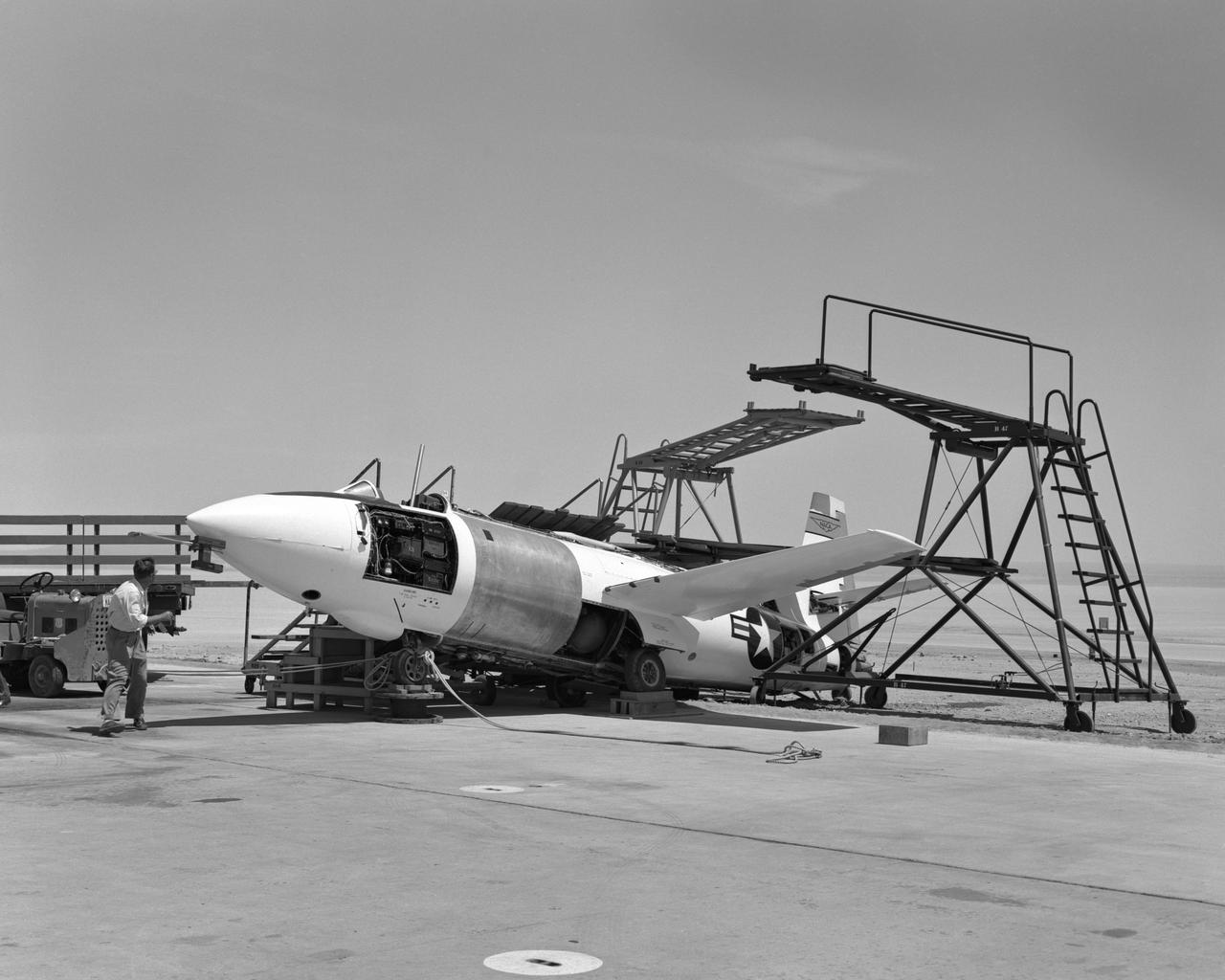

Bell X-1A ejection seat test setup
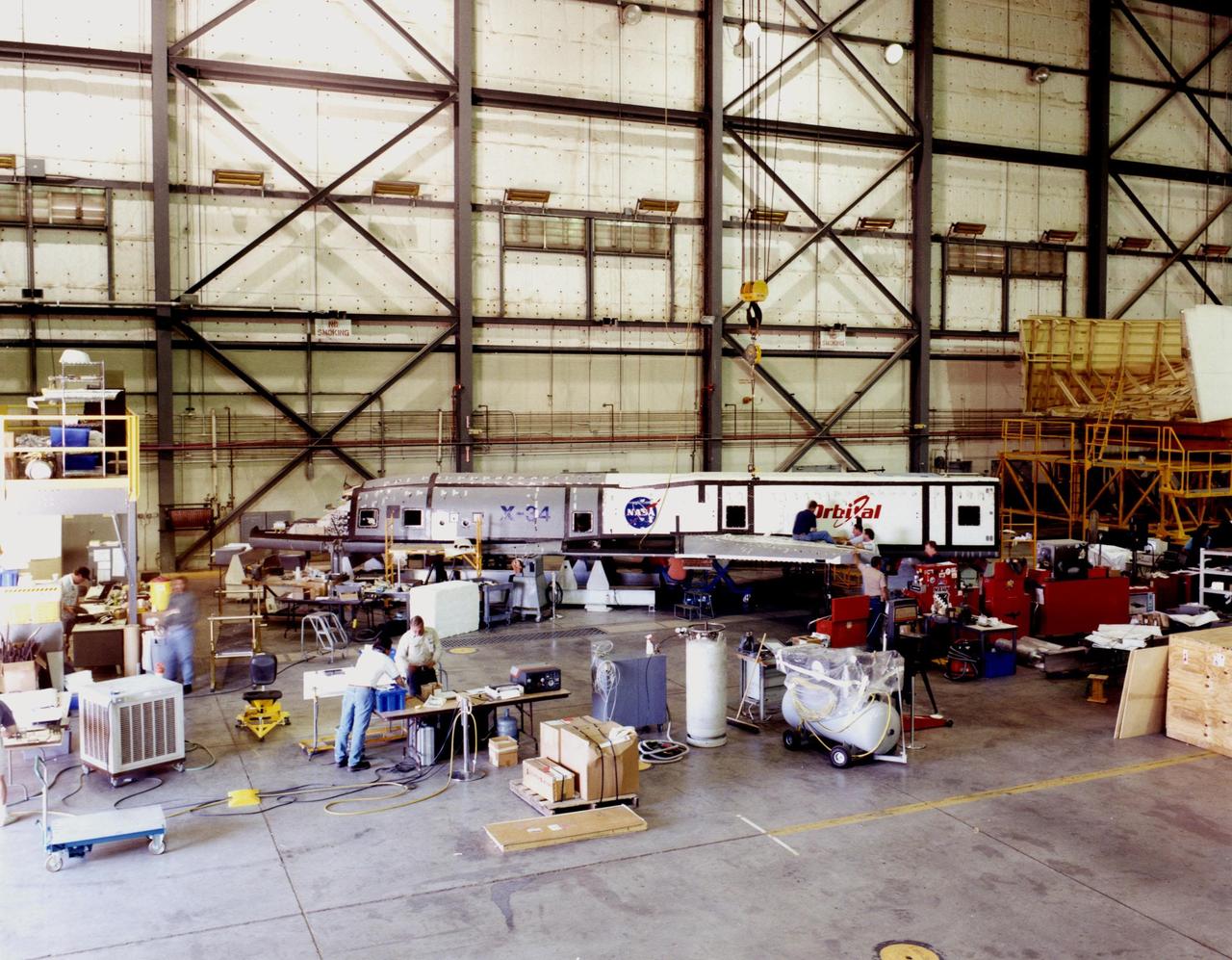

The modified X-34, known as A-1A, rests in the background of the Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., while an integrated team of KSC, Dryden Flight Research Center and Orbital Sciences Corporation engineers and technicians bring the X-34 A-1A vehicle closer to test flight readiness. Since September, eight NASA engineering technicians from KSC's Engineering Prototype Lab have assisted in the complex process of converting the X-34 A-1 vehicle from captive carry status to unpowered flight status, the A-1A. The X-34 is 58.3 feet long, 27.7 feet wide from wing tip to wing tip, and 11.5 feet tall from the bottom of the fuselage to the top of the tail. The autonomously operated technology demonstrator will be air-launched from an L-1011 airplane and should be capable of flying eight times the speed of sound, reaching an altitude of 250,000 feet. The X-34 Project is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala
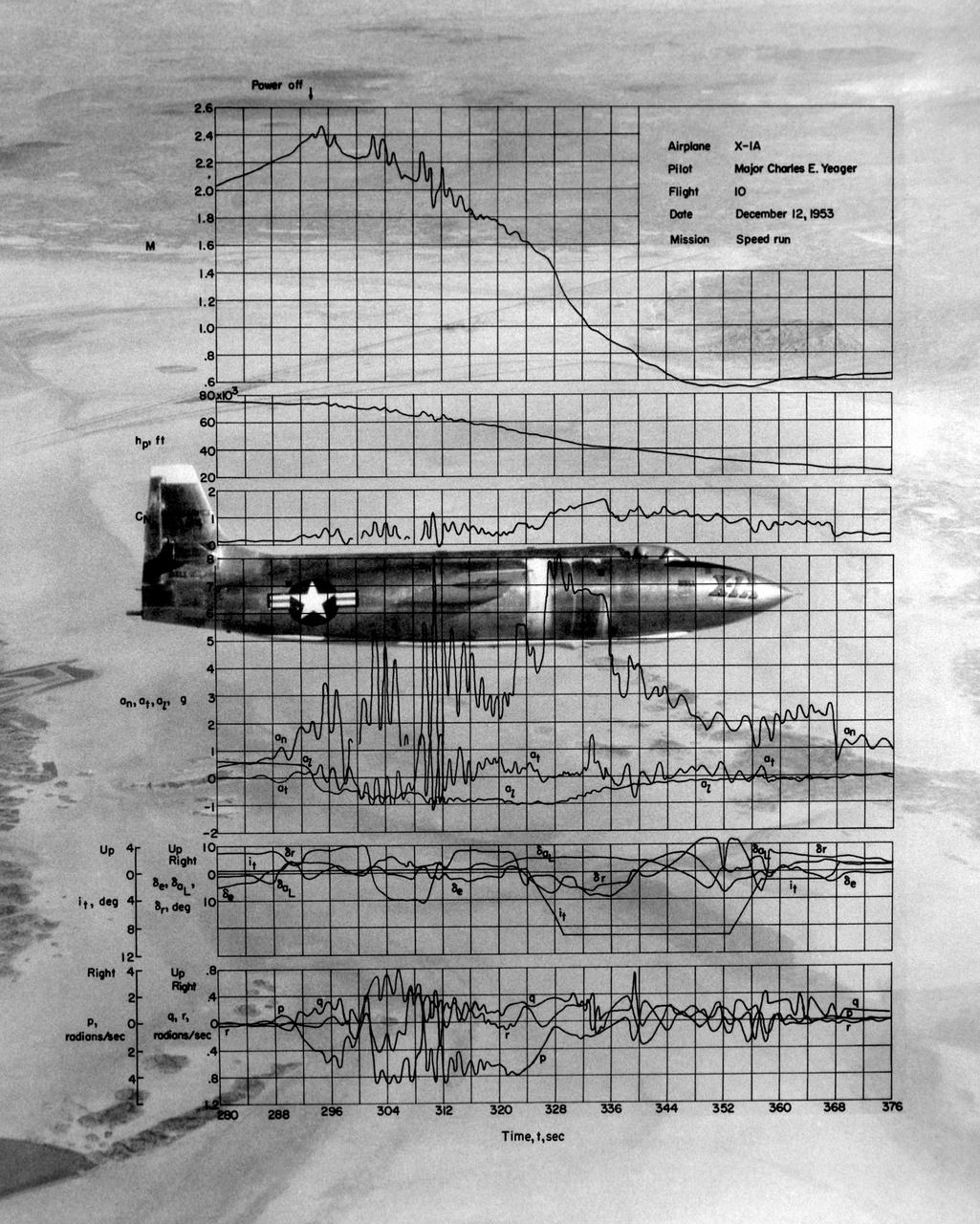
This photo of the X-1A includes graphs of the flight data from Maj. Charles E. Yeager's Mach 2.44 flight on December 12, 1953. (This was only a few days short of the 50th anniversary of the Wright brothers' first powered flight.) After reaching Mach 2.44, then the highest speed ever reached by a piloted aircraft, the X-1A tumbled completely out of control. The motions were so violent that Yeager cracked the plastic canopy with his helmet. He finally recovered from a inverted spin and landed on Rogers Dry Lakebed. Among the data shown are Mach number and altitude (the two top graphs). The speed and altitude changes due to the tumble are visible as jagged lines. The third graph from the bottom shows the G-forces on the airplane. During the tumble, these twice reached 8 Gs or 8 times the normal pull of gravity at sea level. (At these G forces, a 200-pound human would, in effect, weigh 1,600 pounds if a scale were placed under him in the direction of the force vector.) Producing these graphs was a slow, difficult process. The raw data from on-board instrumentation recorded on oscillograph film. Human computers then reduced the data and recorded it on data sheets, correcting for such factors as temperature and instrument errors. They used adding machines or slide rules for their calculations, pocket calculators being 20 years in the future.
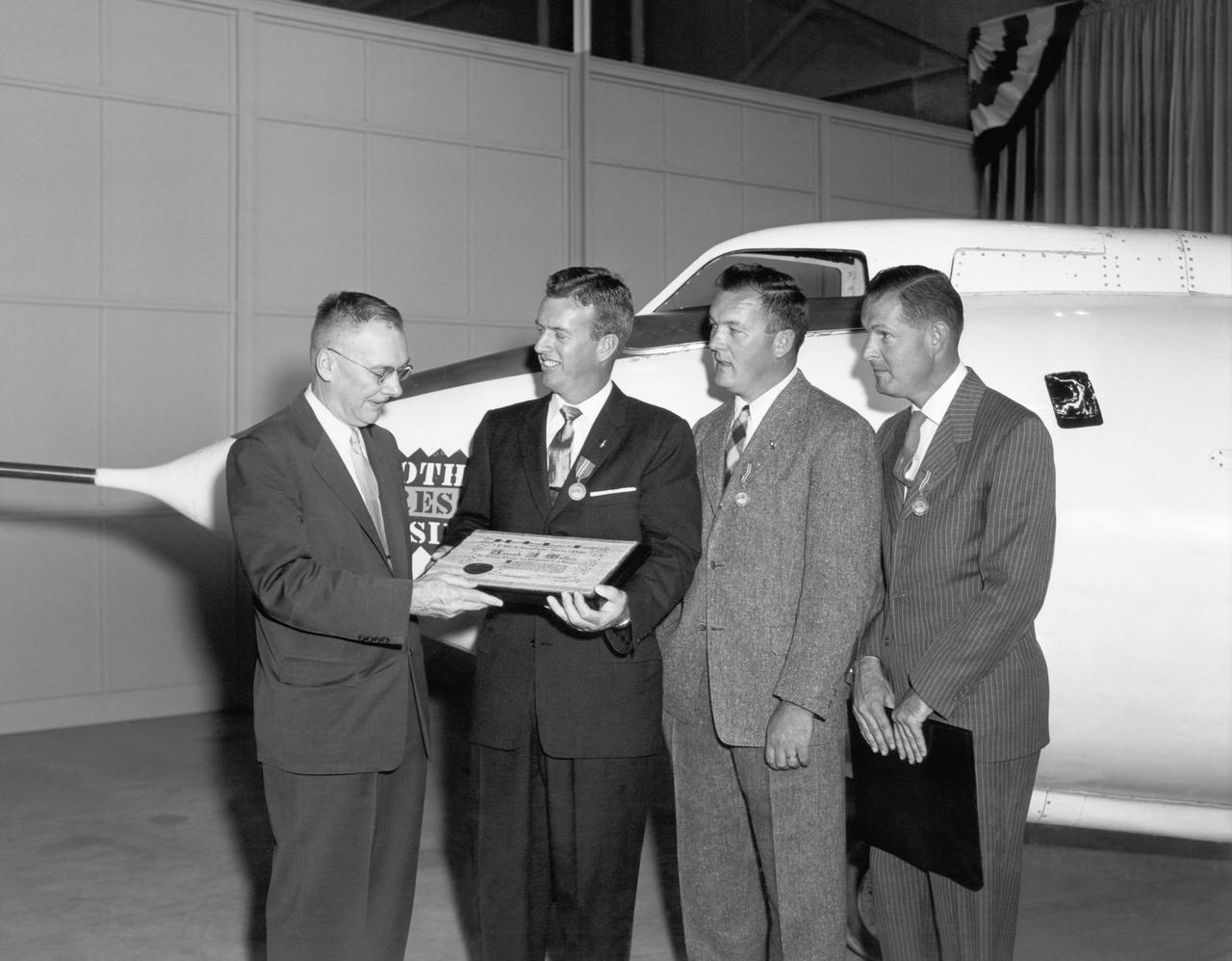

Hugh Dryden (far left) presents the NACA Exceptional Service Medal award at the NACA High Speed Flight Station. He awarded (L-R) Joe Walker (X-1A research pilot), Stan Butchart (pilot of the B-29 mothership),and Richard Payne (X-1A crew chief) in recognition of their research extending knowledge of swept wing flight.
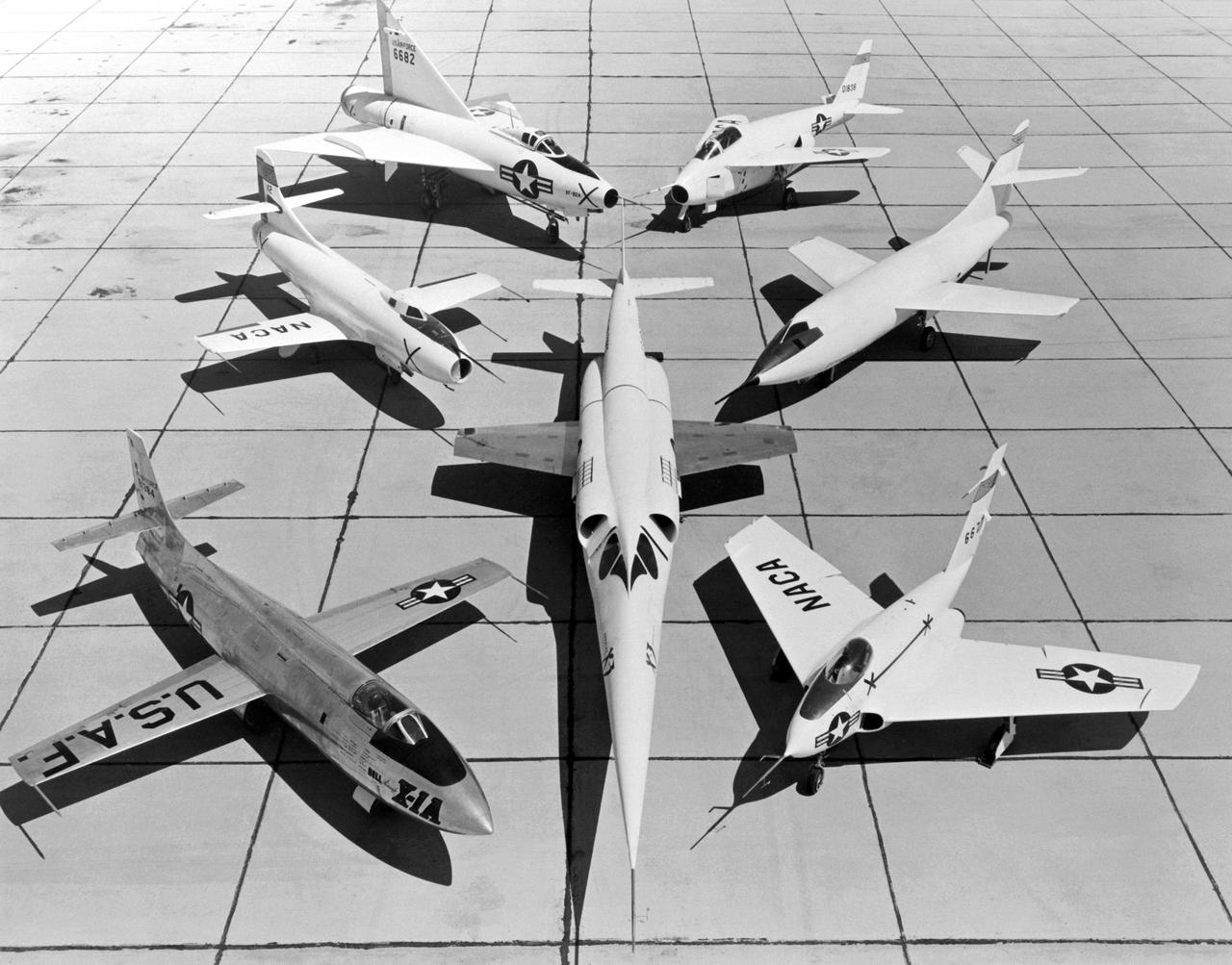

A 1953 photo of some of the research aircraft at the NACA High-Speed Flight Research Station (now known as the the Dryden Flight Research Center). The photo shows the X-3 (center) and, clockwise from left: X-1A (Air Force serial number 48-1384), the third D-558-1 (NACA tail number 142), XF-92A, X-5, D-558-2, and X-4.
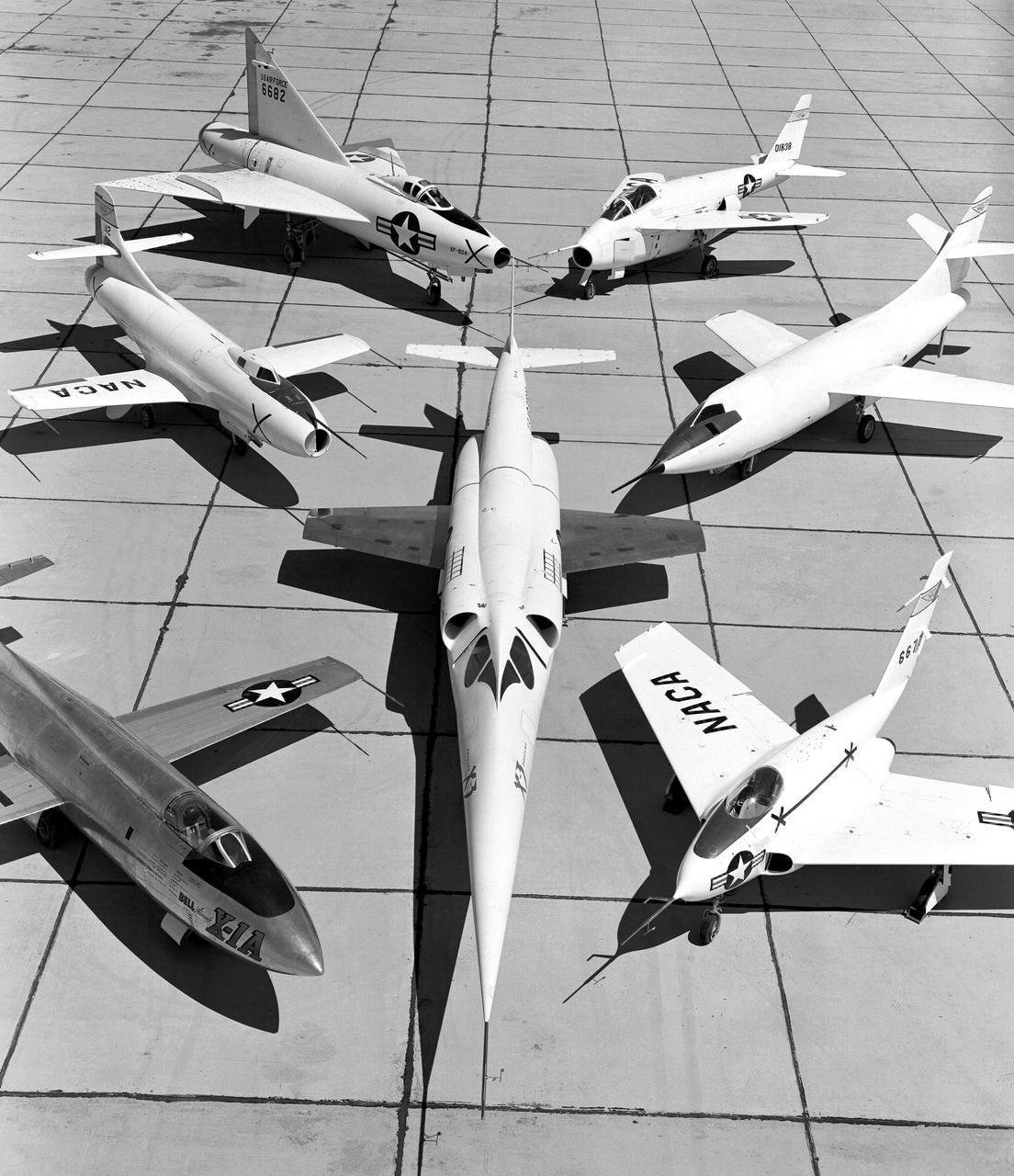

X-3 (center), and clockwise from left: X-1A, D-558-I, XF-92A, X-5, D-558-II, and X-4.
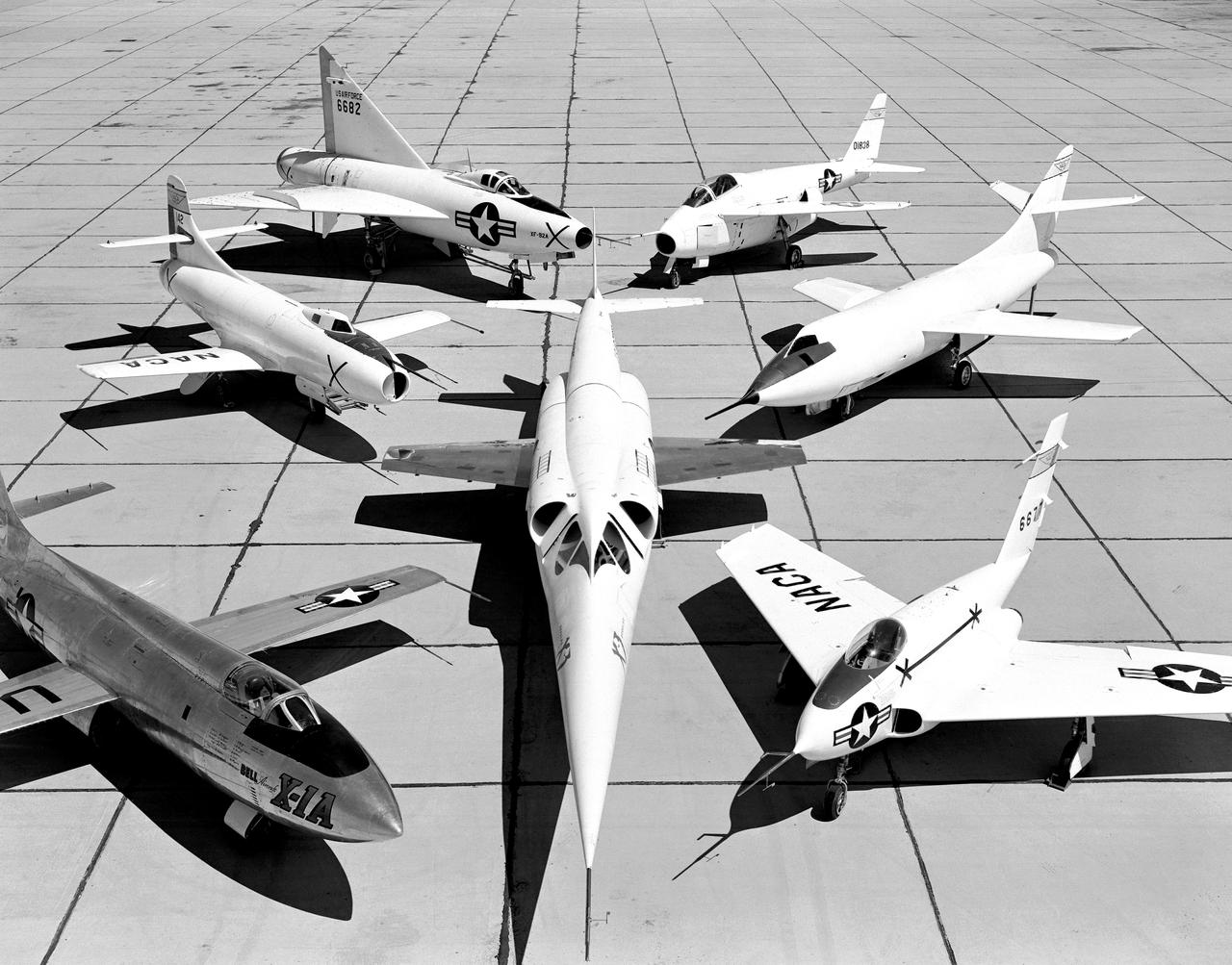

X-3 (center), and clockwise from left: X-1A, D-558-I, XF-92A, X-5, D-558-II, and X-4.
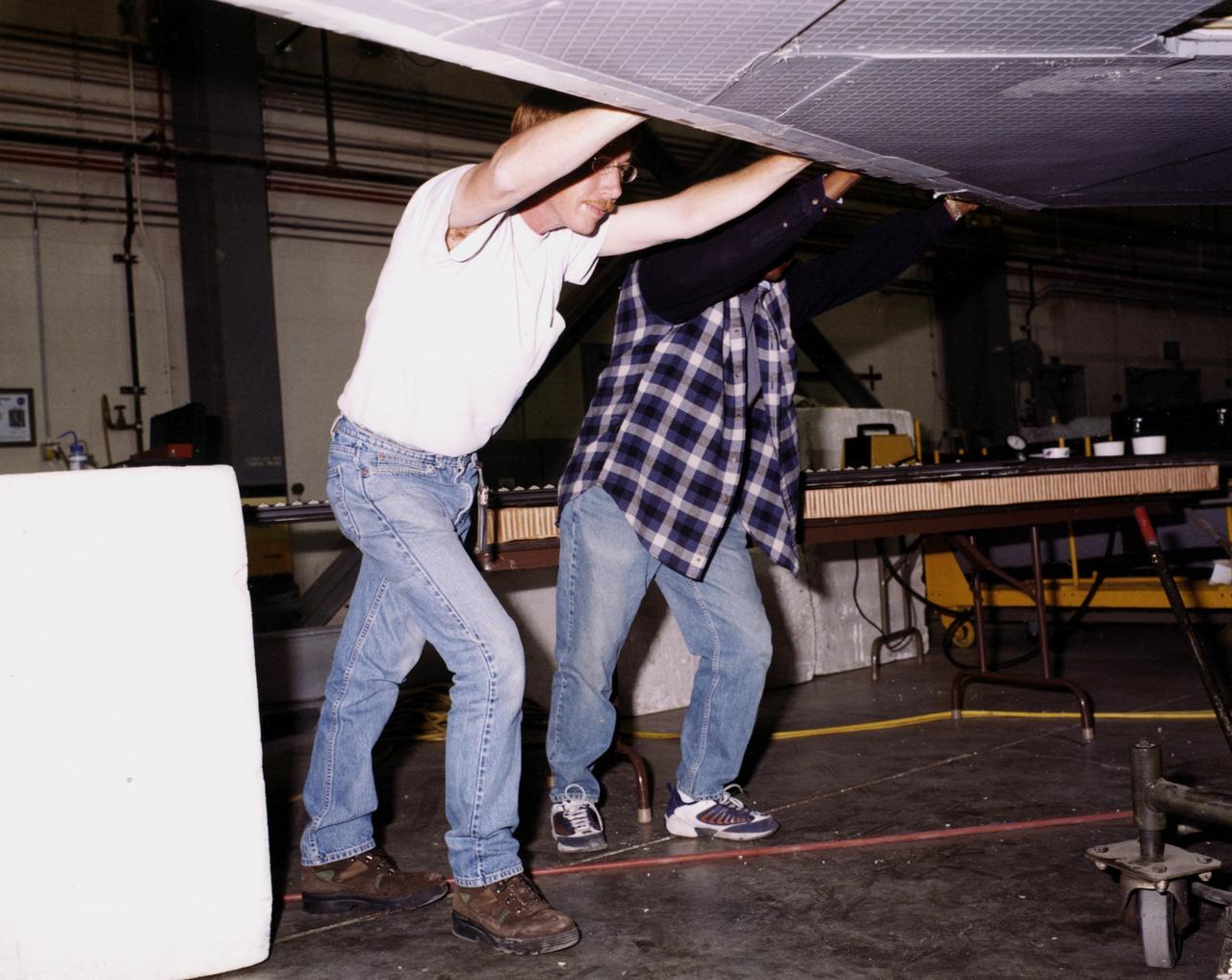

At Dryden Flight Research Center, Calif., KSC technician James Niehoff Jr. (left) helps attach the wing of the modified X-34, known as A-1A. Niehoff is one of eight NASA engineering technicians from KSC's Engineering Prototype Lab who have assisted Orbital Sciences Corporation and Dryden in the complex process of converting the X-34 A-1 vehicle from captive carry status to unpowered flight status, the A-1A. The other KSC technicians are Kevin Boughner, Roger Cartier, Mike Dininny, Mike Lane, Jerry Moscoso, David Rowell and Bryan Taylor. The X-34 is 58.3 feet long, 27.7 feet wide from wing tip to wing tip, and 11.5 feet tall from the bottom of the fuselage to the top of the tail. The autonomously operated technology demonstrator will be air-launched from an L-1011 airplane and should be capable of flying eight times the speed of sound, reaching an altitude of 250,000 feet. The X-34 Project is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala
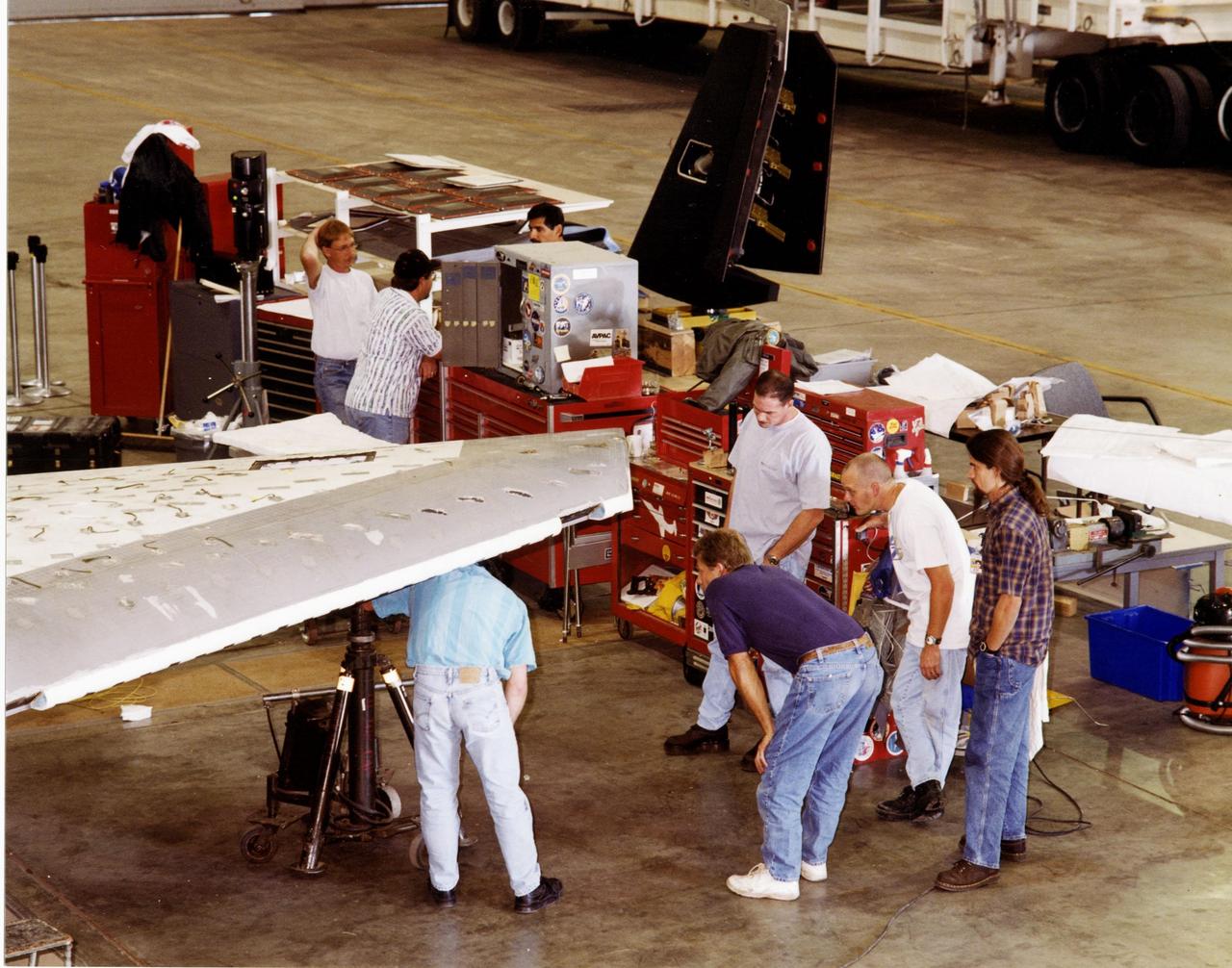

Two of KSC's X-34 technicians (far right), David Rowell and Roger Cartier, look at work being done on the modified A-1A at Dryden Flight Research Center, Calif. Since September, eight NASA engineering technicians from KSC's Engineering Prototype Lab have assisted Orbital Sciences Corporation and NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in the complex process of converting the X-34 A-1 vehicle from captive carry status to unpowered flight status, the A-1A. The other KSC technicians are Kevin Boughner, Mike Dininny, Mike Lane, Jerry Moscoso, James Niehoff Jr. and Bryan Taylor. The X-34 is 58.3 feet long, 27.7 feet wide from wing tip to wing tip, and 11.5 feet tall from the bottom of the fuselage to the top of the tail. The autonomously operated technology demonstrator will be air-launched from an L-1011 airplane and should be capable of flying eight times the speed of sound, reaching an altitude of 250,000 feet. The X-34 Project is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala
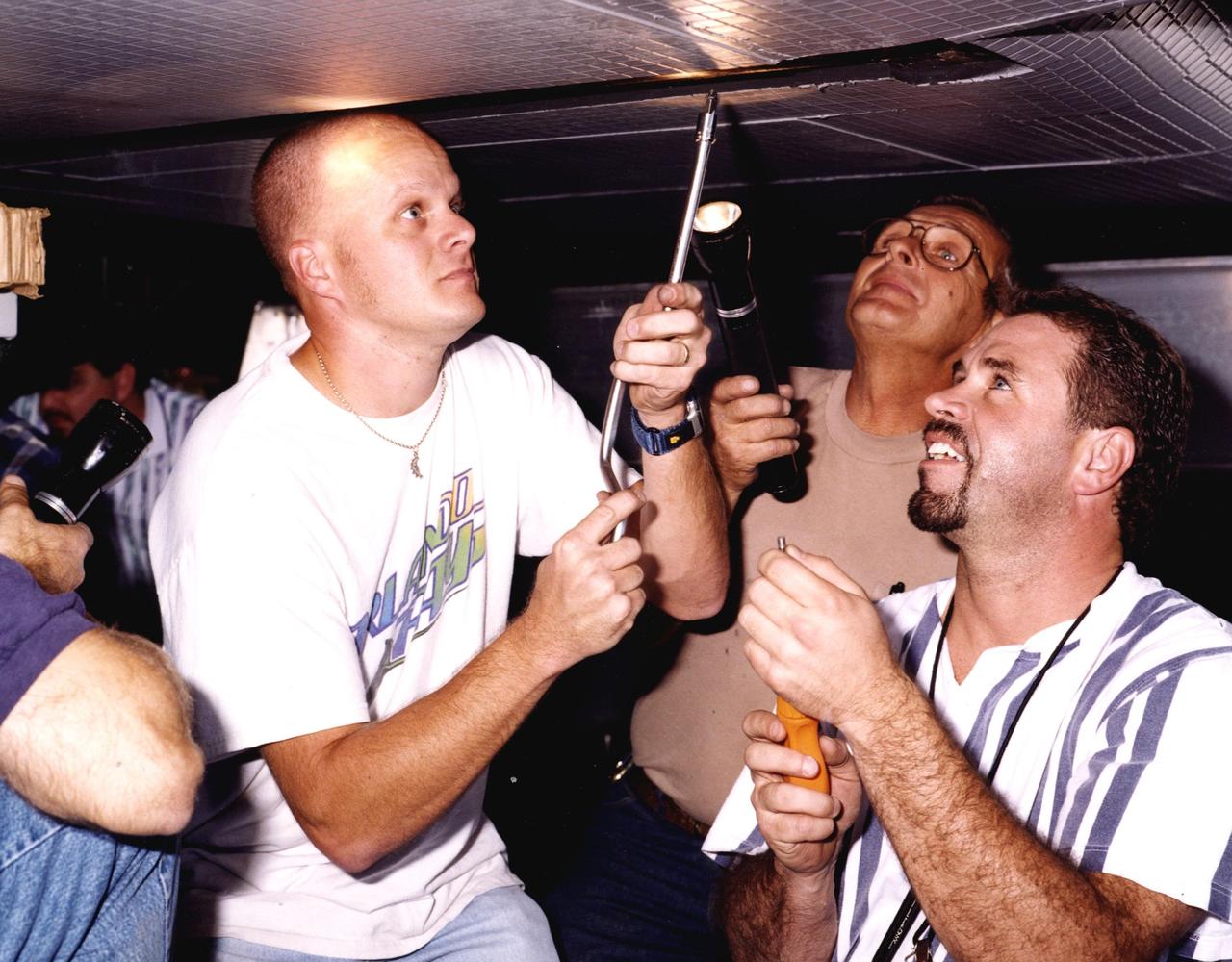

KSC technician David Rowell works on the wing of the modified X-34, known as A-1A, at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Calif. Looking on are Art Cape, with Dryden, and Mike Brainard, with Orbital Sciences Corporation. Rowell is one of eight NASA engineering technicians from KSC's Engineering Prototype Lab who have assisted Orbital and Dryden in the complex process of converting the X-34 A-1 vehicle from captive carry status to unpowered flight status, the A-1A. The other KSC technicians are Kevin Boughner, Roger Cartier, Mike Dininny, Mike Lane, Jerry Moscoso, James Niehoff Jr. and Bryan Taylor. The X-34 is 58.3 feet long, 27.7 feet wide from wing tip to wing tip, and 11.5 feet tall from the bottom of the fuselage to the top of the tail. The autonomously operated technology demonstrator will be air-launched from an L-1011 airplane and should be capable of flying eight times the speed of sound, reaching an altitude of 250,000 feet. The X-34 Project is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala
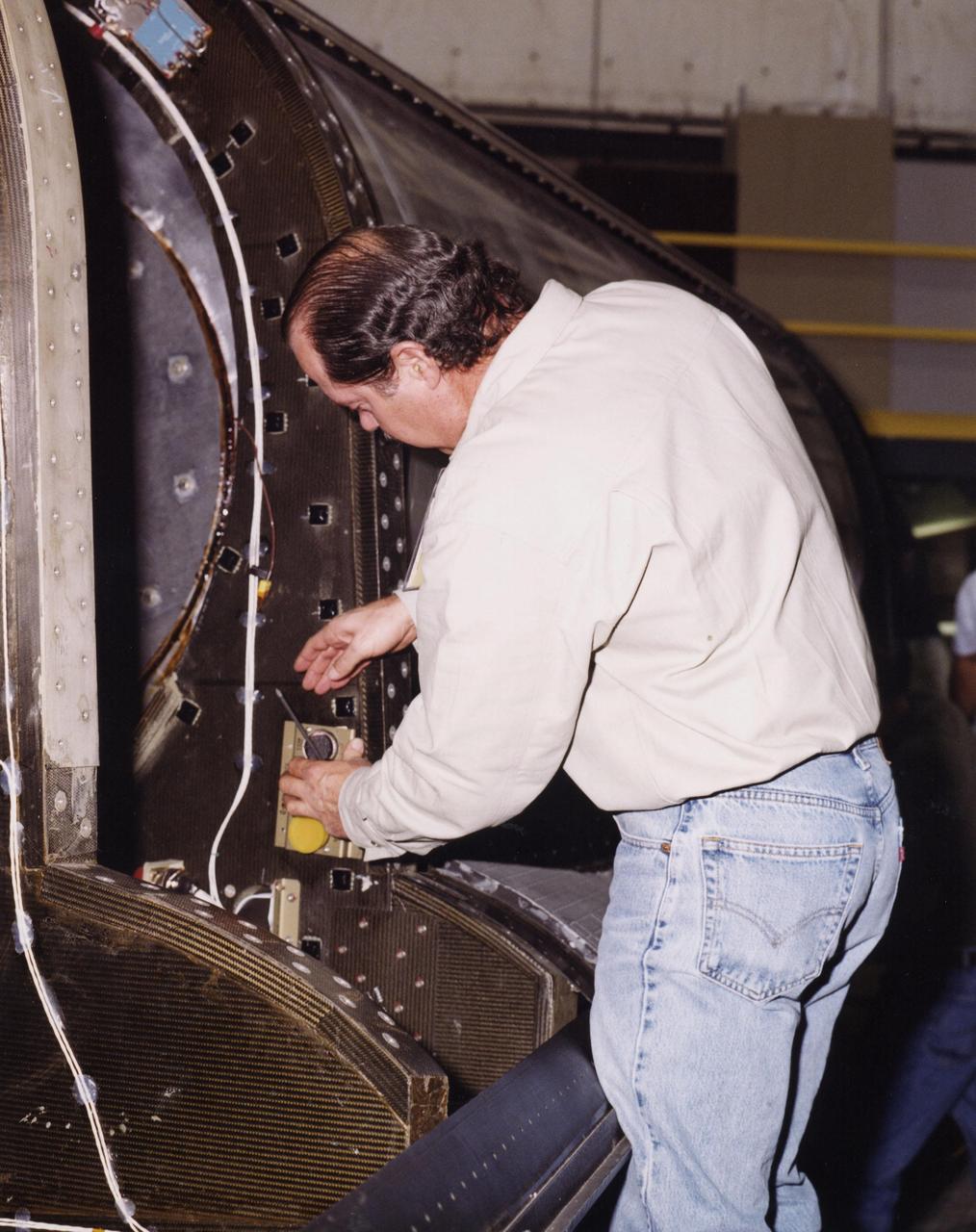

At Dryden Flight Research Center, Calif., KSC technician Bryan Taylor makes an adjustment on the modified X-34, known as A-1A. Taylor is one of eight NASA engineering technicians from KSC's Engineering Prototype Lab who have assisted Orbital Sciences Corporation and Dryden in the complex process of converting the X-34 A-1 vehicle from captive carry status to unpowered flight status, the A-1A. The other KSC technicians are Kevin Boughner, Roger Cartier, Mike Dininny, Mike Lane, Jerry Moscoso, James Niehoff Jr. and David Rowell. The X-34 is 58.3 feet long, 27.7 feet wide from wing tip to wing tip, and 11.5 feet tall from the bottom of the fuselage to the top of the tail. The autonomously operated technology demonstrator will be air-launched from an L-1011 airplane and should be capable of flying eight times the speed of sound, reaching an altitude of 250,000 feet. The X-34 Project is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala
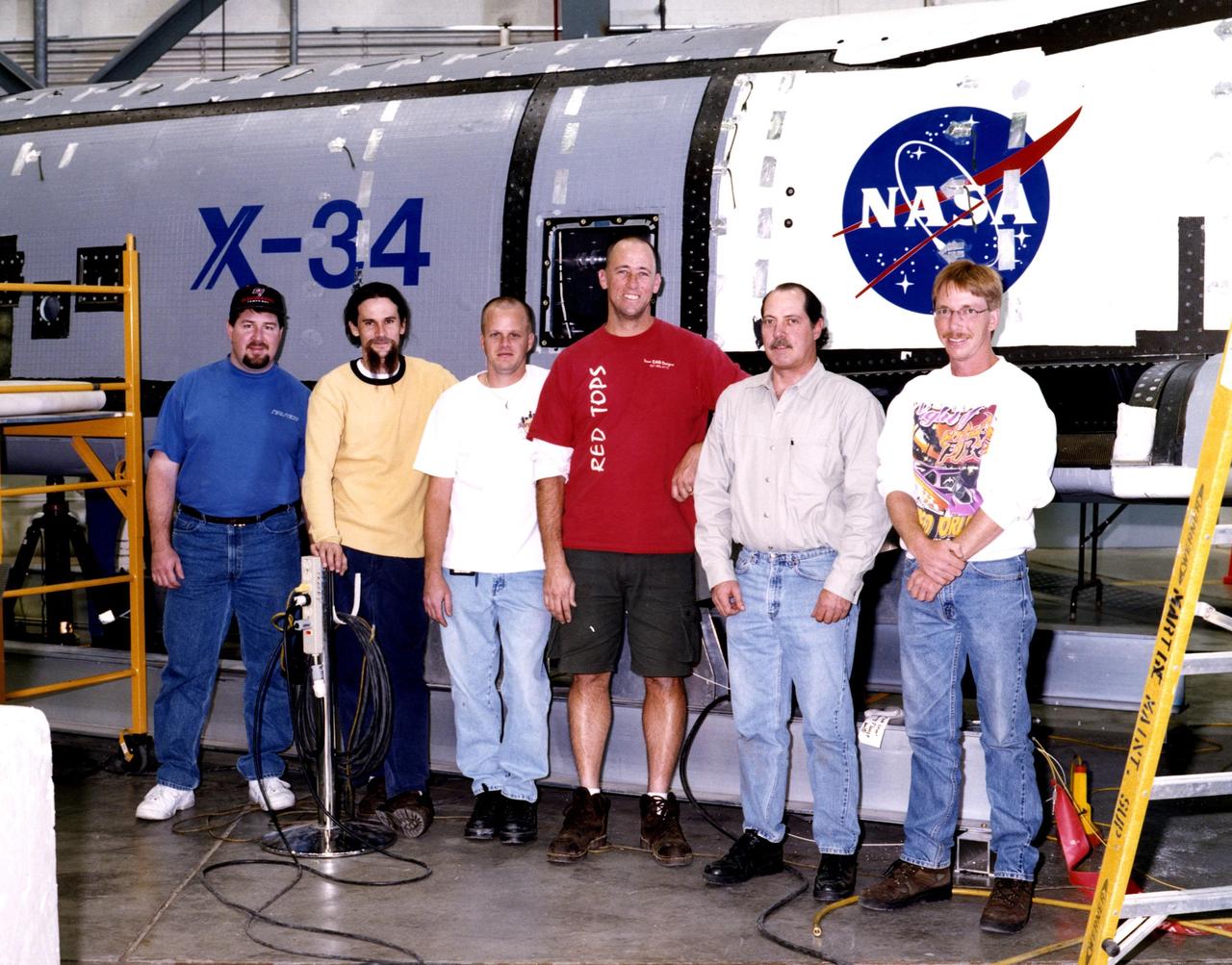

Six of the KSC workers who supported recent X-34 modifications pose in front of the modified A-1A vehicle at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. From left are Mike Lane, Roger Cartier, Dave Rowell, Mike Dininny, Bryan Taylor and James Niehoff Jr. Not shown are Kevin Boughner and Jerry Moscoso. Since September, the eight NASA engineering technicians from KSC's Engineering Prototype Lab have assisted Orbital Sciences Corporation and NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in the complex process of converting the X-34 A-1 vehicle from captive carry status to unpowered flight status, known as A-1A. The X-34 is 58.3 feet long, 27.7 feet wide from wing tip to wing tip, and 11.5 feet tall from the bottom of the fuselage to the top of the tail. The autonomously operated technology demonstrator will be air-launched from an L-1011 airplane and should be capable of flying eight times the speed of sound, reaching an altitude of 250,000 feet. The X-34 Project is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala
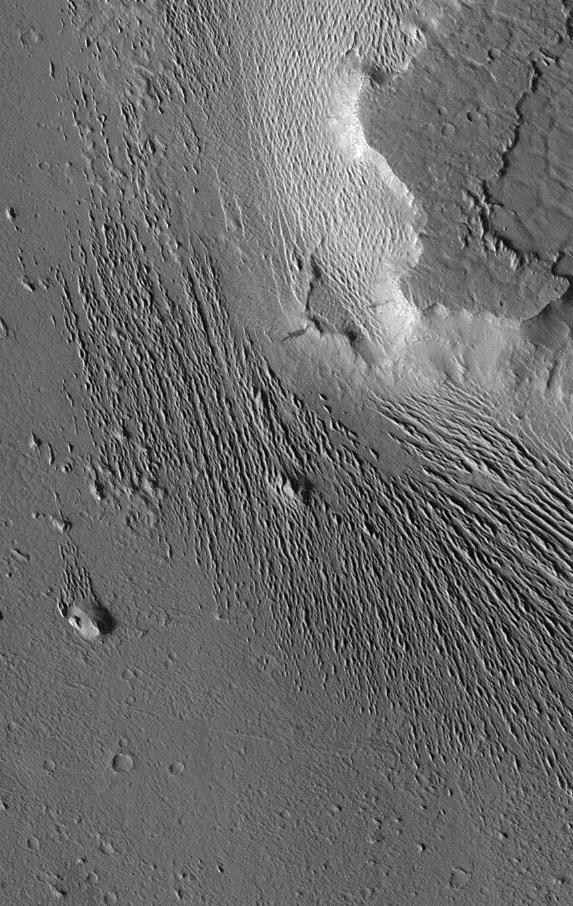

Extensive wind-swept plains of the Medusae Fossae formation on Mars. This northern subframe image, frame 3104, is of a 3.0 x 4.7 km area centered near 2.4 degrees north, 163.8 degrees west. Science Magazine, Volume 279, Number 5357, 13 March 1998, M. C. Malin, et. al., "Early Views of the Martian Surface from the Mars Orbiter Camera of Mars Global Surveyor", pp. 1681-1685 (Fig. 1A) http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00800
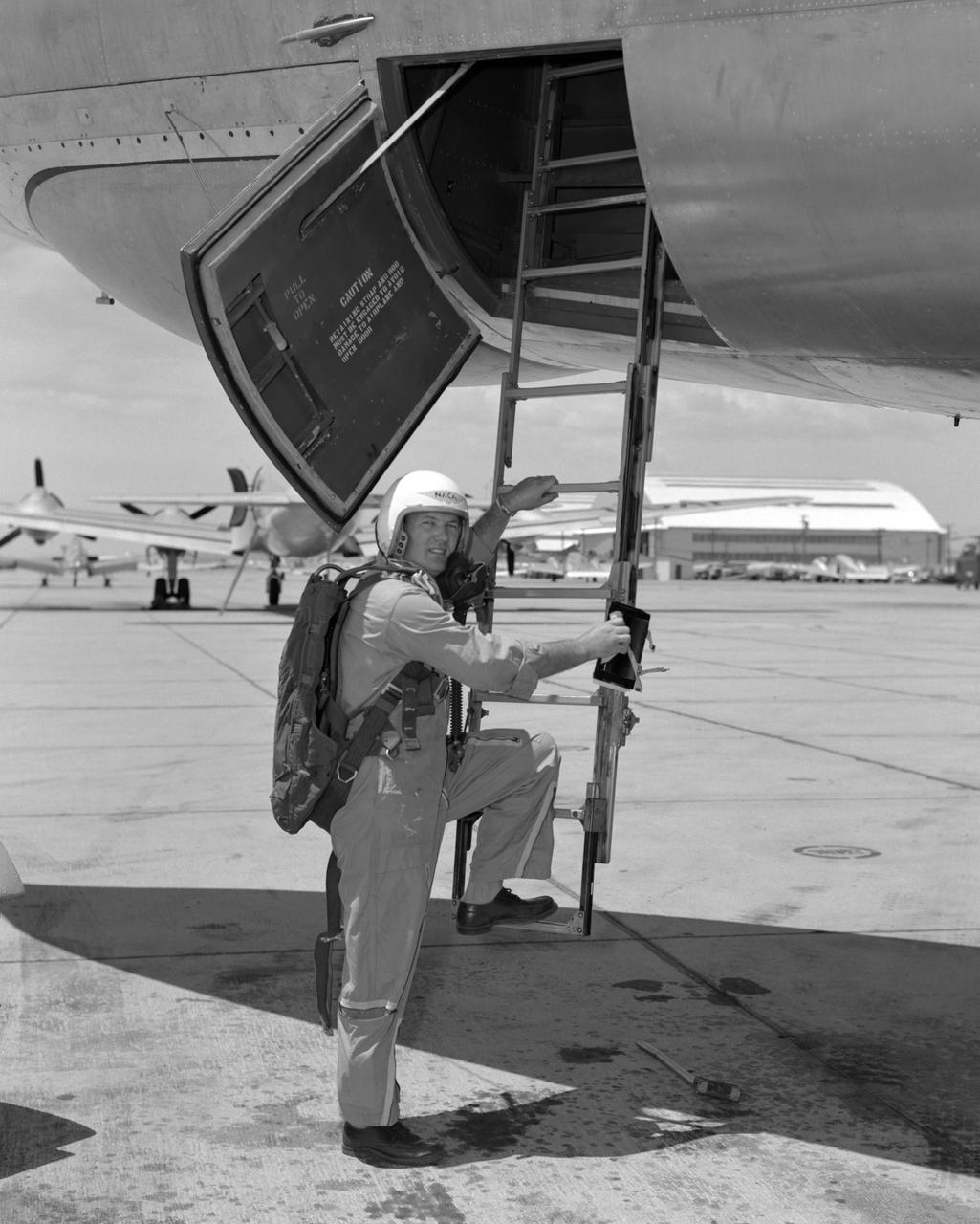

From December 10, 1966, until his retirement on February 27, 1976, Stanley P. Butchart served as Chief (later, Director) of Flight Operations at NASA's Flight Research Center (renamed on March 26, 1976, the Hugh L. Dryden Flight Research Center). Initially, his responsibilities in this position included the Research Pilots Branch, a Maintenance and Manufacturing Branch, and an Operations Engineering Branch, the last of which not only included propulsion and electrical/electronic sections but project engineers for the X-15 and lifting bodies. During his tenure, however, the responsibilities of his directorate came to include not only Flight Test Engineering Support but Flight Systems and Loads laboratories. Before becoming Chief of Flight Operations, Butchart had served since June of 1966 as head of the Research Pilots Branch (Chief Pilot) and then as acting chief of Flight Operations. He had joined the Center (then known as the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics' High-Speed Flight Research Station) as a research pilot on May 10, 1951. During his career as a research pilot, he flew a great variety of research and air-launch aircraft including the D-558-I, D-558-II, B-29 (plus its Navy version, the P2B), X-4, X-5, KC-135, CV-880, CV-990, B-47, B-52, B-747, F-100A, F-101, F-102, F-104, PA-30 Twin Comanche, JetStar, F-111, R4D, B-720, and B-47. Although previously a single-engine pilot, he became the Center's principal multi-engine pilot during a period of air-launches in which the pilot of the air-launch aircraft (B-29 or P2B) basically directed the operations. It was he who called for the chase planes before each drop, directed the positioning of fire rescue vehicles, and released the experimental aircraft after ensuring that all was ready for the drop. As pilot of the B-29 and P2B, Butchart launched the X-1A once, the X-1B 13 times, the X-1E 22 times, and the D-558-II 102 times. In addition, he towed the M2-F1 lightweight lifting body 14 times behind an R4
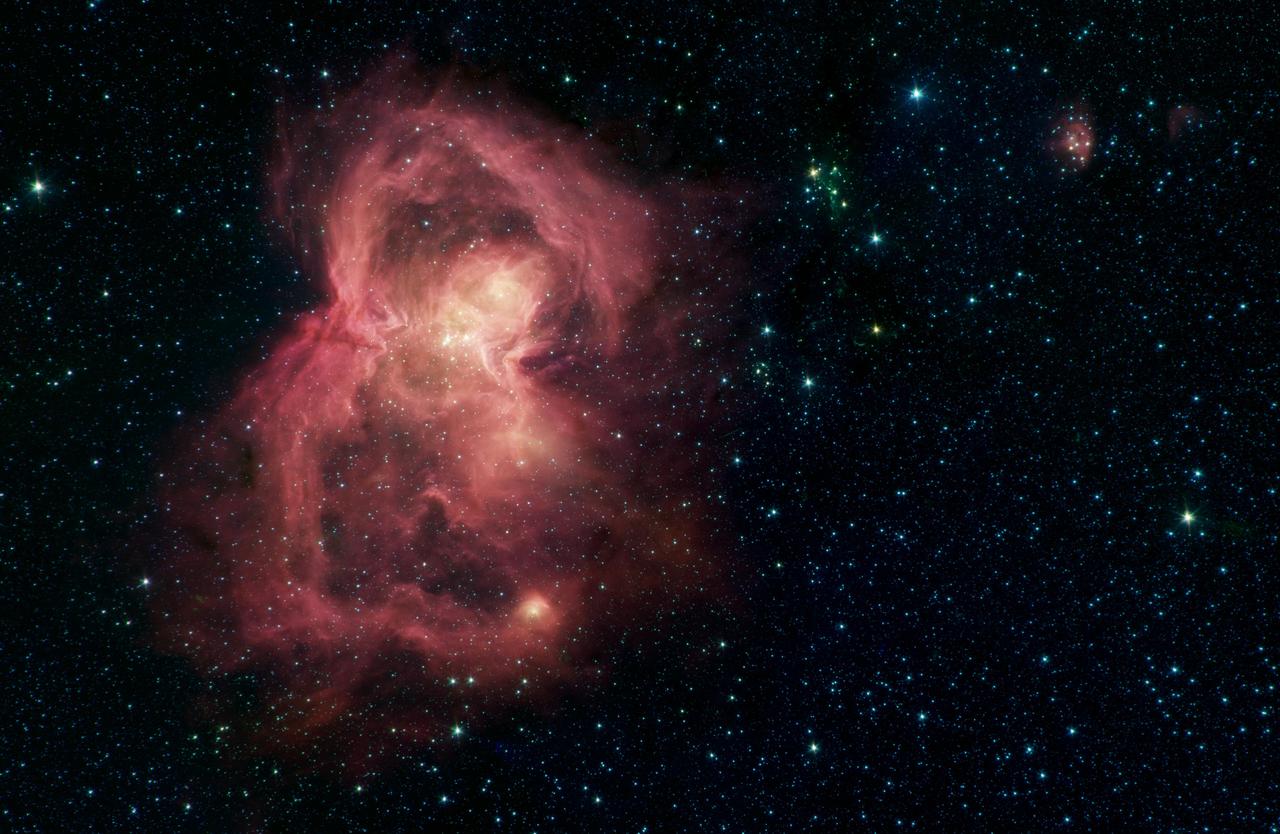

What looks like a red butterfly in space is in reality a nursery for hundreds of baby stars, revealed in this infrared image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Officially named W40, the butterfly is a nebula - a giant cloud of gas and dust in space where new stars may form. The butterfly's two "wings" are giant bubbles of hot, interstellar gas blowing from the hottest, most massive stars in this region. The material that forms W40's wings was ejected from a dense cluster of stars that lies between the wings in the image. The hottest, most massive of these stars, W40 IRS 1a, lies near the center of the star cluster. W40 is about 1,400 light-years from the Sun, about the same distance as the well-known Orion nebula, although the two are almost 180 degrees apart in the sky. They are two of the nearest regions in which massive stars - with masses upwards of 10 times that of the Sun - have been observed to be forming. The W40 star-forming region was observed as part of a Spitzer Legacy Survey, and the resulting mosaic image was published as part of the MYStIX (Massive Young stellar clusters Study in Infrared and X-rays) survey of young stellar objects. The Spitzer picture is composed of four images taken with the telescope's Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) in different wavelengths of infrared light: 3.6, 4.5, 5.8 and 8.0 µm (shown as blue, green, orange and red). Organic molecules made of carbon and hydrogen, called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are excited by interstellar radiation and become luminescent at wavelengths near 8.0 microns, giving the nebula its reddish features. Stars are brighter at the shorter wavelengths, giving them a blue tint. Some of the youngest stars are surrounded by dusty disks of material, which glow with a yellow or red hue. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23121
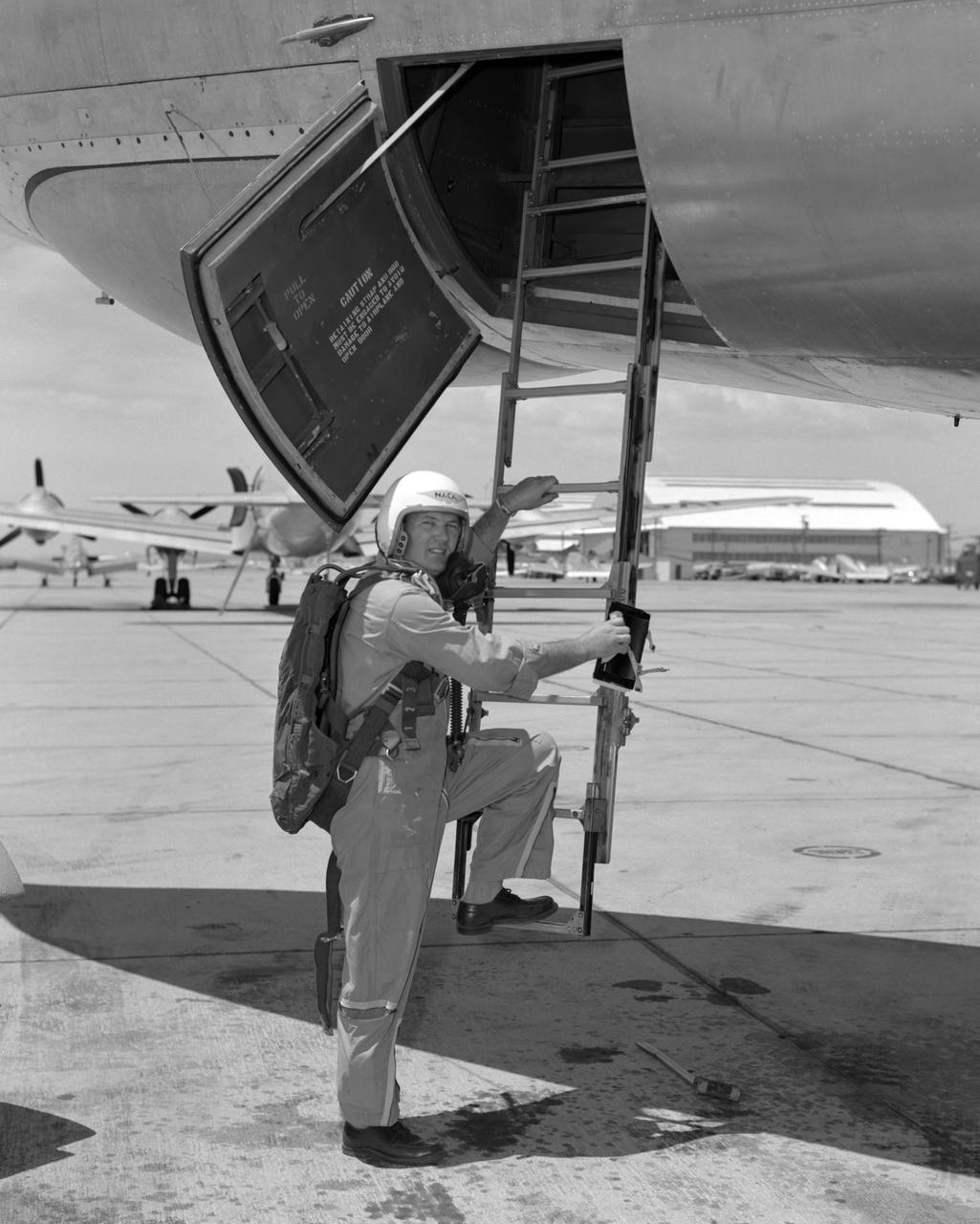

Stan Butchart climbing into B-47.