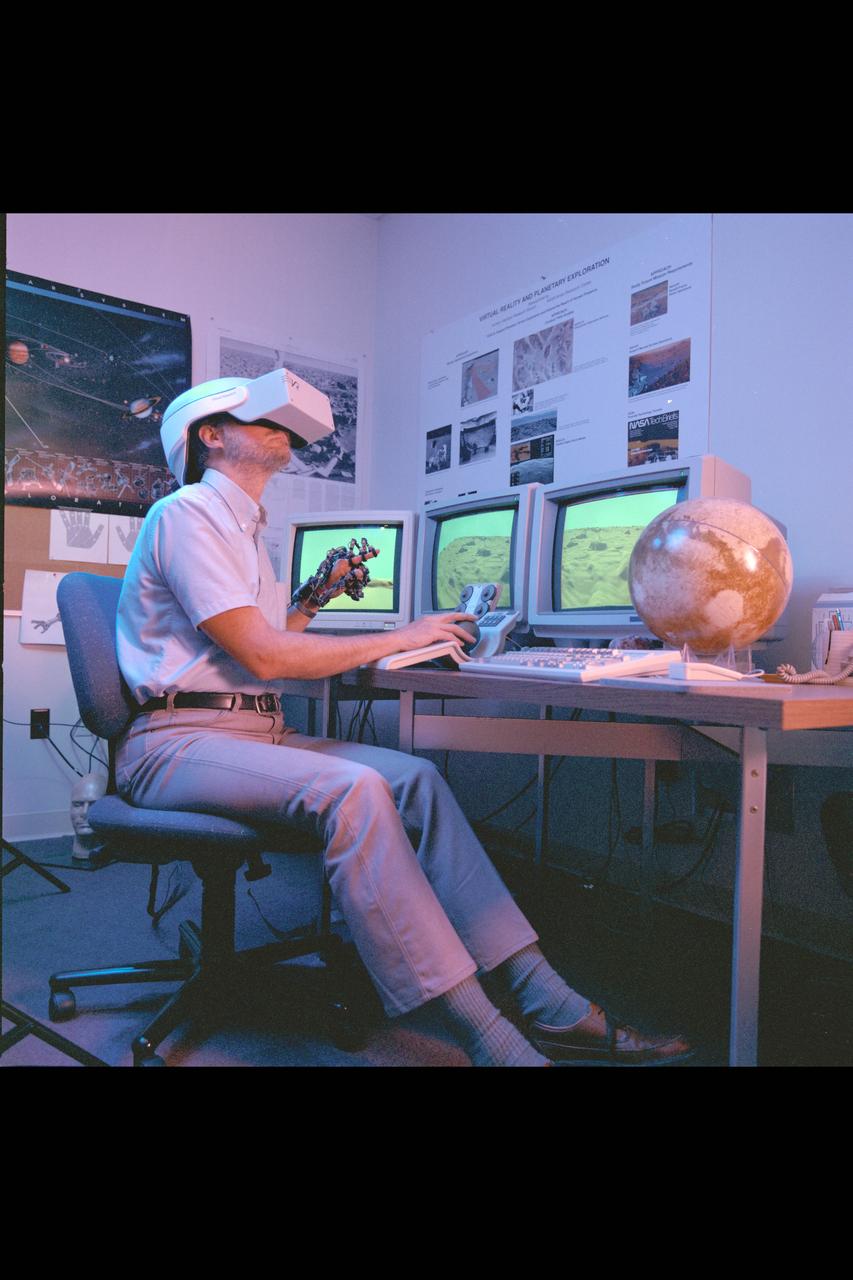

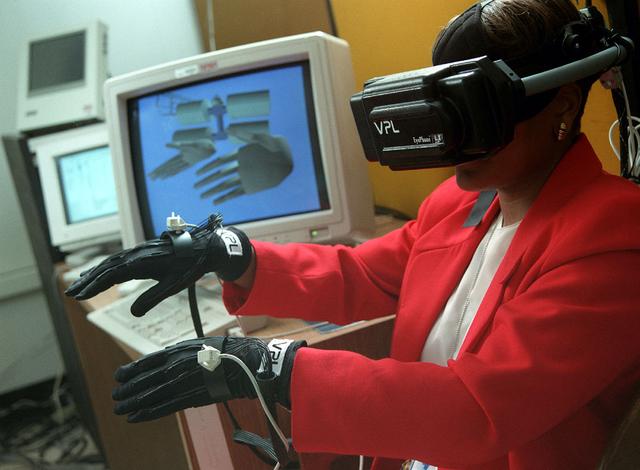
Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
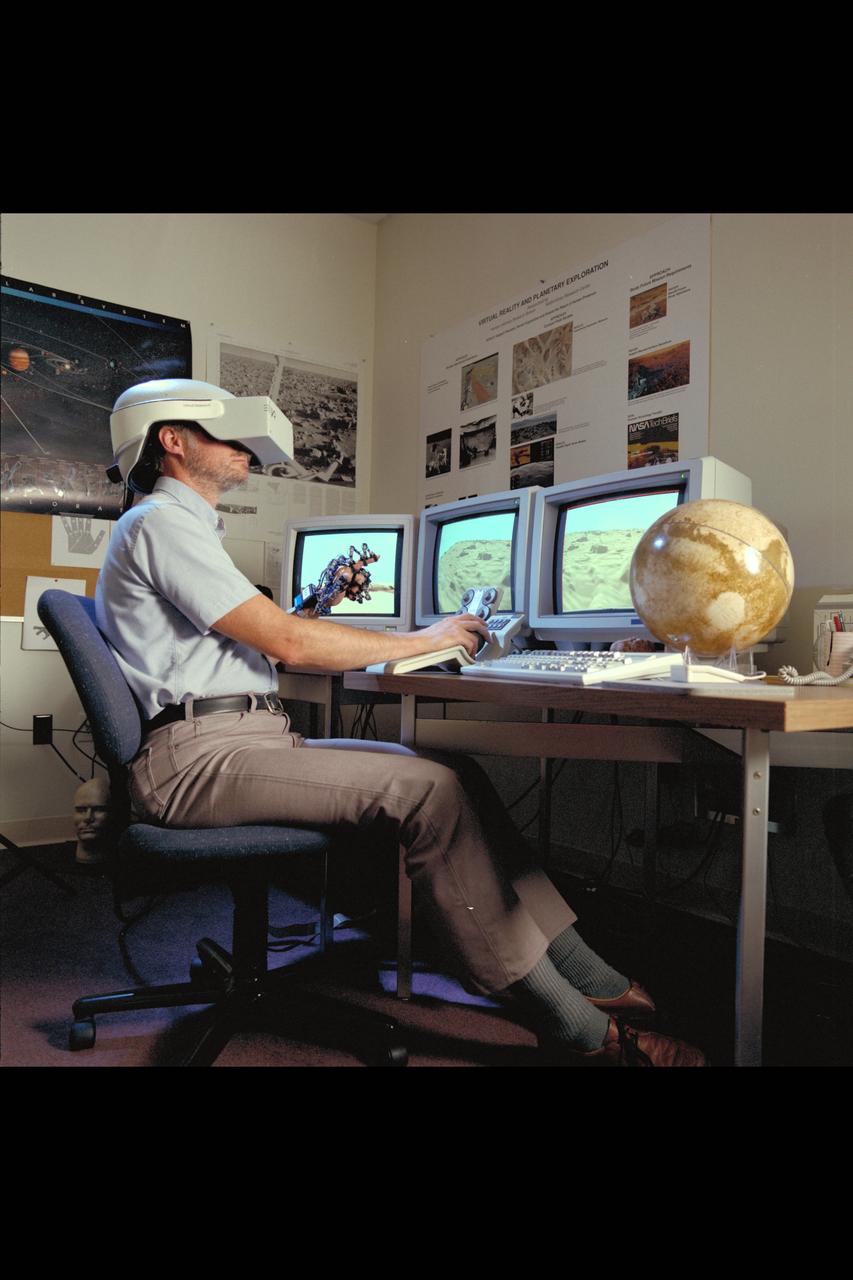

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
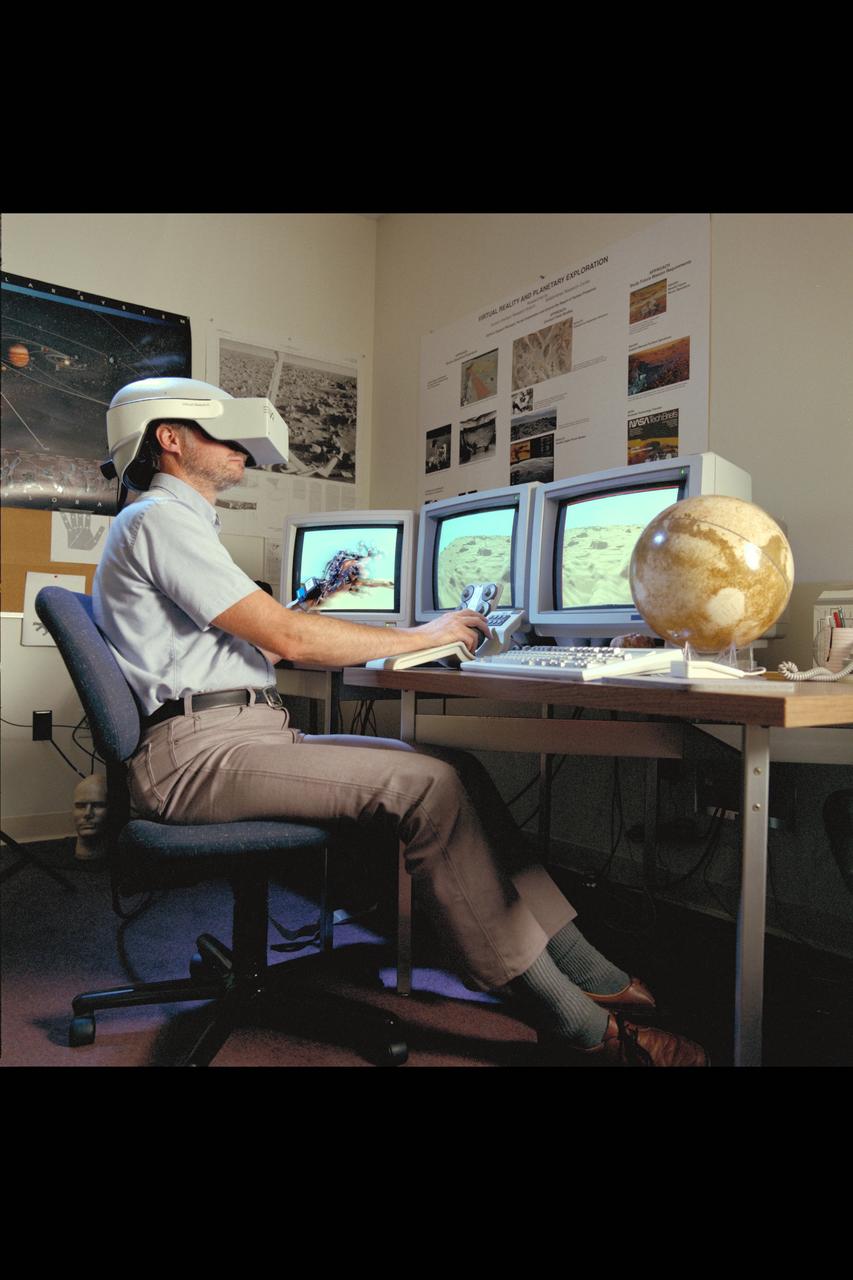

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
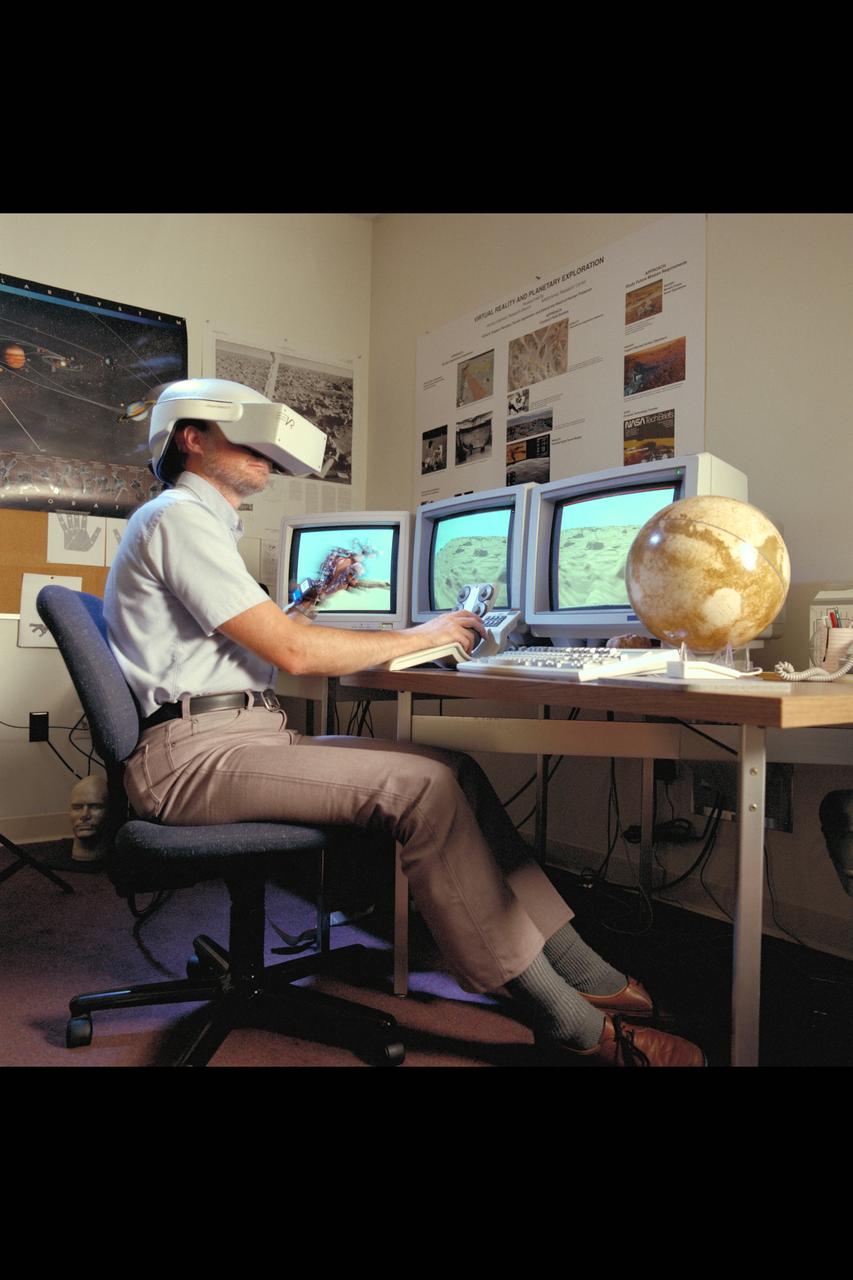

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
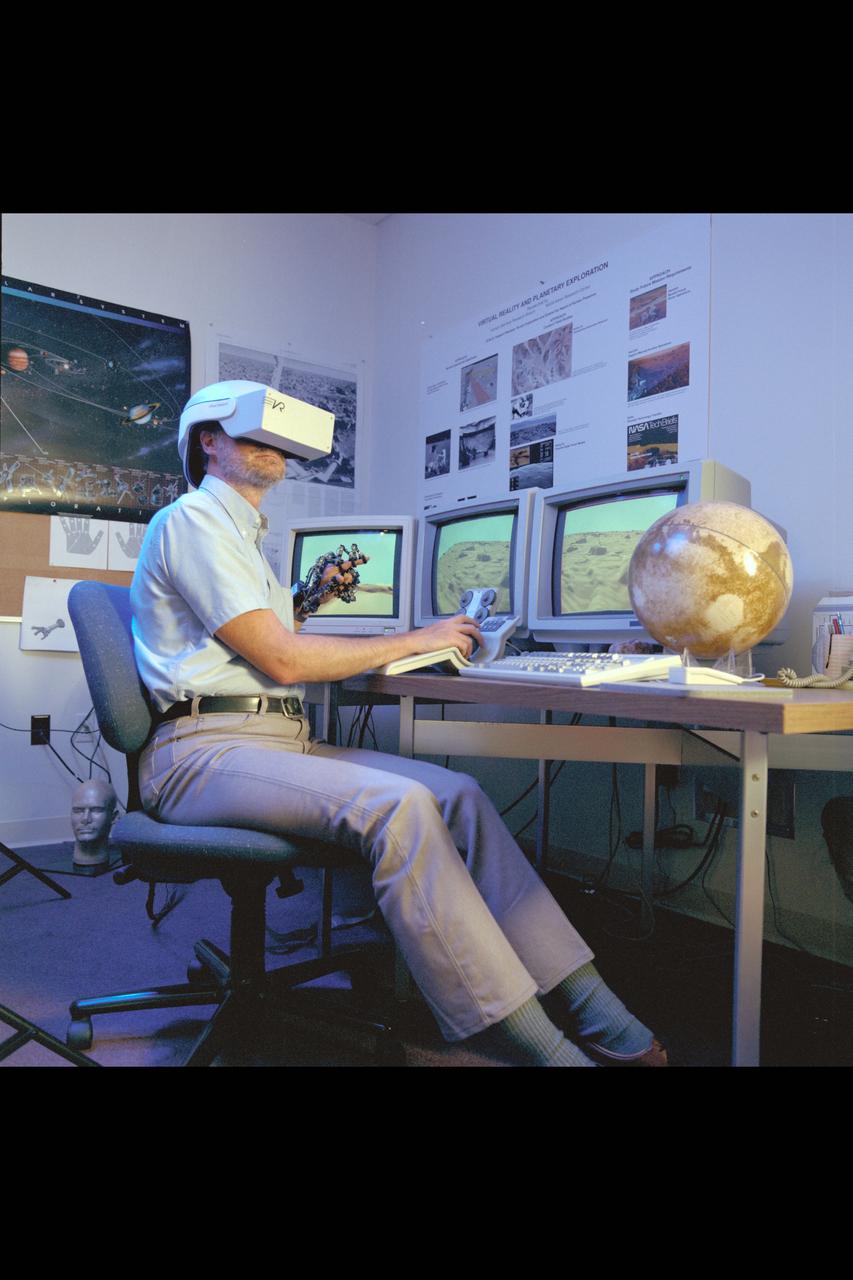

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
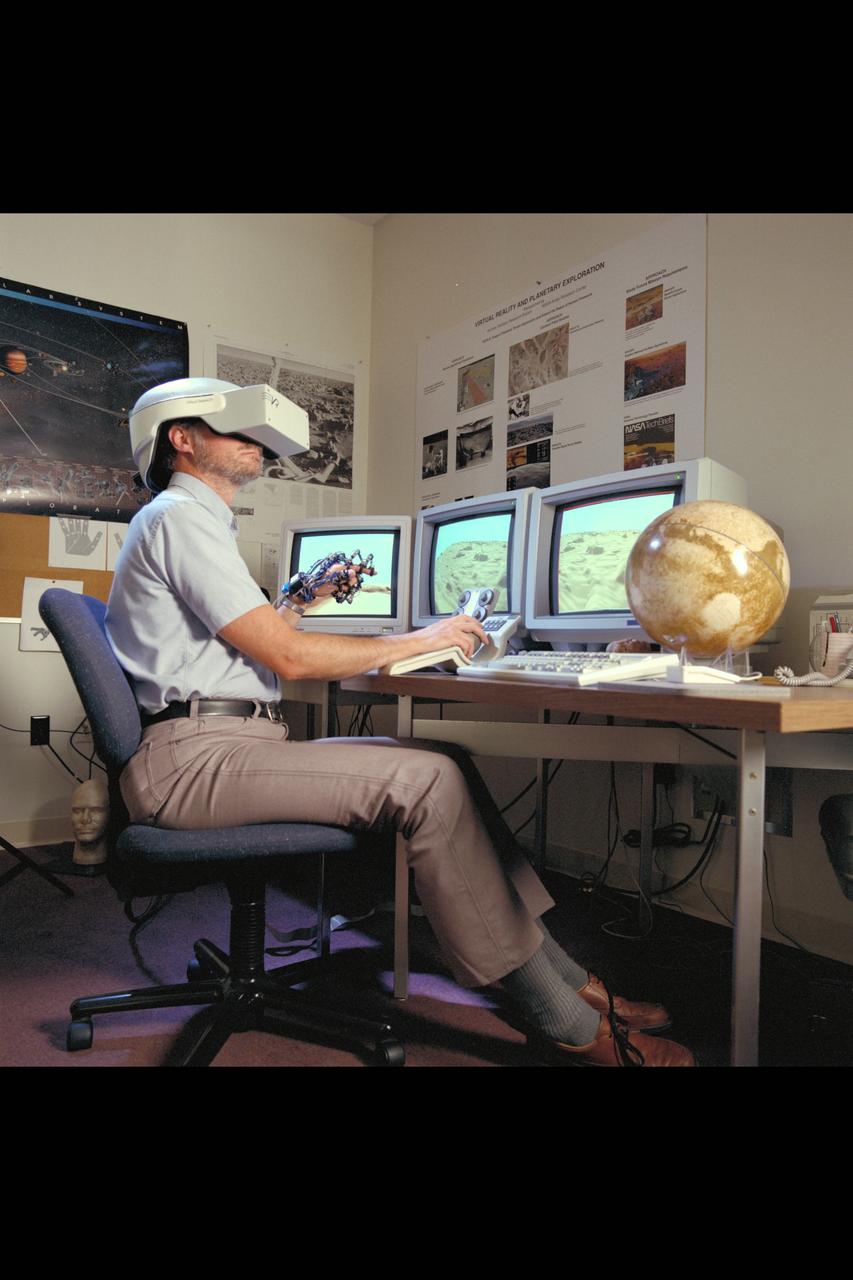

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
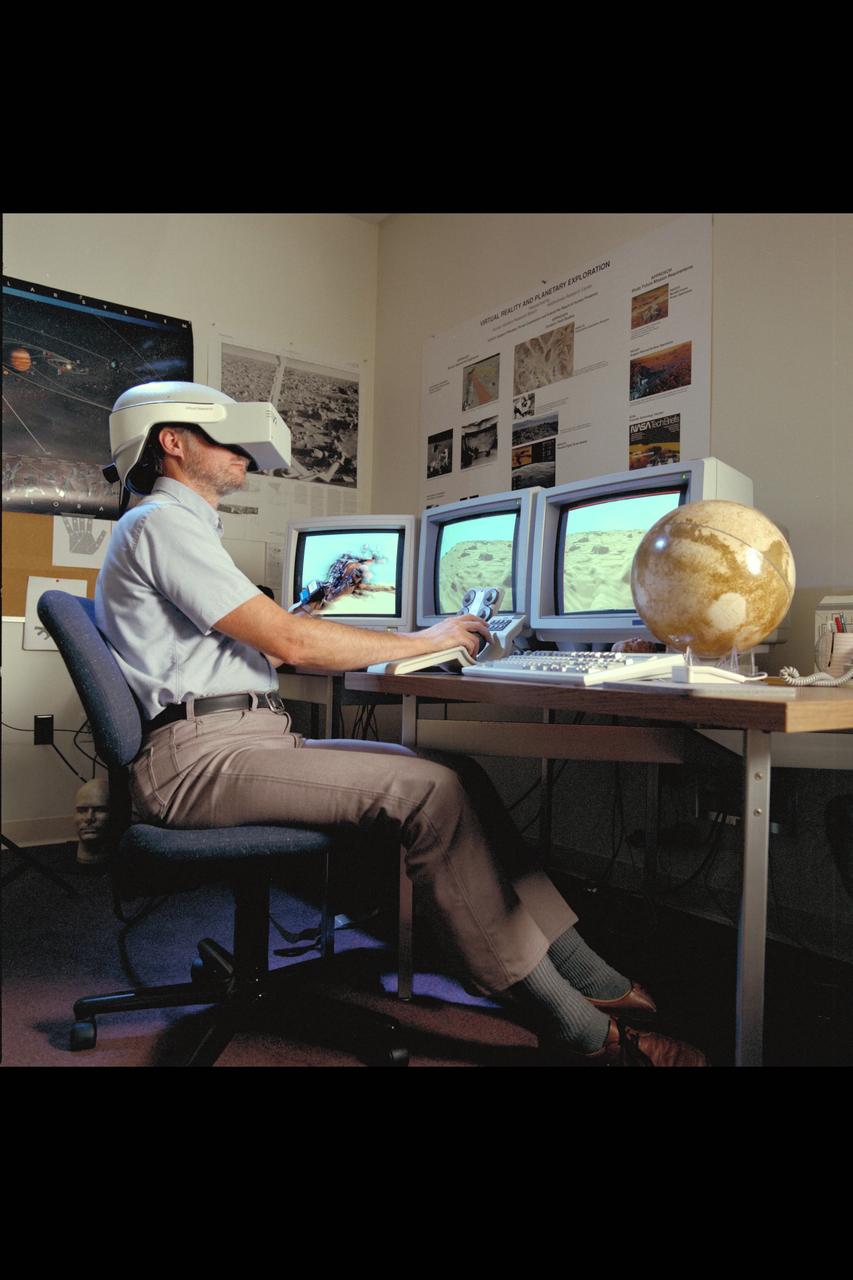

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
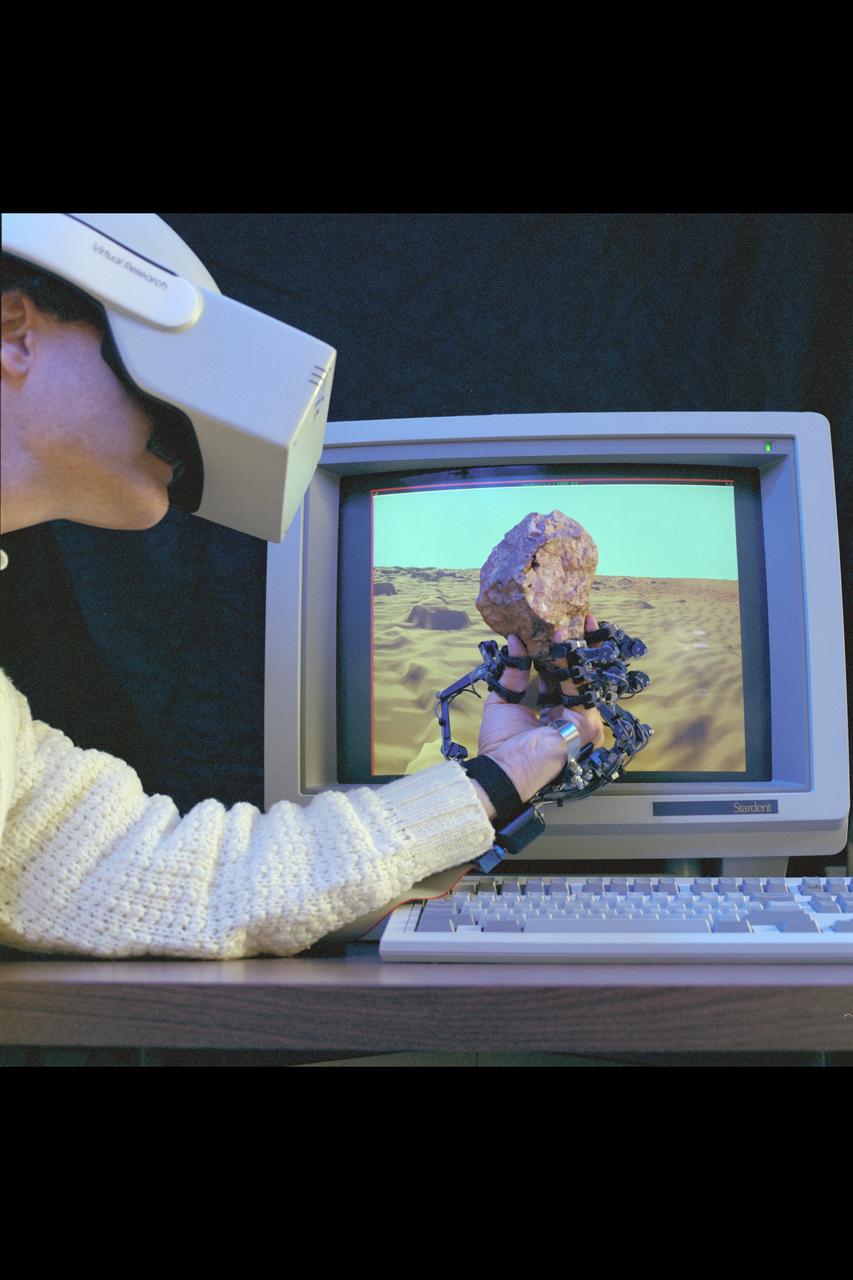

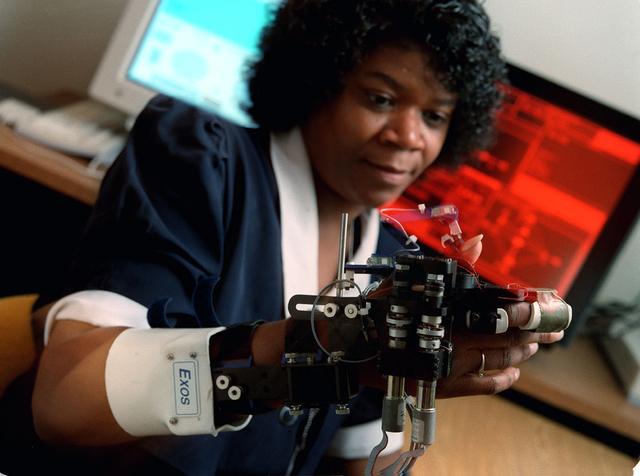
Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Dr Michael McGreevy with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (holding rock in virtual hand)
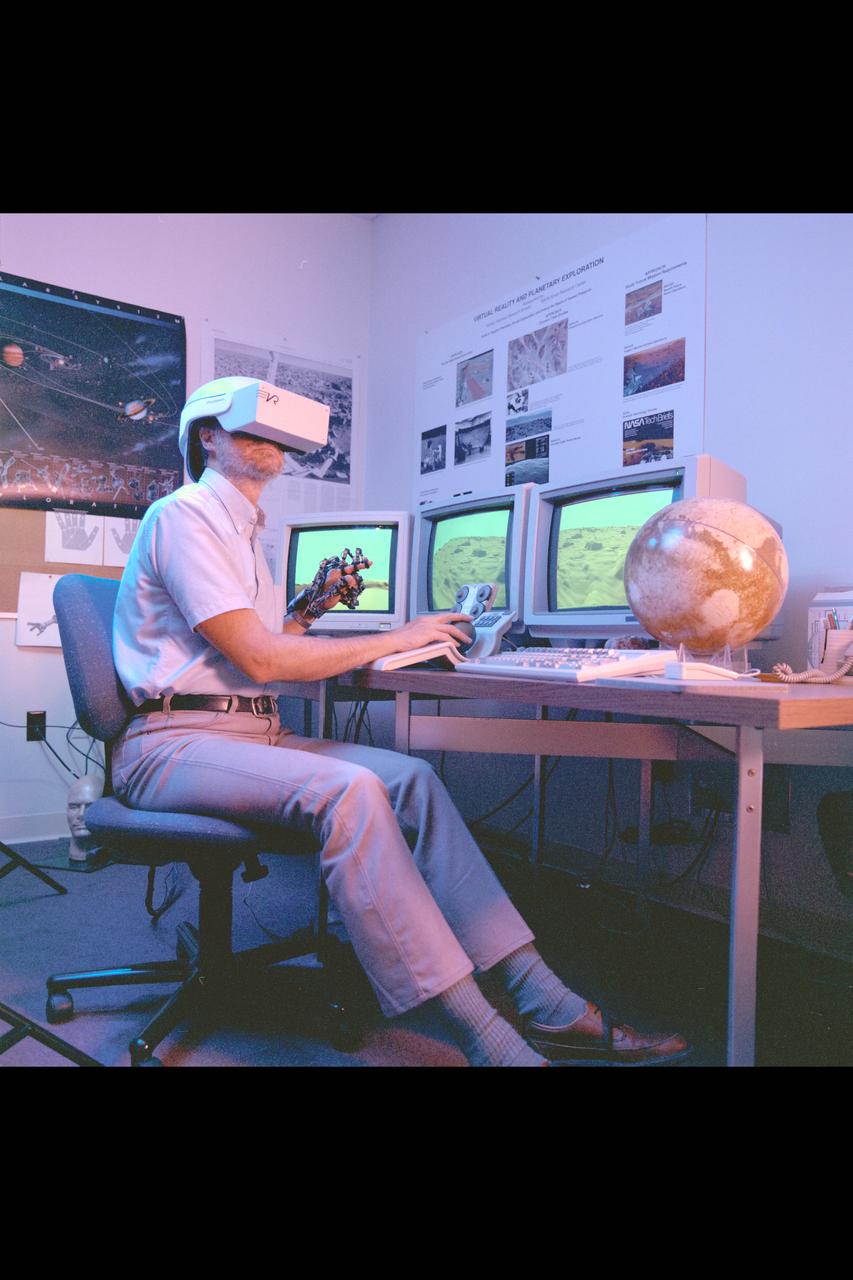

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
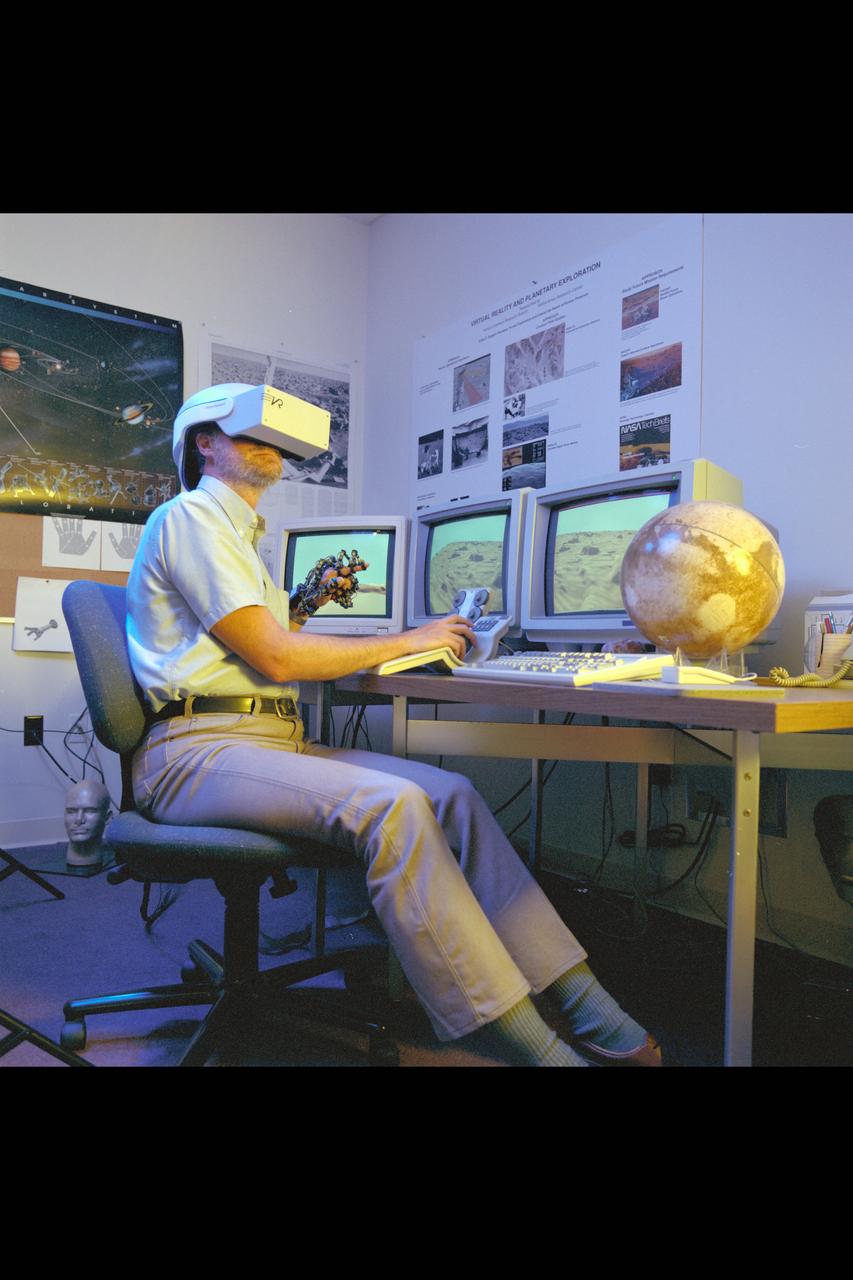

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
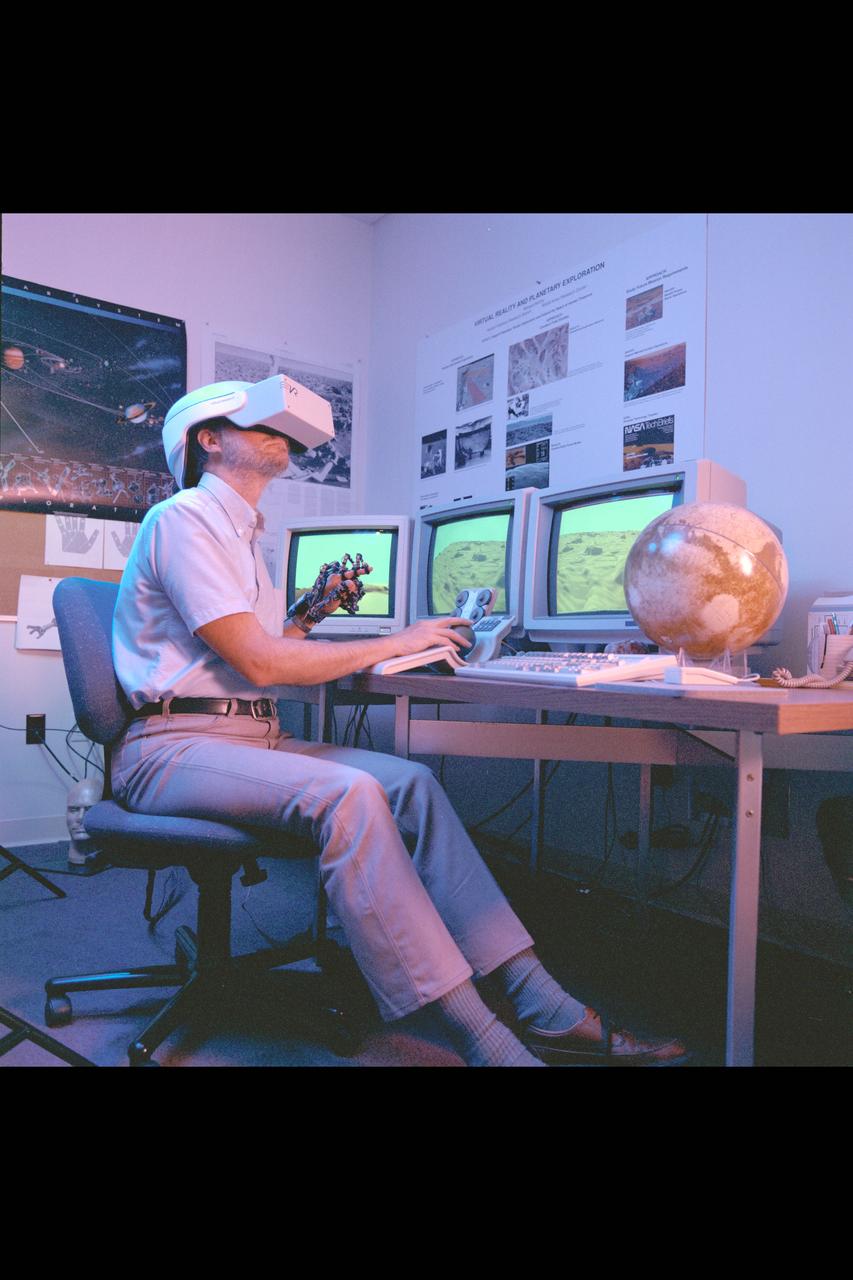

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
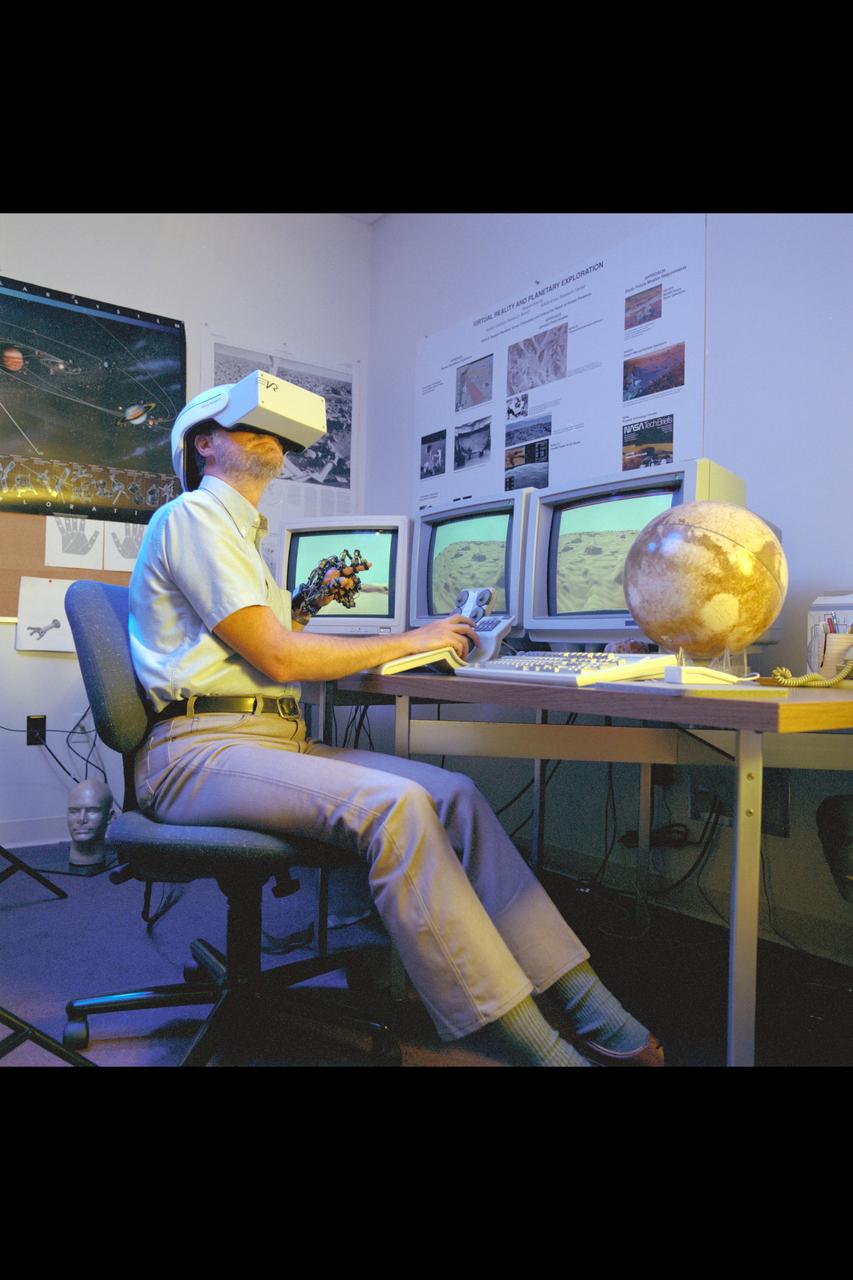

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
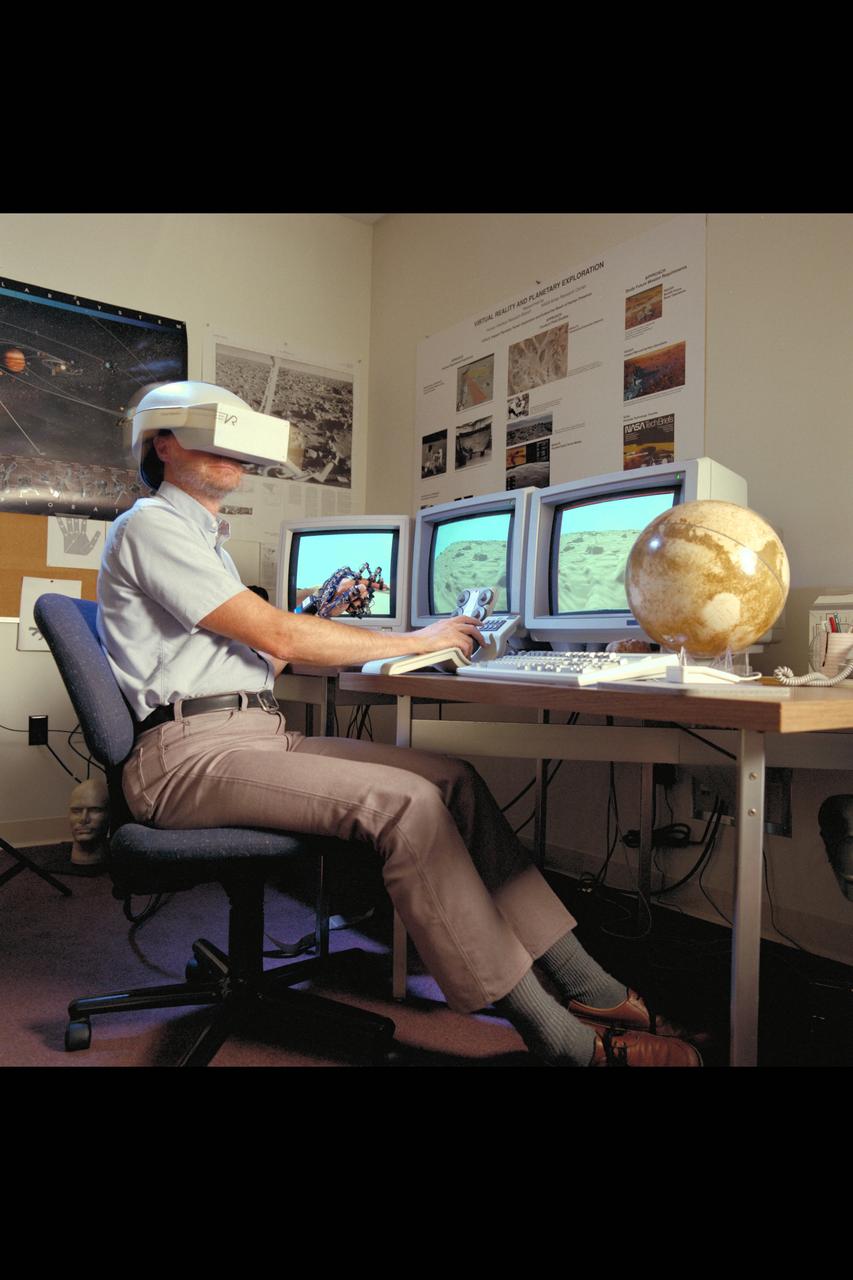

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
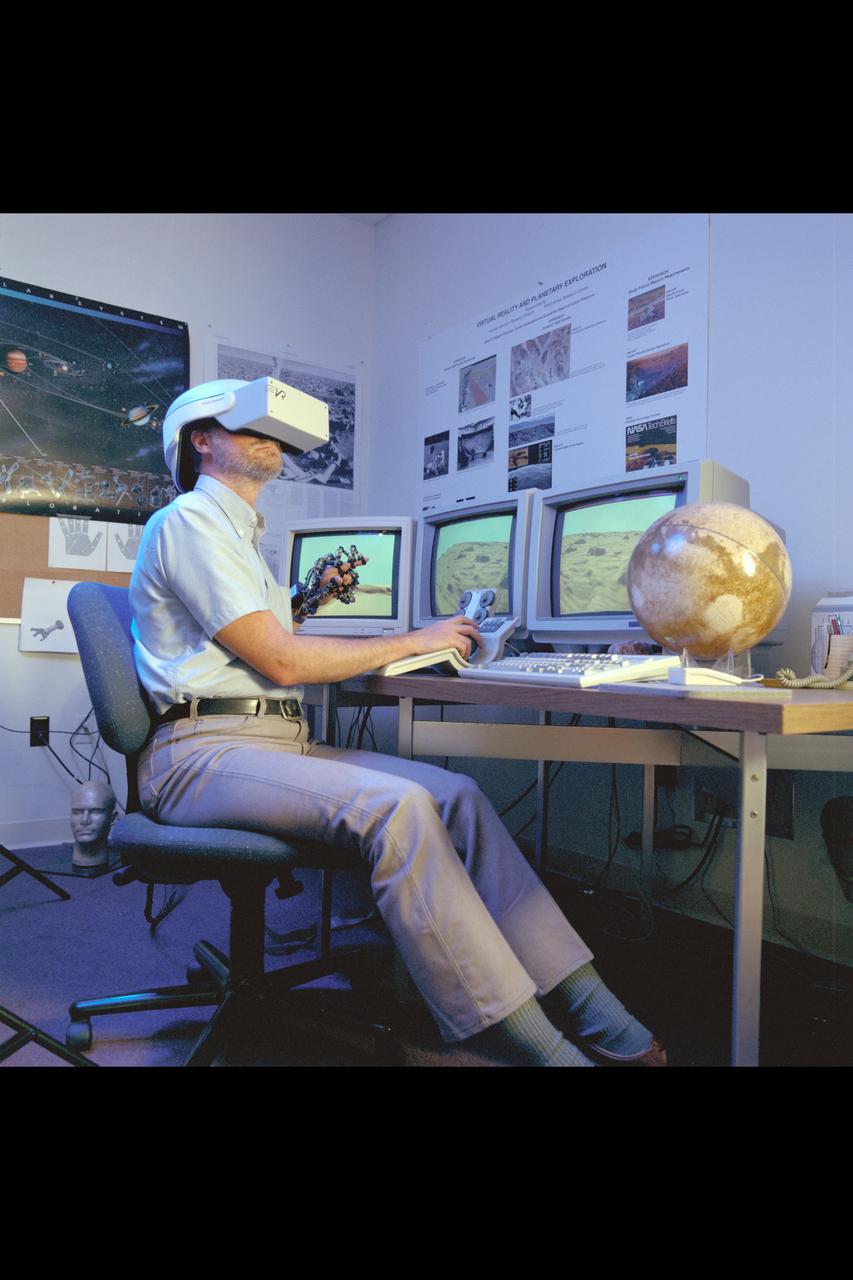

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Lewis Hitchner with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
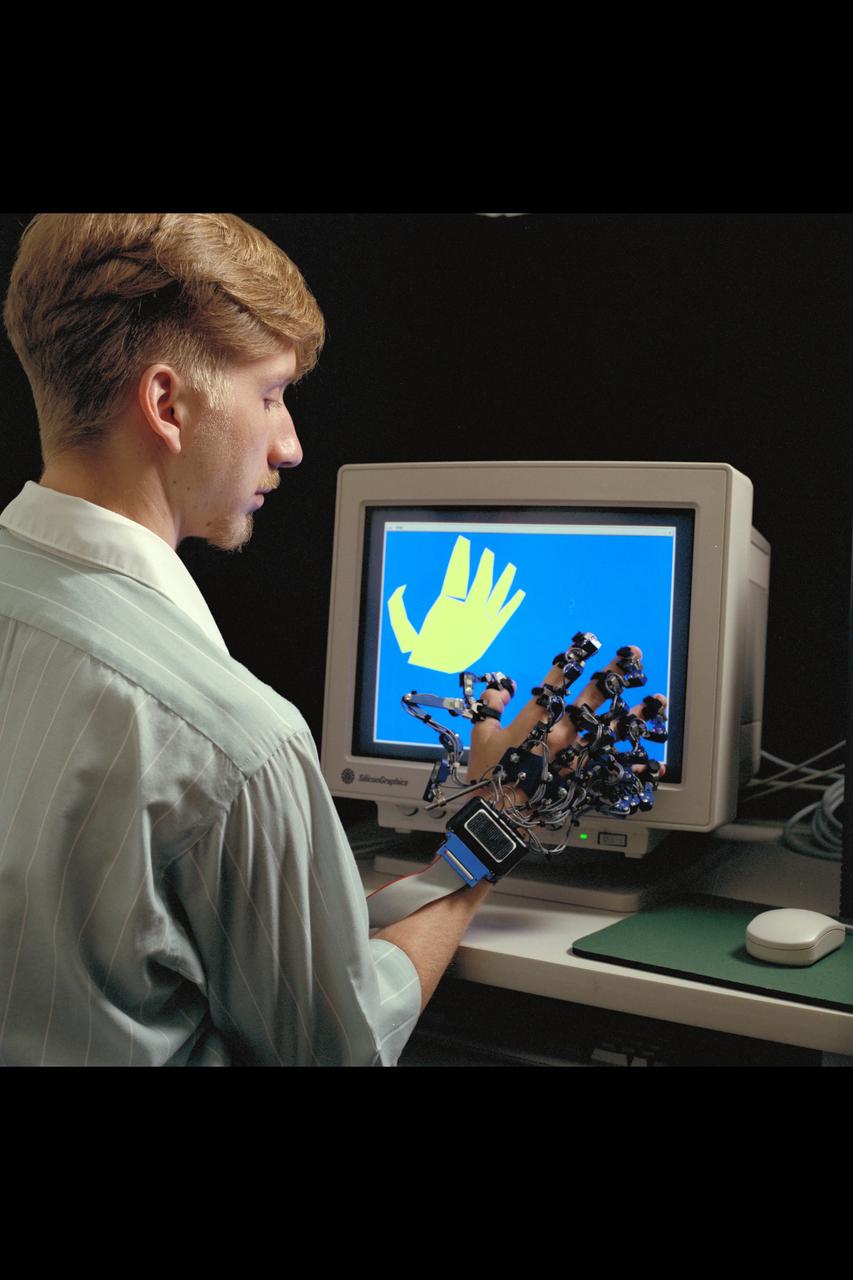

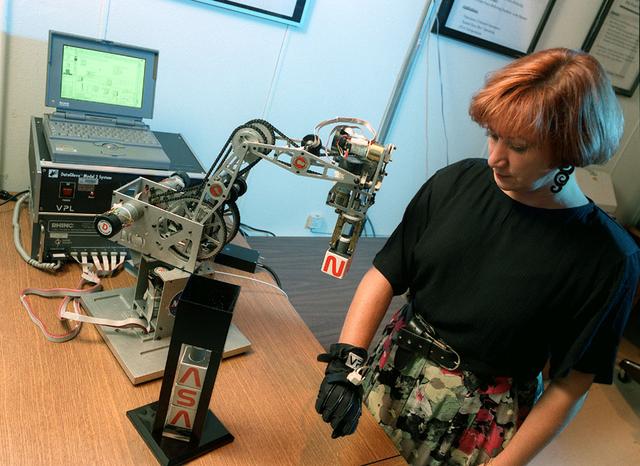
Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows William Briggs with EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows William Briggs with EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
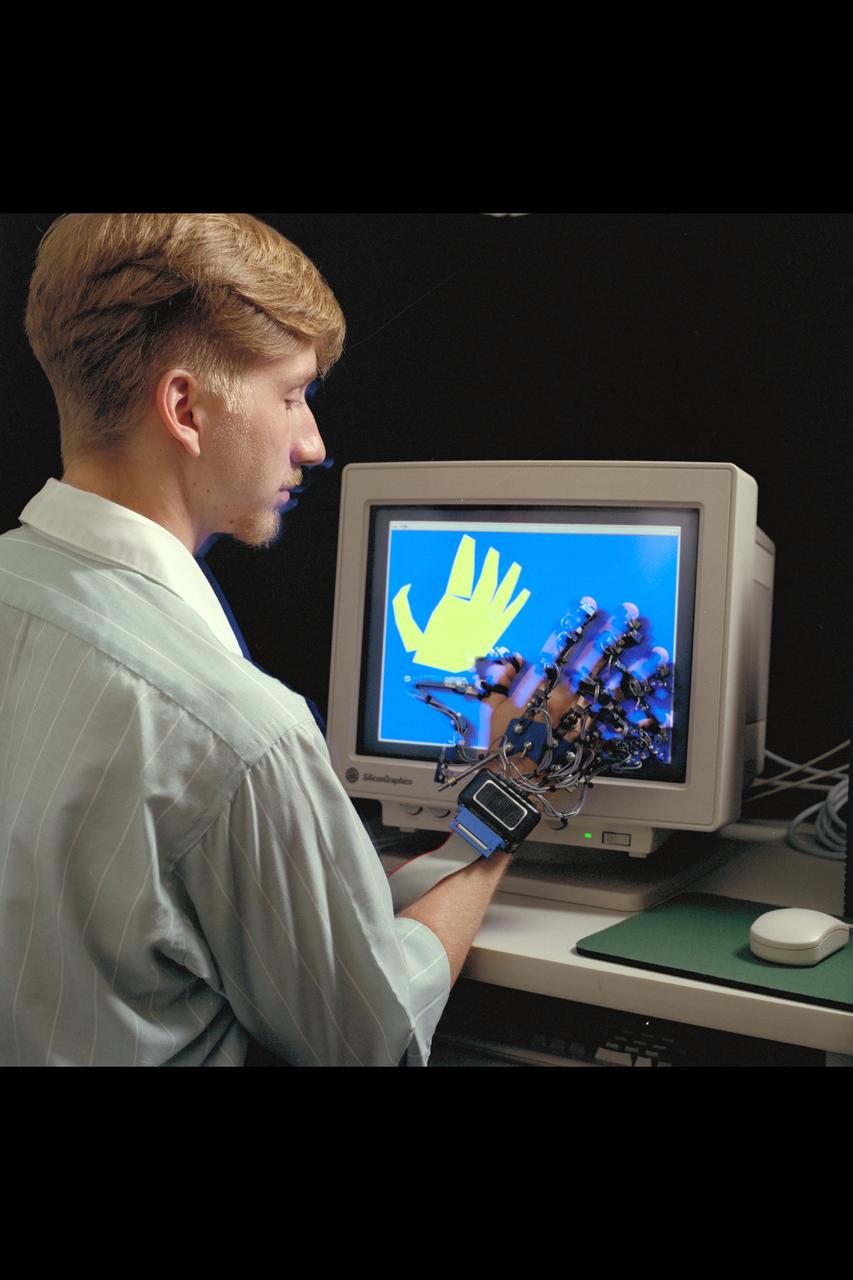

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows William Briggs with EXOS Dexterous interface (virtual hand)
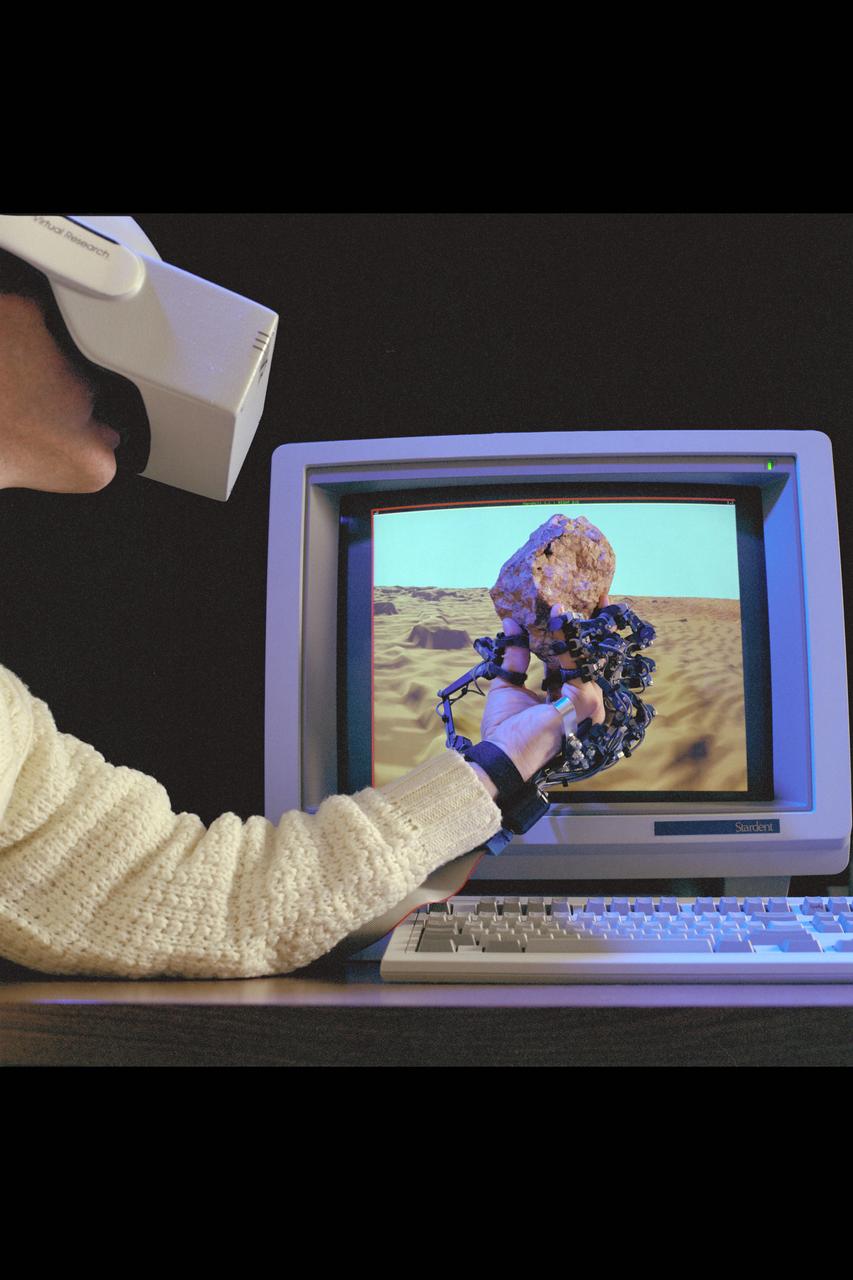

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Dr Michael McGreevy with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (holding rock invirtual hand)
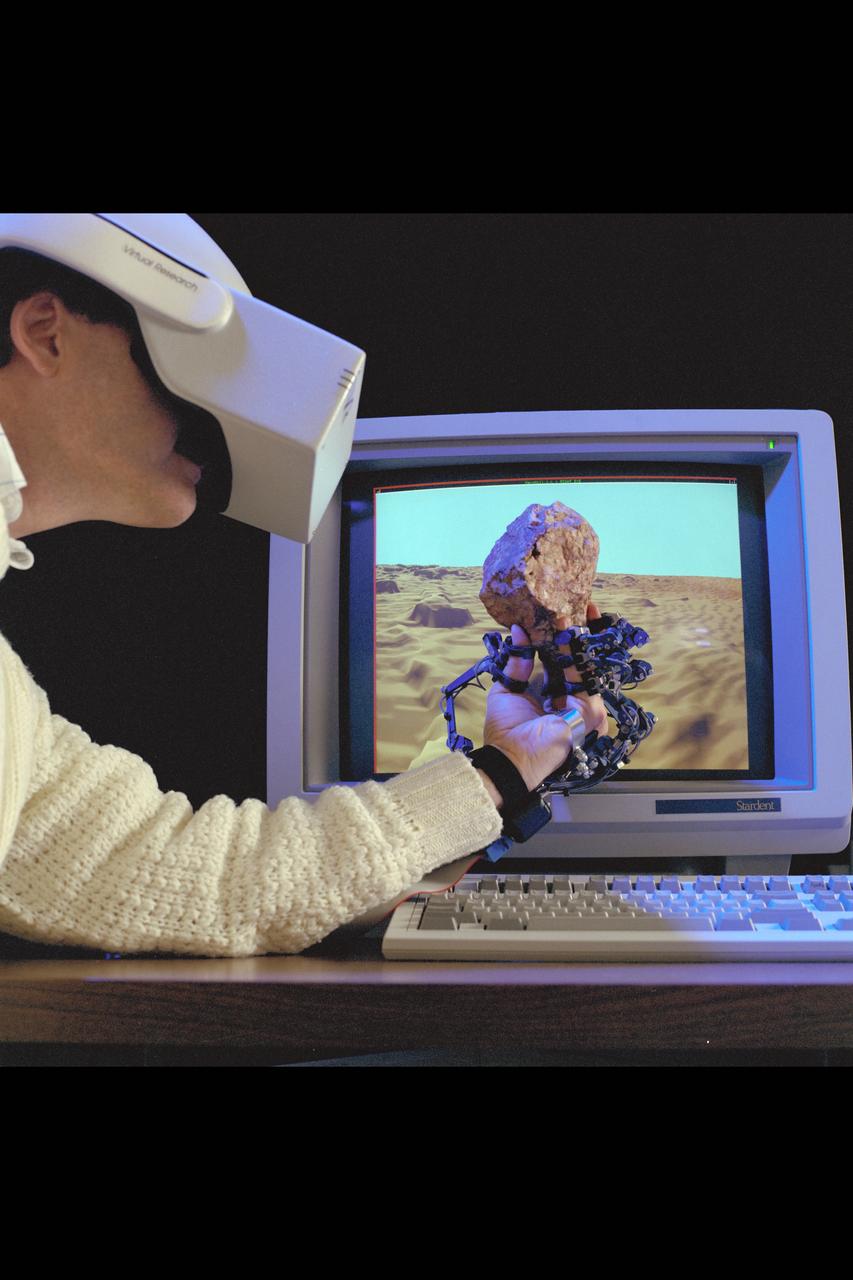

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Dr Michael McGreevy with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (holding rock invirtual hand)
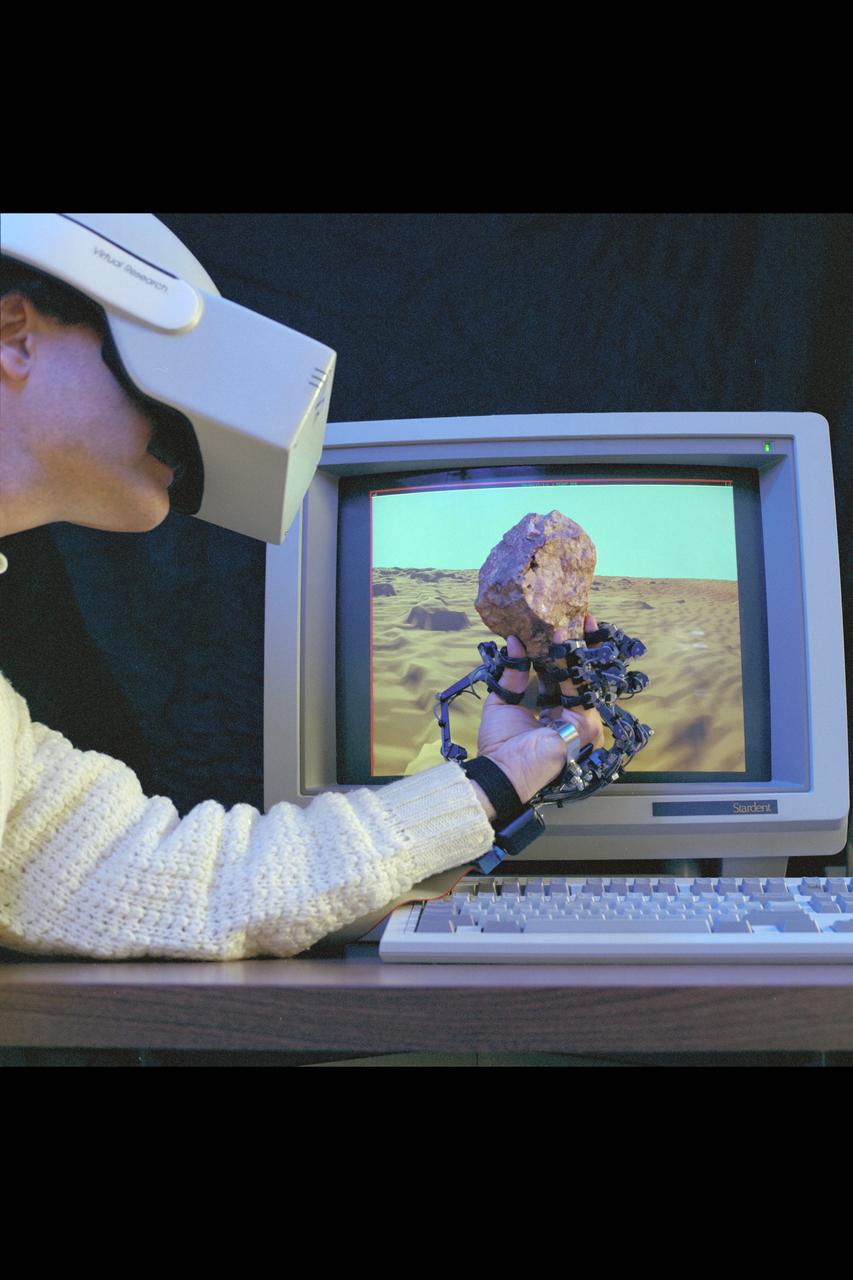

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Dr Michael McGreevy with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (holding rock invirtual hand)
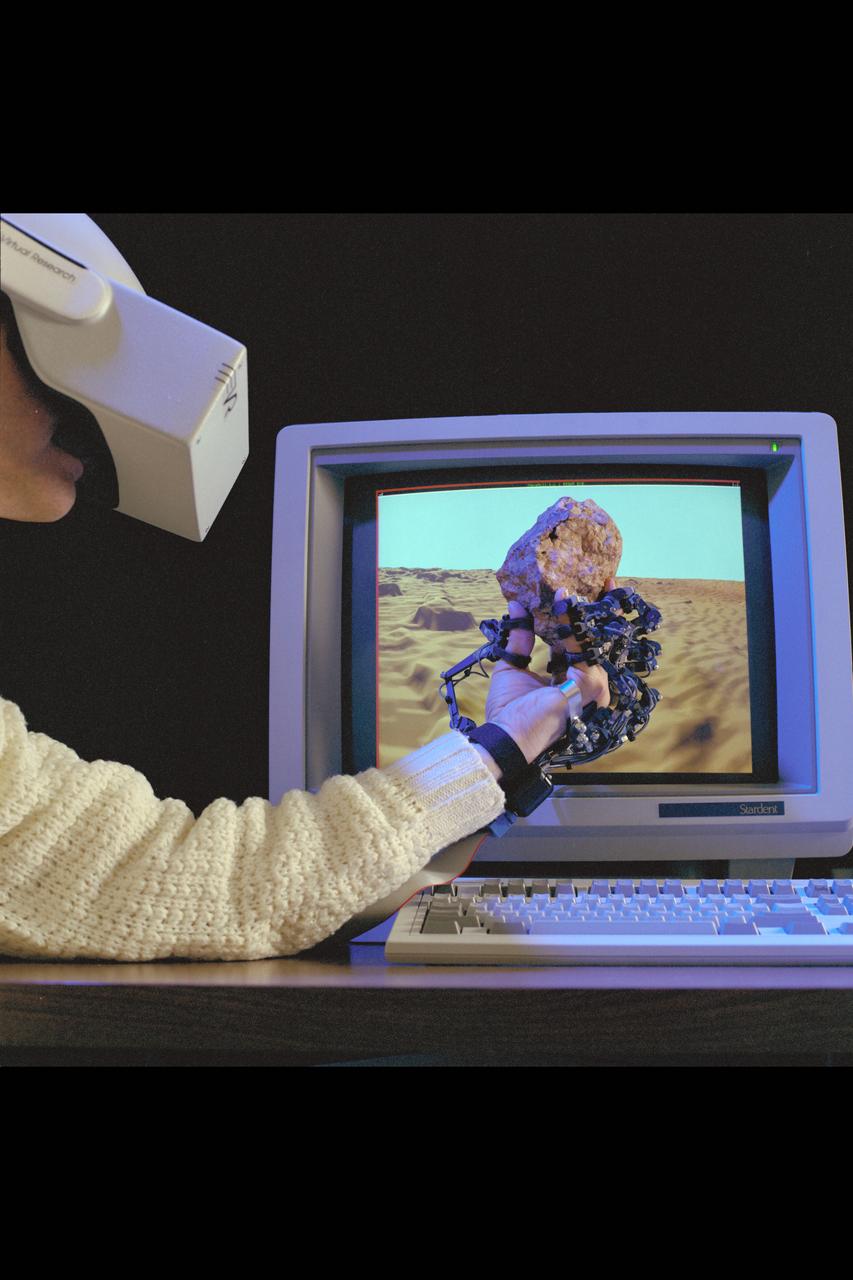

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration shows Dr Michael McGreevy with virtual helmet and EXOS Dexterous interface (holding rock invirtual hand)
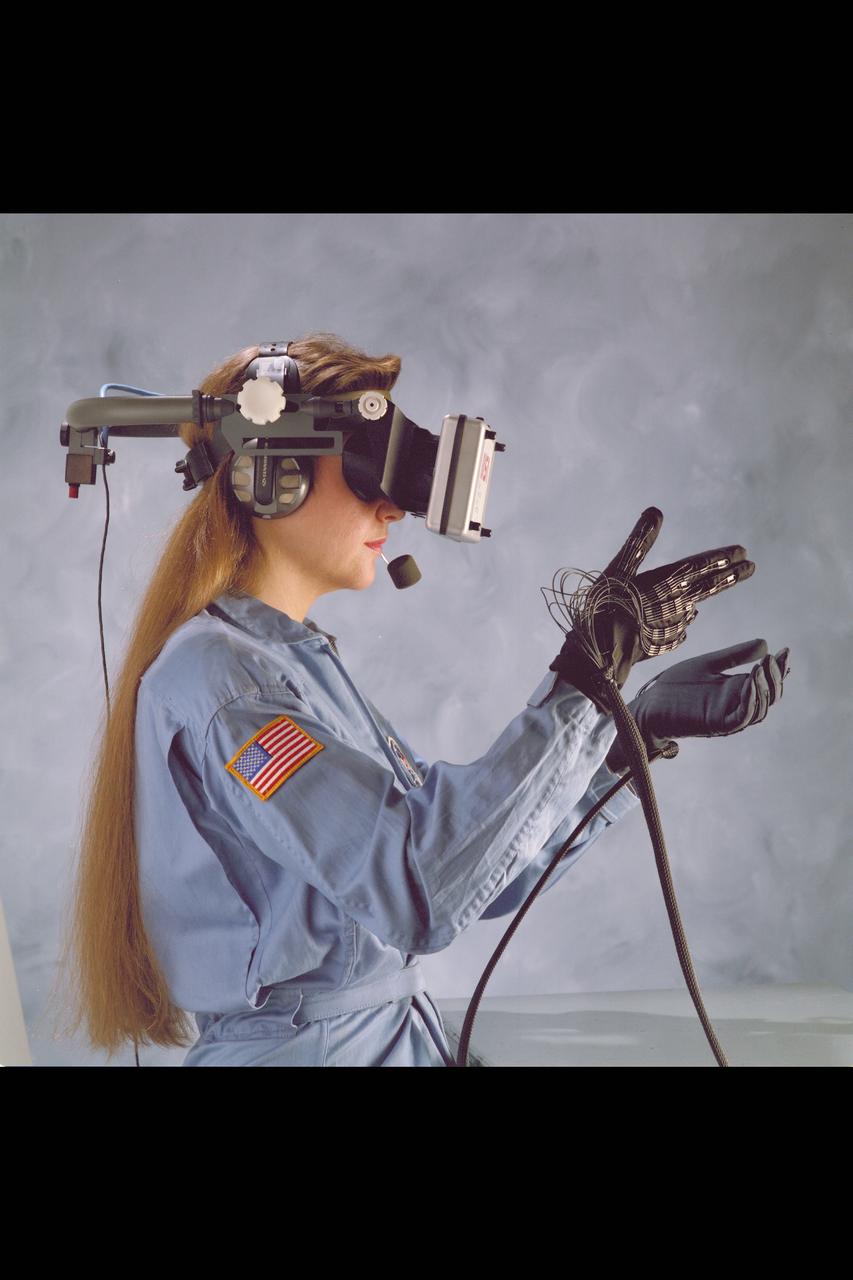

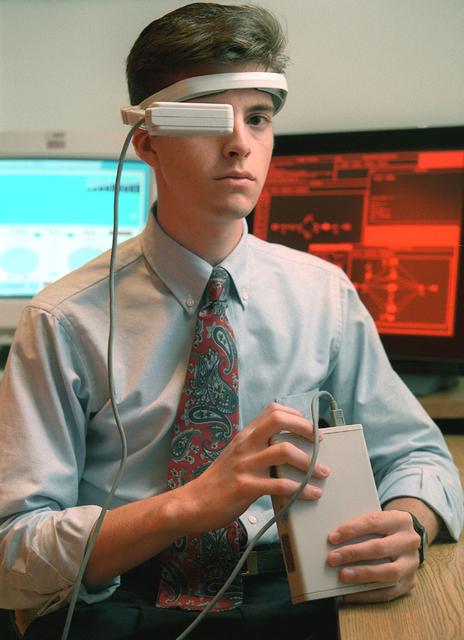
Virtual Environment Reality workstation technology (helmet & gloves)
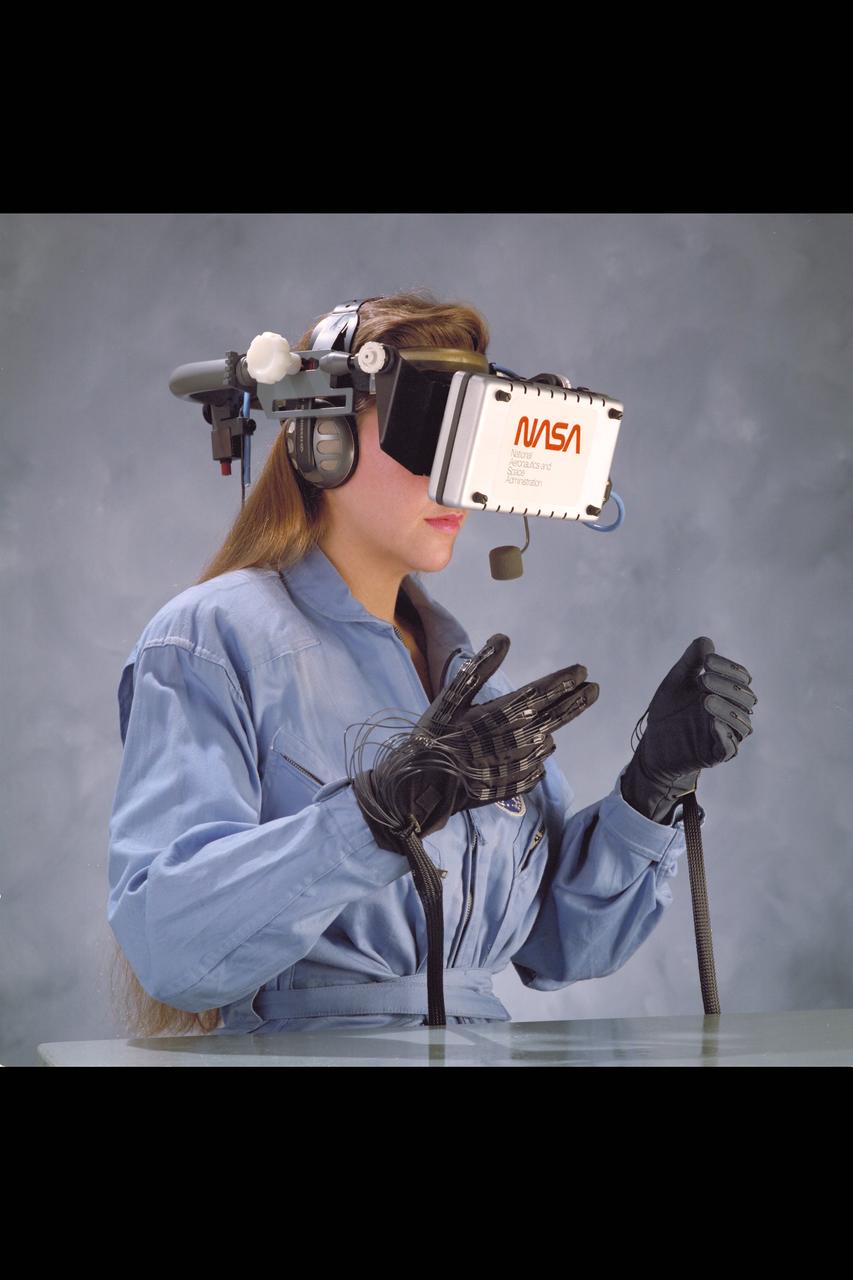

Virtual Environment Reality workstation technology (helmet & gloves)
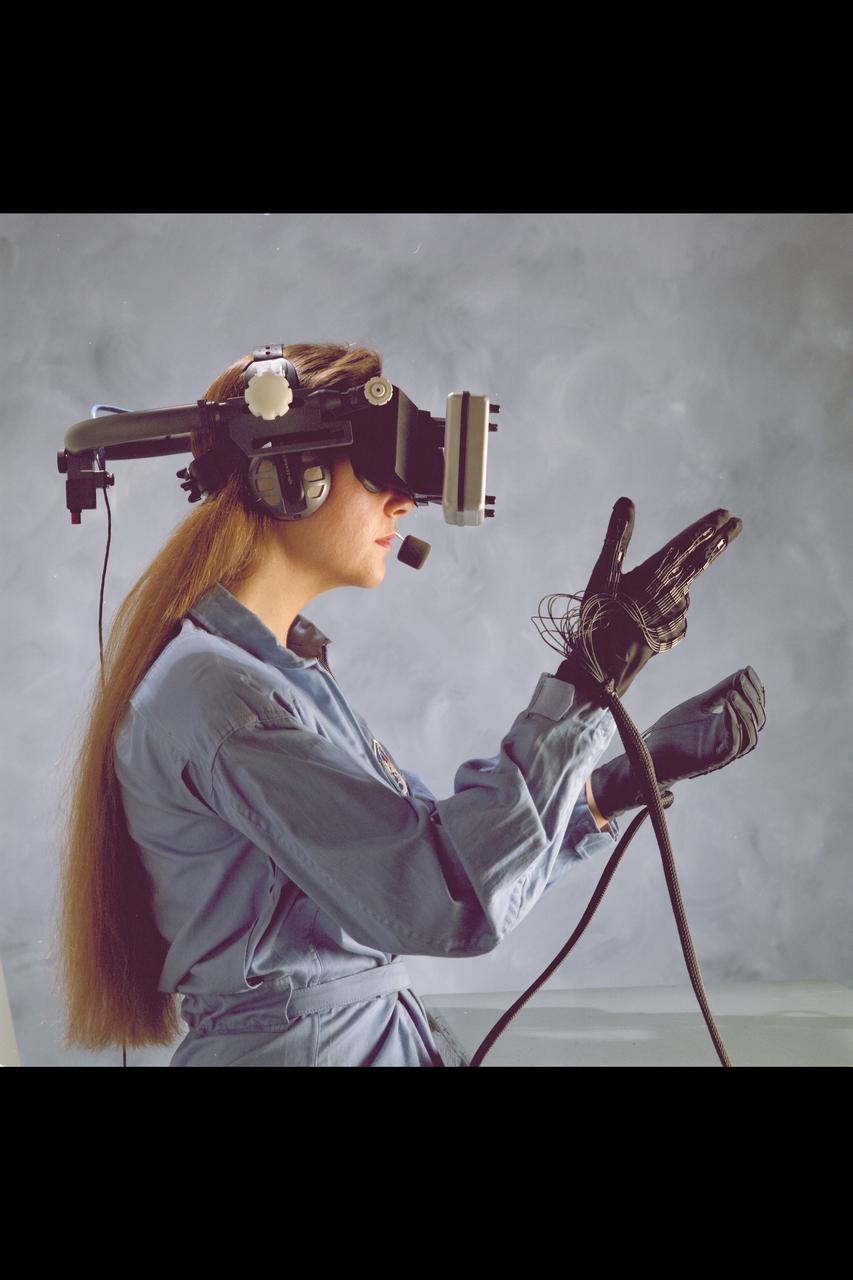

Virtual Environment Reality workstation helmet and gloves
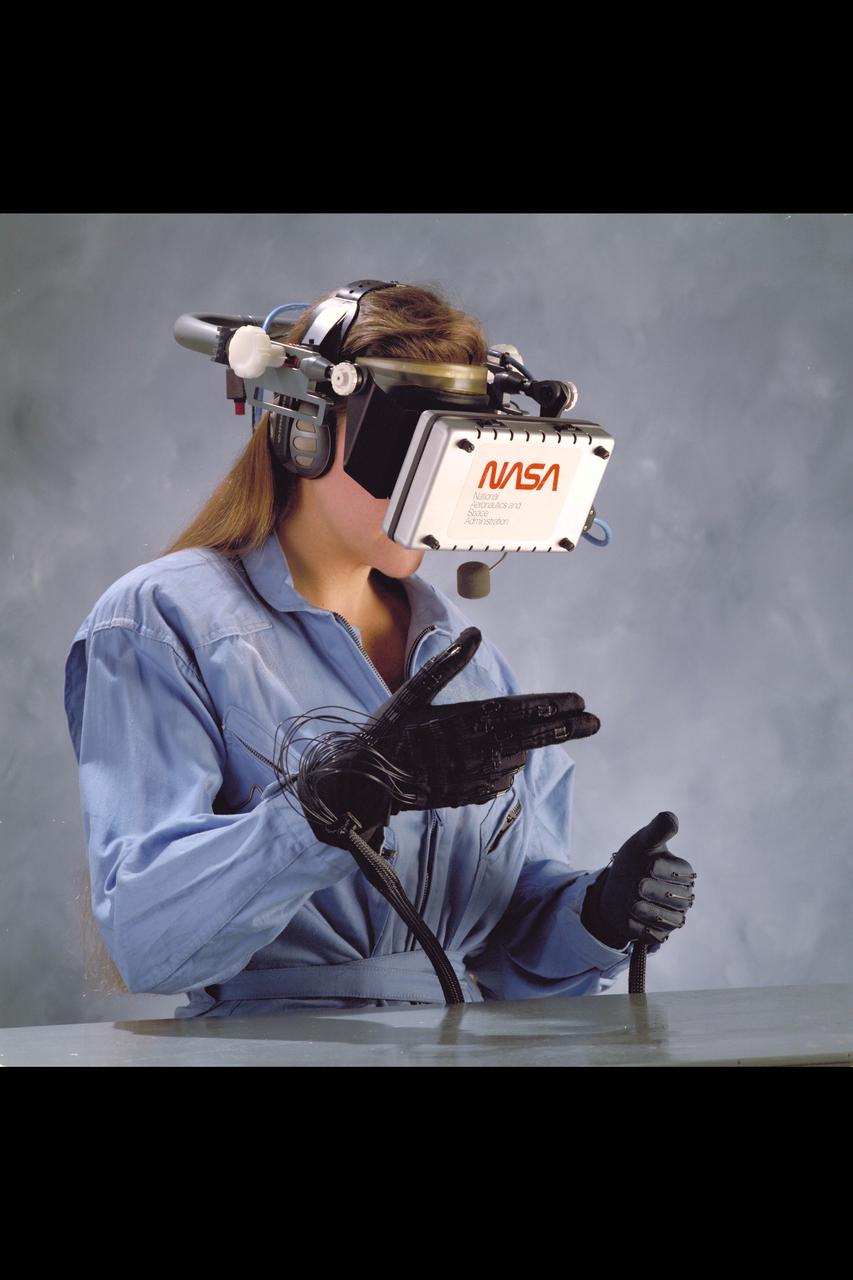

Virtual Environment Reality workstation technology (helmet & gloves)
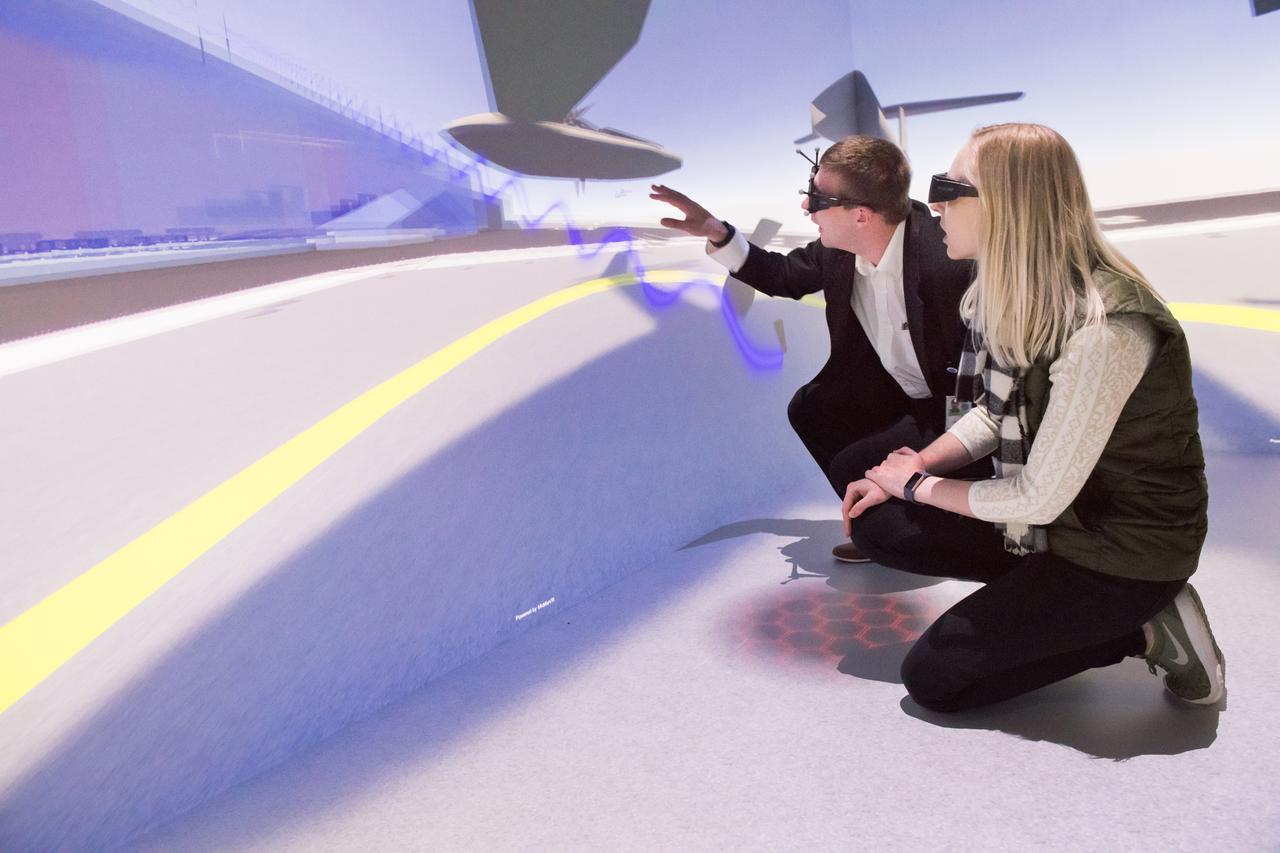

Computer Automatic Virtual Environment, CAVE Tours to Mark the 30th Anniversary of the Graphics and Visualization Lab, GVIS
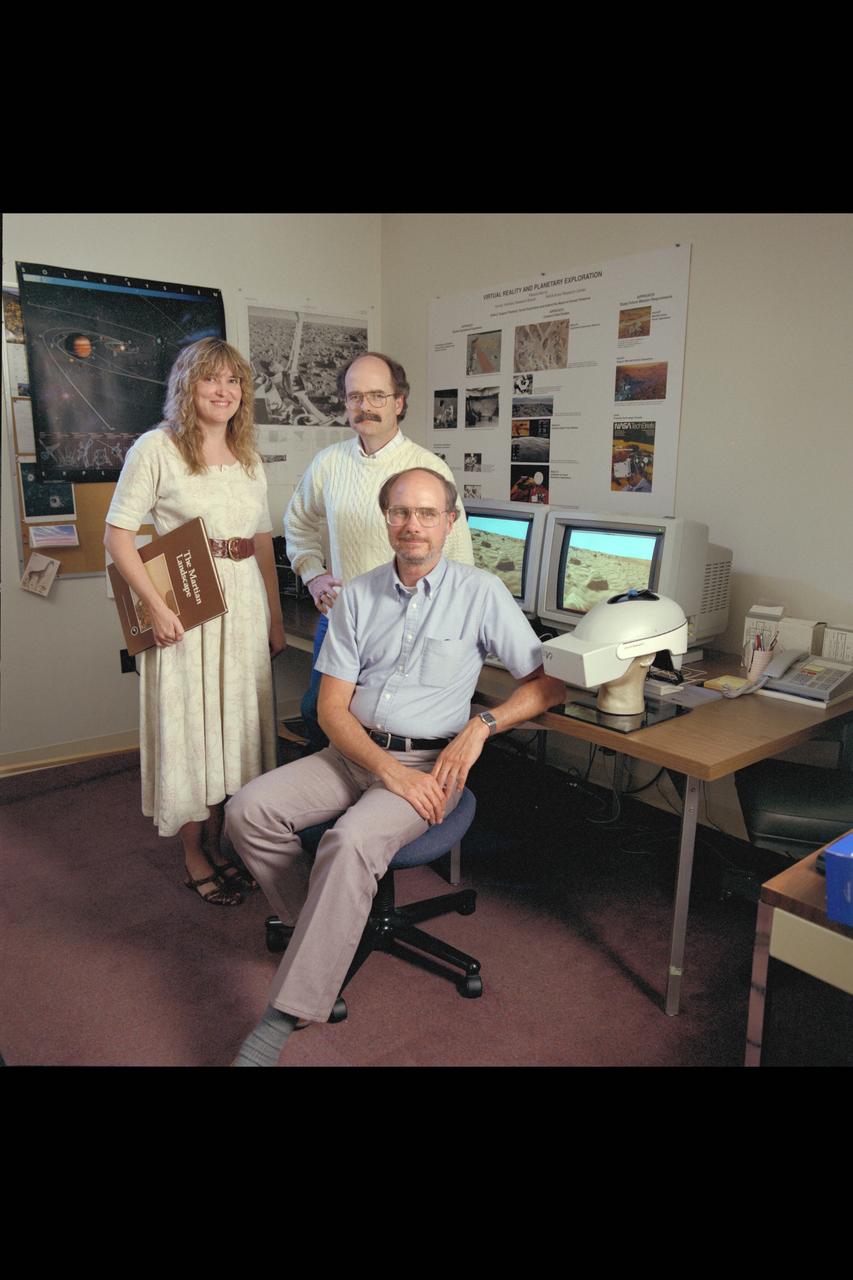

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration group Lewis Hitchner (seated) Cindy Fergouson, Dr Michael McGreevy (standing)
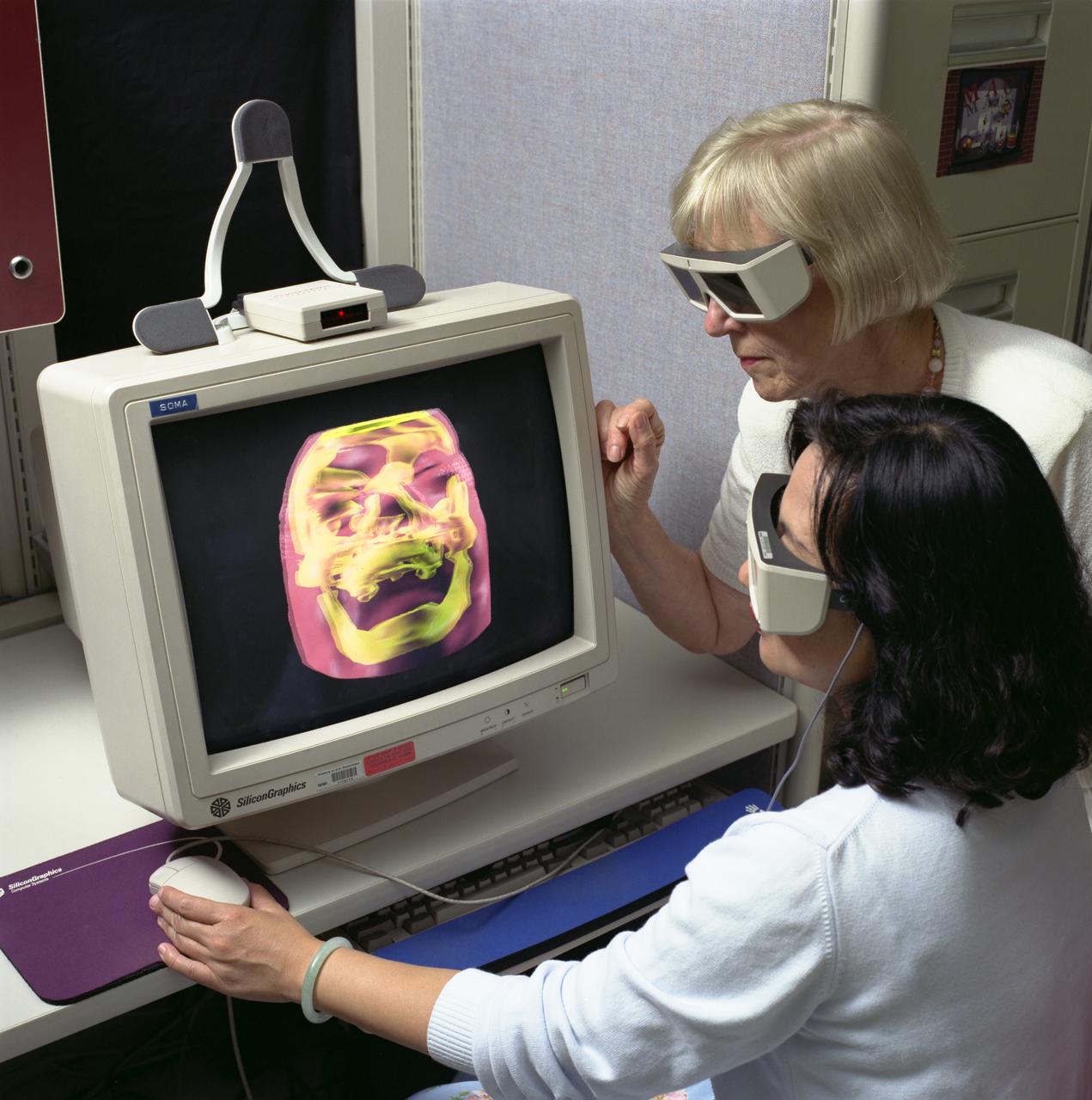
Virtual Environment for (facial) ) reconstructive surgery, Dr Ross and Rei Cheng work with the 3d glasses as they maneuver the skull and tissue for the facial reconstructive surgery
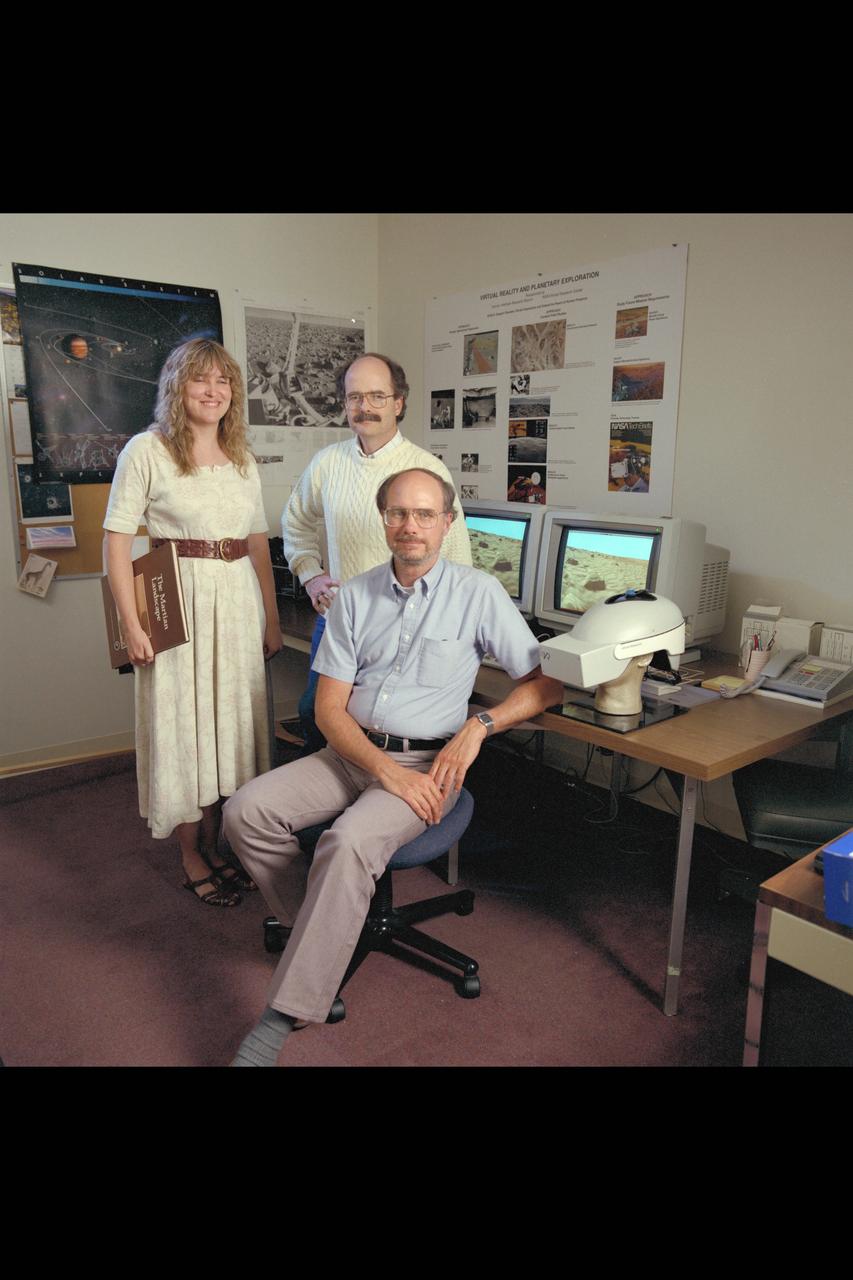

Virtual Environment Telepresence workstation, simulated Mars Exploration group: Lewis Hitchner, (seated) Cindy Fergouson, & Dr Michael McGreevy (standing)

Fernando Figueroa (left), an aerospace technologist at Stennis, and John Schmatzel (center), a professor on loan from Rowan University in Glassboro, N.J., joined Ray Wang, president of Mobitrum Corp., in Silver Springs, Md., to test a virtual sensor instrument in development. The test was performed as part of NASA's Facilitated Access to the Space Environment for Technology Development and Training program.
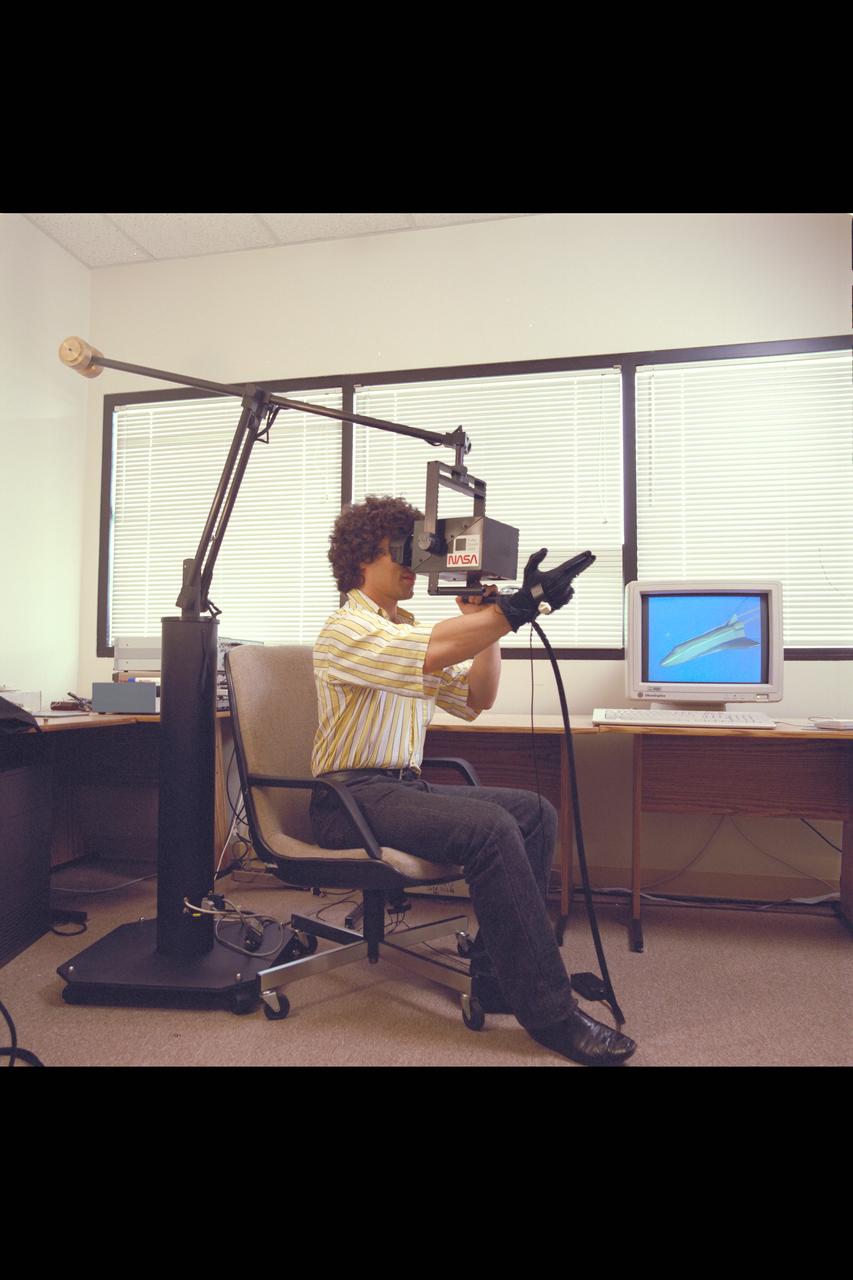

N-258 NAS facility virtual reality workstation, hand-held maneuvering unit , test and virtual environment simulation by Creon Levitt
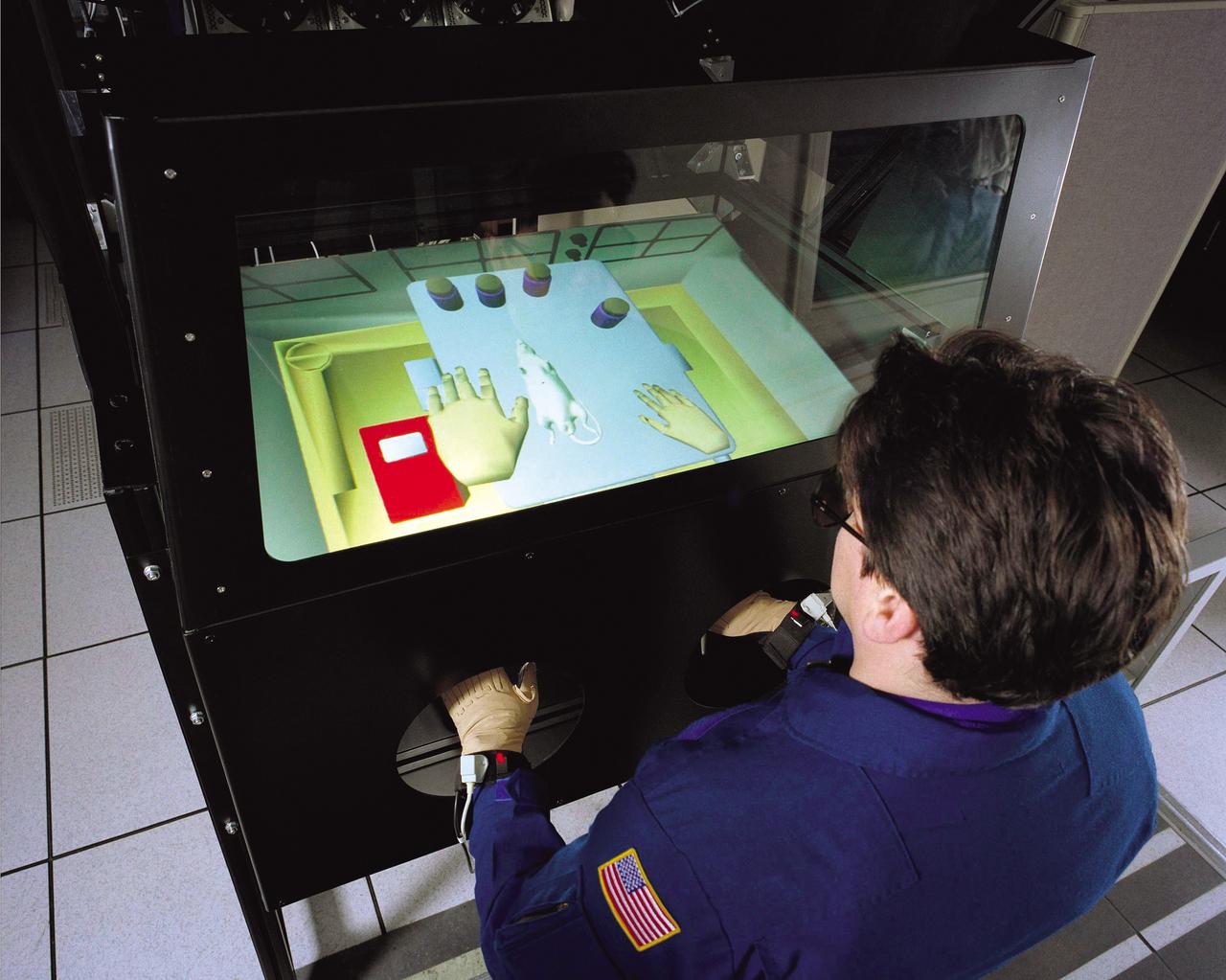

NASA’s Virtual Glovebox (VGX) was developed to allow astronauts on Earth to train for complex biology research tasks in space. The astronauts may reach into the virtual environment, naturally manipulating specimens, tools, equipment, and accessories in a simulated microgravity environment as they would do in space. Such virtual reality technology also provides engineers and space operations staff with rapid prototyping, planning, and human performance modeling capabilities. Other Earth based applications being explored for this technology include biomedical procedural training and training for disarming bio-terrorism weapons.

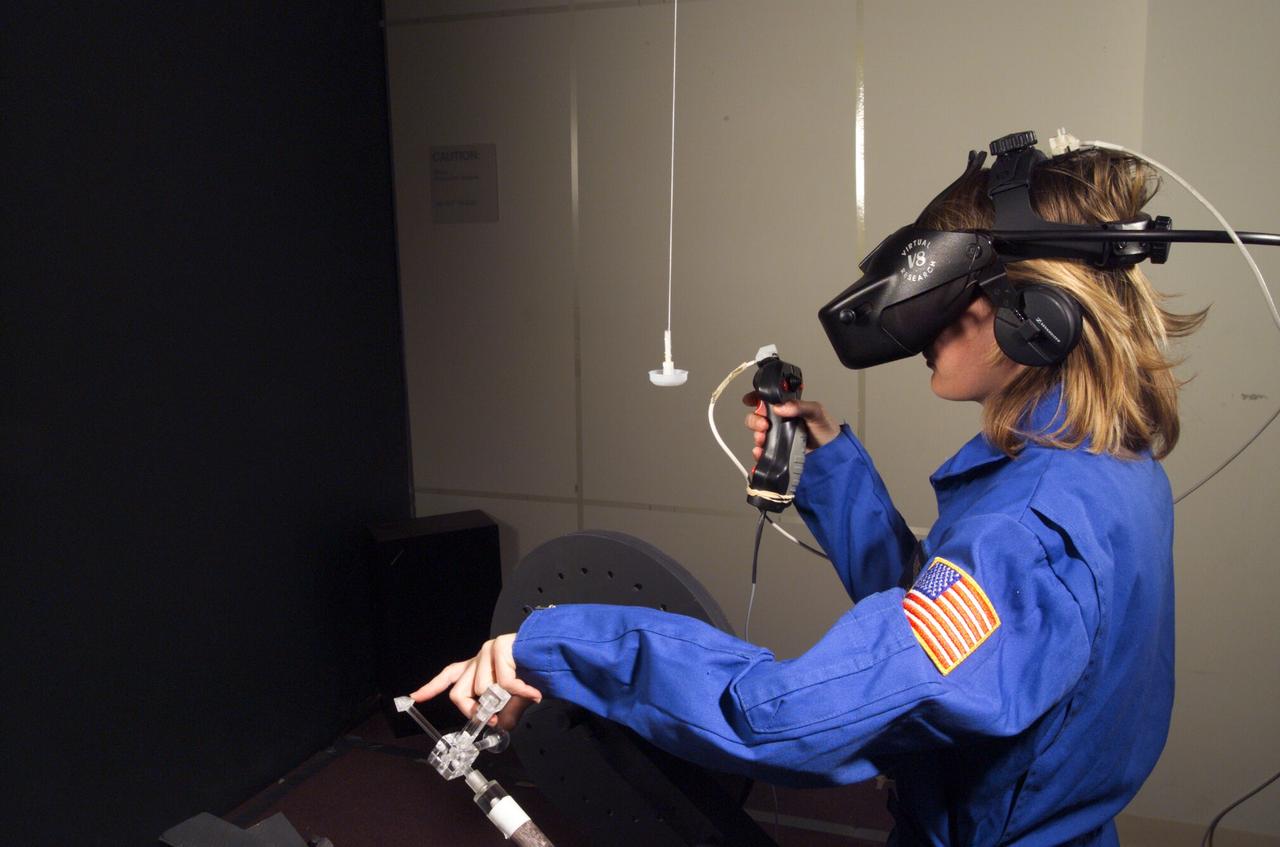
HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: Shown is Heather Smith with headgear and controls
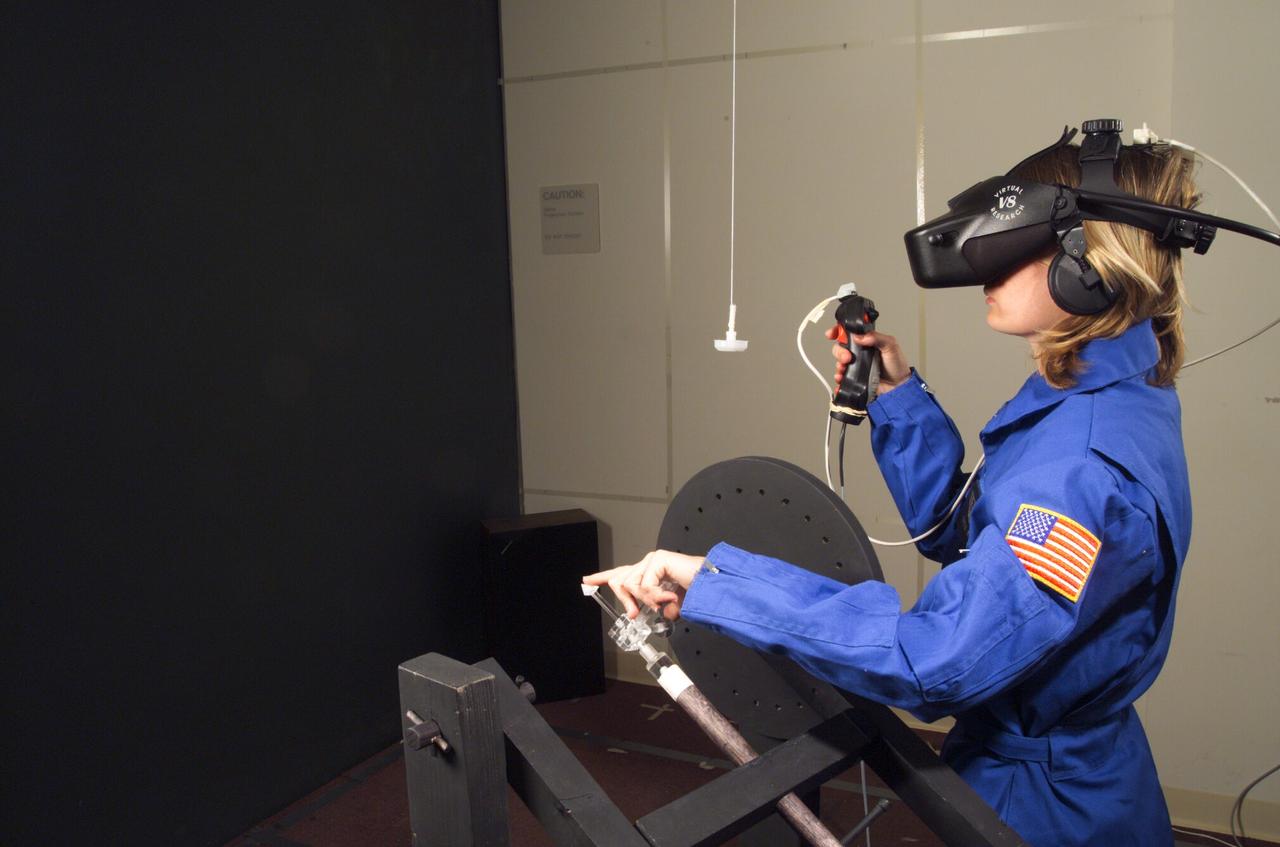

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: Shown is Heather Smith with headgear and controls
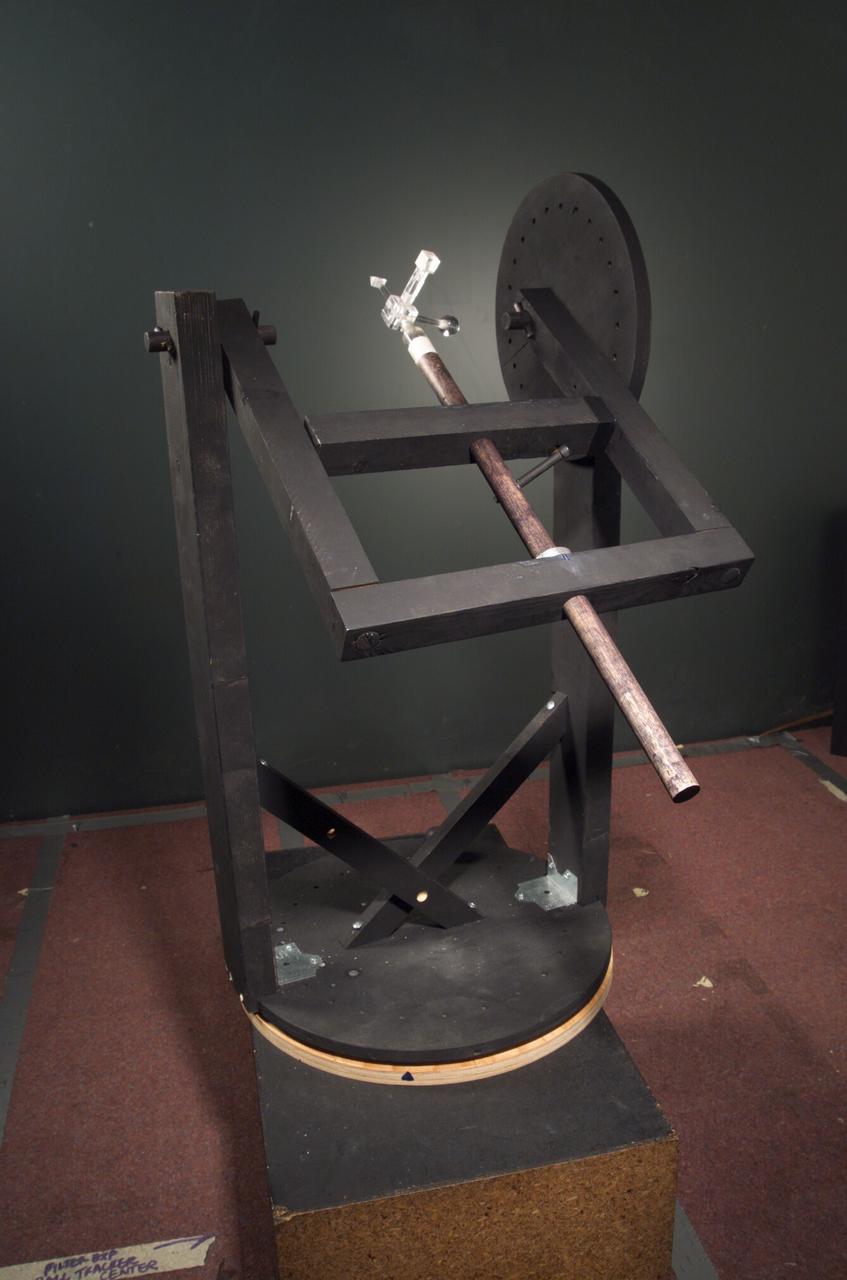

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: system stand

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: Shown is Heather Smith with headgear and controls

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: joystick control
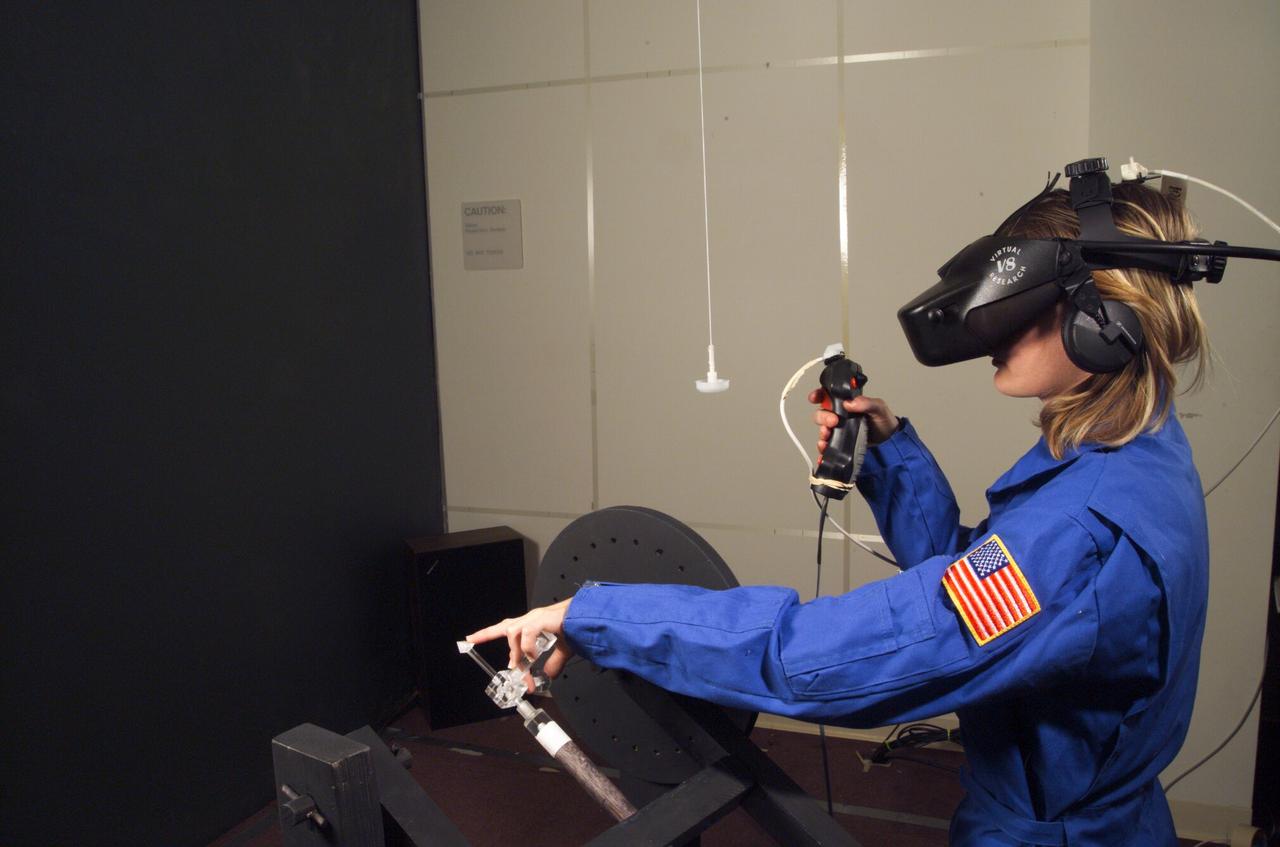

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: Shown is Heather Smith with headgear and controls

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: joystick control
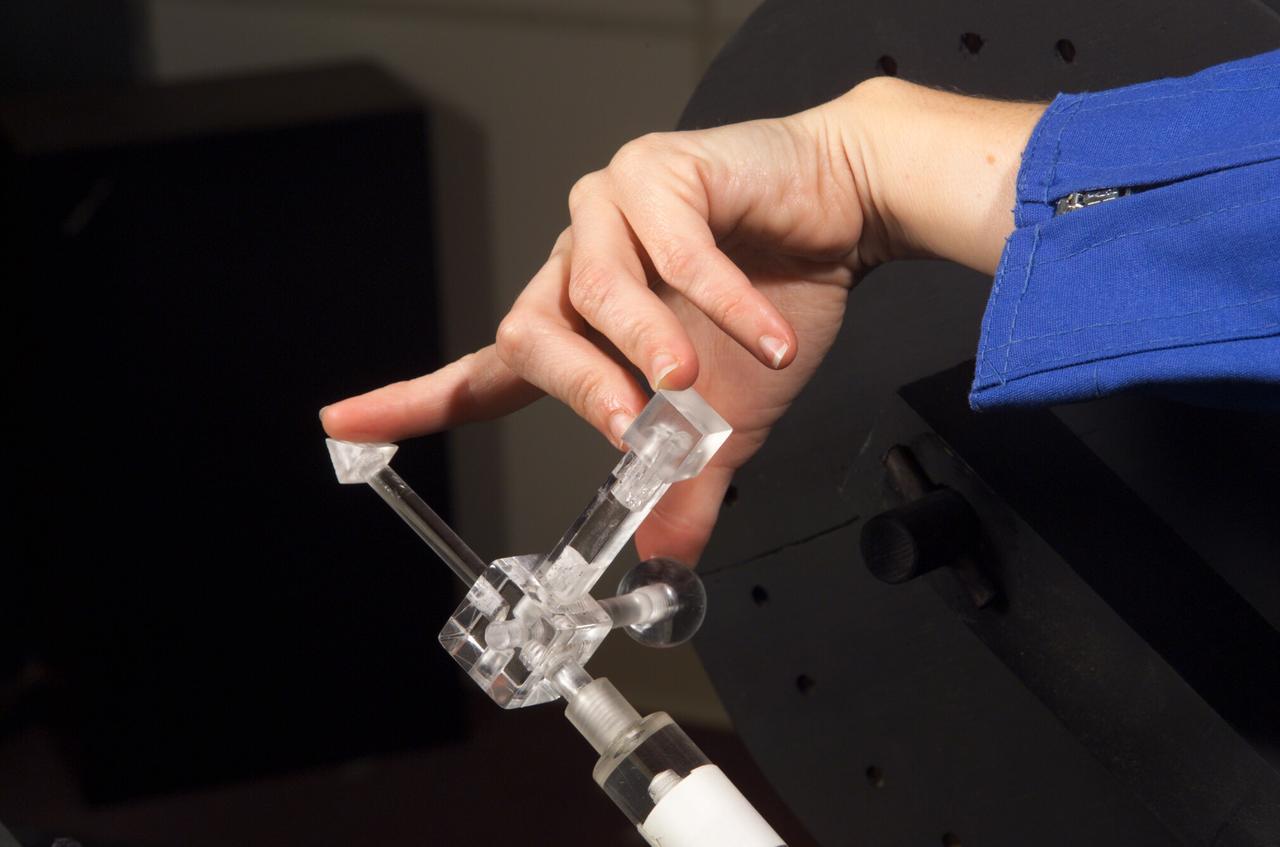
HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: HAPTIC cue stick
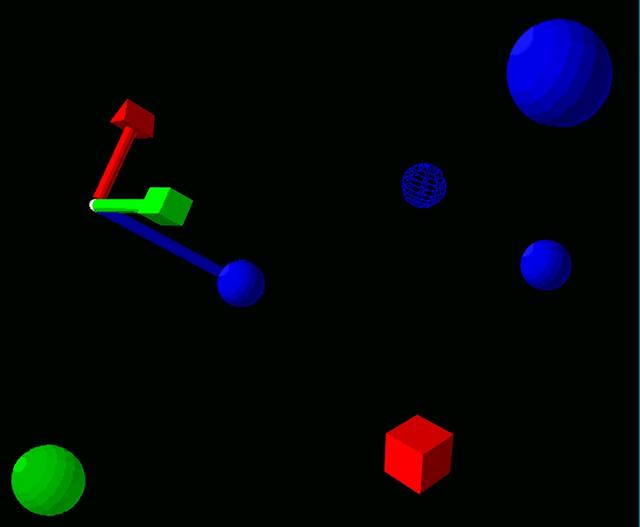
HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: Postmovement VR Displays
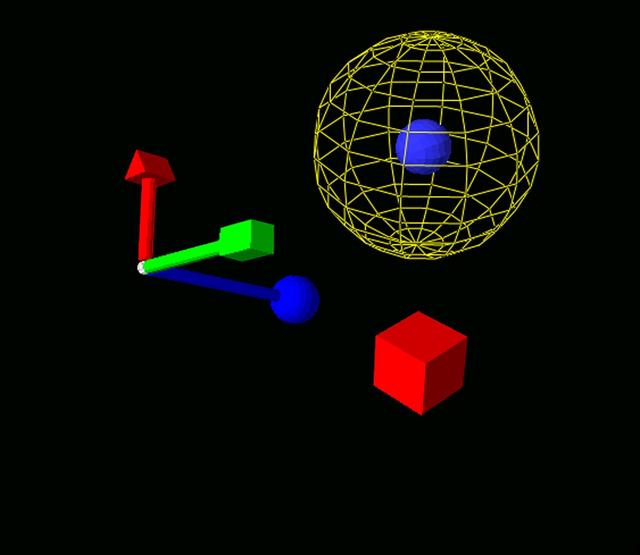
HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: Premovement VR display

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: Shown is Heather Smith with headgear and controls

HAPTIC Cueing Research Study (p.i.: Steve Ellis) Virtual environments: HAPTIC cue stick

A person observes the computational Fluid Dynamics solution for cryogenic storage tank mixing inside the Glenn Reconfigurable User-interface and Virtual Reality Exploration on October 18, 2023. The GRUVE Lab provides a fully interactive virtual reality space in which to observe and analyze data and environments. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

Virtual Reality (VR) can provide cost effective methods to design and evaluate components and systems for maintenance and refurbishment operations. Marshall SPace Flight Center (MSFC) is begirning to utilize VR for design analysis in the X-34 experimental reusable space vehicle. Analysts at MSFC's Computer Applications and Virtual Environments (CAVE) used Head Mounted Displays (HMD) (pictured), spatial trackers and gesture inputs as a means to animate or inhabit a properly sized virtual human model. These models are used in a VR scenario as a way to determine functionality of space and maintenance requirements for the virtual X-34. The primary functions of the virtual X-34 mockup is to support operations development and design analysis for engine removal, the engine compartment and the aft fuselage. This capability provides general visualization support to engineers and designers at MSFC and to the System Design Freeze Review at Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC).
Virtual Reality (VR) can provide cost effective methods to design and evaluate components and systems for maintenance and refurbishment operations. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama began to utilize VR for design analysis in the X-34 experimental reusable space vehicle. Analysts at MSFC's Computer Applications and Virtual Environments (CAVE) used Head Mounted Displays (HMD) (pictured), spatial trackers and gesture inputs as a means to animate or inhabit a properly sized virtual human model. These models were used in a VR scenario as a way to determine functionality of space and maintenance requirements for the virtual X-34. The primary functions of the virtual X-34 mockup was to support operations development and design analysis for engine removal, the engine compartment and the aft fuselage. This capability providedgeneral visualization support to engineers and designers at MSFC and to the System Design Freeze Review at Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC). The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.

Virtual Reality (VR) can provide cost effective methods to design and evaluate components and systems for maintenance and refurbishment operations. Marshall Spce Flight Center (MSFC) is begirning to utilize VR for design analysis in the X-34 experimental reusable space vehicle. Analysts at MSFC's Computer Applications and Virtual Environments (CAVE) used Head Mounted Displays (HMD) (pictured), spatial trackers and gesture inputs as a means to animate or inhabit a properly sized virtual human model. These models are used in a VR scenario as a way to determine functionality of space and maintenance requirements for the virtual X-34. The primary functions of the virtual X-34 mockup is to support operations development and design analysis for engine removal, the engine compartment and the aft fuselage. This capability provides general visualization support to engineers and designers at MSFC and to the System Design Freeze Review at Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC).

Virtual Reality (VR) can provide cost effective methods to design and evaluate components and systems for maintenance and refurbishment operations. The Marshall Space Flight Centerr (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama began to utilize VR for design analysis in the X-34 experimental reusable space vehicle. Analysts at MSFC's Computer Applications and Virtual Environments (CAVE) used Head Mounted Displays (HMD) (pictured), spatial trackers and gesture inputs as a means to animate or inhabit a properly sized virtual human model. These models were used in a VR scenario as a way to determine functionality of space and maintenance requirements for the virtual X-34. The primary functions of the virtual X-34 mockup was to support operations development and design analysis for engine removal, the engine compartment and the aft fuselage. This capability provided general visualization support to engineers and designers at MSFC and to the System Design Freeze Review at Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC). The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
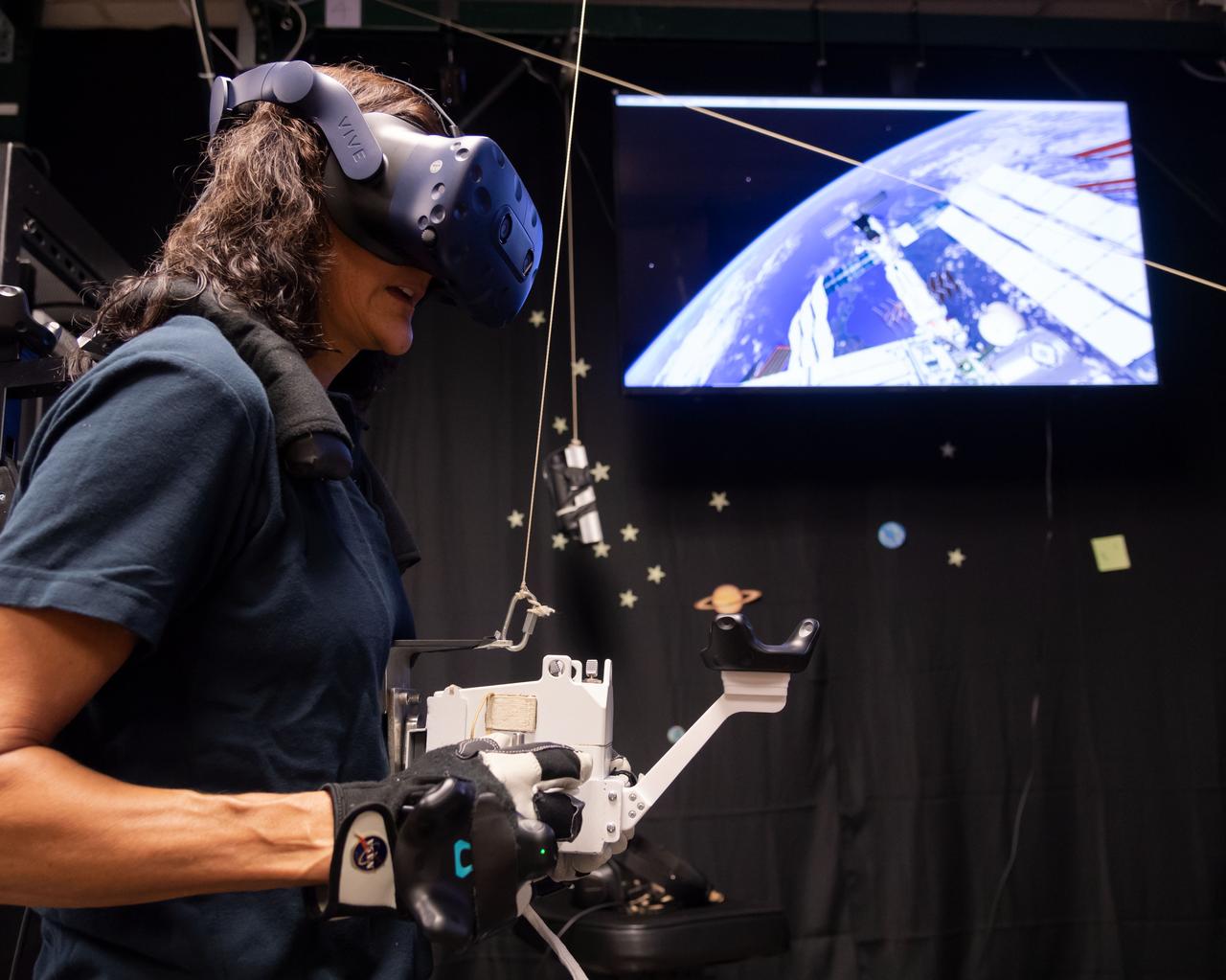

The Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. Commercial Crew Astronaut Suni Williams practices spacewalking in preparation for a mission to the International Space Station in 2019. Williams is assigned to Boeing’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.
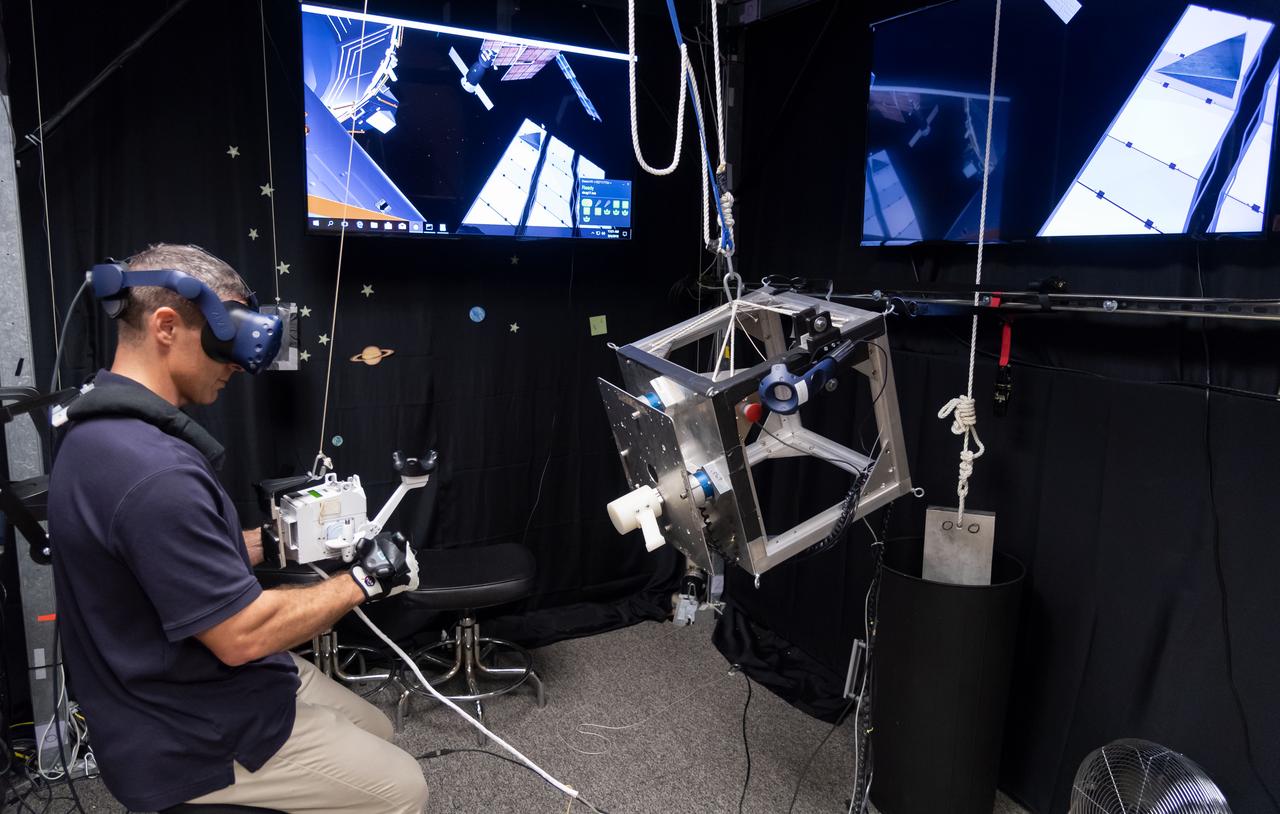

The Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. Commercial Crew Astronaut Mike Hopkins practices spacewalking in preparation for a mission to the International Space Station. Hopkins is assigned to SpaceX’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.
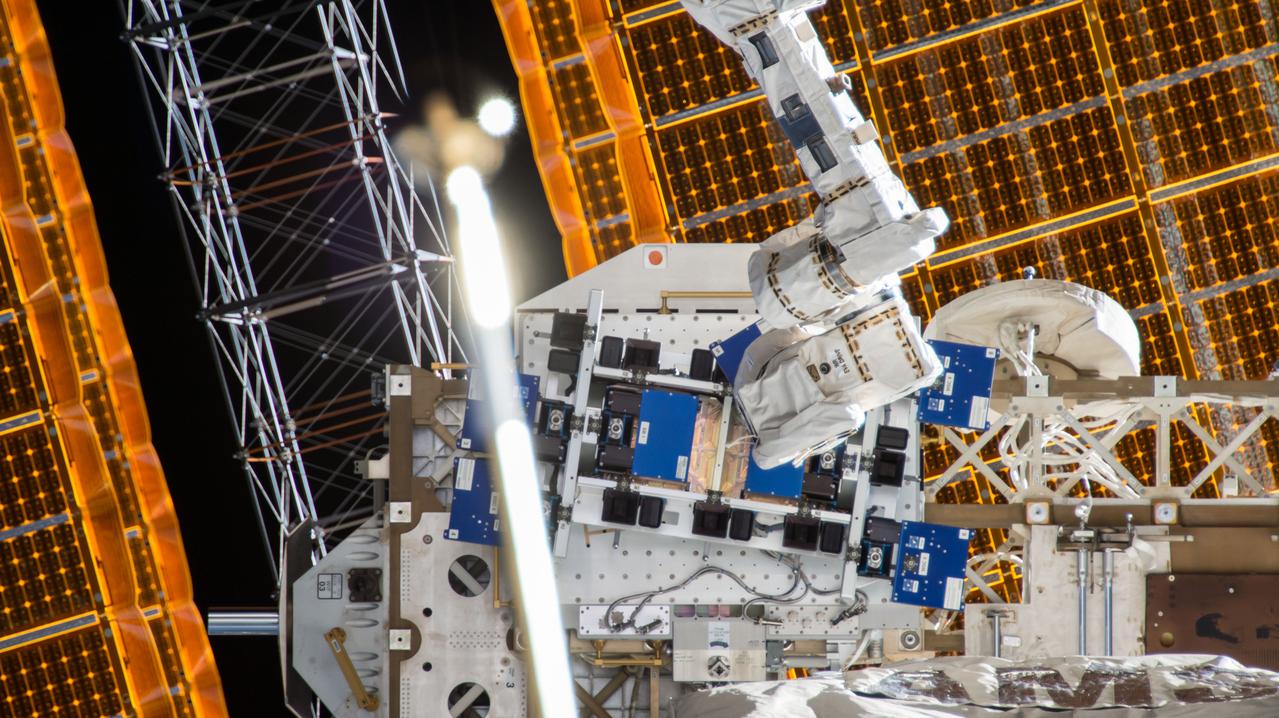

iss055e026913 (4/19/2018) --- View of the Materials ISS Experiment Flight Facility (MISSE-FF) taken by the External High Definition Camera (EHDC1). The MISSE-FF platform provides the ability to test materials, coatings, and components or other larger experiments in the harsh environment of space, which is virtually impossible to do collectively on Earth.
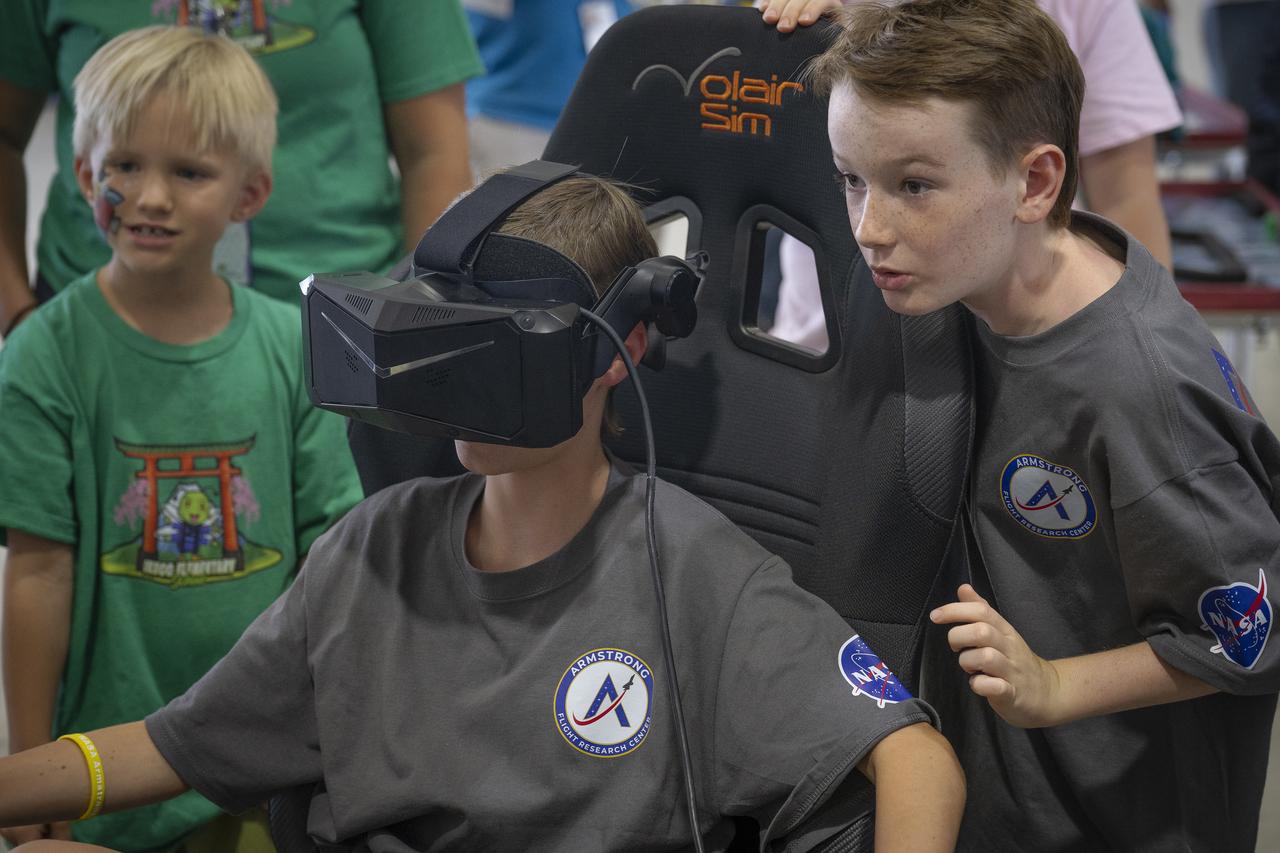

Children explore a virtual reality flight simulator during Bring Kids to Work Day on June 17, 2025, at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The immersive experience introduced participants to aerospace engineering and flight research in an engaging, hands-on environment.
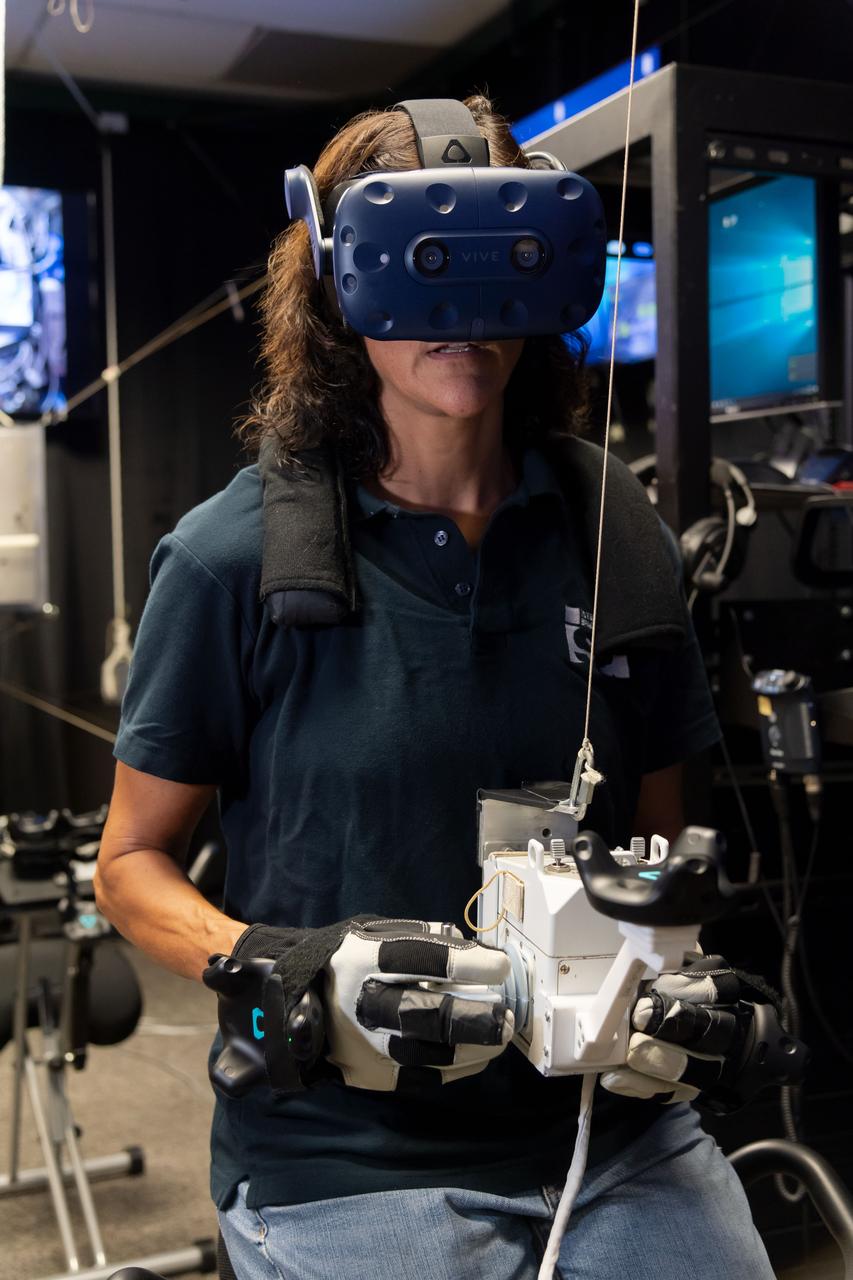

Commercial Crew Astronaut Suni Williams practices spacewalking in the Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston. The training provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is working with Boeing and SpaceX to return human spaceflight launches to the United States in 2019. Williams is assigned to Boeing’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.
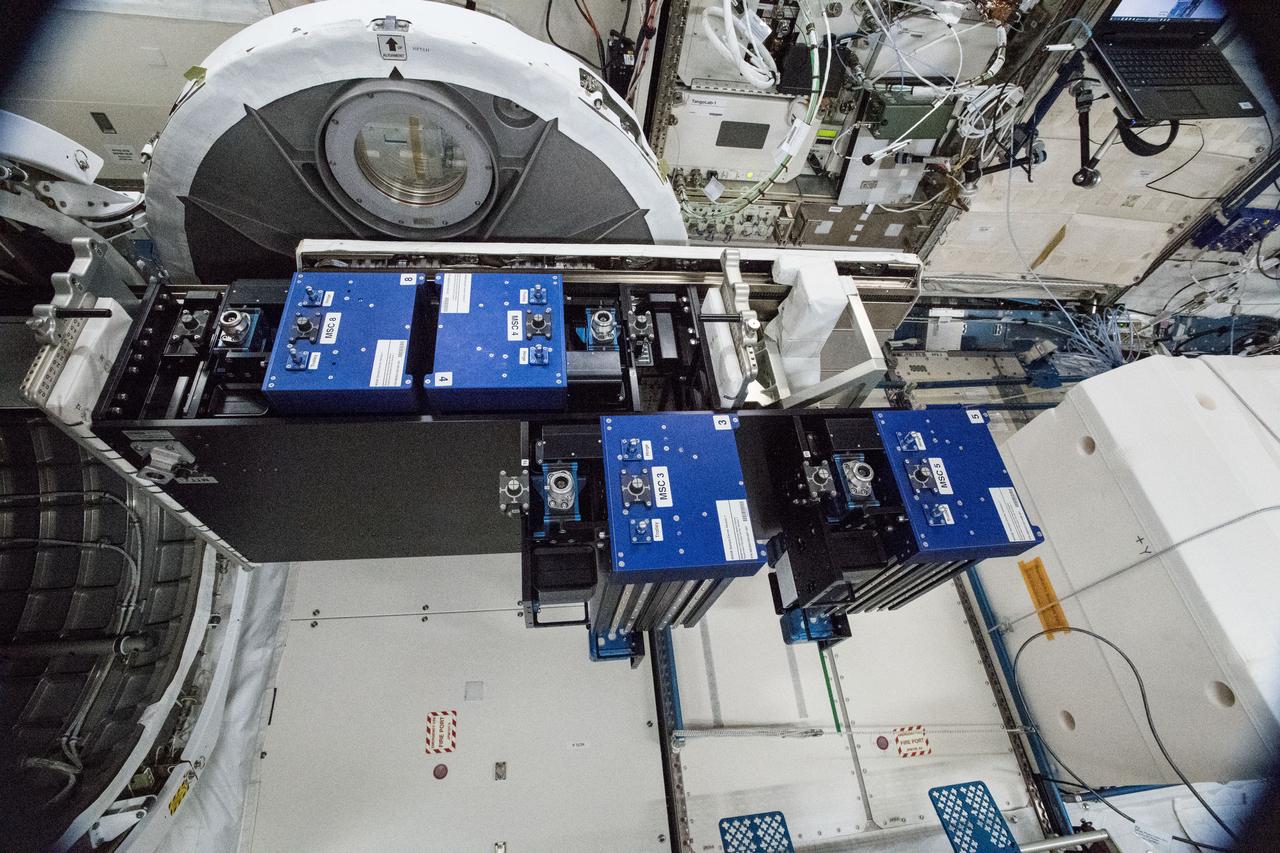

iss055e020137 (4/13/2018) --- Photographic documentation taken in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) during preparations for the install of the Materials ISS Experiment - Flight Facility (MISSEE-FF). The MISSE-FF platform provides the ability to test materials, coatings, and components or other larger experiments in the harsh environment of space, which is virtually impossible to do collectively on Earth.
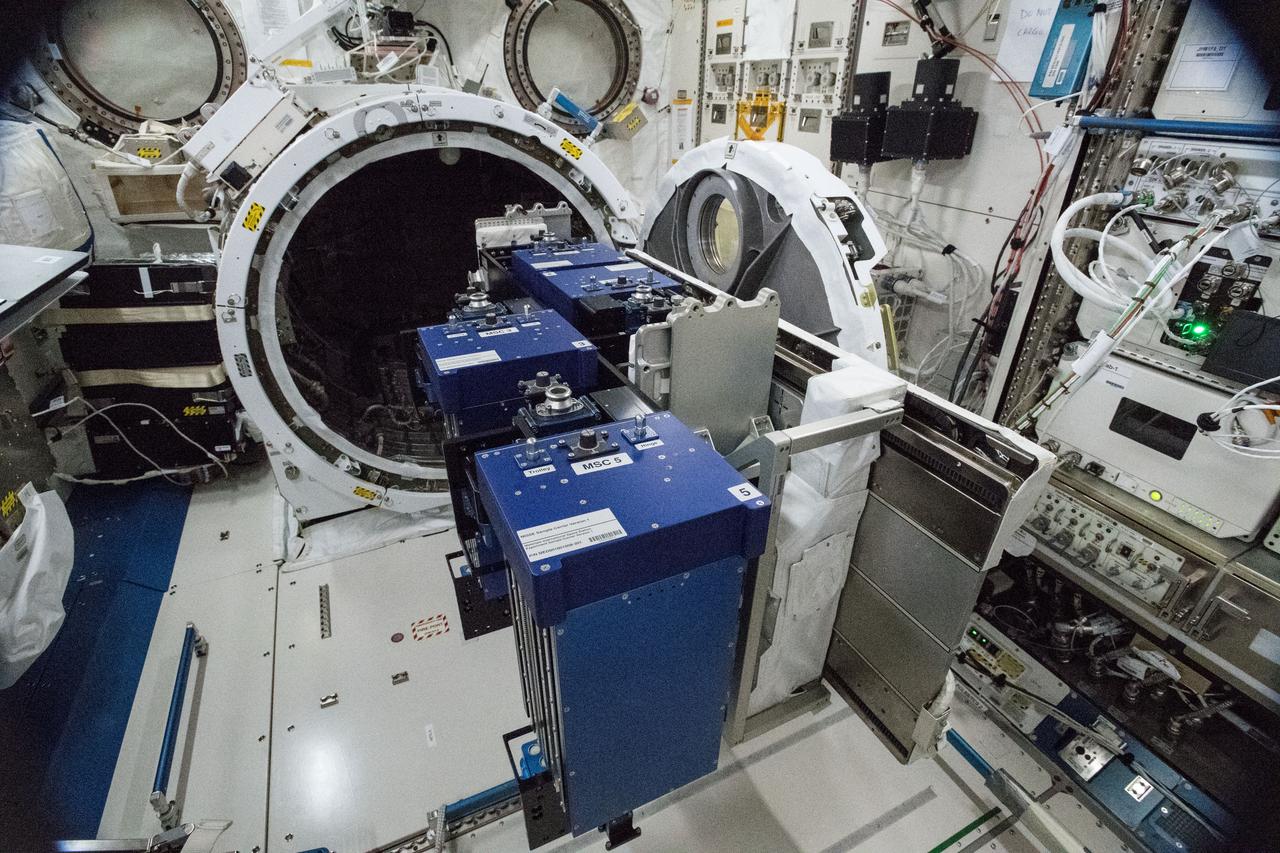
iss055e020134 (4/13/2018) --- Photographic documentation taken in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) during preparations for the install of the Materials ISS Experiment - Flight Facility (MISSEE-FF). The MISSE-FF platform provides the ability to test materials, coatings, and components or other larger experiments in the harsh environment of space, which is virtually impossible to do collectively on Earth.
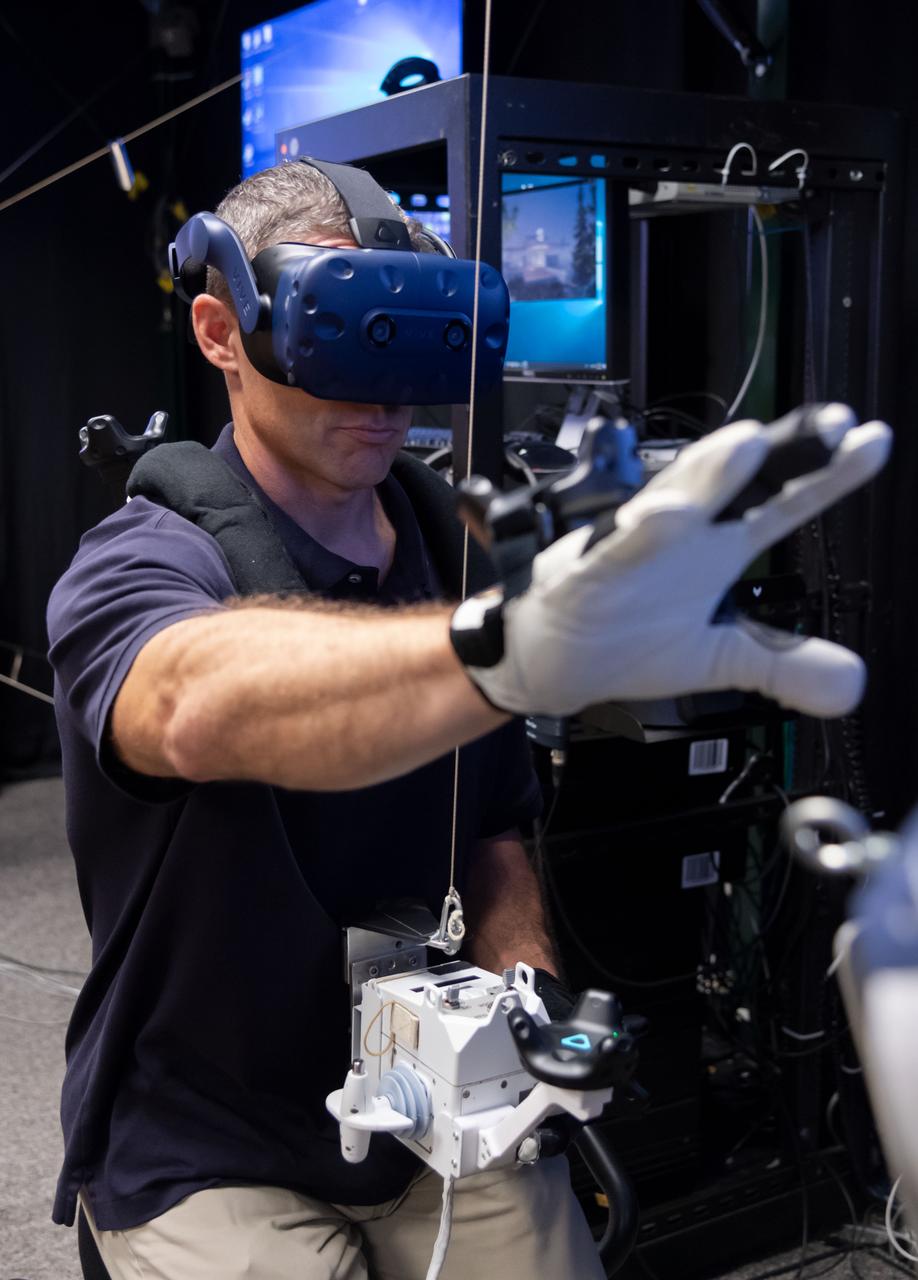

Commercial Crew Astronaut Mike Hopkins practices spacewalking in the Virtual Reality Lab at Johnson Space Center in Houston. The training provides real-time graphics and motion simulators to replicate the space environment. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is working with Boeing and SpaceX to return human spaceflight launches to the United States in 2019. Hopkins is assigned to SpaceX’s first operational mission after the company’s test flight with crew.
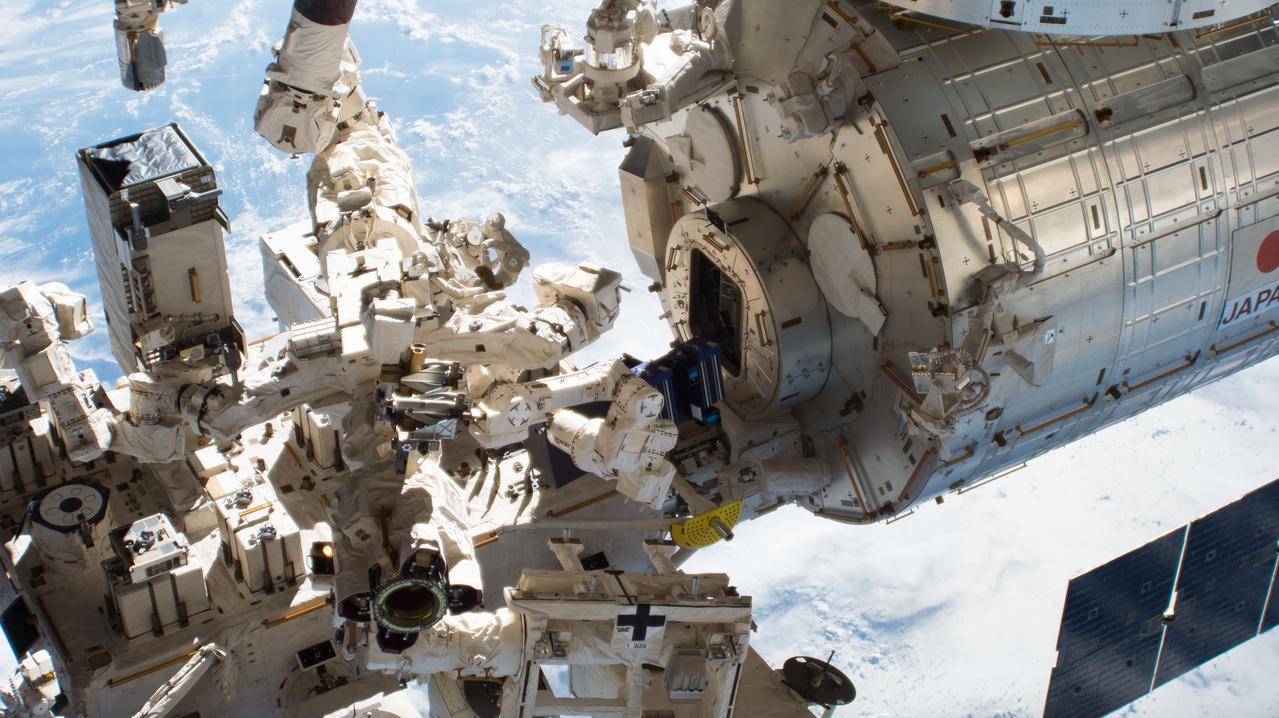

iss055e024241 (4/16/2018) --- View of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Exposed Facility (EF) and the Materials ISS Experiment Flight Facility (MISSE-FF) as it exits the JEM airlock. The MISSE-FF platform provides the ability to test materials, coatings, and components or other larger experiments in the harsh environment of space, which is virtually impossible to do collectively on Earth.

iss056e014352 (June 18, 2018) --- Flight Engineer Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency (ESA) is in quasi-free-floating configuration for the GRASP study taking place inside Europe's Columbus laboratory module. The ESA-sponsored research is studying how the body adapts to the microgravity environment. GRASP uses virtual reality headsets as a way to understand how important gravity is, compared to the other senses, when reaching for an object.
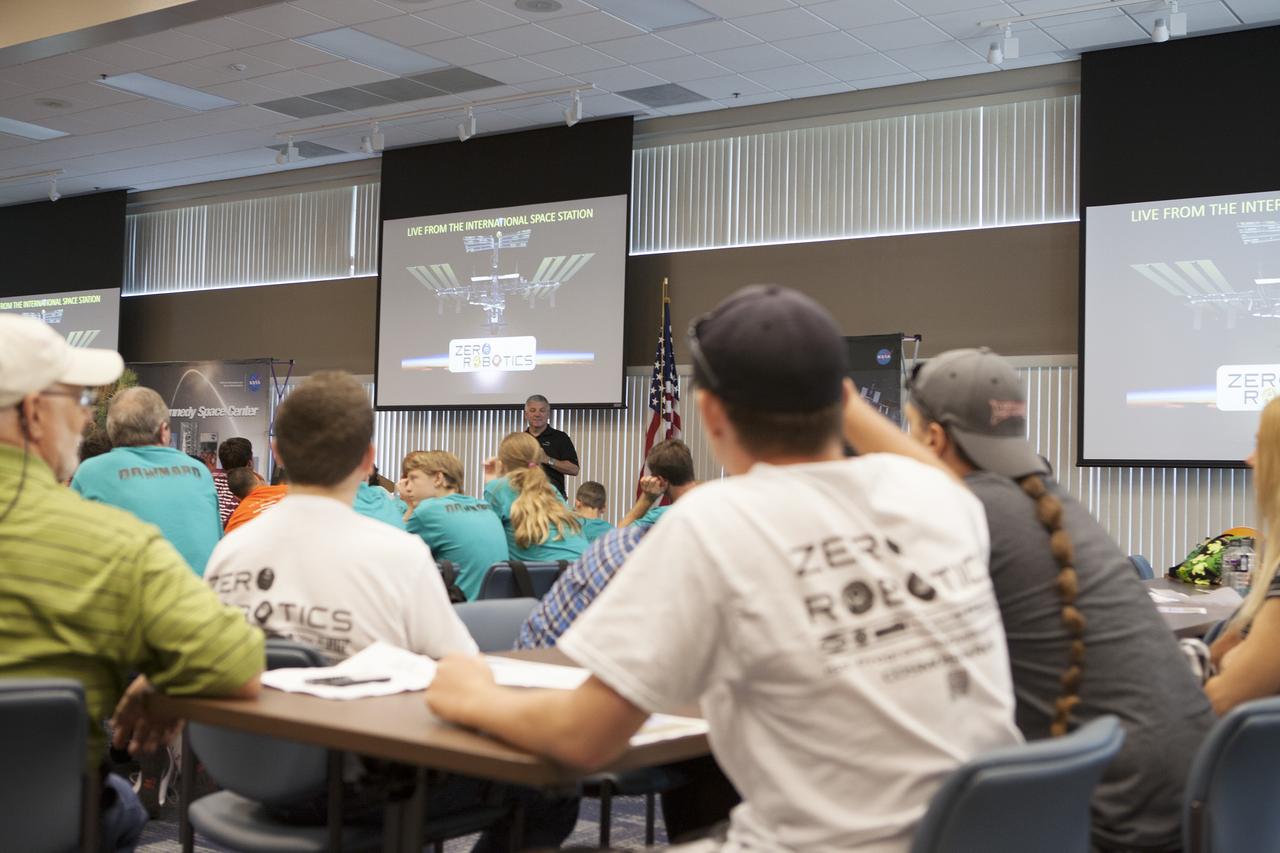

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
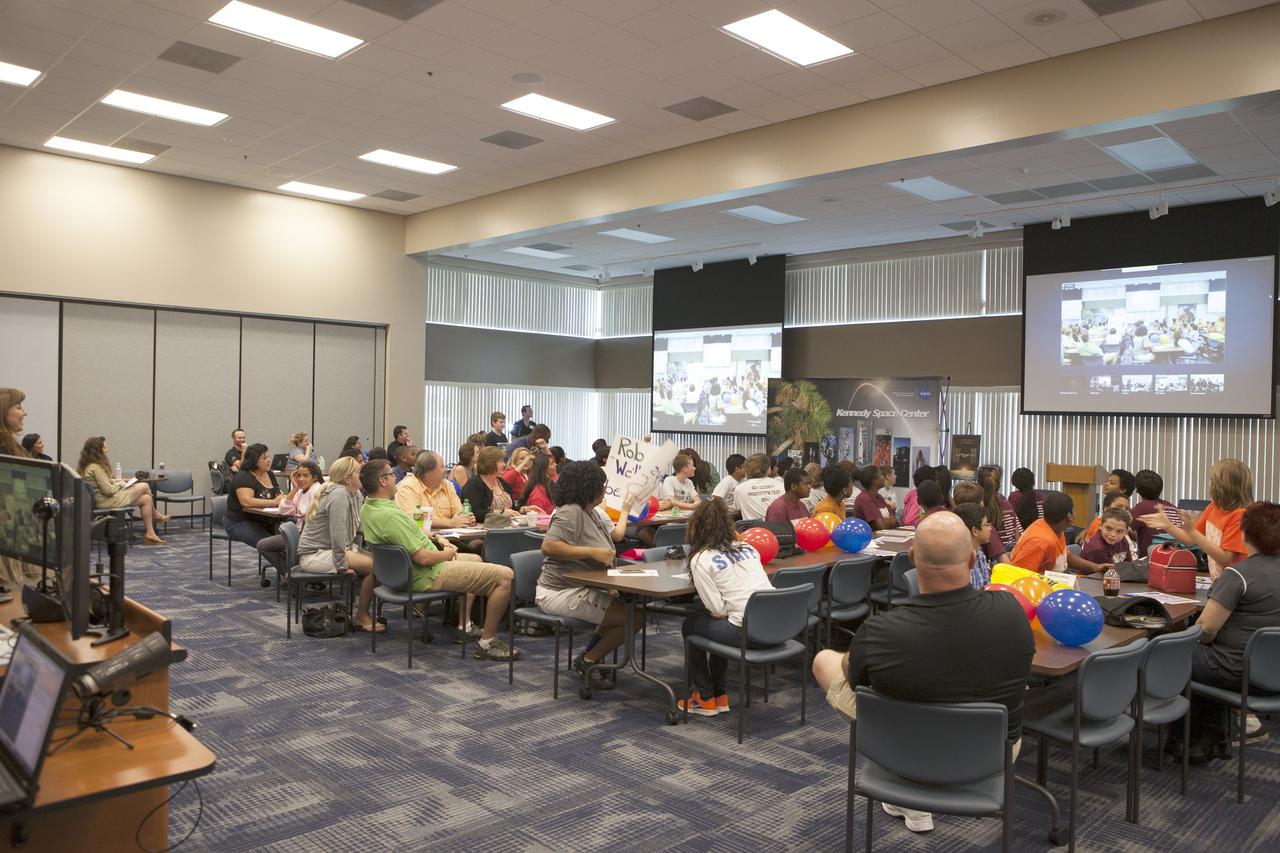

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Florida middle school students and their teachers greet students from other locations via webex before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition. The Florida teams are at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
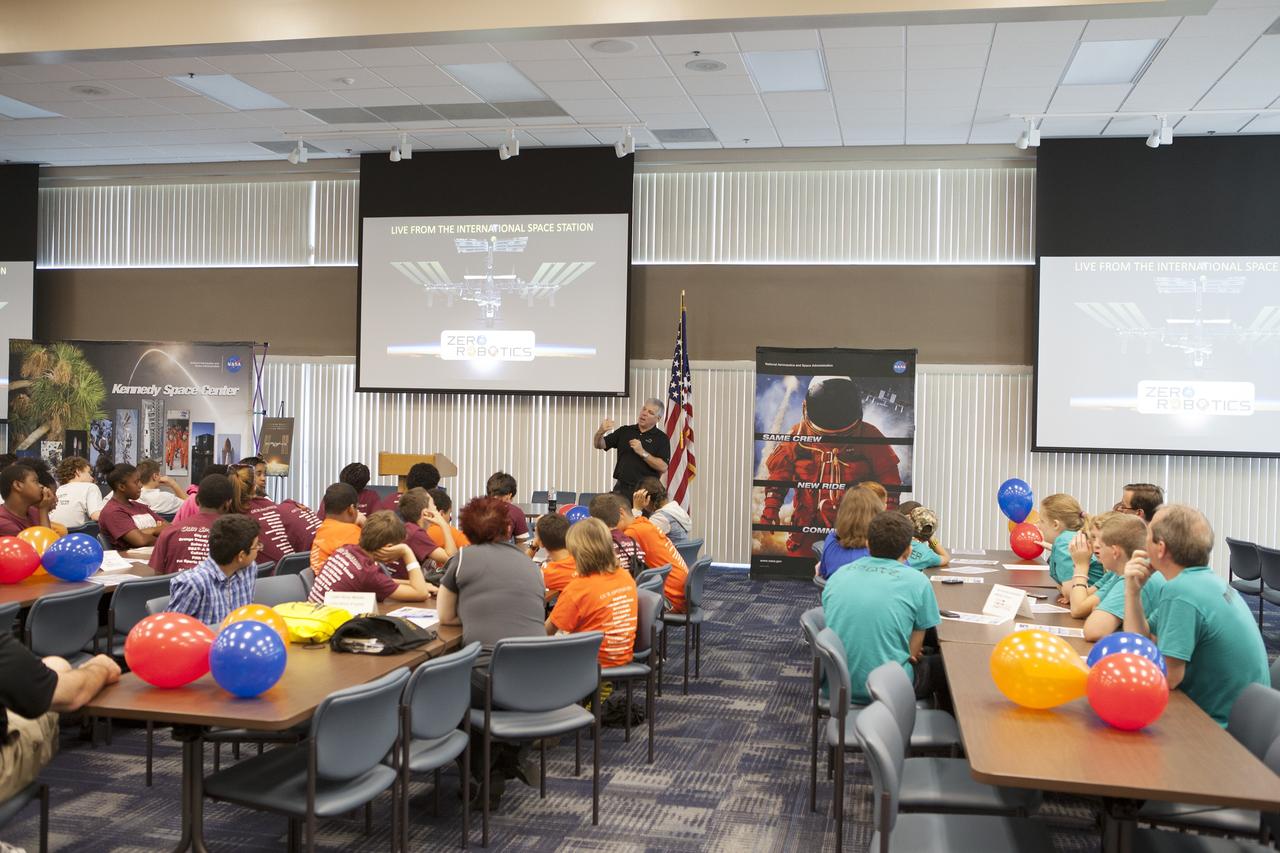

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
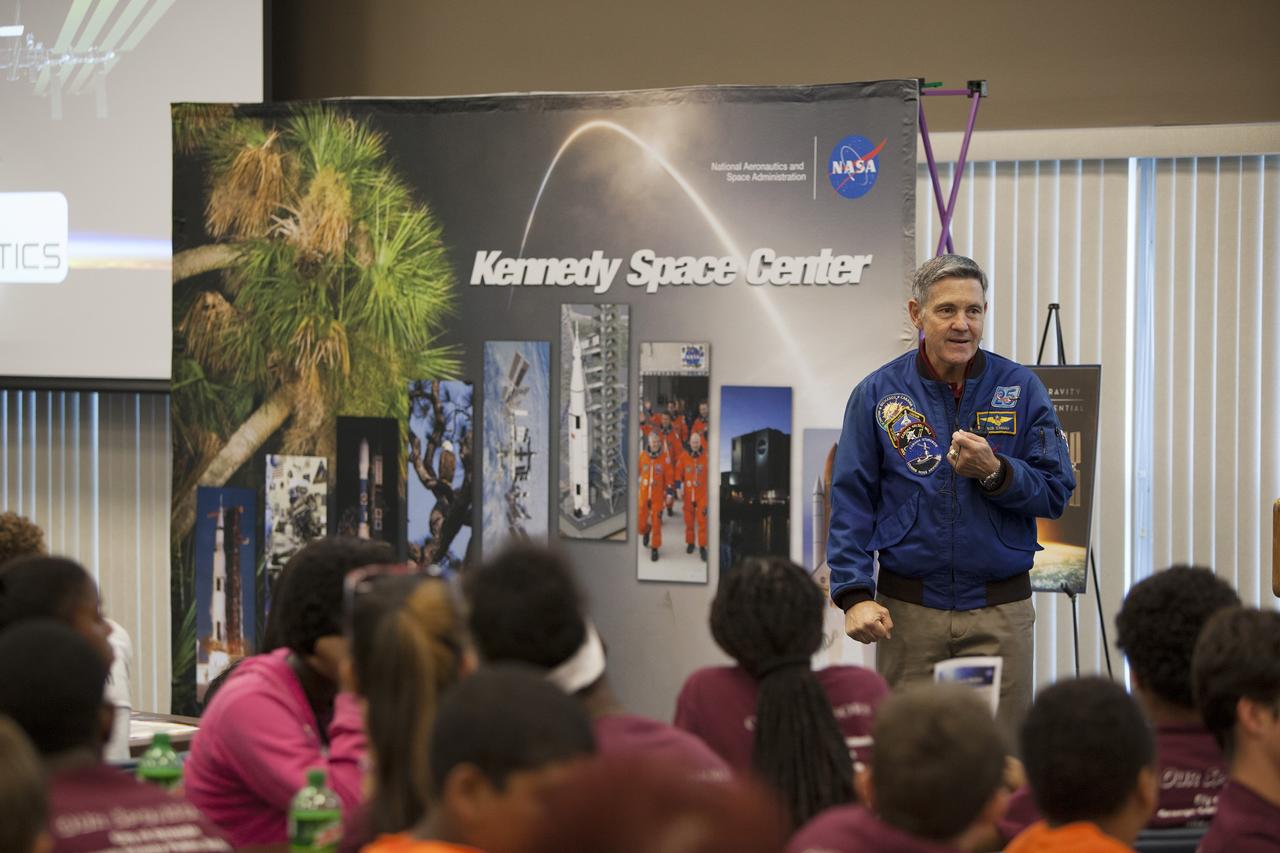

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kennedy Space Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers during the Zero Robotics finals competition at the center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
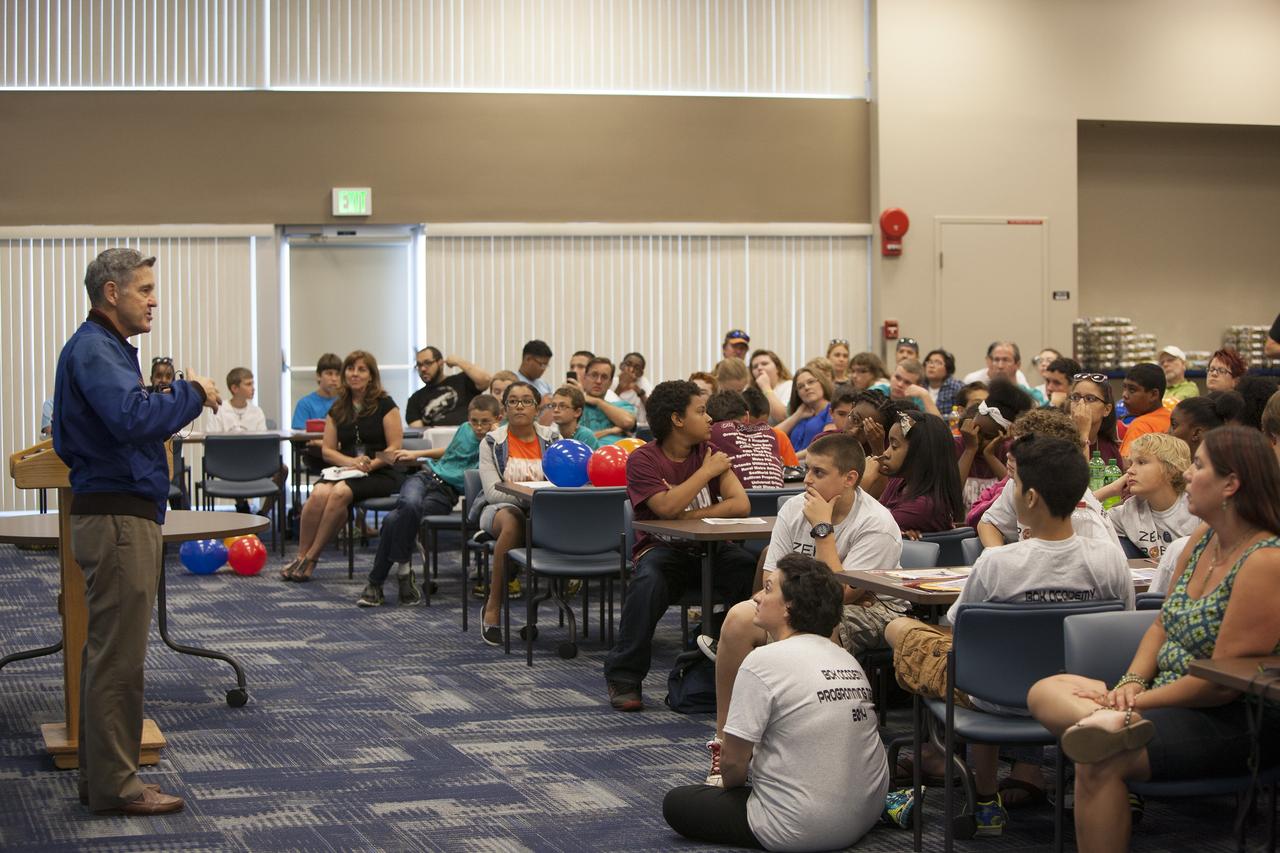

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kennedy Space Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers during the Zero Robotics finals competition at the center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kennedy Space Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers during the Zero Robotics finals competition at the center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
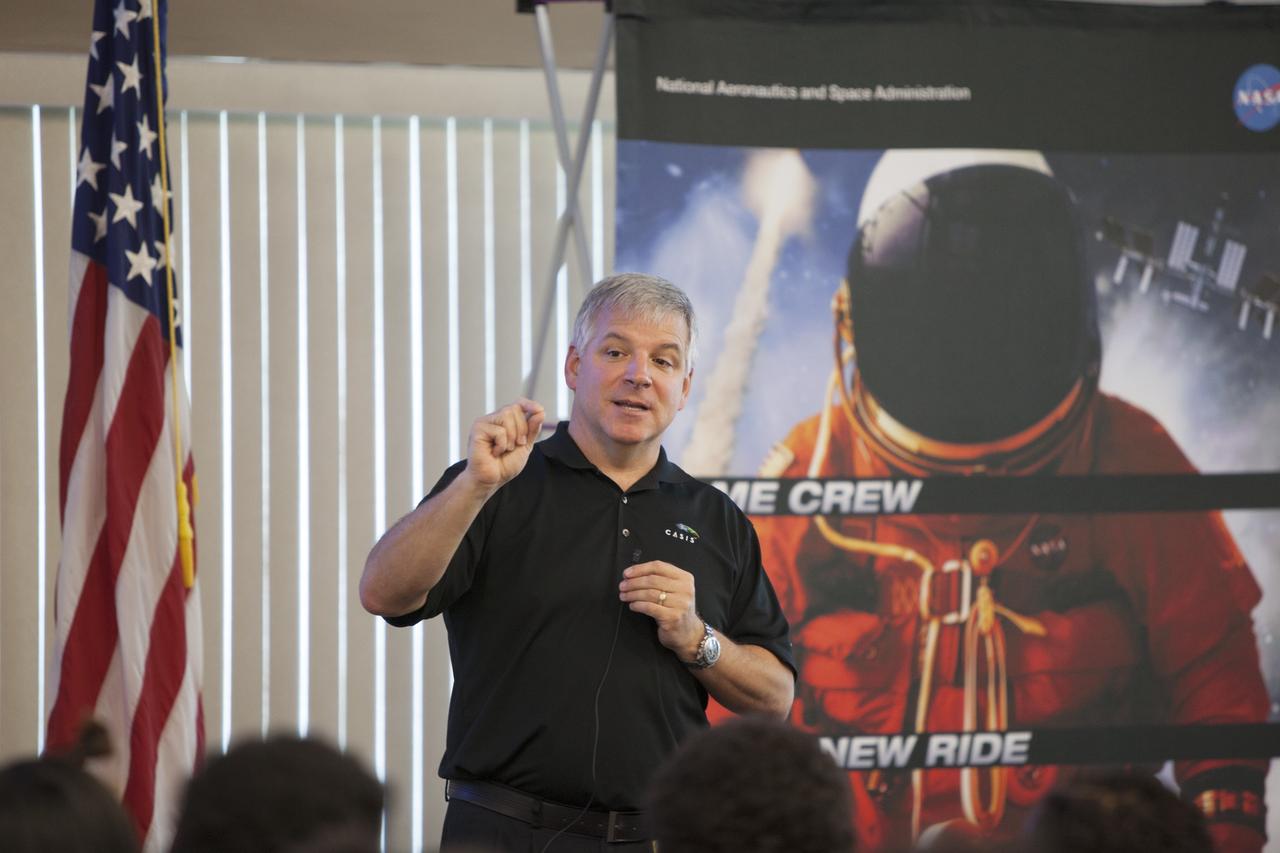

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
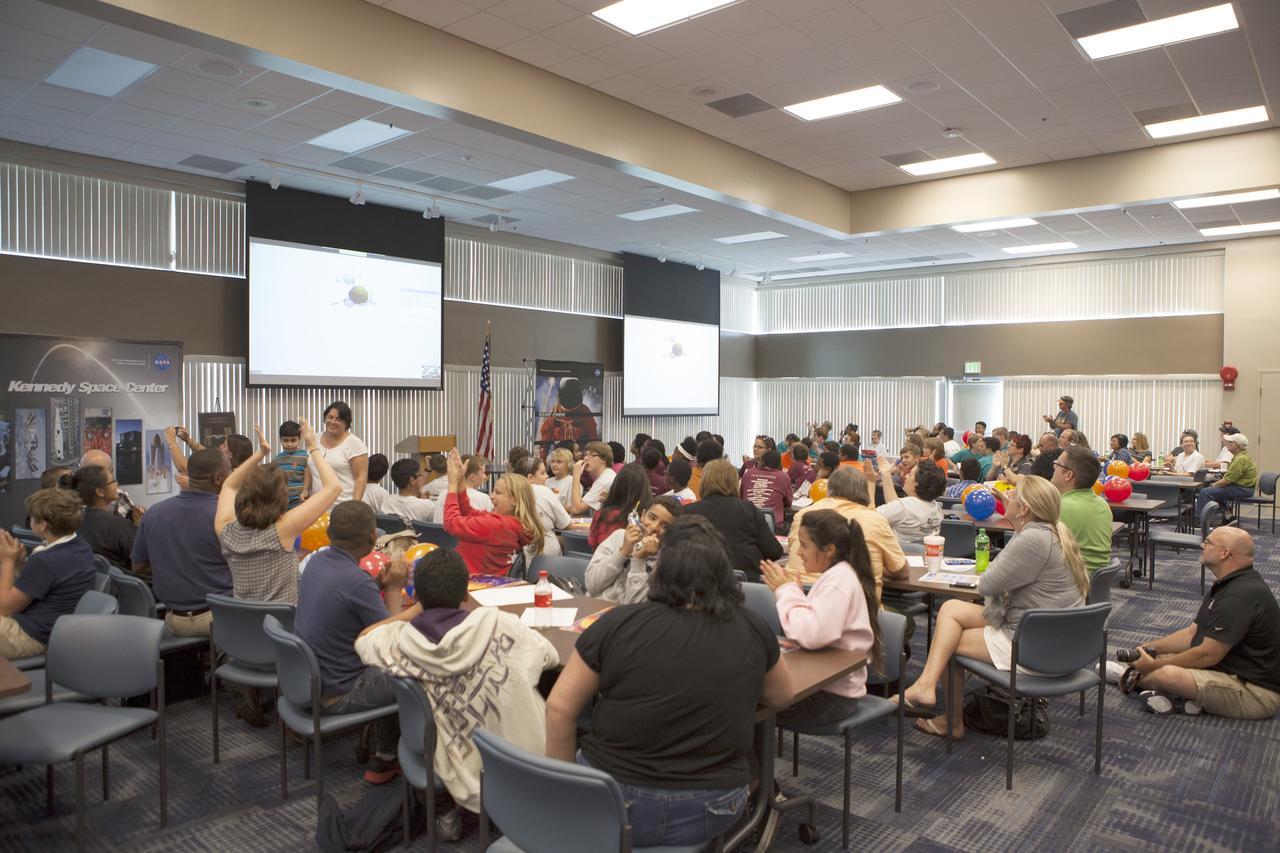

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Florida middle school students and their teachers watch the Zero Robotics finals competition broadcast live via webex from the International Space Station. The Florida teams are at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
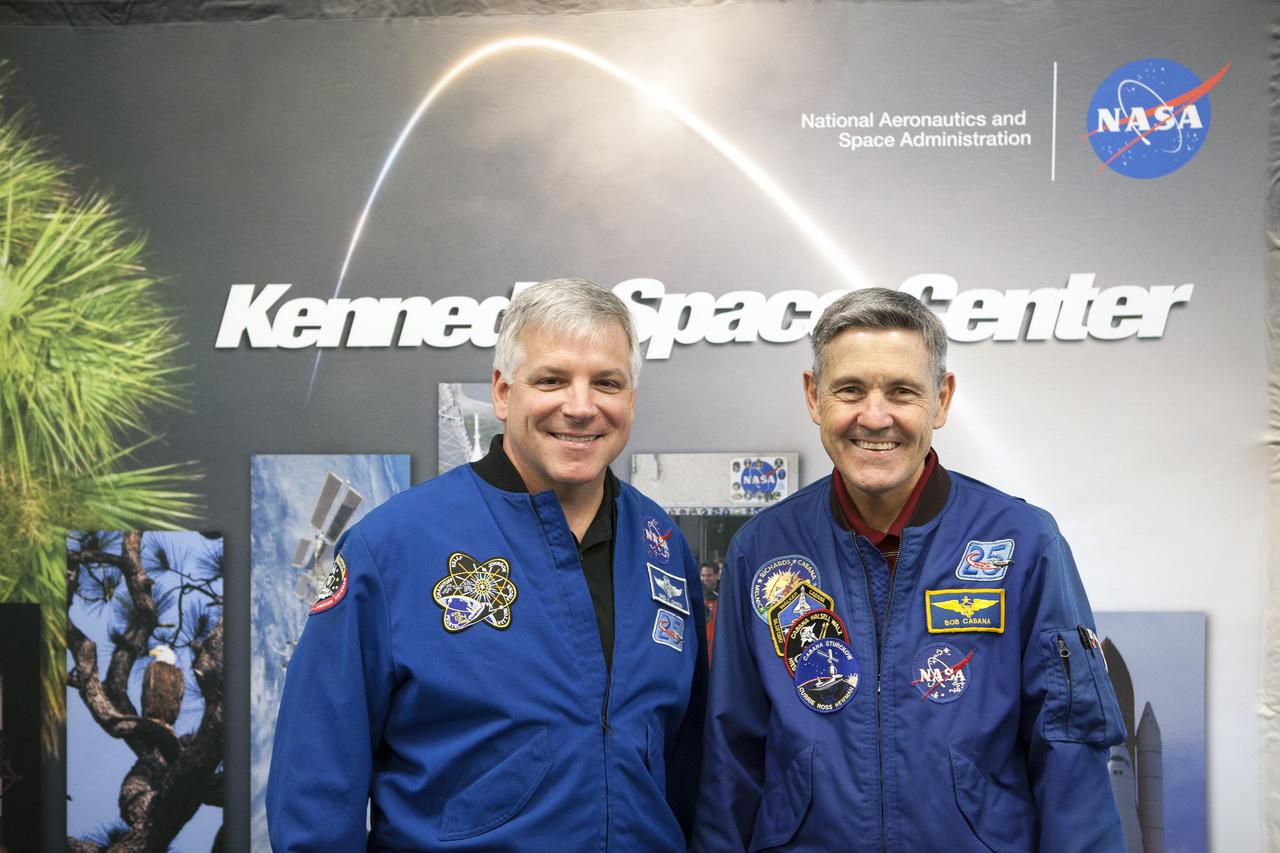

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, at left, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, and NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, visit with Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
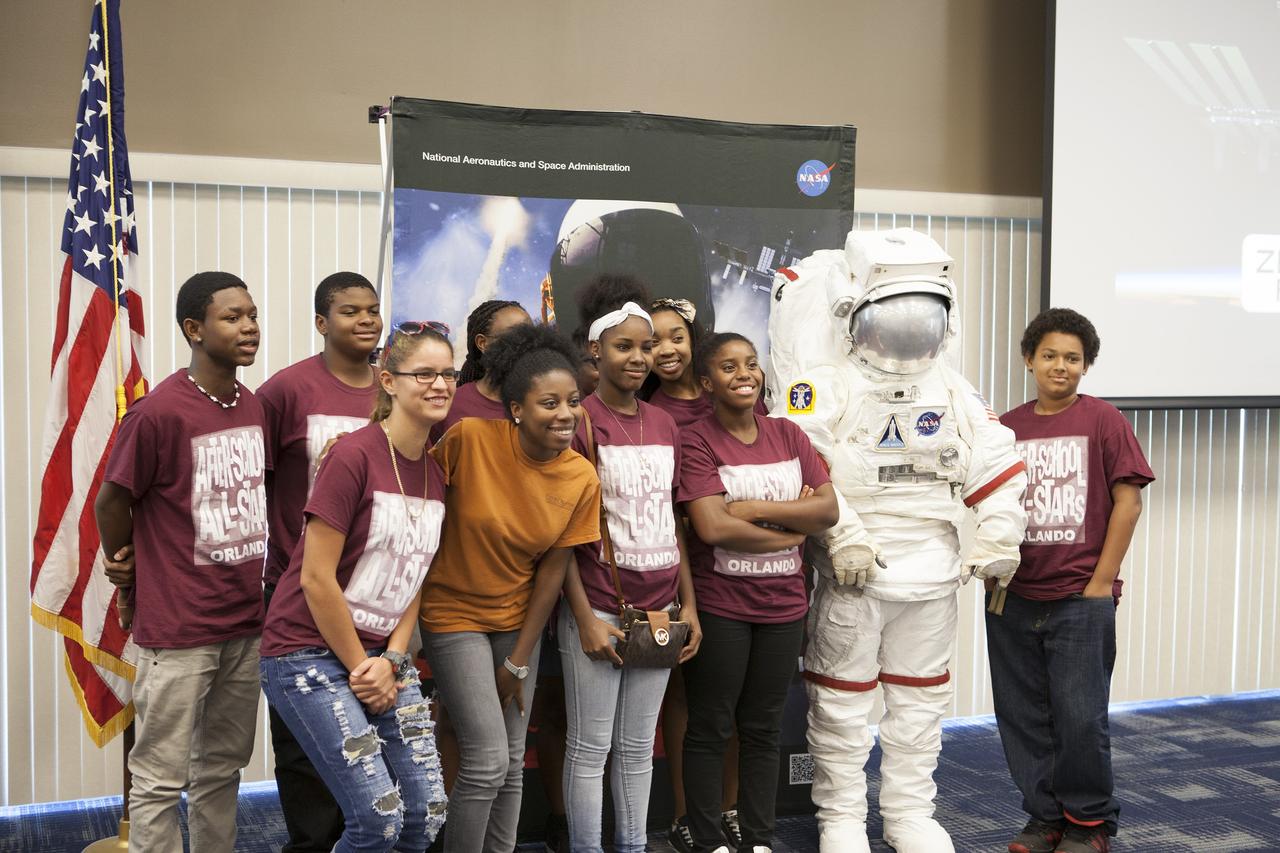

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex Spaceperson poses for a photo with Carver Middle School students and their teacher from Orlando, Florida, during the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. The team, members of the After School All-Stars, were regional winners and advanced to the final competition. For the competition, students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
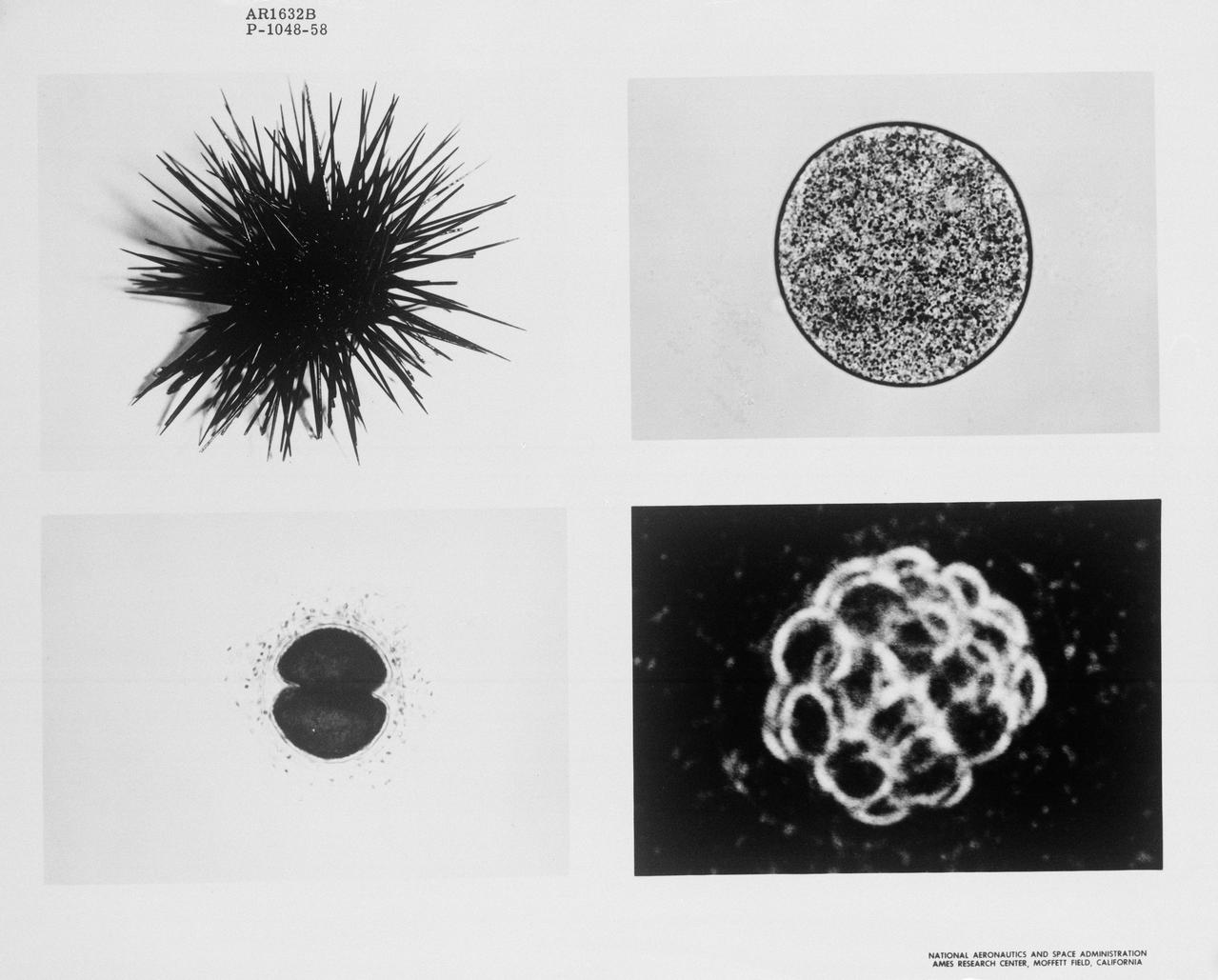
S65-18762 (March 1965) --- Effects of the weightless environment on cell division, the basic growth process for living tissue, will be studied during the Gemini-Titan 3 flight scheduled for March 23, 1965. A spiny black sea urchin (upper left) is stimulated by mild electric shock or potassium chloride. As a result it sheds many thousands of eggs. When fertilized, these eggs become actively dividing cells very similar in basic processes to cells of other animals, including humans. These pictures show stages of cell division. At upper right is a single cell; at lower right cell divisions have produced many cells. Cell photos are magnified about 700 times, and all cells shown are too small to be seen by the naked eye. (Photos at upper right and lower left are of sea urchin eggs. Group of cells at lower right are from a sand dollar, which like the sea urchin, is an Echinoderm. Its eggs are virtually identical and are used interchangeably with those of the sea urchin in NASA Ames Center weightlessness experiments.) The Gemini experiment will involve cell division like that shown here. This will take place during several hours of weightlessness aboard the Gemini spacecraft. The experiment will be flown back to laboratories at Cape Kennedy after spacecraft recovery. It has been designed so that any abnormal cell division found by postflight analysis should suggest that the weightless environment has effects on individual cells. This might mean hazards for prolonged periods of manned spaceflight.
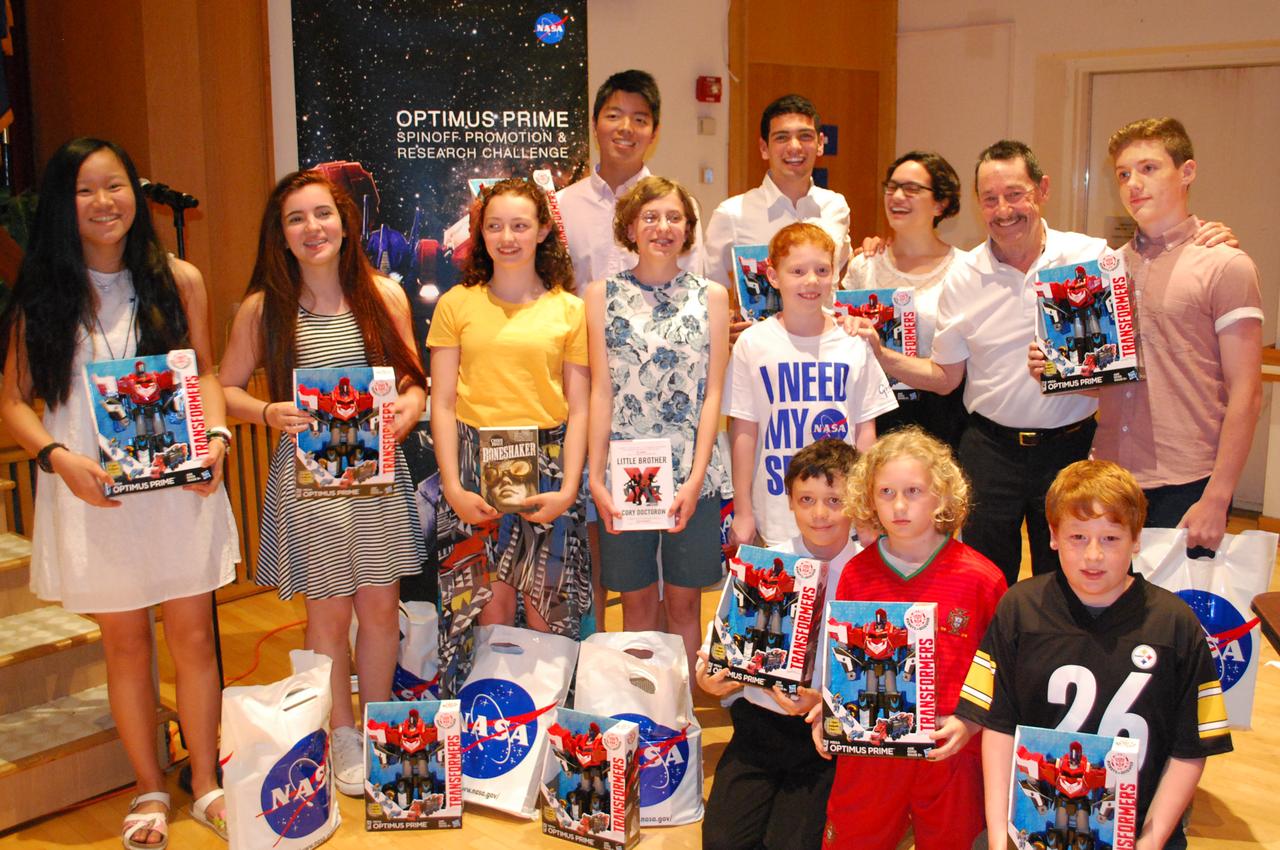

From June 28 through 30, 2016, the OPTIMUS PRIME Spinoff Promotion and Research Challenge (OPSPARC) gave the contest’s winning students the opportunity to explore NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Three teams of students from elementary, middle and high school won the contest by creating the most popular ideas to use NASA technology in new and innovative ways. The students used an online platform called Glogster to make posters about their ideas, and the general public voted for their favorites. Sophia Sheehan won the elementary school prize for her invention of the “blow coat,” which would be powered by solar panels and blow warm air into winter coats, helping people in her hometown of Chicago stay warm in the winter. Heidi Long, Aubrey Nesti, Katherine Valbuena and Jasmine Wu won in the middle school category for their idea called Tent-cordion, which would use spacesuit and satellite insulation materials in a foldable tent to house refugees and the homeless. Finally, Jake Laddis, Alex Li, Isaac Wecht and Isabel Wecht won in the high school category for their idea to use James Webb Space Telescope sunshield technology to shield houses from summer heat and reduce the need for air conditioning around the world. The high school winners also had the opportunity to compete in the NASA InWorld challenge, sponsored by the James Webb Space Telescope project, and continued developing their idea in a virtual world and gaming environment. During their three-day workshop at Goddard, the students toured the center, met with scientists and engineers, took a look at the James Webb Space Telescope in Goddard’s clean room, and even made their own videos in Goddard’s TV studio. One of the students talked about how the experience inspired her. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/298fGdQ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/298fGdQ</a>
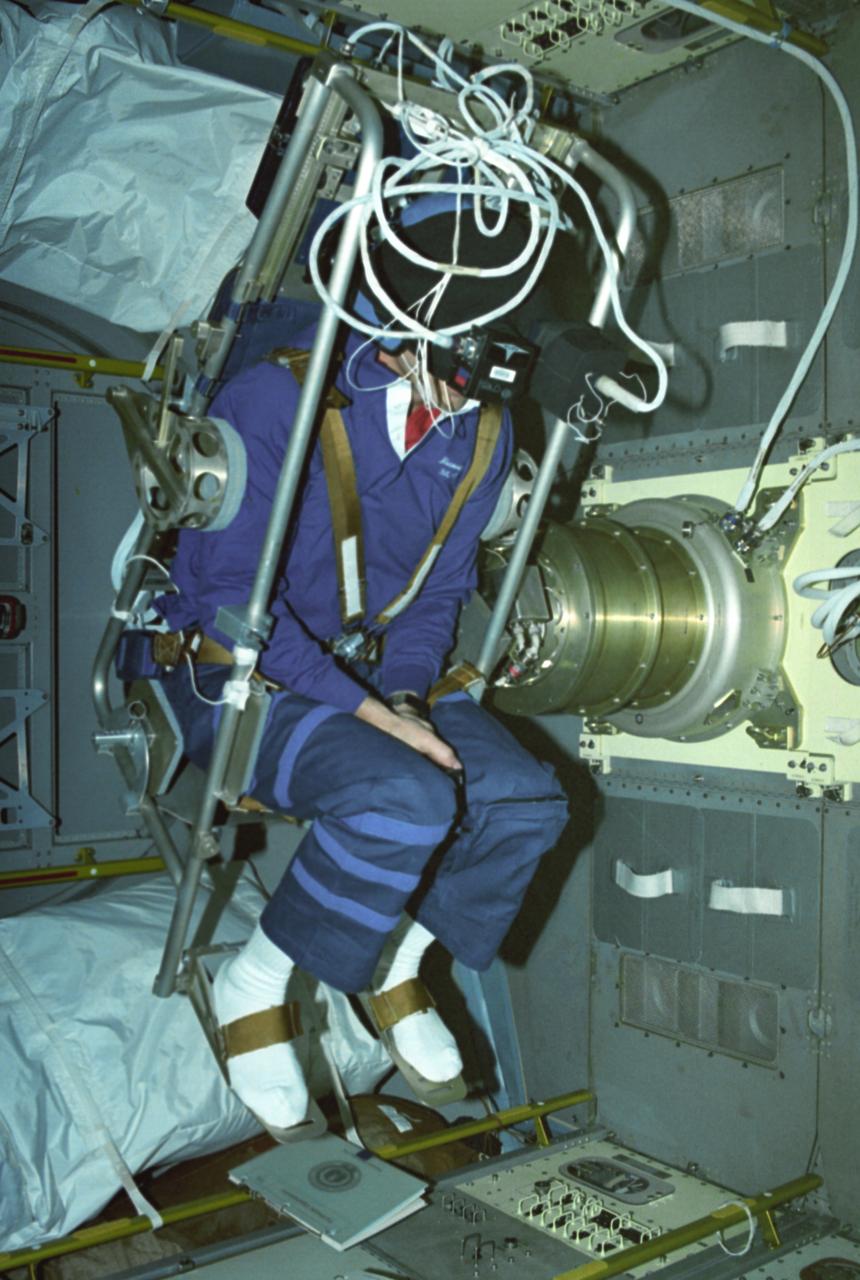

Astronaut David C. Hilmers conducts the Microgravity Vestibular Investigations (MVI) sitting in its rotator chair inside the IML-1 science module. When environmental conditions change so that the body receives new stimuli, the nervous system responds by interpreting the incoming sensory information differently. In space, the free-fall environment of an orbiting spacecraft requires that the body adapts to the virtual absence of gravity. Early in flights, crewmembers may feel disoriented or experience space motion sickness. MVI examined the effects of orbital flight on the human orientation system to obtain a better understanding of the mechanisms of adaptation to weightlessness. By provoking interactions among the vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive systems and then measuring the perceptual and sensorimotor reactions, scientists can study changes that are integral to the adaptive process. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).

This image depicts a vast canyon of dust and gas in the Orion Nebula from a 3-D computer model based on observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and created by science visualization specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md. A 3-D visualization of this model takes viewers on an amazing four-minute voyage through the 15-light-year-wide canyon. Credit: NASA, G. Bacon, L. Frattare, Z. Levay, and F. Summers (STScI/AURA) Go here to learn more about Hubble 3D: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premiere.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/hubble_imax_premier...</a> or <a href="http://www.imax.com/hubble/" rel="nofollow">www.imax.com/hubble/</a> Take an exhilarating ride through the Orion Nebula, a vast star-making factory 1,500 light-years away. Swoop through Orion's giant canyon of gas and dust. Fly past behemoth stars whose brilliant light illuminates and energizes the entire cloudy region. Zoom by dusty tadpole-shaped objects that are fledgling solar systems. This virtual space journey isn't the latest video game but one of several groundbreaking astronomy visualizations created by specialists at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, the science operations center for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The cinematic space odysseys are part of the new Imax film "Hubble 3D," which opens today at select Imax theaters worldwide. The 43-minute movie chronicles the 20-year life of Hubble and includes highlights from the May 2009 servicing mission to the Earth-orbiting observatory, with footage taken by the astronauts. The giant-screen film showcases some of Hubble's breathtaking iconic pictures, such as the Eagle Nebula's "Pillars of Creation," as well as stunning views taken by the newly installed Wide Field Camera 3. While Hubble pictures of celestial objects are awe-inspiring, they are flat 2-D photographs. For this film, those 2-D images have been converted into 3-D environments, giving the audience the impression they are space travelers taking a tour of Hubble's most popular targets. "A large-format movie is a truly immersive experience," says Frank Summers, an STScI astronomer and science visualization specialist who led the team that developed the movie visualizations. The team labored for nine months, working on four visualization sequences that comprise about 12 minutes of the movie. "Seeing these Hubble images in 3-D, you feel like you are flying through space and not just looking at picture postcards," Summers continued. "The spacescapes are all based on Hubble images and data, though some artistic license is necessary to produce the full depth of field needed for 3-D." The most ambitious sequence is a four-minute voyage through the Orion Nebula's gas-and-dust canyon, about 15 light-years across. During the ride, viewers will see bright and dark, gaseous clouds; thousands of stars, including a grouping of bright, hefty stars called the Trapezium; and embryonic planetary systems. The tour ends with a detailed look at a young circumstellar disk, which is much like the structure from which our solar system formed 4.5 billion years ago. Based on a Hubble image of Orion released in 2006, the visualization was a collaborative effort between science visualization specialists at STScI, including Greg Bacon, who sculpted the Orion Nebula digital model, with input from STScI astronomer Massimo Roberto; the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; and the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. For some of the sequences, STScI imaging specialists developed new techniques for transforming the 2-D Hubble images into 3-D. STScI image processing specialists Lisa Frattare and Zolt Levay, for example, created methods of splitting a giant gaseous pillar in the Carina Nebula into multiple layers to produce a 3-D effect, giving the structure depth. The Carina Nebula is a nursery for baby stars. Frattare painstakingly removed the thousands of stars in the image so that Levay could separate the gaseous layers on the isolated Carina pillar. Frattare then replaced the stars into both foreground and background layers to complete the 3-D model. For added effect, the same separation was done for both visible and infrared Hubble images, allowing the film to cross-fade between wavelength views in 3-D. In another sequence viewers fly into a field of 170,000 stars in the giant star cluster Omega Centauri. STScI astronomer Jay Anderson used his stellar database to create a synthetic star field in 3-D that matches recent razor-sharp Hubble photos. The film's final four-minute sequence takes viewers on a voyage from our Milky Way Galaxy past many of Hubble's best galaxy shots and deep into space. Some 15,000 galaxies from Hubble's deepest surveys stretch billions of light-years across the universe in a 3-D sequence created by STScI astronomers and visualizers. The view dissolves into a cobweb that traces the universe's large-scale structure, the backbone from which galaxies were born. In addition to creating visualizations, STScI's education group also provided guidance on the "Hubble 3D" Educator Guide, which includes standards-based lesson plans and activities about Hubble and its mission. Students will use the guide before or after seeing the movie. "The guide will enhance the movie experience for students and extend the movie into classrooms," says Bonnie Eisenhamer, STScI's Hubble Formal Education manager. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) and is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Md. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. The institute is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., Washington, D.C.