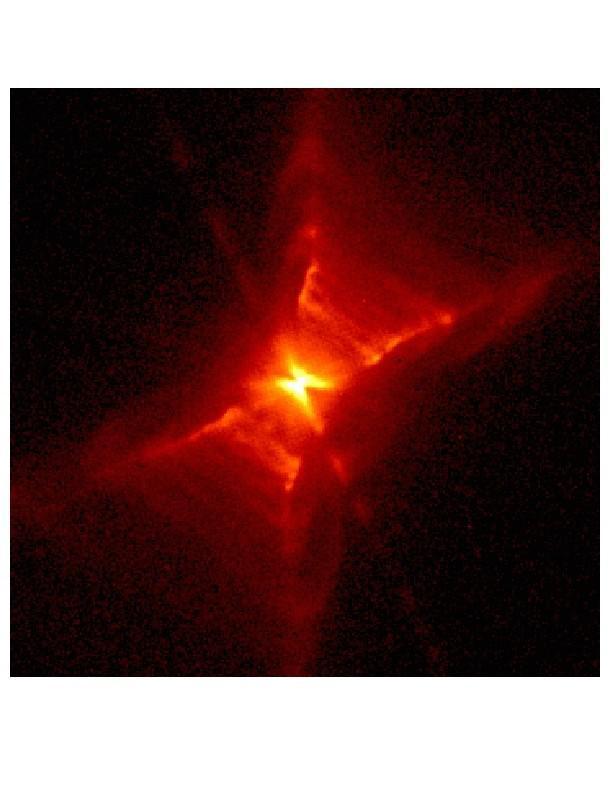

An archival image of the Red Rectangle, or HD44179, taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 onboard NASA Hubble Space Telescope.

This is a photograph of giant twisters and star wisps in the Lagoon Nebula. This superb Hubble Space Telescope (HST) image reveals a pair of one-half light-year long interstellar twisters, eerie furnels and twisted rope structures (upper left), in the heart of the Lagoon Nebula (Messier 8) that lies 5,000 light-years away in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. This image was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field/Planetary Camera 2 (WF/PC2).

This image of the Egg Nebula, also known as CRL-2688 and located roughly 3,000 light-years from us, was taken in red light with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WF/PC2) aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The image shows a pair of mysterious searchlight beams emerging from a hidden star, crisscrossed by numerous bright arcs. This image sheds new light on the poorly understood ejection of stellar matter that accompanies the slow death of Sun-like stars. The image is shown in false color.
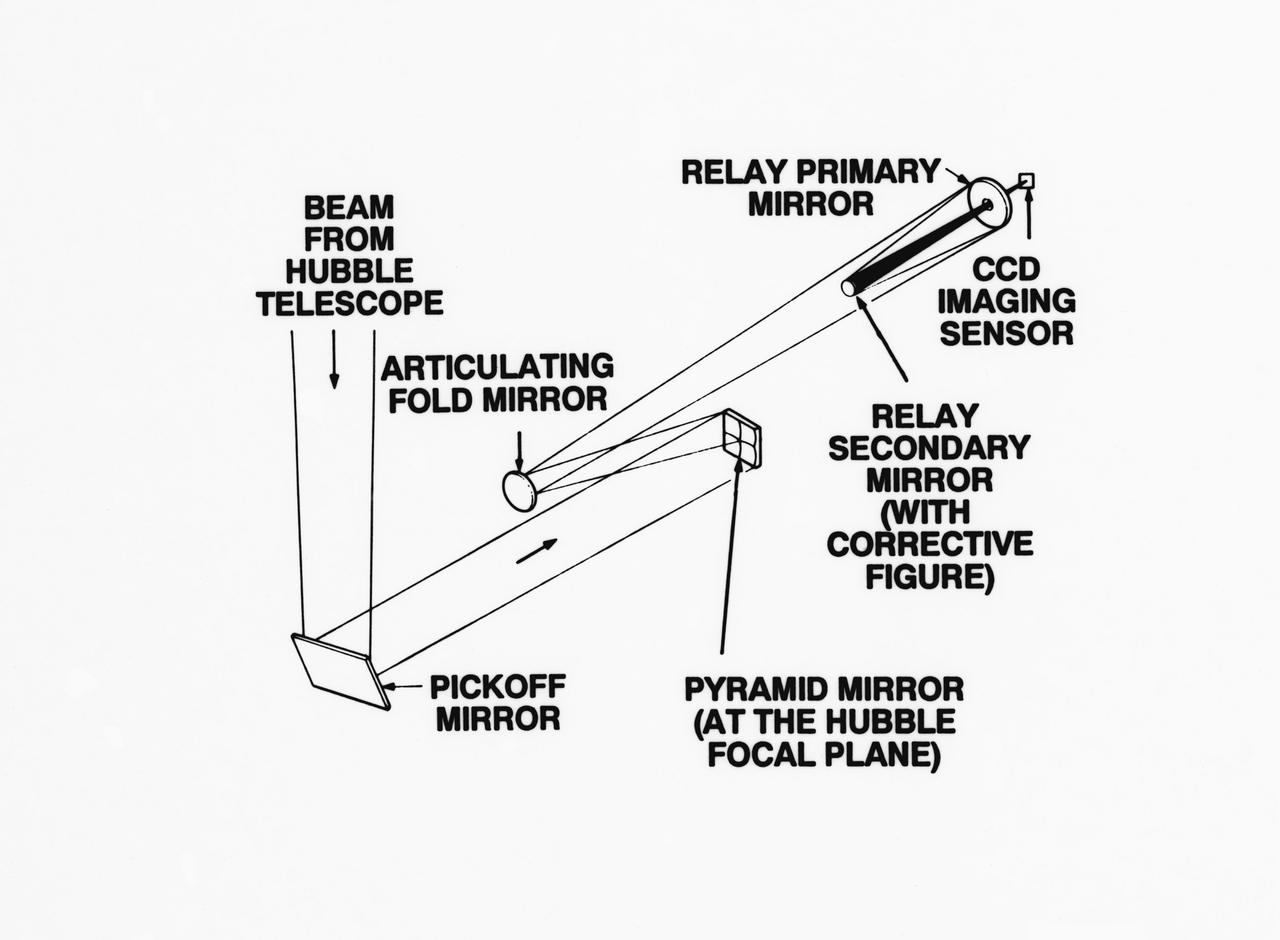
S93-33258 (15 Mar 1993) --- An optical schematic diagram of one of the four channels of the Wide Field\Planetary Camera-2 (WF\PC-2) shows the path taken by beams from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) before an image is formed at the camera's charge-coupled devices. A team of NASA astronauts will pay a visit to the HST later this year, carrying with them the new WF/PC-2 to replace the one currently on the HST. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California has been working on the replacement system for several months. See NASA photo S93-33257 for a close-up view of tiny articulating mirrors designed to realign incoming light in order to make certain the beams fall precisely in the middle of the secondary mirrors.

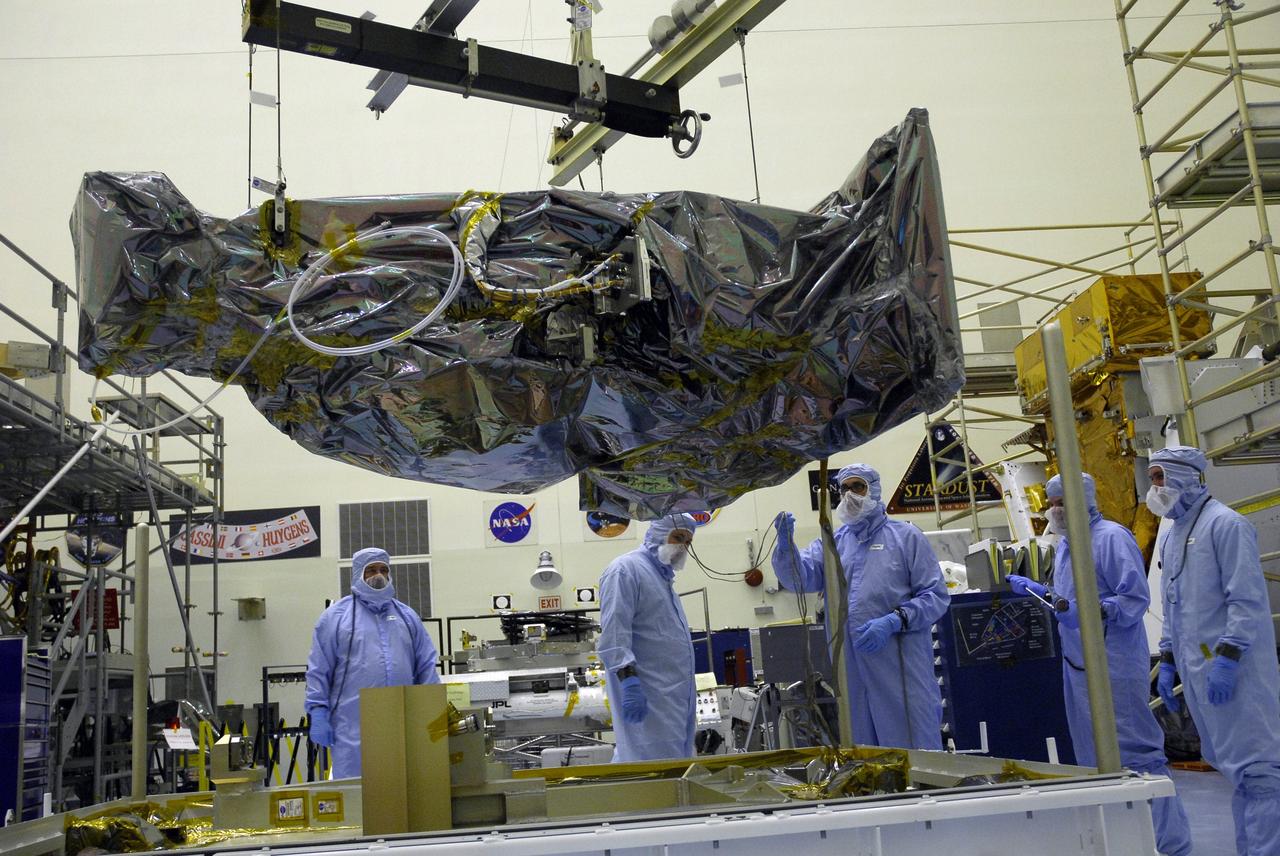
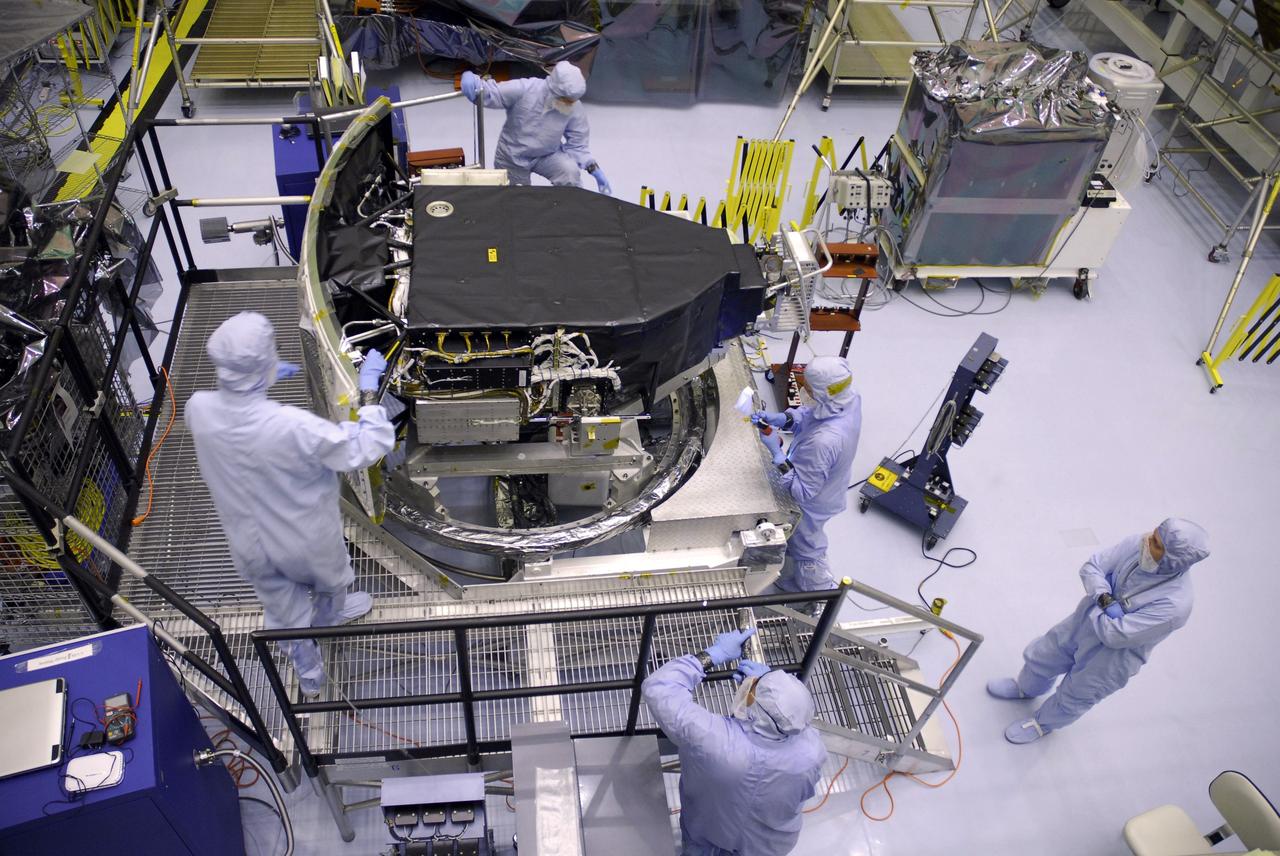
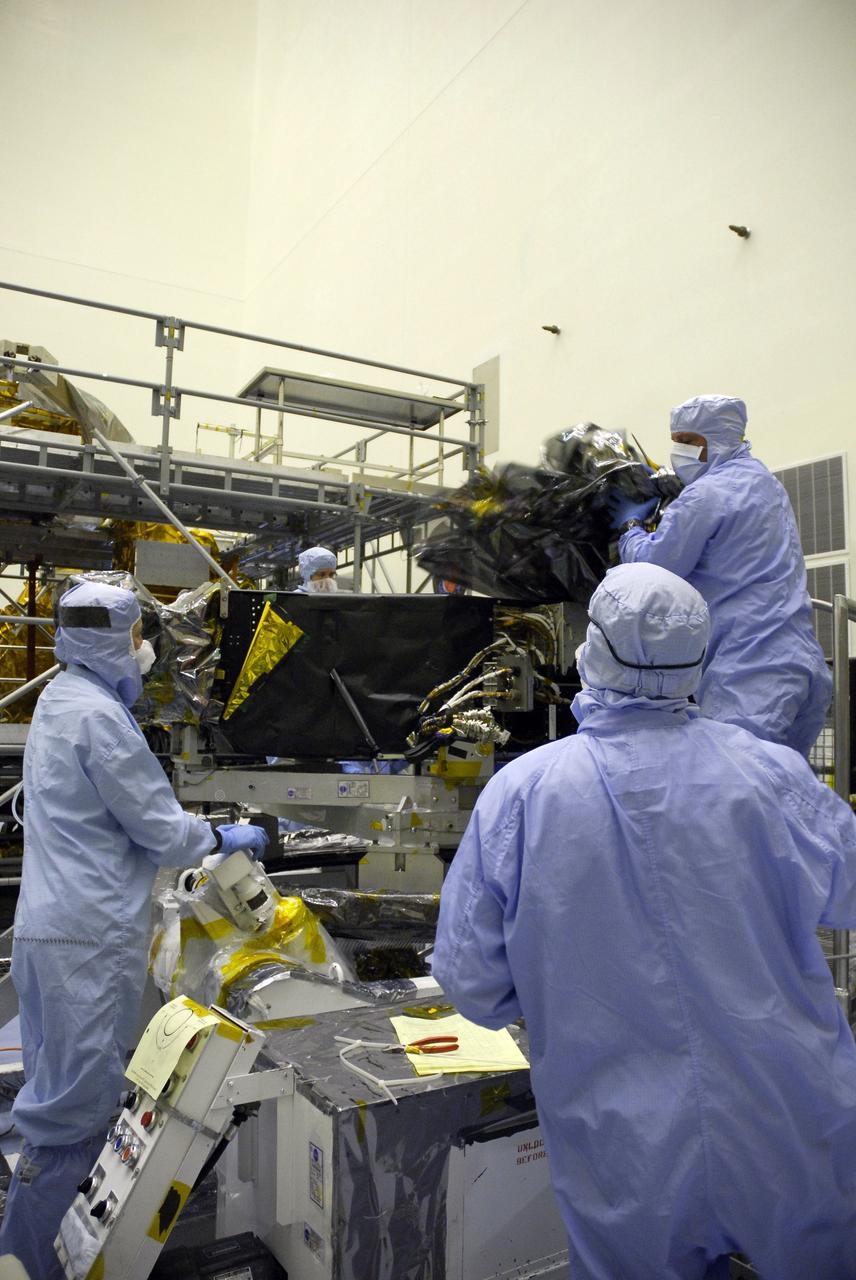
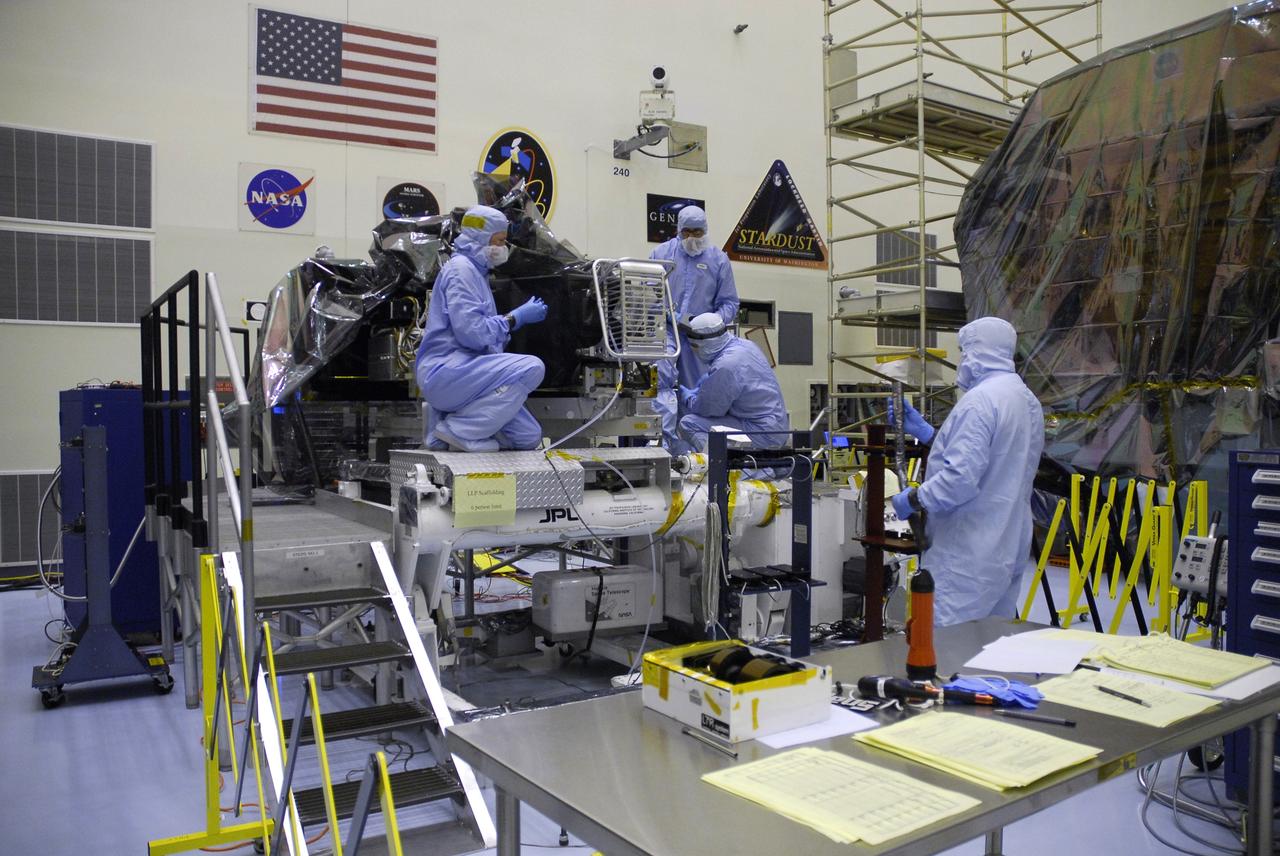
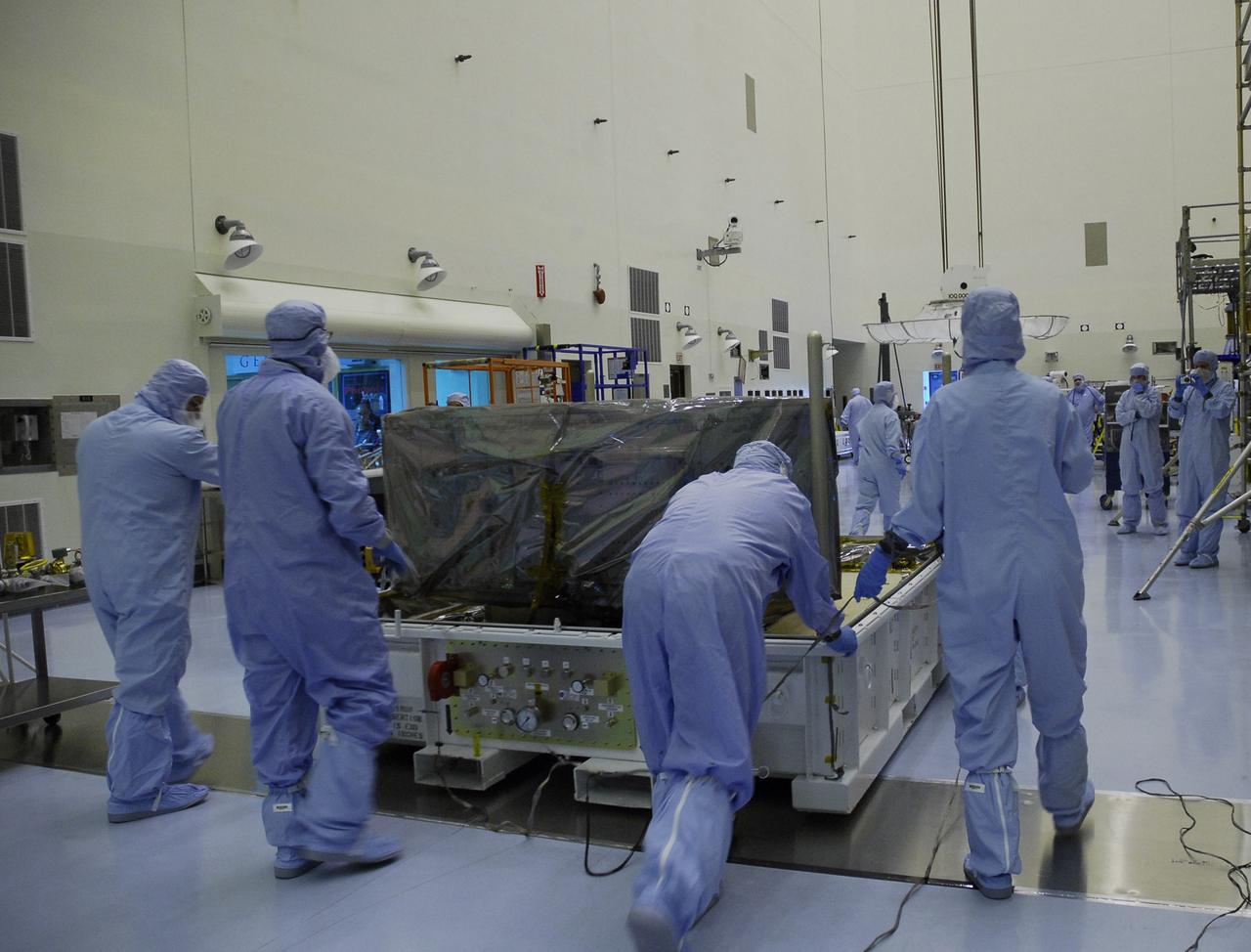
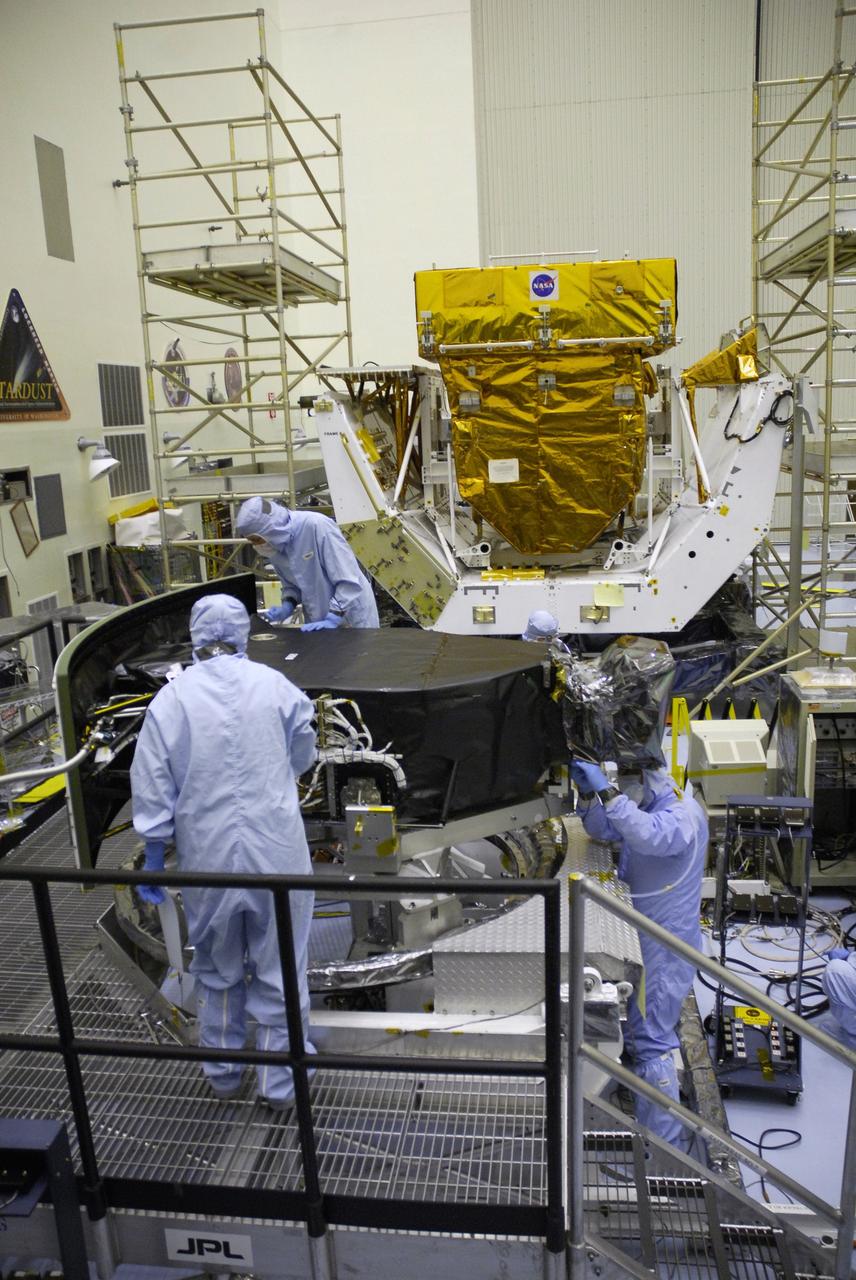
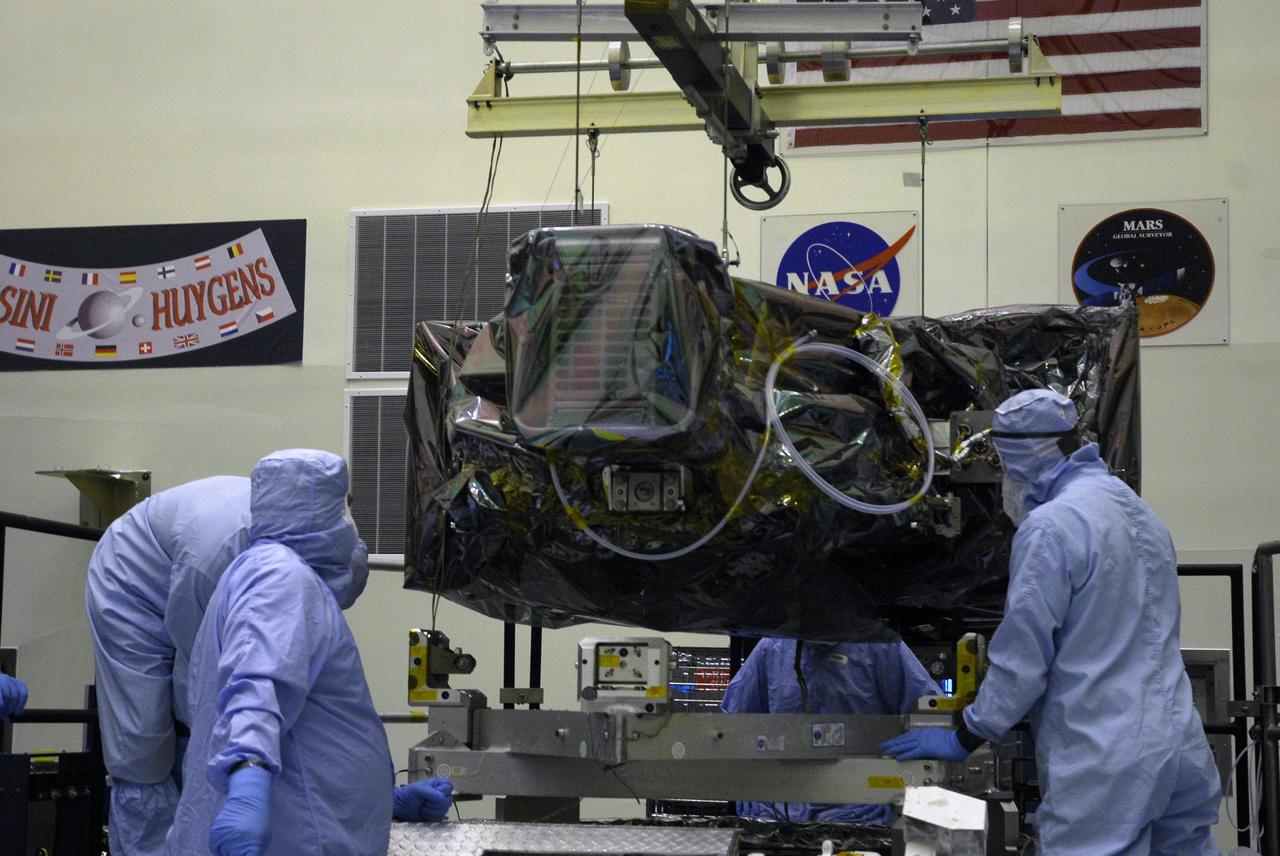
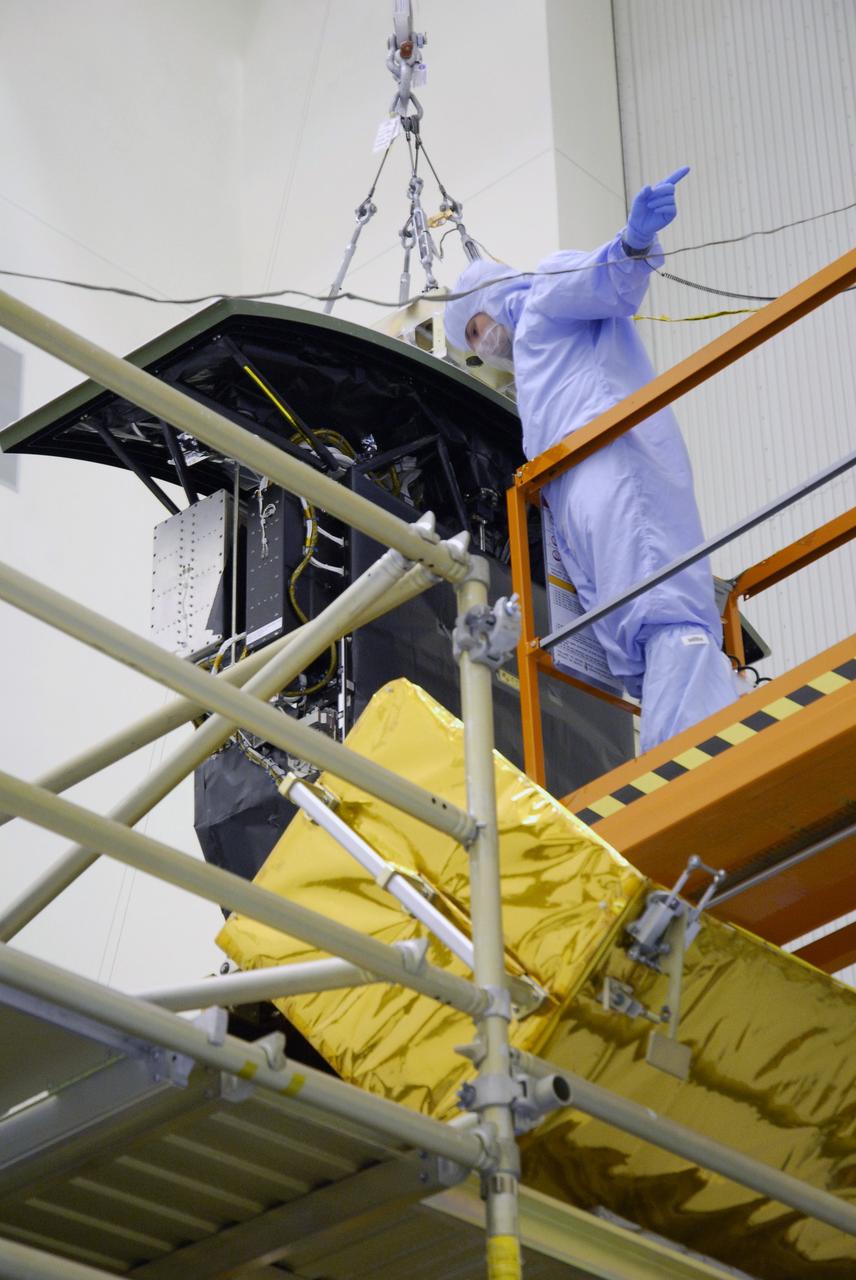
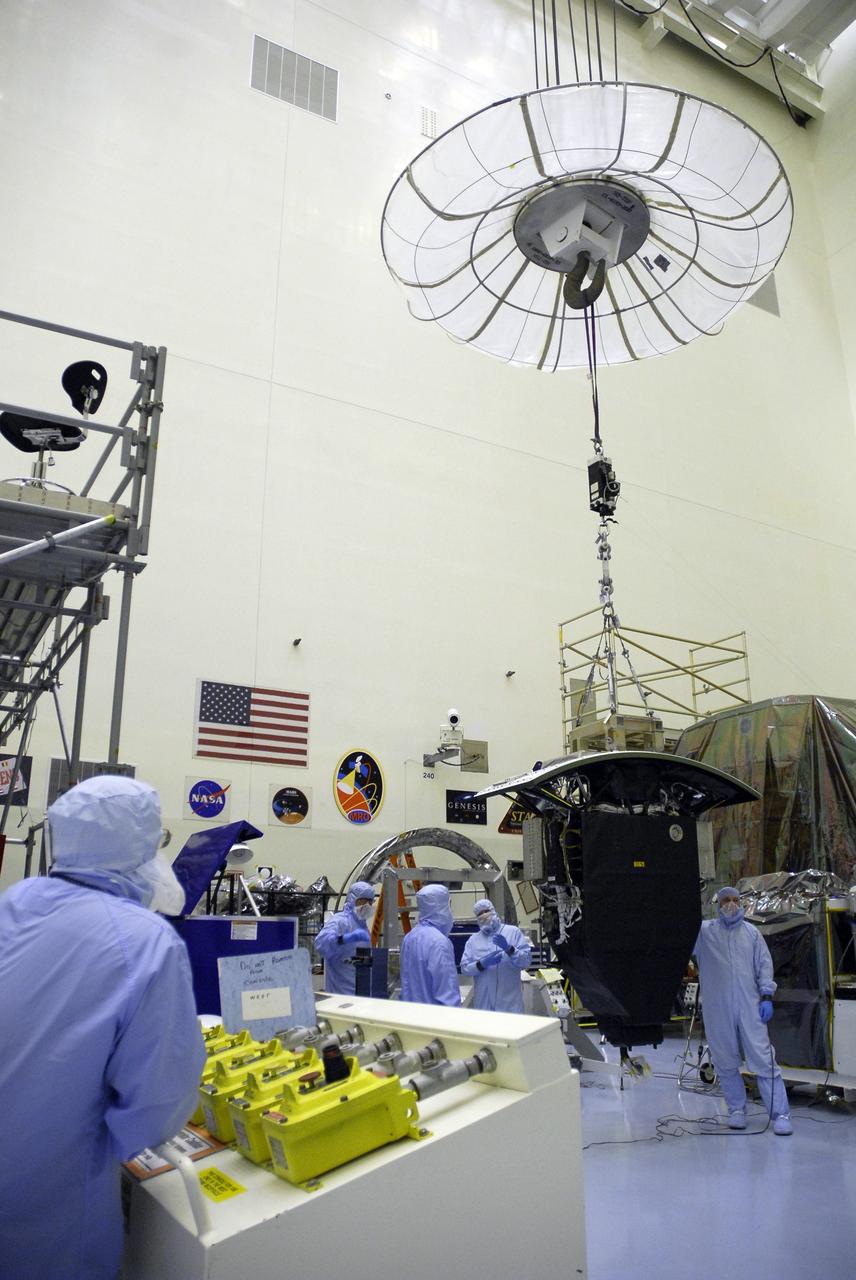
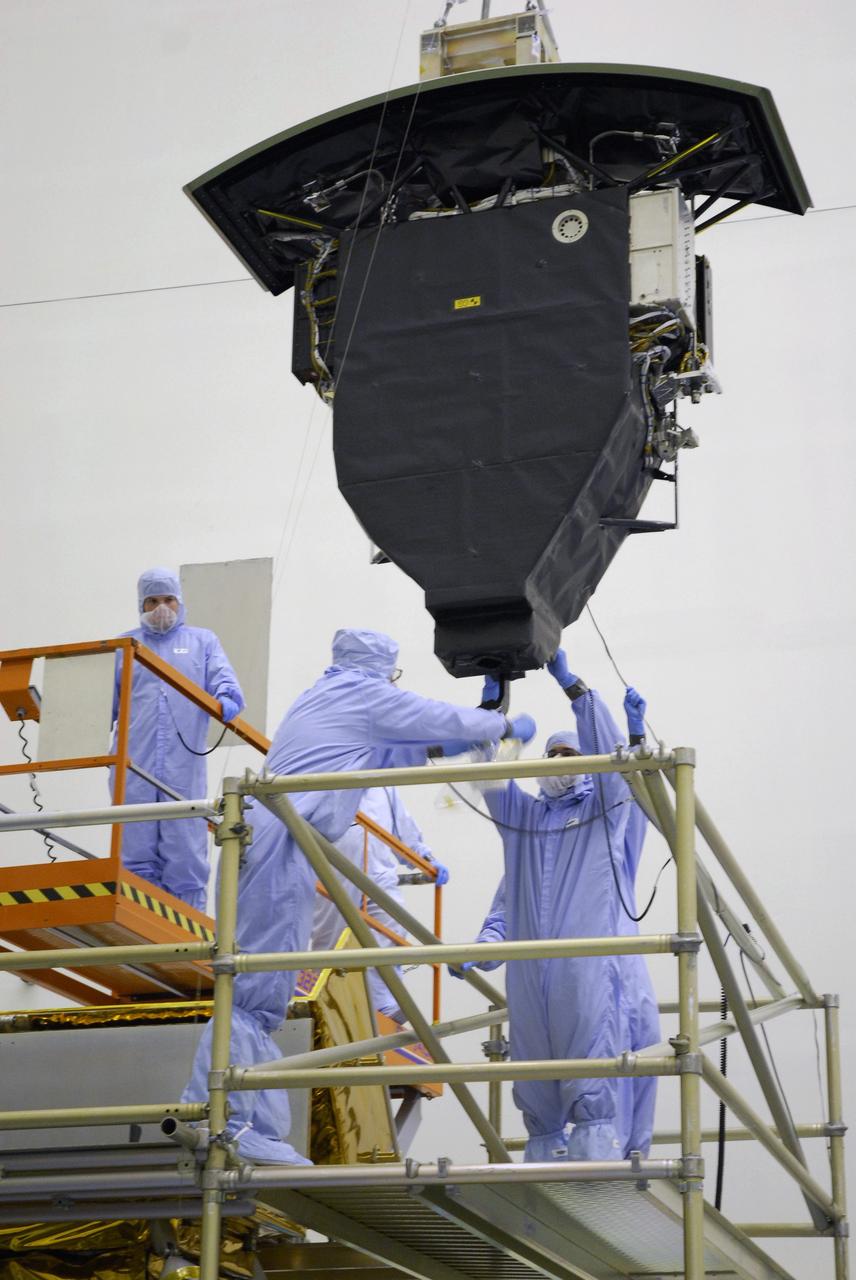
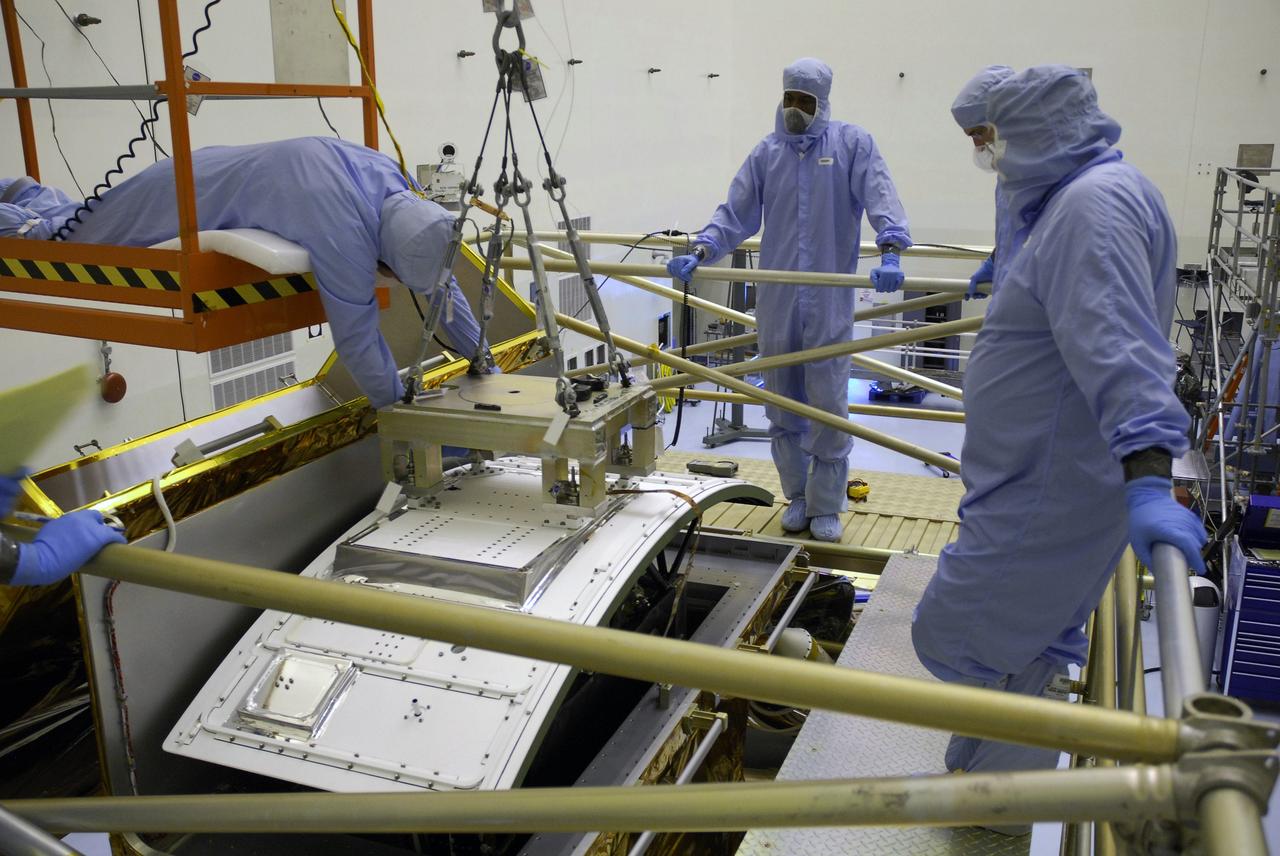
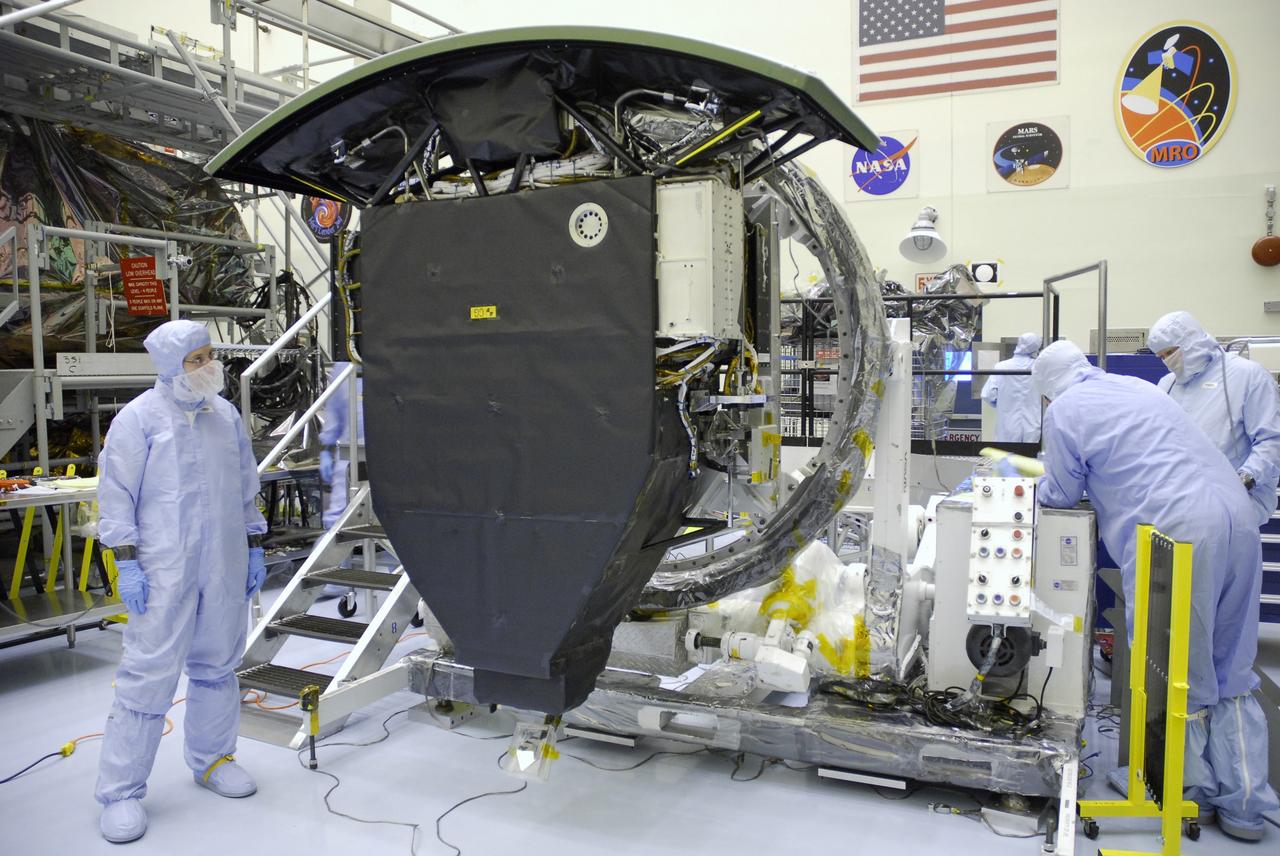
NASA's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 undergoes testing at JPL. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22912
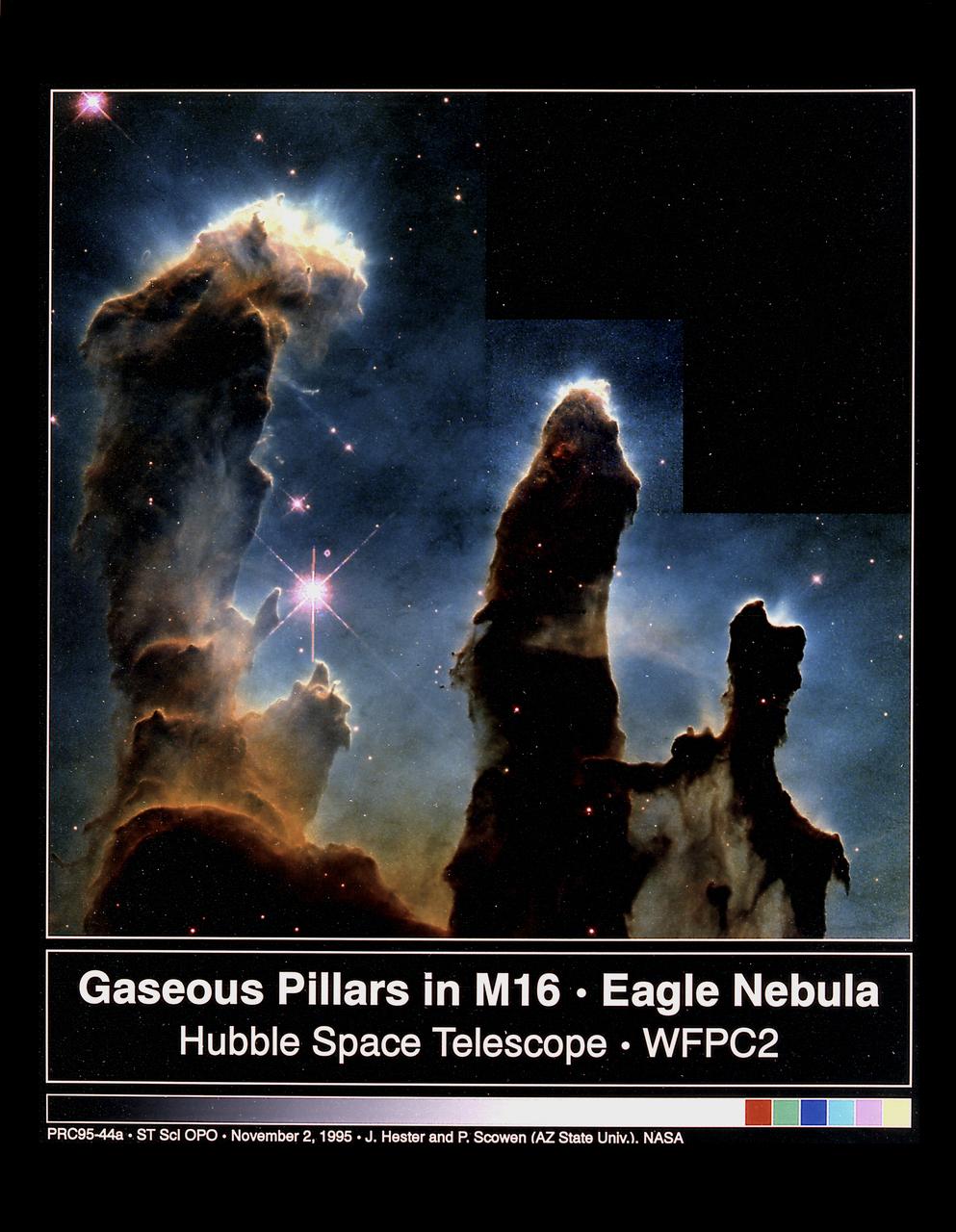
These eerie, dark, pillar-like structures are actually columns of cool interstellar hydrogen gas and dust that are also incubators for new stars. The pillars protrude from the interior wall of a dark molecular cloud like stalagmites from the floor of a cavern. They are part of the Eagle Nebula (also called M16), a nearby star-forming region 7,000 light-years away, in the constellation Serpens. The ultraviolet light from hot, massive, newborn stars is responsible for illuminating the convoluted surfaces of the columns and the ghostly streamers of gas boiling away from their surfaces, producing the dramatic visual effects that highlight the three-dimensional nature of the clouds. This image was taken on April 1, 1995 with the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. The color image is constructed from three separate images taken in the light of emission from different types of atoms. Red shows emissions from singly-ionized sulfur atoms, green shows emissions from hydrogen, and blue shows light emitted by doubly-ionized oxygen atoms.

Taken by the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), this image of MyCn18, a young planetary nebula located about 8,000 light-years away, reveals its true shape to be an hourglass with an intricate pattern of "etchings" in its walls. The arc-like etchings could be the remnants of discrete shells ejected from the star when it was younger, flow instabilities, or could result from the action of a narrow beam of matter impinging on the hourglass walls. According to one theory on the formation of planetary nebulae, the hourglass shape is produced by the expansion of a fast stellar wind within a slowly expanding cloud, which is denser near its equator than near its poles. Hubble has also revealed other features in MyCn18 which are completely new and unexpected. For example, there is a pair of intersecting elliptical rings in the central region which appear to be the rims of a smaller hourglass. This picture has been composed from three separate images taken in the light of ionized nitrogen (represented by red), hydrogen (green) and doubly-ionized oxygen (blue). The results are of great interest because they shed new light on the poorly understood ejection of stellar matter which accompanies the slow death of sun-like stars. An unseen companion star and accompanying gravitational effects may well be necessary in order to explain the structure of MyCn18. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST.

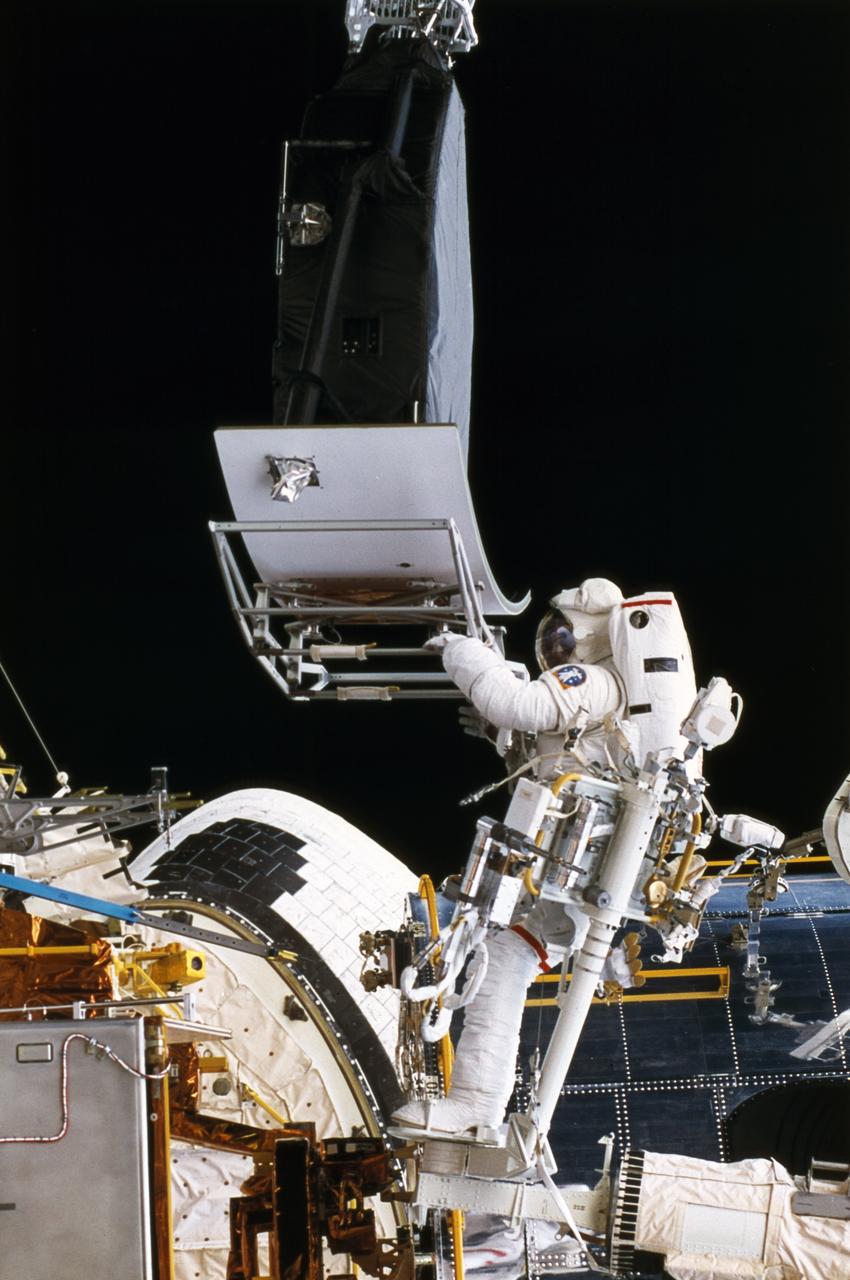
Astronauts Jeffrey Hoffman and Story Musgrave install the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on the Hubble Space Telescope, during SM1 in December, 1993. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22911
The Hubble Space Telescope Structural Dynamic Test Vehicle is seen inside the Space Hall at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum during an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 in Washington, DC. COSTAR and WFPC2 were were installed in Hubble during the first space shuttle servicing mission in 1993 and returned to Earth on the fifth and final servicing mission in 2009. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

John Trauger, former principal investigator for the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) at NASA's Jet Propultion Laboratory (JPL), speaks at an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the WFPC2 on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. COSTAR and WFPC2 were installed in Hubble during the first space shuttle servicing mission in 1993 and returned to Earth on the fifth and final servicing mission in 2009. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

John Grunsfeld, NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, is seen during during an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. Grunsfeld flew on three of space shuttle servicing missions to Hubble, including the fifth and final mission in 2009 which returned COSTAR and WFPC2 to Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks at an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. Administrator Bolden piloted space shuttle Discovery on the mission that deployed the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks at an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. Administrator Bolden piloted space shuttle Discovery on the mission that deployed the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
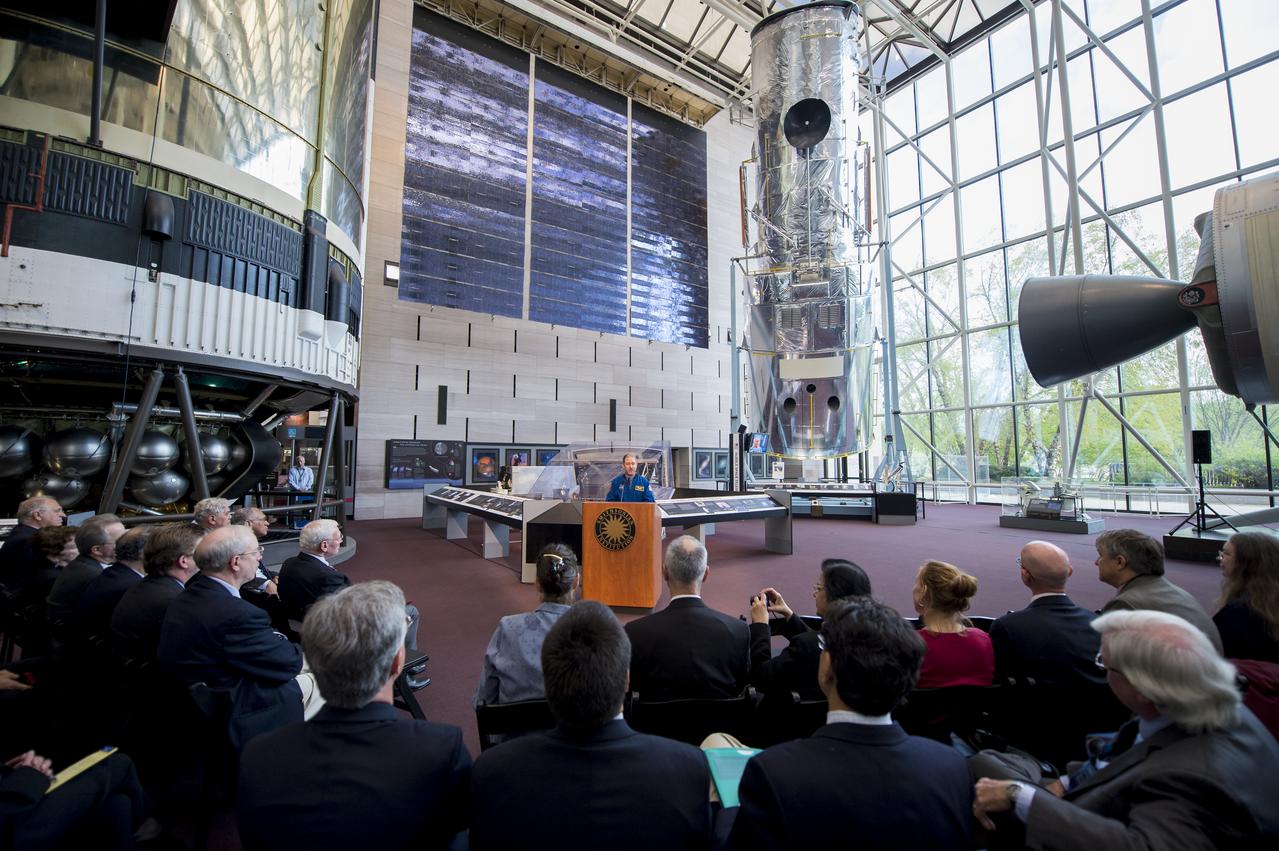

John Grunsfeld, NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, speaks during an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. Grunsfeld flew on three of space shuttle servicing missions to Hubble, including the fifth and final mission in 2009 which returned COSTAR and WFPC2 to Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
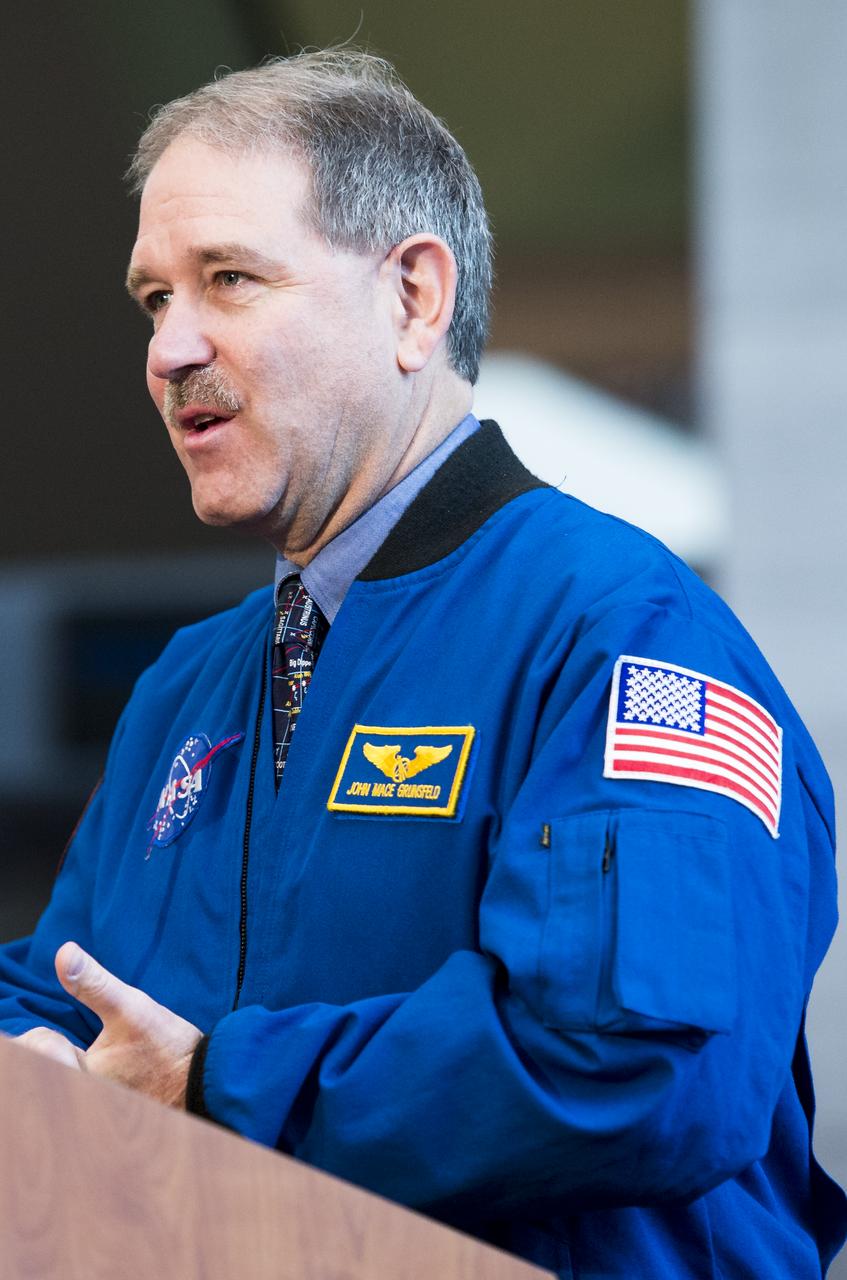

John Grunsfeld, NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, speaks during during an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. Grunsfeld flew on three of space shuttle servicing missions to Hubble, including the fifth and final mission in 2009 which returned COSTAR and WFPC2 to Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
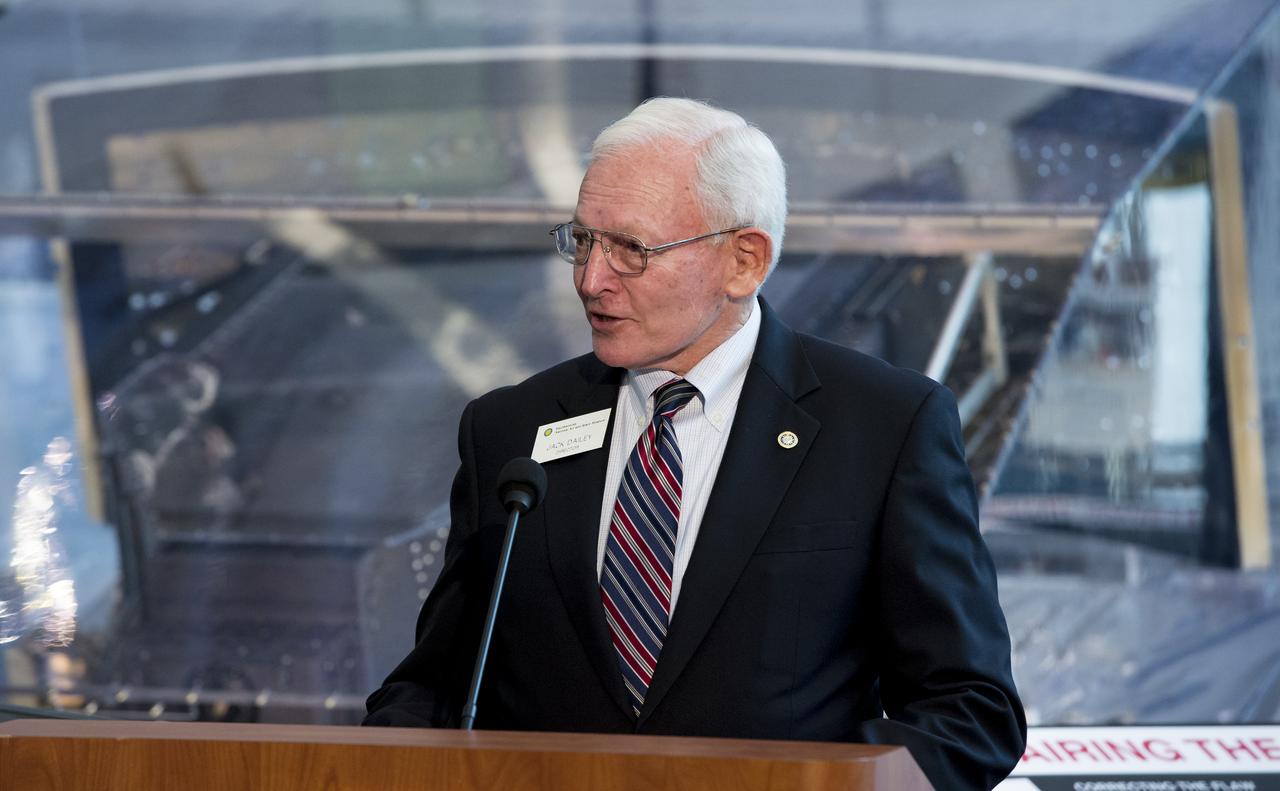

Gen. J.R. "Jack" Dailey, Director of the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum speaks at an event unveiling a new exhibit featuring Hubble's Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) on Wednesday, April 23, 2014 at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. COSTAR and WFPC2 were installed in Hubble during the first space shuttle servicing mission in 1993 and returned to Earth on the fifth and final servicing mission in 2009. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
This image of a dying star, protoplanetary nebula IRAS22036+5306, containing strange, complex structures may help explain the death throes of stars and defy our current understanding of physics. Taken by NASA Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2.
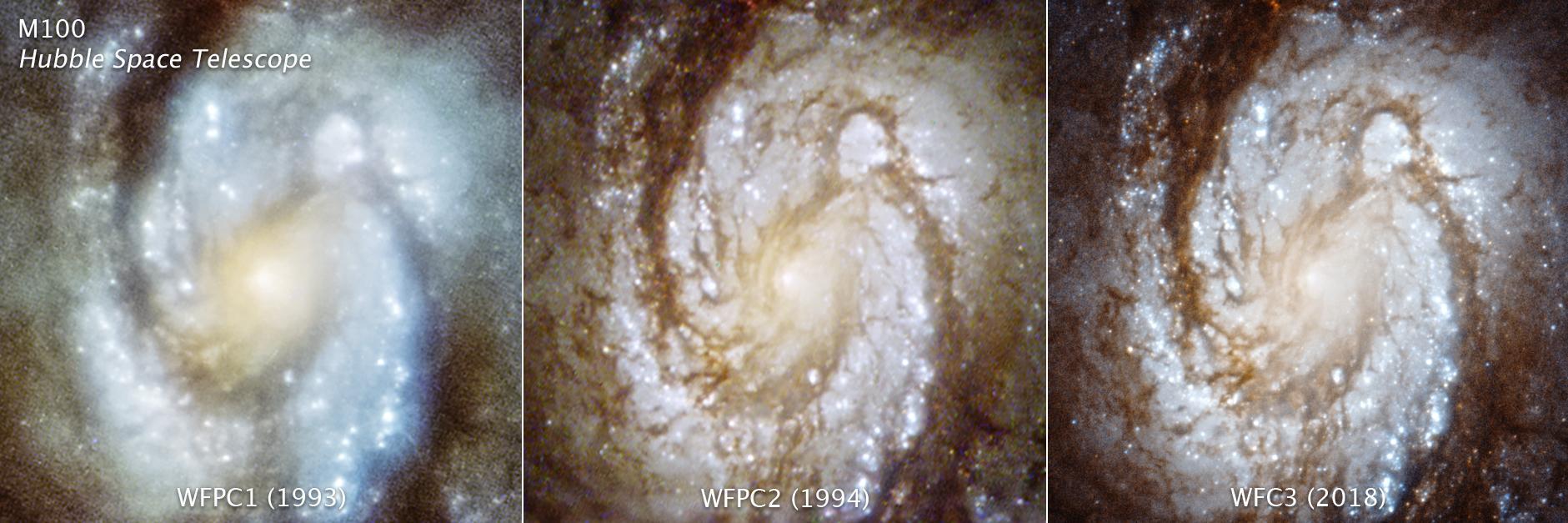

These three images are of the central region of the spiral galaxy M100, taken with three generations of cameras that were sequentially swapped out aboard the Hubble Space Telescope, and document the consistently improving capability of the observatory. The image on the left was taken with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 1 in 1993. The photo is blurry due to a flaw (called spherical aberration) in Hubble's primary mirror. Celestial images could not be brought into a single focus. The middle image was taken in late 1993 with Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 that was installed during the December 2 - 13 space shuttle servicing mission (SM1, STS-61). The camera contained corrective optics to compensate for the mirror flaw, and so the galaxy snapped into sharp focus when photographed. The image on the right was taken with a newer instrument, Wide Field Camera 3, that was installed on Hubble during the space shuttle servicing mission 4 (SM4) in May, 2009. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22913

This image was returned by NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft on July 3, 1989. The planet and its largest satellite, Triton, are captured in view; Triton appears in the lower right corner at about 5 oclock relative to Neptune. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01287
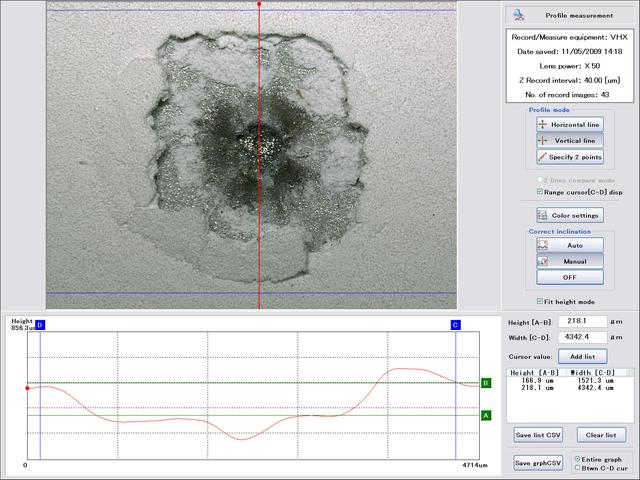
JSC2009-E-054444 (17 July 2009) --- Depth and profile measurements of an impact crater on the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC-2), returned to Earth in May 2009 following the STS-125 mission. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
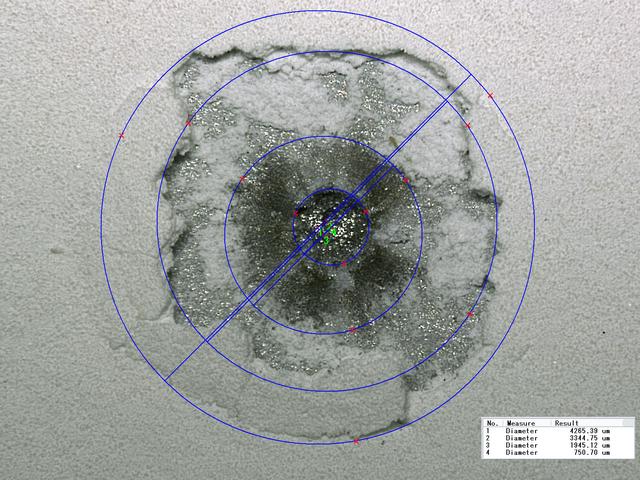
JSC2010-E-054443 (17 July 2009) --- Diameter measurements of an impact crater on the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WFPC-2), returned to Earth in May 2009, following the STS-125 mission. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

This is a color Hubble Space Telescope (HST) heritage image of supernova remnant N49, a neighboring galaxy, that was taken with Hubble's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. Color filters were used to sample light emitted by sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen. The color image was superimposed on a black and white image of stars in the same field also taken with Hubble. Resembling a fireworks display, these delicate filaments are actually sheets of debris from a stellar explosion.

What look like giant twisters are spotted by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). These images are, in actuality, pillars of gases that are in the process of the formation of a new star. These pillars can be billions of miles in length and may have been forming for millions of years. This one formation is located in the Lagoon Nebula and was captured by the Hubble's wide field planetary camera-2 (WFPC-2).
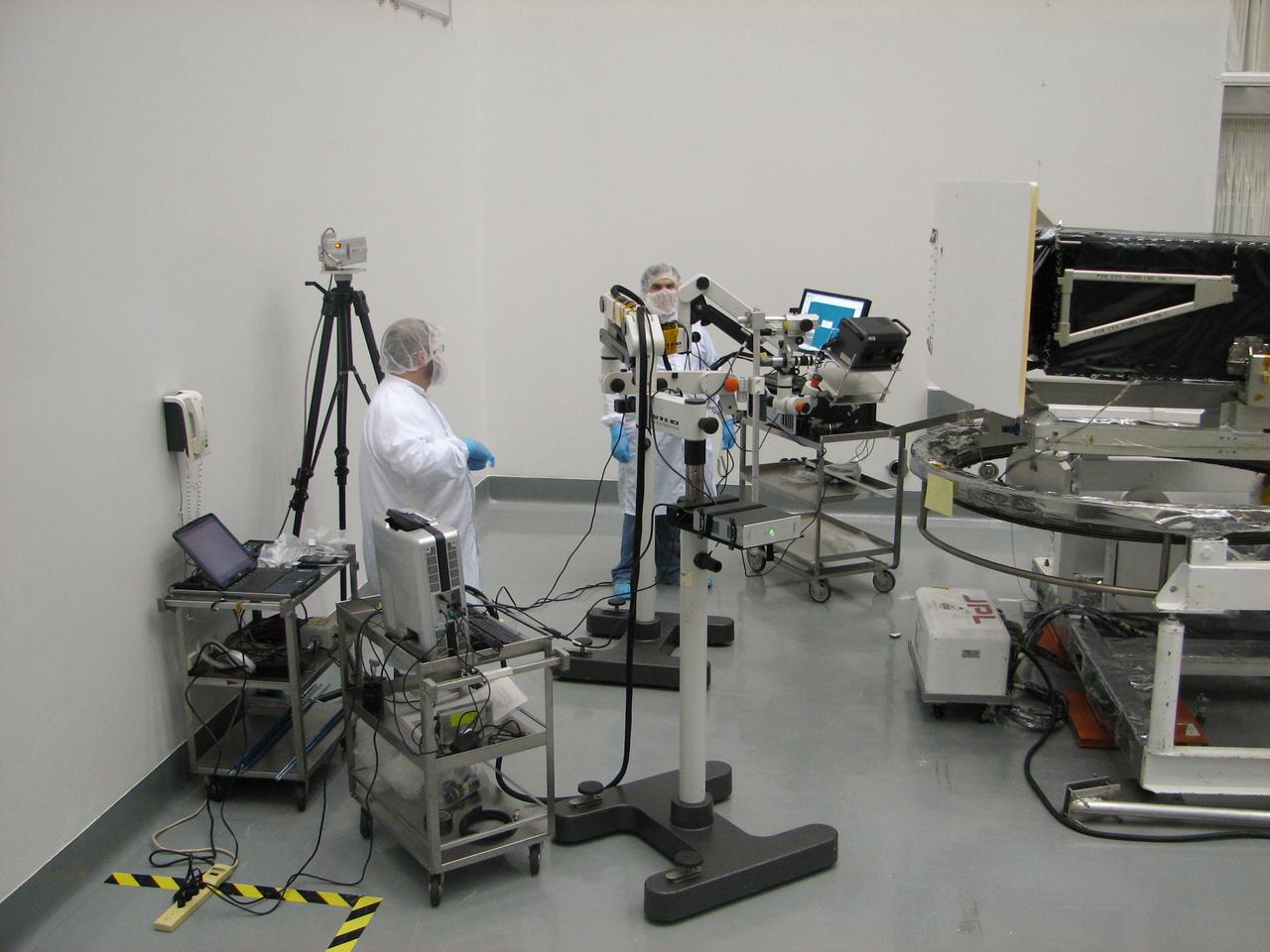

JSC2010-E-054445 (2 July 2009) --- Members of the Orbital Debris Program Office and the Hypervelocity Impact Technology Facility at JSC record images of impact craters and other surface data on the returned Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WFPC-2) of the Hubble Space Telescope. Inspection took place at the Goddard Space Flight Center during the summer of 2009. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
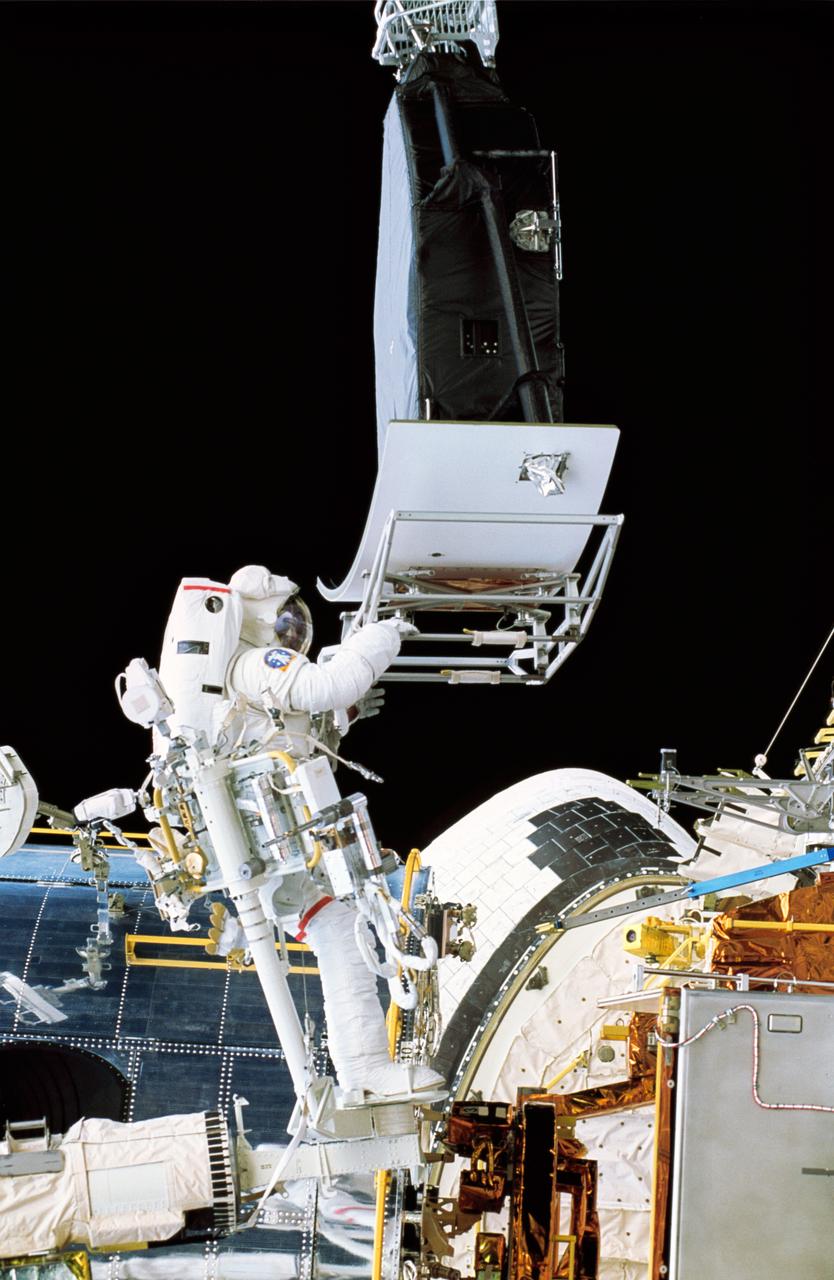

STS061-37-011 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman with Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC 1) during changeout operations. WF/PC-2 has already been installed in cavity (out of frame). Astronauts Hoffman and Story Musgrave are performing Extravehicular Activities (EVA) to repair the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
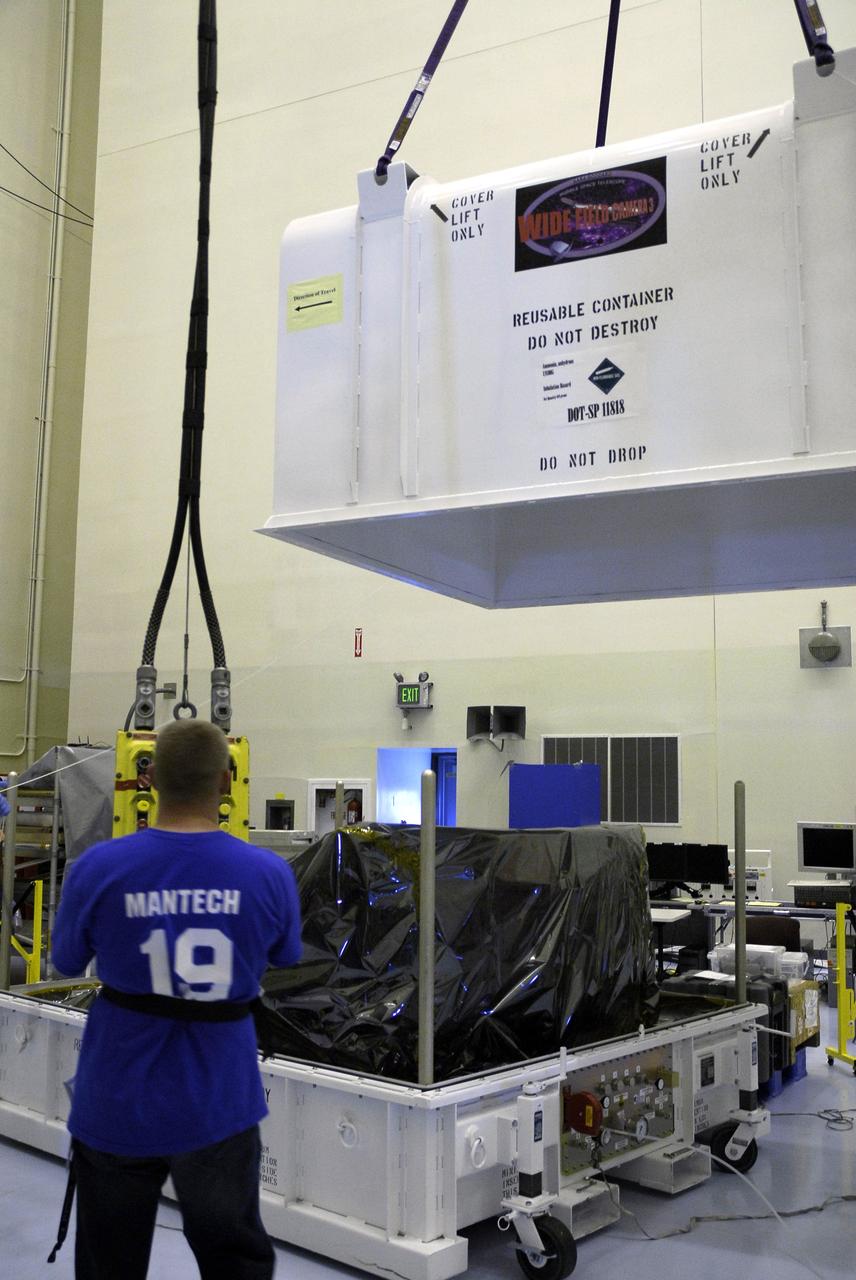

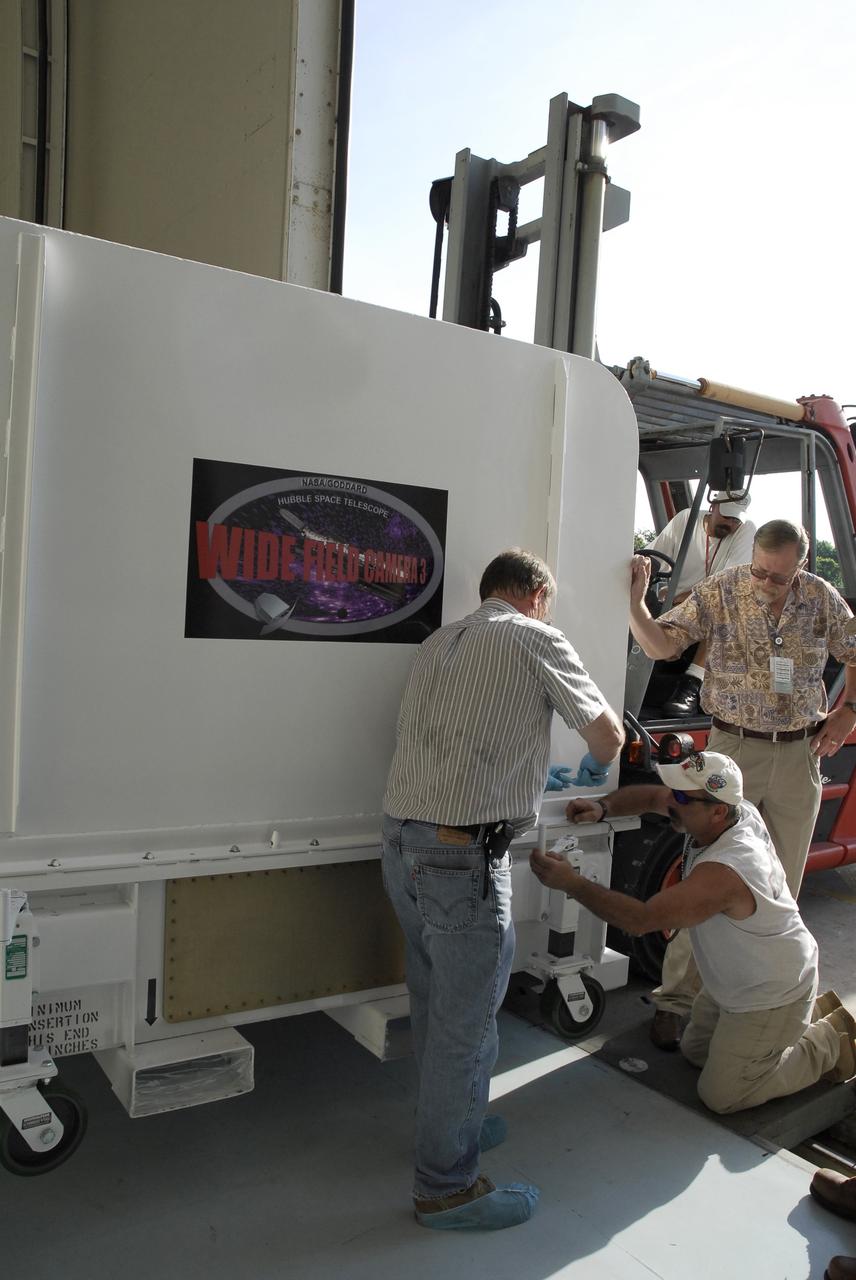
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, shipping container is lifted away from the mobile base. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is ready to be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
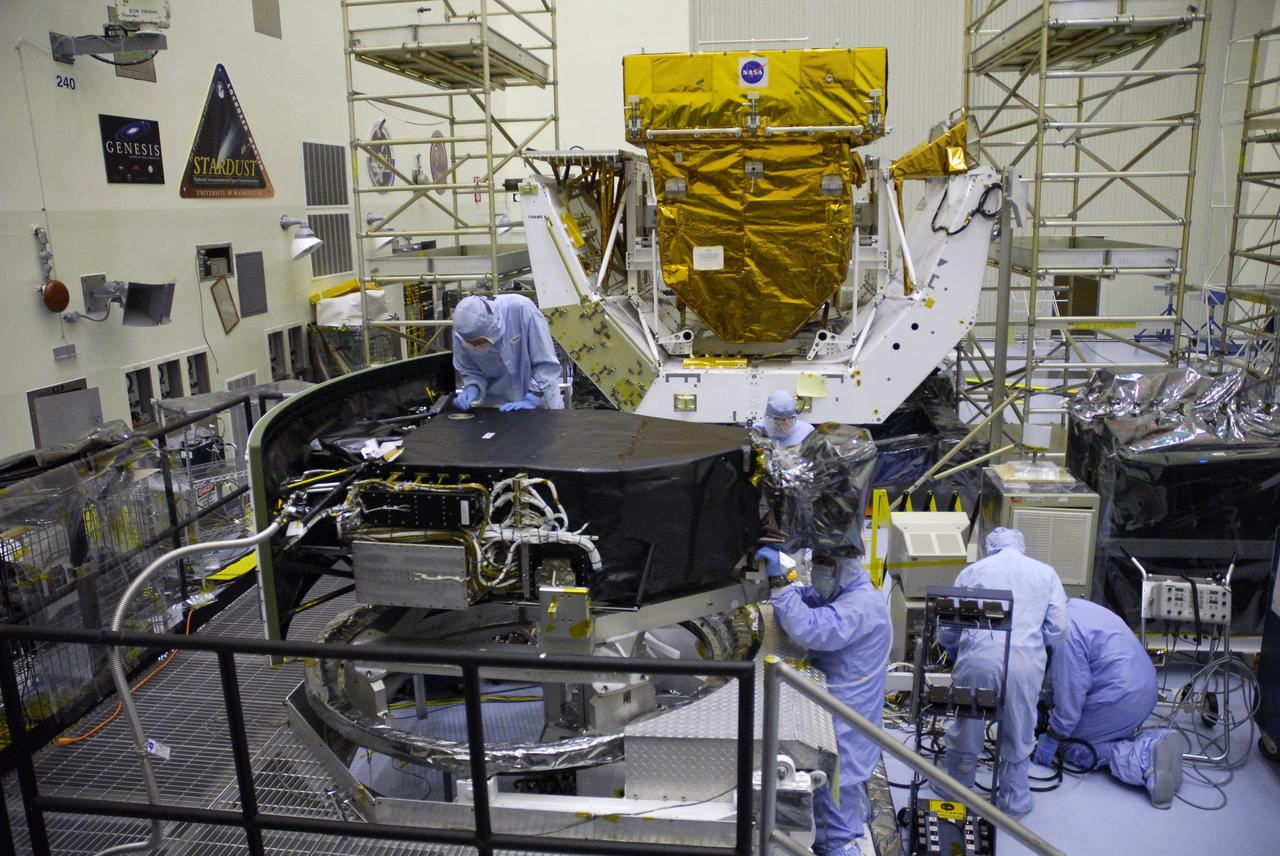

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility complete removal of the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians begin lifting the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, shipping container. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians monitor the movement of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, as the overhead crane transfers it to a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
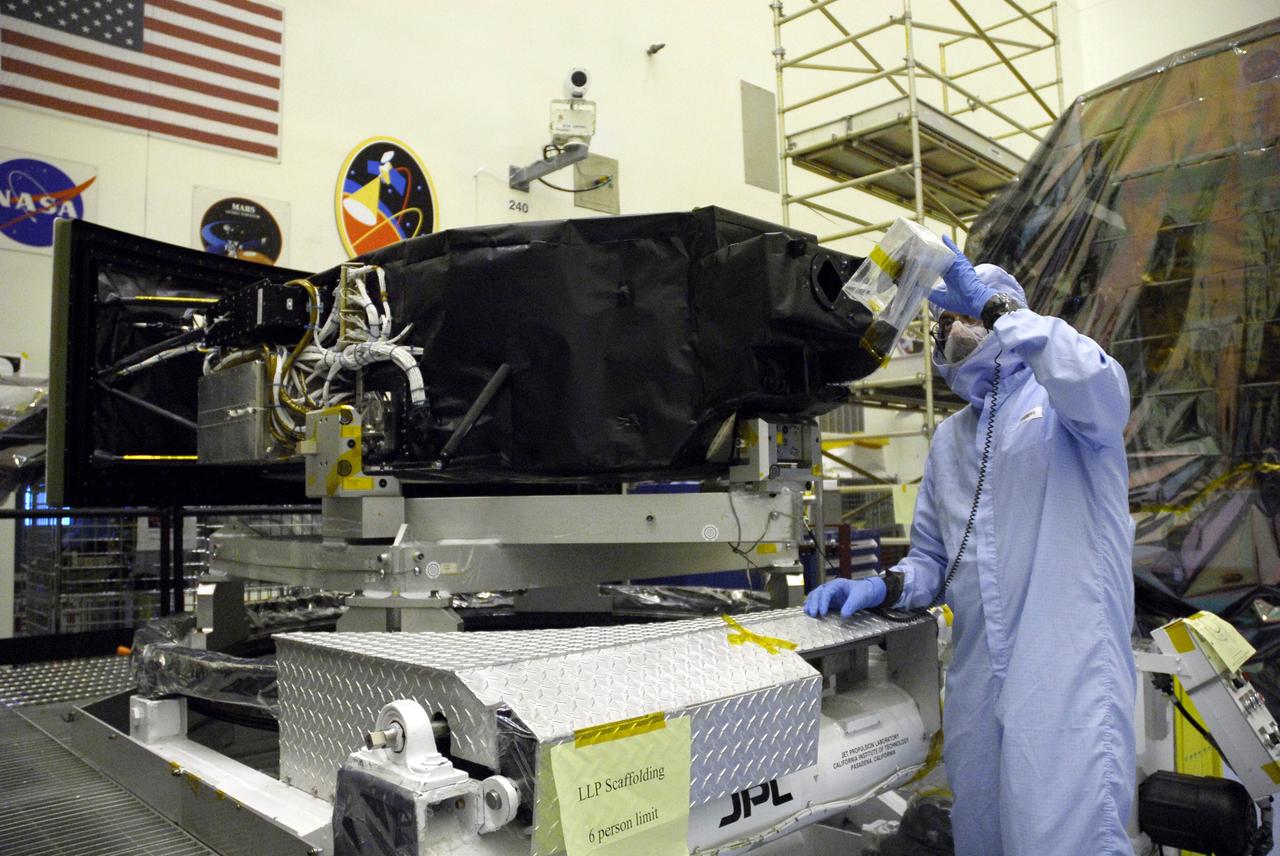

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician checks the pick-off mirror on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, that will be installed on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to Hubble. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, from the base of the shipping container. The WFC3 will be transferred to a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians unlatch the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3,shipping container before removing it. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, after removal of its protective cover. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility begin removing the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
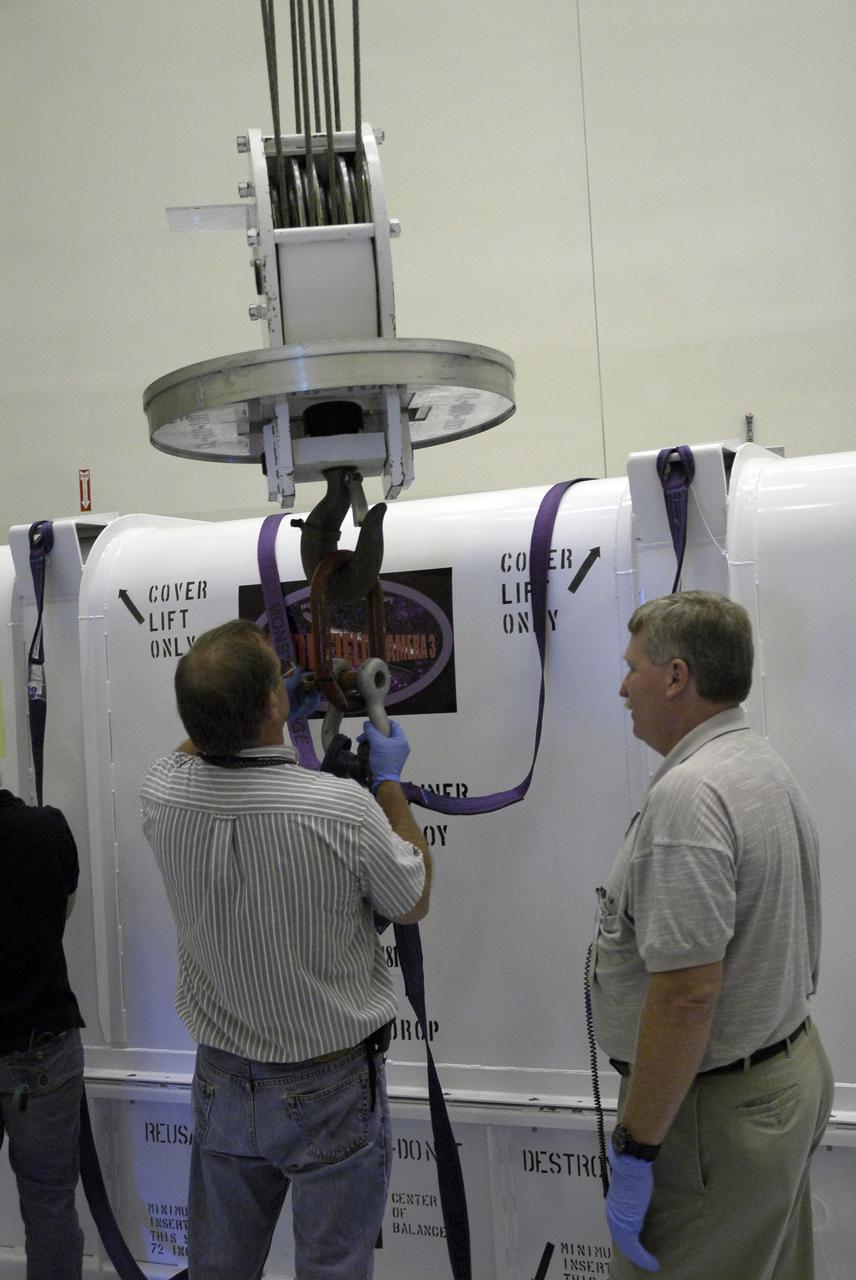

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians attach an overhead crane to the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, shipping container. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, after removal of its protective cover. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is lowered onto the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, rests on a work stand in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility since its arrival Aug. 12. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility remove the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians move the base of the shipping container holding the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, into the high bay. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility complete removal of the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians move the base of the shipping container holding the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians monitor the movement of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, as it is lowered onto a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
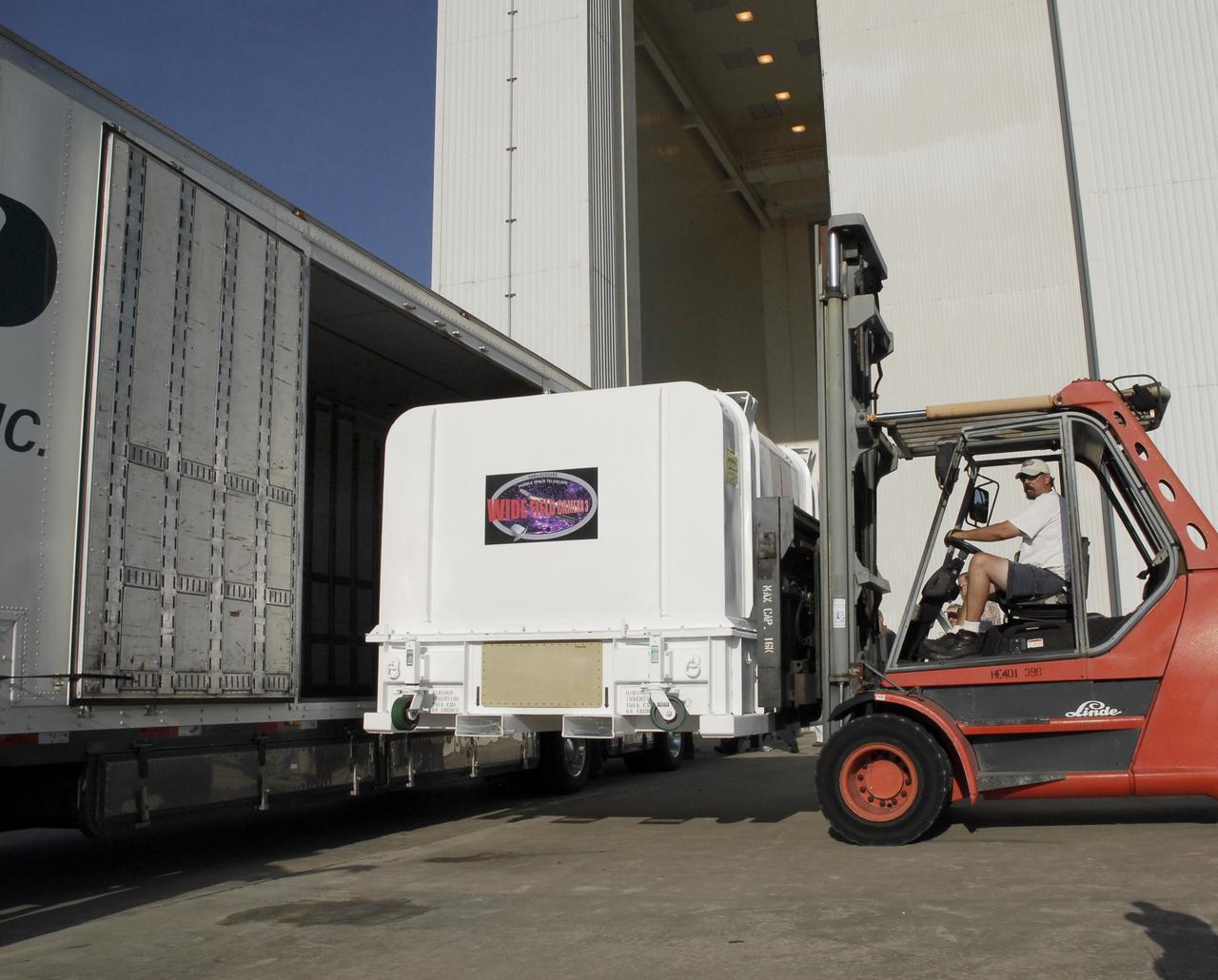

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The shipping container with the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, inside is removed from the truck outside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is lowered toward the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
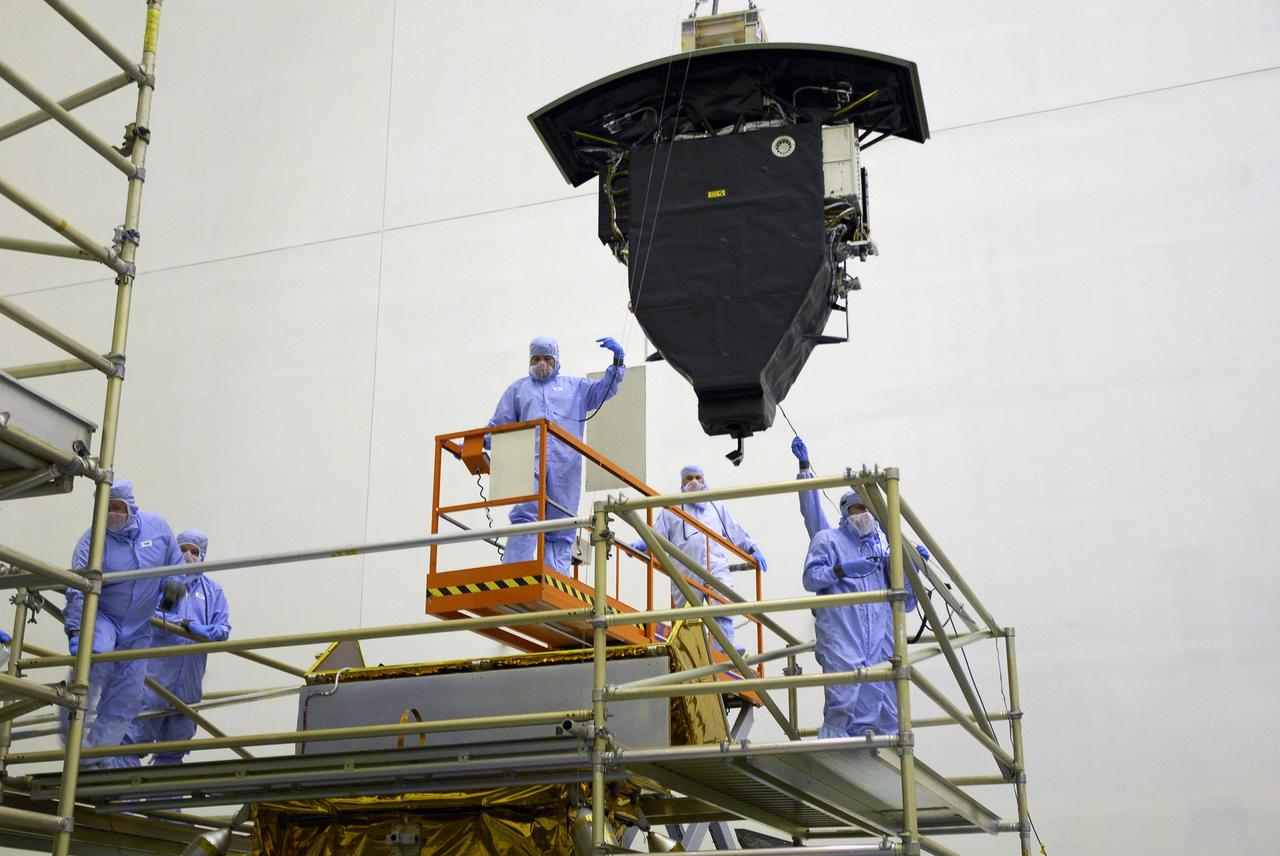

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is moved toward the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
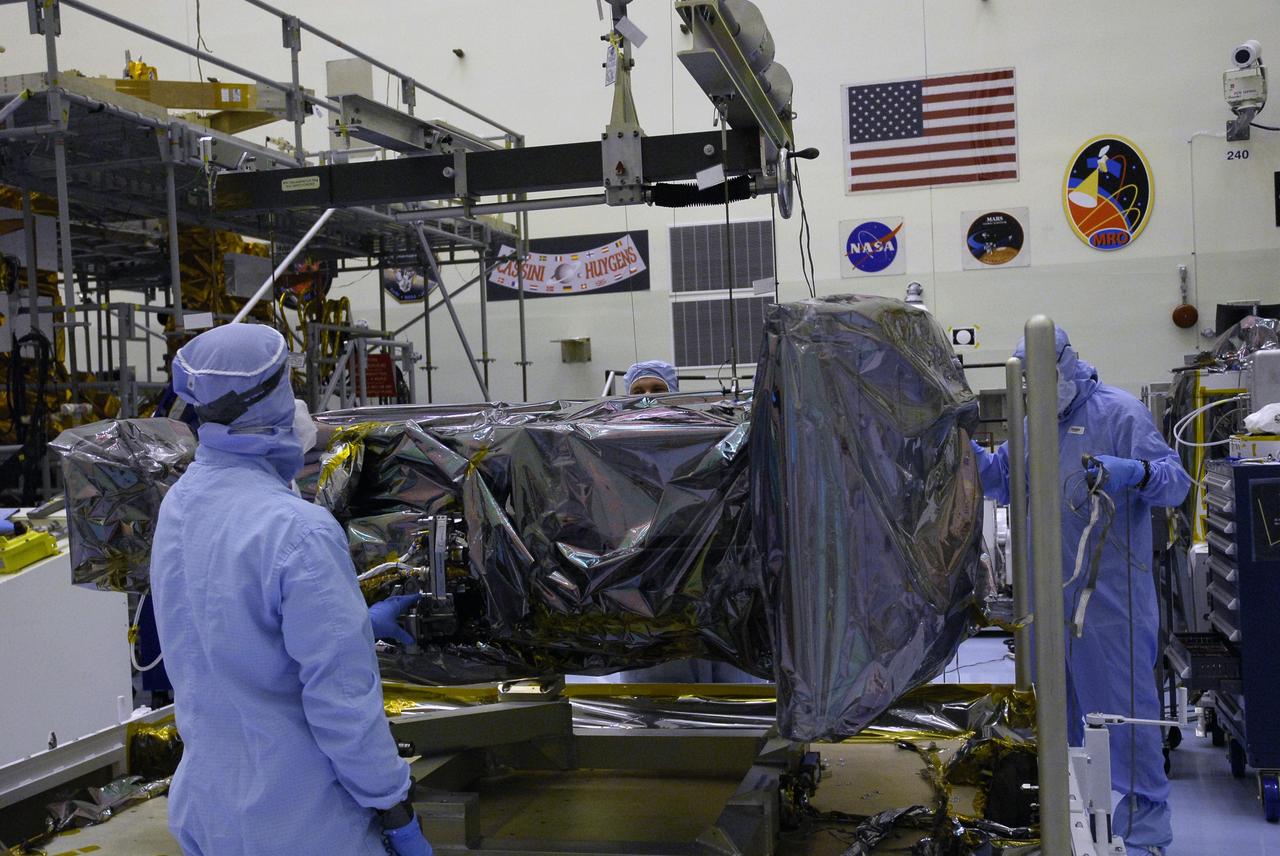

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane begins to lift the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, from the base of the shipping container. The WFC3 will be transferred to a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane is moved above the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, for attachment. The WFC3 will be lifted and transferred to a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
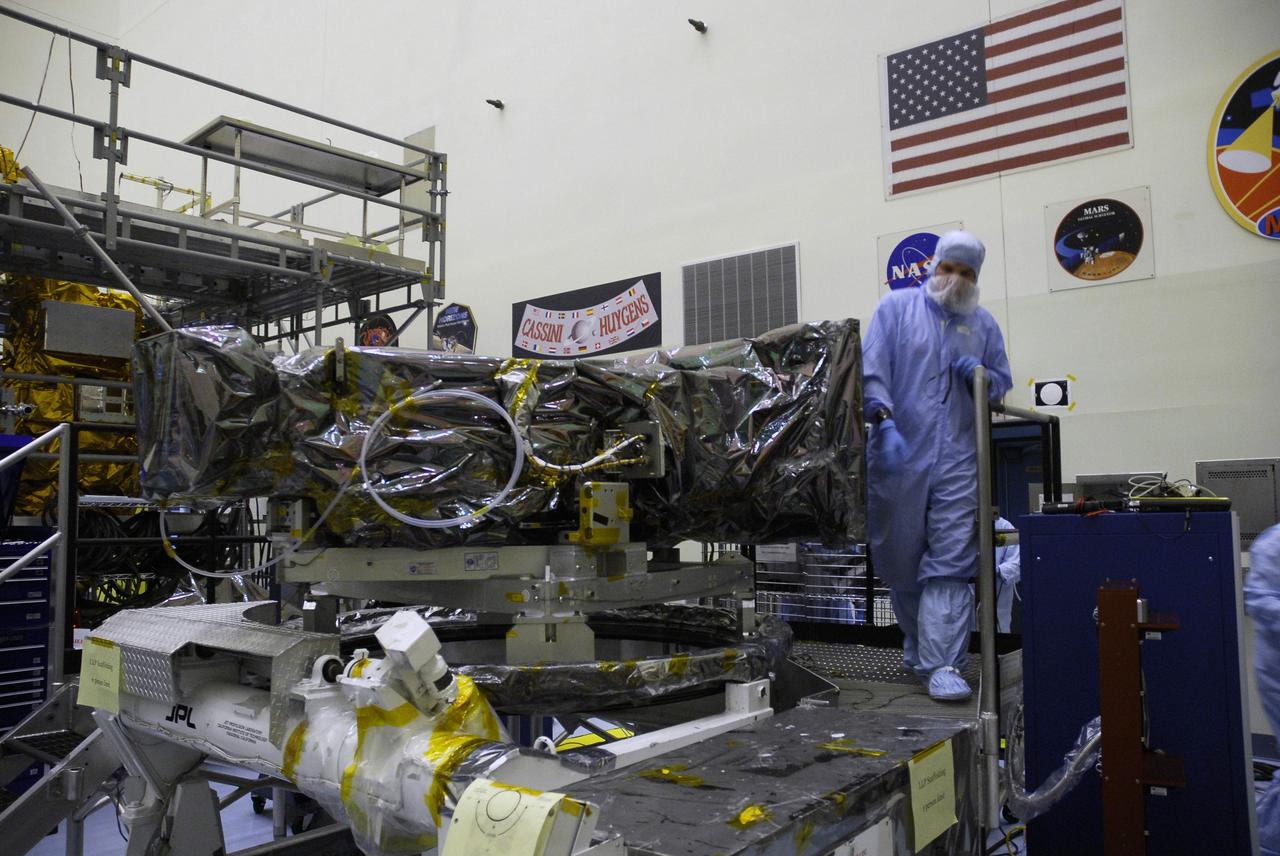

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians monitor the placement of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, on a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
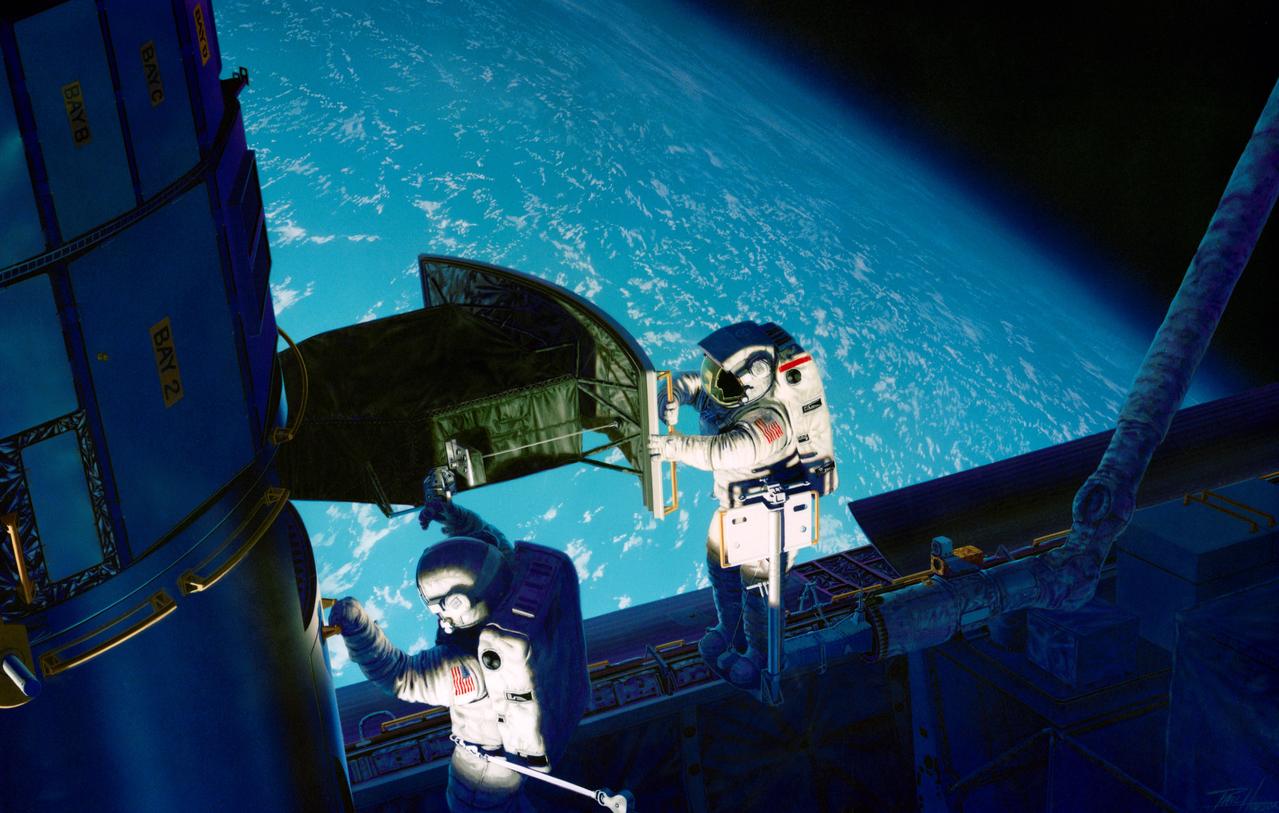

S93-48826 (November 1993) --- This artist's rendition of the 1993 Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission shows astronauts installing the new Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC 2). The instruments to replace the original camera and contains corrective optics that compensate for the telescope's flawed primary mirror. During the 11-plus day mission, astronauts are also scheduled to install the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) -- an optics package that focuses and routes light to the other three instruments aboard the observatory -- a new set of solar array panels, and other hardware and components. The artwork was done for JPL by Paul Hudson.

A comparison image of the M100 Galactic Nucleus, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Wide Field Planetary Camera-1 (WF/PC1) and Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WF/PC2). The HST was placed in a low-Earth orbit by the Space Shuttle Discovery, STS-31 mission, in April 1990. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. During four spacewalks, the STS-61 crew replaced the solar panel with its flexing problems; the WF/PC1 with the WF/PC2, with built-in corrective optics; and the High-Speed Photometer with the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR), to correct the aberration for the remaining instruments. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects.
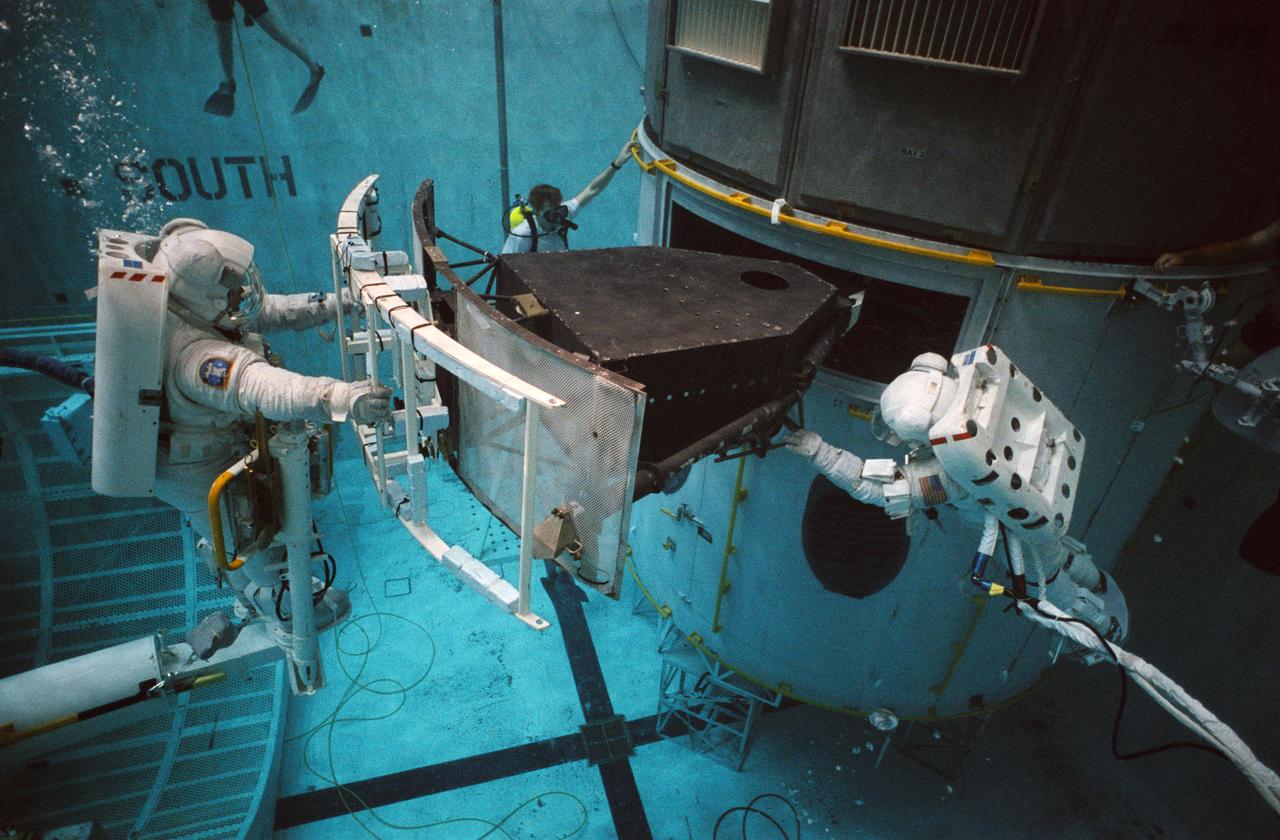
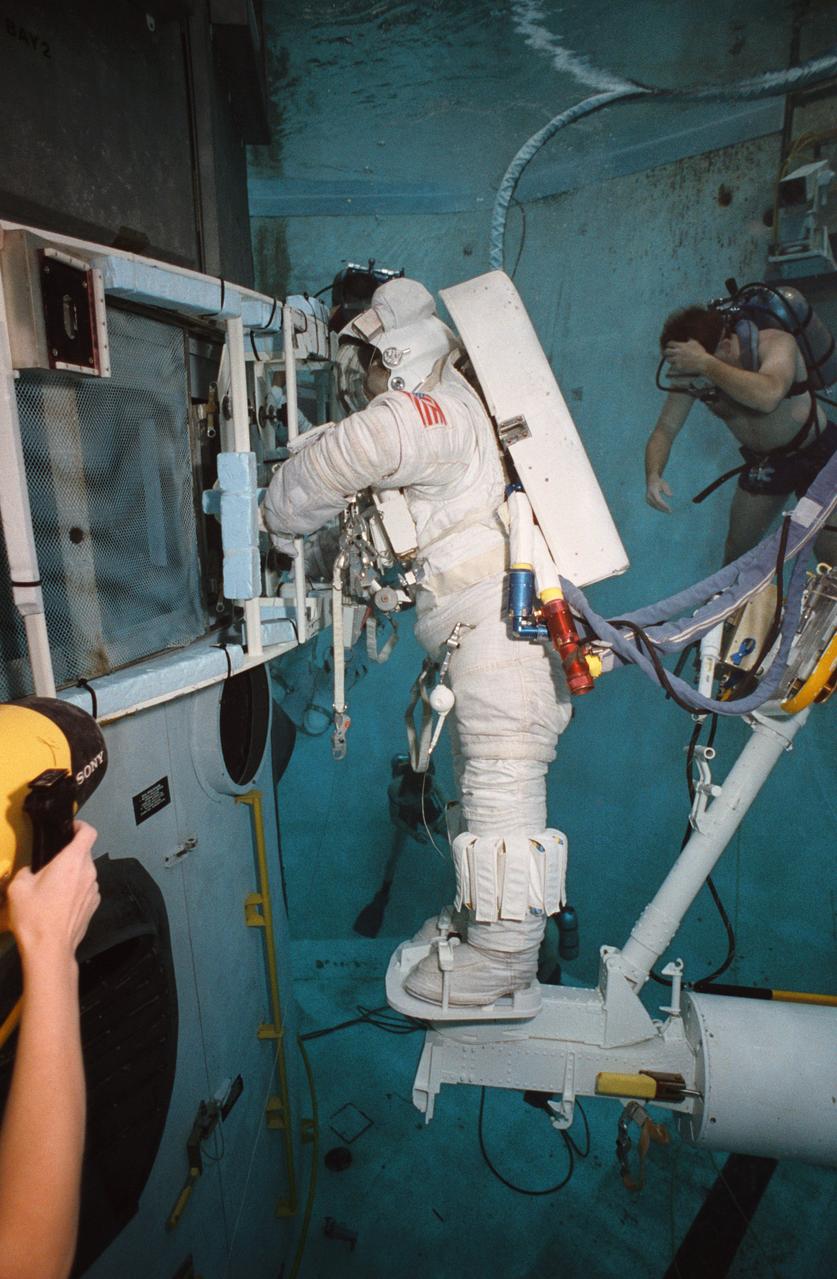
S93-33103 (2 Apr 1993) --- Wearing training versions of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMU), astronauts F. Story Musgrave and Jeffrey A. Hoffman use the giant pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. The two are working with a full-scale training version of the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC). The current WF/PC will be replaced with WF/PC-2. A total of five extravehicular activity (EVA) sessions will be conducted during the scheduled December mission of the Endeavour.
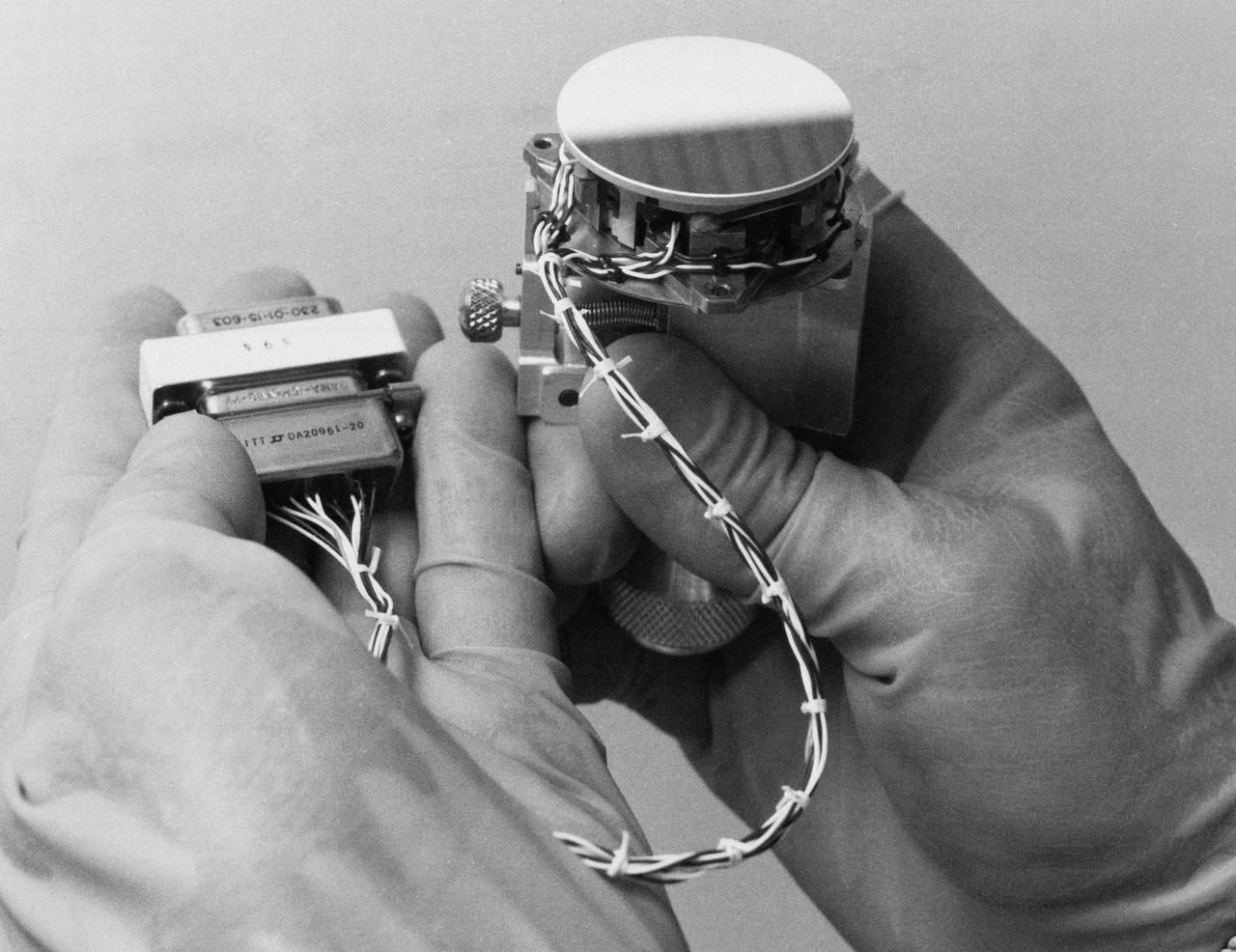
S93-33257 (15 Mar 1993) --- This close-up view features tiny articulating fold mirrors that will go into a replacement camera for the Wide Field\Planetary Camera (WF\PC-1) currently on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). A team of NASA astronauts will pay a visit to the HST later this year, carrying with them the new WF/PC-2 to replace the one currently on the HST. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California has been working on the replacement system for several months. See NASA photo S93-33258 for an optical schematic diagram of one of the four channels of the WF\PC-2 showing the path taken by beams from the HST before an image is formed at the camera's charge-coupled devices.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician cleans the edge of the radiator on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3,that will be installed on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The radiator is the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space. It will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians stand by as the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is rotated. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at left is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, has been rotated. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at top is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, high above the floor for transfer to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, from its stand. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, above the stand holding the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the placement of an overhead crane to the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, that will transfer the WFC3 to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians observe as the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is rotated to vertical. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at top is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
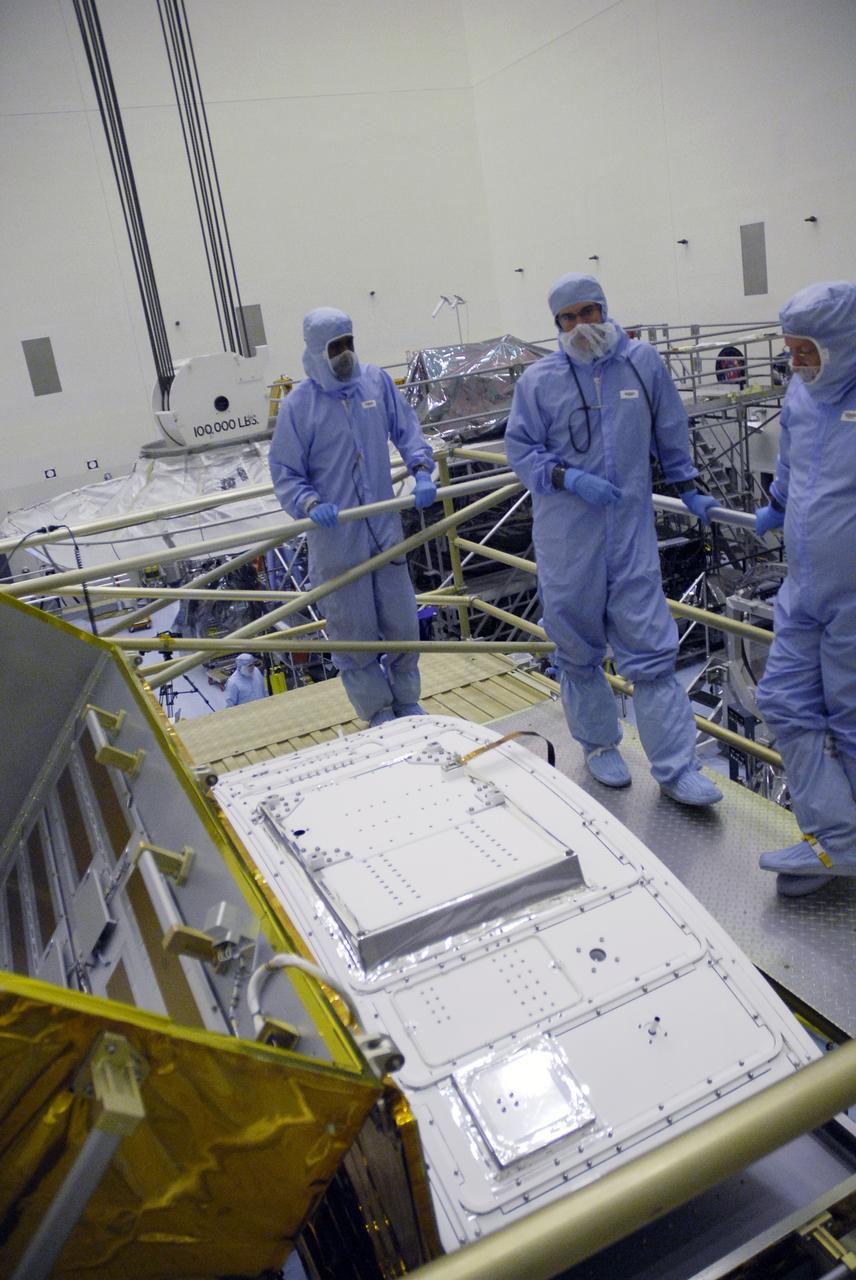

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians wait for the rotation of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, in order to attach a crane. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The part shown here is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

In the center of this image, taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, is the galaxy cluster SDSS J1038+4849 — and it seems to be smiling. You can make out its two orange eyes and white button nose. In the case of this “happy face”, the two eyes are very bright galaxies and the misleading smile lines are actually arcs caused by an effect known as strong gravitational lensing. Galaxy clusters are the most massive structures in the Universe and exert such a powerful gravitational pull that they warp the spacetime around them and act as cosmic lenses which can magnify, distort and bend the light behind them. This phenomenon, crucial to many of Hubble’s discoveries, can be explained by Einstein’s theory of general relativity. In this special case of gravitational lensing, a ring — known as an Einstein Ring — is produced from this bending of light, a consequence of the exact and symmetrical alignment of the source, lens and observer and resulting in the ring-like structure we see here. Hubble has provided astronomers with the tools to probe these massive galaxies and model their lensing effects, allowing us to peer further into the early Universe than ever before. This object was studied by Hubble’s Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) and Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) as part of a survey of strong lenses. A version of this image was entered into the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition by contestant Judy Schmidt. Image Credit: NASA/ESA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians wait for the rotation of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, in order to attach a crane. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at left is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
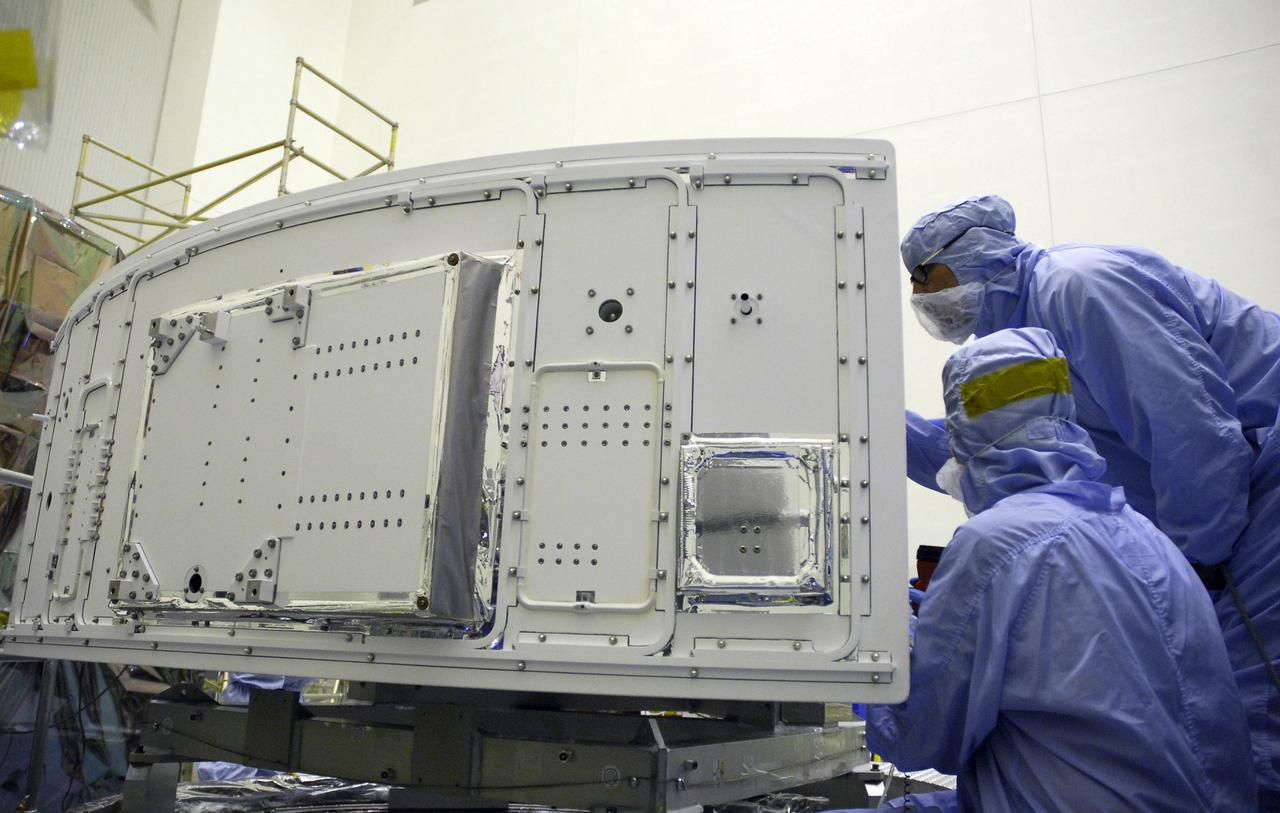

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technicians clean the radiator on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3,that will be installed on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The radiator is the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space. It will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
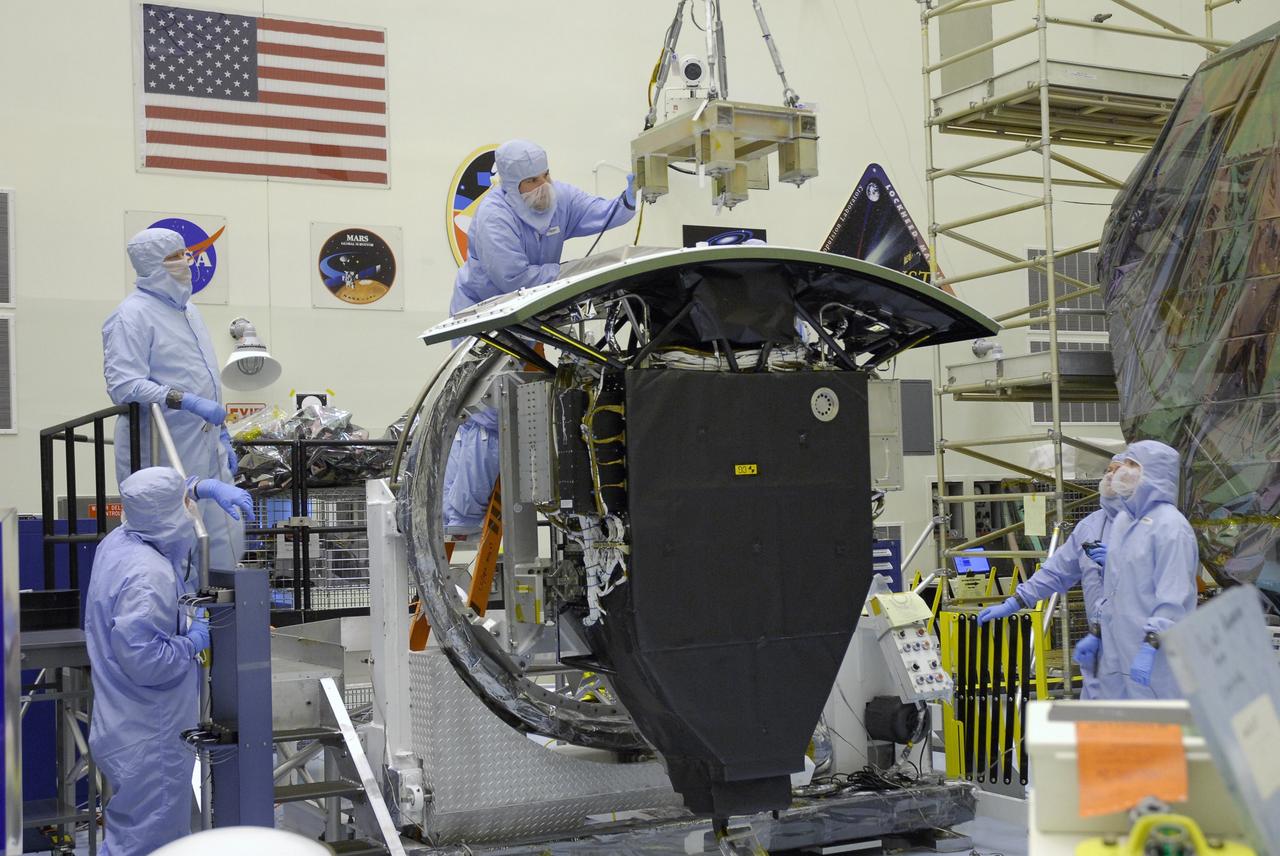

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician guides a crane for attachment to the radiator on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The radiator is the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, waits to be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The part shown here is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rotation of the Wide Field Camera 3 (background left), or WFC3, in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the data. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at top is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
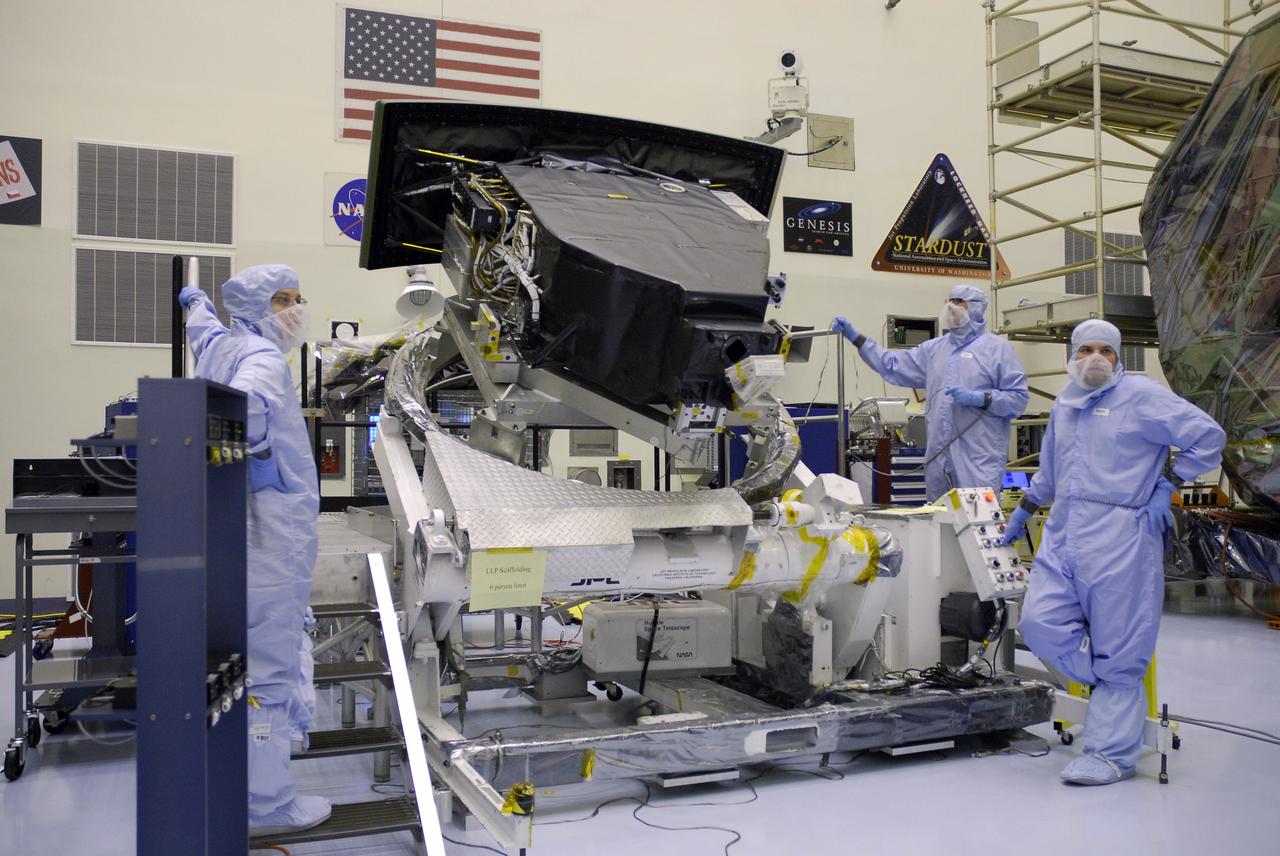

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians observe as the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is rotated. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at the back is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

S93-33101 (5 Apr 1993) --- Wearing a training version of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton uses the giant pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. Standing on a mobile foot restraint connected to the Shuttle's robot arm, Thornton grasps a large structure which attaches to the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC). The current WF/PC on the HST will be replaced with WF/PC-2. Out of frame is astronaut Thomas D. Akers, who will join Thornton in STS-61 EVA. A SCUBA-equipped diver can be seen in the background. A number of divers are on hand for all training sessions in the WET-F. A total of five extravehicular activity (EVA) sessions will be conducted during the scheduled December mission of the Endeavour.
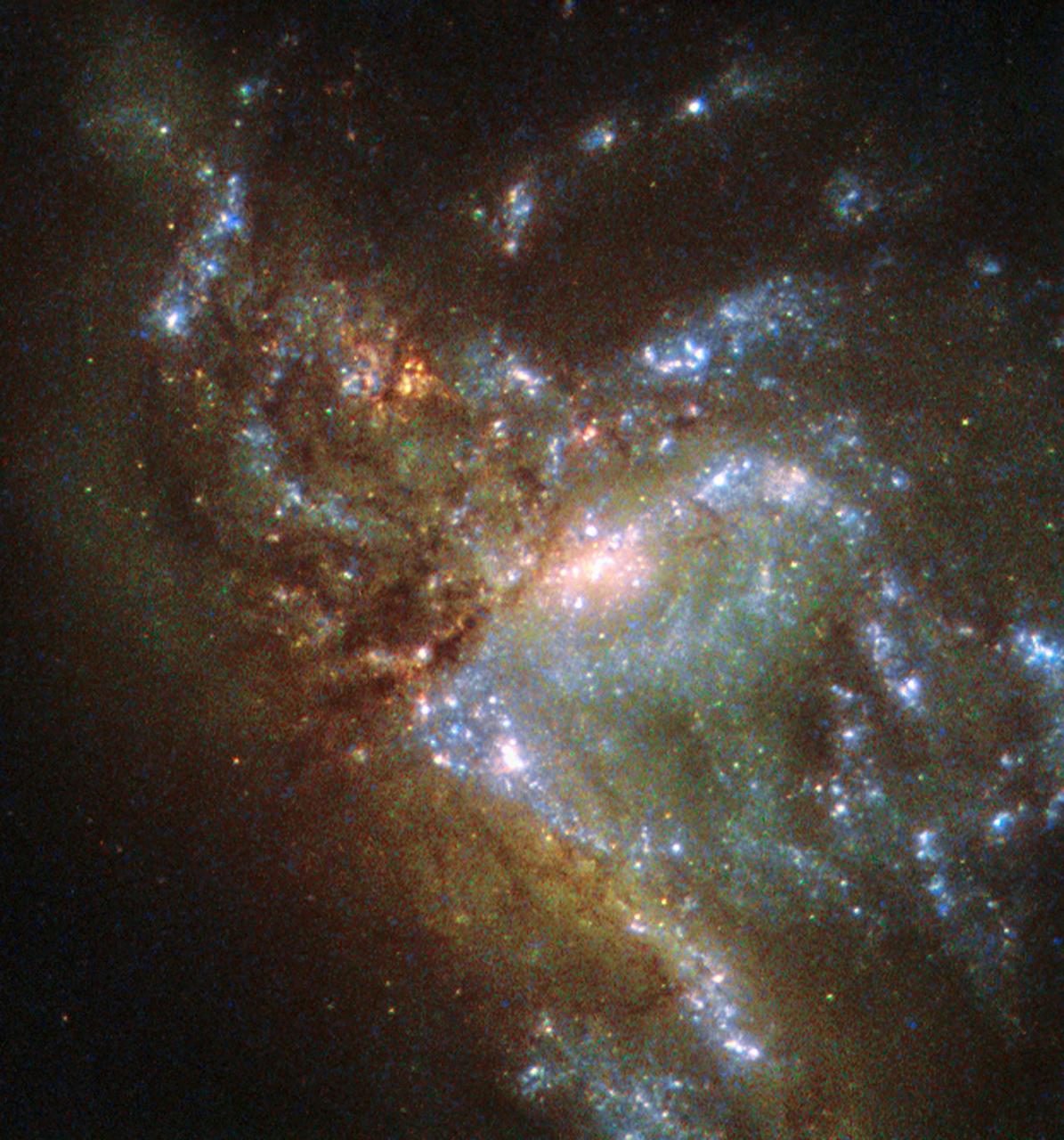

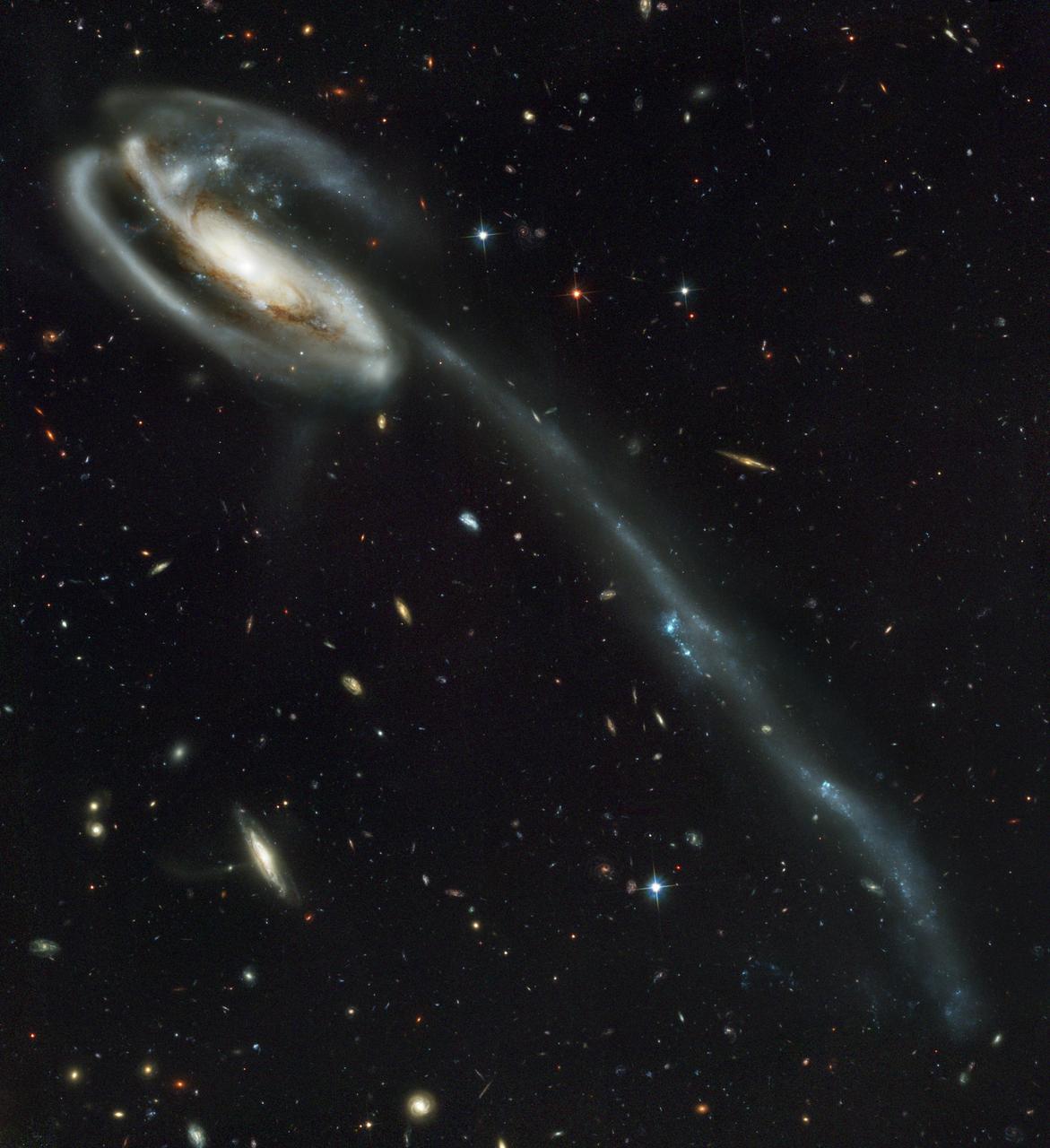
This image, taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 on board the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows the galaxy NGC 6052, located around 230 million light-years away in the constellation of Hercules. It would be reasonable to think of this as a single abnormal galaxy, and it was originally classified as such. However, it is in fact a “new” galaxy in the process of forming. Two separate galaxies have been gradually drawn together, attracted by gravity, and have collided. We now see them merging into a single structure. As the merging process continues, individual stars are thrown out of their original orbits and placed onto entirely new paths, some very distant from the region of the collision itself. Since the stars produce the light we see, the “galaxy” now appears to have a highly chaotic shape. Eventually, this new galaxy will settle down into a stable shape, which may not resemble either of the two original galaxies.
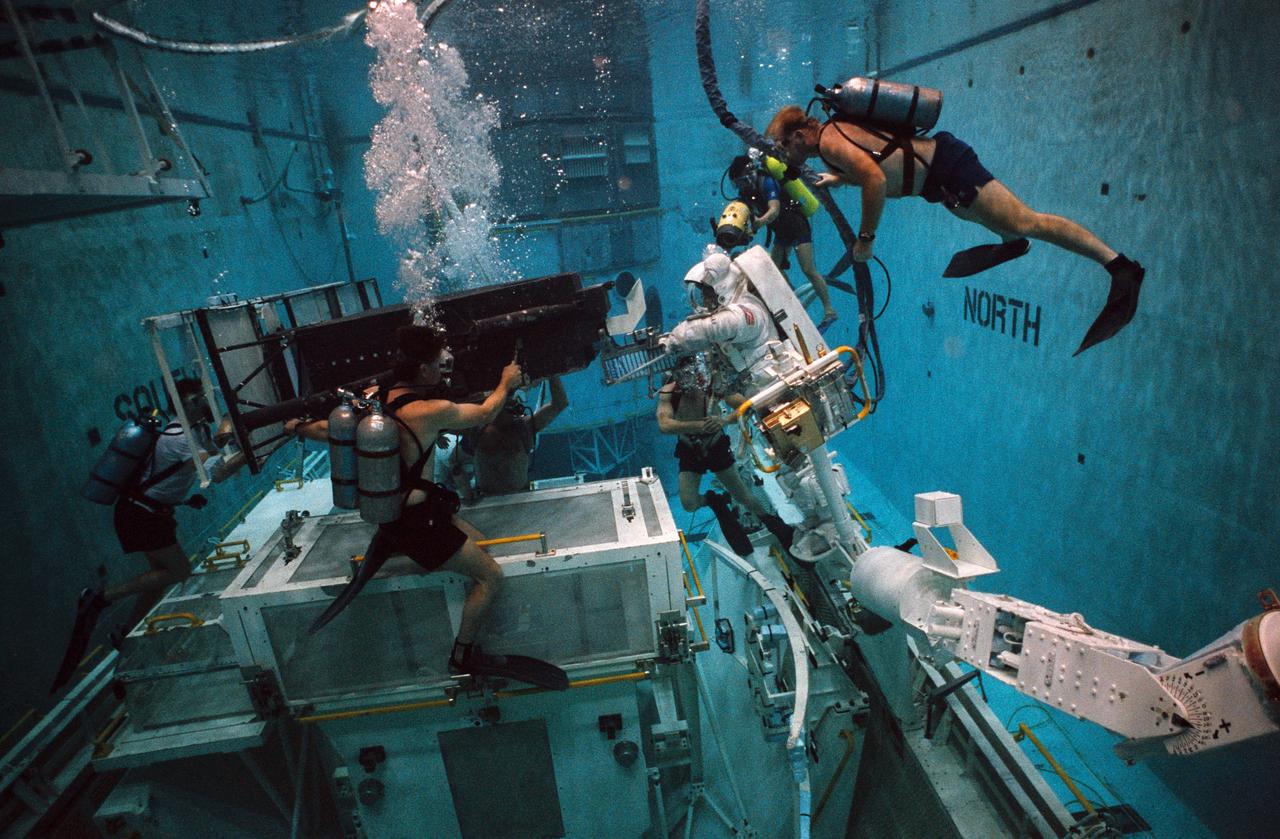

S93-33102 (5 Apr 1993) --- Wearing a training version of Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), astronaut Thomas D. Akers uses the giant pool of the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) to rehearse for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) repair mission. Standing on a mobile foot restraint connected to the Shuttle's robot arm, Akers works with a full-scale training version of the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC). The current WF/PC on the HST will be replaced with WF/PC-2. The giant box is a stowage area for both WF/PC facilities. Out of frame is astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, who will join Akers in STS-61 EVA. Several SCUBA-equipped divers assist in the rehearsal. A total of five extravehicular activity (EVA) sessions will be conducted during the scheduled December mission of the Endeavour.

This deepest-ever view of the universe unveils myriad galaxies back to the begirning of time. Several hundred, never-before-seen, galaxies are visible in this view of the universe, called Hubble Deep Field (HDF). Besides the classical spiral and elliptical shaped galaxies, there is a bewildering variety of other galaxy shapes and colors that are important clues to understanding the evolution of the universe. Some of the galaxies may have formed less than one-billion years after the Big Bang. The image was assembled from many separate exposures with the Wide Field/Planetary Camera 2 (WF/PC2), for ten consecutive days between December 18, 1995 and December 28, 1995. This true-color view was assembled from separate images taken with blue, red, and infrared light. By combining these separate images into a single color picture, astronomers will be able to infer, at least statistically, the distance, age, and composition of galaxies in the field. Blue objects contain young stars and/or are relatively close, while redder objects contain older stellar populations and/or are farther away.

A panoramic view of a vast, sculpted area of gas and dust where thousands of stars are being born has been captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The image, taken by Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2, is online at http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2001/21/image/a/. The camera was designed and built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. The photo offers an unprecedented, detailed view of the entire inner region of the fertile, star-forming 30 Doradus Nebula. The mosaic picture shows that ultraviolet radiation and high-speed material unleashed by the stars in the cluster, called R136 (the large blue blob left of center), are weaving a tapestry of creation and destruction, triggering the collapse of looming gas and dust clouds and forming pillar-like structures that incubate newborn stars. The 30 Doradus Nebula is in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way located 170,000 light-years from Earth. Nebulas like 30 Doradus are signposts of recent star birth. High-energy ultraviolet radiation from young, hot, massive stars in R136 causes surrounding gaseous material to glow. Previous Hubble telescope observations showed that R136 contains several dozen of the most massive stars known, each about 100 times the mass of the Sun and about 10 times as hot. These stellar behemoths formed about 2 million years ago. The stars in R136 produce intense "stellar winds," streams of material traveling at several million miles an hour. These winds push the gas away from the cluster and compress the inner regions of the surrounding gas and dust clouds (seen in the image as the pinkish material). The intense pressure triggers the collapse of parts of the clouds, producing a new star formation around the central cluster. Most stars in the nursery are not visible because they are still encased in cocoons of gas and dust. This mosaic image of 30 Doradus consists of five overlapping pictures taken between January 1994 and September 2000 by the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. Several color filters enhance important details in the stars and the nebula. Blue corresponds to the hot stars. The greenish color denotes hot gas energized by the central cluster of stars. Pink depicts the glowing edges of the gas and dust clouds facing the cluster, which are being bombarded by winds and radiation. Reddish-brown represents the cooler surfaces of the clouds, which are not receiving direct radiation from the central cluster. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04200
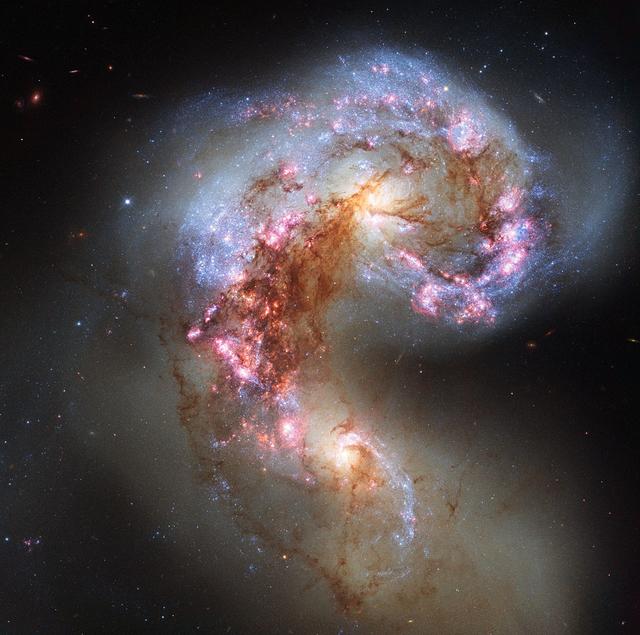

The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has snapped the best ever image of the Antennae Galaxies. Hubble has released images of these stunning galaxies twice before, once using observations from its Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) in 1997, and again in 2006 from the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). Each of Hubble’s images of the Antennae Galaxies has been better than the last, due to upgrades made during the famous servicing missions, the last of which took place in 2009. The galaxies — also known as NGC 4038 and NGC 4039 — are locked in a deadly embrace. Once normal, sedate spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, the pair have spent the past few hundred million years sparring with one another. This clash is so violent that stars have been ripped from their host galaxies to form a streaming arc between the two. In wide-field images of the pair the reason for their name becomes clear — far-flung stars and streamers of gas stretch out into space, creating long tidal tails reminiscent of antennae. This new image of the Antennae Galaxies shows obvious signs of chaos. Clouds of gas are seen in bright pink and red, surrounding the bright flashes of blue star-forming regions — some of which are partially obscured by dark patches of dust. The rate of star formation is so high that the Antennae Galaxies are said to be in a state of starburst, a period in which all of the gas within the galaxies is being used to form stars. This cannot last forever and neither can the separate galaxies; eventually the nuclei will coalesce, and the galaxies will begin their retirement together as one large elliptical galaxy. This image uses visible and near-infrared observations from Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), along with some of the previously-released observations from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). Credit: NASA/European Space Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This colourful bubble is a planetary nebula called NGC 6818, also known as the Little Gem Nebula. It is located in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), roughly 6000 light-years away from us. The rich glow of the cloud is just over half a light-year across — humongous compared to its tiny central star — but still a little gem on a cosmic scale. When stars like the Sun enter retirement, they shed their outer layers into space to create glowing clouds of gas called planetary nebulae. This ejection of mass is uneven, and planetary nebulae can have very complex shapes. NGC 6818 shows knotty filament-like structures and distinct layers of material, with a bright and enclosed central bubble surrounded by a larger, more diffuse cloud. Scientists believe that the stellar wind from the central star propels the outflowing material, sculpting the elongated shape of NGC 6818. As this fast wind smashes through the slower-moving cloud it creates particularly bright blowouts at the bubble’s outer layers. Hubble previously imaged this nebula back in 1997 with its Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, using a mix of filters that highlighted emission from ionised oxygen and hydrogen (opo9811h). This image, while from the same camera, uses different filters to reveal a different view of the nebula. A version of the image was submitted to the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures image processing competition by contestant Judy Schmidt.

This shot from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows a maelstrom of glowing gas and dark dust within one of the Milky Way’s satellite galaxies, the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). This stormy scene shows a stellar nursery known as N159, an HII region over 150 light-years across. N159 contains many hot young stars. These stars are emitting intense ultraviolet light, which causes nearby hydrogen gas to glow, and torrential stellar winds, which are carving out ridges, arcs, and filaments from the surrounding material. At the heart of this cosmic cloud lies the Papillon Nebula, a butterfly-shaped region of nebulosity. This small, dense object is classified as a High-Excitation Blob, and is thought to be tightly linked to the early stages of massive star formation. N159 is located over 160,000 light-years away. It resides just south of the Tarantula Nebula (heic1402), another massive star-forming complex within the LMC. This image comes from Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. The region was previously imaged by Hubble’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which also resolved the Papillon Nebula for the first time. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA

This picture of the galaxy UGC 10214 was was taken by the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), which was installed aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in March 2002 during HST Servicing Mission 3B (STS-109 mission). Dubbed the "Tadpole," this spiral galaxy is unlike the textbook images of stately galaxies. Its distorted shape was caused by a small interloper, a very blue, compact galaxy visible in the upper left corner of the more massive Tadpole. The Tadpole resides about 420 million light-years away in the constellation Draco. Seen shining through the Tadpole's disk, the tiny intruder is likely a hit-and-run galaxy that is now leaving the scene of the accident. Strong gravitational forces from the interaction created the long tail of debris, consisting of stars and gas that stretch our more than 280,000 light-years. The galactic carnage and torrent of star birth are playing out against a spectacular backdrop: a "wallpaper pattern" of 6,000 galaxies. These galaxies represent twice the number of those discovered in the legendary Hubble Deep Field, the orbiting observatory's "deepest" view of the heavens, taken in 1995 by the Wide Field and planetary camera 2. The ACS picture, however, was taken in one-twelfth of the time it took to observe the original HST Deep Field. In blue light, ACS sees even fainter objects than were seen in the "deep field." The galaxies in the ACS picture, like those in the deep field, stretch back to nearly the begirning of time. Credit: NASA, H. Ford (JHU), G. Illingworth (USCS/LO), M. Clampin (STScI), G. Hartig (STScI), the ACS Science Team, and ESA.

A comparison of images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field/Planetary Camera (HST/WFPC) and the Mars Global Surveyor Orbiter Camera (MGS/MOC) shows the progress of a regional dust storm within the Valles Marineris canyons on Mars. The first HST image (left), taken in mid-May, shows no dust within the canyons. The most recent HST image (center), taken on 27 June in support of the Mars Pathfinder landing activities, shows a dust storm filling part of the canyon system and extending into the chaotic terrains at the eastern end of the canyons. The MGS/MOC image (right), acquired on July 2, shows that bright dust continues to fill the valleys. However, it does not appear to have moved significantly north of the previously observed position, suggesting that the storm remains confined to the canyon region, and does not appear to directly threaten the Pathfinder landing site (small black circle). The HST images shown here have been reduced in scale to match that of the MGS/MOC image. Although the HST is 10 times farther from Mars than MGS, its images are sharper because its resolving power is 15 times better than the MOC, and the light gathering area is almost 50 times greater. However, MGS is presently 45,000 times farther from Mars than it will be when the MOC begins its primary photography mission. At 400 km above the martian surface, the MOC wide angle camera will collect daily images at a resolution of 7.5 km/pixel, compared to HST's best of about 20 km/pixel. The narrow angle camera will observe portions of Mars at better than 1.5 m/pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00607
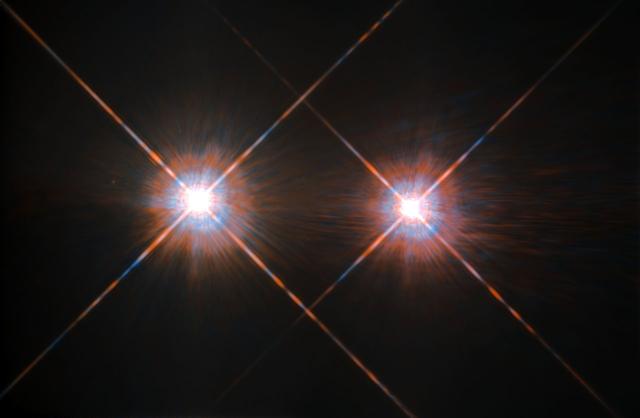

The closest star system to the Earth is the famous Alpha Centauri group. Located in the constellation of Centaurus (The Centaur), at a distance of 4.3 light-years, this system is made up of the binary formed by the stars Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B, plus the faint red dwarf Alpha Centauri C, also known as Proxima Centauri. This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has given us this stunning view of the bright Alpha Centauri A (on the left) and Alpha Centauri B (on the right), shining like huge cosmic headlamps in the dark. The image was captured by the Wide-Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). WFPC2 was Hubble’s most used instrument for the first 13 years of the space telescope’s life, being replaced in 2009 by Wide-Field Camera 3 (WFC3) during Servicing Mission 4. This portrait of Alpha Centauri was produced by observations carried out at optical and near-infrared wavelengths. Compared to the sun, Alpha Centauri A is of the same stellar type, G2, and slightly bigger, while Alpha Centauri B, a K1-type star, is slightly smaller. They orbit a common center of gravity once every 80 years, with a minimum distance of about 11 times the distance between Earth and the sun. Because these two stars are, together with their sibling Proxima Centauri, the closest to Earth, they are among the best studied by astronomers. And they are also among the prime targets in the hunt for habitable exoplanets. Using the European Space Organization's HARPS instrument, astronomers already discovered a planet orbiting Alpha Centauri B. Then on Aug. 24, 2016, astronomers announced the intriguing discovery of a nearly Earth-sized planet in the habitable zone orbiting the star Proxima Centauri Image credit: ESA/NASA
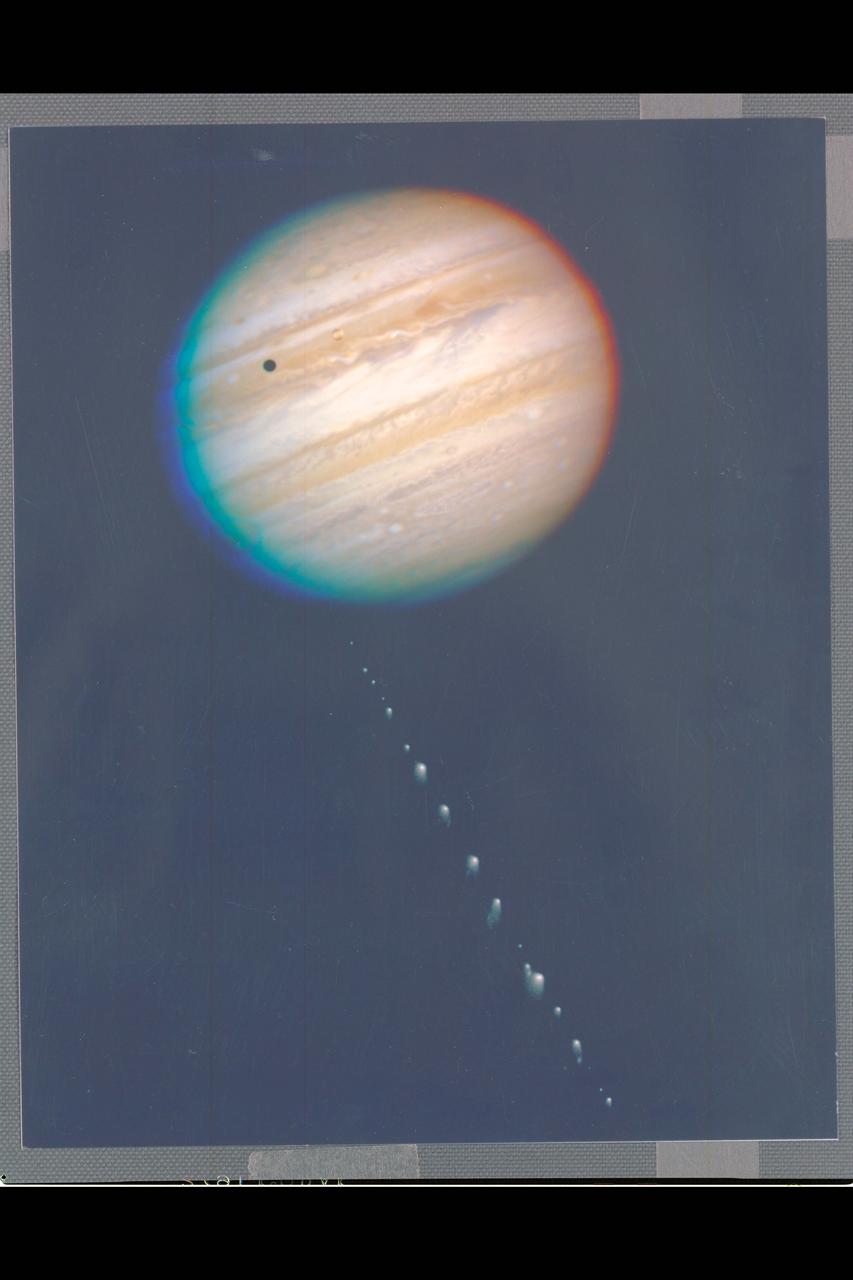

This is a composite photo, assembled from separate images of Jupiter and Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy 9 as imaged by the Wide Field & Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC-2), aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Jupiter was imaged on May 18, 1994, when the giant planet was at a distance of 420 million miles (670 million KM) from Earth. This 'true-color' picture was assembled from separate HST exposures in red, blue, and green light. Jupiter's rotation between exposures creates the blue and red fringe on either side of the disk. HST can resolve details in Jpiter's magnifient cloud belts and zones as small as 200 miles (320 km) across (wide field mode). This detailed view is only surpassed by images from spacecraft that have traveled to Jupiter. The dark spot on the disk of Jupiter is the shadow of the inner moon Io. This volcanic moon appears as an orange and yellow disk just to the upper right of the shadow. Though Io is approximately the size of Earth's Moon (but 2,000 times farther away), HST can resolve surface details. When the comet was observed on May 17, its train of 21 icy fragments stretched across 710 thousand miles (1.1 million km) of space, or 3 times the distance between Earth and the Moon. This required six WFPC exposures along the comet train to include all the nuclei. The image was taken in red light. The apparent angular size of Jupiter relative to the comet, and its angular separation from the comet when the images were taken, have been modified for illustration purposes. CREDIT: H.A. Weaver, T.E. Smith (Space Telescope Science Institute (STSI)) and J.T. Tranuger, R.W. Evans (Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL)) and NASA. (HST ref: STSci-PR94-26a)

Astronaut Hoffman held the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Wide Field/Planetary Camera-1 (WF/PC1) that was replaced by WF/PC2 in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Endeavour during Extravehicular Activity (EVA). The STS-61 mission was the first of the series of the HST servicing missions. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. During four spacewalks, the STS-61 crew replaced the solar panel with its flexing problems; the WF/PC1 with WF/PC2, with built-in corrective optics; and the High-Speed Photometer with the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) to correct the aberration for the remaining instruments. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
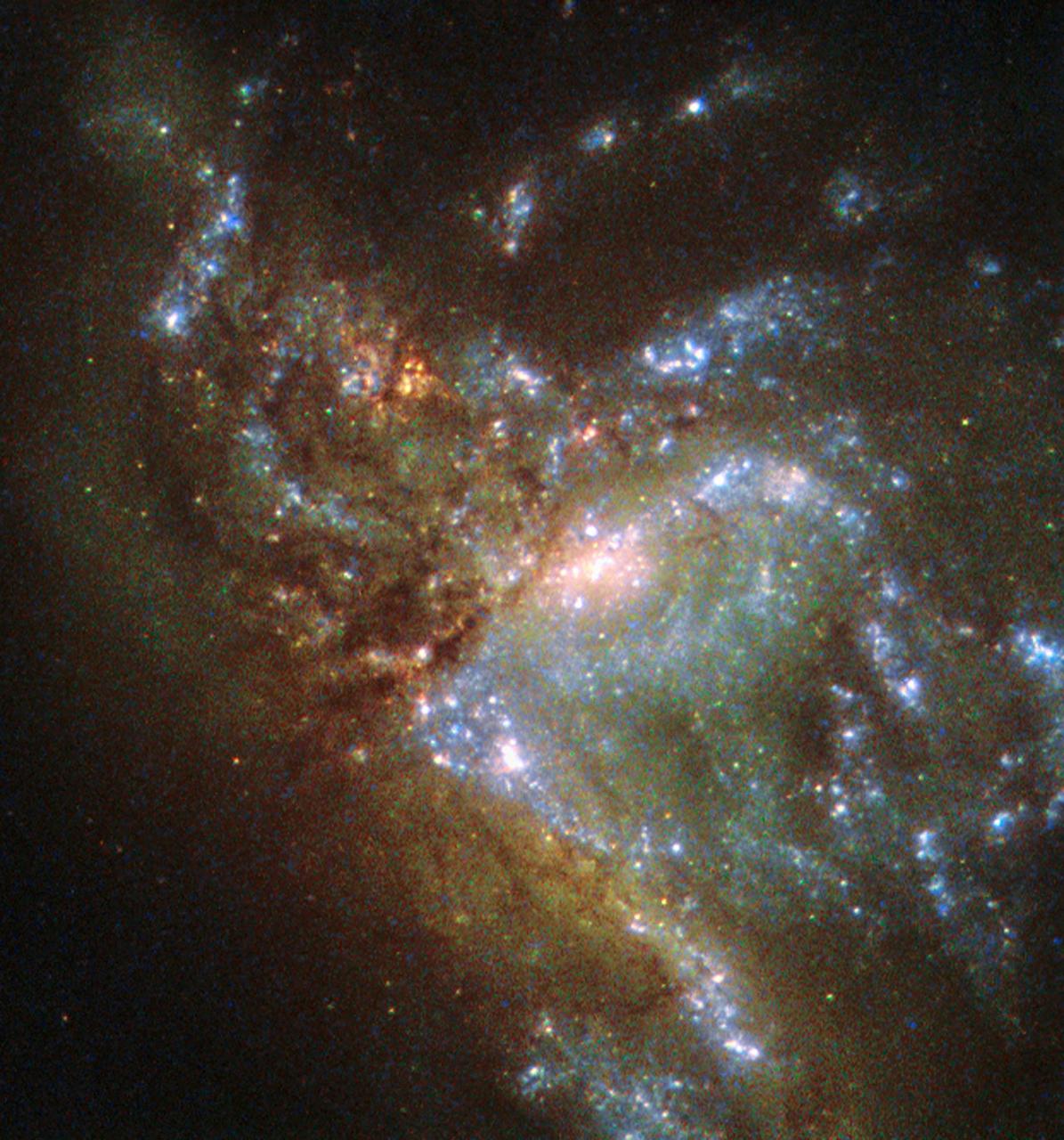

This image, taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 on board the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows the galaxy NGC 6052, located around 230 million light-years away in the constellation of Hercules. It would be reasonable to think of this as a single abnormal galaxy, and it was originally classified as such. However, it is in fact a “new” galaxy in the process of forming. Two separate galaxies have been gradually drawn together, attracted by gravity, and have collided. We now see them merging into a single structure. As the merging process continues, individual stars are thrown out of their original orbits and placed onto entirely new paths, some very distant from the region of the collision itself. Since the stars produce the light we see, the “galaxy” now appears to have a highly chaotic shape. Eventually, this new galaxy will settle down into a stable shape, which may not resemble either of the two original galaxies. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

This colorful bubble is a planetary nebula called NGC 6818, also known as the Little Gem Nebula. It is located in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), roughly 6,000 light-years away from us. The rich glow of the cloud is just over half a light-year across — humongous compared to its tiny central star — but still a little gem on a cosmic scale. When stars like the sun enter "retirement," they shed their outer layers into space to create glowing clouds of gas called planetary nebulae. This ejection of mass is uneven, and planetary nebulae can have very complex shapes. NGC 6818 shows knotty filament-like structures and distinct layers of material, with a bright and enclosed central bubble surrounded by a larger, more diffuse cloud. Scientists believe that the stellar wind from the central star propels the outflowing material, sculpting the elongated shape of NGC 6818. As this fast wind smashes through the slower-moving cloud it creates particularly bright blowouts at the bubble’s outer layers. Hubble previously imaged this nebula back in 1997 with its Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, using a mix of filters that highlighted emission from ionized oxygen and hydrogen. This image, while from the same camera, uses different filters to reveal a different view of the nebula. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release October 19, 2010 Though the universe is chock full of spiral-shaped galaxies, no two look exactly the same. This face-on spiral galaxy, called NGC 3982, is striking for its rich tapestry of star birth, along with its winding arms. The arms are lined with pink star-forming regions of glowing hydrogen, newborn blue star clusters, and obscuring dust lanes that provide the raw material for future generations of stars. The bright nucleus is home to an older population of stars, which grow ever more densely packed toward the center. NGC 3982 is located about 68 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. The galaxy spans about 30,000 light-years, one-third of the size of our Milky Way galaxy. This color image is composed of exposures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2), the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). The observations were taken between March 2000 and August 2009. The rich color range comes from the fact that the galaxy was photographed invisible and near-infrared light. Also used was a filter that isolates hydrogen emission that emanates from bright star-forming regions dotting the spiral arms. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: A. Riess (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

To view a video of this story go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8448332724">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8448332724</a> Working with astronomical image processors at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md., renowned astro-photographer Robert Gendler has taken science data from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) archive and combined it with his own ground-based observations to assemble a photo illustration of the magnificent spiral galaxy M106. Gendler retrieved archival Hubble images of M106 to assemble a mosaic of the center of the galaxy. He then used his own and fellow astro-photographer Jay GaBany's observations of M106 to combine with the Hubble data in areas where there was less coverage, and finally, to fill in the holes and gaps where no Hubble data existed. The center of the galaxy is composed almost entirely of HST data taken by the Advanced Camera for Surveys, Wide Field Camera 3, and Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 detectors. The outer spiral arms are predominantly HST data colorized with ground-based data taken by Gendler's and GaBany's 12.5-inch and 20-inch telescopes, located at very dark remote sites in New Mexico. The image also reveals the optical component of the "anomalous arms" of M106, seen here as red, glowing hydrogen emission. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/m106.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/m106.html</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), R. Gendler (for the Hubble Heritage Team), and G. Bacon (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This Hubble Space Telescope image reveals a rainbow of colors in this dying star, called IC 446. Like many other so-called planetary nebulae, IC 4406 exhibits a high degree of symmetry. The nebula's left and right halves are nearly mirror images of the other. If we could fly around IC 446 in a spaceship, we would see that the gas and dust form a vast donut of material streaming outward from the dying star. We do not see the donut shape in this photograph because we are viewing IC 4406 from the Earth-orbiting HST. From this vantage point, we are seeing the side of the donut. This side view allows us to see the intricate tendrils of material that have been compared to the eye's retina. In fact, IC 4406 is dubbed the "Retina Nebula." The donut of material confines the intense radiation coming from the remnant of the dying star. Gas on the inside of the donut is ionized by light from the central star and glows. Light from oxygen atoms is rendered blue in this image; hydrogen is shown as green, and nitrogen as red. The range of color in the final image shows the differences in concentration of these three gases in the nebula. This image is a composite of data taken by HST's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 in June 2001 and in January 2002 by Bob O'Dell (Vanderbilt University) and collaborators, and in January by the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI). Filters used to create this color image show oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen gas glowing in this object.

Image released 11 Aug 2011. The "Necklace Nebula" is located 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagitta (the Arrow). In this composite image, taken on July 2, 2011, Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 captured the glow of hydrogen (blue), oxygen (green), and nitrogen (red). The object, aptly named the Necklace Nebula, is a recently discovered planetary nebula, the glowing remains of an ordinary, Sun-like star. The nebula consists of a bright ring, measuring 12 trillion miles wide, dotted with dense, bright knots of gas that resemble diamonds in a necklace. <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/necklace-nebula.html" target="_blank" rel="nofollow"></a> <b>Credit:</b> NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This neat little galaxy is known as NGC 4526. Its dark lanes of dust and bright diffuse glow make the galaxy appear to hang like a halo in the emptiness of space in this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Although this image paints a picture of serenity, the galaxy is anything but. It is one of the brightest lenticular galaxies known, a category that lies somewhere between spirals and ellipticals. It has hosted two known supernova explosions, one in 1969 and another in 1994, and is known to have a colossal supermassive black hole at its center that has the mass of 450 million suns. NGC 4526 is part of the Virgo cluster of galaxies. Ground-based observations of galaxies in this cluster have revealed that a quarter of these galaxies seem to have rapidly rotating disks of gas at their centers. The most spectacular of these is this galaxy, NGC 4526, and its spinning disk of gas, dust, and stars reaches out uniquely far from its heart, spanning some seven percent of the galaxy's entire radius. This disk is moving incredibly fast, spinning at more than 250 kilometers per second. The dynamics of this quickly whirling region were actually used to infer the mass of NGC 4526’s central black hole — a technique that had not been used before to constrain a galaxy’s central black hole. This image was taken with Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 and the Advanced Camera for Surveys. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt
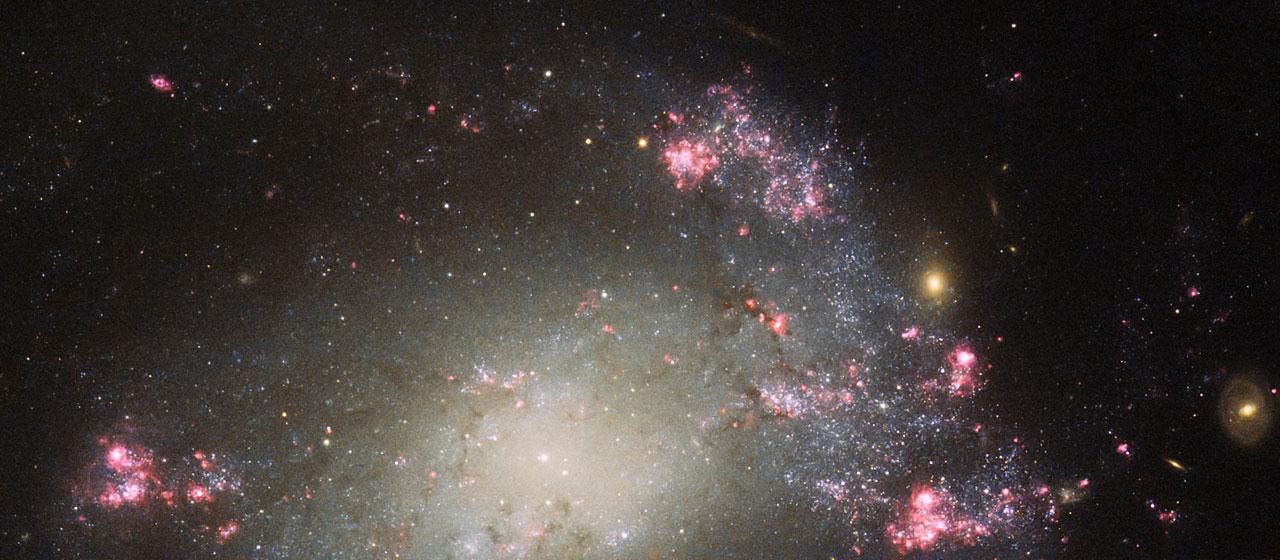

Bursts of pink and red, dark lanes of mottled cosmic dust, and a bright scattering of stars — this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows part of a messy barred spiral galaxy known as NGC 428. It lies approximately 48 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cetus (The Sea Monster). Although a spiral shape is still just about visible in this close-up shot, overall NGC 428’s spiral structure appears to be quite distorted and warped, thought to be a result of a collision between two galaxies. There also appears to be a substantial amount of star formation occurring within NGC 428 — another telltale sign of a merger. When galaxies collide their clouds of gas can merge, creating intense shocks and hot pockets of gas and often triggering new waves of star formation. NGC 428 was discovered by William Herschel in December 1786. More recently a type Ia supernova designated SN2013ct was discovered within the galaxy by Stuart Parker of the BOSS (Backyard Observatory Supernova Search) project in Australia and New Zealand, although it is unfortunately not visible in this image. This image was captured by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) and Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). A version of this image was entered into the Hubble’s Hidden Treasures Image Processing competition by contestants Nick Rose and the Flickr user penninecloud. Links: Nick Rose’s image on Flickr Penninecloud’s image on Flickr

This image, taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 on board the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows the globular cluster Terzan 1. Lying around 20 000 light-years from us in the constellation of Scorpius (The Scorpion), it is one of about 150 globular clusters belonging to our galaxy, the Milky Way. Typical globular clusters are collections of around a hundred thousand stars, held together by their mutual gravitational attraction in a spherical shape a few hundred light-years across. It is thought that every galaxy has a population of globular clusters. Some, like the Milky Way, have a few hundred, while giant elliptical galaxies can have several thousand. They contain some of the oldest stars in a galaxy, hence the reddish colours of the stars in this image — the bright blue ones are foreground stars, not part of the cluster. The ages of the stars in the globular cluster tell us that they were formed during the early stages of galaxy formation! Studying them can also help us to understand how galaxies formed. Terzan 1, like many globular clusters, is a source of X-rays. It is likely that these X-rays come from binary star systems that contain a dense neutron star and a normal star. The neutron star drags material from the companion star, causing a burst of X-ray emission. The system then enters a quiescent phase in which the neutron star cools, giving off X-ray emission with different characteristics, before enough material from the companion builds up to trigger another outburst.
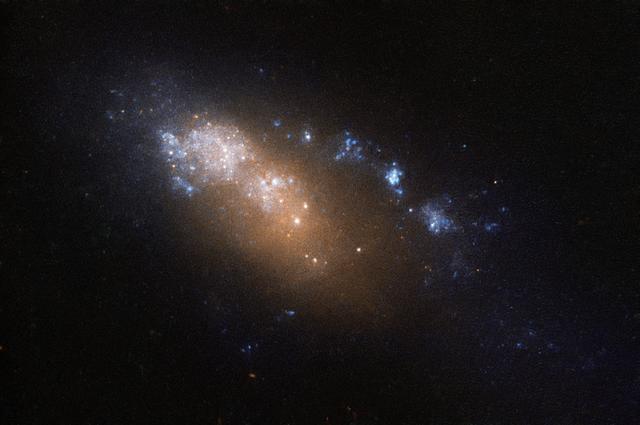

The galaxy, NGC 178 may be small, but it packs quite a punch. Measuring around 40,000 light-years across, its diameter is less than half that of the Milky Way, and it is accordingly classified as a dwarf galaxy. Despite its diminutive size, NGC 178 is busy forming new stars. On average, the galaxy forms stars totaling around half the mass of the Sun per year — enough to label it a starburst galaxy. The galaxy’s discovery is an interesting, and somewhat confusing, story. It was originally discovered by American astronomer Ormond Stone in 1885 and dubbed NGC 178, but its position in the sky was recorded incorrectly — by accident the value for the galaxy’s right ascension (which can be thought of as the celestial equivalent of terrestrial longitude) was off by a considerable amount. In the years that followed NGC 178 was spotted again, this time by French astronomer Stéphane Javelle. As no cataloged object occupied that position in the sky, Javelle believed he had discovered a new galaxy and entered it into the expanded Index Catalog under the name IC 39. Later, American astronomer Herbert Howe also observed the object and corrected Stone’s initial mistake. Many years later, astronomers finally noticed that NGC 178 and IC 39 were actually the same object! This image of NGC 178 comprises data gathered by the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA

Release Date: May 3, 2004 A Dying Star Shrouded by a Blanket of Hailstones Forms the Bug Nebula (NGC 6302) The Bug Nebula, NGC 6302, is one of the brightest and most extreme planetary nebulae known. The fiery, dying star at its center is shrouded by a blanket of icy hailstones. This NASA Hubble Wide Field Plantery Camera 2 image shows impressive walls of compressed gas, laced with trailing strands and bubbling outflows. Object Names: NGC 6302, Bug Nebula Image Type: Astronomical Credit: NASA, ESA and A.Zijlstra (UMIST, Manchester, UK) To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/gallery/album/nebula/pr2004046a/" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/gallery/album/nebula/pr2004046a/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
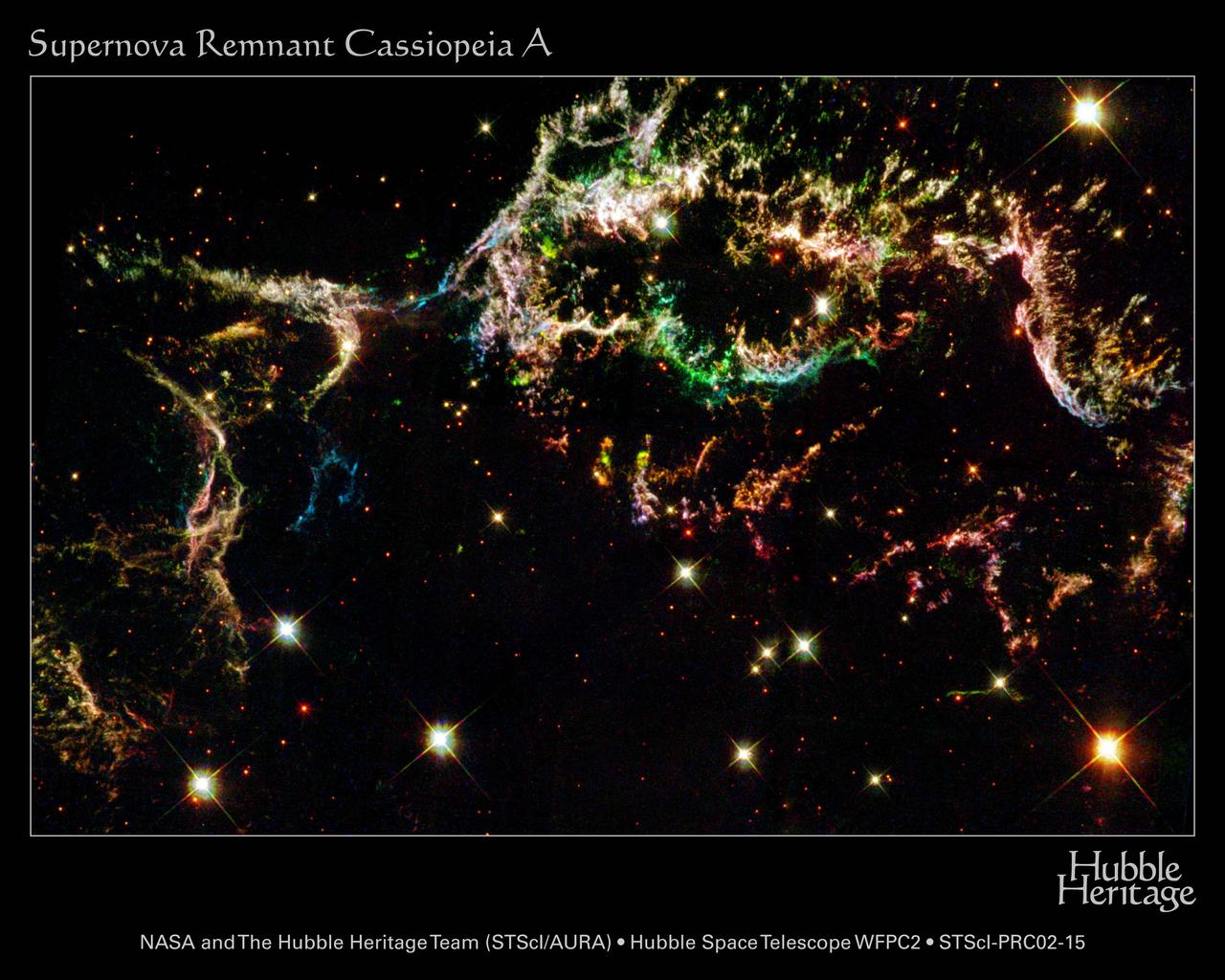
The colorful streamers that float across the sky in this photo taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST) were created by the universe's biggest firecracker, the titanic supernova explosion of a massive star. The light from the exploding star reached Earth 320 years ago, nearly a century before the United States celebrated its birth with a bang. The dead star's shredded remains are called Cassiopeia A, or "Cas A" for short. Cas A is the youngest known supernova remnant in our Milky Way Galaxy and resides 10,000 light-years away in the constellation Cassiopeia, so the star actually blew up 10,000 years before the light reached Earth in the late 1600s. This HST image of Cas A shows for the first time that the debris is arranged into thousands of small, cooling knots of gas. This material eventually will be recycled into building new generations of stars and planets. Our own Sun and planets are constructed from the debris of supernovae that exploded billions of years ago. This photo shows the upper rim of the super nova remnant's expanding shell. Near the top of the image are dozens of tiny clumps of matter. Each small clump, originally just a small fragment of the star, is tens of times larger than the diameter of our solar system. The colors highlight parts of the debris where chemical elements are glowing. The dark blue fragments, for example, are richest in oxygen; the red material is rich in sulfur. The images were taken with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 in January 2000 and January 2002. Image Credit: NASA and HST team (Stoics/AURA). Acknowledgment: R. Fesen (Darmouth) and J. Morse ( Univ. of Colorado).
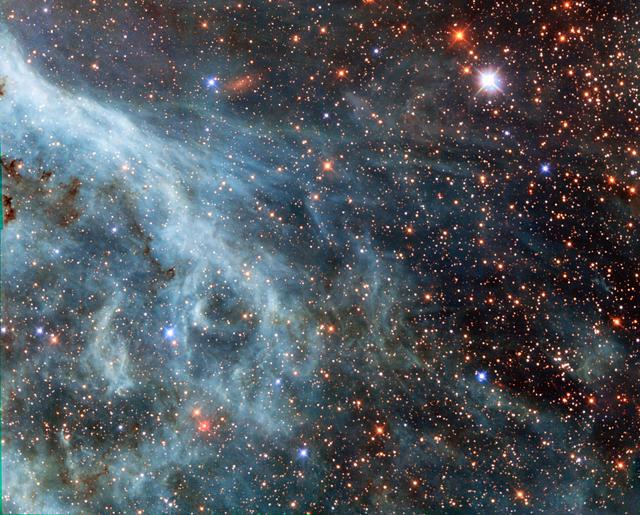

The brightly glowing plumes seen in this image are reminiscent of an underwater scene, with turquoise-tinted currents and nebulous strands reaching out into the surroundings. However, this is no ocean. This image actually shows part of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small nearby galaxy that orbits our galaxy, the Milky Way, and appears as a blurred blob in our skies. The NASA/European Space Agency (ESA) Hubble Space Telescope has peeked many times into this galaxy, releasing stunning images of the whirling clouds of gas and sparkling stars (opo9944a, heic1301, potw1408a). This image shows part of the Tarantula Nebula's outskirts. This famously beautiful nebula, located within the LMC, is a frequent target for Hubble (heic1206, heic1402). In most images of the LMC the color is completely different to that seen here. This is because, in this new image, a different set of filters was used. The customary R filter, which selects the red light, was replaced by a filter letting through the near-infrared light. In traditional images, the hydrogen gas appears pink because it shines most brightly in the red. Here however, other less prominent emission lines dominate in the blue and green filters. This data is part of the Archival Pure Parallel Project (APPP), a project that gathered together and processed over 1,000 images taken using Hubble’s Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, obtained in parallel with other Hubble instruments. Much of the data in the project could be used to study a wide range of astronomical topics, including gravitational lensing and cosmic shear, exploring distant star-forming galaxies, supplementing observations in other wavelength ranges with optical data, and examining star populations from stellar heavyweights all the way down to solar-mass stars. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA: acknowledgement: Josh Barrington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
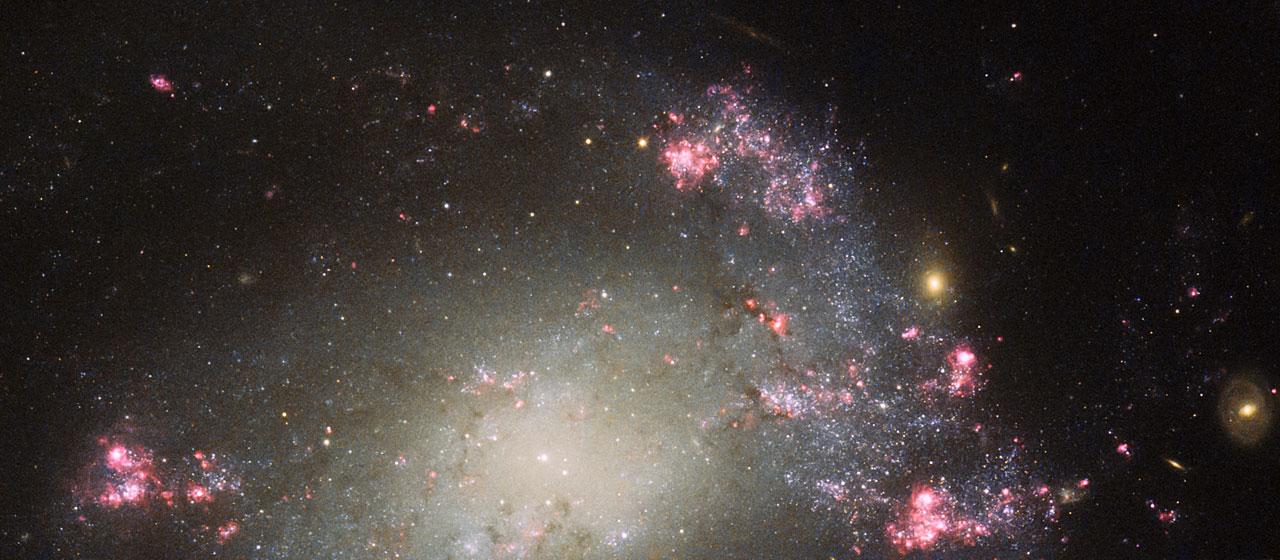

Bursts of pink and red, dark lanes of mottled cosmic dust, and a bright scattering of stars — this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows part of a messy barred spiral galaxy known as NGC 428. It lies approximately 48 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cetus (The Sea Monster). Although a spiral shape is still just about visible in this close-up shot, overall NGC 428’s spiral structure appears to be quite distorted and warped, thought to be a result of a collision between two galaxies. There also appears to be a substantial amount of star formation occurring within NGC 428 — another telltale sign of a merger. When galaxies collide their clouds of gas can merge, creating intense shocks and hot pockets of gas, and often triggering new waves of star formation. NGC 428 was discovered by William Herschel in December 1786. More recently a type of supernova designated SN2013ct was discovered within the galaxy by Stuart Parker of the BOSS (Backyard Observatory Supernova Search) project in Australia and New Zealand, although it is unfortunately not visible in this image. This image was captured by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) and Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). Image credit: ESA/Hubble and NASA and S. Smartt (Queen's University Belfast), Acknowledgements: Nick Rose and Flickr user pennine cloud <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release March 2, 2012 This composite image shows the distribution of dark matter, galaxies, and hot gas in the core of the merging galaxy cluster Abell 520, formed from a violent collision of massive galaxy clusters. The natural-color image of the galaxies was taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and with the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope in Hawaii. Superimposed on the image are "false-colored" maps showing the concentration of starlight, hot gas, and dark matter in the cluster. Starlight from galaxies, derived from observations by the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope, is colored orange. The green-tinted regions show hot gas, as detected by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. The gas is evidence that a collision took place. The blue-colored areas pinpoint the location of most of the mass in the cluster, which is dominated by dark matter. Dark matter is an invisible substance that makes up most of the universe's mass. The dark-matter map was derived from the Hubble Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 observations, by detecting how light from distant objects is distorted by the cluster galaxies, an effect called gravitational lensing. The blend of blue and green in the center of the image reveals that a clump of dark matter resides near most of the hot gas, where very few galaxies are found. This finding confirms previous observations of a dark-matter core in the cluster. The result could present a challenge to basic theories of dark matter, which predict that galaxies should be anchored to dark matter, even during the shock of a collision. Abell 520 resides 2.4 billion light-years away. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/dark-matter-core.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/dark-matter-cor...</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, CFHT, CXO, M.J. Jee (University of California, Davis), and A. Mahdavi (San Francisco State University) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>