
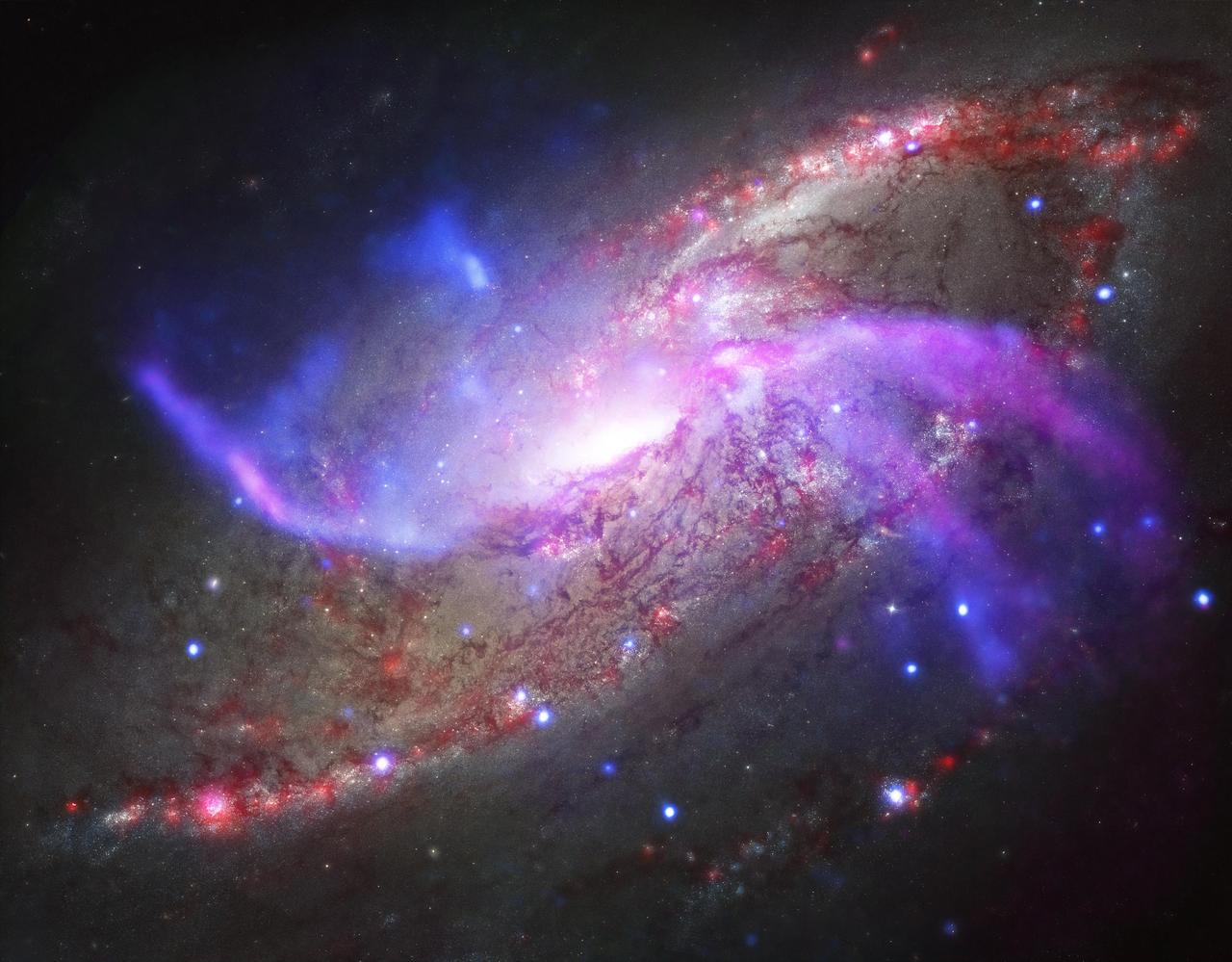
A composite image of the spiral galaxy NGC 4258 showing X-ray emission observed with NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory blue and infrared emission observed with NASA Spitzer Space Telescope red and green.

About 2,400 massive stars in the center of 30 Doradus, the Tarantula Nebula, produce intense radiation and powerful winds as they blow off material seen as infrared emission from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and X-rays from Chandra X-ray Observatory.

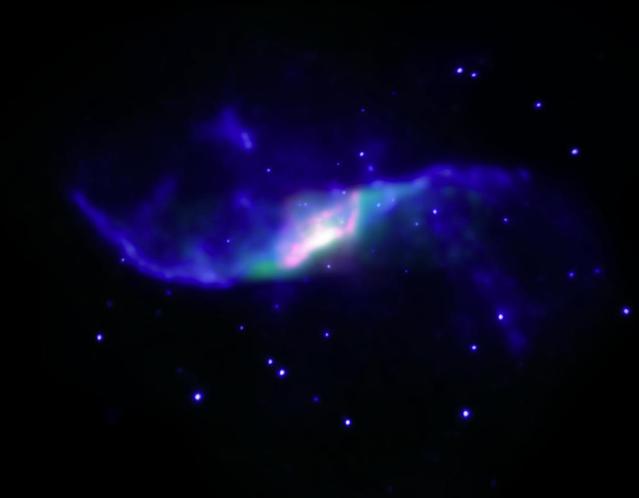
Anomalous arms are seen in this composite image of NGC 4258 from NASA Chandra X-ray Observator, NSF Karl Jansky Very Large Array, NASA Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer Space Telescope.

This chart details Skylab's X-Ray Spectrographic Telescope, an Apollo Telescope Mount facility. It was designed to sequentially photograph solar flares and other active regions in the x-ray spectrum. The Marshall Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
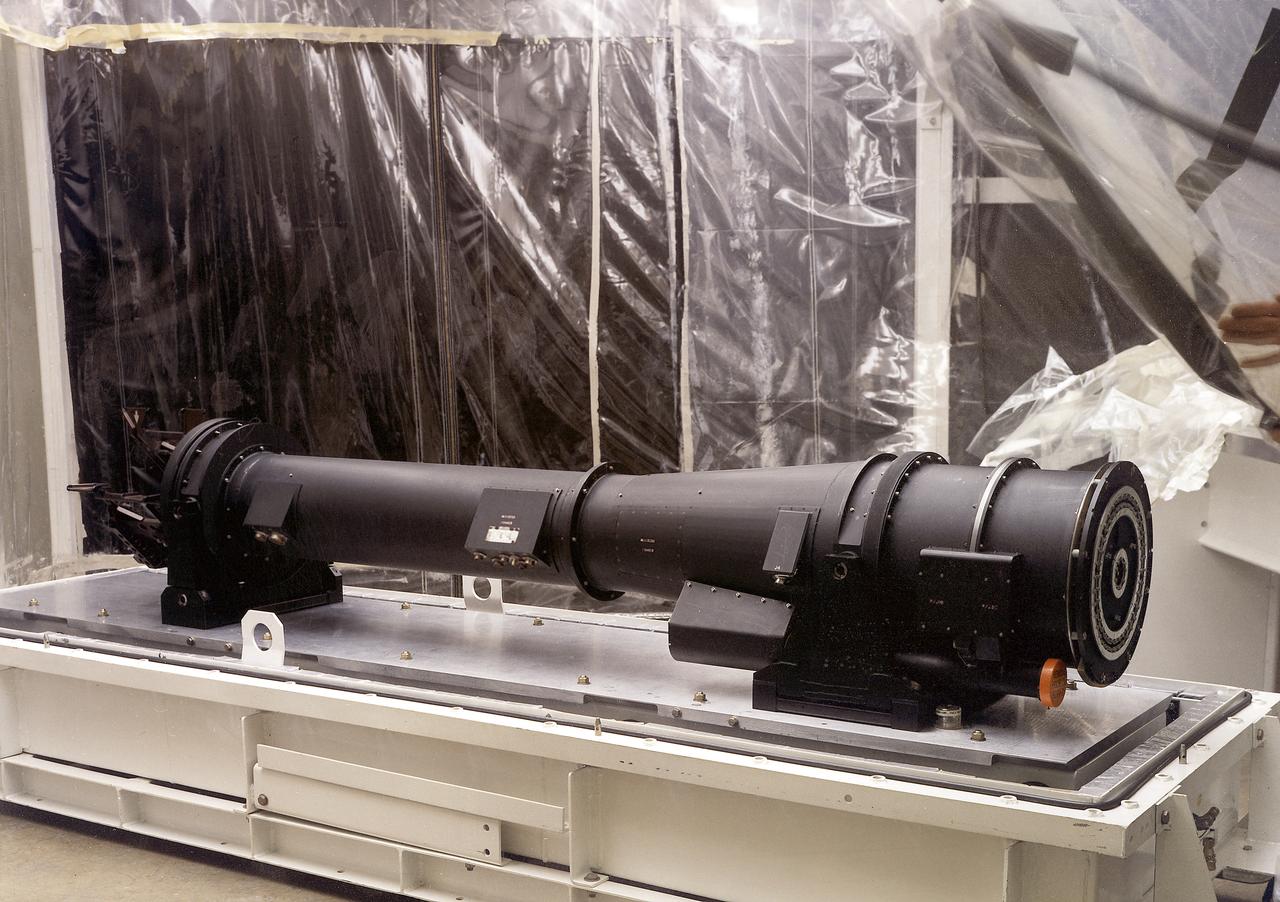

This photograph details Skylab's X-Ray Spectrographic Telescope, an Apollo Telescope Mount facility. It was designed to sequentially photograph solar flares and other active regions in x-ray spectrum. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
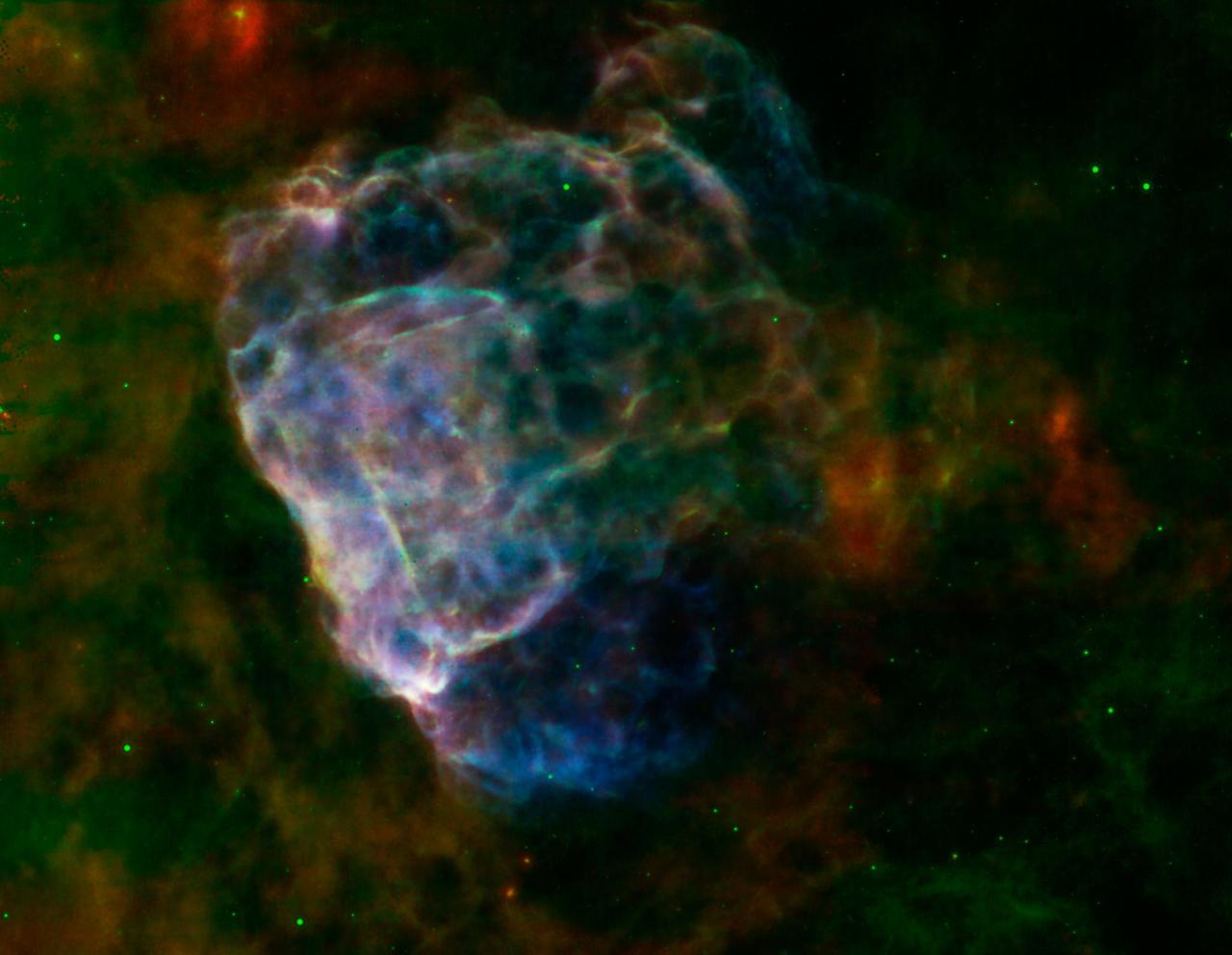
Puppis A, around 7,000 light-years away, is seen in this image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and Chandra X-Ray Observatory, and the European Space Agency XMM-Newton.
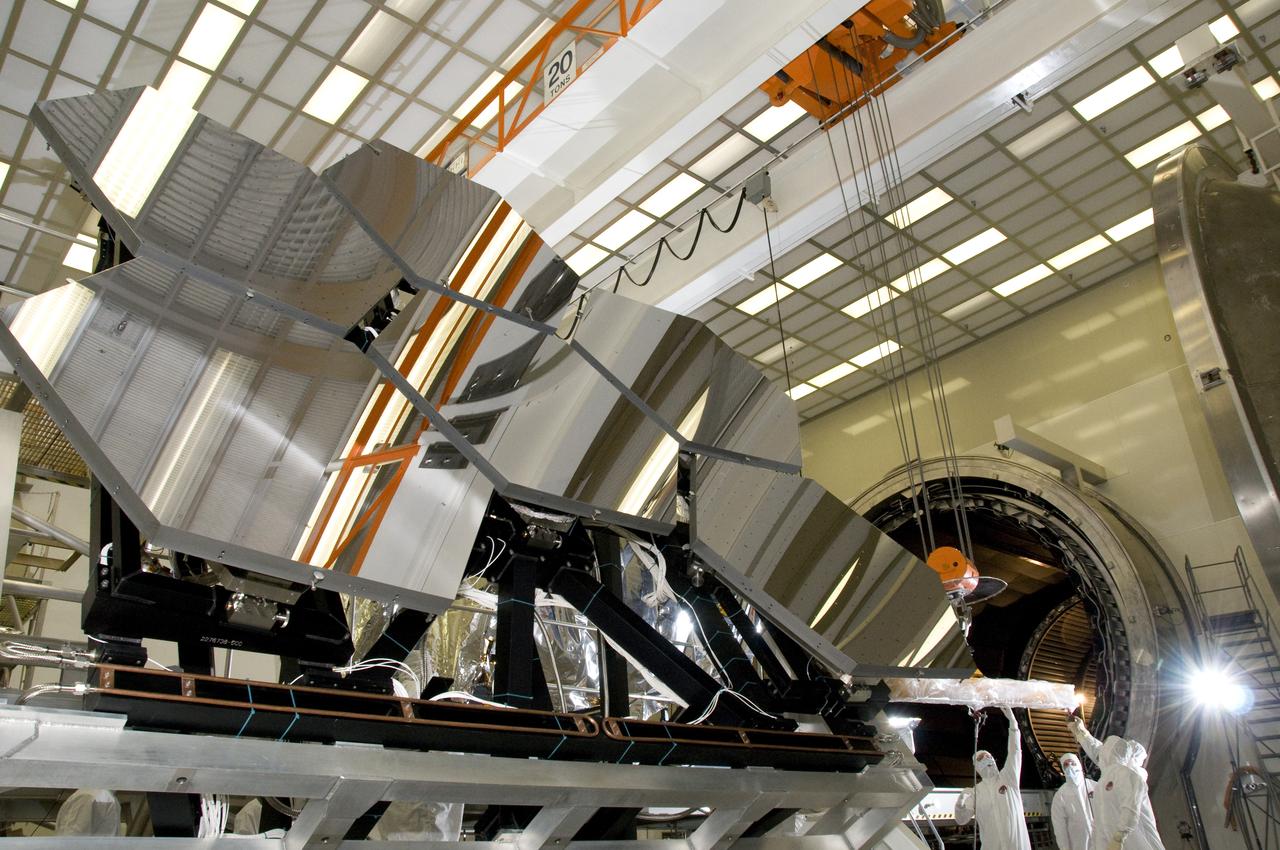

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
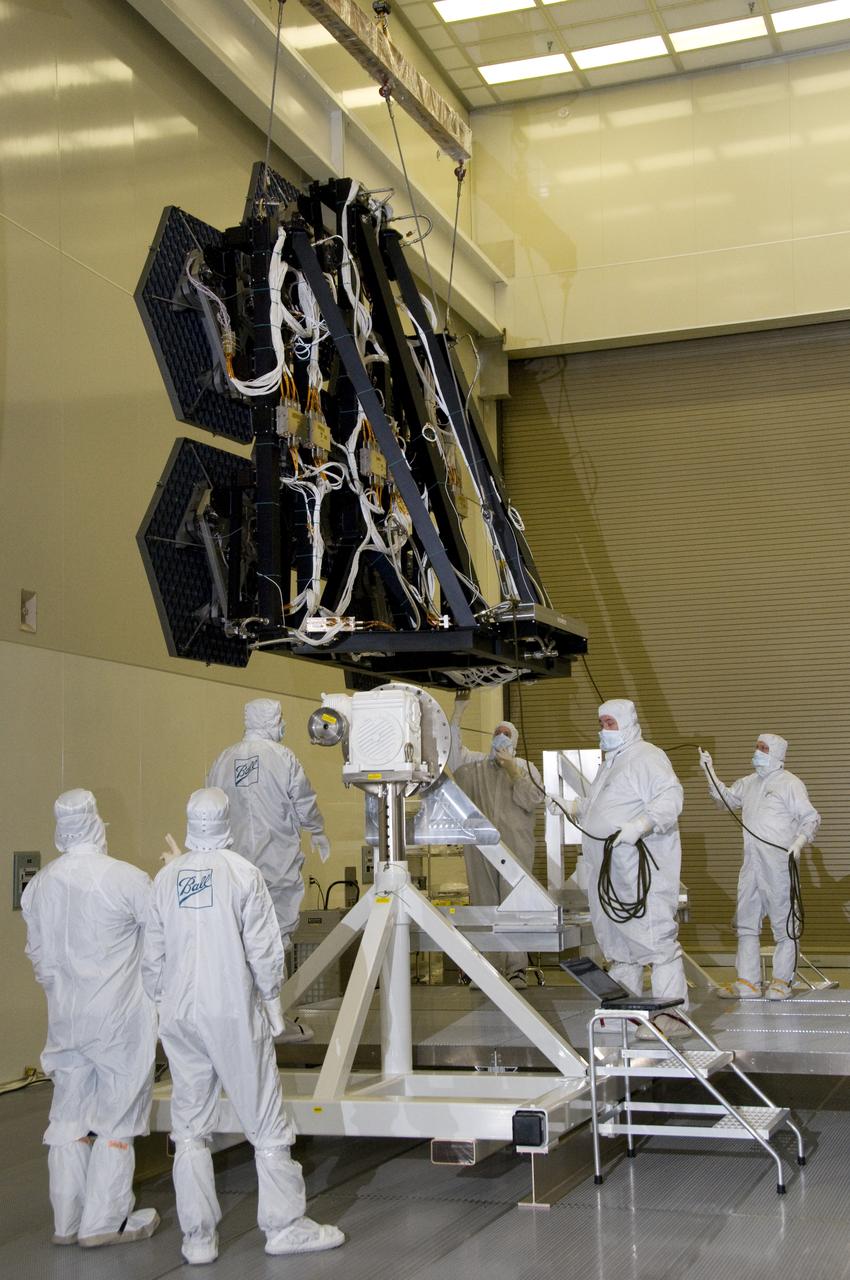

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
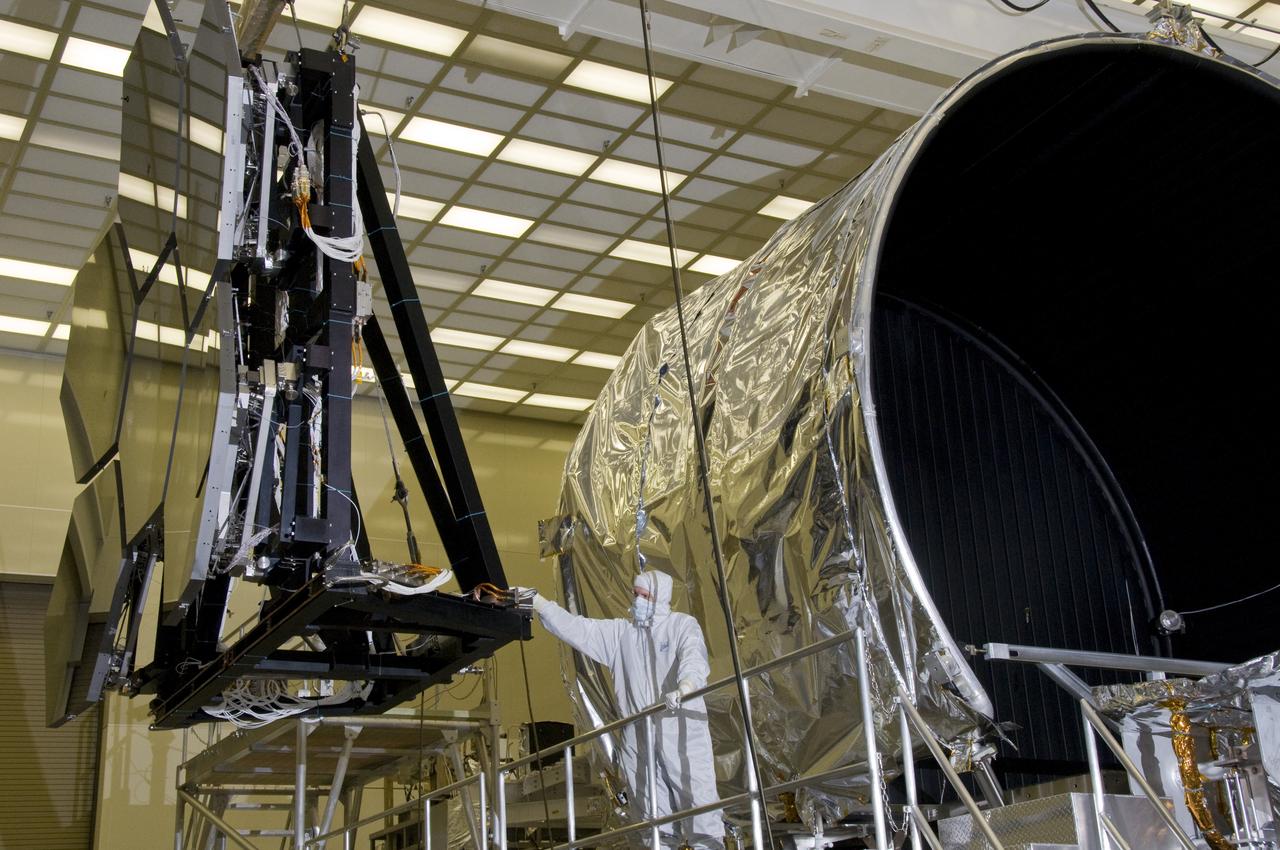

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
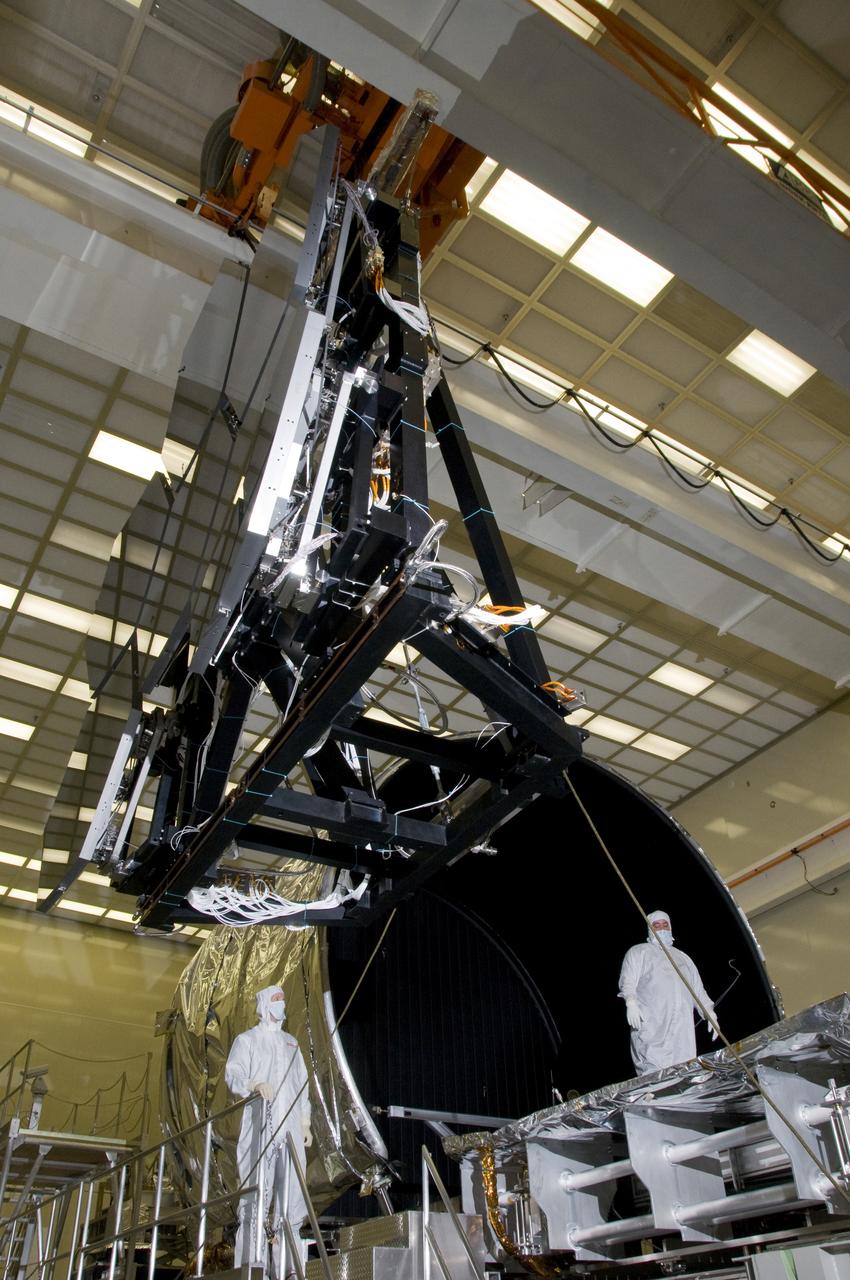

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
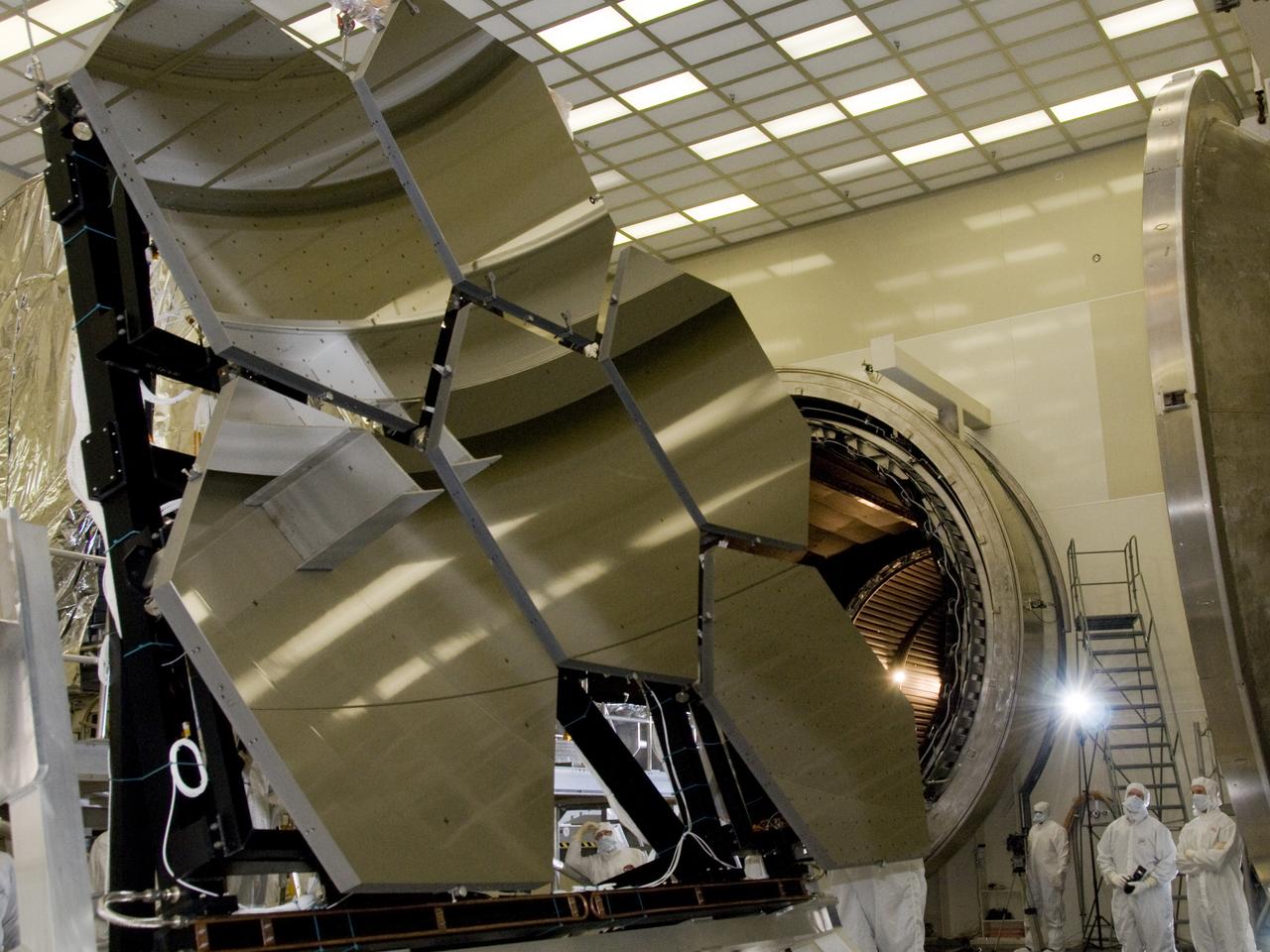

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
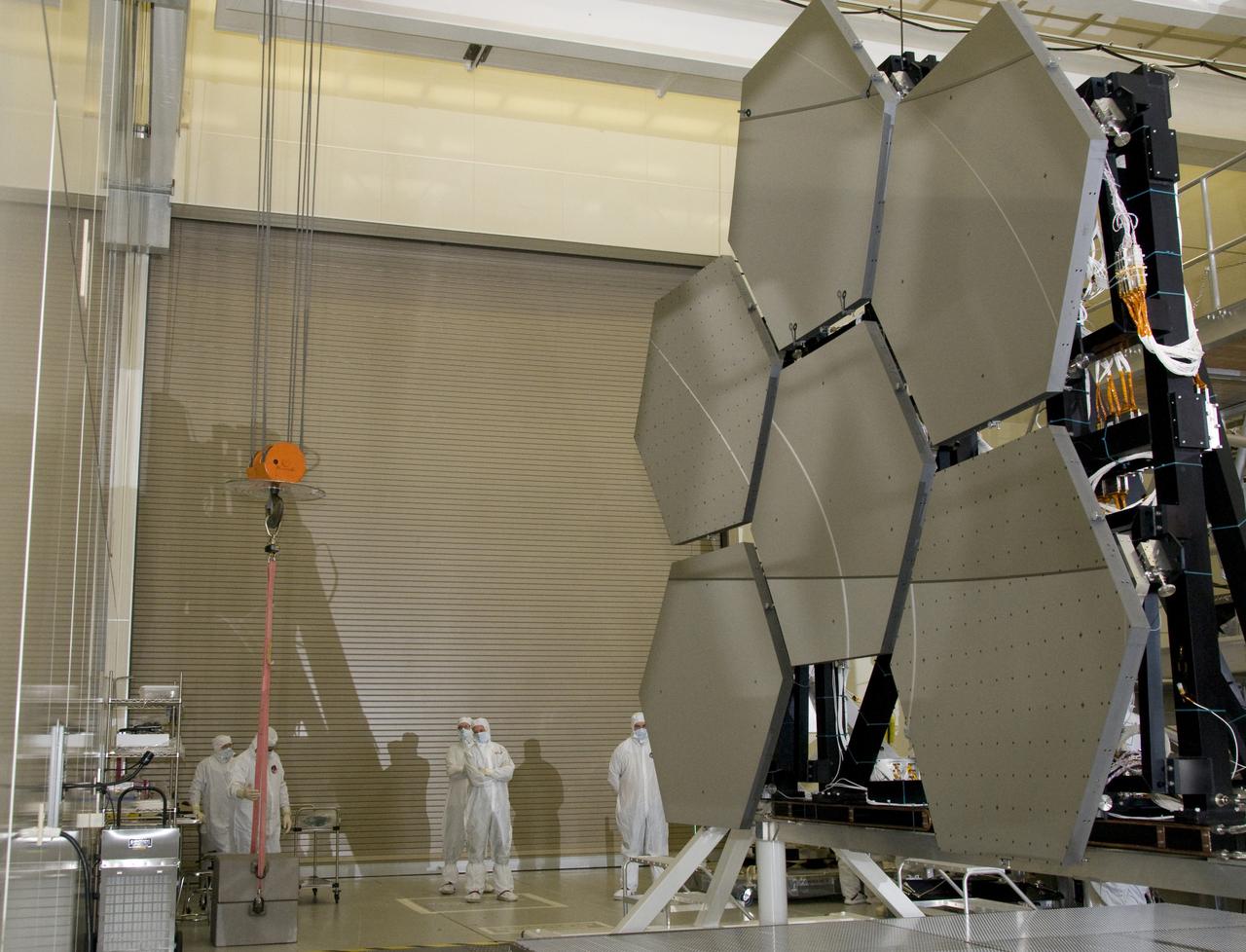

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
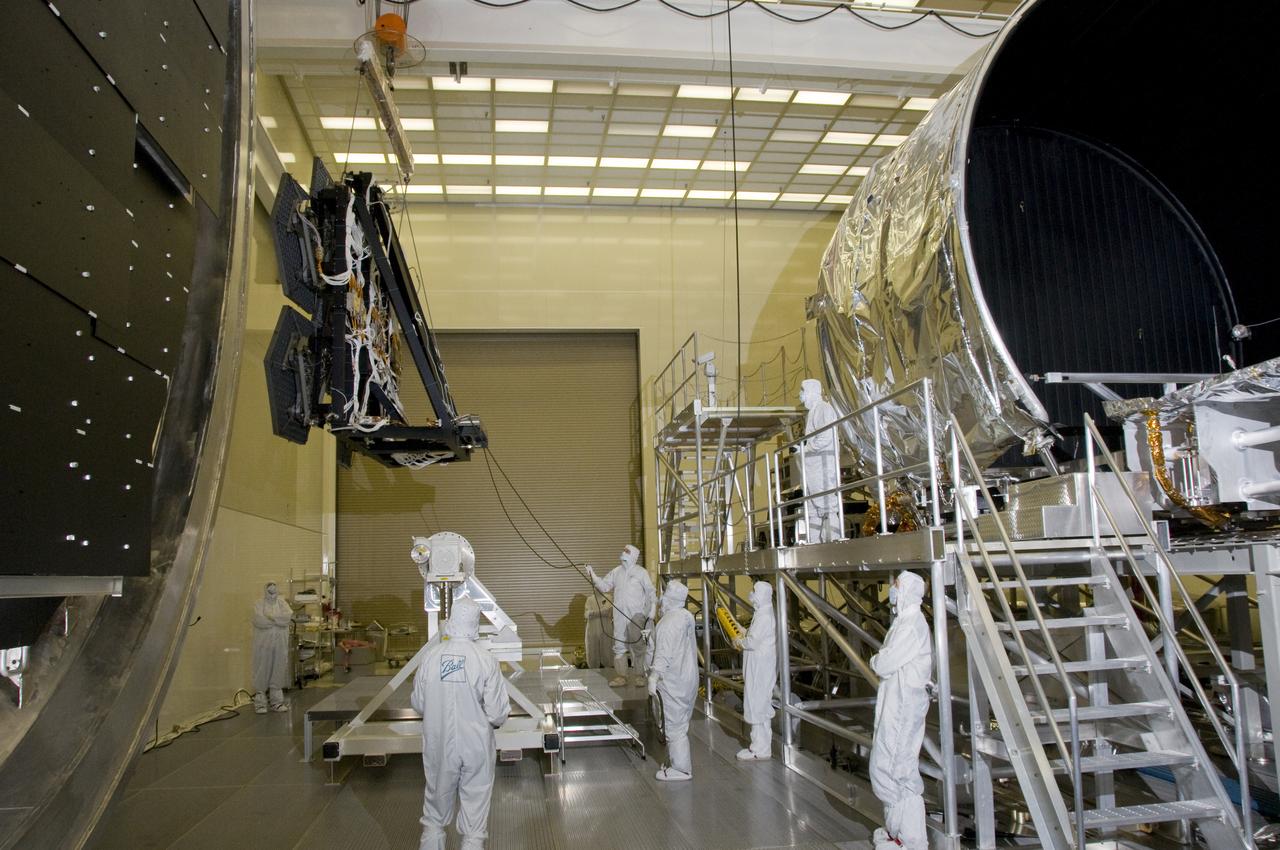

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
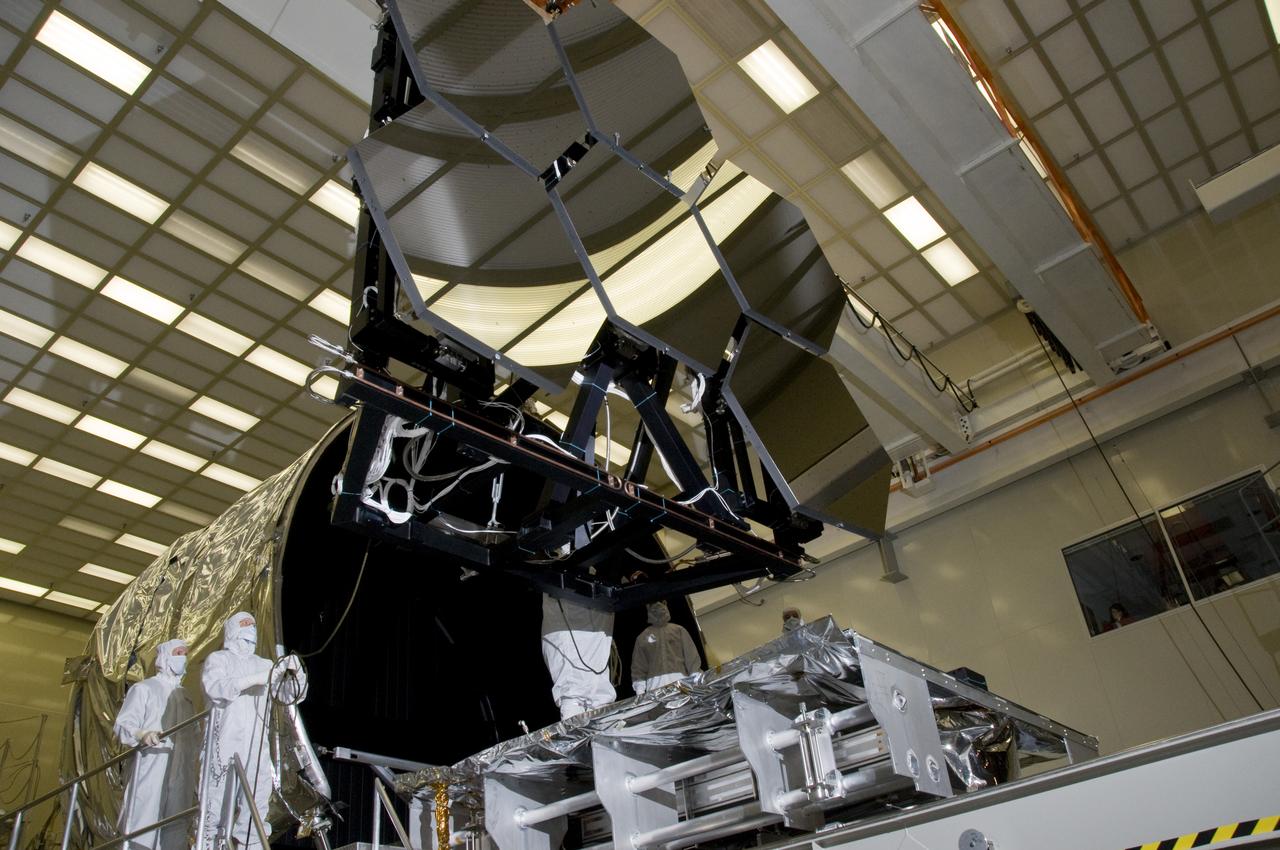

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
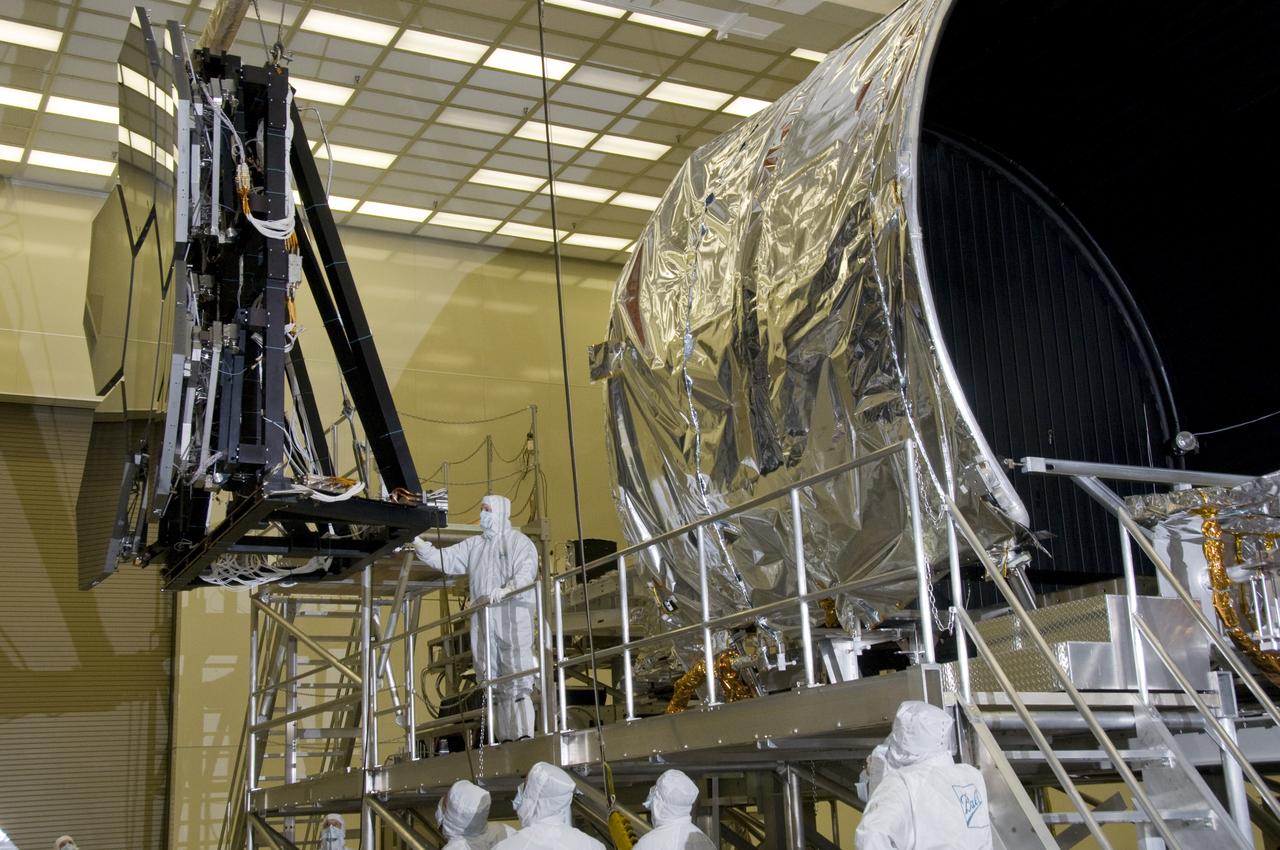

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
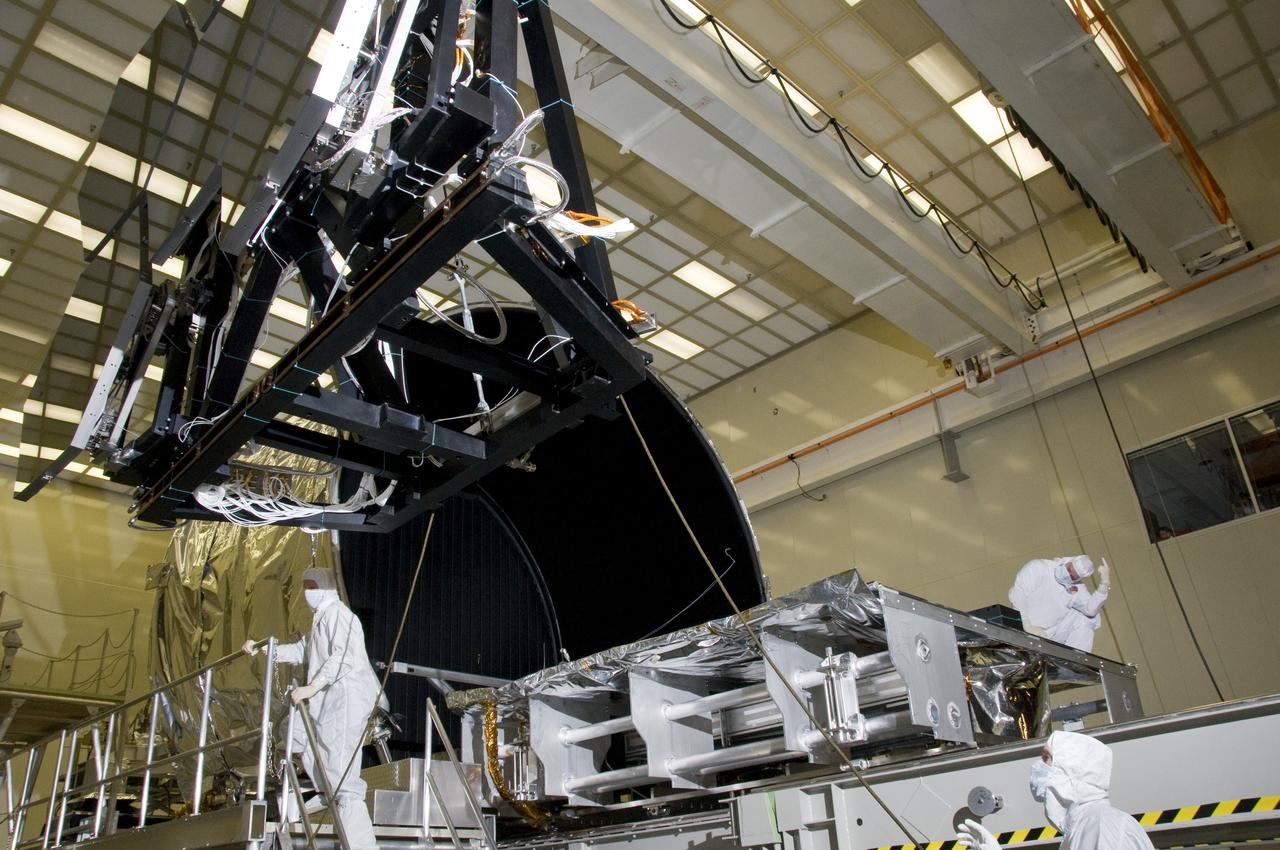

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
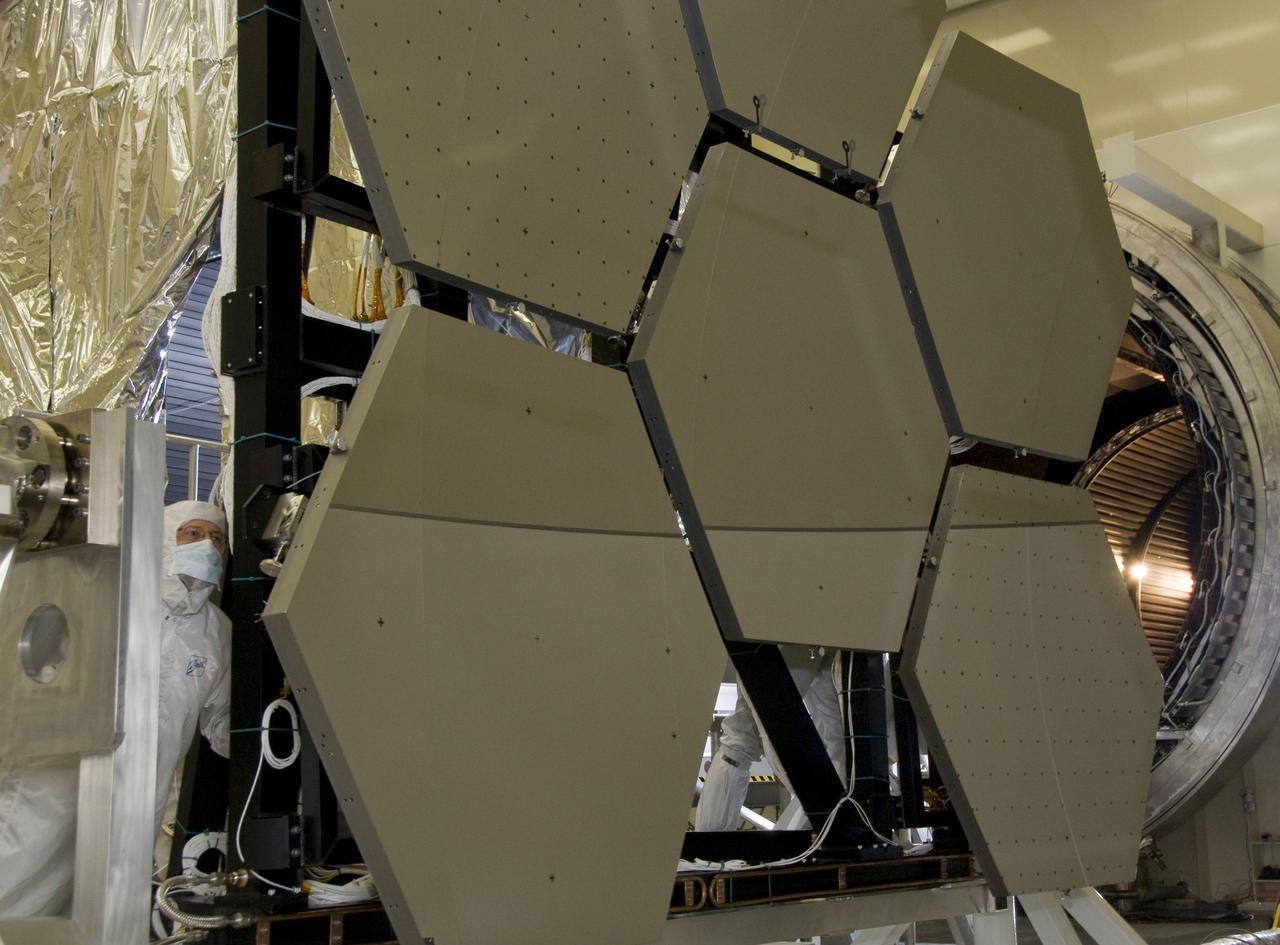

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
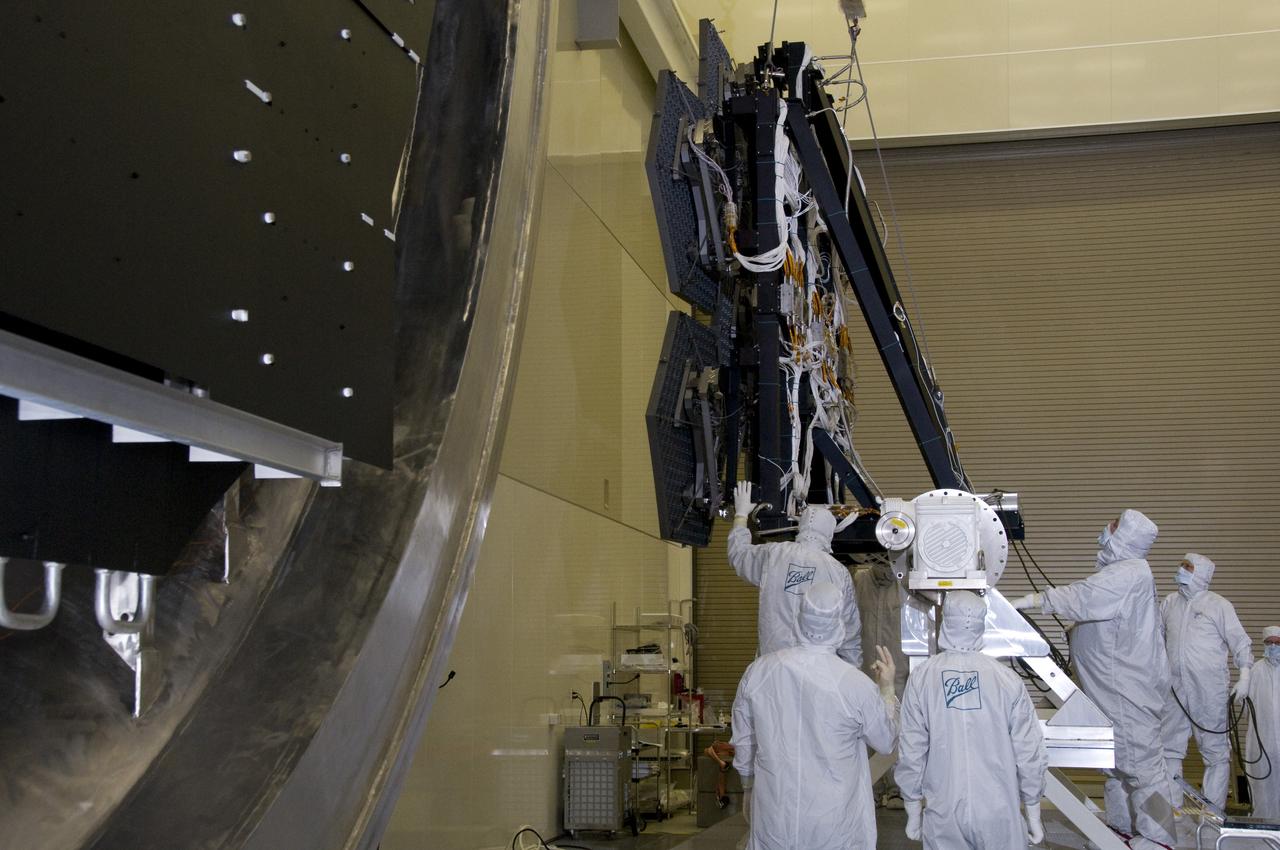

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
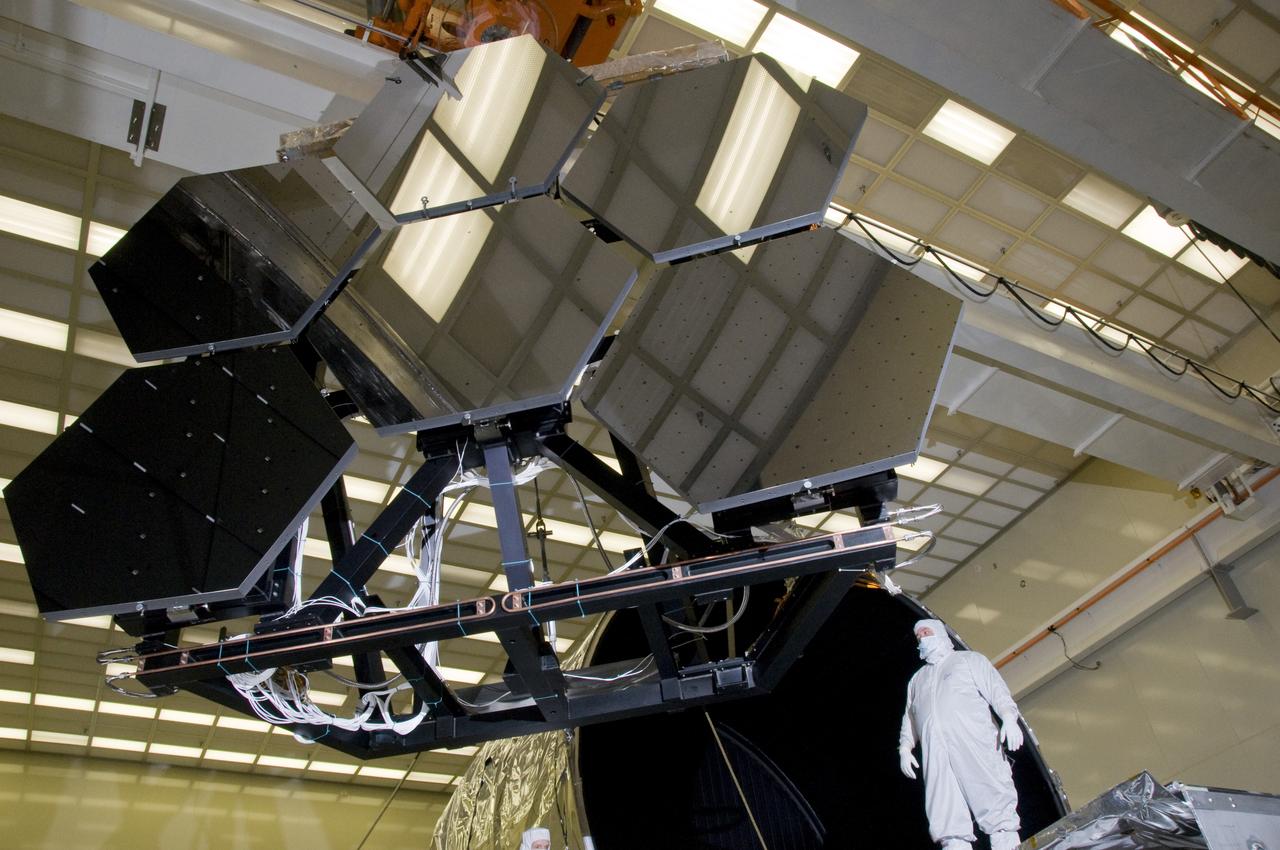

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
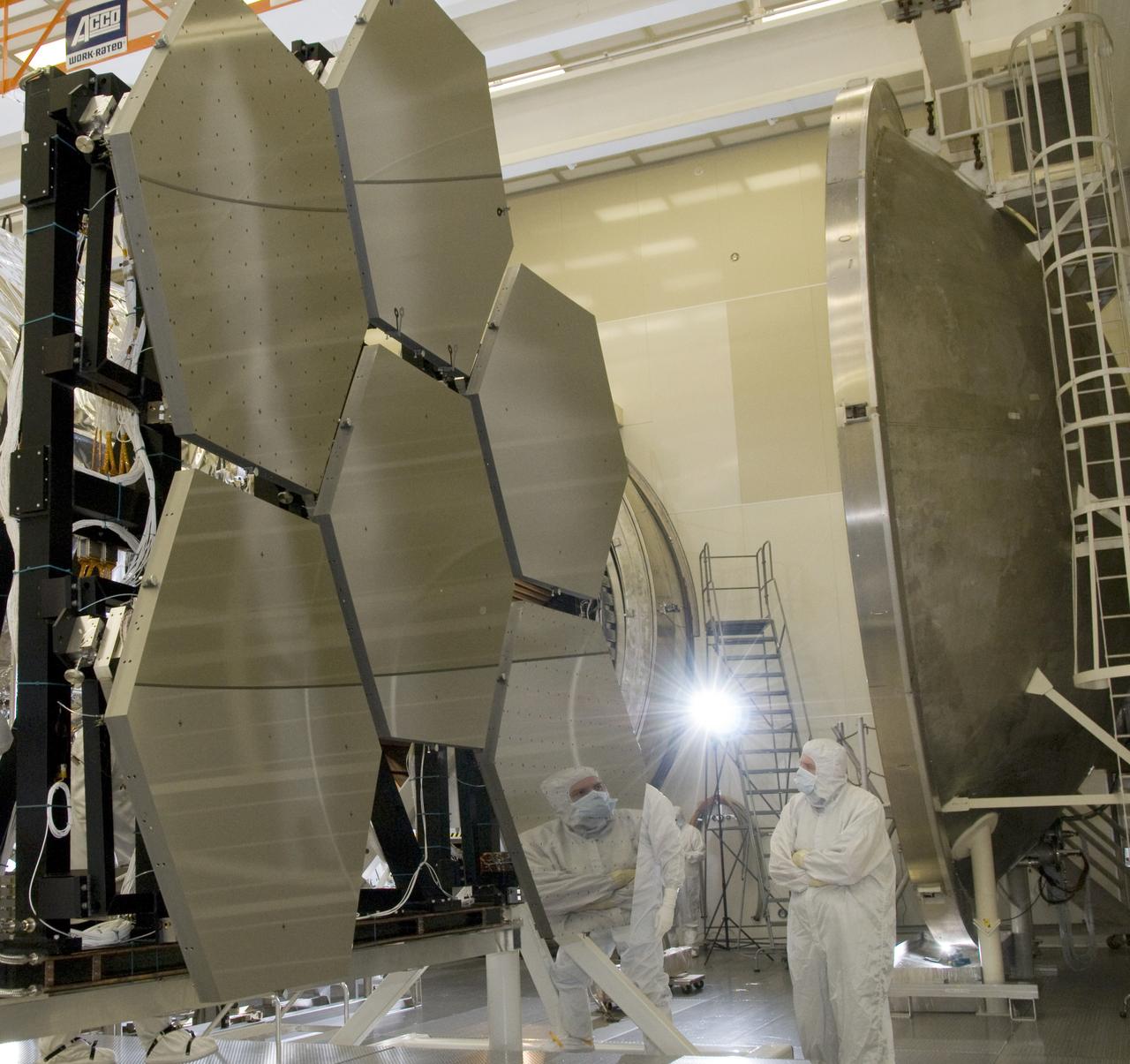

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
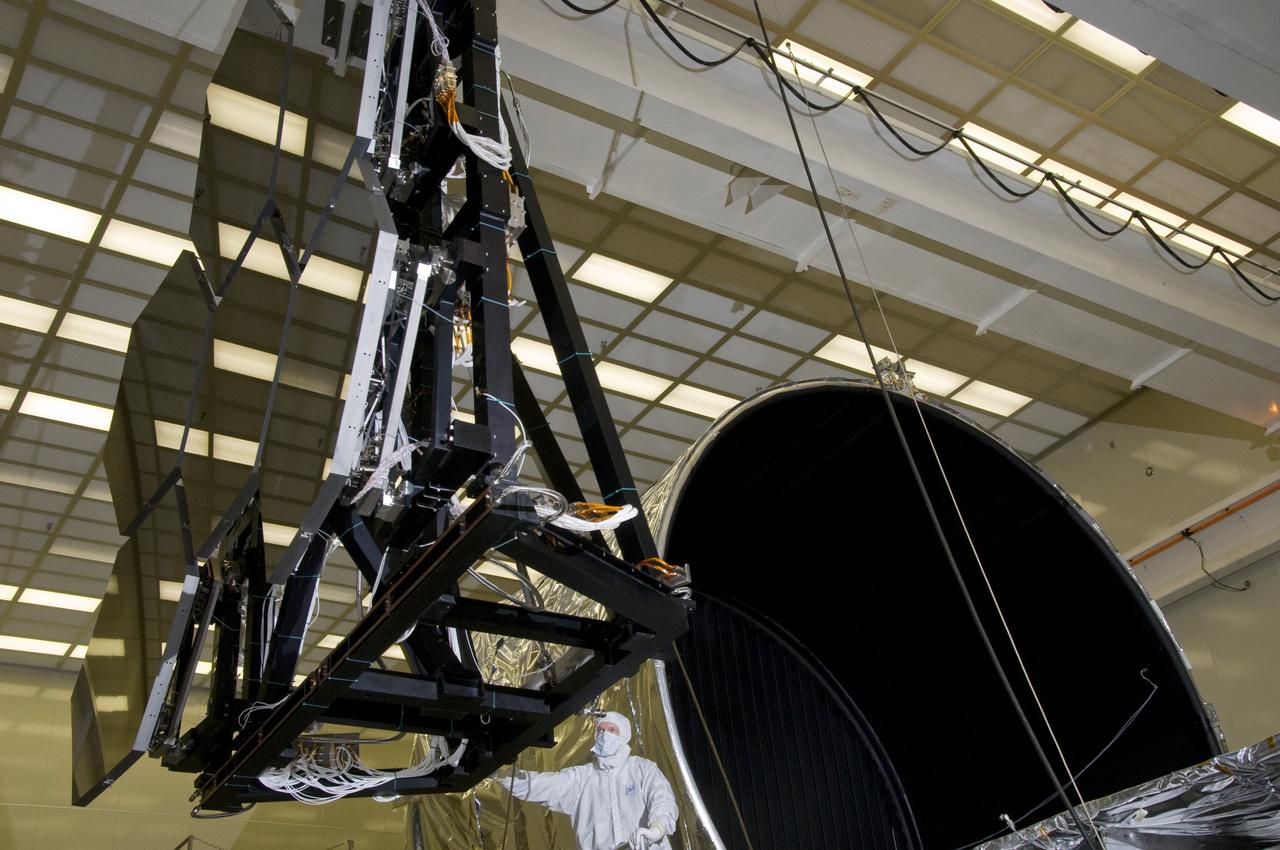

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
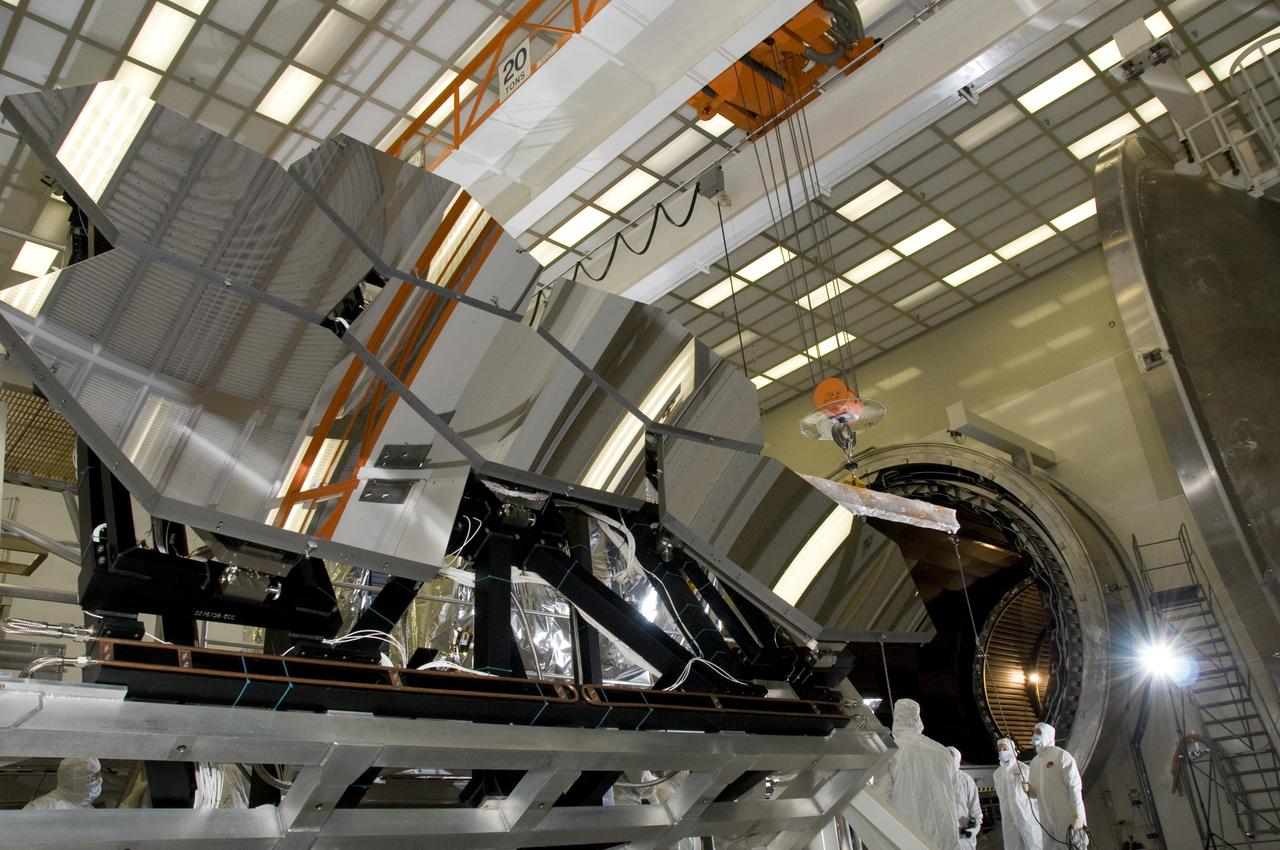

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
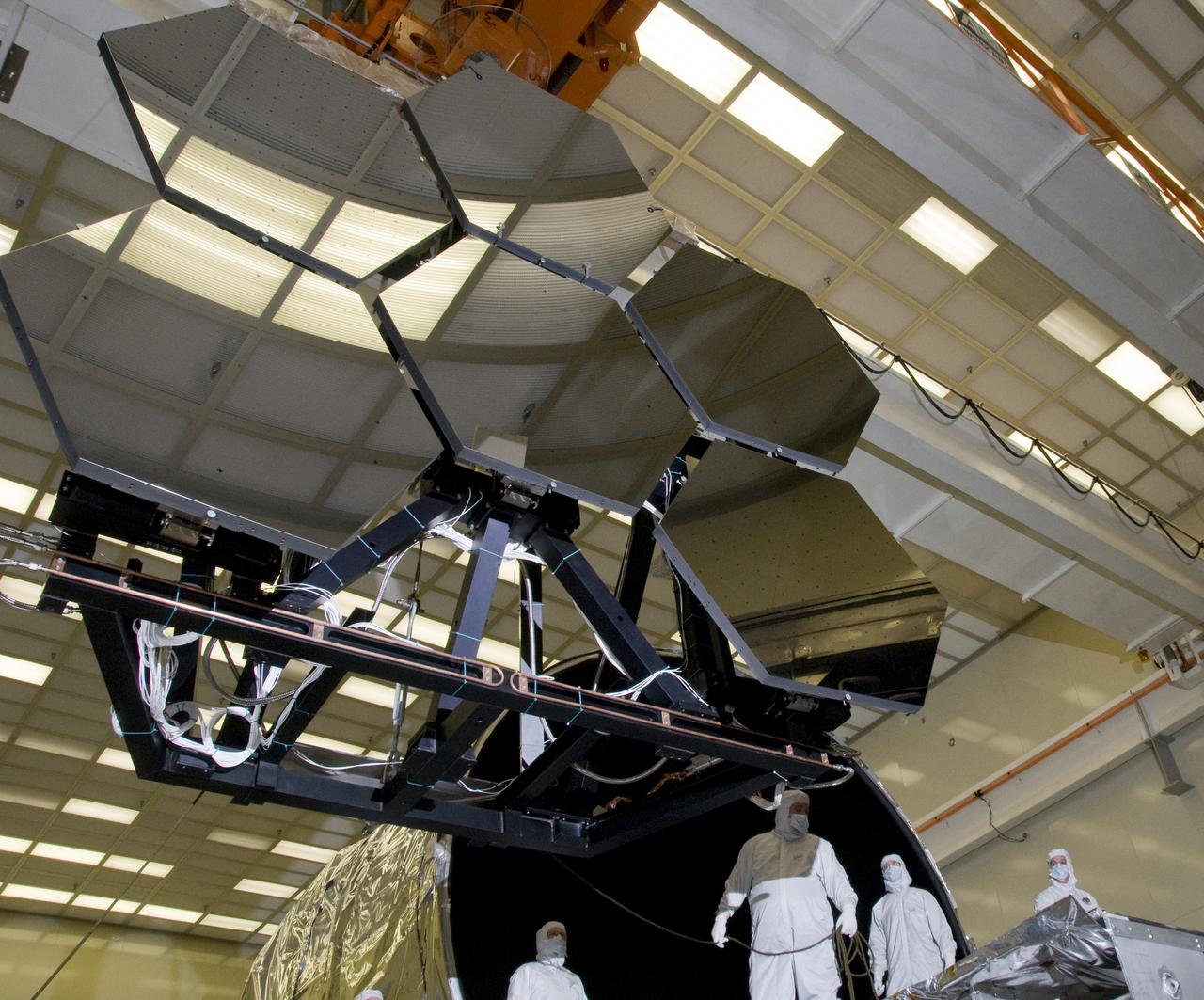

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
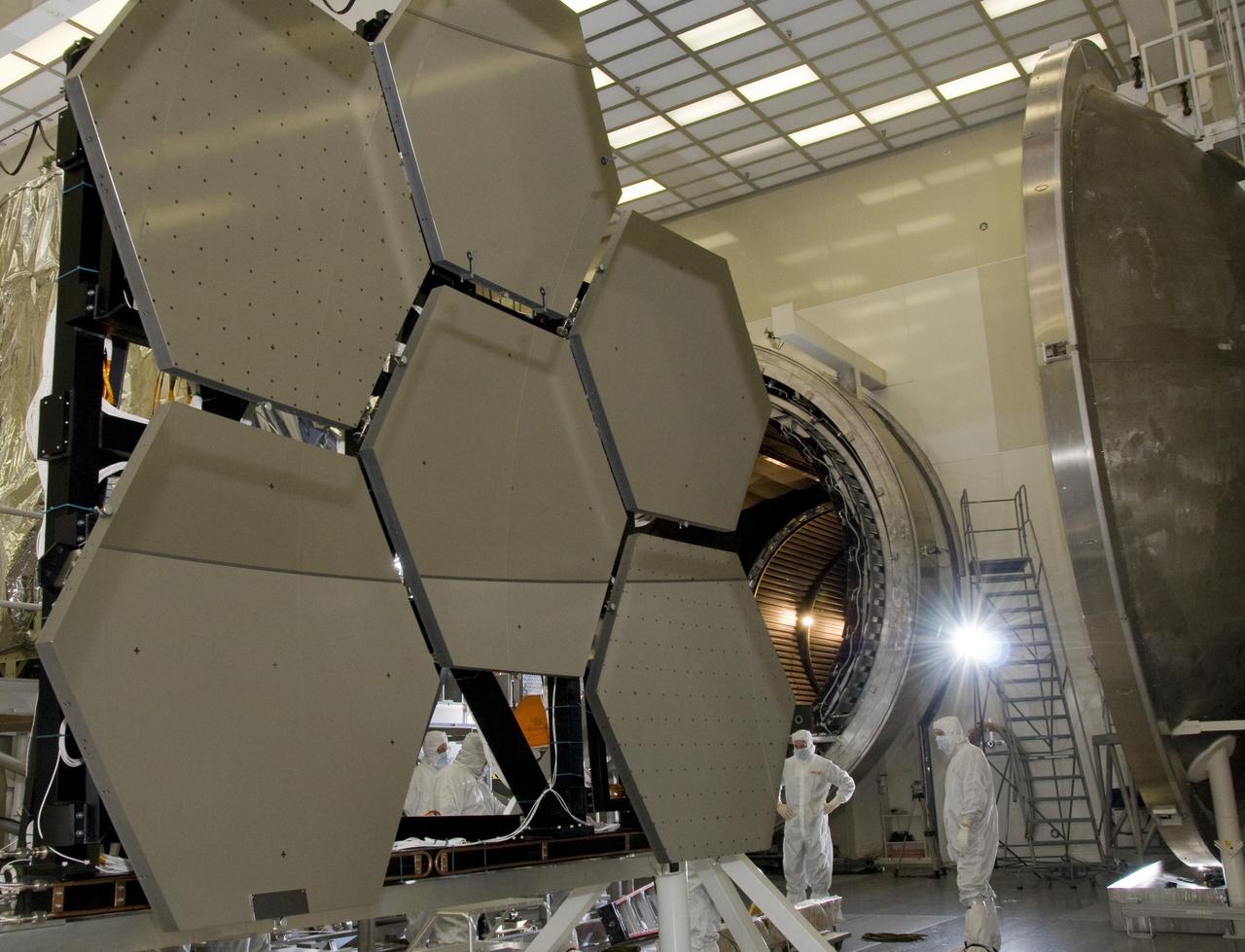

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
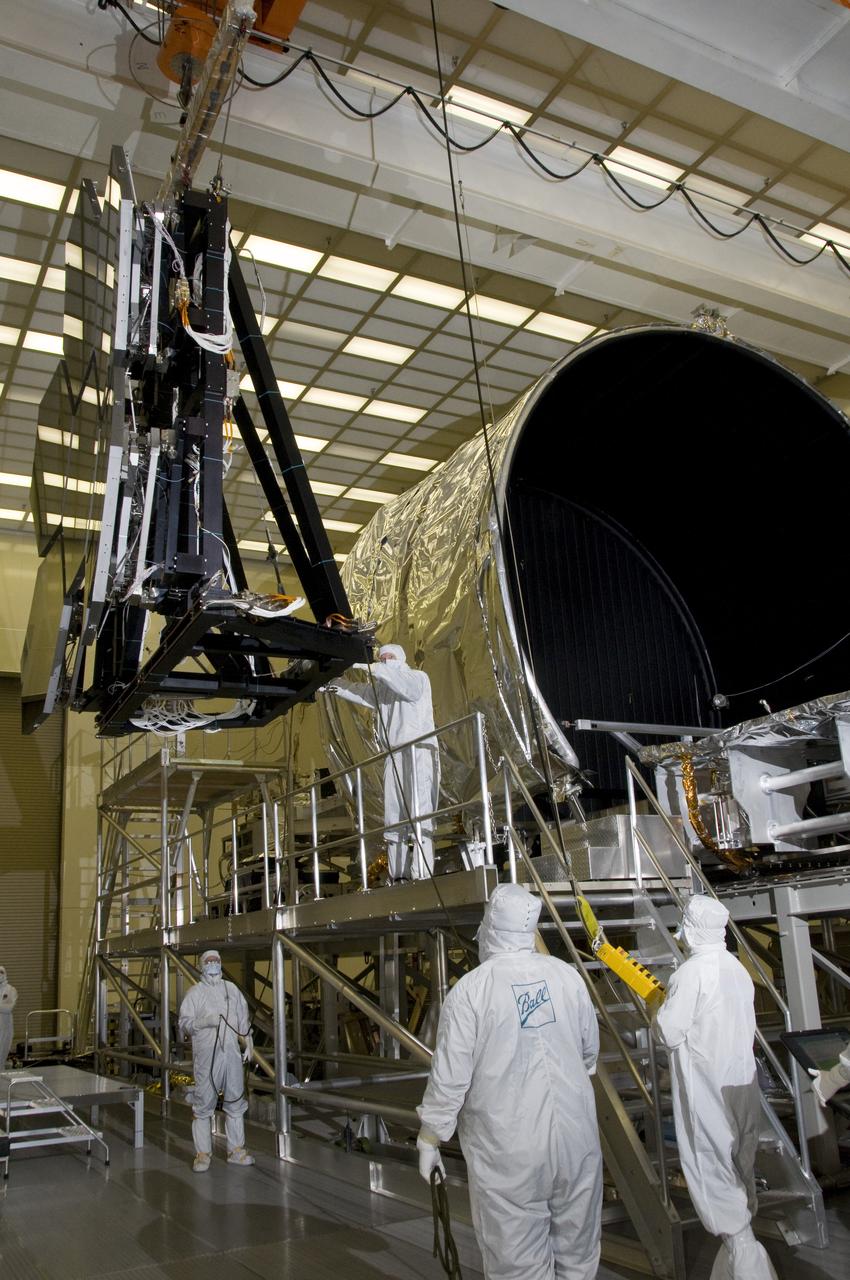

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
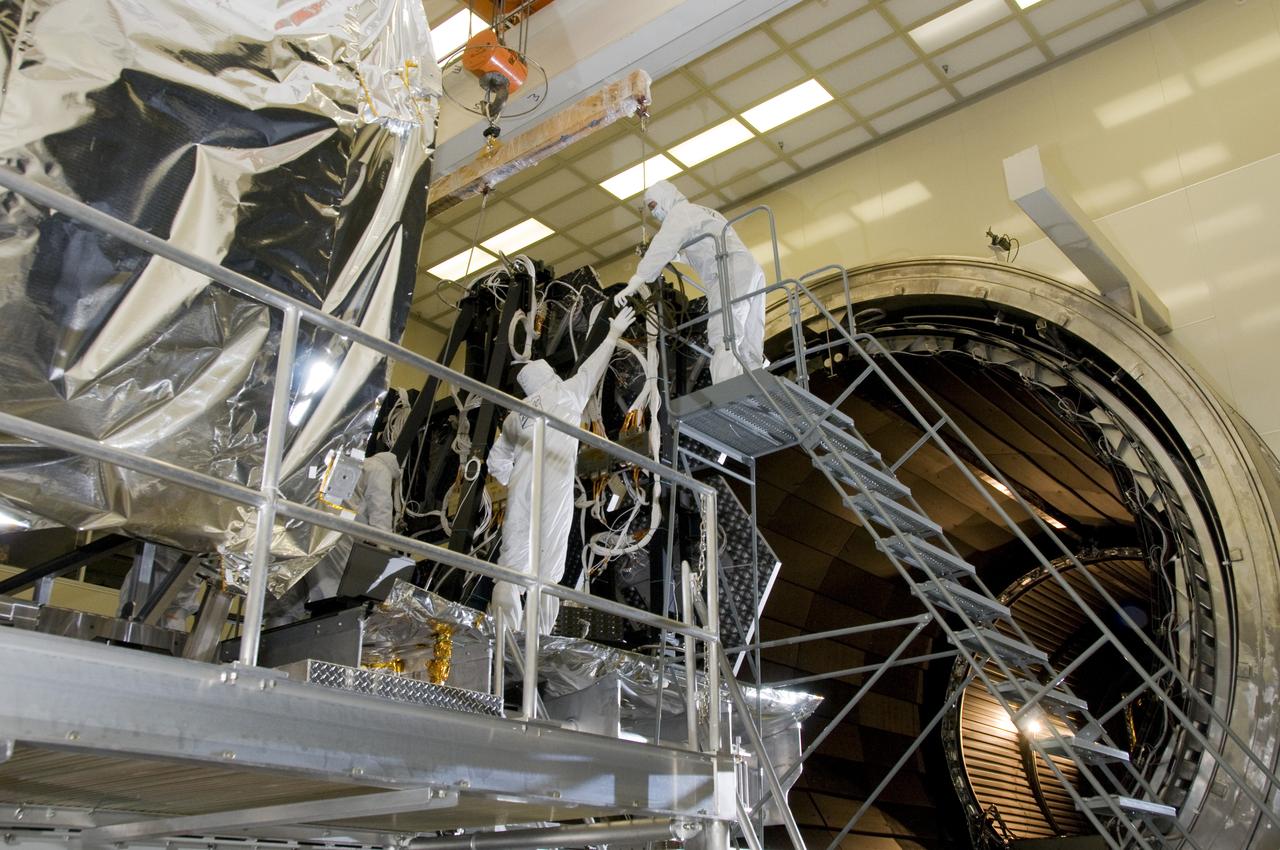

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
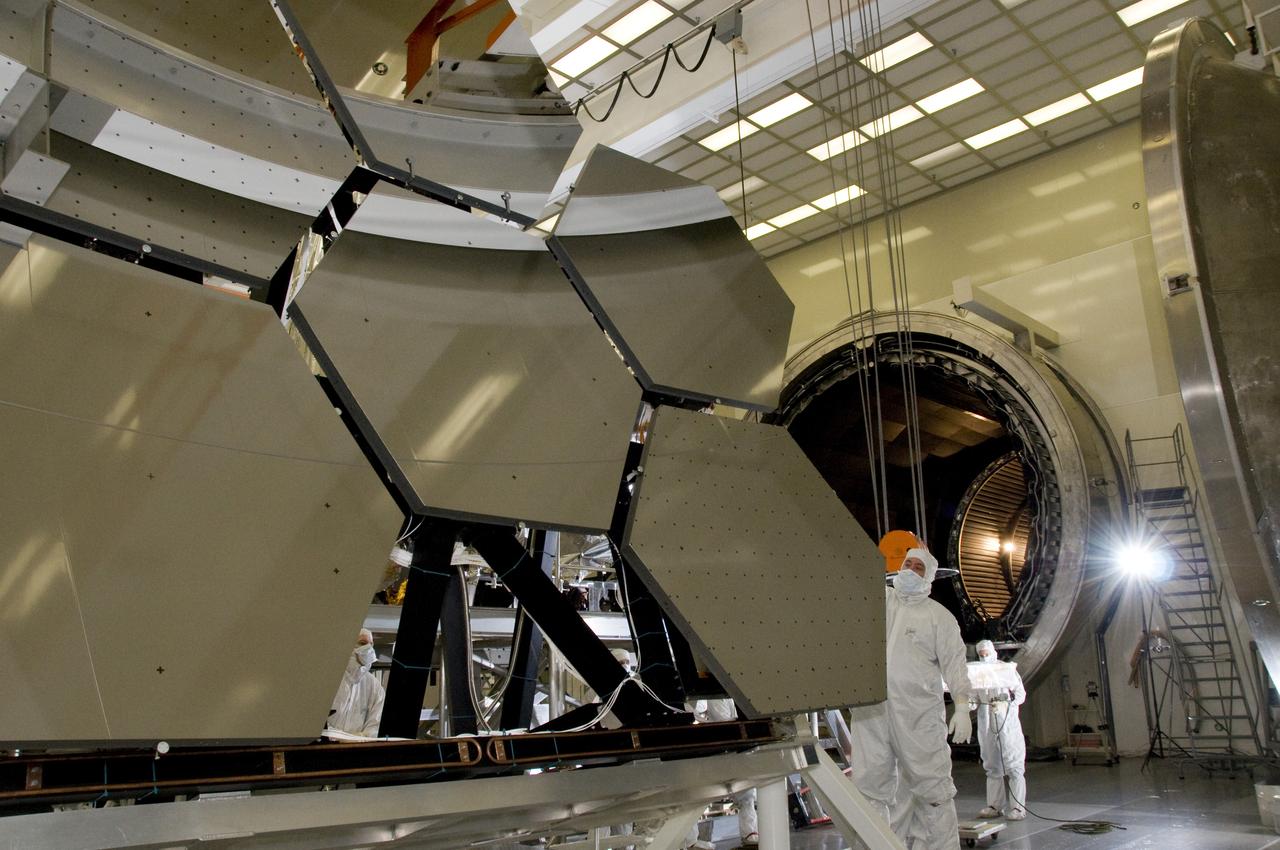

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
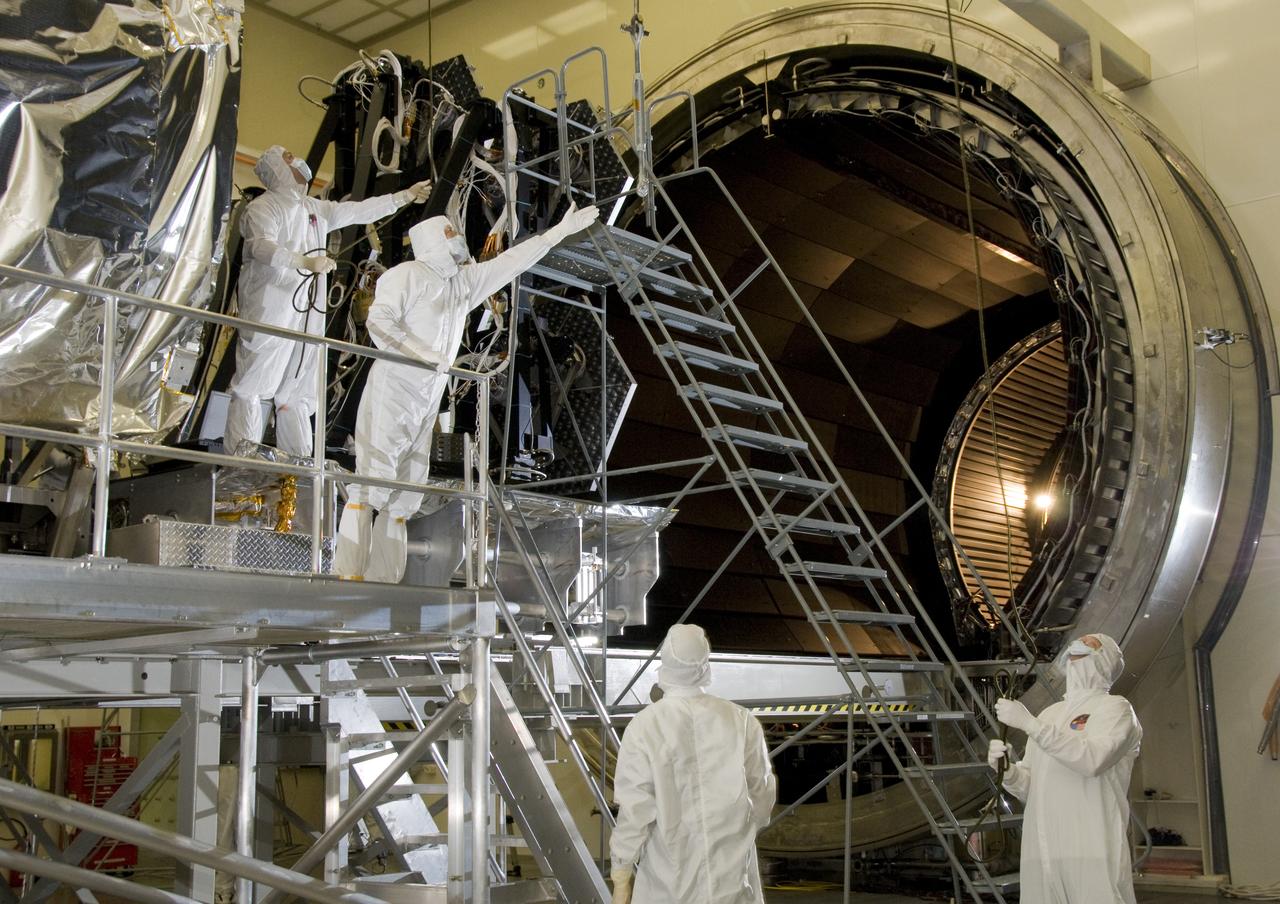

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
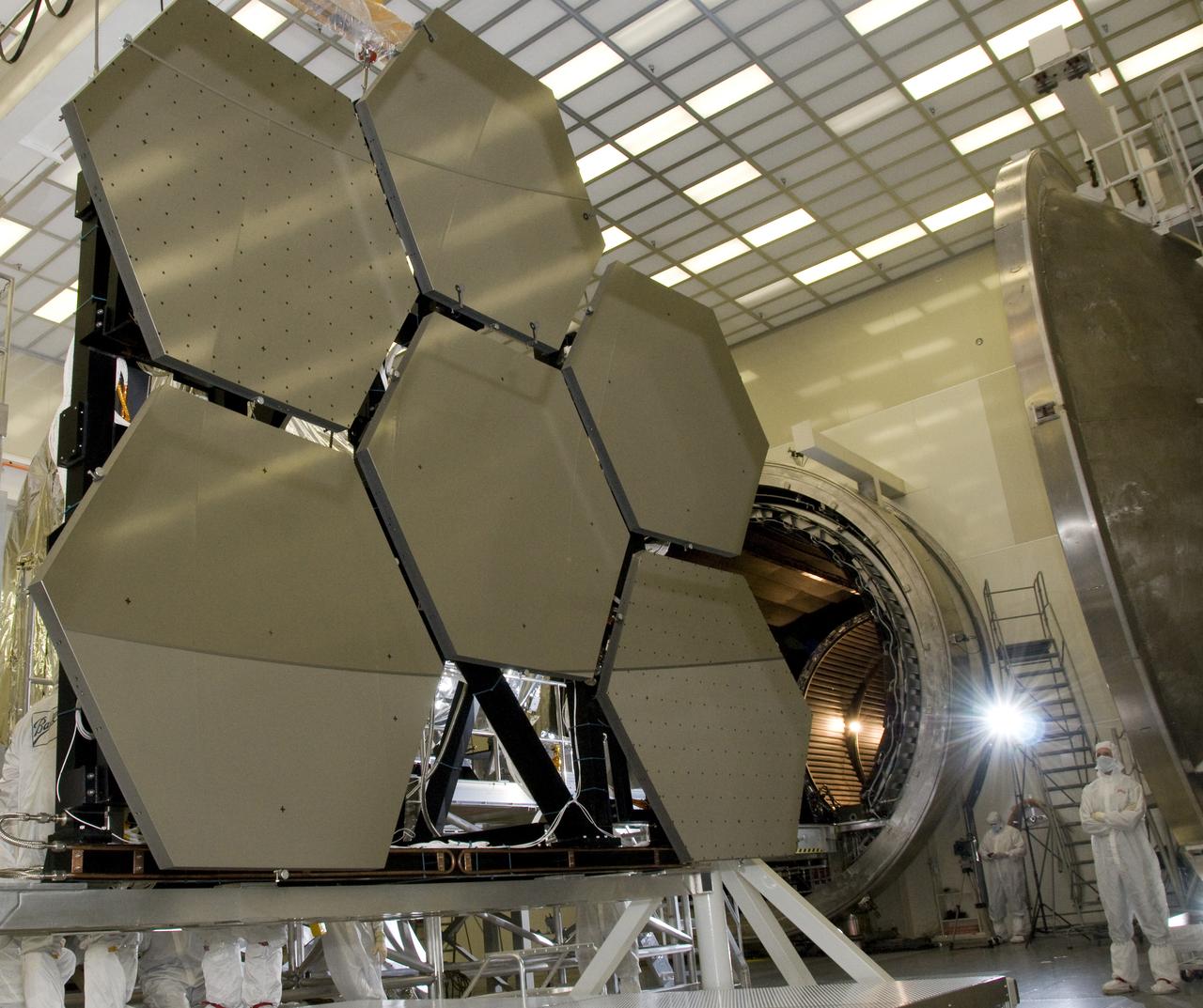

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
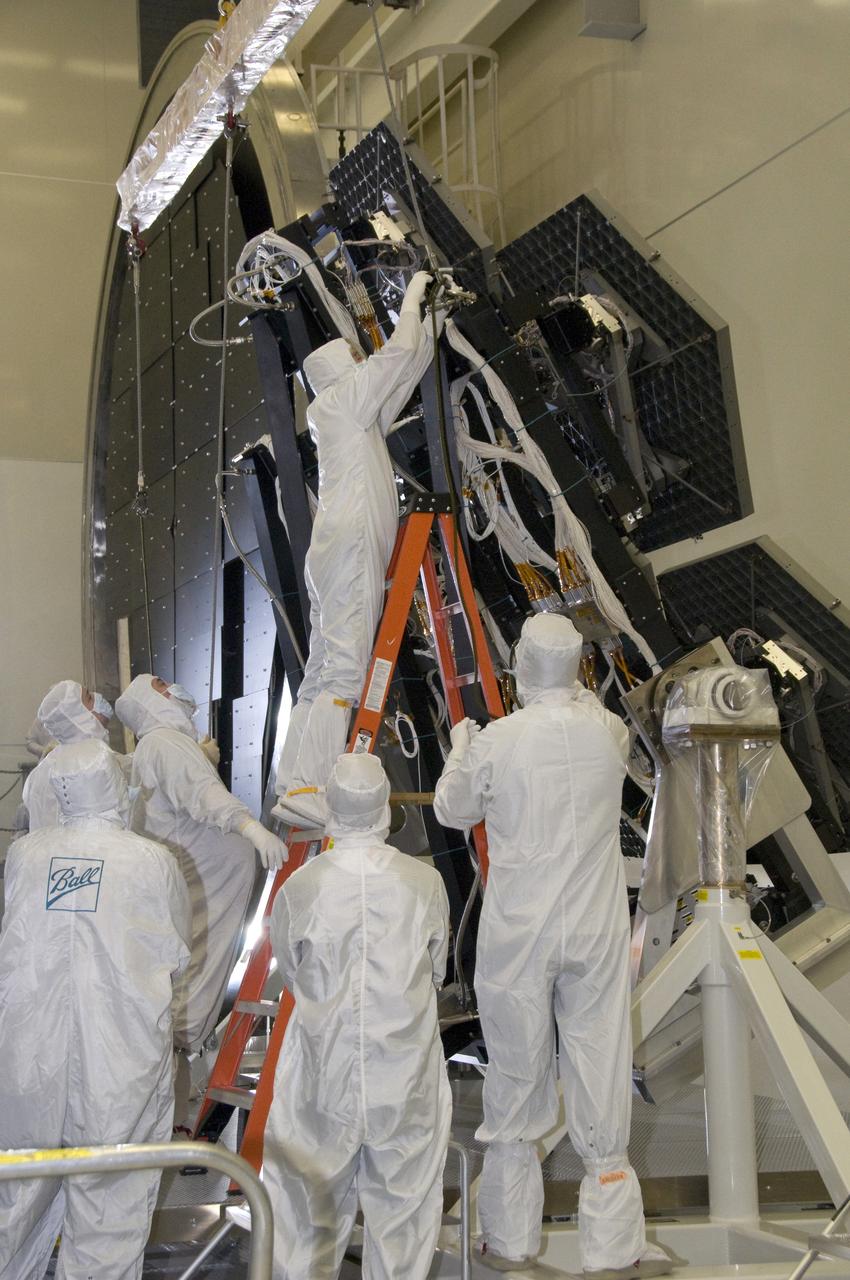

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
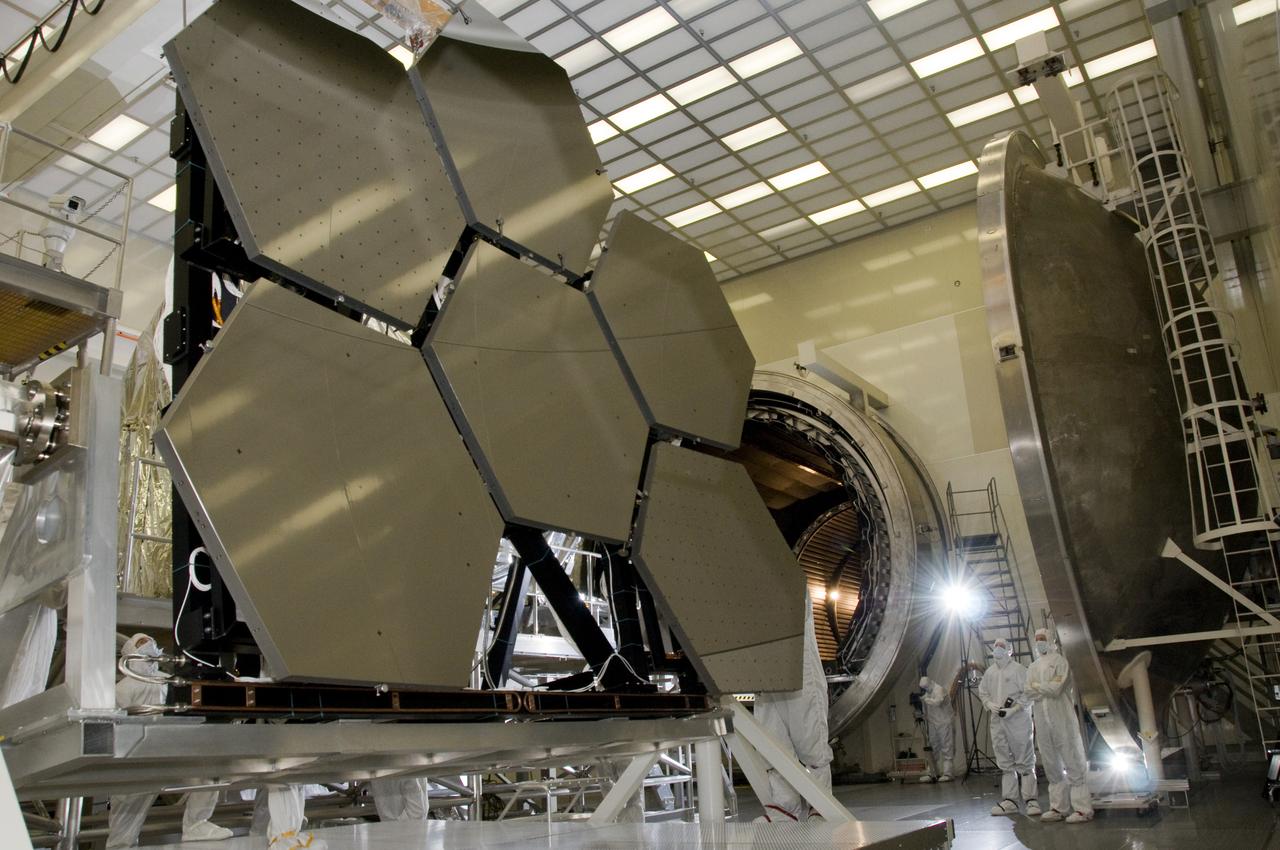

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
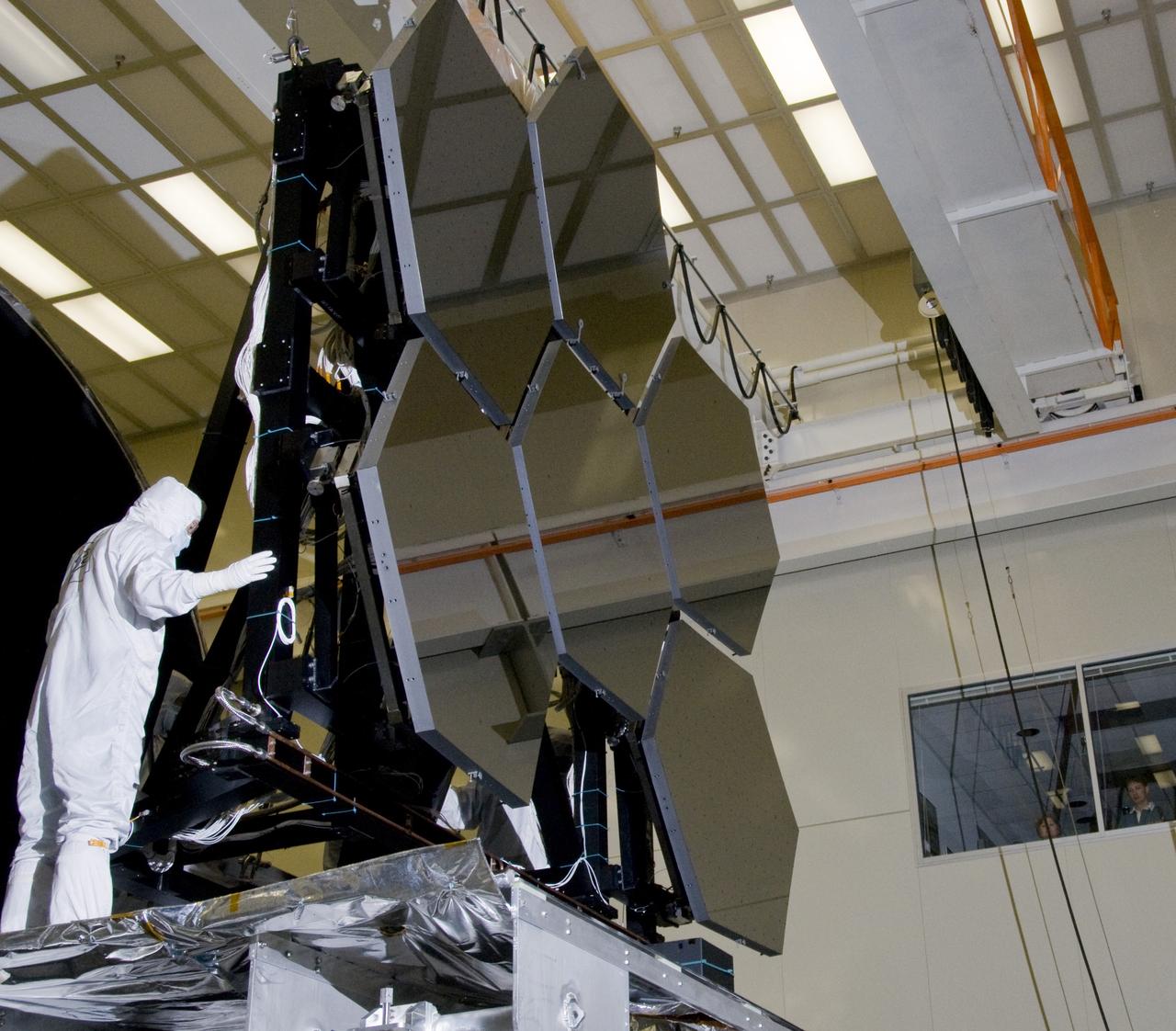

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
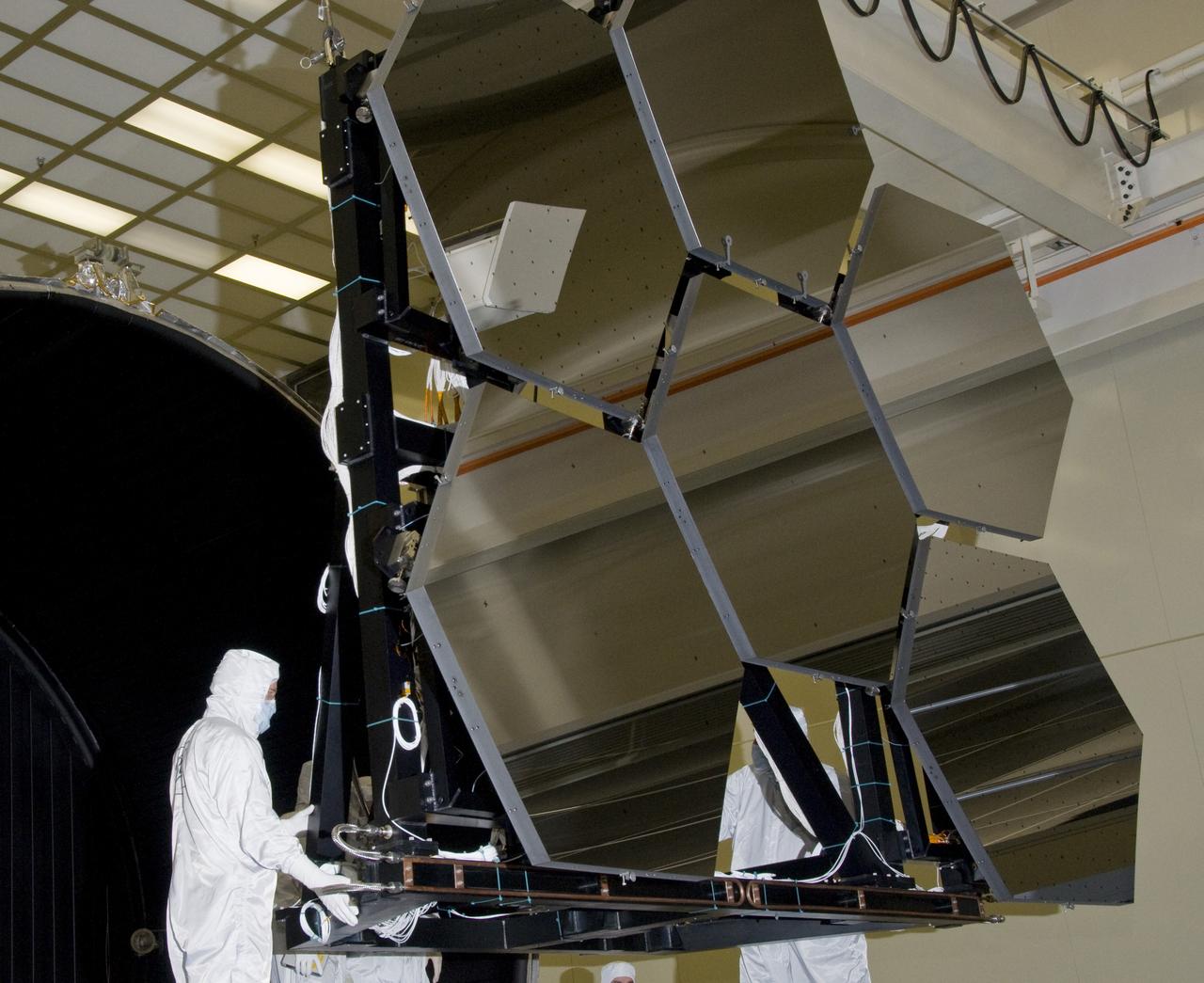

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
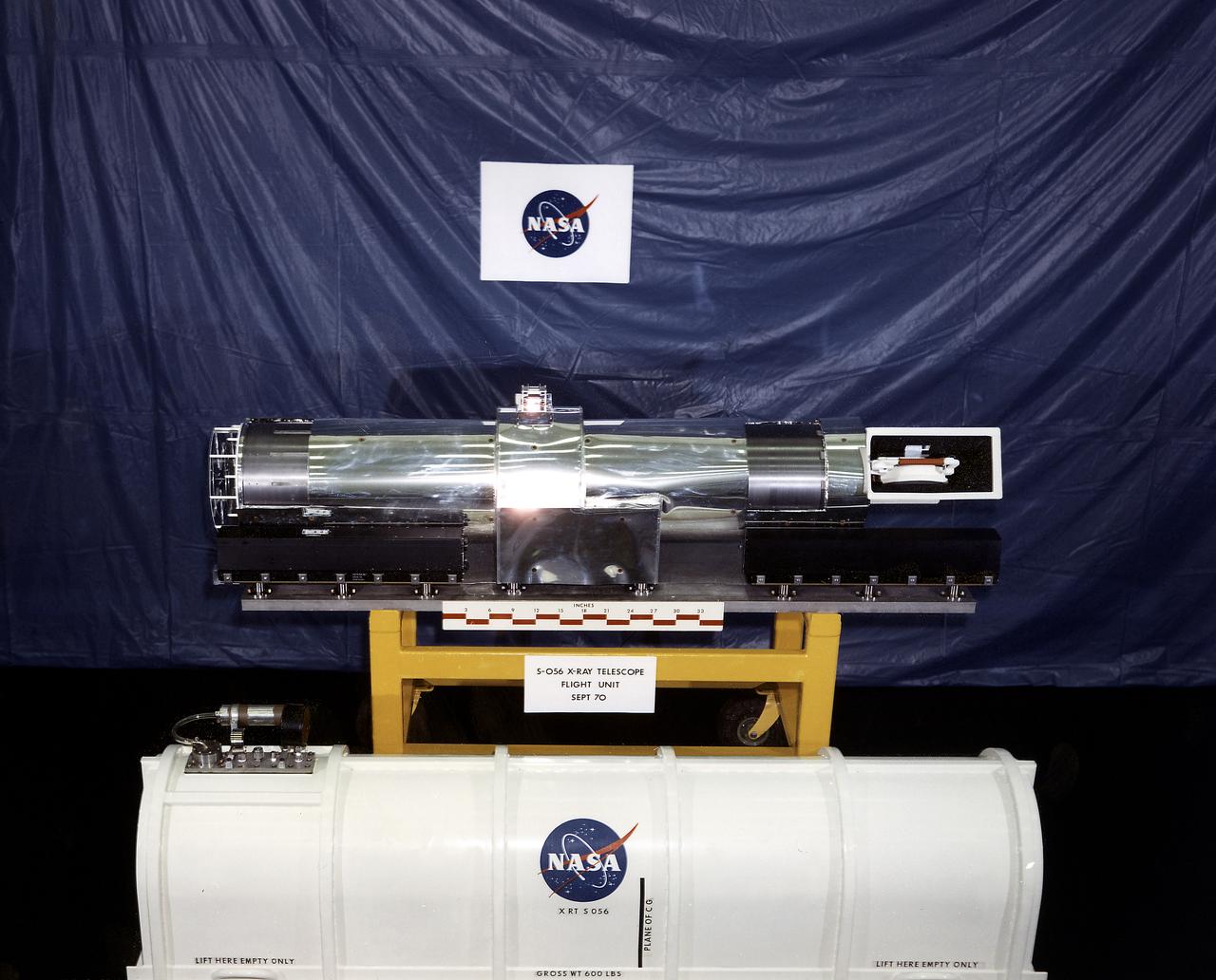

This 1970 photograph shows Skylab's Dual X-Ray Telescopes, an Apollo Telescope Mount facility. It was designed to gather solar radiation data in the x-ray region of the solar spectrum and provide information on physical processes within the solar atmosphere. In support of the two primary telescopes, auxiliary instruments provided a continuous record of the total x-ray flux in two bands. A flare detector was also provided at the control console as an aid to astronauts for monitoring solar activity. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
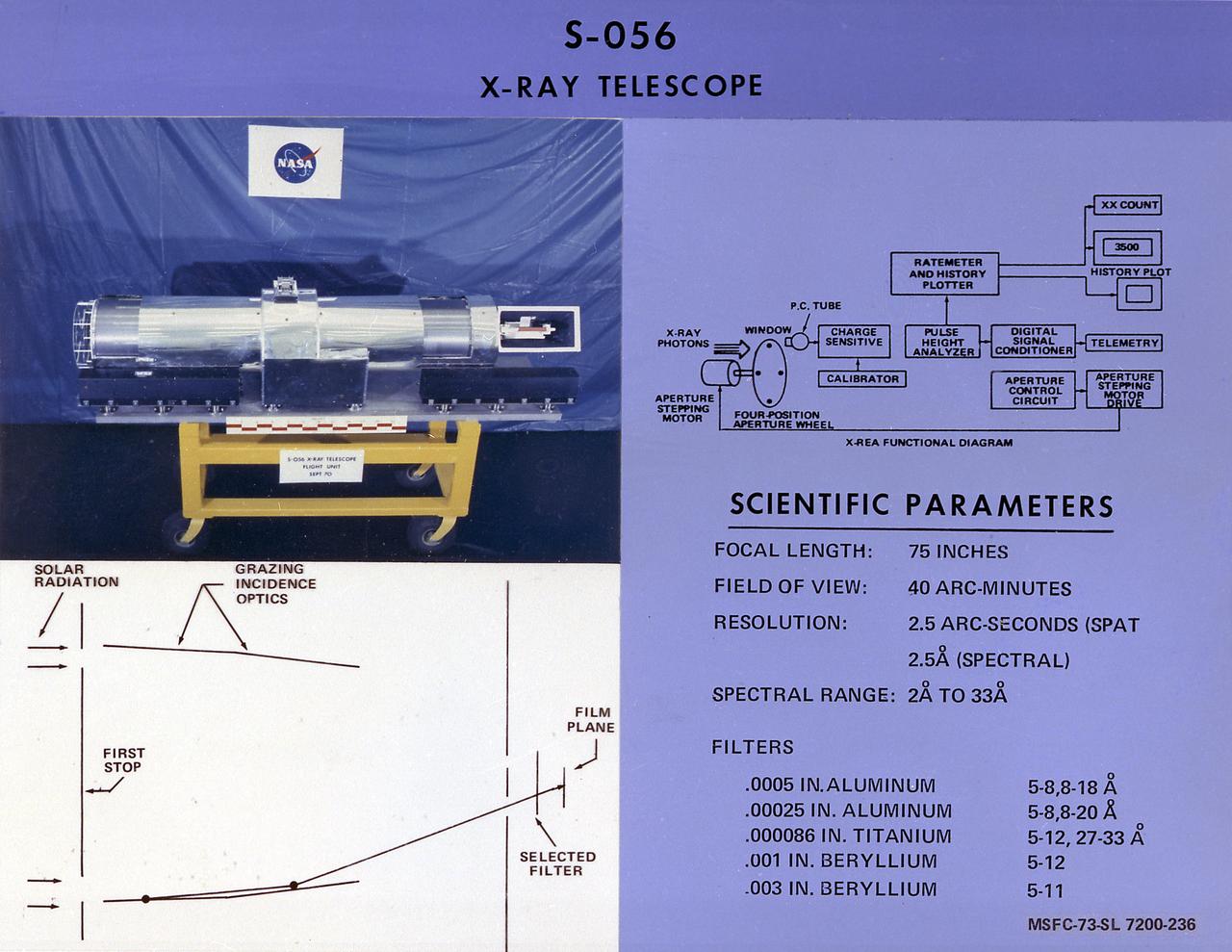
This chart details Skylab's Dual X-Ray Telescopes, one of eight Apollo Telescope Mount facilities. It was designed to gather solar radiation data in the x-ray region of the solar spectrum and provide information on physical processes within the solar atmosphere. In support of the two primary telescopes, auxiliary instruments provided a continuous record of the total x-ray flux in two bands. A flare detector was also provided at the control console as an aid to astronauts for monitoring solar activity. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.

This new composite image of stellar cluster NGC 1333 combines X-rays from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory (pink); infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope (red); and optical data from the Digitized Sky Survey and the National Optical Astronomical Observatories' Mayall 4-meter telescope on Kitt Peak near Tucson, Arizona. The Chandra data reveal 95 young stars glowing in X-ray light, 41 of which had not been seen previously using Spitzer because they lacked infrared emission from a surrounding disk. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19347
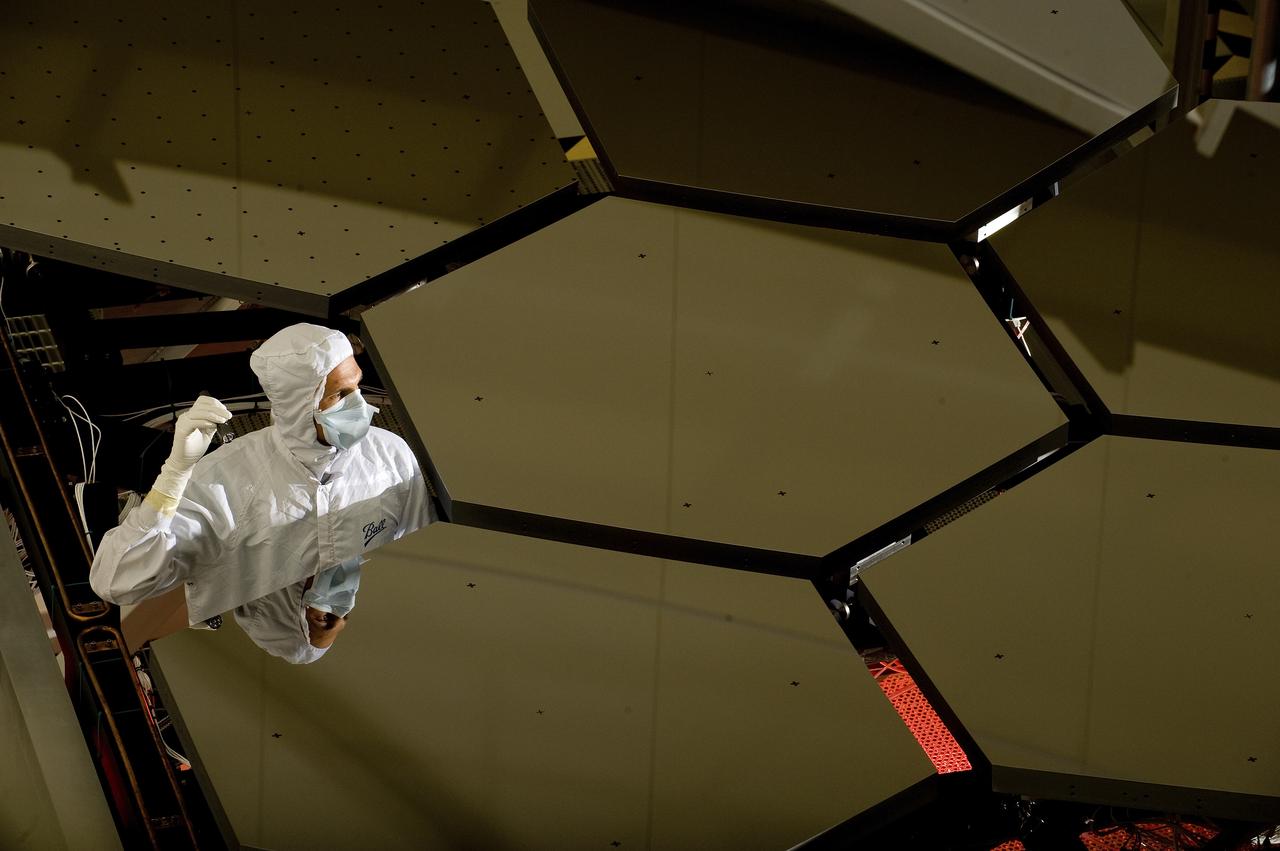

A BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIAN STANDS WITHIN A JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE ARRAY THAT WAS IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING
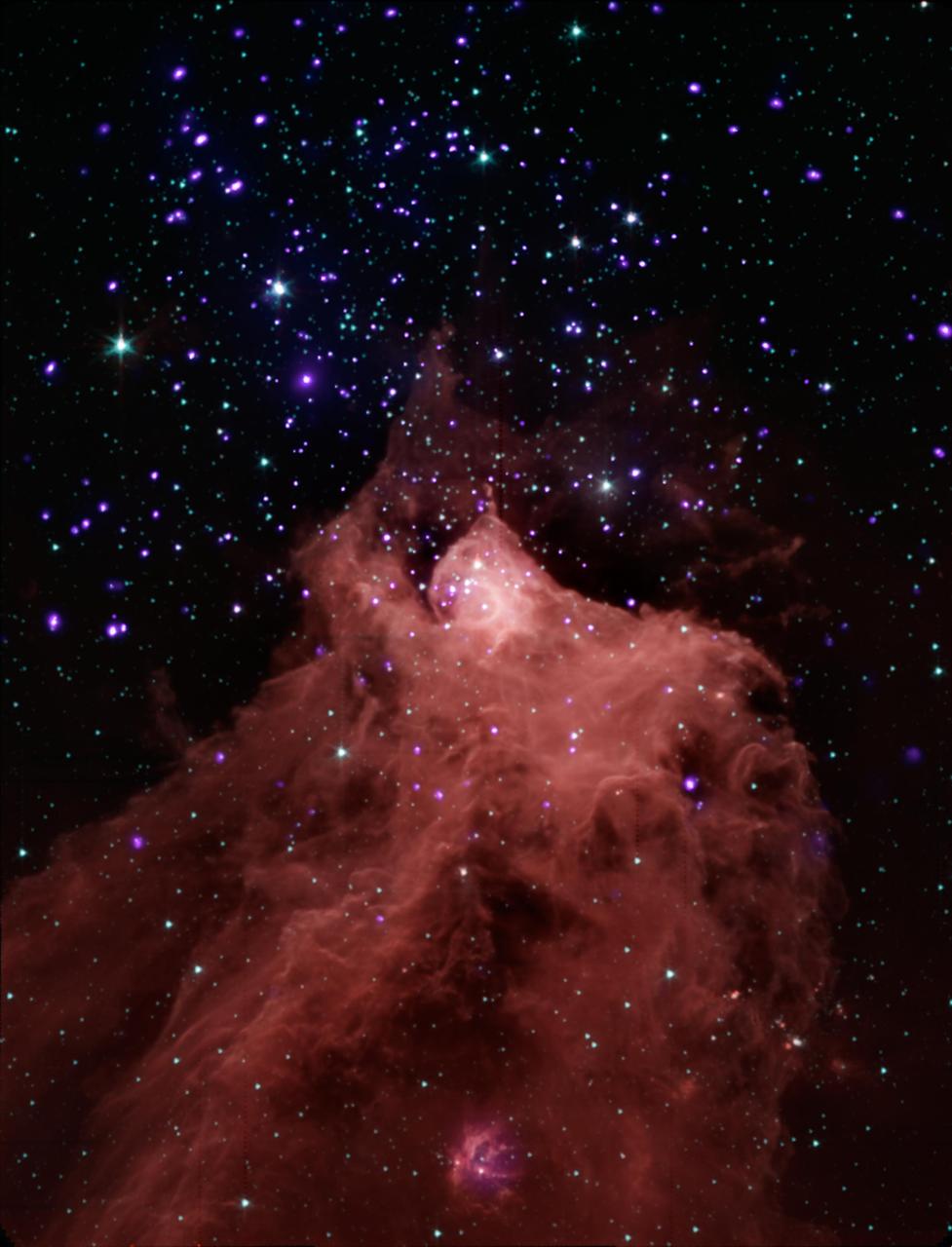

This composite image, combining data from NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory and Spitzer Space Telescope shows the star-forming cloud Cepheus B, located in our Milky Way galaxy about 2,400 light years from Earth

The spiral galaxy NGC 3627, located about 30 million light years from Earth as seen by four NASA telescopes; inset shows the central region, which contains a bright X-ray source that is likely powered by material falling onto a supermassive black hole.
![In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA12348/PIA12348~medium.jpg)
In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348
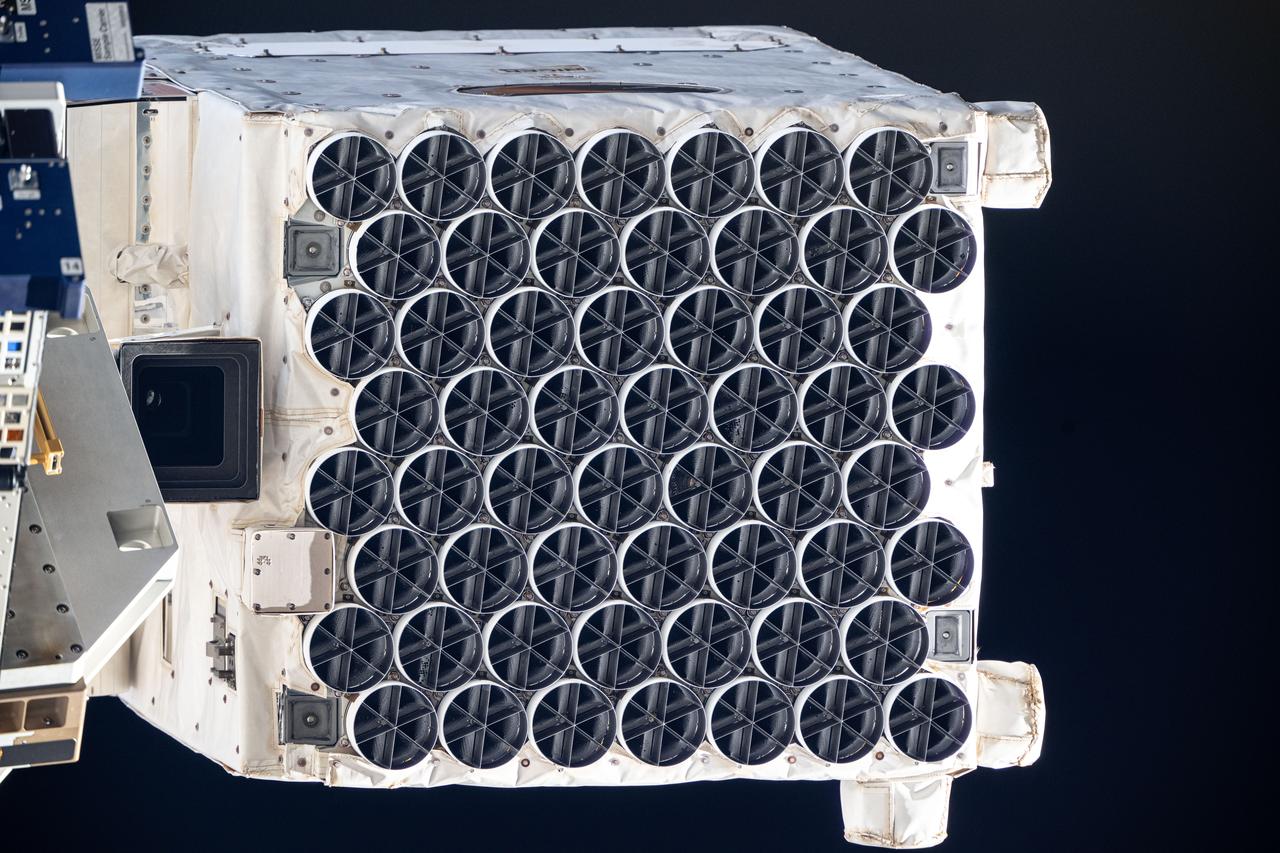
iss072e371351 (Dec. 17, 2024) --- The NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) X-ray telescope is pictured installed on the starboard side of the International Space Station's integrated truss segment. NICER's 56 X-ray concentrators are covered by thermal shields, or filters, that block ultraviolet, infrared, and visible light while allowing X-rays to pass through to the mirrors underneath enabling the observation of neutron stars. Several thermal shields have been damaged allowing unwanted sunlight to "leak" into the astrophysics instrument interfering with X-ray measurements. NASA astronauts Nick Hague and Sun Williams will conduct a spacewalk on Jan. 16 to patch the damaged thermal shields and restore NICER for daytime scientific operations.
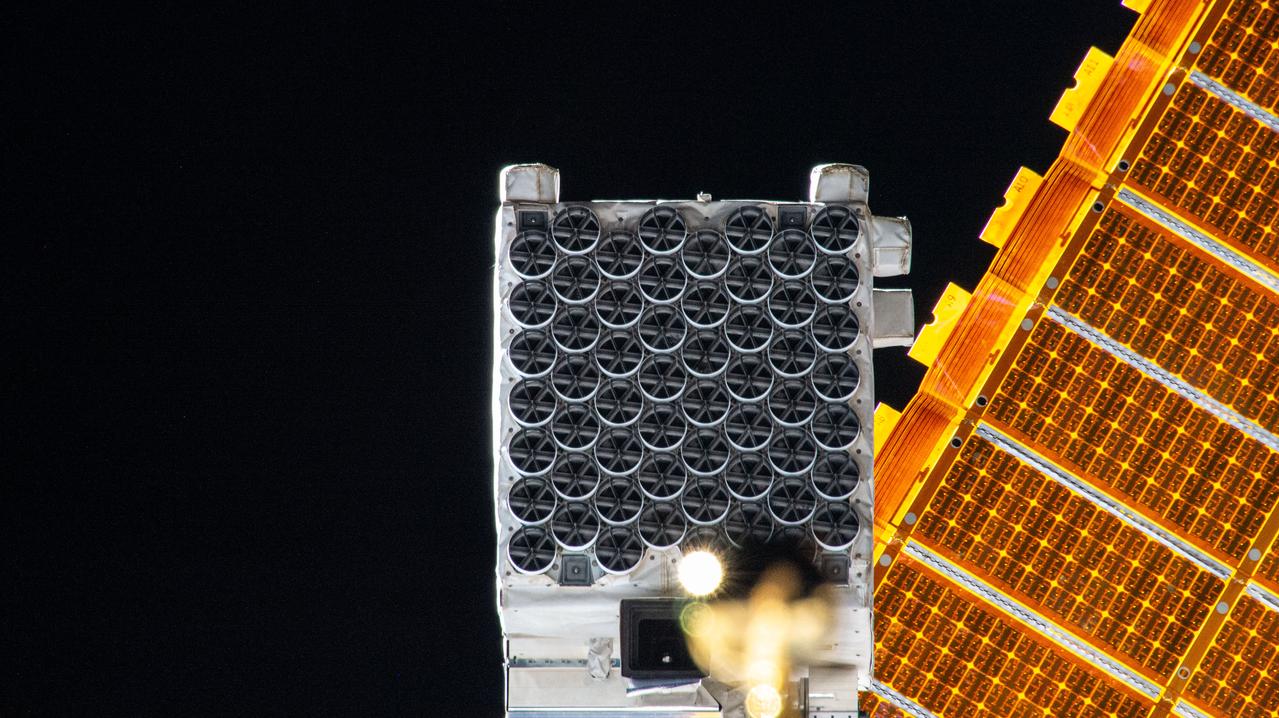
iss072e371305 (Dec. 17, 2024) --- The NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) X-ray telescope is pictured installed on the starboard side of the International Space Station's integrated truss segment. NICER's 56 X-ray concentrators are covered by thermal shields, or filters, that block ultraviolet, infrared, and visible light while allowing X-rays to pass through to the mirrors underneath enabling the observation of neutron stars. Several thermal shields have been damaged allowing unwanted sunlight to "leak" into the astrophysics instrument interfering with X-ray measurements. NASA astronauts Nick Hague and Sun Williams will conduct a spacewalk on Jan. 16 to patch the damaged thermal shields and restore NICER for daytime scientific operations.
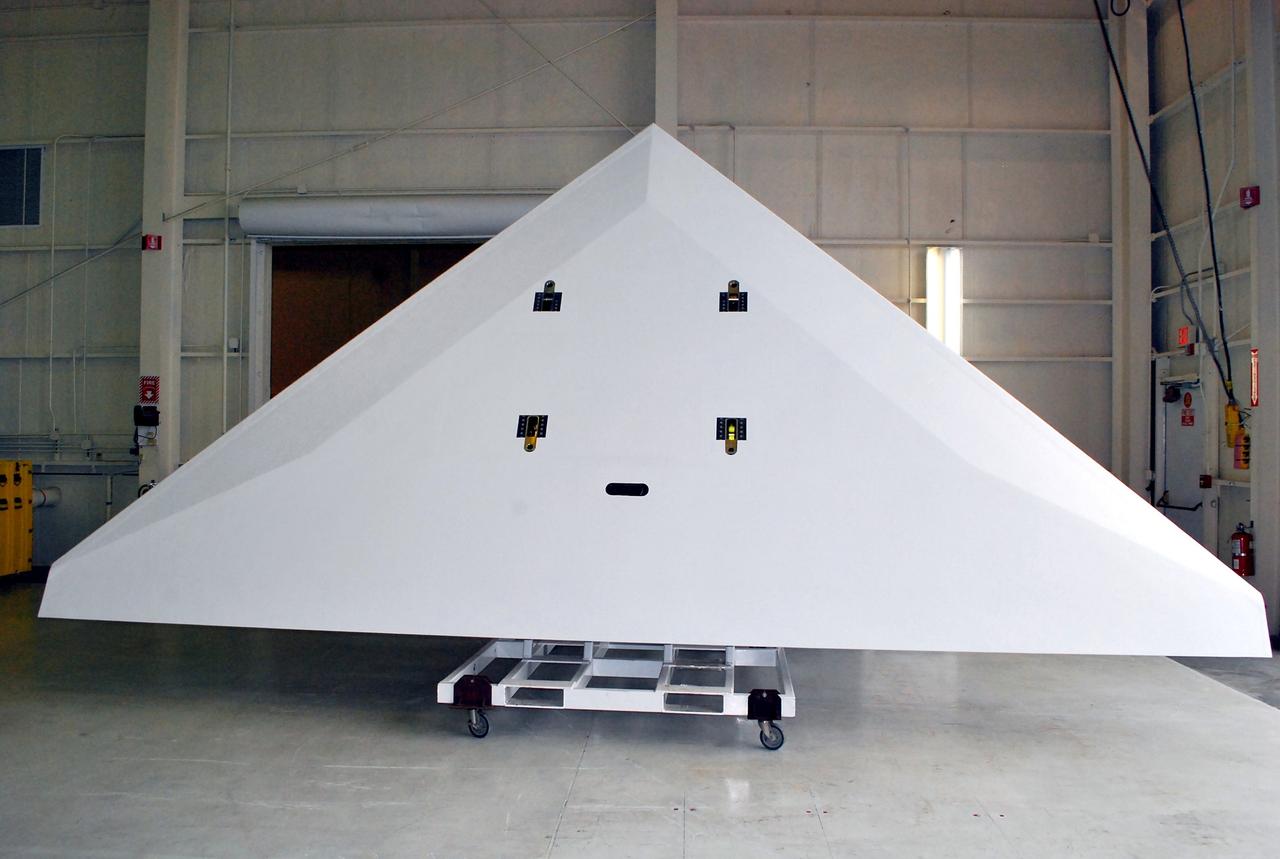

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The wing of the Pegasus XL launch vehicle awaits processing in a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences' L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
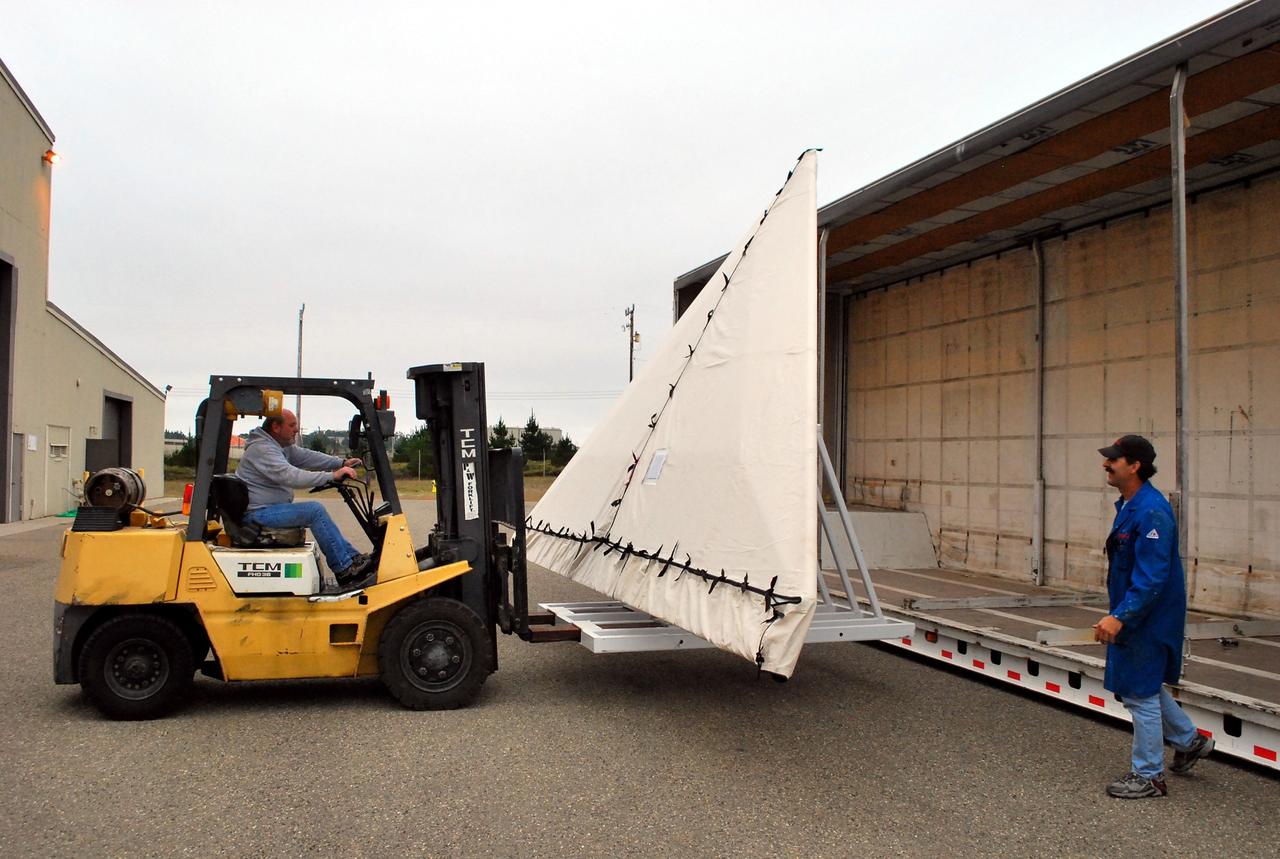

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Orbital Sciences Corp. workers uncrate the wing of the Pegasus XL launch vehicle at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Orbital's Pegasus rocket is being processed to launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences' L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
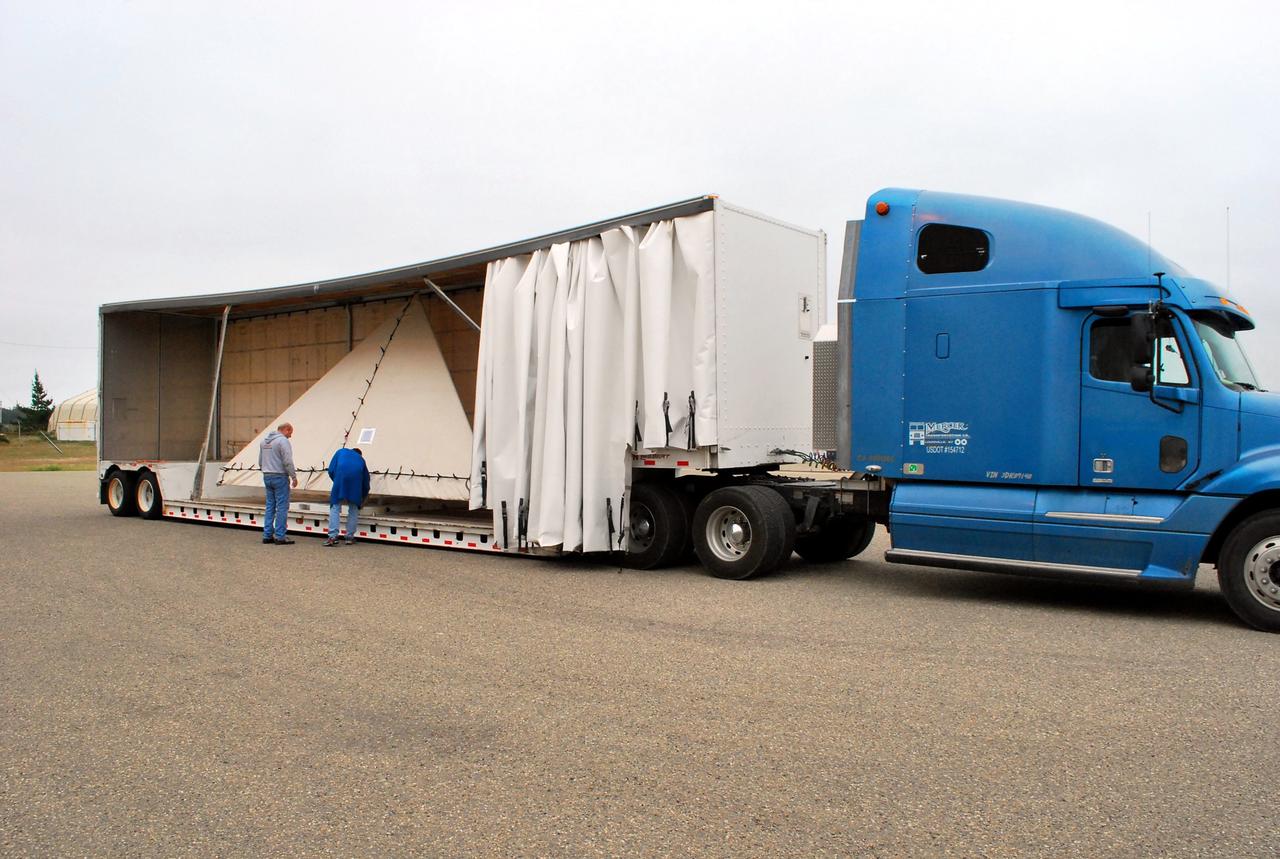

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The wing of the Pegasus XL launch vehicle arrives at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket is being processed to launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences' L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
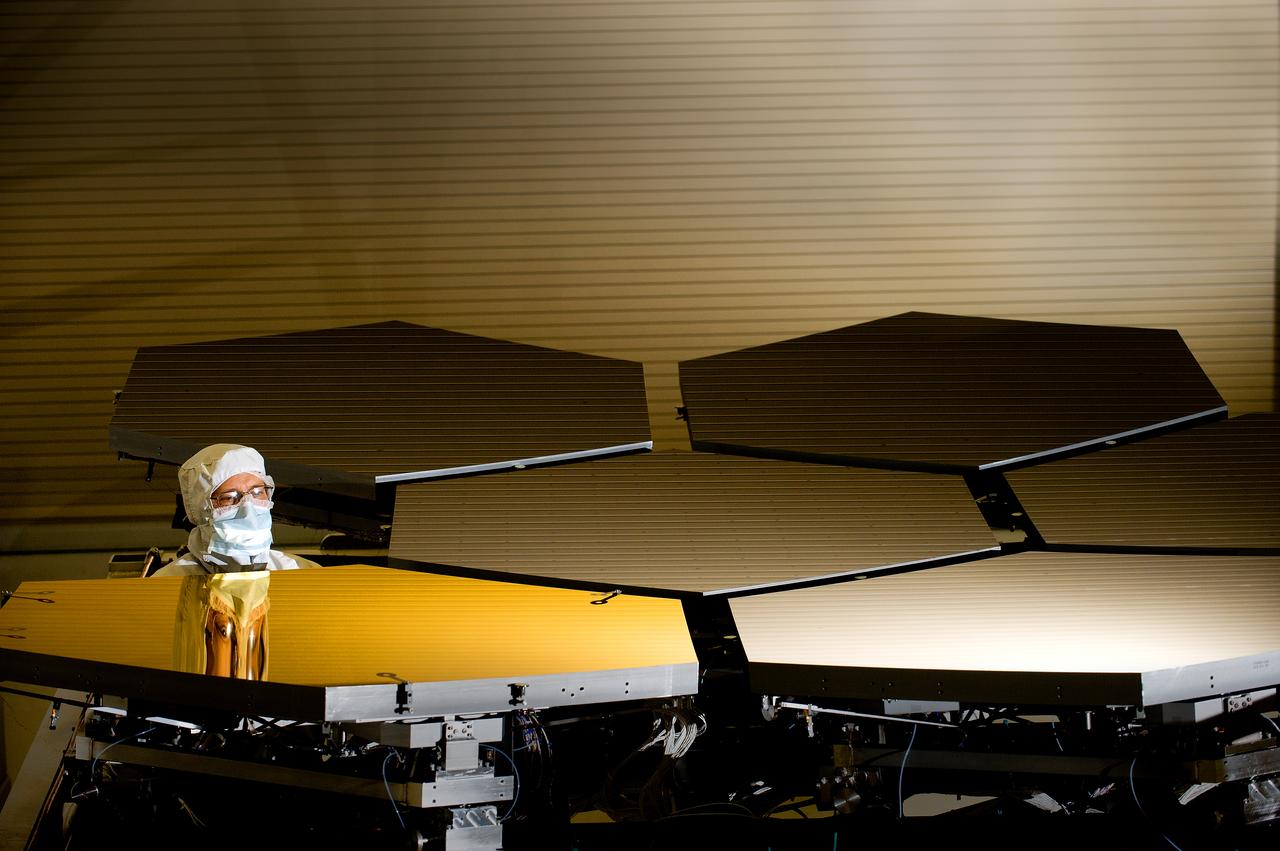

BALL AEROSPACE’S SCOTT MURRAY INSPECTS MIRRORS FOR THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
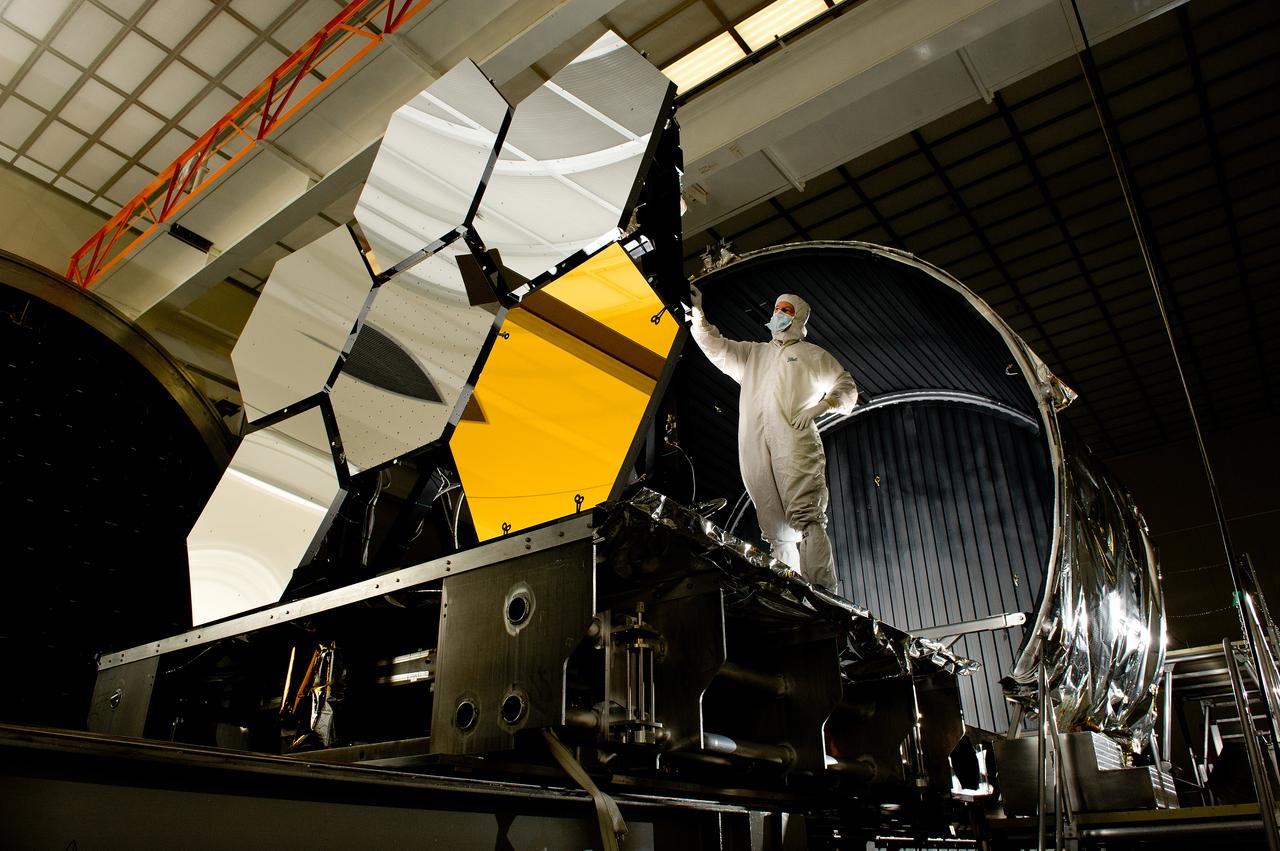

BALL AEROSPACE’S DAVE CHANEY INSPECTS THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
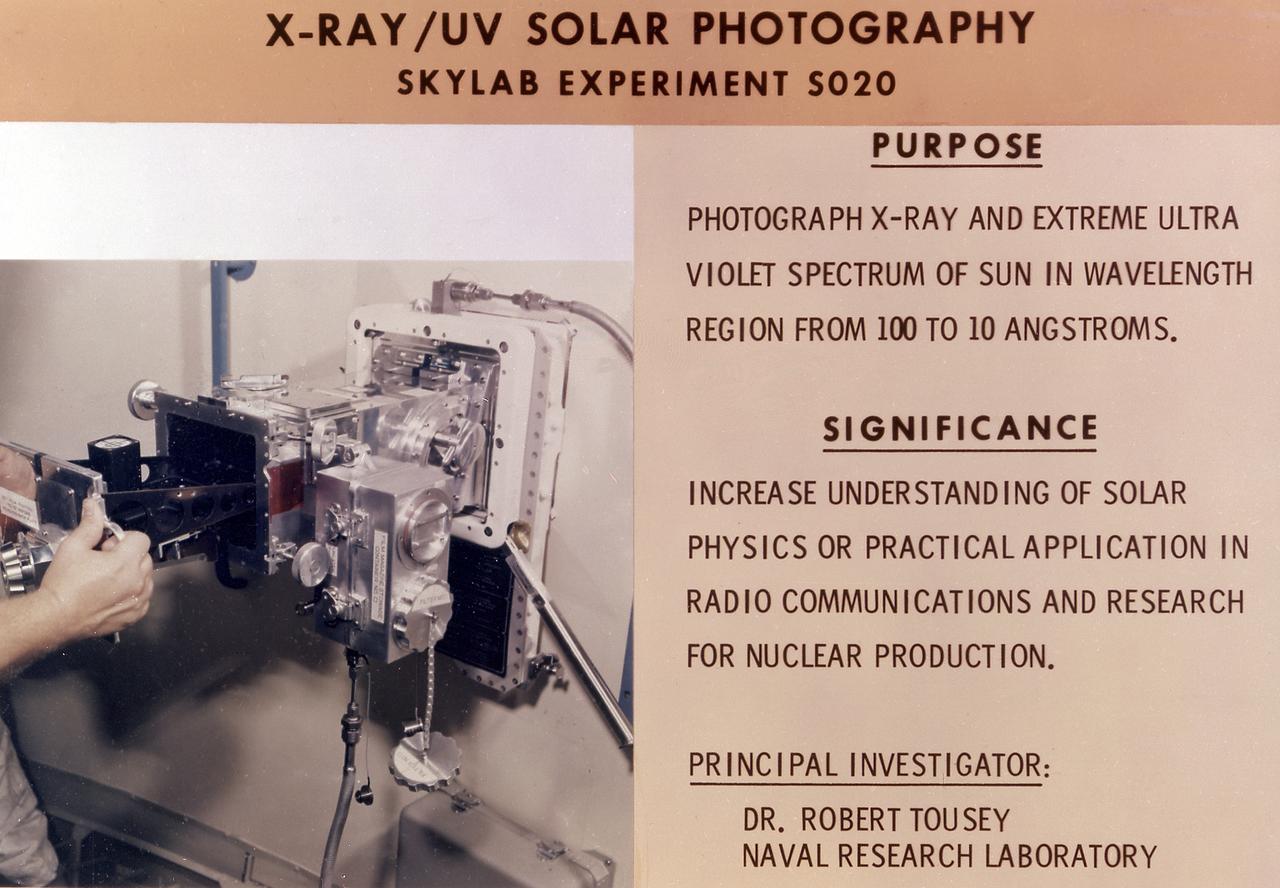
This chart details Skylab's Ultraviolet (UV) X-Ray Solar Photography experiment (S020) in an Apollo Telescope Mount facility. It was designed to photograph normal and explosive areas within the solar atmosphere in the UV and x-ray spectra. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
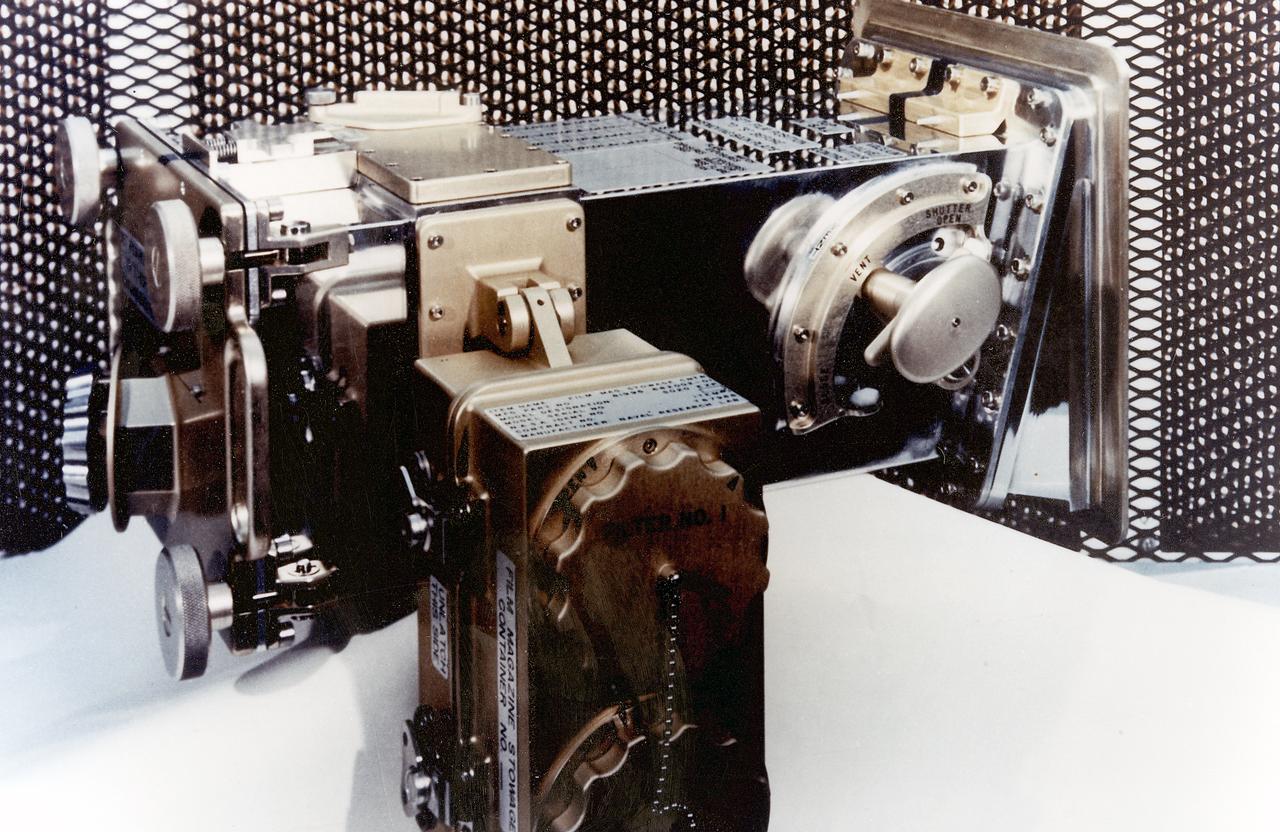
This 1970 photograph shows Skylab's Ultraviolet (UV)/X-Ray Solar Photography instrument, an Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) facility designed to photograph normal and explosive areas in the solar atmosphere in the x-ray and UV spectra. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
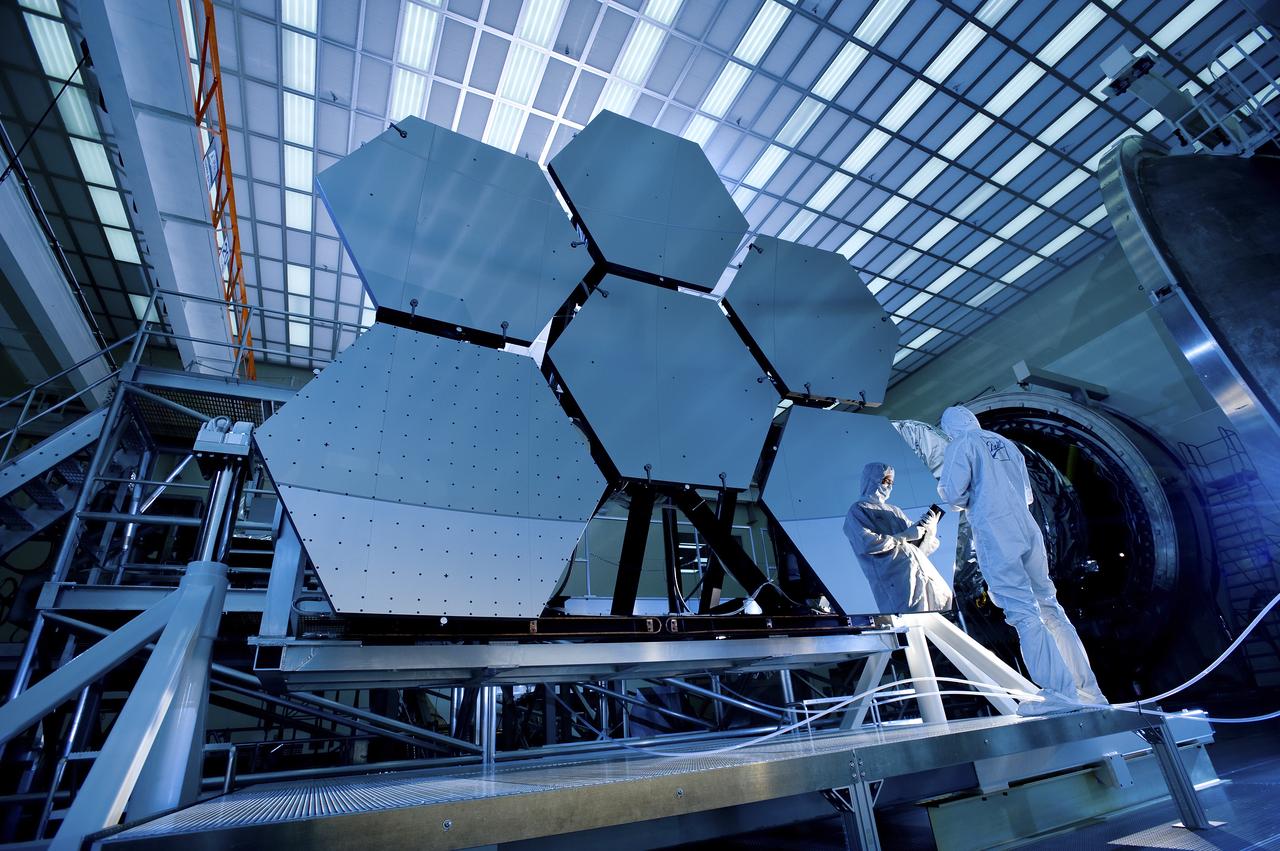

BALL AEROSPACE'S JAKE LEWIS IS REFLECTED IN ONE OF THE MIRRORS ON A JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE ARRAY THAT WAS IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING
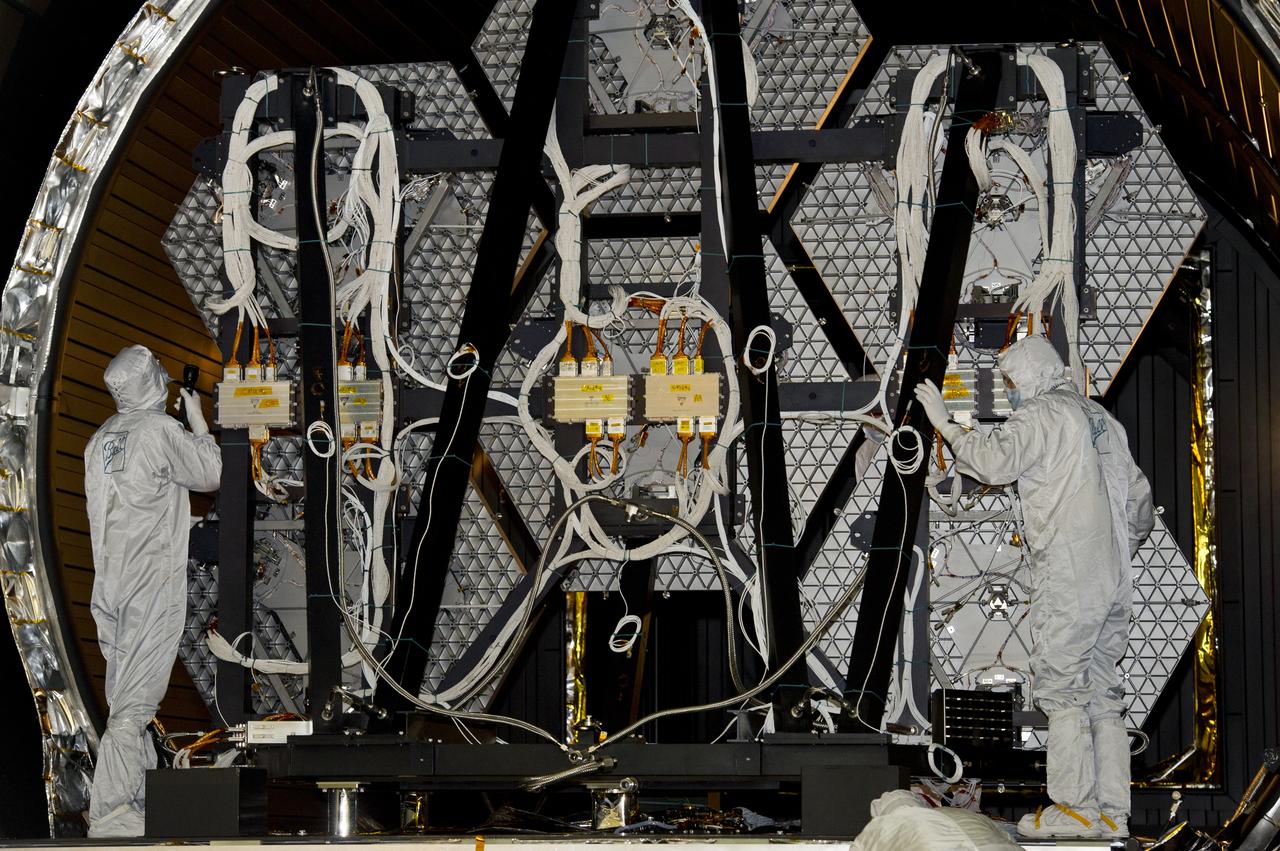
JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
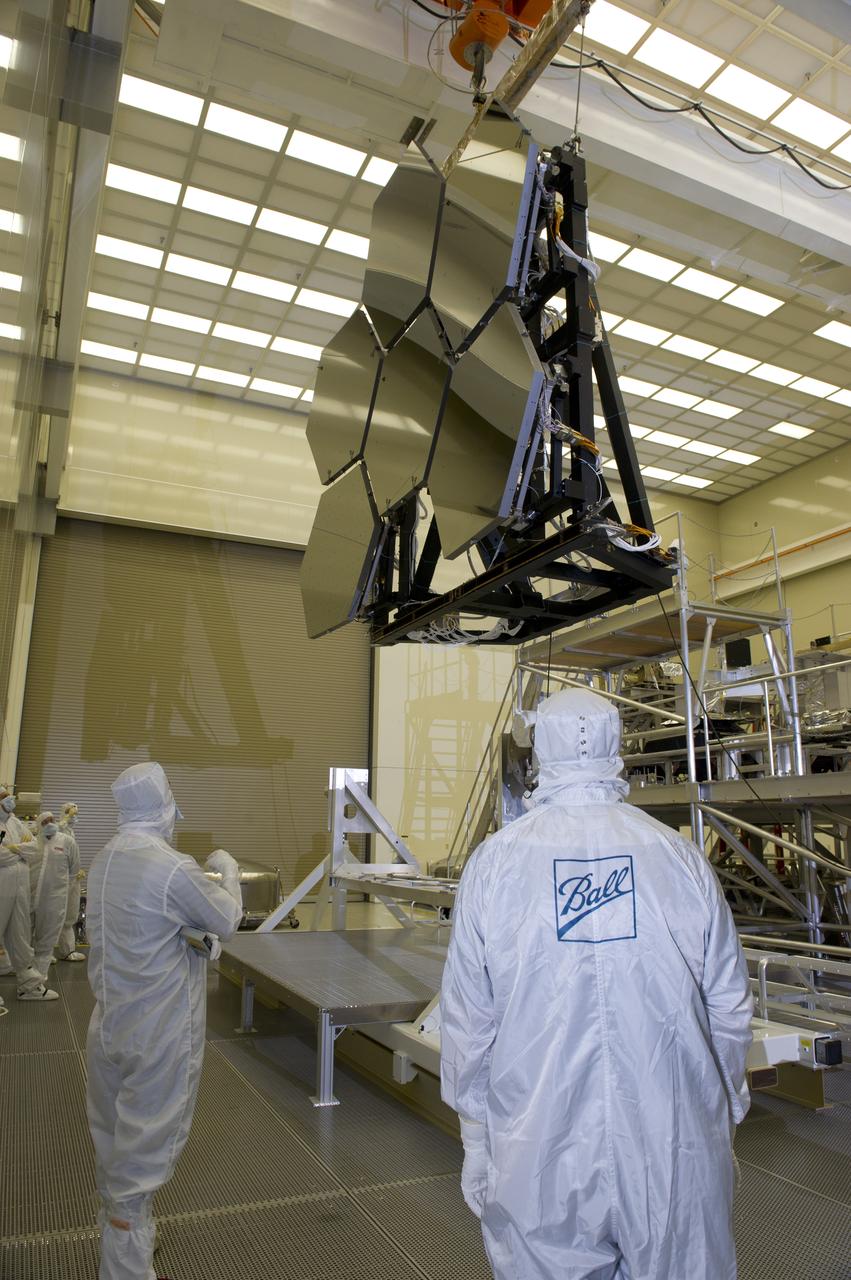

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
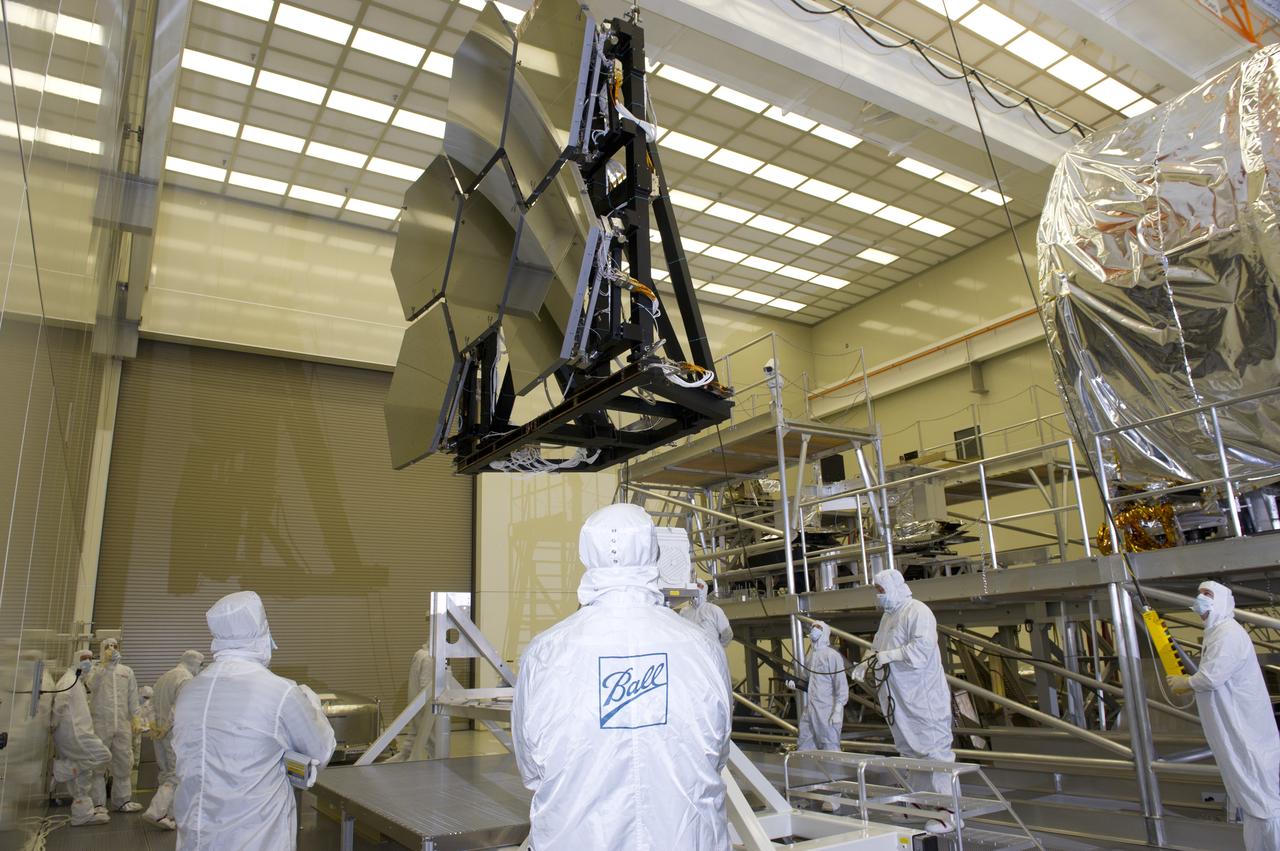

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
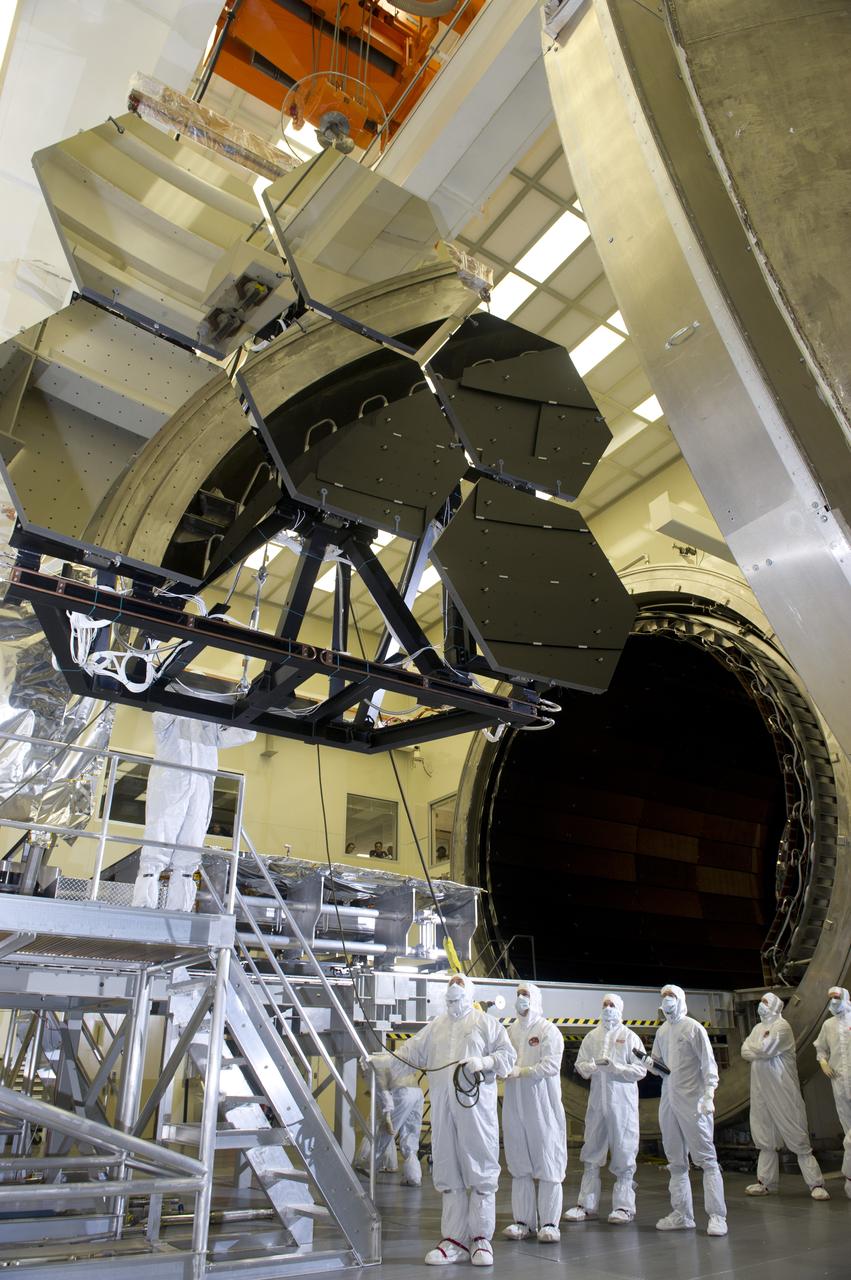

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
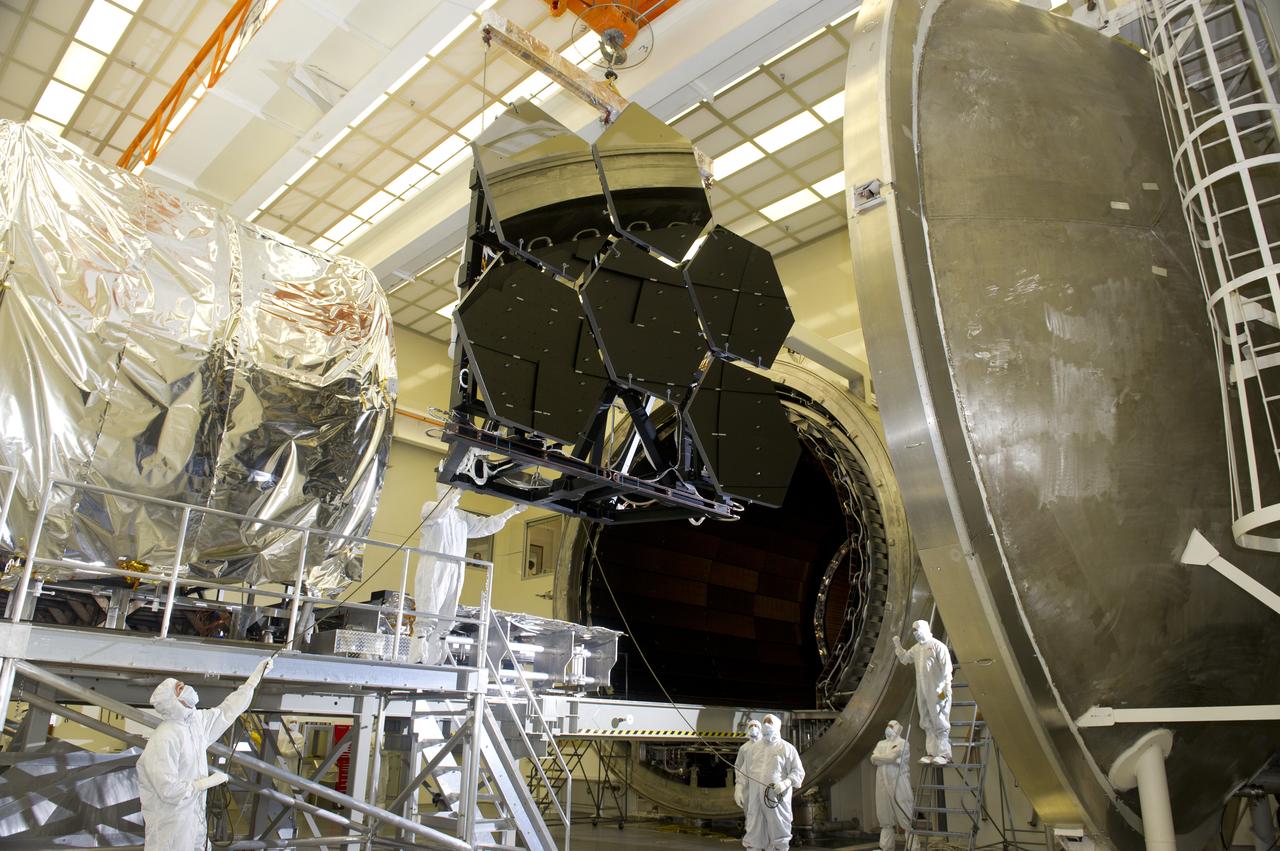

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
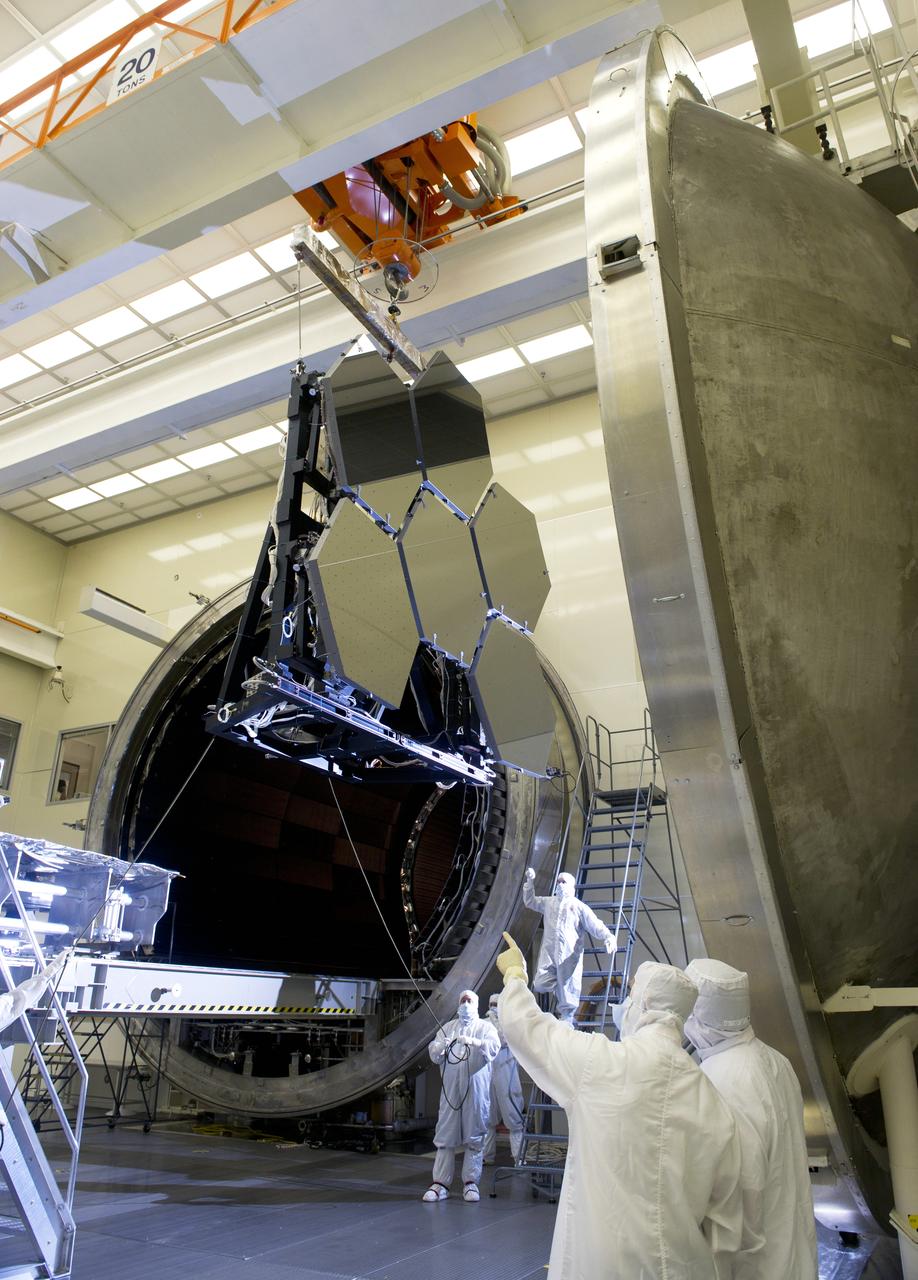

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
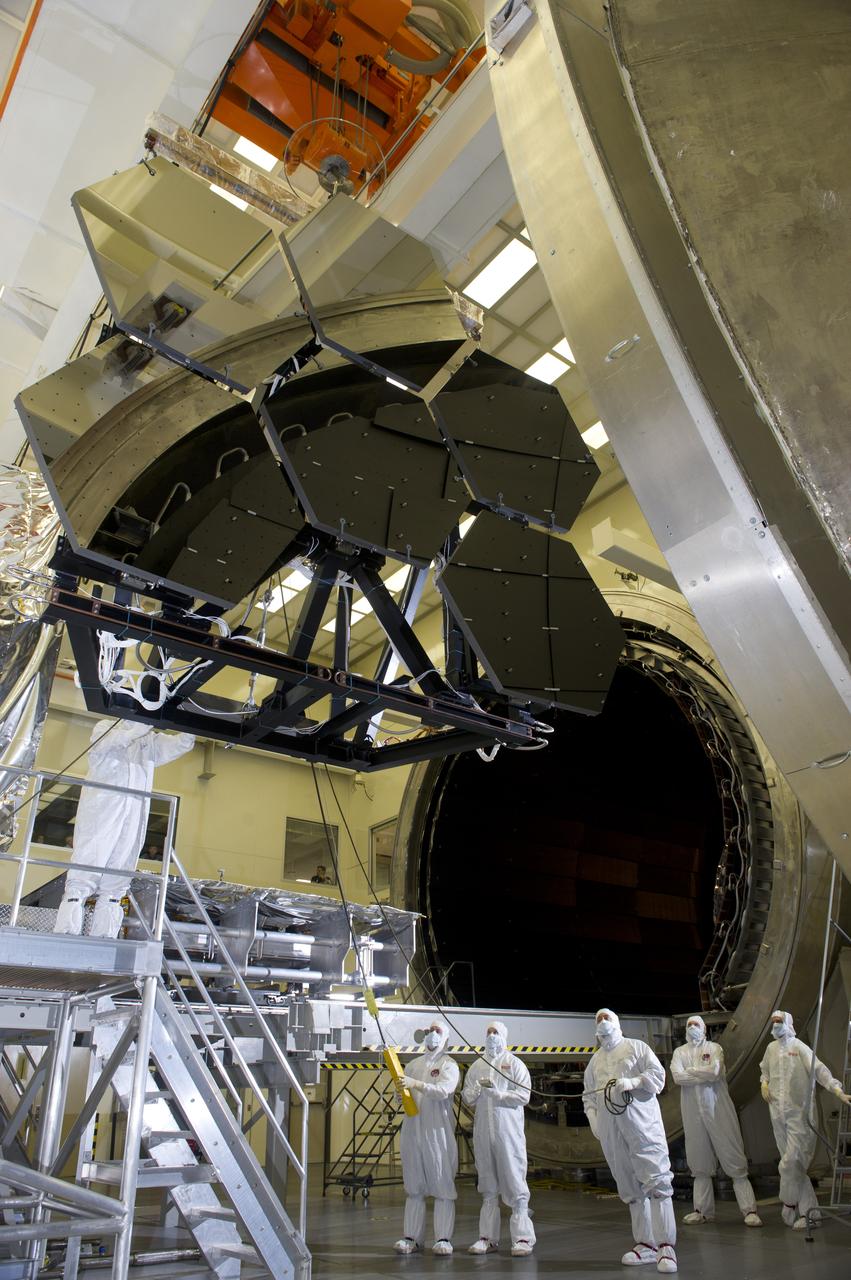

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
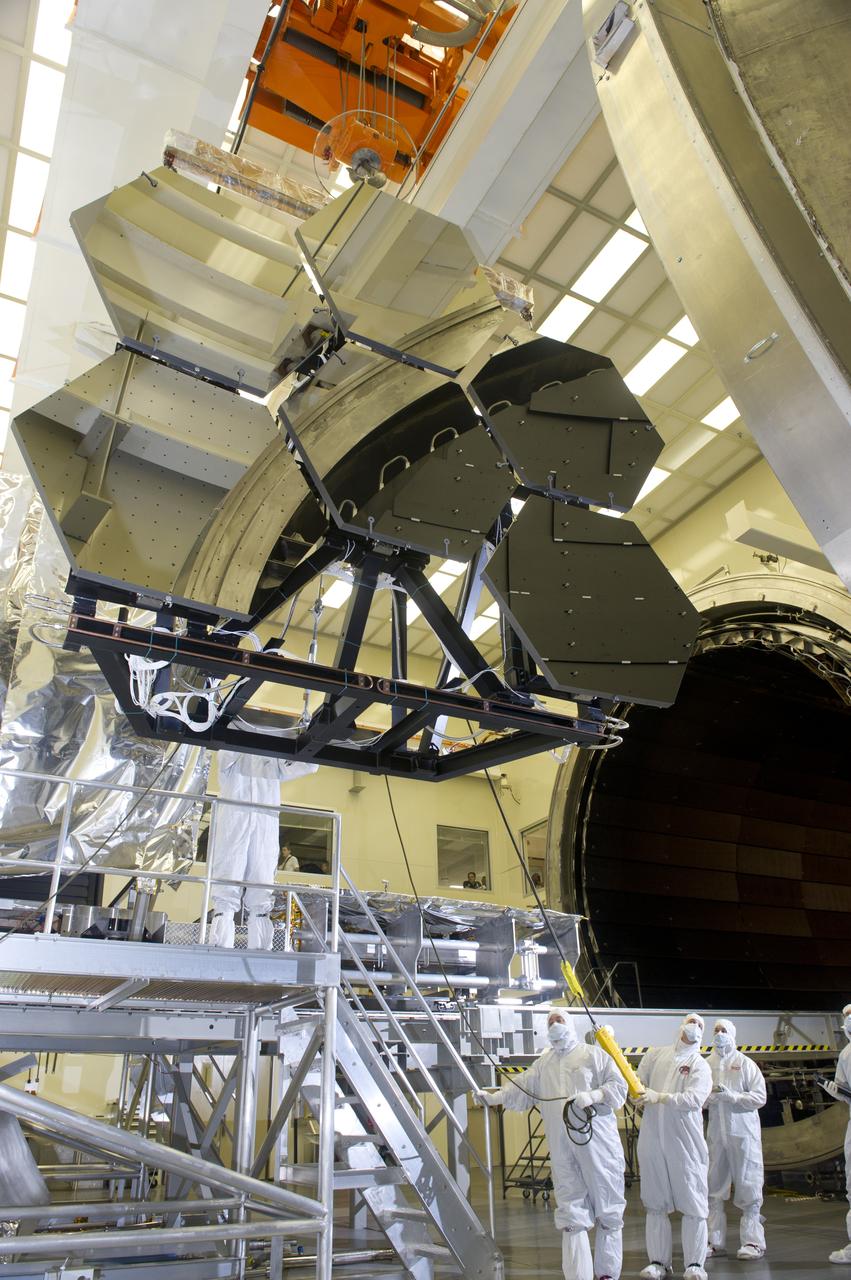

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
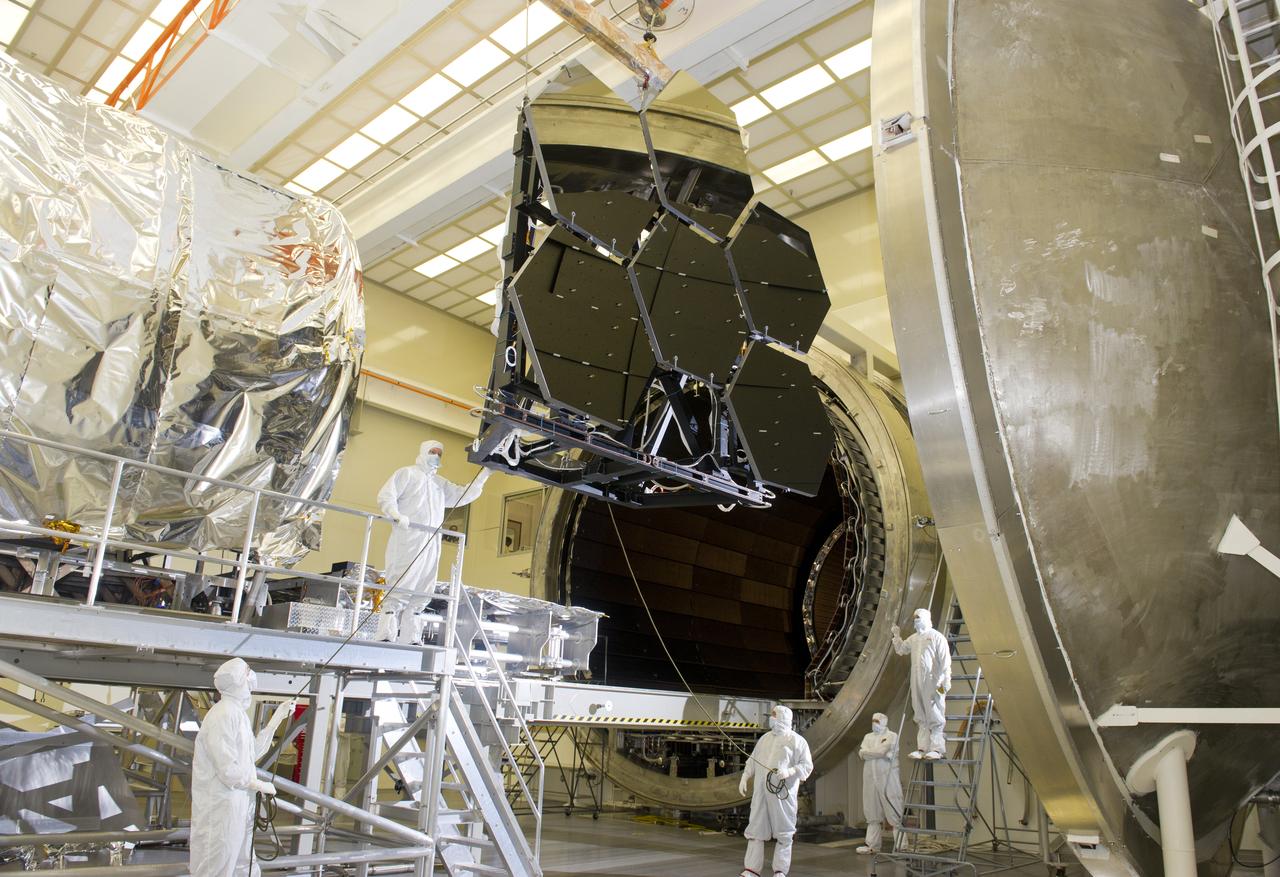

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
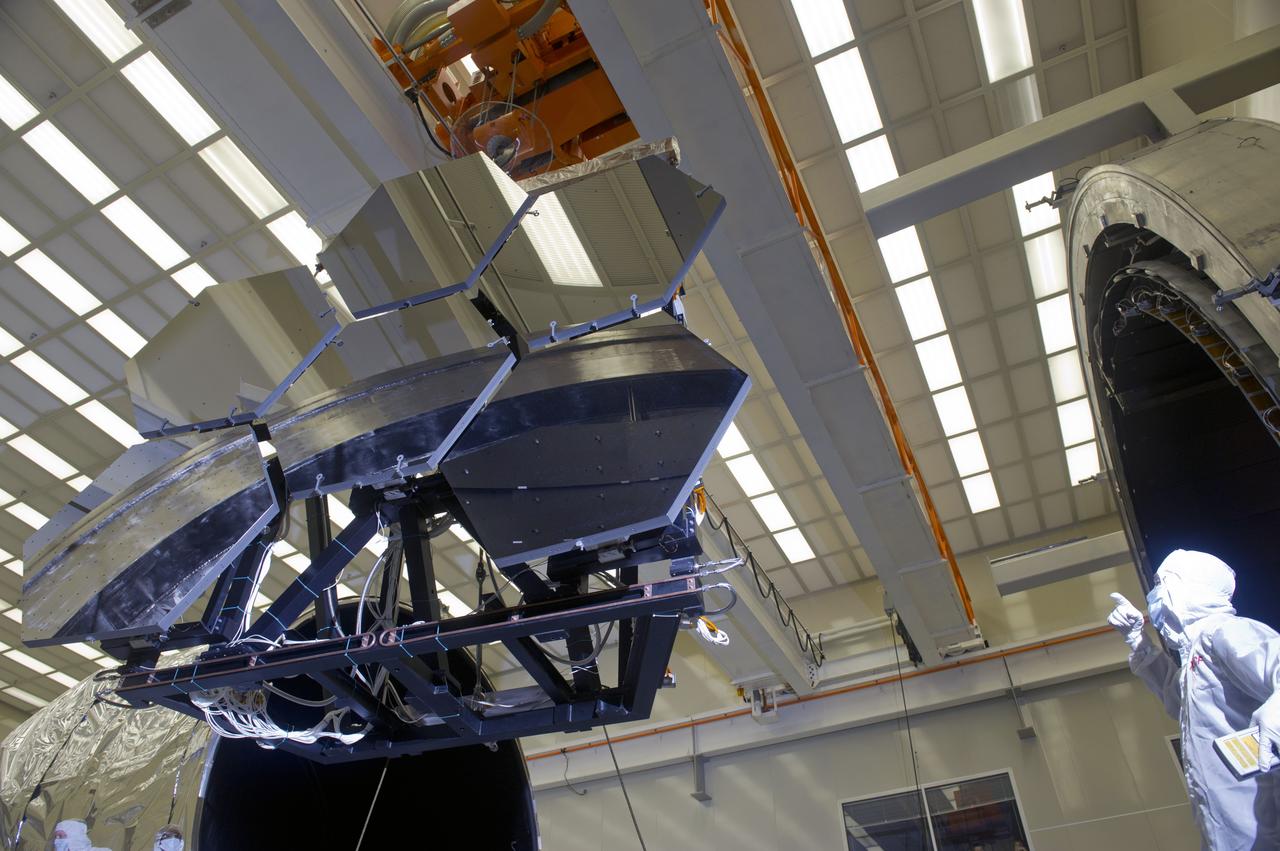

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
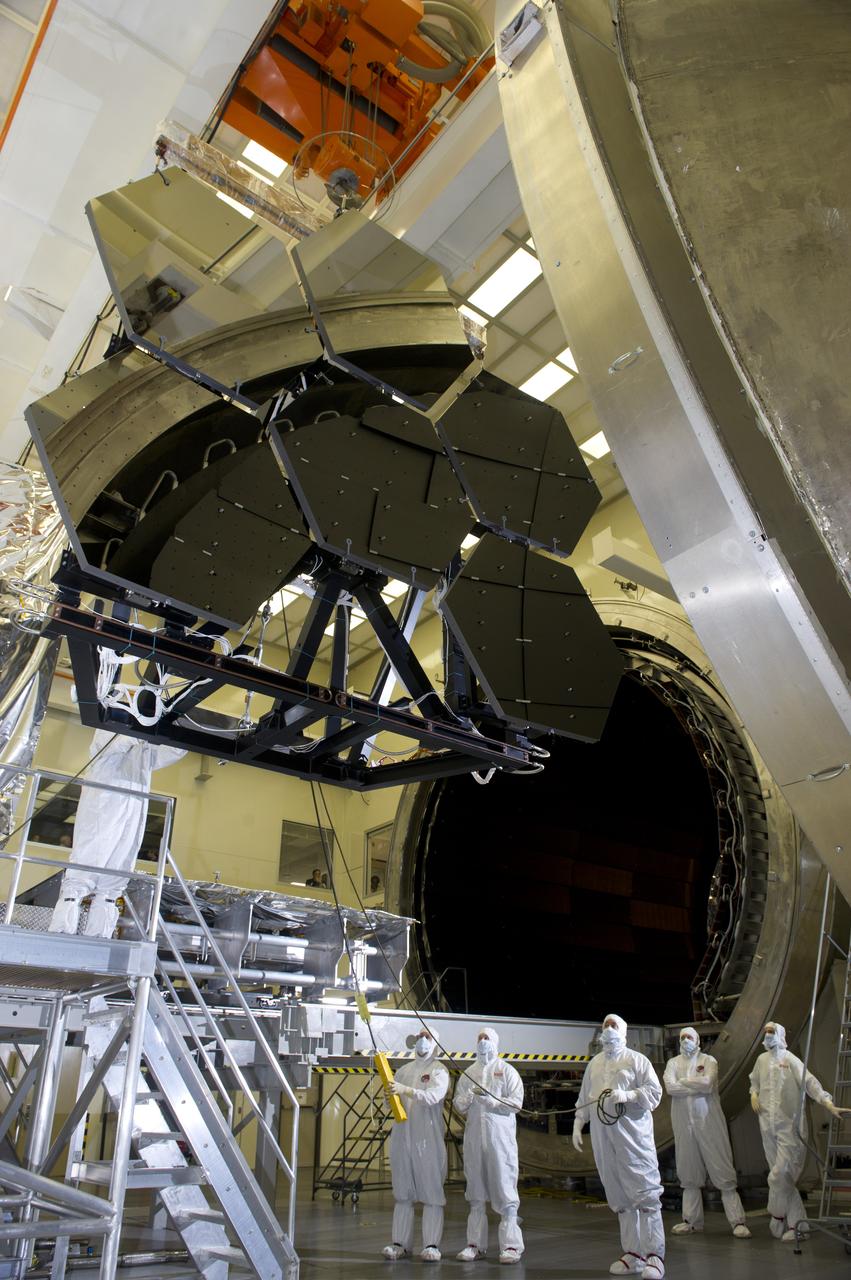

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY

In the summer of the year 1054 AD, Chinese astronomers saw a new "guest star," that appeared six times brighter than Venus. So bright in fact, it could be seen during the daytime for several months. This "guest star" was forgotten about until 700 years later with the advent of telescopes. Astronomers saw a tentacle-like nebula in the place of the vanished star and called it the Crab Nebula. Today we know it as the expanding gaseous remnant from a star that self-detonated as a supernova, briefly shining as brightly as 400 million suns. The explosion took place 6,500 light-years away. If the blast had instead happened 50 light-years away it would have irradiated Earth, wiping out most life forms. In the late 1960s astronomers discovered the crushed heart of the doomed star, an ultra-dense neutron star that is a dynamo of intense magnetic field and radiation energizing the nebula. Astronomers therefore need to study the Crab Nebula across a broad range of electromagnetic radiation, from X-rays to radio waves. This image combines data from five different telescopes: the VLA (radio) in red; Spitzer Space Telescope (infrared) in yellow; Hubble Space Telescope (visible) in green; XMM-Newton (ultraviolet) in blue; and Chandra X-ray Observatory (X-ray) in purple. More images and an animation are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21474
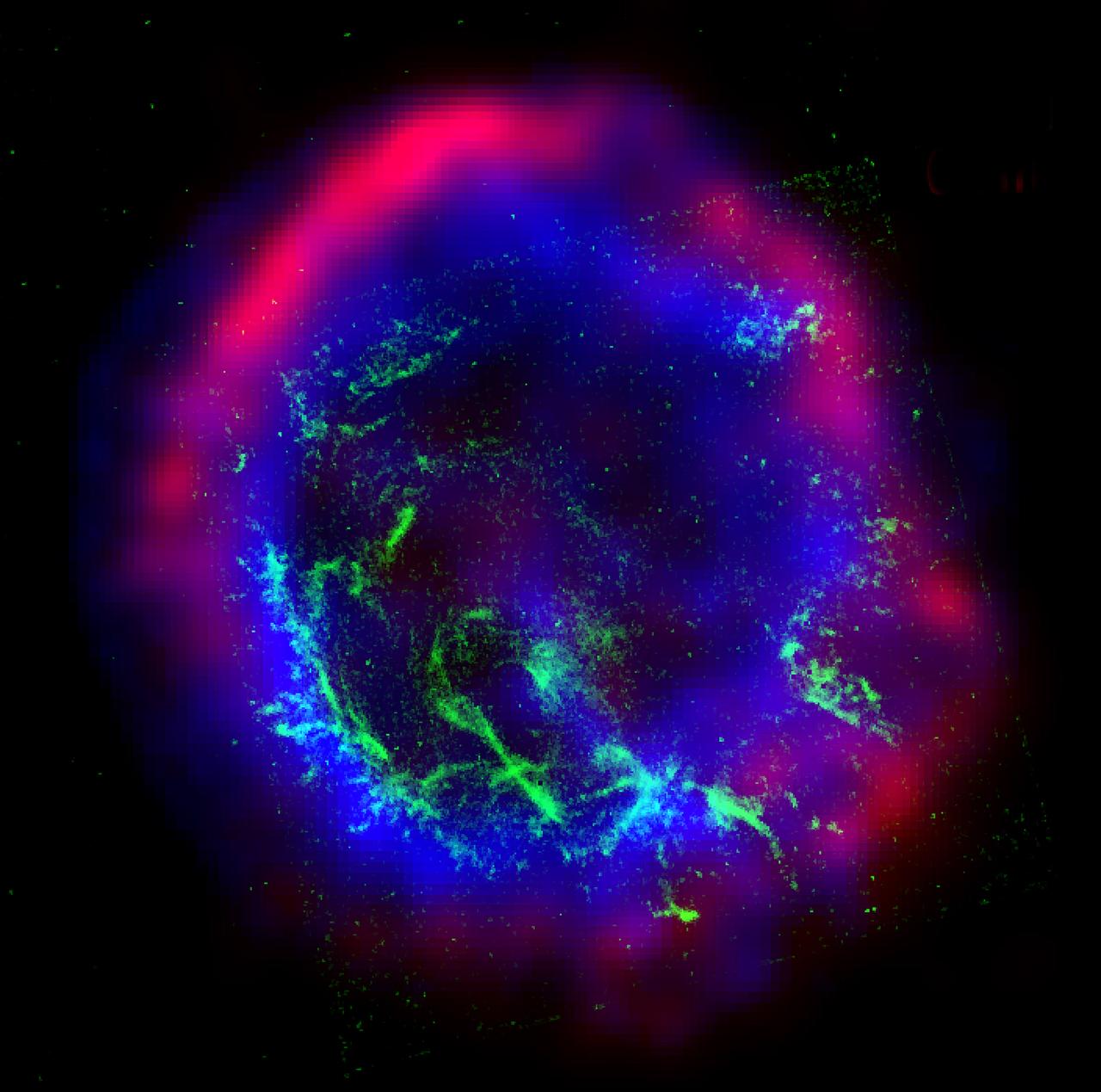
This image is a color composite of the supernova remnant E0102-72: x-ray (blue), optical (green), and radio (red). E0102-72 is the remnant of a star that exploded in a nearby galaxy known as the Small Magellanic Cloud. The star exploded outward at speeds in excess of 20 million kilometers per hour (12 million mph) and collided with surrounding gas. This collision produced two shock waves, or cosmic sonic booms, one traveling outward, and the other rebounding back into the material ejected by the explosion. The radio image, shown in red, was made using the Australia Telescope Compact Array. The radio waves are due to extremely high-energy electrons spiraling around magnetic field lines in the gas and trace the outward moving shock wave. The Chandra X-ray Observatory image, shown in blue, shows gas that has been heated to millions of degrees by the rebounding, or reverse shock wave. The x-ray data show that this gas is rich in oxygen and neon. These elements were created by nuclear reactions inside the star and hurled into space by the supernova. The Hubble Space Telescope optical image, shown in green, shows dense clumps of oxygen gas that have "cooled" to about 30,000 degrees. Photo Credit: X-ray (NASA/CXC/SAO); optical (NASA/HST): radio: (ACTA)
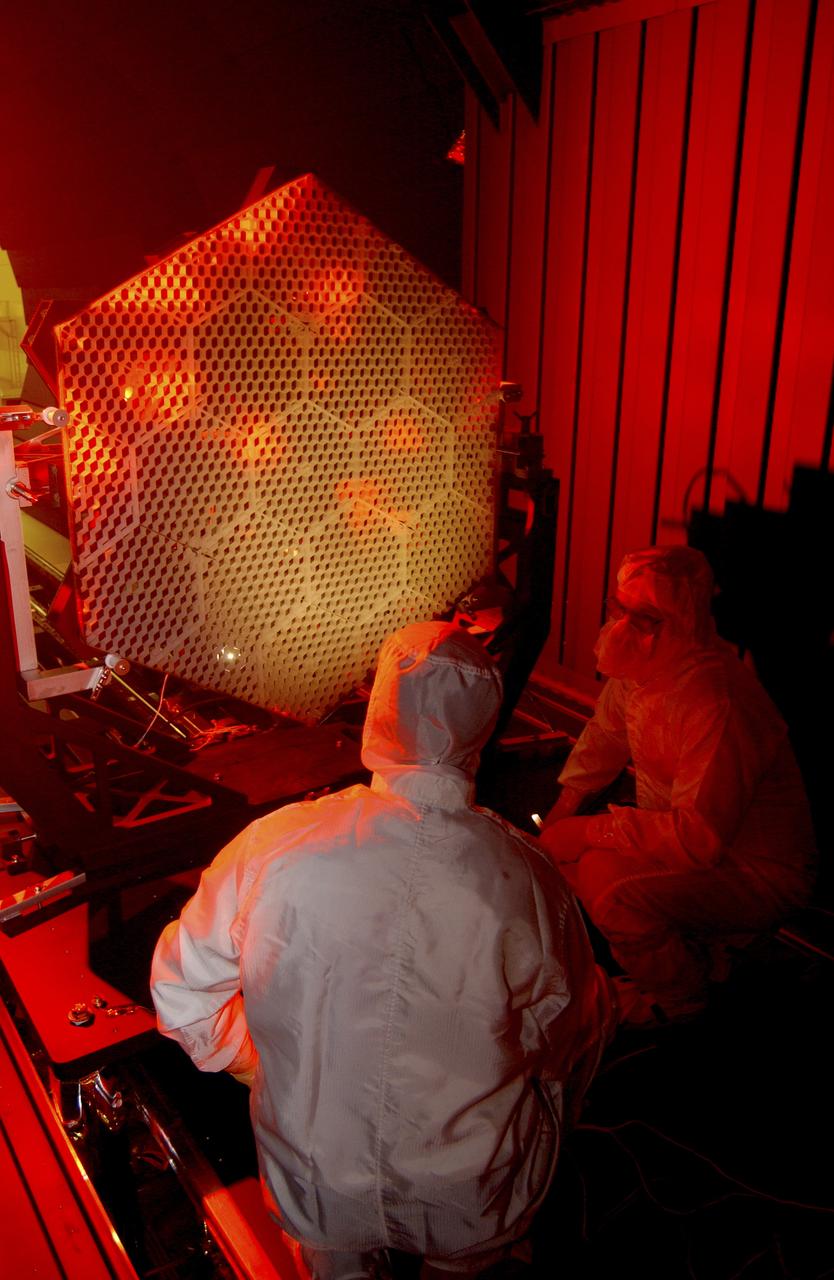

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, one of many segments of the mirror assembly is being set up inside the 24-ft vacuum chamber where it will undergo x-ray calibration tests. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
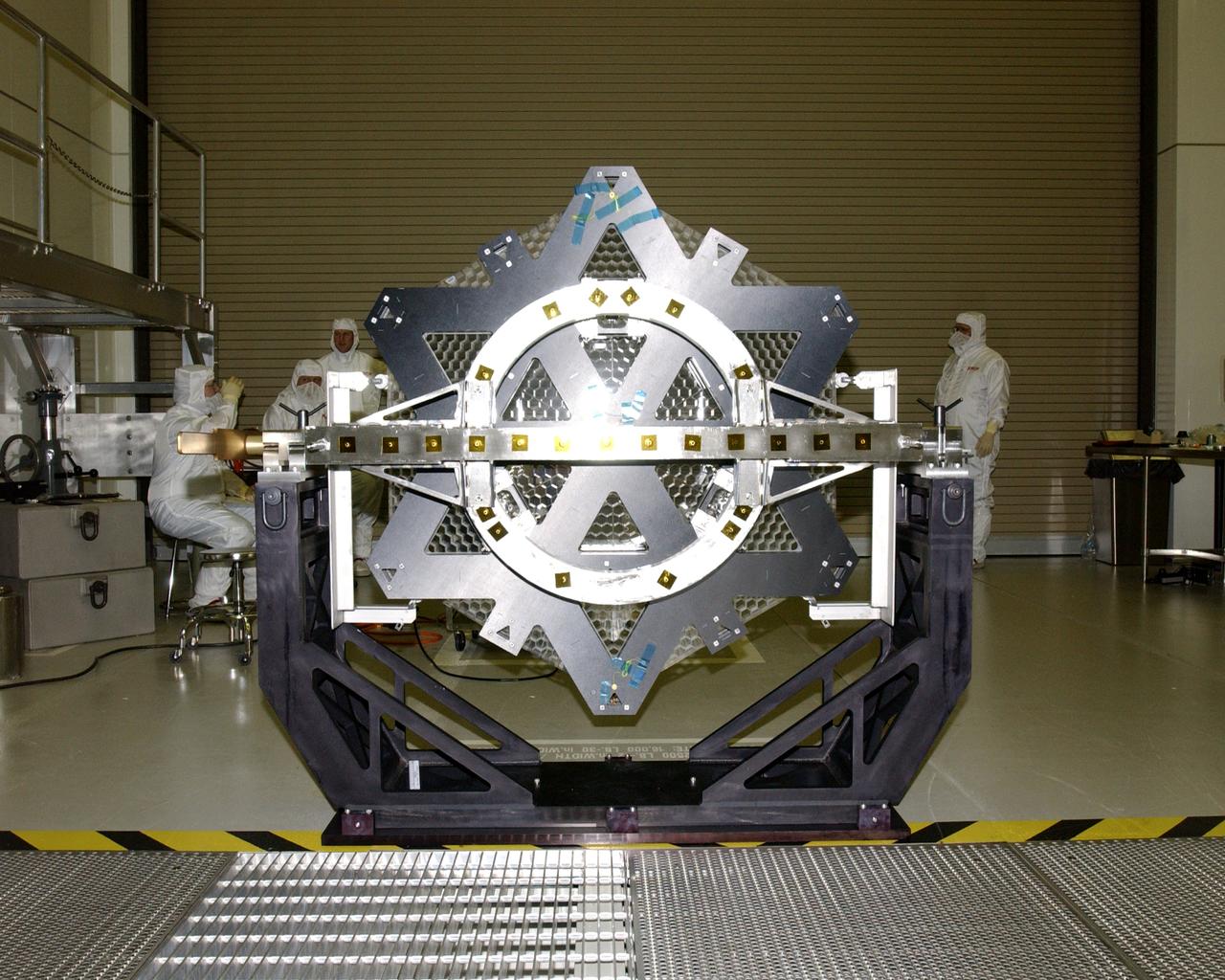
This photo (rear view) is of one of many segments of the Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
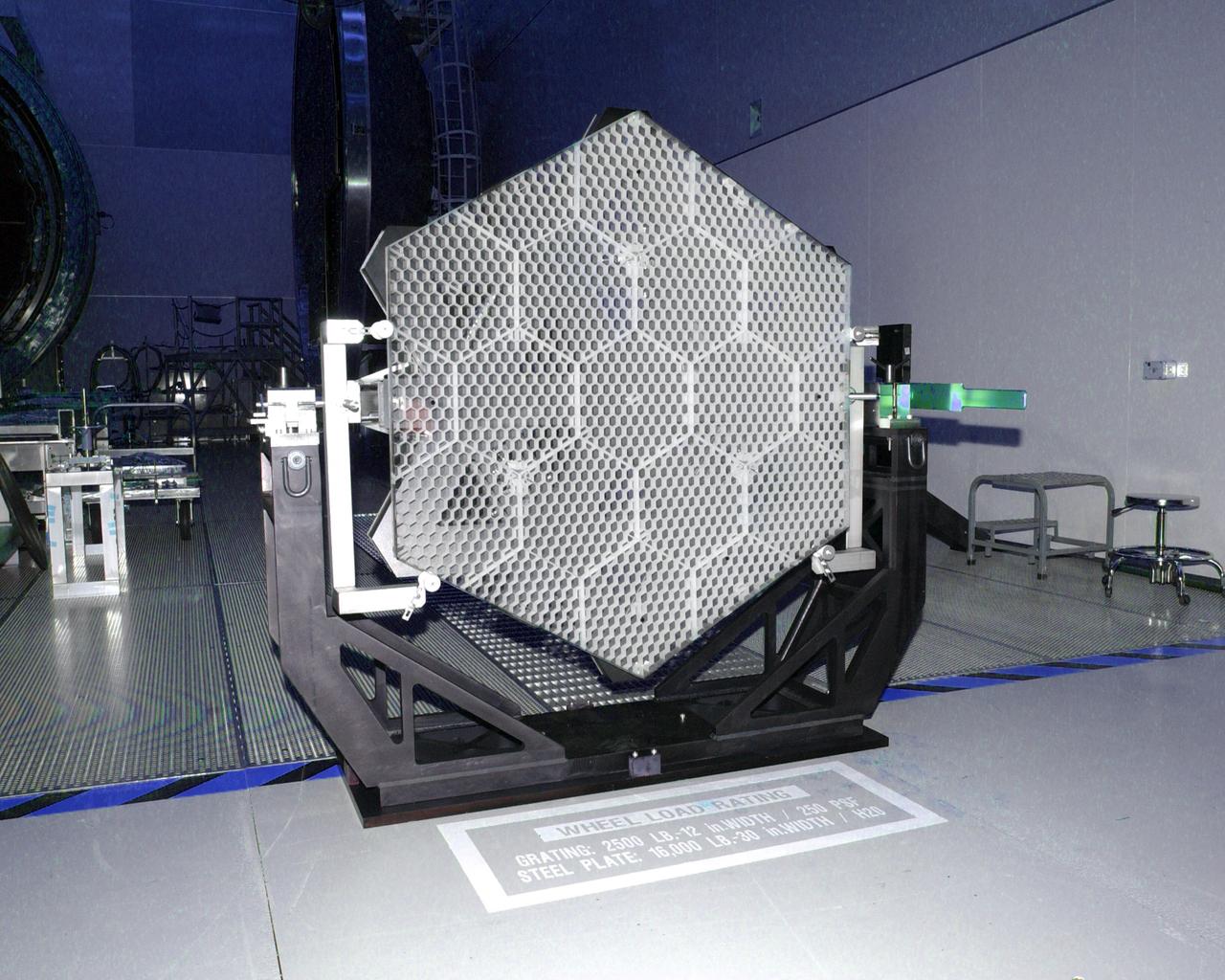
This photo (a frontal view) is of one of many segments of the Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
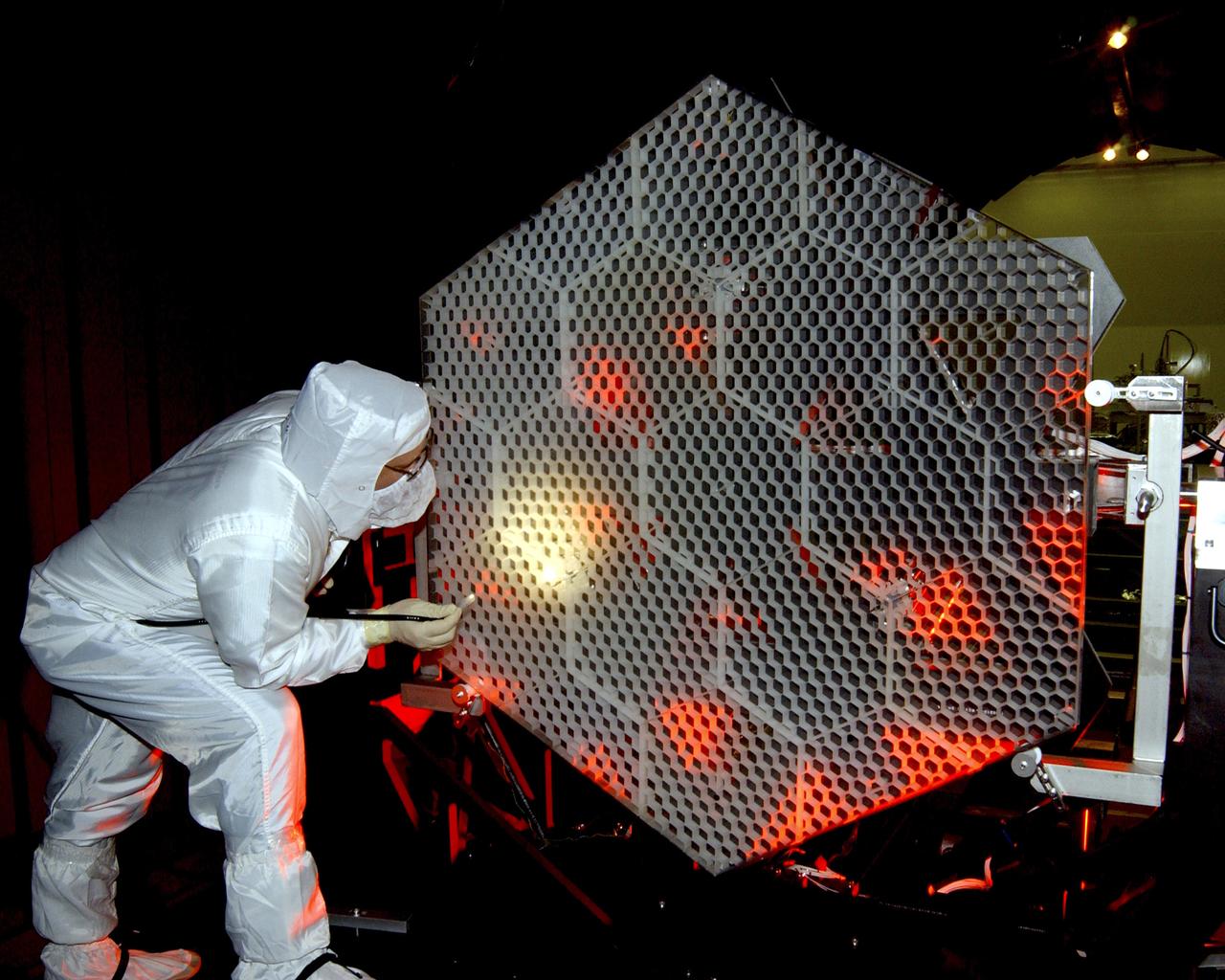

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, an MSFC employee is inspecting one of many segments of the mirror assembly for flaws. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
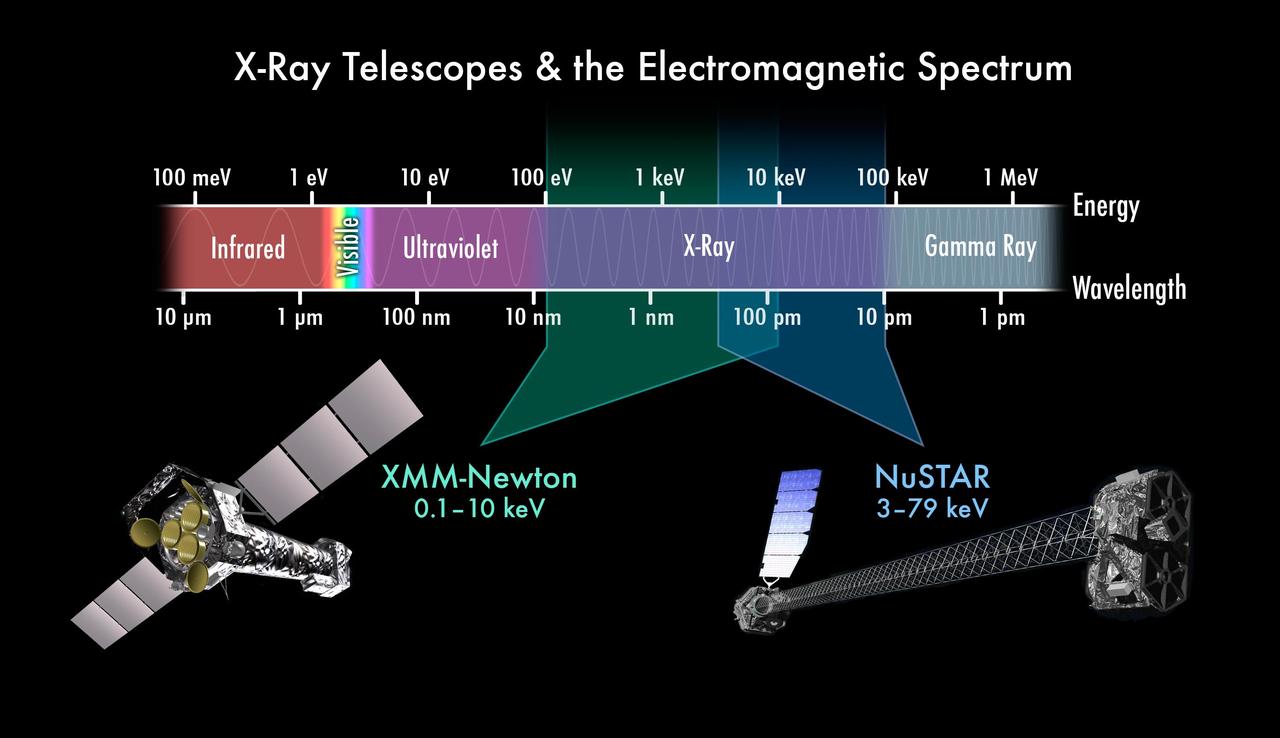
This chart depicts the electromagnetic spectrum, highlighting the X-ray portion. NASA NuSTAR and ESA XMM-Newton telescope complement each other by seeing different colors of X-ray light.
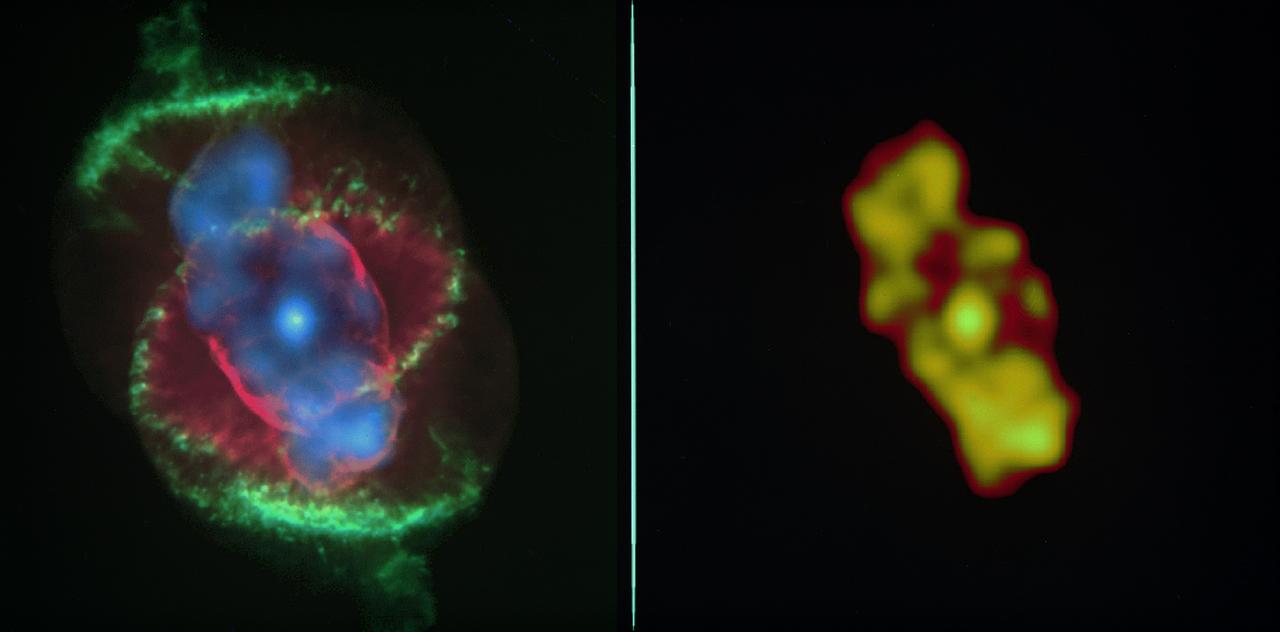
Left image: The x-ray data from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) has revealed a bright central star surrounded by a cloud of multimillion-degree gas in the planetary nebula known as the Cat's Eye. This CXO image, where the intensity of the x-ray emission is correlated to the brightness of the orange coloring, captures the expulsion of material from a star that is expected to collapse into a white dwarf in a few million years. The intensity of x-rays from the central star was unexpected, and it is the first time astronomers have seen such x-ray emission from the central star of a planetary nebula. Right image: An image of Cat's Eye taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). By comparing the CXO data with that from the HST, researchers are able to see where the hotter, x-ray emitting gas appears in relation to the cooler material seen in optical wavelengths by the HST. The CXO team found that the chemical abundance in the region of hot gas (its x-ray intensity is shown in purple) was not like those in the wind from the central star and different from the outer cooler material (the red and green structures.) Although still incredibly energetic and hot enough to radiate x-rays, CXO shows the hot gas to be somewhat cooler than scientists would have expected for such a system. CXO image credit: (NASA/UIUC/Y. Chu et al.) HST image credit: (NASA/HST)
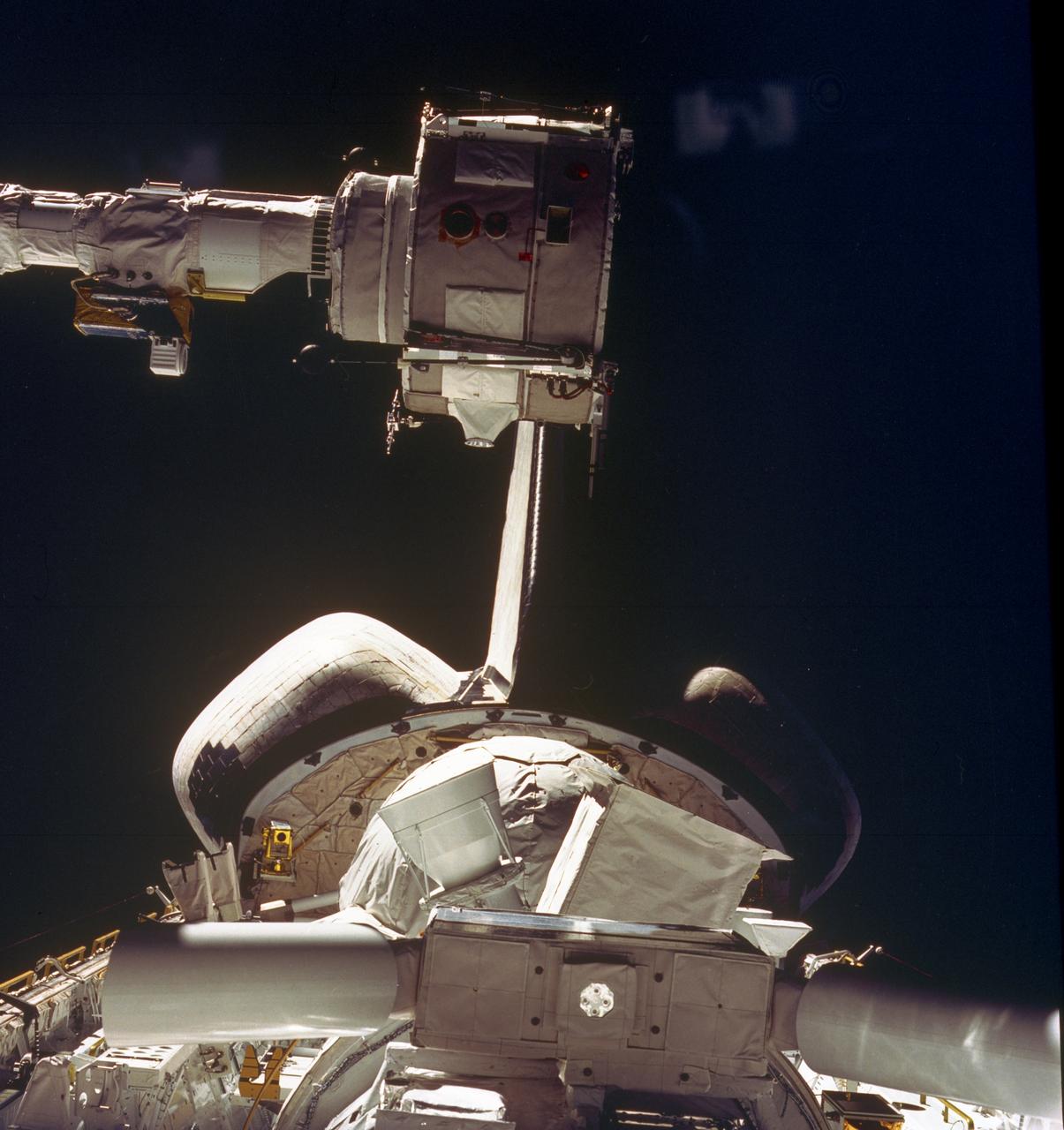

This STS-51F mission onboard Photograph shows some of the Spacelab-2 instruments in the cargo bay of the Orbiter Challenger. The Plasma Diagnostics Package (PDP). shown at the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), used instruments on a subsatellite to study natural plasma processes, orbiter-induced plasma processes, and beam plasma physics. Fourteen instruments were mounted on the PDP for measurements of various plasma characteristics. The X-ray Telescope (XRT), is at the front. The goal of this investigation was to image and examine the X-ray emissions from clusters of galaxies in order to study the mechanisms that cause high-temperature emissions and to determine the weight of galactic clusters. The Small Helium-Cooled Infrared Telescope (IRT) is at the right behind the XRT. The objective of this investigation was to measure and map diffused and discrete infrared astronomical sources while evaluating the Space Shuttle as a platform for infrared astronomy. At the same time, a new large superfluid helium dewar system for cooling the telescope was evaluated. The egg-shaped Cosmic Ray Nuclei experiment (CRNE) is shown at the rear. This investigation was to study the composition of high-energy cosmic rays by using a large instrument exposed to space for a considerable period of time. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on July 29, 1985.
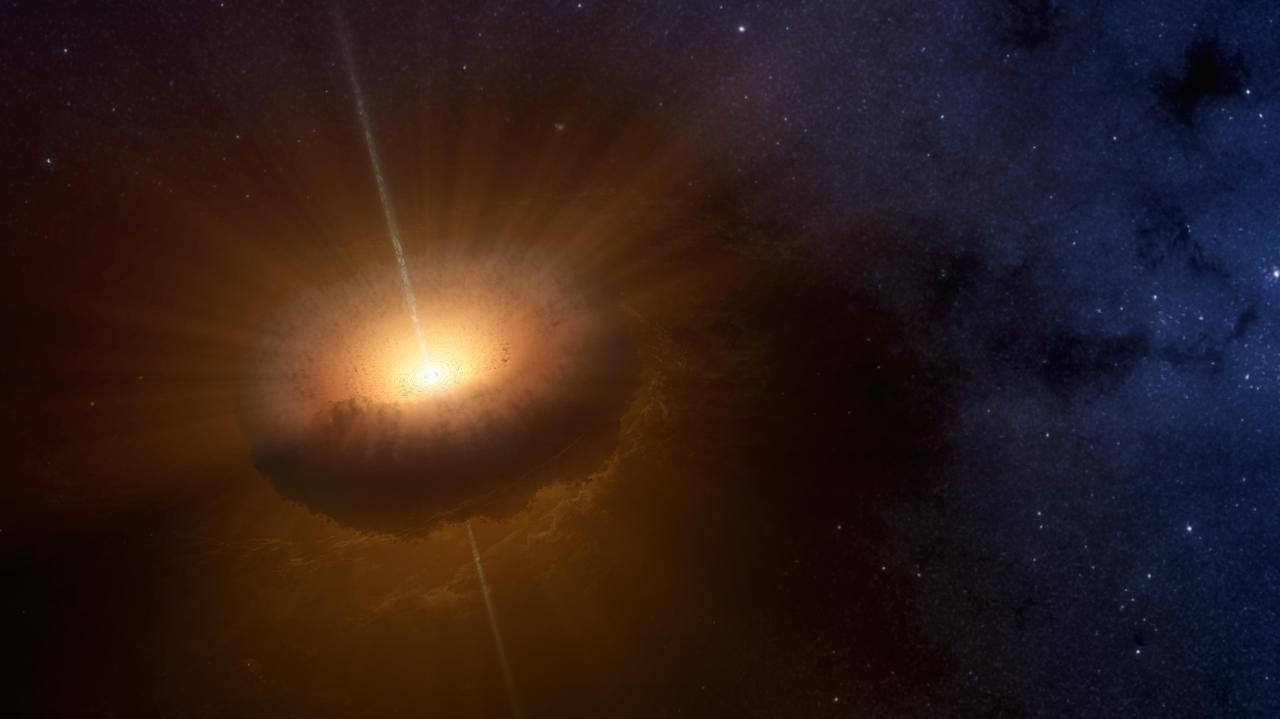

This artist's concept shows an unusual celestial object called CX330 was first detected as a source of X-ray light in 2009 by NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory while it was surveying the bulge in the central region of the Milky Way. A 2016 study in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society found that CX330 is the most isolated young star that has been discovered. Researchers compared NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) data from 2010 with NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope data from 2007 to come to this conclusion. CX330 is not near any star-forming region. As of the most recent observation, which was August 2015, this object was outbursting, meaning it was launching "jets" of material that slam into the gas and dust around it. Astronomers plan to continue studying the object, including with future telescopes that could view CX330 in other wavelengths of light. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20700
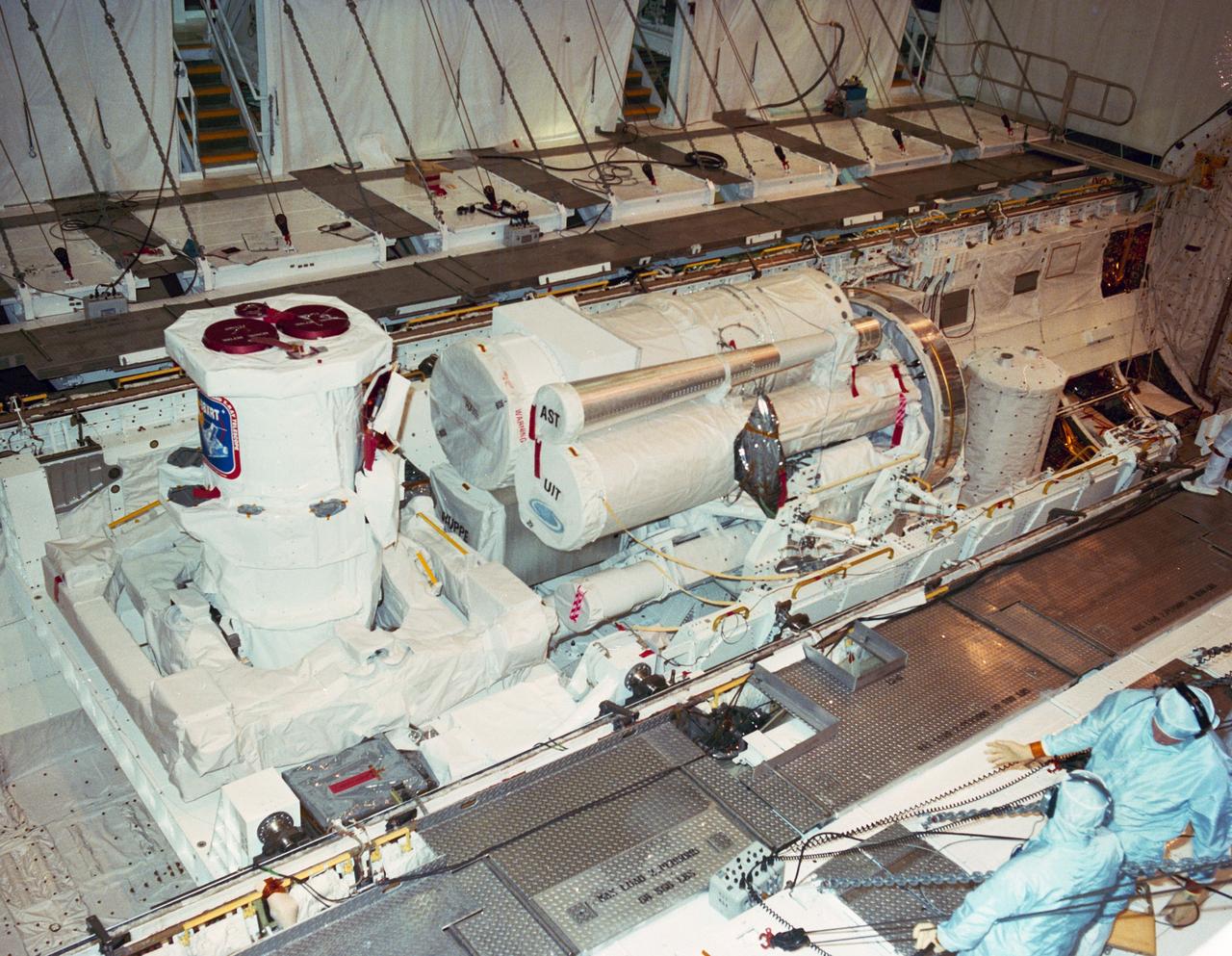
STS-35 Astronomy Laboratory 1 (ASTRO-1) is installed in Columbia's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102's, payload bay (PLB) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF). On the left, in the aft PLB is the Broad Band X Ray Telescope (BBXRT) mounted on the two axis pointing system (TAPS). In the center, the three ultraviolet telescopes - Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE), the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), and the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) - are mounted on the instrument pointing system (IPS) and are in stowed position. At the far right is the Spacelab Pallet System (SPS) igloo. View provided by KSC with alternate number KSSC-90PC-421.

This photograph was taken during the integration of the Astro-1 mission payloads at the Kennedy Space Center on March 20, 1990, showing the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT) at the left, as three telescopes for the Astro-1 Observatory are settled into the Orbiter Columbia payload bay. Above Earth's atmospheric interference, Astro-1 would make precise measurements of objects such as planets, stars, and galaxies in relatively small fields of view and would observe and measure ultraviolet radiation from celestial objects. The Astro-1 used a Spacelab pallet system with an instrument pointing system and a cruciform structure for bearing the three ultraviolet instruments mounted in a parallel configuration. The three instruments were: The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), which was designed to obtain far-ultraviolet spectroscopic data from white dwarfs, emission nebulae, active galaxies, and quasars; the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE) which was to study polarized ultraviolet light from magnetic white dwarfs, binary stars, reflection nebulae, and active galaxies; and the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), which was to record photographic images in ultraviolet light of galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. The star trackers that supported the instrument pointing system, were also mounted on the cruciform. Also in the payload bay was the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT), which was designed to obtain high-resolution x-ray spectra from stellar corona, x-ray binary stars, active galactic nuclei, and galaxy clusters. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the Astro-1 observatory was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35) on December 2, 1990.

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures the activity of WUPPE (Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment) data review at the Science Operations Area during the mission. This image shows mission activities at the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT) Work Station in the Science Operations Area (SOA).
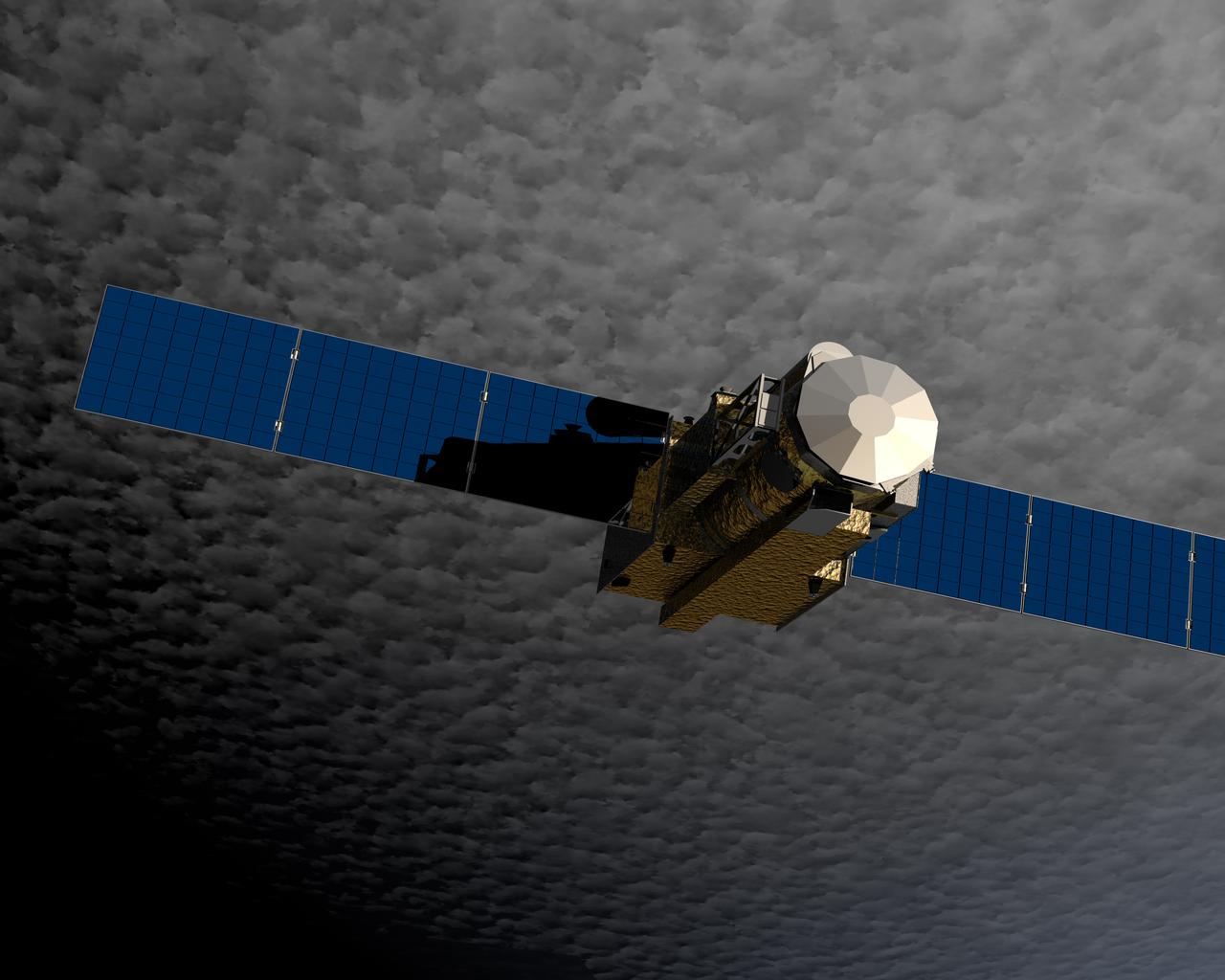

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). Provided by the Multimedia support group at MSFC, this rendering illustrates the Solar-B Spacecraft in earth orbit with its solar panels completely extended.

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). This image of a sunspot, taken by Hinode, is a prime example of what the spacecraft can offer.
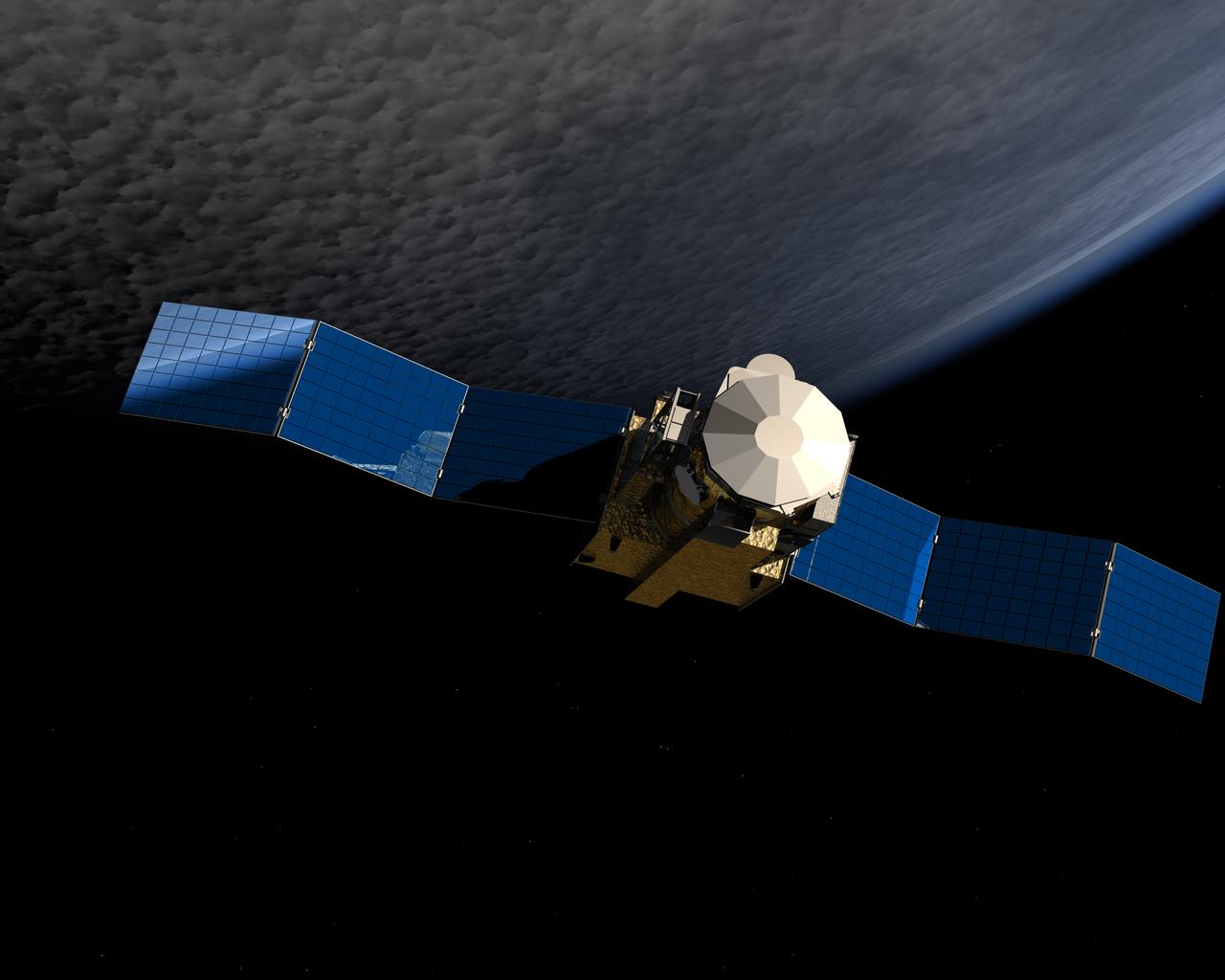

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). Provided by the Multimedia support group at MSFC, this rendering illustrates the Solar-B Spacecraft in earth orbit with its solar panels partially extended.
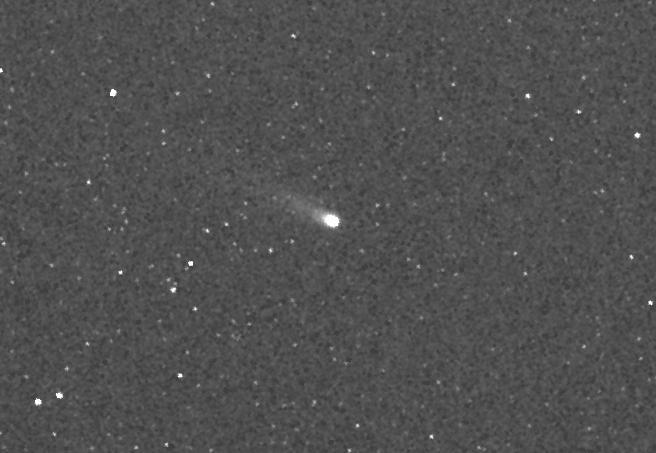

An optical color image of galaxies is seen here overlaid with X-ray data magenta from NASA Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array NuSTAR. Both magenta blobs show X-rays from massive black holes buried at the hearts of galaxies.

This is a composite image of N49, the brightest supernova remnant in optical light in the Large Magellanic Cloud; the image combines data from the Chandra X-ray Telescope blue and NASA Spitzer Space Telescope red.
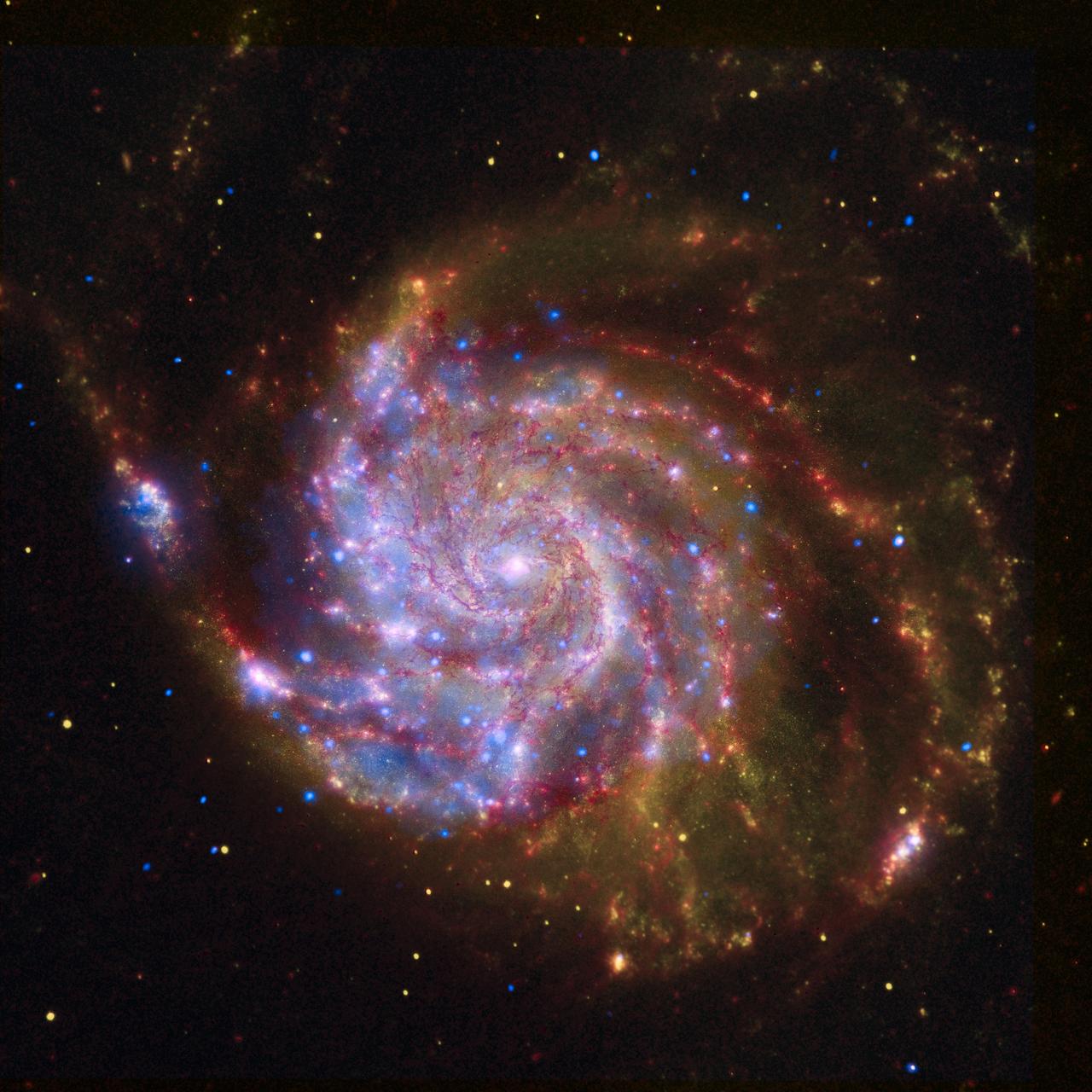

NASA Great Observatories continue Galileo legacy with stunning images and breakthrough science from the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory.
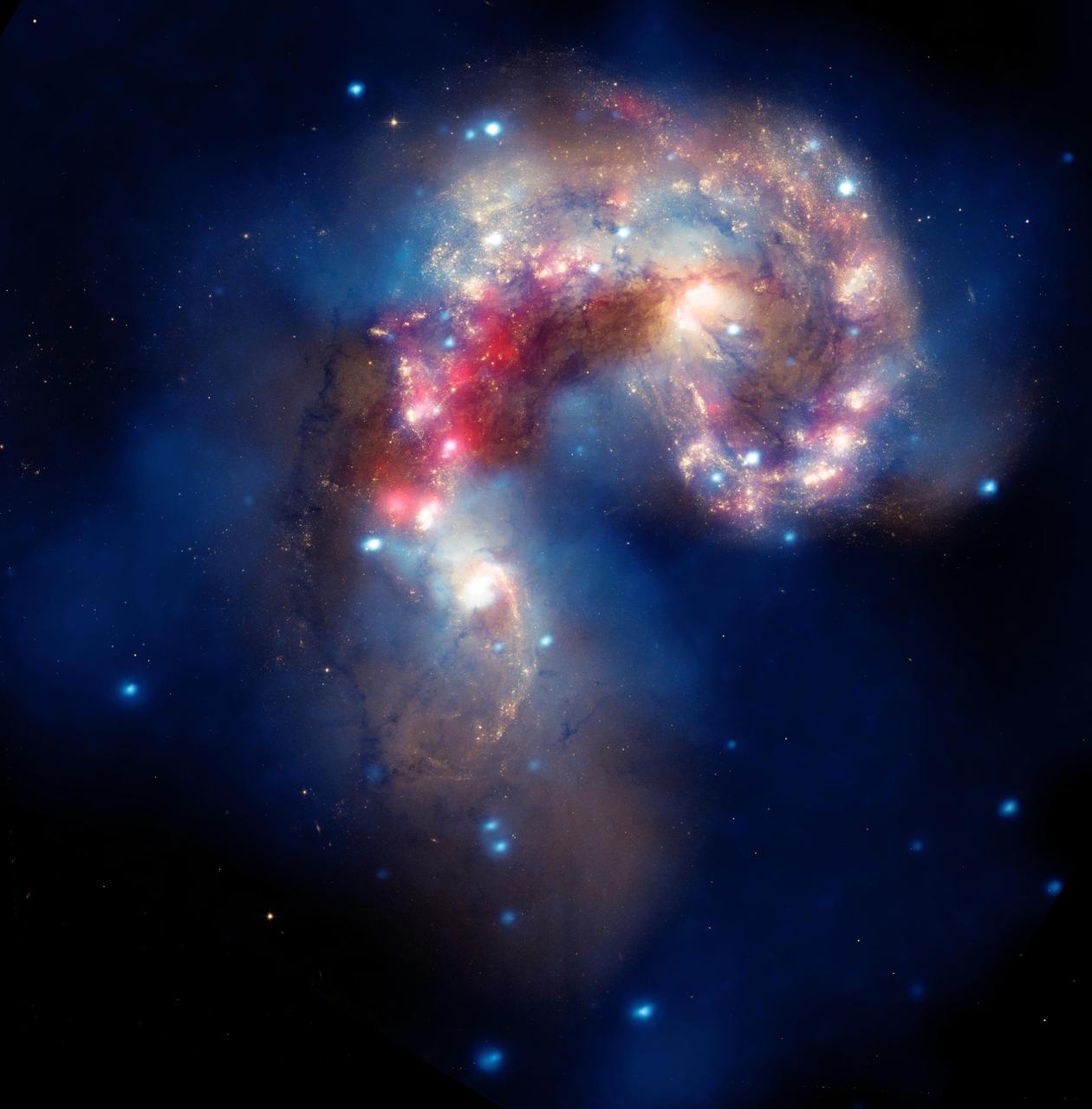

This image of two tangled galaxies has been released by NASA Great Observatories. The Antennae galaxies are shown in this composite image from the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the Hubble Space Telescope, and the Spitzer Space Telescope.
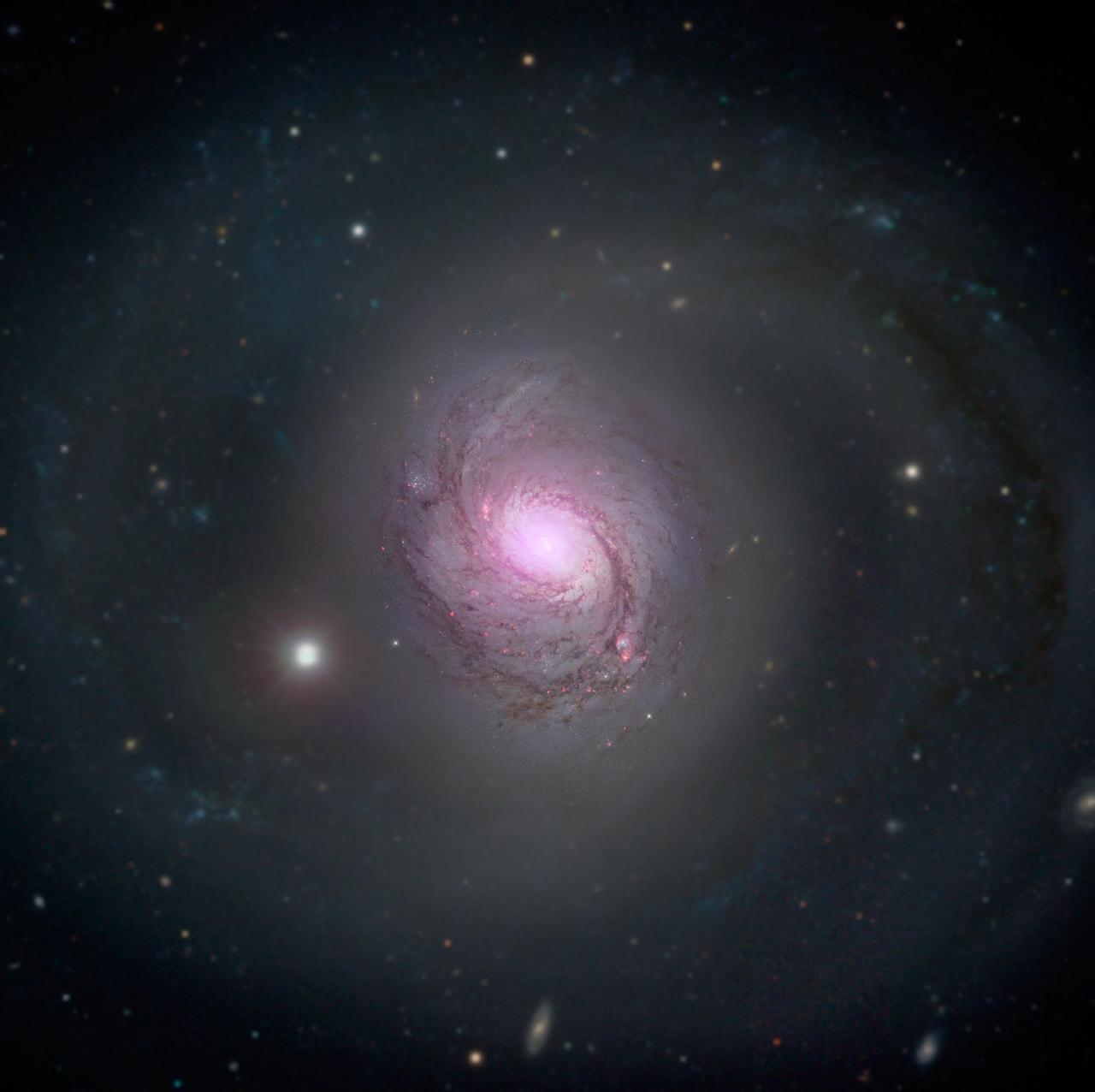

Galaxy NGC 1068 is shown in visible light and X-rays in this composite image. High-energy X-rays (magenta) captured by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, are overlaid on visible-light images from both NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The X-ray light is coming from an active supermassive black hole, also known as a quasar, in the center of the galaxy. This supermassive black hole has been extensively studied due to its relatively close proximity to our galaxy. NGC 1068 is about 47 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus. The supermassive black hole is also one of the most obscured known, blanketed by thick clouds of gas and dust. NuSTAR's high-energy X-ray view is the first to penetrate the walls of this black hole's hidden lair. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20057

In 1986, NASA introduced a Shuttle-borne ultraviolet observatory called Astro. The Astro Observatory was designed to explore the universe by observing and measuring the ultraviolet radiation from celestial objects. Astronomical targets of observation selected for Astro missions included planets, stars, star clusters, galaxies, clusters of galaxies, quasars, remnants of exploded stars (supernovae), clouds of gas and dust (nebulae), and the interstellar medium. Astro-1 used a Spacelab pallet system with an instrument pointing system and a cruciform structure for bearing the three ultraviolet instruments mounted in a parallel configuration. The three instruments were: The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), which was designed to obtain far-ultraviolet spectroscopic data from white dwarfs, emission nebulae, active galaxies, and quasars; the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE) which was to study polarized ultraviolet light from magnetic white dwarfs, binary stars, reflection nebulae, and active galaxies; and the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) which was to record photographic images in ultraviolet light of galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. The star trackers that supported the instrument pointing system were also mounted on the cruciform. Also in the payload bay was the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT), which was designed to obtain high-resolution x-ray spectra from stellar corona, x-ray binary stars, active galactic nuclei, and galaxy clusters. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the Astro-1 observatory was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35) on December 2, 1990.
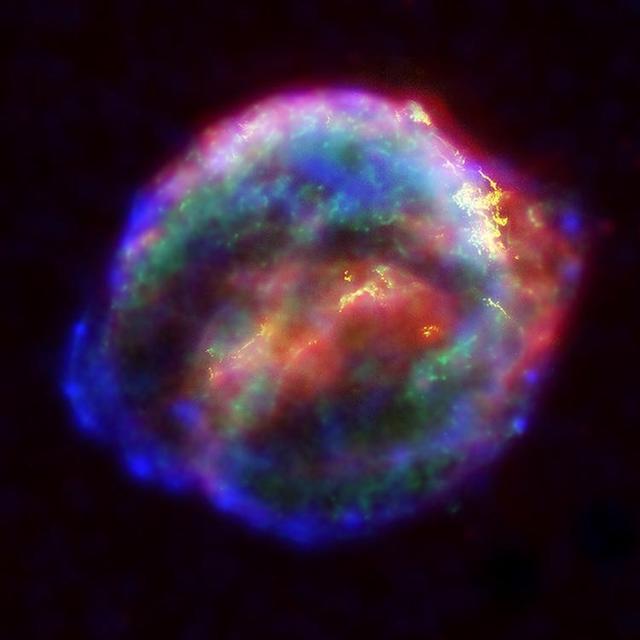
NASA's three Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the SpitzerSpace Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- joined forces to probe theexpanding remains of a supernova, called Kepler's supernova remnant, first seen 400 years ago by sky watchers, including astronomer Johannes Kepler. The combined image unveils a bubble-shaped shroud of gas and dust that is 14light-years wide and is expanding at 4 million miles per hour (2,000 kilometersper second). Observations from each telescope highlight distinct features of thesupernova remnant, a fast-moving shell of iron-rich material from the explodedstar, surrounded by an expanding shock wave that is sweeping up interstellar gasand dust. Each color in this image represents a different region of the electromagneticspectrum, from X-rays to infrared light. These diverse colors are shown in thepanel of photographs below the composite image. The X-ray and infrared datacannot be seen with the human eye. By color-coding those data and combining themwith Hubble's visible-light view, astronomers are presenting a more completepicture of the supernova remnant. Visible-light images from the Hubble telescope (colored yellow) reveal where the supernova shock wave is slamming into the densest regions of surrounding gas.The bright glowing knots are dense clumps from instabilities that form behindthe shock wave. The Hubble data also show thin filaments of gas that look likerippled sheets seen edge-on. These filaments reveal where the shock wave isencountering lower-density, more uniform interstellar material. The Spitzer telescope shows microscopic dust particles (colored red) that havebeen heated by the supernova shock wave. The dust re-radiates the shock wave'senergy as infrared light. The Spitzer data are brightest in the regionssurrounding those seen in detail by the Hubble telescope. The Chandra X-ray data show regions of very hot gas, and extremely high-energyparticles. The hottest gas (higher-energy X-rays, colored blue) is locatedprimarily in the regions directly behind the shock front. These regions alsoshow up in the Hubble observations, and also align with the faint rim of glowingmaterial seen in the Spitzer data. The X-rays from the region on the lower left(colored blue) may be dominated by extremely high-energy electrons that wereproduced by the shock wave and are radiating at radio through X-ray wavelengthsas they spiral in the intensified magnetic field behind the shock front. CoolerX-ray gas (lower-energy X-rays, colored green) resides in a thick interior shelland marks the location of heated material expelled from the exploded star. Kepler's supernova, the last such object seen to explode in our Milky Waygalaxy, resides about 13,000 light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. The Chandra observations were taken in June 2000, the Hubble in August 2003;and the Spitzer in August 2004. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06907
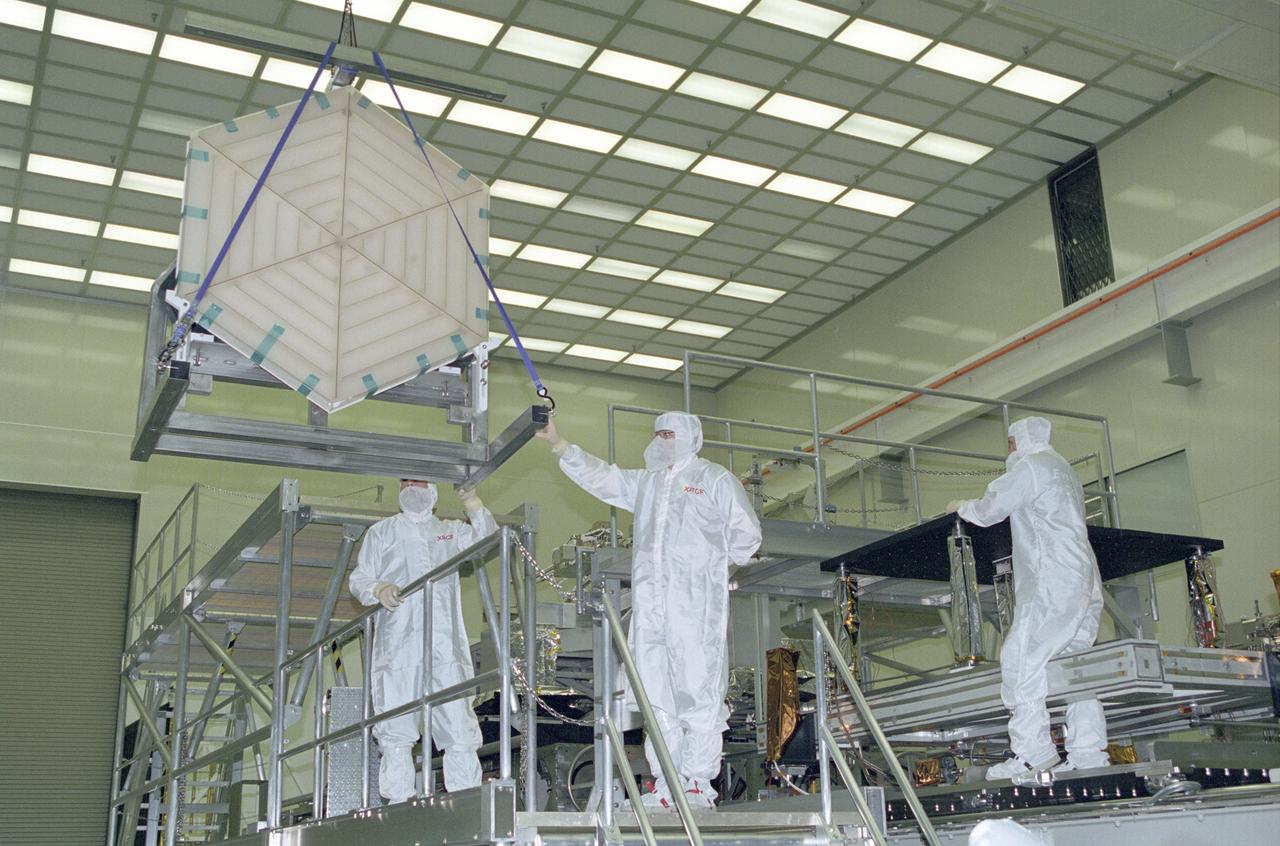

In this photograph, the composite material mirror is tested in the X-Ray Calibration Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The mirror test conducted was to check the ability to accurately model and predict the cryogenic performance of complex mirror systems, and the characterization of cryogenic dampening properties of beryllium. The JWST, a next generation successor to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), was named in honor of James W. Webb, NASA's second administrator, who led NASA in the early days of the fledgling Aerospace Agency. Scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle, the JWST will be able to look deeper into the universe than the HST because of the increased light-collecting power of its larger mirror and the extraordinary sensitivity of its instrument to infrared light.
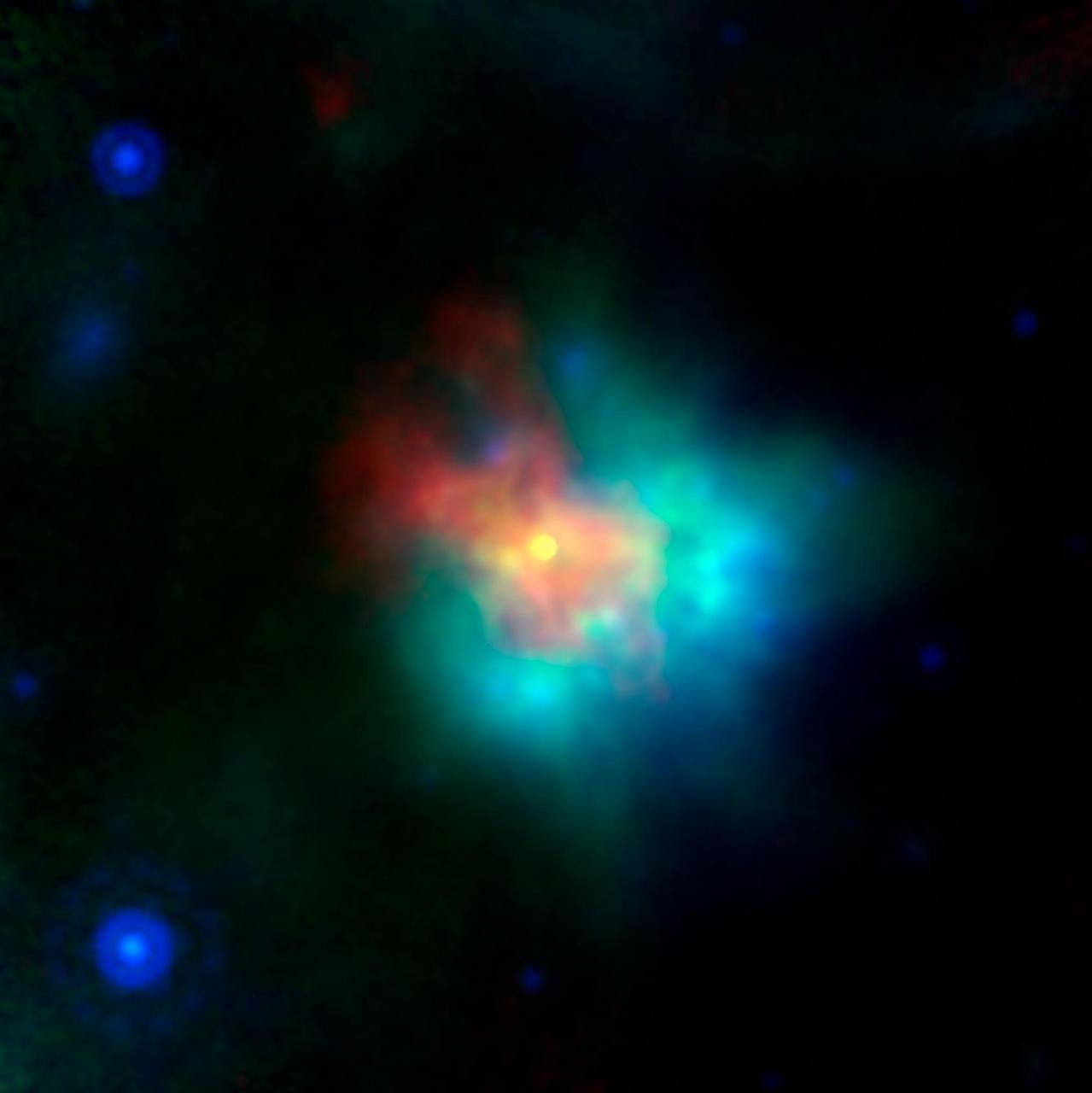

This image of supernova remnant G54.1+0.3 includes radio, infrared and X-ray light. The saturated yellow point at the center of the image indicates strong X-ray source at the center of the supernova remnant. This is an incredibly dense object called a neutron star, which can form as a star runs out of fuel to keep it inflated, and the unsupported material collapses down on to the star's core. G54.1+0.3 contains a special type of neutron star called a pulsar, which emits particularly bright radio and X-ray emissions. The blue and green emissions show the presence of dust, including silica. The red hues correspond to radio data from the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array; green corresponds to 70 µm wavelength infrared light from the European Space Agency's Herschel Space Observatory; blue corresponds to 24 µm wavelength infrared light from the Multiband Imaging Photometer (MIPS) instrument on NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope; yellow corresponds to X-ray data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22569
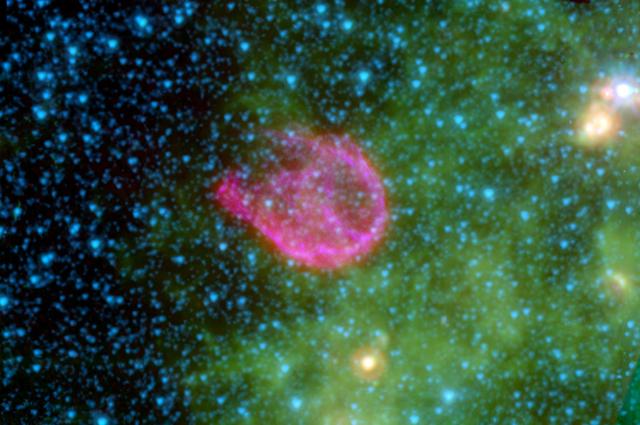

Supernovae are the explosive deaths of the universe most massive stars. This false-color composite from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory shows the remnant of N132D, the wispy pink shell of gas at center.
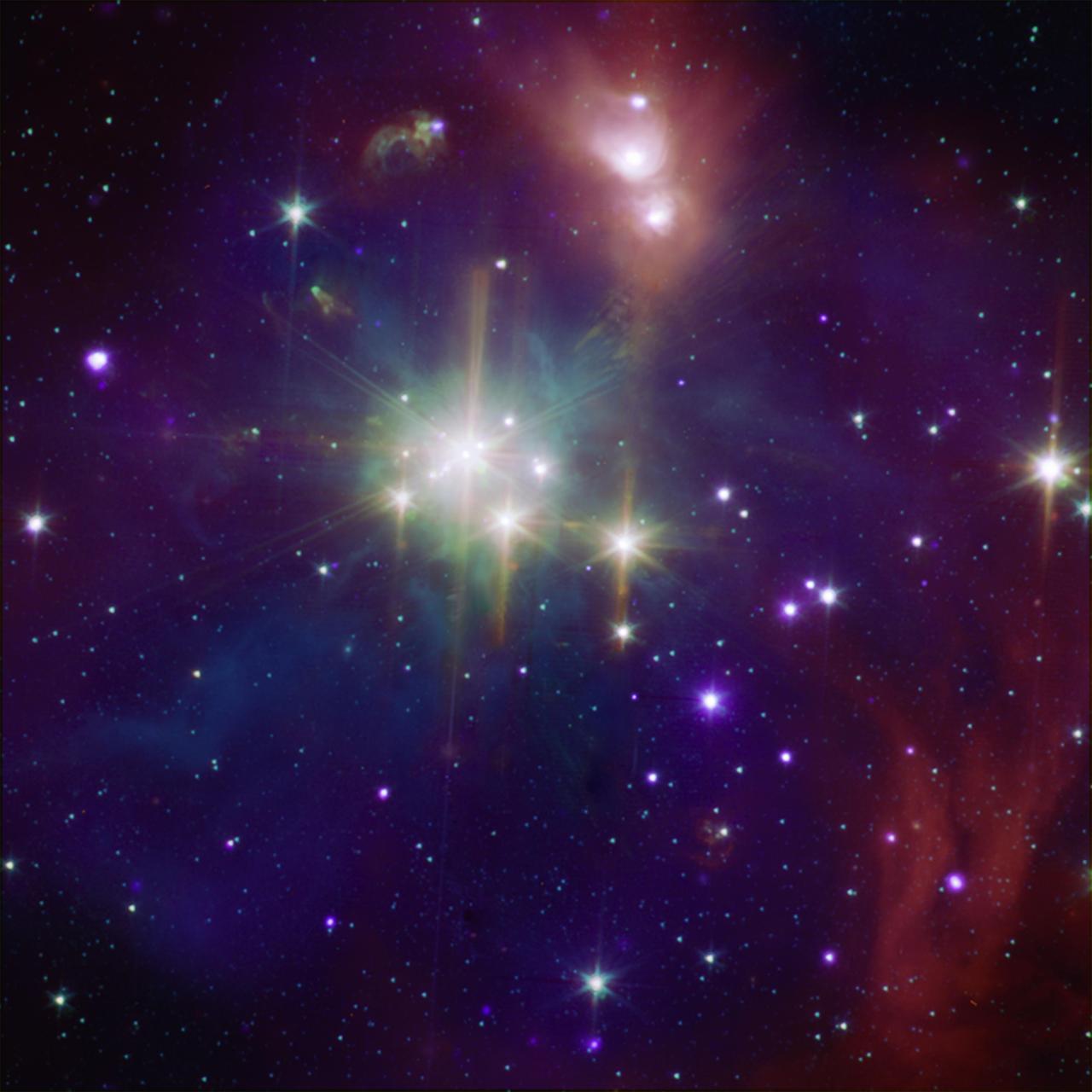

This composite image shows the Coronet in X-rays from Chandra and infrared from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope orange, green, and cyan. The Spitzer data show young stars plus diffuse emission from dust.

This data plot captured by NASA Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, shows X-ray light streaming from regions near a supermassive black hole known as Markarian 335.

NASA Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, has a complex set of mirrors, or optics, that will help it see high-energy X-ray light in greater detail than ever before.
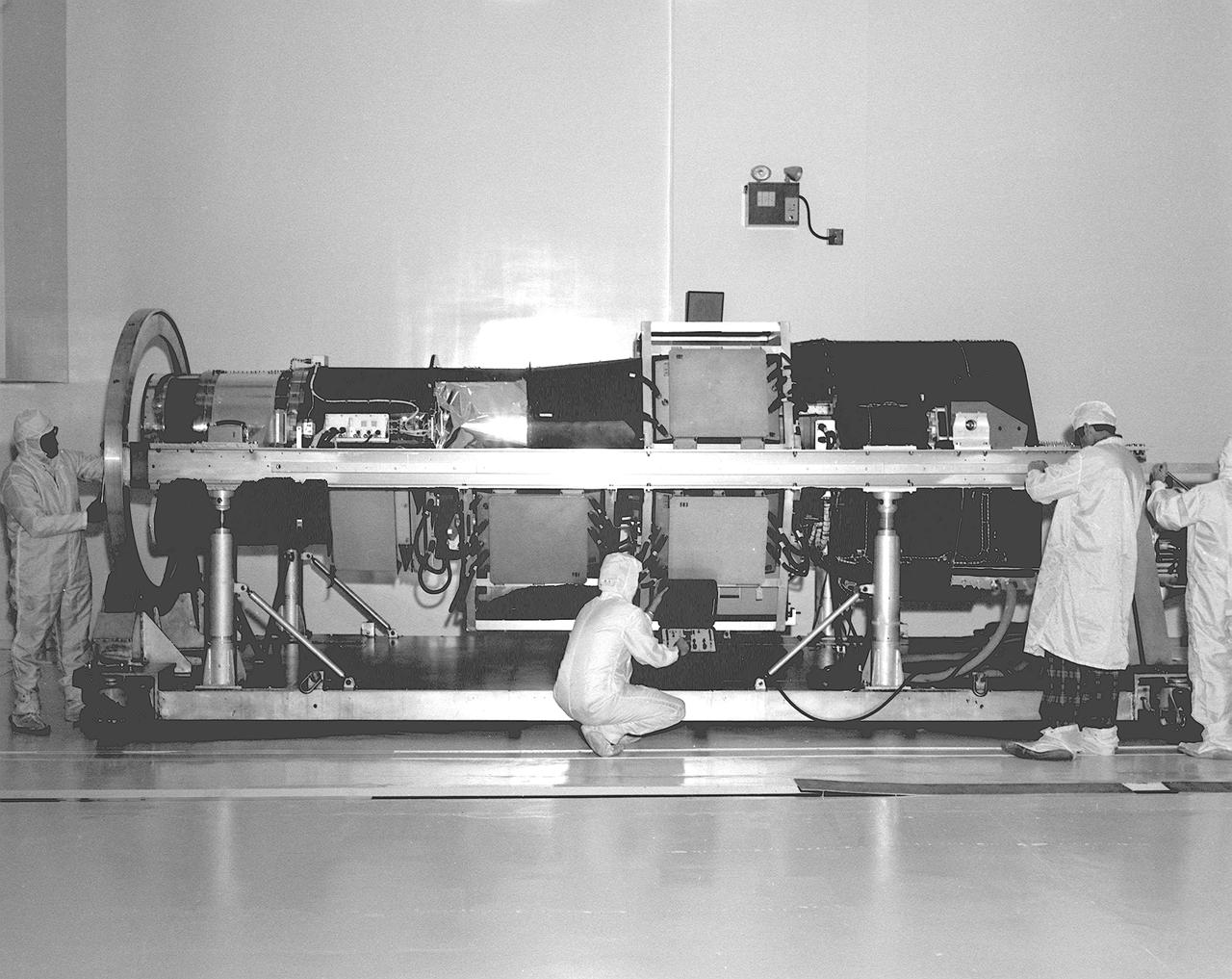
This photograph is of the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2 telescope being checked by engineers in the X-Ray Calibration Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The MSFC was heavily engaged in the technical and scientific aspects, testing and calibration, of the HEAO-2 telescope. The HEAO-2 was the first imaging and largest x-ray telescope built to date. The X-Ray Calibration Facility was built in 1976 for testing MSFC's HEAO-2. The facility is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produced a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performance in space is predicted. The original facility contained a 1,000-foot long by 3-foot diameter vacuum tube (for the x-ray path) cornecting an x-ray generator and an instrument test chamber. Recently, the facility was upgraded to evaluate the optical elements of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, Chandra X-Ray Observatory and Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory.
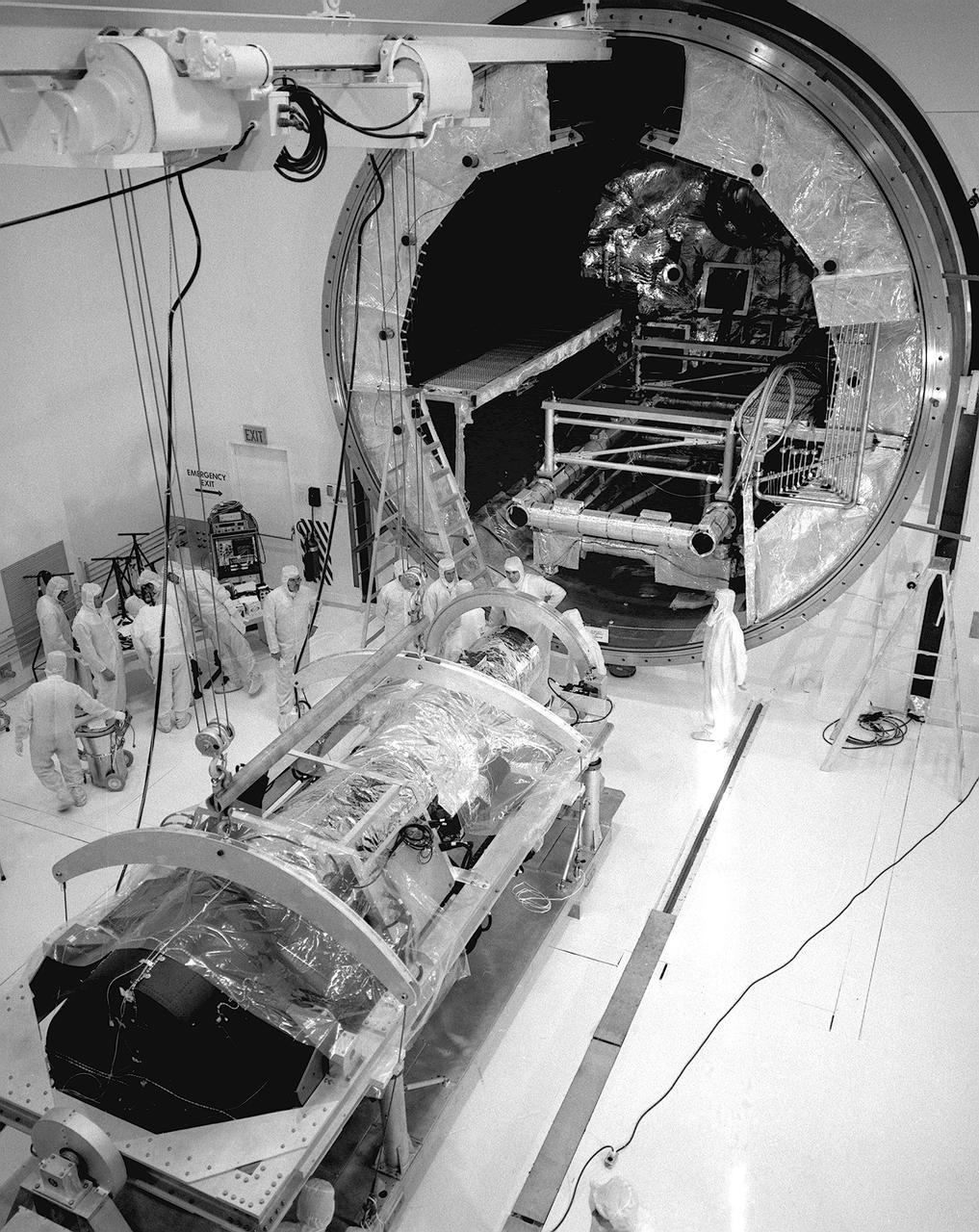
This photograph is of the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2 telescope being evaluated by engineers in the clean room of the X-Ray Calibration Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The MSFC was heavily engaged in the technical and scientific aspects, testing and calibration, of the HEAO-2 telescope The HEAO-2 was the first imaging and largest x-ray telescope built to date. The X-Ray Calibration Facility was built in 1976 for testing MSFC's HEAO-2. The facility is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produced a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performance in space is predicted. The original facility contained a 1,000-foot long by 3-foot diameter vacuum tube (for the x-ray path) cornecting an x-ray generator and an instrument test chamber. Recently, the facility was upgraded to evaluate the optical elements of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, Chandra X-Ray Observatory and Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory.
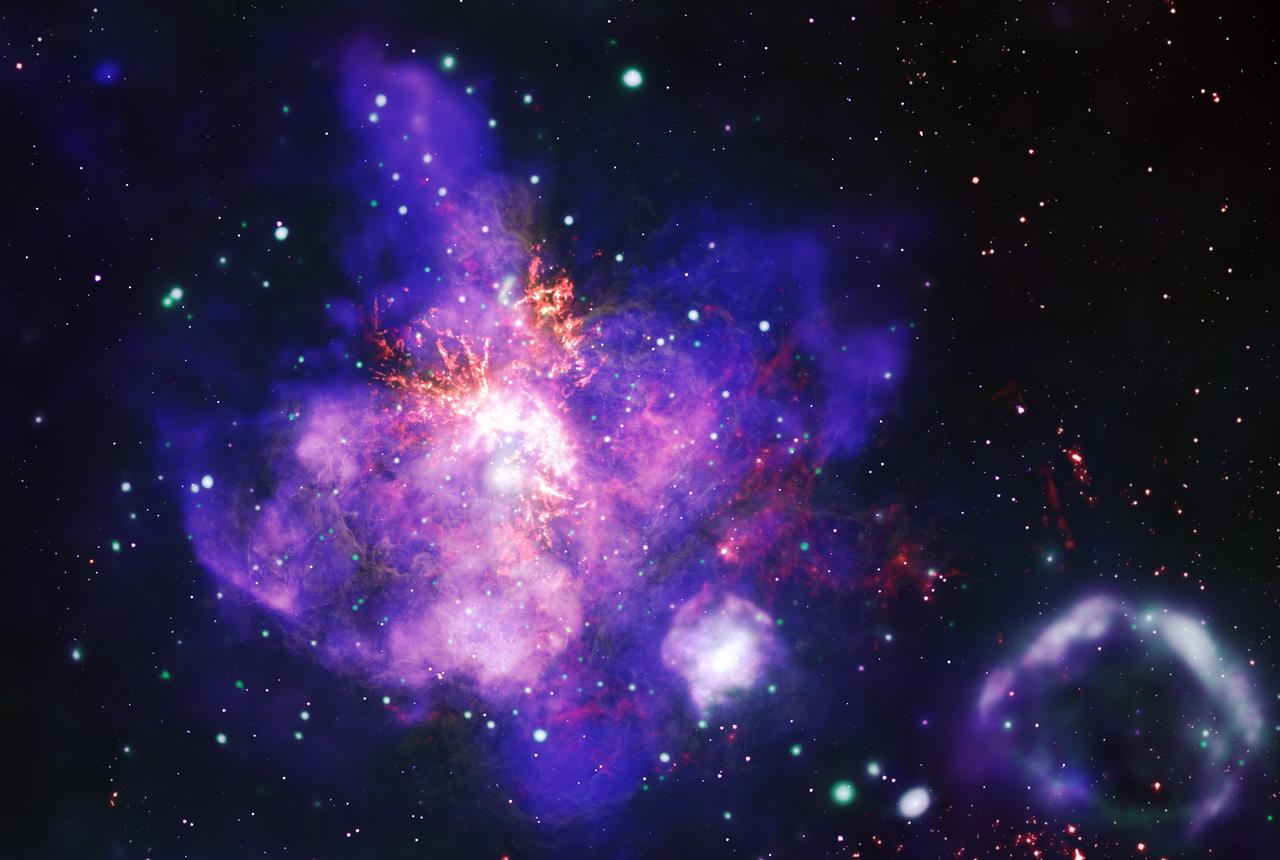

This composite image contains the deepest X-ray image ever made of the spectacular star forming region called 30 Doradus. By combining X-ray data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory (blue and green) with optical data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (yellow) and radio data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (orange), this stellar arrangement comes alive.
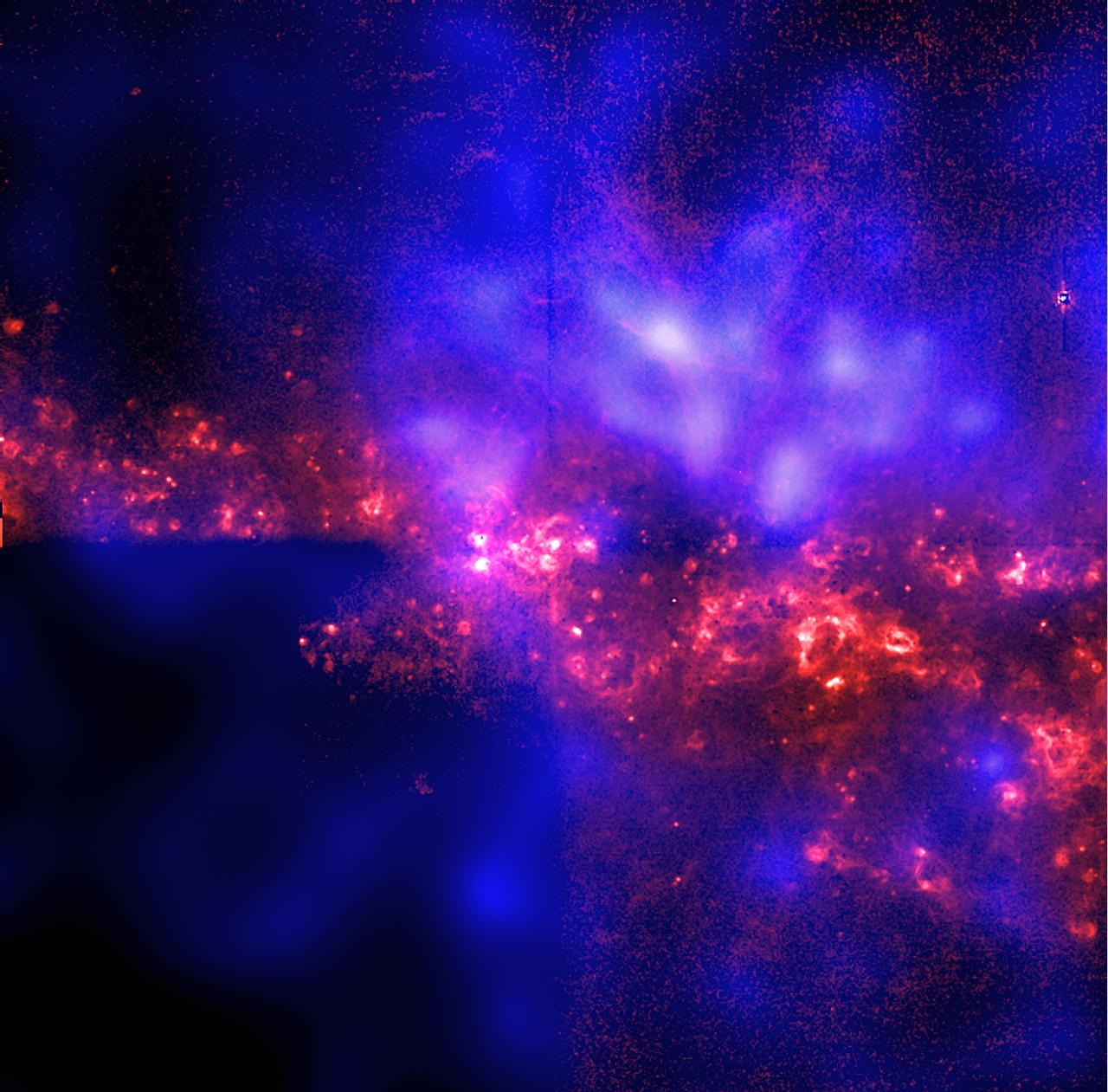

This image shows the central region of the spiral galaxy NGC 4631 as seen edge-on from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Chandra data, shown in blue and purple, provide the first unambiguous evidence for a halo of hot gas surrounding a galaxy that is very similar to our Milky Way. The structure across the middle of the image and the extended faint filaments, shown in orange, represent the observation from the HST that reveals giant bursting bubbles created by clusters of massive stars. Scientists have debated for more than 40 years whether the Milky Way has an extended corona, or halo, of hot gas. Observations of NGC 4631 and similar galaxies provide astronomers with an important tool in the understanding our own galactic environment. A team of astronomers, led by Daniel Wang of the University of Massachusetts at Amherst, observed NGC 4631 with CXO's Advanced Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS). The observation took place on April 15, 2000, and its duration was approximately 60,000 seconds.
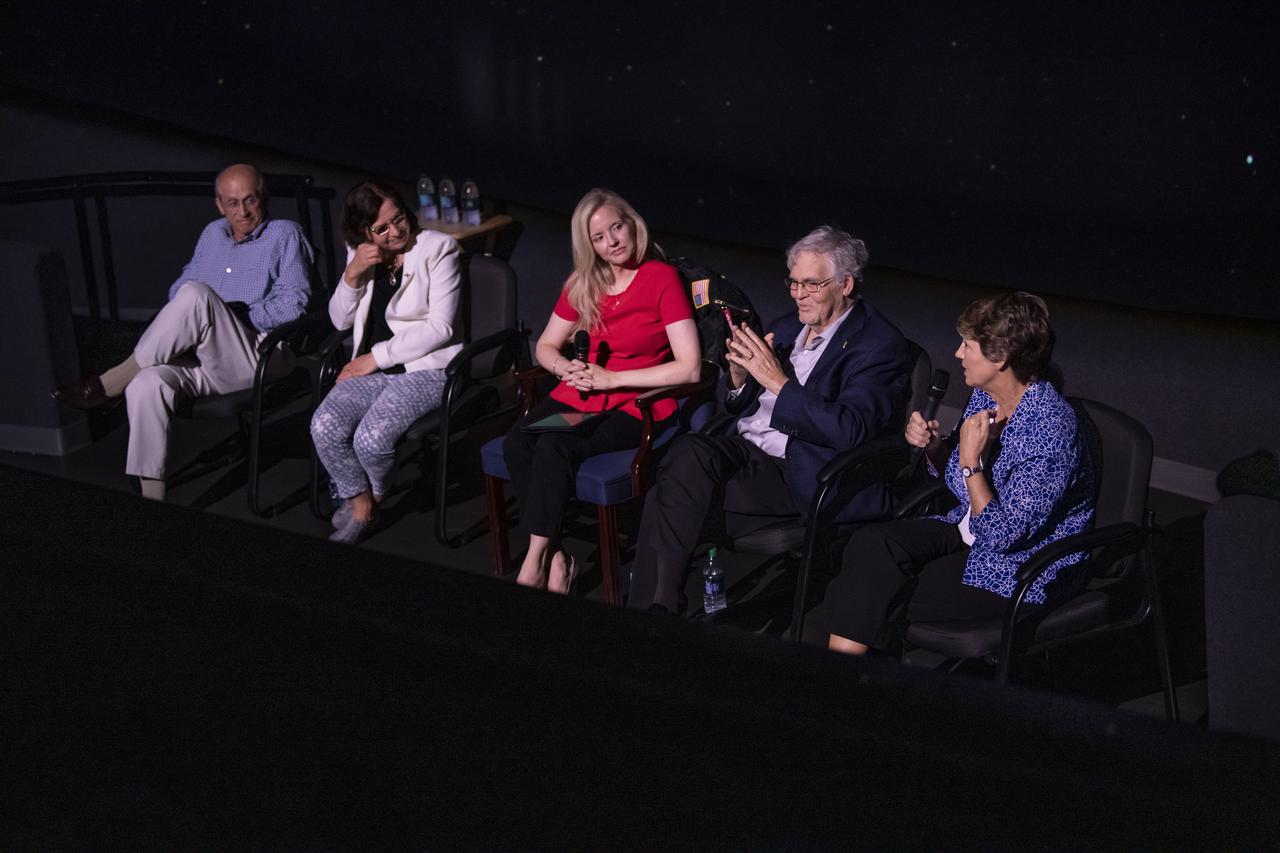

The 20th year of the Chandra X-ray Telescope was celebrated at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center's planetarium. The speakers were retired Astronaut Eileen Collins, Astrophysicist at the "Chandra X-ray Center Aneta Siemiginowska, "Senior Astrophysicist at the Chandra X-ray center Harvey Tananbaum, and Chandra Project Scientist Dr. Martin Weisskopf. The panel discussion was moderated by Kim Kowal Arcand, "Visualizaton Lead at the Chandra X-ray Center.

A star's spectacular death in the constellation Taurus was observed on Earth as the supernova of 1054 A.D. Now, almost a thousand years later, a superdense neutron star left behind by the stellar death is spewing out a blizzard of extremely high-energy particles into the expanding debris field known as the Crab Nebula. This composite image uses data from three of NASA's Great Observatories. The Chandra X-ray image is shown in light blue, the Hubble Space Telescope optical images are in green and dark blue, and the Spitzer Space Telescope's infrared image is in red. The size of the X-ray image is smaller than the others because ultrahigh-energy X-ray emitting electrons radiate away their energy more quickly than the lower-energy electrons emitting optical and infrared light. The neutron star, which has the mass equivalent to the sun crammed into a rapidly spinning ball of neutrons twelve miles across, is the bright white dot in the center of the image. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01320
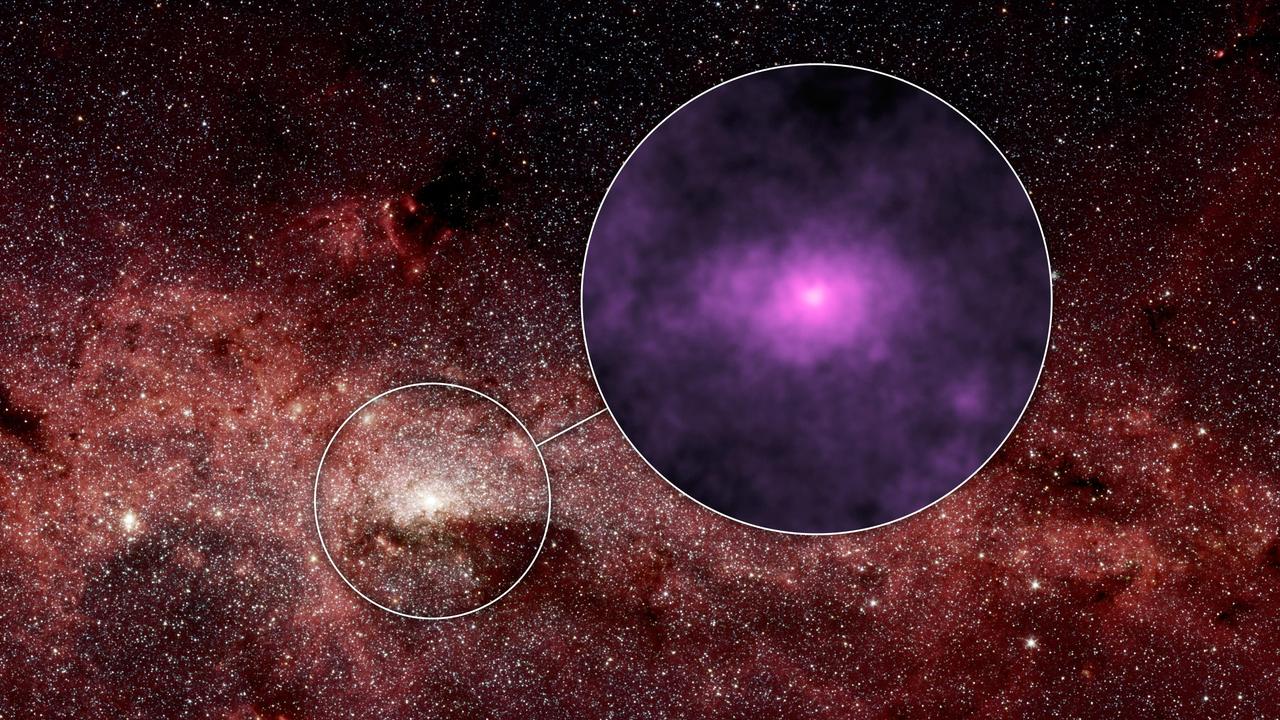
NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, has captured a new high-energy X-ray view (magenta, Figure 1) of the bustling center of our Milky Way galaxy. The smaller circle shows the area where the NuSTAR image was taken -- the very center of our galaxy, where a giant black hole resides. That region is enlarged to the right, in the larger circle, to show the NuSTAR data. The NuSTAR picture is one of the most detailed ever taken of the center of our galaxy in high-energy X-rays. The X-ray light, normally invisible to our eyes, has been assigned the color magenta. The brightest point of light near the center of the X-ray picture is coming from a spinning dead star, known as a pulsar, which is near the giant black hole. While the pulsar's X-ray emissions were known before, scientists were surprised to find more high-energy X-rays than predicted in the surrounding regions, seen here as the elliptical haze. Astronomers aren't sure what the sources of the extra X-rays are, but one possibility is a population of dead stars. The background picture was captured in infrared light by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. The NuSTAR image has an X-ray energy range of 20 to 40 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19334

JWST (JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE) WING #2 INSTALLATION IN THE XRCF (X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY) PRIOR TO TESTING

JWST (JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE) WING #2 INSTALLATION IN THE XRCF (X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY) PRIOR TO TESTING