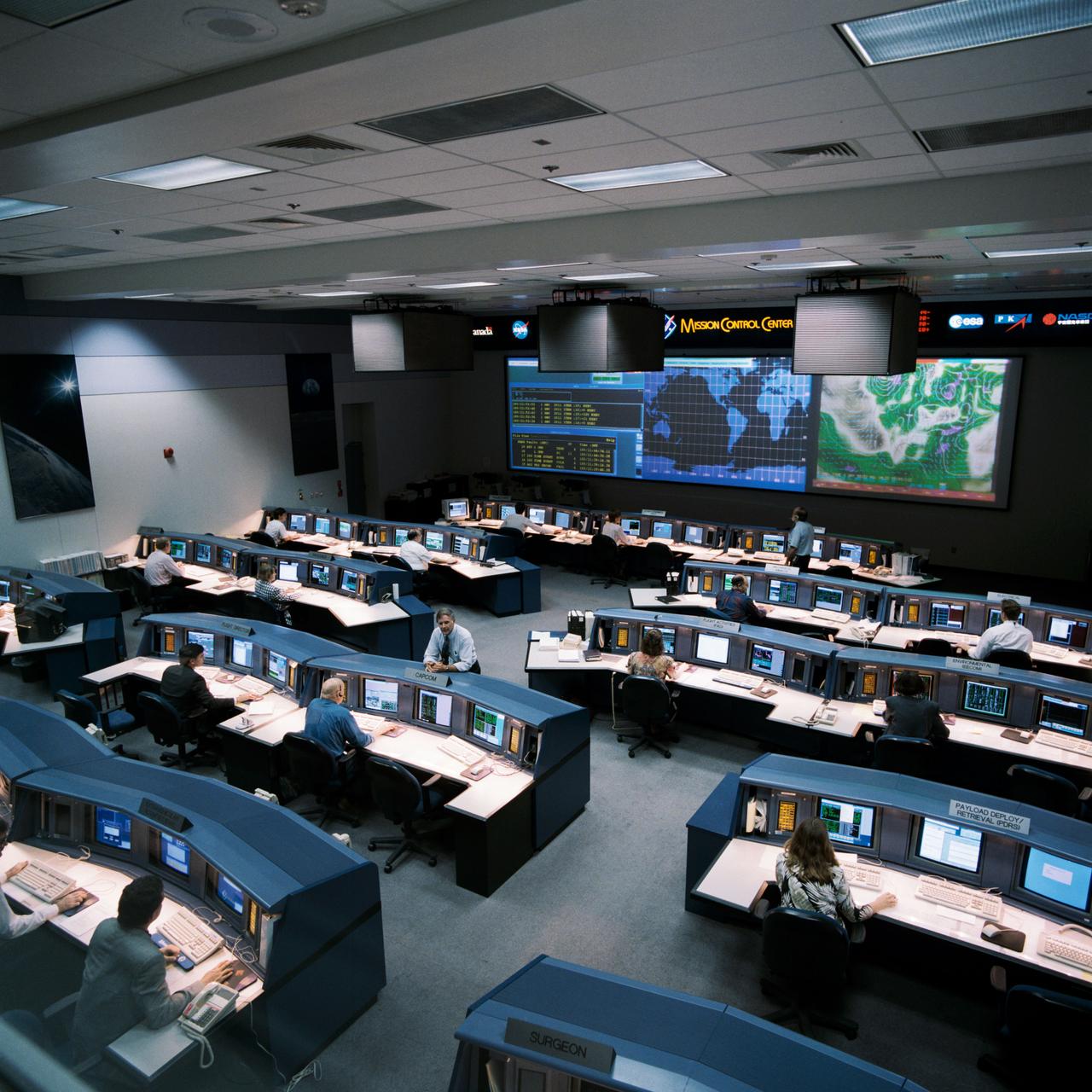

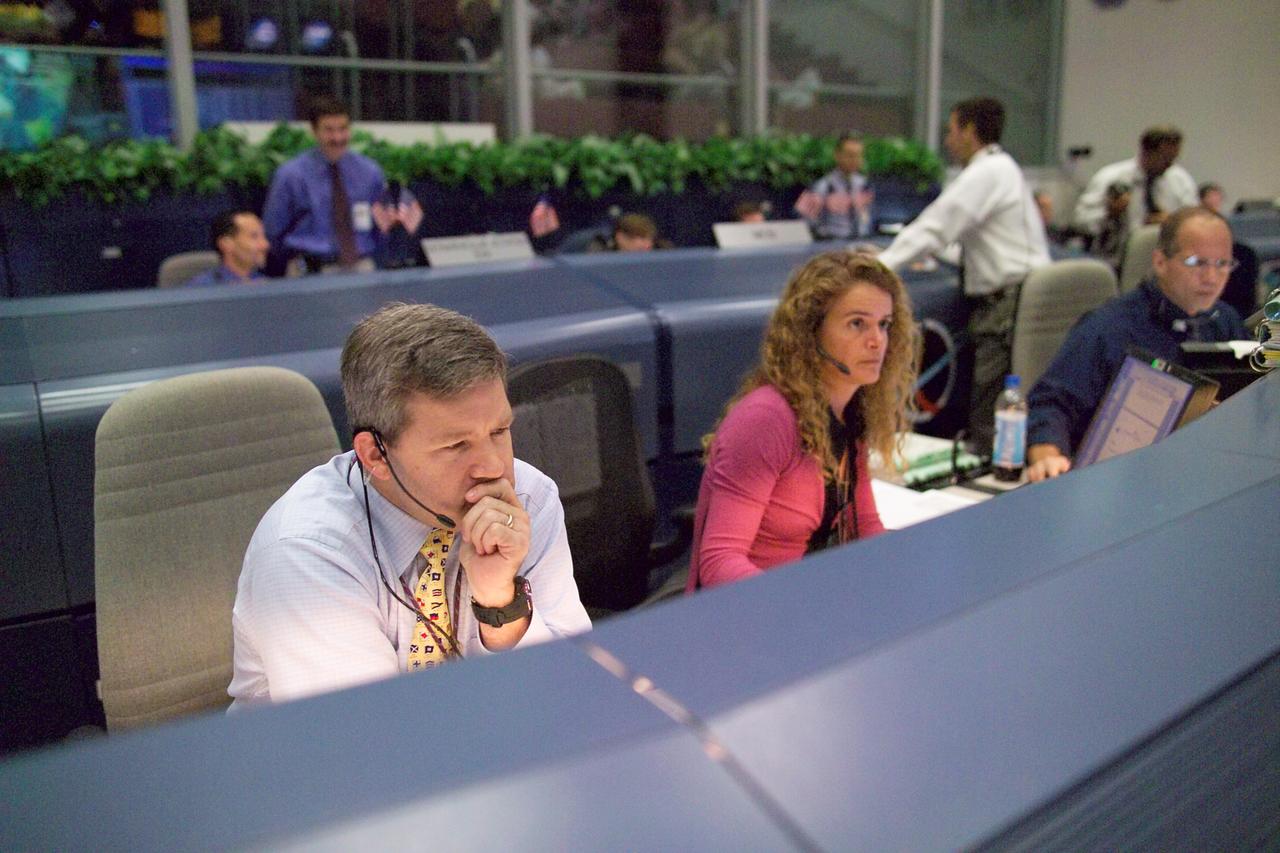
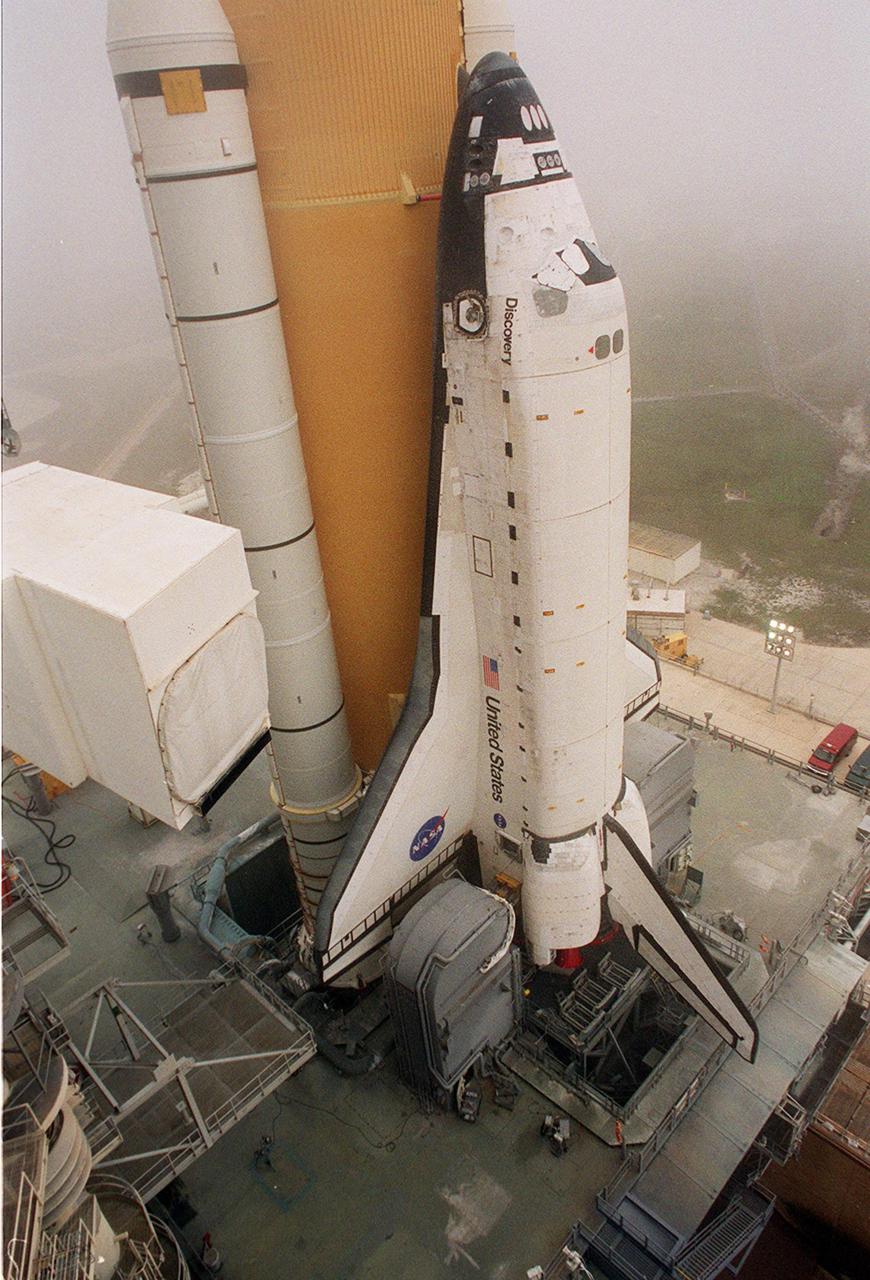
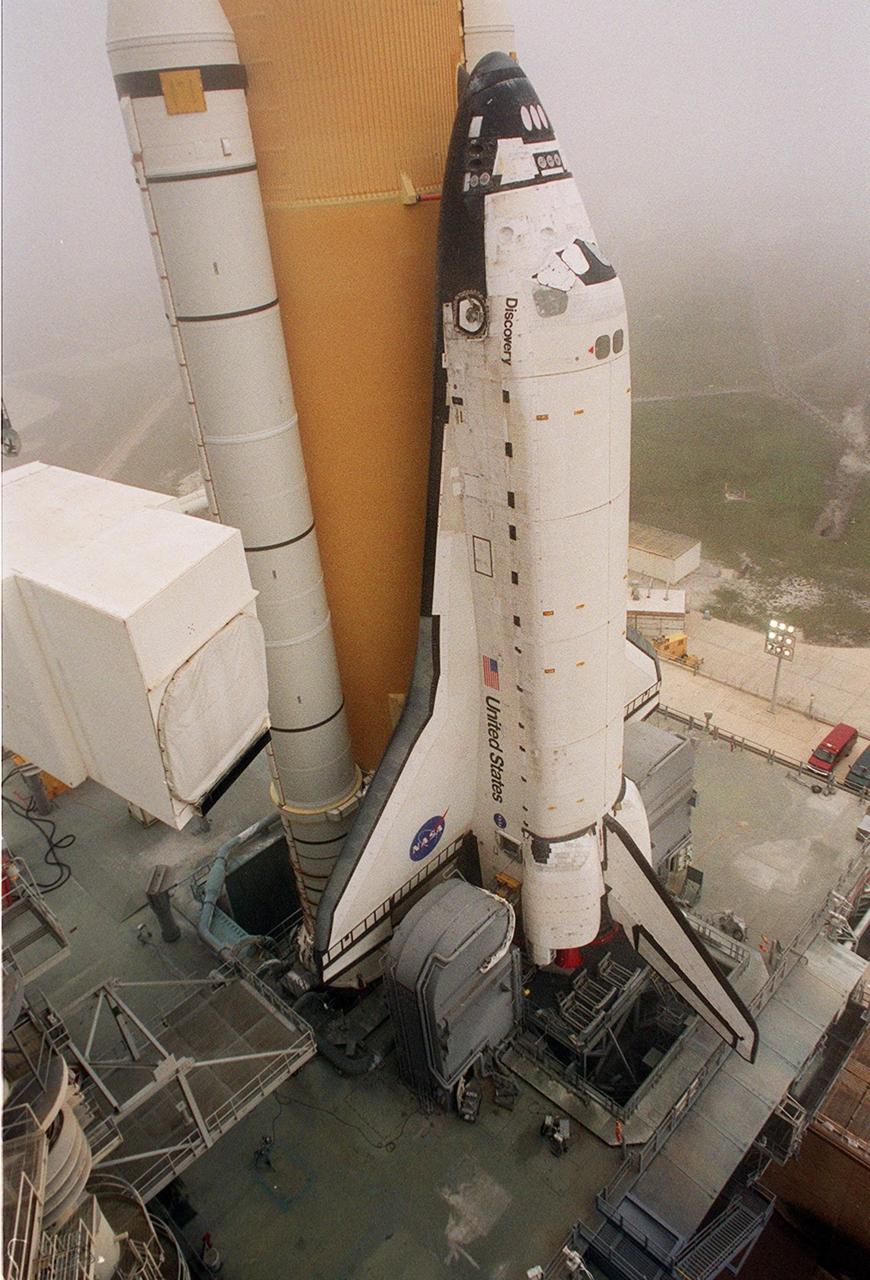
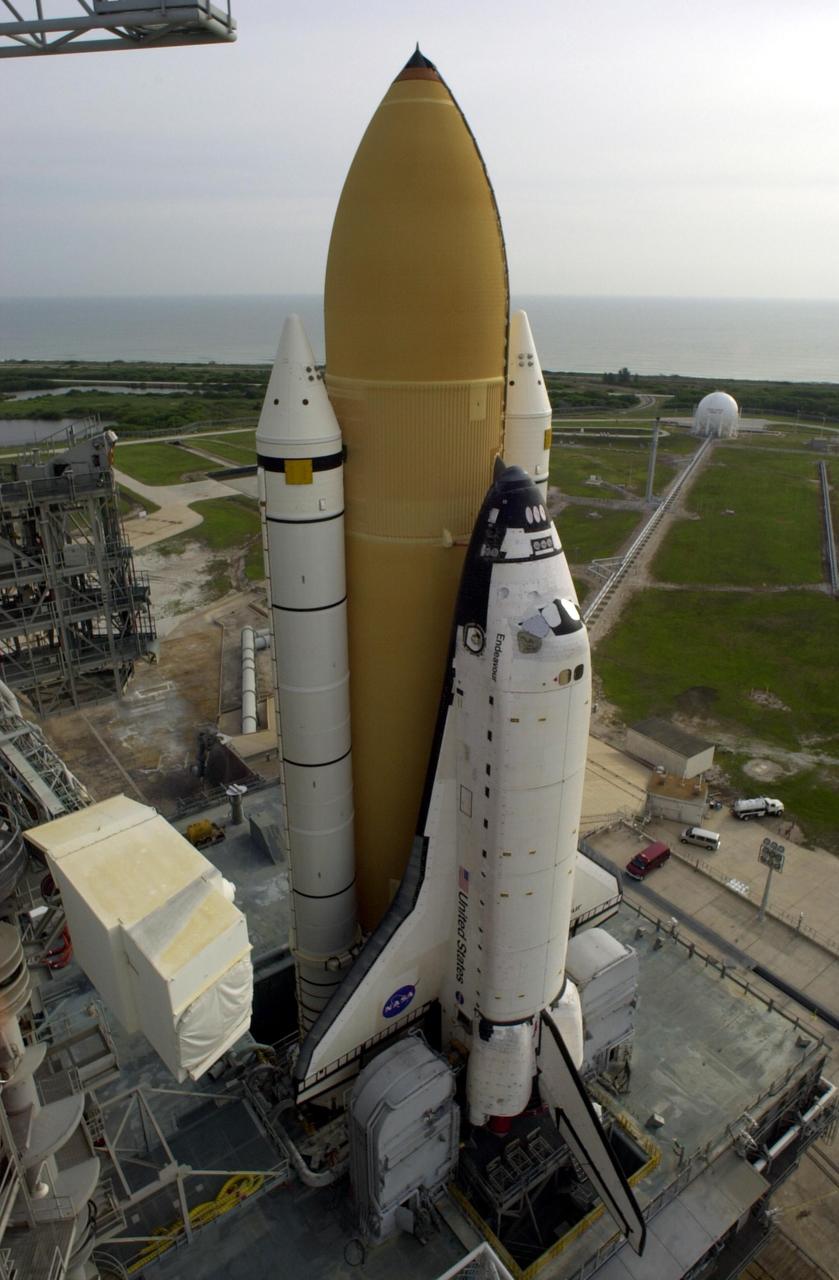
Documentation of the new mission control center White Flight Control Room (FLCR). Excellent overall view of White FLCR with personnel manning console workstations (11221). Fisheye lens perspective from Flight Director station with Brian Austin (11222). Environmental (EECOM) workstation and personnel (11223).
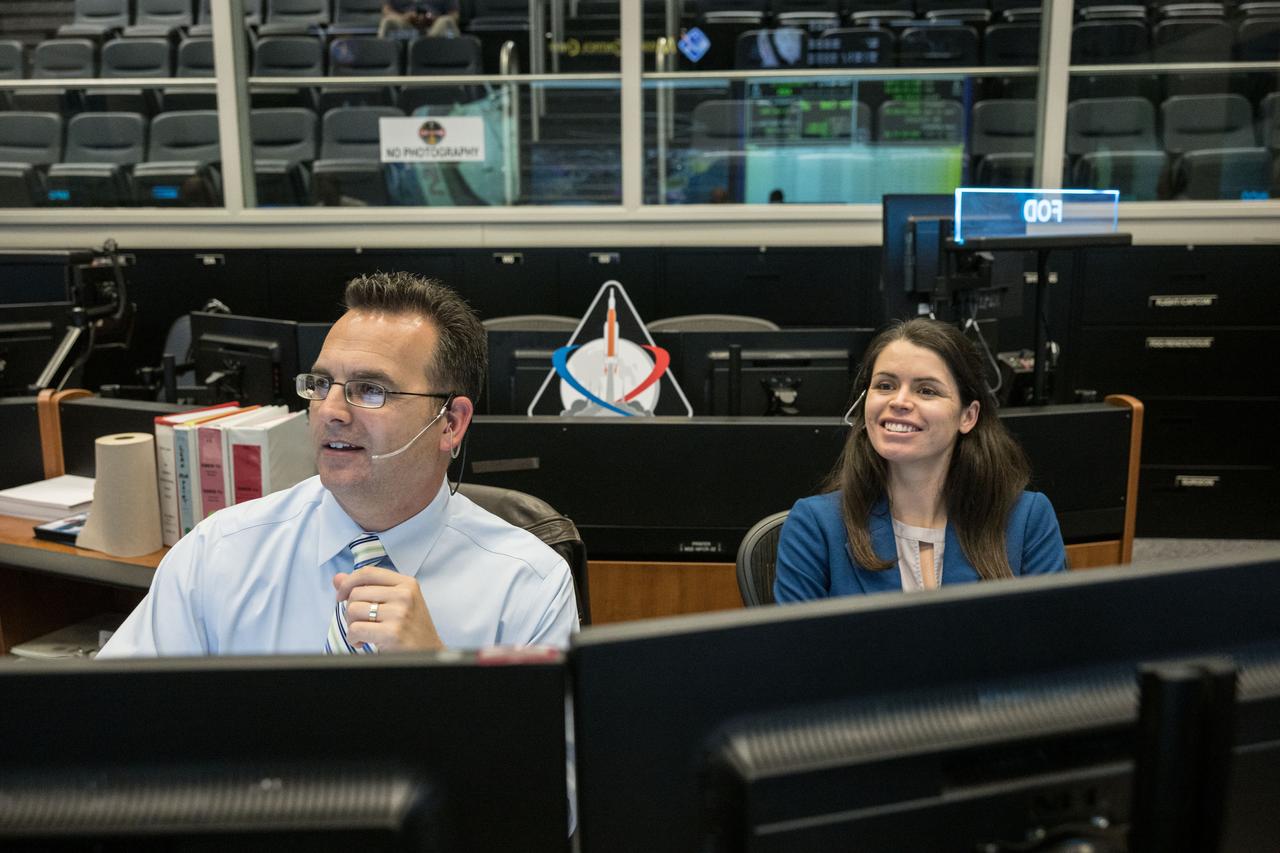

jsc2022e090070: (Nov. 28, 2022): Flight Directors Paul Konyha and Nicole McElroy smile as the Orion spacecraft reaches its record-breaking distance from the Earth, nearly 270,000 miles, on flight day 14 of the Artemis I mission. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

Documentation of flight controllers in the White Flight Control Room (WFCR) on STS-114 Launch Day, July 26, 2005. View of Phil Engelauf and Flight Director Paul Hill standing at the Mission Operations Directorate (MOD) console.
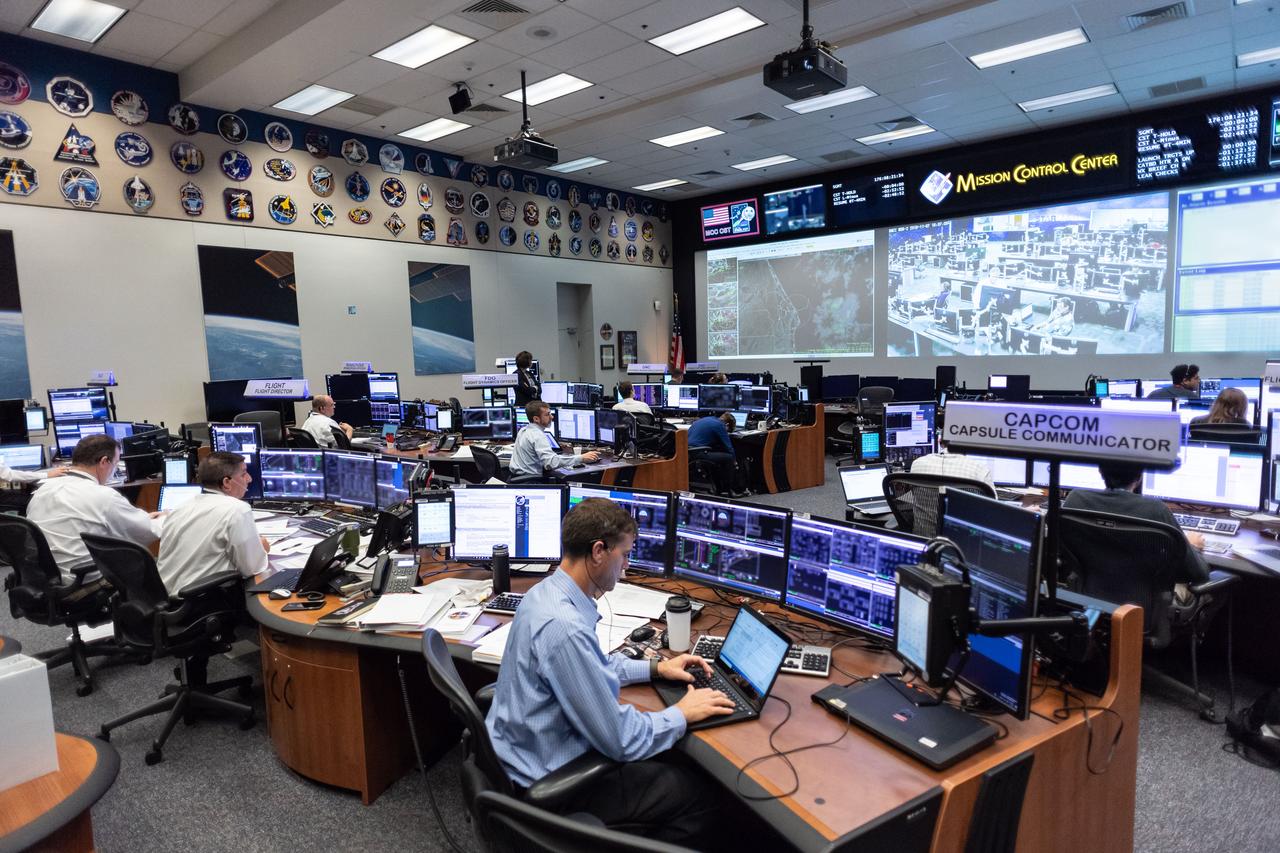

Boeing’s Flight Control Team participated in a rehearsal of prelaunch procedures for the company’s upcoming Orbital Flight Test in the White Flight Control Room in the Mission Control Center at Johnson Space Center in Houston. Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner will fly uncrewed to the International Space Station before NASA will certify the spacecraft to carry astronauts to station.
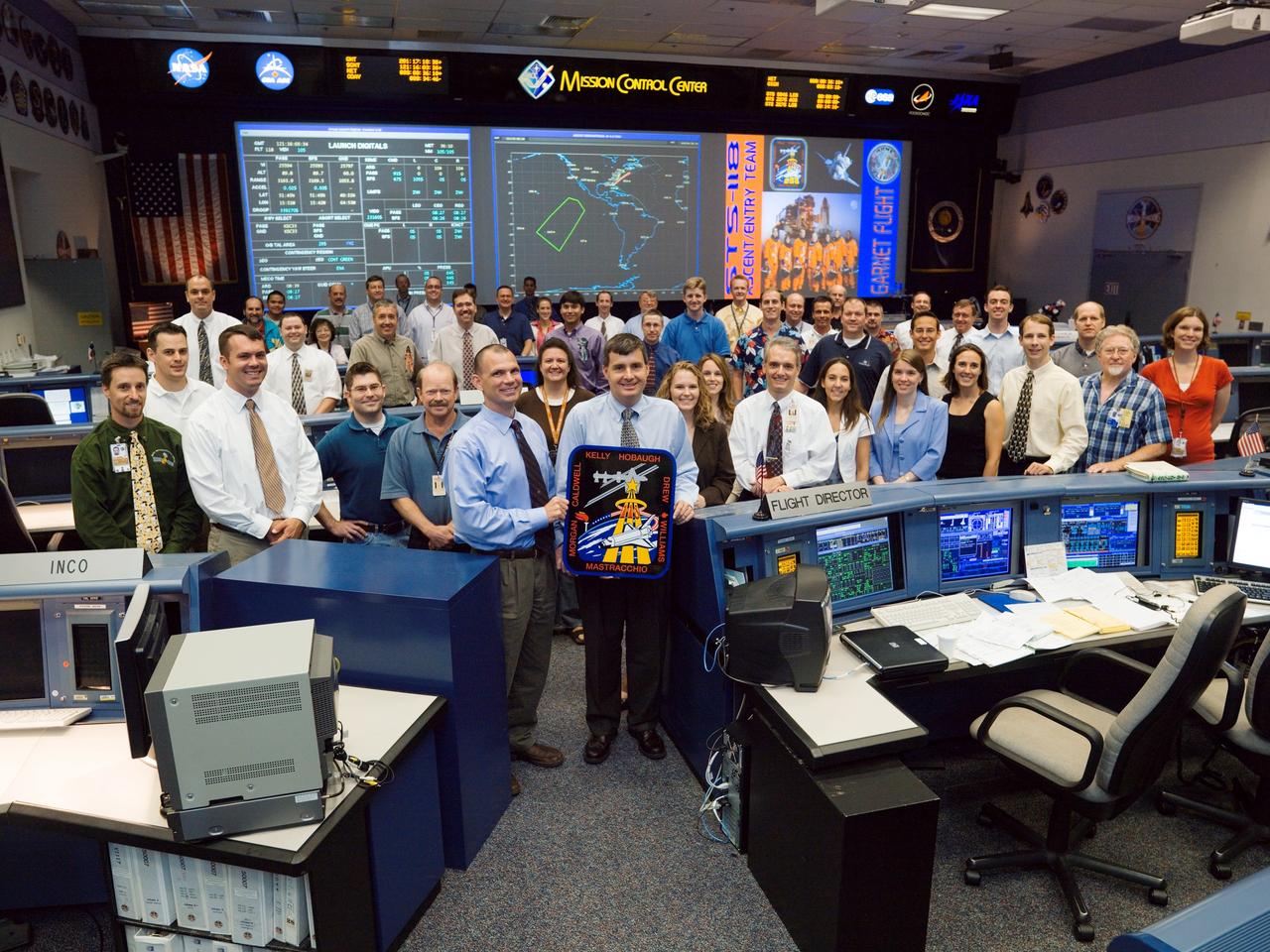

JSC2007-E-41011 (20 July 2007) --- STS-118 Ascent/Entry flight control team pose for a group portrait in the space shuttle flight control room of Houston's Mission Control Center (MCC). Flight director Steve Stich (center right) and astronaut Tony Antonelli, spacecraft communicator (CAPCOM), hold the STS-118 mission logo.

jsc2022e090080 (Nov. 28, 2022): NASA Astronaut Stan Love observes the Orion spacecraft as it reaches its maximum distance from the Earth, nearly 270,000 miles, on flight day 14 of the Artemis I mission from within the Mission Control Center in Houston, Texas. Love is practicing to be capsule communicator, or capcom, during future crewed Artemis missions. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

jsc2022e090130 (Nov. 28, 2022): Flight Directors Paul Konyha and Nicole McElroy monitor the Orion spacecraft as it reaches its record-breaking distance from the Earth, nearly 270,000 miles, on flight day 14 of the Artemis I mission. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

JSC2006-E-39881 (10 Sept. 2006) --- In the Shuttle (White) Flight Control Room of Houston's Mission Control Center, flight director Paul Dye (right) and spacecraft communicator (CAPCOM) Megan McArthur monitor data during the STS-115 inspection of the wings' leading edge and nose cap of the Space Shuttle Atlantis.

The closeout crew in the White Room help STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell with final suitup before entering Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m

The closeout crew in the White Room help STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell with final suitup before entering Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m

(jsc2022e089094_alt) (Nov. 21, 2022) During day 6 of the 25.5 day mission, Vanessa Wyche, Johnson Space Center, Center Director and Flight Director Rick LaBrode, inside the Artemis Mission Control Room or the White Flight Control Room at the Johnson Space Center during the Outbound Powered Flyby (OPF) burn. The Outbound Powered Flyby burn, targeted the DRI burn and was performed as Orion flew by the Moon around 62 mi (100 km)

JSC2005-E-30656 (28 July 2005) --- Rob Navias, Public Affairs Office commentator, describes the activities of a very busy third flight day for STS-114 from the PAO console in the Space Shuttle (White) Flight Control Room.
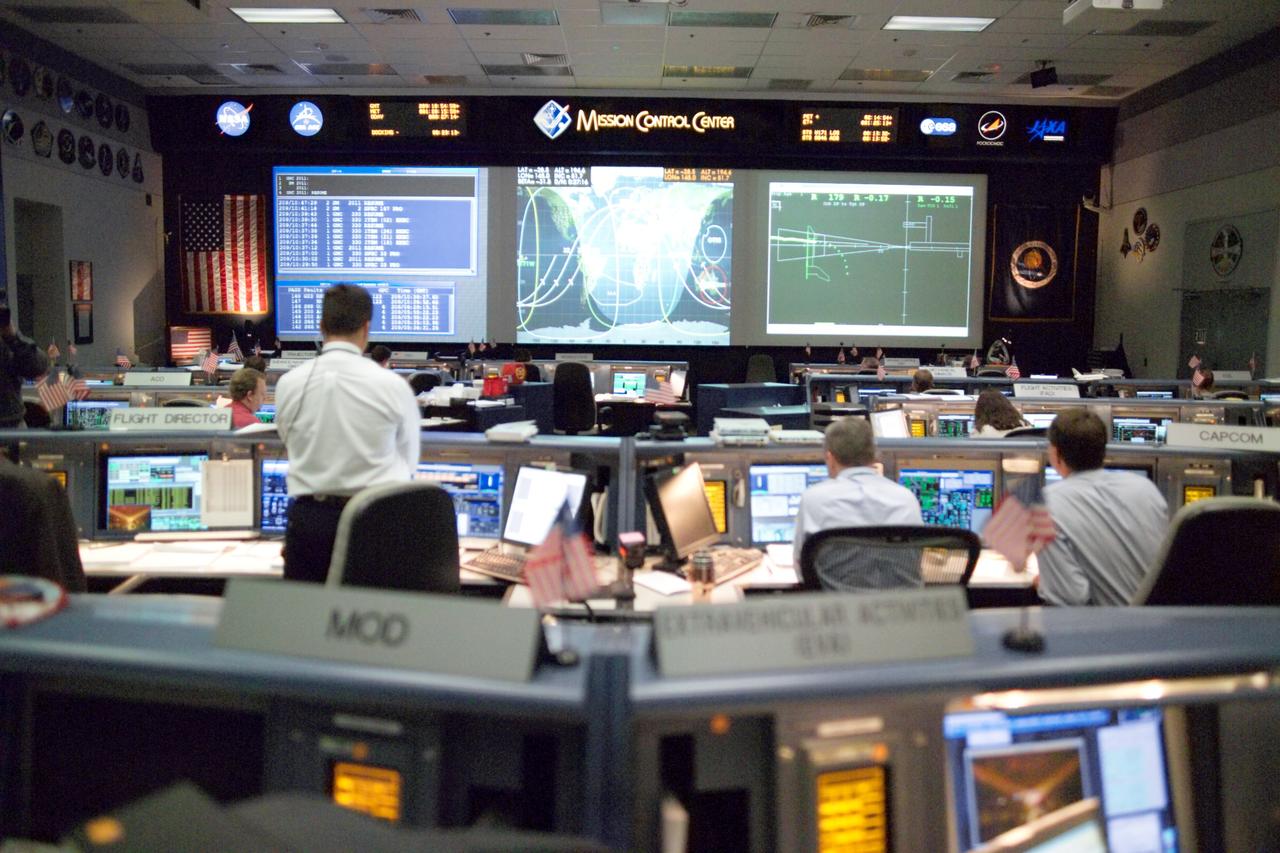

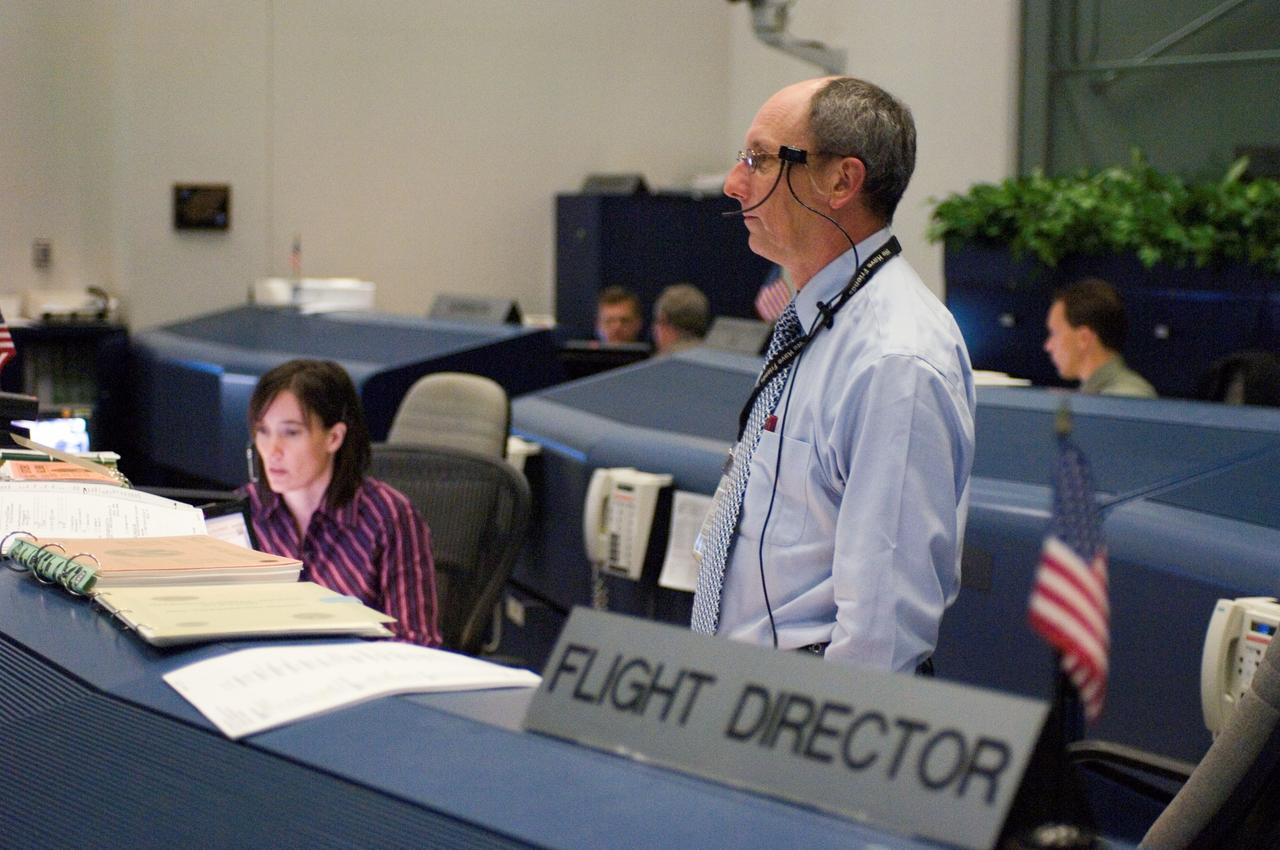
JSC2005-E-30649 (28 July 2005) --- In this wide shot of the Space Shuttle (White) Control Room, STS-114 Lead Flight Director Paul Hill stands at his console during the very busy rendezvous and docking activities between the Discovery and International Space Station.
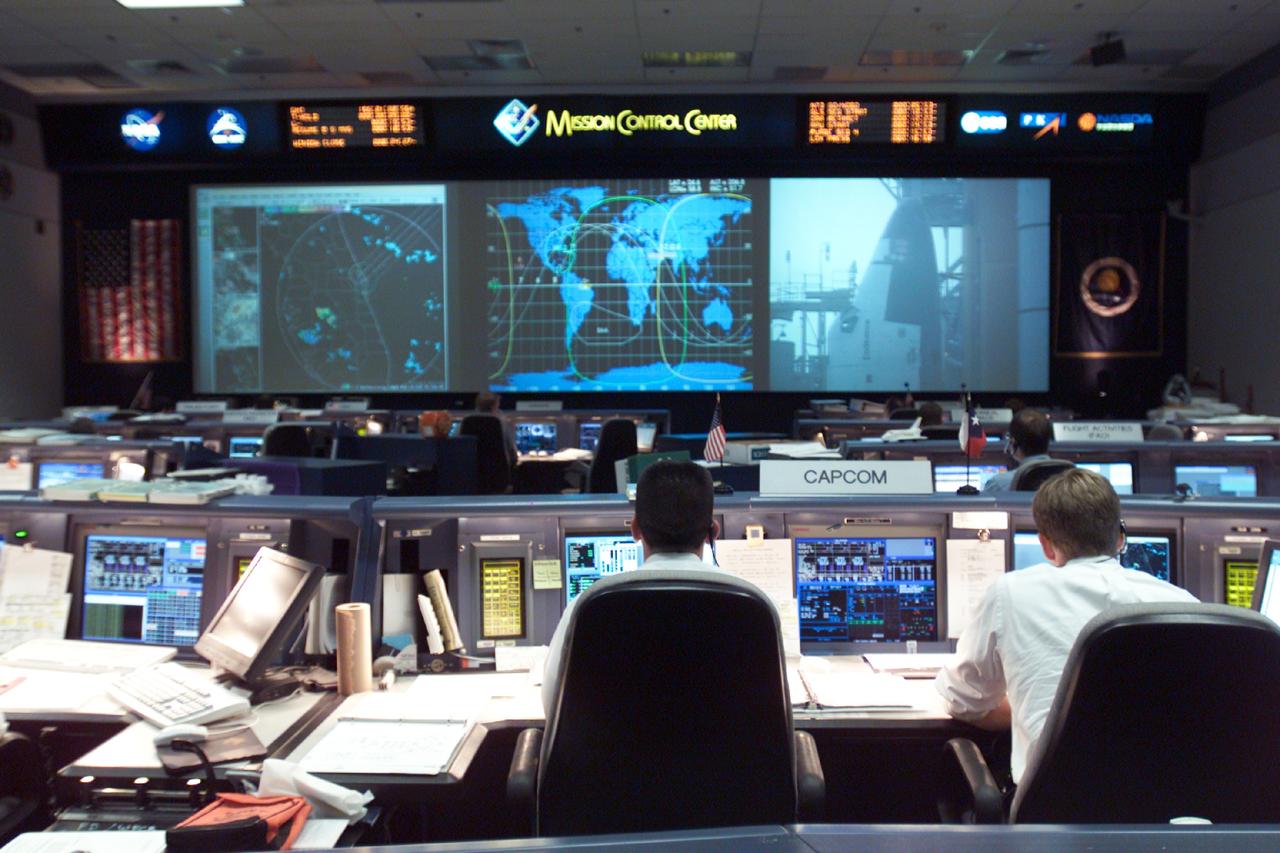

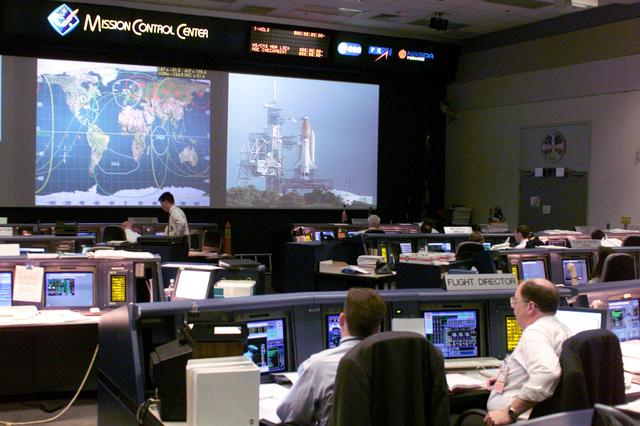
JSC2002-E-23113 (5 June 2002) --- The Space Shuttle Endeavour is shown on the big screen in this overall view of the shuttle flight control room (WFCR) in Houston’s Mission Control Center (MCC) as it is on the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Endeavour launched at 4:23 p.m. (CDT) on June 5, 2002. Once the vehicle cleared the tower in Florida, the Houston-based team of flight controllers took over the ground control of the flight.
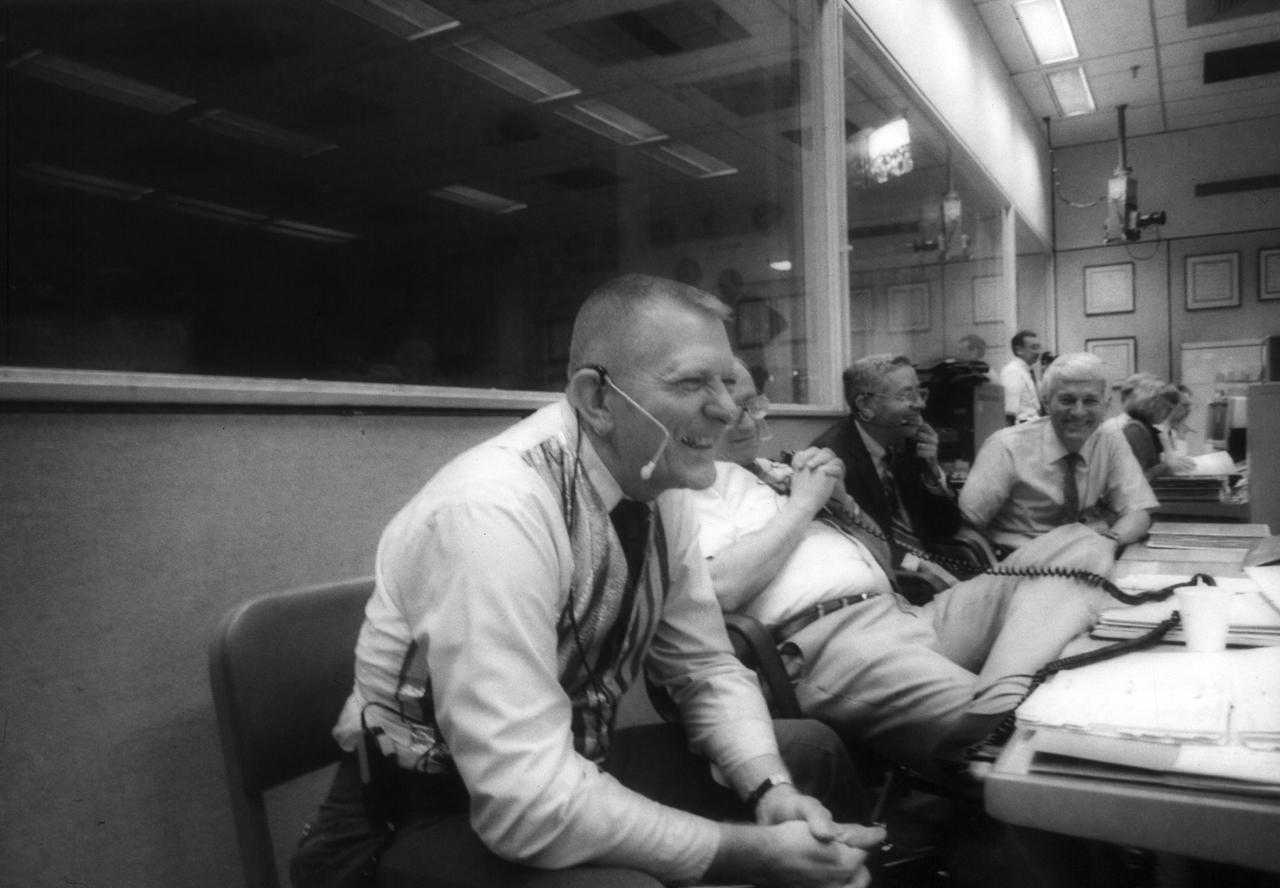

JSC officials, laughing, listen to crewmembers' commentary onboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, during STS-26. In the Flight Control Room (FCR) of JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC) Bldg 30 and seated at the Mission Operations Directorate (MOD) console, MOD Director Eugene F. Kranz (foreground), wearing red, white and blue vest, smiles along with JSC Director Aaron Cohen and Flight Crew Operations Deputy Director Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr. (far right).

In the White Room with the closeout crew, STS-98 Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam sends a message to his wife before entering Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m

In the White Room with the closeout crew, STS-98 Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam sends a message to his wife before entering Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m
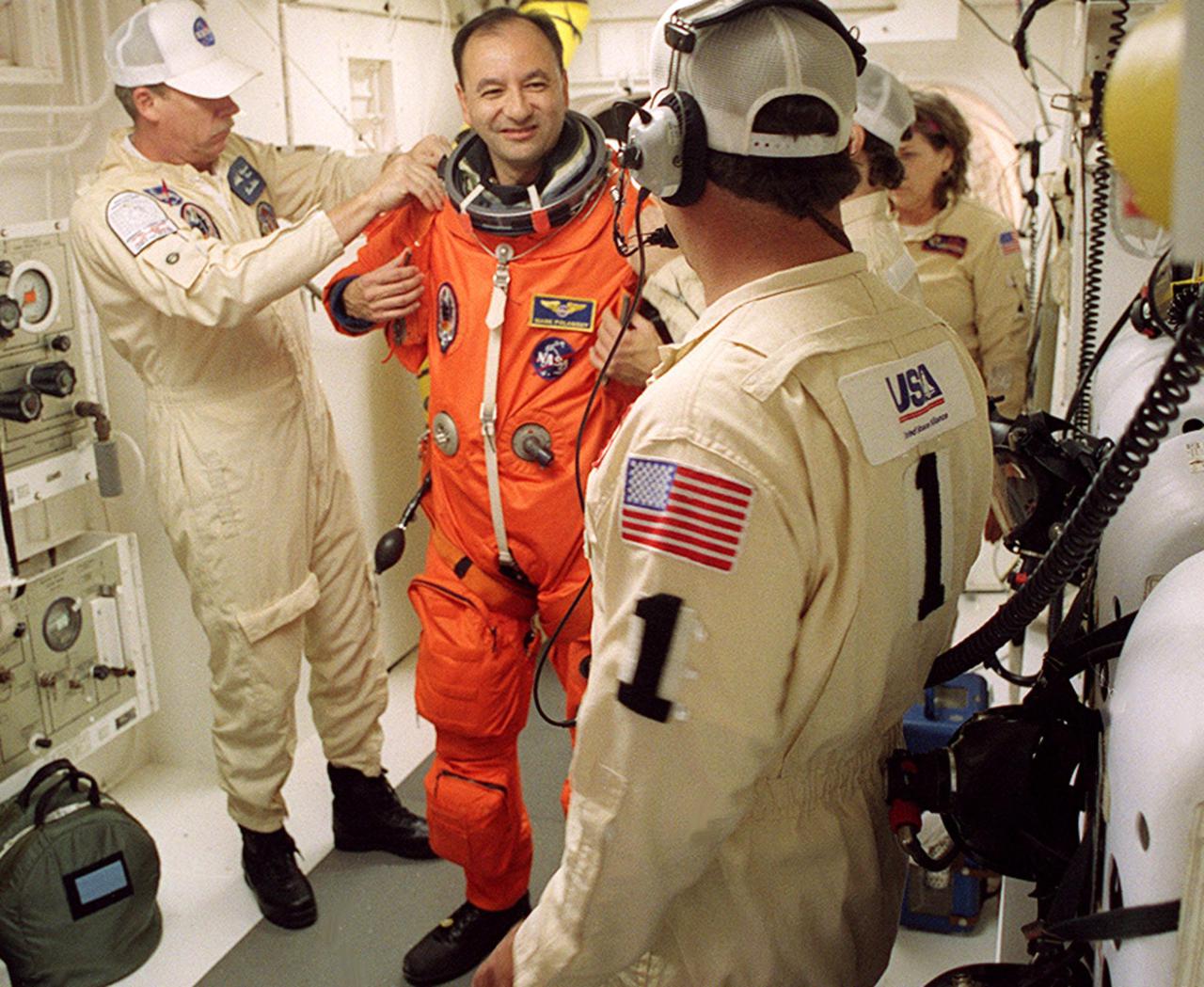

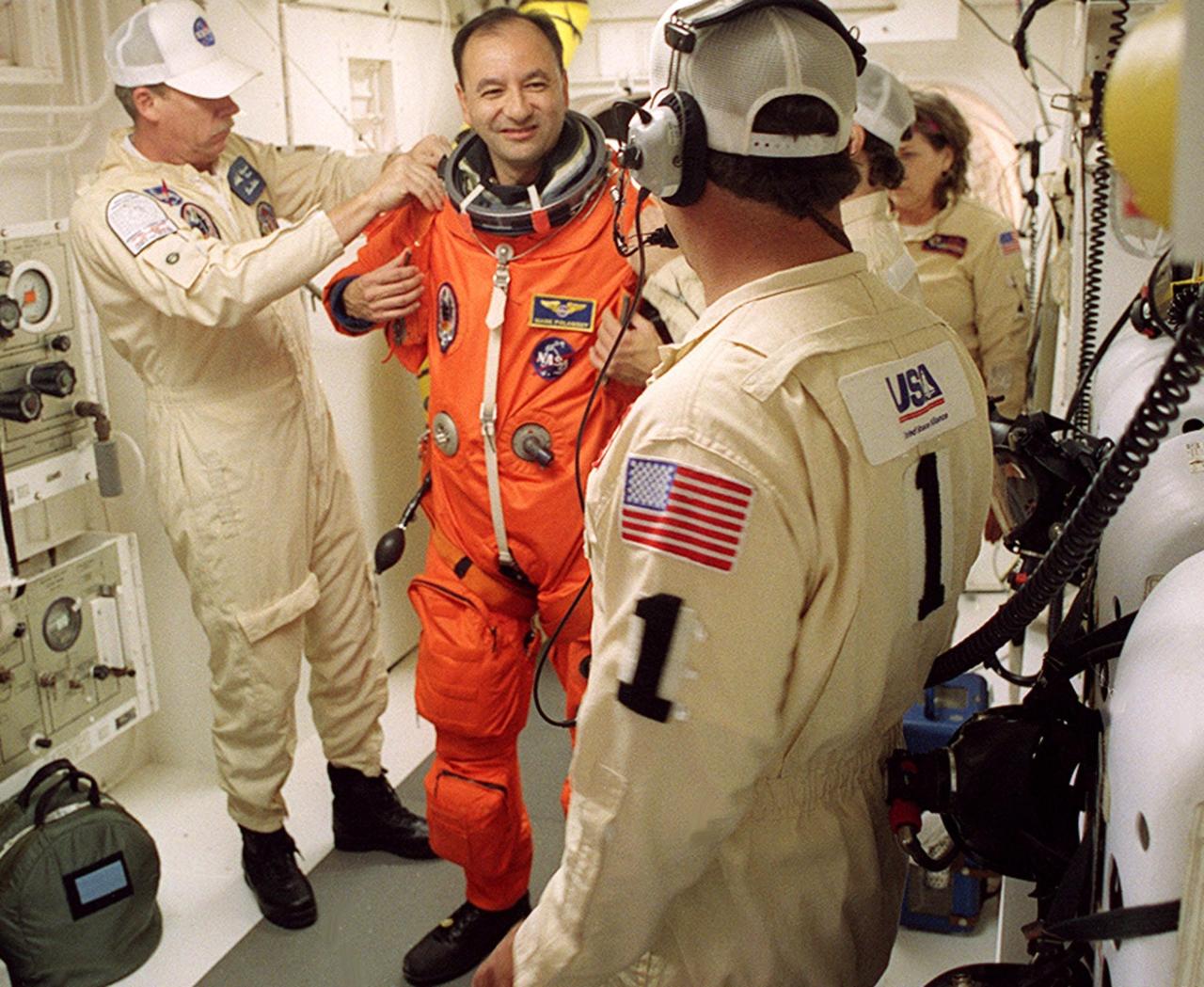
In the White Room with the closeout crew, STS-98 Pilot Mark Polansky happily undergoes final suit preparations before he enters Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m
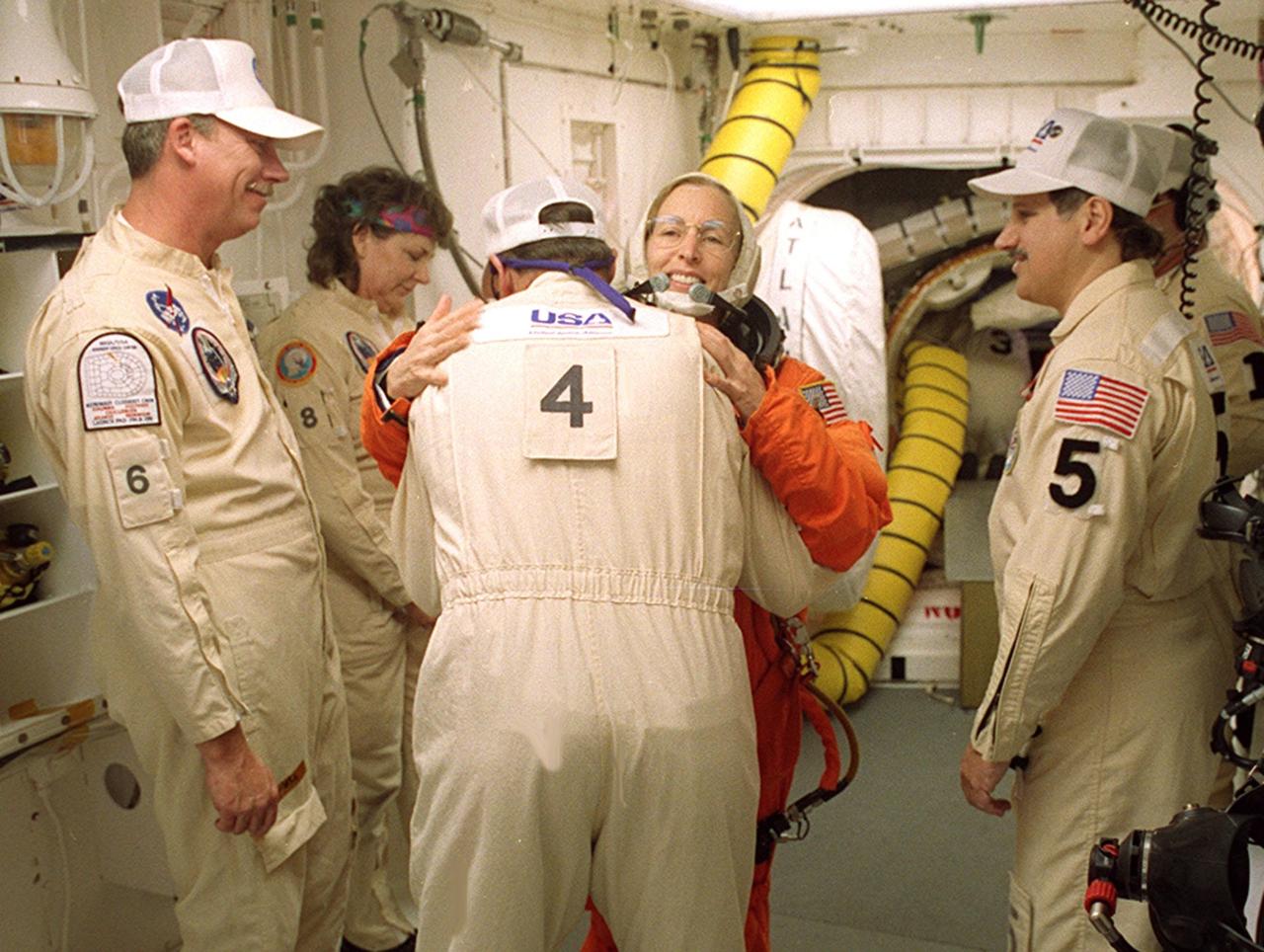

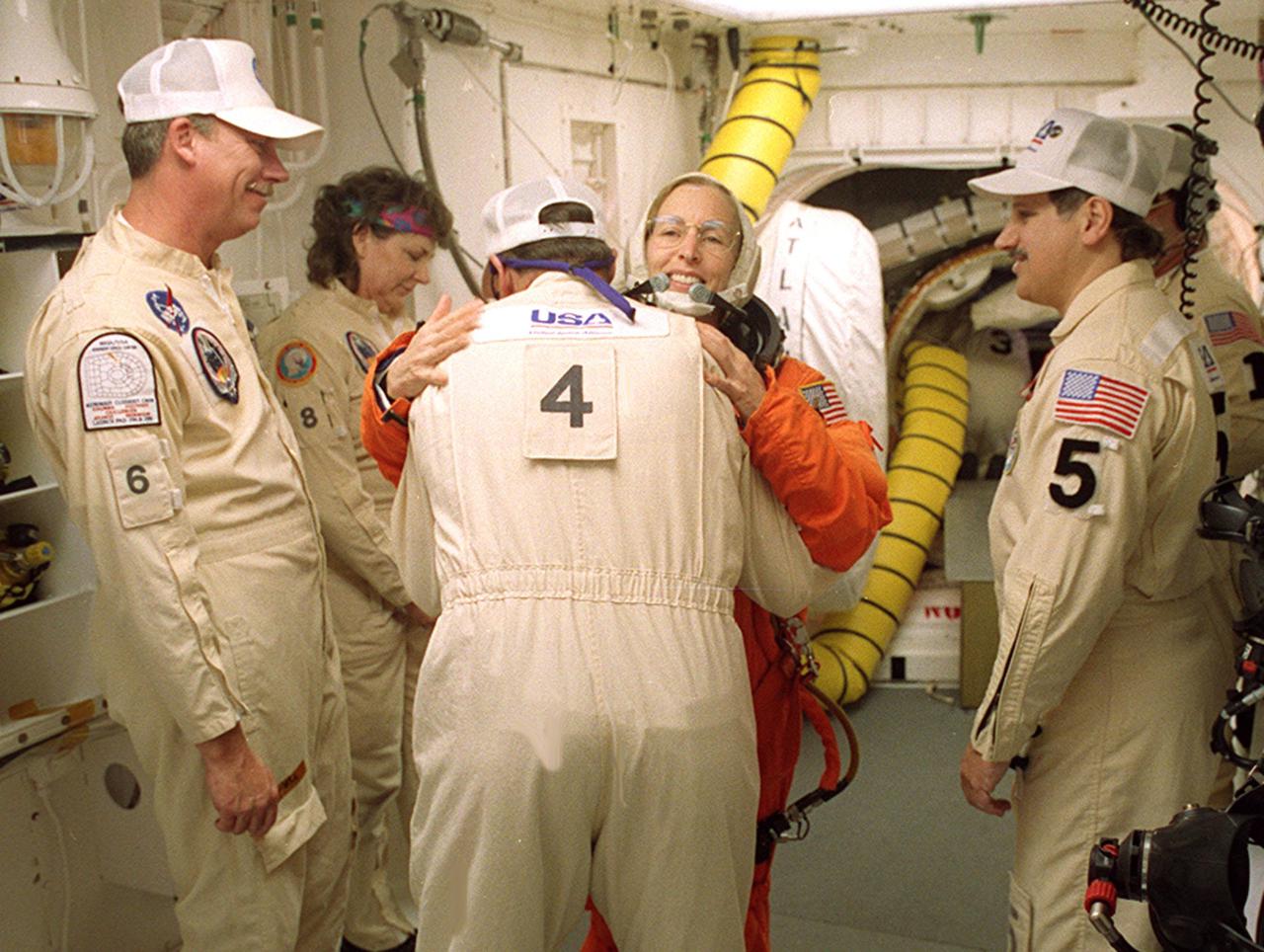
In the White Room before launch, STS-98 Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins gets a hug from a closeout crew member before she enters Space Shuttle Atlantis. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m

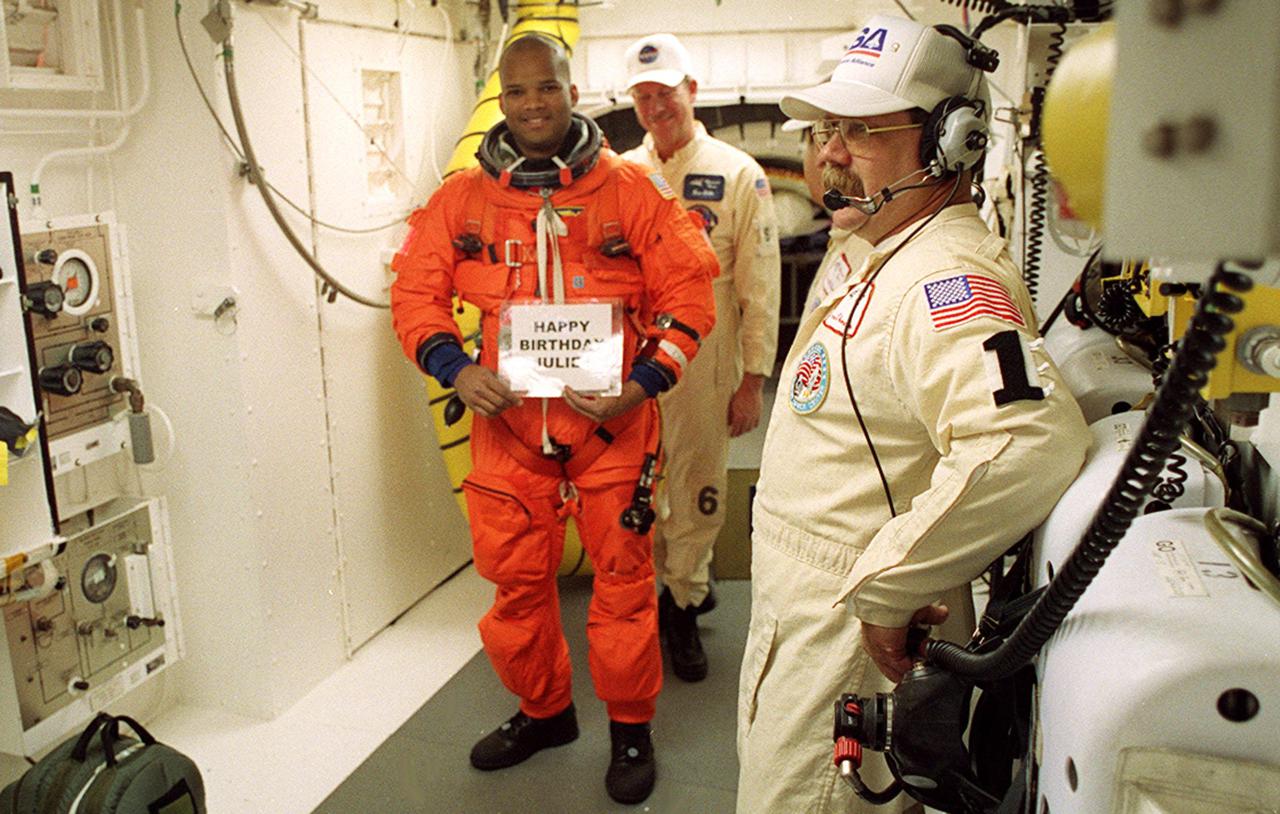
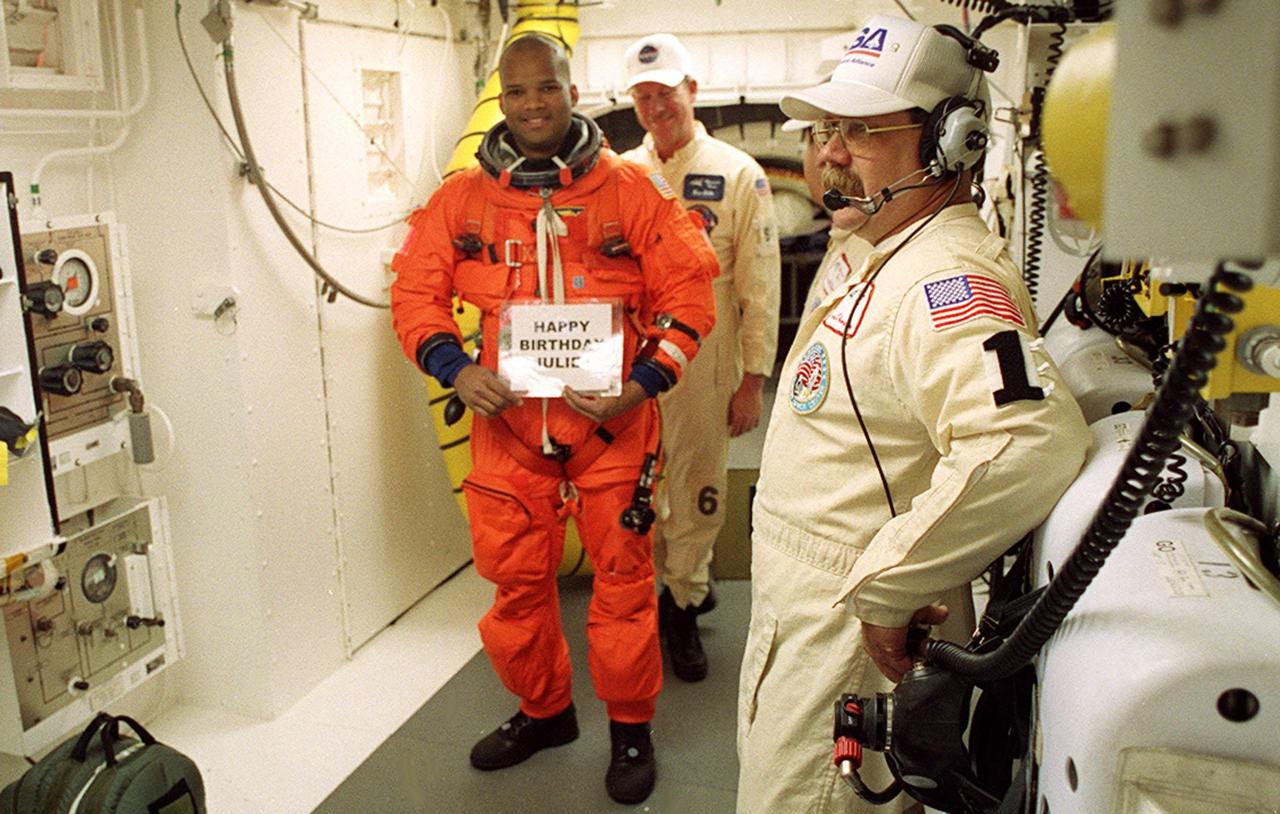
In the White Room with the closeout crew, STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones shows a message to his family before he enters Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m

In the White Room with the closeout crew, STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones shows a message to his family before he enters Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m

In the White Room before launch, STS-98 Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins gets a hug from a closeout crew member before she enters Space Shuttle Atlantis. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m

In the White Room with the closeout crew, STS-98 Pilot Mark Polansky happily undergoes final suit preparations before he enters Space Shuttle Atlantis for launch. The White Room is an environmentally controlled room at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program. The planned landing is at KSC Feb. 18 about 1 p.m
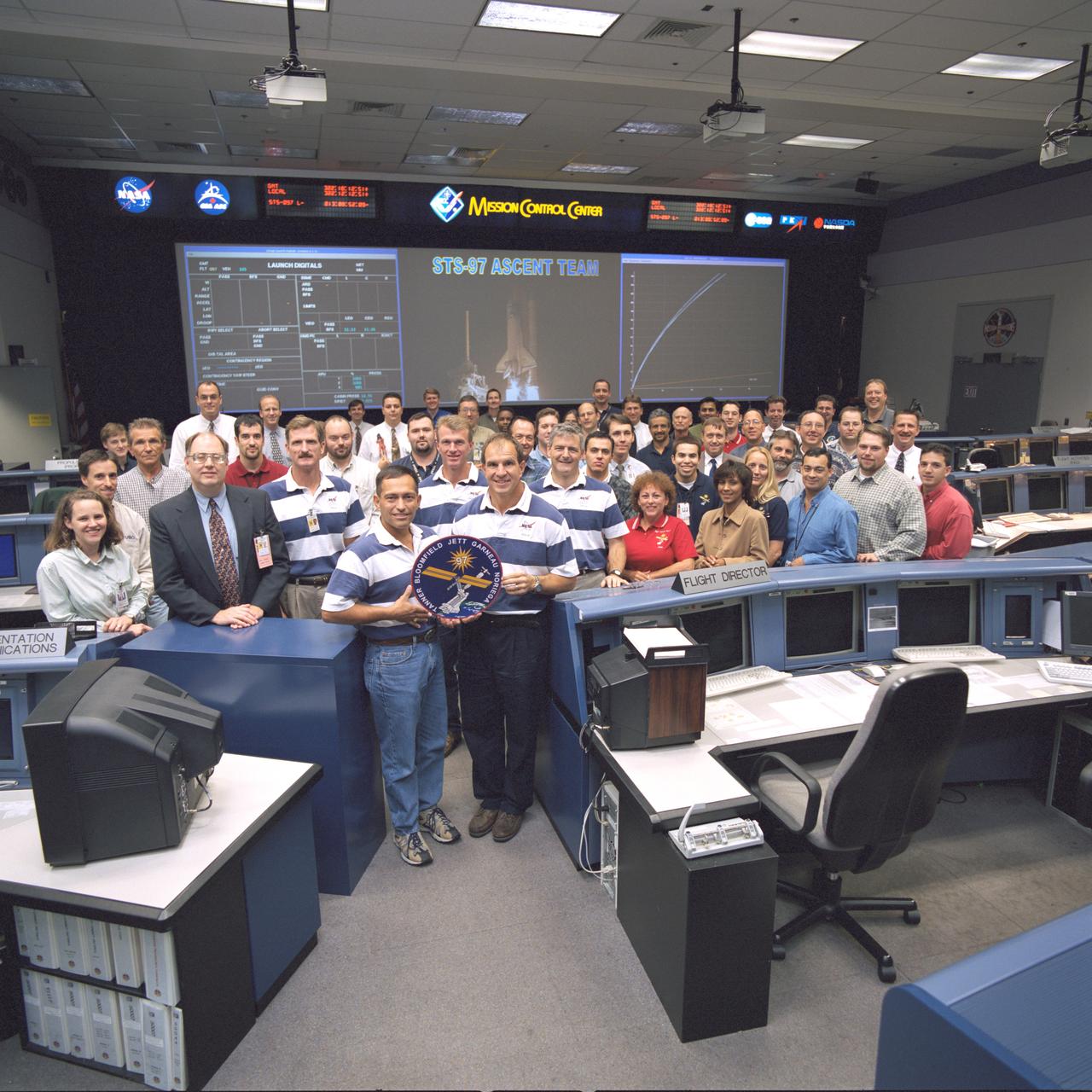

JSC2000-07294 (20 November 2000) --- The 40-odd flight controllers assigned to the STS-97 ascent team and some special guests pose for a group portrait in the shuttle flight control room in Houston's Mission Control Center (JSC). The five guests attired in the blue and white shirts are the flight crew members for the STS-97 crew, scheduled to be launched from Florida on the last day of this month. The astronauts are, from the left, Joseph R. Tanner, Carlos I. Noriega, Brent W. Jett, Jr., Michael J. Bloomfield and Marc Garneau, who represents the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). Ascent shift flight director Wayne Hale stands next to Tanner.
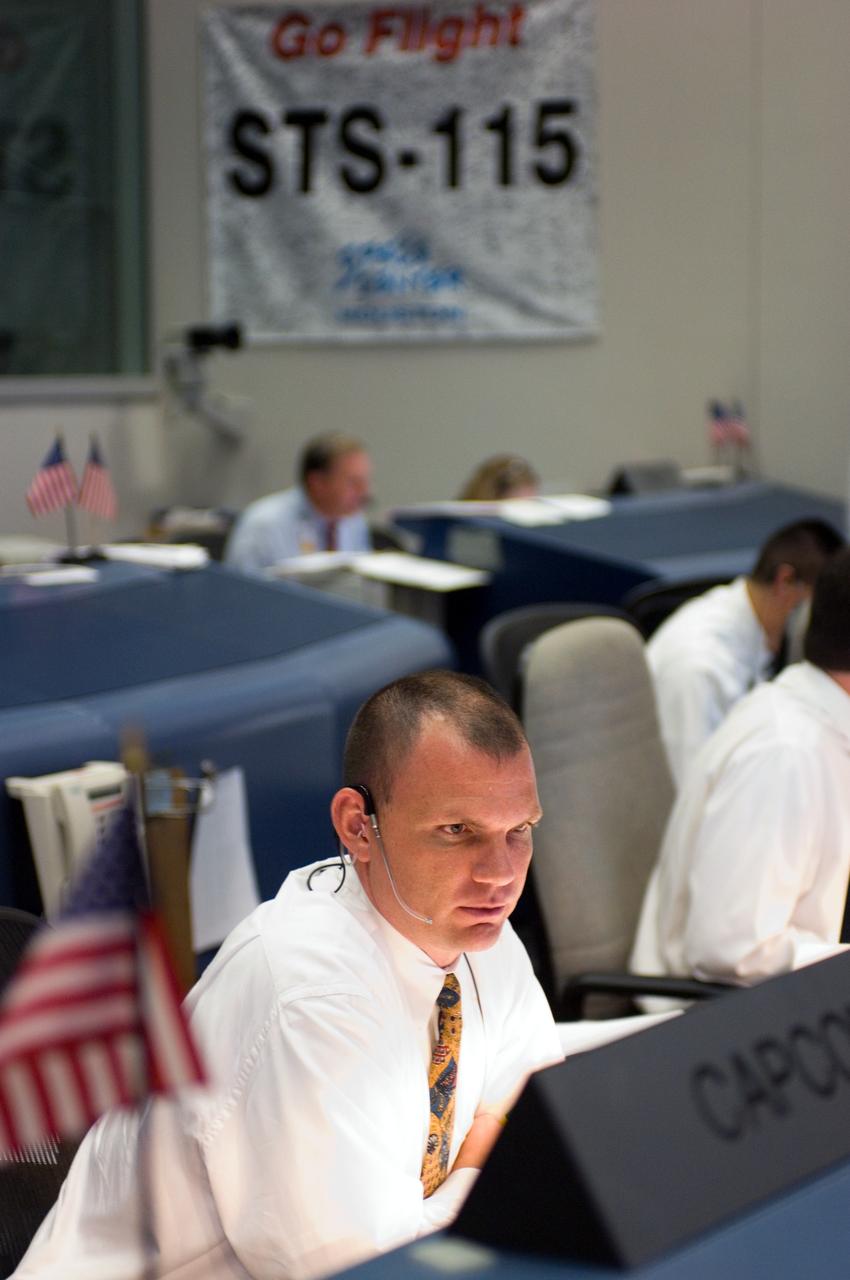

JSC2006-E-39854 (9 Sept. 2006) --- In the Shuttle (White) Flight Control Room of Houston's Mission Control Center, astronaut Dominic A. (Tony) Antonelli monitors launch countdown activities a few hundred miles away in Florida, site of Space Shuttle Atlantis' scheduled STS-115 launch. Antonelli serves as the spacecraft communicator (CAPCOM) for the ascent and entry phases. Liftoff occurred at 11:15 a.m. (EDT) on Sept. 9, 2006 from launch pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center.

JSC2005-E-31936 (3 August 2005) --- Astronauts Julie Payette (Canadian Space Agency) and Stephen N. Frick monitor communications at the spacecraft communicator (CAPCOM) console in the Shuttle (White) Flight Control Room in Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Mission Control Center during the third period of extravehicular activity (EVA) for STS-114.
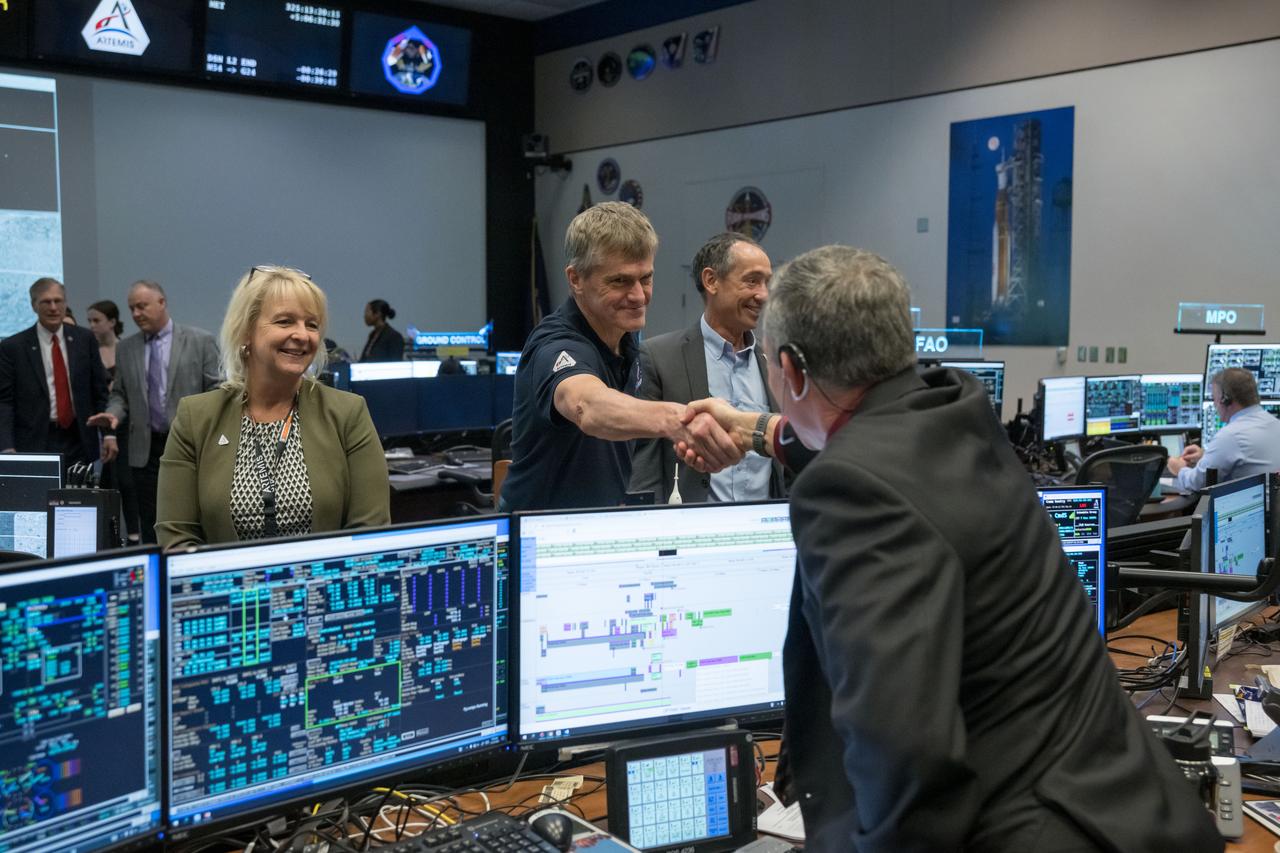

jsc2022e089183 (Nov. 21, 2022) During flight day 6 of the 25.5-day mission, Orion program managers greet Artemis I Lead Flight Director Rick LaBrode in the White Flight Control Room at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. The visit followed during the Outbound Powered Flyby (OPF) burn, which set Orion on a course to fly by the Moon at a closest distance of 81 miles (130.5 kilometers).
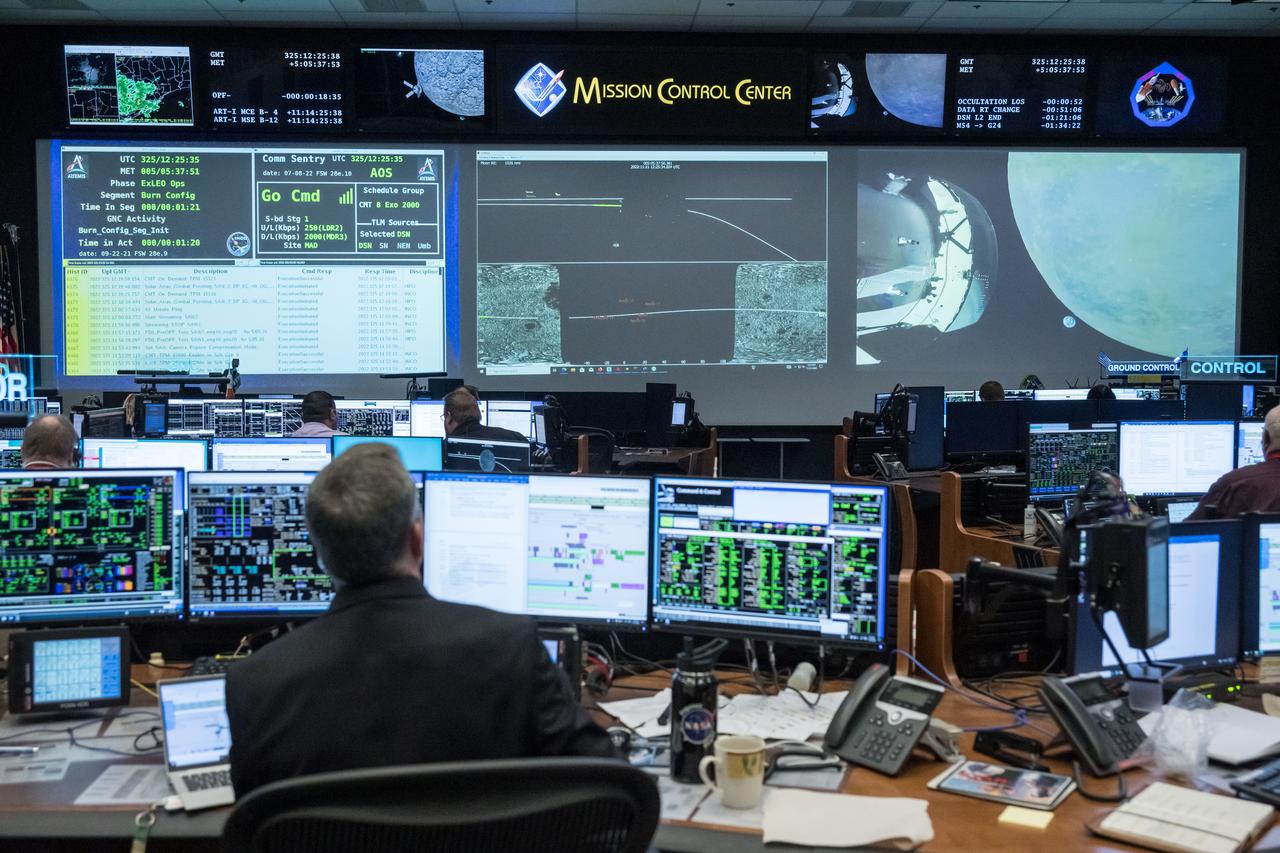

jsc2022e089168 (Nov. 21, 2022) During flight day 6 of the 25.5-day Artemis I mission, Lead Flight Director Rick LaBrode monitors the progress of the Outbound Powered Flyby (OPF) in the White Flight Control Room at Johnson Space Center in Houston. burn monitored by. The OPF burn set Orion on a course to fly by the Moon at a closest distance of 81 miles (130.5 kilometers).
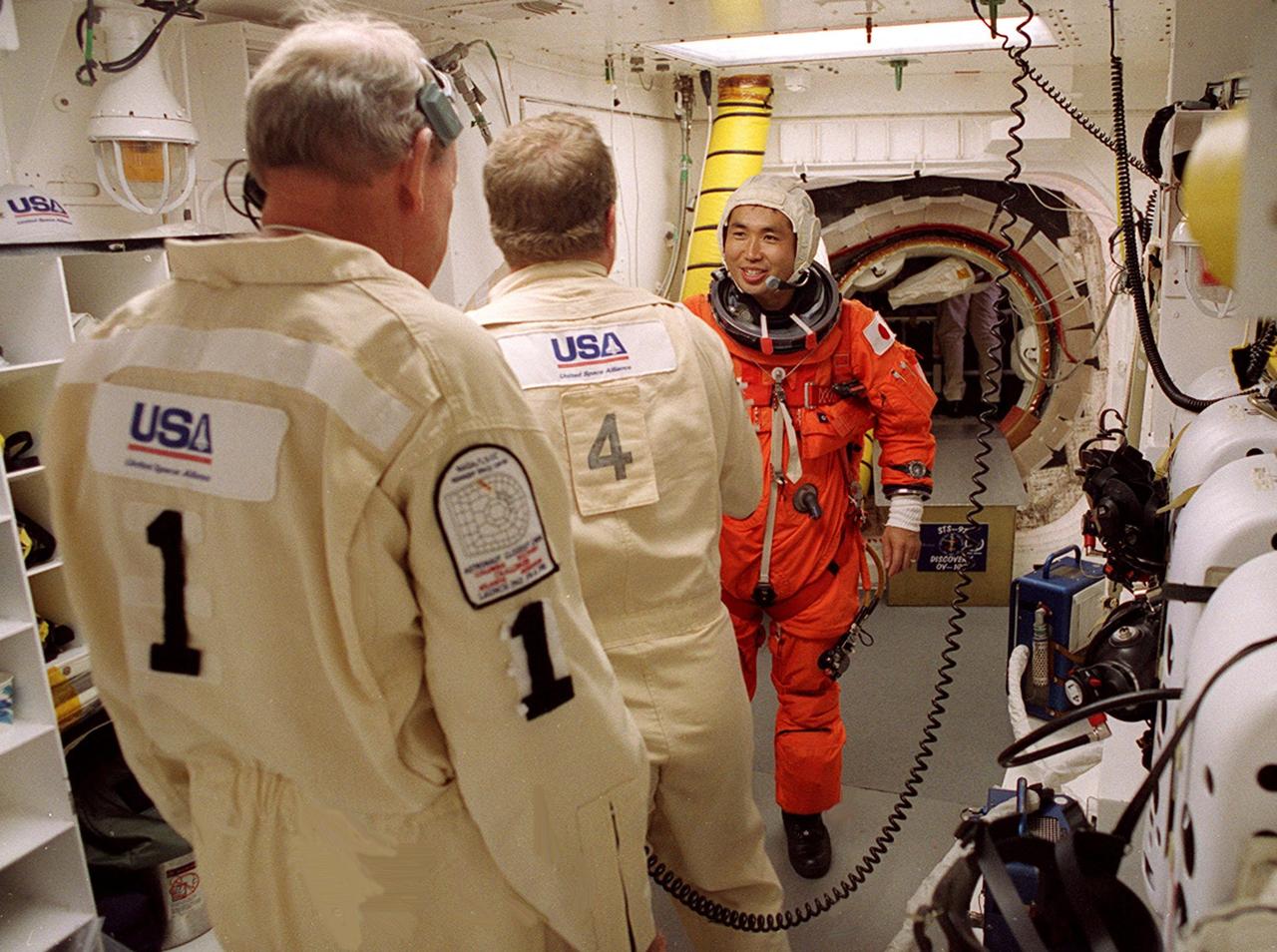

STS-92 Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata of Japan gets a final check of his launch and entry suit in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. Wakata and the rest of the crew are making the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT
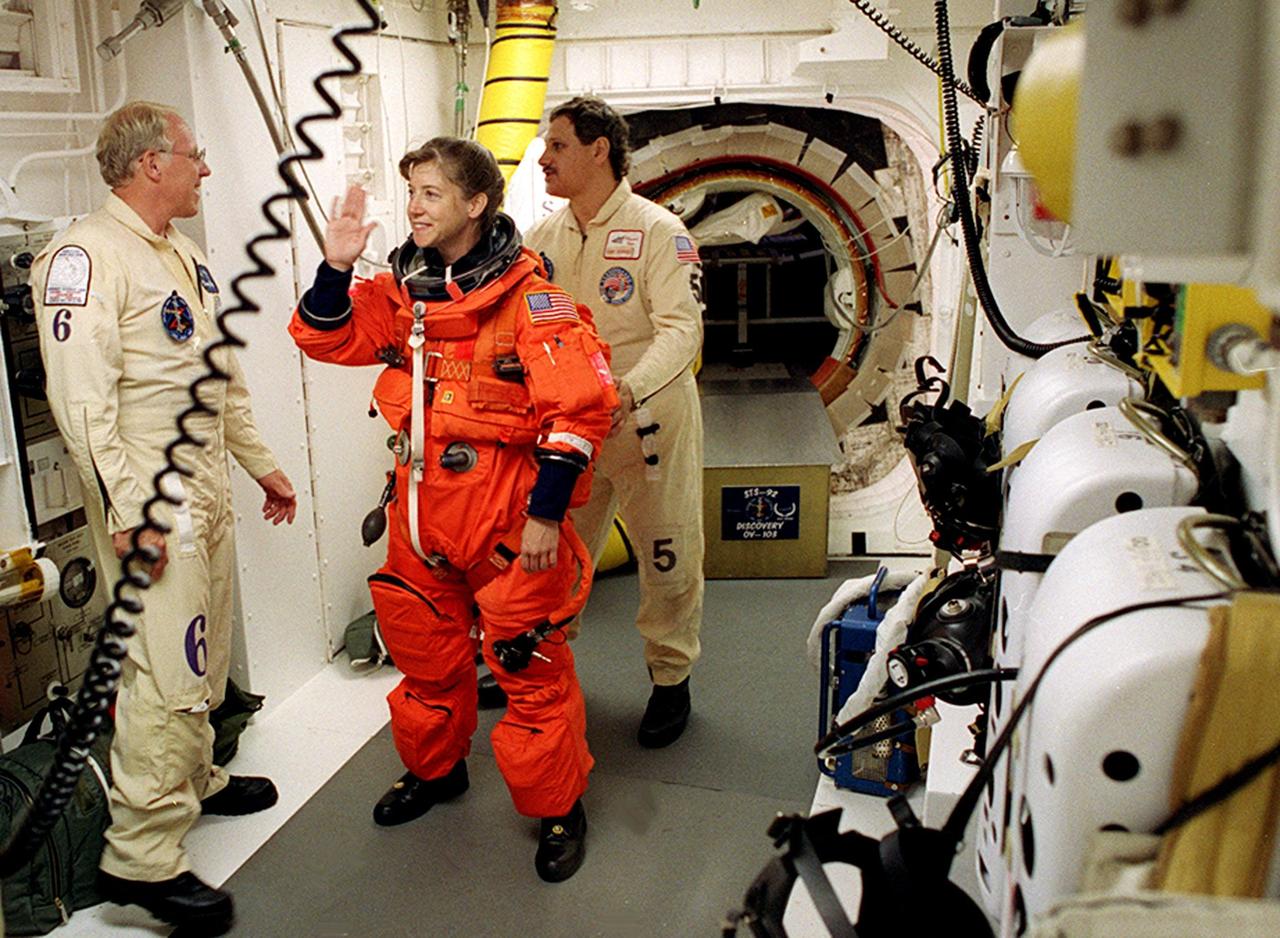

STS-92 Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy has a final check on her launch and entry suit in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. Melroy and the rest of the crew are undertaking the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT
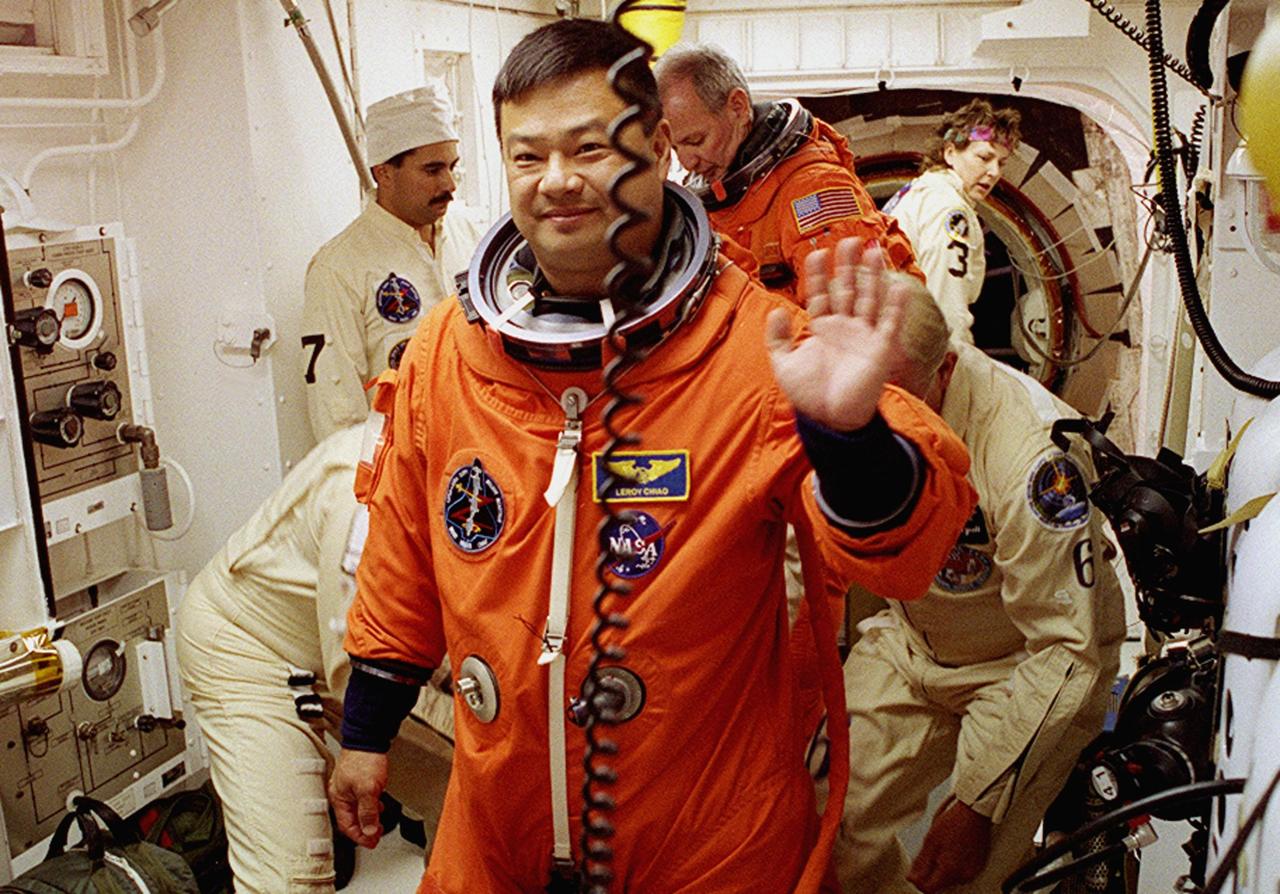

STS-92 Mission Specialist Leroy Chiao waves while waiting for suit check in the White Room. Behind him is Commander Brian Duffy. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. Chiao, Duffy and the rest of the crew are undertaking the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT
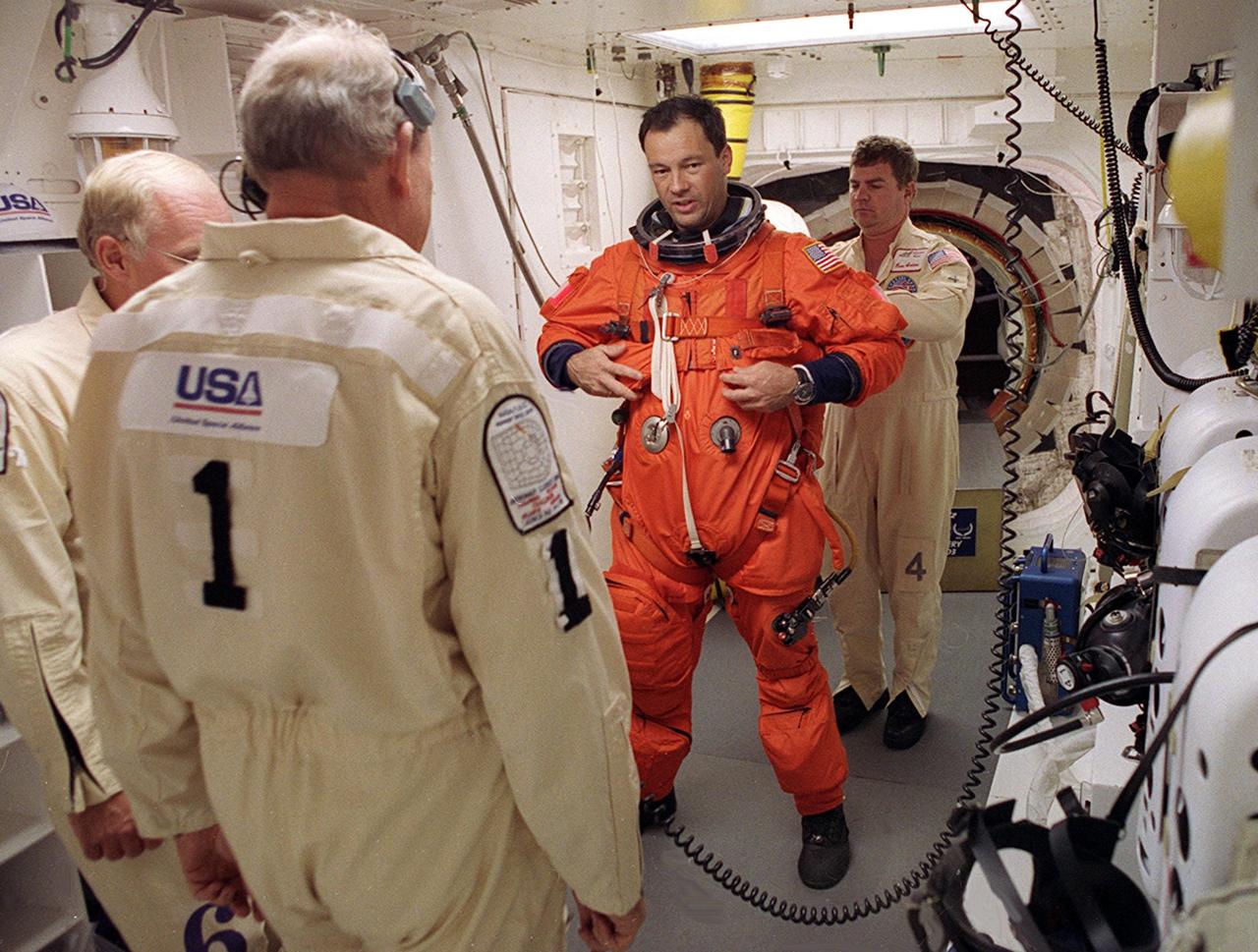

STS-92 Mission Specialist Michael E. Lopez-Alegria gets a final check of his launch and entry suit in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. Lopez-Alegria and the rest of the crew are undertaking the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT
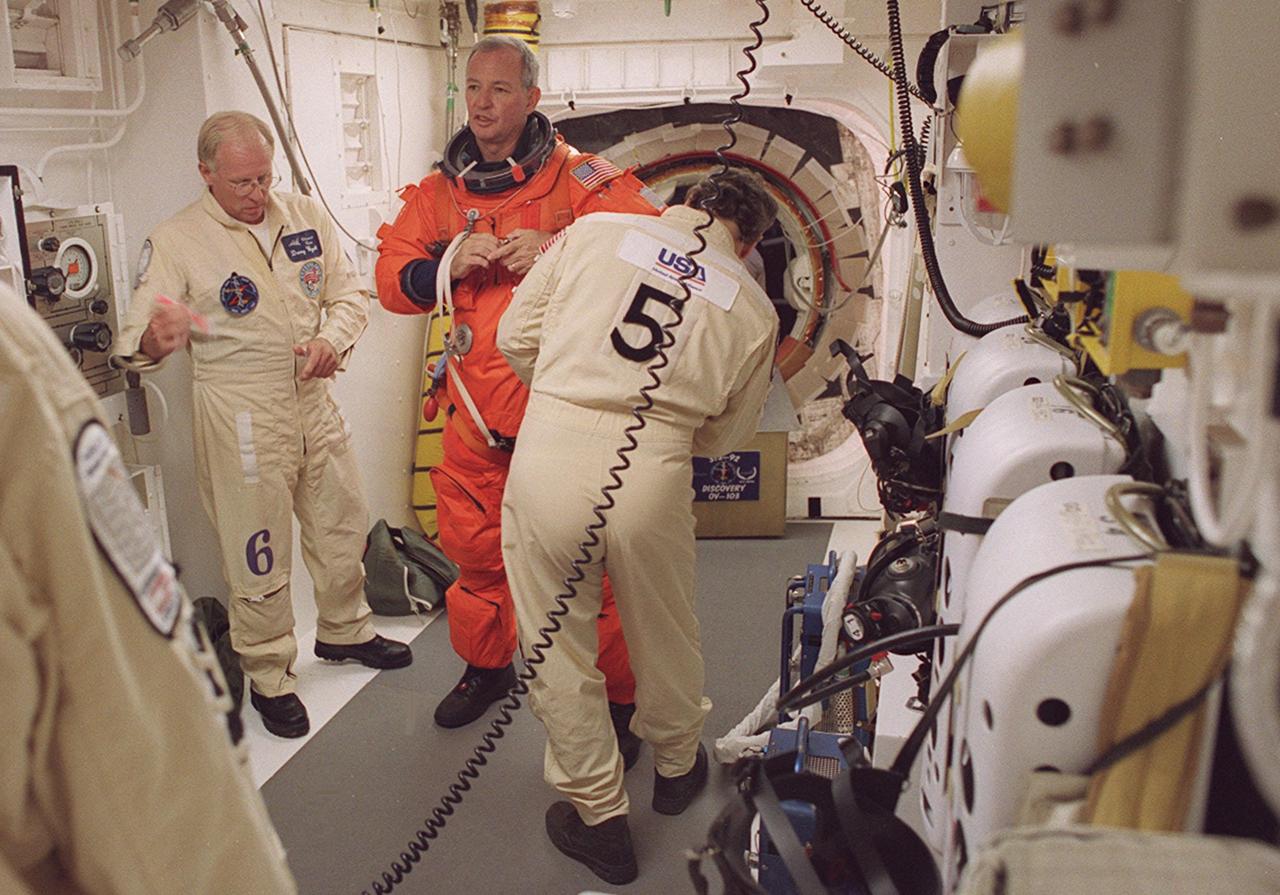

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy is helped with final suit check in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. Duffy and the rest of the crew are undertaking the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT

STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. undergoes final suit check in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. McArthur and the rest of the crew are making the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT

S73-26849 (25 May 1973) --- Four flight directors for the Skylab 1 and 2 mission are grouped around the flight director's console in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center at Johnson Space Center during the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module (CSM) "fly around" inspection of the Skylab 1 space station cluster. They are, going counterclockwise from center foreground, Donald R. Puddy (white shirt), Milton Windler, Philip C. Shaffer and M.P. Frank. A view of the Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop seen from the Skylab 2 CSM is visible on the television monitor in the background. Photo credit: NASA

STS-88 Commander Robert D. Cabana is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39A before entering Space Shuttle Endeavour for launch. During the nearly 12-day mission, the six-member crew will mate the first two elements of the International Space Station the already-orbiting Zarya control module with the Unity connecting module carried by Endeavour. Cabana is making his fourth spaceflight

STS-88 Mission Specialist Jerry L. Ross is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39A before entering Space Shuttle Endeavour for launch. During the nearly 12-day mission, the six-member crew will mate the first two elements of the International Space Station the already-orbiting Zarya control module with the Unity connecting module carried by Endeavour. He is making his sixth spaceflight and is one of two extravehicular activity crew members on this mission

STS-88 Mission Specialist Sergei Konstantinovich Krikalev, a Russian cosmonaut, is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39A before entering Space Shuttle Endeavour for launch. During the nearly 12-day mission, the six-member crew will mate the first two elements of the International Space Station the already-orbiting Zarya control module with the Unity connecting module carried by Endeavour. He is making his fourth spaceflight
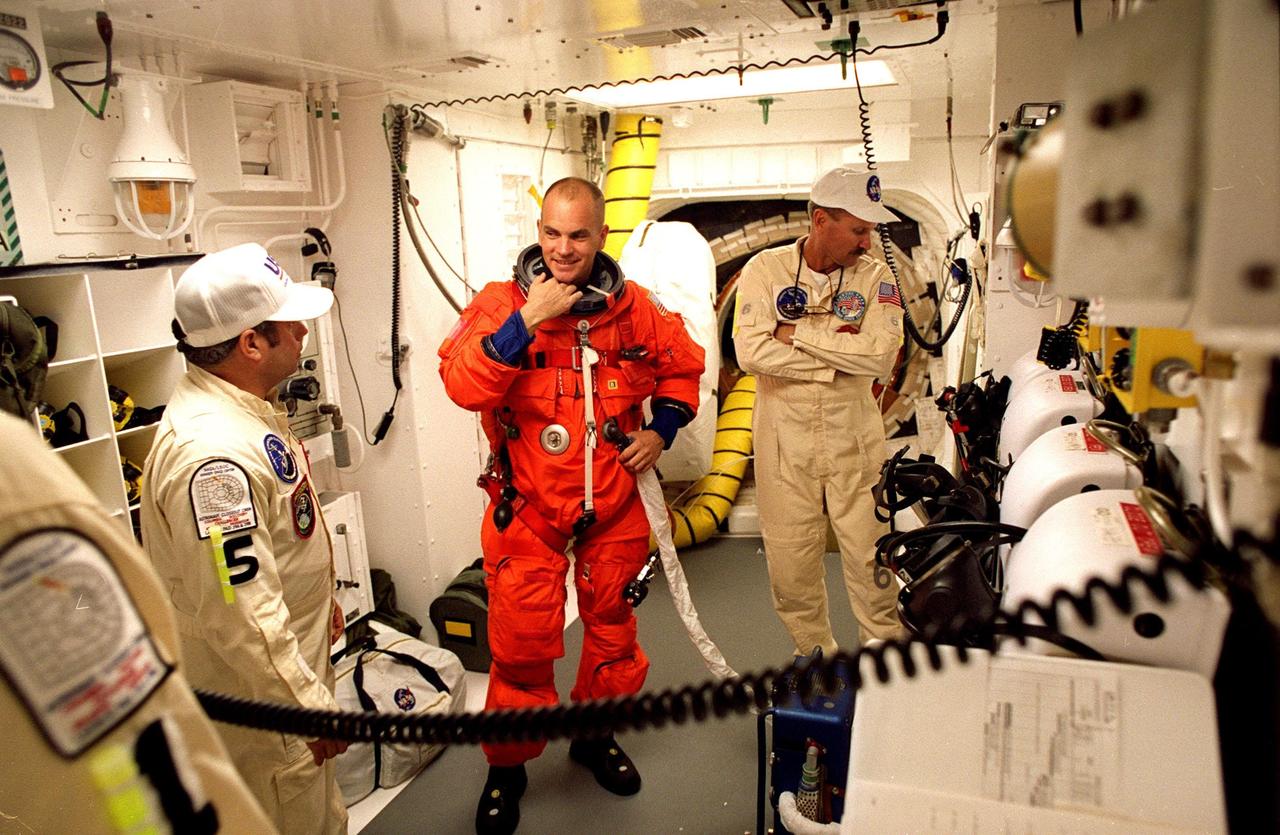

STS-88 Pilot Frederick W. "Rick" Sturckow is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39A before entering Space Shuttle Endeavour for launch. During the nearly 12-day mission, the six-member crew will mate the first two elements of the International Space Station the already-orbiting Zarya control module with the Unity connecting module carried by Endeavour. He is making his first spaceflight
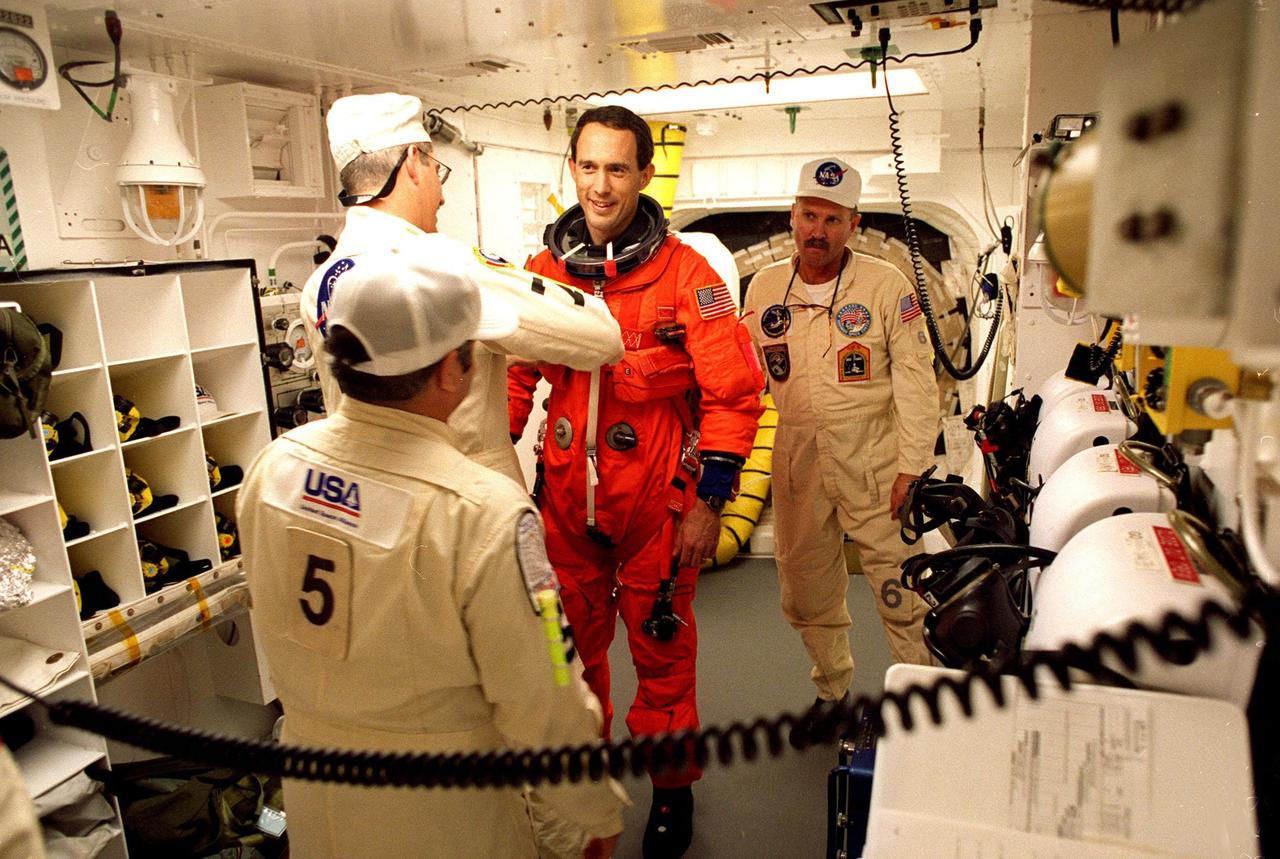

STS-88 Mission Specialist James H. Newman is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39A before entering Space Shuttle Endeavour for launch. During the nearly 12-day mission, the six-member crew will mate the first two elements of the International Space Station the already-orbiting Zarya control module with the Unity connecting module carried by Endeavour. Newman is making his third spaceflight and is one of two extravehicular activity crew members on this mission
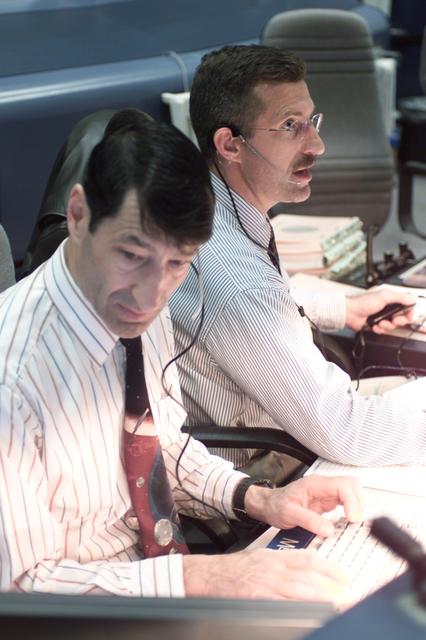

JSC2002-E-08463 (7 March 2002) --- Astronauts Mario Runco, Jr. (foreground) and Daniel C. Burbank, both spacecraft communicators (CAPCOM), monitor data at their consoles in the shuttle flight control room (WFCR) in Houston’s Mission Control Center (MCC) during the STS-109 Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission.
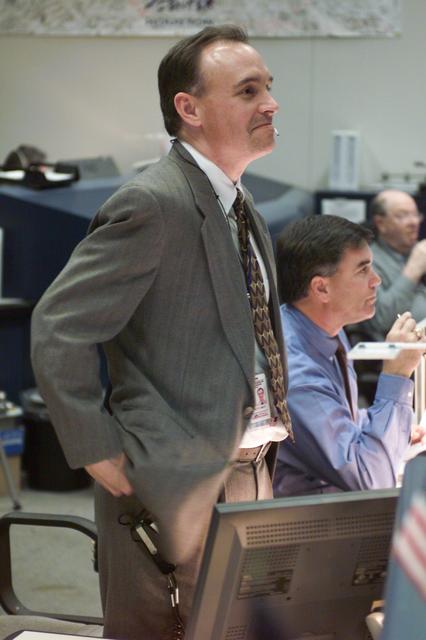

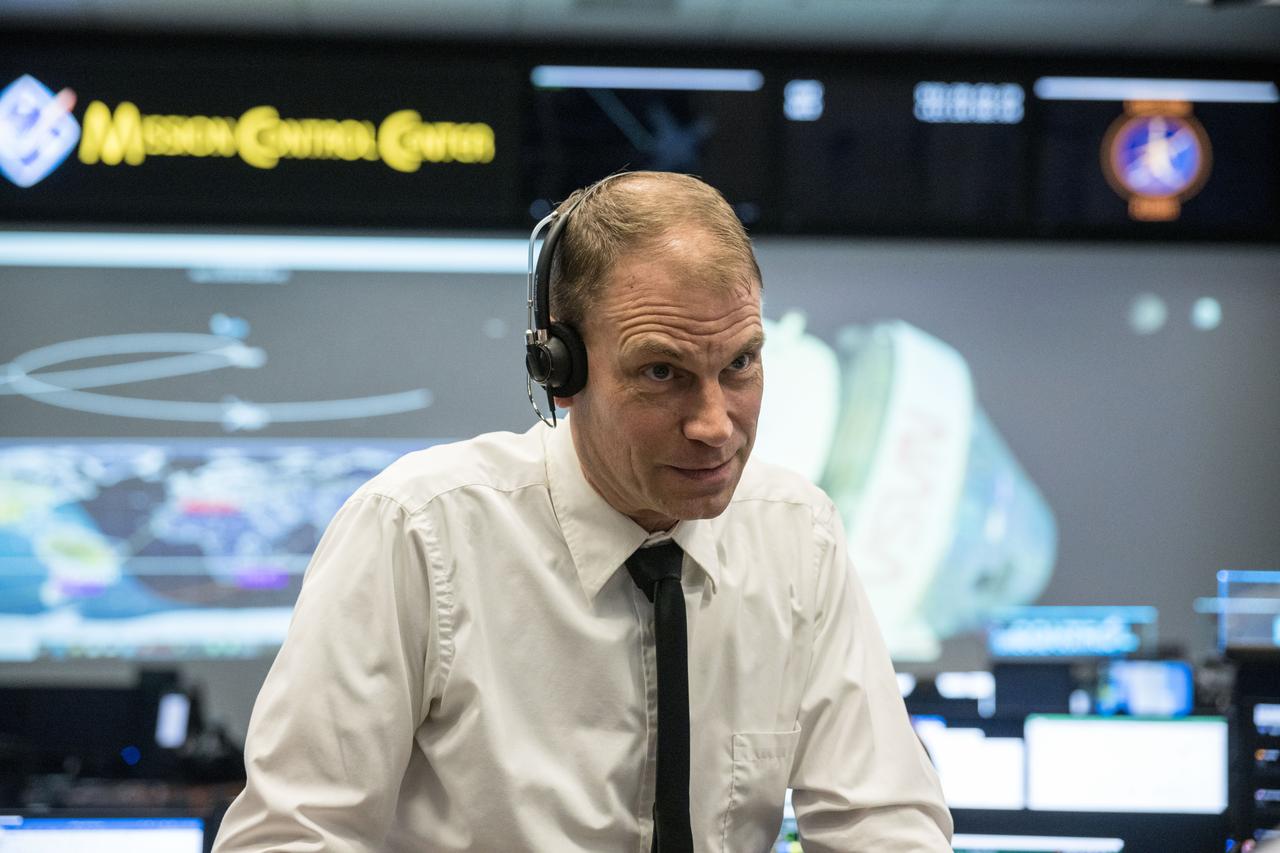
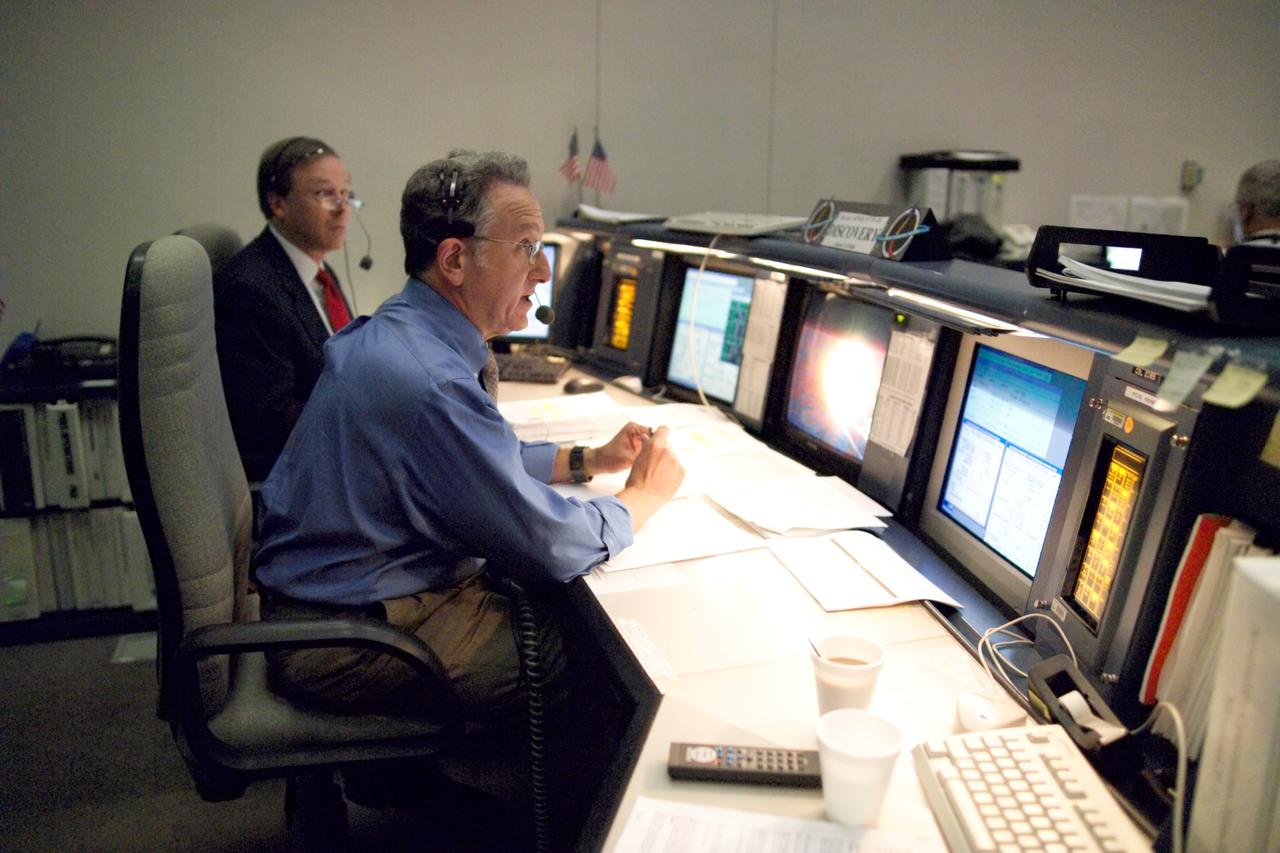
JSC2002-E-08460 (7 March 2002) --- Flight directors Jeff Hanley (standing) and Bryan P. Austin watch the large screens from their consoles in the shuttle flight control room (WFCR) in Houston;s Mission Control Center (MCC) during the STS-109 Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission.

STS-88 Mission Specialist Nancy Jane Currie is assisted with her ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39A before entering Space Shuttle Endeavour for launch. During the nearly 12-day mission, the six-member crew will mate the first two elements of the International Space Station the already-orbiting Zarya control module with the Unity connecting module carried by Endeavour. She is making her third spaceflight as the crew's flight engineer and prime operator of the Remote Manipulator System, the robotic arm
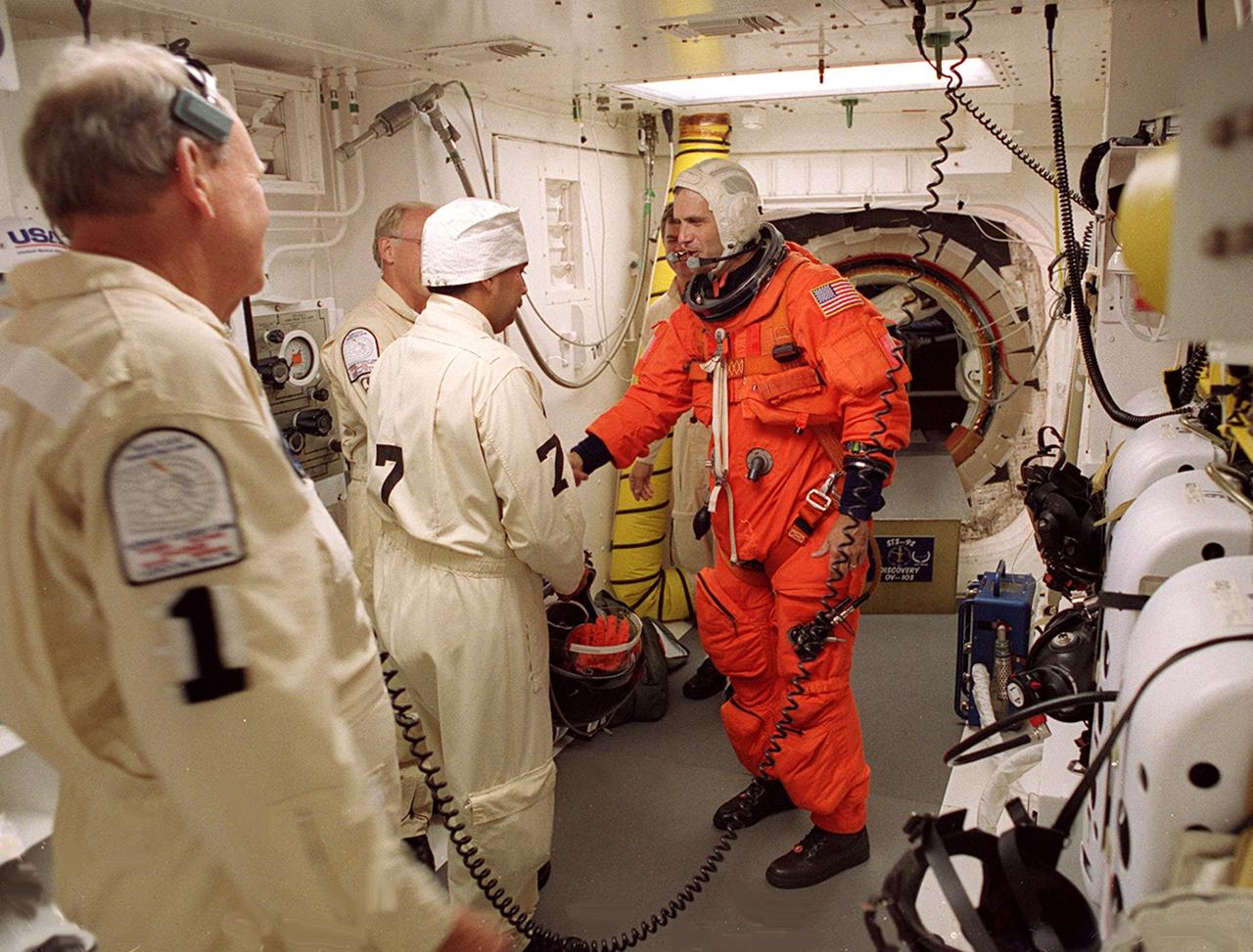

STS-92 Mission Specialist Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff reaches out to shake the hand of Danny Wyatt, KSC NASA Quality Assurance specialist, after completing final check of his launch and entry suit in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. Wisoff and the rest of the crew are undertaking the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT
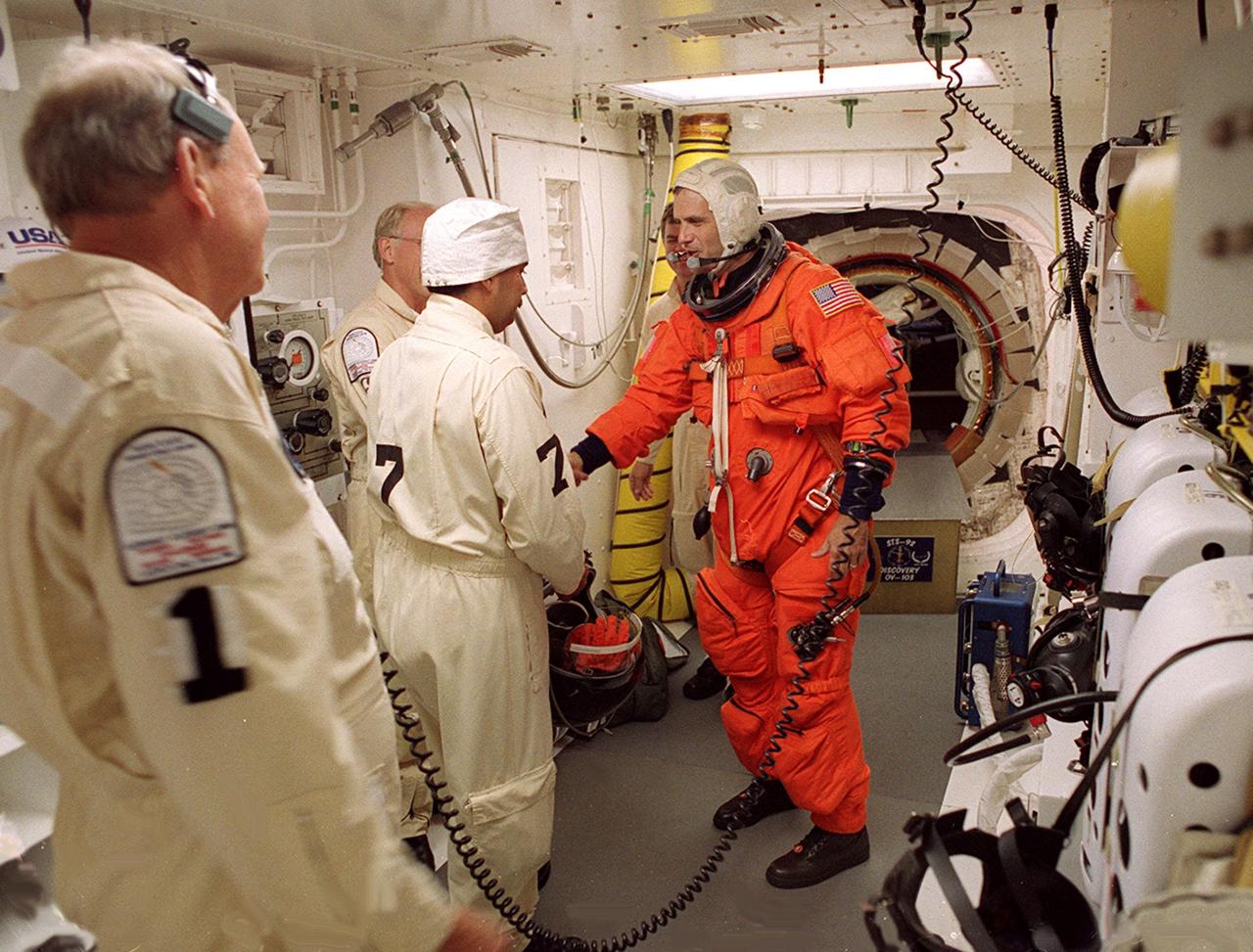

STS-92 Mission Specialist Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff reaches out to shake the hand of Danny Wyatt, KSC NASA Quality Assurance specialist, after completing final check of his launch and entry suit in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. Wisoff and the rest of the crew are undertaking the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT

Space Shuttle Atlantis is revealed after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Extended to the side of Atlantis is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room at its end. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area that provides entry for the crew into Atlantis’s cockpit. Above the yellow-orange external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, with the “beanie cap” vent hood raised. Before cryogenic loading, the hood will be lowered into position over the external tank vent louvers to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the International Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
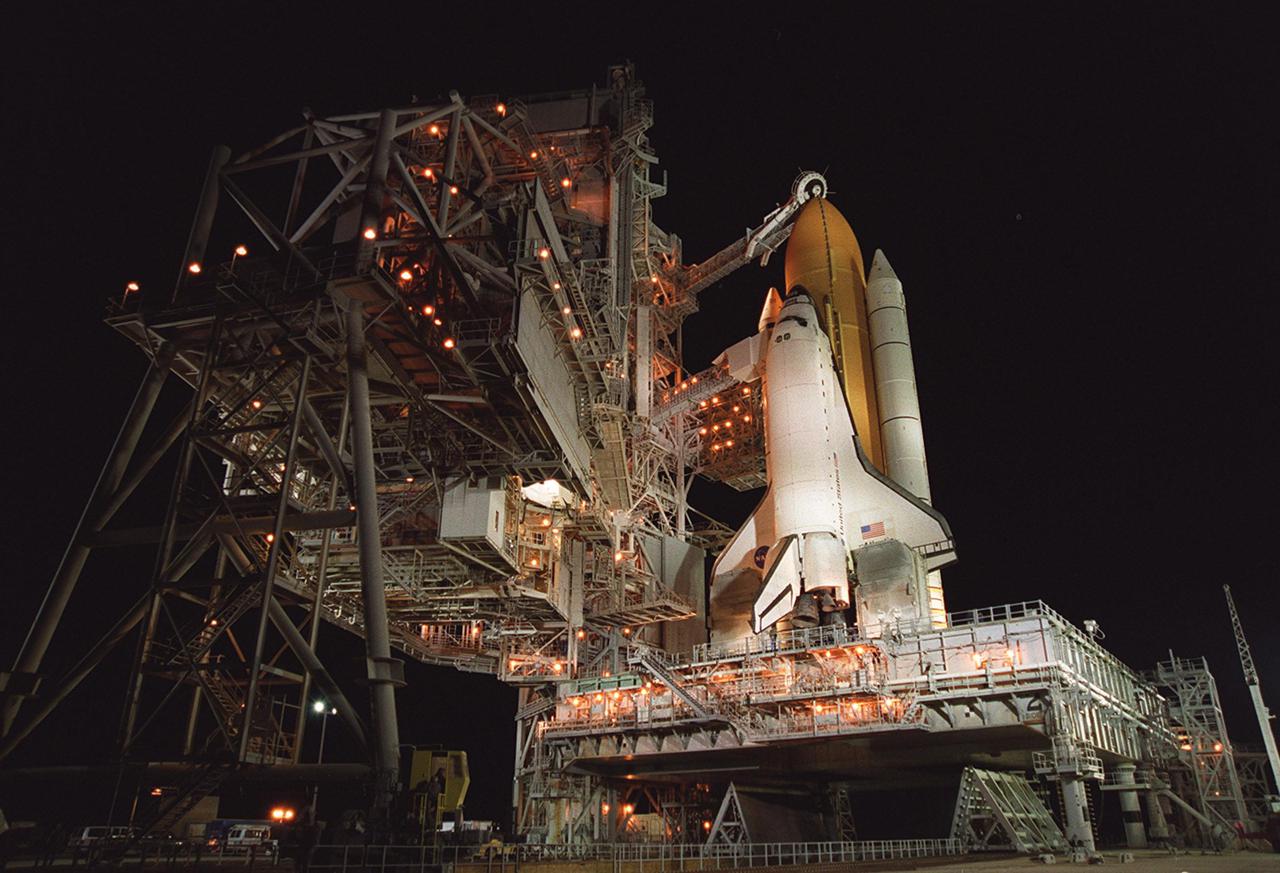

Space Shuttle Atlantis is revealed after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. Extended to the side of Atlantis is the orbiter access arm, with the White Room at its end. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area that provides entry for the crew into Atlantis’s cockpit. Above the yellow-orange external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, with the “beanie cap” vent hood raised. Before cryogenic loading, the hood will be lowered into position over the external tank vent louvers to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the International Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
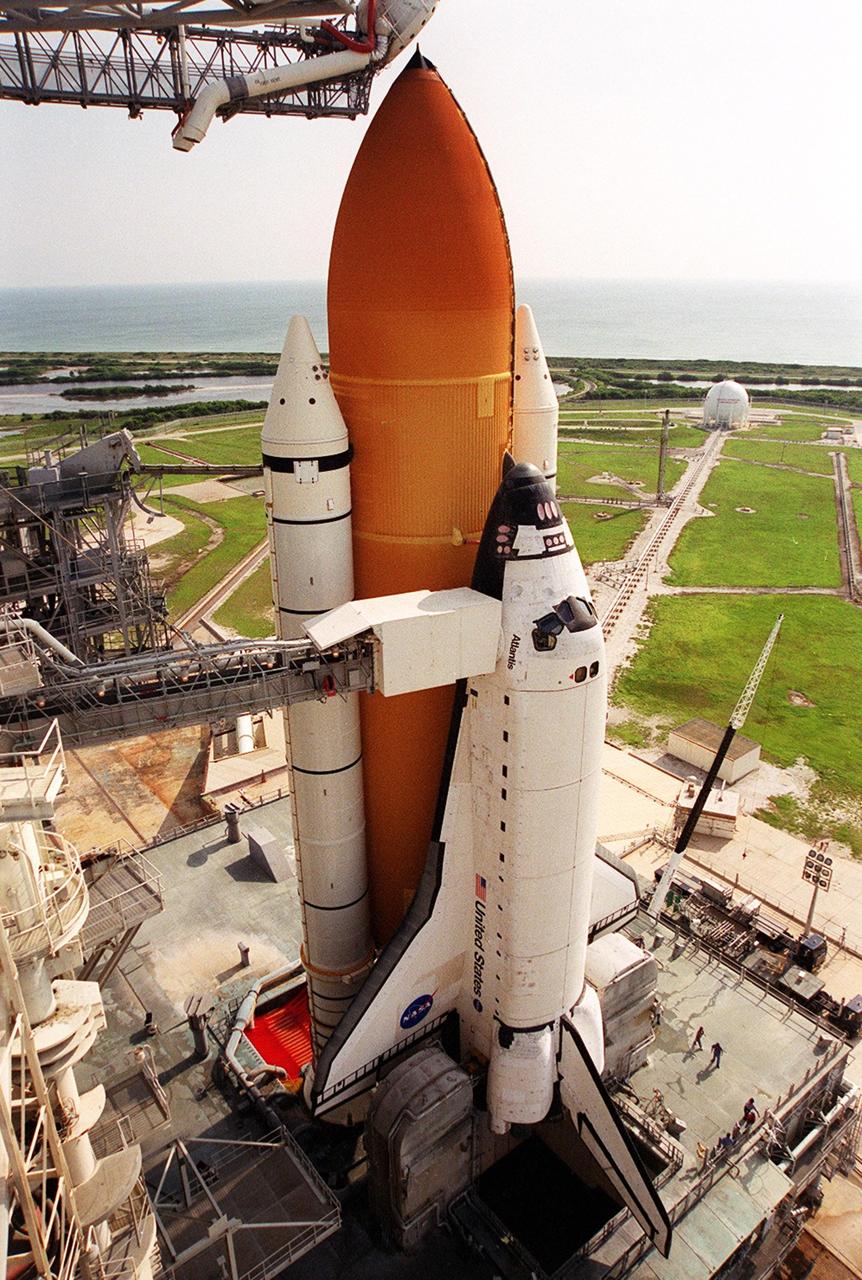

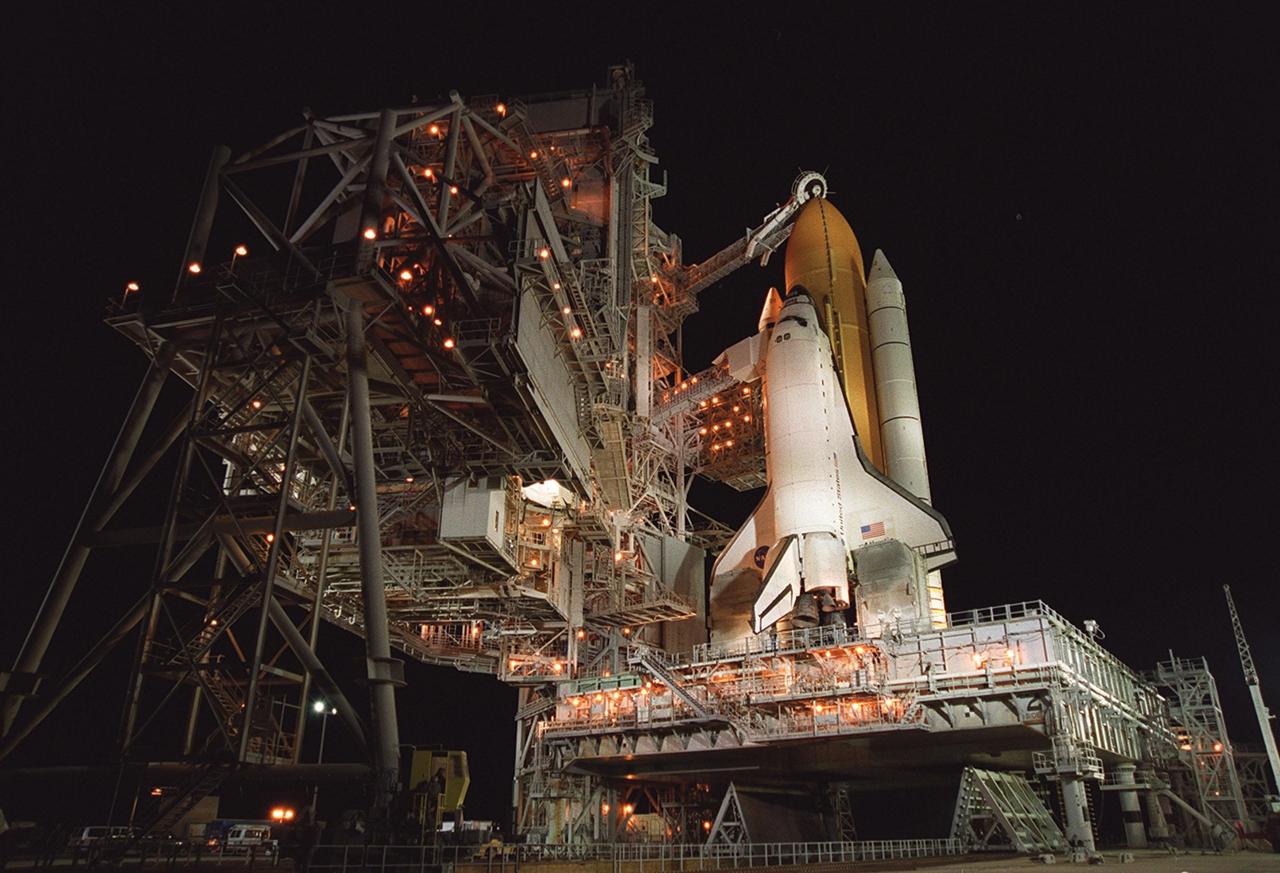
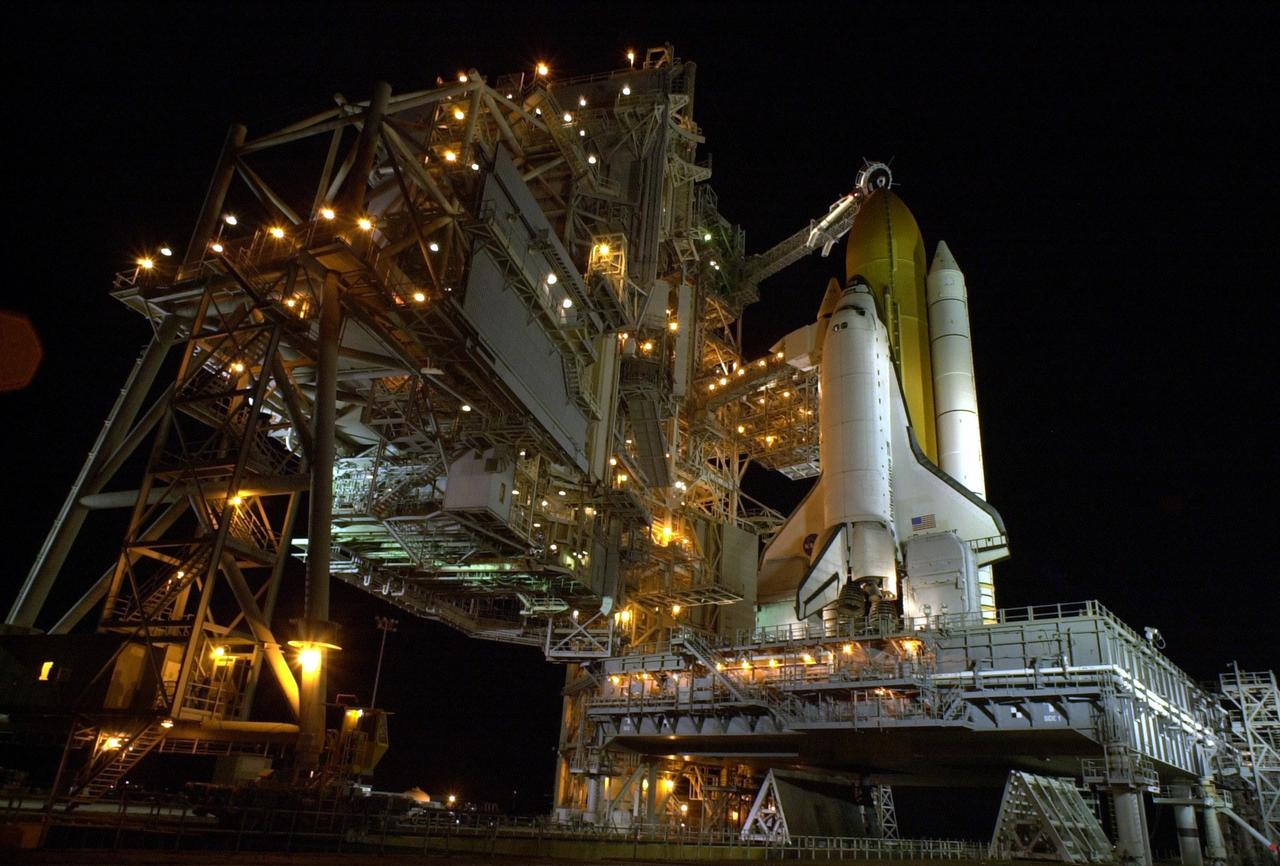
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis is ready for final launch preparations. The orbiter access arm is extended to the orbiter to allow entry into Atlantis. The White Room at the end is the point of entry, and is an environmentally controlled room where the Shuttle crew have final adjustments made to their launch and entry suits. At the lower end of Atlantis are the tail service masts, in front of either wing. The masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Viewed in the background is the Atlantic Ocean. Launch on mission STS-104 is scheduled for 5:04 a.m. July 12. The launch is the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Along with a crew of five, Atlantis will carry the joint airlock module as primary payload
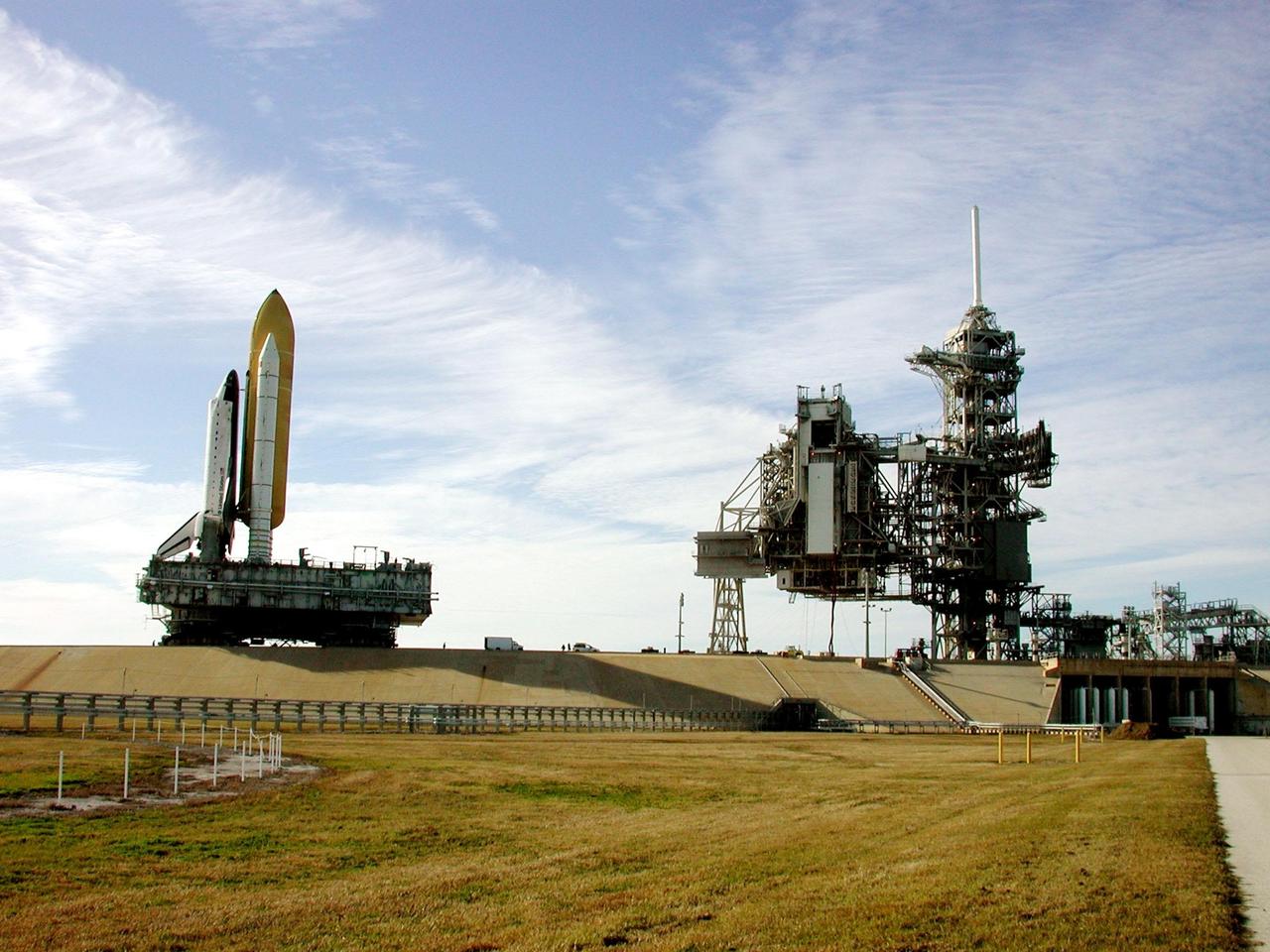

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Under wispy white morning clouds, Space Shuttle Atlantis approaches Launch Pad 39A, which shows the Rotating Service Structure open (left) and the Fixed Service Structure (right). At the RSS, the payload canister is being lifted up to the Payload Changeout Room. This is the Shuttle’s second attempt at rollout. Jan. 2 a failed computer processor on the crawler transporter aborted the rollout and the Shuttle was returned to the Vehicle Assembly Building using a secondary computer processor on the vehicle. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny. The lab will have five system racks already installed inside the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch no earlier than Jan. 19, 2001, with a crew of five
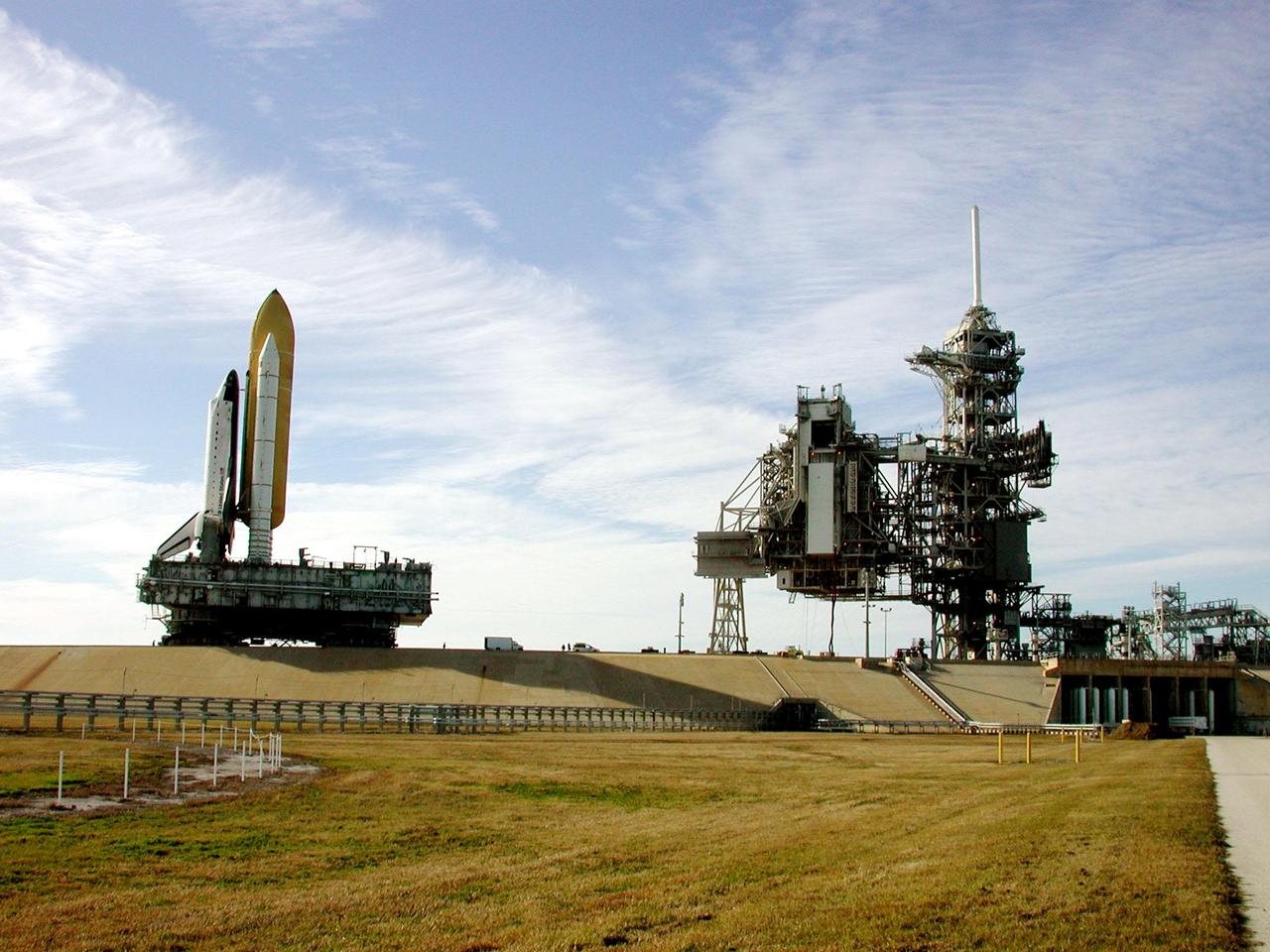

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Under wispy white morning clouds, Space Shuttle Atlantis approaches Launch Pad 39A, which shows the Rotating Service Structure open (left) and the Fixed Service Structure (right). At the RSS, the payload canister is being lifted up to the Payload Changeout Room. This is the Shuttle’s second attempt at rollout. Jan. 2 a failed computer processor on the crawler transporter aborted the rollout and the Shuttle was returned to the Vehicle Assembly Building using a secondary computer processor on the vehicle. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny. The lab will have five system racks already installed inside the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch no earlier than Jan. 19, 2001, with a crew of five
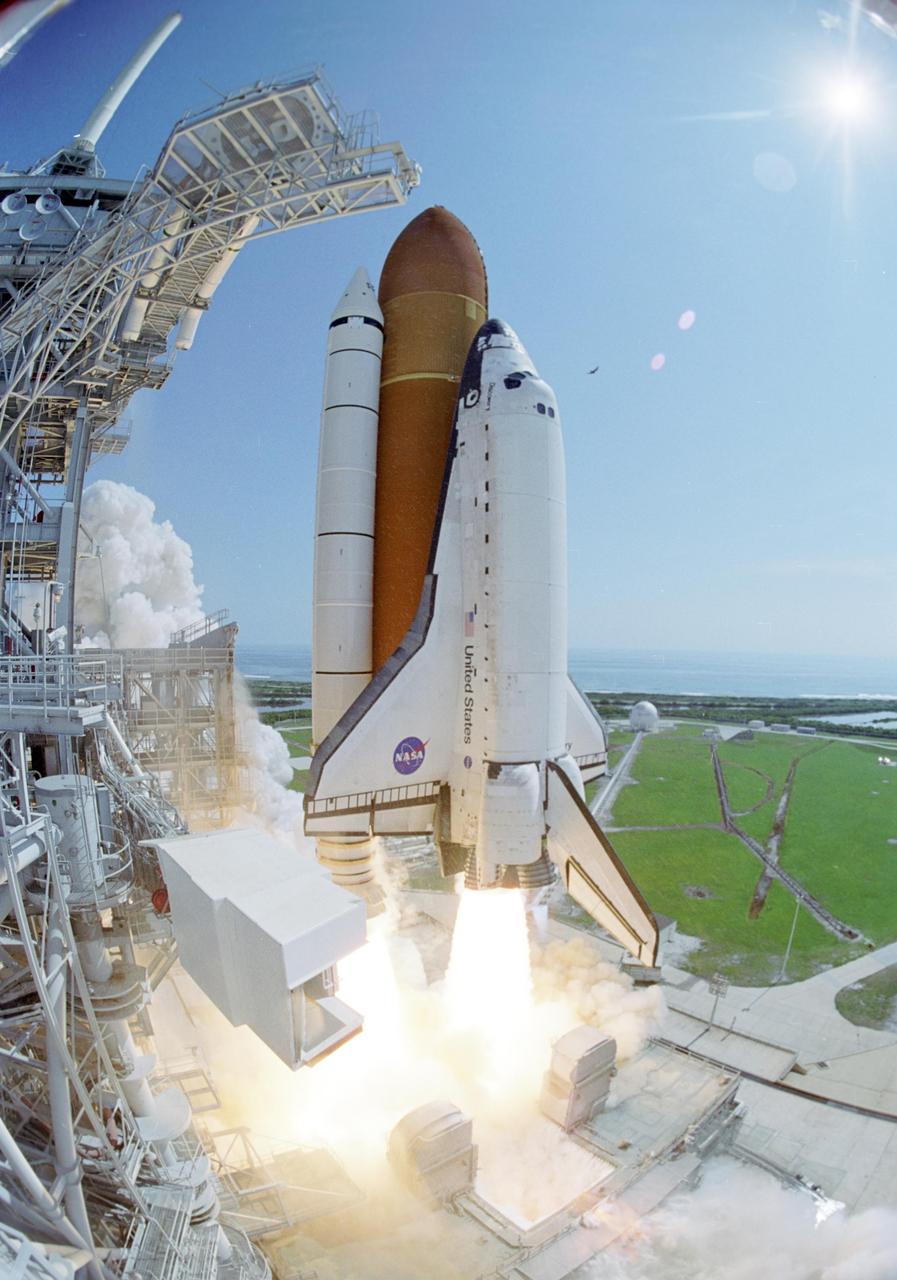

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A fish-eye view shows Space Shuttle Discovery moments after liftoff from Launch Pad 39B on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. At left is the Fixed Service Structure with the White Room appearing to be suspended in mid-air. The White Room provides the astronauts access into the orbiter. The liftoff occurred at 10:39 a.m. EDT. On this mission to the International Space Station the crew will perform inspections on-orbit for the first time of all of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of the wings and the Thermal Protection System tiles using the new Canadian-built Orbiter Boom Sensor System and the data from 176 impact and temperature sensors. Mission Specialists will also practice repair techniques on RCC and tile samples during a spacewalk in the payload bay. During two additional spacewalks, the crew will install the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility on Aug. 7.
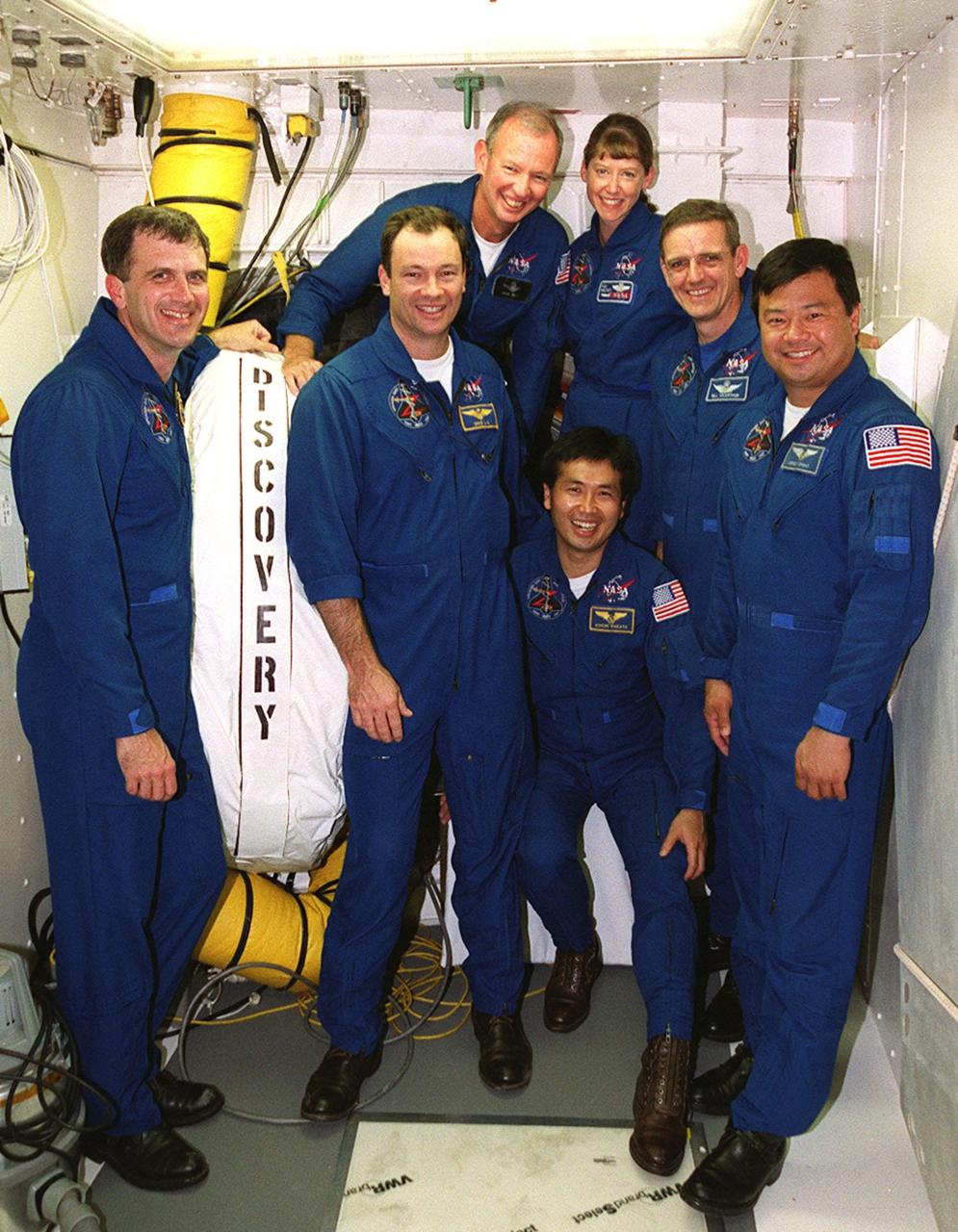

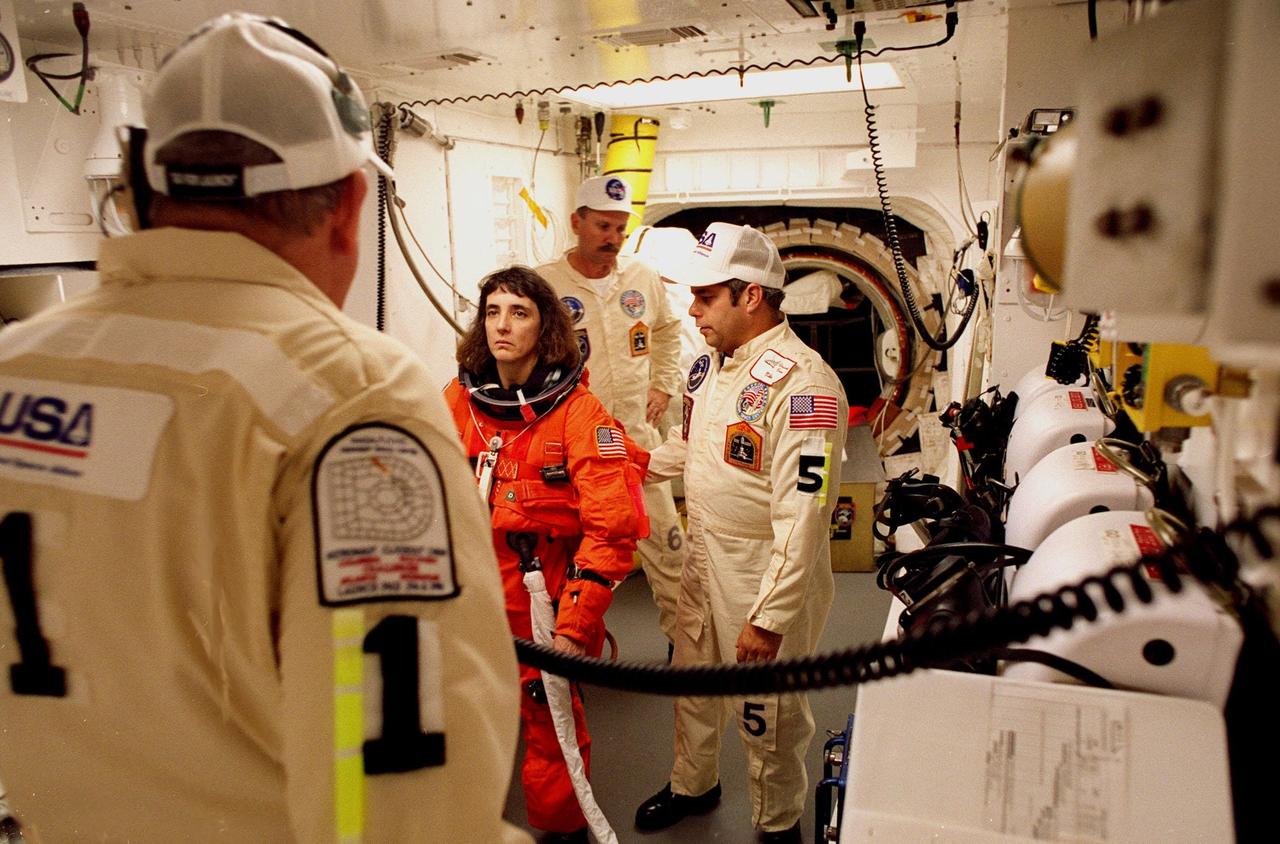
The STS-92 crew poses for a photograph in the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber on the orbiter access arm that provides entry for the crew into the orbiter. Standing, left to right, are Mission Specialists Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria; Commander Brian Duffy; Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy; and Mission Specialists William S. McArthur Jr. and Leroy Chiao. Crouching in front is Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata of Japan. The crew is at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that provide emergency egress training, opportunities to inspect the mission payload, and take part in a simulated countdown. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
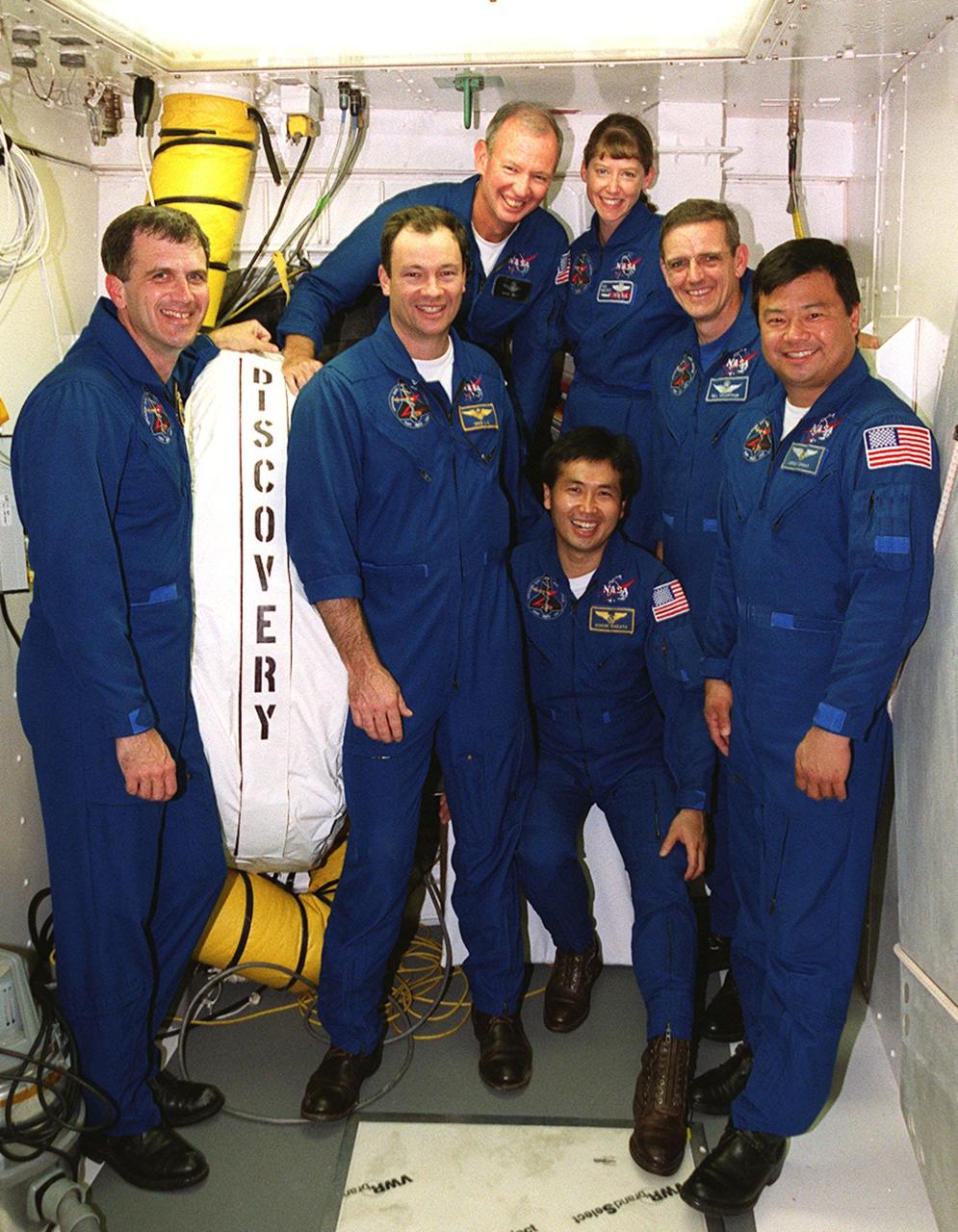

The STS-92 crew poses for a photograph in the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber on the orbiter access arm that provides entry for the crew into the orbiter. Standing, left to right, are Mission Specialists Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria; Commander Brian Duffy; Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy; and Mission Specialists William S. McArthur Jr. and Leroy Chiao. Crouching in front is Mission Specialist Koichi Wakata of Japan. The crew is at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that provide emergency egress training, opportunities to inspect the mission payload, and take part in a simulated countdown. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT on the fifth flight to the International Space Station. It will carry two elements of the Space Station, the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The mission is also the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
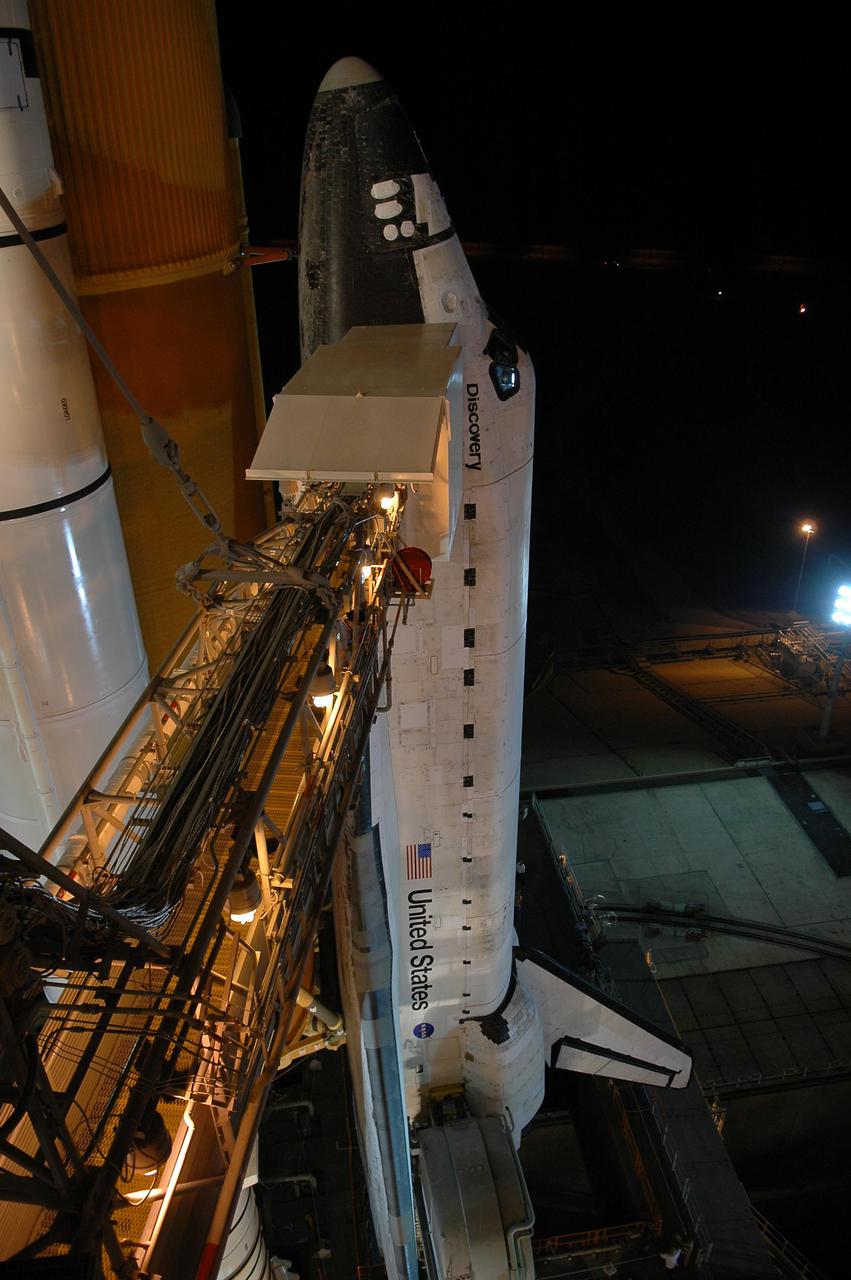

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Following rollback of the Rotating Service Structure, the orbiter access arm is able to be extended to Space Shuttle Discovery. The arm provides access into Discovery through the White Room, where the astronauts are checked by the closeout crew. Discovery is scheduled to launch on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 3:51 p.m. July 13 with a crew of seven. The payload includes the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The astronauts will make three spacewalks, including one to practice repair techniques for the Shuttle’s heat shield and one to install the new gyroscope. This is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 11:06 a.m. July 25.
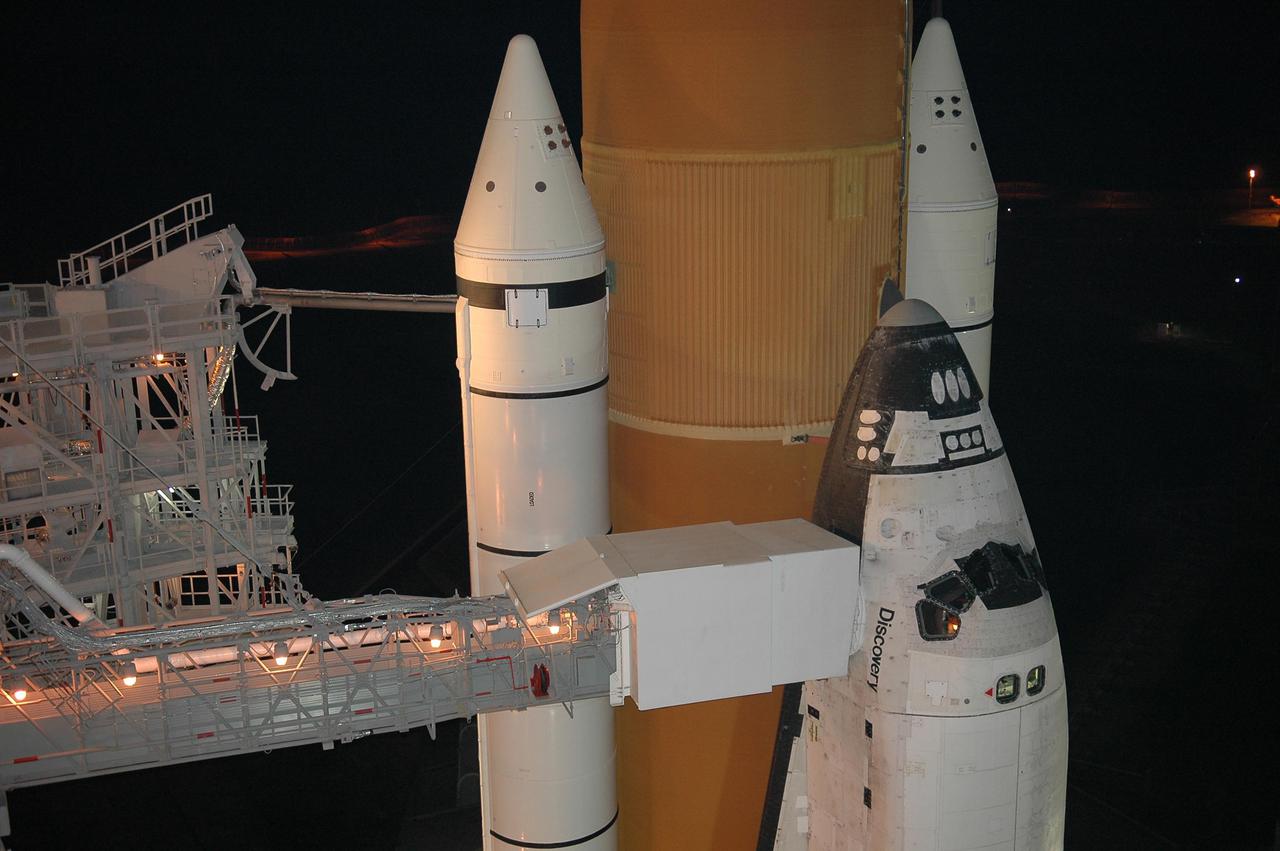

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Following rollback of the Rotating Service Structure, the orbiter access arm is able to be extended to Space Shuttle Discovery. The arm provides access into Discovery through the White Room, where the astronauts are checked by the closeout crew. Behind Discovery is the orange External Tank, flanked by the twin white Solid Rocket Boosters. Discovery is scheduled to launch on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 3:51 p.m. July 13 with a crew of seven. The payload includes the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The astronauts will make three spacewalks, including one to practice repair techniques for the Shuttle’s heat shield and one to install the new gyroscope. This is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 11:06 a.m. July 25.
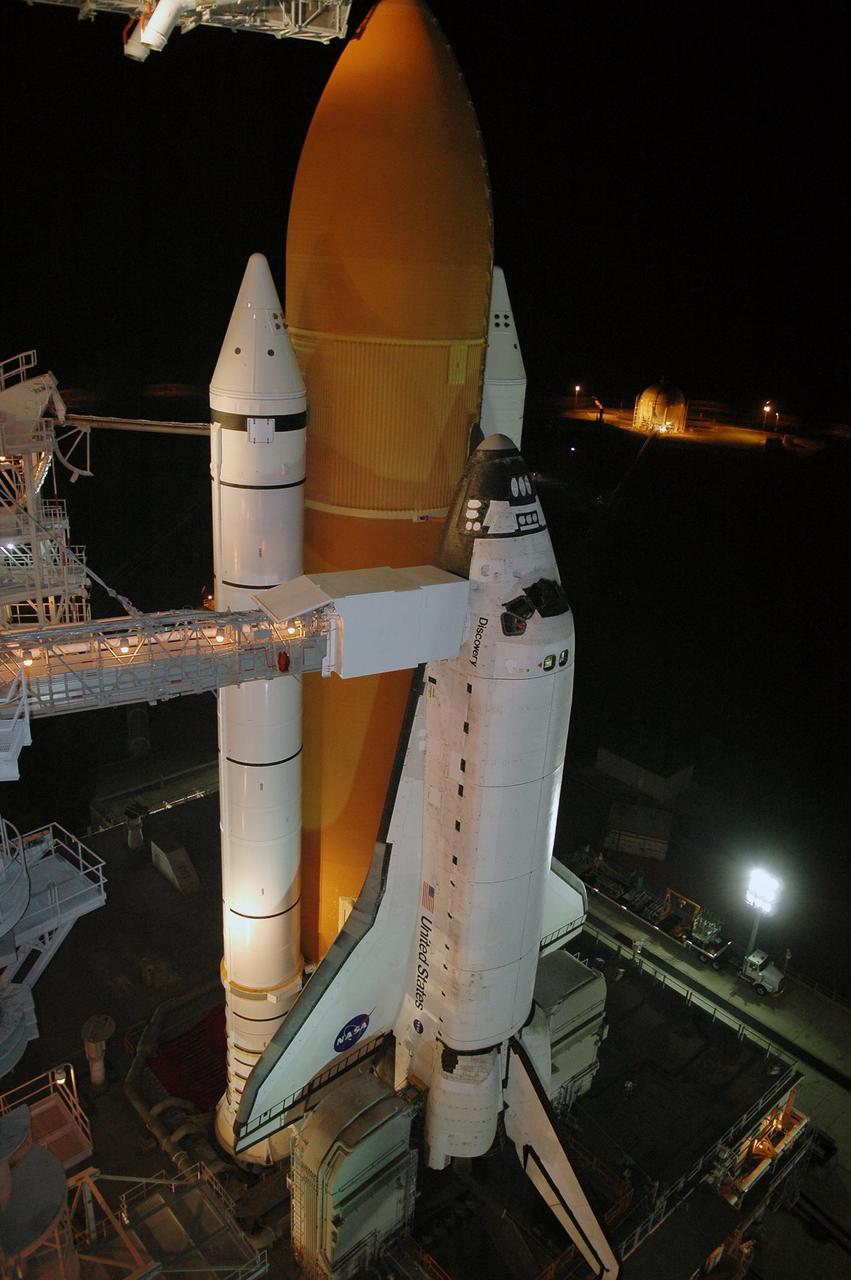

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Following rollback of the Rotating Service Structure, the orbiter access arm is able to be extended to Space Shuttle Discovery. The arm provides access into Discovery through the White Room, where the astronauts are checked by the closeout crew. Behind Discovery is the orange External Tank, flanked by the twin white Solid Rocket Boosters. Discovery is scheduled to launch on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114 at 3:51 p.m. July 13 with a crew of seven. The payload includes the External Stowage Platform-2, equipped with spare part assemblies, and a replacement Control Moment Gyroscope contained in the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure. The astronauts will make three spacewalks, including one to practice repair techniques for the Shuttle’s heat shield and one to install the new gyroscope. This is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 11:06 a.m. July 25.
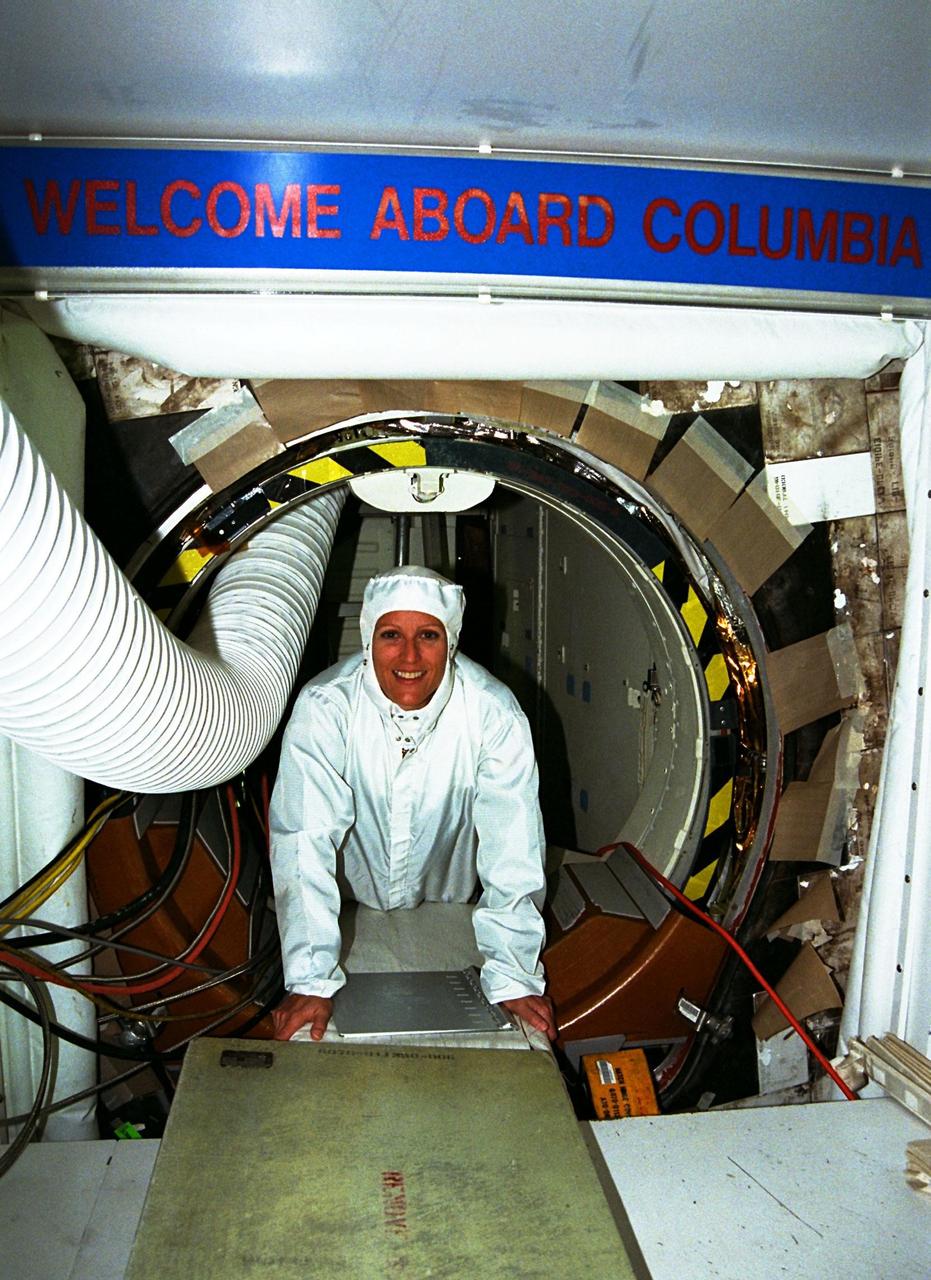

STS-90 Mission Specialist Kathryn (Kay) Hire enjoys the crawl between Columbia and the white room that allows access to the orbiter. The crew of STS-90 recently participated in the Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) in Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. Investigations during the STS-90 Neurolab mission will focus on the effects of microgravity on the nervous system. Specifically, experiments will study the adaptation of the vestibular system, the central nervous system, and the pathways that control the ability to sense location in the absence of gravity, as well as the effect of microgravity on a developing nervous system. STS-90, which will be Hire's first Shuttle flight, is scheduled for launch on April 16 at 2:19 p.m. EDT
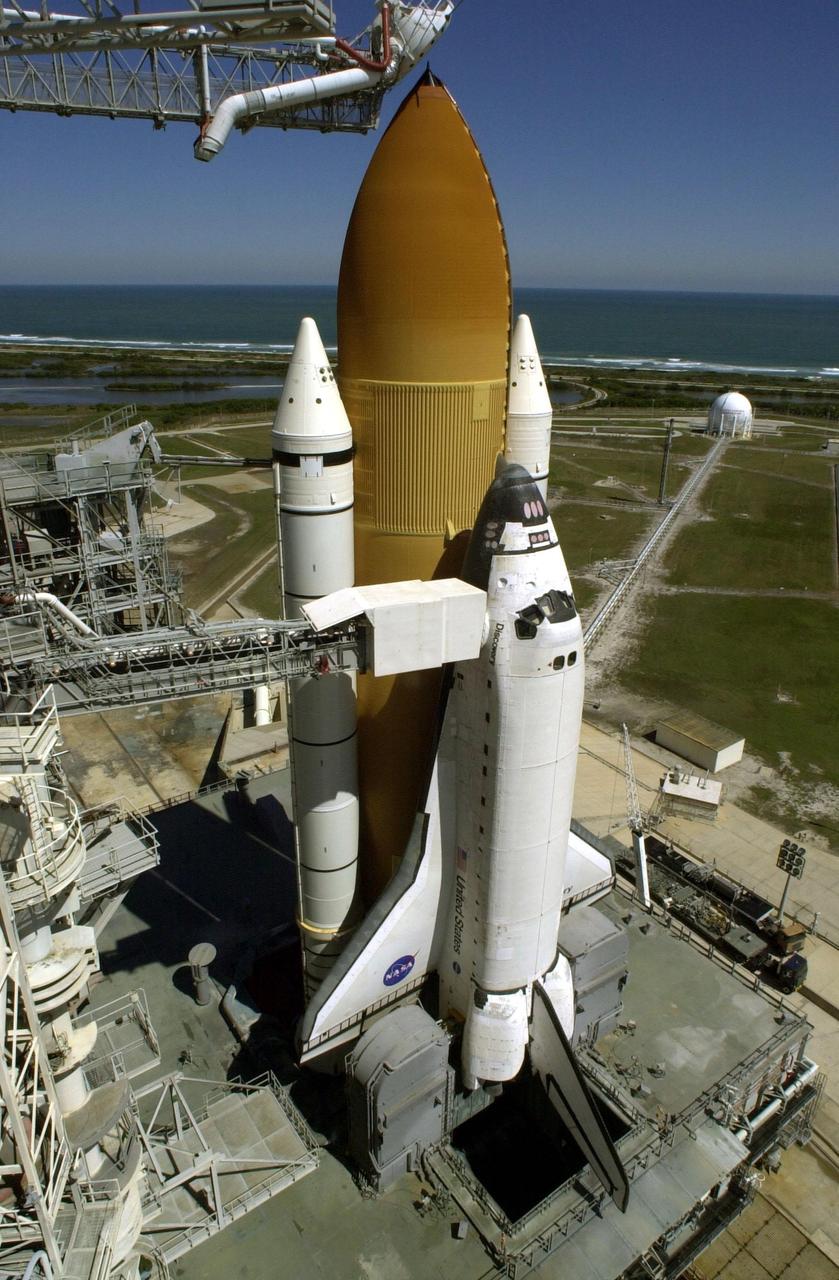

Space Shuttle Discovery sits poised on Launch Pad 39B, ready for launch at 6:42 a.m. EST March 8 on mission STS-102. Situated above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm with the “beanie cap,” a vent hood. The orbiter access arm is extended from the Fixed Service Structure (left) to the orbiter. An environmentally controlled chamber, known as the White Room, is at the end of the arm, providing entrance for the astronaut crew into the orbiter. In the distance, behind the Space Shuttle, can be seen the Atlantic Ocean. On this eighth construction flight to the International Space Station, Discovery carries the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny

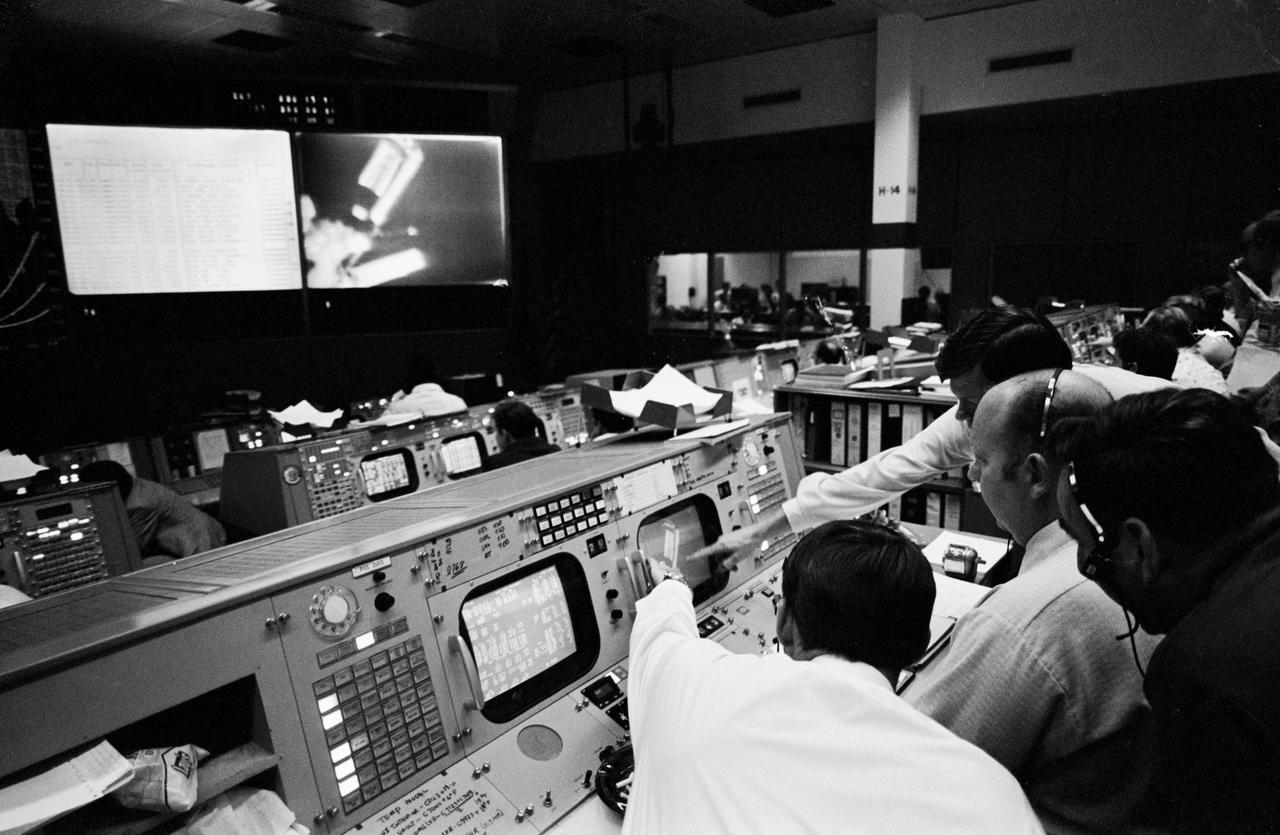
JSC2000-E-22286 (8 September 2000) --- An overall shot in Houston's Mission Control Center (MCC) shows flight controllers awaiting the launch of the Space Shuttle Atlantis from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. The vehicle later launched on schedule, at 8:46 a.m. (EDT), September 8, 2000, as the Johnson Space Center (JSC) flight control team took the baton from KSC's launch controllers. According to flight director Bill Reeves, "The picture referenced was taken less than an hour before launch for STS-106, before we changed the front screens for ascent operations. Wayne Hale (in glasses) is the Flight director for ascent and LeRoy Cain seated to his left was serving as "Weather Flight" for Wayne. The console in the front right corner of the room next to the screens is the Ground Control position, where I was supporting at this time. The man with white hair is Norn Talbott, who will be retiring after this flight with more than 35 years at NASA. Ray Grossman is next to him, who is training to take his place on the GC Ascent Team. I am in fron of and slightly to the right of Ray. As you can see by the boxes at the consoel behind us (Mechanical), we come well prepared for all contingencies, including donuts for early morning shifts. We were on console by 2:00 am central time for the 7:45 am launch." Reference: https://spaceflight.nasa.gov/feedback/expert/answer/mcc/sts-106/09_14_09_35_19.html

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the White Room at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-134 Pilot Greg H. Johnson, left, and Mission Specialist Greg Chamitoff prepare to board space shuttle Endeavour through the crew hatch in the background. Members of the Closeout Crew, in white uniforms, are there to assist astronauts with their launch-and-entry suits and the boarding process. Johnson piloted space shuttle Endeavour during its STS-123 mission in 2008. Chamitoff last served as flight engineer and science officer aboard the International Space Station in 2008. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. May 16 at 8:56 a.m. will be the second launch attempt for Endeavour. The first attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the White Room at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-134 Mission Specialist Michael Fincke prepares to board space shuttle Endeavour through the crew hatch in the background. Members of the Closeout Crew, in white uniforms, are there to assist astronauts with their launch-and-entry suits and the boarding process. Fincke last served as a member of the Expedition 18 crew of the International Space Station in 2009. This will be Fincke's first flight aboard a space shuttle. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. May 16 at 8:56 a.m. will be the second launch attempt for Endeavour. The first attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
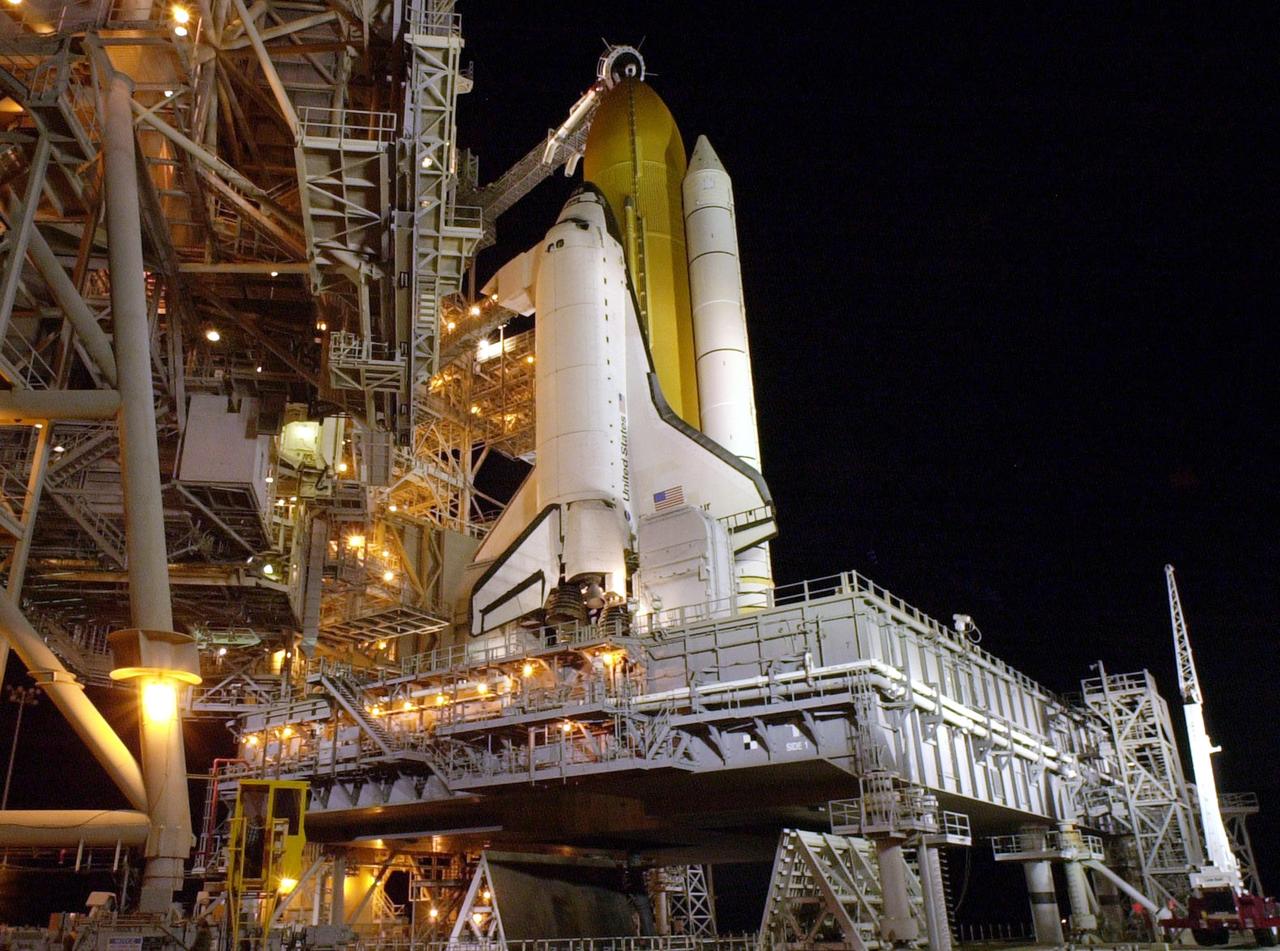

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour is revealed after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
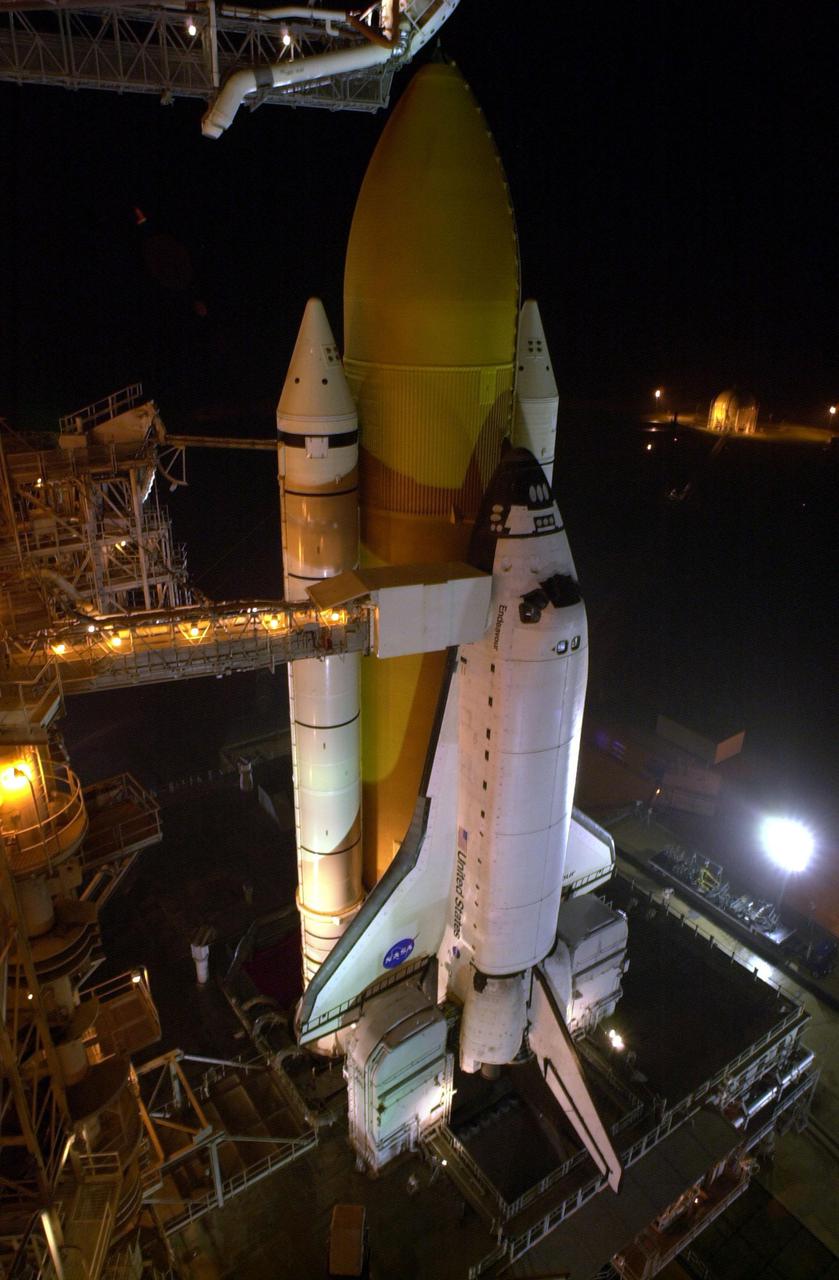

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
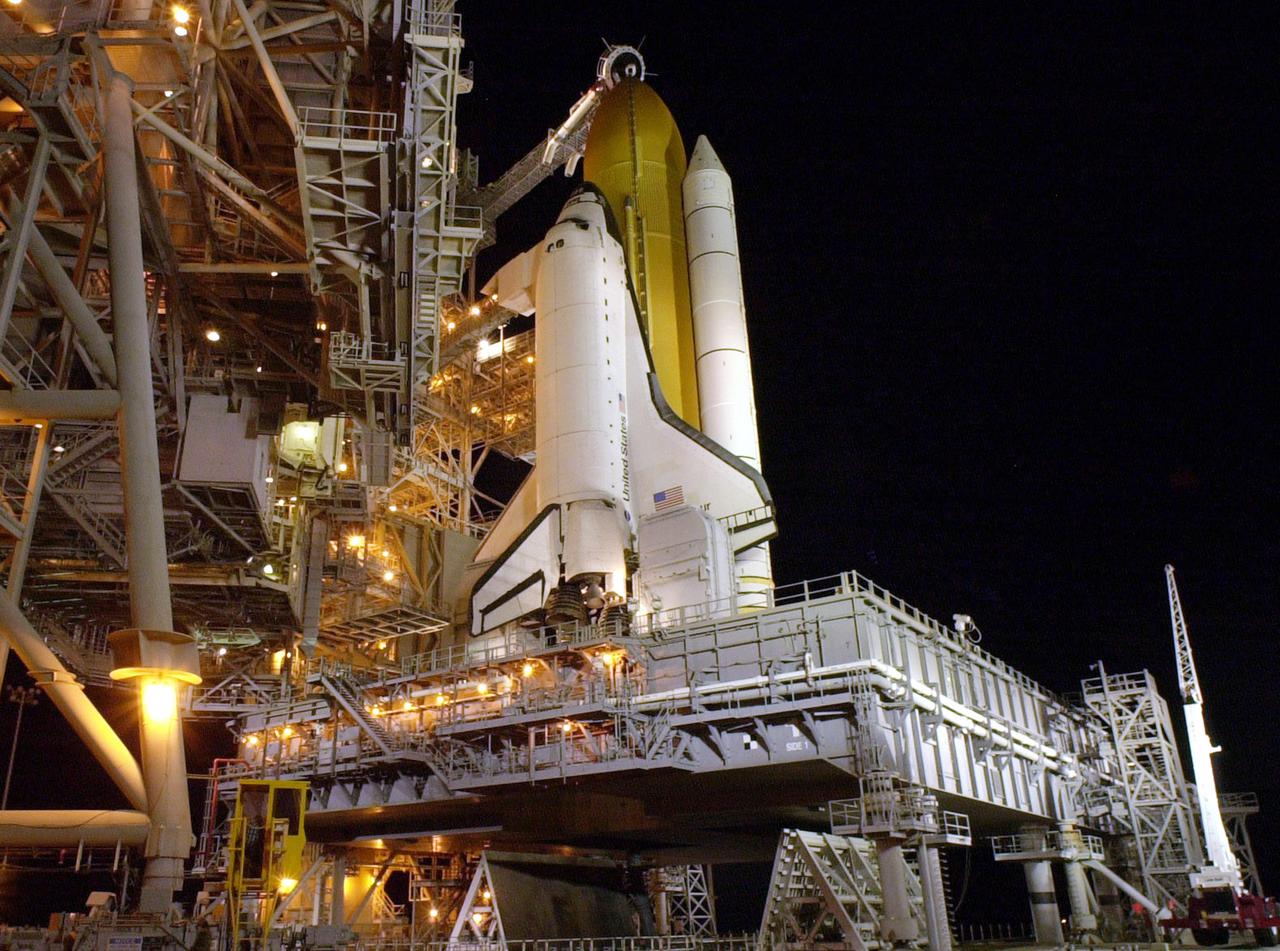

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour is revealed after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
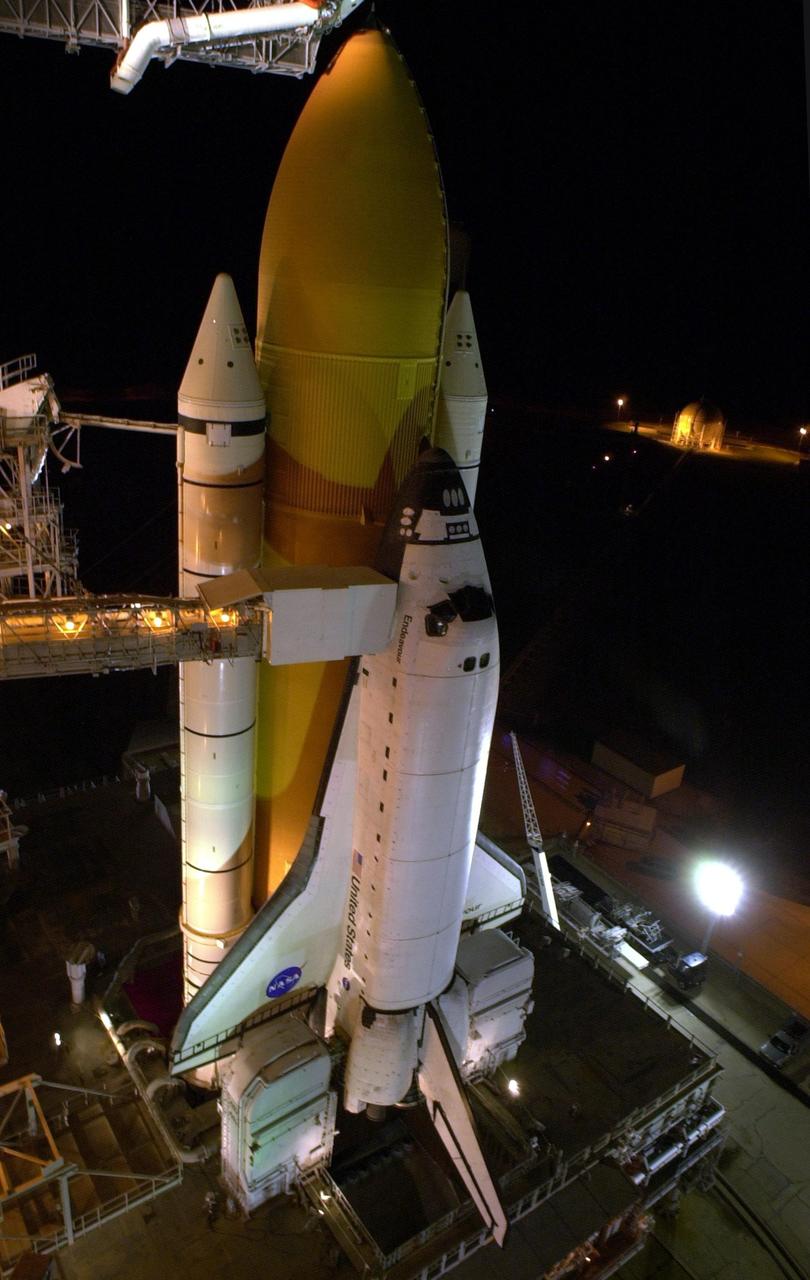

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour stands ready for launch after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen are the twin solid rocket boosters flanking the orange external tank. Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. Below Endeavour is the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
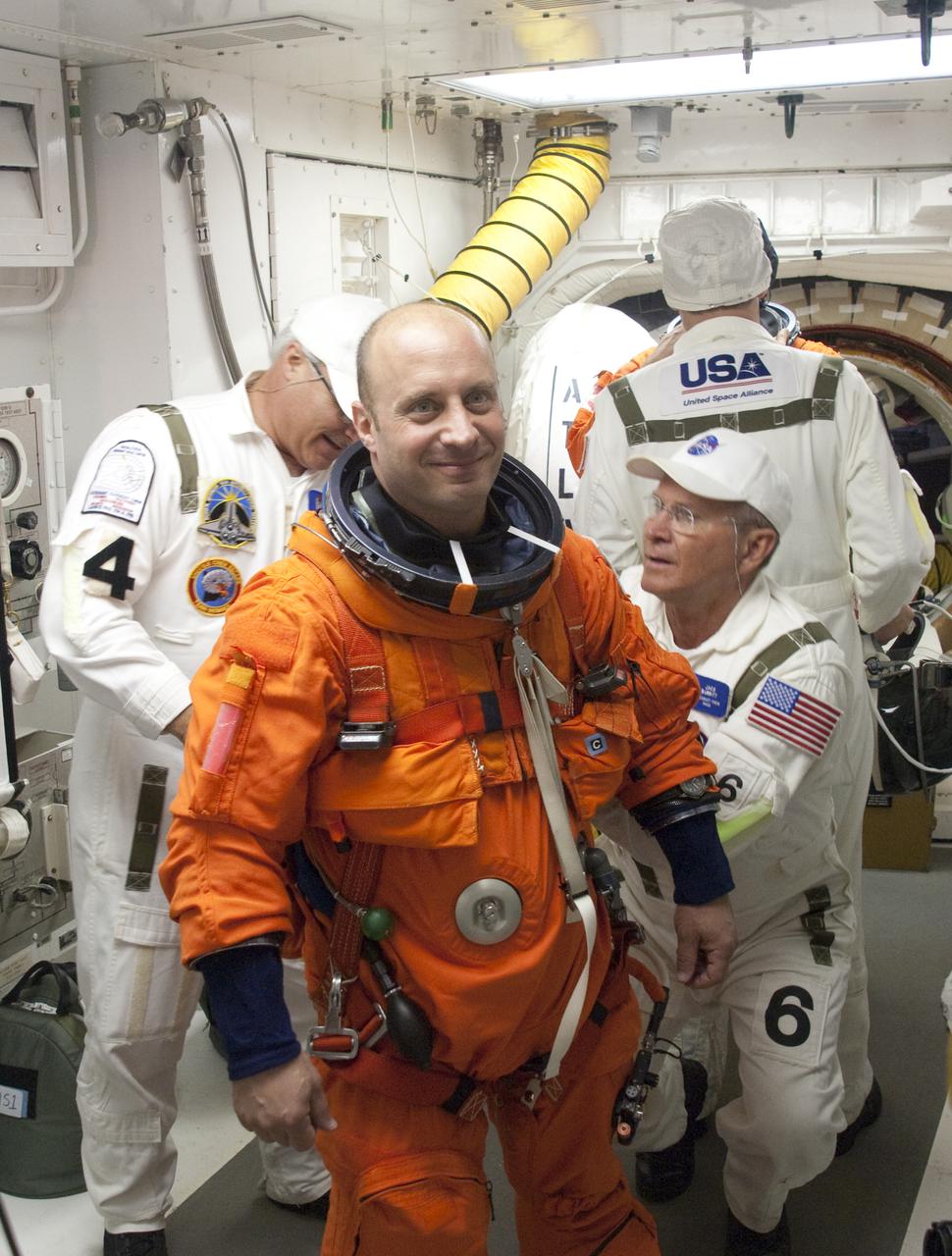

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the White Room at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance space suit technicians help STS-132 Mission Specialist Garrett Reisman put on the parachute for his launch-and-entry suit before he enters space shuttle Atlantis through the crew hatch in the background. Reisman was a flight engineer on the International Space Station's Expedition 16 and 17. Liftoff of the STS-132 mission is set for 2:20 p.m. EDT on May 14. The six-member STS-132 crew will deliver the Russian-built Mini Research Module-1 to the International Space Station. Named Rassvet, Russian for 'dawn,' the module is the second in a series of new pressurized components for Russia and will be permanently attached to the Earth-facing port of the Zarya control module. Rassvet will be used for cargo storage and will provide an additional docking port to the station. Also aboard Atlantis is an Integrated Cargo Carrier, or ICC, an unpressurized flat bed pallet and keel yoke assembly used to support the transfer of exterior cargo from the shuttle to the station. STS-132 is the 34th mission to the station and the last scheduled flight for Atlantis. For more information on the STS-132 mission objectives, payload and crew, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo Credit: NASA_Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
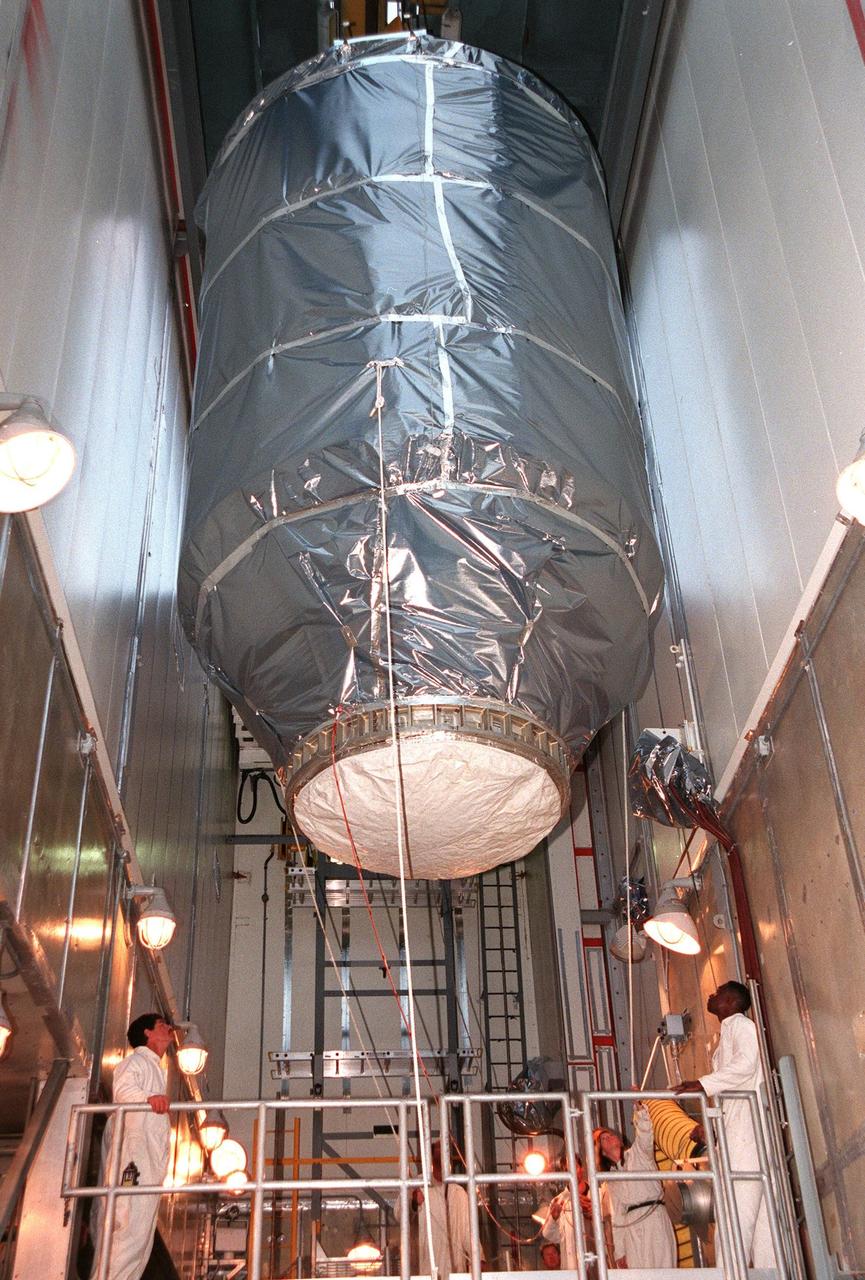

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17A at Cape Canaveral Air Station, Deep Space 1 is lowered in the white room for installation on a Boeing Delta 7326 rocket . The spacecraft is targeted for launch on Oct. 25. Deep Space 1 is the first flight in NASA's New Millennium Program, and is designed to validate 12 new technologies for scientific space missions of the next century, including the engine. Propelled by the gas xenon, the engine is being flight-tested for future deep space and Earth-orbiting missions. Deceptively powerful, the ion drive emits only an eerie blue glow as ionized atoms of xenon are pushed out of the engine. While slow to pick up speed, over the long haul it can deliver 10 times as much thrust per pound of fuel as liquid or solid fuel rockets. Other onboard experiments include software that tracks celestial bodies so the spacecraft can make its own navigation decisions without the intervention of ground controllers. Deep Space 1 will complete most of its mission objectives within the first two months, but will also do a flyby of a near-Earth asteroid, 1992 KD, in July 1999
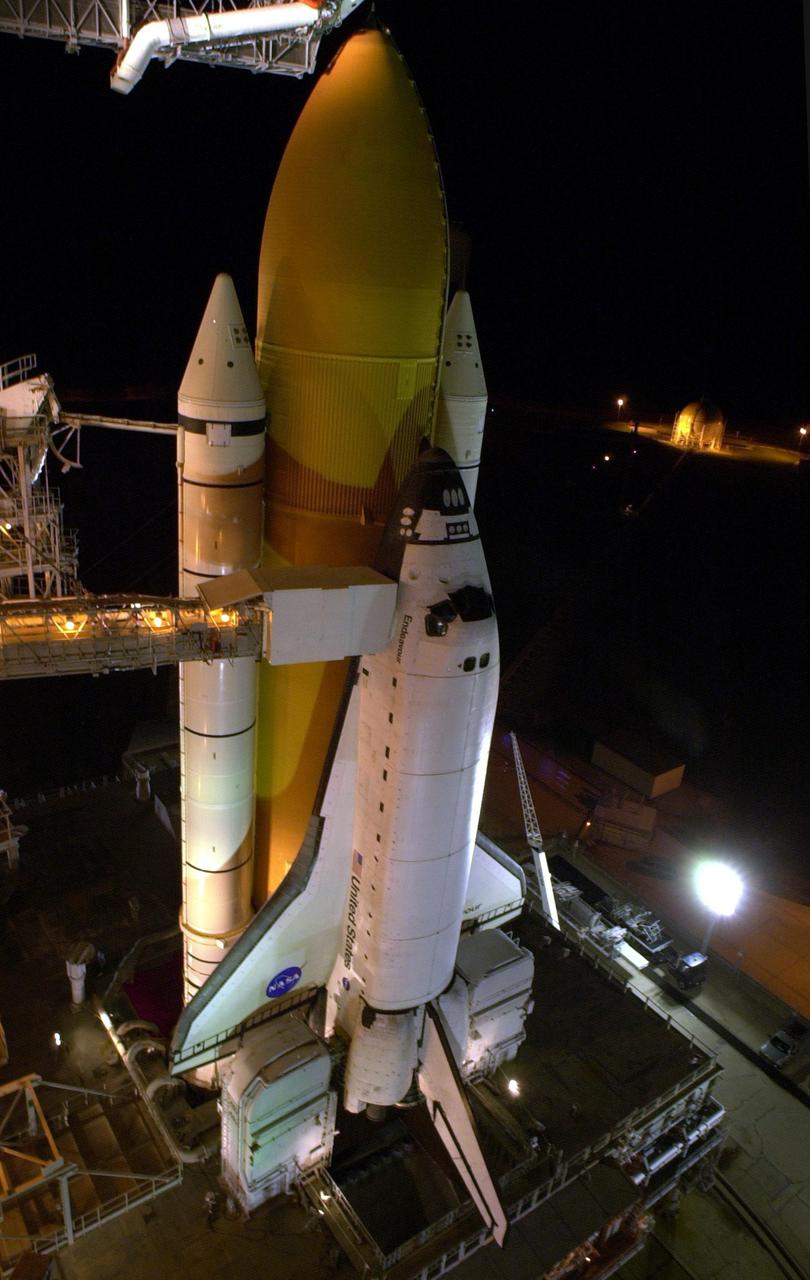

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour stands ready for launch after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B. Seen are the twin solid rocket boosters flanking the orange external tank. Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. Below Endeavour is the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
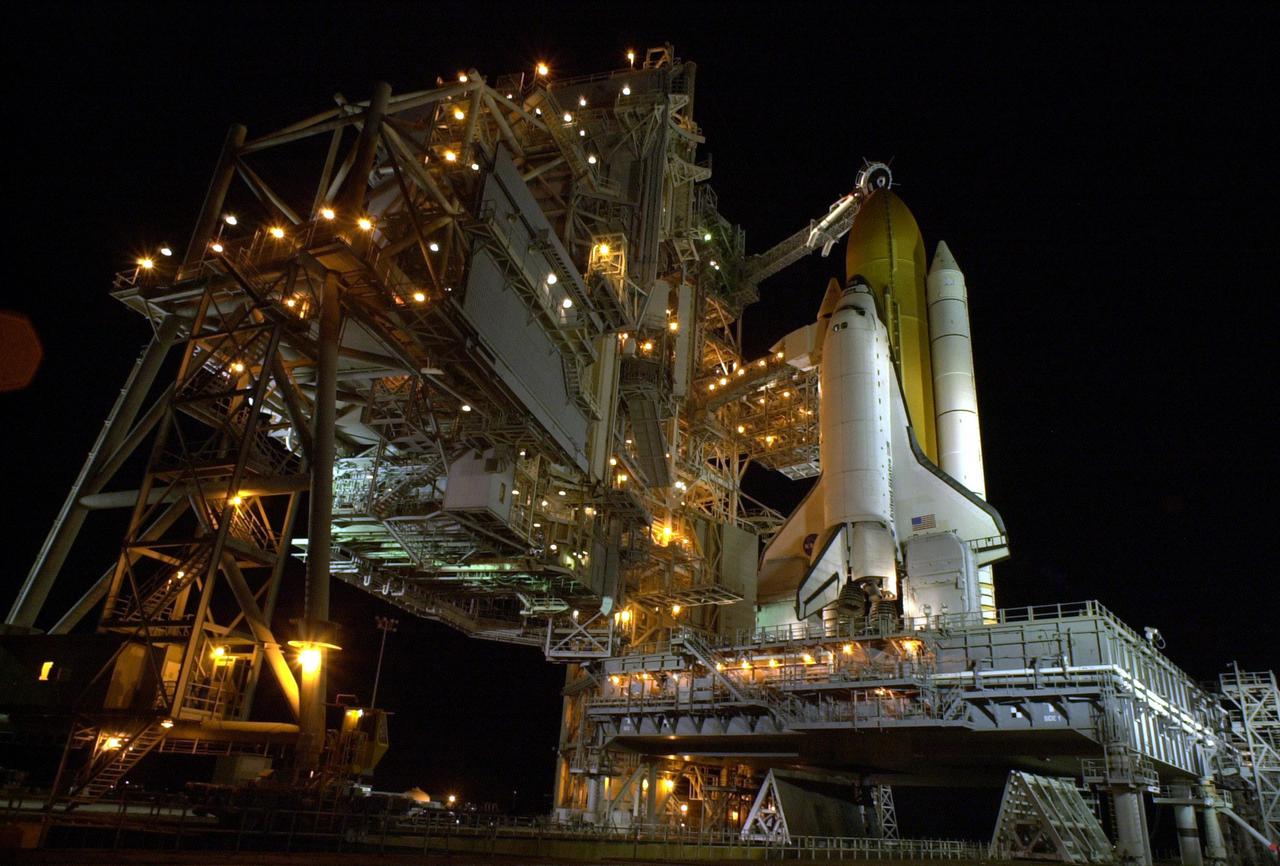

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Seen is one of the twin solid rocket boosters that flank the orange external tank. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching to the crew hatch on the side is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Nov. 29 at 7:41 p.m. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After rollback of the Rotating Service Structure on Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Endeavour is bathed in light. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-132 Mission Specialist Garrett Reisman prepares to enter space shuttle Atlantis from the pad's White Room. Reisman was a flight engineer on the International Space Station's Expedition 16 and 17. The six-member STS-132 crew is participating in a dress rehearsal for launch, known as the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test, from their seats in the crew compartment of space shuttle Atlantis. Launch is targeted for 2:19 p.m. EDT on May 14. On the STS-132 mission, the crew will deliver an Integrated Cargo Carrier, or ICC, and the Russian-built Mini-Research Module-1, or MRM-1, to the International Space Station. The ICC is an unpressurized flat bed pallet and keel yoke assembly used to support the transfer of exterior cargo from the shuttle to the space station. The MRM-1, known as Rassvet, is the second in a series of new pressurized components for Russia and will be permanently attached to the Earth-facing port of the Zarya control module. Rassvet, which translates to 'dawn,' will be used for cargo storage and provide an additional docking port to the station. STS-132 is the 34th mission to the station and the 132nd shuttle mission overall. For information on the STS-132 mission, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Endeavour rests on Launch Pad 39A after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Shuttle comprises the orbiter, in front, and the taller orange external tank behind it flanked by twin solid rocket boosters. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform that straddles the flame trench below. On either side of Endeavour's tail and main engines are the tail service masts that support the fluid,, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxyen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. In the foreground, left, is the White Room, located at the end of the orbiter access arm. This environmentally controlled area provides access to the cockpit of the orbiter. Mission STS-111 is designated UF-2, the 14th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Endeavour's payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and Mobile Base System. The mission also will swap resident crews on the Station, carrying the Expedition 5 crew and returning to Earth Expedition 4. Liftoff of Endeavour is scheduled between 4 and 8 p.m. May 30, 2002
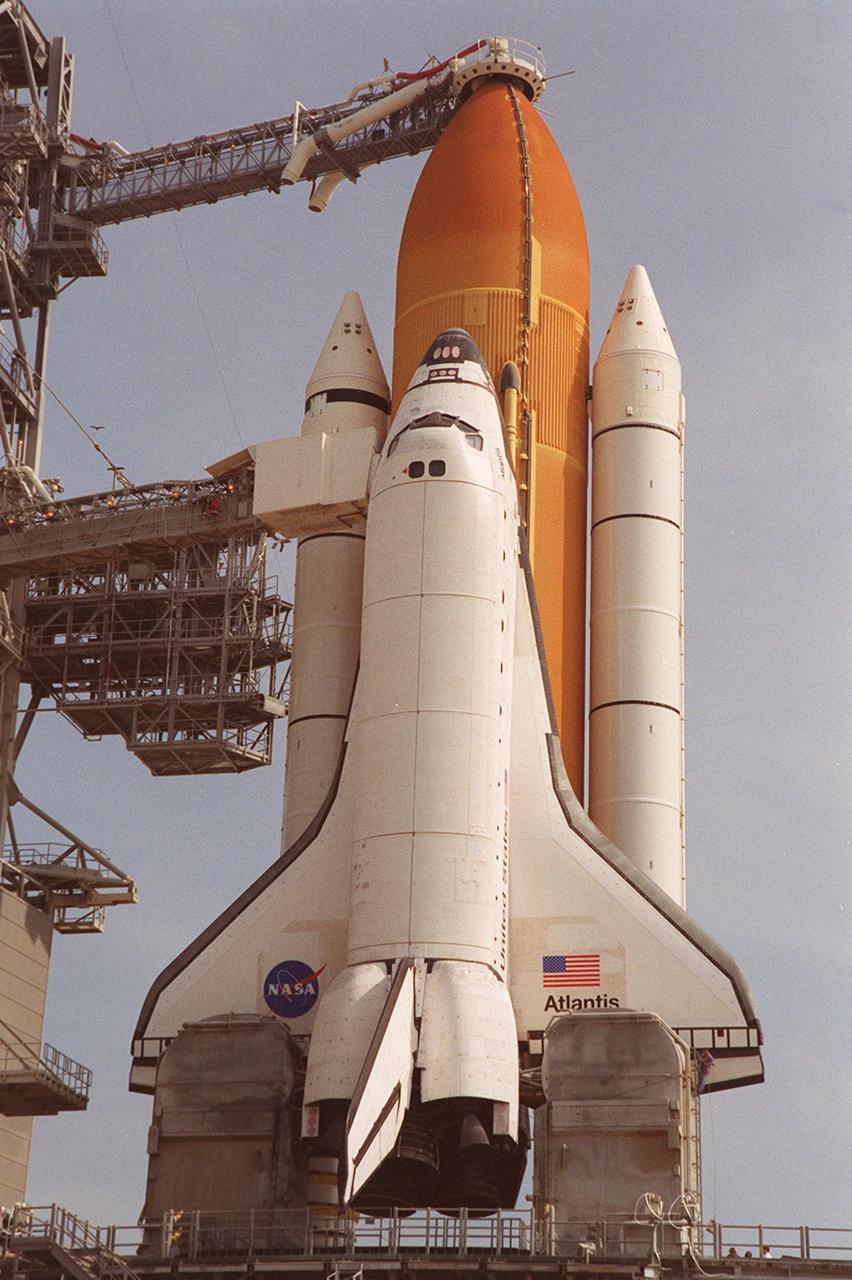
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After RSS rollback, Space Shuttle Atlantis is ready for final launch preparations. The orbiter access arm, with the environmentally controlled White Room at the end, is extended to the orbiter to allow entry into Atlantis. Above it is the gaseous oxygen vent arm with its characteristic “beanie cap” or hood placed over the external tank. The retractable arm and vent hood assembly allows gaseous oxygen vapors to vent away from the Space Shuttle vehicle. The vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boils off. At the lower end of Atlantis are the tail service masts, in front of either wing. The masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Launch on mission STS-104 is scheduled for 5:04 a.m. July 12. The launch is the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. Along with a crew of five, Atlantis will carry the joint airlock module as primary payload
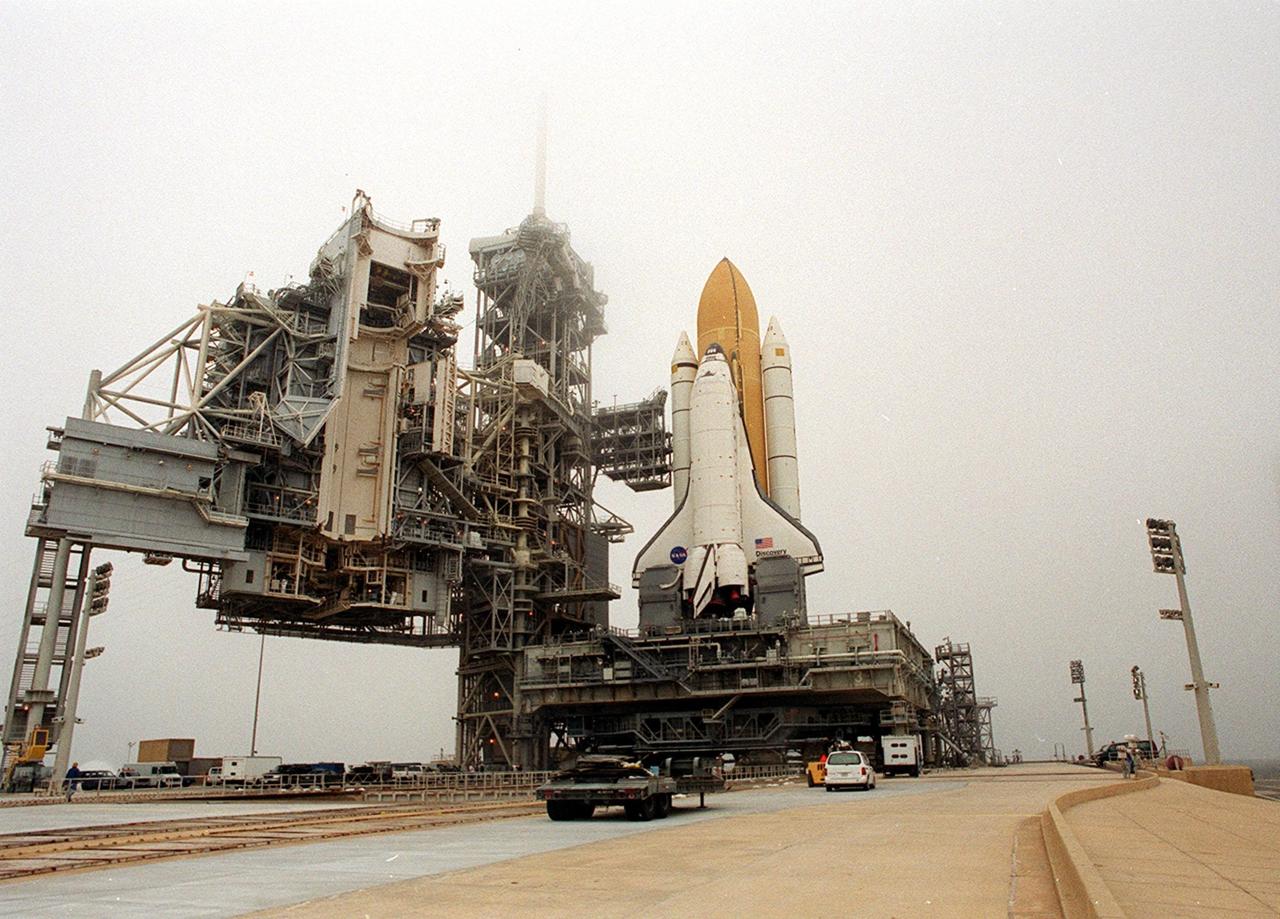

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
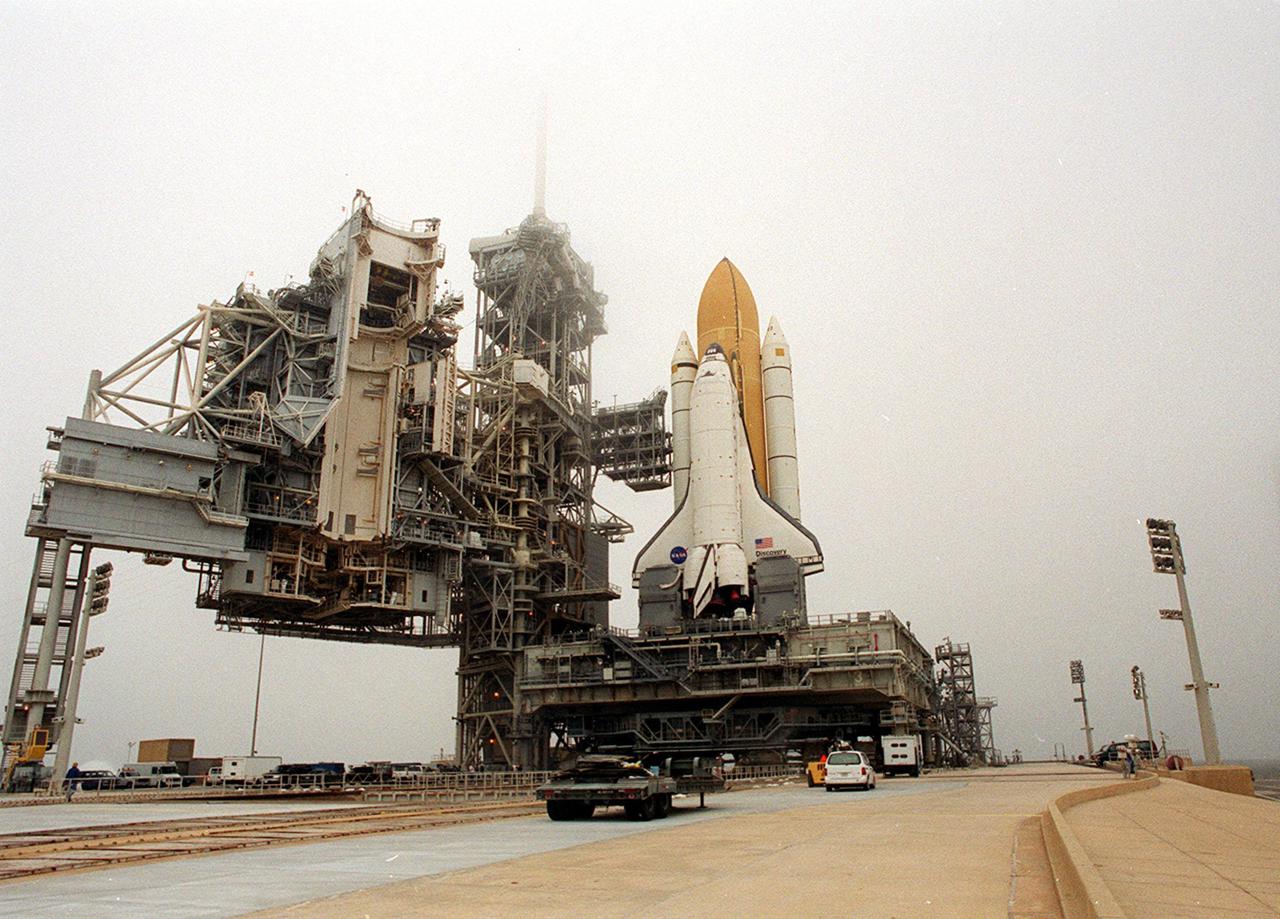

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on Launch Pad 39B after its approximately 5-hour rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At center left can be seen the White Room, the environmentally controlled chamber that provides entry into the orbiter for the astronaut crews. The chamber is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, which has not been extended yet. At the bottom of Discovery’s left wing is the tail service mast, one of two belonging to the Mobile Launcher Platform on which the Shuttle rests. The tail service mast is 31 feet high, 15 feet long and 9 feet wide. A second TSM is on the other side. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Discovery will be flying on mission STS-102 to the International Space Station. Its payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, a “moving van,” to carry laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies to and from the Space Station aboard the Space Shuttle. The flight will also carry the Expedition Two crew up to the Space Station, replacing Expedition One, who will return to Earth on Discovery. Launch is scheduled for March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
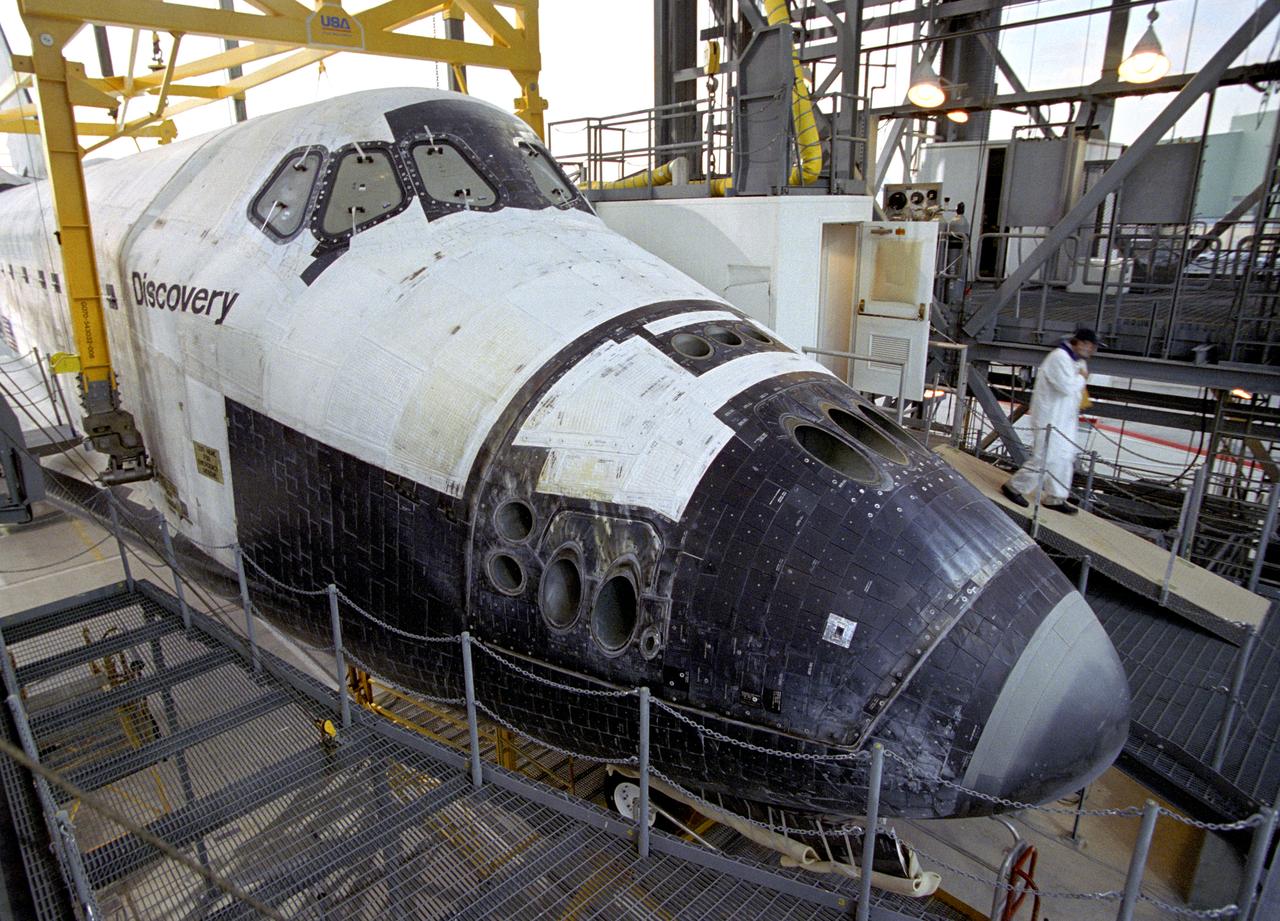

A technician leaves the 'white room', the access point for entering the Space Shuttle Discovery during post-flight processing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
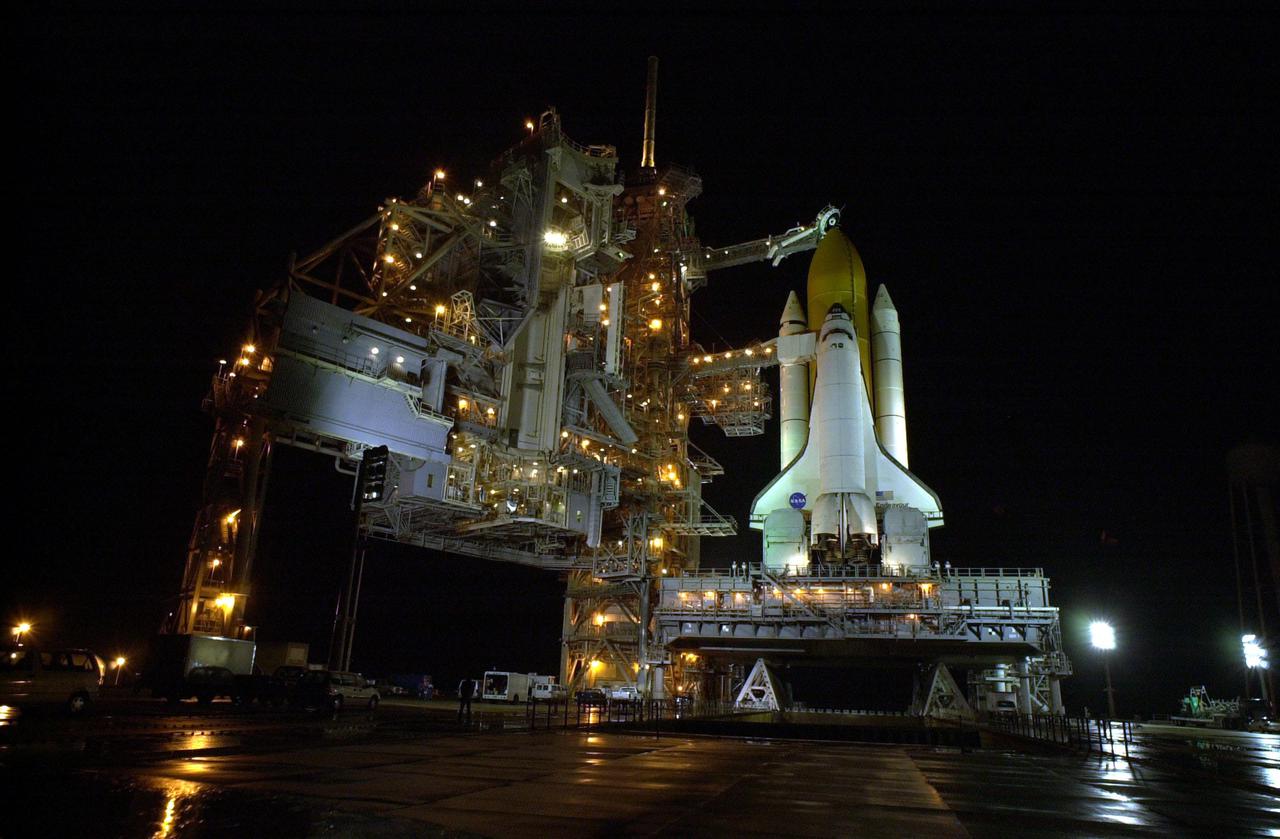

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Rain on the ground around Space Shuttle Endeavour on Launch Pad 39B reflects the many lights illluminating the Rotating Service Structure (at left), Fixed Service Structure and Shuttle. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the 'beanie cap.' Stretching from the FSS to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
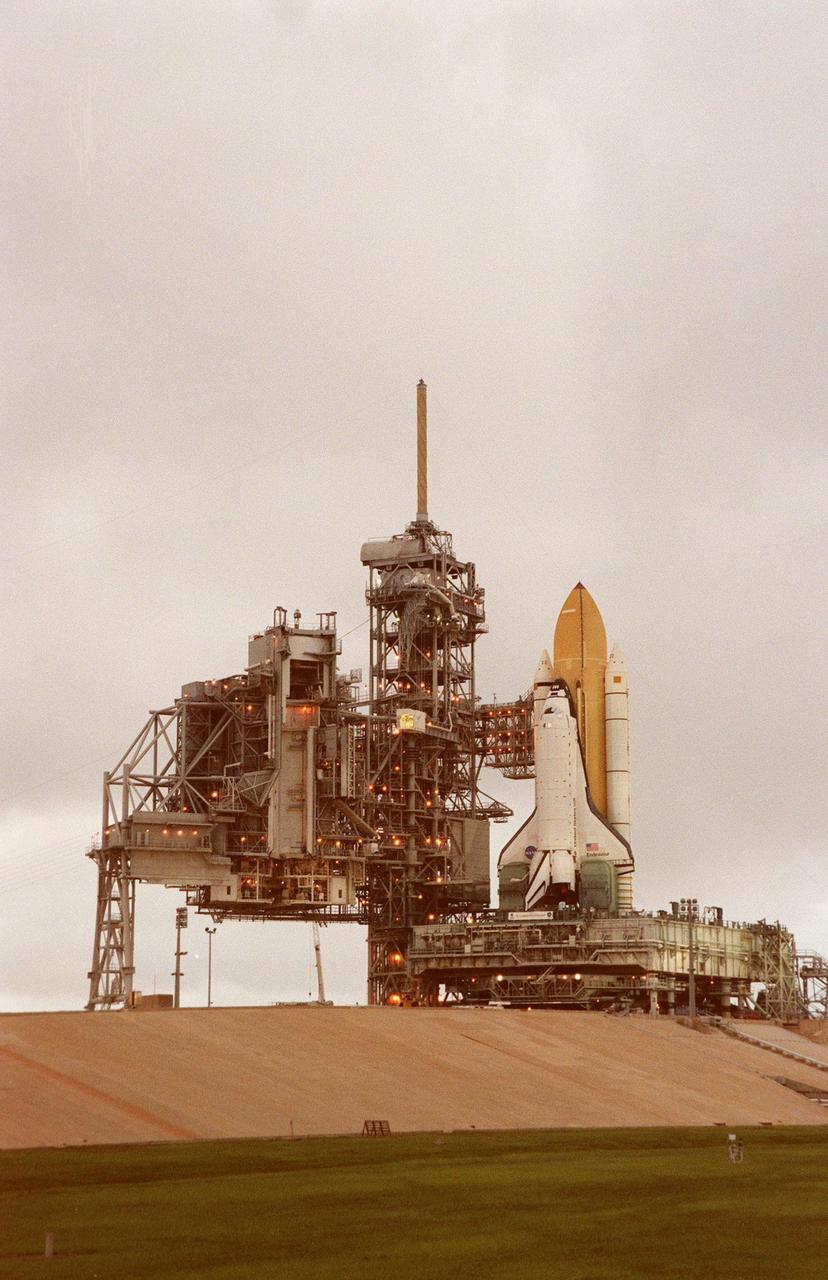

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the cloud-dimmed light of early morning, Space Shuttle Endeavour sits in place at Launch Pad 39A , atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter, after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At its left are the Rotating Service Structure and Fixed Service Structure with the orbiter access arm extended. The access arm swings out to the orbiter crew compartment hatch to allow personnel to enter the crew compartment. At its outer end is the white room, an environmental chamber, that mates with the orbiter. While at the pad, the orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-88 launch targeted for Dec. 3, 1998. Mission STS-88 is the first U.S. flight for the assembly of the International Space Station and will carry the Unity connecting module. While on orbit, the flight crew will deploy Unity from the payload bay and connect it to the Russian-built Zarya control module which will be in orbit at that time. Unity will be the main connecting point for later U.S. station modules and components. More than 40 launches are planned over five years involving the resources and expertise of 16 cooperating nations. Comprising the STS-88 crew are Commander Robert D. Cabana, Pilot Frederick W. "Rick" Sturckow, Mission Specialists Nancy J. Currie, Jerry L. Ross, James H. Newman and Russian cosmonaut Sergei Konstantinovich Krikalev. Ross and Newman will make three spacewalks to connect power, data and utility lines and install exterior equipment
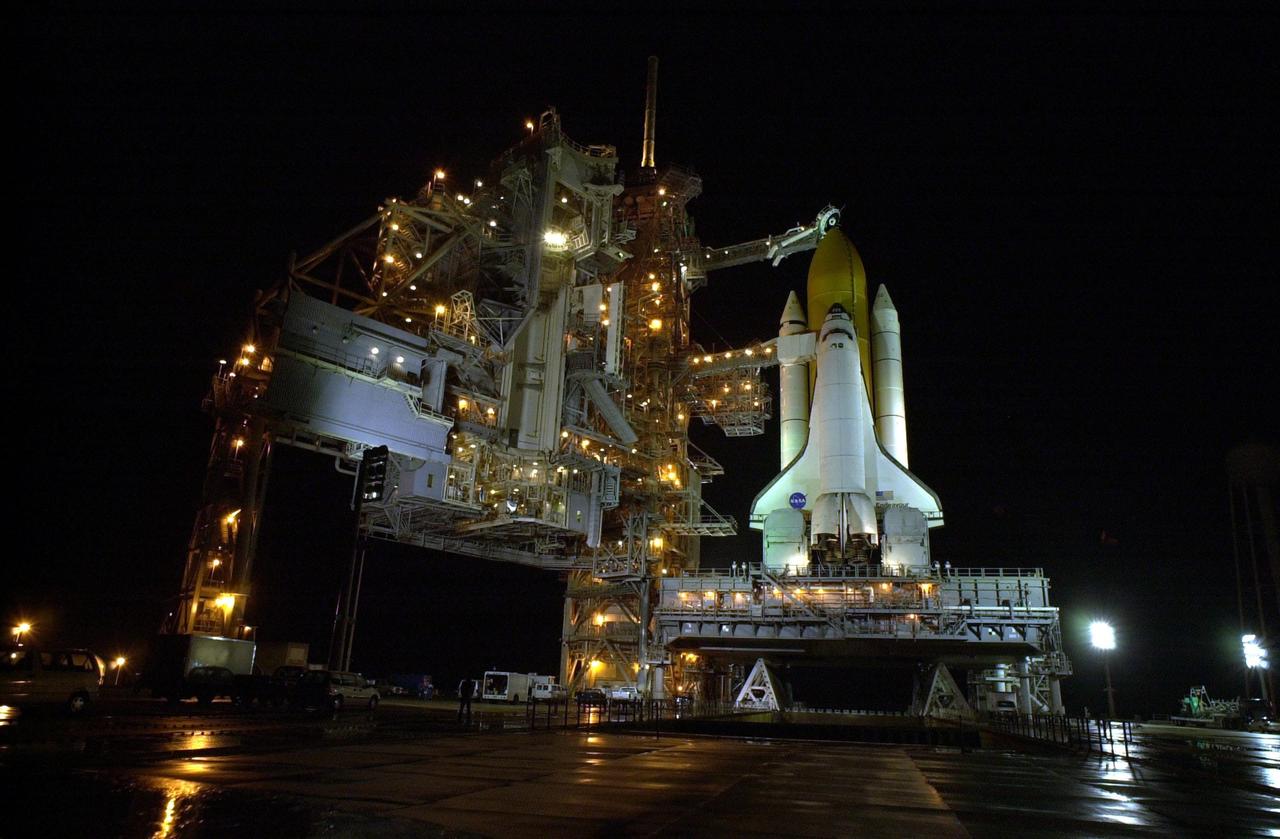

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Rain on the ground around Space Shuttle Endeavour on Launch Pad 39B reflects the many lights illluminating the Rotating Service Structure (at left), Fixed Service Structure and Shuttle. Twin solid rocket boosters flank the orange external tank behind Endeavour. Above the external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm that vents gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Shuttle. The vent hood assembly at the end is often referred to as the "beanie cap." Stretching from the FSS to the crew hatch on the side of Endeavour is the Orbiter Access Arm with its environmentally controlled White Room at the end, through which the crew enters the vehicle. The Shuttle sits on the Mobile Launcher Platform with the two service tail masts on either side of the main engines. The tail masts support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter's liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Each tail mast is 31 feet (9.4 meters) high, 15 feet (4.6 meters) long and 9 feet (3.1 meters) wide. Endeavour is scheduled to launch on mission STS-108 Dec. 4 at 5:45 p.m. EST. On this 12th flight to the International Space Station, known as a Utilization Flight, Endeavour will carry a crew of four plus the Expedition 4 crew, who will replace Expedition 3 aboard the ISS. The payload includes the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies, equipment and experiments
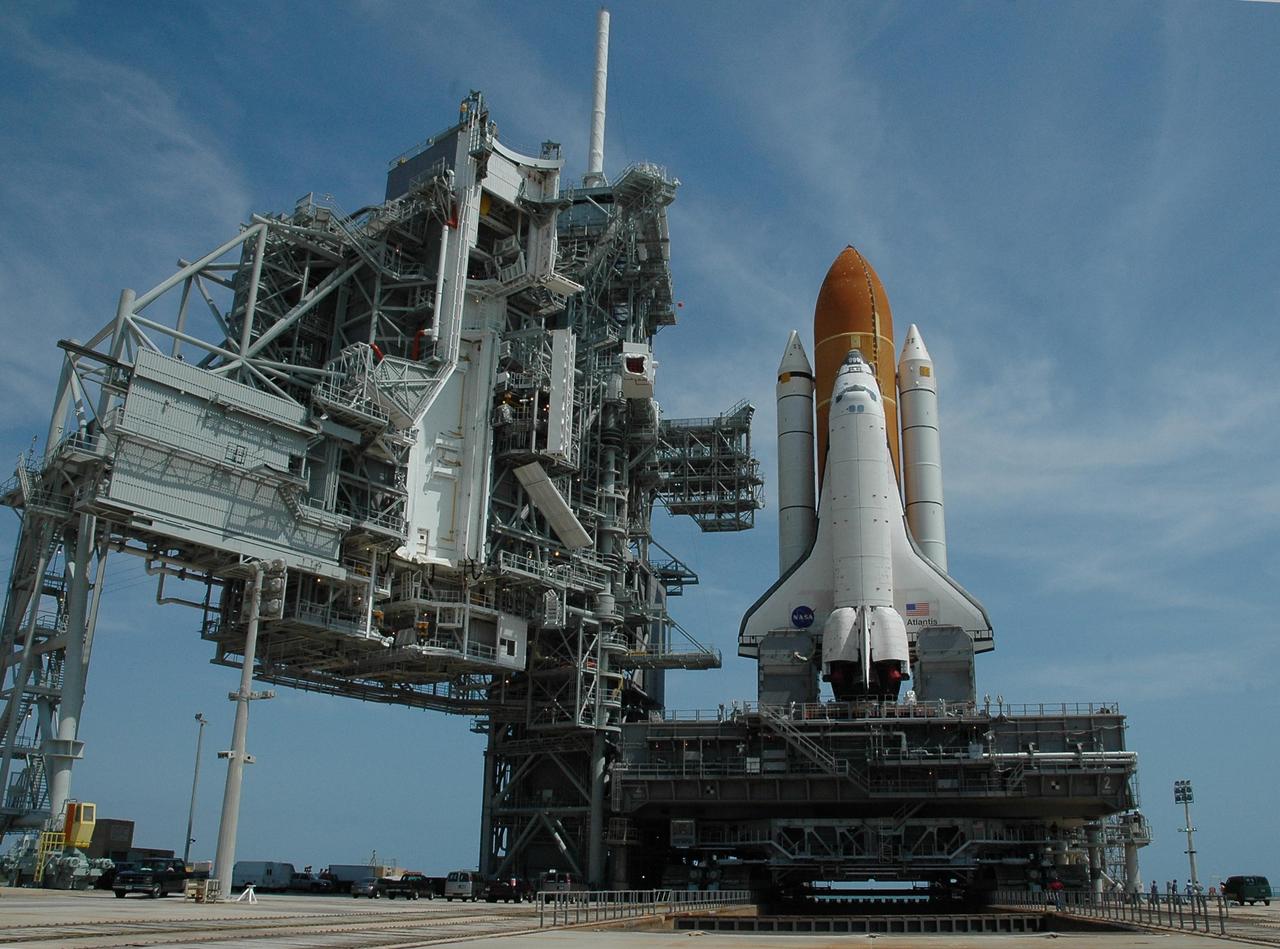

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, mounted on a mobile launch platform, finally rests on the hard stand of Launch Pad 39A, straddling the flame trench. This is the second rollout for the shuttle. The flame trench transecting the pad's mound at ground level is 490 feet long, 58 feet wide and 40 feet high. It is made of concrete and refractory brick. Pad structures are insulated from the intense heat of launch by the flame deflector system, which protects the flame trench floor and the pad surface along the top of the flame trench. On the left of the shuttle are the fixed service structure and rotating service structure in open position. When closed, the rotating structure provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. The white area in the center is the Payload Changeout Room, an enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports payload delivery at the launch pad and subsequent vertical installation in the orbiter payload bay. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 5:02 a.m. EDT. In late February, while Atlantis was on the launch pad, Atlantis' external tank received hail damage during a severe thunderstorm that passed through the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 area. The hail caused visible divots in the giant tank's foam insulation, as well as minor surface damage to about 26 heat shield tiles on the shuttle's left wing. The shuttle was returned to the VAB for repairs. The launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-117 is now targeted for June 8. A flight readiness review will be held on May 30 and 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder