
Application of blowing-type boundry-layer control to the leading-and trailing-edge flaps of a Change Vought XF8U-1 wing
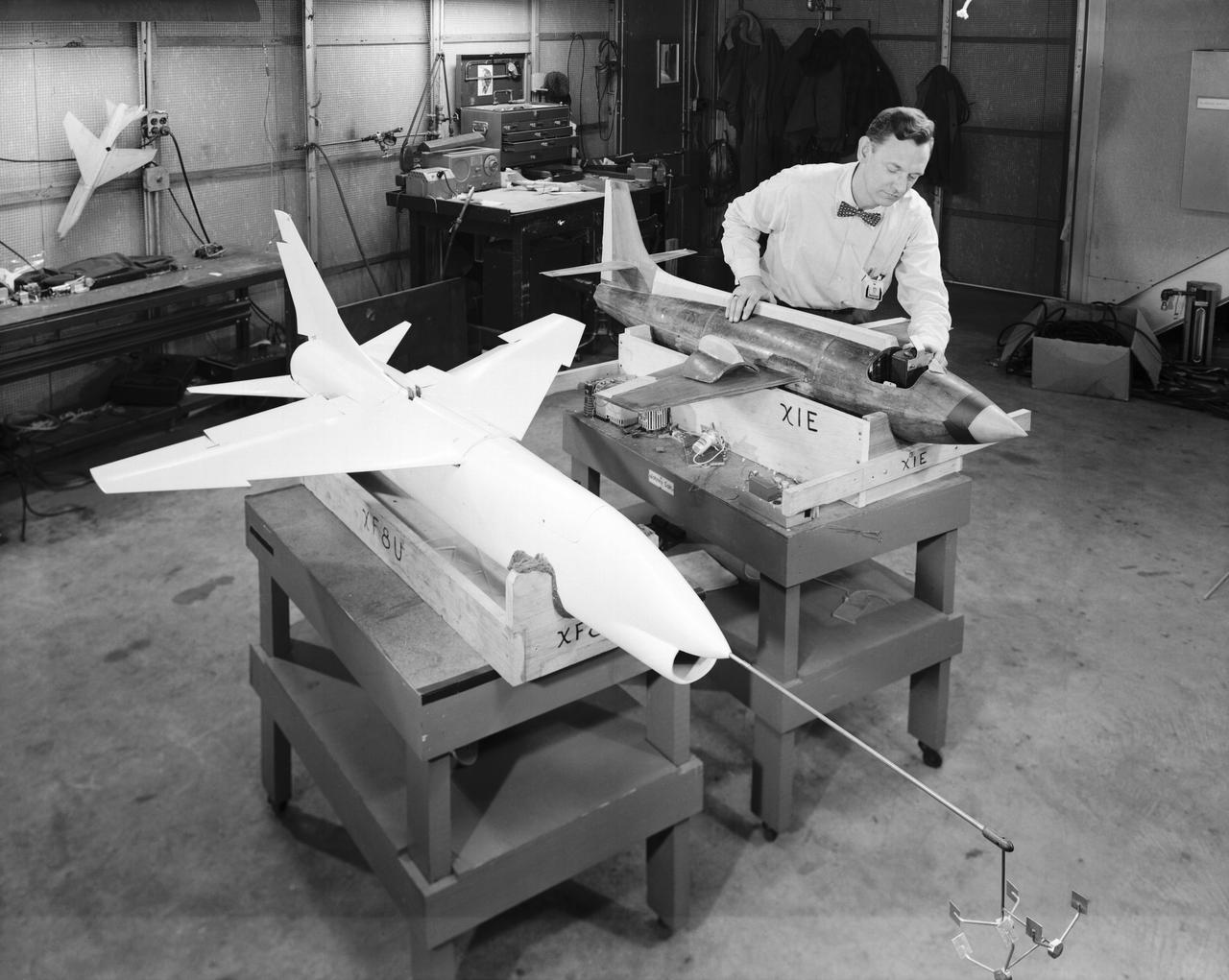

L57-660 A technician prepares dynamic models of the Bell X-1E and the Vought XF-8U Crusader for wind tunnel testing in 1957. The Crusader was then the Navy's fastest aircraft- maximum speed Mach 1.75 at 35,000 Feet. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 307.
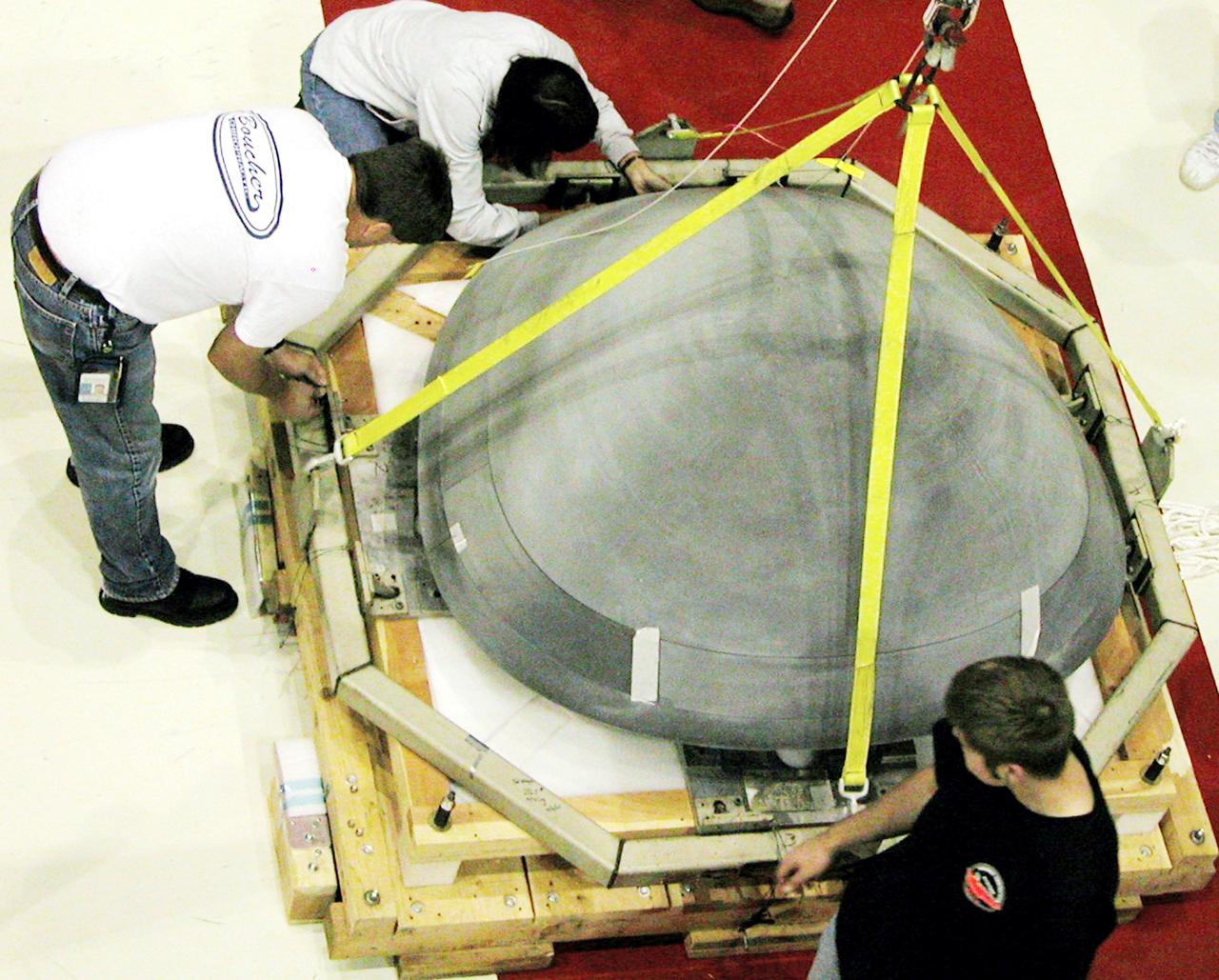

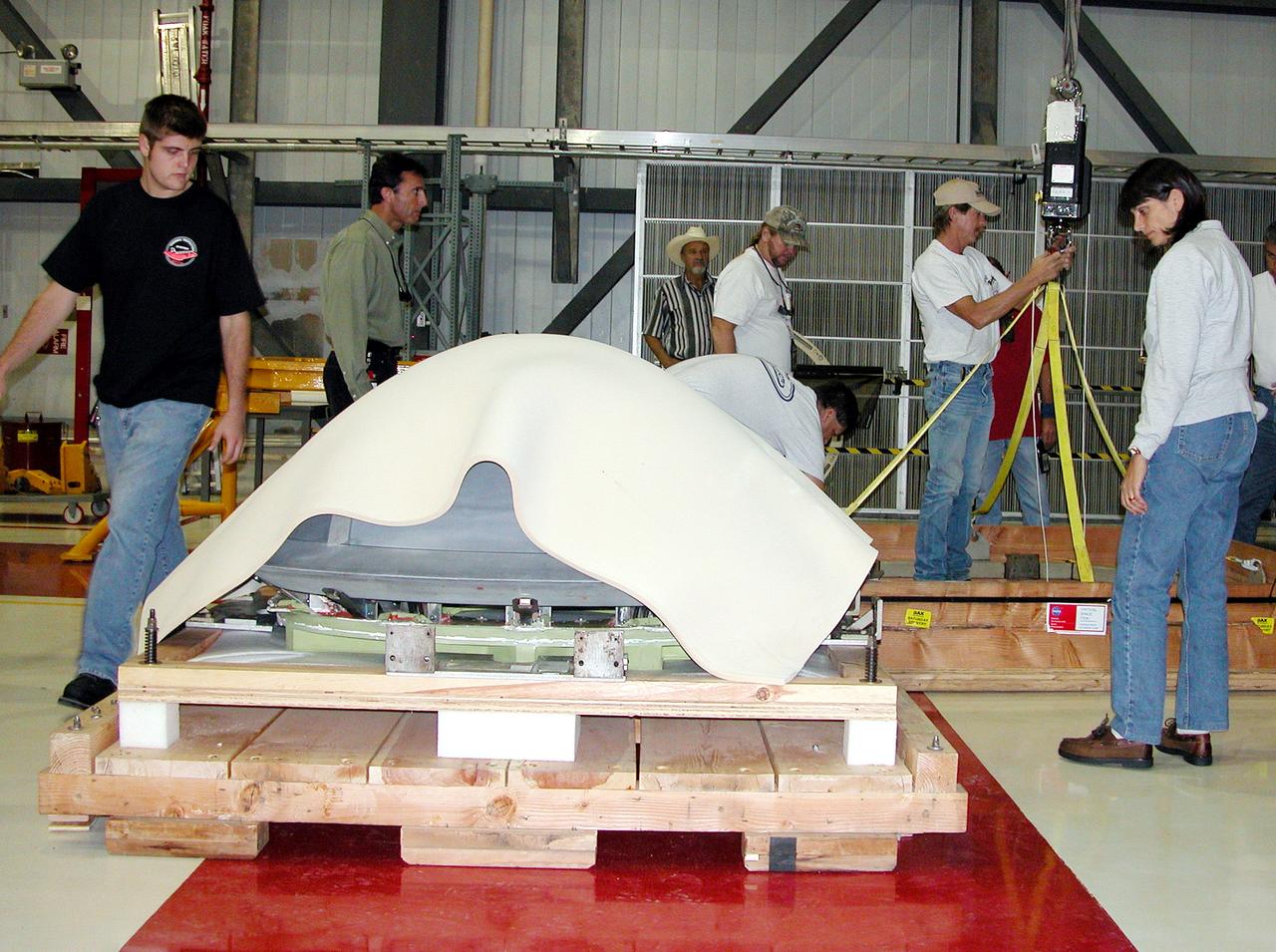
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap from Atlantis is secured on a shipping pallet. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap from Atlantis is lowered toward a shipping pallet. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

CHANCE VOUGHT F7U-3 #656 AIRPLANE at NACA Ames for testing of PRESSURE PROBE ON TAIL PIPE (afterburners)

Navy CHANCE VOUGHT F7U-3 #656 AIRPLANE on NACA Ames flight line
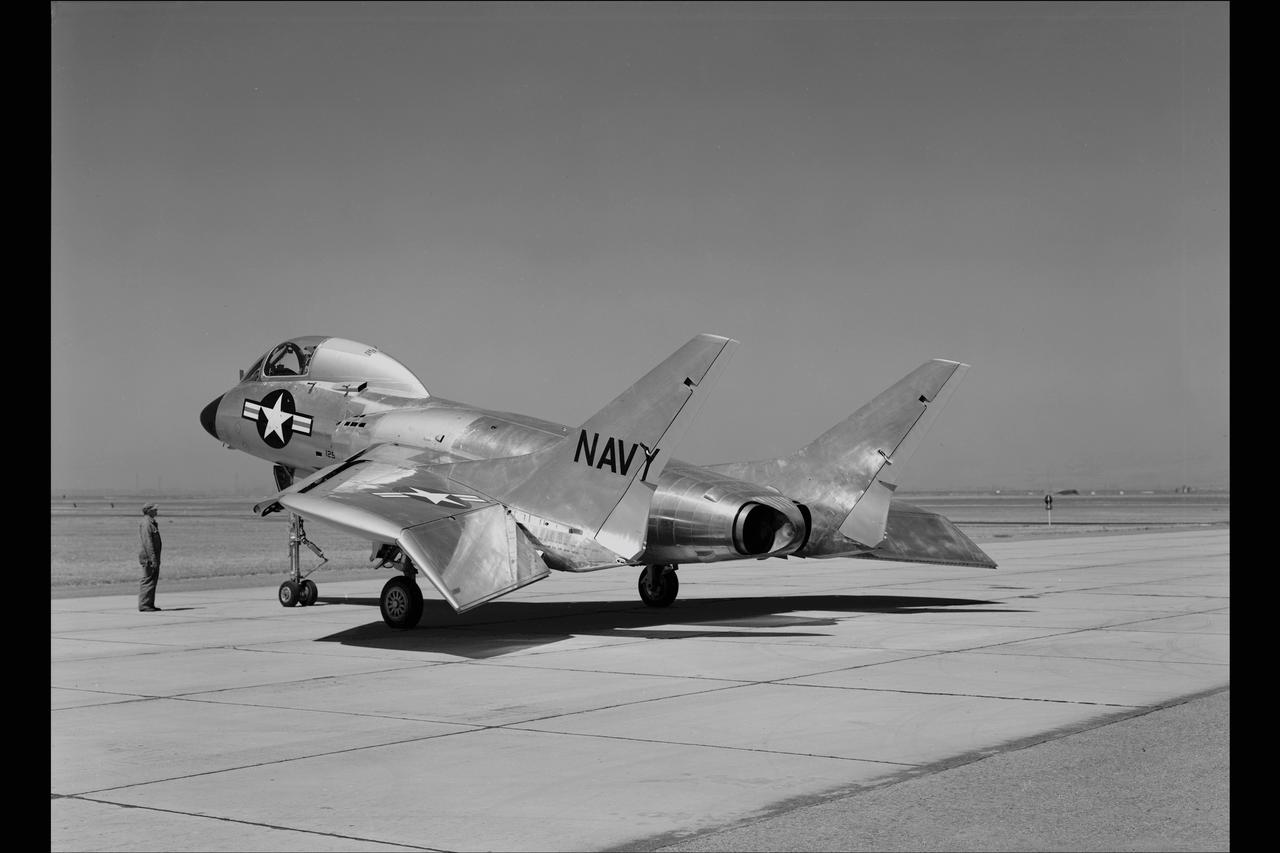

Navy CHANCE VOUGHT F7U-3 #656 AIRPLANE on NACA Ames flight line
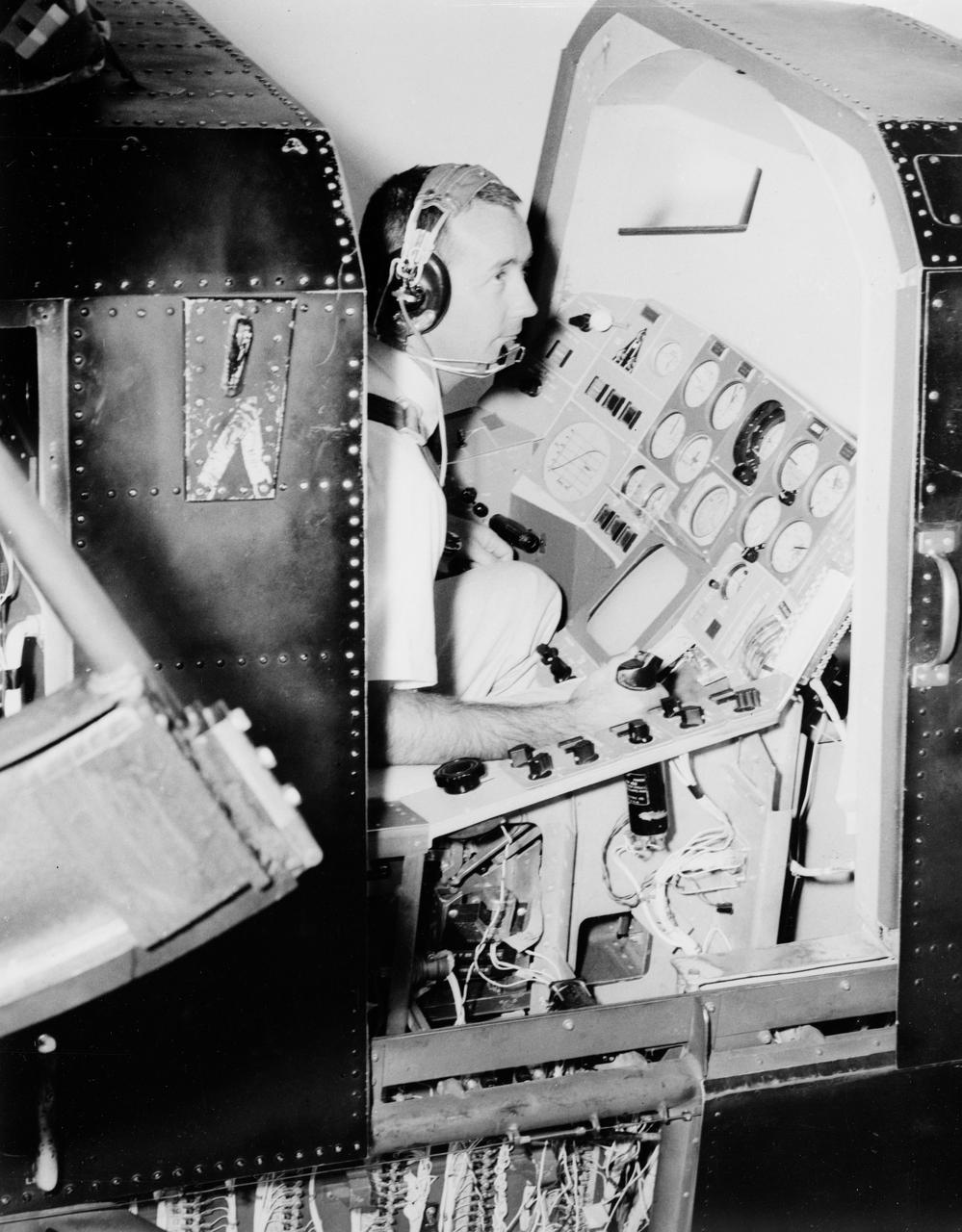
S65-19472 (10 May 1965) --- Astronaut James A. McDivitt is shown in the gondola of a realistic manned spaceflight simulator developed by the Astronautics Division of Ling-Temco-Vought in Dallas, Texas.
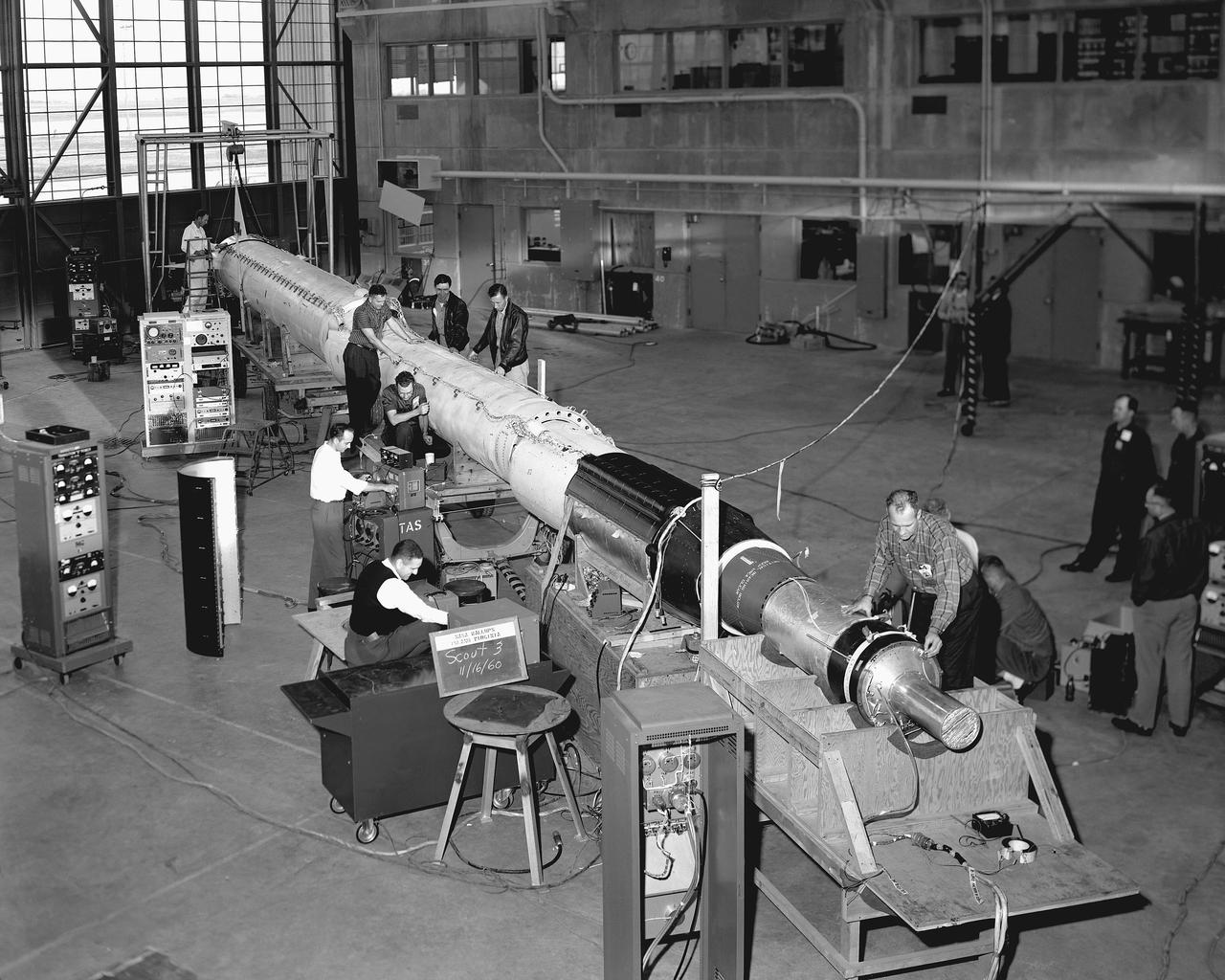

Employees of Vought Astronautic, Scout's prime contractor, work with NASA technicians to prepare ST-3 for launch. Unfortunately, this rocket would fail because of the second-stage misfire.
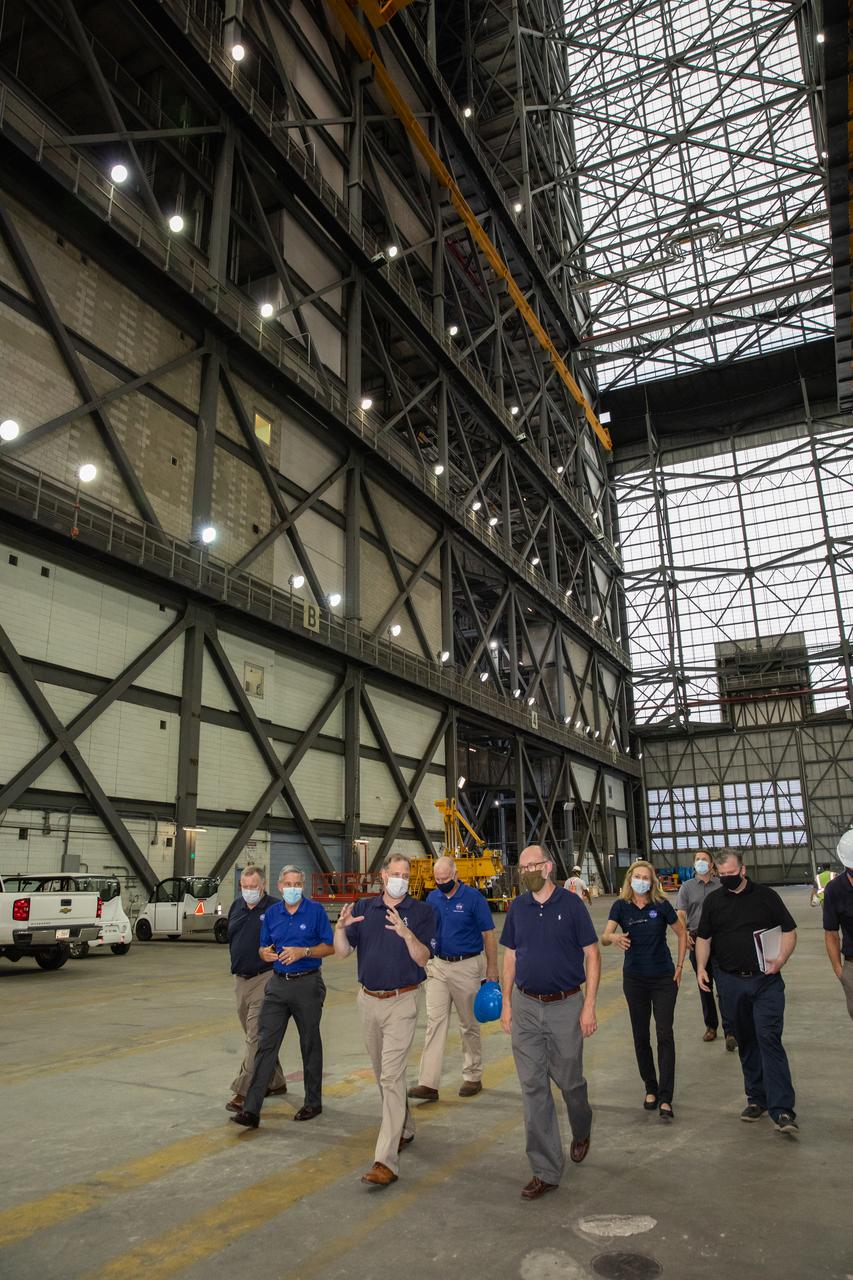

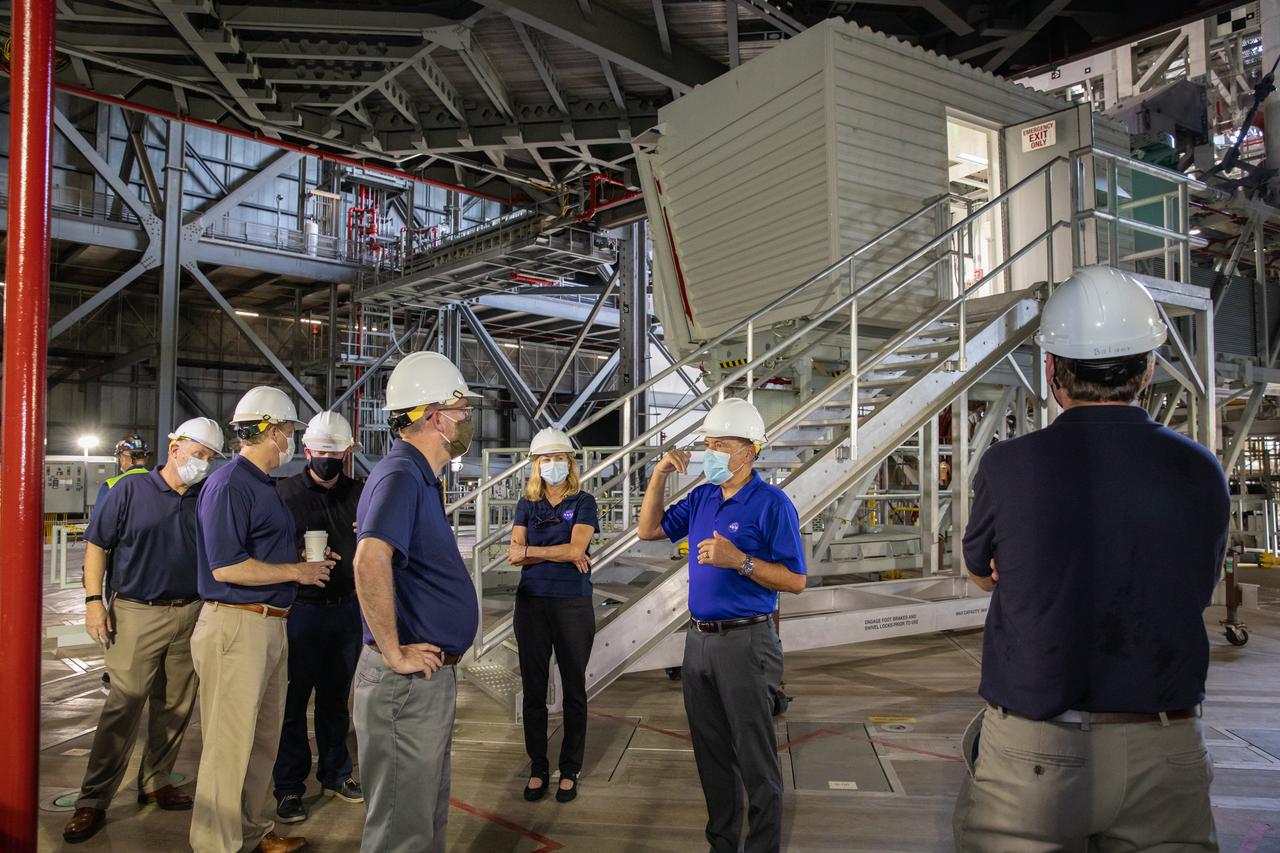
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, in the center, tours the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2020, with Russell Vought, in front at right, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget. Accompanying them is Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, second from left. Behind Vought is Kennedy Deputy Director Janet Petro. At right, next to Petro, is Brian McCormack, associate director of the White House Office of Management and Budget. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, second from right, speaks to Russell Vought, across from him, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, during a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 28, 2020. Standing to the left of Vought is NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine. Third from right is Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, packing material is placed over the nose cap that was removed from Atlantis. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.
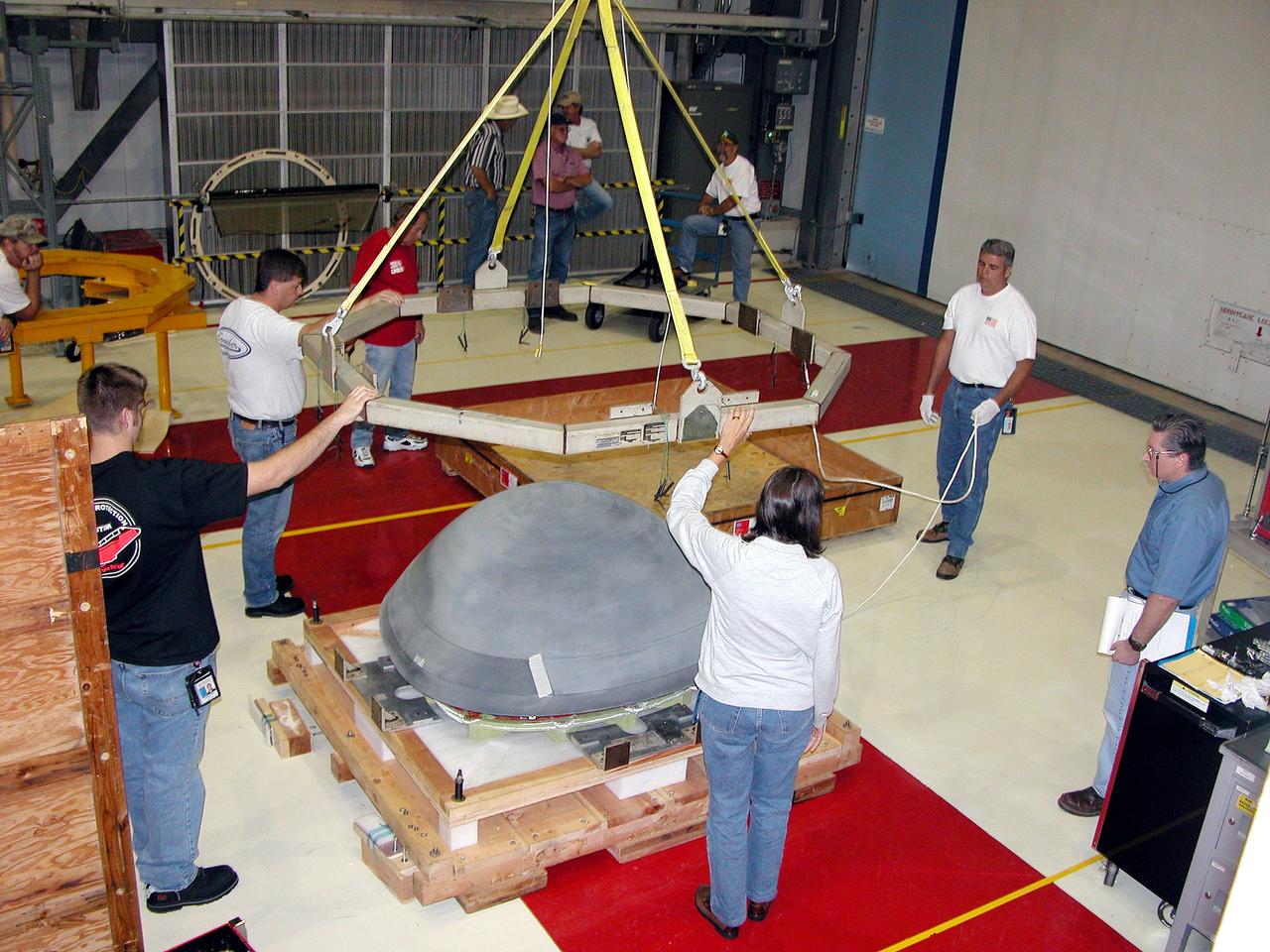

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers remove the overhead crane from the nose cap that was removed from Atlantis. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.
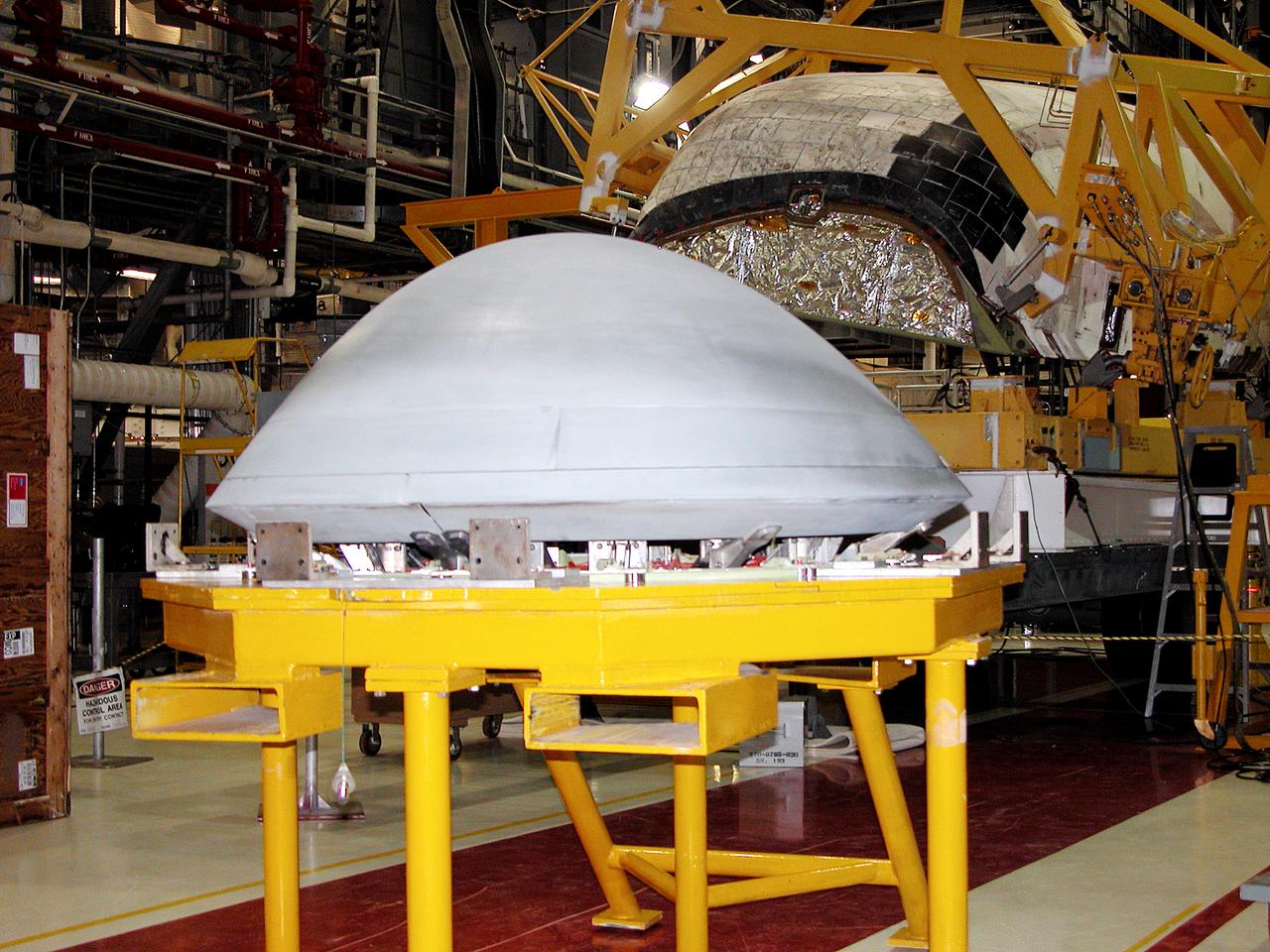

In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap (foreground) removed from Atlantis (behind) waits to be shipped to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

Wings for large scale model aircraft.
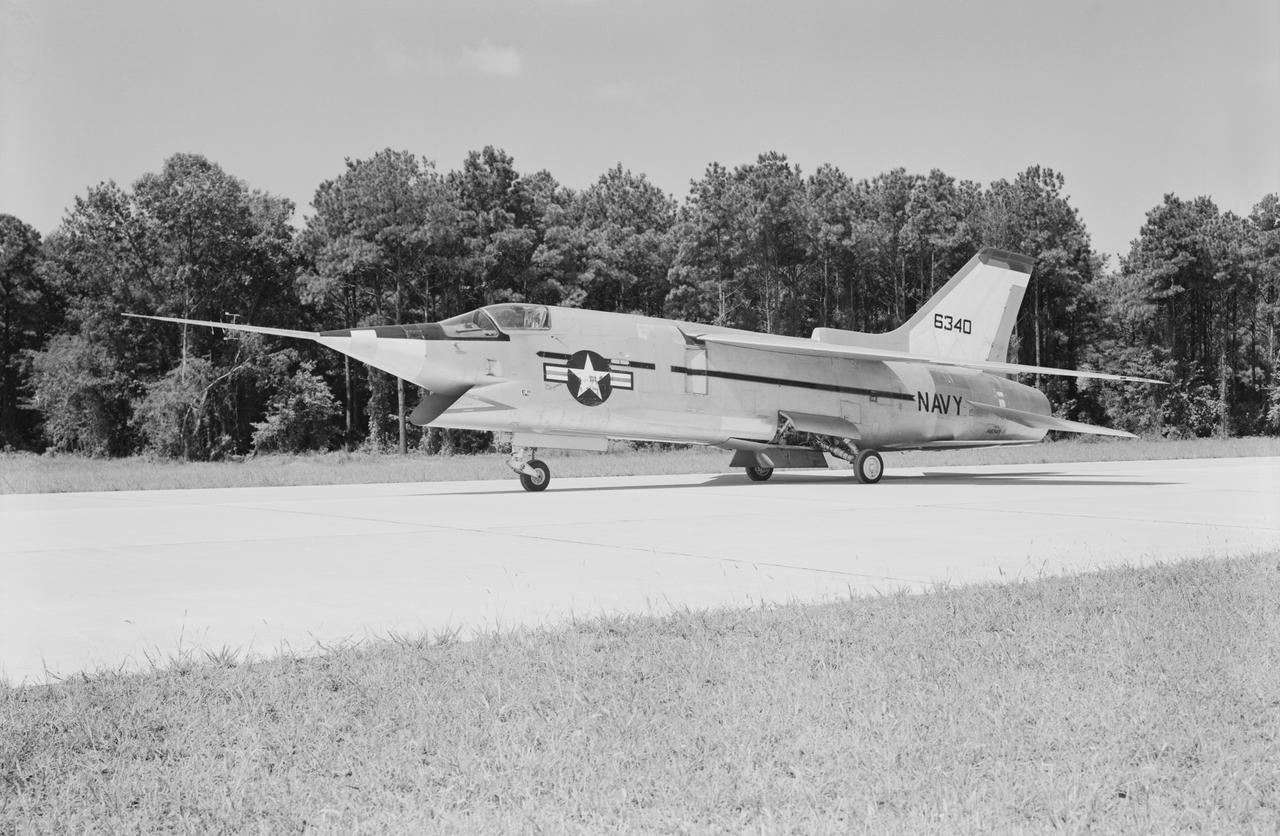

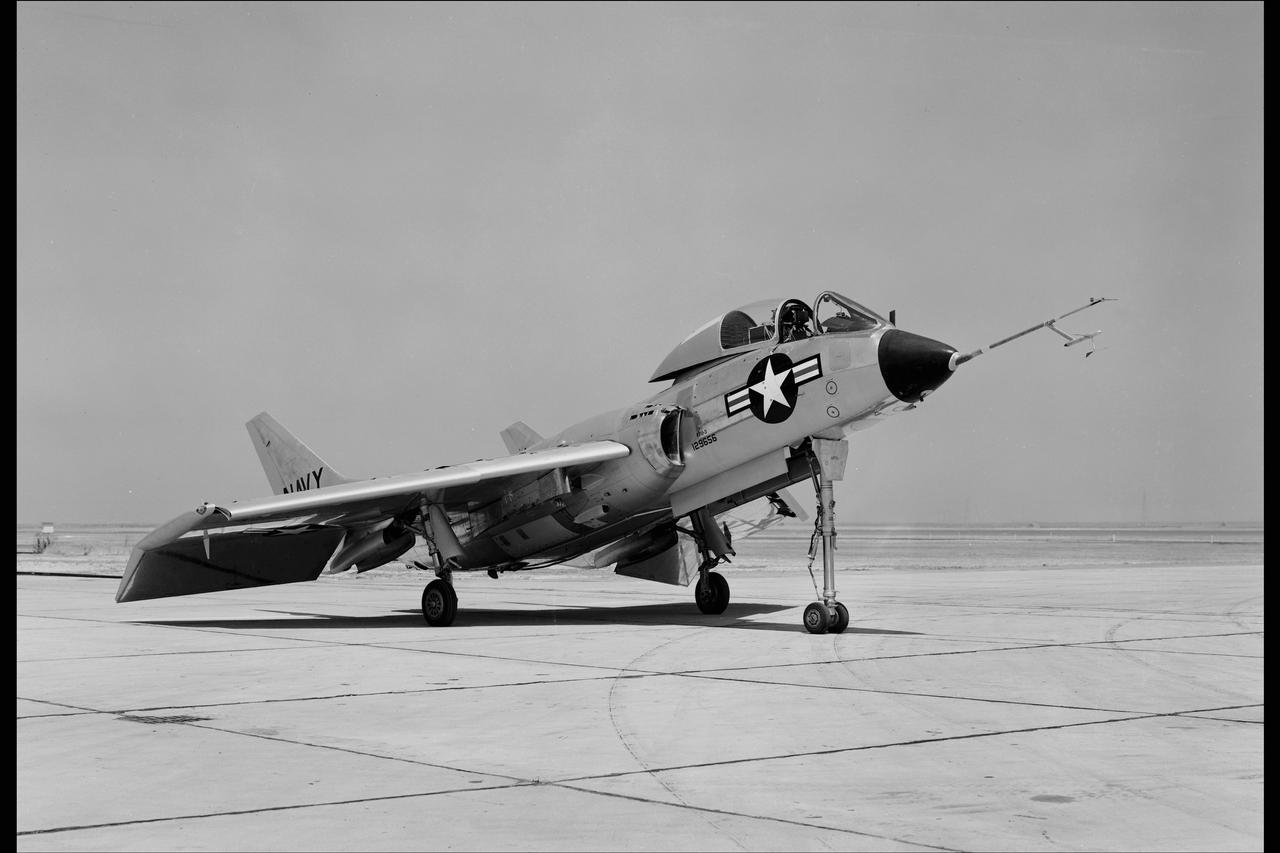
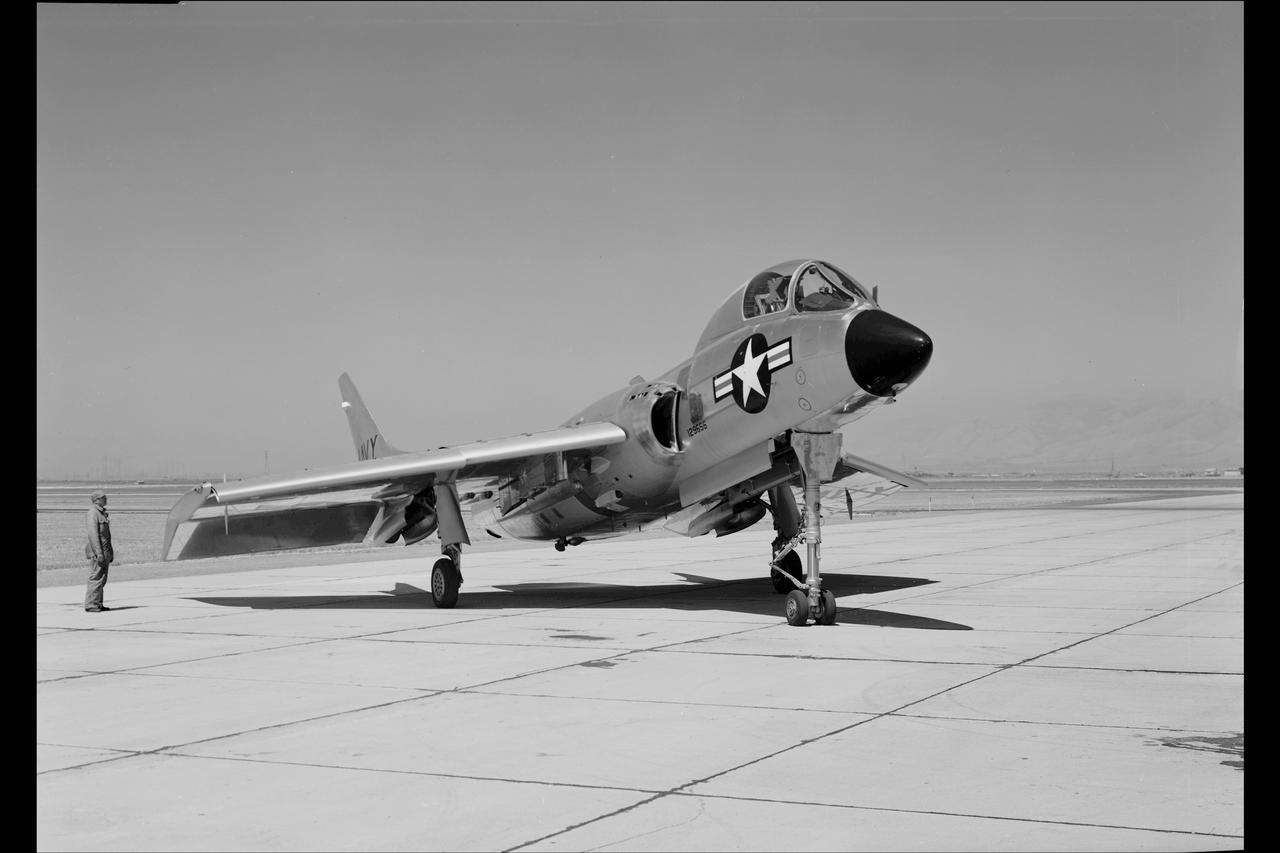
Crusader on runway. Navy aircraft number 6340. L59-6101 caption: The Navy's Vought XF8U-3 Supersonic Fighter was an entirely new design as compared to the earlier F8U Crusader series. This jet plane lost in competition with the McDonnell F4H, however, and was never put into production. Langley used the XF8U-3 in some of the first flight measurements of sonic boom intensity. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 507. Caption: Chance Vought F8U-3 airplane used in sonic boom investigation at Wallops, June-August 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 672.
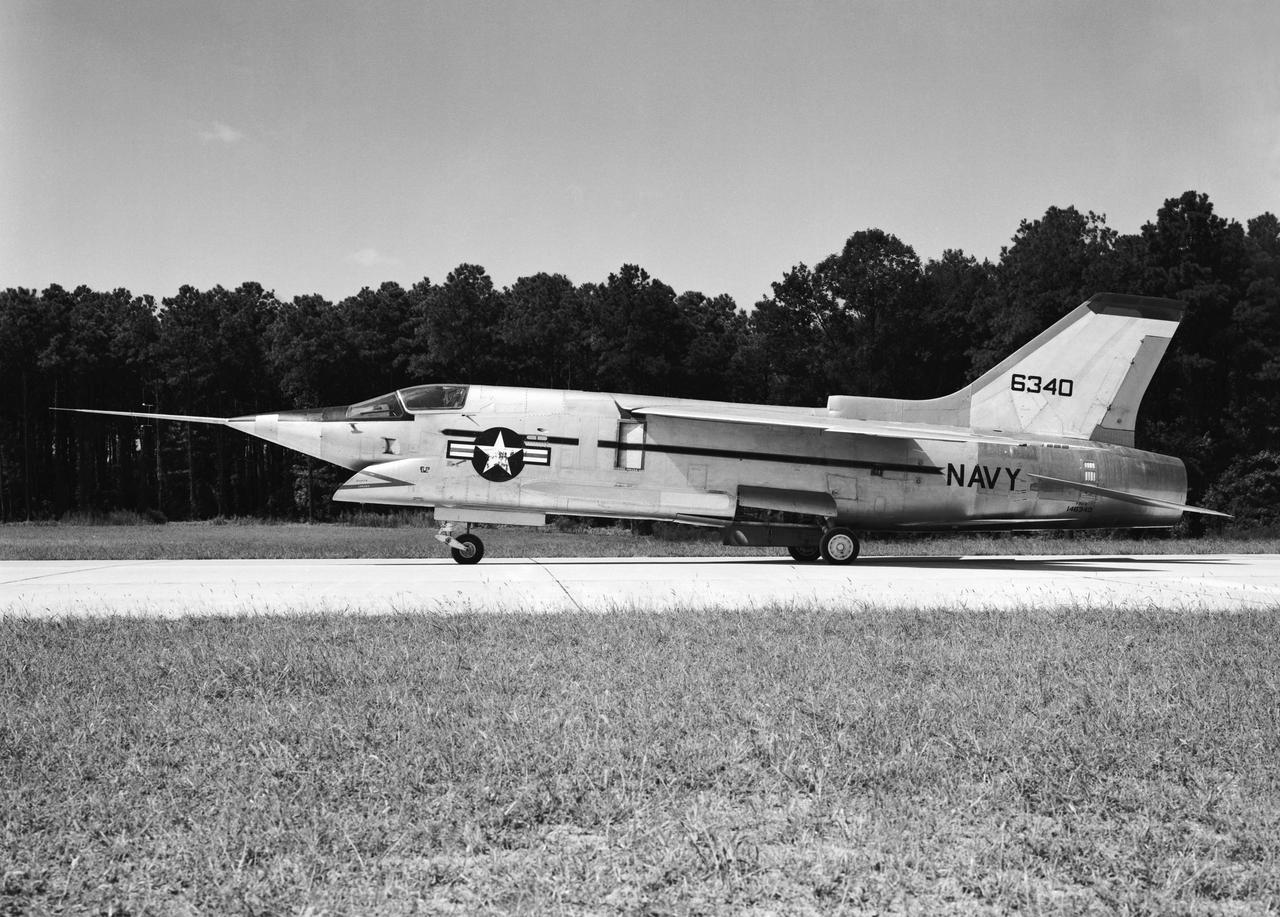

Crusader on runway. Navy aircraft number 6340. L59-6101 caption: The Navy's Vought XF8U-3 Supersonic Fighter was an entirely new design as compared to the earlier F8U Crusader series. This jet plane lost in competition with the McDonnell F4H, however, and was never put into production. Langley used the XF8U-3 in some of the first flight measurements of sonic boom intensity. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 507. Caption: Chance Vought F8U-3 airplane used in sonic boom investigation at Wallops, June-August 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 672.
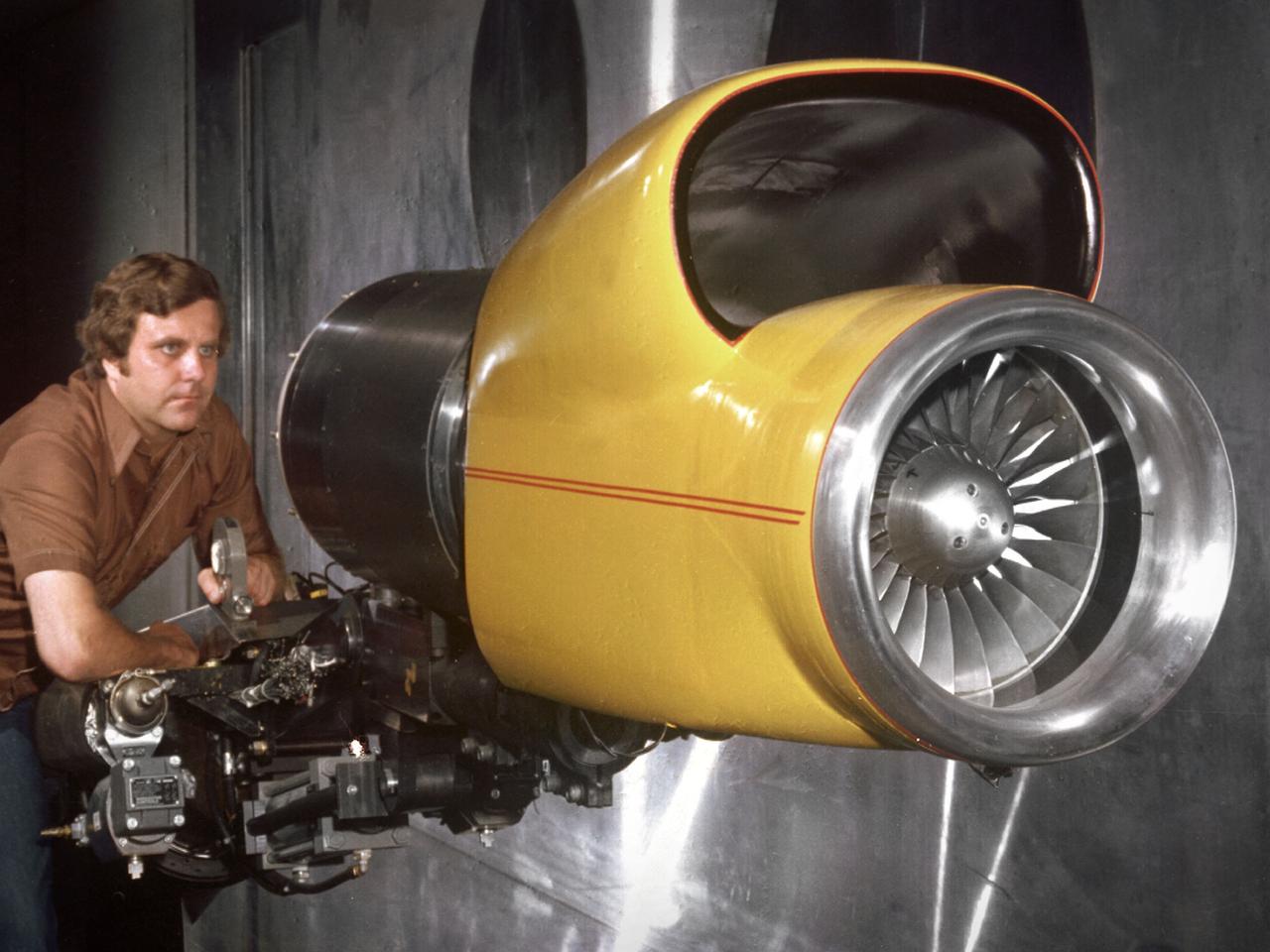
A technician checks a 0.25-scale engine model of a Vought Corporation V-530 engine in the test section of the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Vought created a low-drag tandem-fan Vertical/Short and Takeoff and Landing (V/STOL) engine in the mid-1970s, designated as the V-530. The first fan on the tandem-fan engine was supplied with air through a traditional subsonic inlet, seen on the lower front of the engine. The air was exhausted through the nacelle during normal flight and directed down during takeoffs. The rear fan was supplied by the oval-shaped top inlet during all phases of the flight. The second fan exhausted its air through a rear vectorable nozzle. NASA Lewis and Vought partnered in the late 1970s to collect an array of inlet and nozzle design information on the tandem fan engines for the Navy. Vought created this .25-scale model of the V-530 for extensive testing in Lewis' 10- by 10-foot tunnel. During an early series of tests, the front fan was covered, and a turbofan simulator was used to supply air to the rear fan. The researchers then analyzed the performance of only the front fan inlet. During the final series of tests, the flow from the front fan was used to supply airflow to the rear fan. The researchers studied the inlet's recovery, distortion, and angle-of-attack limits over various flight conditions.

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, far right, accompanies Russell Vought, second from right, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, and NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, far left, on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 28, 2020. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Shown in front of the Artemis I spacecraft, Larry Price, at left, Lockheed Martin Orion program manager, accompanies Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, during a tour of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2020. Orion spacecraft are being prepared for Artemis I and Artemis II. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
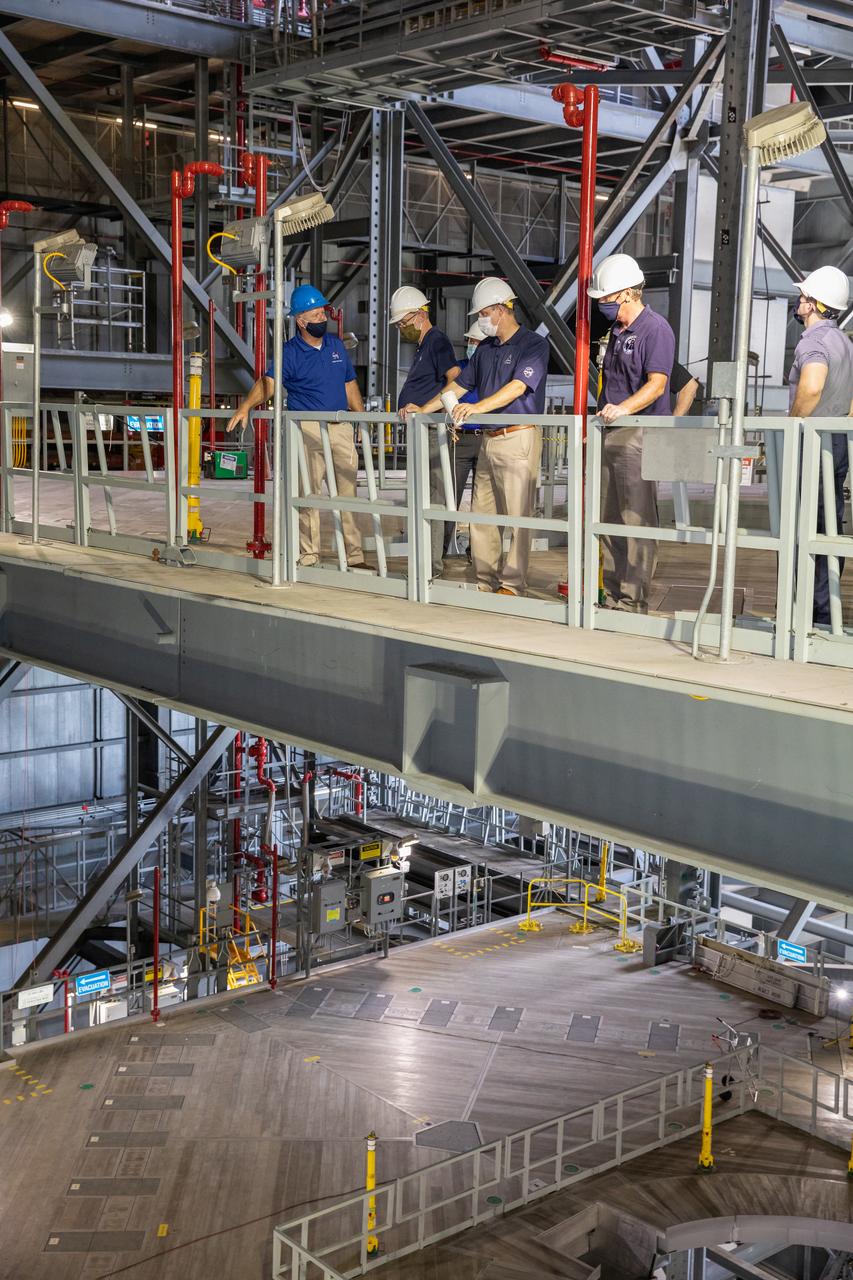

Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, second from left, and NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, are on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 28, 2020. In this photo, they are viewing one of the levels of new service platforms in High Bay 3. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, far left, Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, second from left, and Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, far right, are on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 28, 2020. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
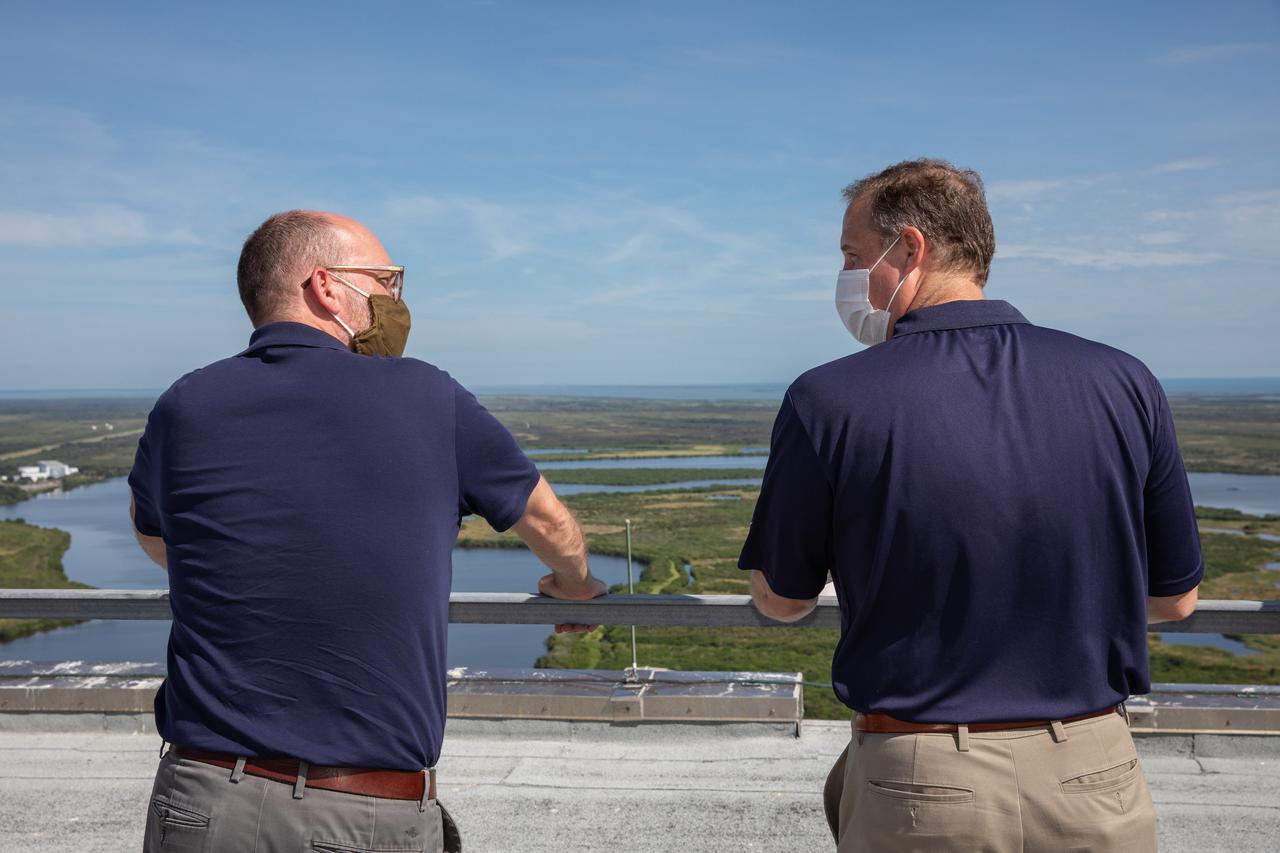

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, at right, and Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, are on the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) during a tour of the spaceport on Aug. 28, 2020. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
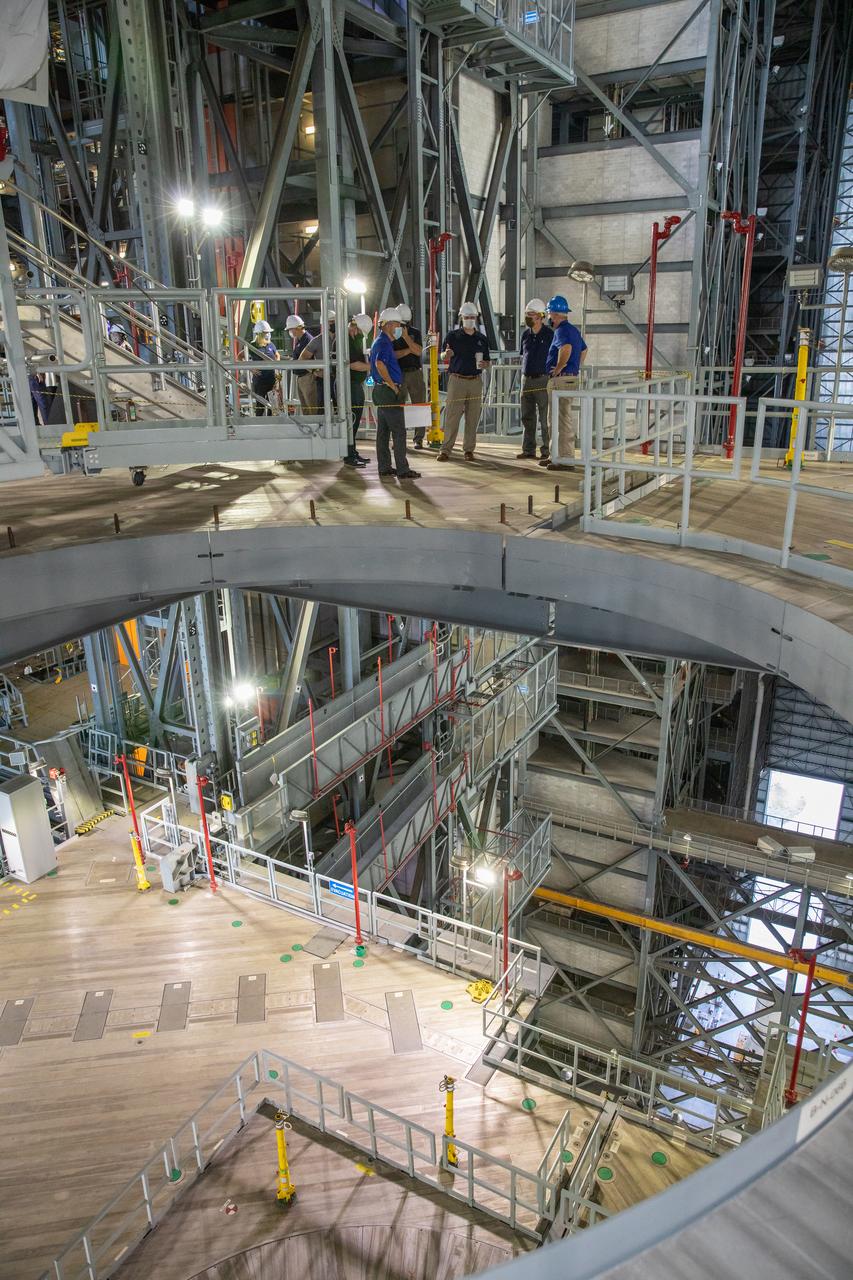

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana accompanies NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, and Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 28, 2020. In this photo, they are viewing one of the levels of new service platforms in High Bay 3. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
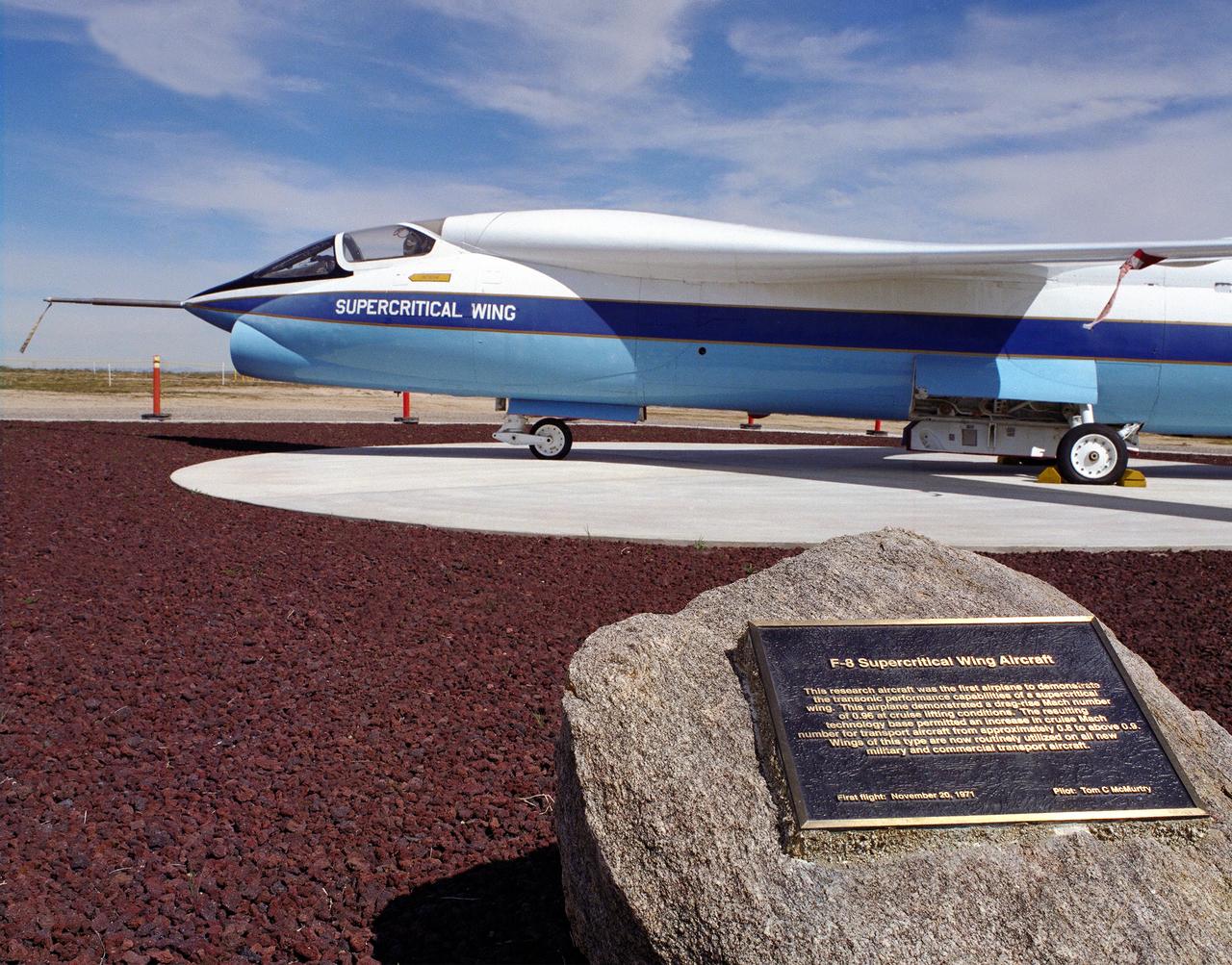

A Vought F-8A Crusader was selected by NASA as the testbed aircraft (designated TF-8A) to install an experimental Supercritical Wing (SCW) in place of the conventional wing. The unique design of the Supercritical Wing reduces the effect of shock waves on the upper surface near Mach 1, which in turn reduces drag. In the photograph the TF-8A Crusader with the Supercritical Wing is shown on static display in front of the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The F-8 SCW aircraft, along with the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire aircraft were placed on display on May 27, 1992, at a conference marking the 20th anniversary of the start of the two programs.
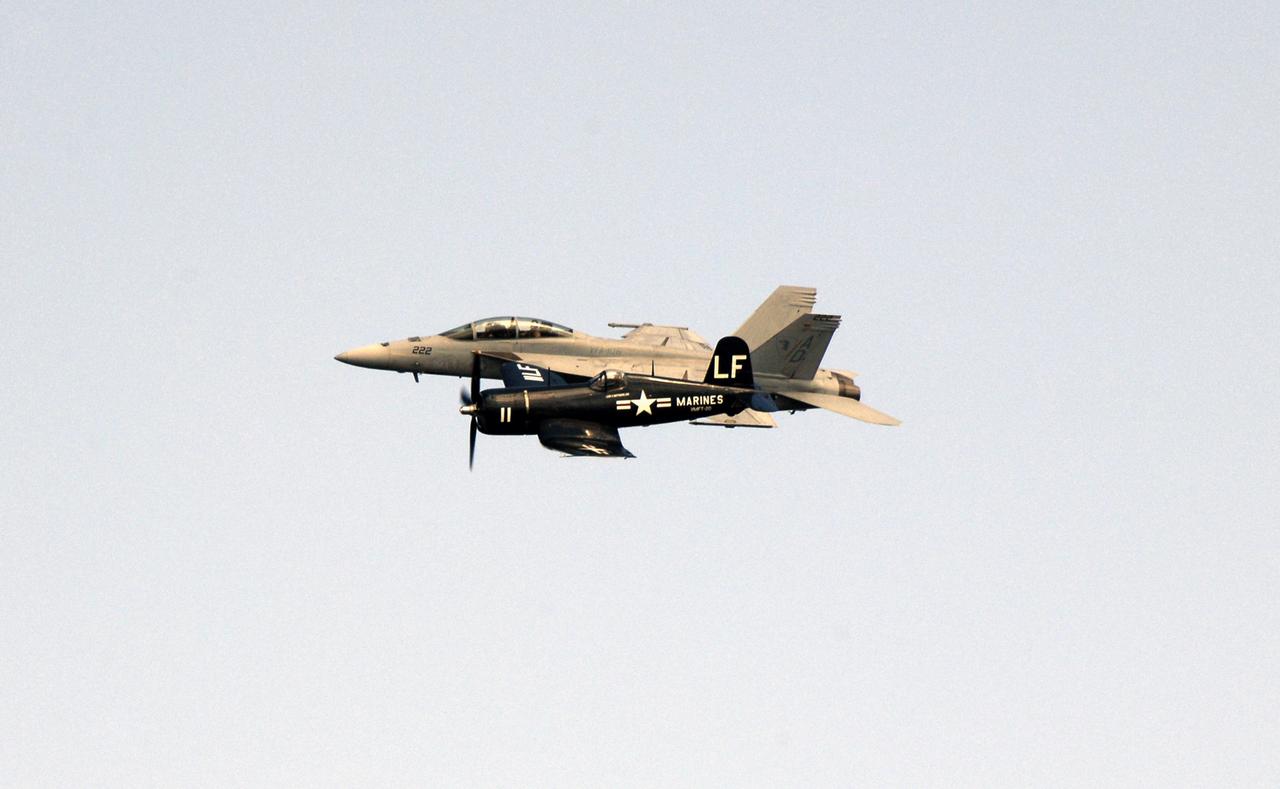

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A contrast in speed and design, the F/A-18 Super Hornet jet (behind) flies alongside a World War II Vought F4U Corsair during the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex Space and Air Show Nov. 8-9 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This year’s show brought together the best in military aircraft, such as the F/A-18 Super Hornet and F-16 Fighting Falcon, coupled with precision pilots and veteran astronauts to celebrate spaceflight and aviation. The event included a water rescue demonstration by the 920th Rescue Wing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

On the Vehicle Assembly Building roof at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, far left, accompanies NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from left, and Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 28, 2020. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
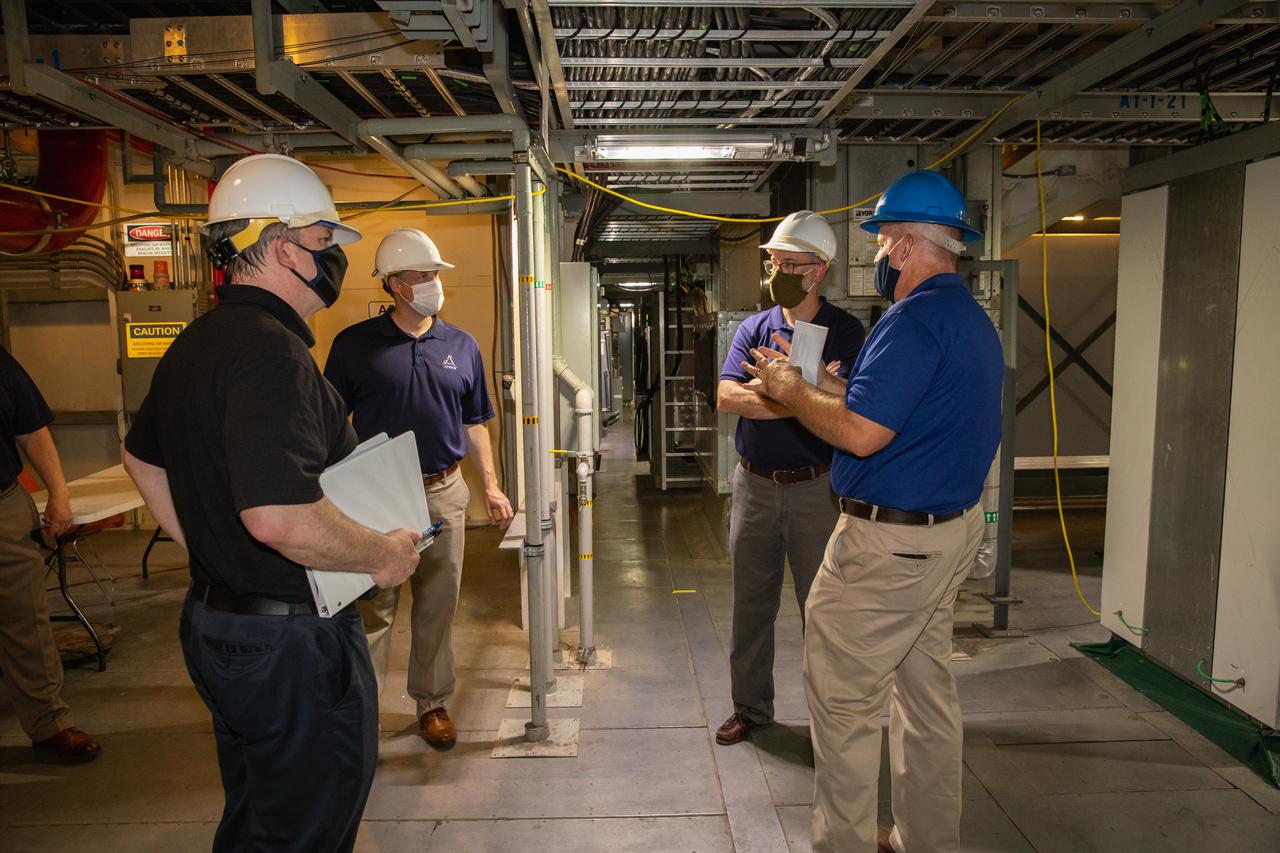

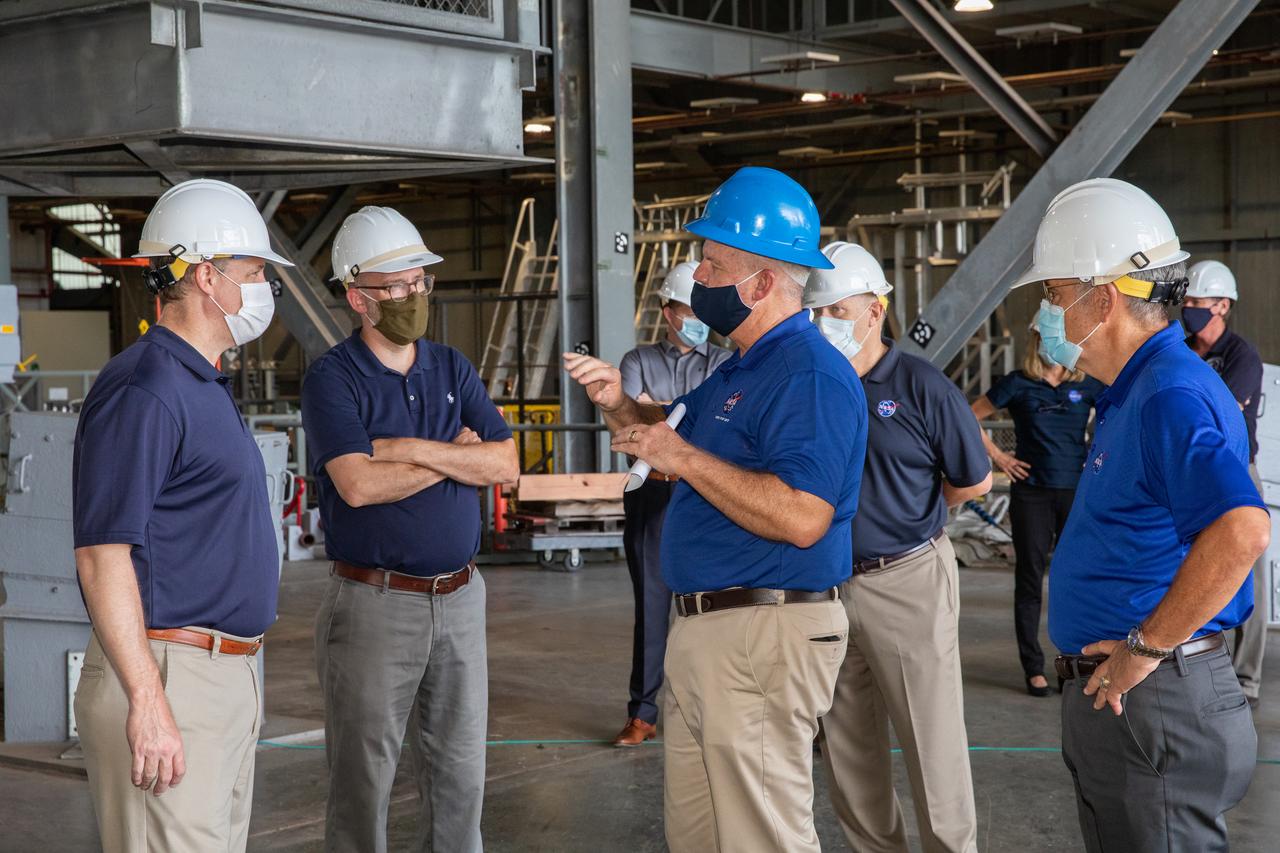
Darrell Foster, far right, chief of the Project Management Division in Exploration Ground Systems, briefs from left, Brian McCormack, associate director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, and Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, while on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 28, 2020. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Closest to the Artemis I spacecraft, Larry Price, at left, Lockheed Martin Orion program manager, talks with Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, and NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, third from left in front, during a tour of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2020. Orion spacecraft are being prepared for Artemis I and Artemis II. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
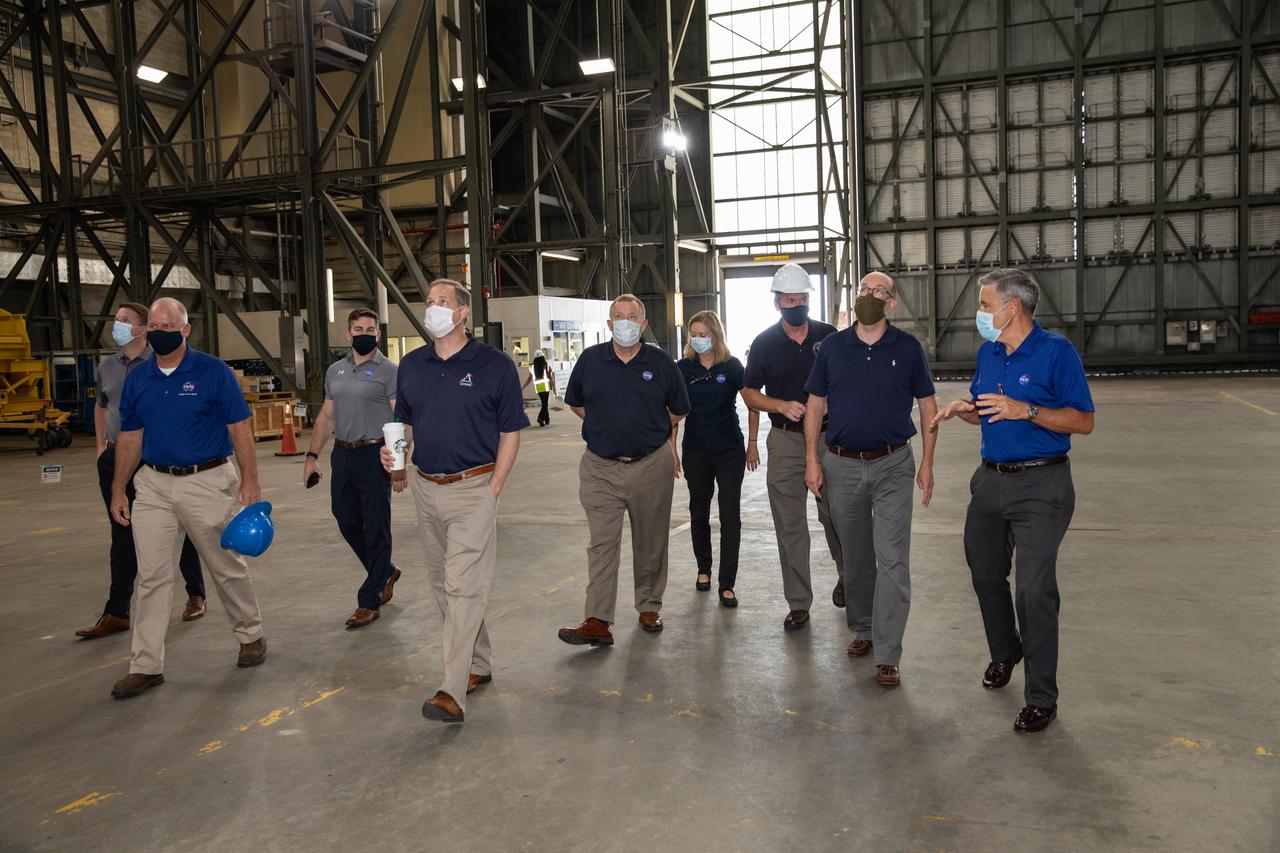

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, far right, accompanies Russell Vought, second from right, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 28, 2020. Leading the group, in front, is NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, along with NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro, and Mike Bolger, manager of Kennedy’s Exploration Ground Systems Directorate. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
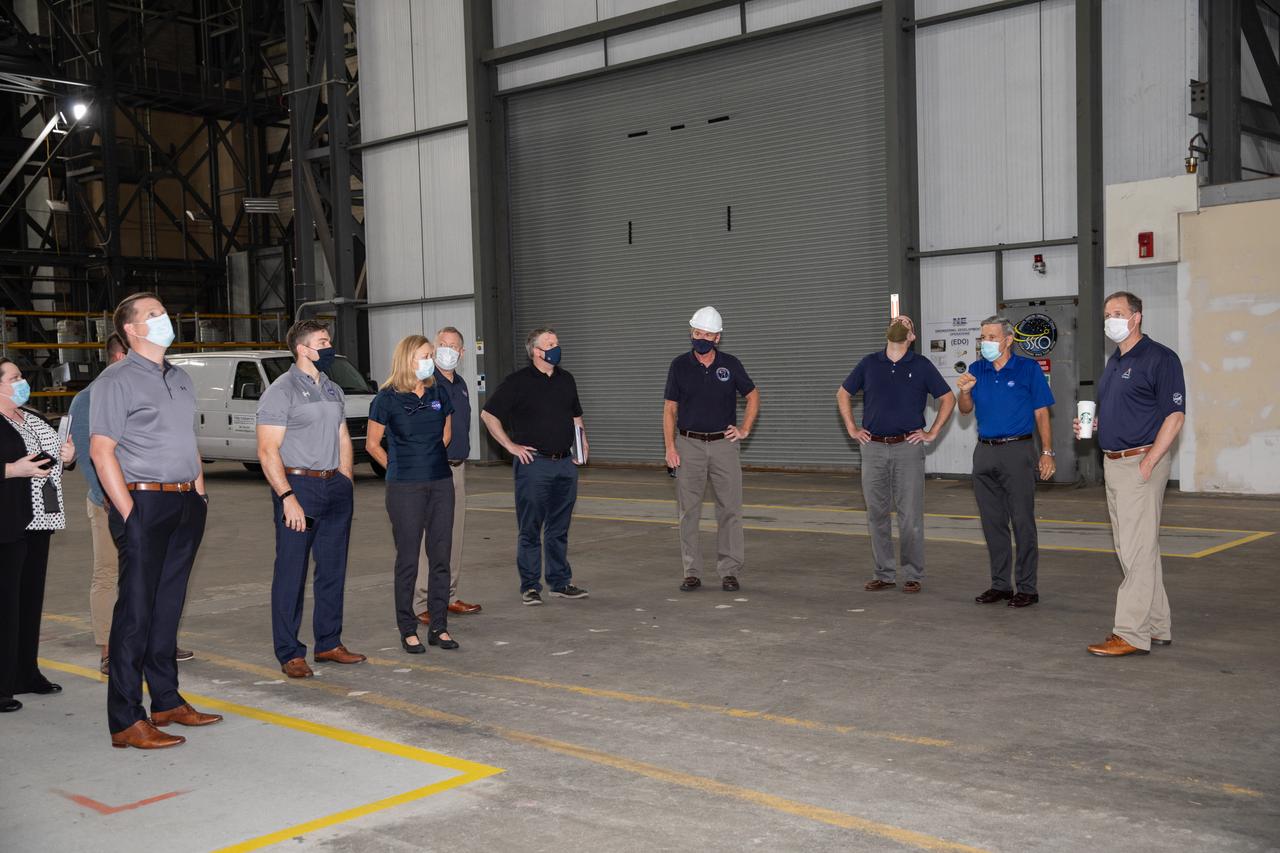

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, second from right, accompanies Russell Vought, third from right, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, and NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, far right, on a tour of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 28, 2020. Third from left is Kennedy Deputy Director Janet Petro, and fourth from right is Mike Bolger, manager of Kennedy’s Exploration Ground Systems Directorate. The VAB is critical to the assembly of the Space Launch System rocket for NASA’s Artemis program. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Dr. Eric H. Thoemmes, third from left, vice president of Space, Missile Defense and Strategic with Lockheed Martin, speaks to Russell Vought, second from left, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, during a tour of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2020. At far left is Larry Price, Lockheed Martin Orion Program manager. To the right of Thoemmes is NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard, and Brian McCormack, associate director of the White House Office of Management and Budget. In view in the background is the heatshield for Artemis II. Inside the high bay, Orion spacecraft are being prepared for Artemis I and Artemis II. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

From left, Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Assembly, Test and Launch Operations; Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana; NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget; and Larry Price, Lockheed Martin Orion Program Manager, tour the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2020. In the center, behind them from left, are Brian McCormack, associate director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, and Glenn Chin, Deputy Manager of Orion Production Operations. Inside the high bay, Orion spacecraft are being prepared for Artemis I and Artemis II, with the Crew Module Adapter for Artemis II shown in the background. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Representatives from NASA, Lockheed Martin and the White House Office of Management and Budget pause for a group photograph in front of the Artemis I spacecraft during a tour of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2020. From left, are Kennedy Deputy Director Janet Petro; Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Assembly, Test and Launch Operations; Brian McCormack, associate director of the White House Office of Management and Budget; NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard; Larry Price, Lockheed Martin Orion program manager; Dr. Eric H. Thoemmes, vice president of Space, Missile Defense and Strategic with Lockheed Martin; NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget; Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana; Glenn Chin, Deputy Manager of Orion Production Operations; and Joe Mayer, director of Government Relations with Lockheed Martin. Orion spacecraft are being prepared for Artemis I and Artemis II. In the background is the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Larry Price, closest to the Artemis I spacecraft, Lockheed Martin Orion Program manager, accompanies Russell Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, during a tour of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2020. Behind them, from left, are Brian McCormack, White House associate director of the Office of Management and Budget, and Kennedy Space Director Bob Cabana. At far right, from the front, are Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Assembly, Test and Launch Operations, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, and Glenn Chin, Deputy Manager of Orion Production Operations. In the foreground, from left are Dr. Eric Thoemmes, vice president, Lockheed Martin Space, Missile Defense and Strategic, and NASA Deputy Administrator Jim Morhard. Inside the high bay, Orion spacecraft are being prepared for Artemis I and Artemis II. The Office of Management and Budget is working with the U.S. Congress to line up the necessary resources to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

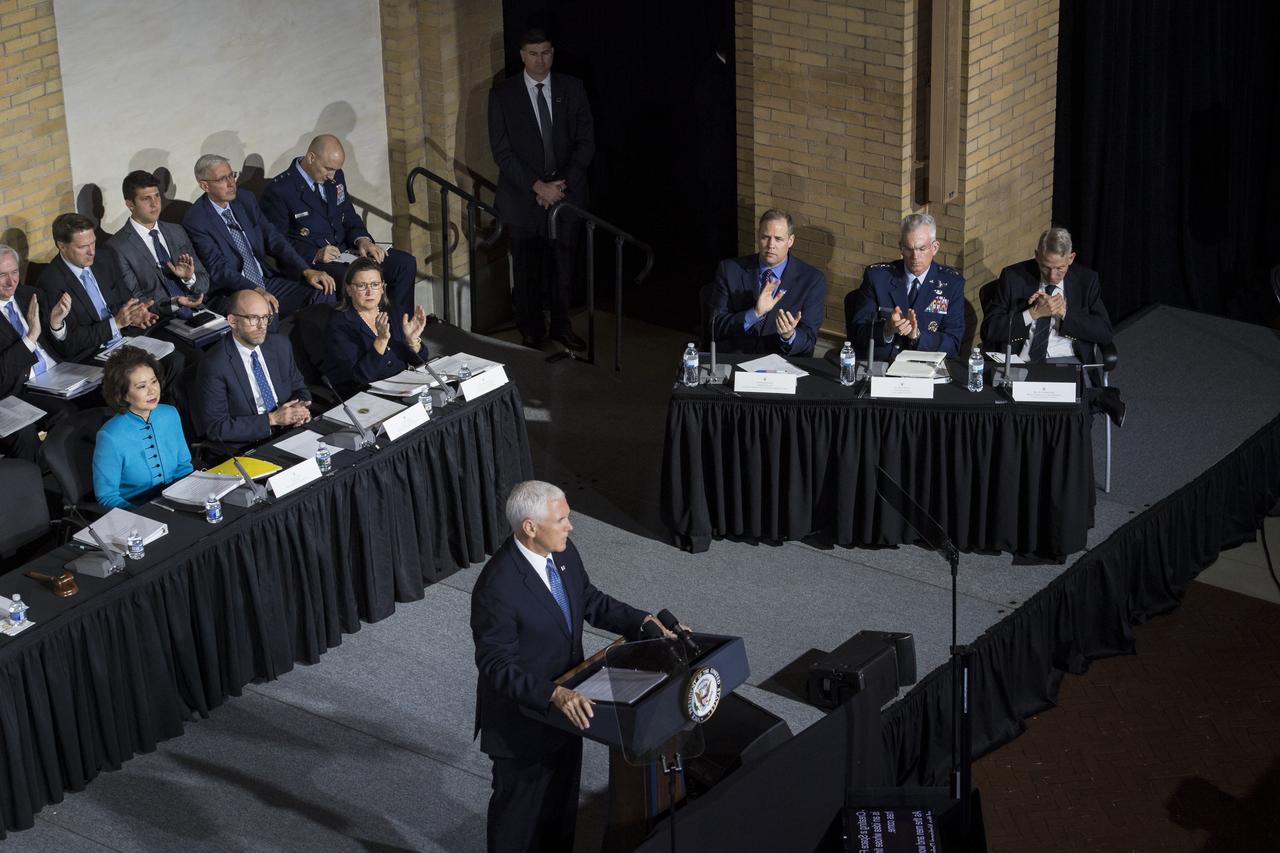
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks during the National Space Council meeting titled, Moon, Mars, and Worlds Beyond, Winning the Next Frontier, Tuesday, Oct. 23, 2018 at the National War College at Fort Lesley J. McNair in Washington. Chaired by the Vice President, the council's role is to advise the President regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

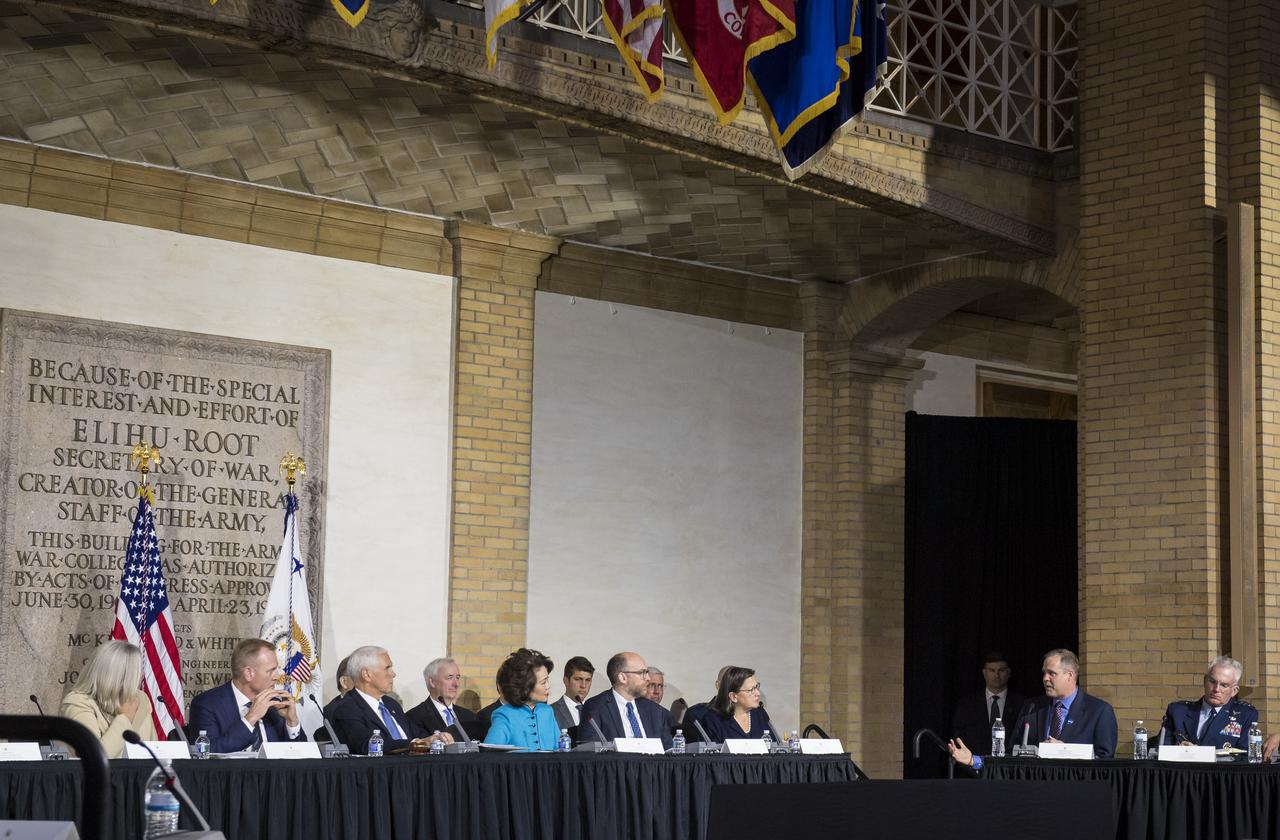
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, third from right, applauds as Vice President Mike Pence delivers opening remarks during the National Space Council meeting titled, Moon, Mars, and Worlds Beyond, Winning the Next Frontier, Tuesday, Oct. 23, 2018 at the National War College at Fort Lesley J. McNair in Washington. Chaired by the Vice President, the council's role is to advise the President regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
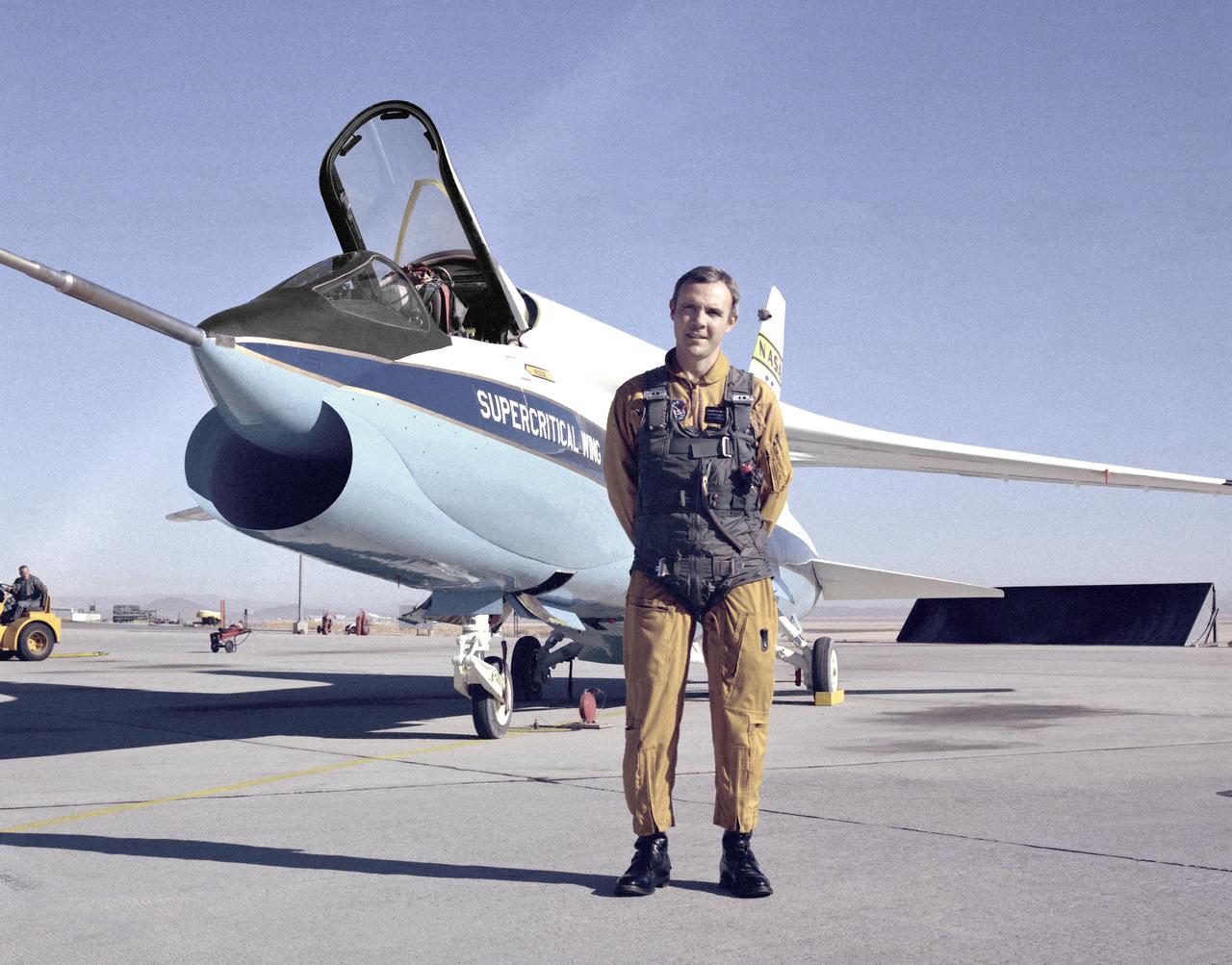

A Vought F-8A Crusader was selected by NASA as the testbed aircraft (designated TF-8A) to install an experimental Supercritical Wing (SCW) in place of the conventional wing. The unique design of the Supercritical Wing reduces the effect of shock waves on the upper surface near Mach 1, which in turn reduces drag. In this photograph the TF-8A Crusader with Supercritical Wing is shown on the ramp with project pilot Tom McMurtry standing beside it. McMurtry received NASA's Exceptional Service Medal for his work on the F-8 SCW aircraft. He also flew the AD-1, F-15 Digital Electronic Engine Control, the KC-130 winglets, the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire and other flight research aircraft including the remotely piloted 720 Controlled Impact Demonstration and sub-scale F-15 research projects. In addition, McMurtry was the 747 co-pilot for the Shuttle Approach and Landing Tests and made the last glide flight in the X-24B. McMurtry was Dryden’s Director for Flight Operations from 1986 to 1998, when he became Associate Director for Operations at NASA Dryden. In 1982, McMurtry received the Iven C. Kincheloe Award from the Society of Experimental Test Pilots for his contributions as project pilot on the AD-1 Oblique Wing program. In 1998 he was named as one of the honorees at the Lancaster, Calif., ninth Aerospace Walk of Honor ceremonies. In 1999 he was awarded the NASA Distinguished Service Medal. He retired in 1999 after a distinguished career as pilot and manager at Dryden that began in 1967.