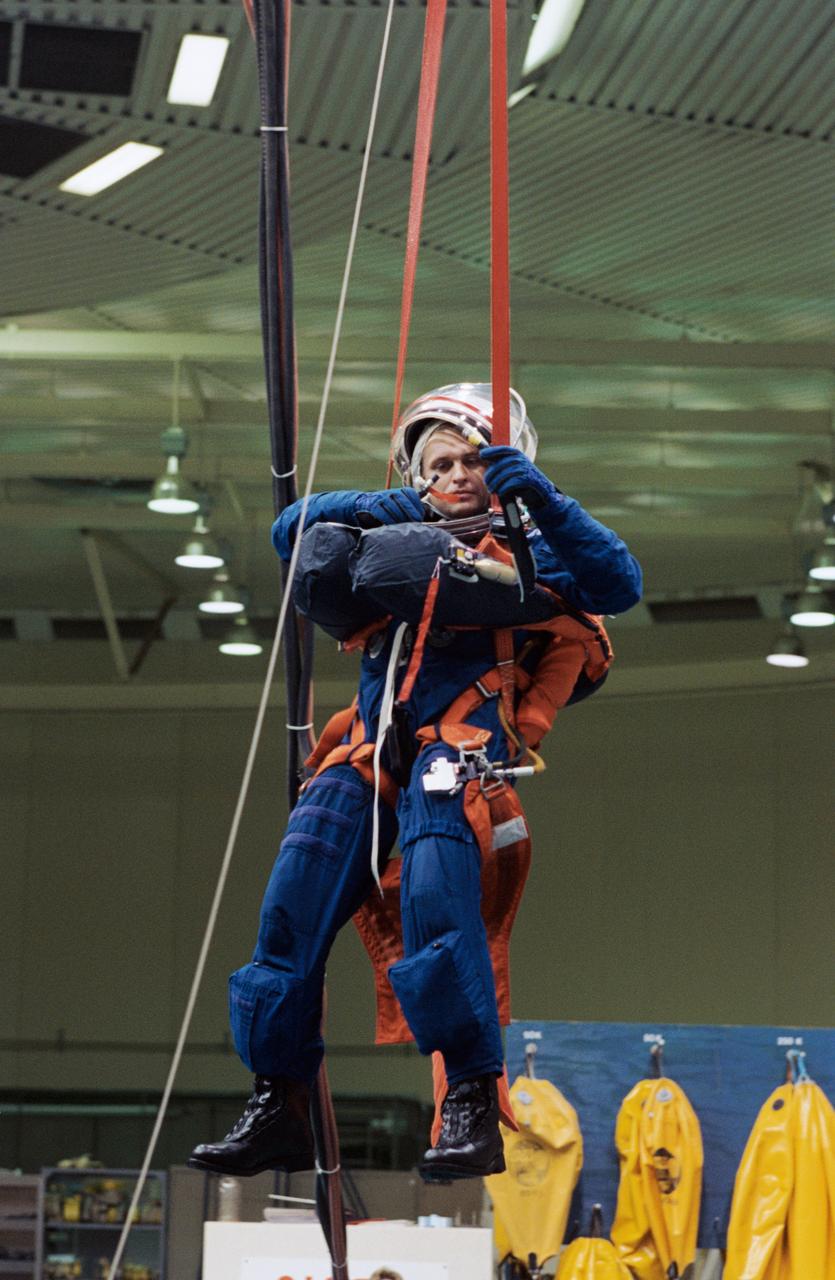

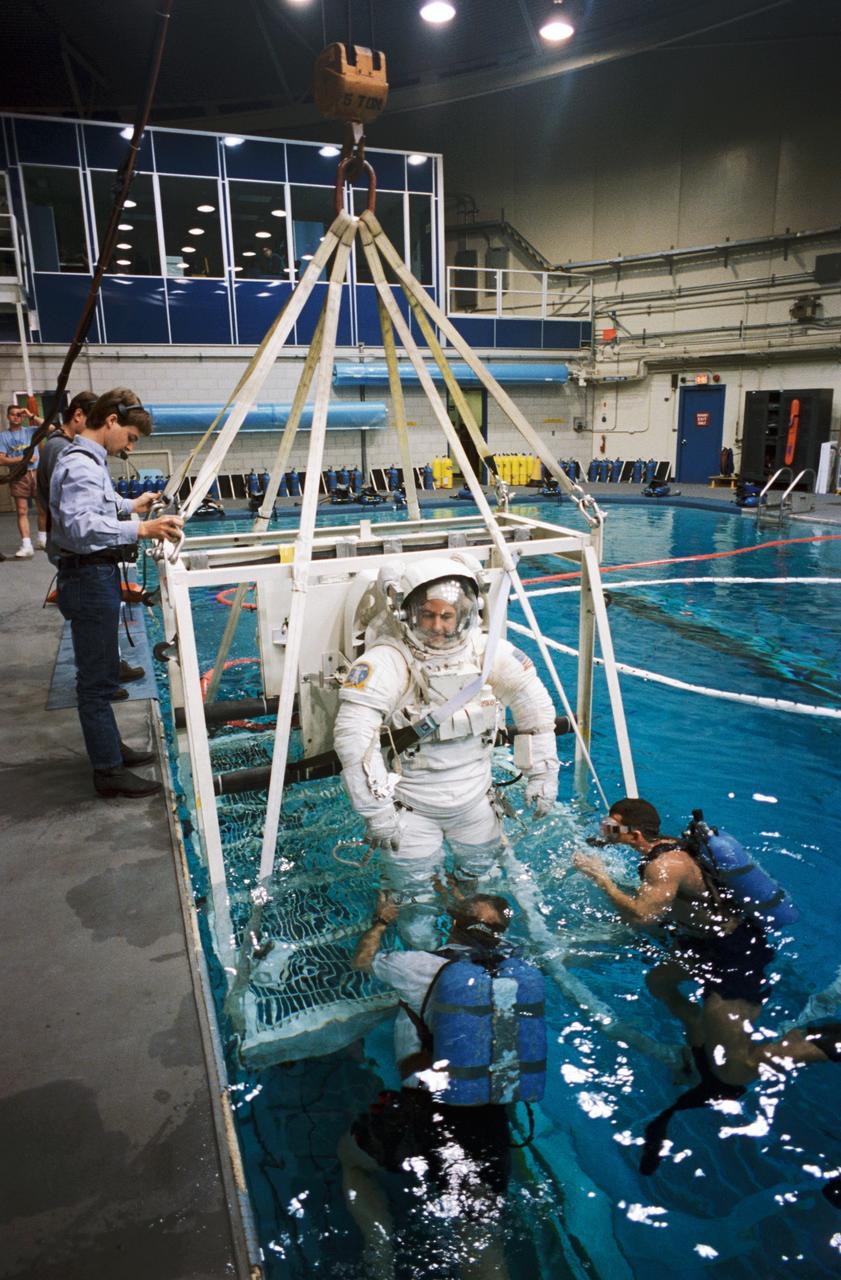
S94-47232 (13 Oct 1994) --- Cosmonaut Yuriy I. Onufriyenko (right), in the United States to participate in training for joint Russia-United States space missions, simulates a parachute drop into water. The training took place in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) because it contains a 25-feet-deep pool. Onufriyenko, a Mir reserve team member, and a number of other cosmonauts and astronauts participating in the joint program were in Houston, Texas to prepare for upcoming missions which involve crewmembers from the two nations.
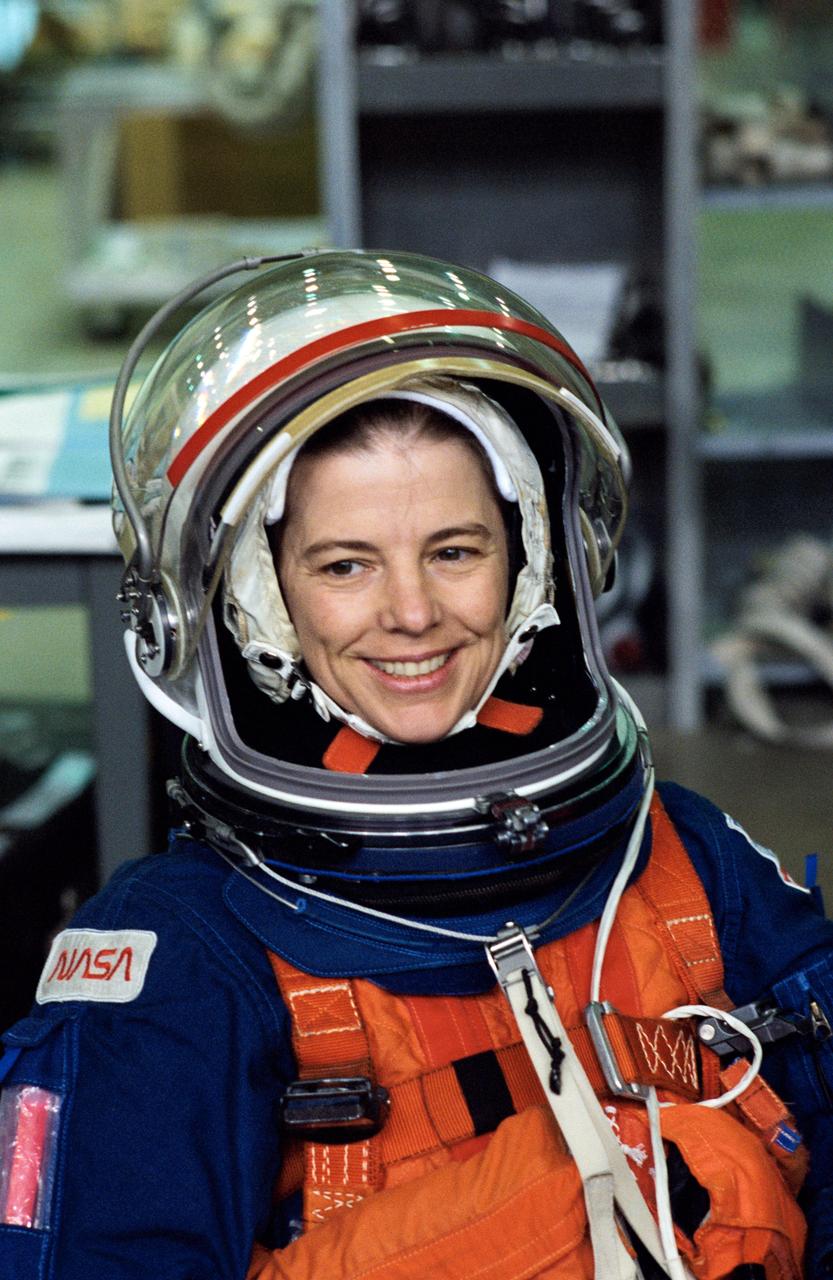

S94-47256 (13 Oct 1994) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, STS-71 mission specialist, smiles as she watches a crew mate (out of frame) make a simulated parachute landing in nearby water. The action came as part of an emergency bailout training session in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility's (WET-F) 25-feet-deep pool.

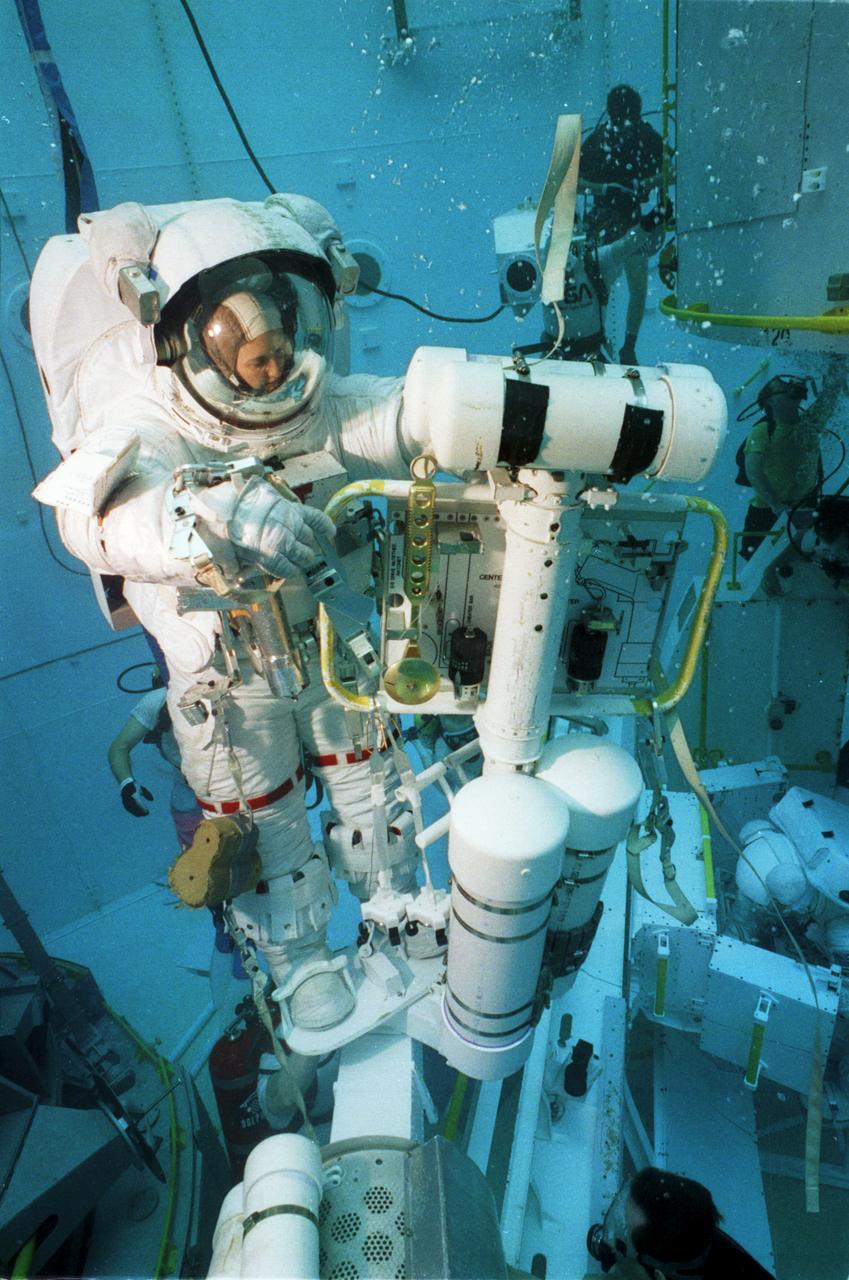
STS-38 Mission Specialist (MS) Carl J. Meade, wearing extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) upper torso, takes a breather from suit donning activities in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. Meade is preparing for an underwater extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation. During the training exercise, Meade will rehearse contingency EVA procedures for the STS-38 mission aboard Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104.

S94-39770 (August 1994) --- Astronaut Carl J. Meade, STS-64 mission specialist, is being submerged prior to an underwater simulation of a spacewalk scheduled for his September mission. Meade, who shared the rehearsal in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) pool with crewmate astronaut Mark C. Lee (partially visible at left), is equipped with a training version of new extravehicular activity (EVA) hardware called the Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER) system. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

S94-39762 (August 1994) --- Astronaut Carl J. Meade, STS-64 mission specialist, listens to ground monitors prior to a simulation of a spacewalk scheduled for his September mission. Meade, who shared the rehearsal in Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) pool with crewmate astronaut Mark C. Lee (out of frame), is equipped with a training version of new extravehicular activity (EVA) hardware called the Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER) system. The hardware includes a mobility-aiding back harness and a chest-mounted hand control module. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
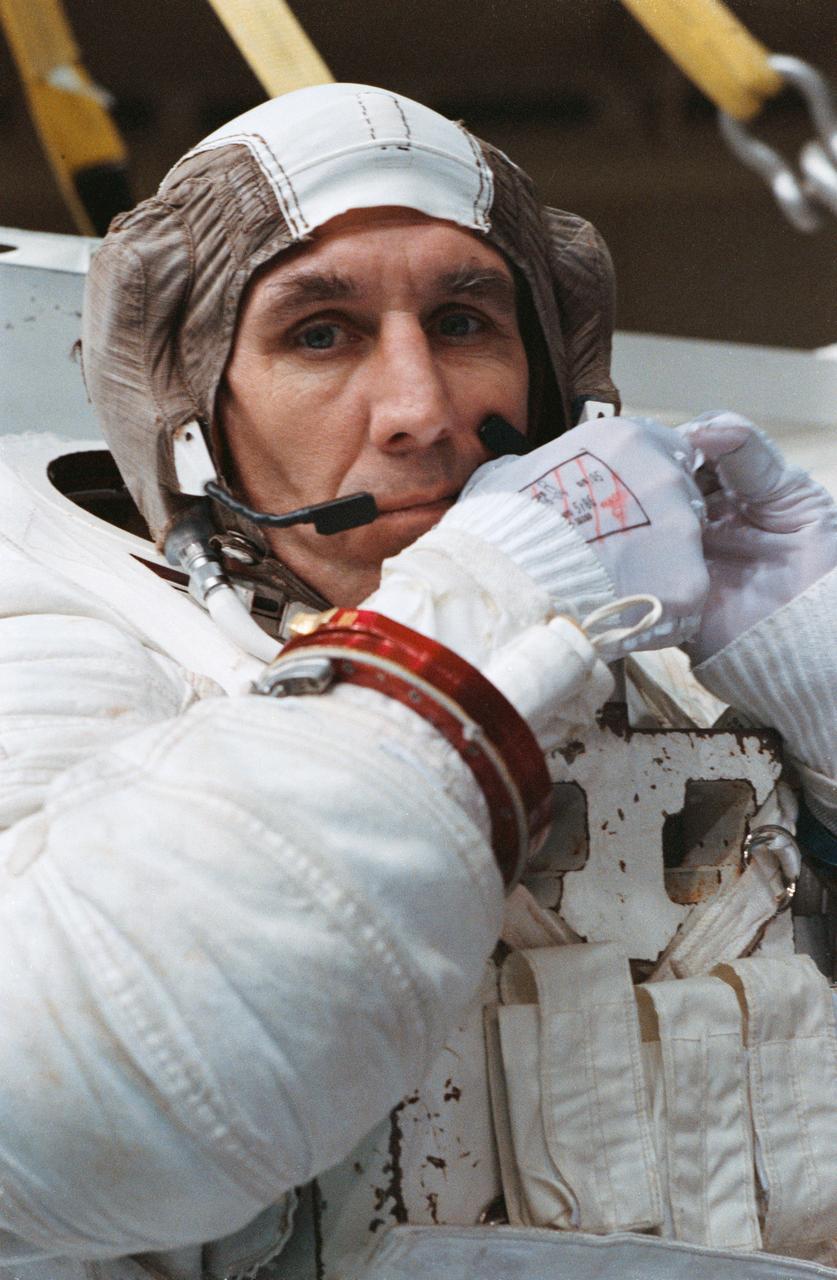

STS-38 Mission Specialist (MS) Robert C. Springer, wearing extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), fastens the strap on his communications carrier assembly (CCA) cap during suit donning in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. Positioned on the WETF platform at pool side, Springer is preparing for an underwater extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation. During the training exercise, Springer will rehearse contingency EVA procedures for the STS-38 mission aboard Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104.
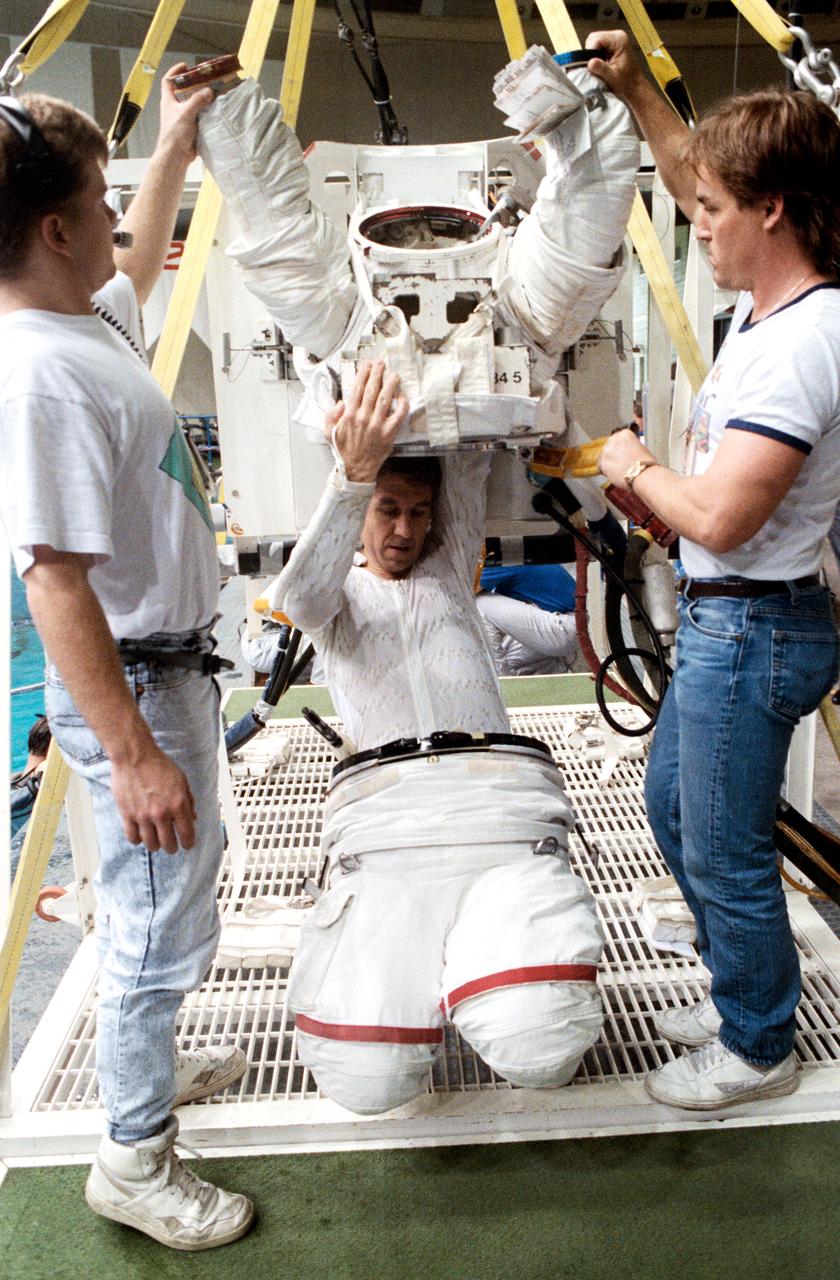

STS-38 Mission Specialist (MS) Robert C. Springer dons extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) upper torso with technicians' assistance in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. Positioned on the WETF platform at pool side, Springer is preparing for an underwater extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation. During the training session, Springer will rehearse contingency EVA procedures for the STS-38 mission aboard Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104.
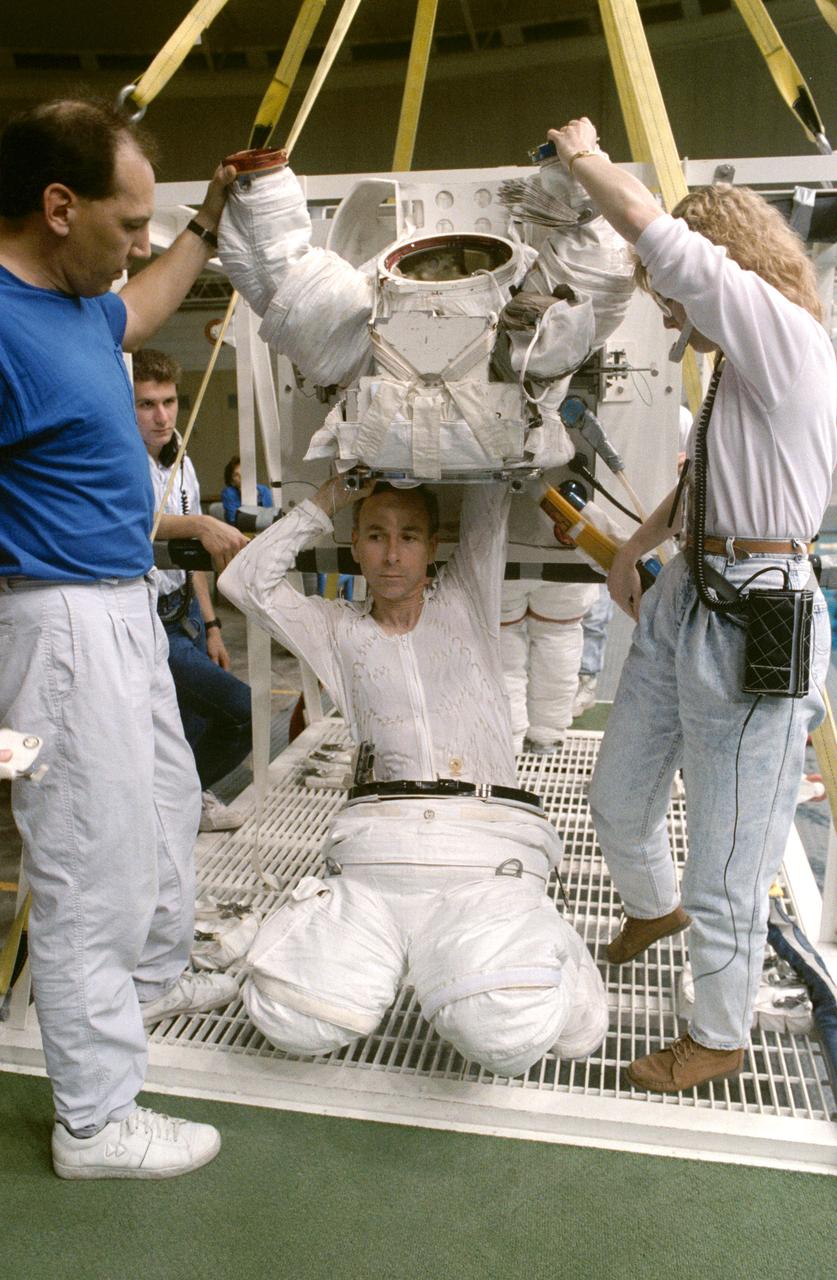

STS-38 Mission Specialist (MS) Carl J. Meade, wearing liquid cooling and ventilation garment (LCVG) and extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) lower torso, crouches under EMU upper torso. Technicians extend the EMU sleeves as Meade reaches into upper torso during suit donning in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. Positioned on the WETF platform at pool side, Meade is preparing for an underwater extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation. During the training exercise, Meade will rehearse contingency EVA procedures for the STS-38 mission aboard Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104.
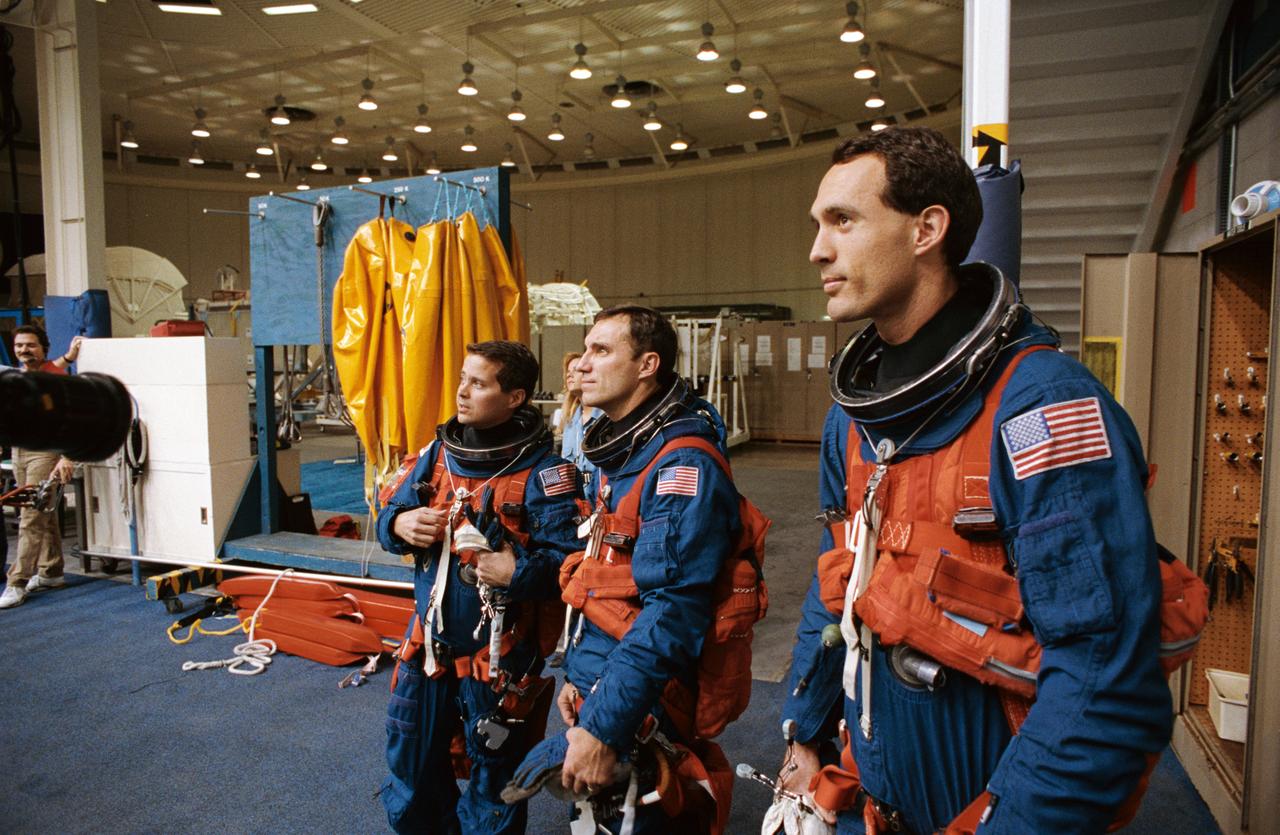

S93-31929 (24 March 1993) --- The three mission specialists for NASA's STS-51 mission watch as a crewmate (out of frame) simulates a parachute jump into water during emergency bailout training exercises at the Johnson Space Center's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Left to right are astronauts Daniel W. Bursch, Carl E. Walz and James H. Newman. Out of frame are astronauts Frank L. Culbertson and William F. Readdy, commander and pilot, respectively.

STS-48 Mission Specialist (MS) James F. Buchli, wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), is watched by SCUBA-equipped divers as the platform he is standing on is lowered into JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. When completely underwater, Buchli will be released from the platform and will perform contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) operations. This underwater simulation of a spacewalk is part of the training required for Buchli's upcoming mission aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103.
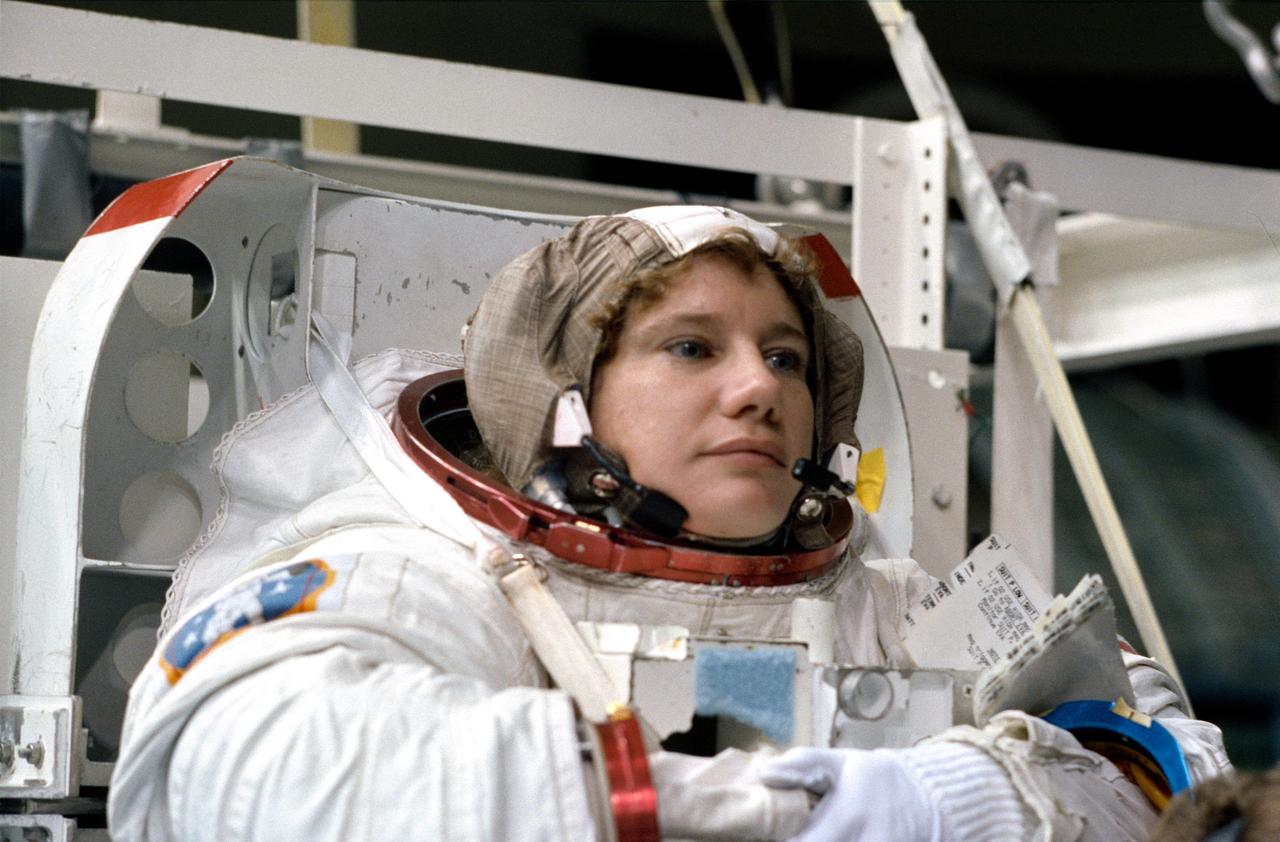

S92-42755 (31 July 1992) --- Astronaut Susan J. Helms, mission specialist assigned to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour for the STS-54 mission, completes the donning of her spacesuit before a training exercise. Though not assigned to the scheduled extravehicular activity (EVA), Helms is trained in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F). She will aid astronauts Gregory J. Harbaugh and Mario Runco Jr. in their planned EVA, scheduled for January of next year, and serve a backup role. Wearing this high fidelity training version of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), Helms was later lowered into the 25-ft. deep WET-F pool. The pressurized suit is weighted so as to allow Helms to achieve neutral buoyancy and simulate the various chores of the spacewalk.
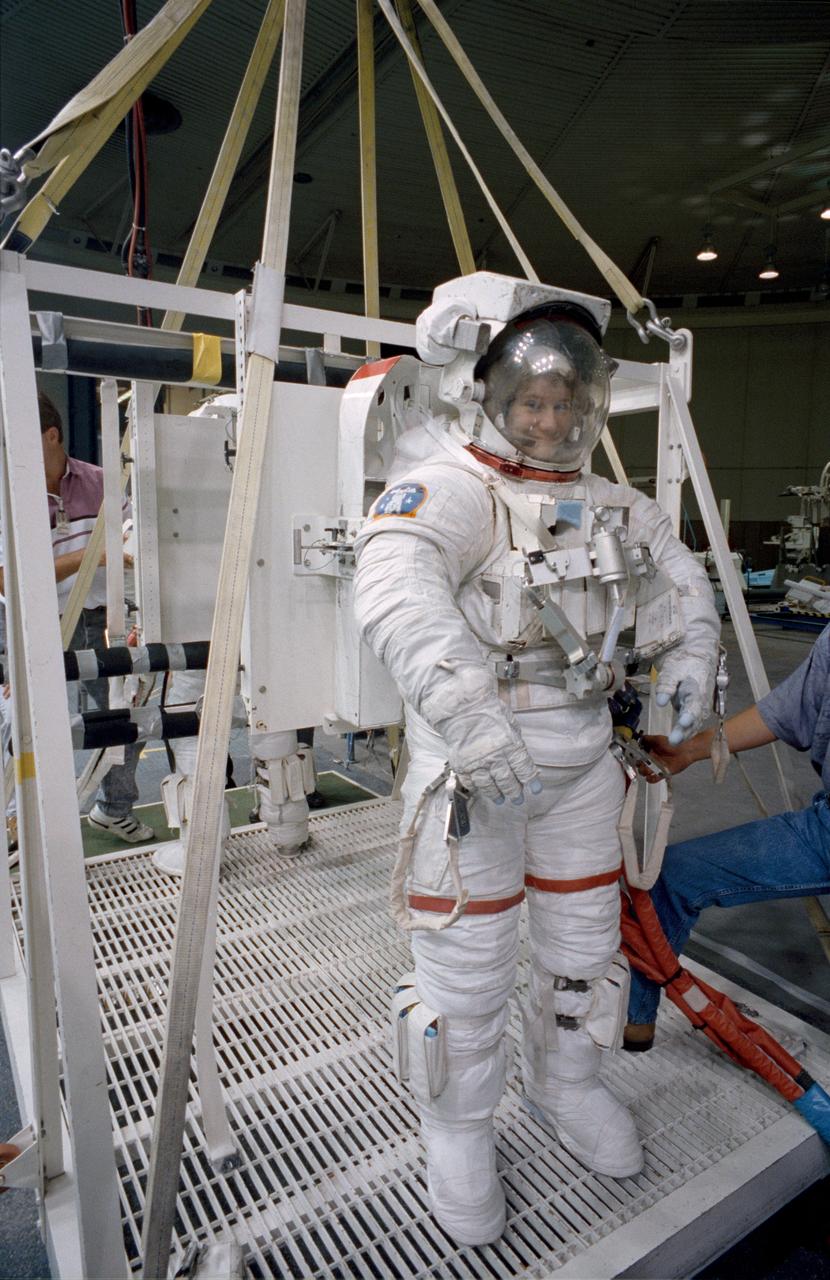

S92-42754 (31 July 1992) --- Astronaut Susan J. Helms, mission specialist assigned to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour for the STS-54 mission, gets assistance to complete the donning of her spacesuit. Though not assigned to the scheduled extravehicular activity (EVA), Helms is trained in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F). She will aid astronauts Gregory J. Harbaugh and Mario Runco Jr. in their planned EVA, scheduled for January of next year, and serve a backup role. Wearing this high fidelity training version of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), Helms was later lowered into the 25-ft. deep WET-F pool. The pressurized suit is weighted so as to allow Helms to achieve neutral buoyancy and simulate the various chores of the spacewalk.
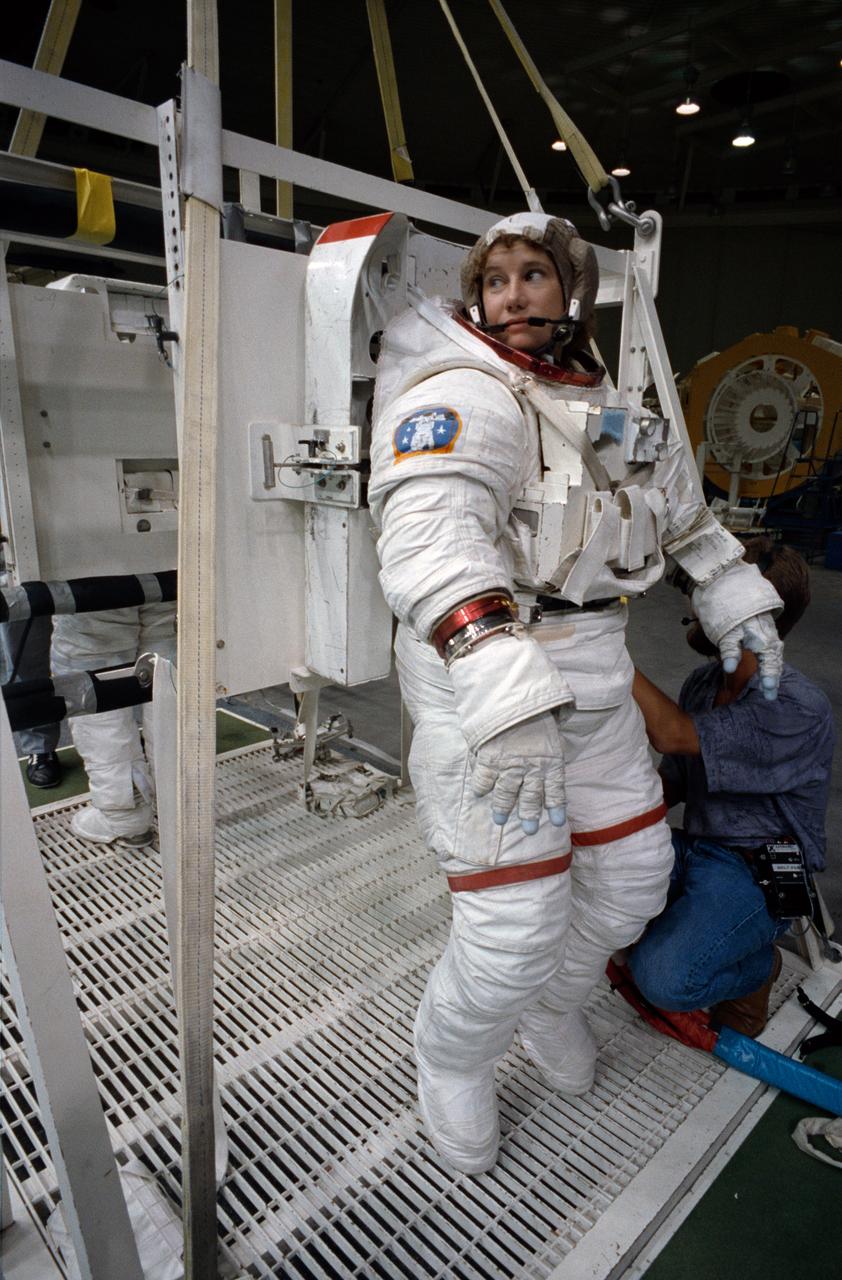

S92-42753 (31 July 1992) --- Astronaut Susan J. Helms, mission specialist assigned to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour for the STS-54 mission, gets assistance to complete the donning of her spacesuit. Though not assigned to the scheduled extravehicular activity (EVA), Helms is trained in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F). She will aid astronauts Gregory J. Harbaugh and Mario Runco Jr. in their planned EVA, scheduled for January of next year, and serve a backup role. Wearing this high fidelity training version of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), Helms was later lowered into the 25-ft. deep WET-F pool. The pressurized suit is weighted so as to allow Helms to achieve neutral buoyancy and simulate the various chores of the spacewalk.
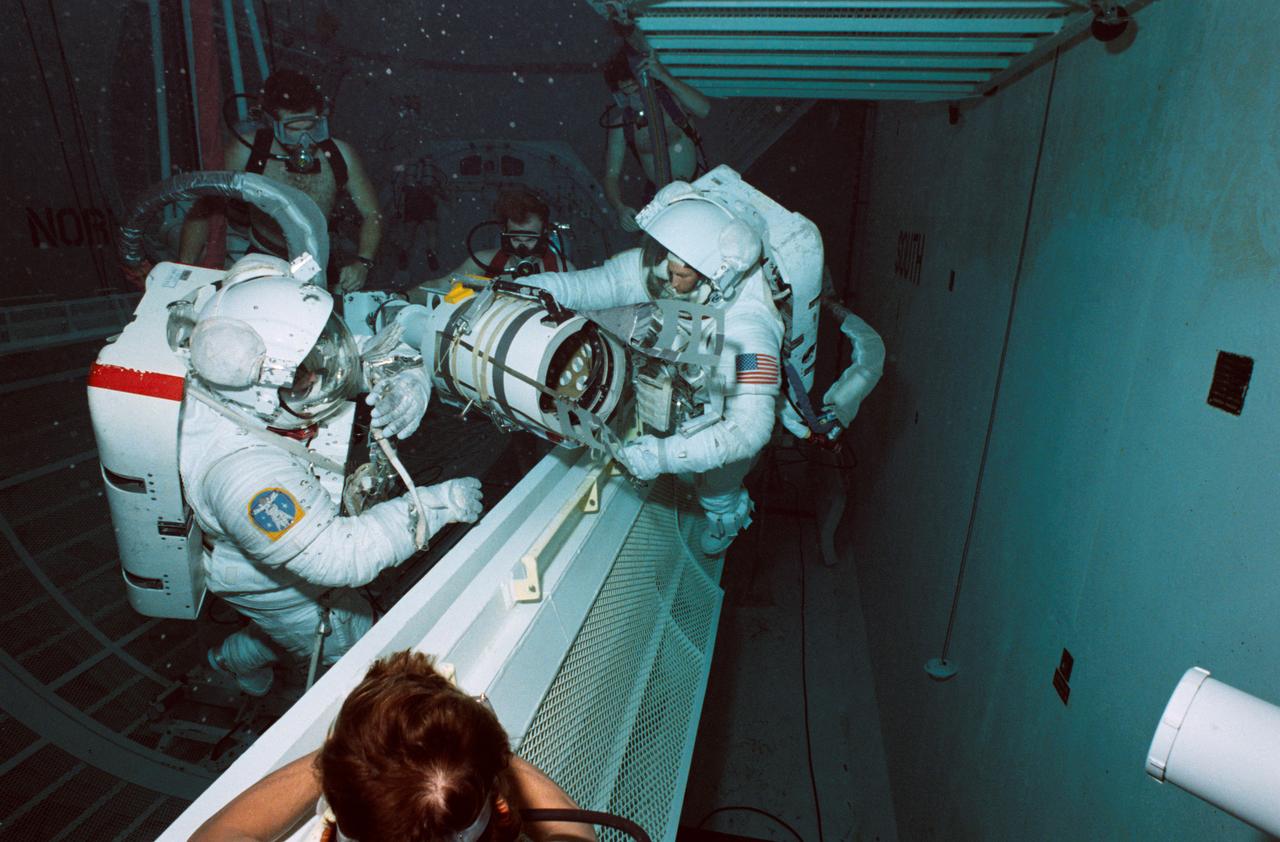
Underwater EVA Simulation of "Flyswatter" attachment in the Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF), 04/15/1985. JSC, HOUSTON, TX
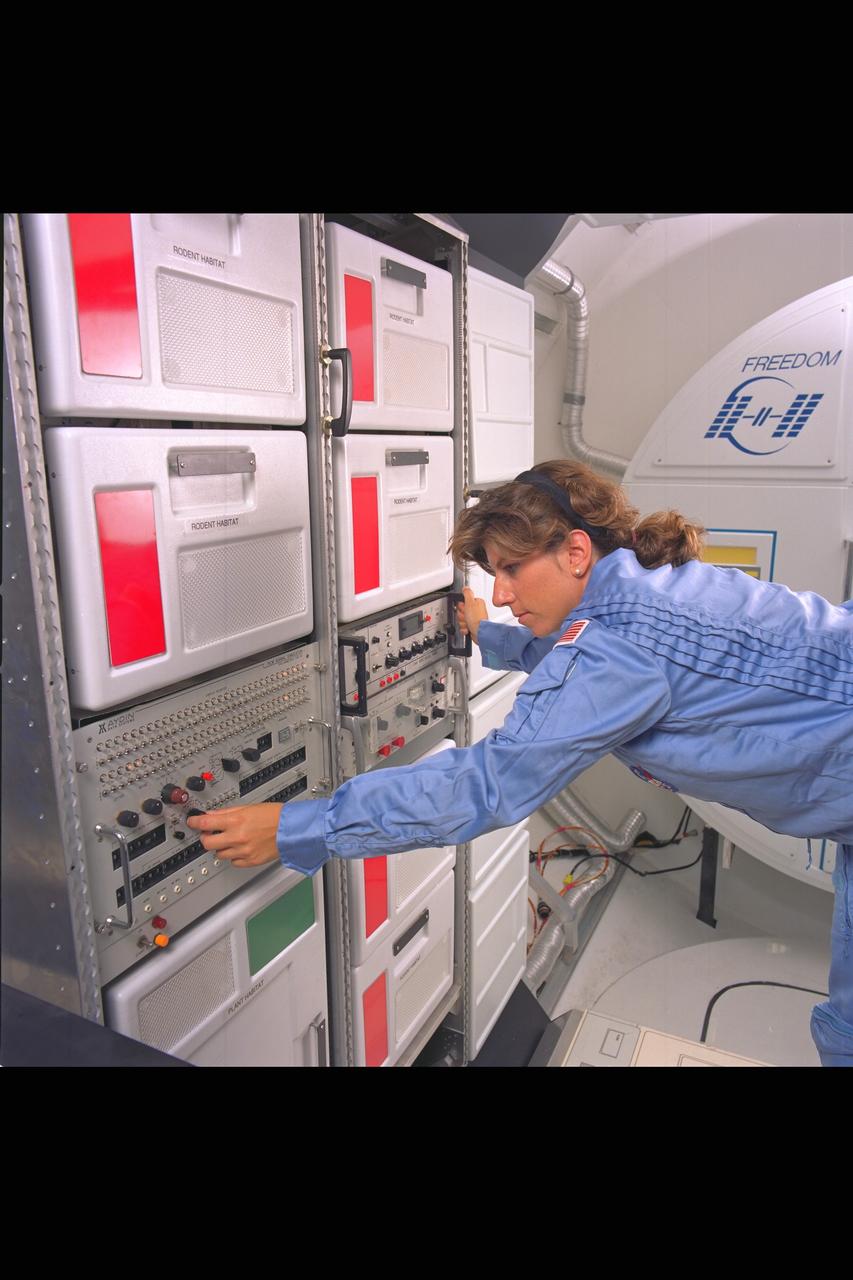

Space Station Gravitational Biology Facility Project Mock-up with Kristine Guerra (2.5) with Biolab (simulating weightlessness in space)

This photograph was taken during testing of an emergency procedure to free jammed solar array panels on the Skylab workshop. A metal strap became tangled over one of the folded solar array panels when Skylab lost its micrometeoroid shield during the launch. This photograph shows astronauts Schweickart and Gibson in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) using various cutting tools and methods developed by the MSFC to free the jammed solar wing. Extensive testing and many hours of practice in simulators such as the NBS tank helped prepare the Skylab crewmen for extravehicular performance in the weightless environment. This huge water tank simulated the weightless environment that the astronauts would encounter in space.

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, submerges after spending some time under water in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, submerges after spending some time under water in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.
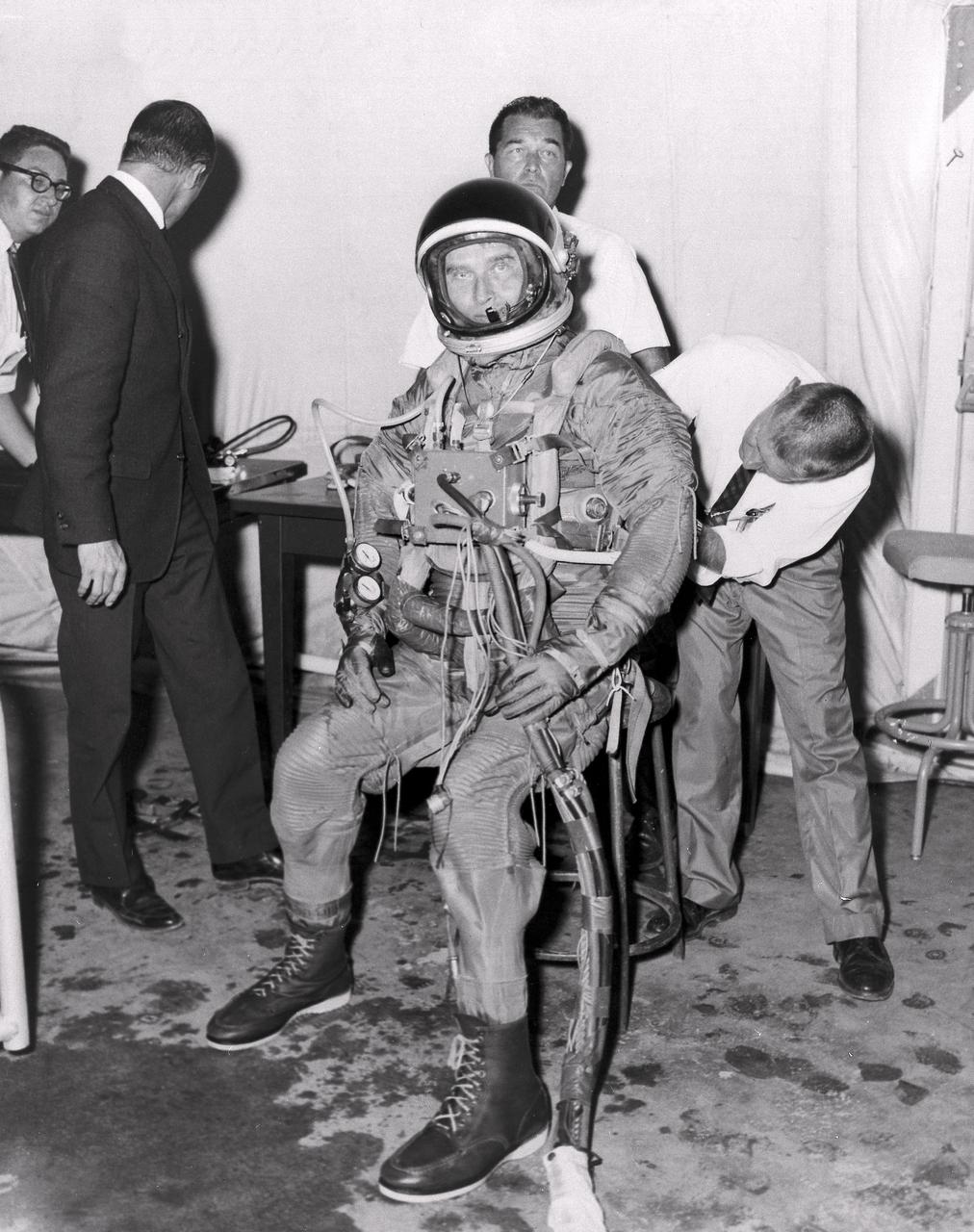

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, is shown fitted with suit and diving equipment as he prepares for a tryout in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.
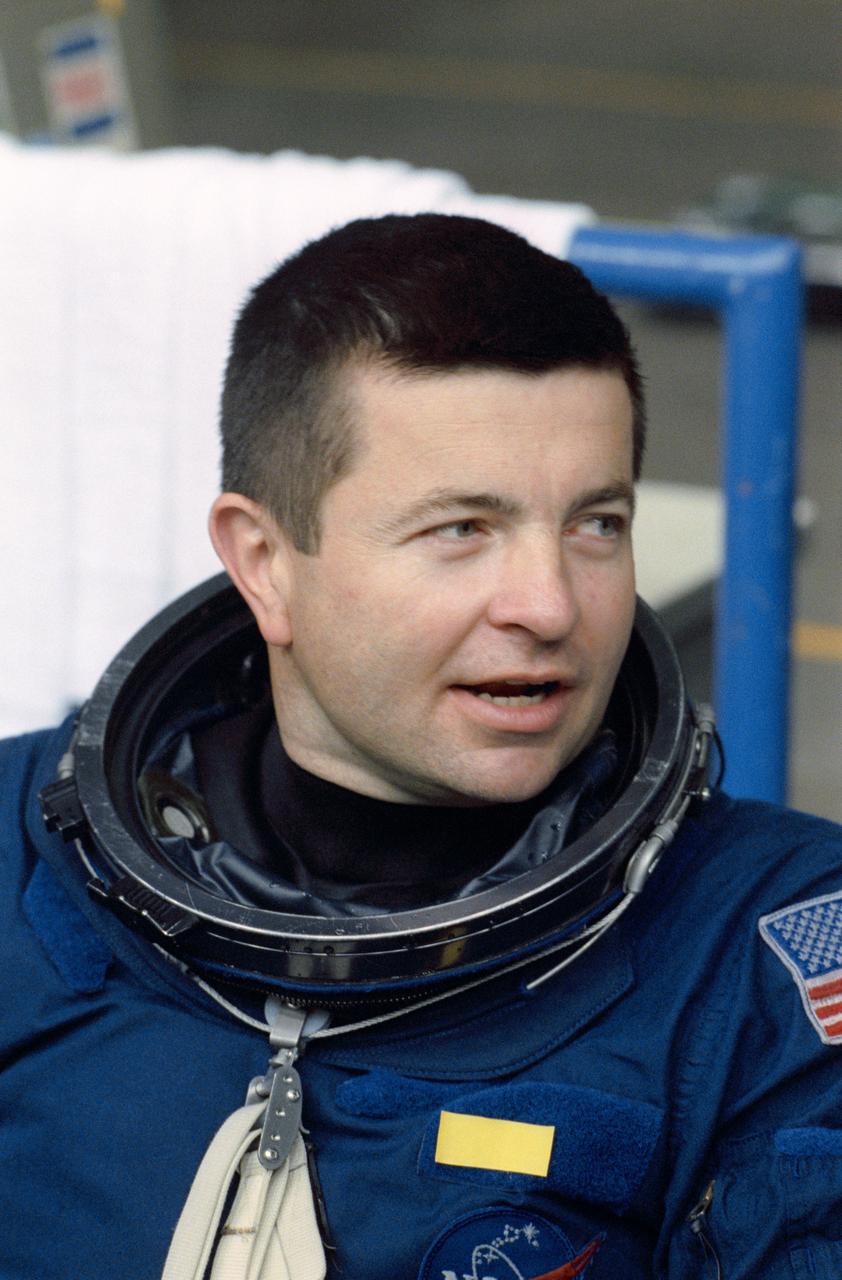

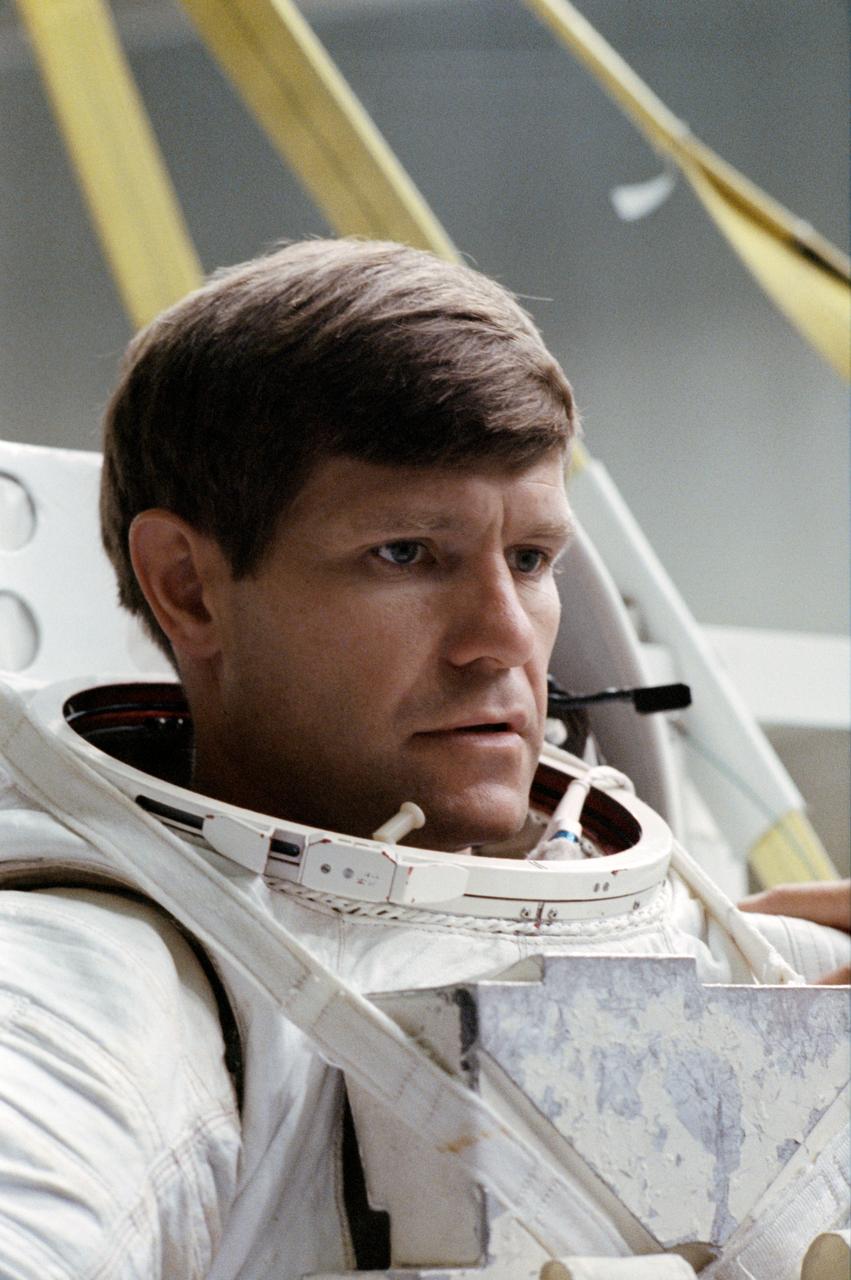
STS-37 Pilot Kenneth D. Cameron, wearing launch and entry suit (LES), discusses simulated emergency egress training on the pool side of JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. Cameron will be dropped into a simulated ocean, the WETF's 25-ft pool, into which a parachute landing might be made.
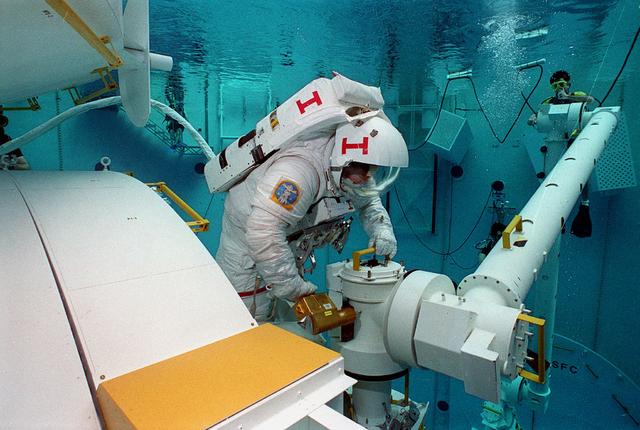

This photograph was taken in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) during the testing of the Japanese Experimental Module. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of extra-vehicular activities.
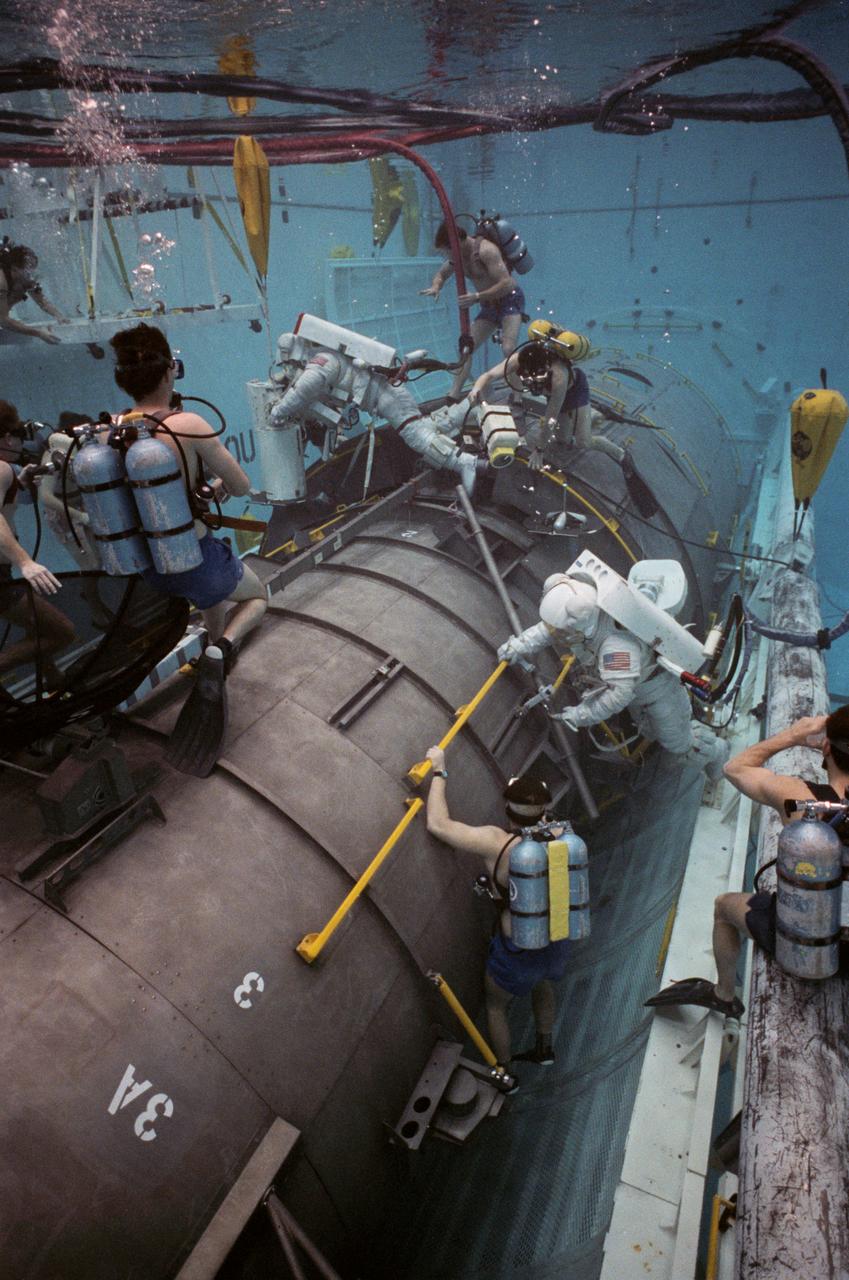

This overall view shows STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II (left) and MS Kathryn D. Sullivan making a practice space walk in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. McCandless works with a mockup of the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector which is attached to a grapple fixture on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) mockup. Sullivan manipulates HST hardware on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. SCUBA-equipped divers monitor the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) suited crewmembers during this simulated extravehicular activity (EVA). No EVA is planned for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment, but the duo has trained for contingencies which might arise during the STS-31 mission aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Photo taken by NASA JSC photographer Sheri Dunnette.
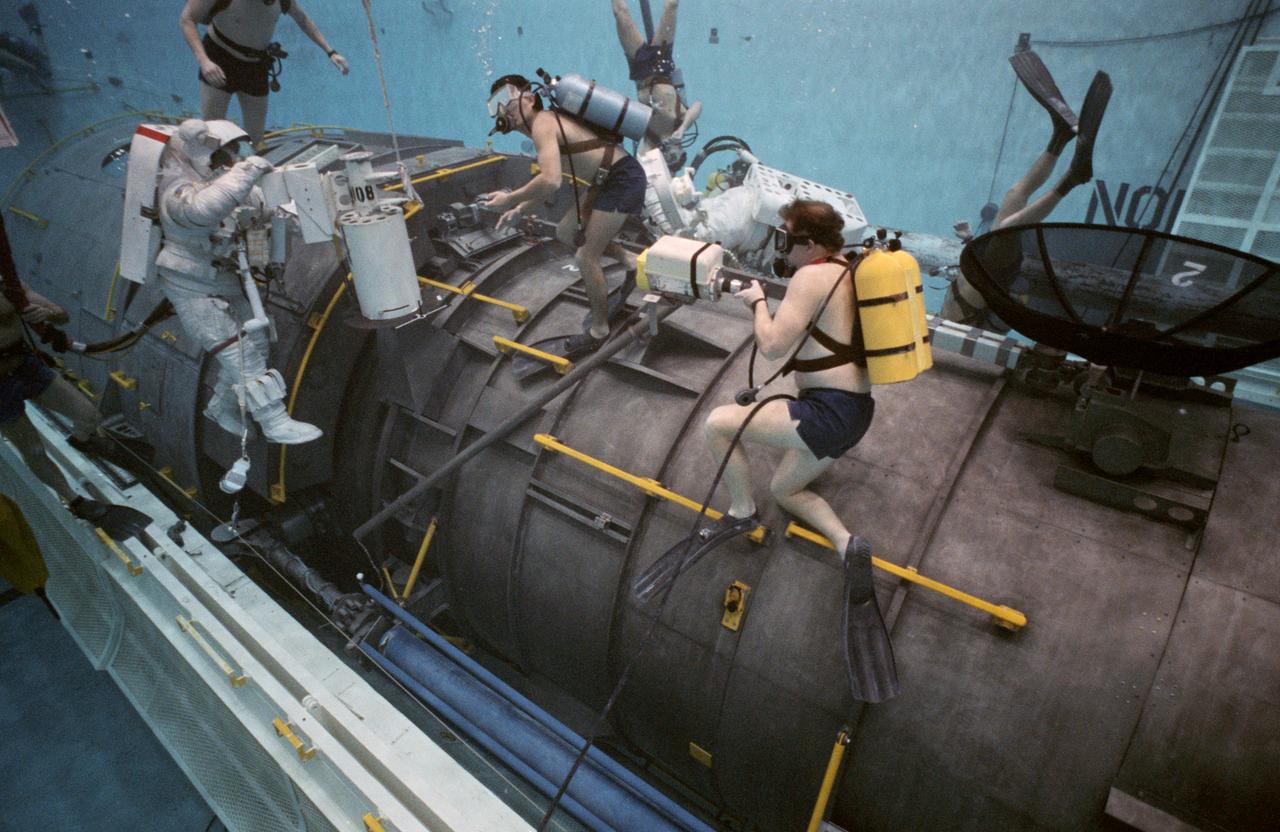

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II (left), wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), maneuvers his way around a mockup of the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector during an underwater simulation in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. The end effector is attached to a grapple fixture on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) mockup. As McCandless performs contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) procedures, fellow crewmember MS Kathryn D. Sullivan, in EMU, works on the opposite side of the HST mockup, and SCUBA-equipped divers monitor the activity. Though no EVA is planned for STS-31, the two crewmembers train for contingencies that would necessitate leaving the shirt sleeve environment of Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, crew cabin and performing chores with the HST payload or related hardware in the payload bay (PLB).
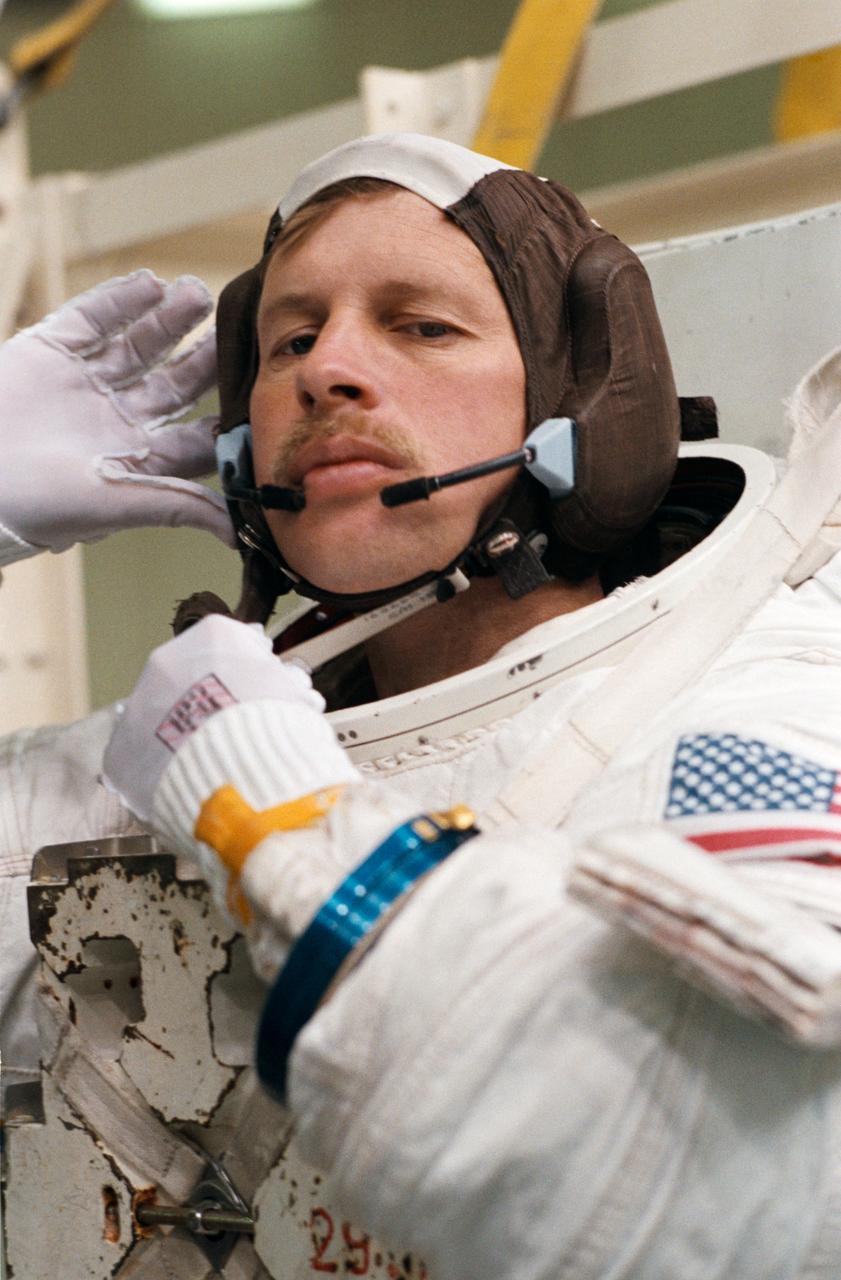

Astronaut Sherwood Springer prepares for an underwater test at Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) in response to the discovery of problems with the 04/13 deployed Syncom IV (LEASAT) communications satellite. Activities, Bldg. 29, WETF for the STS-23/51D Extravehicular Activity (EVA) Simulation for Syncom IV, 04/14/1985. 1. Shuttle - Simulation (SYNCOM IV) 2. Astronaut Jerry L. Ross - Simulation (SYNCOM) 3. Astronaut Sherwood C. Spring - Simulation (SYNCOM IV) JSC, Houston, TX
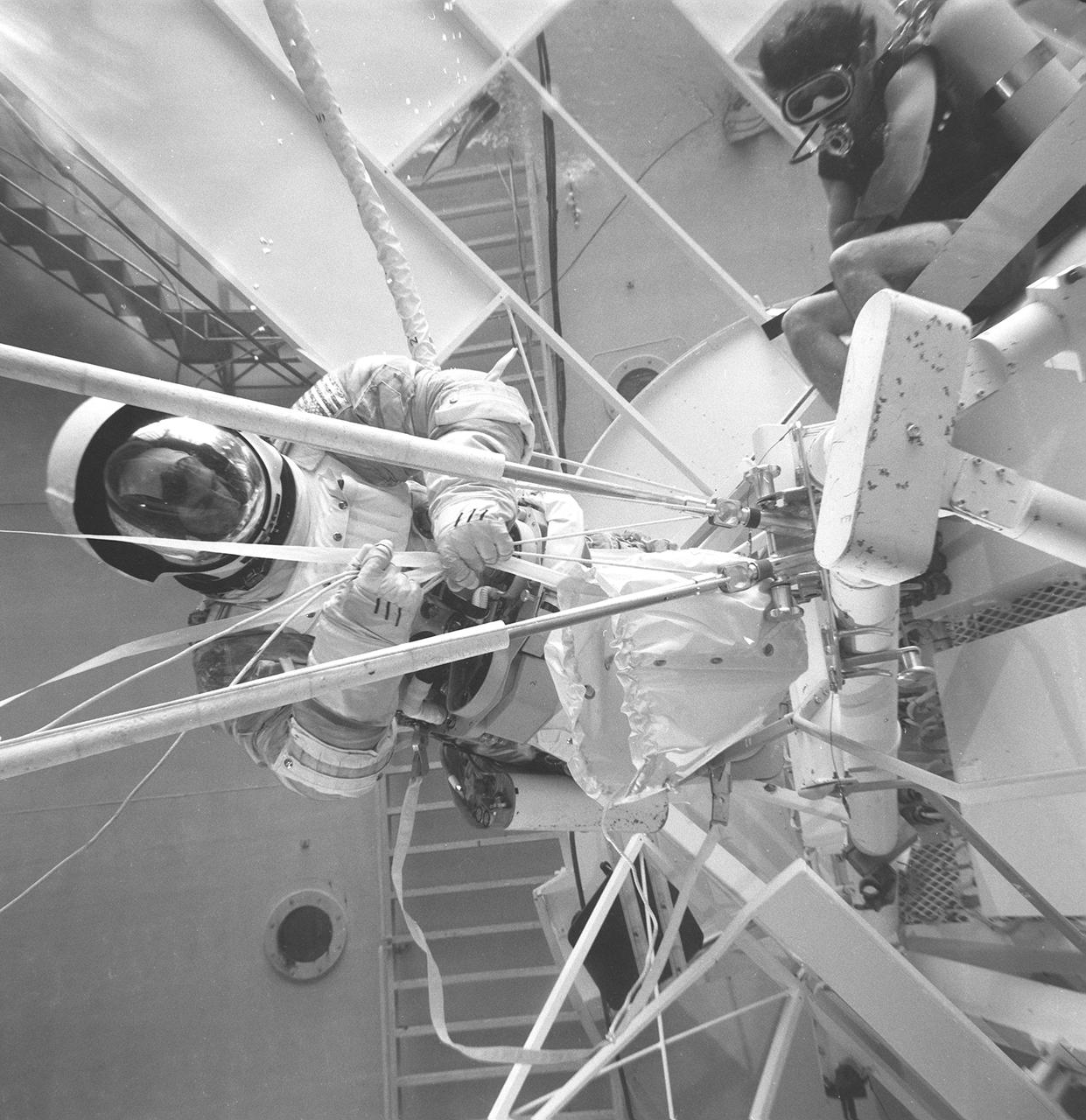

This photograph was taken in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) during the testing of an emergency procedure to deploy a twin-pole sunshade to protect the orbiting workshop from overheating due to the loss of its thermal shield. The spacecraft suffered damage to its sunshield during its launch on May 14, 1973. This photograph shows the base plate used to hold the twin-pole in place, the bag to hold the fabric sail, and the lines that were used to draw the sail into place. Extensive testing and many hours of practice in simulators, such as the NBS, helped prepare the Skylab crewmen for extravehicular performance in the weightless environment. This huge water tank simulated the weightless environment that the astronauts would encounter in space.
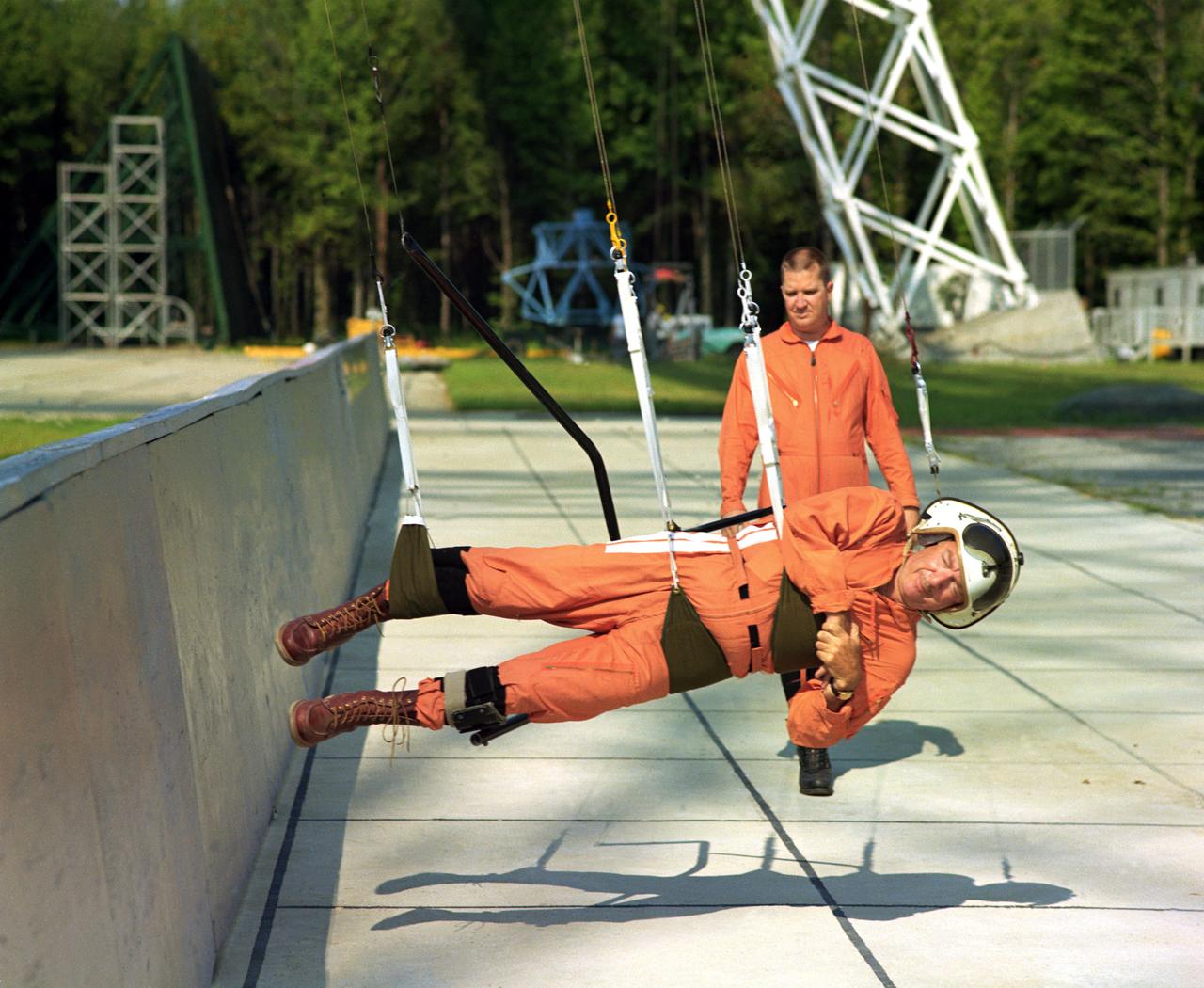

Walter Cronkite in the Reduced Gravity Simulator. Various views of Cronkite in the Lunar Landing Research Facility's Reduced Gravity Simulator which was used to train the astronauts for weightlessness. L68-8308 Caption: "During a 1968 visit to Langley, then CBS News Anchorman Walter Cronkite tries out the Reduced Gravity Simulator, a series of cable-supported slings designed to approximate the Moon's gravity, 1/6th that of Earth's." Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, p 91, by James Schultz.
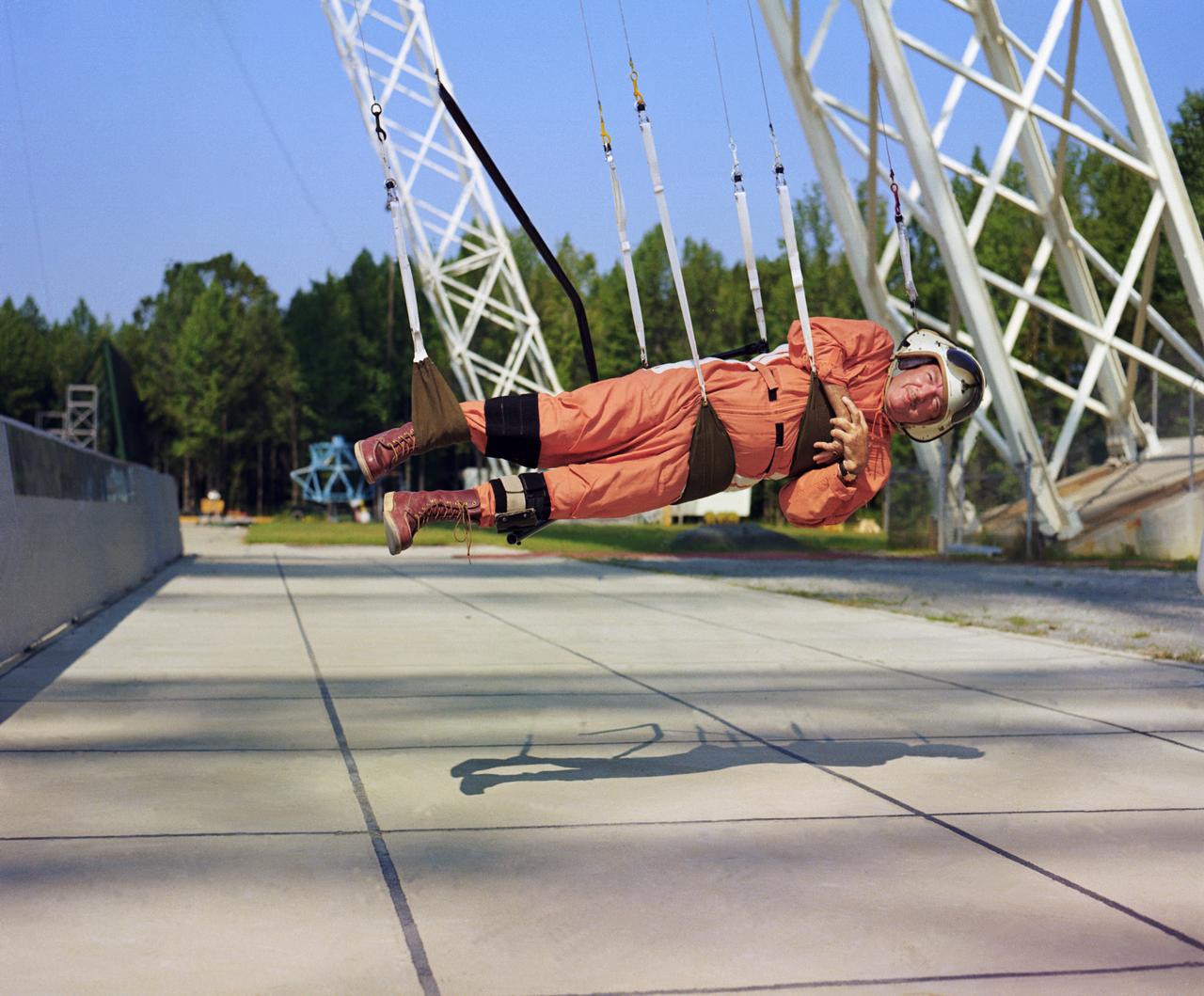

Walter Cronkite in the Reduced Gravity Simulator. Various views of Cronkite in the Lunar Landing Research Facility's Reduced Gravity Simulator which was used to train the astronauts for weightlessness. L68-8308 Caption: "During a 1968 visit to Langley, then CBS News Anchorman Walter Cronkite tries out the Reduced Gravity Simulator, a series of cable-supported slings designed to approximate the Moon's gravity, 1/6th that of Earth's." Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, p 91, by James Schultz.
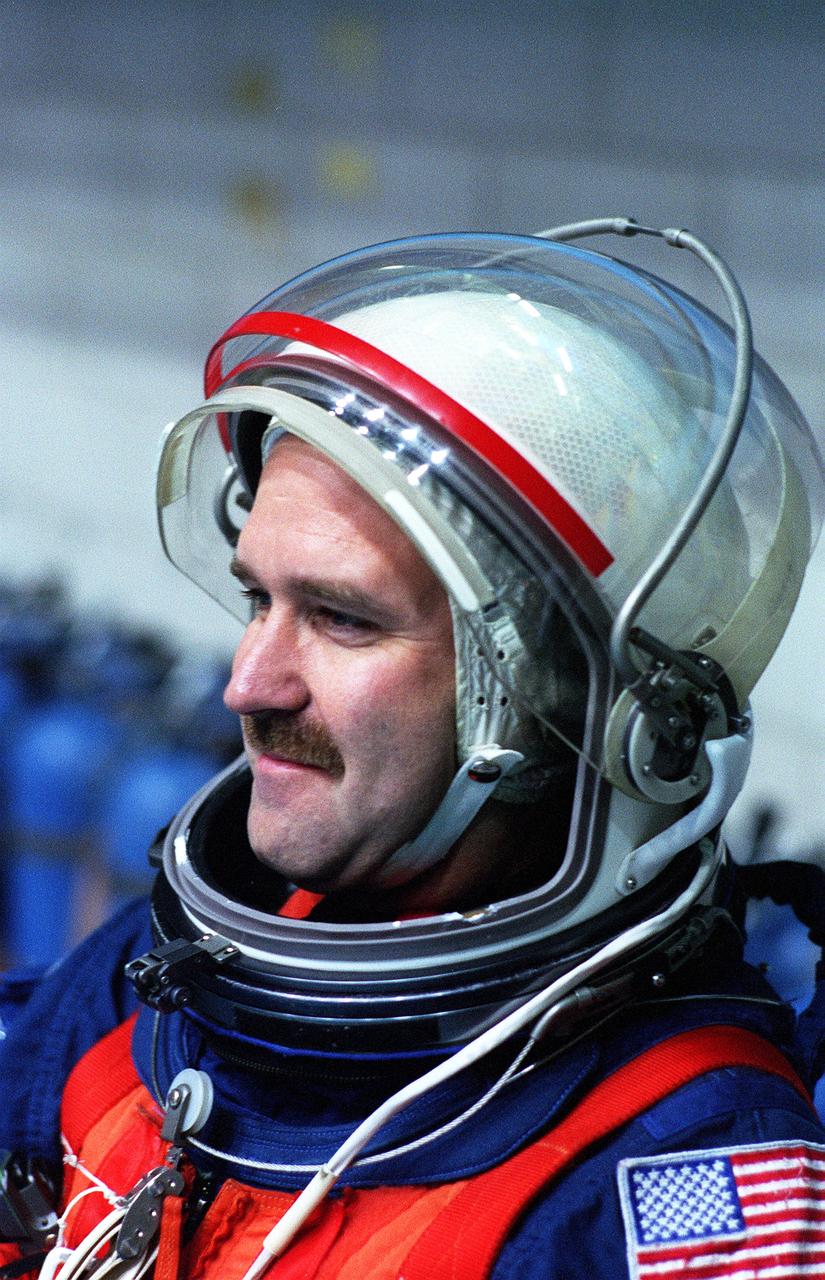

S96-15402 (26 Sept. 1996) --- In the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility, astronaut John M. Grunsfeld, STS-81 mission specialist, prepares to simulate a parachute drop into water. Five STS-81 crewmates, out of frame, joined him for the bailout training exercises.
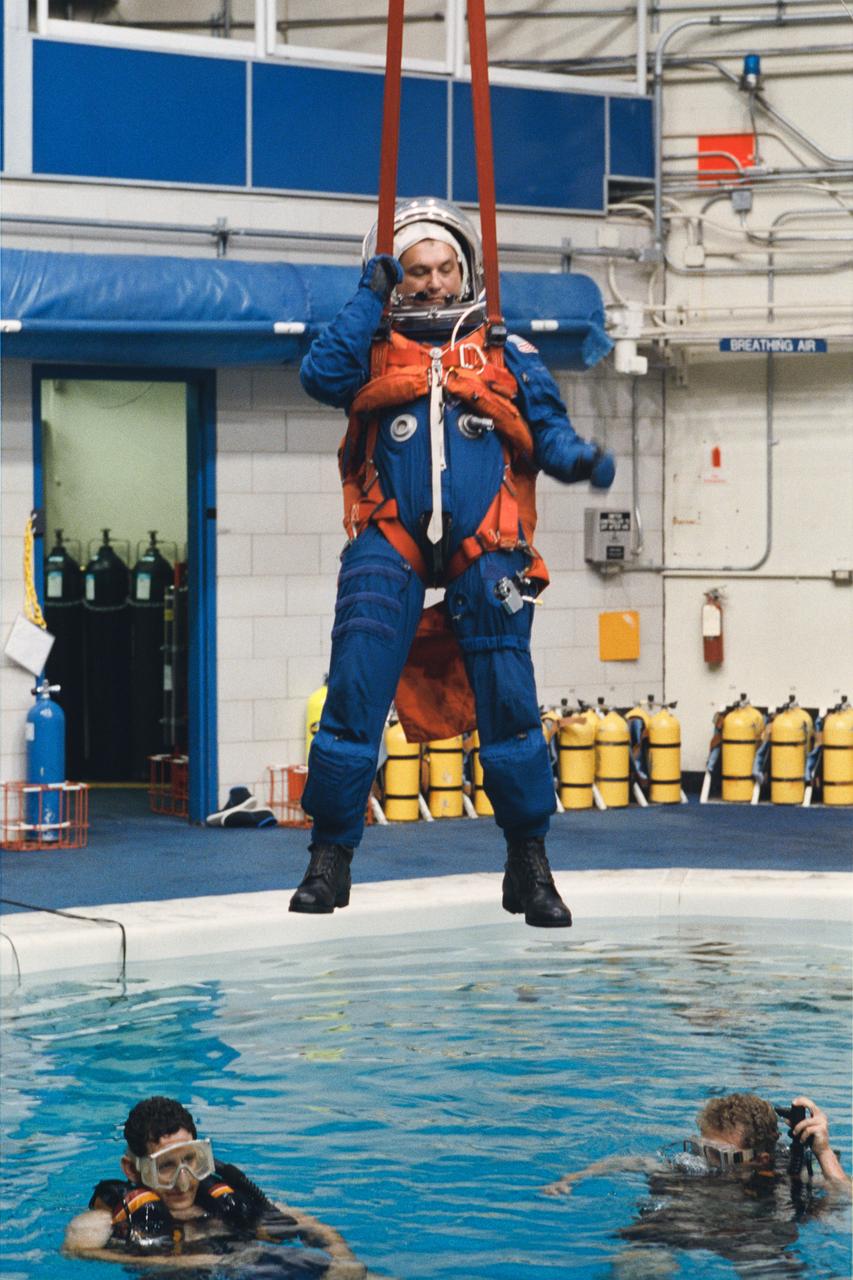

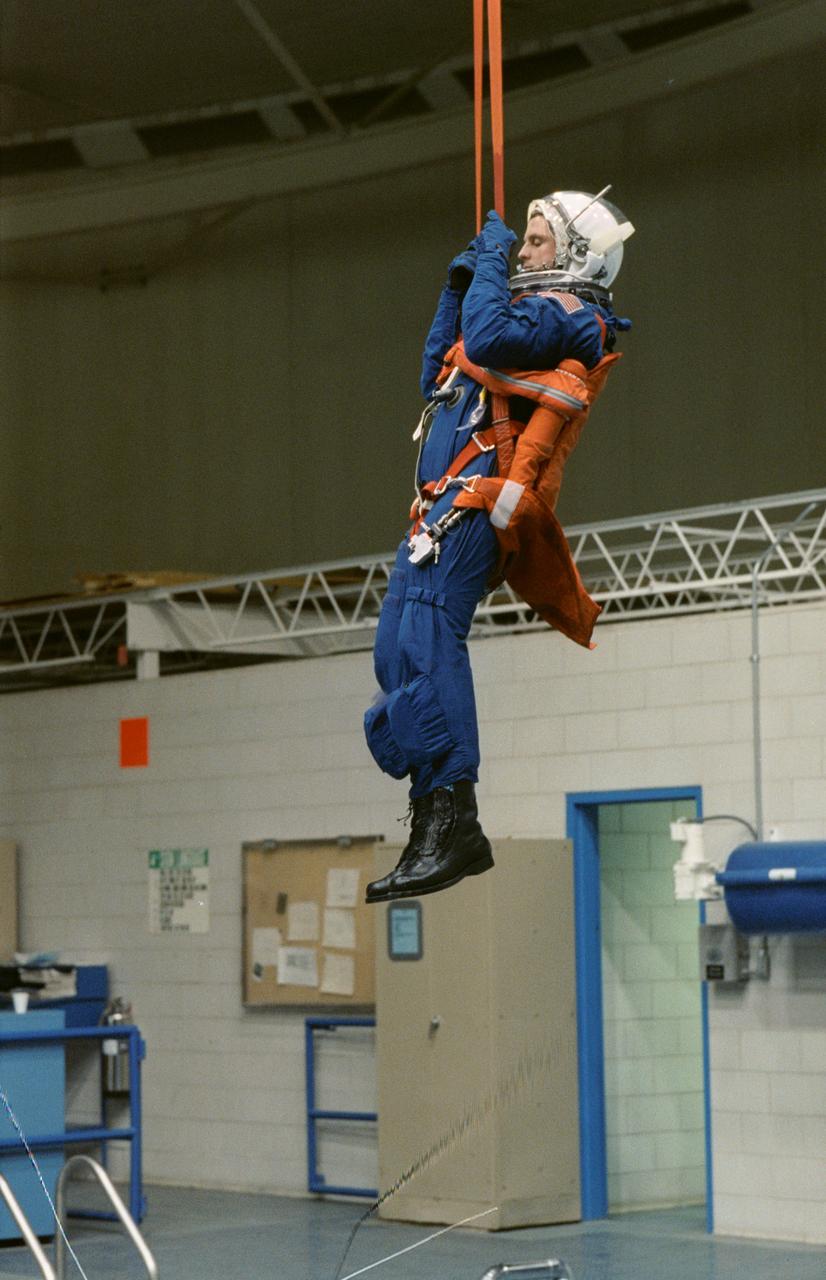
Cosmanaut Vladimir Titov, an alternate mission specialist for STS-60, simulates a parachute glide into water during a bailout training exercise at JSC. This phase of emergency egress training took place in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF).
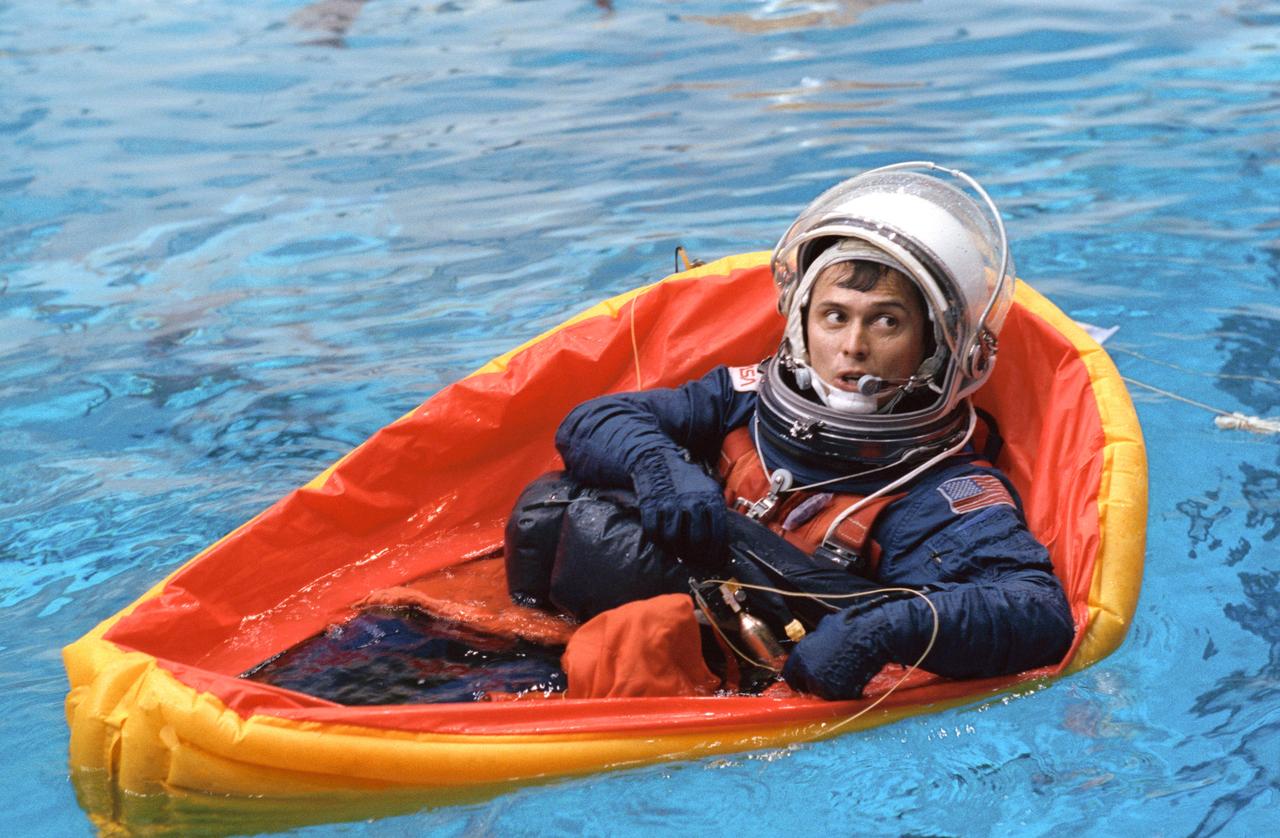

S92-33478 (12 March 1992) --- Astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, mission specialist, relies on a one-person life raft to get him to "safety" during a STS-46 bailout simulation exercise. The training took place in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility.
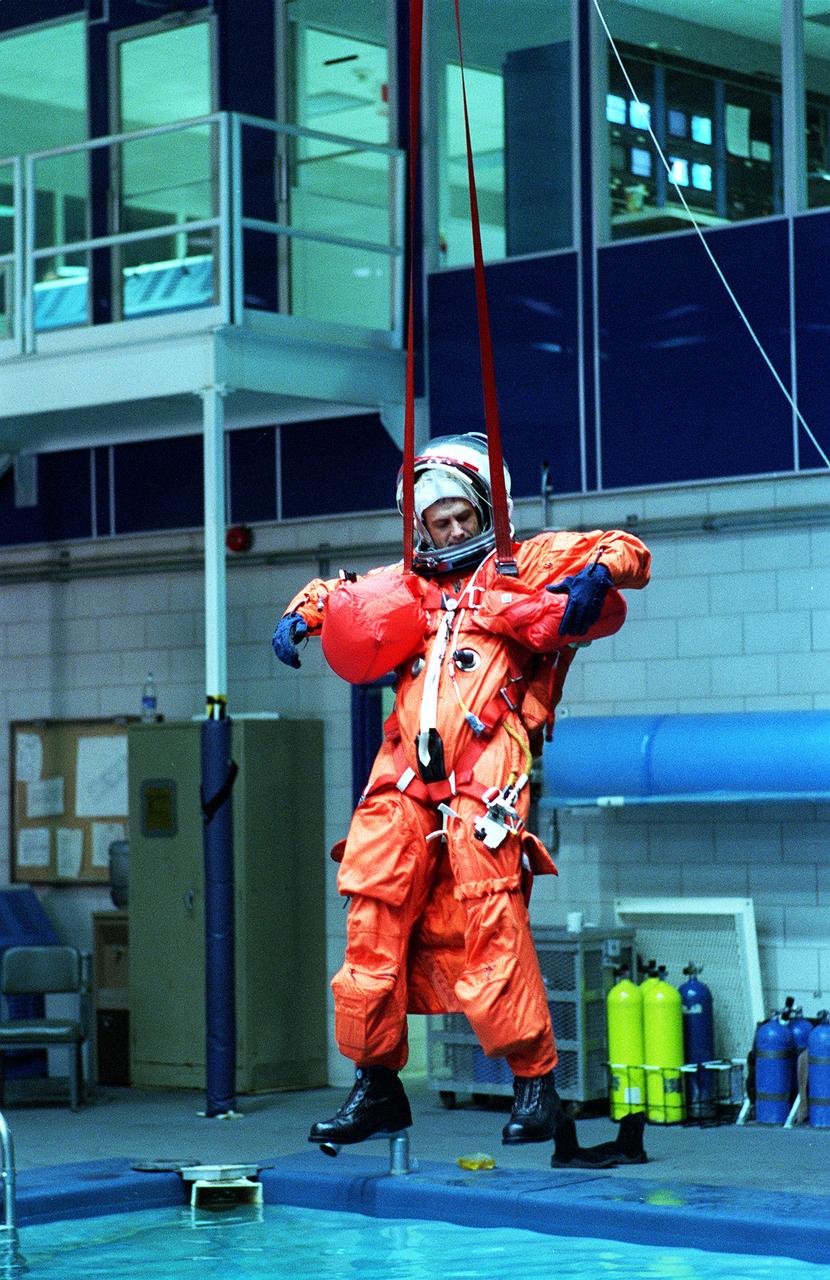

S96-15407 (26 Sept. 1996) --- In the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility, astronaut Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff, STS-81 mission specialist, simulates a parachute drop into water. Five STS-81 crewmates, out of frame, joined him for the bailout training exercises.
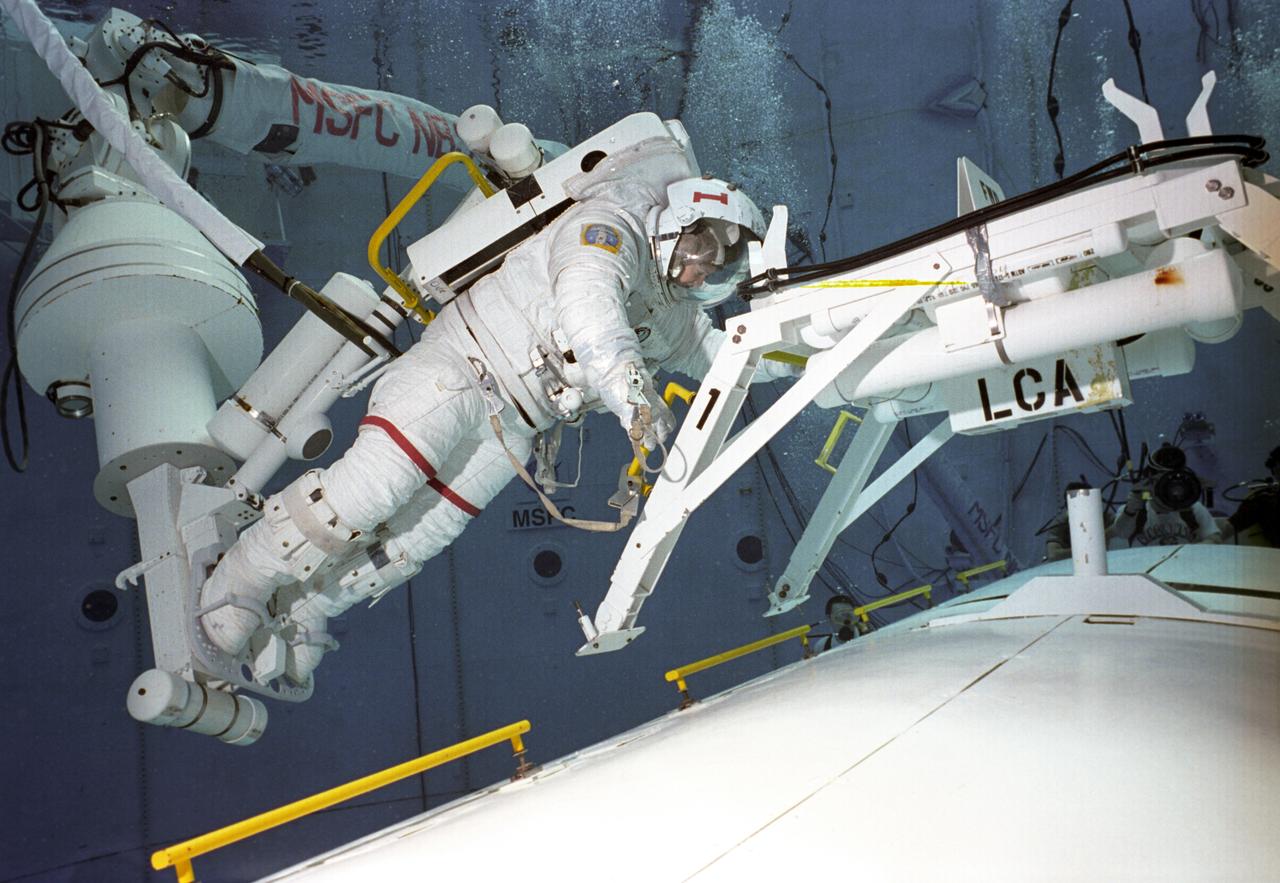

Astronauts Susan Helms (#1) and Carl Walz (#2) are training in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at Marshall Space Flight center with an exercise for International Space Station Alpha. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA).
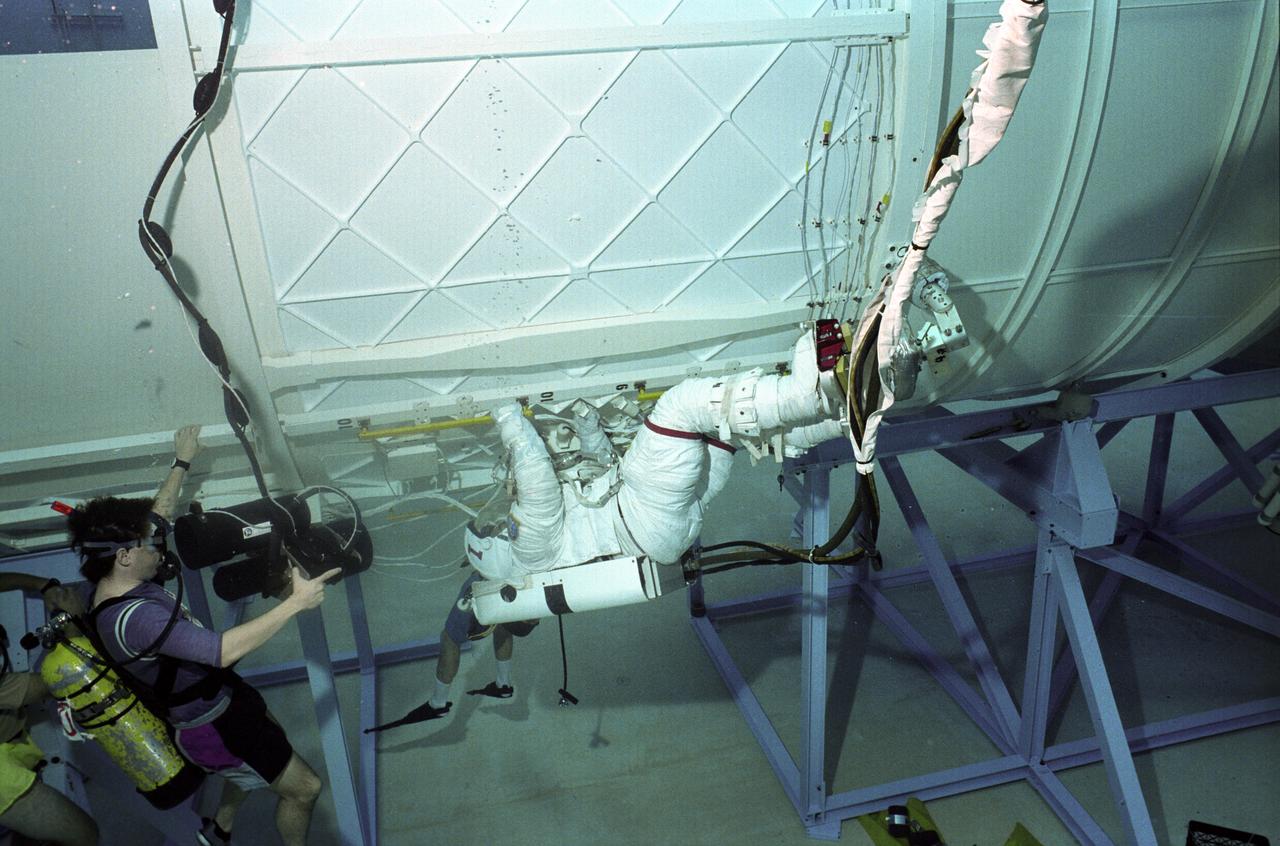

Astronauts Tamara Jernigan (#1) and David Wolf (#2) are training in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at Marshall Space Flight center with an exercise for International Space Station Alpha. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA).
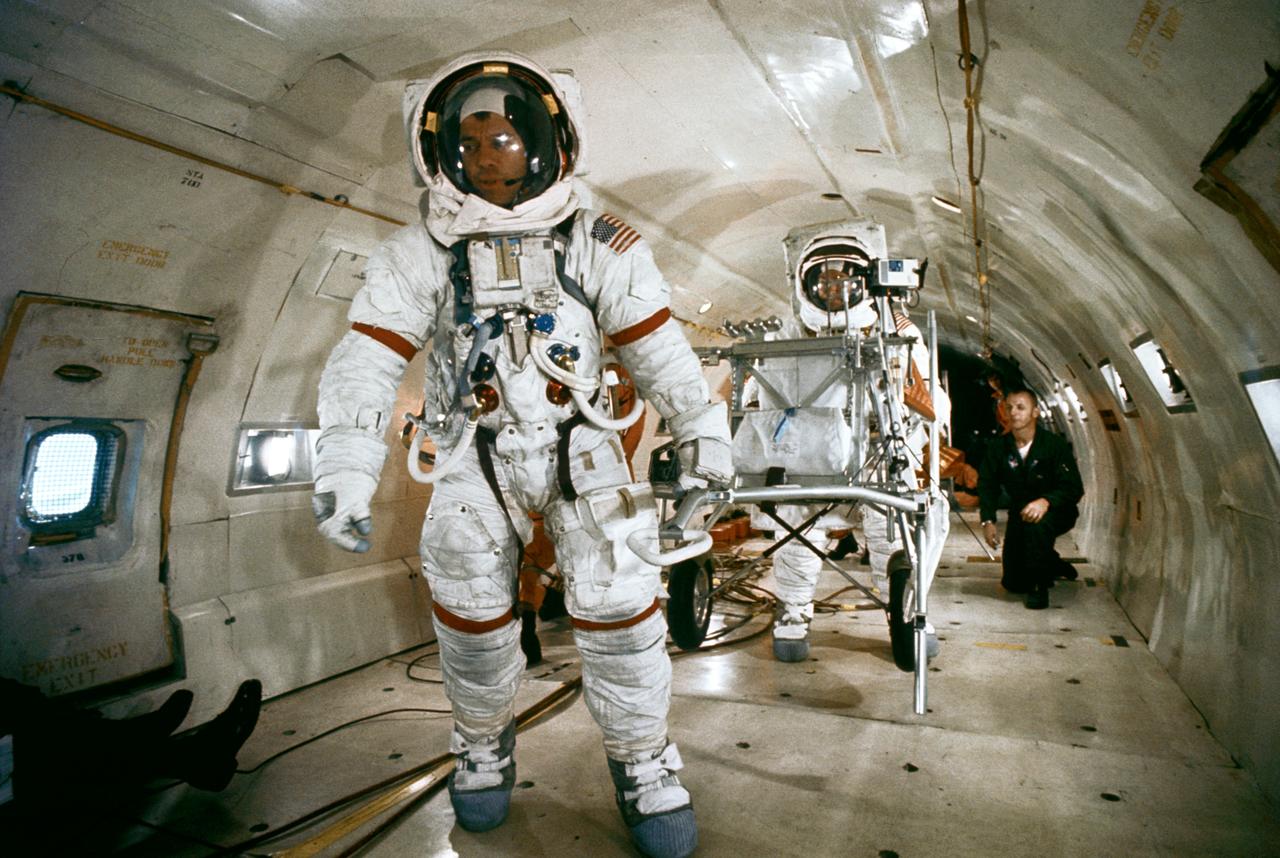

S70-53479 (4 Nov. 1970) -- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 commander, pulls the modular equipment transporter (MET) under weightless conditions aboard an Air Force KC-135 out of Patrick Air Force Base. Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, Apollo 14 lunar module pilot, is behind the MET. The KC-135 aircraft, flying a parabolic curve, creates a weightless environment providing a training exercise in preparation for the astronauts' extravehicular activities (EVA) on the lunar surface. This training simulates the 1/6 gravity the astronauts will encounter on the moon.
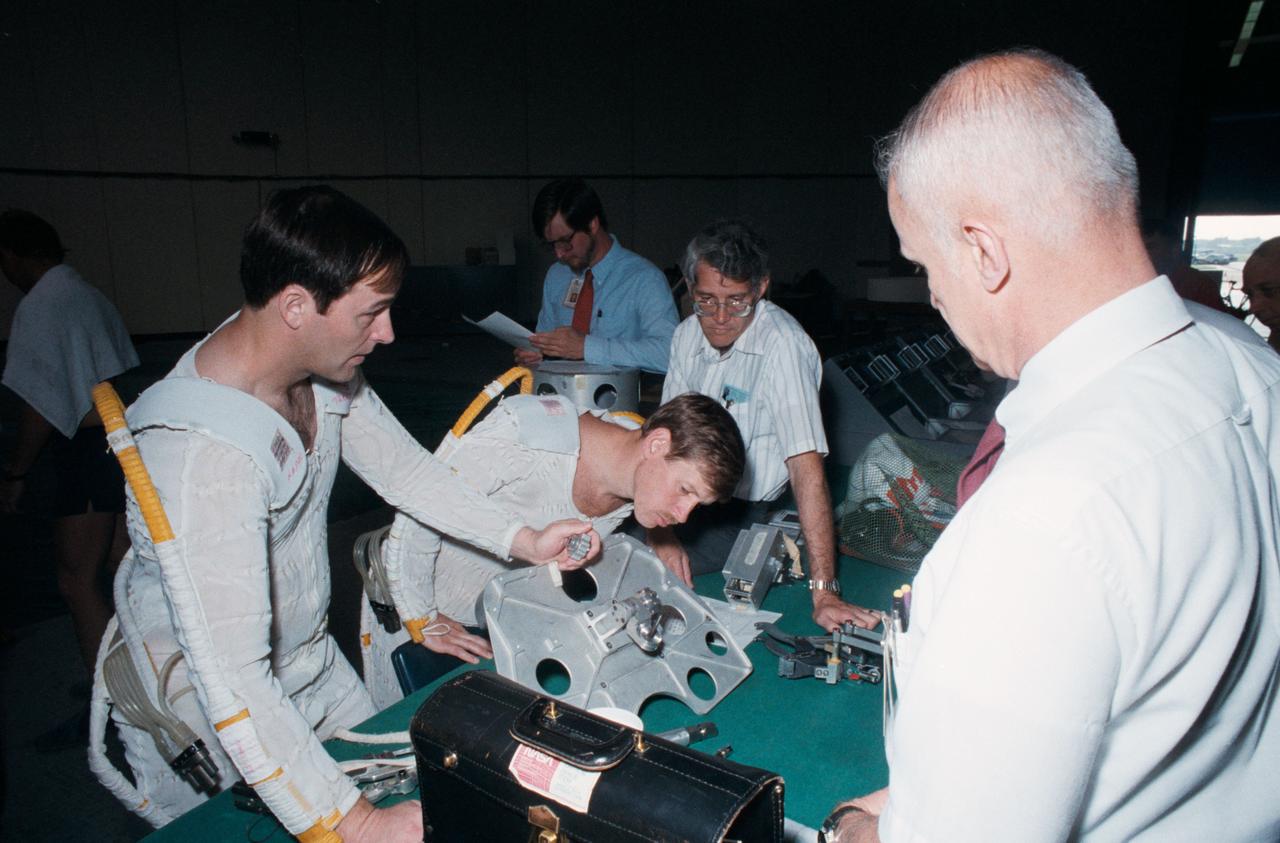

Astronauts Jerry L. Ross (left) and Sherwood Springer (center), look over a foot restraint like that on the currently orbiting Shuttle Discovery. At right is Astronaut Bruce McCandless II. Activities, Bldg. 29, Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) for the STS-23/51D Extravehicular Activity (EVA) Simulation for Syncom IV, 04/14/1985. 1. SHUTTLE - SIMULATION (SYNCOM IV) 2. ASTRONAUT ROSS, JERRY L. - SIMULATION (SYNCOM) 3. ASTRONAUT SPRING, SHERWOOD C. - SIMULATION (SYNCOM IV) JSC, HOUSTON, TX

S94-33357 (1994) --- Scott Bleiseth, top, prepares to spin Mike Hess, a fellow EVA engineer, during a test on the air-bearing floor in the Shuttle Mock-up and Integration Laboratory at NASA's Johnson Space Center. The hardware being tested is part of the Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER). The pair was developing techniques by which the non-SAFER equipped spacewalker will impart a rotation to the SAFER-using spacewalker during the STS-64 mission. Once the SAFER astronaut is spinning, the device will be activated and its automatic attitude hold capability will be tested. SAFER is to fly on STS-76 as well. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

S90-45238 (25 June 1990) ---- Astronaut Linda M. Godwin, STS 37 mission specialist, simulates emergency egress from a Space Shuttle. The training session was held in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) weightless environment training facility (WET-F). The 25-ft. pool in the facility served as a simulated ocean into which a parachute landing might be made. Early next year, Godwin, along with four other astronauts, will fly onboard Atlantis for a five-day mission.

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Dr. Ernst Stuhlinger, Director of Research Projects Office; and Dr. Wernher von Braun, center director, along with others, took a swim in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at MSFC. A safety diver adjusts scuba equipment worn by von Braun, while Stuhlinger adjusts his weight belt prior to entering the tank. In the NBS, subjects were weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition underwater to perform and practice tasks in a simulated weightless condition as would be encountered in space.
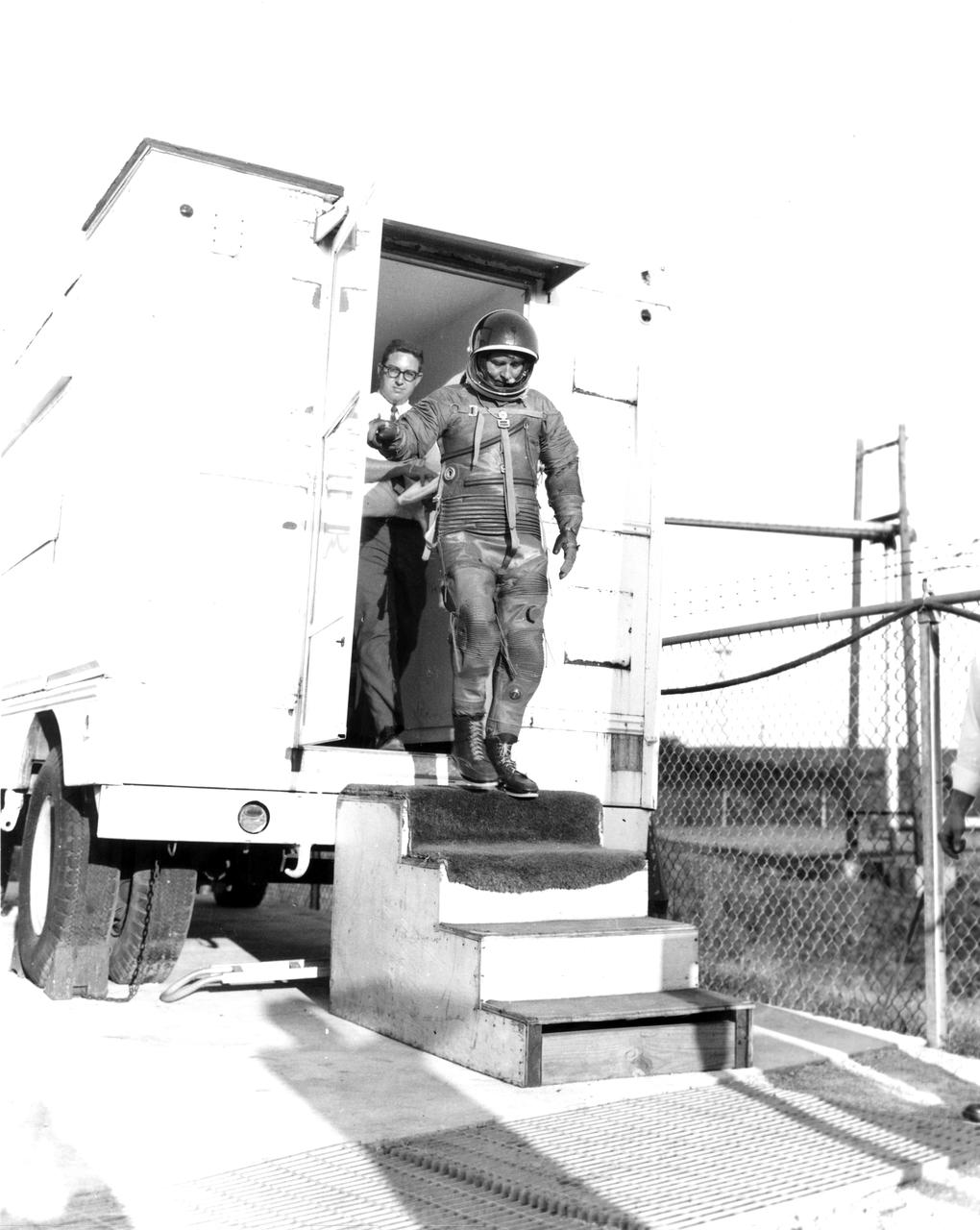

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun, is shown leaving the suiting-up van wearing a pressure suit prepared for a tryout in the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.
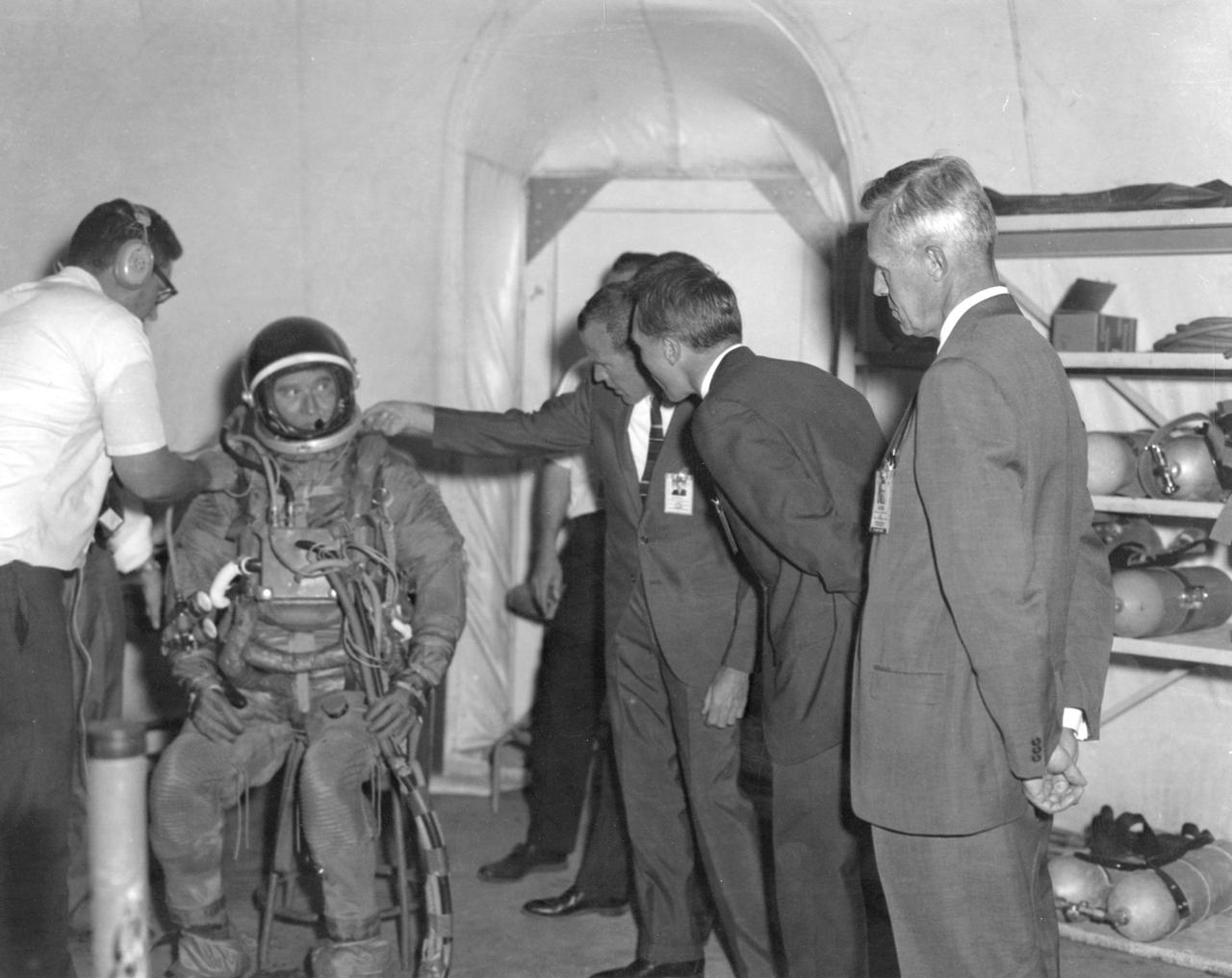

Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper checks the neck ring of a space suit worn by Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. von Braun before he submerges into the water of the MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Wearing a pressurized suit and weighted to a neutrally buoyant condition, Dr. von Braun was able to perform tasks underwater which simulated weightless conditions found in space.
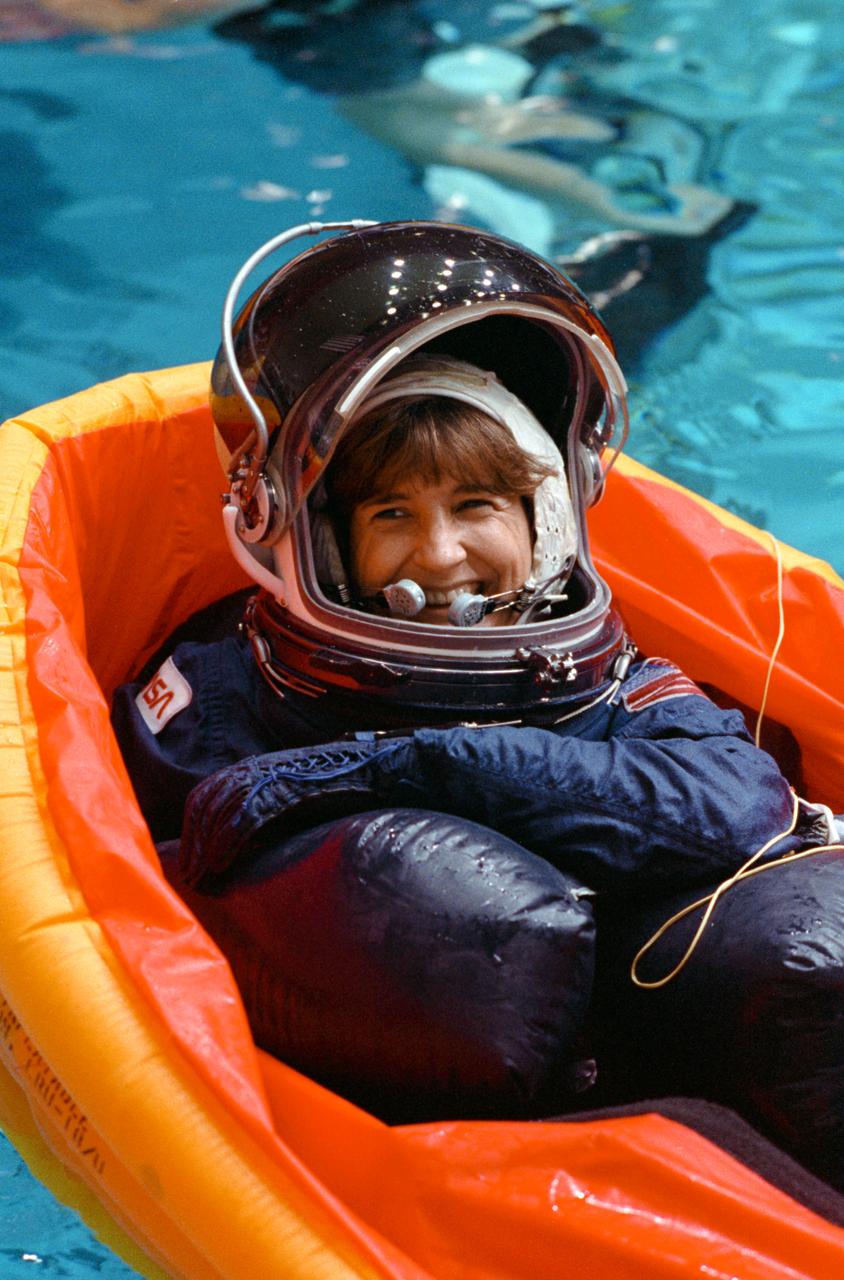

S90-45229 (25 June 1990) --- Astronaut Linda M. Godwin, STS-37 mission specialist, floats in a one-person life raft. She was simulating steps involved in emergency egress from a space shuttle. The training session was held in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). The 25-ft. deep pool in the facility served as a simulated ocean into which a parachute landing might be made. Early next year, Godwin, along with four other astronauts, will fly onboard Atlantis for a five-day mission.
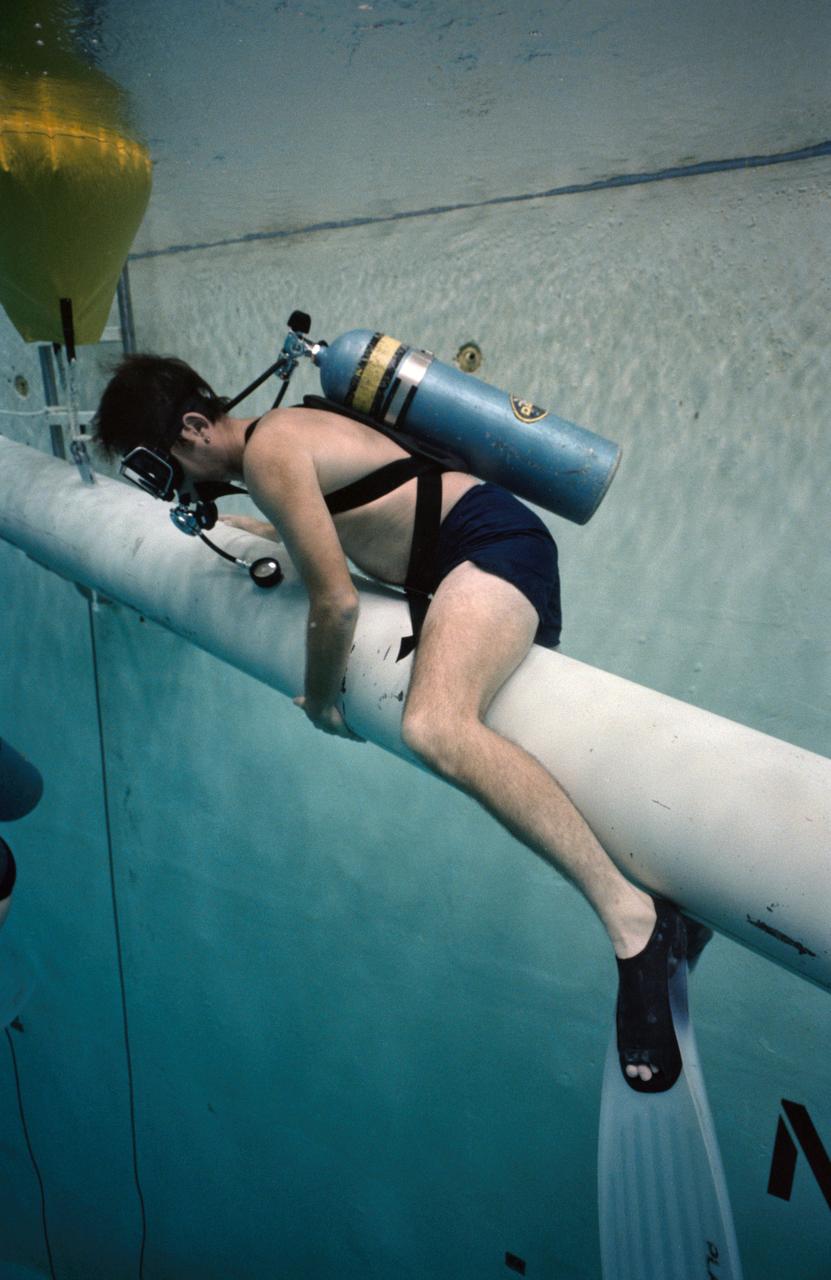

S84-36958 (29 June 1984) --- Astronaut Robert L. Crippen, 41-G crew commander, perches nearby an underwater simulation scene in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Purpose of the rehearsal was to train two of the 41-G crew's mission specialists for a scheduled extravehicular activity (EVA). Out of frame are Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan, Jon A. McBride and David Leestma. Dr. Sullivan and Leestma donned extravehicular mobility units (EMU) for the simulation while Crippen and McBride monitored the activity. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
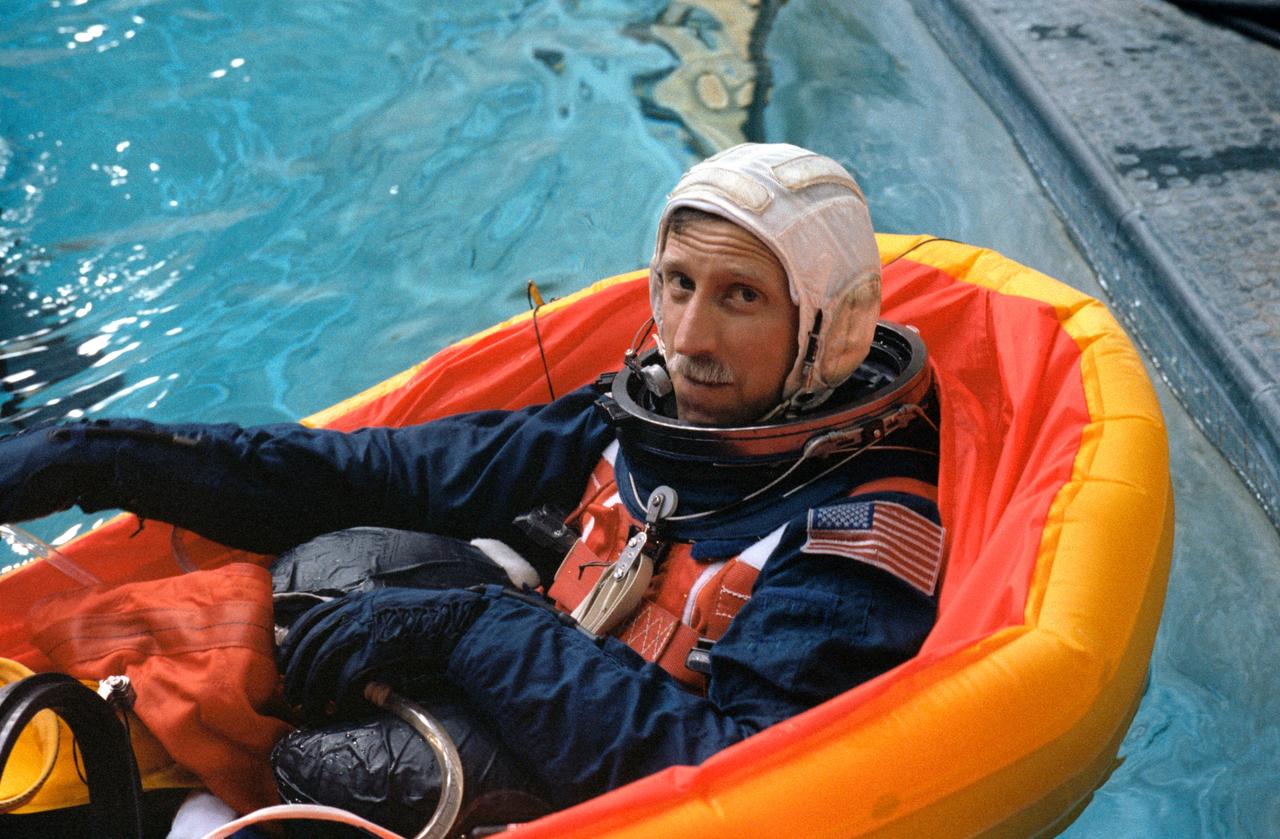

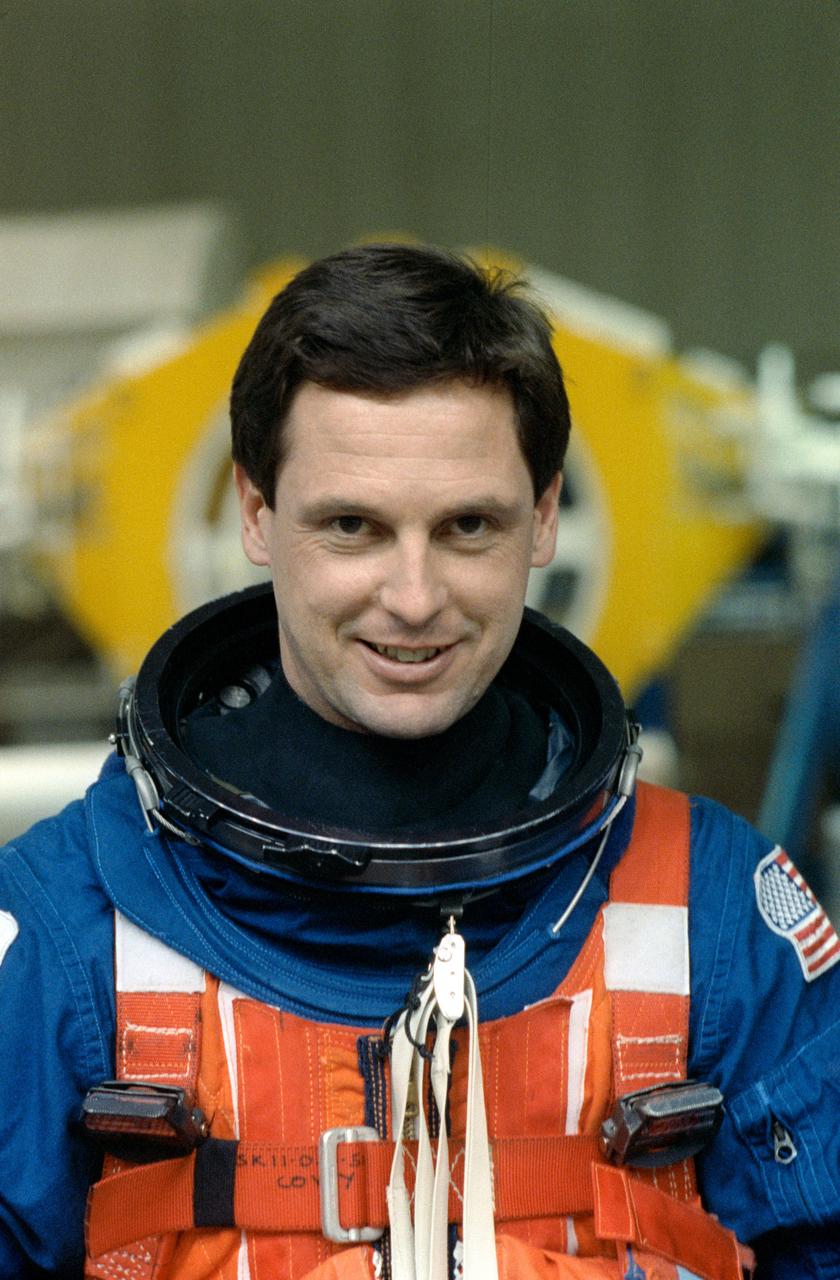
S88-42425 (20 July 1988) --- STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Pilot Richard O. Covey, wearing the newly designed launch and entry suit (LES), floats in single-occupant life raft in JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. The simulation of the escape and rescue operations utilized the crew escape system (CES) pole method of egress from the Space Shuttle.
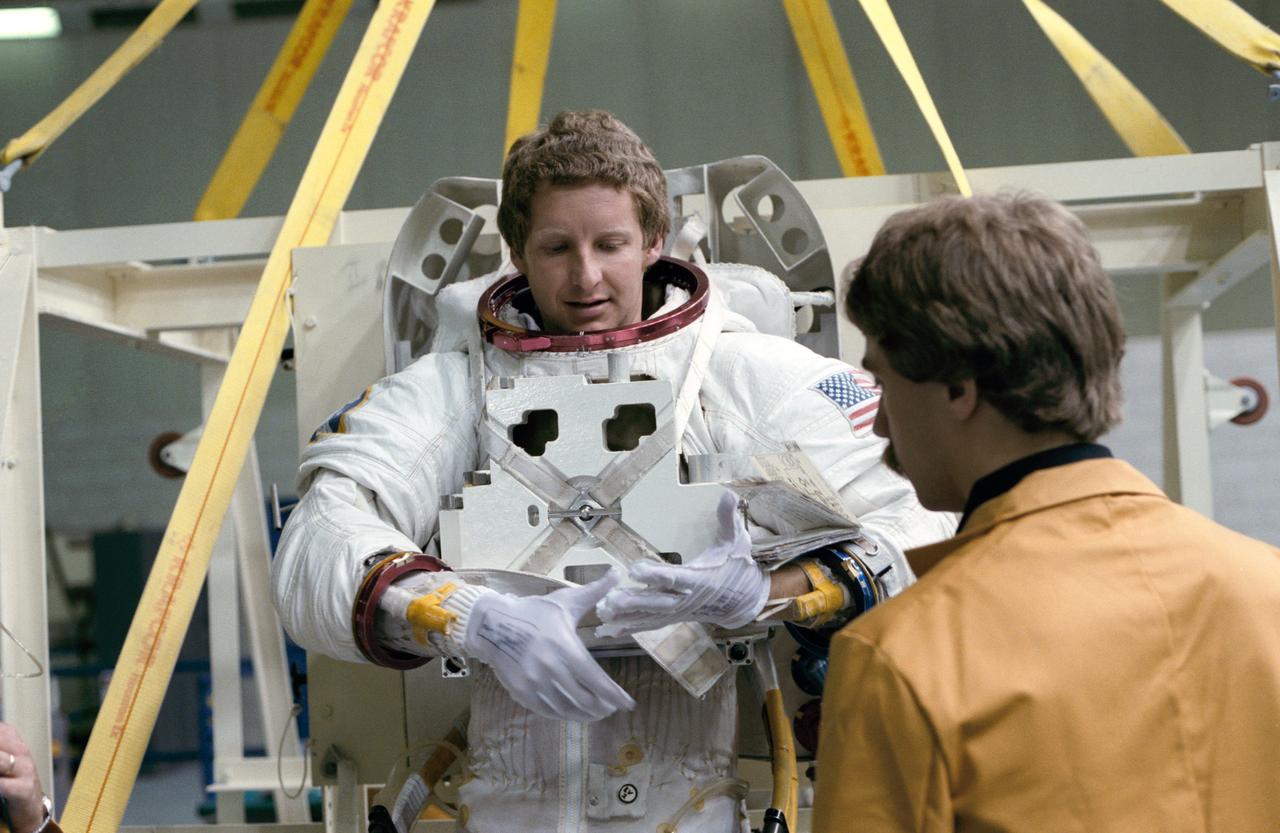

S84-28203 (24 Feb 1984) --- Astronaut Steven A. Hawley, 41-D mission specialists, completes suiting up procedures before being submerged in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) 25 ft. deep weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Obscured behind Dr. Hawley is astronaut Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, 41-D mission specialist. later the pair were lowered into the facility for an underwater simulation of a contingent extravehicular activity for the week-long flight.
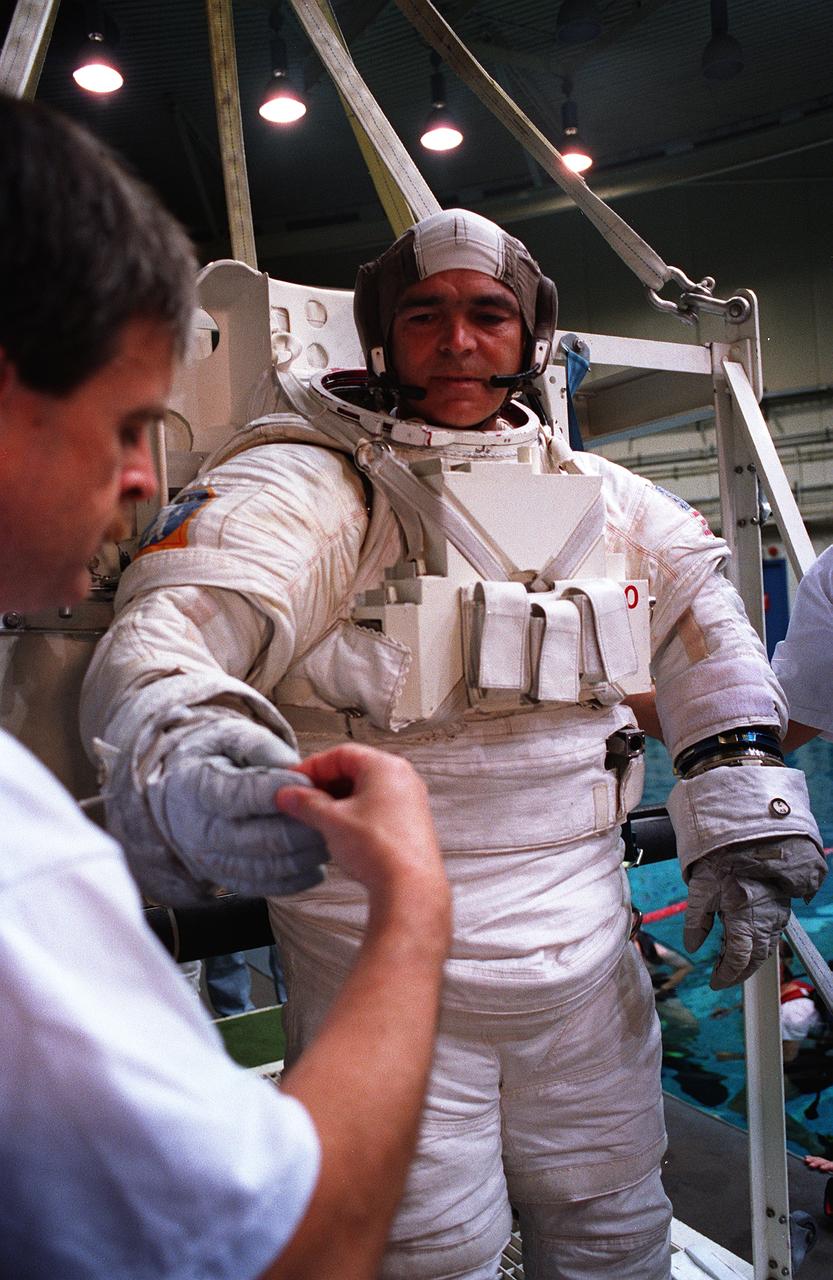

S95-21279 (September 1995) --- Astronaut Michael R. (Rich) Clifford, mission specialist, checks his gloves before being submerged in a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Wearing high fidelity training versions of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit, both Clifford and Linda M. Godwin were later simulating Extravehicular Activity (EVA) chores in the pool. Launch aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis is scheduled for March of 1996.
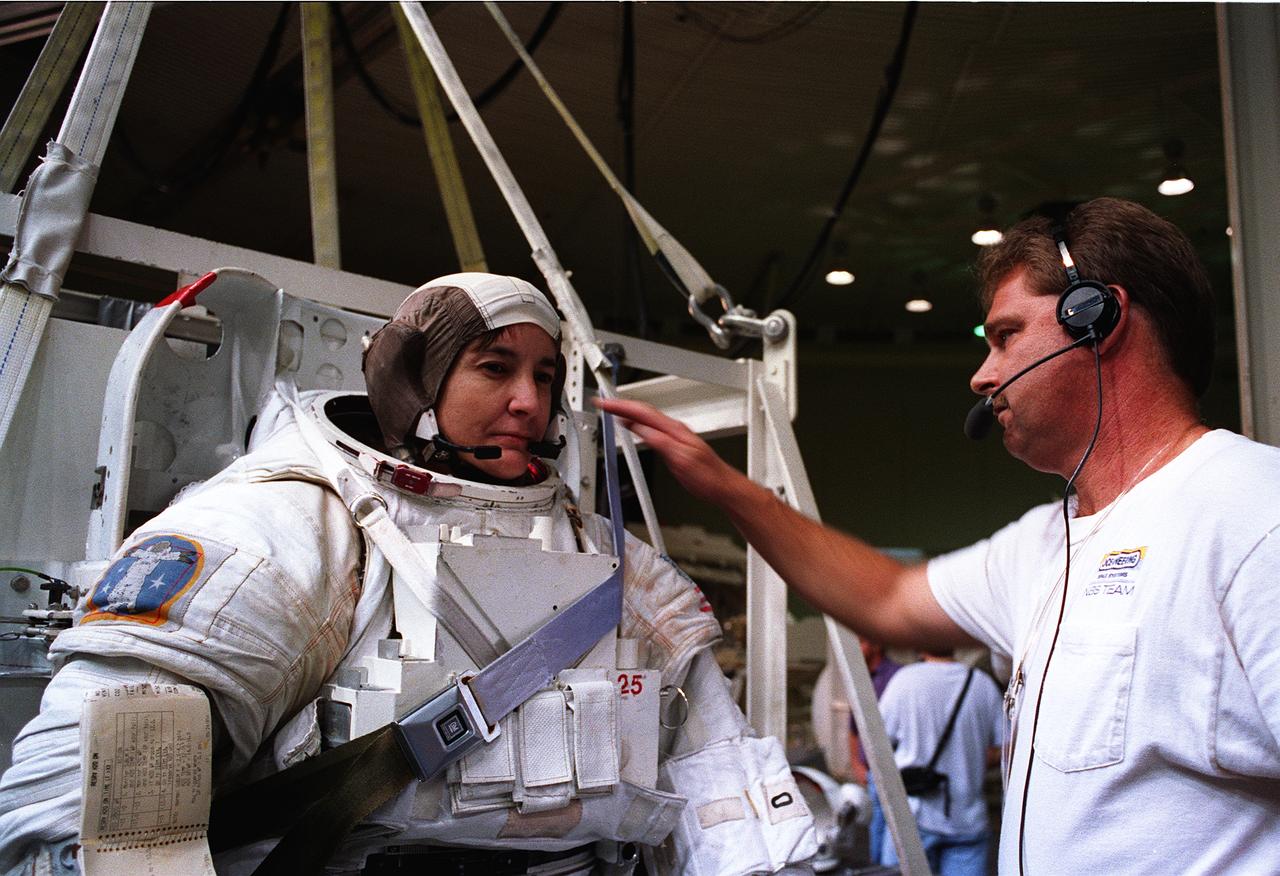

S95-21280 (September 1995) --- Astronaut Linda M. Godwin, mission specialist, checks communications systems before being submerged in a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Wearing high fidelity training versions of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit, both Godwin and Michael R. (Rich) Clifford were later simulating Extravehicular Activity (EVA) chores in the pool. Launch aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis is scheduled for March of 1996.
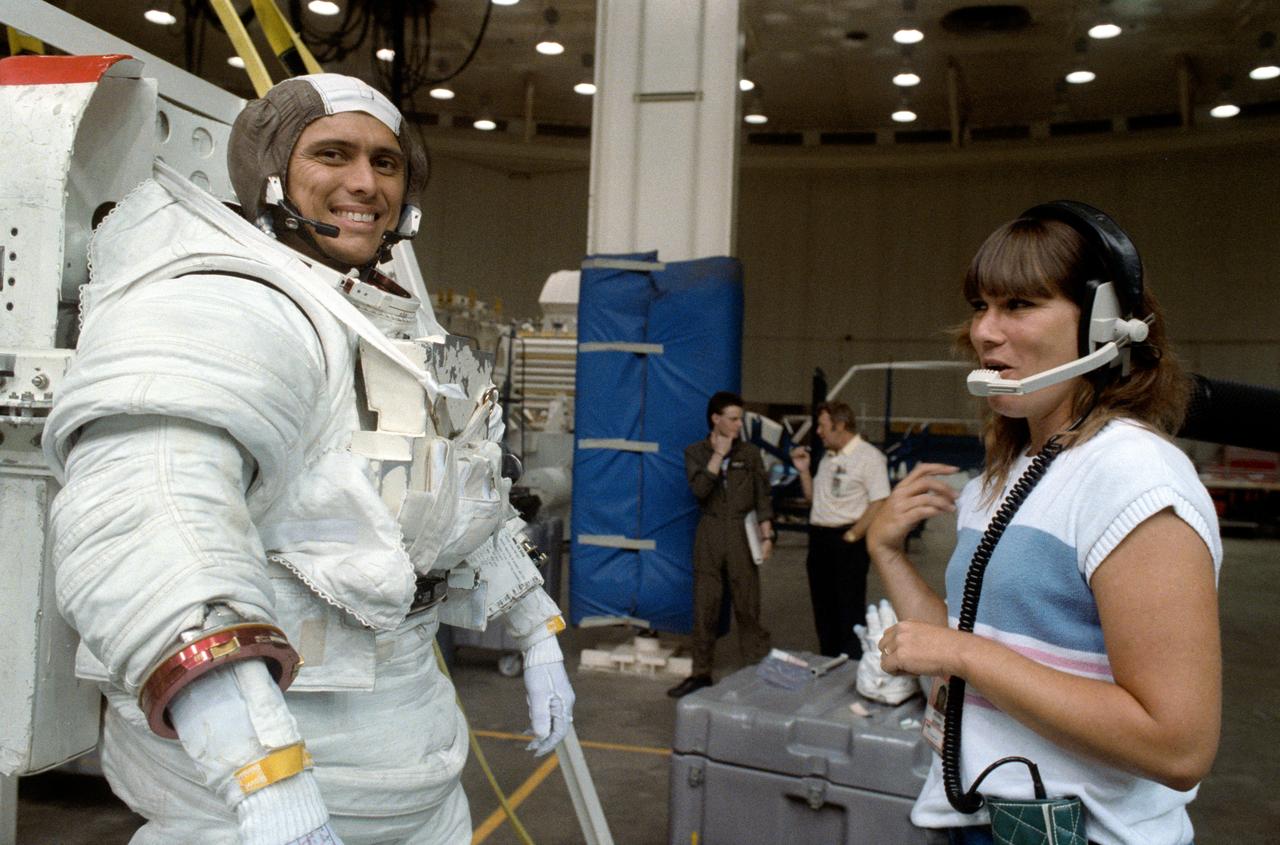

S89-42667 (24 Aug 1989) --- Astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Diaz tests his communications gear with Pam S. Peters of RSO, prior to participating in an underwater simulation of a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for his mission specialist assignment on NASA's STS-34 mission. He stands on a platform that will lower him into a 25-ft. deep pool, part of JSC's weightless environmental test facility (WET-F). Also participating in the contingency EVA rehearsal was astronaut Ellen S. Baker (out of frame).
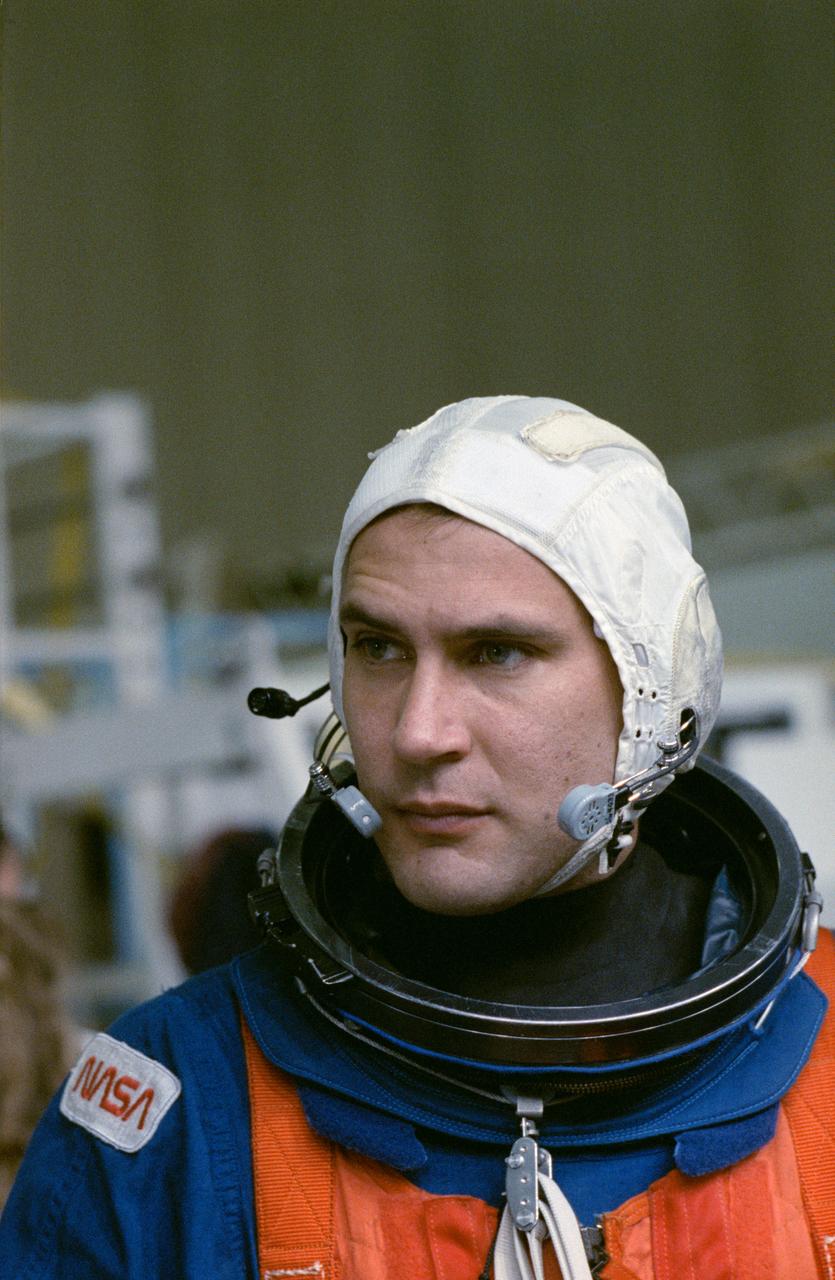

S90-54750 (7 Dec 1990) --- Astronaut Richard J. Hieb, mission specialist, listens attentively as a trainer (out of frame) briefs the STS-39 crewmembers on emergency egress measures. The seven astronauts were in JSC's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). This type training uses the WET-F's 25 ft. deep pool to simulate an ocean parachute landing.
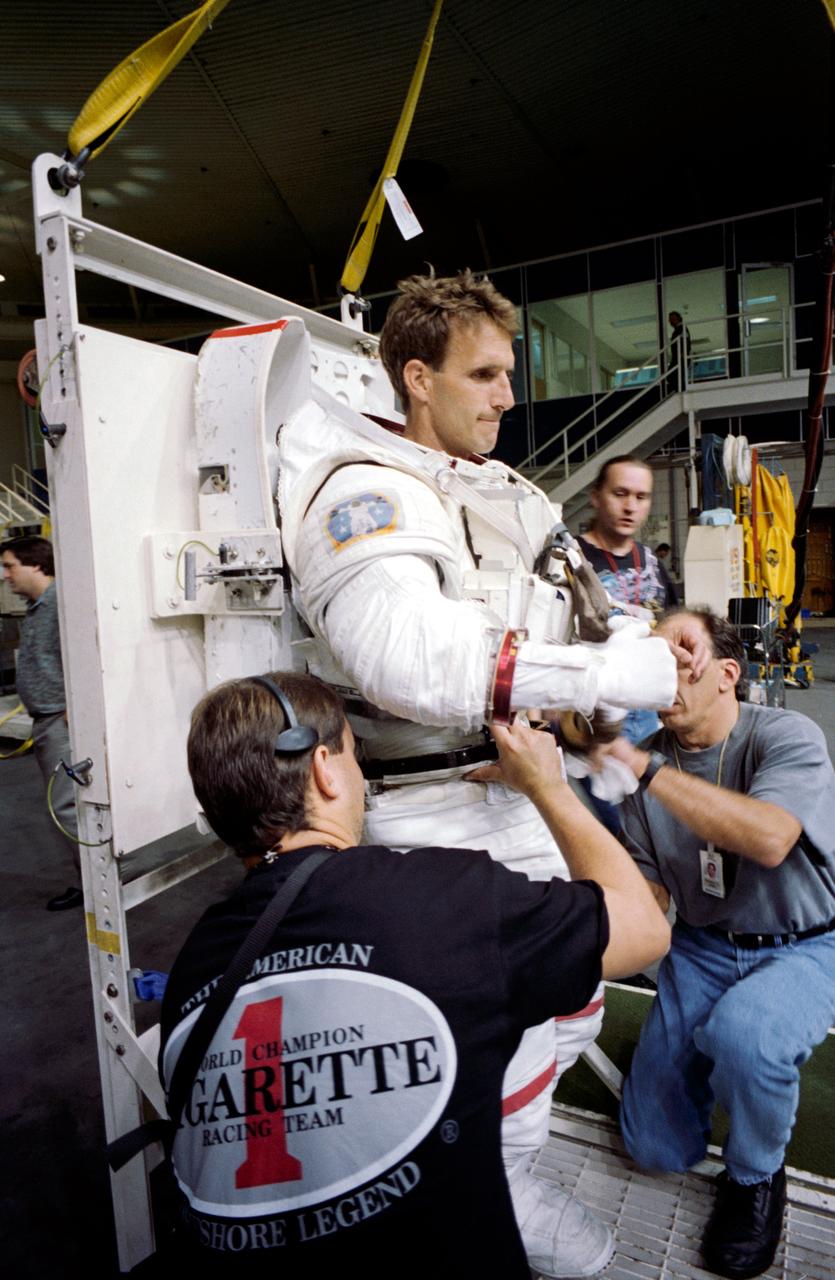

COLOR 13 SEPTEMBER 1996 S96-14353 JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS STS-81 TRAINING VIEW --- In the Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F), astronaut Jerry M. Linenger, STS-81 mission specialist, prepares for an underwater simulation of a contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA). Linenger, attired in a training version will utilize the nearby 25-feet deep pool, in which he will be able to achieve a neutrally buoyant state.
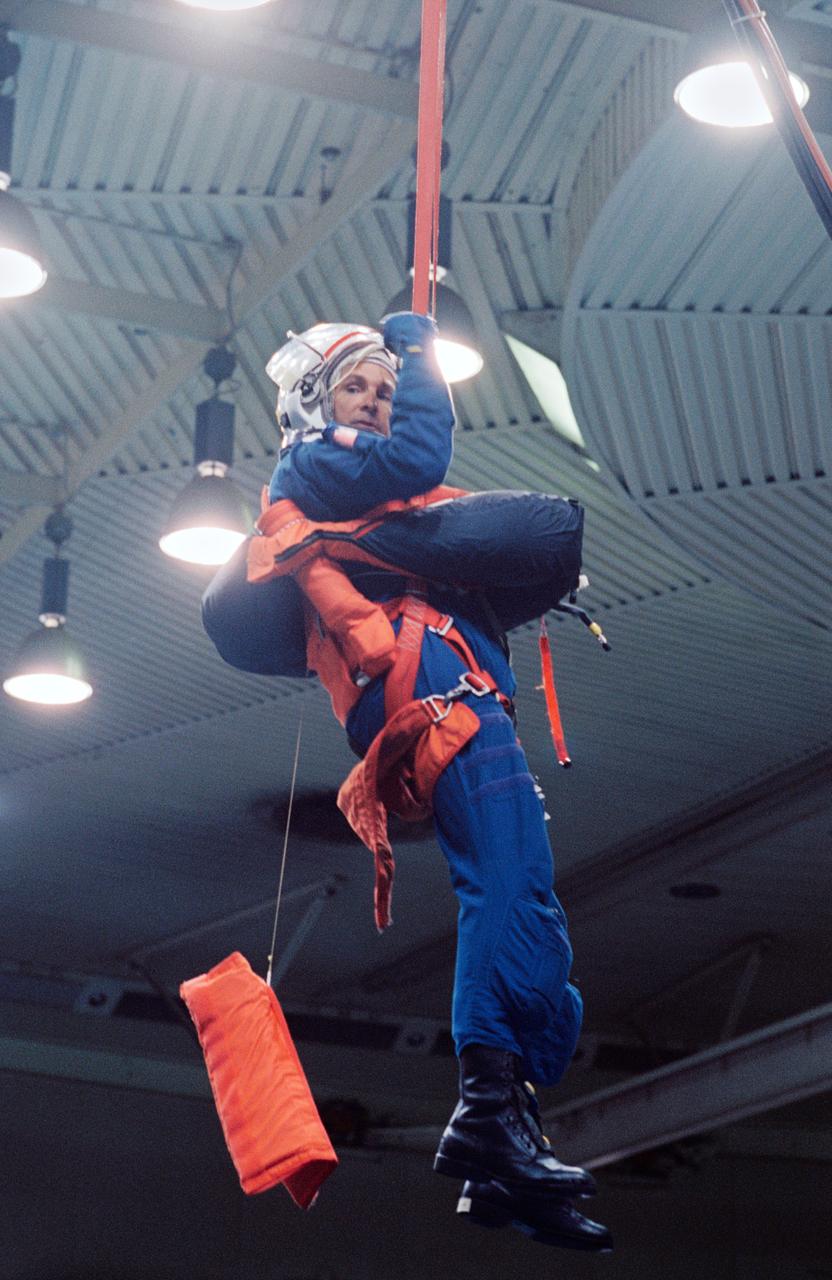

S94-37516 (28 June 1994) --- Astronaut Curtis L. Brown is suspended by a simulated parachute gear during an emergency bailout training exercise in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Making his second flight in space, Brown will join four other NASA astronauts and a European mission specialist for a week and a half in space aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis in support of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
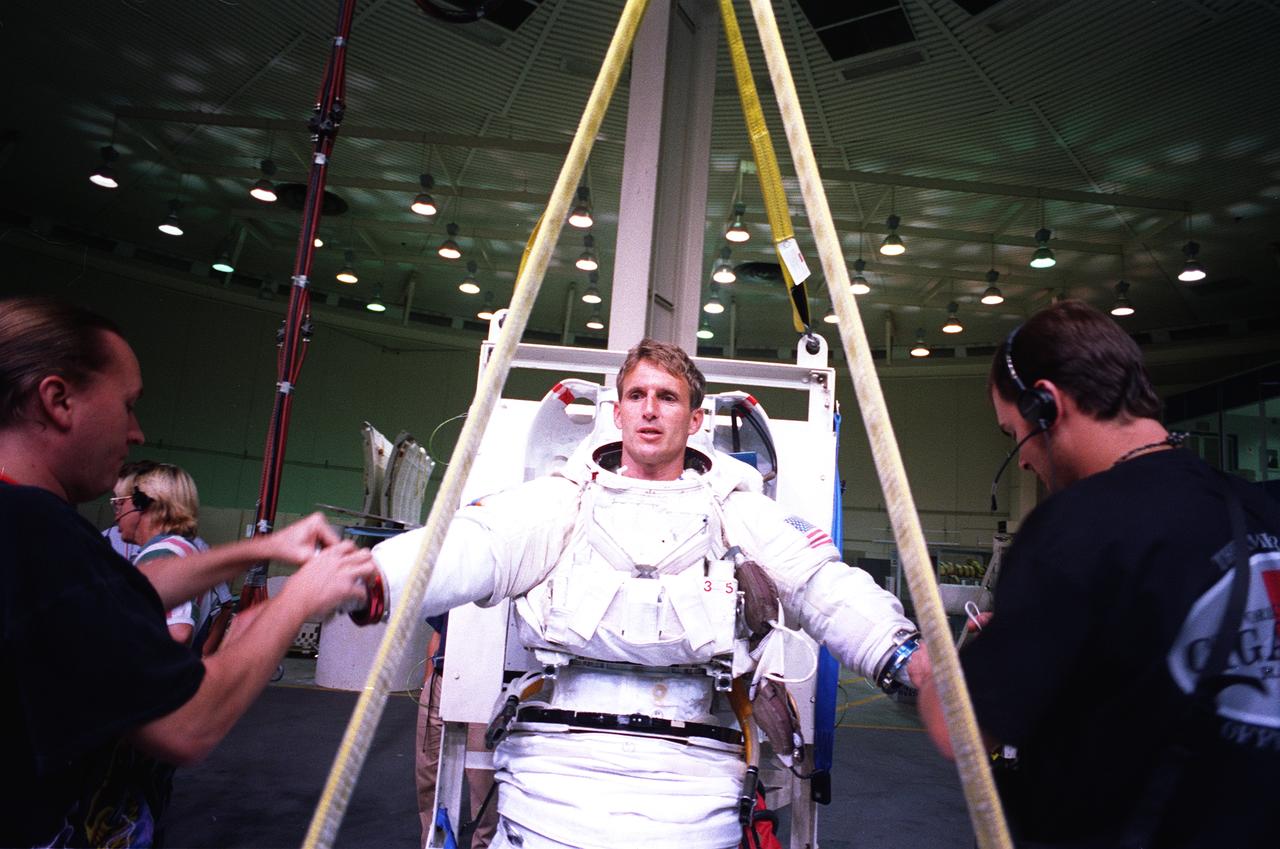

S96-14344 (13 Sept. 1996) --- In the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility, astronaut Jerry M. Linenger, STS-81 mission specialist, prepares for an underwater simulation of a contingency space walk. Linenger, attired in a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU ) will utilize the nearby 25-ft. deep pool, in which he will be able to achieve a neutrally buoyant state.
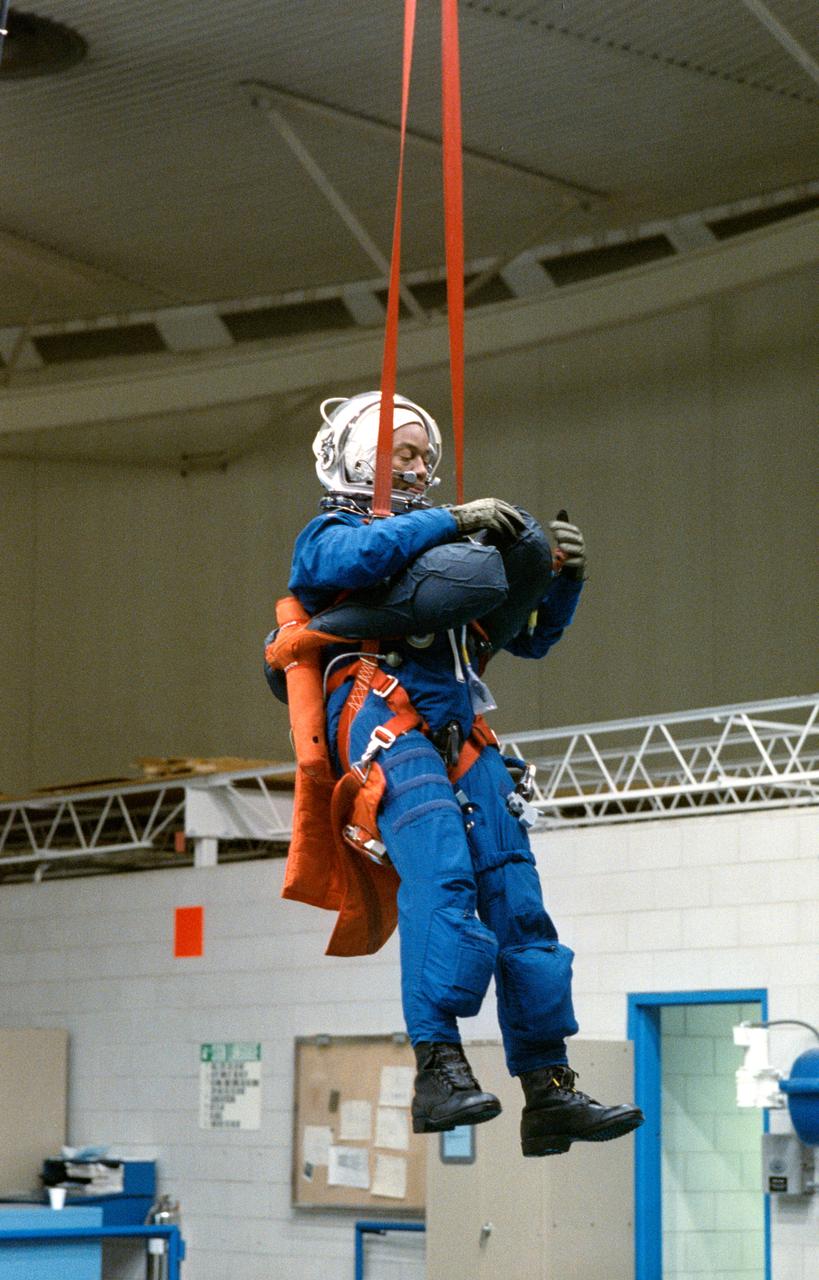

S90-54755 (13 Dec 1990) --- Astronaut Guion S. Bluford, Jr., STS-39 Mission Specialist wearing launch and entry suit (LES) and launch and entry helmet (LEH), is suspended above JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool via his parachute harness. Bluford will be dropped from the harness into the WETF's 25 ft deep pool to simulate an emergency egress bailout from the Space Shuttle into the ocean.
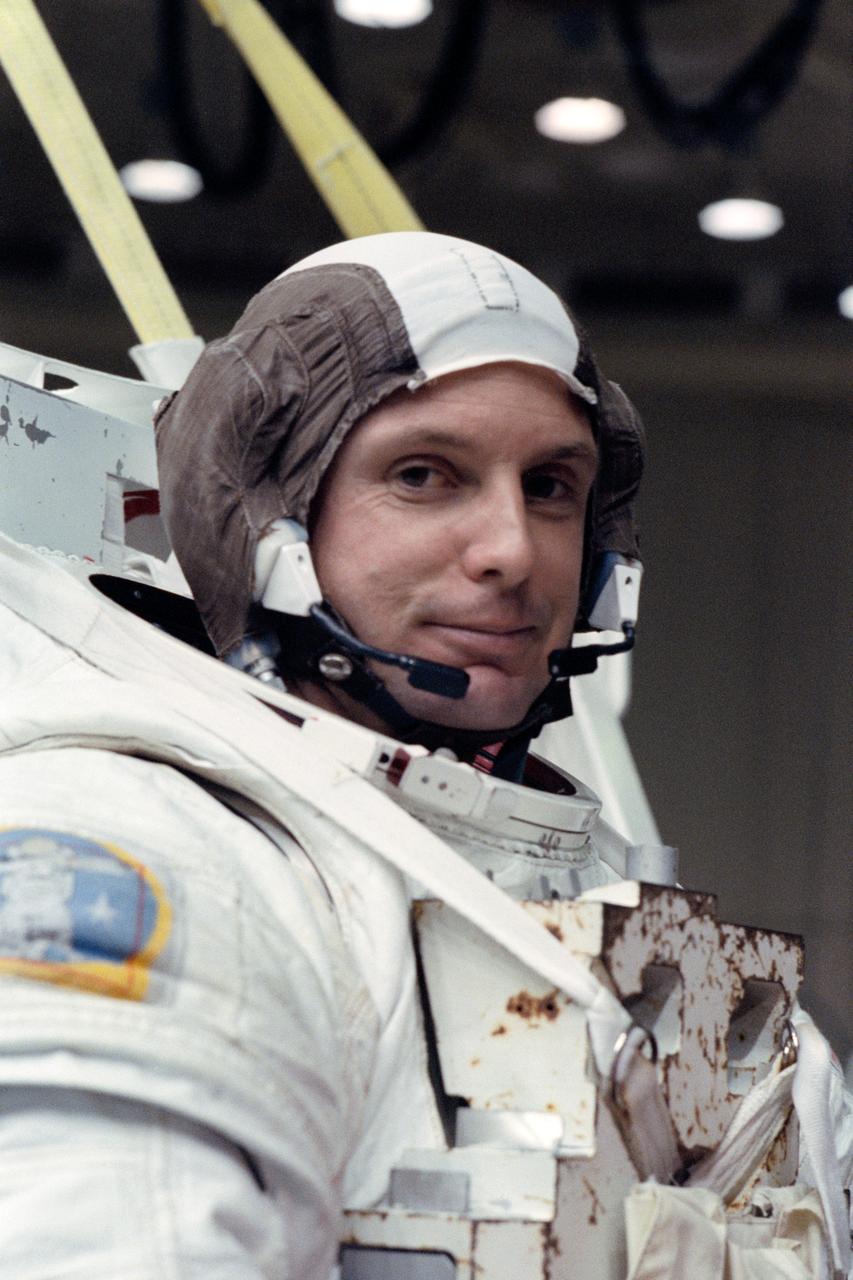

S90-41497 (Aug 1990) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh, STS-39 mission specialist, completes suiting up process for a training exercise in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Harbaugh and fellow crewmembers are using JSC's WET-F facility to participate in simulations of contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the flight.
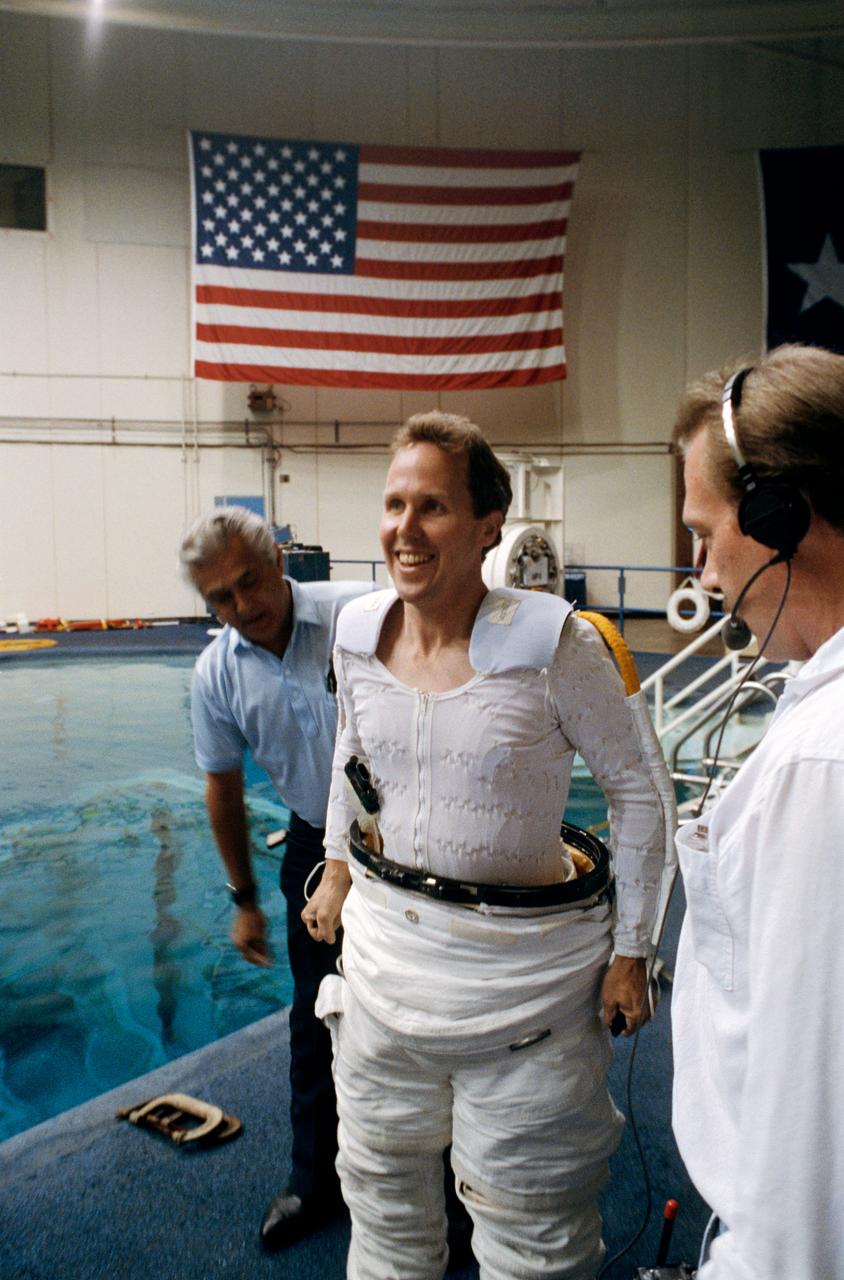

Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, dons a space suit prior to participating in contingency space walk simulations at the JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF). Jones is assisted by Frank Hernandez (left) and suit technician Charles Hudson of Hamilton Standard. Jones suit is weighted to that he can achieve a neutrally buoyant state once under water. Extravehicular tasks are not planned for the STS-59 mission, but a number of chores are rehearsed in case of failure of remote systems to perform those jobs.
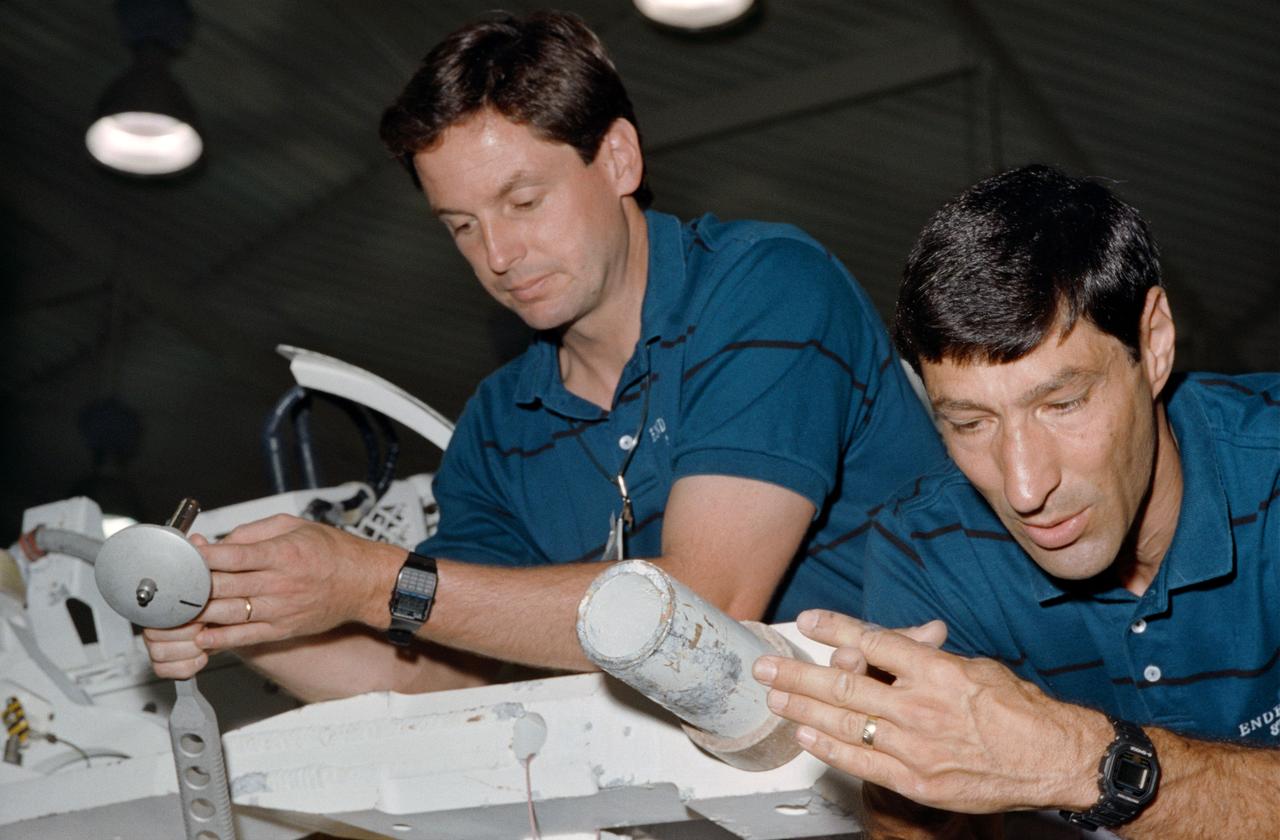

STS-54 Endeavour, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105, Mission Specialist 1 (MS1) Mario Runco, Jr (right) and MS2 Gregory J. Harbaugh, holding an ESSEX wrench, examine mockup and tools prior to an underwater simulation in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. Runco and Harbaugh discuss the trunnion / payload retention latch assembly (PRLA) configuration.

S90-41500 (Aug 1990) --- Astronaut Donald R. McMonagle checks communication gear on his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-ft. deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). McMonagle was preparing to participate in the simulation of a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the mission, scheduled for Discovery in the spring of 1991.

S92-42679 (28 July 1992) --- STS-53 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Mission Specialist James S. Voss, wearing extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) and communications carrier assembly (CCA), dons his gloves with assistance from two technicians. Voss is preparing for an underwater contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation in JSC?s Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg.29 pool.
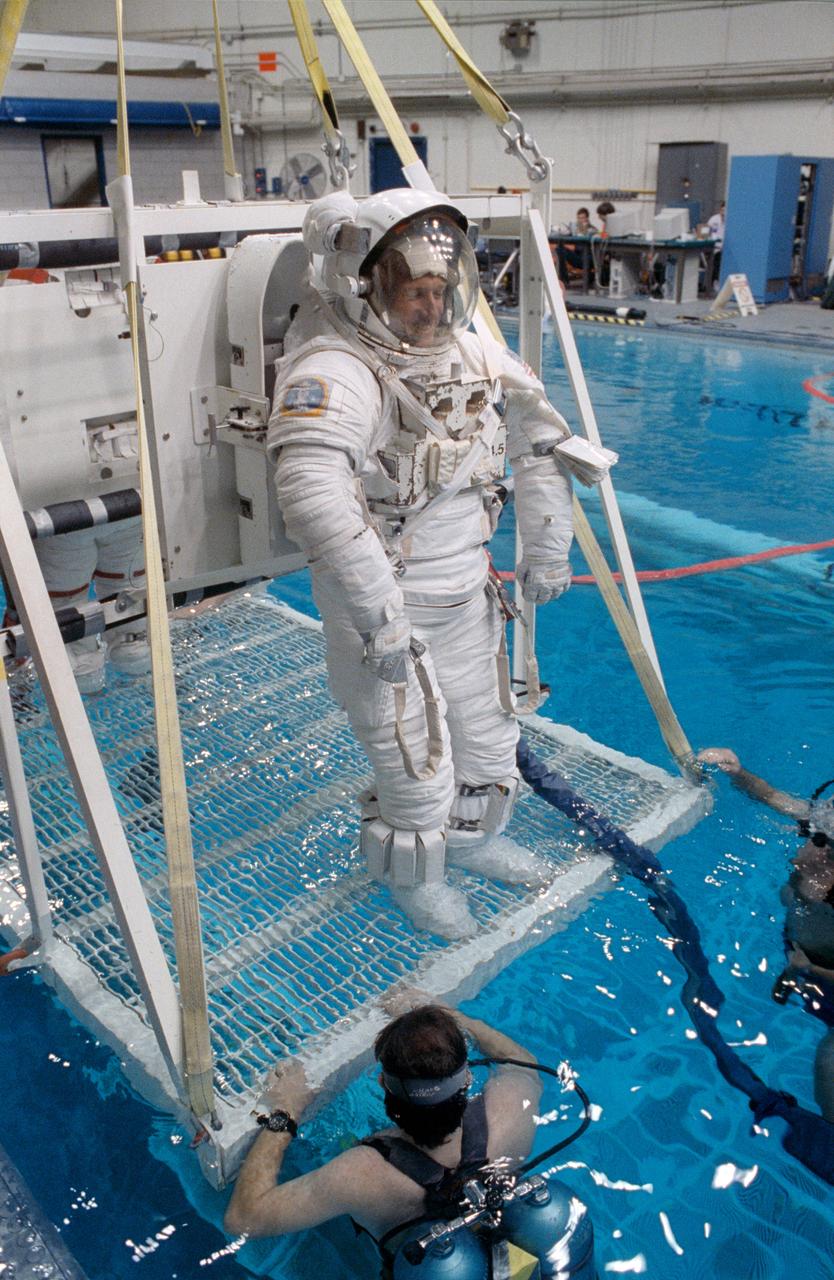

S91-30197 (1 March 1991) --- A wider shot of astronaut C. Michael Foale, mission specialist, standing on a platform which is part of a system that will lower him into a 25-ft. deep pool. Foale used the pool in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F) to rehearse a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA). Two SCUBA-equipped swimmers assist. Astronauts wear pressurized spacesuits configured for achieving a neutrally buoyant condition in the water to simulate both planned and contingency EVAs.

S90-54764 (7 Dec 1990) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh, mission specialist, listens attentively as a trainer (out of frame) briefs the STS-39 crewmembers on emergency egress measures. The seven astronauts were in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) weightless environment training facility (WET-F). This type training uses the WET-F's 25 ft. deep pool to simulate an ocean parachute landing.

S90-46036 (Aug 1990) --- Astronaut Donald R. McMonagle awaits arrival of helmet gear for his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-ft. deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). McMonagle was preparing to participate in the simulation of a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the mission, scheduled for Discovery in the spring of 1991.
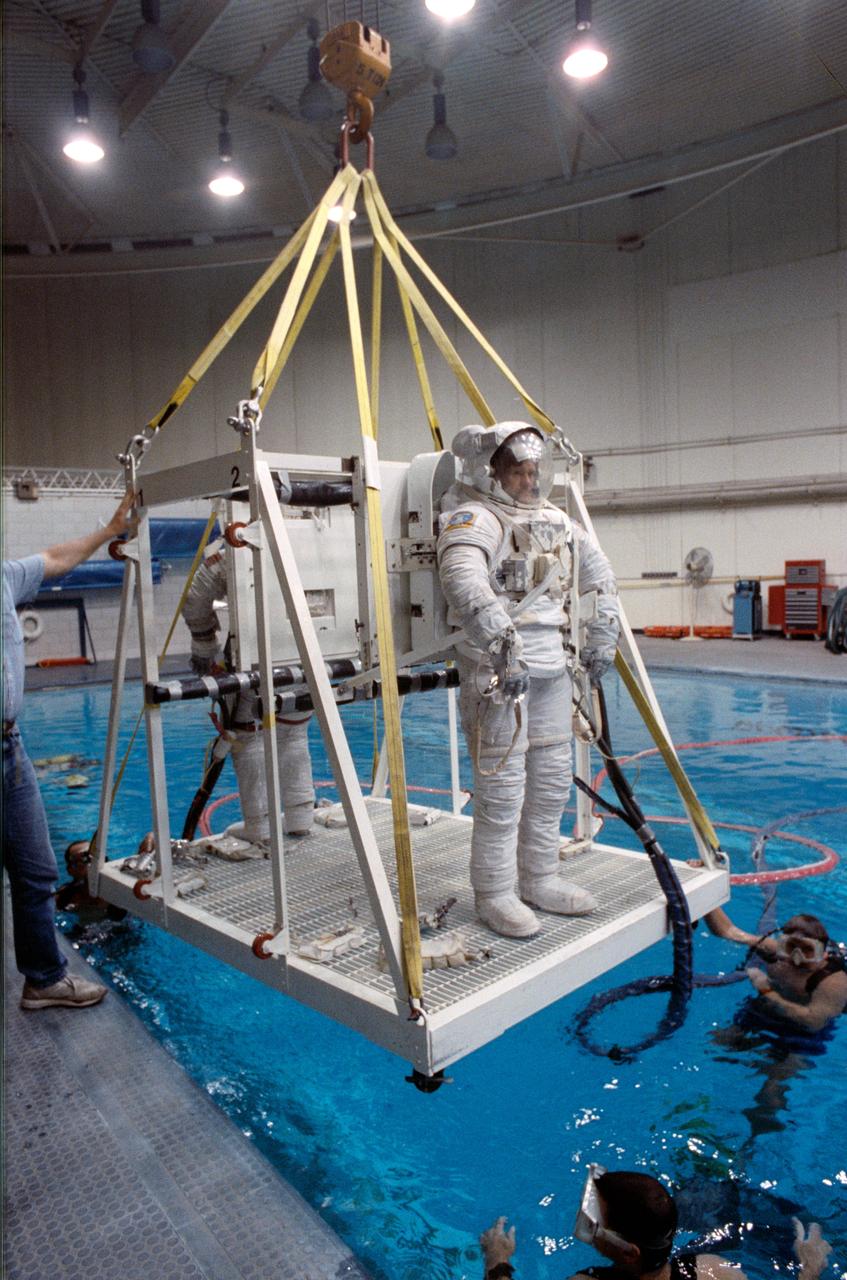
S90-46030 (Aug 1990) --- Astronaut Donald R. McMonagle (foreground) wears an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-ft. deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh, a fellow STS 39 mission specialist, shares the moveable platform with McMonagle and prepares to join him in the simulation of a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the mission, scheduled for Discovery in the spring of 1991. A number of SCUBA-equipped divers assist in the training session.
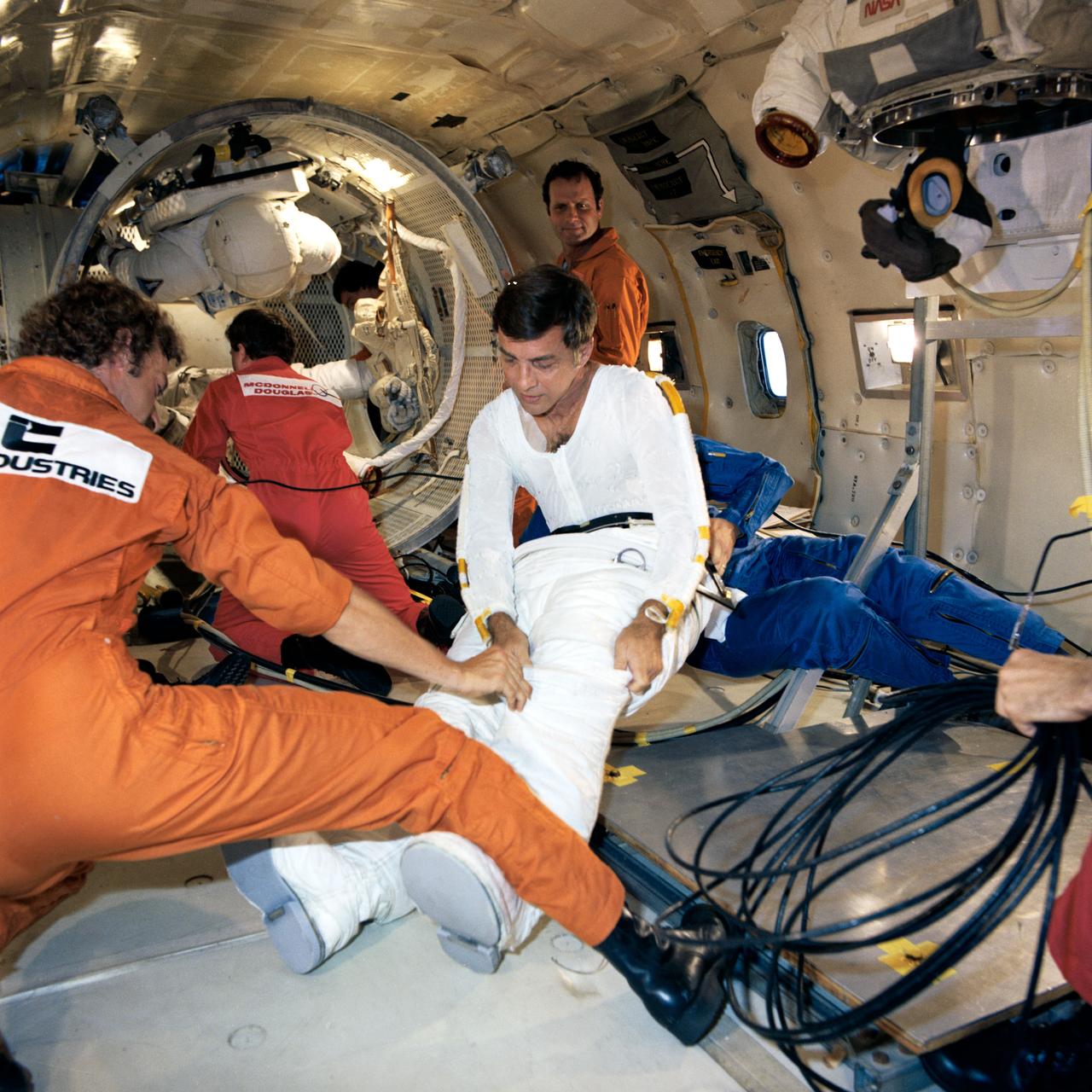

Spacesuit Donning and Doffing in Zero-G Training for Don Peterson of the STS-6 Crew with Astronaut Jerry Ross assisting; and, apparatus for testing the JSC Mechanically-Induced Settling Technology (MIST) Experiment. The training is being held aboard the KC-135 to simulate weightlessness. He is being assisted to don the lower torso of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) by an ILC Technician. 1. ASTRONAUT ROSS, JERRY L. - ZERO-G SUITING 2. SHUTTLE - EXPERIMENTS (MIST)

S90-46492 (16 Aug 1990) --- Astronaut Tamara E. Jernigan, STS-40 mission specialist, is pictured in a training version of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit. Dr. Jernigan was about to be submerged in the Johnson Space Center's 25-ft. deep weightless environment training facility (WET-F) pool to simulate a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA). There is no EVA scheduled for STS-40, the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) mission.
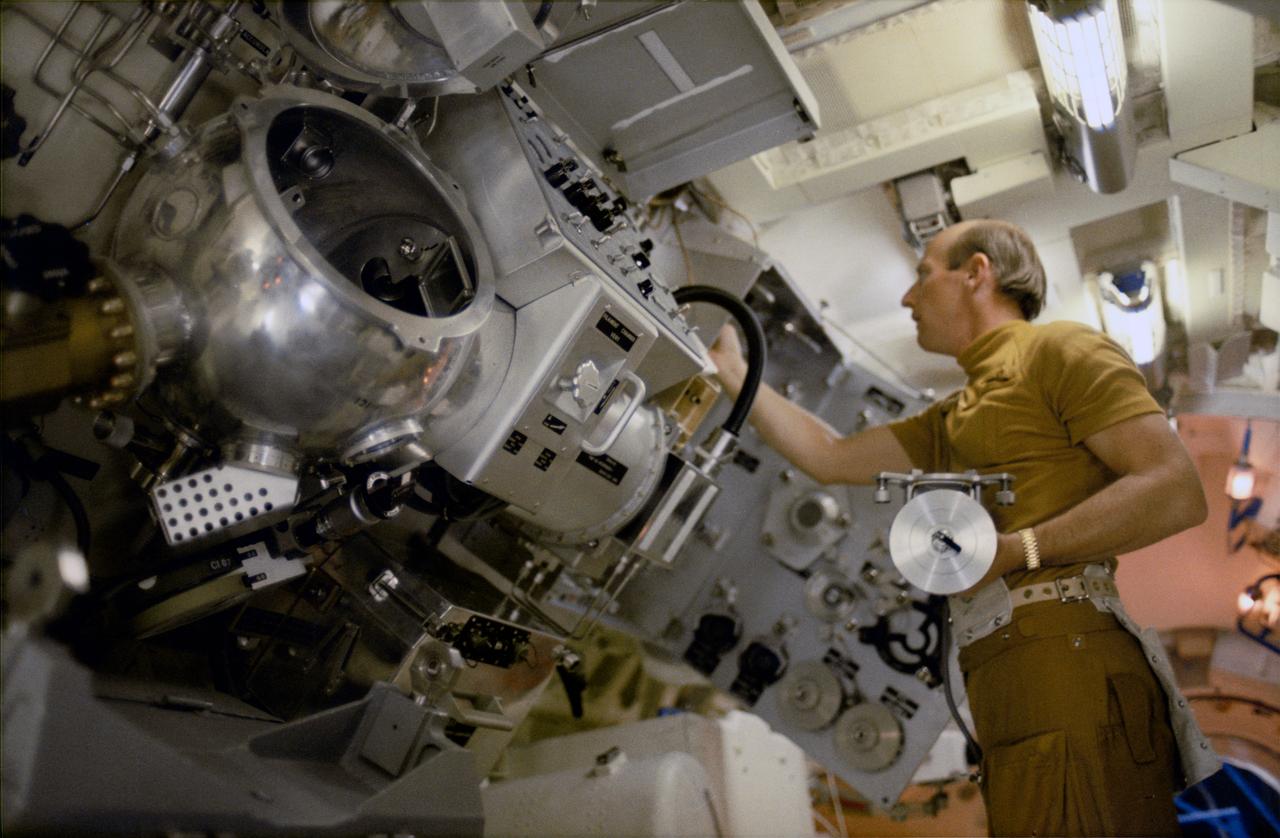

S73-20759 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the first manned Skylab mission, takes items from the M512 materials processing equipment storage assembly during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Conrad is standing in the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) trainer in the JSC Mission Simulation and Training Facility. The assembly holds equipment designed to explore space manufacturing capability in a weightless state. Conrad is holding one of the experiment parts in his left hand. Photo credit: NASA
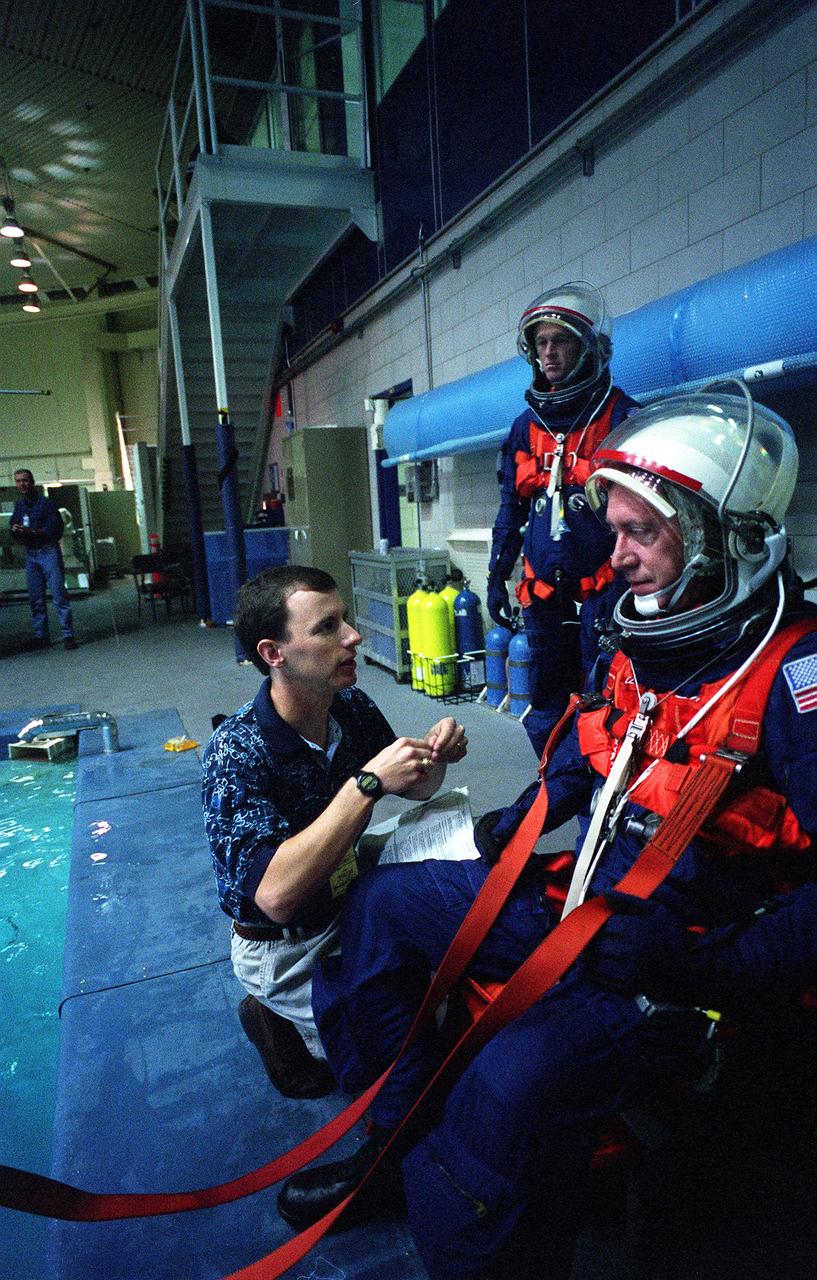

S96-15388 (26 Sept. 1996) --- In the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility, astronaut Michael Baker, STS-81 mission commander, prepares to simulate a parachute drop into water. David Pogue helps with the final touches on Baker's training version of the launch and entry suit, as Brent W. Jett (background), pilot, looks on.
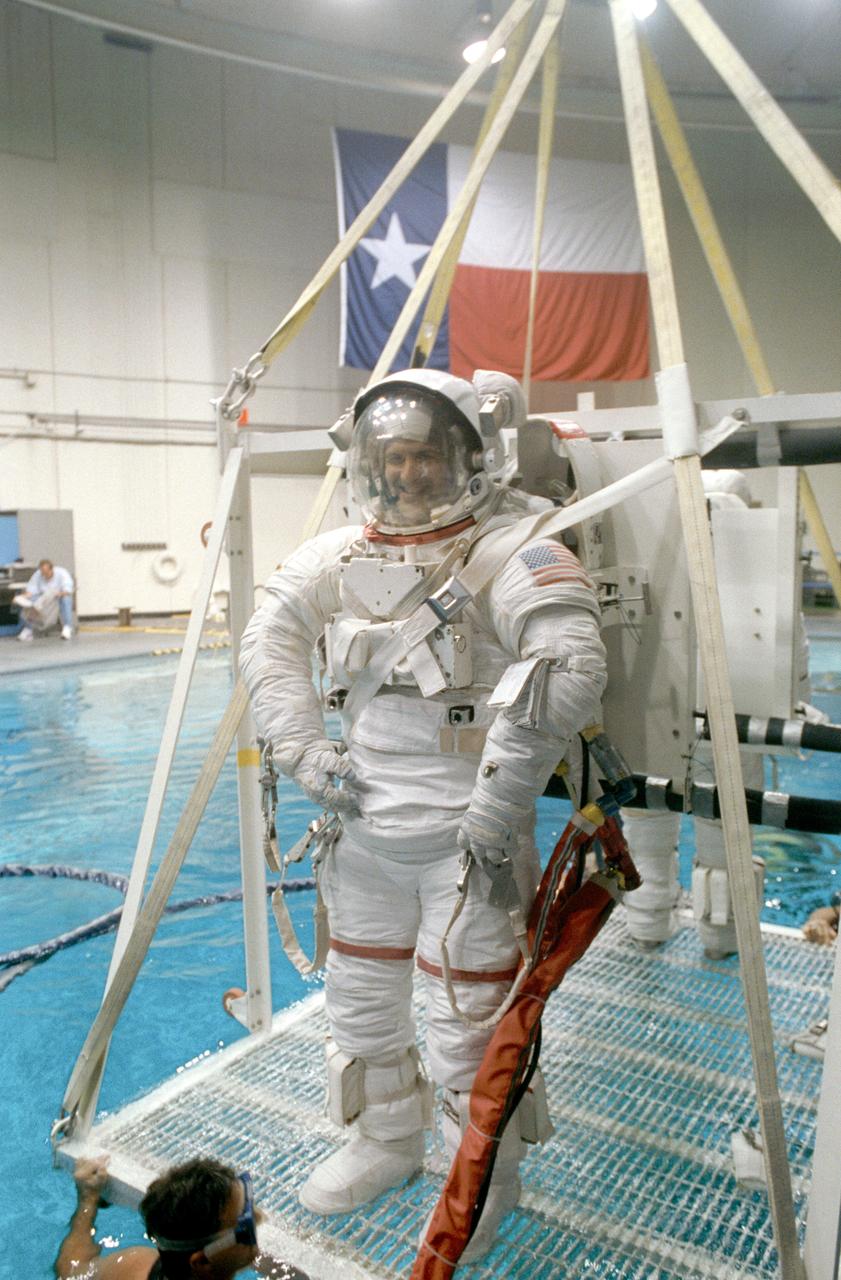

S92-40378 (1 July 1992) --- Astronaut Peter J.K. Wisoff, STS-57 mission specialist, fully suited in an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) and helmet and standing on a platform, is lowered into the 25 foot deep pool of Johnson Space Center?s (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29. Once underwater, Wisoff will participate in an underwater extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation. A scuba-equipped diver already in the pool guides the platform into the water.
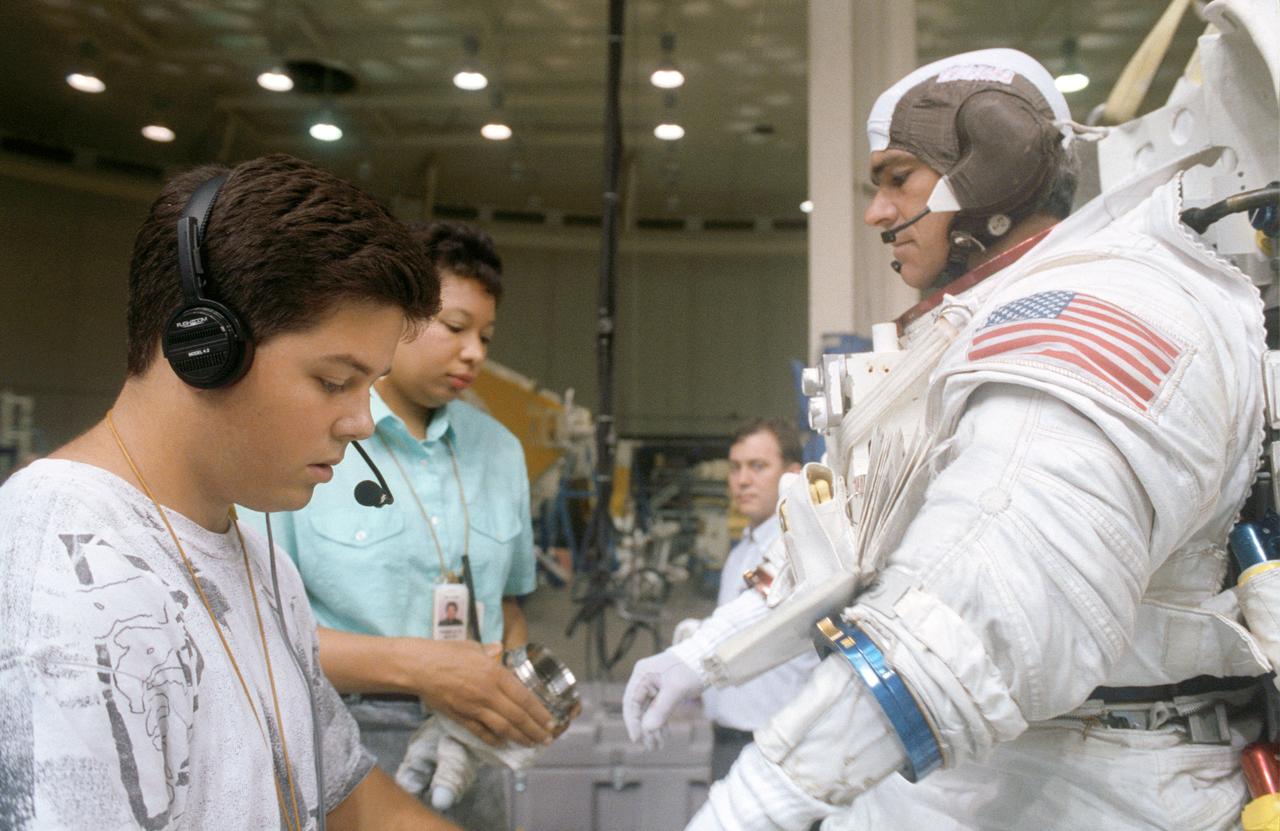

S92-42681 (28 July 1992) --- STS-53 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Mission Specialist (MS) Michael R.U. Clifford, wearing extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) and communications carrier assembly (CCA), dons gloves with assistance from two technicians. Clifford is preparing for an underwater contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) simulation in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool.
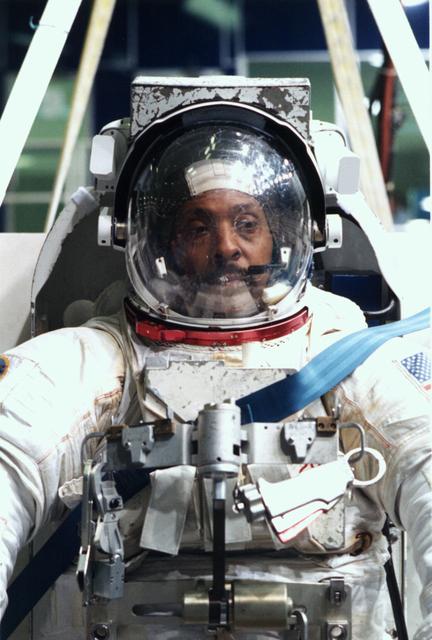

S95-04113 (24 February 1995) --- Wearing a training version of the Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Winston E. Scott, mission specialist, prepares to go underwater for a Extravehicular Activity (EVA) simulation at Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). In less than a year from now, Scott is scheduled to perform an EVA in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Endeavour in support of the STS-72 mission.
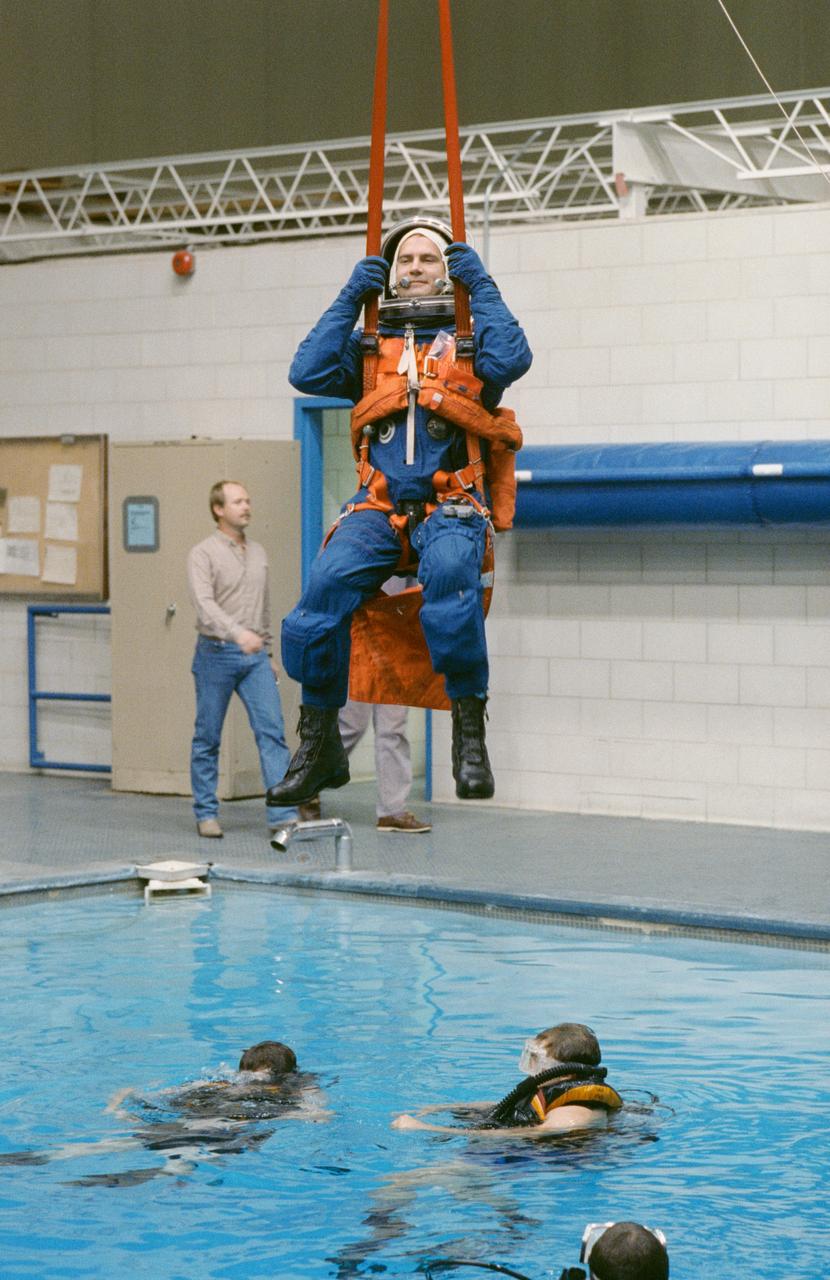

S90-54760 (7 Dec 1990) --- Astronaut Richard J. Hieb, mission specialist, participates in emergency egress training. Hieb and six fellow STS 39 astronauts were in JSC's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). This type training uses the WET-F's 25 ft. deep pool to simulate an ocean parachute landing. A number of SCUBA-equipped divers assist in the training session.

S96-12924 (14 February 1996) --- astronaut Stephen K. Robinson stands on a platform connected to a hoist that will lower him and astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. (view obscured, other side of platform) into Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Test Facility (WET-F) pool. The two were about to participate in an underwater simulation of contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) that might be needed to support the scheduled 11-day August 1997 STS-85 mission.
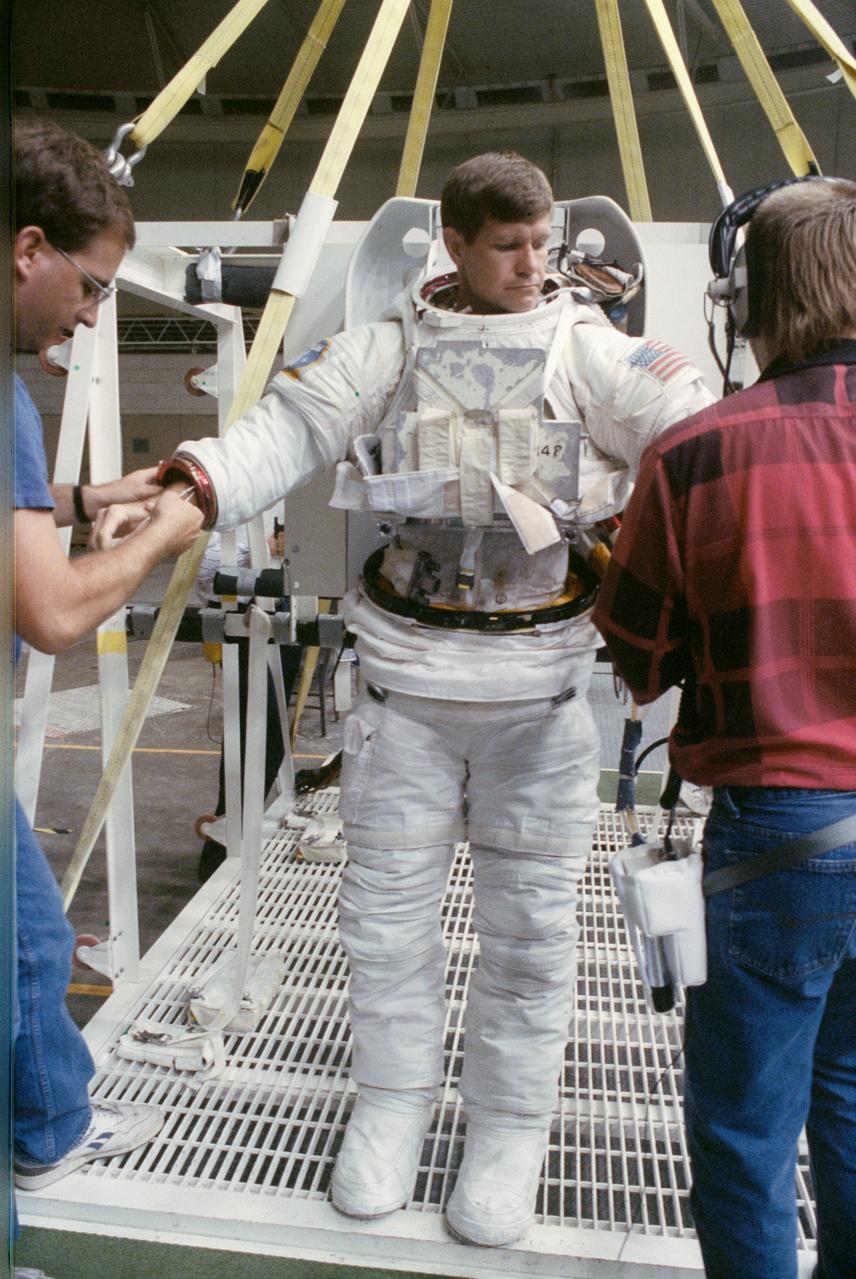

S90-41498 (Aug 1990) --- Astronaut Donald R. McMonagle is about to don gloves for his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-ft. deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC)weightless environment training facility (WET-F). McMonagle was preparing to participate in the simulation of a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the mission, scheduled for Discovery in the spring of 1991.
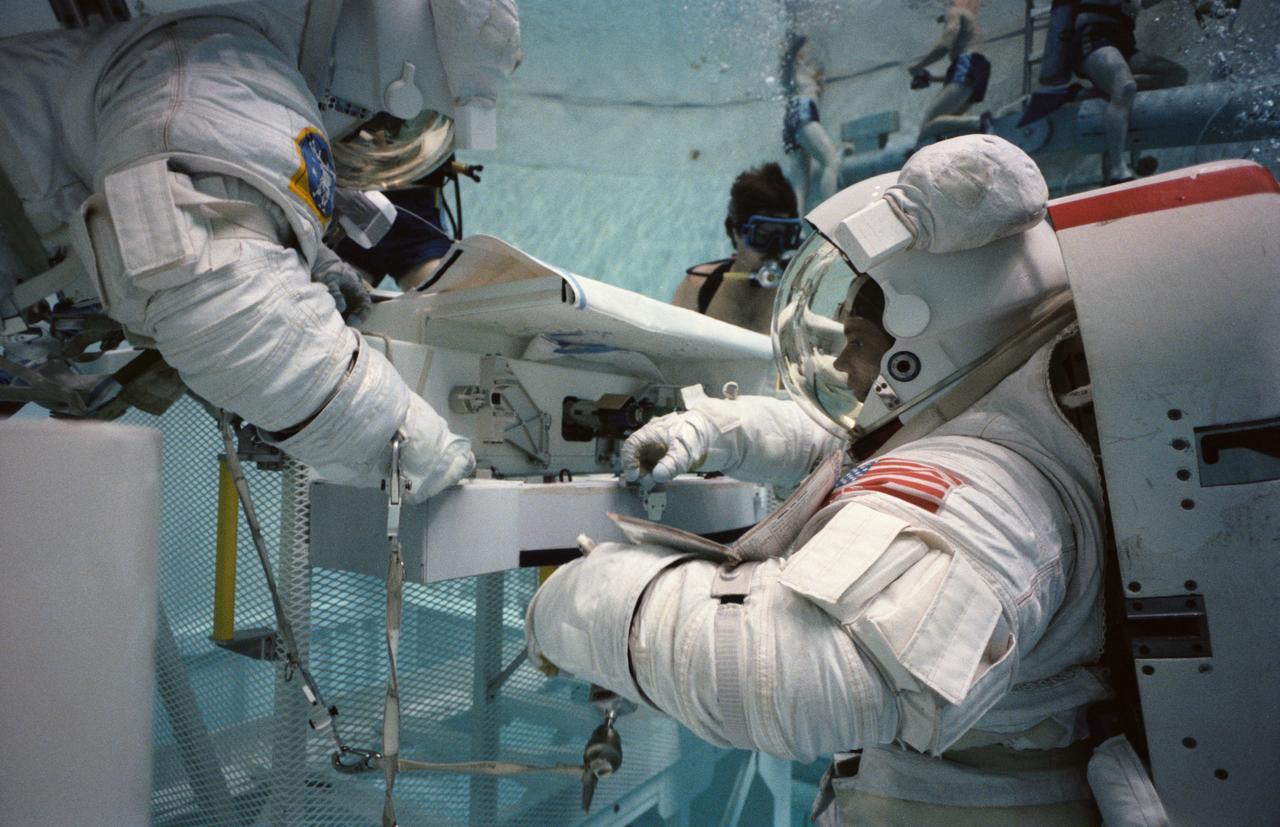

S84-36960 (5 July 1984) --- Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan, left, and David C. Leestma, Mission 41-G crewmembers, simulate the transfer of cryogenics in space during an Earth-bound underwater session in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). The two mission specialists will be joined by three NASA astronauts and two payload specialists for a flight aboard the Columbia later this year. The photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
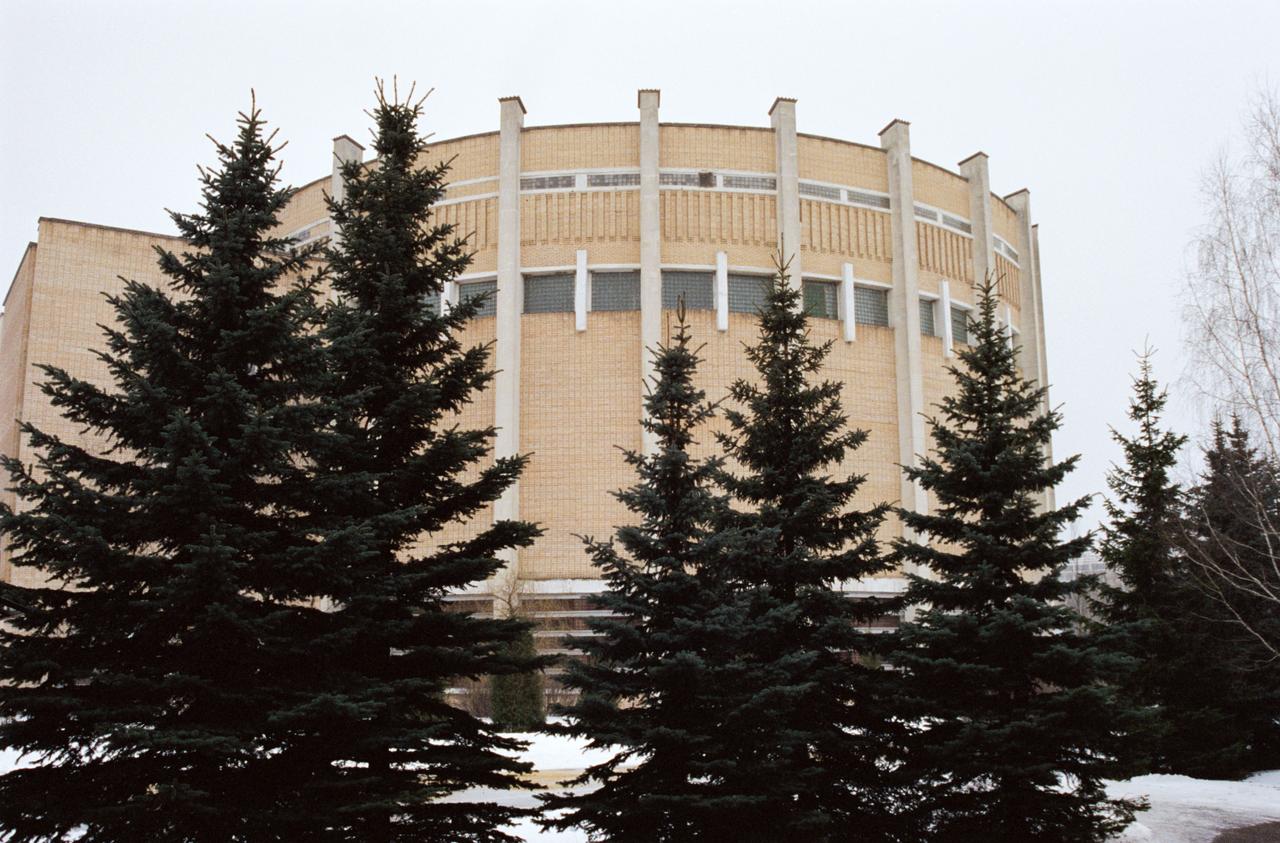

S95-04319 (22 Feb 1995) --- The neutral buoyancy facility at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City, Russia, is used for underwater training for missions aboard the Russian Mir Space Station. The facility is similar to NASA's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston, Texas, and the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama.

S96-12935 (14 Feb. 1996) --- Attired in a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Stephen K. Robinson is lowered into Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Test Facility (WET-F) pool. Astronauts Robinson and Robert L. Curbeam were about to participate in an underwater simulation of contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) that might be needed to support the scheduled 11-day August 1997 STS-85 mission.

S90-54763 (7 Dec 1990) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh. Mission specialist, participates in emergency egress training. Harbaugh and some of his fellow STS 39 astronauts were in JSC's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Harbaugh is actually suspended over water. This type training uses the WET-F's 25 ft. deep pool to simulate an ocean parachute landing.

S87-26630 (March 1987) --- Astronaut Charles D. (Sam) Gemar, wearing a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit, prepares to be emersed in the 25-ft. deep waters of the Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Once underwater, Gemar was able to achieve a neutrally buoyant state and to simulate the floating type activities of an astronaut in microgravity. Gemar began training as an astronaut candidate in the summer of 1985.
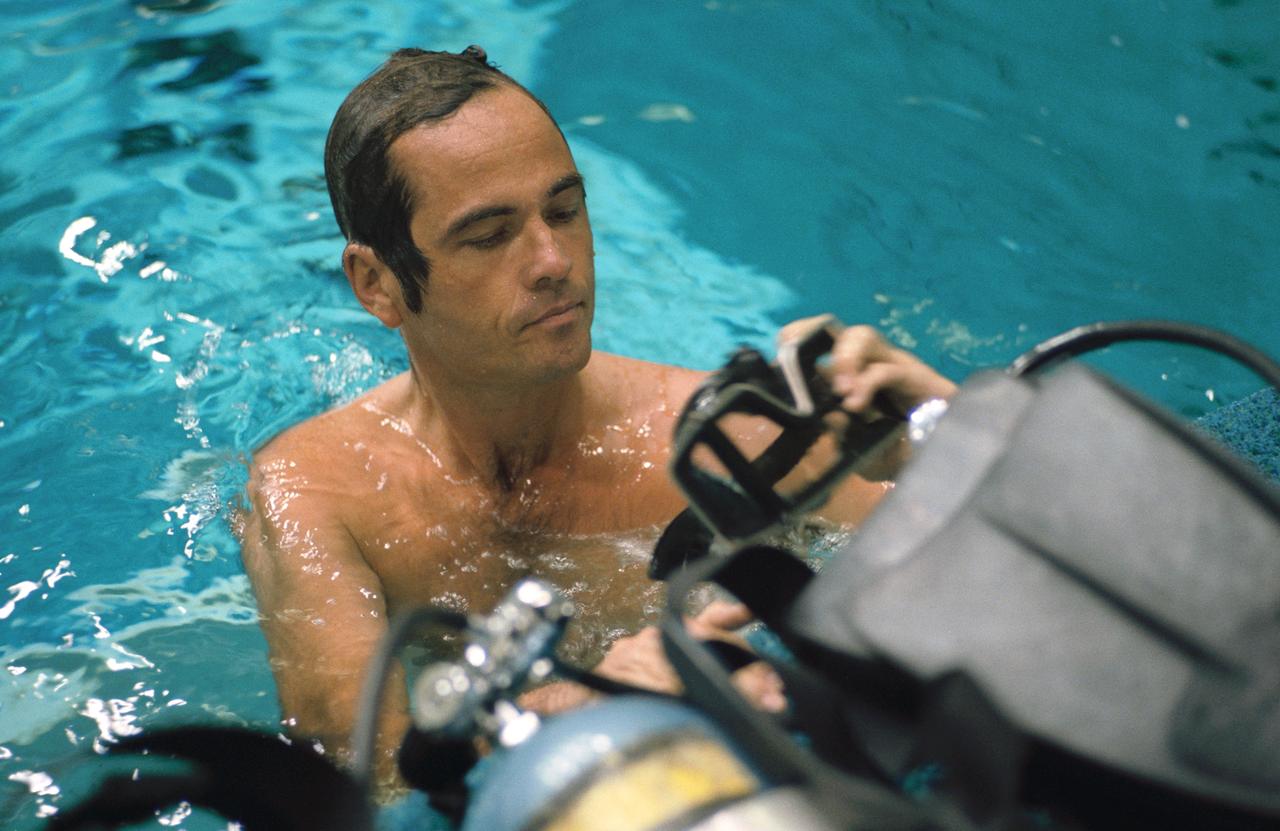

S84-36956 (1 July 1984) --- Astronaut Robert L. Crippen, 41-G crew commander, prepares his SCUBA mask prior to submerging into the weightless environment training facility's 25 ft. deep pool to observe a simulation exercise for two fellow 41-G crewmembers assigned to an extravehicular activity (EVA) in space. Not pictured are Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, mission specialists who will perform the EVA during the eight-day mission scheduled for October of this year.

S96-12948 (14 February 1996) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. stands on a platform connected to a hoist that will lower him and astronaut Stephen L. Robinson (out of frame) into Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Test Facility (WET-F) pool. The two, attired in training versions of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), were about to participate in an underwater simulation of contingency Extravehicular Activity (EVA) for the scheduled 11-day August 1997 STS-85 mission.
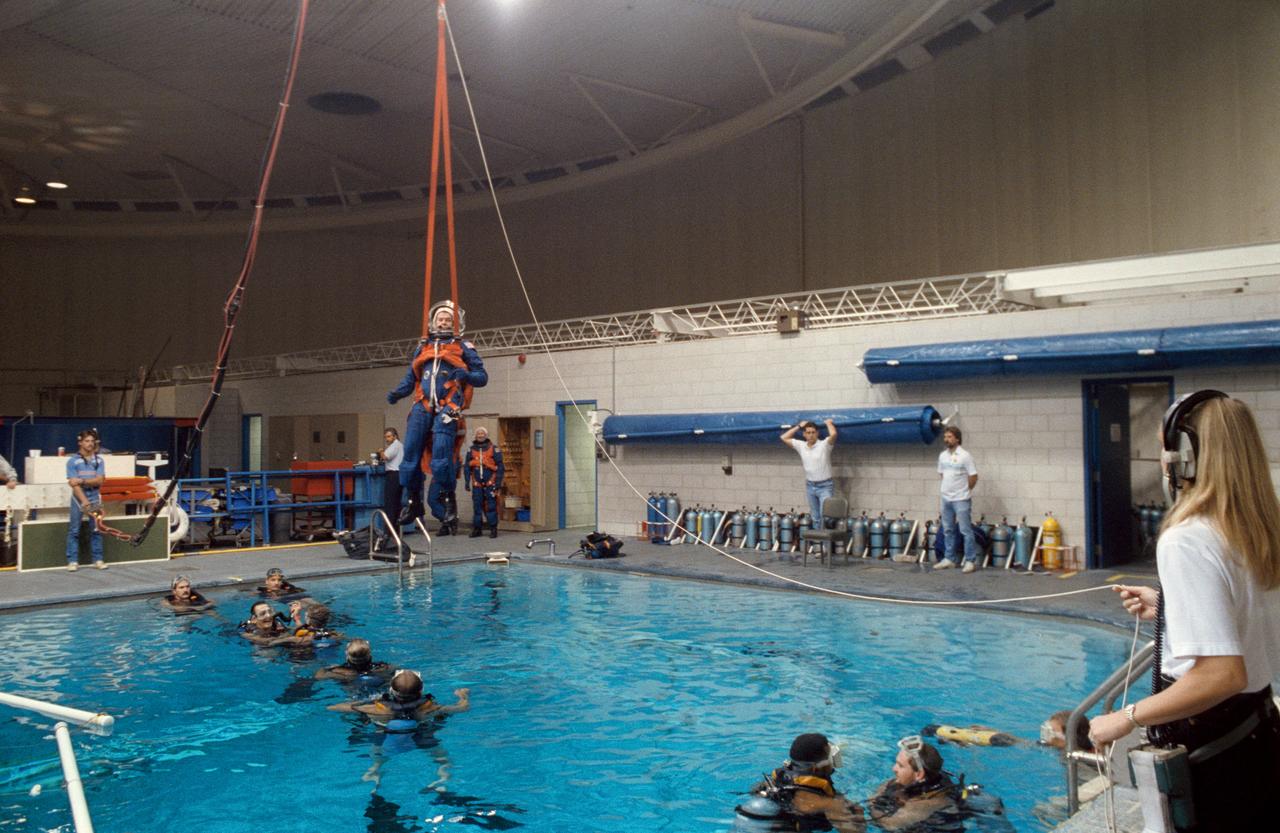

S91-52074 (26 Nov 1991) --- Charles R. (Rick) Chappell, alternate payload specialist, equipped with simulated parachute gear, descends into the water during bail-out training exercises in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). In this phase of the training program, Shuttle crewmembers learn the proper measures to take in the event of ejection and subsequent parachute landing into a body of water. A number of SCUBA-equipped swimmers who assisted in the training are pictured.
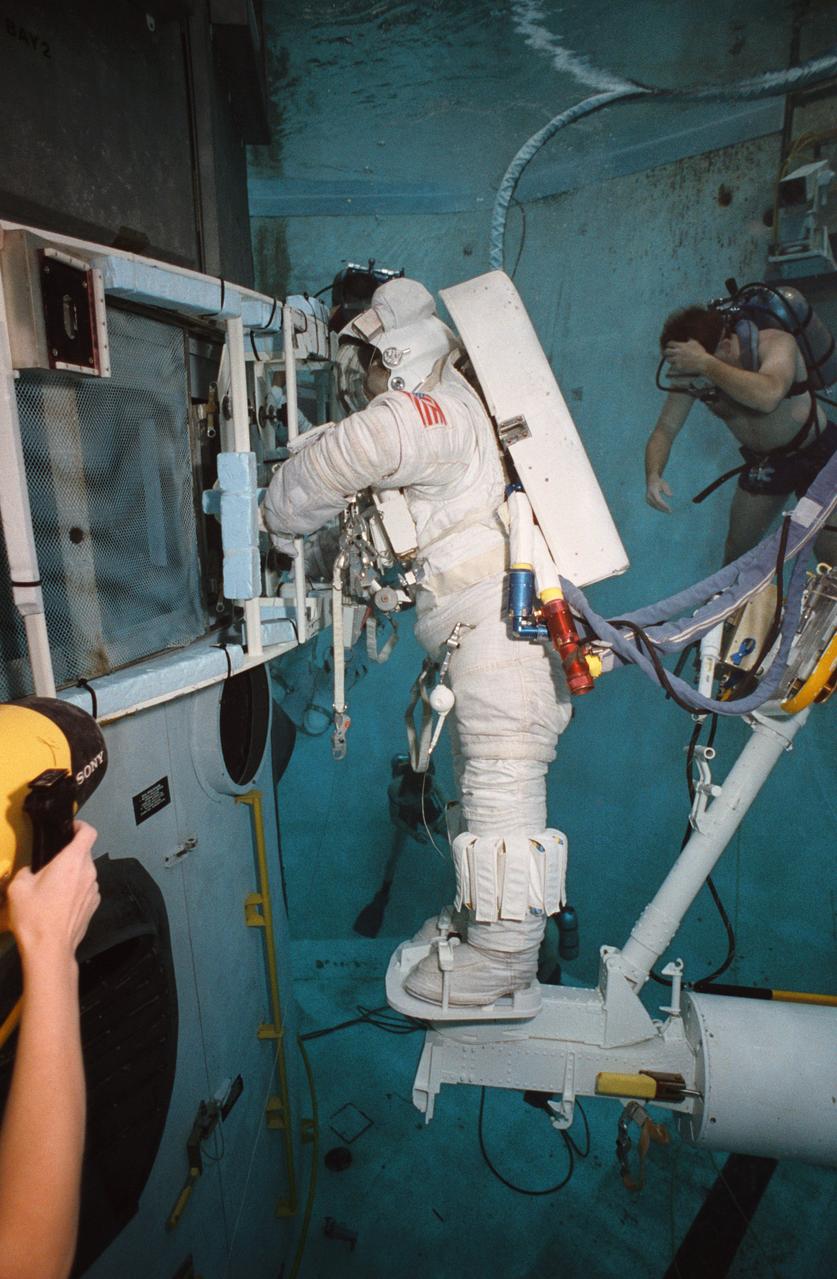

S93-33101 (5 Apr 1993) --- Wearing a training version of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton uses the giant pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. Standing on a mobile foot restraint connected to the Shuttle's robot arm, Thornton grasps a large structure which attaches to the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC). The current WF/PC on the HST will be replaced with WF/PC-2. Out of frame is astronaut Thomas D. Akers, who will join Thornton in STS-61 EVA. A SCUBA-equipped diver can be seen in the background. A number of divers are on hand for all training sessions in the WET-F. A total of five extravehicular activity (EVA) sessions will be conducted during the scheduled December mission of the Endeavour.
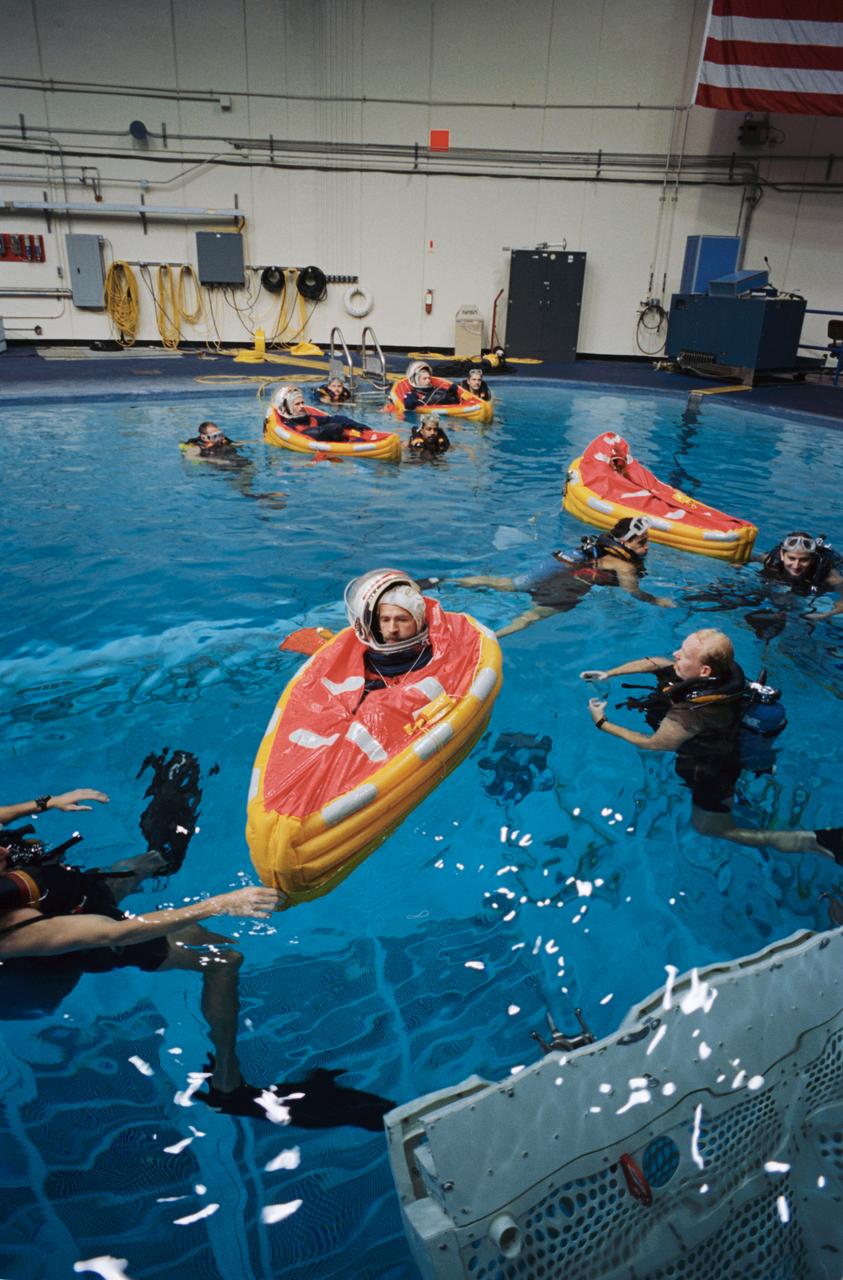

S94-47226 (13 Oct 1994) --- Using small life rafts, several cosmonauts and astronauts participating in joint Russia - United States space missions take part in an emergency bailout training session in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility's (WET-F) 25-feet-deep pool. In the foreground is cosmonaut Alexsandr F. Poleshchuk, a member of the Mir reserve crew. A number of SCUBA-equipped divers assist the trainees.
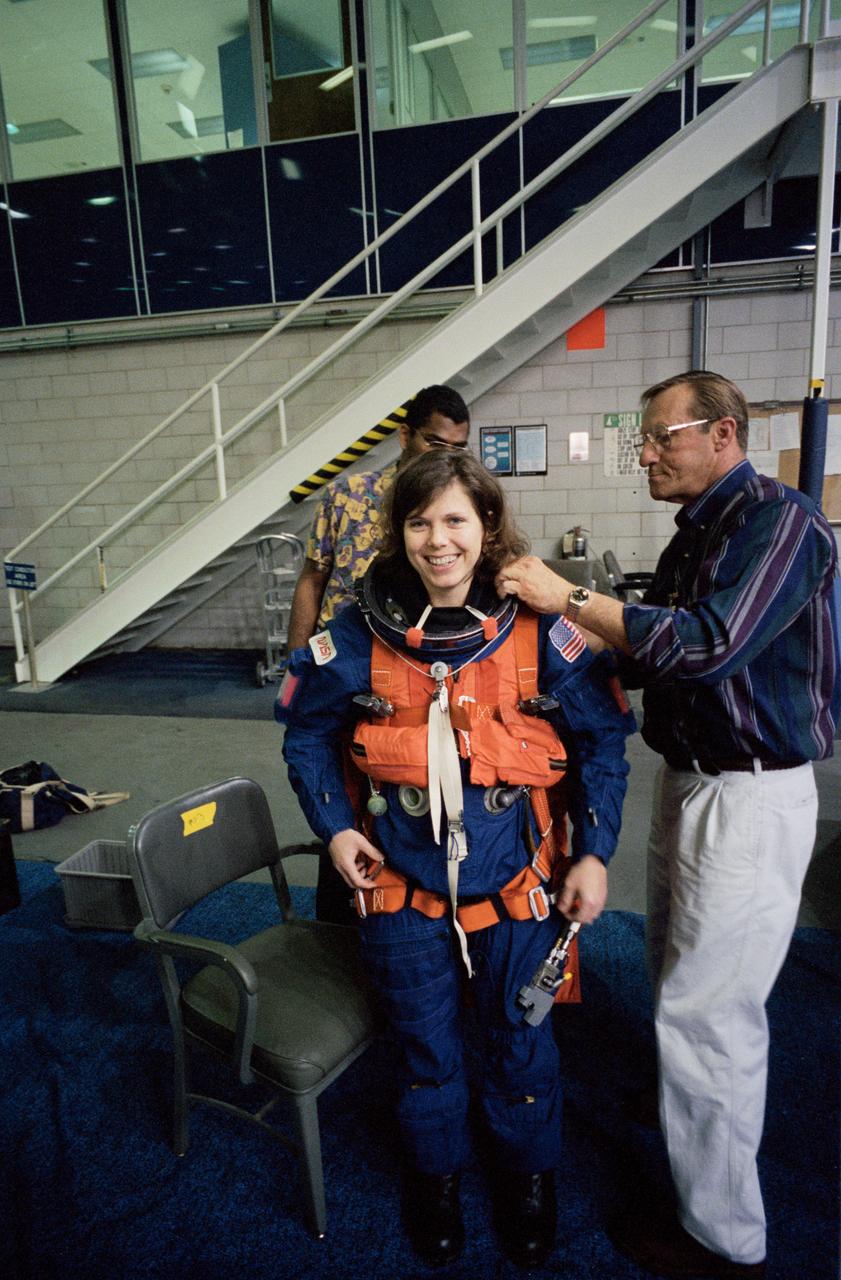

S95-03469 (16 FEB 1995) --- Attired in a training version of the Shuttle launch and entry garment, astronaut Mary Ellen Weber gets help with the final touches of suit donning during a training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Helping out is Rockwell's William L. Todd (right), while Staffon Isaacs looks on. Training as a mission specialist for the STS-70 mission, Weber was about to rehearse emergency bailout. The crew members made use of a nearby 25-feet deep pool to practice parachute landings in water and subsequent deployment of life rafts.
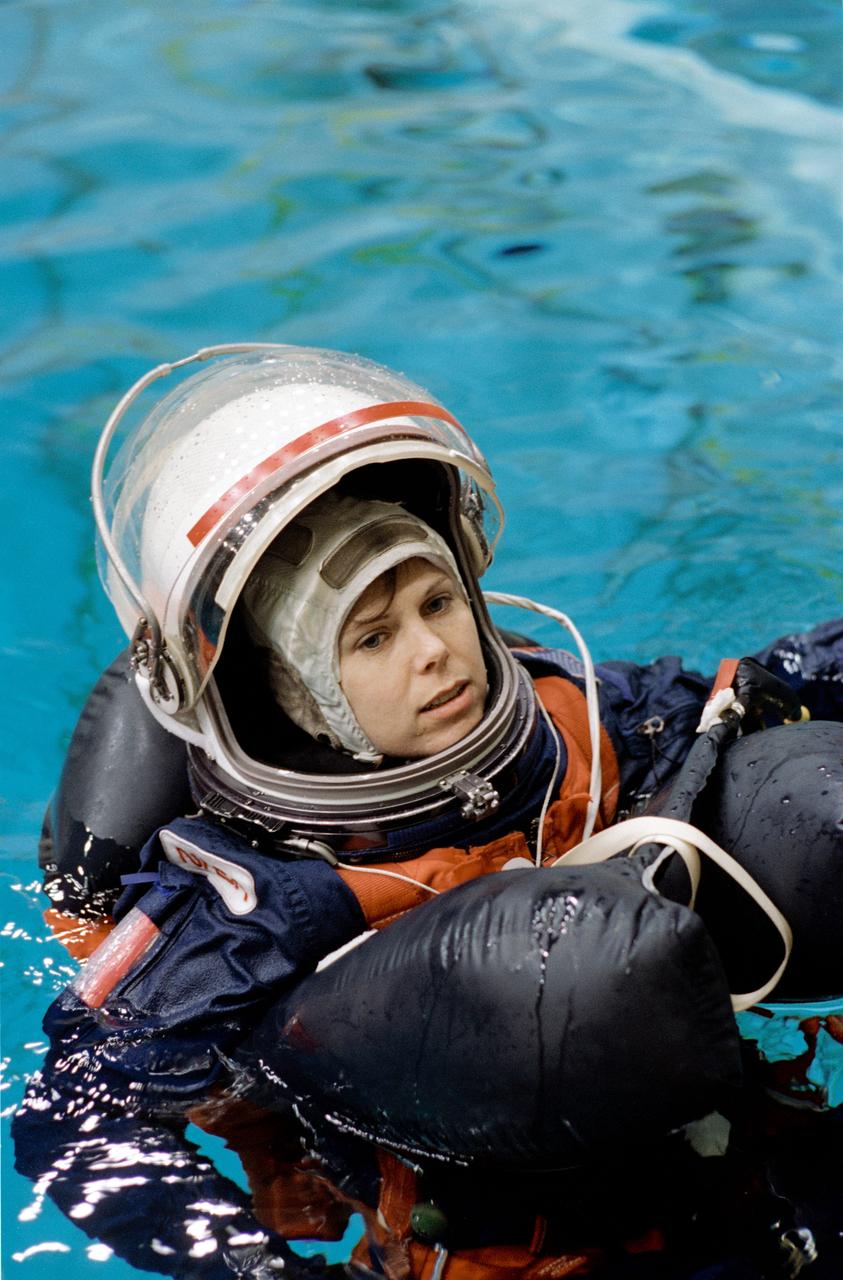

S95-03501 (16 FEB 1995) --- Astronaut Mary Ellen Weber prepares to deploy a life raft during a training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Training as a mission specialist for the STS-70 mission, Weber was joined by four crew mates in the emergency bailout rehearsal.
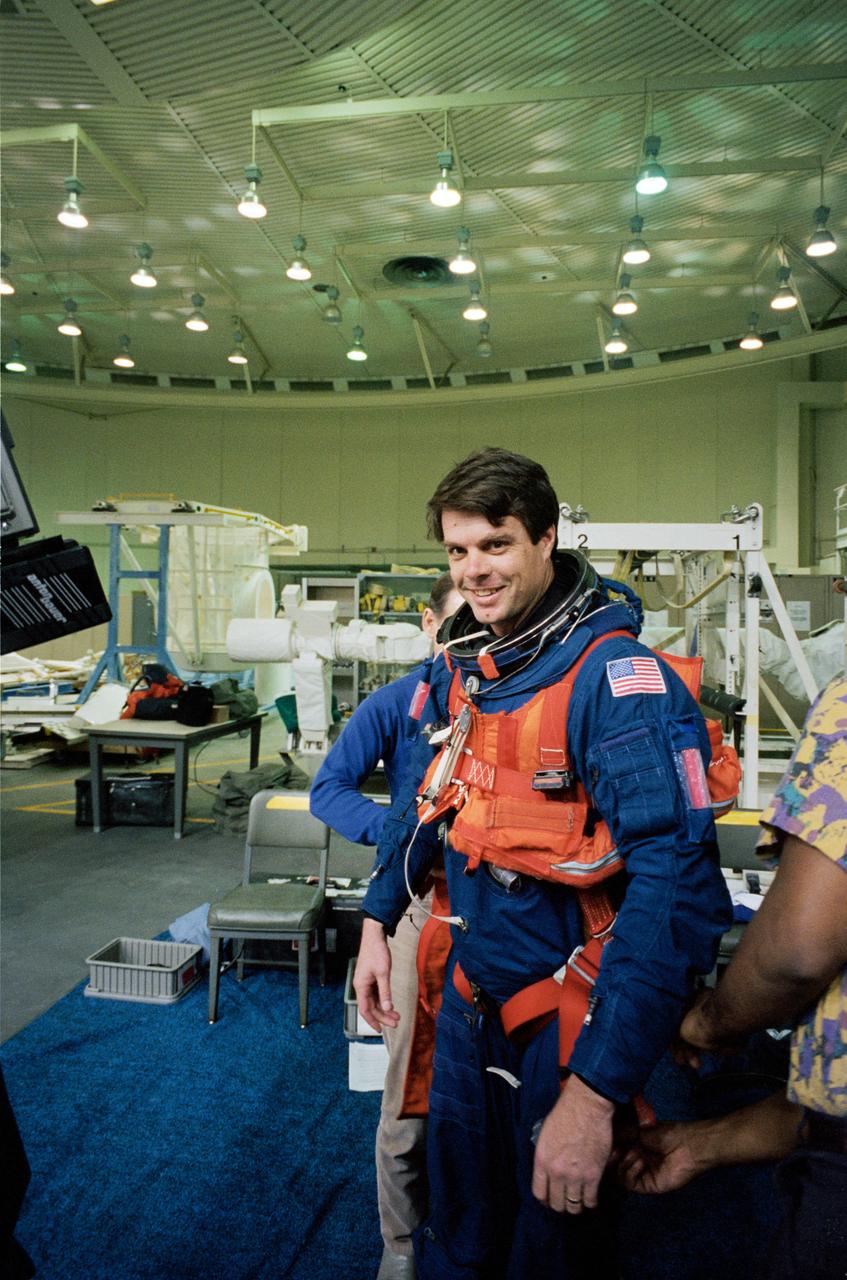

S95-03465 (16 Feb 1995) --- Attired in a training version of the Shuttle launch and entry garment, astronaut Kevin R. Kregel gets help with the final touches of suit donning during a training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Assigned as pilot for the STS-70 mission, Kregel was about to rehearse emergency bailout. The crew members made use of a nearby 25-feet deep pool to practice parachute landings in water and subsequent deployment of life rafts.
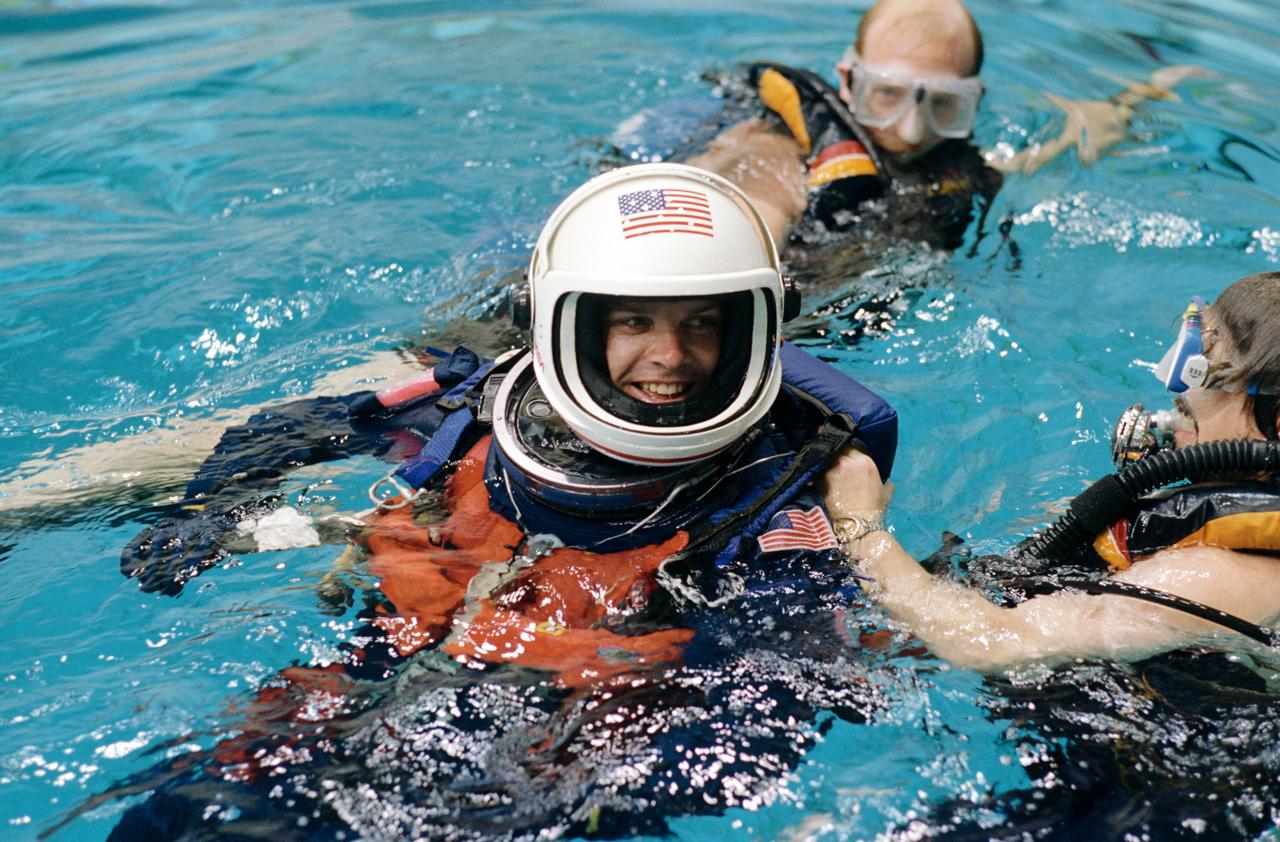

S95-03480 (16 FEB 1995) --- Attired in a training version of the Shuttle launch and entry garment, astronaut Kevin R. Kregel, pilot, gets help from SCUBA-equipped divers during a training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). As part of the emergency bailout phase of their training agenda, the STS-70 crew members made use of this 25-feet deep pool to practice parachute landings in water and subsequent deployment of life rafts.
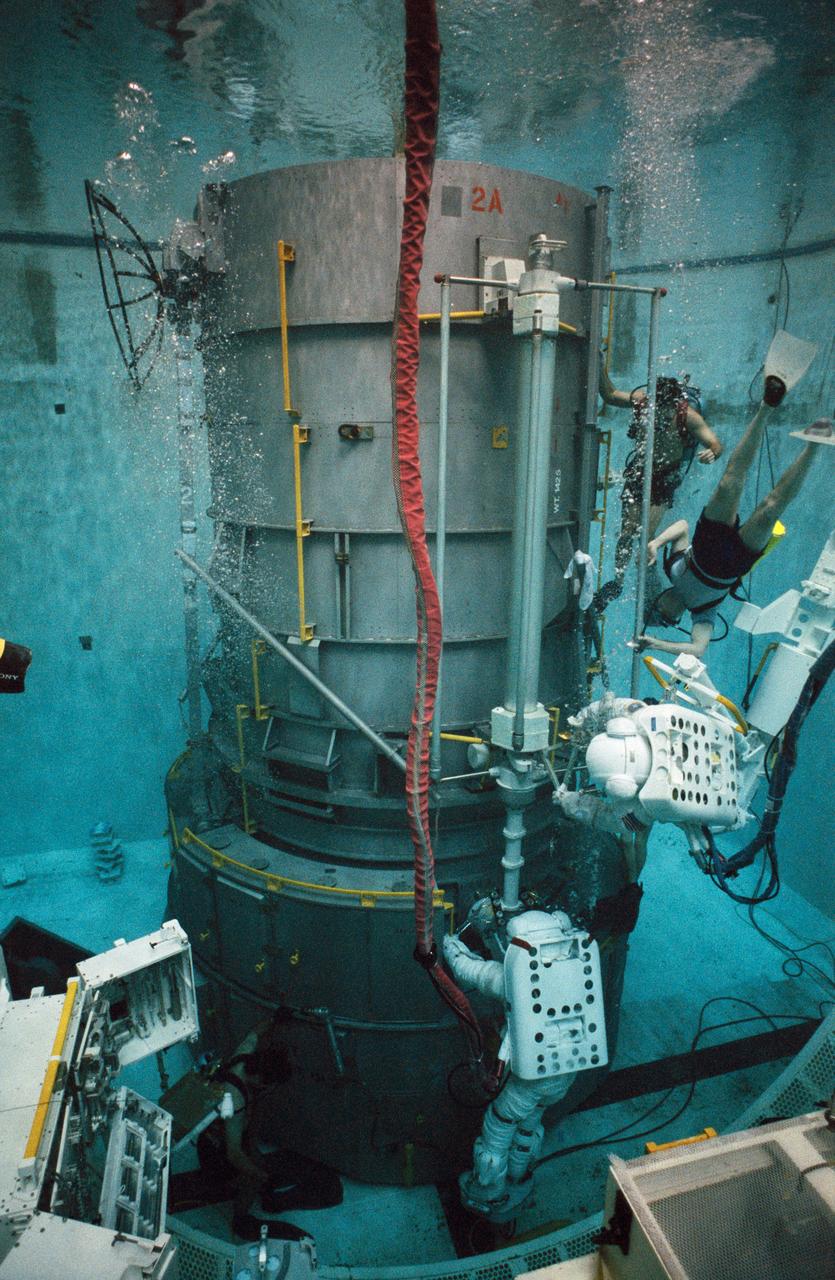
S93-30237 (5 Mar 1993) --- Wearing training versions of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMU), astronauts Thomas D. Akers (red stripe) and Kathryn C. Thornton use the spacious pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. They are working with part of a full-scale mockup of HST.
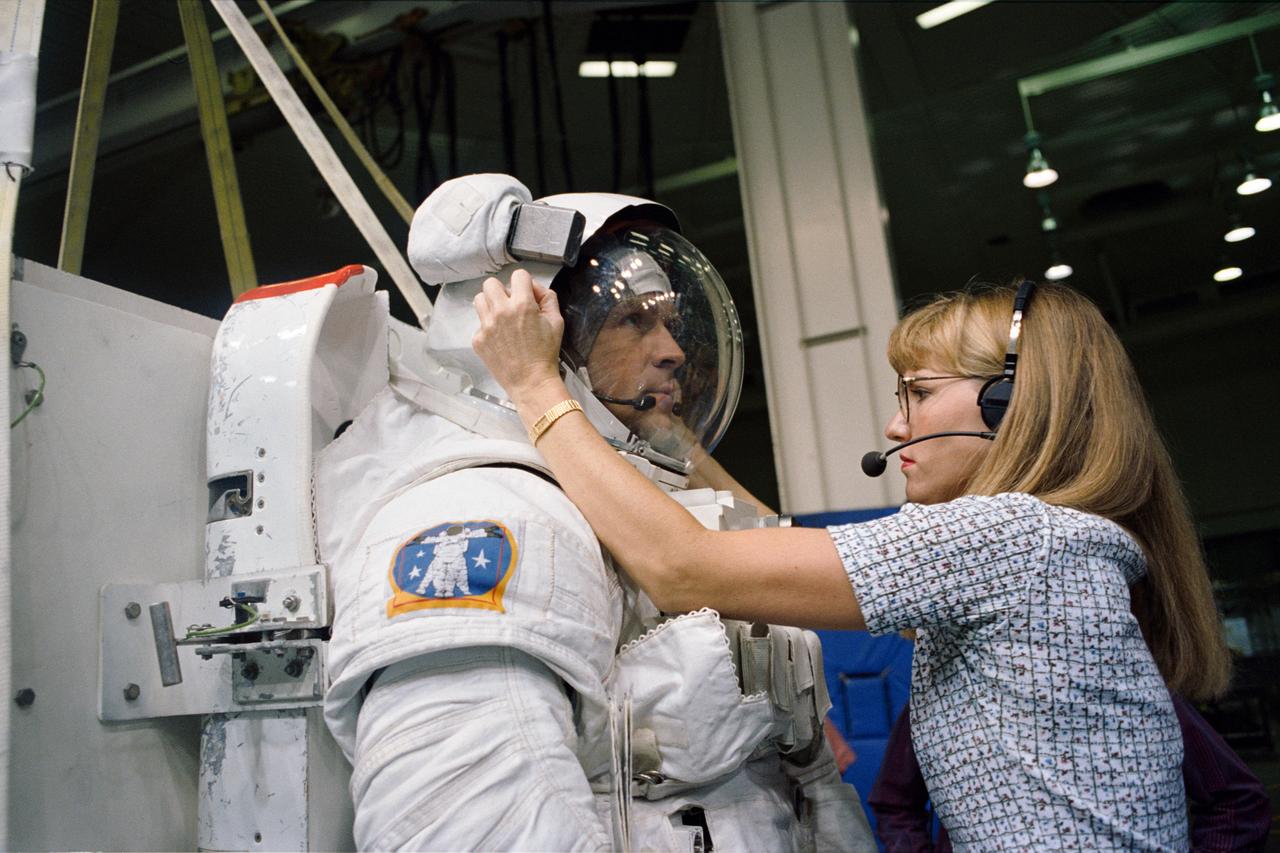

S94-39774 (August 1994) --- Boeing's Kari Rueter checks the helmet of astronaut Mark C. Lee prior to the mission specialist's participation in an underwater rehearsal for an extravehicular activity (EVA). Lee's spacewalk is scheduled for the September STS-64 mission. New rescue gear for use on future space shuttle missions will be evaluated during the mission's single spacewalk, involving astronauts Lee and Carl J. Meade, mission specialists. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
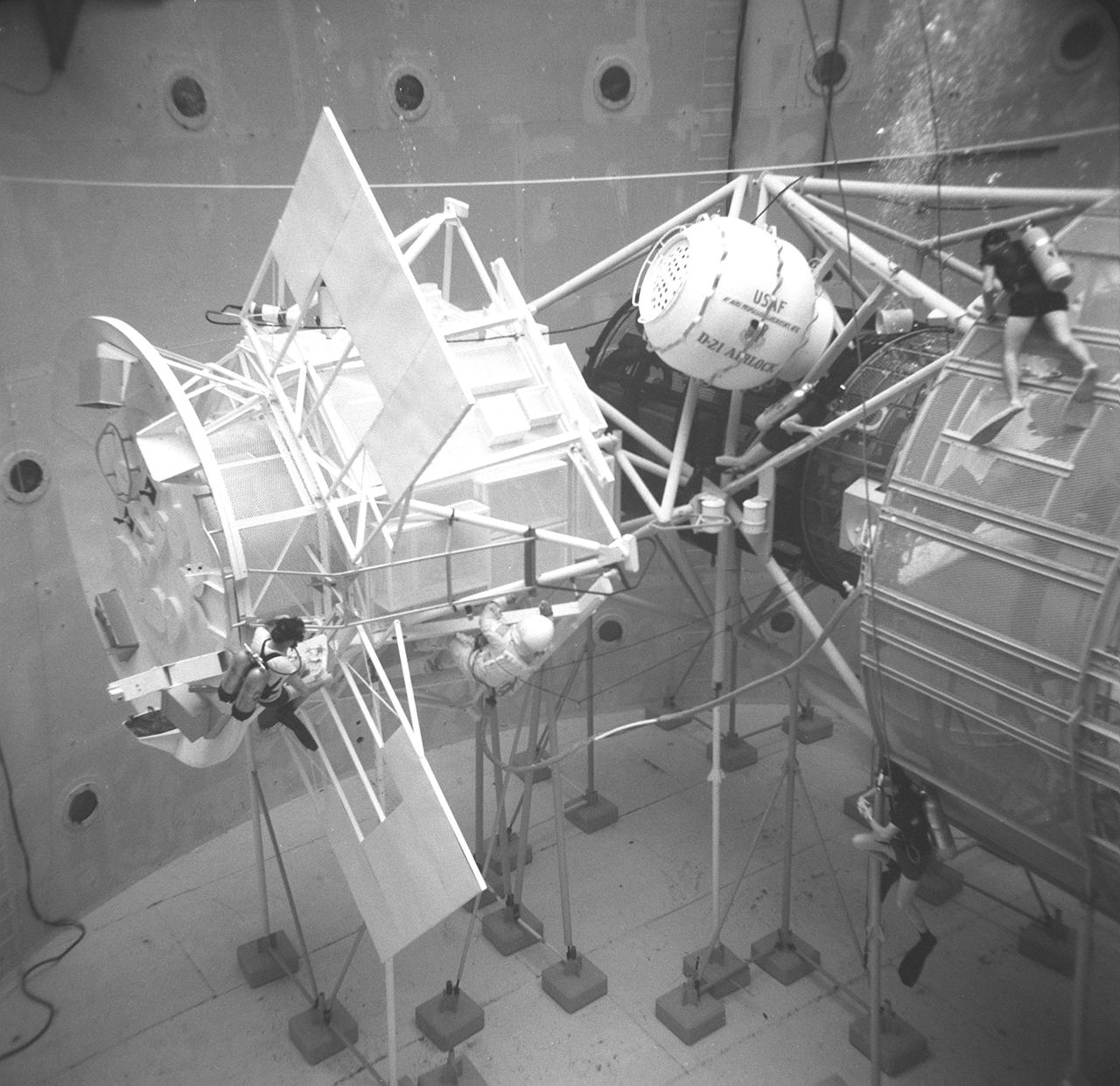

After the end of the Apollo missions, NASA's next adventure into space was the marned spaceflight of Skylab. Using an S-IVB stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle, Skylab was a two-story orbiting laboratory, one floor being living quarters and the other a work room. The objectives of Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. At the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), astronauts and engineers spent hundreds of hours in an MSFC Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) rehearsing procedures to be used during the Skylab mission, developing techniques, and detecting and correcting potential problems. The NBS was a 40-foot deep water tank that simulated the weightlessness environment of space. This photograph shows astronaut Ed Gibbon (a prime crew member of the Skylab-4 mission) during the neutral buoyancy Skylab extravehicular activity training at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) mockup. One of Skylab's major components, the ATM was the most powerful astronomical observatory ever put into orbit to date.

S84-36900 (29 June 1984) ---Astronauts Robert L. Crippen (right) and Jon A. McBride, crew commander and pilot, respectively, for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission, don self contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) gear prior to their underwater to observe a simulation of an extravehicular activity (EVA) to be performed on their mission. Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, two of three mission specialists on the seven-member crew, are scheduled for the EVA. The underwater training took place in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F).
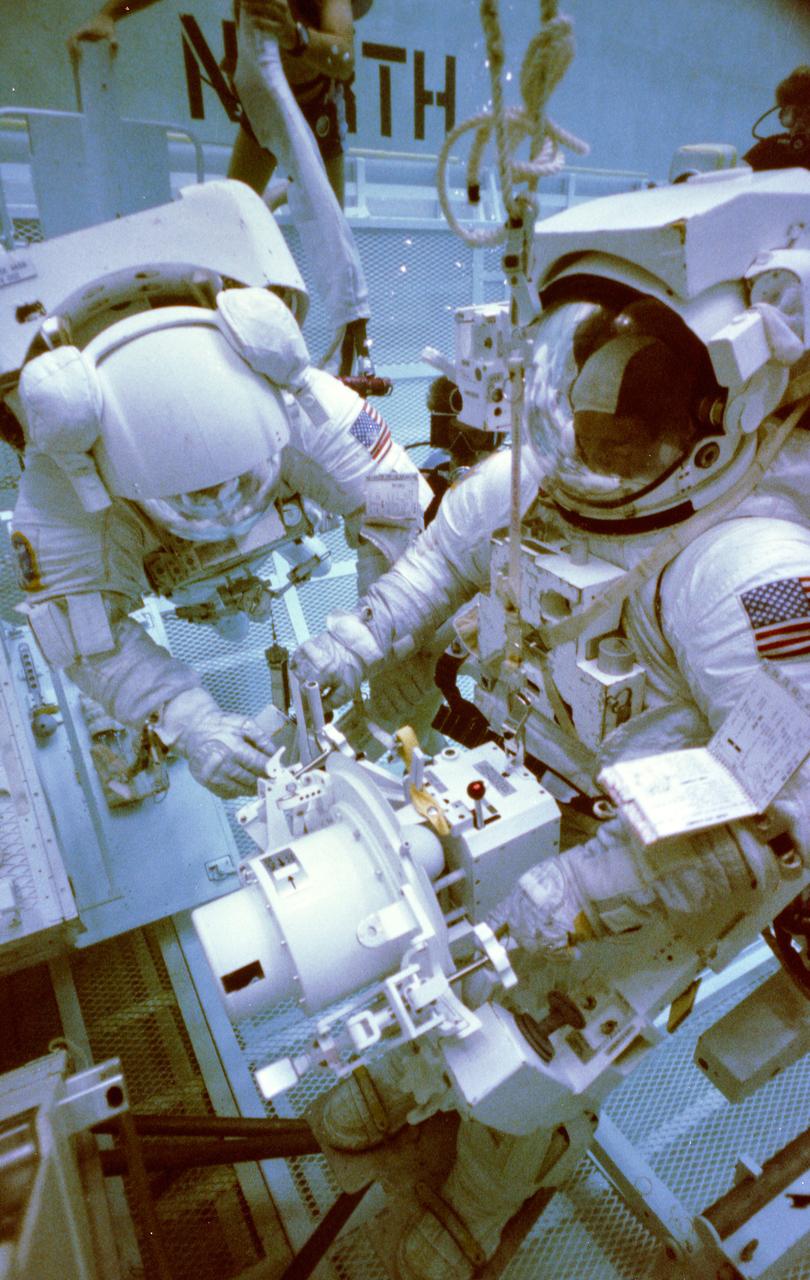
S83-42893 (19 Oct 1983) ---- Astronauts George D. Nelson and James D. van Hoften, two of three STS-41C mission specialists, share an extravehicular activity (EVA) task in this simulation of a Solar Maximum Satellite (SMS) repair visit. The two are making use of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Dr. Nelson is equipped with the manned maneuvering unit (MMU) trainer and he handles the trunion pin attachment device (TPAD), a major tool to be used on the mission. The photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
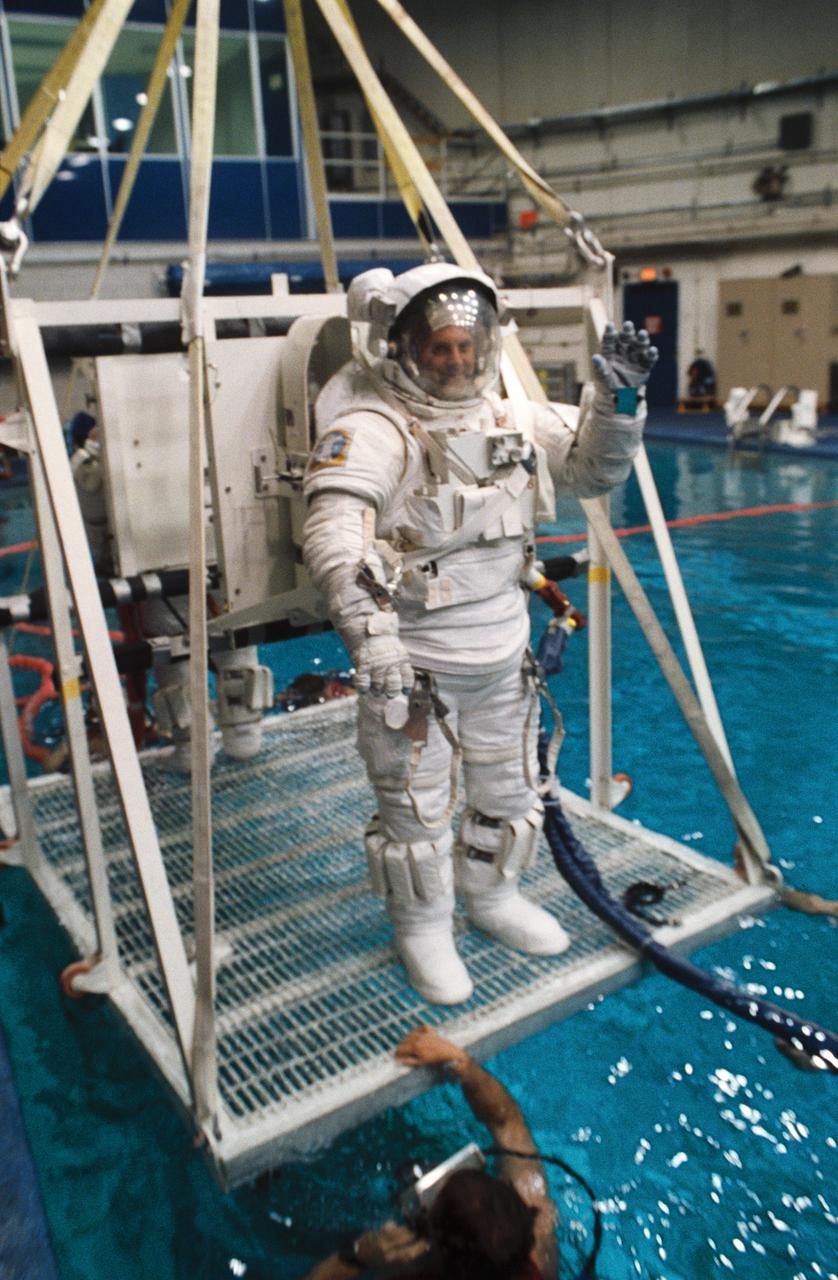

S93-31702 (3 April 1993) --- Astronaut David A. Wolf participates in training for contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) for the STS-58 mission. Behind Wolf, sharing the platform with him is astronaut Shannon W. Lucid. For simulation purposes, the two mission specialists were about to be submerged to a point of neutral buoyancy in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Though the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) mission does not include a planned EVA, all crews designate members to learn proper procedures to perform outside the spacecraft in the event of failure of remote means to accomplish those tasks.
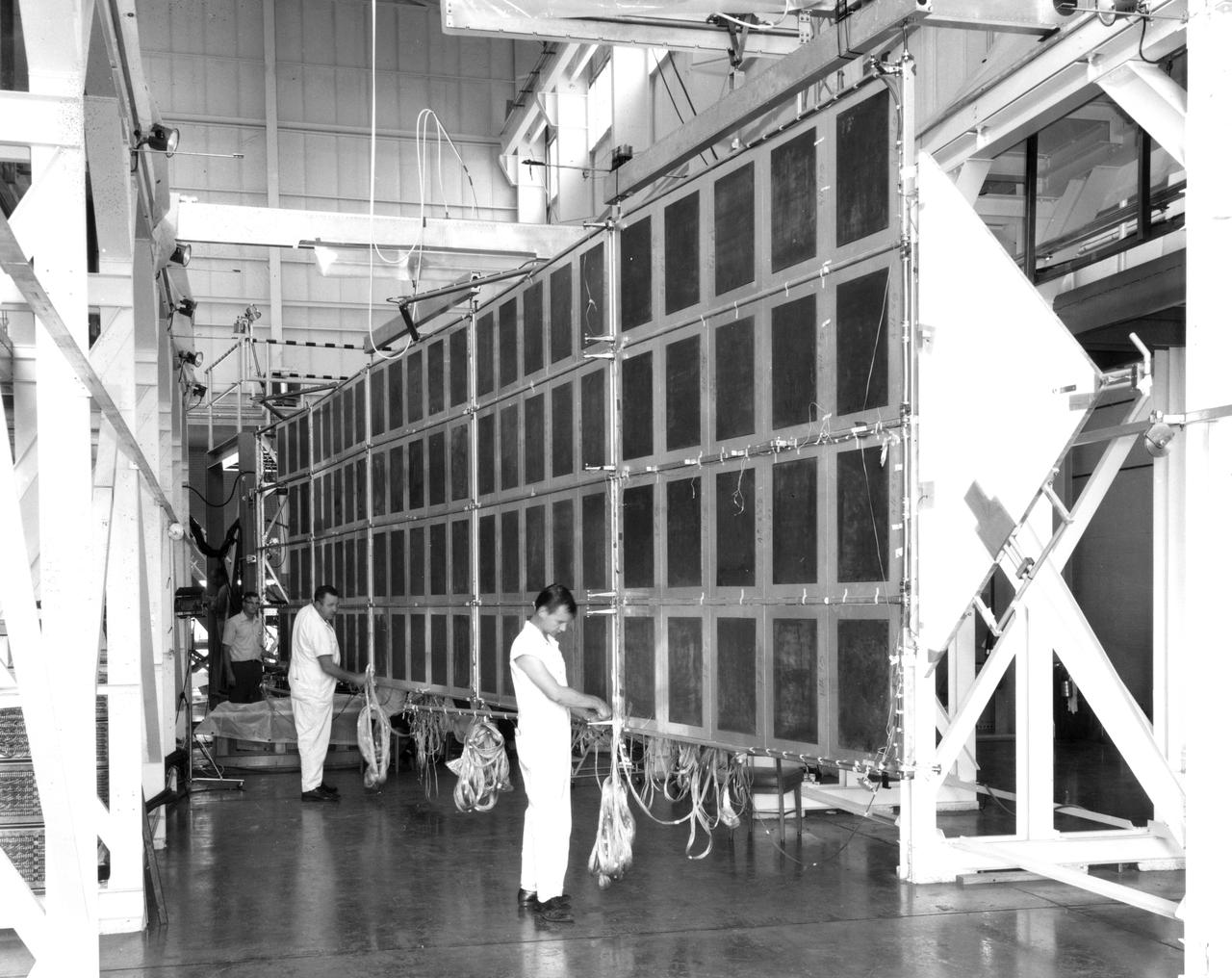

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center check the wiring on a mechanical test article of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) solar array. Four such arrays were joined in a cross to provide electric power for the ATM in Earth orbit. The deployment mechanism for extending the wing to the fully open position had just been tested when this photograph was taken. The array was suspended from beams riding on air bearings to closely simulate the weightless conditions under which it would be deployed in space. The wings are folded against the sides of the ATM for launch and are deployed by a scissors mechanism in Earth’s orbit.
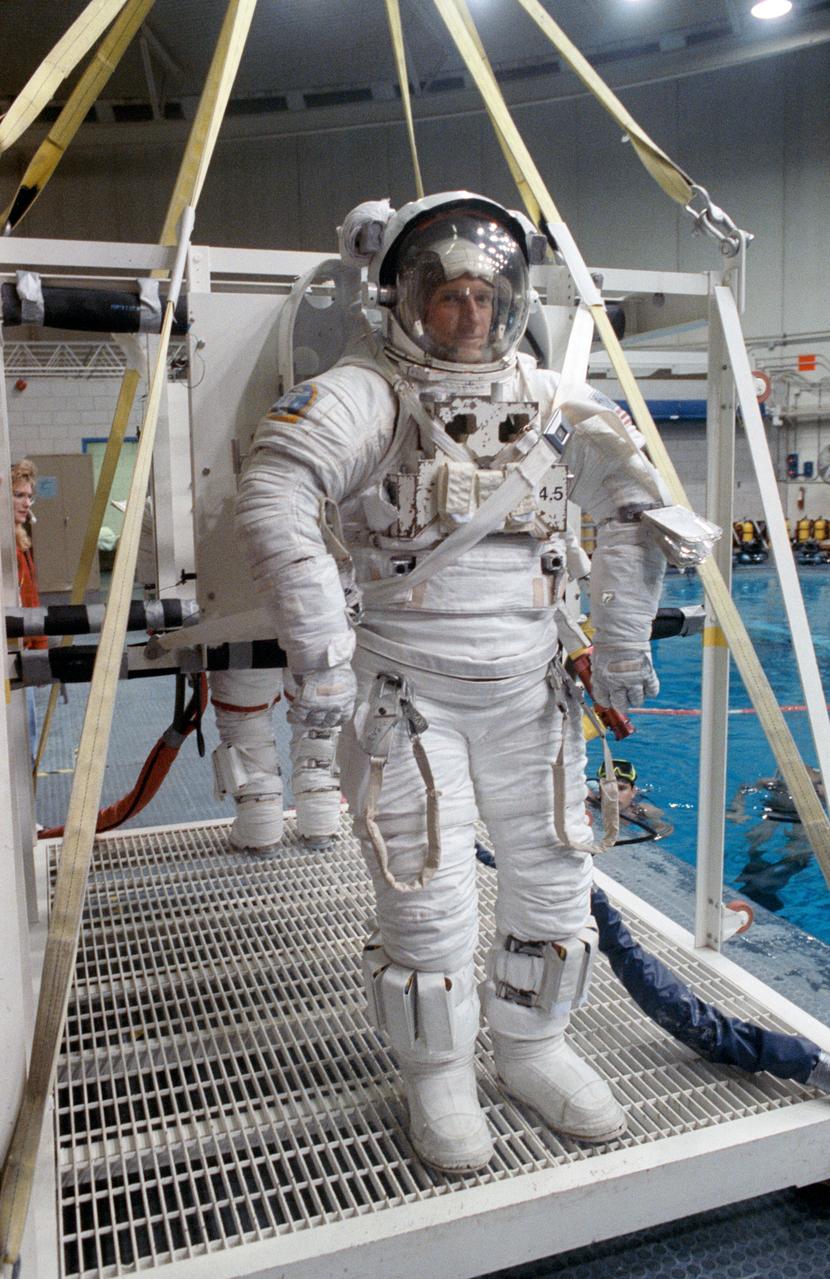

S91-30196 (1 March 1991) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, mission specialist, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, payload commander (barely visible in background), stand on a platform (out of frame) which is part of a system that will lower them into a 25-ft. deep pool. The payload commander and mission specialist used the pool in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F) to rehearse a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts wear pressurized spacesuits configured for achieving a neutrally buoyant condition in the water to simulate both planned and contingency EVAs. Two SCUBA-equipped swimmers assisting the training are seen in the background.
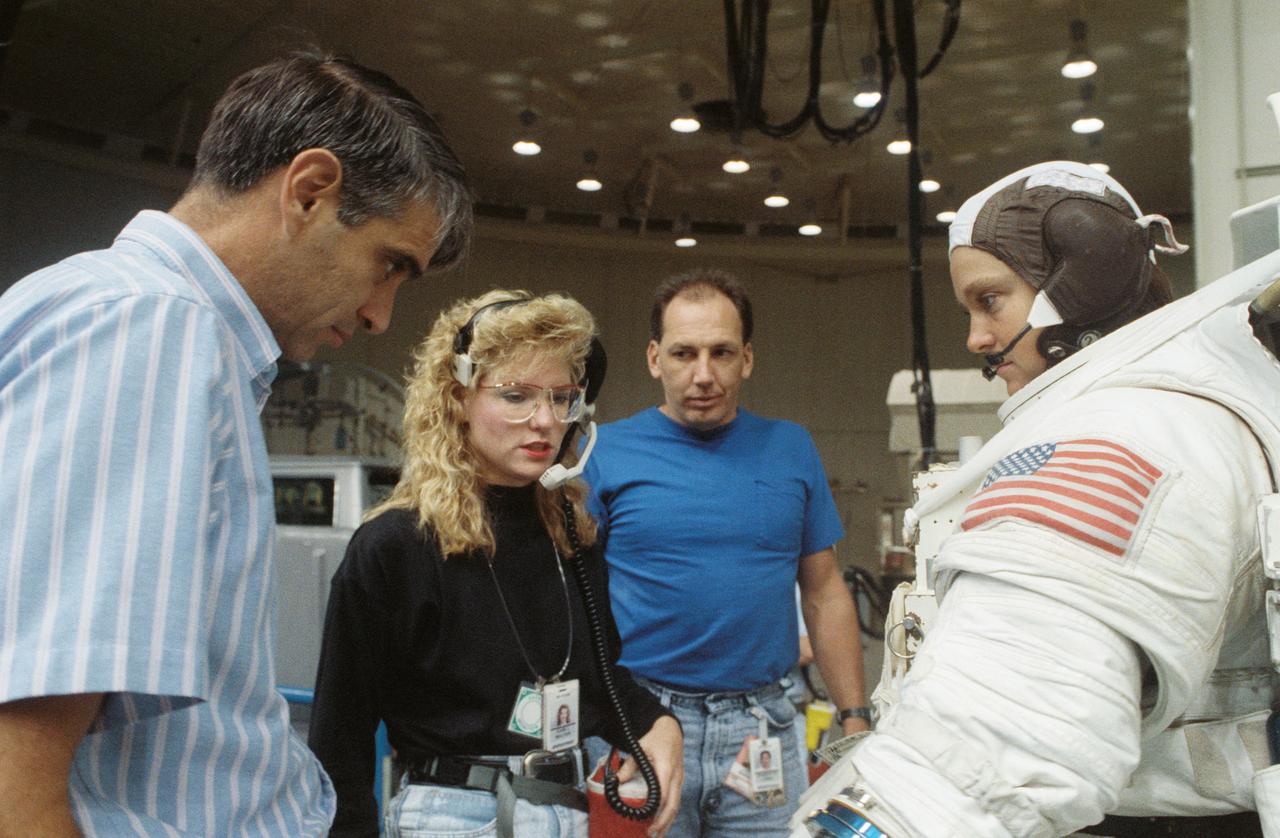

S90-45785 (16 Aug 1990) --- Astronaut Tamara E. Jernigan, STS-40 mission specialist, is pictured in a training version of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) spacesuit talking with a fellow crewmember and members of the crew training staff. At left is astronaut Sidney M. Gutierrez, pilot for the flight. Dr. Jernigan was about to be submerged in the Johnson Space Center's 25-ft. deep weightless environment training facility (WET-F) pool to simulate a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA). There is no EVA scheduled for STS-40, the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) mission.
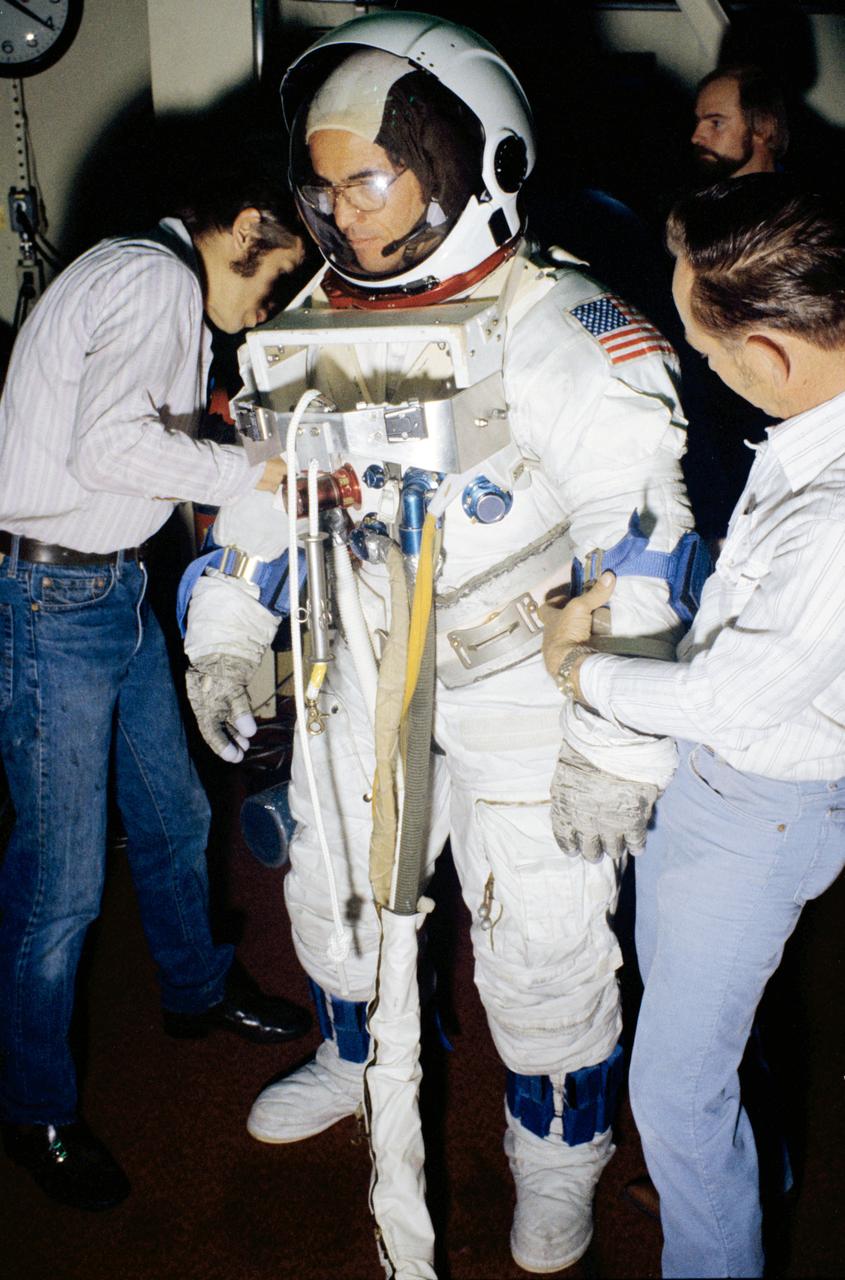

S79-25007 (13 Dec. 1978) --- Astronaut Robert L. Crippen, pilot for the first space shuttle orbital flight test (STS-1), is assisted by technicians prior to entering a water immersion facility (WIF) during a training session. The zero-gravity familiarization took place in the Johnson Space Center?s training and test center (Building 260). The WIF afford one of two ways to simulate the feeling of weightlessness experienced during space extravehicular activity (EVA), the other being inside aircraft flying a parabolic curve. Crippen will be joined by astronaut John W. Young for the STS-1 flight. Photo credit: NASA
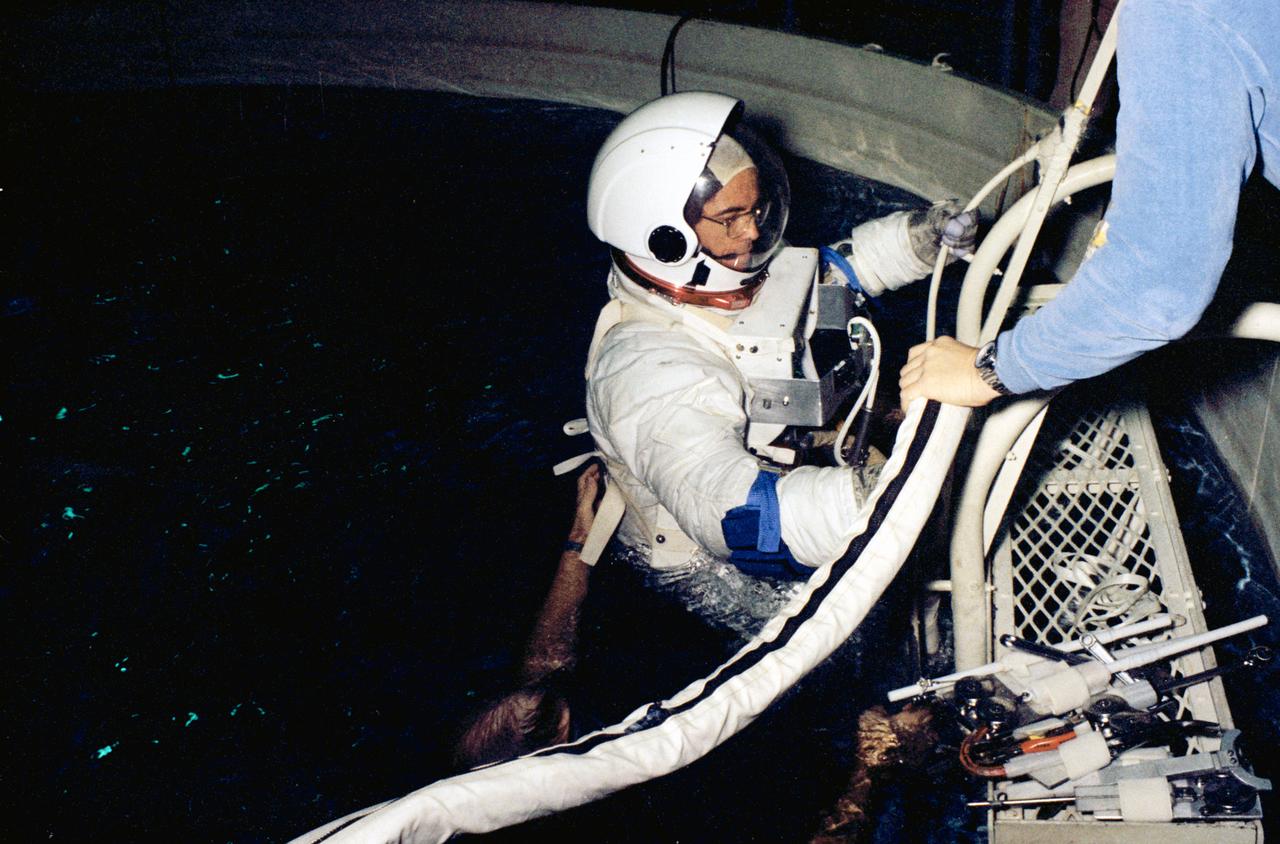

S79-25014 (13 Dec. 1978) --- Astronaut Robert L. Crippen, pilot of the first space shuttle orbital flight test (STS-1), eases into a water immersion facility (WIF) during a training session in the Johnson Space Center?s training and test facility (Bldg. 260). The WIF affords one of two ways to simulate the feeling of weightlessness experienced during space extravehicular activity (EVA), the other being inside aircraft flying a parabolic curve. Crippen will be joined by astronaut John W. Young, commander for the STS-1 flight. Photo credit: NASA
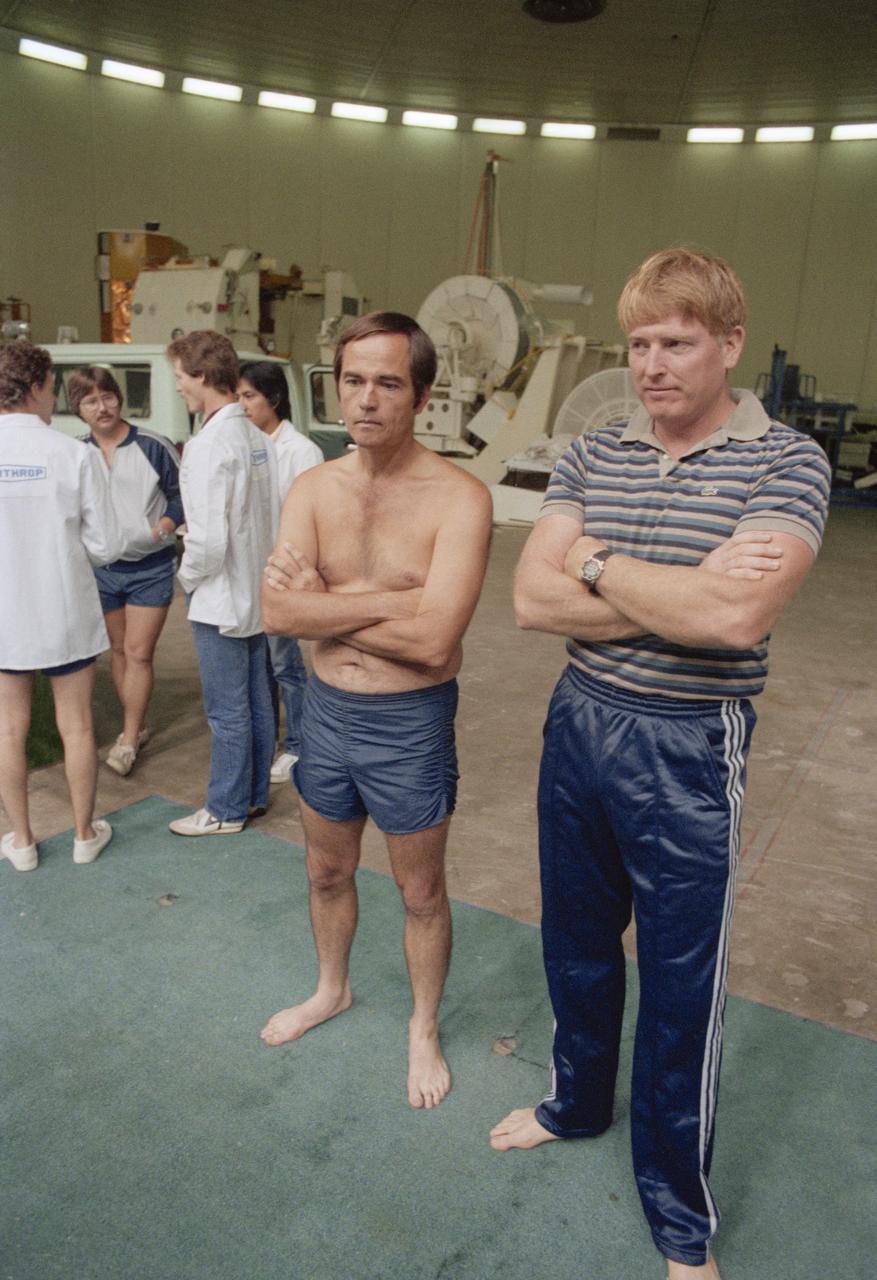

S84-36898 (29 June 1984) --- Astronauts Robert L. Crippen (left) and Jon A. McBride, crew commander and pilot, respectively for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission, await the delivery of self contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) gear prior to their going underwater to observe a simulation of an extravehicular activity (EVA) scheduled for their mission. The EVA will be performed by Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, two of three mission specialists named for the seven-member crew. The underwater training took place in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F).
This close-up of astronaut and mission specialist, Kathryn Thornton, was captured under water in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neural Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) where she is participating in a training session for the STS-61 mission. The NBS provided the weightless environment encountered in space needed for testing and the practices of Extravehicular Activities (EVA). Launched on December 2, 1993 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor, STS-61 was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) serving mission. During the 2nd EVA of the mission, Thornton, along with astronaut and mission specialist Thomas Akers, performed the task of replacing the solar arrays. The EVA lasted 6 hours and 35 minutes.
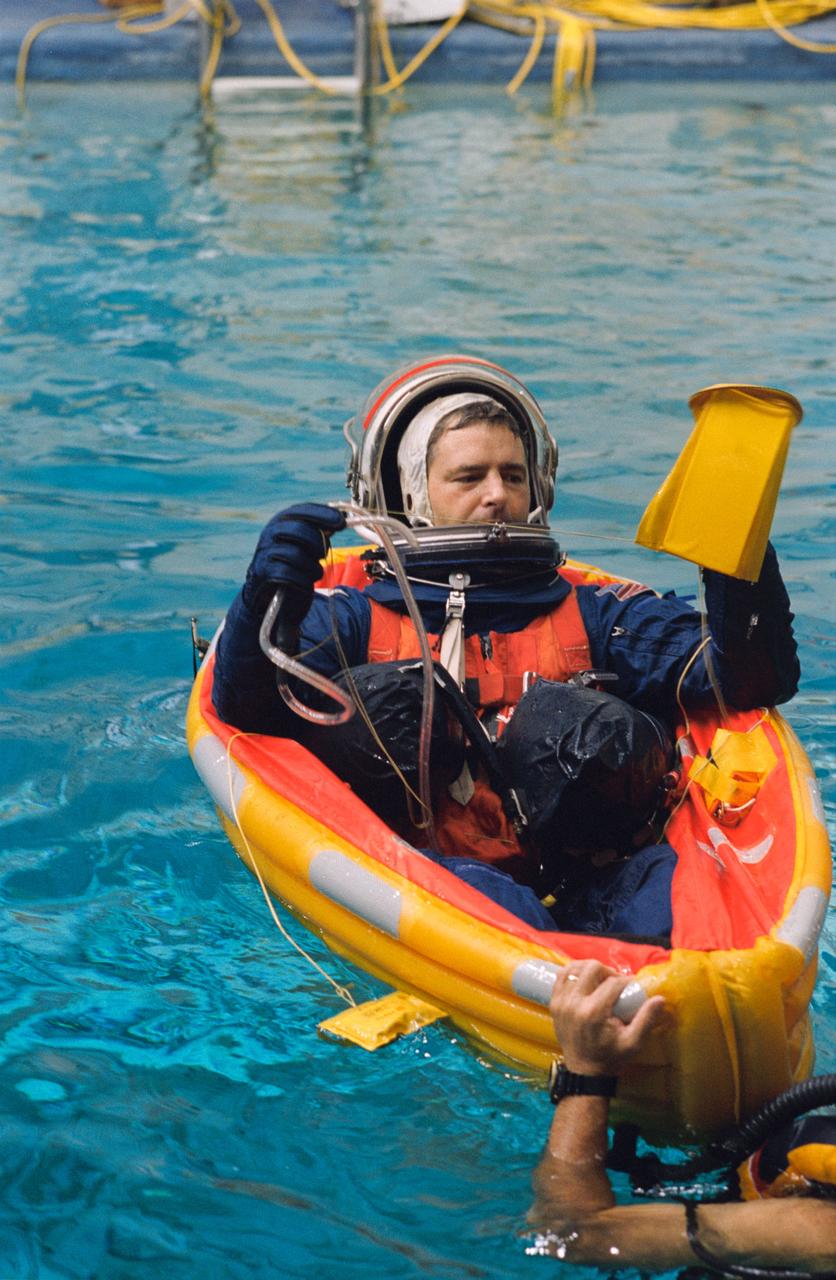

S93-45726 (7 Oct. 1993) --- Canadian astronaut candidate Marc Garneau, later named as a mission specialist for NASA's STS-77 mission, participates in emergency bailout training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Garneau was in the 1992 class of Astronaut Candidates (ASCAN). Wearing full parachute gear following a simulated parachute drop, Garneau has deployed a small life raft in a 25-feet deep pool in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). This portion of an astronaut's training is to prepare him or her for proper measures to take in the event of bailout over water. Garneau is assisted here by one of several SCUBA-equipped divers in the pool.
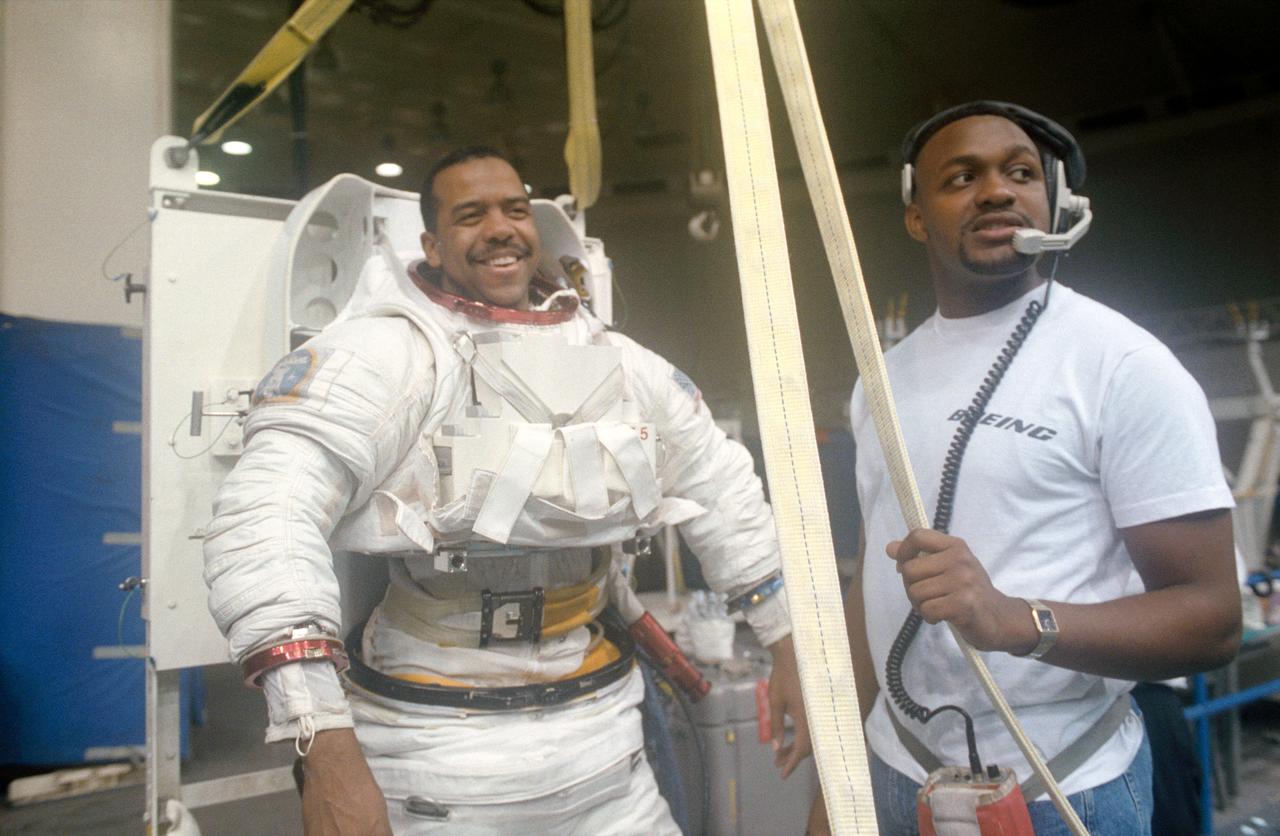

S91-51063 (Dec 1991) --- Partially attired in a special training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit, astronaut Bernard J. Harris Jr. is pictured before a training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Harris, STS-55 mission specialist, is assisted by Laney Lee. Minutes later, Harris was in a 25-feet deep pool, simulating a contingency extravehicular activity (EVA). There is no scheduled EVA for the 1993 flight but each spaceflight crew includes astronauts trained for a variety of contingency tasks that could require exiting the shirt-sleeve environment of a Shuttle's cabin.