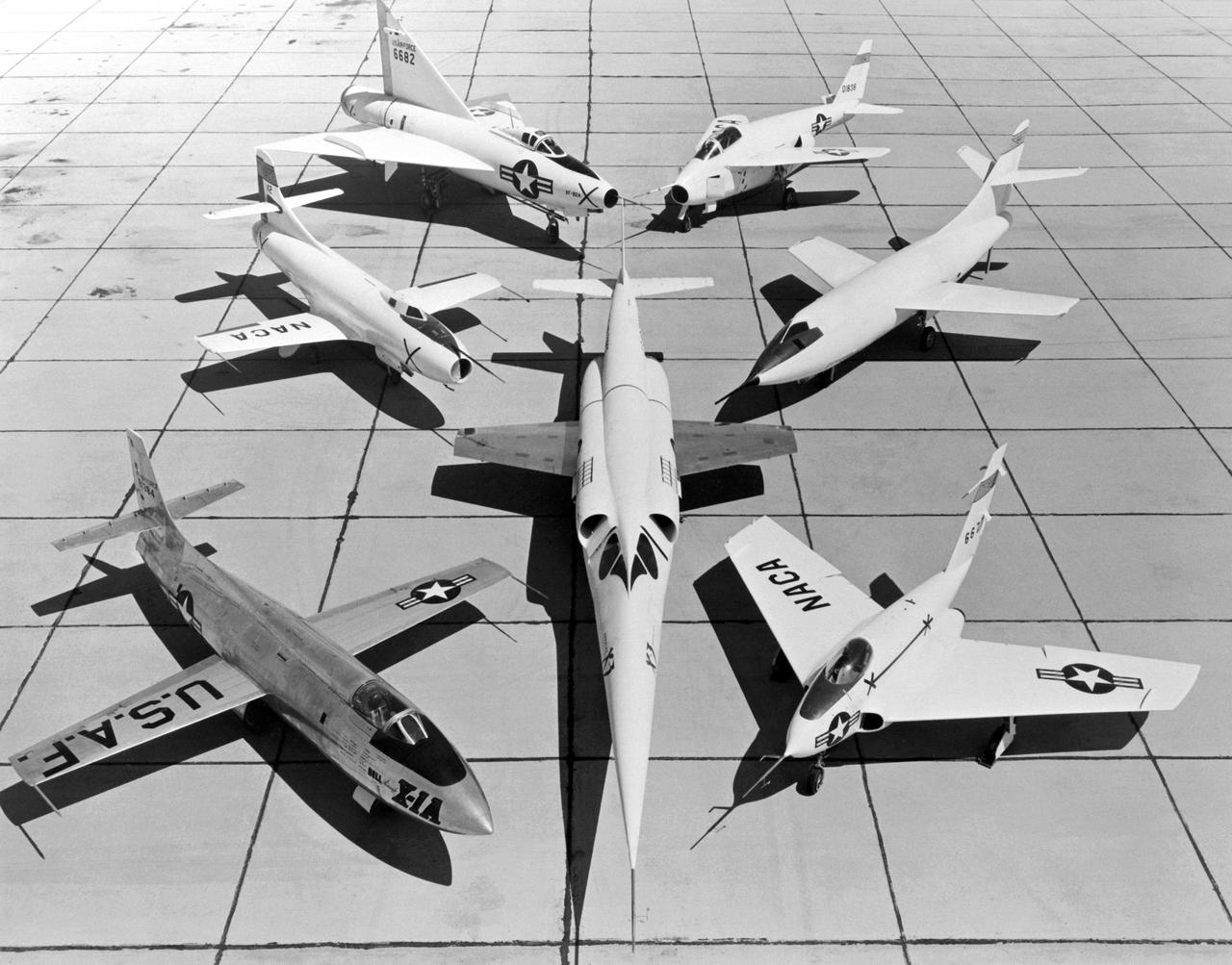

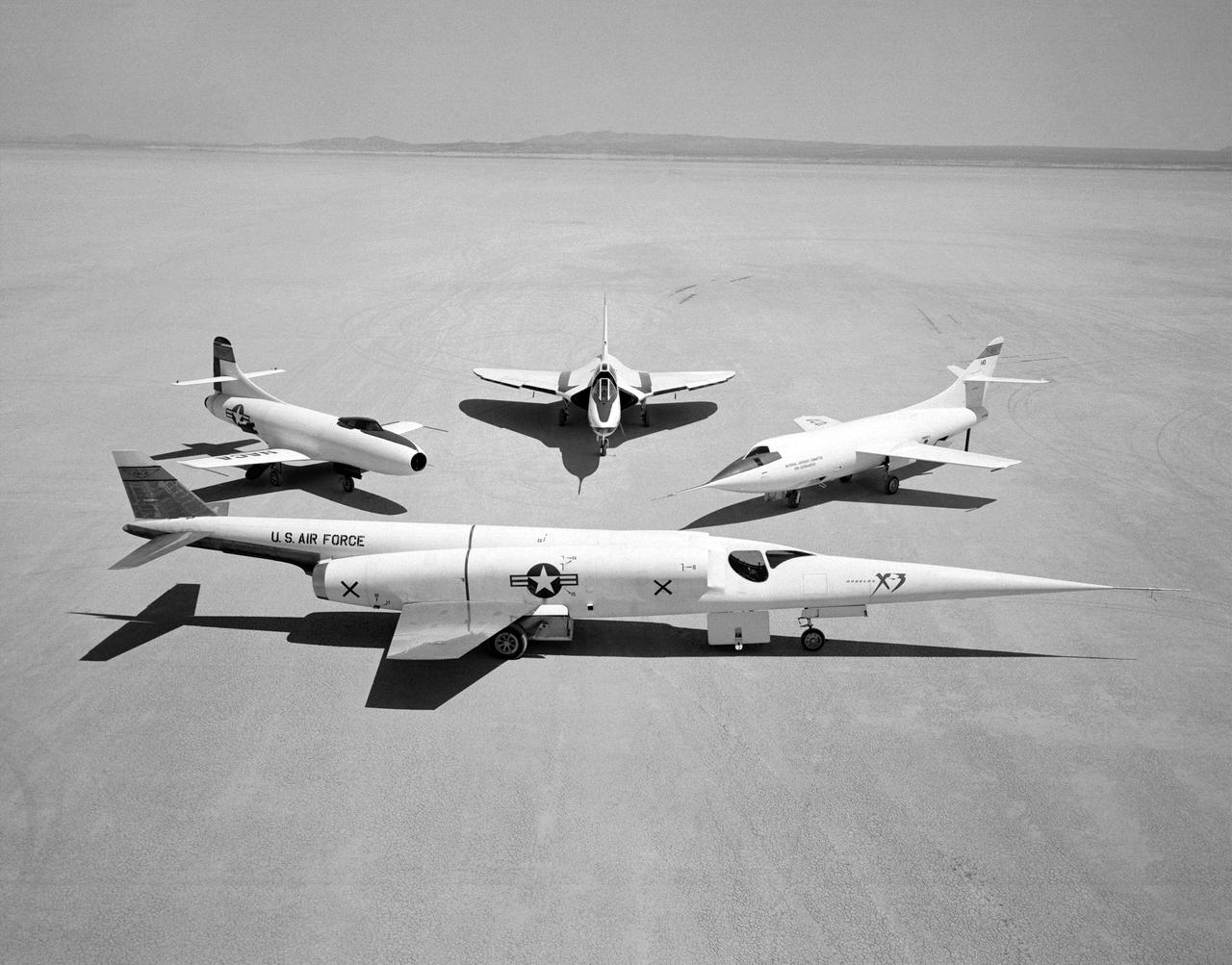
A 1953 photo of some of the research aircraft at the NACA High-Speed Flight Research Station (now known as the the Dryden Flight Research Center). The photo shows the X-3 (center) and, clockwise from left: X-1A (Air Force serial number 48-1384), the third D-558-1 (NACA tail number 142), XF-92A, X-5, D-558-2, and X-4.
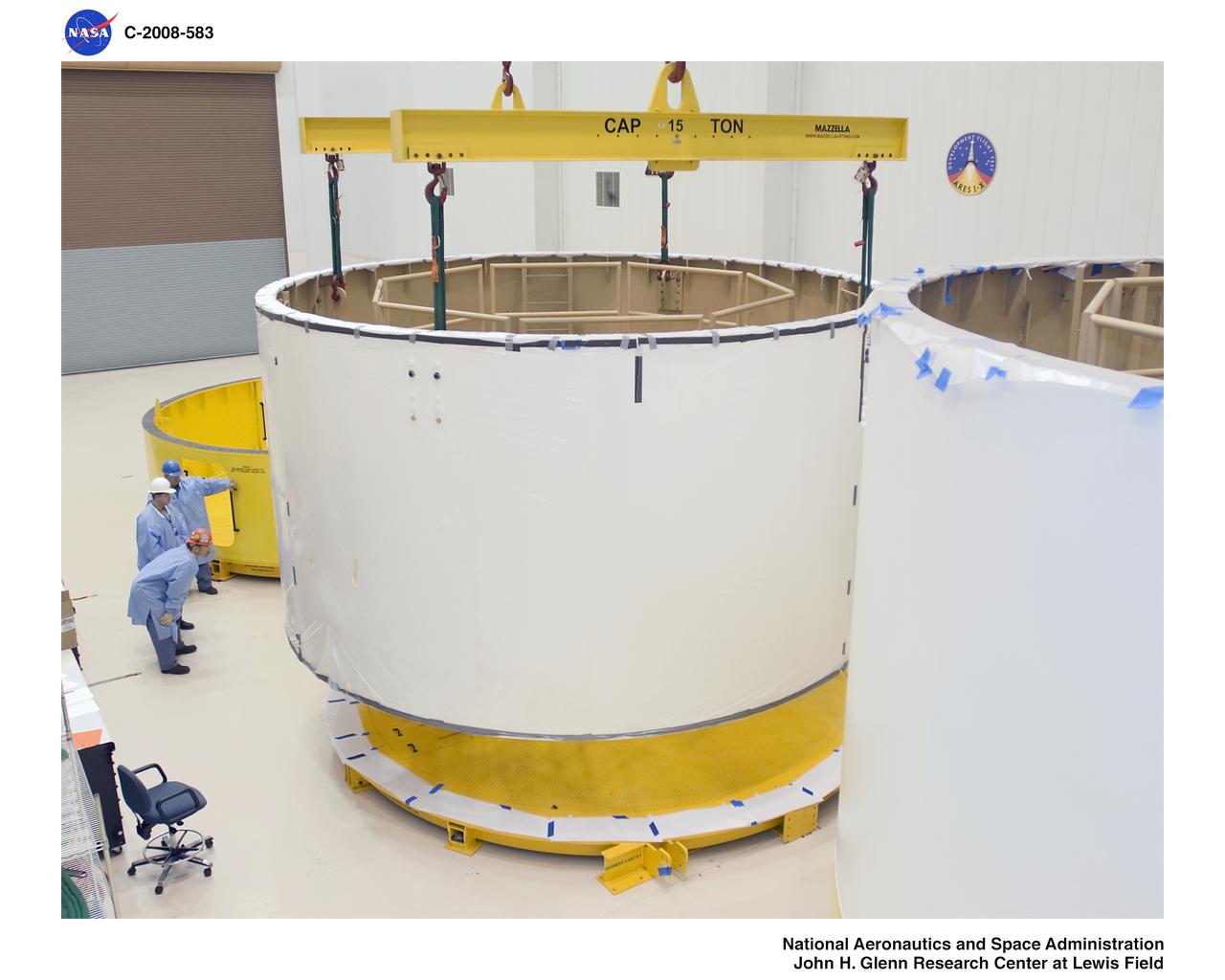

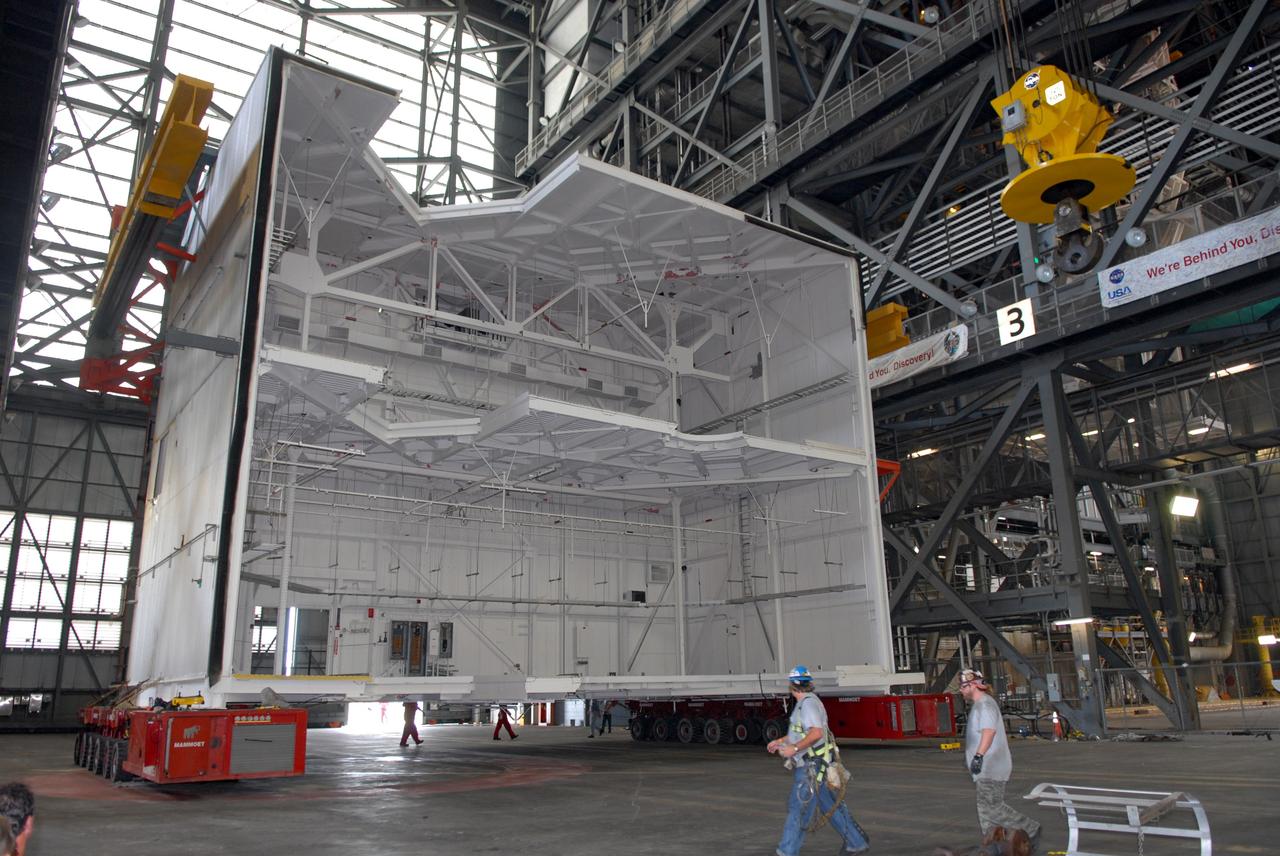
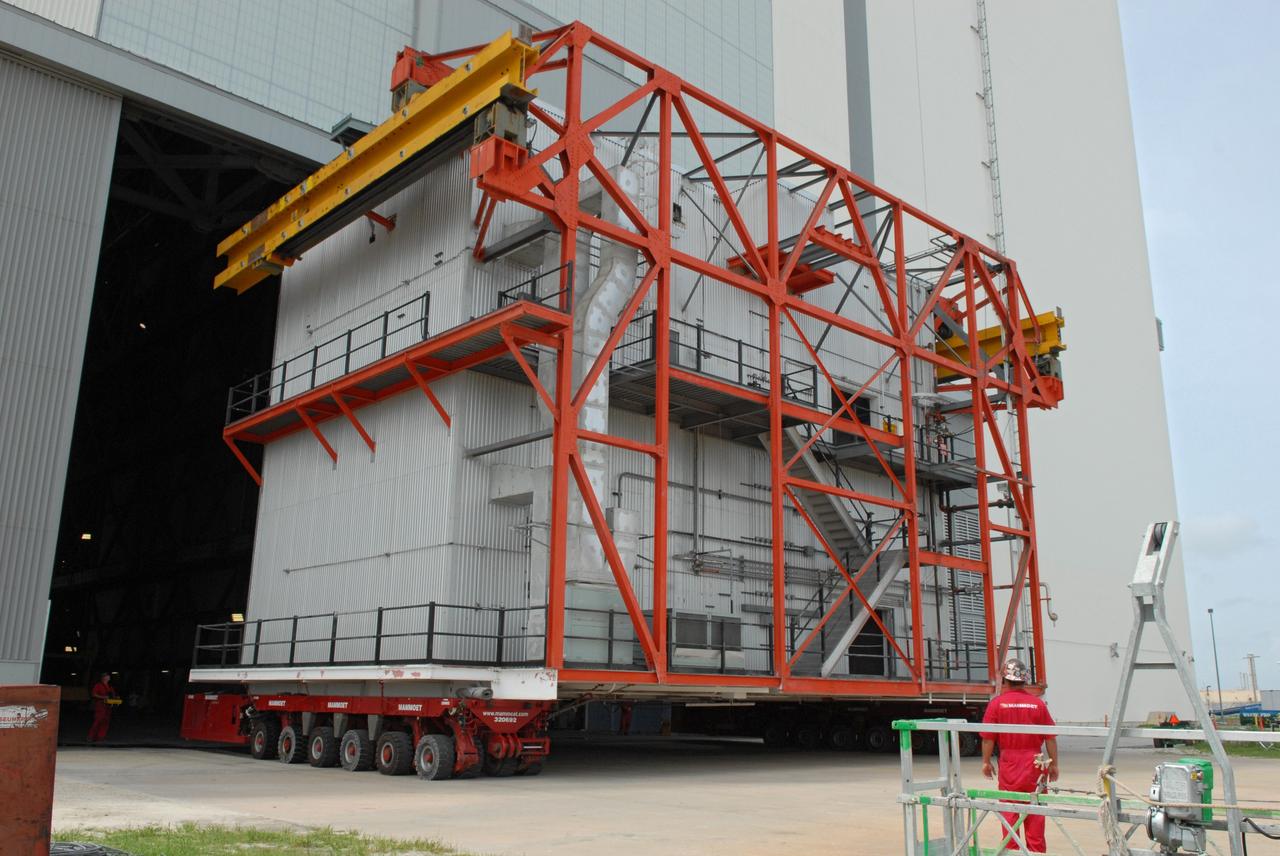
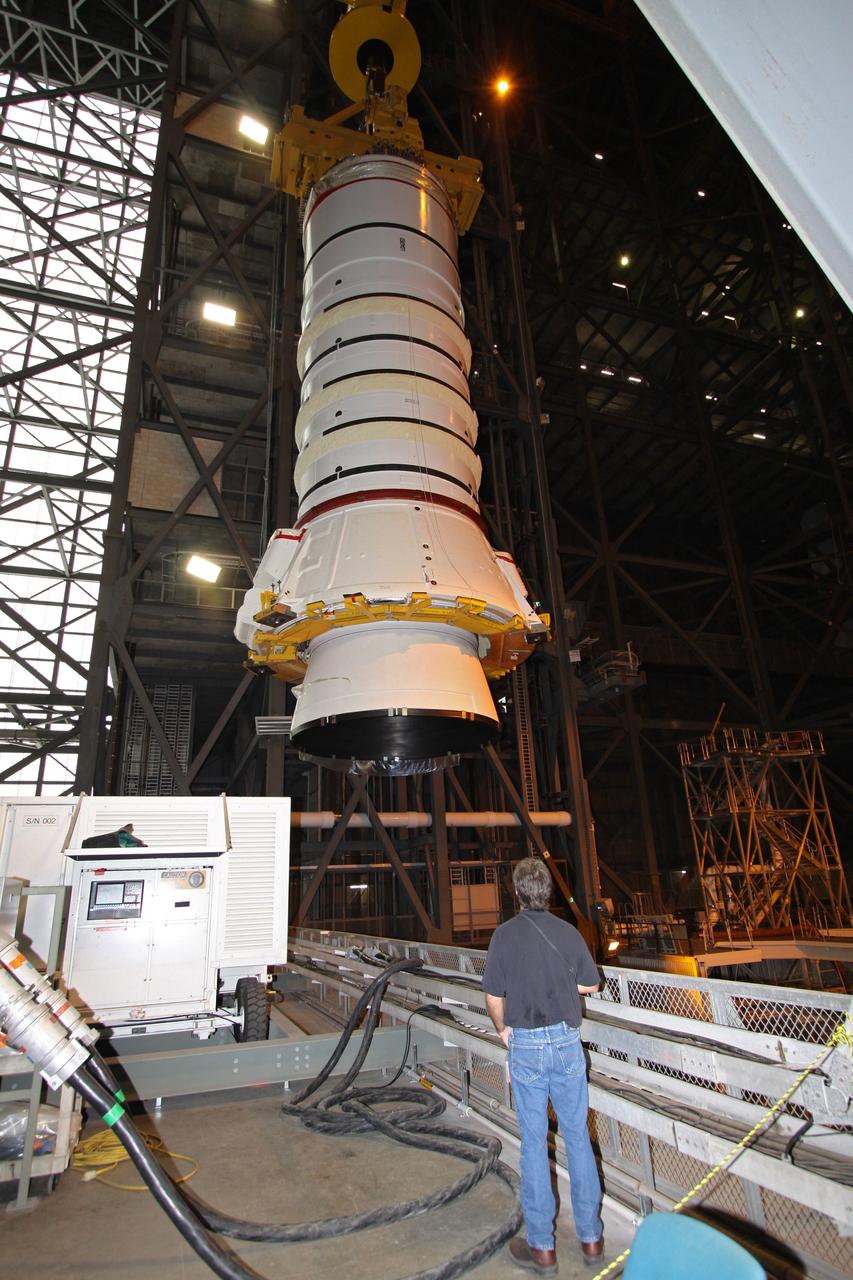
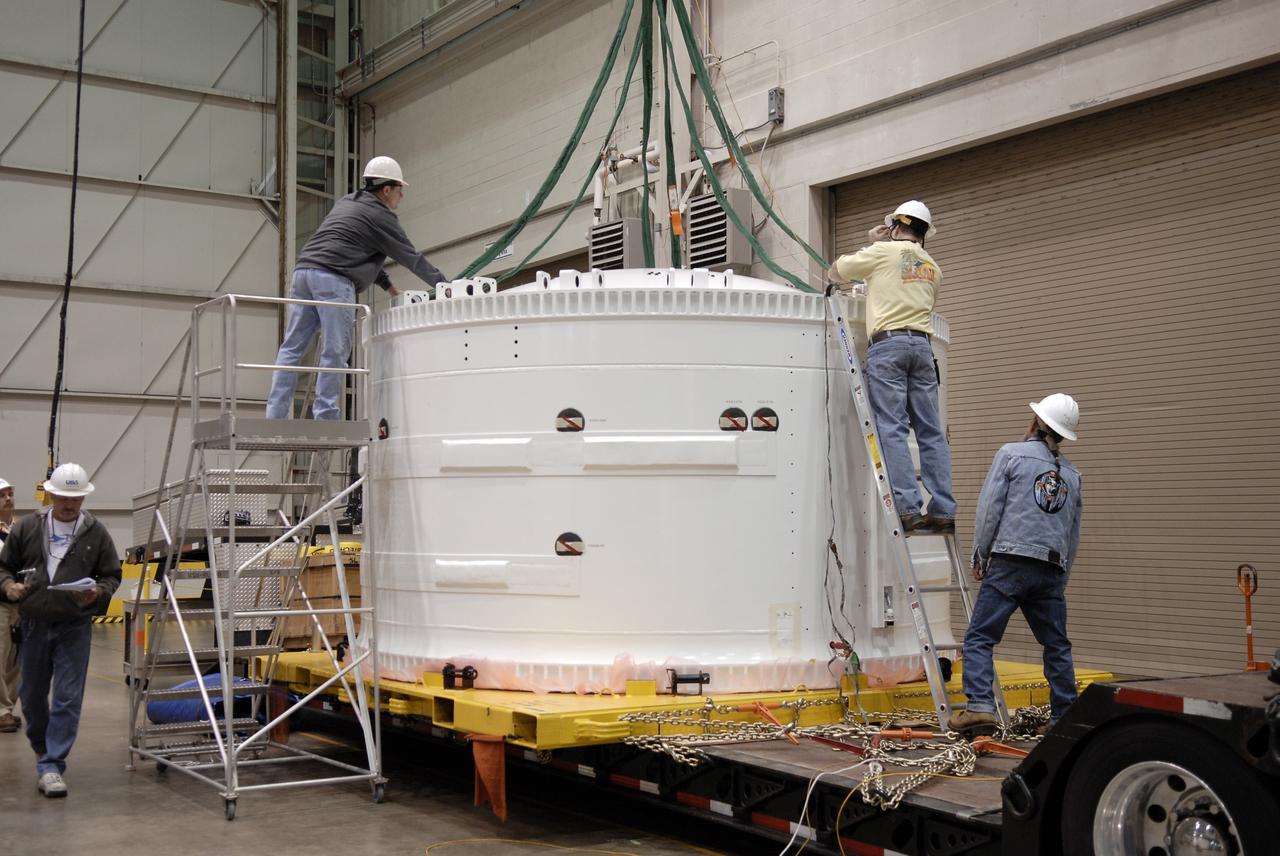
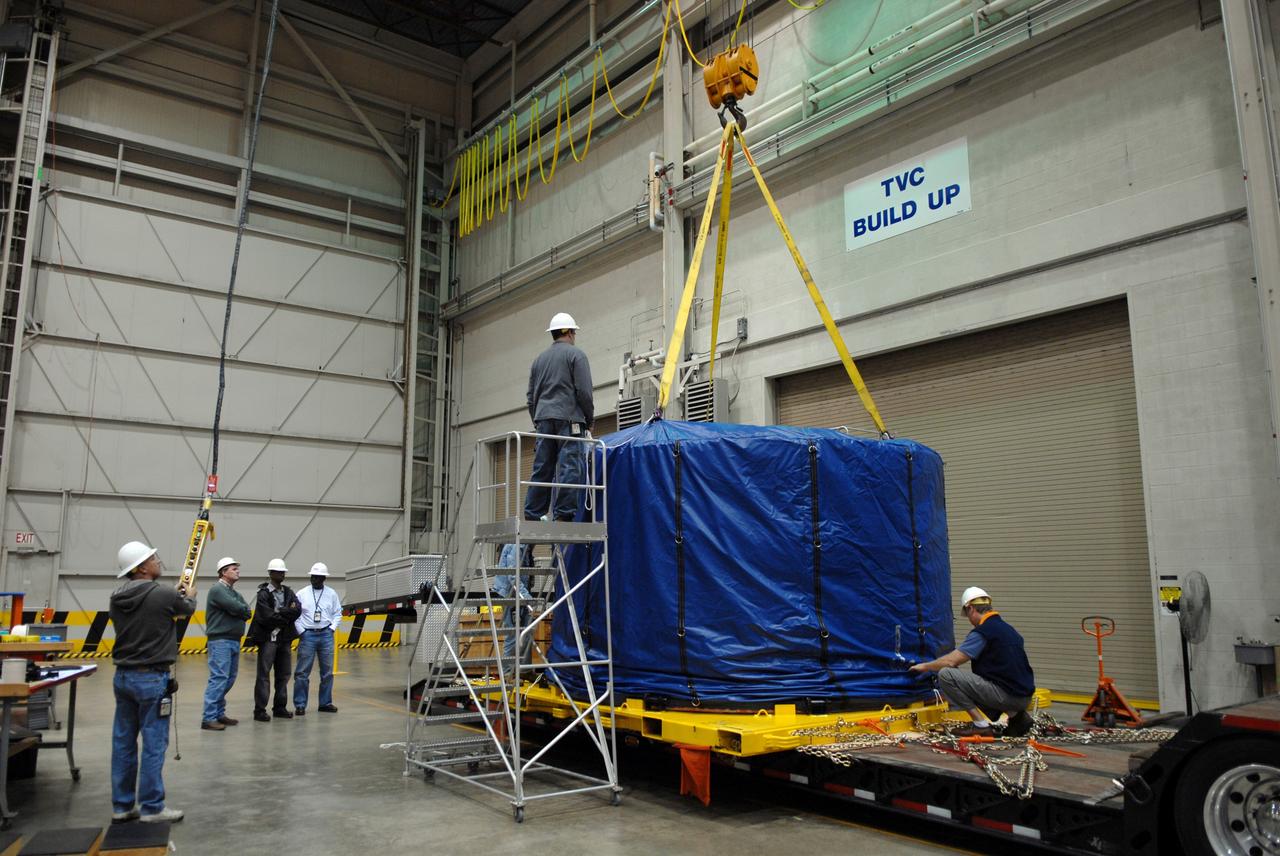
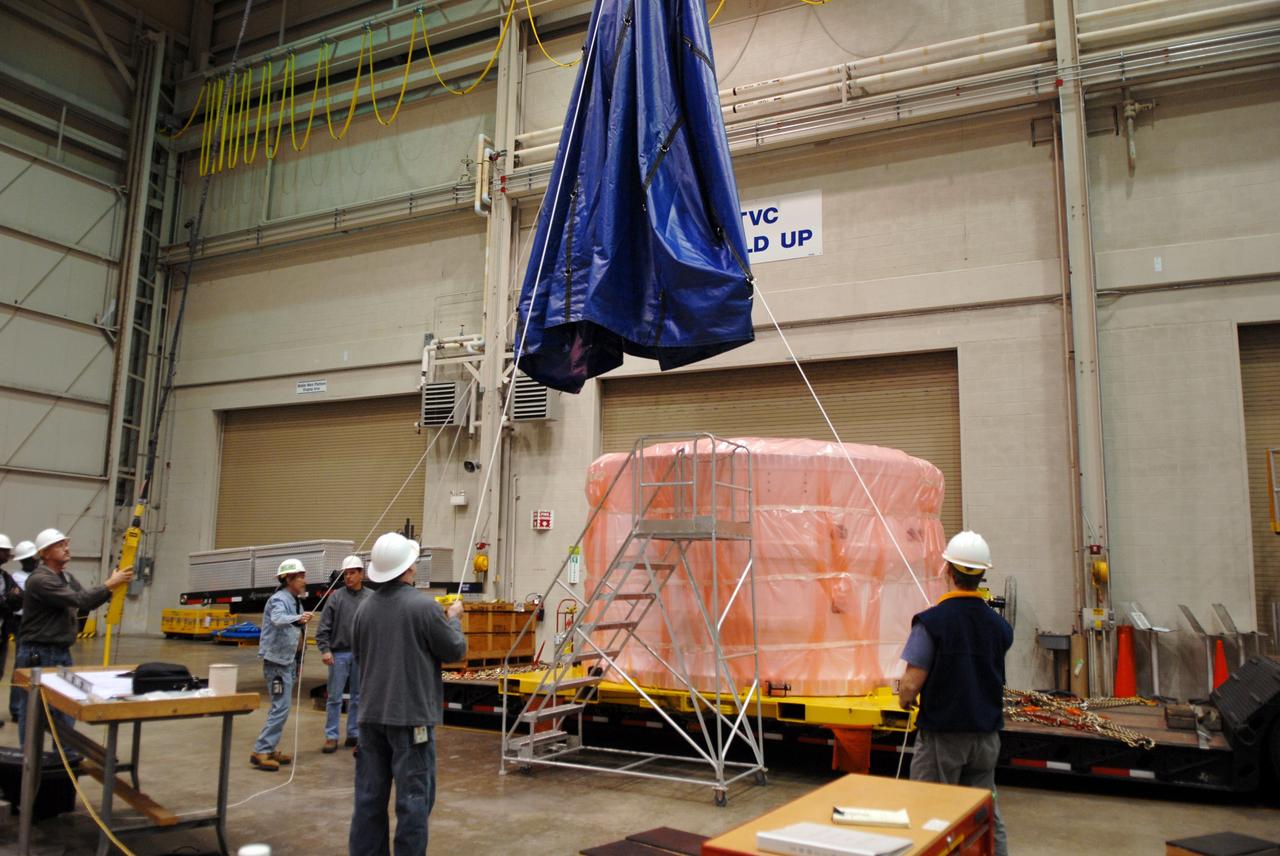
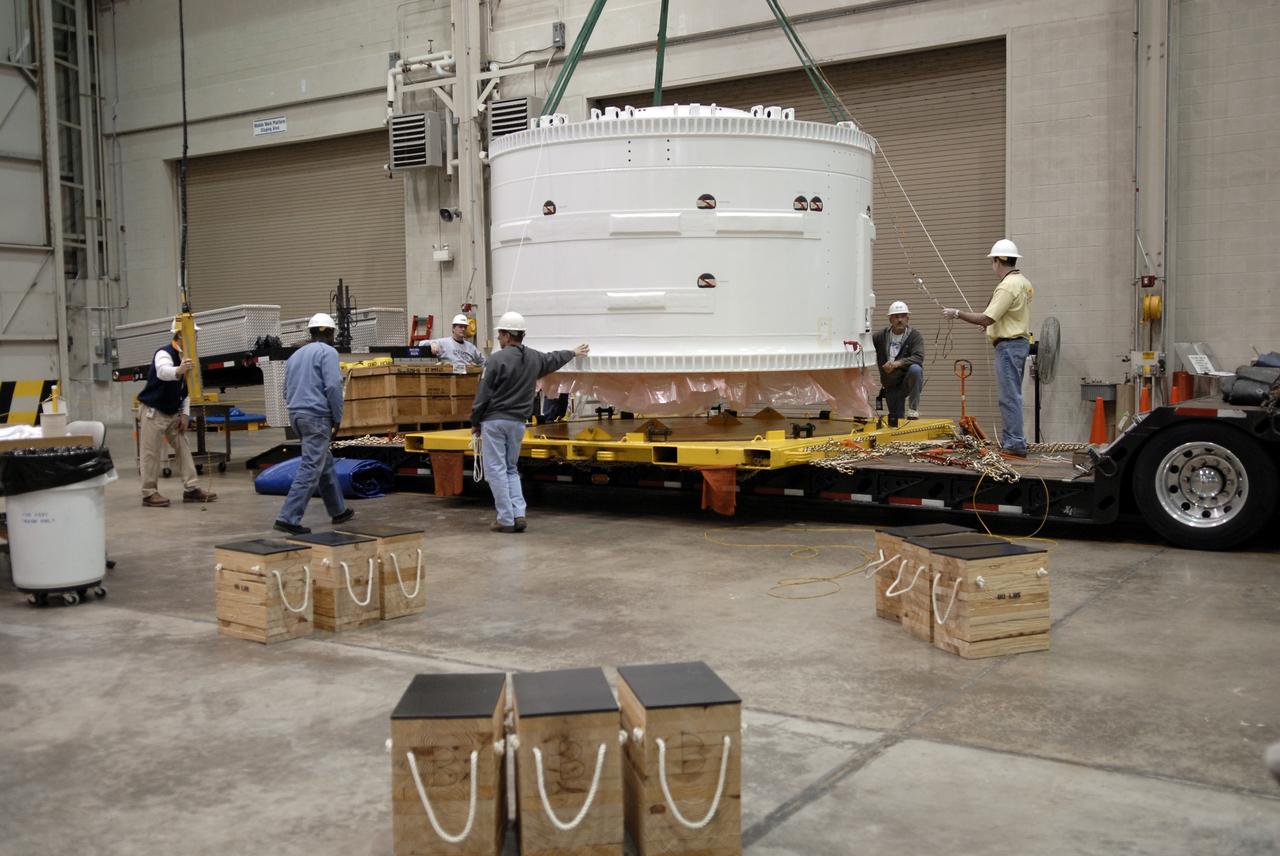
Ares 1-X segment US-3 being lifted onto the cart prior to being stacked onto US-2 to start forming the Ares 1-X USS Super Stack
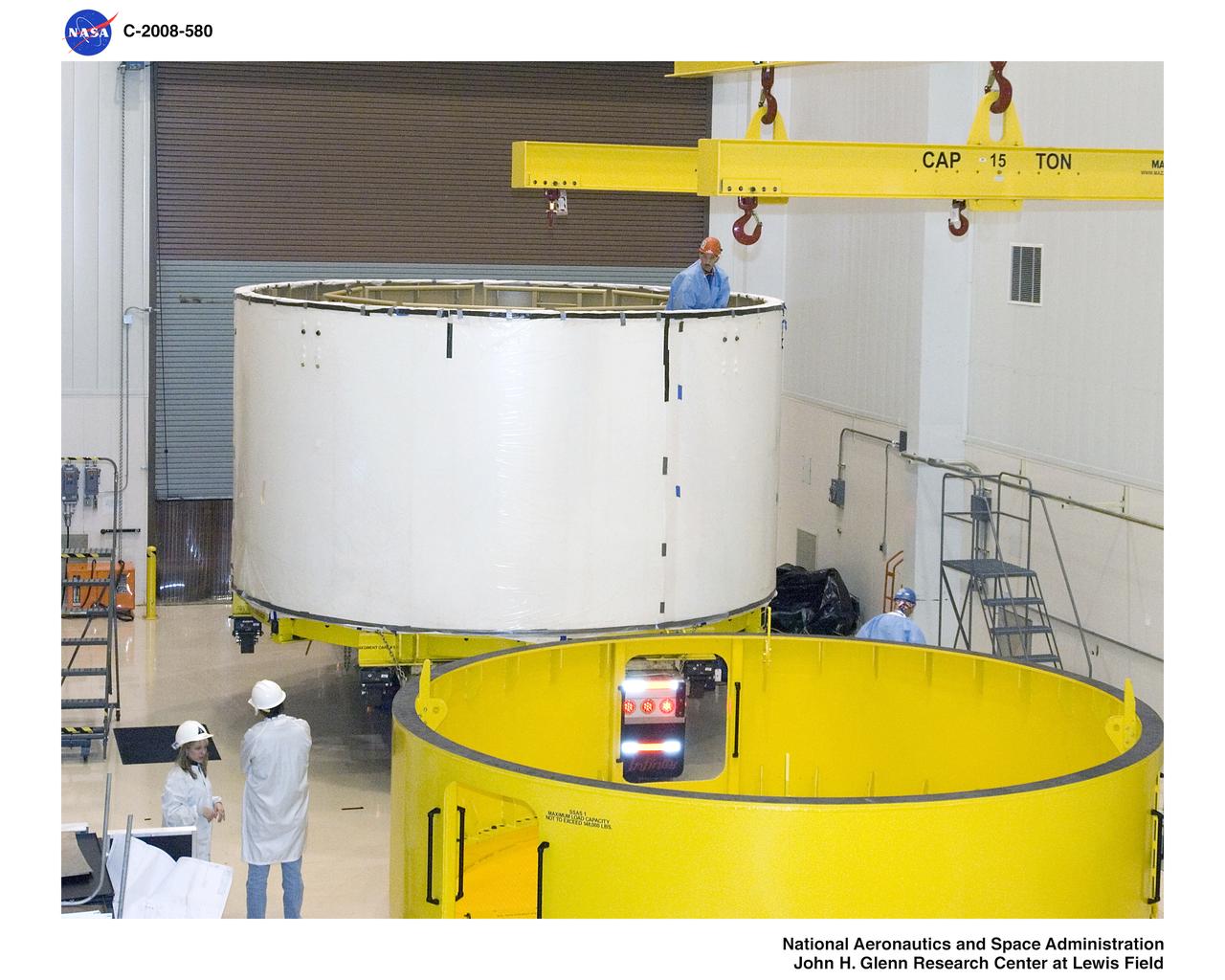

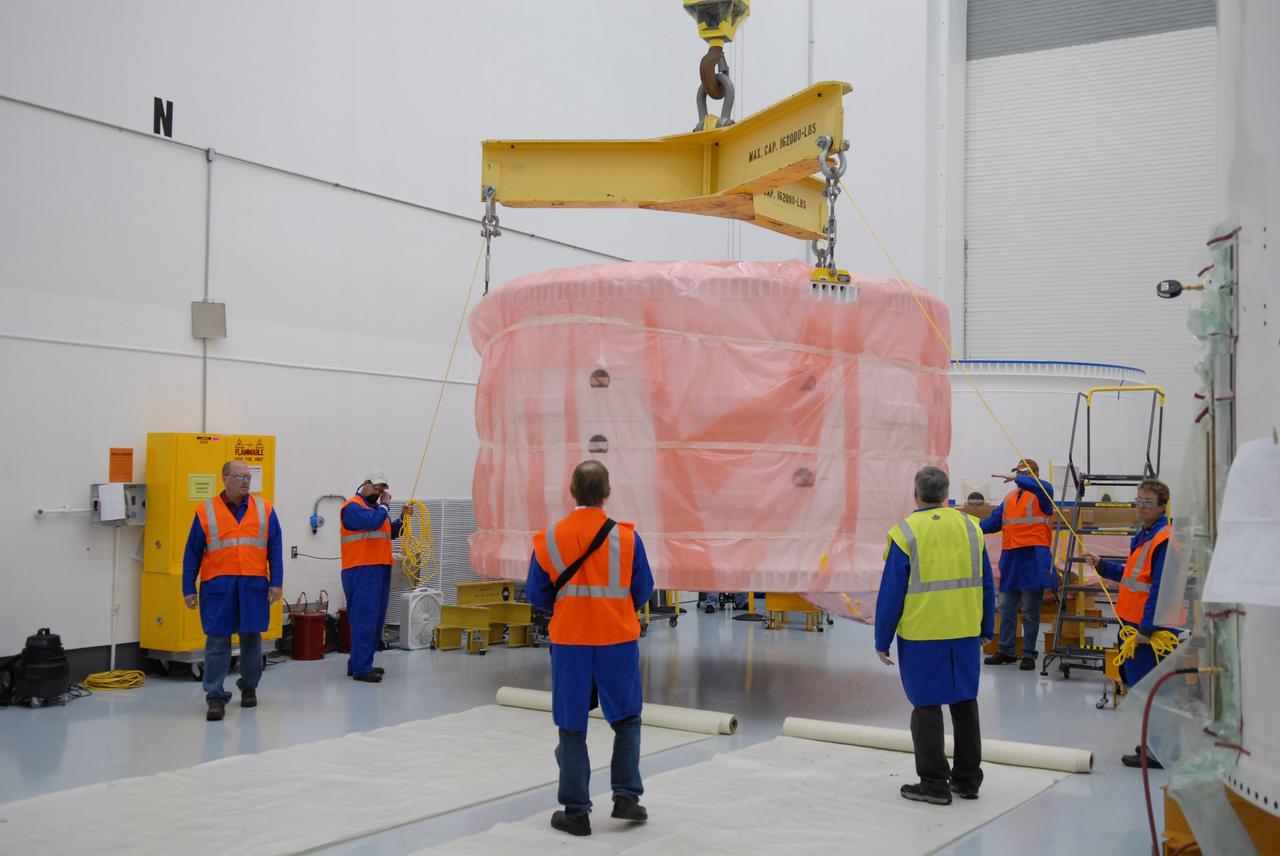
Ares 1-X Segment US-3 being lifted from the truck in Building 333

Originally devised to observe Saturn stage separation during Apollo flights, Marshall Space Flight Center's Miniature Television Camera, measuring only 4 x 3 x 1 1/2 inches, quickly made its way to the commercial telecommunications market.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3, the Ares I-X "super stack 1" is being attached to the forward motor segment. Super stack 1 comprises the frustum, forward skirt, forward skirt extension, interstages 1 and 2 and the fifth segment simulator. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending forma NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
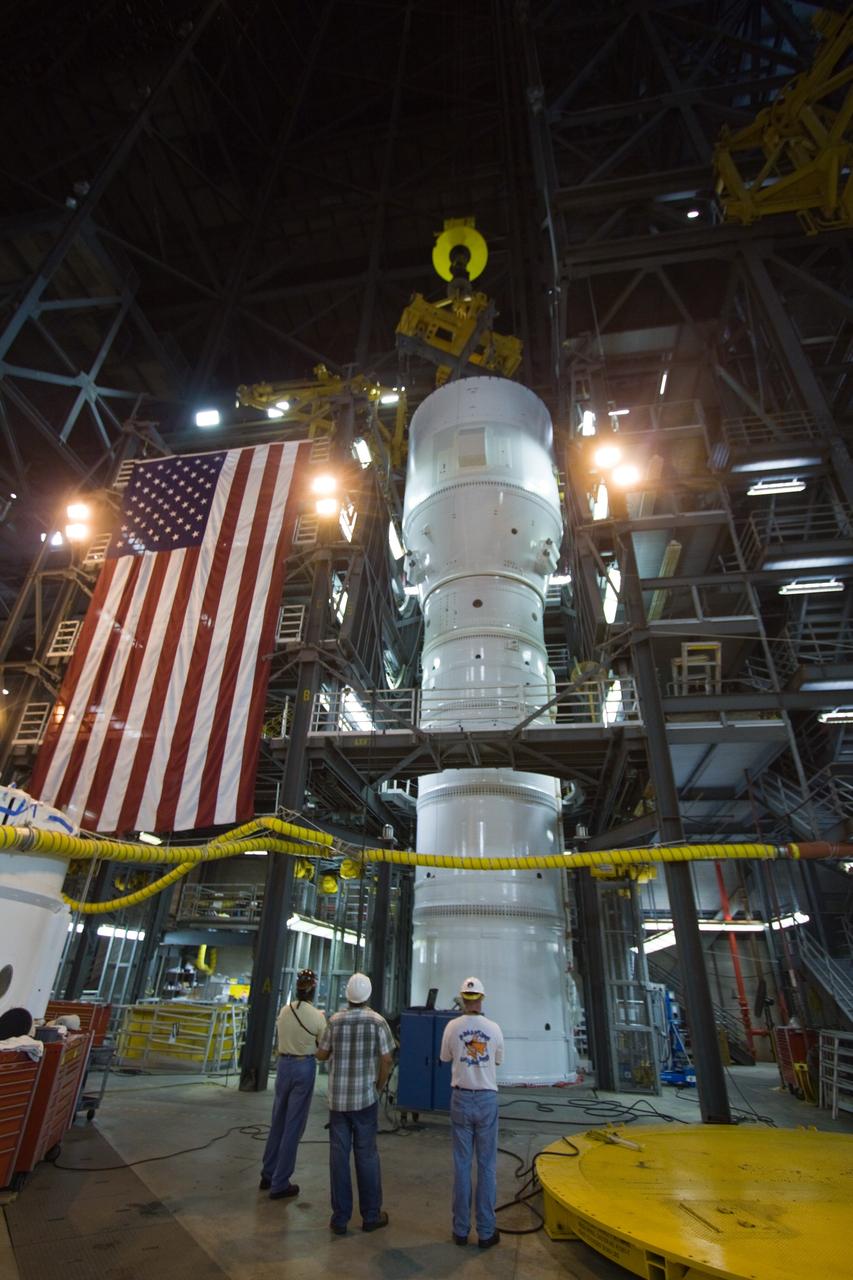

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, the Ares I-X "super stack 1" is to be lifted into High Bay 3 and attached to the forward motor segment. Super stack 1 comprises the frustum, forward skirt, forward skirt extension, interstages 1 and 2 and the fifth segment simulator. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending forma NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3, the Ares I-X "super stack 1" is being attached to the forward motor segment. Super stack 1 comprises the frustum, forward skirt, forward skirt extension, interstages 1 and 2 and the fifth segment simulator. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending forma NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
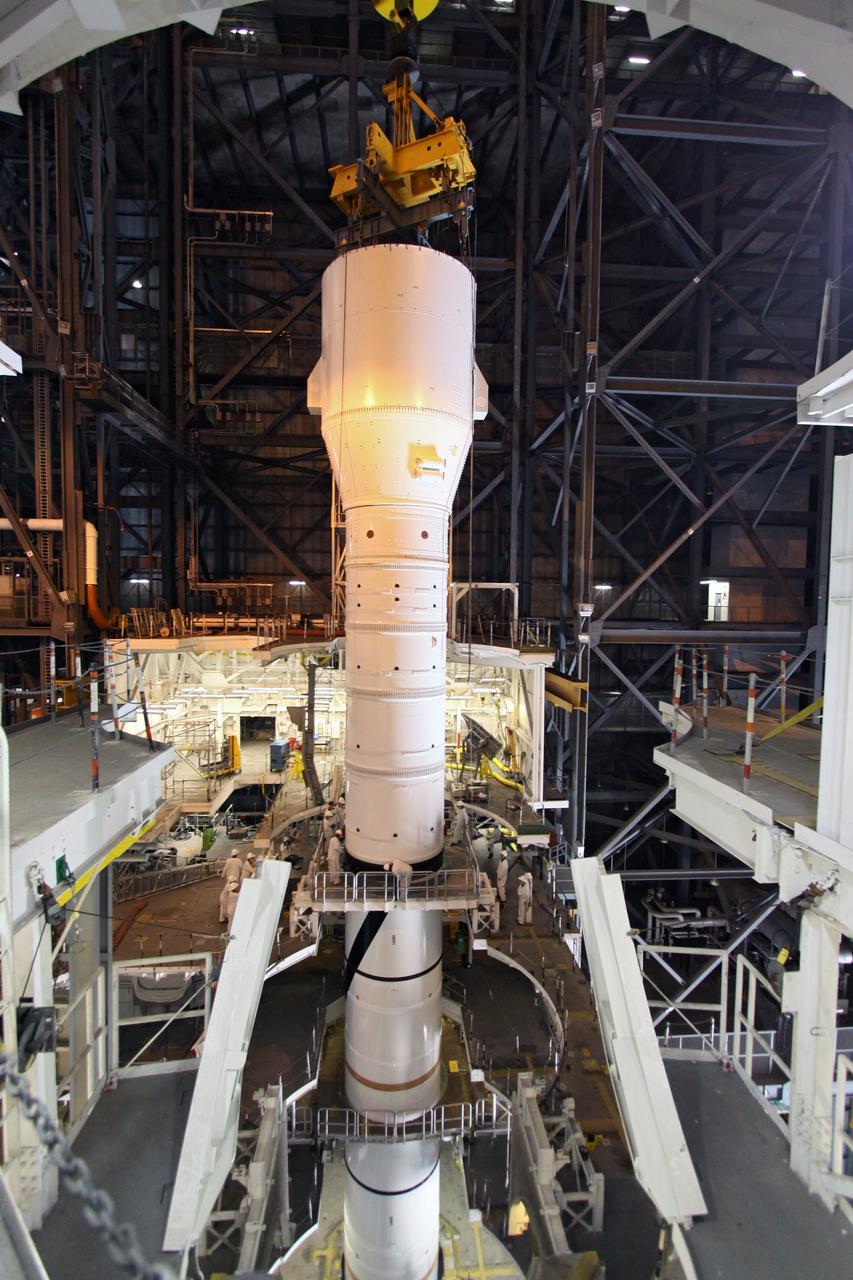

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3, the Ares I-X "super stack 1" is being attached to the forward motor segment. Super stack 1 comprises the frustum, forward skirt, forward skirt extension, interstages 1 and 2 and the fifth segment simulator. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending forma NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
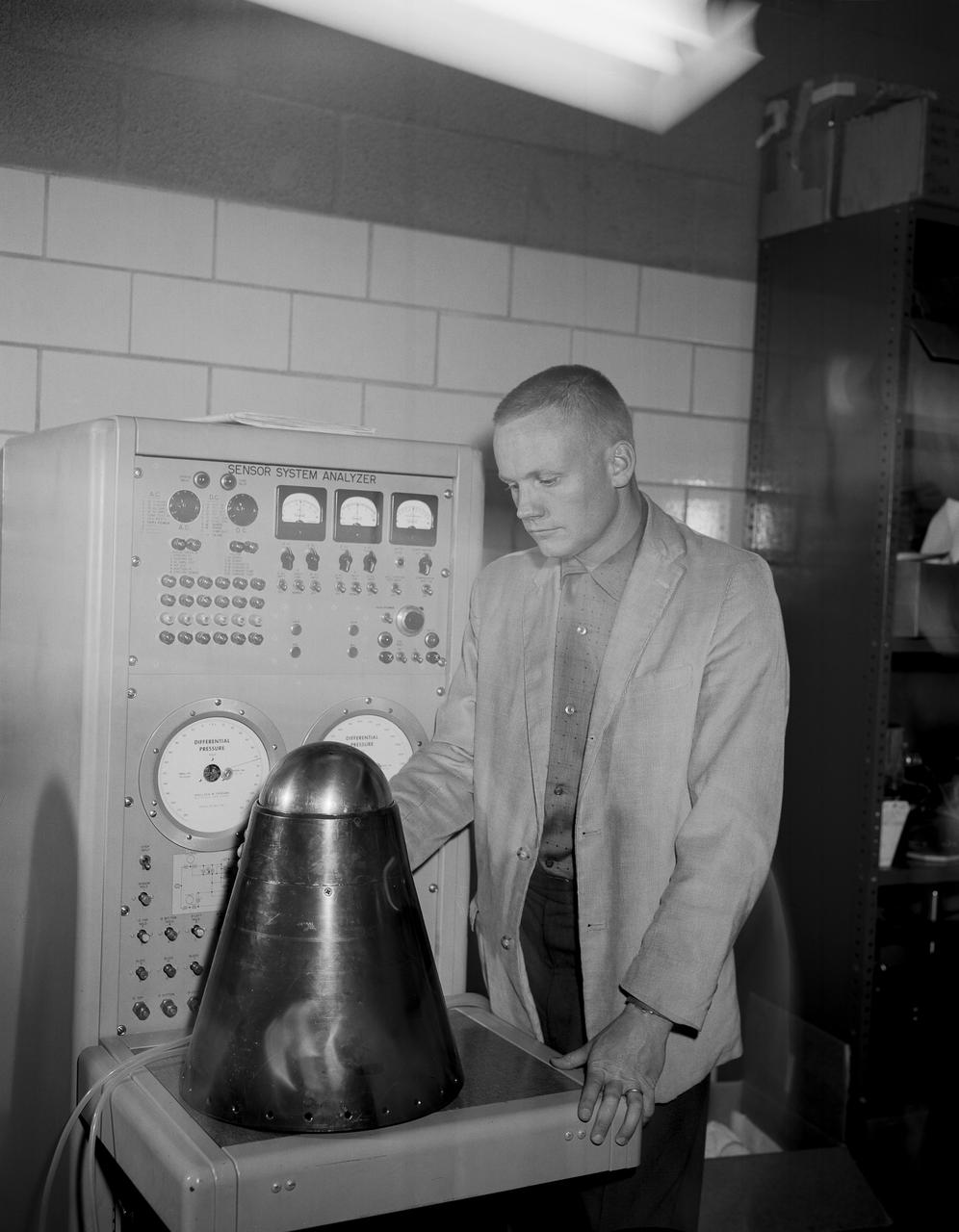

From the program’s inception, Neil Armstrong was actively engaged in both the piloting and engineering aspects of the X-15. He flew the first mission using a new flow-direction sensor (ball nose) and the first flight with a self-adaptive flight control system. Collaborating closely with designers and engineers on the system’s development, he made seven flights in the X-15 between December 1960 and July 1962. During these missions, he reached a peak altitude of 207,500 feet in the X-15-3 and a top speed of 3,989 mph (Mach 5.74) in the X-15-1.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Platform C is moved away from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center to allow refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle in high bay 3. The platform will be demolished. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Platform C is being moved from high bay 3 to allow refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle. The platform will be removed from the VAB and demolished. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
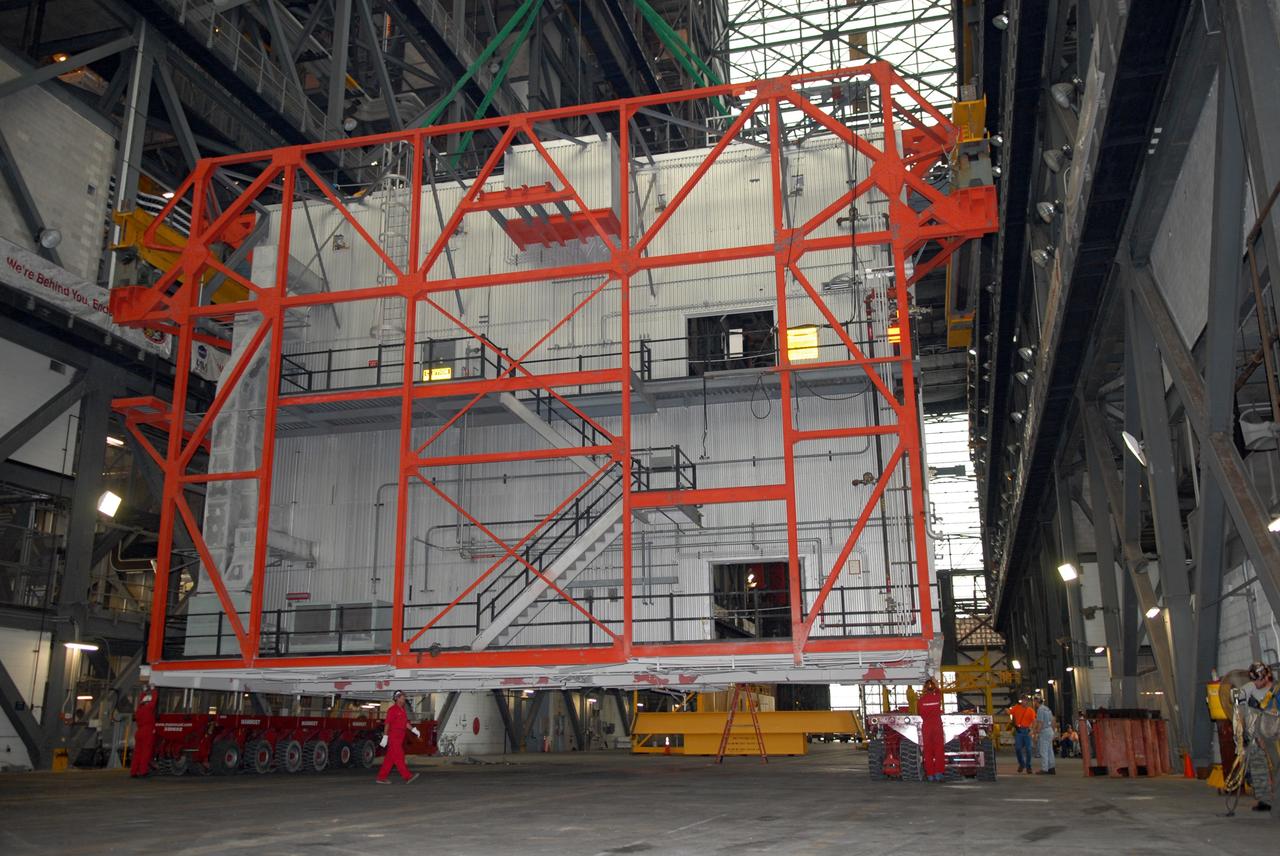

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Platform C is being moved from high bay 3 to allow refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle. The platform will be removed from the VAB and demolished. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Platform C is moved out of Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center to allow refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle in high bay 3. The platform will be demolished. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
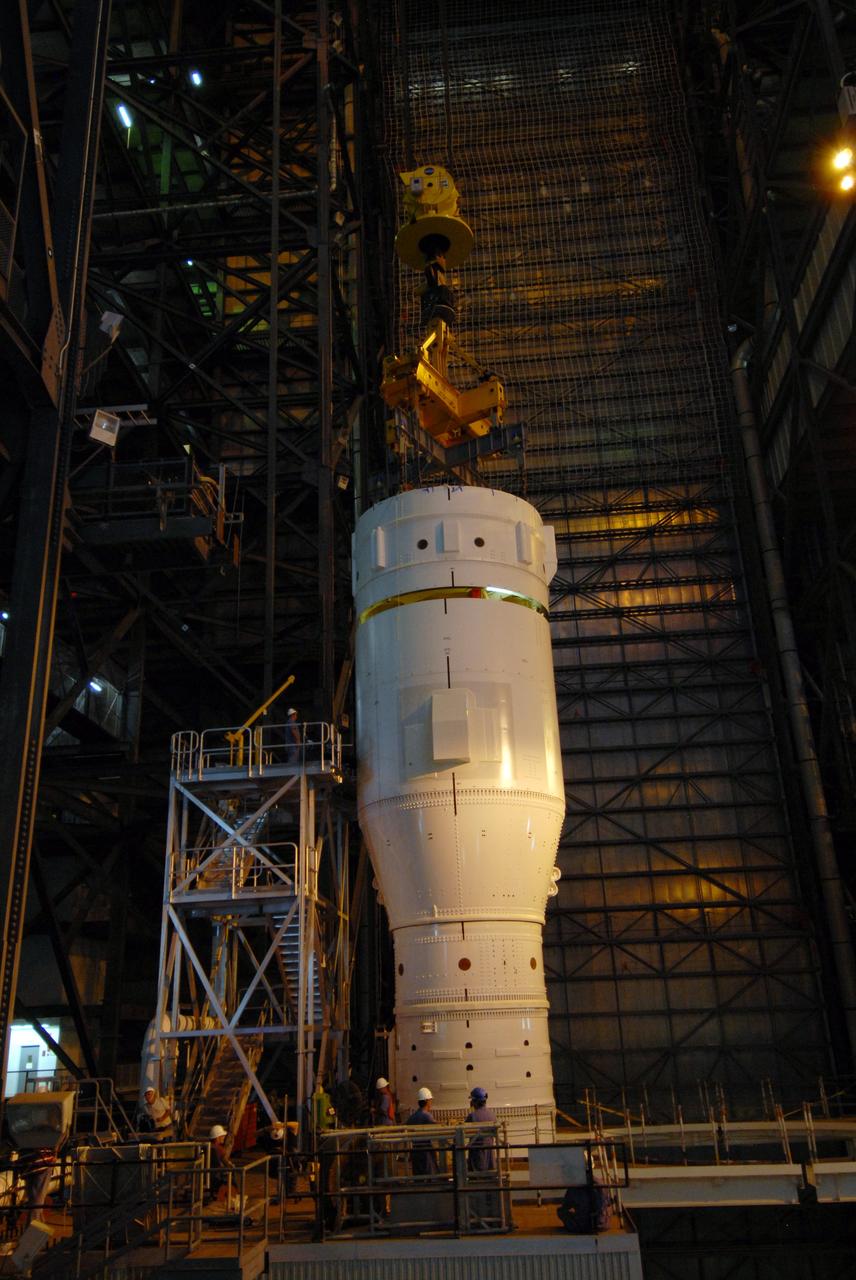

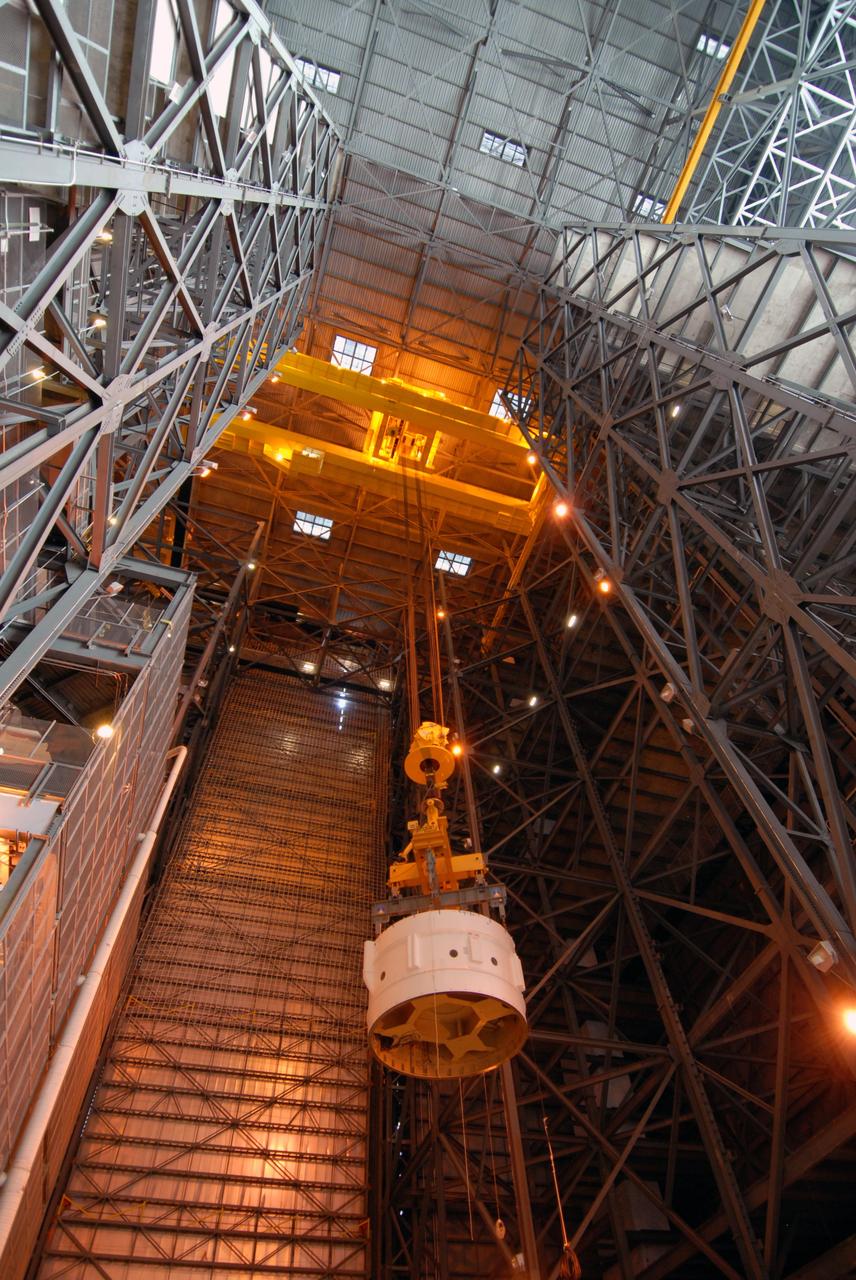
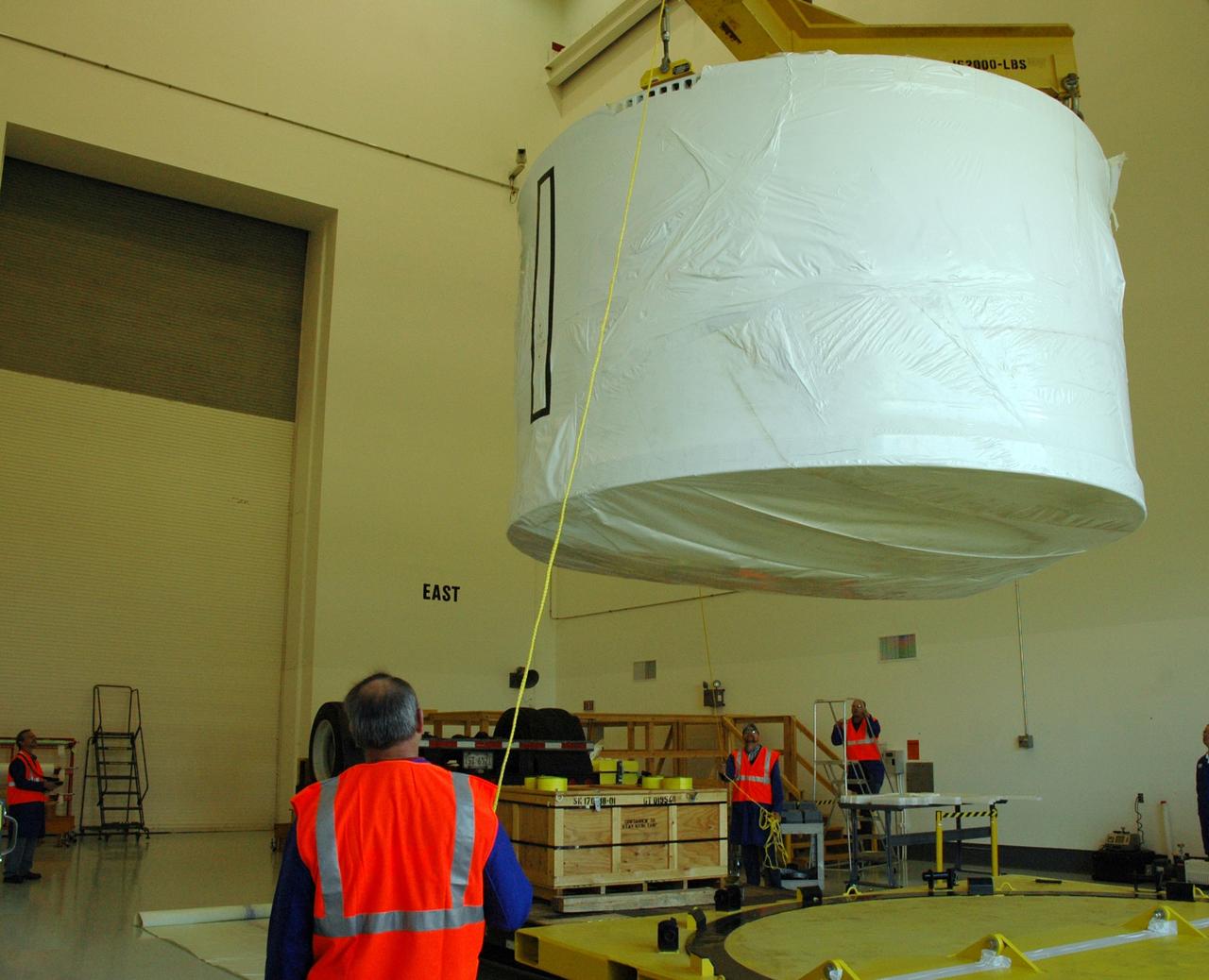
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage, for attachment with Super Stack 1 below. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
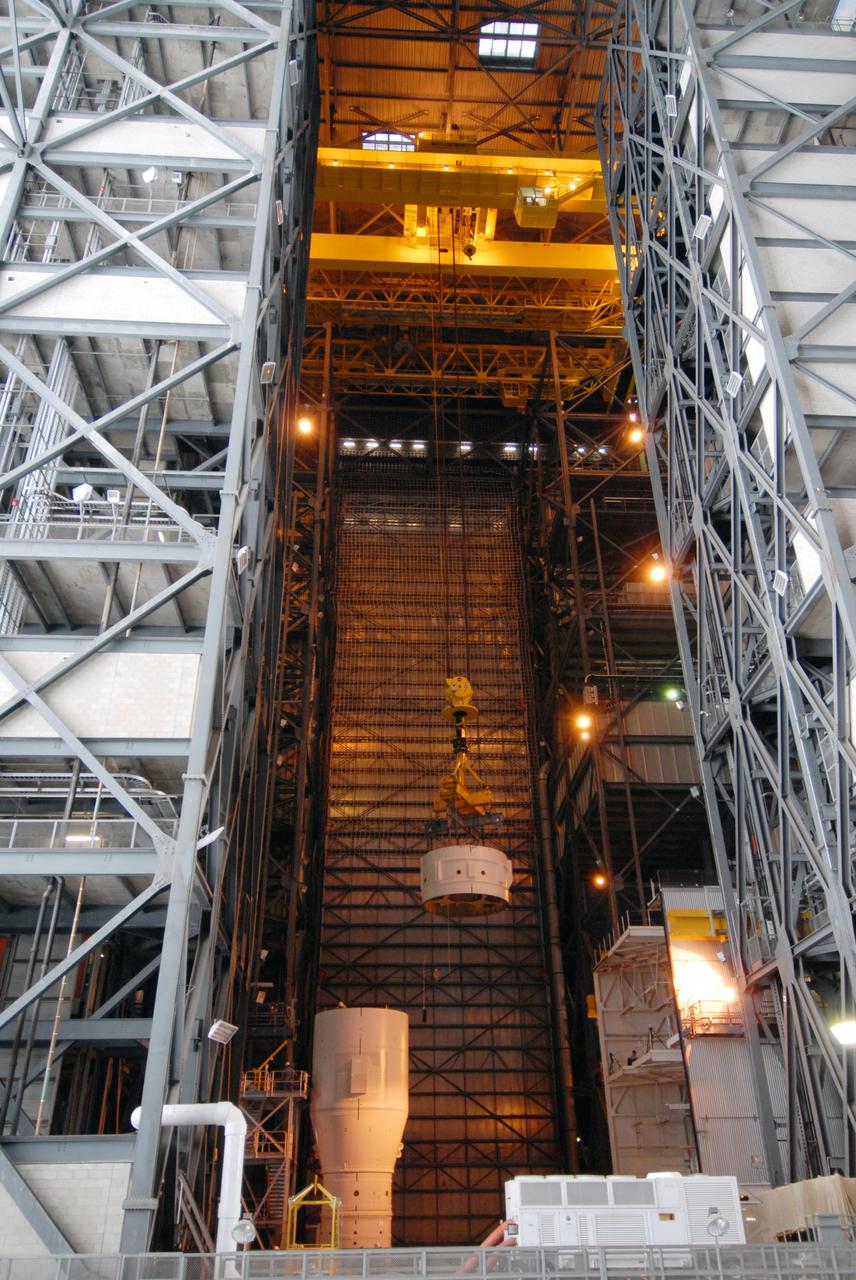
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage, for integration with Super Stack 1. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
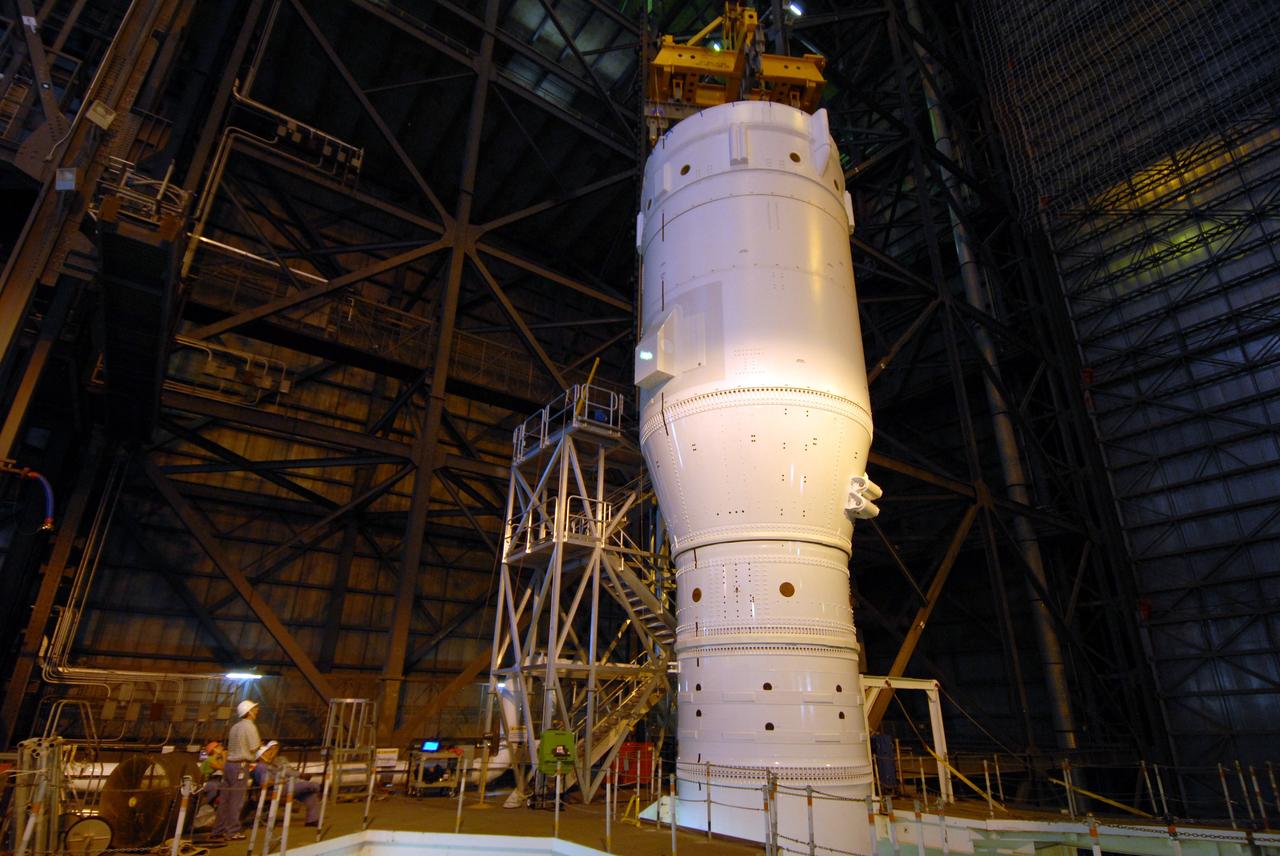

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage, onto Super Stack 1 for integration. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
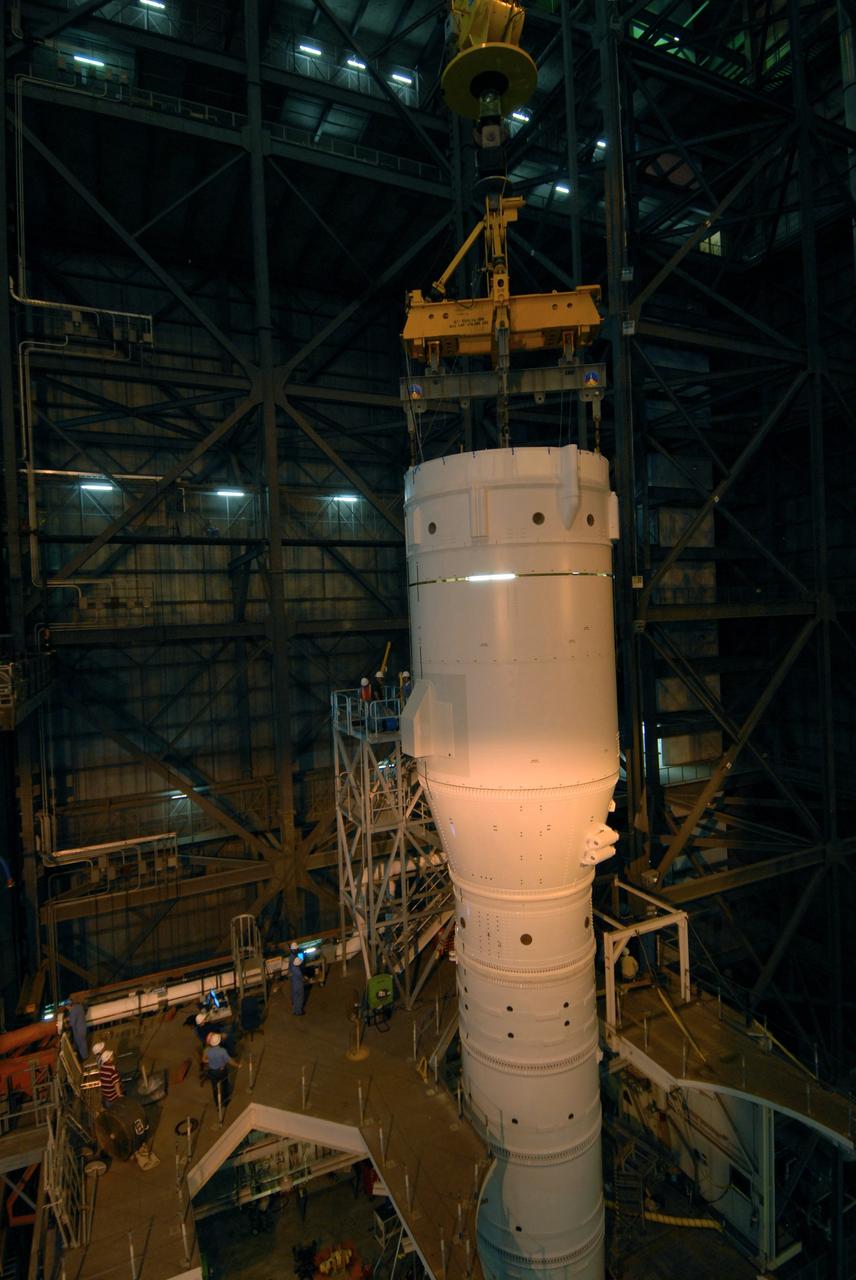

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage, onto Super Stack 1 for integration. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
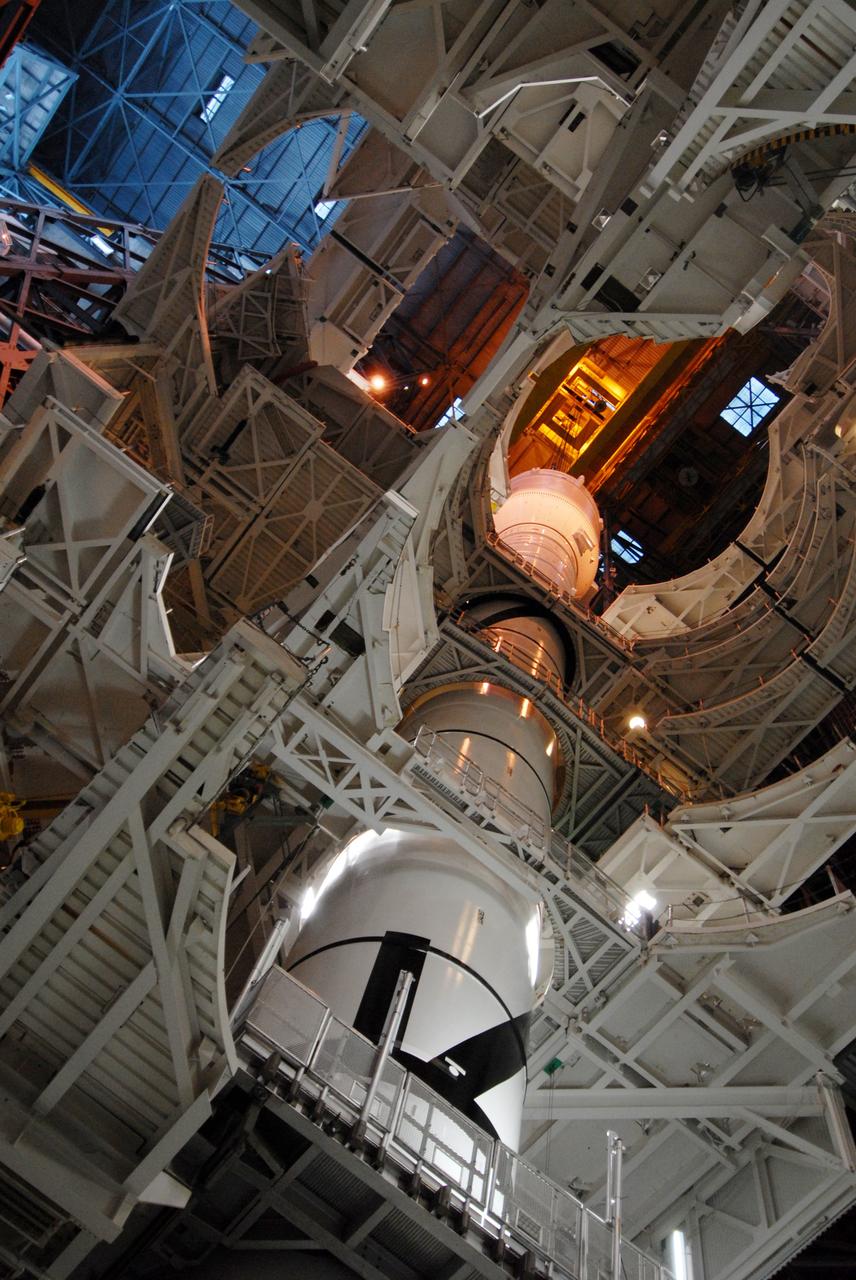

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane has lowered Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage, onto Super Stack 1 for integration atop the first stage, which comprises four solid rocket booster segments, on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane has lowered Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage, onto Super Stack 1 for assembly. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

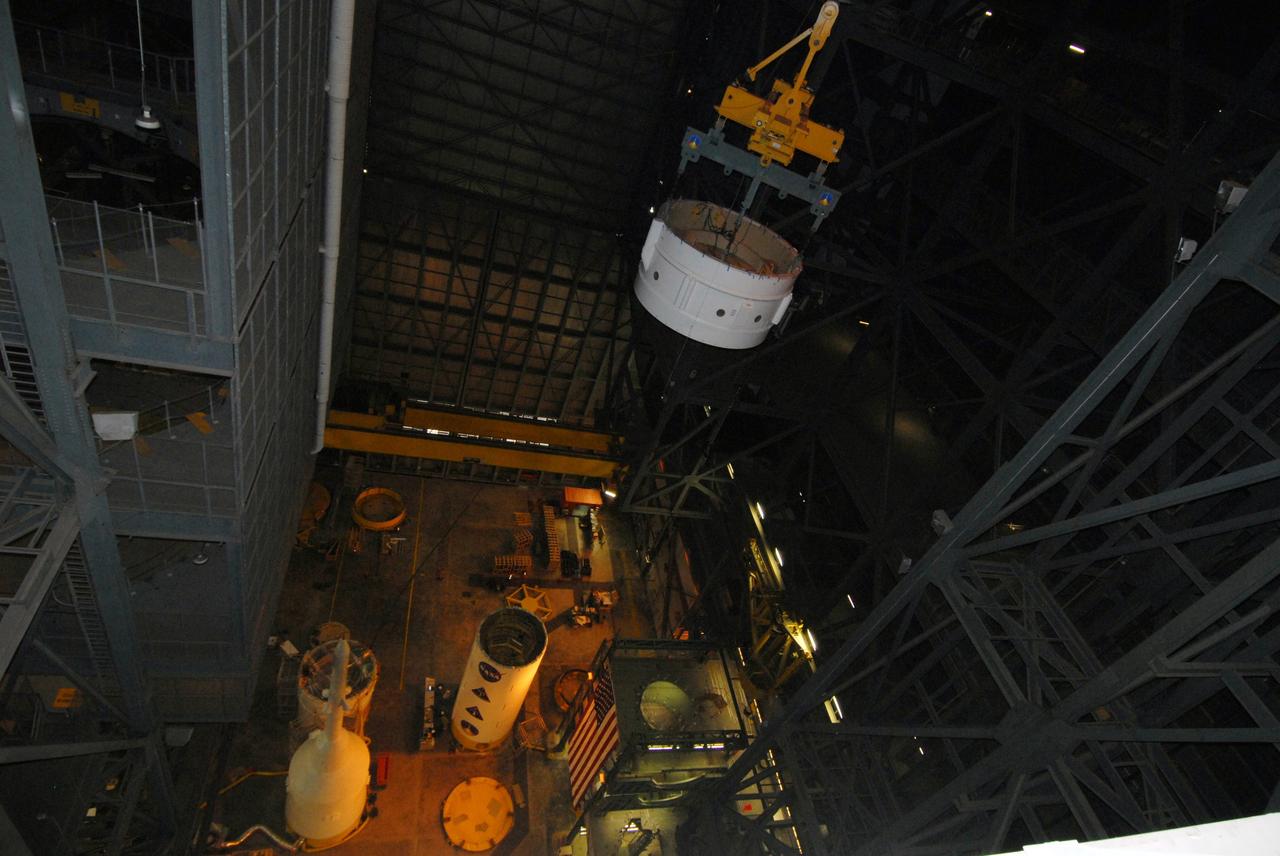
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is moved to High Bay 1 where it will be lowered onto the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

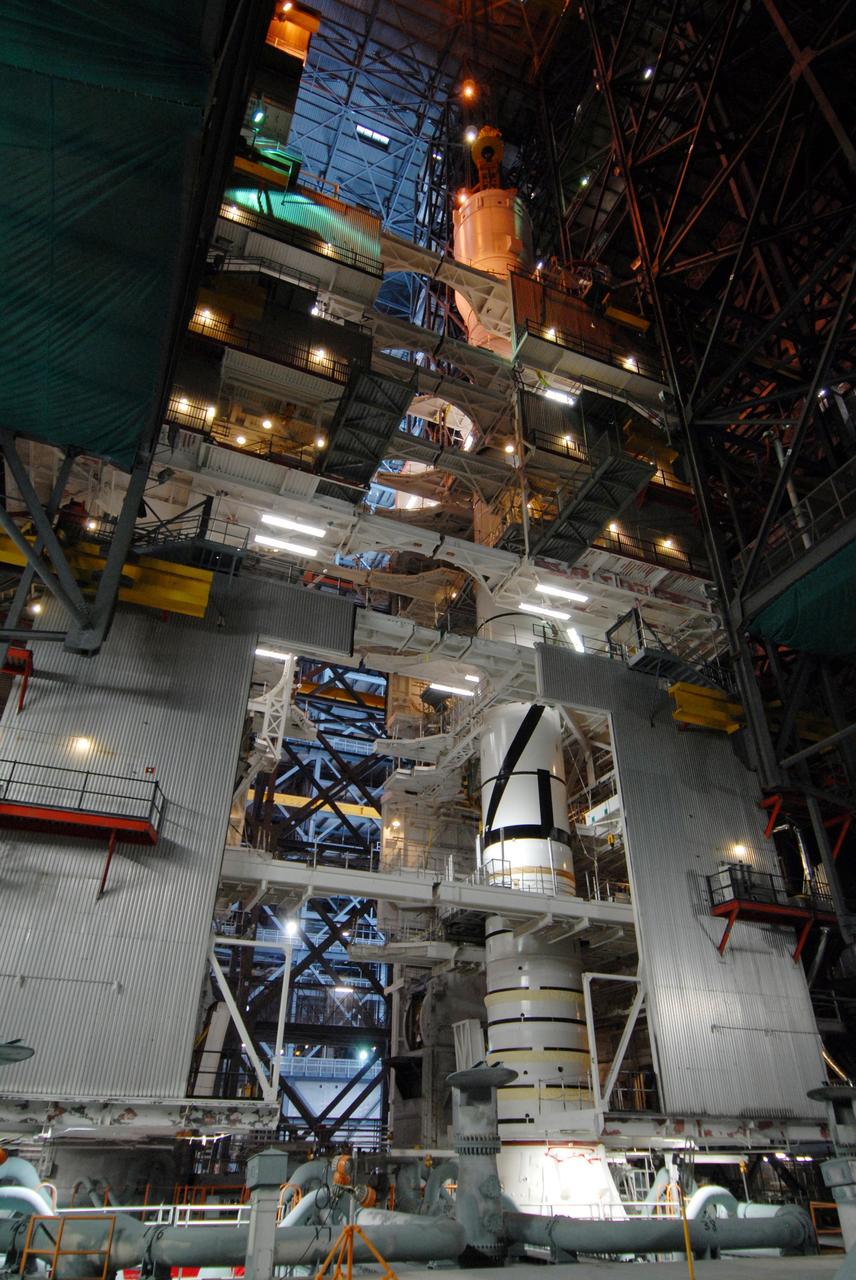
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage. The stack will be attached to Super Stack 1 across the transfer aisle in High Bay 3. At left is Super Stack 3. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage. The stack is being moved across the transfer aisle for attachment to Super Stack 1 in High Bay 3. Beneath is seen Super Stack 3 and at left is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
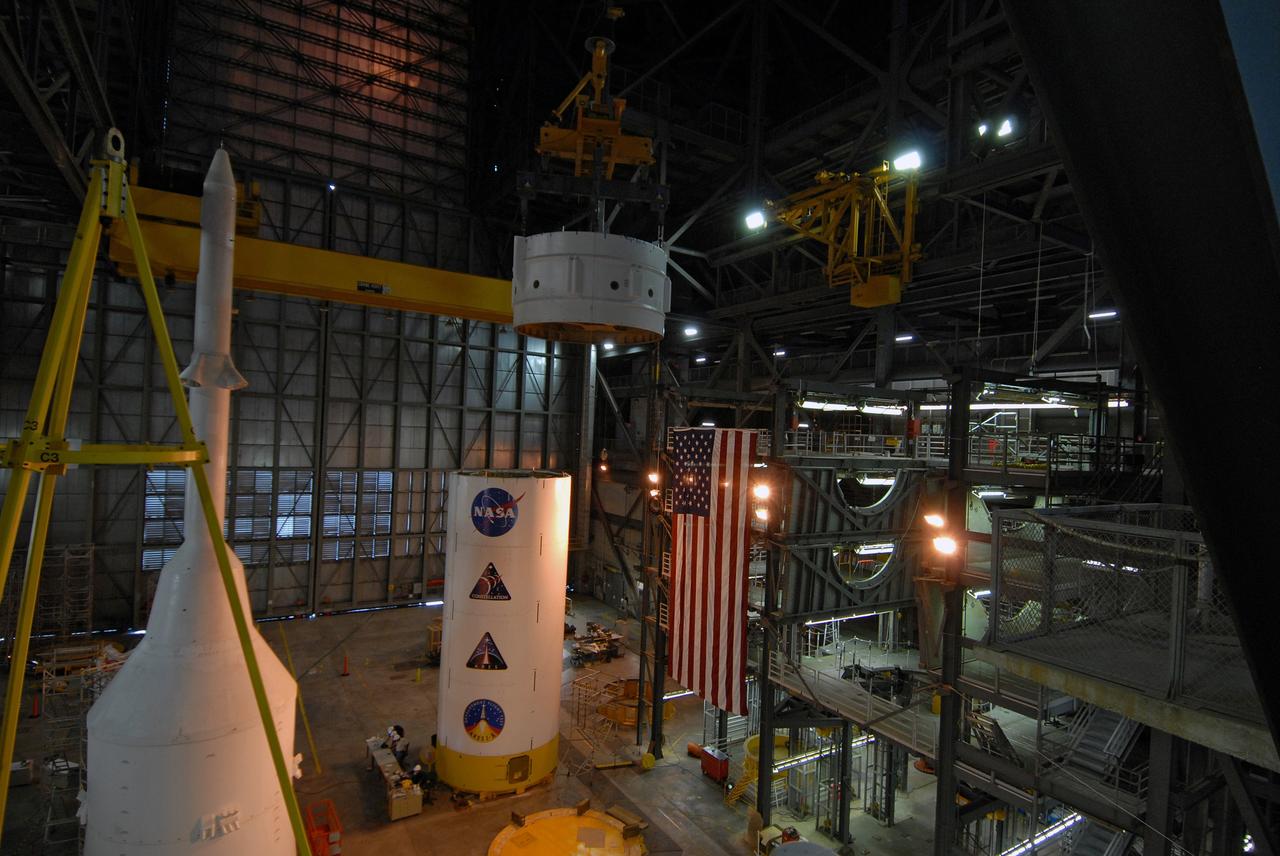

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage. The stack is being moved across the transfer aisle for attachment to Super Stack 1 in High Bay 3. Beneath is seen Super Stack 3 and at left is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
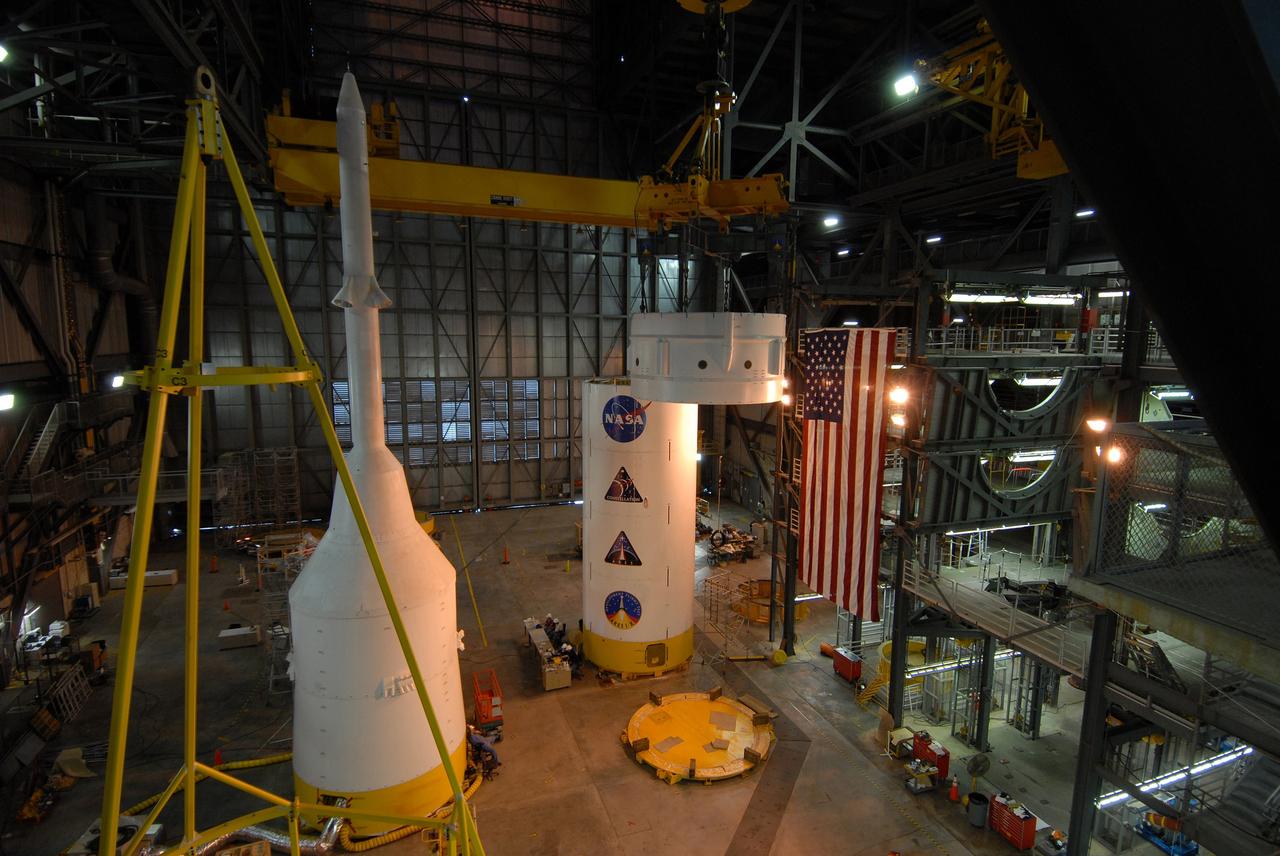

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage. The stack is being moved across the transfer aisle for attachment to Super Stack 1 in High Bay 3. Beneath can be seen Super Stack 3 and at left is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
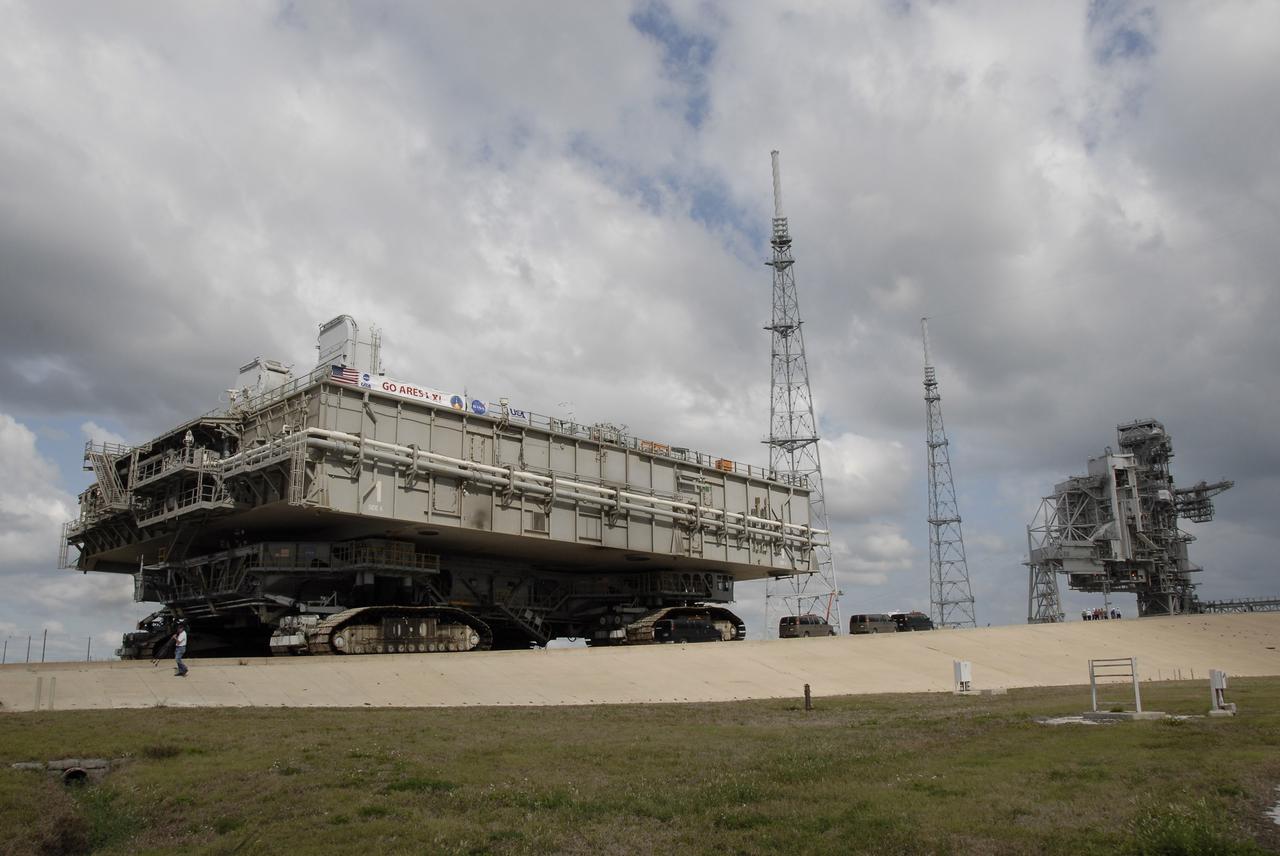

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1 is moving to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the crawler-transporter underneath. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Seen around the service structures on the pad are the new 600-foot lightning towers and masts erected for the Ares launches. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
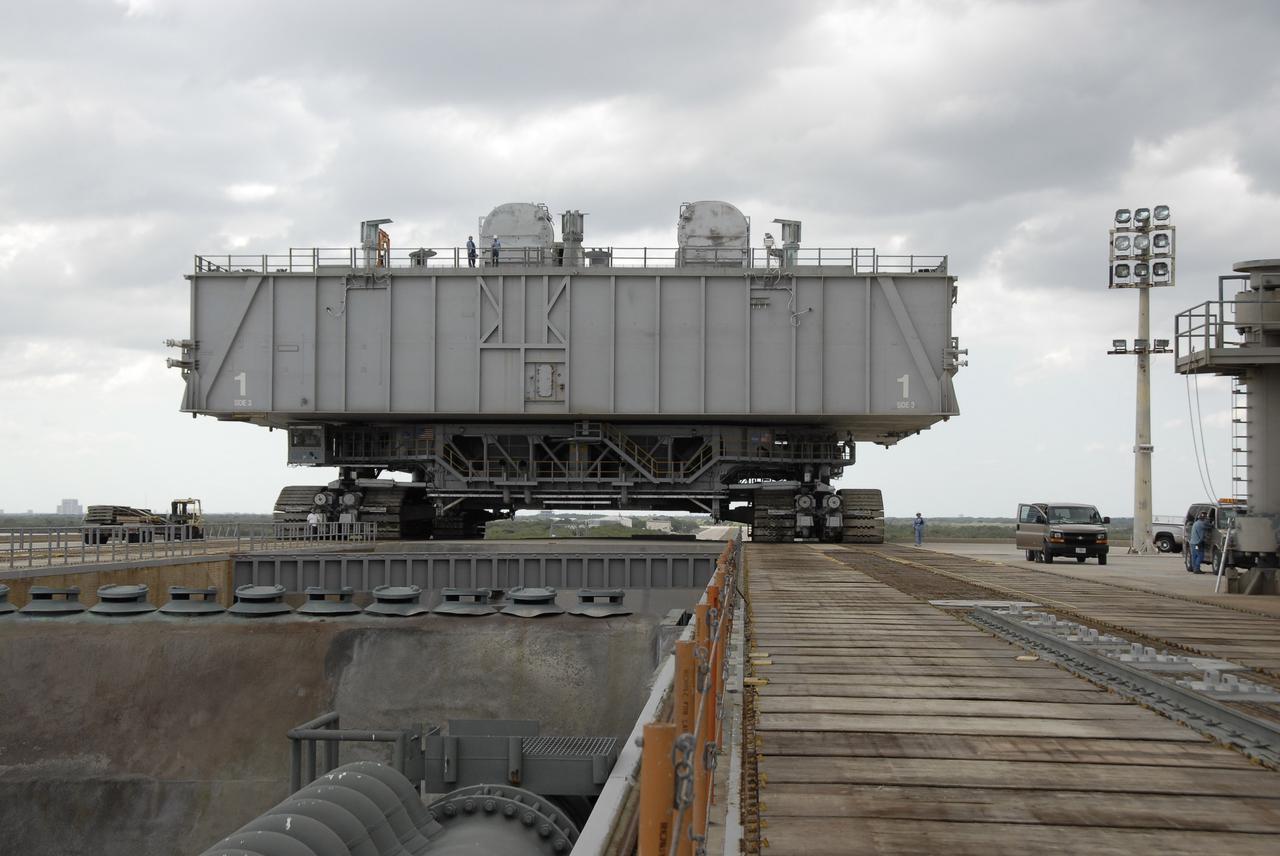

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1, on top of the crawler-transporter, nears the flame trench (lower left) on the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
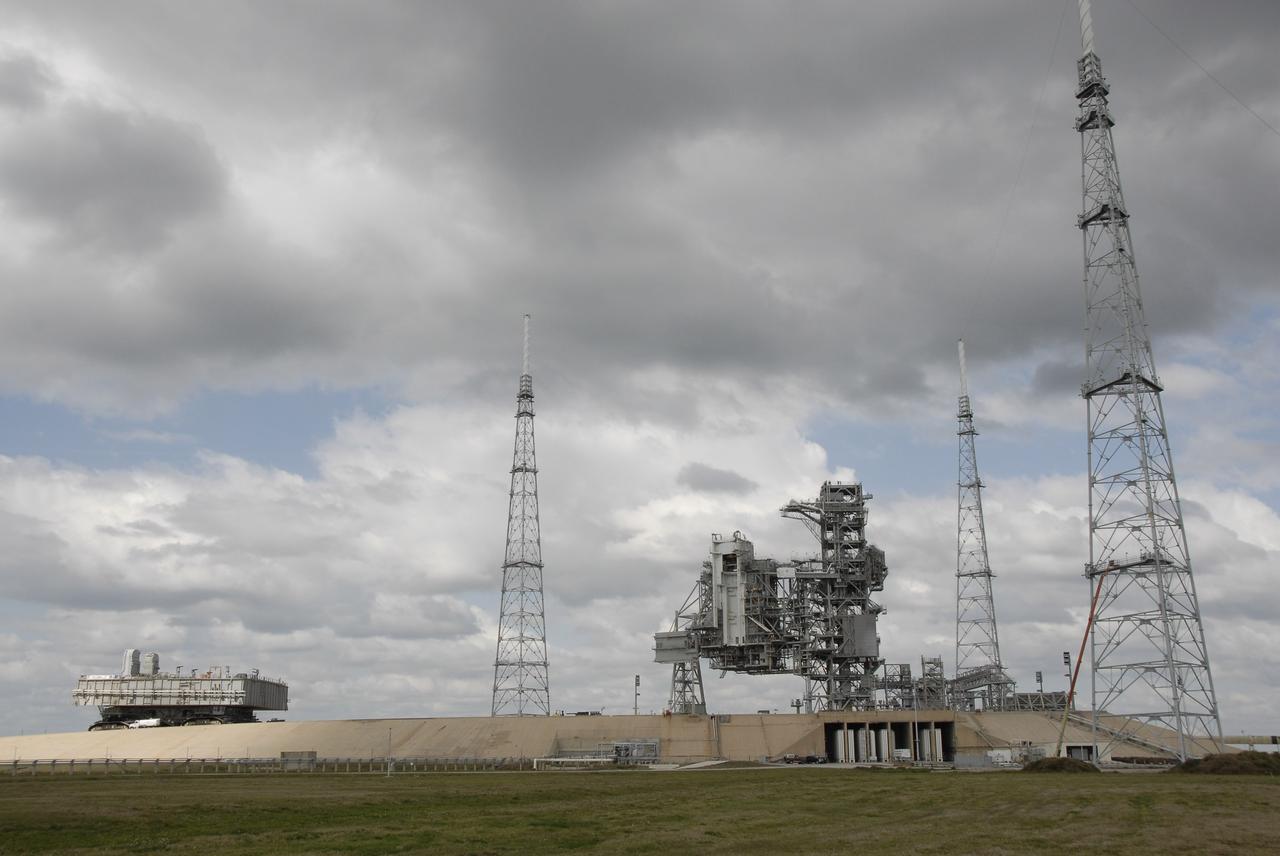

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1 nears the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the crawler-transporter underneath. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Seen around the service structures on the pad are the new 600-foot lightning towers and masts erected for the Ares launches. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
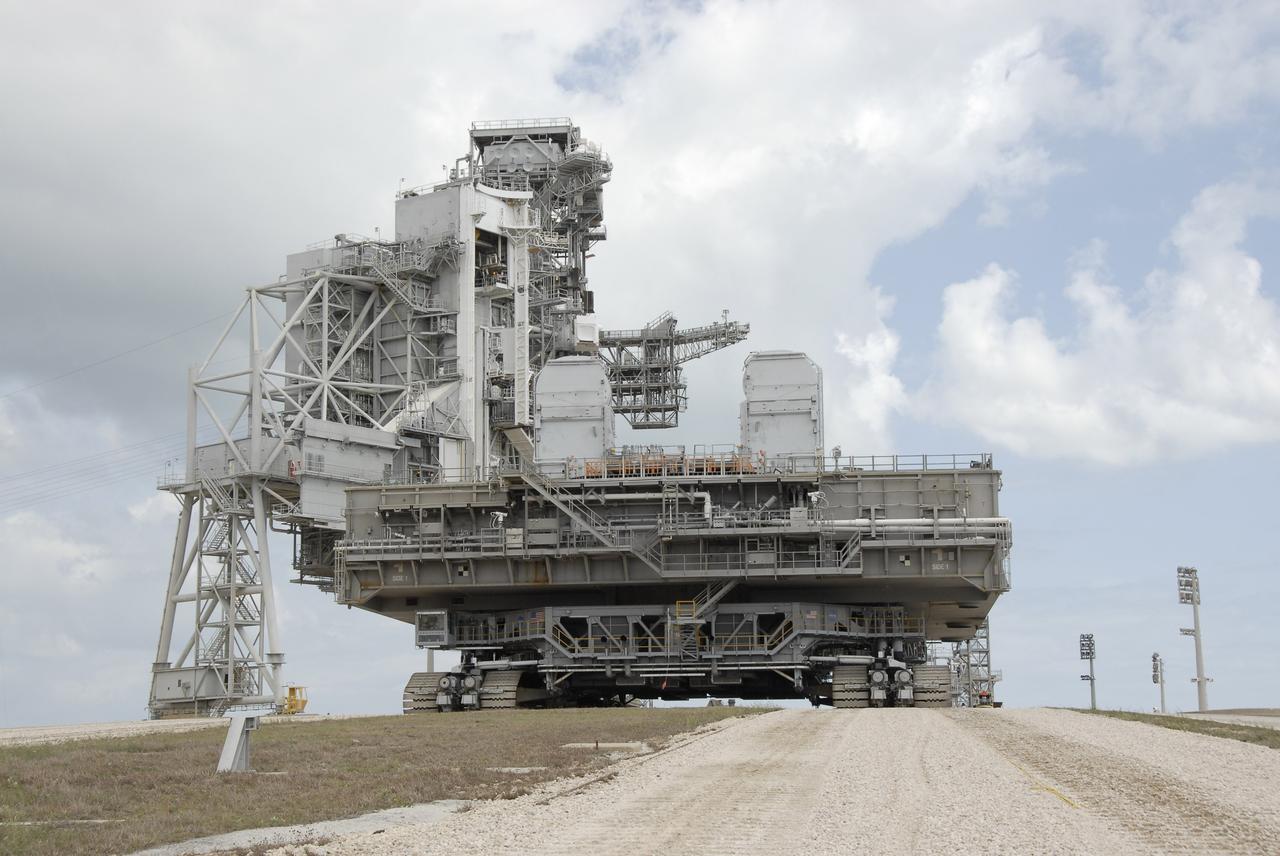

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1, on top of the crawler-transporter, reaches the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
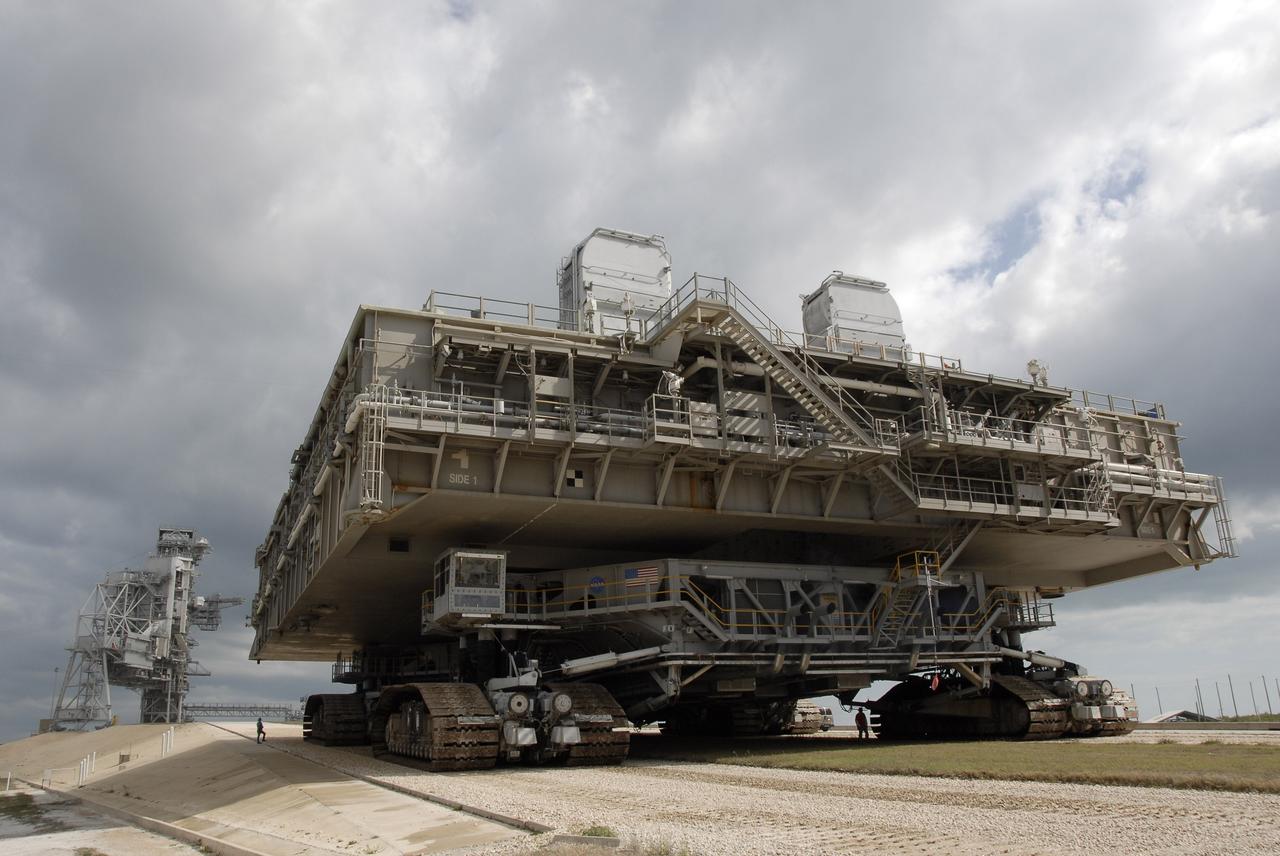

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1 is moving to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the crawler-transporter underneath. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1, on top of the crawler-transporter, reaches the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

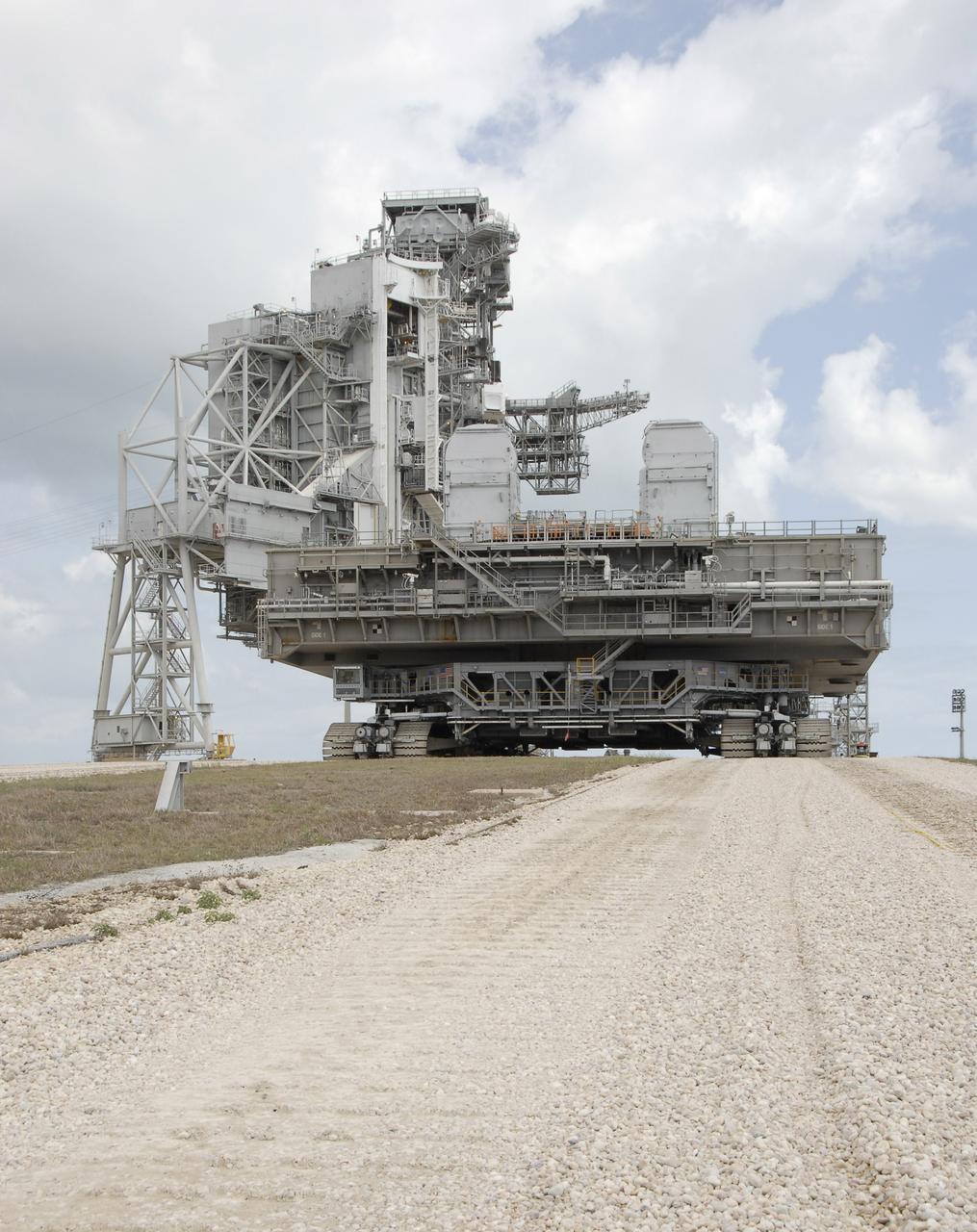
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1 nears the top of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the crawler-transporter underneath. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mobile Launcher Platform-1 is moving to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the crawler-transporter underneath. The MLP has been handed over to the Constellation Program for its future use for the Ares I-X flight test in the summer of 2009. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The MLP is being moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Following this testing, MLP-1 will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 to begin stacking, or assembling, Ares I-X. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
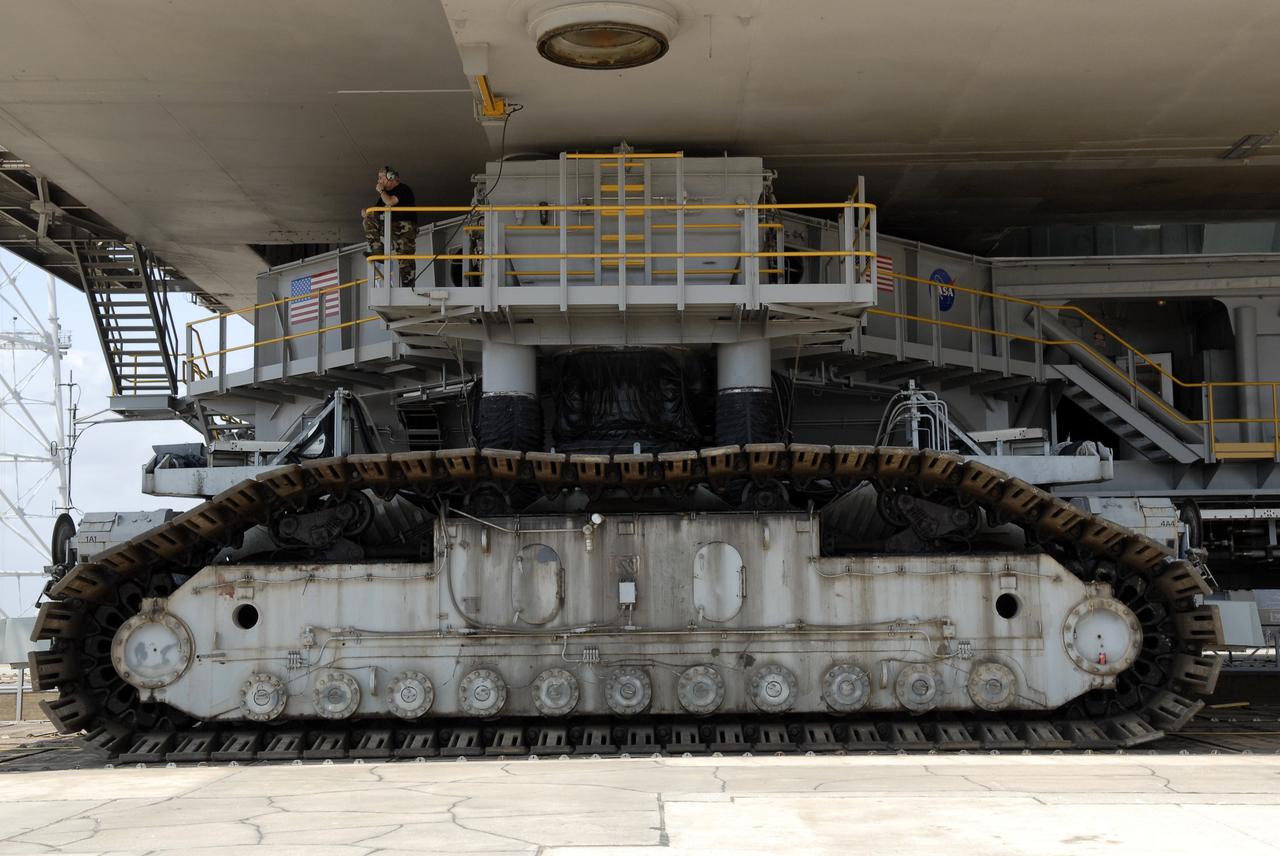

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the crawler-transporter is underneath the mobile launcher platform to move it from Kennedy's Launch Pad 39B to the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. The platform was turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
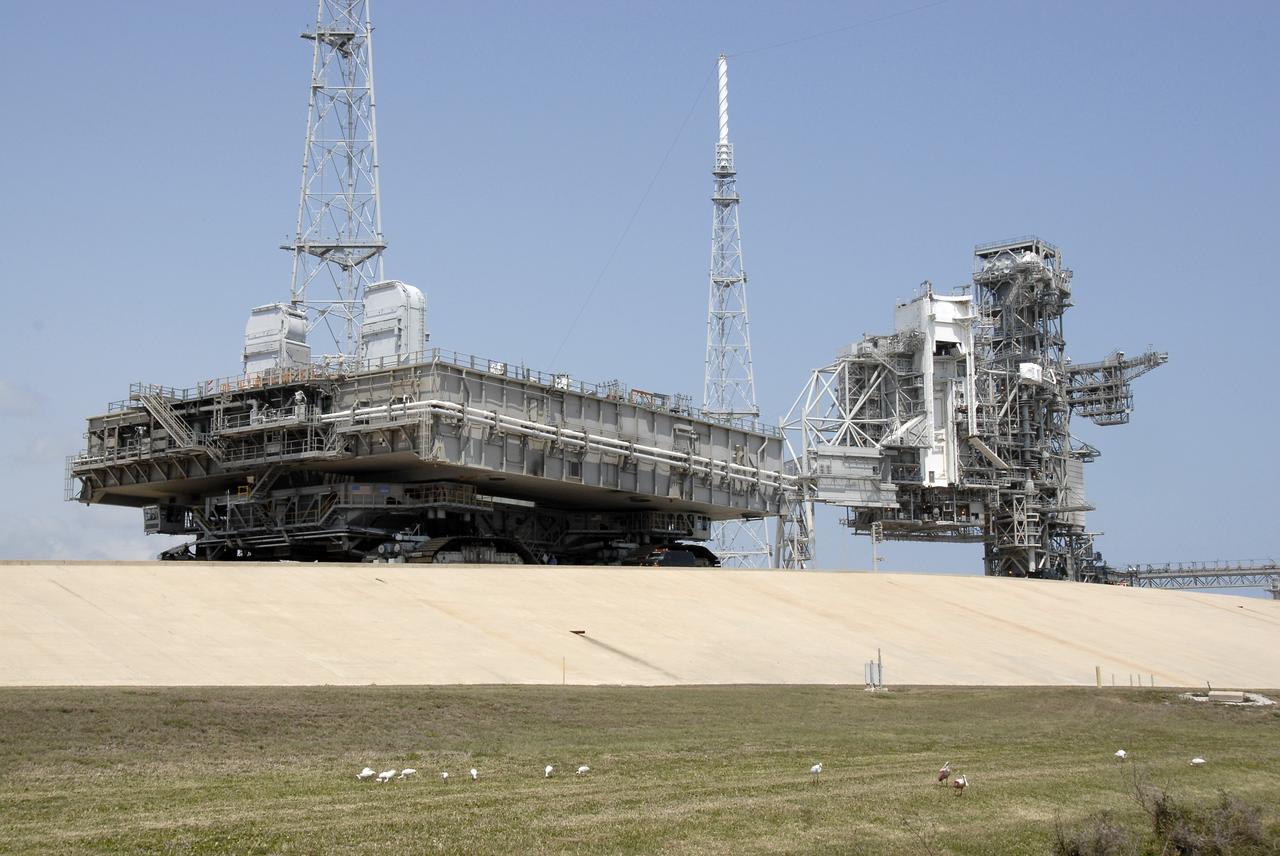

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mobile launcher platform that was turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month is being moved from Kennedy's Launch Pad 39B via the crawler-transporter underneath. The platform will be rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
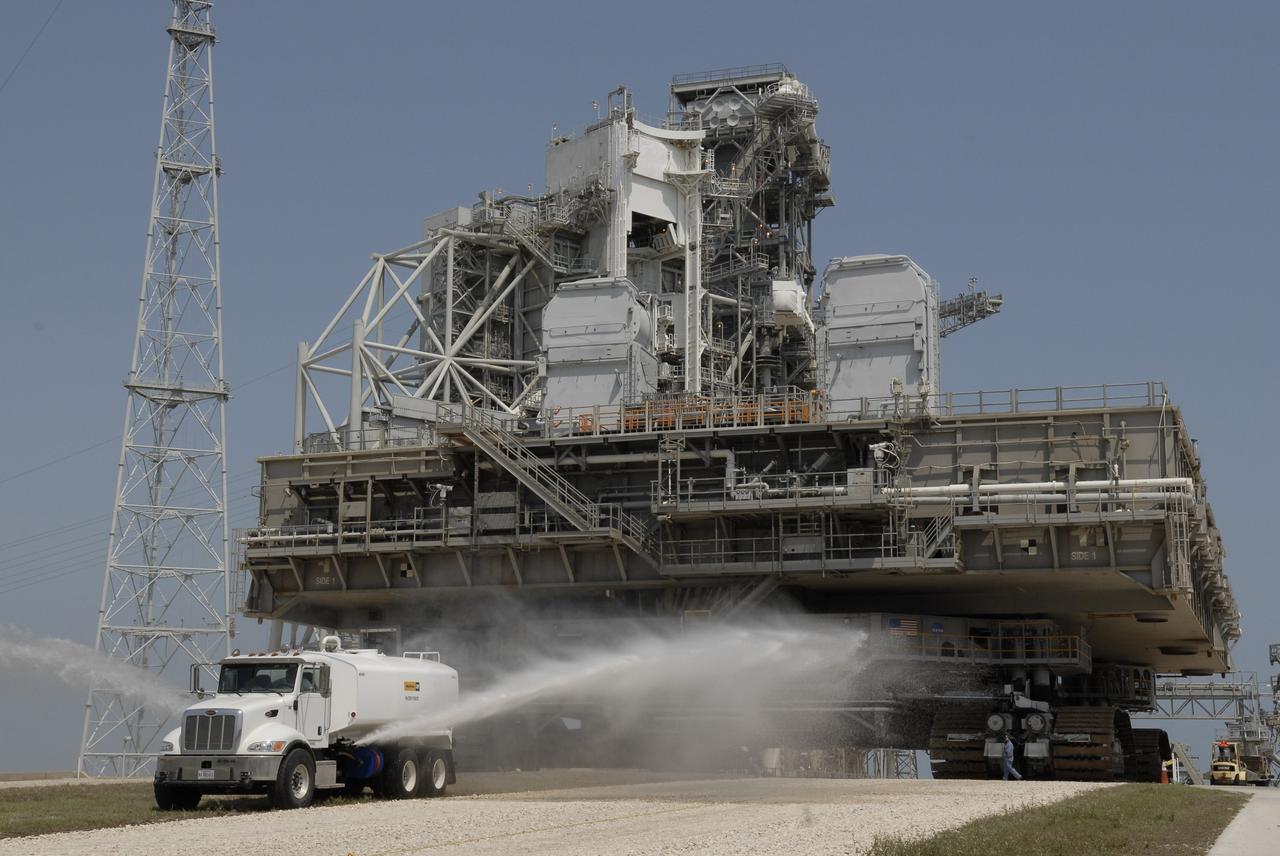

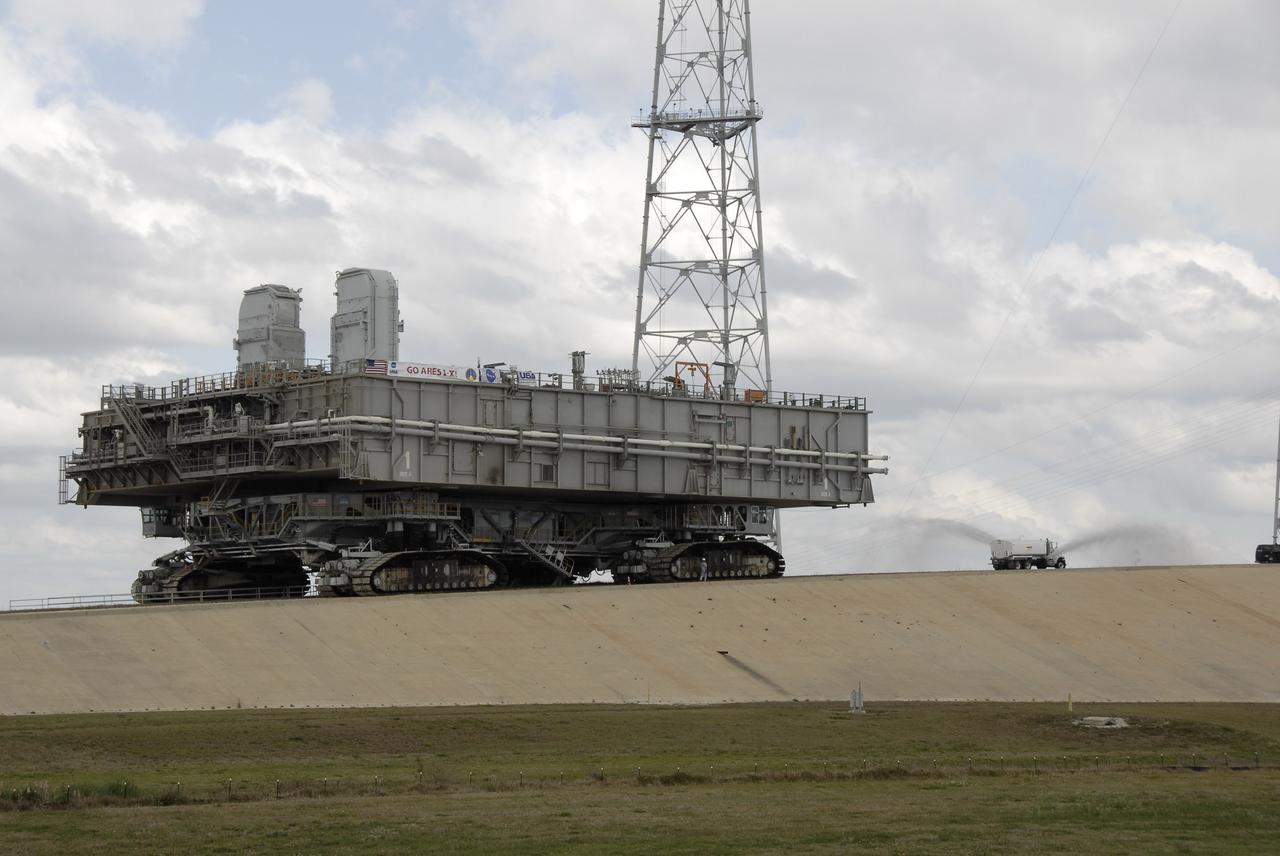
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a water truck sprays the dry crawlerway in front of the crawler-transporter carrying the mobile launcher platform on top as it moves away from Kennedy's Launch pad 39B. The platform, turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month, will be rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
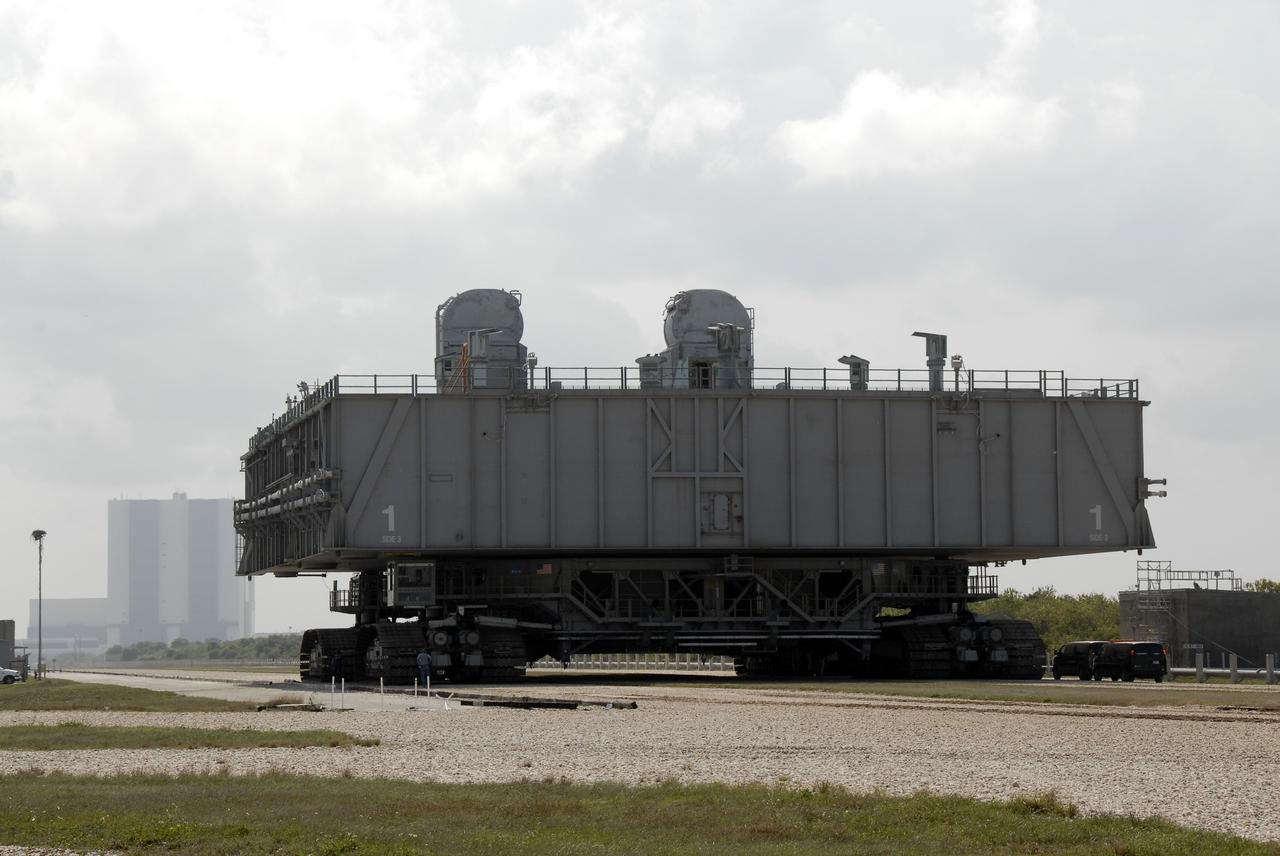

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mobile launcher platform that was turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month moves along the crawlerway via the crawler-transporter underneath. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The platform will be rolled into the VAB's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
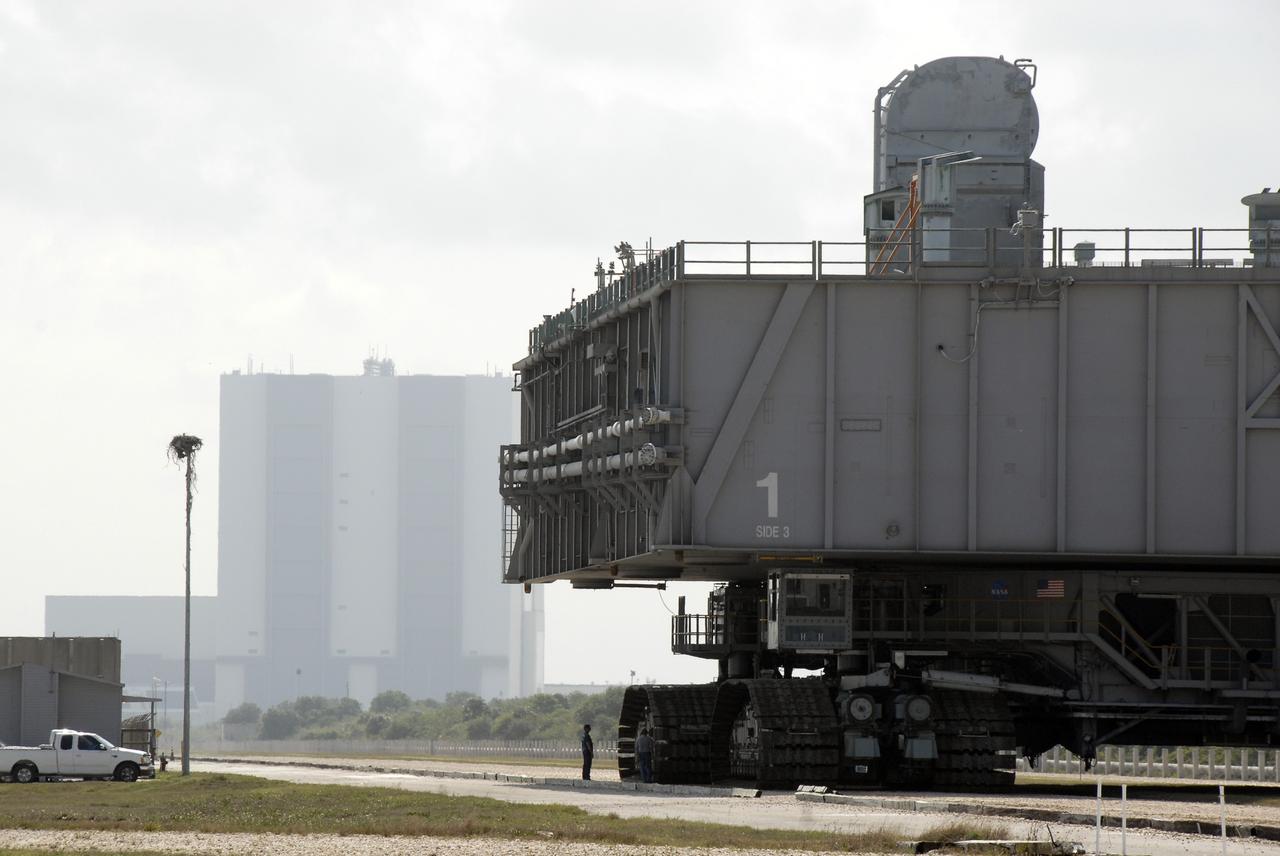

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A worker is dwarfed by the giant crawler-transporter and mobile launcher platform moving along the crawlerway toward the Vehicle Assembly Building. The platform will be rolled into the VAB's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
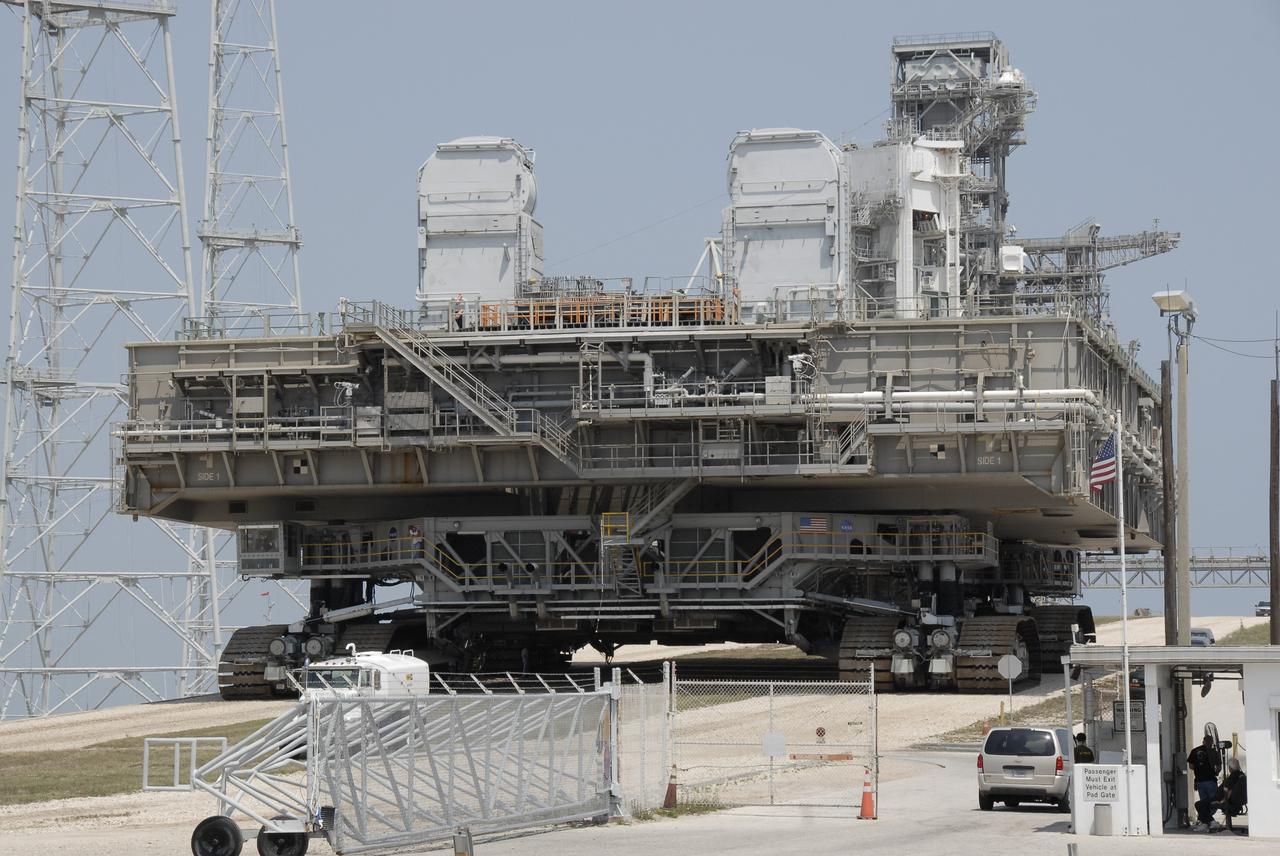

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mobile launcher platform that was turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month moves off Kennedy's Launch Pad 39B via the crawler-transporter underneath. The platform will be rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
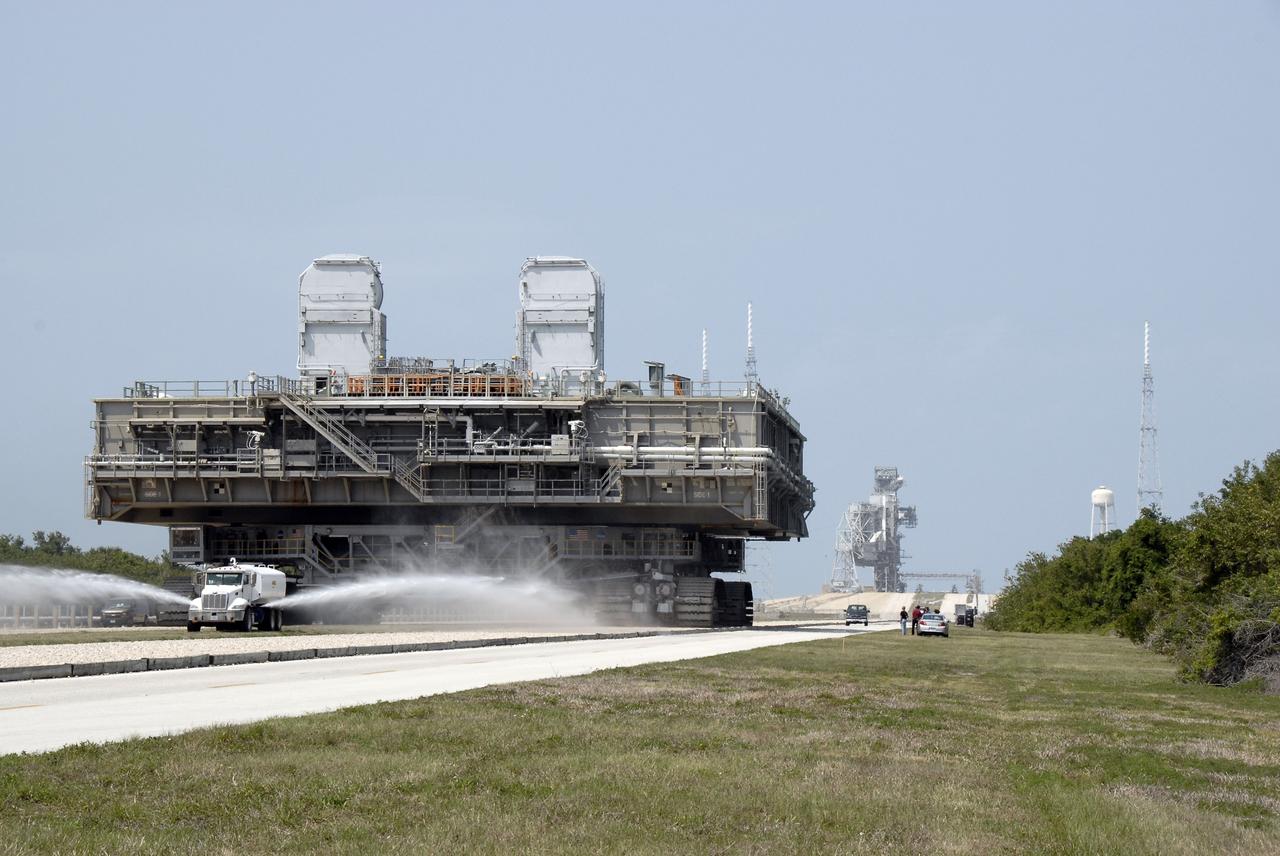

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a water truck continues to spray the dry crawlerway in front of the crawler-transporter as it moves the mobile launcher platform on top away from Kennedy's Launch pad 39B. The platform, turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month, will be rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
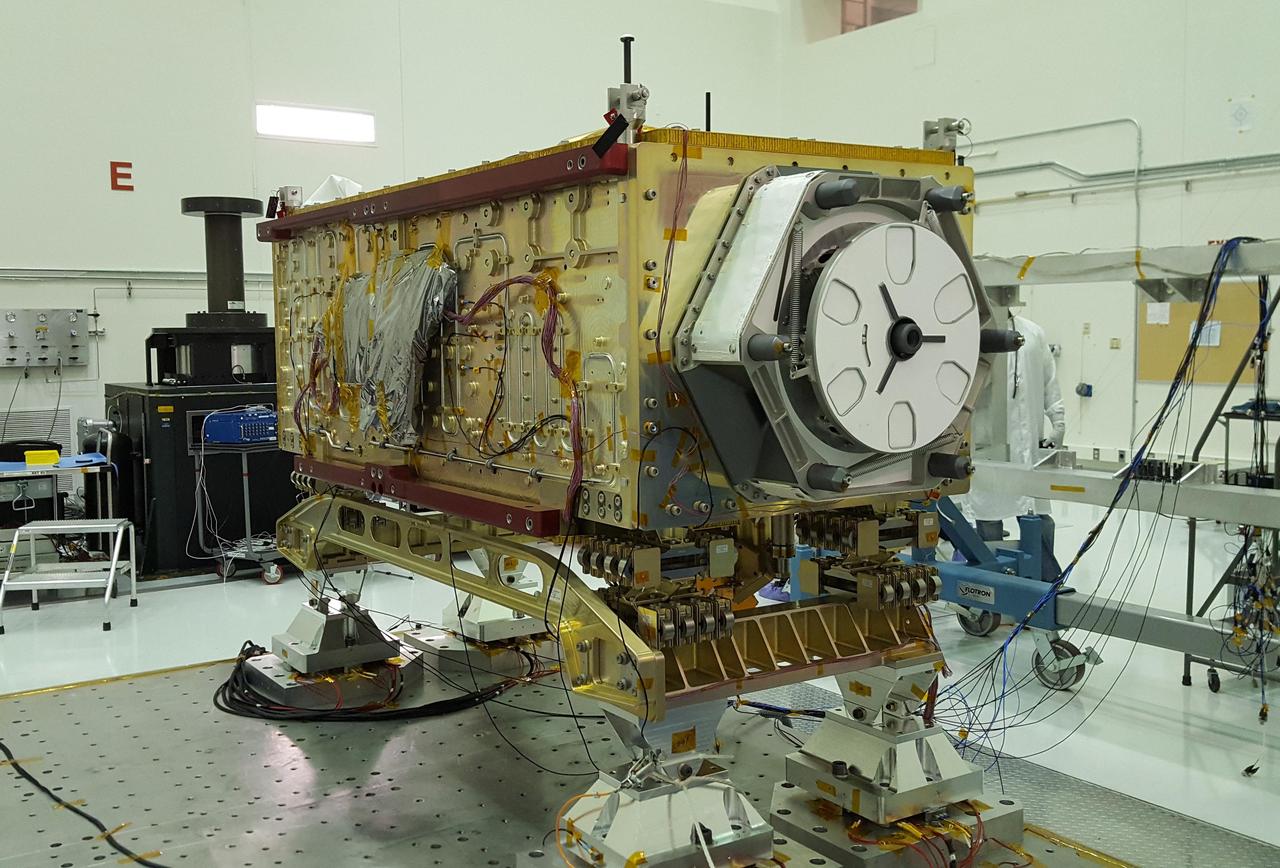

OCO-3 sits on the large vibration table (known as the "shaker") in the Environmental Test Lab at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The exposed wires lead to sensors used during dynamics and thermal-vacuum testing. Thermal blankets will be added to the instrument at Kennedy Space Center, where a Space-X Dragon capsule carrying OCO-3 will launch in on a Falcon 9 rocket to the space station on May 1, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23211
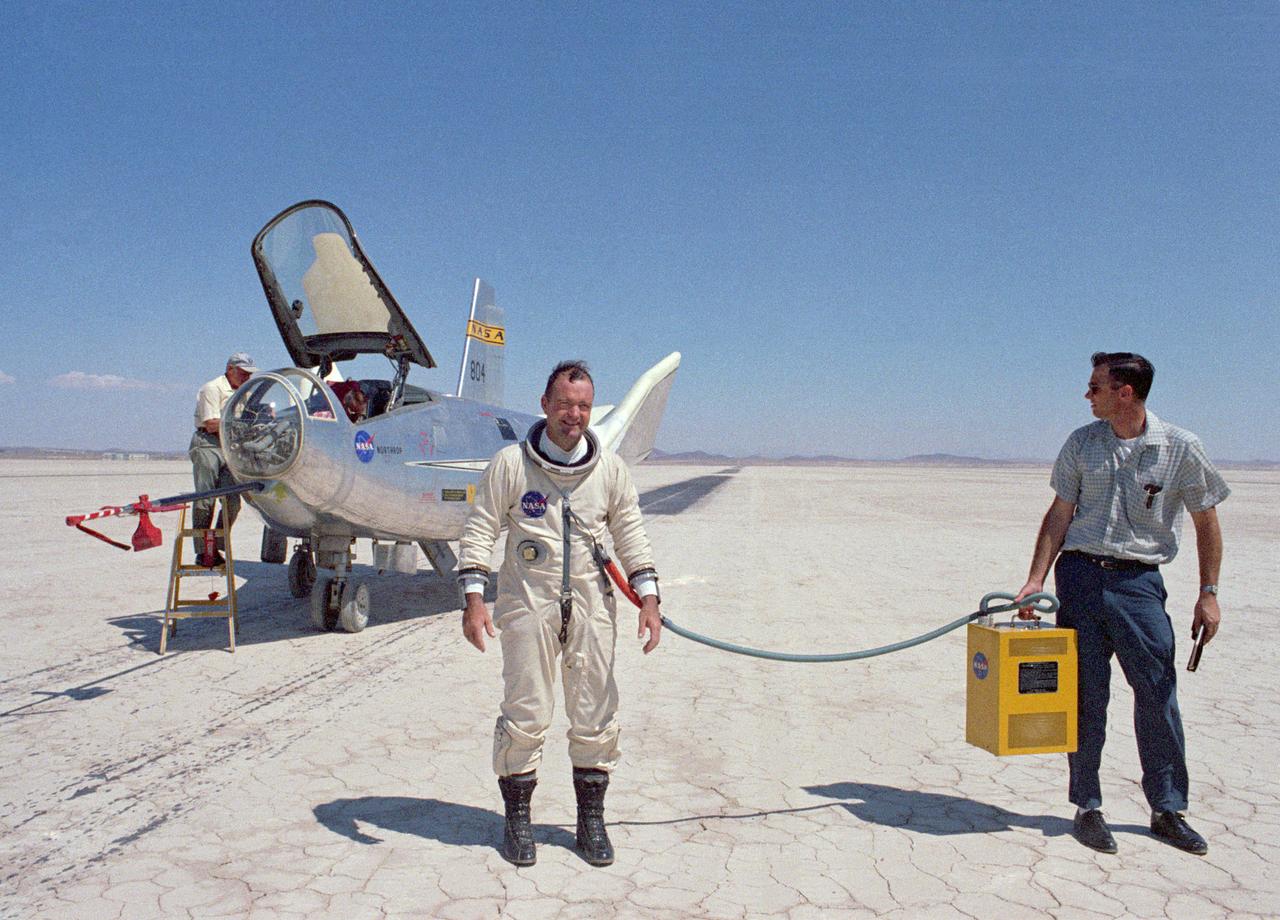

NASA research pilot Bill Dana after his fourth free flight (1 glide and 3 powered) in the HL-10. This particular flight reached a maximum speed of Mach 1.45. Dana made a total of nine HL-10 flights (1 glide and 8 powered), and his lifting body experience as a whole included several car tow and 1 air tow flights in the M2-F1; 4 glide and 15 powered flights in the M2-F3; and 2 powered flights in the X-24B. He is wearing a pressure suit for protection against the cockpit depressurizing at high altitudes. The air conditioner box held by the ground crewman provides cool air to prevent overheating.

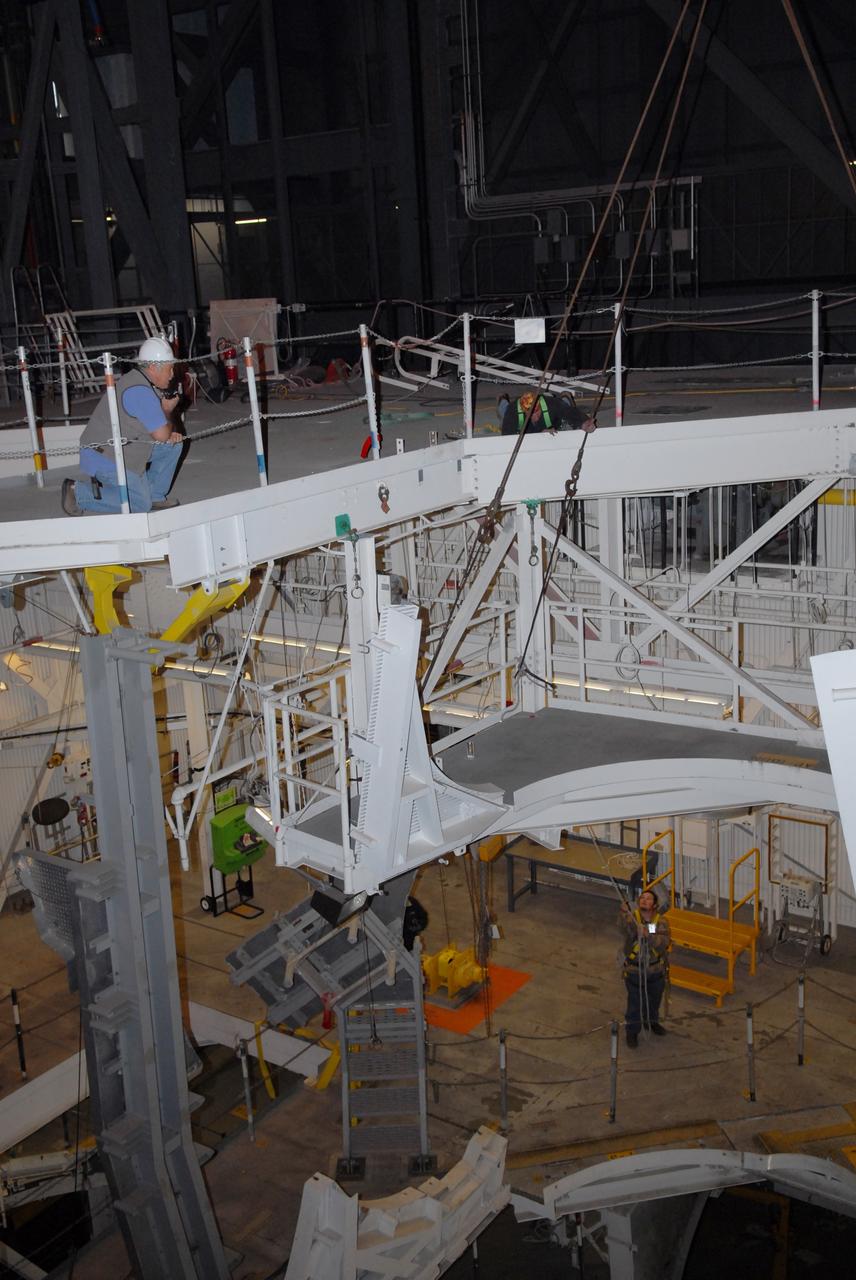
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts Super Stack 2, part of the Ares I-X upper stage, into the upper levels. The stack is being moved across the transfer aisle for attachment to Super Stack 1 in High Bay 3. The upper stage comprises five super stacks, which are integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage on the mobile launch platform. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
![There are many dust devils on Mars -- little twisters that raise dust from the surface. They have also cleaned dust off of the solar panels of the rovers Opportunity and Spirit, improving the solar power production. (Spirit became stuck in 2009 and ceased communication a year later.) HiRISE sees many dust-devil tracks on Mars, but rarely captures an active feature because the images cover such small areas and because the typical time of day near 3 p.m. is past the peak heating and dust-devil activity. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 29.5 centimeters (11.6 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning) to 58.9 centimeters (23.2 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning)]. North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21457](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21457/PIA21457~medium.jpg)
There are many dust devils on Mars -- little twisters that raise dust from the surface. They have also cleaned dust off of the solar panels of the rovers Opportunity and Spirit, improving the solar power production. (Spirit became stuck in 2009 and ceased communication a year later.) HiRISE sees many dust-devil tracks on Mars, but rarely captures an active feature because the images cover such small areas and because the typical time of day near 3 p.m. is past the peak heating and dust-devil activity. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 29.5 centimeters (11.6 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning) to 58.9 centimeters (23.2 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning)]. North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21457

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the platform is being lifted from an upper level in high bay 3. Its removal is part of the refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle. The Ares I and Ares V rockets will be more than 325 feet tall, considerably taller than the space shuttle atop its mobile launcher platform. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this platform will be removed from high bay 3 as part of the refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle. The Ares I and Ares V rockets will be more than 325 feet tall, considerably taller than the space shuttle atop its mobile launcher platform. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

This ASTER image covers an area of 10.5 x 15 km in southern Afghanistan and was acquired on August 20, 2000. The band 3-2-1 composite shows part of an extensive field of barchan sand dunes south of Kandahar. The shape of the dunes indicates that the prevailing wind direction is from the west. The image is located at 30.7 degrees north latitude and 65.7 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11099

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this platform is lifted from an upper level in high bay 3. Its removal is part of the refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle. The Ares I and Ares V rockets will be more than 325 feet tall, considerably taller than the space shuttle atop its mobile launcher platform. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

A group picture of Douglas Airplanes, taken for a photographic promotion in 1954, at what is now known as the Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, California. The photo includes the X-3 (in front--Air Force serial number 49-2892) then clockwise D-558-I, XF4D-1 (a Navy jet fighter prototype not flown by the NACA), and the first D-558-II (NACA tail number 143, Navy serial number 37973), which was flown only once by the NACA.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this platform is being removed from high bay 3 as part of the refurbishment of the facility for the Constellation Program's Ares 1-X vehicle. The Ares I and Ares V rockets will be more than 325 feet tall, considerably taller than the space shuttle atop its mobile launcher platform. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
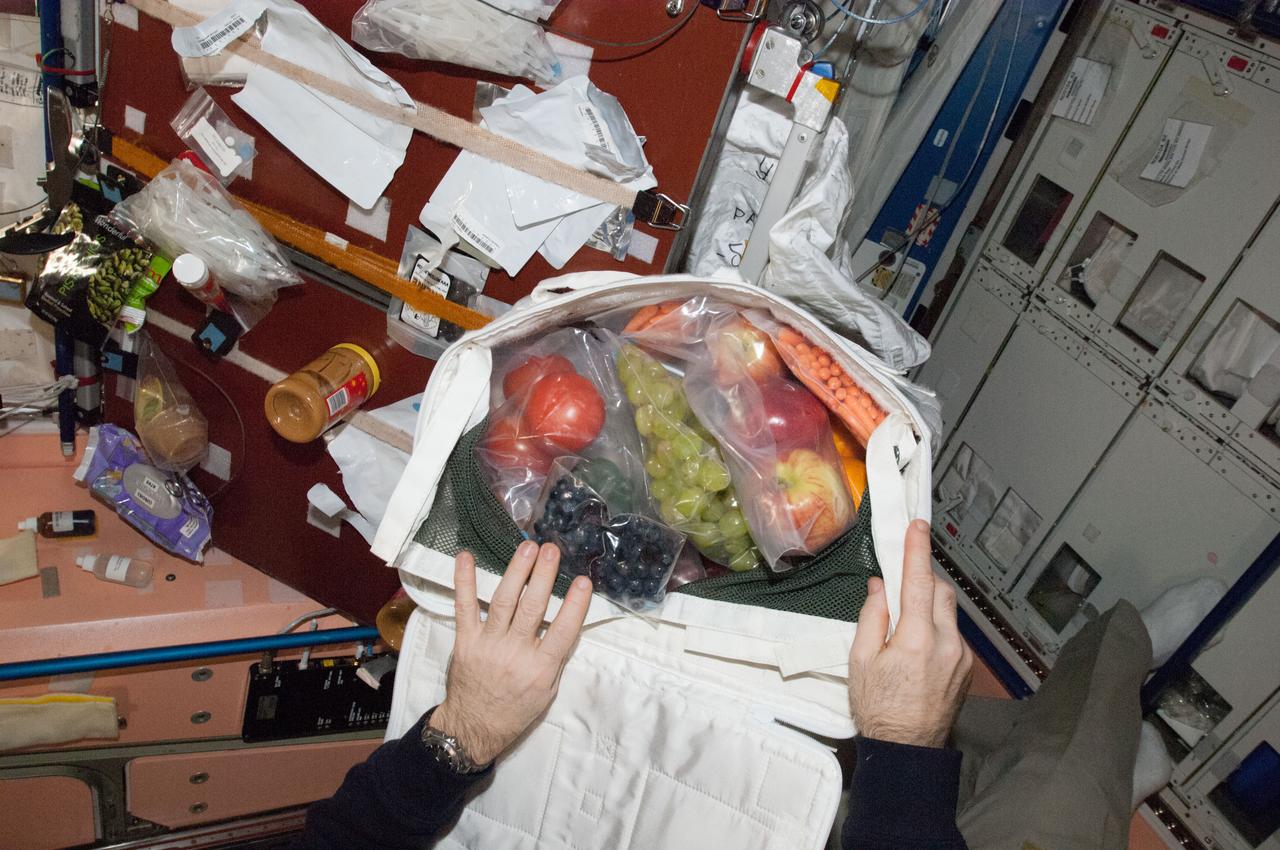
ISS034-E-062087 (3 March 2013) --- The hands of Expedition 34 Commander Kevin Ford, NASA astronaut, open a bag revealing a highly welcomed aggregate of fruit which was sent up from Earth a couple of days earlier and which arrived at the International Space Station on March 3. It was just a very small portion of all the fresh supplies which arrived aboard the unmanned Space X Dragon spacecraft. The scene, being witnessed by many of the astronauts and cosmonauts out of the camera's view, took place in Node 1 or Unity.

NASA Ames Graphics MAJOR NATIONAL FULL-SCALE AERODYNAMICS COMPLEX (NFAC) ROTORCRAFT TESTS SINCE 1977 COMPOSITE. Sikosky S-76 Rotor AC77-0045, Bell 222 fuselage AC77-1388-1, Bell XV-15 Aircraft AC78-0579-3, Kaman CCR Rotor AC78-0731-1, Lokcheed X-Wing Rorotr AC79-0367-4, Boeing VERTOL BMR Rotor AC80-0120-2, Sikordky ABC Helicopter AC80-0467-17, MBB BO-105 Rotor AC83-0309-157
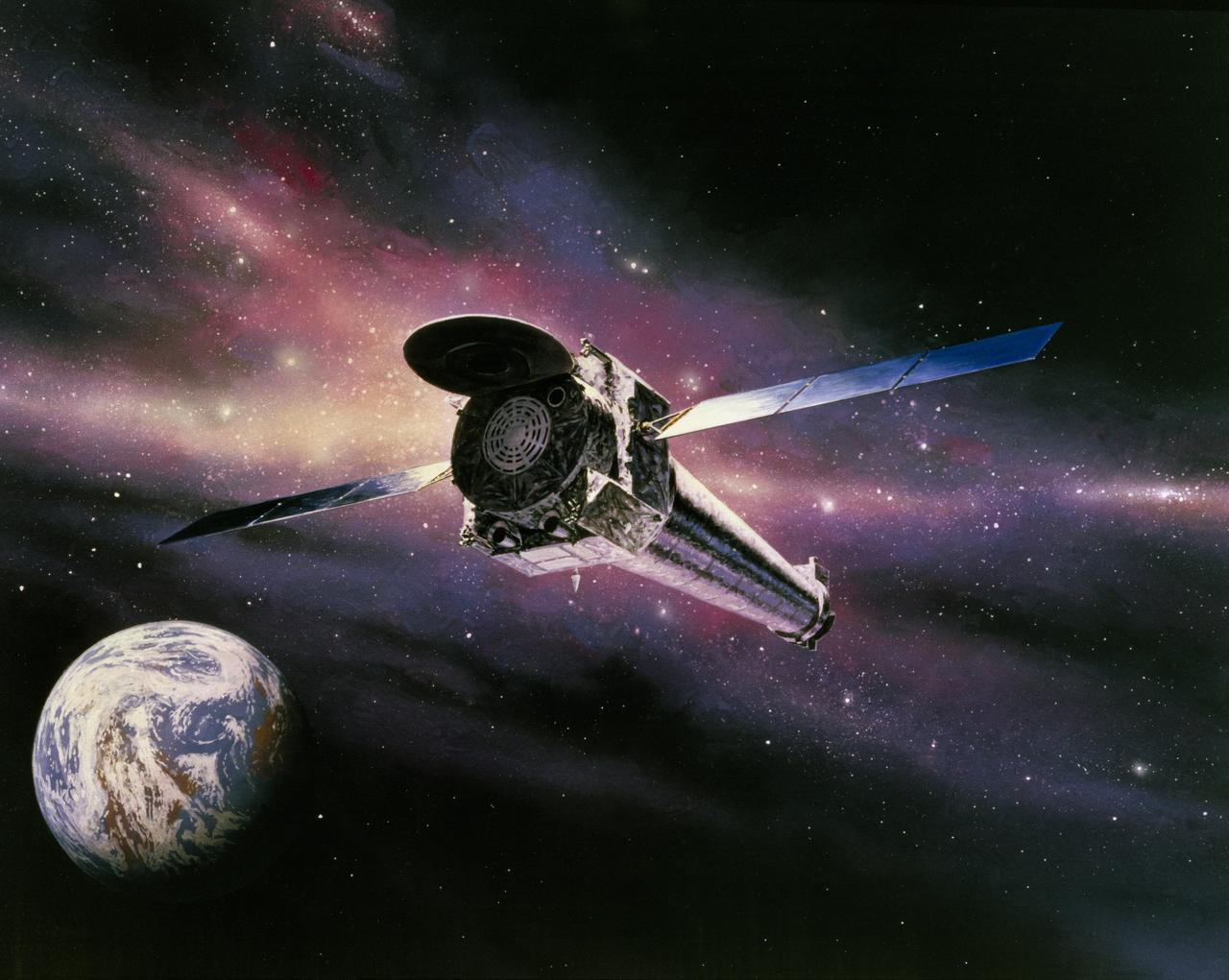

This is an artist's concept of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), fully developed in orbit in a star field with Earth. In 1999, the AXAF was renamed the CXO in honor of the late Indian-American Novel Laureate Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It is designed to observe x-rays from high energy regions of the Universe, such as hot gas in the renmants of exploded stars. It produces picture-like images of x-ray emissions analogous to those made in visible light, as well as gathers data on the chemical composition of x-ray radiating objects. The CXO helps astronomers world-wide better understand the structure and evolution of the universe by studying powerful sources of x-ray such as exploding stars, matter falling into black holes, and other exotic celestial objects. The Observatory has three major parts: (1) the x-ray telescope, whose mirrors will focus x-rays from celestial objects; (2) the science instruments that record the x-rays so that x-ray images can be produced and analyzed; and (3) the spacecraft, which provides the environment necessary for the telescope and the instruments to work. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development the CXO and NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Observatory was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, STS-93 mission. (Image courtesy of TRW).
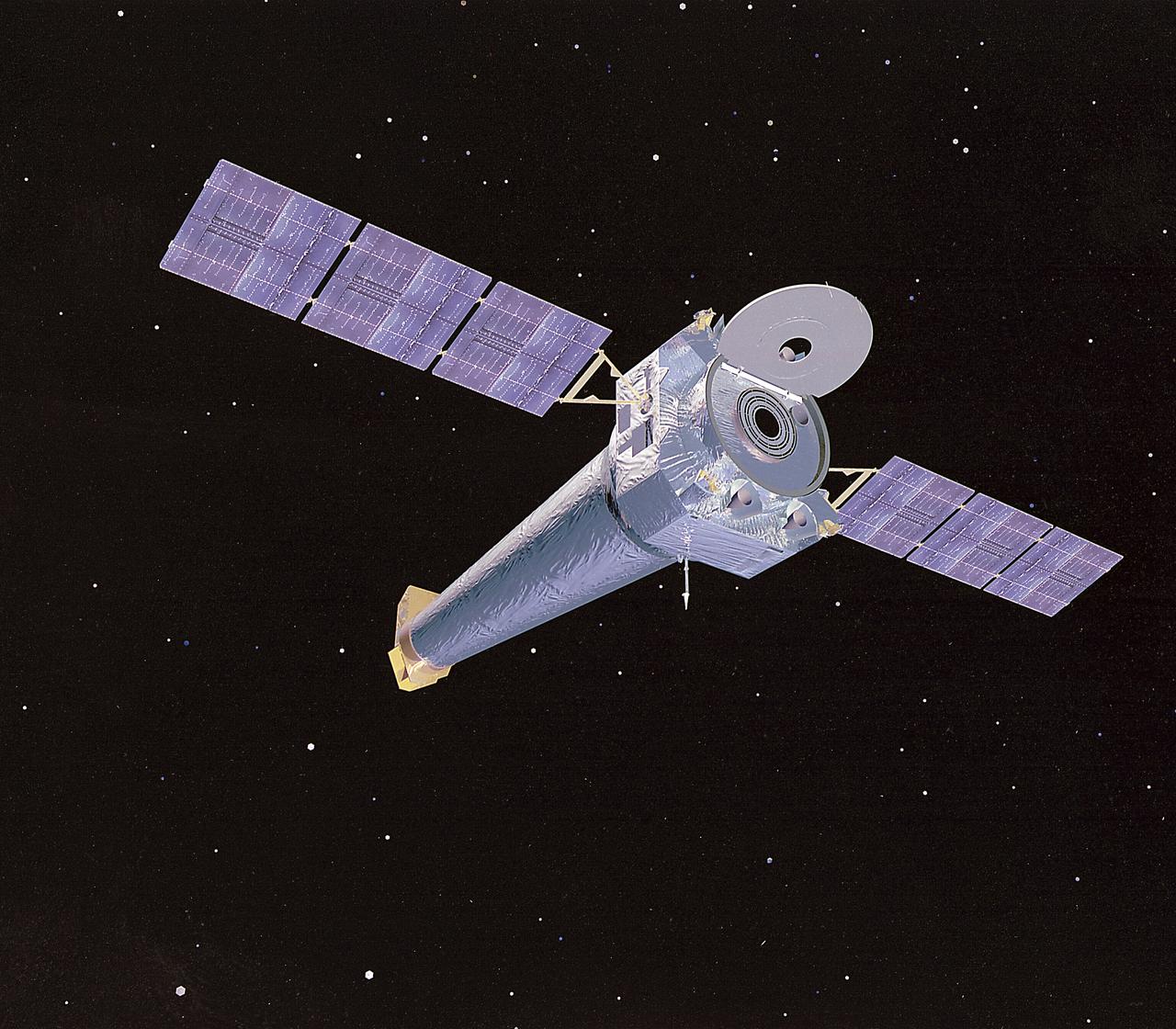
This is a computer rendering of the fully developed Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF). In 1999, the AXAF was renamed the CXO in honor of the late Indian-American Novel Laureate Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It is designed to observe x-rays from high energy regions of the Universe, such as hot gas in the renmants of exploded stars. It produces picture-like images of x-ray emissions analogous to those made in visible light, as well as gathers data on the chemical composition of x-ray radiating objects. The CXO helps astronomers world-wide better understand the structure and evolution of the universe by studying powerful sources of x-ray such as exploding stars, matter falling into black holes, and other exotic celestial objects. The Observatory has three major parts: (1) the x-ray telescope, whose mirrors will focus x-rays from celestial objects; (2) the science instruments that record the x-rays so that x-ray images can be produced and analyzed; and (3) the spacecraft, which provides the environment necessary for the telescope and the instruments to work. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Observatory was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, STS-93 mission. (Image courtesy of TRW).
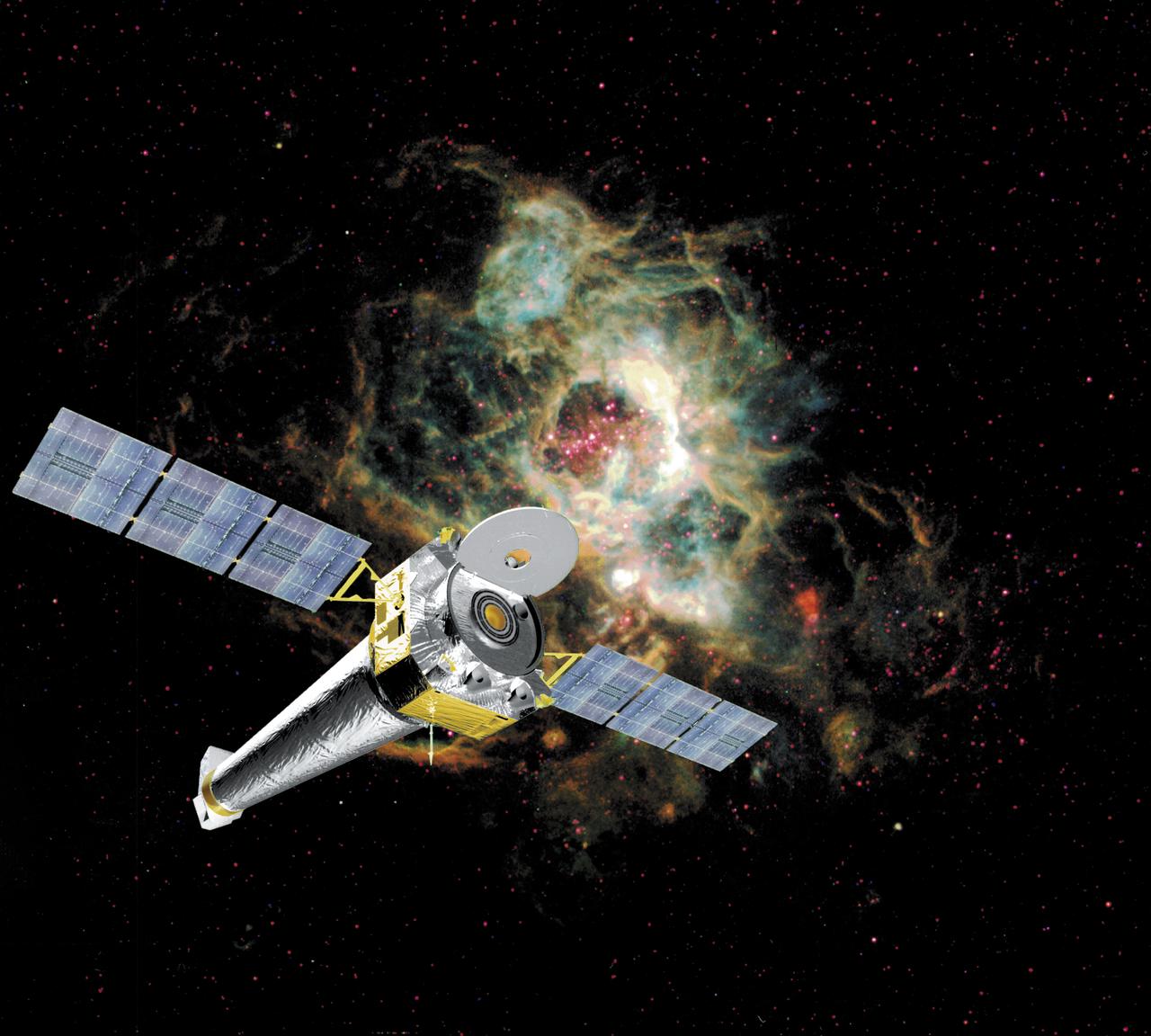

This is a computer rendering of the fully developed Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), in orbit in a star field. In 1999, the AXAF was renamed the CXO in honor of the late Indian-American Novel Laureate Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It is designed to observe x-rays from high energy regions of the Universe, such as hot gas in the renmants of exploded stars. It produces picture-like images of x-ray emissions analogous to those made in visible light, as well as gathers data on the chemical composition of x-ray radiating objects. The CXO helps astronomers world-wide better understand the structure and evolution of the universe by studying powerful sources of x-rays such as exploding stars, matter falling into black holes, and other exotic celestial objects. The Observatory has three major parts: (1) the x-ray telescope, whose mirrors will focus x-rays from celestial objects; (2) the science instruments that record the x-rays so that x-ray images can be produced and analyzed; and (3) the spacecraft, which provides the environment necessary for the telescope and the instruments to work. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Observatory was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, STS-93 mission. (Image courtesy of TRW).
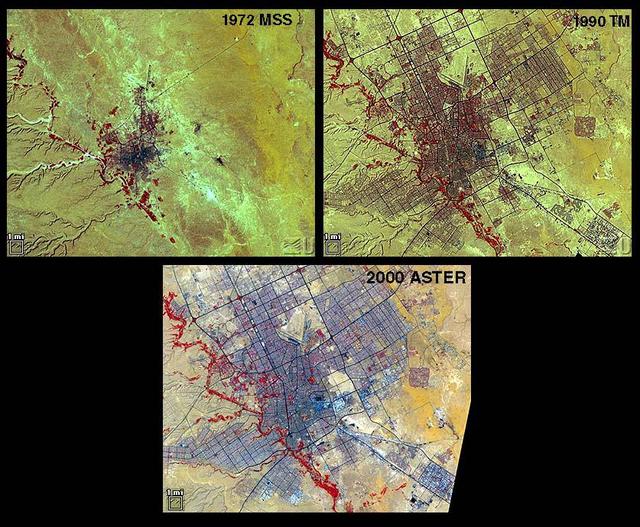
Riyadh, the national capital of Saudi Arabia, is shown in 1972, 1990 and 2000. Its population grew in these years from about a half million to more than two million. Saudi Arabia experienced urbanization later than many other countries; in the early 1970s its urban-rural ratio was still about 1:3. By 1990 that had reversed to about 3:1. The city grew through in-migration from rural areas, and from decreases in the death rate while birthrates remained high. The 1972 image is a Landsat MSS scene; the 1990 image is a Landsat Thematic Mapper scene; and the 2000 image is an ASTER scene. All three images cover an area of about 27 x 34 km. The image is centered at 24.6 degrees north latitude, 46.6 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11087
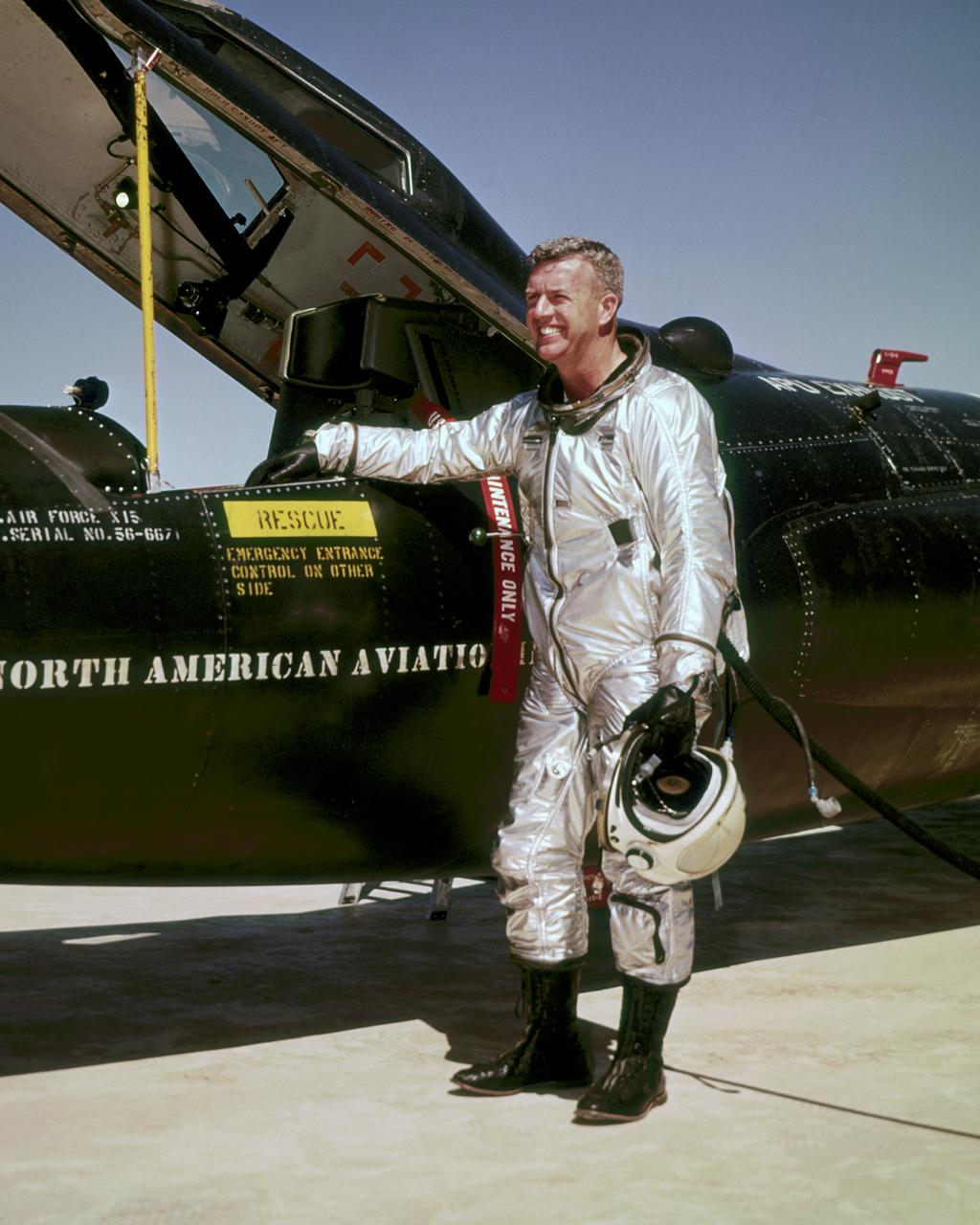

Joseph A. Walker was a Chief Research Pilot at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center during the mid-1960s. He joined the NACA in March 1945, and served as project pilot at the Edwards flight research facility on such pioneering research projects as the D-558-1, D-558-2, X-1, X-3, X-4, X-5, and the X-15. He also flew programs involving the F-100, F-101, F-102, F-104, and the B-47. Walker made the first NASA X-15 flight on March 25, 1960. He flew the research aircraft 24 times and achieved its fastest speed and highest altitude. He attained a speed of 4,104 mph (Mach 5.92) during a flight on June 27, 1962, and reached an altitude of 354,300 feet on August 22, 1963 (his last X-15 flight). He was the first man to pilot the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) that was used to develop piloting and operational techniques for lunar landings. Walker was born February 20, 1921, in Washington, Pa. He lived there until graduating from Washington and Jefferson College in 1942, with a B.A. degree in Physics. During World War II he flew P-38 fighters for the Air Force, earning the Distinguished Flying Cross and the Air Medal with Seven Oak Clusters. Walker was the recipient of many awards during his 21 years as a research pilot. These include the 1961 Robert J. Collier Trophy, 1961 Harmon International Trophy for Aviators, the 1961 Kincheloe Award and 1961 Octave Chanute Award. He received an honorary Doctor of Aeronautical Sciences degree from his alma mater in June of 1962. Walker was named Pilot of the Year in 1963 by the National Pilots Association. He was a charter member of the Society of Experimental Test Pilots, and one of the first to be designated a Fellow. He was fatally injured on June 8, 1966, in a mid-air collision between an F-104 he was piloting and the XB-70.
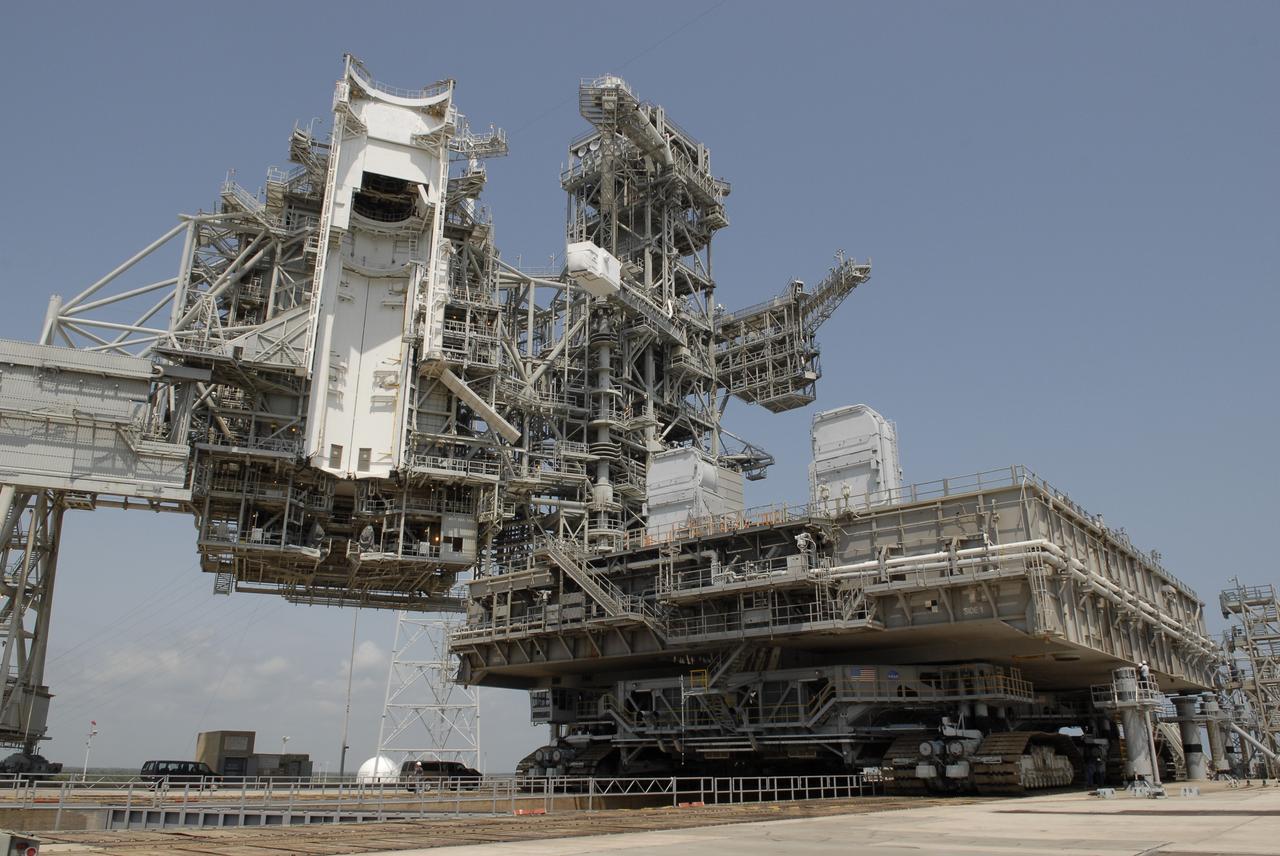

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mobile launcher platform that was turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month is being moved from Kennedy's Launch Pad 39B via the crawler-transporter underneath. At left is seen the payload changeout room in the open rotating service structure. The platform will be rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
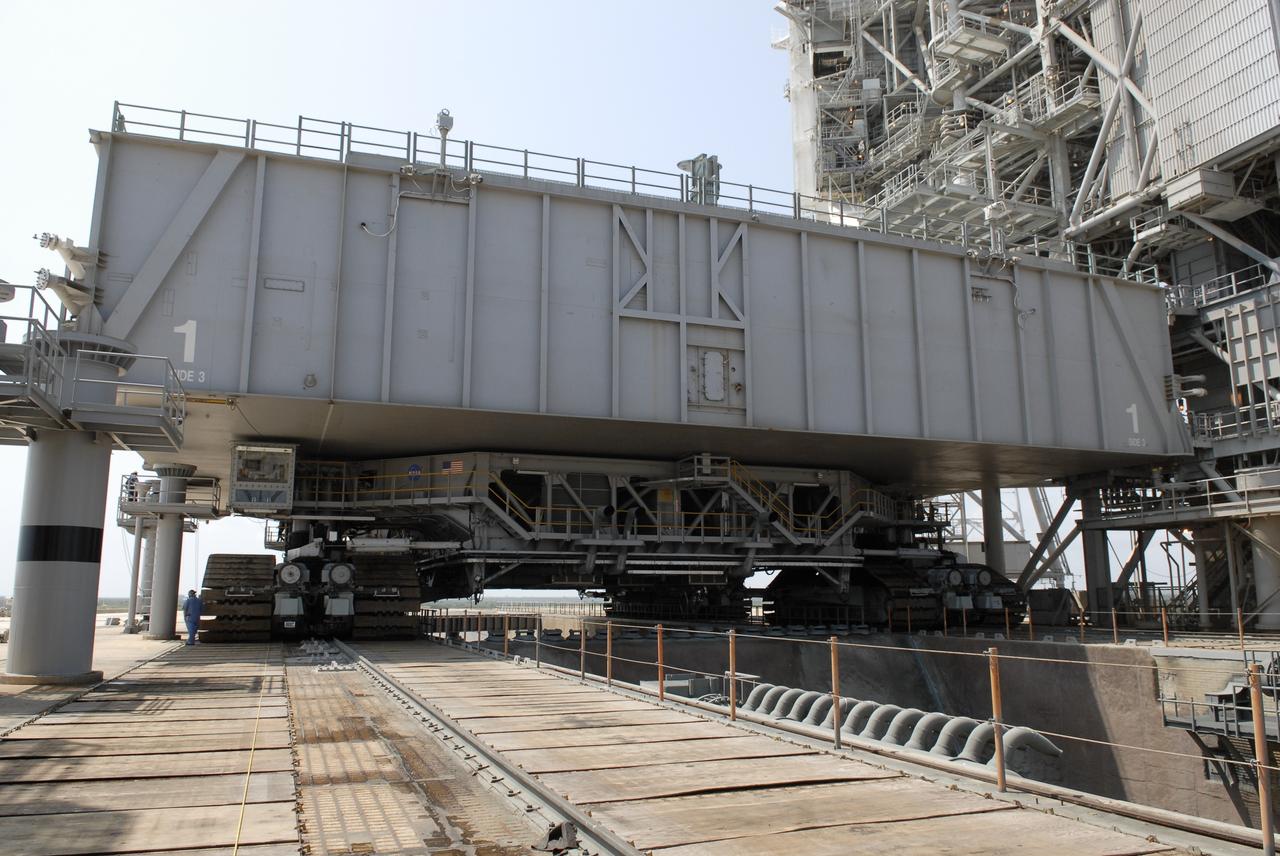

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mobile launcher platform that was turned over from the shuttle program to the Constellation Program last month is being moved from Kennedy's Launch Pad 39B via the crawler-transporter underneath. Here, the platform and crawler can be seen straddling the flame trench on the launch pad. The platform will be rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 in preparation for the Ares I-X flight test this summer. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. Ground Control System hardware was installed in MLP-1 in December 2008. The platform was moved to the launch pad to check out the installed hardware with the Launch Control Center Firing Room 1 equipment, using the actual circuits that will be used when the fully stacked Ares I-X vehicle is rolled out later this year for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
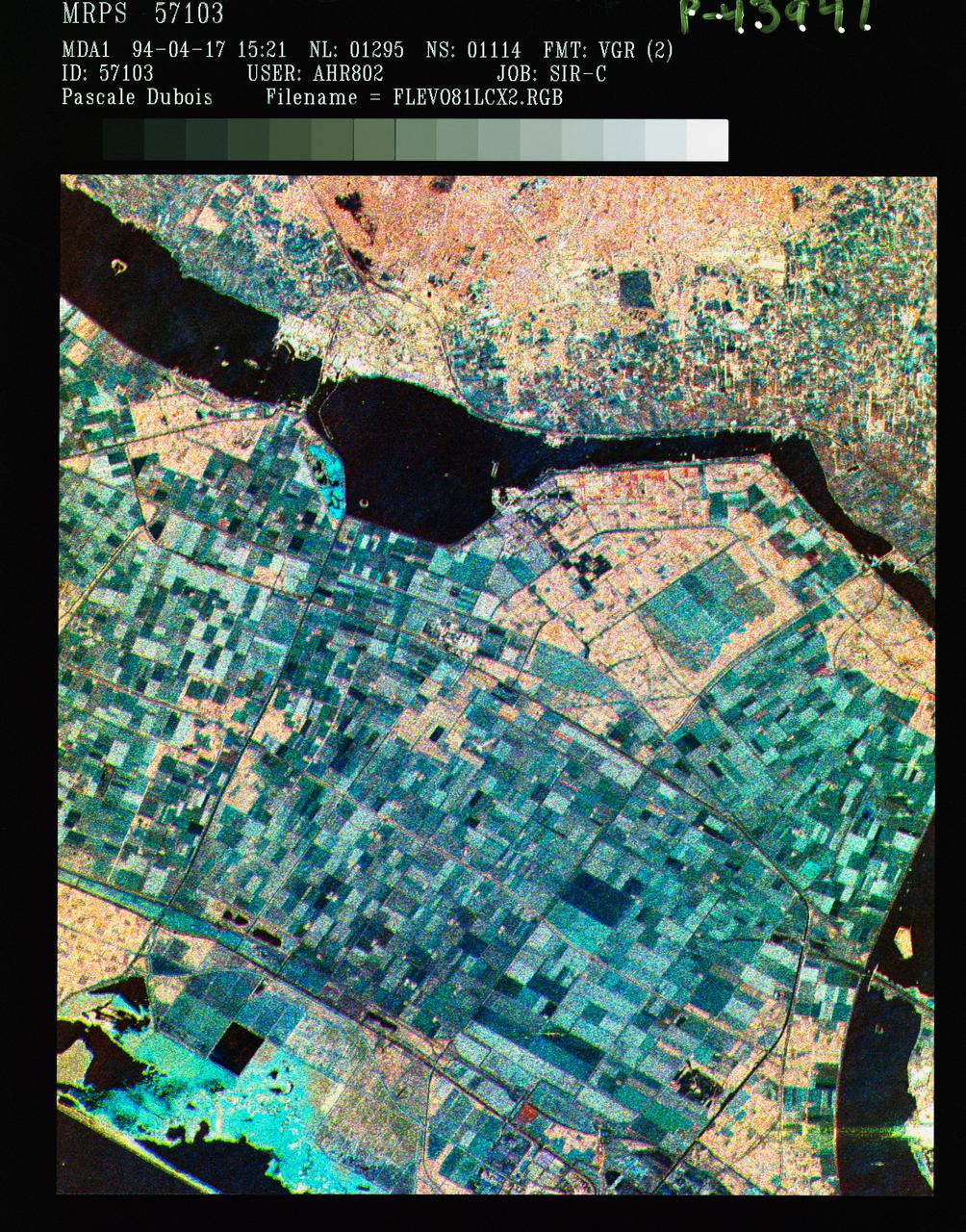

STS059-S-086 (18 April 1994) --- This is a three-frequency false-color image of Flevoland, the Netherlands, centered at 52.4 degrees north latitude, and 5.4 degrees east longitude. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on April 14, 1994. It was produced by combining data from the X-Band, C-Band and L-Band radar's. The area shown is approximately 25 by 28 kilometers (15 1/2 by 17 1/2 miles). Flevoland, which fills the lower two-thirds of the image, is a very flat area that is made up of reclaimed land that is used for agriculture and forestry. At the top of the image, across the canal from Flevoland, is an older forest shown in red; the city of Harderwijk is shown in white on the shore of the canal. At this time of the year, the agricultural fields are bare soil, and they show up in this images in blue. The changes in the brightness of the blue areas are equal to the changes in roughness. The dark blue areas are water and the small dots in the canal are boats. This SIR-C/X-SAR supersite is being used for both calibration and agricultural studies. Several soil and crop ground-truth studies will be conducted during the Shuttle flight. In addition, about 10 calibration devices and 10 corner reflectors have been deployed to calibrate and monitor the radar signal. One of these transponders can be seen as a bright star in the lower right quadrant of the image. This false-color image was made using L-Band total power in the red channel, C-Band total power in the green channel, and X-Band VV polarization in the blue channel. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43941
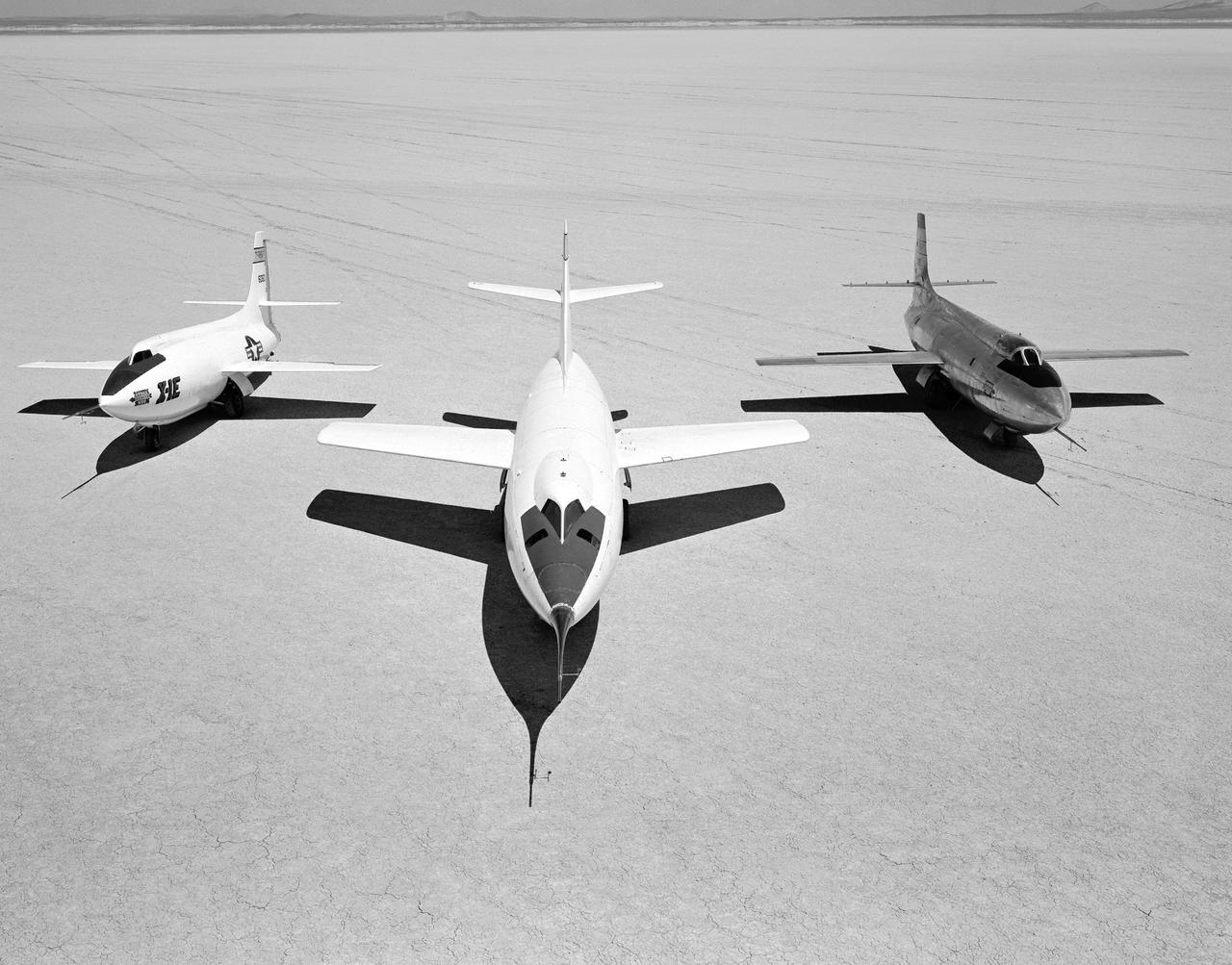

Early NACA research aircraft on the lakebed at the High Speed Research Station in 1955: Left to right: X-1E, D-558-II, X-1B
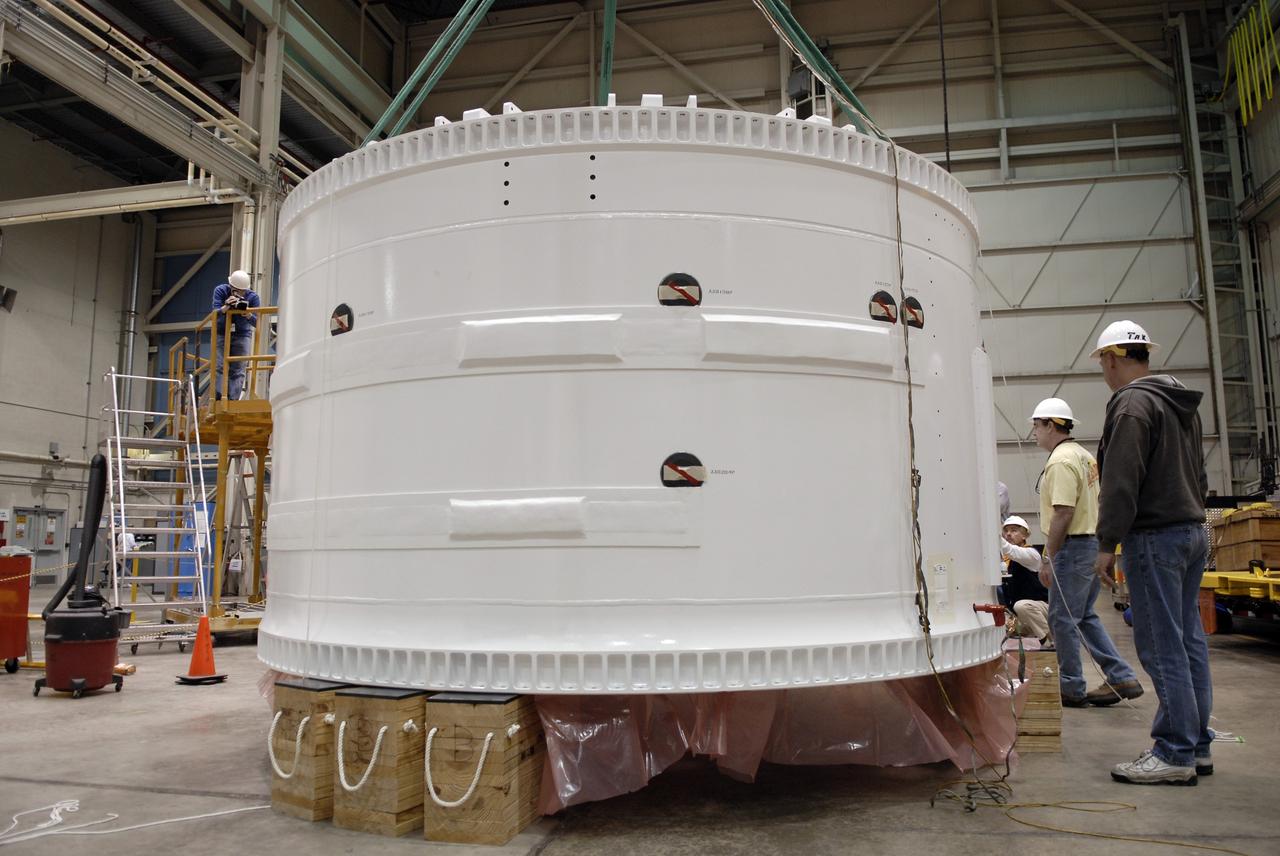

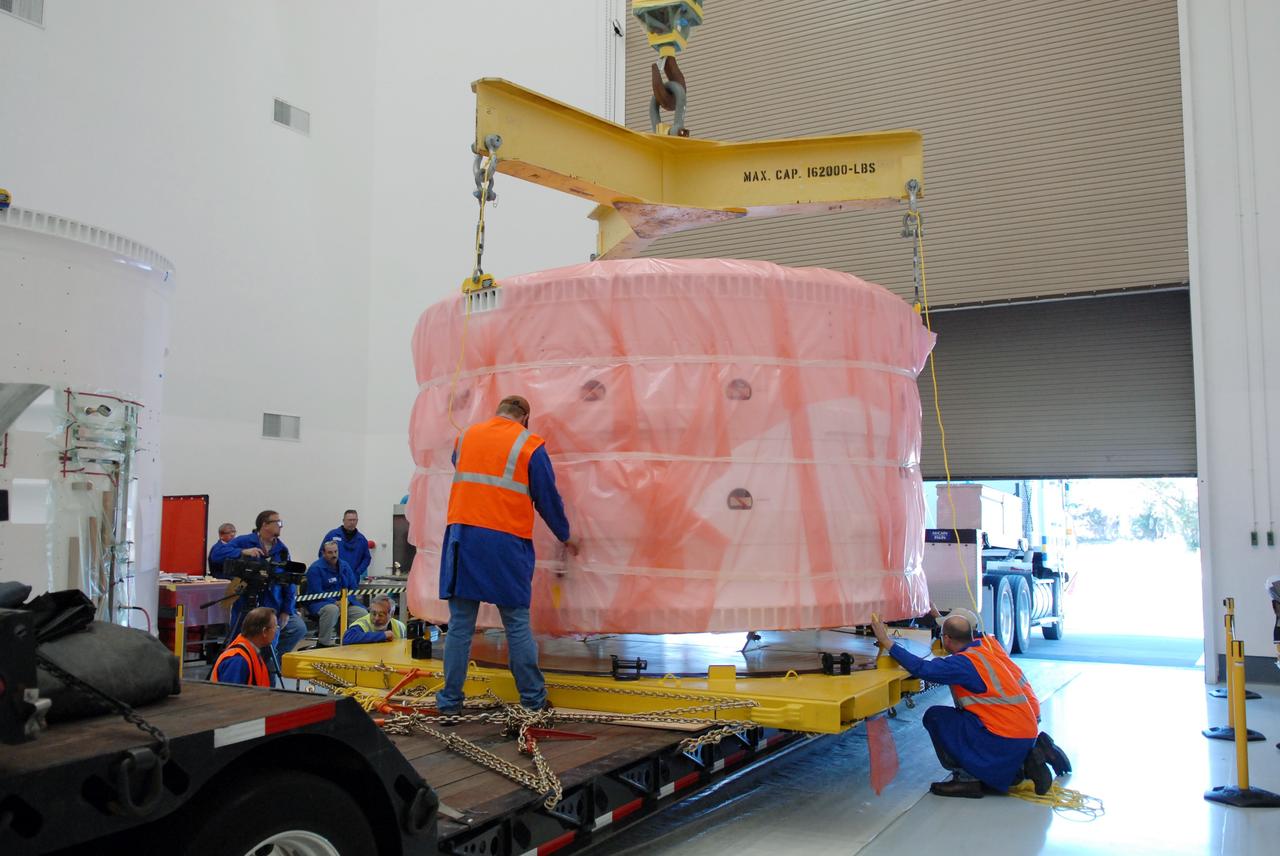
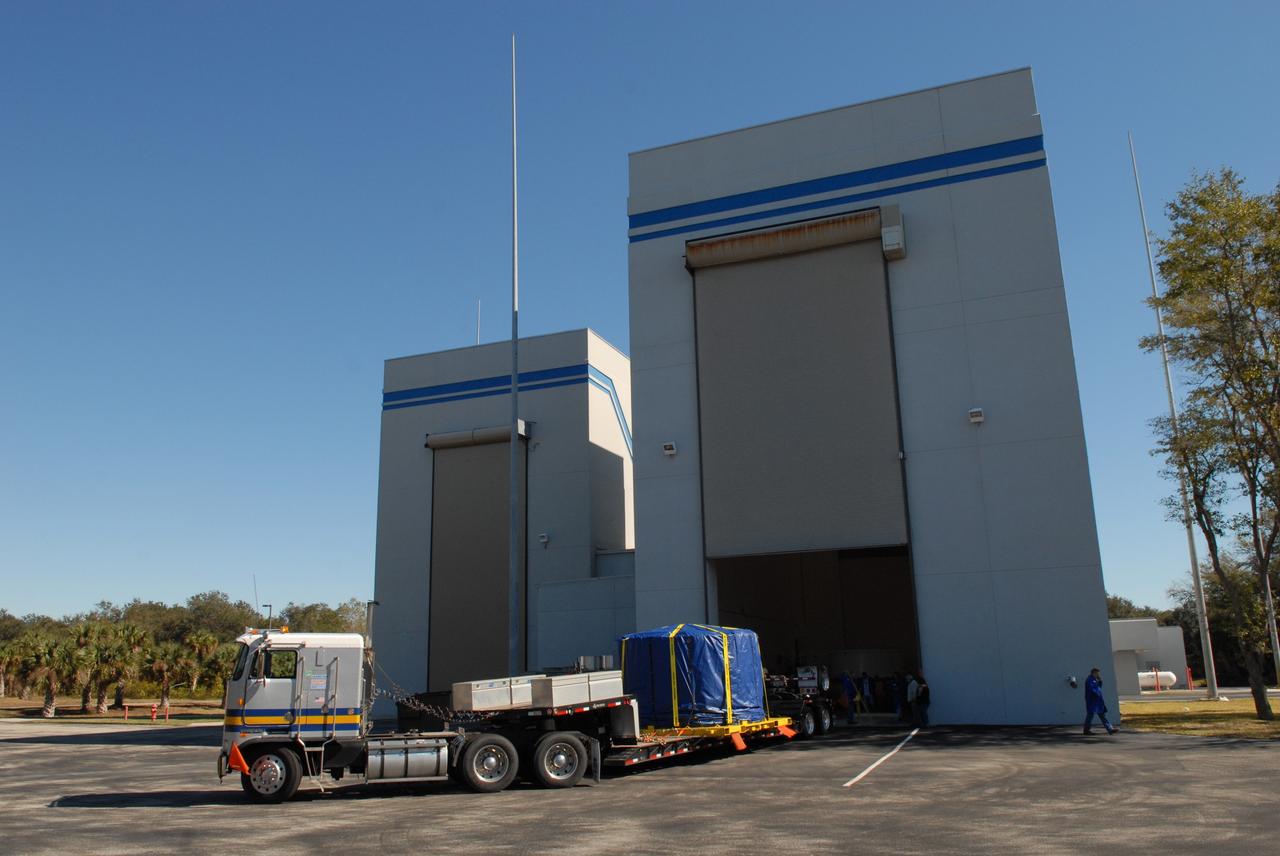
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward skirt is lowered onto supports on the floor. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
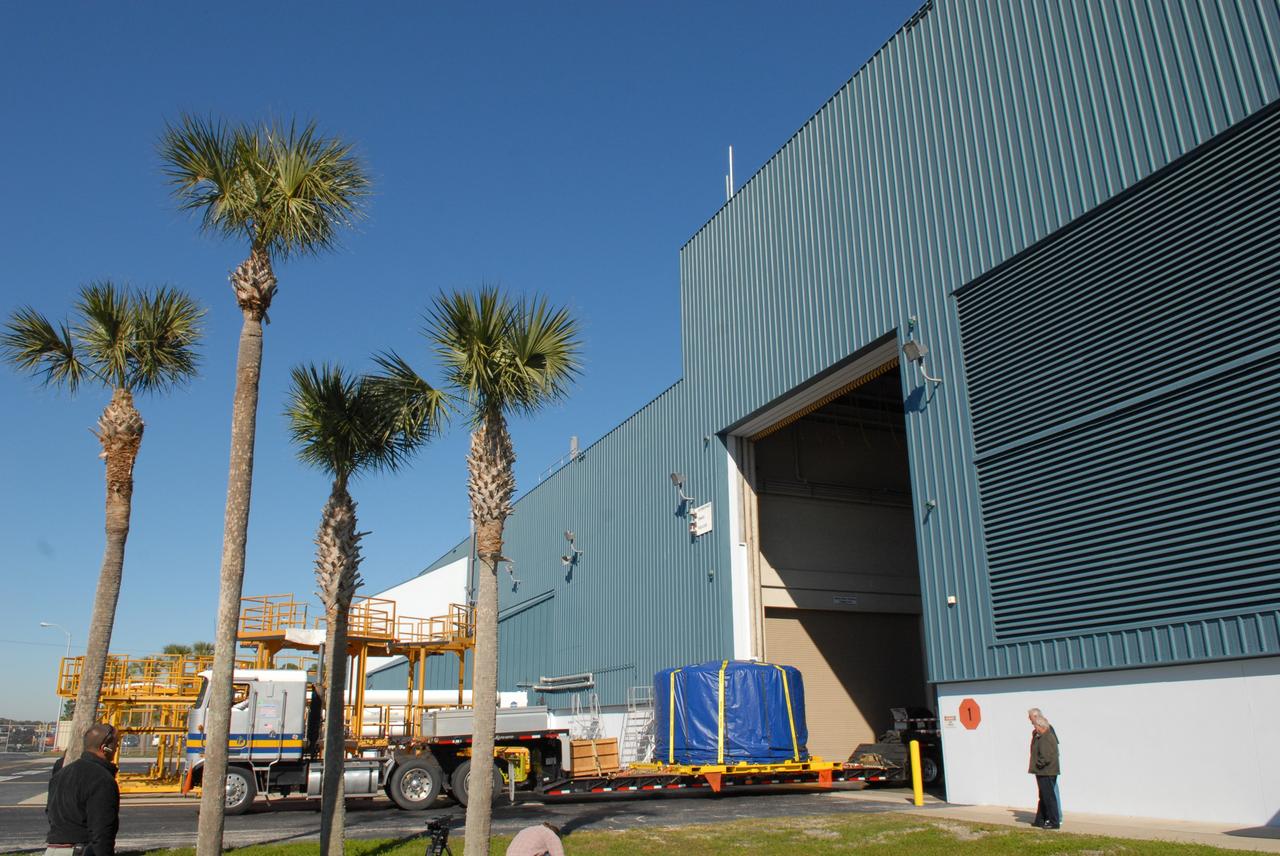

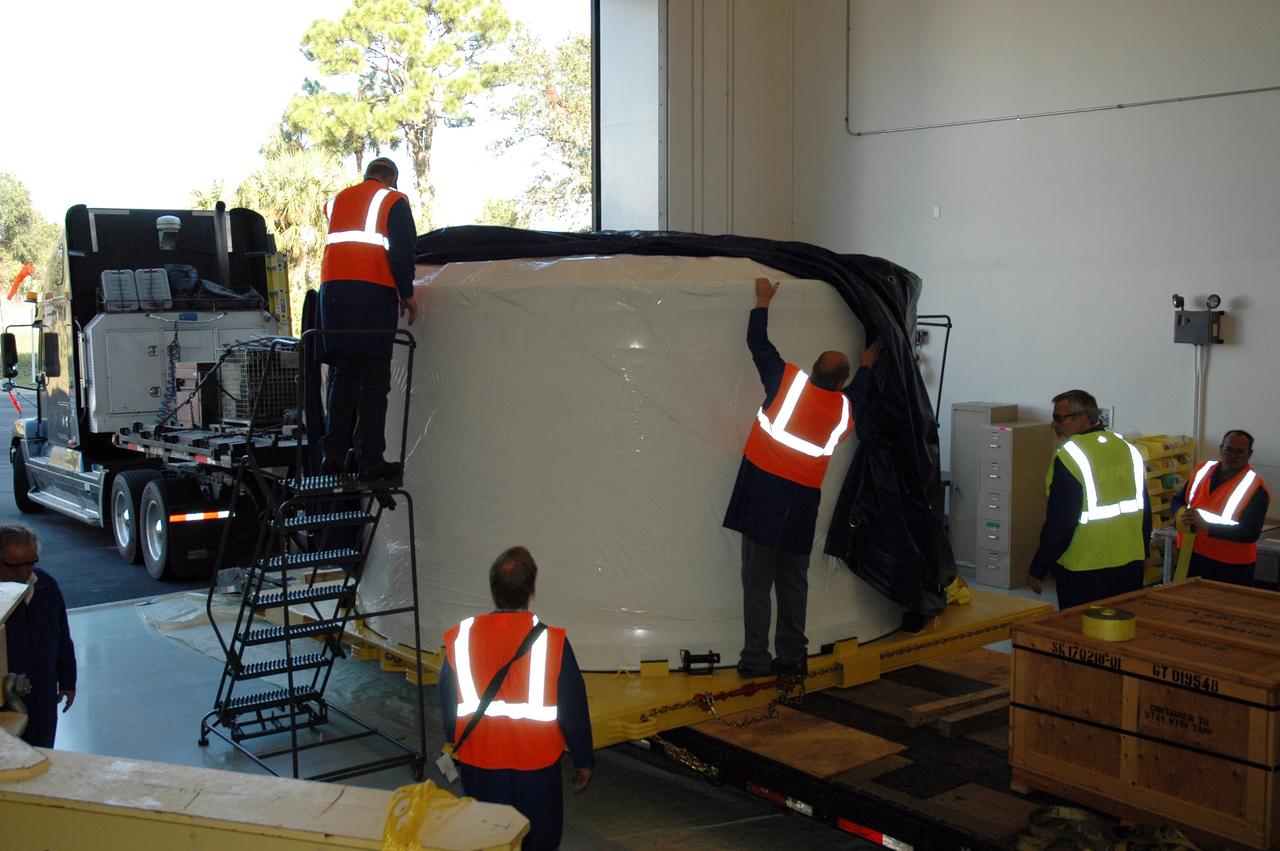
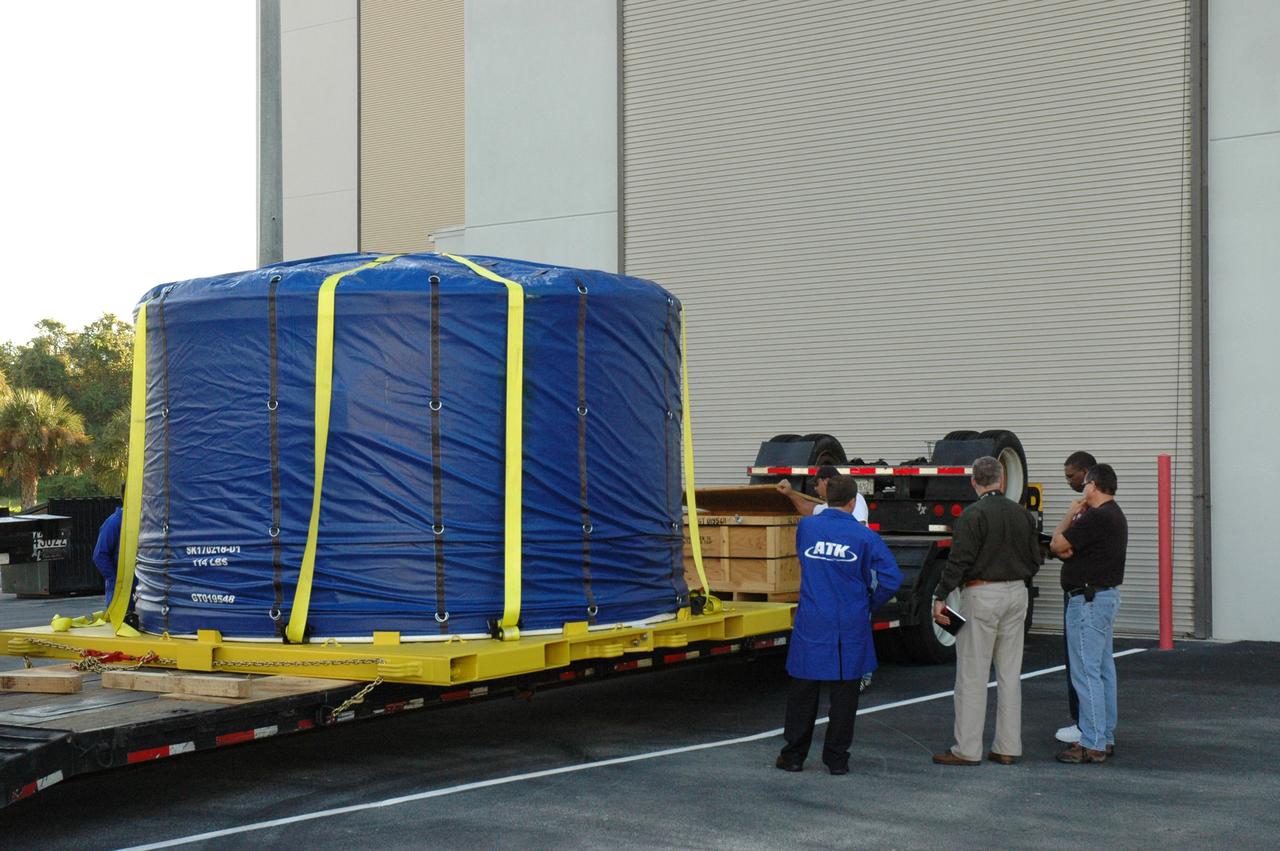
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Wrapped and strapped, the Ares I-X forward skirt arrives at the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
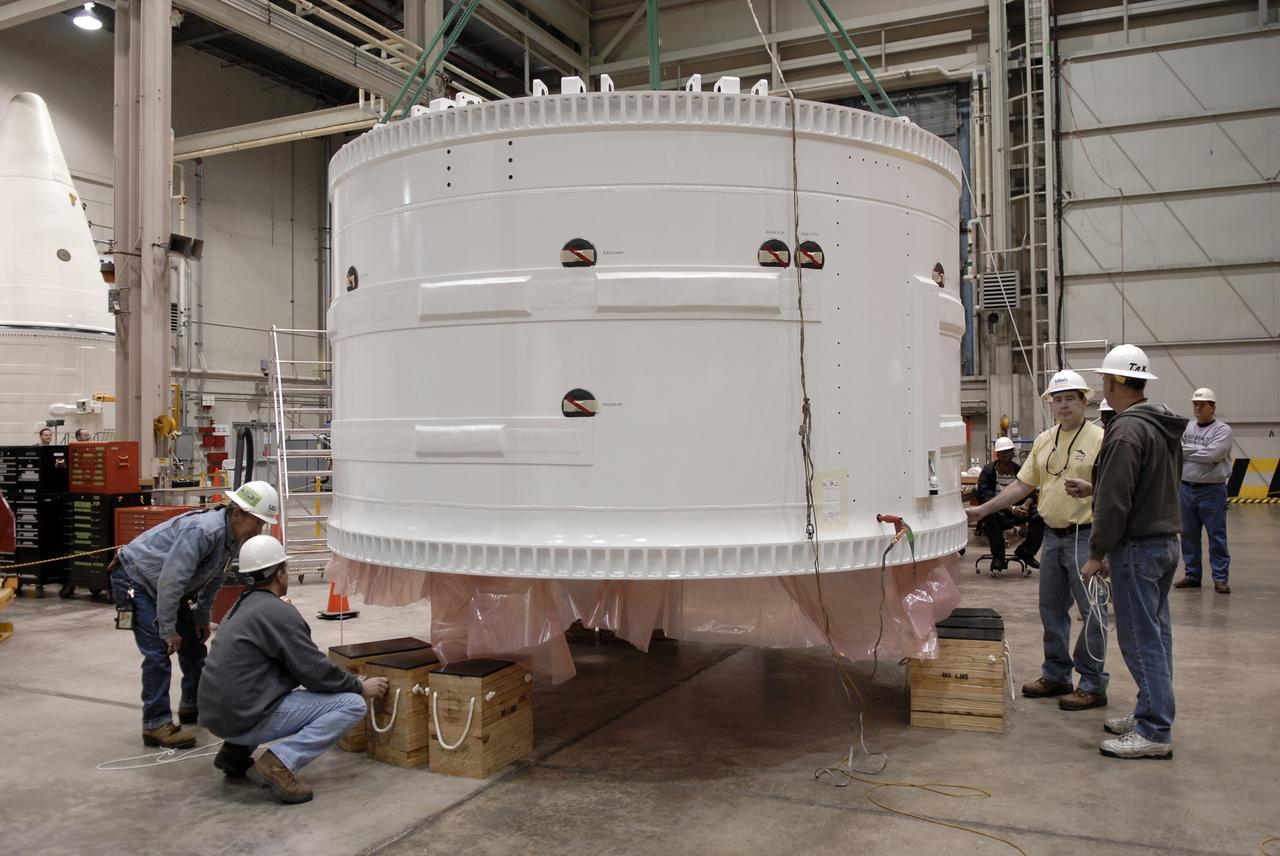

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward skirt is lowered onto supports on the floor. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
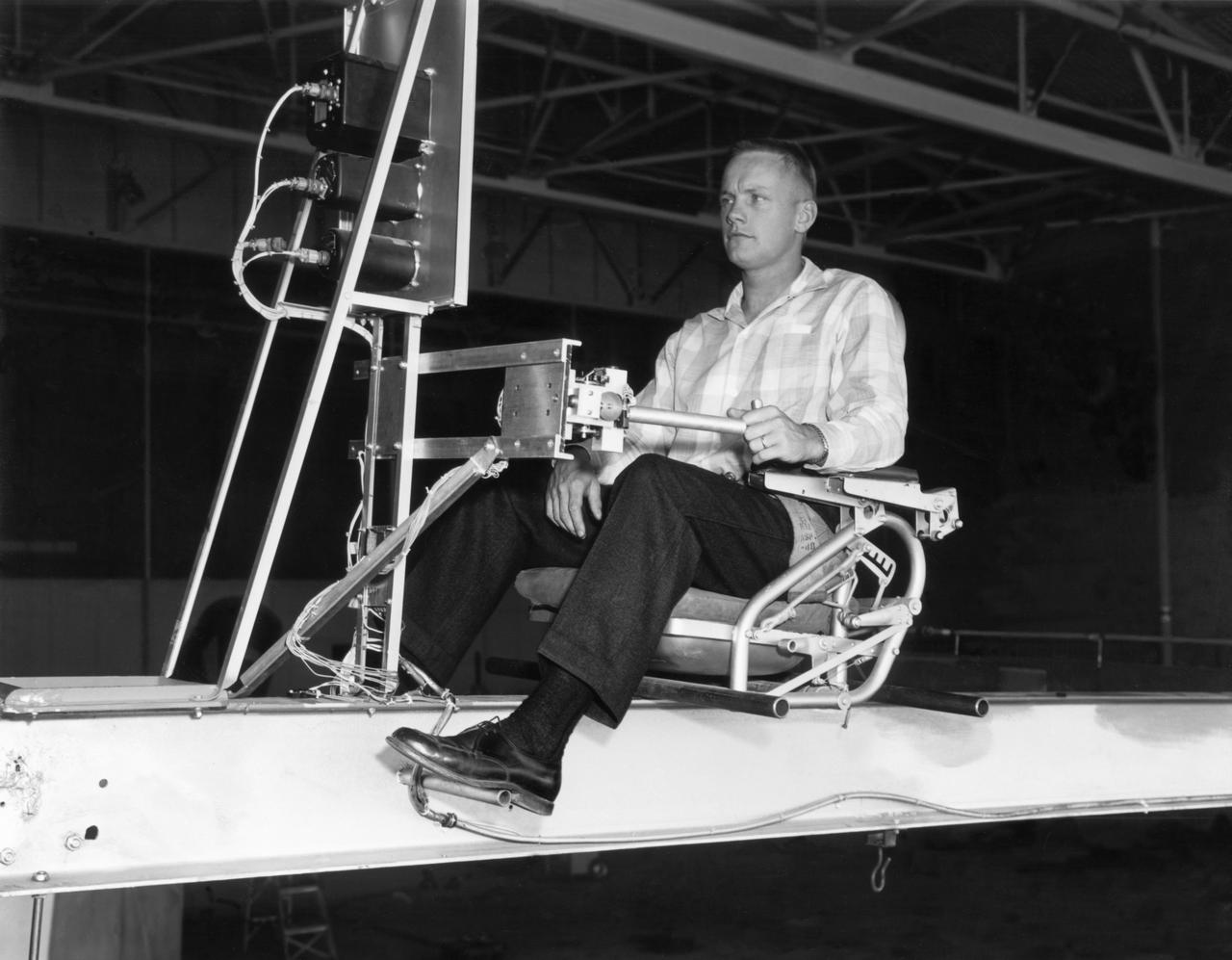

Famed astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, the first man to set foot on the moon during the historic Apollo 11 space mission in July 1969, served for seven years as a research pilot at the NACA-NASA High-Speed Flight Station, now the Dryden Flight Research Center, at Edwards, California, before he entered the space program. Armstrong joined the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) at the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory (later NASA's Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, and today the Glenn Research Center) in 1955. Later that year, he transferred to the High-Speed Flight Station at Edwards as an aeronautical research scientist and then as a pilot, a position he held until becoming an astronaut in 1962. He was one of nine NASA astronauts in the second class to be chosen. As a research pilot Armstrong served as project pilot on the F-100A and F-100C aircraft, F-101, and the F-104A. He also flew the X-1B, X-5, F-105, F-106, B-47, KC-135, and Paresev. He left Dryden with a total of over 2450 flying hours. He was a member of the USAF-NASA Dyna-Soar Pilot Consultant Group before the Dyna-Soar project was cancelled, and studied X-20 Dyna-Soar approaches and abort maneuvers through use of the F-102A and F5D jet aircraft. Armstrong was actively engaged in both piloting and engineering aspects of the X-15 program from its inception. He completed the first flight in the aircraft equipped with a new flow-direction sensor (ball nose) and the initial flight in an X-15 equipped with a self-adaptive flight control system. He worked closely with designers and engineers in development of the adaptive system, and made seven flights in the rocket plane from December 1960 until July 1962. During those fights he reached a peak altitude of 207,500 feet in the X-15-3, and a speed of 3,989 mph (Mach 5.74) in the X-15-1. Armstrong has a total of 8 days and 14 hours in space, including 2 hours and 48 minutes walking on the Moon. In March 1966 he was commander of the Gemini 8 or

S72-03145 (October 1972) --- A vertical view of the Apollo 17 Taurus-Littrow site with an overlay to illustrate the three planned Apollo 17 traverses using the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The EVA-1 traverse has a single station (1); the EVA-2 traverse has four stations (2,3,4,5); and the EVA-3 traverse has five stations (6,7,8,9,10). Stations 10-A and 10-B are alternate locations for Station 10. In addition to the major stations mentioned above, brief stops are planned for sampling between stations using the LRV sampler tool (note diamond-shaped figures), and for deploying explosive charges associated with the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (LSPE - note black x-marks).

File name :DSC_0749.JPG File size :1.1MB(1174690Bytes) Date taken :2003/03/07 13:51:29 Image size :2000 x 1312 Resolution :300 x 300 dpi Number of bits :8bit/channel Protection attribute :Off Hide Attribute :Off Camera ID :N/A Camera :NIKON D1H Quality mode :FINE Metering mode :Matrix Exposure mode :Shutter priority Speed light :No Focal length :20 mm Shutter speed :1/500second Aperture :F11.0 Exposure compensation :0 EV White Balance :Auto Lens :20 mm F 2.8 Flash sync mode :N/A Exposure difference :0.0 EV Flexible program :No Sensitivity :ISO200 Sharpening :Normal Image Type :Color Color Mode :Mode II(Adobe RGB) Hue adjustment :3 Saturation Control :N/A Tone compensation :Normal Latitude(GPS) :N/A Longitude(GPS) :N/A Altitude(GPS) :N/A

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers attach cables to the Ares I-X forward skirt, which was transported from the Astrotech facility. The segment will be lifted off the transporter and placed on supports on the floor. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X forward skirt is lifted from the transporter that delivered it to Astrotech in Titusville, Fla. The forward skirt will be moved to a stand. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alliant Techsystems Inc. workers at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., remove an internal cover from around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The hardware was delivered from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the Ares I-X forward skirt is revealed after its delivery from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the Ares I-X forward skirt, wrapped in a protective cover, is lifted by a crane for a move to a transporter. The segment will be transferred to the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alliant Techsystems Inc. workers at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., remove the protective outer shipping cover from the Ares I-X forward skirt after its arrival from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the padding is being removed from around the Ares I-X forward skirt. It was transferred from the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Fla. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alliant Techsystems Inc. workers at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., attach an overhead crane to the Ares I-X forward skirt just arrived from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. The forward skirt will be lifted and moved to a stand. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

The family of High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO) instruments consisted of three unmarned scientific observatories capable of detecting the x-rays emitted by the celestial bodies with high sensitivity and high resolution. The celestial gamma-ray and cosmic-ray fluxes were also collected and studied to learn more about the mysteries of the universe. High-Energy rays cannot be studied by Earth-based observatories because of the obscuring effects of the atmosphere that prevent the rays from reaching the Earth's surface. They had been observed initially by sounding rockets and balloons, and by small satellites that do not possess the needed instrumentation capabilities required for high data resolution and sensitivity. The HEAO carried the instrumentation necessary for this capability. In this photograph, an artist's concept of three HEAO spacecraft is shown: HEAO-1, launched on August 12, 1977; HEAO-2, launched on November 13, 1978; and HEAO-3, launched on September 20. 1979.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers lift the padding away from the Ares I-X forward skirt transferred from the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Fla. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward skirt is lifted off the transporter that carried it from the Astrotech facility. The segment will be lifted off the transporter and placed on supports on the floor. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers place protective covers around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The segment will be transferred to the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alliant Techsystems Inc. workers at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., begin removing an internal cover from around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The hardware was delivered from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers place padding and cables over the Ares I-X forward skirt for its transfer to the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X forward skirt arrives at the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Fla., after its journey from Major Tool & Machine Inc. in Indiana. Major Tool is subcontractor to Ares I prime contractor Alliant Techsystems Inc., or ATK, in Utah. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will integrate and assemble the forward skirt components in the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the Ares I-X forward skirt, wrapped in a protective cover, is lowered by crane onto a transporter. The segment will be transferred to the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Wrapped and strapped, the Ares I-X forward skirt is transported away from Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., heading for the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
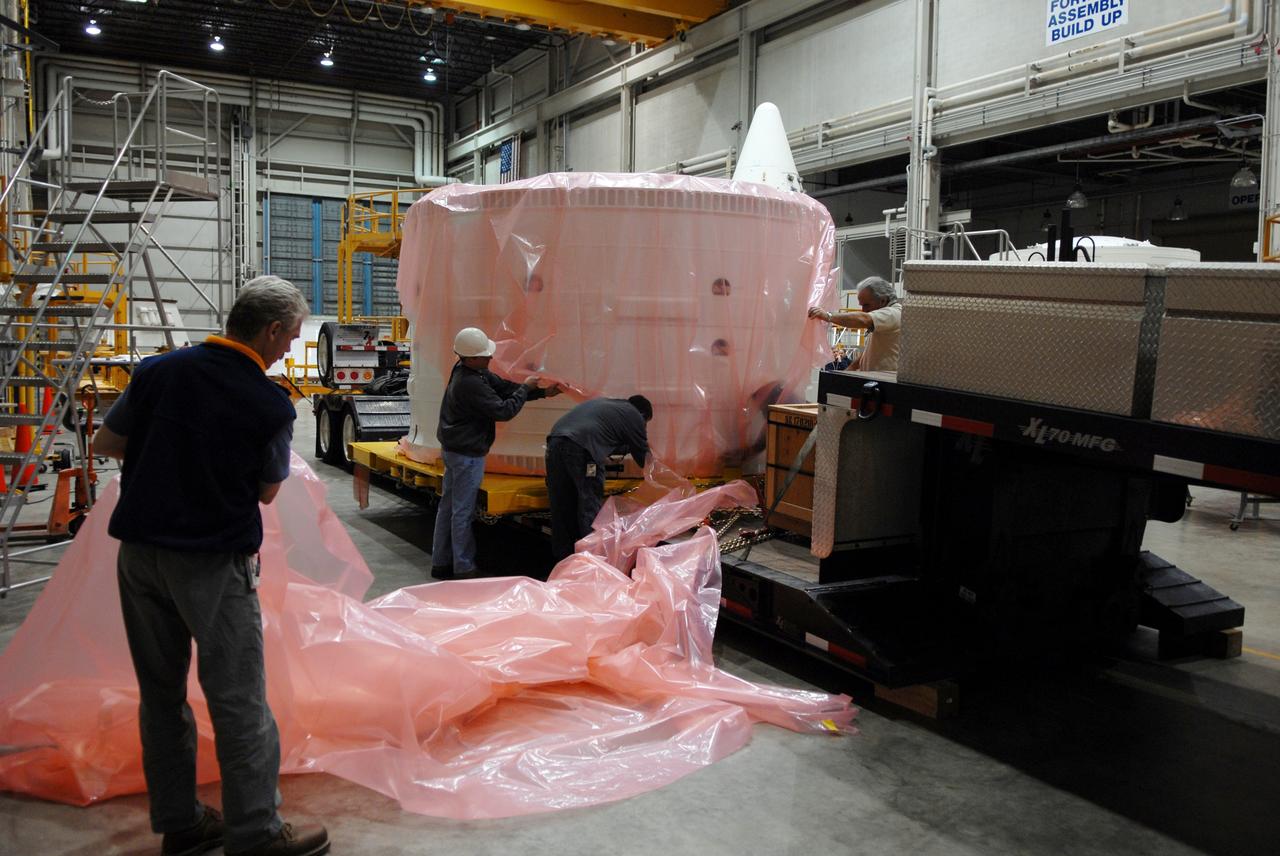

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers begin removing the protective cover from around the Ares I-X forward skirt. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
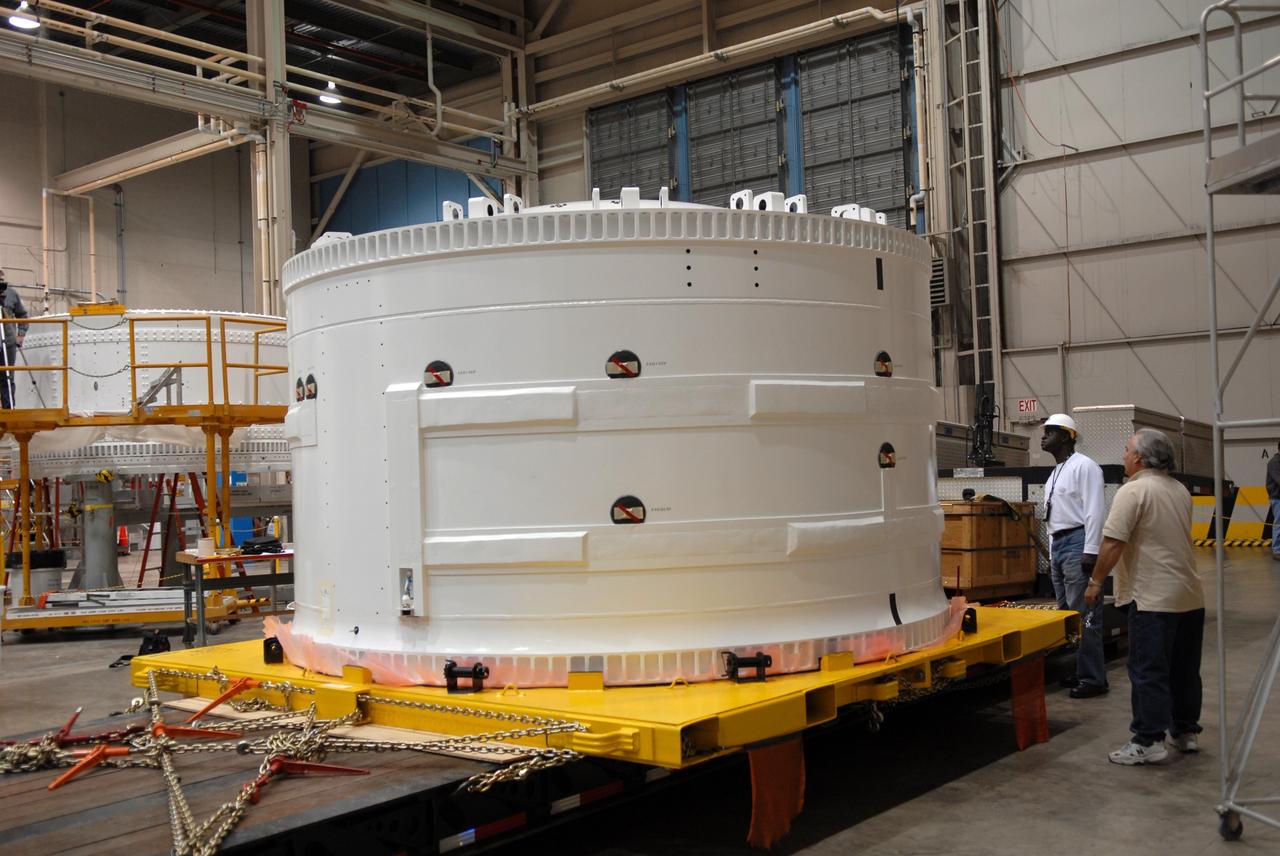

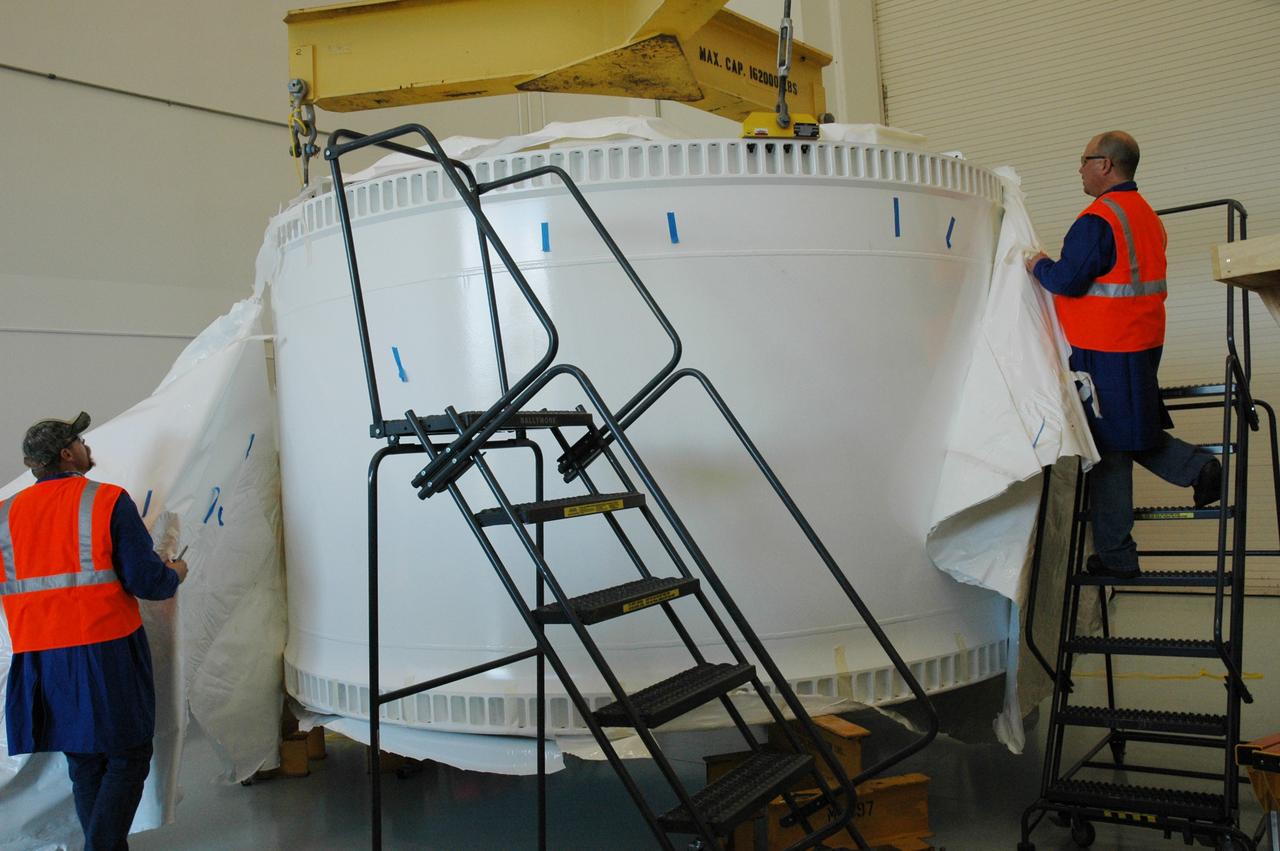
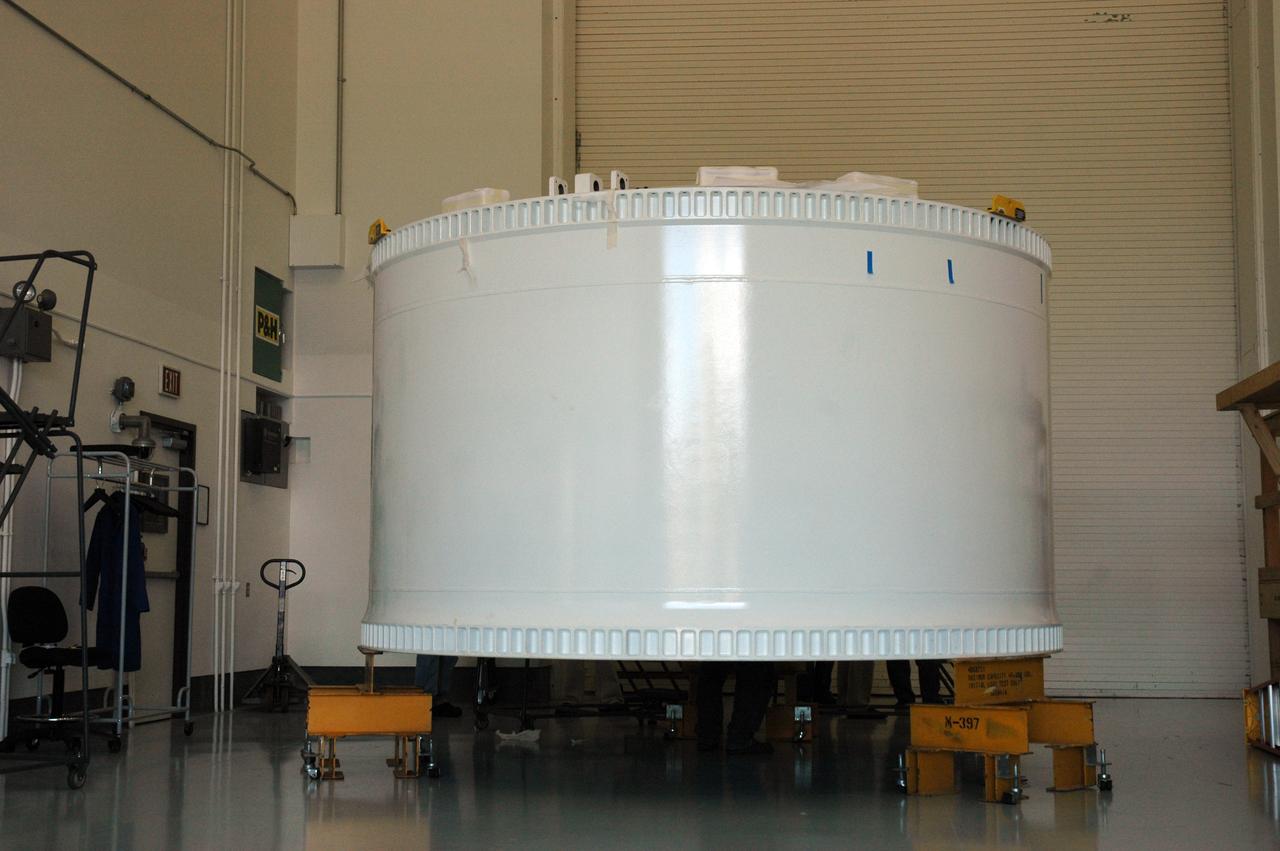
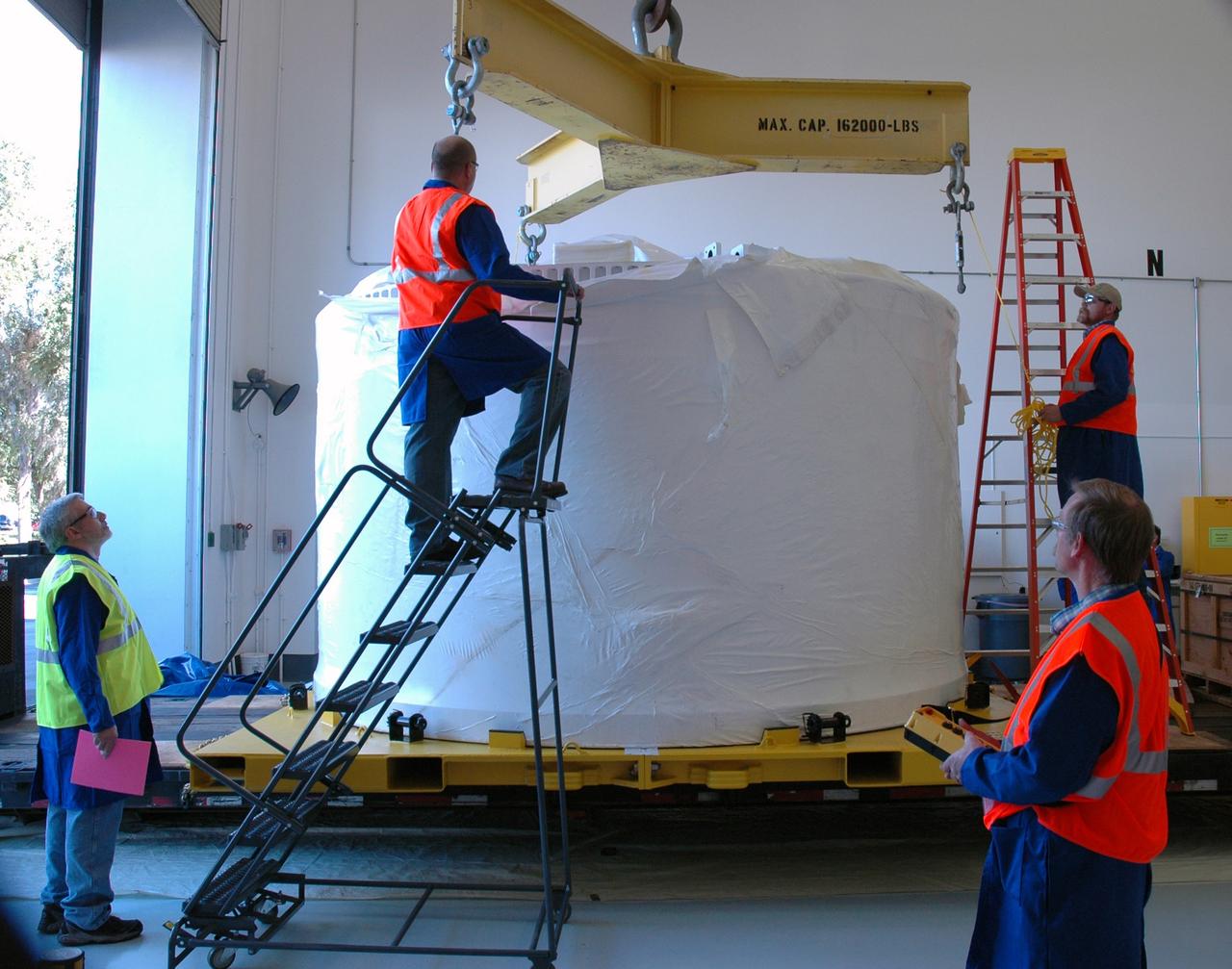
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, or ARF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the pristine Ares I-X forward skirt is examined by workers after the protective cover was removed. The forward skirt is the initial piece of first-stage hardware in preparation for the July 2009 test flight of the agency's next-generation spacecraft and launch vehicle system. Built entirely of armored steel, the 14,000-pound segment is seven feet tall and 12-1/4 feet wide. United Space Alliance, under a subcontract to ATK, will complete the integration and assembly of the forward skirt components in the ARF. It will then be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 for stacking operations. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
This Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar color composite shows a portion of the Weddell Sea, which is adjacent to the continent of Antarctica. The image shows extensive coverage of first-year sea ice mixtures and patches of open water inside the ice margin. The image covers a 100 kilometer by 30 kilometer (62 mile by 18.5 mile) region of the southern ocean, centered at approximately 57 degrees south latitude and 3 degrees east longitude, which was acquired on October 3, 1994. Data used to create this image were obtained using the L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received) in red; the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received) in green; and the C-band (horizontally transmitted and received) in blue. The sea ice, which appears rust-brown in the image, is composed of loosely packed floes from approximately 1 meter to 2 meters (3 feet to 6.5 feet) thick and ranging from 1 meter to 20 meters (3 feet to 65.5 feet) in diameter. Large patches of open water, shown as turquoise blue, are scattered throughout the area, which is typical for ice margins experiencing off-ice winds. The thin, well-organized lines clearly visible in the ice pack are caused by radar energy reflected by floes riding the crest of ocean swells. The wispy, black features seen throughout the image represent areas where new ice is forming. Sea ice, because it acts as an insulator, reduces the loss of heat between the relatively warm ocean and cold atmosphere. This interaction is an important component of the global climate system. Because of the unique combination of winds, currents and temperatures found in this region, ice can extend many hundreds of kilometers north of Antarctica each winter, which classifies the Weddell Sea as one of nature's greatest ice-making engines. During the formation of sea ice, great quantities of salt are expelled from the frozen water. The salt increases the density of the upper layer of sea water, which then sinks to great depths. Oceanographers believe this process forms most of the oceans' deep water. Sea ice covering all of the southern oceans, including the Weddell Sea, typically reaches its most northerly extent in about September. As periods of daylight become gradually longer in the Southern Hemisphere, ice formation stops and the ice edge retreats southward. By February, most of the sea ice surrounding Antarctica disappears. Imaging radar is extremely useful for studying the polar regions because of the long periods of darkness and extensive cloud cover. The multiple frequencies of the SIR-C/X-SAR instruments allow further study into ways of improving the separation of the various thickness ranges of sea ice, which are vital to understanding the heat balance in the ice, ocean and atmospheric system. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01737

An oil slick in the Gulf of Mexico following Hurricane Ida – a high-end Category 4 when it made landfall near Port Fourchon, Louisiana, on Aug. 29, 2021 – appears as a green trail in the inset false-color graphic provided by NASA's Delta-X project, while the surrounding seawater appears orange. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) regularly monitors U.S. coastal waters for potential spills and noticed slicks that appeared just off the coast after the hurricane. They were able to use this information from Delta-X to corroborate other data they had about oil slicks in the area (satellite image in the second inset picture). The blue-green swath crossing from the Gulf of Mexico over the Louisiana coast denotes the flight path of the Delta-X radar instrument on Sept. 1, just before 11:30 a.m. CDT. Charged with studying the Mississippi River Delta, Delta-X was gearing up to collect data on Louisiana's coastal wetlands when Hurricane Ida barreled ashore in late August. The storm damaged buildings and infrastructure alike, resulting in power outages, flooding, and oil slicks in the Gulf of Mexico. Oil tends to smooth out the bumps on the ocean's surface, which results in a distinct radar signal that the Delta-X mission was able to pick out of their data. Delta-X added flight paths to their planned schedule – with the support of NASA's Applied Science Disaster Program – in order to collect information over the gulf in areas of interest to NOAA. Delta-X is studying two wetlands – the Atchafalaya and Terrebonne Basins – by land, boat, and air to quantify water and sediment flow as well as vegetation growth. While the Atchafalaya Basin has been gaining land through sediment accumulation, Terrebonne Basin, which is right next to the Atchafalaya, has been rapidly losing land. The data collected by the project will be applied to models used to forecast which areas of the delta are likely to gain or lose land under various sea level rise, river flow, and watershed management scenarios. The mission uses several instruments to collect its data. Affixed to the bottom of a Gulfstream-III airplane, one of those instruments, the all-weather Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR), bounces radar signals off of Earth's surface, forming a kind of image of a particular area. Repeated images of the same regions, captured at different times, enable researchers to detect changes in those areas, such as fluctuating water levels beneath the vegetation as the tides move in and out of these wetlands. In addition to radar measurements, teams from Caltech, Louisiana State University, Florida International University, and other collaborating institutions gather water and vegetation samples – among other data – by boat, other airborne sensors, and from instruments on the ground. Funded by NASA's Earth Venture Suborbital (EVS-3) program, Delta-X is managed by the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. Fall 2021 was Delta-X's last scheduled field campaign, although the five-year mission will run through the end of 2023. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24540
![In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA12348/PIA12348~medium.jpg)
In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348
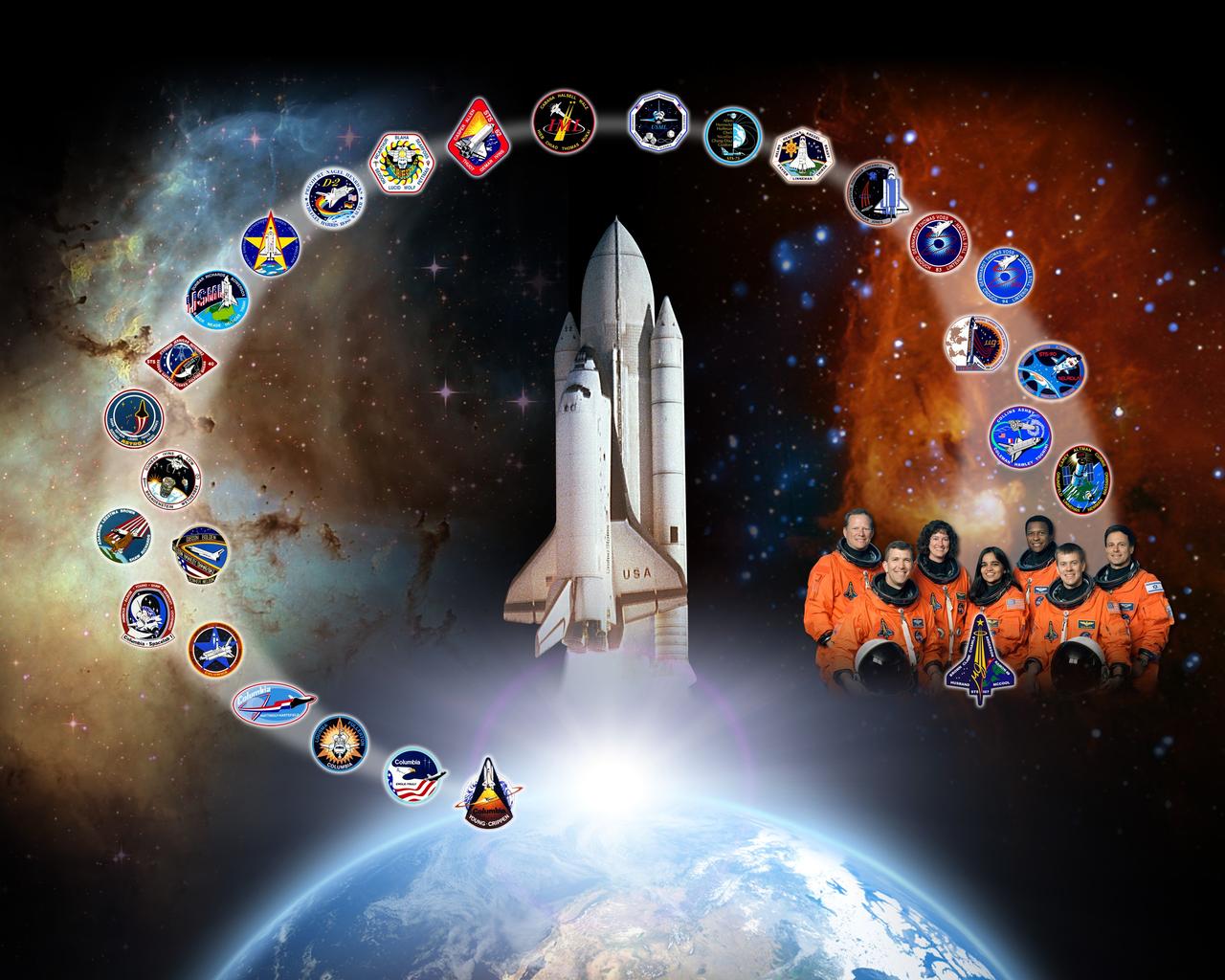

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This orbiter tribute of space shuttle Columbia, or OV-102, hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tribute features Columbia, the “first of the fleet," rising above Earth at the dawn of the Space Shuttle Program. Columbia's accomplishments include the launch and deployment of NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory on STS-93, the first shuttle landing at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico on STS-3, the first deployment of commercial satellites and the first four-member crew during STS-5, the first Spacelab mission and first six-member crew on STS-9, the first female commander, Eileen Collins, on STS-93, as well as several laboratory missions with international partners. Crew-designed patches for each of Columbia’s missions lead from Earth toward a remembrance of the STS-107 crew, which was lost during re-entry on Feb. 1, 2003. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a version of space shuttle Columbia's orbiter tribute, or OV-102, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tribute features Columbia, the “first of the fleet," rising above Earth at the dawn of the Space Shuttle Program. Columbia's accomplishments include the launch and deployment of NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory on STS-93, the first shuttle landing at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico on STS-3, the first deployment of commercial satellites and the first four-member crew during STS-5, the first Spacelab mission and first six-member crew on STS-9, the first female commander, Eileen Collins, on STS-93, as well as several laboratory missions with international partners. Crew-designed patches for each of Columbia’s missions lead from Earth toward a remembrance of the STS-107 crew, which was lost during re-entry on Feb. 1, 2003. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-163-KSC

This image, received today, shows the trench excavated by NASA's Viking 1 surface sampler. The trench was dug by extending the surface sampler collection head in a direction from lower right toward the upper left and then withdrawing the surface sampler collector head. Lumpy piles of material at end of trench at lower right was pulled by plowing from trench by the backhoe which will be used to dig trenches later in the mission. Area around trench has ripple marks produced by Martian wind. The trench which was dug early on Sol 8, is about 3 inches wide, 2 inches deep and 6 inches long. Steep dark crater walls show the grains of the Martian surface material stick together (have adhesion). The doming of the surface at far end of the trench show the granular material is dense. The Martian surface material behaves somewhat like moist sand on Earth. Evidence from the trench indicate a sample was collected and delivered to the experiments after repeated tries. The biology experiment level full indicator indicates a sample was received for analysis. The X-Ray fluorescence experiment has no indication to show it received a sample. The GCMS experiment level full indicator suggests no sample was received but this matter is being investigated. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00389
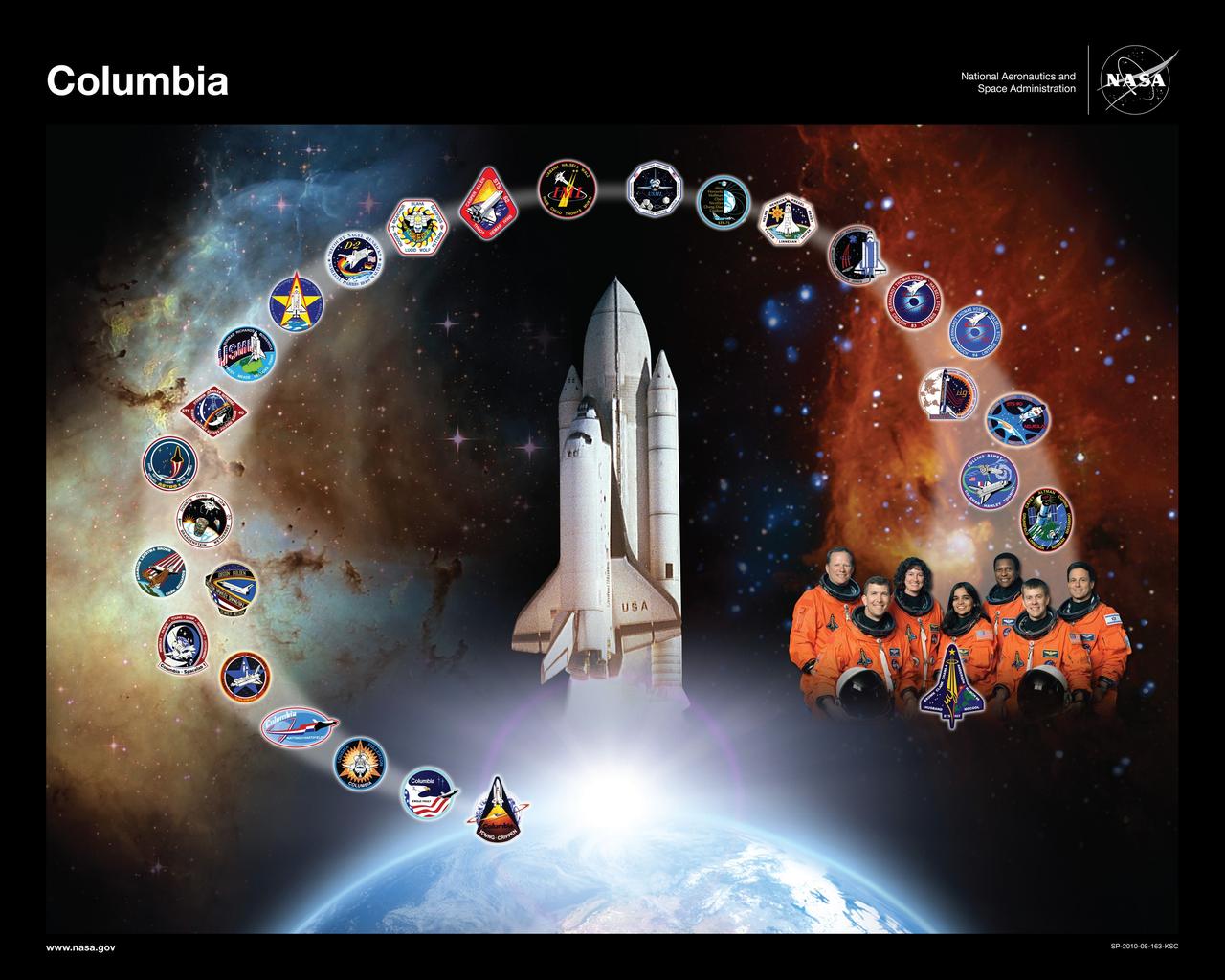

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a printable version of space shuttle Columbia's orbiter tribute, or OV-102, which hangs in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tribute features Columbia, the “first of the fleet," rising above Earth at the dawn of the Space Shuttle Program. Columbia's accomplishments include the launch and deployment of NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory on STS-93, the first shuttle landing at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico on STS-3, the first deployment of commercial satellites and the first four-member crew during STS-5, the first Spacelab mission and first six-member crew on STS-9, the first female commander, Eileen Collins, on STS-93, as well as several laboratory missions with international partners. Crew-designed patches for each of Columbia’s missions lead from Earth toward a remembrance of the STS-107 crew, which was lost during re-entry on Feb. 1, 2003. Five orbiter tributes are on display in the firing room, representing Atlantis, Challenger, Columbia, Endeavour and Discovery. Graphic design credit: NASA/Amy Lombardo. NASA publication number: SP-2010-08-163-KSC
This portion of NASA Mars Odyssey image covers NASA Viking 2 landing site shown with the X. The second landing on Mars took place September 3, 1976 in Utopia Planitia. The exact location of Lander 2 is not as well established as Lander 1 because there were no clearly identifiable features in the lander images as there were for the site of Lander 1. The Utopia landing site region contains pedestal craters, shallow swales and gentle ridges. The crater Goldstone was named in honor of the Tracking Station in the desert of California. The two Viking Landers operated for over 6 years (nearly four martian years) after landing. This one band IR (band 9 at 12.6 microns) image shows bright and dark textures, which are primarily due to differences in the abundance of rocks on the surface. The relatively cool (dark) regions during the day are rocky or indurated materials, fine sand and dust are warmer (bright). Many of the temperature variations are due to slope effects, with sun-facing slopes warmer than shaded slopes. The dark rings around several of the craters are due to the presence of rocky (cool) material ejected from the crater. These rocks are well below the resolution of any existing Mars camera, but THEMIS can detect the temperature variations they produce. Daytime temperature variations are produced by a combination of topographic (solar heating) and thermophysical (thermal inertia and albedo) effects. Due to topographic heating the surface morphologies seen in THEMIS daytime IR images are similar to those seen in previous imagery and MOLA topography. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04023

STS068-S-052 (3 October 1994) --- This is a radar image of Mount Rainier in Washington state. The volcano last erupted about 150 years ago and numerous large floods and debris flows have originated on its slopes during the last century. Today the volcano is heavily mantled with glaciers and snow fields. More than 100,000 people live on young volcanic mud flows less than 10,000 years old and, are within the range of future, devastating mud slides. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its 20th orbit on October 1, 1994. The area shown in the image is approximately 59 by 60 kilometers (36.5 by 37 miles). North is toward the top left of the image, which was composed by assigning red and green colors to the L-Band, horizontally transmitted and vertically, and the L-Band, horizontally transmitted and vertically received. Blue indicates the C-Band, horizontally transmitted and vertically received. In addition to highlighting topographic slopes facing the Space Shuttle, SIR-C records rugged areas as brighter and smooth areas as darker. The scene was illuminated by the Shuttle's radar from the northwest so that northwest-facing slopes are brighter and southeast-facing slopes are dark. Forested regions are pale green in color, clear cuts and bare ground are bluish or purple; ice is dark green and white. The round cone at the center of the image is the 14,435 feet (4,399 meters) active volcano, Mount Rainier. On the lower slopes is a zone of rock ridges and rubble (purple to reddish) above coniferous forests (in yellow/green). The western boundary of Mount Rainier National Park is seen as a transition from protected, old-growth forest to heavily logged private land, a mosaic of recent clear cuts (bright purple/blue) and partially re-grown timber plantations (pale blue). The prominent river seen curving away from the mountain at the top of the image (to the northwest) is the White River, and the river leaving the mountain at the bottom right of the image (south) is the Nisqually River, which flows out of the Nisqually glacier on the mountain. The river leaving to the left of the mountain is the Carbon River, leading west and north toward heavily populated regions near Tacoma. The dark patch at the top right of the image is Bumping Lake. Other dark areas seen to the right of ridges throughout the image are radar shadow zones. Radar images can be used to study the volcanic structure and the surrounding regions with linear rock boundaries and faults. In addition, the recovery of forested lands from natural disasters and the success of re-forestation programs can also be monitored. Ultimately this data may be used to study the advance and retreat of glaciers and other forces of global change. Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. (P-44703)

Four Extreme Ultraviolet and X-ray Irradiance Sensors or EXIS instruments that will fly aboard four of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-R or GOES-R Series spacecraft were recently lined up like babies in a nursery. The EXIS Team at NOAA's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) in Boulder, Colorado took a short timeout during the week of January 20, 2014 to take advantage of a rare photo opportunity. Each EXIS instrument will fly aboard one of the GOES-R series of spacecraft that include GOES-R, S, T, and U. All four EXIS instruments happened to be in the clean room at the same time. It is expected that this will probably be the last time that all four siblings will be in one place together as Flight Model 1 (seen on the left) is being shipped on February 3 to begin integration and testing onto the GOES-R spacecraft at a Lockheed Martin facility in Littleton, Colo. The other instruments have already dispersed to other areas at LASP for continued build and test operations. The EXIS instruments on the GOES-R series satellites are critical to understanding and monitoring solar irradiance in the upper atmosphere, that is, the power and effect of the Sun’s electromagnetic radiation per unit of area. EXIS will be able to detect solar flares that could interrupt communications and reduce navigational accuracy, affecting satellites, high altitude airlines and power grids on Earth. On board the EXIS are two main sensors, the Extreme Ultraviolet Sensor (EUVS) and the X-Ray Sensor (XRS), which will help scientists monitor activity on the sun. The GOES-R series is a collaborative development and acquisition effort between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA. The GOES-R satellites will provide continuous imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth’s Western Hemisphere and space weather monitoring. For more information about the GOES-R series, visit: <a href="http://www.goes-r.gov" rel="nofollow">www.goes-r.gov</a> Credit: NOAA/NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This Chandra X-Ray Observatory image of the mysterious superstar Eta Carinae reveals a surprising hot irner core, creating more questions than answers for astronomers. The image shows three distinct structures: An outer, horseshoe shaped ring about 2 light-years in diameter, a hot inner core about 3 light-months in diameter, and a hot central source less than a light-month in diameter which may contain the superstar. In 1 month, light travels a distance of approximately 489 billion miles (about 788 billion kilometers). All three structures are thought to represent shock waves produced by matter rushing away from the superstar at supersonic speeds. The temperature of the shock-heated gas ranges from 60 million degrees Kelvin in the central regions to 7 million degrees Kelvin on the outer structure. Eta Carinae is one of the most enigmatic and intriguing objects in our galaxy. Between 1837 and 1856, it increased dramatically in brightness to become the most prominent star in the sky except for Sirius, even through it is 7,500 light-years away, more than 80 times the distance to Sirius. This "Great Eruption," as it is called, had an energy comparable to a supernova, yet did not destroy the star, which faded to become a dim star, invisible to the naked eye. Since 1940, Eta Carinae has begun to brighten again, becoming visible to the naked eye. Photo credit: NASA/CXC/SAO

Women Scientists: Lucille Coltrane, Jean Clark Keating, Katherine Cullie Speegle, Doris 'Dot' Lee, Ruth Whitman, and Emily Stephens Mueller,Lucille Coltrane is at the far left. She was a computer and worked for Norm Crabill who provided positive identification. Lucille authored a NACA Research Memorandum, Investigation of Two Bluff Shapes in Axial Free Flight Over a Mach Number Range From 0.35 to 2.15 in 1958. Next to Lucille is Jean Clark Keating. Jean was identified by Mary Woerner who said that both Jean and her husband Jerry are now deceased. The third woman from the left is Katherine Cullie Speegle. Katherine co-authored two research papers: Preliminary Results From a Free-Flight Investigation of Boundary-Layer Transition and Heat Transfer on a Highly Polished 8-Inch-Diameter Hemisphere-Cylinder at Mach Numbers up to 3 and Reynolds Numbers Based on a Length of 1 Foot up to 17.7 x 10 to the 6th and Heat Transfer For Mach Numbers Up to 2.2 and Pressure Distributions for Mach Numbers Up to 4.7 From Flight Investigations of a Flat-Face Cone and a Hemisphere-Cone. Norm remembered the woman standing as Doris. Mary Alice identified her as Doris 'Dot' Lee, who worked with Katherine Speegle. Dot was married to a NASA engineer named John Lee. Next to Doris is Ruth Whitman. Norm remembered she and her husband owned a Howard DGA 15 at the airport in WEst Point. That prompted Mary Alice to remember her name and that her husband was Jim. The woman seated on the right is Emily Stephens Mueller. Norm remembers that Emily went to Houston as part of the Space Task Group, but retired back here on the peninsula. In 2008, Emily attended the NACA Reunion X11. She walked over to a table of books about the history of NACA, former NACA facilities and the organization's aviation pioneers and saw a book about women of flight from the Dryden Research Center and paused, then pointed somewhat in amazement. "That’s me," she said of a picture on the cover of her on the far left of a li

Women Scientists: Lucille Coltrane, Jean Clark Keating, Katherine Cullie Speegle, Doris 'Dot' Lee, Ruth Whitman, and Emily Stephens Mueller,Lucille Coltrane is at the far left. She was a computer and worked for Norm Crabill who provided positive identification. Lucille authored a NACA Research Memorandum, Investigation of Two Bluff Shapes in Axial Free Flight Over a Mach Number Range From 0.35 to 2.15 in 1958. Next to Lucille is Jean Clark Keating. Jean was identified by Mary Woerner who said that both Jean and her husband Jerry are now deceased. The third woman from the left is Katherine Cullie Speegle. Katherine co-authored two research papers: Preliminary Results From a Free-Flight Investigation of Boundary-Layer Transition and Heat Transfer on a Highly Polished 8-Inch-Diameter Hemisphere-Cylinder at Mach Numbers up to 3 and Reynolds Numbers Based on a Length of 1 Foot up to 17.7 x 10 to the 6th and Heat Transfer For Mach Numbers Up to 2.2 and Pressure Distributions for Mach Numbers Up to 4.7 From Flight Investigations of a Flat-Face Cone and a Hemisphere-Cone. Norm remembered the woman standing as Doris. Mary Alice identified her as Doris 'Dot' Lee, who worked with Katherine Speegle. Dot was married to a NASA engineer named John Lee. Next to Doris is Ruth Whitman. Norm remembered she and her husband owned a Howard DGA 15 at the airport in WEst Point. That prompted Mary Alice to remember her name and that her husband was Jim. The woman seated on the right is Emily Stephens Mueller. Norm remembers that Emily went to Houston as part of the Space Task Group, but retired back here on the peninsula. In 2008, Emily attended the NACA Reunion X11. She walked over to a table of books about the history of NACA, former NACA facilities and the organization's aviation pioneers and saw a book about women of flight from the Dryden Research Center and paused, then pointed somewhat in amazement. "That’s me," she said of a picture on the cover of her on the far left of a li

Women Scientists: Lucille Coltrane, Jean Clark Keating, Katherine Cullie Speegle, Doris "Dot" Lee, Ruth Whitman, and Emily Stephens Mueller,Lucille Coltrane is at the far left. She was a computer and worked for Norm Crabill who provided positive identification. Lucille authored a NACA Research Memorandum, Investigation of Two Bluff Shapes in Axial Free Flight Over a Mach Number Range From 0.35 to 2.15 in 1958. Next to Lucille is Jean Clark Keating. Jean was identified by Mary Woerner who said that both Jean and her husband Jerry are now deceased. The third woman from the left is Katherine Cullie Speegle. Katherine co-authored two research papers: Preliminary Results From a Free-Flight Investigation of Boundary-Layer Transition and Heat Transfer on a Highly Polished 8-Inch-Diameter Hemisphere-Cylinder at Mach Numbers up to 3 and Reynolds Numbers Based on a Length of 1 Foot up to 17.7 x 10 to the 6th and Heat Transfer For Mach Numbers Up to 2.2 and Pressure Distributions for Mach Numbers Up to 4.7 From Flight Investigations of a Flat-Face Cone and a Hemisphere-Cone. Norm remembered the woman standing as Doris. Mary Alice identified her as Doris 'Dot' Lee, who worked with Katherine Speegle. Dot was married to a NASA engineer named John Lee. Next to Doris is Ruth Whitman. Norm remembered she and her husband owned a Howard DGA 15 at the airport in WEst Point. That prompted Mary Alice to remember her name and that her husband was Jim. The woman seated on the right is Emily Stephens Mueller. Norm remembers that Emily went to Houston as part of the Space Task Group, but retired back here on the peninsula. In 2008, Emily attended the NACA Reunion X11. She walked over to a table of books about the history of NACA, former NACA facilities and the organization's aviation pioneers and saw a book about women of flight from the Dryden Research Center and paused, then pointed somewhat in amazement. "ThatÕs me," she said of a picture on the cover of her on the far left of a line of women. She was at Dryden from 1948-49.