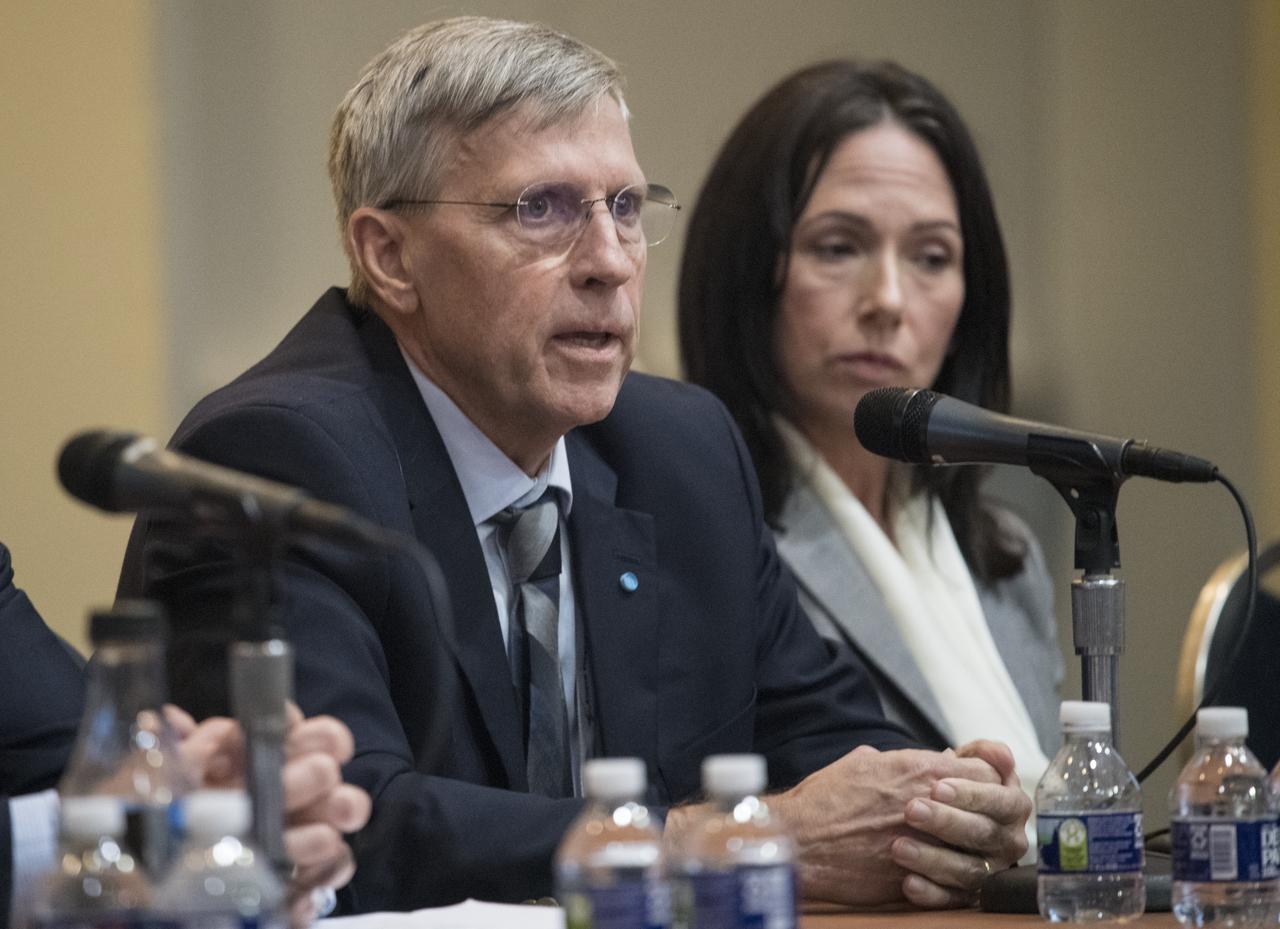

William Paloski, Director of NASA’s Human Research Program, is seen during a discussion titled “ISS-Moon-Mars: Using Spaceflight Platforms to Study and Simulate Future Missions” during the the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Monday, Oct. 21, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
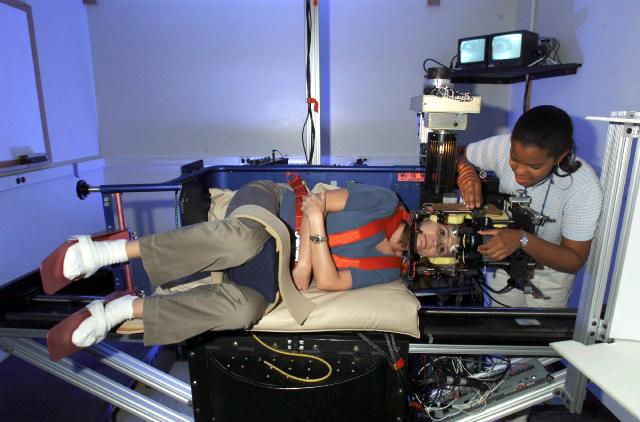
The short-arm centrifuge subjects an astronaut to conflicting sensory input and study the astronaut's perception of motion. It is one of several instruments used in the Spatial Reorientation Following Space Flight investigation to be conducted on crewmembers. During space flight, the vestibular organs no longer respond in a familiar way. Instead, inputs from the irner ear do not match those coming from the eyes. While on Earth, you can open your eyes to see if you truly are spinning, but astronauts do not have this luxury. Astronauts can see the floor, but have no sense of down; when they bend their heads forward, the otoliths are not stimulated properly. This state, called sensory conflict, must be resolved by the brain to maintain orientation. When they first return to Earth, astronauts are again disoriented because of sensory conflict. They undergo a period of spatial reorientation, as their brains reconcile what their eyes see and what their vestibular system senses. Recovery can take anywhere from hours to days depending on the length of the mission. Principal Investigator: Dr. William Paloski, Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX.
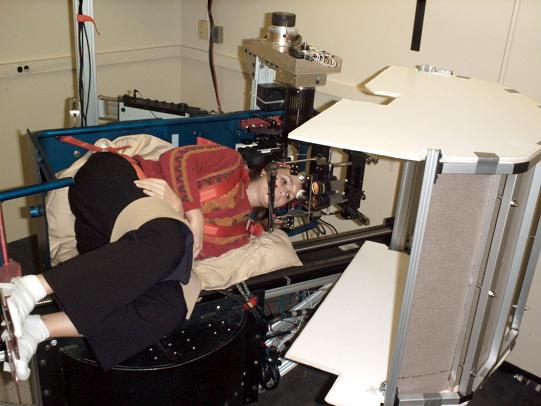

The short-arm centrifuge subjects an astronaut to conflicting sensory input and study the astronaut's perception of motion. It is one of several instruments used in the Spatial Reorientation Following Space Flight investigation to be conducted after astronauts return to Earth. During space flight, the vestibular organs no longer respond in a familiar way. Instead, inputs from the irner ear do not match those coming from the eyes. While on Earth, you can open your eyes to see if you truly are spinning, but astronauts do not have this luxury. Astronauts can see the floor, but have no sense of down; when they bend their heads forward, the otoliths are not stimulated properly. This state, called sensory conflict, must be resolved by the brain to maintain orientation. When they first return to Earth, astronauts are again disoriented because of sensory conflict. They undergo a period of spatial reorientation, as their brains reconcile what their eyes see and what their vestibular system senses. Recovery can take anywhere from hours to days depending on the length of the mission. Principal Investigator: Dr. William Paloski, Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX.