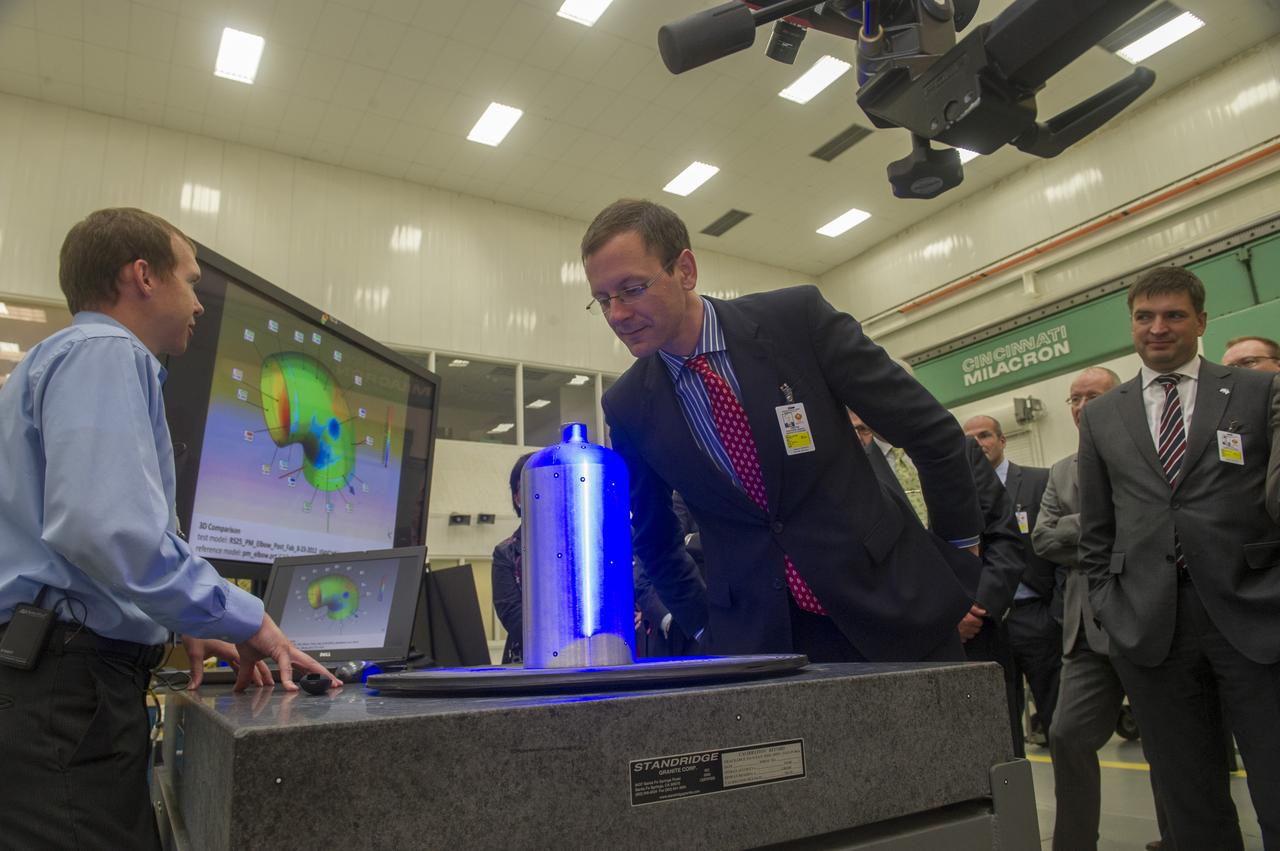

MSFC MECHANICAL ENGINEER BRIAN WEST, (L), DEMONSTRATES STRUCTURED LIGHT SCANNING PROCESS TO MEMBERS OF THE BREMEN, GERMANY, BUSINESS DELEGATION WHO VISITED MARSHALL RECENTLY. SENATOR MARTIN GÜNTHNER, MINISTRY OF ECONOMIC AFFAIRS, LABOUR AND PORTS (CENTER) VIEWS THE PRESSURE VESSEL BEING SCANNED. AT RIGHT IS BERND SCHMELING, SENIOR MANAGER PROCUREMENT, AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH

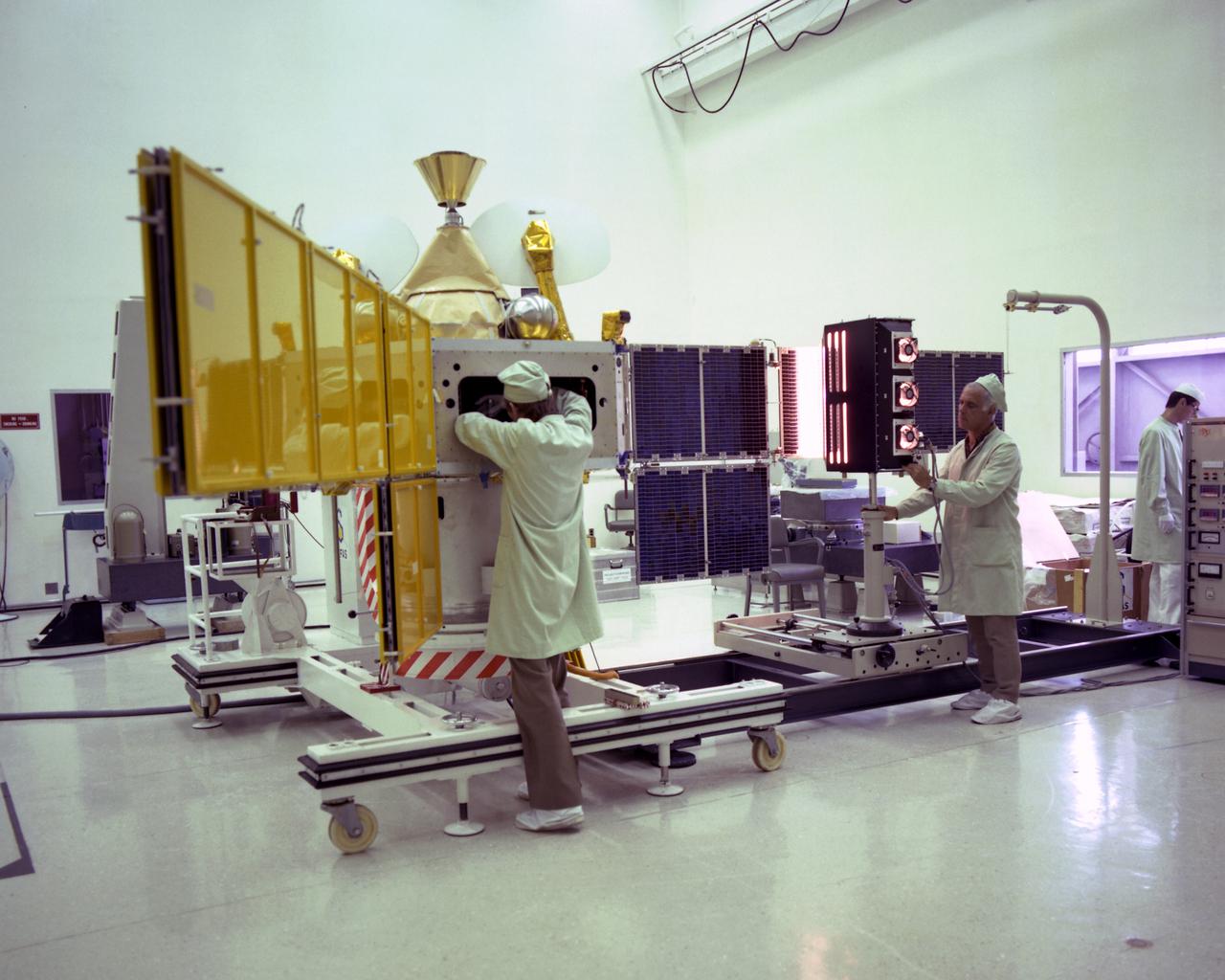
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians check out the Symphonie-B spacecraft during launch preparations at KSC. Symphonie is a synchronous-orbit communications satellite, jointly owned and managed by West Germany and France. Photo credit: NASA
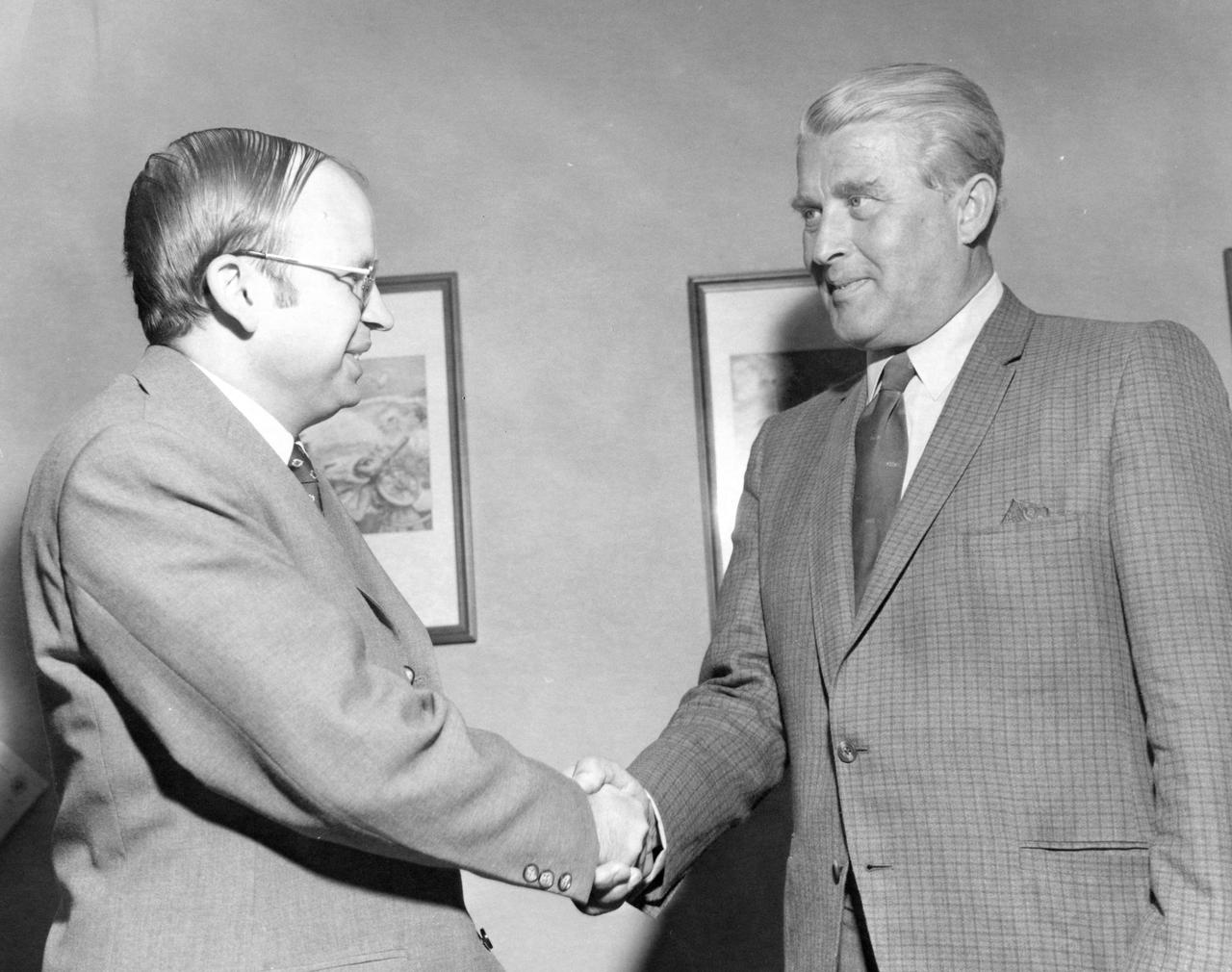

In this photograph, Guenter Ogger of Capitol Magazine, West Germany, greets Marshall Space Flight Center Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun. Mr. Ogger interviewed the famous rocket scientist for his magazine.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians check out the Symphonie-B spacecraft during launch preparations at KSC. Symphonie is a synchronous-orbit communications satellite, jointly owned and managed by West Germany and France. Photo credit: NASA
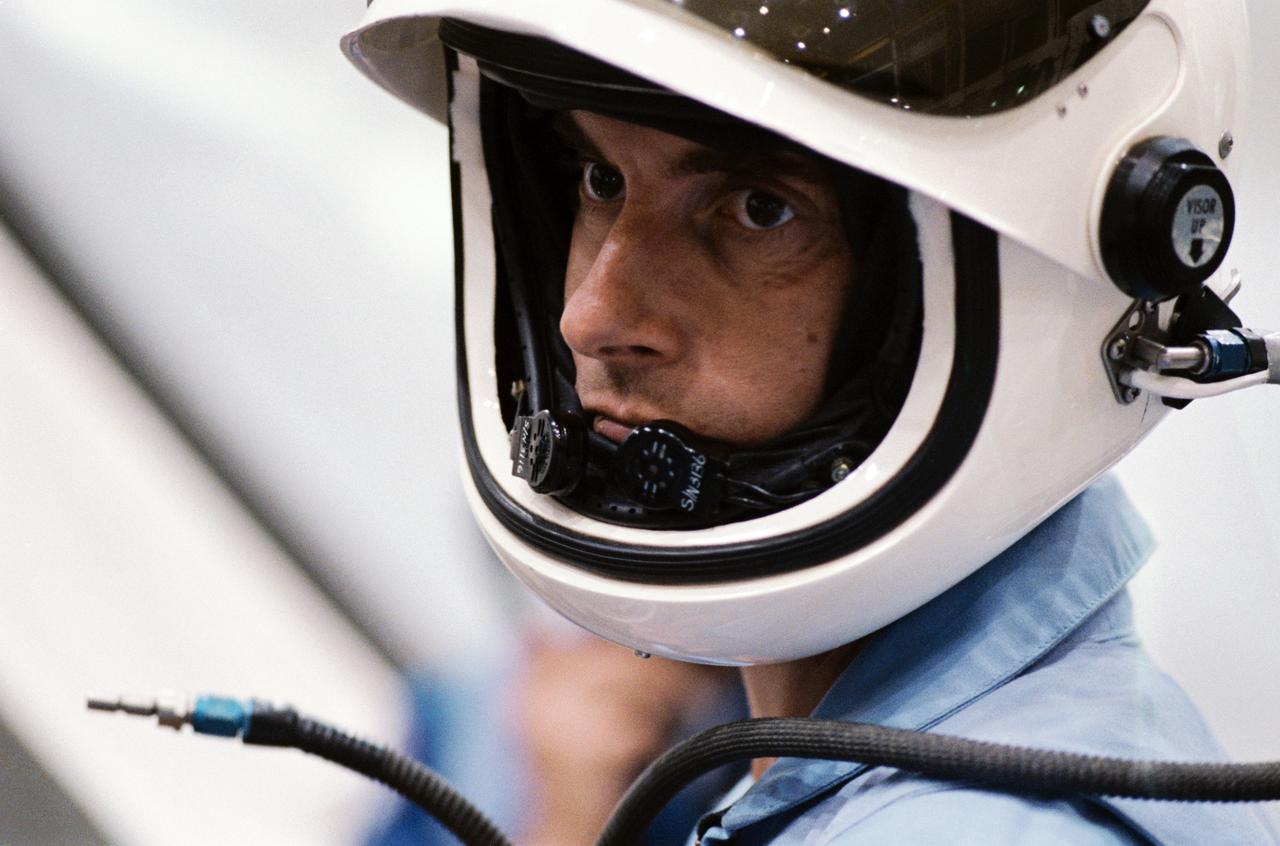

S83-41190 (9 September 1983) --- A close-up view of the serious countenance of West German Physicist Ulf Merbold was captured during a training session with all six STS-9 crewmembers in the Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Shuttle Mockup and Integration Laboratory. Dr. Merbold is SL-1 payload specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA). Dr. Merbold, from Max-Planck Institute in Stuttgart, is a specialist in crystal lattice defects and low-temperature physics. The photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
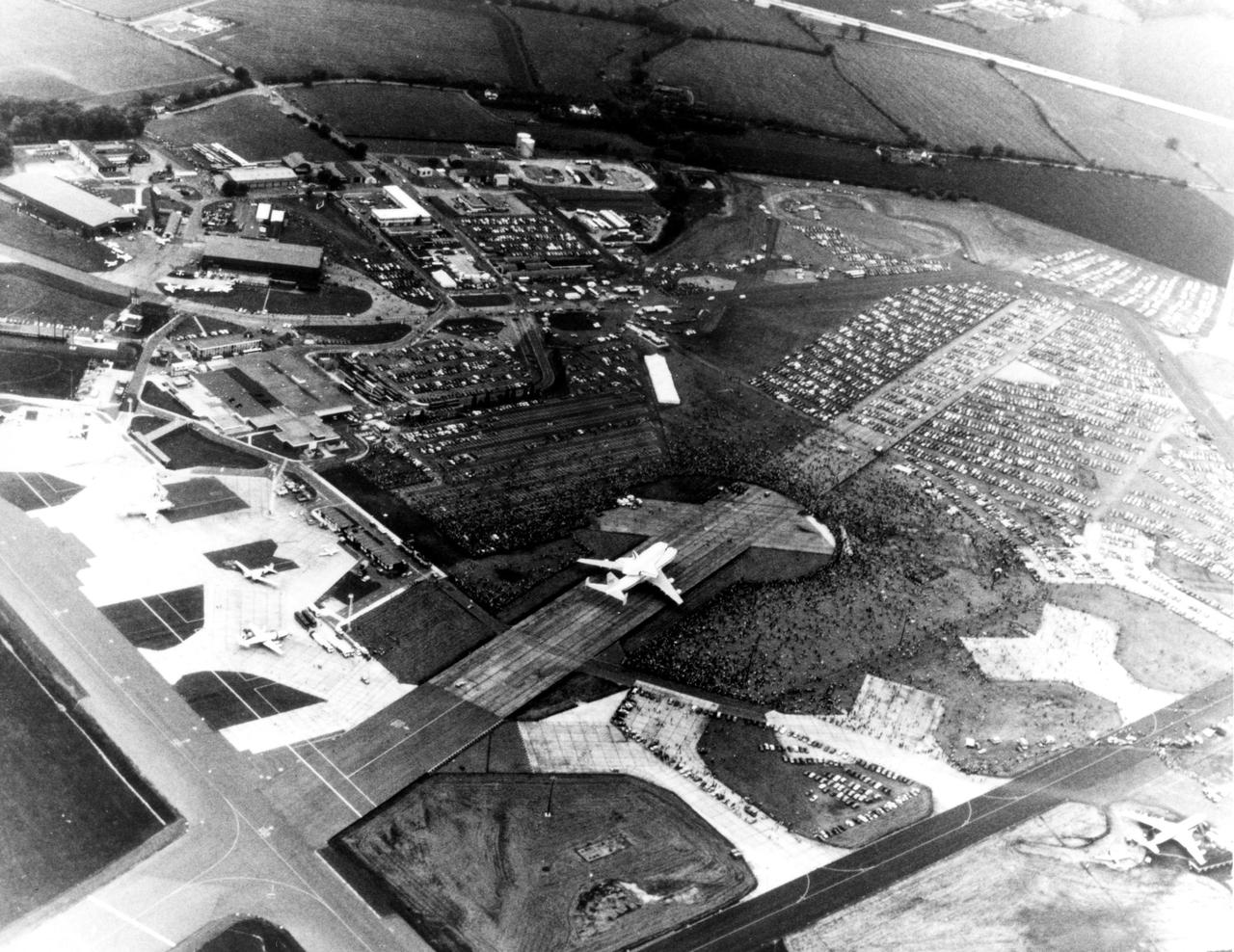

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Thousands of Britons surround the Space Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise at Stansted Airport, near London. The Enterprise atop its 747 carrier aircraft was viewed in London, Bonn-Cologne, West Germany, Rome and Ottawa, Canada, in addition to being shown at the Paris Air Show in June 1983.
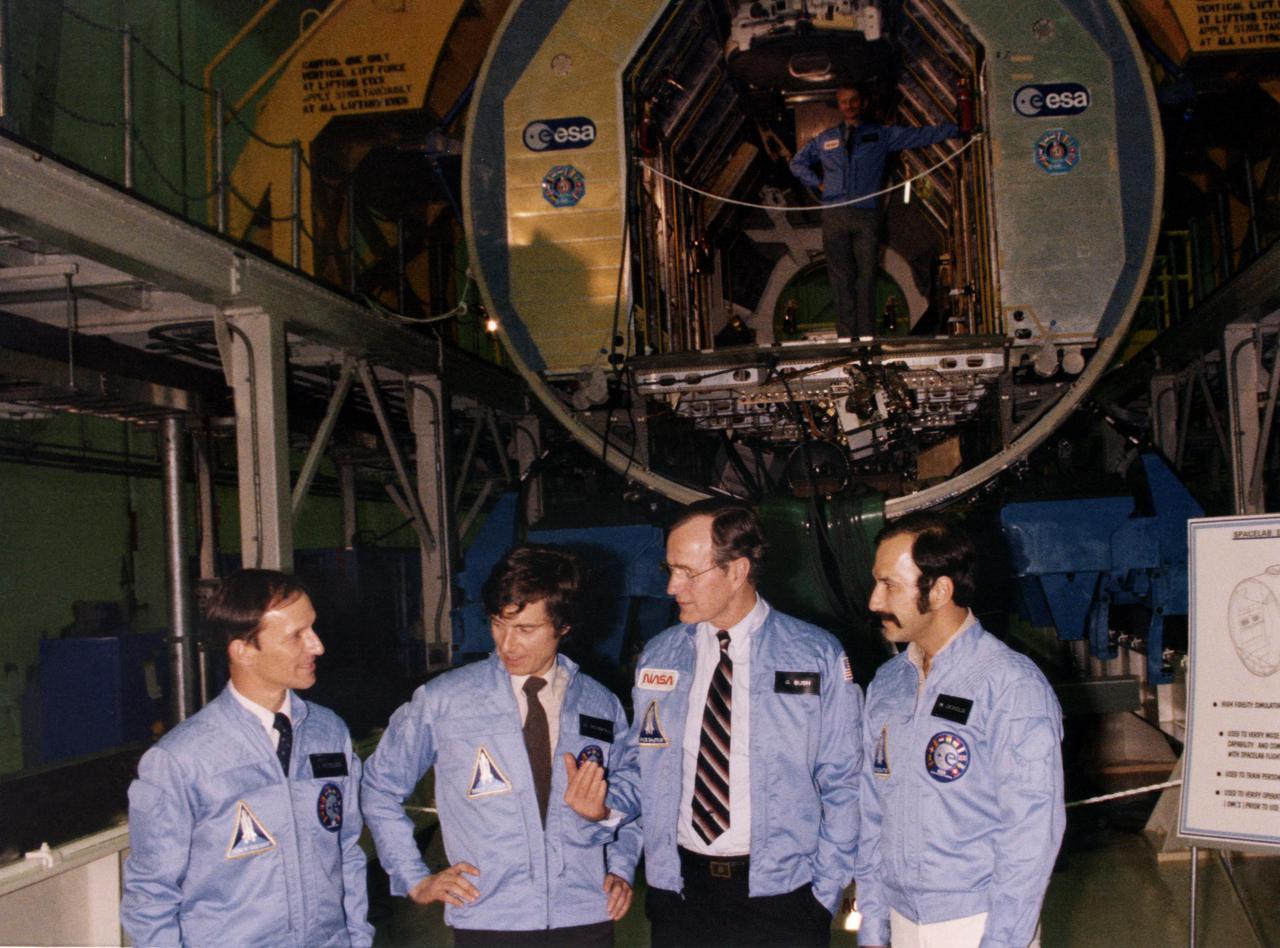

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Vice President George H.W. Bush, third from left, is pictured with the Spacelab engineering module at the Spacelab Arrival Ceremony in the Operations and Checkout Building as he visits with, from left, astronaut Claude Nicollier, European Space Agency, and payload specialists Ulf Marbod, West Germany, and Wubbo Ockels, the Netherlands. Overhead, in the module, is Owen K. Garriott, U.S. astronaut. The European-built Spacelab, designed to provide a shirt-sleeve environment for scientists working in Earth orbit, is scheduled to fly its first mission in the payload bay of the Space Shuttle in 1983.
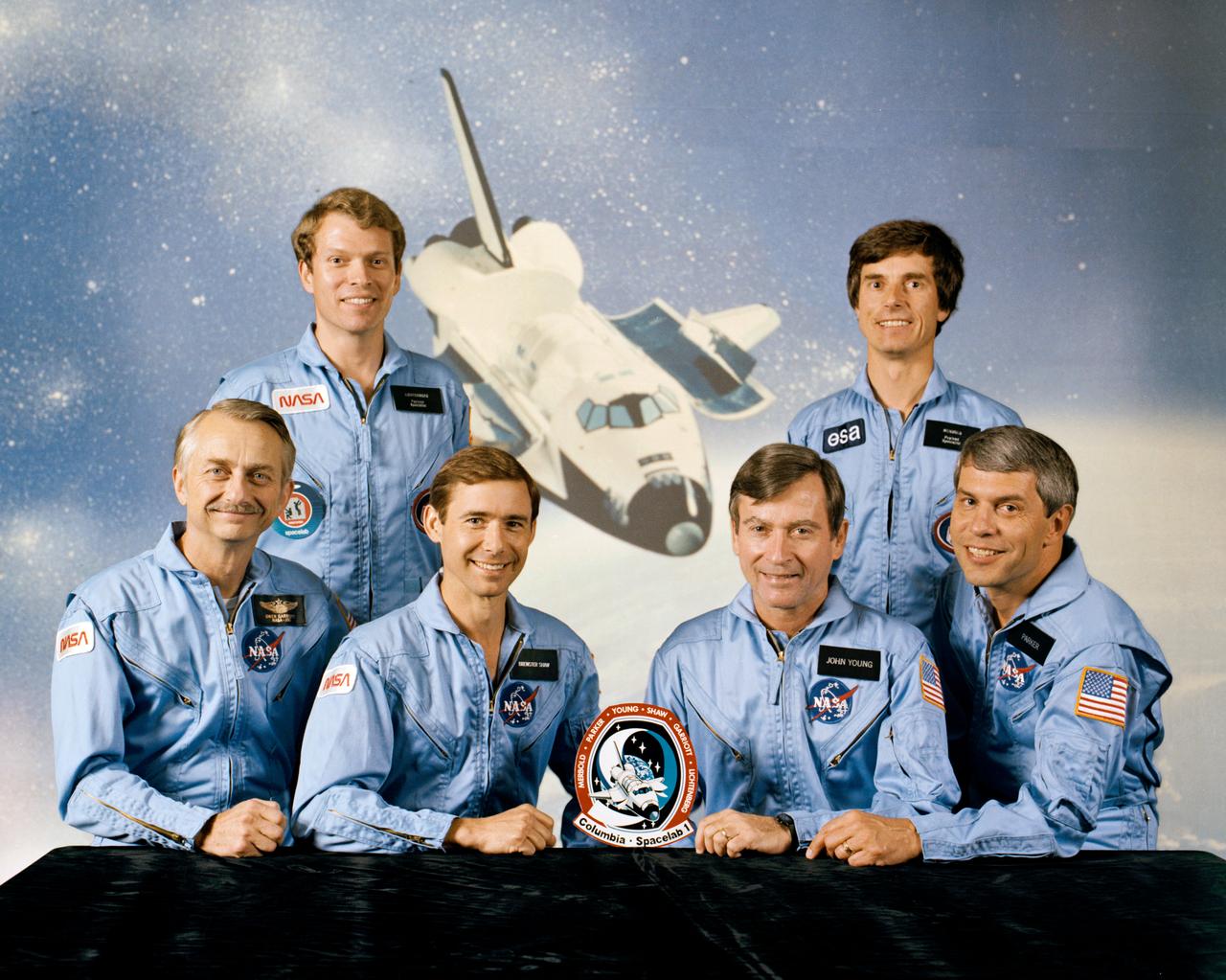

S83-35017 (June 1983) --- These six men represent the first crewmembers to man the Columbia when it gets reactivated later this year. The four NASA astronauts are joined by a European and MIT scientist payload specialist and the Spacelab module and experiment array for STS-9. On the front row are Astronauts Owen K. Garriott, mission specialist; Brewster H. Shaw, Jr., pilot; John W. Young, commander; and Robert A. R. Parker, mission specialist. Byron K. Lichtenberg of the Massachusetts of Technology, left and Ulf Merbold of the Republic of West Germany and the European Space Agency stand in front of an orbital scene featuring the Columbia. Columbia was used for the first five Space Transportation System missions in 1981 and 1982.
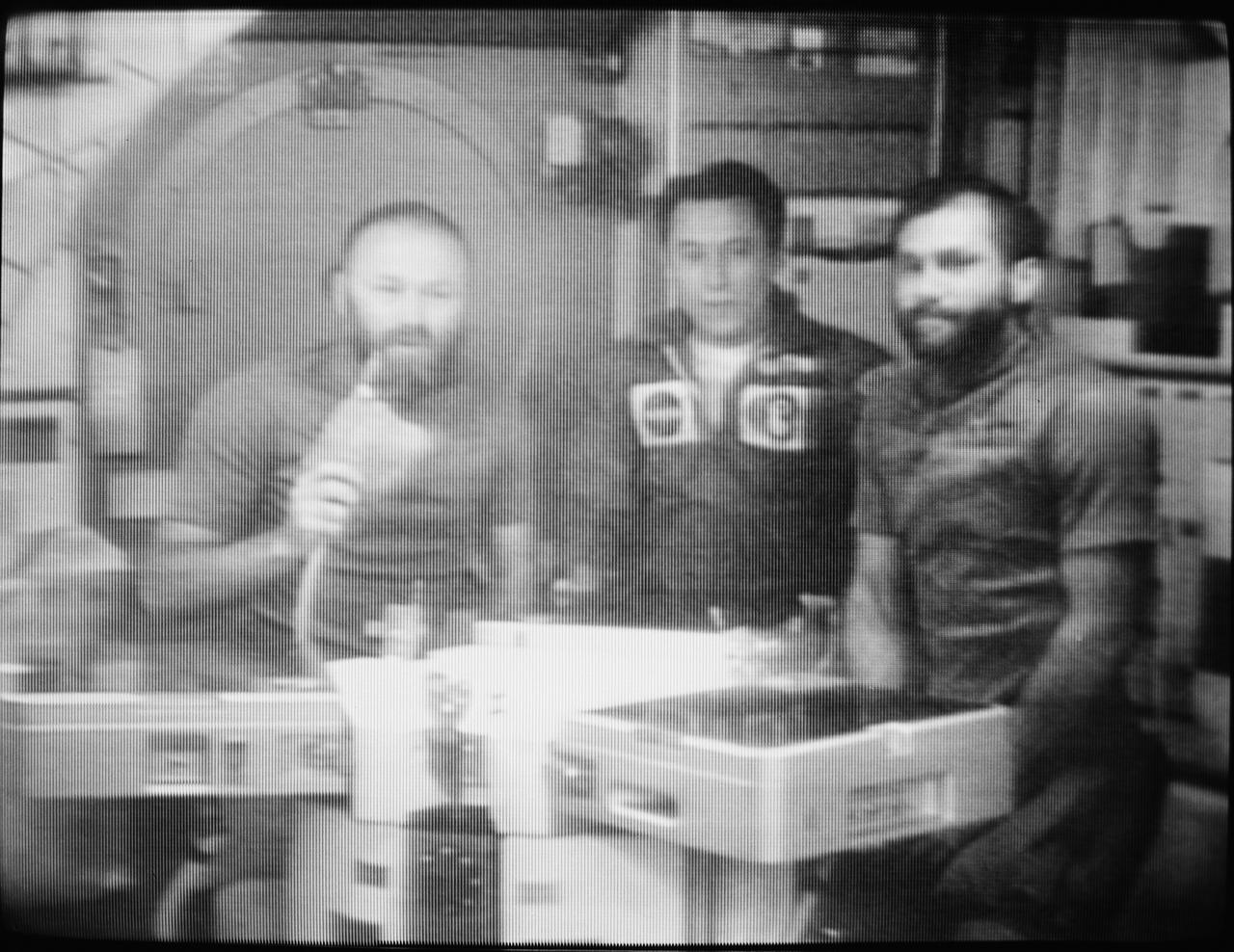

S73-38962 (28 Dec. 1973) --- The three members of the Skylab 4 crew confer via television communication with Dr. Lubos Kohoutek, discoverer of the Comet Kohoutek. This picture of the three astronauts was reproduced from a TV transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station in Earth orbit. They are, left to right, Gerald P. Carr, commander; Edward G. Gibson, science pilot; and William R. Pogue, pilot. They are seated in the crew quarters wardroom of the Orbital Workshop. Professor Kohoutek, who is employed at the Hamburg Observatory in West Germany, was visiting the Johnson Space Center in Houston when he conferred with the Skylab 4 crewmen. Photo credit: NASA
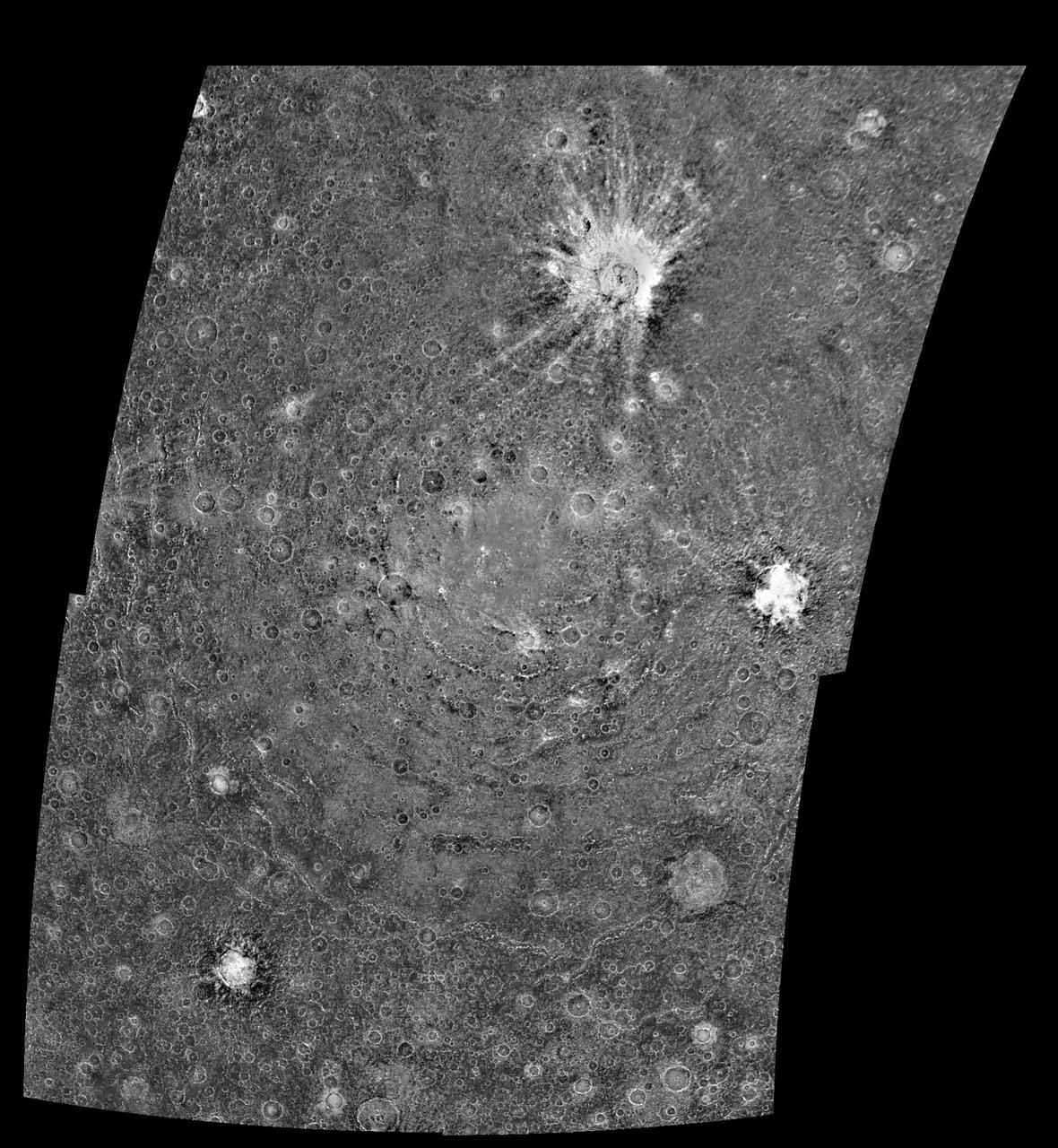
This four-frame mosaic shows the ancient impact structure Asgard on Jupiter's moon Callisto. This image is centered at 30 degrees north, 142 degrees west. The Asgard structure is approximately 1700 km across (1,056 mi) and consists of a bright central zone surrounded by discontinuous rings. The rings are tectonic features with scarps near the central zone and troughs at the outer margin. Several large impacts have smashed into Callisto after the formation of Asgard. The very young, bright-rayed crater Burr is located on the northern part of Asgard. This mosaic has been projected to show a uniform scale between the four mosaiced images. The image was processed by Deutsche Forschungsanstalt fuer Luftund Raumfahrt e.V., Berlin, Germany. This image was taken on November 4, 1996, at a distance of 111,891 kilometers (69,070 miles) by the solid state imaging television camera onboard the Galileo spacecraft during its third orbit around Jupiter. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00517
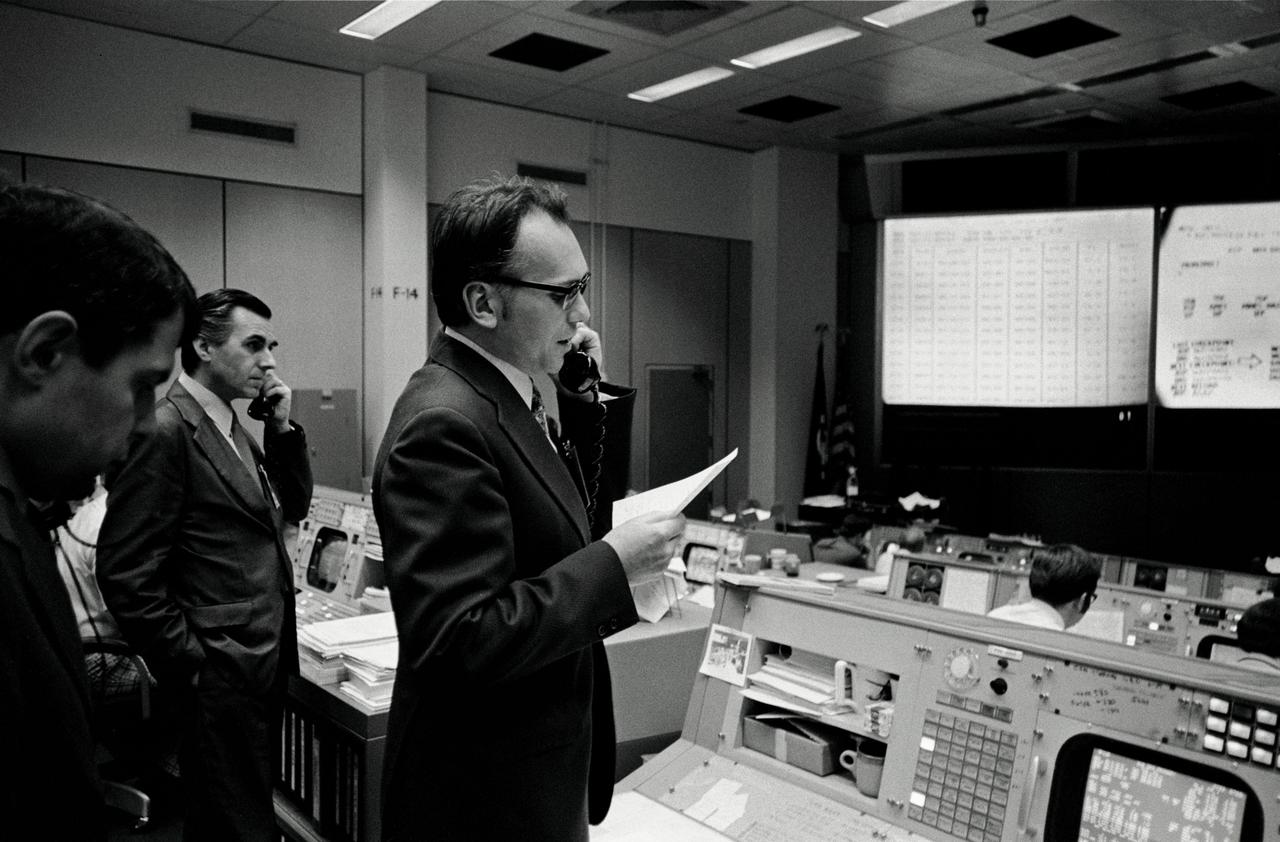

S74-15064 (28 Dec. 1973) --- Dr. Lubos Kohoutek, discoverer of the Comet Kohoutek, is seen in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center during a visit to the Johnson Space Center. He is talking over a radio-telephone with the Skylab 4 crewmen in the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Professor Kohoutek, a well-known Czechoslovakian astronomer who works at the Hamburg Observatory in West Germany, discussed the comet with astronauts Gerald P. Carr, Edward G. Gibson and William R. Pogue. One of the major objectives of the Skylab 4 mission is to monitor the passing of the Comet Kohoutek. Dr. Zdenek Sekania, who accompanied Dr. Kohoutek on the visit to JSC, is on the telephone in the left background. Dr. Sekania is with the Smithsonian Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Photo credit: NASA

S83-32900 (25 May 1983) --- This is the official insignia for STS-9, the major payload of which is Spacelab-1, depicted in the cargo bay of the space shuttle Columbia. The nine stars and the path of the orbiter tell the flight's numerical designation in the Space Transportation System's mission sequence. Astronaut John W. Young is crew commander; Brewster H. Shaw Jr., pilot. NASA astronauts Owen K. Garriott and Robert A.R. Parker are mission specialists. Byron K. Lichtenberg of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Ulf Merbold of the Republic of West Germany are the Spacelab-1 payload specialists. Launch has been set for late 1983. Merbold is a physicist representing the European Space Agency (ESA). The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
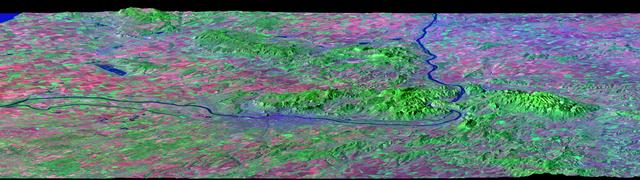
After draining the northern flank of the Alps Mountains in Germany and Austria, the Danube River flows east as it enters this west-looking scene (upper right) and forms the border between Slovakia and Hungary. The river then leaves the border as it enters Hungary and transects the Transdanubian Mountains, which trend southwest to northeast. Upon exiting the mountains, the river turns southward, flowing past Budapest (purplish blue area) and along the western margin of the Great Hungarian Plain. South and west of the Danube, the Transdanubian Mountains have at most only about 400 meters (about 1300 feet) of relief but they exhibit varied landforms, which include volcanic, tectonic, fluvial (river), and eolian (wind) features. A thick deposit of loess (dust deposits likely blown from ancient glacial outwash) covers much of this area, and winds from the northwest, funneled between the Alps and the Carpathian Mountains, are apparently responsible for a radial pattern of erosional streaks across the entire region. This image was generated from a Landsat satellite image draped over an elevation model produced by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). The view uses a 3-times vertical exaggeration to enhance topographic expression. The false colors of the scene result from displaying Landsat bands 1, 4, and 7 in blue, green, and red, respectively. Band 1 is visible blue light, but bands 4 and 7 are reflected infrared light. This band combination maximizes color contrasts between the major land cover types, namely vegetation (green), bare ground (red), and water (blue). Shading of the elevation model was used to further highlight the topographic features. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04952
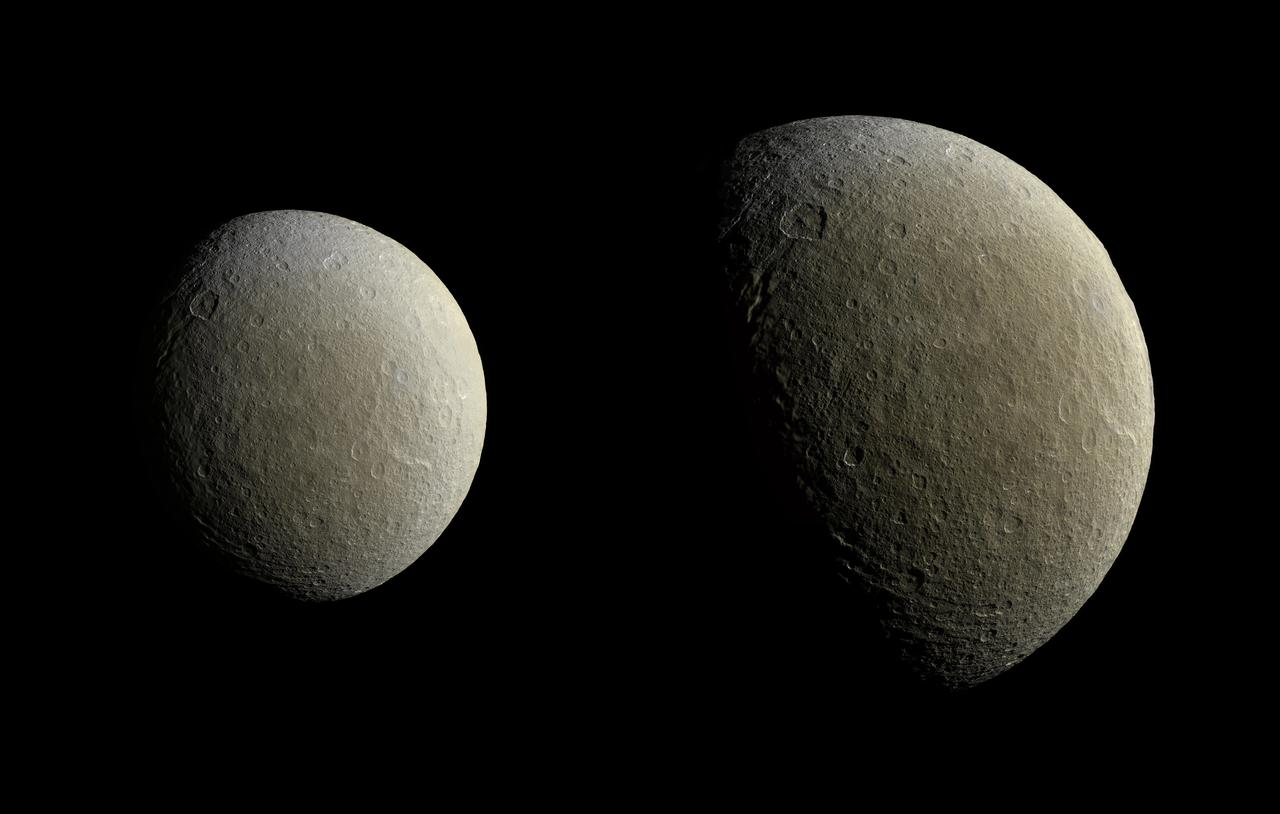

After a couple of years in high-inclination orbits that limited its ability to encounter Saturn's moons, NASA's Cassini spacecraft returned to Saturn's equatorial plane in March 2015. As a prelude to its return to the realm of the icy satellites, the spacecraft had its first relatively close flyby of an icy moon (apart from Titan) in almost two years on Feb. 9. During this encounter Cassini's cameras captured images of the icy moon Rhea, as shown in these in two image mosaics. The views were taken about an hour and a half apart as Cassini drew closer to Rhea. Images taken using clear, green, infrared and ultraviolet spectral filters were combined to create these enhanced color views, which offer an expanded range of the colors visible to human eyes in order to highlight subtle color differences across Rhea's surface. The moon's surface is fairly uniform in natural color. The image at right represents one of the highest resolution color views of Rhea released to date. A larger, monochrome mosaic is available in PIA07763. Both views are orthographic projections facing toward terrain on the trailing hemisphere of Rhea. An orthographic view is most like the view seen by a distant observer looking through a telescope. The views have been rotated so that north on Rhea is up. The smaller view at left is centered at 21 degrees north latitude, 229 degrees west longitude. Resolution in this mosaic is 450 meters (1,476 feet) per pixel. The images were acquired at a distance that ranged from about 51,200 to 46,600 miles (82,100 to 74,600 kilometers) from Rhea. The larger view at right is centered at 9 degrees north latitude, 254 degrees west longitude. Resolution in this mosaic is 300 meters (984 feet) per pixel. The images were acquired at a distance that ranged from about 36,000 to 32,100 miles (57,900 to 51,700 kilometers) from Rhea. The mosaics each consist of multiple narrow-angle camera (NAC) images with data from the wide-angle camera used to fill in areas where NAC data was not available. The image was produced by Heike Rosenberg and Tilmann Denk at Freie Universität in Berlin, Germany. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19057
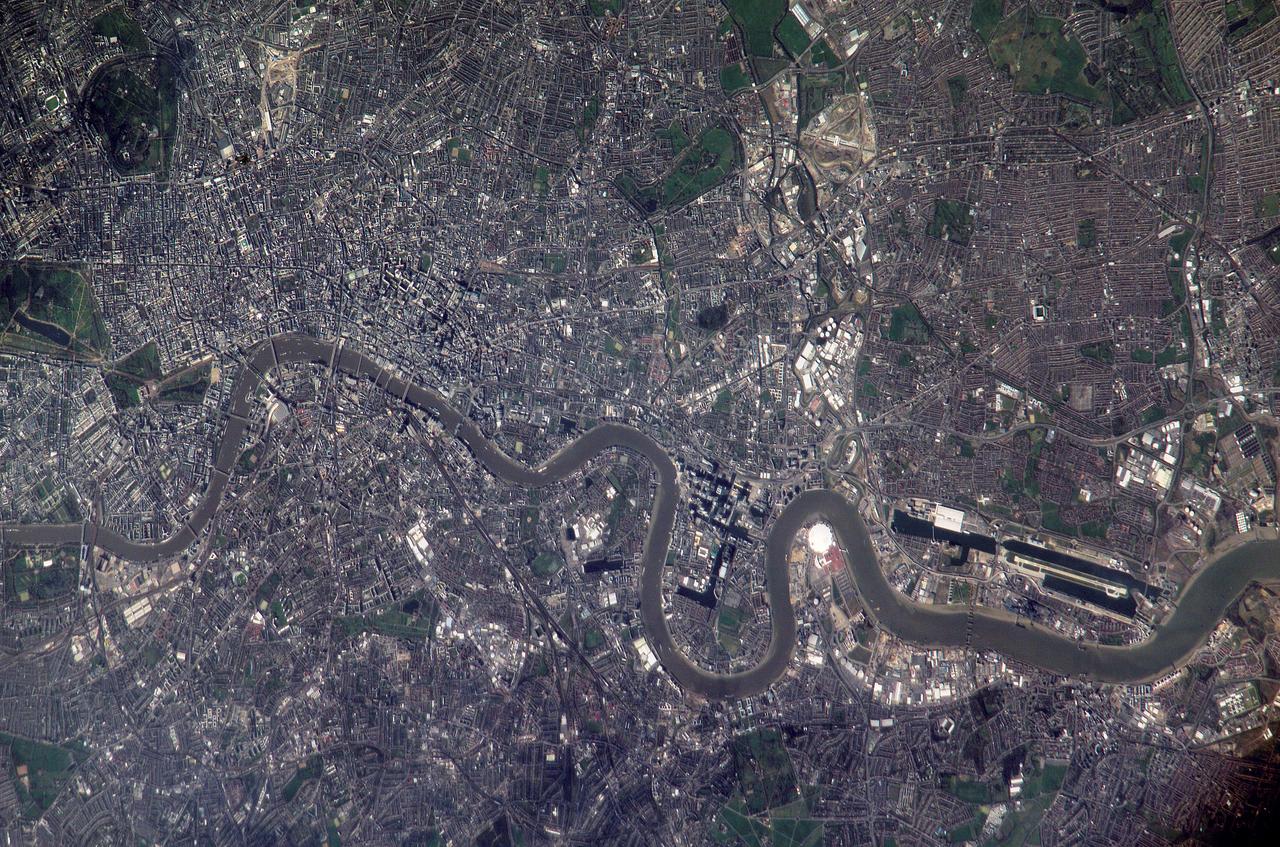

ISS010-E-22495 (2 April 2005) --- Numerous recognizable features appear in this detailed view of London, United Kingdom, photographed by an Expedition 10 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). The photographer had to look back along track for the shot, from a position over northern Germany. The most striking visual features are green open spaces such as Regent’s Park, Hyde Park and St. James’s Park east of Buckingham Palace. Many smaller parks indicate why Londoners are proud of being able to walk miles through the city mainly on grass. The River Thames—with its bridges and barges (some of the more than 14,000 craft registered to sail the Thames)—is the axis upon which the city was founded in Roman times. The relatively small area known as the City of London coincides with the ancient walled Roman city of Londinium on the north bank of the river (the line of the wall is marked closely for almost its entire length by modern streets), and includes St. Paul’s Cathedral near where the Roman temple stood. For scale, the river is 265 meters wide near St. Paul’s. The City is the financial center while Westminster is the center of government, including the Houses of Parliament and Downing Street, where the British Prime Minister lives. Several large structures visible in this image are railroad stations; three serving areas north of London (Euston, St. Pancras and King’s Cross), and Waterloo Station serving southern Britain. The London Eye, a famous Ferris wheel 140 meters high, is situated on an oval island in the River Thames, visible just west of Waterloo Station. Many larger buildings can also be identified, partly because they cast shadows—Buckingham Palace, St Paul’s Cathedral, and the Tate Modern art museum (a converted power station, the 99-meter chimney was designed to fall just short of the crest of St Paul’s dome).

S73-35082 (July-Sept. 1973) --- A near vertical view of a portion of west Africa ravaged by drought for the past five years is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The semi-desert scene is in southeastern Niger about 200 nautical miles east-northeast of the capital city of Niamey. A polygonal-shaped area (dark) in the lower right corner of the picture represents a range-management ranch. The dry stream beds trending diagonally across the photograph locally contain some water or vegetation (green). The beds are sources of water through shallow drilling and contain soils suitable for production of crops. The variety of tans, browns and grays are typical desert colors that represent barren rocks and soil or sand-filled ancient stream valleys. Absence of vegetation is the singular feature of the area. Dr. G. Stuckmann of the Geographic Institute, University of Technology, Mannover, Federal Republic of Germany, will use this photograph in the study of the hydrologic regime of the region through analysis of fossil drainage patterns, geological structures and accumulations of surface water. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. (Alternate number SL3-86-166) Photo credit: NASA
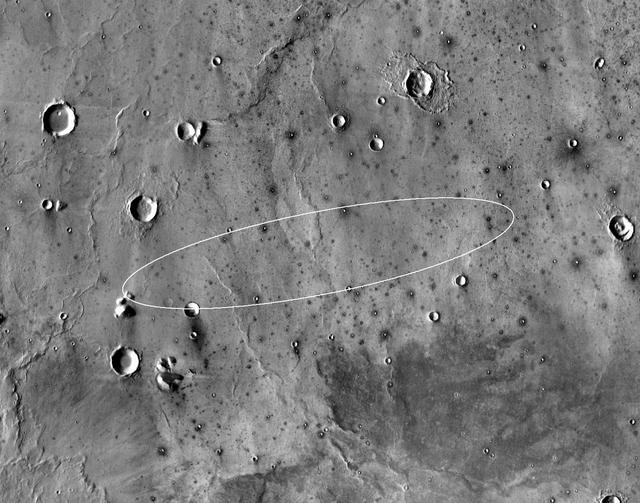

This map shows the single area under continuing evaluation as the InSight mission's Mars landing site, as of a year before the mission's May 2016 launch. The finalist ellipse marked within the northern portion of flat-lying Elysium Planitia is centered at about 4.5 degrees north latitude and 136 degrees east longitude. InSight -- an acronym for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport -- will study the interior of Mars to improve understanding of the processes that formed and shaped rocky planets, including Earth. The mission's launch period begins March 4, 2016, and lasts until late March. Whichever day during that period the launch occurs, landing is scheduled for Sept. 28, 2016. The landing ellipse on this map covers an area within which the spacecraft has about 99 percent chance of landing when targeted for the center of the ellipse. It is about 81 miles (130 kilometers) long, generally west to east, and about 17 miles (27 kilometers) wide. This ellipse covers the case of a launch at the start of the launch period. If the launch occurs later in the period, orientation of the landing ellipse would shift slightly clockwise. Four semifinalist sites in Elysium Planitia were evaluated as safe for InSight landing. This one was selected as having the largest proportion of its area classified as smooth terrain. If continuing analysis identifies unexpected problems with this site, another of the semifinalists could be reconsidered before final selection later this year. The InSight lander will deploy two instruments directly onto the ground using a robotic arm. One is a seismometer contributed by France's space agency (CNES) with components from Germany, Switzerland, the United Kingdom and the United States. The seismometer will measure microscopic ground motions, providing detailed information about the interior structure of Mars. The other instrument to be deployed by the arm is a heat-flow probe contributed by the German Aerospace Center (DLR), designed to hammer itself three to five meters (about 10 to 16 feet) deep. It will monitor heat coming from the planet's interior. The mission will also track the lander's radio to measure wobbles in the planet's rotation that relate to the size of its core. A suite of environmental sensors will monitor the weather and variations in the magnetic field. The base map is a mosaic of daytime thermal images from the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) on NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter. THEMIS was developed and is operated by Arizona State University, Tempe. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19143
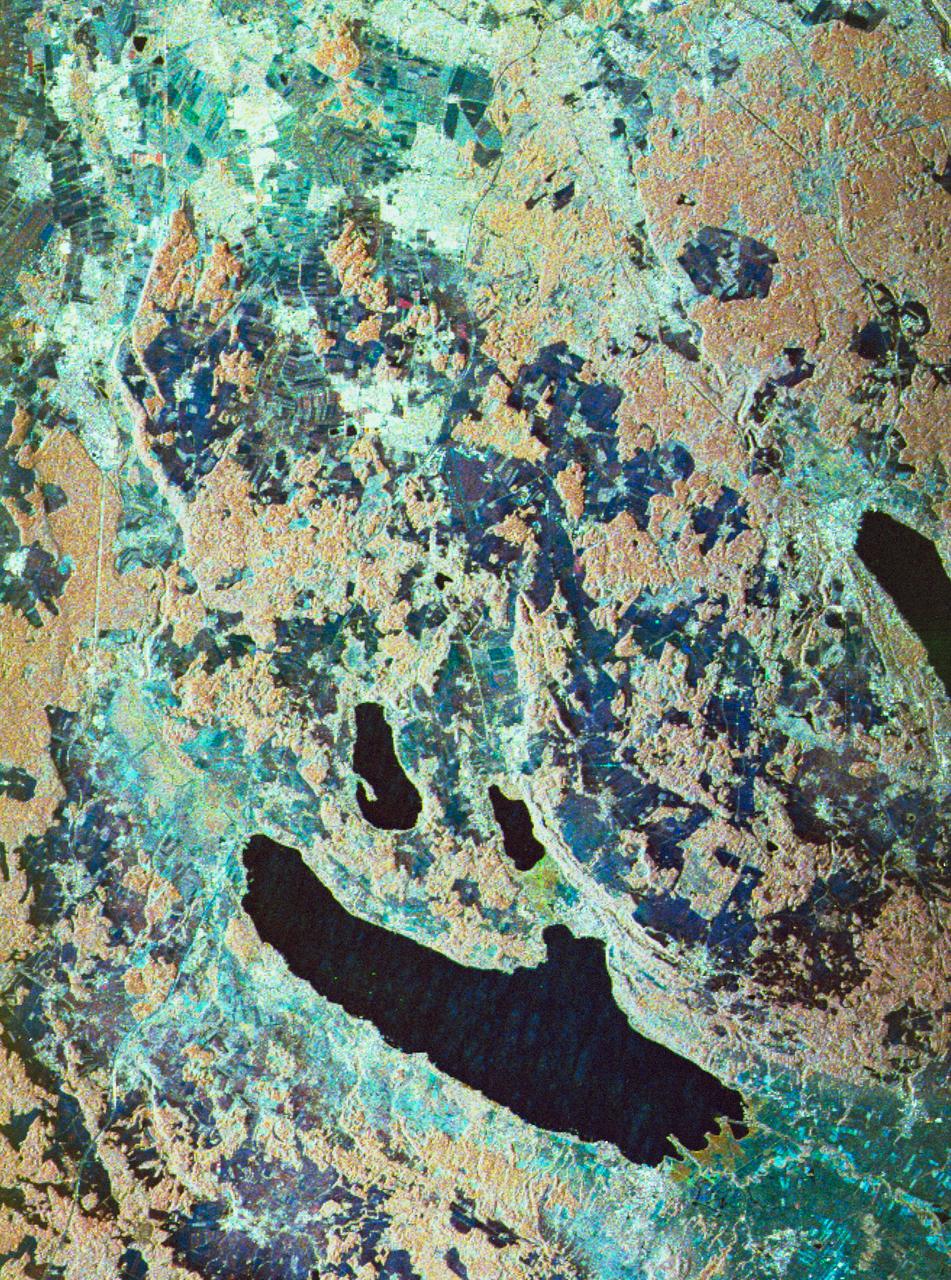
STS059-S-080 (18 April 1994) --- This is a false-color three frequency image of the Oberpfaffenhofen supersite, an area just south-west of Munich in southern Germany. The colors show the different conditions that the three radars (X-Band, C-Band and L-Band) can see on the ground. The image covers a 27 by 36 kilometer area. The center of the site is 48.09 degrees north and 11.29 degrees east. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on April 11, 1994. The dark area on the left is Lake Ammersee. The two smaller lakes are the Woerthsee and the Pilsensee. On the bottom is the tip of the Starnbergersee. The city of Munich is located just beyond the right of the image. The Oberpfaffenhofen supersite is the major test site for SIR-C/X-SAR calibration and scientific investigations concerning agriculture, forestry, hydrology and geology. This color composite image is a three frequency overlay. L-Band total power was assigned red, the C-Band total power is shown in green and the X-Band VV polarization appears blue. The colors on the image stress the differences between the L-Band, C-Band, X-Band images. If the three radar antennas were getting an equal response from objects on the ground, this image would appear in black and white. However, in this image, the blue areas corresponds to area for which the X-Band backscatter is relatively higher than the backscatter at L and C-Bands. This behavior is characteristic of grasslands, clear cuts and shorter vegetation. Similarly, the forested areas have a reddish tint (L-Band). The green areas seen near both the Ammersee and the Pilsensee lakes indicate marshy areas. The agricultural fields in the upper right hand corner appear mostly in blue and green (X-Band and C-Band). The white areas are mostly urban areas, while the smooth surfaces of the lakes appear very dark. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43930