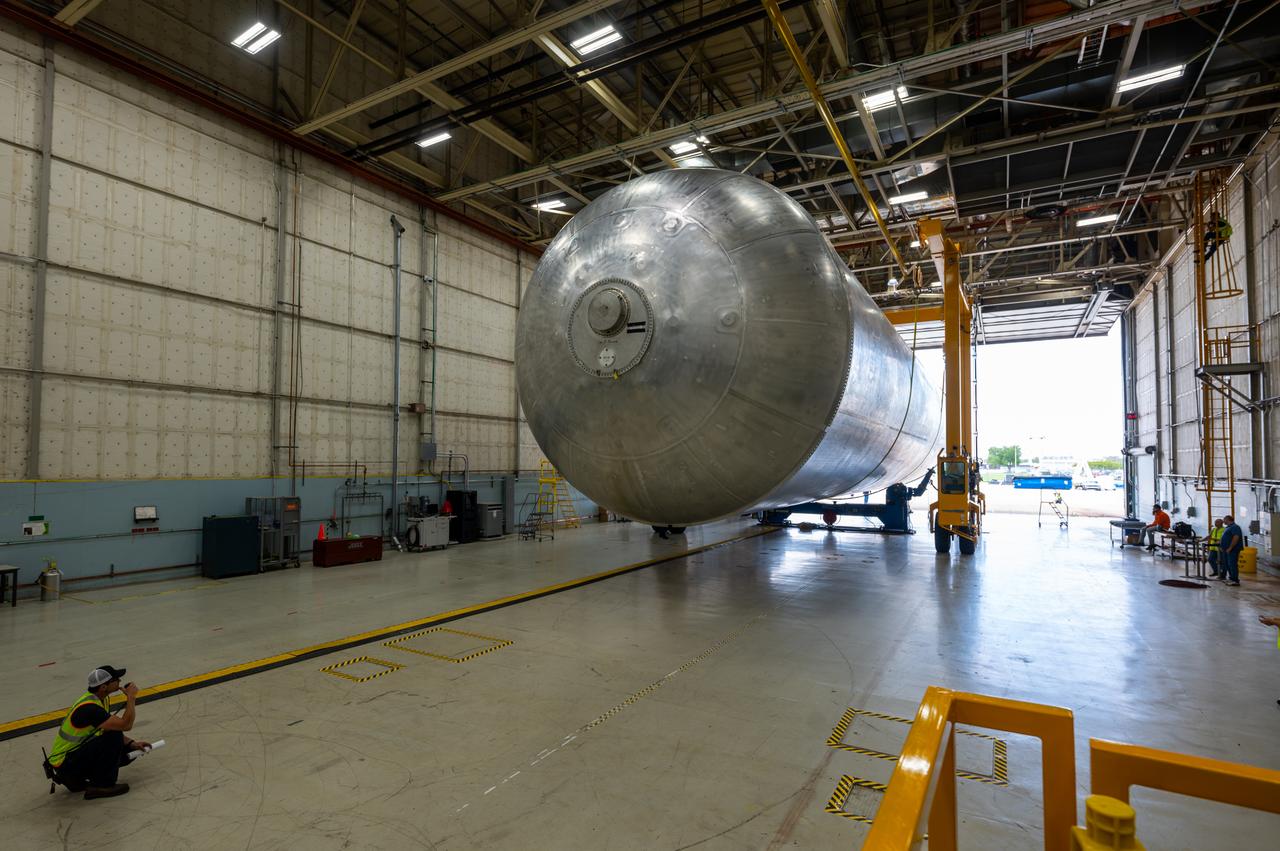

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
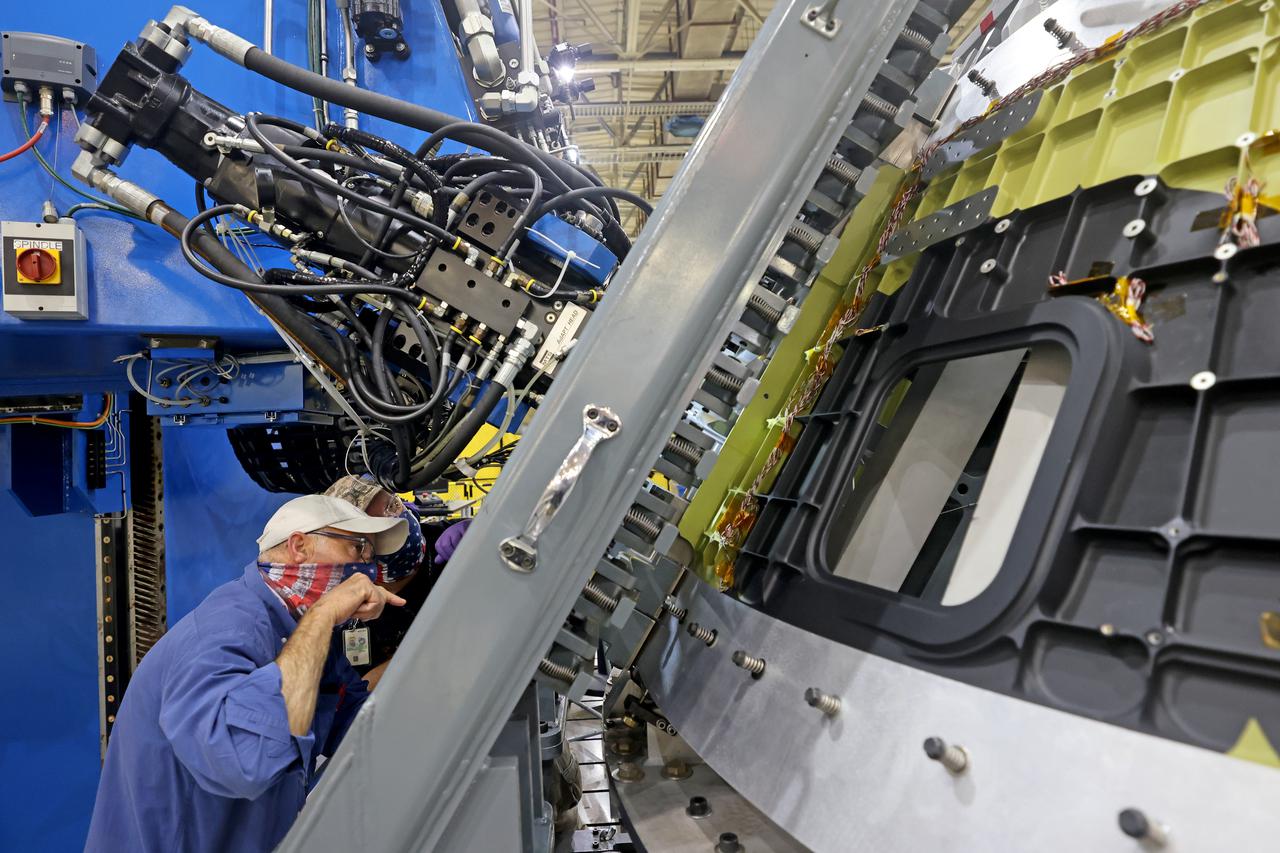

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
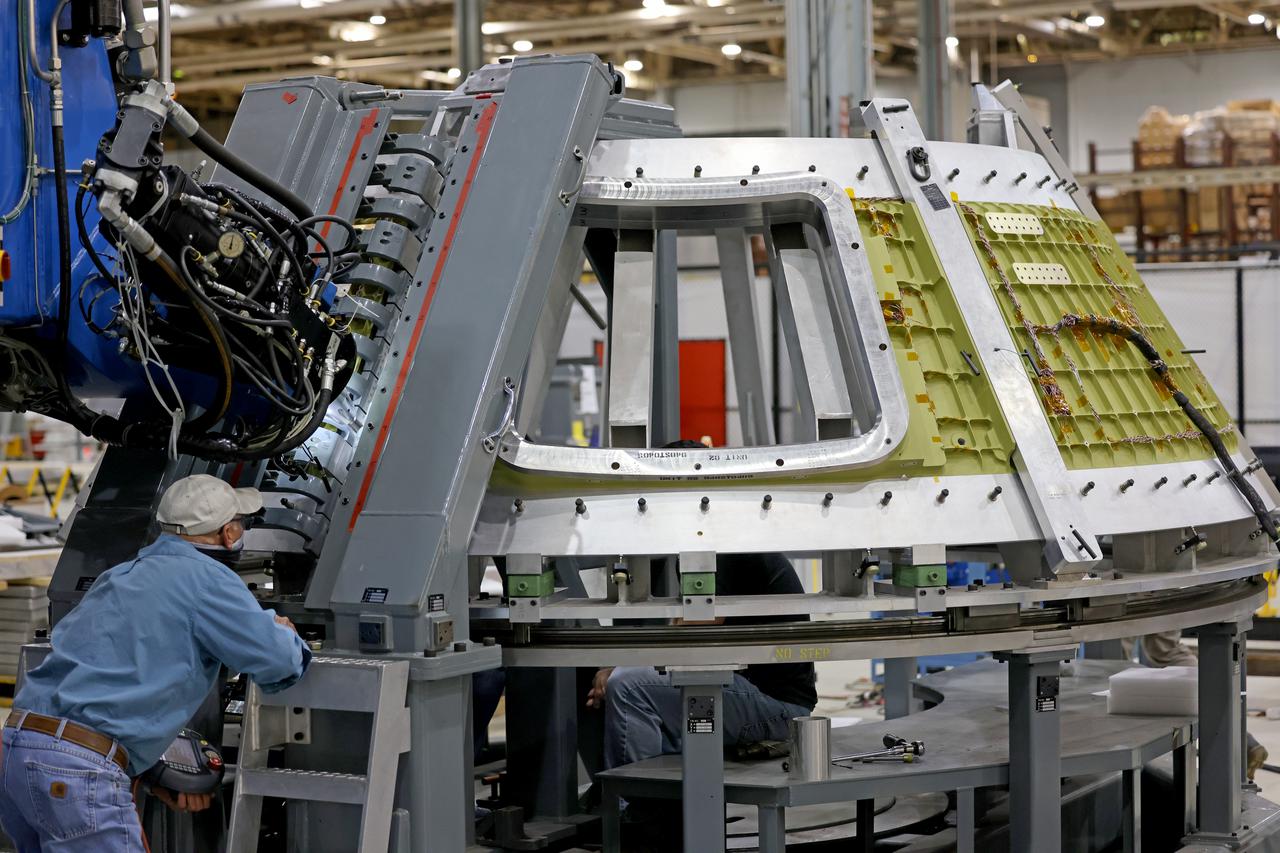
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
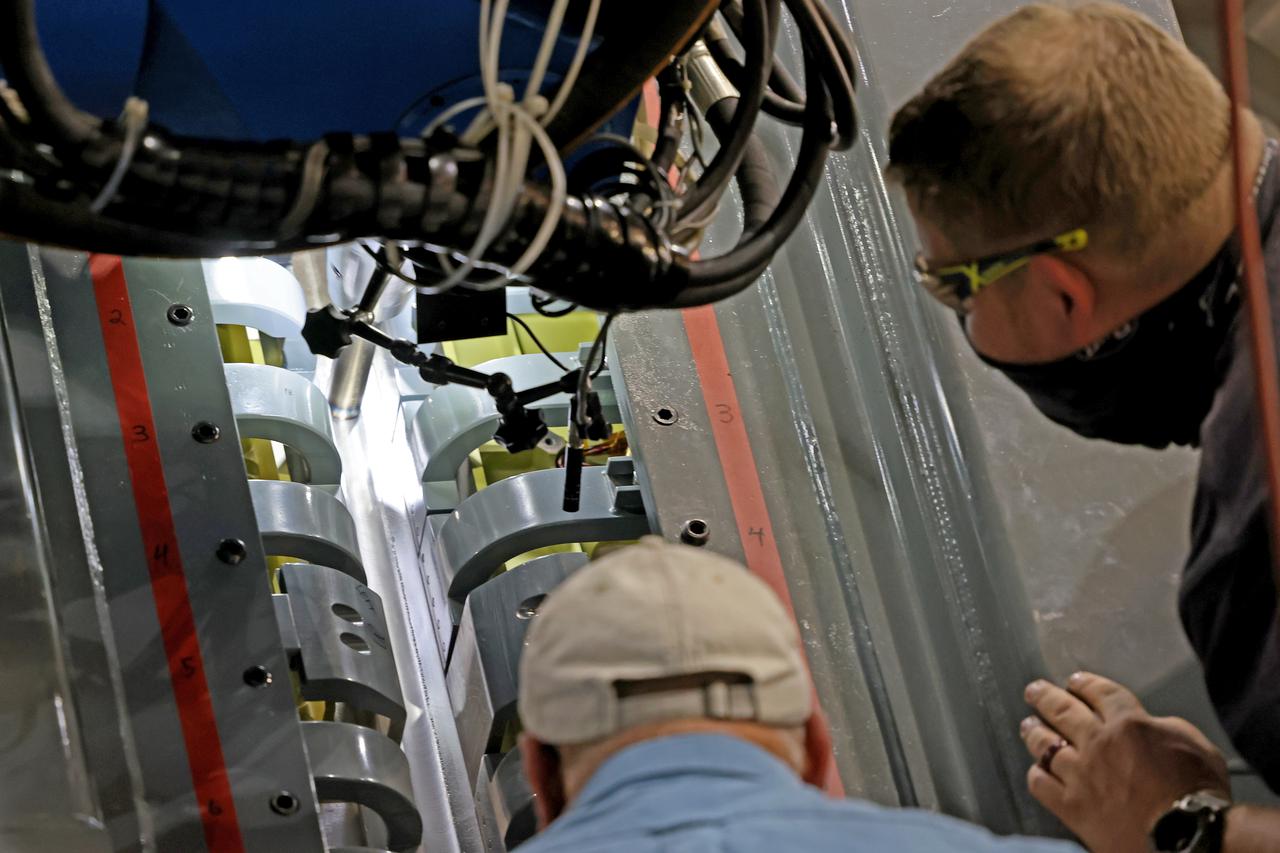

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
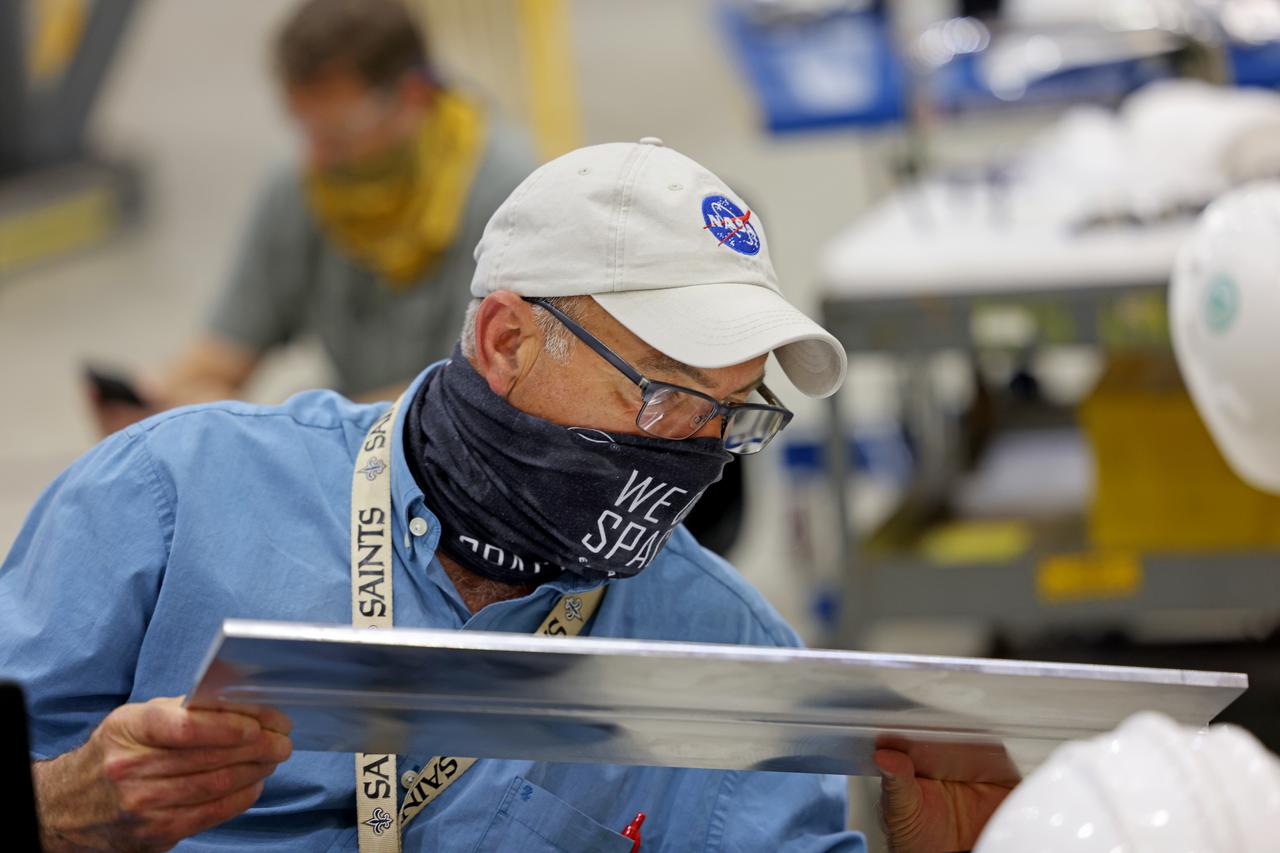

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
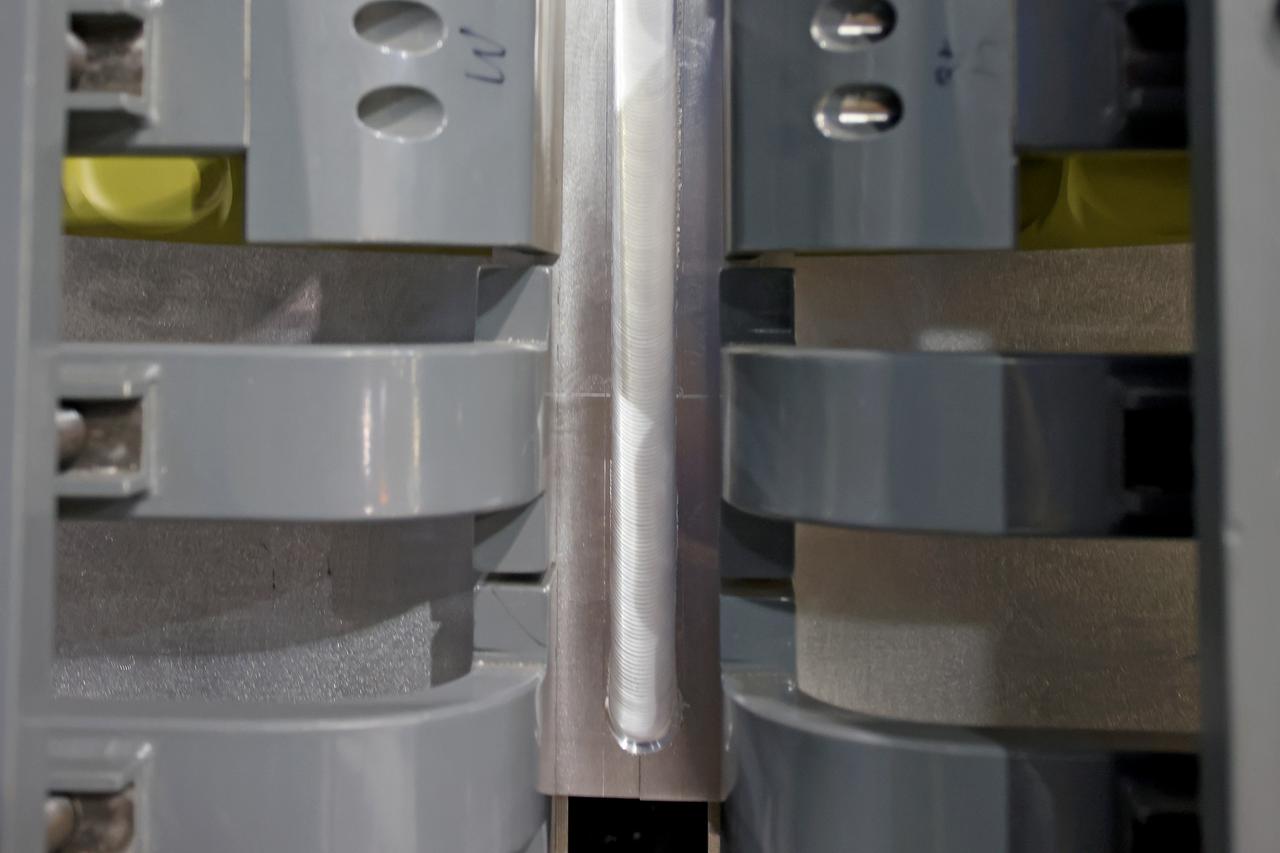

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
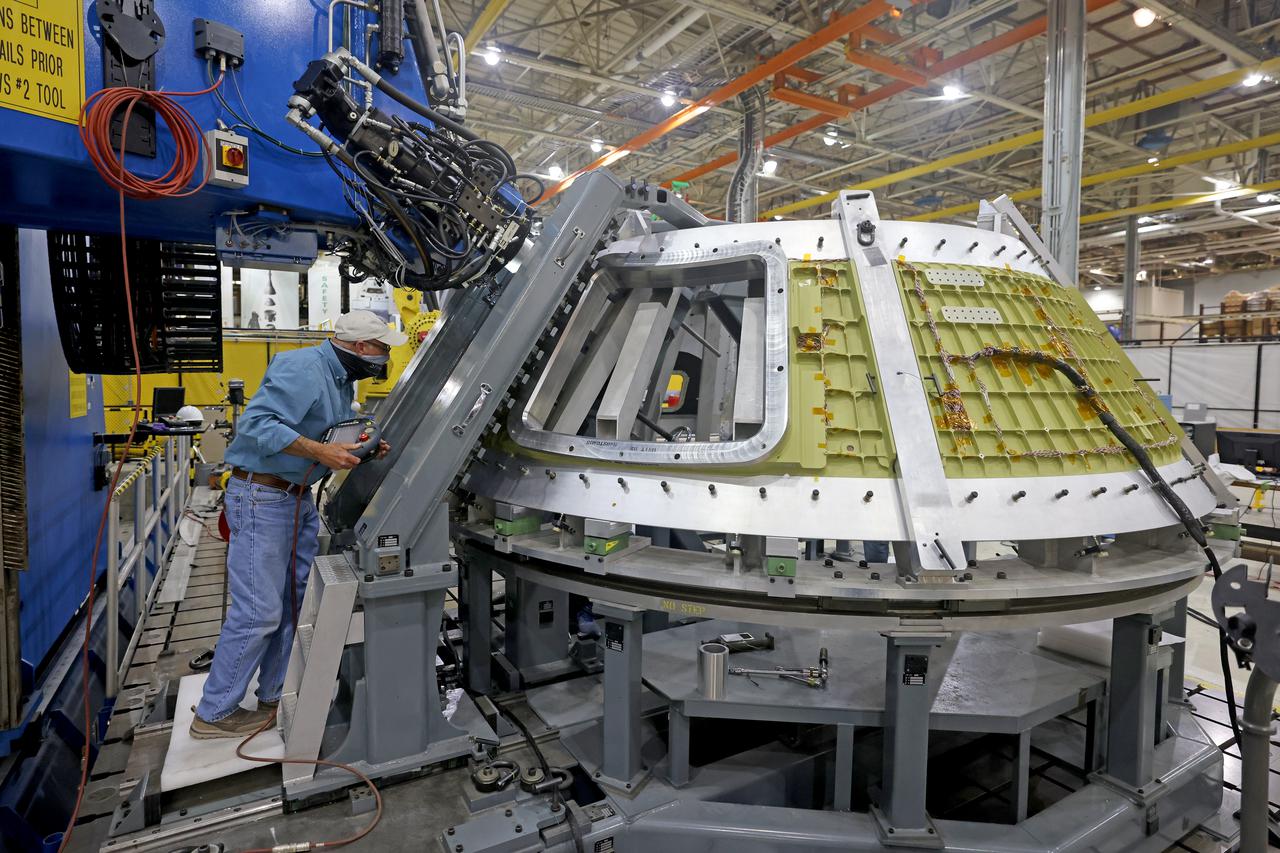

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
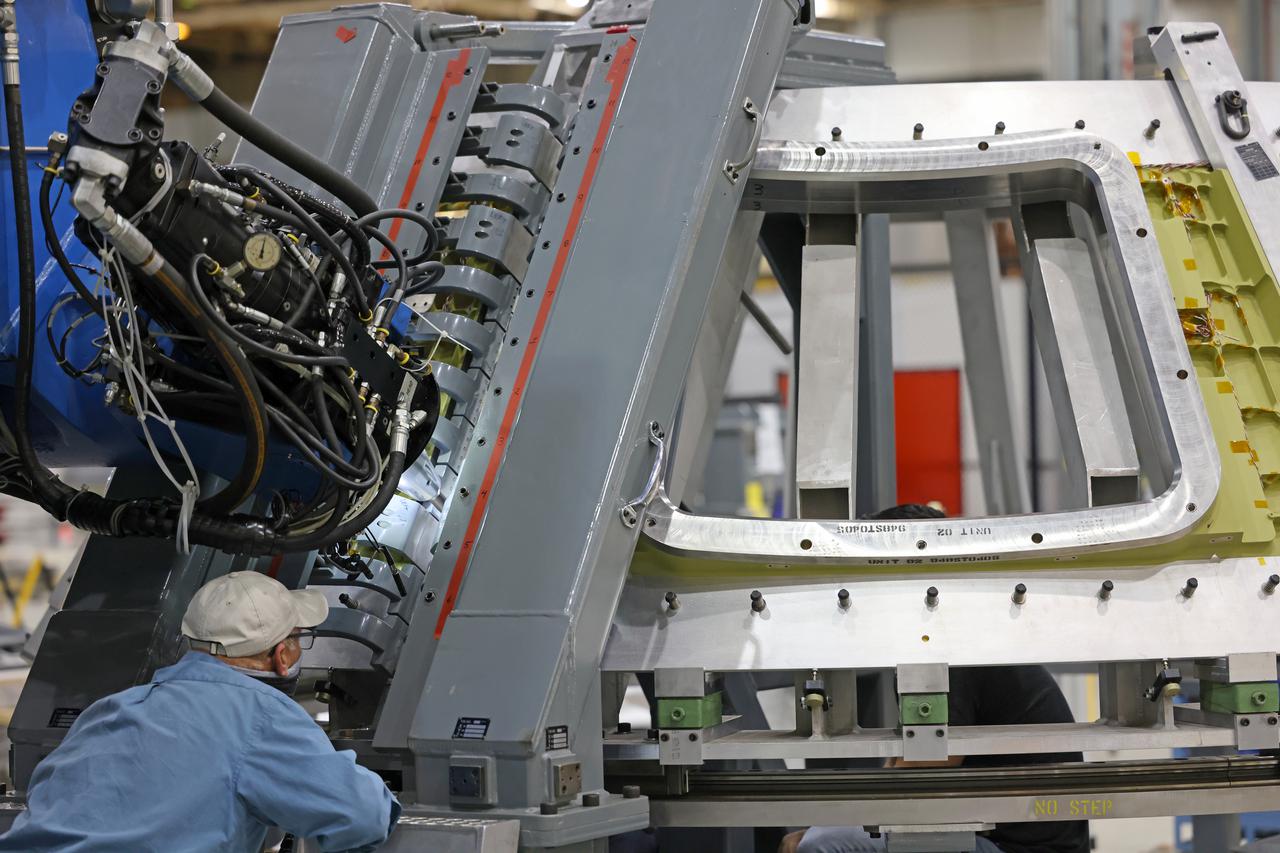
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
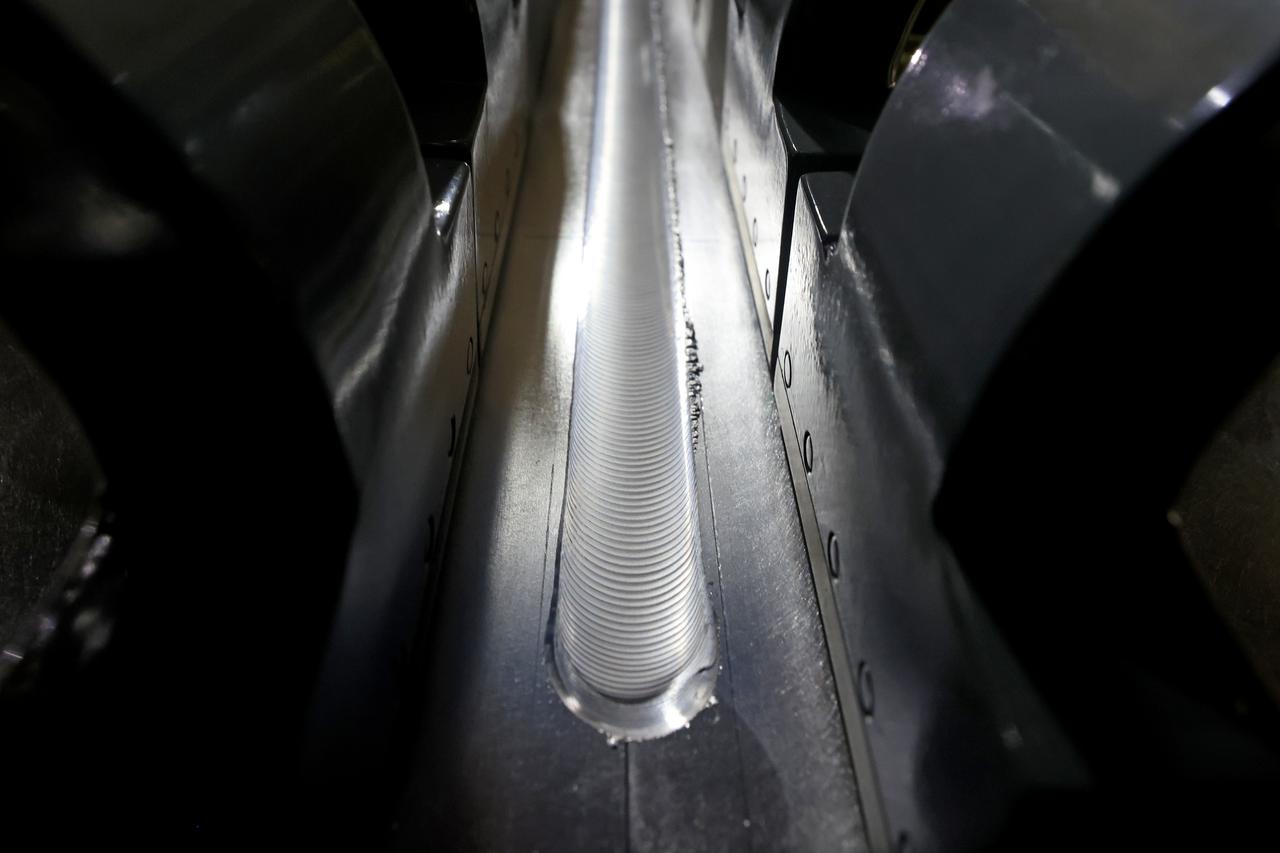

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
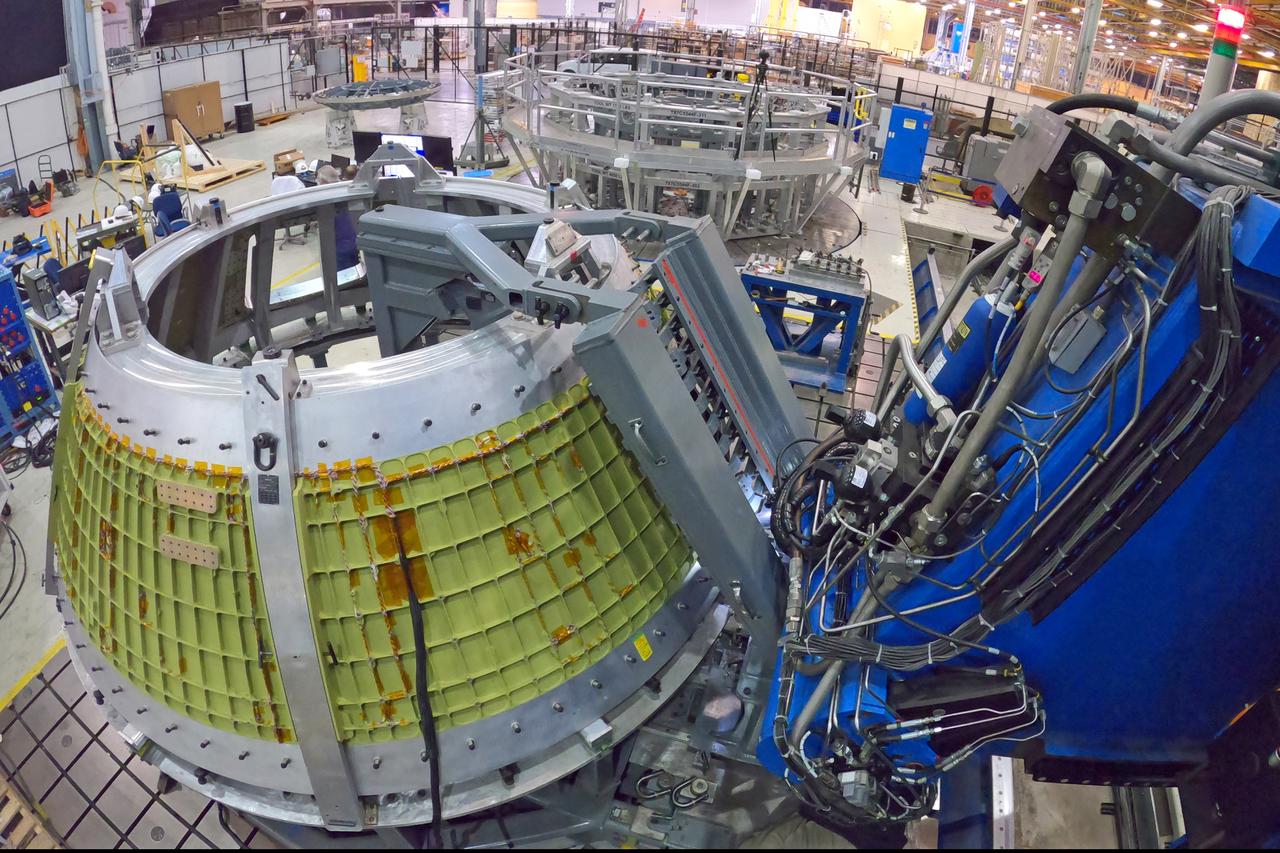
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
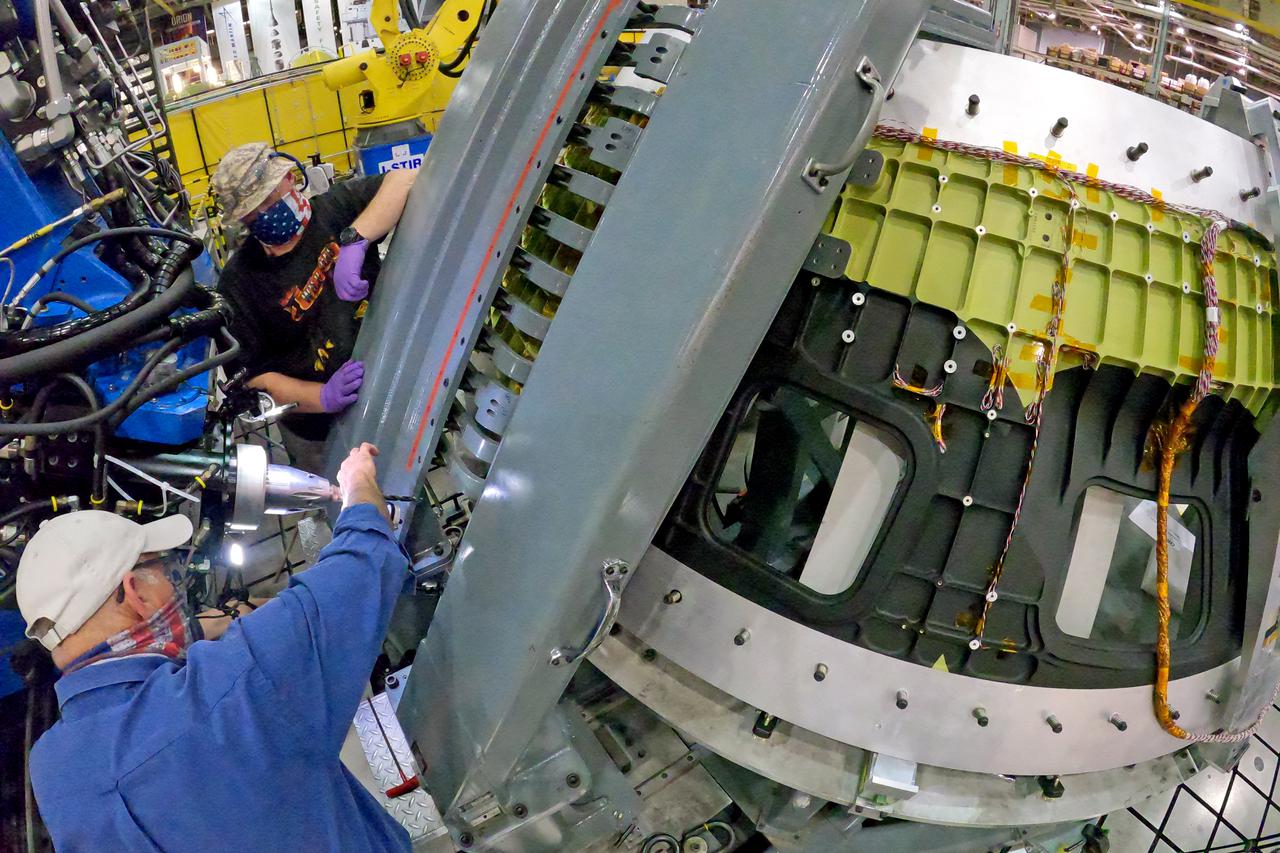

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
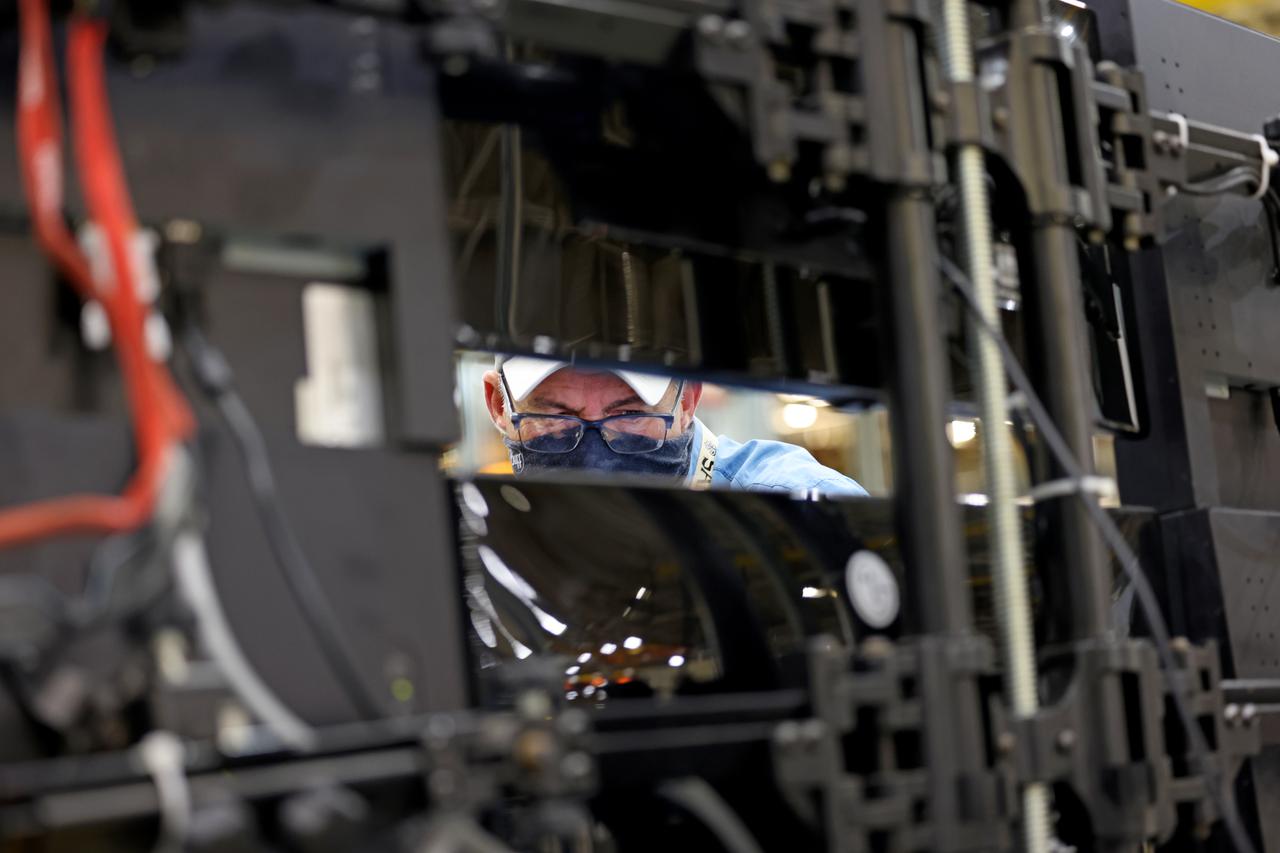

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
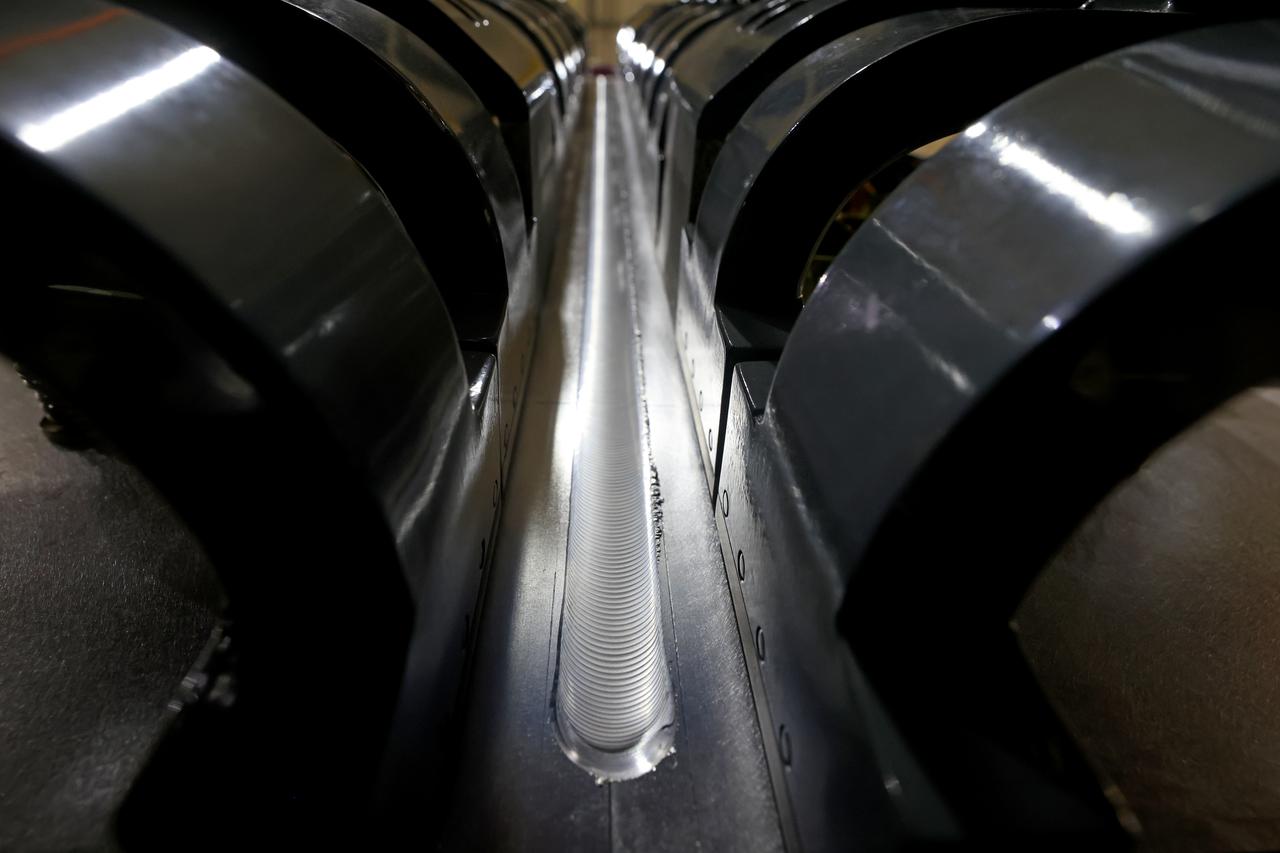

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
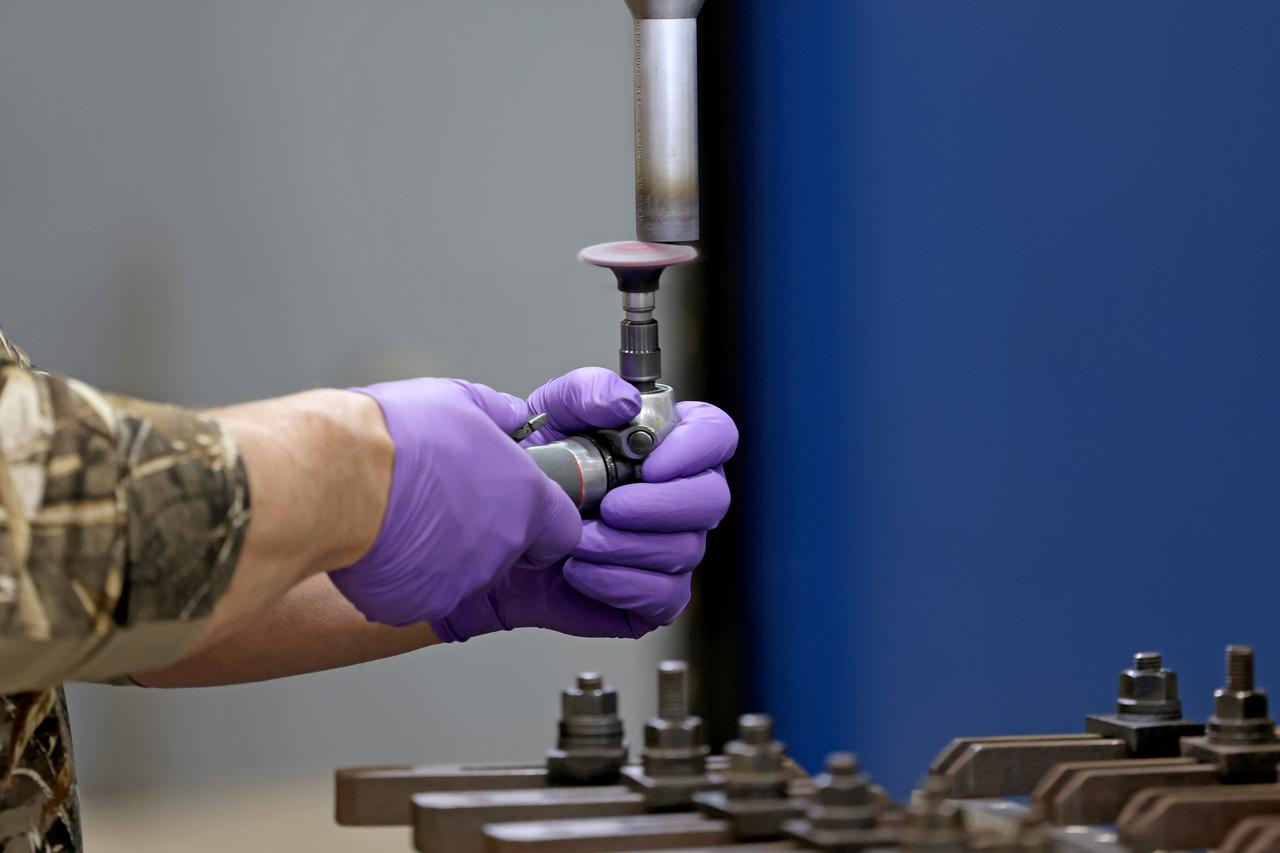

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
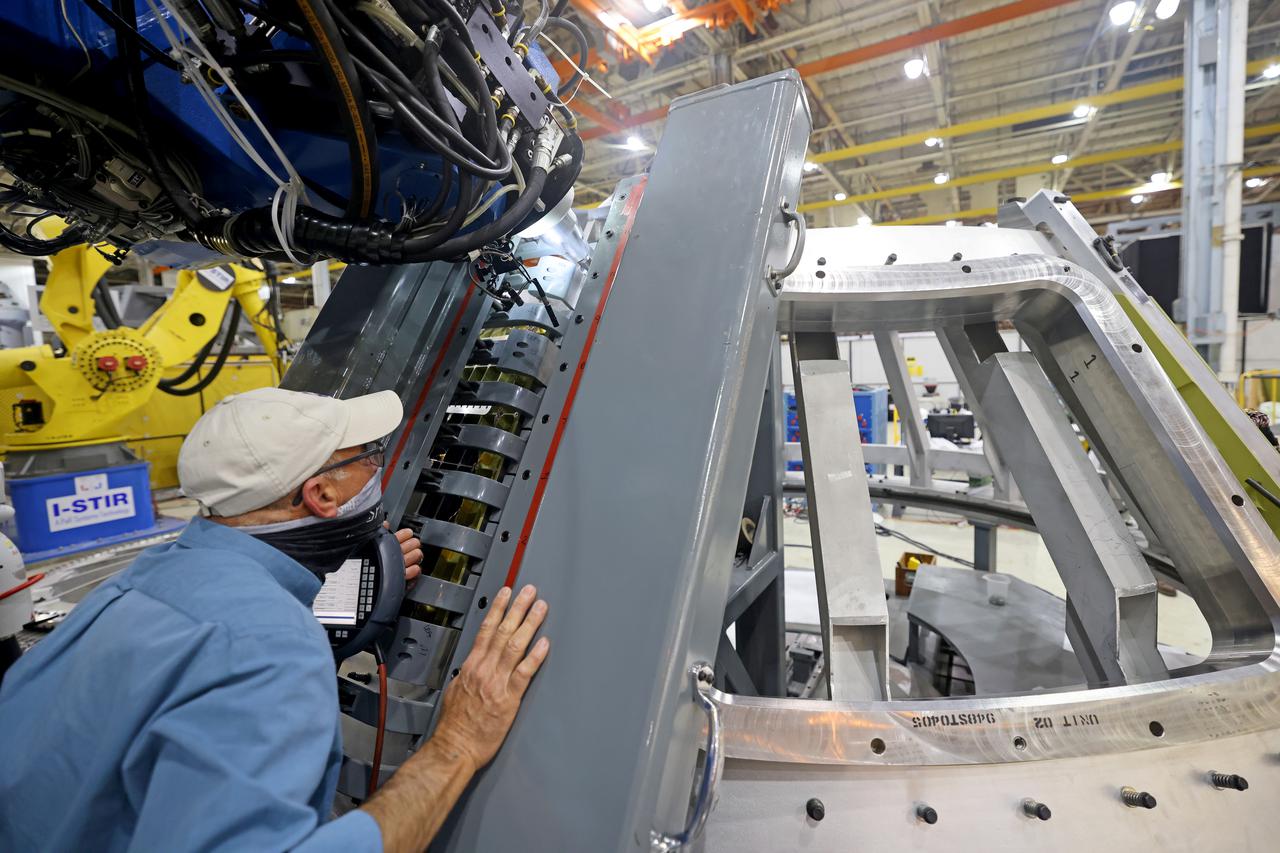

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
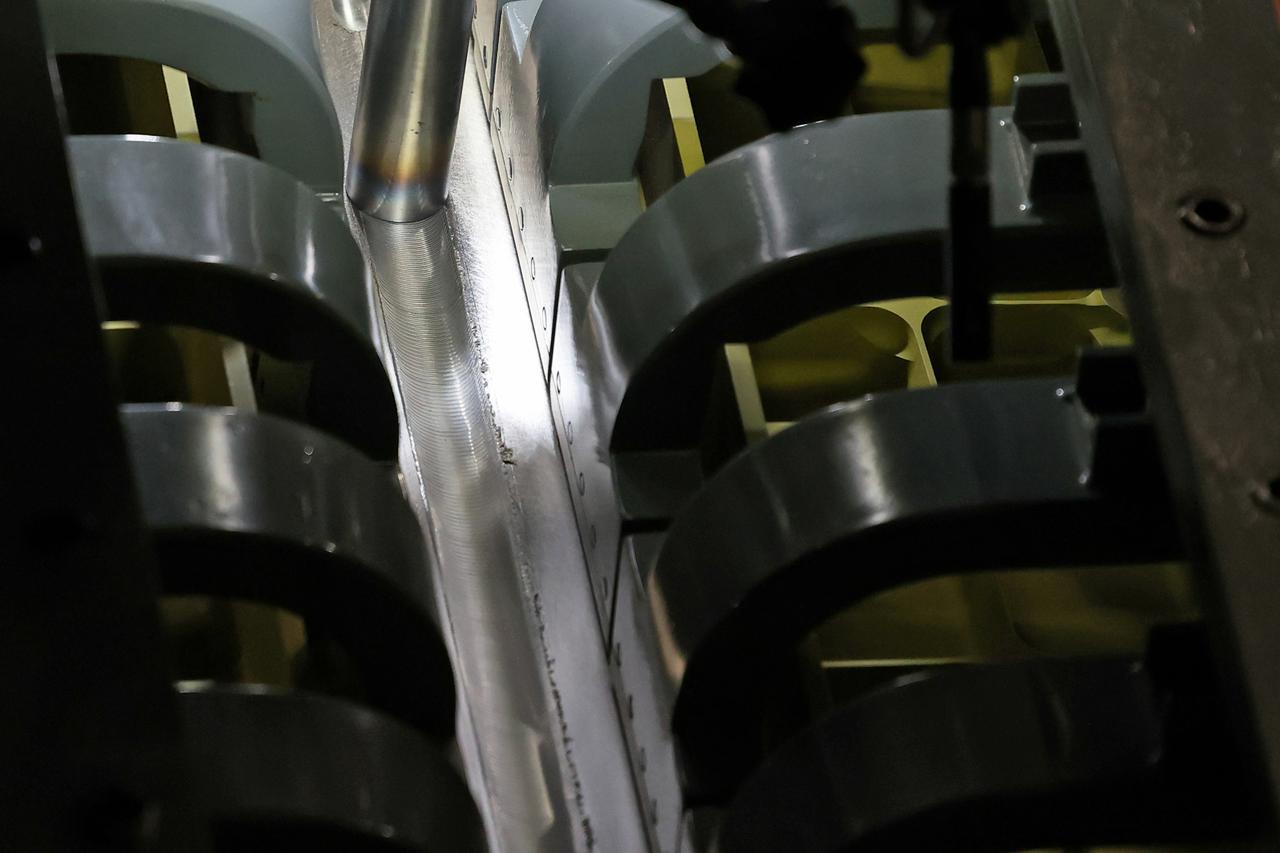

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
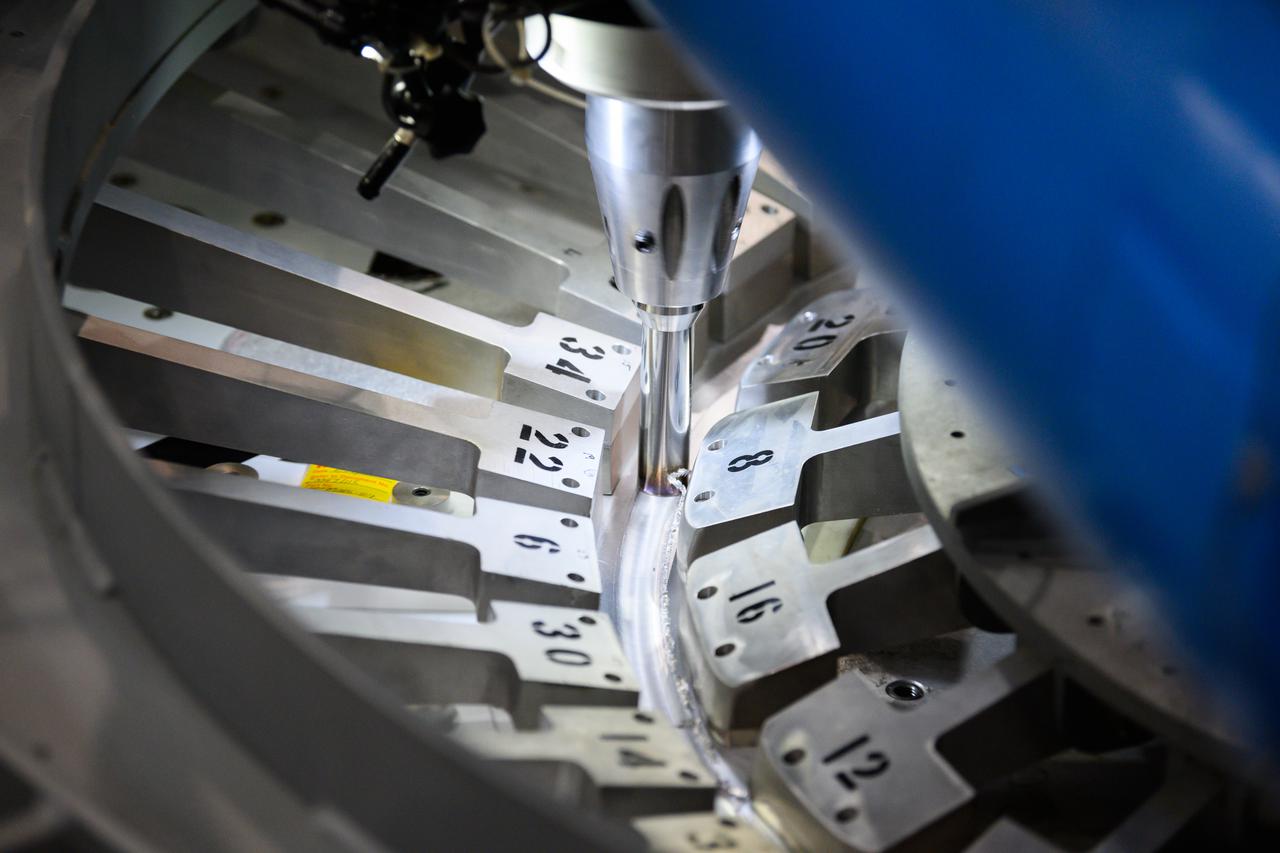

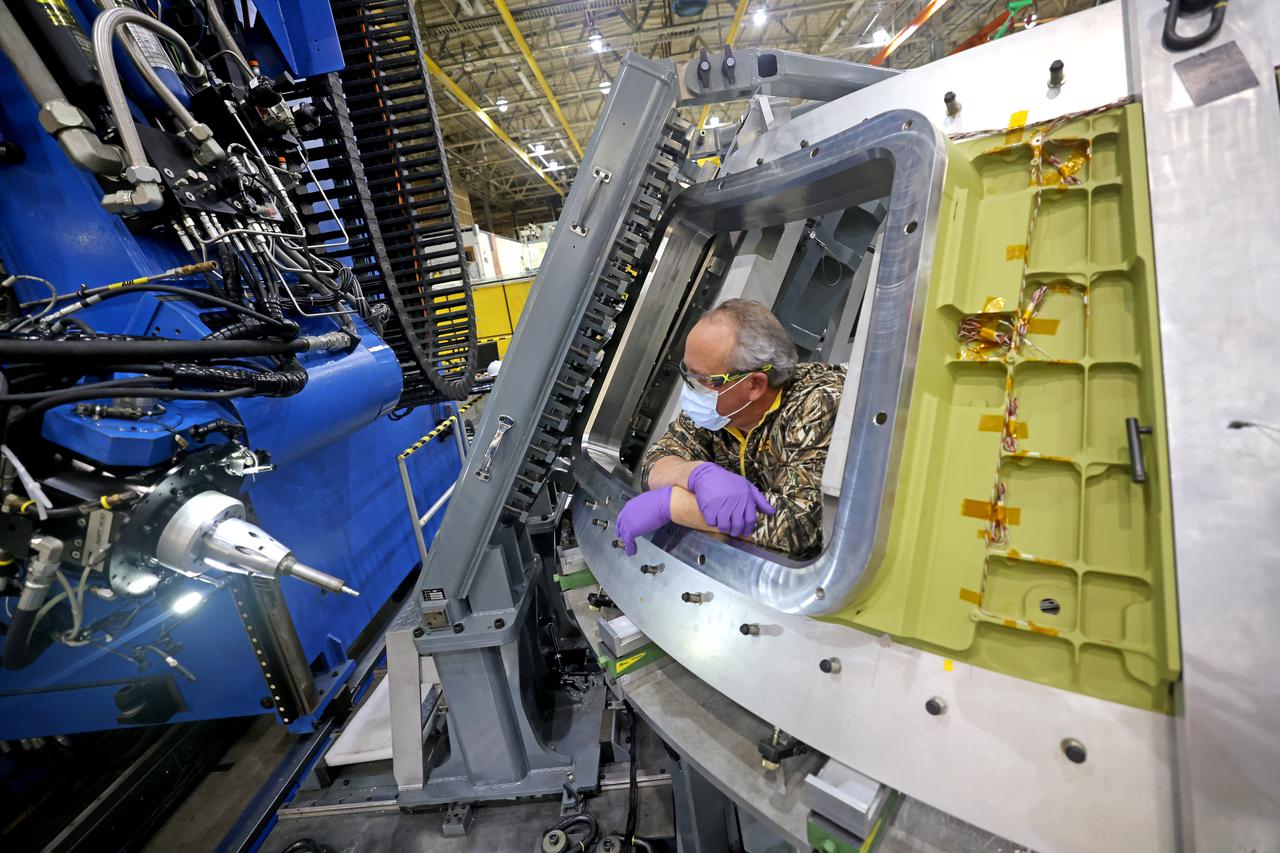
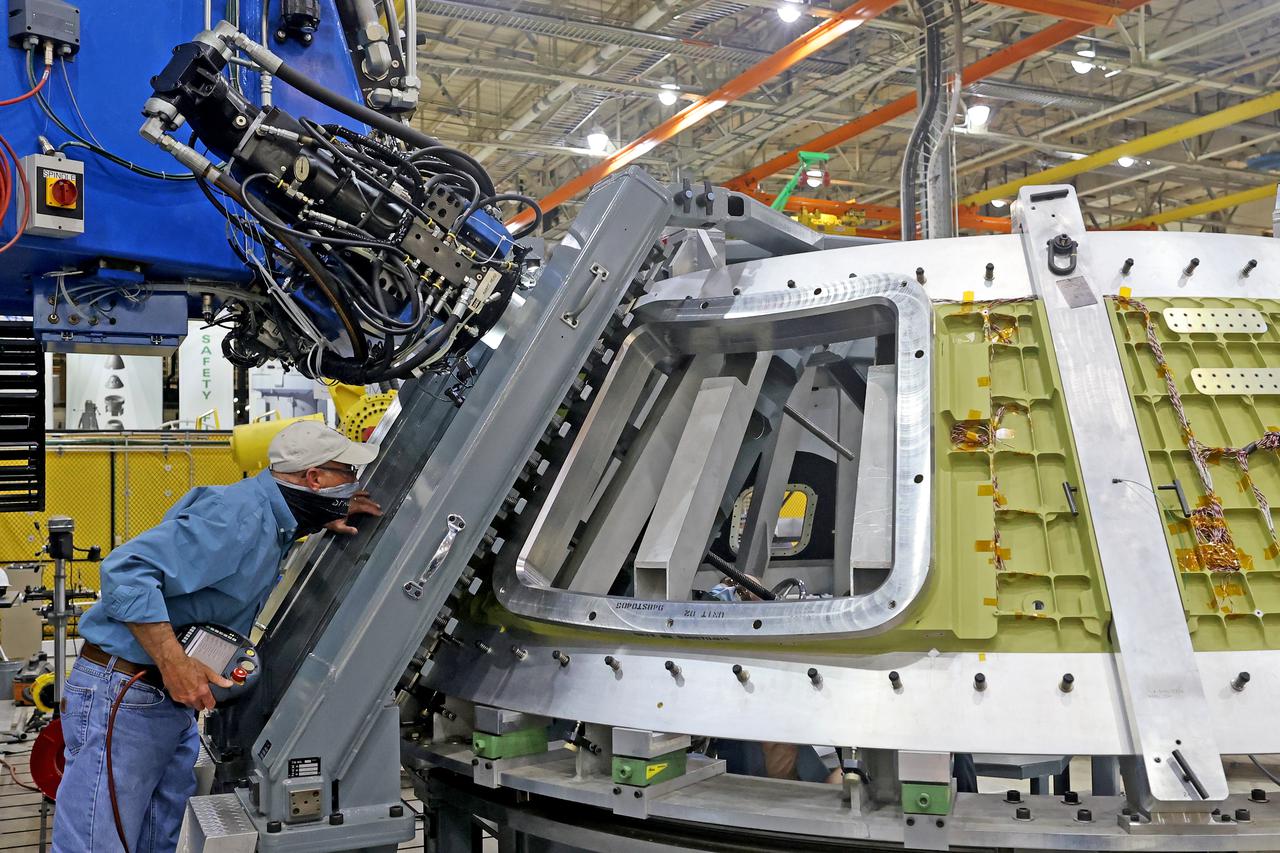
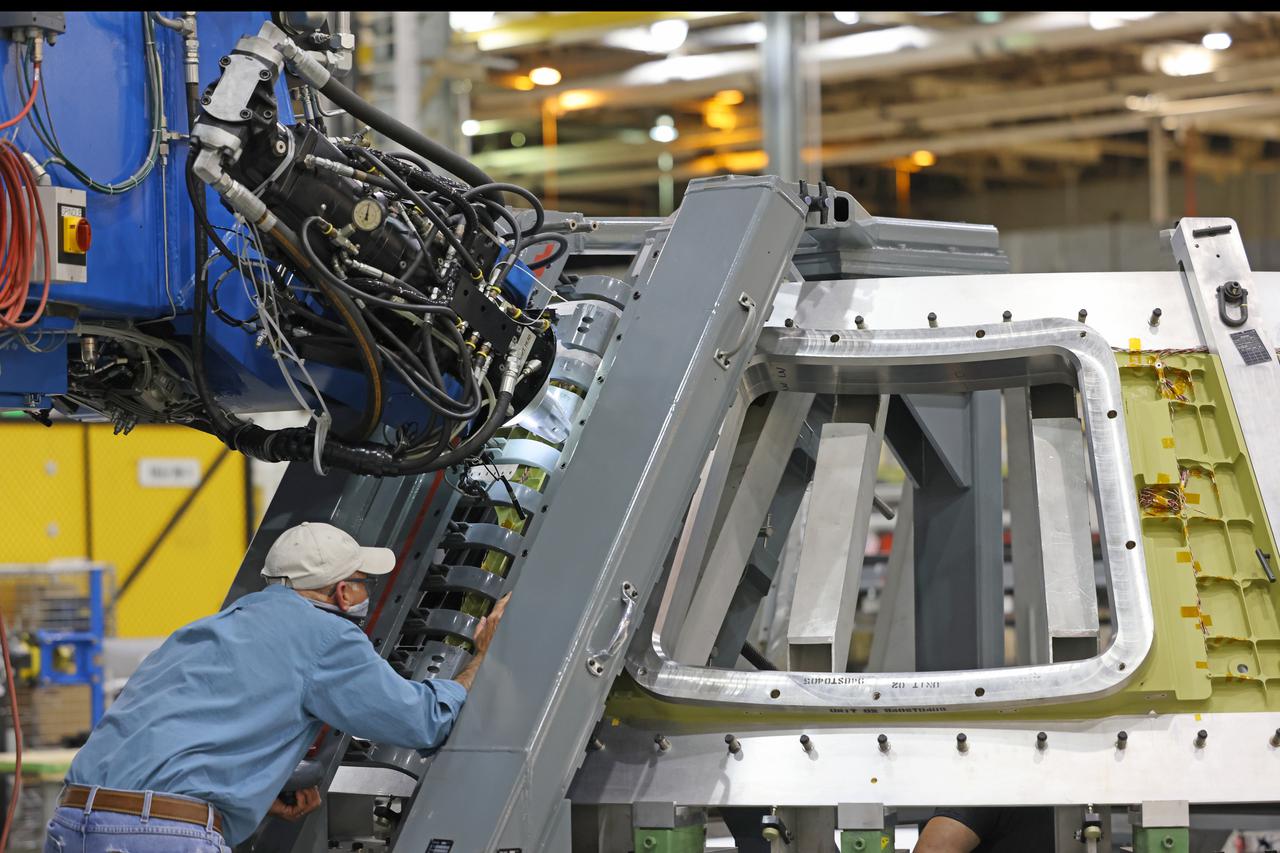
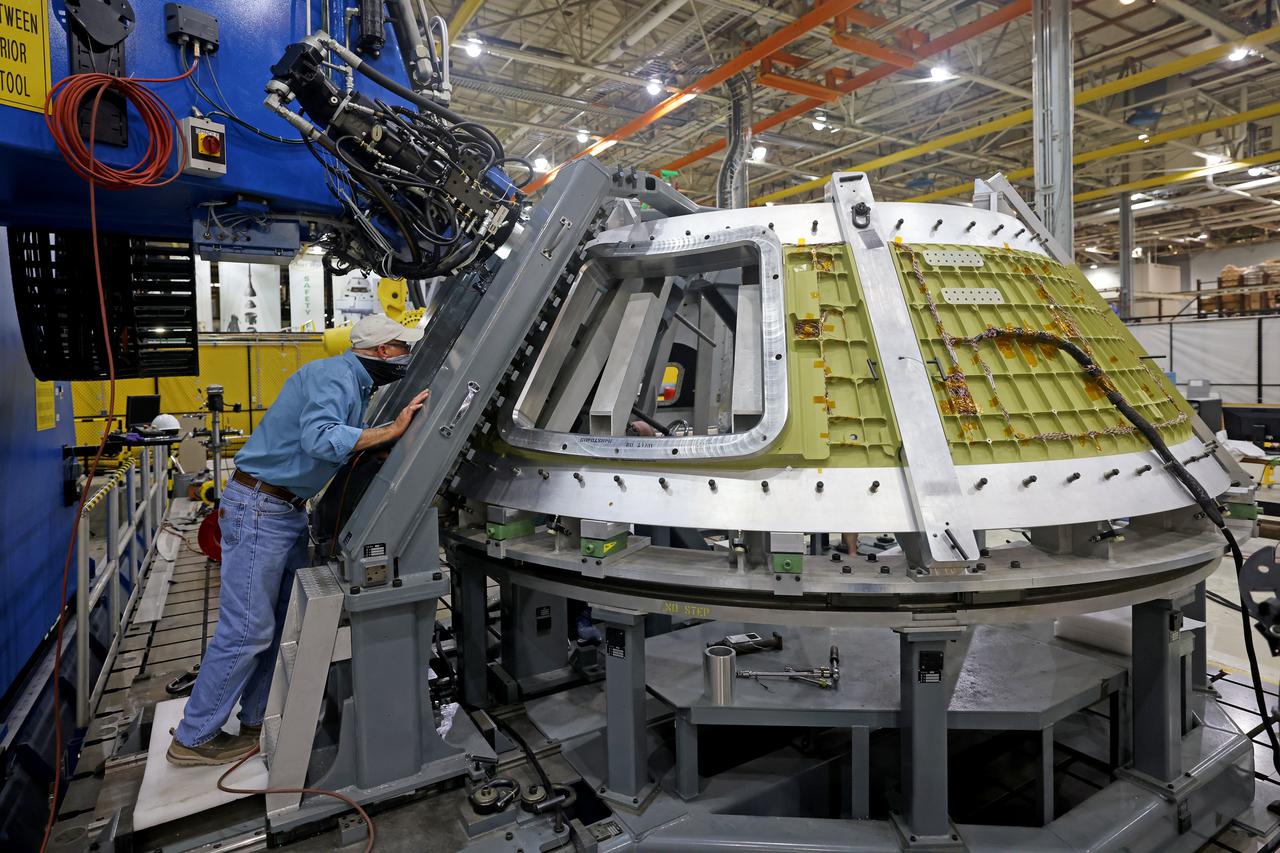
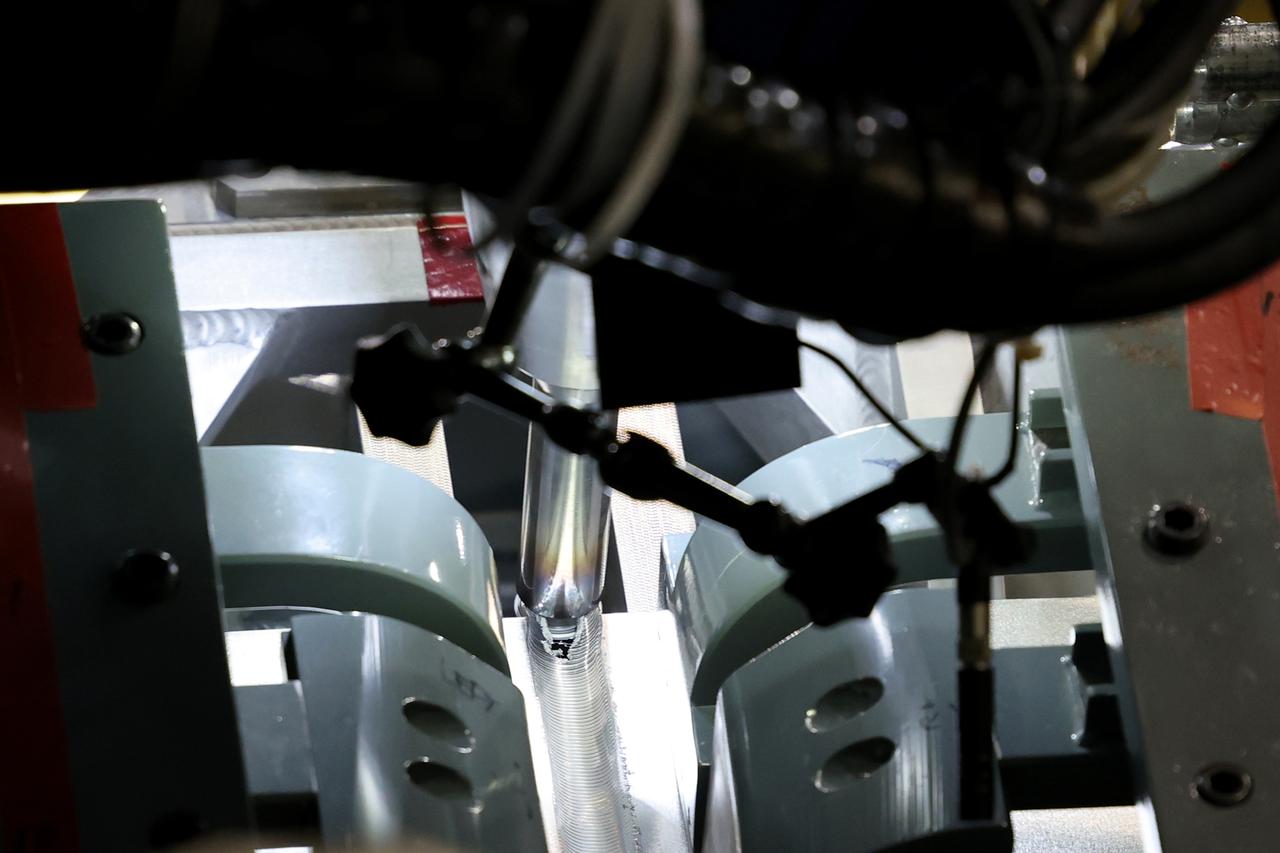
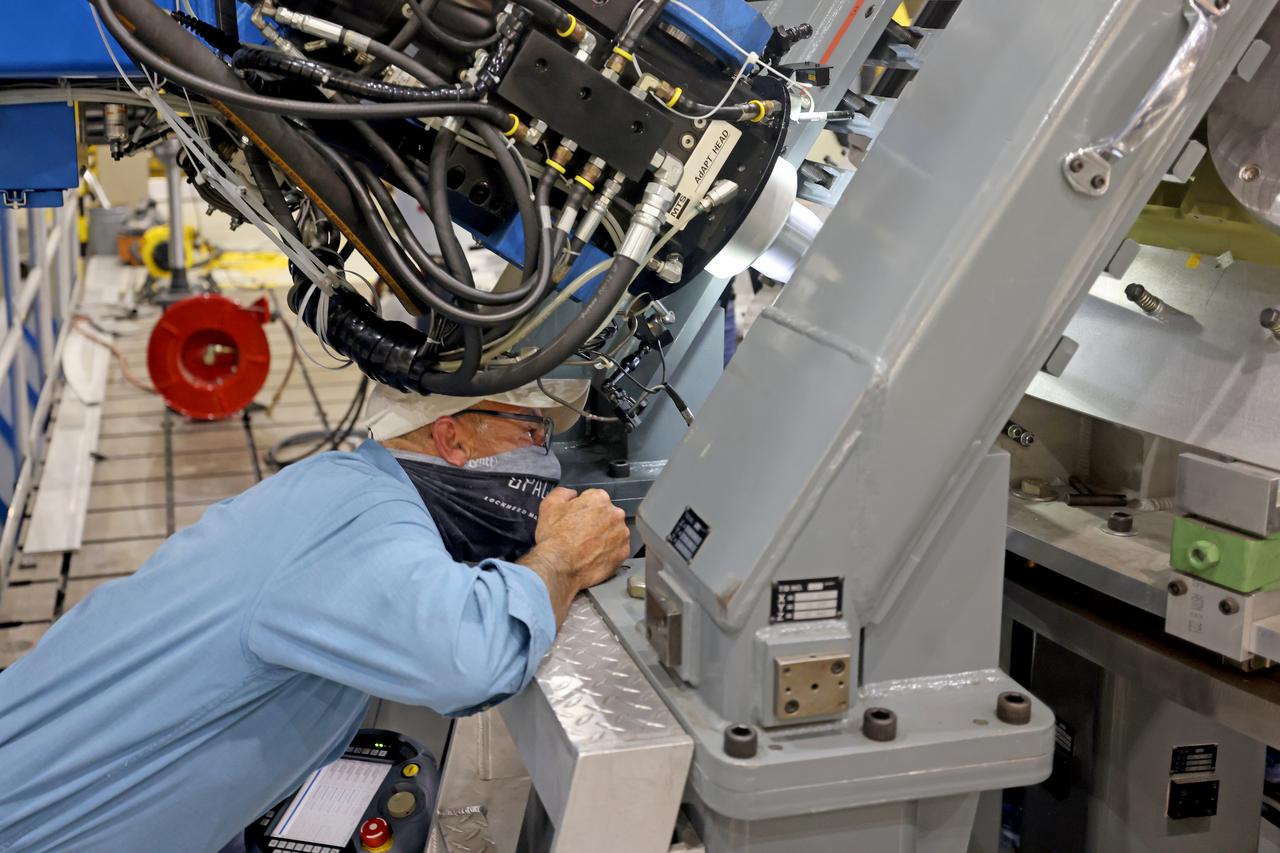
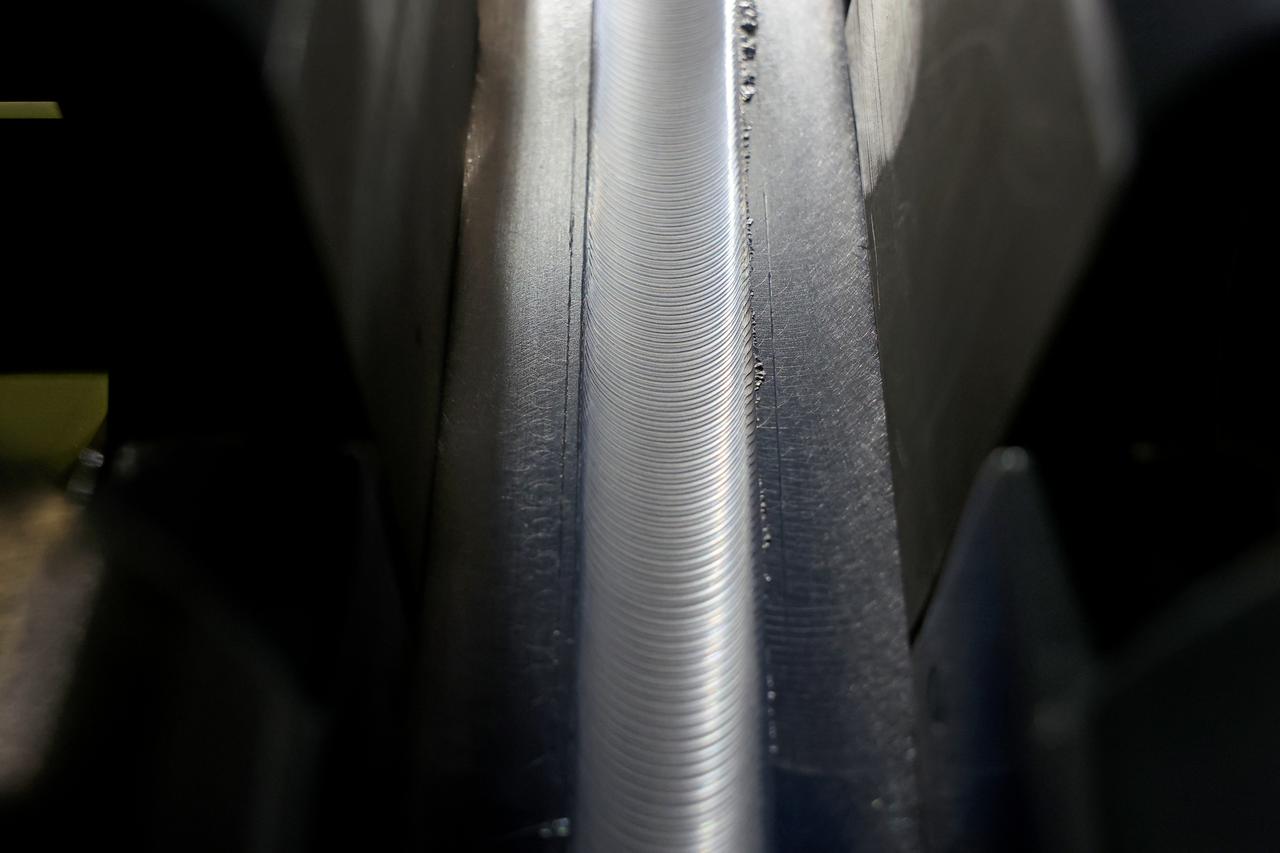
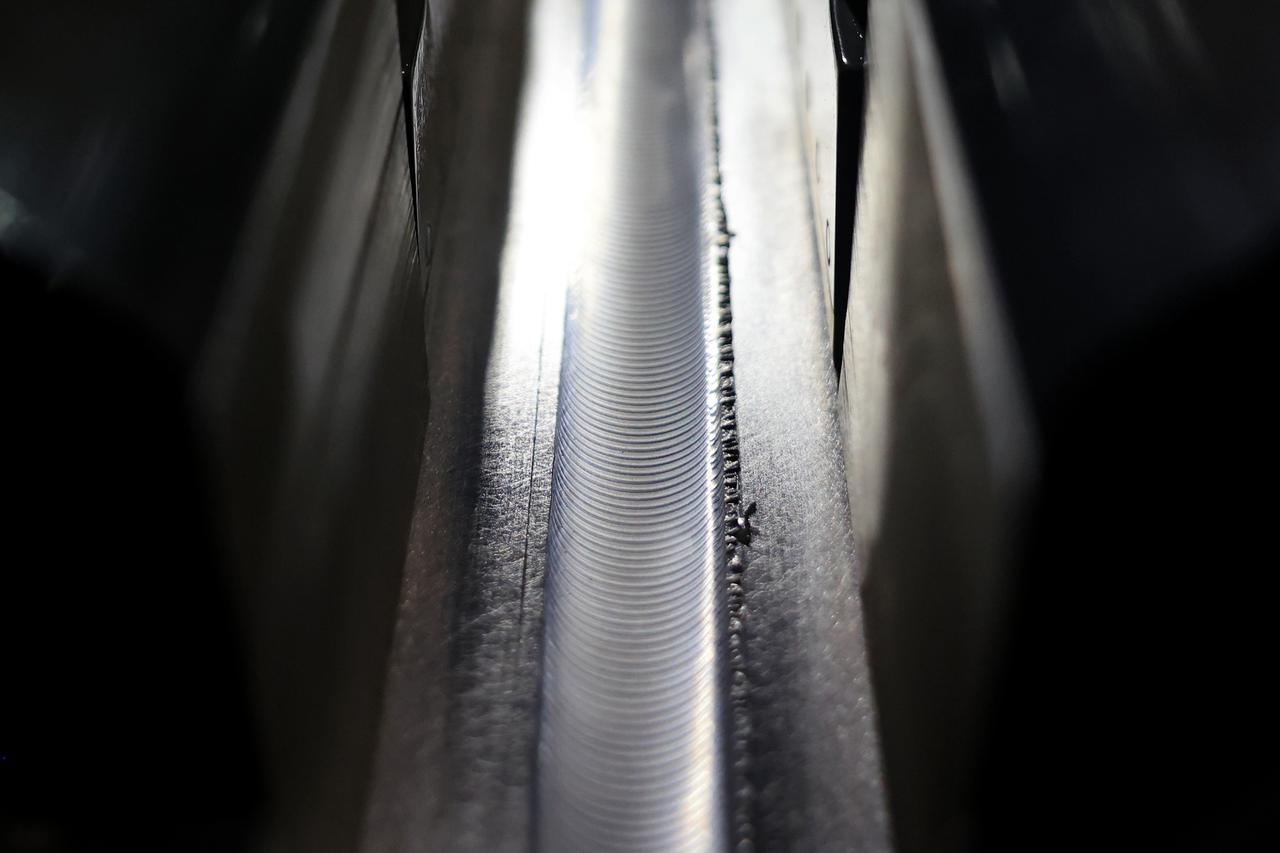
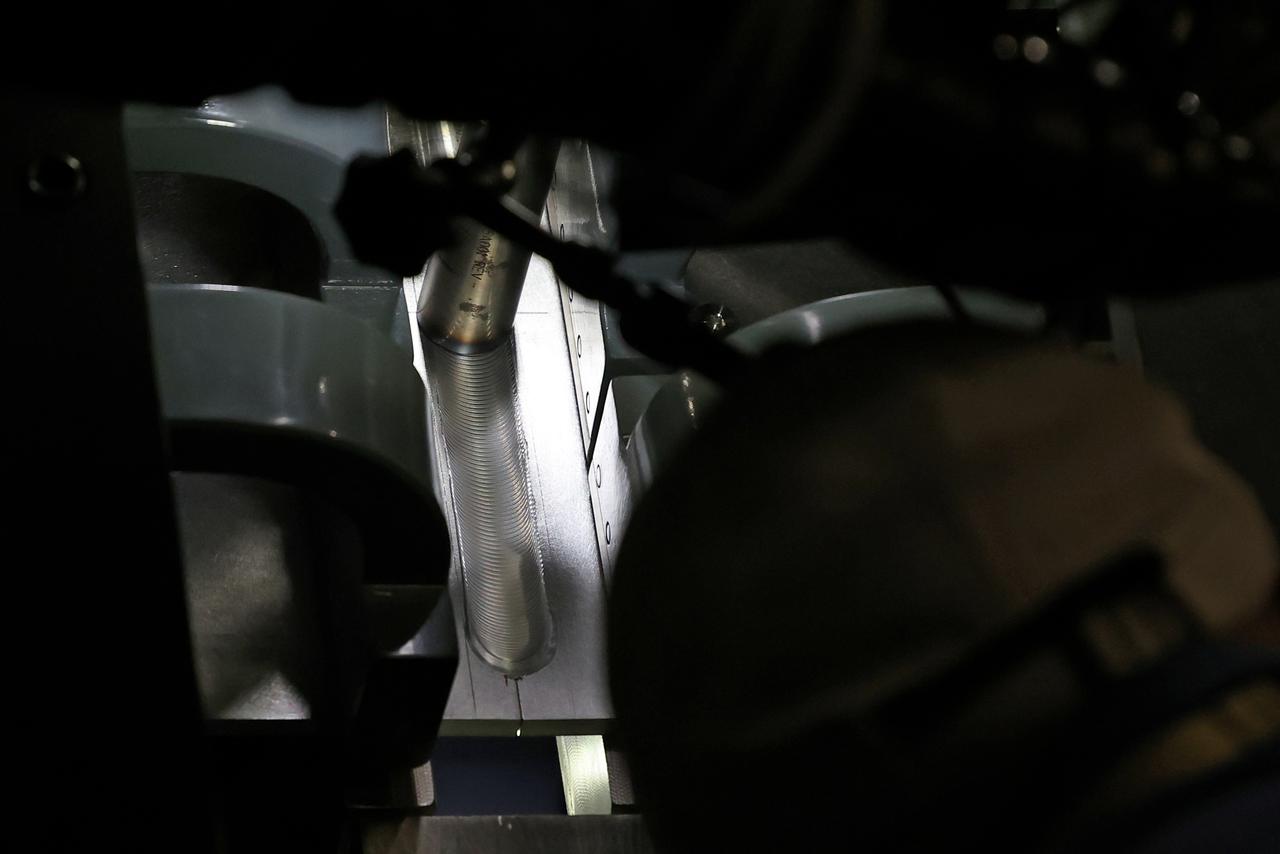
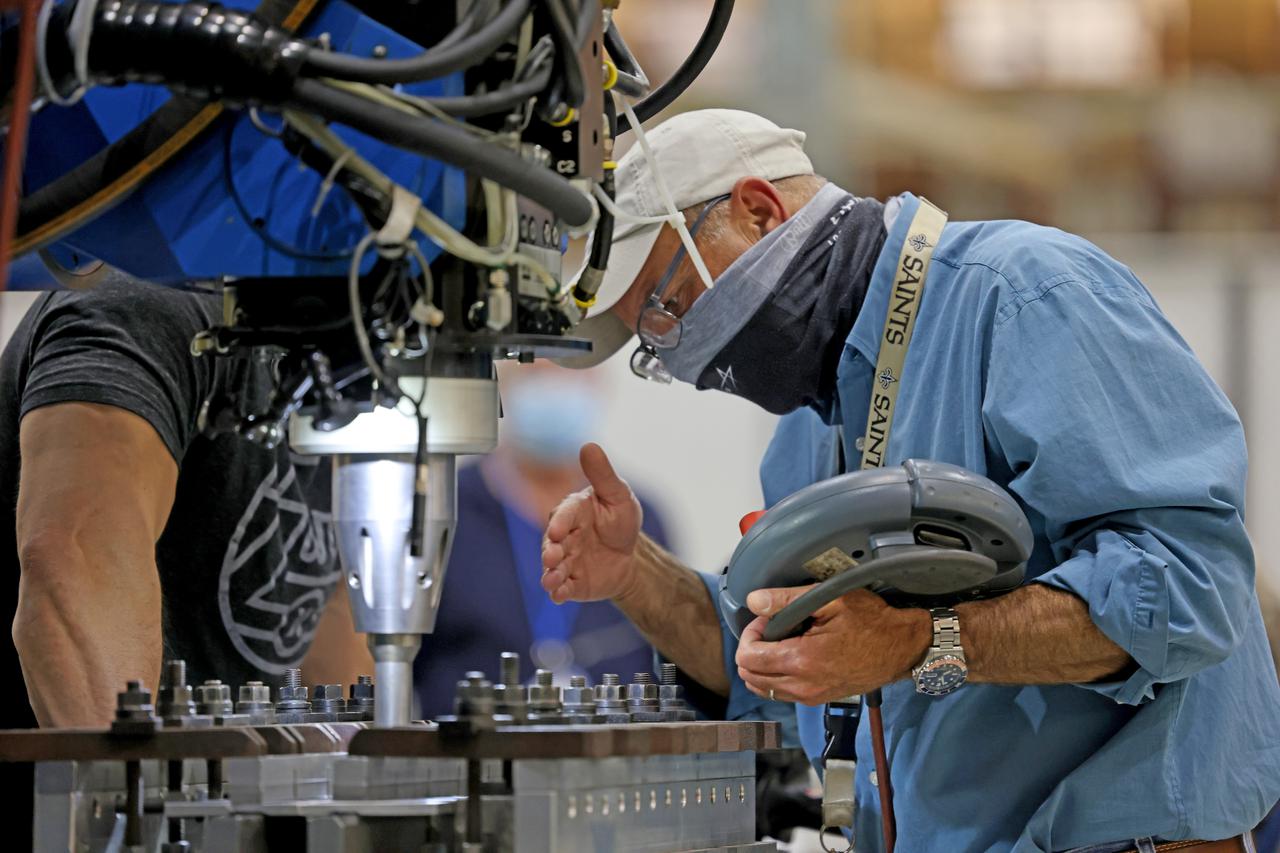
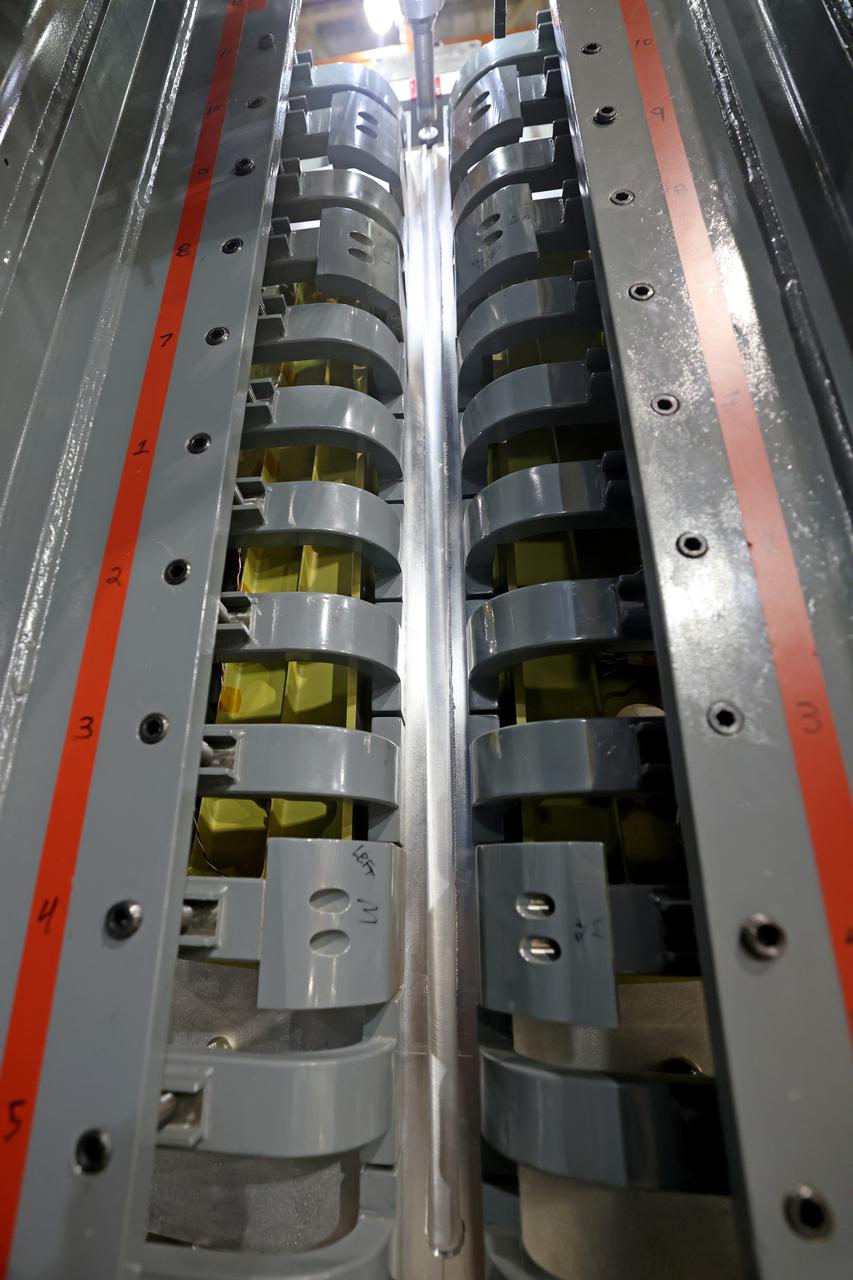
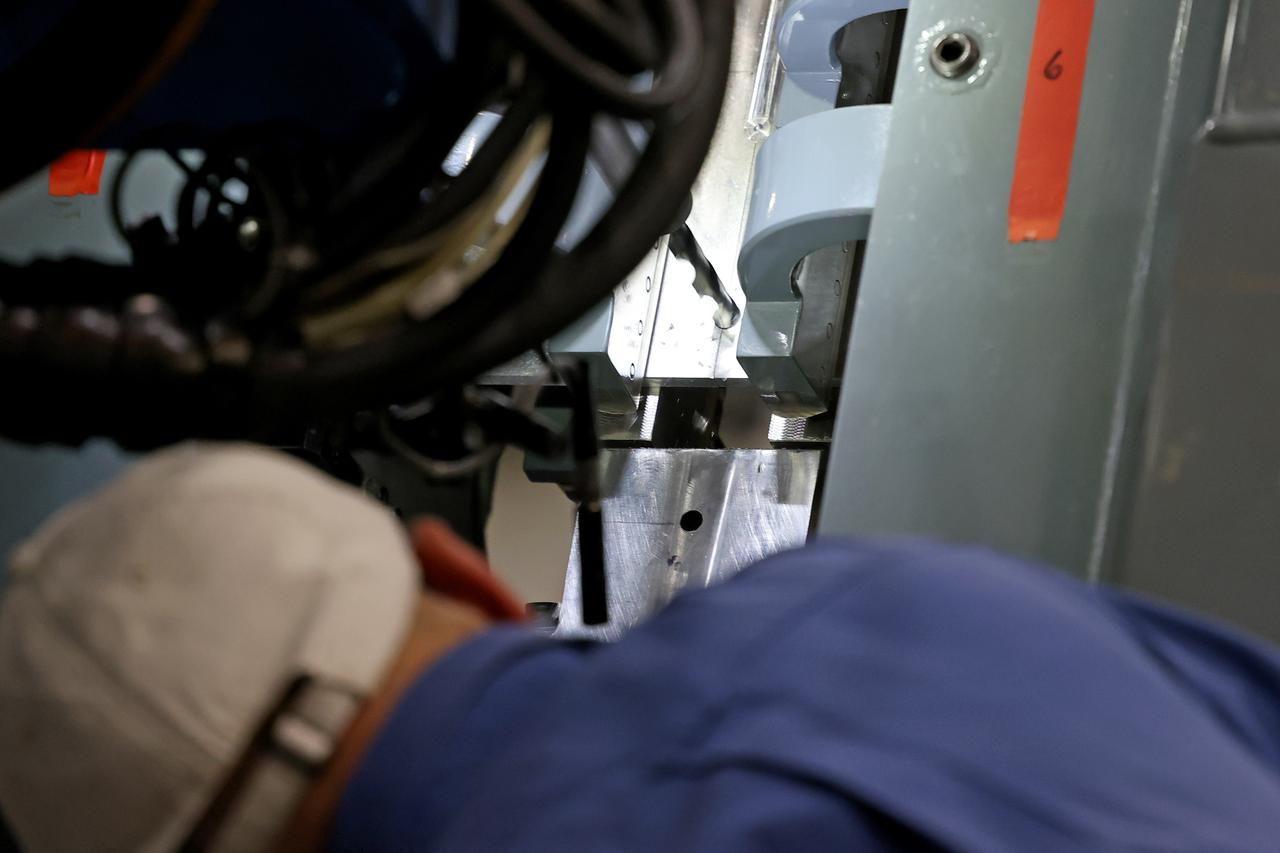
Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
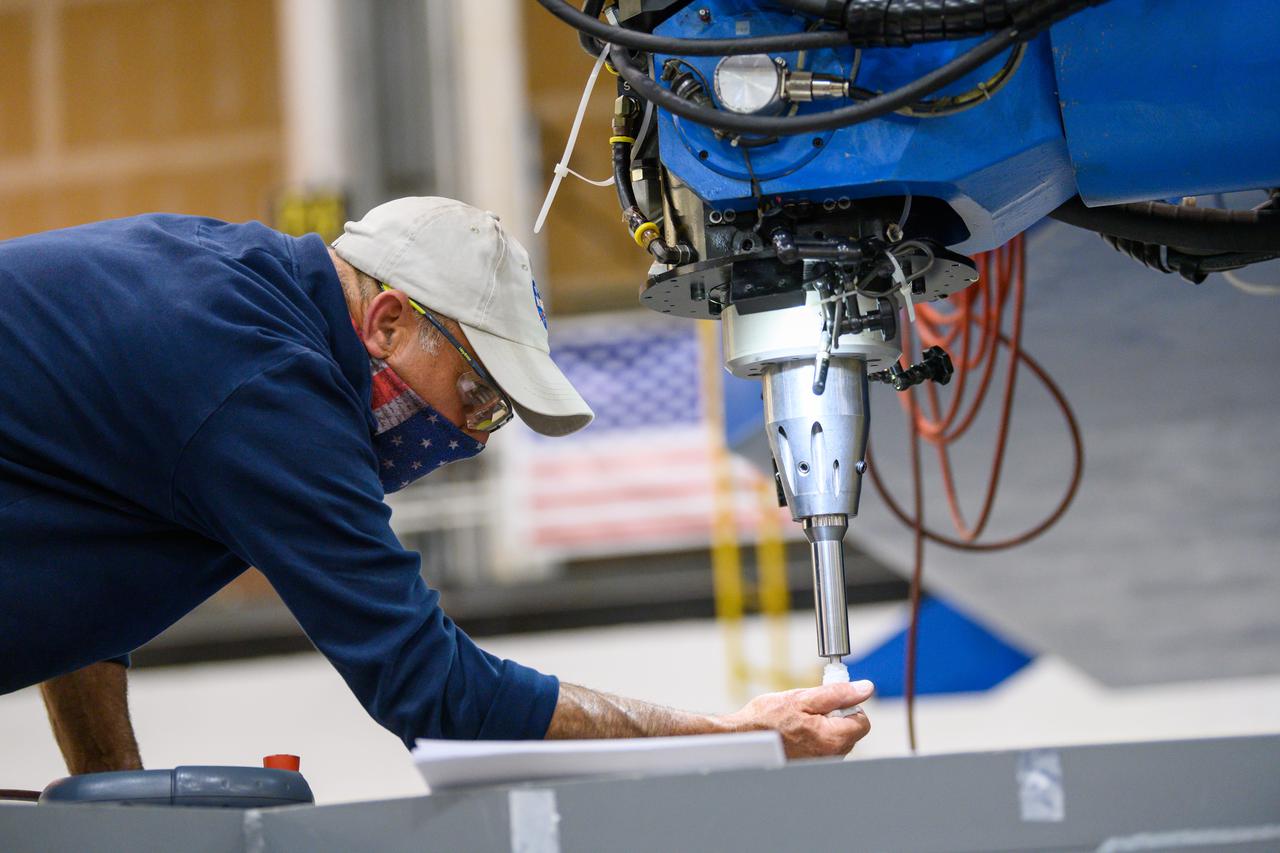
Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
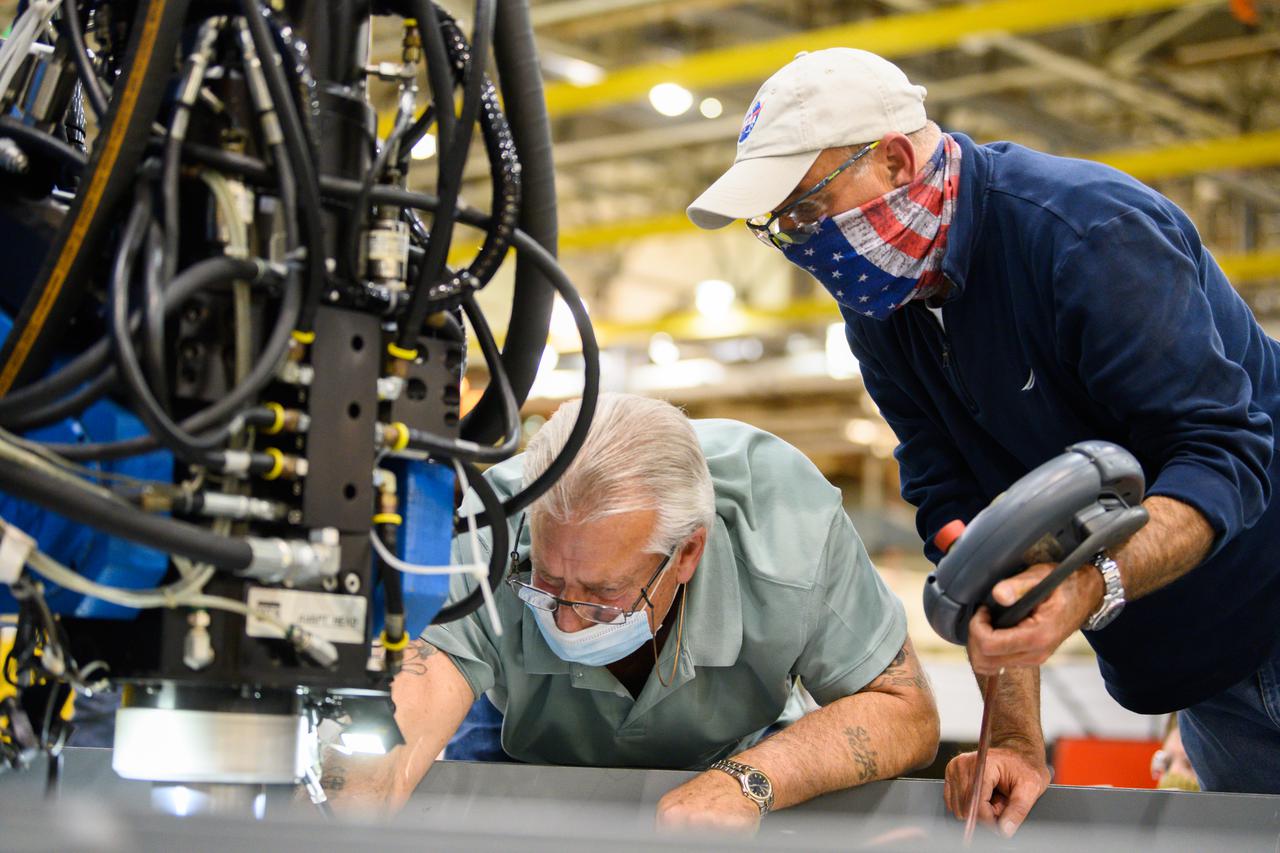

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
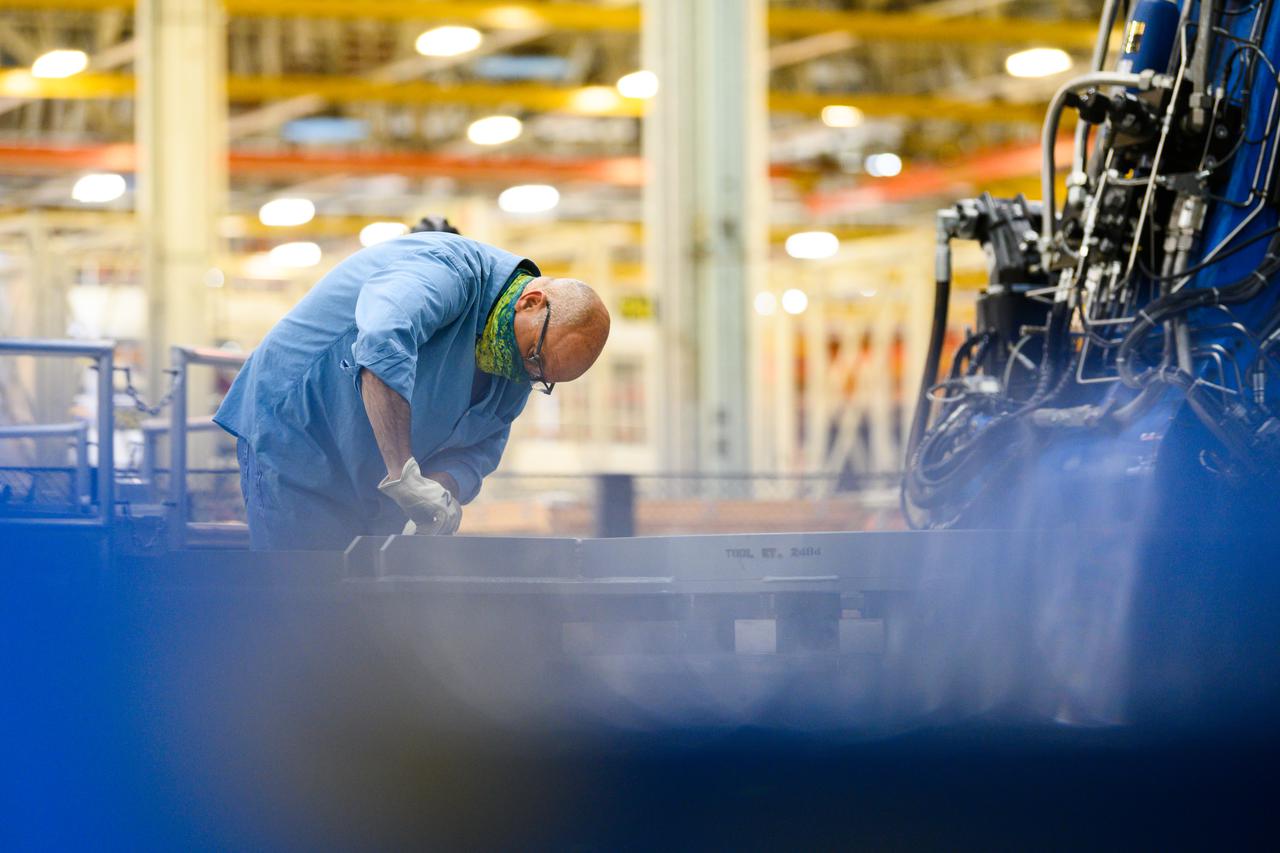

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
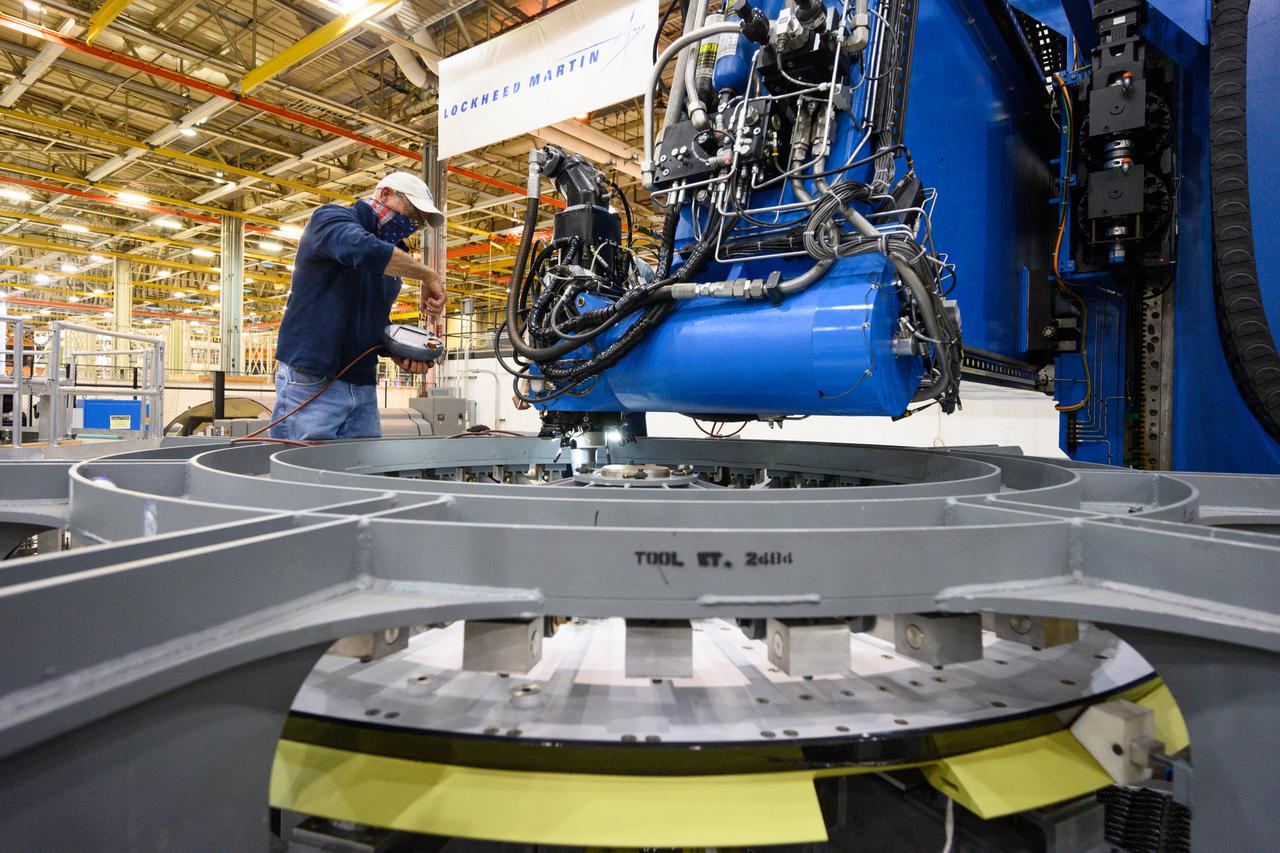

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
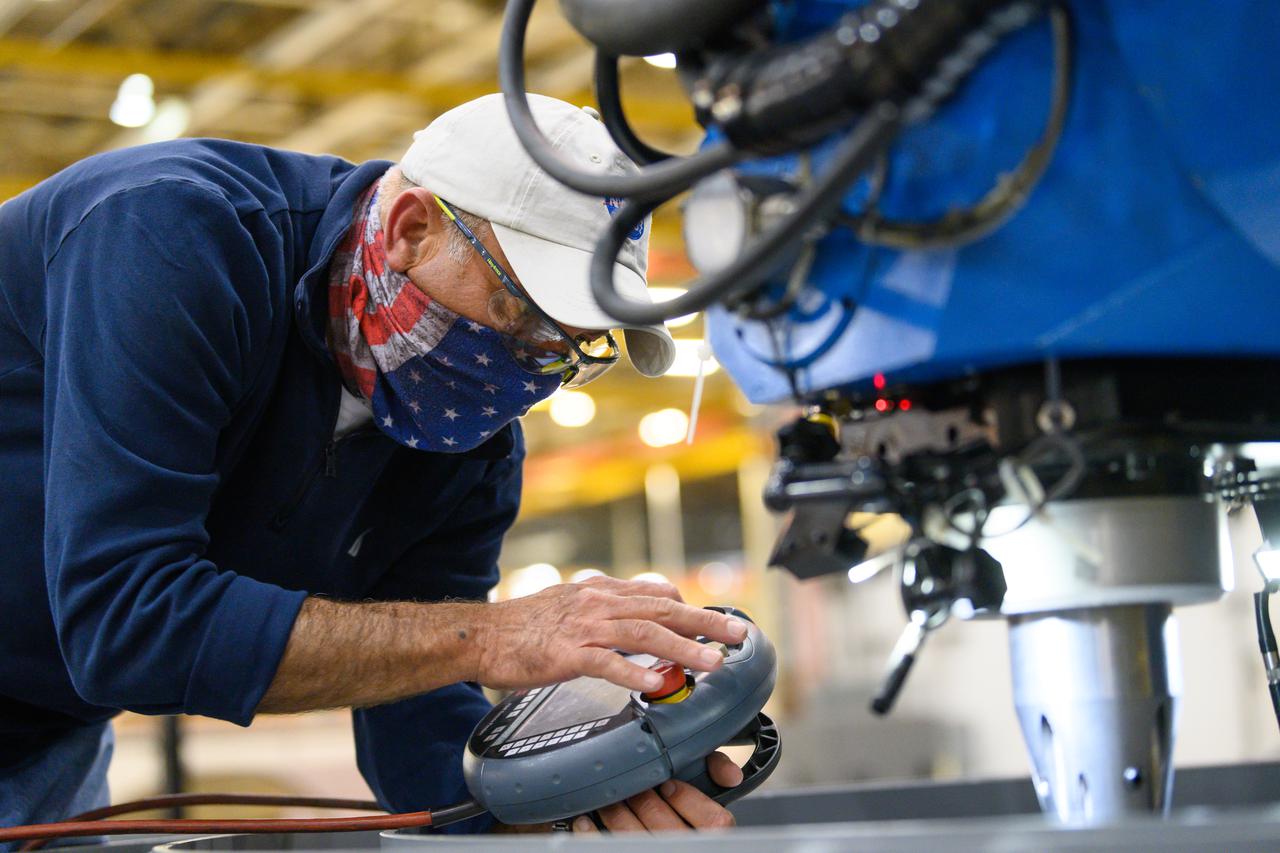

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
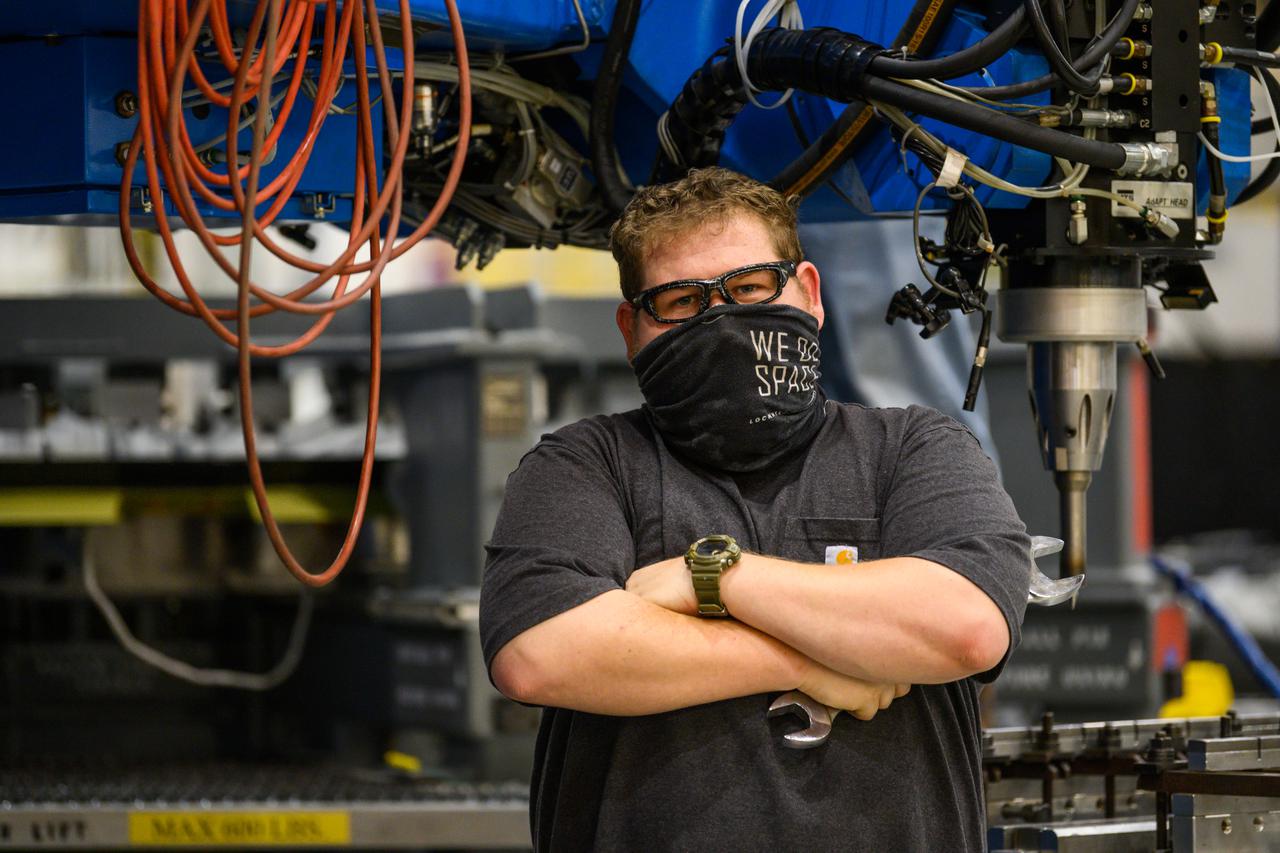

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
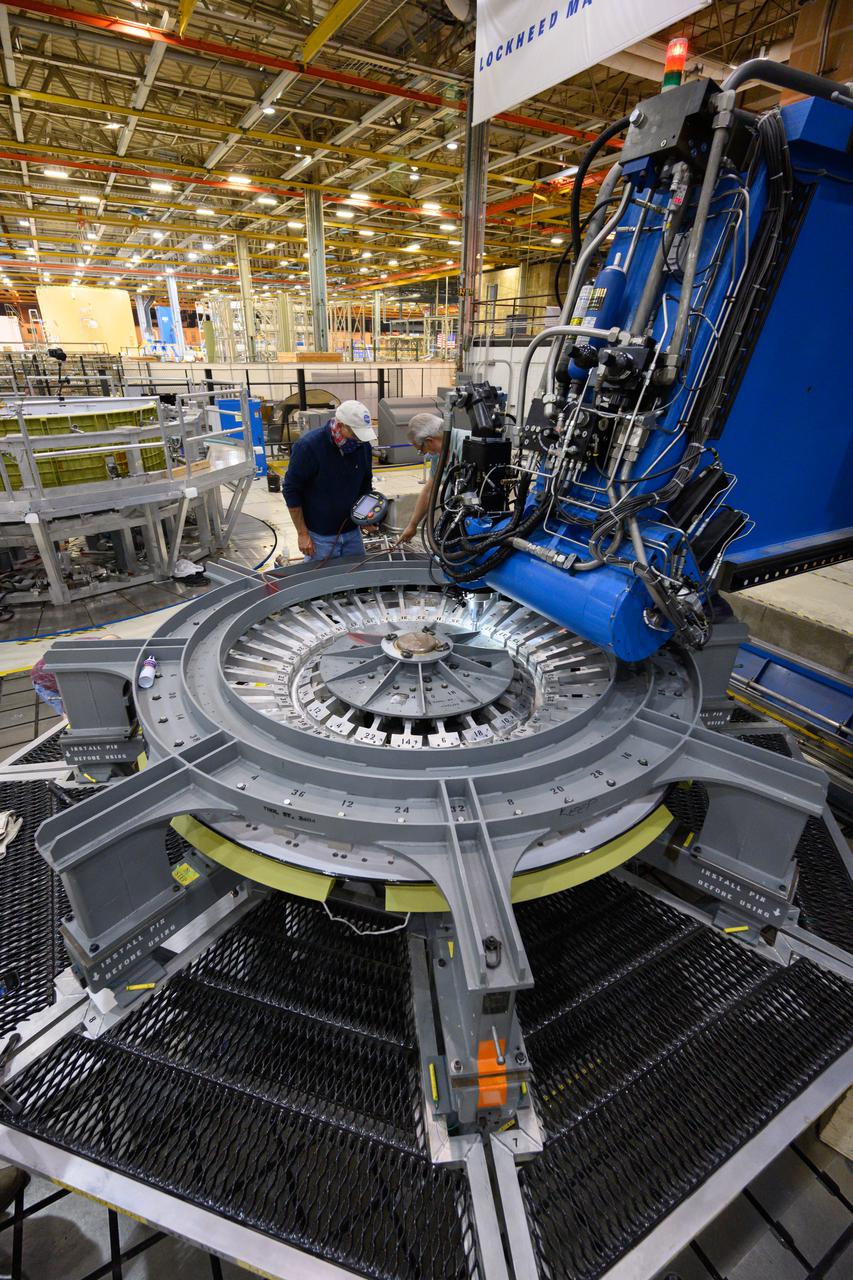

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
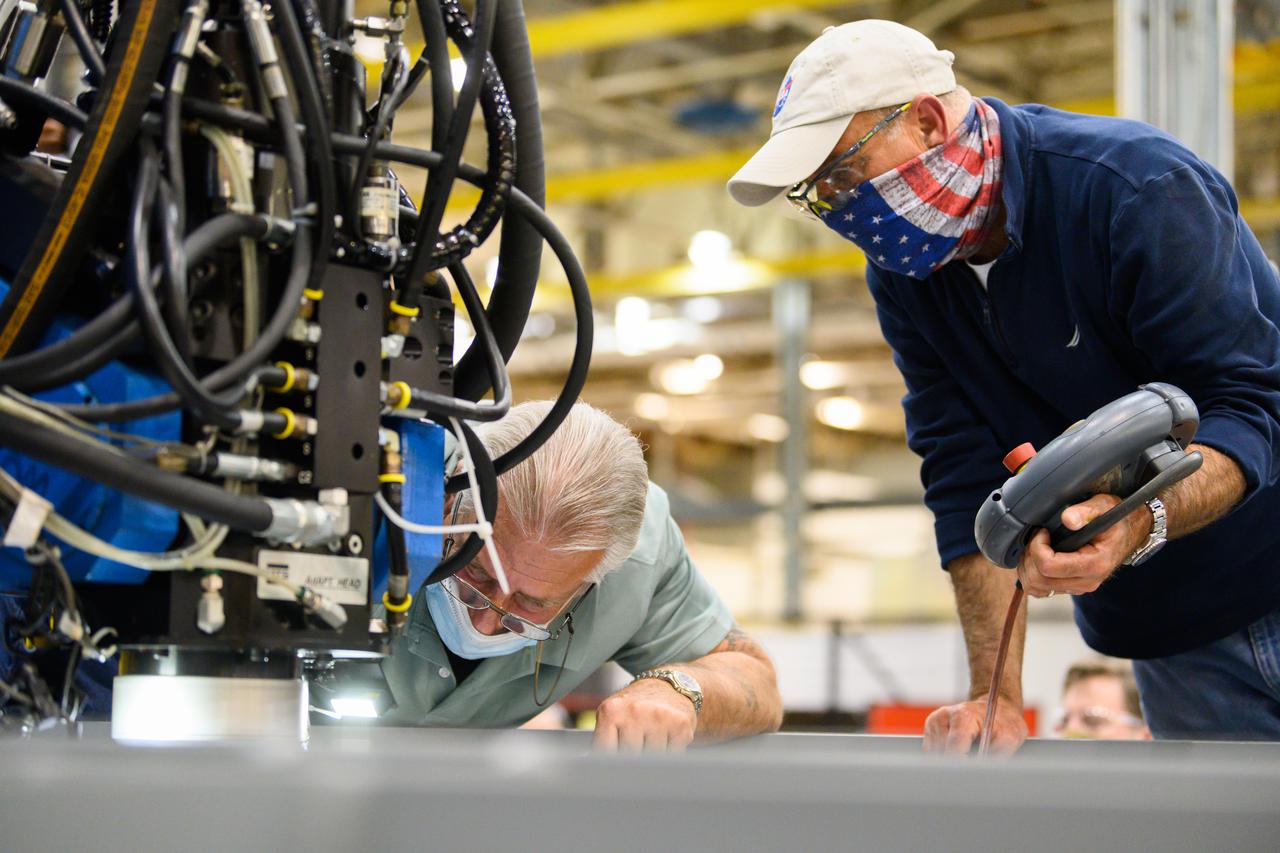

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
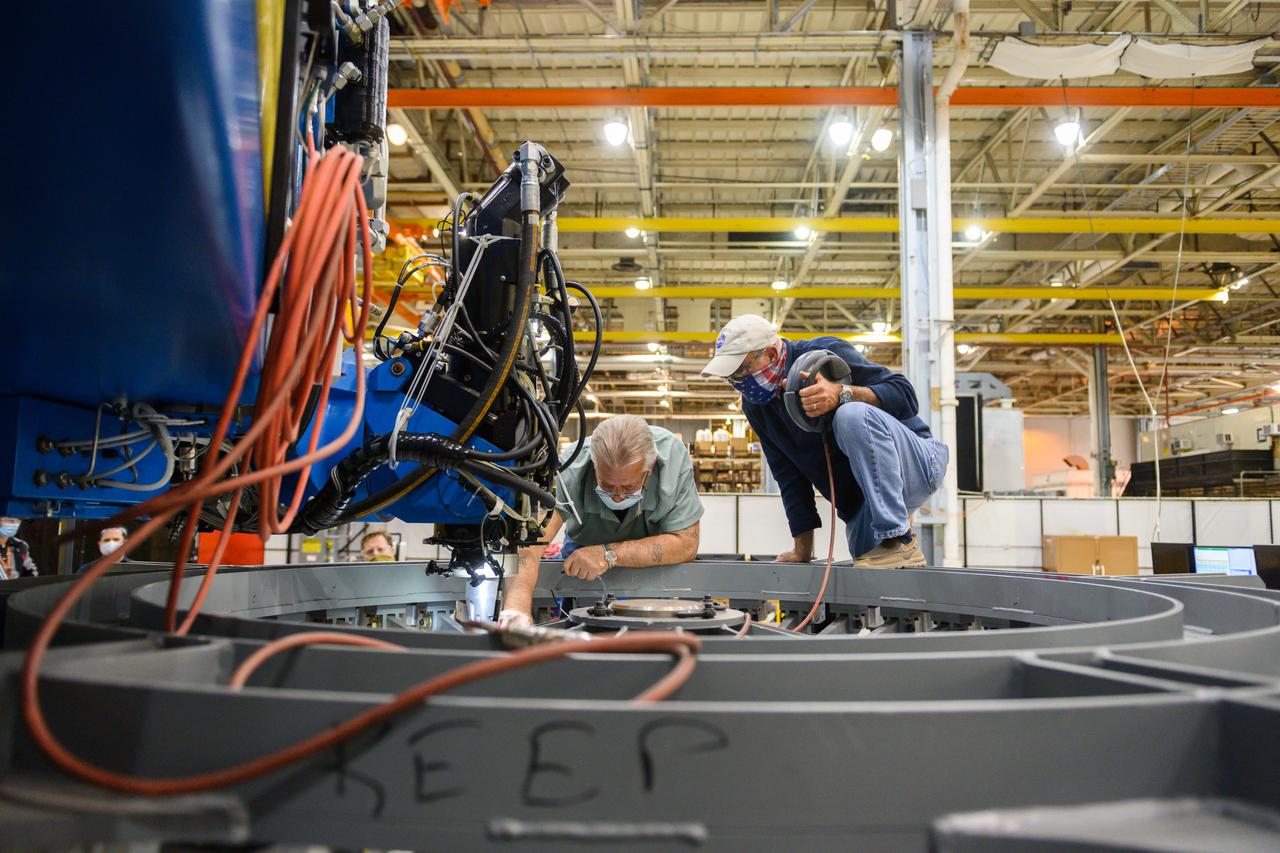

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
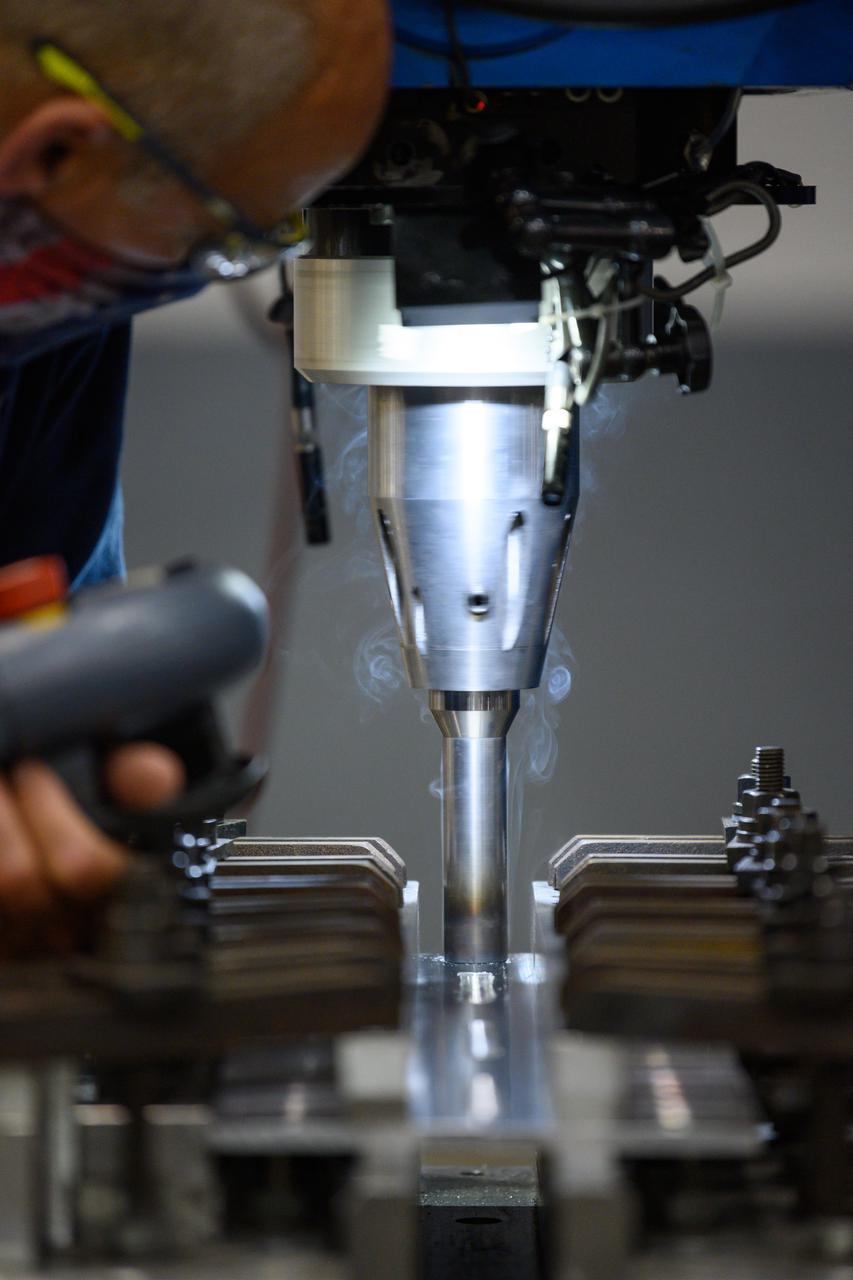

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
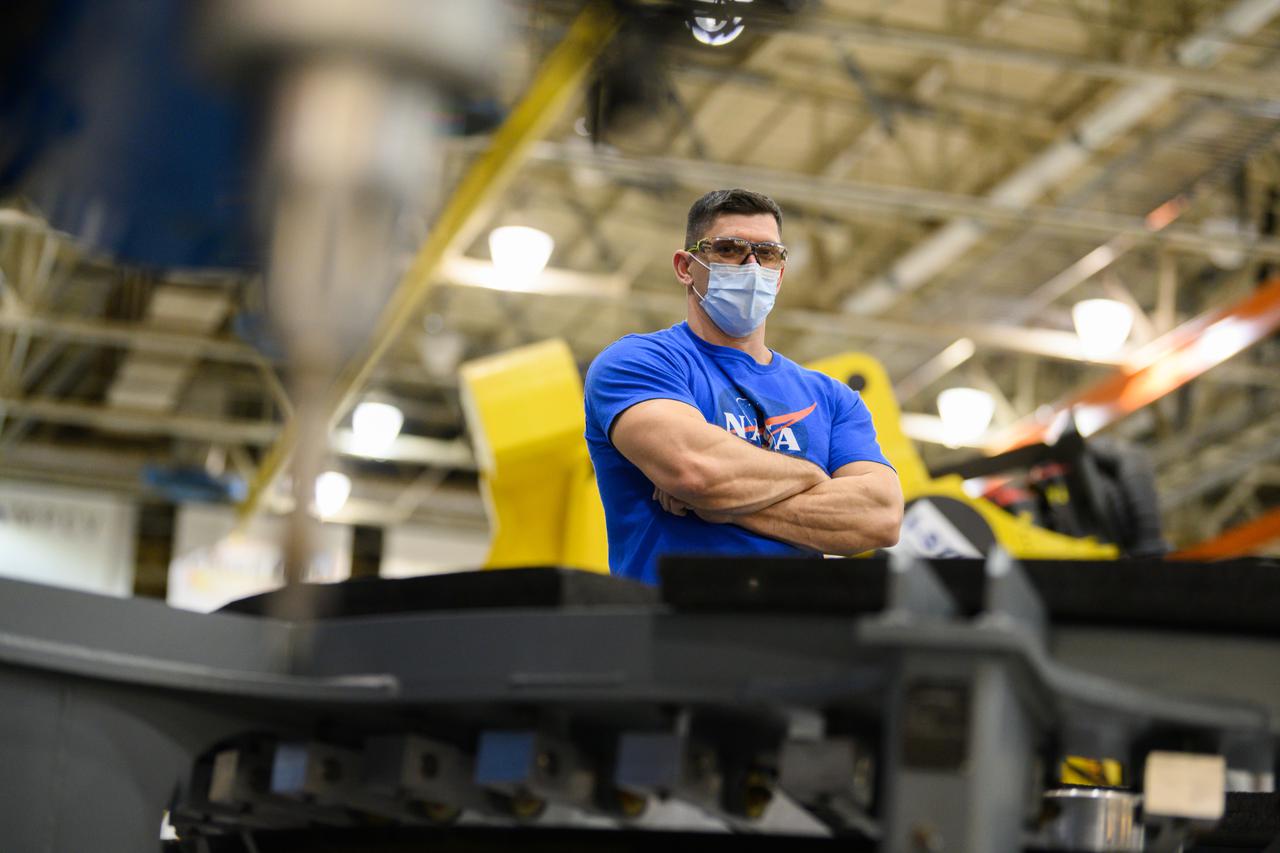

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
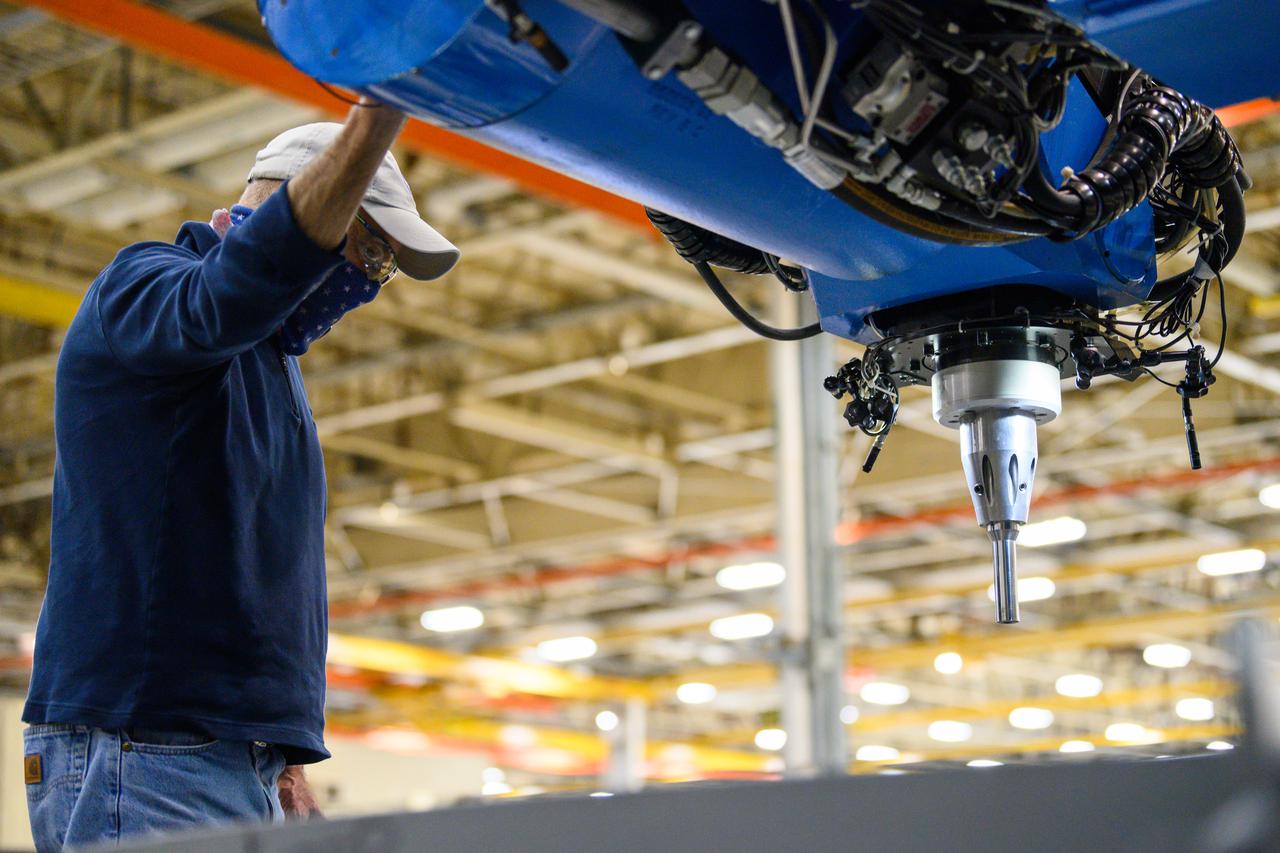

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
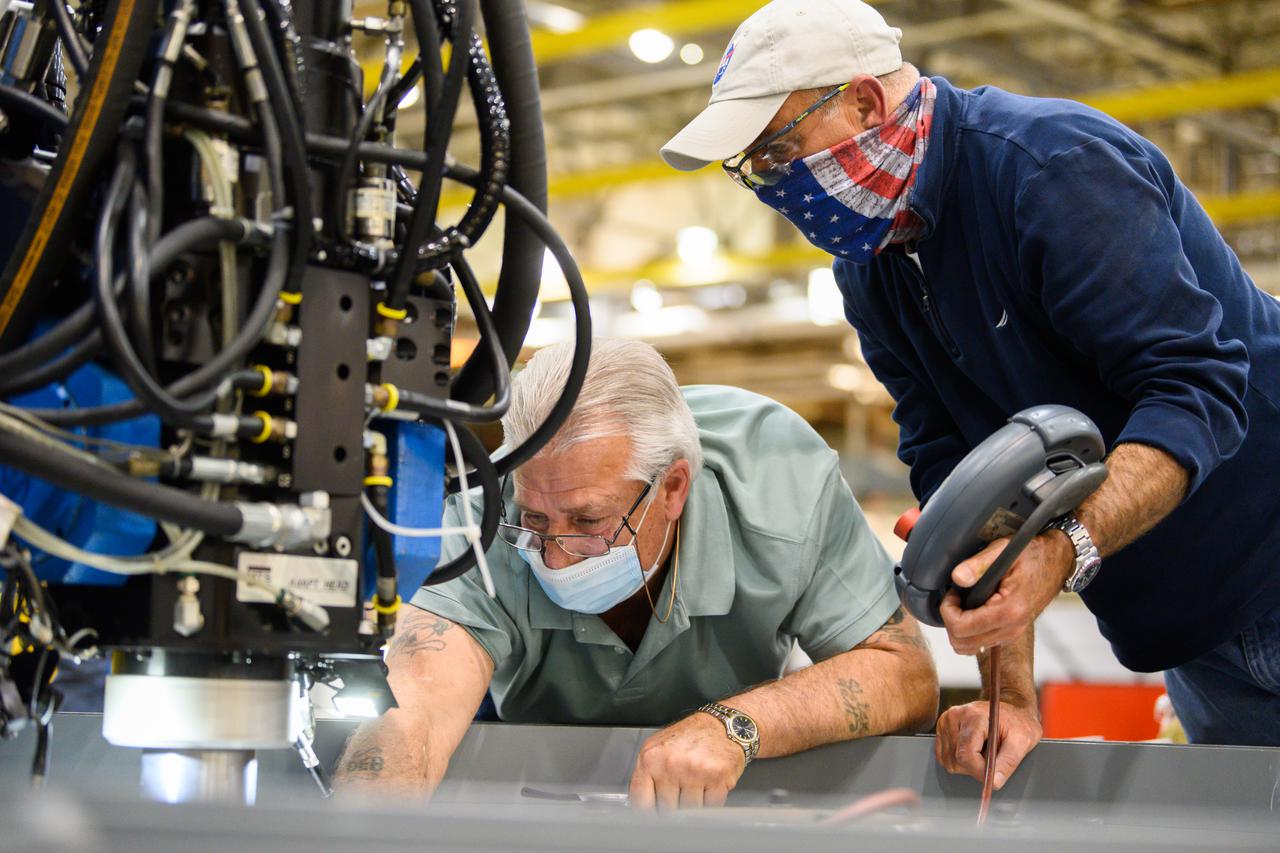

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
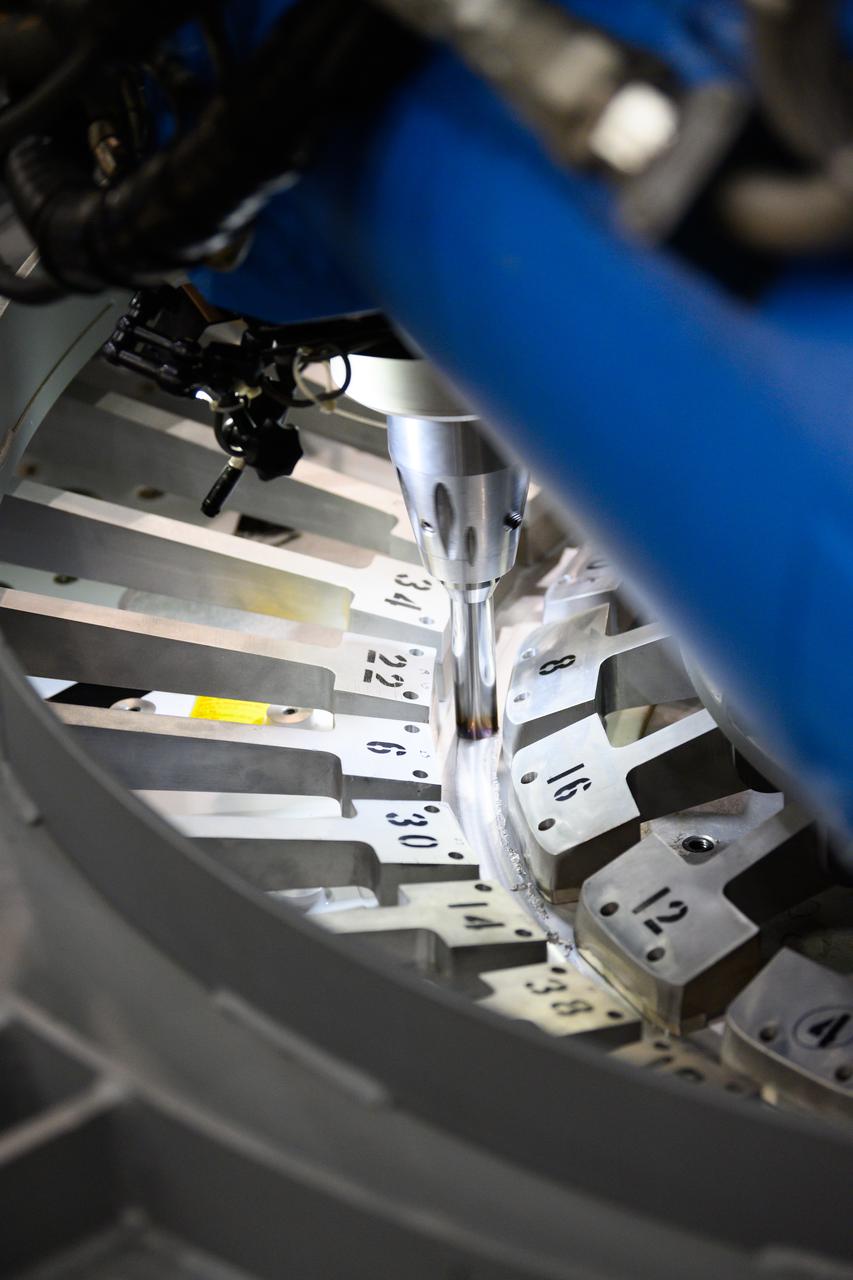

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
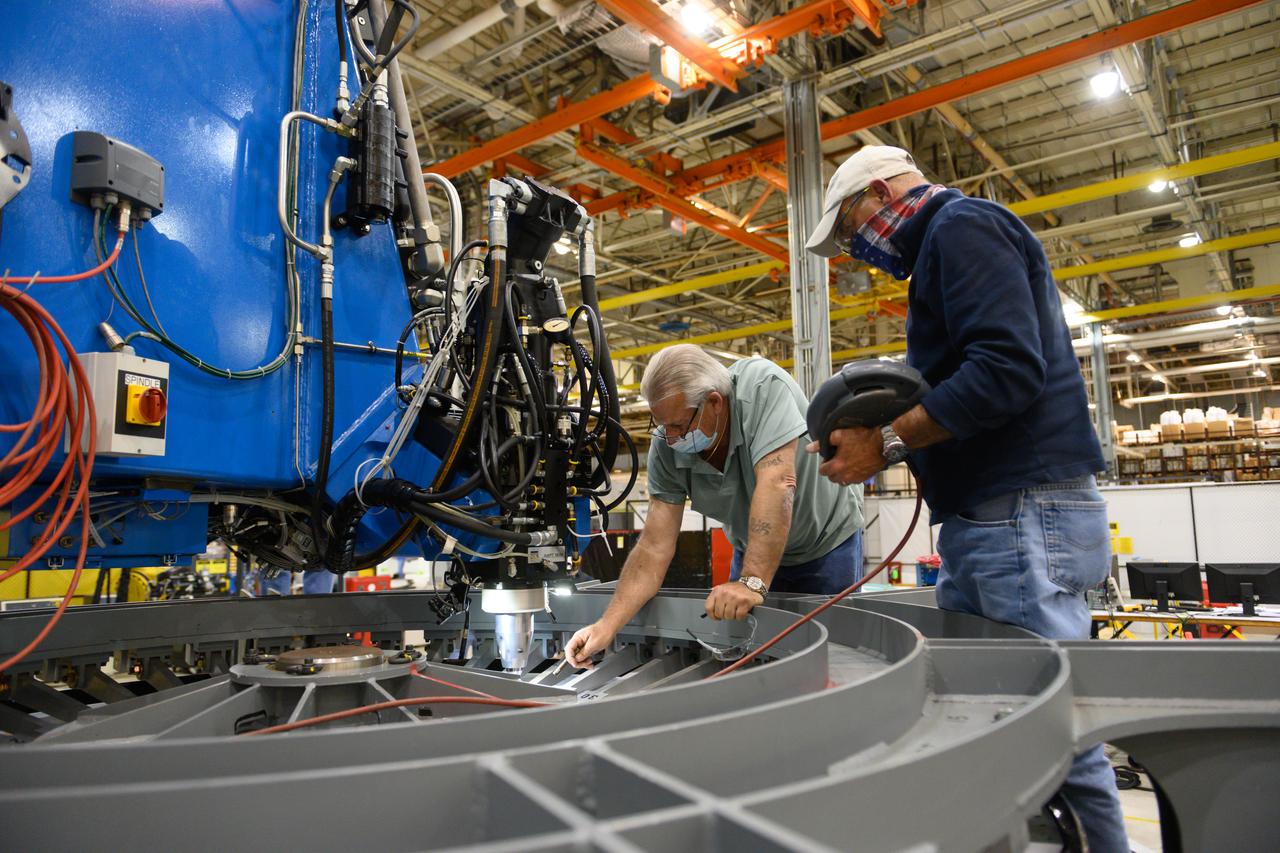

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
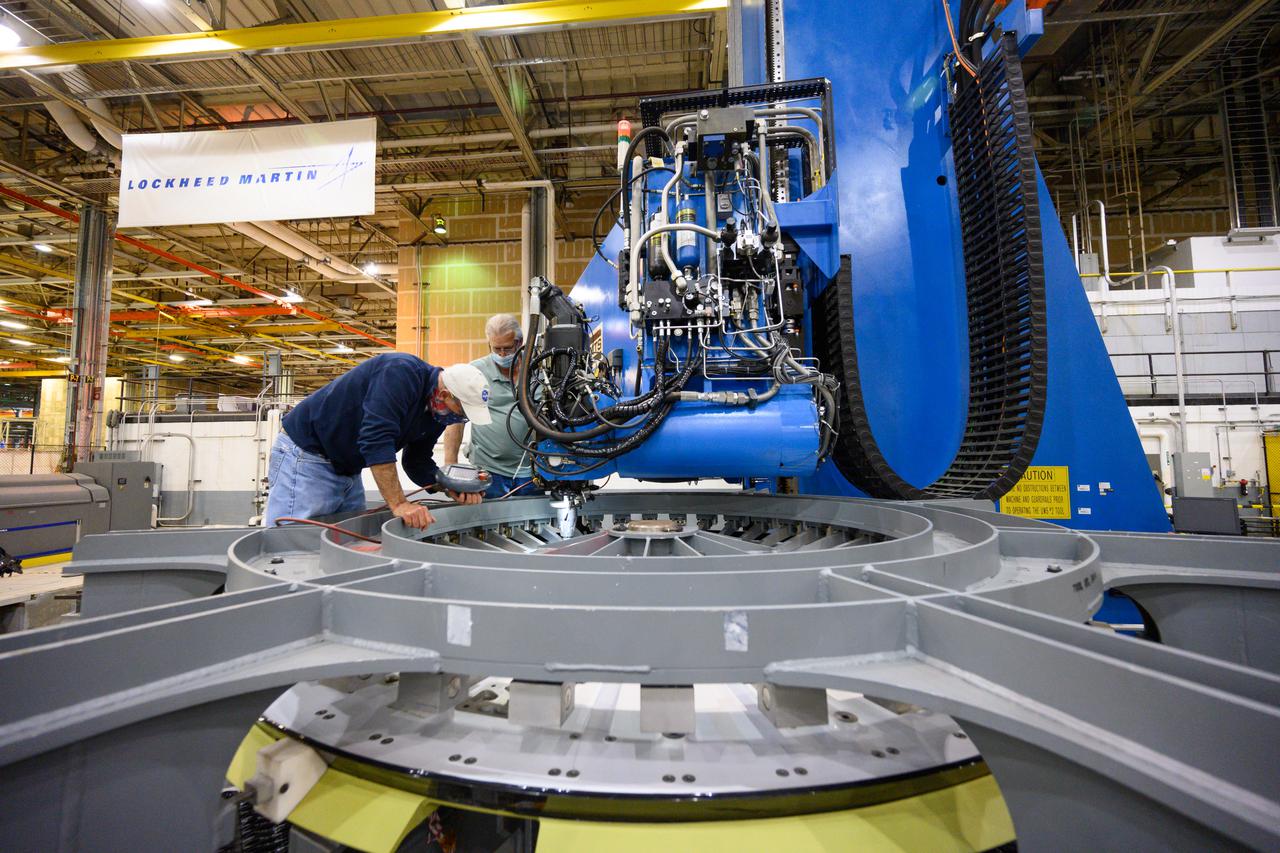

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
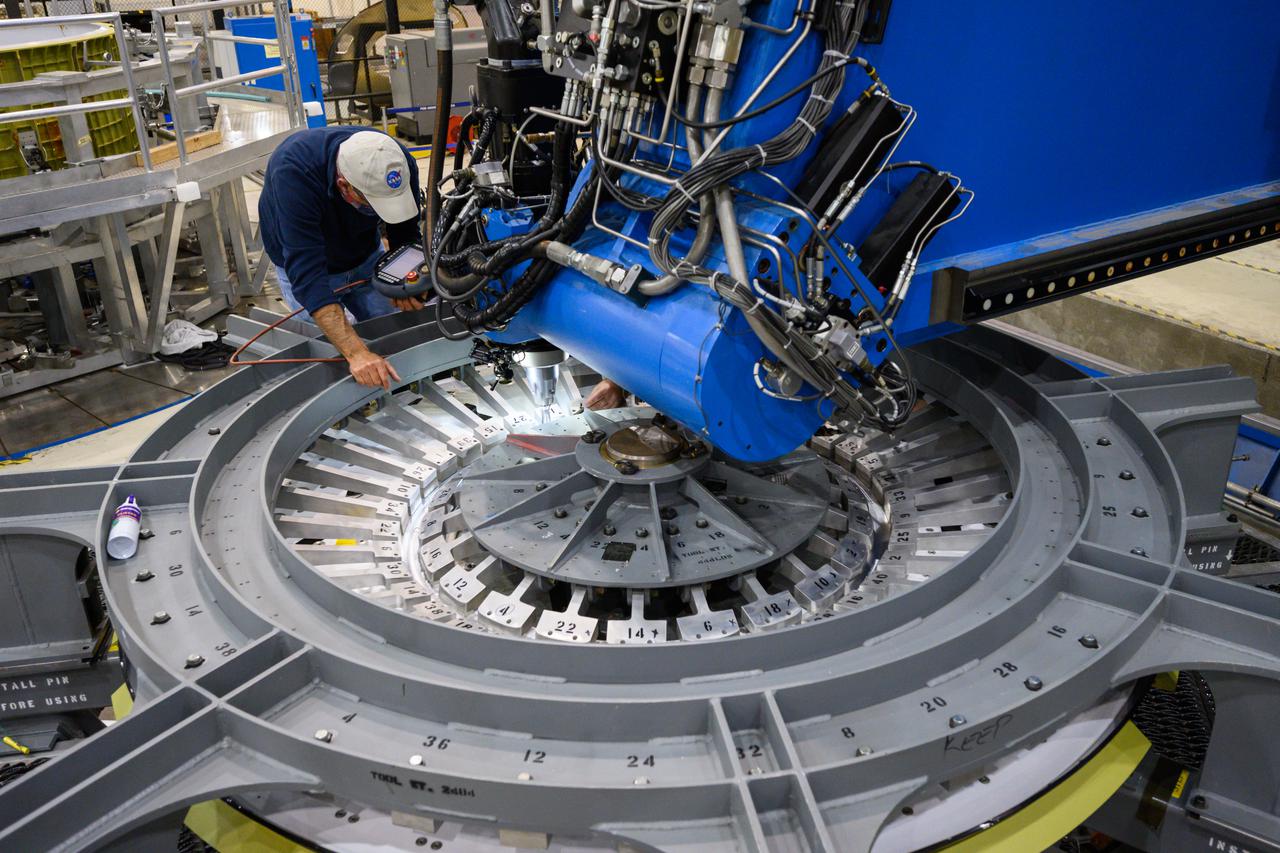

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
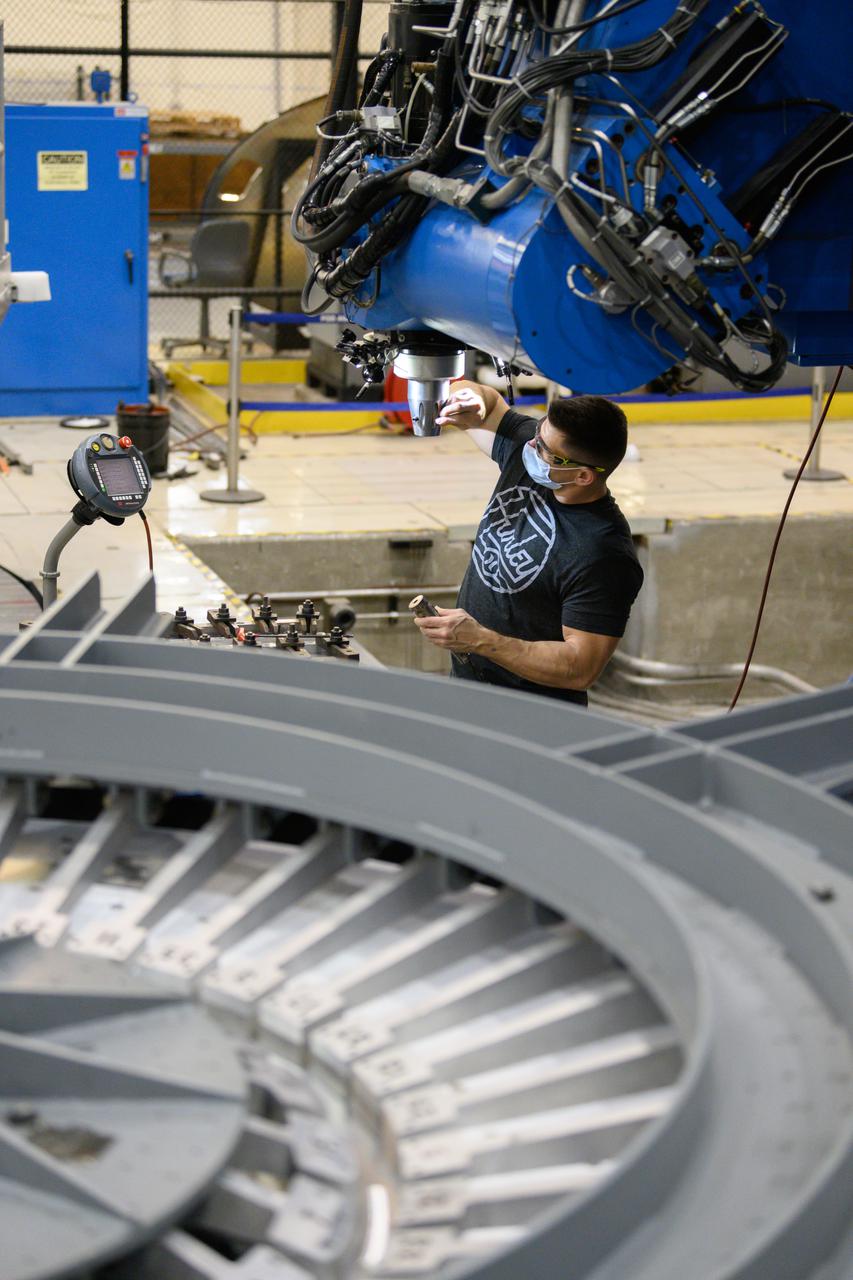

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
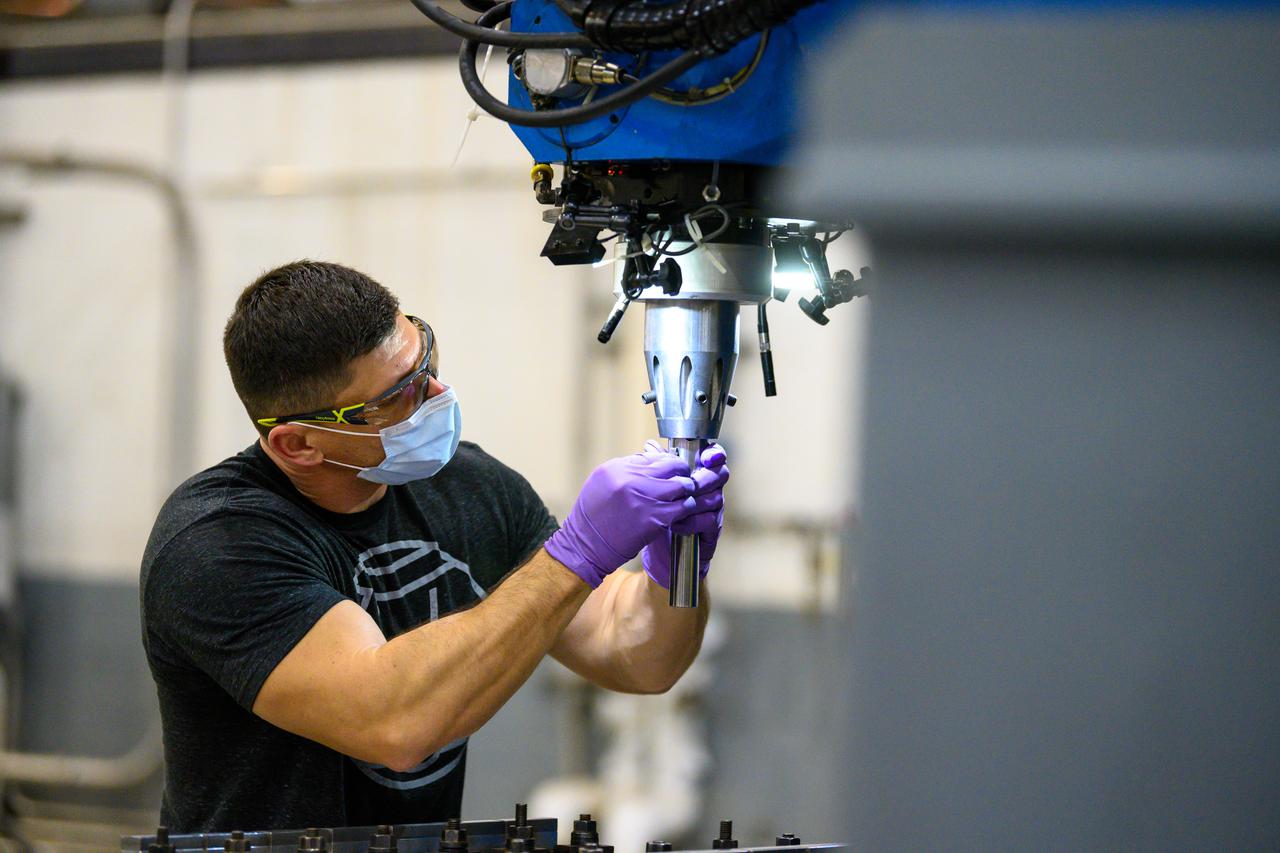

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
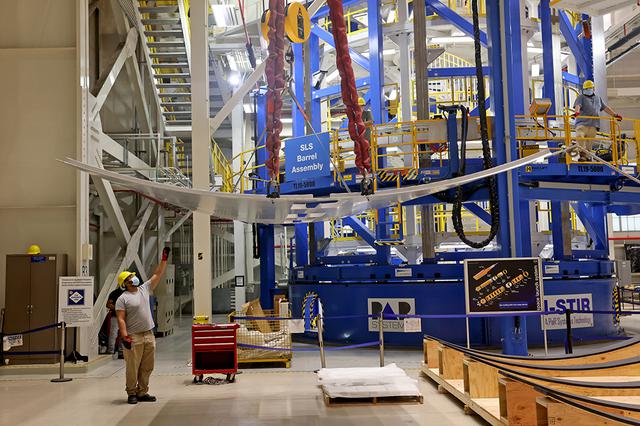

Lift of three EUS test panels in VWC at Michoud Assembly Facility on Thursday, February 11, 2021. Technicians are manufacturing and testing the first in a series of initial weld confidence articles for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) for future flights of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The Exploration Upper Stage weld confidence panels are first produced in the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud, then small sections of the panels are removed for mechanical testing and analysis in another area of the factory. Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures, interfaces between the tooling and hardware, and the structural integrity of the welds. Testing of the EUS weld confidence articles will help engineers and technicians validate welding parameters for manufacturing EUS hardware. The first three SLS flights of NASA’s Artemis program will use an interim cryogenic propulsion stage with one RL10 engine to send Orion to the Moon. The SLS Exploration Upper Stage for flights beyond Artemis III has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing the Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
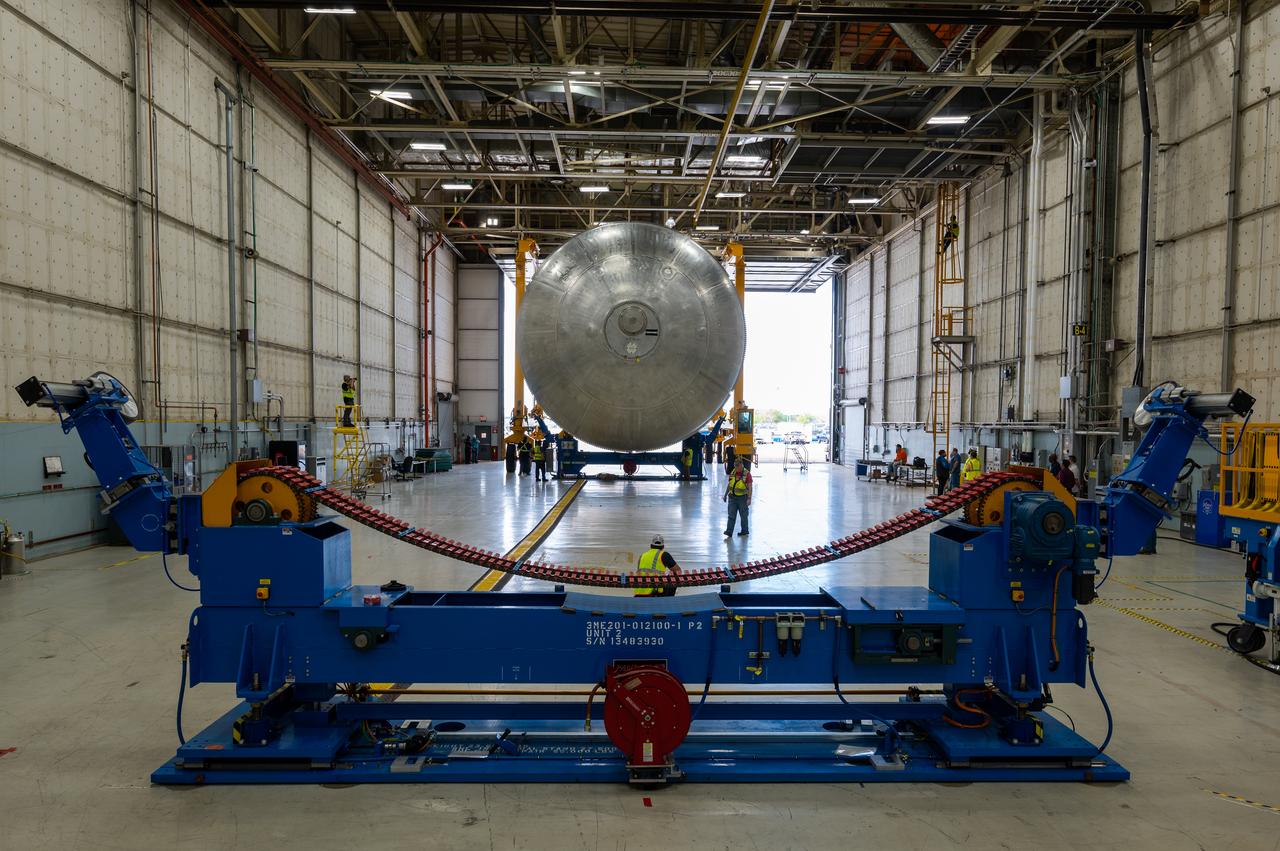

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
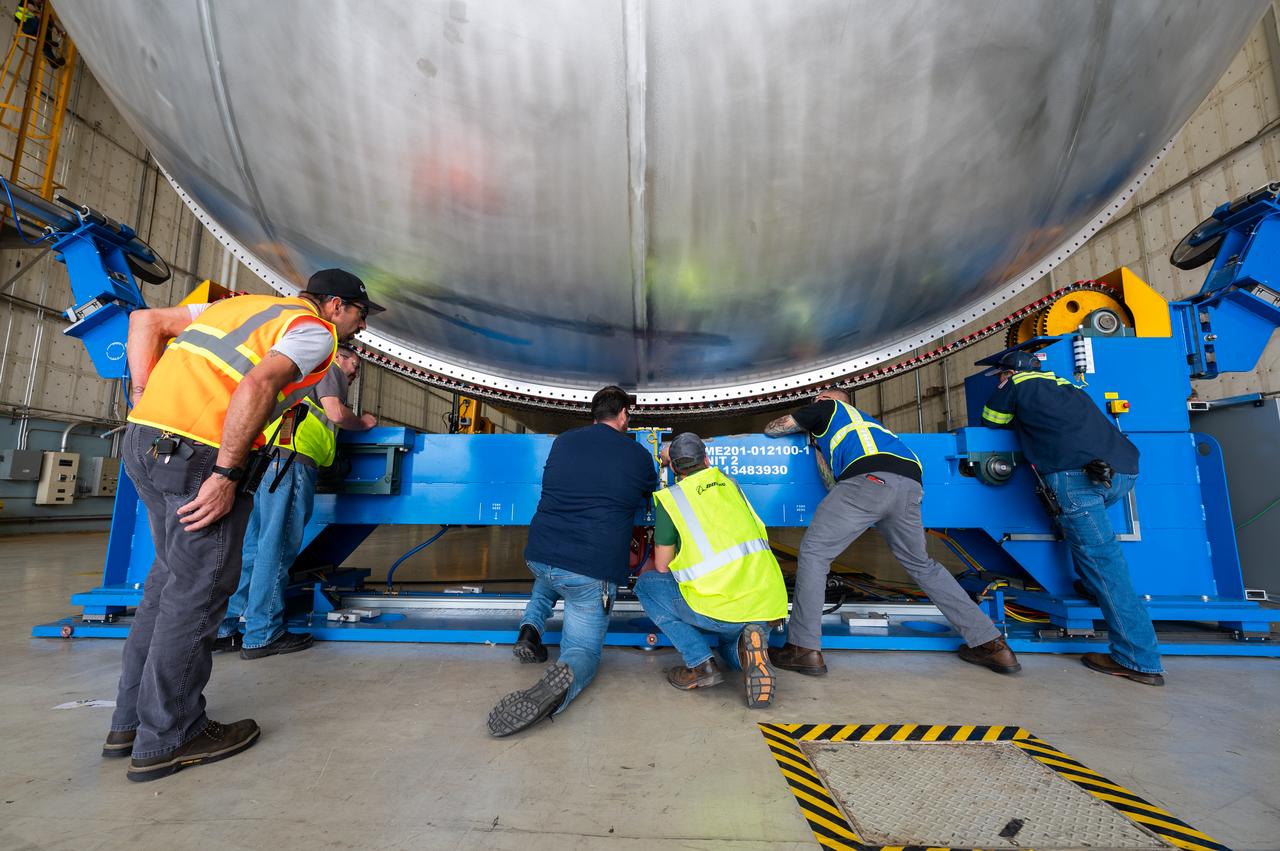

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
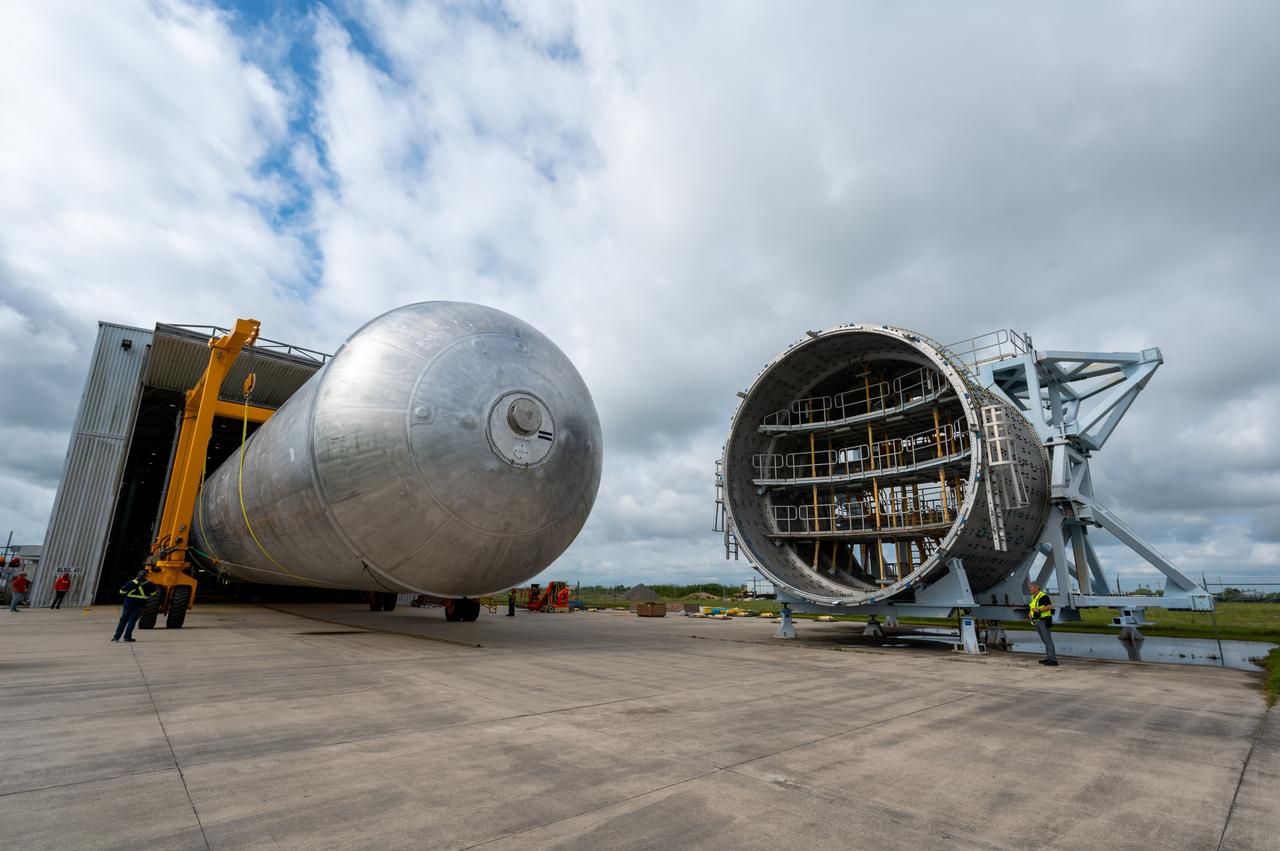

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
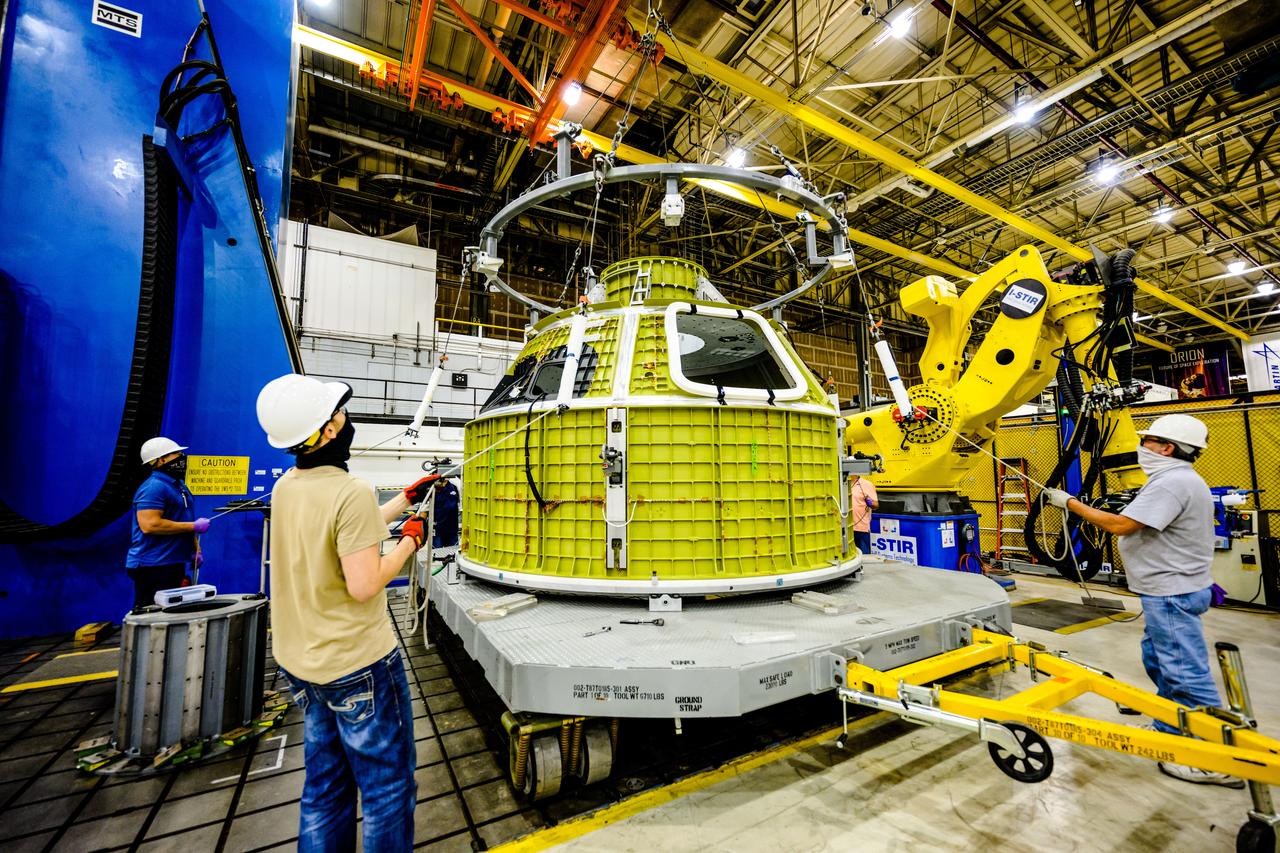

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
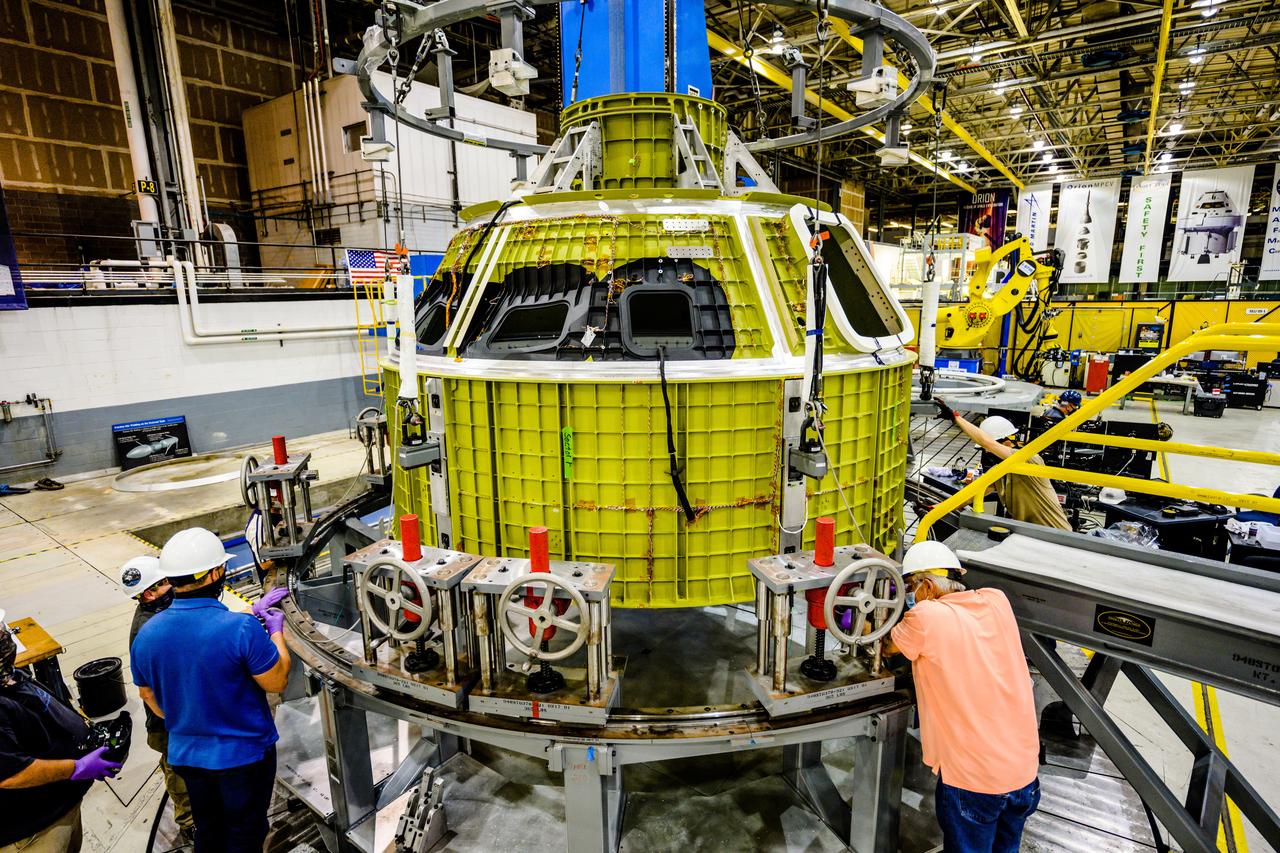

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
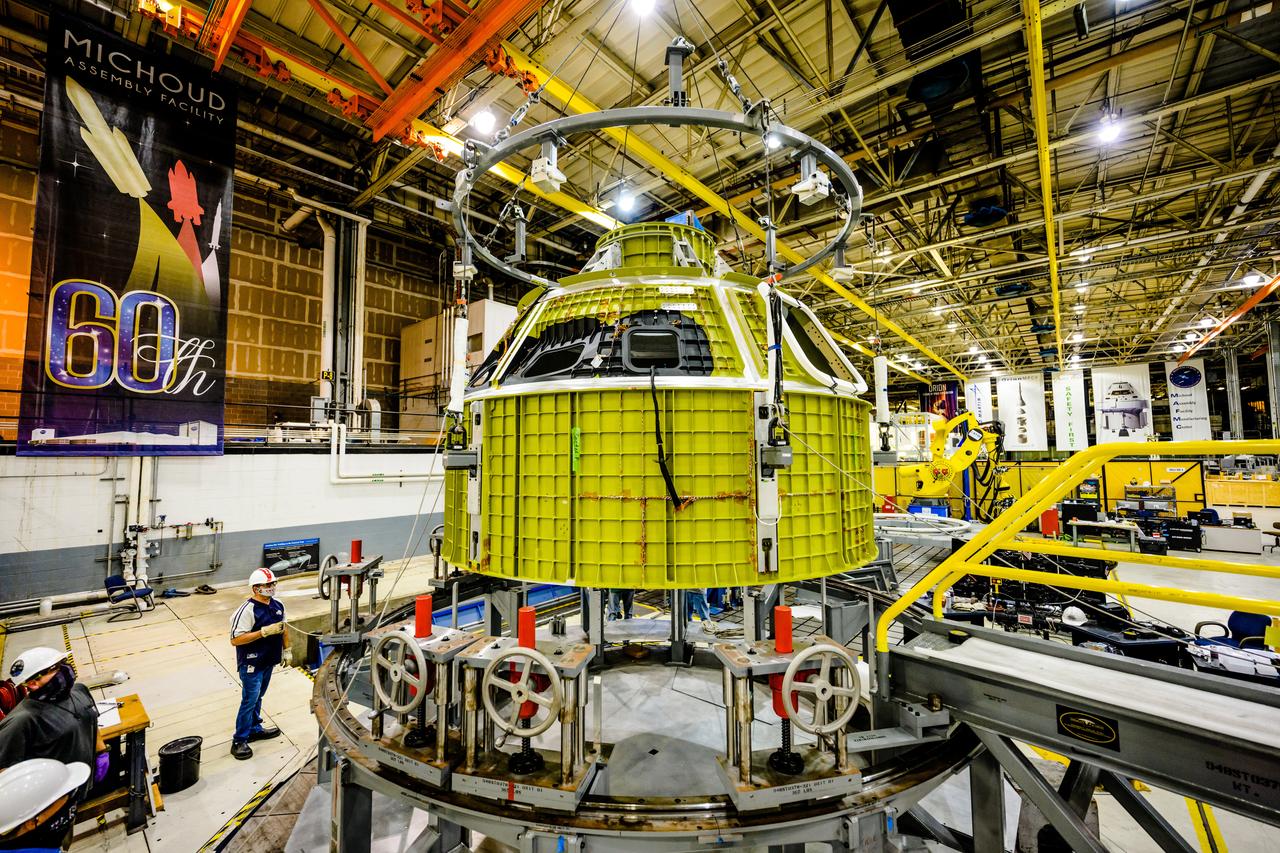

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
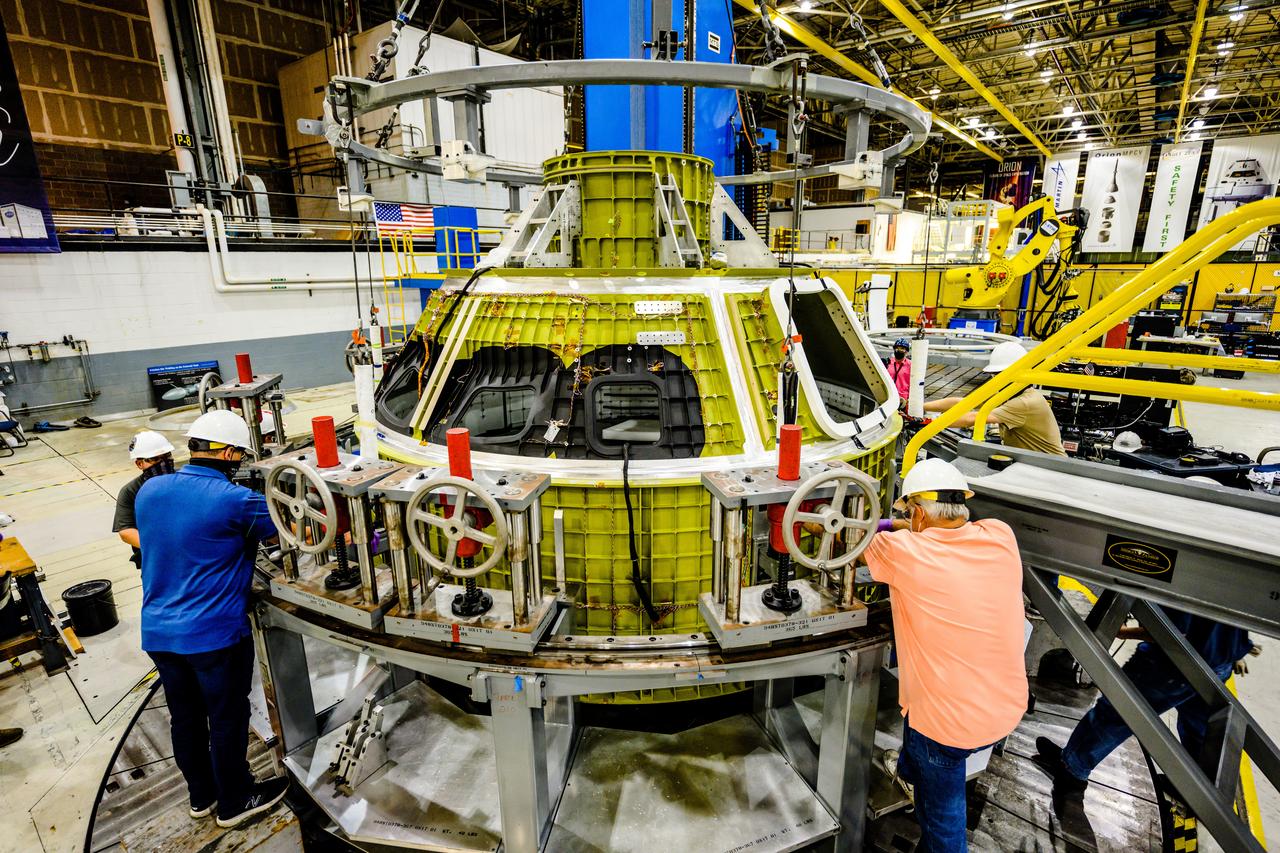

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
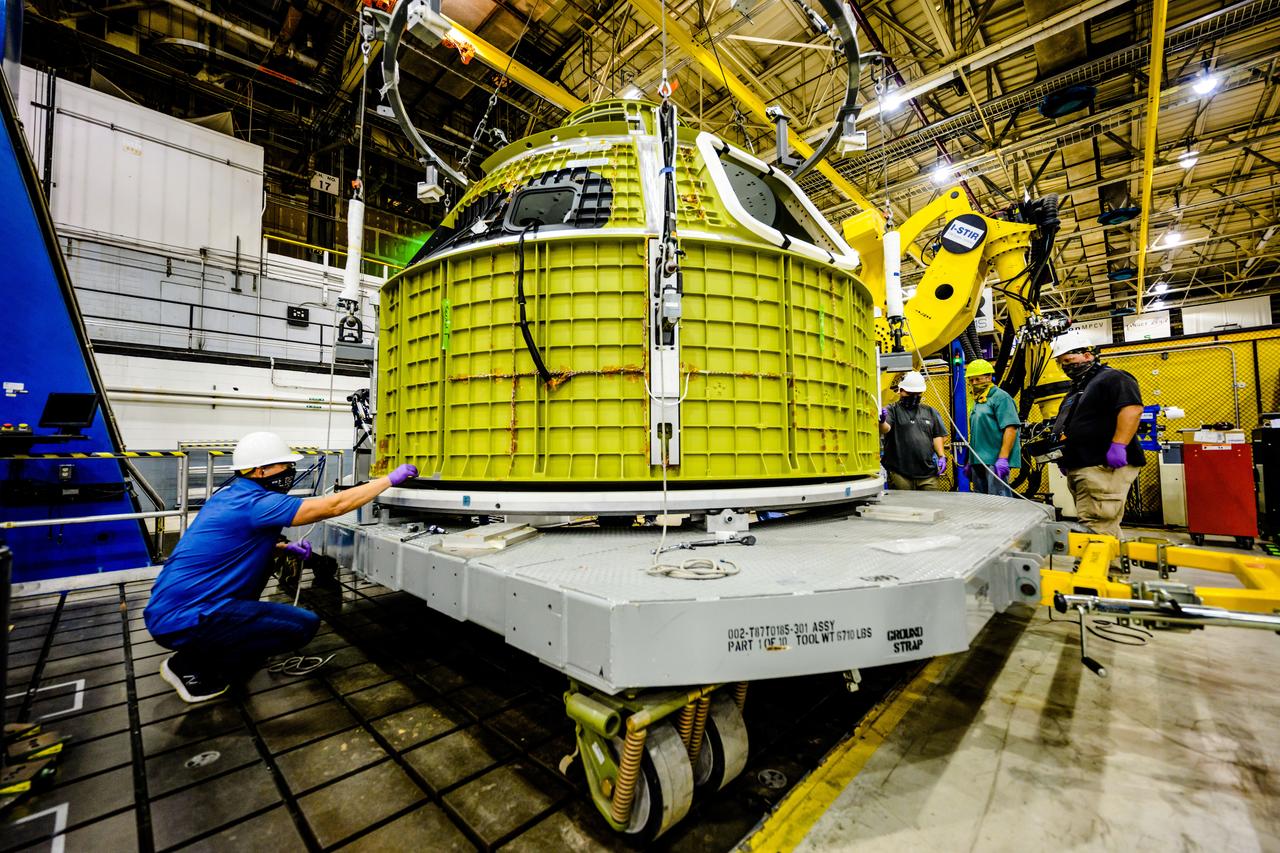

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
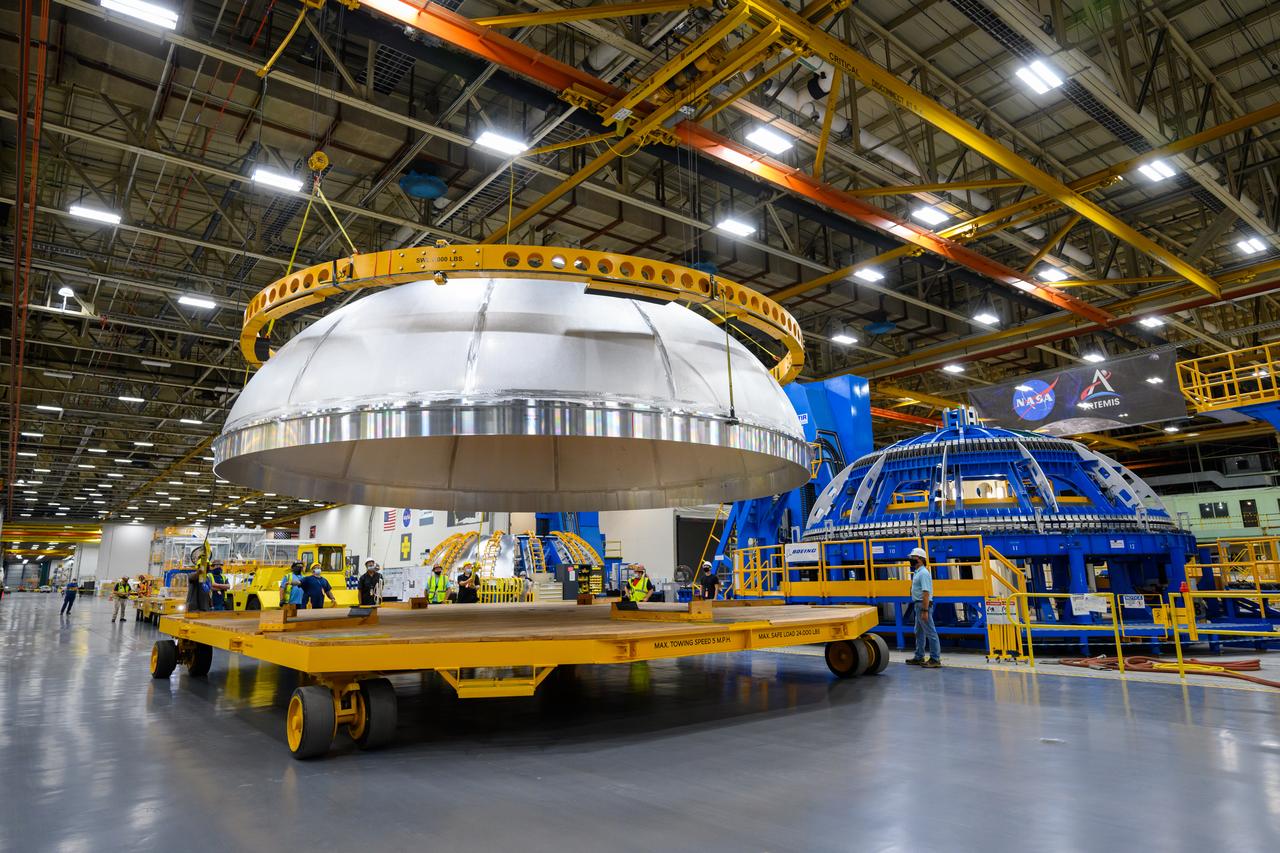

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
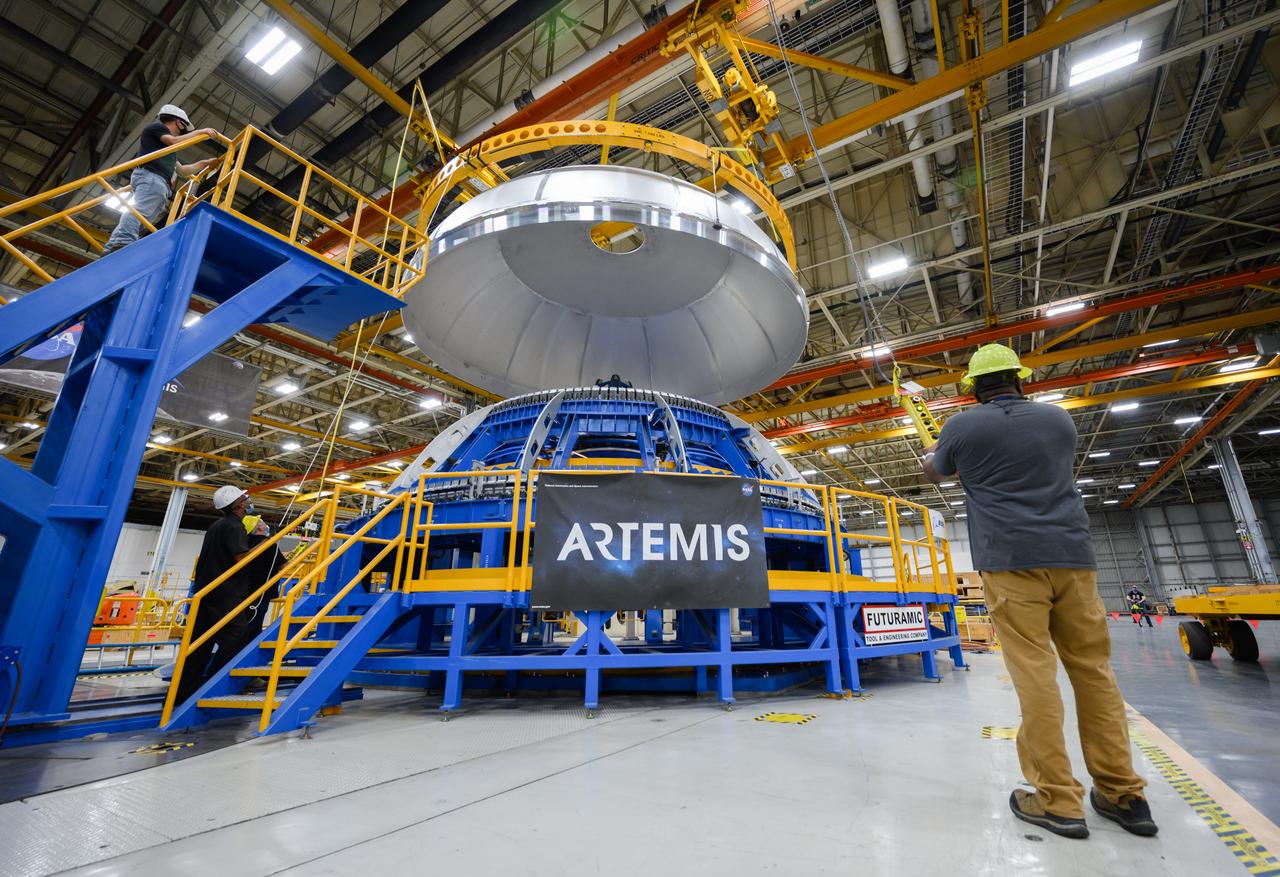

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
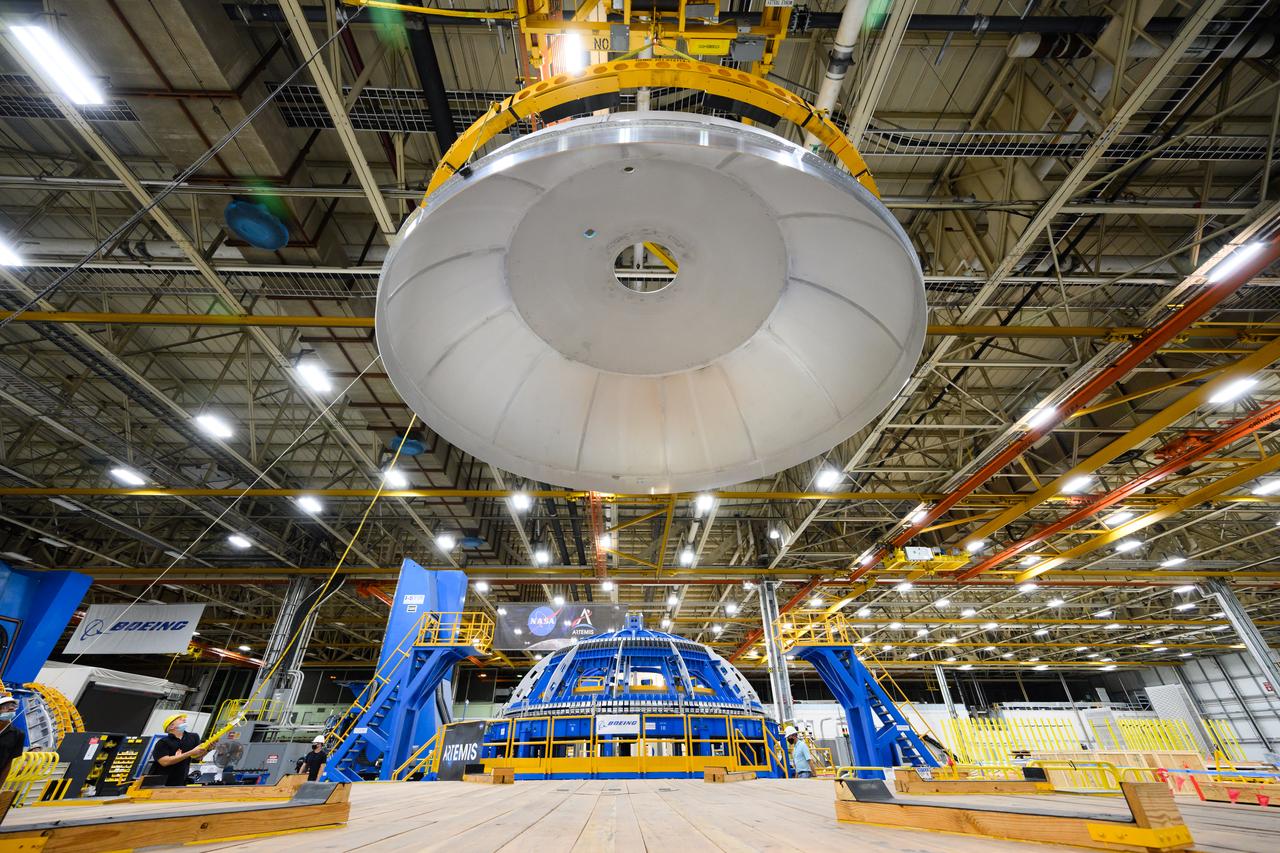

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
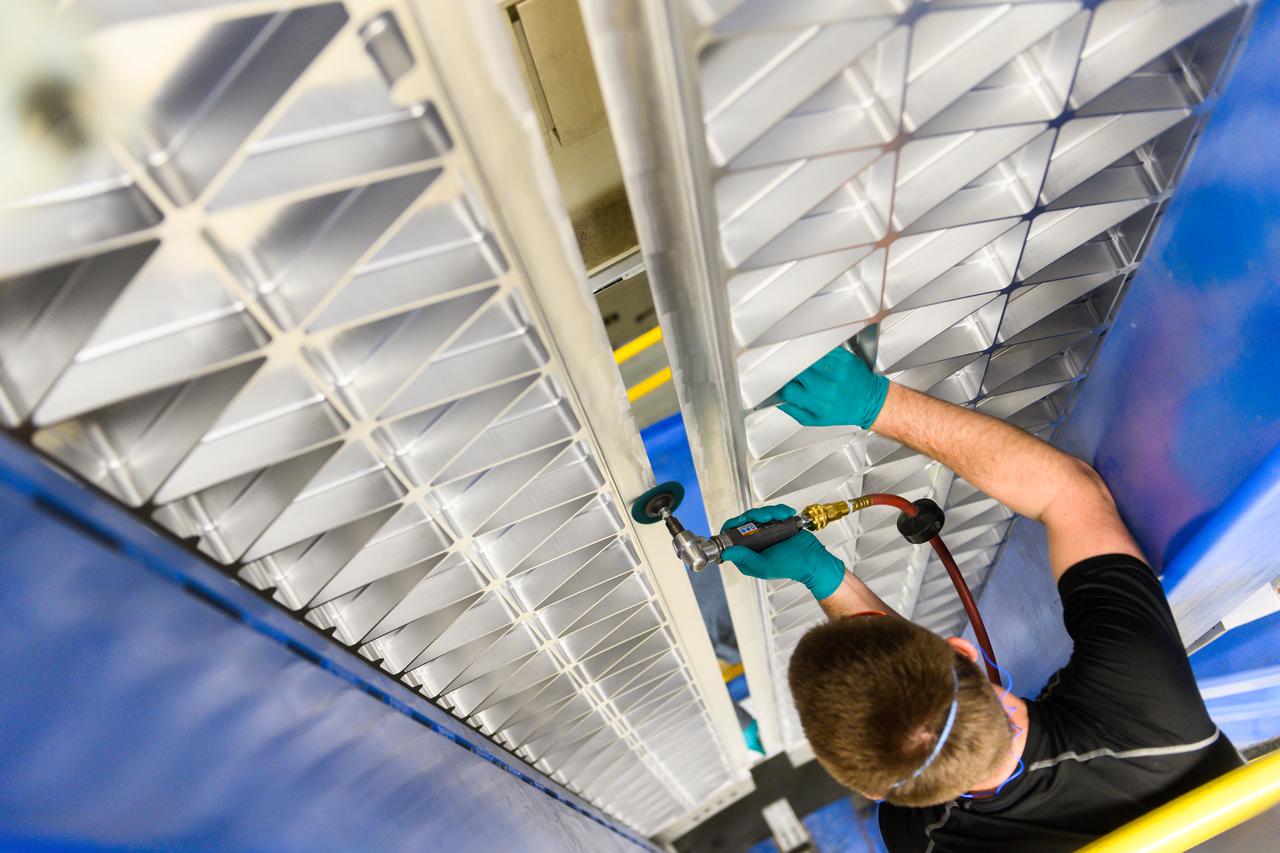

Technicians are manufacturing and testing the first in a series of initial weld confidence articles for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) for future flights of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The Exploration Upper Stage weld confidence panels are first produced in the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud, then small sections of the panels are removed for mechanical testing and analysis in another area of the factory. Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures, interfaces between the tooling and hardware, and the structural integrity of the welds. Testing of the EUS weld confidence articles will help engineers and technicians validate welding parameters for manufacturing EUS hardware. The first three SLS flights of NASA’s Artemis program will use an interim cryogenic propulsion stage with one RL10 engine to send Orion to the Moon. The SLS Exploration Upper Stage for flights beyond Artemis III has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing the Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
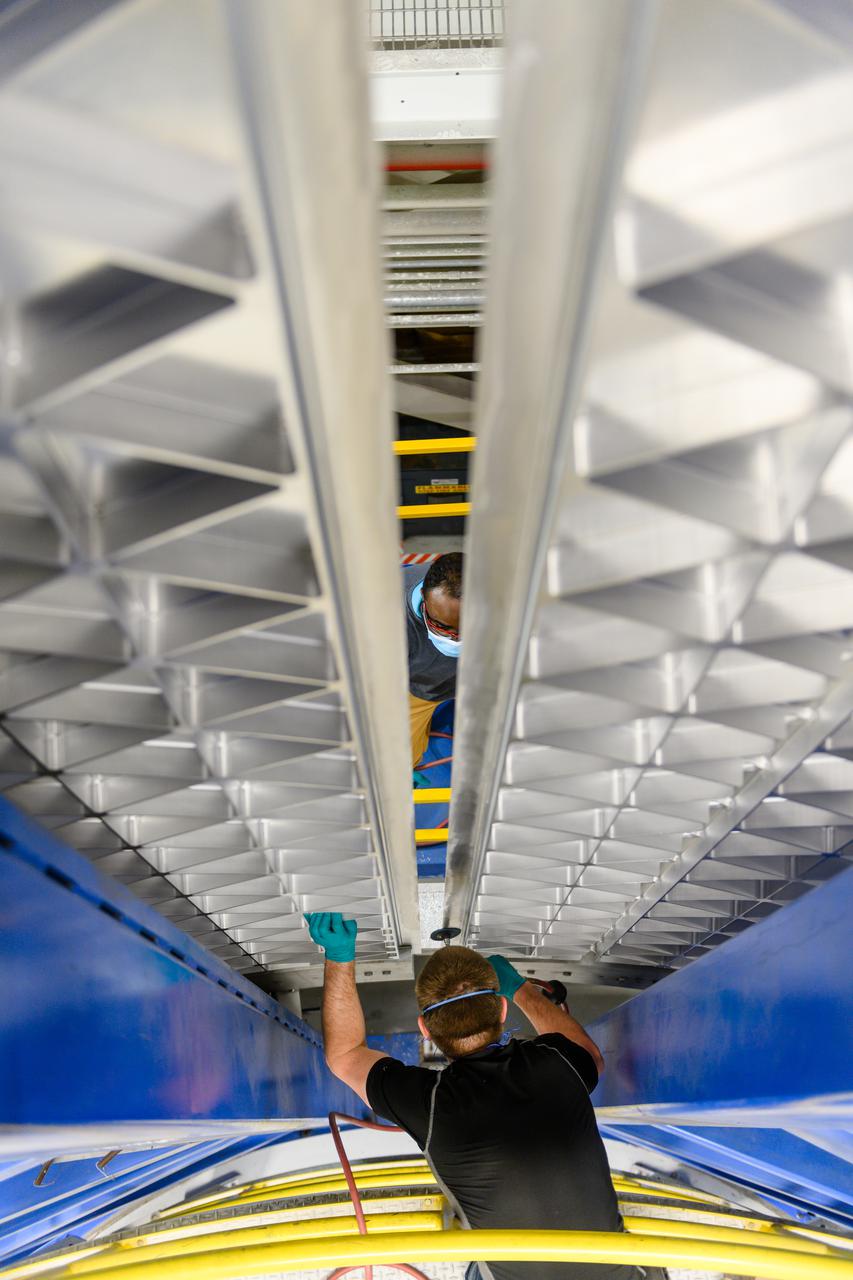

Technicians are manufacturing and testing the first in a series of initial weld confidence articles for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) for future flights of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The Exploration Upper Stage weld confidence panels are first produced in the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud, then small sections of the panels are removed for mechanical testing and analysis in another area of the factory. Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures, interfaces between the tooling and hardware, and the structural integrity of the welds. Testing of the EUS weld confidence articles will help engineers and technicians validate welding parameters for manufacturing EUS hardware. The first three SLS flights of NASA’s Artemis program will use an interim cryogenic propulsion stage with one RL10 engine to send Orion to the Moon. The SLS Exploration Upper Stage for flights beyond Artemis III has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing the Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
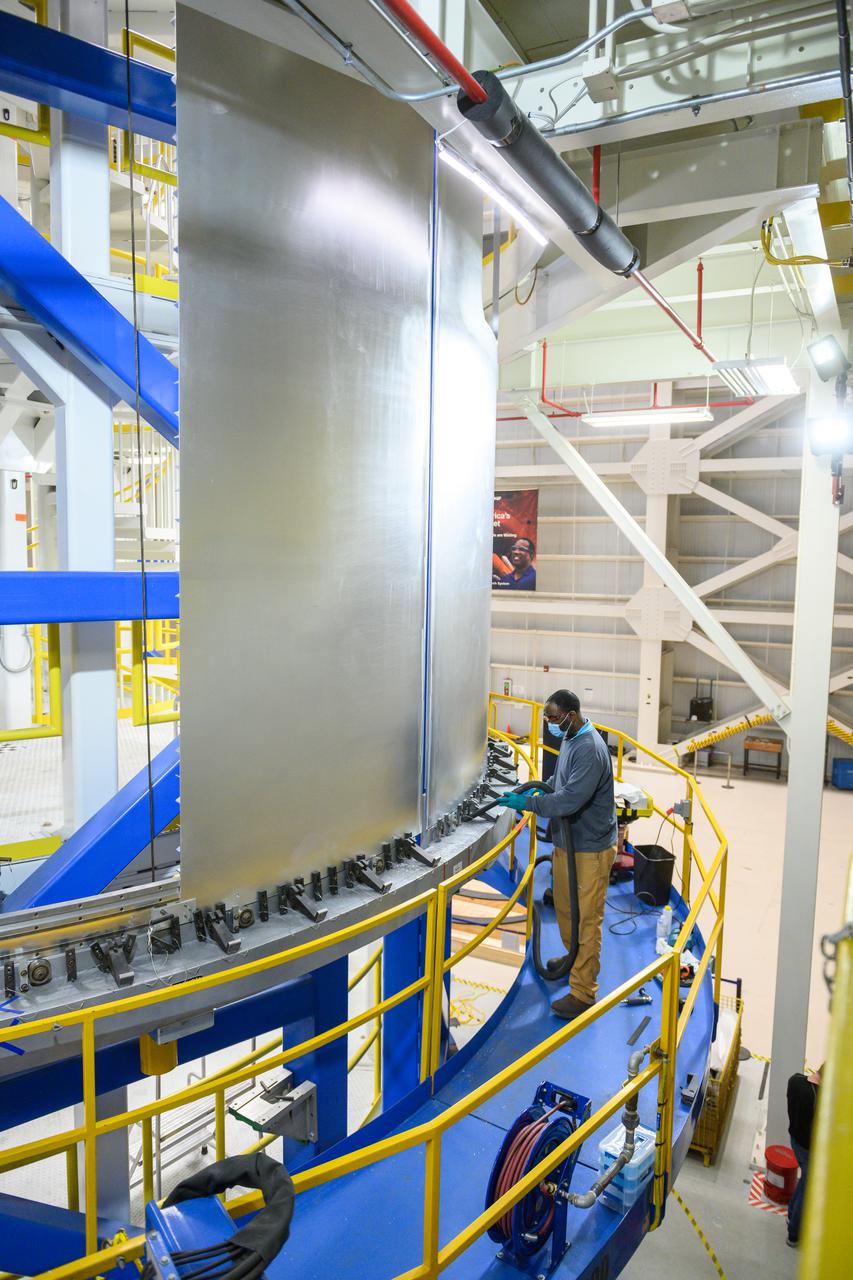

Technicians are manufacturing and testing the first in a series of initial weld confidence articles for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) for future flights of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The Exploration Upper Stage weld confidence panels are first produced in the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud, then small sections of the panels are removed for mechanical testing and analysis in another area of the factory. Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures, interfaces between the tooling and hardware, and the structural integrity of the welds. Testing of the EUS weld confidence articles will help engineers and technicians validate welding parameters for manufacturing EUS hardware. The first three SLS flights of NASA’s Artemis program will use an interim cryogenic propulsion stage with one RL10 engine to send Orion to the Moon. The SLS Exploration Upper Stage for flights beyond Artemis III has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing the Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
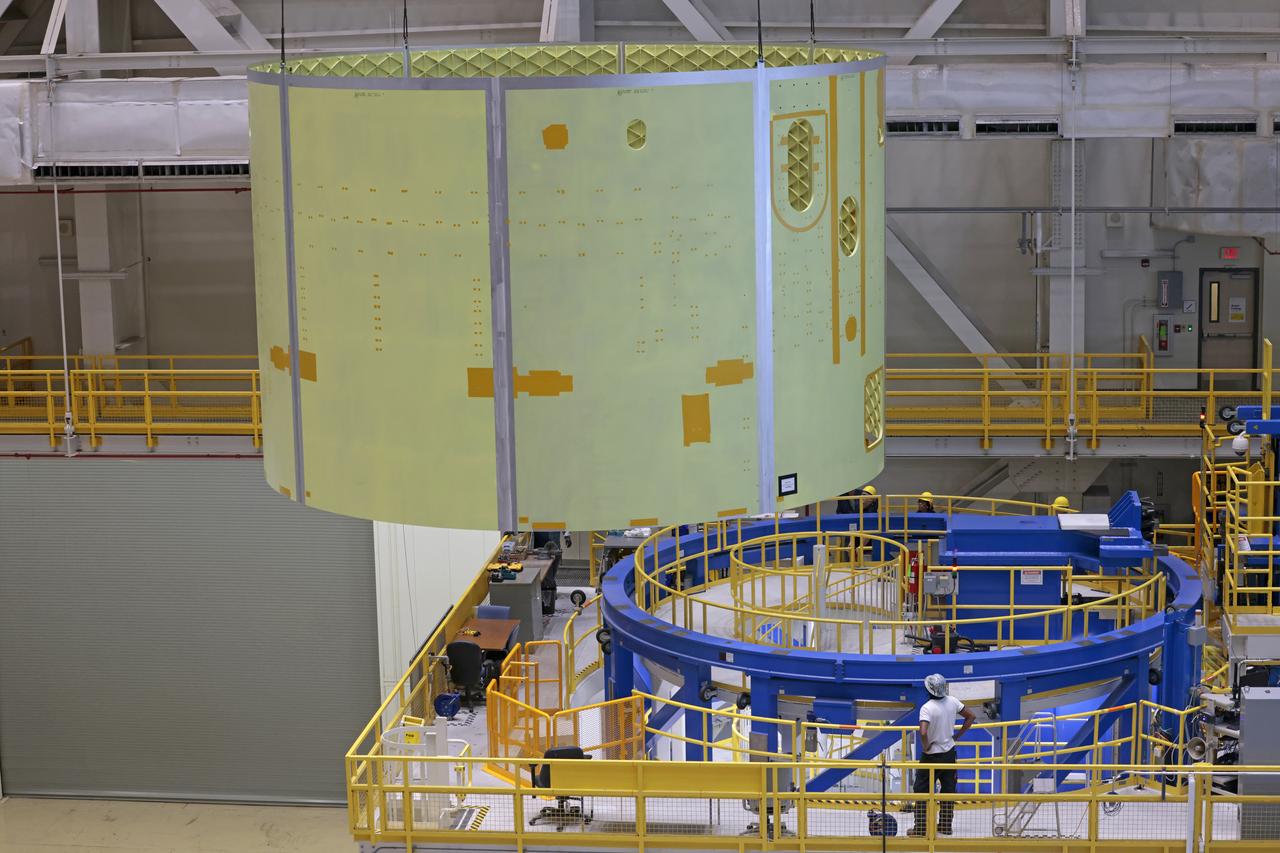

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis V on December 18, 2024, at NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA. Throughout 2024, new tooling was erected in bldg. 115 for the upcoming iterations of the Space Launch System (SLS), Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and the test articles required to develop and assemble each efficiently and effectively. This barrel is the sixty-fourth produced for the Space Launch System program since its inception and is the first barrel weld completed for the core stage of the Artemis V mission. This engine section will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. According to a Boeing engineer, as of this barrel, the VWC has now completed 515 production welds, with friction-stir welding a cumulative distance of 111,568 inches. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis V on December 18, 2024, at NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA. Throughout 2024, new tooling was erected in bldg. 115 for the upcoming iterations of the Space Launch System (SLS), Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and the test articles required to develop and assemble each efficiently and effectively. This barrel is the sixty-fourth produced for the Space Launch System program since its inception and is the first barrel weld completed for the core stage of the Artemis V mission. This engine section will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. According to a Boeing engineer, as of this barrel, the VWC has now completed 515 production welds, with friction-stir welding a cumulative distance of 111,568 inches. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis V on December 18, 2024, at NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA. Throughout 2024, new tooling was erected in bldg. 115 for the upcoming iterations of the Space Launch System (SLS), Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and the test articles required to develop and assemble each efficiently and effectively. This barrel is the sixty-fourth produced for the Space Launch System program since its inception and is the first barrel weld completed for the core stage of the Artemis V mission. This engine section will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. According to a Boeing engineer, as of this barrel, the VWC has now completed 515 production welds, with friction-stir welding a cumulative distance of 111,568 inches. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
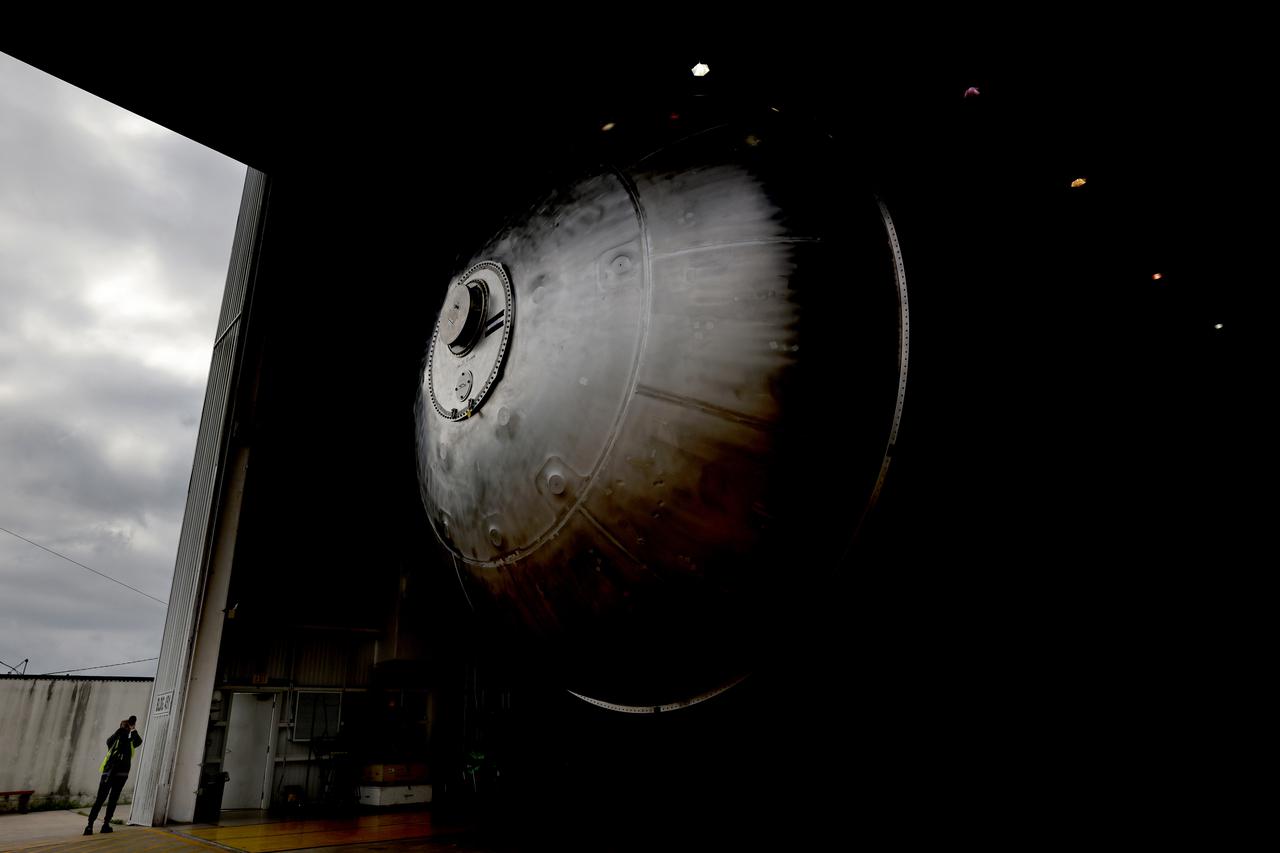

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
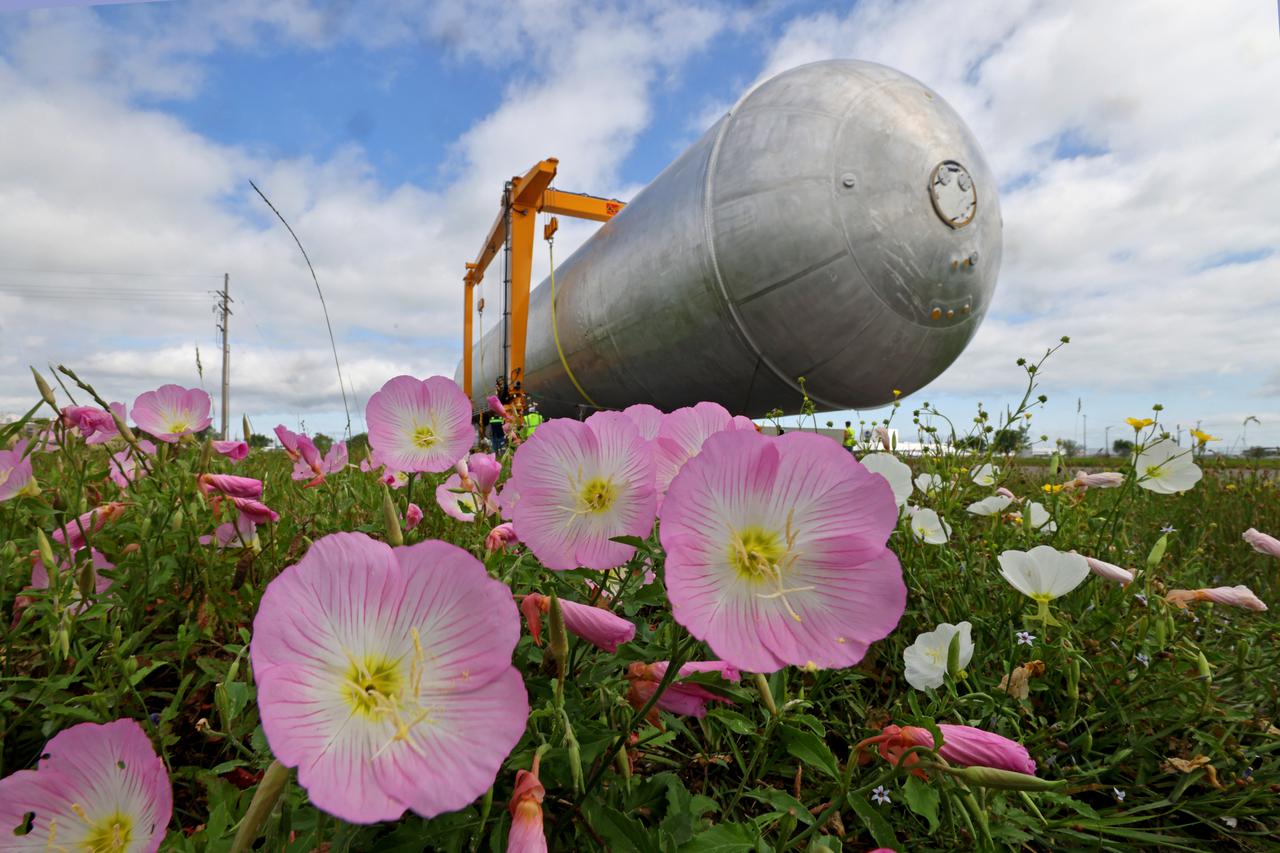

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
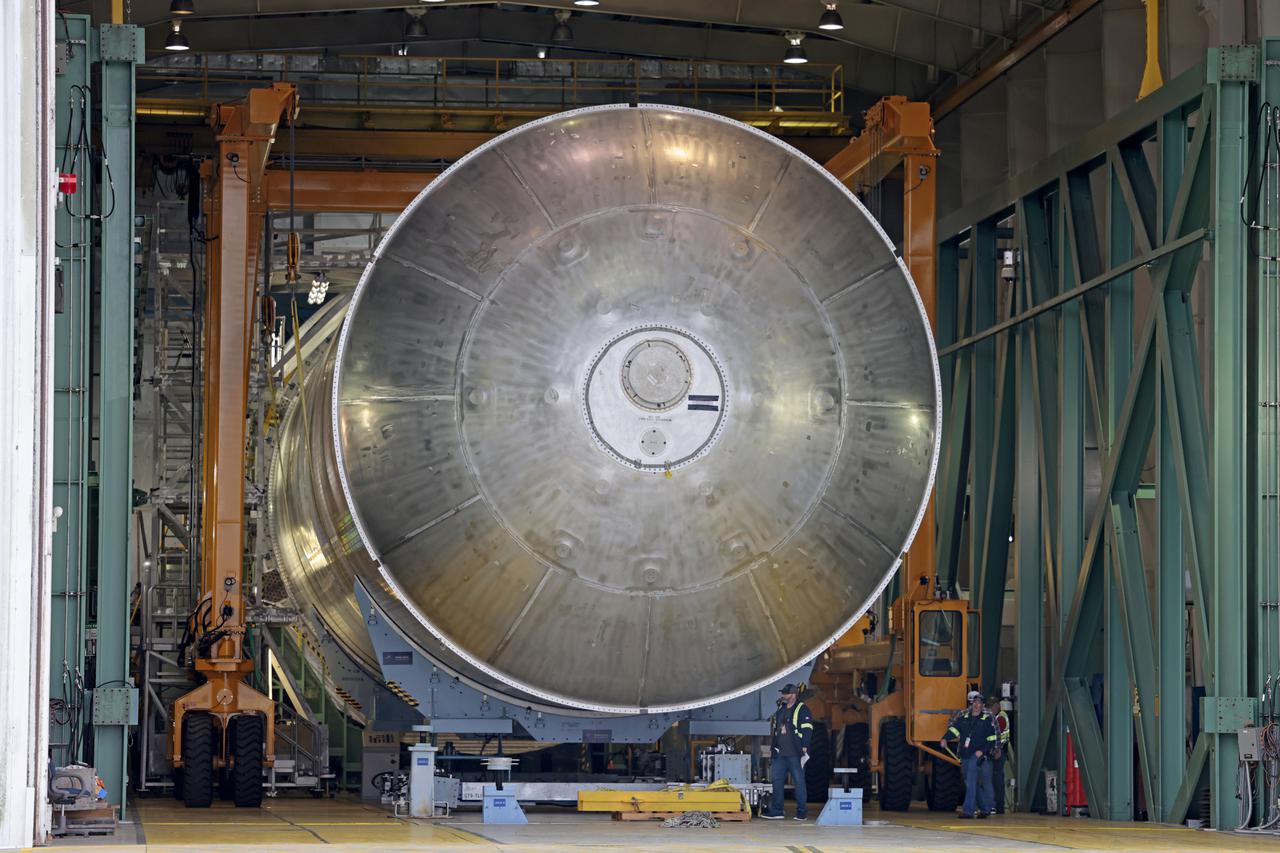

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
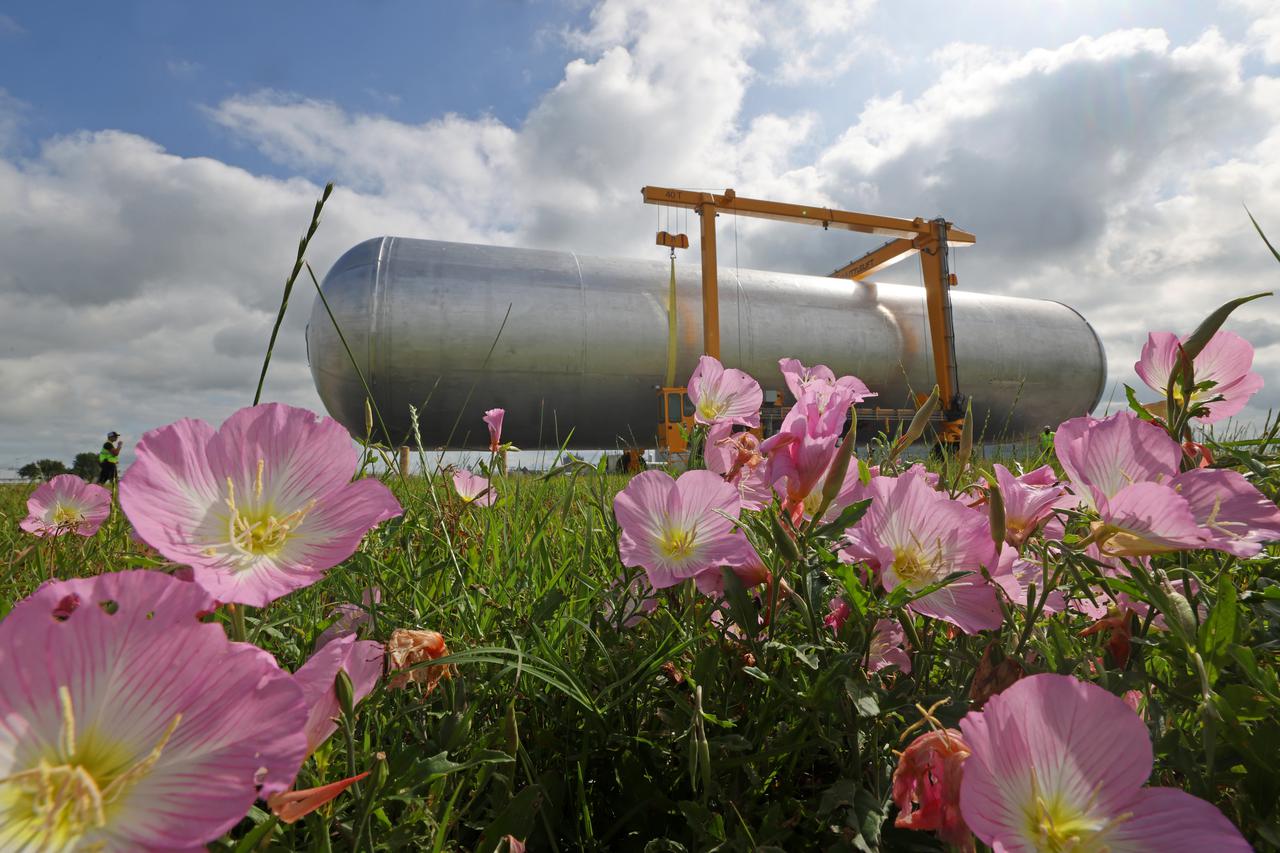

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
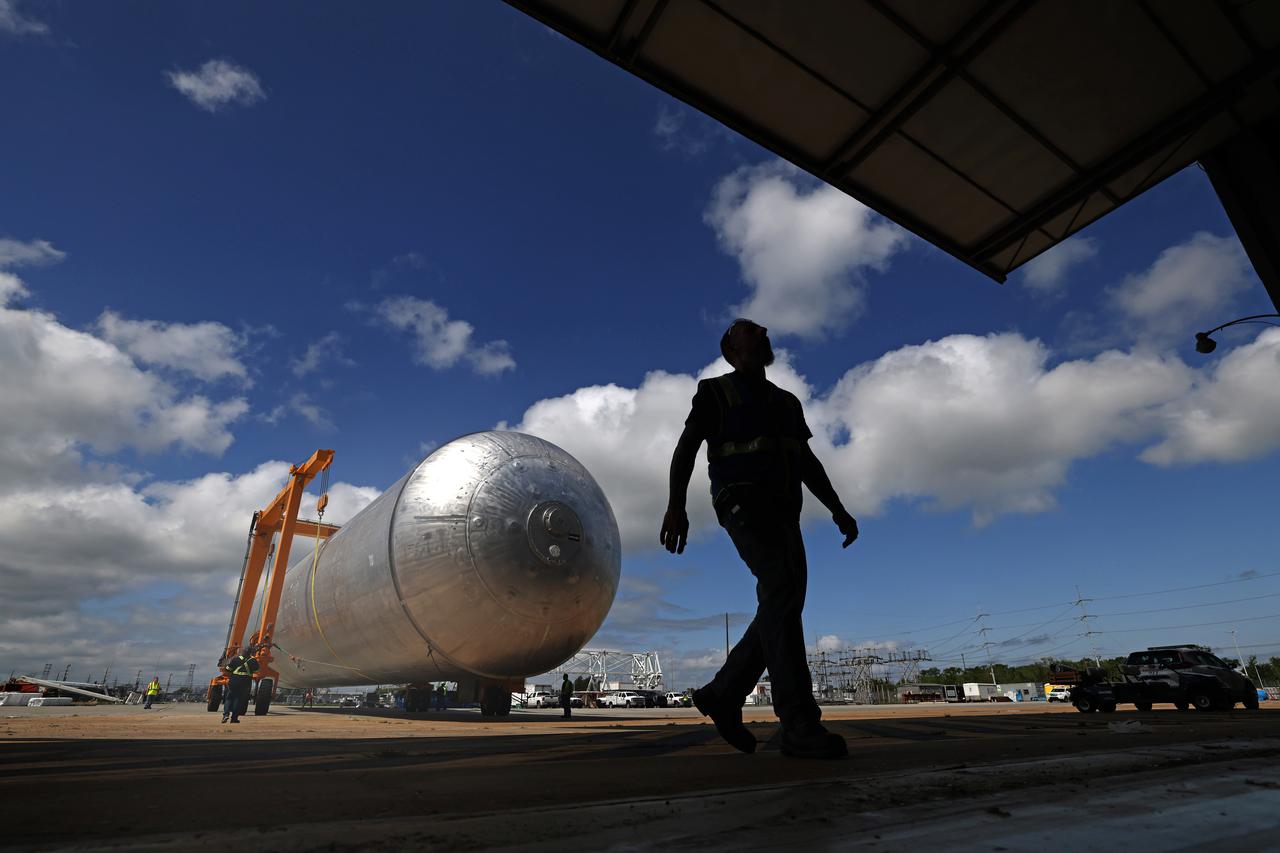

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
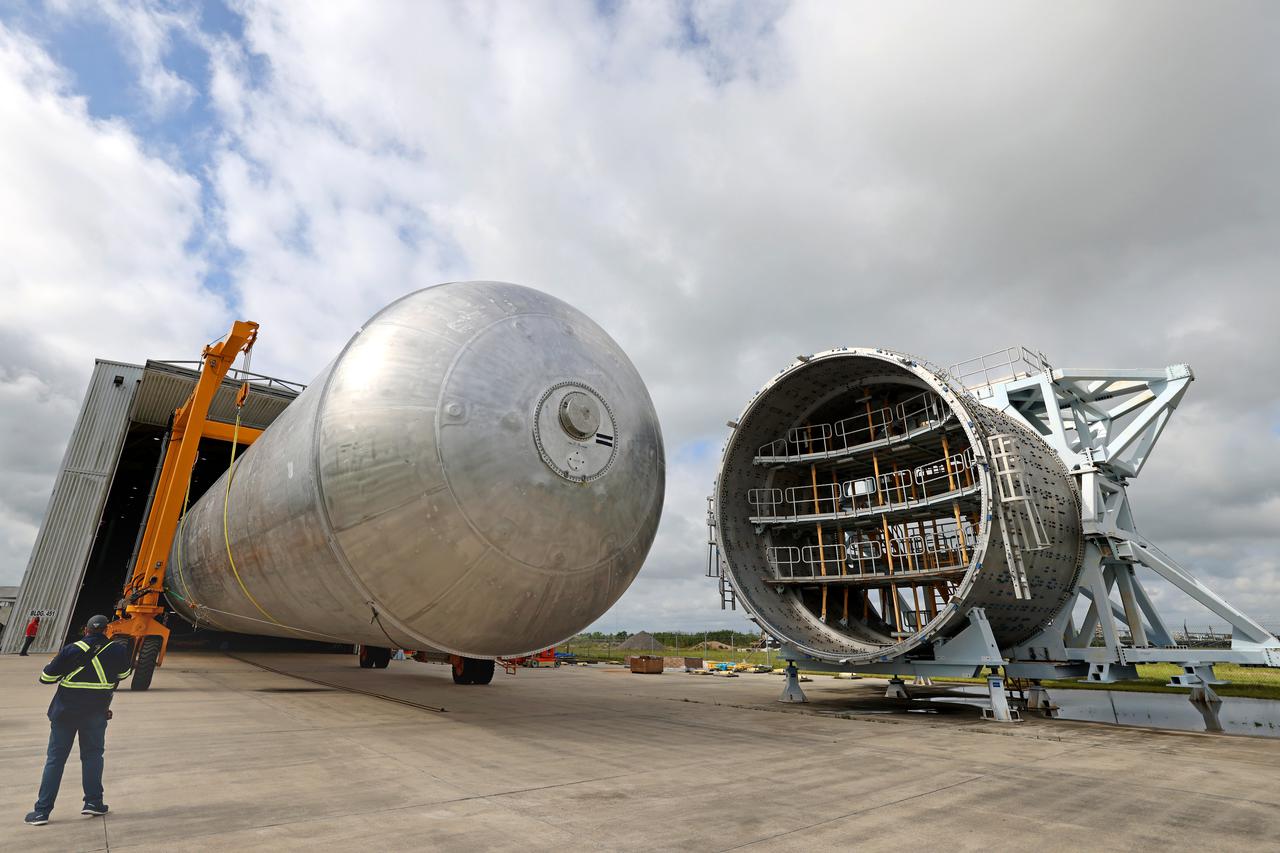

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans removing a weld-confidence article from a robotic welding tool in December 2023. This article features pieces of a liquid hydrogen tank dome that were welded as a test to make sure the dome used for flight will be welded correctly. The dome will be part of the new, four-engine EUS (exploration upper stage) for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. EUS will be used for the Artemis IV lunar mission, replacing the single-engine interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) used for the first three Artemis missions. The evolved in-space stage will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The weld-confidence article pictured here will not be used for flight but is instead helping teams prepare and certify the procedures needed to manufacture flight hardware. NASA is working to land the first woman and person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans removing a weld-confidence article from a robotic welding tool in December 2023. This article features pieces of a liquid hydrogen tank dome that were welded as a test to make sure the dome used for flight will be welded correctly. The dome will be part of the new, four-engine EUS (exploration upper stage) for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. EUS will be used for the Artemis IV lunar mission, replacing the single-engine interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) used for the first three Artemis missions. The evolved in-space stage will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The weld-confidence article pictured here will not be used for flight but is instead helping teams prepare and certify the procedures needed to manufacture flight hardware. NASA is working to land the first woman and person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans removing a weld-confidence article from a robotic welding tool in December 2023. This article features pieces of a liquid hydrogen tank dome that were welded as a test to make sure the dome used for flight will be welded correctly. The dome will be part of the new, four-engine EUS (exploration upper stage) for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. EUS will be used for the Artemis IV lunar mission, replacing the single-engine interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) used for the first three Artemis missions. The evolved in-space stage will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The weld-confidence article pictured here will not be used for flight but is instead helping teams prepare and certify the procedures needed to manufacture flight hardware. NASA is working to land the first woman and person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans removing a weld-confidence article from a robotic welding tool in December 2023. This article features pieces of a liquid hydrogen tank dome that were welded as a test to make sure the dome used for flight will be welded correctly. The dome will be part of the new, four-engine EUS (exploration upper stage) for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. EUS will be used for the Artemis IV lunar mission, replacing the single-engine interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) used for the first three Artemis missions. The evolved in-space stage will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The weld-confidence article pictured here will not be used for flight but is instead helping teams prepare and certify the procedures needed to manufacture flight hardware. NASA is working to land the first woman and person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans removing a weld-confidence article from a robotic welding tool in December 2023. This article features pieces of a liquid hydrogen tank dome that were welded as a test to make sure the dome used for flight will be welded correctly. The dome will be part of the new, four-engine EUS (exploration upper stage) for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. EUS will be used for the Artemis IV lunar mission, replacing the single-engine interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) used for the first three Artemis missions. The evolved in-space stage will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to the Moon. The weld-confidence article pictured here will not be used for flight but is instead helping teams prepare and certify the procedures needed to manufacture flight hardware. NASA is working to land the first woman and person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
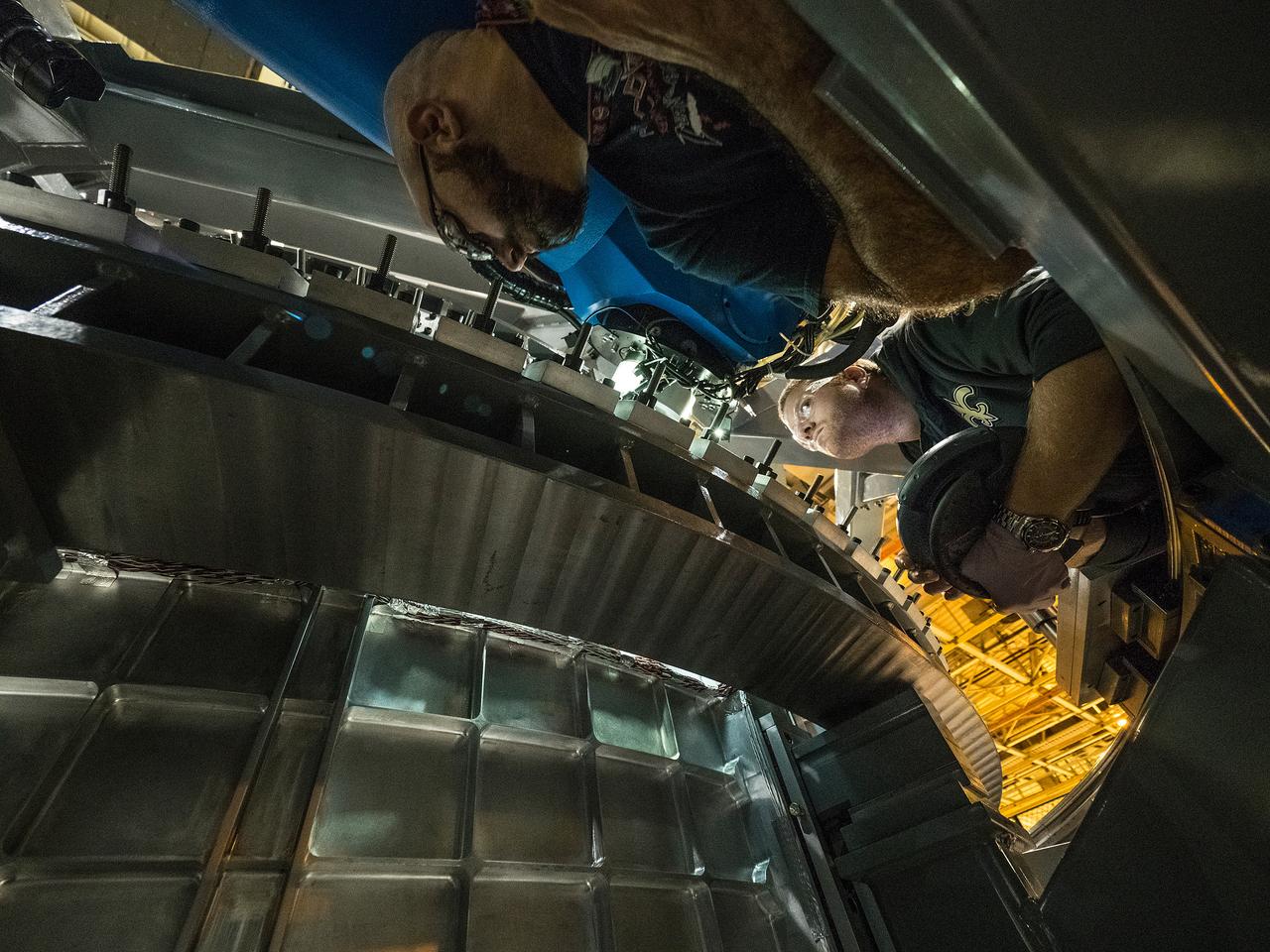

Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 15, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
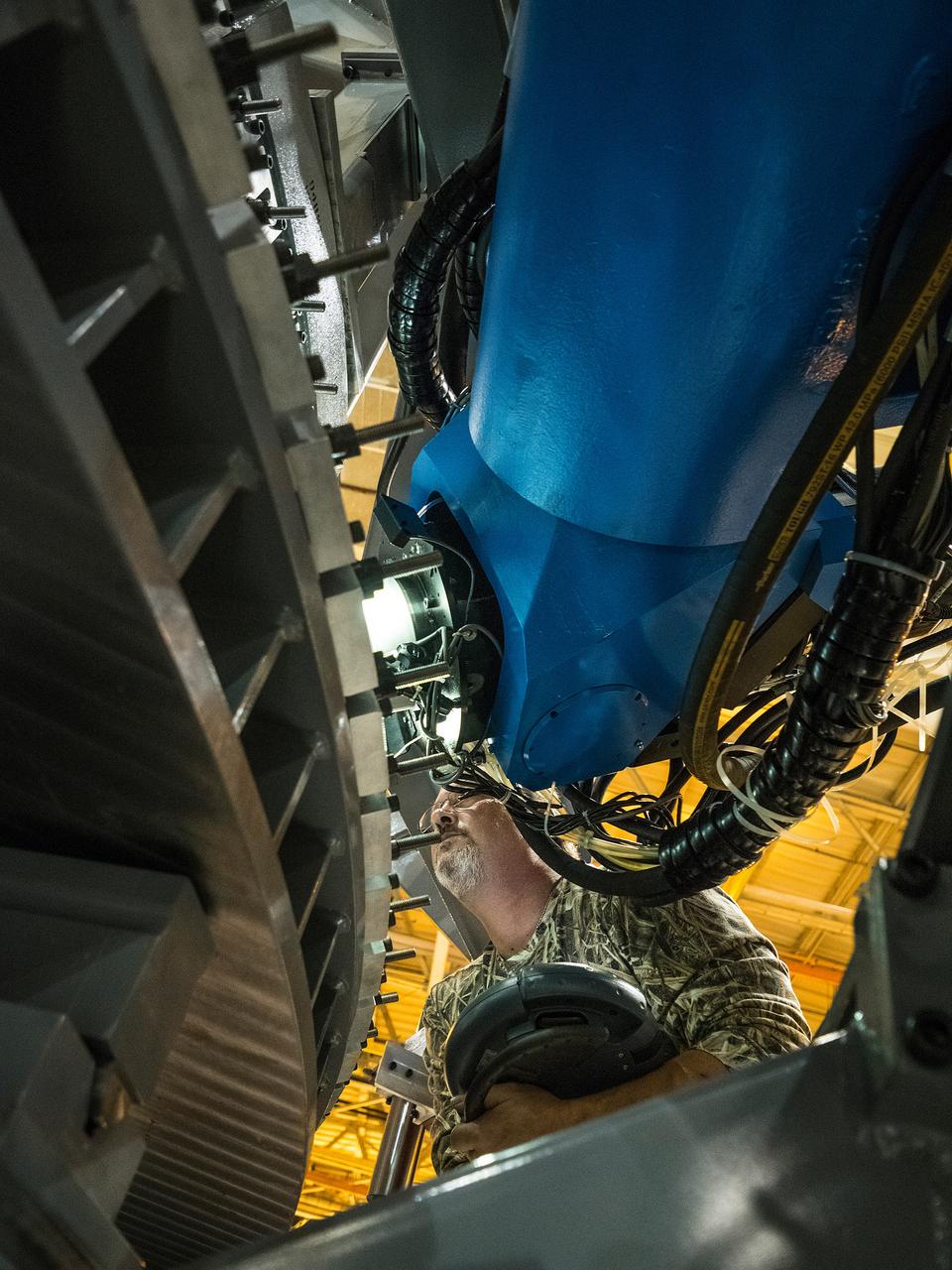

Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 16, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
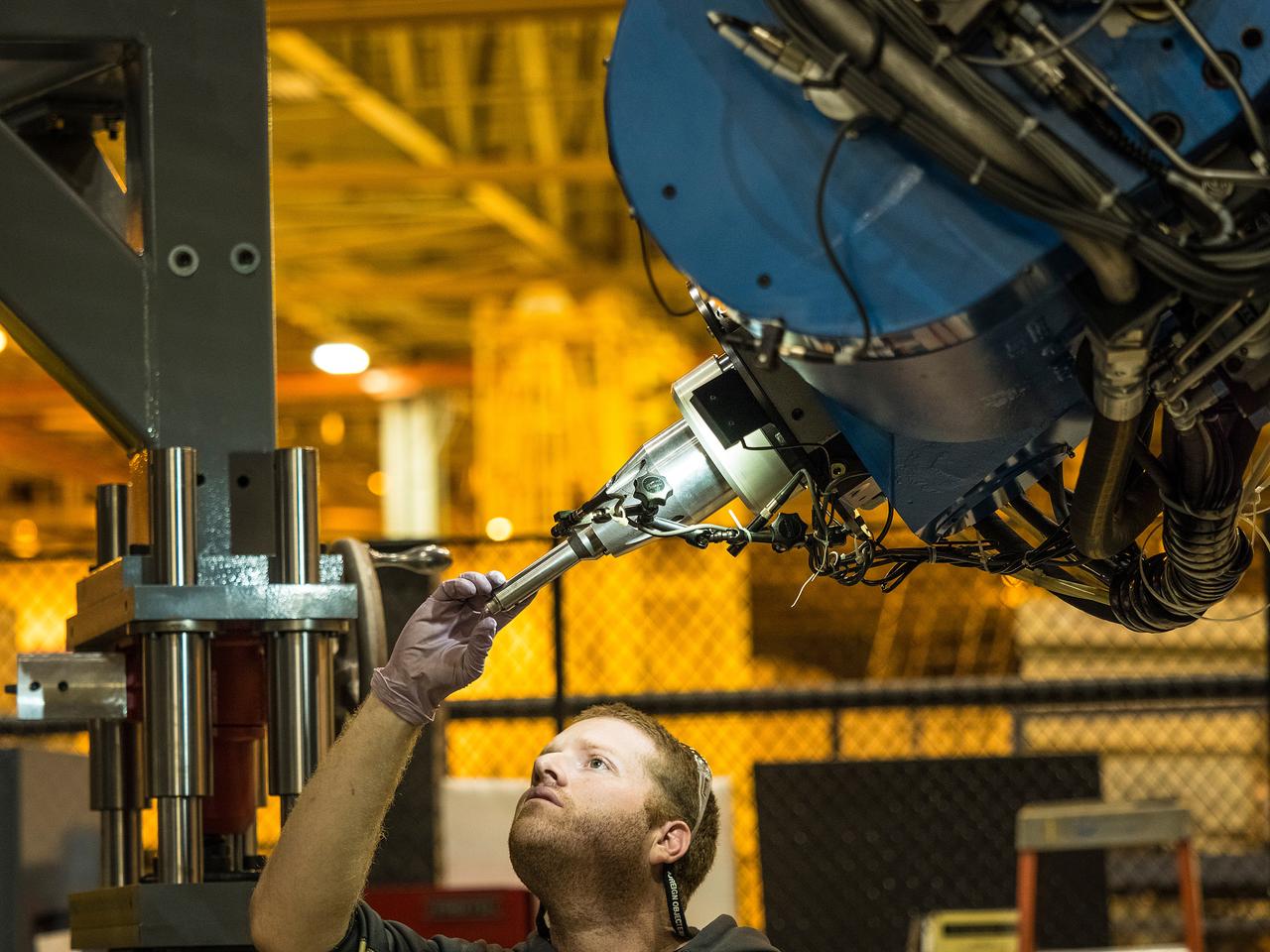

Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 15, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
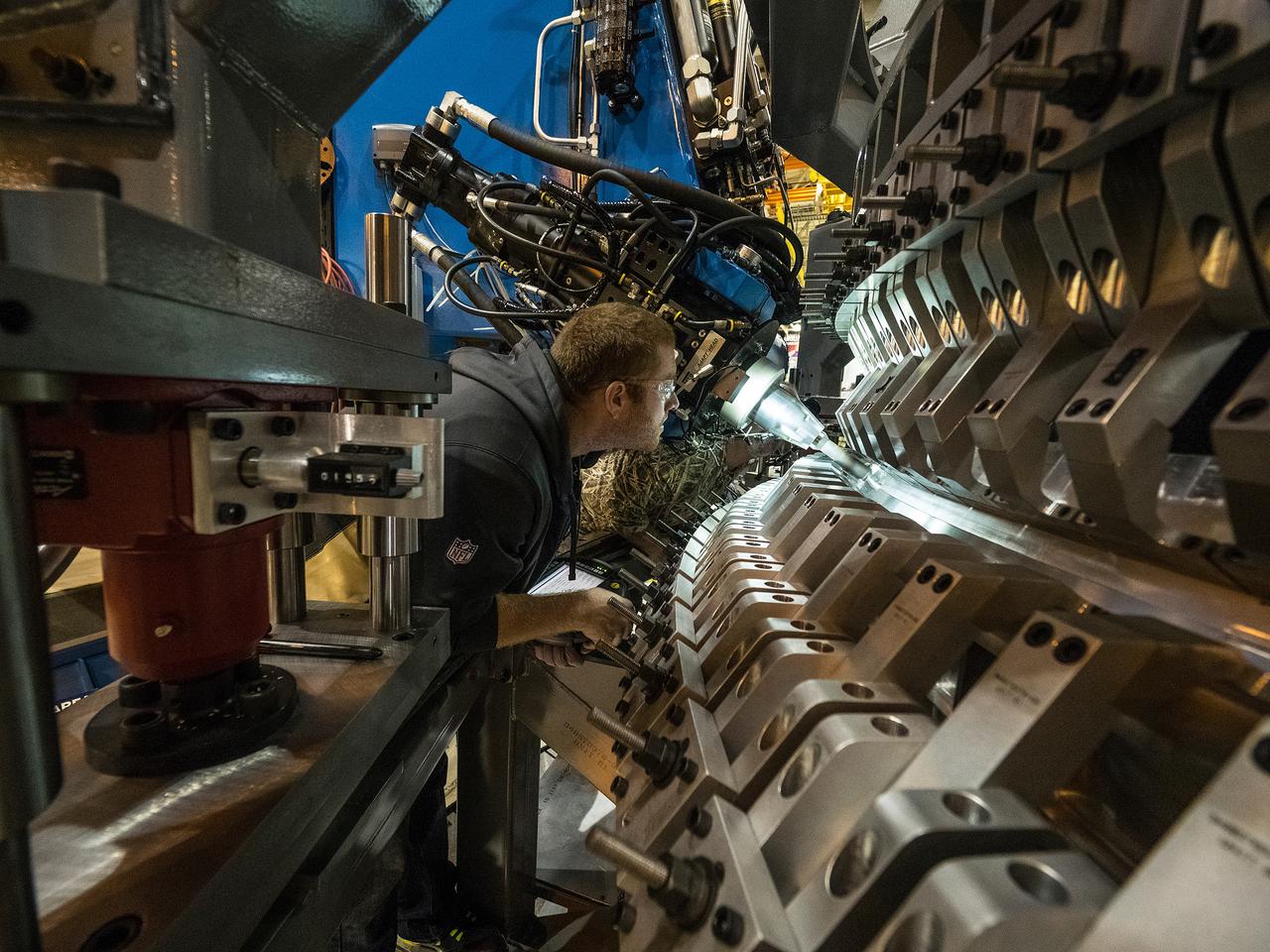
Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 16, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
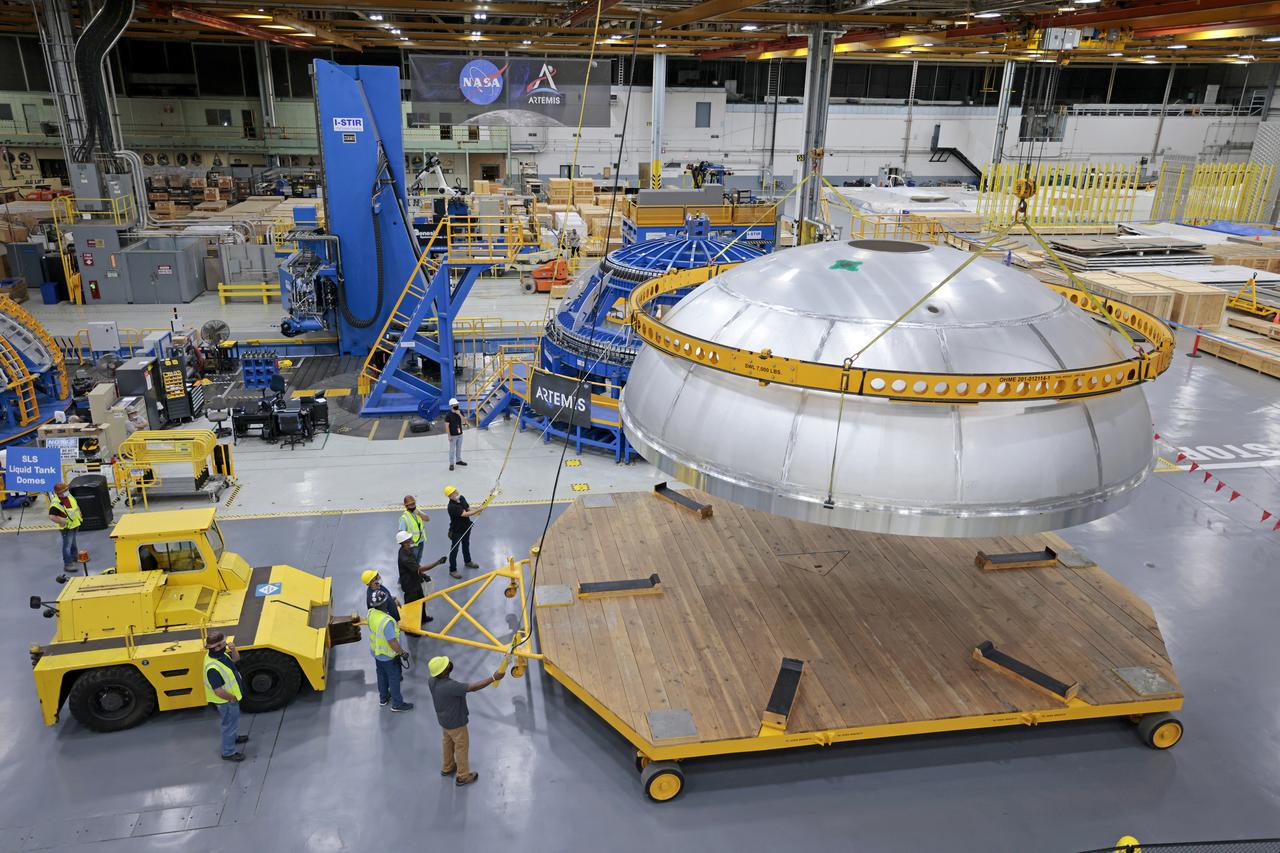

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
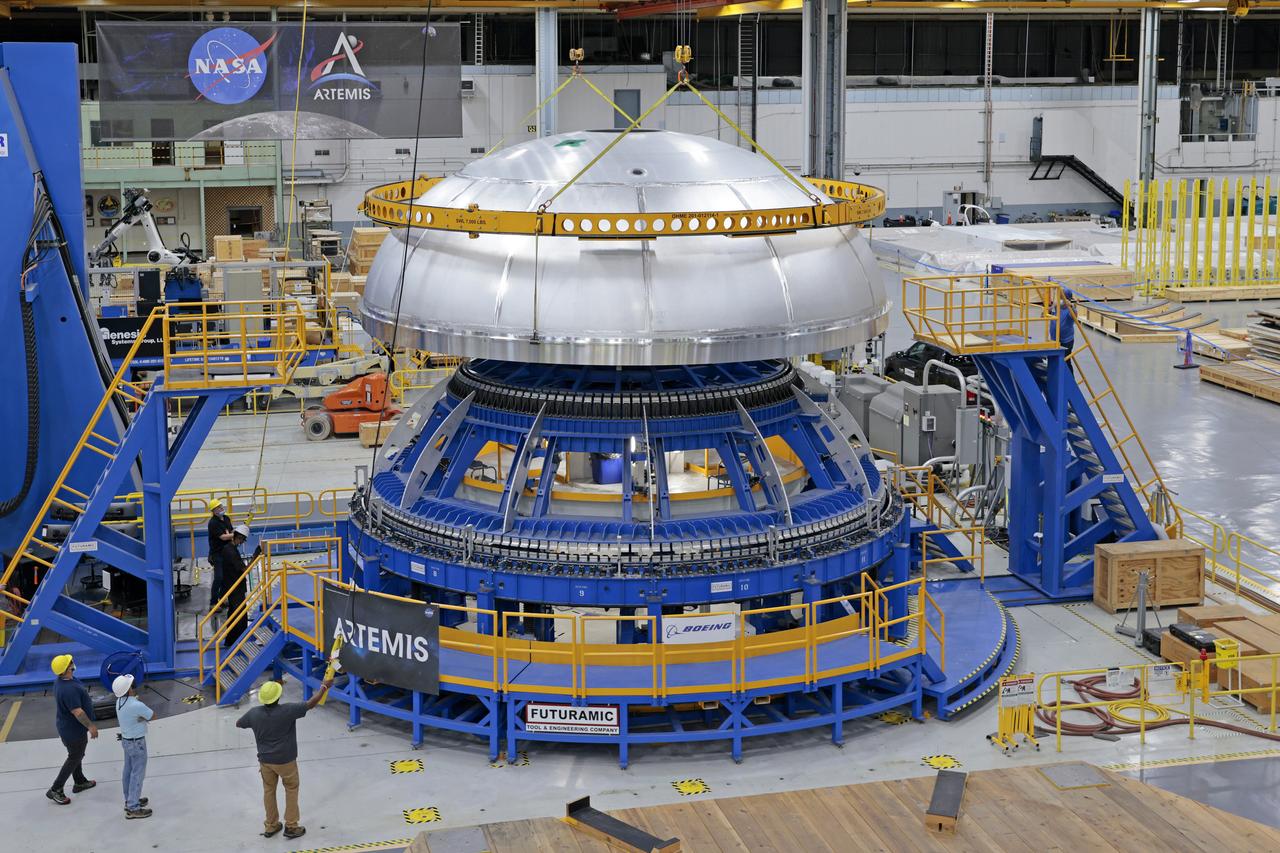
Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lifting and installing the liquid oxygen dome weld confidence article for a future upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket onto the LTAC (LOX Tank Assembly Center) in Building 115 at Michoud for the next phase of manufacturing in July 2023. The dome makes up a portion of the liquid oxygen tank weld confidence article for the EUS (exploration upper stage). Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures and structural integrity of the welds to manufacture structural test and flight versions of the hardware. EUS flight hardware is in early production at Michoud. The more powerful upper stage and its four RL10 engines will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for the SLS core stage and EUS, are manufacturing SLS stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the facility. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
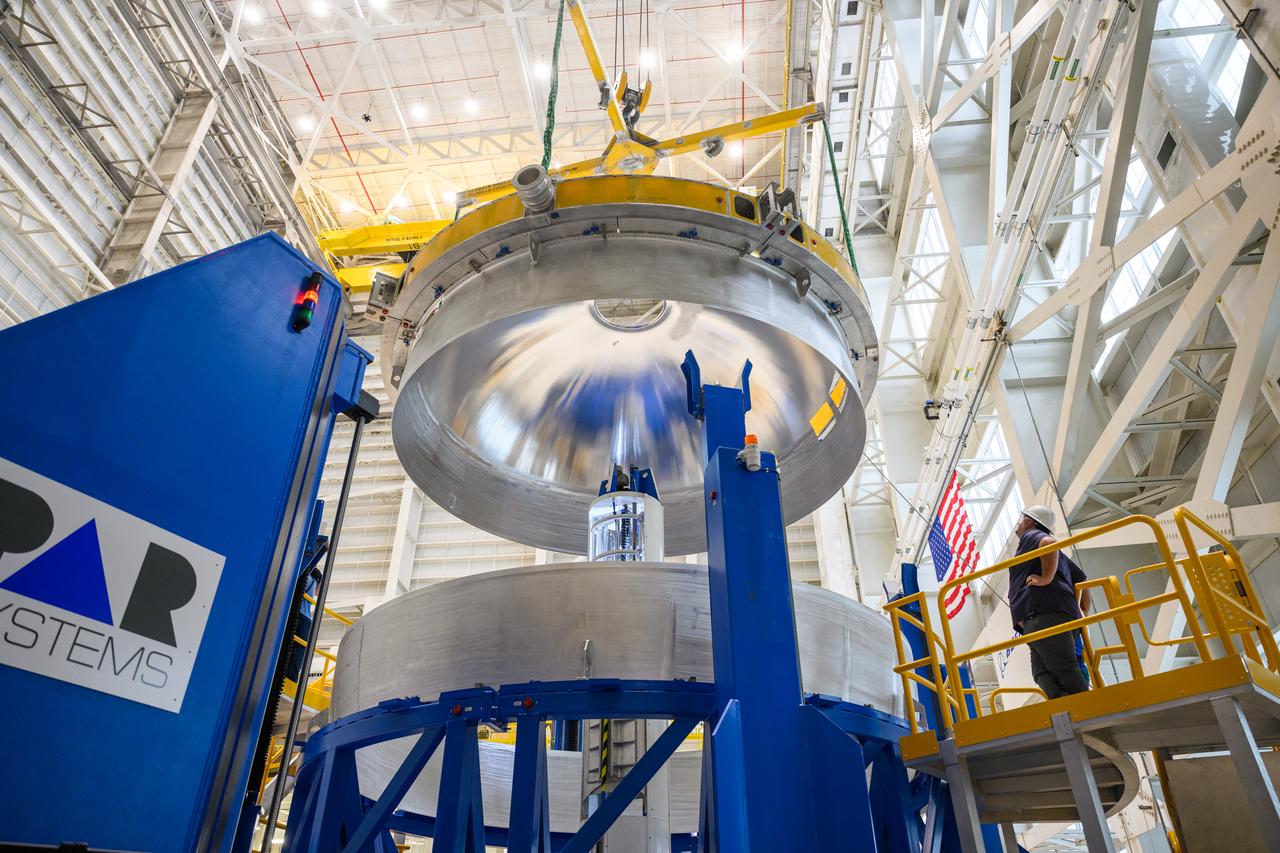

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lifting and installing the liquid oxygen dome weld confidence article for a future upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket onto the LTAC (LOX Tank Assembly Center) in Building 115 at Michoud for the next phase of manufacturing in July 2023. The dome makes up a portion of the liquid oxygen tank weld confidence article for the EUS (exploration upper stage). Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures and structural integrity of the welds to manufacture structural test and flight versions of the hardware. EUS flight hardware is in early production at Michoud. The more powerful upper stage and its four RL10 engines will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for the SLS core stage and EUS, are manufacturing SLS stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the facility. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
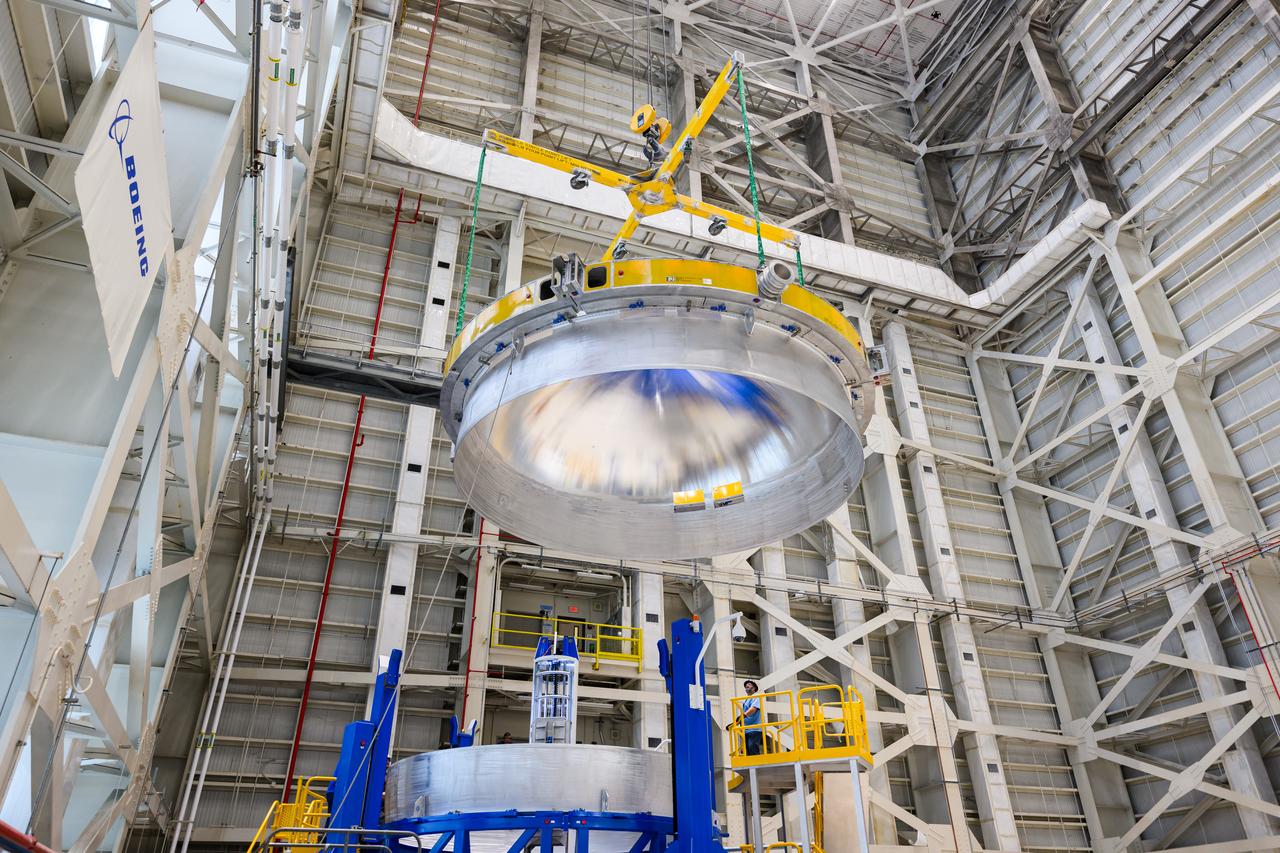

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lifting and installing the liquid oxygen dome weld confidence article for a future upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket onto the LTAC (LOX Tank Assembly Center) in Building 115 at Michoud for the next phase of manufacturing in July 2023. The dome makes up a portion of the liquid oxygen tank weld confidence article for the EUS (exploration upper stage). Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures and structural integrity of the welds to manufacture structural test and flight versions of the hardware. EUS flight hardware is in early production at Michoud. The more powerful upper stage and its four RL10 engines will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for the SLS core stage and EUS, are manufacturing SLS stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the facility. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
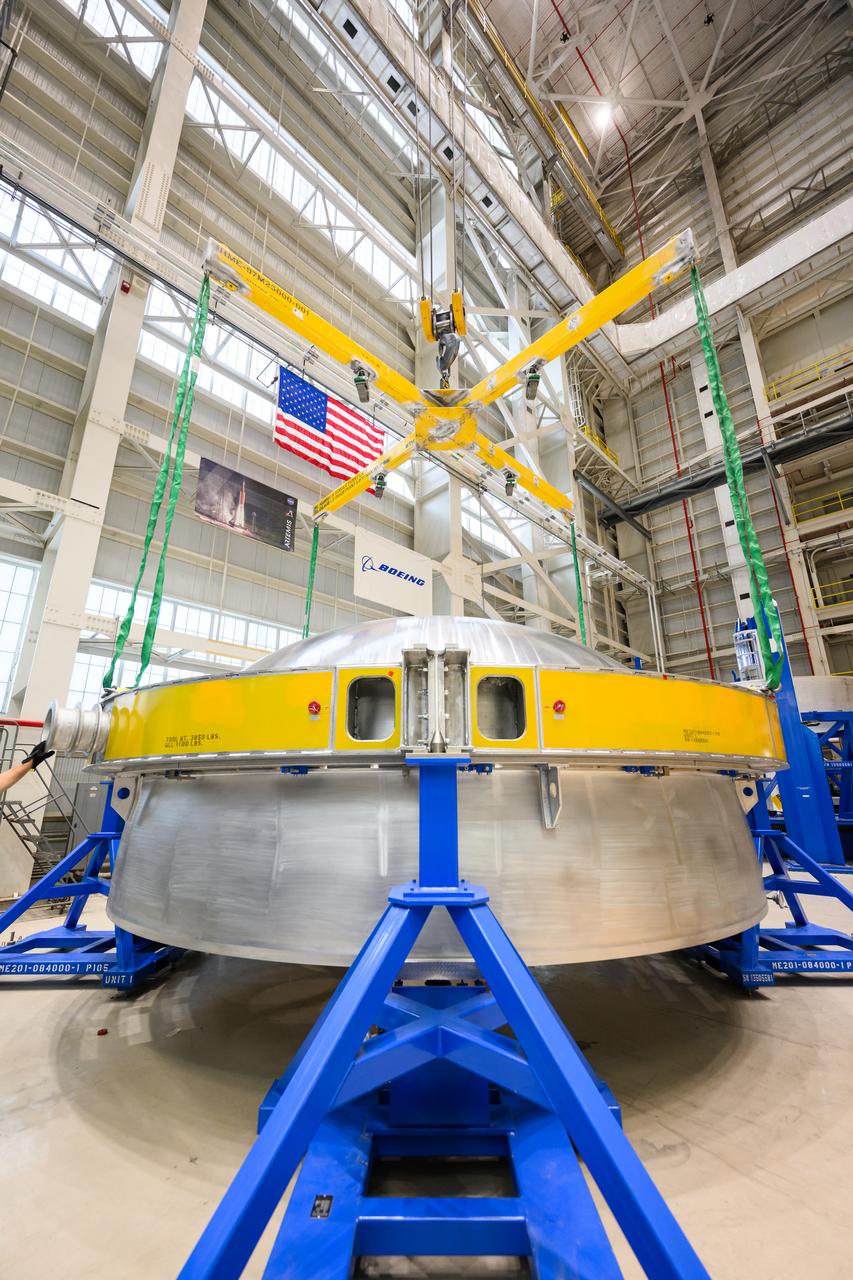

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lifting and installing the liquid oxygen dome weld confidence article for a future upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket onto the LTAC (LOX Tank Assembly Center) in Building 115 at Michoud for the next phase of manufacturing in July 2023. The dome makes up a portion of the liquid oxygen tank weld confidence article for the EUS (exploration upper stage). Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures and structural integrity of the welds to manufacture structural test and flight versions of the hardware. EUS flight hardware is in early production at Michoud. The more powerful upper stage and its four RL10 engines will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for the SLS core stage and EUS, are manufacturing SLS stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the facility. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
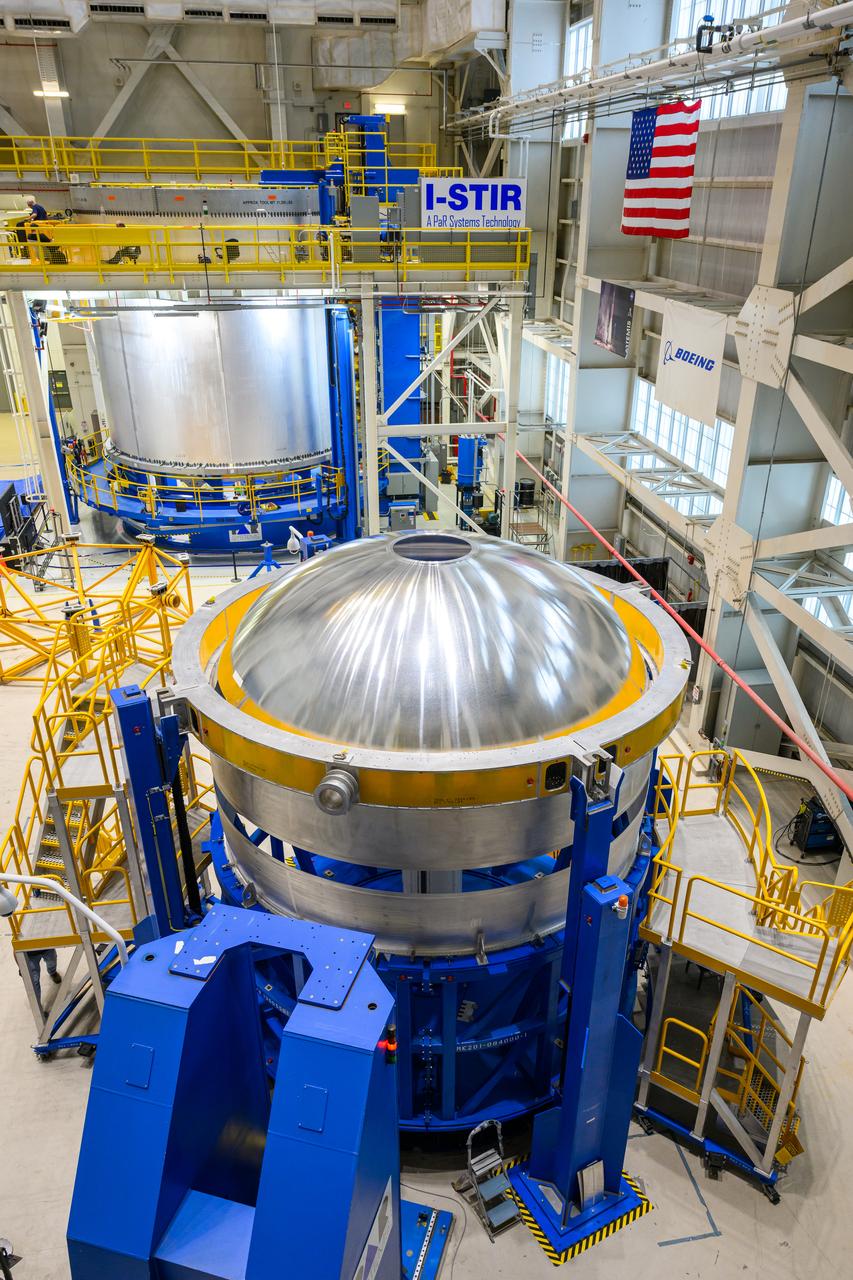

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lifting and installing the liquid oxygen dome weld confidence article for a future upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket onto the LTAC (LOX Tank Assembly Center) in Building 115 at Michoud for the next phase of manufacturing in July 2023. The dome makes up a portion of the liquid oxygen tank weld confidence article for the EUS (exploration upper stage). Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures and structural integrity of the welds to manufacture structural test and flight versions of the hardware. EUS flight hardware is in early production at Michoud. The more powerful upper stage and its four RL10 engines will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for the SLS core stage and EUS, are manufacturing SLS stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the facility. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
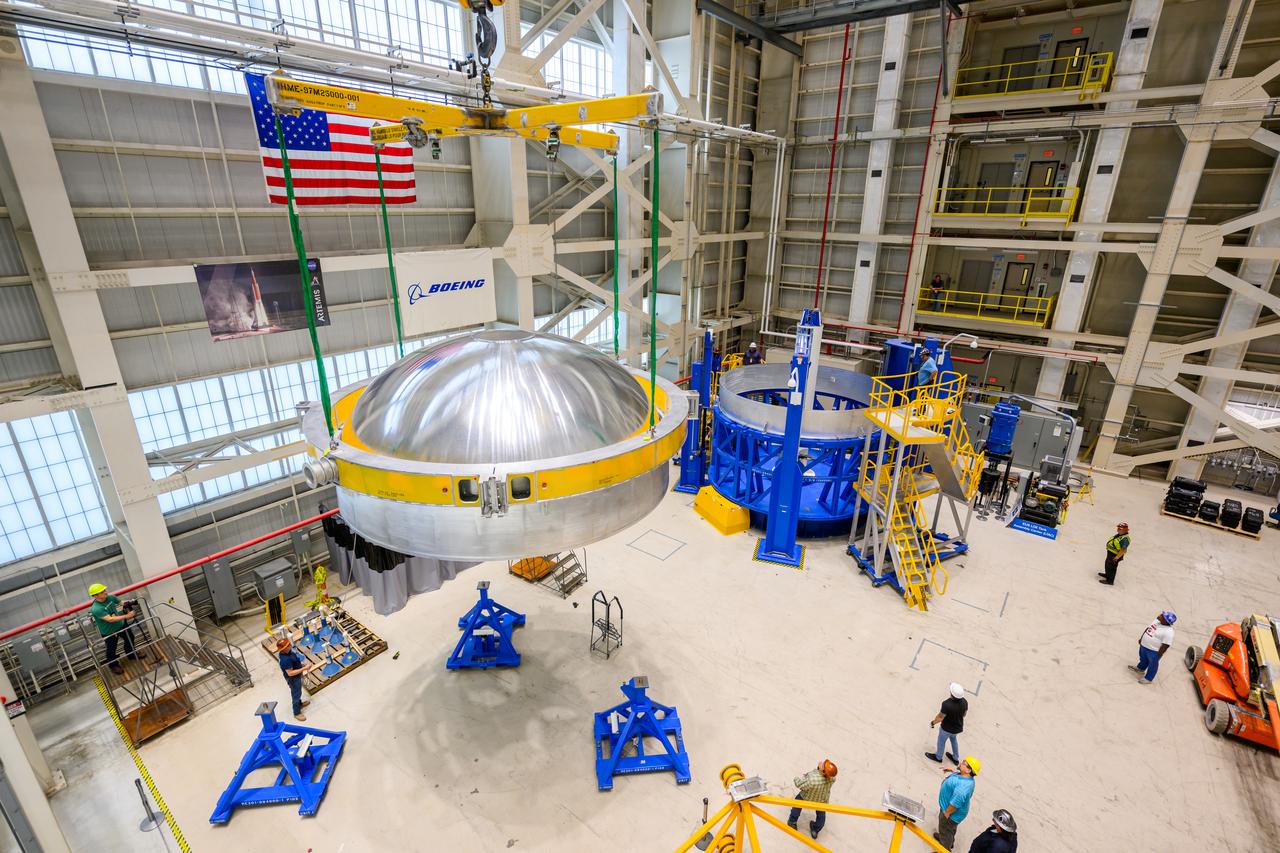

These images show technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lifting and installing the liquid oxygen dome weld confidence article for a future upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket onto the LTAC (LOX Tank Assembly Center) in Building 115 at Michoud for the next phase of manufacturing in July 2023. The dome makes up a portion of the liquid oxygen tank weld confidence article for the EUS (exploration upper stage). Teams use weld confidence articles to verify welding procedures and structural integrity of the welds to manufacture structural test and flight versions of the hardware. EUS flight hardware is in early production at Michoud. The more powerful upper stage and its four RL10 engines will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for the SLS core stage and EUS, are manufacturing SLS stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the facility. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
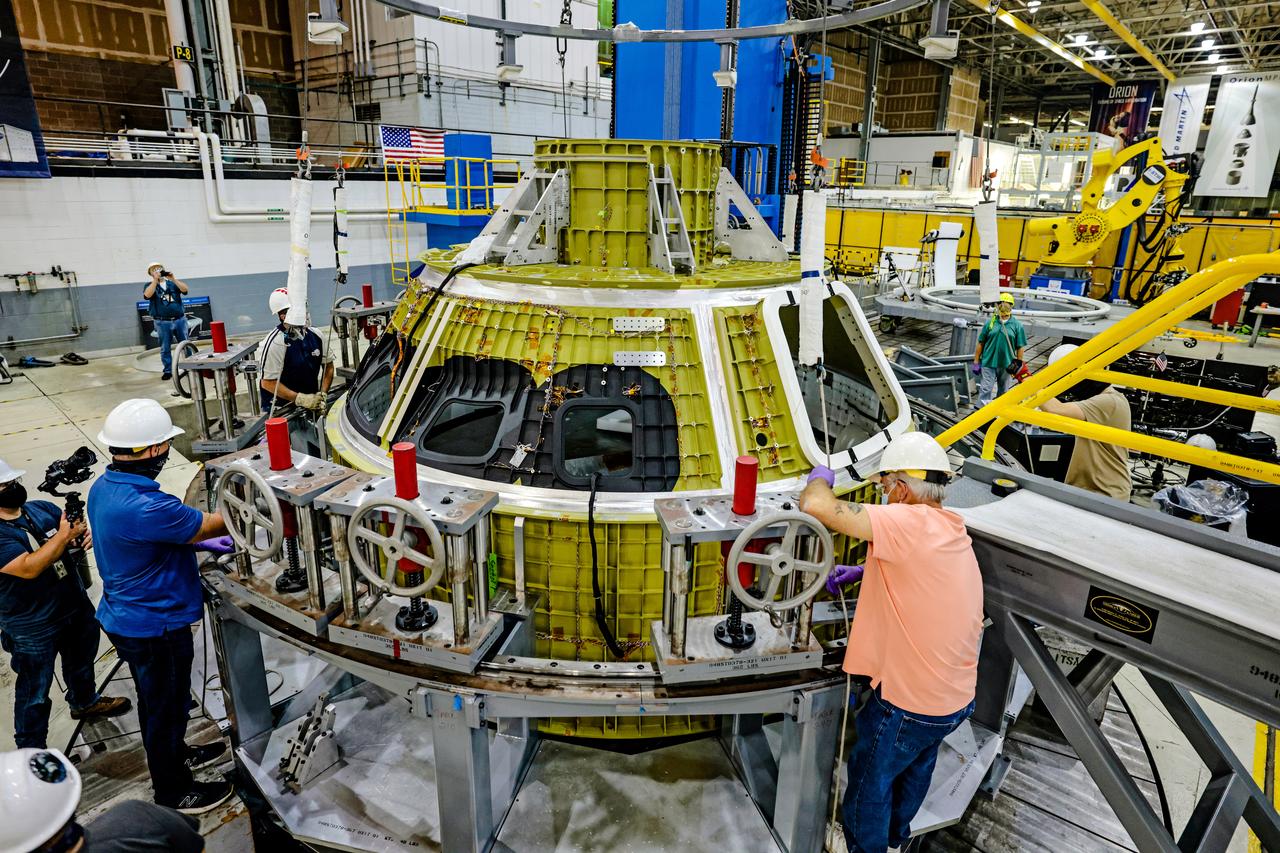

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
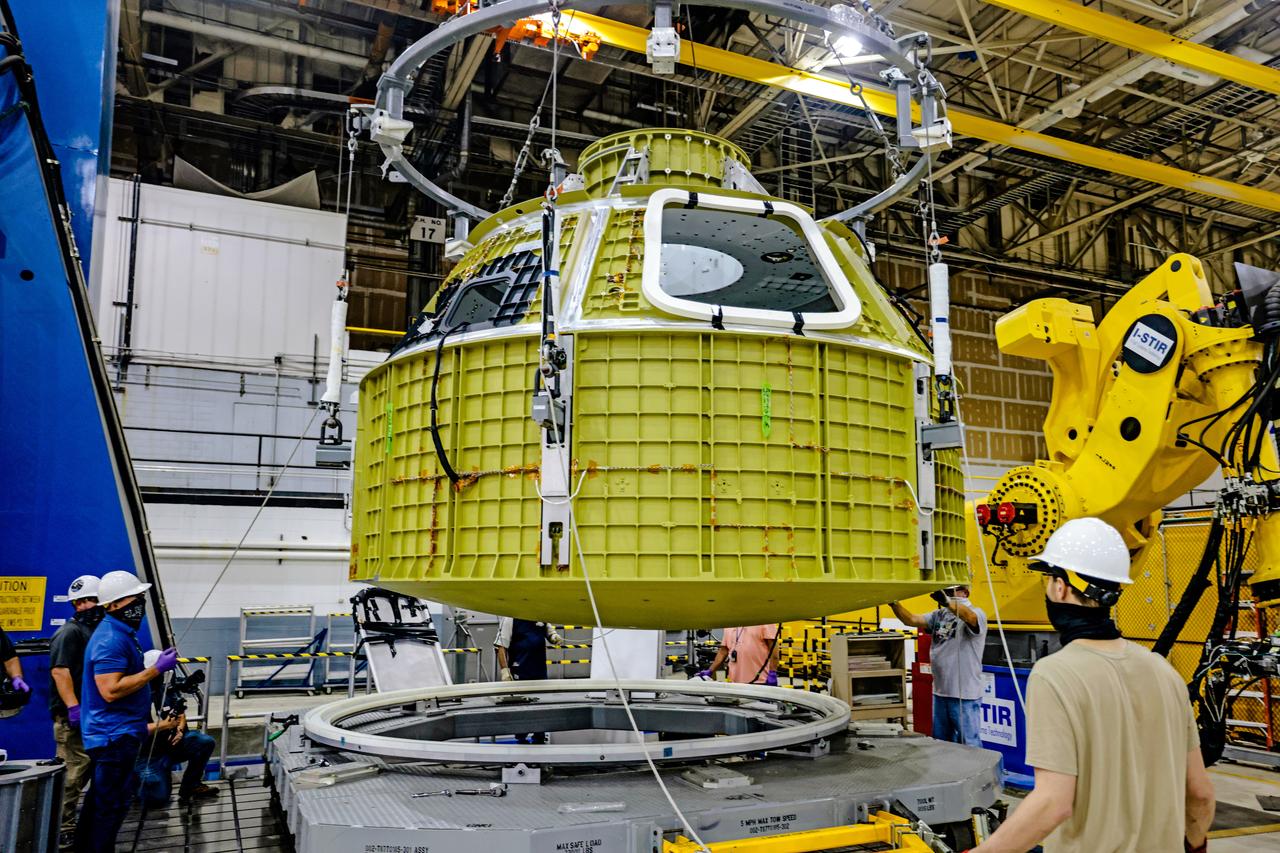

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
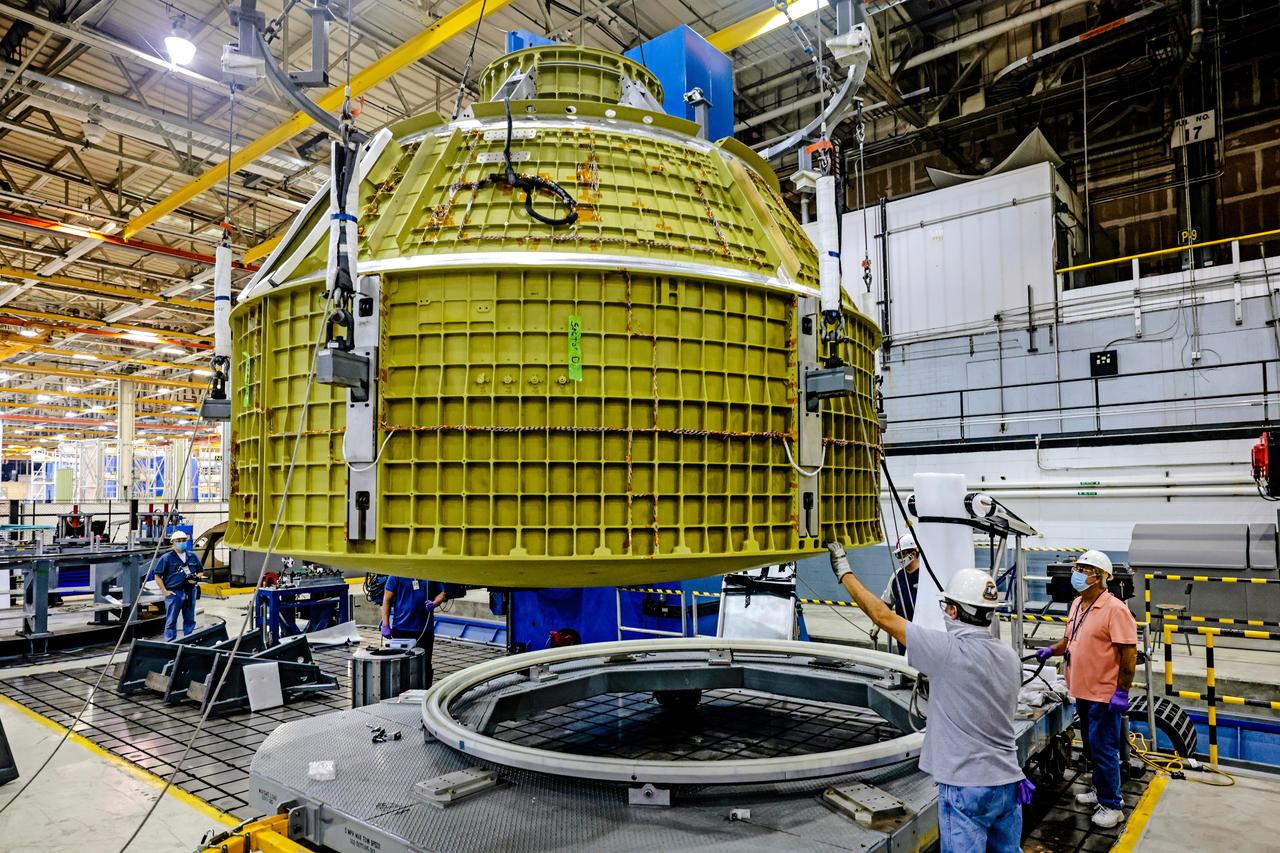

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
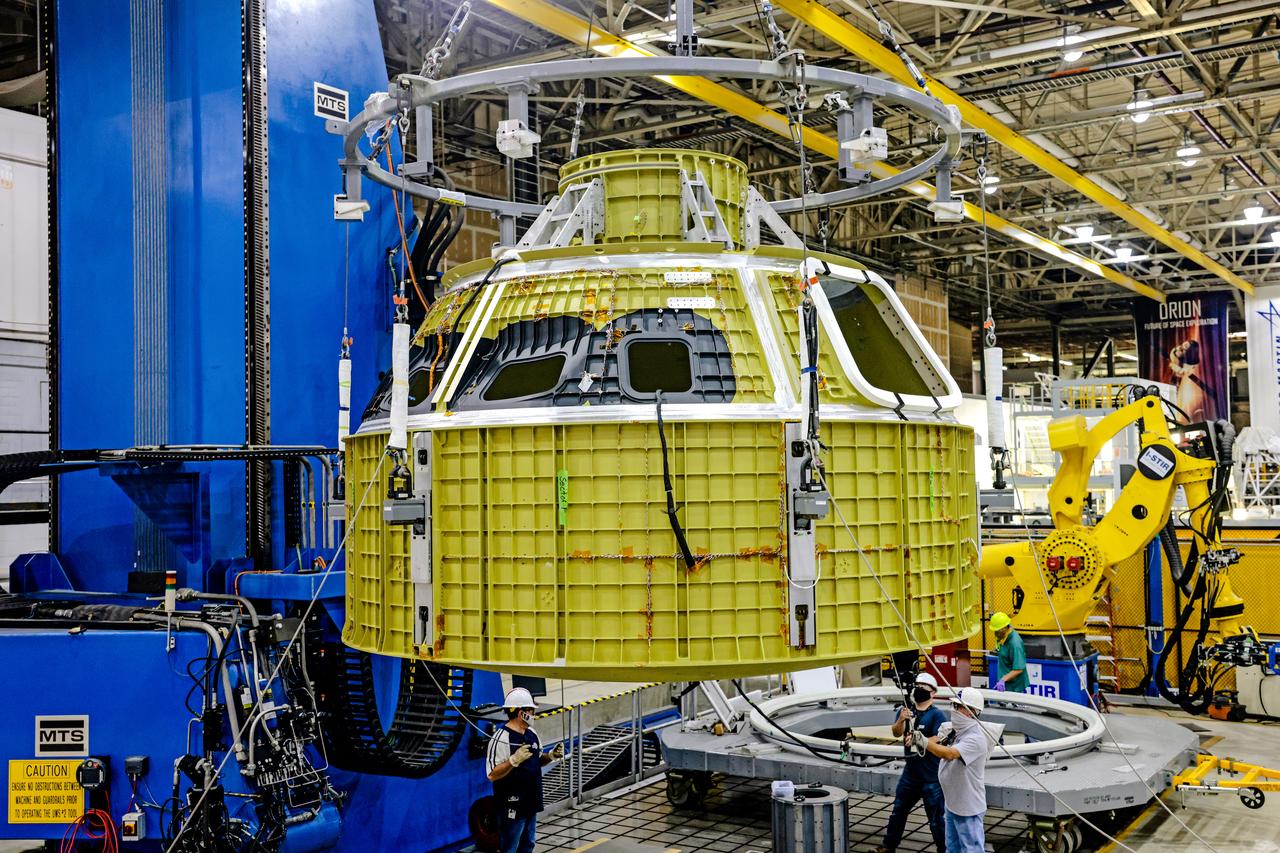

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.