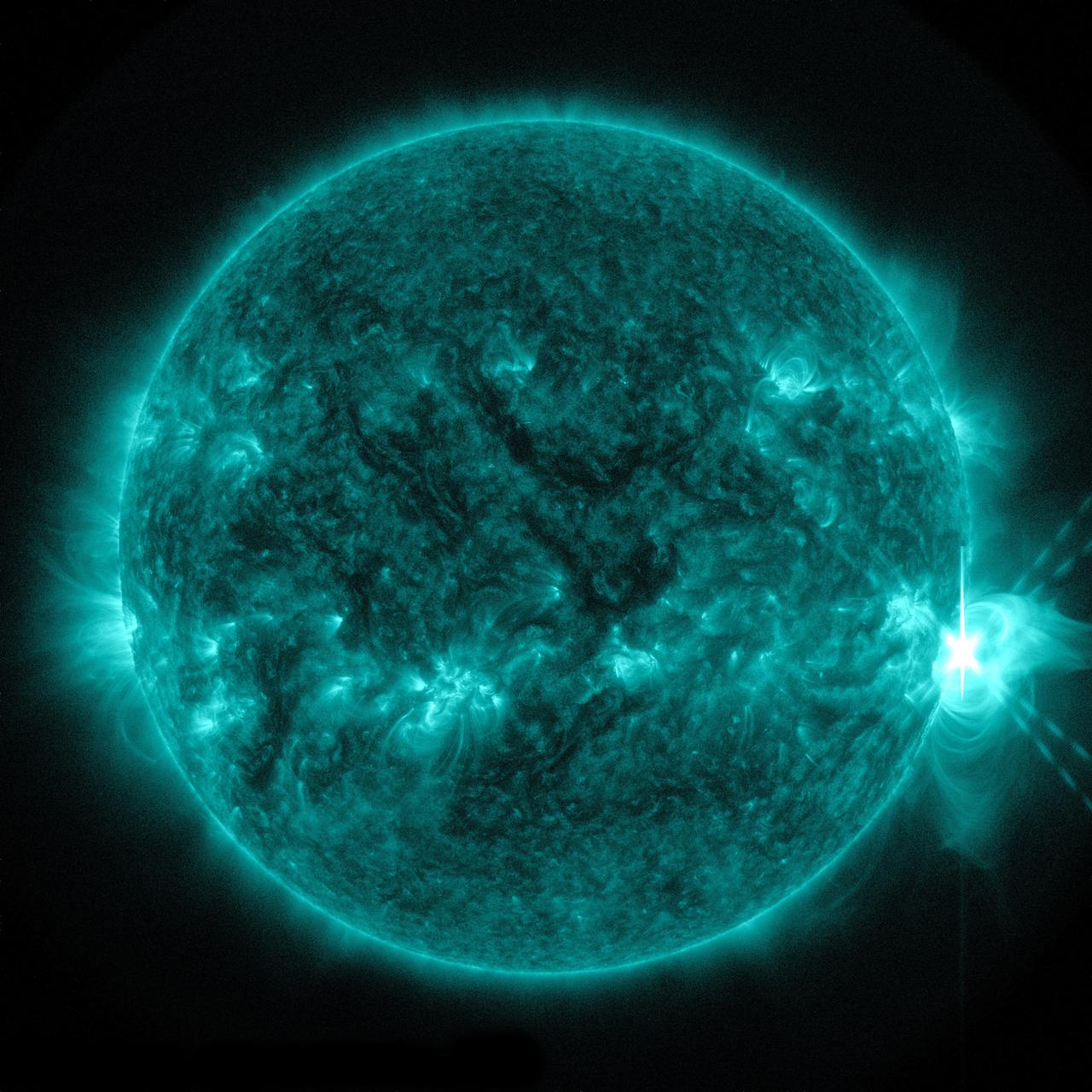

The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 8:27 p.m. EDT on April 24, 2014. Images of the flare were captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. To see how this event may impact Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at <a href="http://spaceweather.gov" rel="nofollow">spaceweather.gov</a>, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings. This flare is classified as an X1.4 flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO Credit: NASA/SDO

Veterans of the X-15 flight research program, most of them now retired, reunited at Dryden on the 40th anniversary of the last X-15 flight on Oct. 24, 1968 for a historical colloquium on the X-15 by noted aerospace historian and author Dennis Jenkins on Oct. 24, 2008. Gathered in front of the replica of X-15 #3 the were (from left) Johnny Armstrong, Betty Love, Paul Reukauf, Bob Hoey, Dave Stoddard, Dean Webb, Vince Capasso, Bill Dana (who flew the last flight), John McTigue and T.D. Barnes. Jenkins, the author of "X-15: Extending the Frontiers of Flight," maintained during his presentation that despite setbacks, the X-15 program became the most successful of all the X-plane research programs due to the can-do, fix-the-problem and go-fly-again attitude of the X-15's cadre of engineers and technicians.
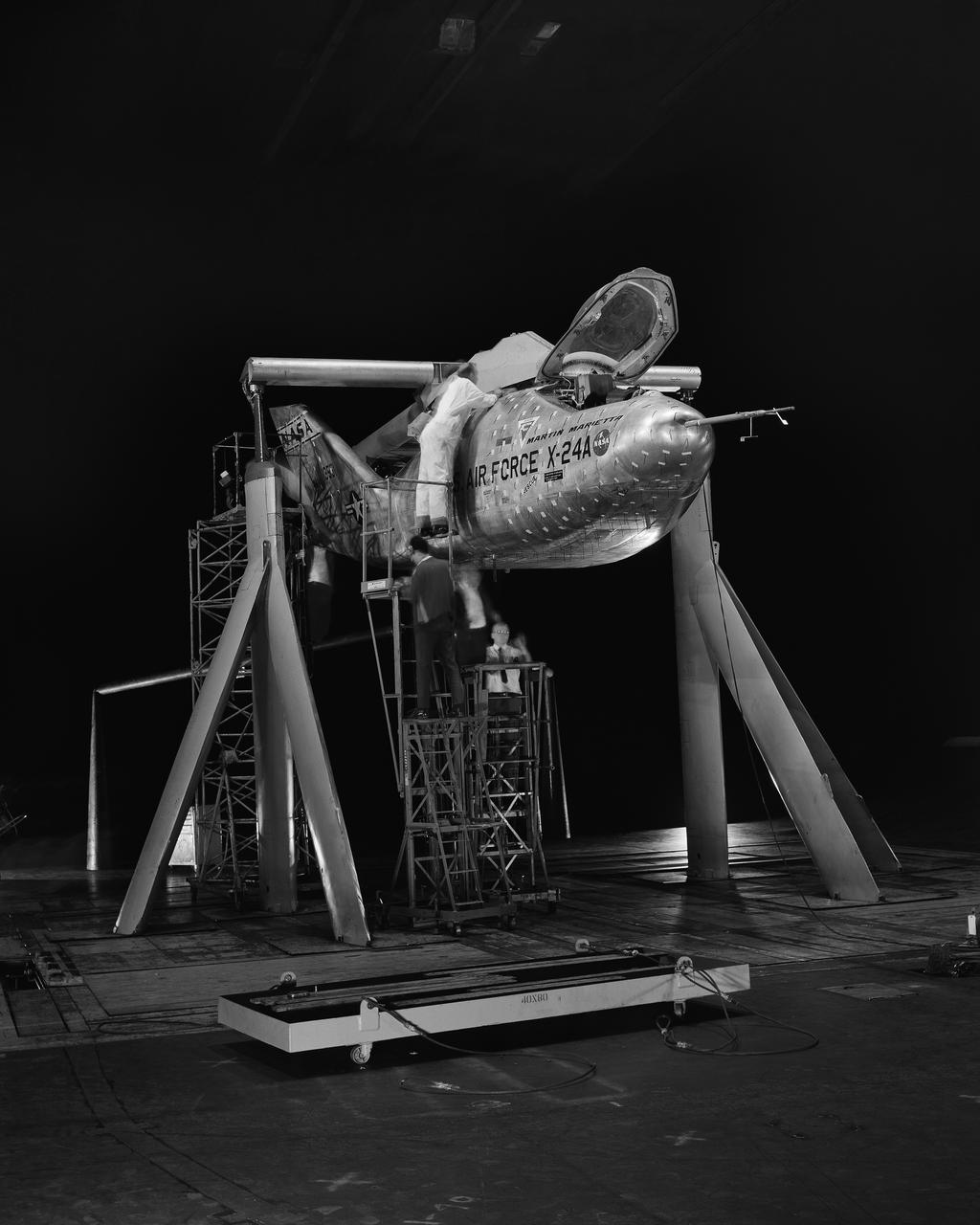

3/4 front view of Martin X-24A lifting body, mounted on B-52 mount.
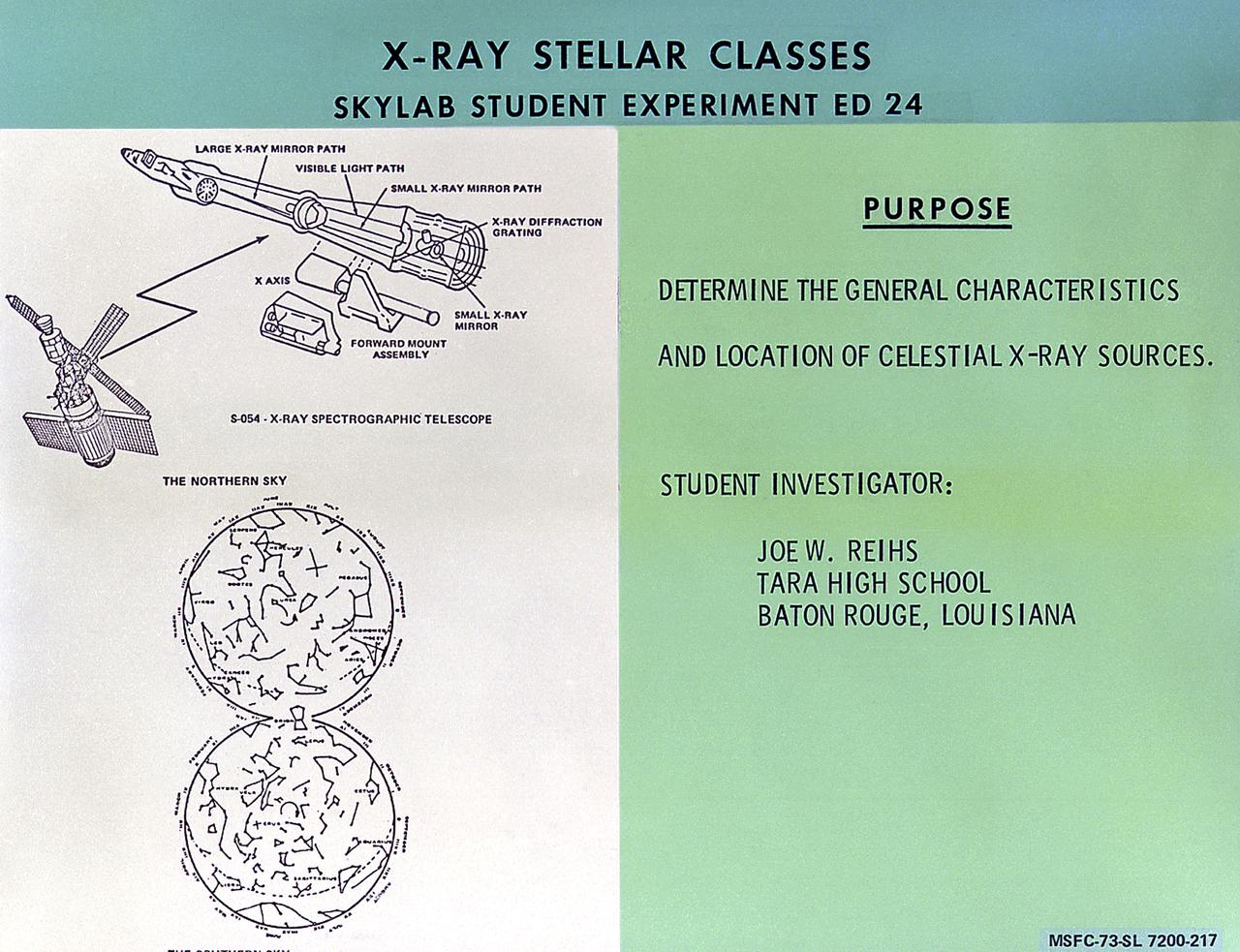
This chart describes the Skylab student experiment X-Ray Stellar Classes, proposed by Joe Reihs of Baton Rouge, Louisiana. This experiment utilized Skylab's X-Ray Spectrographic Telescope to observe and determine the general characteristics and location of x-ray sources. In March 1972, NASA and the National Science Teachers Association selected 25 experiment proposals for flight on Skylab. Science advisors from the Marshall Space Flight Center aided and assisted the students in developing the proposals for flight on Skylab.
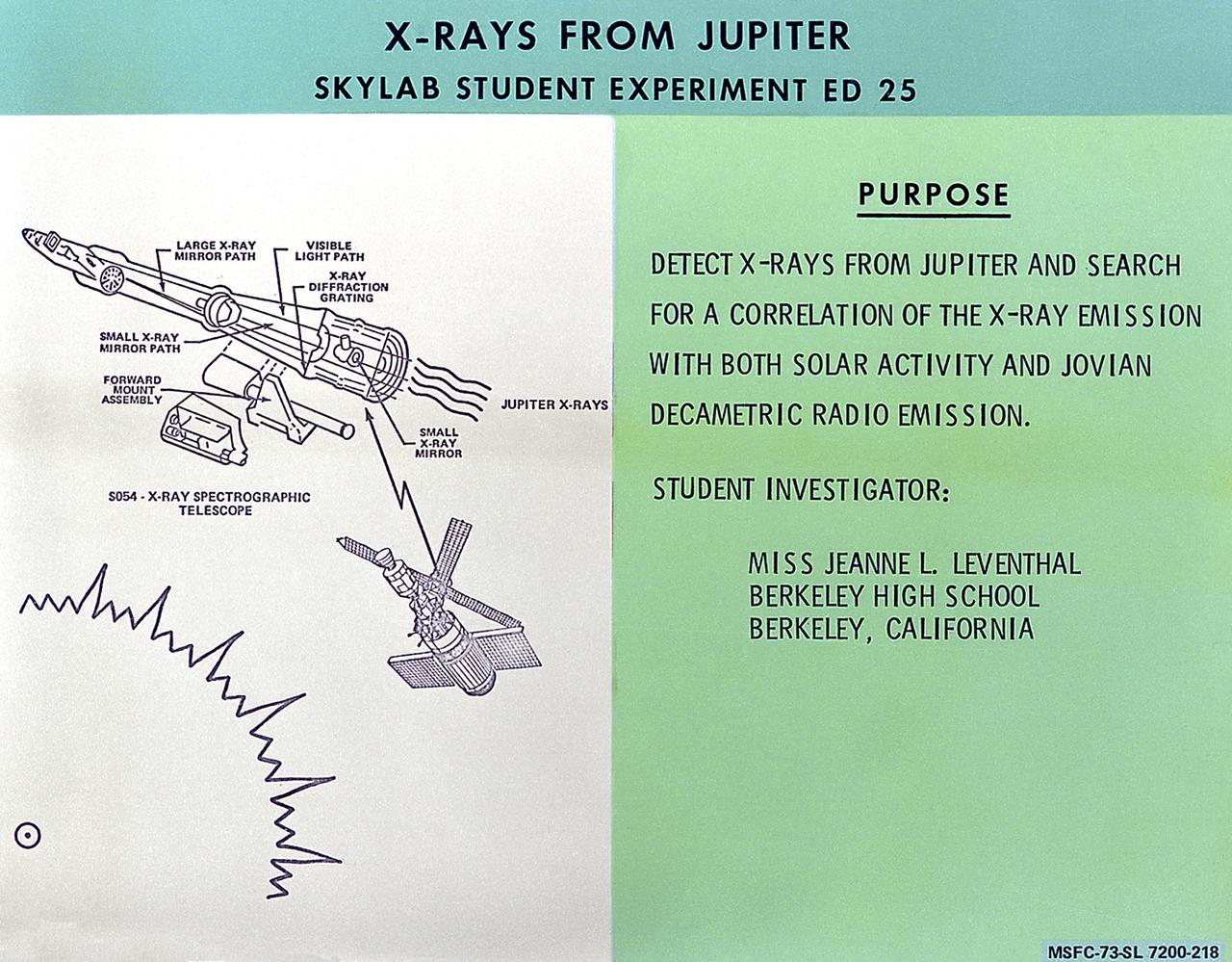
This chart describes the Skylab student experiment X-Rays from Jupiter, proposed by Jearne Leventhal of Berkeley, California. This experiment was an investigation to detect x-rays from the planet Jupiter and determine any correlation with solar flare activity. In March 1972, NASA and the National Science Teachers Association selected 25 experiment proposals for flight on Skylab. Science advisors from the Marshall Space Flight Center aided and assisted the students in developing the proposals for flight on Skylab.

The blue dots in this field of galaxies, known as the COSMOS field, show galaxies that contain supermassive black holes emitting high-energy X-rays. The black holes were detected by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Array, or NuSTAR, which spotted 32 such black holes in this field and has observed hundreds across the whole sky so far. The other colored dots are galaxies that host black holes emitting lower-energy X-rays, and were spotted by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra data show X-rays with energies between 0.5 to 7 kiloelectron volts, while NuSTAR data show X-rays between 8 to 24 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20865

The blue dots in this field of galaxies, known as the COSMOS field, show galaxies that contain supermassive black holes emitting high-energy X-rays. The black holes were detected by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Array, or NuSTAR, which spotted 32 such black holes in this field and has observed hundreds across the whole sky so far. The other colored dots are galaxies that host black holes emitting lower-energy X-rays, and were spotted by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra data show X-rays with energies between 0.5 to 7 kiloelectron volts, while NuSTAR data show X-rays between 8 to 24 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20865

jsc2021e037879 (8/24/2021) --- A preflight view of the Touching Surfaces investigation hardware. The Touch Array (136 mm x 45 mm x 8 mm). Housing : Aluminum (EN-AW 7075 T7351). (Panel A) Nine metallic test surfaces: 3 x steel, copper, brass (from left to right) – with no greater than 3 ?m and less than 3 ?m laser structure (from top to bottom); (Panel B) in each Touch Array two 3 printed humidity detectors are mounted. Image Courtesy DLR
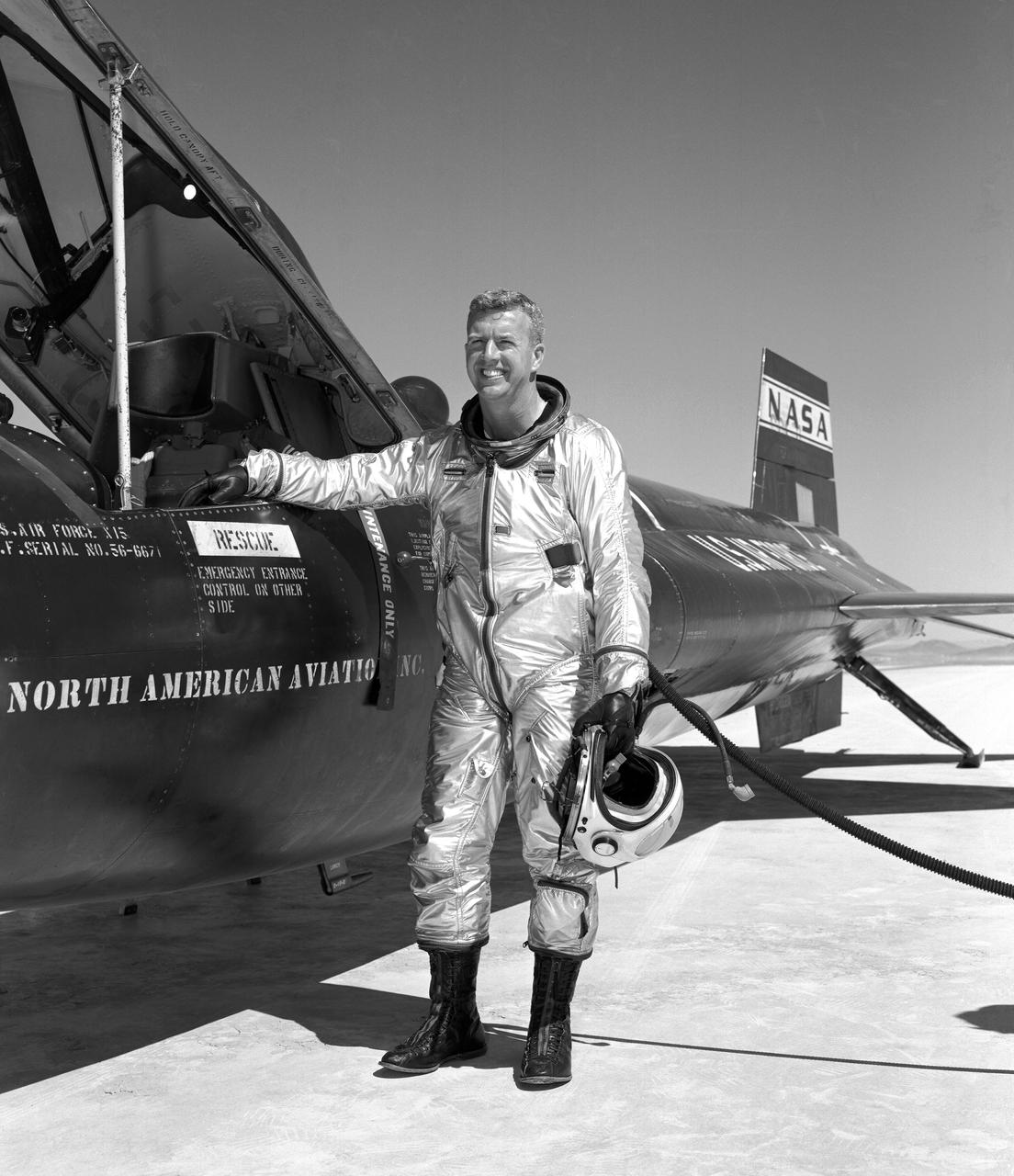

Walker made the first NASA-piloted X-15 flight March 25, 1960, and flew the aircraft 24 times, achieving its highest altitude (354,300 ft.) Aug. 22, 1963. He died piloting a F-104 that was caught up in a vortex of the XB-70.

File name :DSC_0047.JPG File size :2.8MB(2931574Bytes) Date taken :2002/02/24 10:06:57 Image size :3008 x 2000 Resolution :300 x 300 dpi Number of bits :8bit/channel Protection attribute :Off Hide Attribute :Off Camera ID :N/A Camera :NIKON D100 Quality mode :N/A Metering mode :Matrix Exposure mode :Shutter priority Speed light :Yes Focal length :24 mm Shutter speed :1/180second Aperture :F20.0 Exposure compensation :+0.3 EV White Balance :N/A Lens :N/A Flash sync mode :N/A Exposure difference :N/A Flexible program :N/A Sensitivity :N/A Sharpening :N/A Image Type :Color Color Mode :N/A Hue adjustment :N/A Saturation Control :N/A Tone compensation :N/A Latitude(GPS) :N/A Longitude(GPS) :N/A Altitude(GPS) :N/A

STS059-86-059 (9-20 April 1994) --- This oblique handheld Hasselblad 70mm photo shows Death Valley, near California's border with Nevada. The valley -- the central feature of Death Valley National Monument -- extends north to south for some 140 miles (225 kilometers). Hemmed in to the east by the Amargosa Range and to the west by the Panamints, its width varies from 5 to 15 miles (8 to 24 kilometers). Using Spaceborne Imaging Radar (SIR-C) and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (X-SAR) onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, the crew was able to record a great deal of data on this and other sites, as part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth.

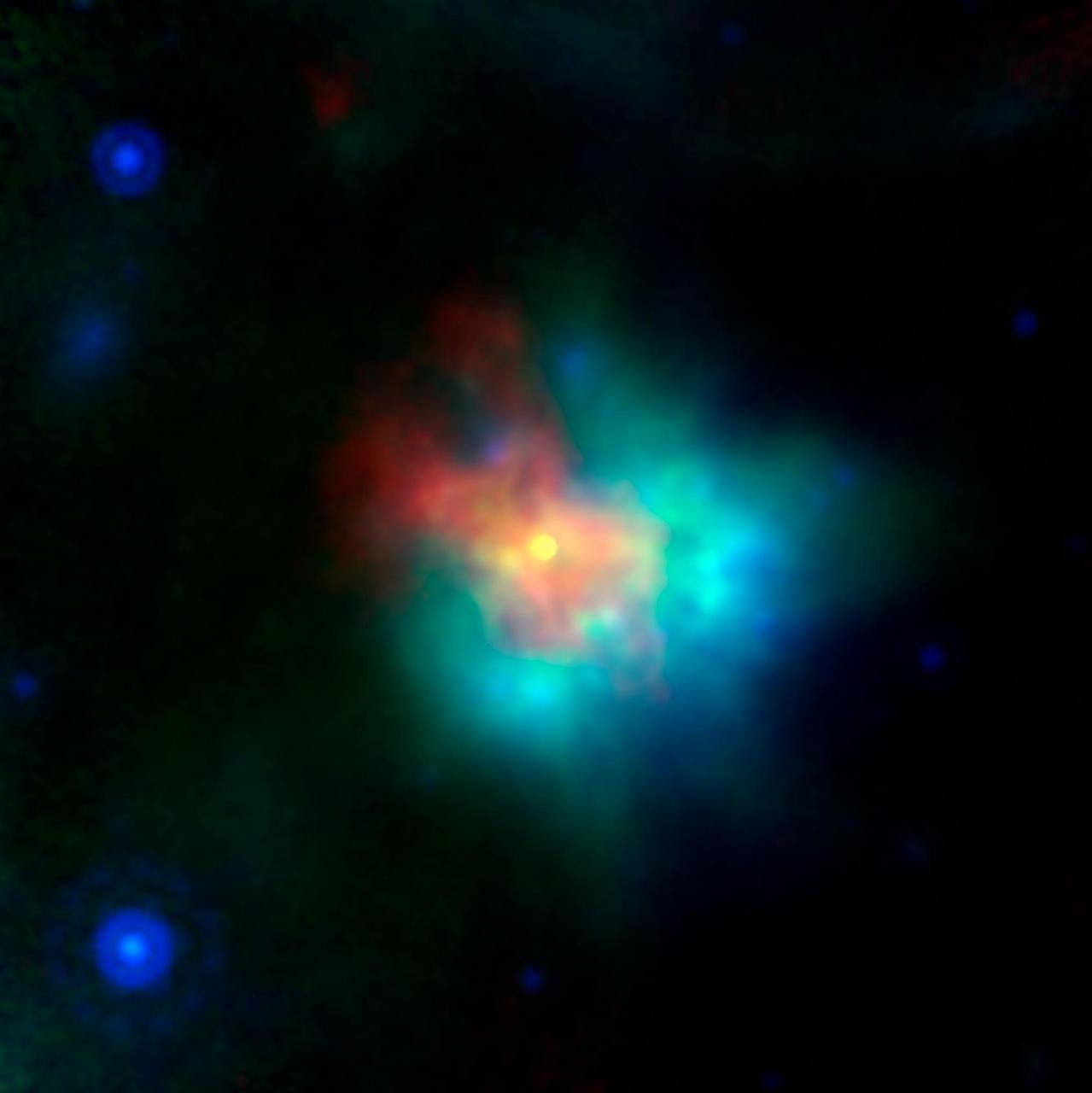
This Spitzer false-color image is a composite of data from the 24 micron channel of Spitzer's multiband imaging photometer (red), and three channels of its infrared array camera: 8 micron (yellow), 5.6 micron (blue), and 4.8 micron (green). Stars are most prominent in the two shorter wavelengths, causing them to show up as turquoise. The supernova remnant is most prominent at 24 microns, arising from dust that has been heated by the supernova shock wave, and re-radiated in the infrared. The 8 micron data shows infrared emission from regions closely associated with the optically emitting regions. These are the densest regions being encountered by the shock wave, and probably arose from condensations in the surrounding material that was lost by the supernova star before it exploded. The composite above (PIA06908, PIA06909, and PIA06910) represent views of Kepler's supernova remnant taken in X-rays, visible light, and infrared radiation. Each top panel in the composite above shows the entire remnant. Each color in the composite represents a different region of the electromagnetic spectrum, from X-rays to infrared light. The X-ray and infrared data cannot be seen with the human eye. Astronomers have color-coded those data so they can be seen in these images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06910

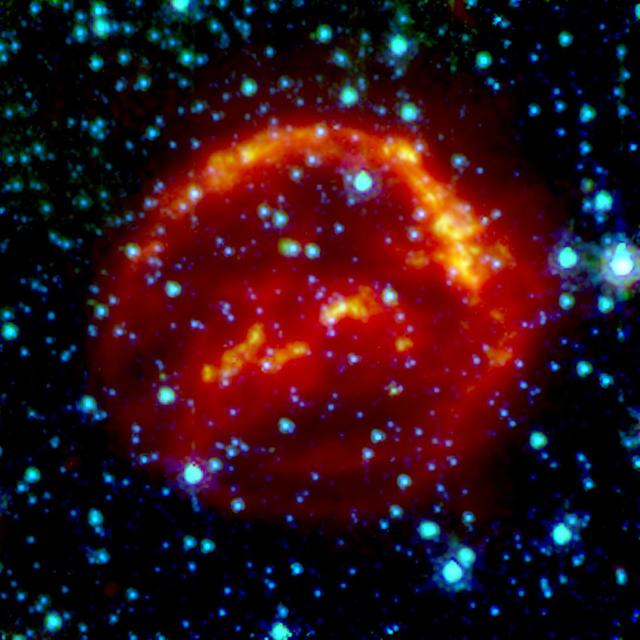
This image of supernova remnant G54.1+0.3 includes radio, infrared and X-ray light. The saturated yellow point at the center of the image indicates strong X-ray source at the center of the supernova remnant. This is an incredibly dense object called a neutron star, which can form as a star runs out of fuel to keep it inflated, and the unsupported material collapses down on to the star's core. G54.1+0.3 contains a special type of neutron star called a pulsar, which emits particularly bright radio and X-ray emissions. The blue and green emissions show the presence of dust, including silica. The red hues correspond to radio data from the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array; green corresponds to 70 µm wavelength infrared light from the European Space Agency's Herschel Space Observatory; blue corresponds to 24 µm wavelength infrared light from the Multiband Imaging Photometer (MIPS) instrument on NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope; yellow corresponds to X-ray data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22569
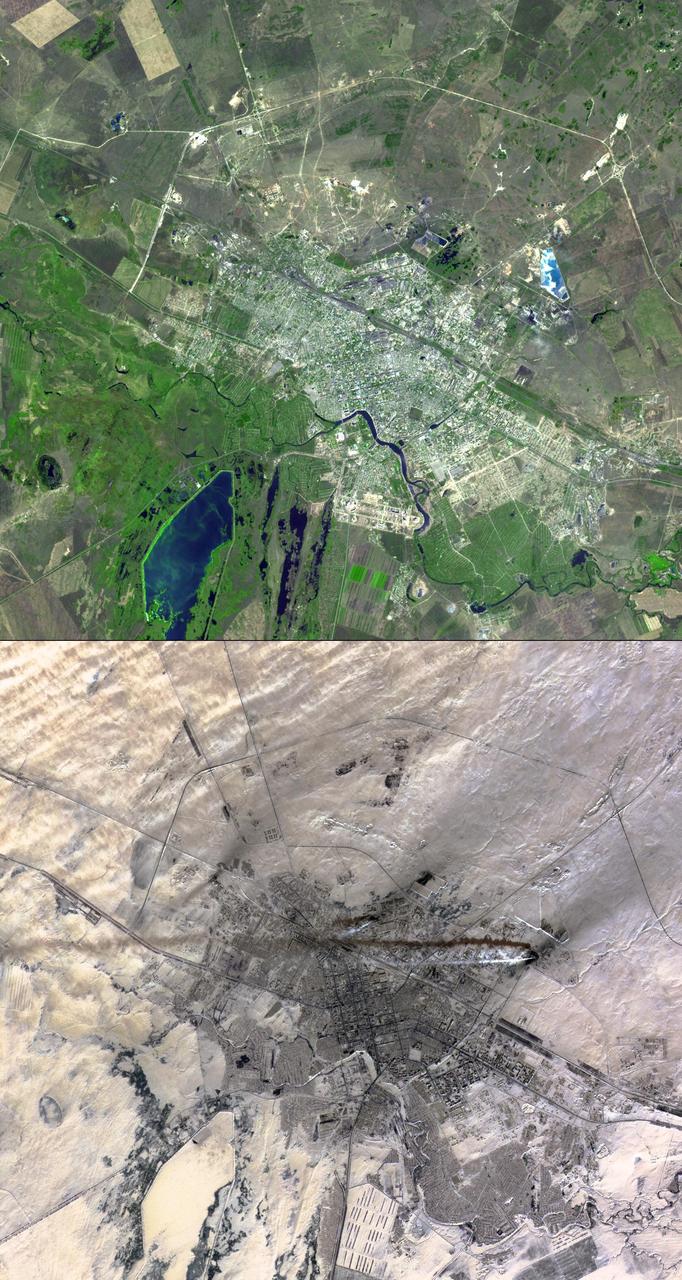

Astana is the capital and second largest city of Kazakhstan, with a population of about 600,000. It was founded as a fort in 1824 on the Ishim River by Siberian Cossacks, and became a railway junction in the early 20th century. Astana became the capital of the newly-independent Kazakhstan in 1997. These two images were acquired March 20, 2001 and September 5, 2003, cover an area of 22.5 x 24 km, and are located near 51.2 degrees north latitude, 71.4 degrees east longitude. This image is from NASA Terra satellite. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10612
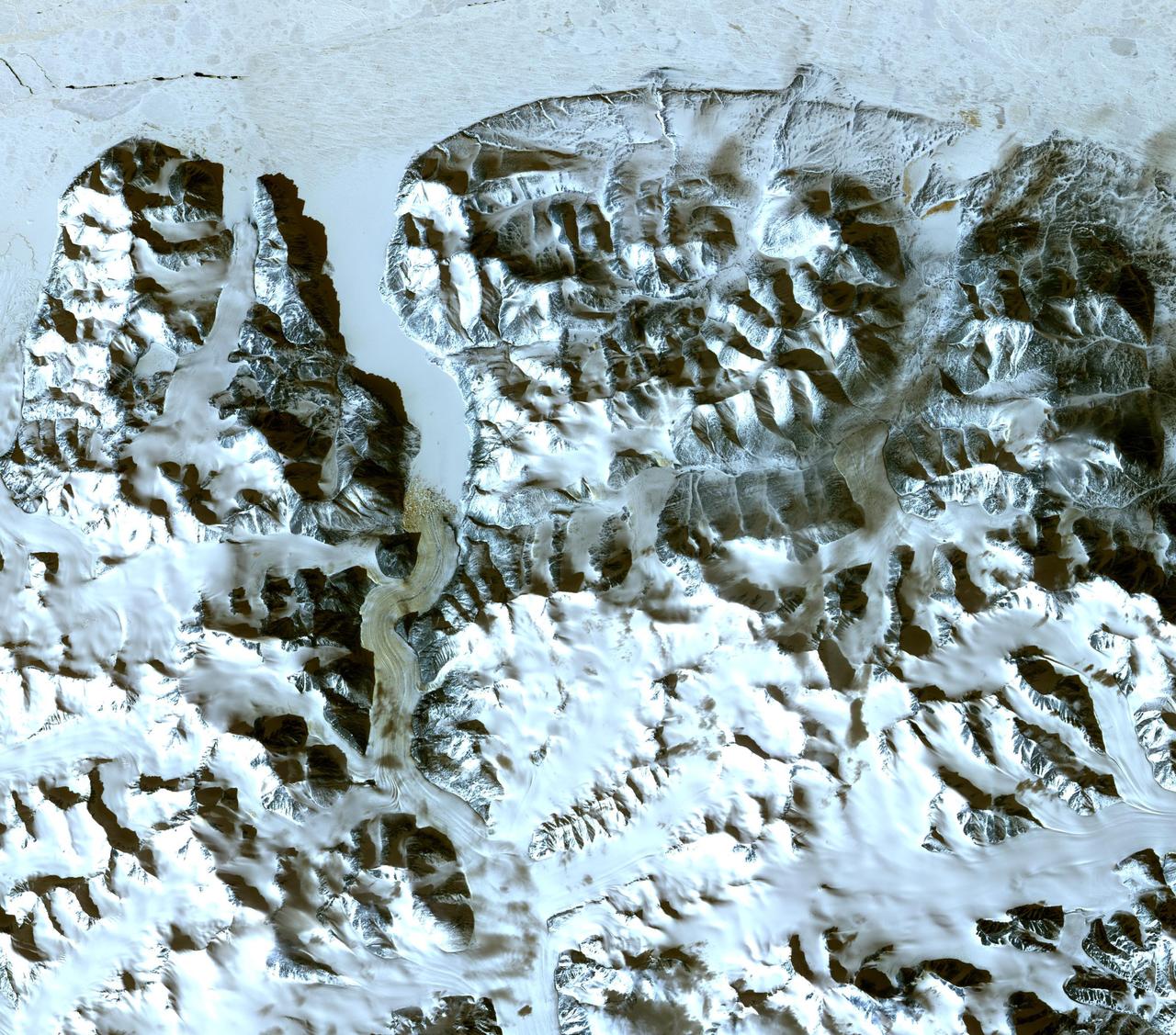

The northernmost land in the world is located in Pearyland, Greenland, at a latitude of 83 degrees, 39.6 minutes. This is a land of permanent snows, glaciers, and 24-hours of daylight during the summer months. The ASTER image was acquired May 17, 2003, covers an area of 47.9 x 42.1 km, and is located at 83.6 degrees north latitude, 33.4 degrees west longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11169
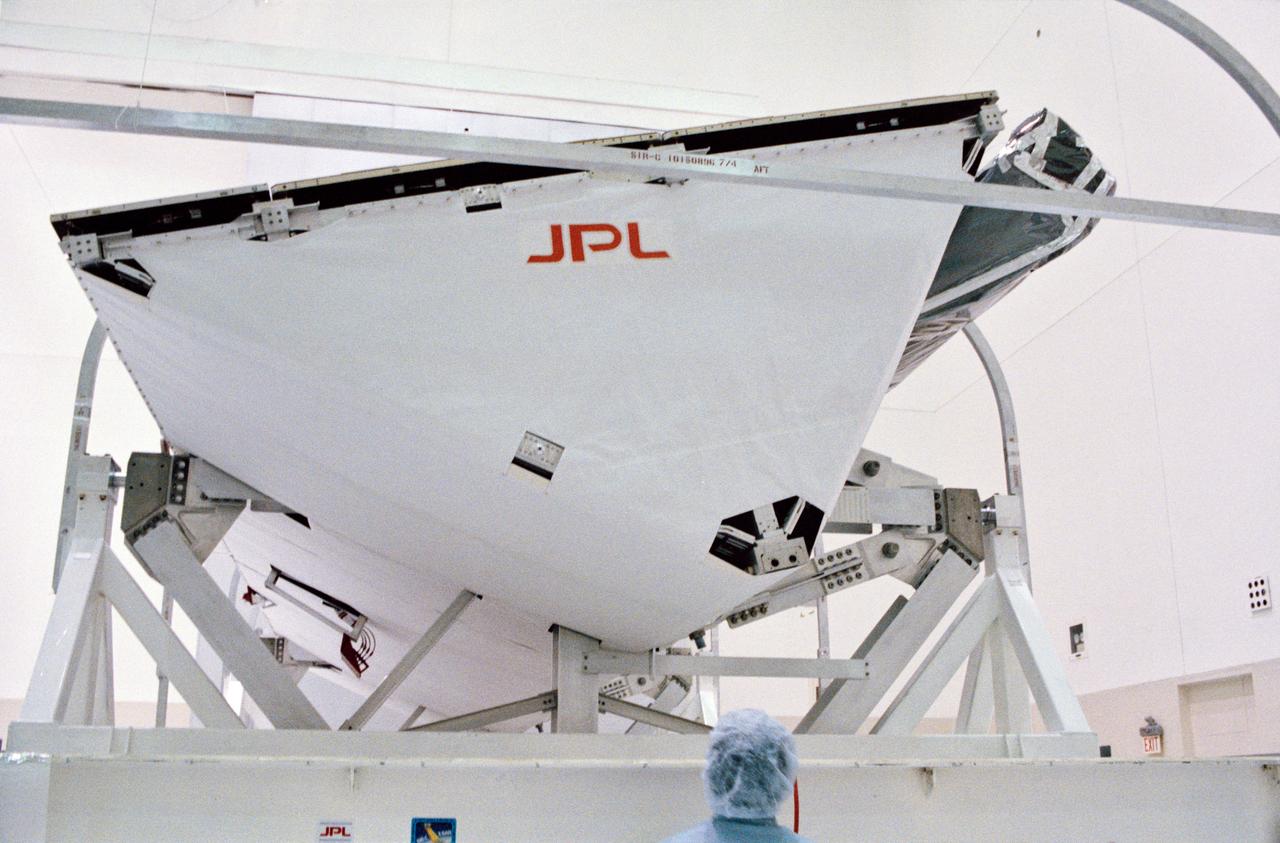

S93-48551 (October 1993) --- The Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) antenna, developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) as part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE), will fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The radar antenna uses microwave energy which gives it the ability to collect data over virtually any region at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. The radar waves can penetrate clouds, and under certain conditions the radar can also see through vegetation, ice and dry sand. In many cases, spaceborne radar is the only way scientists can explore large-scale and inaccessible regions of the Earth's surface. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm) and X-Ban (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to monitor global environmental processes with a focus on climate change. The MTPE spaceborne data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity.
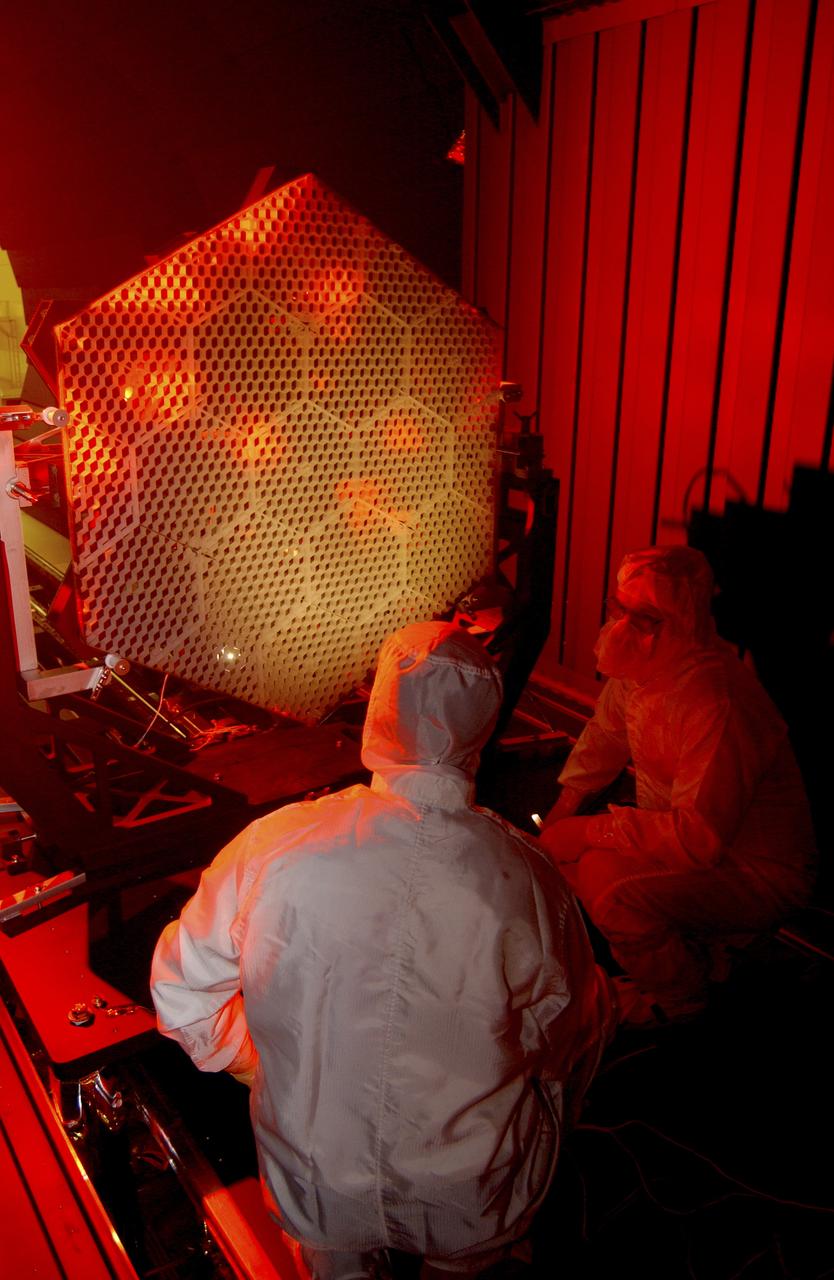

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, one of many segments of the mirror assembly is being set up inside the 24-ft vacuum chamber where it will undergo x-ray calibration tests. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
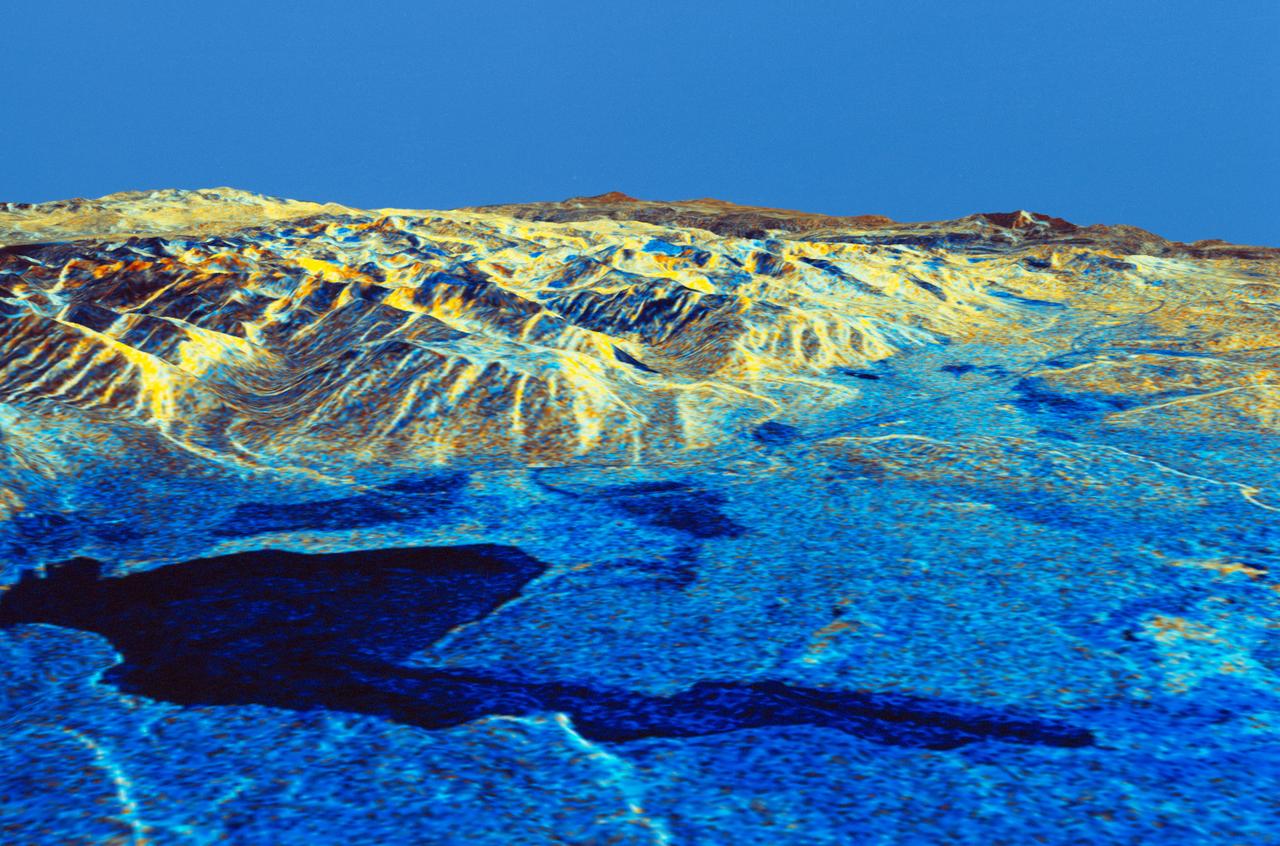
STS059-S-084 (17 April 1994) --- This is a three-dimensional perspective of Mammoth Mountain, California. This view was constructed by overlaying a SIR-C radar image on a U.S. Geological Survey digital elevation map. Vertical exaggeration is 2x. The image is centered at 37.6 degrees north, 119.0 degrees west. It was acquired from the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its 67th orbit, April 13, 1994. In this color representation, red is C-Band HV-polarization, green is C-Band VV-polarization and blue is the ratio of C-Band VV to C-Band HV. Blue areas are smooth and yellow areas are rock outcrops with varying amounts of snow and vegetation. Crowley Lake is in the foreground and Highway 395 crosses in the middle of the image. Mammoth Mountain is shown in the upper right. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43933
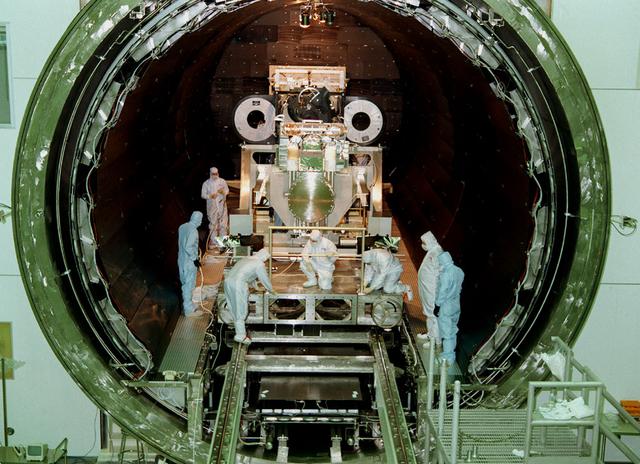

This photo shows the High Resolution Camera (HRC) for the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), being integrated with the High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) in Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) 24-foot Vacuum Chamber at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most poweful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRC is one of the two instruments used at the focus of CXO, where it will detect x-rays reflected from an assembly of eight mirrors. The unique capabilities of the HRC stem from the close match of its imaging capability to the focusing of the mirrors. When used with CXO mirrors, the HRC makes images that reveal detail as small as one-half an arc second. This is equivalent to the ability to read a newspaper at a distance of 1 kilometer. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components relatedto x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
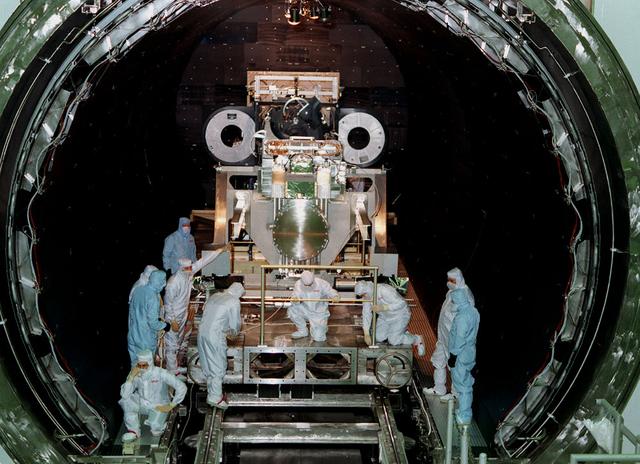

This photo shows the High Resolution Camera (HRC) for the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), being integrated with the High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) in Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) 24-foot Vacuum Chamber at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRC is one of the two instruments used at the focus of CXO, where it will detect x-rays reflected from an assembly of eight mirrors. The unique capabilities of the HRC stem from the close match of its imaging capability to the focusing of the mirrors. When used with CXO mirrors, the HRC makes images that reveal detail as small as one-half an arc second. This is equivalent to the ability to read a newspaper at a distance of 1 kilometer. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
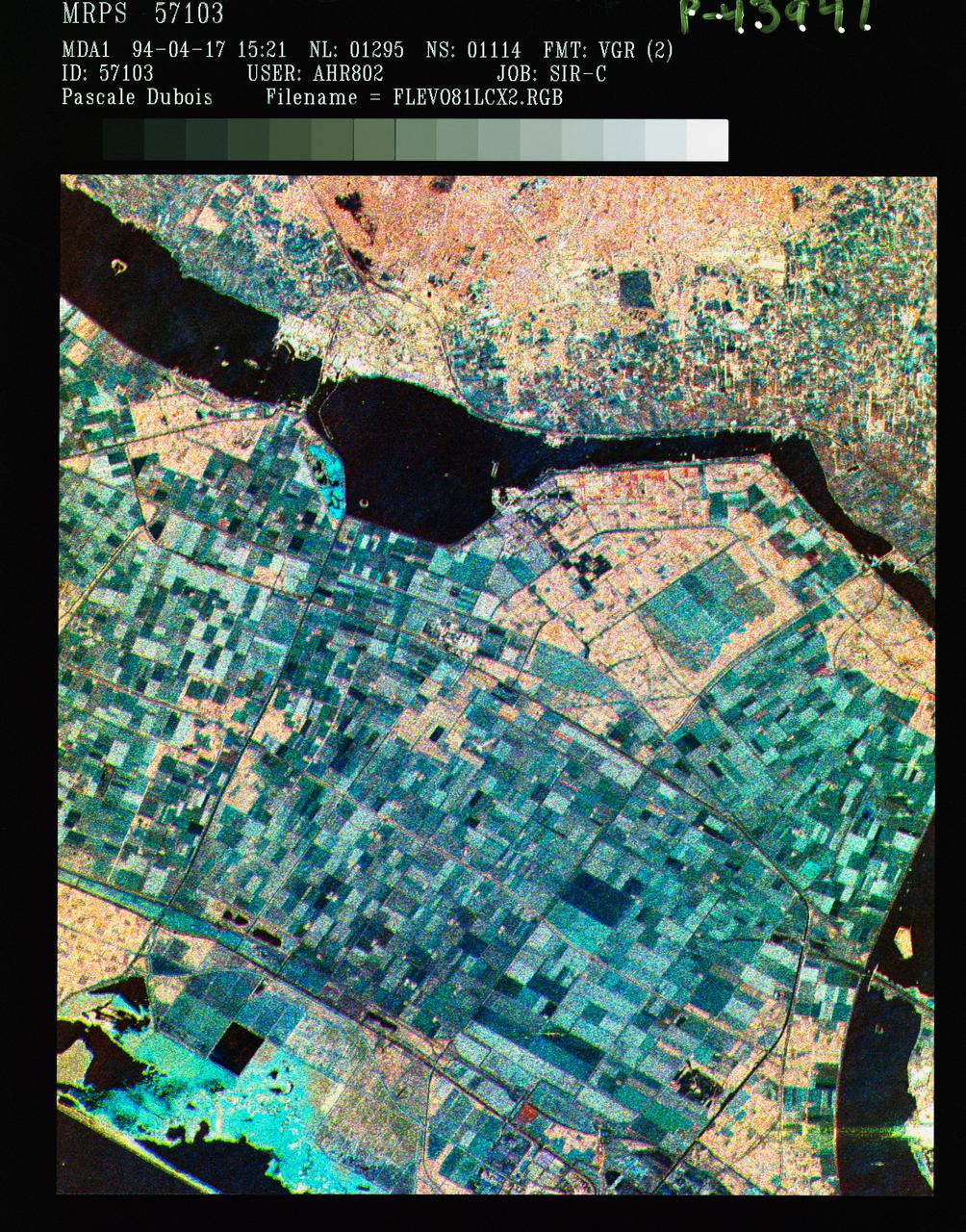

STS059-S-086 (18 April 1994) --- This is a three-frequency false-color image of Flevoland, the Netherlands, centered at 52.4 degrees north latitude, and 5.4 degrees east longitude. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on April 14, 1994. It was produced by combining data from the X-Band, C-Band and L-Band radar's. The area shown is approximately 25 by 28 kilometers (15 1/2 by 17 1/2 miles). Flevoland, which fills the lower two-thirds of the image, is a very flat area that is made up of reclaimed land that is used for agriculture and forestry. At the top of the image, across the canal from Flevoland, is an older forest shown in red; the city of Harderwijk is shown in white on the shore of the canal. At this time of the year, the agricultural fields are bare soil, and they show up in this images in blue. The changes in the brightness of the blue areas are equal to the changes in roughness. The dark blue areas are water and the small dots in the canal are boats. This SIR-C/X-SAR supersite is being used for both calibration and agricultural studies. Several soil and crop ground-truth studies will be conducted during the Shuttle flight. In addition, about 10 calibration devices and 10 corner reflectors have been deployed to calibrate and monitor the radar signal. One of these transponders can be seen as a bright star in the lower right quadrant of the image. This false-color image was made using L-Band total power in the red channel, C-Band total power in the green channel, and X-Band VV polarization in the blue channel. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43941
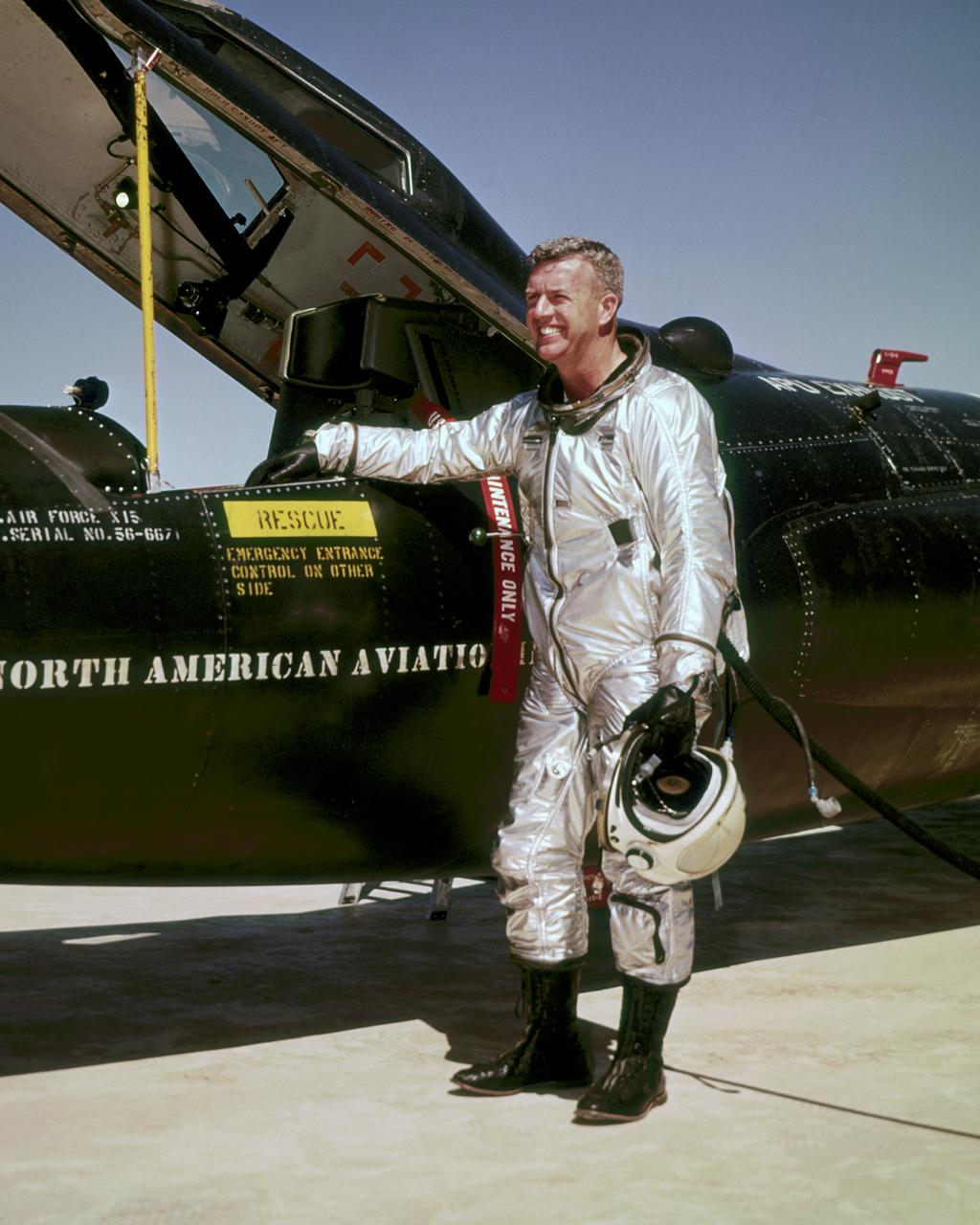

Joseph A. Walker was a Chief Research Pilot at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center during the mid-1960s. He joined the NACA in March 1945, and served as project pilot at the Edwards flight research facility on such pioneering research projects as the D-558-1, D-558-2, X-1, X-3, X-4, X-5, and the X-15. He also flew programs involving the F-100, F-101, F-102, F-104, and the B-47. Walker made the first NASA X-15 flight on March 25, 1960. He flew the research aircraft 24 times and achieved its fastest speed and highest altitude. He attained a speed of 4,104 mph (Mach 5.92) during a flight on June 27, 1962, and reached an altitude of 354,300 feet on August 22, 1963 (his last X-15 flight). He was the first man to pilot the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) that was used to develop piloting and operational techniques for lunar landings. Walker was born February 20, 1921, in Washington, Pa. He lived there until graduating from Washington and Jefferson College in 1942, with a B.A. degree in Physics. During World War II he flew P-38 fighters for the Air Force, earning the Distinguished Flying Cross and the Air Medal with Seven Oak Clusters. Walker was the recipient of many awards during his 21 years as a research pilot. These include the 1961 Robert J. Collier Trophy, 1961 Harmon International Trophy for Aviators, the 1961 Kincheloe Award and 1961 Octave Chanute Award. He received an honorary Doctor of Aeronautical Sciences degree from his alma mater in June of 1962. Walker was named Pilot of the Year in 1963 by the National Pilots Association. He was a charter member of the Society of Experimental Test Pilots, and one of the first to be designated a Fellow. He was fatally injured on June 8, 1966, in a mid-air collision between an F-104 he was piloting and the XB-70.
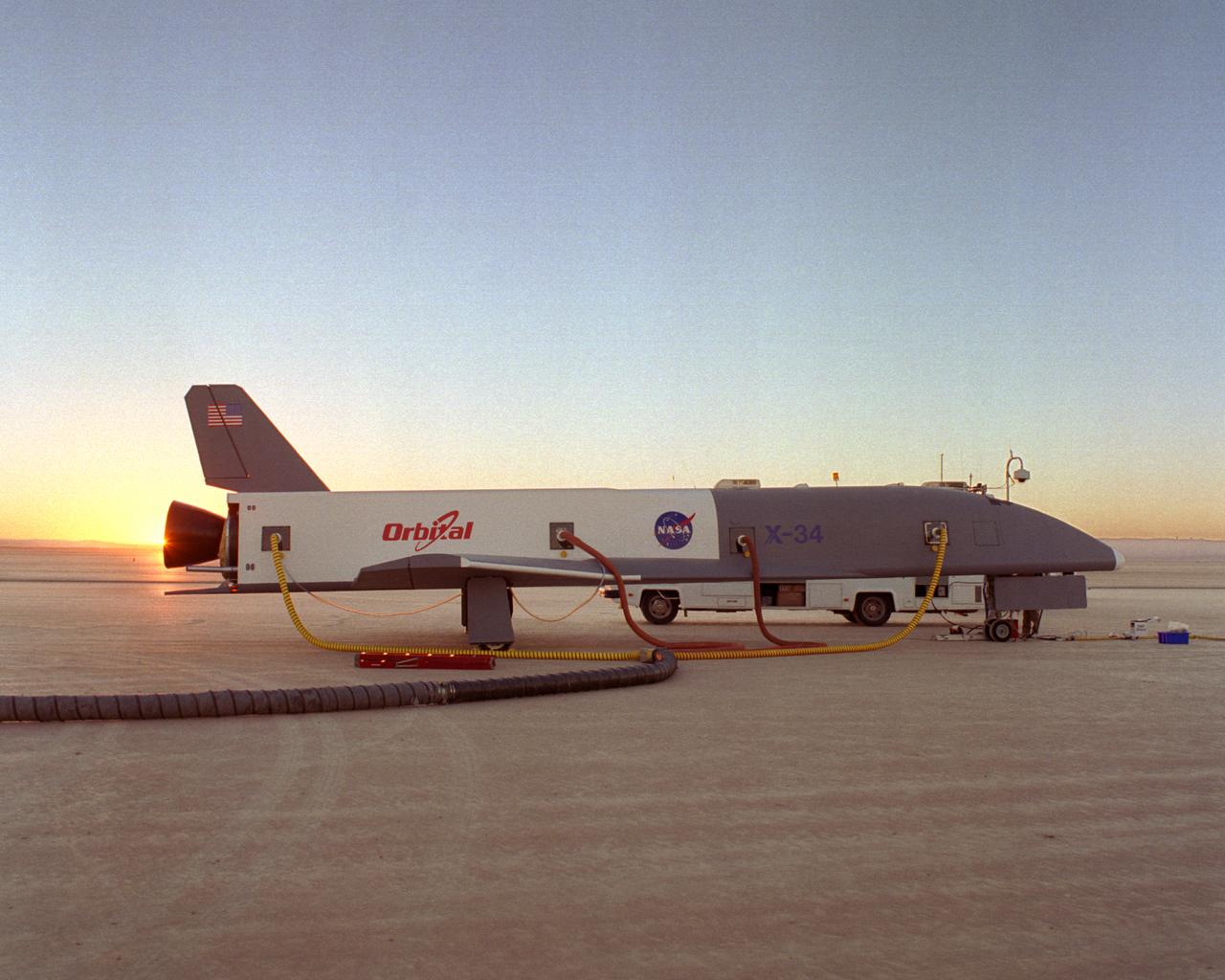

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.
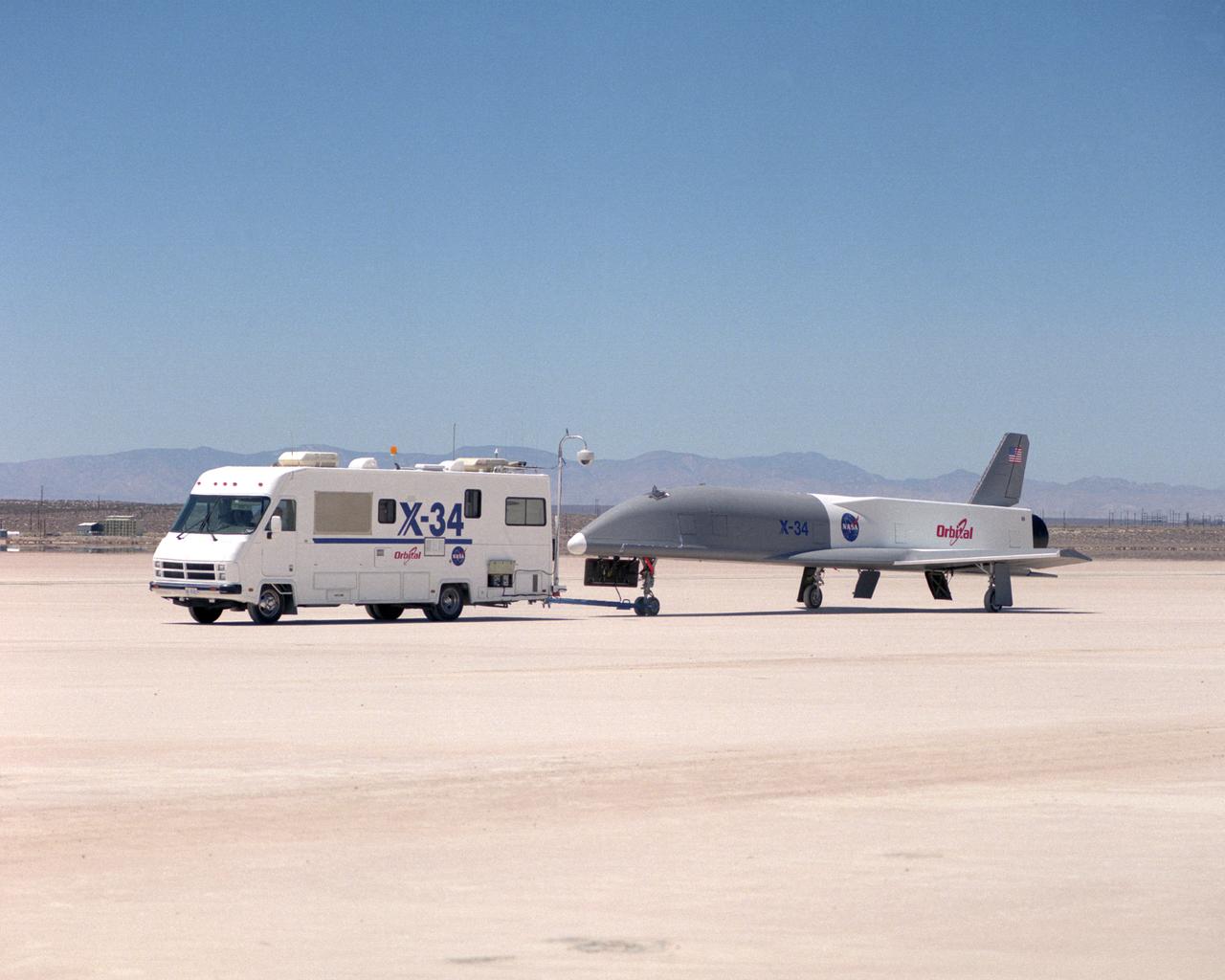

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.
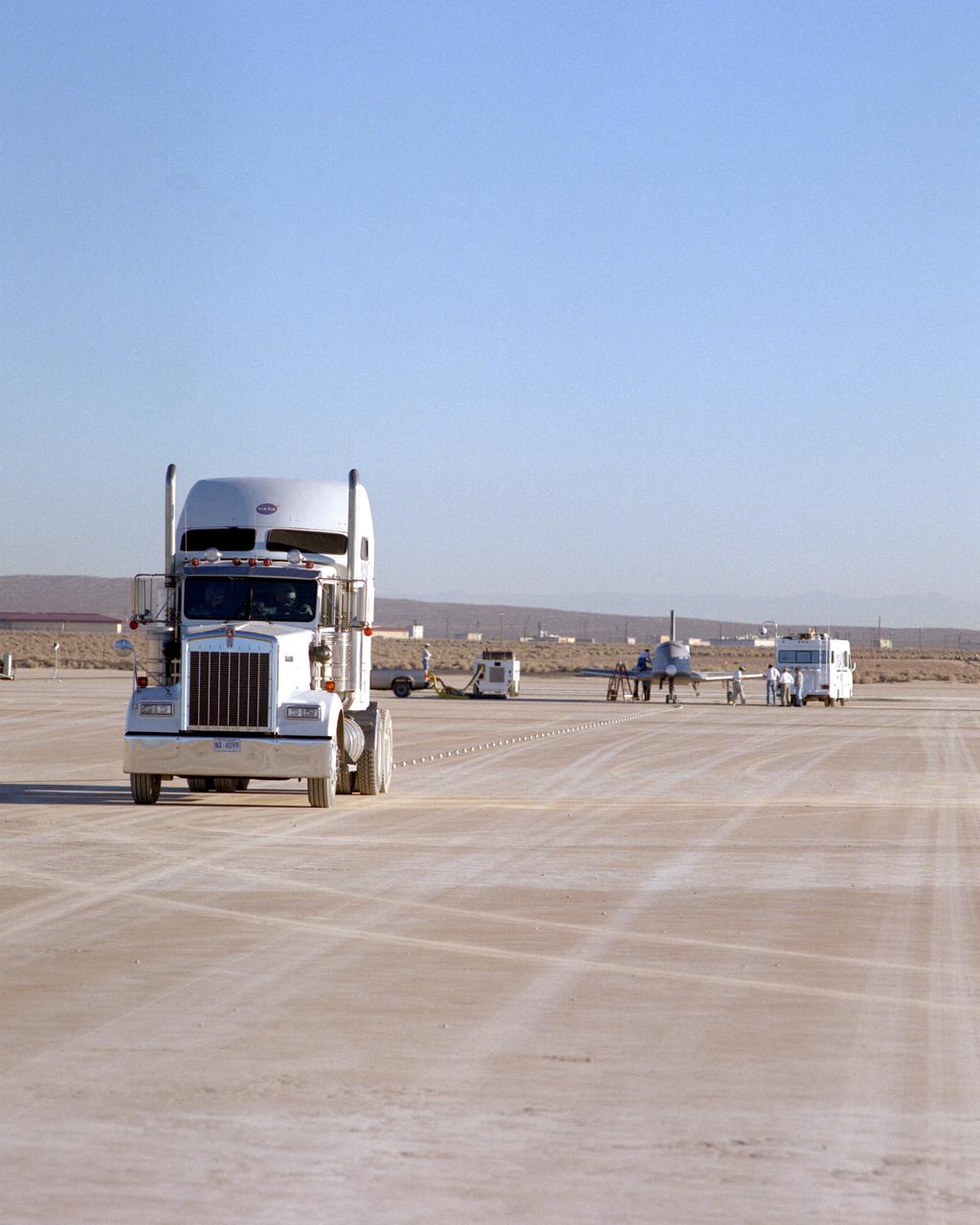

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.
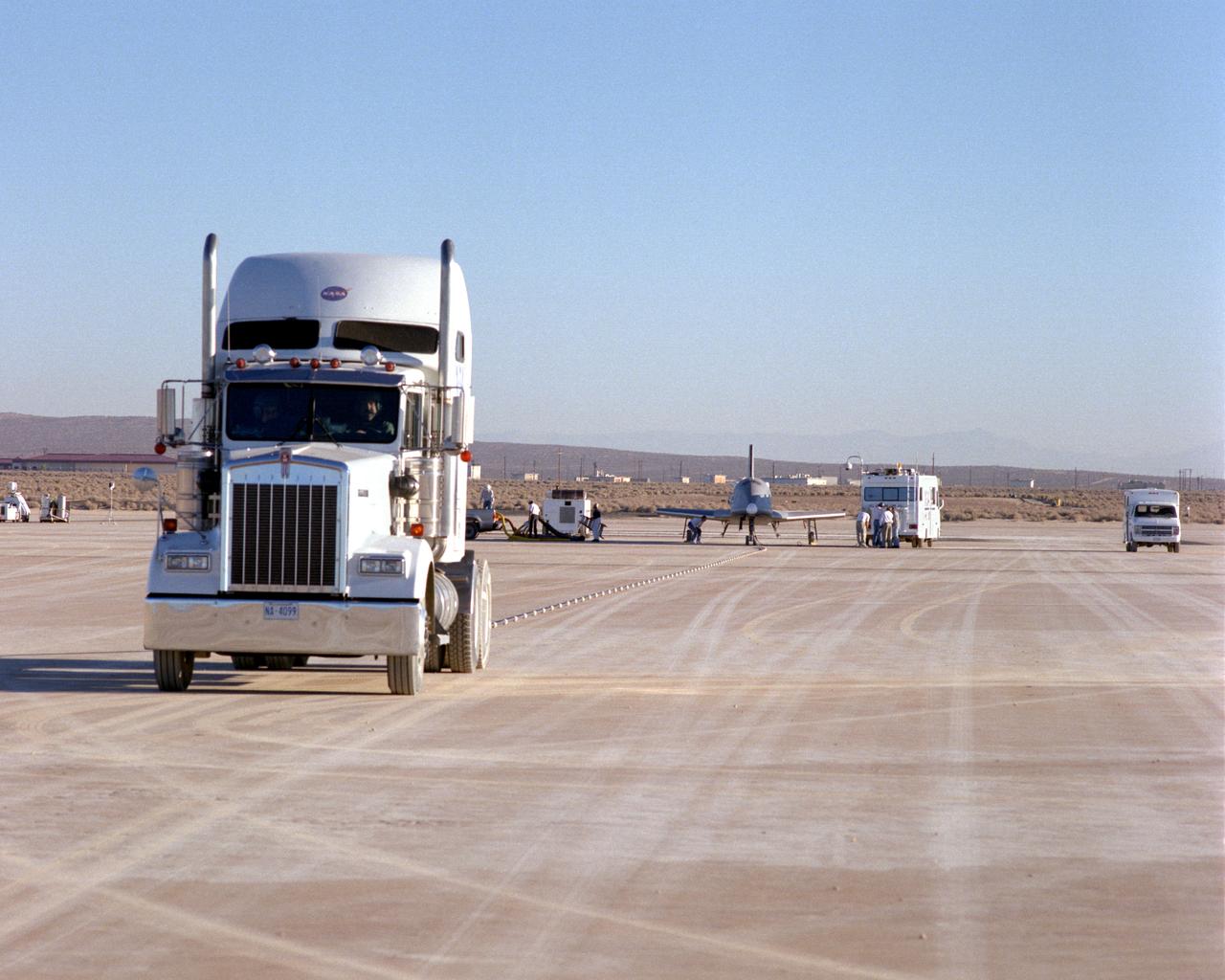

Following initial captive flight tests last year at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California, the X-34 technology demonstrator began a new series of tests last week in which it is being towed behind a semi-truck and released to coast on the Edwards dry lakebed. On July 20, 2000, it was towed and released twice at speeds of five and 10 miles per hour. On July 24, 2000, it was towed and released twice at 10 and 30 miles per hour. Twelve tests are planned during which the X-34 will be towed for distances up to 10,000 feet and released at speeds up to 80 miles per hour. The test series is expected to last at least six weeks.

File name :DSC_0028.JPG File size :2.8MB(2950833Bytes) Date taken :2002/02/19 09:49:01 Image size :3008 x 2000 Resolution :300 x 300 dpi Number of bits :8bit/channel Protection attribute :Off Hide Attribute :Off Camera ID :N/A Camera :NIKON D100 Quality mode :N/A Metering mode :Matrix Exposure mode :Shutter priority Speed light :Yes Focal length :24 mm Shutter speed :1/60second Aperture :F3.5 Exposure compensation :0 EV White Balance :N/A Lens :N/A Flash sync mode :N/A Exposure difference :N/A Flexible program :N/A Sensitivity :N/A Sharpening :N/A Image Type :Color Color Mode :N/A Hue adjustment :N/A Saturation Control :N/A Tone compensation :N/A Latitude(GPS) :N/A Longitude(GPS) :N/A Altitude(GPS) :N/A
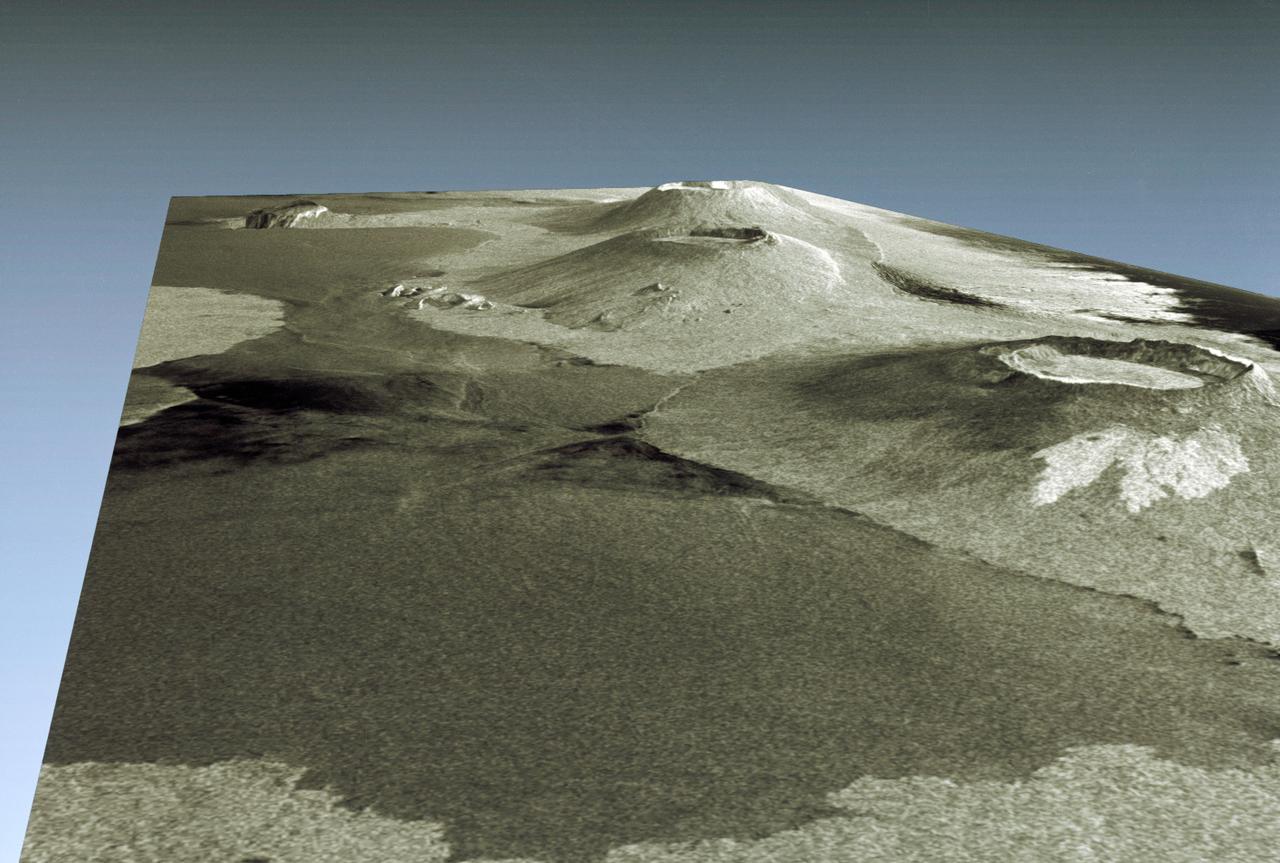

STS059-S-085 (18 April 1994) --- This is a three-dimensional perspective view of part of Isla Isabela in the western Galapagos Islands. It was taken by the L-Band radar in HH polarization from the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) on the 40th orbit of the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This view was constructed by overlaying a SIR-C radar image on a U.S. Geological Survey digital elevation map. The image is centered at about .5 degrees south latitude and 91 degrees west longitude, and covers an area of 75 by 60 kilometers. The radar incidence angle at the center of the image is about 20 degrees. The western Galapagos Islands, which lie about 1200 kilometers west of Ecuador in the eastern Pacific, have six active volcanoes similar to the volcanoes found in Hawaii. Since the time of Charles Darwin's visit to the area in 1835, there have been over 60 recorded eruptions on these volcanoes. This SIR-C/X-SAR image of Alcedo and Sierra Negra volcanoes shows the rougher lava flows as bright features, while ash deposits and smooth pahoehoe lava flows appear dark. The Galapagos Islands are one of the SIR-C/X-SAR supersites and data of this area will be taken several times during the flight to allow scientists to conduct topographic change studies and to search for different lava flow types, ash deposits and fault lines. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43938
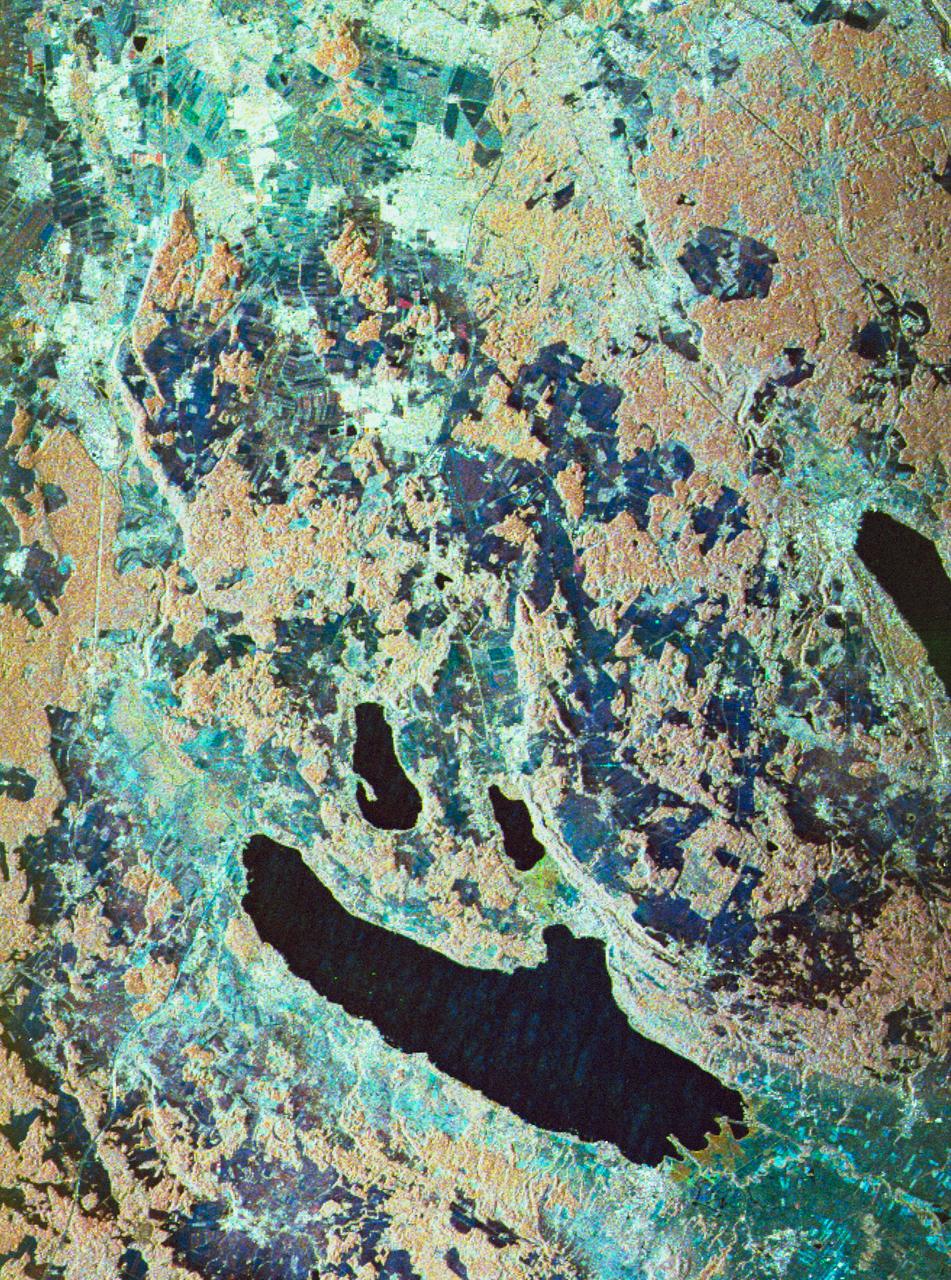
STS059-S-080 (18 April 1994) --- This is a false-color three frequency image of the Oberpfaffenhofen supersite, an area just south-west of Munich in southern Germany. The colors show the different conditions that the three radars (X-Band, C-Band and L-Band) can see on the ground. The image covers a 27 by 36 kilometer area. The center of the site is 48.09 degrees north and 11.29 degrees east. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on April 11, 1994. The dark area on the left is Lake Ammersee. The two smaller lakes are the Woerthsee and the Pilsensee. On the bottom is the tip of the Starnbergersee. The city of Munich is located just beyond the right of the image. The Oberpfaffenhofen supersite is the major test site for SIR-C/X-SAR calibration and scientific investigations concerning agriculture, forestry, hydrology and geology. This color composite image is a three frequency overlay. L-Band total power was assigned red, the C-Band total power is shown in green and the X-Band VV polarization appears blue. The colors on the image stress the differences between the L-Band, C-Band, X-Band images. If the three radar antennas were getting an equal response from objects on the ground, this image would appear in black and white. However, in this image, the blue areas corresponds to area for which the X-Band backscatter is relatively higher than the backscatter at L and C-Bands. This behavior is characteristic of grasslands, clear cuts and shorter vegetation. Similarly, the forested areas have a reddish tint (L-Band). The green areas seen near both the Ammersee and the Pilsensee lakes indicate marshy areas. The agricultural fields in the upper right hand corner appear mostly in blue and green (X-Band and C-Band). The white areas are mostly urban areas, while the smooth surfaces of the lakes appear very dark. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43930
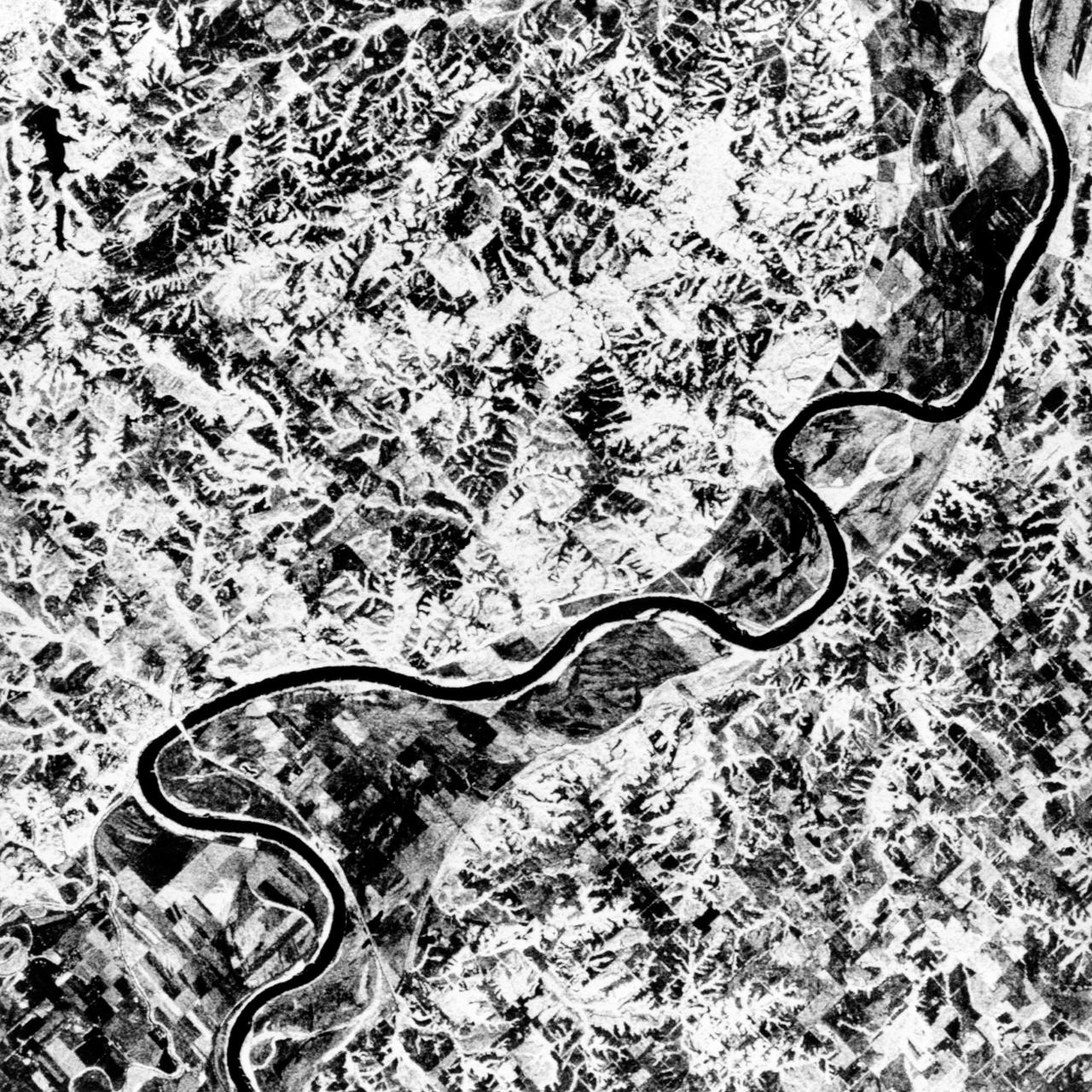
STS068-S-055 (7 October 1994) --- This is a false-color L-Band image of an area near Glasgow, Missouri, centered at about 39.2 degrees north latitude and 92.8 degrees west longitude. The image was acquired using the L-Band radar channel (horizontally transmitted and received and horizontally transmitted and vertically received) polarization's combined. The data were acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on orbit 50 on October 3, 1994. The area shown is approximately 37 by 25 kilometers (23 by 16 miles). The radar data, coupled with pre-flood aerial photography and satellite data and post-flood topographic and field data, are being used to evaluate changes associated with levee breaks in land forms, where deposits formed during the widespread flooding in 1993 along the Missouri and Mississippi Rivers. The distinct radar scattering properties of farmland, sand fields and scoured areas will be used to inventory flood plains along the Missouri River and determine the processes by which these areas return to preflood conditions. The image shows one such levee break near Glasgow, Missouri. In the upper center of the radar image, below the bend of the river, is a region covered by several meters of sand, shown as dark regions. West (left) of the dark areas, a gap in the levee tree canopy shows the area where the levee failed. Radar data such as these can help scientists more accurately assess the potential for future flooding in this region and how that might impact surrounding communities. Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. The radars illuminate Earth with microwaves, allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses the three microwave wavelengths: the L-Band (24 centimeters), C-Band (6 centimeters) and X-Band (3 centimeters). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornier and Alenia Spazio companies for the German space agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian space agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI), with the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt fuer Luft und Raumfahrt e.v. (DLR), the major partner in science, operations and data processing of X-SAR. (P-44734)
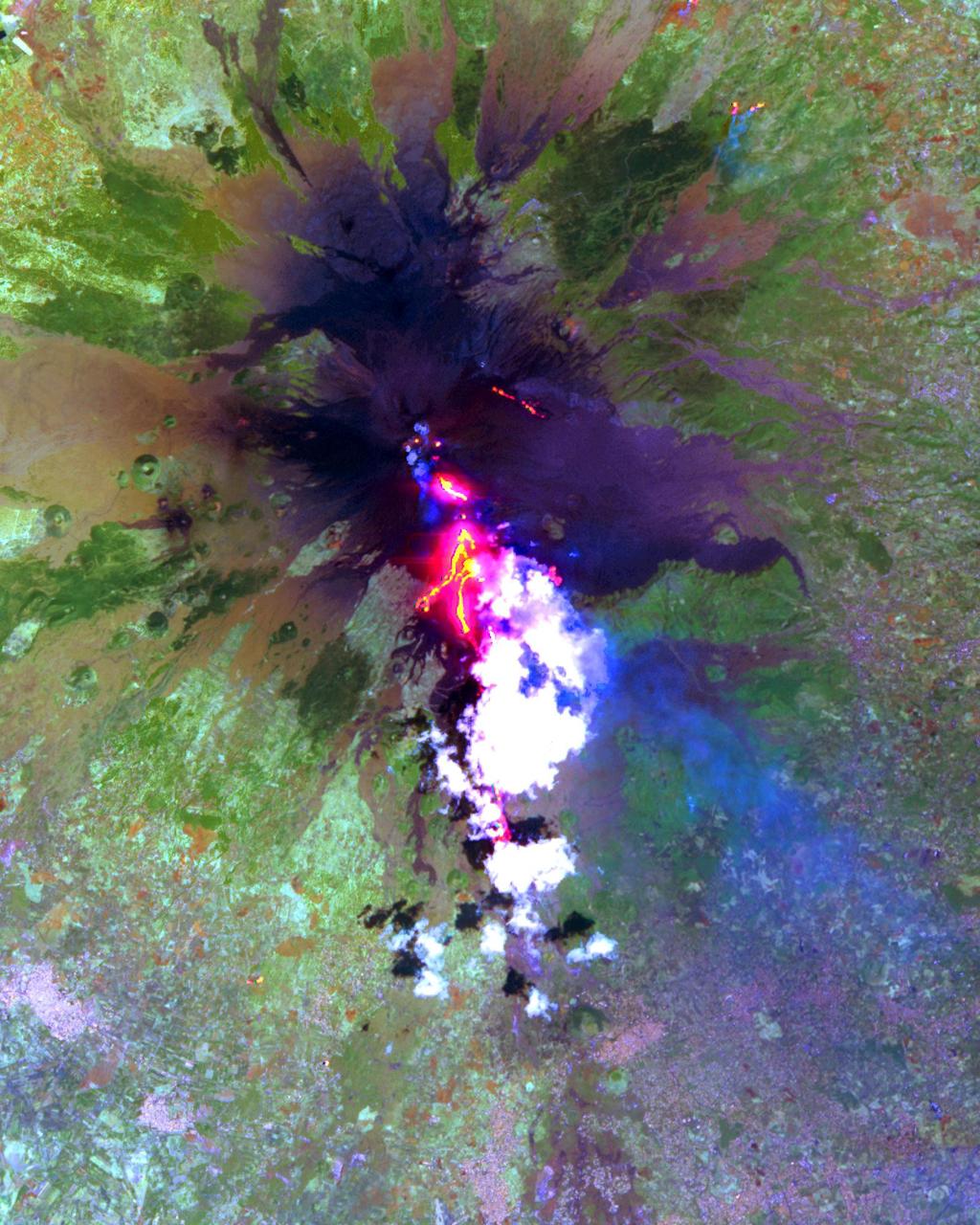

The current eruption of Mt. Etna started on July 17, and has continued to the present. This ASTER image was acquired on Sunday, July 29 and shows advancing lava flows on the southern flank of Mt. Etna above the town of Nicolosi, which is potentially threatened if the eruption increases in magnitude. Also visible are glowing summit craters above the main lava flows, and a small fissure eruption. The bright puffy clouds were formed from water vapor released during the eruption. The image covers an area of 24 x 30 km. The image is centered at 37.7 degrees north latitude, 15 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02677
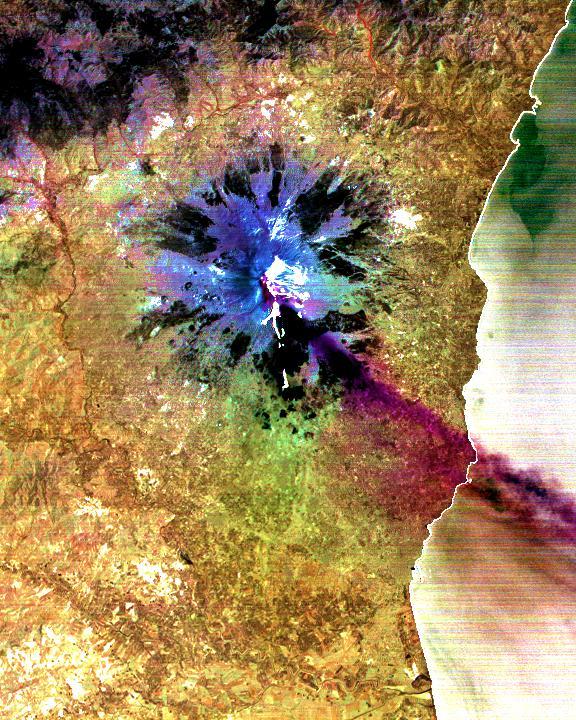
The current eruption of Mt. Etna started on July 17, and has continued to the present. This ASTER image was acquired on Sunday, July 29 and shows the sulfur dioxide plume (in purple) originating form the summit, drifting over the city of Catania, and continuing over the Ionian Sea. ASTER's unique combination of multiple thermal infrared channels and high spatial resolution allows the determination of the thickness and position of the SO2 plume. The image covers an area of 24 x 30 km. The image is centered at 37.7 degrees north latitude, 15 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02678
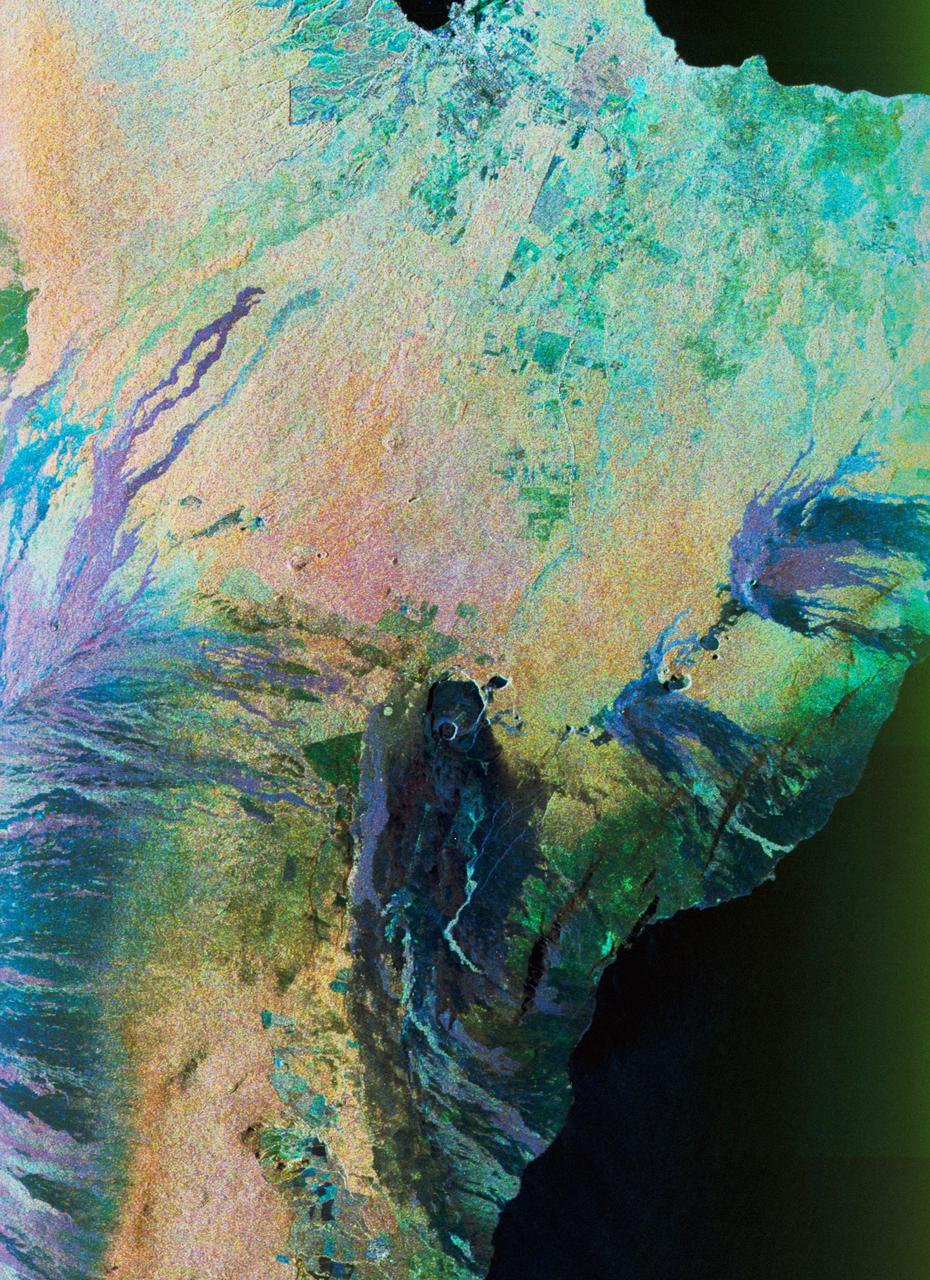

STS059-S-074 (15 April 1994) --- This color composite C-Band and L-Band image of the Kilauea volcano on the big island of Hawaii was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) flying on the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The city of Hilo can be seen at the top. The image shows the different types of lava flows around the crater Pu'u O'o. Ash deposits which erupted in 1790 from the summit of Kilauea volcano show up as dark in this image, and fine details associated with lava flows which erupted in 1919 and 1974 can be seen to the south of the summit in an area called the Ka'u Desert. In addition, the other historic lava flows created in 1881 and 1984 from Mauna Loa volcano (out of view to the left of this image) can easily be seen despite the fact that the surrounding area is covered by forest. Such information will be used to map the extent of such flows, which can pose a hazard to the subdivisions of Hilo. Highway 11 is the linear feature running from Hilo to the Kilauea volcano. The Kilauea volcano has been almost continuously active for more than the last 11 years. Field teams that were on the ground specifically to support these radar observations report that there was vigorous surface activity about 400 meters (one-quarter mile) inland from the coast. A moving lava flow about 200 meters (660 feet) in length was observed at the time of the Shuttle over flight, raising the possibility that subsequent images taken during this mission will show changes in the landscape. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43918
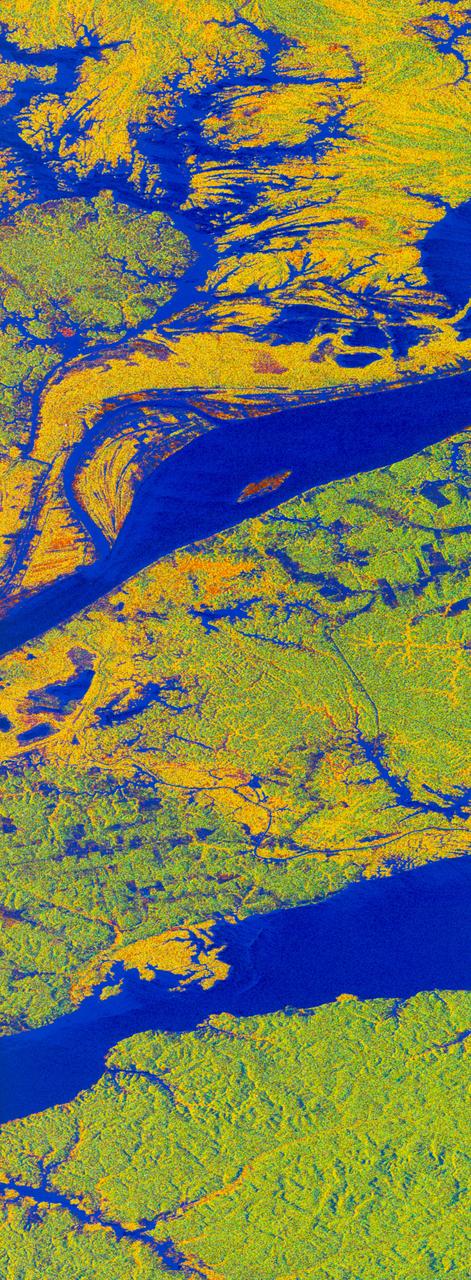

STS059-S-068 (13 April 1994) --- This false-color L-Band image of the Manaus region of Brazil was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on orbit 46 of the mission. The area shown is approximately 8 kilometers by 40 kilometers (5 by 25 miles). At the top of the image are the Solimoes and Rio Negro Rivers just before they combine at Manaus to form the Amazon River. The image is centered at about 3 degrees south latitude, and 61 degrees west longitude. The false colors are created by displaying three L-Band polarization channels; red areas correspond to high backscatter at HH polarization, while green areas exhibit high backscatter at HV polarization. Blue areas show low returns at VV polarization; hence the bright blue colors of the smooth river surfaces. Using this color scheme, green areas in the image are heavily forested, while blue areas are either cleared forest or open water. The yellow and red areas are flooded forest. Between Rio Solimoes and Rio Negro a road can be seen running from some cleared areas (visible as blue rectangles north of Rio Solimoes) north towards a tributary of Rio Negro. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43895

STS059-S-079 (18 April 1994) --- This is a false-color, three frequency image of Prince Albert, Canada, centered at 53.91 north latitude and 104.69 west longitude. It was produced using data from the X-Band, C-Band and L-Band radars that comprise the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR). SIR-C/X-SAR acquired this image on the 20th orbit of the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The area is located 40 kilometers north and 30 kilometers east of the town of Prince Albert in the Saskatchewan province of Canada. The image covers the area east of the Candle Lake, between gravel surface Highways 120 and 106 and west of 106. The area in the middle of the image covers the entire Nipawin (Narrow Hills) provincial park. The look angle of the radar is 30 degrees and the size of the image is approximately 20 by 50 kilometers. The red, green, and blue colors represent L-Band total power, C-Band total power, and XVV respectively. The changes in the intensity of each color are related to various surface conditions such as frozen or thawed forest, fire, deforestation and areas of regrowth. Most of the dark blue areas in the image are the ice covered lakes. The dark area on the top right corner of the image is the White Gull Lake north of the intersection of Highway 120 and 913. The right middle part of the image shows Lake Ispuchaw and Lower Fishing Lake. The deforested areas are shown by light blue in the image. Since most of the logging practice at the Prince Albert area is around the major highways, the deforested areas can be easily detected as small geometrically shaped dark regions along the roads. At the time these data were taken, a major part of the forest was either frozen or undergoing the spring thaw. In such conditions, due to low volume of water in the vegetation, a deeper layer of the canopy is imaged by the radar, revealing valuable information about the type of trees, the amount of vegetation biomass and the condition of the surface. As the frequency increases, the penetration depth in the canopy decreases. Over forest canopies, the X-Band radar contains information about the top of the canopy. Whereas, C-Band and L-Band radar returns show contributions from the crown and trunk areas respectively. The bright areas in the image are dense mixed aspen and old jackpine forests where the return from all three bands is high. The reddish area corresponds to more sparse old jack pine (12 to 17 meters in height and 60 to 75 years old) where the L-Band signal penetrates deeper in the canopy and dominates C-Band and X-Band returns. Comparison of the image with the forest cover map of the area indicates that the three band radar can be used to classify various stands. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43929
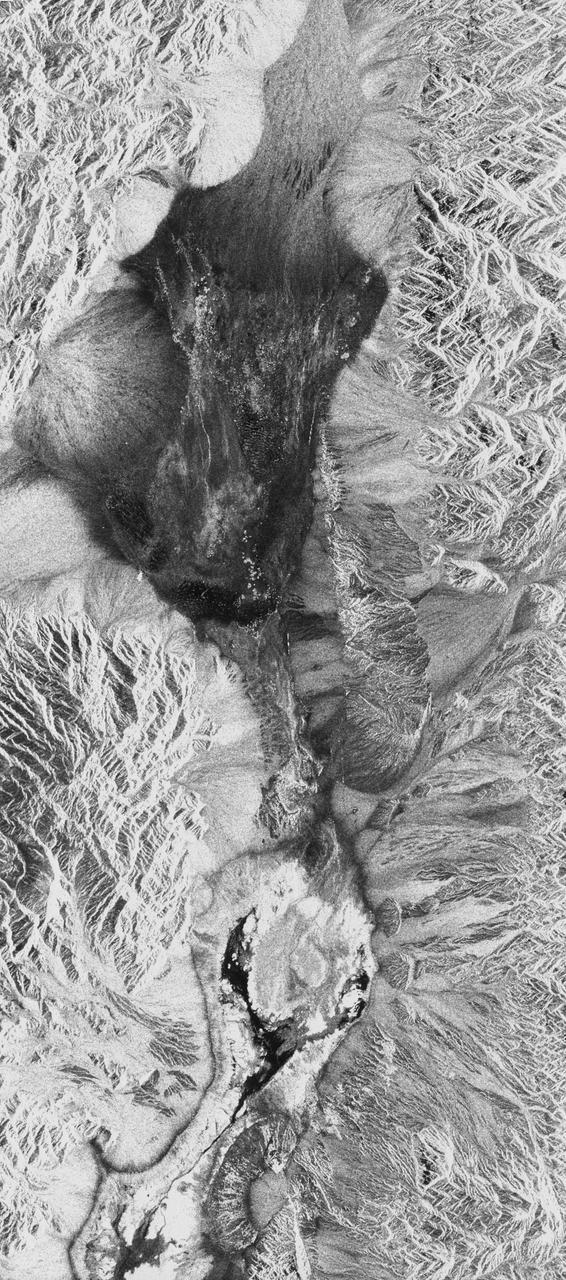
STS059-S-026 (11 April 1994) --- This is an image of Death Valley, California, centered at 36.629 degrees north latitude, 117.069 degrees west longitude. The image shows Furnace Creek alluvial fan and Furnace Creek Ranch at the far right, and the sand dunes near Stove Pipe Wells at the center. The dark fork-shaped feature between Furnace Creek fan and the dunes is a smooth flood-plain which encloses Cottonball Basin. The SIR-C/X-SAR supersite is an area of extensive field investigations and has been visited by both Space Radar Lab astronaut crews. Elevations in the Valley range from 70 meters below sea level, the lowest in the United States, to more than 3300 meters above sea level. Scientists are using SIR-C/X-SAR data from Death Valley to help answer a number of different questions about the Earth's geology. One question concerns how alluvial fans are formed and change through time under the influence of climatic changes and earthquakes. Alluvial fans are gravel deposits that wash down from the mountains over time. They are visible in the image as circular, fan-shaped bright areas extending into the darker valley floor from the mountains. Information about the alluvial fans help scientists study Earth's ancient climate. Scientists know the fans are bulit up through climatic and tectonic processes and they will use the SIR-C/X-SAR data to understand the nature and rates of weathering processes on the fans, soil formation, and the transport of sand and dust by the wind. SIR-C/X-SAR's sensitivity to centimeter-scale (or inch-scale) roughness provides detailed maps of surface texture. Such information can be used to study the occurrence and movement of dust storms and sand dunes. the goal of these studies is to gain a better understanding of the record of past climatic changes and the effects of those changes on a sensitive environment. This may lead to a better ability to predict future response of the land to different potential global cimate-change scenarios. Death Valley is also one of the primary calibration sites for SIR-C/X-SAR. The bright dots near the center of the image are corner reflectors that have been set-up to calibrate the radar as the Shuttle passes overhead. Thirty triangular-shaped reflectors (they look like aluminum pyramids) have been deployed by the calibration team from JPL over a 40 kilometer by 40 kilometer area in and around Death Valley. The calibration team will also deploy transponders (electronic reflectors) and recievers to measure the radar signals from SIR-C/X-SAR on the ground. Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). The radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was develpoed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43883

Caption: An X-class solar flare erupted on the left side of the sun on the evening of Feb. 24, 2014. This composite image, captured at 7:59 p.m. EST, shows the sun in X-ray light with wavelengths of both 131 and 171 angstroms. Credit: NASA/SDO More info: The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 7:49 p.m. EST on Feb. 24, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which keeps a constant watch on the sun, captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation, appearing as giant flashes of light in the SDO images. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This flare is classified as an X4.9-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
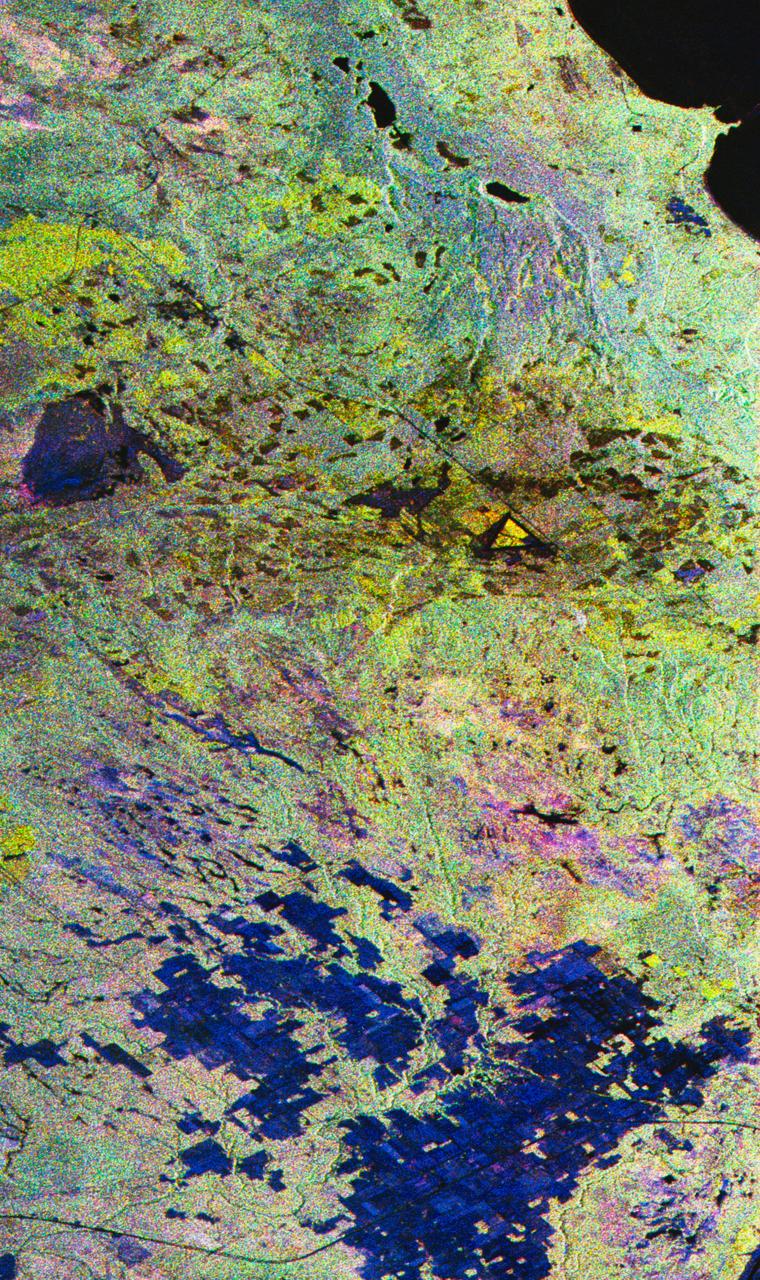
STS059-S-027 (10 April 1994) --- This image is a false-color composite of Raco, Michigan, centered at 46.39 degrees north latitude, 84.88 degrees east longitude. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its 6th orbit and during the first full-capacity test of the instrument. This image was produced using both L-Band and C-Band data. The area shown is approximately 20 kilometers by 50 kilometers. Raco is located at the eastern end of Michigan's upper peninsula, west of Sault Ste. Marie and south of Whitefish Bay on Lake Superior. The site is located at the boundary between the boreal forests and the northern temperate forests, a transitional zone that is expected to be ecologically sensitive to anticipated global changes resulting from climatic warming. On any given day, there is a 60 percent chance that this area will be obscured to some extent by cloud cover which makes it difficult to image using optical sensors. In this color representation (Red=LHH, Green=LHV, Blue=CHH), darker areas in the image are smooth surfaces such as frozen lakes and other non-forested areas. The colors are related to the types of trees and the brightness is related to the amount of plant material covering the surface, called forest biomass. Accurate information about land-cover is important to area resource managers and for use in regional- to global-scale scientific models used to understand global change. SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43882

Many of NICER’s 56 X-ray “concentrators” seen from within the instrument optical bench. Light reflected from the gold surfaces of the 24 concentric foils in each concentrator is focused onto detectors slightly more than 1 meter (3.5 feet) away. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NICER Optics Lead Takashi Okajima installs one of NICER’s 56 X-ray “concentrators,” each consisting of 24 concentric foils. To minimize the effects of Earth’s gravity on their alignment, the concentrator assemblies were installed from the outside edges toward the center of the plate that houses them. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

STS059-S-072 (13 April 1994) --- This image is a false-color composite of Oetztal, Austria located in the Central Alps, centered at 46.8 degrees north latitude, and 10.70 degrees east longitude, at the border between Switzerland (top), Italy (left) and Austria (right and bottom). The area shown is 50 kilometers (30 miles) south of Innsbruck, Austria. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its 14th orbit. Oetztal is a SIR-C/X-SAR hydrology supersite. Approximately one quarter of this image is covered by glaciers, the largest of which, Gepatschferner, is visible as a triangular yellow patch in the center of the scene. The summits of the main peaks reach elevations between 3,500 and 3,768 meters (11,500 and 12,362 feet) above sea level. The tongues of the glaciers are descending from elevated plateaus down into narrow valleys which were formed during the last ice age. This color image was produced in C-Band using multi-polarization information (Red=CHV, Green=CVV, Blue=CVV/CHV). The blue areas are lakes (Gepatsch Dam at center right; Lake Muta at top right) and glacier ice. The yellow areas are slopes facing the radar and areas of dry snow. Purple corresponds to slopes facing away from the radar. Yellow in the valley bottom corresponds to tree covered areas. There is 30 to 50 centimeters (12 to 20 inches) of dry, fresh snow on the glaciers, and about 10 centimeters (4 inches) in the valley at the city of Vent, Austria (center). At these data were taken, the weather was cold, with snow and thick fog. The entire area would appear white to an optical sensor because it is all covered under a winter snowpack. Researchers are interested in Oetztal because knowing how glaciers shrink and grow over time is an important indication of climatic change. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43890
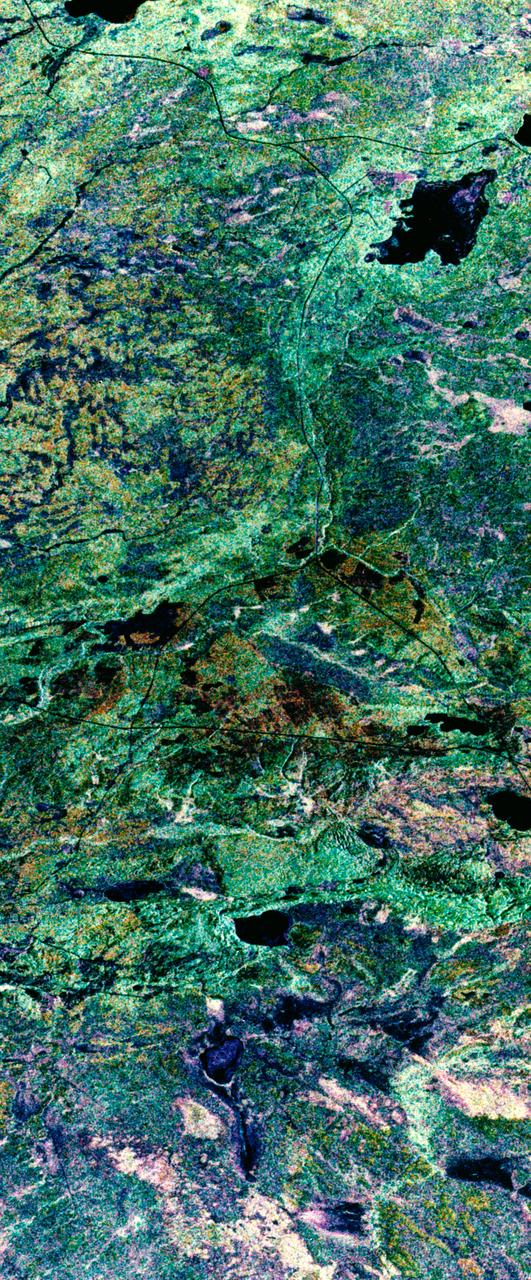

STS059-S-039 (11 April 1994) --- This is a false-color composite of Prince Albert, Canada, centered at 53.91 north latitude and 104.69 west longitude. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its 20th orbit. The area is located 40 kilometers (25 miles) north and 30 kilometers (20 miles) east of the town of Prince Albert in the Saskatchewan province of Canada. The image covers the area east of the Candle Lake, between gravel surface Highways 120 and 106 and west of 106. The area in the middle of the image covers the entire Nipawin (Narrow Hills) provincial park. The look angle of the radar is 30 degrees and the size of the image is approximately 20 kilometers by 50 kilometers (12 by 30 miles). The image was produced by using only the L-Band. The three polarization channels HH, HV and VV are illustrated by red, green and blue respectively. The changes in the intensity of each color are related to various surface conditions such as variations in forest stands, frozen or thawed condition of the surface, disturbances (fire and deforestation), and areas of re-growth. Most of the dark areas in the image are the ice-covered lakes in the region. The dark area on the top right corner of the image is the White Gull Lake north of the intersection of Highway 120 and 913. The right middle part of the image shows Lake Ispuchaw and Lower Fishing Lake. The deforested areas are also shown by dark areas in the image. Since most of the logging practice at the Prince Albert area is around the major highways, the deforested areas can be easily detected as small geometrically shaped dark regions along the roads. At the time of the SIR-C/X-SAR overpass, a major part of the forest is either frozen or undergoing the spring thaw. The L-Band HH shows a high return in the jack pine forest. The reddish areas in the image are old jack pine forest, 12-17 meters (40-55 feet) in height and 60-75 years old. The orange-greenish areas are young jack pine trees, 3-5 meters (10-16 feet) in height and 11-16 years old. The green areas are due to the relative high intensity of the HV channel which is strongly correlated with the amount of biomass. L-Band HV channel shows the biomass variations over the entire region. Most of the green areas, when compared to the forest cover maps are identified as black spruce trees. The dark blue and dark purple colors show recently harvested or re-growth areas respectively. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43886
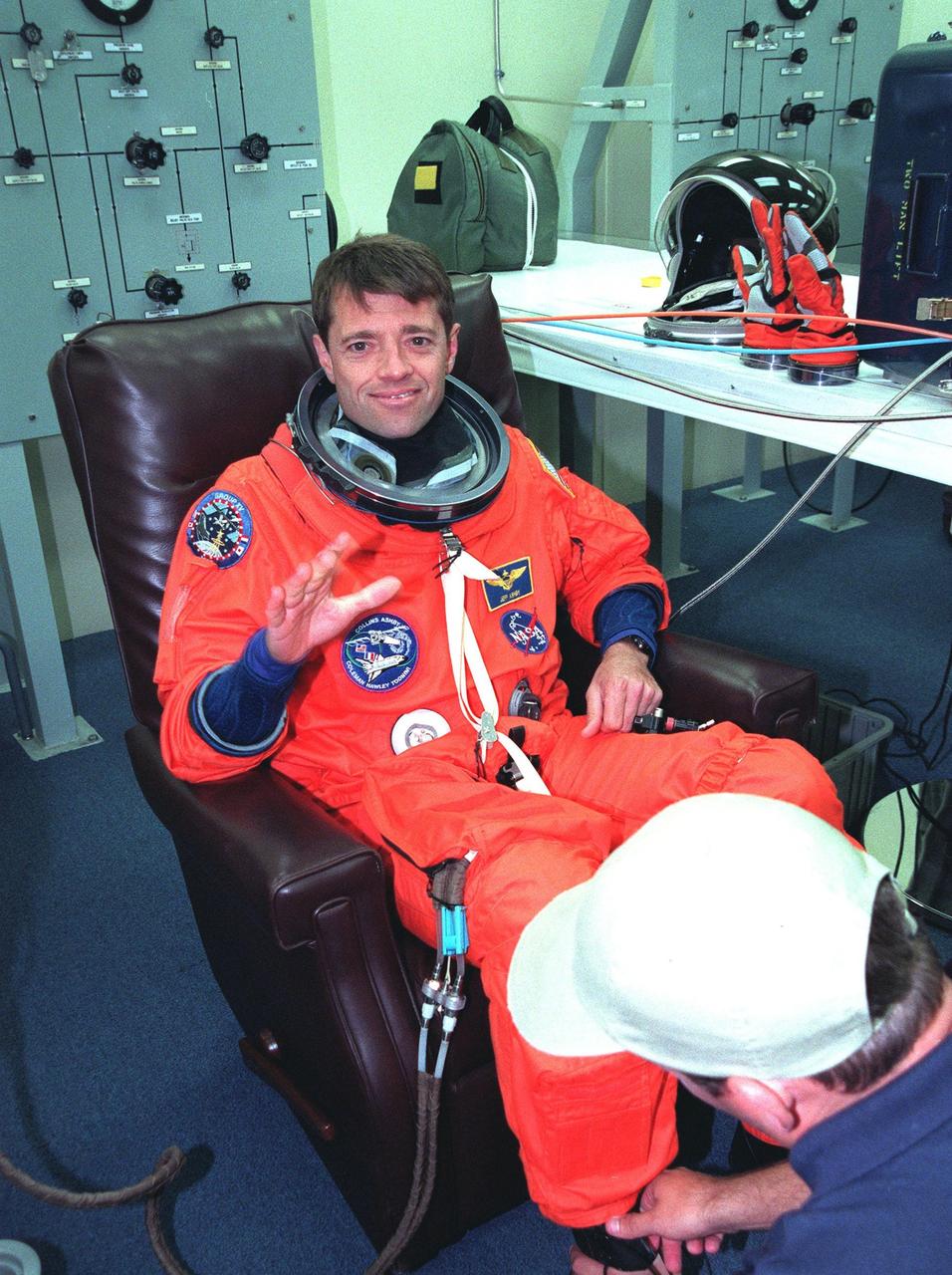

In the Operations and Checkout Building during final launch preparations for the second time, STS-93 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby waves after donning his launch and entry suit while a suit tech adjusts his boot. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
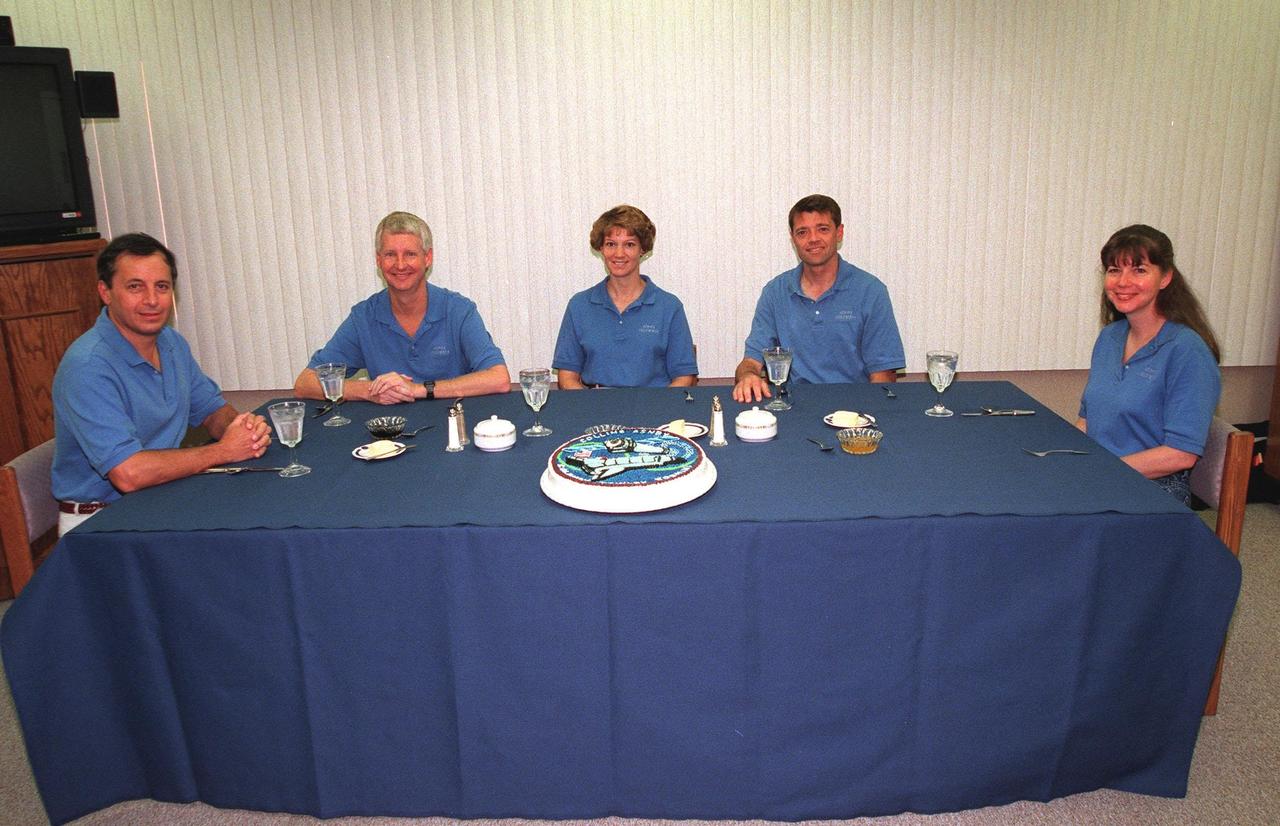

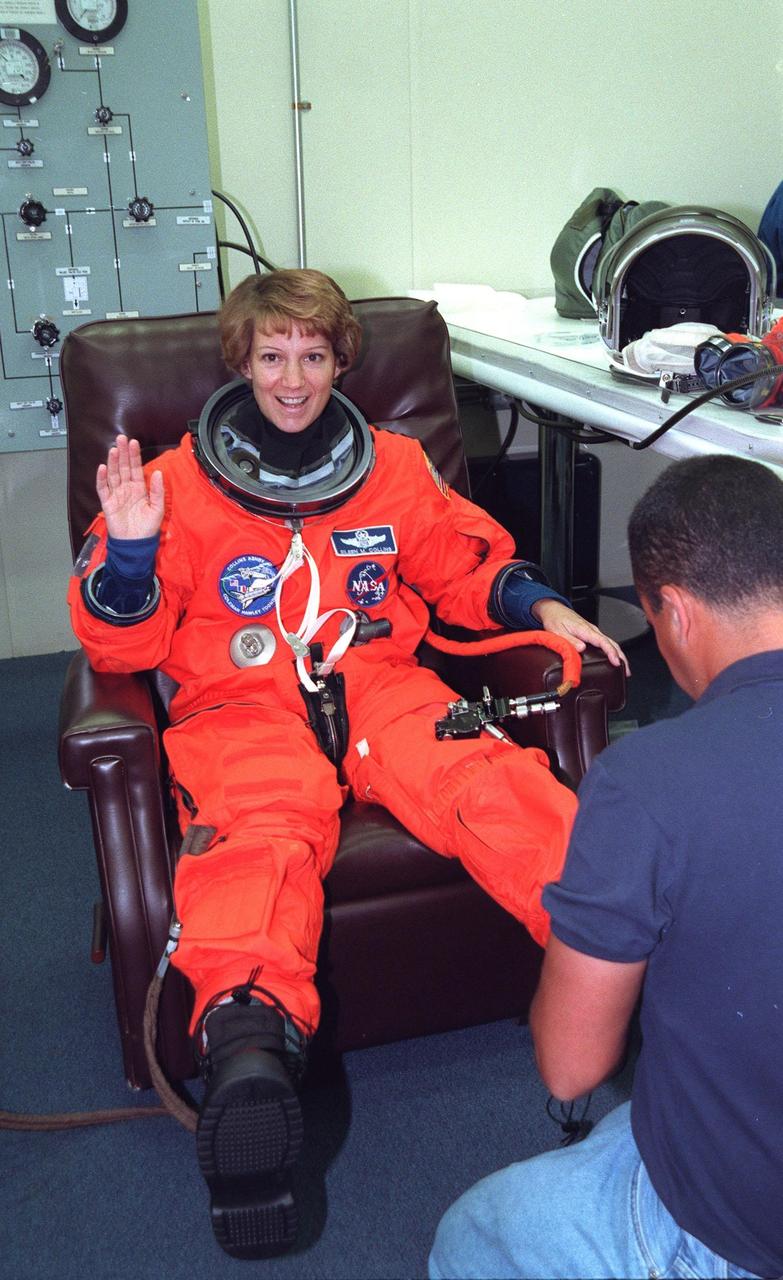
The STS-93 crew gathers a second time for a pre-launch breakfast in the Operations and Checkout Building before suiting up for launch. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. Seated from left are Mission Specialists Michel Tognini, of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), and Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.). STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a Shuttle mission. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), waves after donning his launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Tognini. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission. STS-93 is scheduled to lift off at 12:36 a.m. EDT July 20. The target landing date is July 24 at 11:30 p.m. EDT
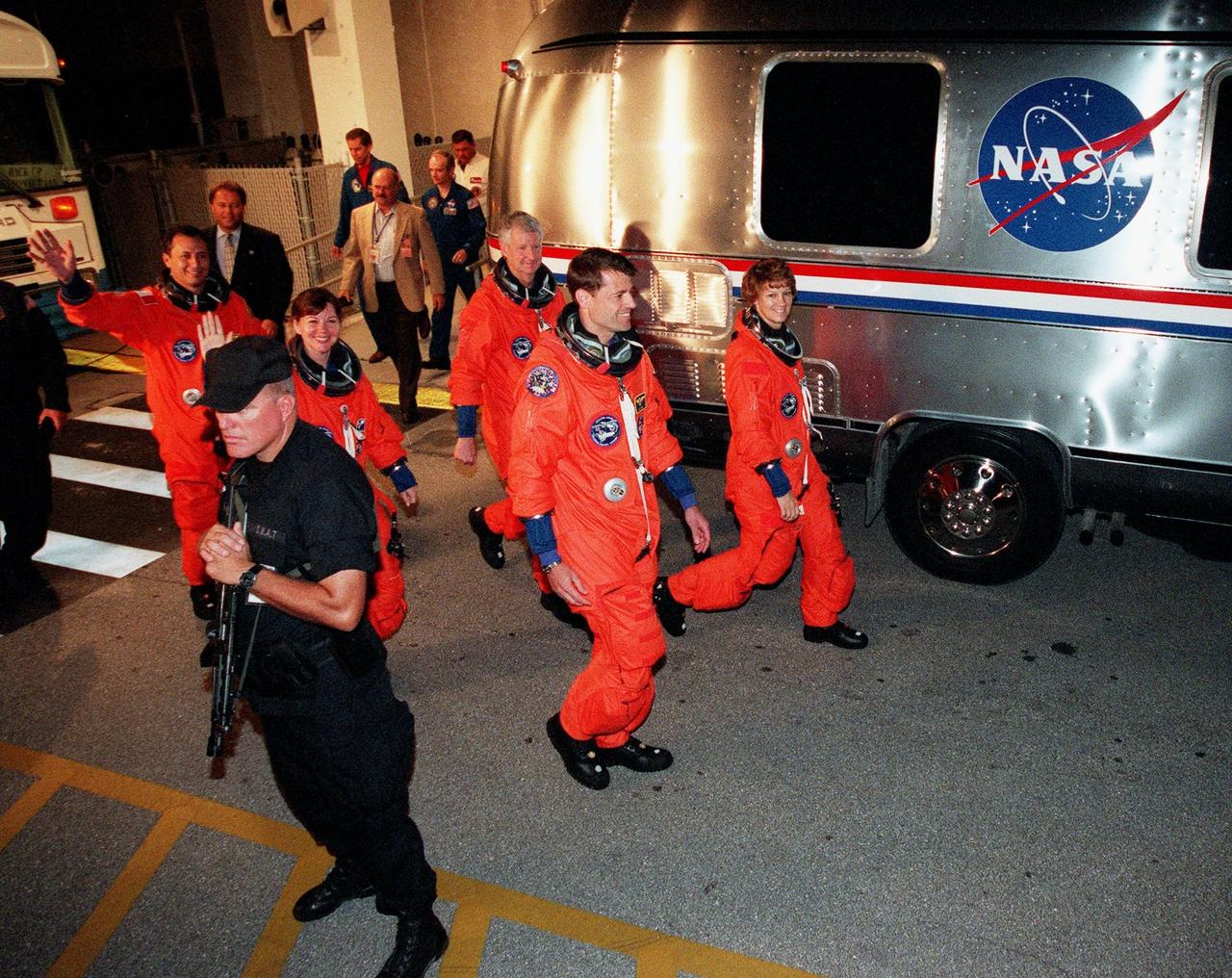

Flanked by security, the STS-93 crew wave to onlookers as they head for the "Astrovan" a second time to take them to Launch Pad 39-B and liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia. After the July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. In their orange launch and entry suits, they are (starting at rear, left to right) Mission Specialists Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.), and Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.); Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby; and Commander Eileen M. Collins. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a Shuttle mission
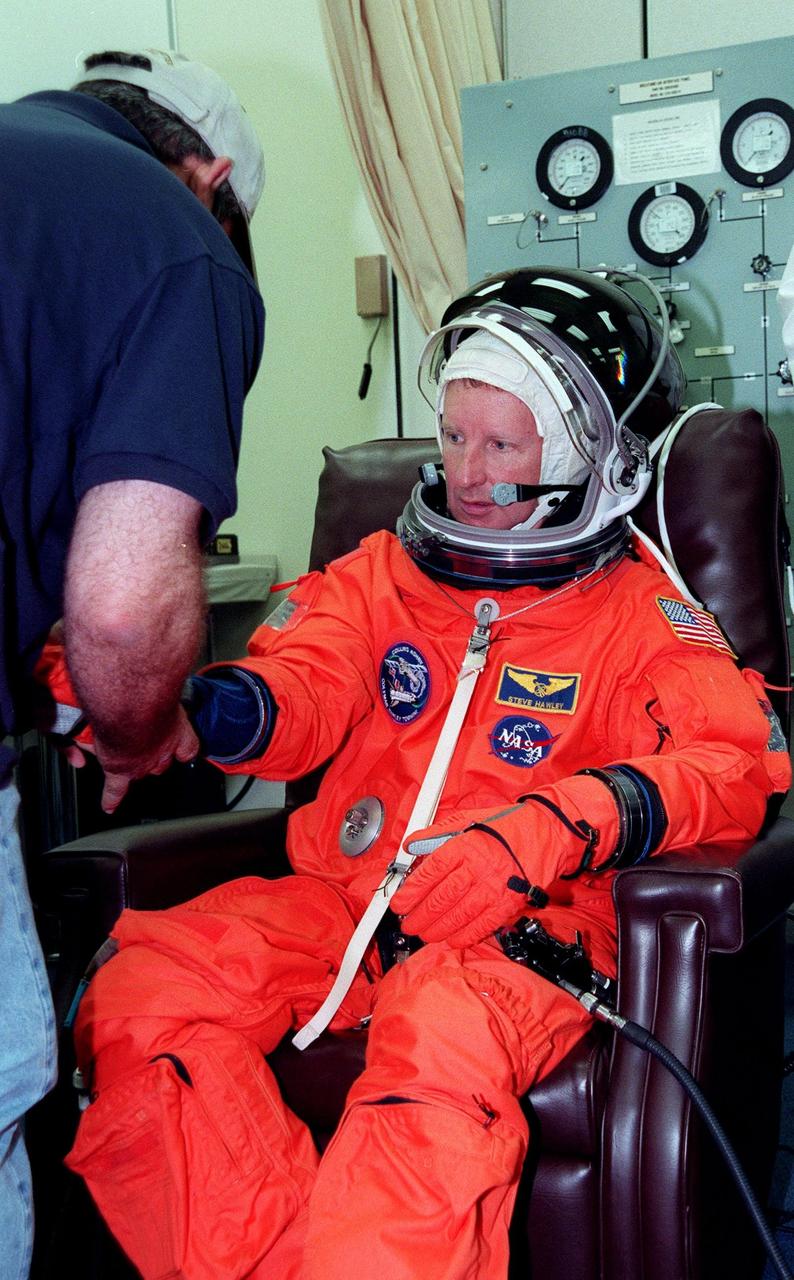

During final launch preparations in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.)gets help donning his launch and entry suit from a suit tech. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Hawley, Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
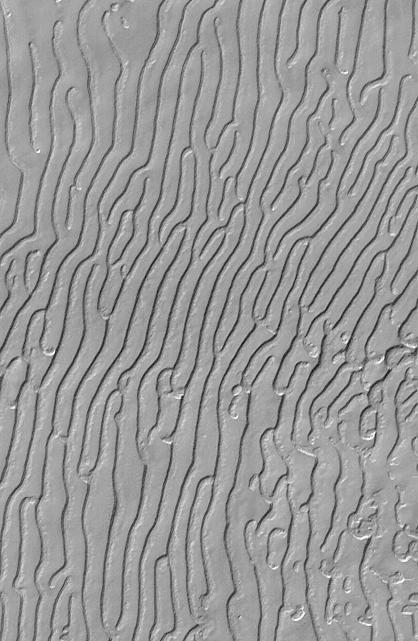

This picture is illuminated by sunlight from the upper left. Some portions of the martian south polar residual cap have long, somewhat curved troughs instead of circular pits. These appear to form in a layer of material that may be different than that in which "swiss cheese" circles and pits form, and none of these features has any analog in the north polar cap or elsewhere on Mars. This picture shows the "fingerprint" terrain as a series of long, narrow depressions considered to have formed by collapse and widening by sublimation of ice. Unlike the north polar cap, the south polar region stays cold enough in summer to retain frozen carbon dioxide. Viking Orbiter observations during the late 1970s showed that very little water vapor comes off the south polar cap during summer, indicating that any frozen water that might be there remains solid throughout the year. This Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) image was obtained in early southern spring on August 4, 1999. It shows an area 3 x 5 kilometers (1.9 x 3.1 miles) at a resolution of about 7.3 meters (24 ft) per pixel. Located near 86.0°S, 53.9°W. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02373
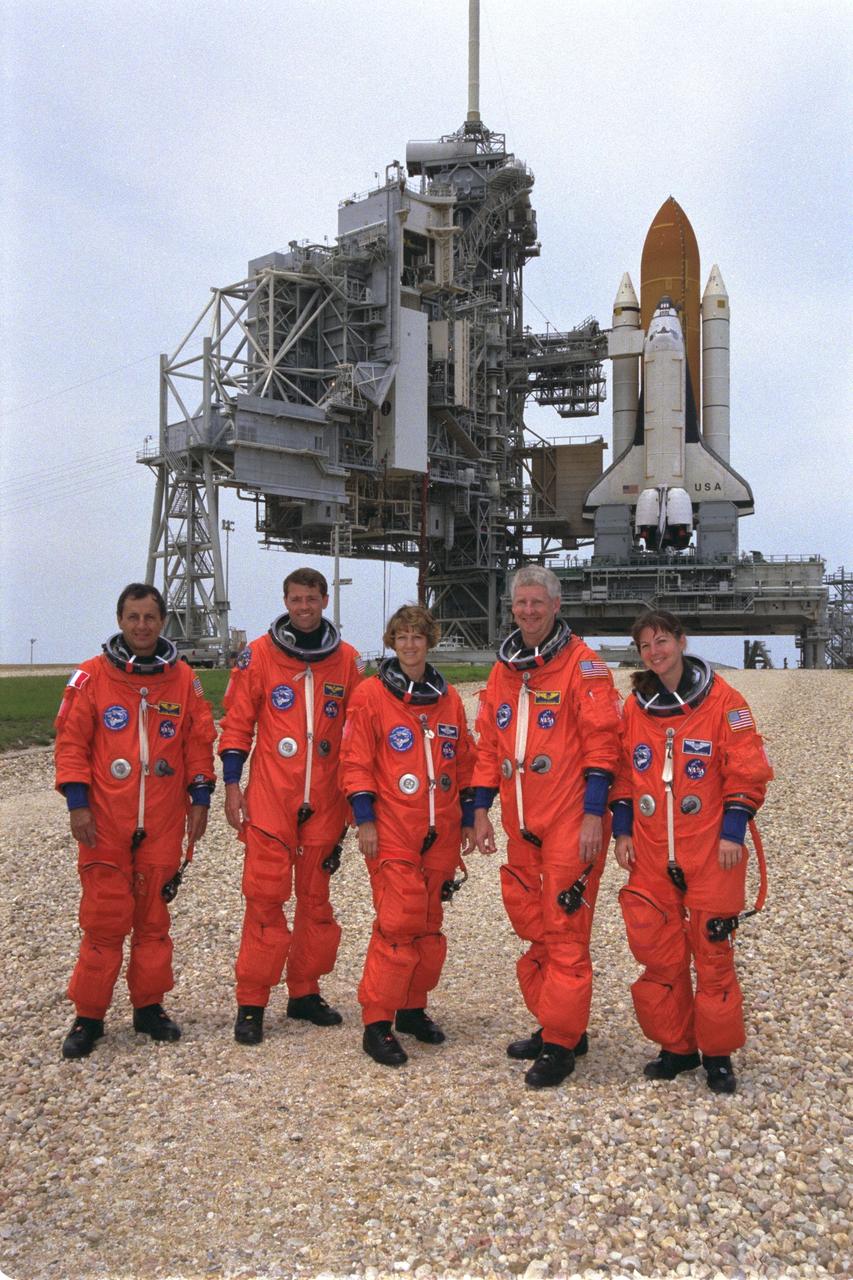

STS093-S-012 (24 June 1999) --- With the Space Shuttle Columbia sitting on Launch Pad 39B in the background, the STS-93 crew members pose for a photo during a break in training at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). From the left are astronauts Michel Tognini, Jeffrey S. Ashby, Eileen M. Collins, Steven A. Hawley and Catherine G. Coleman. Tognini represents the European Space Agency (ESA). Collins will be the first woman to serve as a shuttle commander. The crew members have been taking part in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test, which familiarizes the astronauts with the mission, provides training in emergency egress from the orbiter and the launch pad, and includes the dress rehearsal culminating with a simulated main engine cut-off (MECO). The primary mission of this crew is the release of the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which is expected to allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of the exotic environments in space to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe.
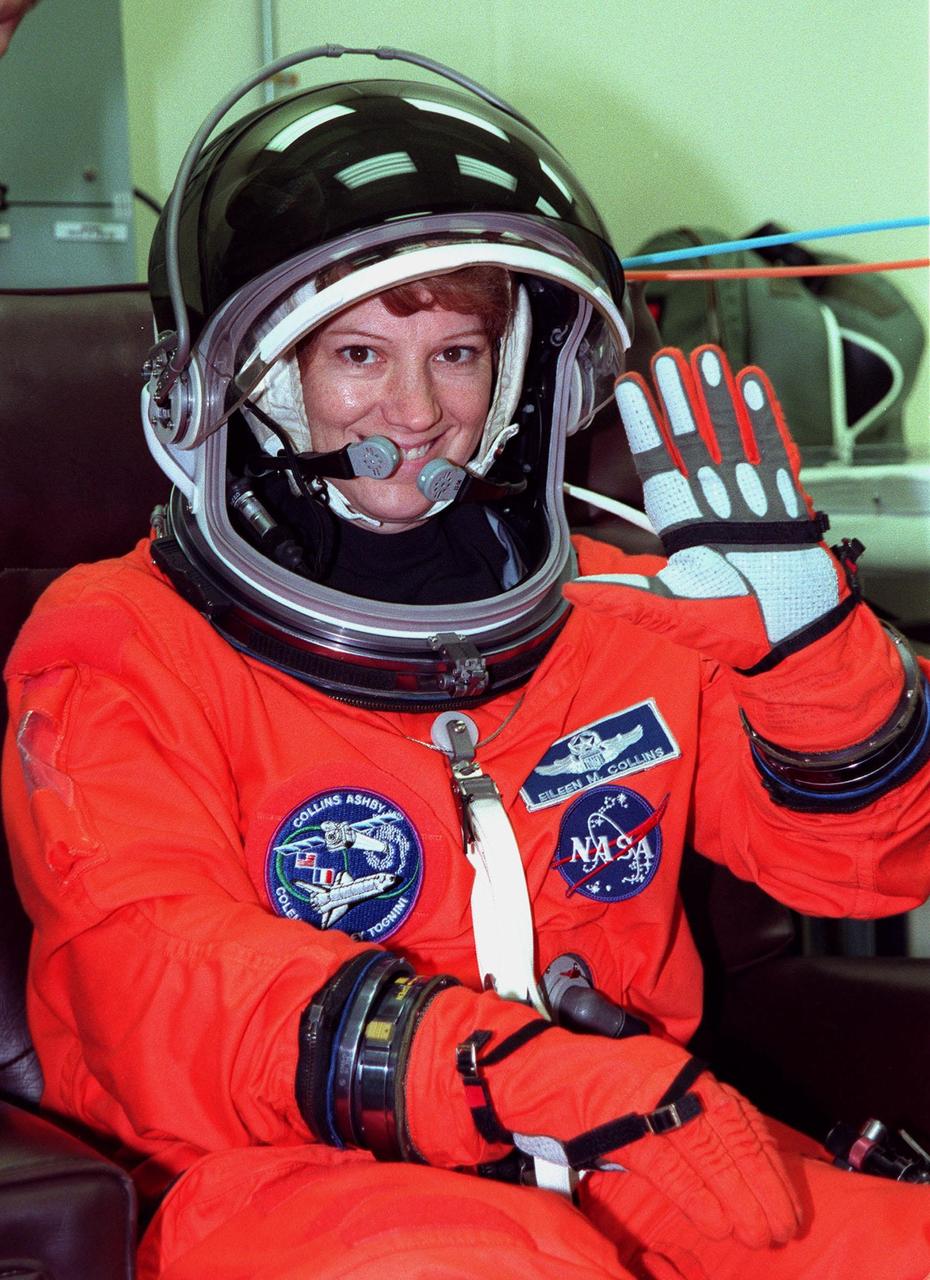

During final launch preparations in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Commander Eileen M. Collins waves after donning her launch and entry suit. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
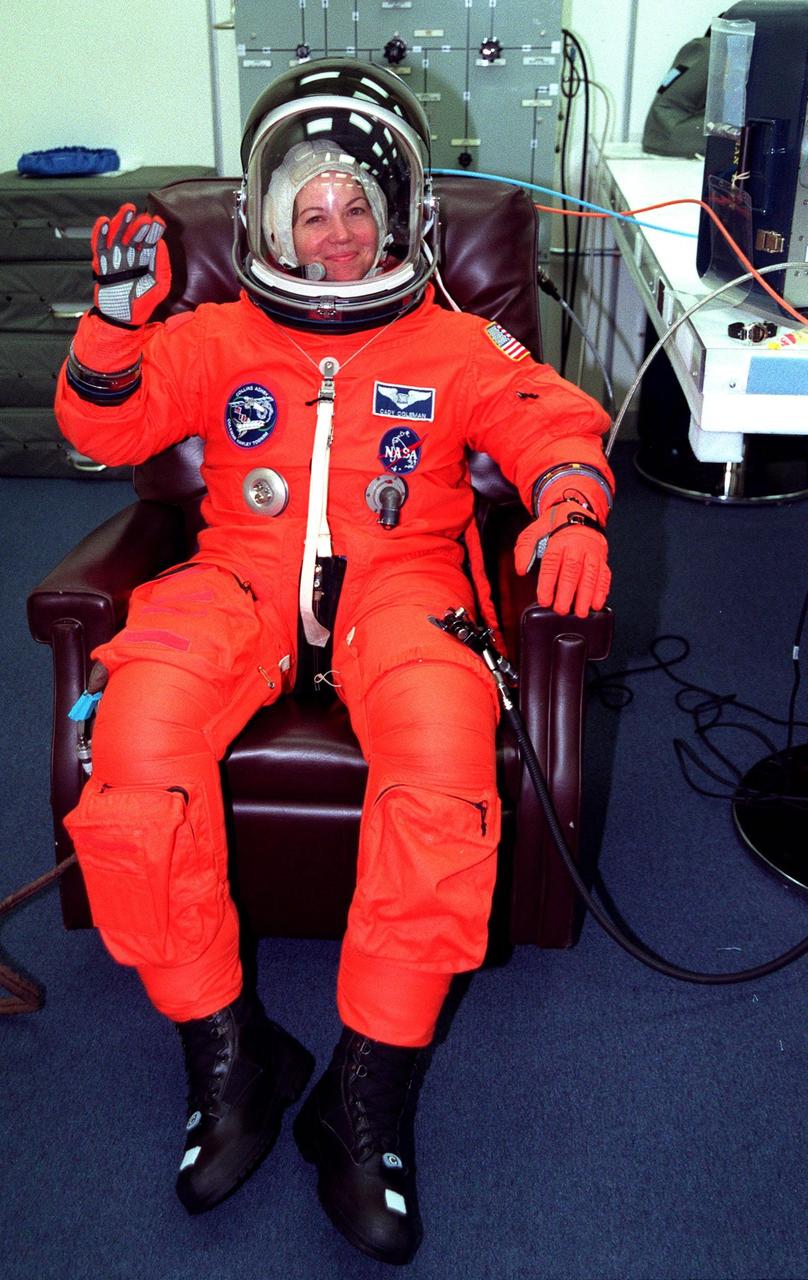

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) waves after donning her launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Coleman and Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission. STS-93 is scheduled to lift off at 12:36 a.m. EDT July 20. The target landing date is July 24 at 11:30 p.m. EDT

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.) smiles after donning his launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Hawley, Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission. STS-93 is scheduled to lift off at 12:36 a.m. EDT July 20. The target landing date is July 24 at 11:30 p.m. EDT
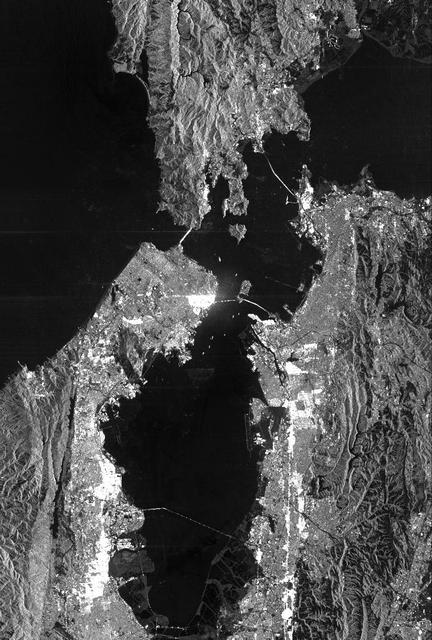

This is a radar image of San Francisco, California, taken on October 3,1994. The image is about 40 kilometers by 55 kilometers (25 miles by 34 miles) with north toward the upper right. Downtown San Francisco is visible in the center of the image with the city of Oakland east (to the right) across San Francisco Bay. Also visible in the image is the Golden Gate Bridge (left center) and the Bay Bridge connecting San Francisco and Oakland. North of the Bay Bridge is Treasure Island. Alcatraz Island appears as a small dot northwest of Treasure Island. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on orbit 56. The image is centered at 37 degrees north latitude, 122degrees west longitude. This single-frequency SIR-C image was obtained by the L-band (24 cm) radar channel, horizontally transmitted and received. Portions of the Pacific Ocean visible in this image appear very dark as do other smooth surfaces such as airport runways. Suburban areas, with the low-density housing and tree-lined streets that are typical of San Francisco, appear as lighter gray. Areas with high-rise buildings, such as those seen in the downtown areas, appear in very bright white, showing a higher density of housing and streets which run parallel to the radar flight track. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01751

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Commander Eileen M. Collins waves while a suit tech adjusts her boot, part of the launch and entry suit, during final launch preparations. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission. STS-93 is scheduled to lift off at 12:36 a.m. EDT July 20. The target landing date is July 24 at 11:30 p.m. EDT
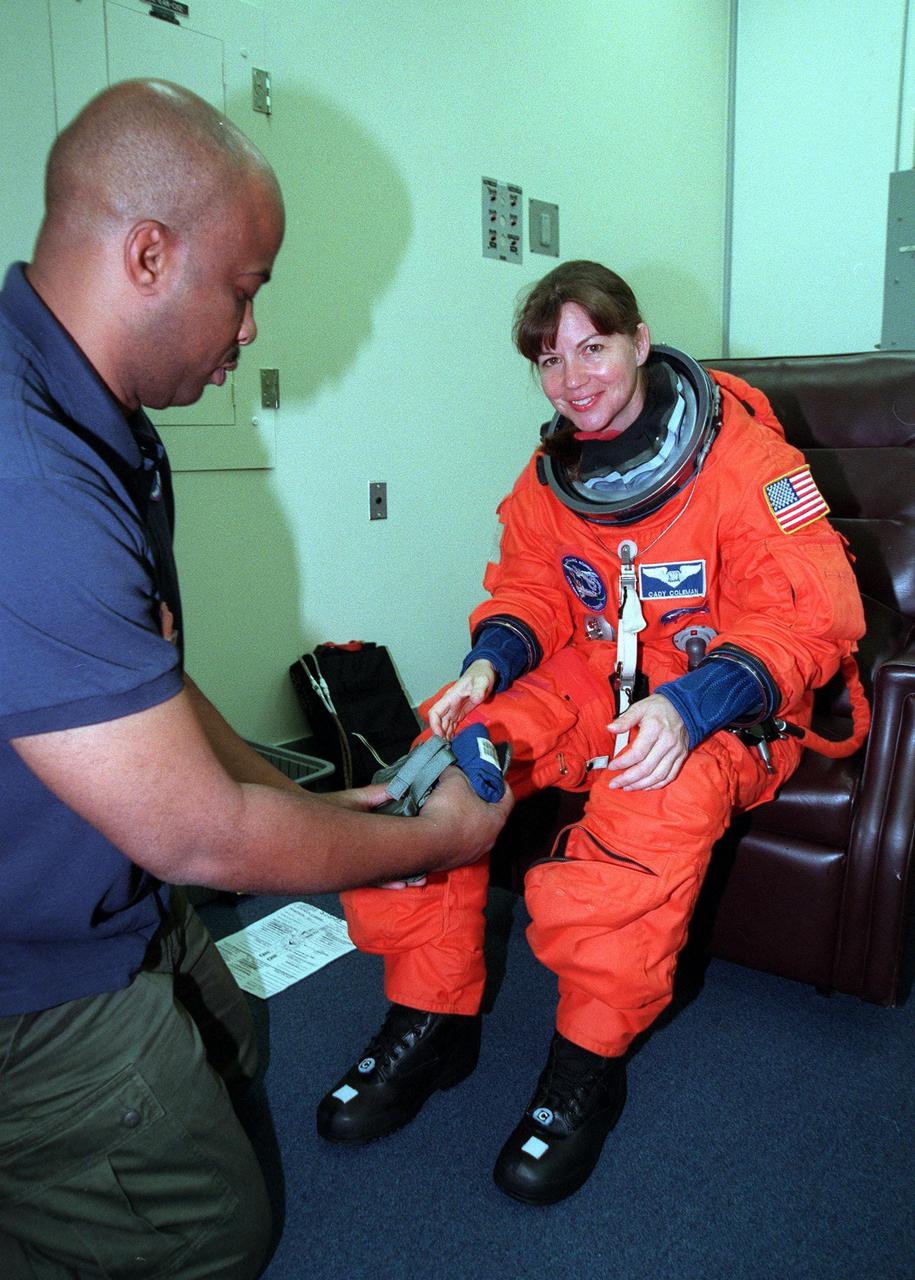

During final launch preparations in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) gets help with her launch and entry suit from a suit tech. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Coleman and Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
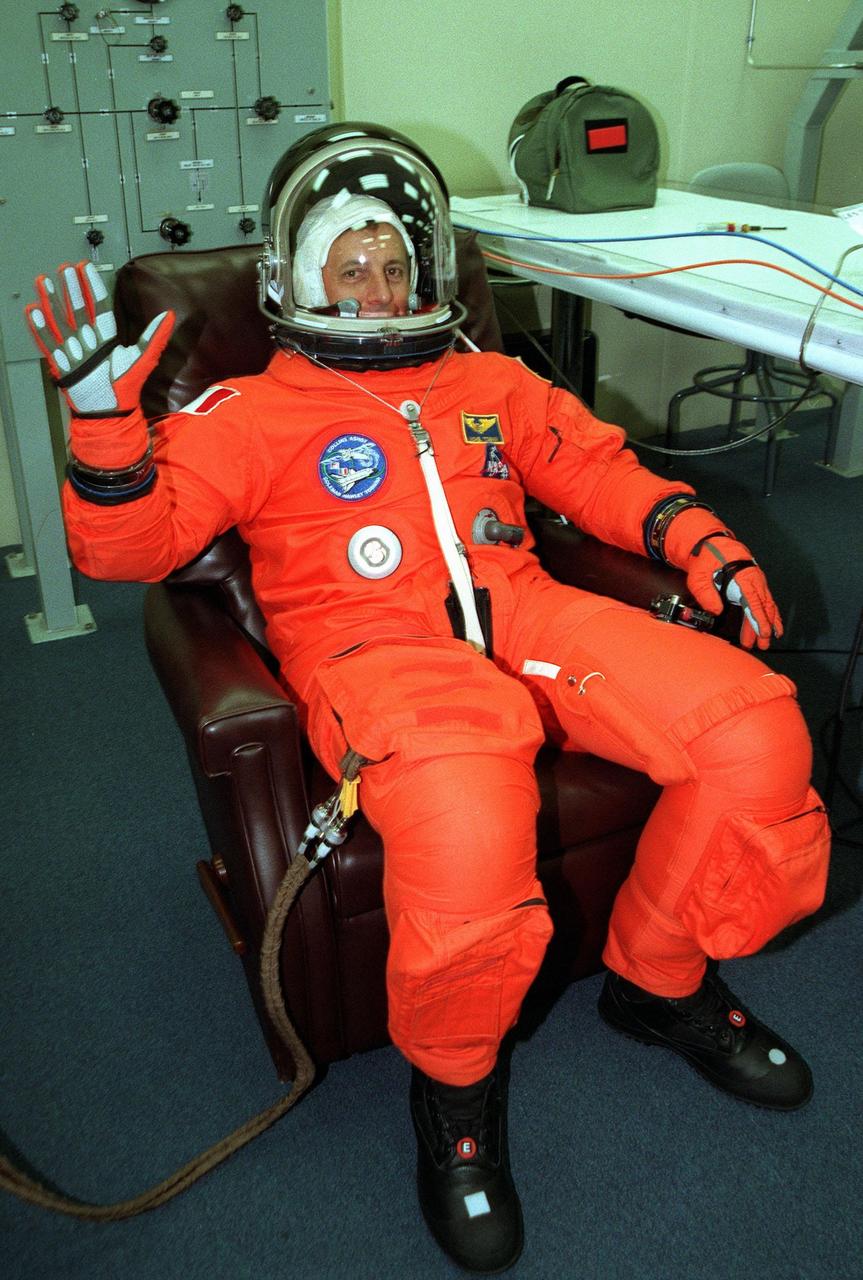

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), waves after donning his launch and entry suit during final launch preparations for the second time. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Tognini. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
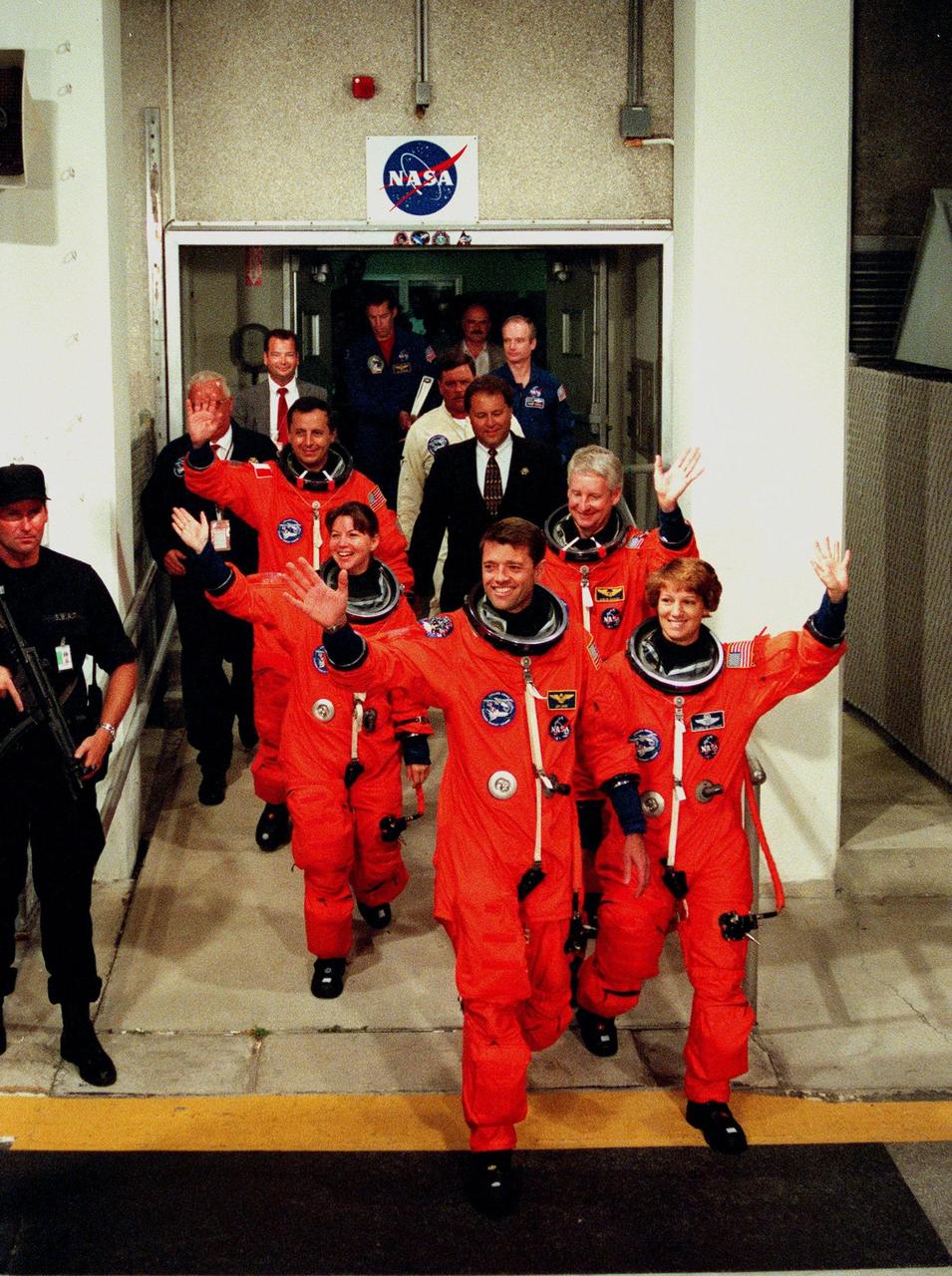

The STS-93 crew wave to onlookers as they walk out of the Operations and Checkout Building enroute to Launch Pad 39-B and liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia. In their orange launch and entry suits, they are (starting at rear, left to right) Mission Specialists Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), and Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.); Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby; Mission Specialist Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.); and Commander Eileen M. Collins. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a Shuttle mission. STS-93 is scheduled to lift off at 12:36 a.m. EDT July 20. The target landing date is July 24 at 11:31 p.m. EDT
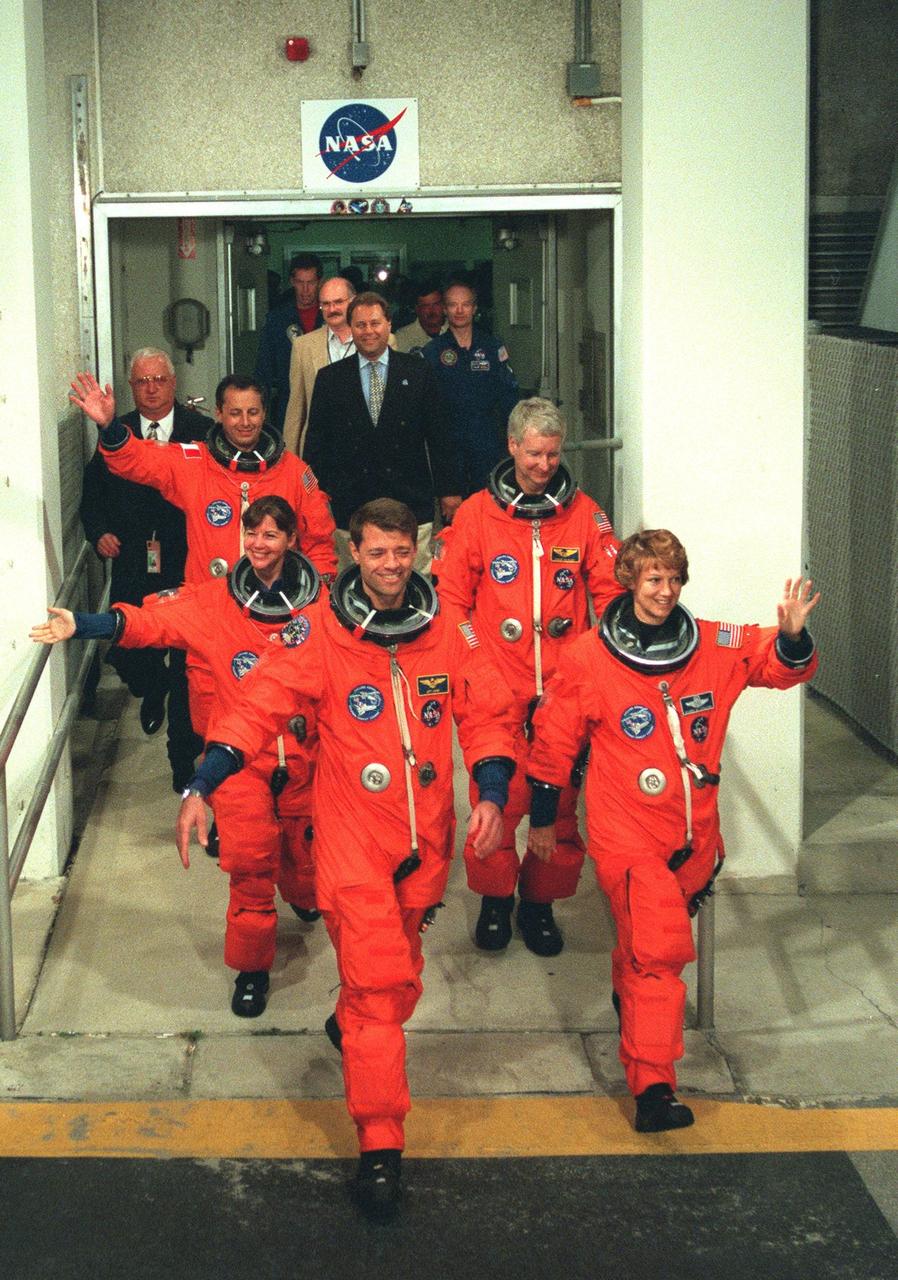

The STS-93 crew wave to onlookers as they walk out of the Operations and Checkout Building for the second time enroute to Launch Pad 39-B and liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. In their orange launch and entry suits, they are (starting at rear, left to right) Mission Specialists Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), and Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.); Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby; Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.); and Commander Eileen M. Collins. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a Shuttle mission
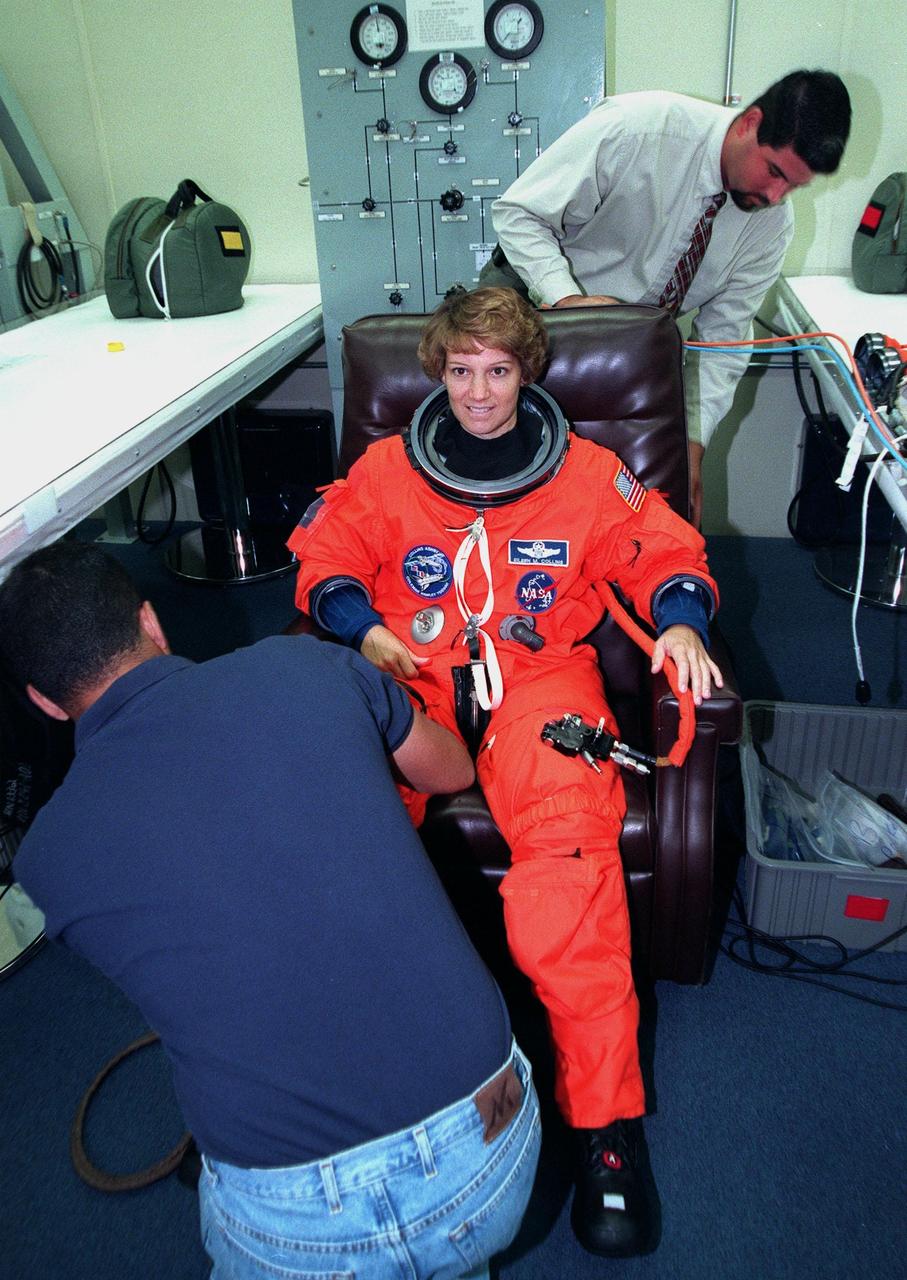

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Commander Eileen M. Collins gets help donning her launch and entry suit. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 launch attempt was scrubbed at the T-7 second mark in the countdown, the launch was rescheduled for Thursday, July 22, at 12:28 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 26, 1999, at 11:24 p.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
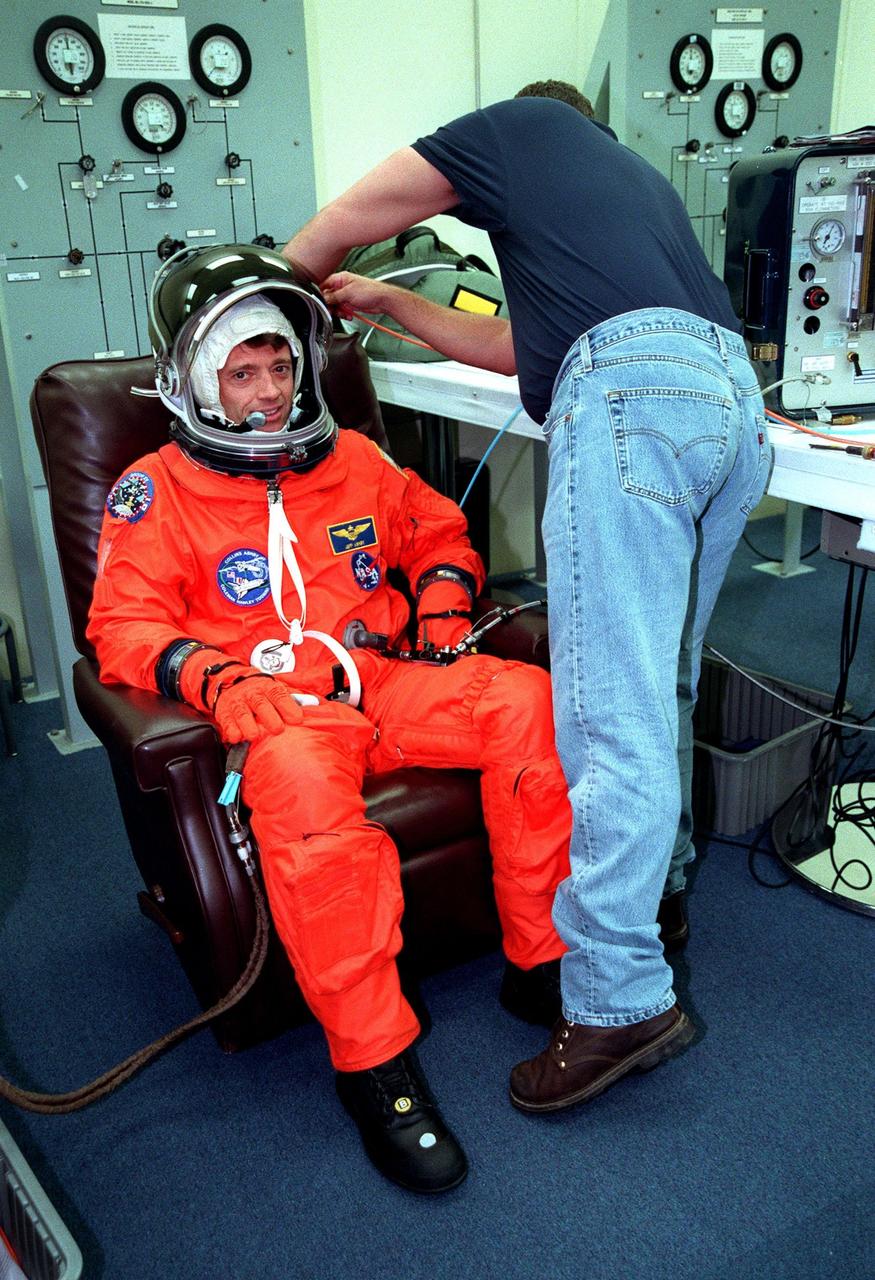

In the Operations and Checkout Building during final launch preparations, STS-93 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby waits after donning his launch and entry suit while a suit tech adjusts his helmet. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Ashby, and Mission Specialists Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission. STS-93 is scheduled to lift off at 12:36 a.m. EDT July 20. The target landing date is July 24 at 11:30 p.m. EDT
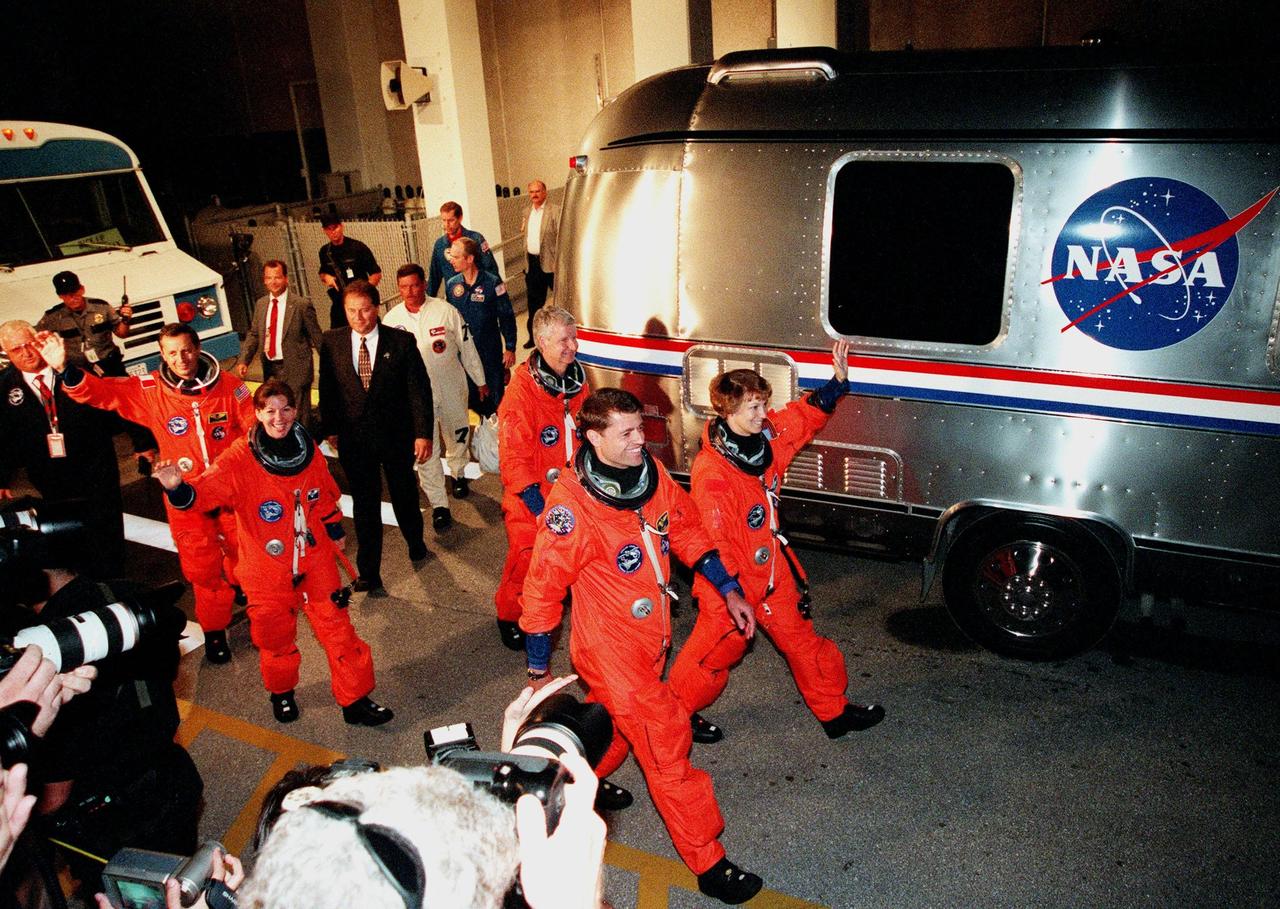

The STS-93 crew wave to onlookers as they walk to the "Astrovan," which will transport them to Launch Pad 39-B and liftoff of Space Shuttle Columbia. In their orange launch and entry suits, they are (starting at rear, left to right) Mission Specialists Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.), and Mission Specialist Stephen A. Hawley (Ph.D.); Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby; and Commander Eileen M. Collins. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The new telescope is 20 to 50 times more sensitive than any previous X-ray telescope and is expected unlock the secrets of supernovae, quasars and black holes. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a Shuttle mission. STS-93 is scheduled to lift off at 12:36 a.m. EDT July 20. The target landing date is July 24 at 11:31 p.m. EDT
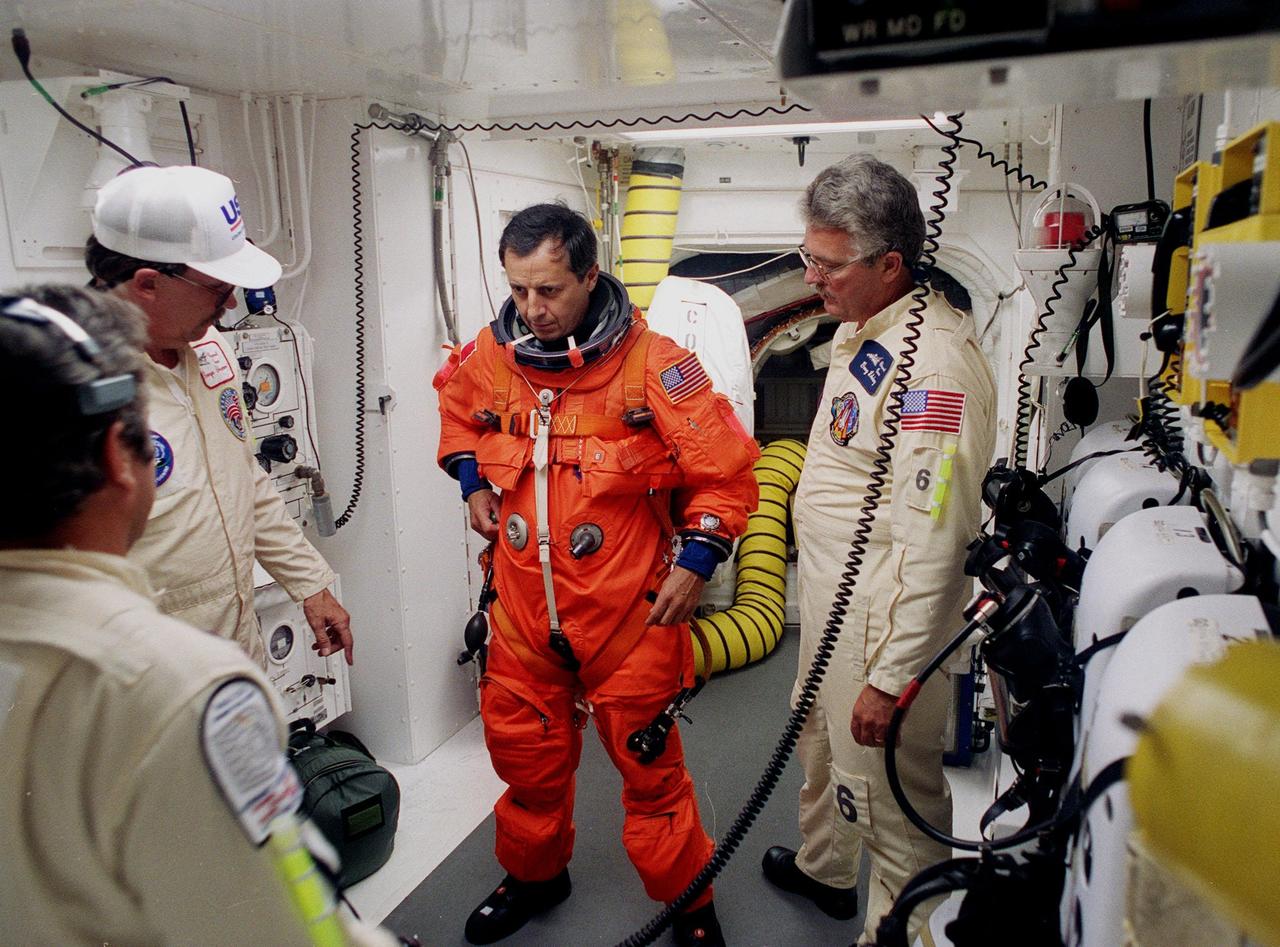

STS-93 Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France is checked out by white room closeout crew members before entering the orbiter Columbia. Tognini is with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). The white room is an environmental chamber at the end of the orbiter access arm that provides entry to the orbiter crew compartment. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 27 at 11:20 p.m. EDT
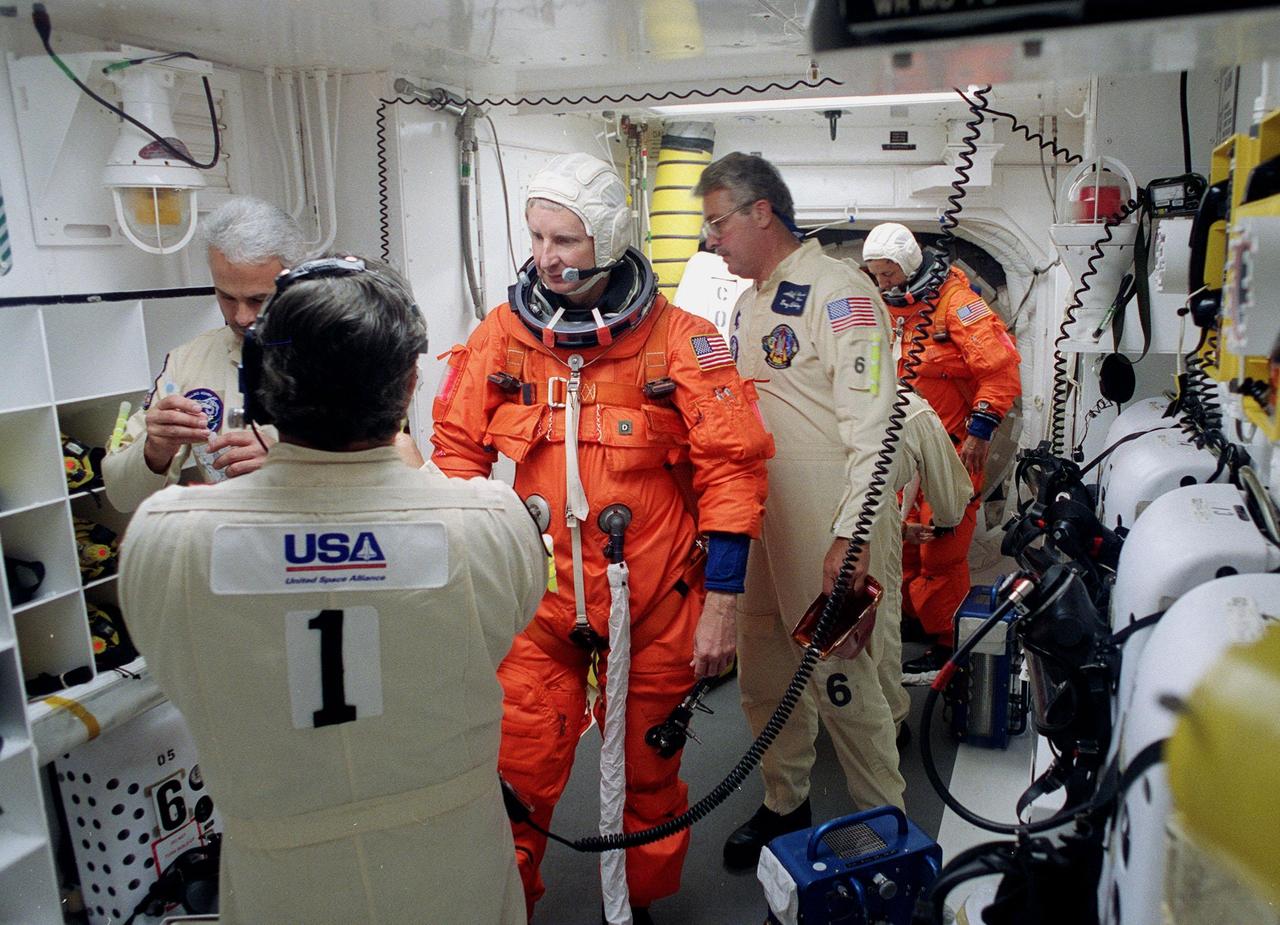

STS-93 Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.) is checked out by white room closeout crew members before entering the orbiter Columbia. In the background is Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France, waiting to enter Columbia. The white room is an environmental chamber at the end of the orbiter access arm that provides entry to the orbiter crew compartment. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 27 at 11:20 p.m. EDT
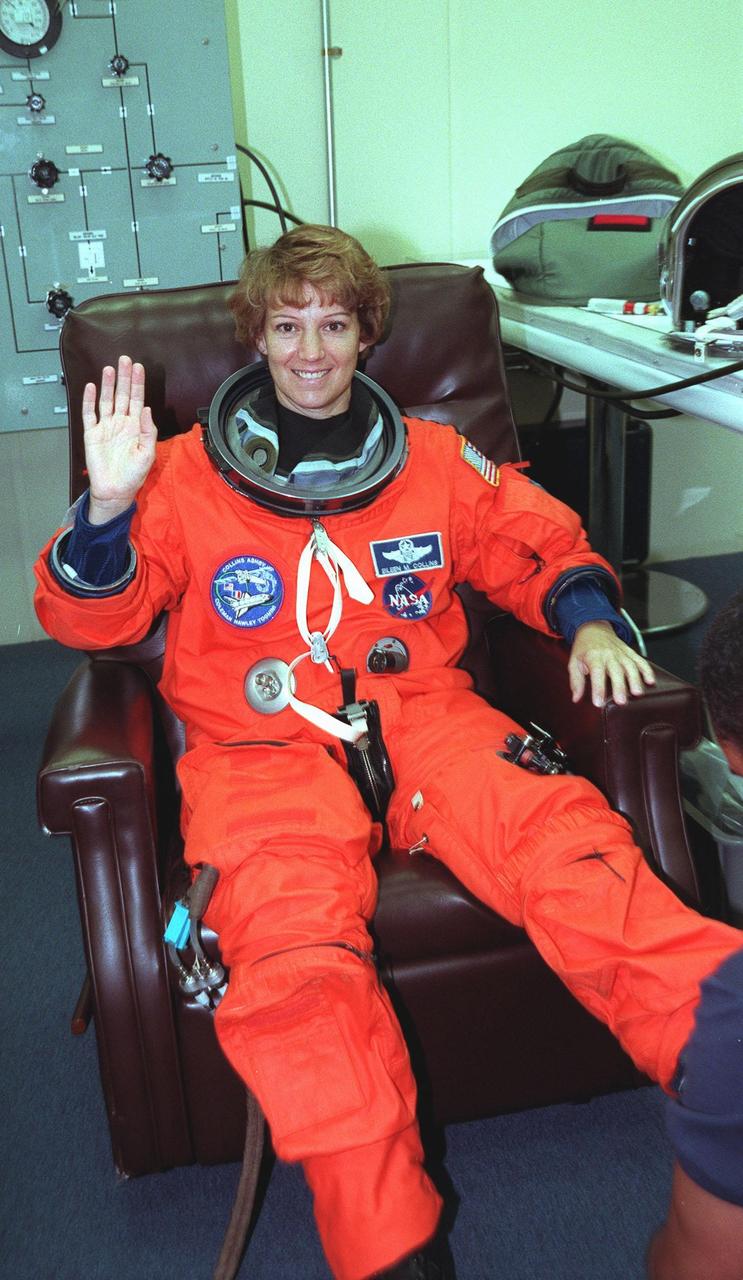

During the third launch preparations in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Commander Eileen M. Collins waves while having her launch and entry suit checked. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
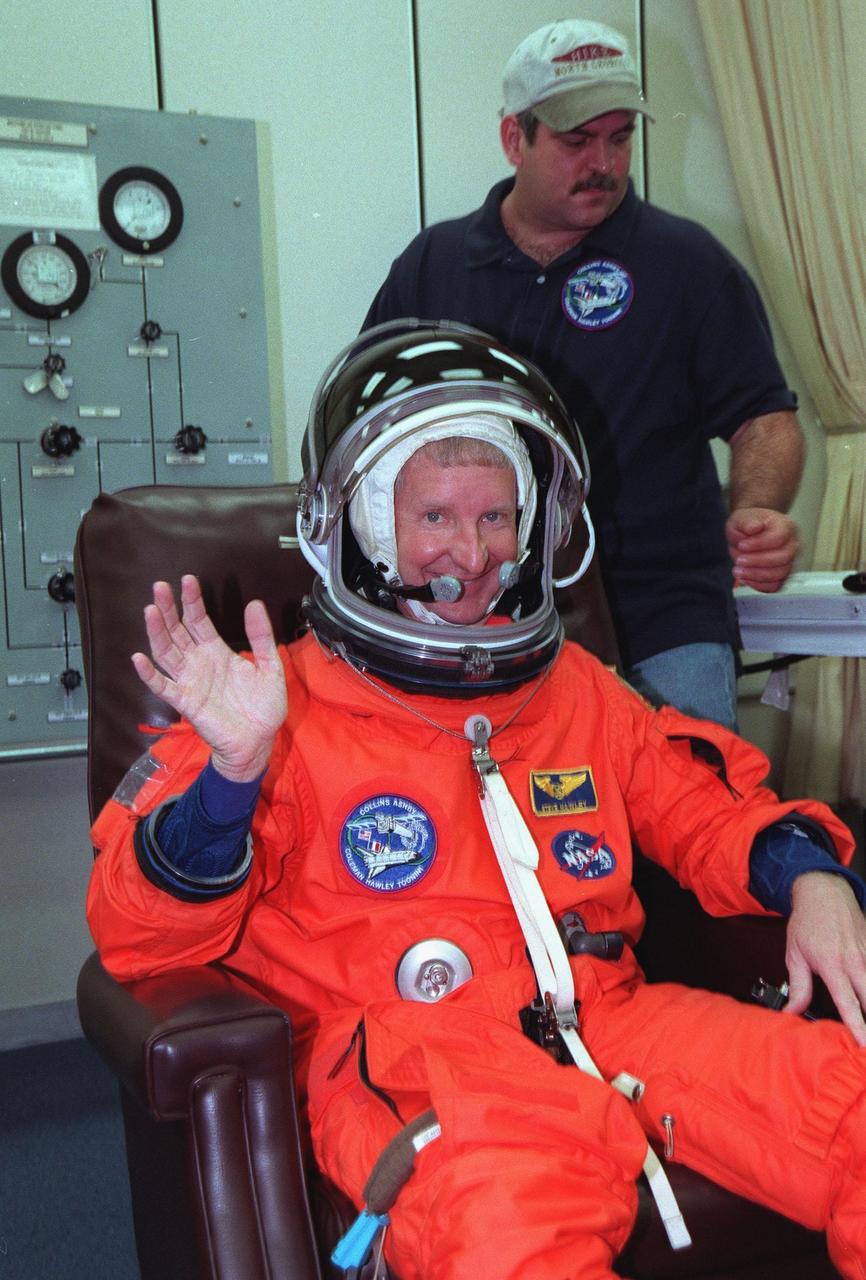

For the third time, during final launch preparations in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.) waves after donning his launch and entry suit. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Hawley, Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
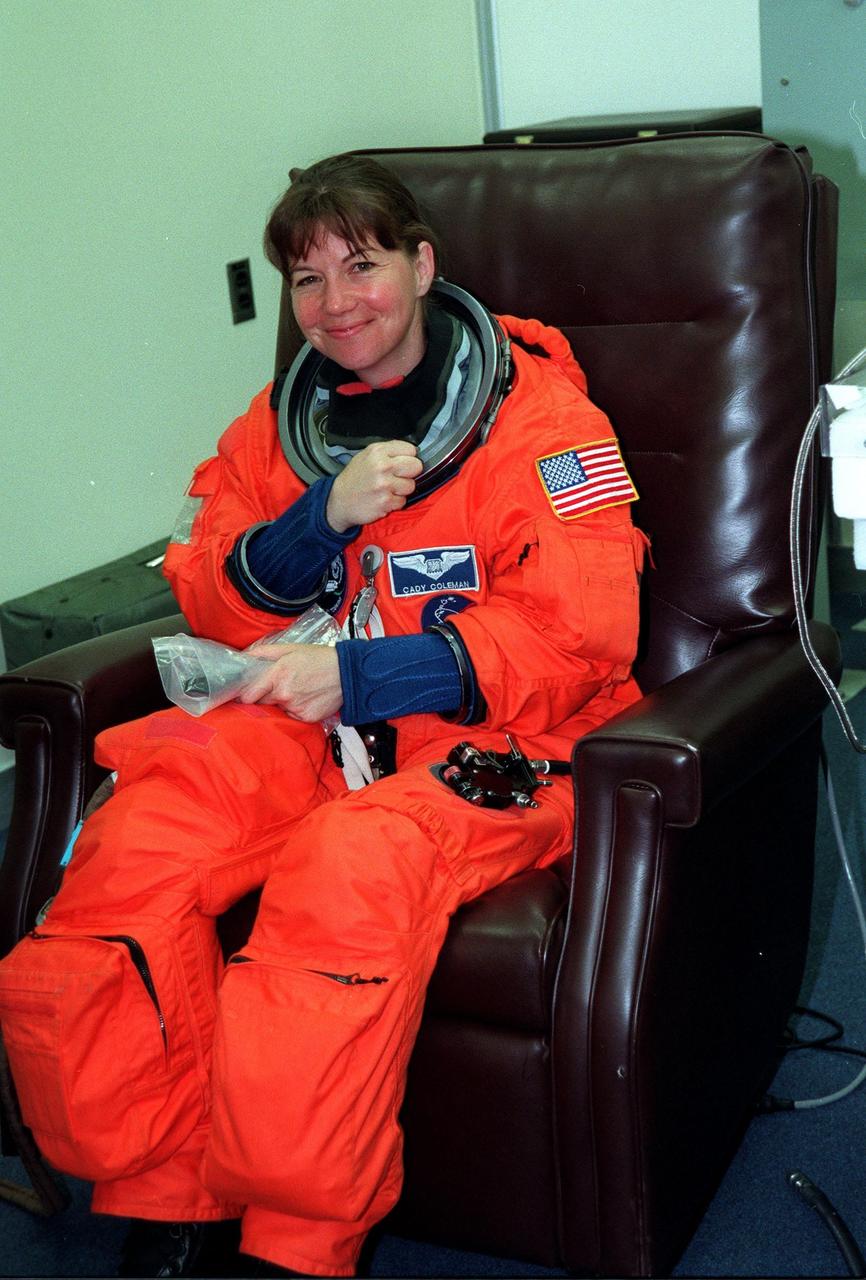

For the third time, during final launch preparations in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) dons her launch and entry suit. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Coleman, and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
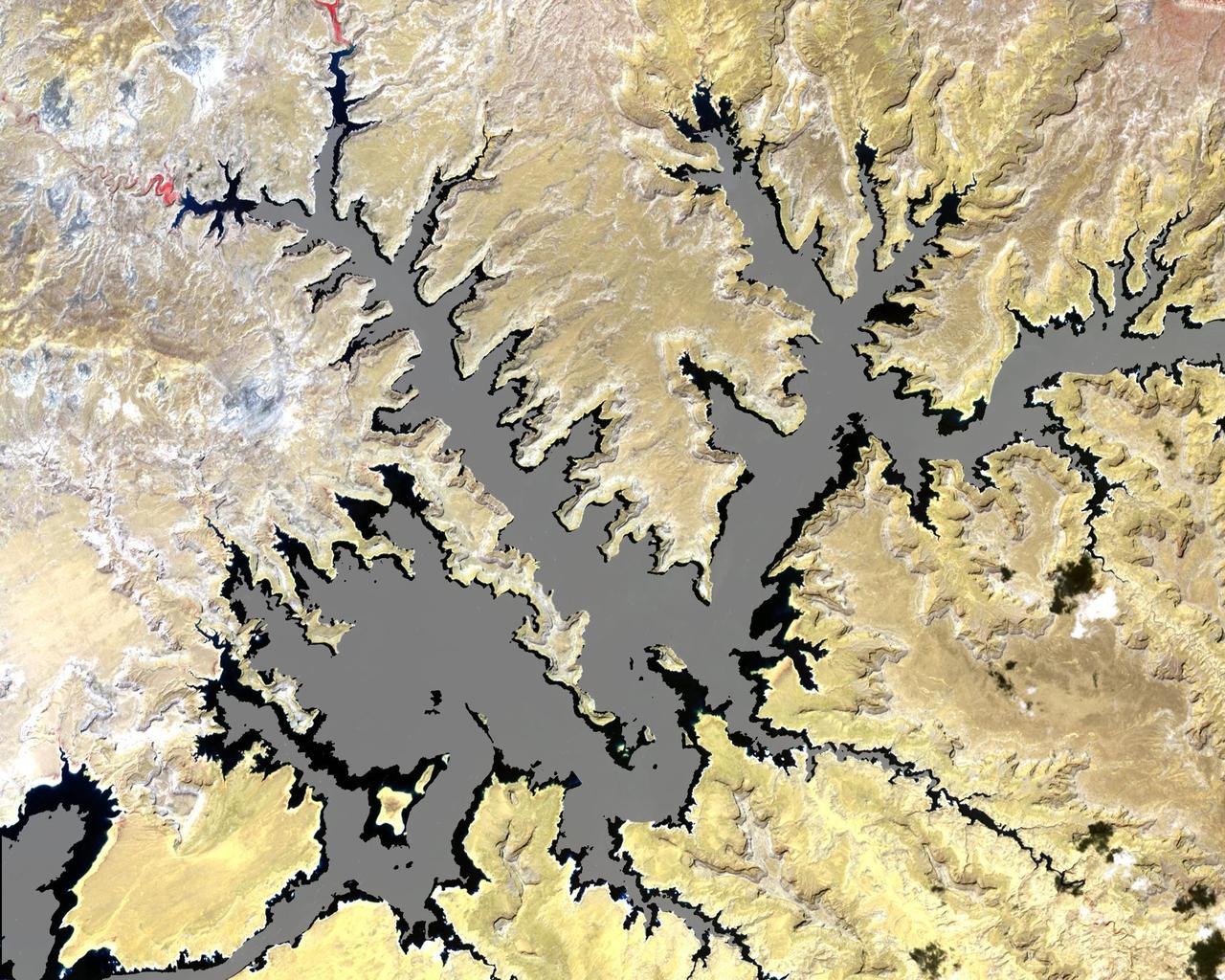
The white ring around Lake Powell tells the story. The surface is down 98 feet. This is critical, because Powell, Lake Mead, and other lakes along the Colorado River provide water for millions of people in five states. We are in the eighth year of a drought on the Colorado River. This year was the driest year ever reported in Southern California, and there is a severe drought in Northern California, down to less than 30-percent of snow pack. This ASTER image of part of Lake Powell was acquired in 2001. The gray area depicts the shrunken, reduced 2007 lake extent compared to the extended, larger black area in 2001. The image covers an area of 24 x 30 km, and is centered near 37.1 degrees north latitude, 111.3 degrees west longitude. This image from NASA Terra satellite. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10614
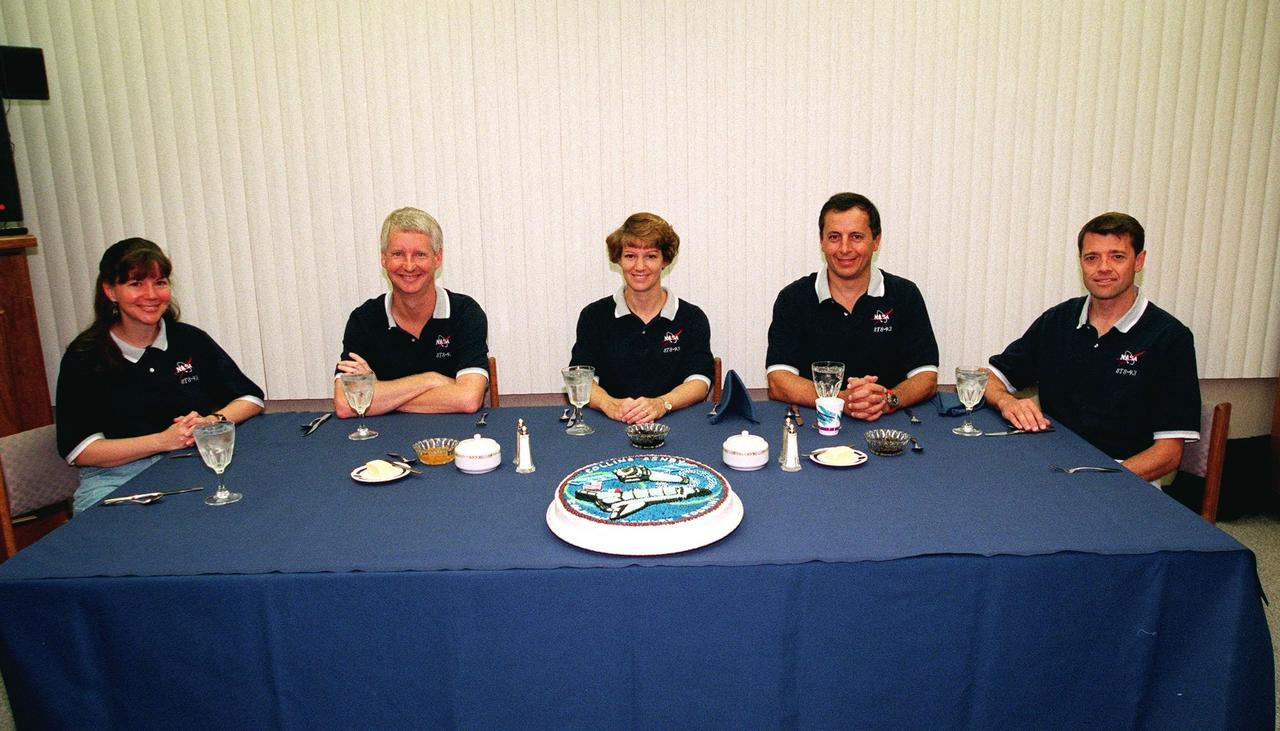

The STS-93 crew gathers a third time for a pre-launch breakfast in the Operations and Checkout Building before suiting up for launch. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 22 launch attempt was scrubbed due to the weather, the launch was rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. Seated from left are Mission Specialists Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.); Commander Eileen M. Collins; Mission Specialist Michel Tognini, of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES); and Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a Shuttle mission. The target landing date is July 27, 1999, at 11:20 p.m. EDT

For the third time, in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Commander Eileen M. Collins tries on her helmet with her launch and entry suit. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
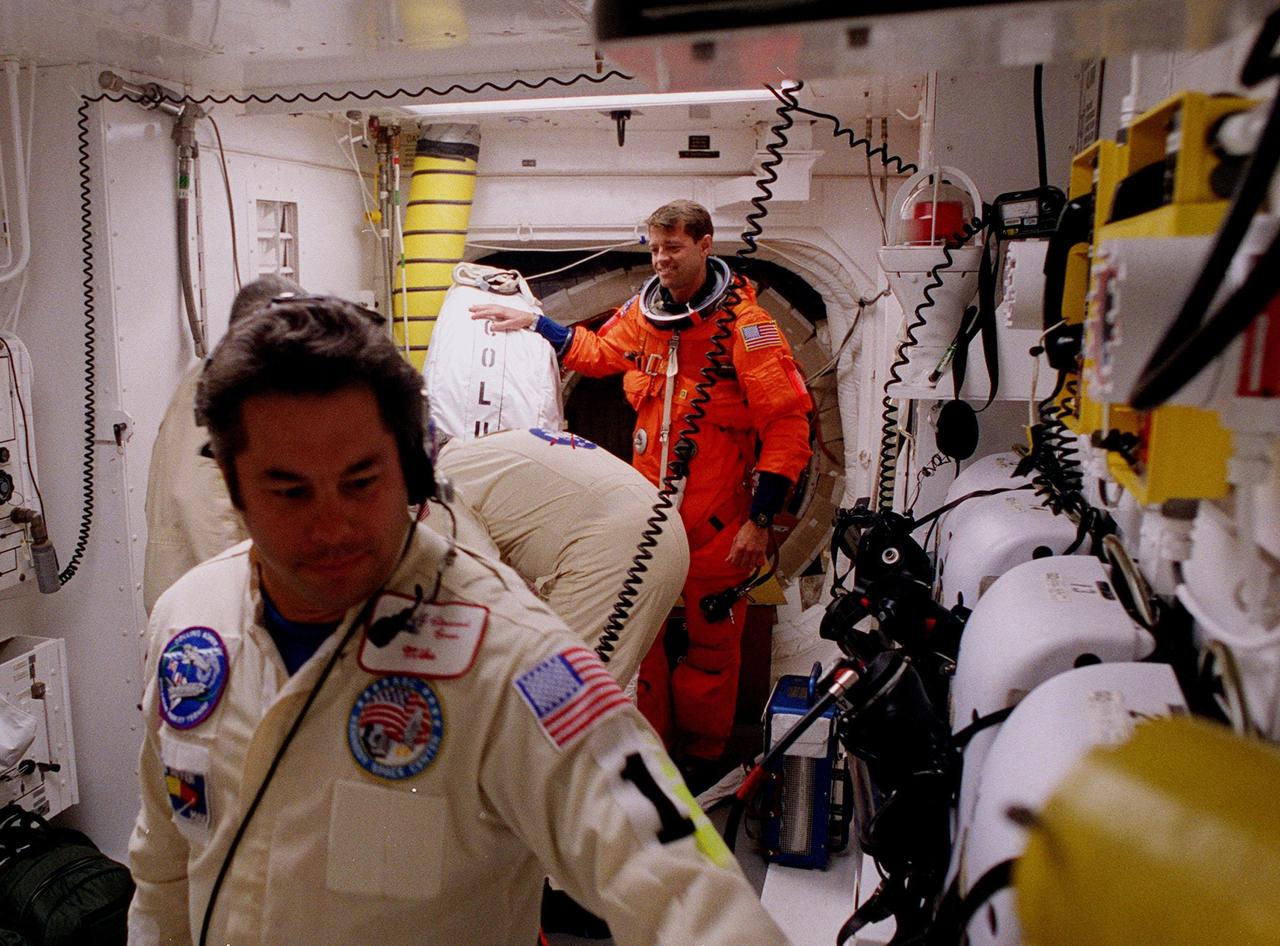

STS-93 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby is checked out by white room closeout crew members before entering the orbiter Columbia. The white room is an environmental chamber at the end of the orbiter access arm that provides entry to the orbiter crew compartment. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 27 at 11:20 p.m. EDT
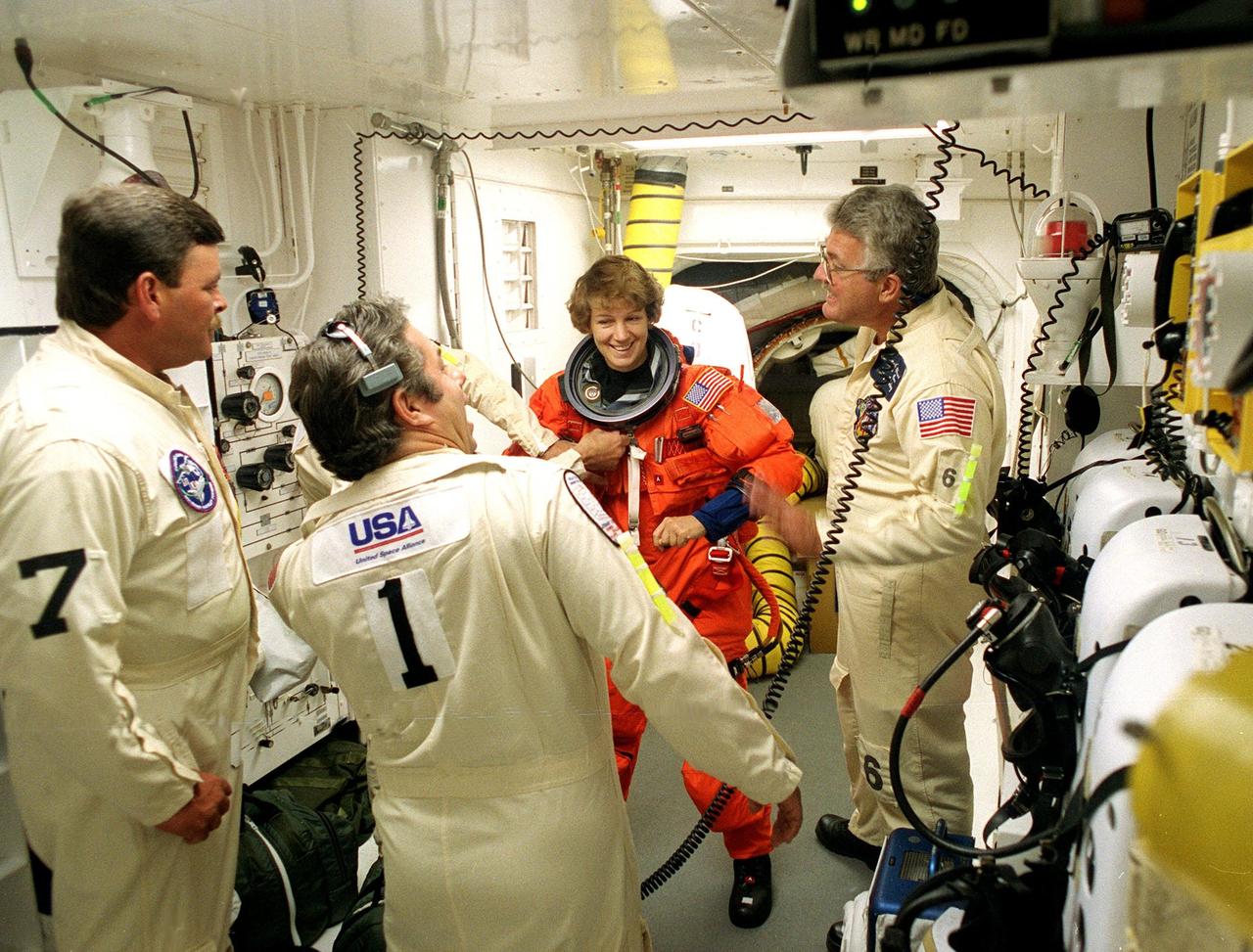

STS-93 Commander Eileen M. Collins is checked out by white room closeout crew members before entering the orbiter Columbia. The white room is an environmental chamber at the end of the orbiter access arm that provides entry to the orbiter crew compartment. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 27 at 11:20 p.m. EDT

For the third time, in the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-93 Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), waves after donning his launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen M. Collins, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Tognini. Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
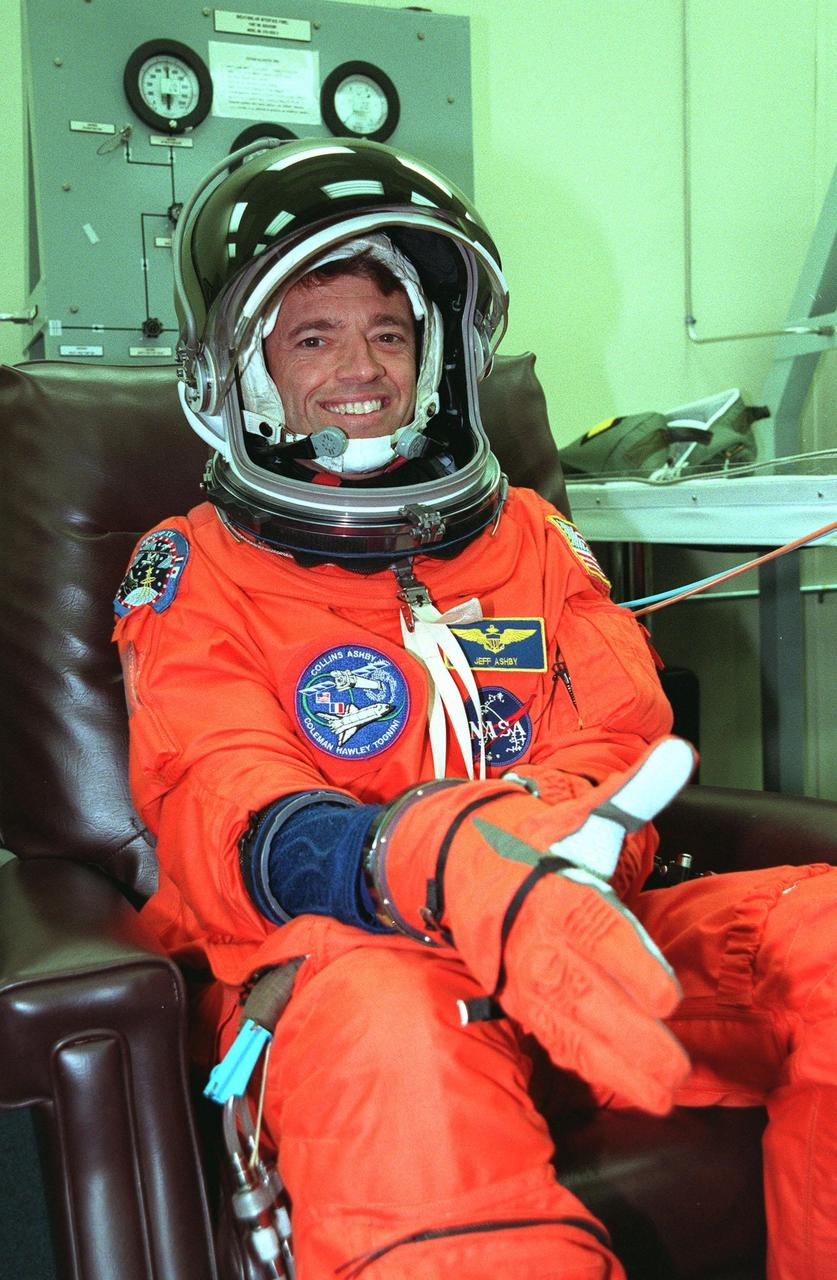

In the Operations and Checkout Building during final launch preparations for the third time, STS-93 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby pulls on his glove, part of his launch and entry suit. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. The STS-93 crew numbers five: Commander Eileen Collins, Ashby, and Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) and Michel Tognini of France, with the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as commander of a shuttle mission
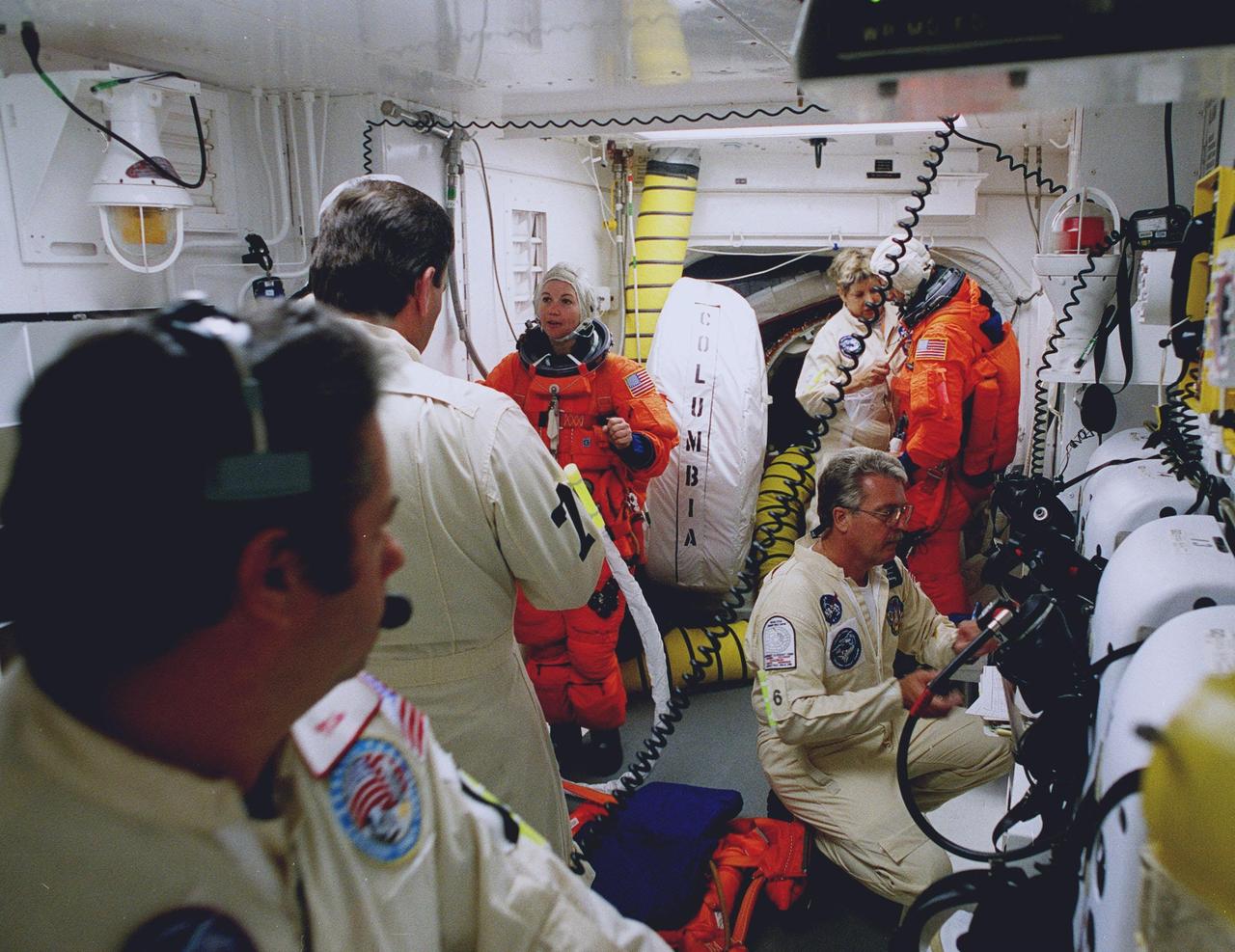

STS-93 Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.) (left) and Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby (right) are checked out by white room closeout crew members before entering the orbiter Columbia. The white room is an environmental chamber at the end of the orbiter access arm that provides entry to the orbiter crew compartment. STS-93 is a five-day mission primarily to release the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to study some of the most distant, powerful and dynamic objects in the universe. After Space Shuttle Columbia's July 20 and 22 launch attempts were scrubbed, the launch was again rescheduled for Friday, July 23, at 12:24 a.m. EDT. The target landing date is July 27 at 11:20 p.m. EDT

Caption: These SDO images from 7:25 p.m. EST on Feb. 24, 2014, show the first moments of an X-class flare in different wavelengths of light -- seen as the bright spot that appears on the left limb of the sun. Hot solar material can be seen hovering above the active region in the sun's atmosphere, the corona. Credit: NASA/SDO More info: The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 7:49 p.m. EST on Feb. 24, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which keeps a constant watch on the sun, captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation, appearing as giant flashes of light in the SDO images. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This flare is classified as an X4.9-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: These SDO images from 7:25 p.m. EST on Feb. 24, 2014, show the first moments of an X-class flare in different wavelengths of light -- seen as the bright spot that appears on the left limb of the sun. Hot solar material can be seen hovering above the active region in the sun's atmosphere, the corona. Credit: NASA/SDO More info: The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 7:49 p.m. EST on Feb. 24, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which keeps a constant watch on the sun, captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation, appearing as giant flashes of light in the SDO images. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This flare is classified as an X4.9-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
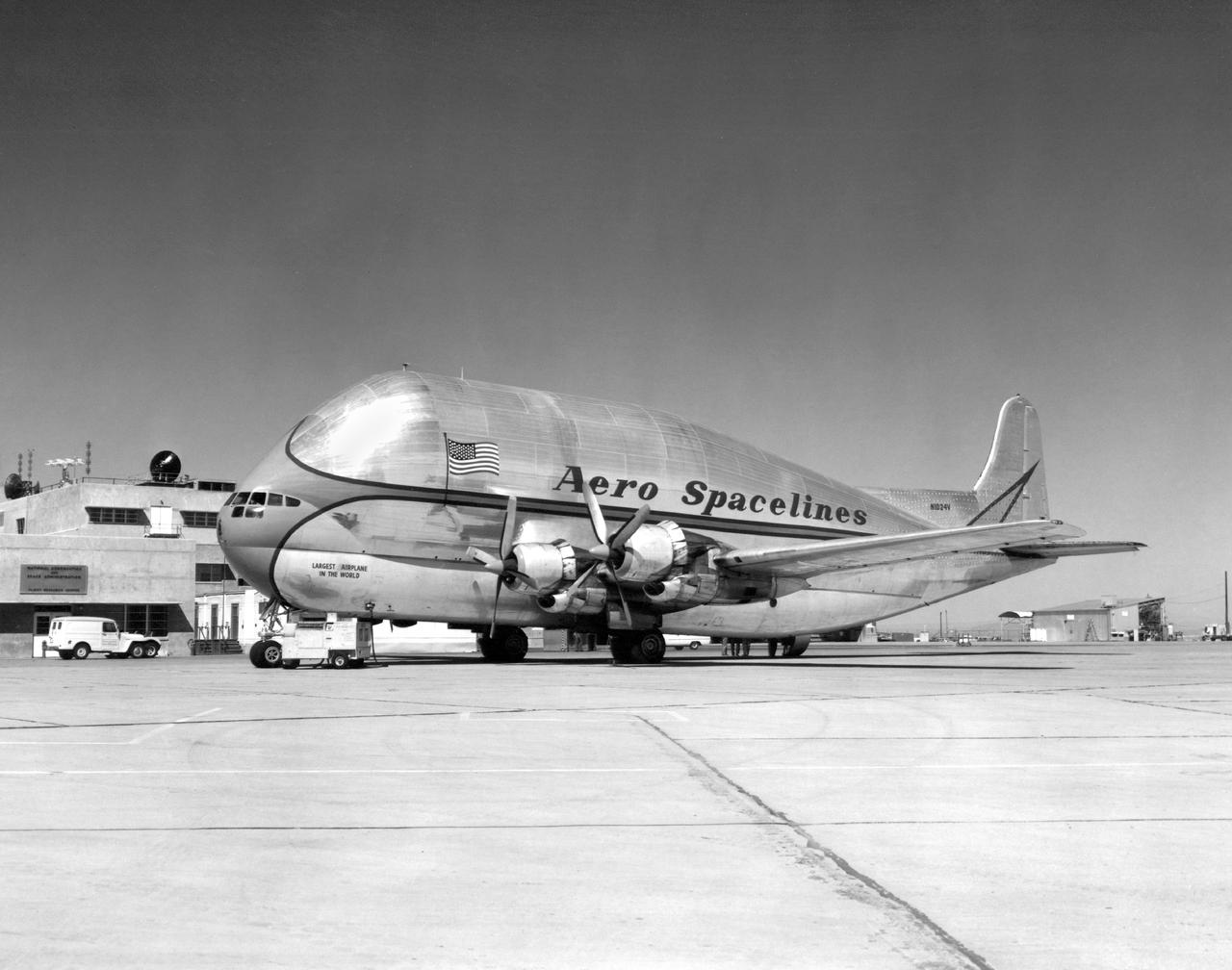

Aero Spacelines B-377PG Pregnant Guppy on ramp in preparation for flight tests and pilot evaluation

This time-lapse video, which has been sped up by 24 times, uses an engineering model of one of the instruments aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover to show how the instrument evaluates safe placement against a rock. If it's determined to be safe, the rover places the instrument, called the Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry (PIXL), close to the targeted rock for science observations. This test occurred at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on June 8, 2023. Located on the end of Perseverance's robotic arm, PIXL scans postage stamp-size areas on rocks with an X-ray beam the width of a human hair, determining which elements are present. Scientists use this information to infer what minerals and chemicals are in a rock and help decide whether Perseverance should collect a rock core using its drill. The X-ray beam exits the circular opening at the center of PIXL; colored LED lights around that circle can light up a surface, allowing an internal camera to take images. Those images allow PIXL to autonomously place itself – very slowly and precisely – as little as 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) away from a surface to collect its data. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26204

SDO AIA image of the X3.1 flare in 131 angstrom light from 21:43 UT on October 24, 2014. Credit:NASA/SDO More info: The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 5:40 p.m. EDT on Oct. 24, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This flare is classified as an X3.1-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. The flare erupted from a particularly large active region -- labeled AR 12192 -- on the sun that is the largest in 24 years. This is the fourth substantial flare from this active region since Oct. 19. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Active region AR 12192 on the sun erupted with a strong flare on Oct. 24, 2014, as seen in the bright light of this image captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. This image shows extreme ultraviolet light that highlights the hot solar material in the sun's atmosphere. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO More info: The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 5:40 p.m. EDT on Oct. 24, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This flare is classified as an X3.1-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. The flare erupted from a particularly large active region -- labeled AR 12192 -- on the sun that is the largest in 24 years. This is the fourth substantial flare from this active region since Oct. 19. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, the environmentally controlled shipping container is lifted from around NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), wrapped in a protective shroud. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will carry NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space awaits integration with the spacecraft in the clean room of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip which began Jan. 24 from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va. The spacecraft will be removed from the shipping container in the airlock and transferred into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
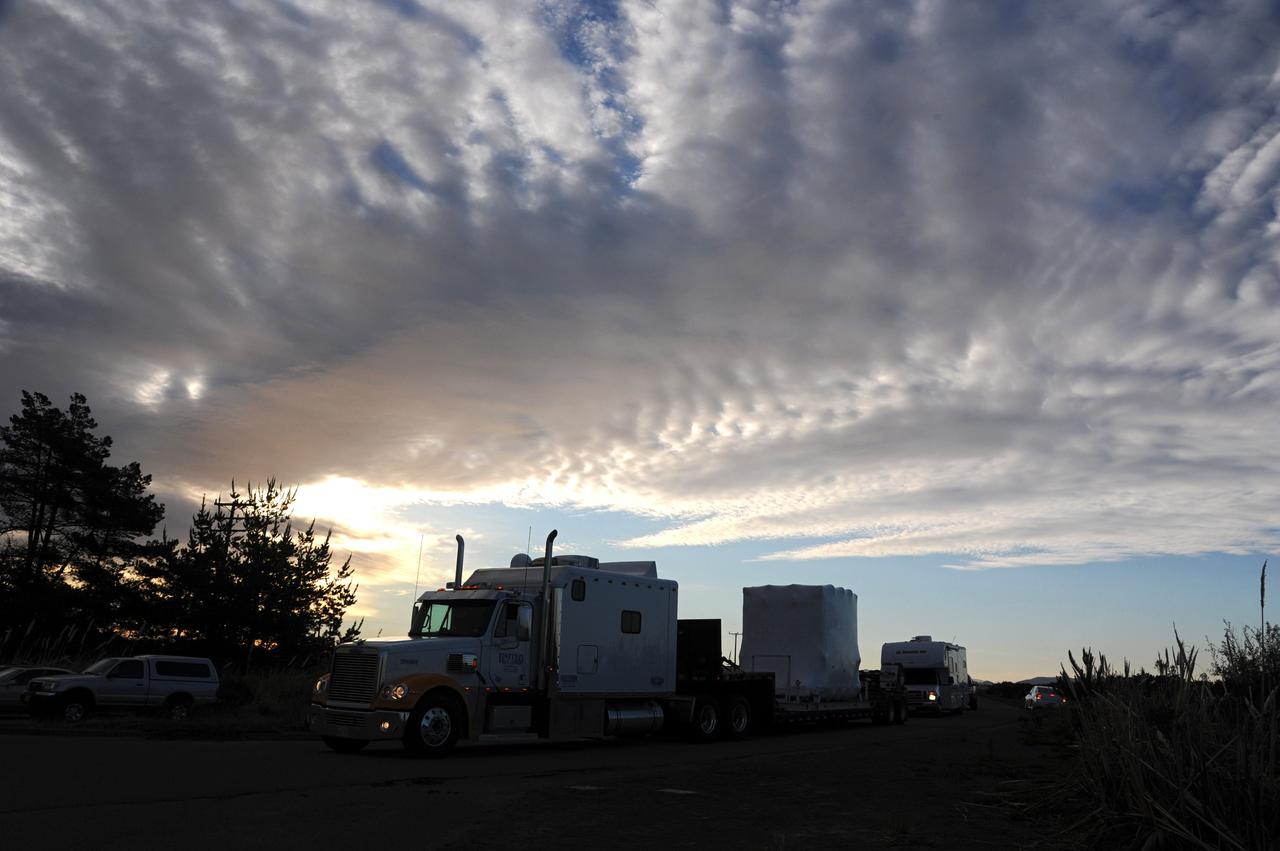

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A tractor-trailer delivers NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), enclosed in an environmentally controlled shipping container, to processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip which began Jan. 24 from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va. The spacecraft will be removed from the shipping container in the airlock and transferred into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
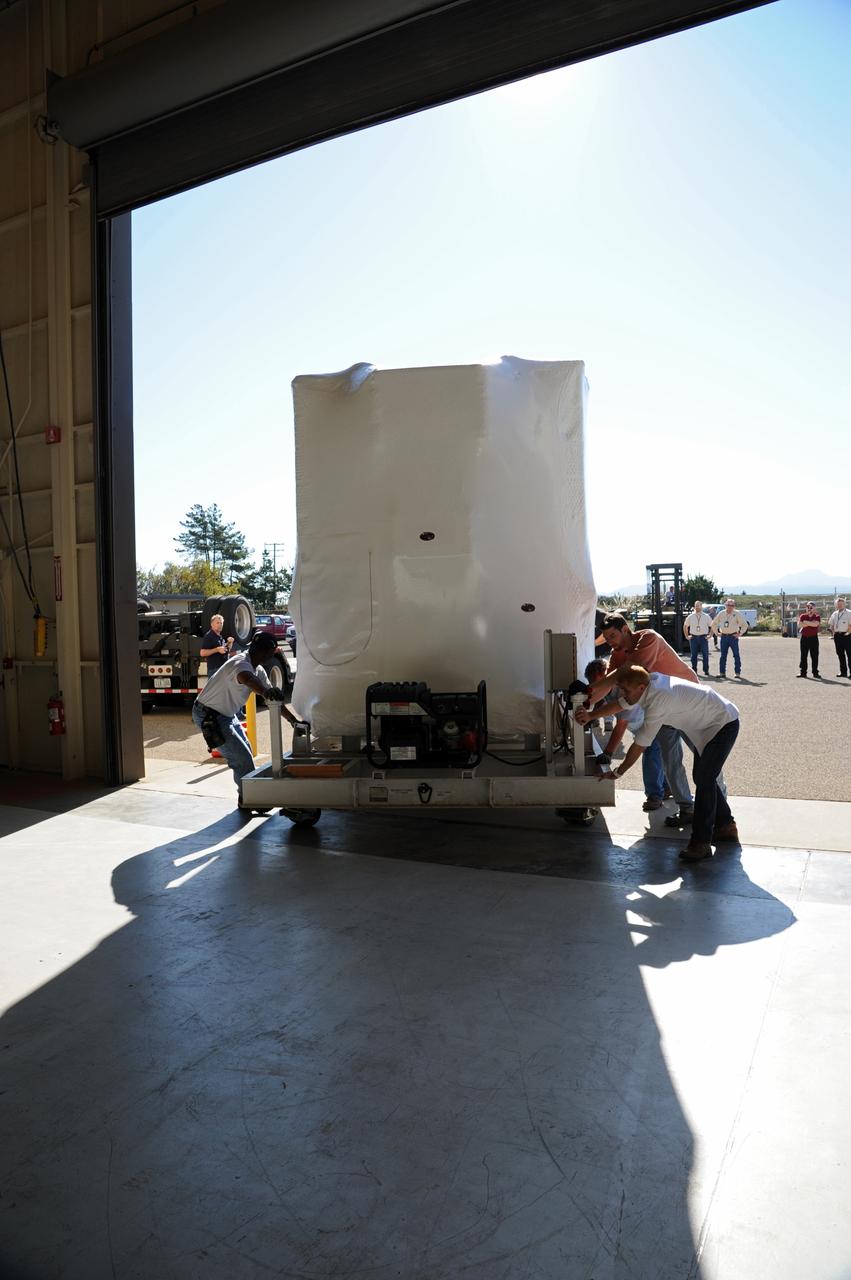

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers roll the environmentally controlled shipping container enclosing NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) through the door of the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip which began Jan. 24 from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va. The spacecraft will be removed from the shipping container in the airlock and transferred into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, a lifting fixture is employed to hoist NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) from its shipping container. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
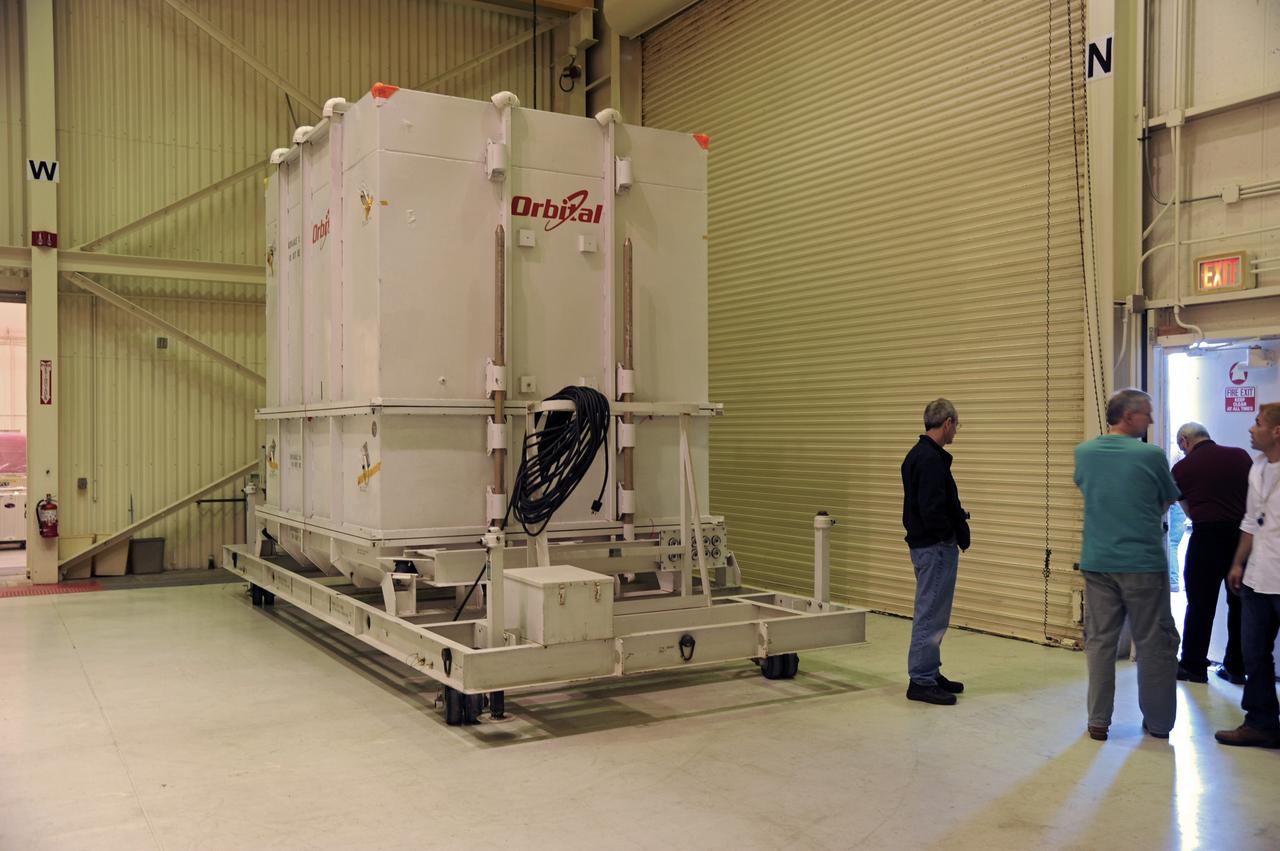

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The payload transporter carrying the environmentally controlled shipping container enclosing NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) is parked in the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip which began Jan. 24 from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va. The spacecraft will be removed from the shipping container in the airlock and transferred into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
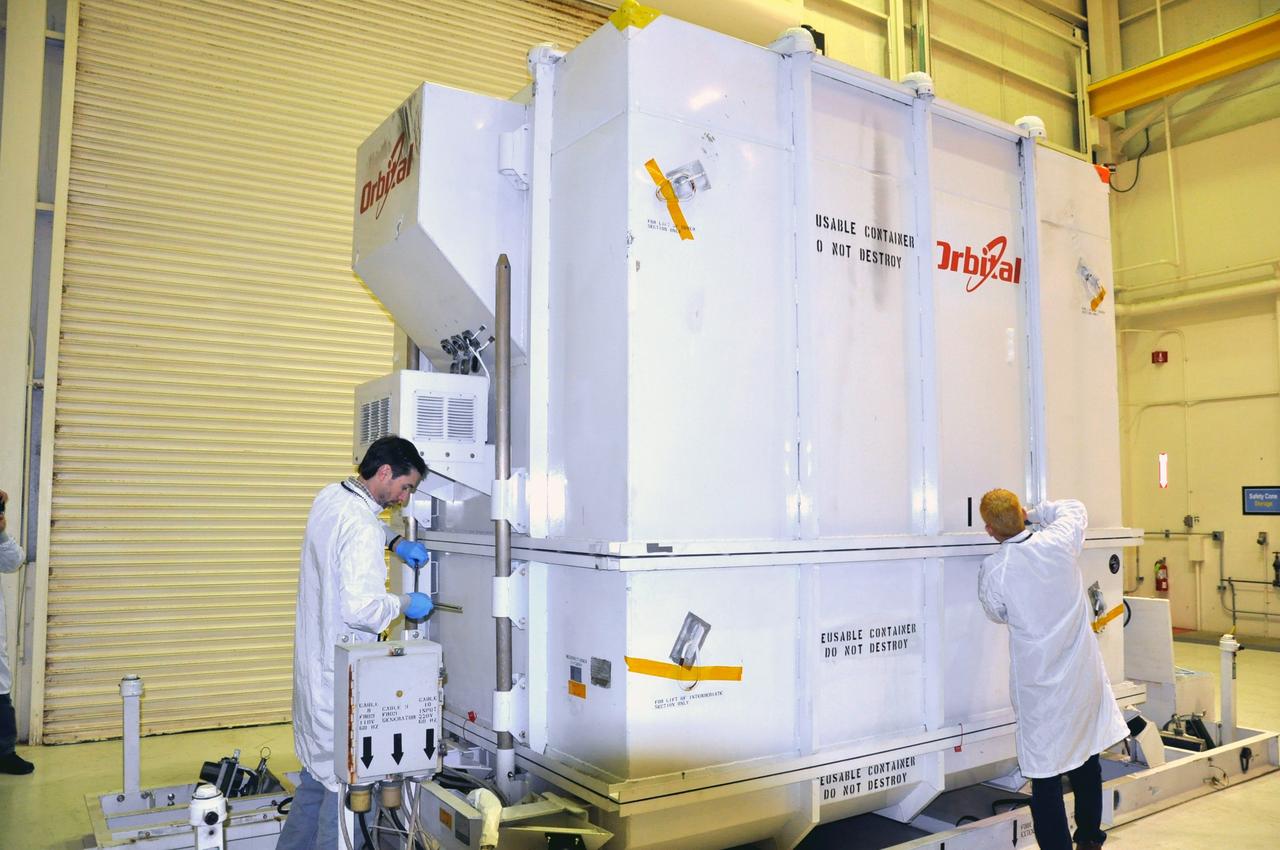

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, preparations are under way to remove the environmentally controlled shipping container from around NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR). The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
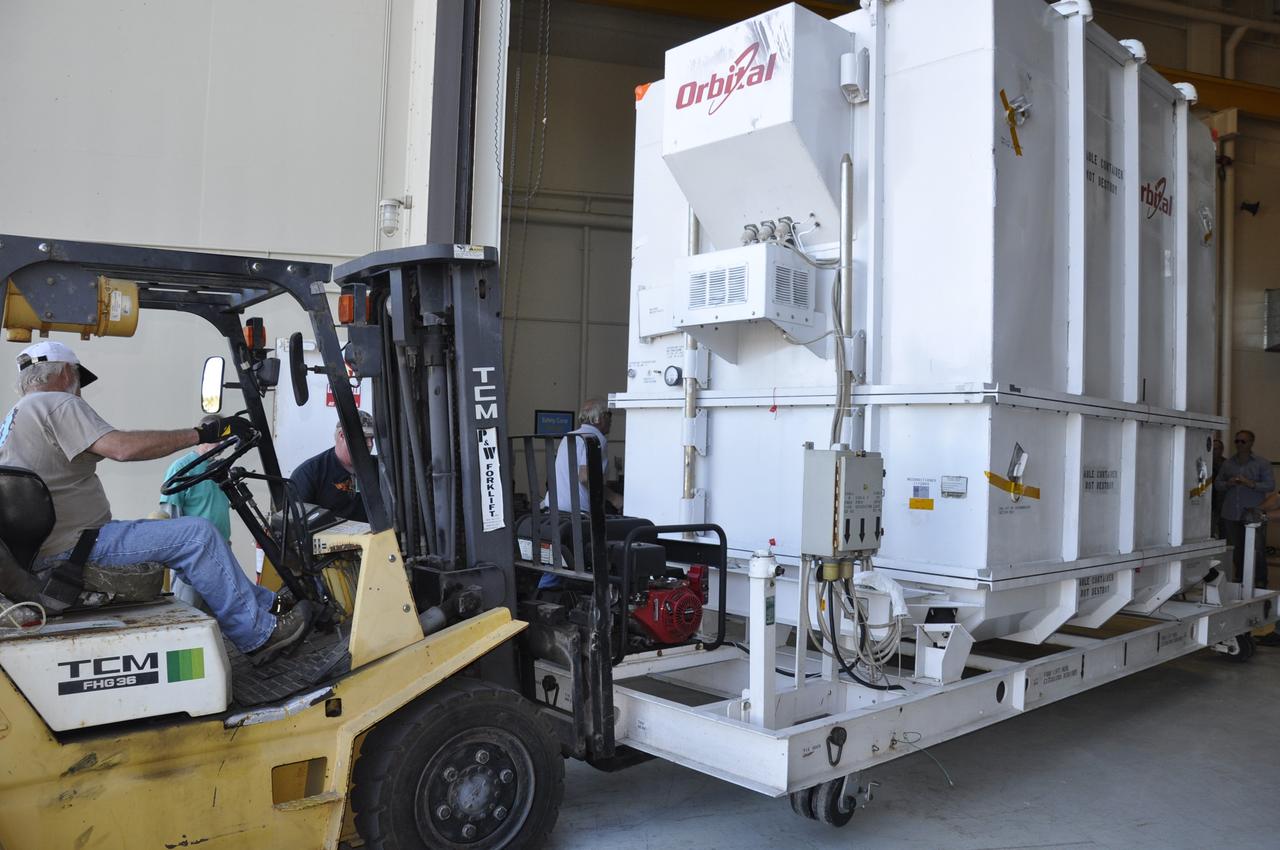

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A forklift is enlisted to transfer the environmentally controlled shipping container enclosing NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) from the airlock to the high bay of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., which began Jan. 24. The spacecraft will be offloaded into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After NuSTAR is removed from its shipping container, checkout and other processing activity will begin. The spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. After processing is completed, the rocket and spacecraft will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
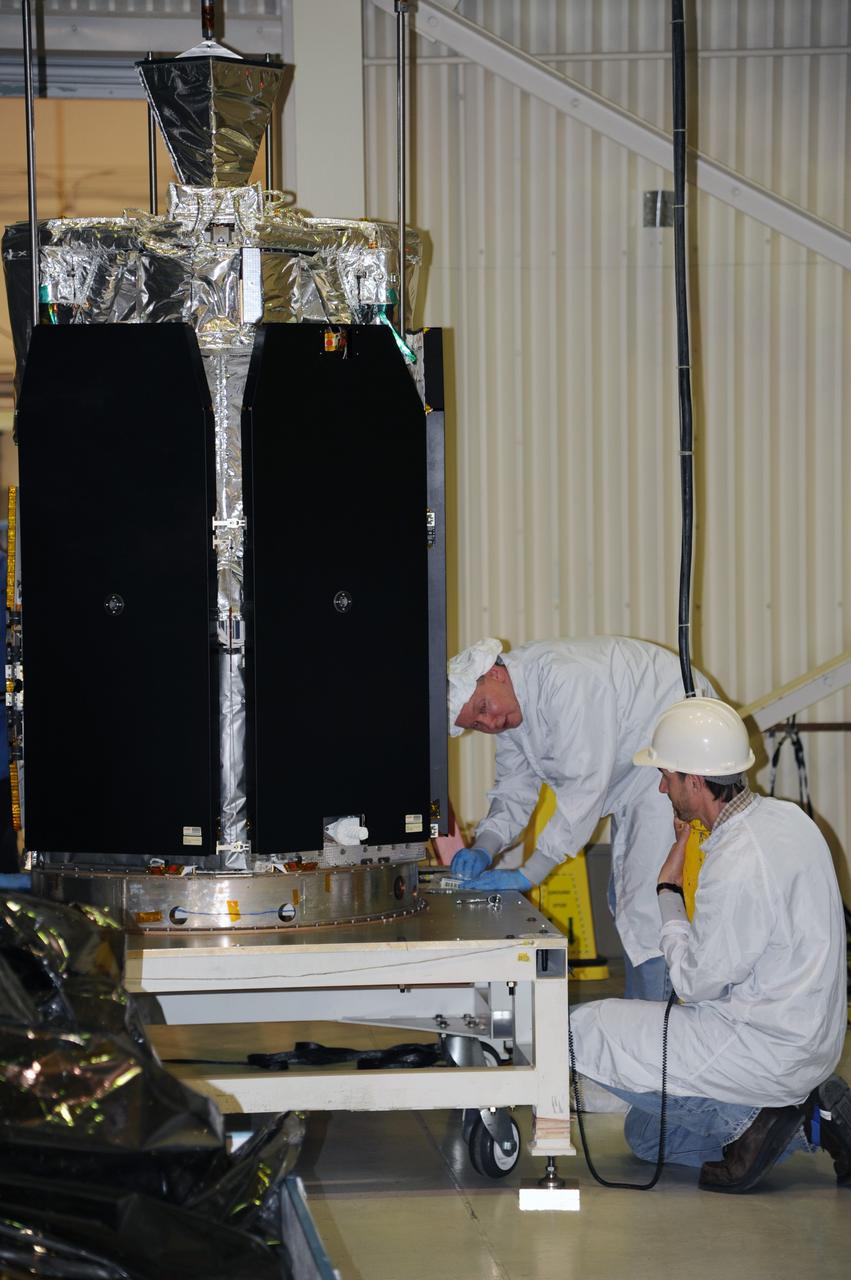

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, workers secure NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) onto a handling dolly. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
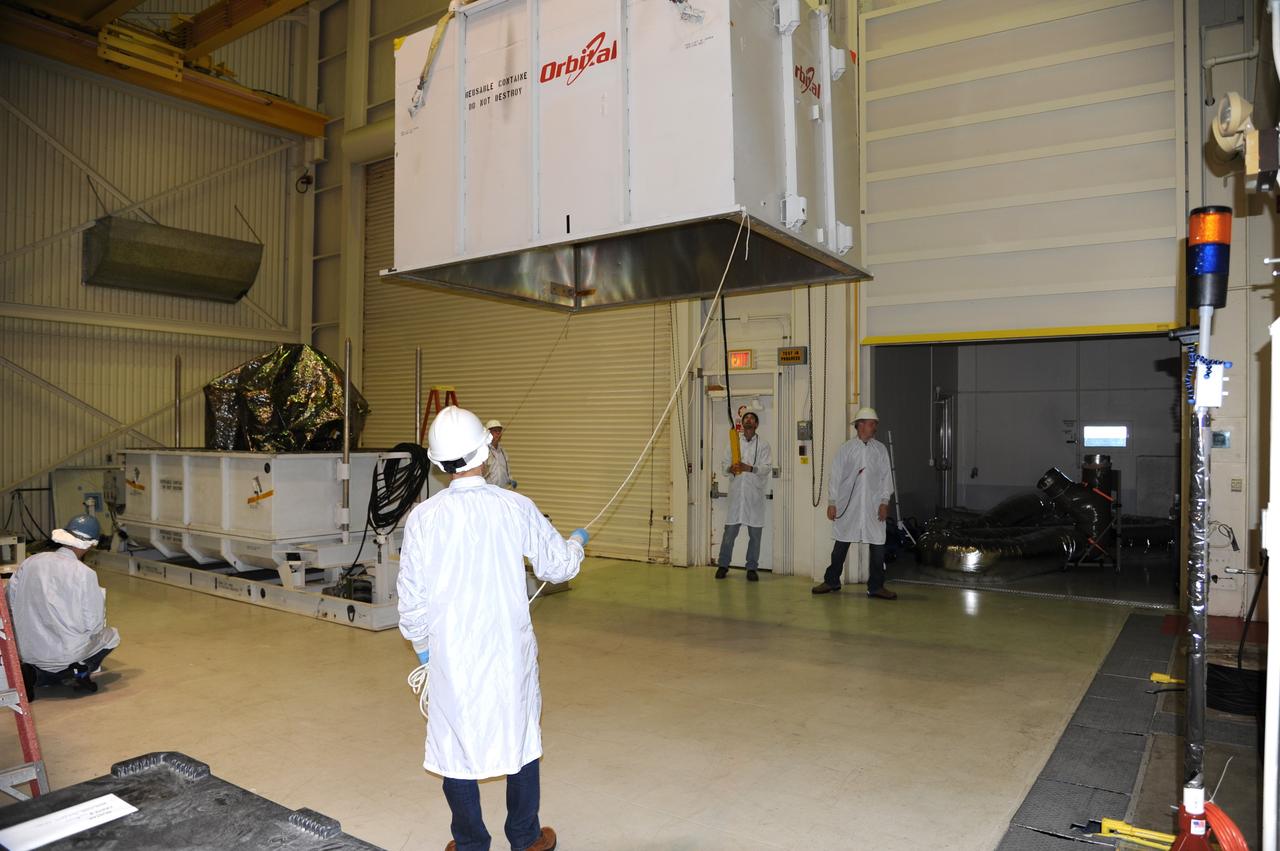

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, the top half of the shipping container is lifted away from NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), wrapped in a protective shroud. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
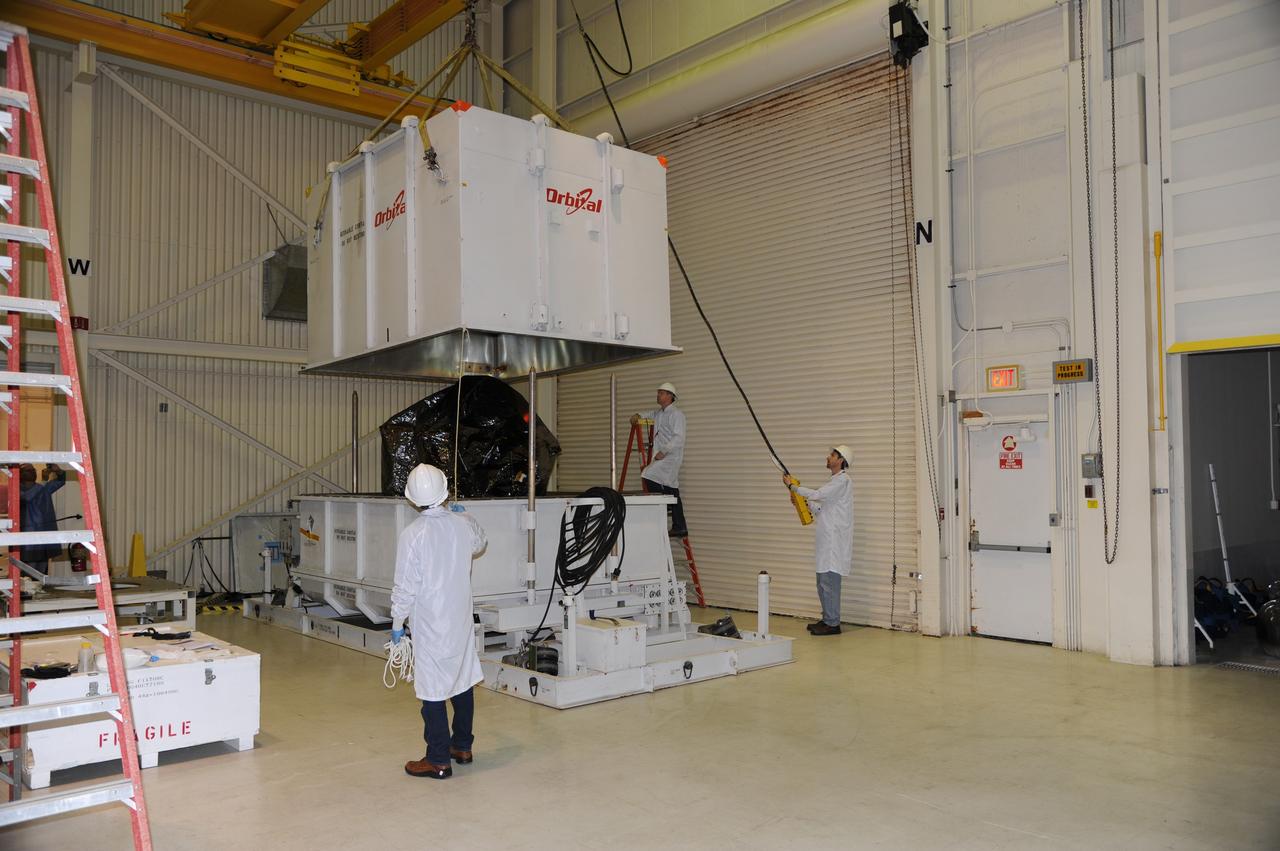

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, workers lift the top half of the shipping container from around NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), wrapped in a protective shroud. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
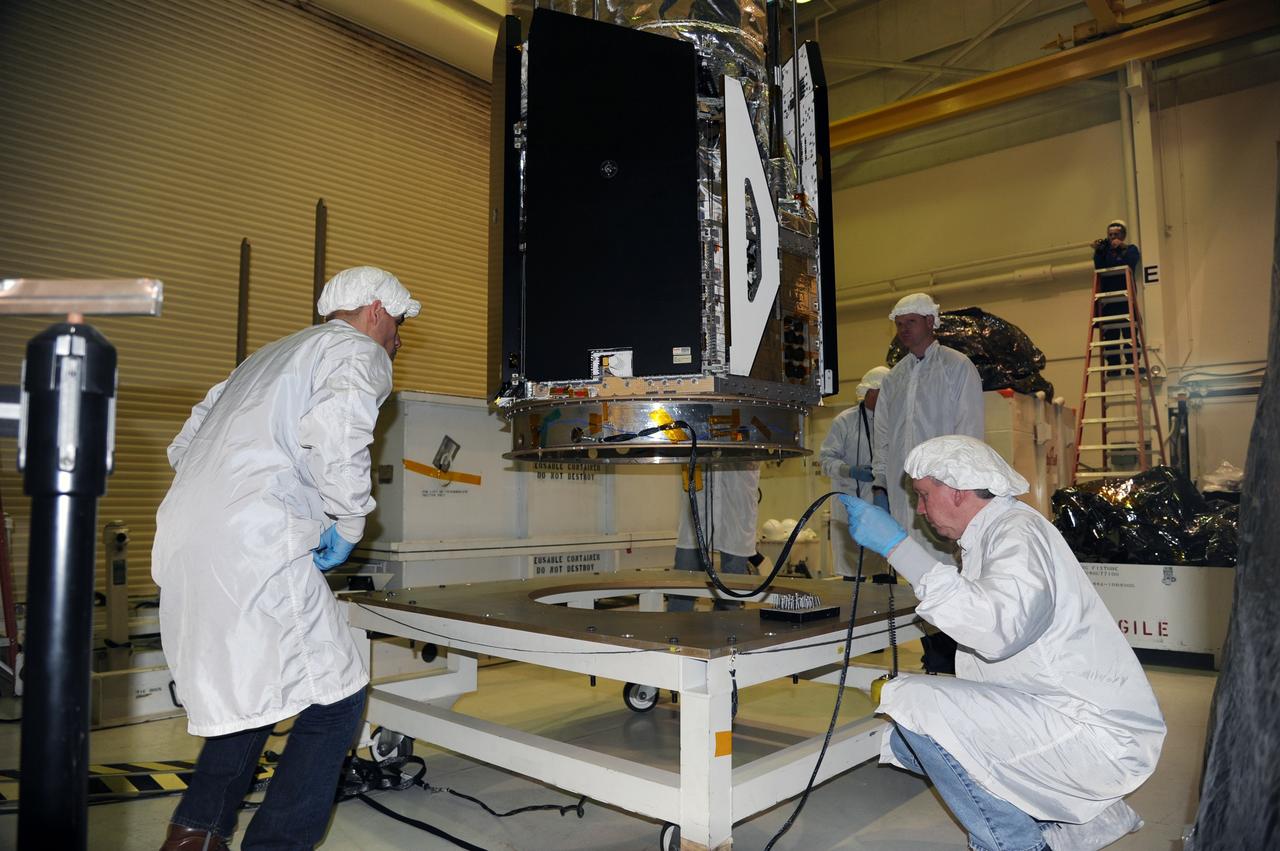

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, workers monitor NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) as it is lowered onto a handling dolly. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
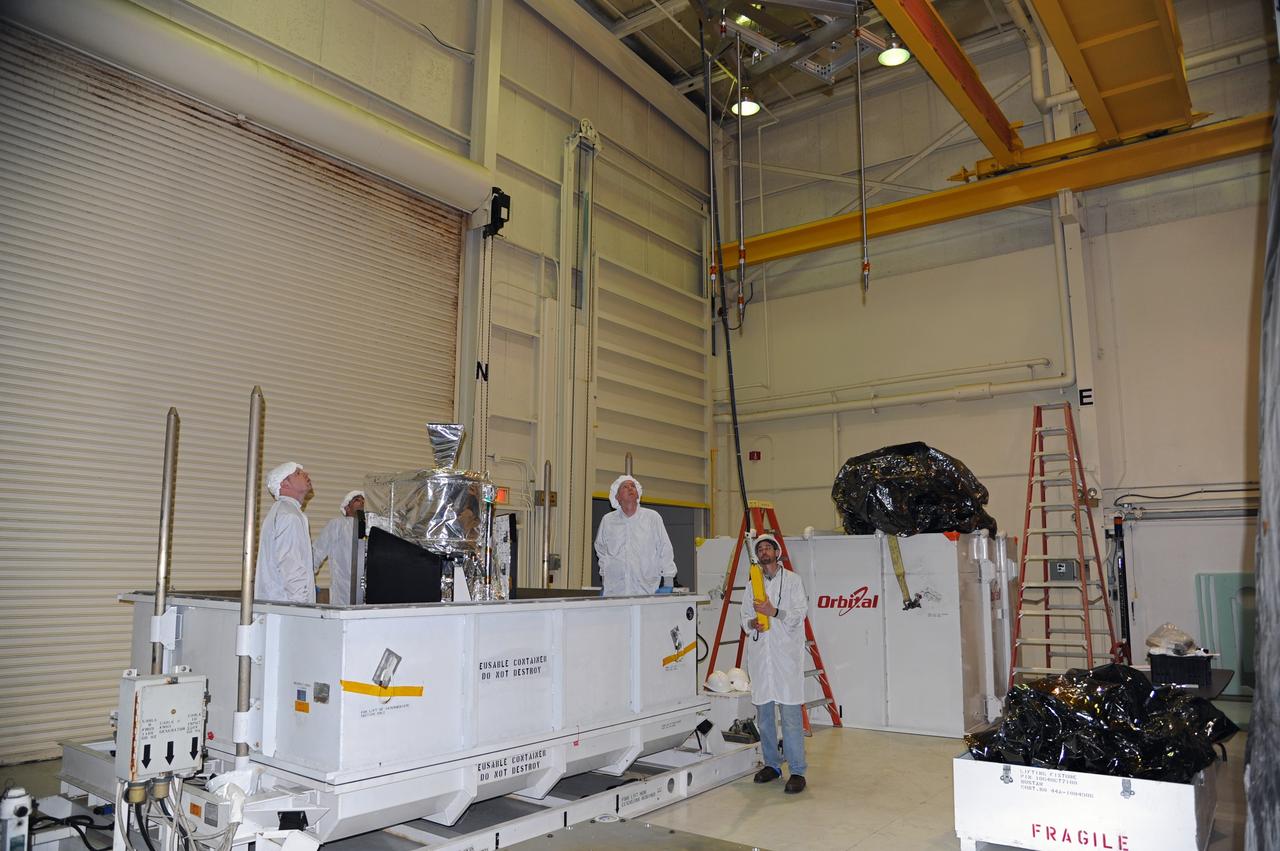

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, workers position a lifting fixture toward NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) during preparations to hoist it from its shipping container. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers position NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), enclosed in an environmentally controlled shipping container, onto a payload transporter for transfer of the telescope into the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., which began Jan. 24. The spacecraft will be offloaded into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After NuSTAR is removed from its shipping container, checkout and other processing activity will begin. The spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. After processing is completed, the rocket and spacecraft will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), enclosed in an environmentally controlled shipping container, is trucked by trailer to processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., which began Jan. 24. The spacecraft will be offloaded into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After NuSTAR is removed from its shipping container, checkout and other processing activity will begin. The spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. After processing is completed, the rocket and spacecraft will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers maneuver the payload transporter carrying the environmentally controlled shipping container enclosing NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into position in the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip which began Jan. 24 from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va. The spacecraft will be removed from the shipping container in the airlock and transferred into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
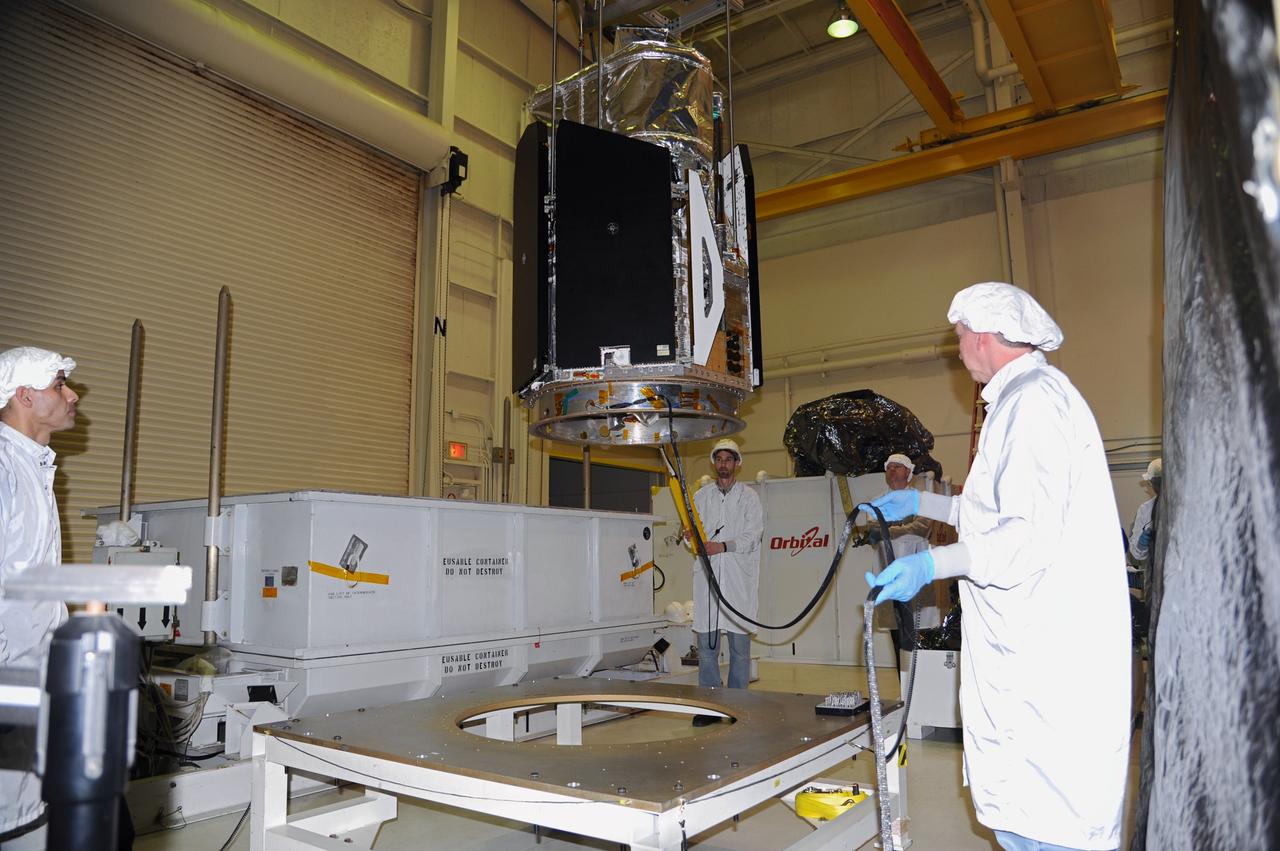

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) moves slowly toward a handling dolly. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
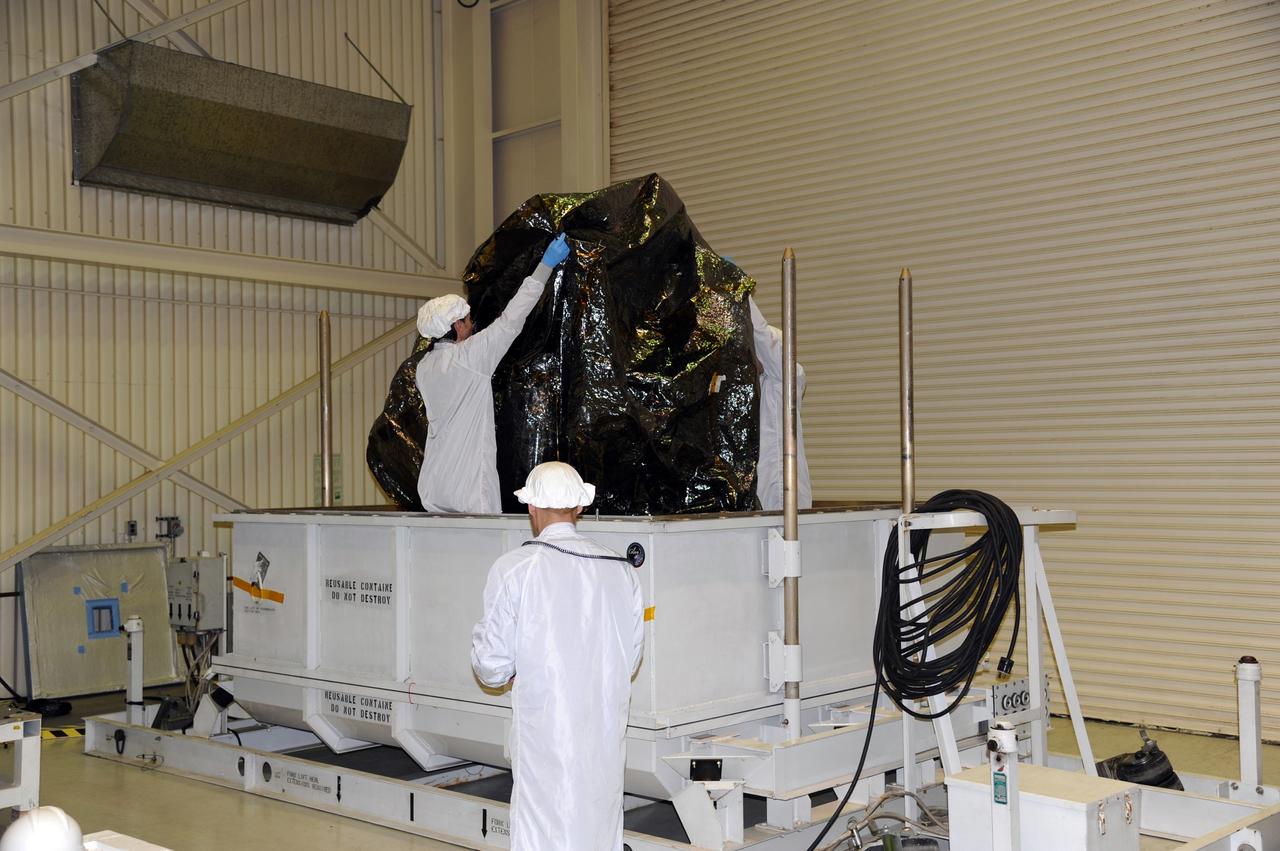

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- In the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California, workers start to remove the protective shroud from around NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) as it rests in the bottom half of a shipping container. The spacecraft arrived at VAFB Jan. 27 after a cross-country trip which began from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., on Jan. 24. Next, NuSTAR will be transferred from the airlock into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After checkout and other processing activities are complete, the spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. The rocket and spacecraft then will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
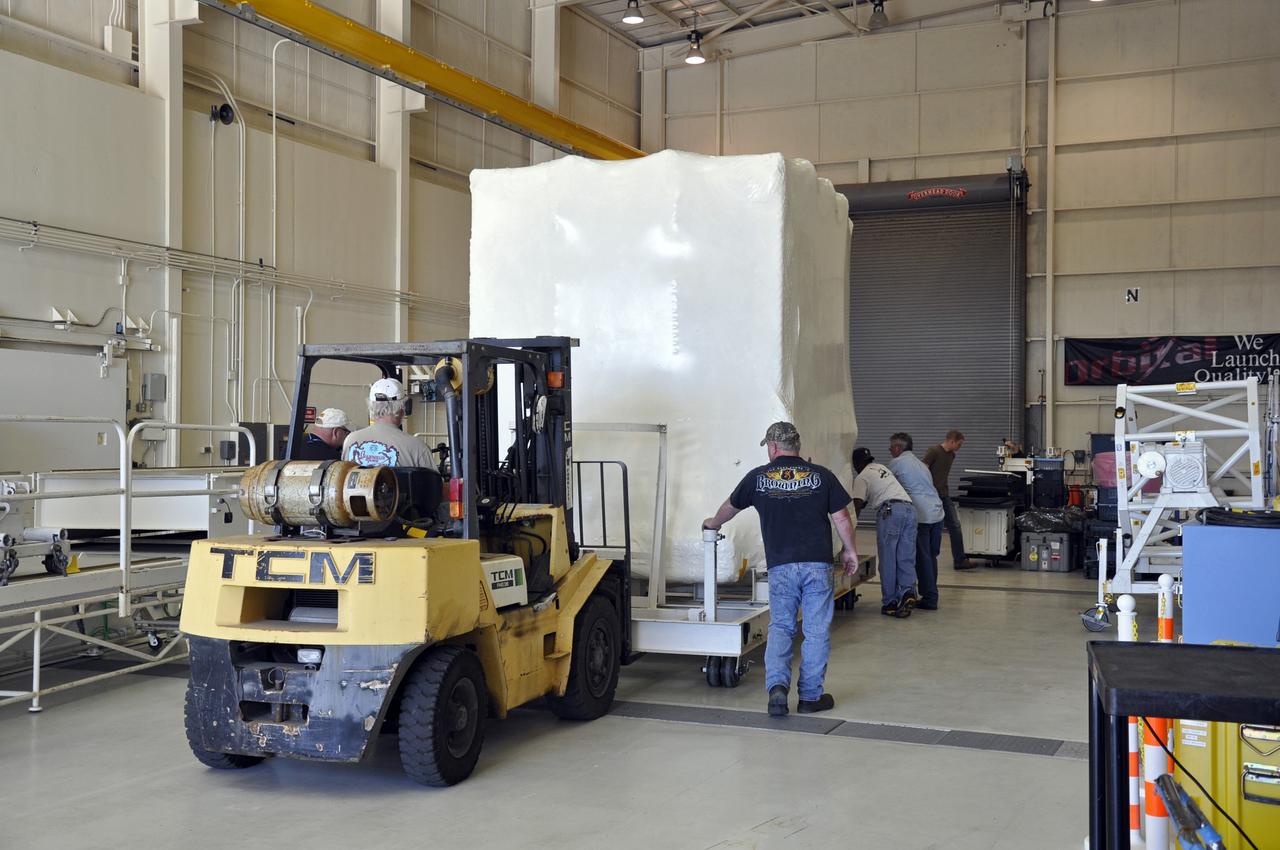

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers position the environmentally controlled shipping container enclosing NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) in the airlock of processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., which began Jan. 24. The spacecraft will be offloaded into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After NuSTAR is removed from its shipping container, checkout and other processing activity will begin. The spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. After processing is completed, the rocket and spacecraft will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
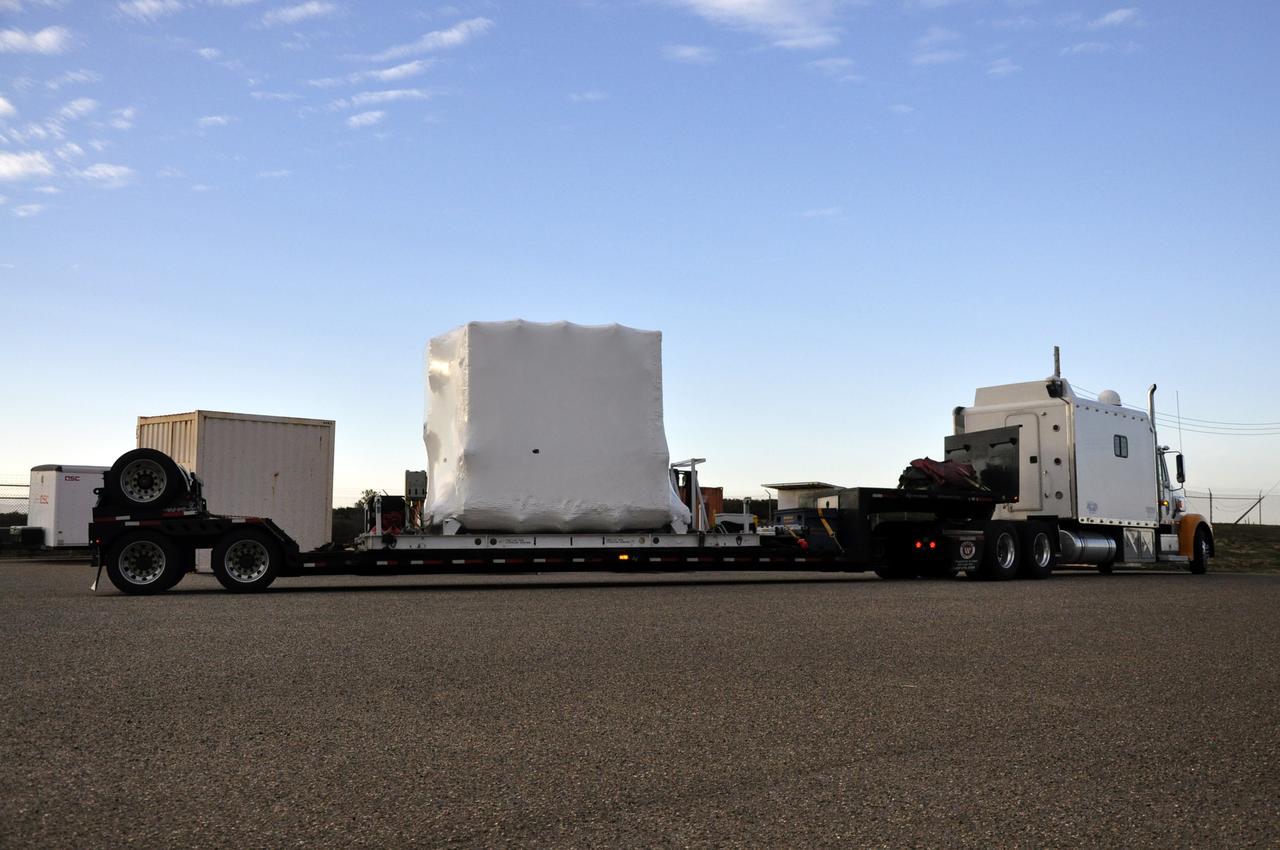

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), enclosed in an environmentally controlled shipping container, arrives at processing facility 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. The spacecraft arrived at 7:52 a.m. PST after a cross-country trip from Orbital Sciences' manufacturing plant in Dulles, Va., which began Jan. 24. The spacecraft will be offloaded into the processing hangar, joining the Pegasus XL rocket that is set to carry it to space. After NuSTAR is removed from its shipping container, checkout and other processing activity will begin. The spacecraft will be integrated with the Pegasus in mid-February and encapsulation in the vehicle fairing will follow. After processing is completed, the rocket and spacecraft will be flown on Orbital's L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch in March. The high-energy x-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB