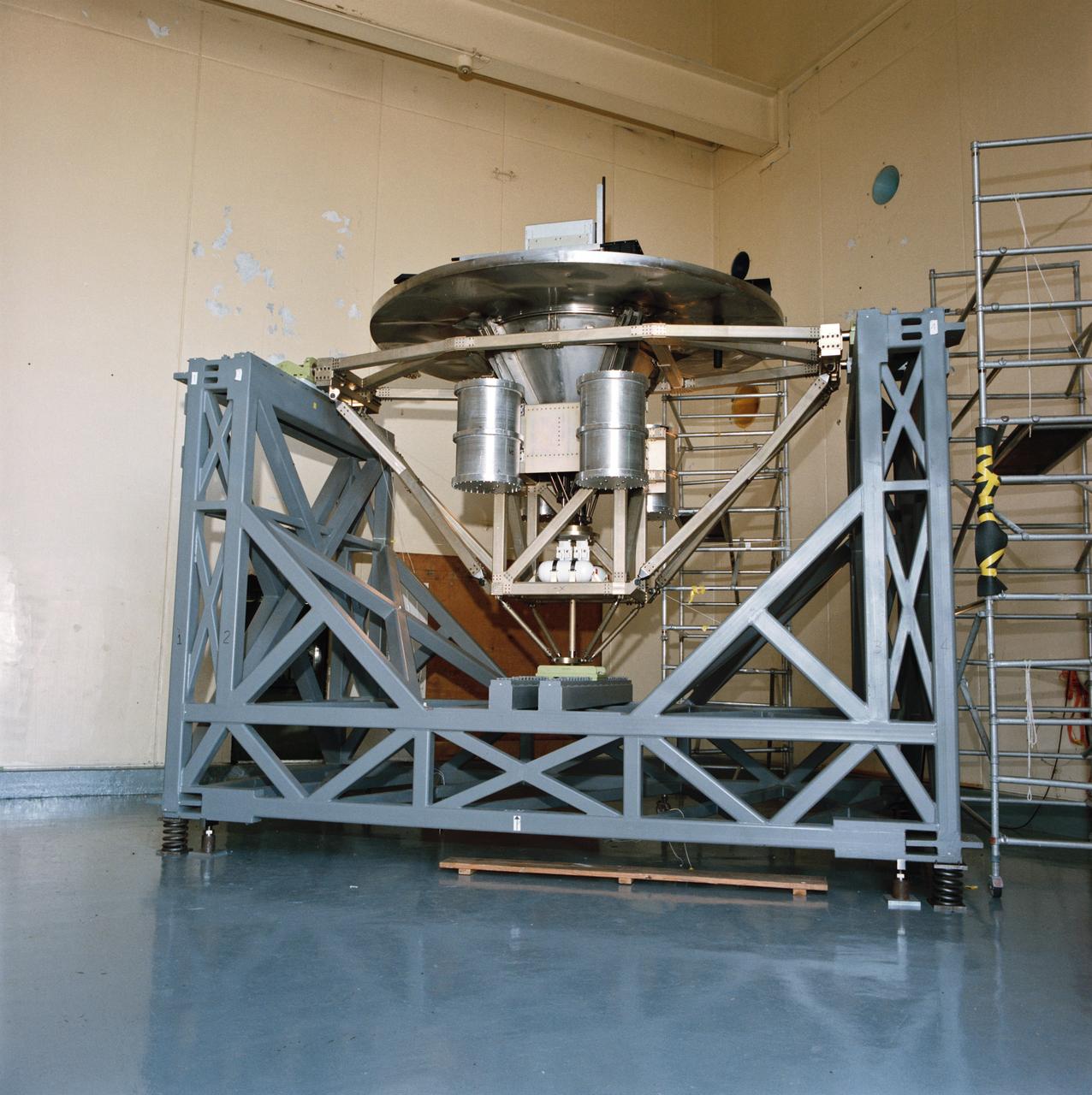

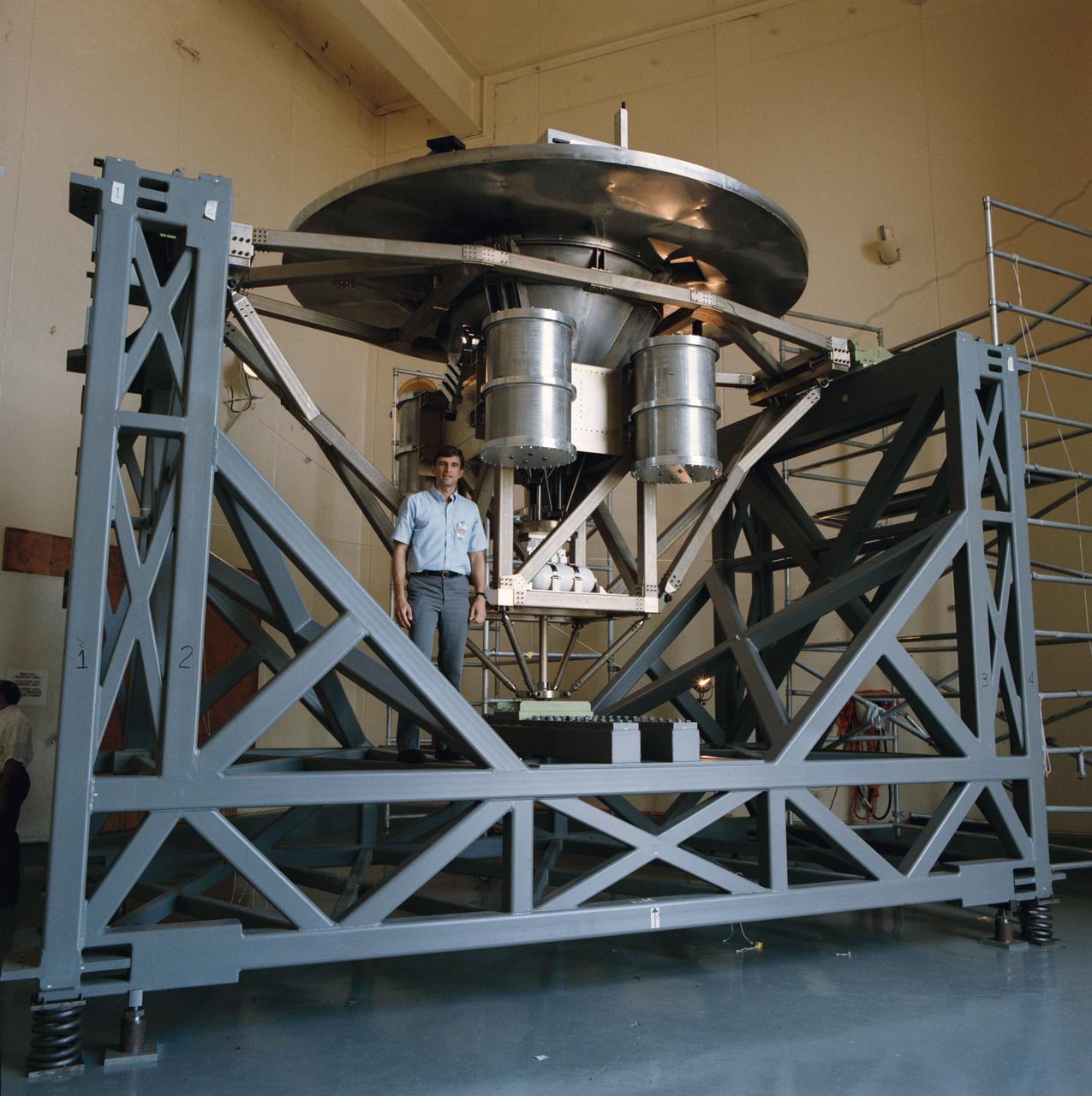
Pictured on a test stand at JSC is the Wake Shield Facility scheduled to fly on STS-60.
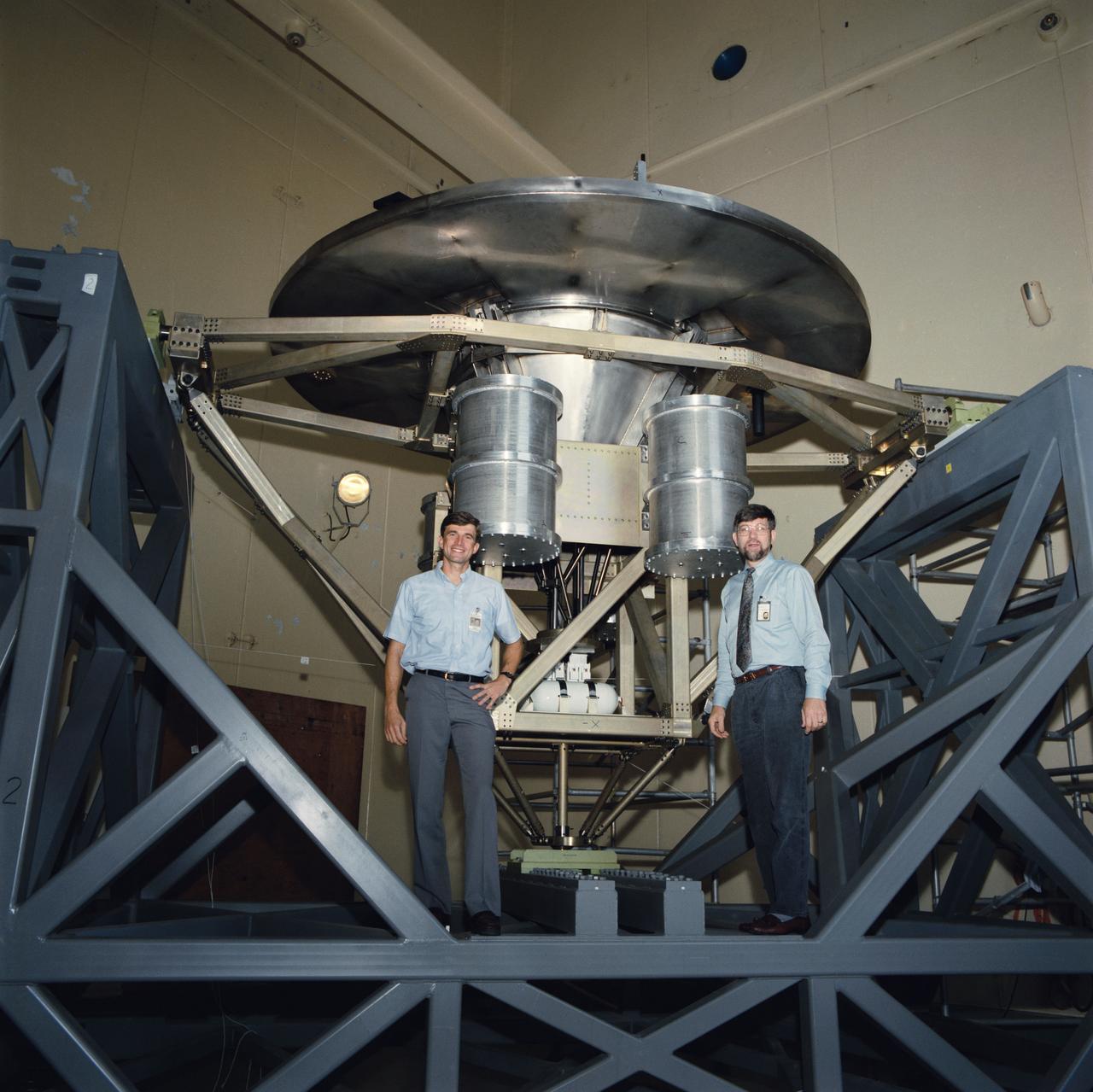

The Wake Shield Facility is displayed on a test stand at JSC. Astronaut Ronald M. Sega, mission specialist for STS-60, is seen with the facility during a break in testing in the acoustic and vibration facility at JSC.
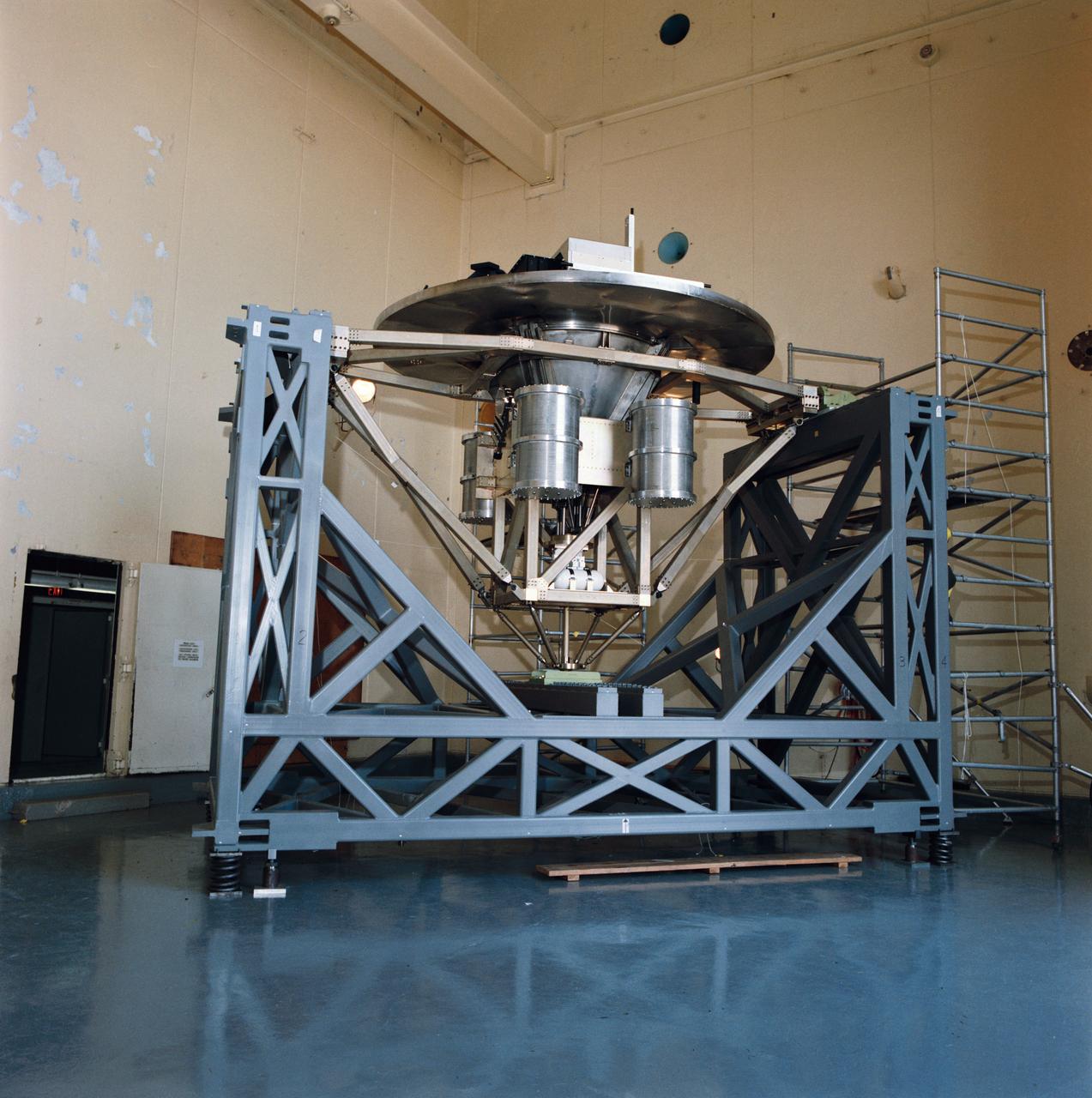

Pictured on a test stand at JSC is the Wake Shield Facility scheduled to fly on STS-60.
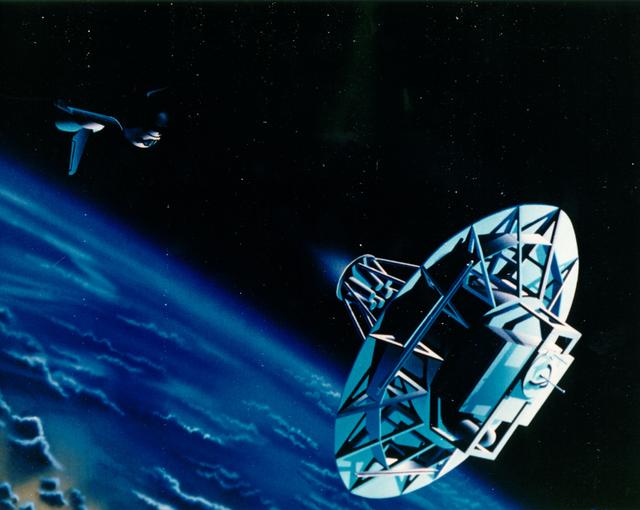

The Wake Shield Facility is a free-flying research and development facility that is designed to use the pure vacuum of space to conduct scientific research in the development of new materials. The thin film materials technology developed by the WSF could some day lead to applications such as faster electronics components for computers. The WSF Free-Flyer is a 12-foot-diameter stainless steel disk that, while traveling in orbit at approximately 18,000 mph, leaves in its wake a vacuum 1,000 to 10,000 times better than the best vacuums currently achieved on Earth. While it is carried into orbit by the Space Shuttle, the WSF is a fully equipped spacecraft in its own right, with cold gas propulsion for separation from the orbiter and a momentum bias attitude control system. All WSF functions are undertaken by a spacecraft computer with the WSF remotely controlled from the ground. The ultra vacuum, nearly empty of all molecules, is then used to conduct a series of thin film growths by a process called epitaxy which produces exceptionally pure and atomically ordered thin films of semiconductor compounds such as gallium arsenide. Using this process, the WSF offers the potential of producing thin film materials, and the devices they will make possible.
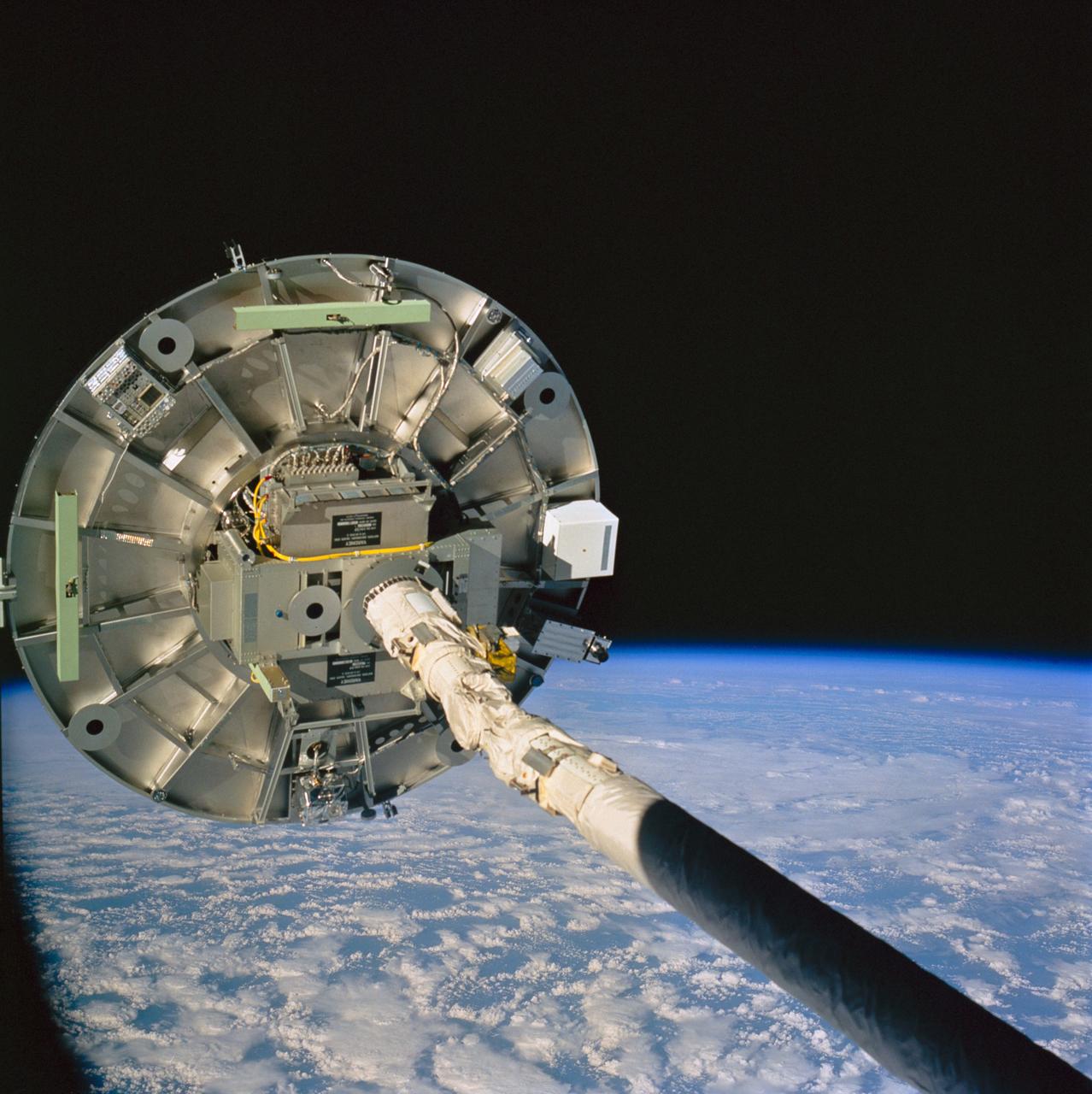

STS060-76-095 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The ram side of the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm is featured in this 70mm frame. Clouds over the Atlantic Ocean and the blackness of space share the backdrop for the picture. Five NASA astronauts and a Russian cosmonaut spent eight days in Earth orbit in support of the STS-60 mission.
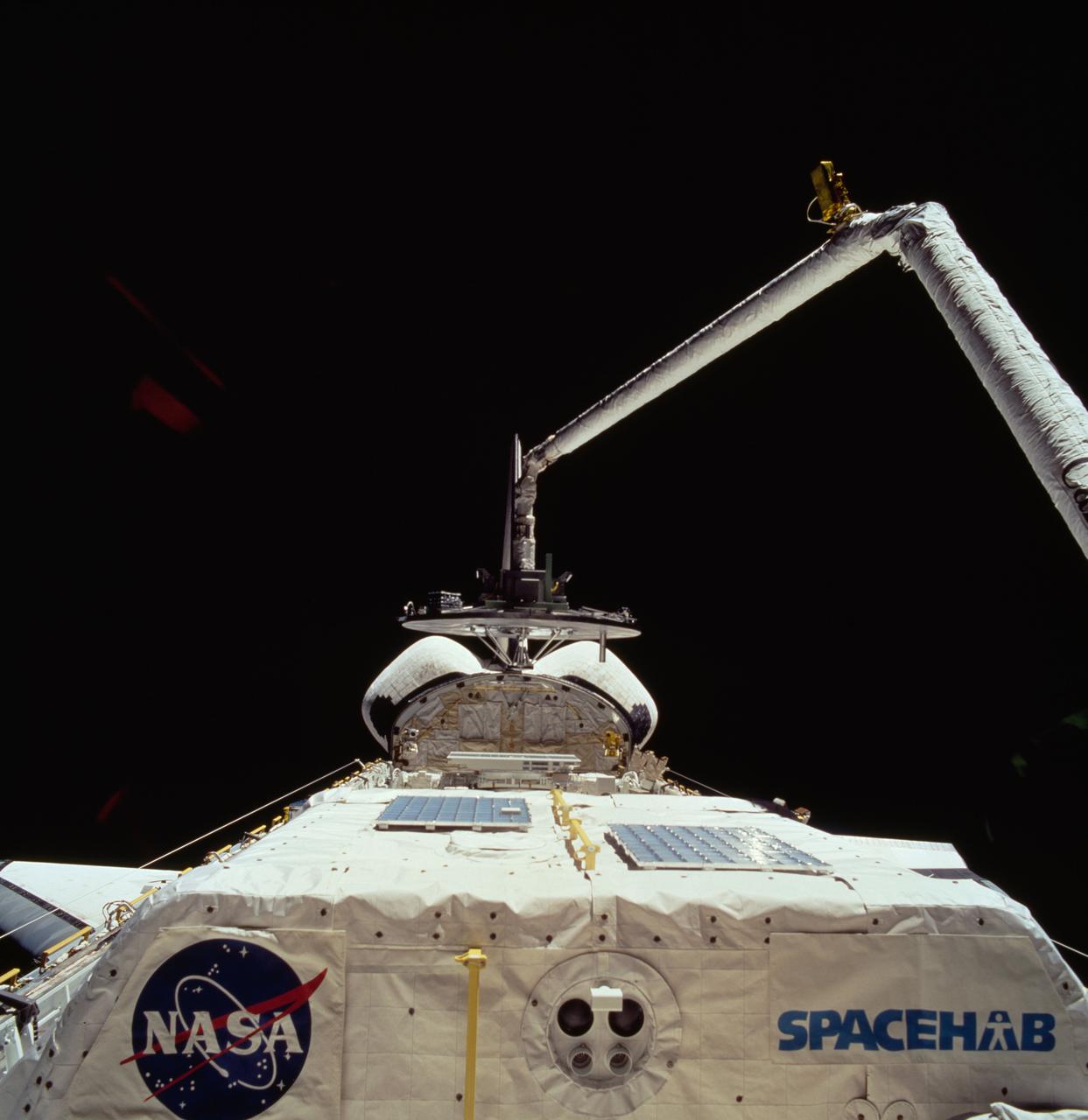

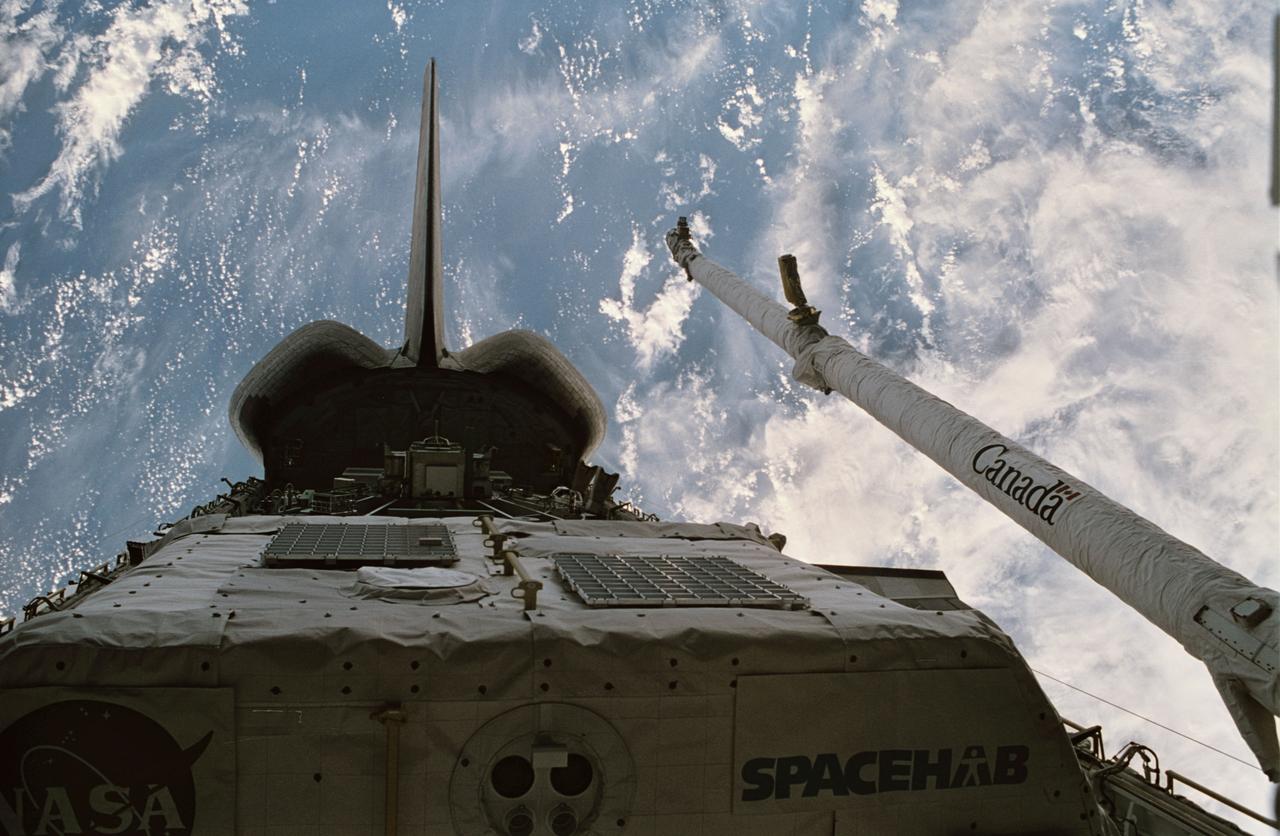
STS060-74-054 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The Wake Shield Facility (WSF) is held in the grasp of Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The 70mm image, backdropped against the blackness of space, also shows the SPACEHAB module in the forward cargo area.

Astronaut Ronald M. Sega stands beside the University of Houston's Wake Shield Facility before it undergoes a Modal Survey Test in the Vibration and Acoustic Test Facility Building 49, prior to being flown on space shuttle mission STS-60.
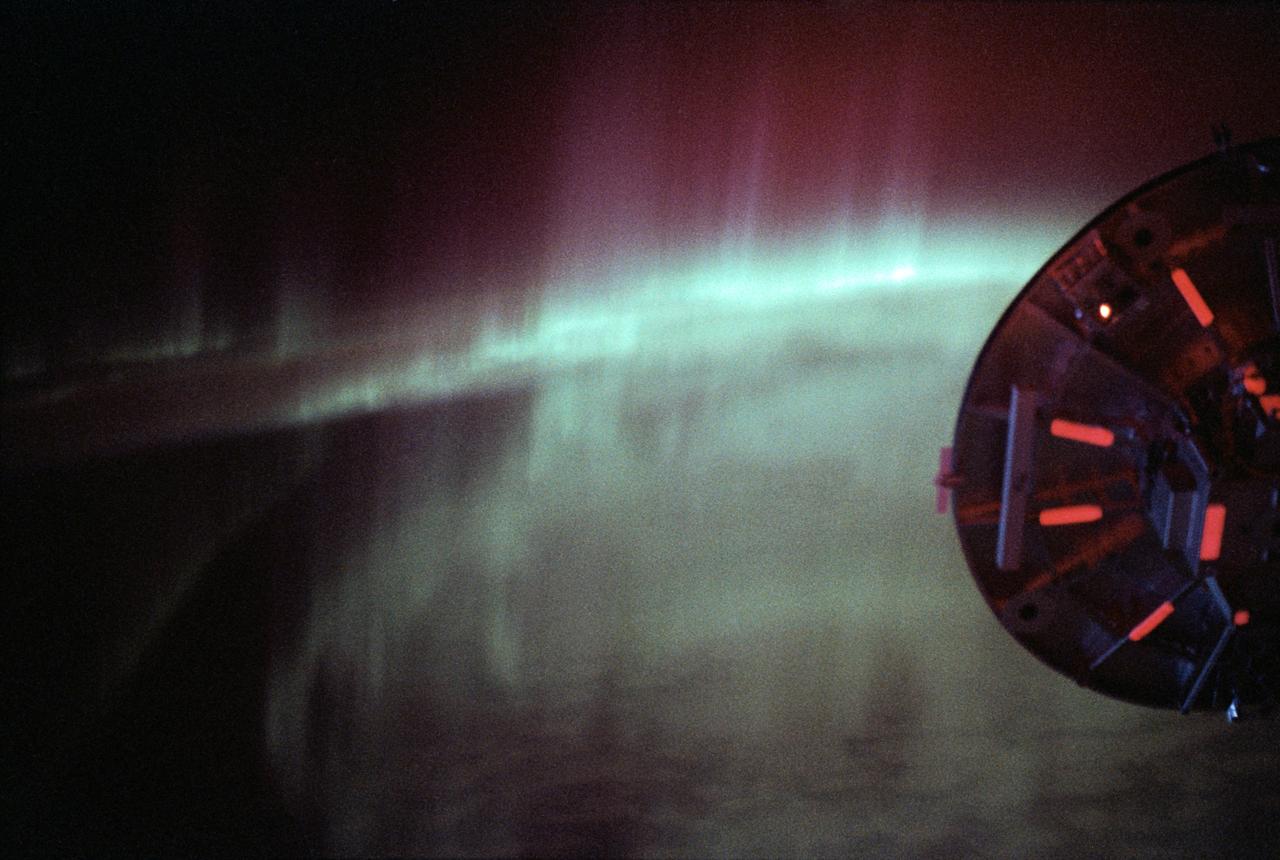
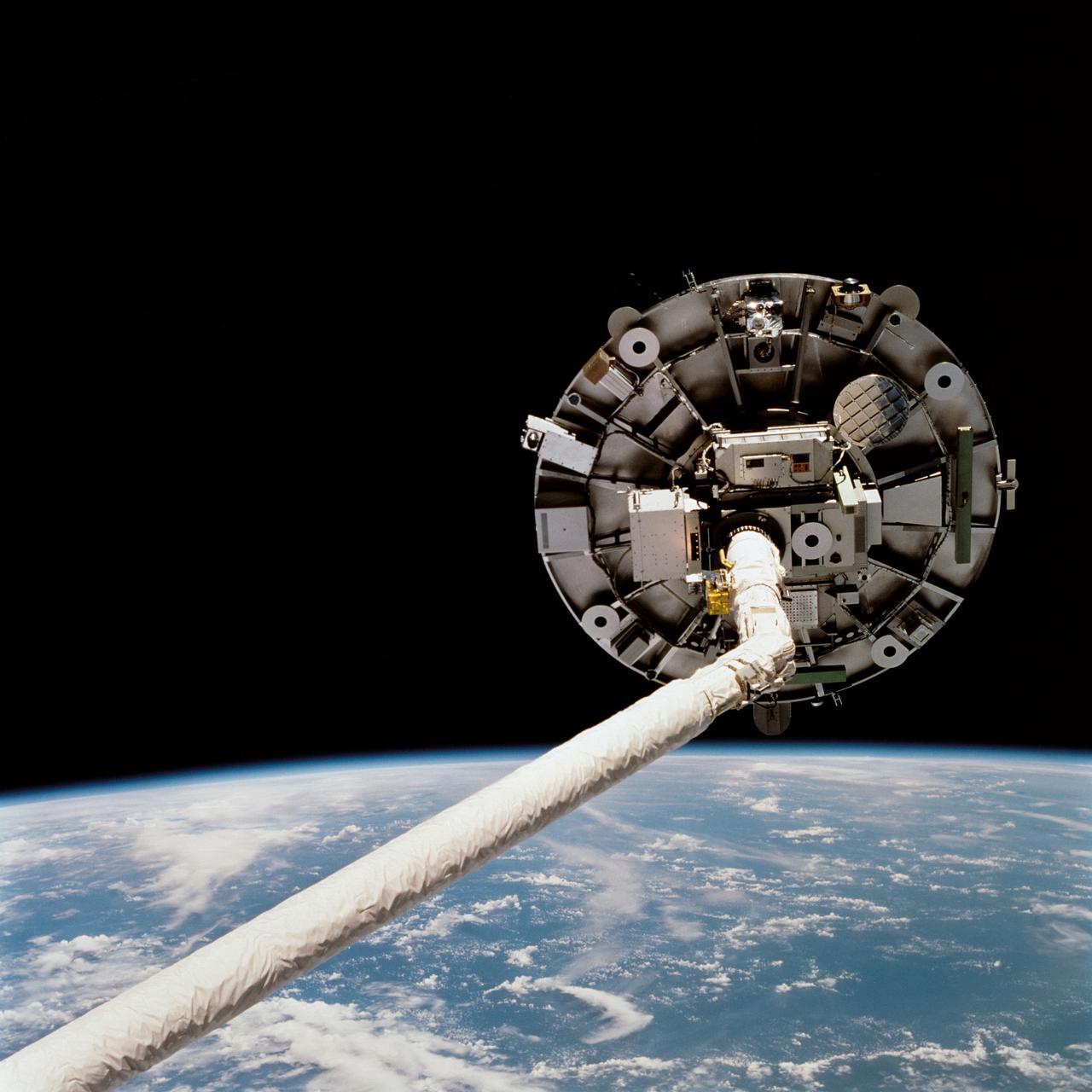
STS060-09-024 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- As the Space Shuttle Discovery flew over a point between New Zealand and Australia, one of the STS-60 crew members used a 35mm camera to capture this image featuring three-fourths of the disc of the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) back dropped against the Southern Lights. The WSF was in the grasp of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) end effector (out of frame at right).

STS069-723-072 (11 September 1995) --- Prior to being released by Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) for a period of time, the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) is backdropped against the darkness of space over a blue and white Earth. The picture was taken shortly after midnight Houston time on September 11, 1995. The Endeavour, with a five-member crew, launched on September 7, 1995, from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and ended its mission there on September 18, 1995, with a successful landing on Runway 33. The multifaceted mission carried a crew of astronauts David M. Walker, mission commander; Kenneth D. Cockrell, pilot; and James S. Voss (payload commander), James H. Newman and Michael L. Gernhardt, all mission specialists.
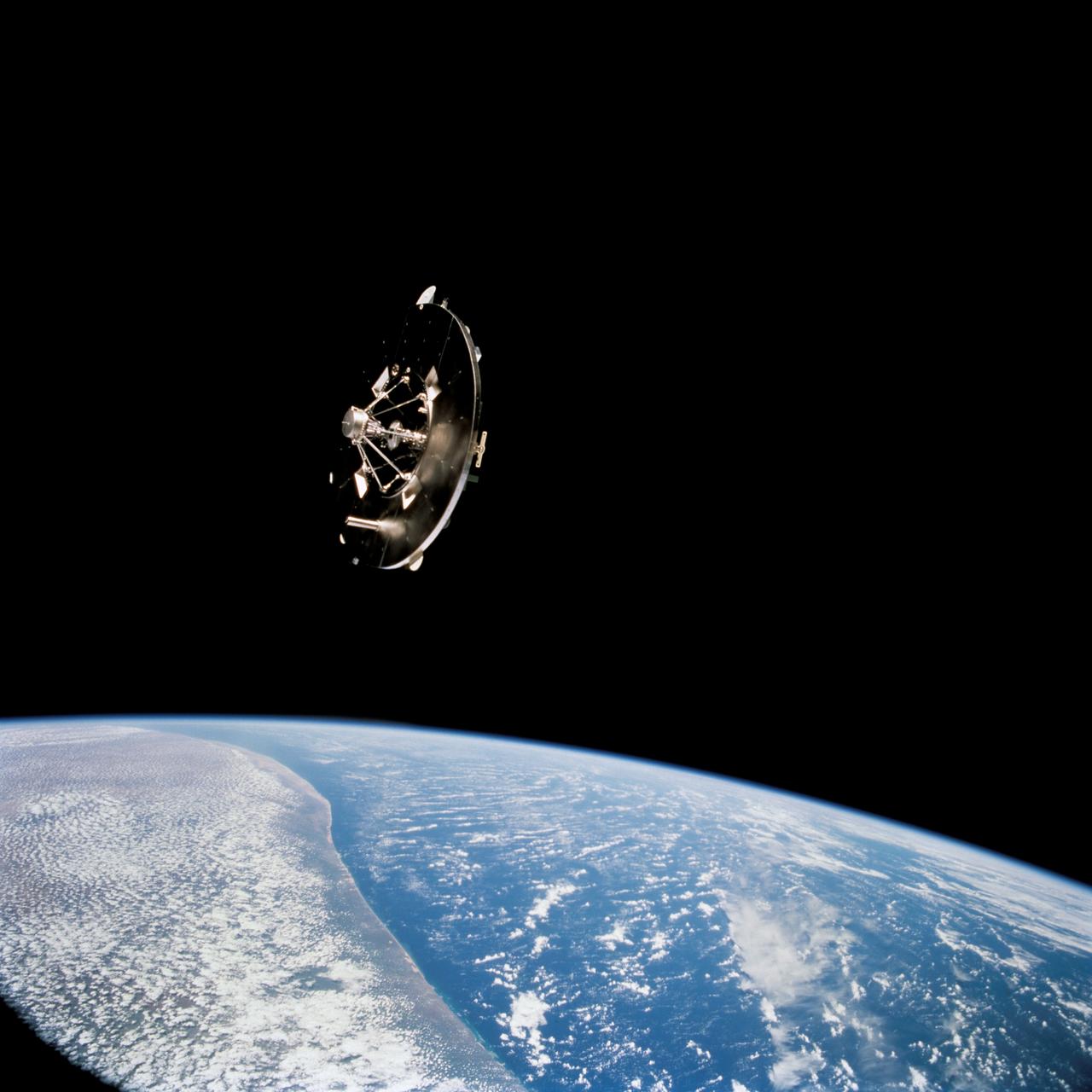

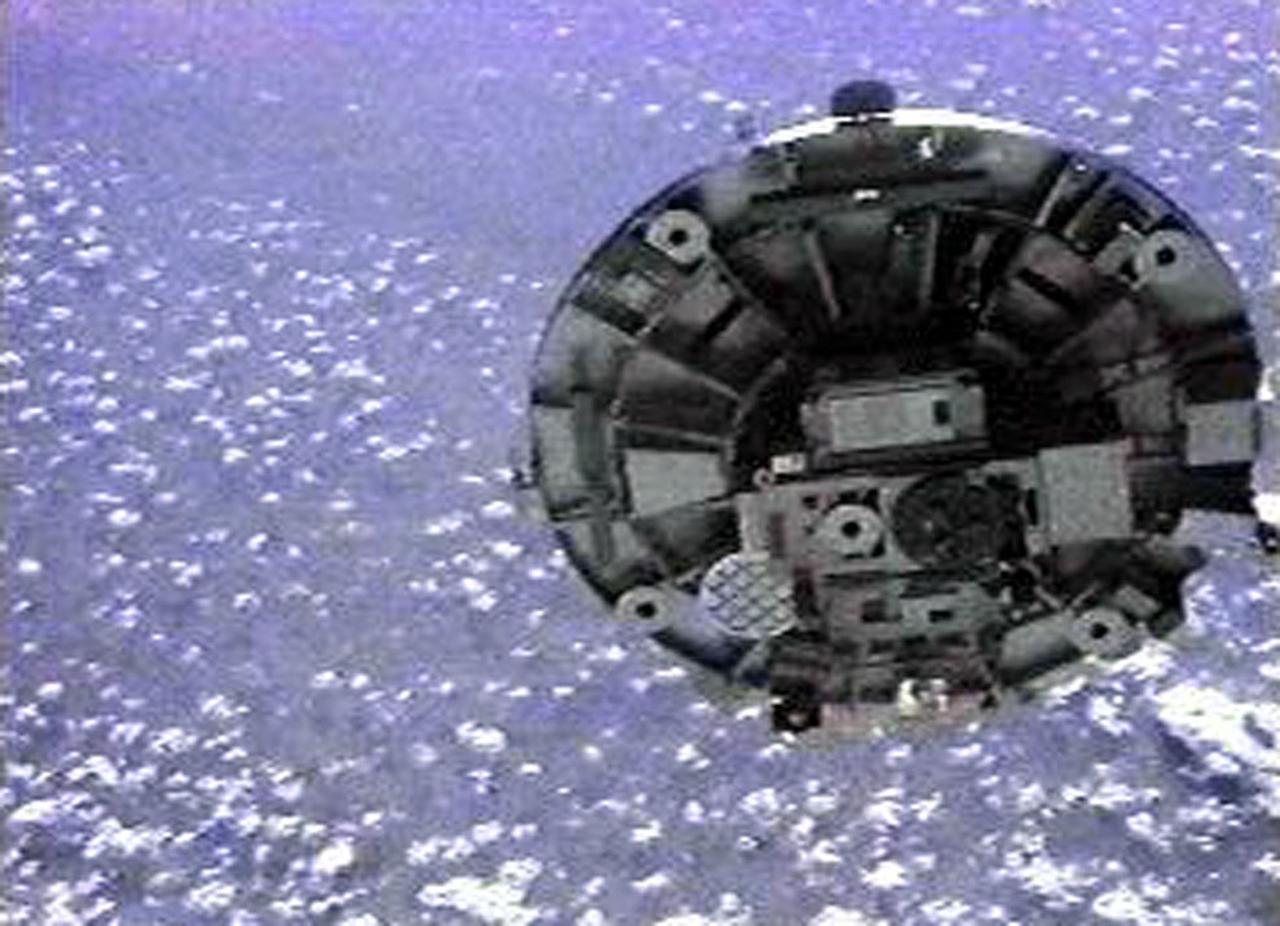
STS069-732-048 (11 September 1995) --- Having earlier been released by the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS), the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) moves away from the Space Shuttle. The coast of Somalia can be seen in the lower left quadrant of the frame. STS-69 and the Space Shuttle Endeavour, with a five-member crew, launched on September 7, 1995, from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and ended its mission there on September 18, 1995, with a successful landing on Runway 33. The multifaceted mission carried a crew of astronauts David M. Walker, mission commander; Kenneth D. Cockrell, pilot; and James S. Voss (payload commander), James H. Newman and Michael L. Gernhardt, all mission specialists.
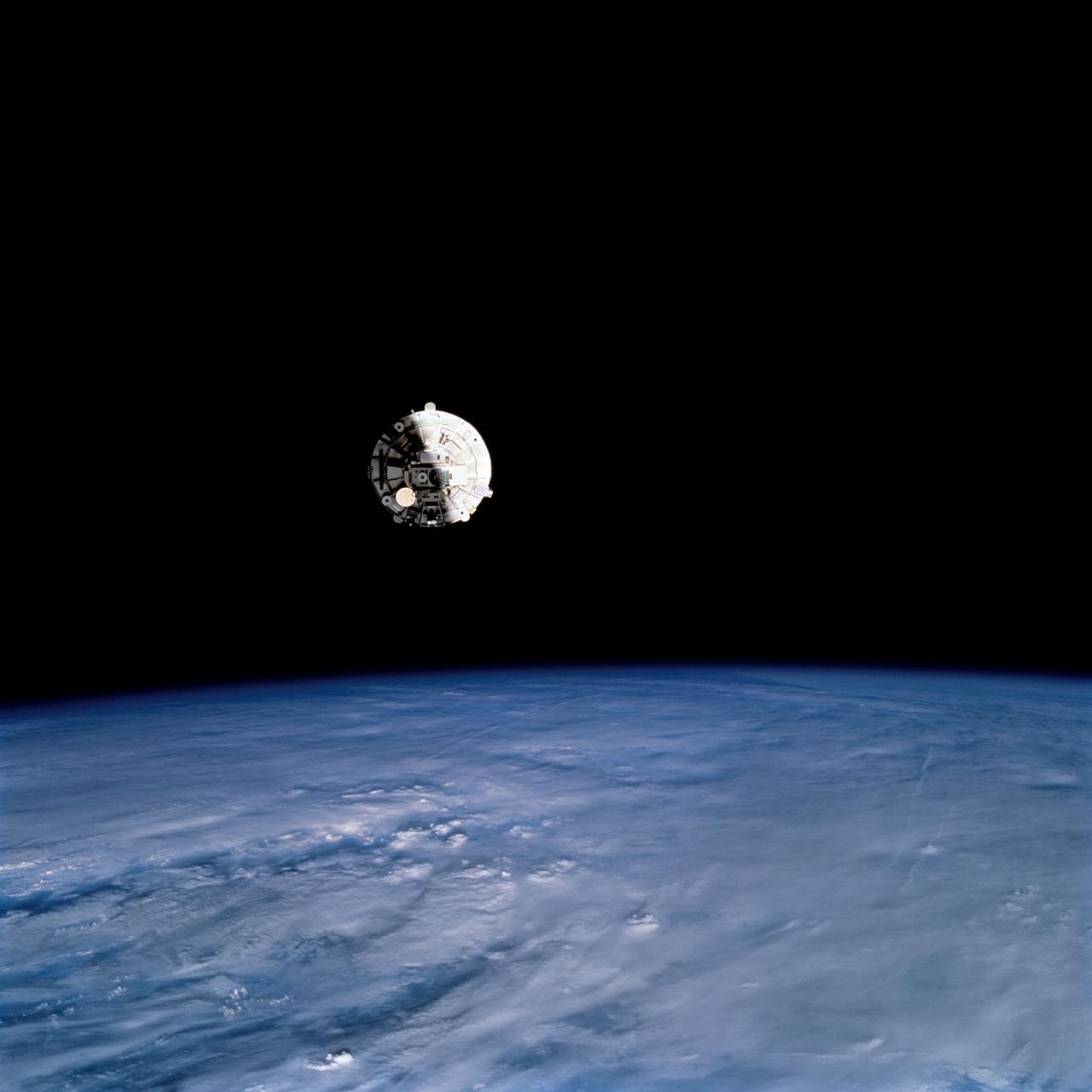

STS069-724-095 (7-18 September 1995) --- Prior to being re-captured by Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS), the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) was recorded on film, backdropped against the darkness of space over a heavily cloud-covered Earth. Endeavour, with a five-member crew, launched on September 7, 1995, from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and ended its mission there on September 18, 1995, with a successful landing on Runway 33. The multifaceted mission carried a crew of astronauts David M. Walker, mission commander; Kenneth D. Cockrell, pilot; and James S. Voss (payload commander), James H. Newman and Michael L. Gernhardt, all mission specialists.
Space Vacuum Epitaxy Center works with industry and government laboratories to develop advanced thin film materials and devices by utilizing the most abundant free resource in orbit: the vacuum of space. SVEC, along with its affiliates, is developing semiconductor mid-IR lasers for environmental sensing and defense applications, high efficiency solar cells for space satellite applications, oxide thin films for computer memory applications, and ultra-hard thin film coatings for wear resistance in micro devices. Performance of these vacuum deposited thin film materials and devices can be enhanced by using the ultra-vacuum of space for which SVEC has developed the Wake Shield Facility---a free flying research platform dedicated to thin film materials development in space.
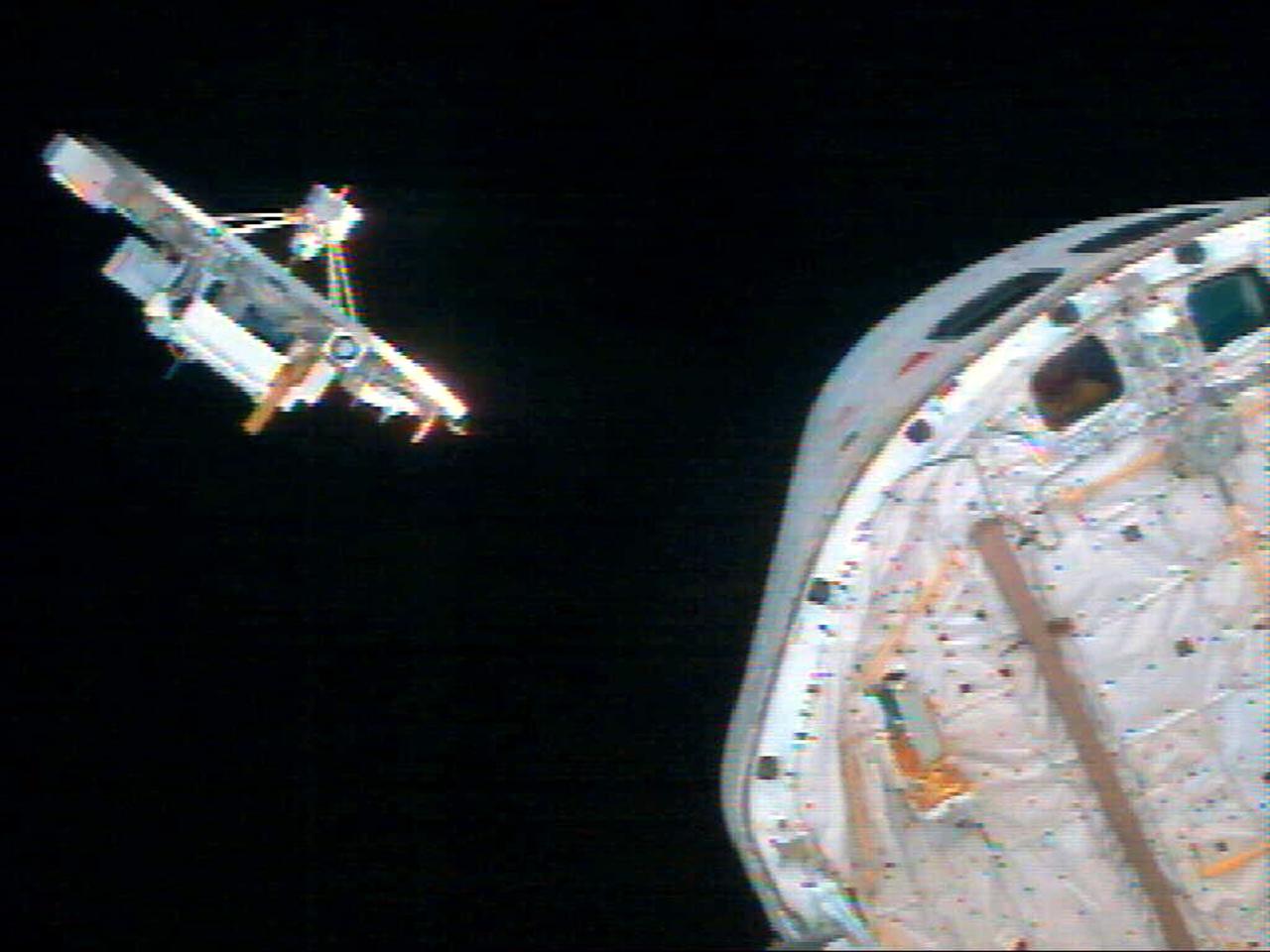

Space Vacuum Epitaxy Center works with industry and government laboratories to develop advanced thin film materials and devices by utilizing the most abundant free resource in orbit: the vacuum of space. SVEC, along with its affiliates, is developing semiconductor mid-IR lasers for environmental sensing and defense applications, high efficiency solar cells for space satellite applications, oxide thin films for computer memory applications, and ultra-hard thin film coatings for wear resistance in micro devices. Performance of these vacuum deposited thin film materials and devices can be enhanced by using the ultra-vacuum of space for which SVEC has developed the Wake Shield Facility---a free flying research platform dedicated to thin film materials development in space.
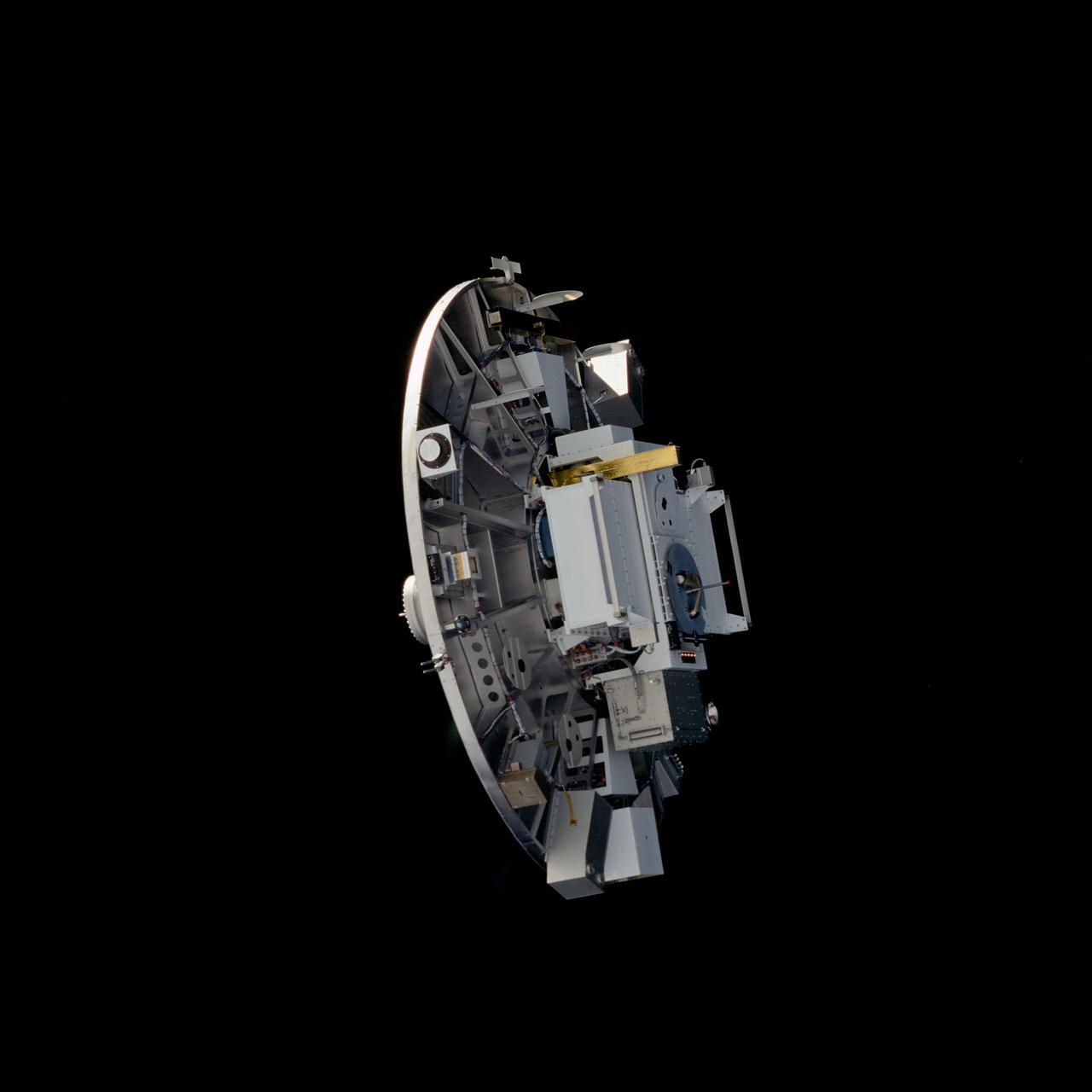
STS080-755-016 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Taken with a 70mm handheld camera, this photograph captures the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) in free flight backdropped against the blackness of space.

STS080-762-049 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Taken with a 70mm handheld camera, this photograph captures the berthing by the space shuttle Columbia's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Wake Shield Facility (WSF).
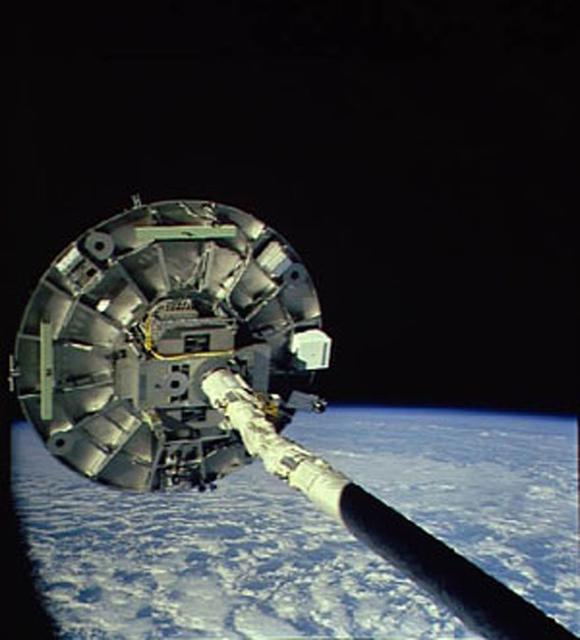

The Wake Shield Facility (WSF) is a free-flying research and development facility that is designed to use the pure vacuum of space to conduct scientific research in the development of new materials. The thin film materials technology developed by the WSF could some day lead to applications such as faster electronics components for computers.
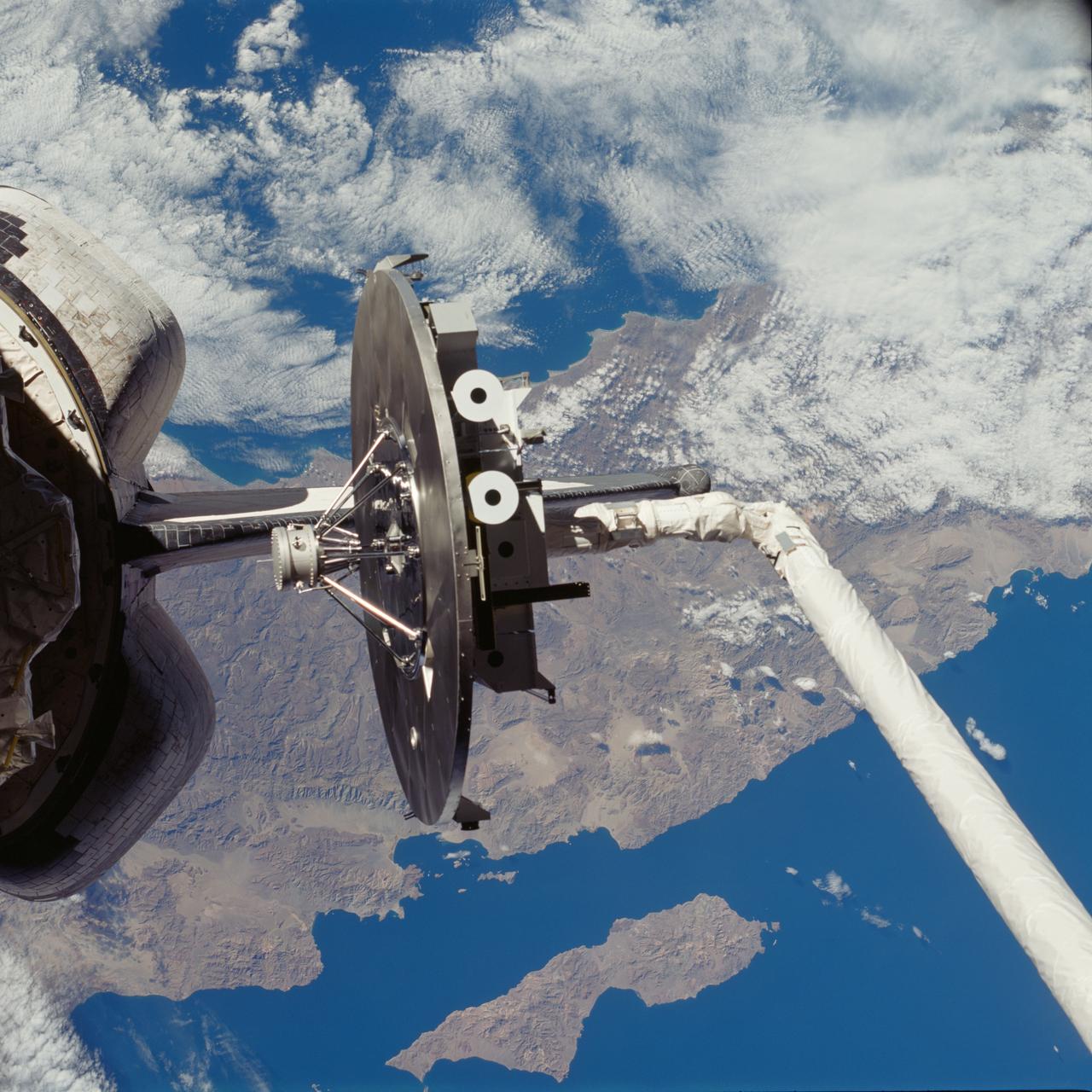

STS080-708-065 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Backdropped against part of Baja California, the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) is about to be re-berthed in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia. Columbia's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) was used extensively during operations with the experiment.
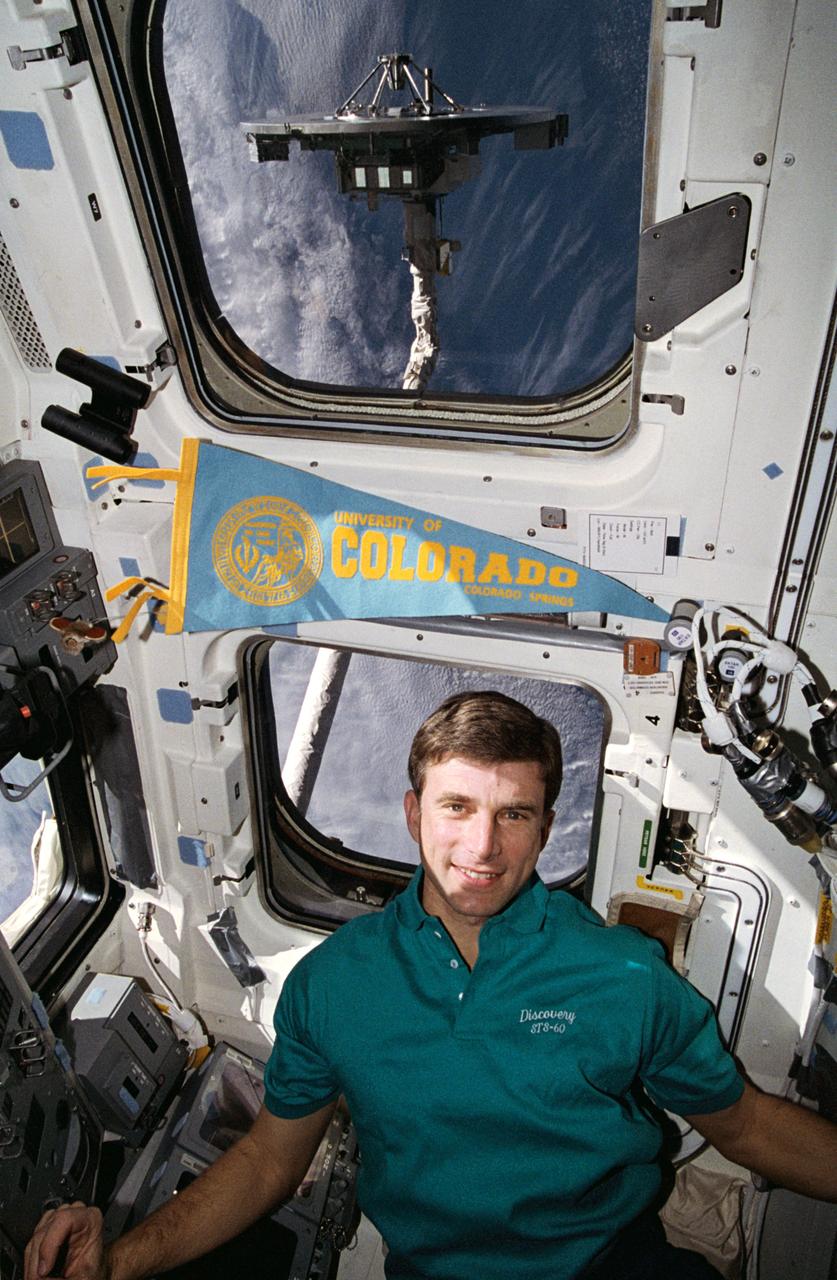

STS060-57-033 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- Astronaut Ronald M. Sega suspends himself in the weightlessness aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery's crew cabin, as the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm holds the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) aloft. The mission specialist is co-principal investigator on the WSF project.

STS080-334-002 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Cockrell, STS-80 mission commander, looks through a window on the space shuttle Columbia's aft flight deck during rendezvous operations with the Wake Shield Facility (WSF).
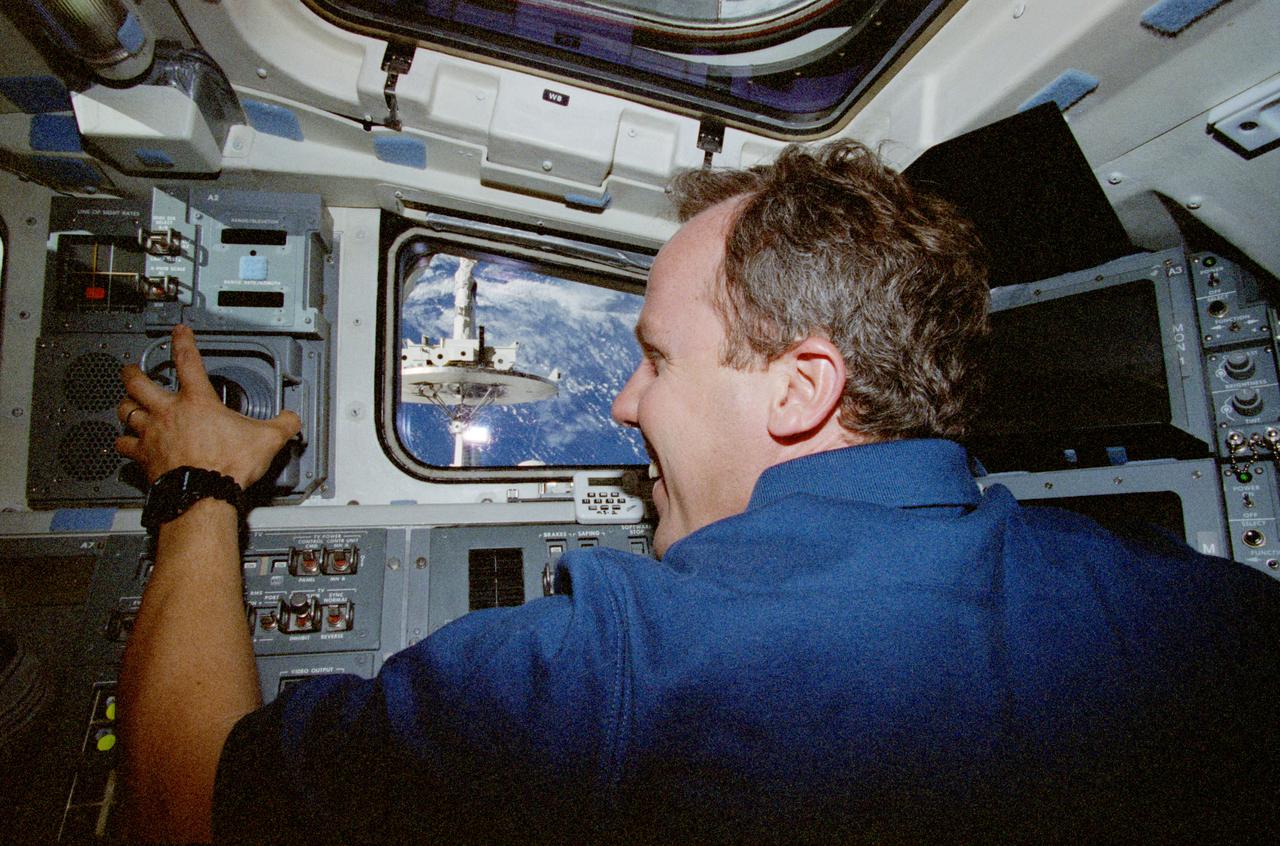

STS080-337-026 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-80 mission specialist, uses the controls of the space shuttle Columbia's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) to conduct a test with the captured Wake Shield Facility (WSF) seen through window at frame center.

Designed by the mission crew members, the patch for STS-69 symbolizes the multifaceted nature of the flight's mission. The primary payload, the Wake Shield Facility (WSF), is represented in the center by the astronaut emblem against a flat disk. The astronaut emblem also signifies the importance of human beings in space exploration, reflected by the planned space walk to practice for International Space Station (ISS) activities and to evaluate space suit design modifications. The two stylized Space Shuttles highlight the ascent and entry phases of the mission. Along with the two spiral plumes, the stylized Space Shuttles symbolize a NASA first, the deployment and recovery on the same mission of two spacecraft (both the Wake Shield Facility and the Spartan). The constellations Canis Major and Canis Minor represent the astronomy objectives of the Spartan and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH) payload. The two constellations also symbolize the talents and dedication of the support personnel who make Space Shuttle missions possible.
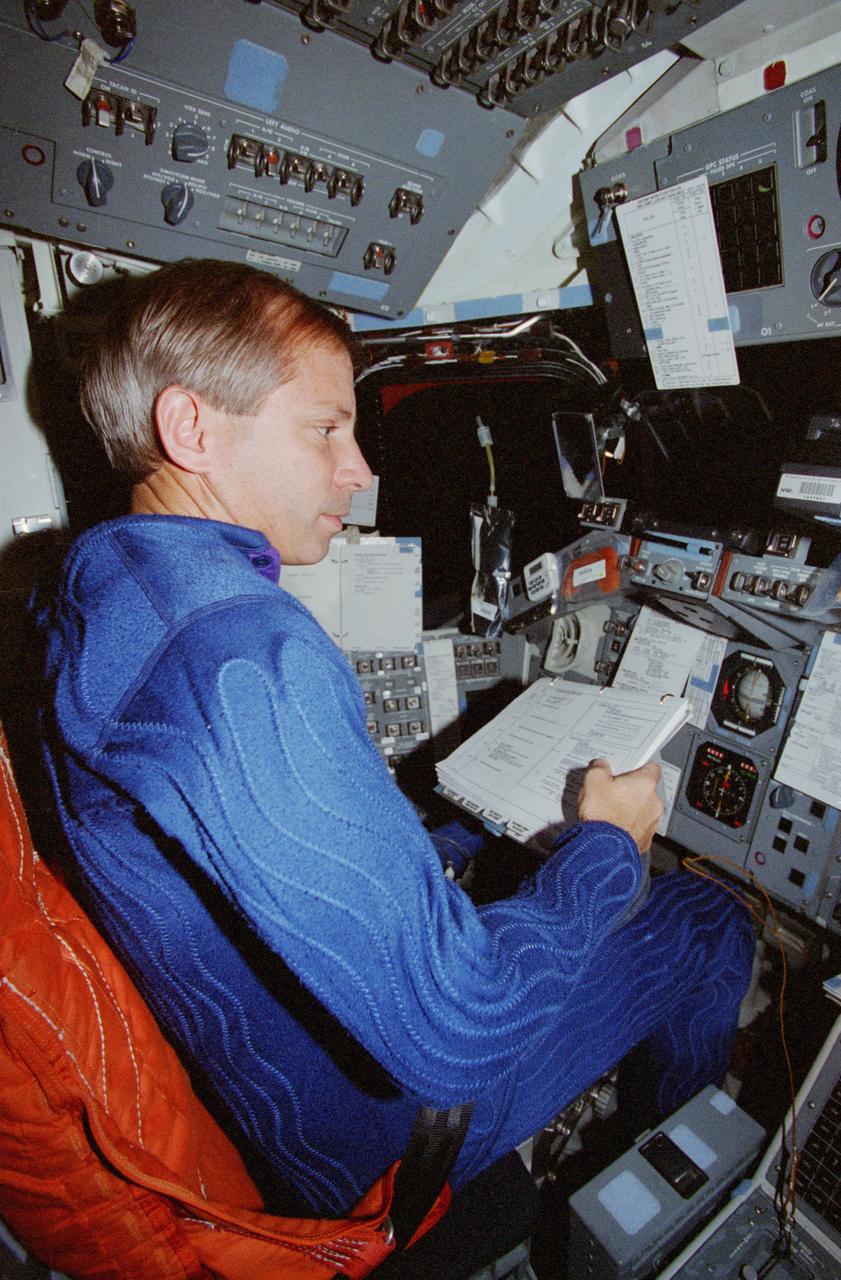

STS080-360-002 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- From the commander's station on the port side of the space shuttle Columbia's forward flight deck, astronaut Kenneth D. Cockrell prepares for a minor firing of Reaction Control System (RCS) engines during operations with the Wake Shield Facility (WSF). The activity was recorded with a 35mm camera on flight day seven. The commander is attired in a liquid-cooled biological garment.
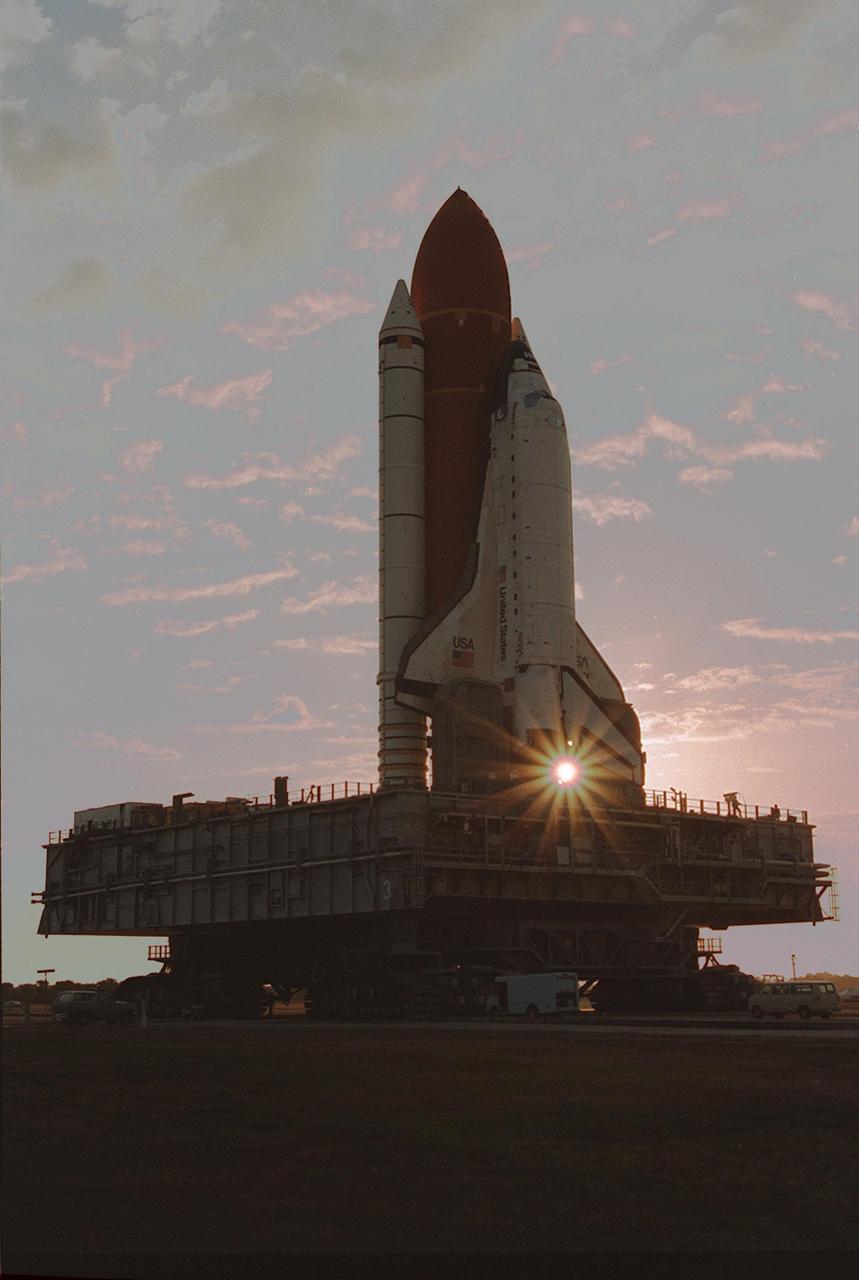

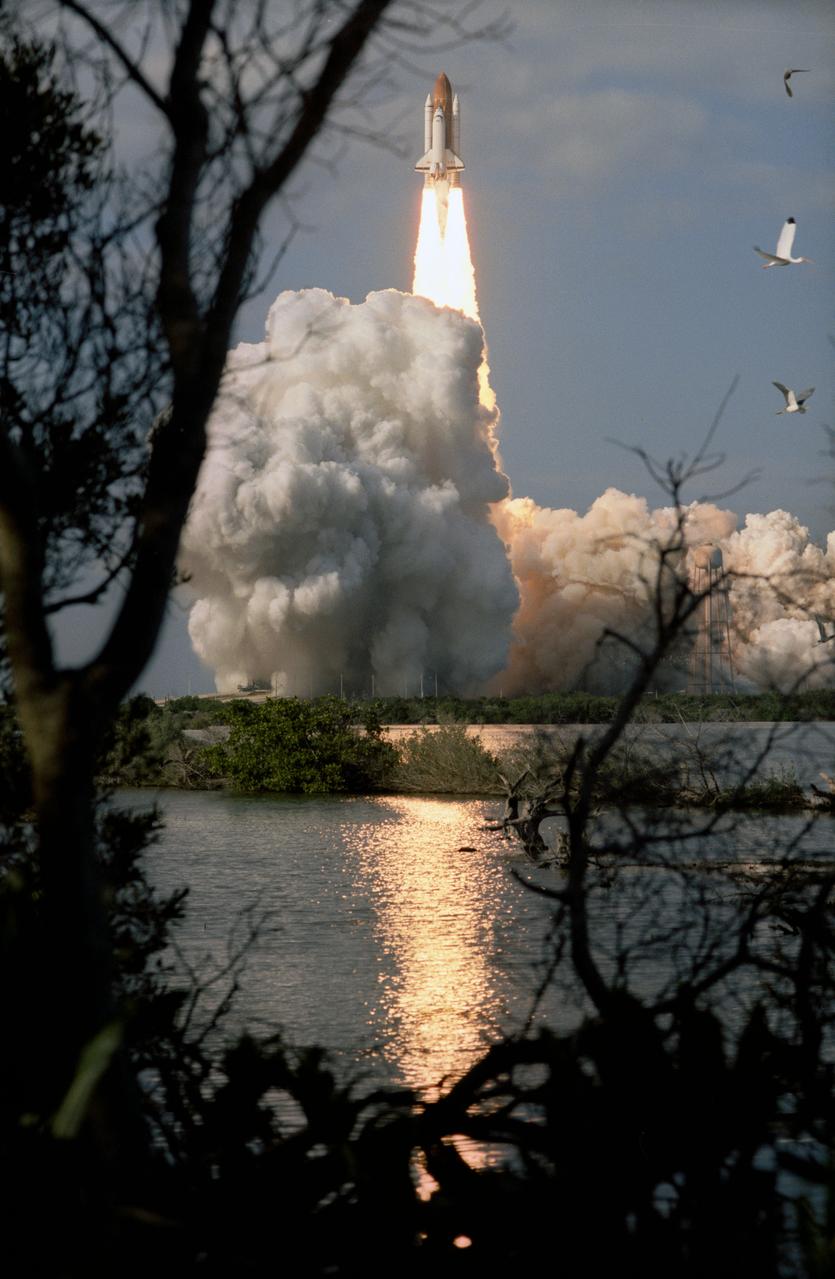
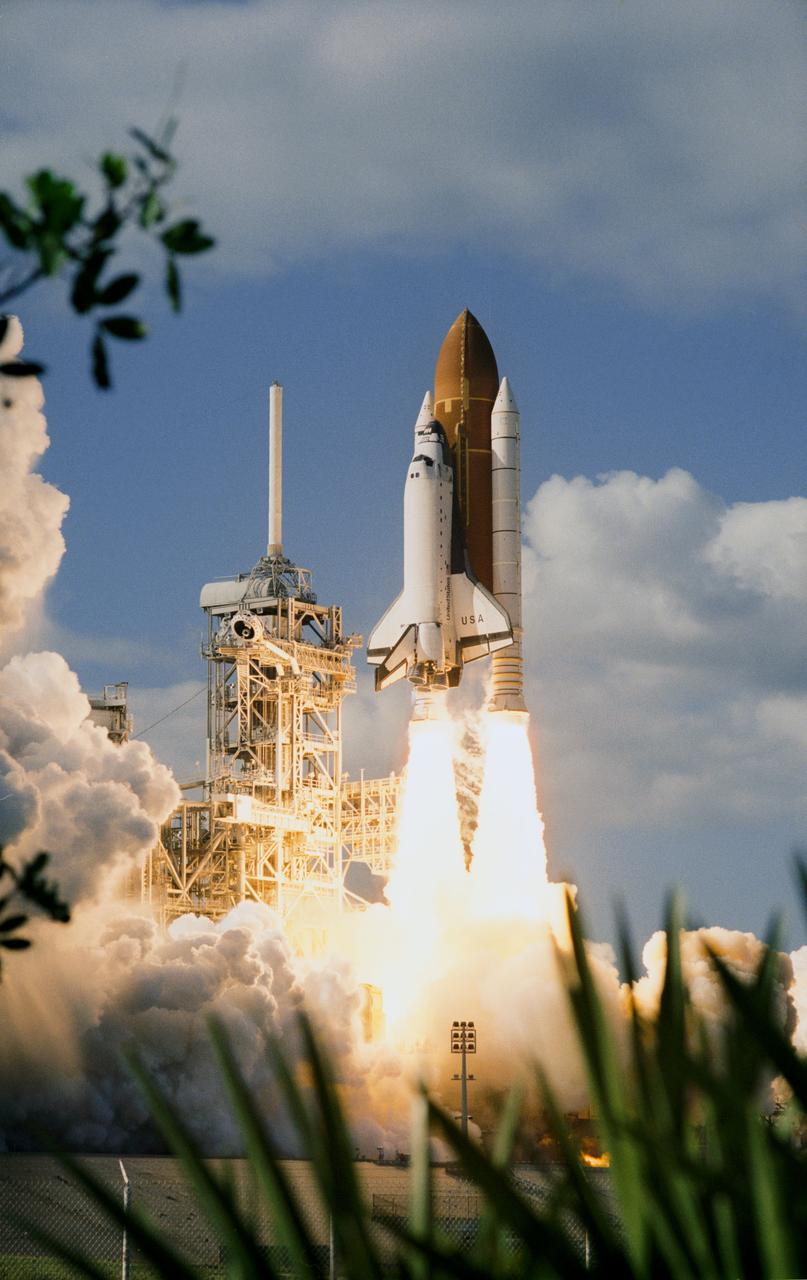
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Leaving the Vehicle Assembly Building for Launch Pad 39A on a crisp, clear winter day, the Space Shuttle Discovery makes the final Earth-bound leg of a journey into space. Once at the pad, two of the payloads for Discovery's upcoming flight, mission STS-60, will be installed. The Wake Shield Facility-1 and Get Away Special bridge assembly will be joining SPACEHAB-2 in the orbiter's payload bay. Liftoff of the first Space Shuttle flight of 1994 is currently targeted for around Feb. 3
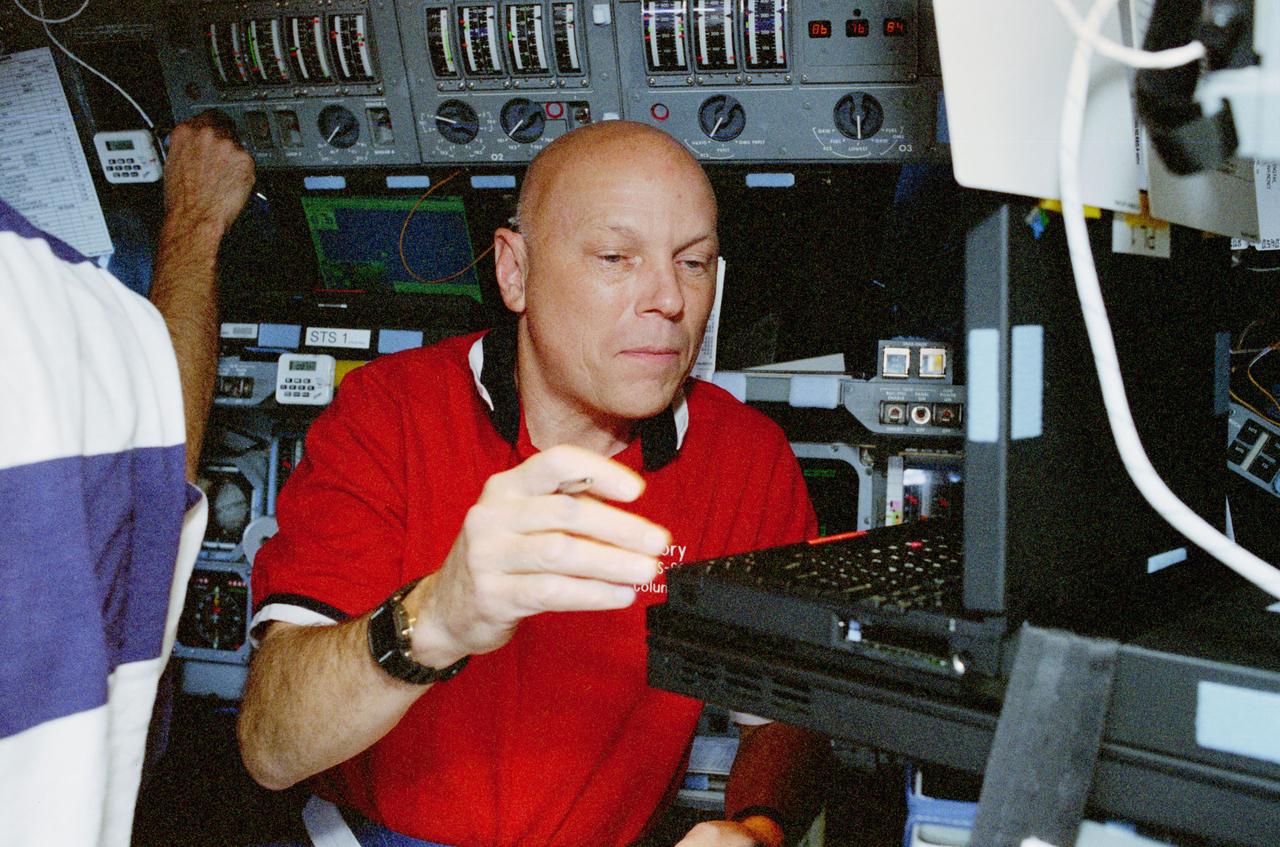

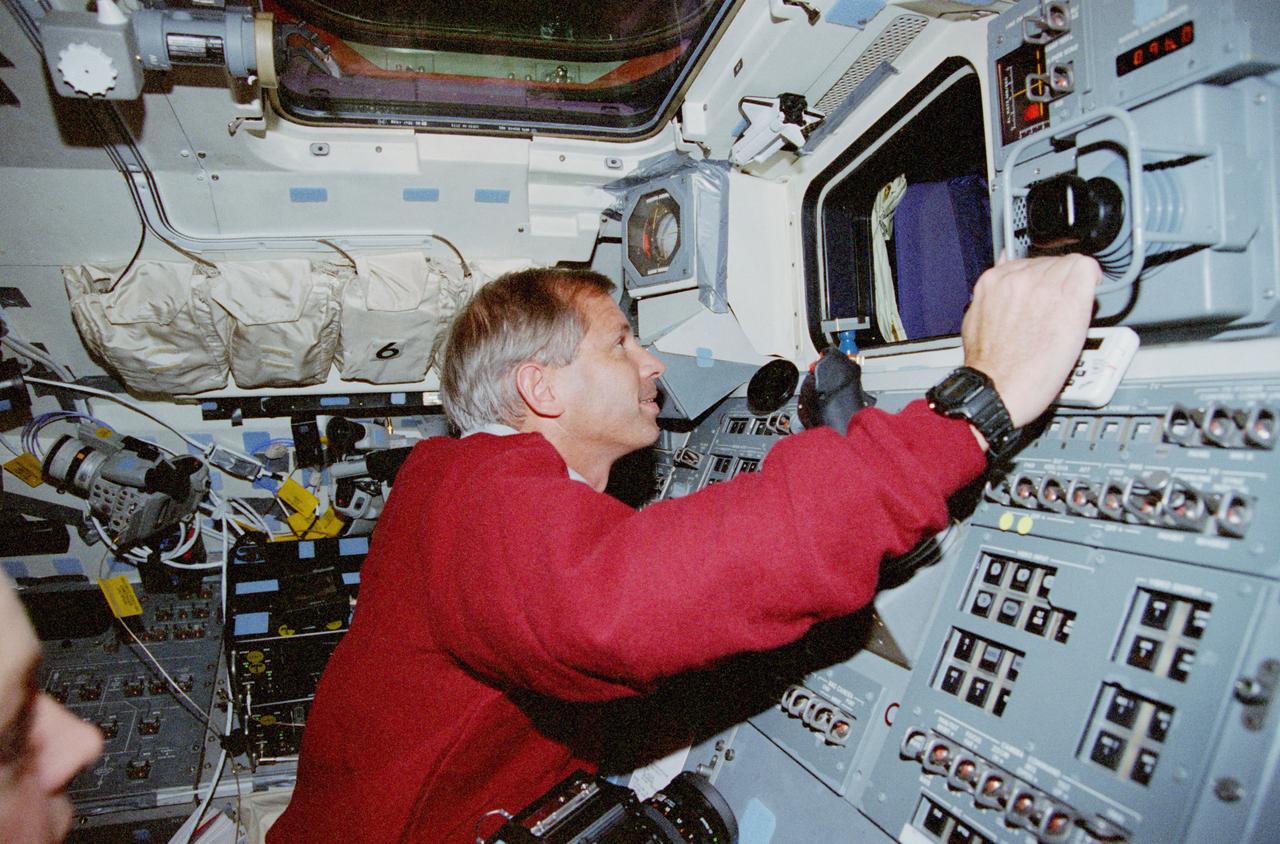
STS080-314-003 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Story Musgrave, STS-80 mission specialist, works with a pair of computers dedicated to Wake Shield Facility (WSF) operations onboard the space shuttle Columbia's flight deck. Musgrave marked his sixth appearance on a space shuttle flight during this duration record-setting space flight.

STS080-708-084 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space and a cloud covered portion of Earth, the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) is turned loose by the space shuttle Columbia's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) to begin a period of free-flight. The image was photographed with a handheld 70mm camera aimed through windows on Columbia's aft flight deck.
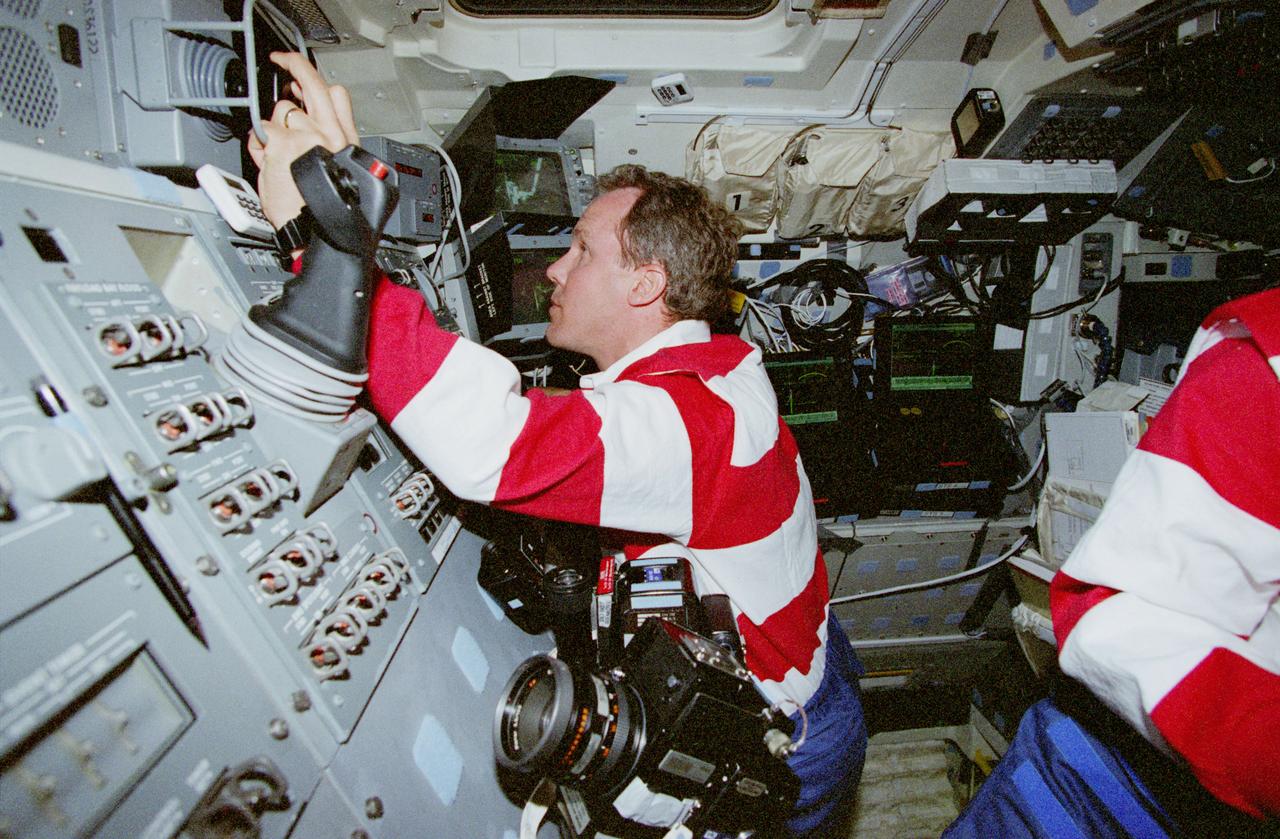

STS080-330-023 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-80 mission specialist, operates the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) controls during operations with the Wake Shield Facility (WSF). When this picture was taken, the part time free-flying WSF was in the grasp of the RMS' end effector, as evidenced by the scene on the space shuttle Columbia's aft flight deck monitor in upper right.
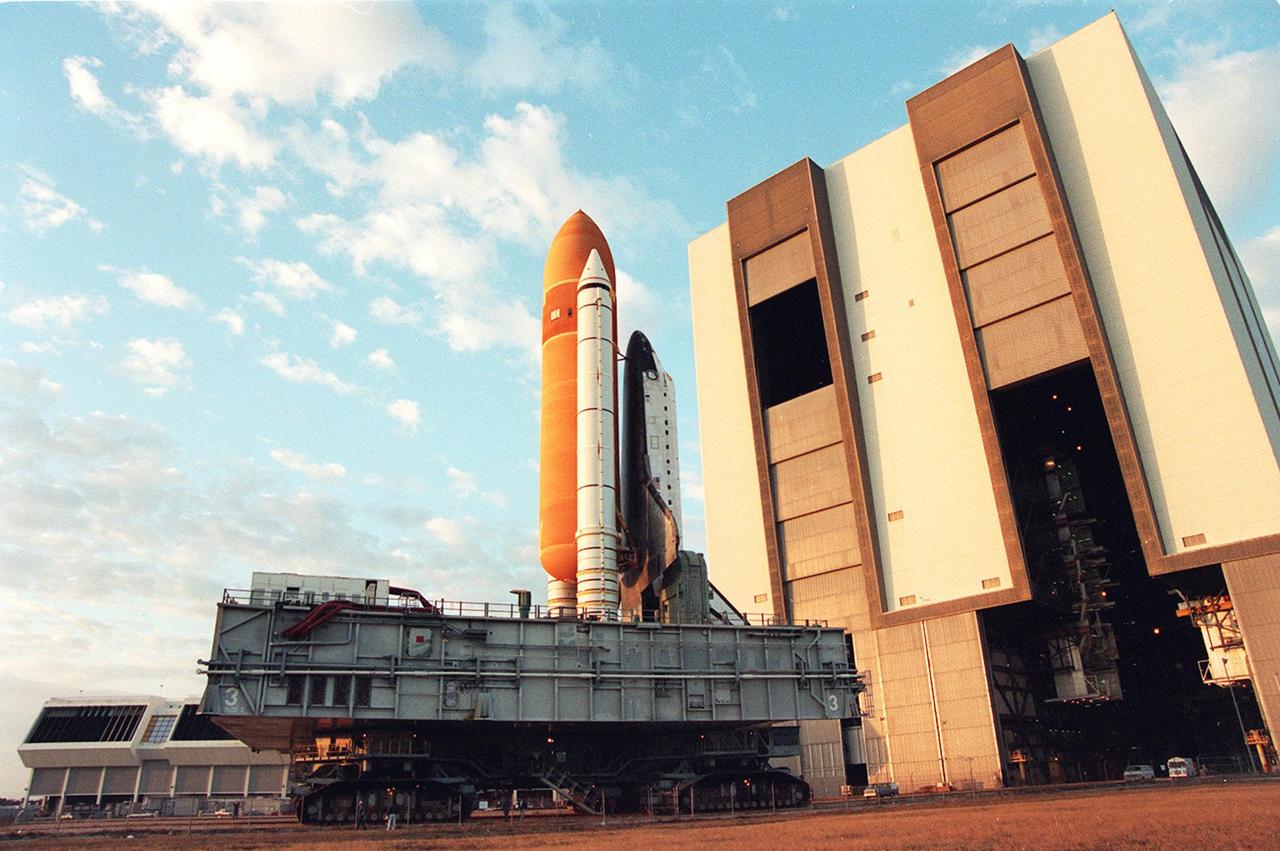

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Leaving the Vehicle Asembly Building for Launch Pad 39A on a crisp, clear winter day, the Space Shuttle Discovery makes the final Earth-bound leg of a journey into space. Once at the pad, two of the payloads for Discovery's upcoming flight, mission STS-60, will be installed. The Wake Shield Facility-1 and Get Away Special bridge assembly will be joining SPACEHAB-2 in the orbiter's payload bay. Liftoff of the first Space Shuttle flight of 1994 is currently targeted for around Feb. 3
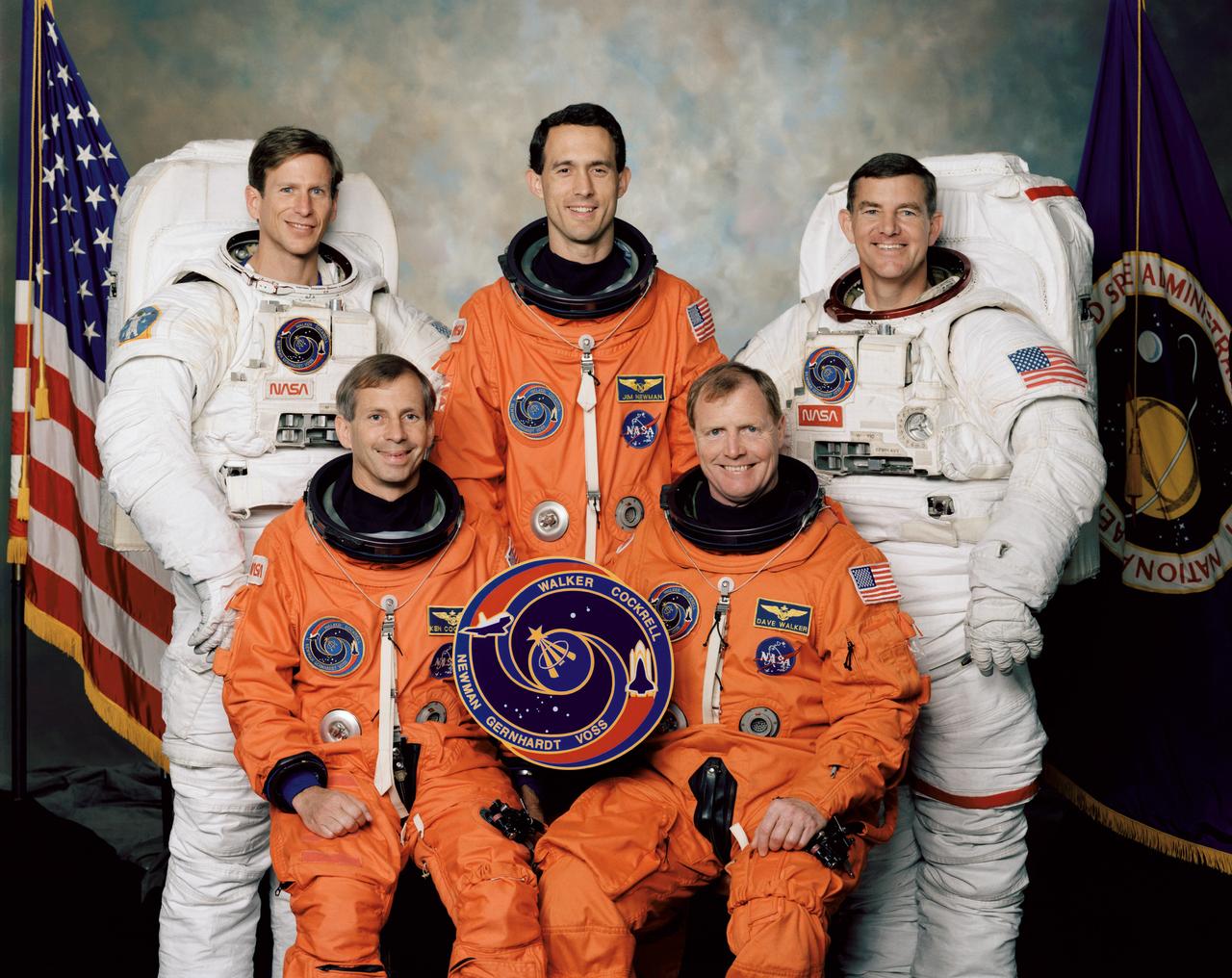

These five NASA astronauts were the crew members for the STS-69 mission that launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour September 7, 1995. Pictured on the front row (left to right) are David M. Walker, mission commander; and Kenneth D. Cockrell, pilot. On the back row (left to right) are Michael L. Gernhardt and James H. Newman, both mission specialists; and James S. Voss, payload commander. The mission’s two primary payloads included the Spartan 201-3 and Wake Shield Facility-2 (WSF-2).

STS069-S-001 (May 1995) --- Designed by the crew members, the patch for STS-69 symbolizes the multifaceted nature of the flight's mission. The primary payload, Wake Shield Facility (WSF), is represented in the center by the astronaut emblem against a flat disk. The astronaut emblem also signifies the importance of human beings in space exploration, reflected by the planned spacewalk supporting space station assembly. The two stylized space shuttles highlight the ascent and entry phases of the mission. Along with the two spiral plumes, the stylized space shuttles symbolize a NASA first - the deployment and recovery on the same mission of two spacecraft (both the Wake Shield Facility and the Spartan). The constellations Canis Major and Canis Minor represent the astronomy objectives of the Spartan and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH) payload. The two constellations also symbolize the talents and dedication of the support personnel who make space shuttle missions possible. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
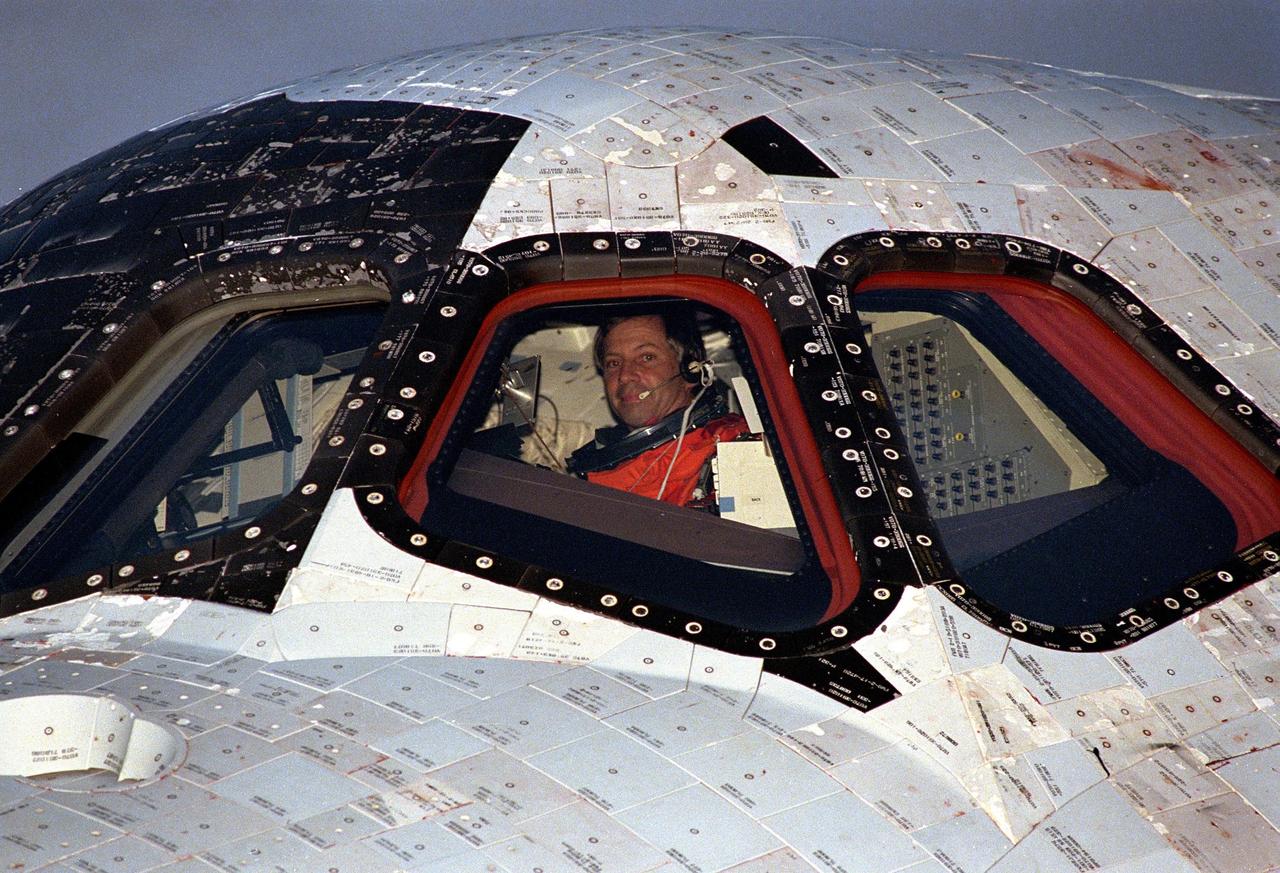

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-80 Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell peers out the window of the orbiter Columbia minutes after guiding the spacecraft to a successful landing on KSC’s Runway 33. Main gear touchdown occurred at 6:49:04 a.m. EST, Dec. 7. On board with Cockrell are four fellow crew members, Pilot Kent V. Rominger, and Mission Specialists Story Musgrave, Thomas D. Jones, and Tamara E. Jernigan, and the two primary payloads of the mission, the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).
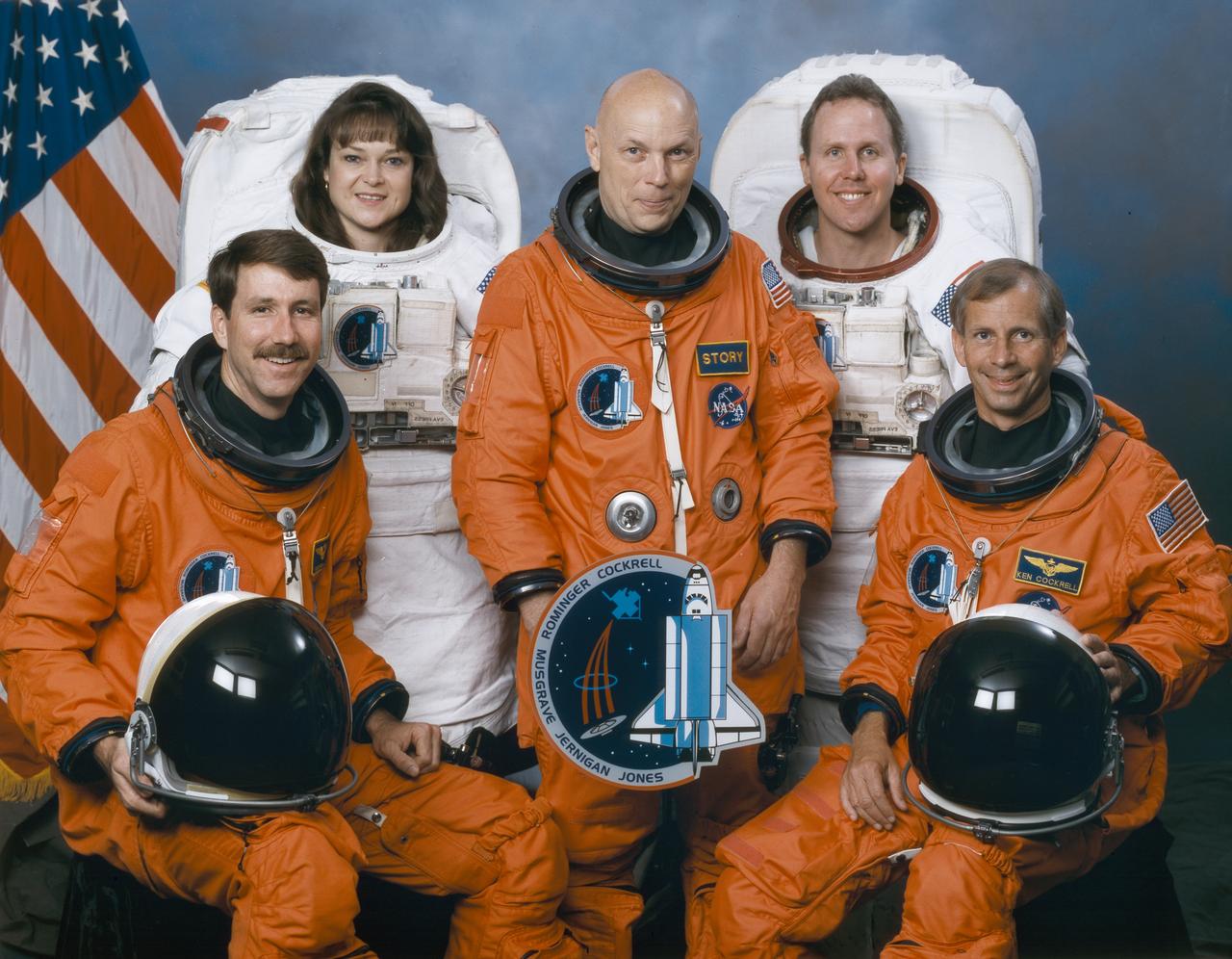

The crew assigned to the STS-79 mission included (seated left to right) Kent V. Rominger, pilot; and Kenneth D. Cockrell, commander. Standing (left to right) are mission specialists Tamara E. Jernigan, F. Story Musgrave, and Thomas D. Jones. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on November 19, 1996 at 2:55:47 pm (EST), the STS-80 mission marked the final flight of 1996. The crew successfully deployed and operated the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II), and deployed and retrieved the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3).
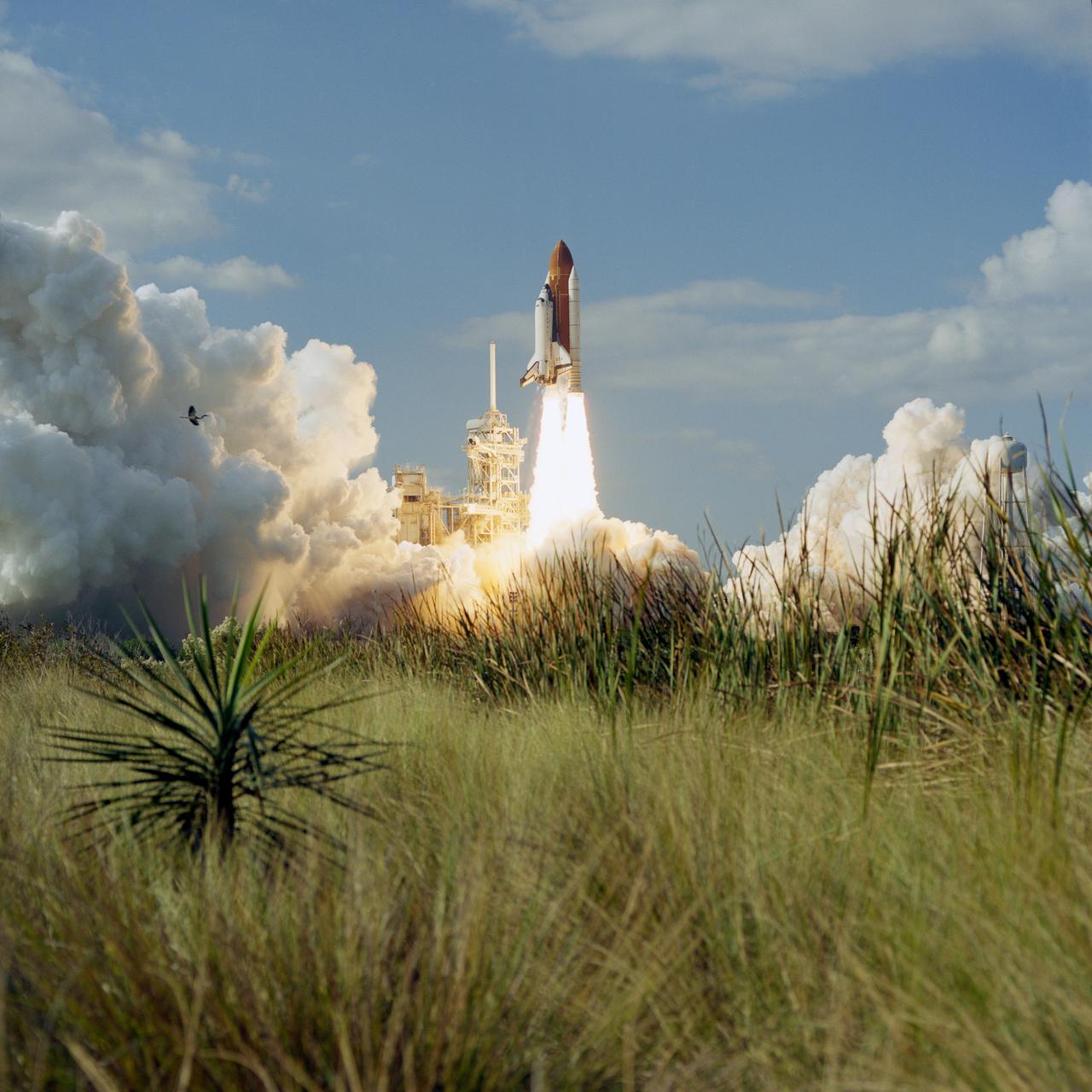

STS080-S-005 (19 Nov. 1996) --- The space shuttle Columbia lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. (EST), Nov. 19, 1996. Onboard are astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; along with Story Musgrave, Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones, all mission specialists. The two primary payloads for STS-80 stowed in Columbia's cargo bay for later deployment and testing are the Wake Shield Facility (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer (ORFEUS) with its associated Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS).

STS060-15-003 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This 35mm frame shows the major payloads of the Space Shuttle Discovery's STS-60 mission, backdropped against clouds over the Atlantic Ocean. In the foreground is the SPACEHAB module, with the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) partially visible in its berthed position near the Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) pods and the vertical stabilizer. Television cameras on the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) were being used for a survey of the cargo. Five NASA astronauts and a Russian cosmonaut went on to spend eight days in Earth orbit in support of the mission.

STS080-S-003 (19 Nov. 1996) --- The space shuttle Columbia lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. (EST), November 19, 1996. Onboard are astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; along with Story Musgrave, Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones, all mission specialists. The two primary payloads for STS-80 stowed in Columbia's cargo bay for later deployment and testing are the Wake Shield Facility (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer (ORFEUS) with its associated Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS).

STS080-S-004 (19 Nov. 1996) --- The space shuttle Columbia lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. (EST), Nov. 19, 1996. Onboard are astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, STS-80 mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; along with Story Musgrave, Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones, all mission specialists. The two primary payloads for STS-80 stowed in Columbia's cargo bay for later deployment and testing are the Wake Shield Facility (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer (ORFEUS) with its associated Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS).
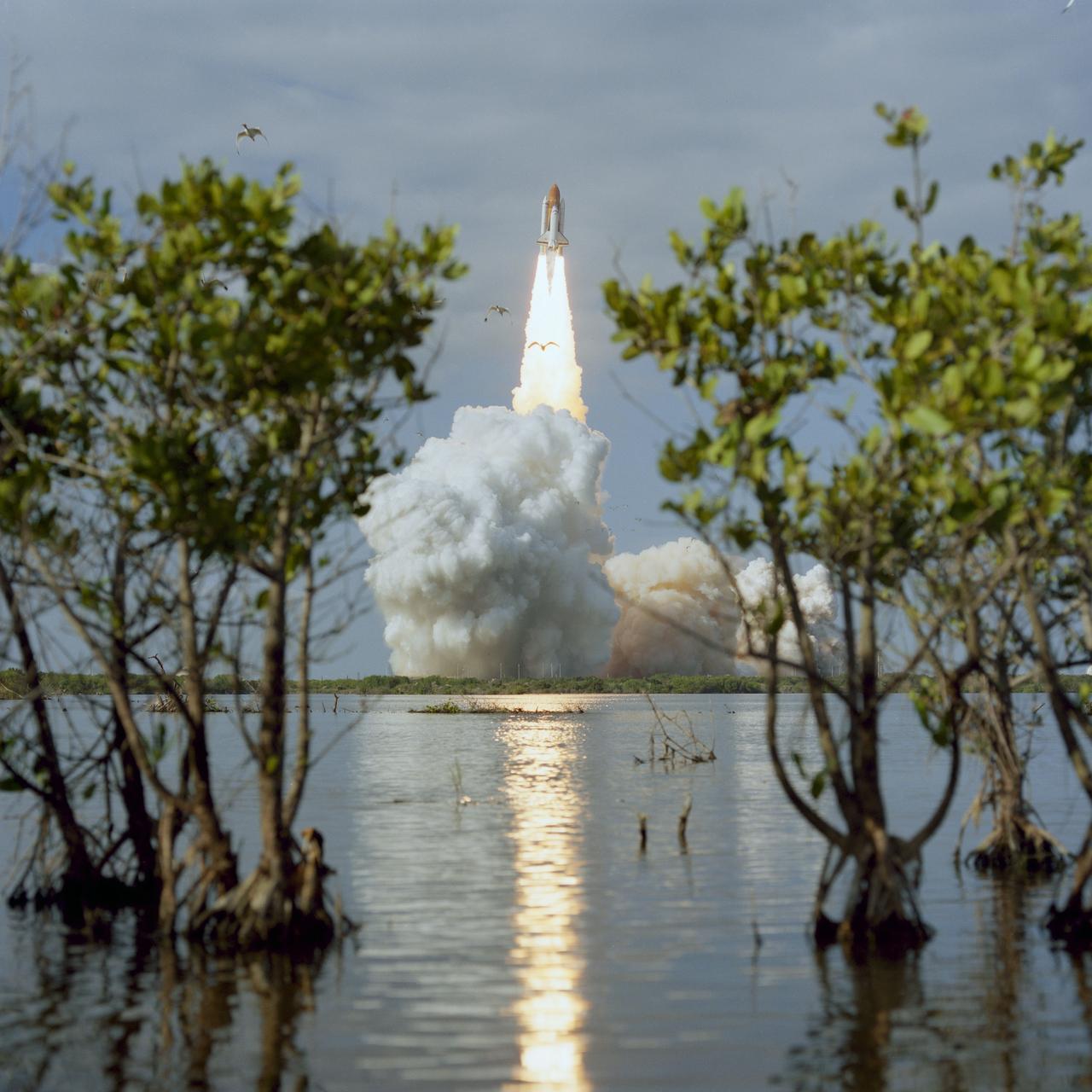

STS080-S-006 (19 Nov. 1996) --- The space shuttle Columbia lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. (EST), Nov. 19, 1996. Onboard are astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; along with Story Musgrave, Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones, all mission specialists. The two primary payloads for STS-80 stowed in Columbia's cargo bay for later deployment and testing are the Wake Shield Facility (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer (ORFEUS) with its associated Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS).
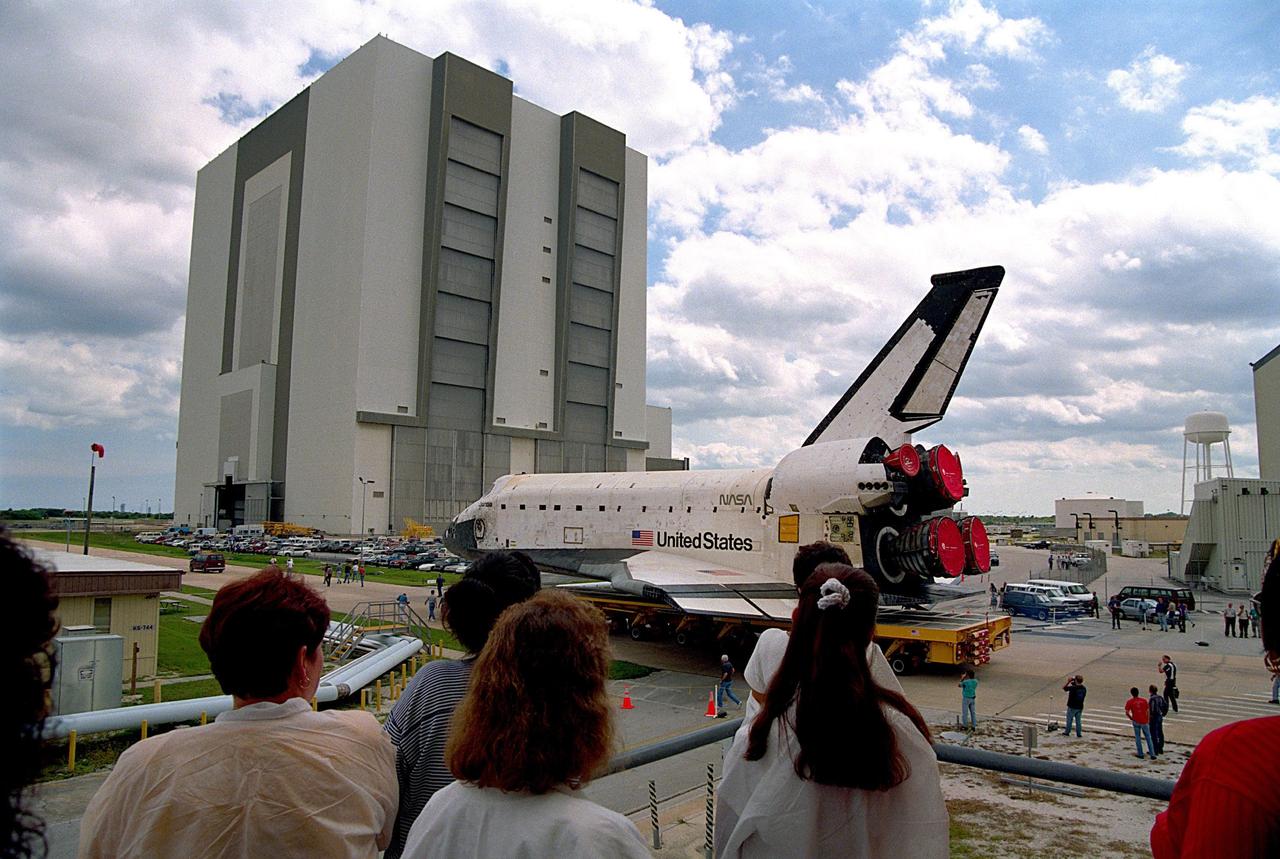

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Columbia completes the short journey from Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 1 to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). During its approximately one-week stay inside the VAB, the spaceplane will be mated to the external tank and twin solid rocket boosters, and electrical and mechanical interfaces will be verified. Rollout to Launch Pad 39B is planned for Oct. 16, where the two primary payloads of the upcoming STS-80 mission -- the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (ORFEUS-SPAS-2) -- will be installed. Liftoff on the final Shuttle flight of 1996 is targeted for no earlier than Nov 8 at 2:47 p.m. EST
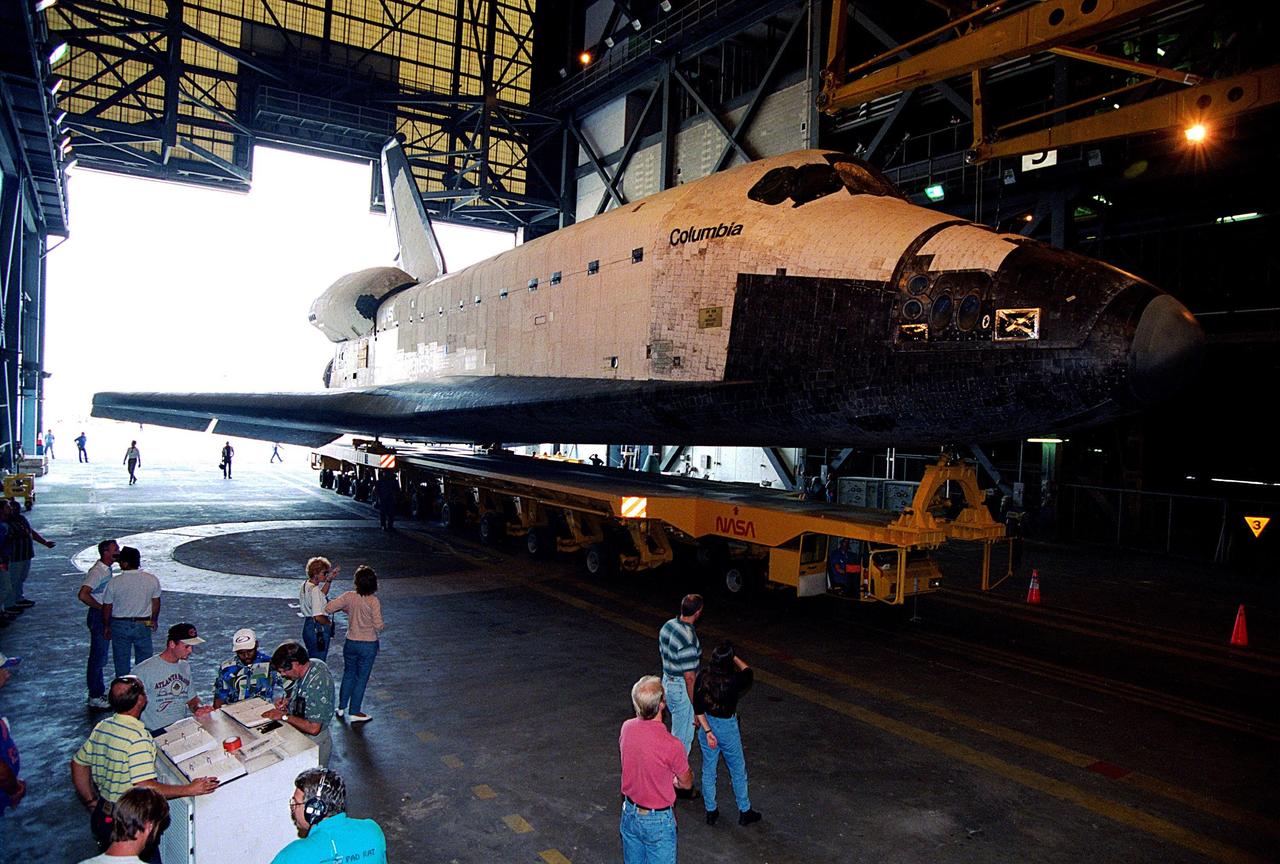

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Columbia completes the short journey from Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 1 to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). During its approximately one-week stay inside the VAB, the spaceplane will be mated to the external tank and twin solid rocket boosters, and electrical and mechanical interfaces will be verified. Rollout to Launch Pad 39B is planned for Oct. 16, where the two primary payloads of the upcoming STS-80 mission -- the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (ORFEUS-SPAS-2) -- will be installed. Liftoff on the final Shuttle flight of 1996 is targeted for no earlier than Nov 8 at 2:47 p.m. EST
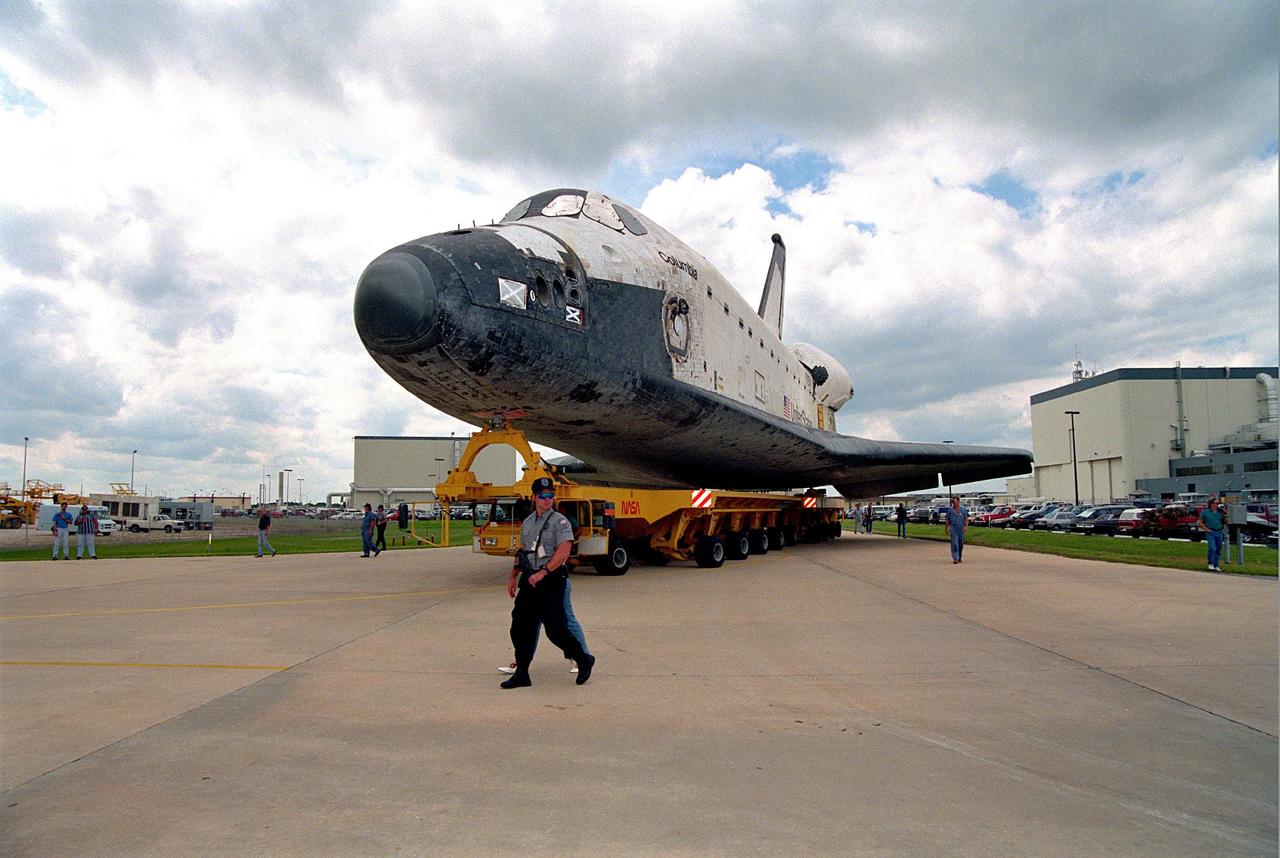

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Columbia completes the short journey from Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 1 to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). During its approximately one-week stay inside the VAB, the spaceplane will be mated to the external tank and twin solid rocket boosters, and electrical and mechanical interfaces will be verified. Rollout to Launch Pad 39B is planned for Oct. 16, where the two primary payloads of the upcoming STS-80 mission -- the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 (ORFEUS-SPAS-2) -- will be installed. Liftoff on the final Shuttle flight of 1996 is targeted for no earlier than Nov 8 at 2:47 p.m. EST.
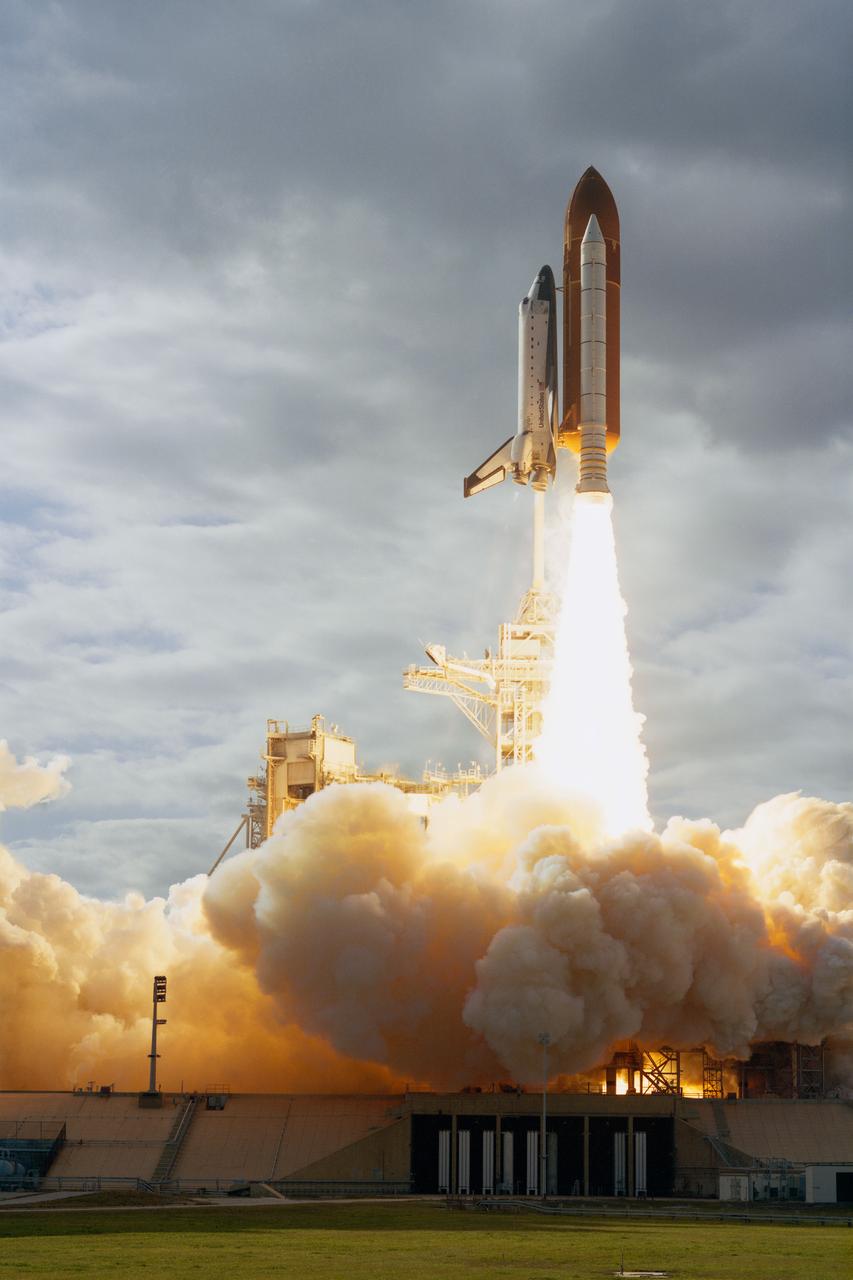

STS080-S-007 (19 Nov. 1996) --- One of the nearest remote camera stations to Launch Pad B captured this profile image of space shuttle Columbia's liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Launch Complex 39 at 2:55:47 p.m. (EST), November 19, 1996. Onboard are astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Kent V. Rominger, pilot; along with Story Musgrave, Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones, all mission specialists. The two primary payloads for STS-80 stowed in Columbia?s cargo bay for later deployment and testing are the Wake Shield Facility (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer (ORFEUS) with its associated Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS).
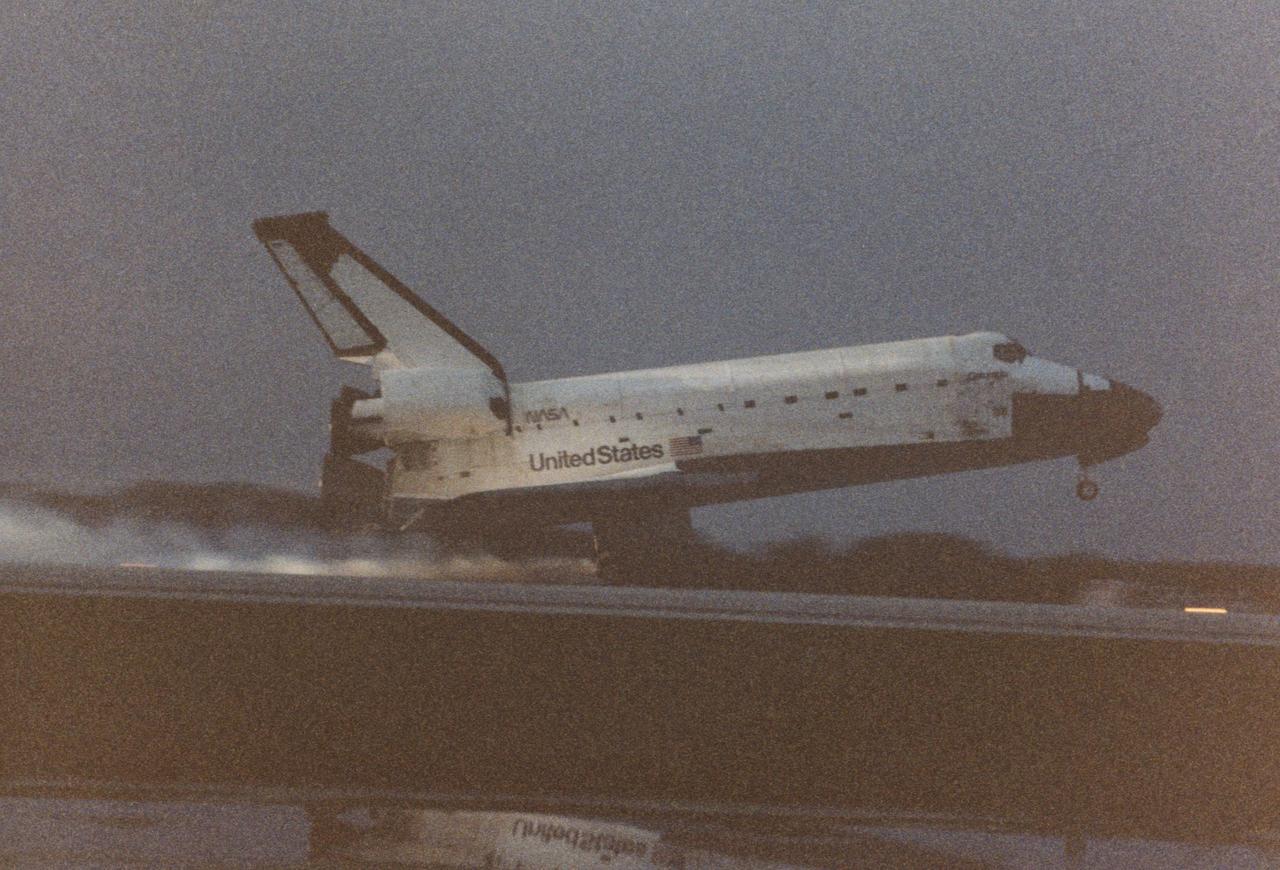

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The final Space Shuttle flight of 1996 comes to a successful close as the orbiter Columbia touches down on Runway 33 of KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown occurred at 6:49:05 a.m. EST, Dec. 7. The mission duration of 17 days, 15 hours and 53 minutes establishes a new record for extended Shuttle flight. The five- member STS-80 crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell and Pilot Kent V. Rominger. The three mission specialists on board are Tamara E. Jernigan, Thomas D. Jones and Story Musgrave. At age 61, Musgrave is the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also becomes the first person to fly six times on the Shuttle. The two primary payloads of the 80th Shuttle flight are the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II) and the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3).
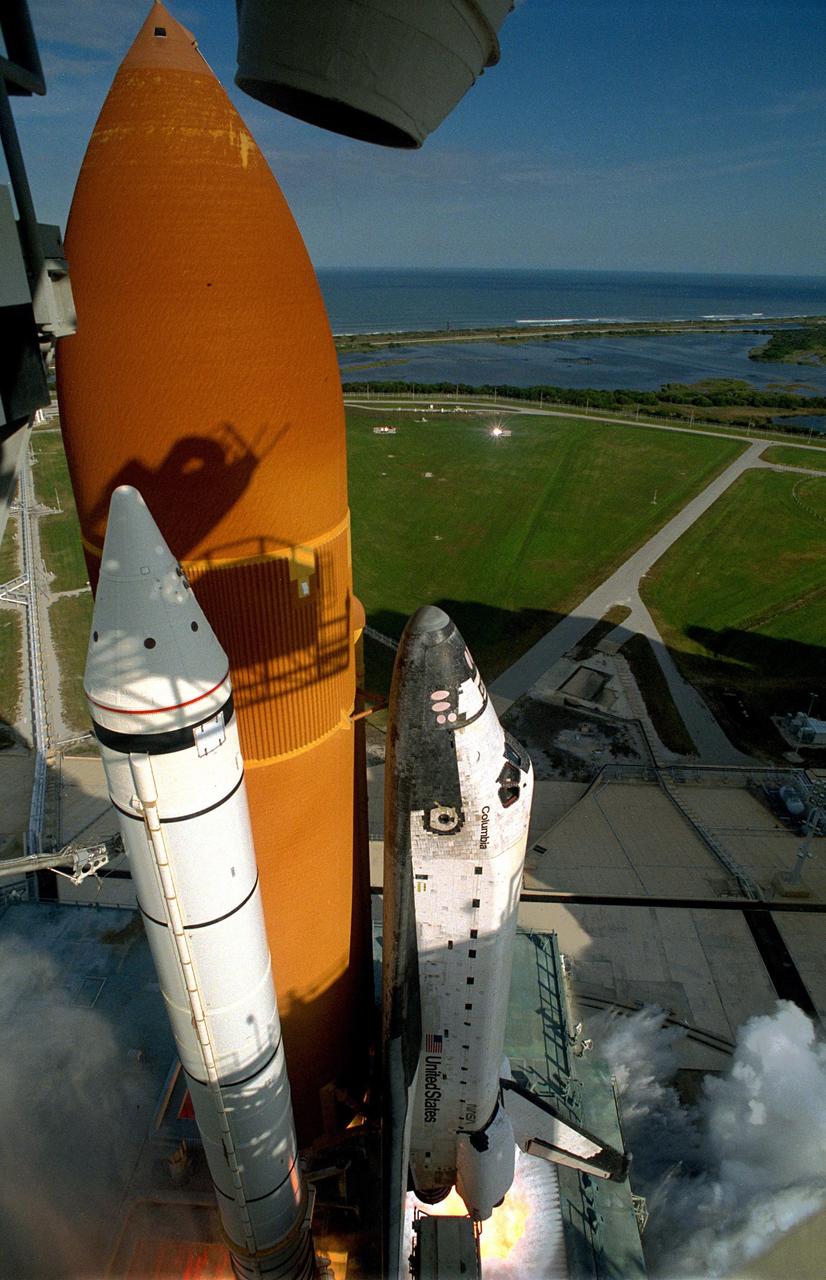

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs into orbit from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. During Mission STS- 80, Columbia’s five-person crew will deploy and retrieve two free-flying spacecraft, conduct two spacewalks and perform a variety of microgravity research experiments in the Shuttle’s middeck area. The veteran crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).
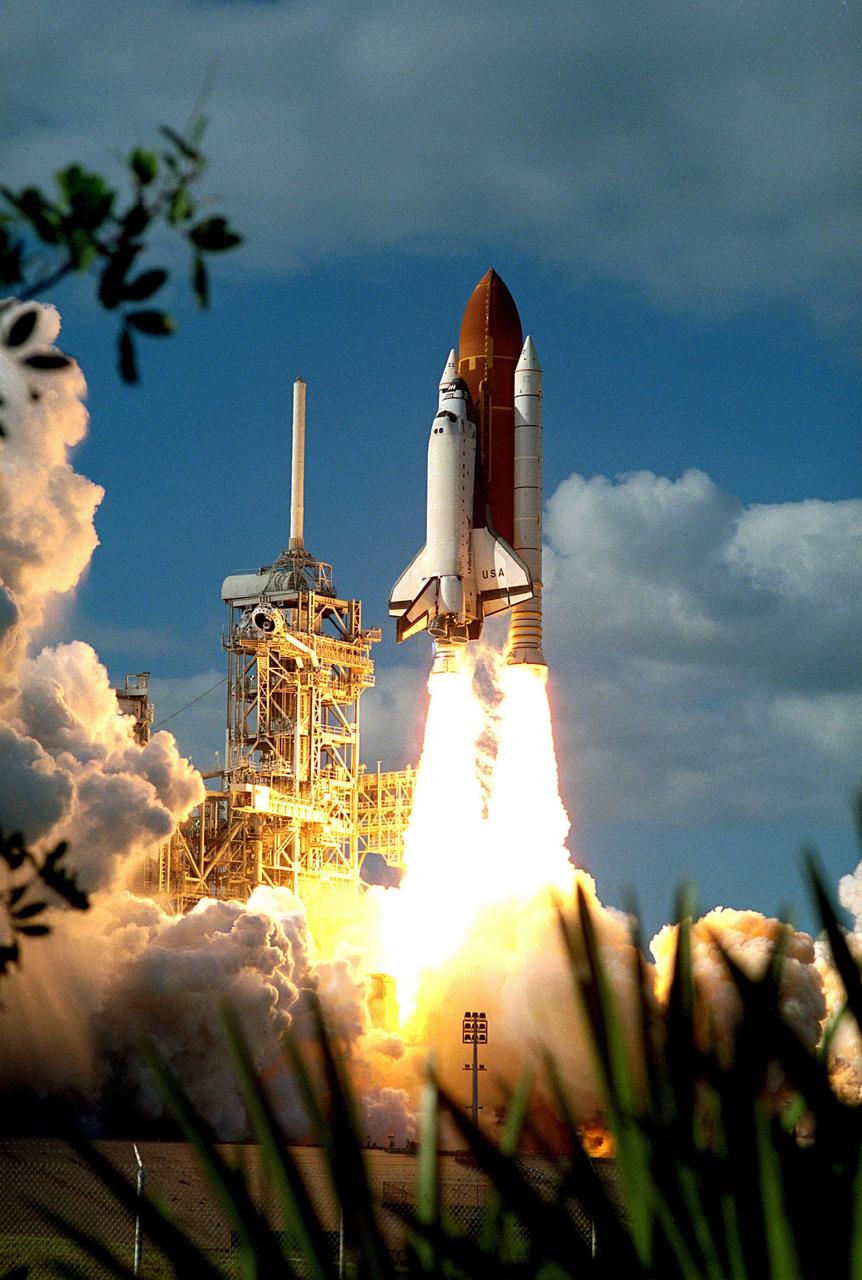

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs into orbit from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, November 19, 1996. During Mission STS-80, Columbia's five-person crew will deploy and retrieve two free-flying spacecraft, conduct two spacewalks and perform a variety of microgravity research experiments in the Shuttleþs middeck area. The veteran crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young's record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA's reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).
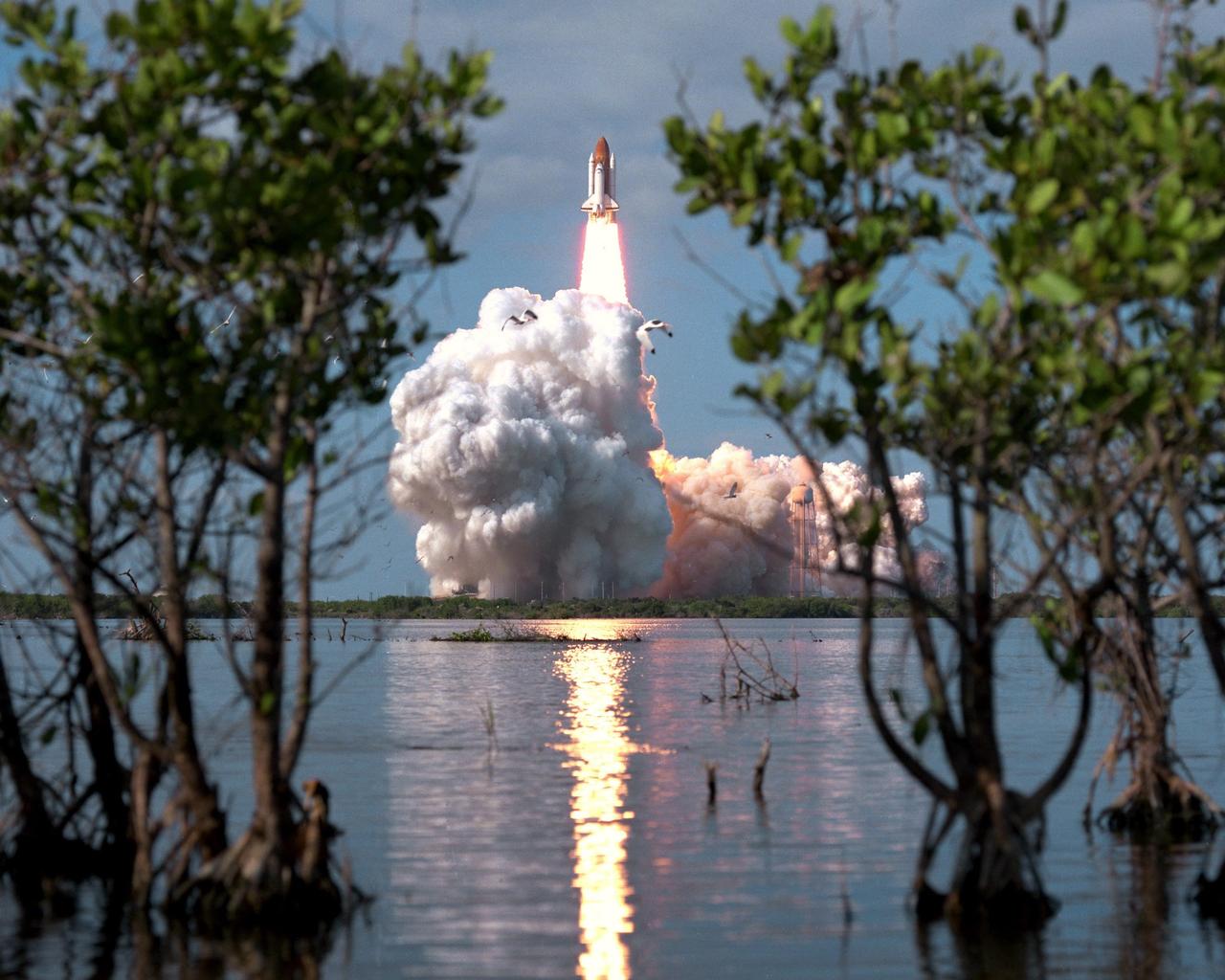

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs into orbit from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. During Mission STS- 80, Columbia’s five-person crew will deploy and retrieve two free-flying spacecraft, conduct two spacewalks and perform a variety of microgravity research experiments in the Shuttle’s middeck area. The veteran crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).

STS080-S-001 (August 1996) --- This STS-80 mission patch depicts the space shuttle Columbia and the two research satellites its crew will deploy into the blue field of space. The uppermost satellite is the Orbiting Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (ORFEUS-SPAS), a telescope aimed at unraveling the life cycles of stars and understanding the gases that drift between them. The lower satellite is the Wake Shield Facility (WSF), flying for the third time. It will use the vacuum of space to create advanced semiconductors for the nation’s electronics industry. ORFEUS and WSF are joined by the symbol of the Astronaut Corps, representing the human contribution to scientific progress in space. The two bright blue stars represent the mission’s extravehicular activities (EVA), final rehearsals for techniques and tools to be used in assembly of the International Space Station (ISS). Surrounding Columbia is a constellation of 16 stars, one for each day of the mission, representing the stellar talents of the ground and flight teams that share the goal of expanding knowledge through a permanent human presence in space. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
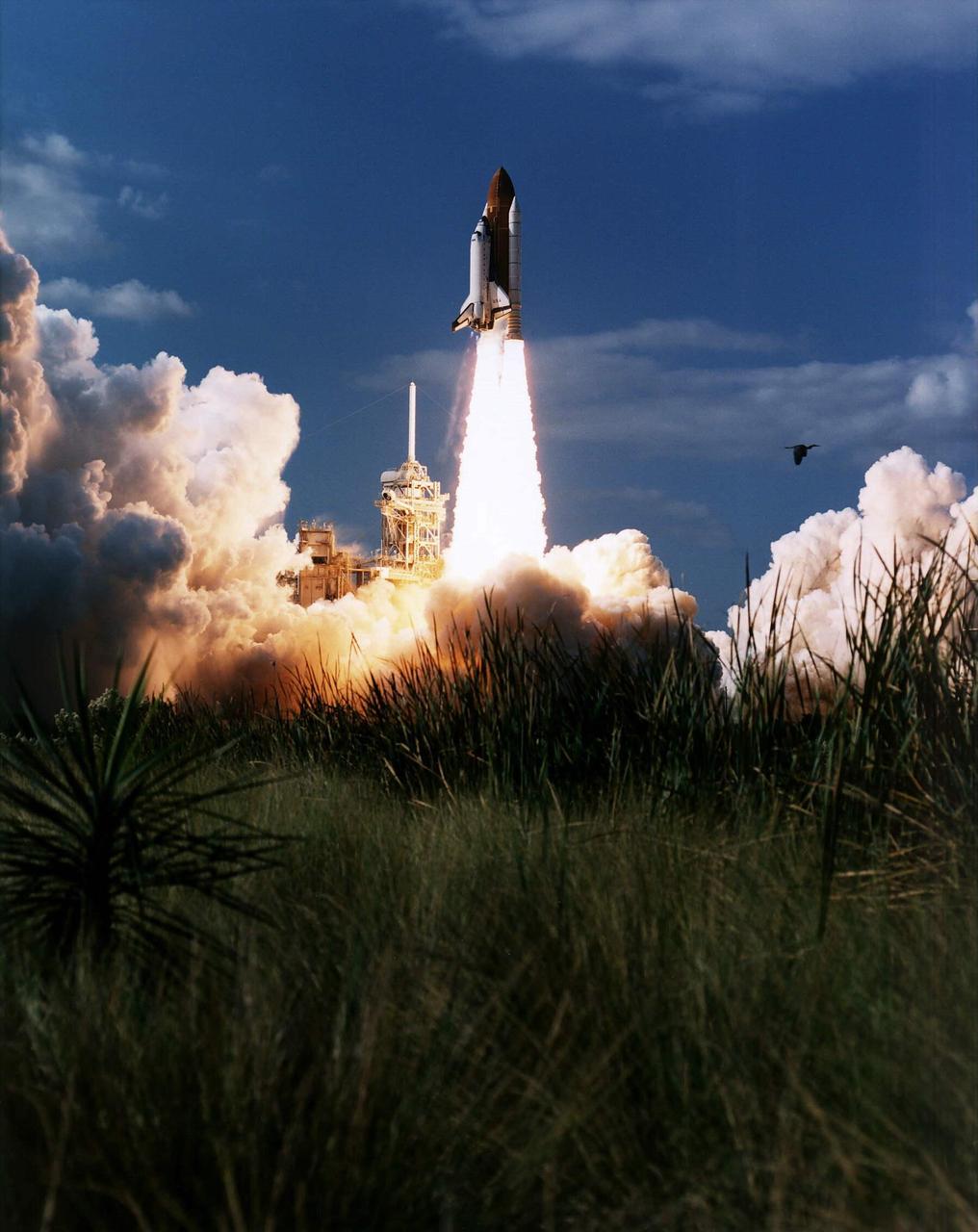

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Vividly framed by a tranquil Florida landscape, the Space Shuttle Columbia lifts off from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. Leading the veteran crew of Mission STS-80 is Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II). Two spacewalks also will be performed during the nearly 16-day mission. Mission STS-80 closes out the Shuttle flight schedule for 1996; it marks the 21st flight for Columbia and the 80th in Shuttle program history.
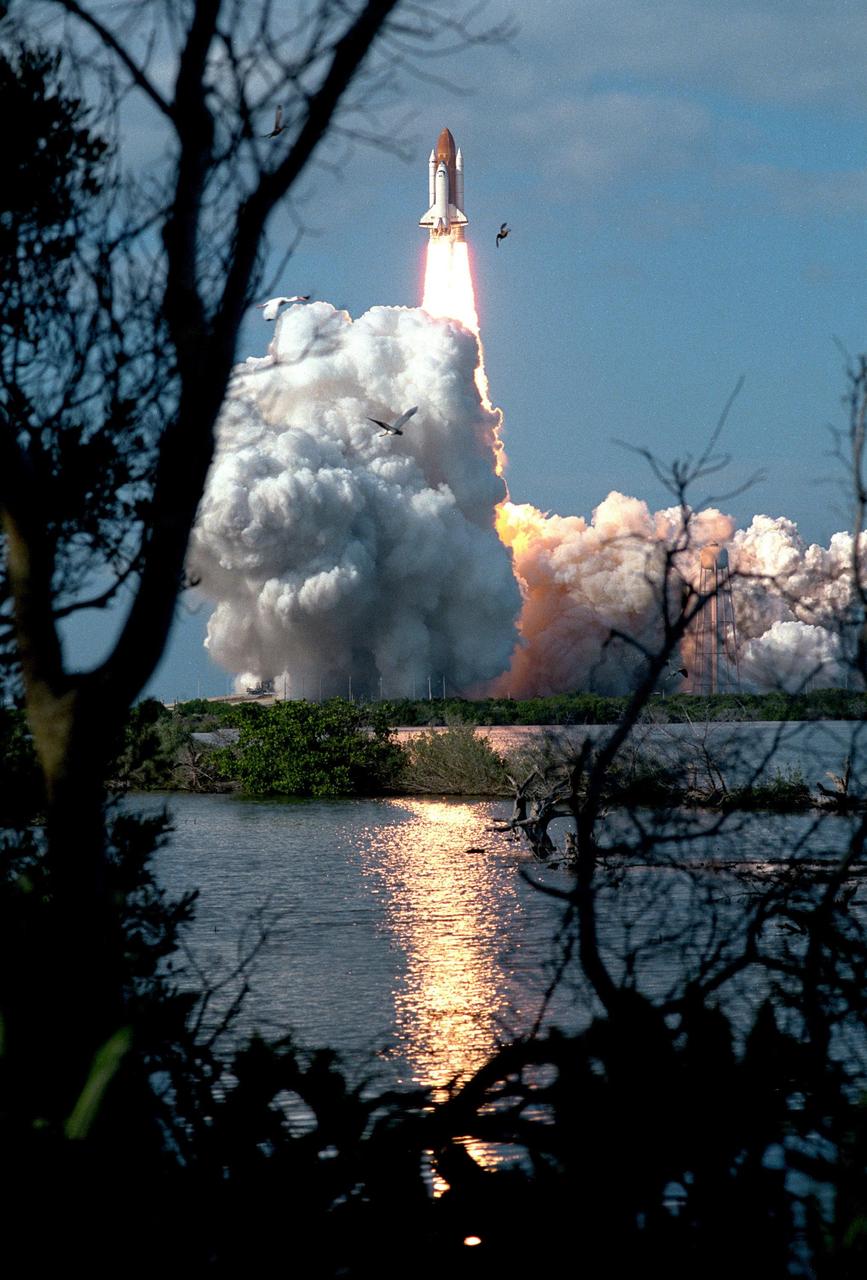

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs skyward from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. Leading the veteran crew of Mission STS-80 is Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II). Two spacewalks also will be performed during the nearly 16-day mission. Mission STS-80 closes out the Shuttle flight schedule for 1996; it marks the 21st flight for Columbia and the 80th in Shuttle program history.
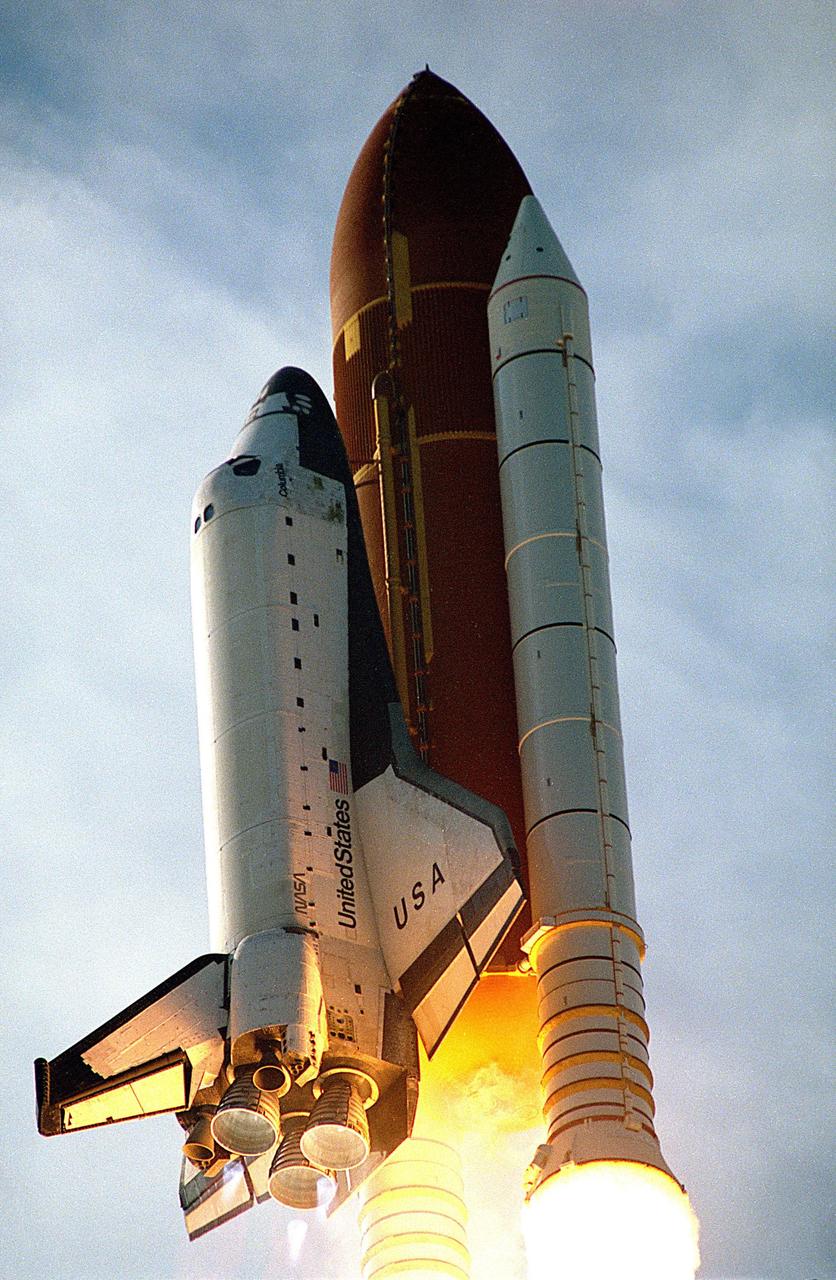

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs skyward from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. Leading the veteran crew of Mission STS-80 is Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II). Two spacewalks also will be performed during the nearly 16-day mission. Mission STS-80 closes out the Shuttle flight schedule for 1996; it marks the 21st flight for Columbia and the 80th in Shuttle program history.
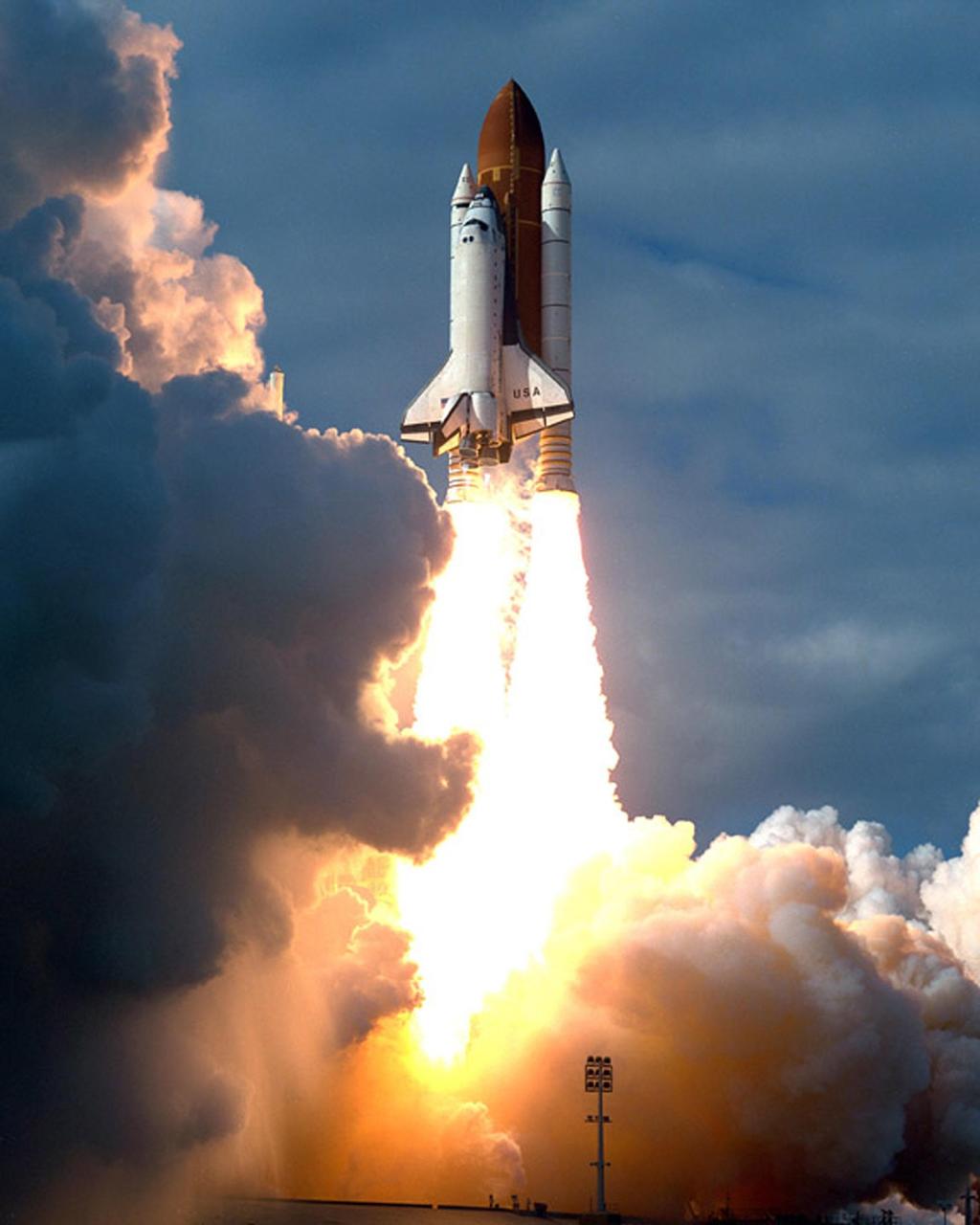

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs into orbit from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. During Mission STS- 80, Columbia’s five-person crew will deploy and retrieve two free-flying spacecraft, conduct two spacewalks and perform a variety of microgravity research experiments in the Shuttle’s middeck area. The veteran crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).
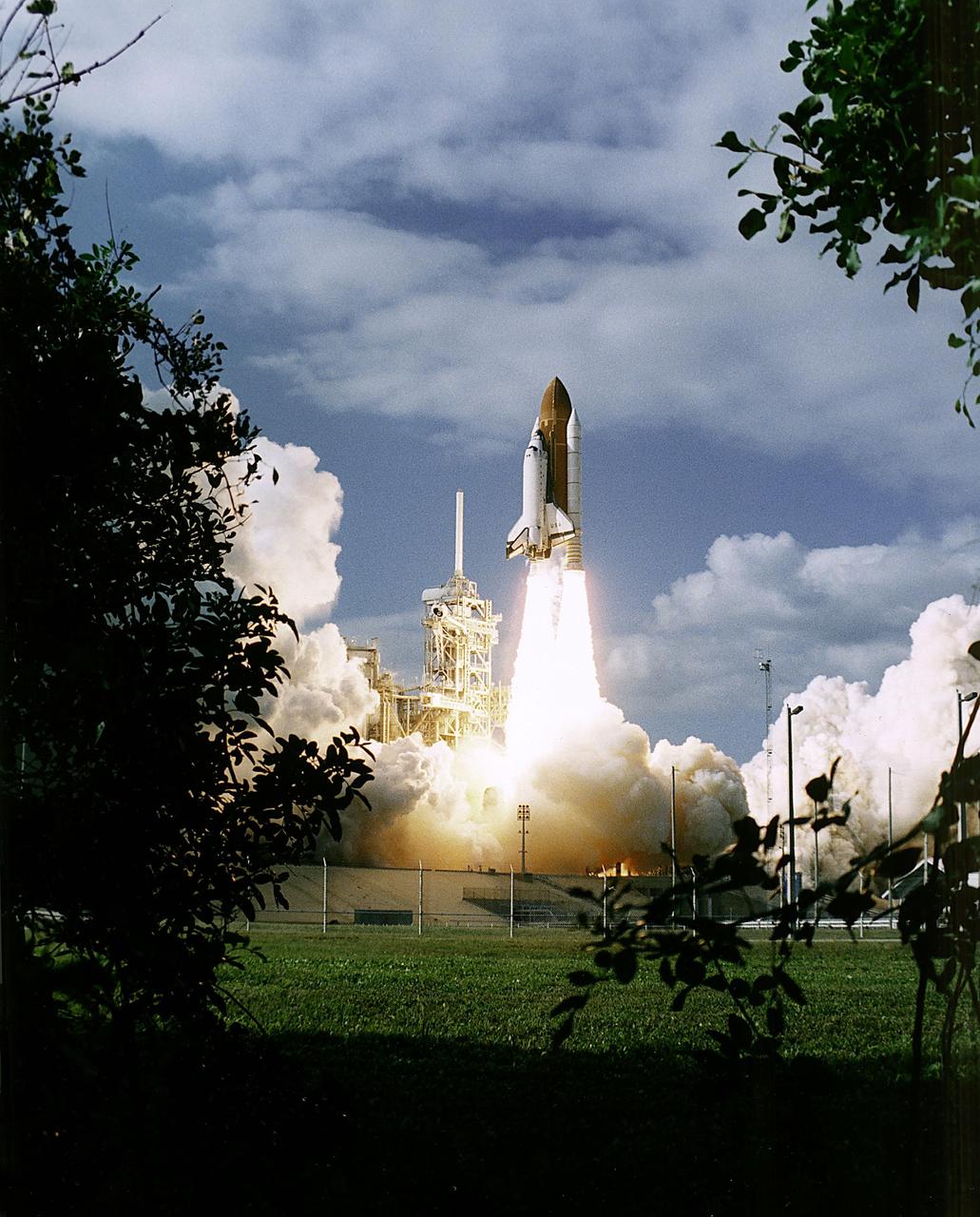

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs into orbit from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, November 19, 1996. During Mission STS-80, Columbia's five-person crew will deploy and retrieve two free-flying spacecraft, conduct two spacewalks and perform a variety of microgravity research experiments in the Shuttle's middeck area. The veteran crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young's record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA's reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).
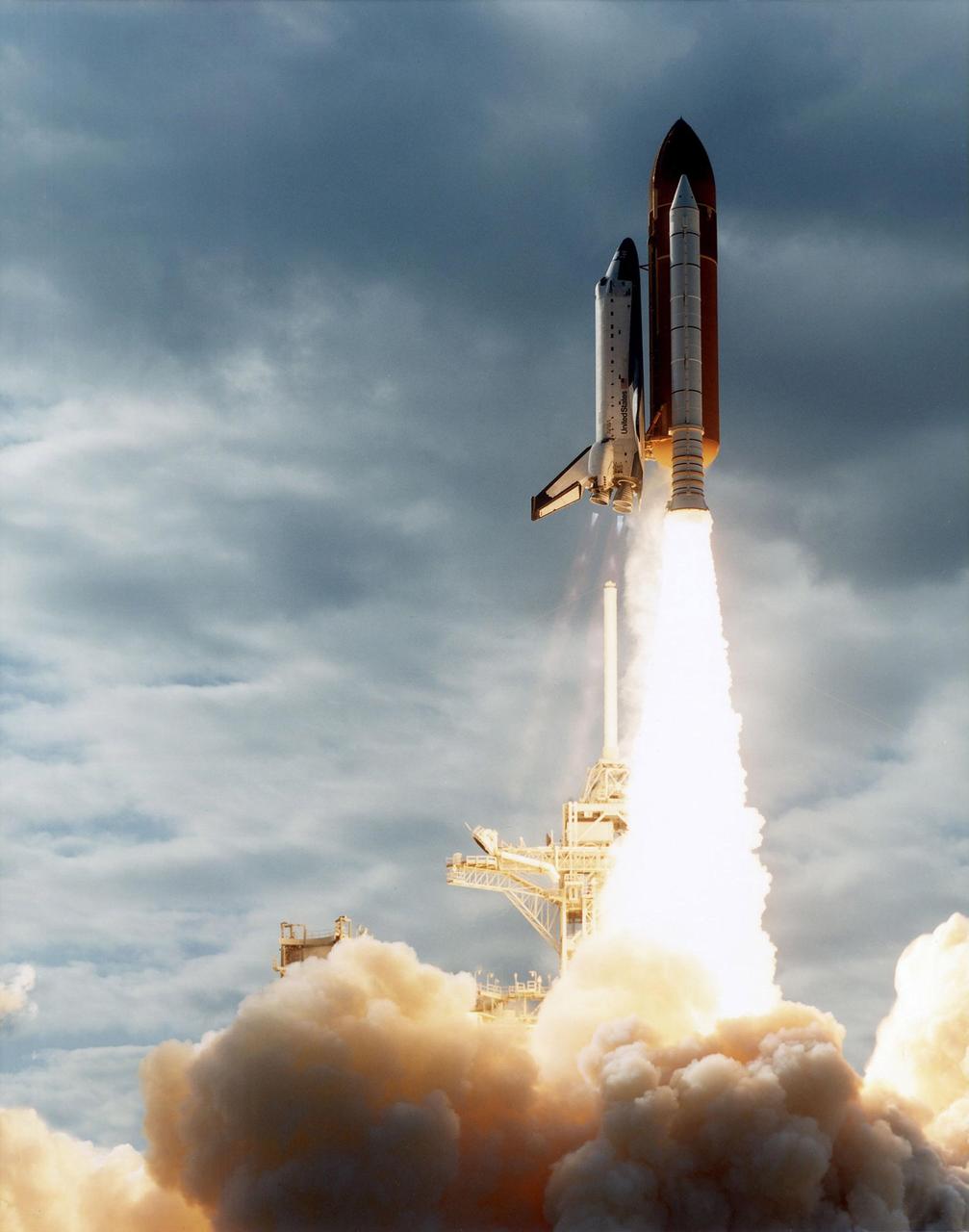

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs into orbit from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. During Mission STS- 80, Columbia’s five-person crew will deploy and retrieve two free-flying spacecraft, conduct two spacewalks and perform a variety of microgravity research experiments in the Shuttle’s middeck area. The veteran crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).
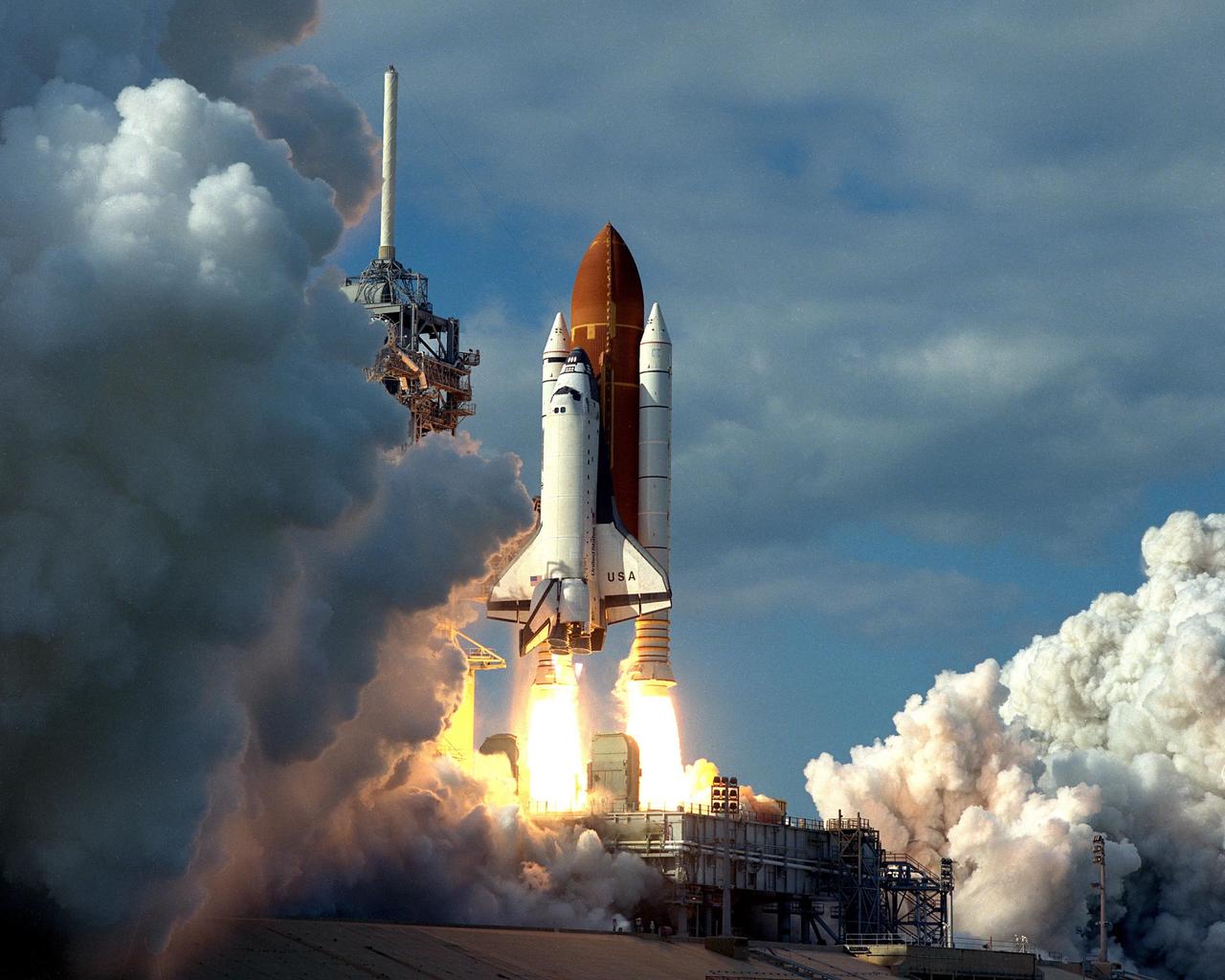

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs into orbit from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. During Mission STS- 80, Columbia’s five-person crew will deploy and retrieve two free-flying spacecraft, conduct two spacewalks and perform a variety of microgravity research experiments in the Shuttle’s middeck area. The veteran crew is led by Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II).

This mission patch for mission STS-80 depicts the Space Shuttle Columbia and the two research satellites its crew deployed into the blue field of space. The uppermost satellite is the Orbiting Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrograph-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (ORFEUS-SPAS), a telescope aimed at unraveling the life cycles of stars and understanding the gases that drift between them. The lower satellite is the Wake Shield Facility (WSF), flying for the third time. It will use the vacuum of space to create advanced semiconductors for the nation's electronics industry. ORFEUS and WSF are joined by the symbol of the Astronaut Corps, representing the human contribution to scientific progress in space. The two bright blue stars represent the mission's Extravehicular Activities (EVA), final rehearsals for techniques and tools to be used in assembly of the International Space Station (ISS). Surrounding Columbia is a constellation of 16 stars, one for each day of the mission, representing the stellar talents of the ground and flight teams that share the goal of expanding knowledge through a permanent human presence in space.