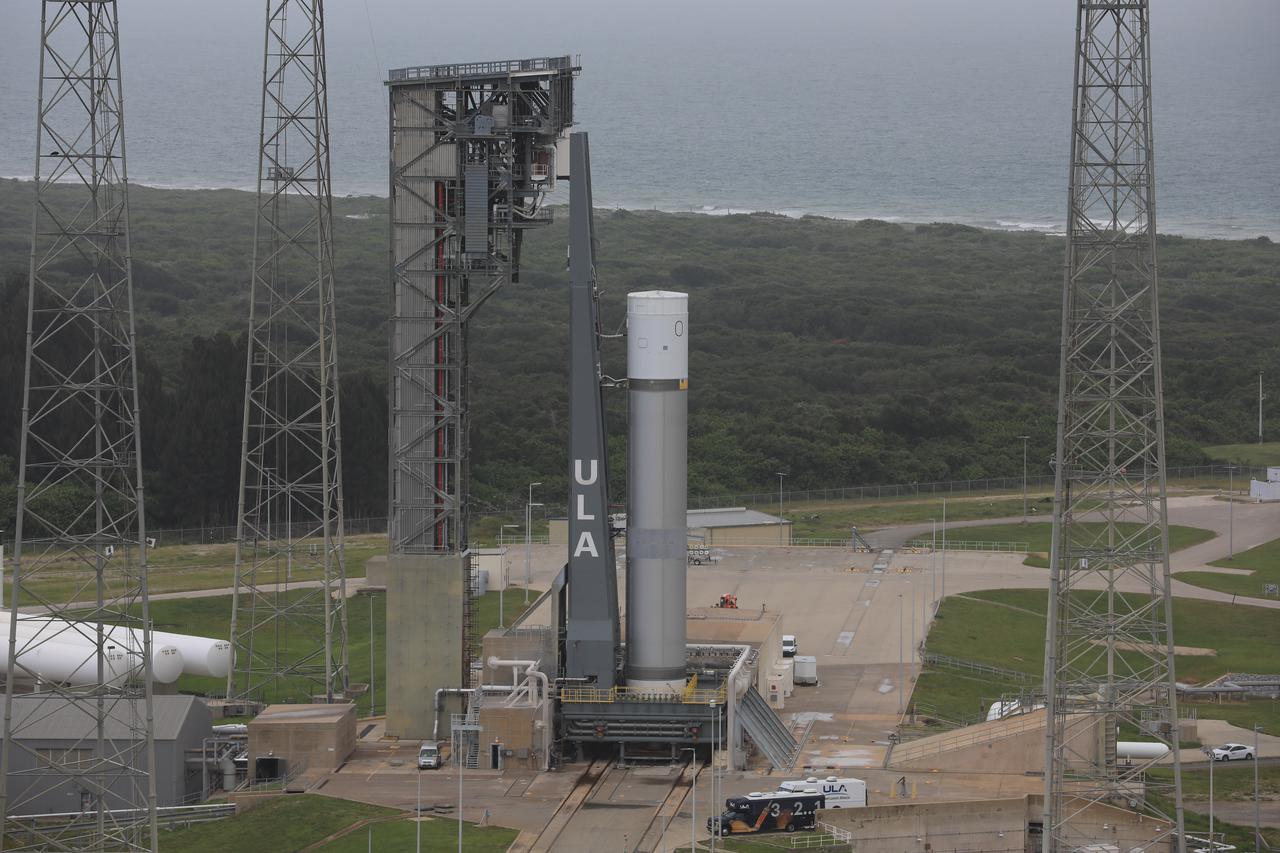

A pathfinder test article of United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Vulcan Centaur rocket is seen at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Aug. 26, 2021. The pathfinder booster is undergoing a series of fueling tests to validate the infrastructure in place at the launch pad and allow the launch team to rehearse countdown operations before the Vulcan’s first flight.
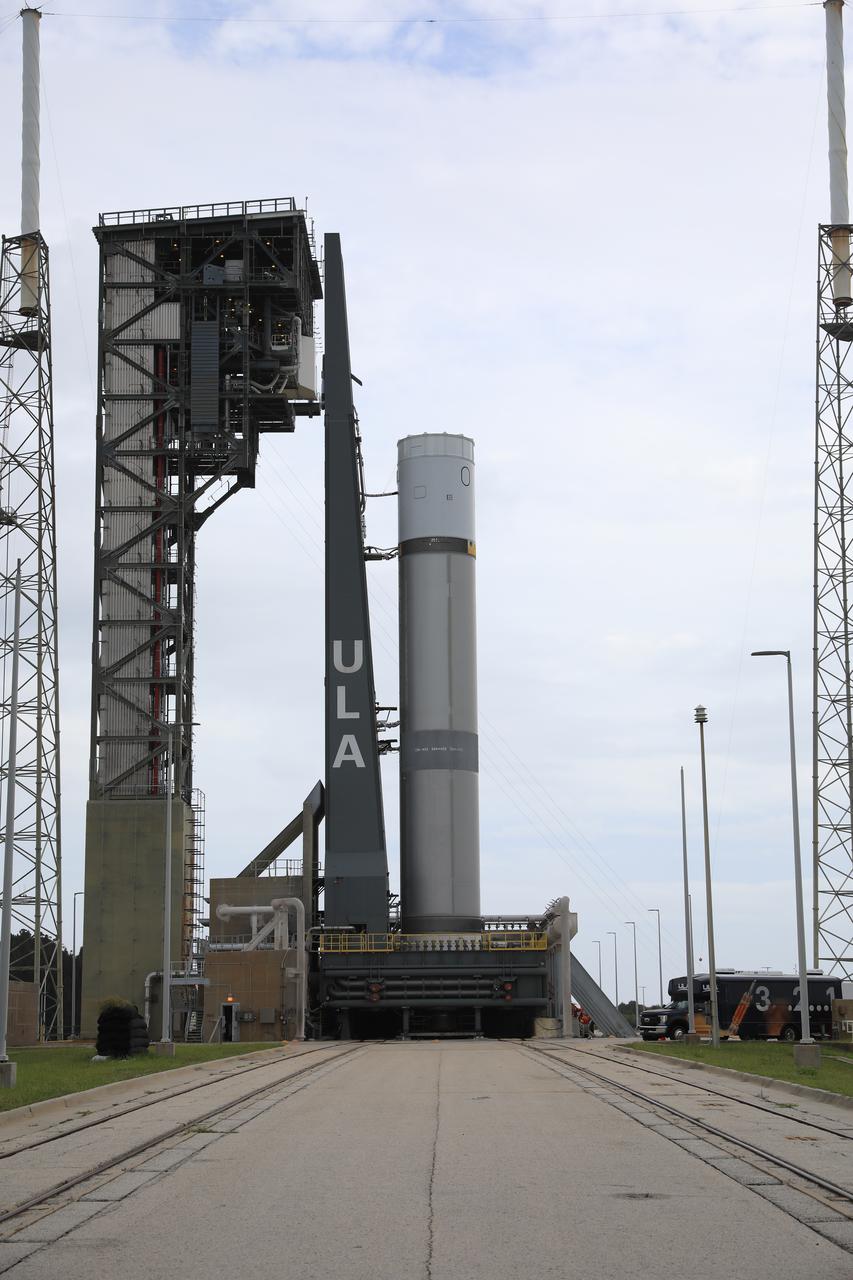

A pathfinder test article of United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Vulcan Centaur rocket is seen at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Aug. 26, 2021. The pathfinder booster is undergoing a series of fueling tests to validate the infrastructure in place at the launch pad and allow the launch team to rehearse countdown operations before the Vulcan’s first flight.
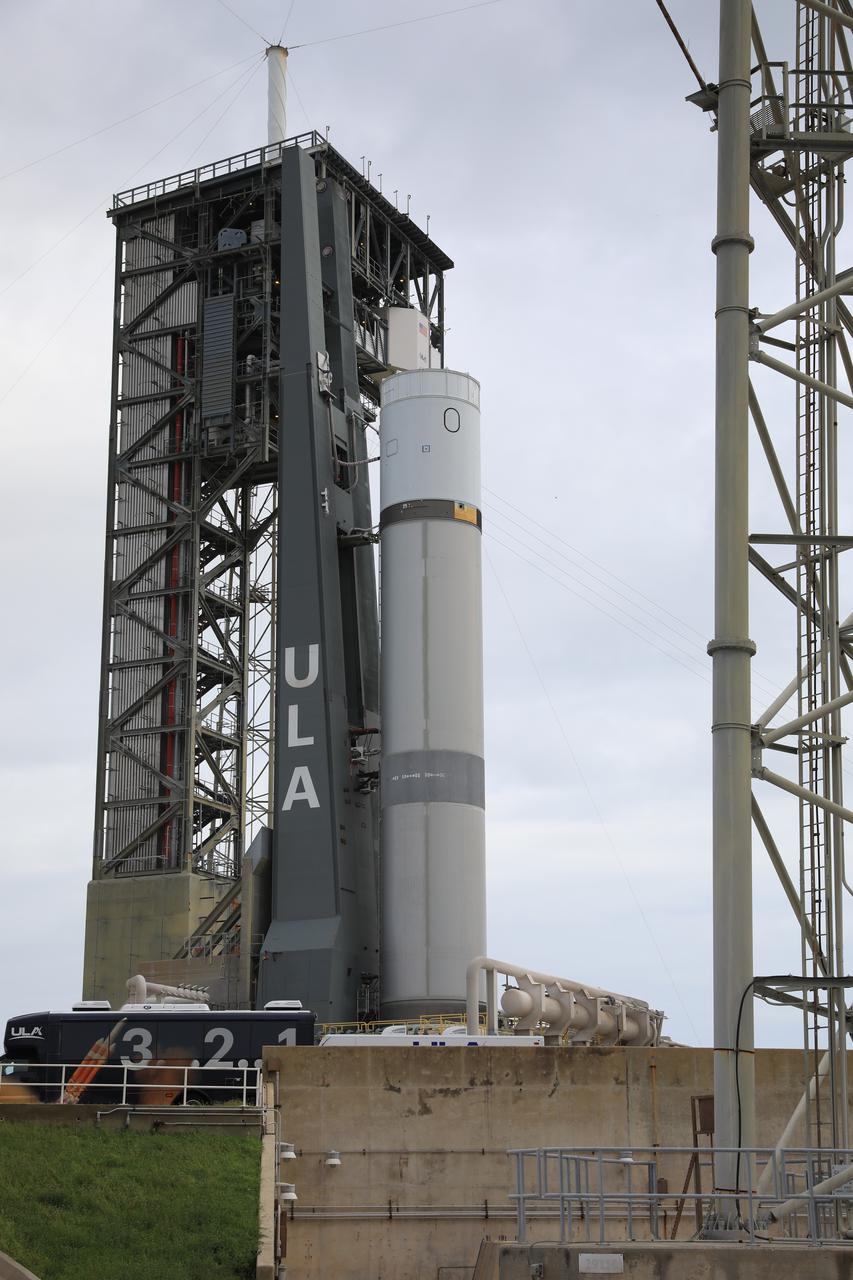

A pathfinder test article of United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Vulcan Centaur rocket is seen at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Aug. 26, 2021. The pathfinder booster is undergoing a series of fueling tests to validate the infrastructure in place at the launch pad and allow the launch team to rehearse countdown operations before the Vulcan’s first flight.

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
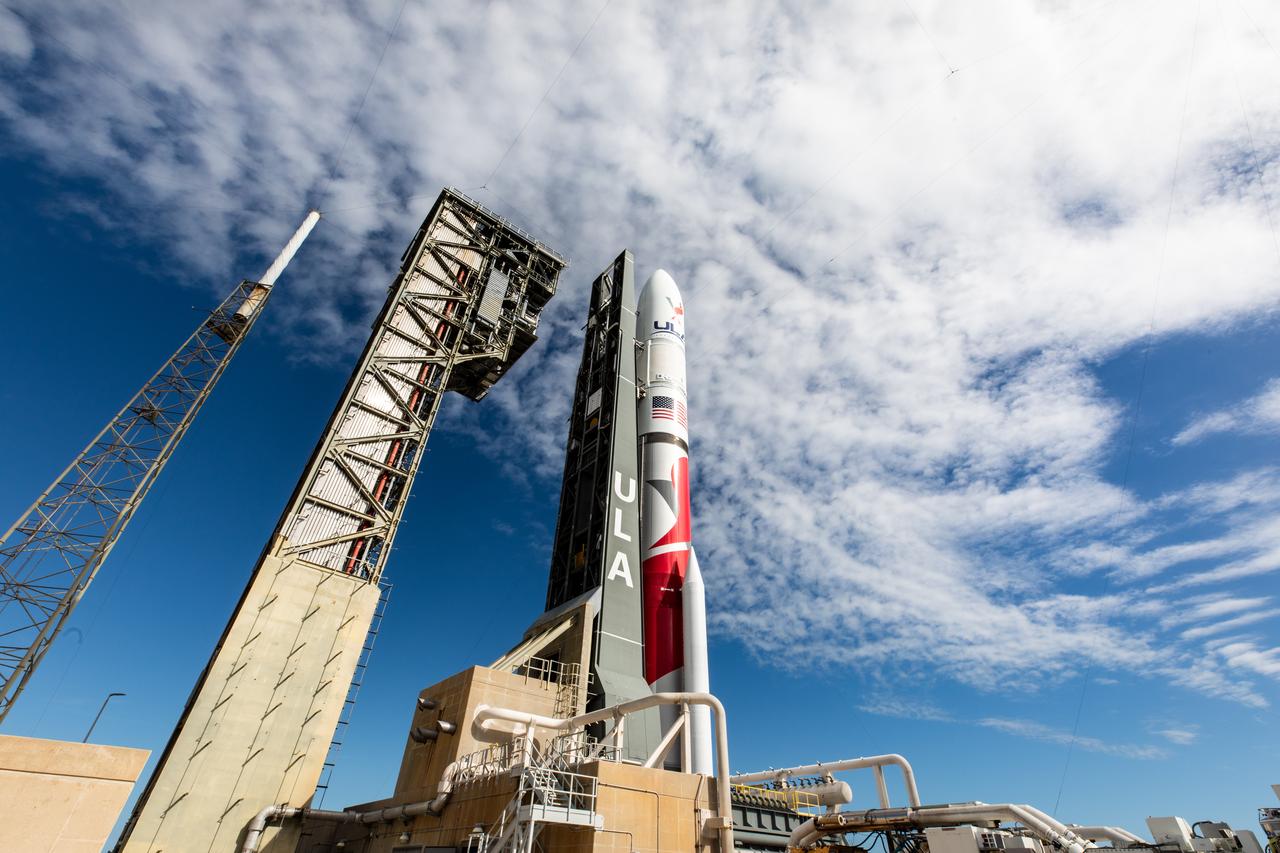

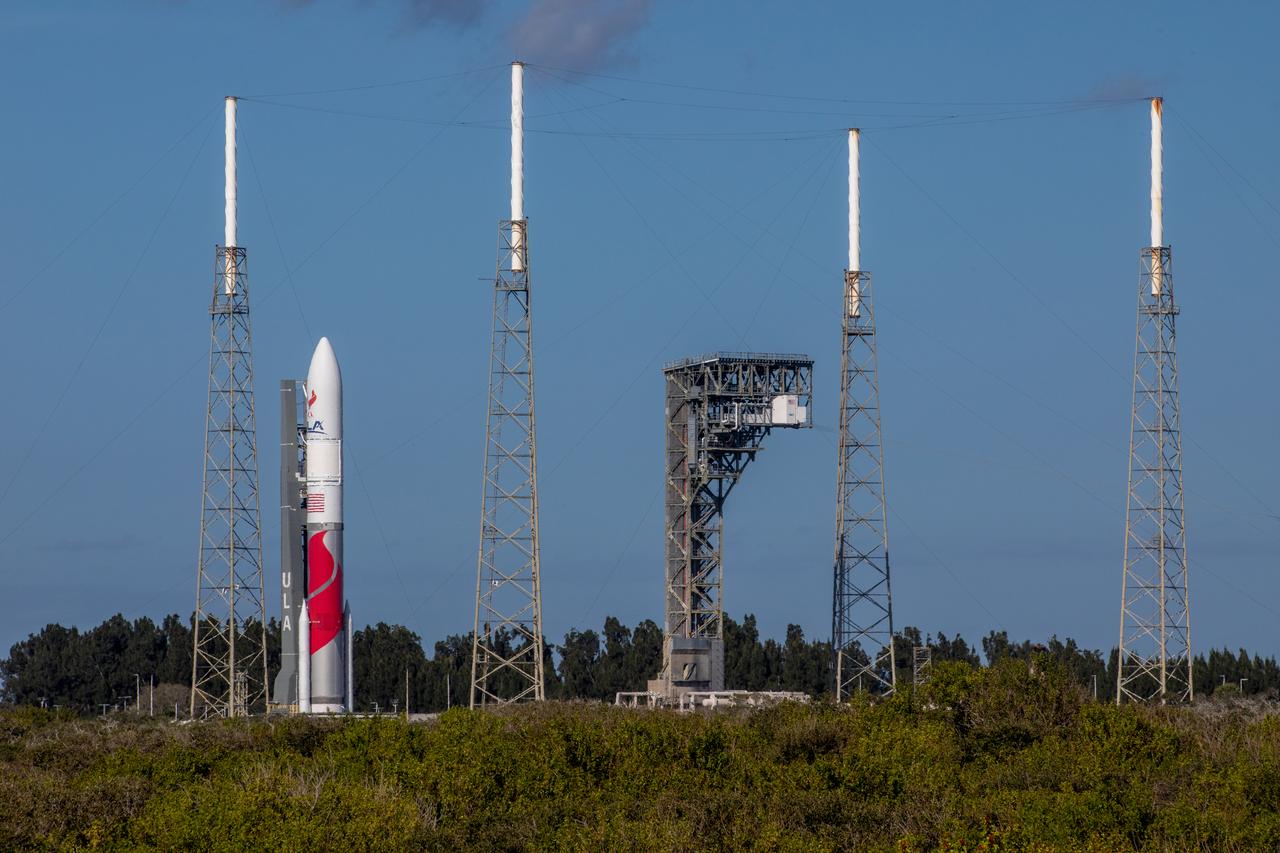
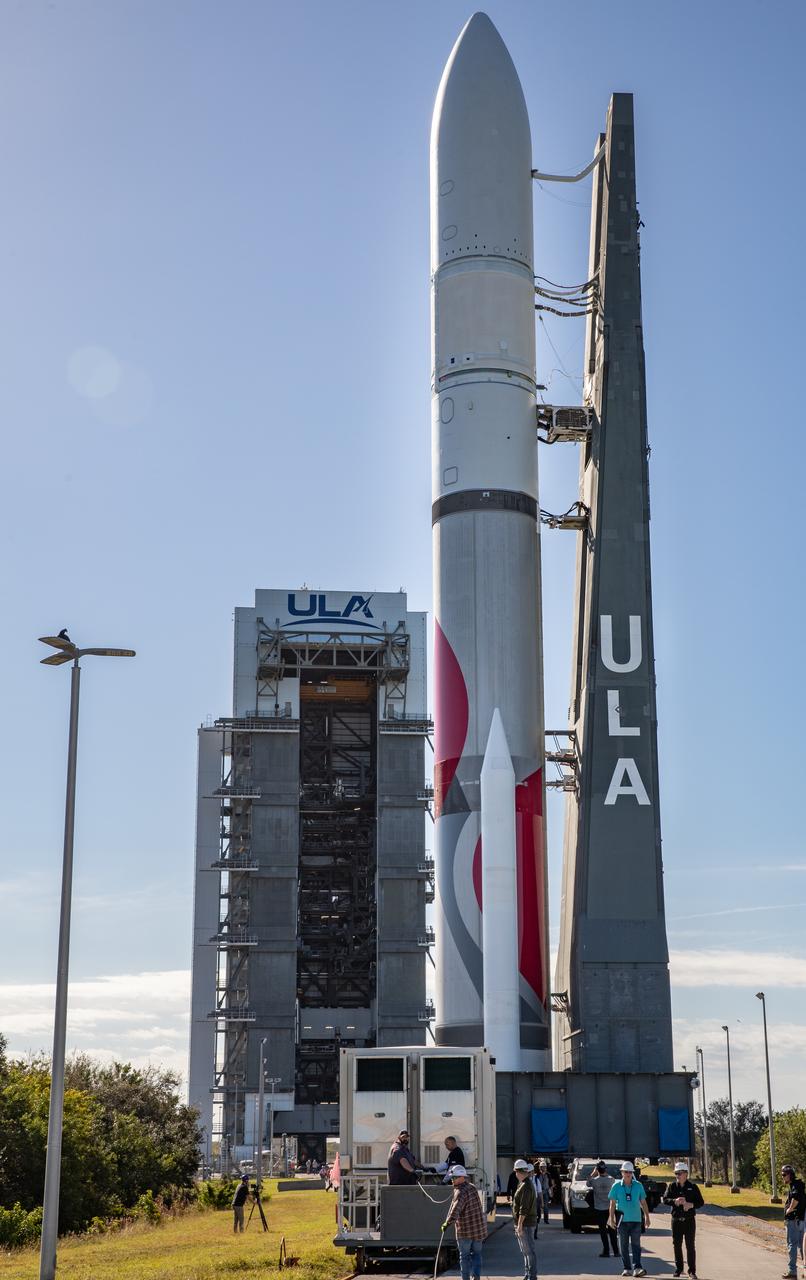
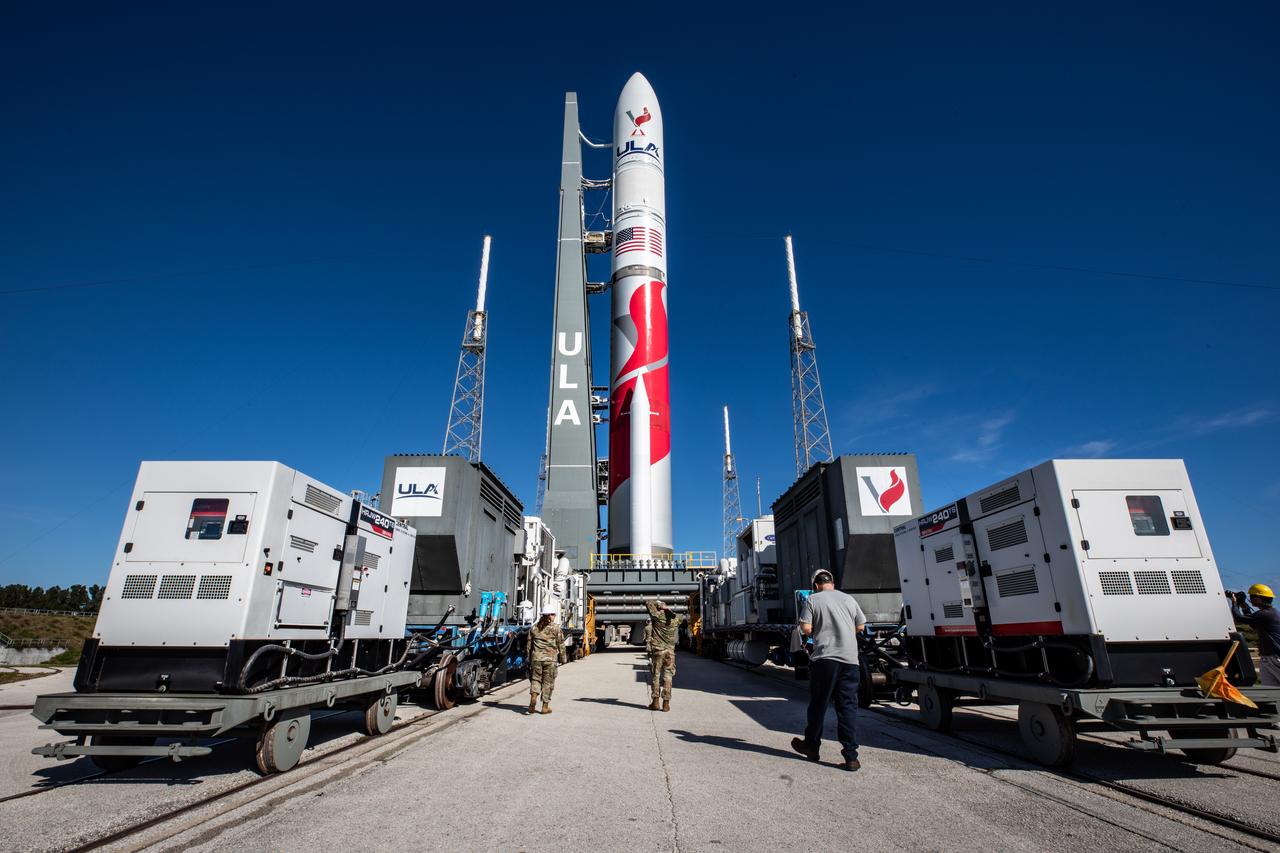
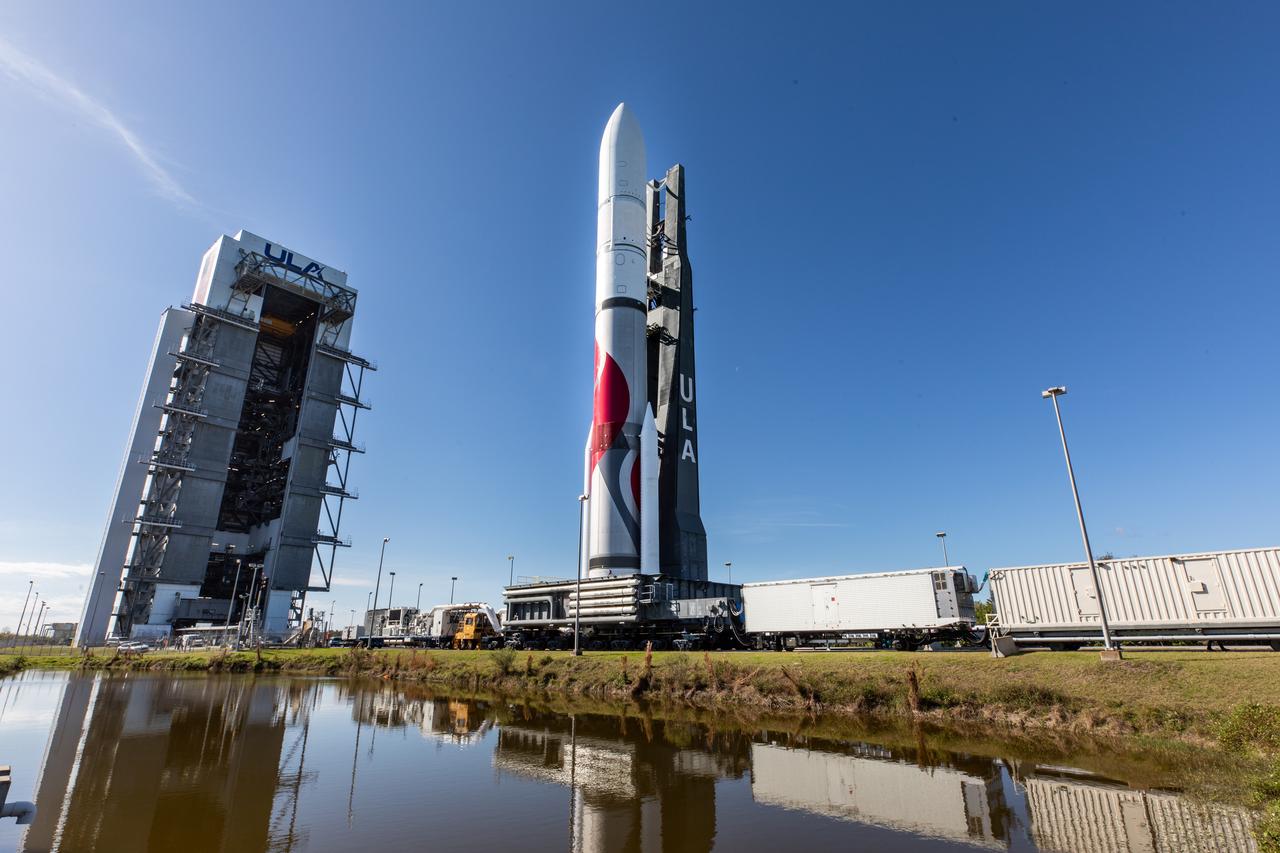
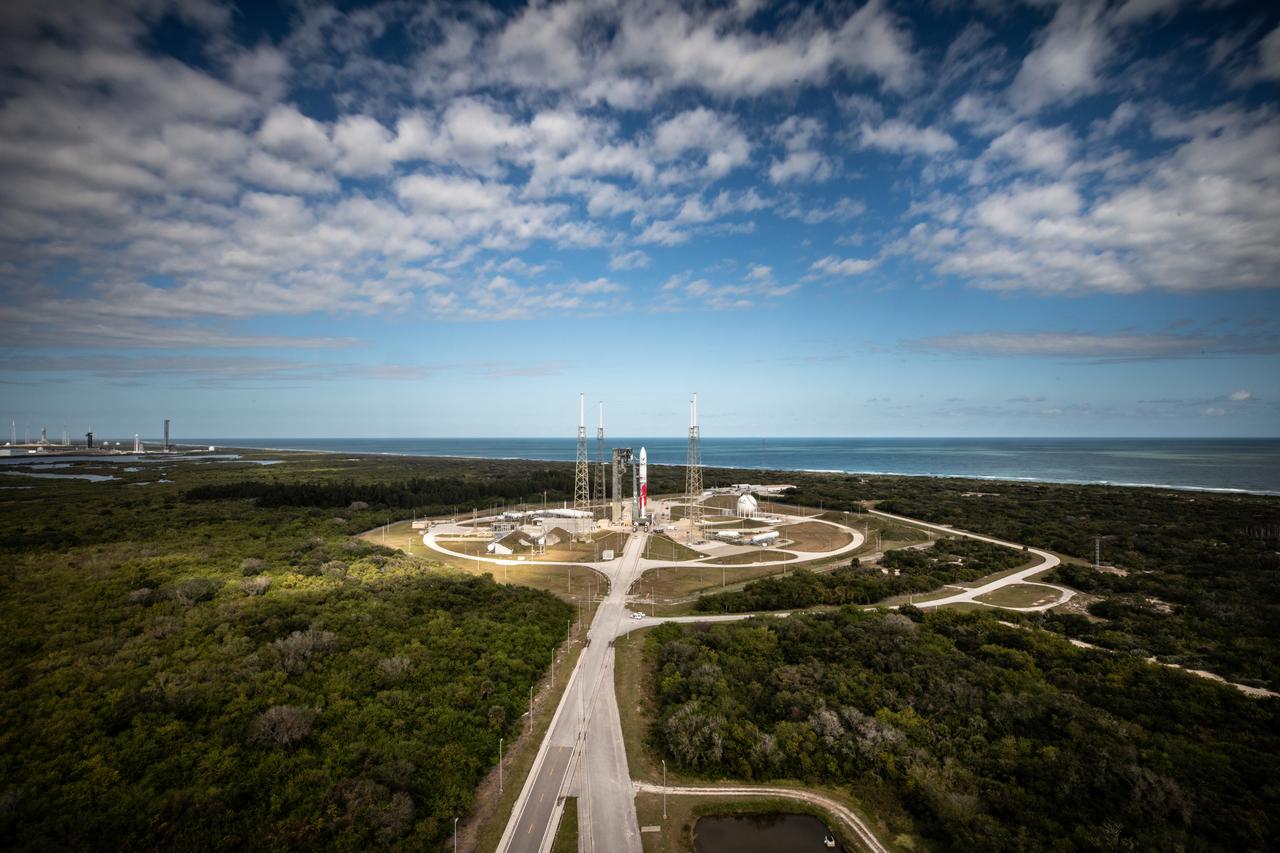
On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
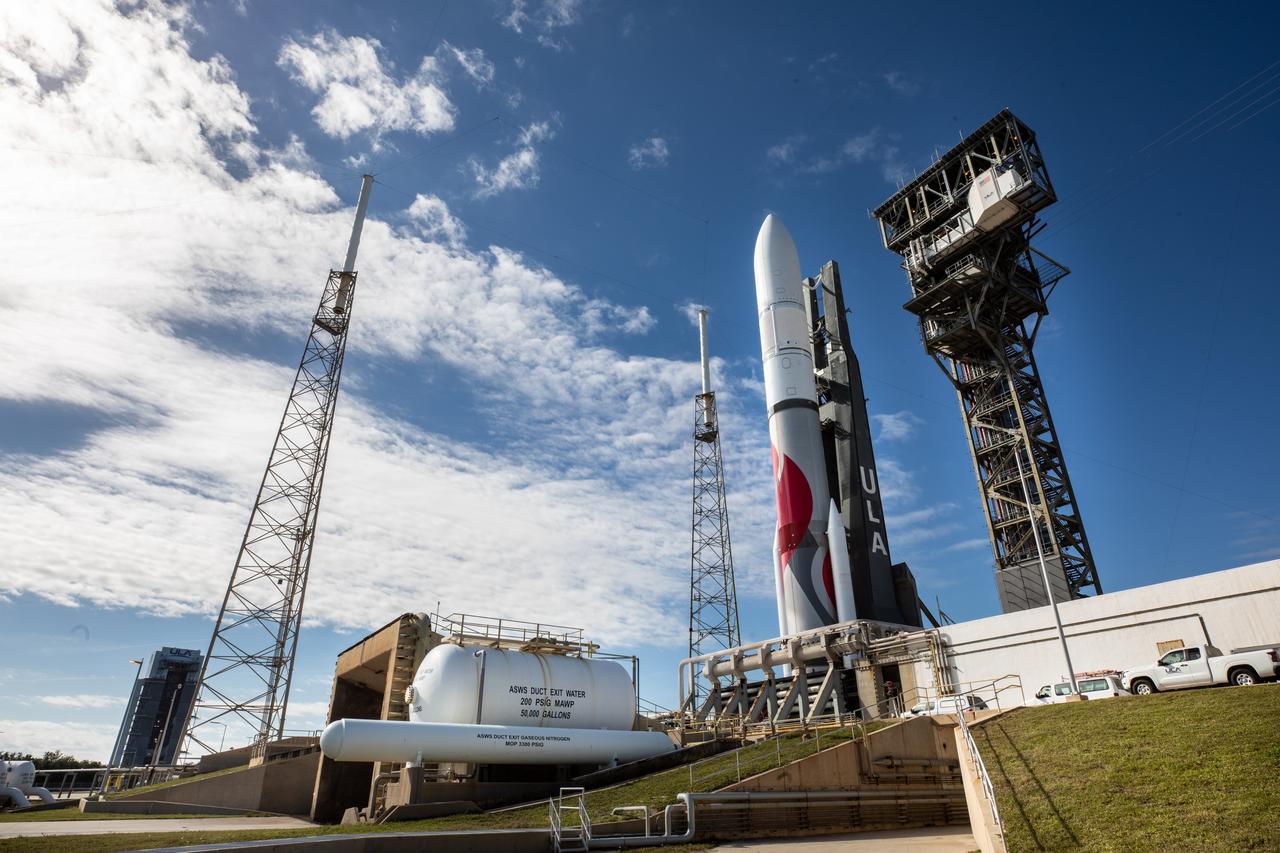

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
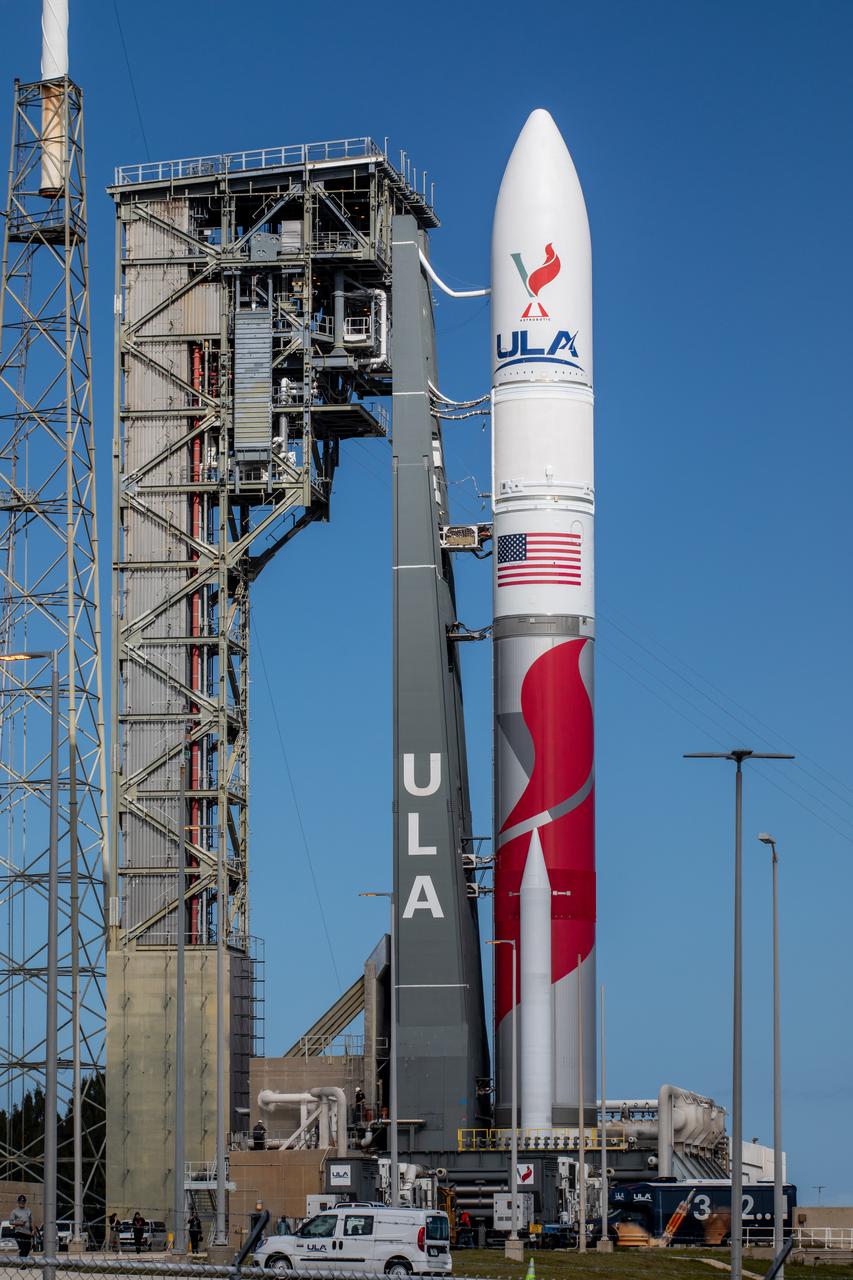

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
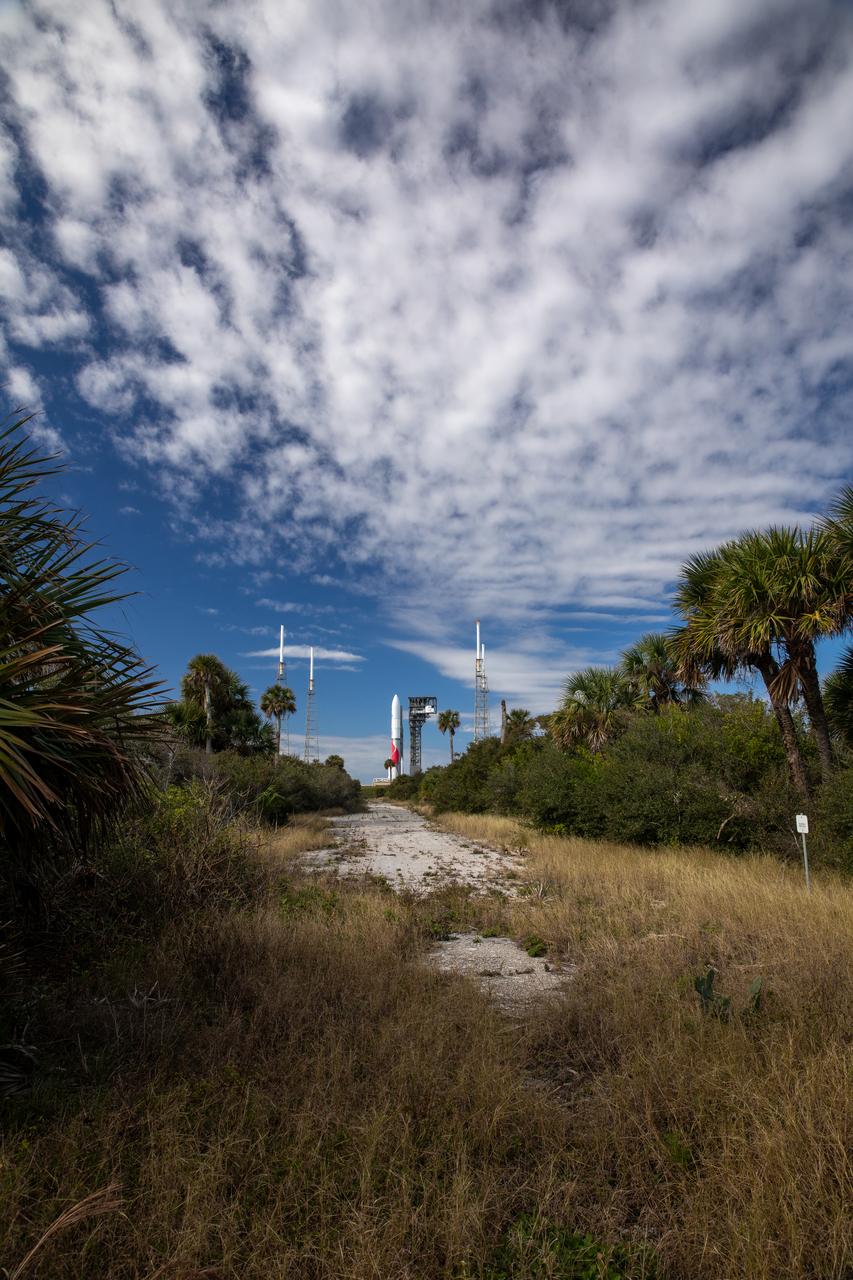

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
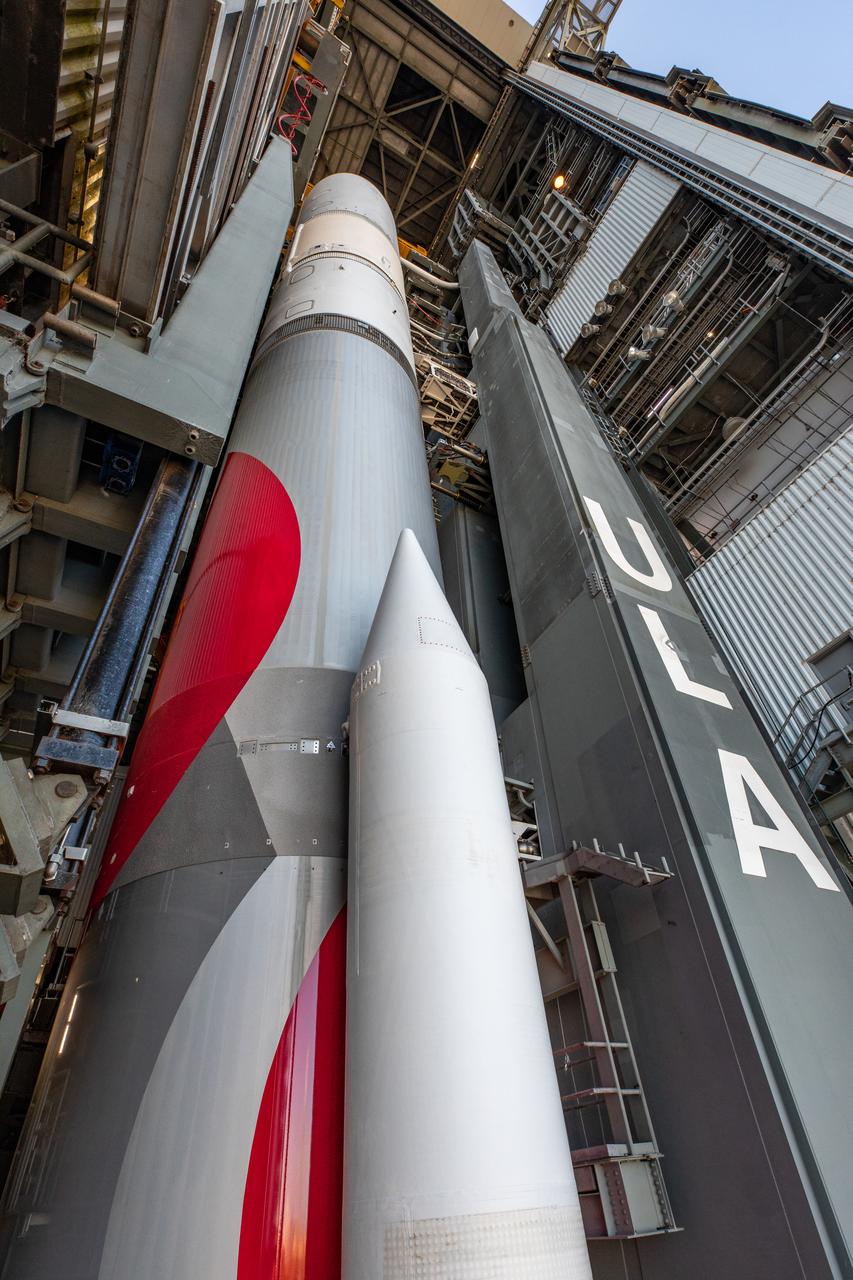

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
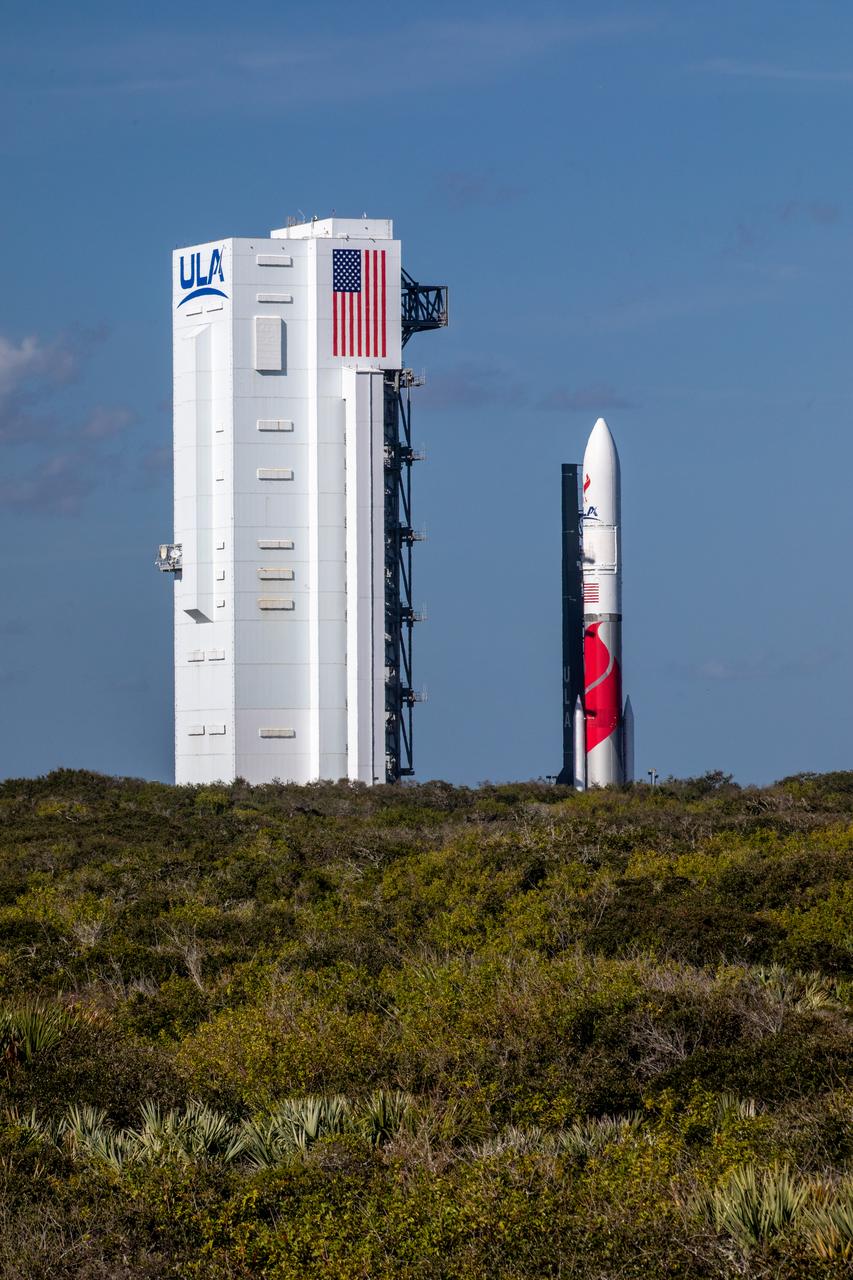

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
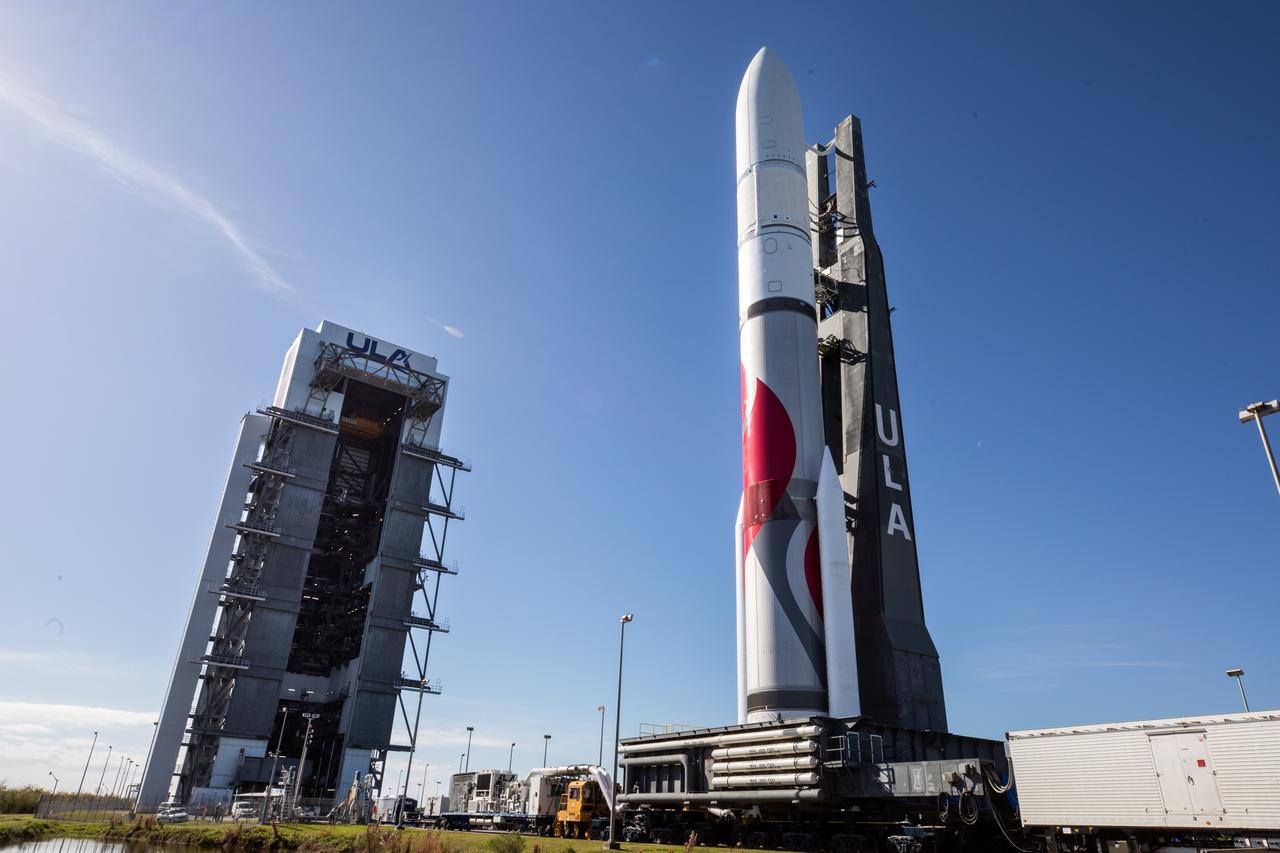

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
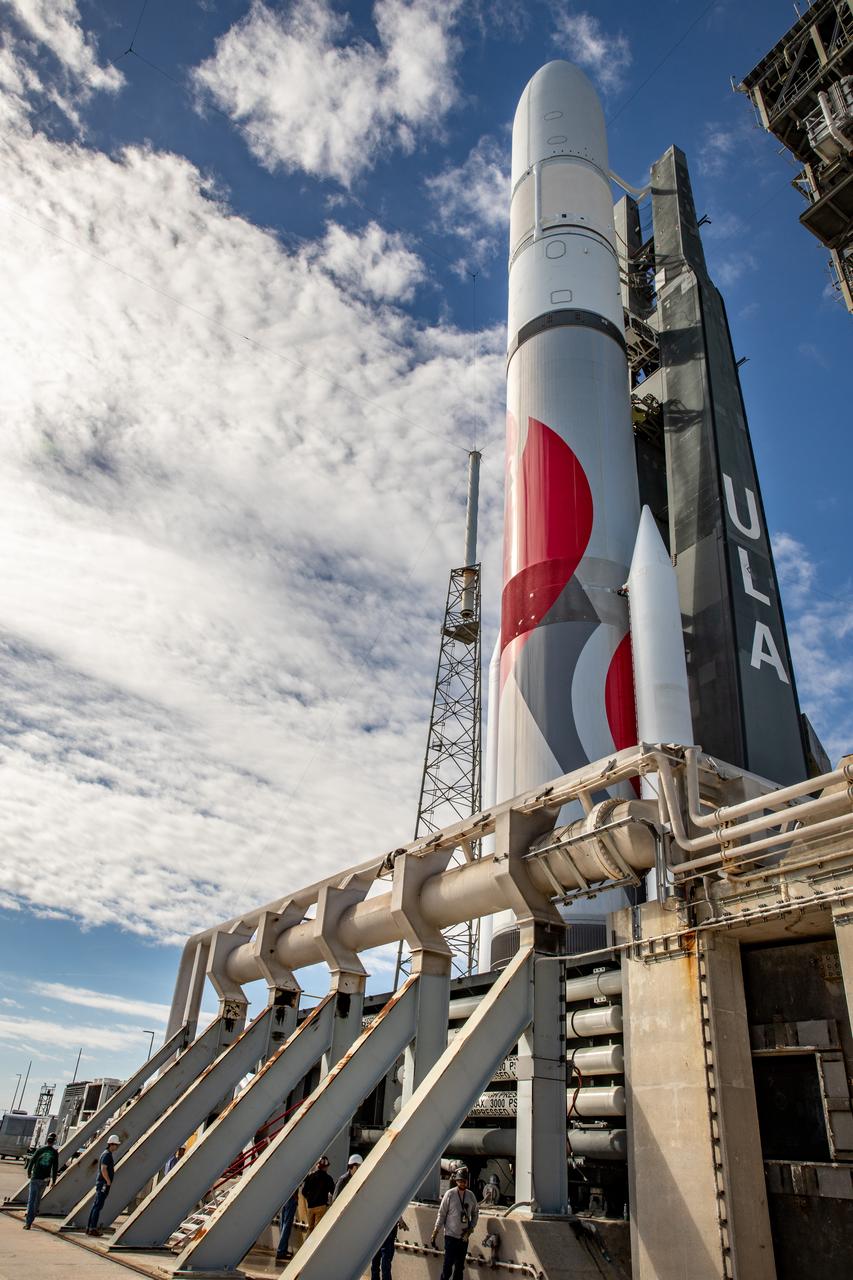

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
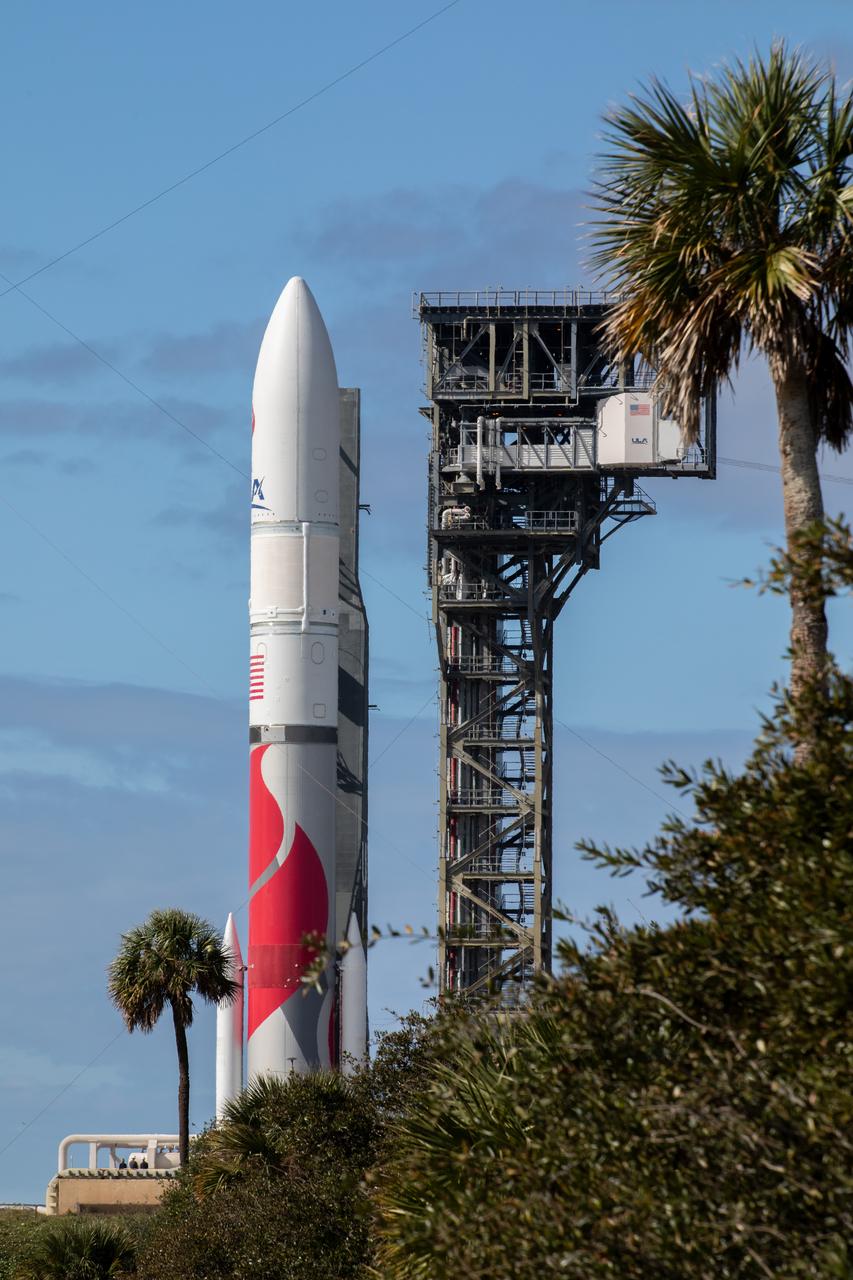

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
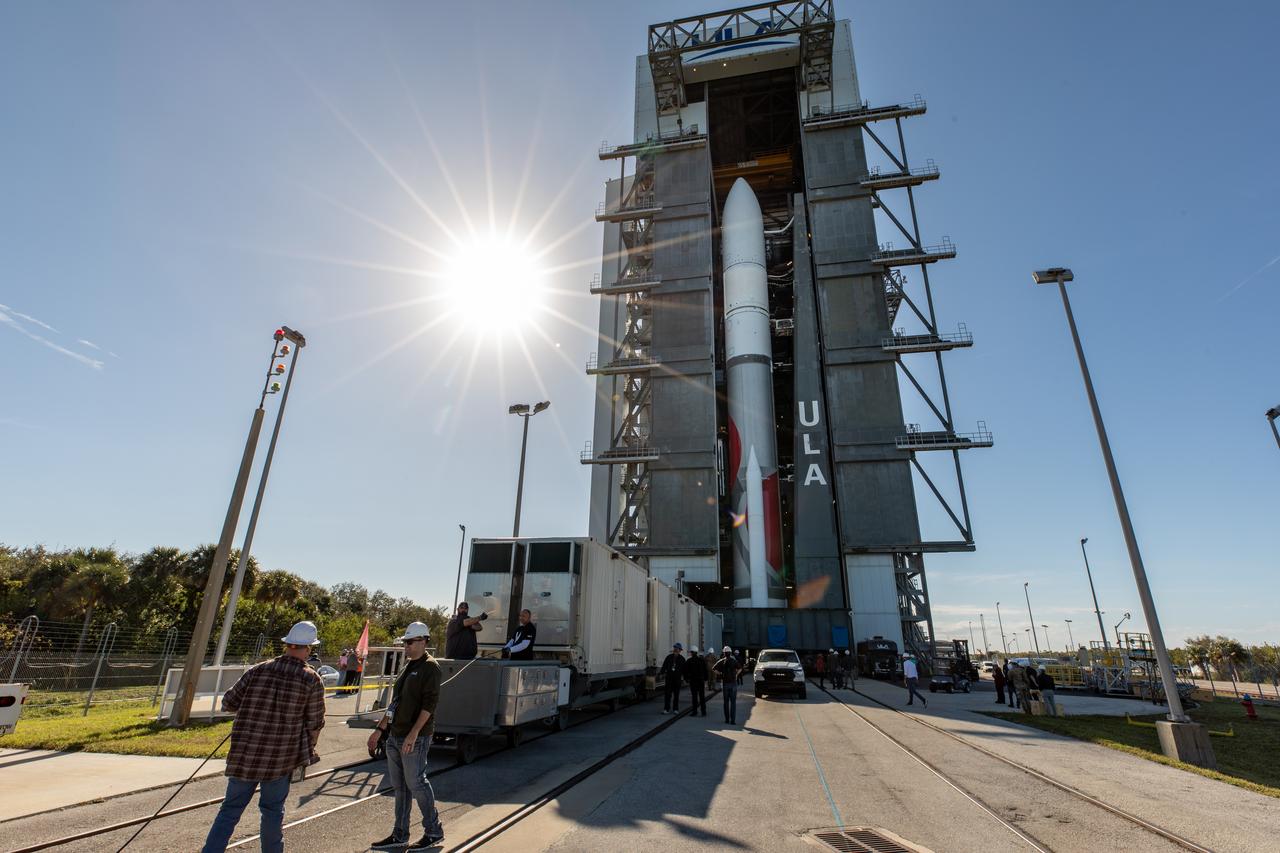

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
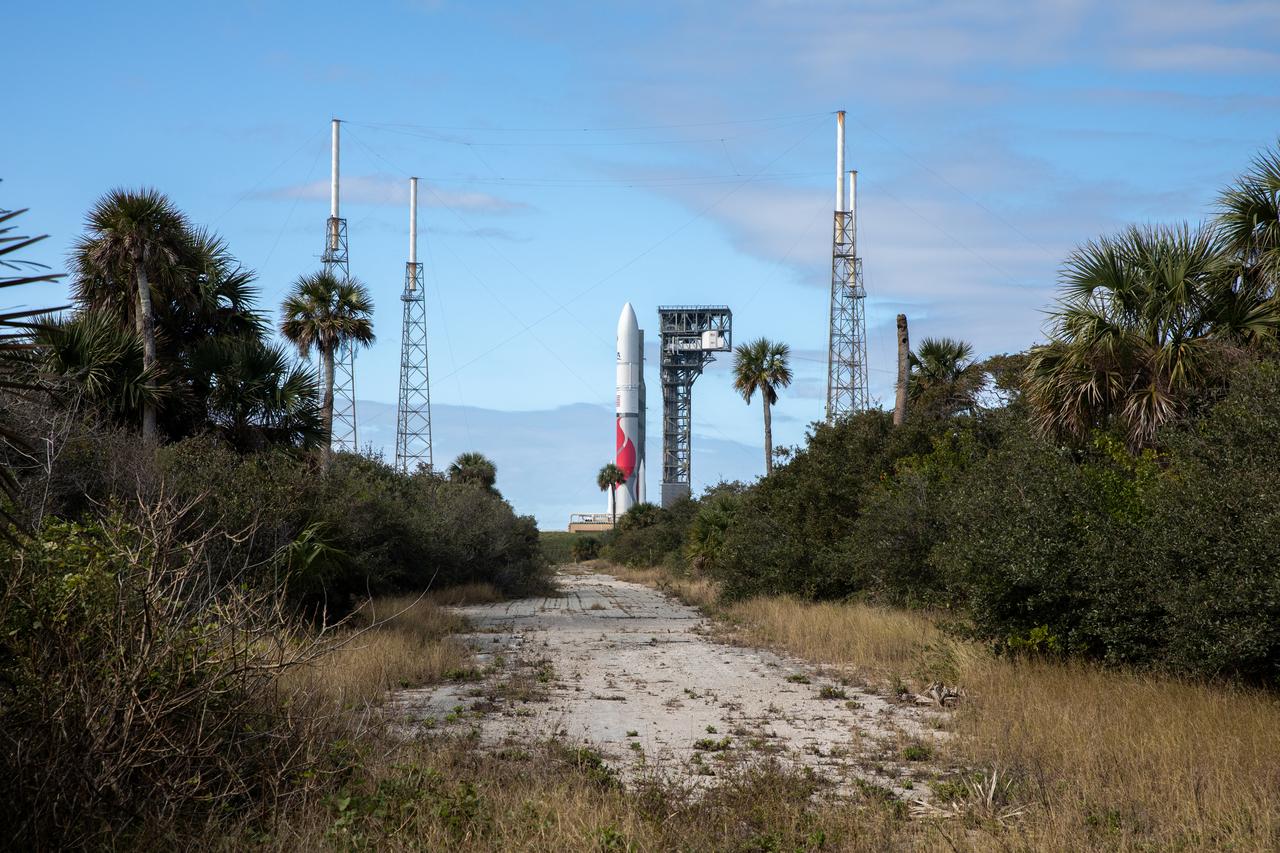

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
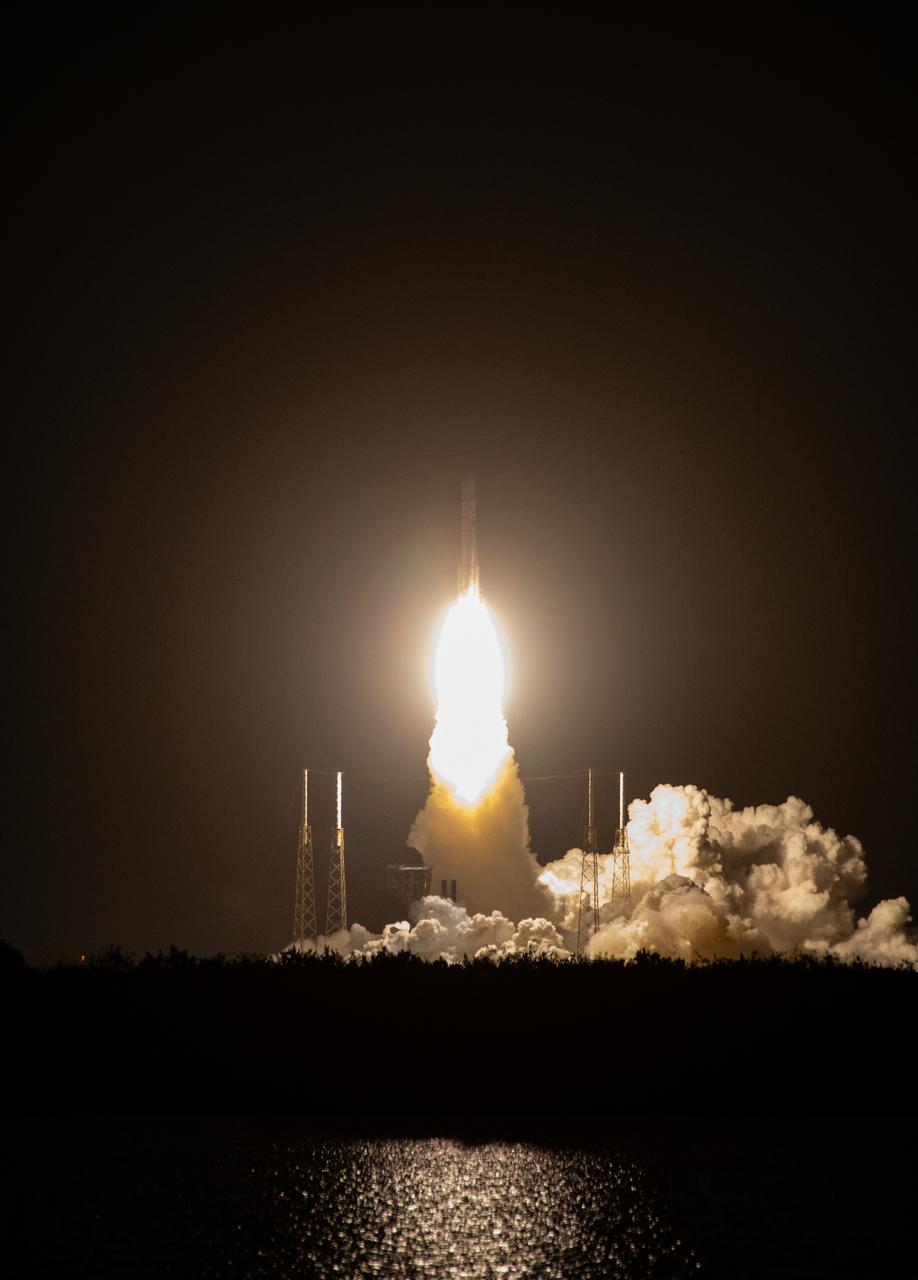

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
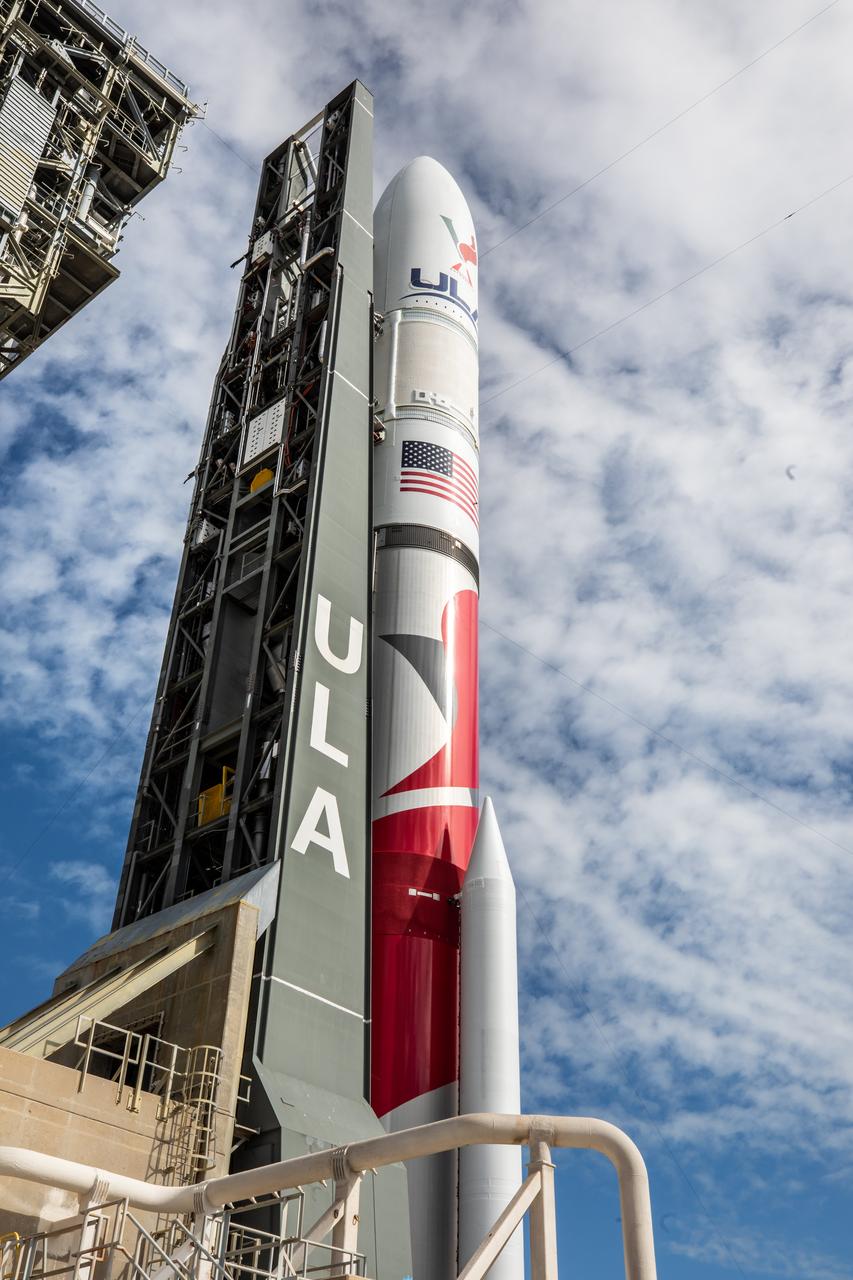
On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
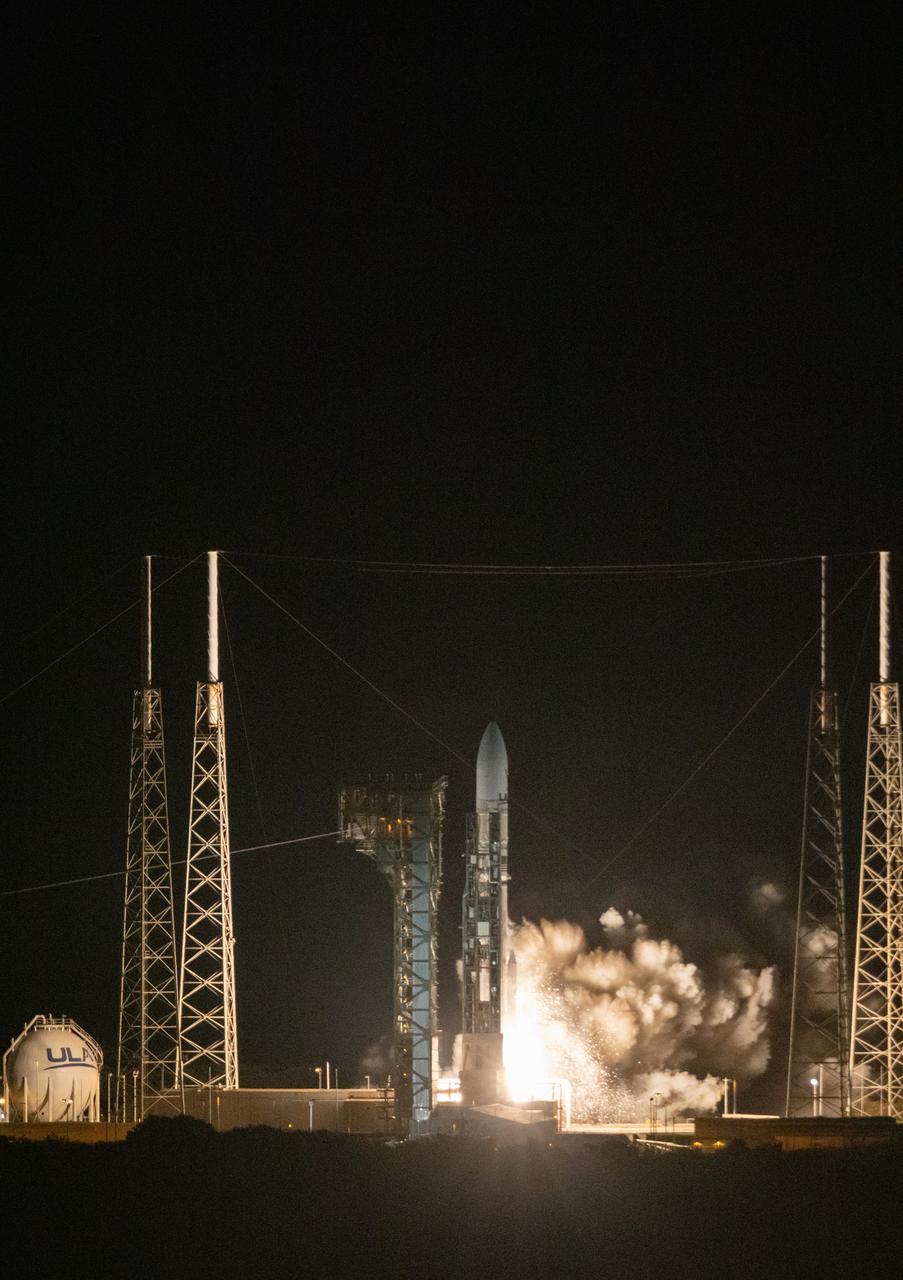

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
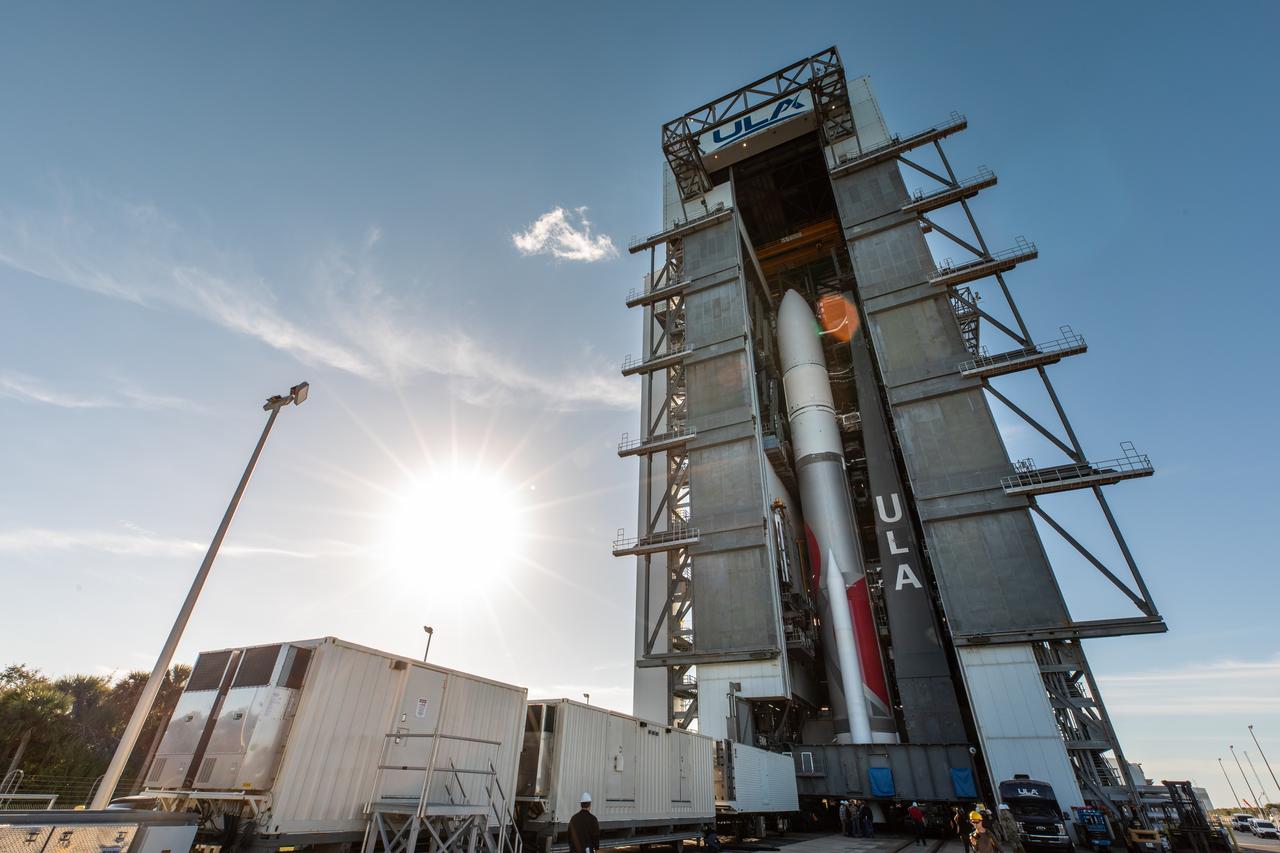

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
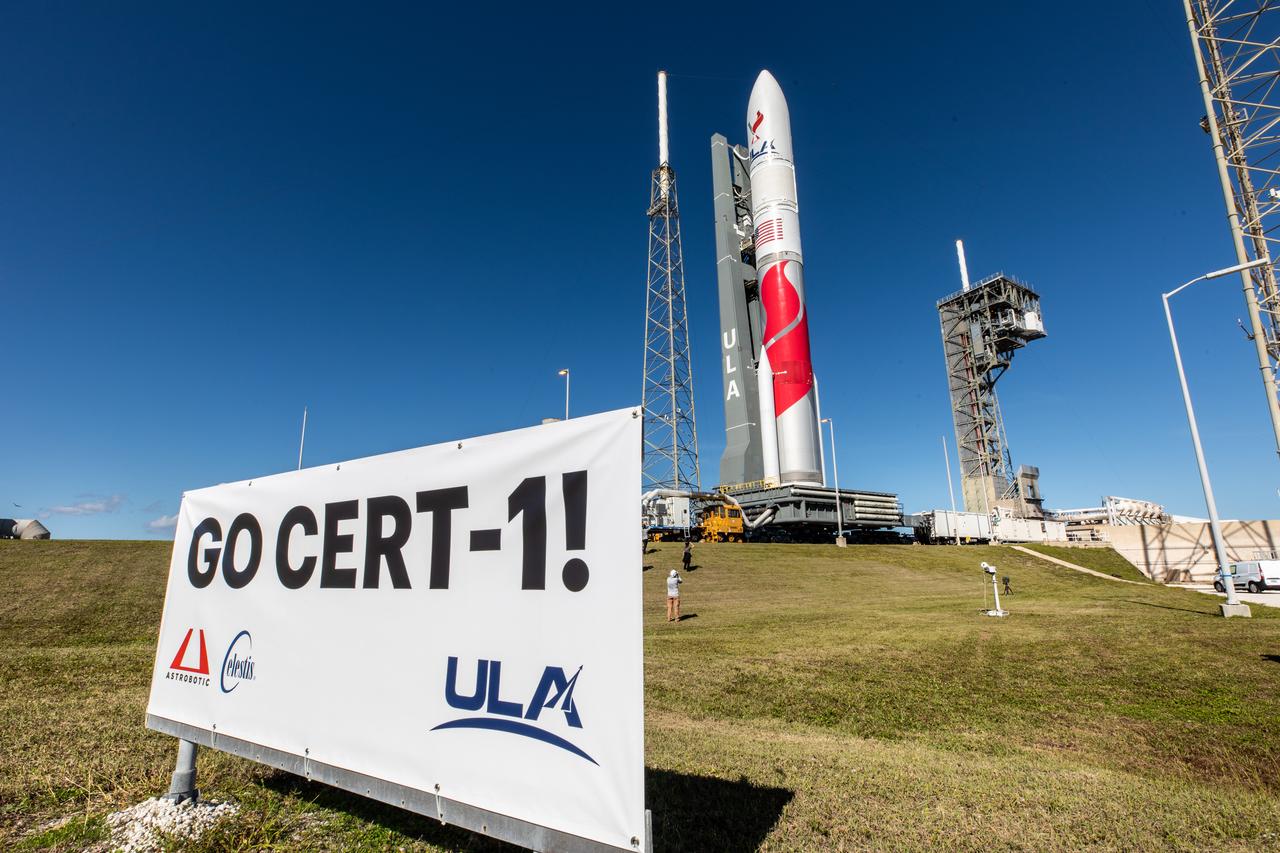

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
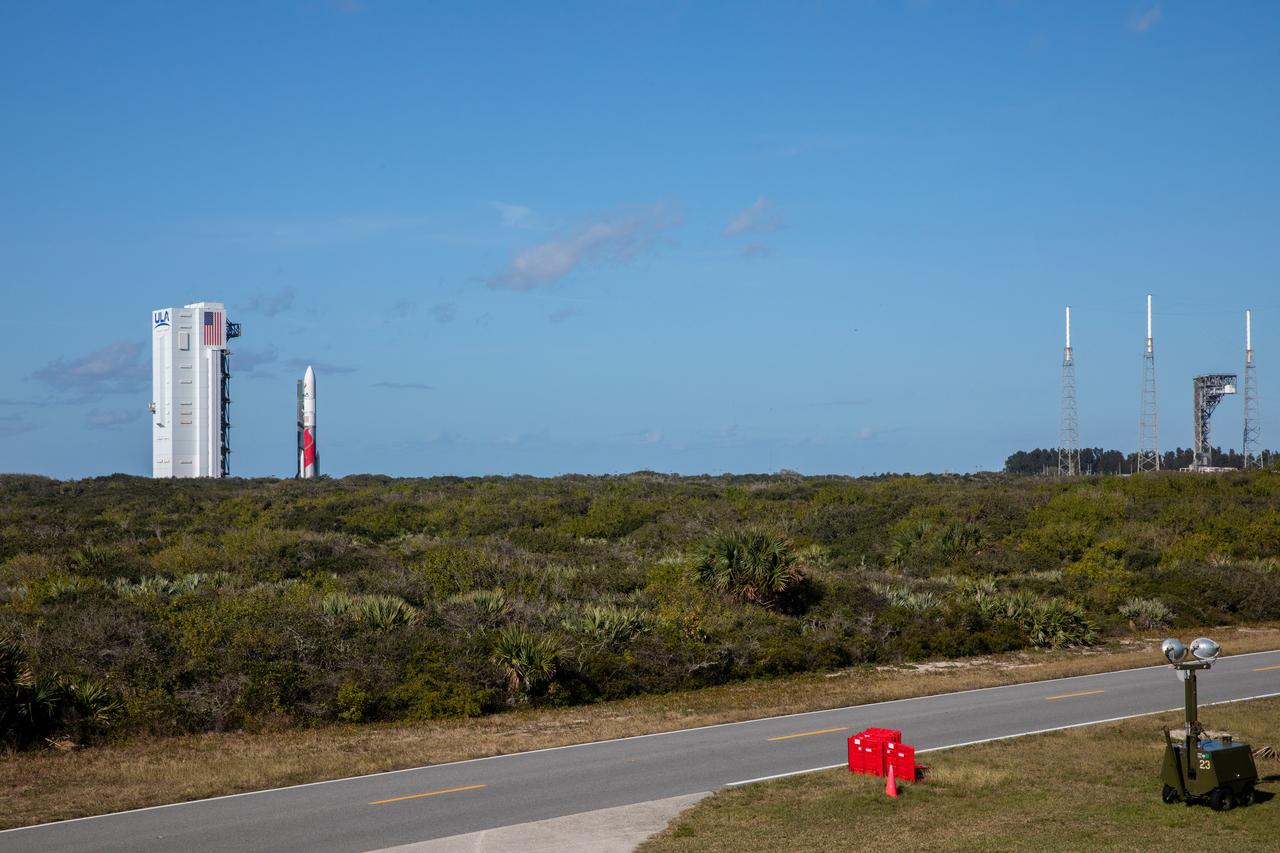

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
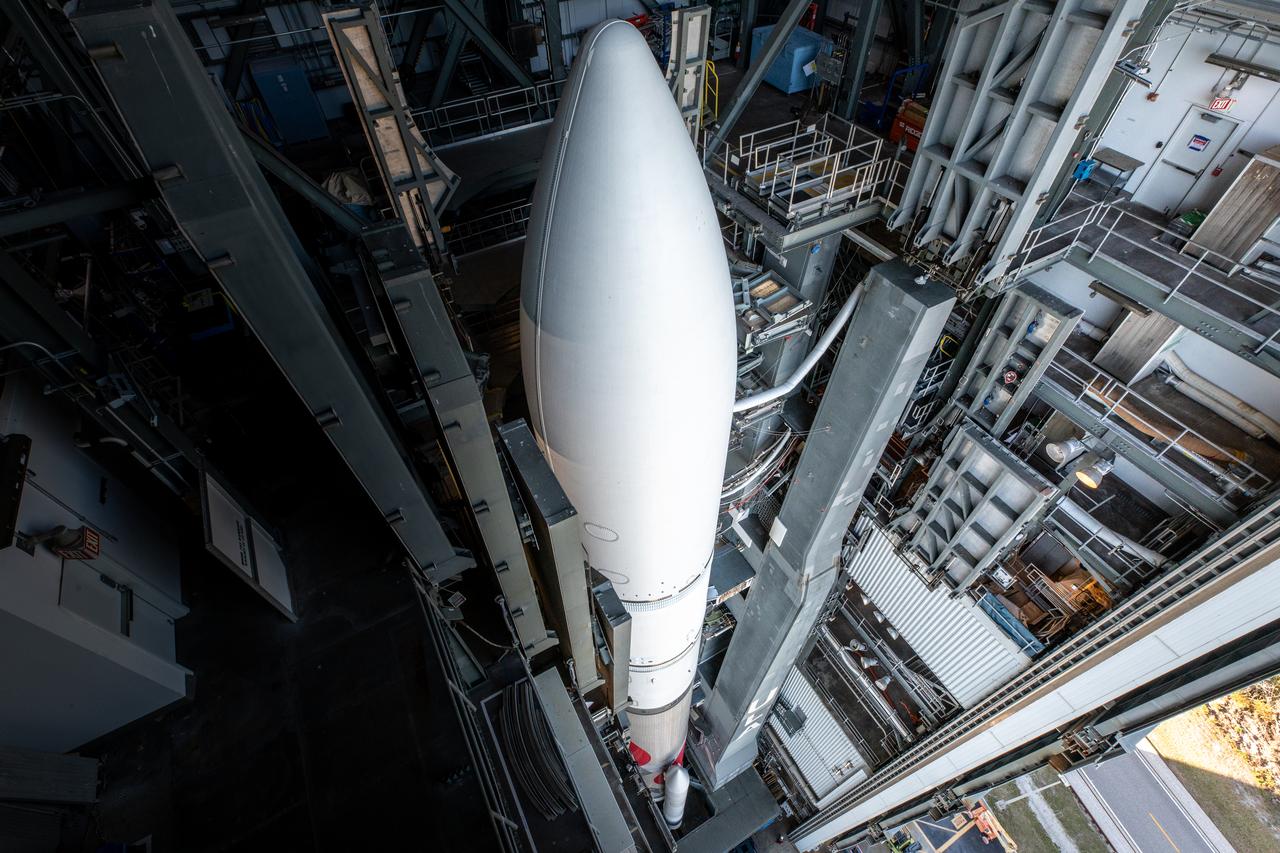

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
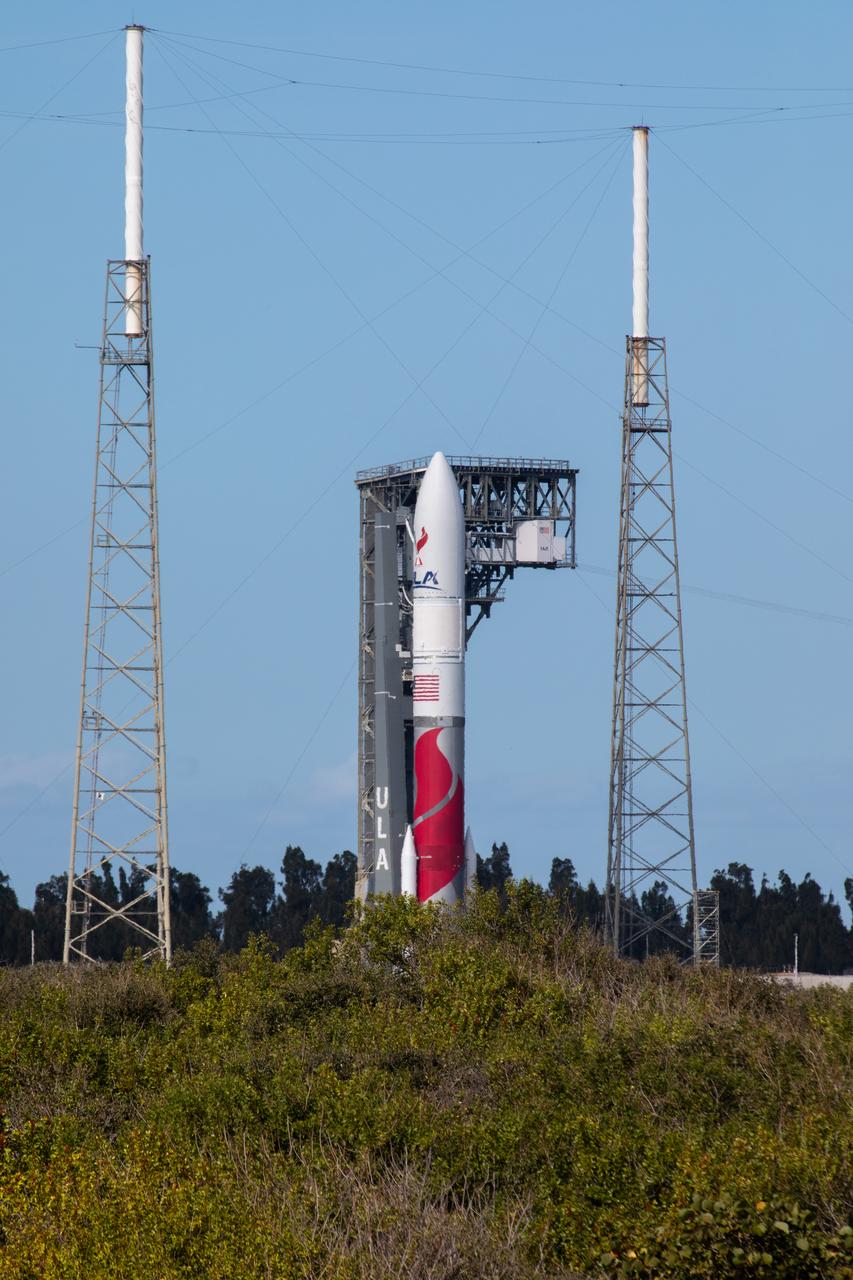

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
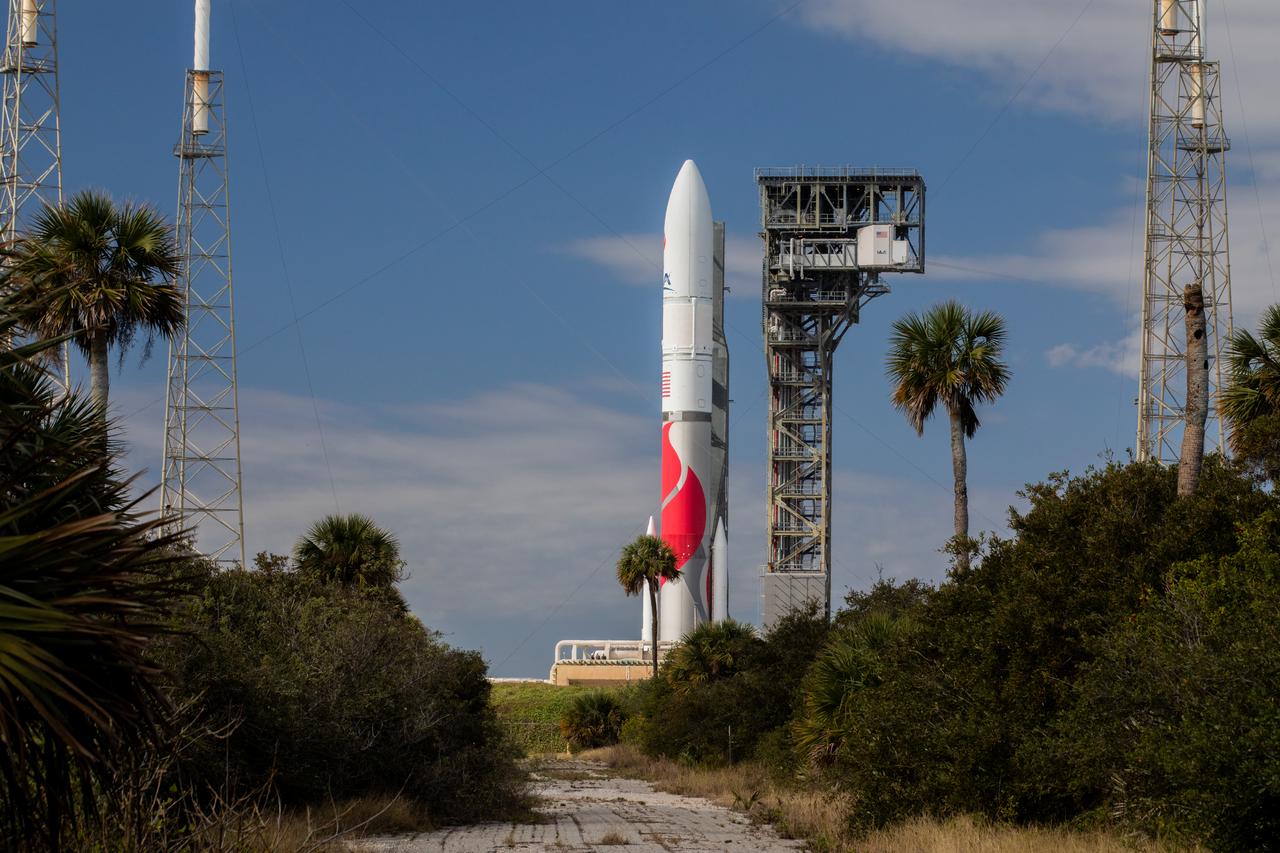

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
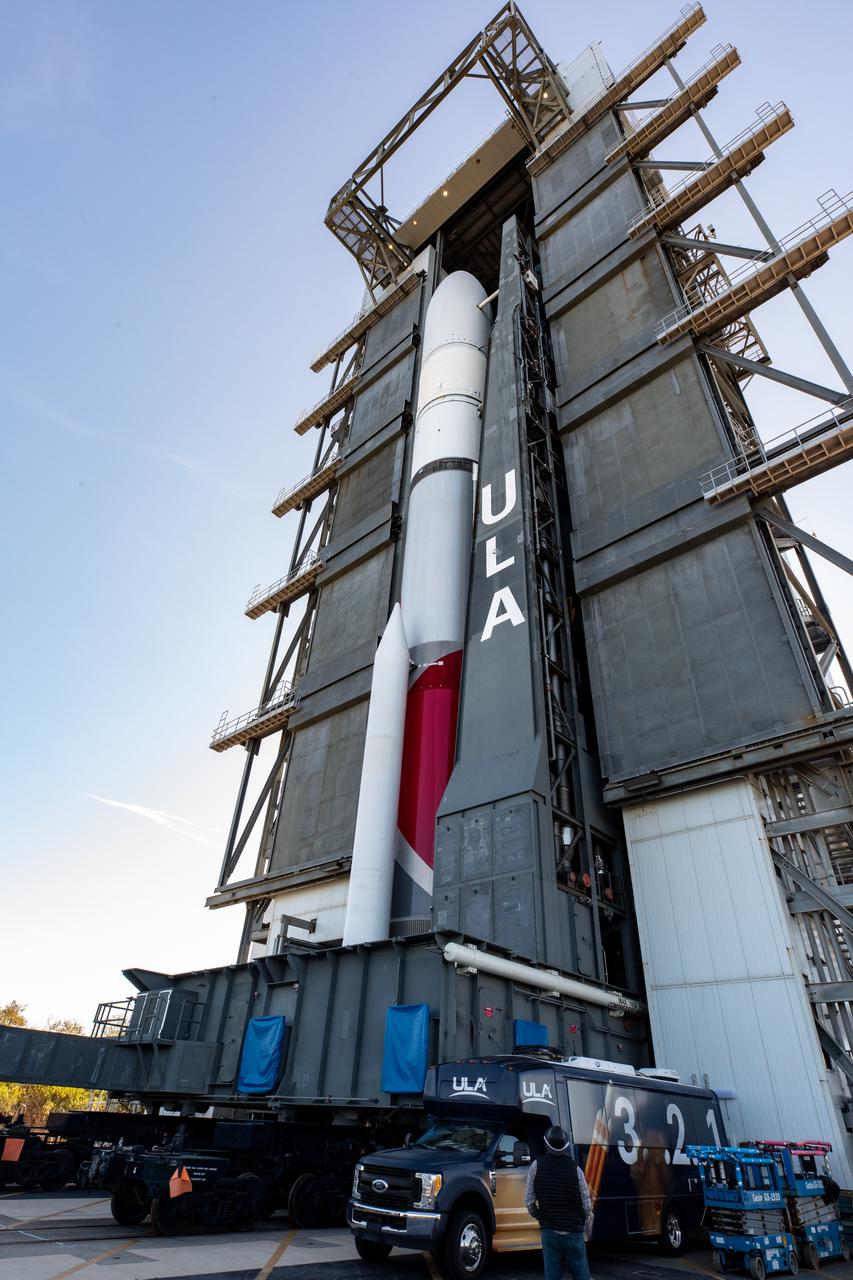

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
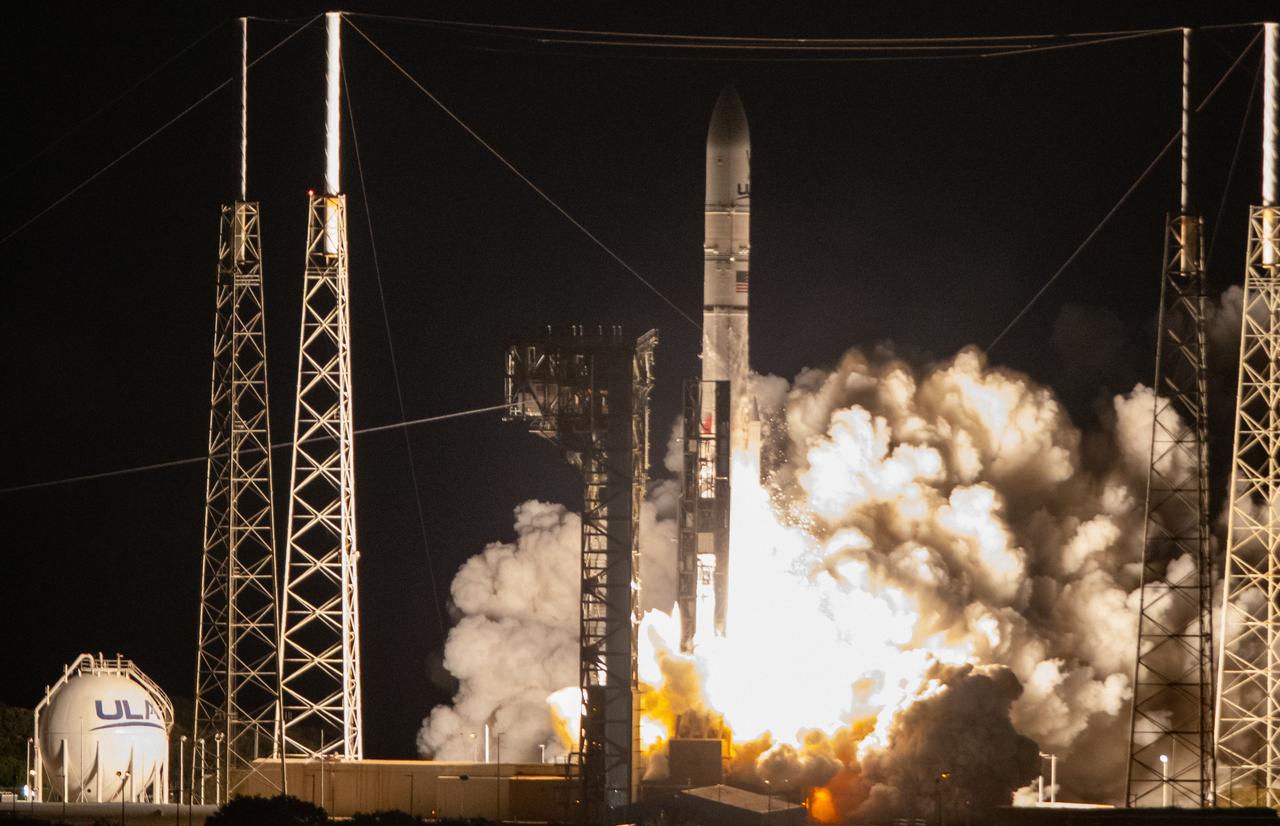

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

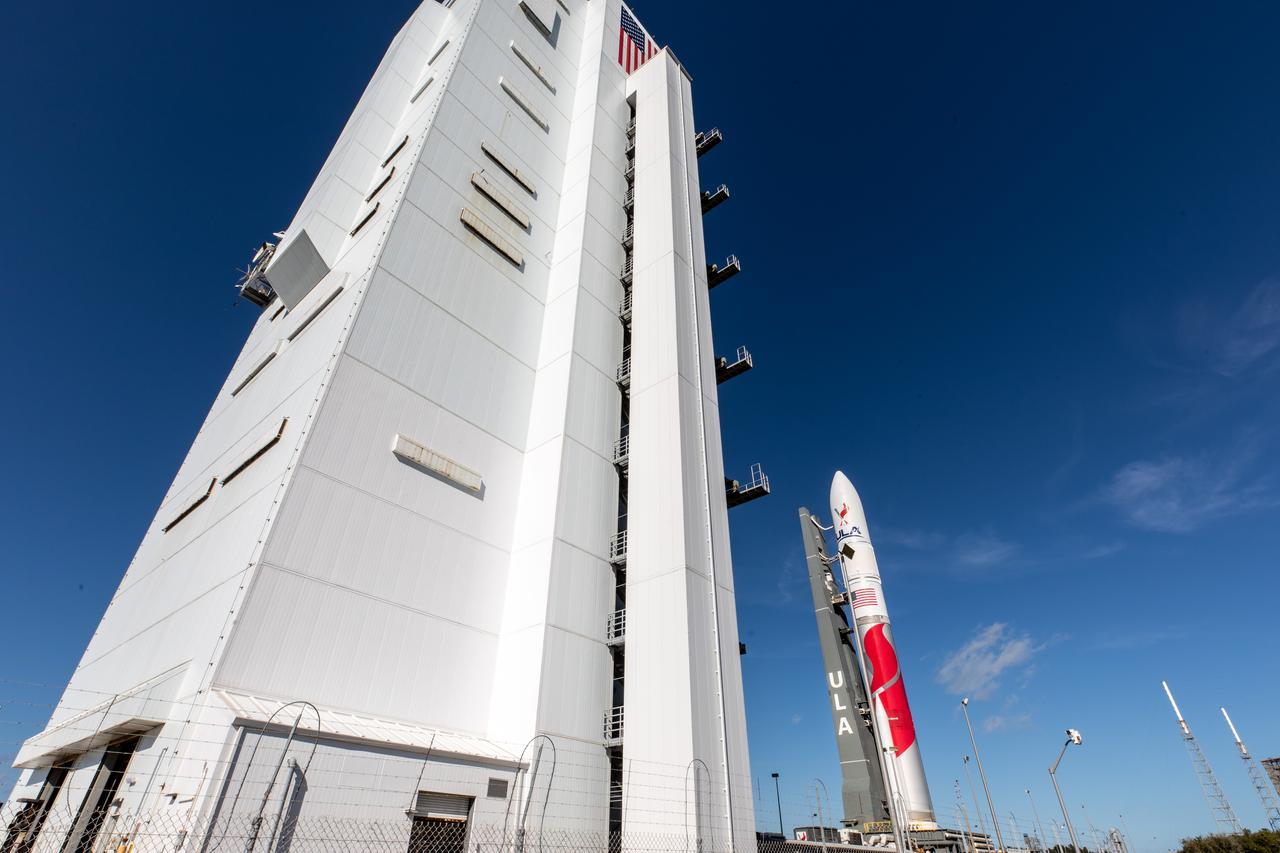
On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
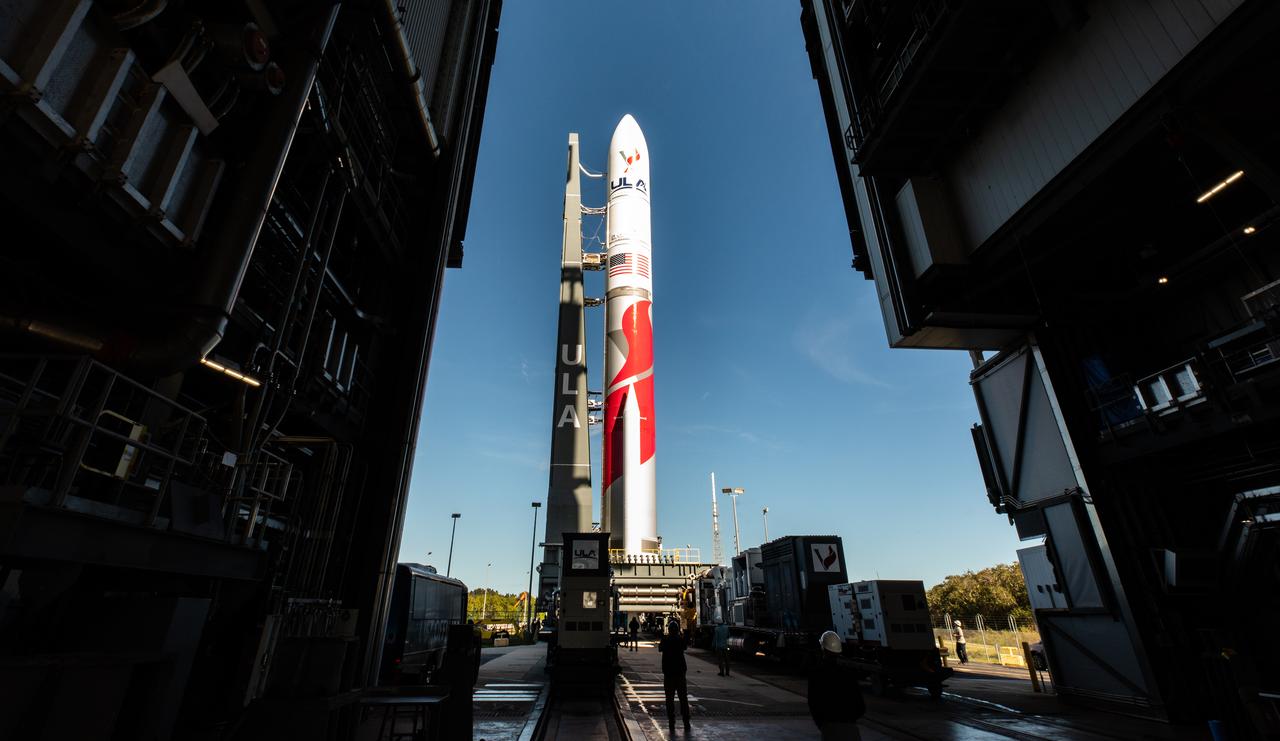

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
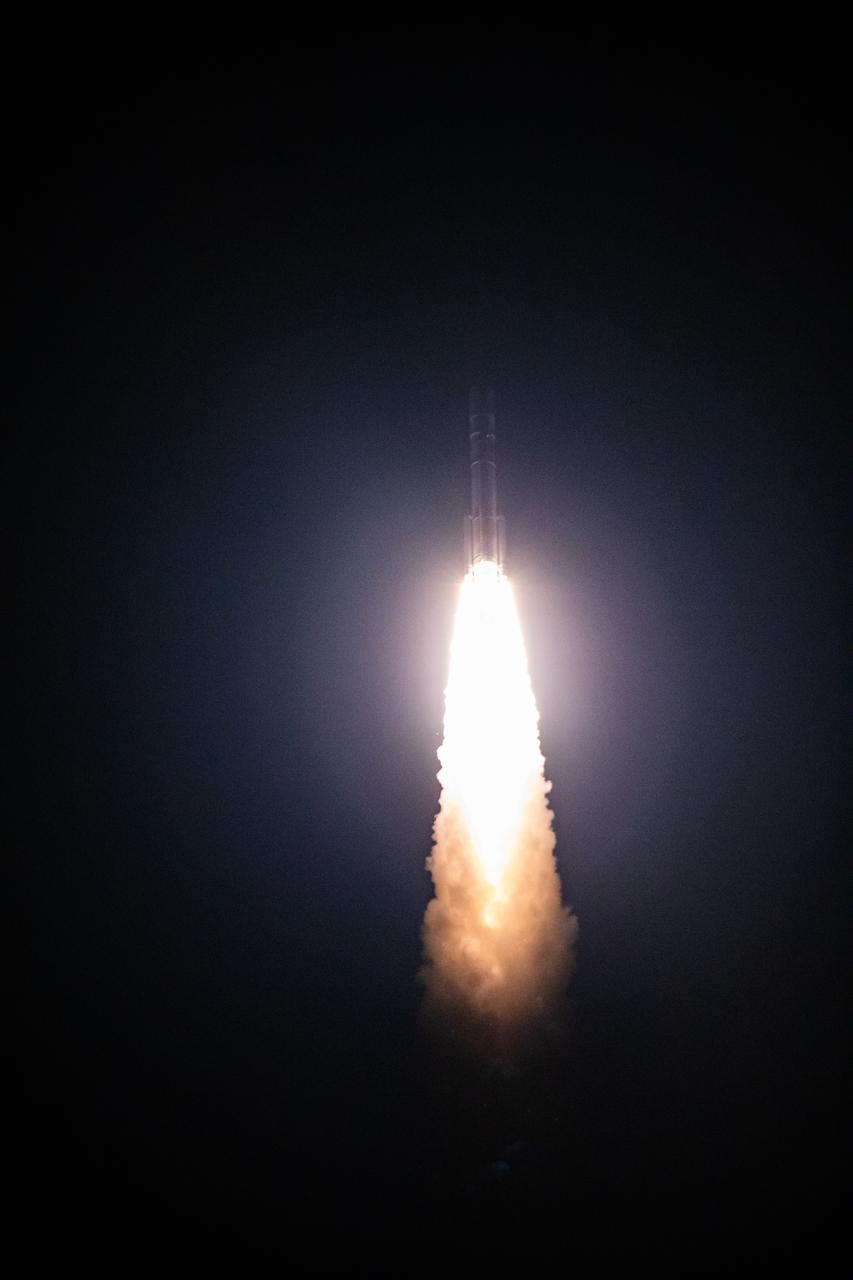

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
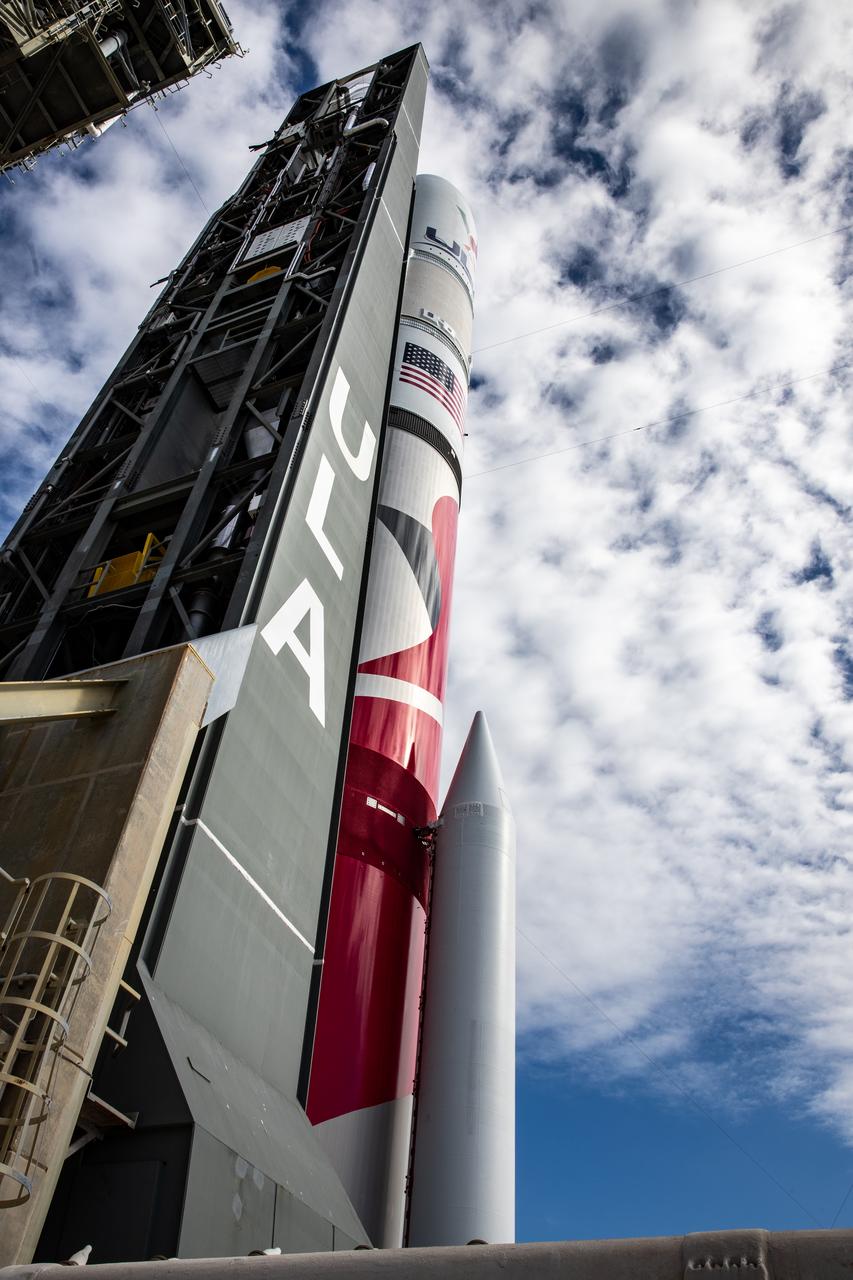

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
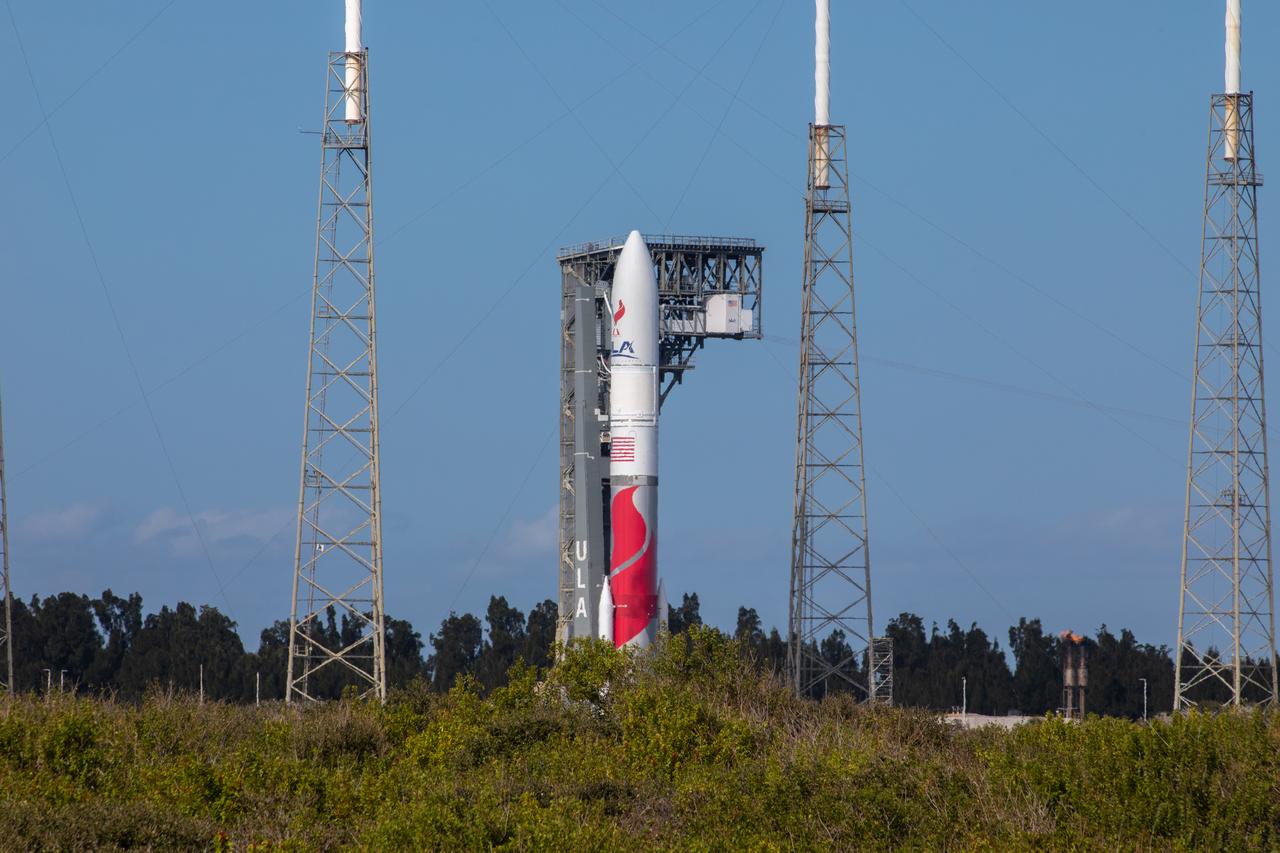

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is preparing to be encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Star Trek composer Michael Giacchino does the Vulcan salute after conducting the National Symphony Orchestra during the "Space, the Next Frontier" event celebrating NASA's 60th Anniversary, Friday, June 1, 2018 at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts in Washington. The event featured music inspired by space including artists will.i.am, Grace Potter, Coheed & Cambria, John Cho, and guest Nick Sagan, son of Carl Sagan. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
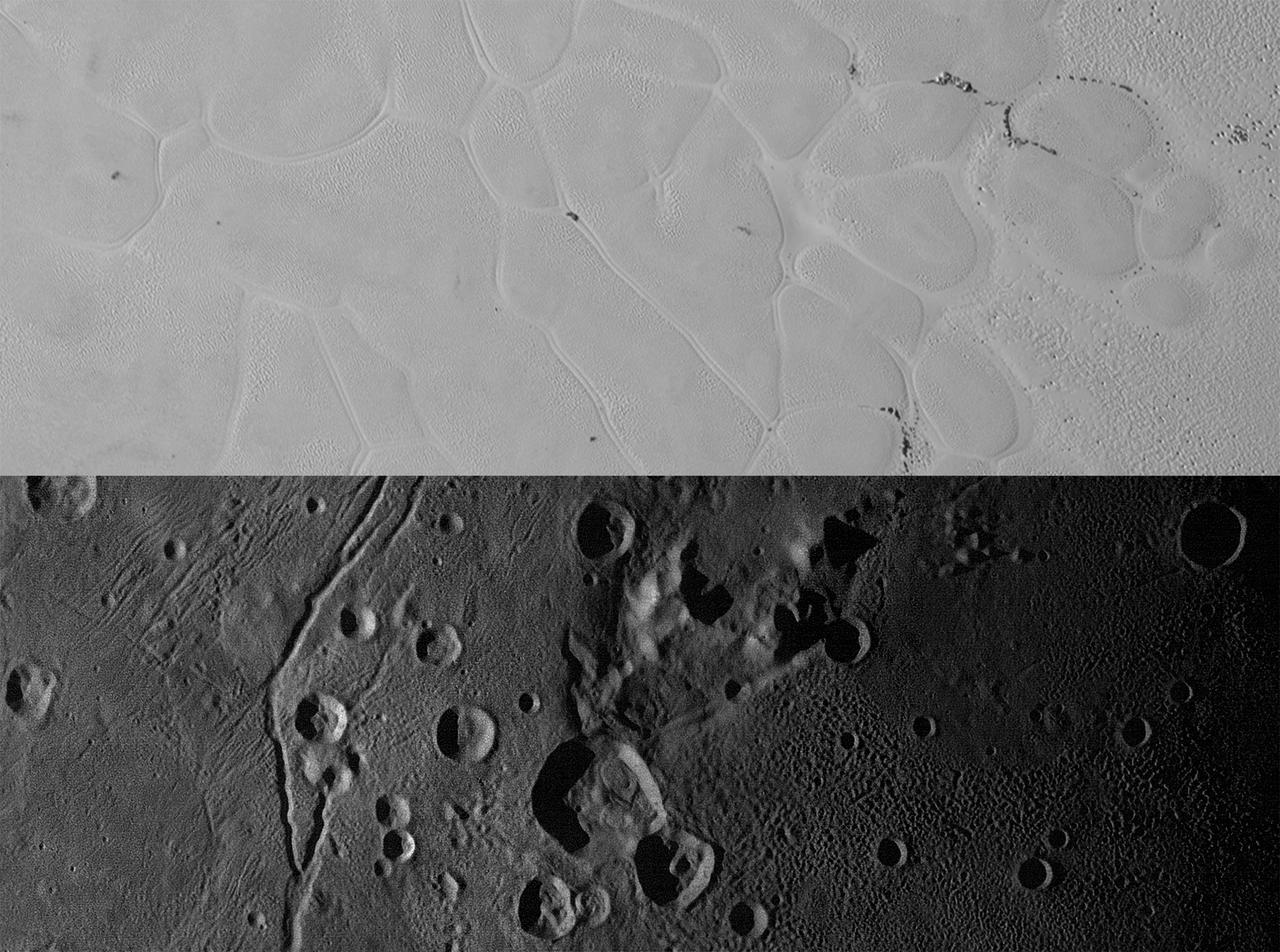
New Horizons views of the informally named Sputnik Planum on Pluto (top) and the informally named Vulcan Planum on Charon (bottom). Both scale bars measure 20 miles (32 kilometers) long; illumination is from the left in both instances. The Sputnik Planum view is centered at 11°N, 180°E, and covers the bright, icy, geologically cellular plains. Here, the cells are defined by a network of interconnected troughs that crisscross these nitrogen-ice plains. At right, in the upper image, the cellular plains yield to pitted plains of southern Sputnik Planum. This observation was obtained by the Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) at a resolution of 1,050 feet (320 meters) per pixel. The Vulcan Planum view in the bottom panel is centered at 4°S, 4°E, and includes the "moated mountain" Clarke Mons just above the center of the image. As well as featuring impact craters and sinuous troughs, the water ice-rich plains display a range of surface textures, from smooth and grooved at left, to pitted and hummocky at right. This observation was obtained by the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) at a resolution of 525 feet (160 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20535
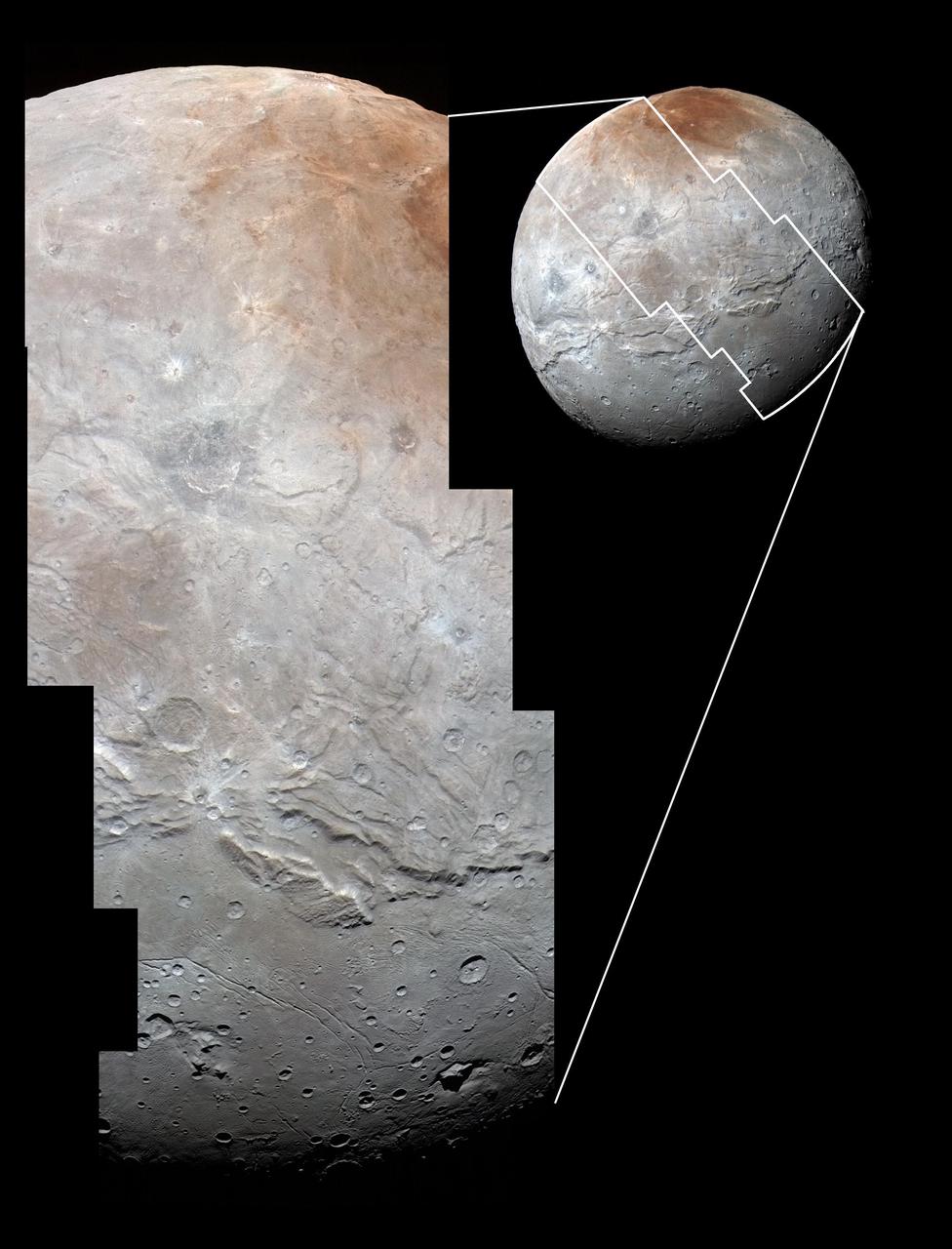

High-resolution images of Charon were taken by the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) on NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, shortly before closest approach on July 14, 2015, and overlaid with enhanced color from the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). Charon's cratered uplands at the top are broken by series of canyons, and replaced on the bottom by the rolling plains of the informally named Vulcan Planum. The scene covers Charon's width of 754 miles (1,214 kilometers) and resolves details as small as 0.5 miles (0.8 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19967

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.

Teams with Astrobotic install the NASA meatball decal on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Peregrine will launch onboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket targeted for no earlier than Dec. 24, 2023, from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The lander will carry a suite of NASA payloads to the Moon as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program.
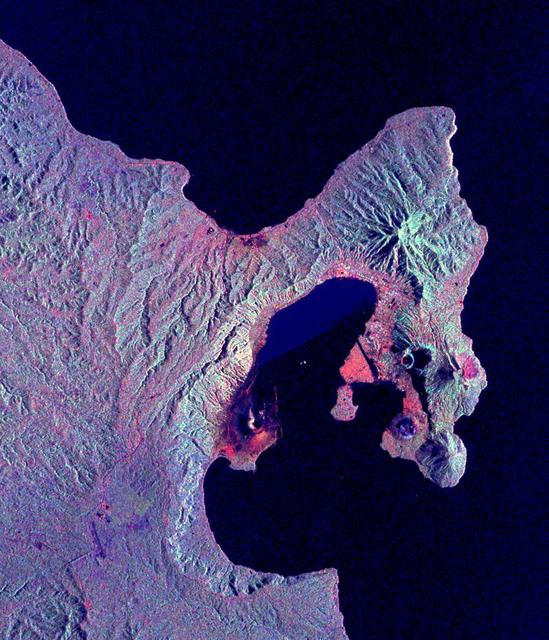

This is a radar image of the Rabaul volcano on the island of New Britain, Papua, New Guinea taken almost a month after its September 19, 1994, eruption that killed five people and covered the town of Rabaul and nearby villages with up to 75 centimeters (30 inches) of ash. More than 53,000 people have been displaced by the eruption. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on its 173rd orbit on October 11, 1994. This image is centered at 4.2 degrees south latitude and 152.2 degrees east longitude in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The area shown is approximately 21 kilometers by 25 kilometers (13 miles by 15.5 miles). North is toward the upper right. The colors in this image were obtained using the following radar channels: red represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received); green represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received); blue represents the C-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received). Most of the Rabaul volcano is underwater and the caldera (crater) creates Blanche Bay, the semi-circular body of water that occupies most of the center of the image. Volcanic vents within the caldera are visible in the image and include Vulcan, on a peninsula on the west side of the bay, and Rabalanakaia and Tavurvur (the circular purple feature near the mouth of the bay) on the east side. Both Vulcan and Tavurvur were active during the 1994 eruption. Ash deposits appear red-orange on the image, and are most prominent on the south flanks of Vulcan and north and northwest of Tavurvur. A faint blue patch in the water in the center of the image is a large raft of floating pumice fragments that were ejected from Vulcan during the eruption and clog the inner bay. Visible on the east side of the bay are the grid-like patterns of the streets of Rabaul and an airstrip, which appears as a dark northwest-trending band at the right-center of the image. Ashfall and subsequent rains caused the collapse of most buildings in the town of Rabaul. Mudflows and flooding continue to pose serious threats to the town and surrounding villages. Volcanologists and local authorities expect to use data such as this radar image to assist them in identifying the mechanisms of the eruption and future hazardous conditions that may be associated with the vigorously active volcano. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01767
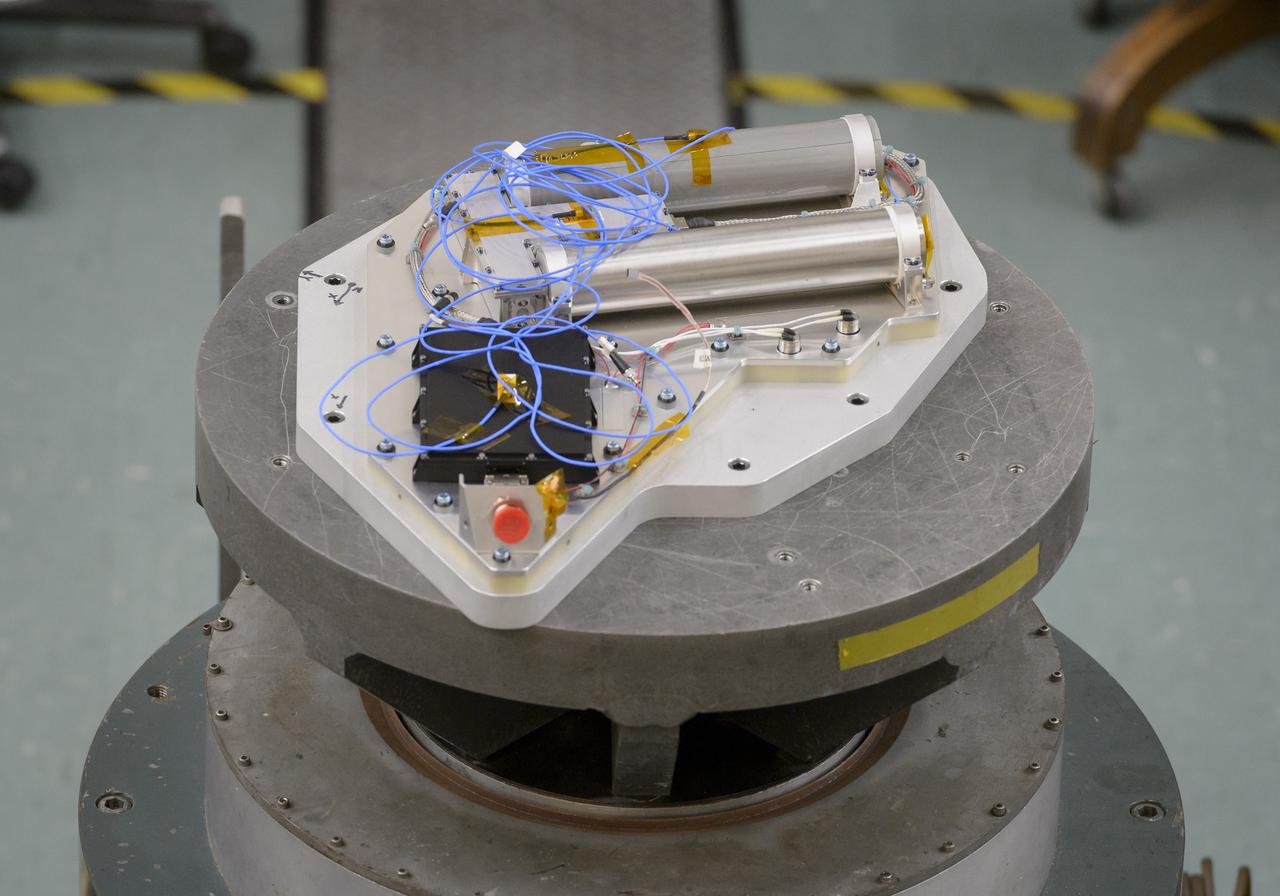
Researchers at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley complete a successful vibration test of the Neutron Spectrometer System or NSS, designed to sniff out water below the surface of the Moon, successfully sailed through a “shake” test to simulate the turbulent conditions of launch. . This is one of the final tests needed to prepare the instrument for a flight to the Moon aboard Astrobotic Technology’s Peregrine lander, as part of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services program. The vibration test simulates the forces the instrument will be subjected to during launch when the lander blasts off aboard a United Launch Alliance Vulcan Centaur rocket. The NSS will fly on the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER.
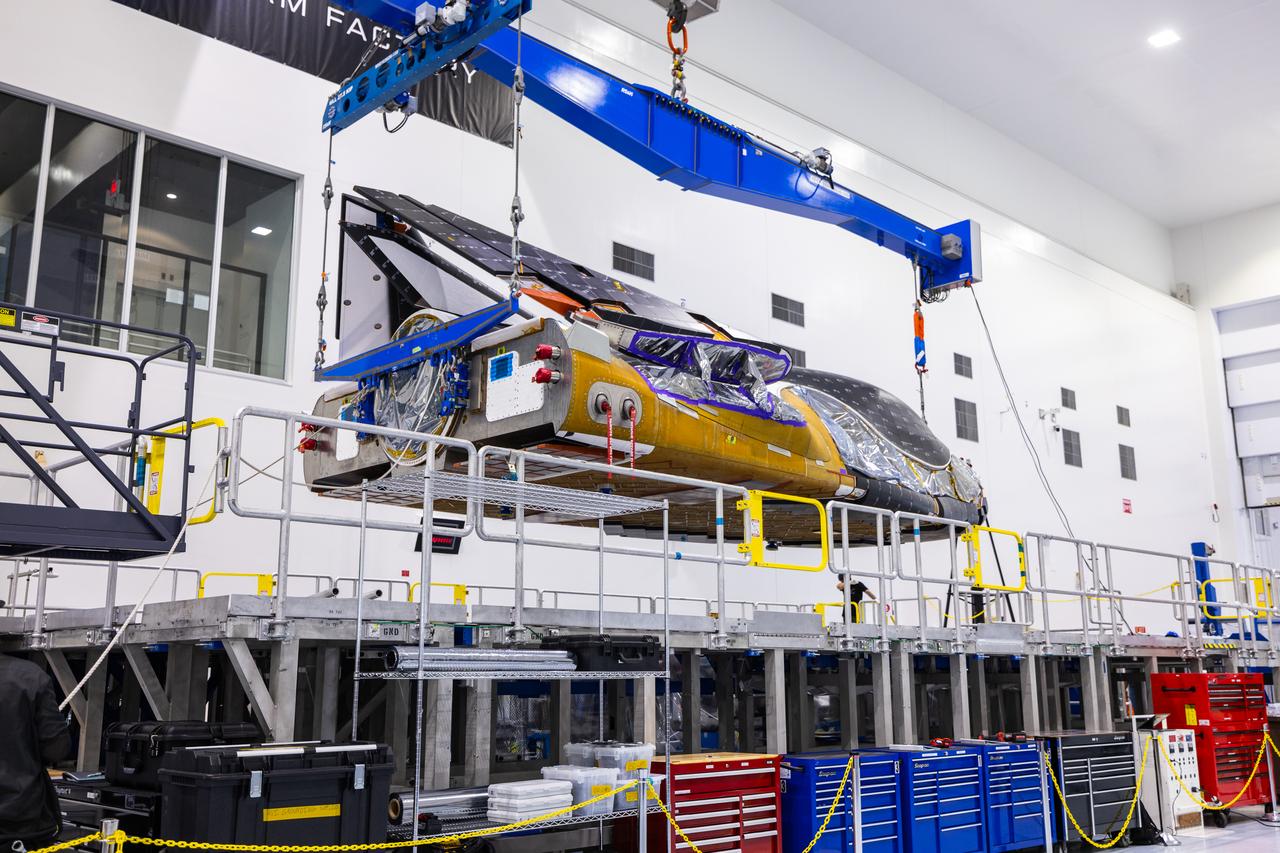

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is lifted and moved by crane inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
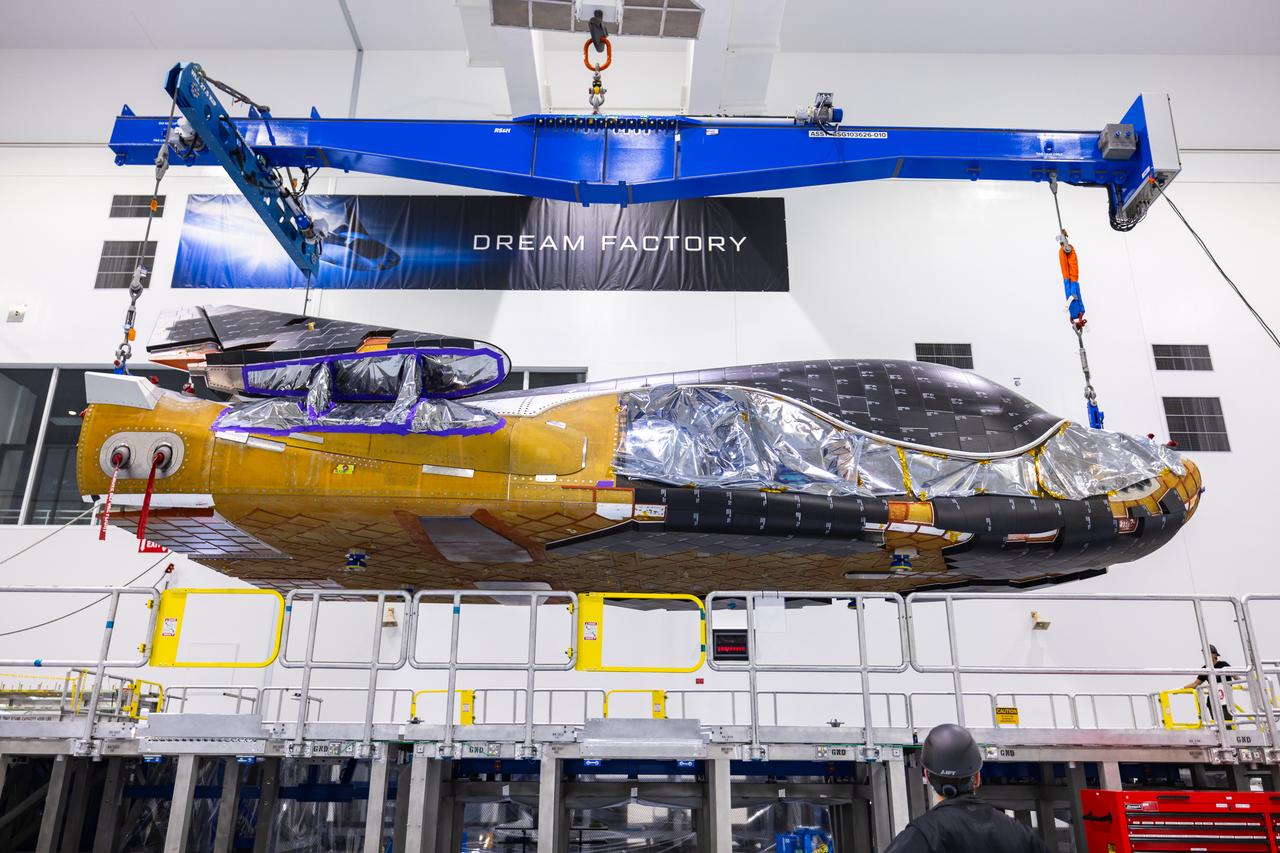

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is lifted and moved by crane inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
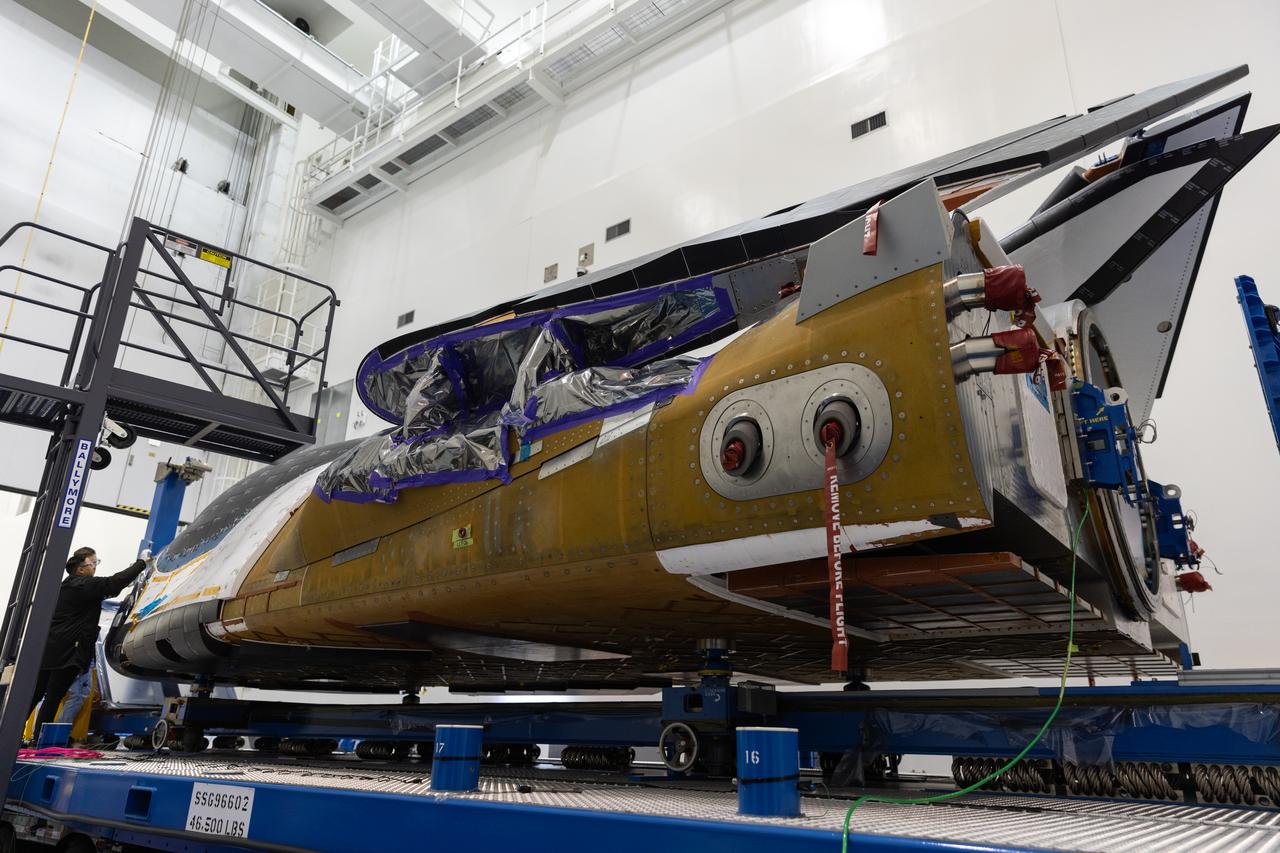

Teams process Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane, inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, following its arrival from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
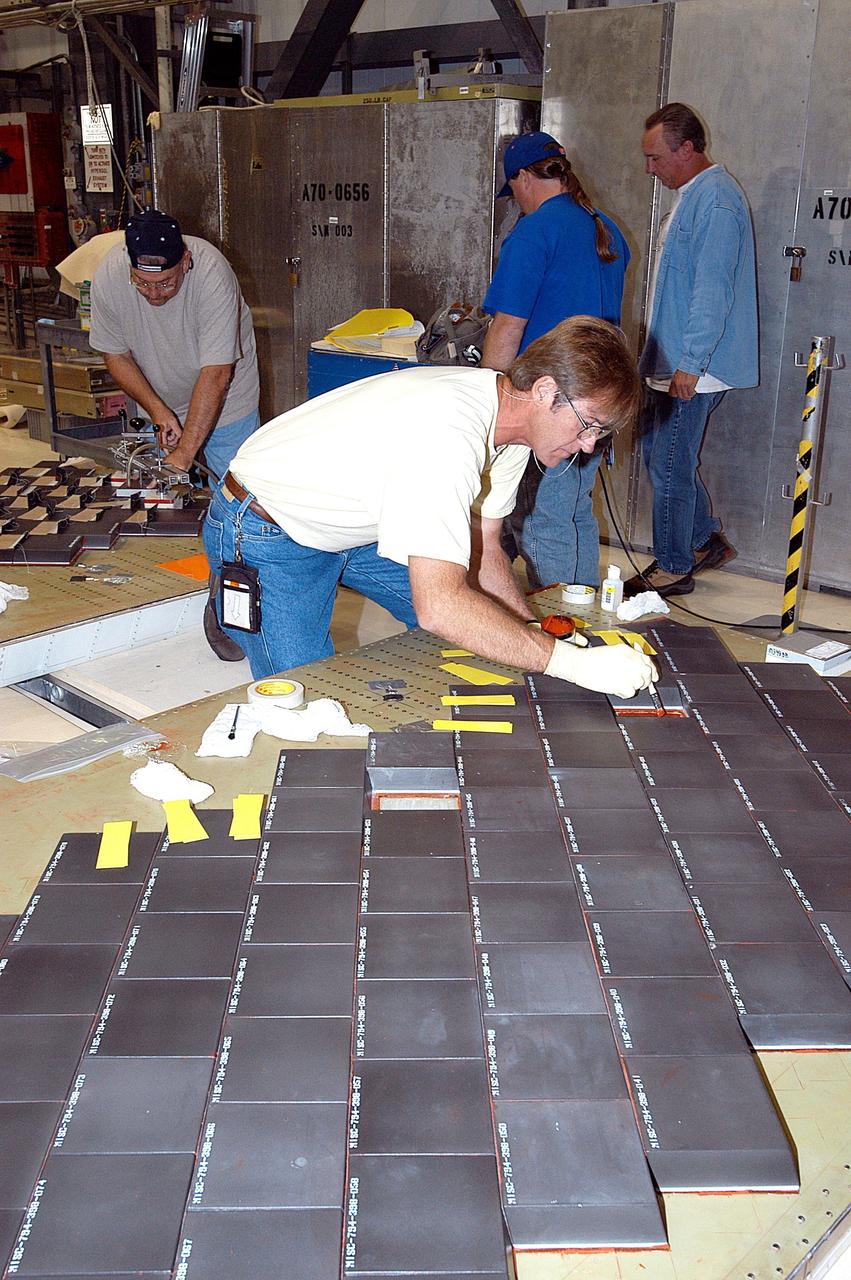

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts applies RTV, a room-temperature vulcanizing silicone adhesive, to a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) on which Thermal Protection System tiles are being installed. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
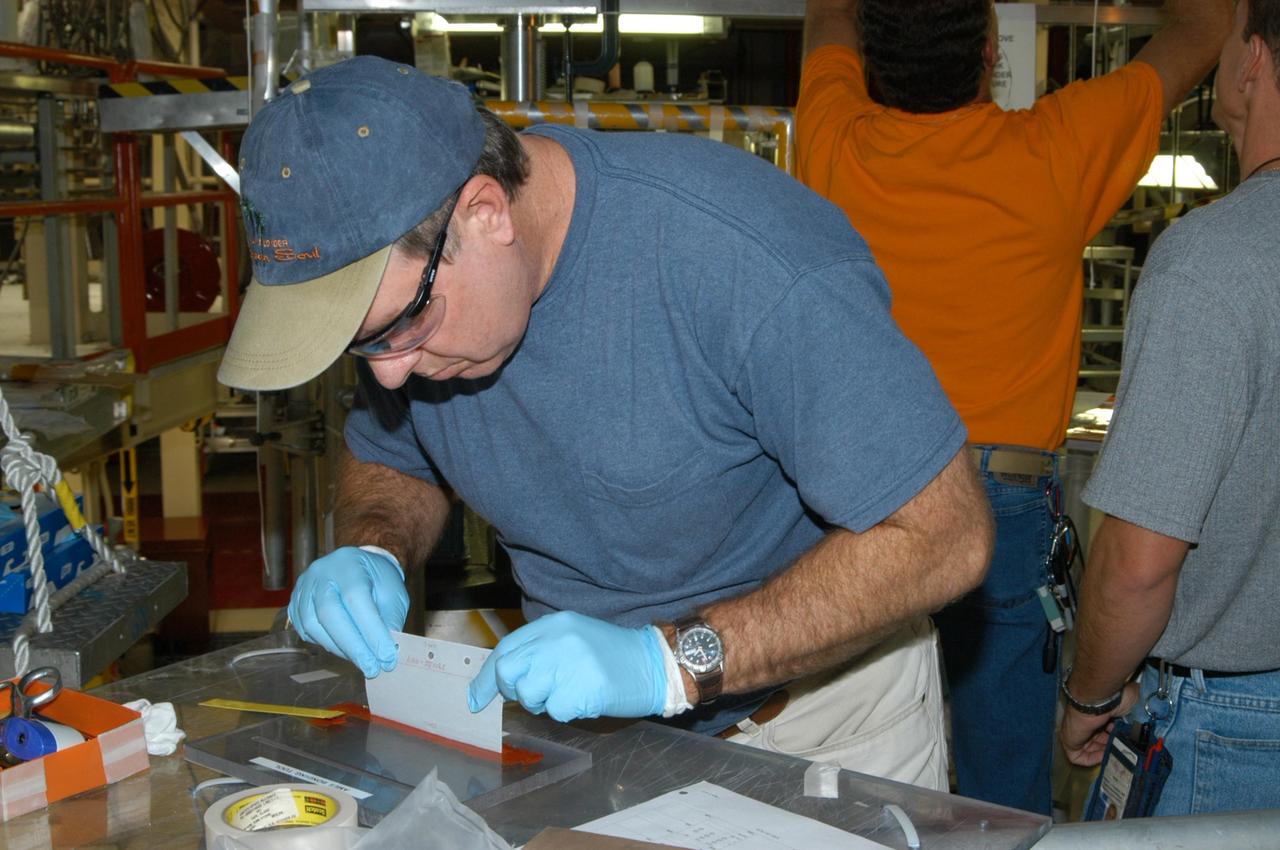

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technician Dell Chapman applies the glue (red) known as RTV, or room temperature vulcanization, to a strip of gap filler before installation on the orbiter Discovery, which is being processed in Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. This work is being performed due to two gap fillers that were protruding from the underside of Discovery on the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114. New installation procedures have been developed to ensure the gap fillers stay in place and do not pose any hazard during the shuttle's re-entry to the atmosphere. Discovery is the scheduled orbiter for the second space shuttle mission in the return-to-flight sequence.
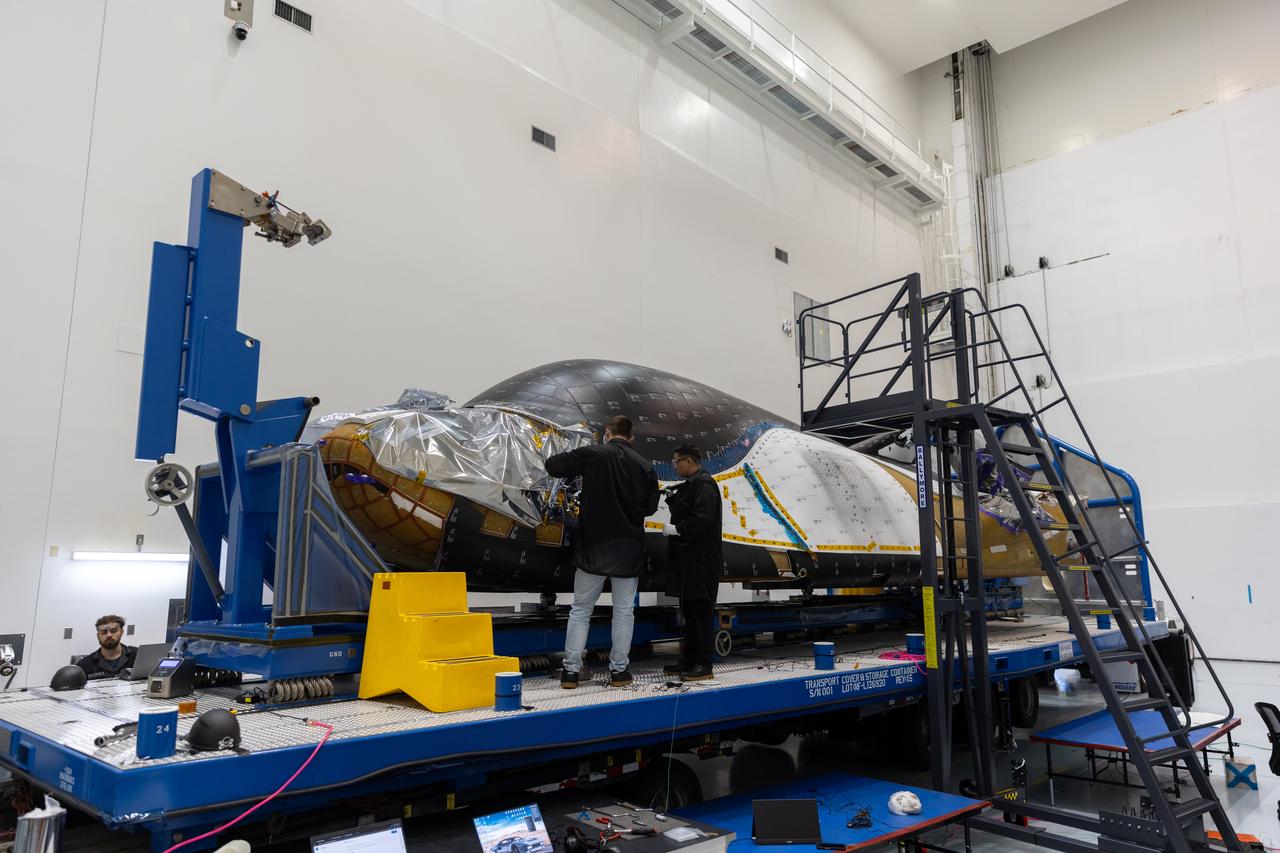

Teams process Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane, inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, following its arrival from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
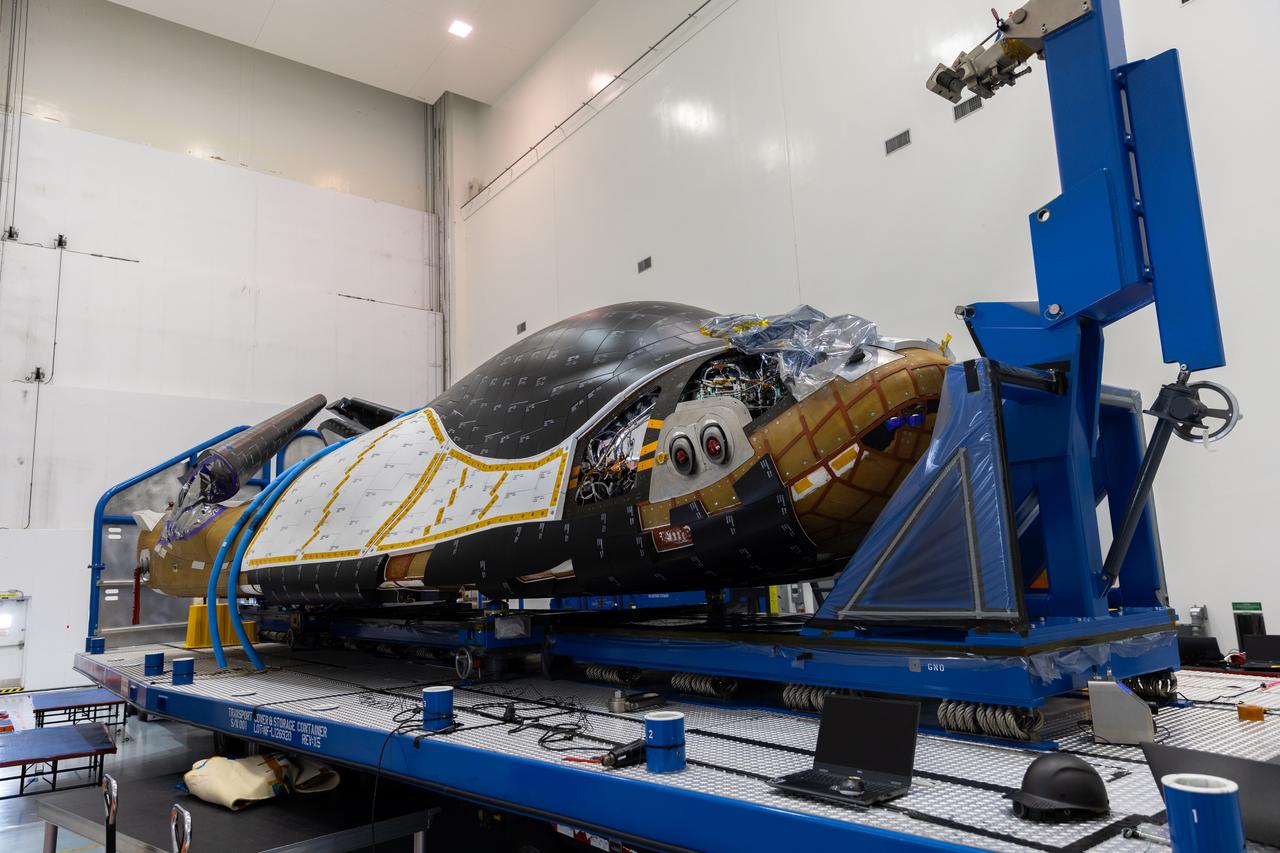

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is processed inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, after arriving by truck inside a climate-controlled transportation container, completing the journey from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
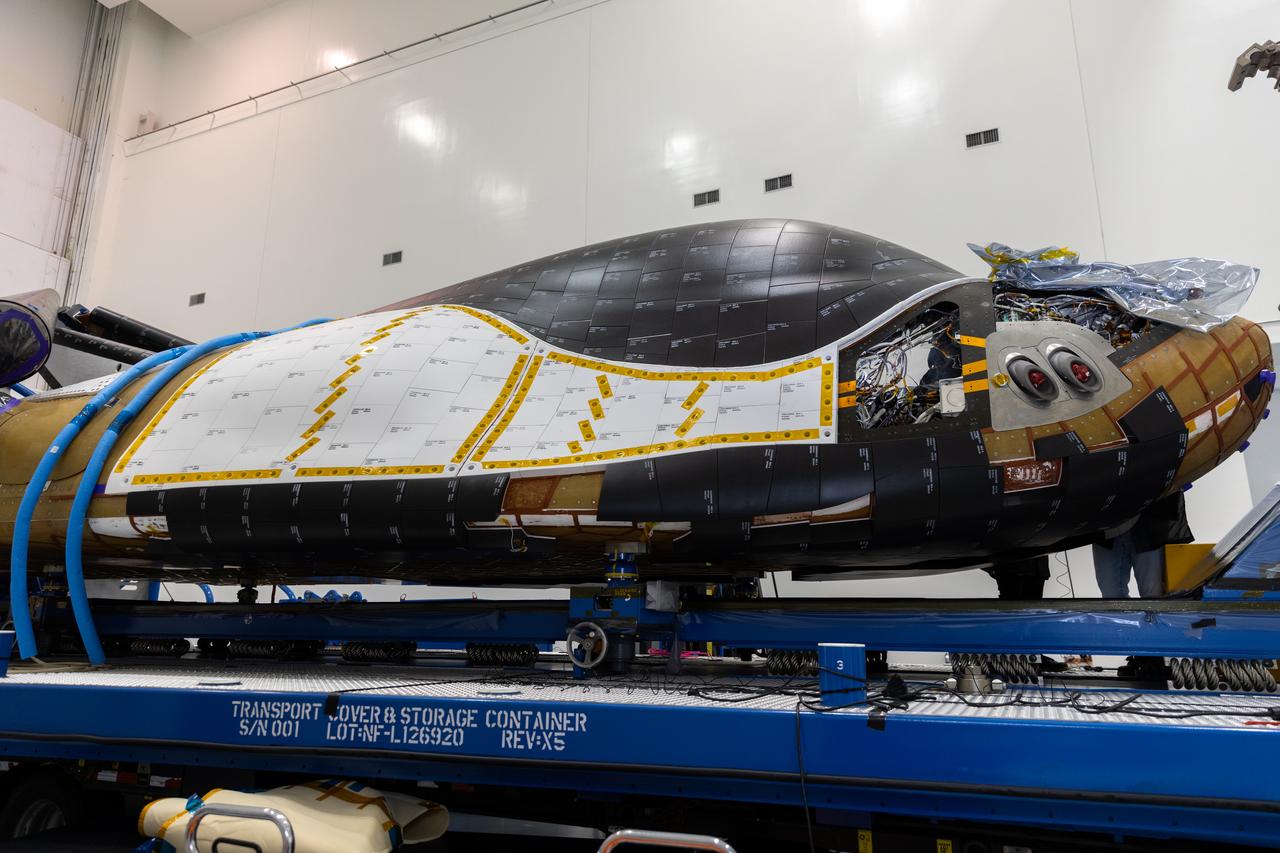

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is processed inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, after arriving by truck inside a climate-controlled transportation container, completing the journey from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
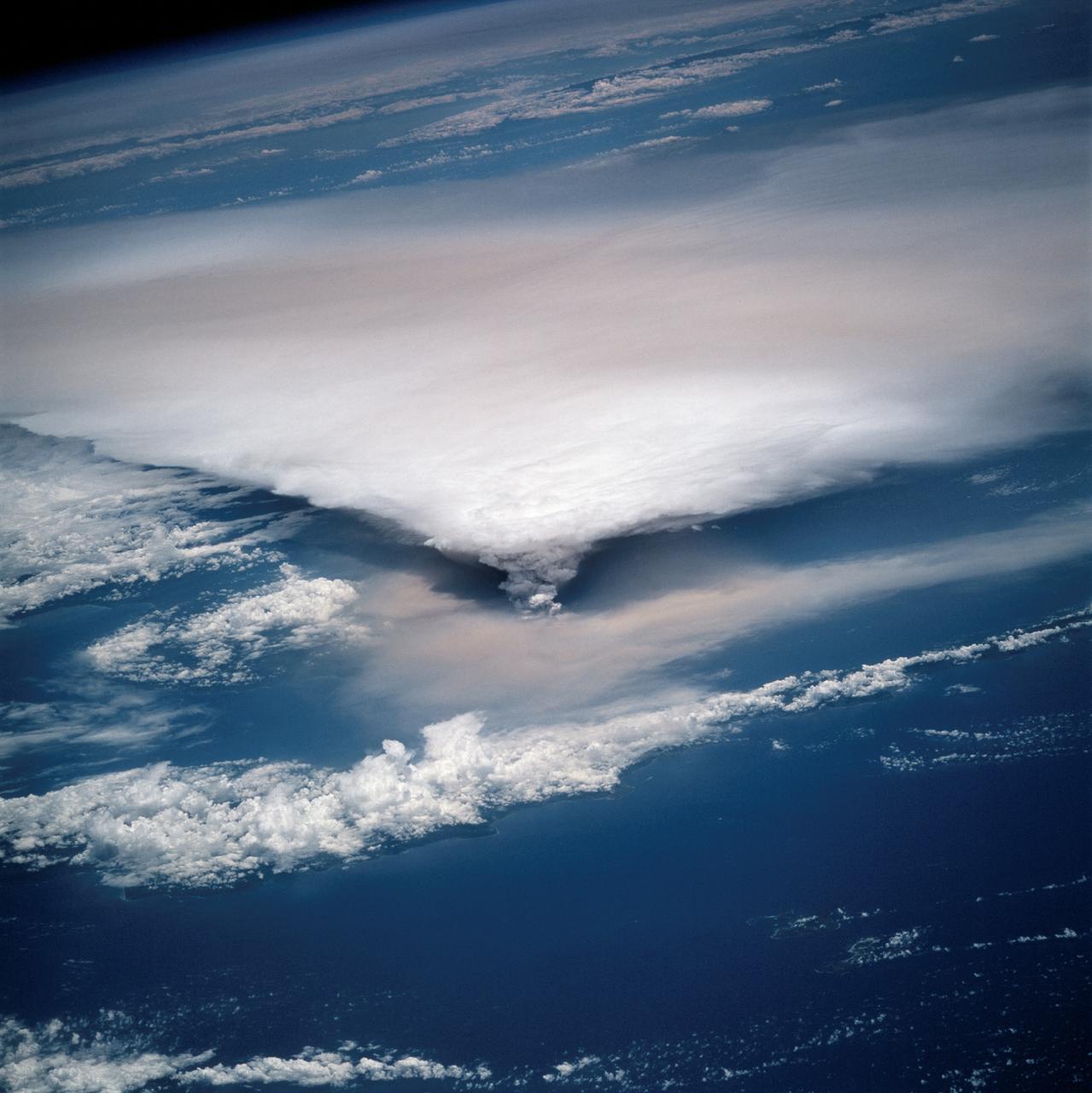

STS064-116-064 (20 Sept. 1994) --- Near the end of the mission, the crew aboard space shuttle Discovery was able to document the beginning of the second day of activity of the Rabaul volcano, on the east end of New Britain. On the morning of Sept. 19, 1994, two volcanic cones on the opposite sides of the 6-kilometer sea crater had begun to erupt with very little warning. Discovery flew just east of the eruption roughly 24 hours after it started and near the peak of its activity. New Ireland, the cloud-covered area in the foreground, lies just east of Rabaul harbor. The eruption, which sent a plume up to over 60,000 feet into the atmosphere, caused over 50,000 people to evacuate the area. Because winds were light at the time of the eruption, most of the ash was deposited in a region within 20 kilometers of the eruption zone. This photo shows the large white billowing eruption plume is carried in a westerly direction by the weak prevailing winds. At the base of the eruption column is a layer of yellow-brown ash being distributed by lower level winds. A sharp boundary moving outward from the center of the eruption in the lower cloud is a pulse of laterally-moving ash which results from a volcanic explosion. Geologists theorize that the large white column and the lower gray cloud are likely from the two main vents on each side of the harbor. The bay and harbor of Rabaul are covered with a layer of ash, possibly partly infilled with volcanic material. Matupit Island and the airport runway have disappeared into the bay. More than a meter of ash has fallen upon the city of Rabaul. Up to five vents were reported to have erupted at once, including the two cones Vulcan and Tavurvur, which are opposites of the harbor as well as new vents below the bay. Half of the Vulcan cone has collapsed into the sea. The extra day in space due to bad weather at the landing site afforded the crew the opportunity for both still and video coverage of the event. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
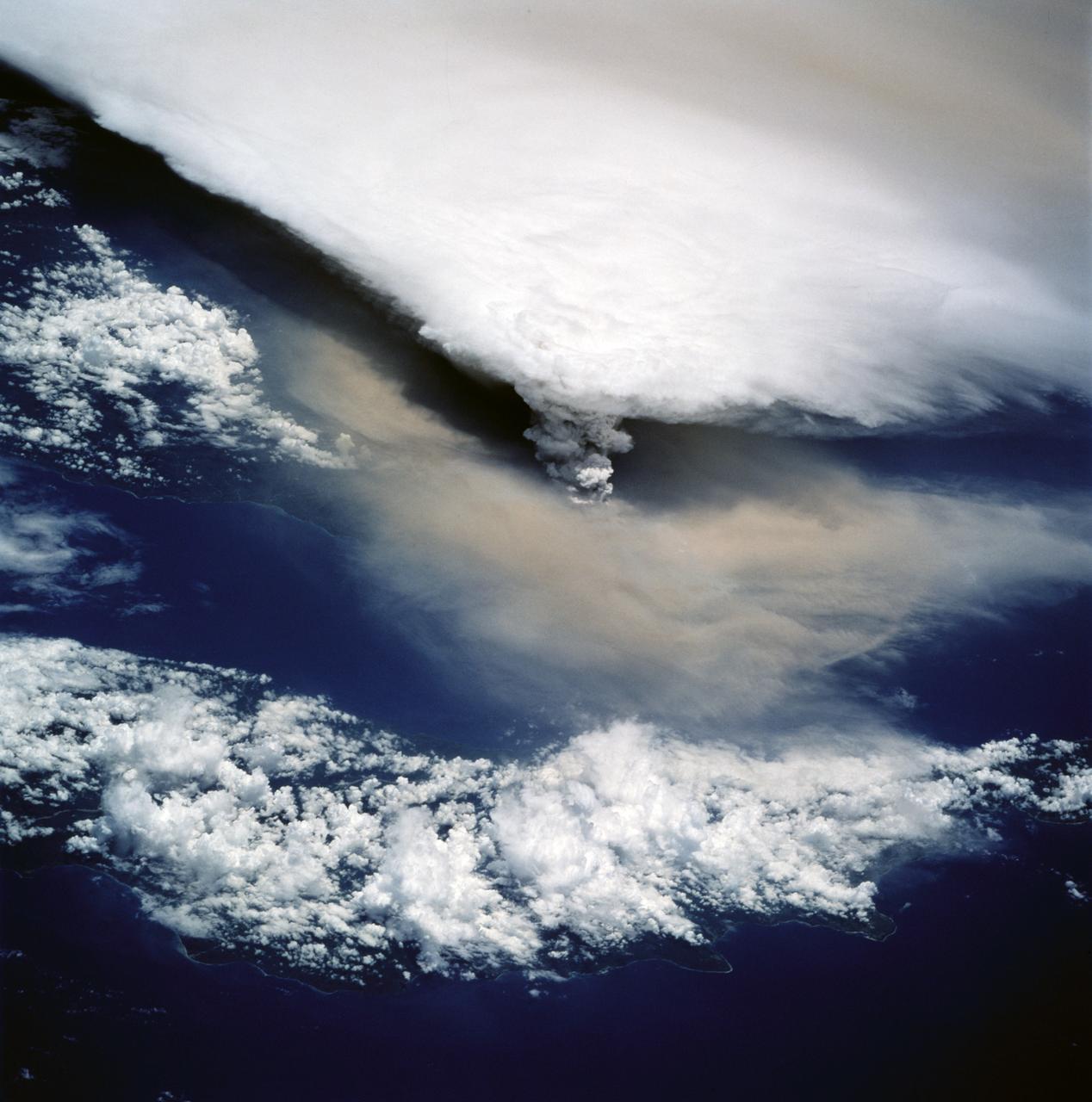

STS064-116-055 (20 Sept. 1994) --- Near the end of its mission, the crew aboard space shuttle Discovery was able to document the beginning of the second day of activity of the Rabaul volcano, on the east end of New Britain. On the morning of Sept. 19, 1994, two volcanic cones on the opposite sides of the 6-kilometer sea crater had begun to erupt with very little warning. Discovery flew just east of the eruption roughly 24 hours after it started and near the peak of its activity. The eruption, which sent a plume up to over 60,000 feet into the atmosphere, caused over 50,000 people to evacuate the area. Because winds were light at the time of the eruption, most of the ash was deposited in a region within 20 kilometers of the eruption zone. This photo shows the large white billowing eruption plume is carried in a westerly direction by the weak prevailing winds. At the base of the eruption column is a layer of yellow-brown ash being distributed by lower level winds. A sharp boundary moving outward from the center of the eruption in the lower cloud is a pulse of laterally-moving ash which results from a volcanic explosion. Geologists theorize that the large white column and the lower gray cloud are likely from the two main vents on each side of the harbor. The cloud-covered island in the foreground is New Ireland. The bay and harbor of Rabaul are covered with a layer of ash, possibly partly infilled with volcanic material. Matupit Island and the airport runway have disappeared into the bay. More than a meter of ash has fallen upon the city of Rabaul. Up to five vents were reported to have erupted at once, including the cones Vulcan and Tavurvur, which are opposites of the harbor as well as new vents below the bay. Half of the Vulcan cone has collapsed into the sea. The extra day in space due to bad weather at the landing site afforded the crew the opportunity for both still and video coverage of the event. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
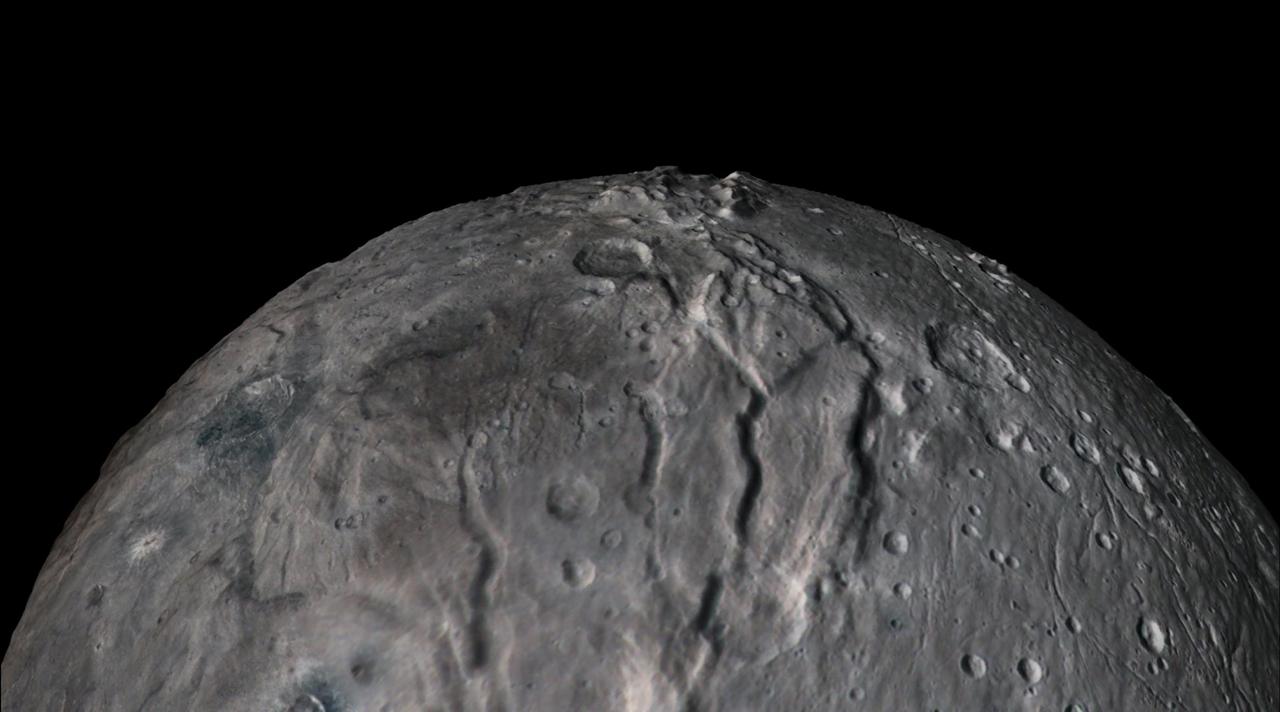

In July 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft sent home the first close-up pictures of Pluto and its moons. Using actual New Horizons data and digital elevation models of Pluto and its largest moon, Charon, mission scientists created flyover movies that offer spectacular new perspectives of the many unusual features that were discovered and which have reshaped our views of the Pluto system -- from a vantage point even closer than a ride on New Horizons itself. The flight over Charon begins high over the hemisphere New Horizons saw on its closest approach, then descends over the deep, wide canyon of Serenity Chasma. The view moves north, passing over Dorothy Gale crater and the dark polar hood of Mordor Macula. The flight then turns back south, covering the northern terrain of Oz Terra before ending over the relatively flat equatorial plains of Vulcan Planum and the "moated mountains" of Clarke Montes. (Note that all feature names are informal.) The topographic relief is exaggerated by a factor of 2 to 3 in these movies to emphasize topography; the surface colors have also been enhanced to bring out detail. Digital mapping and rendering were performed by Paul Schenk and John Blackwell of the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston. A video is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21864

Engineer Emmanuel Decrossas of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California makes an adjustment to an antenna's connector, part of a NASA telecommunications payload called User Terminal, at Firefly Aerospace's facility in Cedar Park, Texas, in August 2025. Figure A (https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/figures/PIA26596_figA.jpg) shows members of the team from JPL and NASA (dark blue) and Firefly (white) with the User Terminal antenna, radio, and other components on the bench behind them. Managed by JPL, the User Terminal will test a new, low-cost lunar communications system that future missions to the Moon's far side could use to transfer data to and from Earth via lunar relay satellite. The User Terminal payload will be installed atop Firefly's Blue Ghost Mission 2 lunar lander, which is slated to launch to the Moon's far side in 2026 under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. NASA's Apollo missions brought large and powerful telecommunications systems to the lunar near-side surface to communicate directly with Earth. But spacecraft on the far side will not have that option because only the near side of the Moon is visible to Earth. Sending messages between the Moon and Earth via a relay orbiter enables communication with the lunar far side and improves it at the Moon's poles. The User Terminal will for the first time test such a setup for NASA by using a compact, lightweight software defined radio, antenna, and related hardware to communicate with a satellite that Blue Ghost Mission 2 is delivering to lunar orbit: ESA's (the European Space Agency's) Lunar Pathfinder. The User Terminal radio and antenna installed on the Blue Ghost lander will be used to commission Lunar Pathfinder, sending test data back and forth. After the lander ceases operations as planned at the end of a single lunar day (about 14 Earth days), a separate User Terminal radio and antenna installed on LuSEE-Night – another payload on the lander – will send LuSEE-Night's data to Lunar Pathfinder, which will relay the information to a commercial network of ground stations on Earth. LuSEE-Night is a radio telescope that expected to operate for at least 1½ years; it is a joint effort by NASA, the U.S. Department of Energy, and University of California, Berkeley's Space Sciences Laboratory. Additionally, User Terminal will be able to communicate with another satellite that's being delivered to lunar orbit by Blue Ghost Mission 2: Firefly's own Elytra Dark orbital vehicle. The hardware on the lander is only part of the User Terminal project, which was also designed to implement a new S-band two-way protocol, or standard, for short-range space communications between entities on the lunar surface (such as rovers and landers) and lunar orbiters, enabling reliable data transfer between them. The standard is a new version of a space communications protocol called Proximity-1 that was initially developed more than two decades ago for use at Mars by an international standard body called the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS), of which NASA is a member agency. The User Terminal team made recommendations to CCSDS on the development of the new lunar S-band standard, which was specified in 2024. The new standard will enable lunar orbiters and surface spacecraft from various entities – NASA and other civil space agencies as well as industry and academia – to communicate with each other, a concept known as interoperability. At Mars, NASA rovers communicate with various Red Planet orbiters using the Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) radio band version of the Proximity-1 standard. On the Moon's far side, use of UHF is reserved for radio astronomy science; so a new lunar standard was needed using a different frequency range, S-band, as were more efficient modulation and coding schemes to better fit the available frequency spectrum specified by the new standard. User Terminal is funded by NASA's Exploration Science Strategy and Integration Office, part of the agency's Science Mission Directorate, which manages the CLPS initiative. JPL manages the project and supported development of the new S-band radio standard and the payload in coordination with Vulcan Wireless in Carlsbad, California, which built the radio. Caltech in Pasadena manages JPL for NASA. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26596