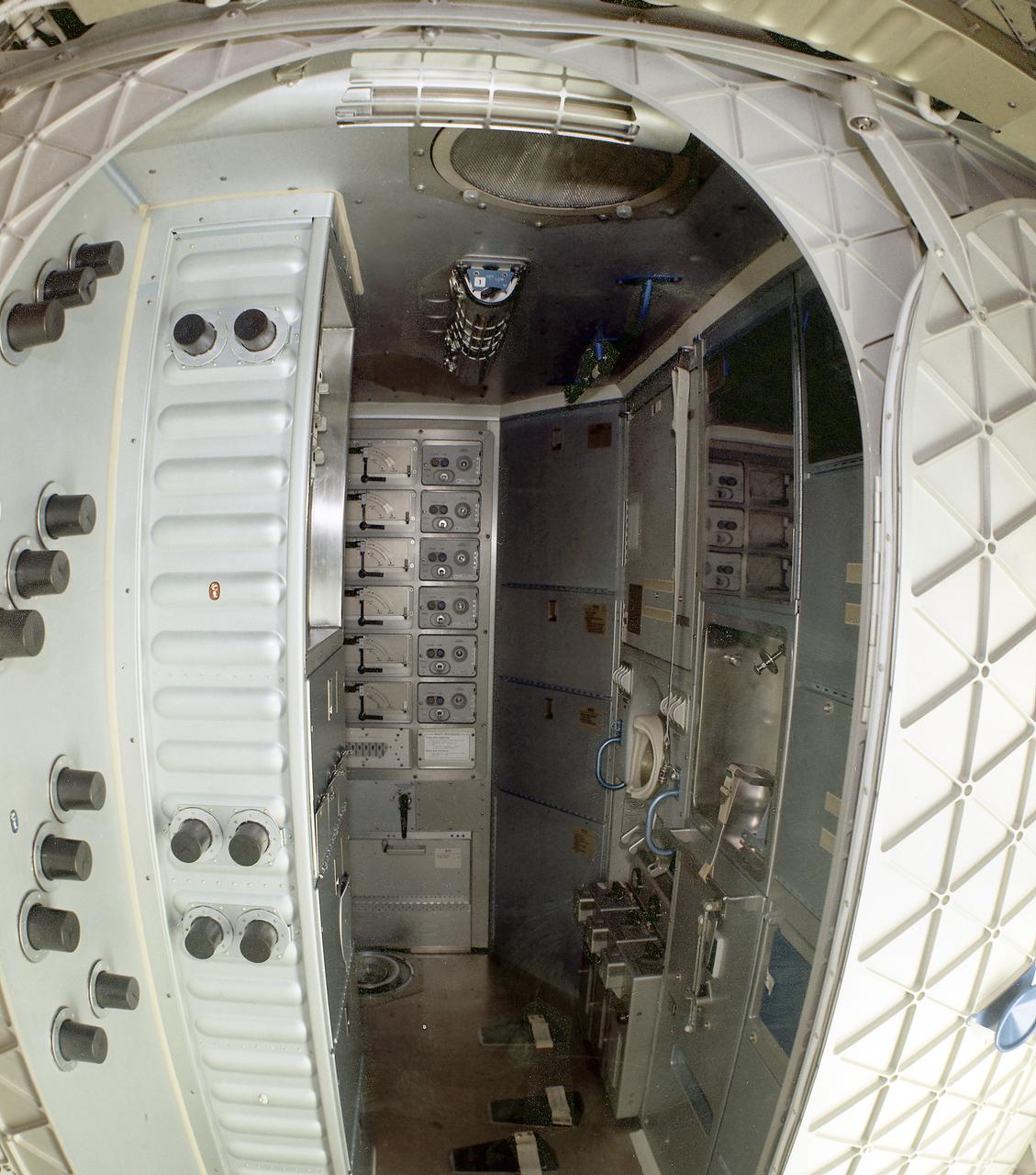

This image is a wide-angle view of the Orbital Workshop waste management compartment. The waste management facilities presented a unique challenge to spacecraft designers. In addition to collection of liquid and solid human wastes, there was a medical requirement to dry all solid human waste products and to return the residue to Earth for examination. Liquid human waste (urine) was frozen for return to Earth. Total quantities of each astronaut's liquid and solid wastes were precisely measured. Cabin air was drawn into the toilet, shown on the wall at right in this photograph, and over the waste products to generate a flow of the waste in the desired direction. The air was then filtered for odor control and antiseptic purposes prior to being discharged back into the cabin.
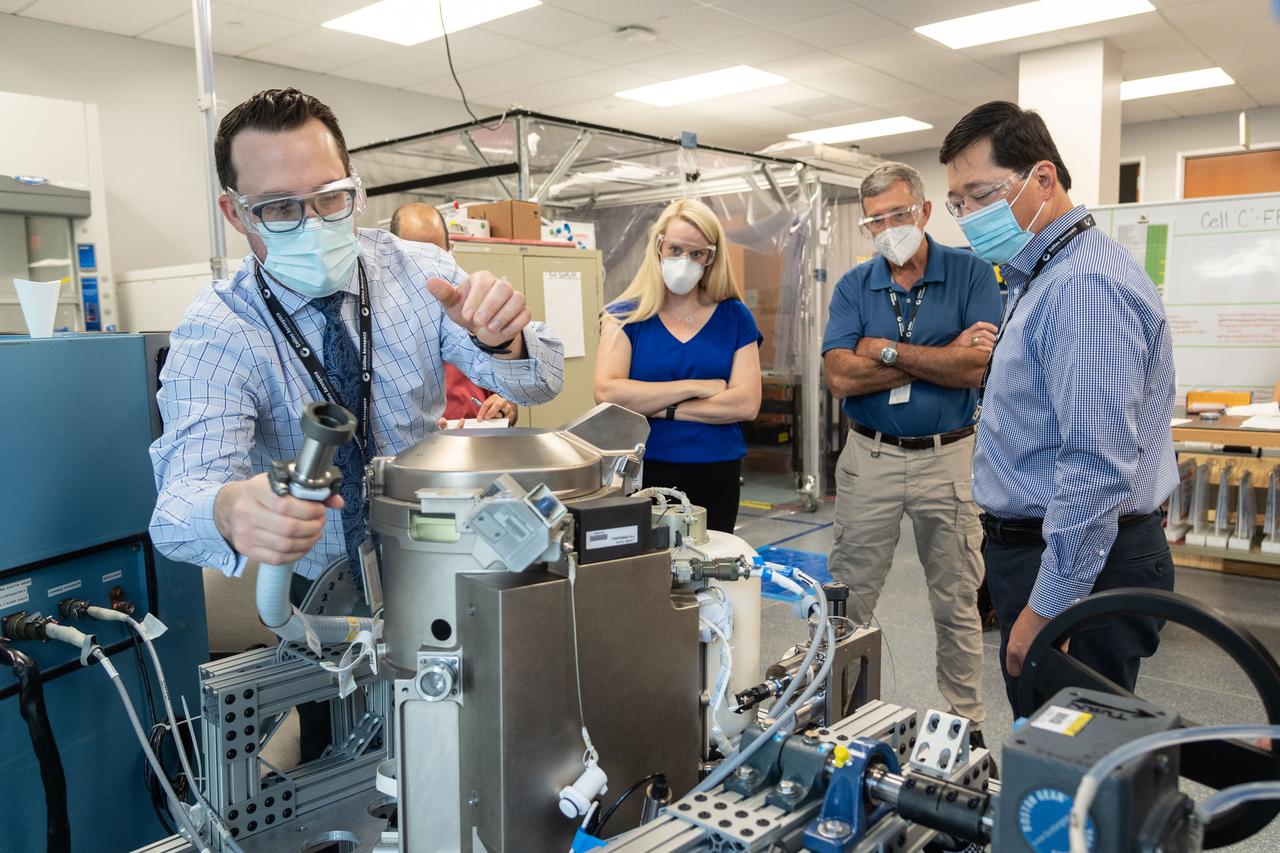

jsc2020e026648 (June 18, 2020) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins and support personnel review the Universal Waste Management System, the advanced space toilet due to be delivered to the International Space Station in October aboard Northrop Grumman's Cygnus space freighter.
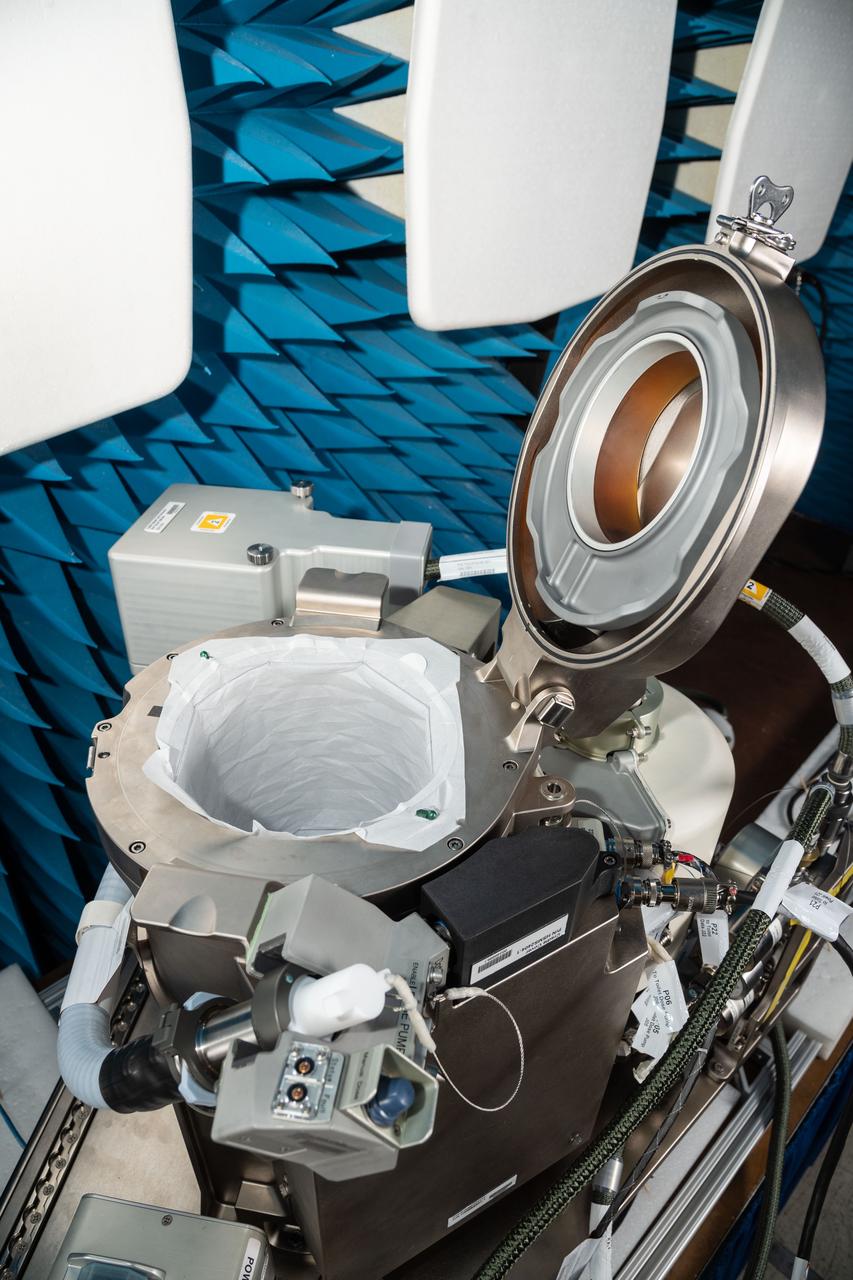

jsc2019e070461 (12/13/2019) --- A preflight view taken of the ISS Universal Waste Management System, Unit 1 during EMI/EMC Testing. This technology provides additional waste disposal points to the International Space Station (ISS) and aids in planning for future exploration missions including Deep Space Gateway (DSG). A smaller, more comfortable and more reliable waste-disposal method allows the crew to focus on other activities and enables further exploration in space.
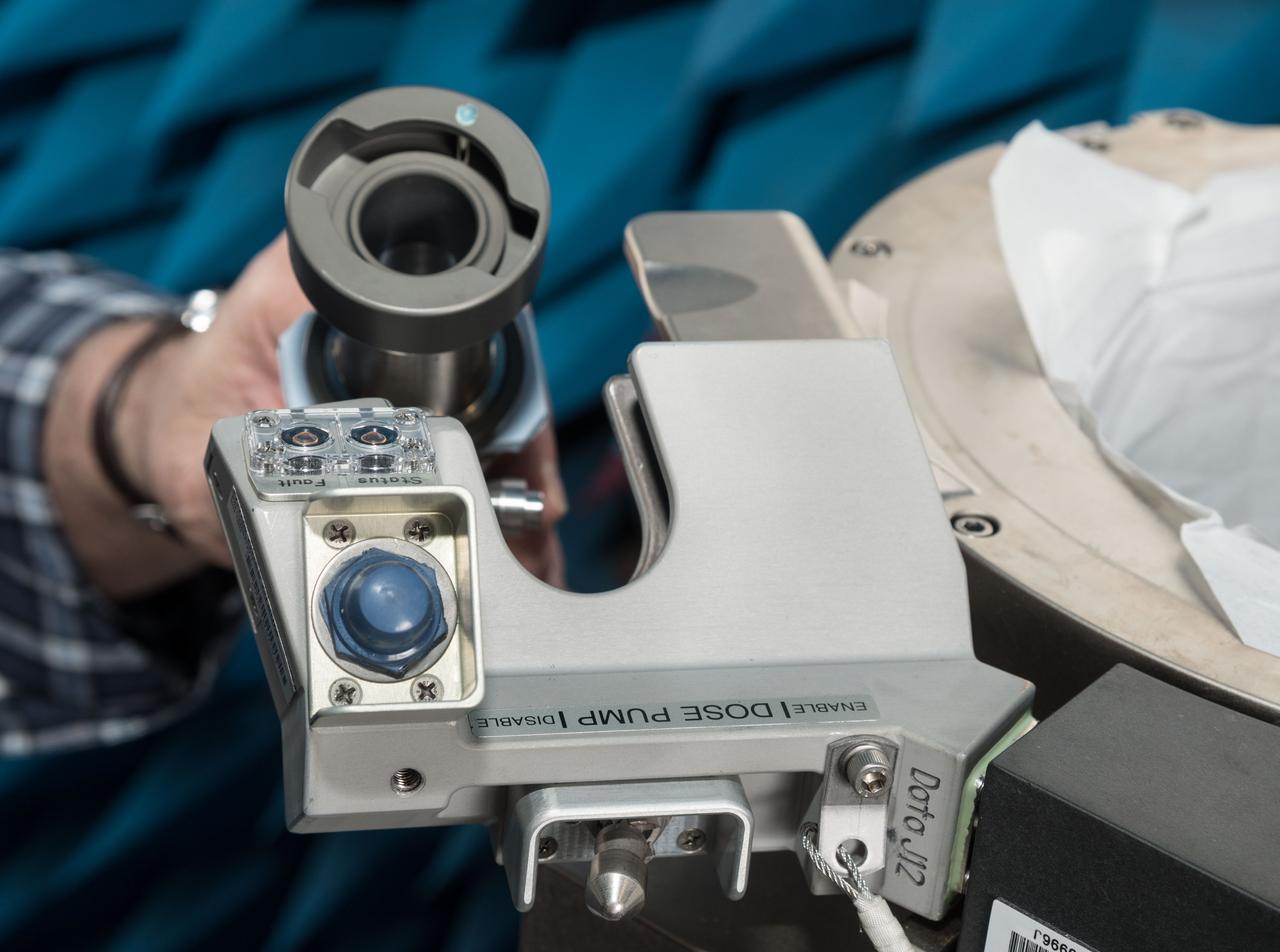

jsc2019e070463 (12/13/2019) --- A preflight view taken of the ISS Universal Waste Management System, Unit 1 during EMI/EMC Testing. This technology provides additional waste disposal points to the International Space Station (ISS) and aids in planning for future exploration missions including Deep Space Gateway (DSG). A smaller, more comfortable and more reliable waste-disposal method allows the crew to focus on other activities and enables further exploration in space.
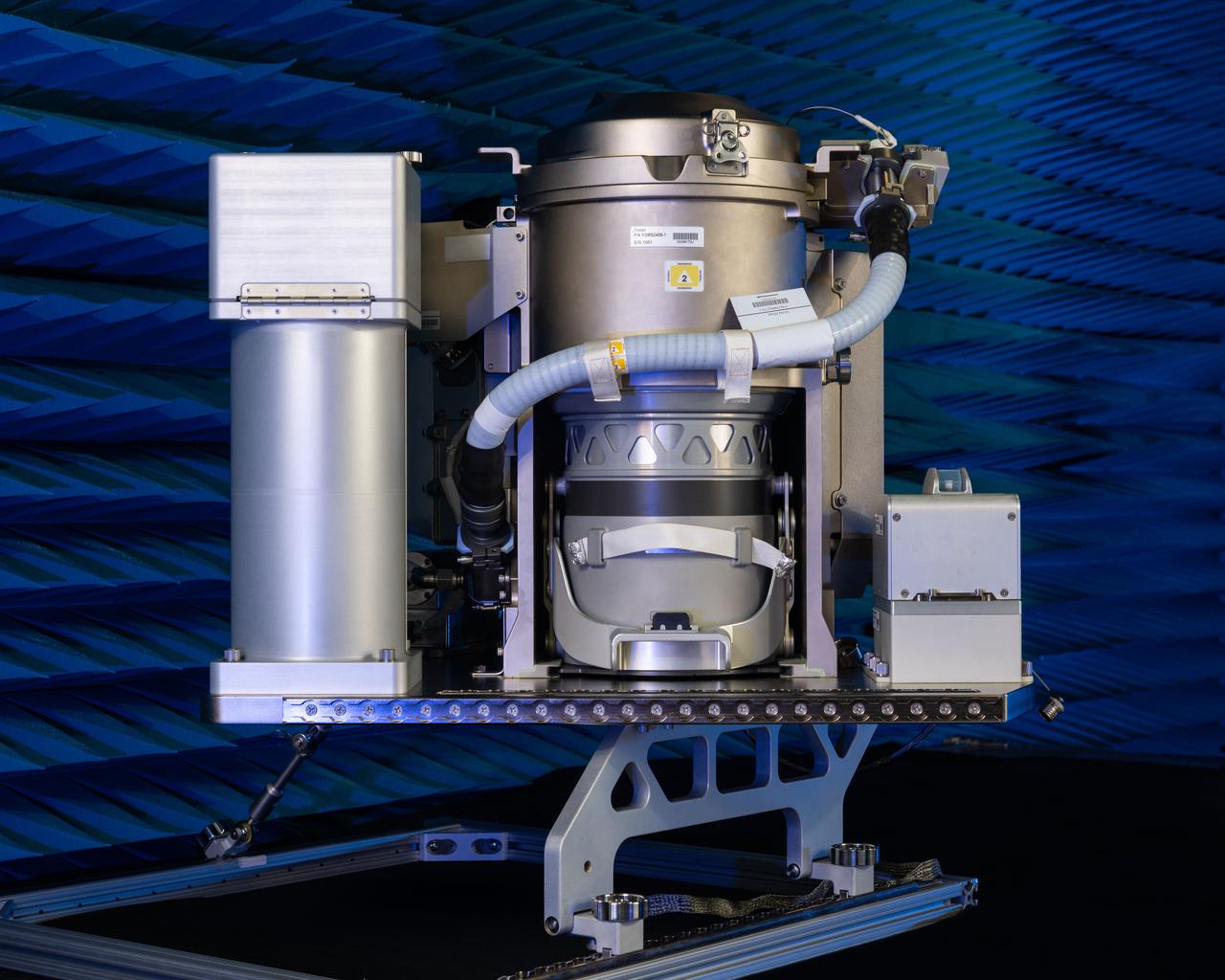

jsc2019e070684_alt (12/16/2019) --- A preflight view taken of the ISS Universal Waste Management System, Unit 1 during EMI/EMC Testing. This technology provides additional waste disposal points to the International Space Station (ISS) and aids in planning for future exploration missions including Deep Space Gateway (DSG). A smaller, more comfortable and more reliable waste-disposal method allows the crew to focus on other activities and enables further exploration in space.
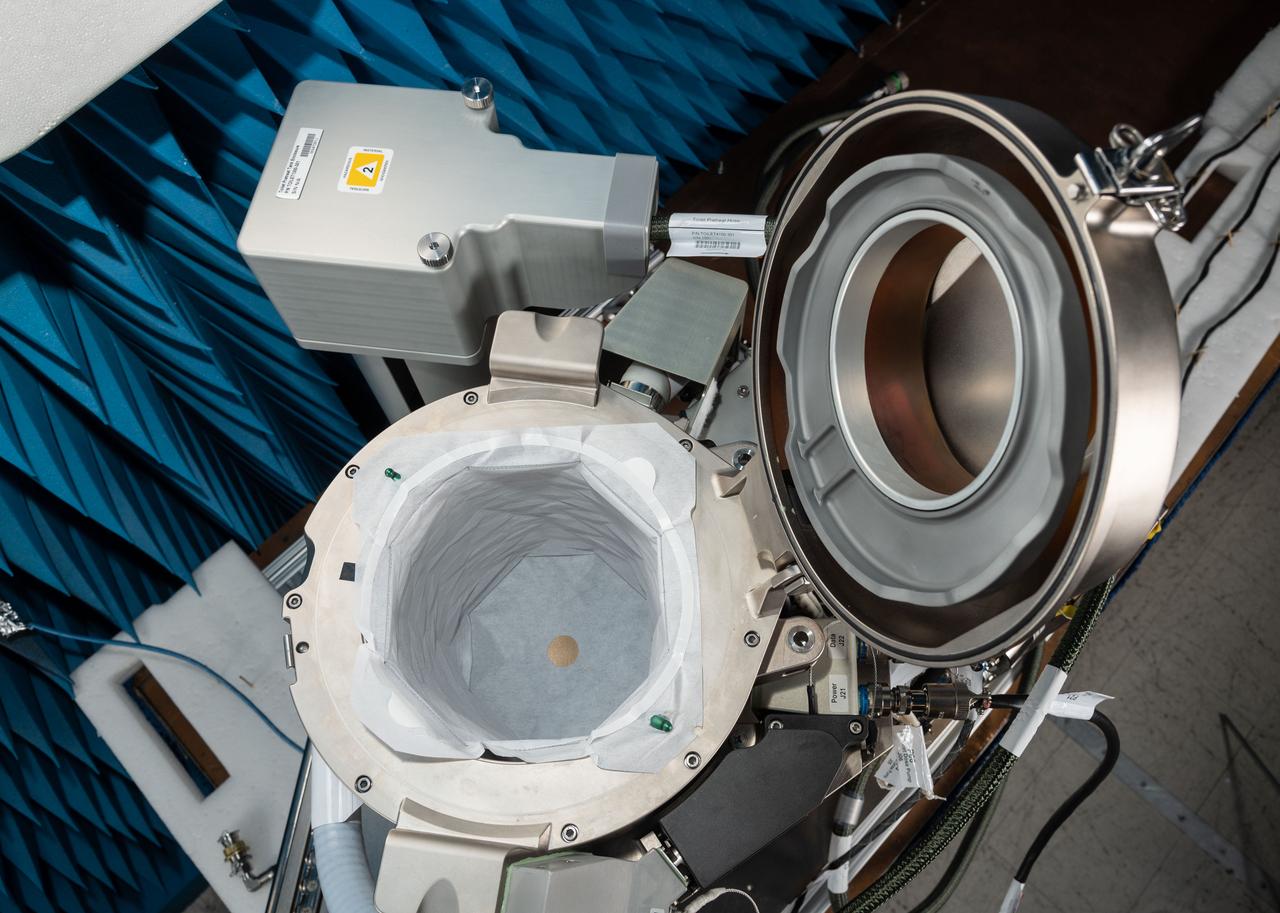
jsc2019e070462 (12/13/2019) --- A preflight view taken of the ISS Universal Waste Management System, Unit 1 during EMI/EMC Testing. This technology provides additional waste disposal points to the International Space Station (ISS) and aids in planning for future exploration missions including Deep Space Gateway (DSG). A smaller, more comfortable and more reliable waste-disposal method allows the crew to focus on other activities and enables further exploration in space.
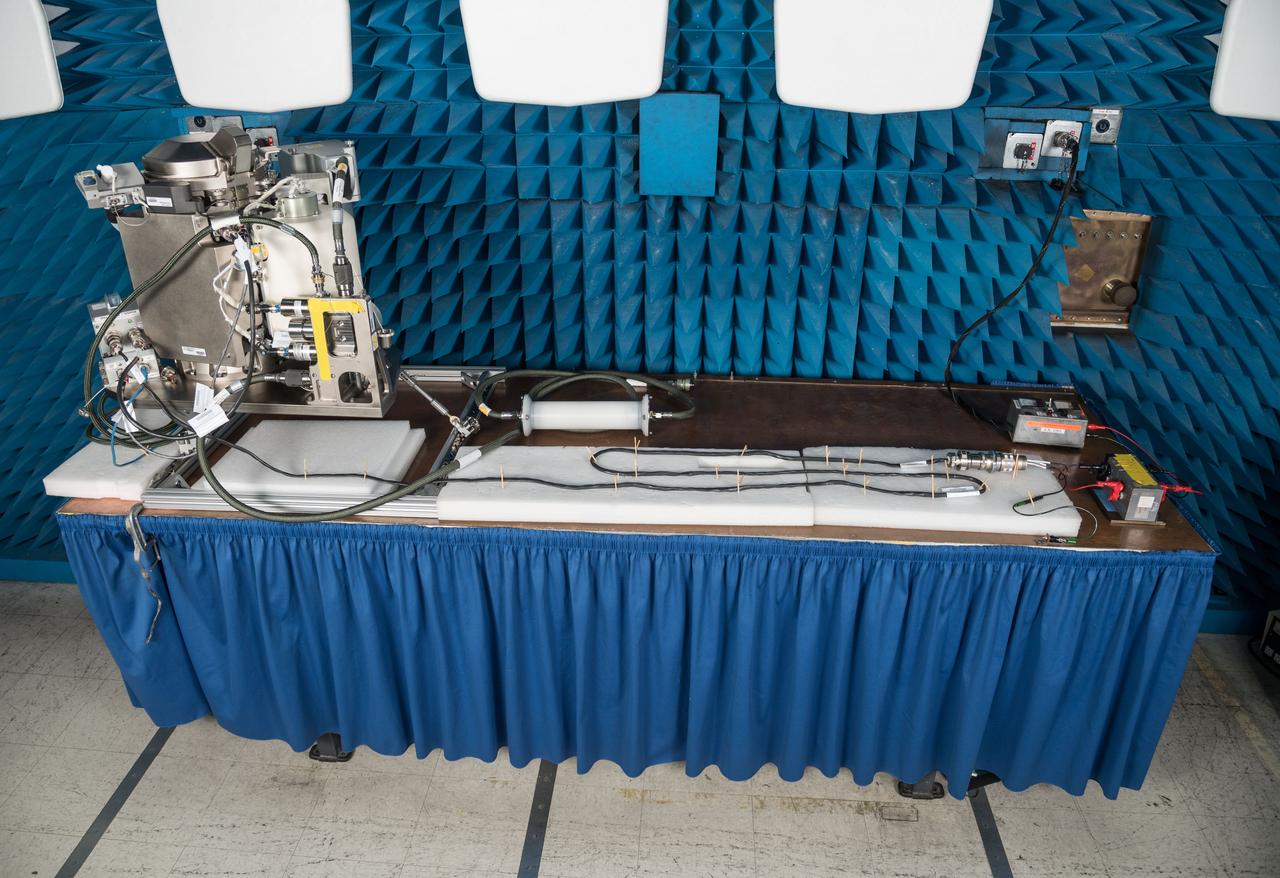

jsc2019e070457 (12/13/2019) --- A preflight view taken of the ISS Universal Waste Management System, Unit 1 during EMI/EMC Testing. This technology provides additional waste disposal points to the International Space Station (ISS) and aids in planning for future exploration missions including Deep Space Gateway (DSG). A smaller, more comfortable and more reliable waste-disposal method allows the crew to focus on other activities and enables further exploration in space.
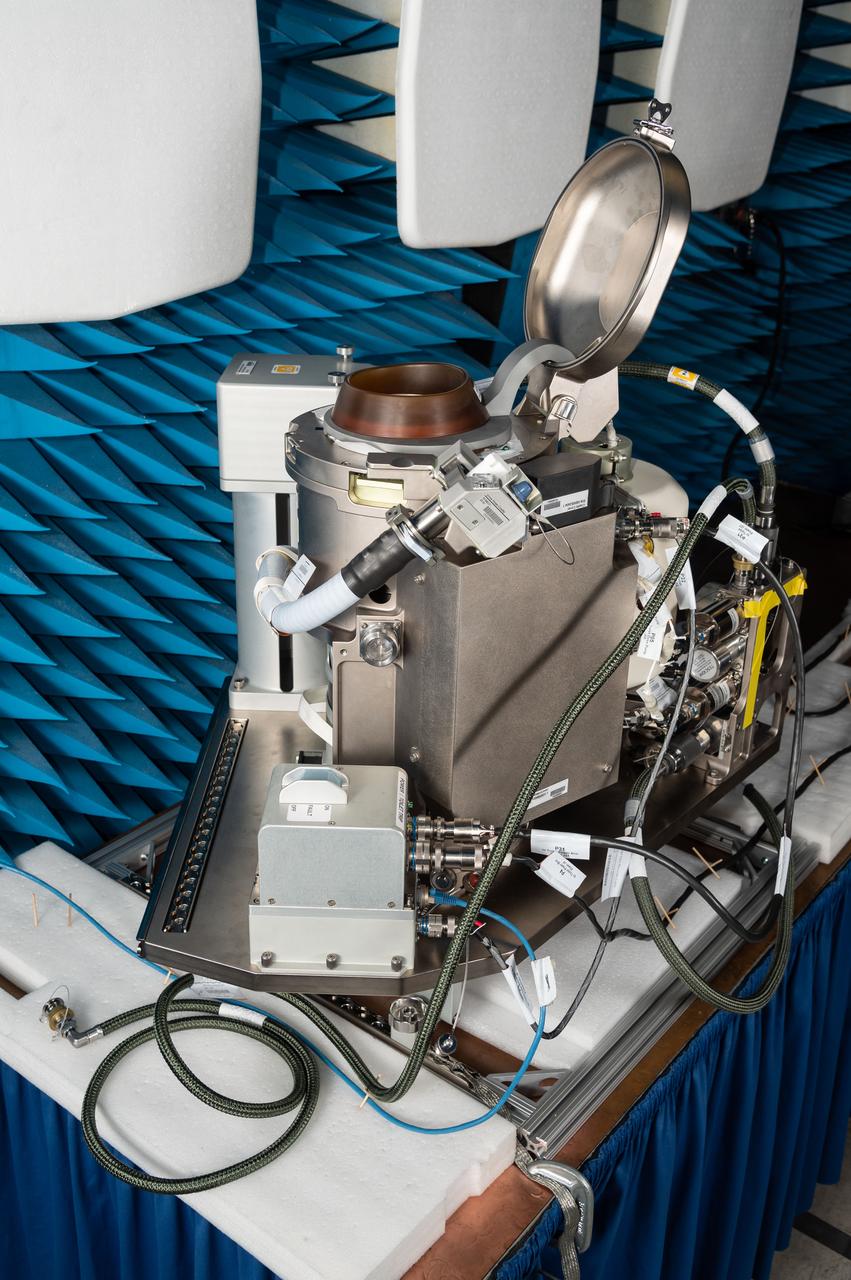

jsc2019e070459 (12/13/2019) --- A preflight view taken of the ISS Universal Waste Management System, Unit 1 during EMI/EMC Testing. This technology provides additional waste disposal points to the International Space Station (ISS) and aids in planning for future exploration missions including Deep Space Gateway (DSG). A smaller, more comfortable and more reliable waste-disposal method allows the crew to focus on other activities and enables further exploration in space.
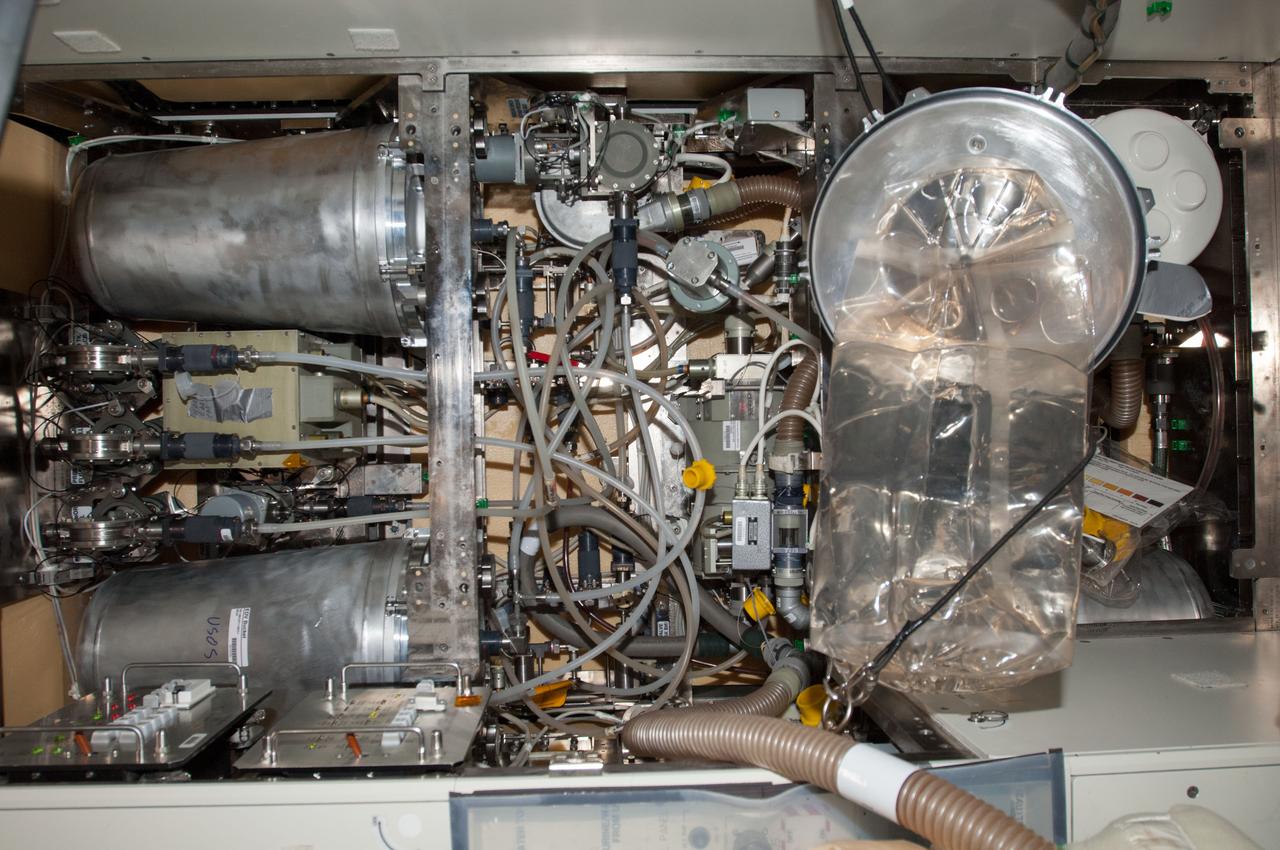

Internal view of Waste and Hygiene Compartment (WHC) taken during maintenance by the Expedition 40 crew.
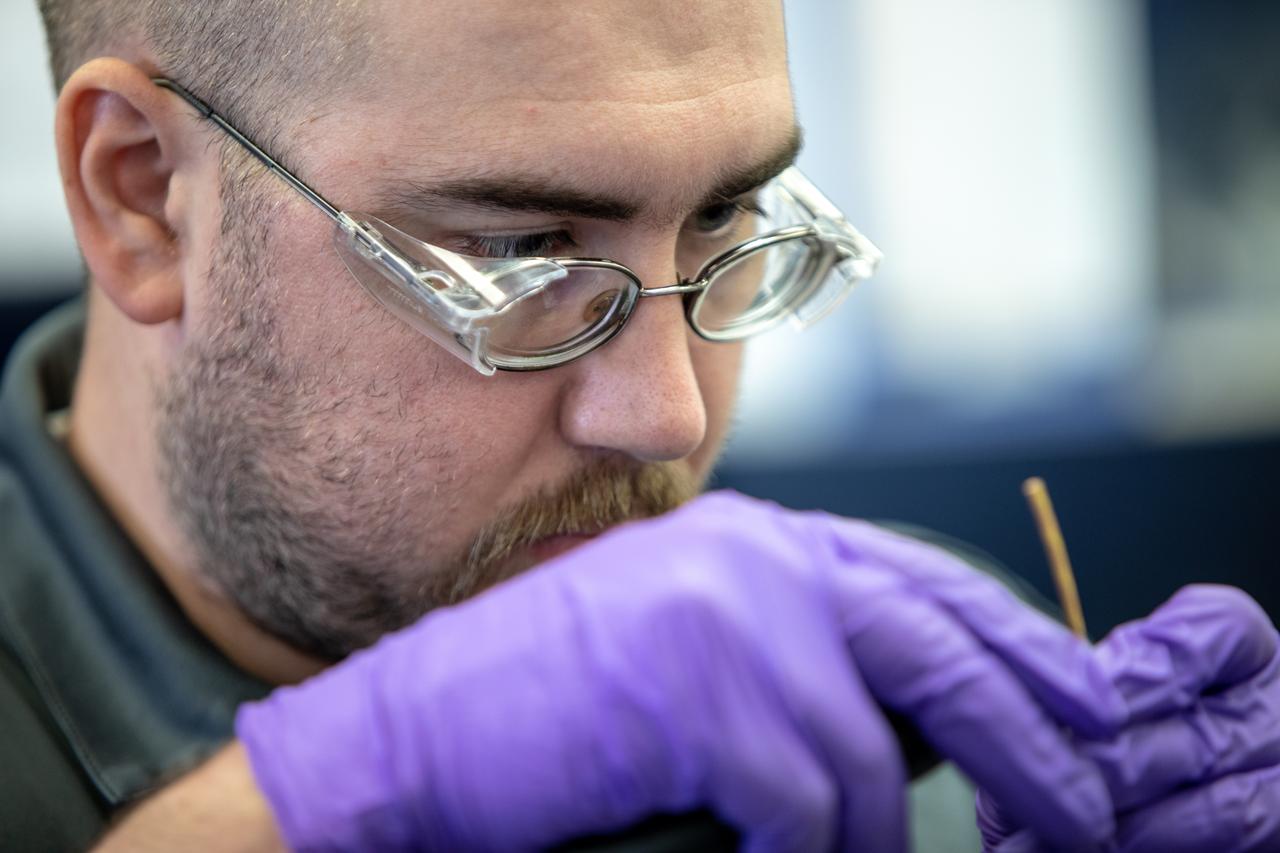

Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
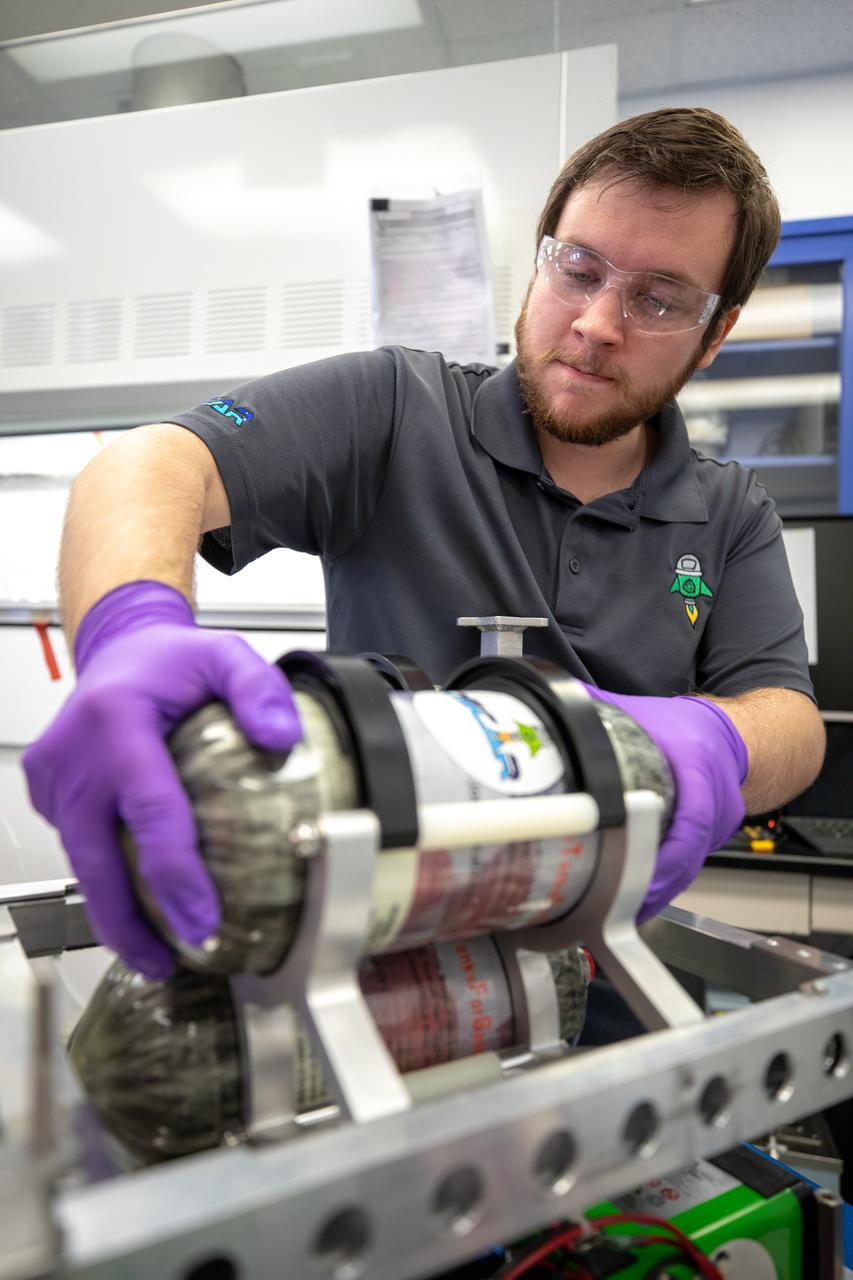

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, installs OSCAR to the flight hardware that will carry it on its suborbital flight test. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees have worked on constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
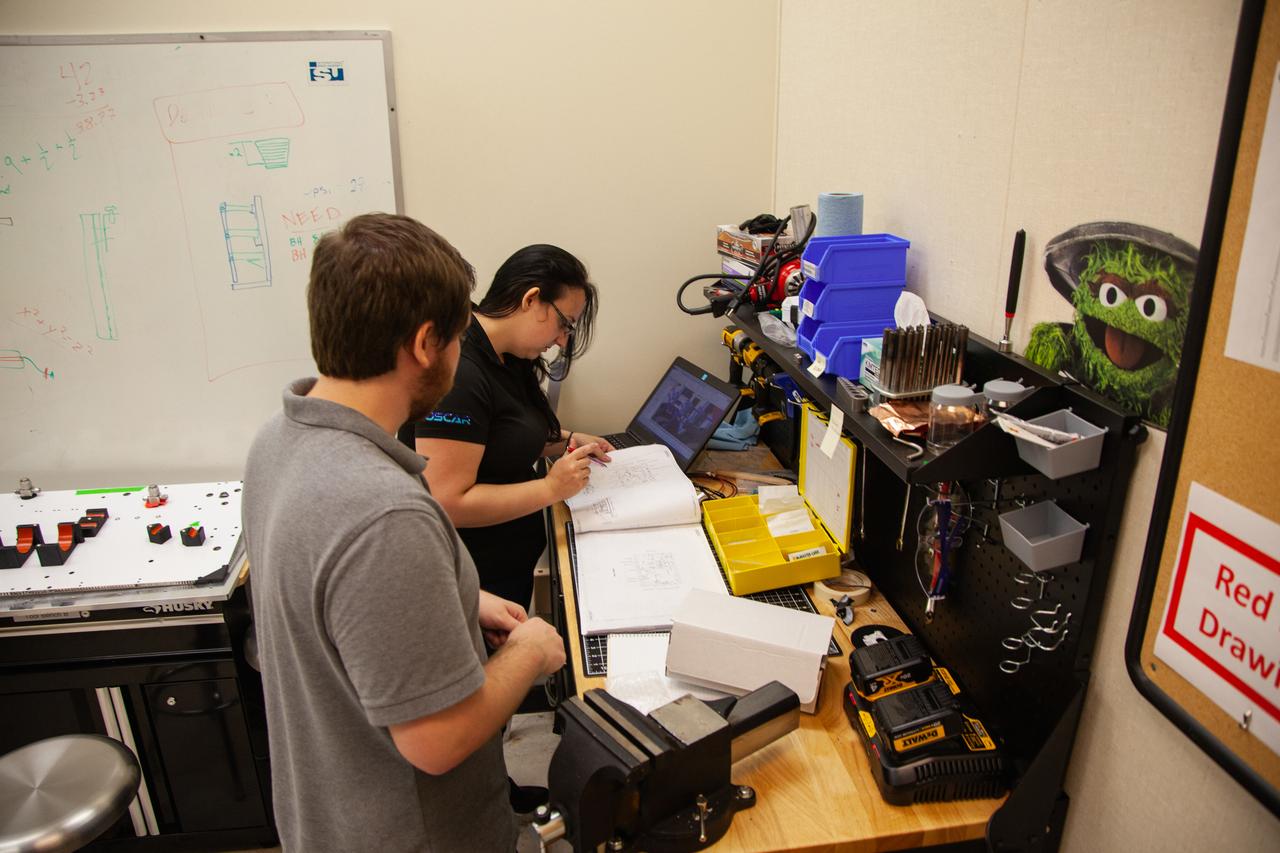

Kennedy Space Center employees are working on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
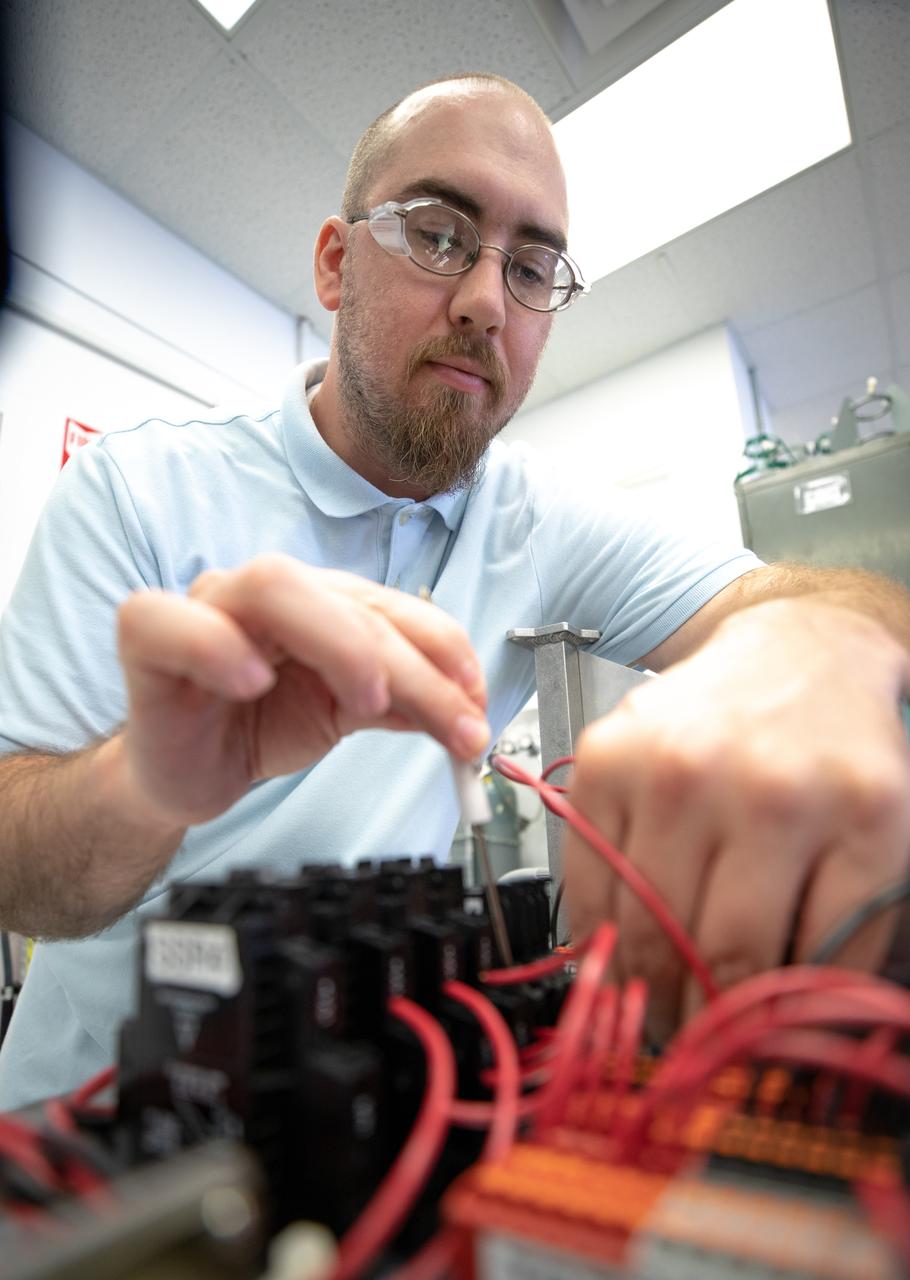
Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
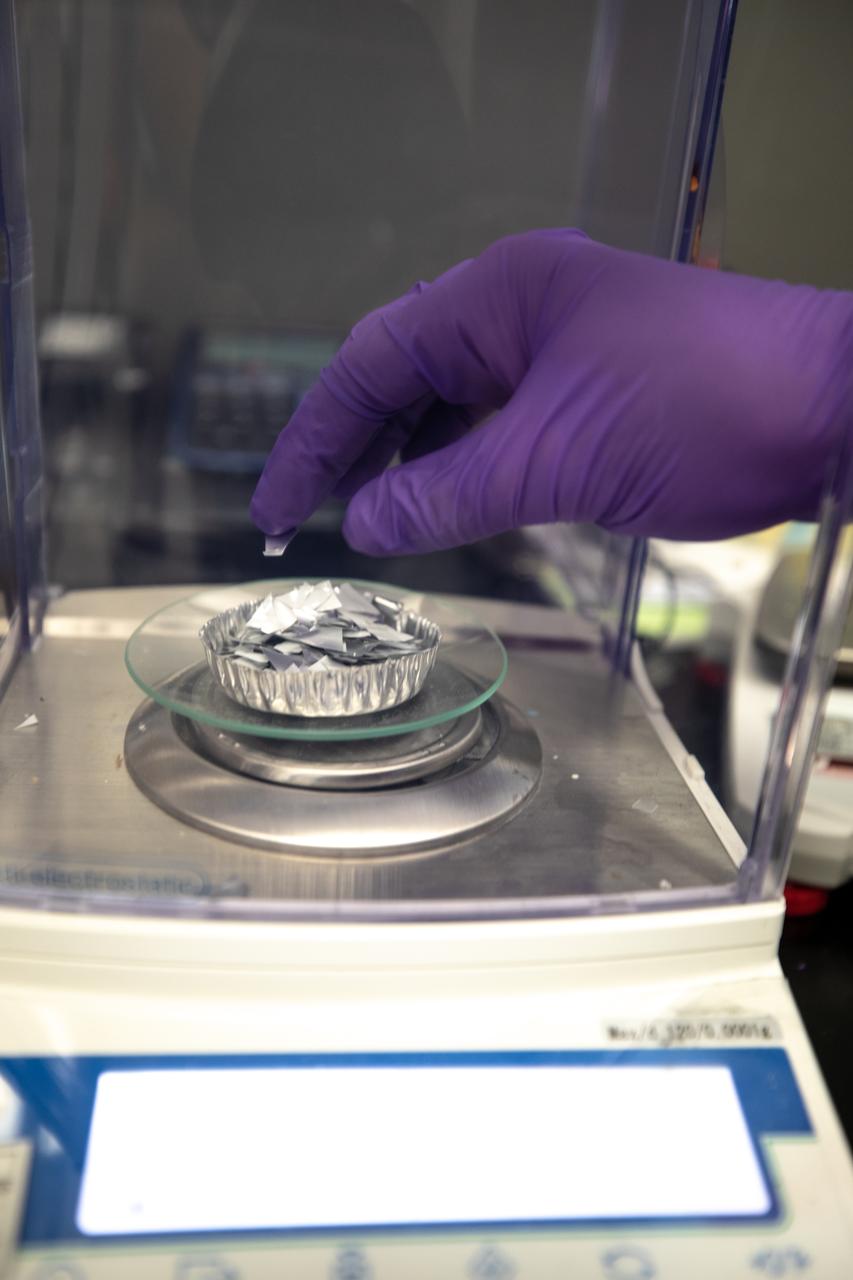
A Kennedy Space Center intern weighs trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
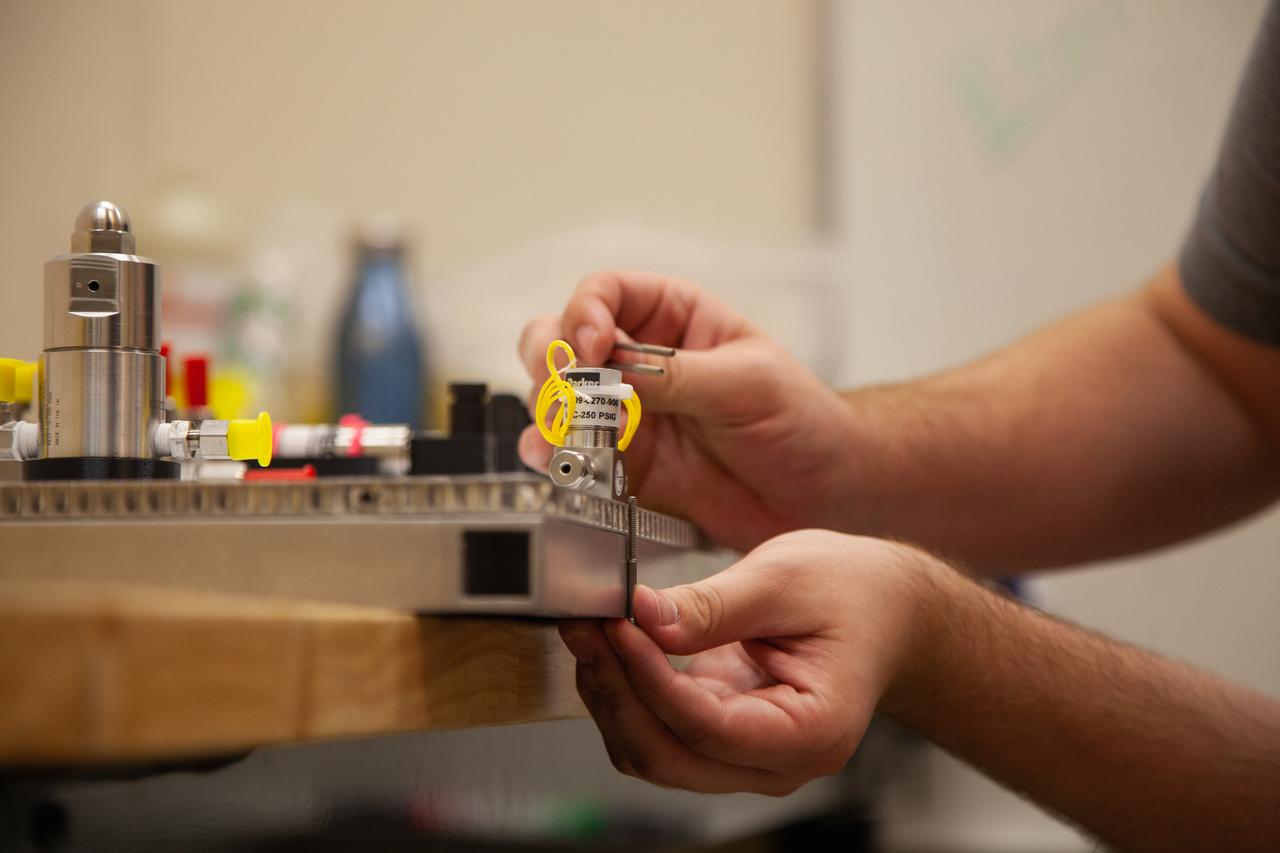

A Kennedy Space Center employee works on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
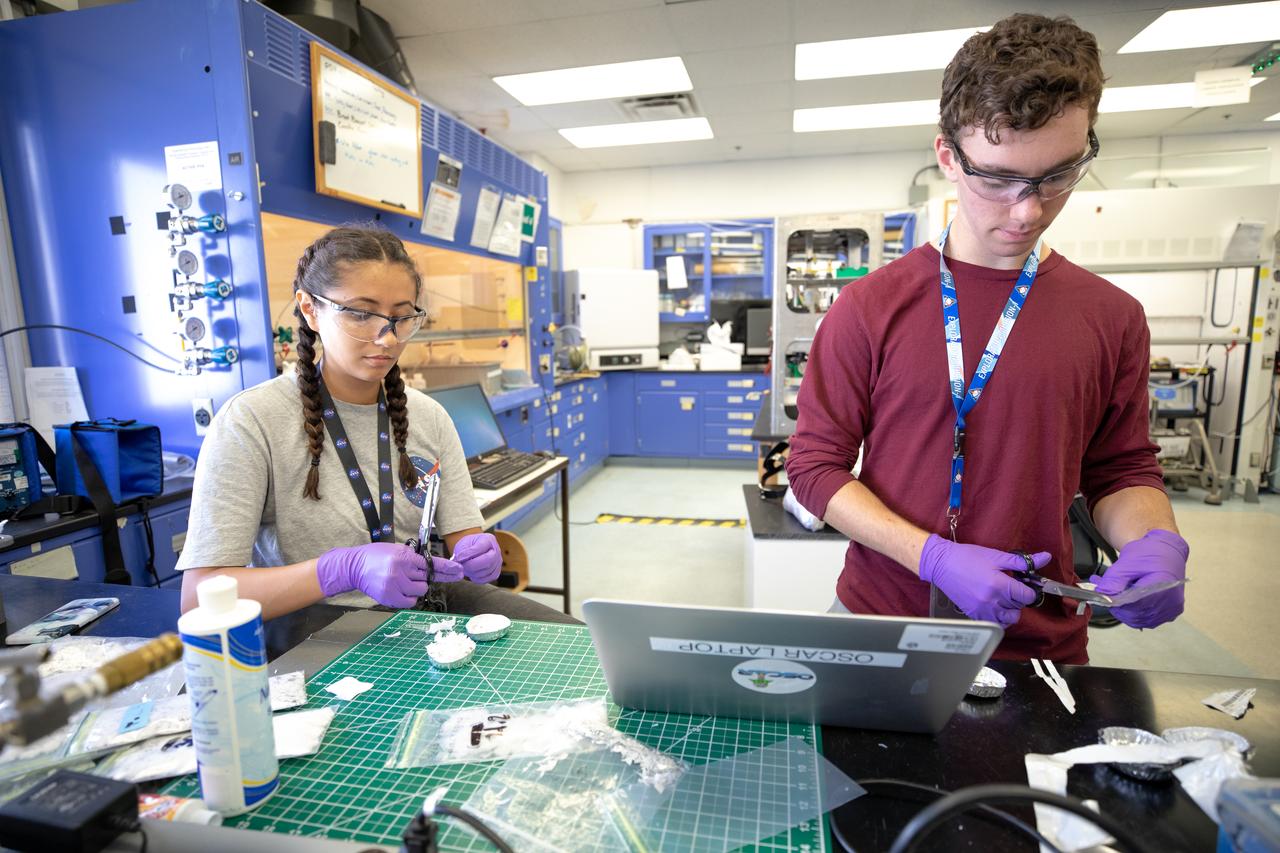

From left, interns Isabella Aviles and Patrick Follis at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cut up different types of material for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, to use as a trash simulant during microgravity testing. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, recover water from trash and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
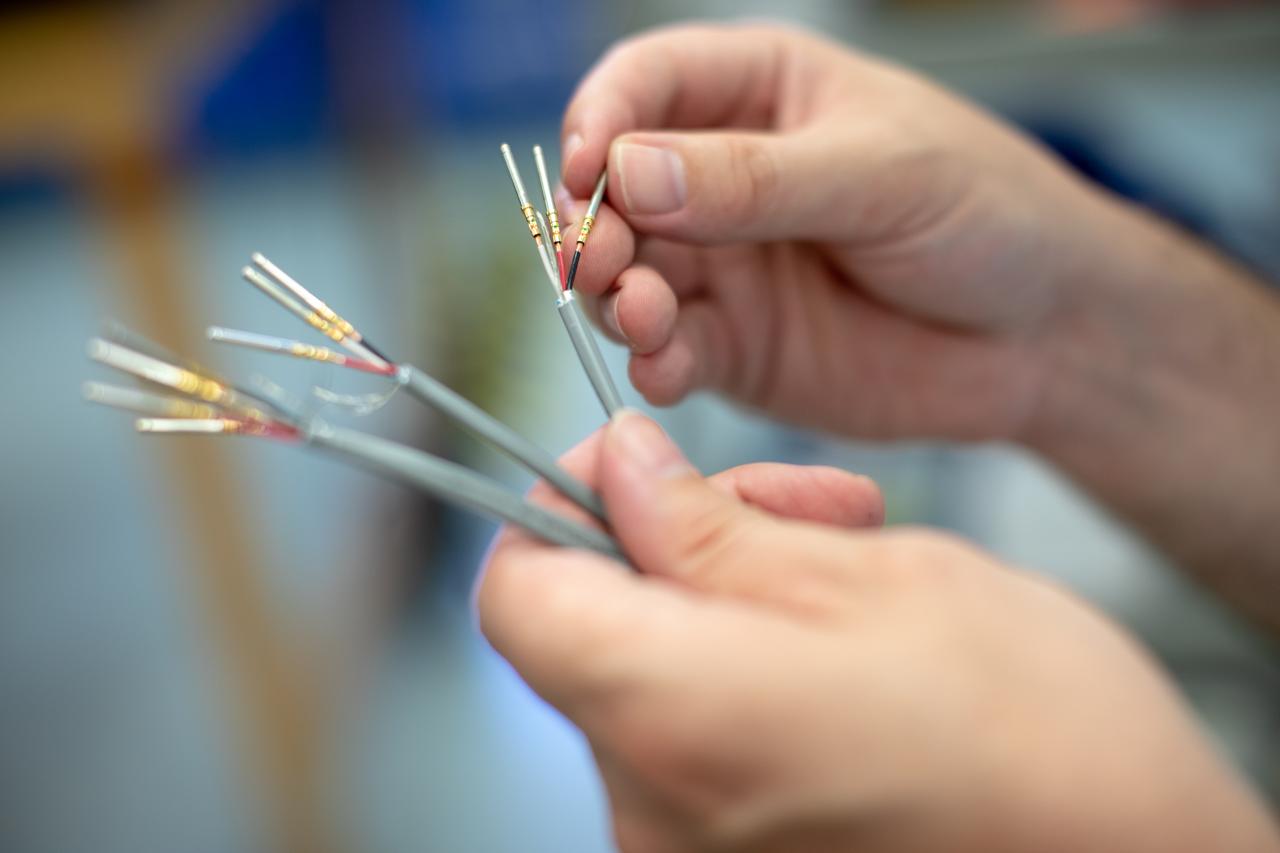
Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Rector, or OSCAR, is photographed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
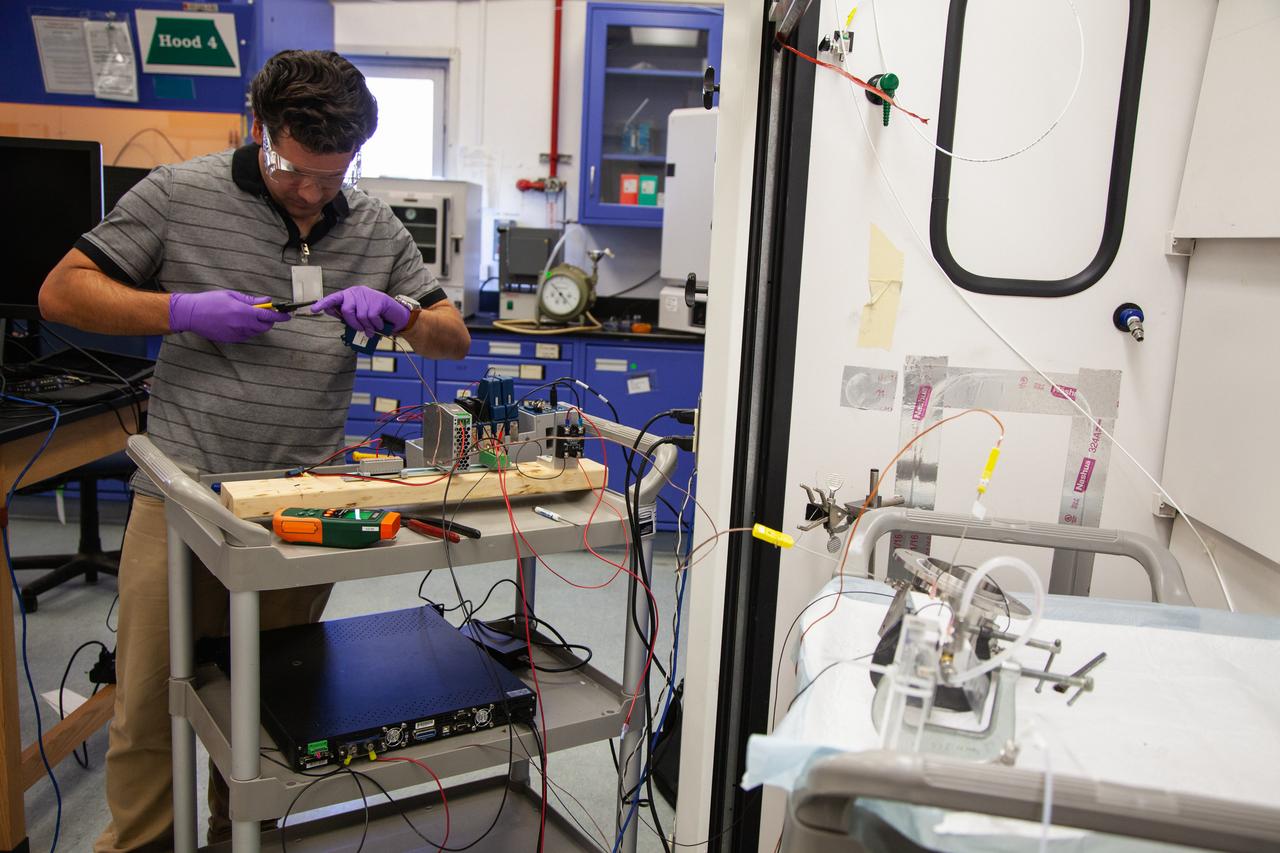
A Kennedy Space Center employee works on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
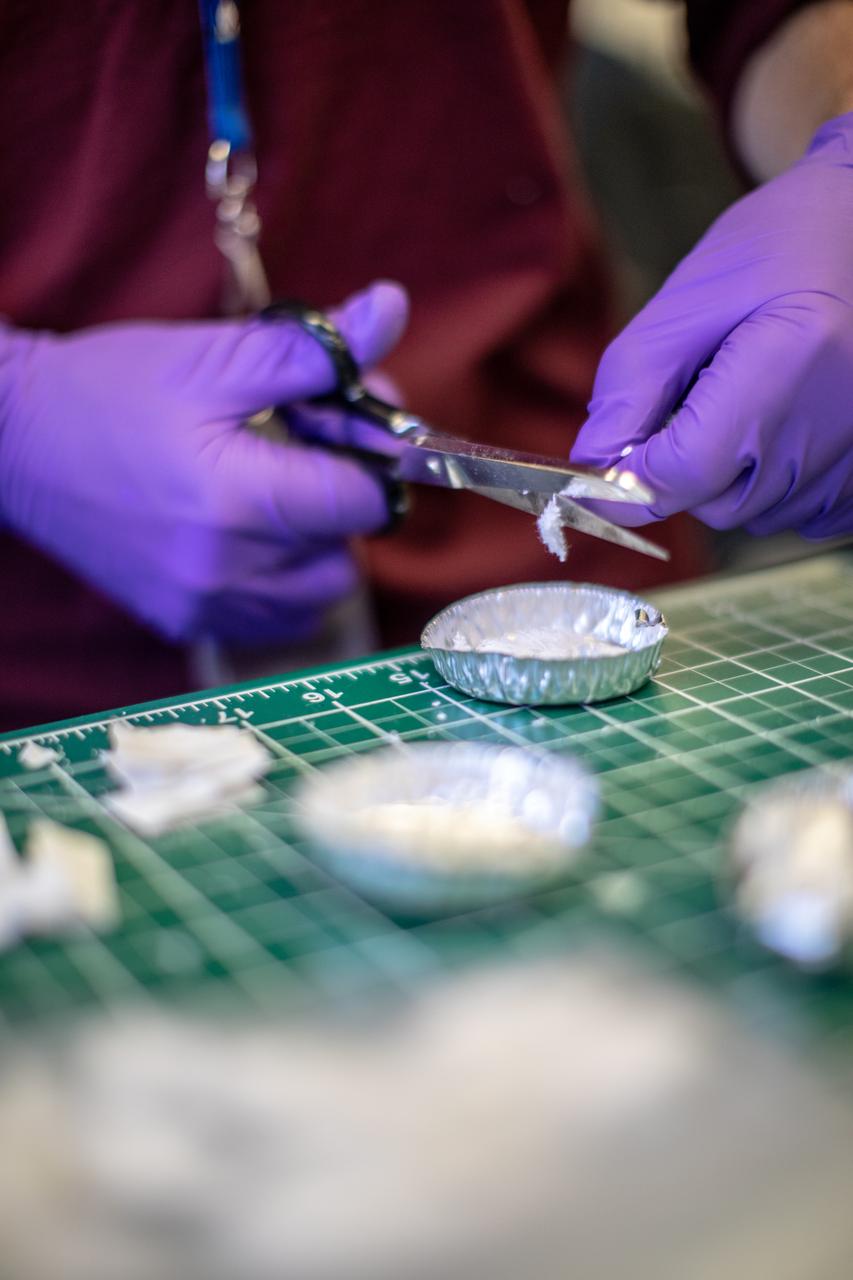

An intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts up different types of material to be utilized as trash simulant for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
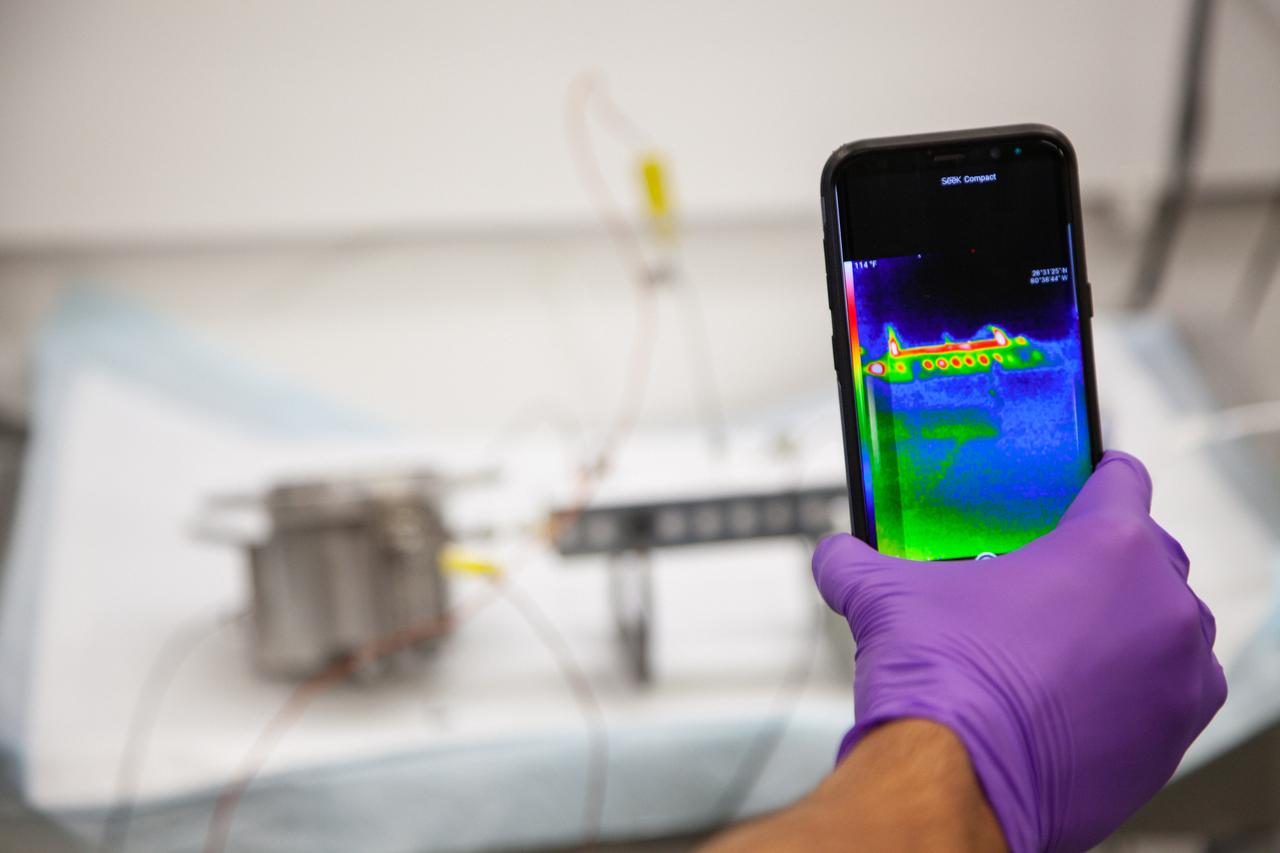

A Kennedy Space Center employee conducts thermal testing of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
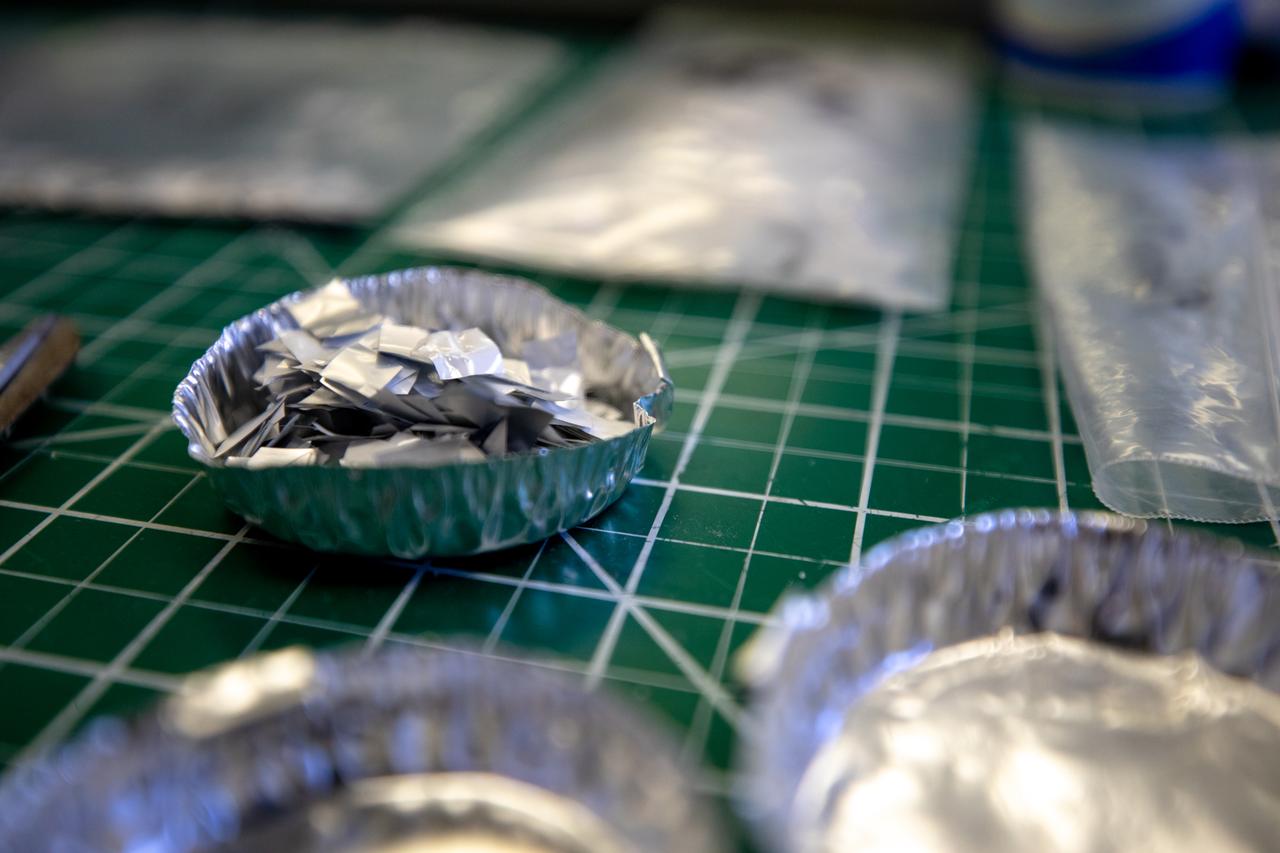

Pictured at Kennedy Space Center is trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
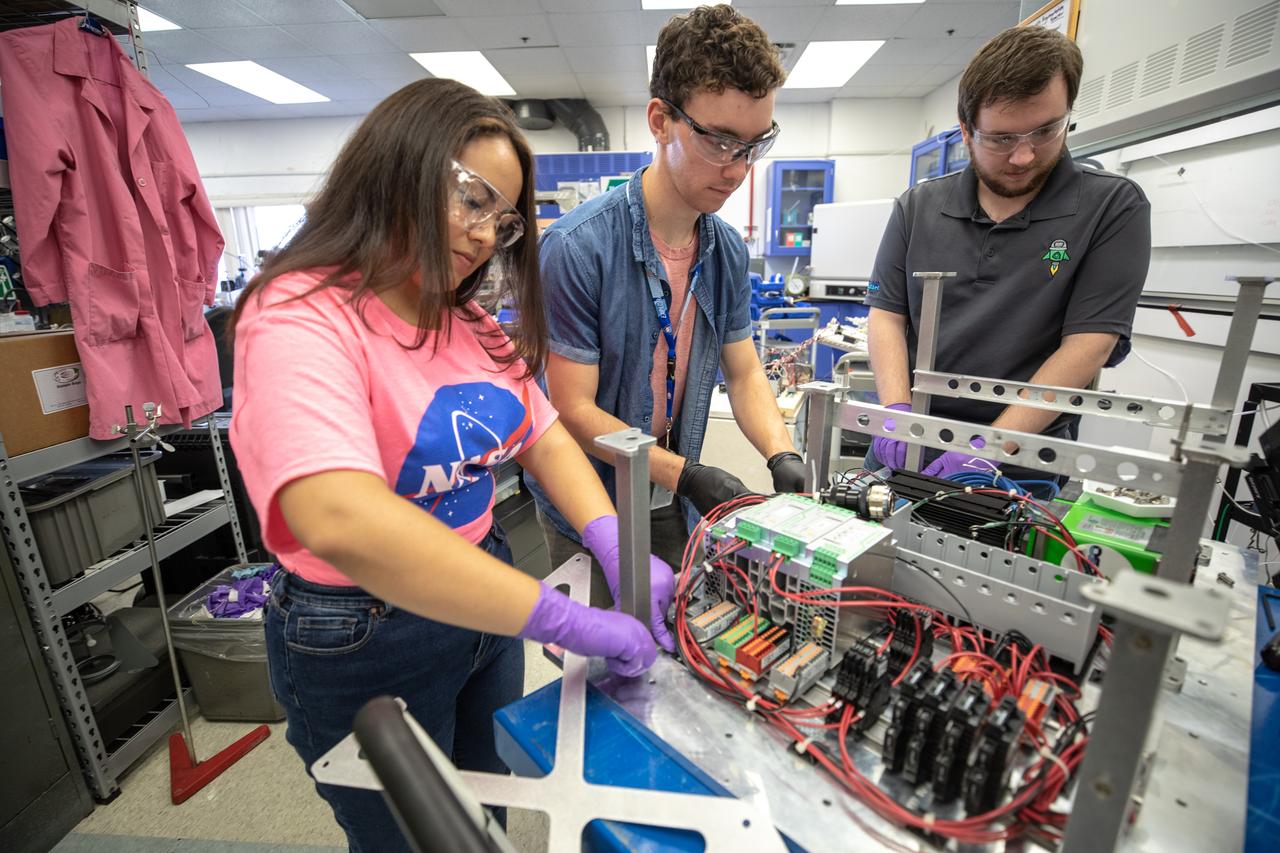

From left, Kennedy Space Center interns Brianna Sandoval and Patrick Follis, and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
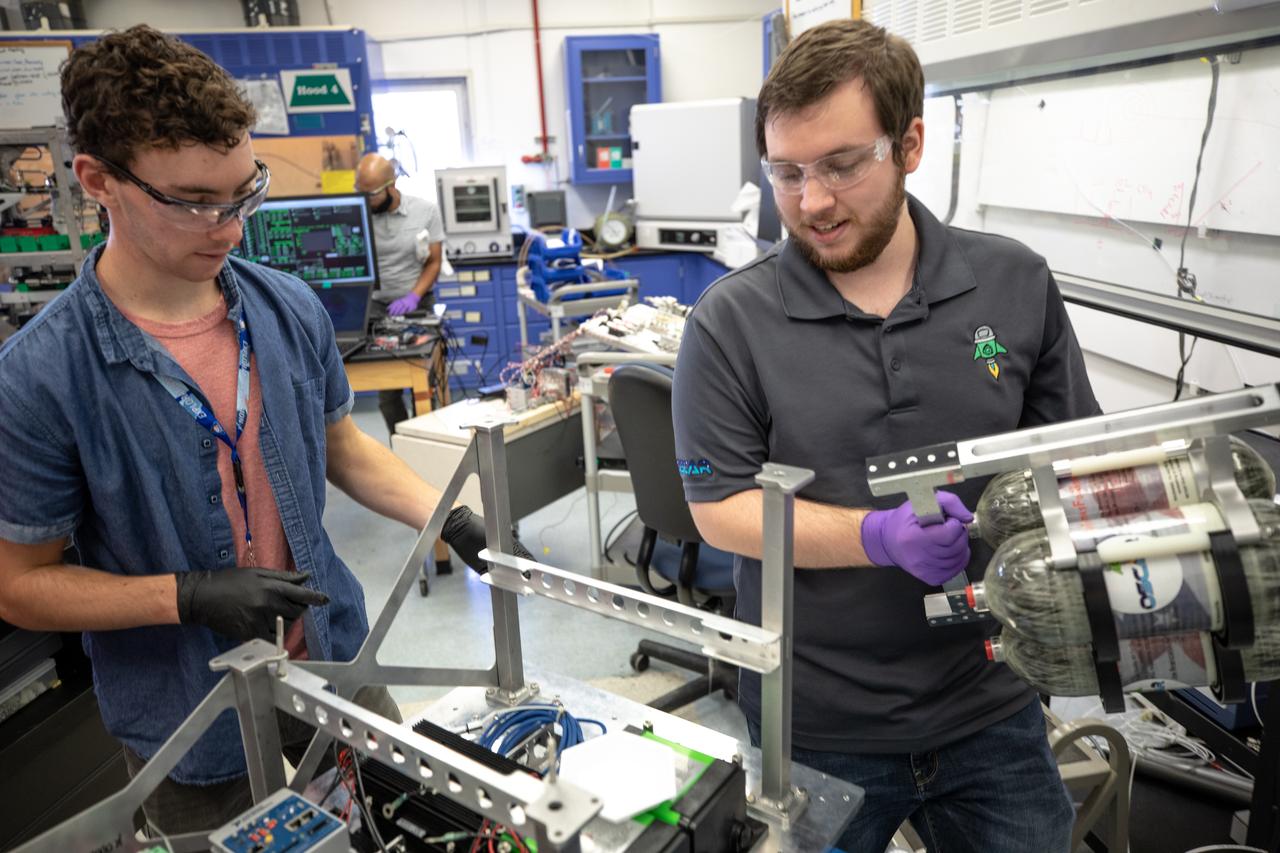
Kennedy Space Center employee Jonathan Gleeson (right) and Kennedy intern Patrick Follis assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
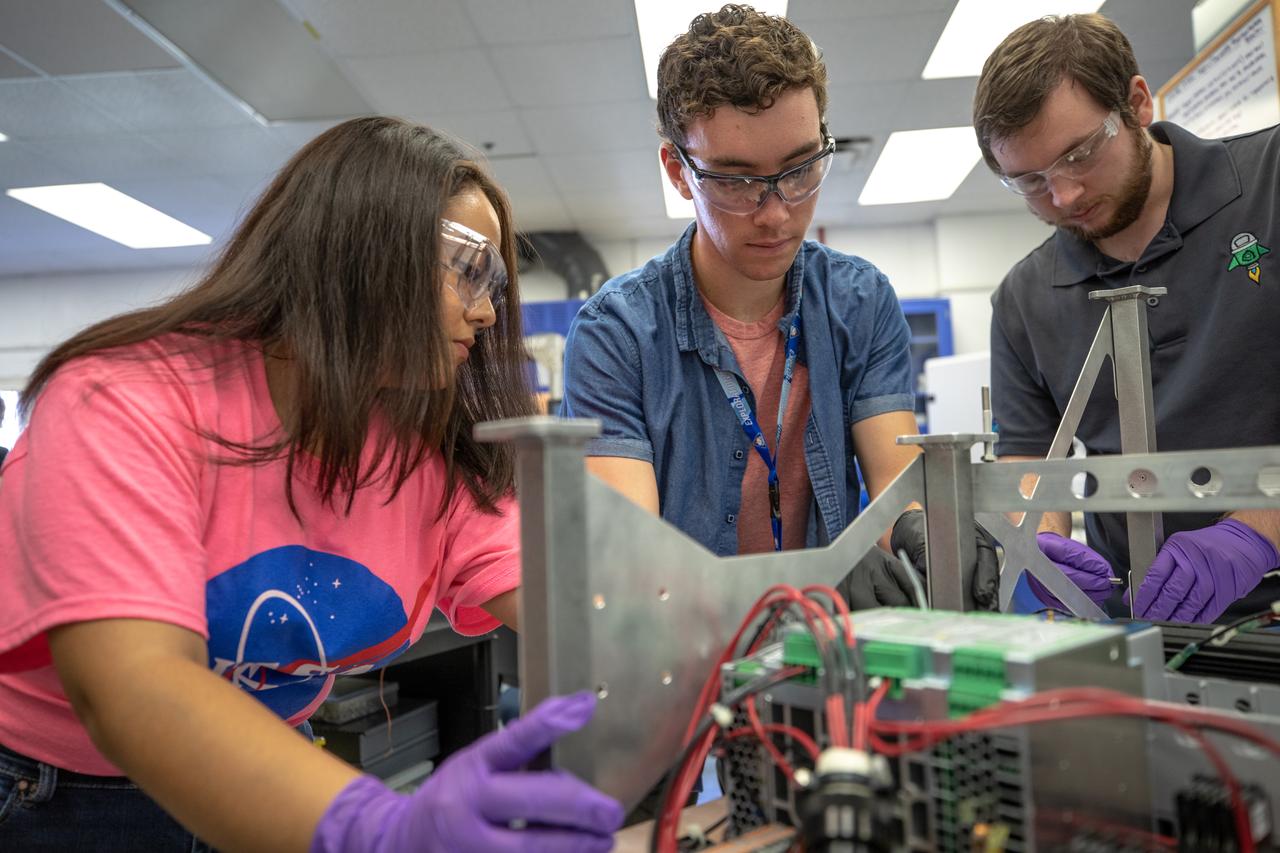

From left, Kennedy Space Center interns Brianna Sandoval and Patrick Follis, and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
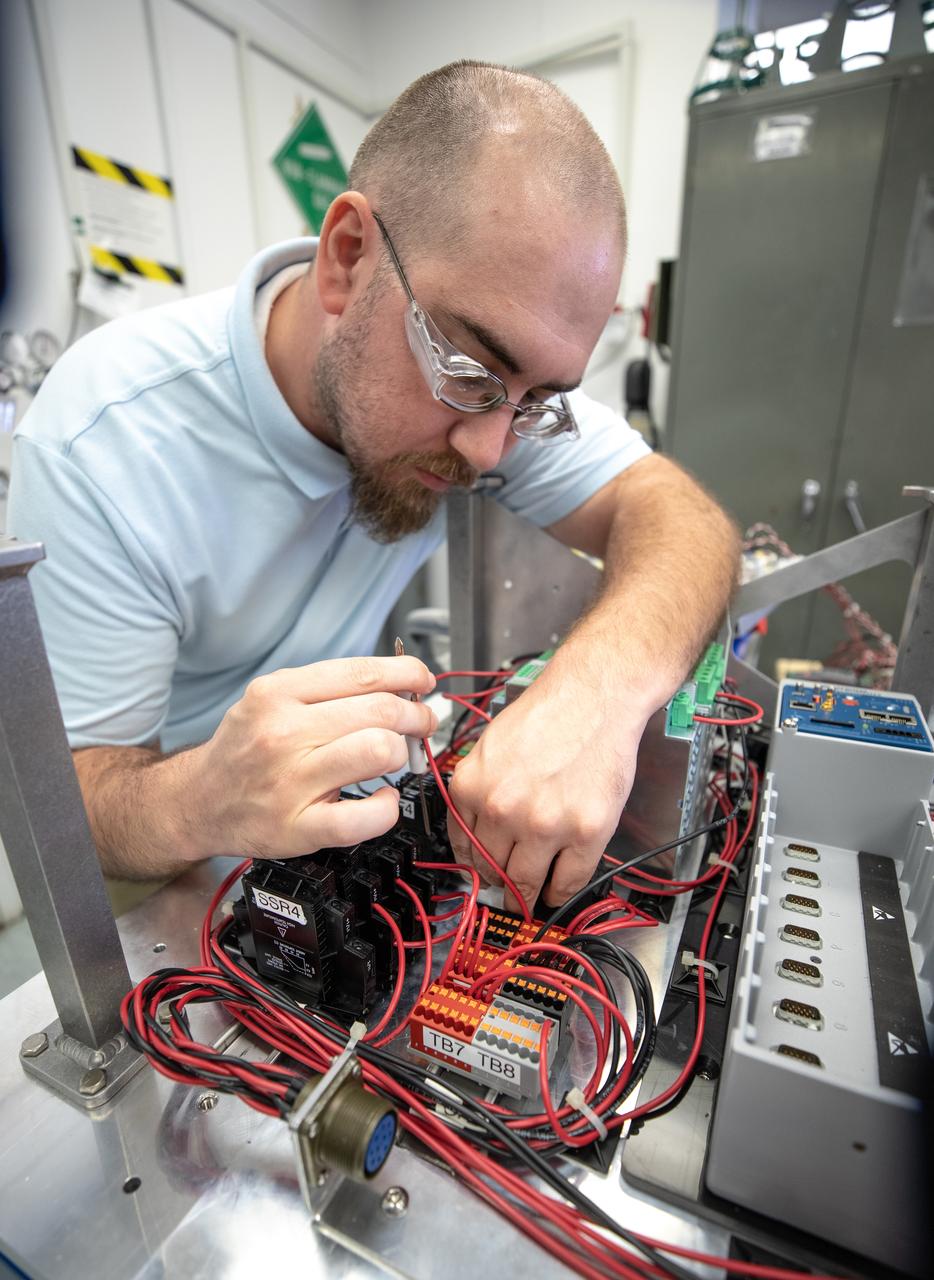

Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
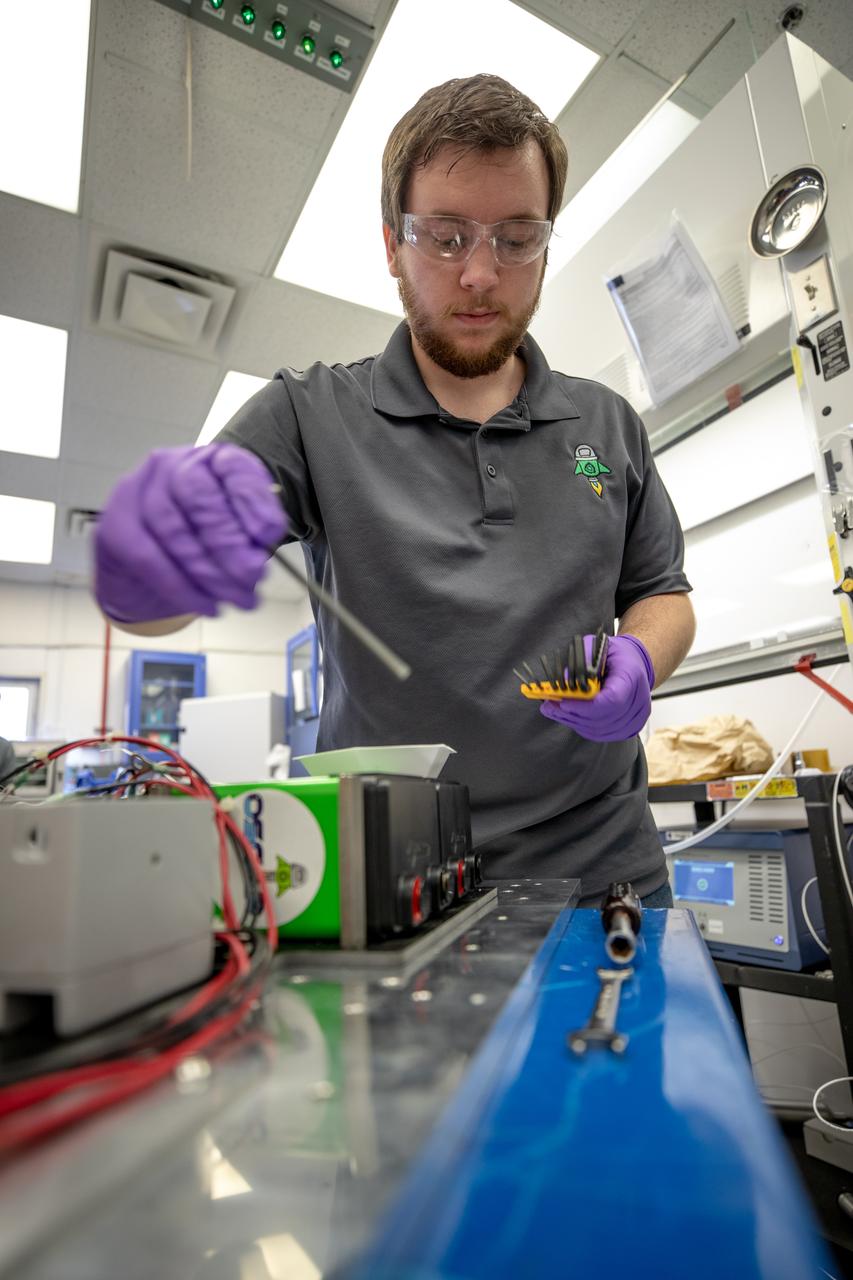

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
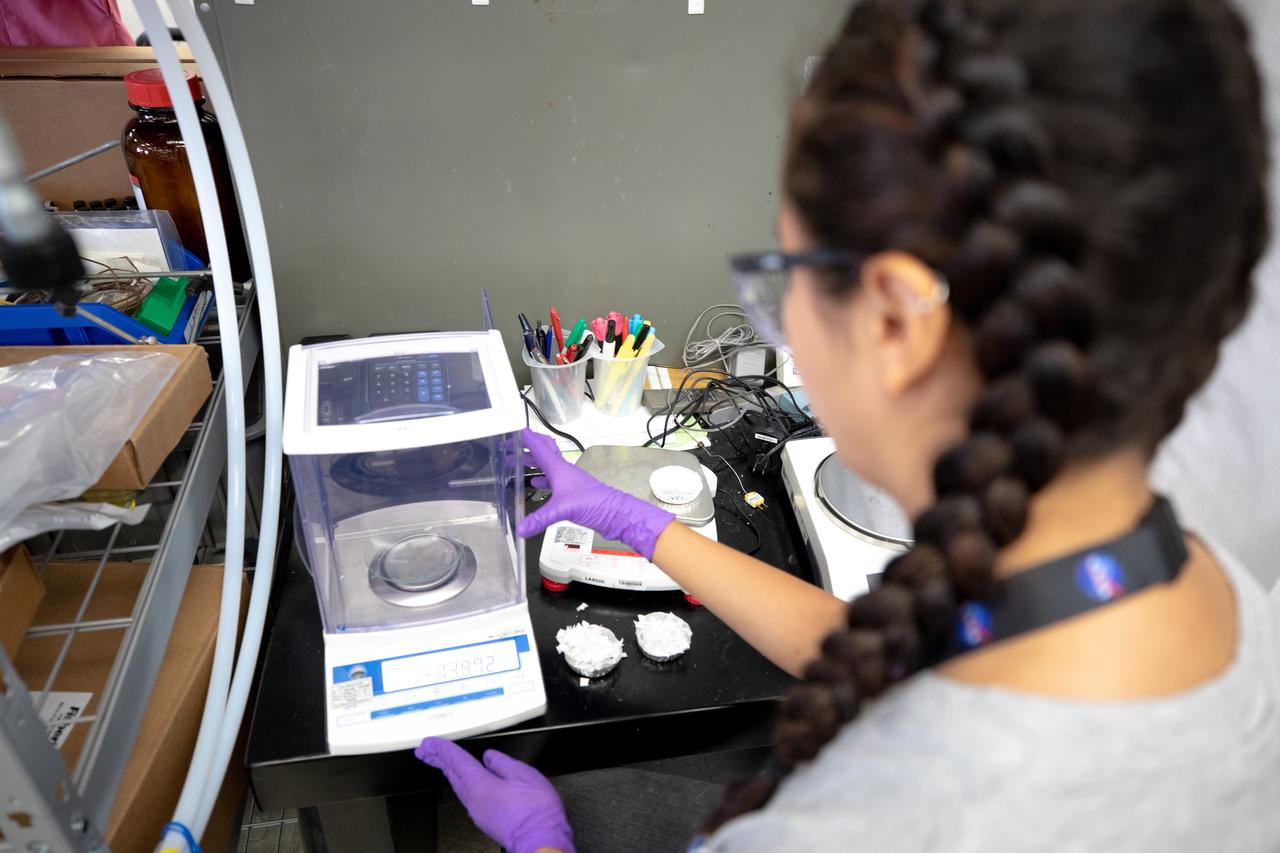
Isabella Aviles, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, weighs trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
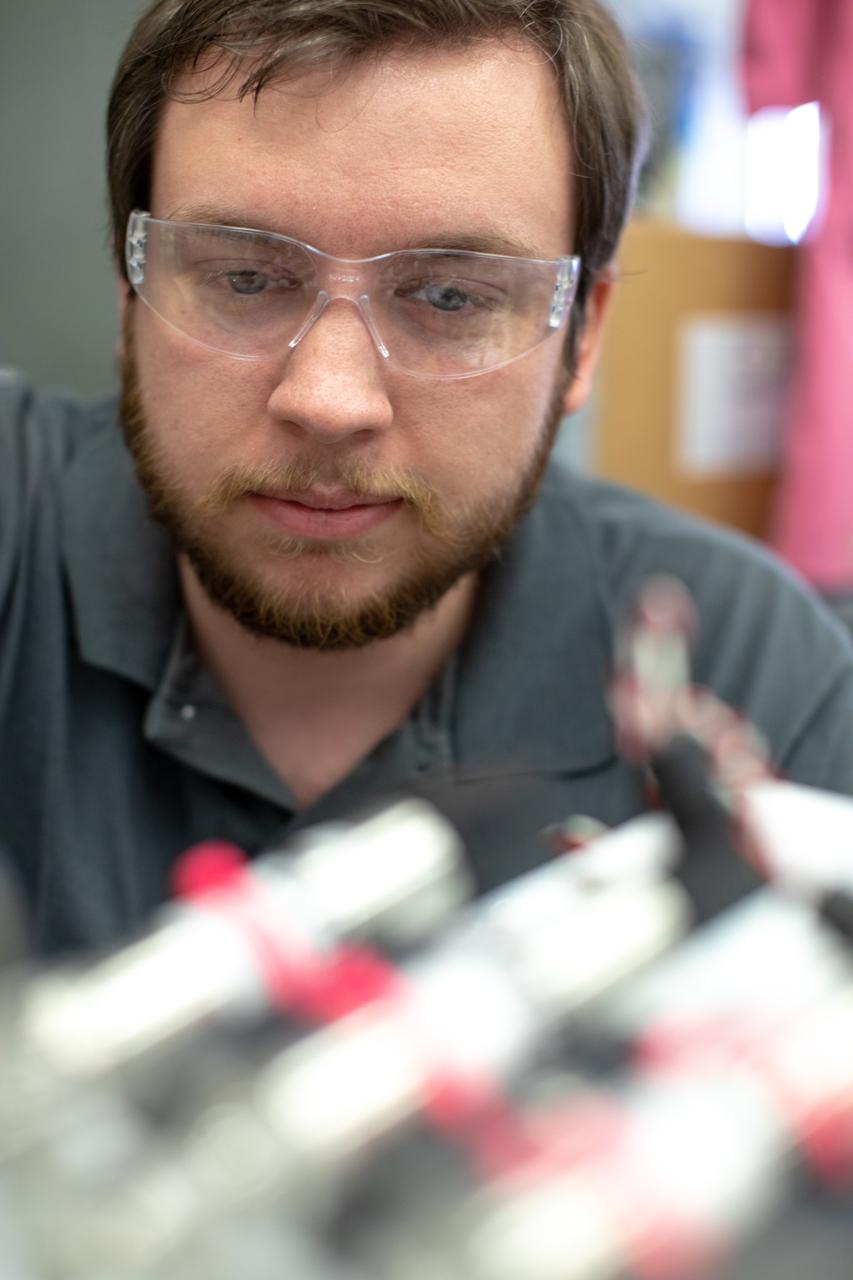

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
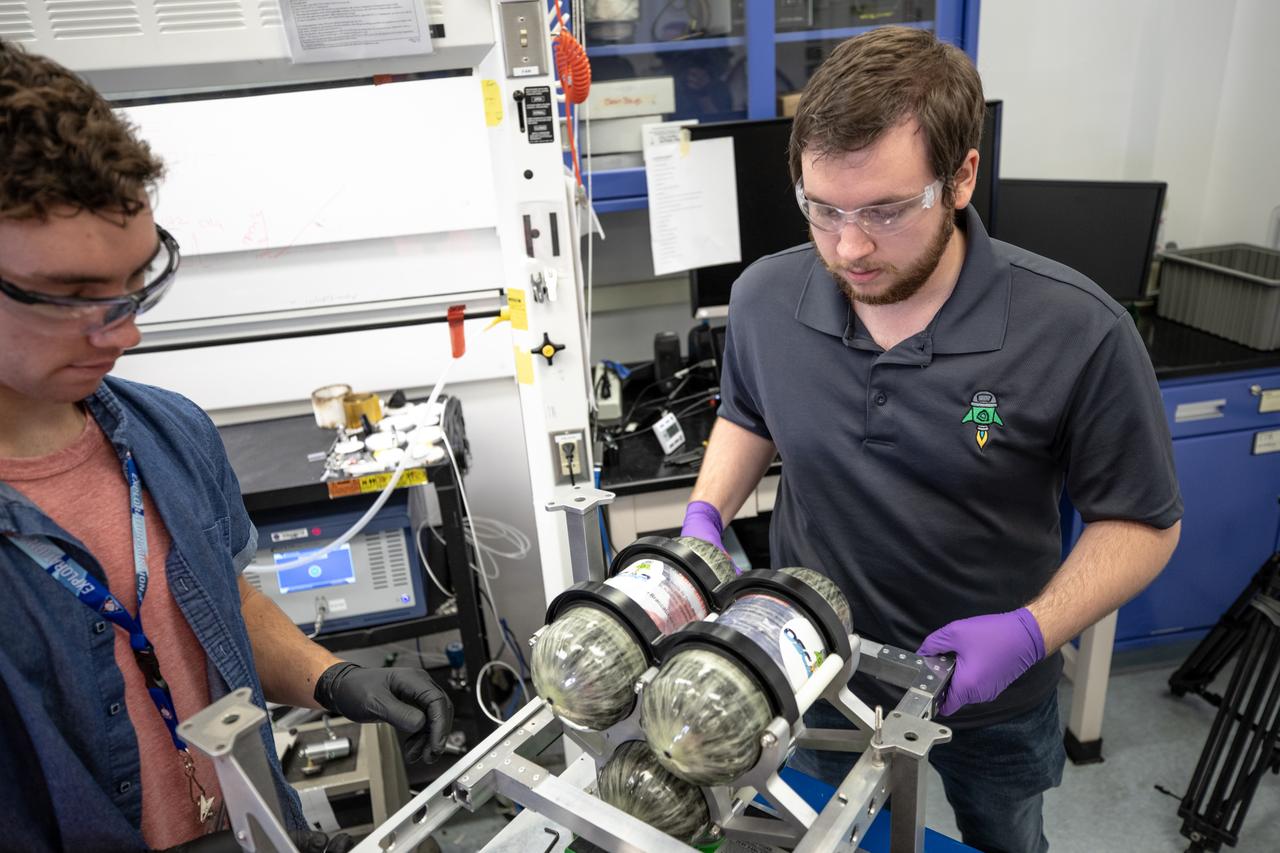

Kennedy Space Center employee Jonathan Gleeson (right) and Kennedy intern Patrick Follis assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
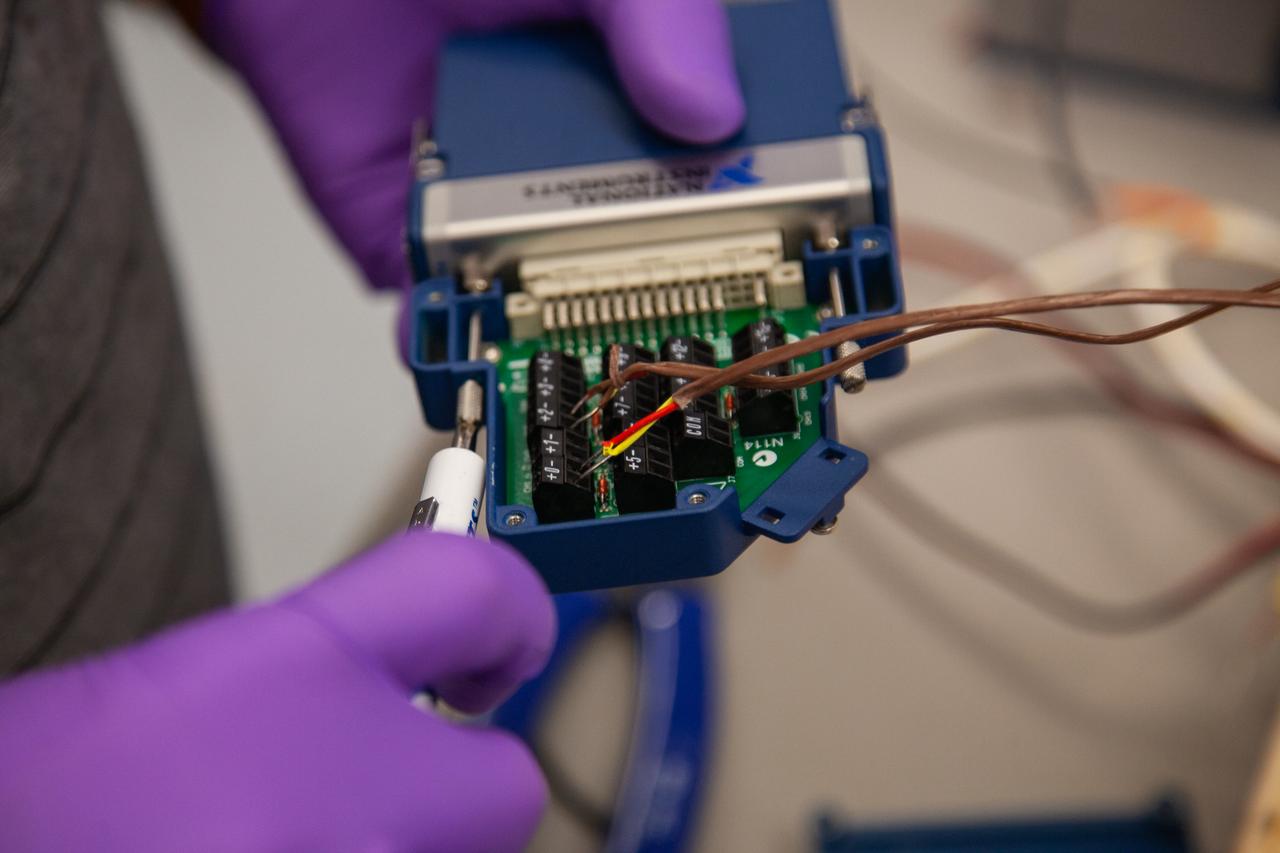
A Kennedy Space Center employee works on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
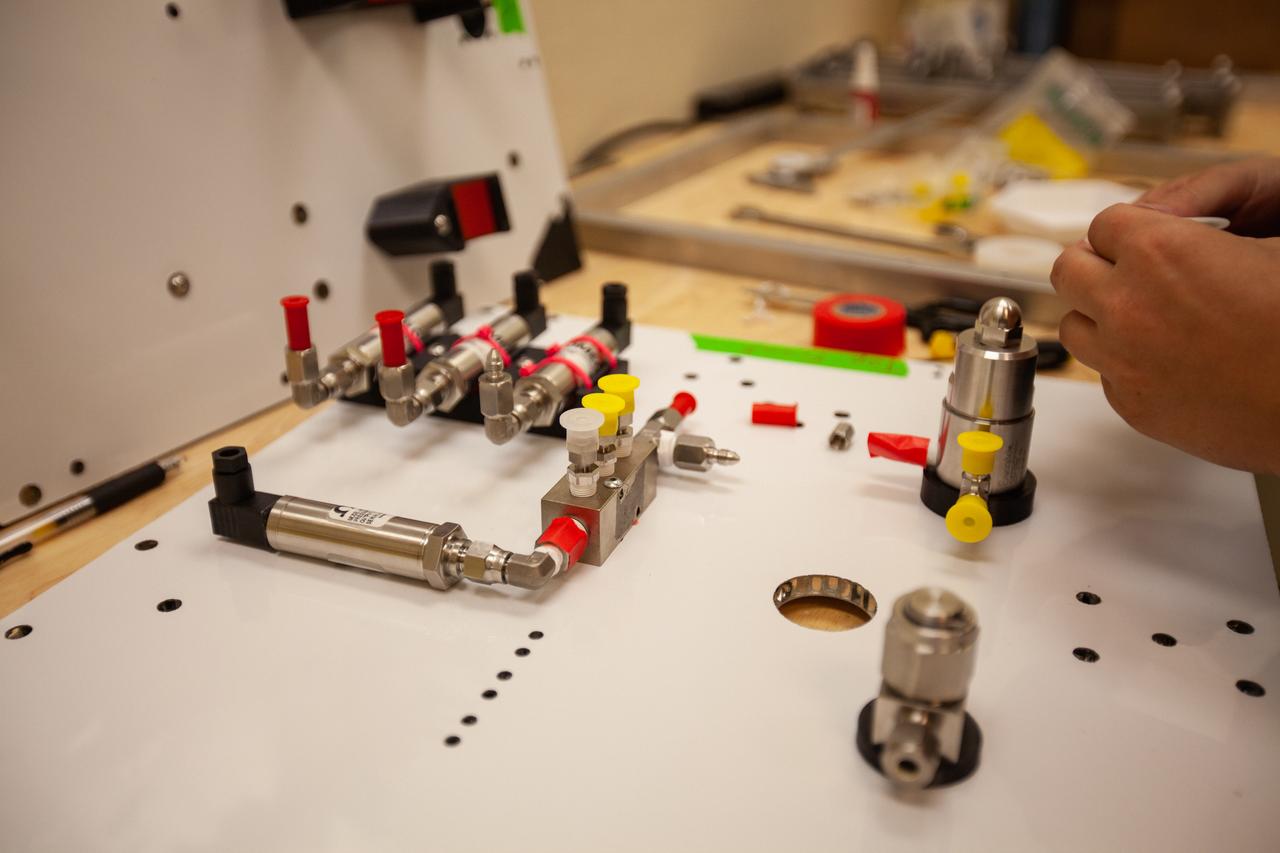
A Kennedy Space Center employee works on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
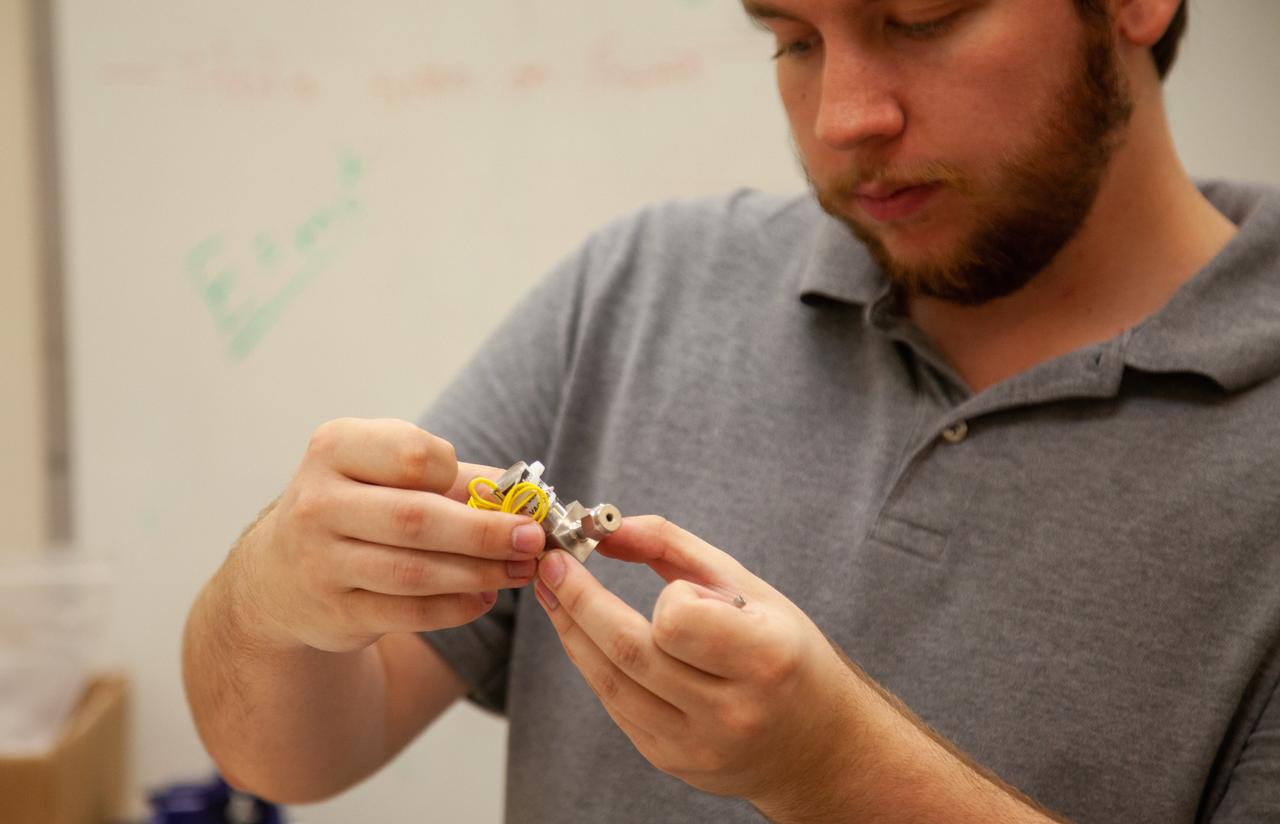

A Kennedy Space Center employee works on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Patrick Follis, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, assembles the flight hardware for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is being prepared for suborbital flight testing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for the suborbital flight test.
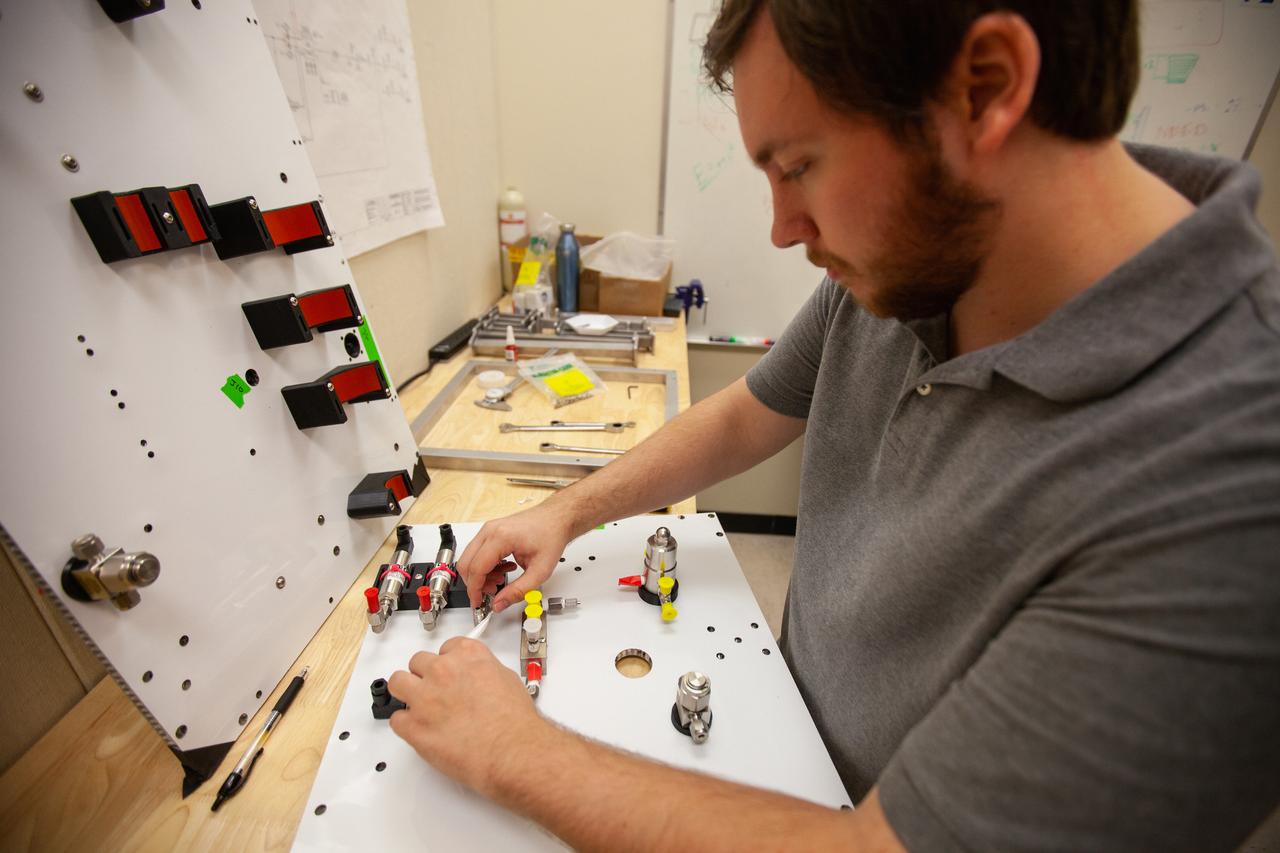

A Kennedy Space Center employee works on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
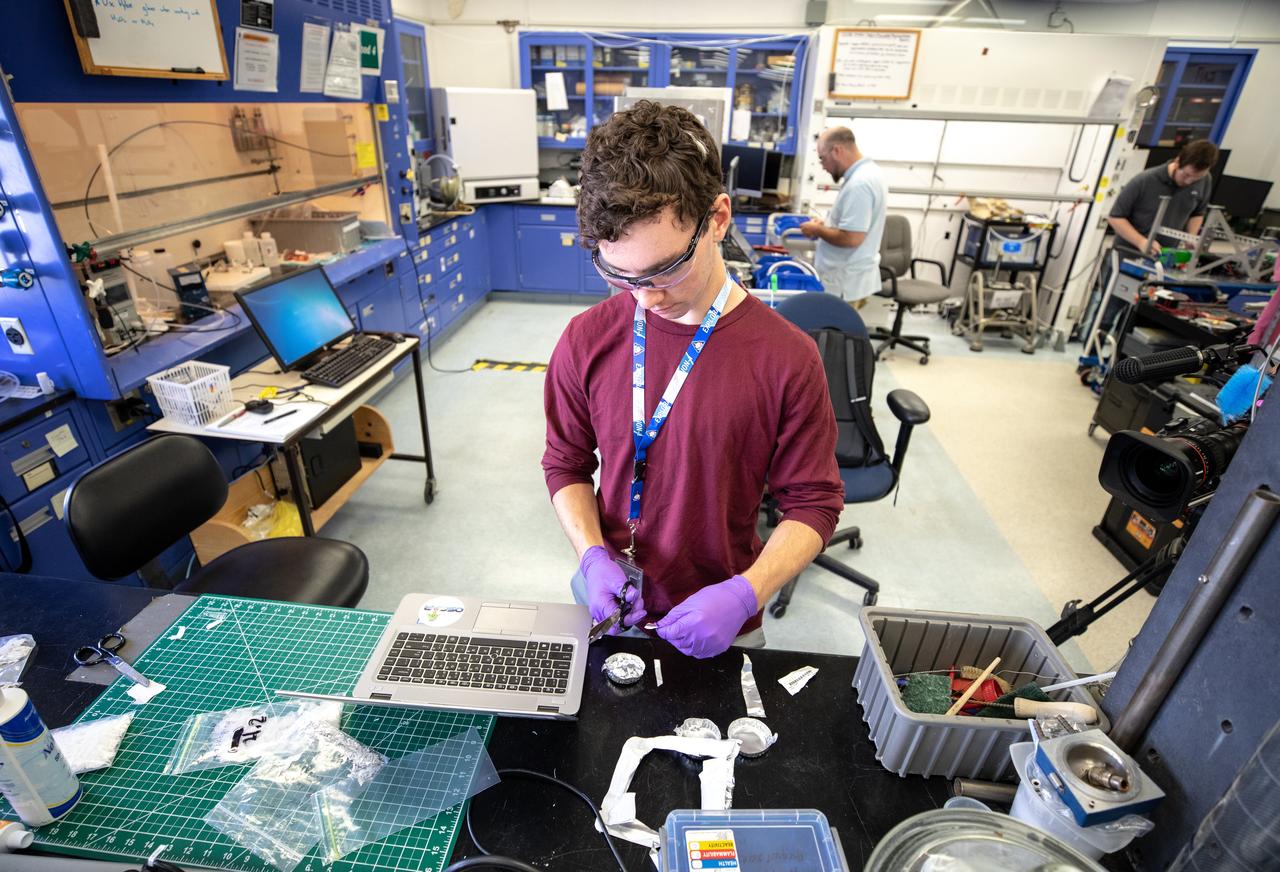

Patrick Follis, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cuts up different types of material for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, to use as a trash simulant during microgravity testing. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
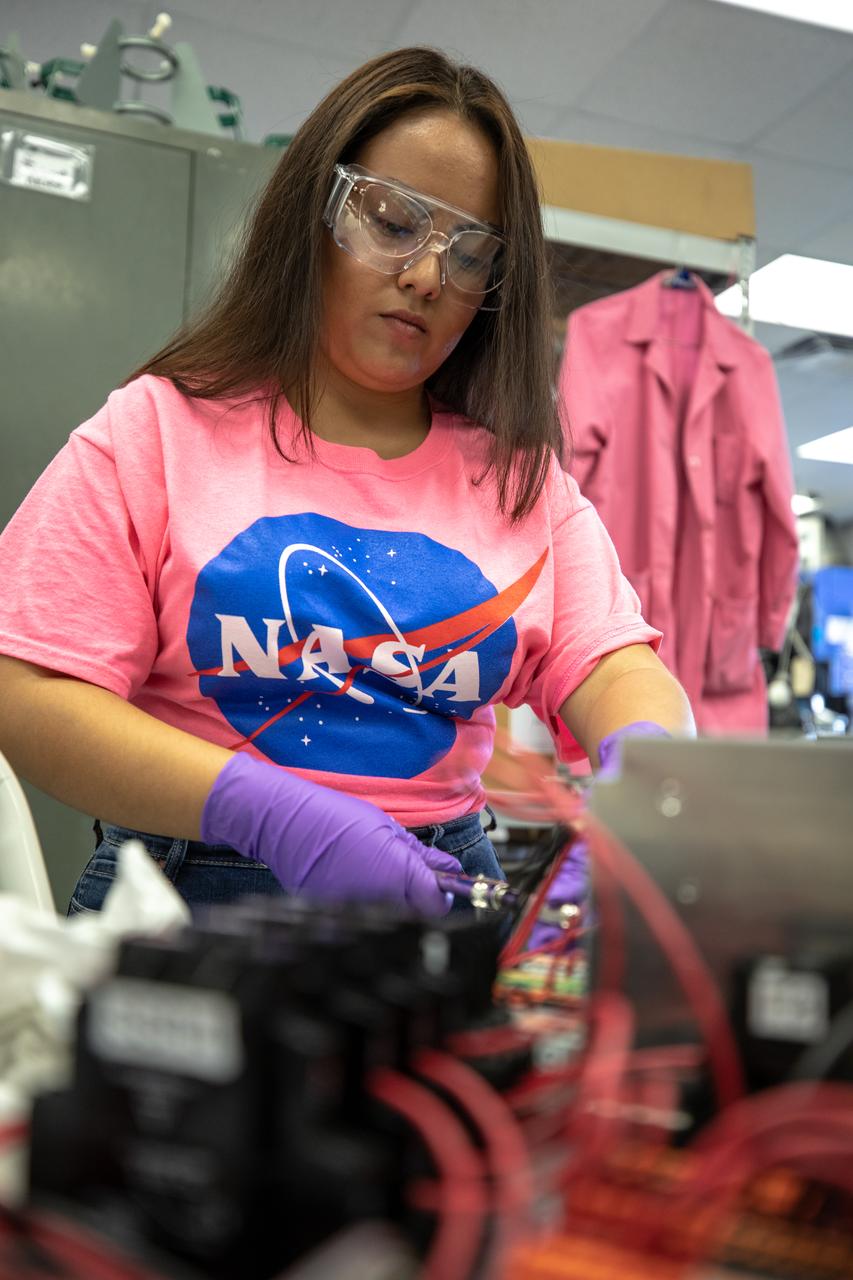

Brianna Sandoval, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, assembles the flight hardware of the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Kennedy Space Center employees assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Kennedy Space Center intern Patrick Follis (left) and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
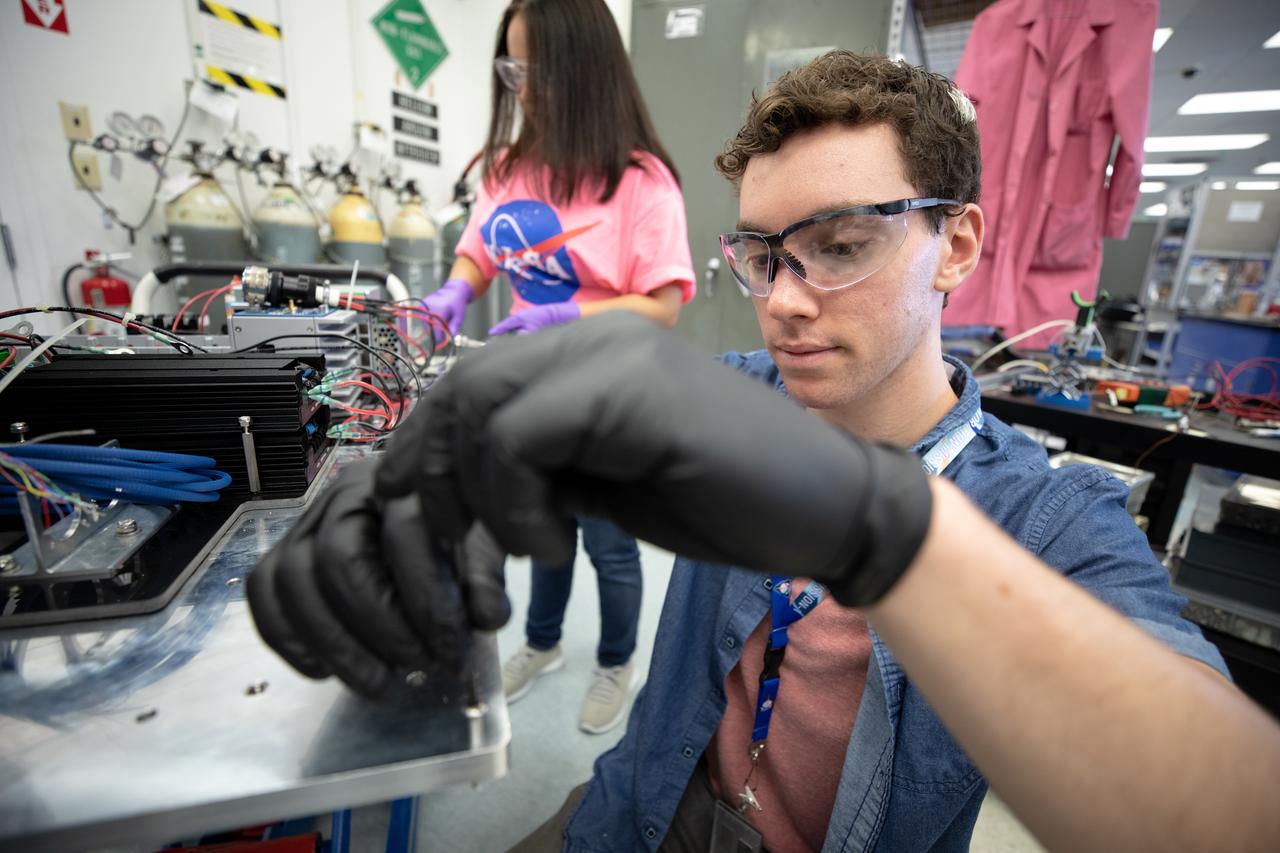

Interns Brianna Sandoval (left) and Patrick Follis at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida assemble the flight hardware for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
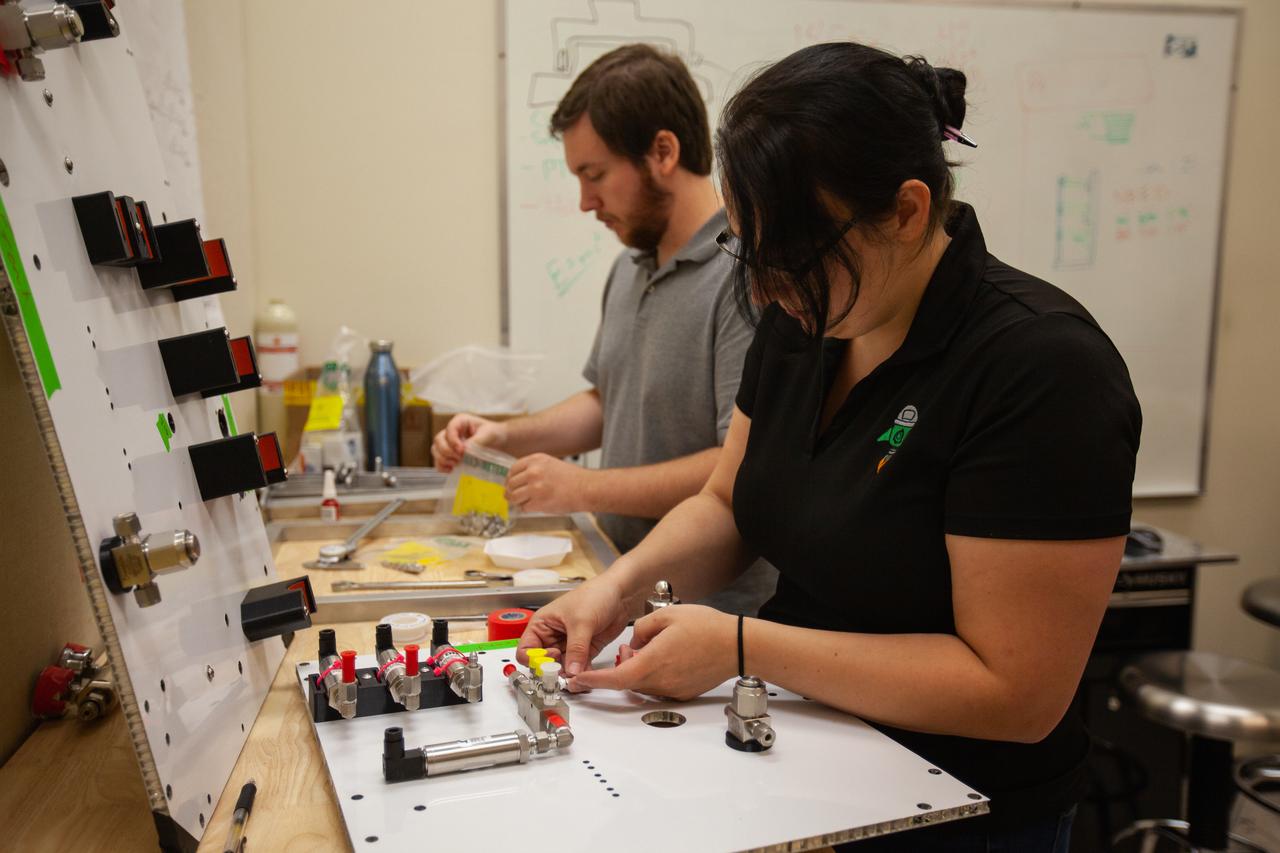

Kennedy Space Center employees assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
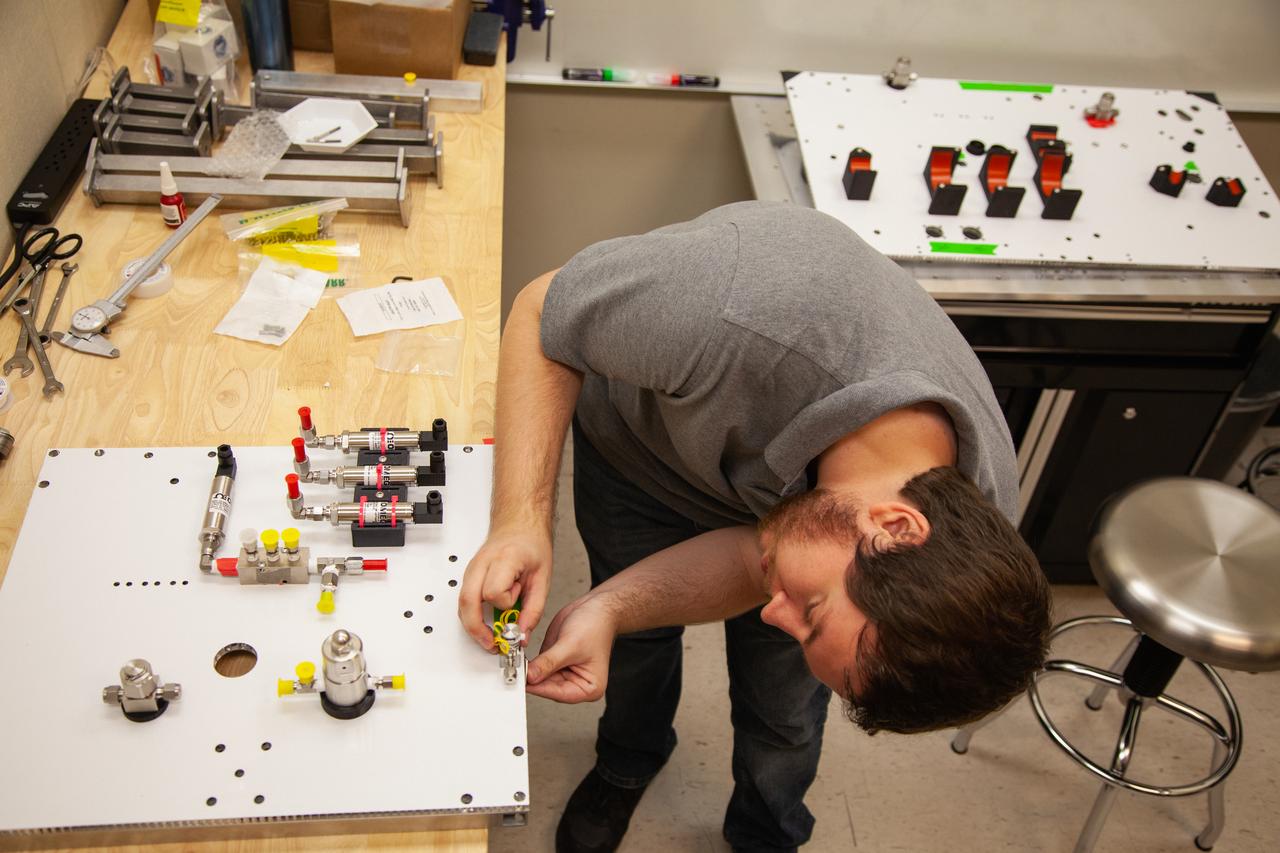

A Kennedy Space Center employee works on assembling the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has already been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

iss064e012310 (Dec. 14, 2020) --- NASA astronauts and Expedition 64 Flight Engineers Shannon Walker and Michael Hopkins work on installing components for the station's new Universal Waste Management System, or bathroom, located inside the Tranquility module.
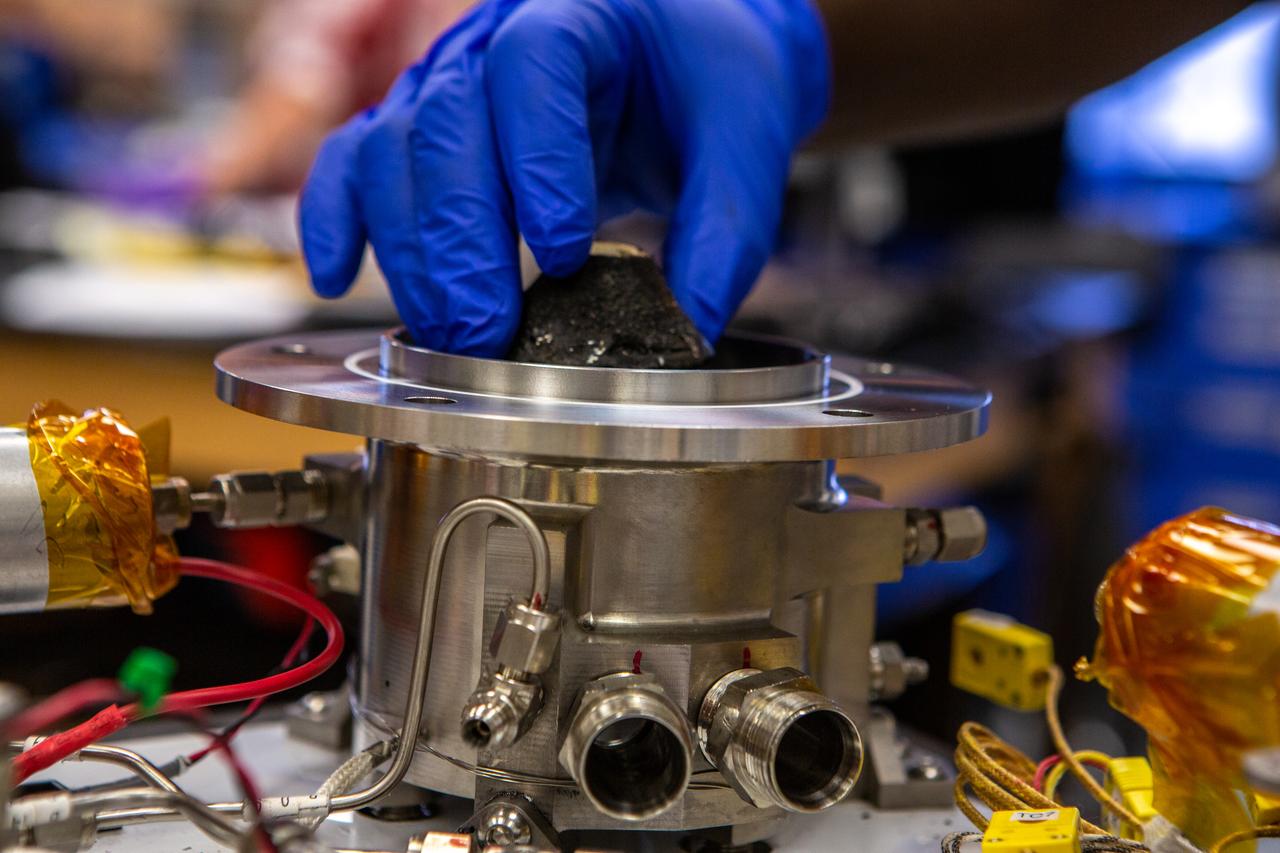
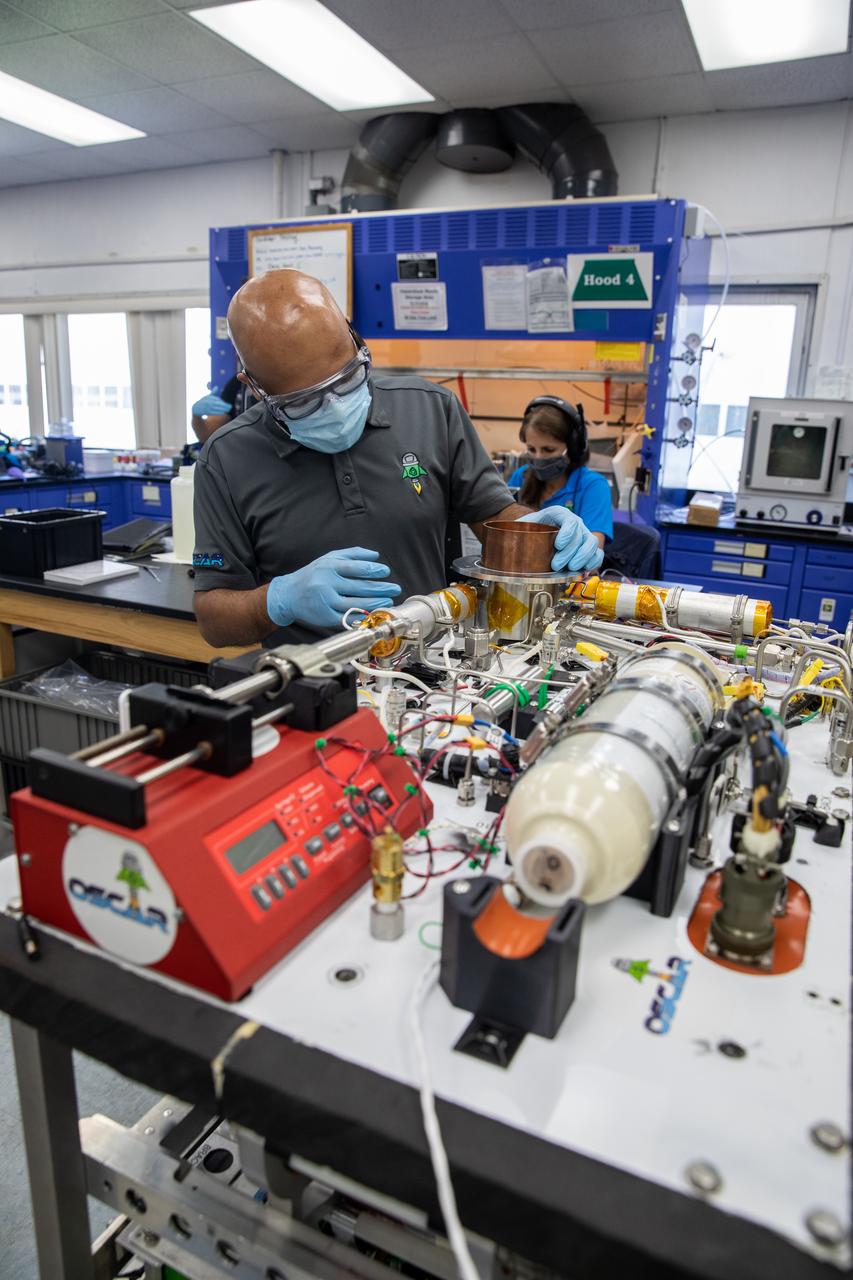
Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
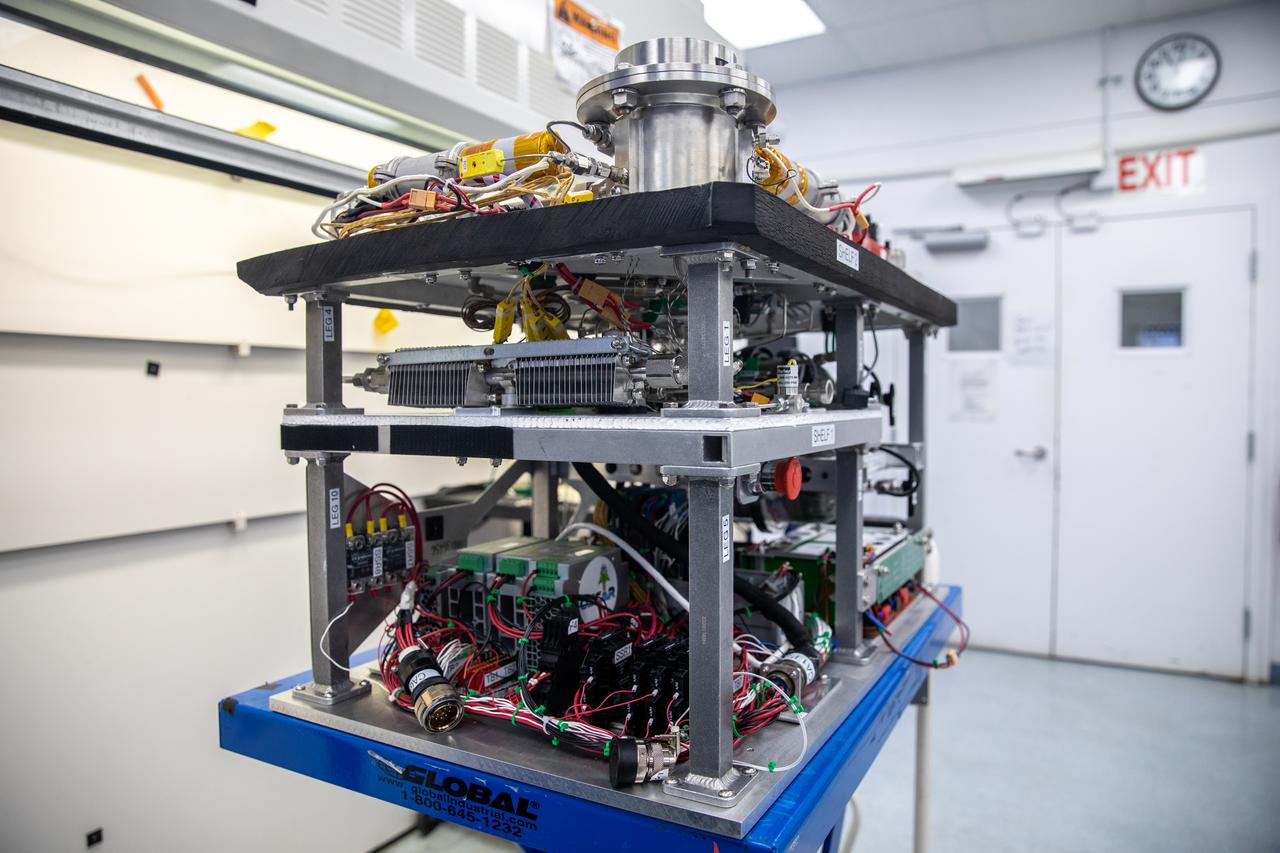
Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is inside the Applied Physics Lab inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is in view inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
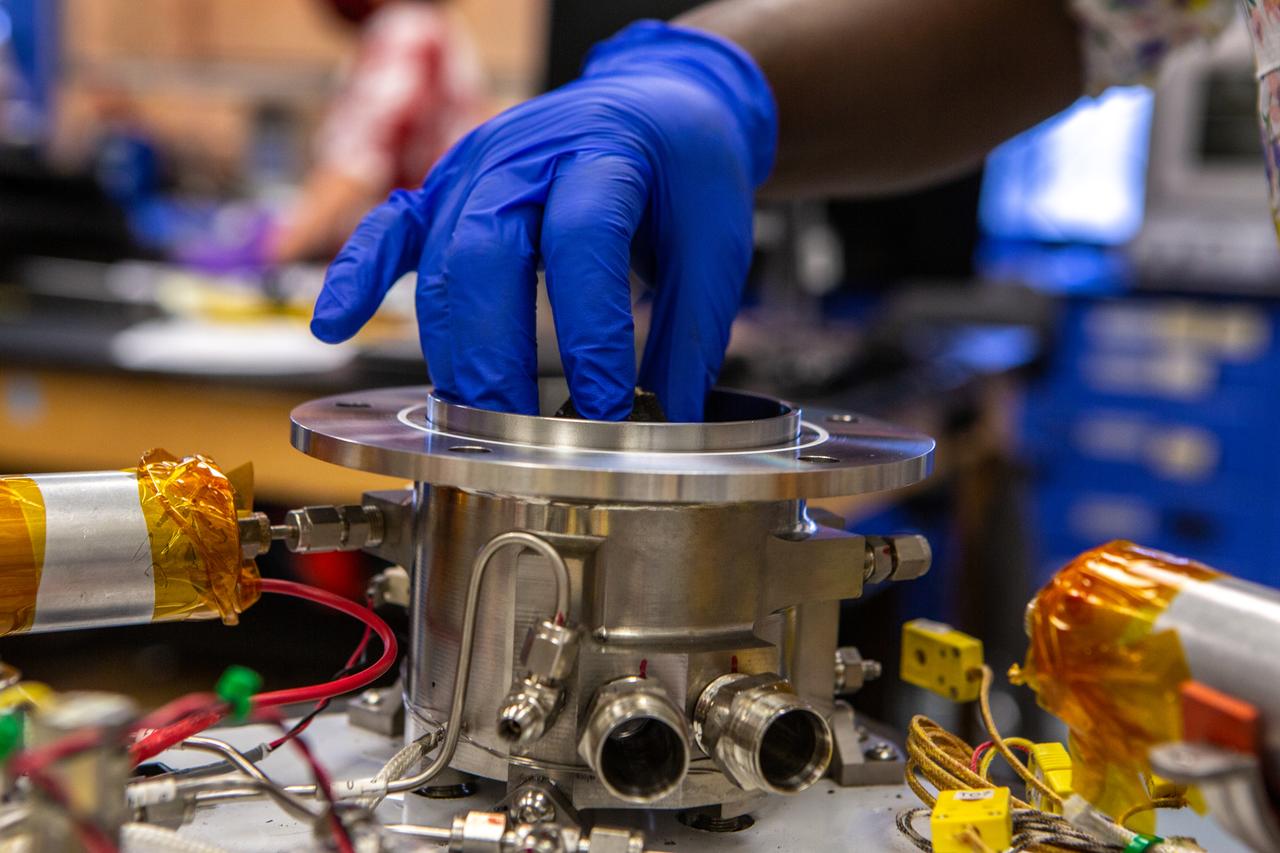
Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
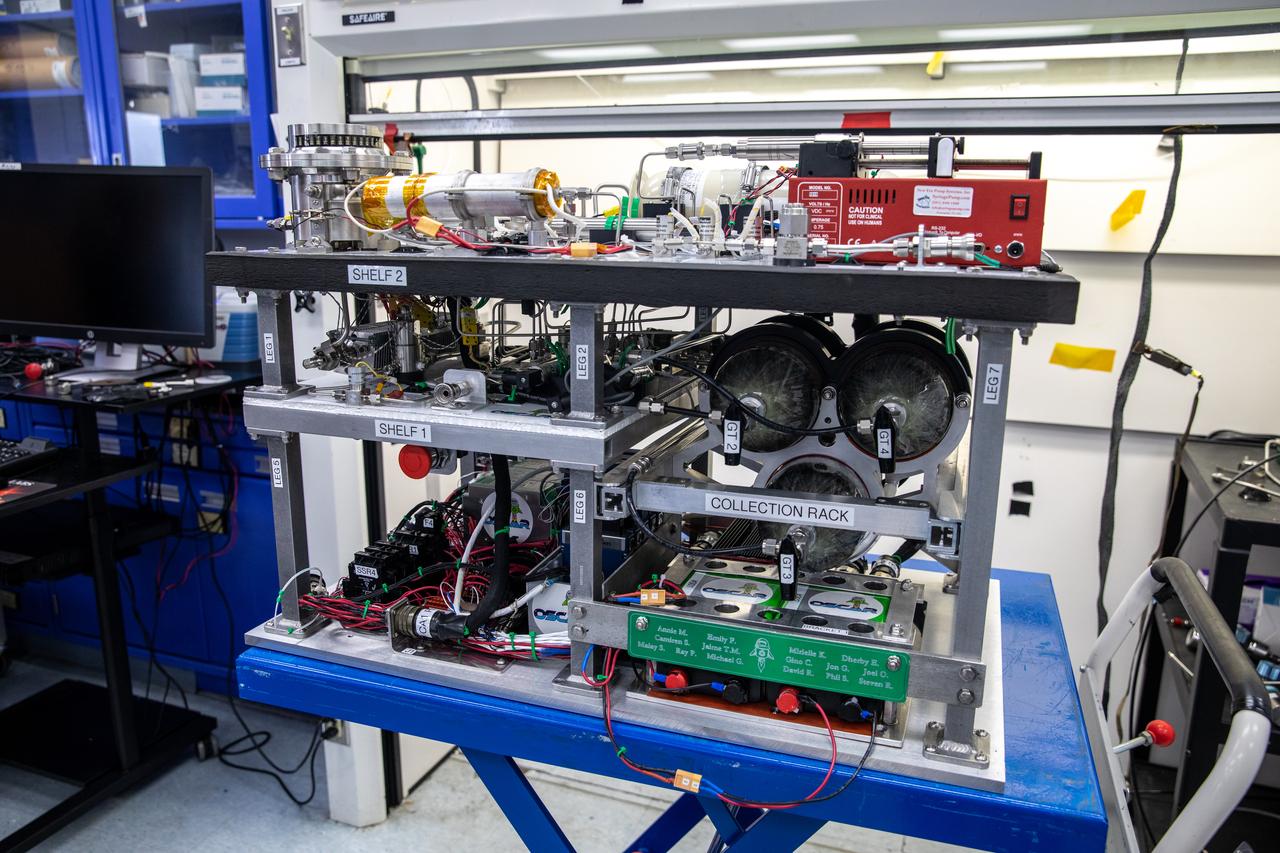
Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is inside the Applied Physics Lab inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
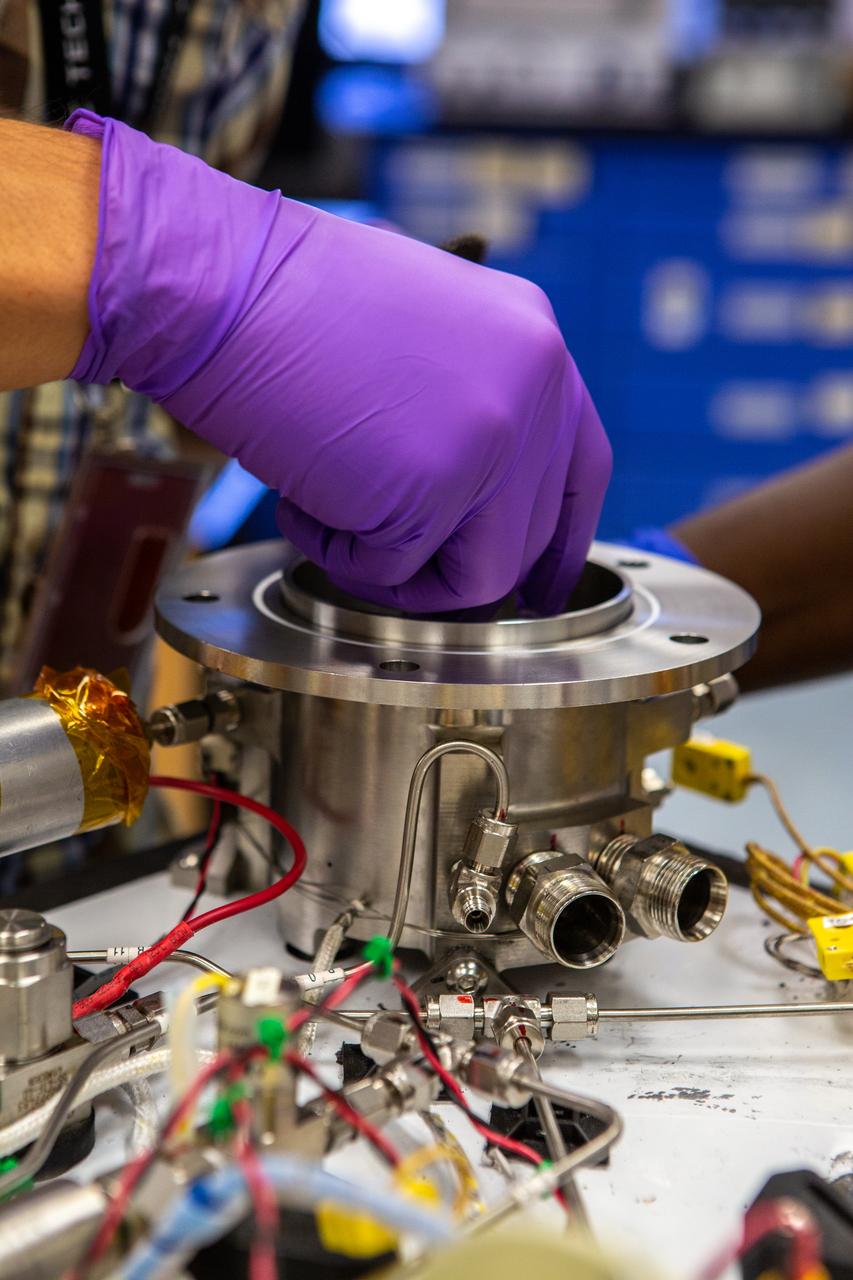

Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
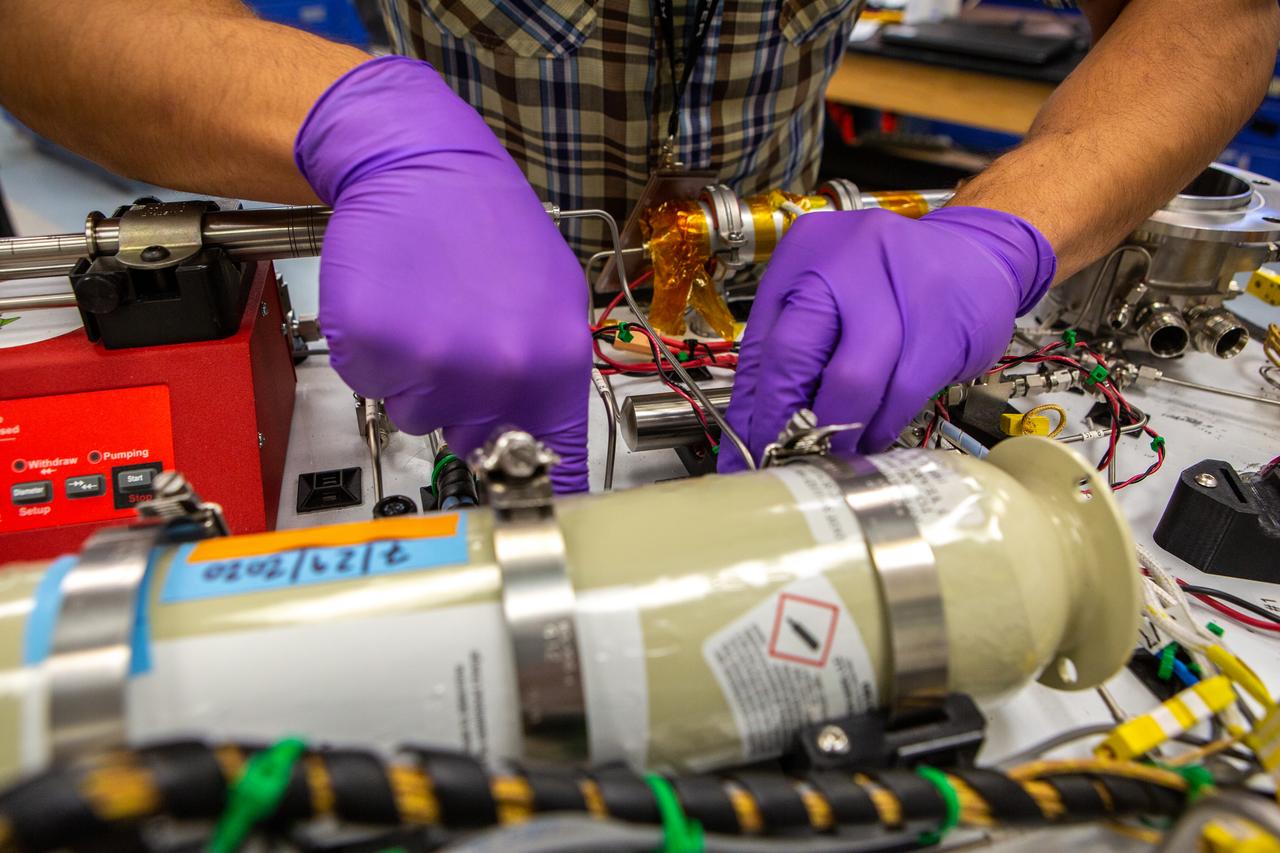

Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is inside the Applied Physics Lab inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
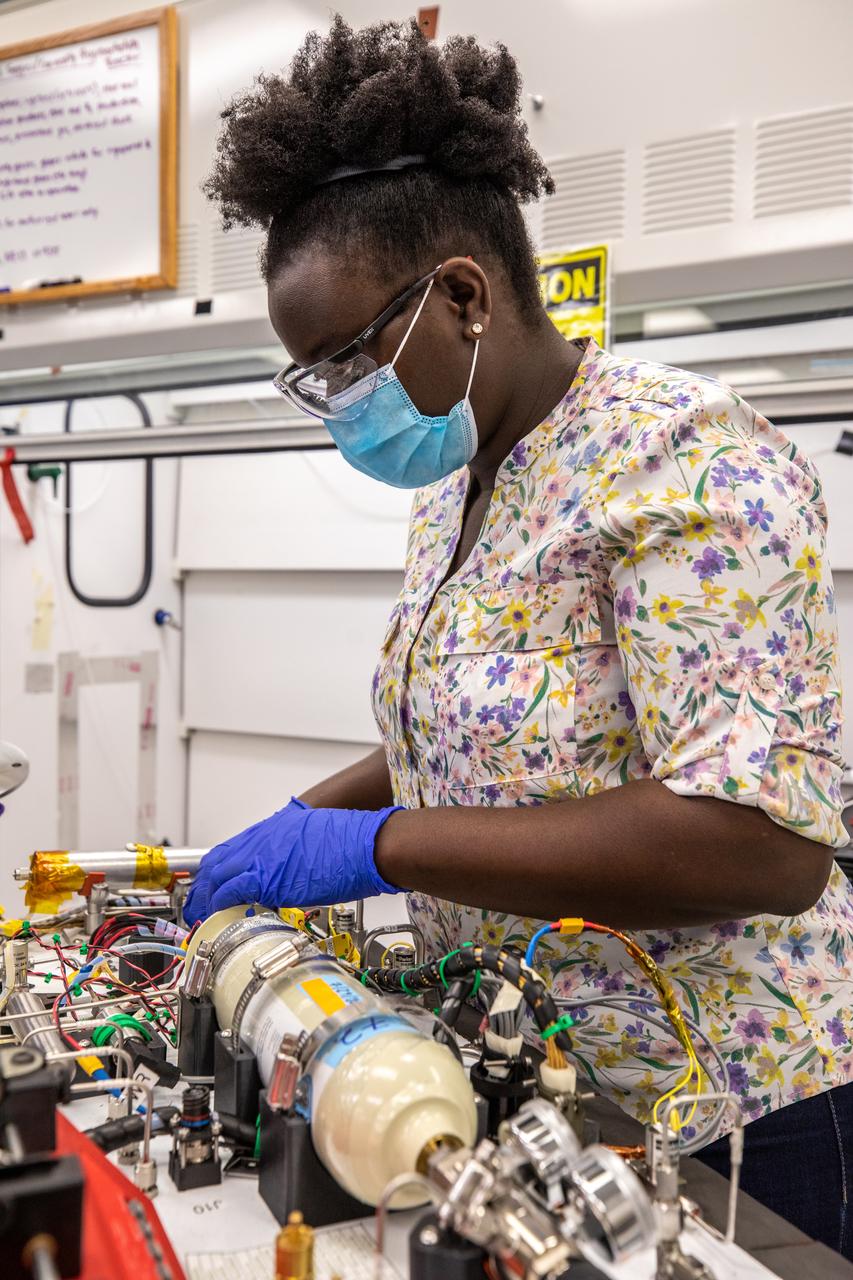

Technicians wearing protective equipment perform work for a future mission on flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 10, 2020. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
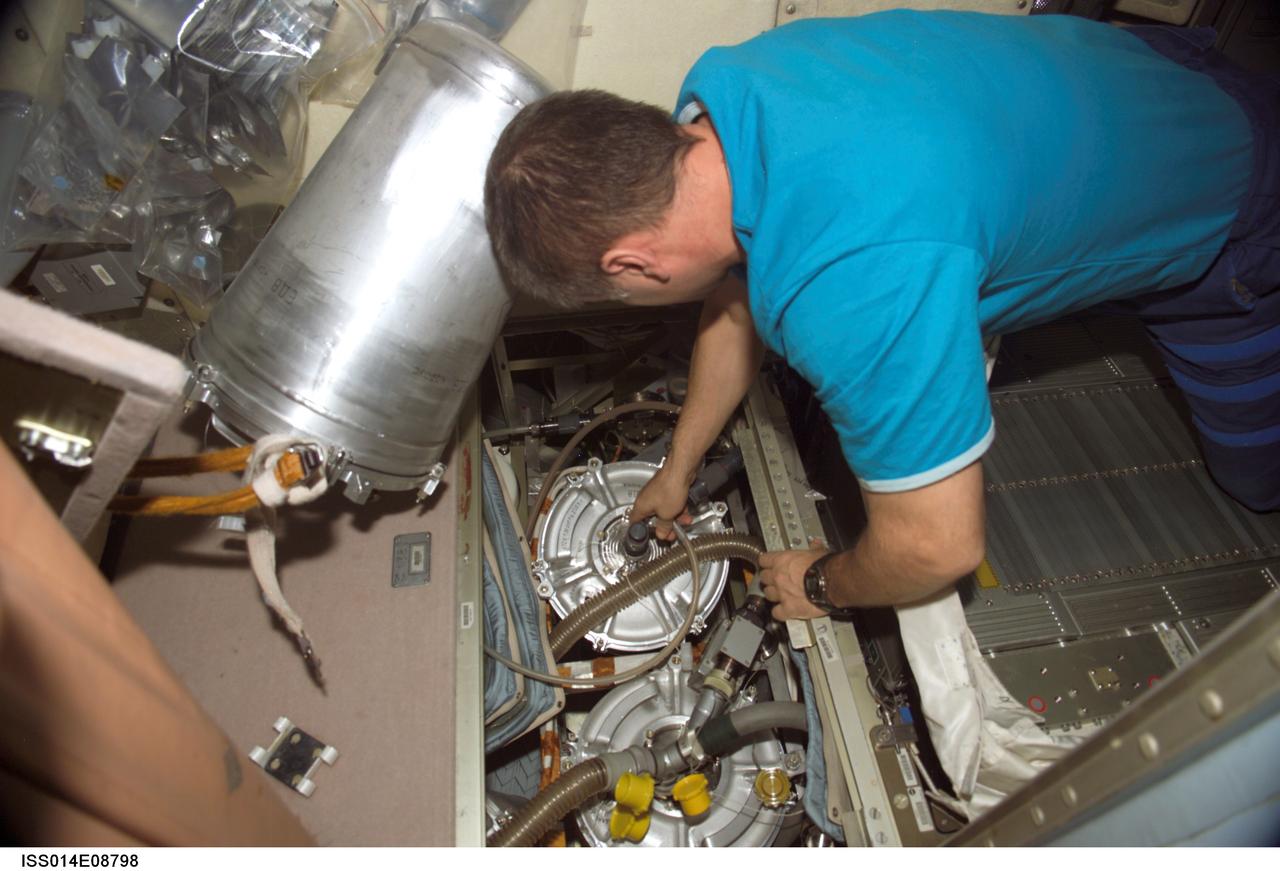

ISS014-E-08798 (29 Nov. 2006) --- Cosmonaut Mikhail Tyurin, Expedition 14 flight engineer, replaces the E-K pre-treat container and hose in the waste management system in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
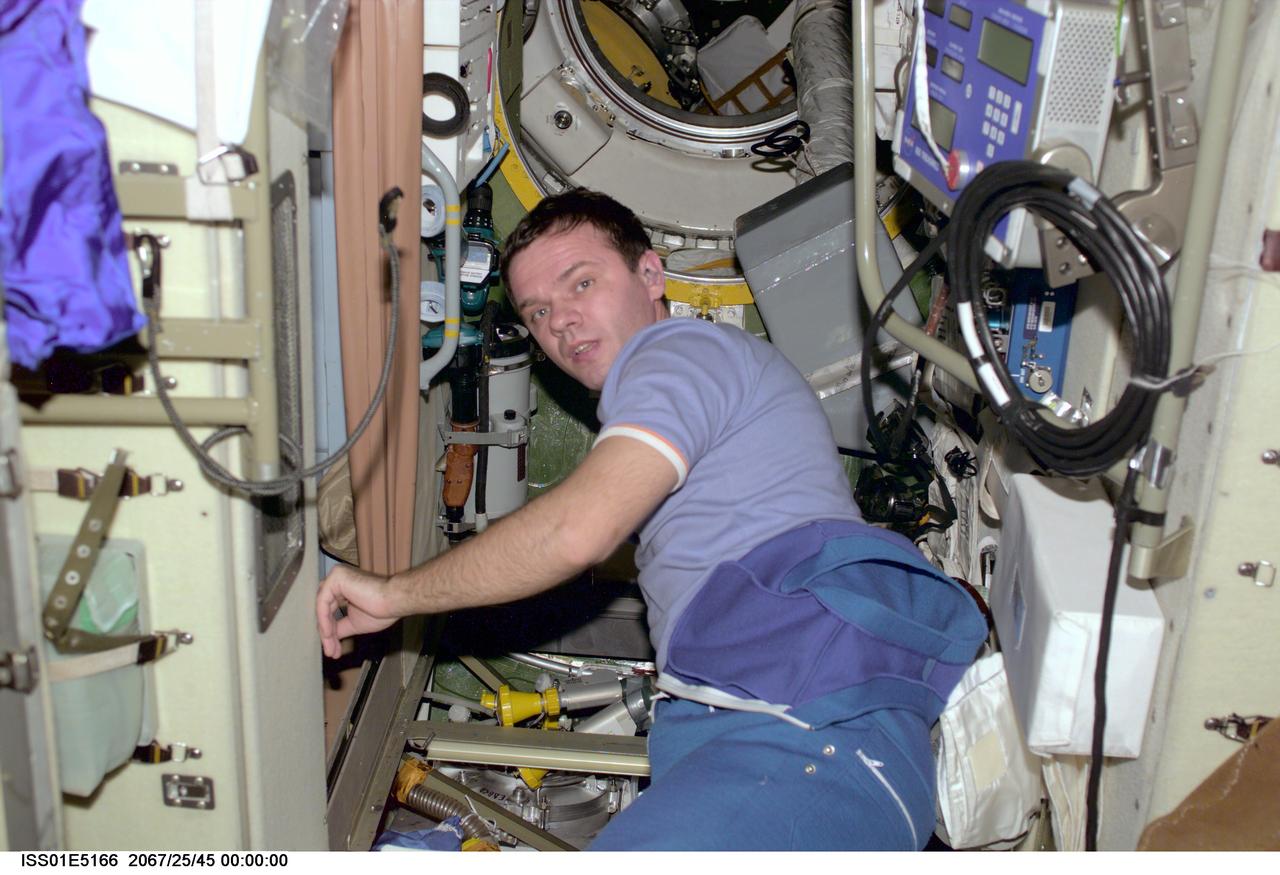

ISS01-E-5166 (December 2000) --- Cosmonaut Yuri P. Gidzenko, Soyuz commander for Expedition One, performs some electrician's work just outside the waste management compartment in the Zvezda Service Module of the Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS).
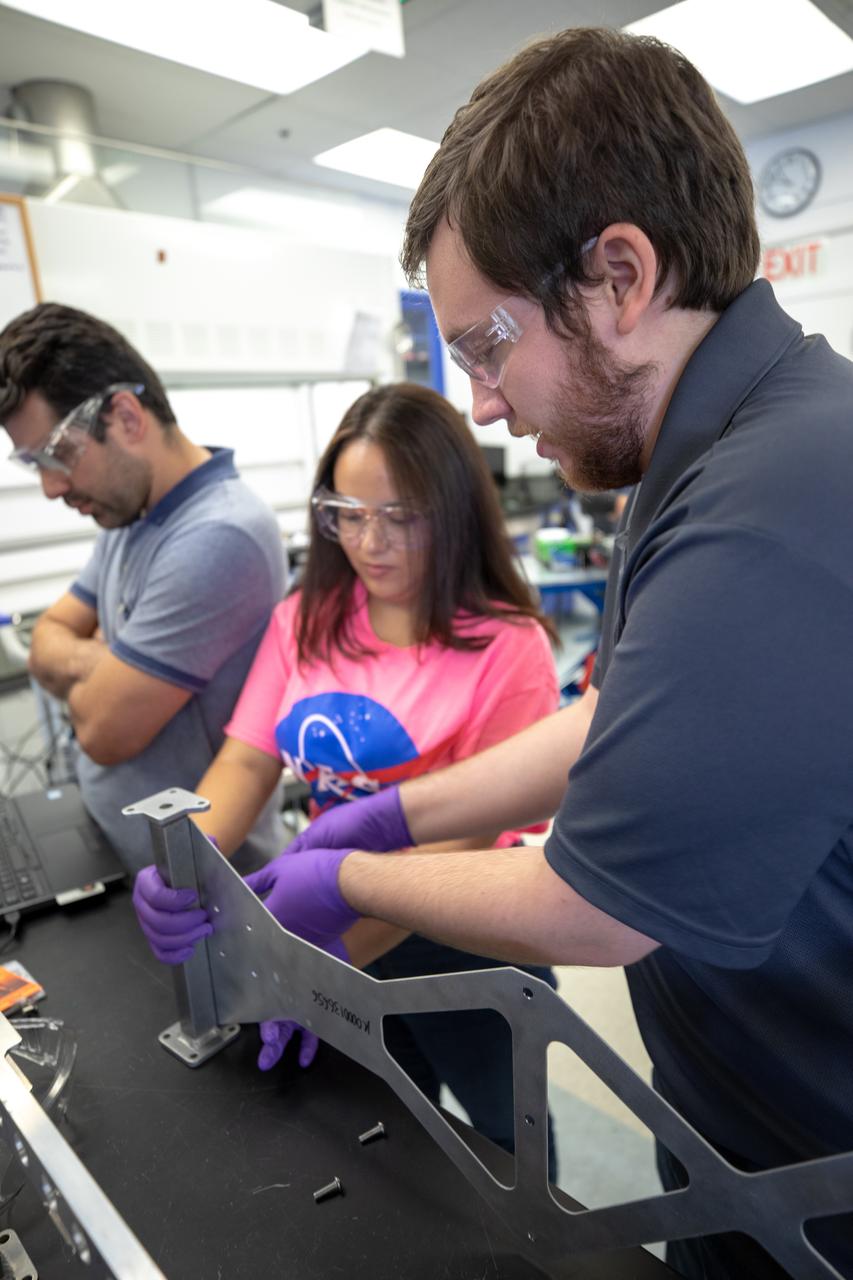

From left, Kennedy Space Center Mechanical Engineer Jaime Toro, NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) data acquisition and testing; Brianna Sandoval, OSCAR intern; and Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy employee providing support for OSCAR under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assemble the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
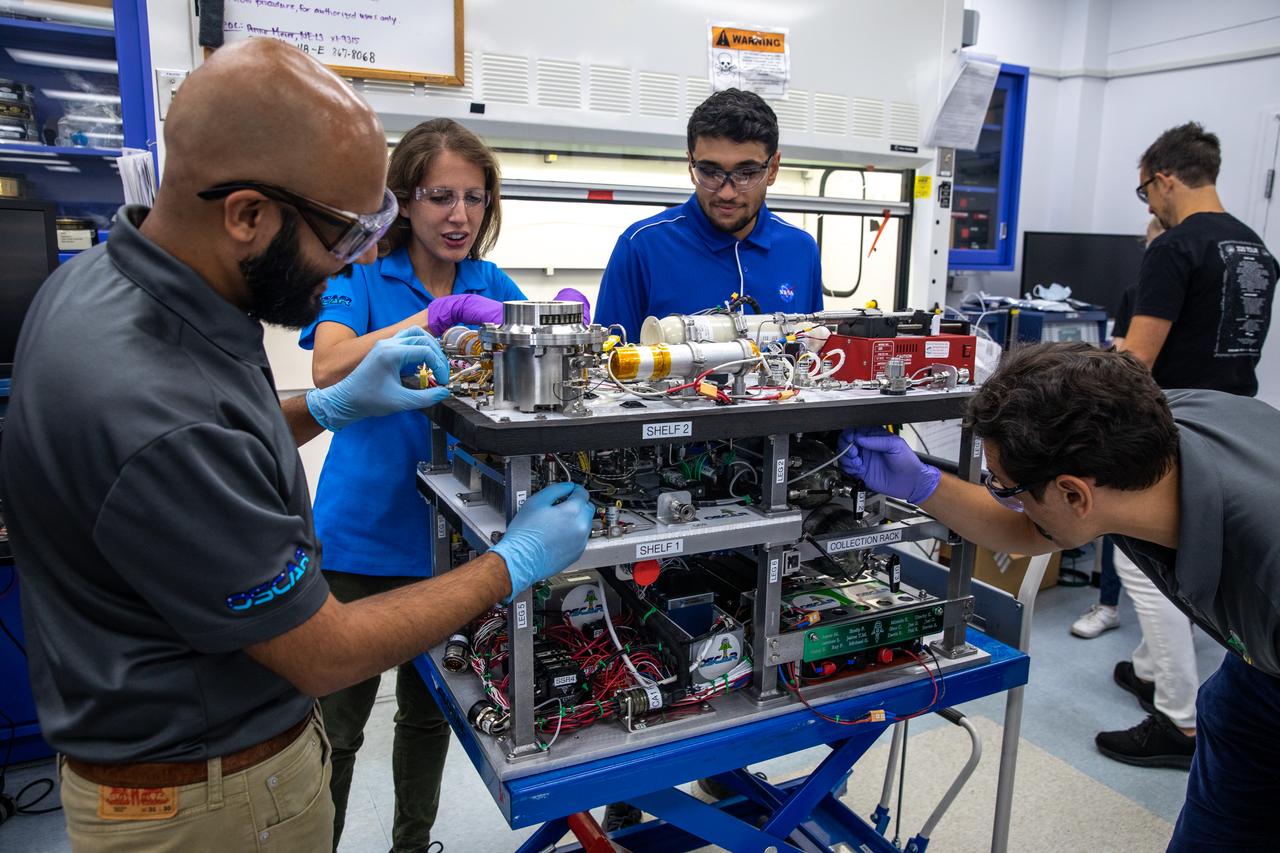
The Trash to Gas team members prepare flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
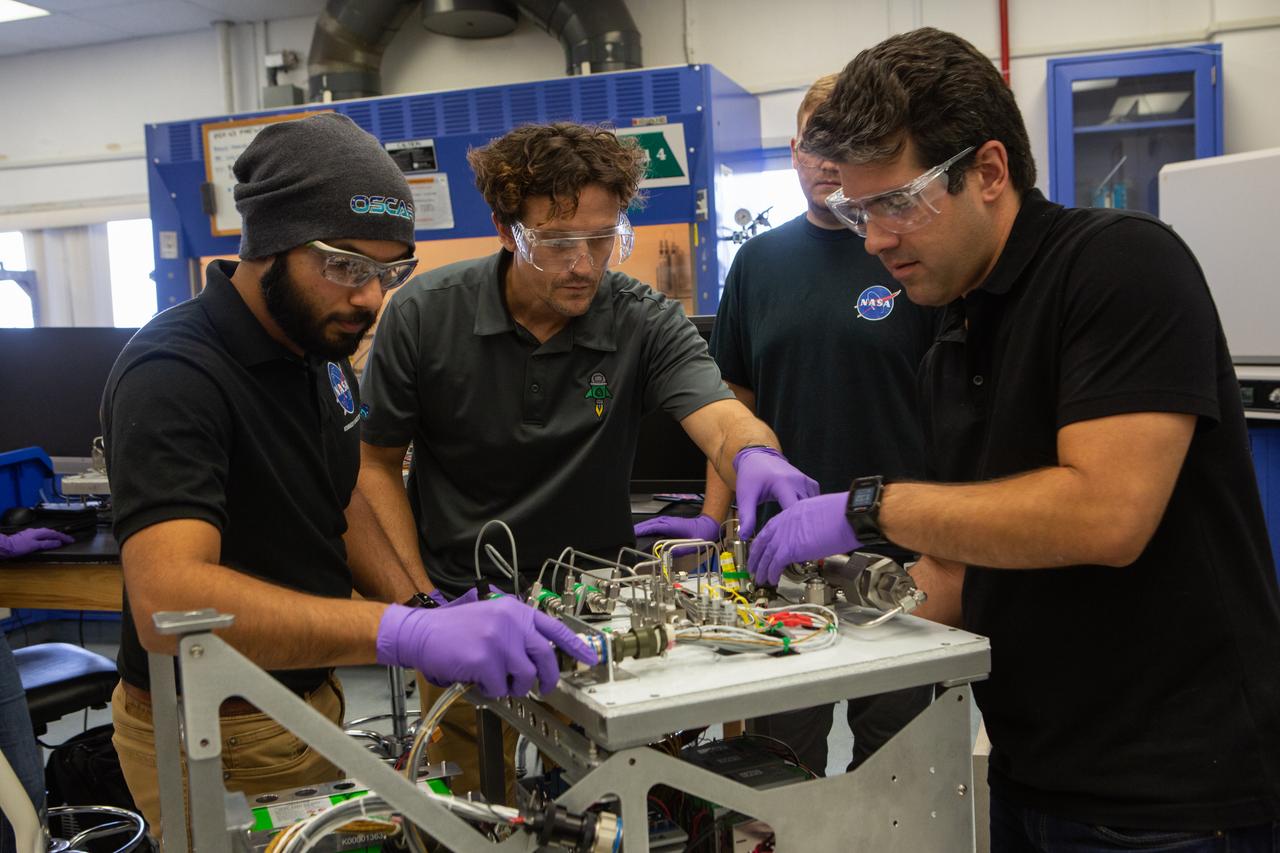

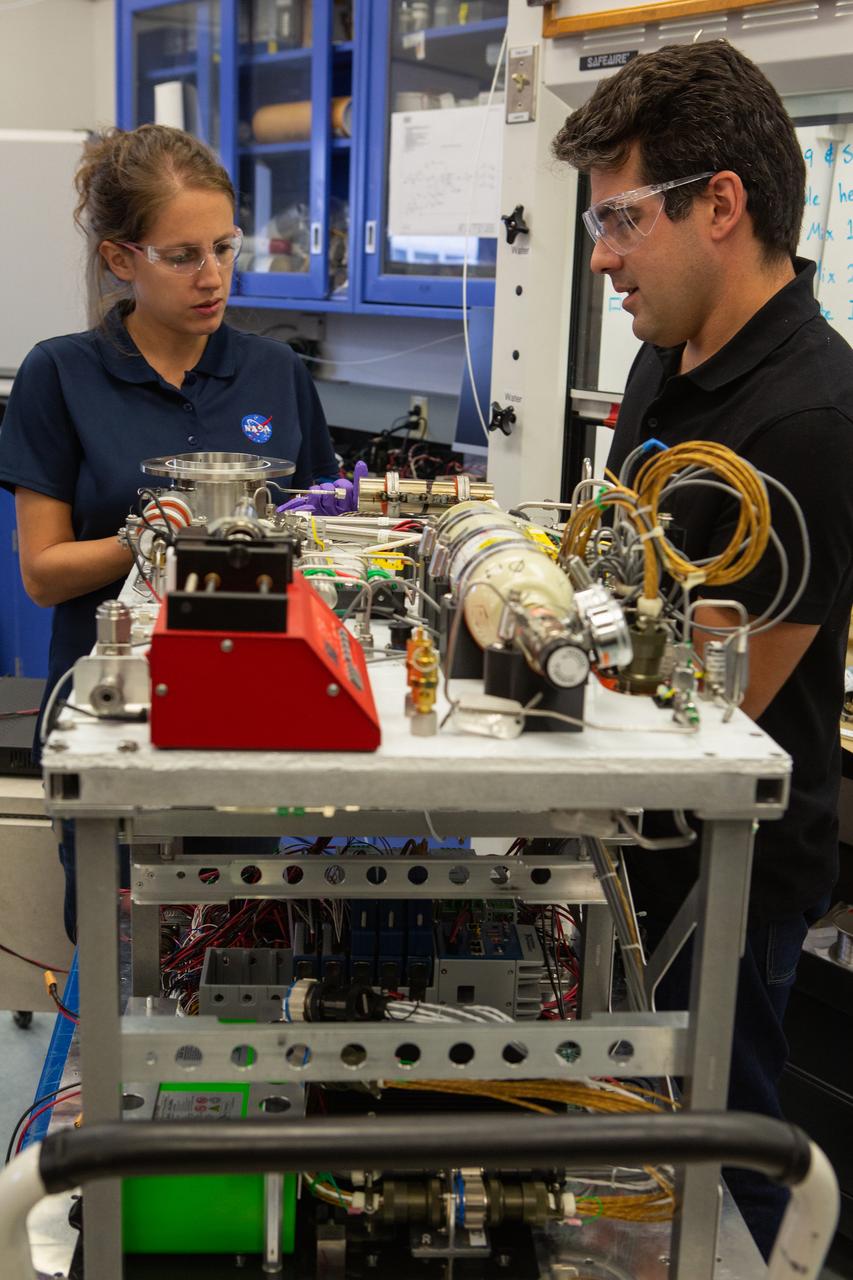
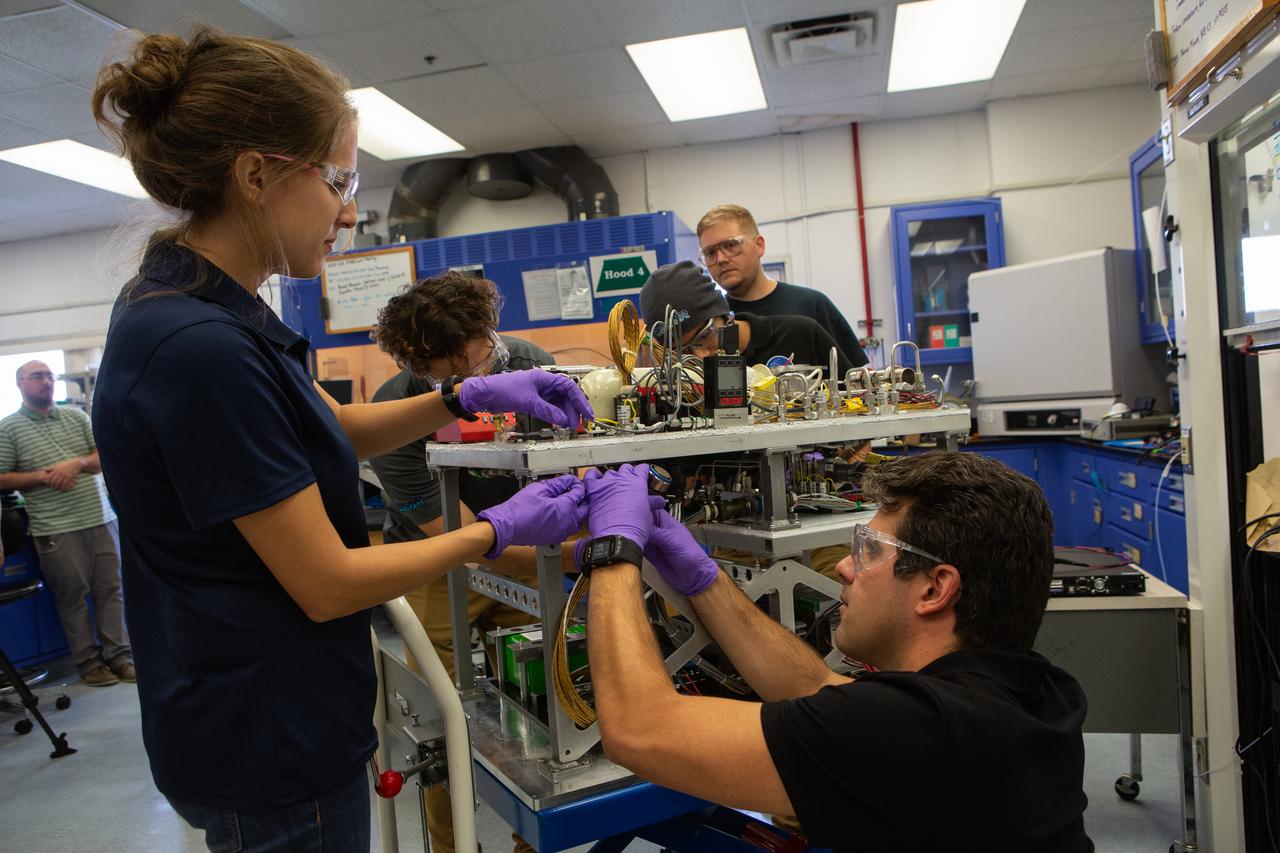
From left, team members Malay Shah, Gino Carro, Evan Bell and Jamie Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
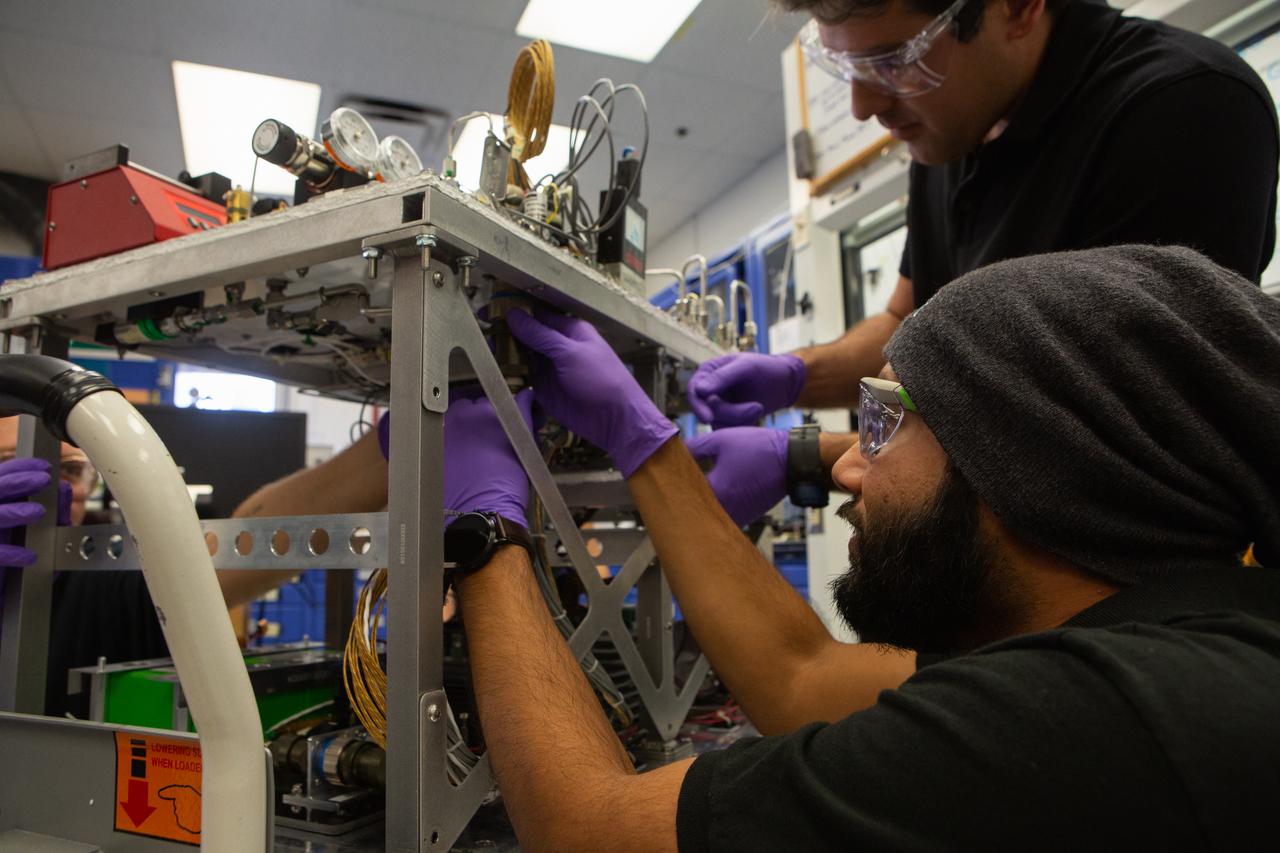
Team members Malay Shah, foreground, and Gino Carro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
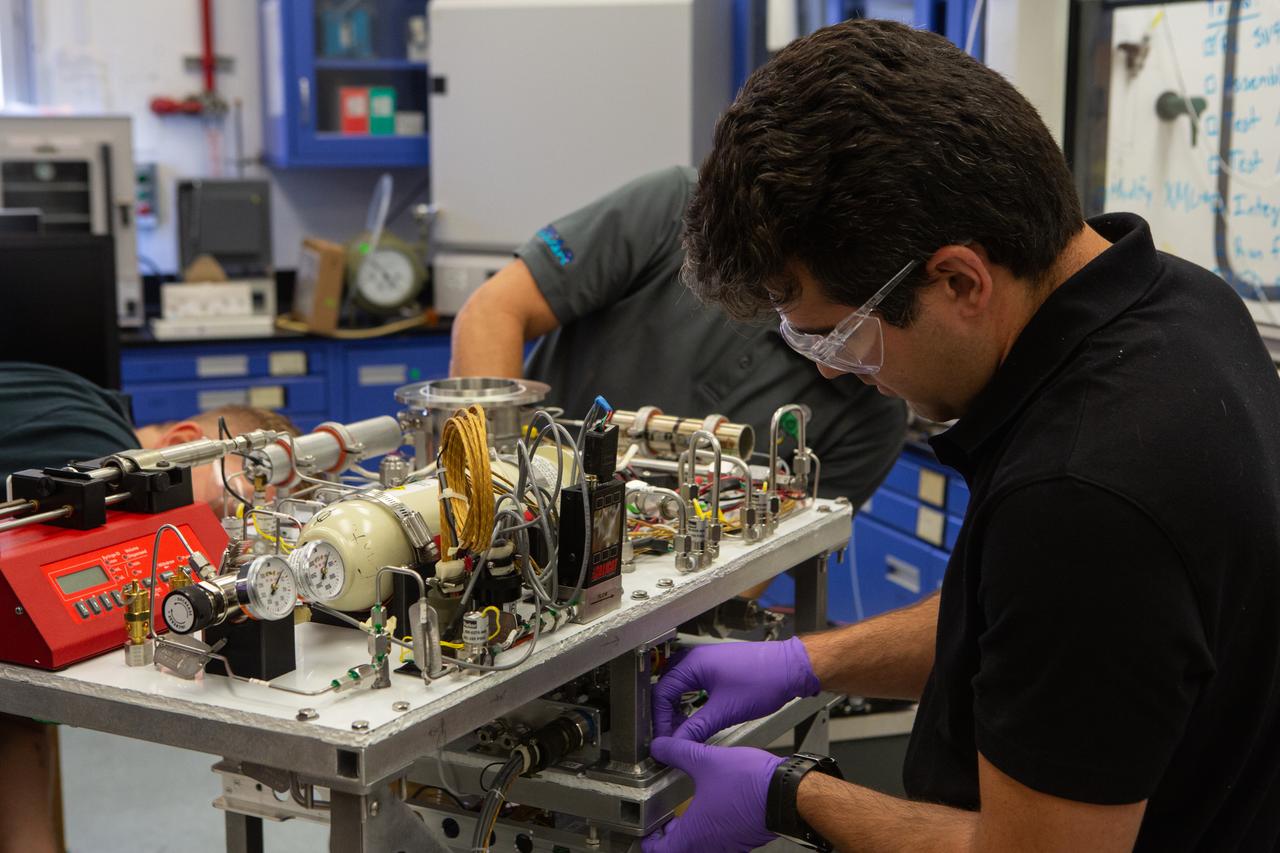
Jaime Toro assembles the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
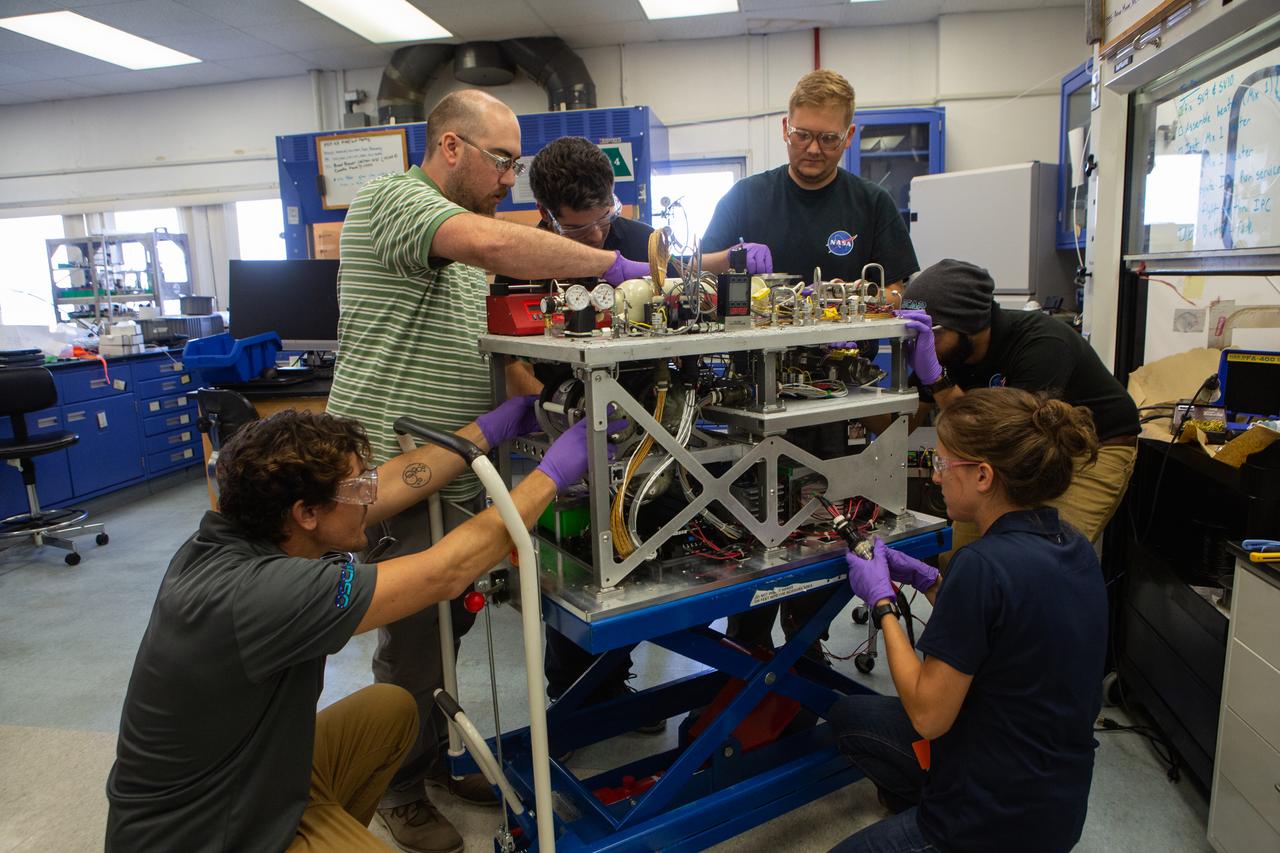

Team members assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Gino Carro, Tom Cauvel, Jaime Toro, Evan Bell, Malay Shah and Annie Meier. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
The Trash to Gas team members prepare flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
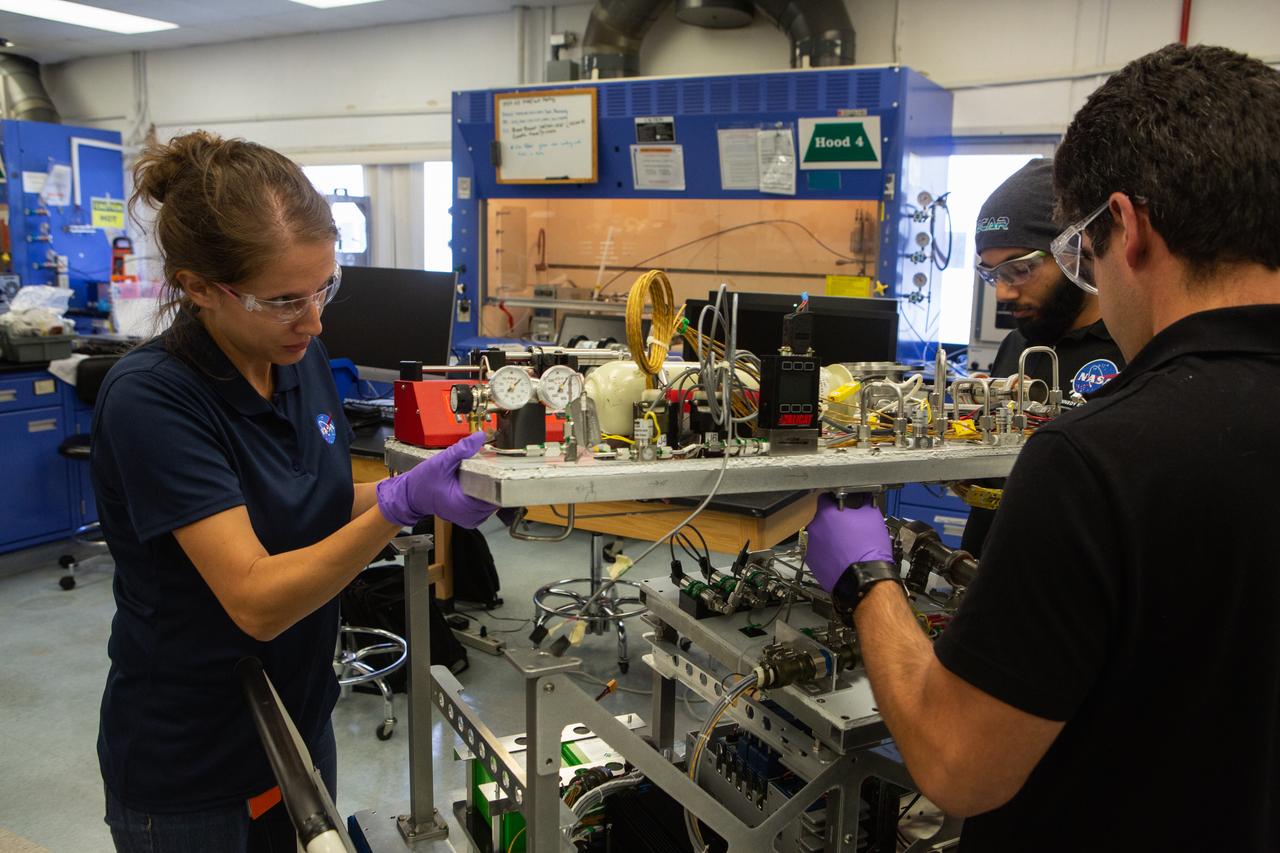

From left, team members Annie Meier, Malay Shah and Jamie Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
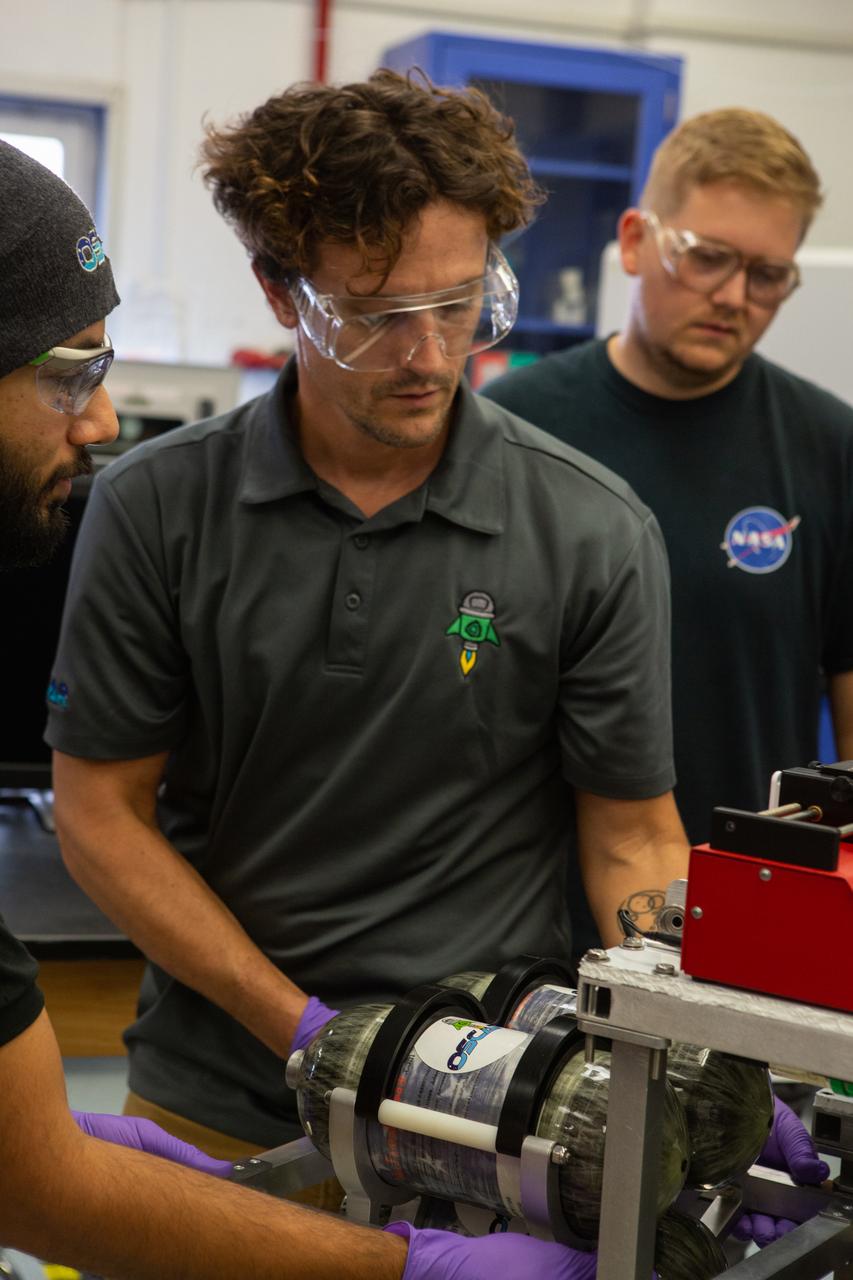

From left, team members Malay Shah, Gino Carro and Evan Bell assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
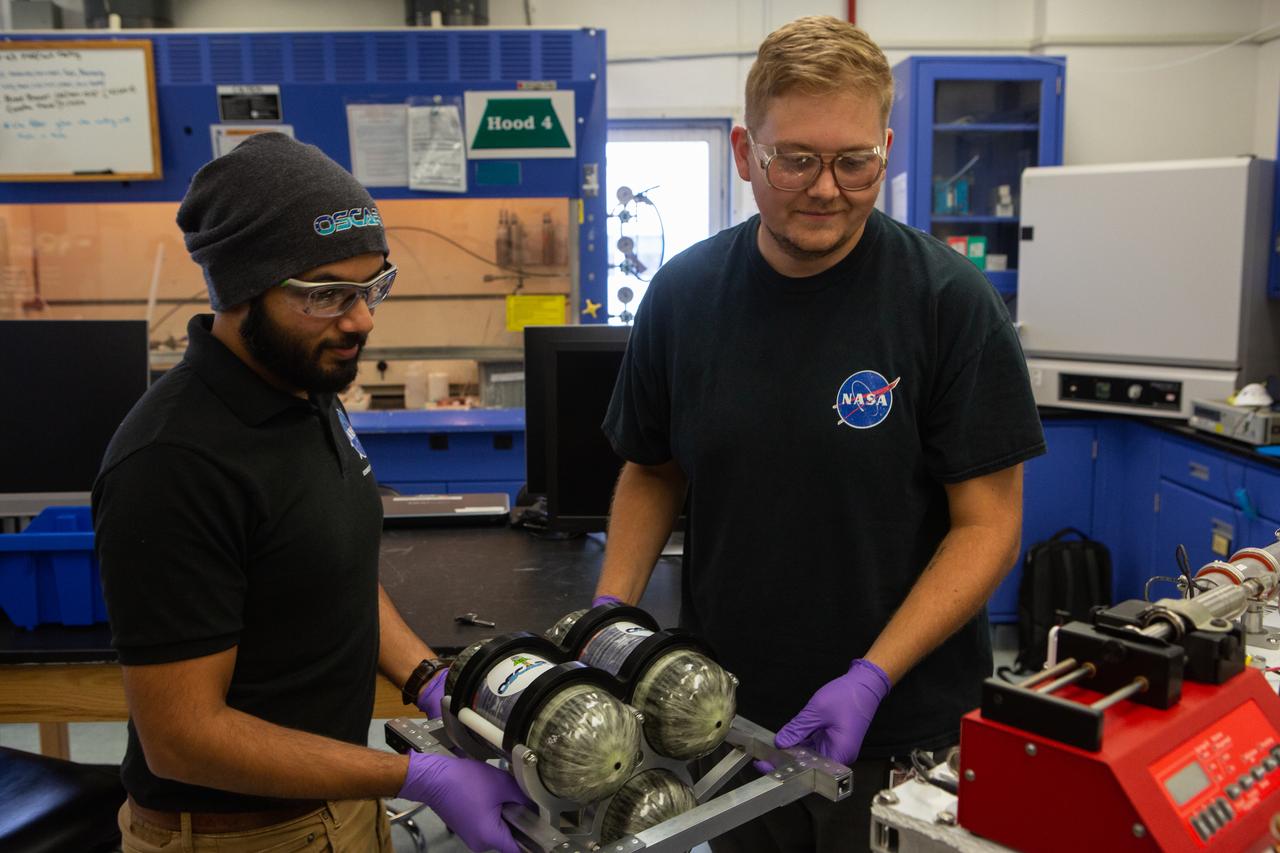

Team members Malay Shah, left, and Evan Bell assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.

The Trash to Gas team members prepare flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside Applied Physics lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
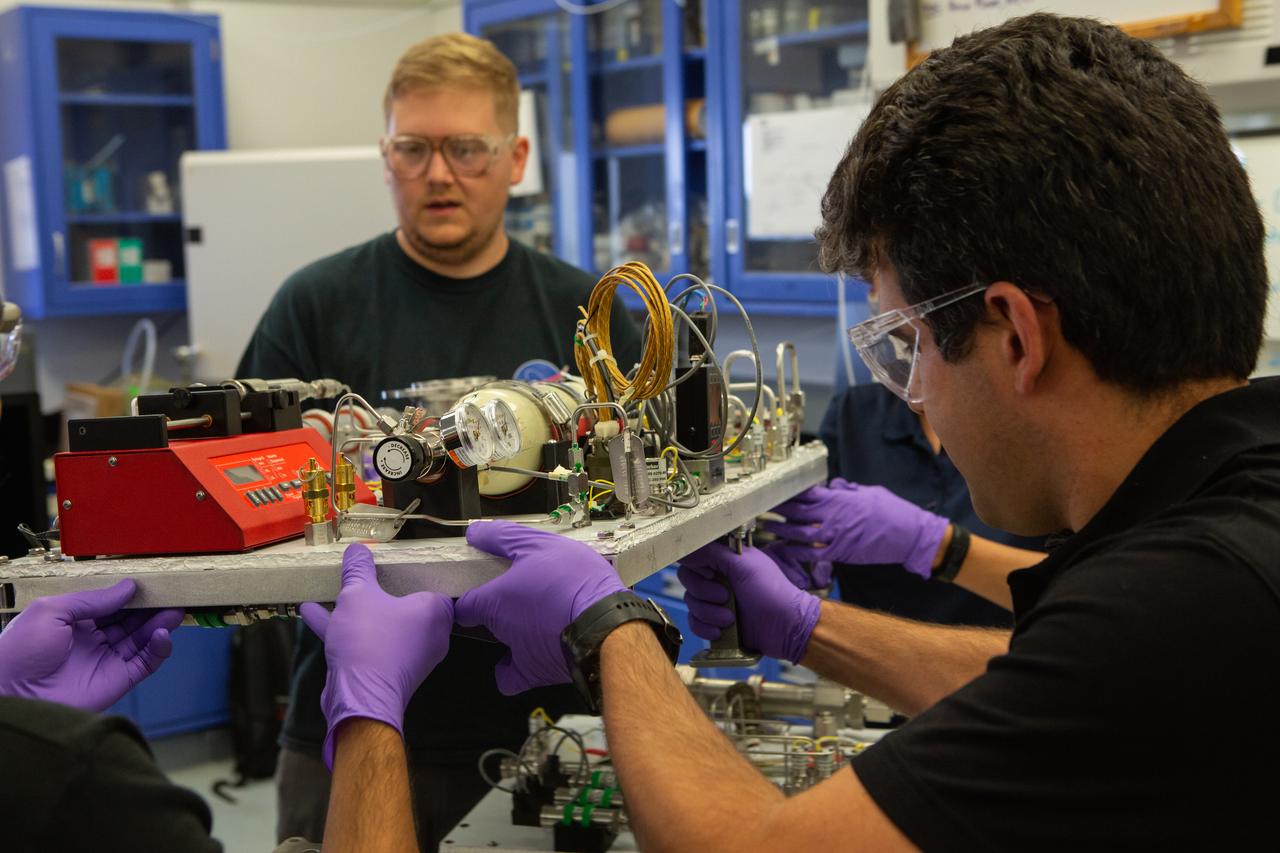
Team members Evan Bell, left, and Jaime Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
The Trash to Gas team members gather around the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

Team members Annie Meier, left, and Jamie Toro assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.

Team members assemble the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Annie Meier, Gino Carro, Evan Bell and Jamie Toro. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
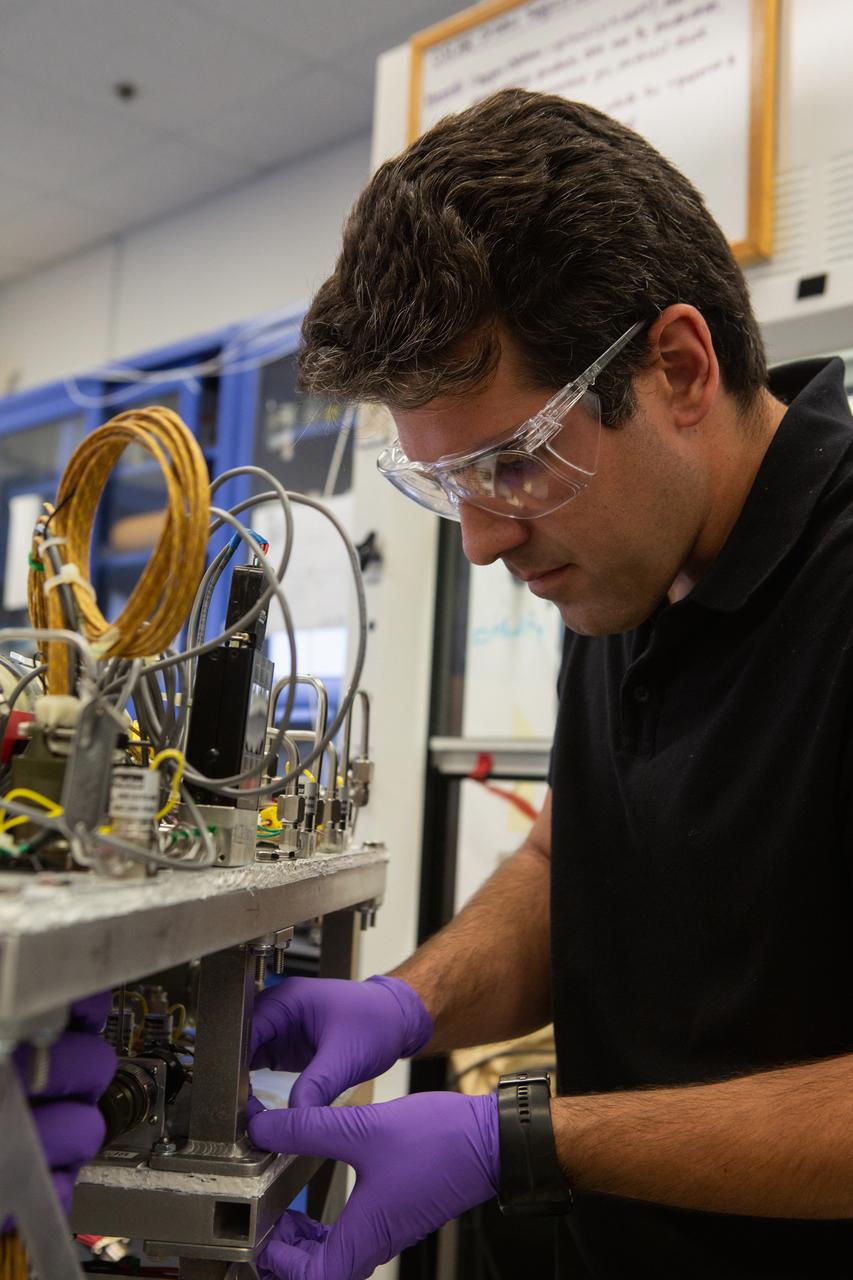

Jaime Toro assembles the flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.

A Trash to Gas team member prepares flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, inside the Applied Physics Lab in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 21, 2022. OSCAR began as an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
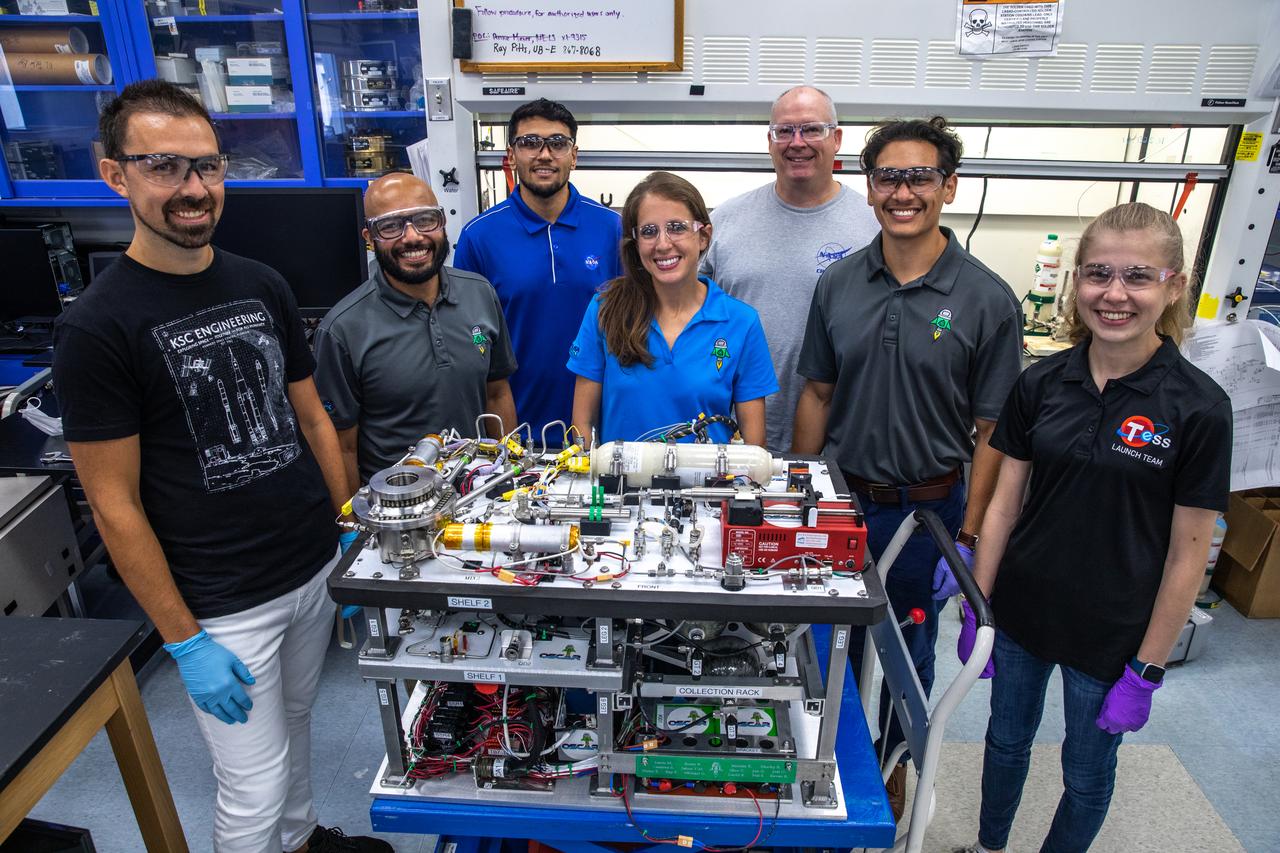
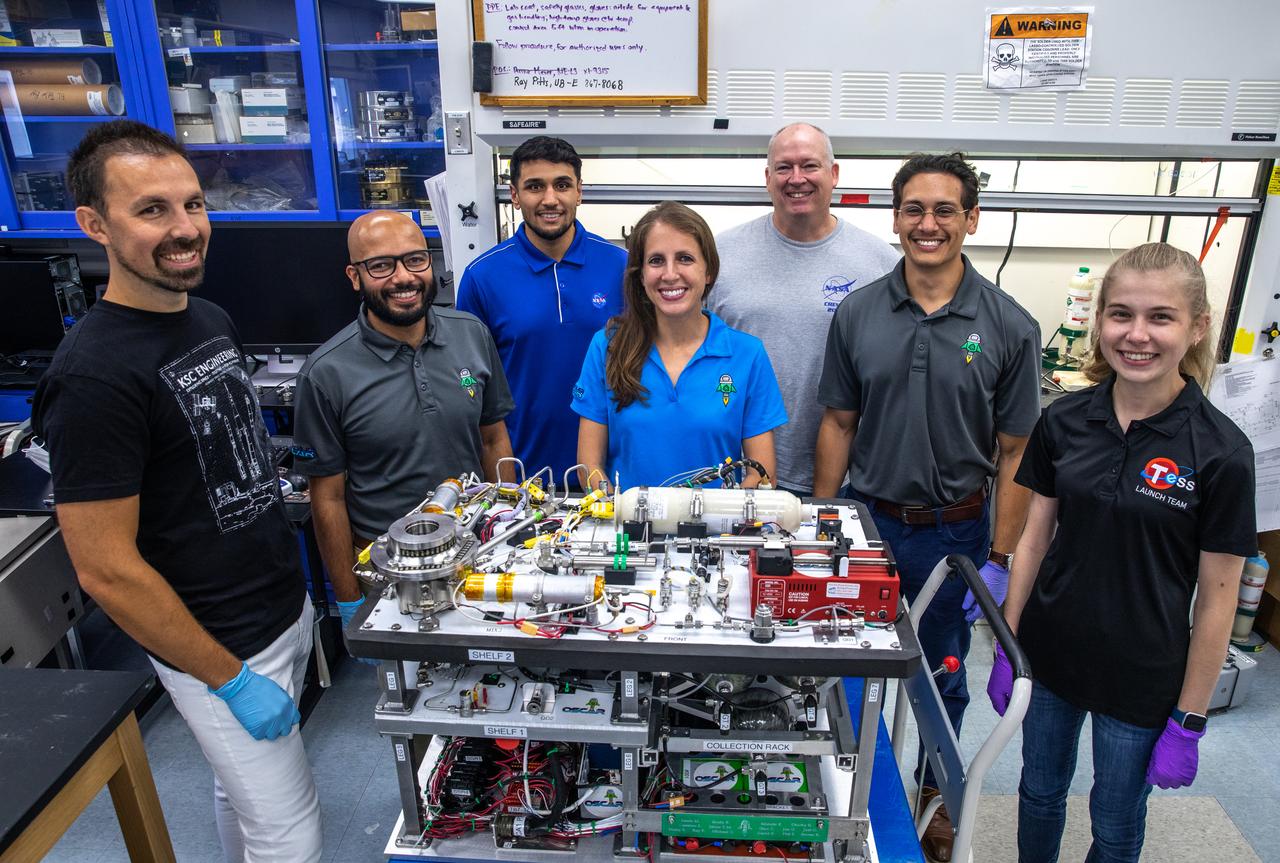
Members of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, team pause for a photo with the flight hardware on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Gino Carro, Tom Cauvel, Jaime Toro, Evan Bell, Malay Shah and Annie Meier. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
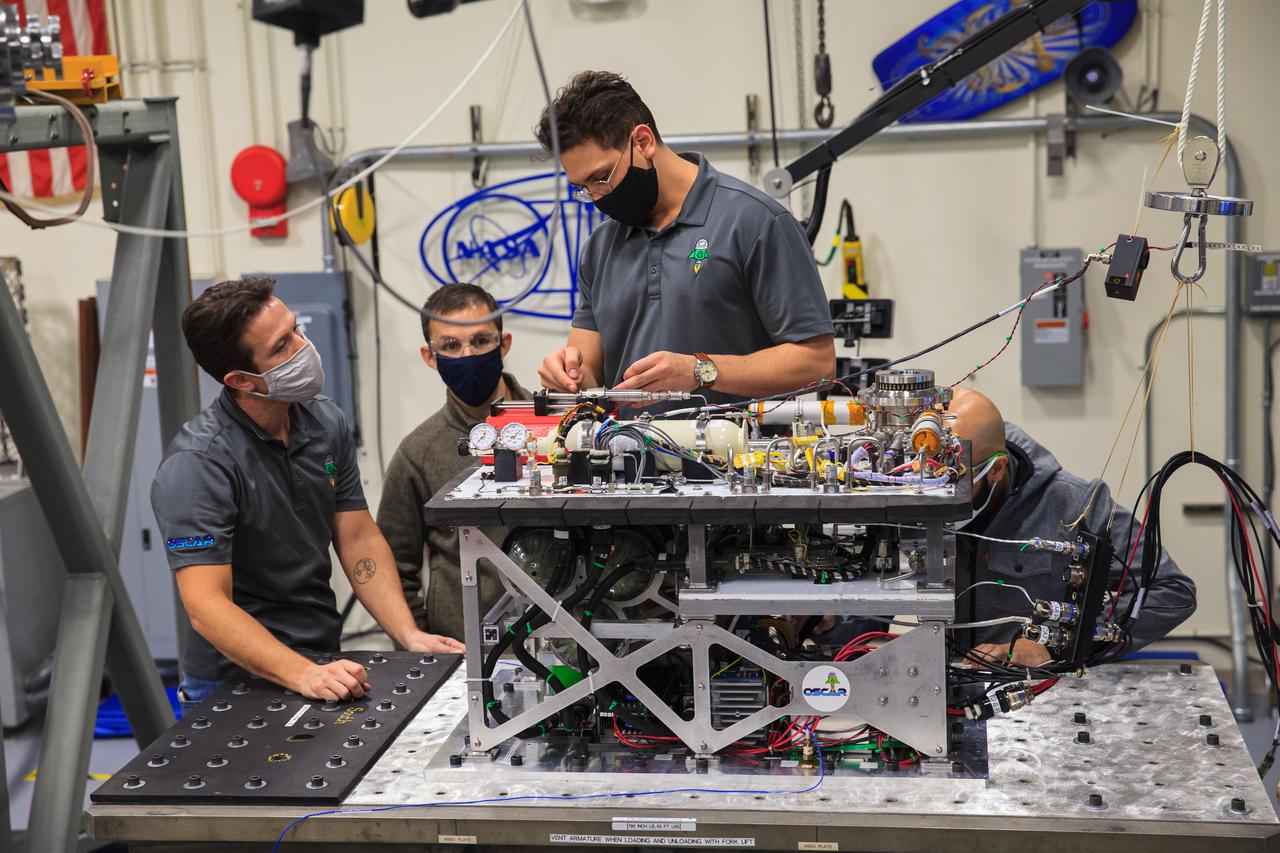
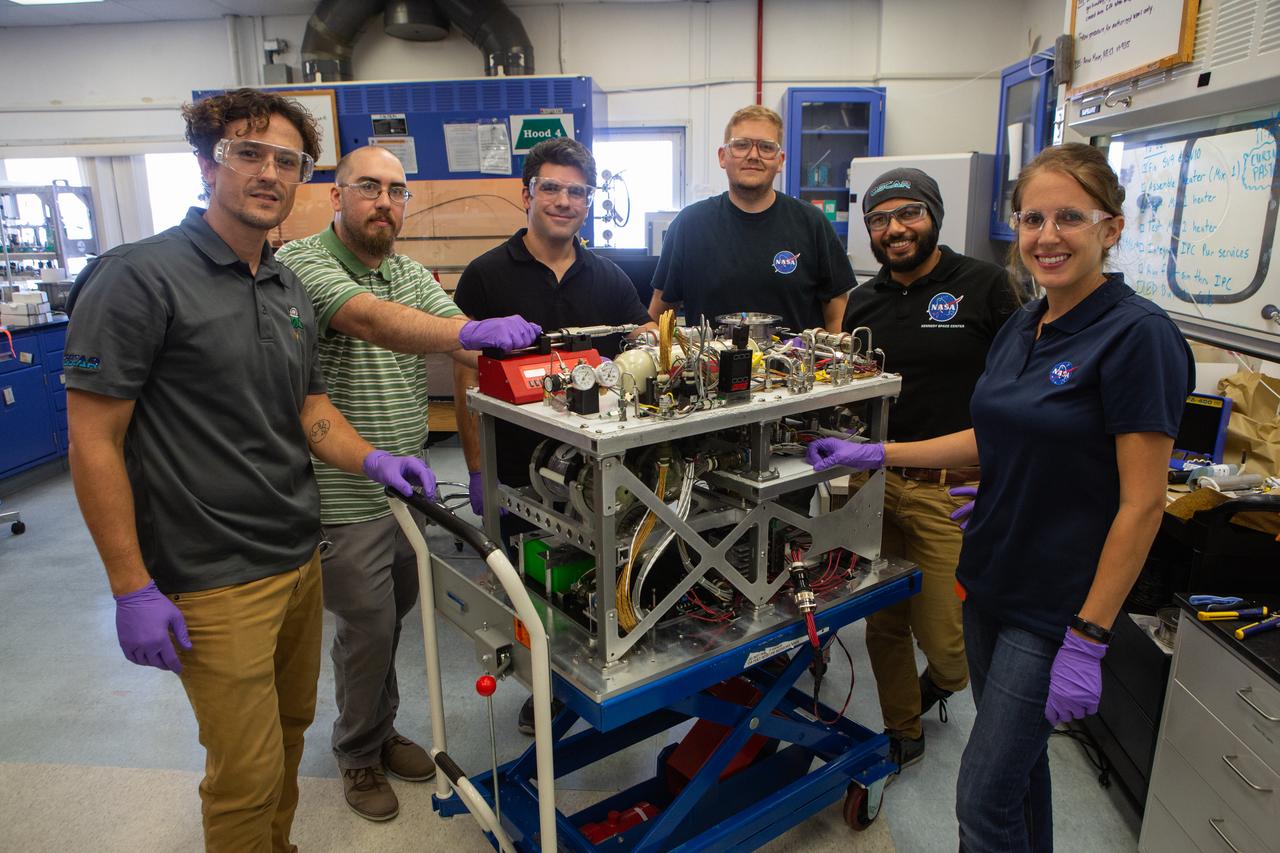
Kennedy Space Center engineers conduct vibration tests inside the Florida spaceport’s Vibration Test Lab on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the suborbital flight of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, slated for later this year. From left are Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract; David Rinderknecht, NASA chemical engineer; Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for OSCAR; and Malay Shah, NASA thermal/fluid analysis engineer. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.
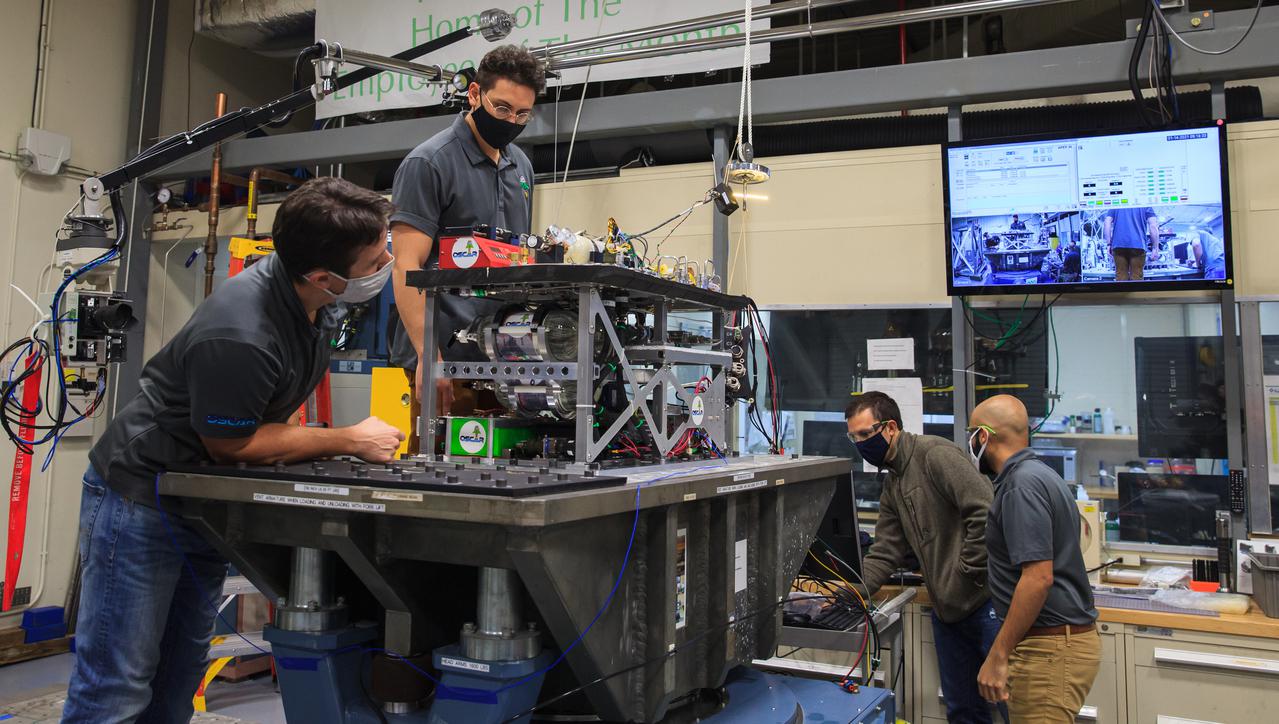
Kennedy Space Center engineers conduct vibration tests inside the Florida spaceport’s Vibration Test Lab on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the suborbital flight of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, slated for later this year. From left are Gino Carro, a pressure vessels and systems engineer for the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract; Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for OSCAR; David Rinderknecht, NASA chemical engineer; and Malay Shah, NASA thermal/fluid analysis engineer. Beginning as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space.

This image depicts a layout of the Skylab workshop 1-G trainer crew quarters. At left, in the sleep compartment, astronauts slept strapped to the walls of cubicles and showered at the center. Next right was the waste management area where wastes were processed and disposed. Upper right was the wardroom where astronauts prepared their meals and foods were stored. In the experiment operation area, upper left, against the far wall, was the lower-body negative-pressure device (Skylab Experiment M092) and the Ergometer for the vectorcardiogram experiment (Skylab Experiment M063). The trainers and mockups were useful in the developmental phase, while engineers and astronauts were still working out optimum designs. They provided much data applicable to the manufacture of the flight articles.
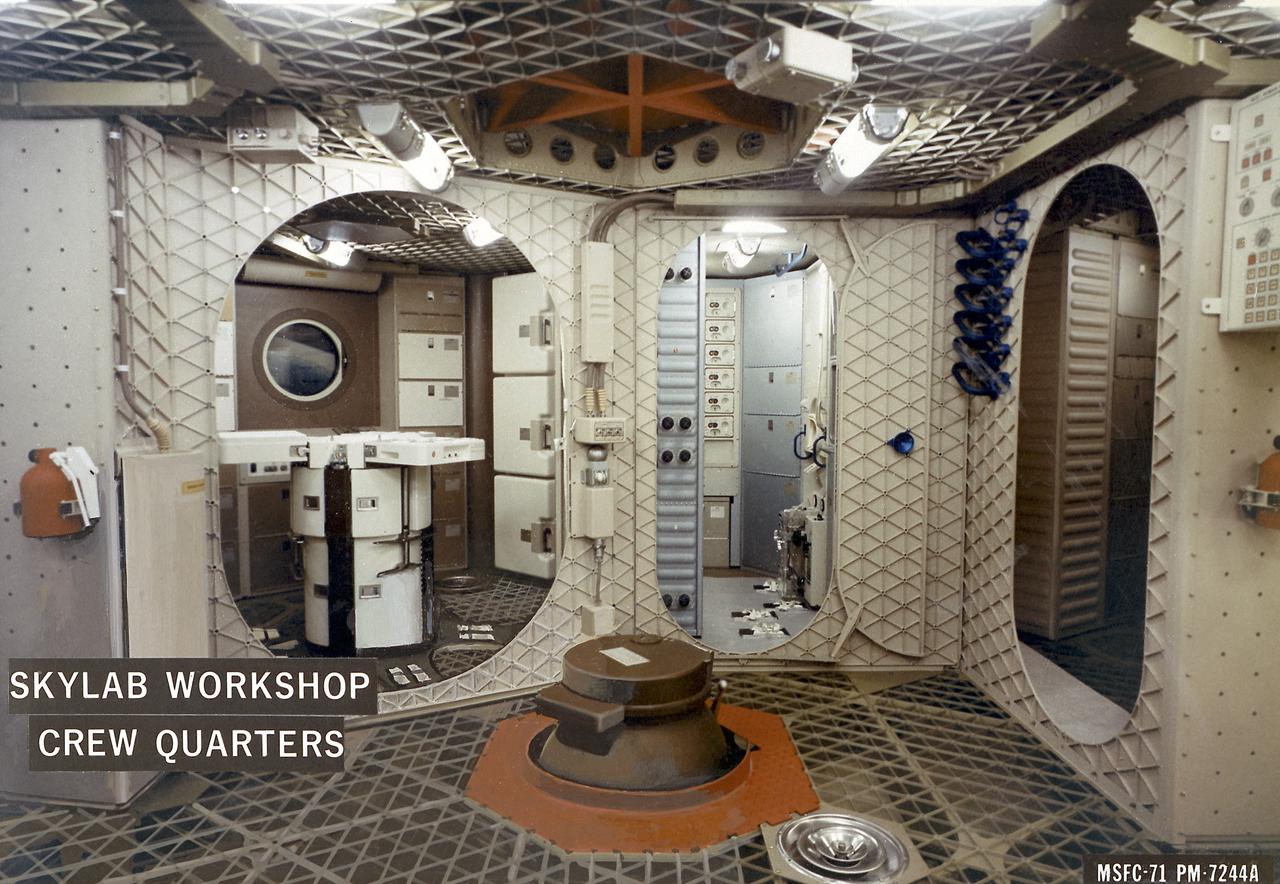

The wardroom deck of the Orbital Workshop, showing the living quarters arrangement, is seen here in good detail. From left to right is the dining area, waste management, and sleeping quarters. Portable restraints are on the wall beside the sleeping quarters. The ergometer for the vectorcardiograph (Experiment - M093) and lower-body Negative Pressure (Experiment M092) unit, used in some of the medical experiments, are in the foreground. The round brown object in the center of the room is the trash disposal airlock.
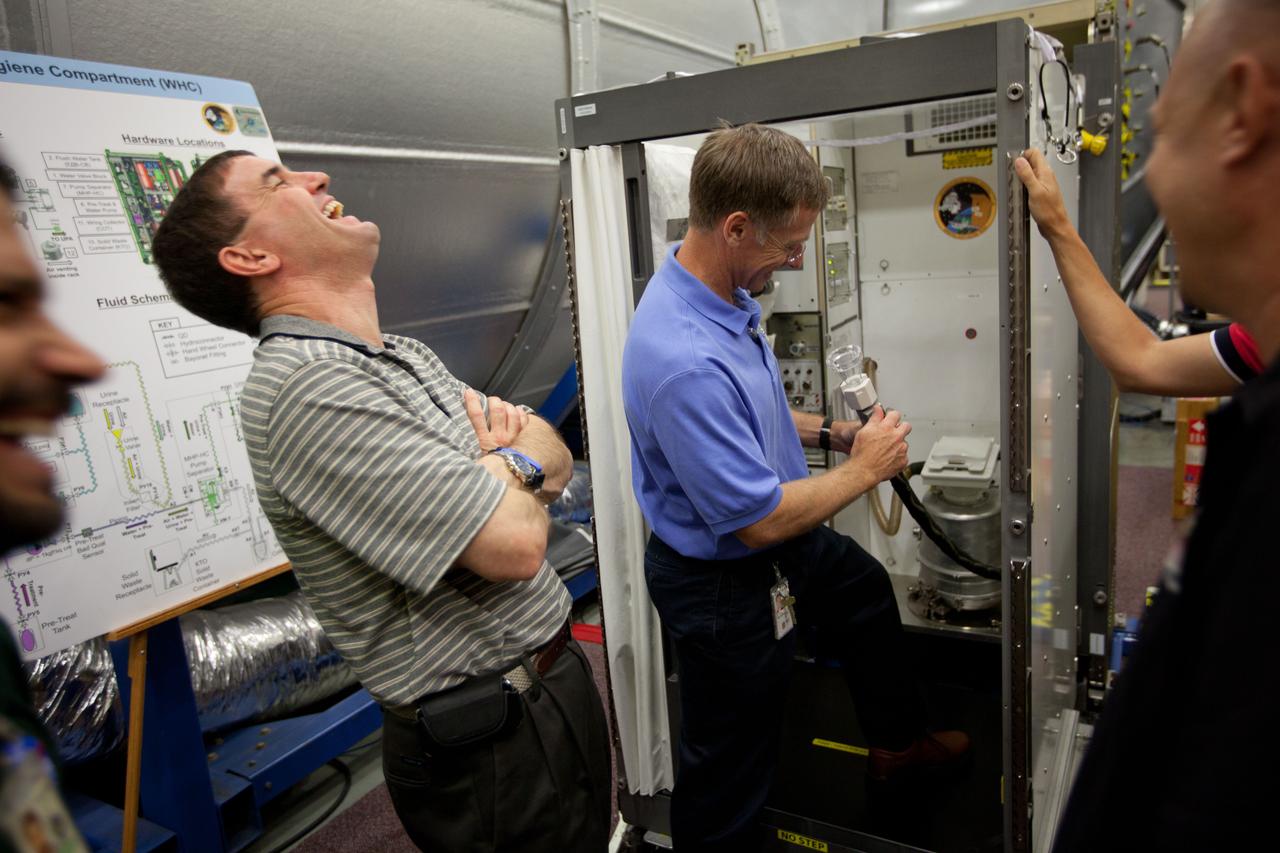

JSC2011-E-060140 (29 June 2011) --- NASA astronaut Rex Walheim laughs with his crewmates as STS-135 commander Chris Ferguson gets a refresher on the use of the waste management system on the International Space Station as the crew trains at NASA?s Johnson Space Center June 29, 2011. The day's training marked the crew's final scheduled sessions in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at JSC. Photo credit: NASA Photo/Houston Chronicle, Smiley N. Pool
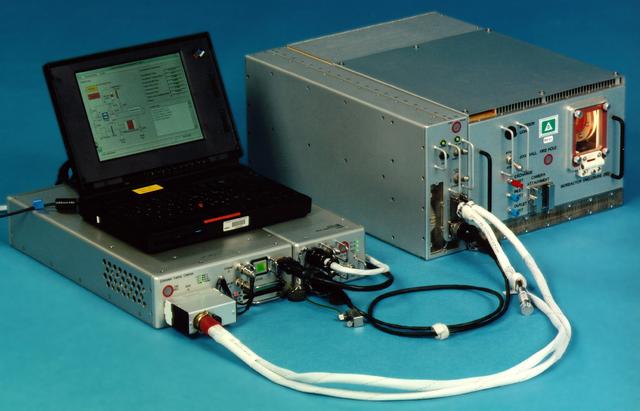

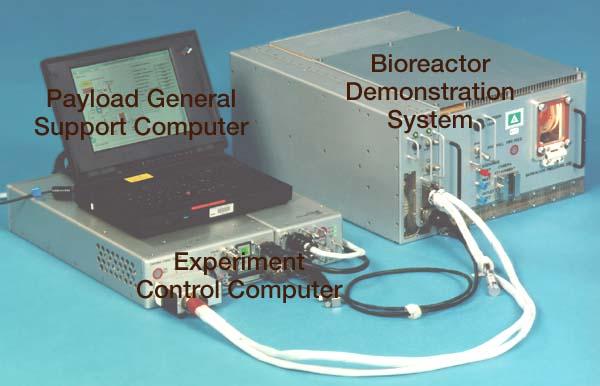
Bioreactor Demonstration System (BDS) comprises an electronics module, a gas supply module, and the incubator module housing the rotating wall vessel and its support systems. Nutrient media are pumped through an oxygenator and the culture vessel. The shell rotates at 0.5 rpm while the irner filter typically rotates at 11.5 rpm to produce a gentle flow that ensures removal of waste products as fresh media are infused. Periodically, some spent media are pumped into a waste bag and replaced by fresh media. When the waste bag is filled, an astronaut drains the waste bag and refills the supply bag through ports on the face of the incubator. Pinch valves and a perfusion pump ensure that no media are exposed to moving parts. An Experiment Control Computer controls the Bioreactor, records conditions, and alerts the crew when problems occur. The crew operates the system through a laptop computer displaying graphics designed for easy crew training and operation. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators. See No. 0101824 for a version with labels, and No. 0103180 for an operational schematic.
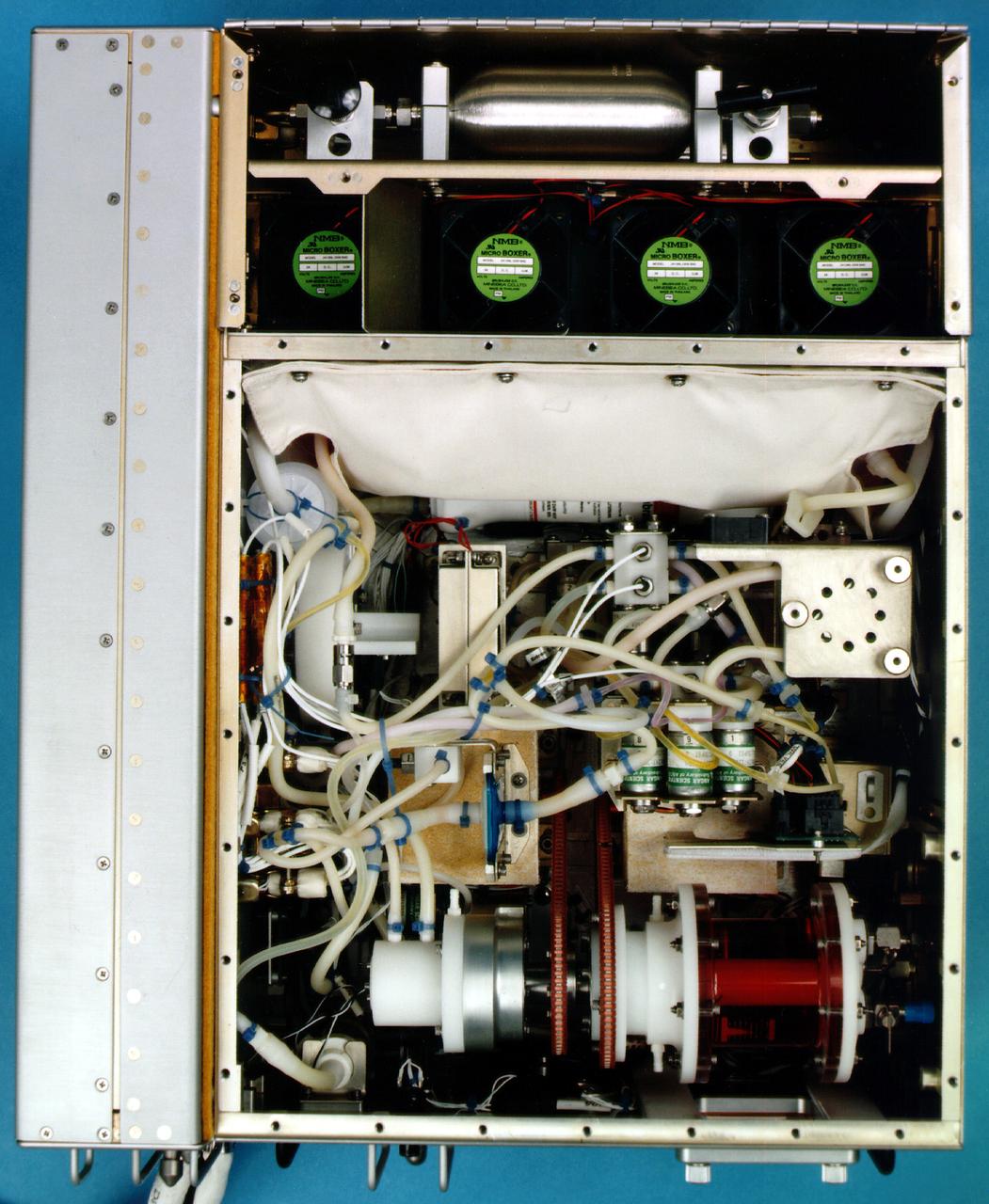
Bioreactor Demonstration System (BDS) comprises an electronics module, a gas supply module, and the incubator module housing the rotating wall vessel and its support systems. Nutrient media are pumped through an oxygenator and the culture vessel. The shell rotates at 0.5 rpm while the irner filter typically rotates at 11.5 rpm to produce a gentle flow that ensures removal of waste products as fresh media are infused. Periodically, some spent media are pumped into a waste bag and replaced by fresh media. When the waste bag is filled, an astronaut drains the waste bag and refills the supply bag through ports on the face of the incubator. Pinch valves and a perfusion pump ensure that no media are exposed to moving parts. An Experiment Control Computer controls the Bioreactor, records conditions, and alerts the crew when problems occur. The crew operates the system through a laptop computer displaying graphics designed for easy crew training and operation. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators. See No. 0101825 for a version with major elements labeled, and No. 0103180 for an operational schematic. 0101816

Bioreactor Demonstration System (BDS) comprises an electronics module, a gas supply module, and the incubator module housing the rotating wall vessel and its support systems. Nutrient media are pumped through an oxygenator and the culture vessel. The shell rotates at 0.5 rpm while the irner filter typically rotates at 11.5 rpm to produce a gentle flow that ensures removal of waste products as fresh media are infused. Periodically, some spent media are pumped into a waste bag and replaced by fresh media. When the waste bag is filled, an astronaut drains the waste bag and refills the supply bag through ports on the face of the incubator. Pinch valves and a perfusion pump ensure that no media are exposed to moving parts. An Experiment Control Computer controls the Bioreactor, records conditions, and alerts the crew when problems occur. The crew operates the system through a laptop computer displaying graphics designed for easy crew training and operation. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators. See No. 0101816 for a version without labels, and No. 0103180 for an operational schematic.
Bioreactor Demonstration System (BDS) comprises an electronics module, a gas supply module, and the incubator module housing the rotating wall vessel and its support systems. Nutrient media are pumped through an oxygenator and the culture vessel. The shell rotates at 0.5 rpm while the irner filter typically rotates at 11.5 rpm to produce a gentle flow that ensures removal of waste products as fresh media are infused. Periodically, some spent media are pumped into a waste bag and replaced by fresh media. When the waste bag is filled, an astronaut drains the waste bag and refills the supply bag through ports on the face of the incubator. Pinch valves and a perfusion pump ensure that no media are exposed to moving parts. An Experiment Control Computer controls the Bioreactor, records conditions, and alerts the crew when problems occur. The crew operates the system through a laptop computer displaying graphics designed for easy crew training and operation. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators. See No. 0101823 for a version without labels, and No. 0103180 for an operational schematic.

The Test and Operations Support Contract (TOSC) Kimberly-Clark RightCycle program team of April Smith and An Huynh recently earned a Fiscal Year 2021 Sustainable Environment Awareness (SEA) Award Citation. The Kennedy Space Center employees received the honor in SEA’s Waste Management category. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is being replaced with Kimberly-Clark brand, where possible, as collection containers are placed in all applicable TOSC facilities at Kennedy. All supplier PPE is collected, placed in a container, and shipped back to the company to be recycled into usable products.

jsc2021e036649 (8/4/2021) --- From left to right: Eng. Michele Cioffi Program Manager, Eng.Marco Fabio Miceli System & Test Engineer, Eng. Pasquale Pellegrino Test Engineer from ALI S.c.a r.l. and Eng.Maurizio Ruggiero Electronic Specialist from Euro.Soft s.r.l.. REducing Arthritis Dependent Inflammation First Phase (READI FP) evaluates how microgravity and space radiation affect the generation of bone tissue. It also examines the potential protective effects of bio-collagen and bioactive metabolites such as antioxidants during spaceflight. The source of these metabolites are vegetal extracts produced as waste products in wine production.
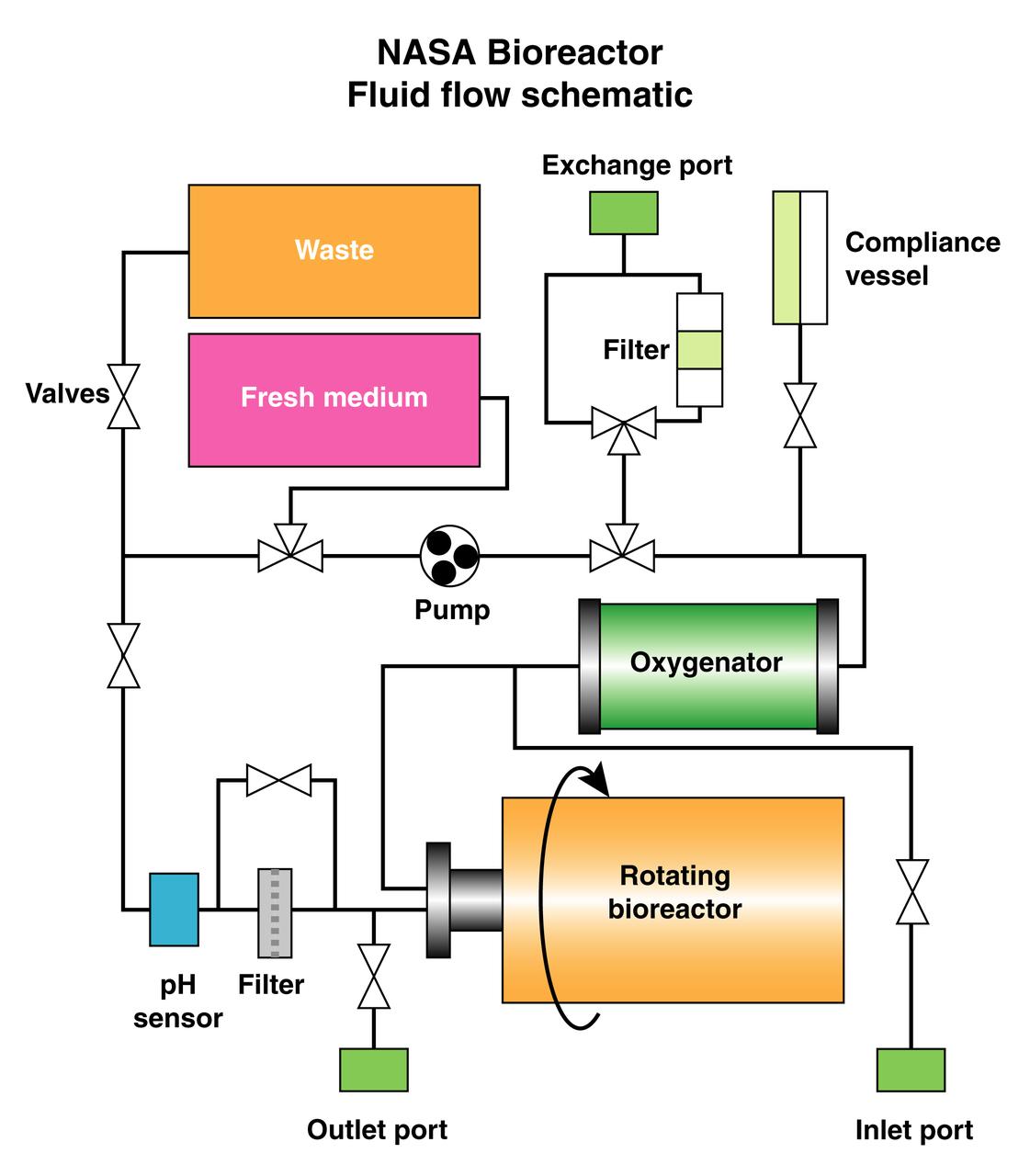
The schematic depicts the major elements and flow patterns inside the NASA Bioreactor system. Waste and fresh medium are contained in plastic bags placed side-by-side so the waste bag fills as the fresh medium bag is depleted. The compliance vessel contains a bladder to accommodate pressure transients that might damage the system. A peristolic pump moves fluid by squeezing the plastic tubing, thus avoiding potential contamination. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators.

Astronaut John Blaha replaces an exhausted media bag and filled waste bag with fresh bags to continue a bioreactor experiment aboard space station Mir in 1996. NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators. This image is from a video downlink. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC).
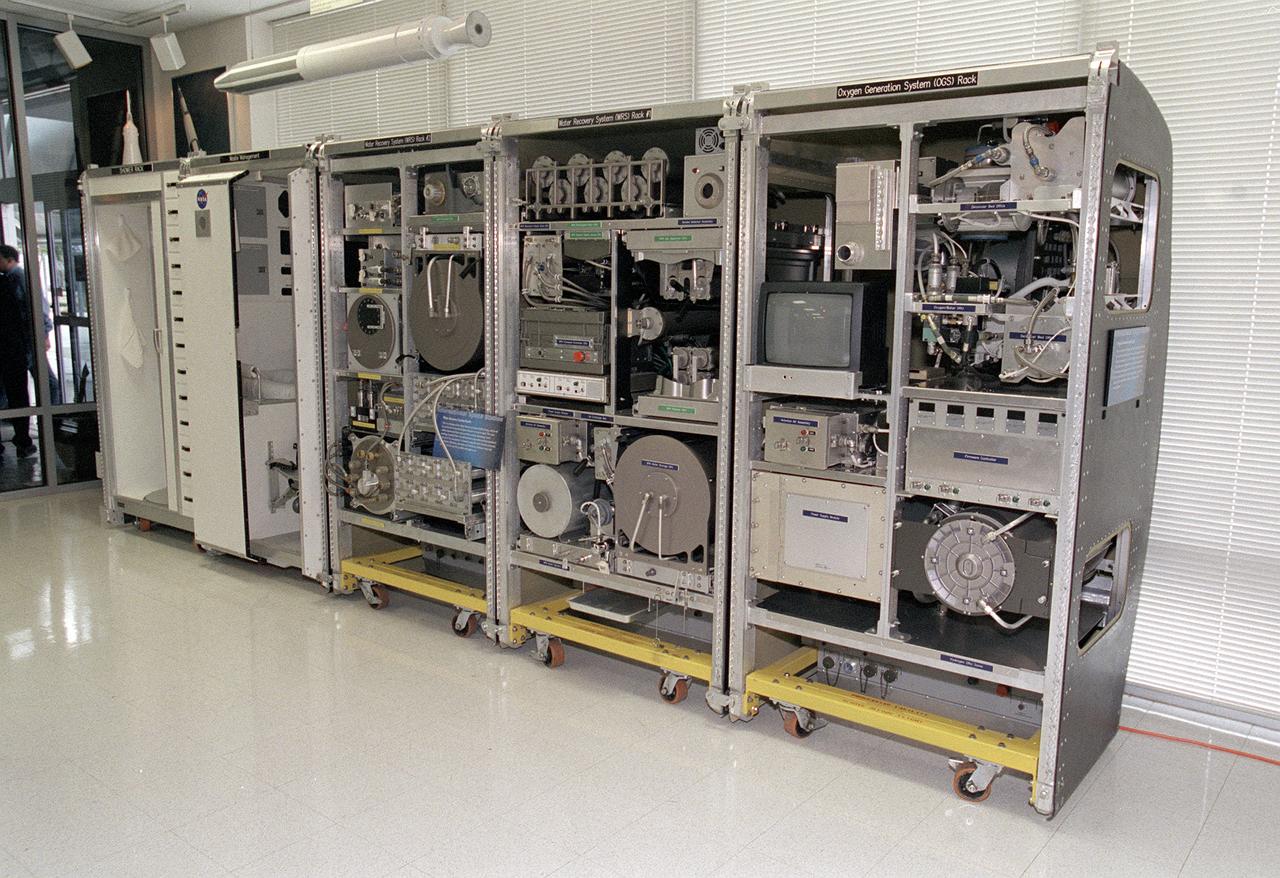

The Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) Group of the Flight Projects Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, is responsible for designing and building the life support systems that will provide the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) a comfortable environment in which to live and work. This photograph shows the mockup of the the ECLSS to be installed in the Node 3 module of the ISS. From left to right, shower rack, waste management rack, Water Recovery System (WRS) Rack #2, WRS Rack #1, and Oxygen Generation System (OGS) rack are shown. The WRS provides clean water through the reclamation of wastewaters and is comprised of a Urine Processor Assembly (UPA) and a Water Processor Assembly (WPA). The UPA accepts and processes pretreated crewmember urine to allow it to be processed along with other wastewaters in the WPA. The WPA removes free gas, organic, and nonorganic constituents before the water goes through a series of multifiltration beds for further purification. The OGS produces oxygen for breathing air for the crew and laboratory animals, as well as for replacing oxygen loss. The OGS is comprised of a cell stack, which electrolyzes (breaks apart the hydrogen and oxygen molecules) some of the clean water provided by the WRS, and the separators that remove the gases from the water after electrolysis.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bob Bagdigian talks to the media about the Water Recovery System being delivered to the International Space Station on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission. Bagdigian is a project manager with NASA's Regenerative Environmental Control and Life Support System at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. Behind Bagdigian is a mockup of the two racks that will be used. The two units of the Water Recovery System are designed to provide drinking-quality water through the reclamation of wastewater, including urine and hygiene wastes. The water that’s produced will be used to support the crew and work aboard the station. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Dressed for a little exercise, Deputy Program Manager of Launch Services Chuck Dovale addresses the employees who have turned out during their lunchtime for a ribbon-cutting ceremony opening the new fitness trail next to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The one-mile-long track will provide employees with a safe place off Kennedy's roadways to walk or run. The more than 6 tons of green waste removed to create the trail's footprint will be mulched and used for cover at Kennedy's landfill. Approximately 1,594 tons of crawler fines -- ground-up crawler rock removed from the crawlerway in the Launch Complex 39 area -- was used for the foundation of the trail. Fitness equipment has been ordered and will be installed on a concrete slab at the trail's west end. After the equipment has been installed, the slab will be coated to provide a rubberized exercise pad. At Kennedy Space Center, the health and safety of every employee is paramount. To learn more about Kennedy, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
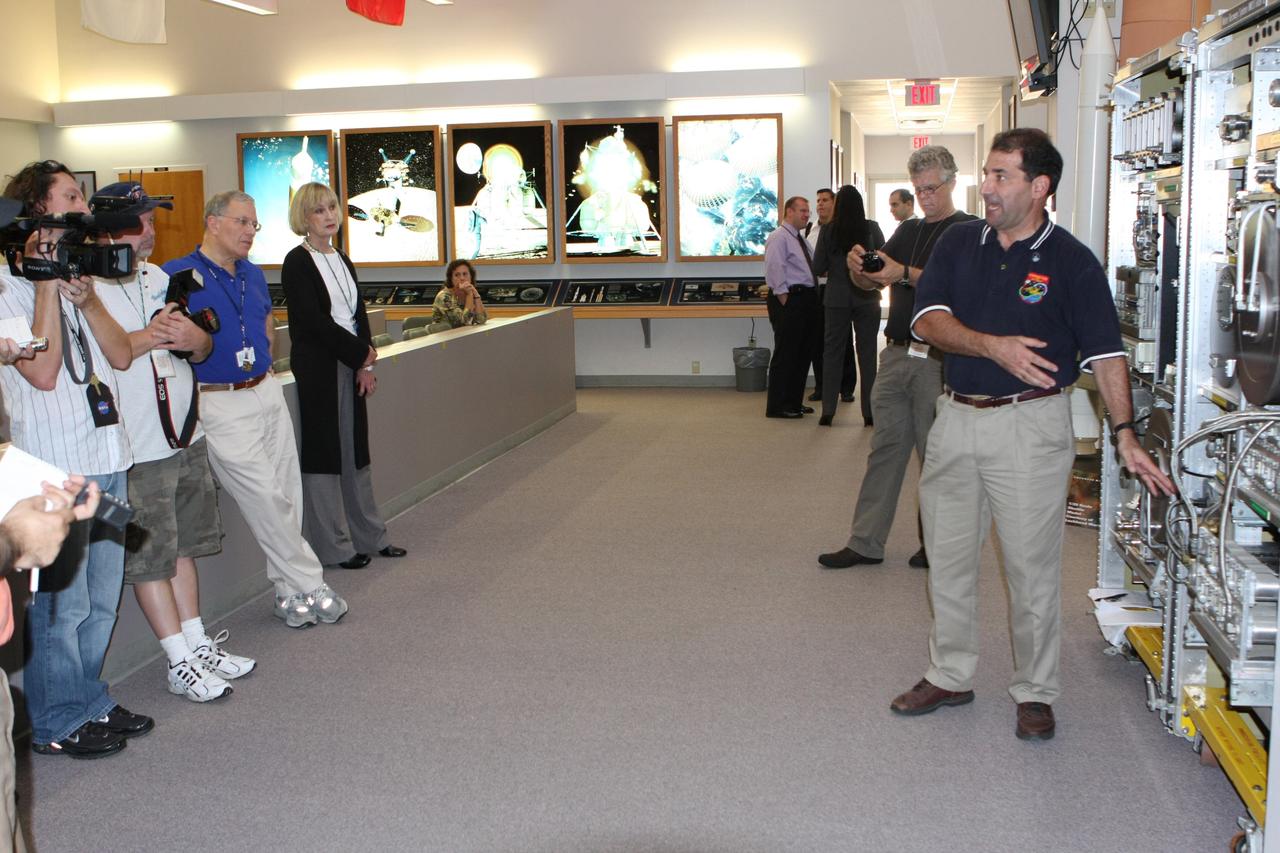

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In In the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bob Bagdigian (right) talks to the media about the Water Recovery System being delivered to the International Space Station on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission. Bagdigian is a project manager with NASA's Regenerative Environmental Control and Life Support System at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. Behind Bagdigian is a mockup of the two racks that will be used. The two units of the Water Recovery System are designed to provide drinking-quality water through the reclamation of wastewater, including urine and hygiene wastes. The water that’s produced will be used to support the crew and work aboard the station. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
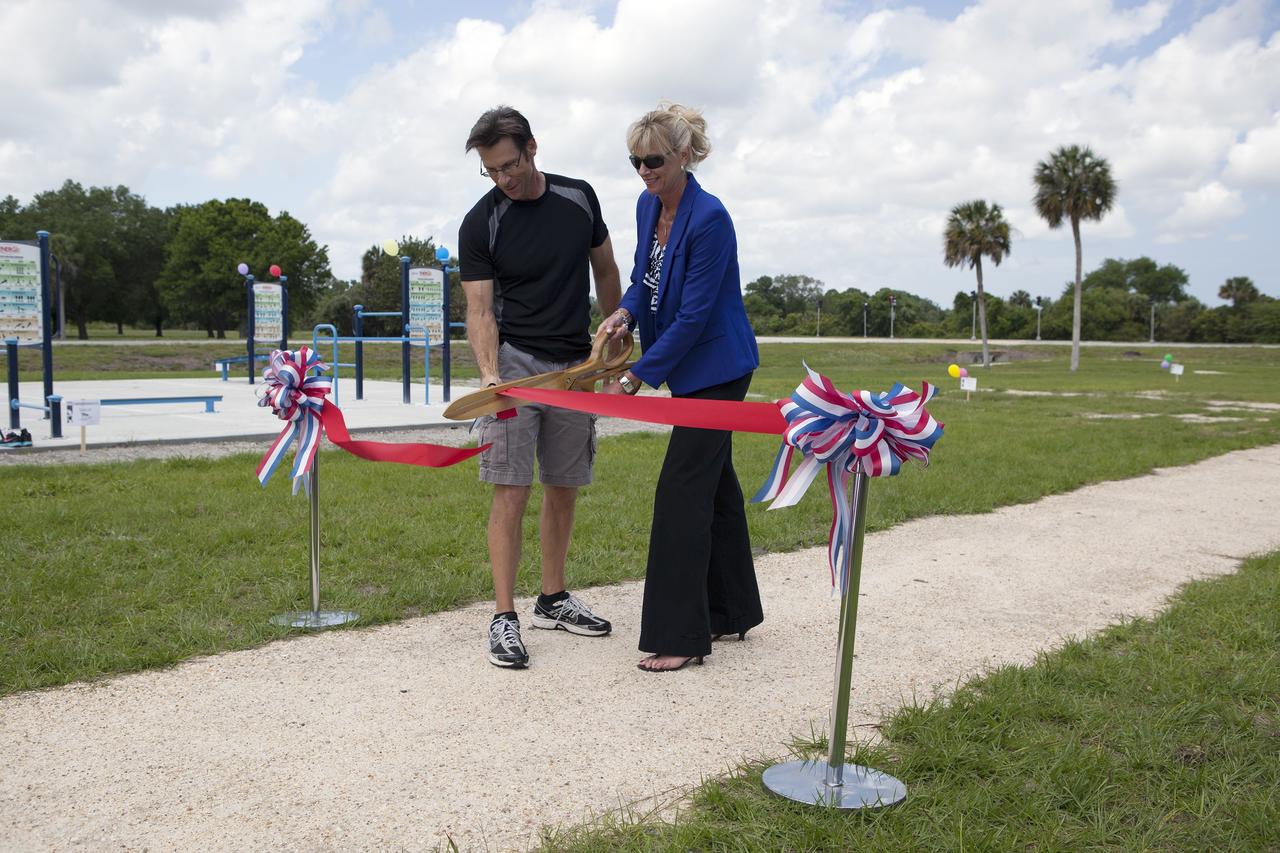

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Chuck Dovale, at left, deputy program manager of Launch Services, and Nancy Bray, director of Center Operations, cut a ribbon officially opening the new fitness trail next to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The one-mile-long track will provide employees with a safe place off Kennedy's roadways to walk or run. The more than 6 tons of green waste removed to create the trail's footprint will be mulched and used for cover at Kennedy's landfill. Approximately 1,594 tons of crawler fines -- ground-up crawler rock removed from the crawlerway in the Launch Complex 39 area -- was used for the foundation of the trail. Fitness equipment has been ordered and will be installed on a concrete slab at the trail's west end. After the equipment has been installed, the slab will be coated to provide a rubberized exercise pad. At Kennedy Space Center, the health and safety of every employee is paramount. To learn more about Kennedy, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
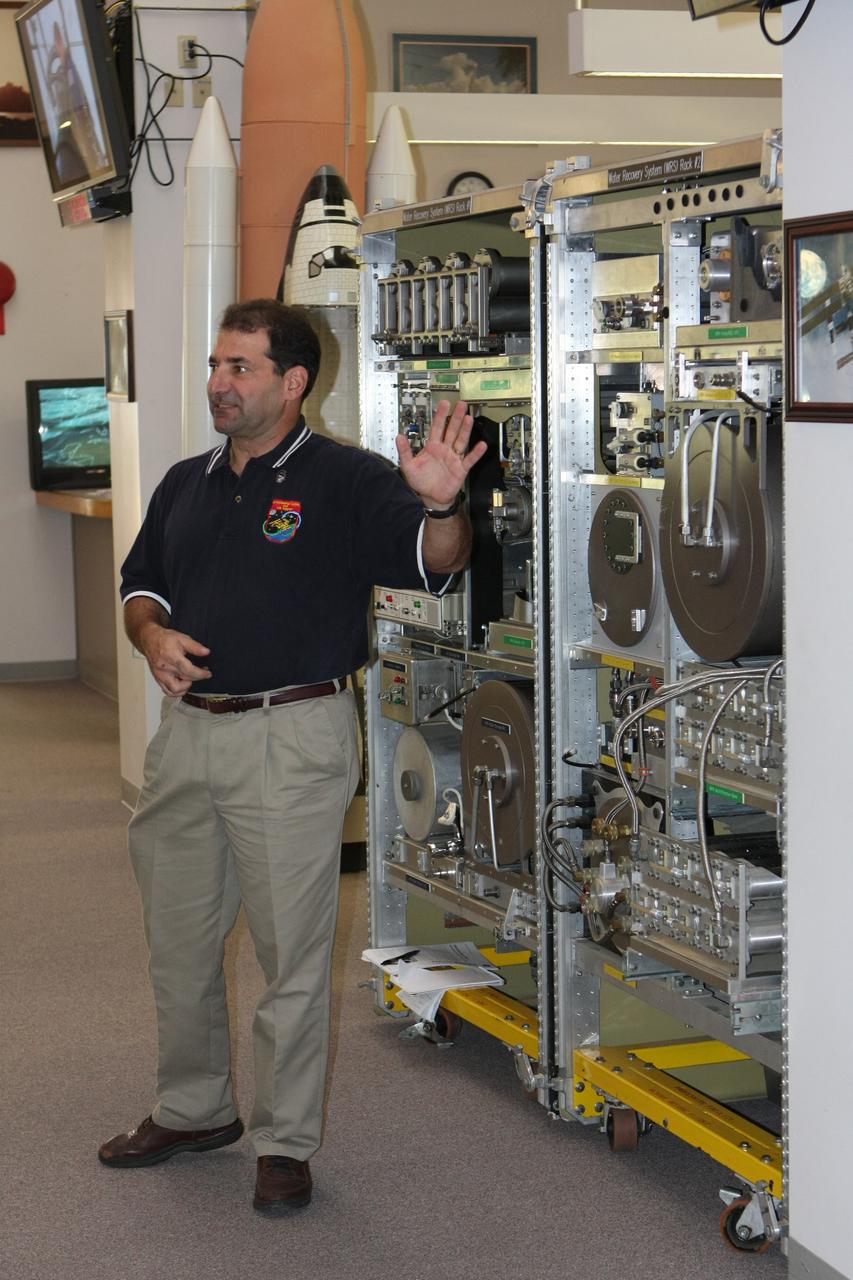

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bob Bagdigian talks to the media about the Water Recovery System being delivered to the International Space Station on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission. Bagdigian is a project manager with NASA's Regenerative Environmental Control and Life Support System at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. Behind Bagdigian is a mockup of the two racks that will be used. The two units of the Water Recovery System are designed to provide drinking-quality water through the reclamation of wastewater, including urine and hygiene wastes. The water that’s produced will be used to support the crew and work aboard the station. STS-126 is the 124th space shuttle flight and the 27th flight to the International Space Station. The mission will feature four spacewalks and work that will prepare the space station to house six crew members for long- duration missions. Liftoff is scheduled for 7:55 p.m. EST Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
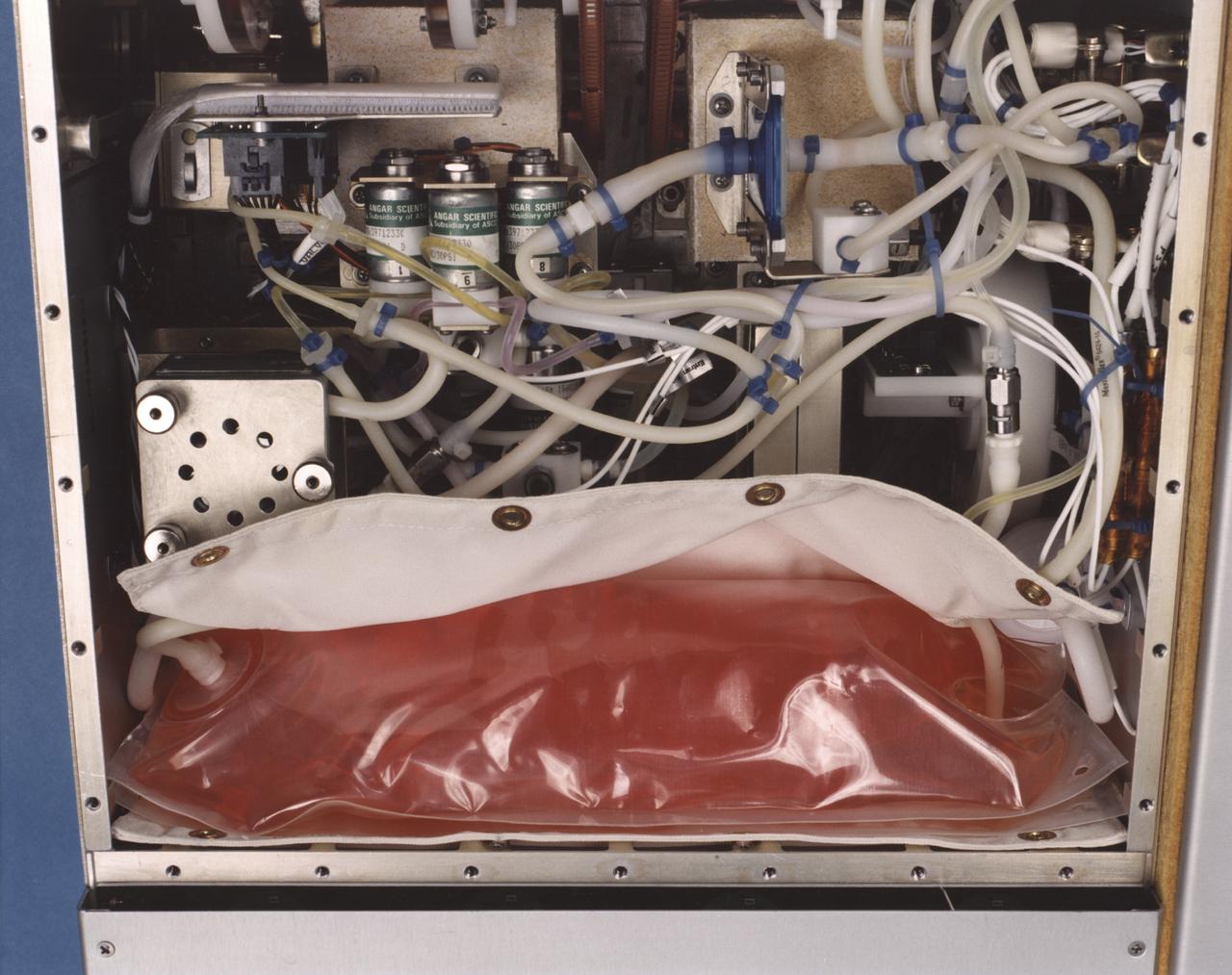
Close-up view of the interior of a NASA Bioreactor shows the plastic plumbing and valves (cylinders at center) to control fluid flow. A fresh nutrient bag is installed at top; a flattened waste bag behind it will fill as the nutrients are consumed during the course of operation. The drive chain and gears for the rotating wall vessel are visible at bottom center center. The NASA Bioreactor provides a low turbulence culture environment which promotes the formation of large, three-dimensional cell clusters. The Bioreactor is rotated to provide gentle mixing of fresh and spent nutrient without inducing shear forces that would damage the cells. Due to their high level of cellular organization and specialization, samples constructed in the bioreactor more closely resemble the original tumor or tissue found in the body. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators.
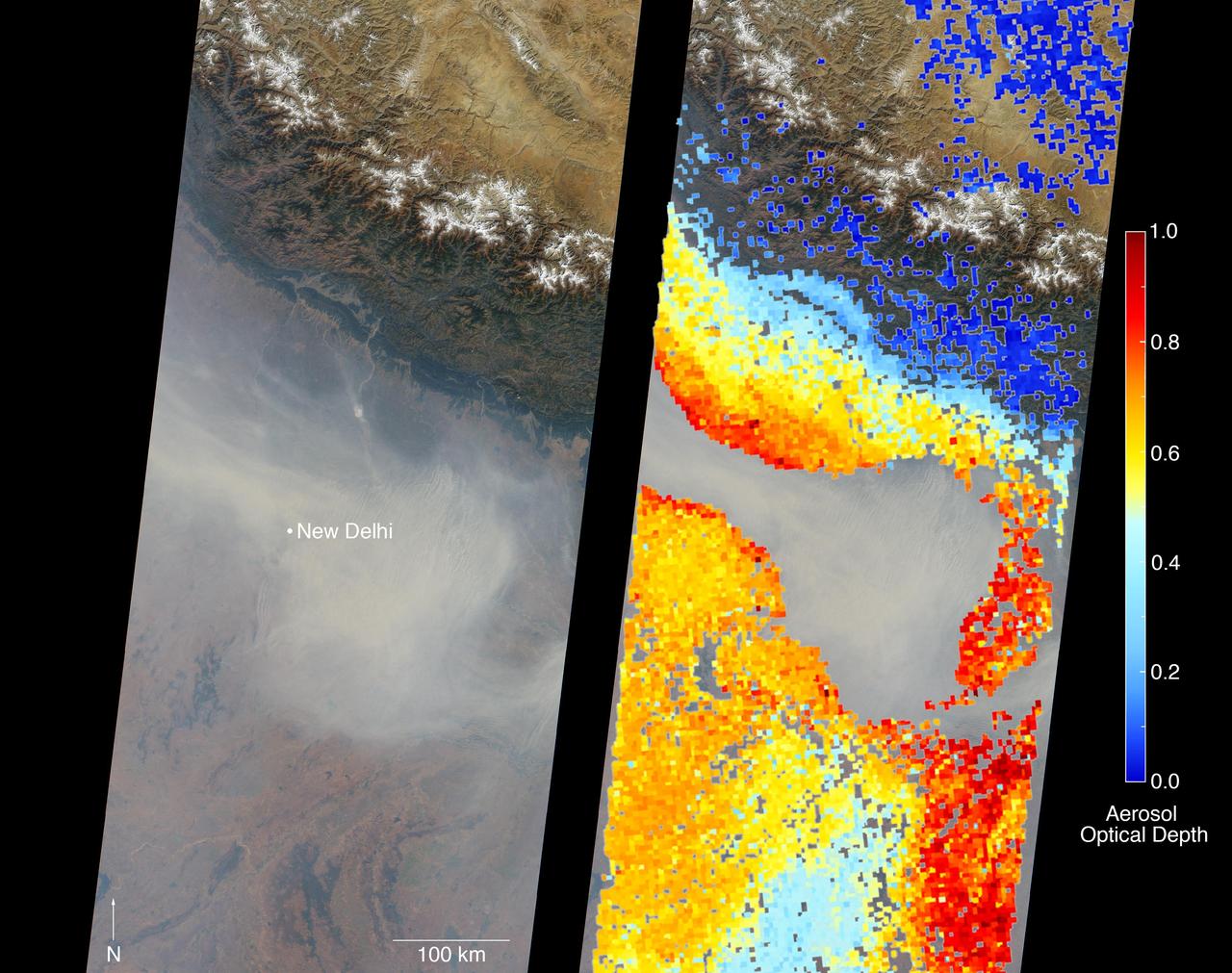
New Delhi, India's capital city, is currently suffering though a period of particularly poor air quality. In early November 2016, monitors at various locations in the area posted air quality index measurements as high as the 900s (the most severe ranking, "hazardous," is any air quality index measurement over 300). Thousands of schools have been closed, and a survey by the Associate Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India reports that 10 percent of the city's workers called in sick due to air-pollution-related health issues. According to several published news reports, the extreme air pollution may be due to a combination of nearby agricultural burning after harvest, urban construction and solid-waste burning, as well as remnants of firecracker smoke and additional car emissions after the celebration of Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights, on October 30. The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite passed over the region on Saturday, Nov. 5, 2016, at around 11:05 a.m. local time. At left is an image acquired from MISR's vertical viewing camera. The Himalayas stretch across the northern portion of the image. This towering mountain range tends to concentrate pollution in the region immediately to the south, including New Delhi, by preventing pollutants from blowing northwards. New Delhi, whose location is indicated on the image, is under a patch of especially thick haze. At 6:00 a.m. local time on that date, the U.S. Mission India NowCast Air Quality Index for New Delhi was reported at 751, more than twice the threshold for hazardous air quality. At right, a map of aerosol optical depth is superimposed on the image. Optical depth is a quantitative measure of the abundance of aerosols (tiny particles in the atmosphere). Optical depths for the area around New Delhi have not been calculated because the haze is so thick that the algorithm has classified the area as a cloud. In the region immediately surrounding the thick haze, optical depths approach 1.0. An optical depth of 1.0 means that only about 37 percent of direct sunlight reaches the surface due to interactions with particles in the atmosphere. These data were acquired during Terra orbit 89805. Other MISR data are available through the NASA Langley Research Center; for more information, go to https://eosweb.larc.nasa.gov/project/misr/misr_table. MISR was built and is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Terra spacecraft is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland. The MISR data were obtained from the NASA Langley Research Center Atmospheric Science Data Center, Hampton, Virginia. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21100
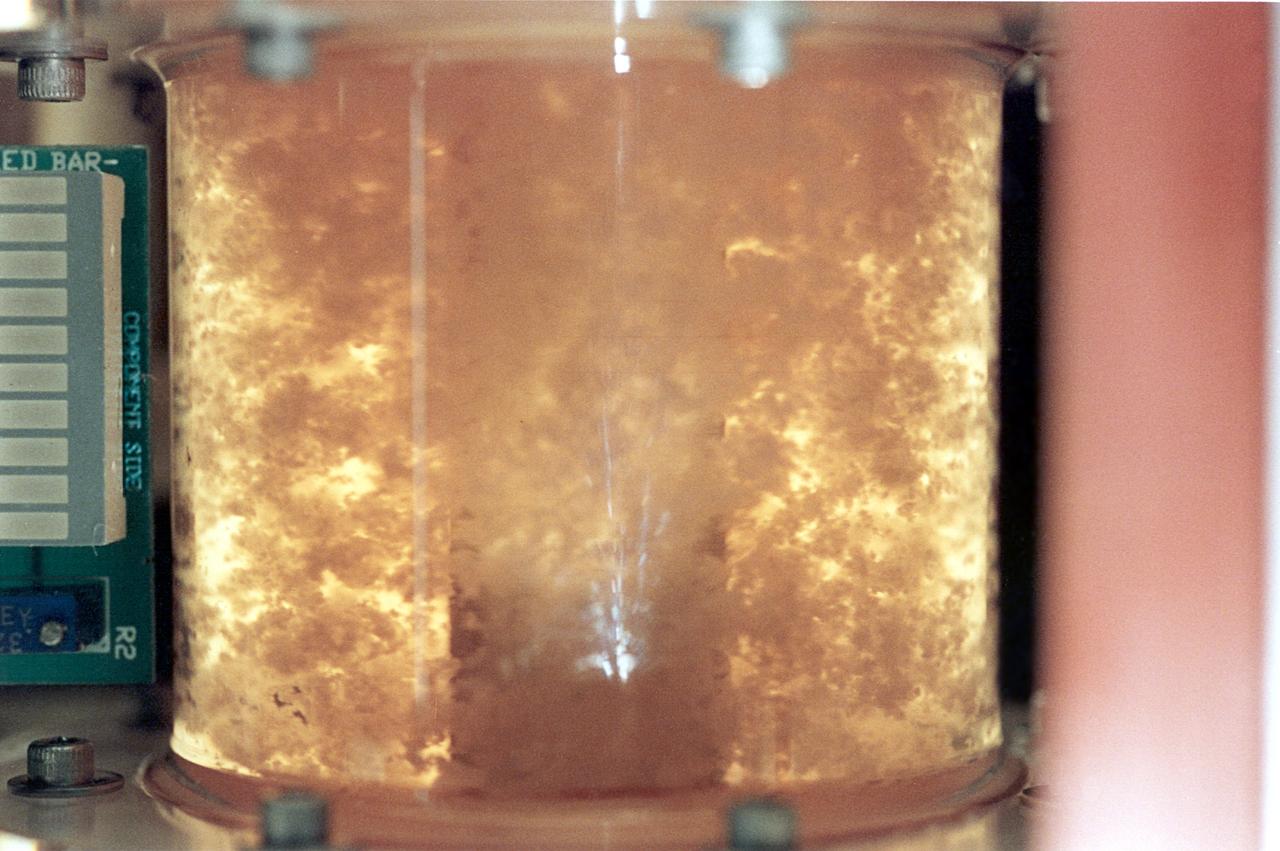
For 5 days on the STS-70 mission, a bioreactor cultivated human colon cancer cells, which grew to 30 times the volume of control specimens grown on Earth. This significant result was reproduced on STS-85 which grew mature structures that more closely match what are found in tumors in humans. Shown here, clusters of cells slowly spin inside a bioreactor. On Earth, the cells continually fall through the buffer medium and never hit bottom. In space, they are naturally suspended. Rotation ensures gentle stirring so waste is removed and fresh nutrient and oxygen are supplied. The NASA Bioreactor provides a low turbulence culture environment which promotes the formation of large, three-dimensional cell clusters. Due to their high level of cellular organization and specialization, samples constructed in the bioreactor more closely resemble the original tumor or tissue found in the body. The Bioreactor is rotated to provide gentle mixing of fresh and spent nutrient without inducing shear forces that would damage the cells. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators.