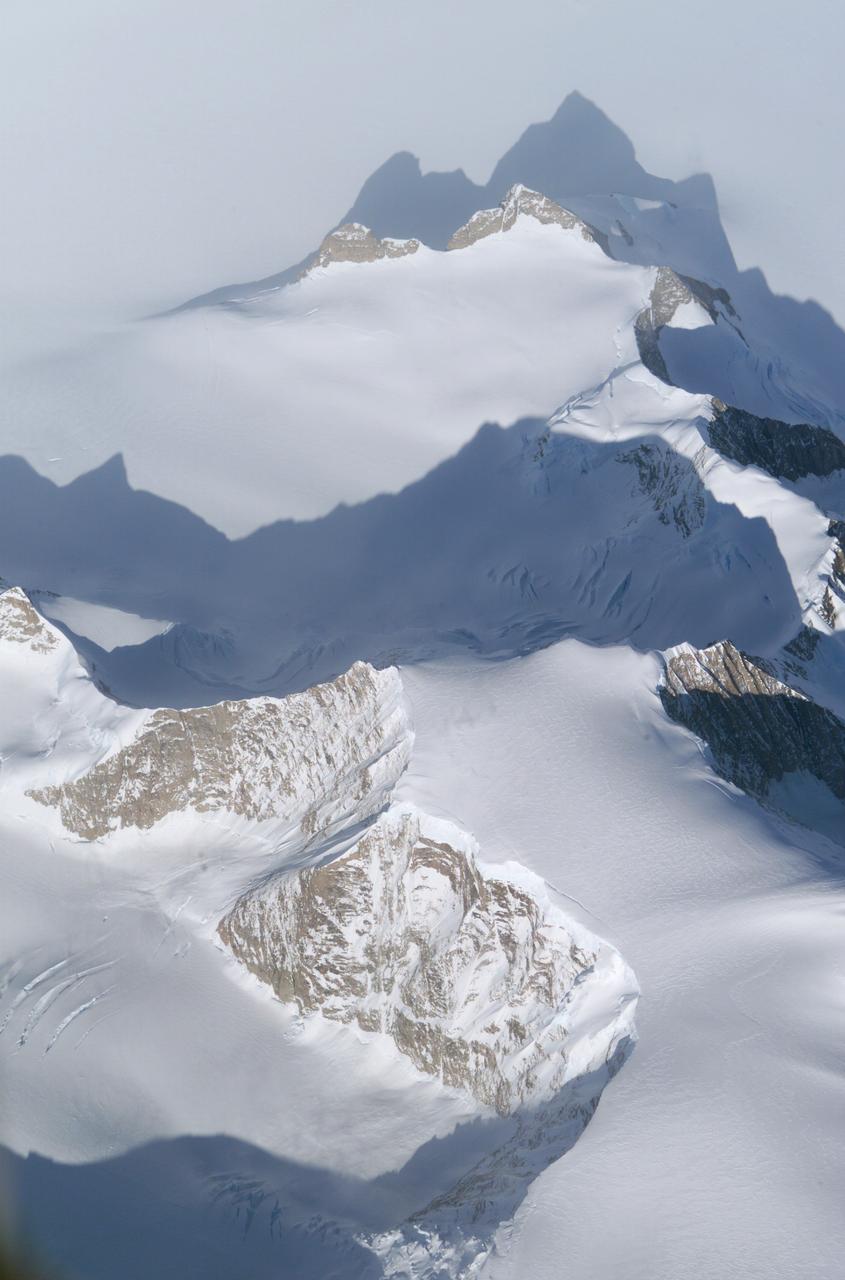

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
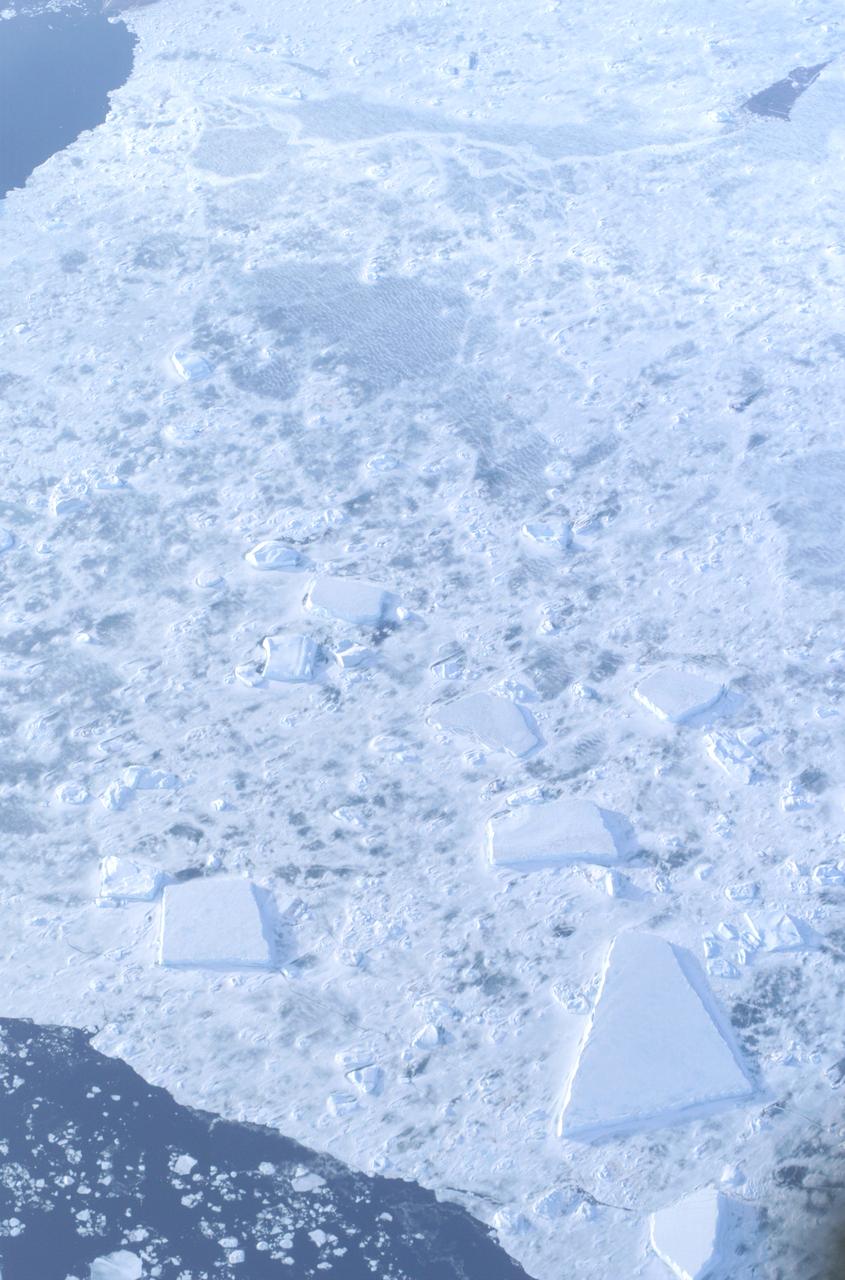

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
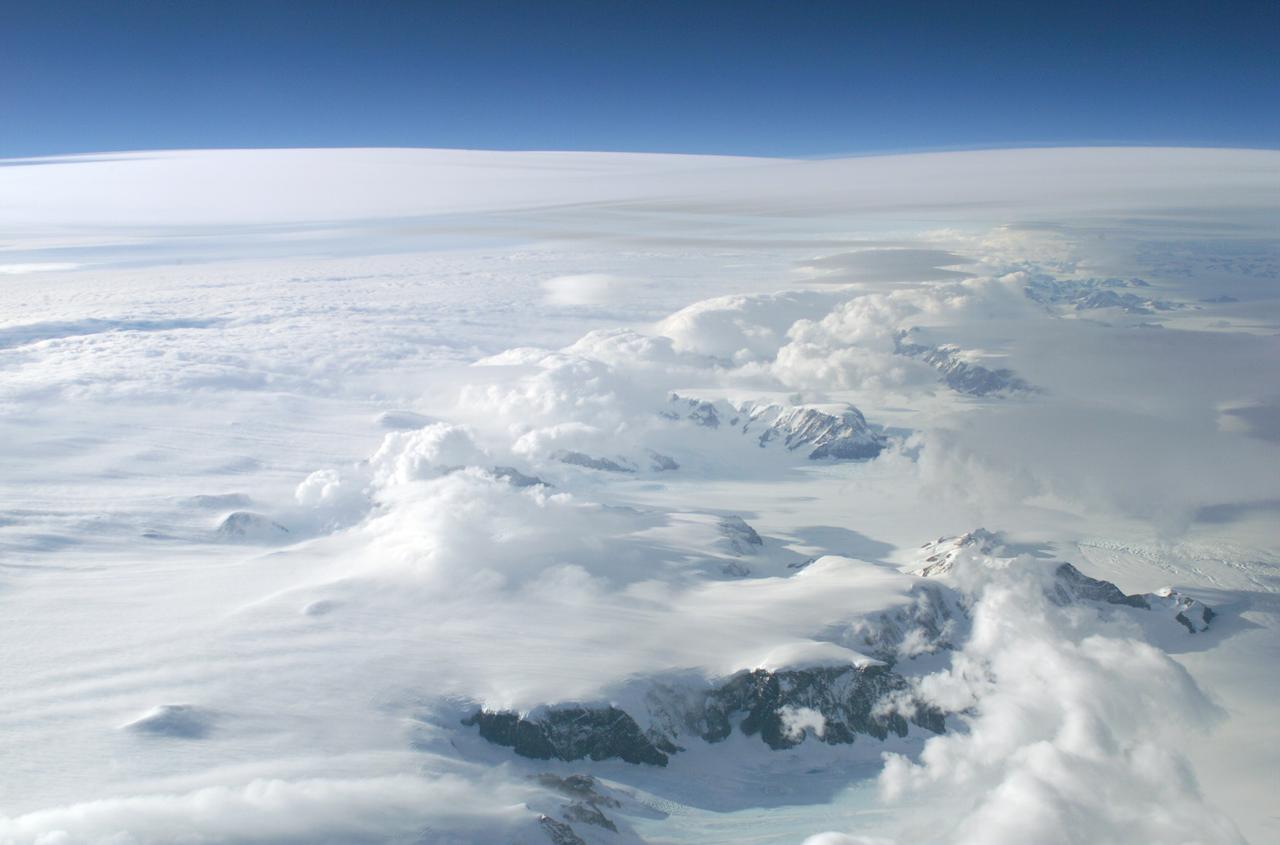

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
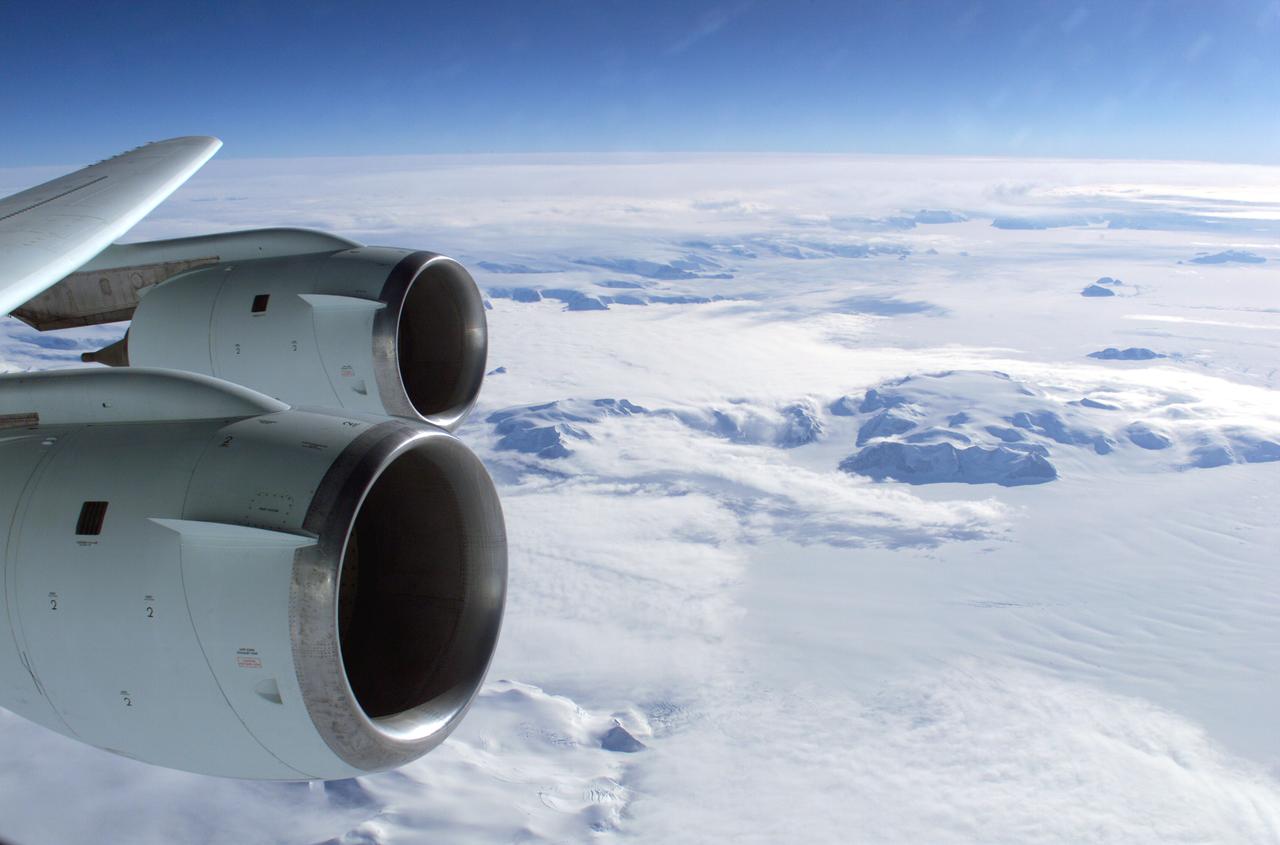

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
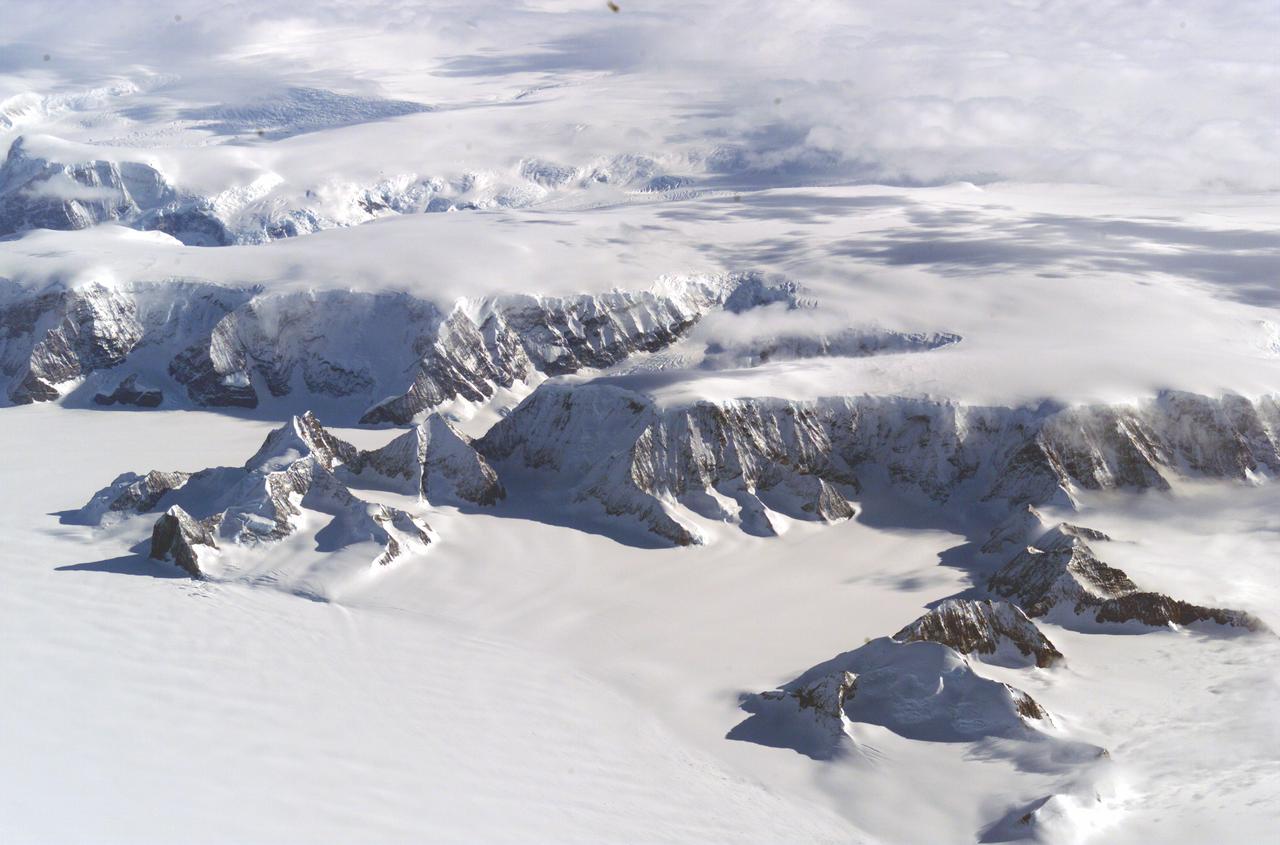

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

This image of the moon was obtained by the Galileo Solid State imaging system on Dec. 8 at 7 p.m. PST as NASA Galileo spacecraft passed the Earth and was able to view the lunar surface from a vantage point not possible from the Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00225
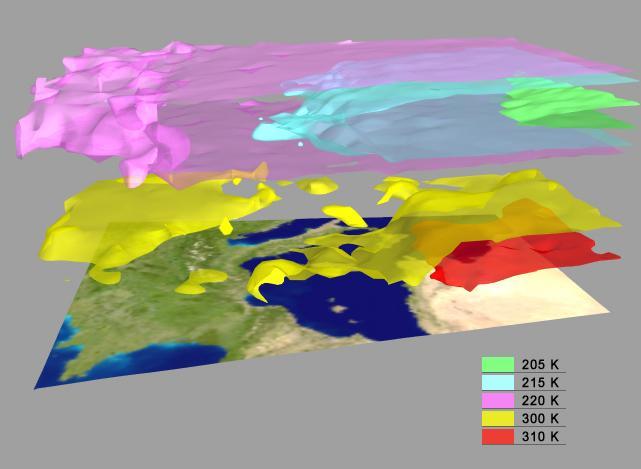
AIRS Retrieved Temperature Isotherms over Southern Europe viewed from the west, September 8, 2002. The isotherms in this map made from AIRS onboard NASA Aqua satellite data show regions of the same temperature in the atmosphere. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00513
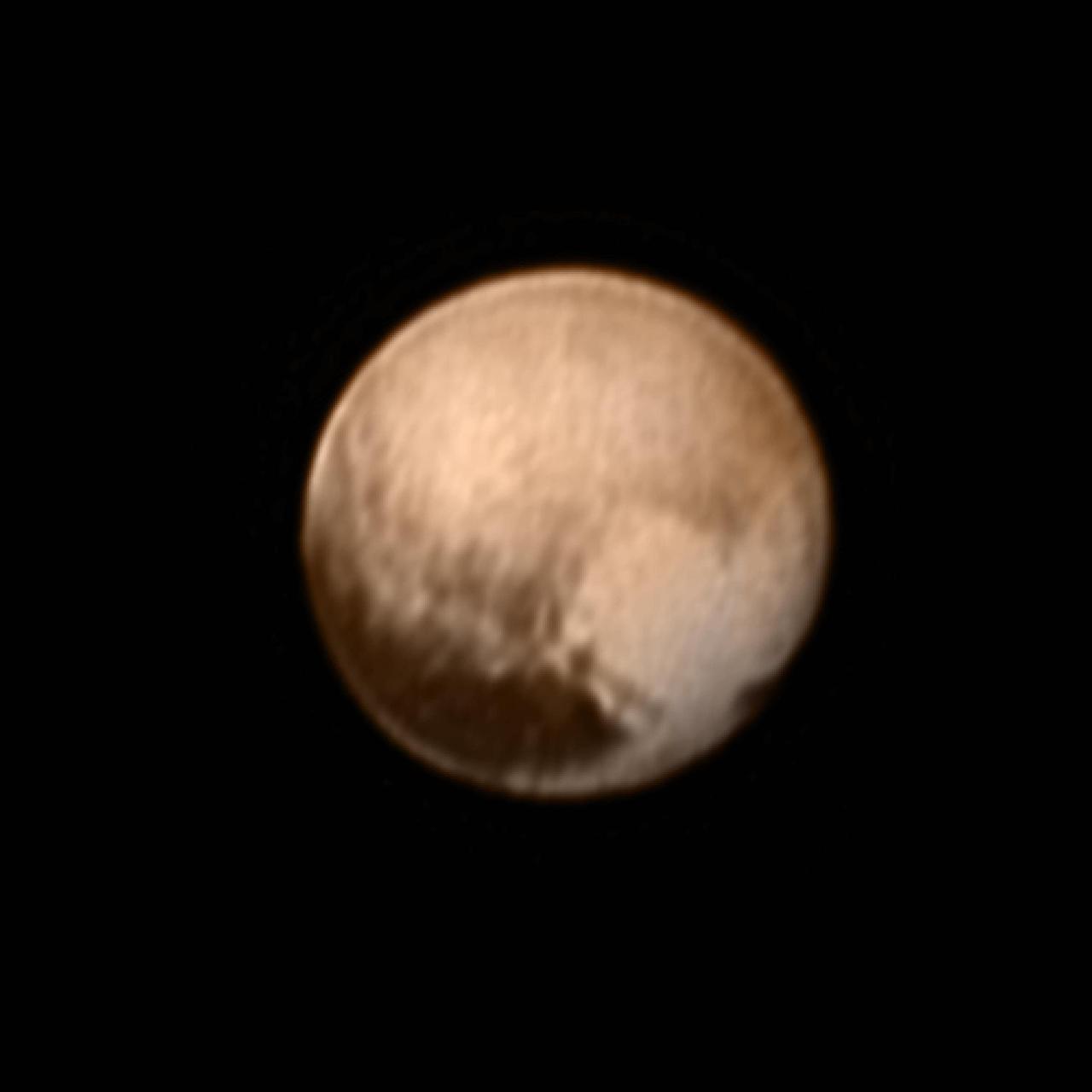

In the early morning hours of July 8, 2015, mission scientists received this new view of Pluto -- the most detailed yet returned by the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons. The image was taken on July 7, when the NASA spacecraft was just under 5 million miles (8 million kilometers) from Pluto, and is the first to be received since the July 4 anomaly that sent the spacecraft into safe mode. This view is centered roughly on the area that will be seen close-up during New Horizons' July 14 closest approach. This side of Pluto is dominated by three broad regions of varying brightness. Most prominent are an elongated dark feature at the equator, informally known as "the whale," and a large heart-shaped bright area measuring some 1,200 miles (2,000 kilometers) across on the right. Above those features is a polar region that is intermediate in brightness. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19702
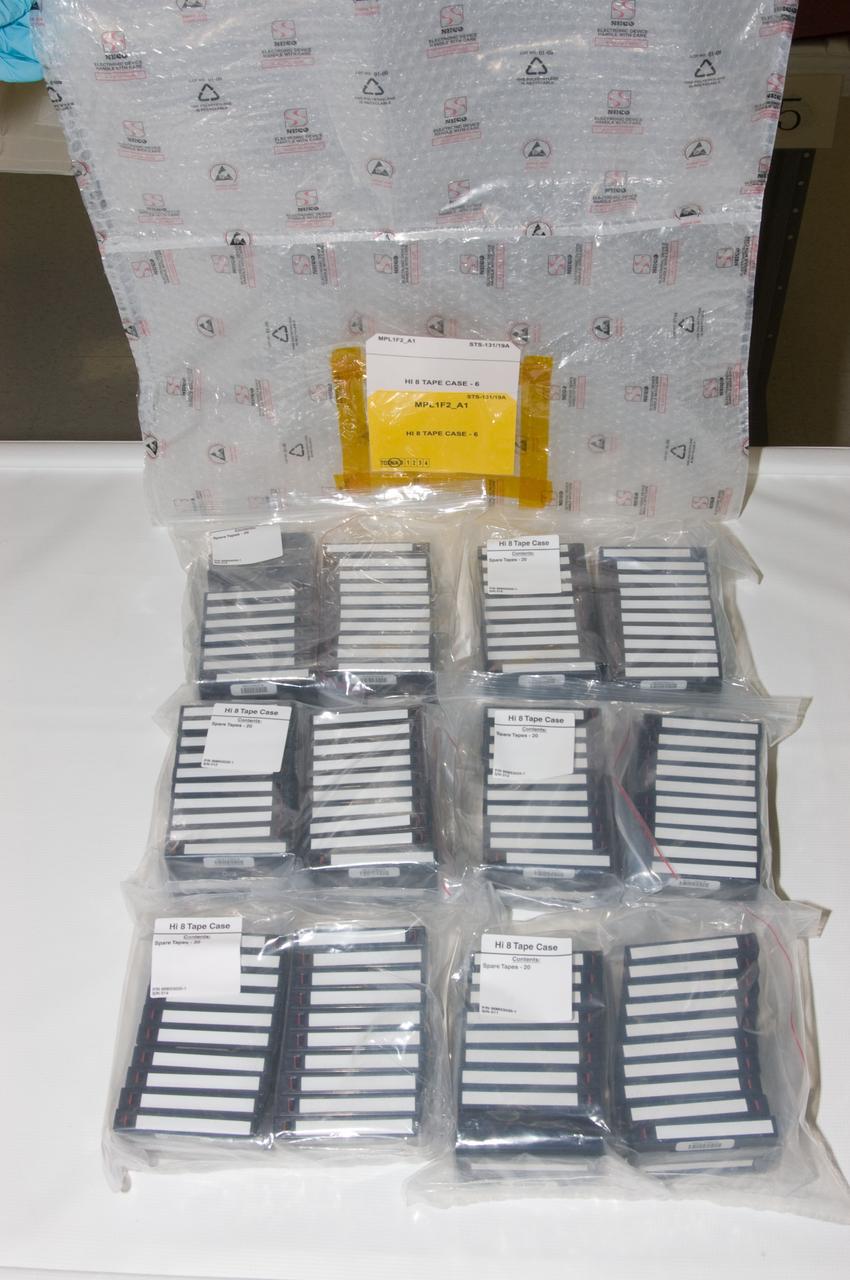

View of a Hi 8 Video Storage Bag and multiple Hi 8 Video Tape cases.
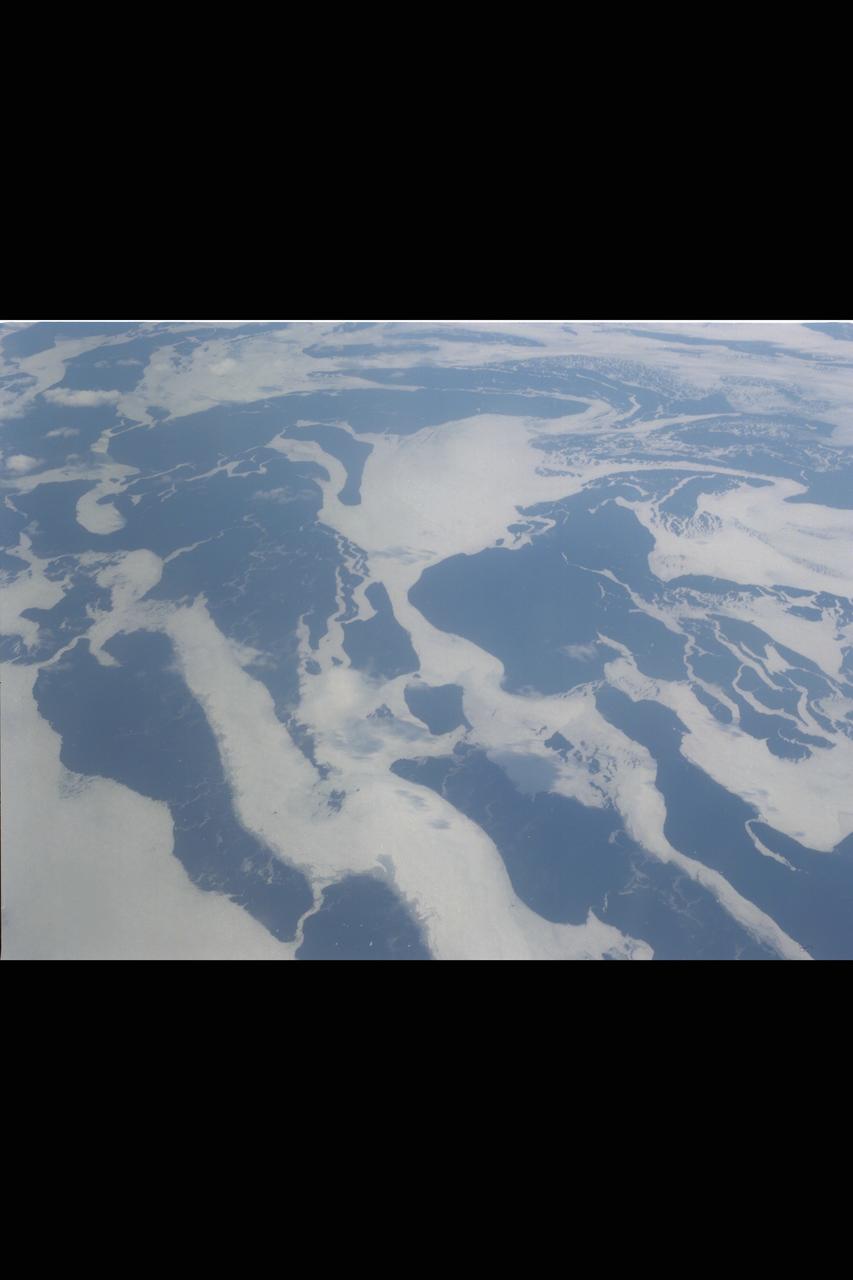

DC-8 (NASA-717) Antarctic Ozone Experiment: (Summer in Antarctic - aerial view from DC-8)
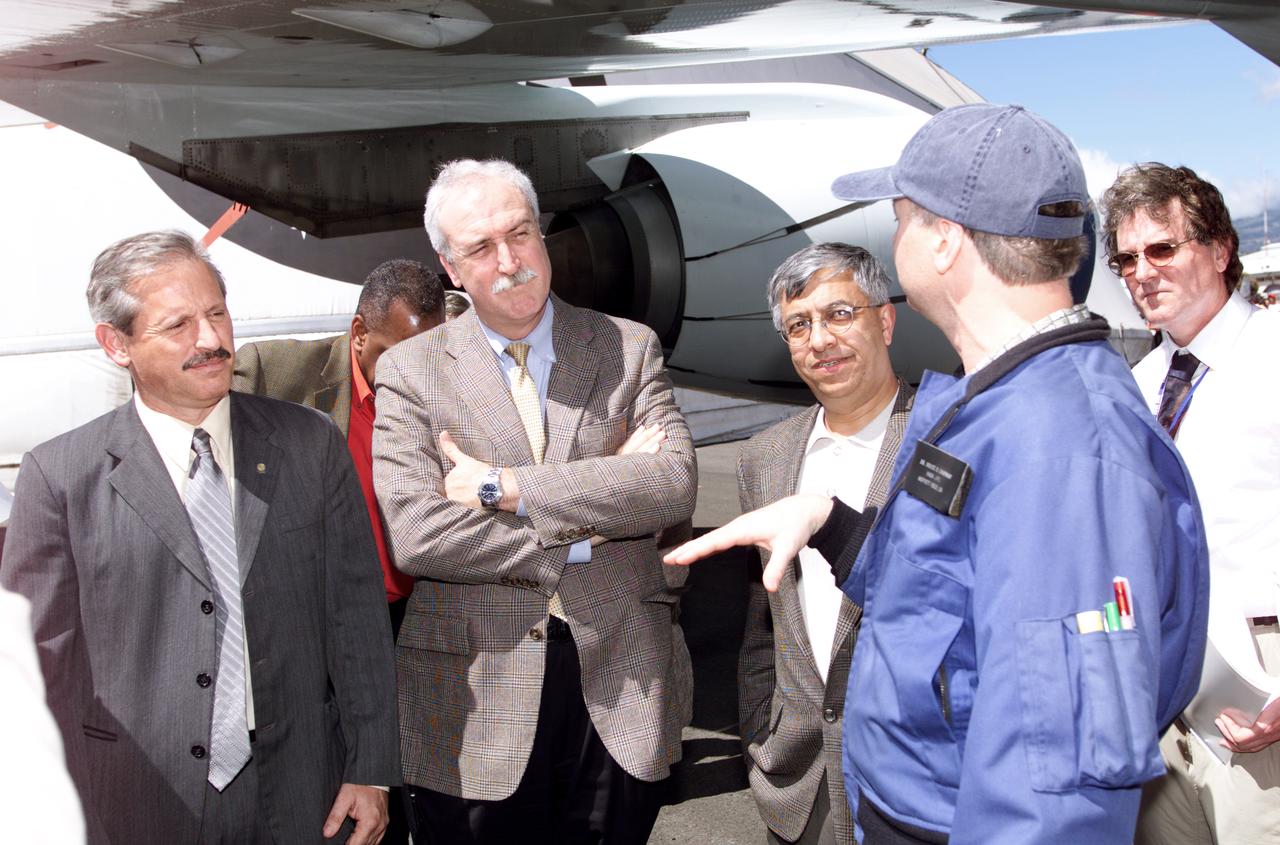

Personnel viewing AirSAR hardware while touring the outside of NASA's DC-8 during a stop-off on the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign, L-R: Fernando Gutierrez, Costa Rican Minister of Science and Technology(MICIT); NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe; Dr. Gahssem Asrar, NASA Associate Administrator for Earth Science Enterprises; JPL scientist Bruce Chapman; and Craig Dobson, NASA Program Manager for AirSAR. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.

This view, made using images taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft, features a tall conical mountain on Ceres. Elevations span a range of about 5 miles (8 kilometers) from the lowest places in this region to the highest terrains. Blue represents the lowest elevation, and brown is the highest. The white streaks seen running down the side of the mountain are especially bright parts of the surface. The image was generated using two components: images of the surface taken during Dawn's High Altitude Mapping Orbit (HAMO) phase, where it viewed the surface at a resolution of about 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel, and a shape model generated using images taken at varying sun and viewing angles during Dawn's lower-resolution Survey phase. The image of the region is color-coded according to elevation, and then draped over the shape model to give this view. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19976
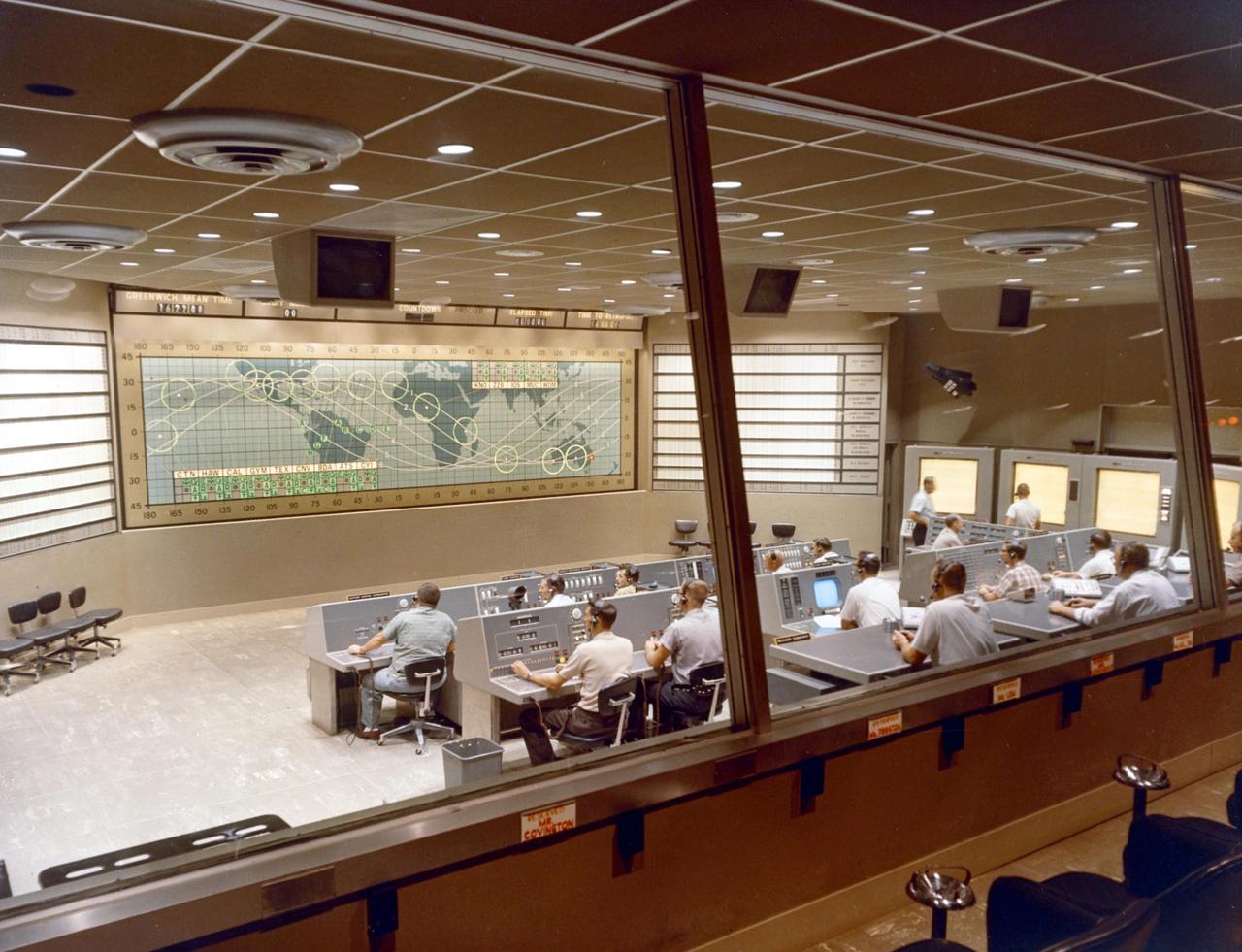

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Interior view of the Mission Control Center during the launch sequence of Mercury-Atlas 8 MA-8).

S66-24406 (16 March 1966) --- Close-up view of astronaut David R. Scott, pilot of the Gemini-8 spaceflight, making final adjustments and checks in the spacecraft during the Gemini-8 prelaunch countdown. In the background almost out of view is astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, command pilot. Photo credit: NASA
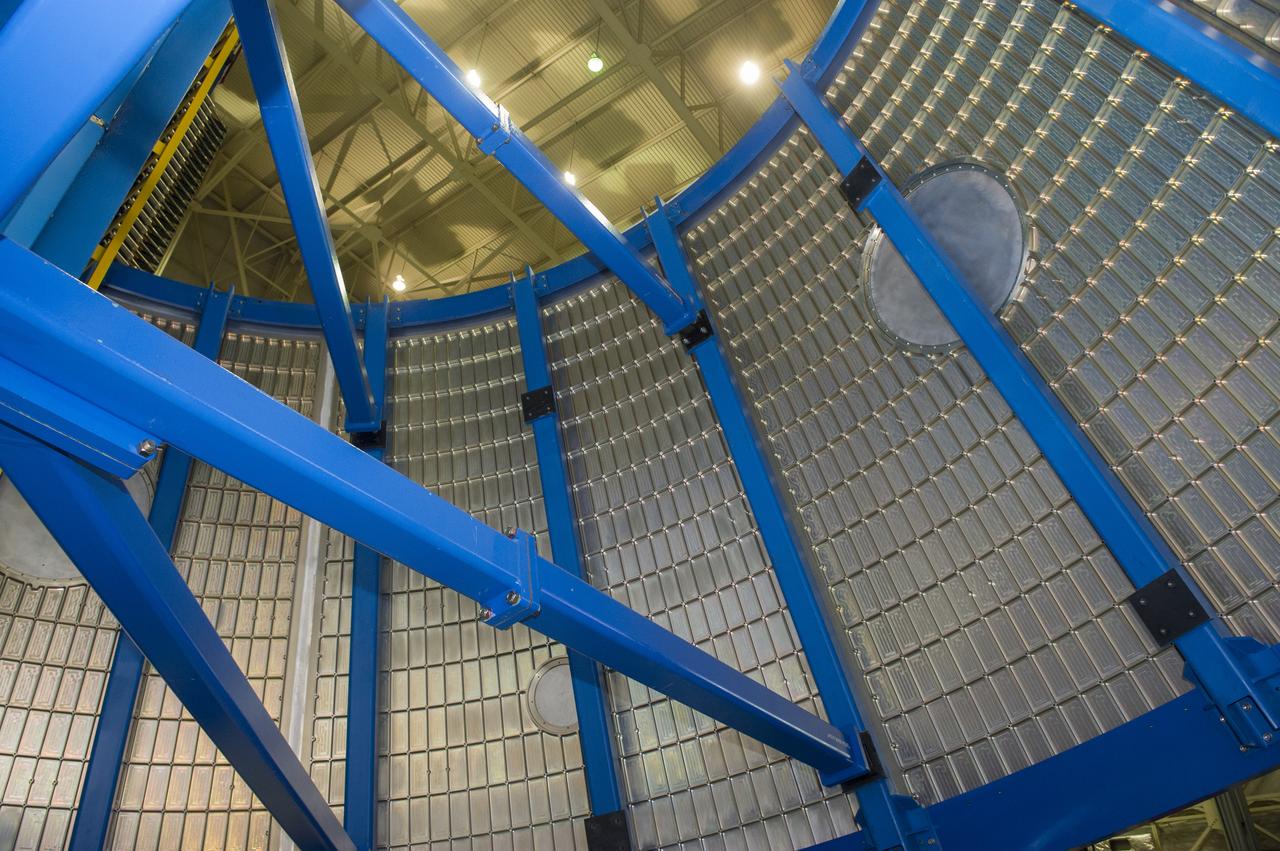

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE
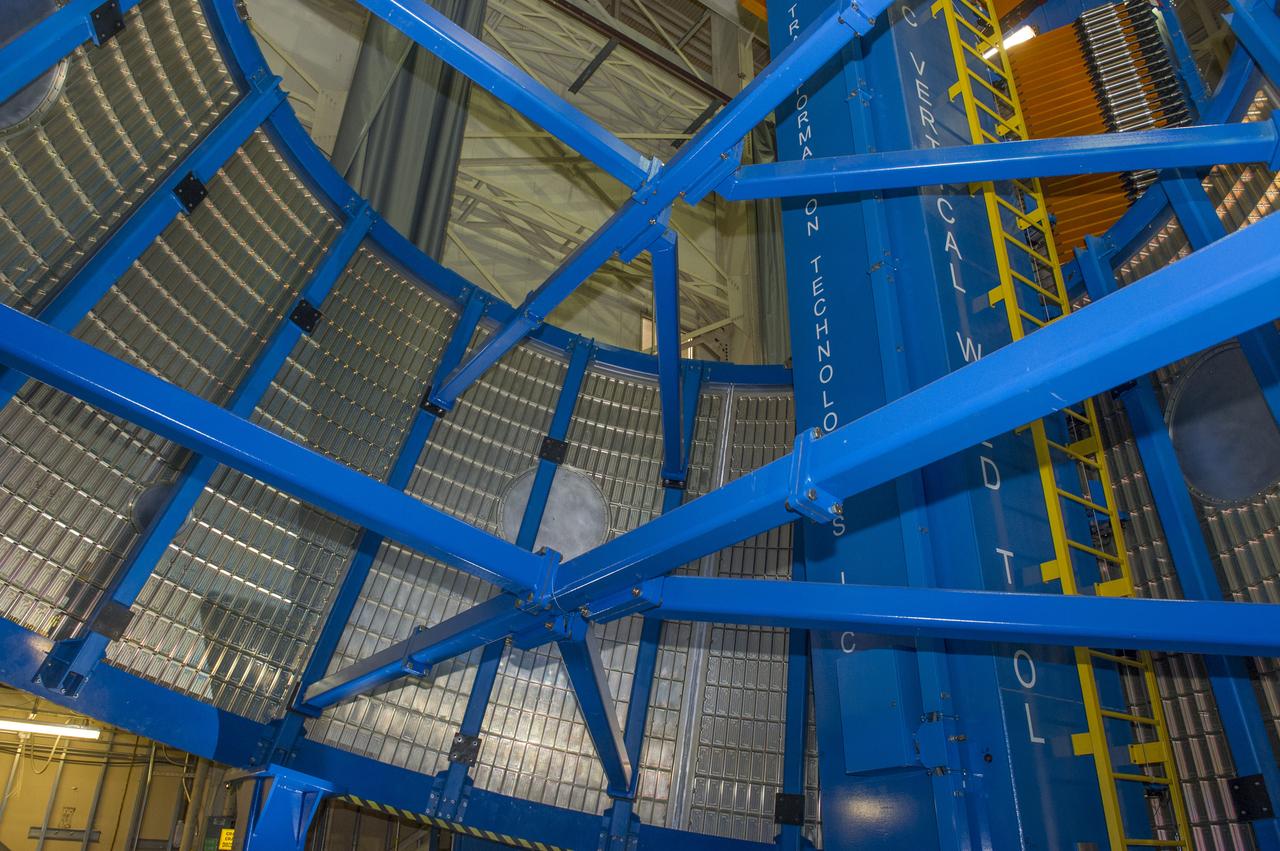

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE
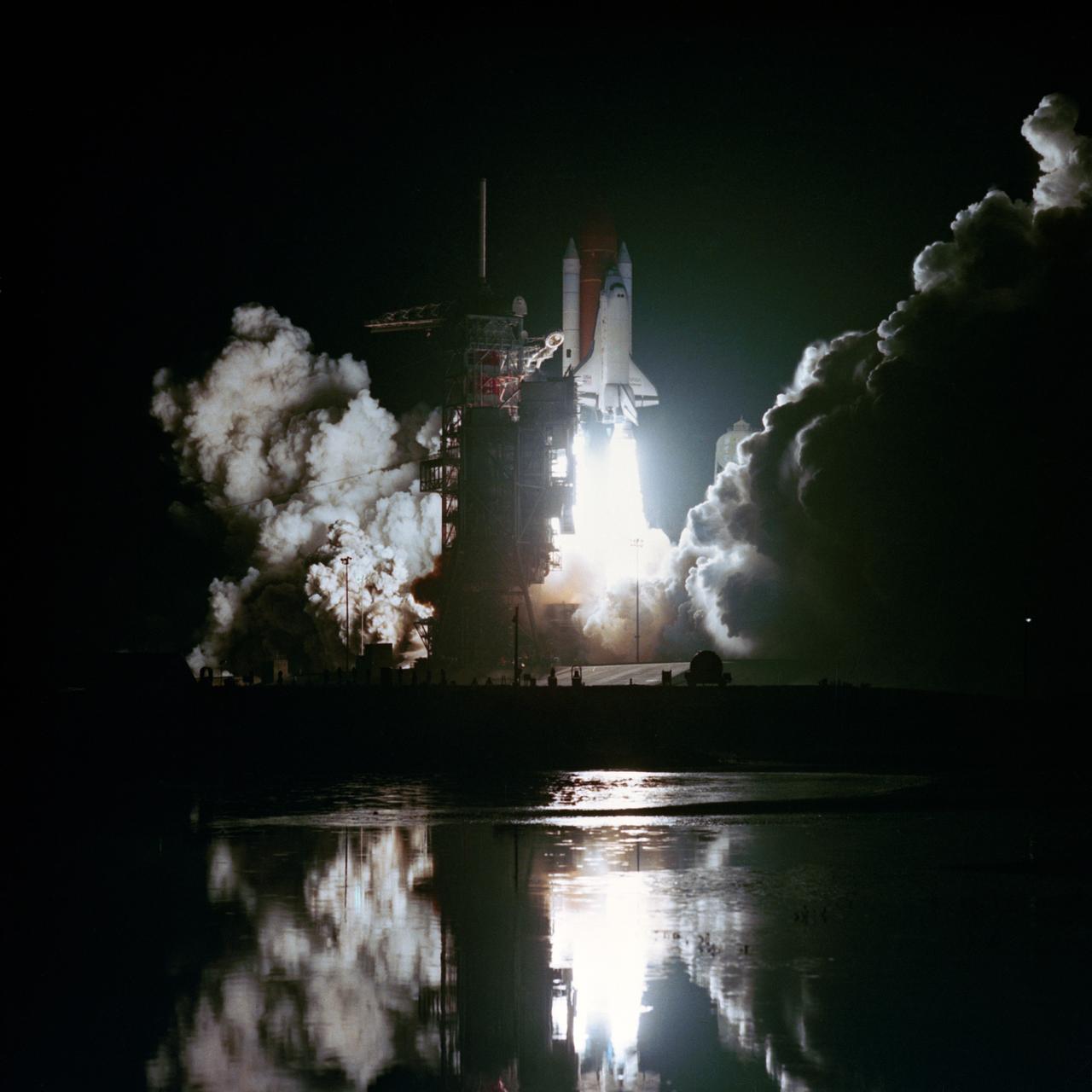

Night launch view of STS-8. Very nice shot. KSC, FL

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE
LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE
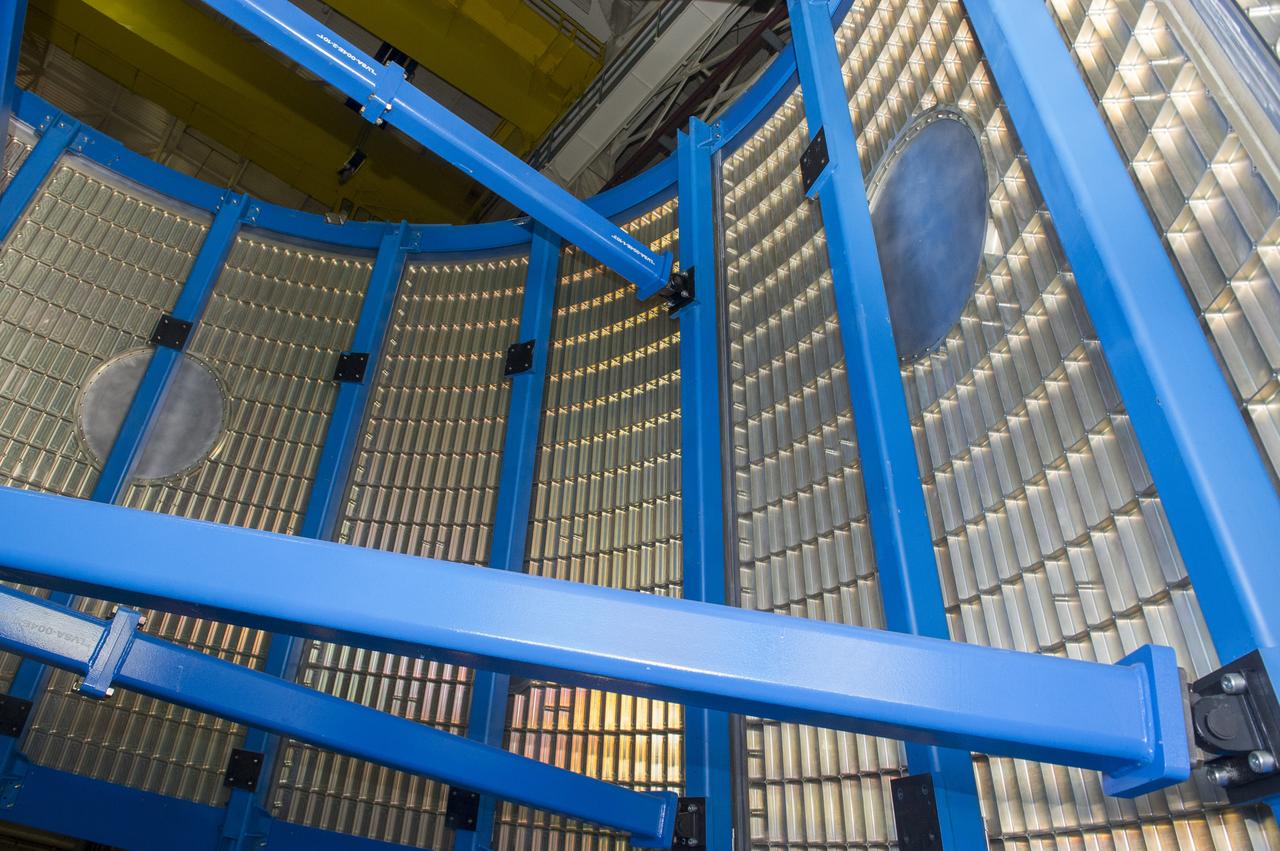

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE
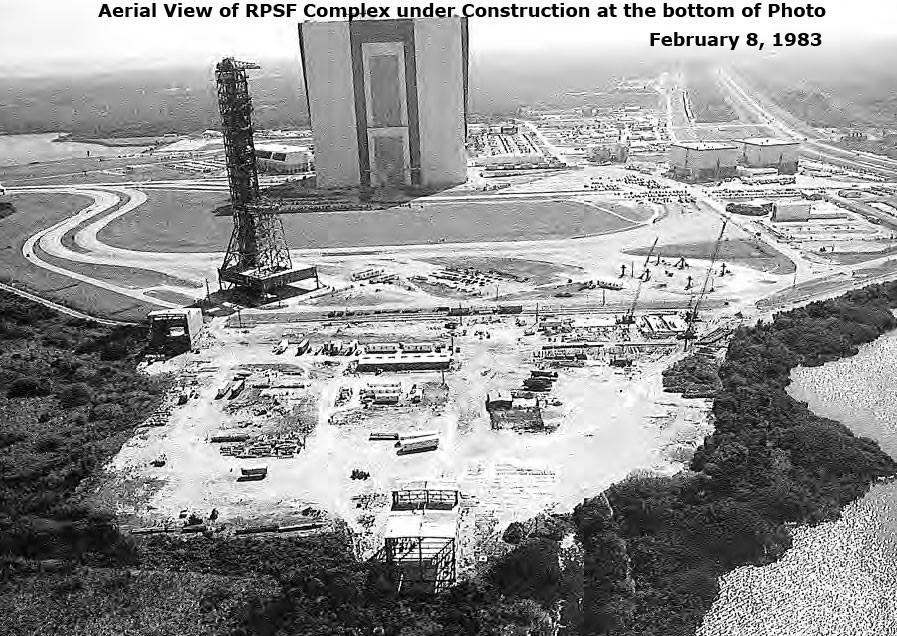

Aerial View of RPSF Complex under construction, February 8, 1983

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE
LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 INTERIOR VIEW OF CONE
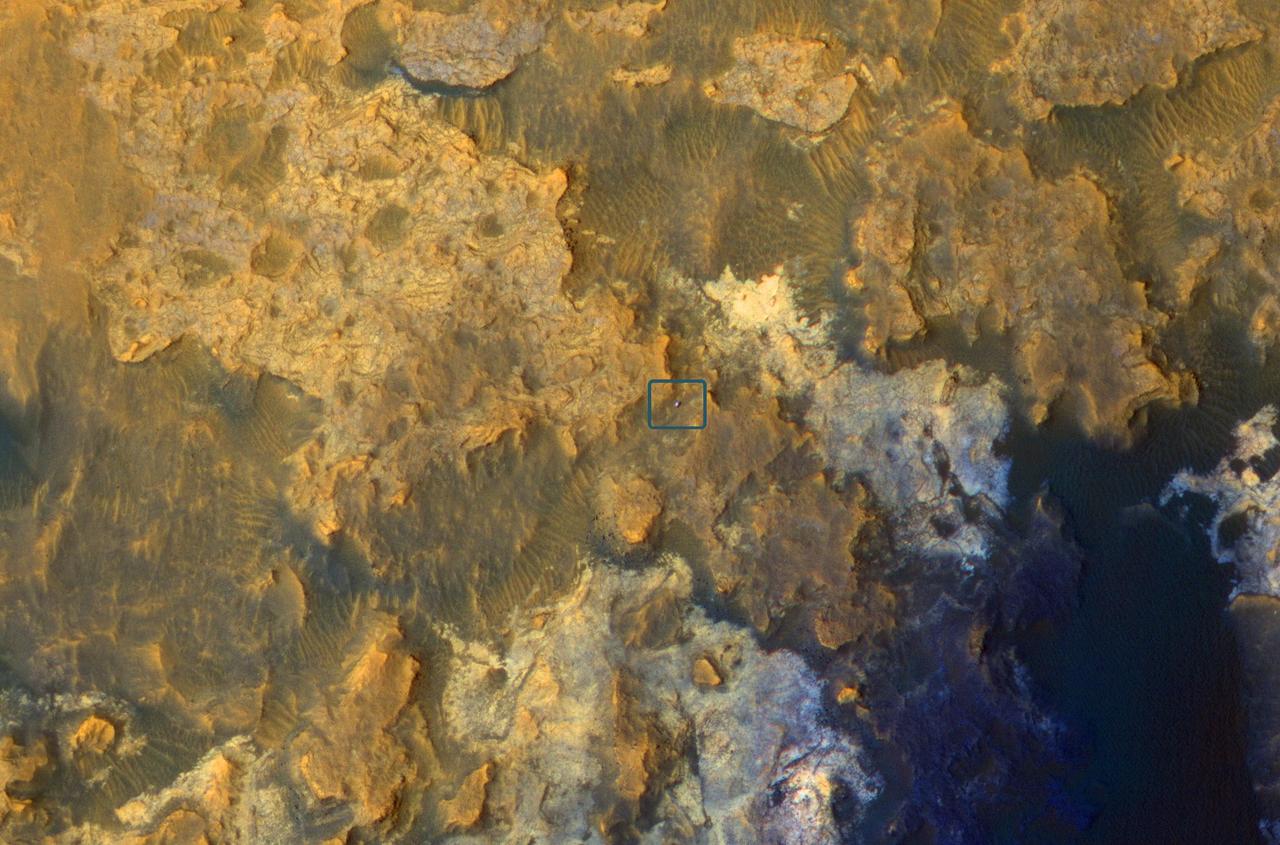

A view from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on April 8, 2015, catches sight of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover passing through a valley called "Artist's Drive" on the lower slope of Mount Sharp. The image is from the orbiter's High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera. It shows the rover's position after a drive of about 75 feet (23 meters) during the 949th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. North is toward the top. The rover's location, with its shadow extending toward the right, is indicated with an inscribed rectangle. The view in this image covers an area about 550 yards (500 meters) across. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19392
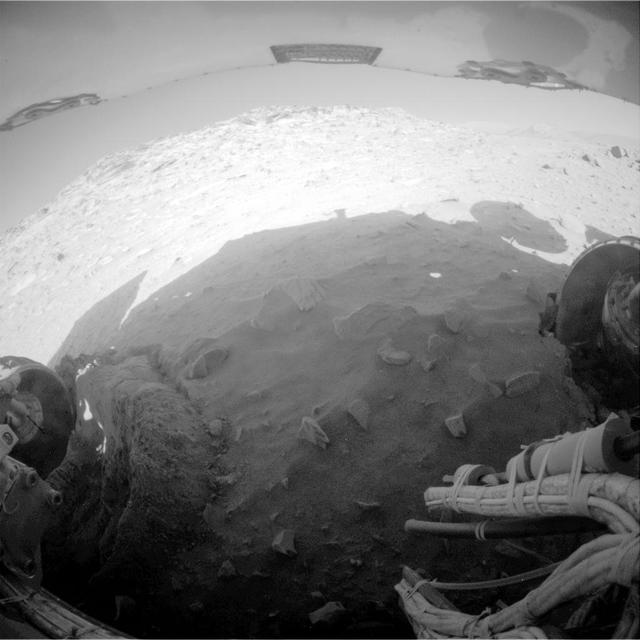

NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit recorded this fisheye view after completing a drive during on Mars on Feb. 8, 2010. The drive left Spirit in the position where the rover will stay parked during the upcoming Mars southern-hemisphere winter.

This crescent view of Earth Moon in infrared wavelengths comes from a camera test by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft on its way to Mars. This image was taken by taken by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment camera Sept. 8, 2005.
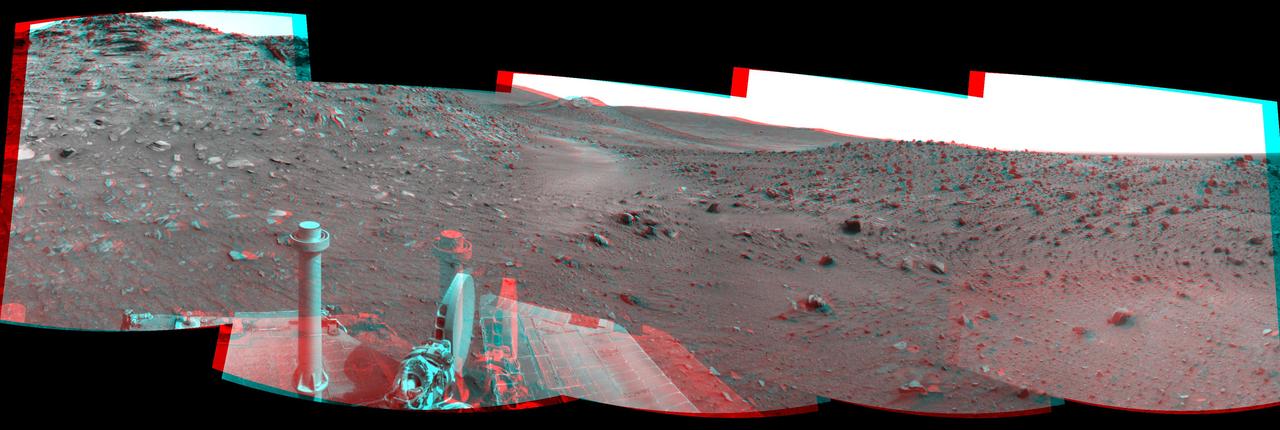

This stereo scene combines frames taken by the navigation camera on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit during the 1,871st Martian day, or sol, of Spirit mission on Mars April 8, 2009. You will need 3-D glasses to view this image.
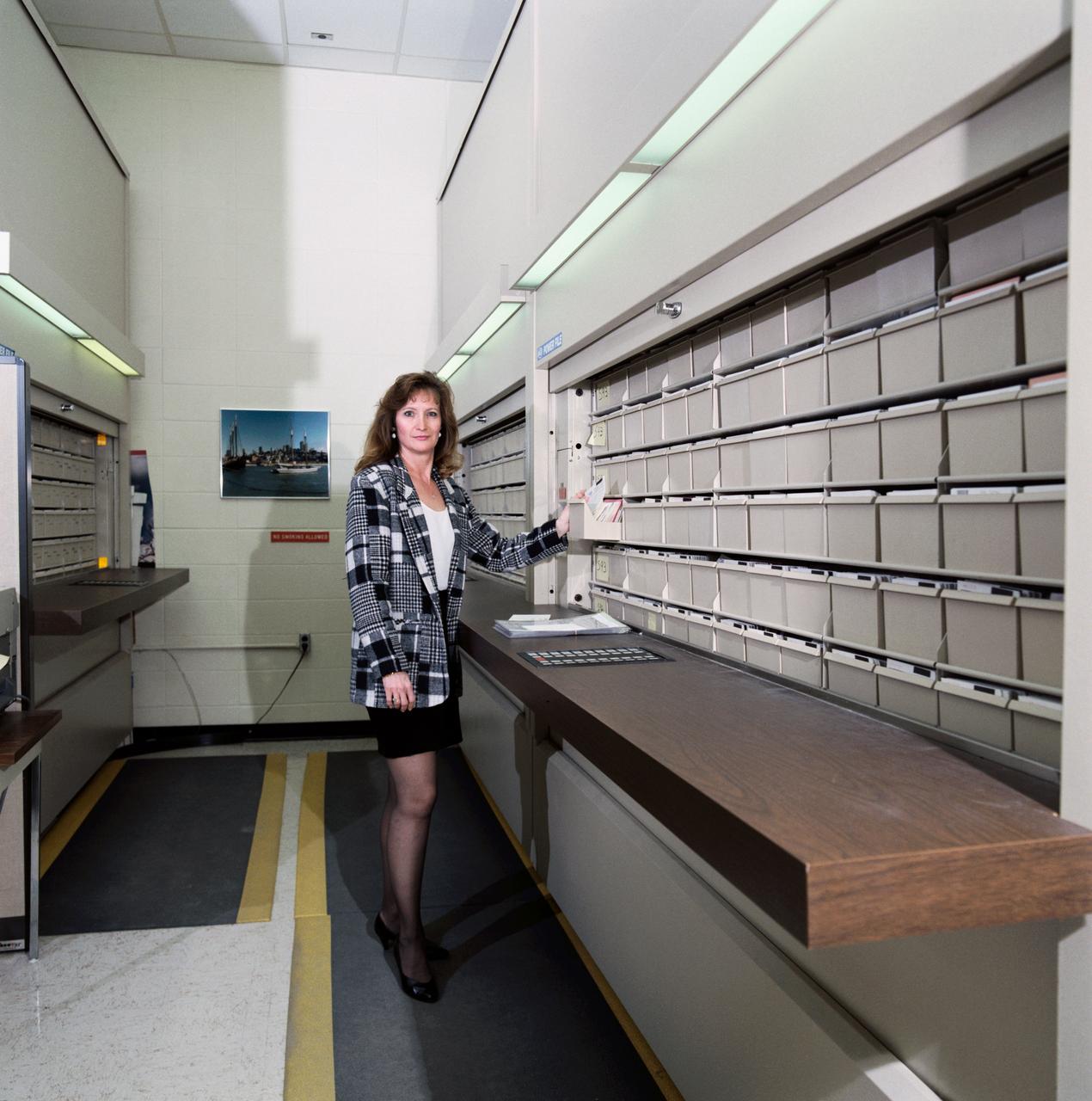

Views of Image Sciences Division activities in bldg 8 and 424 for use in presentation by George Abbey, Deputy Center Director. Views include Taft Broadcasting employee Dexter Herbert in television editing suite in bldg 8 (26624); RMS Photographic Services employee Kelly St. Germaine at IAMS viewing station in the lobby of bldg 8 (26625); RMS employee Irene Jenkins standing in front of automated files used for negative storage in bldg 424 (26626); RMS employee Irma Rodriguez at barcoding and checkout station in bldg 424 (26627).
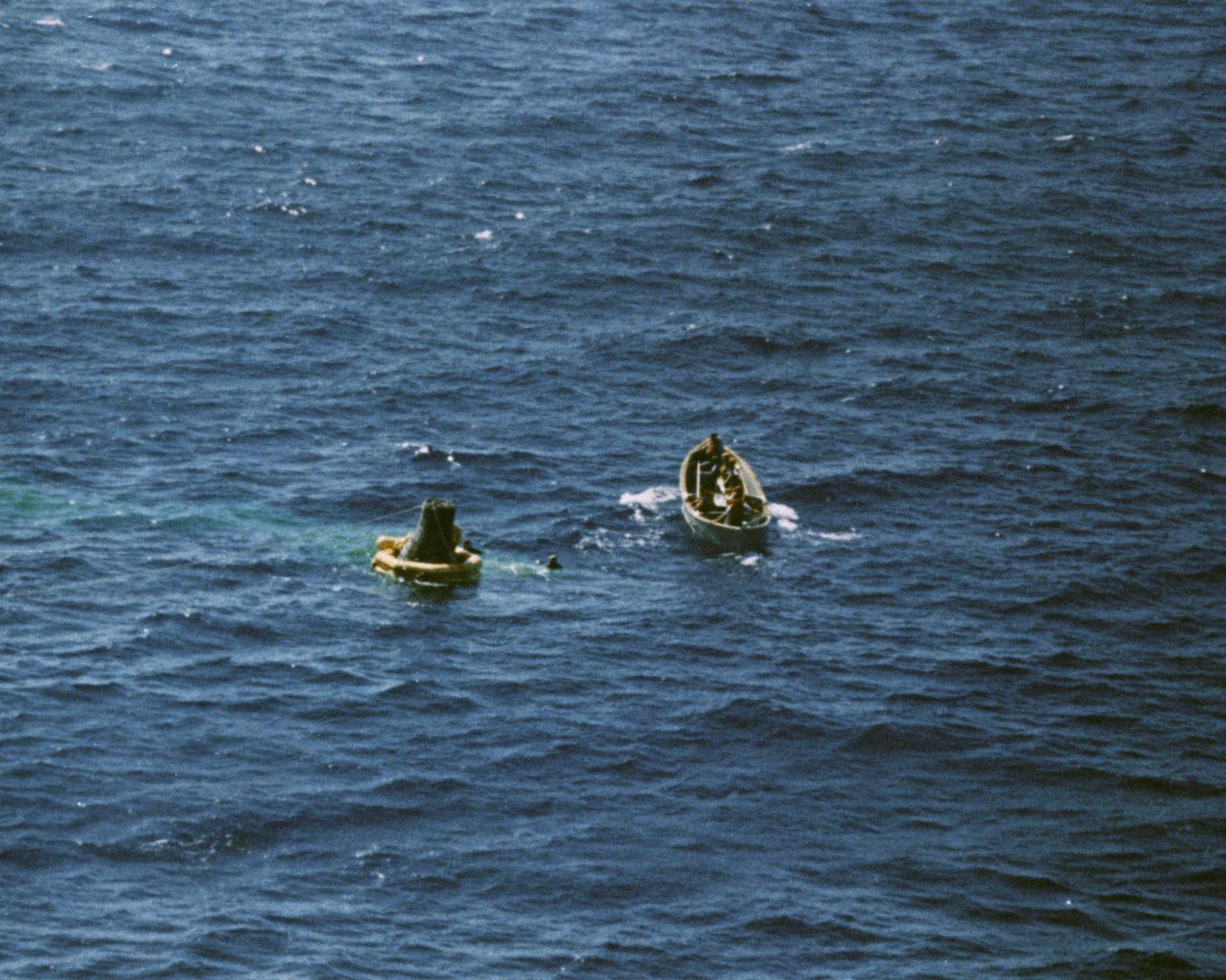

S62-09049 (3 Oct. 1962) --- Aerial view of a life boat from the USS Kearsarge, recovery ship, approaching the floating Sigma 7 capsule for the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) mission. Photo credit: NASA
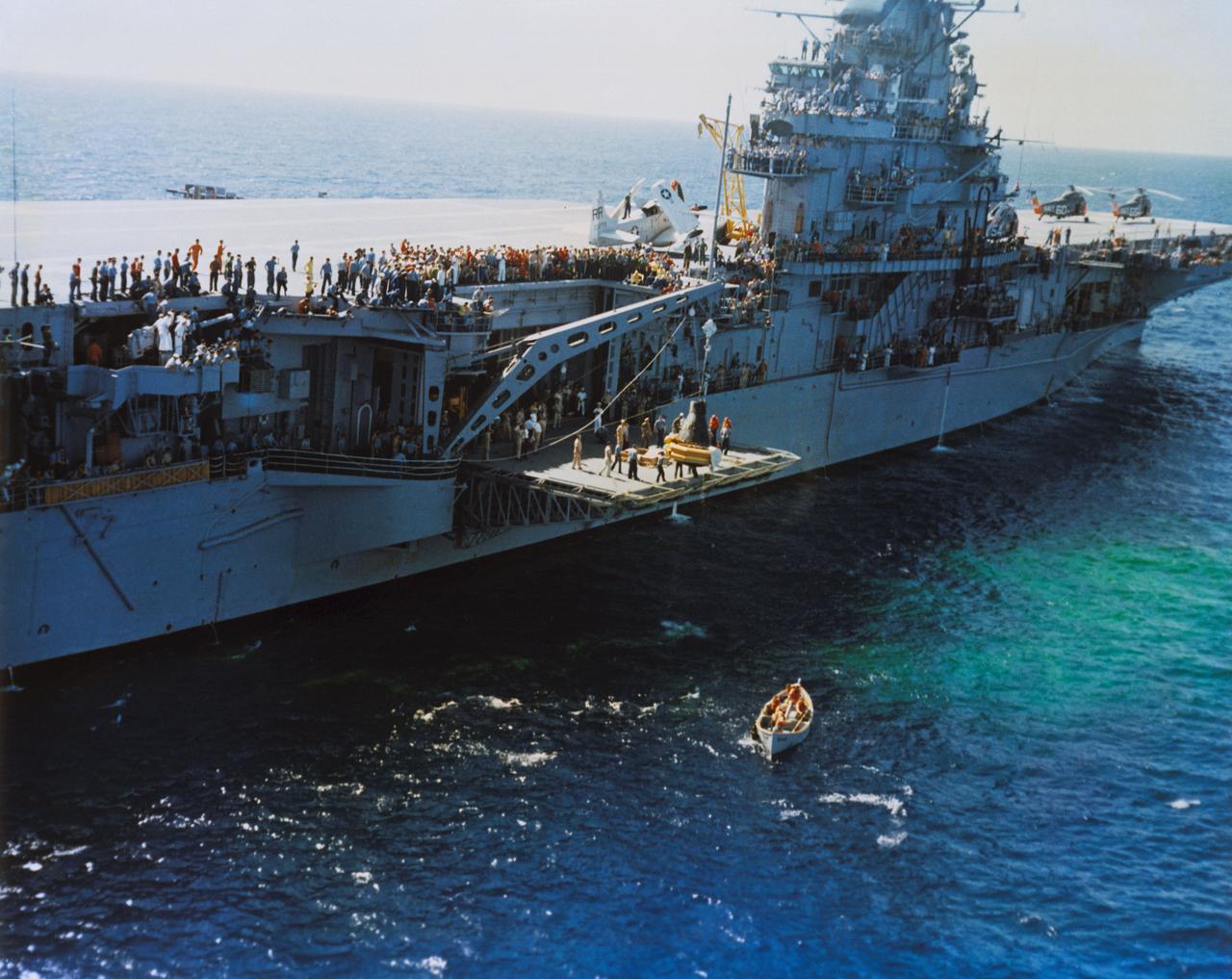

S62-09050 (3 Oct. 1962) --- Aerial view of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) Sigma 7 capsule being lowered to the deck of the carrier USS Kearsarge. Photo credit: NASA
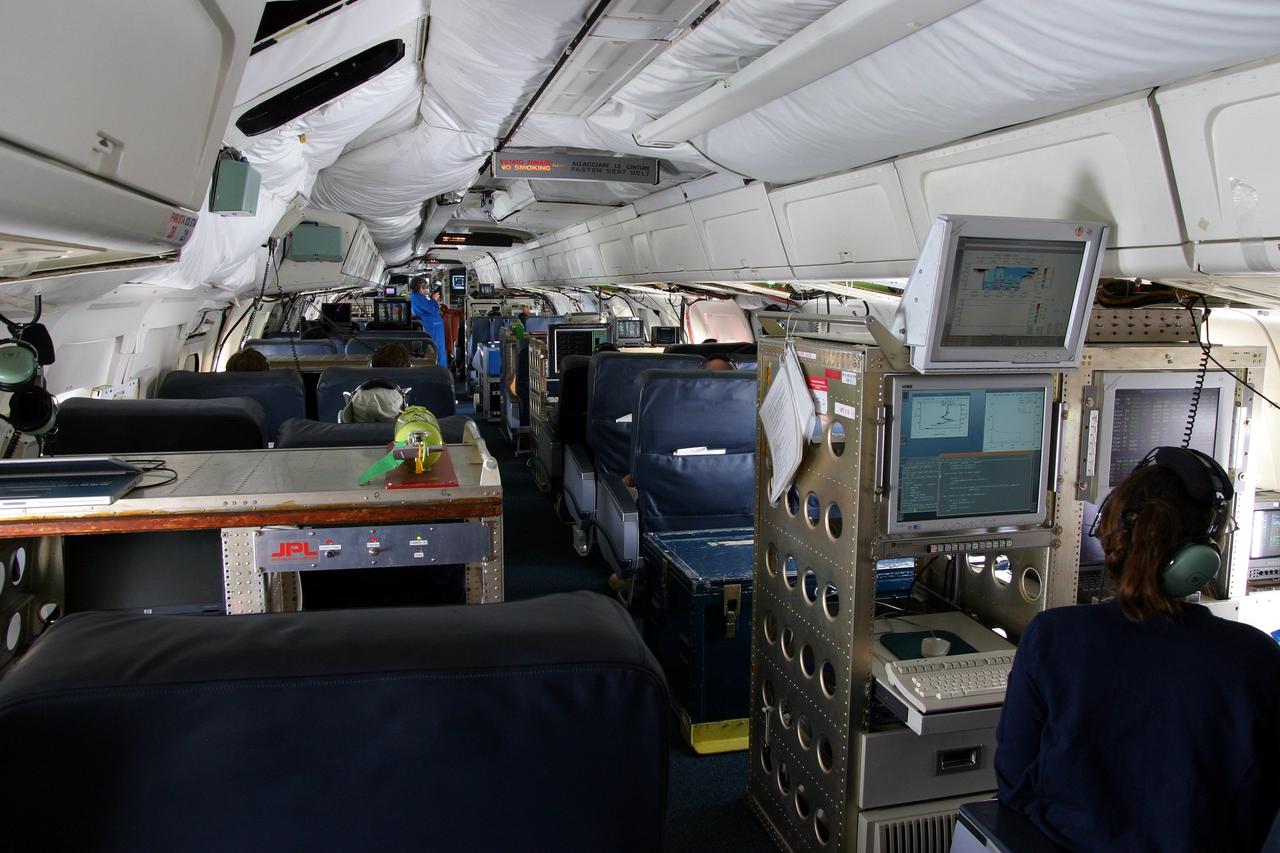

DC-8 NAMMA MISSION TO CAPE VERDE, AFRICA: a view of NASA's DC-8 cabin during a science flgiht to fly above, under and through Tropical Storm Debby.
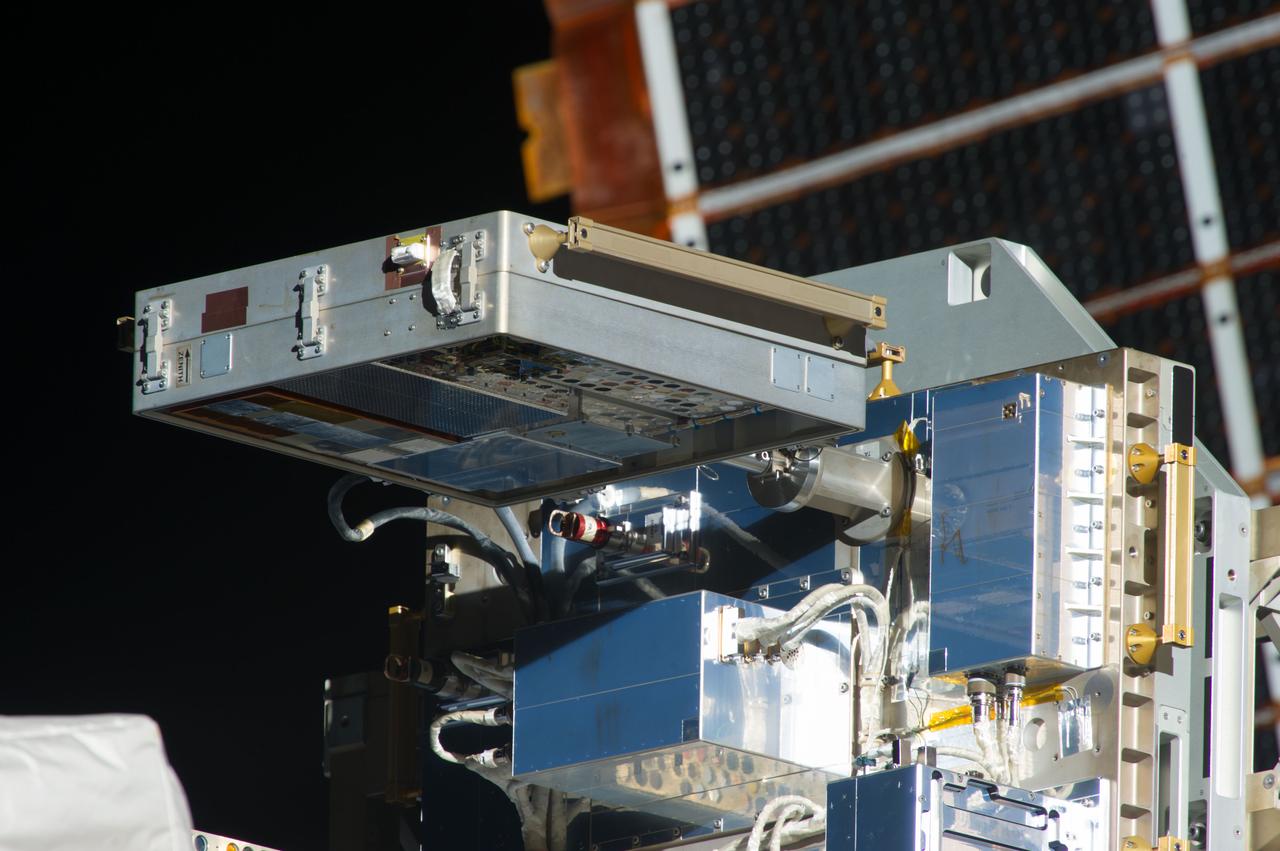
iss036e004042 (5/24/2013) --- View of Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8) which is installed on the ExPRESS Logistics Carrier 2 (ELC-2),located on the S3 Truss Outboard Zenith site.
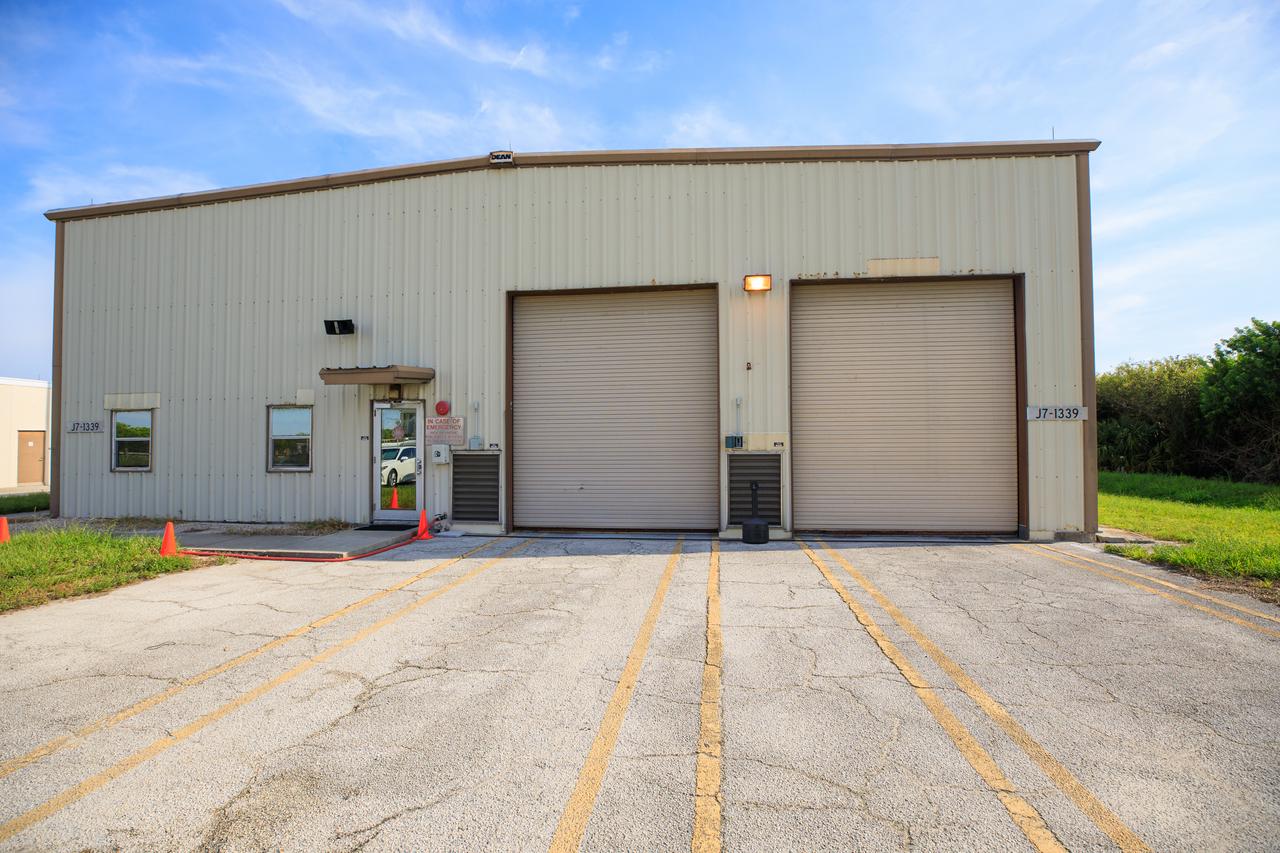

An exterior view of Fire Station 3 at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 8, 2022.
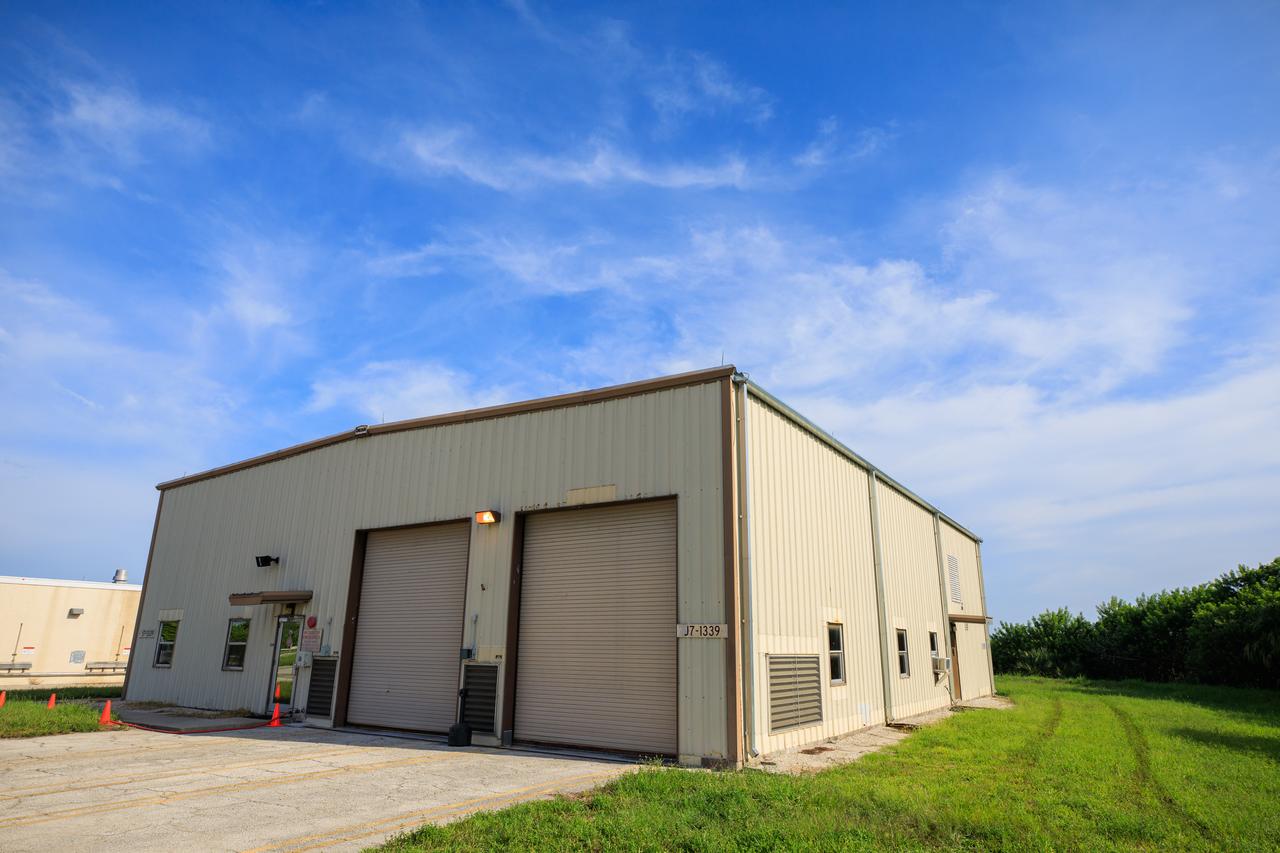

An exterior view of Fire Station 3 at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 8, 2022.
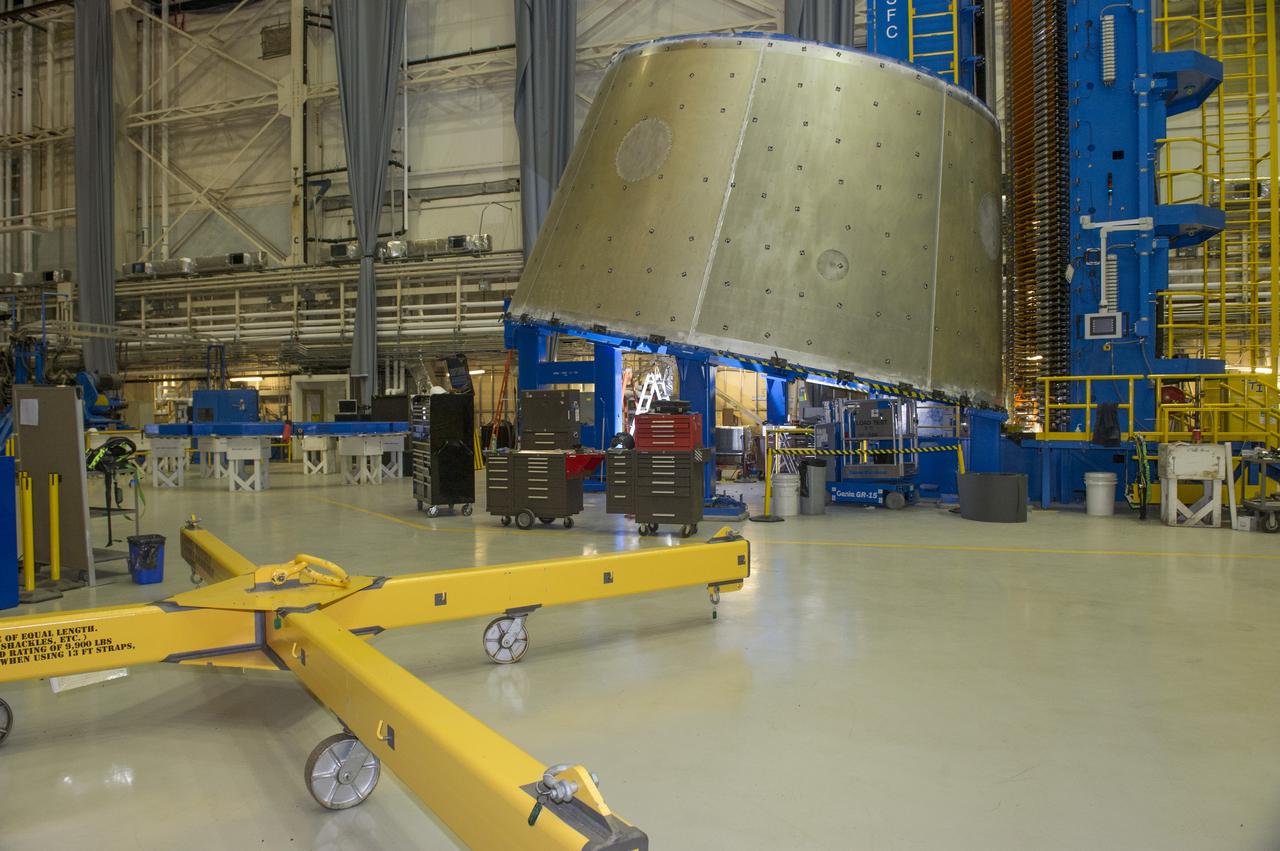

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 EXTERIOR VIEWS OF LVSA AFT CONE
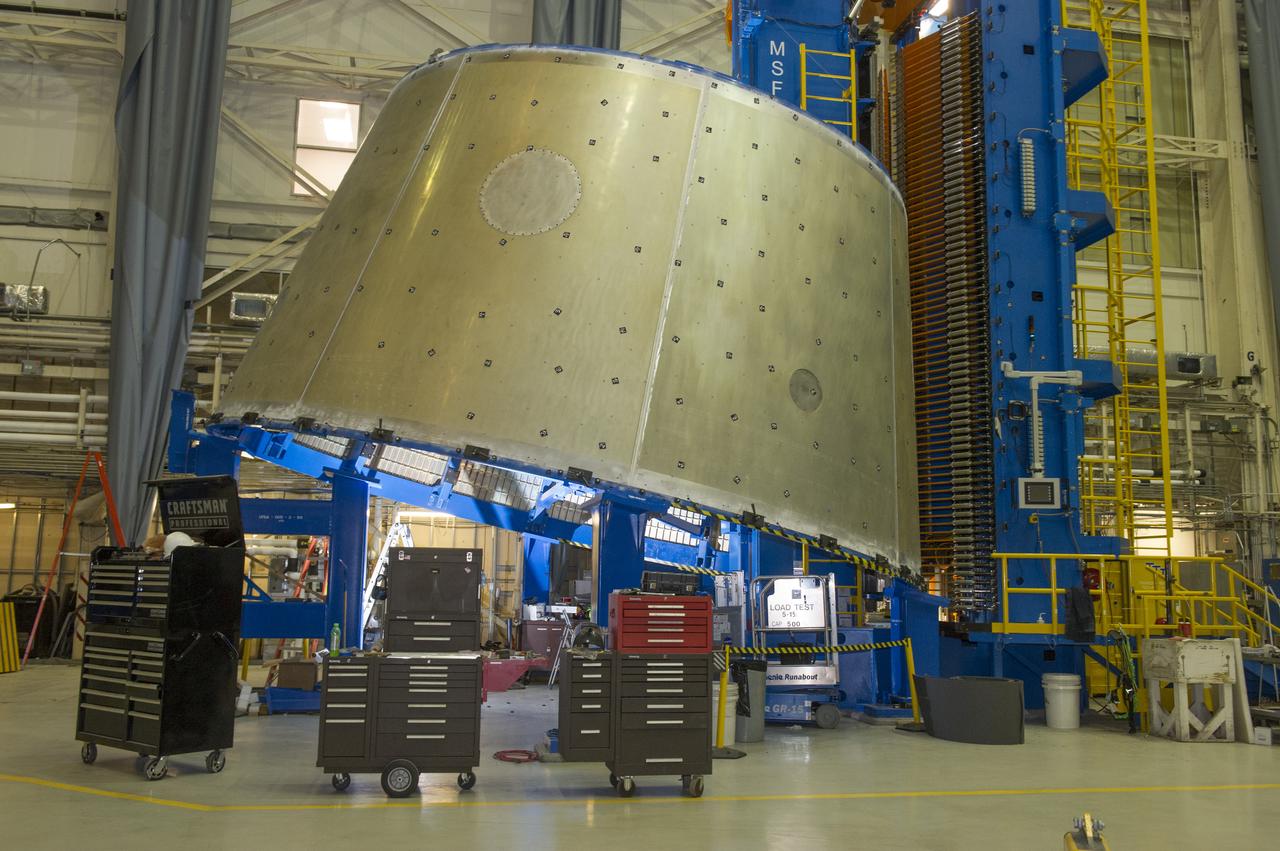

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 EXTERIOR VIEWS OF LVSA AFT CONE
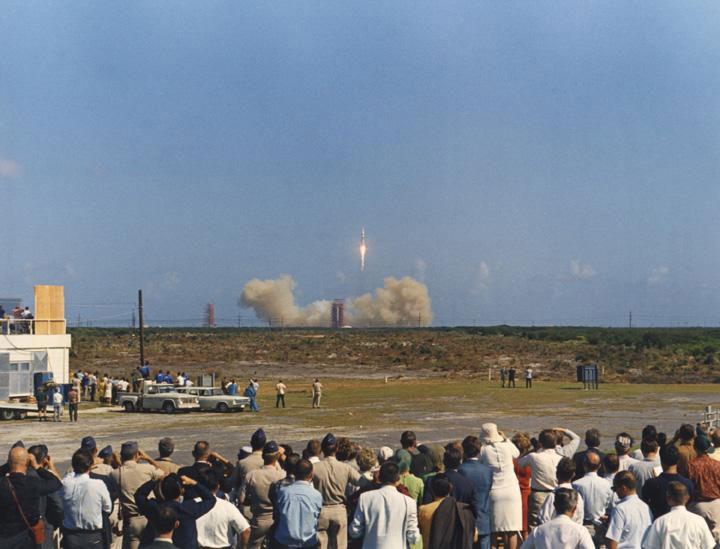

View of Press Site 2, CCAFS, during launch of Apollo 8, October 11, 1968
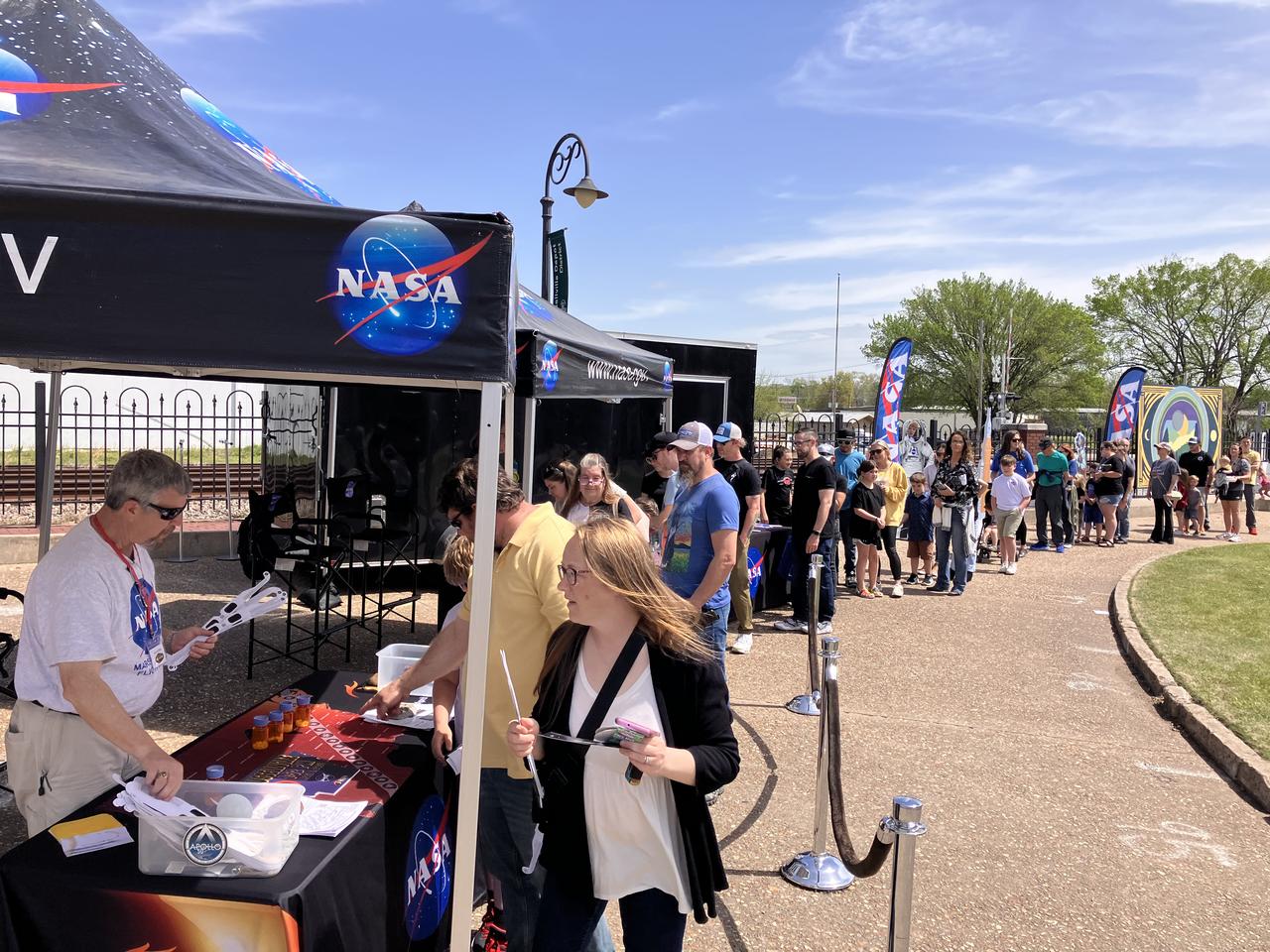

NASA gives out solar eclipse glasses for people to safely view the eclipse on April 8 in Russellville, Arkansas.

View of OPF High Bay No. 1, Level 13 platform installation, July 8, 1977

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 EXTERIOR VIEWS OF LVSA AFT CONE

An exterior view of Fire Station 3 at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 8, 2022.
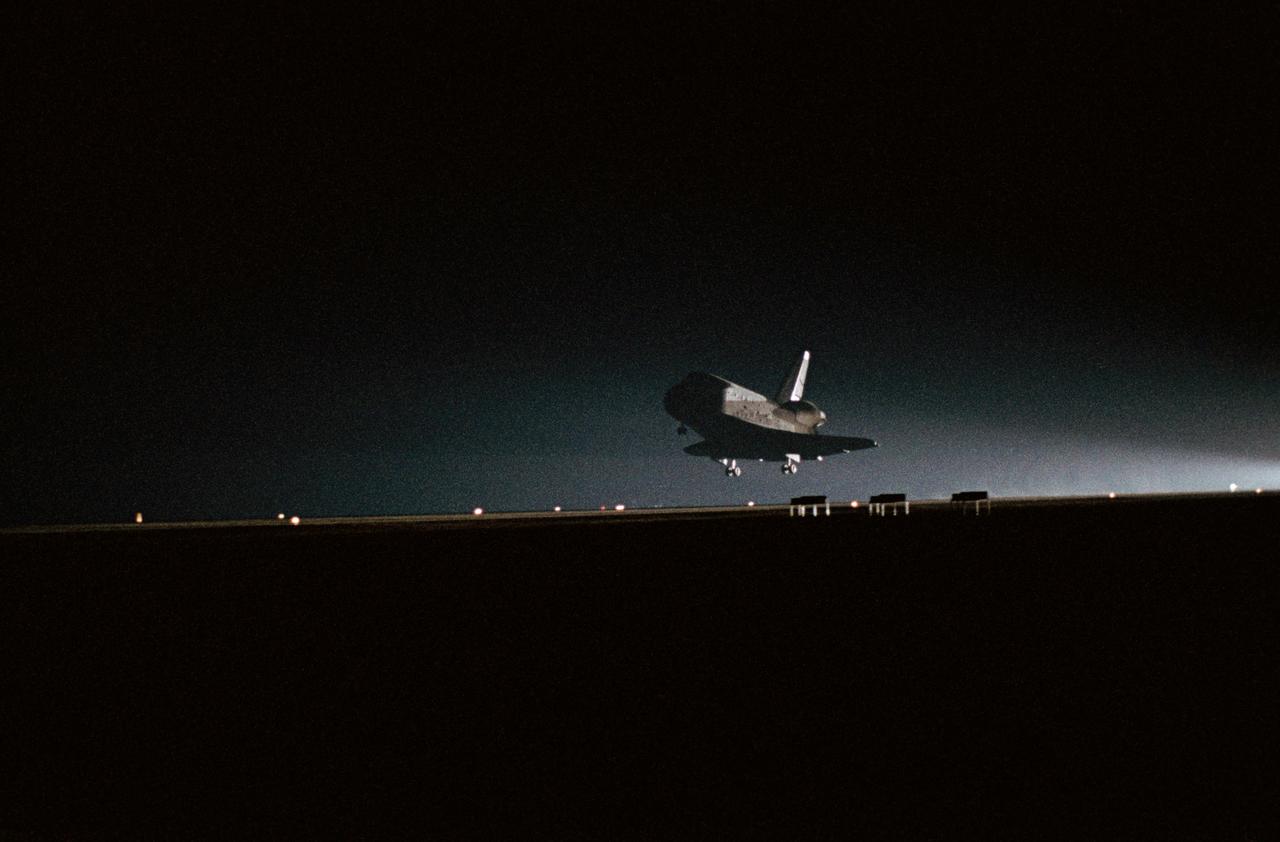

Night view, Challenger STS-8 as it is coming in for a landing. EDWARDS AFB (EAFB), CA
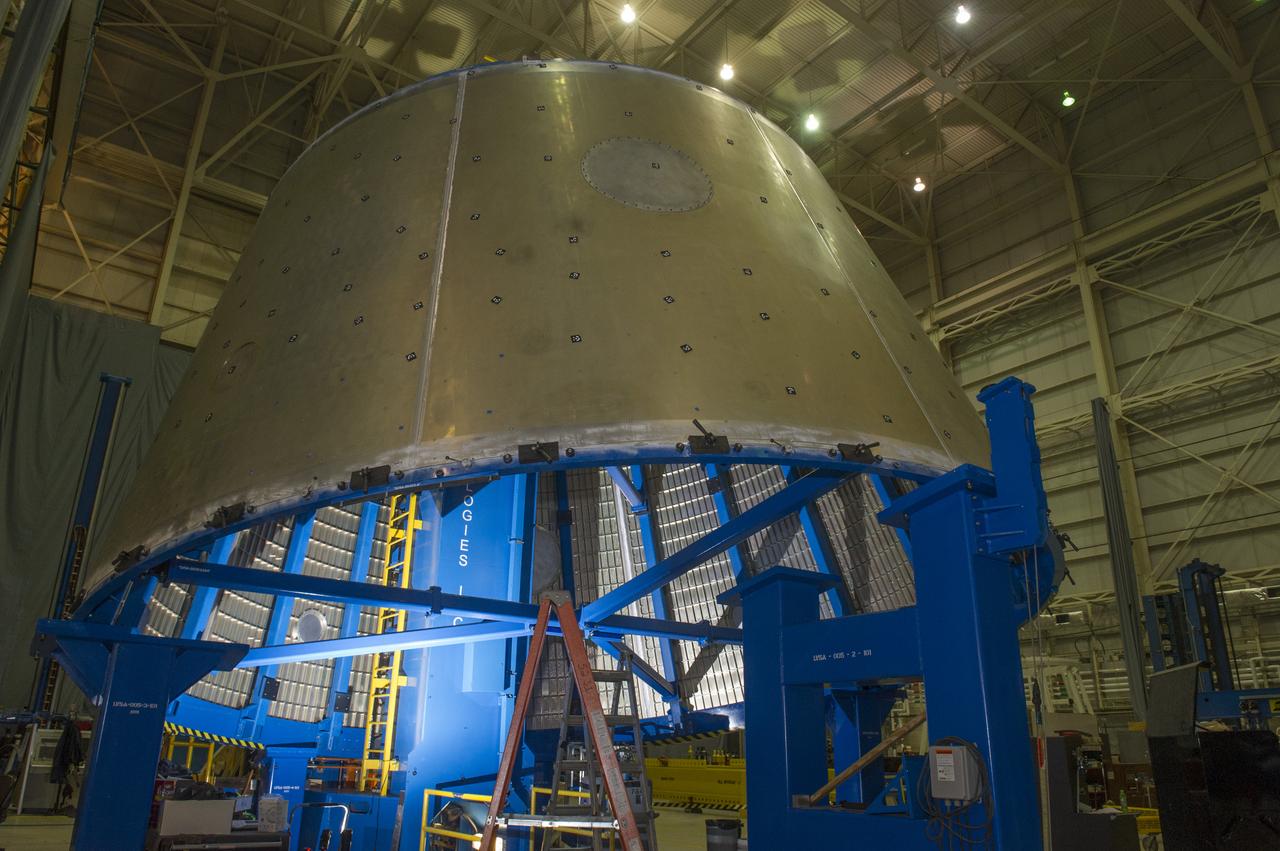

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 EXTERIOR VIEWS OF LVSA AFT CONE
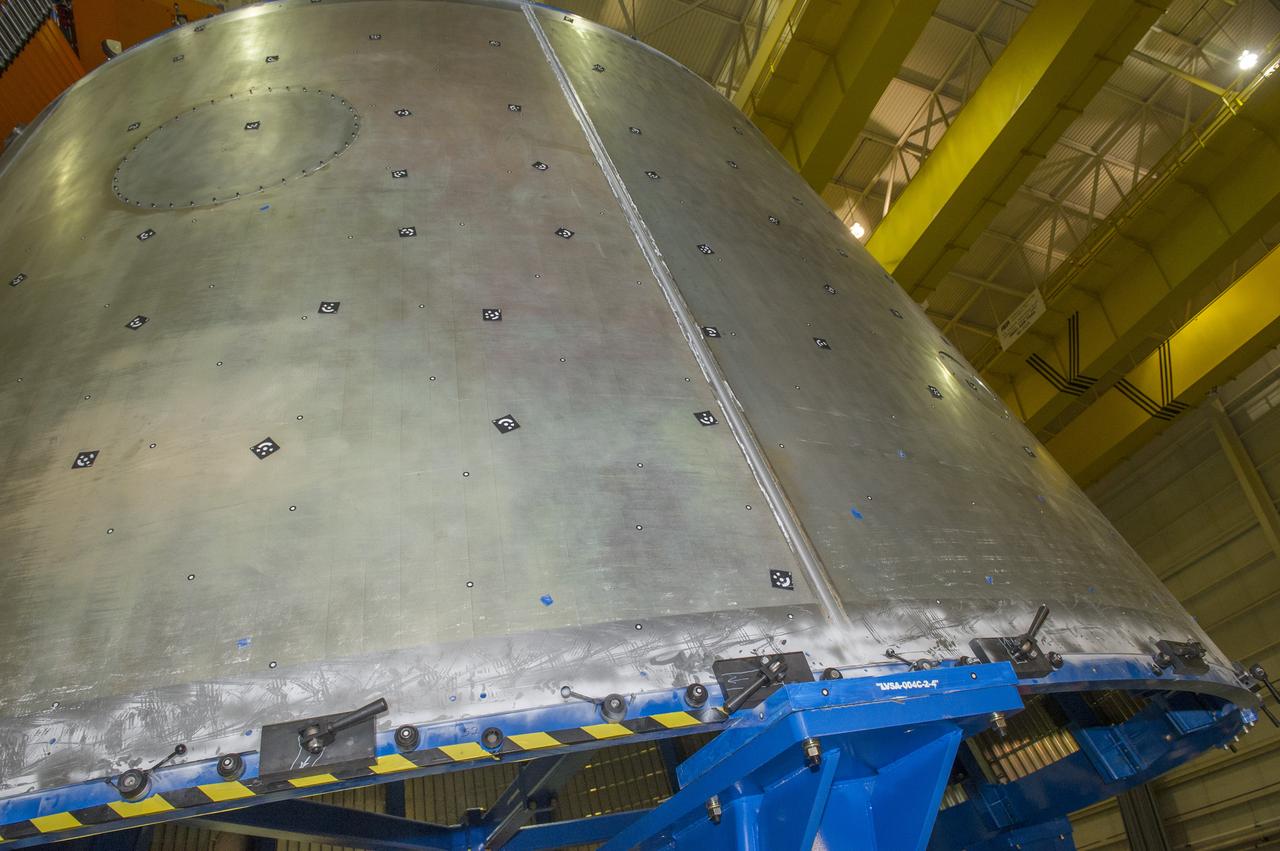

LVSA AFT CONE SECTION POST WELD #8 EXTERIOR VIEWS OF LVSA AFT CONE
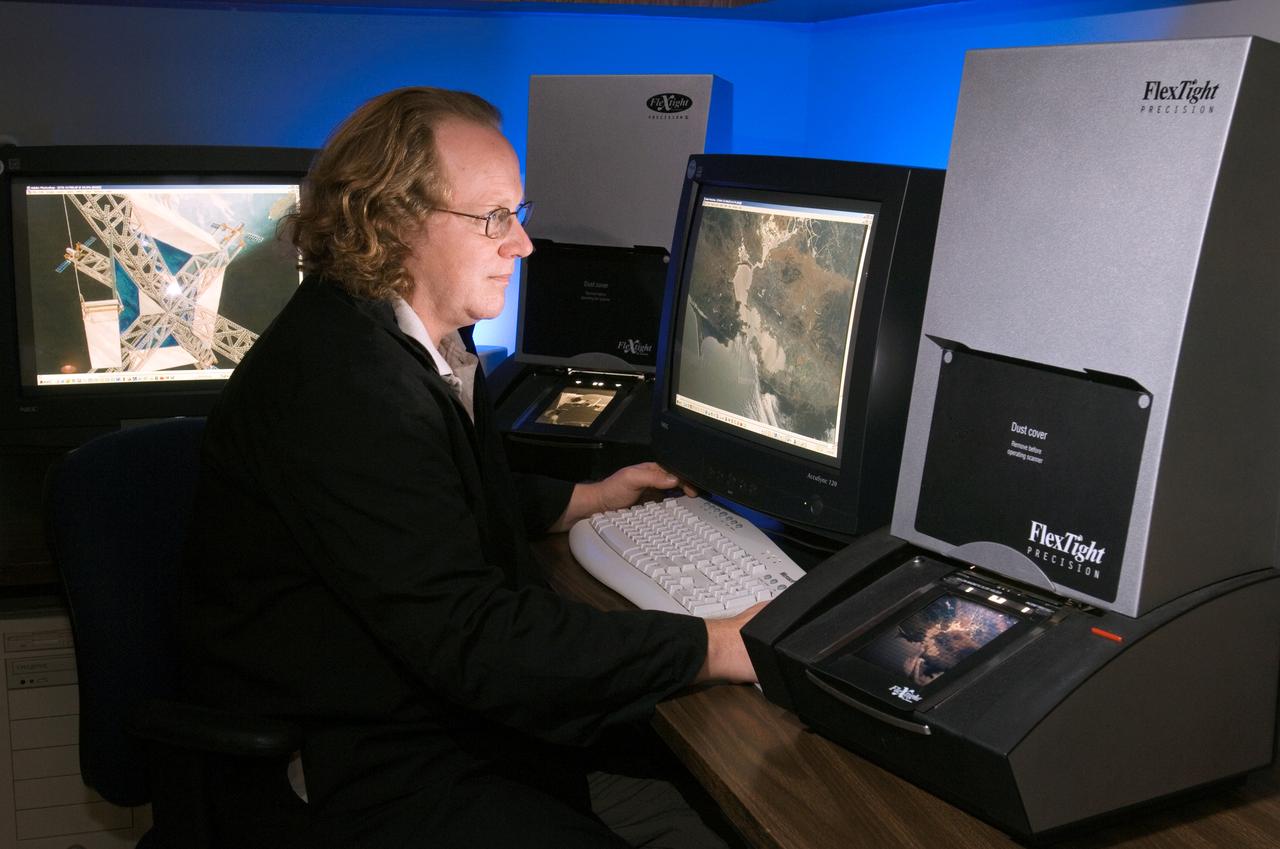

View of Larry Jefferson in the Building 8 photo lab scanning area working with Environmental Photos.
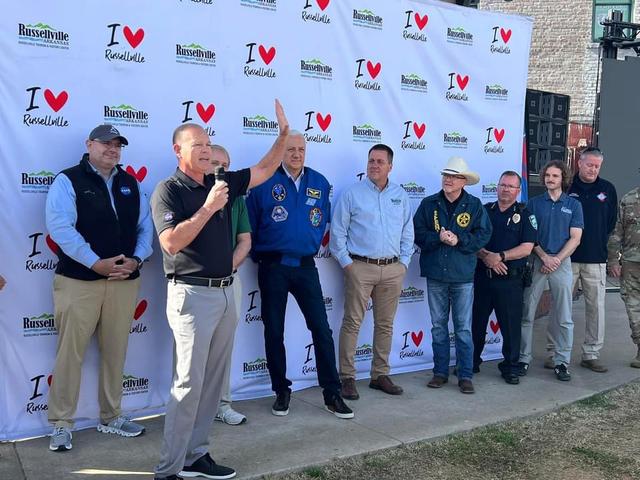

NASA Stennis Acting Center Director John Bailey, front left, speaks to people gathered to view the total solar eclipse in Russellville, Arkansas, on April 8.
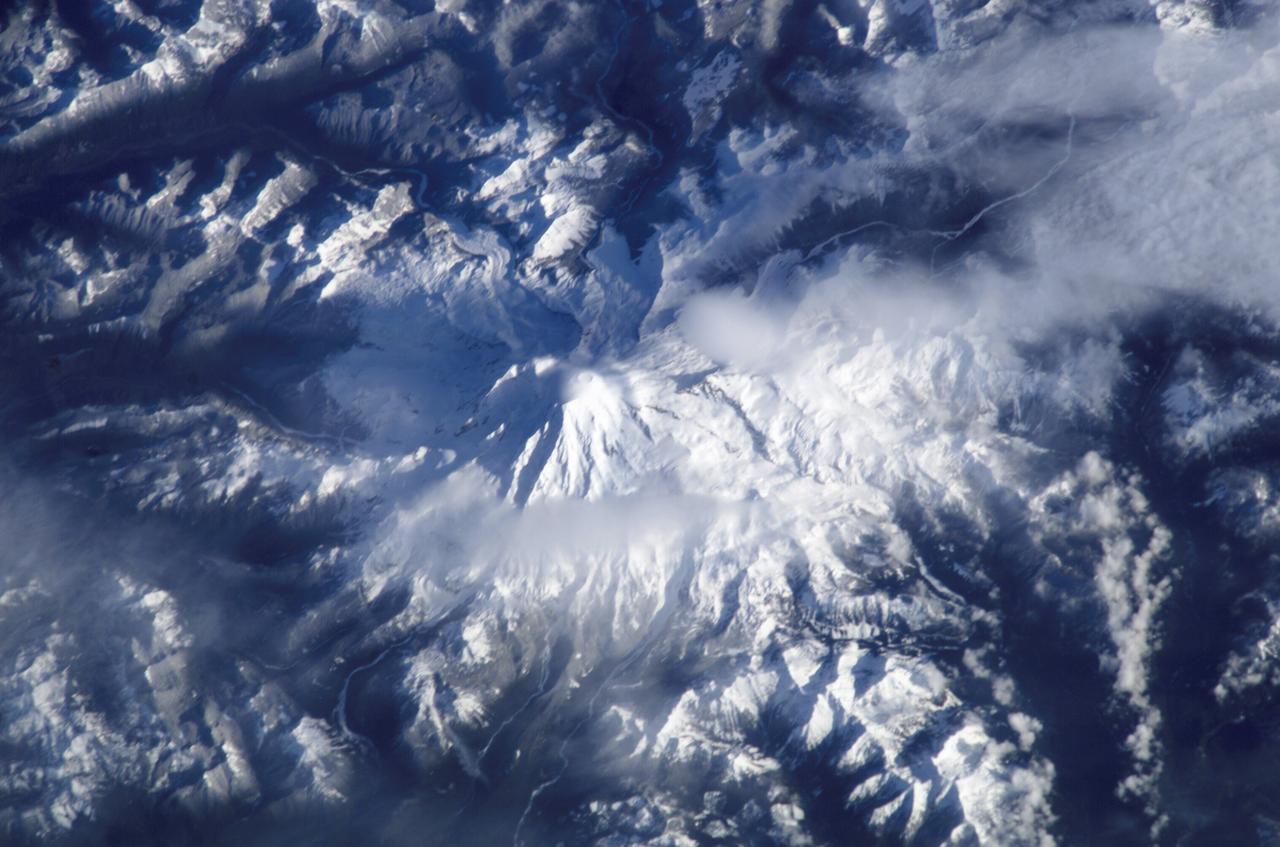

ISS008-E-17649 (29 February 2004) --- This view featuring Mount Rainer, Washington, was photographed by an Expedition 8 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS).
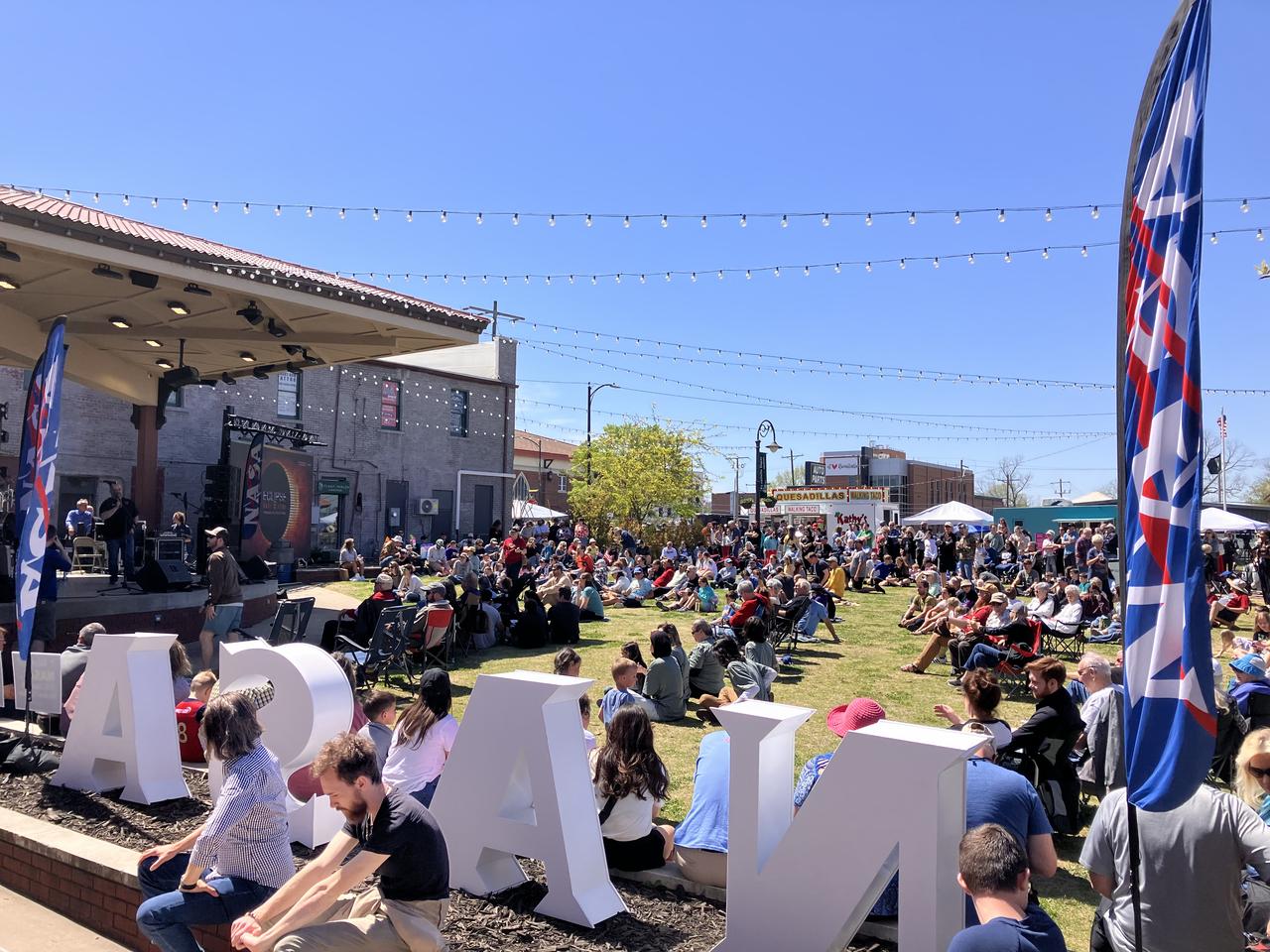

A crowd of people in Russellville, Arkansas, prepare to watch the total solar eclipse on April 8 as Forbes ranked the city as a top spot for viewing.
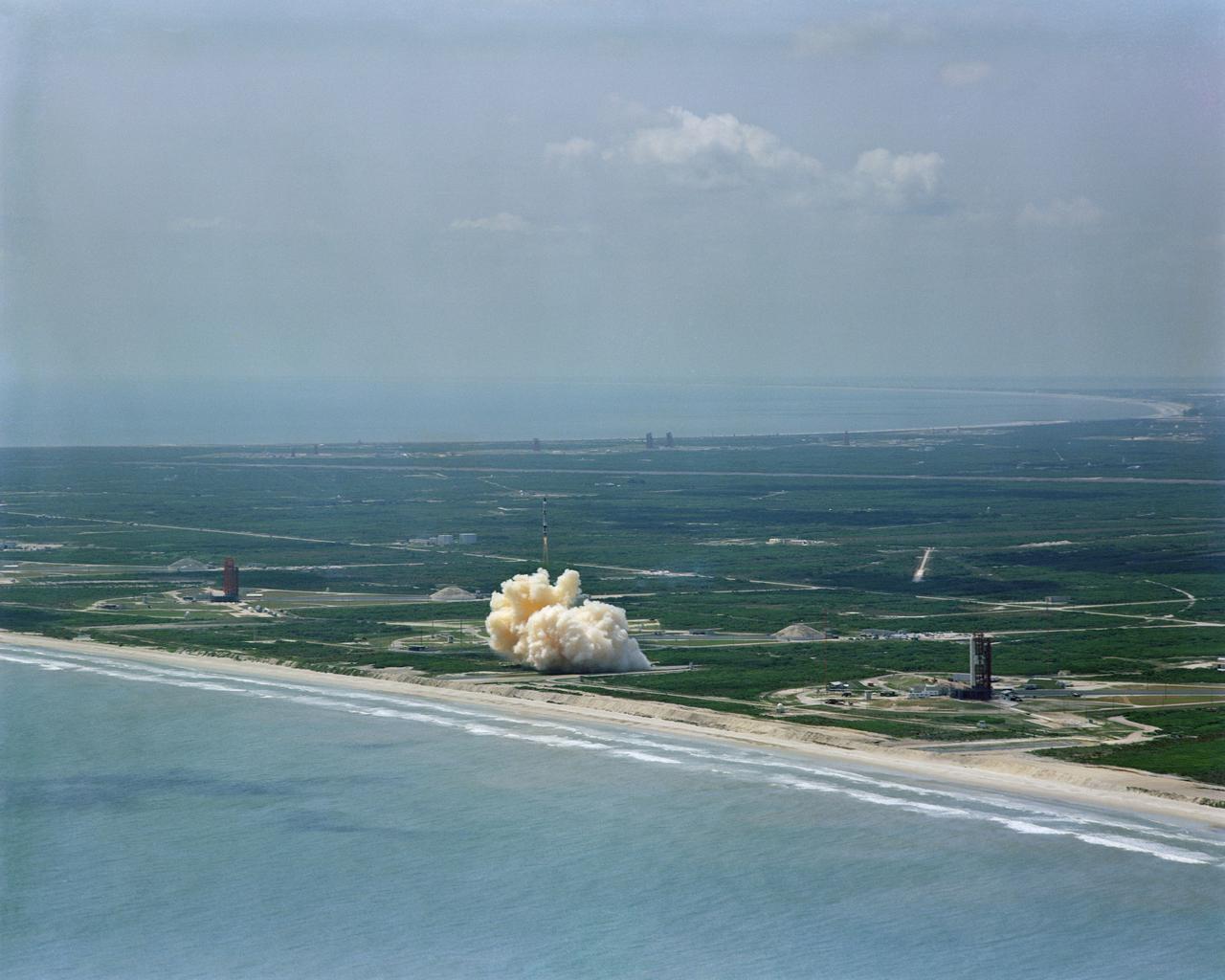

S64-22412 (8 April 1964) --- Aerial view of the Gemini/Titan-II launch vehicle #1 liftoff at Cape Kennedy, Florida.
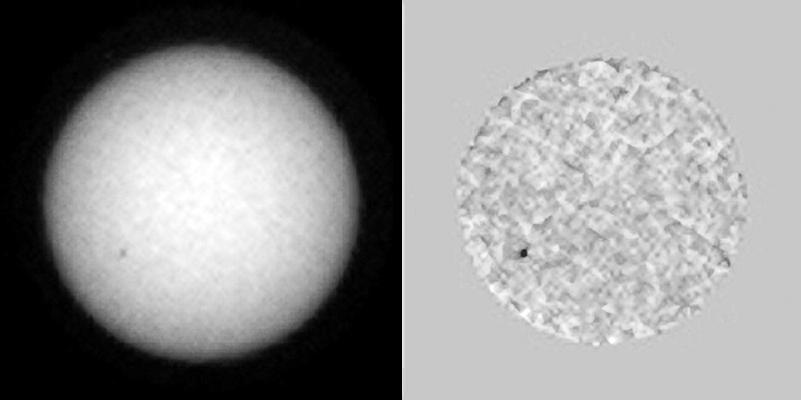
This single frame from a sequence of images shows sunspots as viewed by NASA Curiosity Mars rover from June 27 to July 8, 2015; the rover was in position to see the opposite side of the sun from the side facing Earth during this period. One sunspot seen in this series emerged while under Curiosity's view, subsequently rotated out of view over the July 4 weekend. That sunspot's location showed up a few days later observable from Earth's point of view as an area of solar eruptions and source of a coronal mass ejection. The coronal mass ejection affected interplanetary space weather, though not in Earth's direction. The images were taken by the right-eye camera of Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam), which has a 100-millimeter telephoto lens. The view on the left of each pair in this sequence has little processing other than calibration and putting north toward the top of each frame. The view on the right of each pair has been enhanced to make sunspots more visible. The apparent granularity throughout these enhanced images is an artifact of this processing. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19801