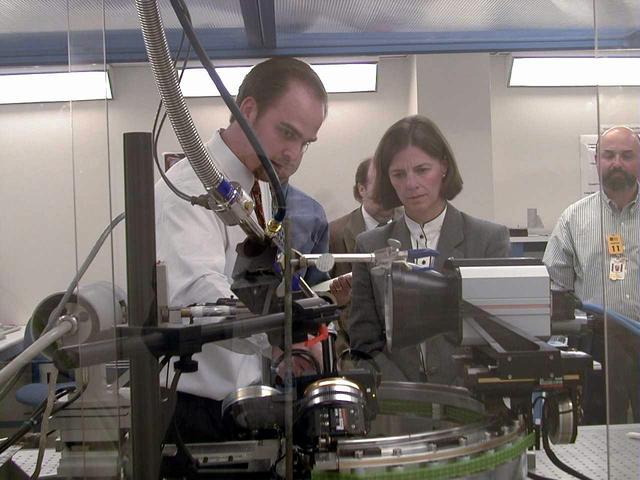

University of Alabama engineer Lance Weiss briefs NASA astronaut Dr. Bornie Dunbar about the design and capabilities of the X-ray Crystallography Facility under development at the Center for Macromolecular Crystallography of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, AL, April 21, 1999. The X-ray Crystallography Facility is designed to speed the collection of protein structure information from crystals grown aboard the International Space Station. By measuring and mapping the protein crystal structure in space, researchers will avoid exposing the delicate crystals to the rigors of space travel and make important research data available to scientists much faster. The X-ray Crystallography facility is being designed and developed by the Center for Macromolecular Crystallography of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, a NASA Commercial Space Center.
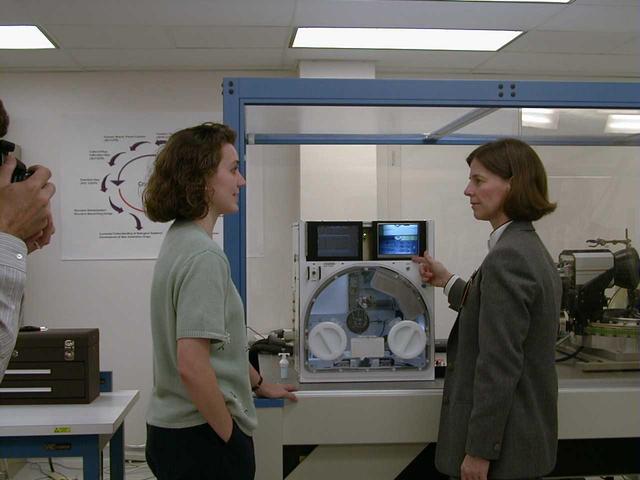

University of Alabama engineer Stacey Giles briefs NASA astronaut Dr. Bornie Dunbar about the design and capabilities of the X-ray Crystallography Facility under development at the Center for Macromolecular Crystallography of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, AL, April 21, 1999. The X-ray Crystallography Facility is designed to speed the collection of protein structure information from crystals grown aboard the International Space Station. By measuring and mapping the protein crystal structure in space, researchers will avoid exposing the delicate crystals to the rigors of space travel and make important research data available to scientists much faster. The X-ray Crystallography facility is being designed and developed by the Center for Macromolecular Crystallography of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, a NASA Commercial Space Center.

Edward Snell, a National Research Council research fellow at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), prepares a protein crystal for analysis by x-ray crystallography as part of NASA's structural biology program. The small, individual crystals are bombarded with x-rays to produce diffraction patterns, a map of the intensity of the x-rays as they reflect through the crystal.
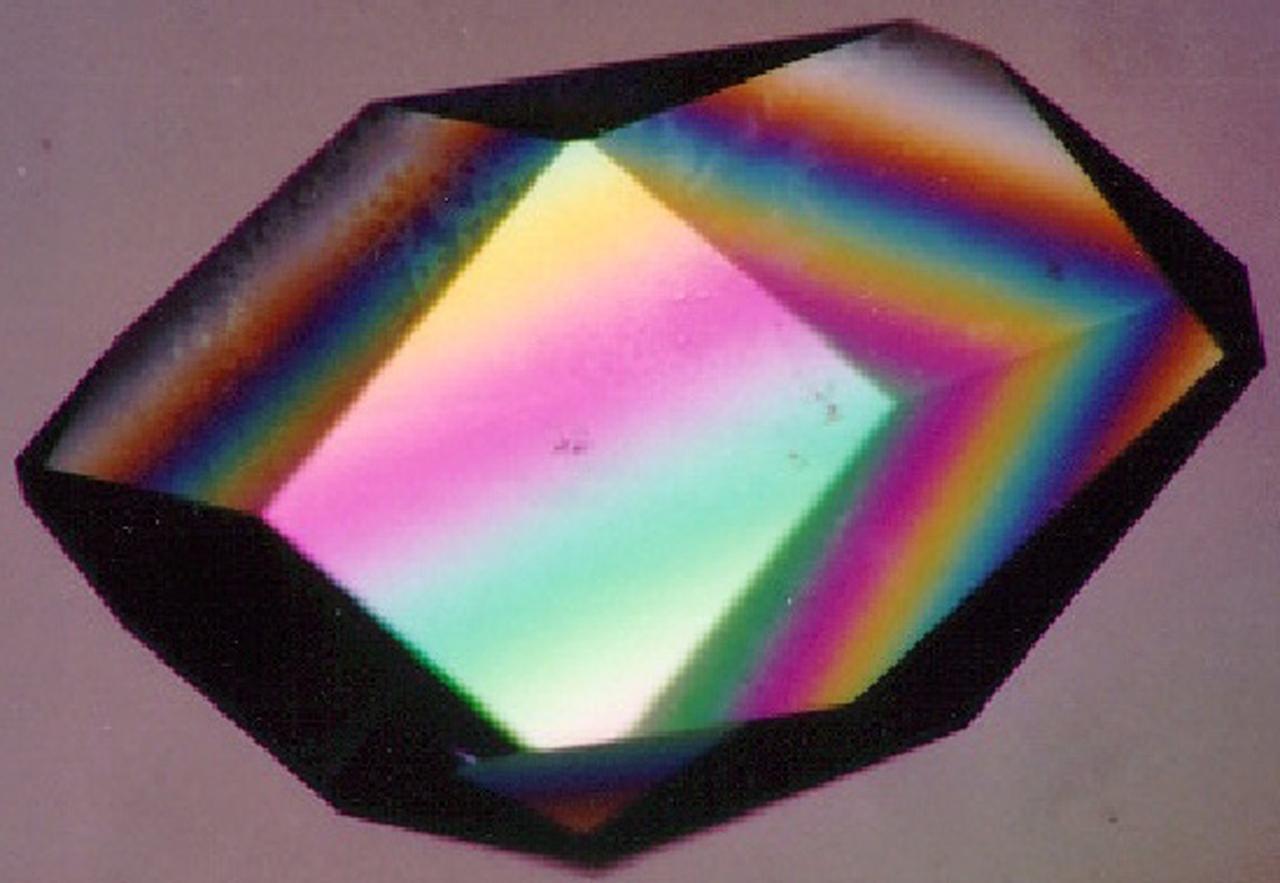
To the crystallographer, this may not be a diamond but it is just as priceless. A Lysozyme crystal grown in orbit looks great under a microscope, but the real test is X-ray crystallography. The colors are caused by polarizing filters. Proteins can form crystals generated by rows and columns of molecules that form up like soldiers on a parade ground. Shining X-rays through a crystal will produce a pattern of dots that can be decoded to reveal the arrangement of the atoms in the molecules making up the crystal. Like the troops in formation, uniformity and order are everything in X-ray crystallography. X-rays have much shorter wavelengths than visible light, so the best looking crystals under the microscope won't necessarily pass muster under the X-rays. In order to have crystals to use for X-ray diffraction studies, crystals need to be fairly large and well ordered. Scientists also need lots of crystals since exposure to air, the process of X-raying them, and other factors destroy them. Growing protein crystals in space has yielded striking results. Lysozyme's structure is well known and it has become a standard in many crystallization studies on Earth and in space.
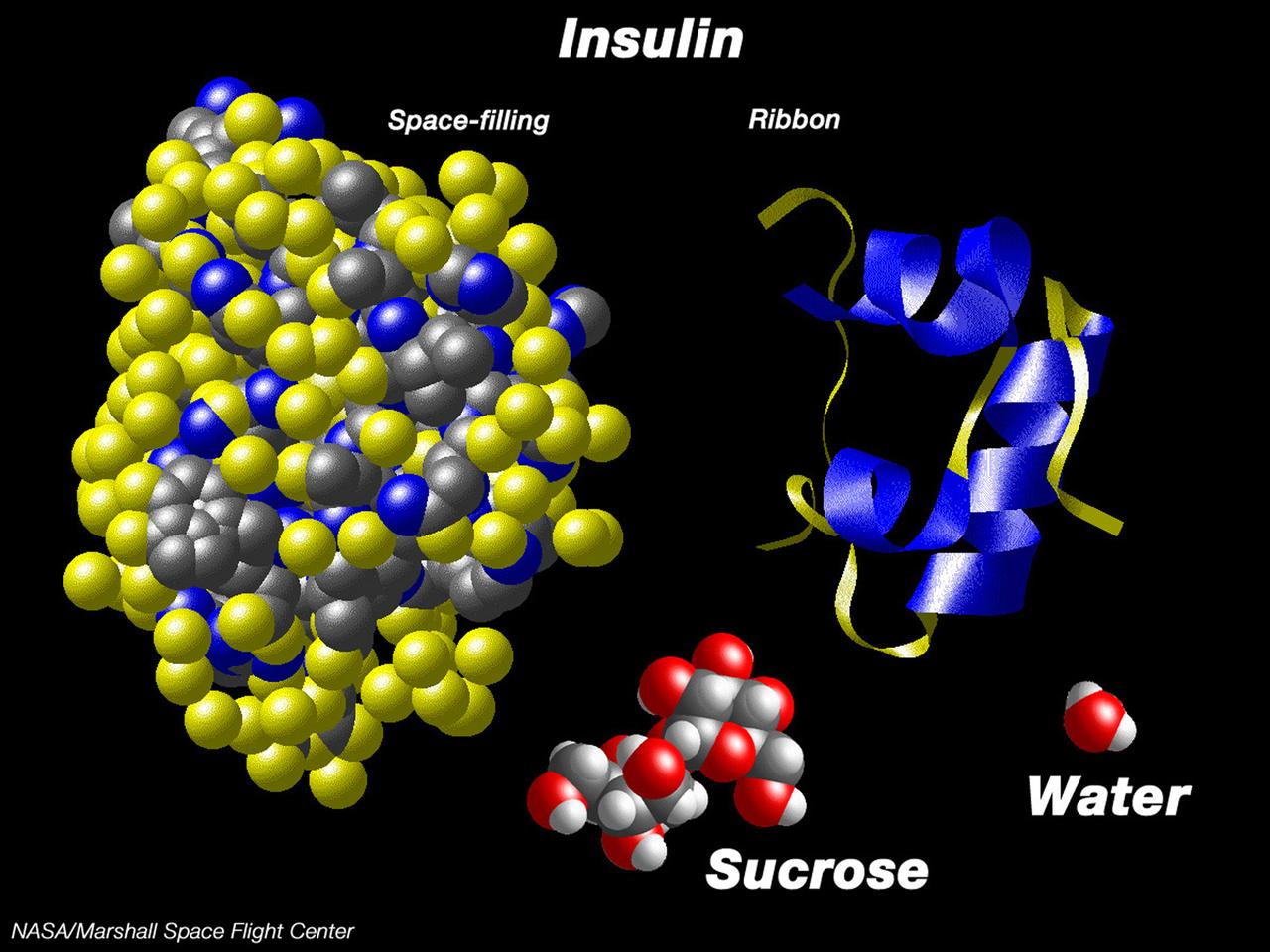
This computer graphic depicts the relative complexity of crystallizing large proteins in order to study their structures through x-ray crystallography. Insulin is a vital protein whose structure has several subtle points that scientists are still trying to determine. Large molecules such as insuline are complex with structures that are comparatively difficult to understand. For comparison, a sugar molecule (which many people have grown as hard crystals in science glass) and a water molecule are shown. These images were produced with the Macmolecule program. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)