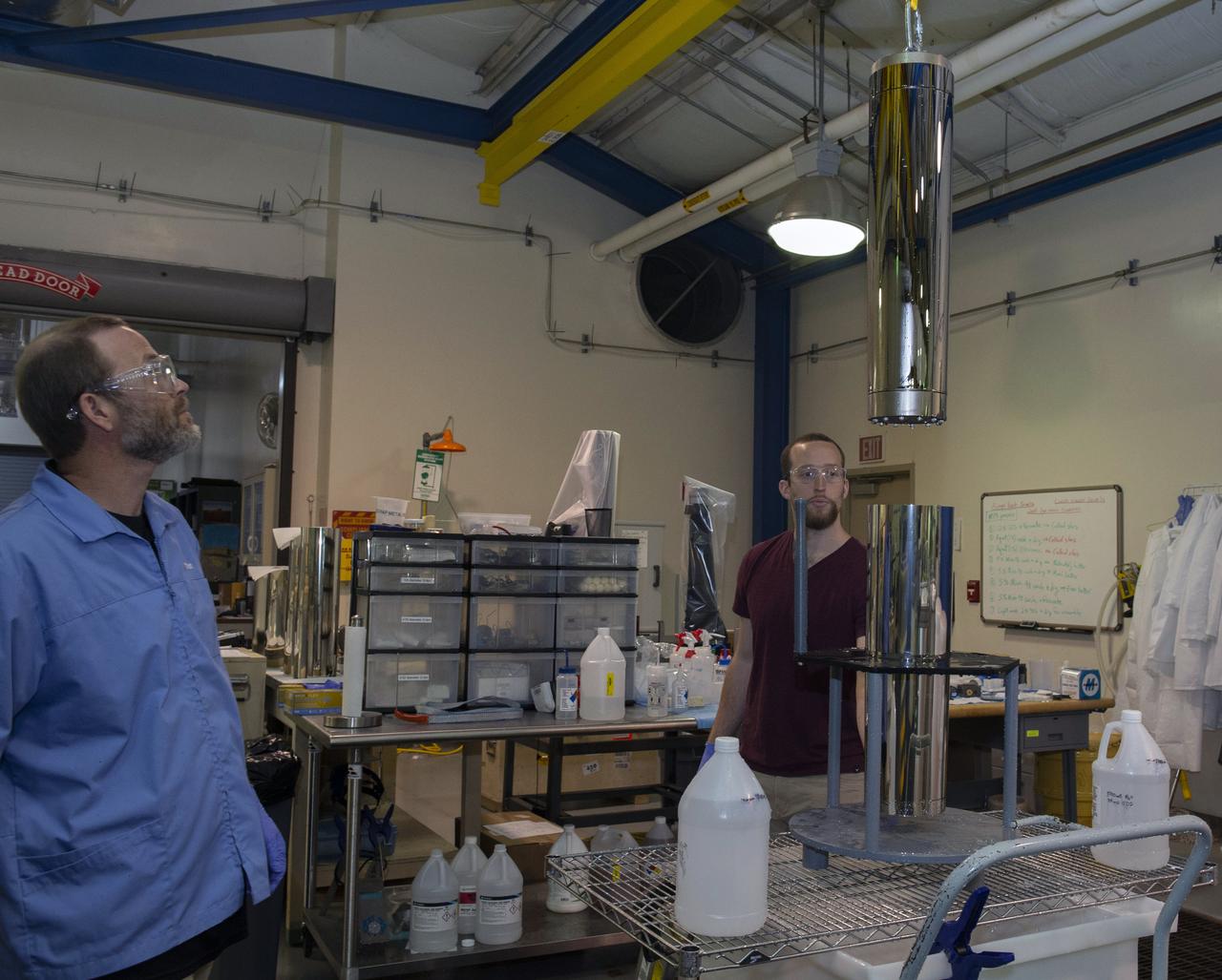

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
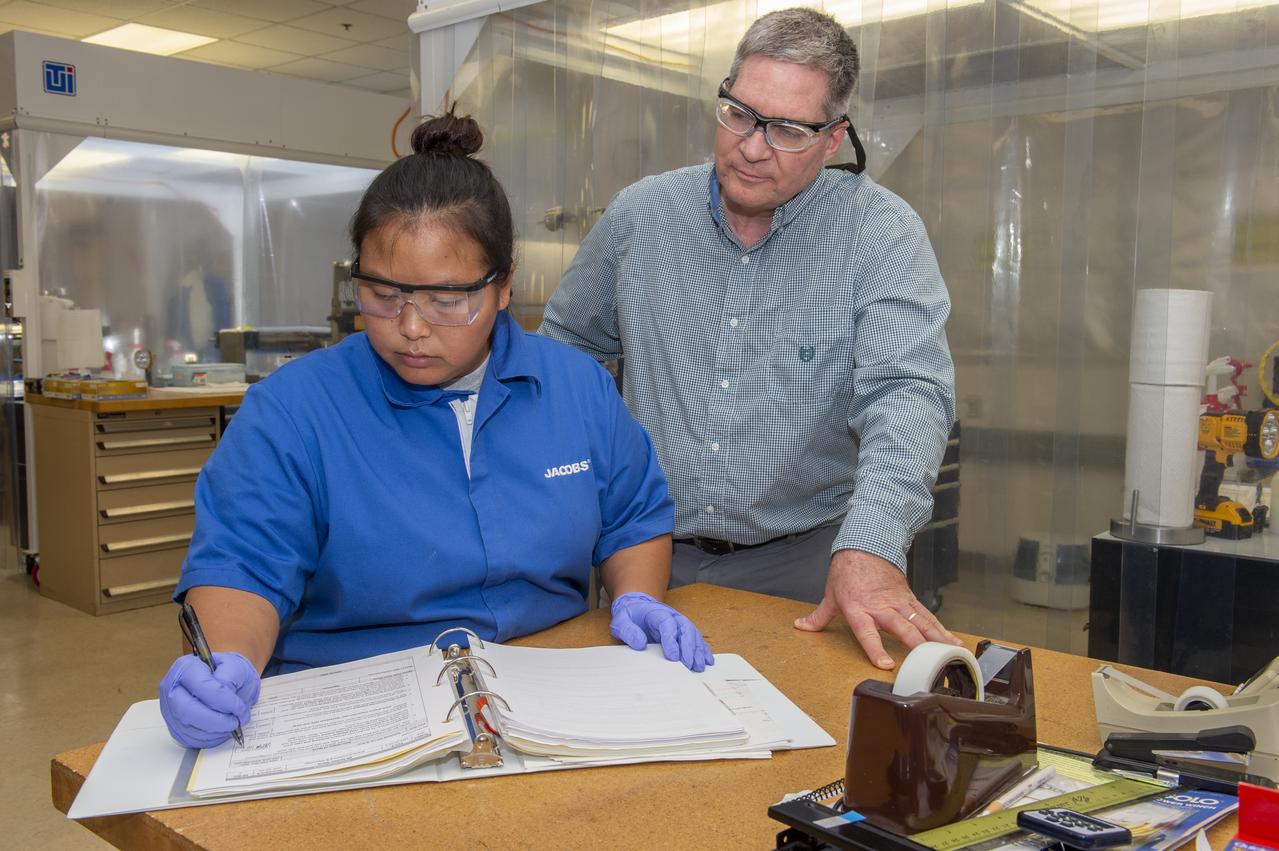

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
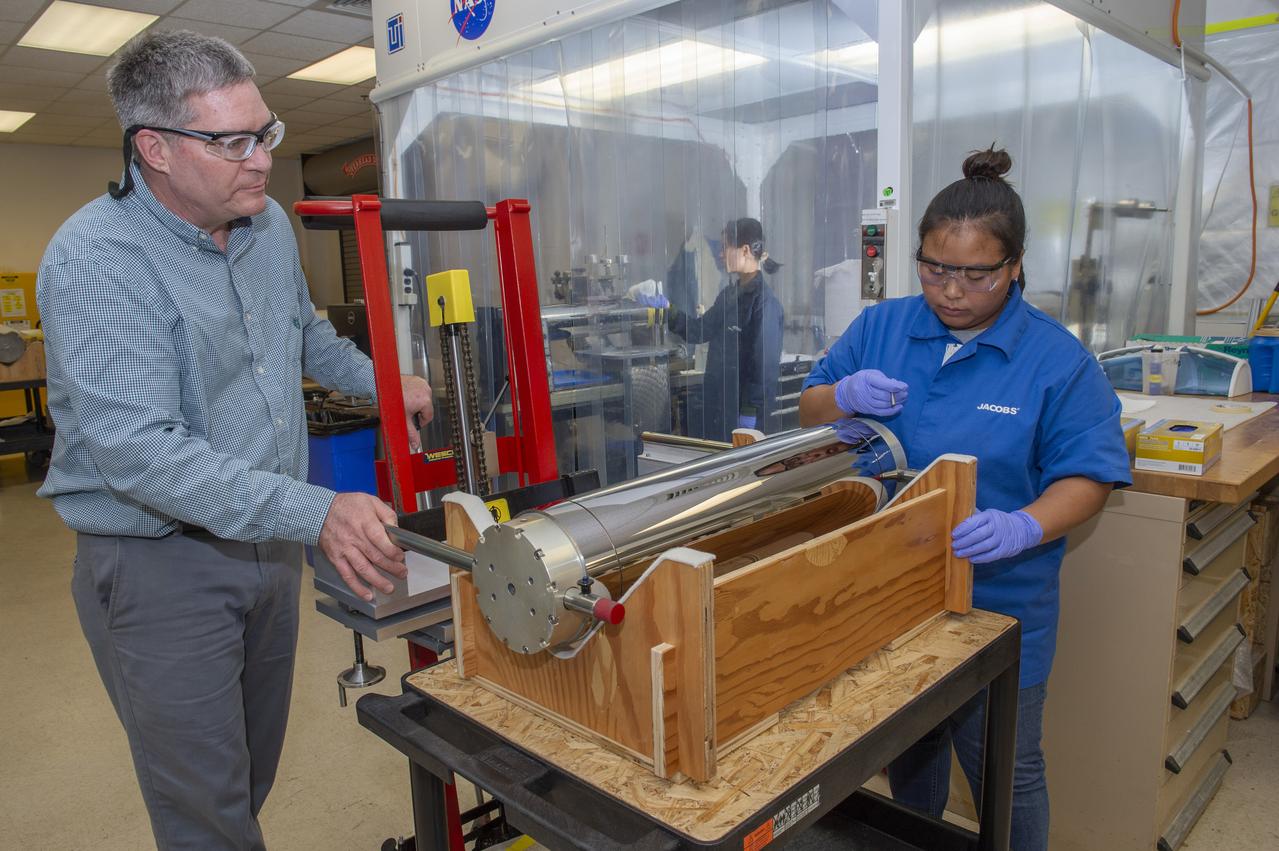

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
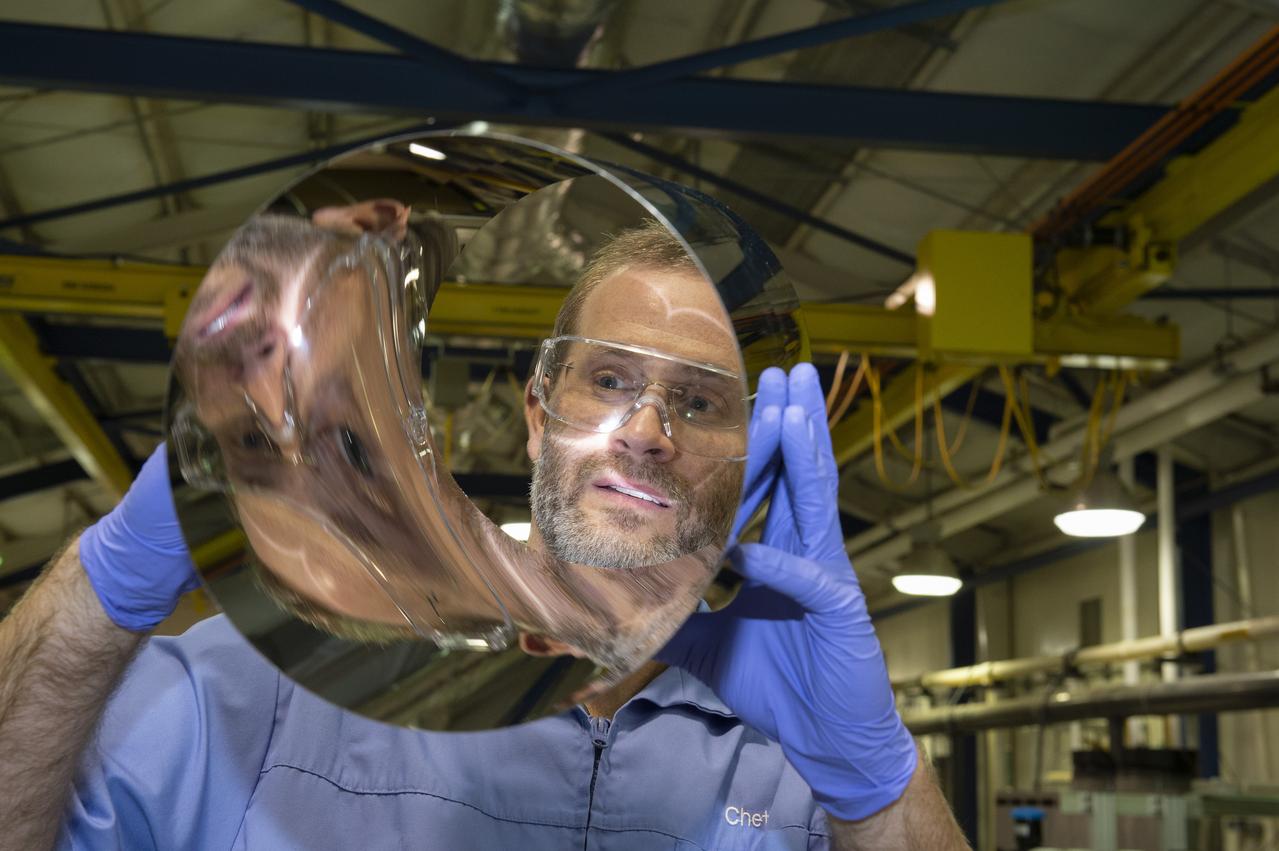

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
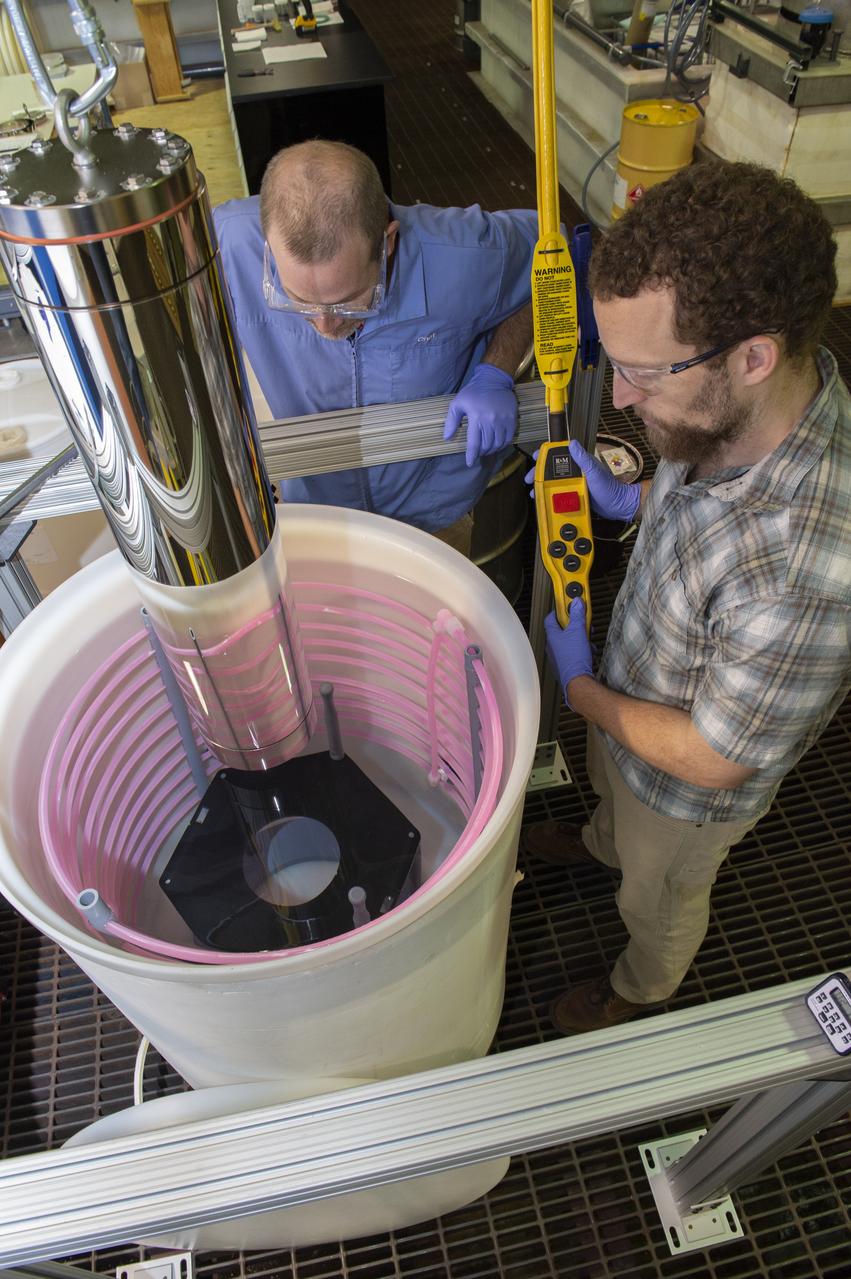

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
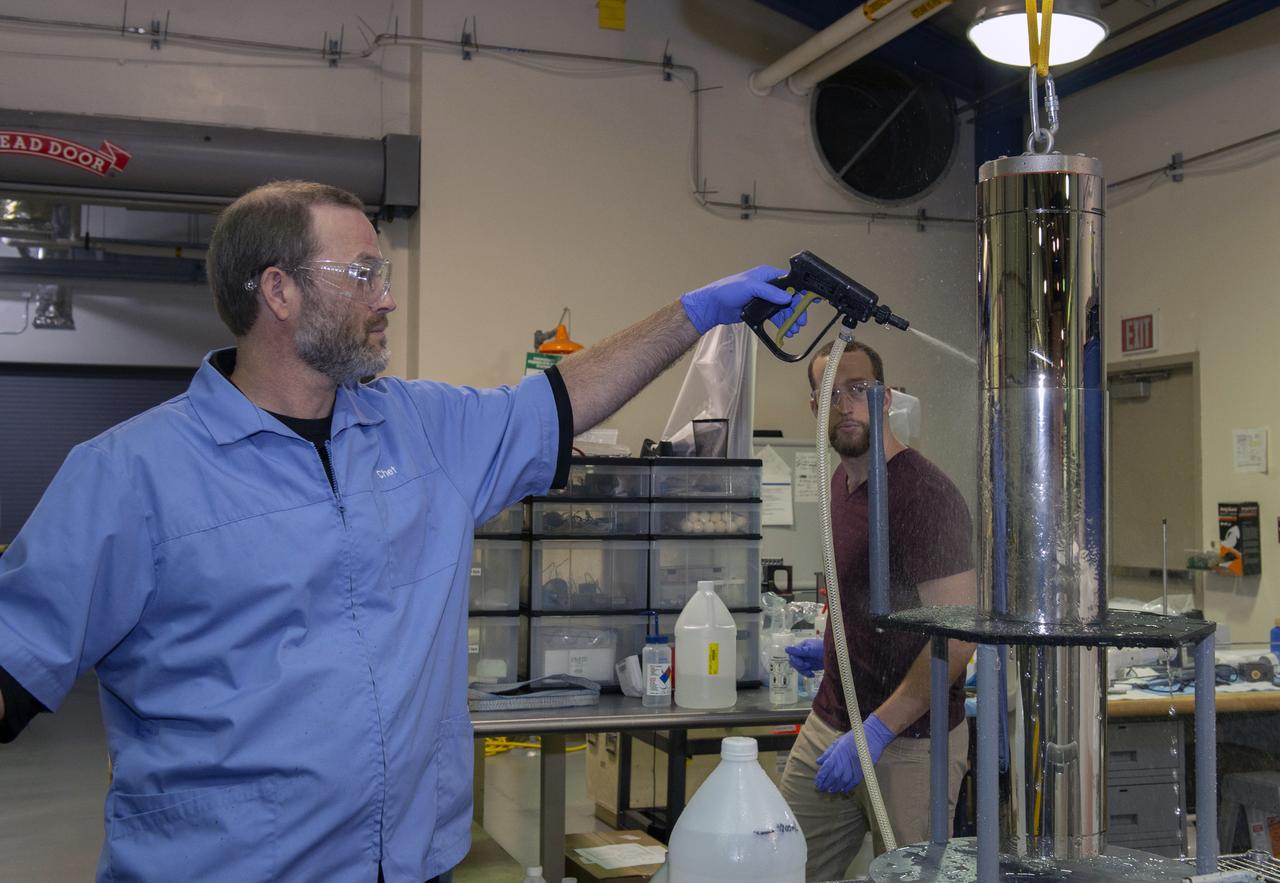

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
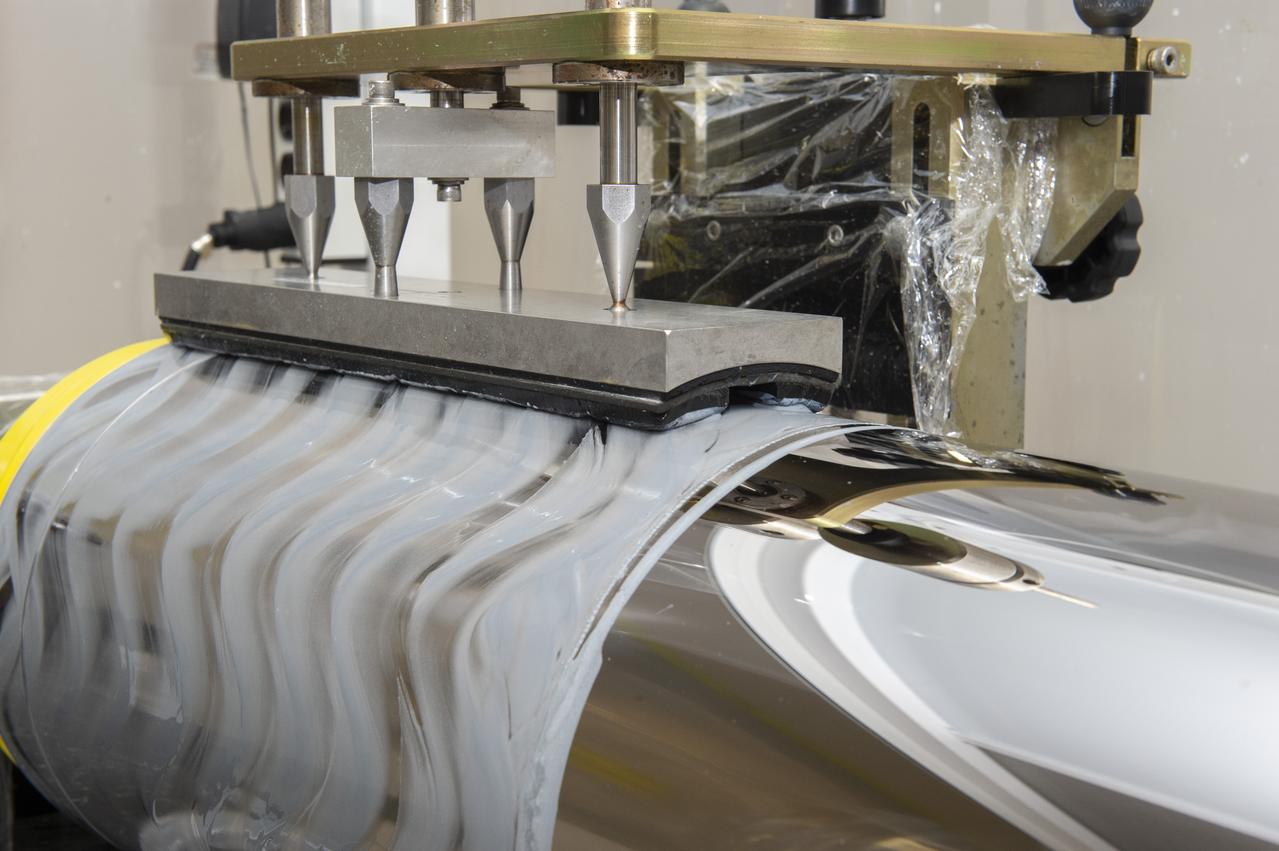

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
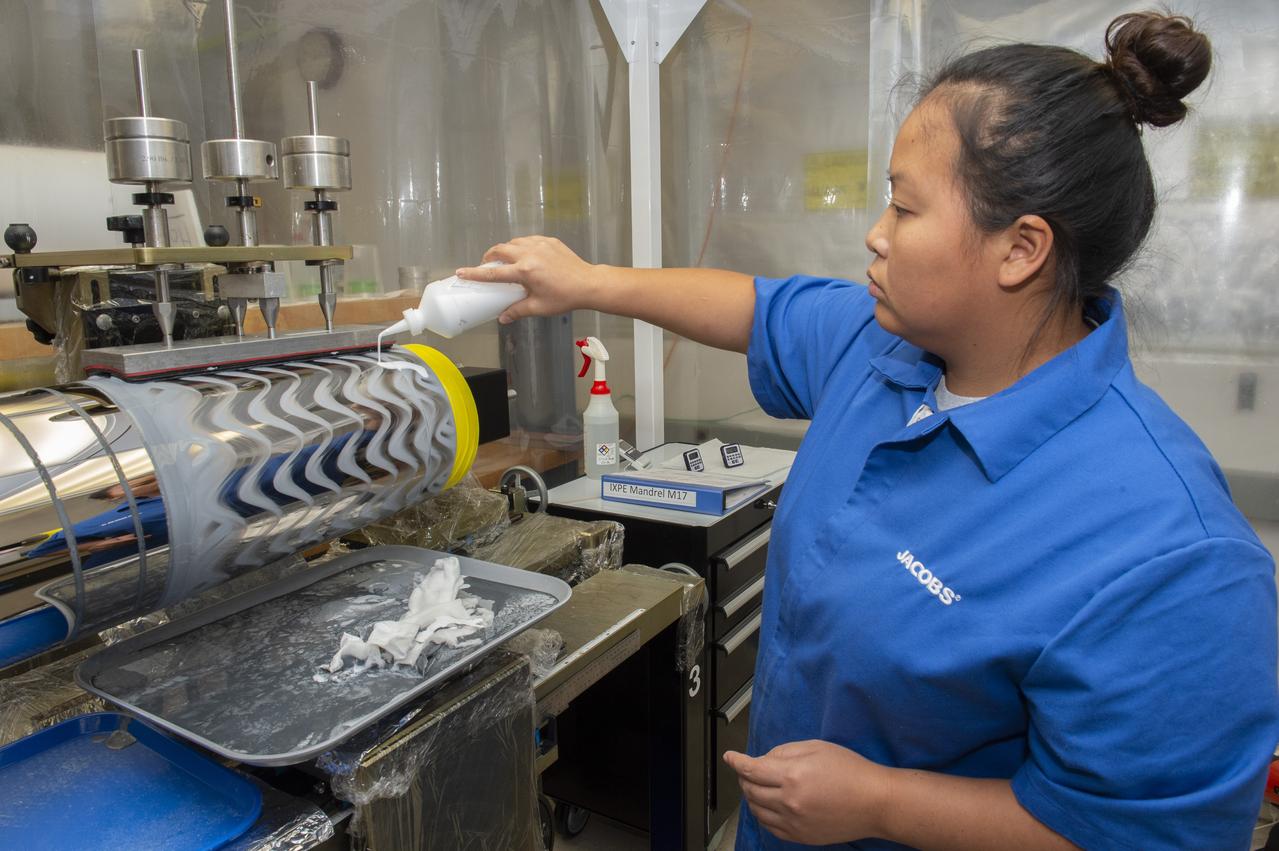

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
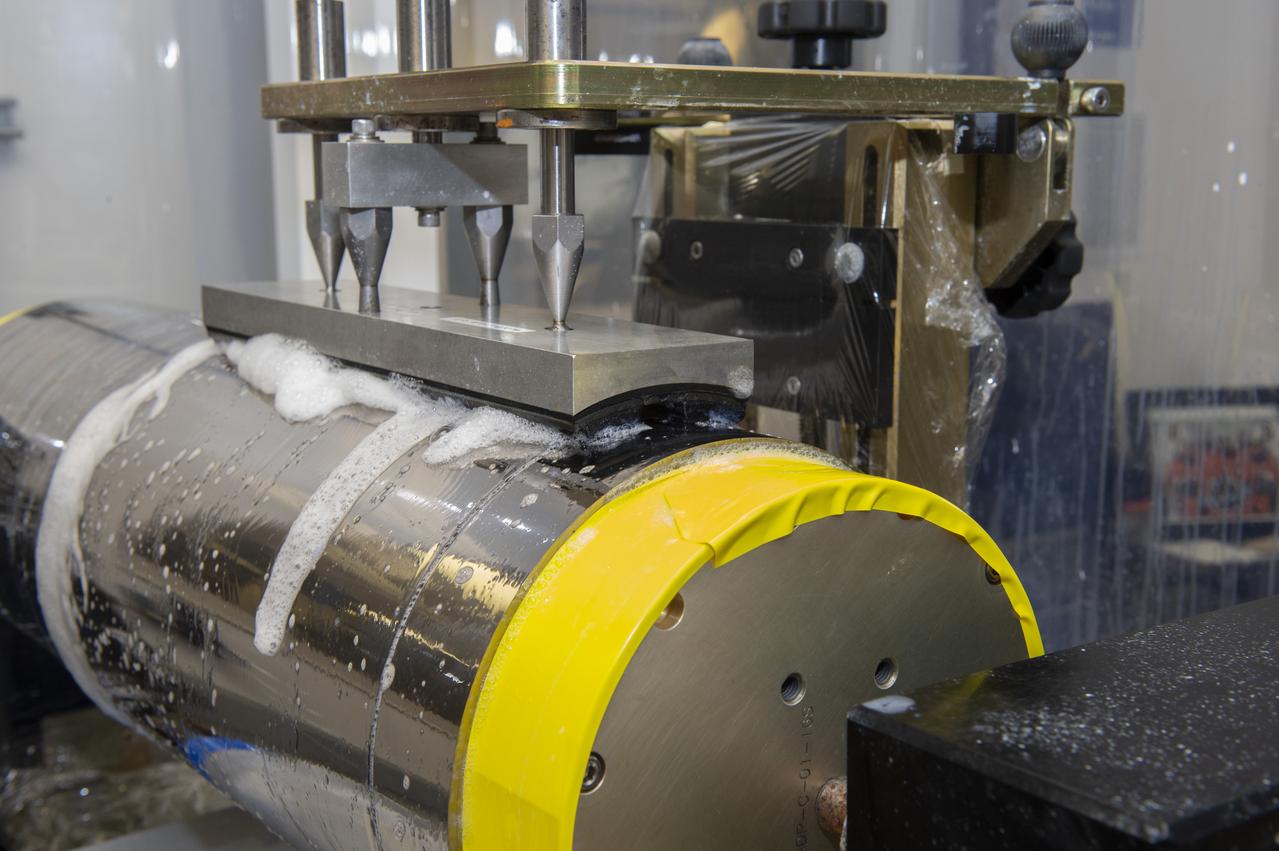

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM
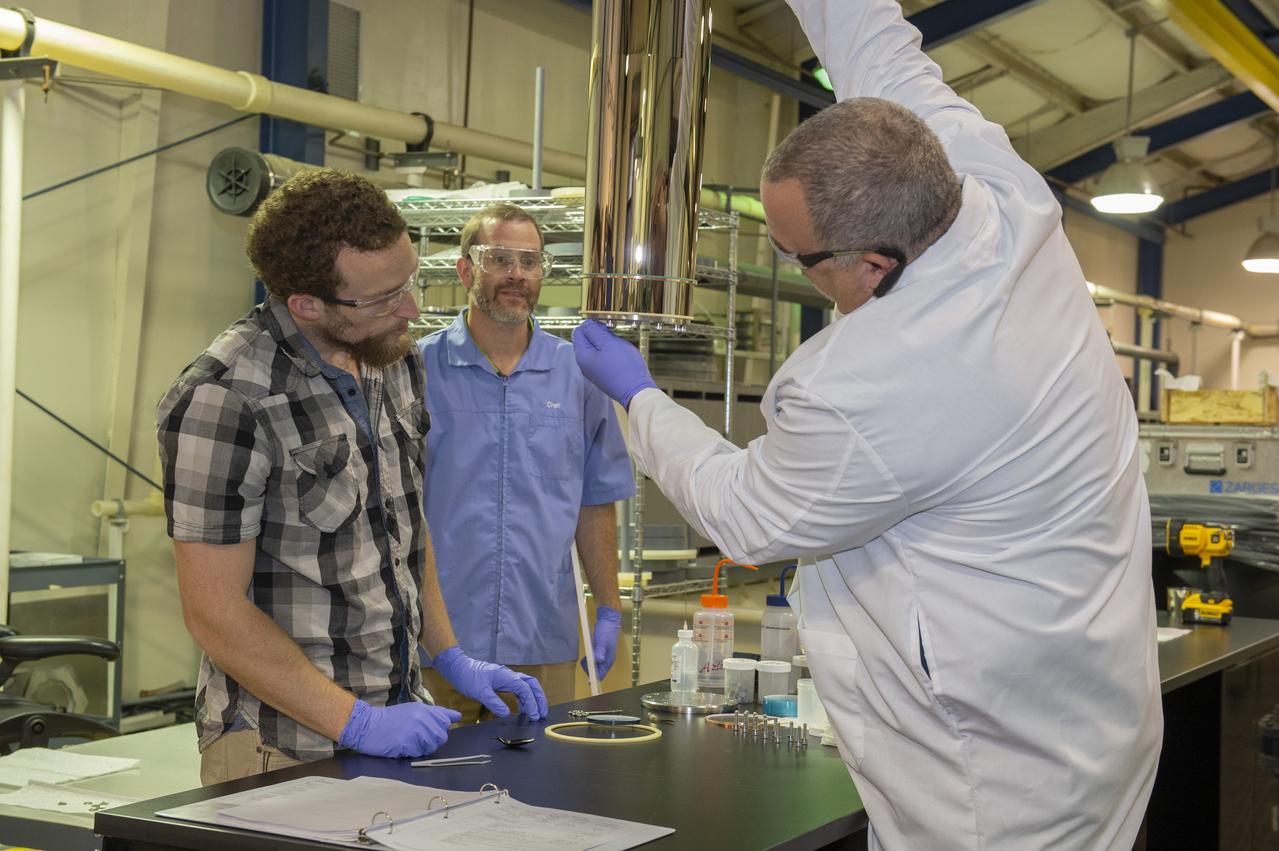

X-RAY MIRROR REPLICATION AND SHELL SEPARATION PROCESS: CHET SPEEGLE, JOHN HOOD, KEITH BOWEN, CARL WIDRIG, RATANA MEEKHAM, AMY MEEKHAM

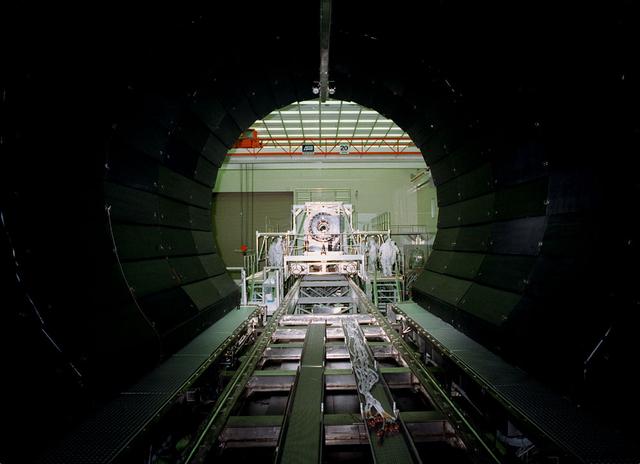
TESTING OF THE KODAK ADVANCE MIRROR SYSTEM DEMONSTRATOR IN THE X-RAY CALIBRATION FACILITY

This photograph shows the mirrors of the High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) for the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), being assembled in the Eastman Kodak Company in Rochester, New York. The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRMA, the heart of the telescope system, is contained in the cylindrical "telescope" portion of the observatory. Since high-energy x-rays would penetrate a normal mirror, special cylindrical mirrors were created. The two sets of four nested mirrors resemble tubes within tubes. Incoming x-rays graze off the highly polished mirror surface and are furneled to the instrument section for detection and study. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for its project management. The Observatory was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, STS-93 mission.

This is a photograph of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) integration at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRMA, the heart of the telescope system, is contained in the cylindrical "telescope" portion of the observatory. Since high-energy x-rays would penetrate a normal mirror, special cylindrical mirrors were created. The two sets of four nested mirrors resemble tubes within tubes. Incoming x-rays graze off the highly polished mirror surface and are furneled to the instrument section for detection and study. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSCF was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
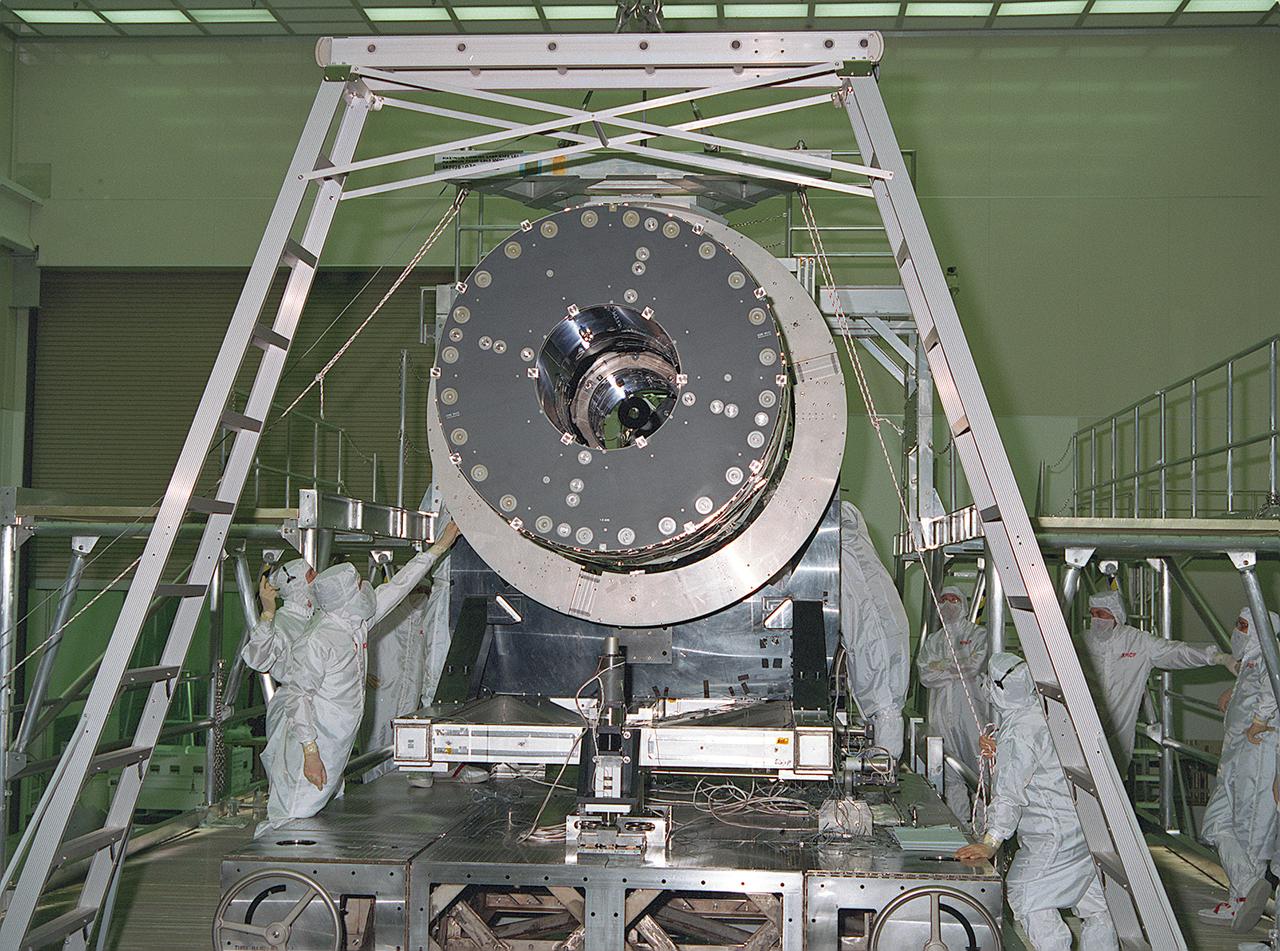
This photograph shows the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) being removed from the test structure in the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRMA, the heart of the telescope system, is contained in the cylindrical "telescope" portion of the observatory. Since high-energy x-rays would penetrate a normal mirror, special cylindrical mirrors were created. The two sets of four nested mirrors resemble tubes within tubes. Incoming x-rays graze off the highly polished mirror surface and are furneled to the instrument section for detection and study. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
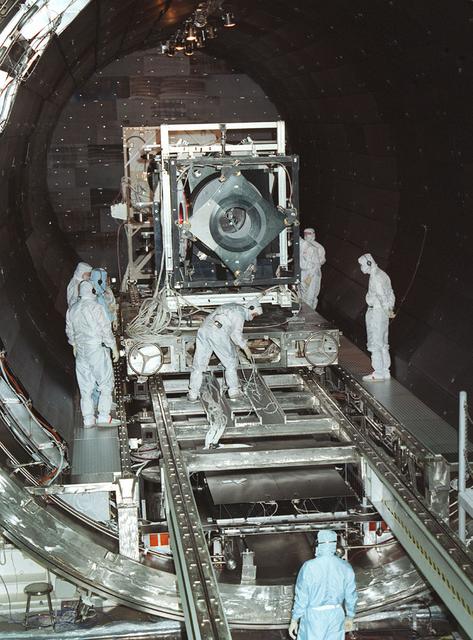

This is a photograph of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) integration at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRMA, the heart of the telescope system, is contained in the cylindrical "telescope" portion of the observatory. Since high-energy x-rays would penetrate a normal mirror, special cylindrical mirrors were created. The two sets of four nested mirrors resemble tubes within tubes. Incoming x-rays graze off the highly polished mirror surface and are furneled to the instrument section for detection and study. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
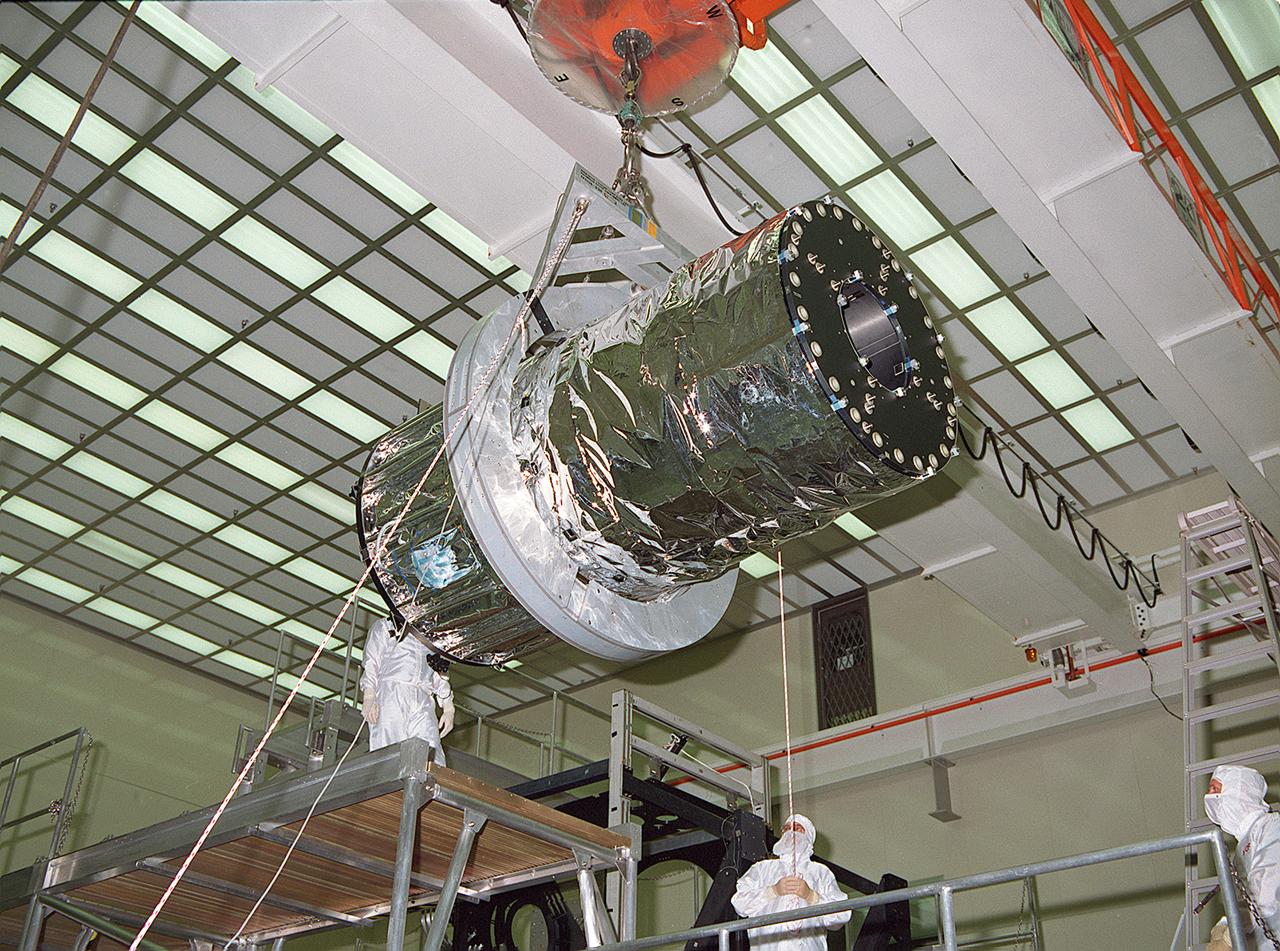

This photograph shows the Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) being removed from the test structure in the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRMA, the heart of the telescope system, is contained in the cylindrical "telescope" portion of the observatory. Since high-energy x-rays would penetrate a normal mirror, special cylindrical mirrors were created. The two sets of four nested mirrors resemble tubes within tubes. Incoming x-rays graze off the highly polished mirror surface and are furneled to the instrument section for detection and study. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
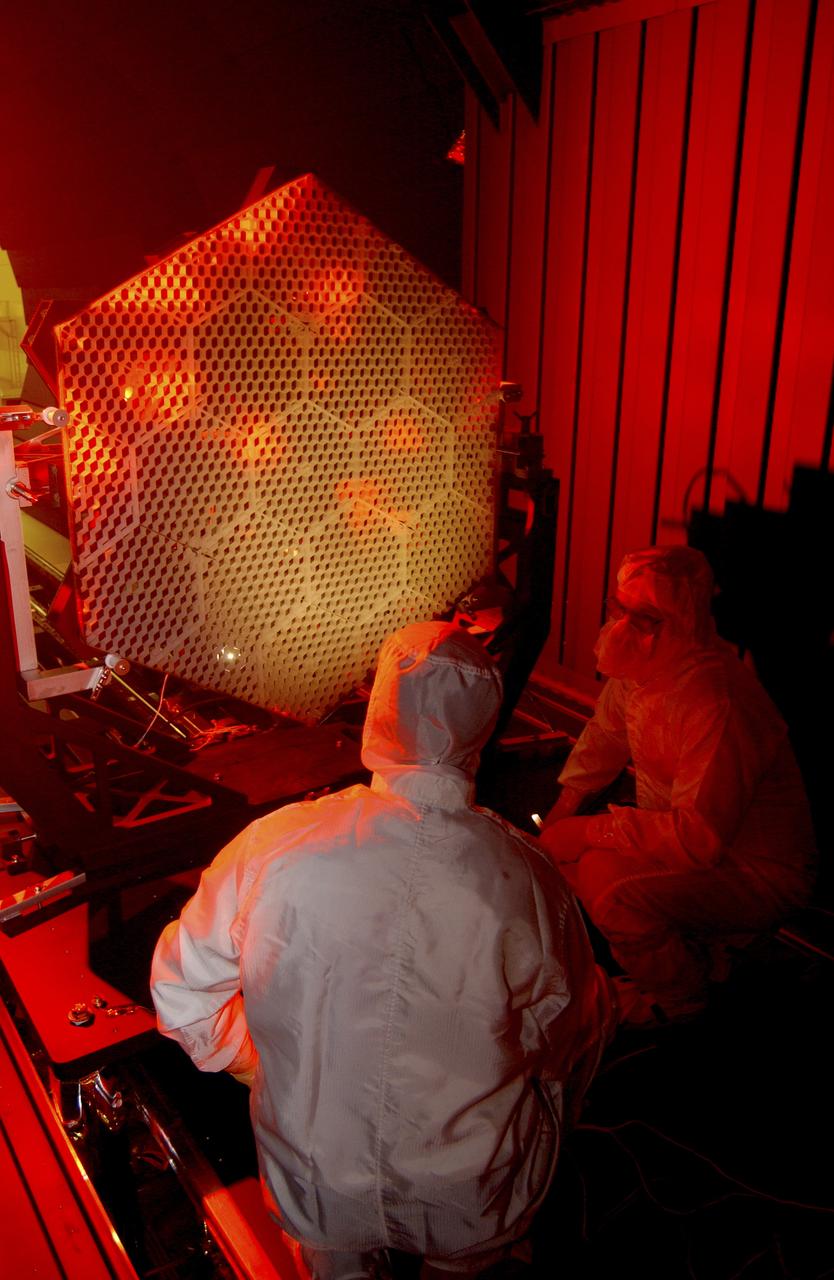

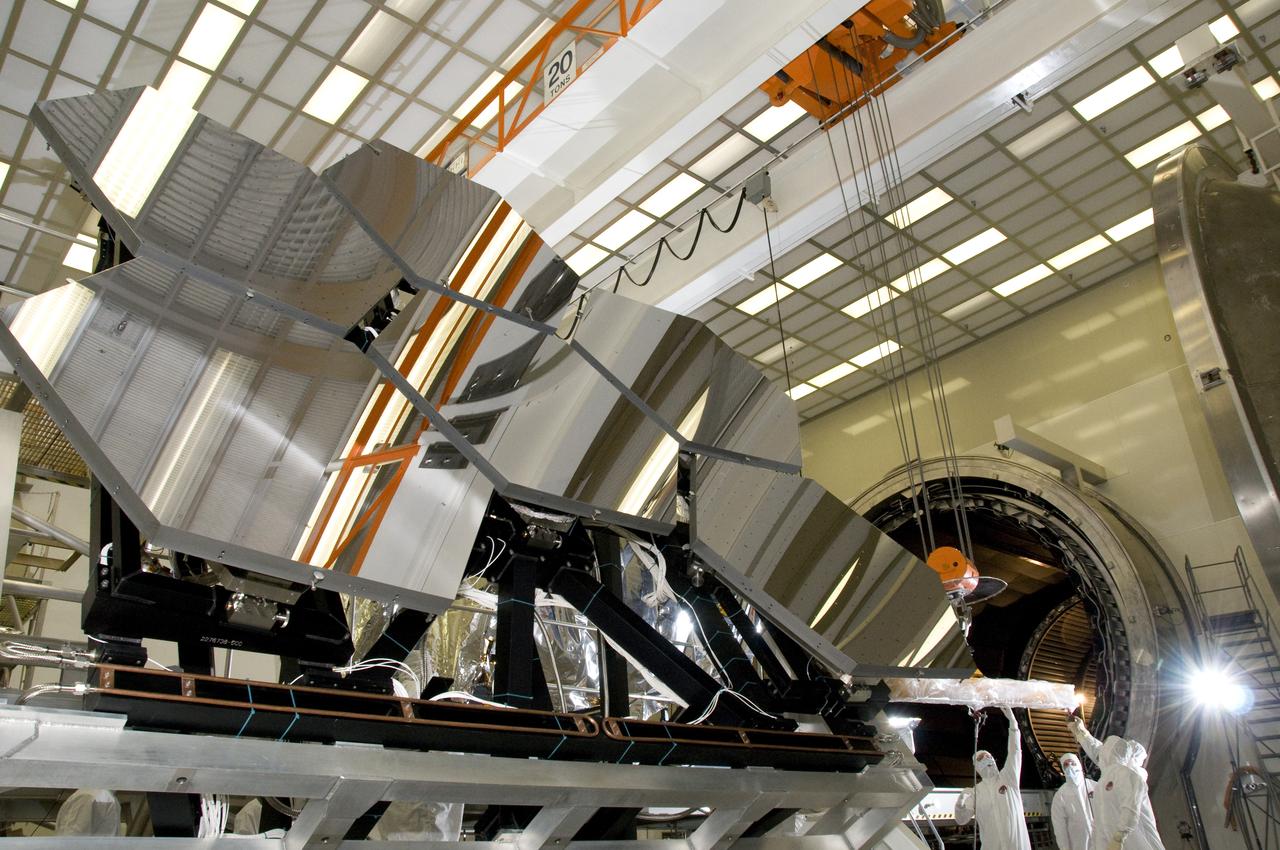
The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, one of many segments of the mirror assembly is being set up inside the 24-ft vacuum chamber where it will undergo x-ray calibration tests. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
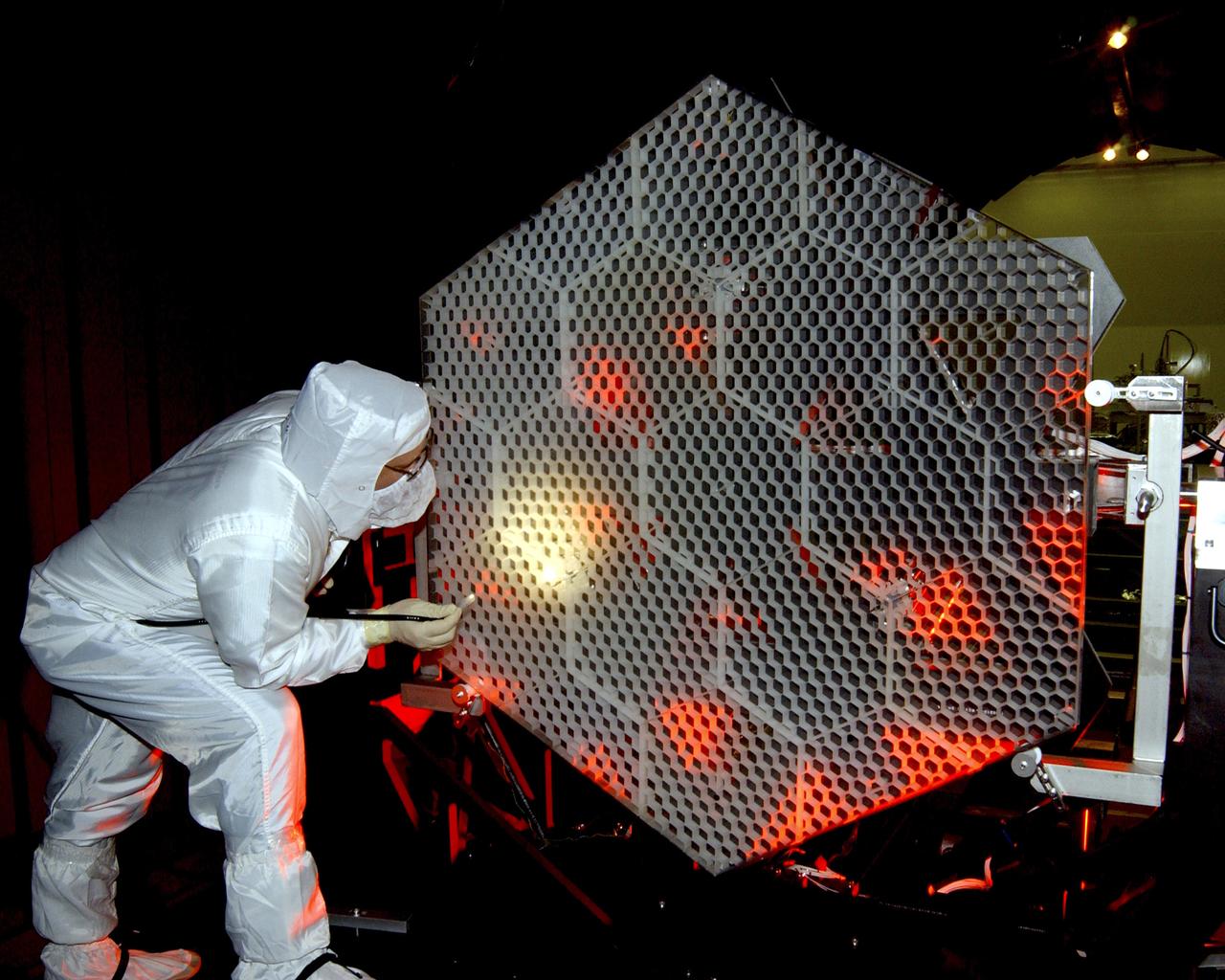

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, an MSFC employee is inspecting one of many segments of the mirror assembly for flaws. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
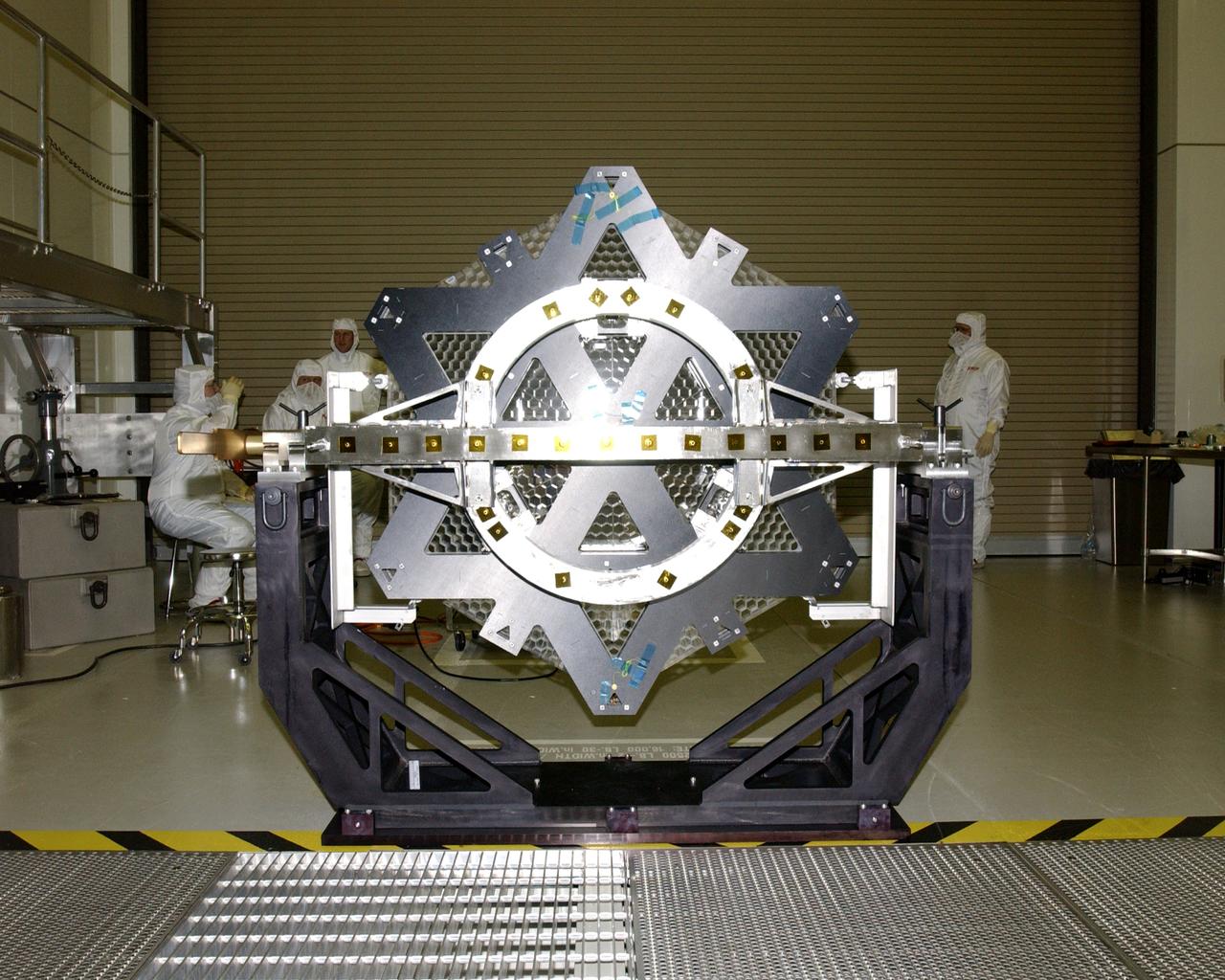
This photo (rear view) is of one of many segments of the Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
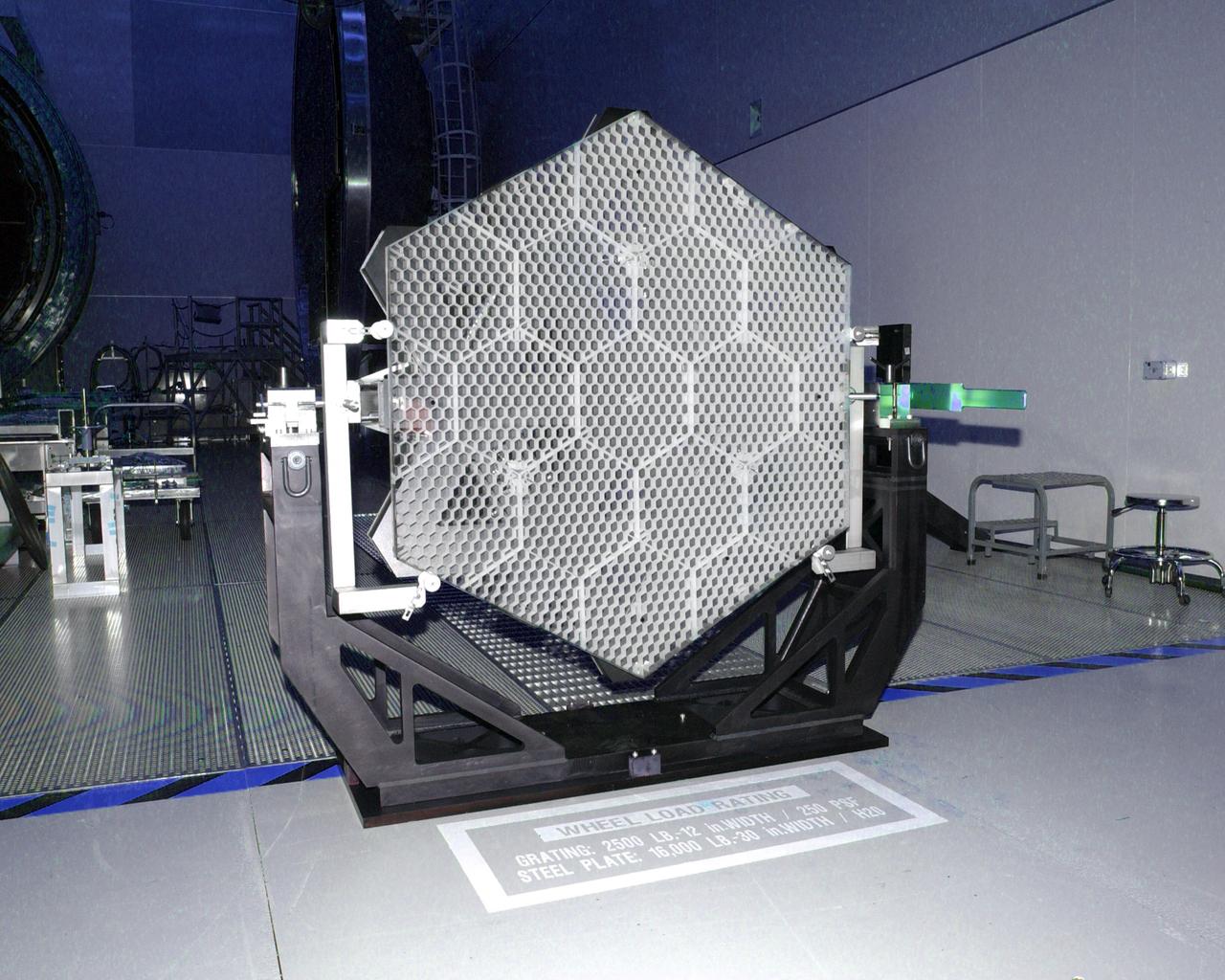
This photo (a frontal view) is of one of many segments of the Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
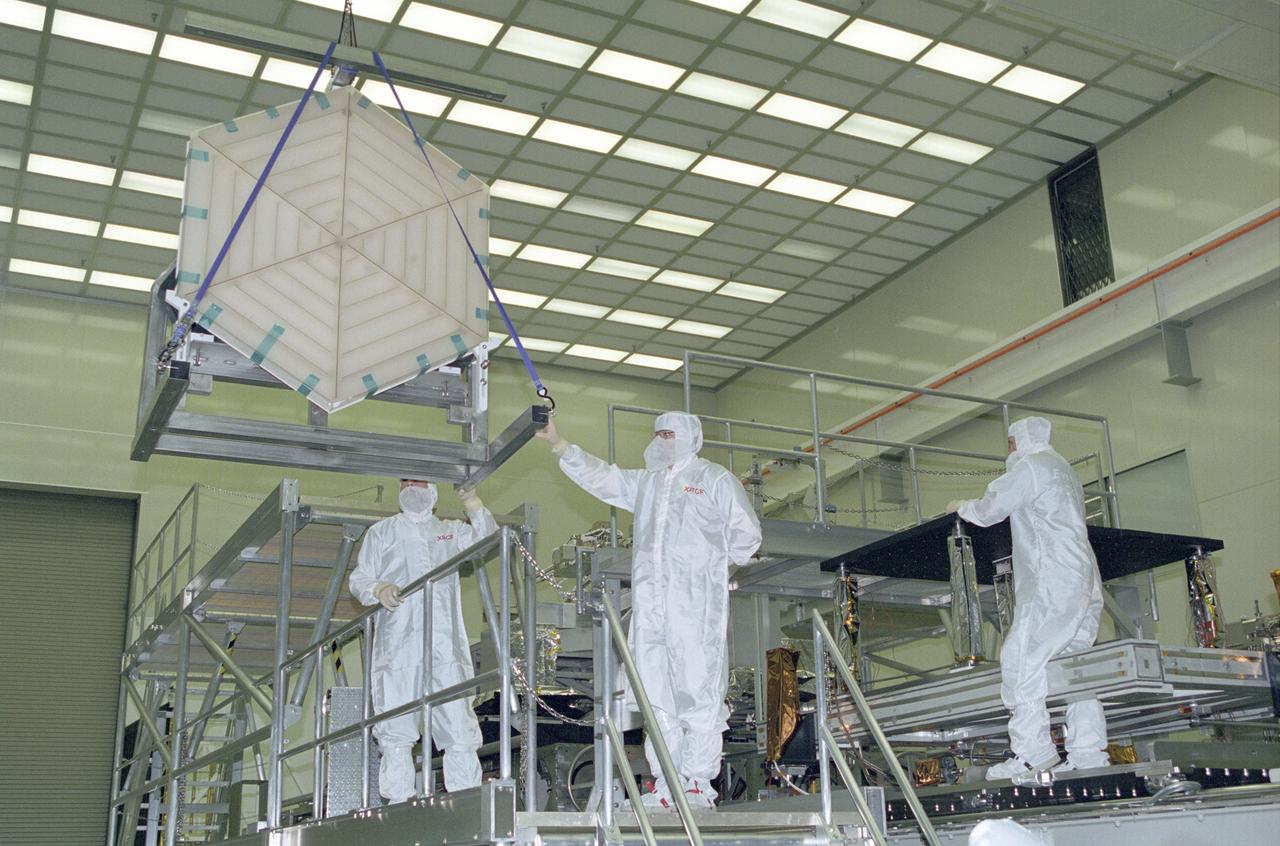

In this photograph, the composite material mirror is tested in the X-Ray Calibration Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The mirror test conducted was to check the ability to accurately model and predict the cryogenic performance of complex mirror systems, and the characterization of cryogenic dampening properties of beryllium. The JWST, a next generation successor to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), was named in honor of James W. Webb, NASA's second administrator, who led NASA in the early days of the fledgling Aerospace Agency. Scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle, the JWST will be able to look deeper into the universe than the HST because of the increased light-collecting power of its larger mirror and the extraordinary sensitivity of its instrument to infrared light.

NASA Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, has a complex set of mirrors, or optics, that will help it see high-energy X-ray light in greater detail than ever before.

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
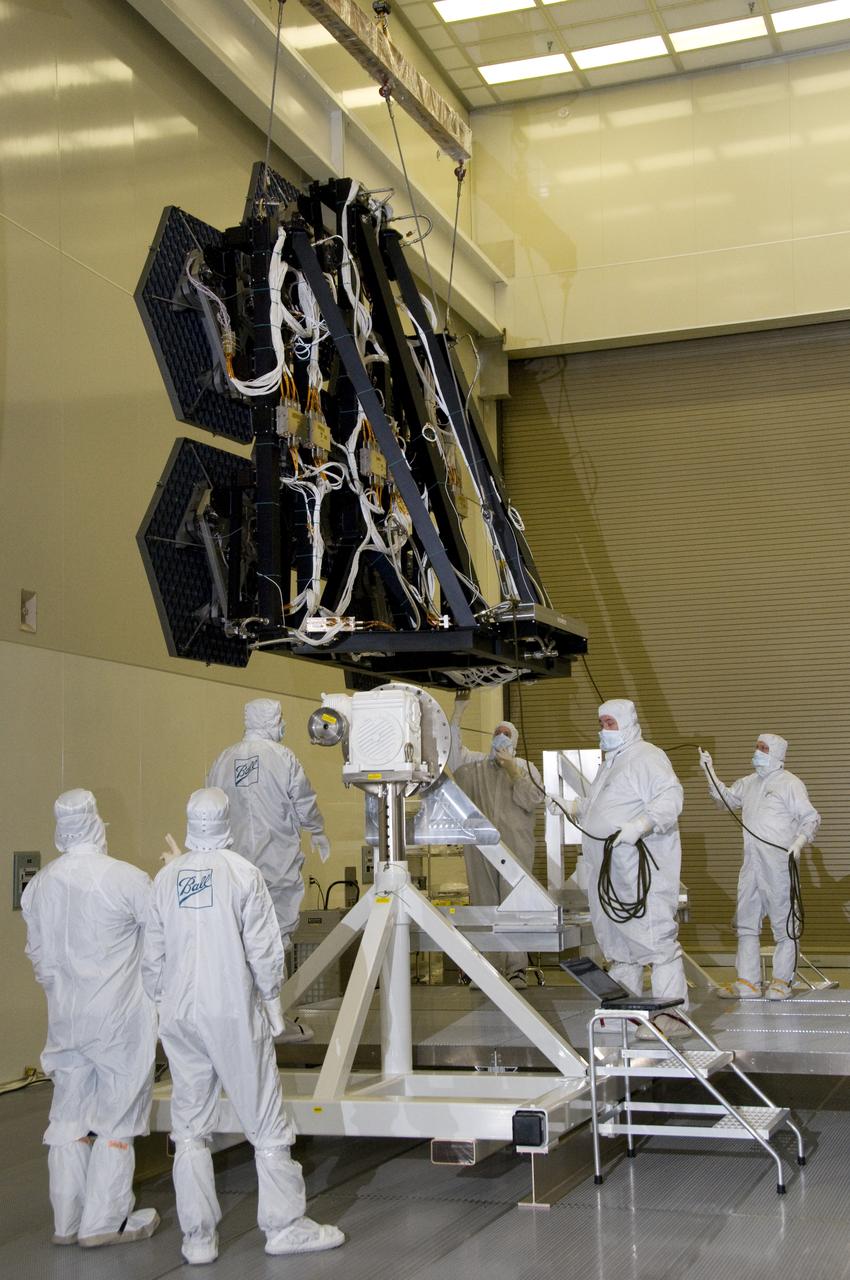

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
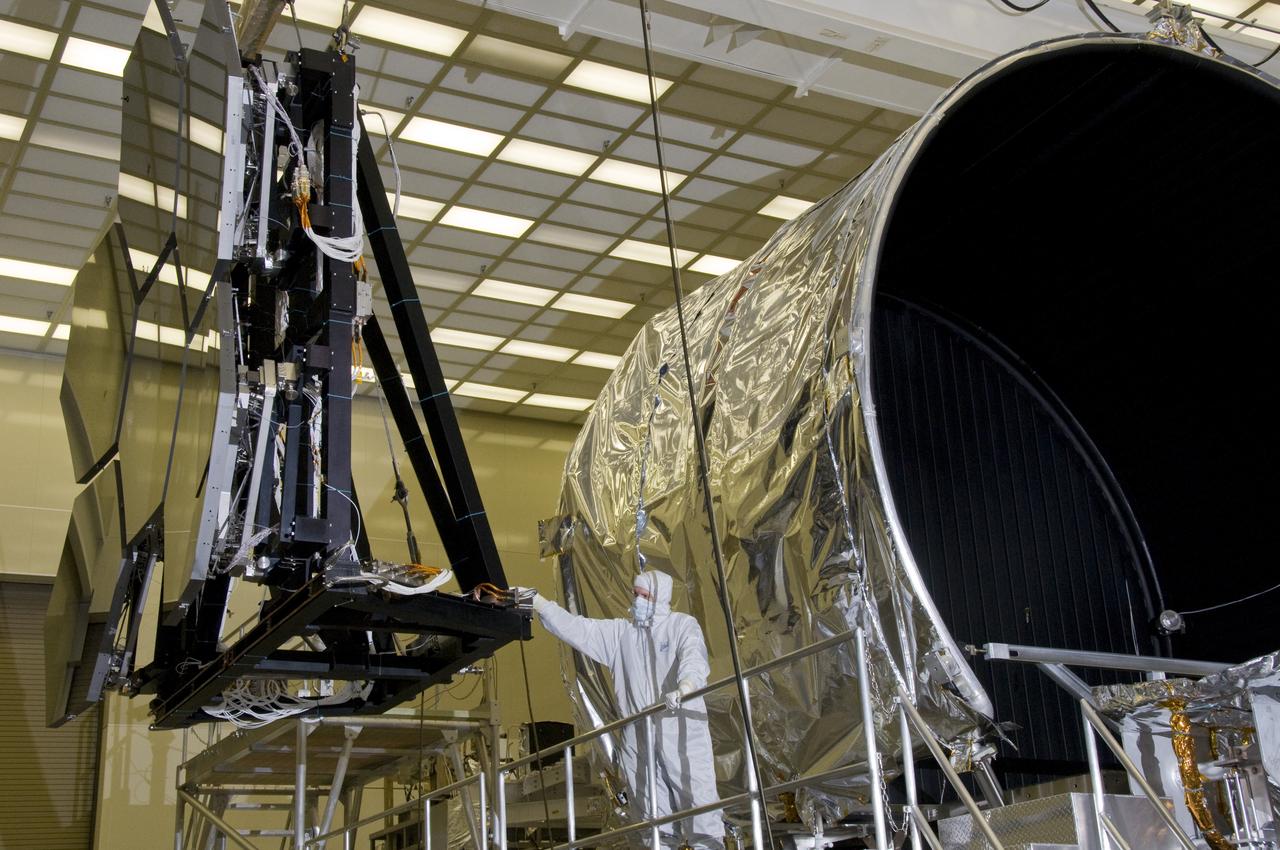

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
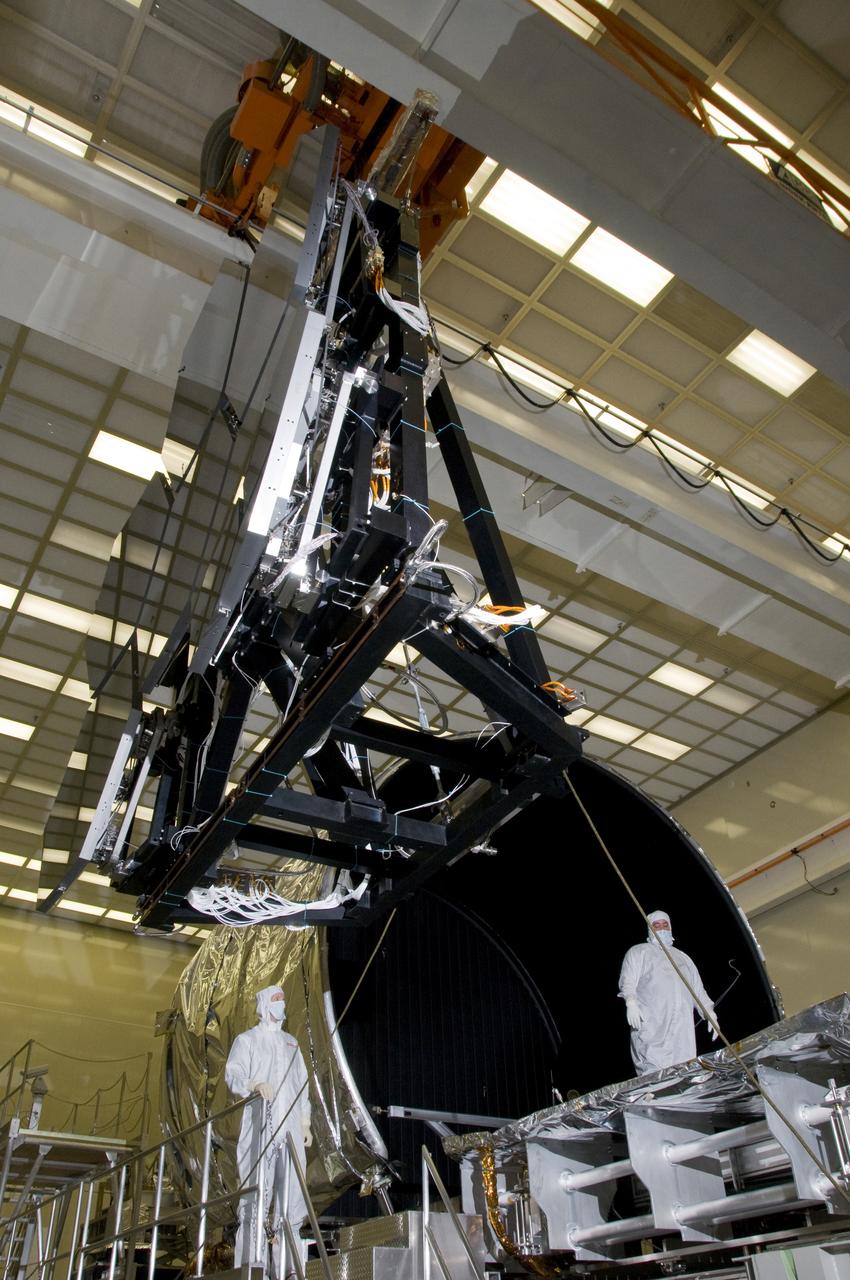

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
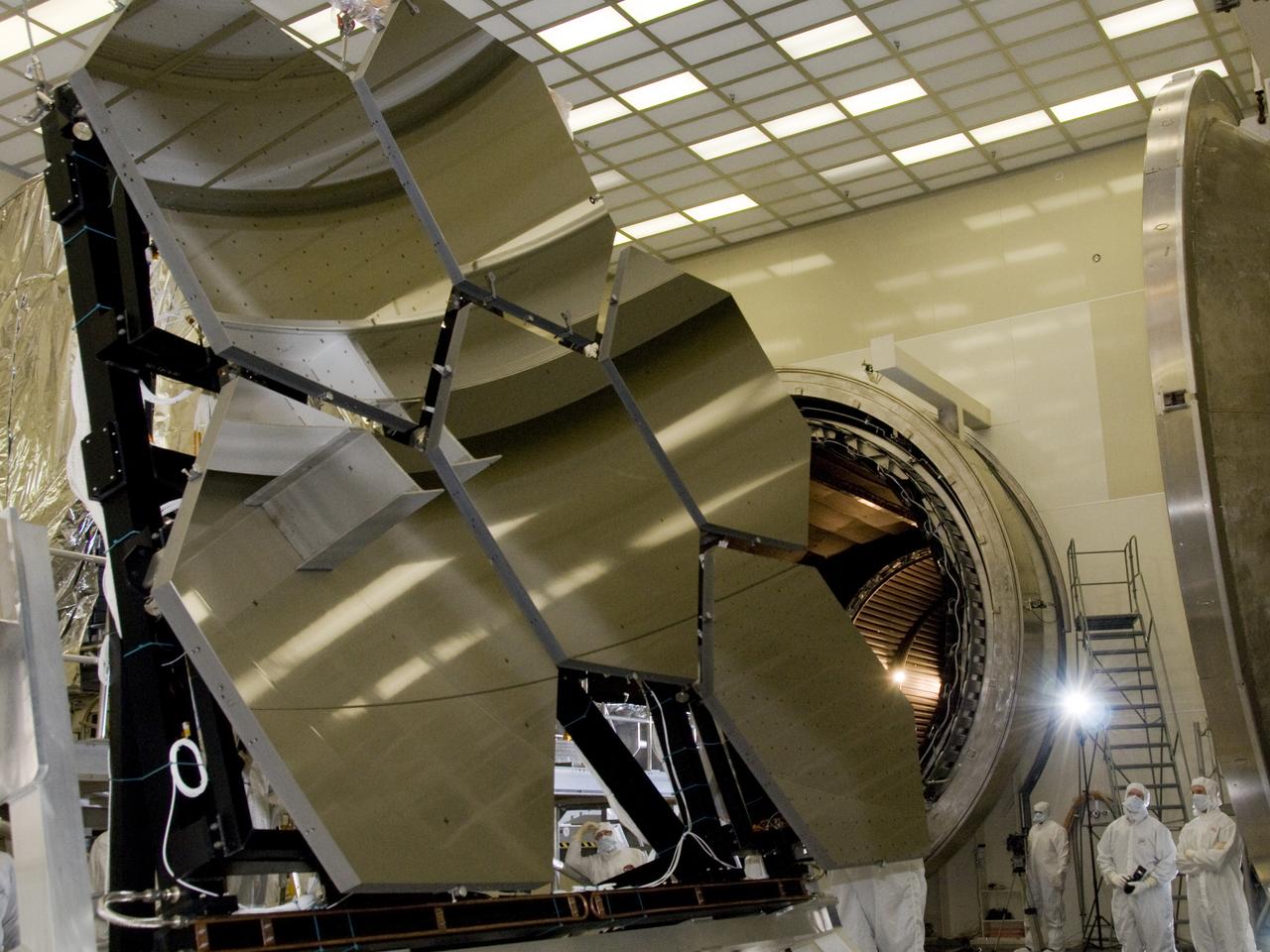

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
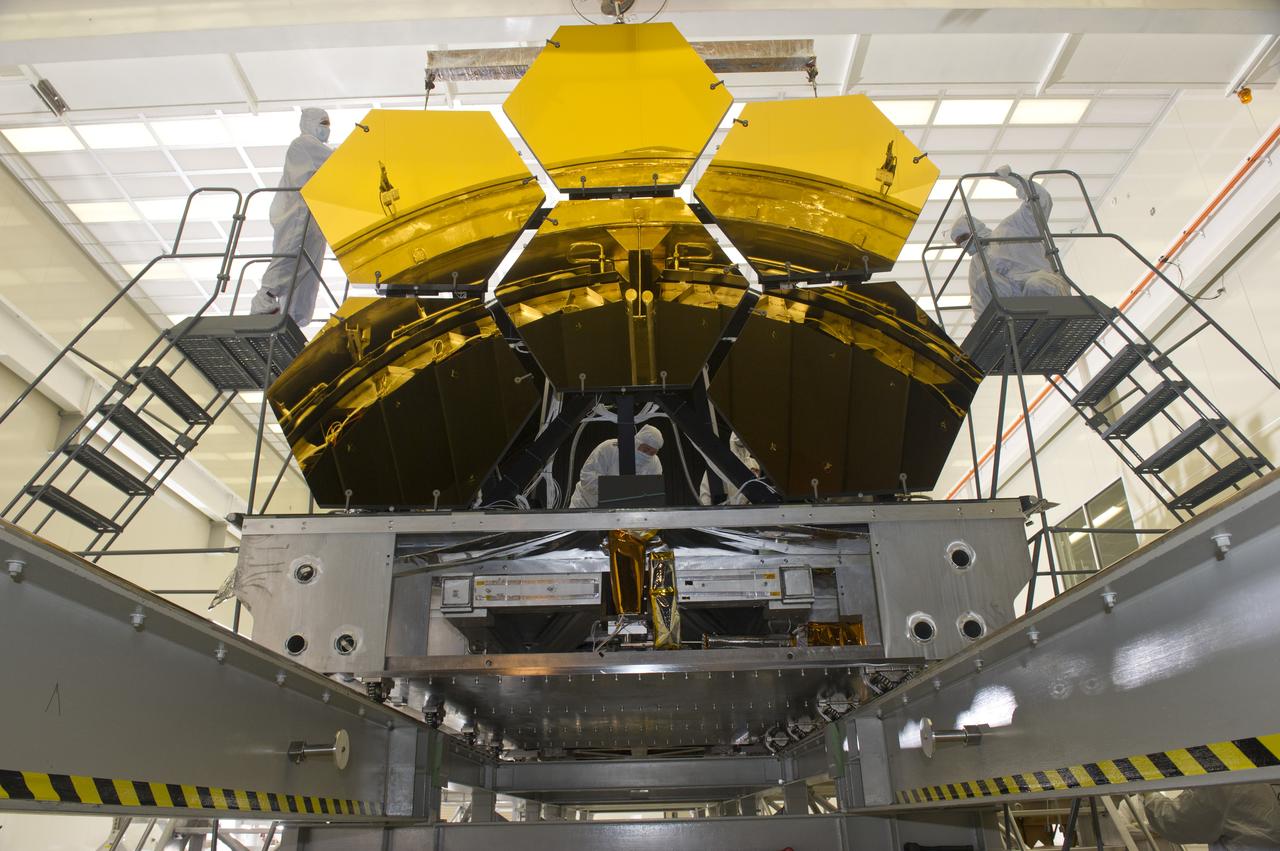

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
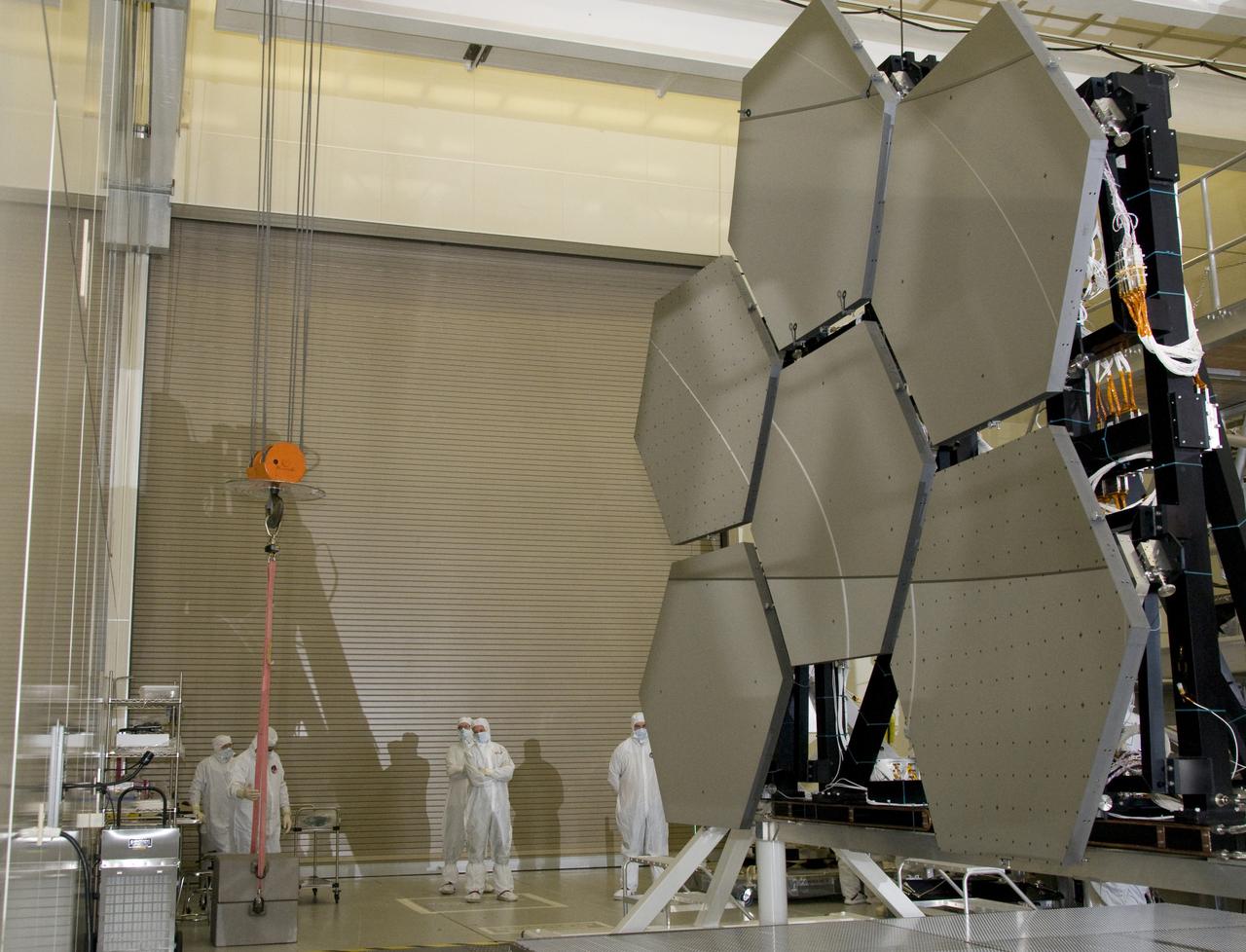

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
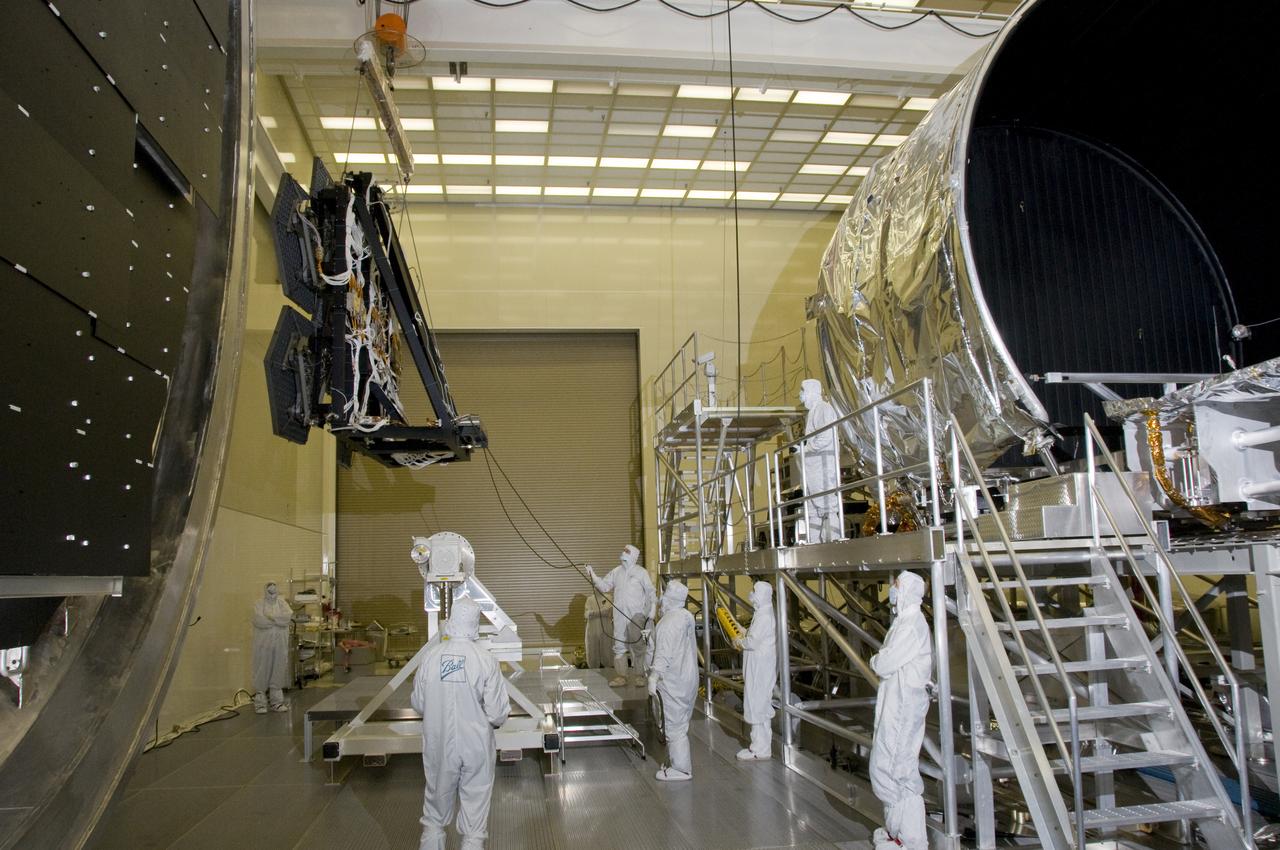

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
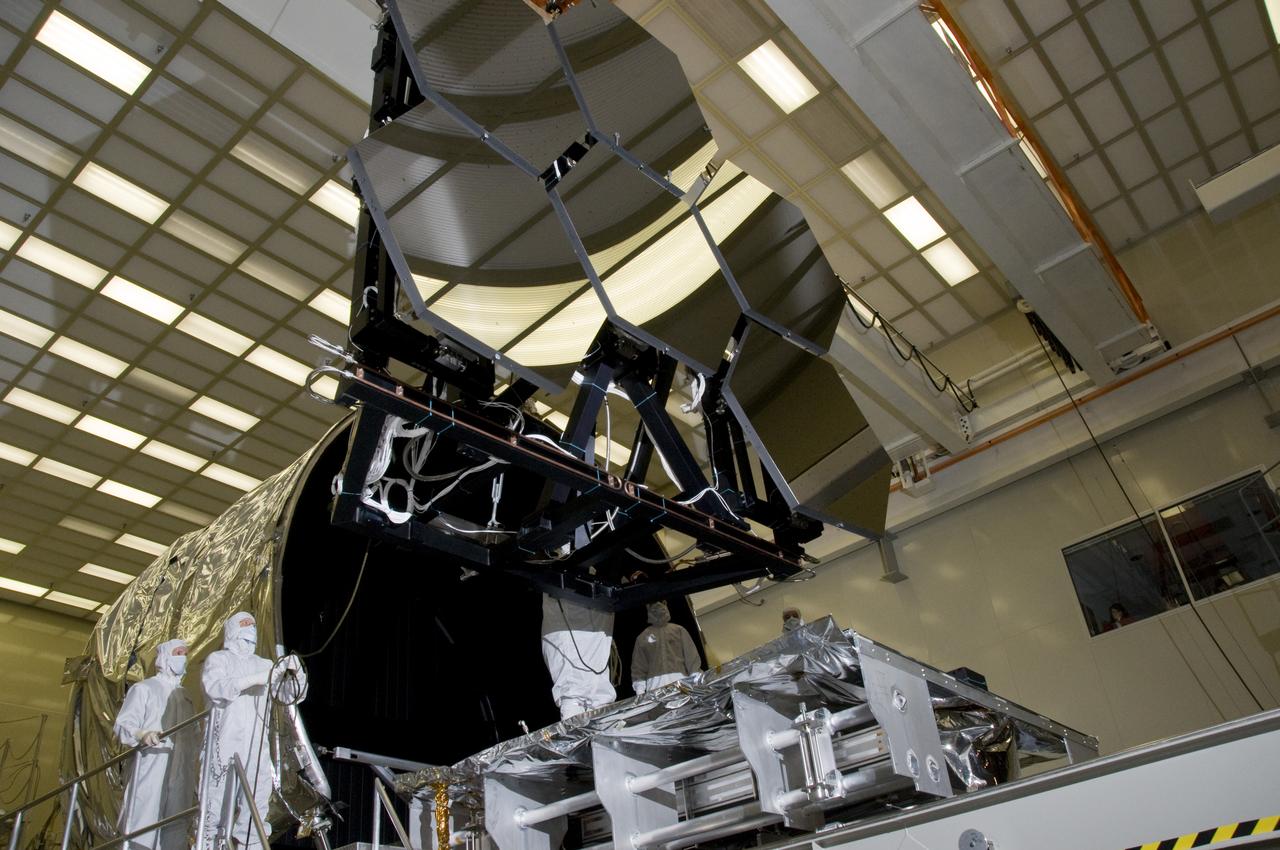

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
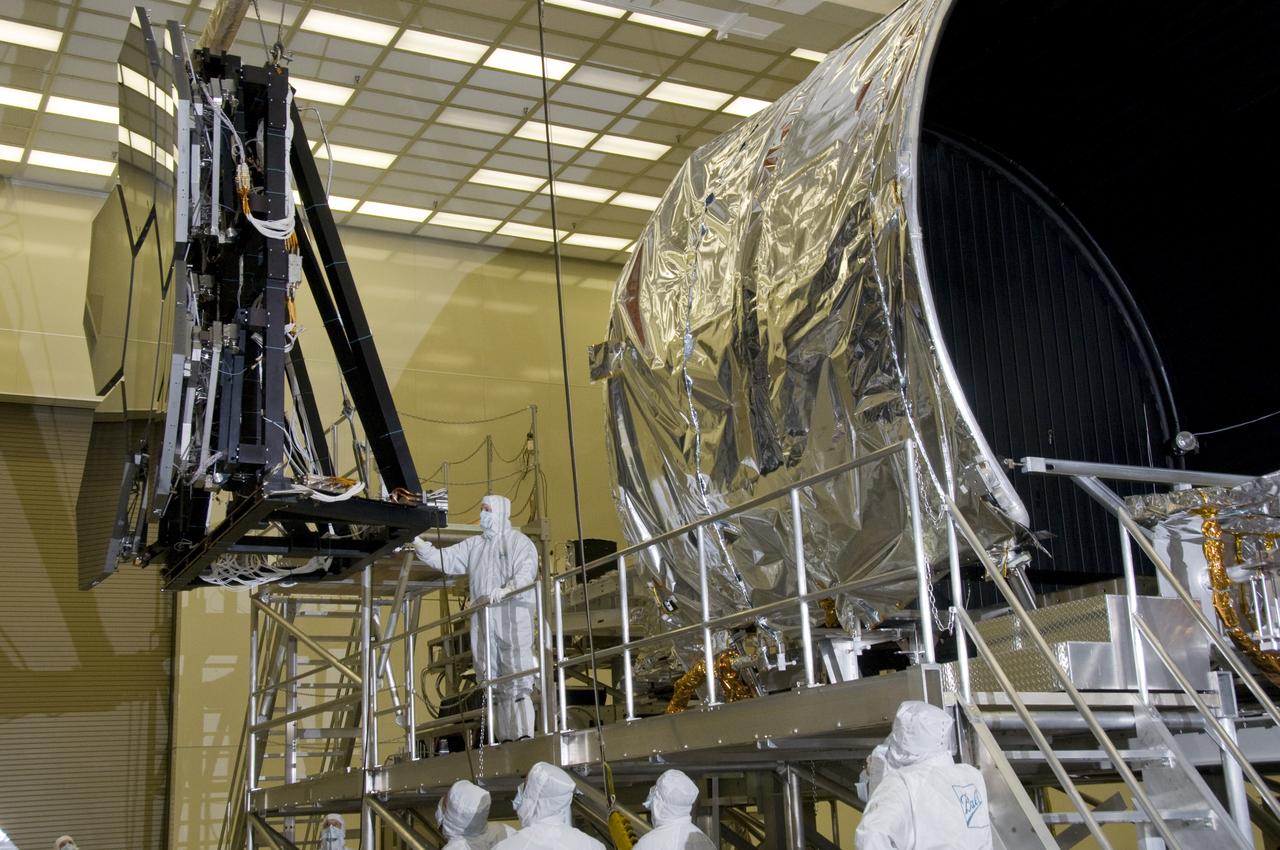

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
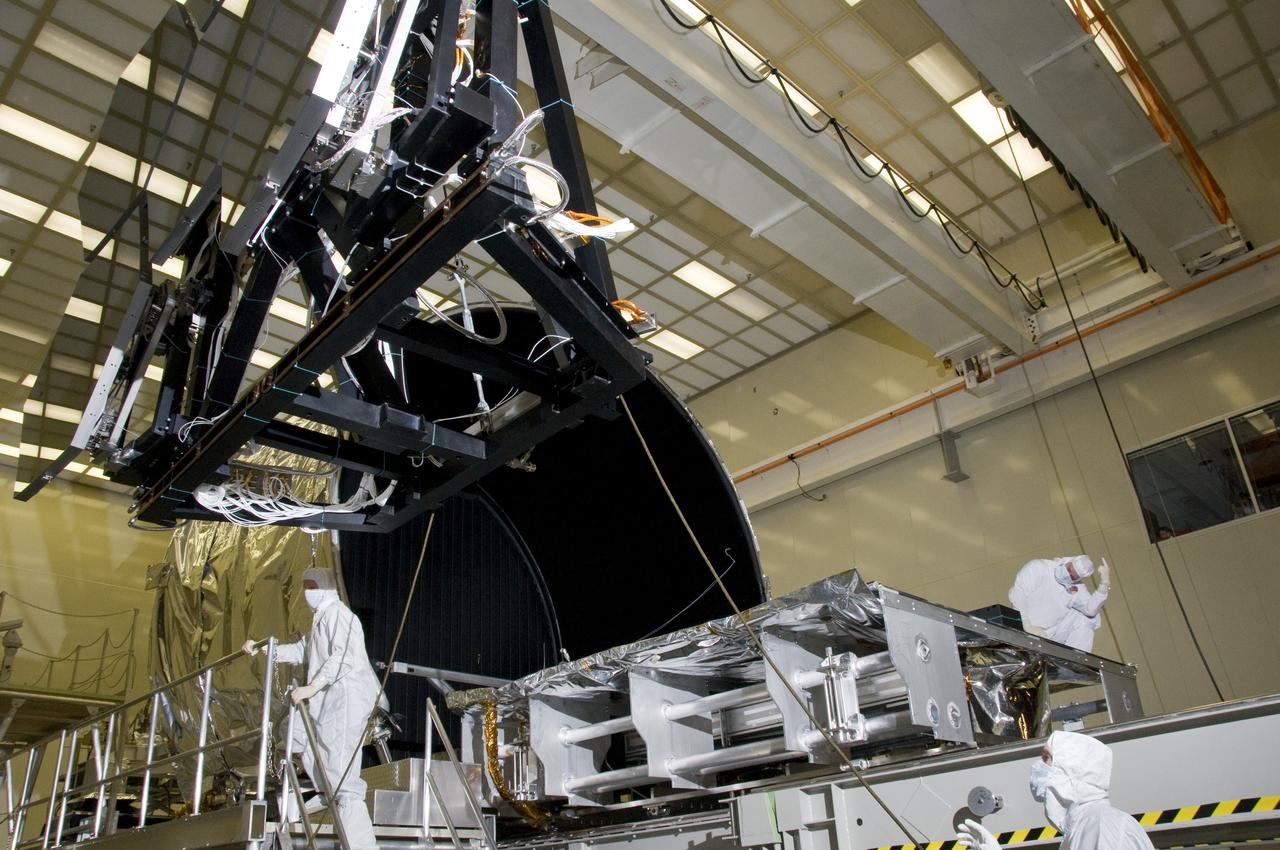

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
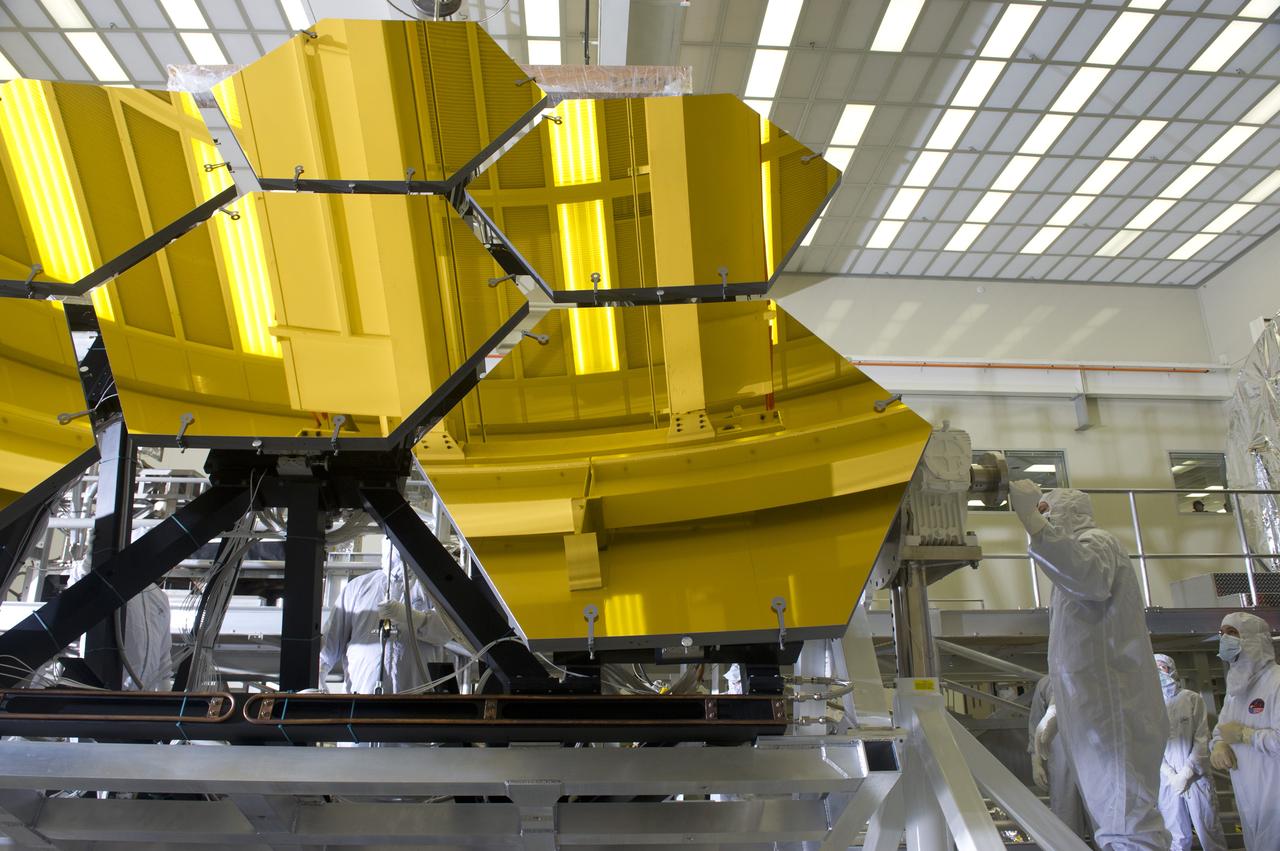

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
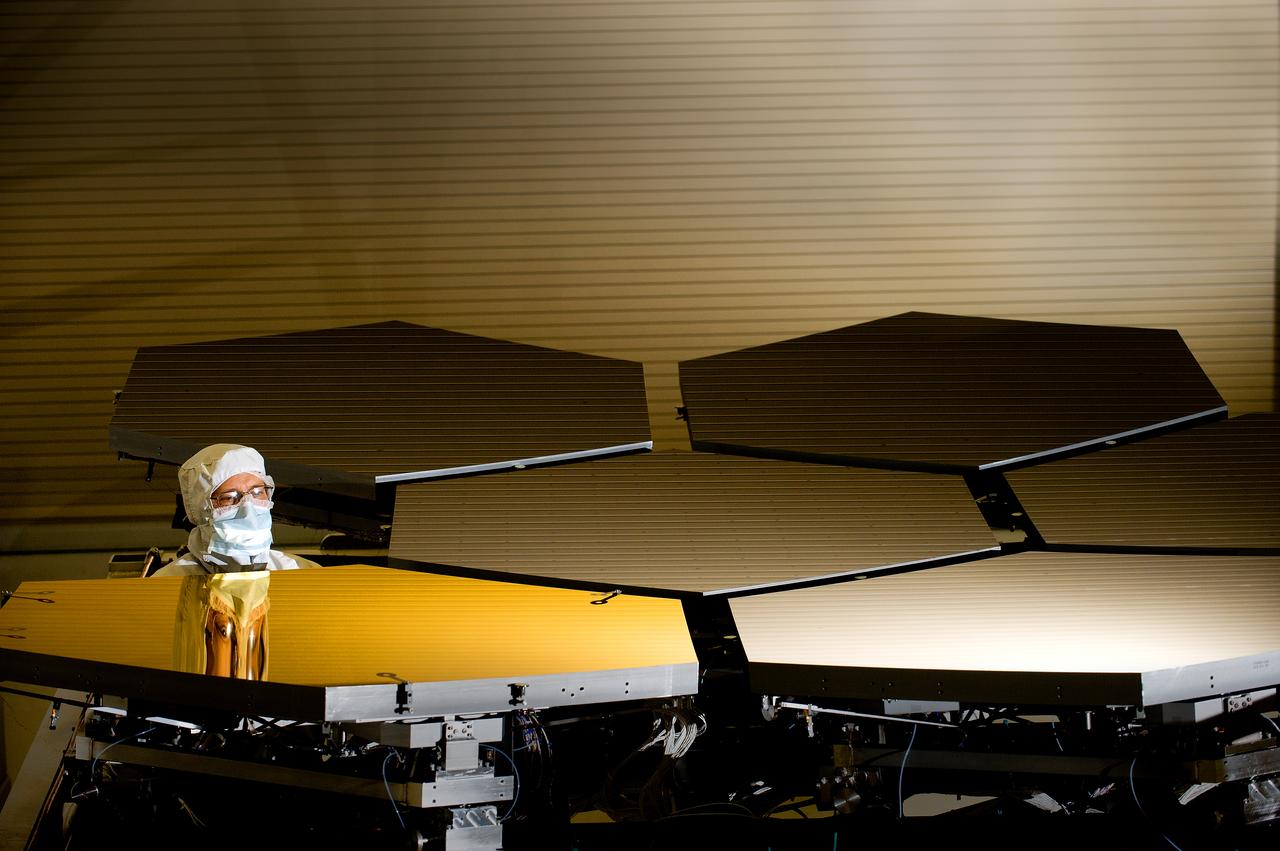

BALL AEROSPACE’S SCOTT MURRAY INSPECTS MIRRORS FOR THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
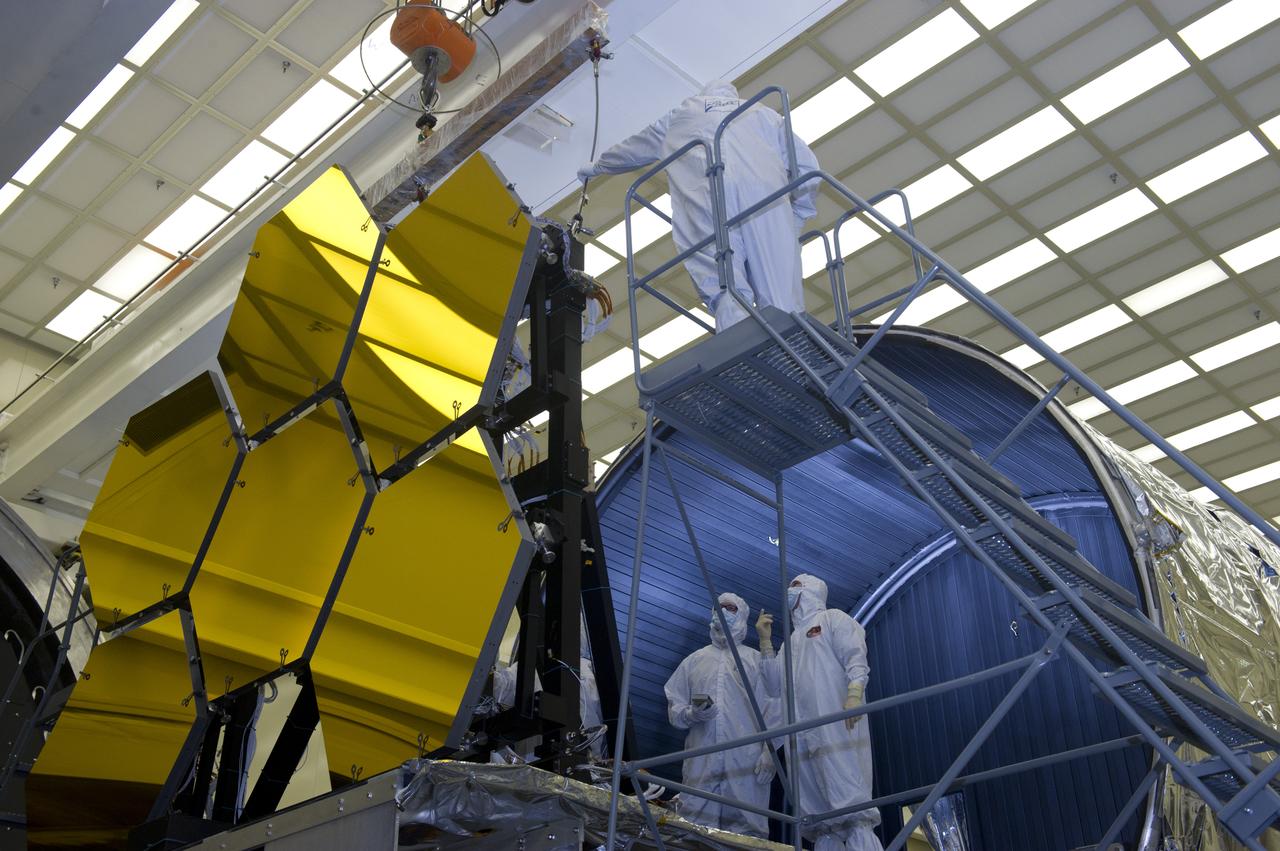

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
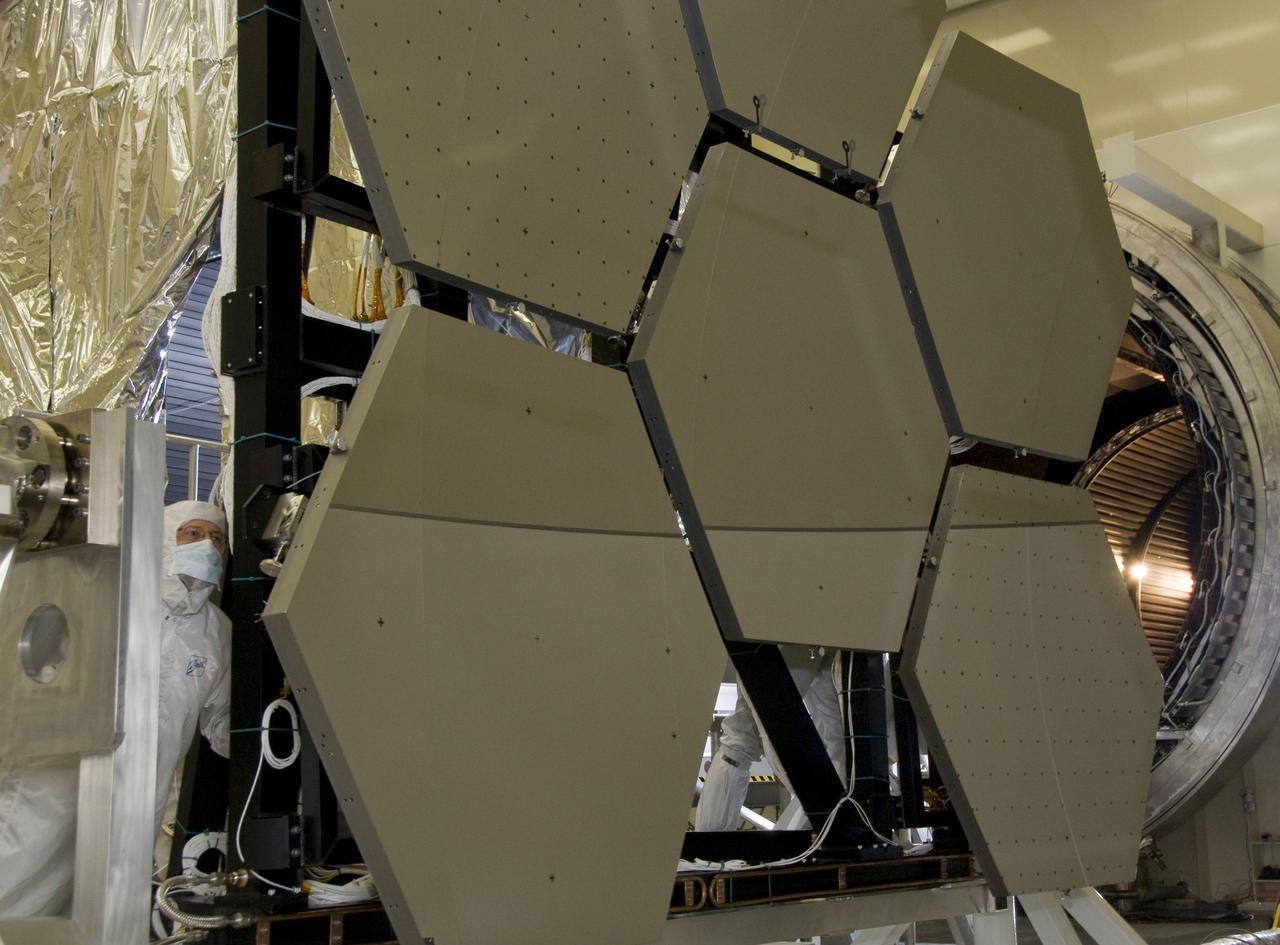

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
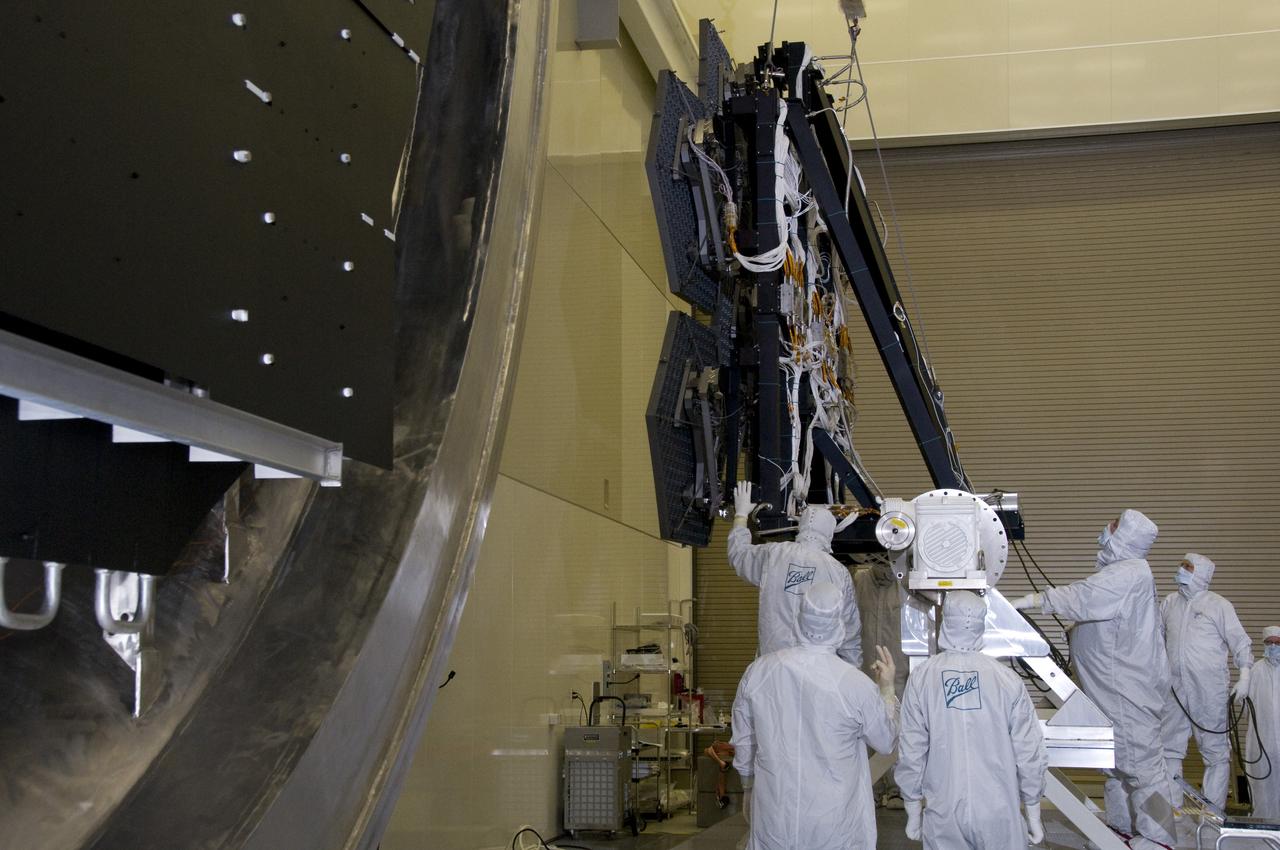

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
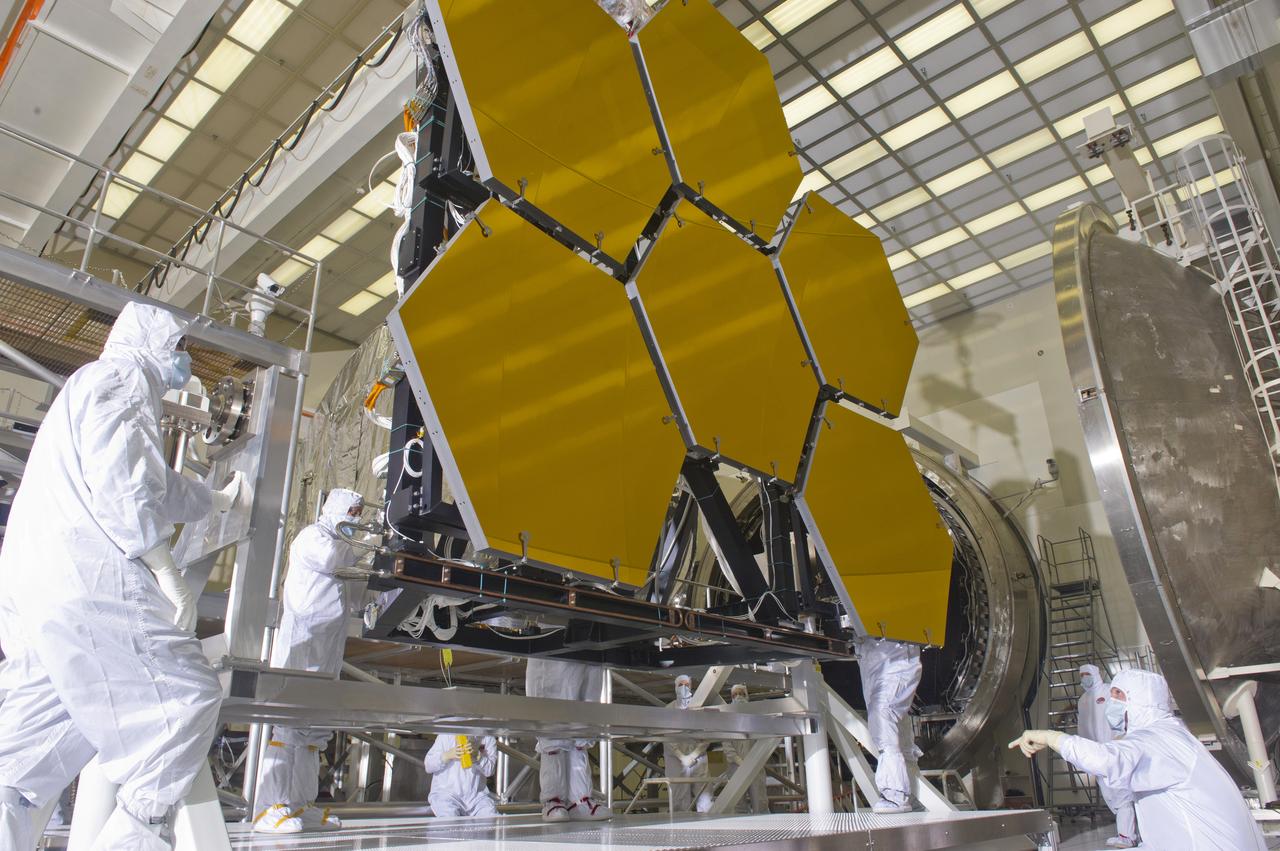

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
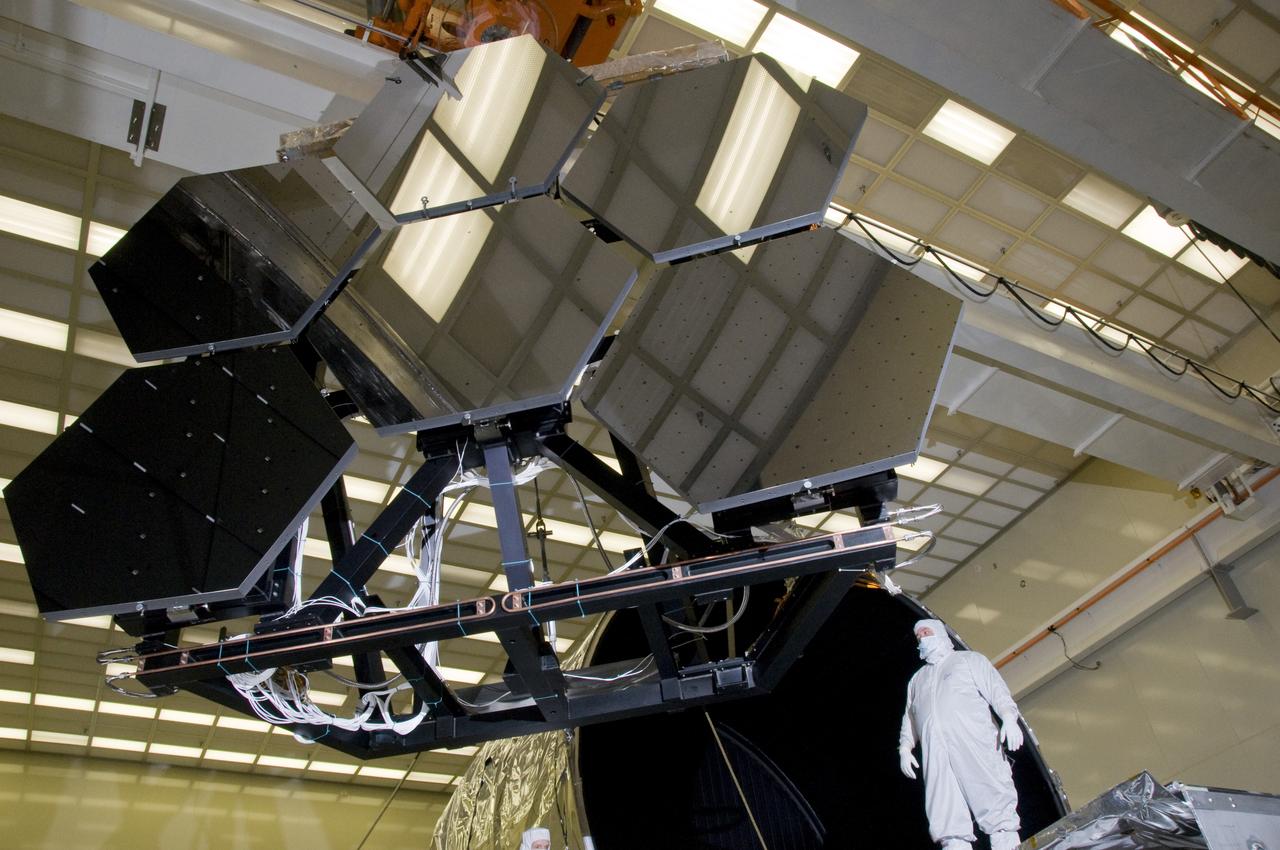

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
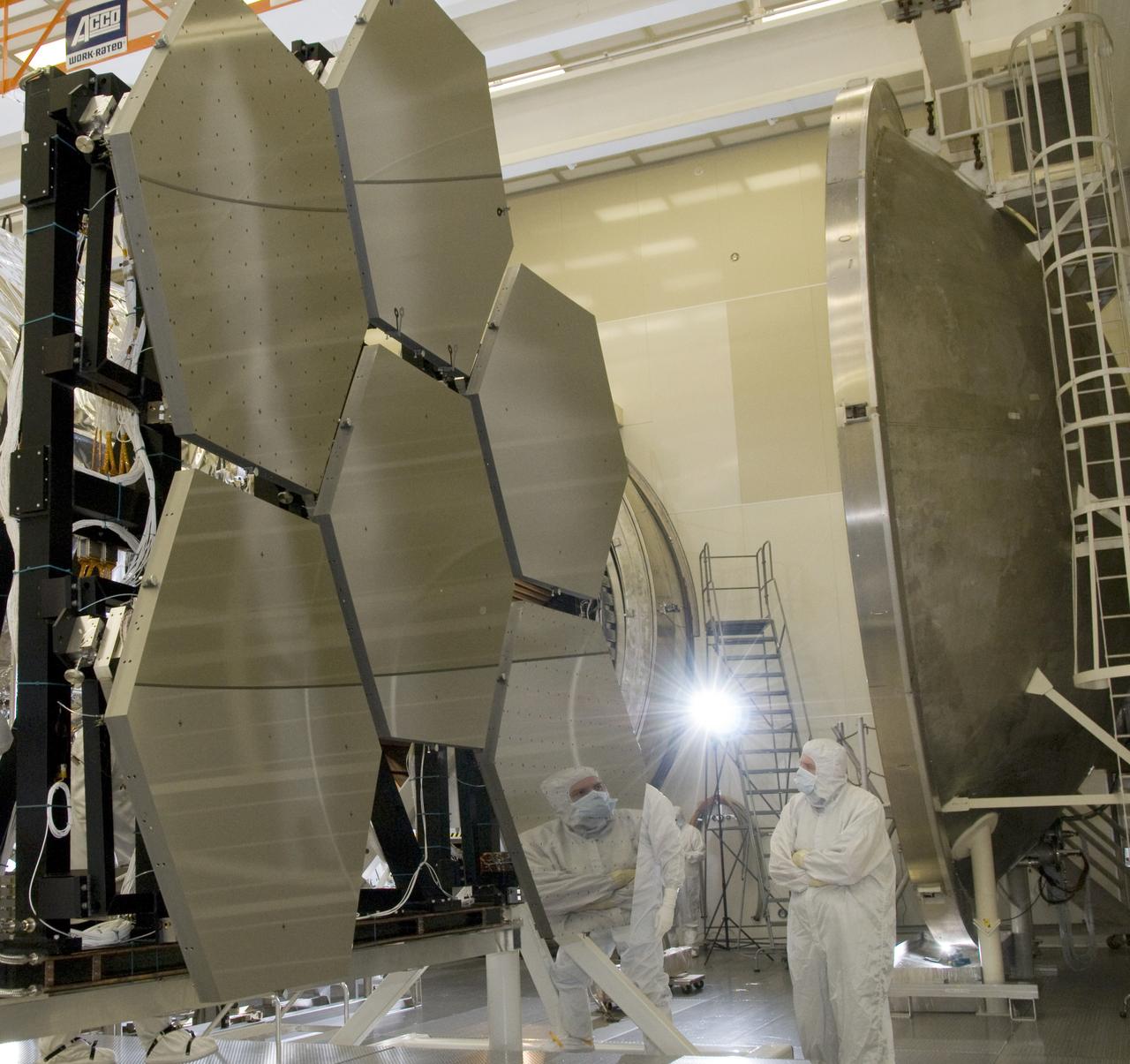

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
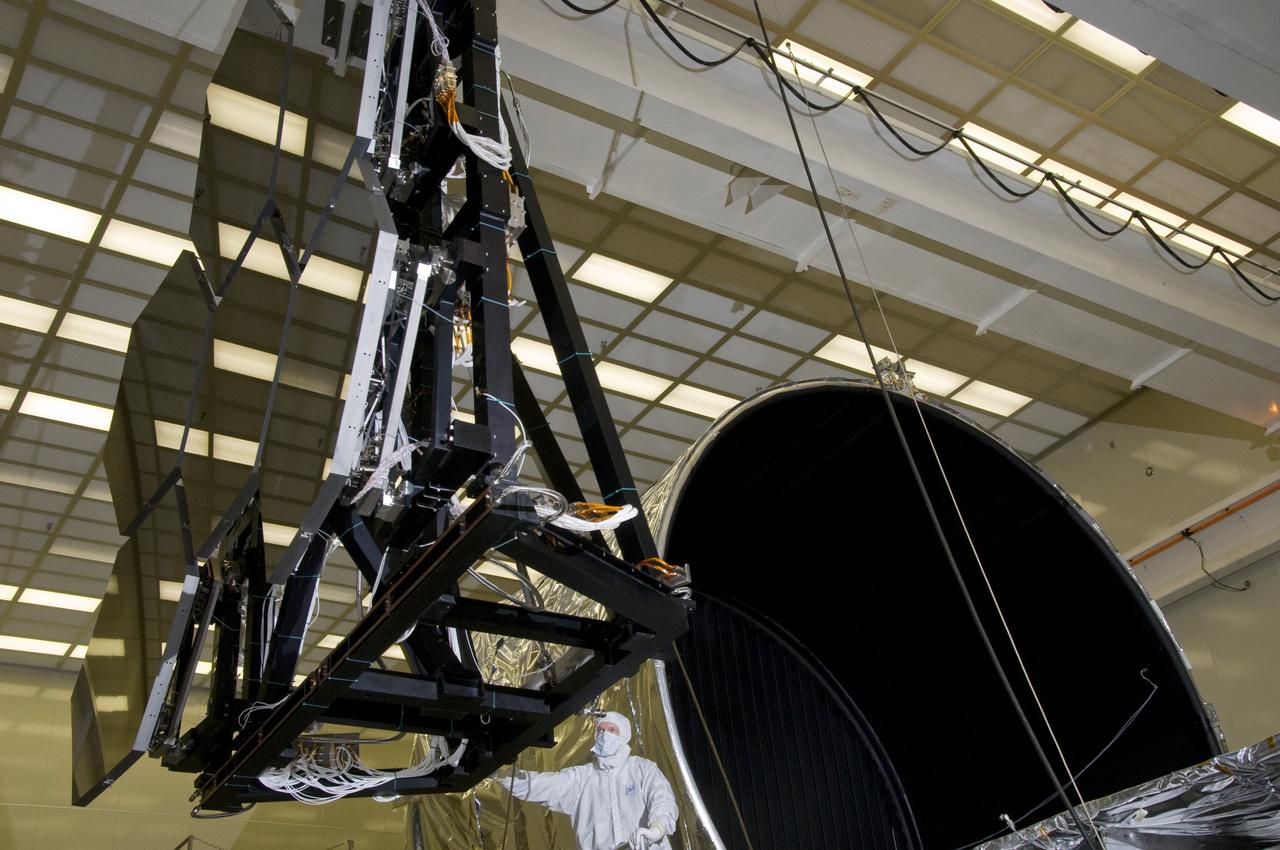

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
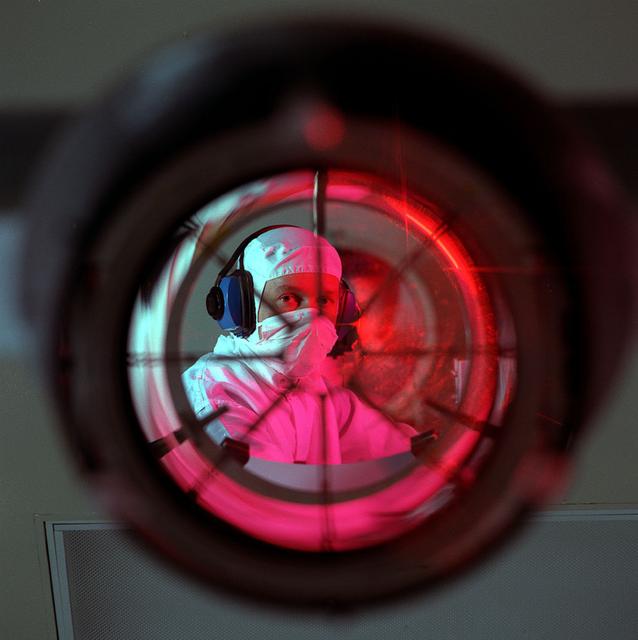

Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility-S (AXAF-S) nickel prototype mirror optical test setup.
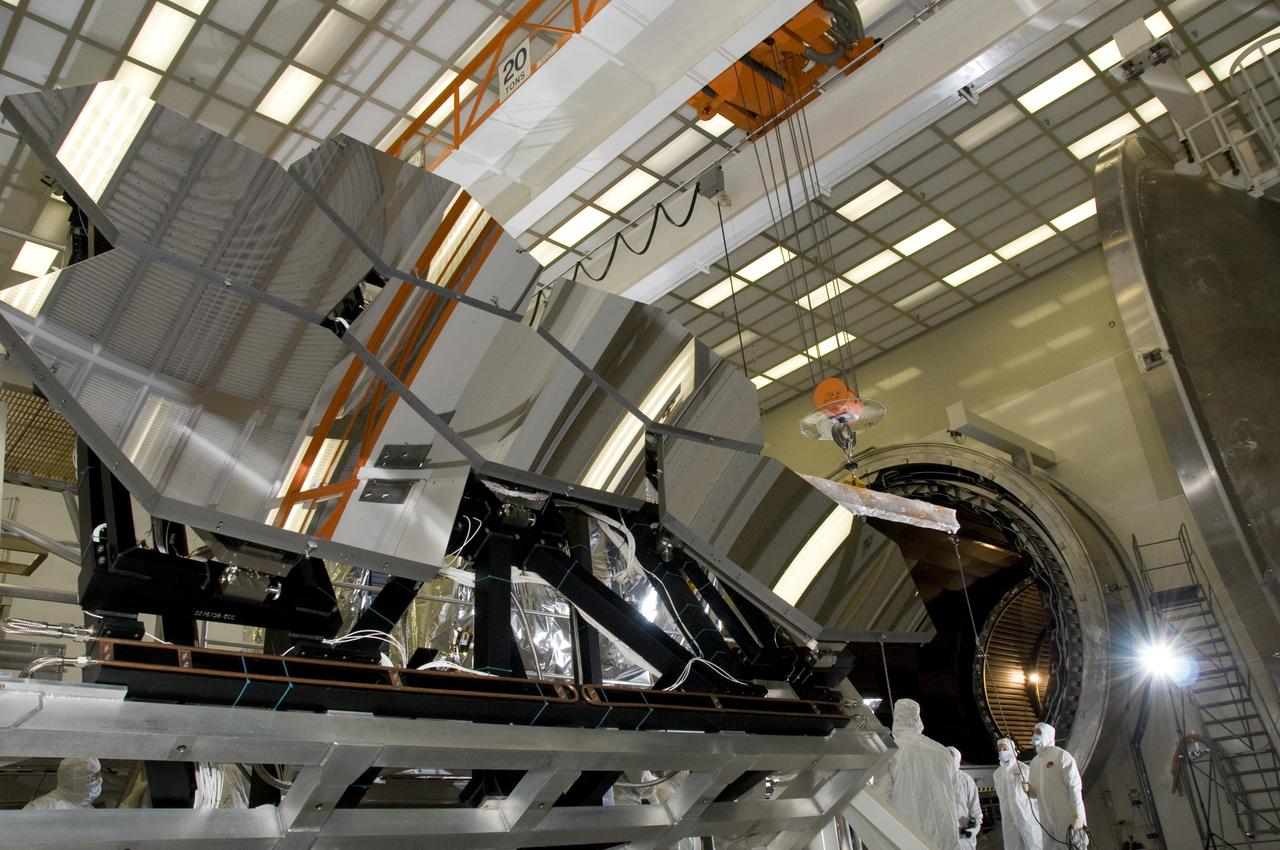

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
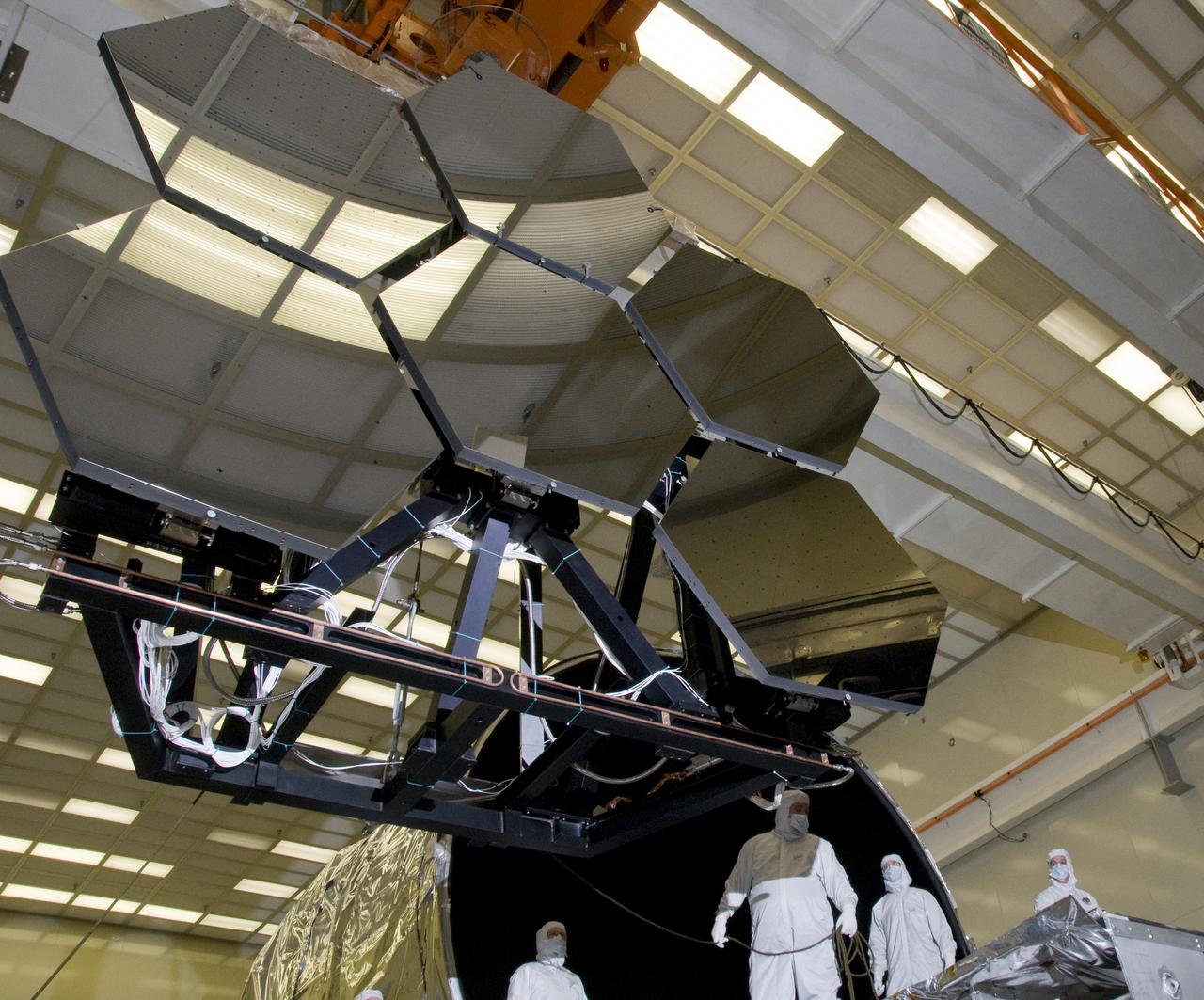

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
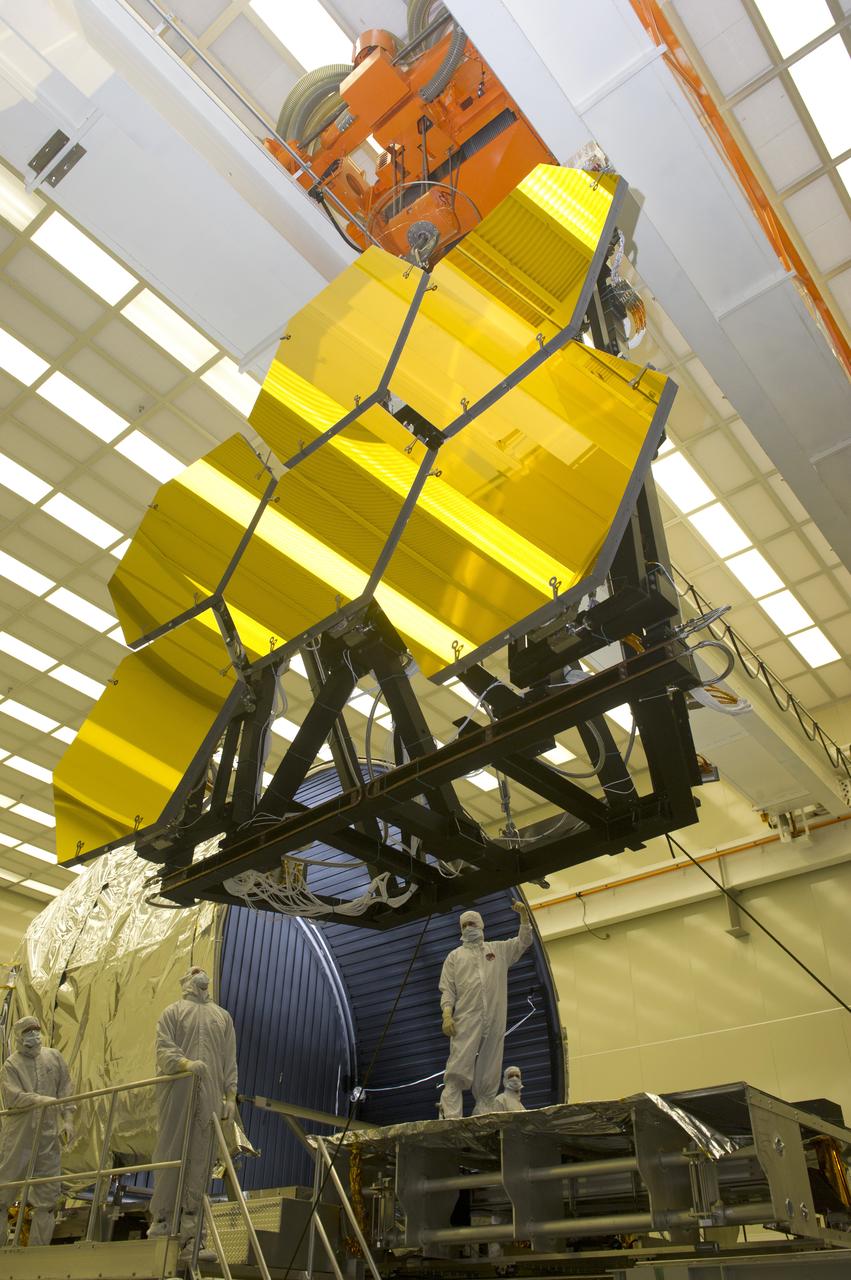

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
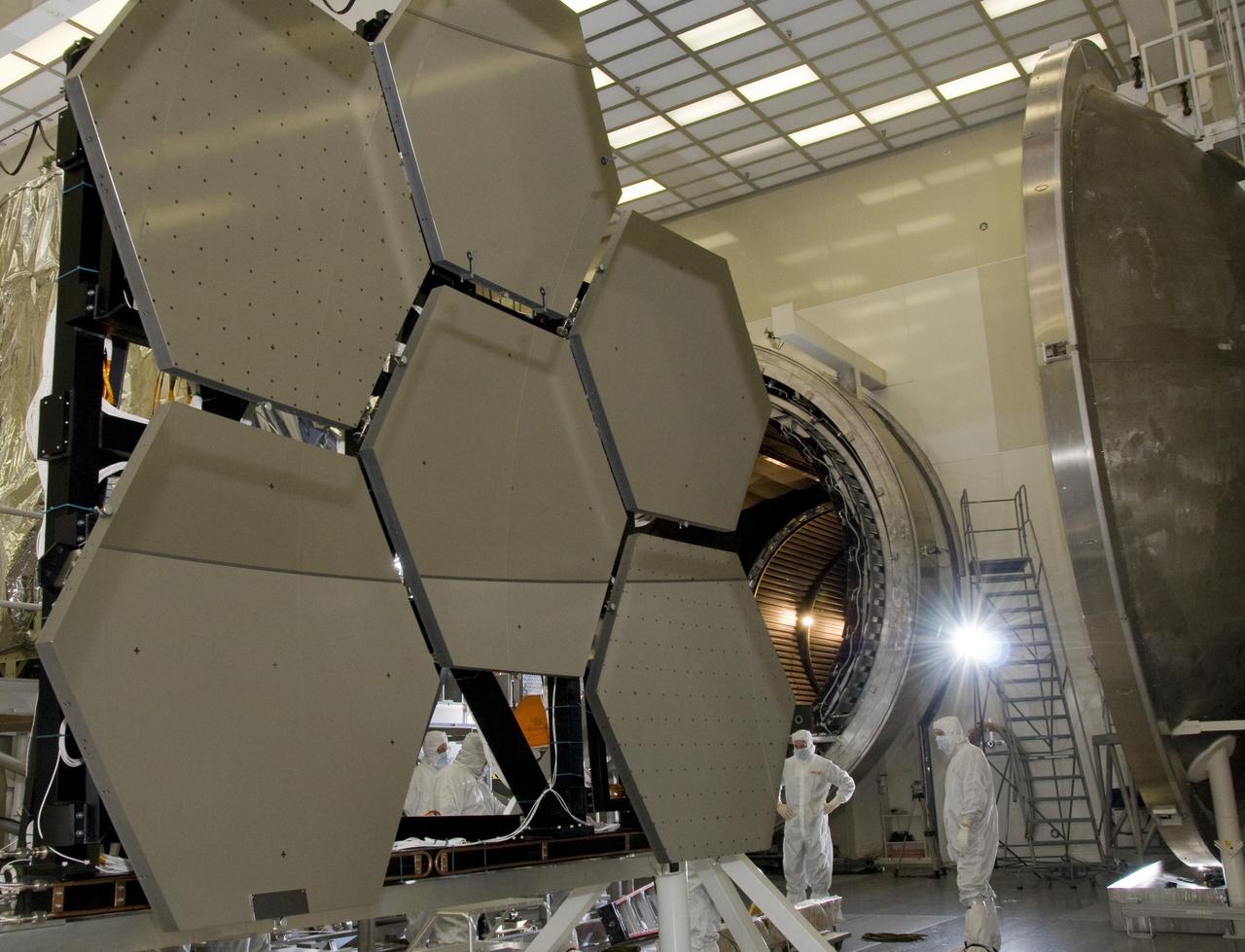

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
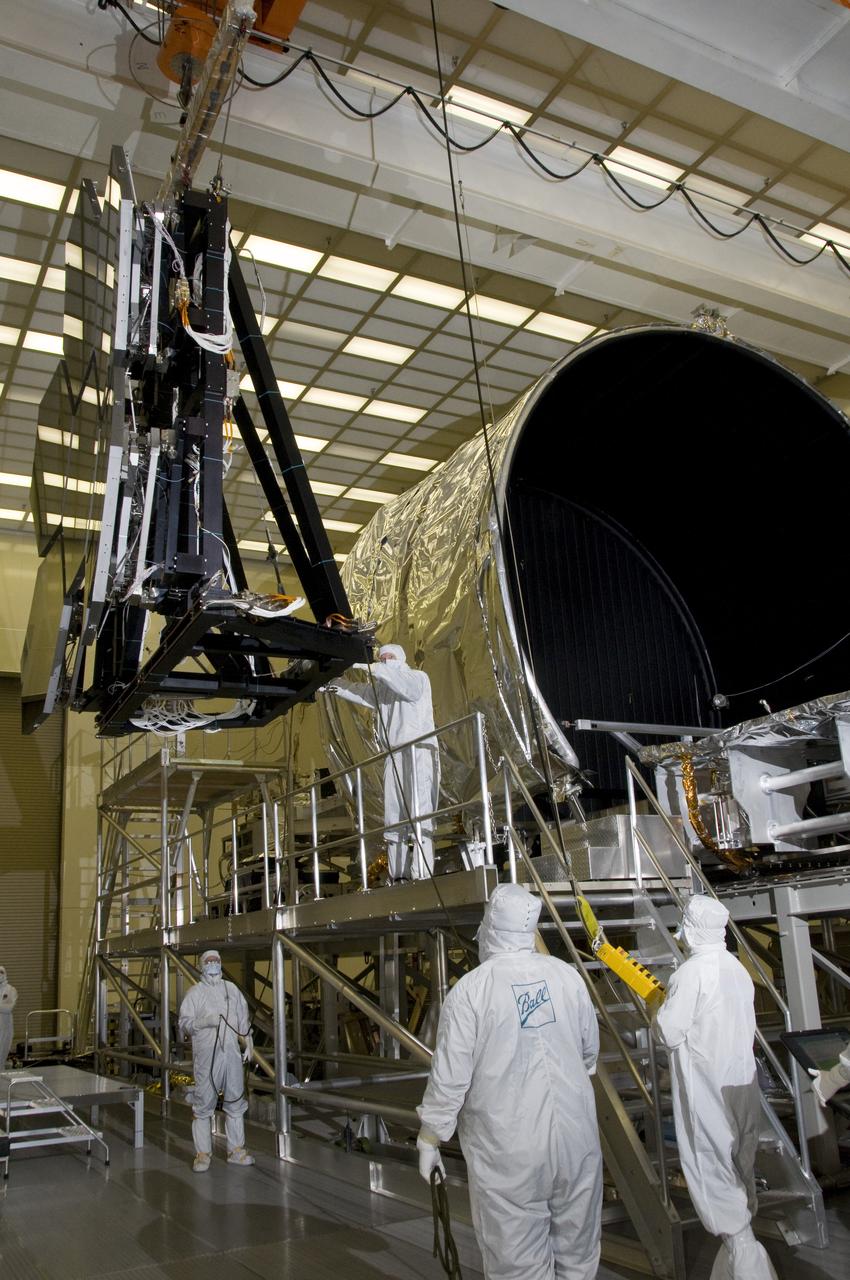

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
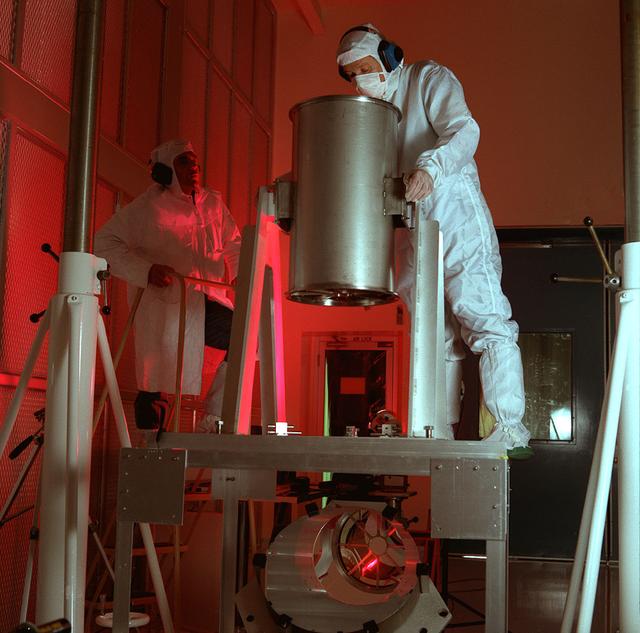

Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility-S (AXAF-S) nickel prototype mirror optical test setup.
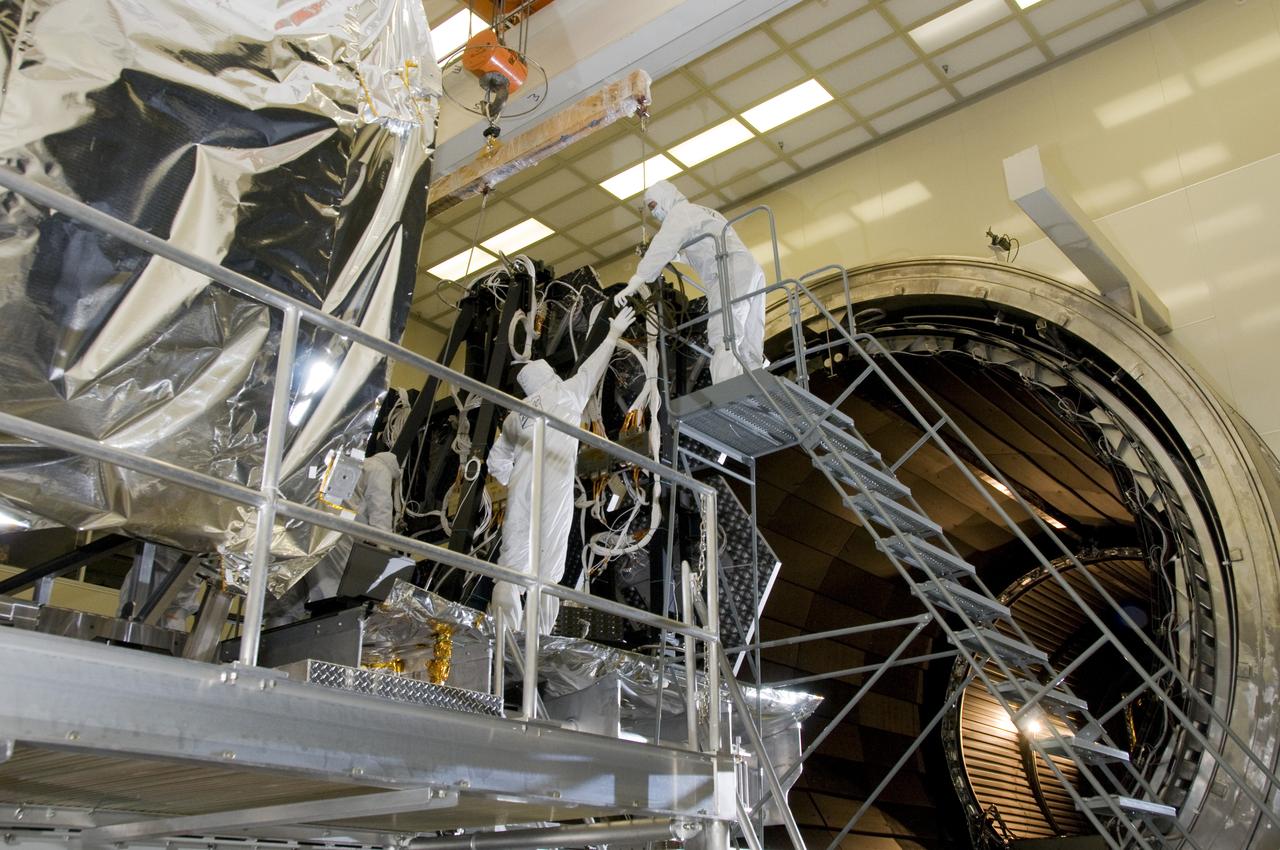

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
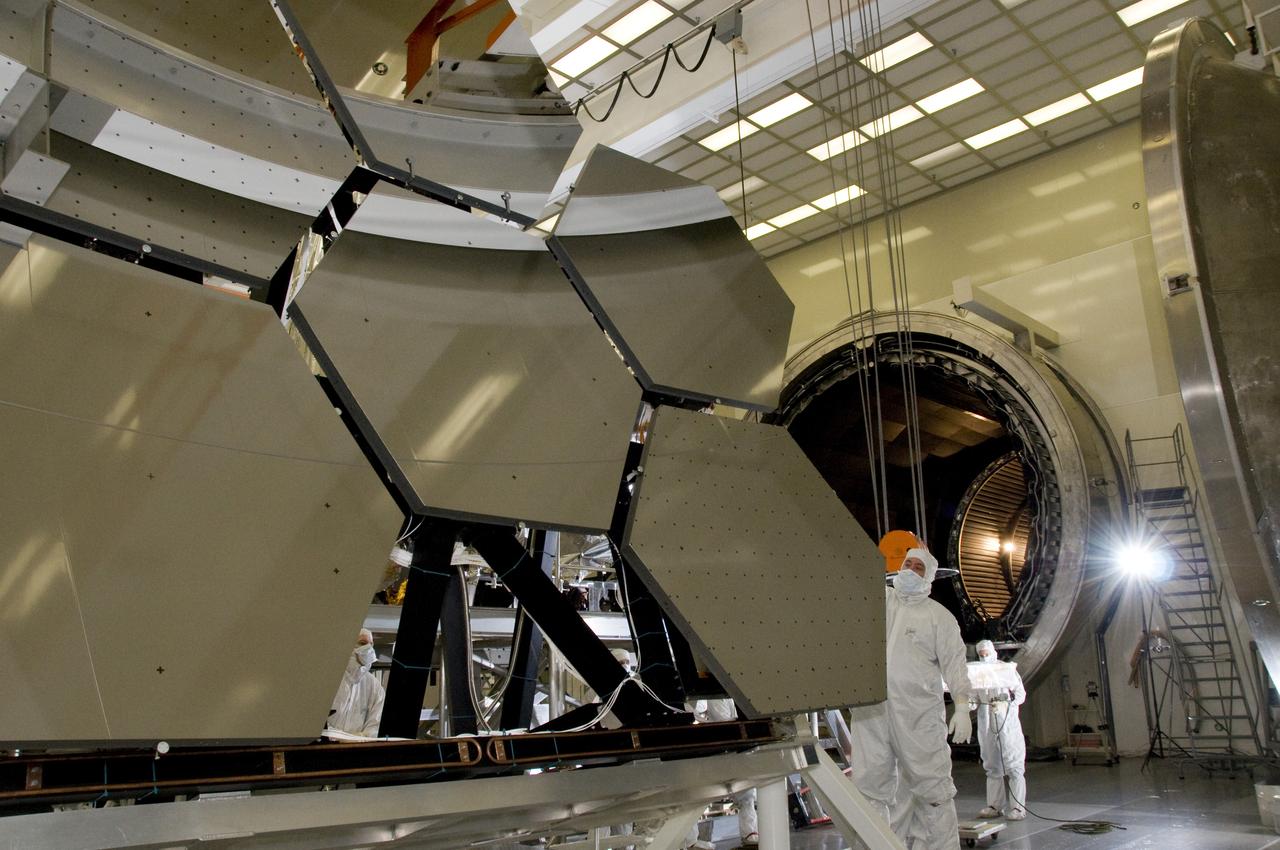

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
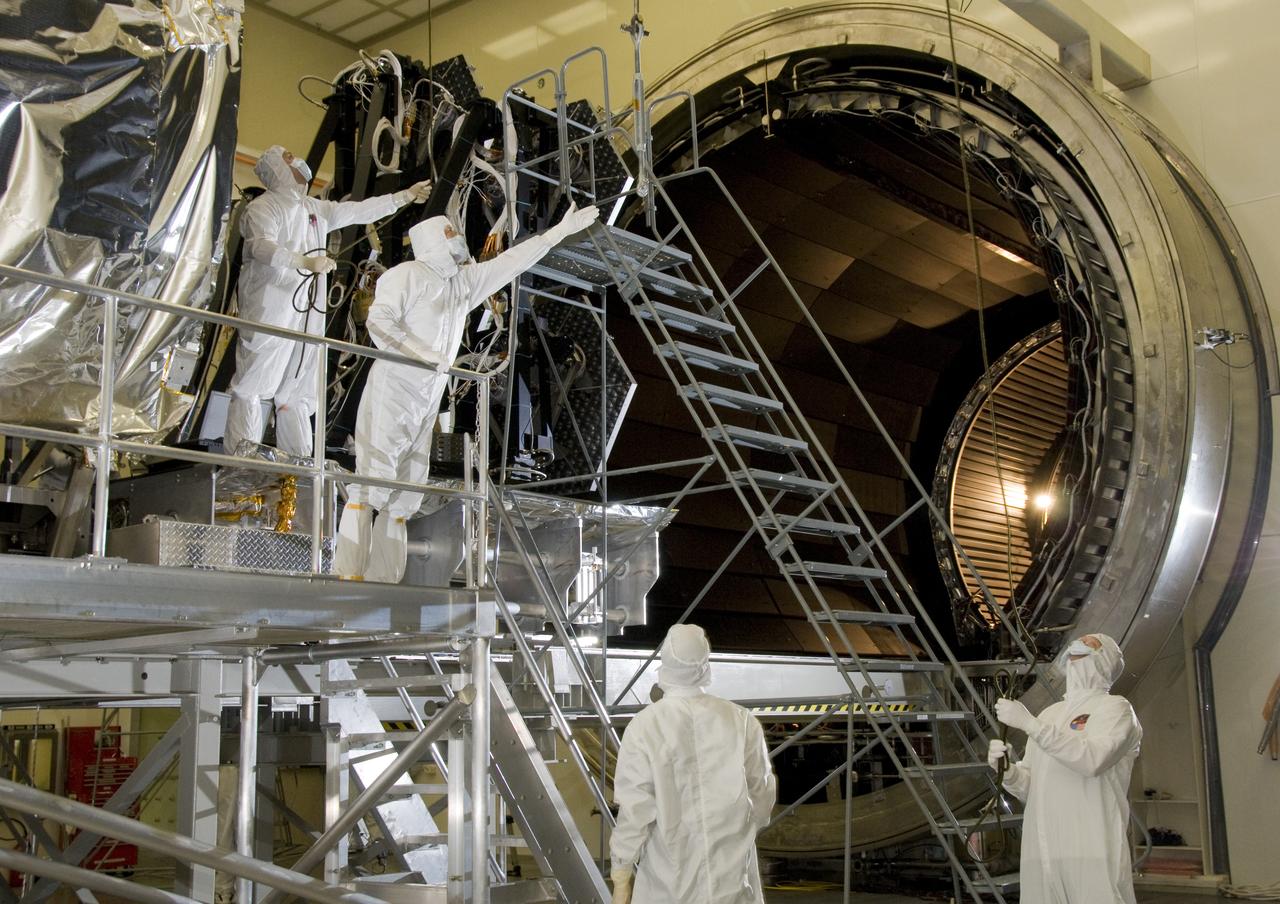

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
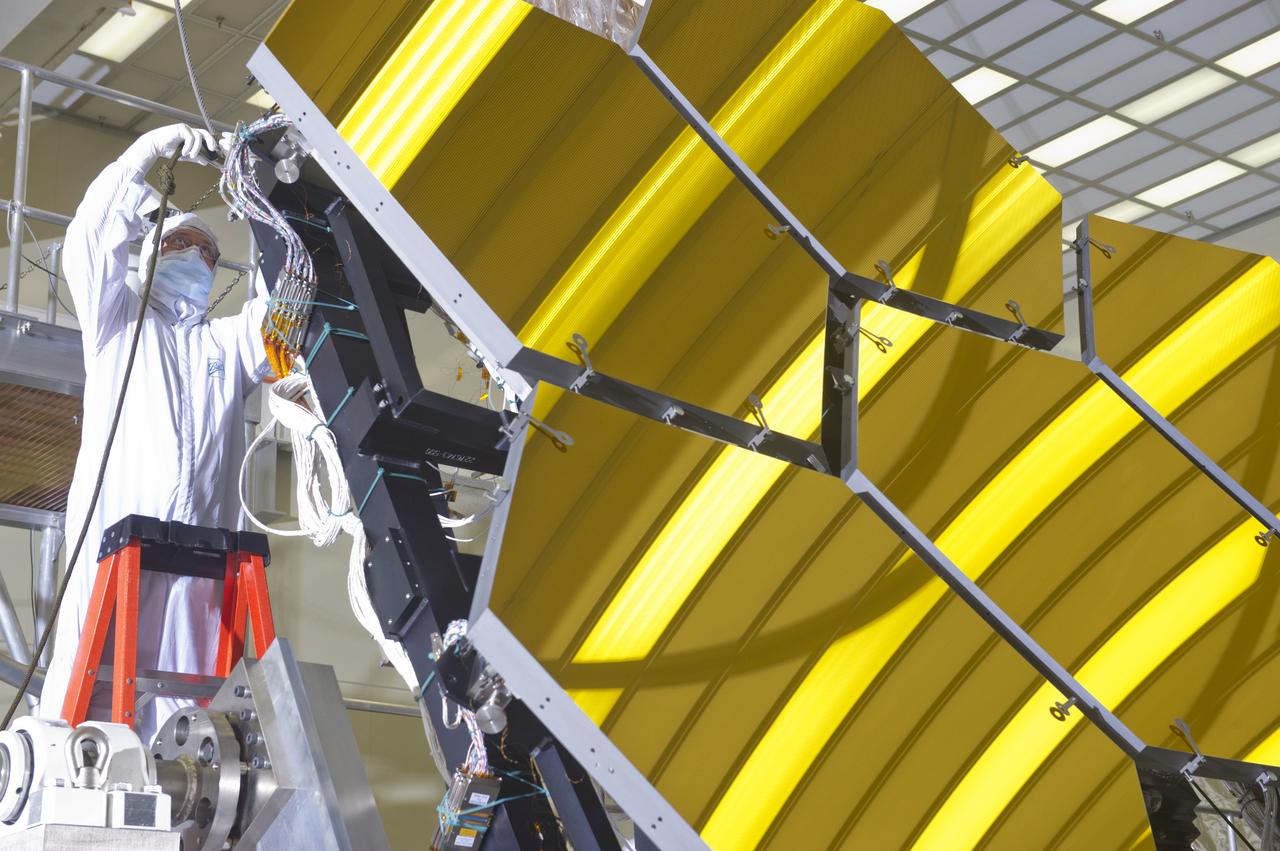

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
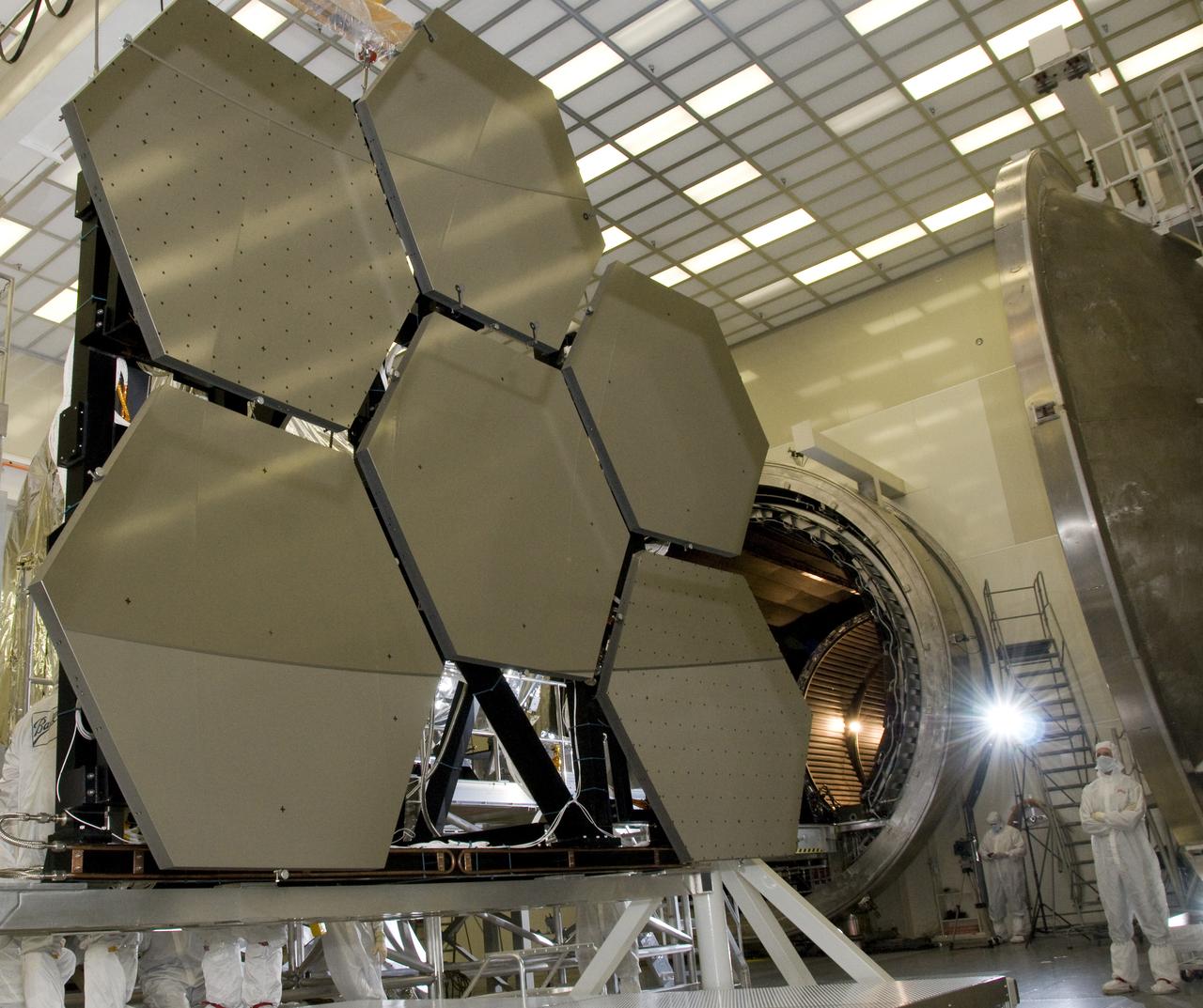

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
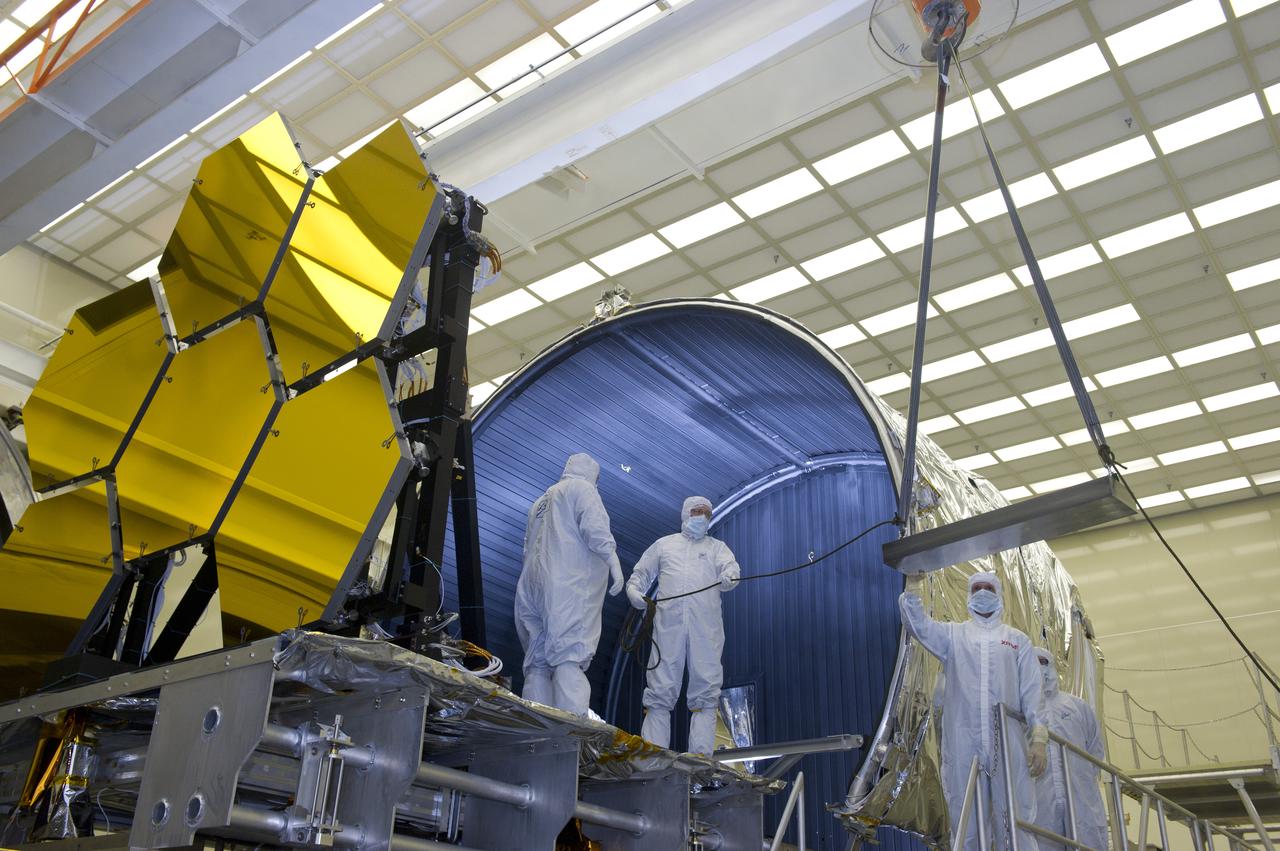

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
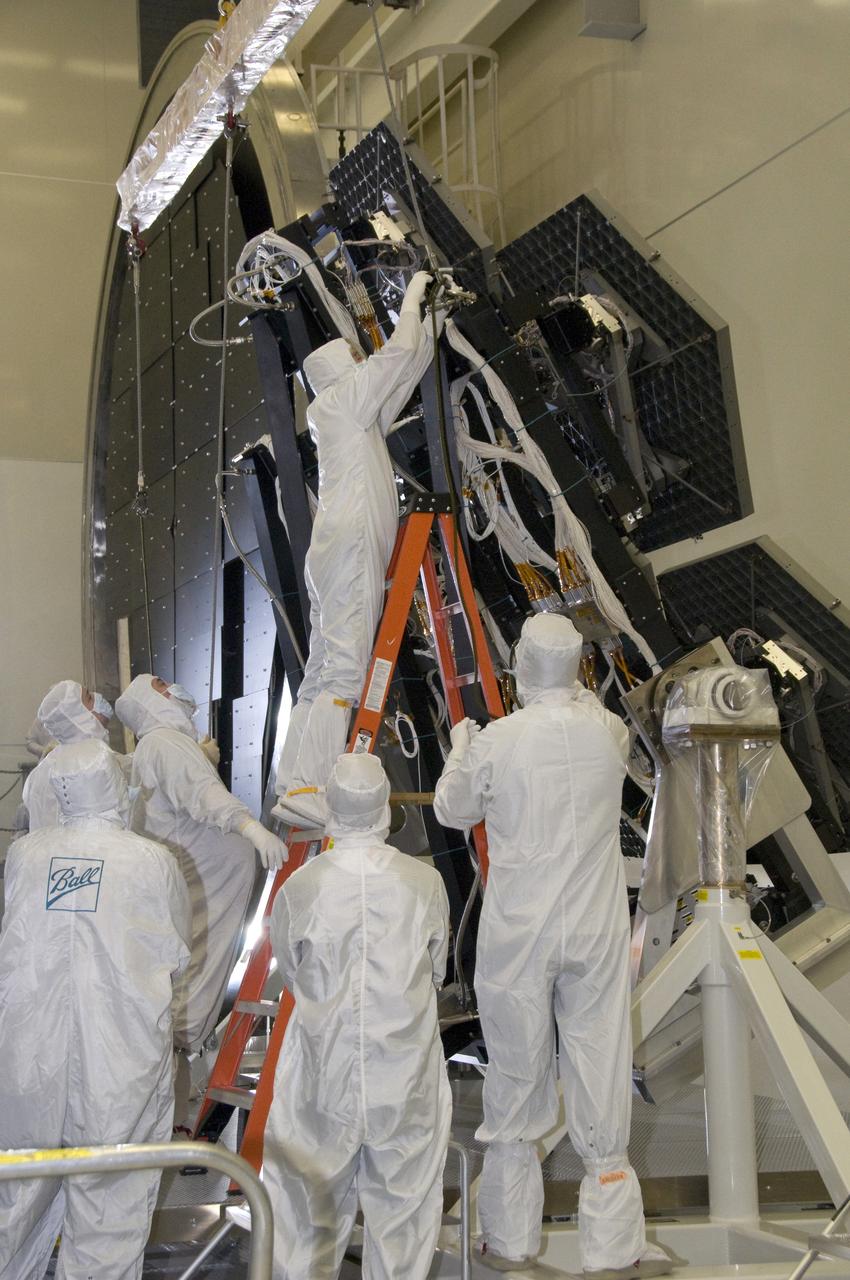

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
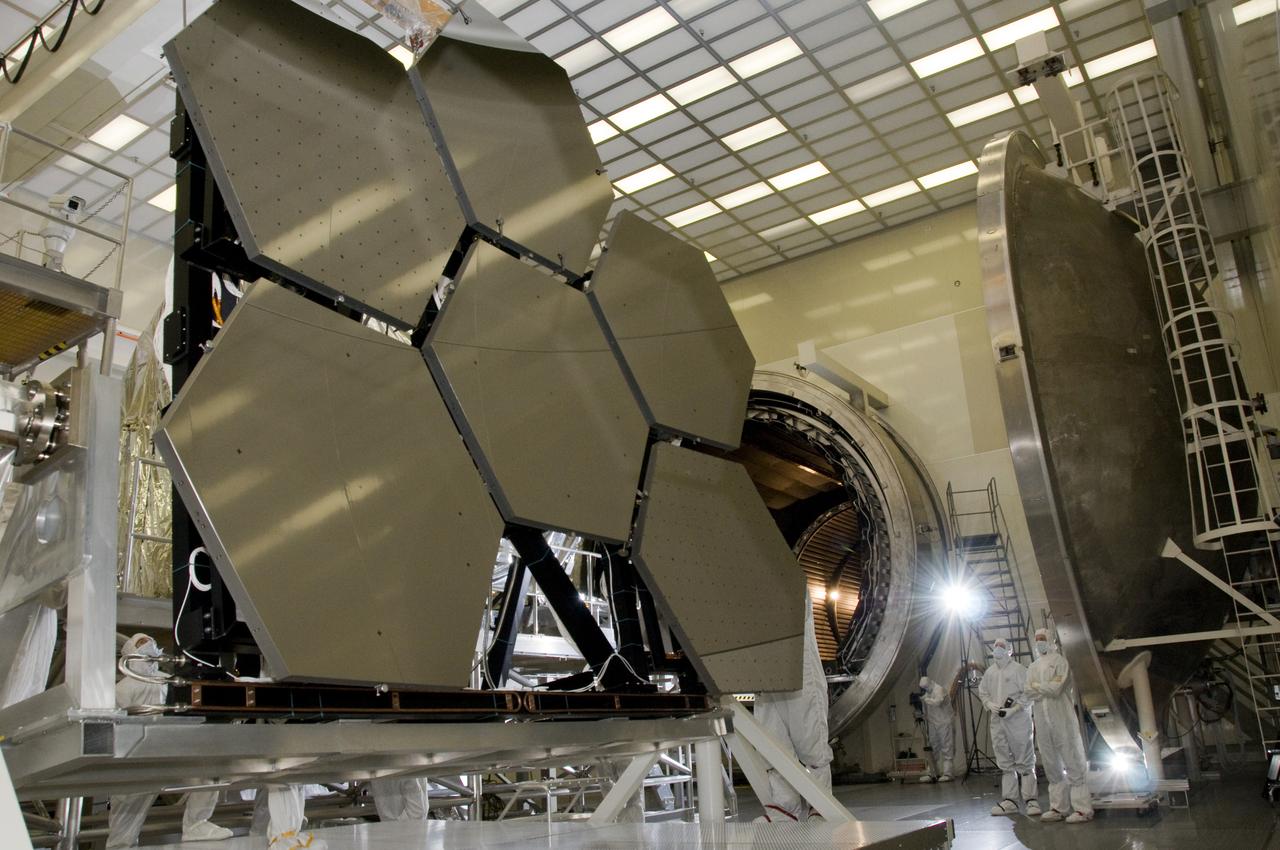

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
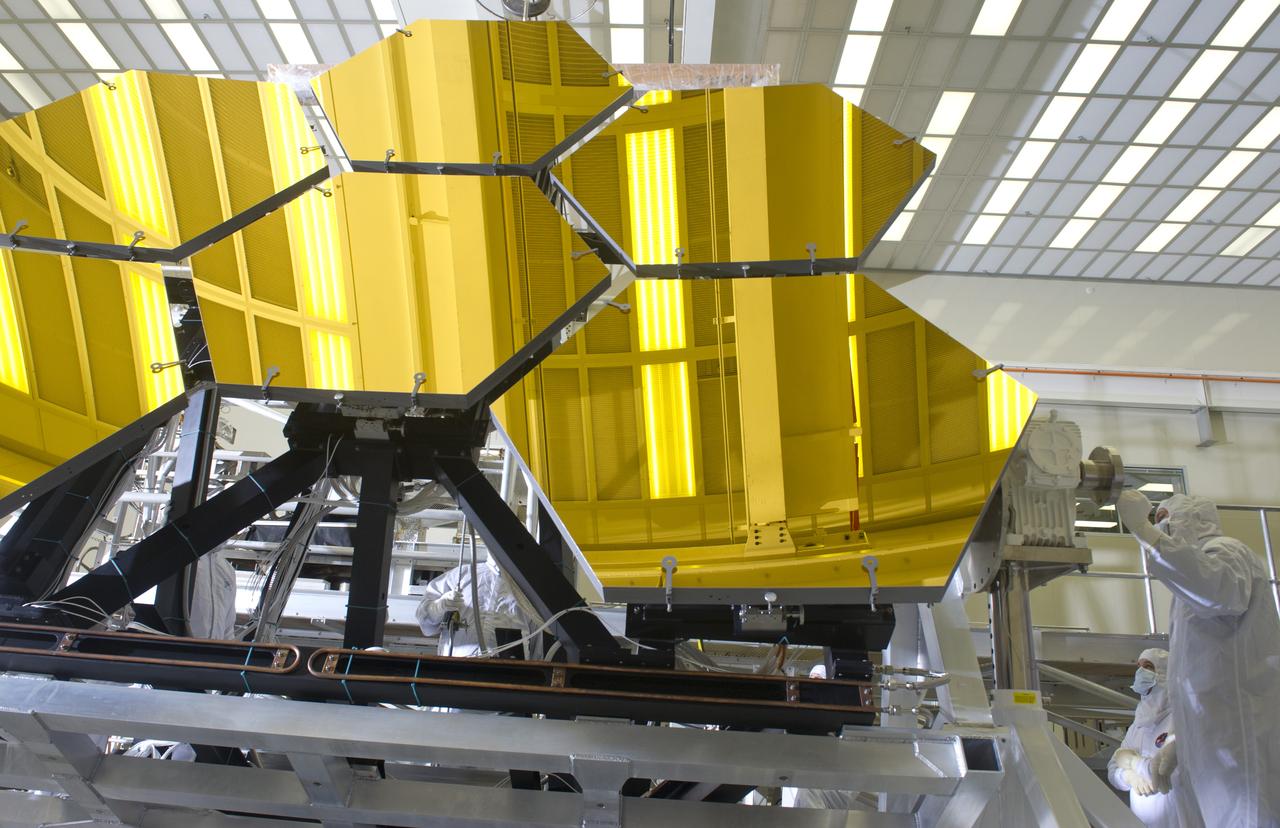

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
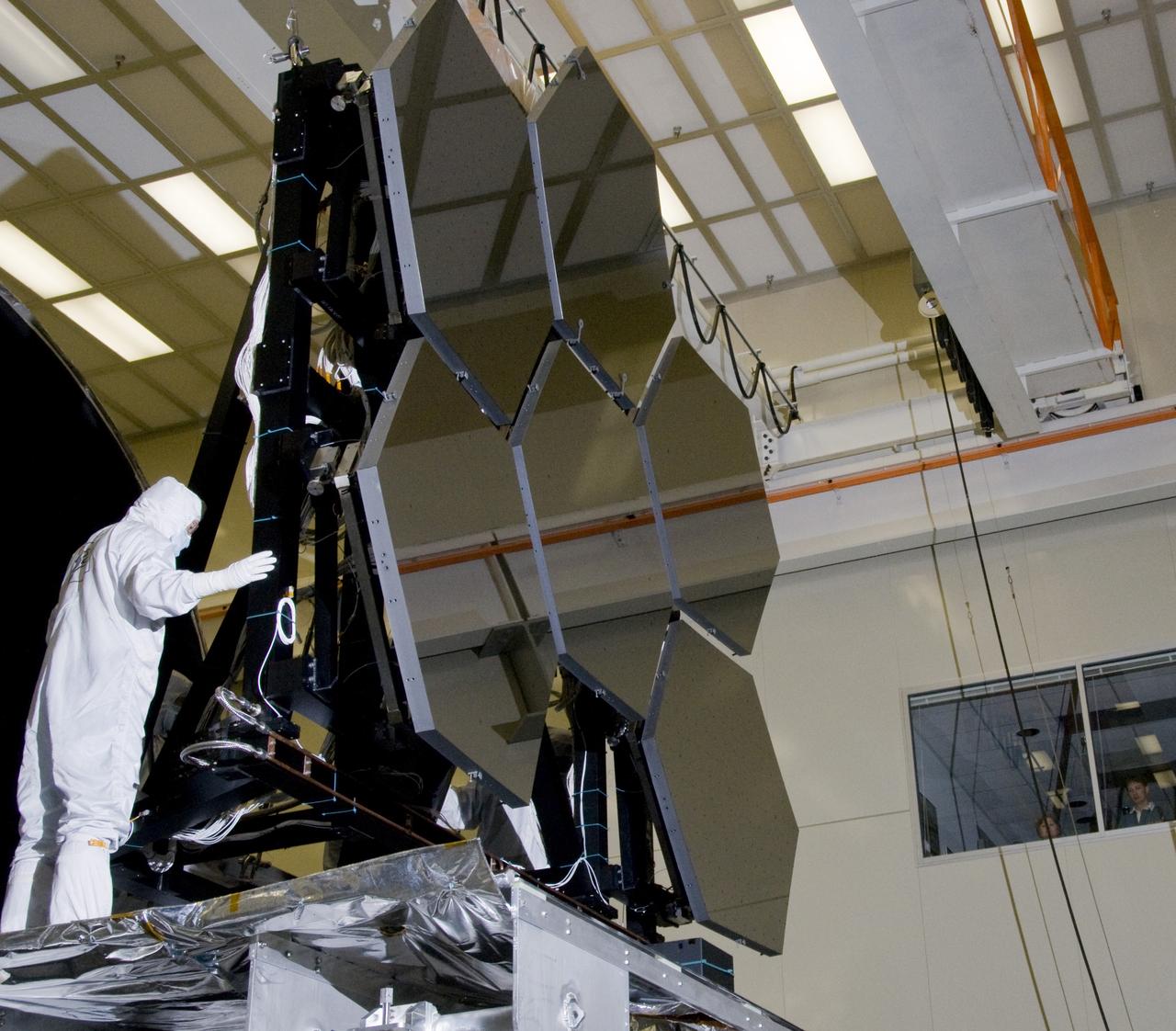

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
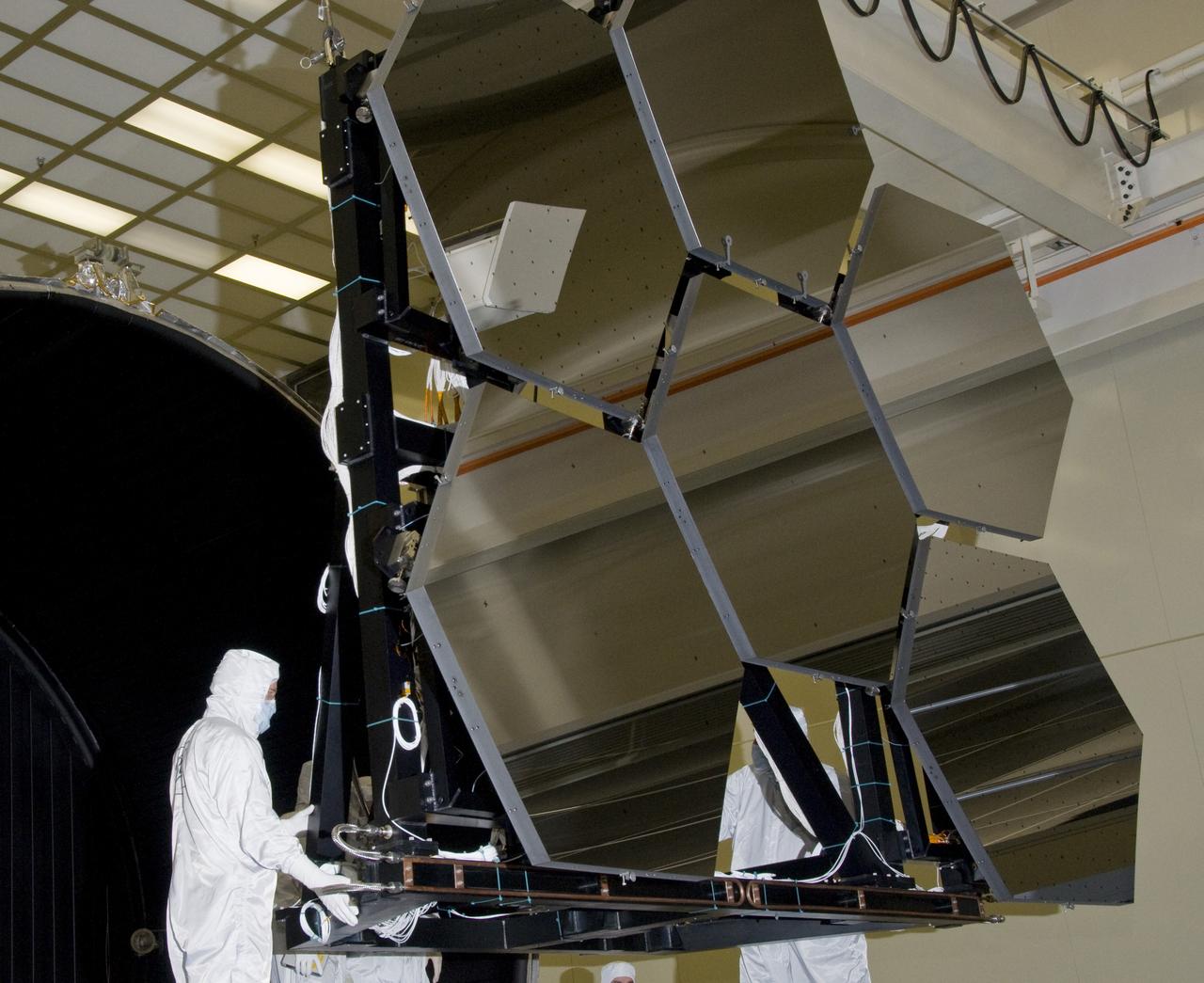

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
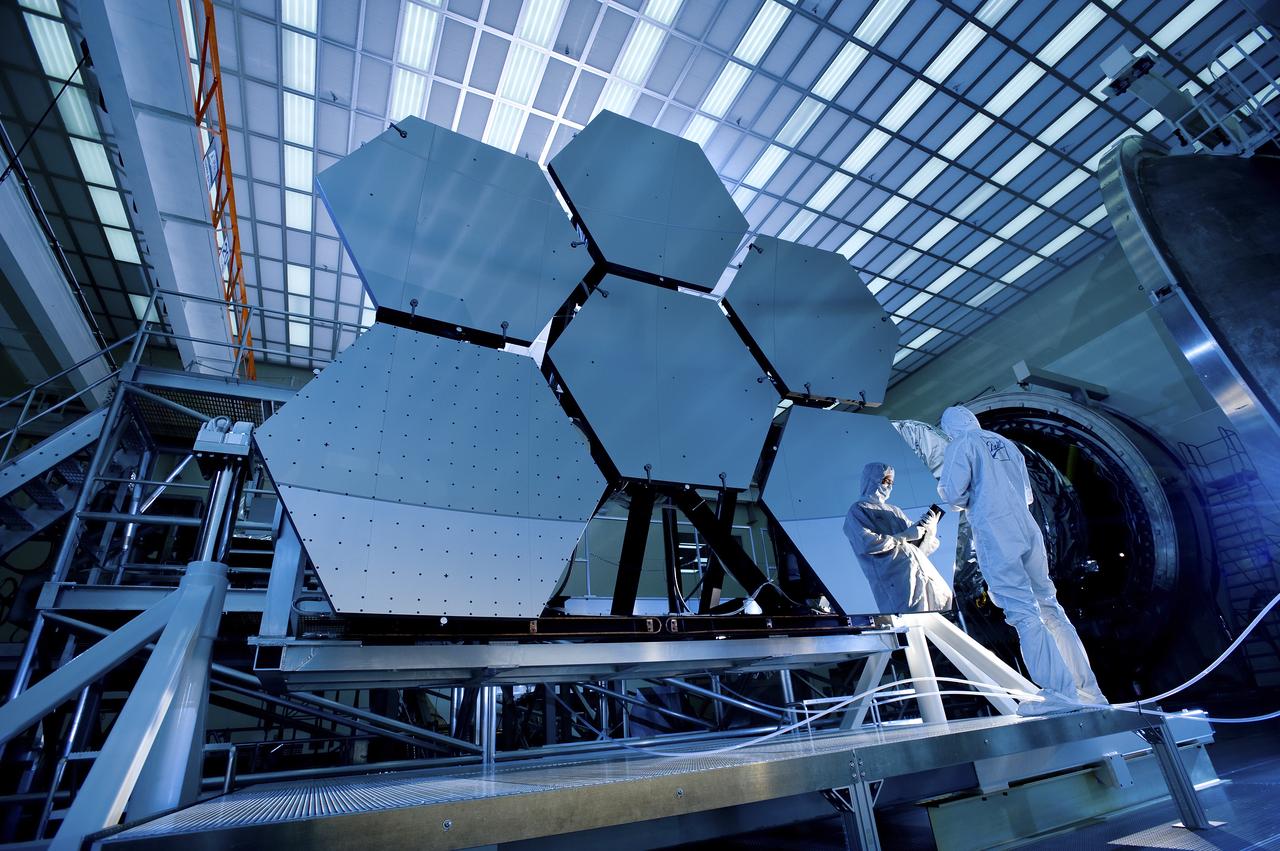

BALL AEROSPACE'S JAKE LEWIS IS REFLECTED IN ONE OF THE MIRRORS ON A JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE ARRAY THAT WAS IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING
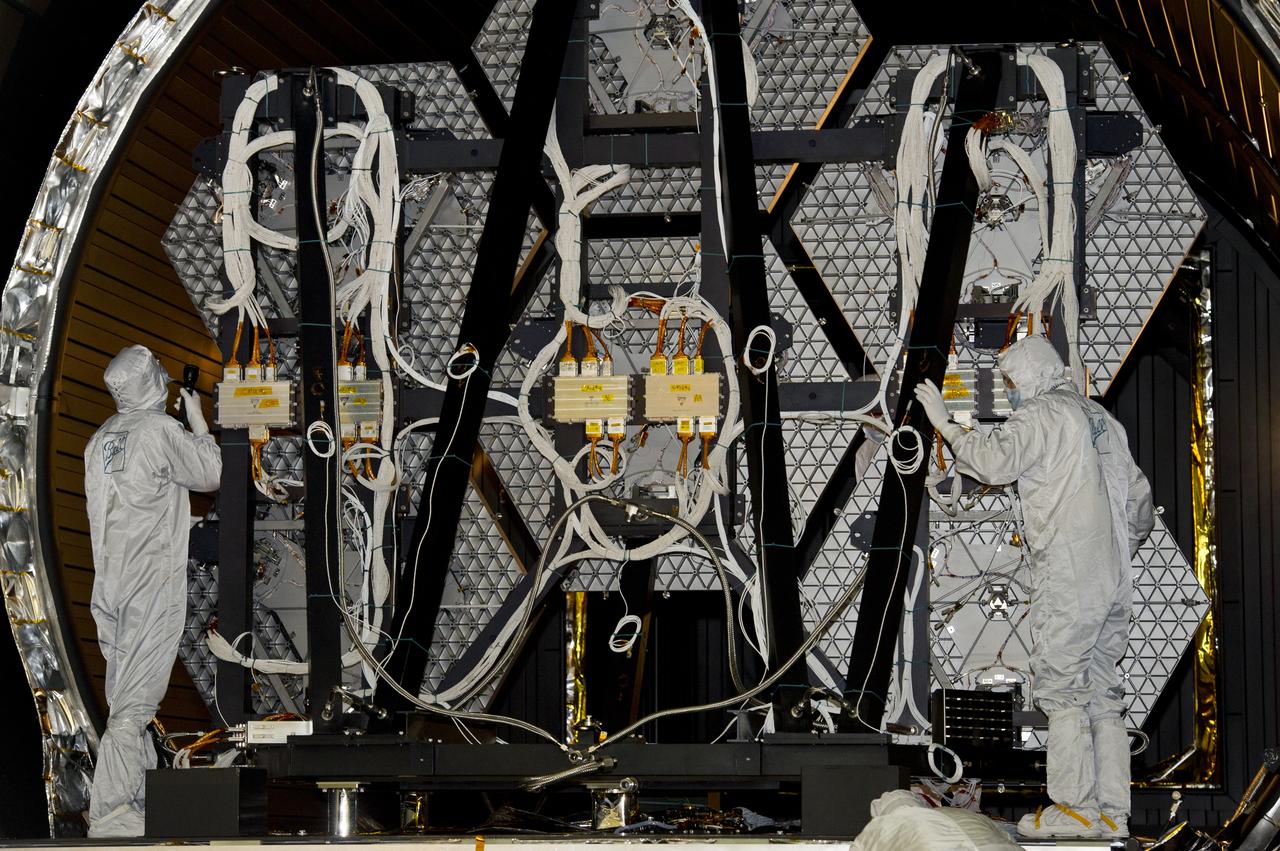
JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
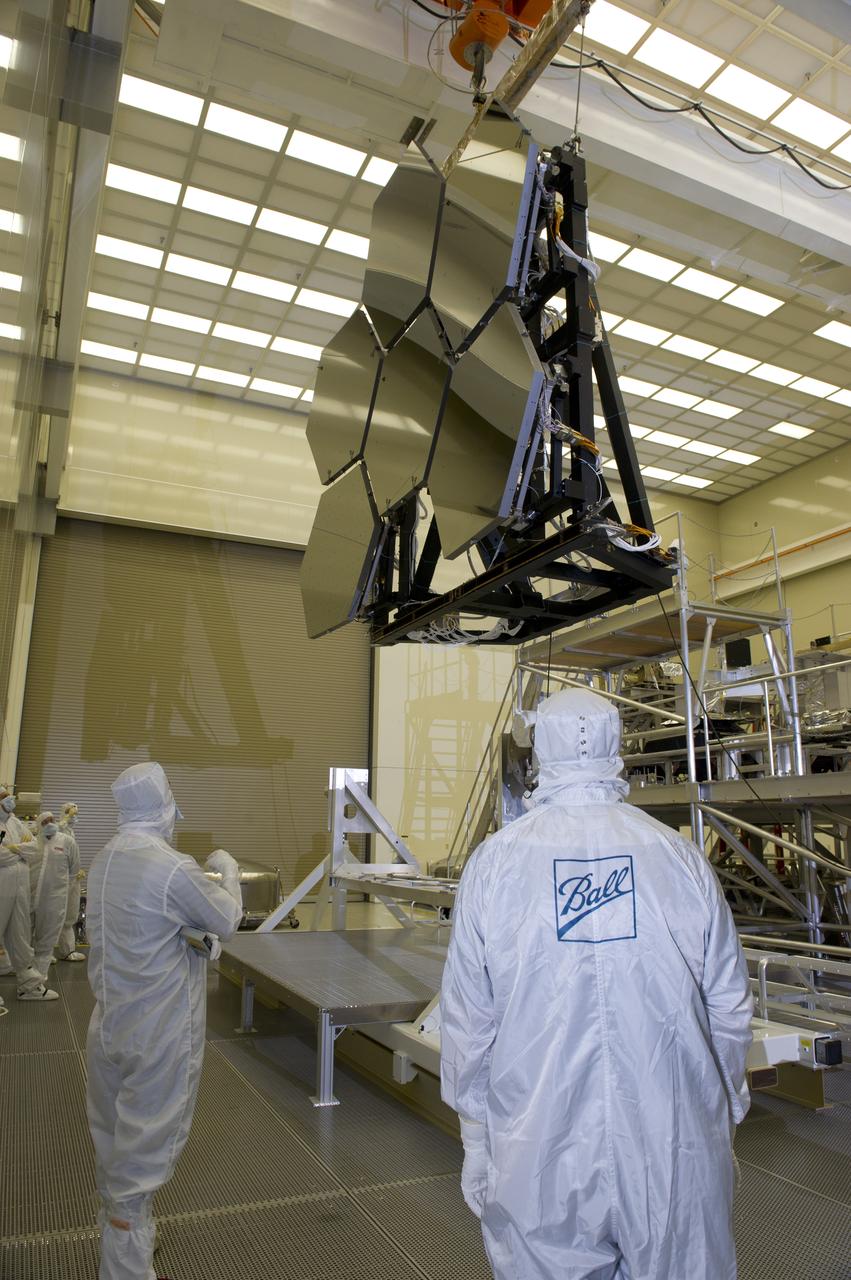

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
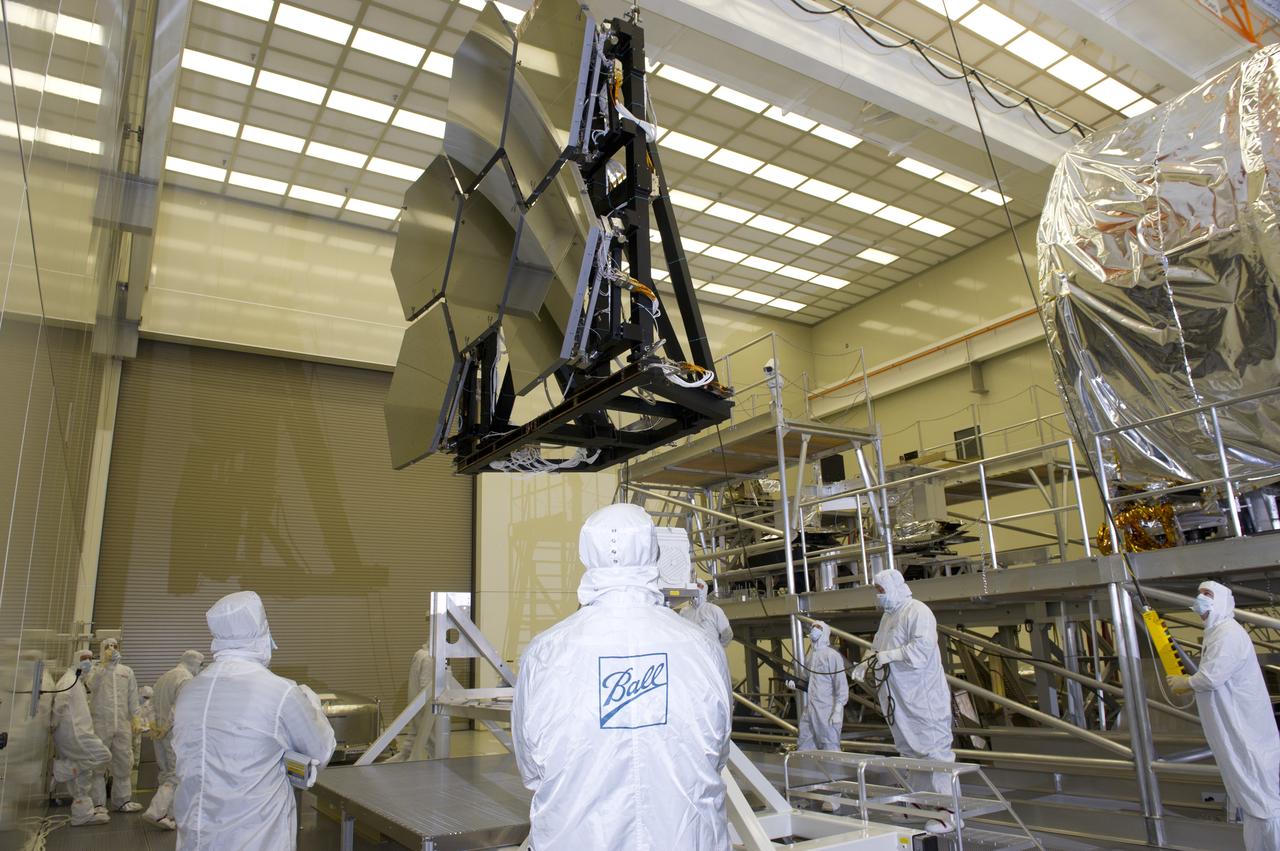

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
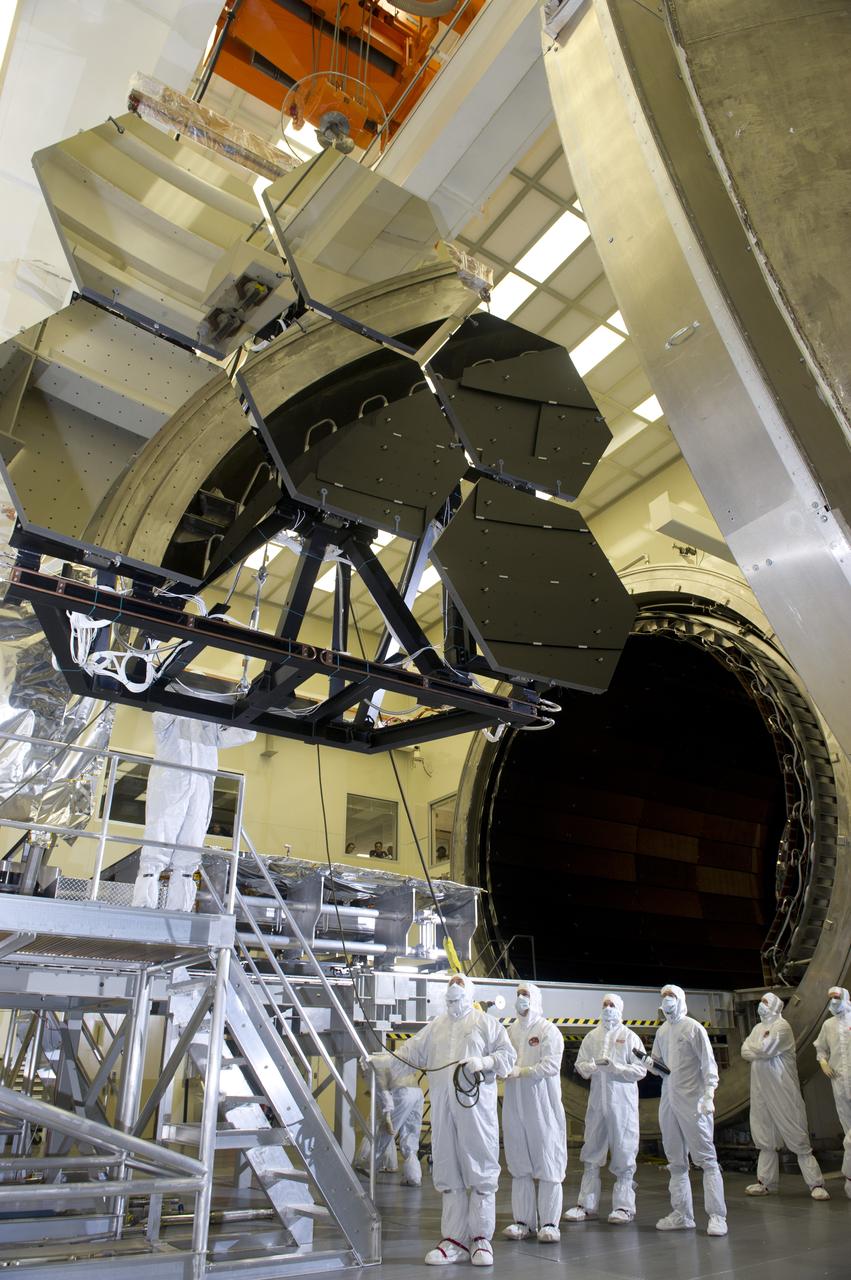

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
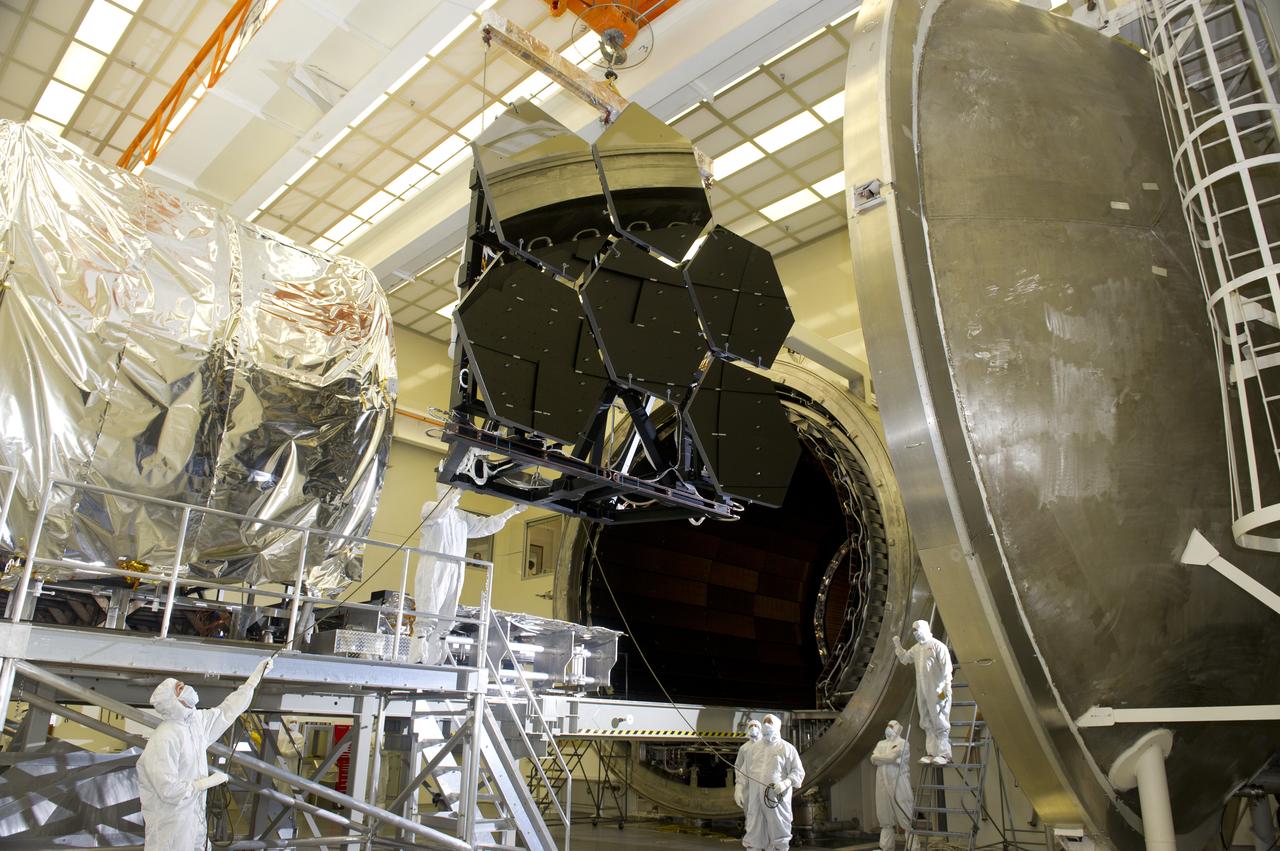

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
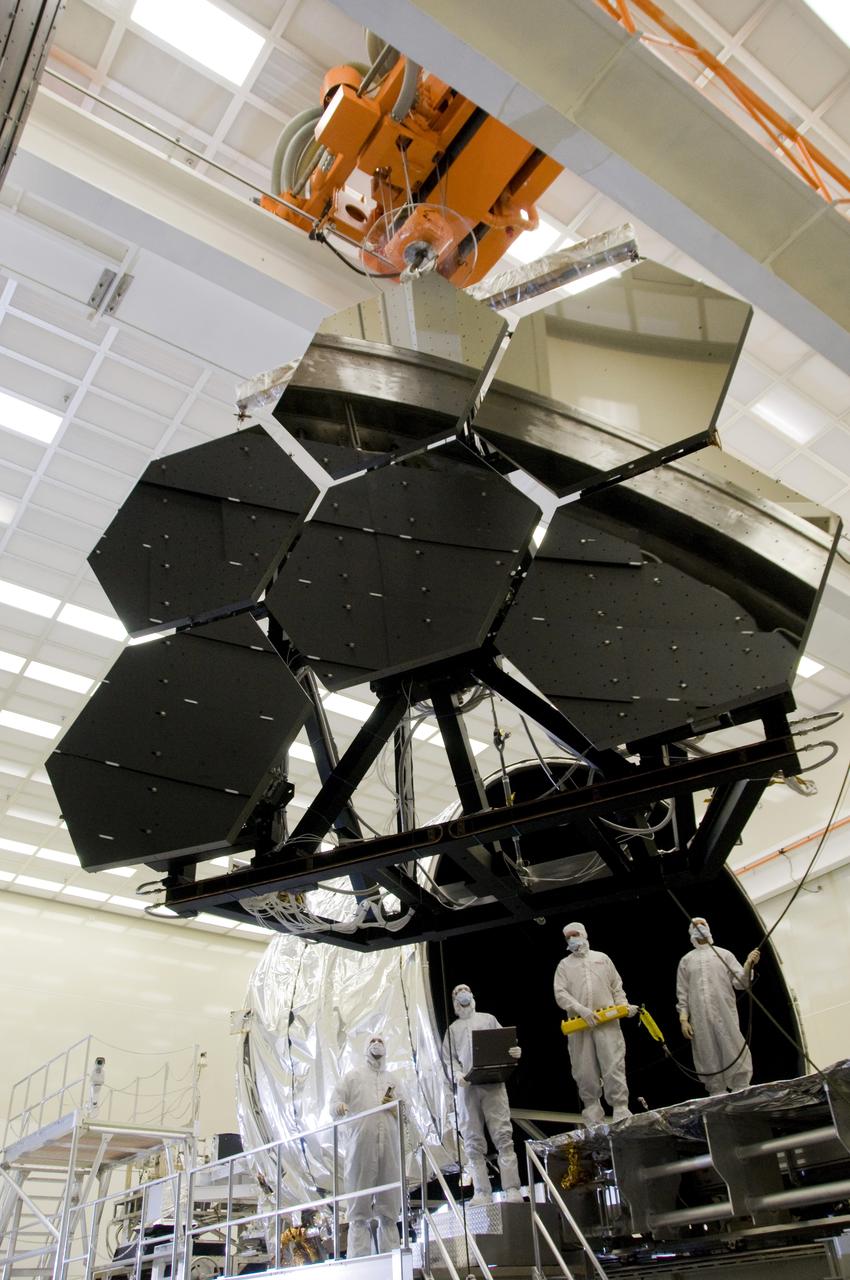

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE PRIMARY MIRROR SEGMENTS BEING LIFTED INTO POSITION FOR CRYOGENIC-OPTICAL EVALUATION AT NASA’S X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
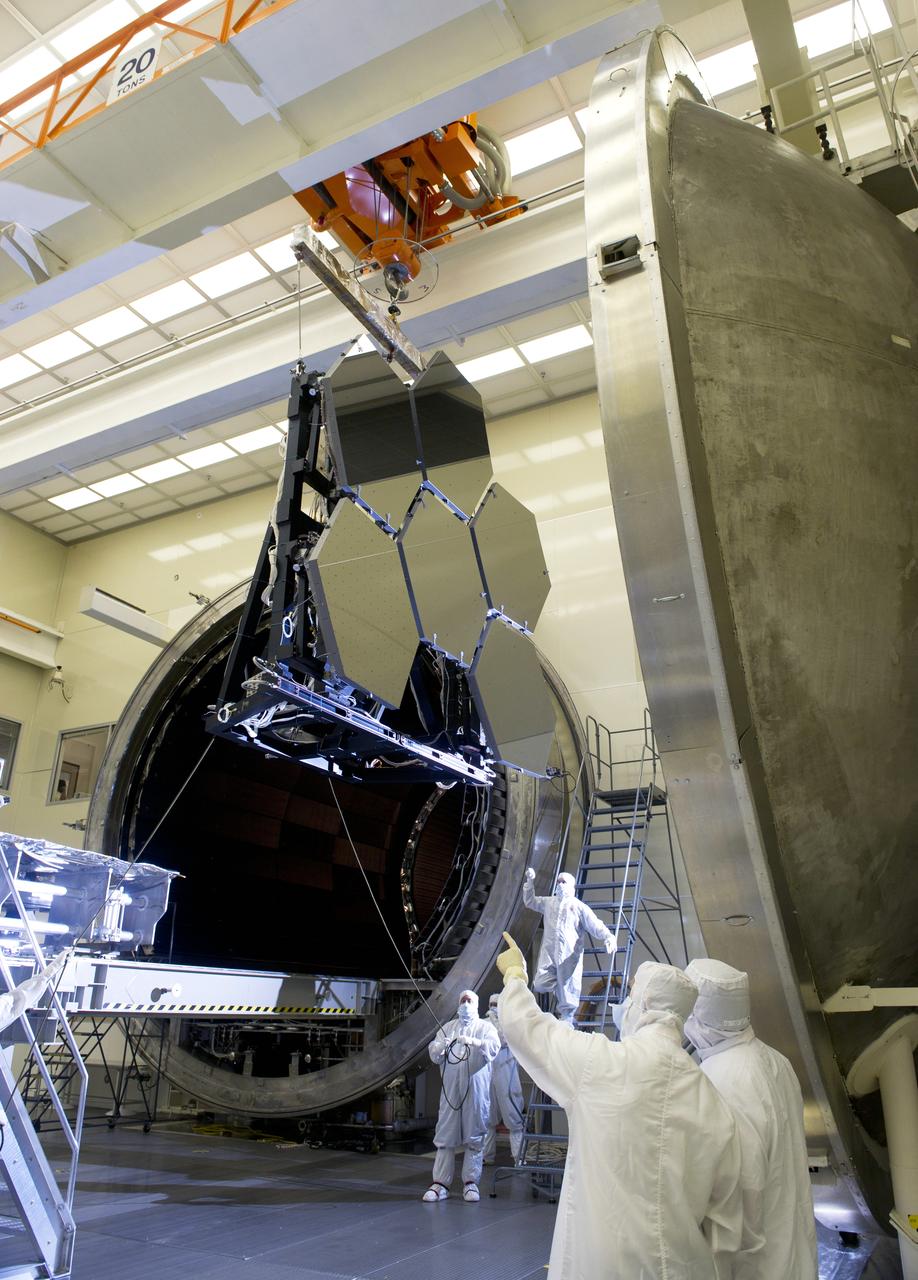

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
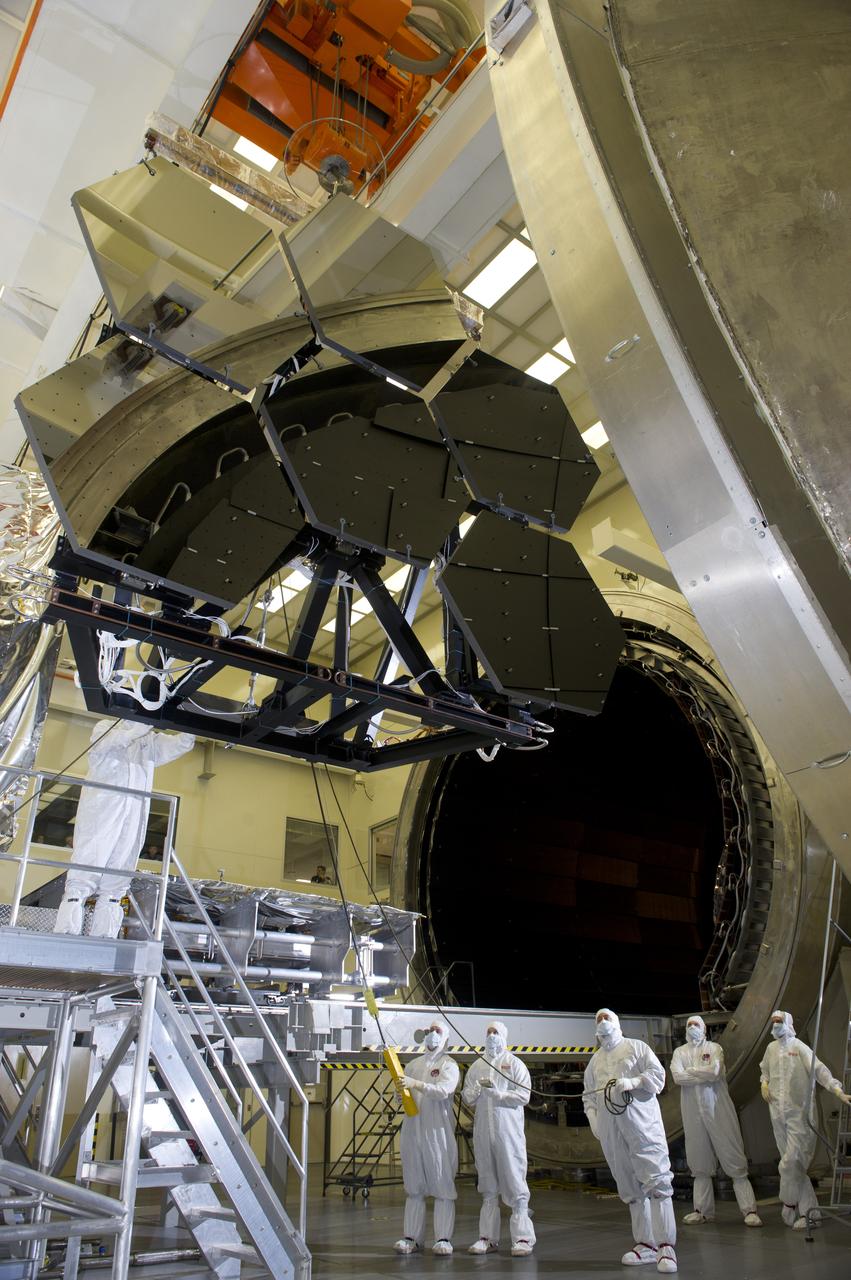

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
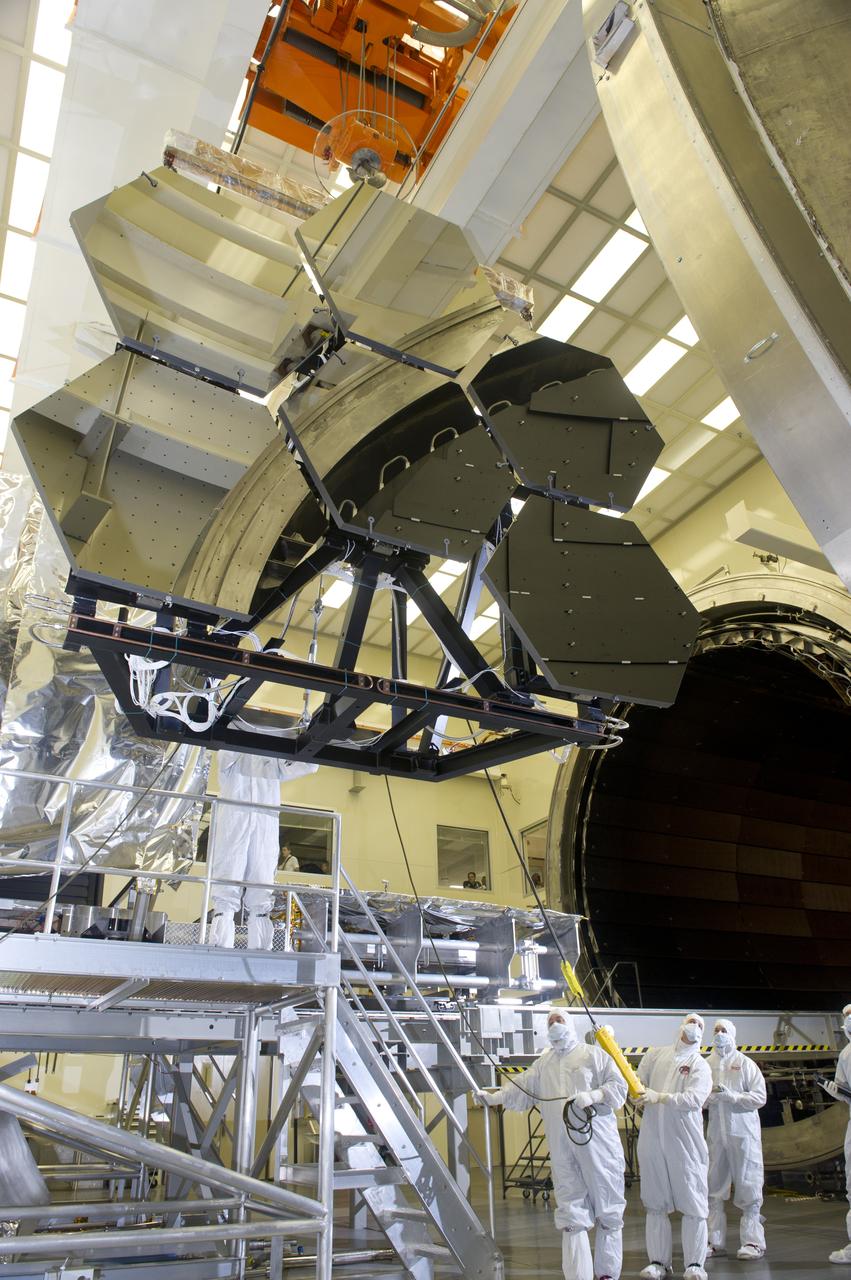

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
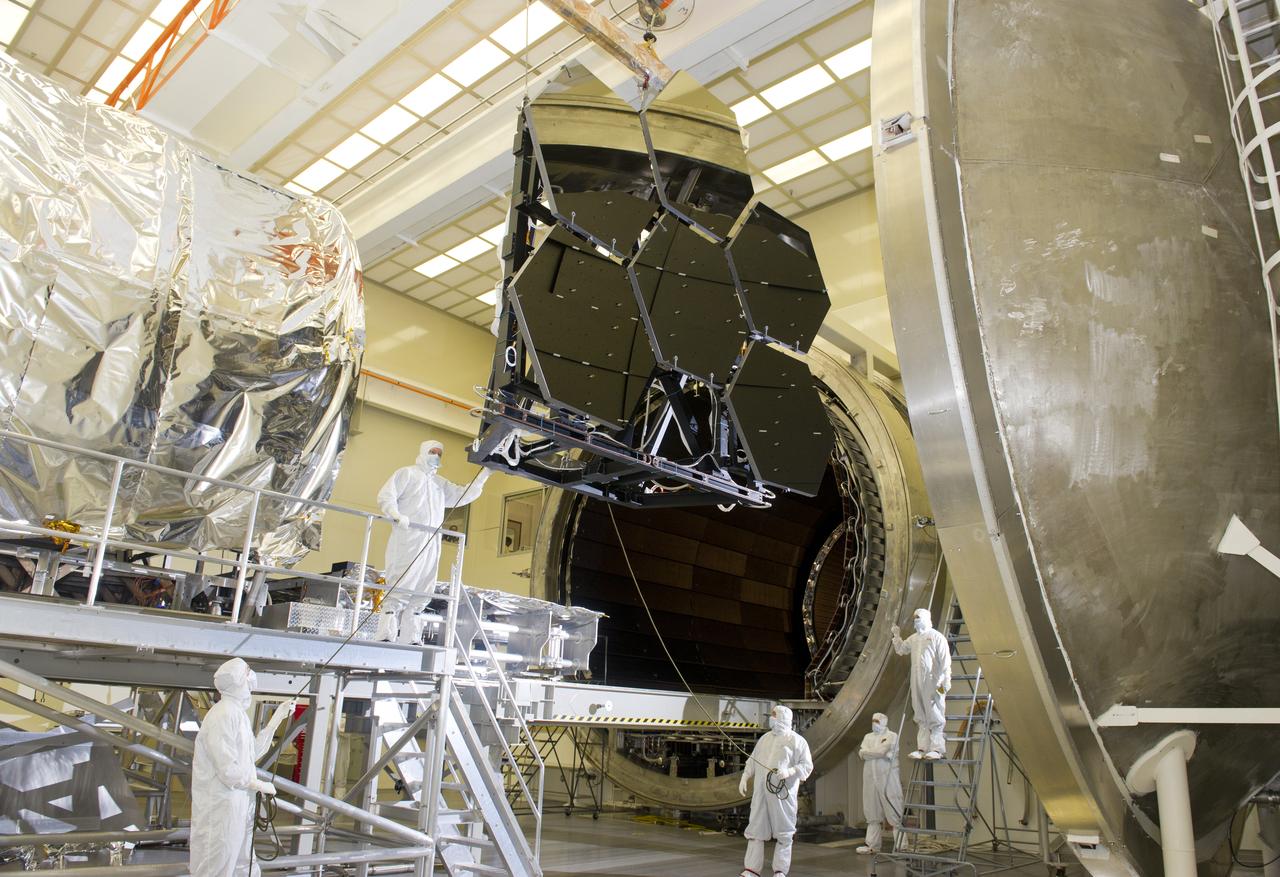

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
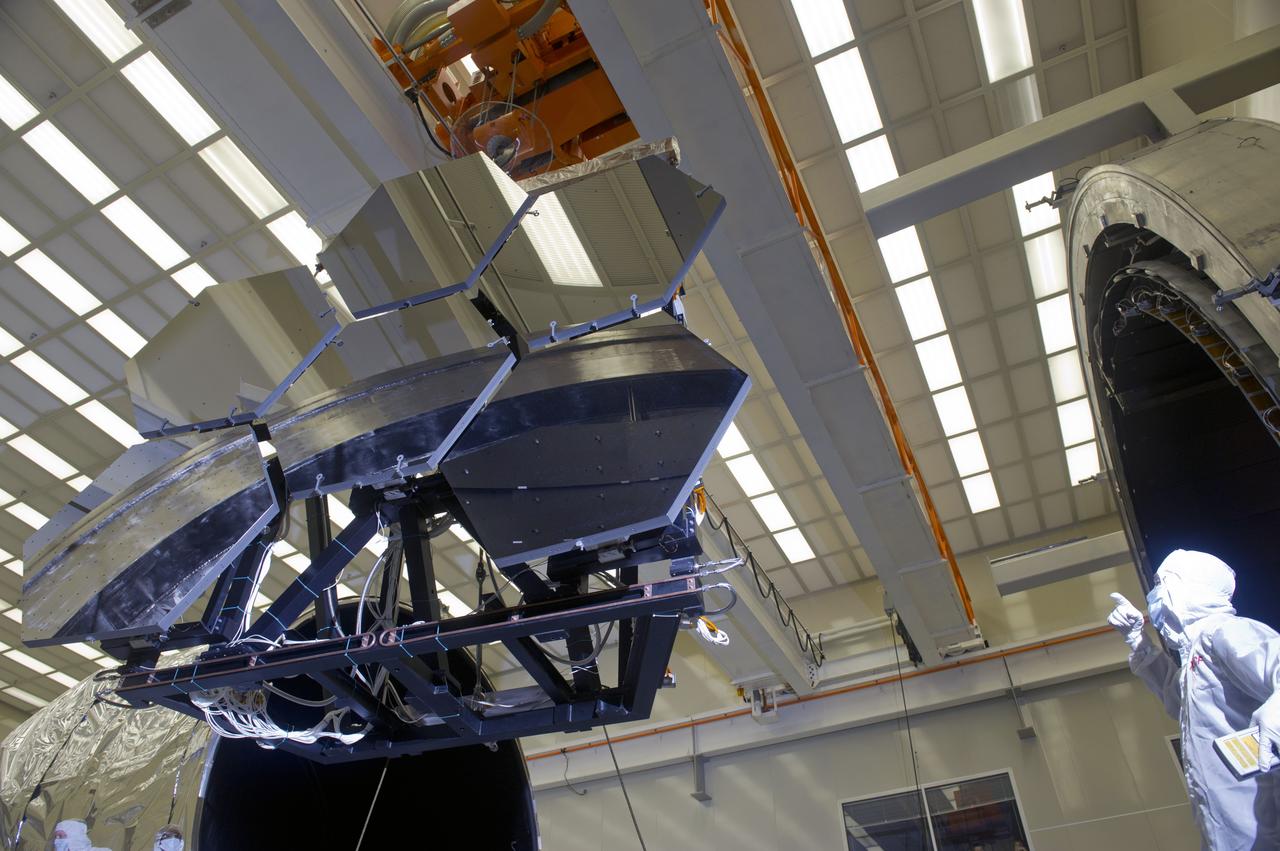

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
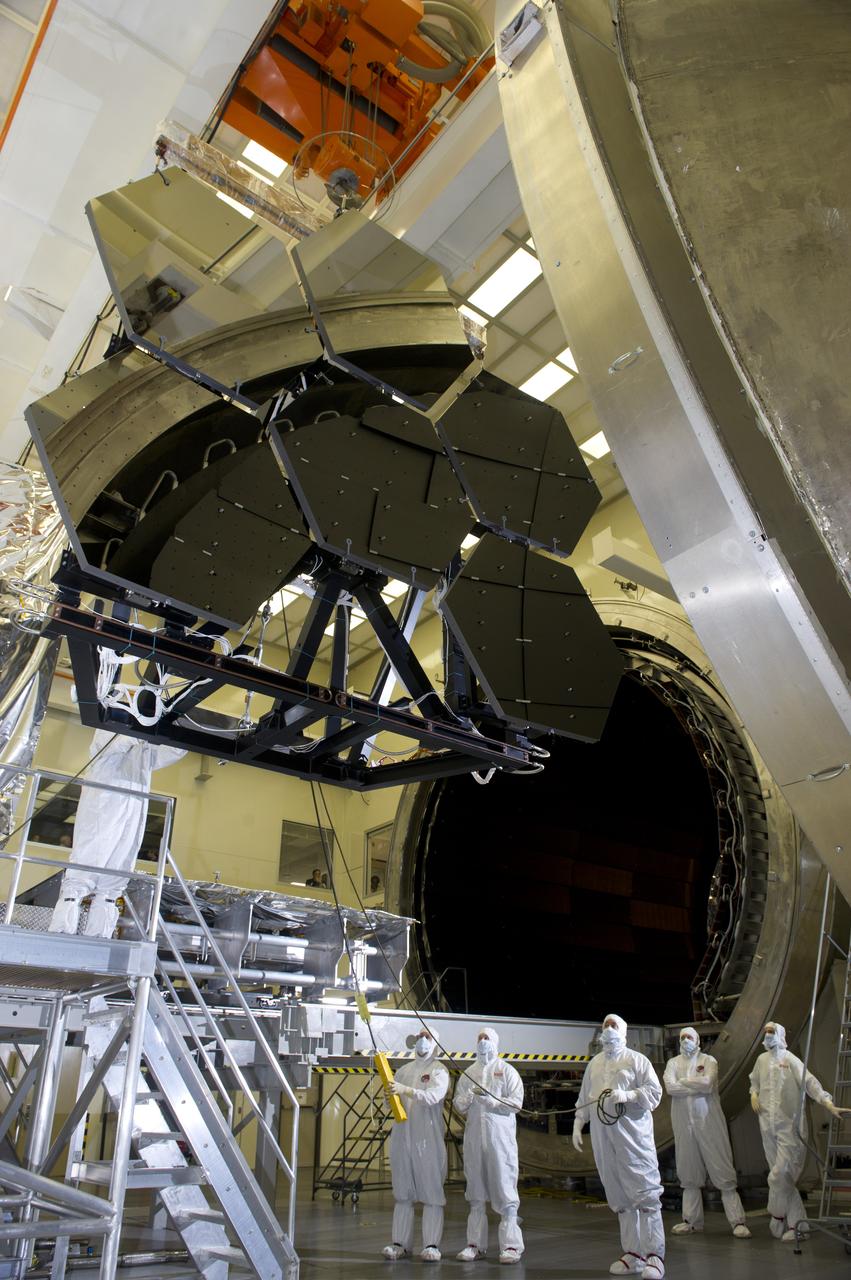

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
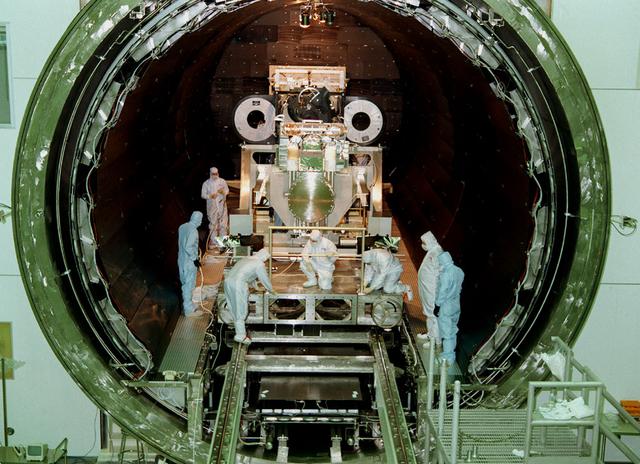

This photo shows the High Resolution Camera (HRC) for the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), being integrated with the High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) in Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) 24-foot Vacuum Chamber at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most poweful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRC is one of the two instruments used at the focus of CXO, where it will detect x-rays reflected from an assembly of eight mirrors. The unique capabilities of the HRC stem from the close match of its imaging capability to the focusing of the mirrors. When used with CXO mirrors, the HRC makes images that reveal detail as small as one-half an arc second. This is equivalent to the ability to read a newspaper at a distance of 1 kilometer. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components relatedto x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
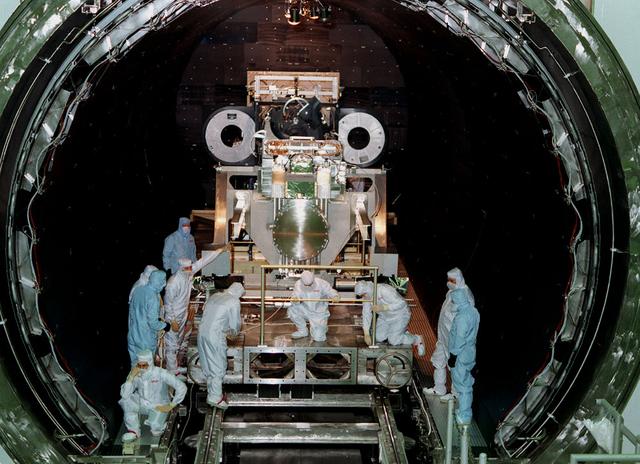

This photo shows the High Resolution Camera (HRC) for the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), being integrated with the High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) in Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) 24-foot Vacuum Chamber at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRC is one of the two instruments used at the focus of CXO, where it will detect x-rays reflected from an assembly of eight mirrors. The unique capabilities of the HRC stem from the close match of its imaging capability to the focusing of the mirrors. When used with CXO mirrors, the HRC makes images that reveal detail as small as one-half an arc second. This is equivalent to the ability to read a newspaper at a distance of 1 kilometer. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
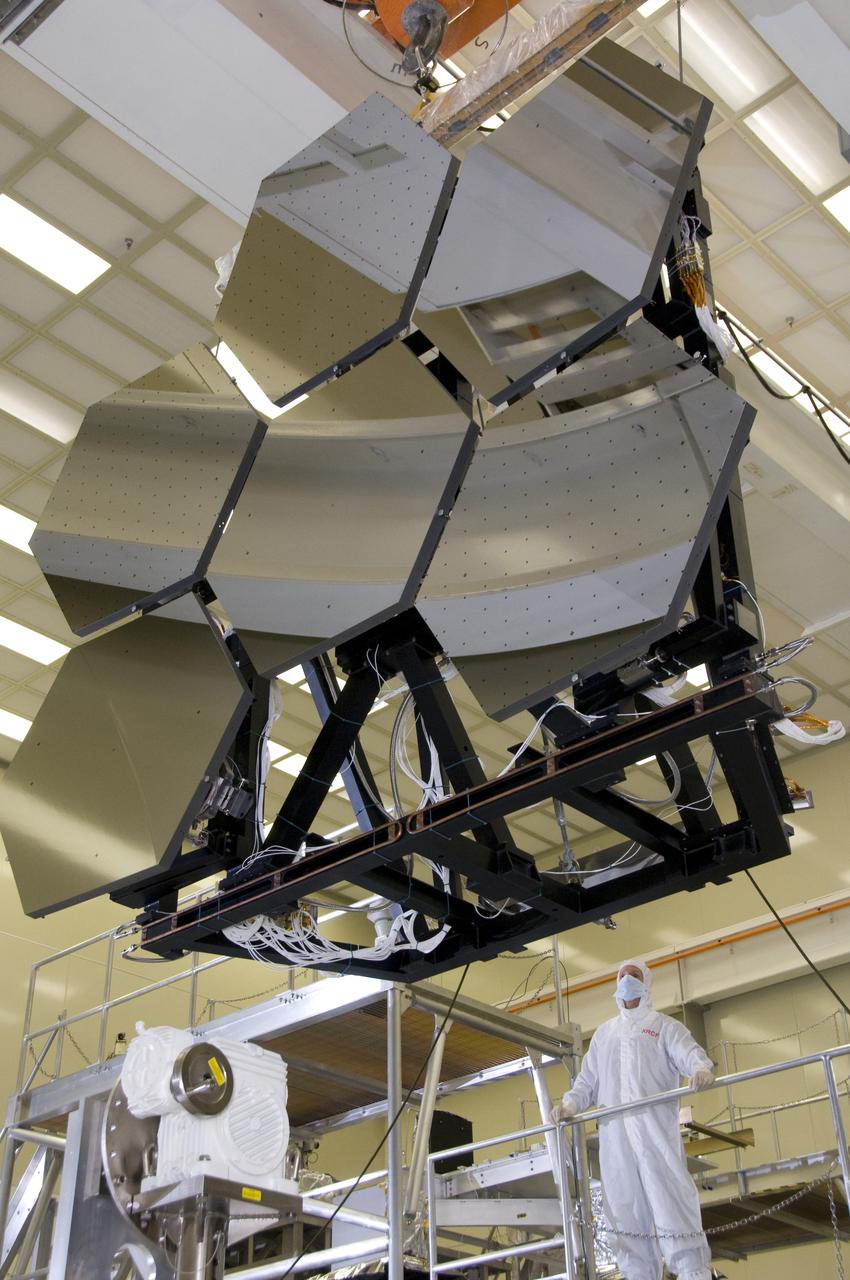

ERNIE WRIGHT, TEST DIRECTOR, MONITORS MOVE OF TEST STAND WITH SIX JWST (JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE) PRIMARY MIRROR SEGMENT ASSEMBLIES AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
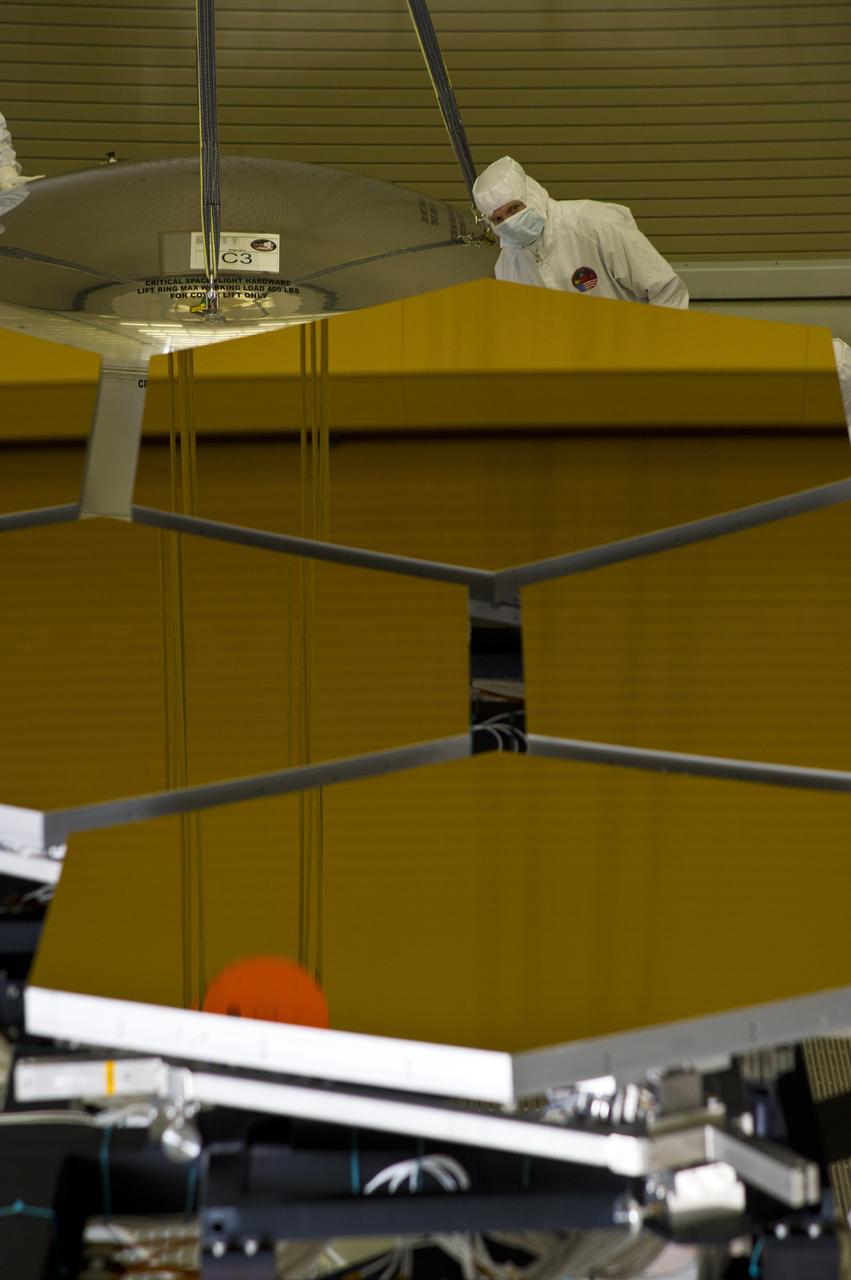

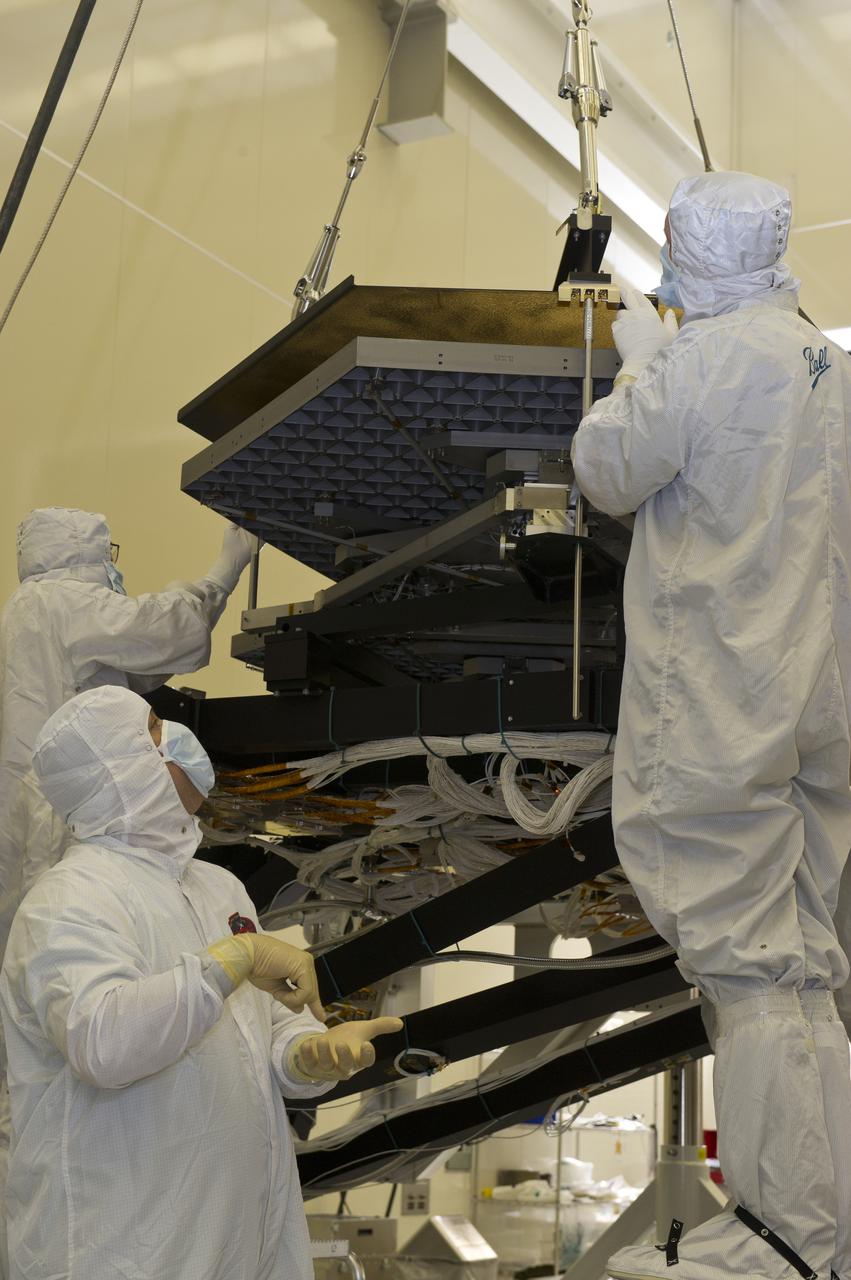
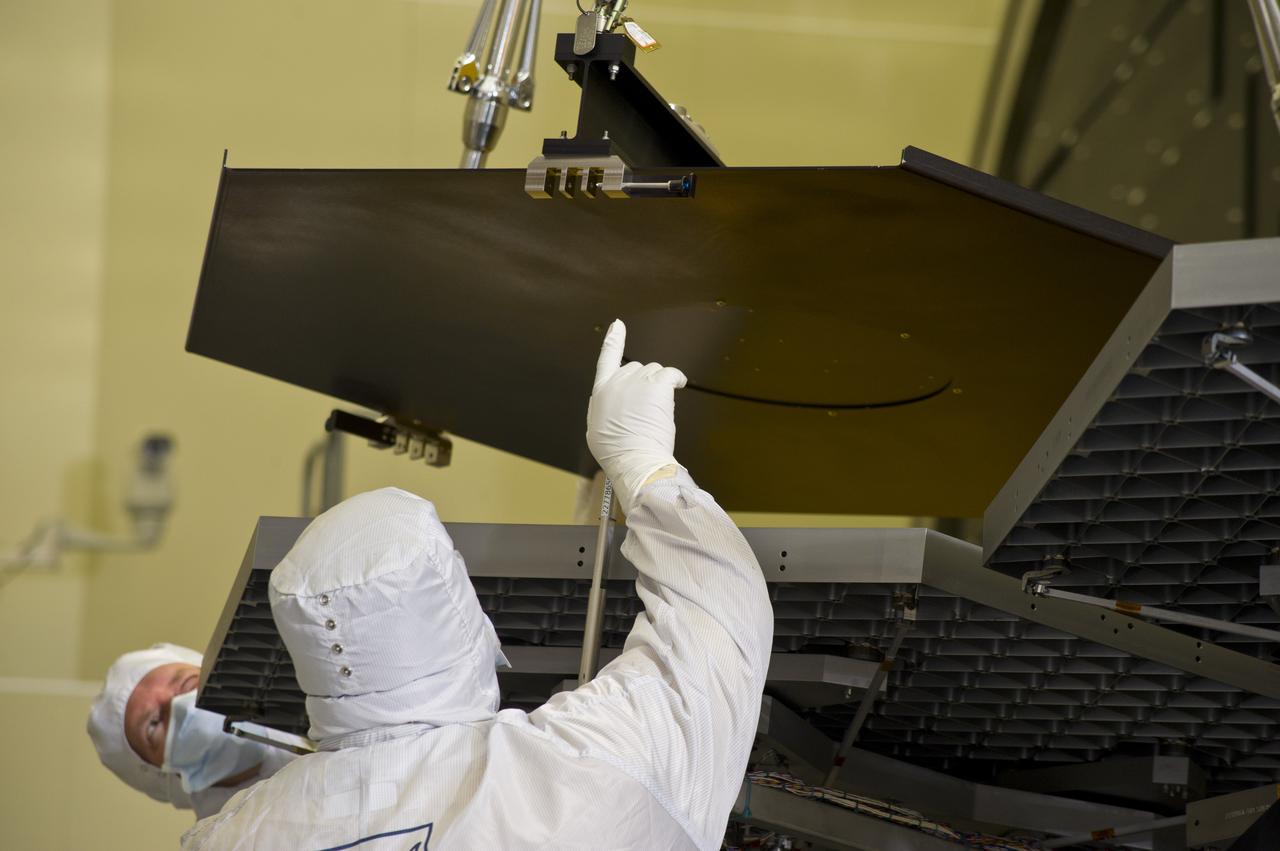
BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
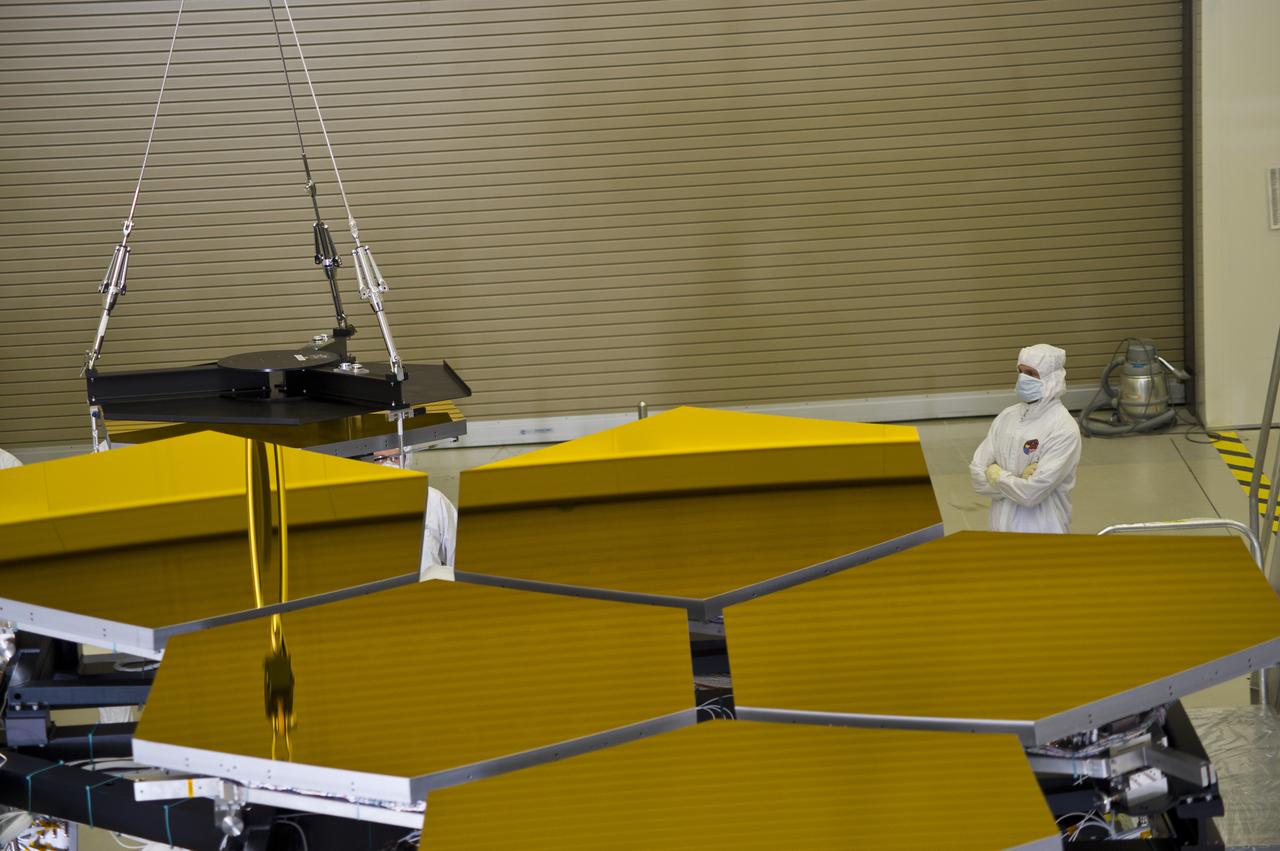

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
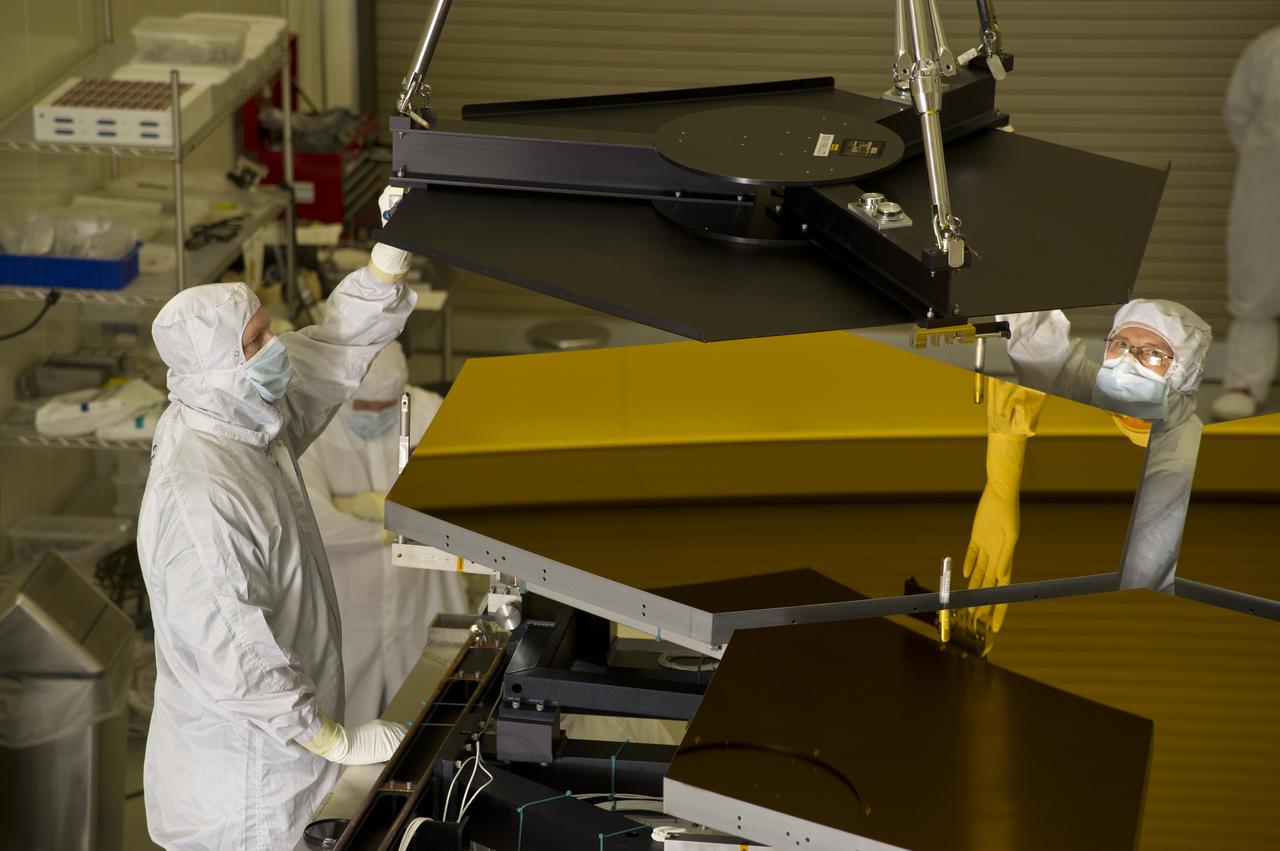

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
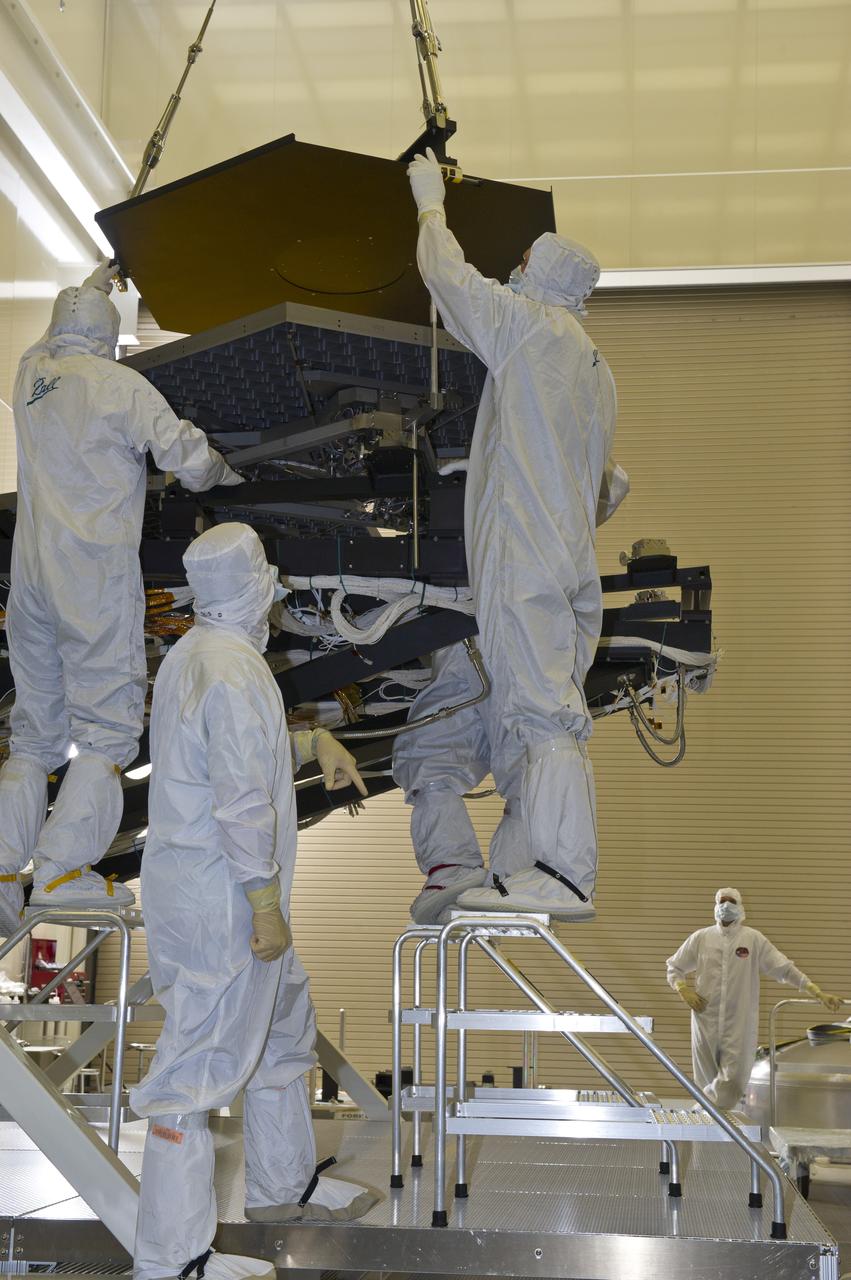

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
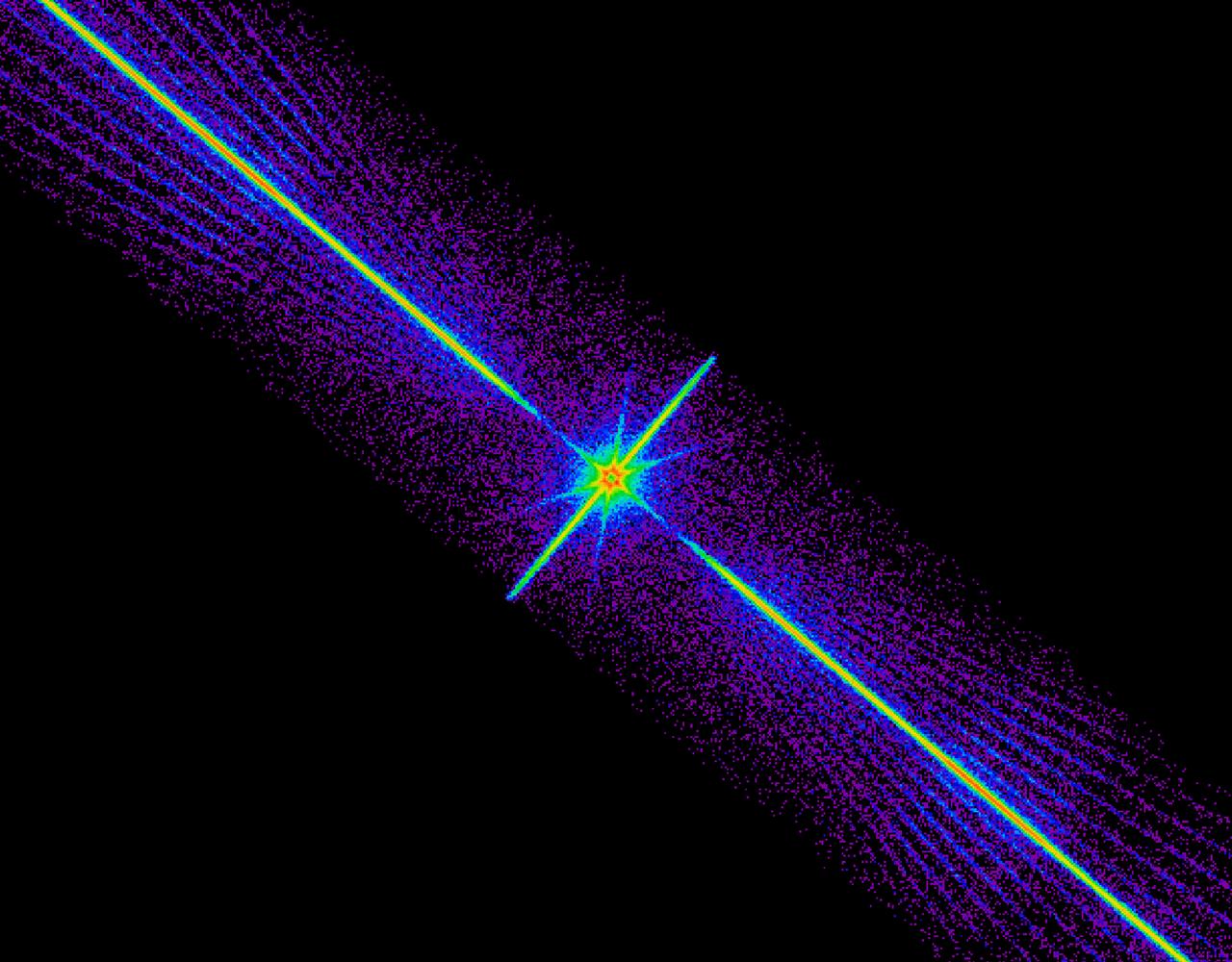
This Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) image is a spectrum of a black hole, which is similar to the colorful spectrum of sunlight produced by a prism. The x-rays of interest are shown here recorded in bright stripes that run rightward and leftward from the center of the image. These x-rays are sorted precisely according to their energy with the highest-energy x-rays near the center of the image and the lower-energy x-rays farther out. The spectrum was obtained by using the Low Energy Transmission Grating (LETG), which intercepts x-rays and changes their direction by the amounts that depend sensitively on the x-ray energy. The assembly holds 540 gold transmission gratings. When in place behind the mirrors, the gratings intercept the x-rays reflected from the telescope. The bright spot at the center is due to a fraction of the x-ray radiation that is not deflected by the LETG. The spokes that intersect the central spot and the faint diagonal rays that flank the spectrum itself are artifacts due to the structure that supports the LETG grating elements. (Photo credit: NASA Cfa/J. McClintock et al)

Leon Van Speybroeck of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge Massachusetts was awarded the 2002 Bruno Rossi Prize of the High-Energy Astrophysics Division of the American Astronomy Society. The Rossi Prize is an arnual recognition of significant contributions in high-energy astrophysics in honor of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's late Professor Bruno Rossi, an authority on cosmic ray physics and a pioneer in the field of x-ray astronomy. Van Speybroeck, who led the effort to design and make the x-ray mirrors for NASA's premier Chandra X-Ray Observatory, was recognized for a career of stellar achievements in designing precision x-ray optics. As Telescope Scientist for Chandra, he has worked for more than 20 years with a team that includes scientists and engineers from the Harvard-Smithsonian, NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, TRW, Inc., Huhes-Danbury (now B.F. Goodrich Aerospace), Optical Coating Laboratories, Inc., and Eastman-Kodak on all aspects of the x-ray mirror assembly that is the heart of the observatory.
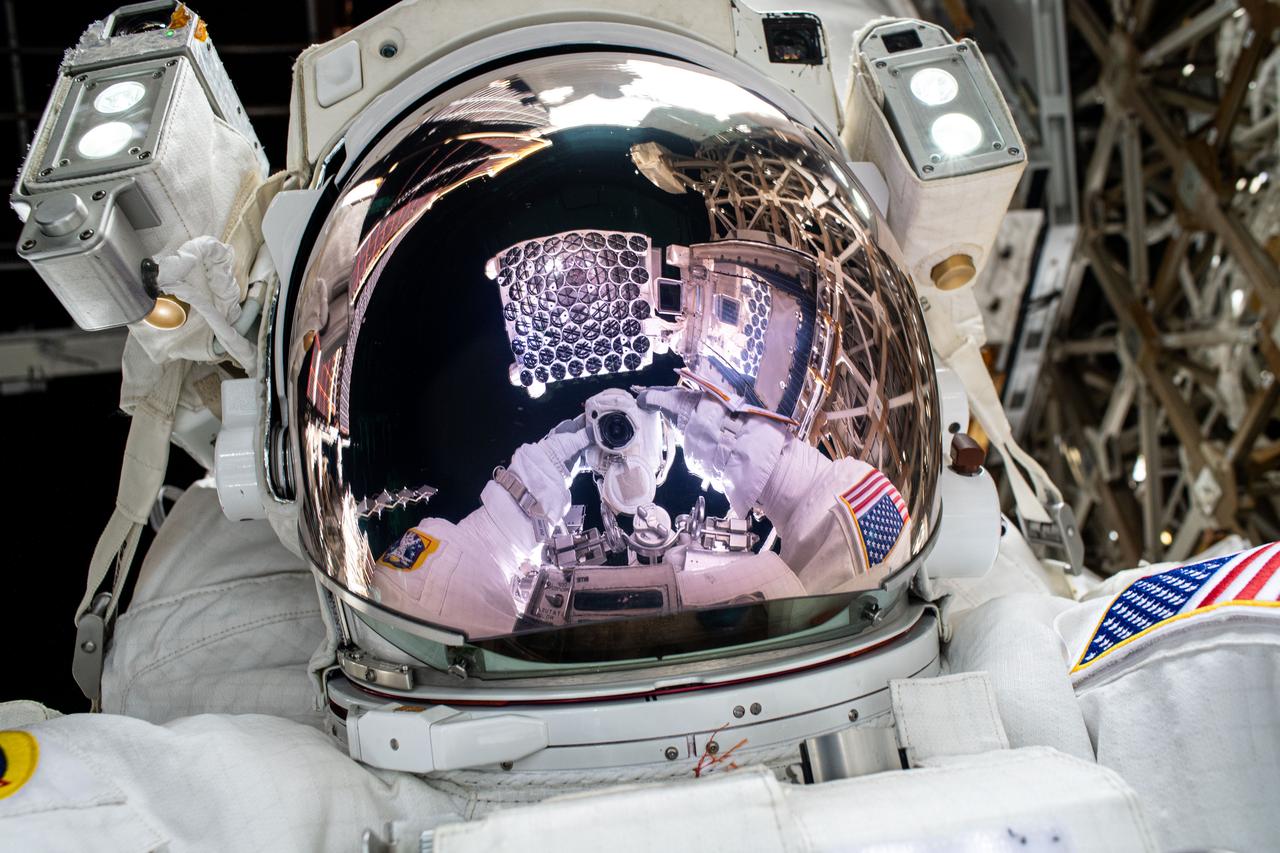

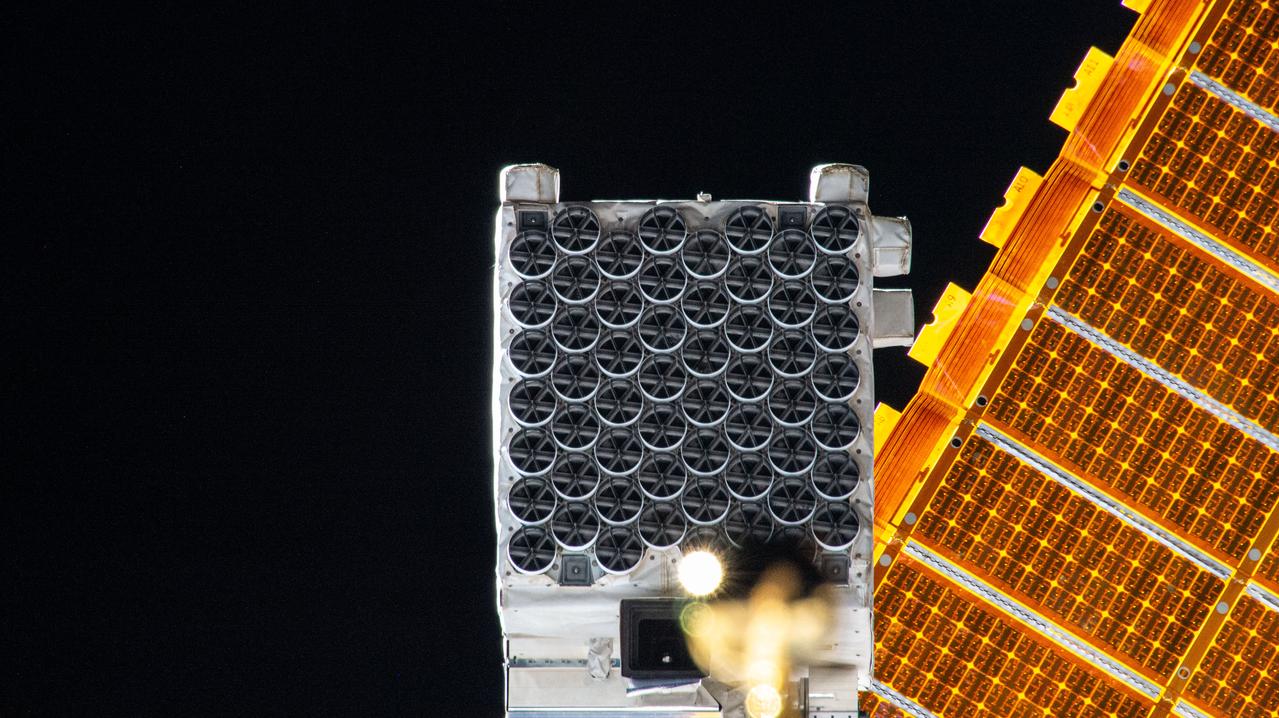
iss072e487911 (Jan. 16, 2025) --- The NICER X-ray telescope is reflected on NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Nick Hague's spacesuit helmet visor in this high-flying "space-selfie." Also, visible in Hague's visor is the camera he is pointing toward himself to take this photograph. During the six-hour spacewalk, Hague patched light leaks on some of NICER's 56 X-ray concentrators that block ultraviolet, infrared, and visible light while allowing X-rays to pass through to the mirrors underneath enabling the observation of neutron stars.
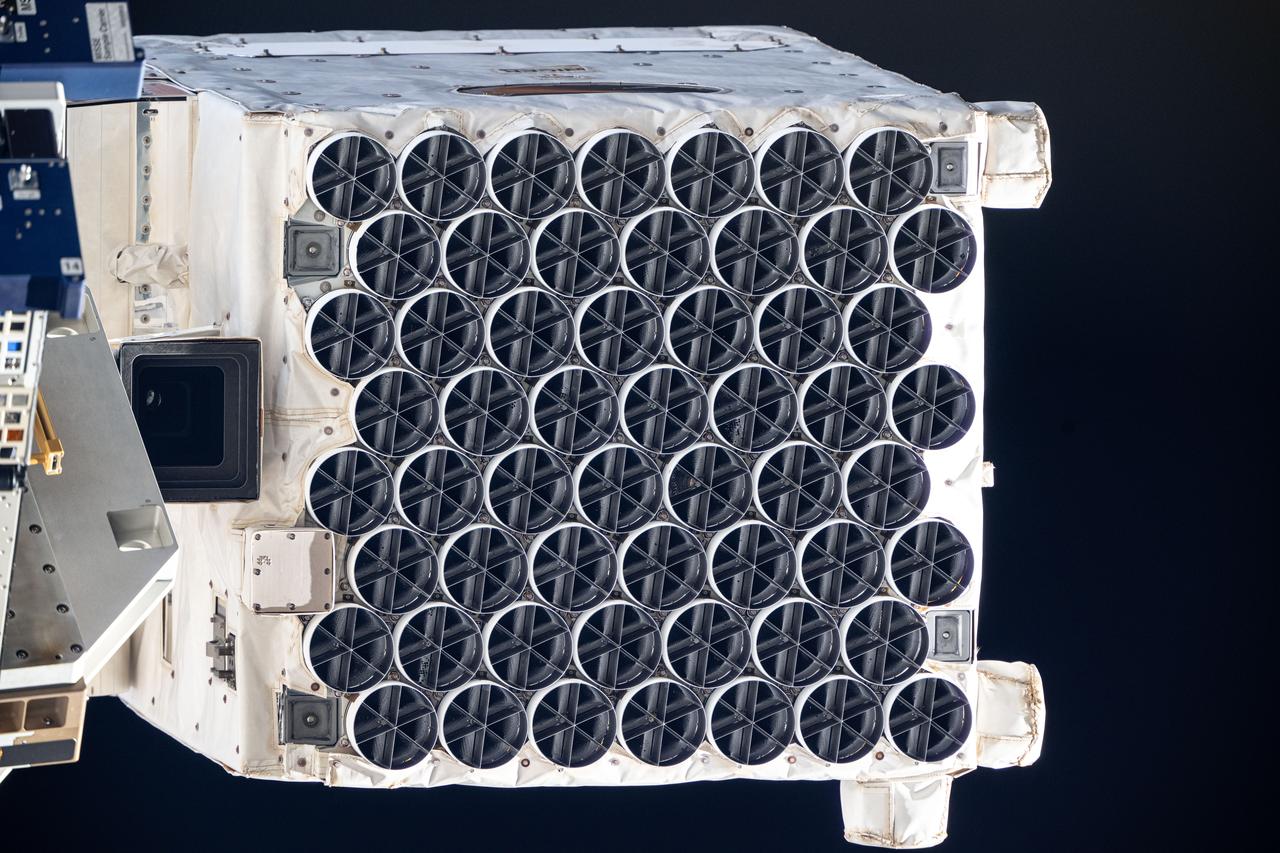
iss072e371351 (Dec. 17, 2024) --- The NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) X-ray telescope is pictured installed on the starboard side of the International Space Station's integrated truss segment. NICER's 56 X-ray concentrators are covered by thermal shields, or filters, that block ultraviolet, infrared, and visible light while allowing X-rays to pass through to the mirrors underneath enabling the observation of neutron stars. Several thermal shields have been damaged allowing unwanted sunlight to "leak" into the astrophysics instrument interfering with X-ray measurements. NASA astronauts Nick Hague and Sun Williams will conduct a spacewalk on Jan. 16 to patch the damaged thermal shields and restore NICER for daytime scientific operations.
iss072e371305 (Dec. 17, 2024) --- The NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) X-ray telescope is pictured installed on the starboard side of the International Space Station's integrated truss segment. NICER's 56 X-ray concentrators are covered by thermal shields, or filters, that block ultraviolet, infrared, and visible light while allowing X-rays to pass through to the mirrors underneath enabling the observation of neutron stars. Several thermal shields have been damaged allowing unwanted sunlight to "leak" into the astrophysics instrument interfering with X-ray measurements. NASA astronauts Nick Hague and Sun Williams will conduct a spacewalk on Jan. 16 to patch the damaged thermal shields and restore NICER for daytime scientific operations.
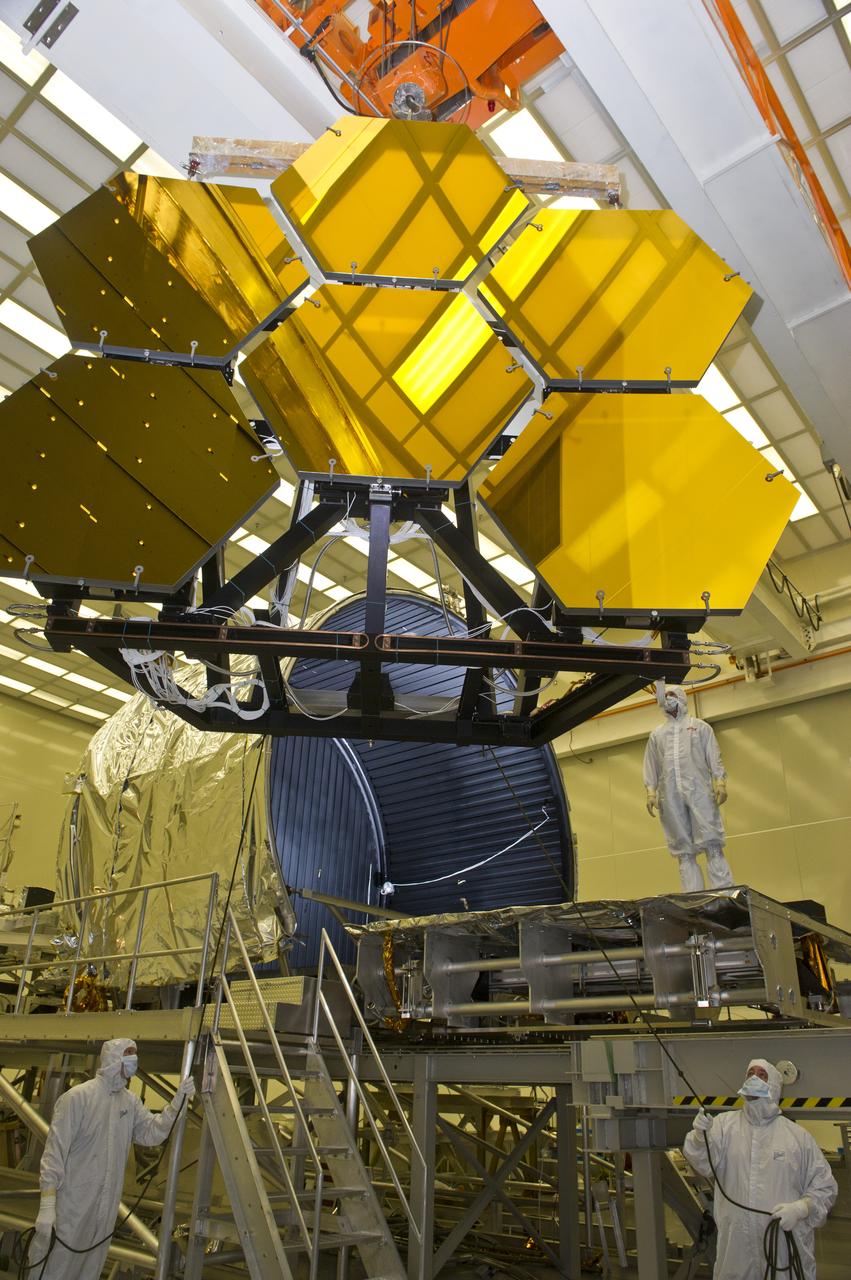

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
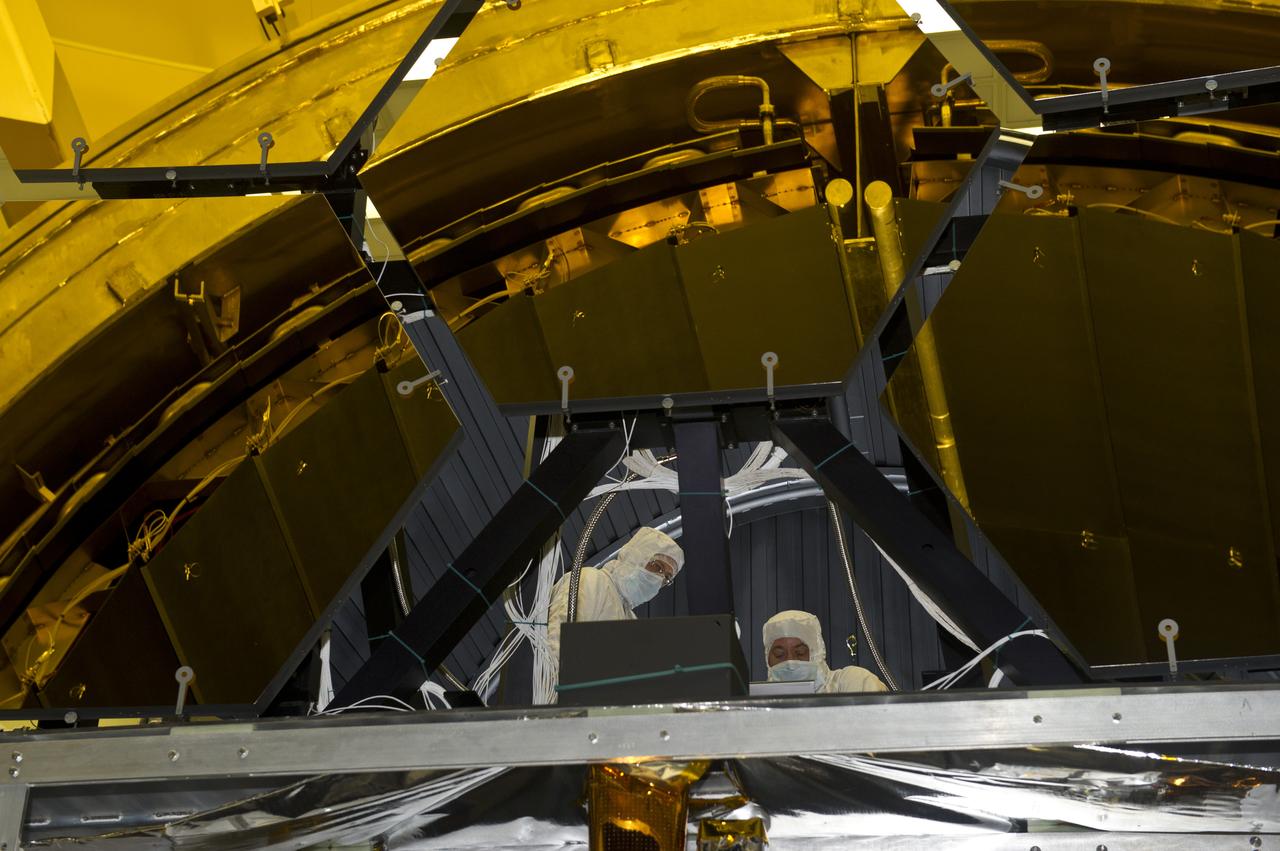

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
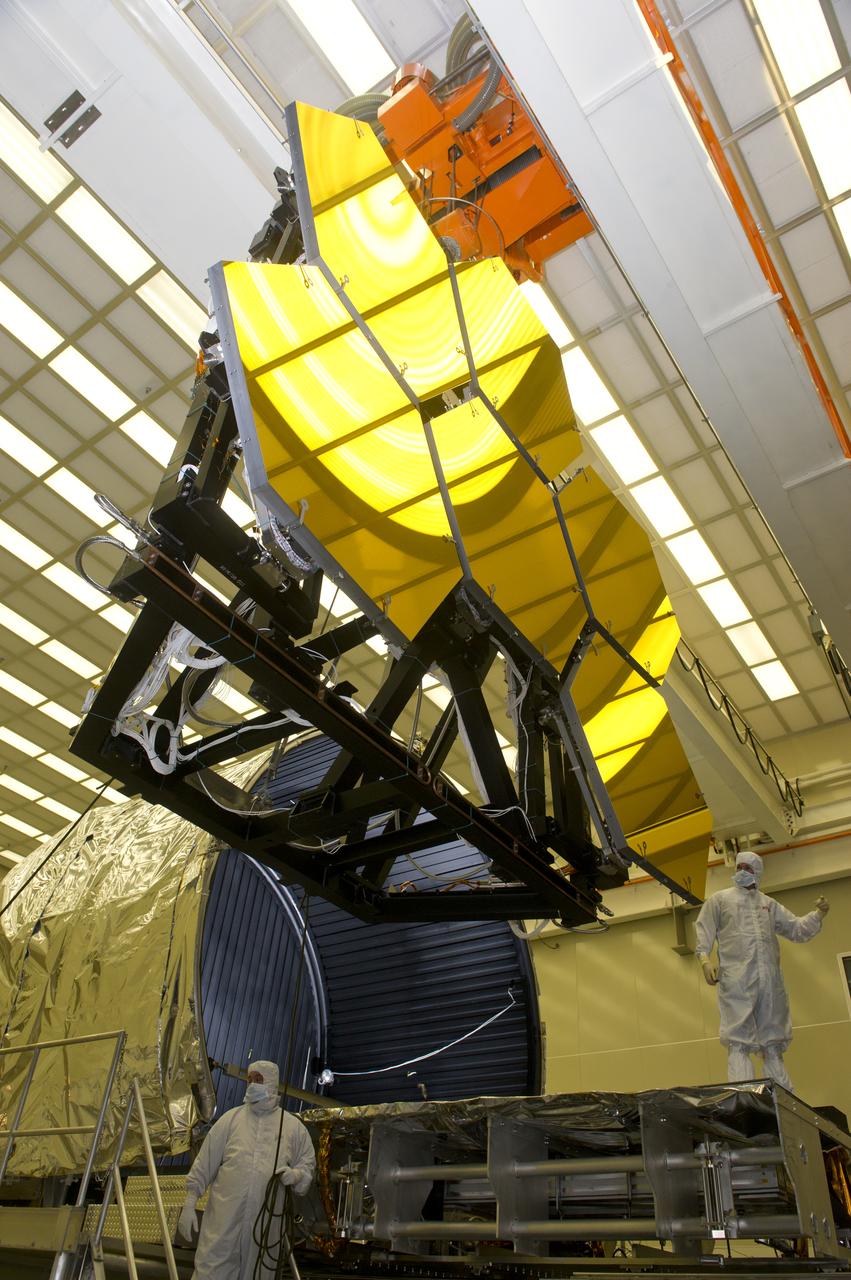

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
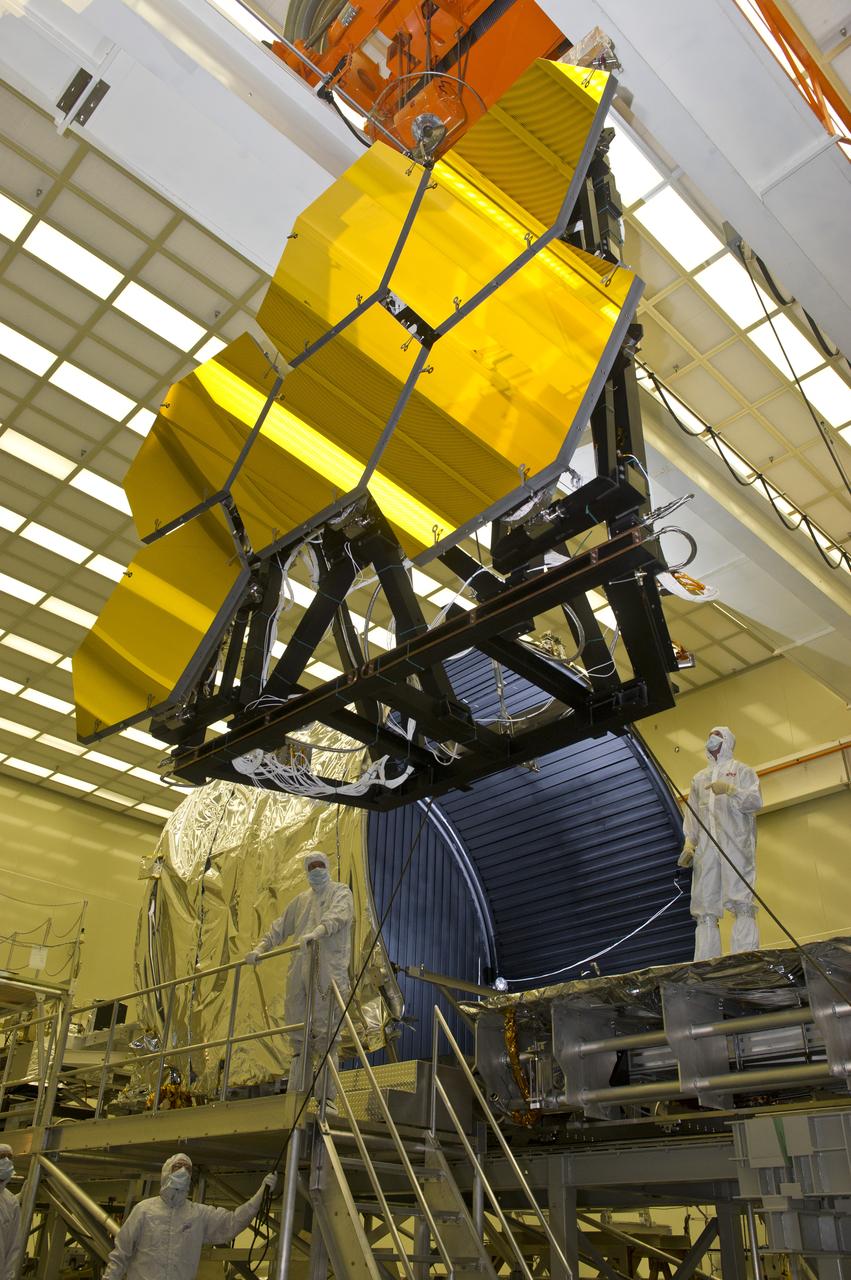

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
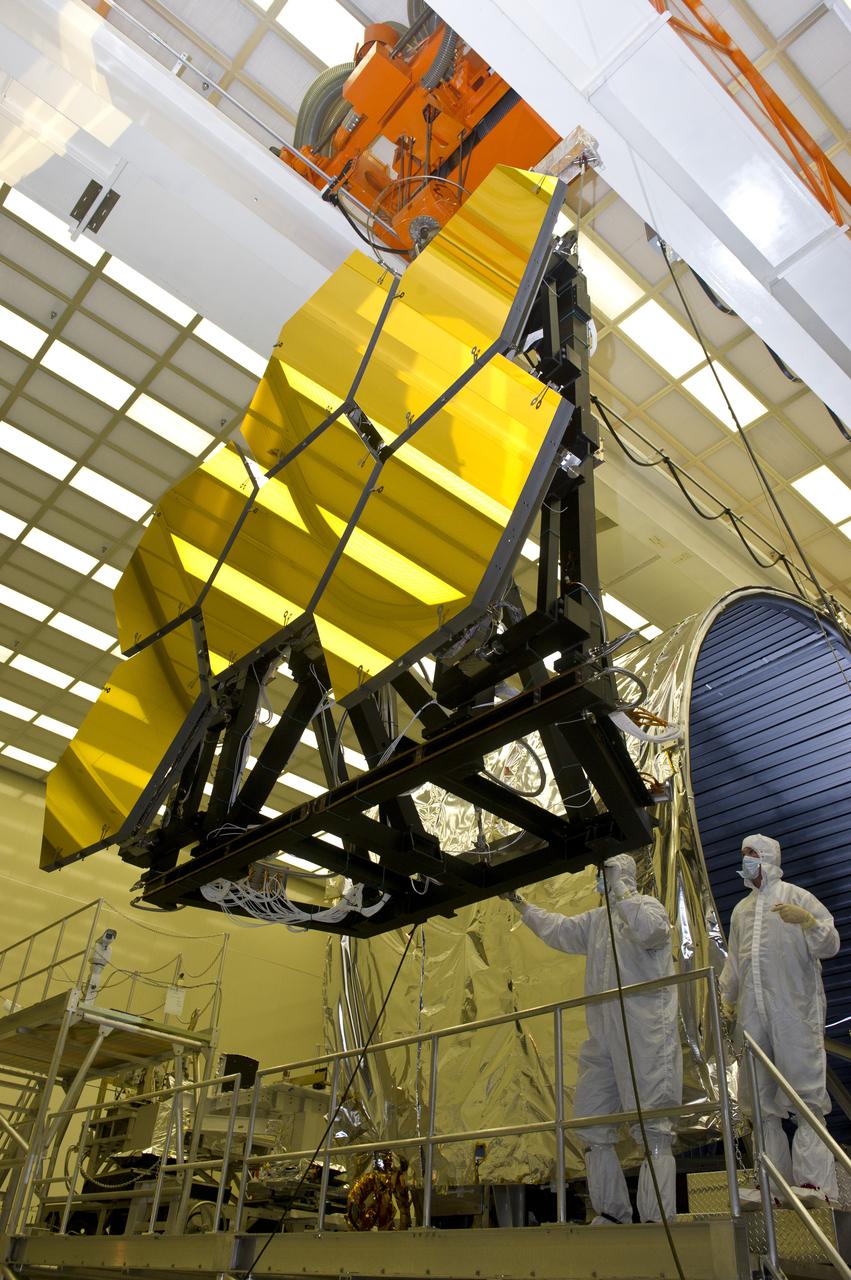

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
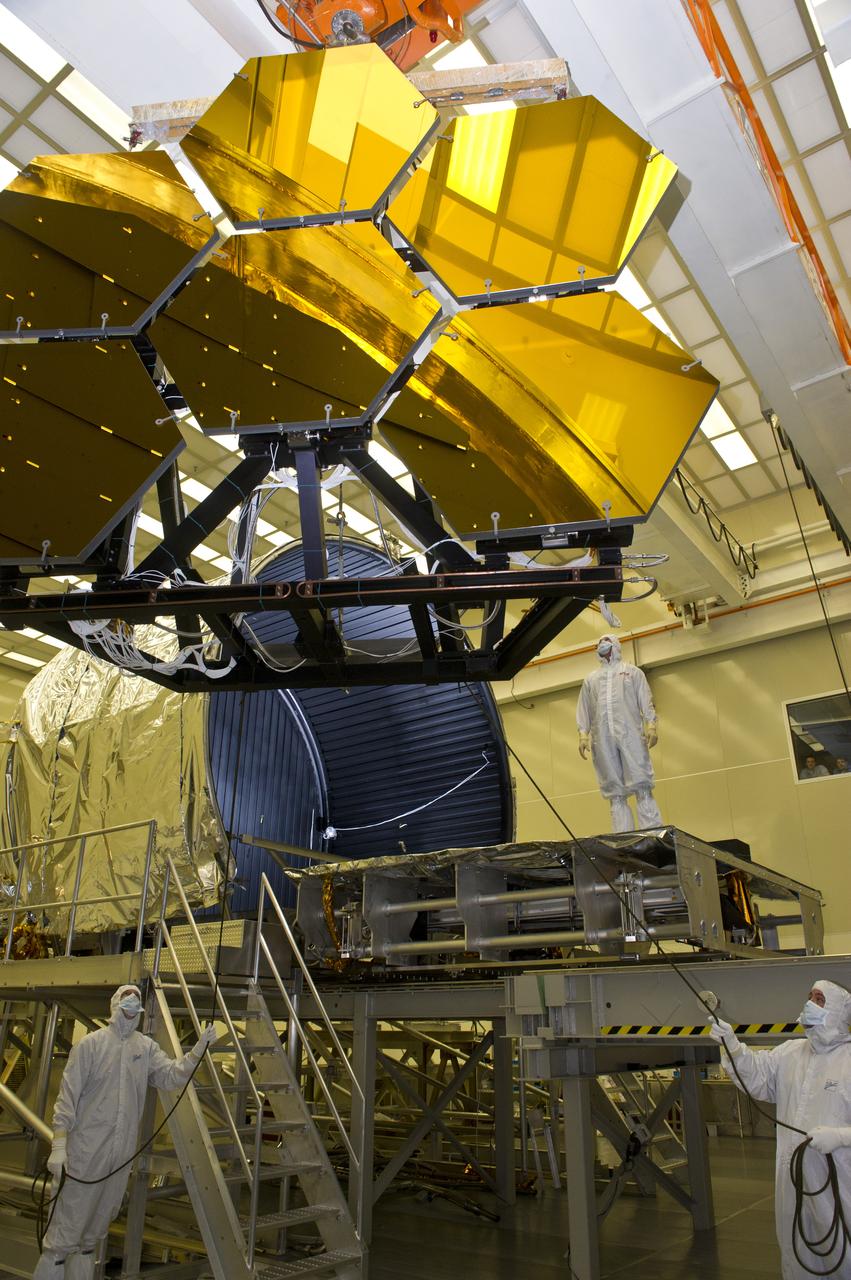

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
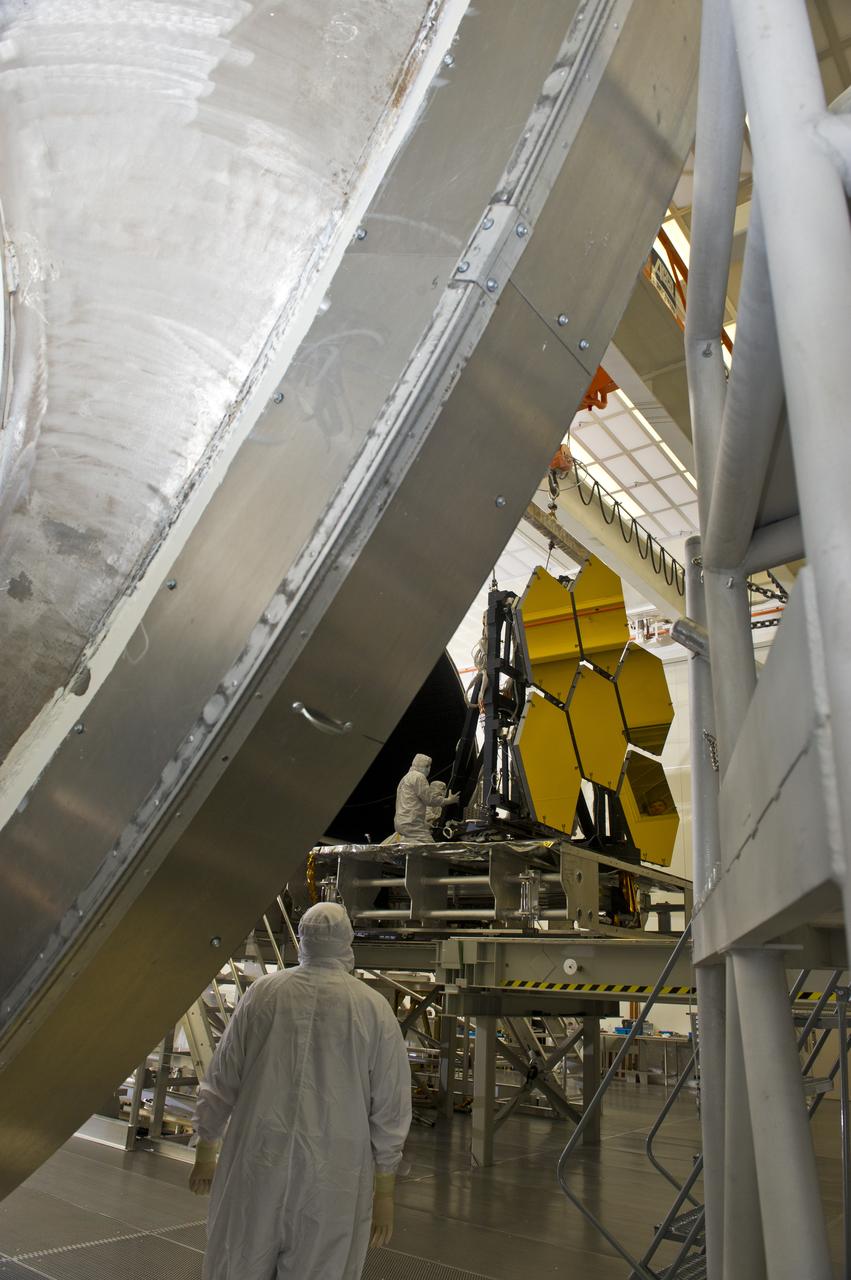

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
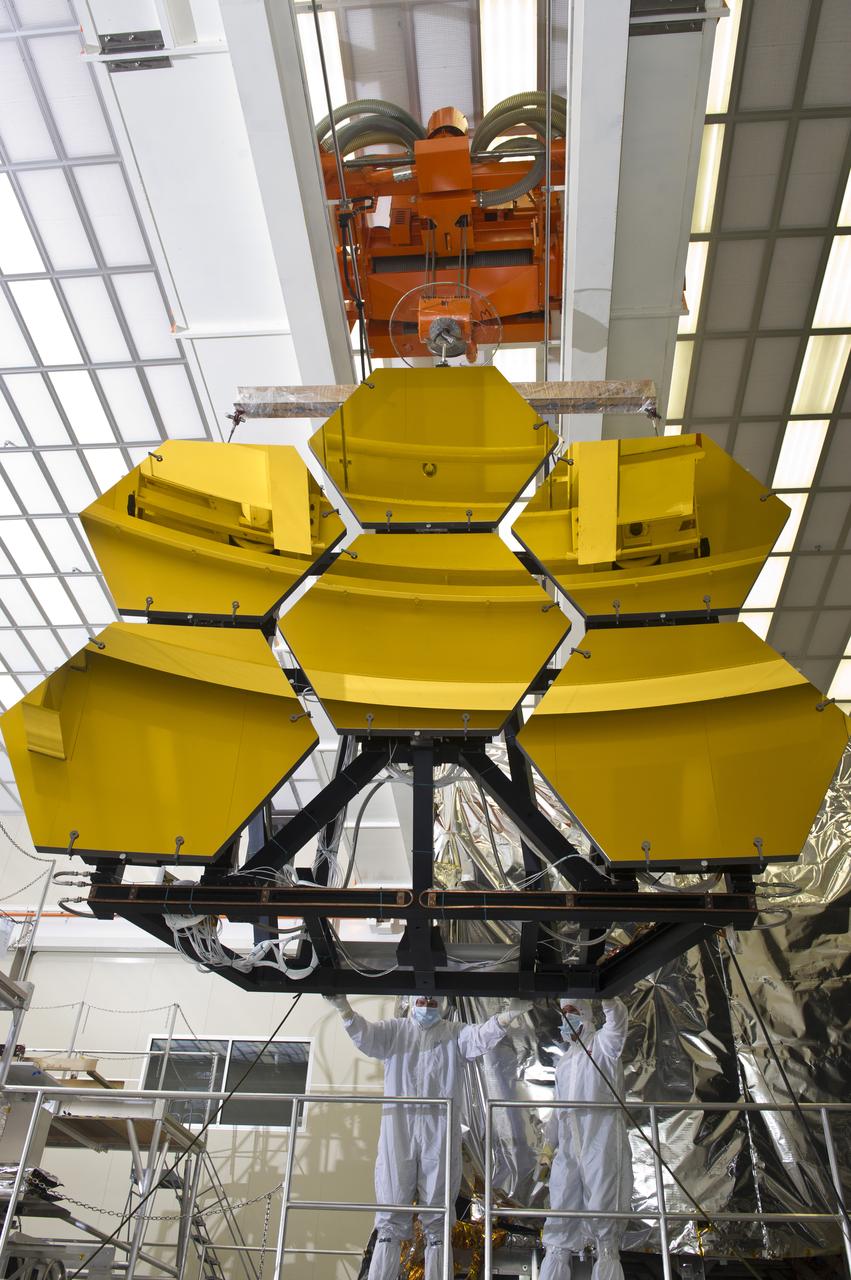

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY

NASA ADMINISTRATOR CHARLES BOLDEN LISTENS AS BALL AEROSPACE TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION PRINCIPLE OPTICAL ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY EXPLAINS HOW MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY CHILLS THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS TO -414 DEGREES FAHRENHEIT TO SIMULATE THE COLD TEMPERATURES OF SPACE.
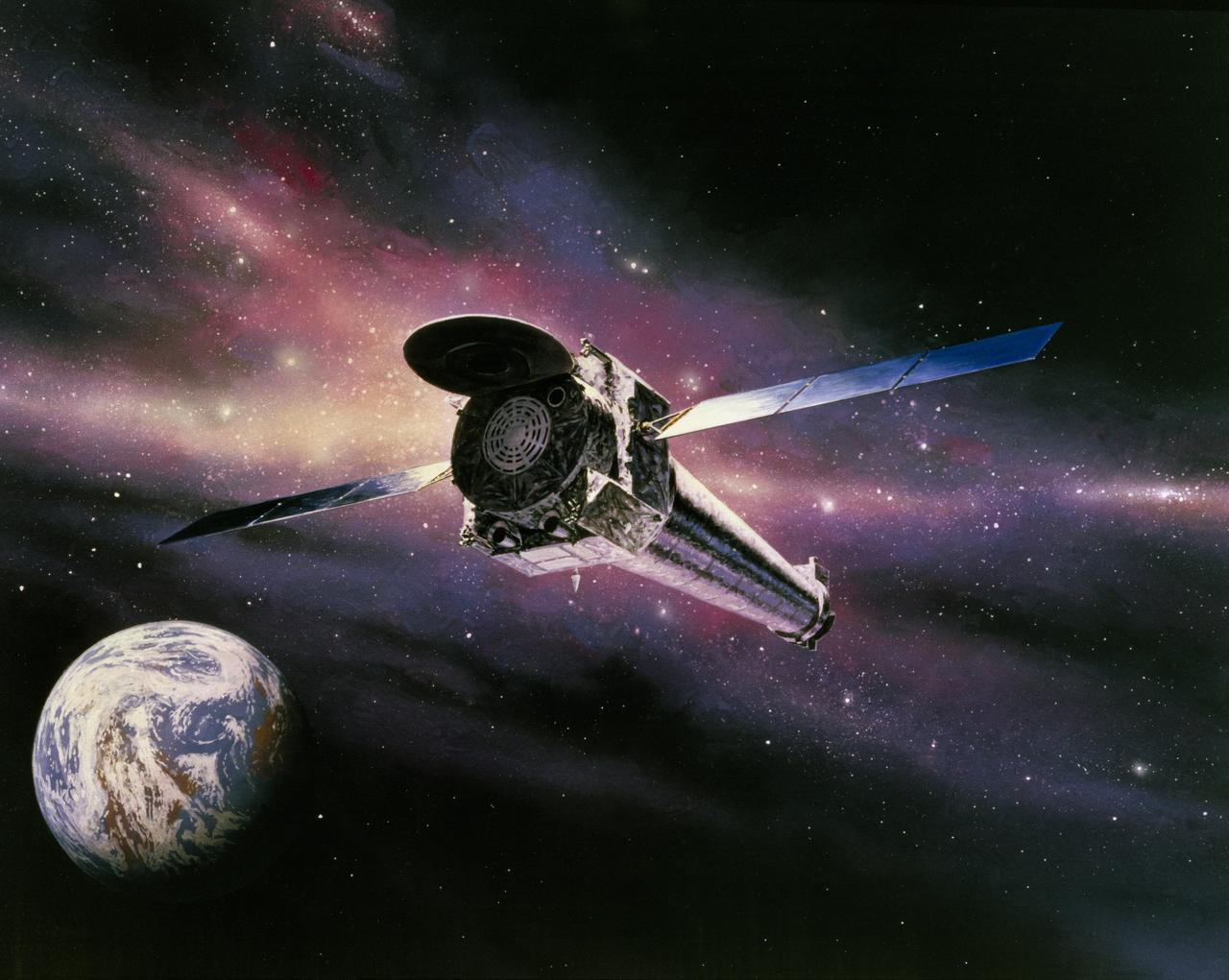

This is an artist's concept of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), fully developed in orbit in a star field with Earth. In 1999, the AXAF was renamed the CXO in honor of the late Indian-American Novel Laureate Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It is designed to observe x-rays from high energy regions of the Universe, such as hot gas in the renmants of exploded stars. It produces picture-like images of x-ray emissions analogous to those made in visible light, as well as gathers data on the chemical composition of x-ray radiating objects. The CXO helps astronomers world-wide better understand the structure and evolution of the universe by studying powerful sources of x-ray such as exploding stars, matter falling into black holes, and other exotic celestial objects. The Observatory has three major parts: (1) the x-ray telescope, whose mirrors will focus x-rays from celestial objects; (2) the science instruments that record the x-rays so that x-ray images can be produced and analyzed; and (3) the spacecraft, which provides the environment necessary for the telescope and the instruments to work. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development the CXO and NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Observatory was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, STS-93 mission. (Image courtesy of TRW).
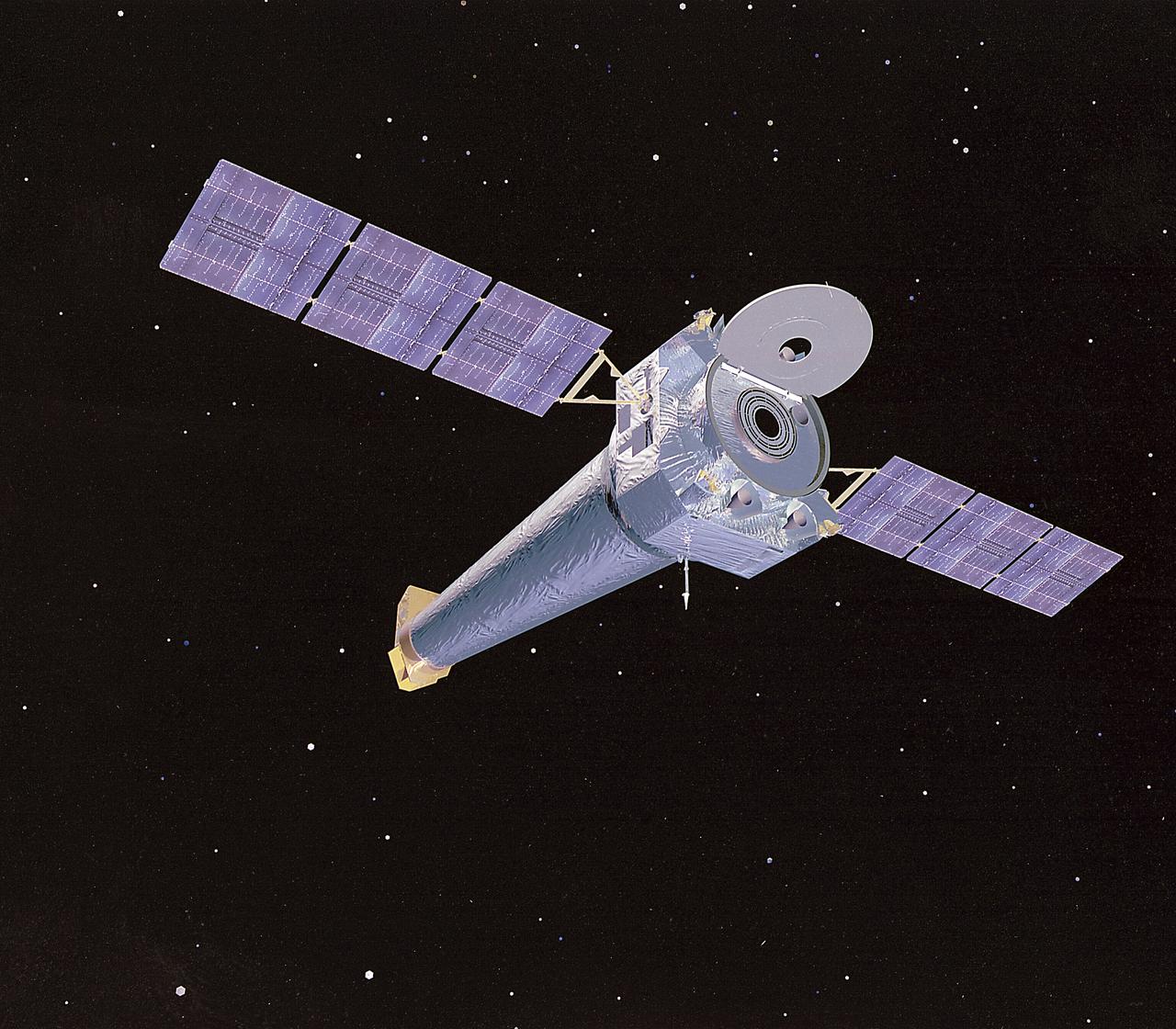
This is a computer rendering of the fully developed Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF). In 1999, the AXAF was renamed the CXO in honor of the late Indian-American Novel Laureate Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It is designed to observe x-rays from high energy regions of the Universe, such as hot gas in the renmants of exploded stars. It produces picture-like images of x-ray emissions analogous to those made in visible light, as well as gathers data on the chemical composition of x-ray radiating objects. The CXO helps astronomers world-wide better understand the structure and evolution of the universe by studying powerful sources of x-ray such as exploding stars, matter falling into black holes, and other exotic celestial objects. The Observatory has three major parts: (1) the x-ray telescope, whose mirrors will focus x-rays from celestial objects; (2) the science instruments that record the x-rays so that x-ray images can be produced and analyzed; and (3) the spacecraft, which provides the environment necessary for the telescope and the instruments to work. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Observatory was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, STS-93 mission. (Image courtesy of TRW).