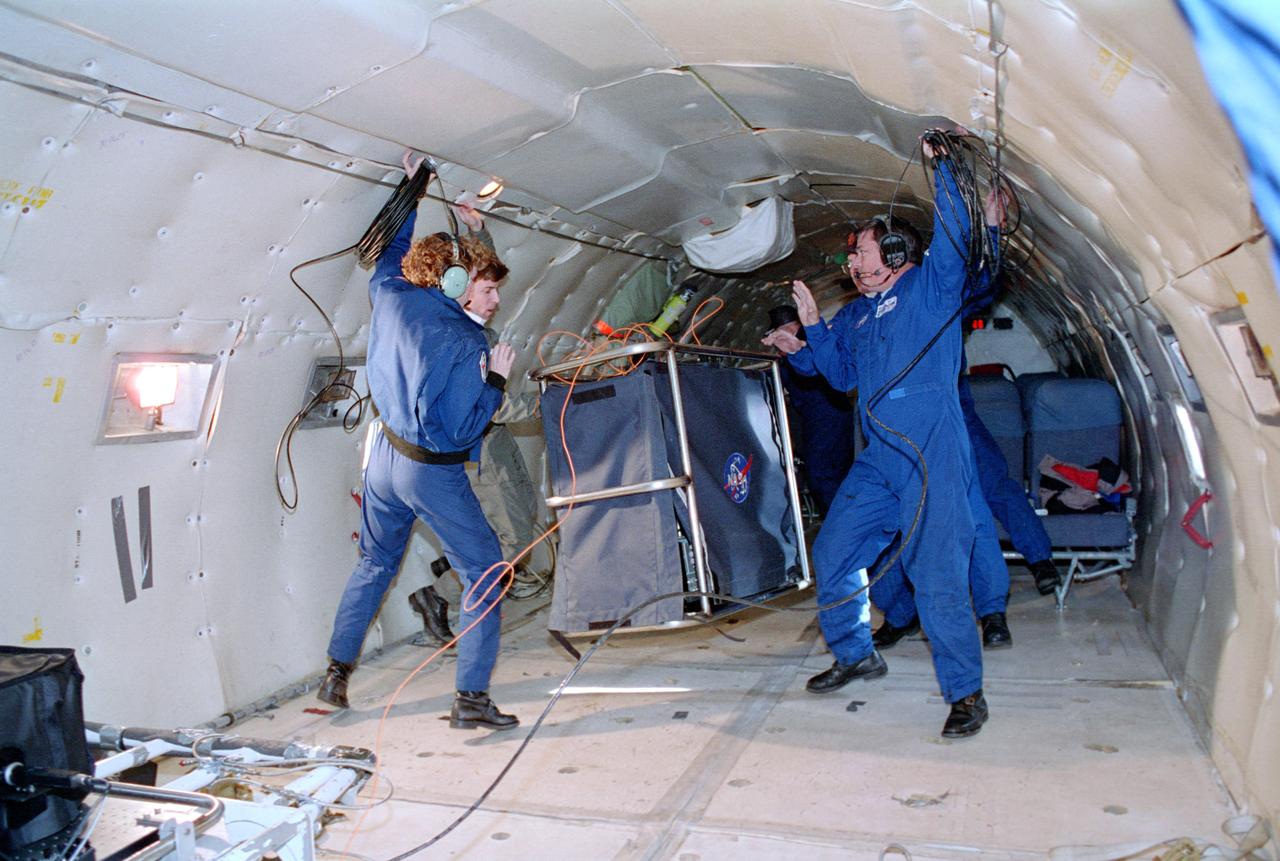

ZERO GRAVITY AIRCRAFT KC135 FLIGHTS AT LEWIS RESEARCH CENTER (Glenn Research Center)
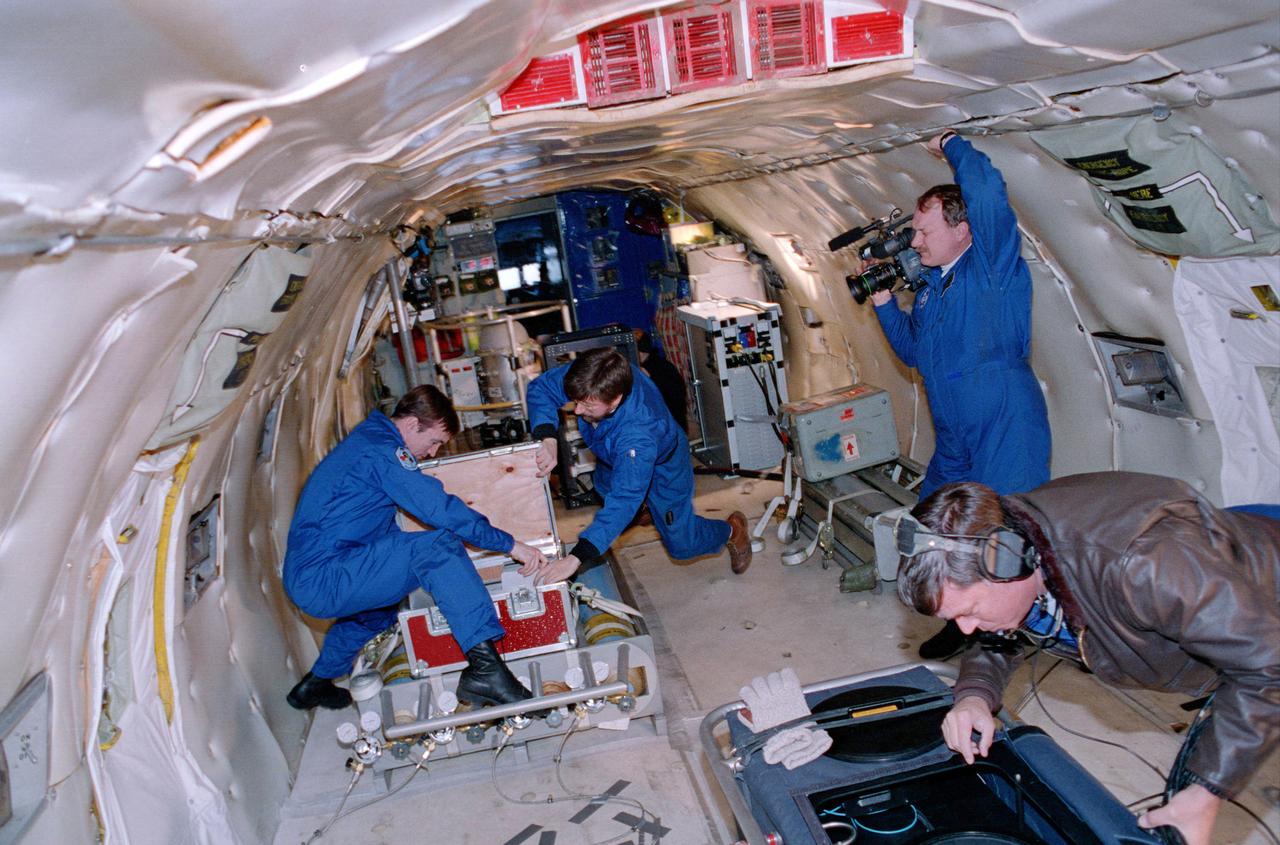

ZERO GRAVITY AIRCRAFT KC135 FLIGHTS AT LEWIS RESEARCH CENTER

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to 1 meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No.1 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to one-meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 3 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)
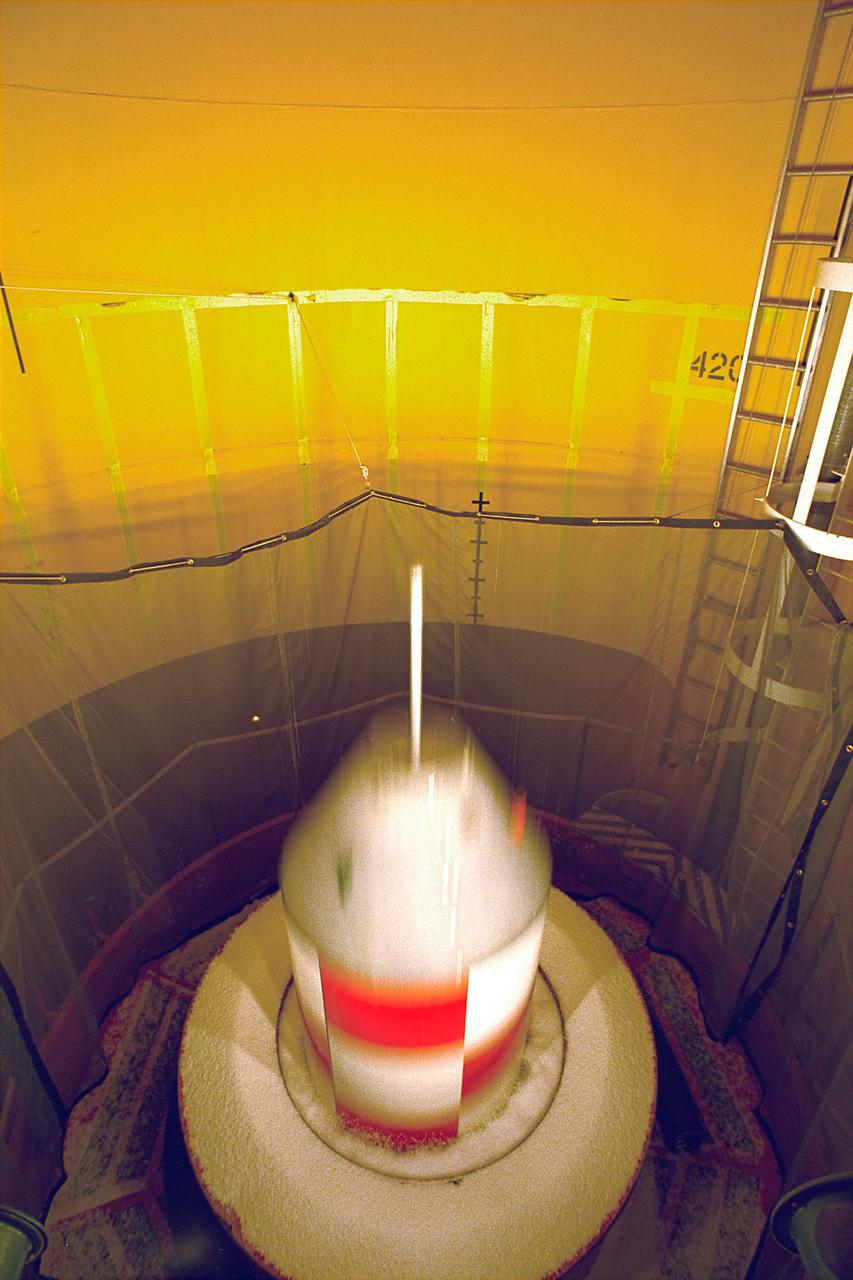
An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physcis, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to 1 meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 2 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to one meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 4 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)
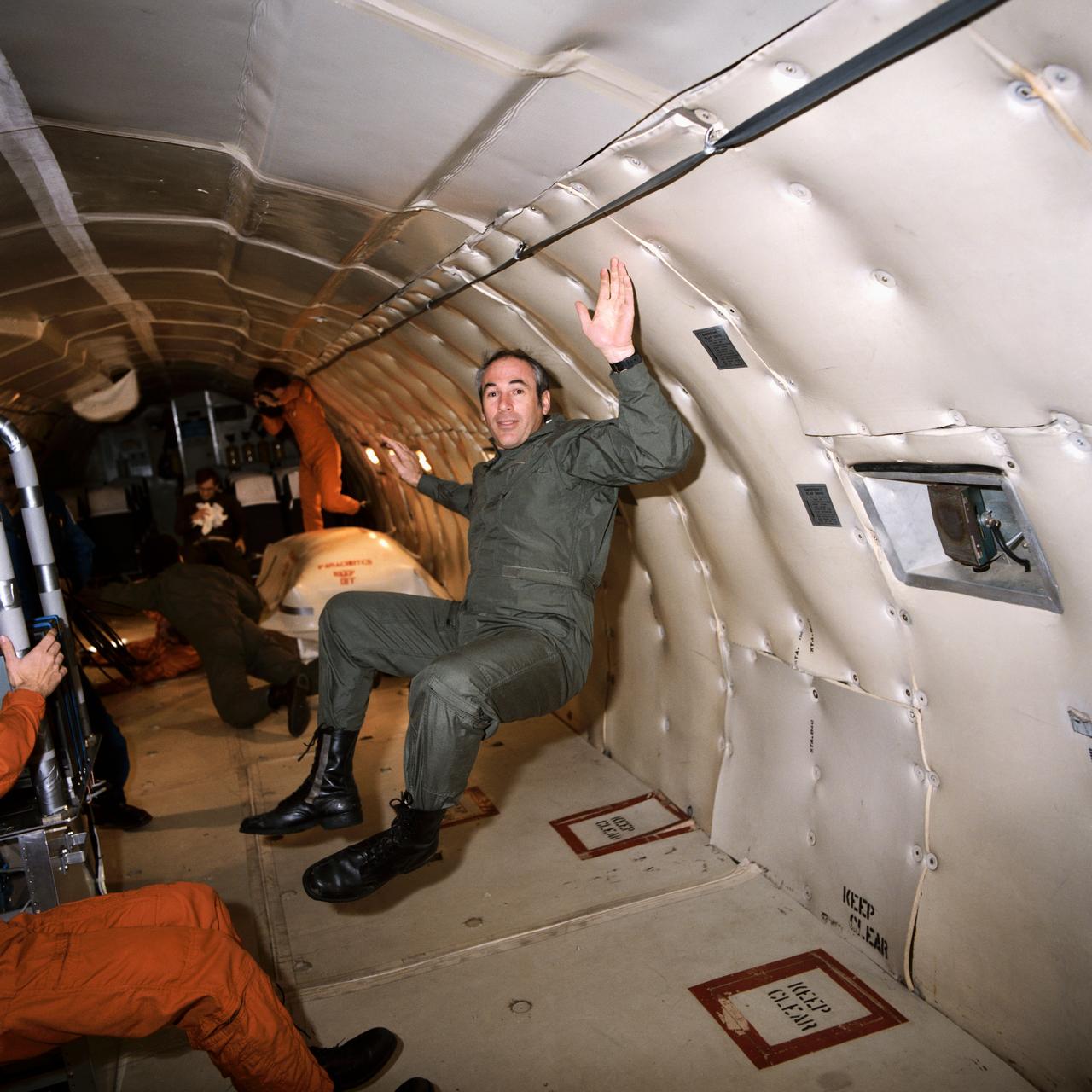

S85-26106 (25 Jan. 1985) --- Astronaut Gregory Jarvis gets a familiarization session in weightlessness aboard a KC-135 "zero gravity" aircraft. Jarvis was originally assigned as payload specialist to STS-51D but was reassigned to STS-51L. Photo credit: NASA
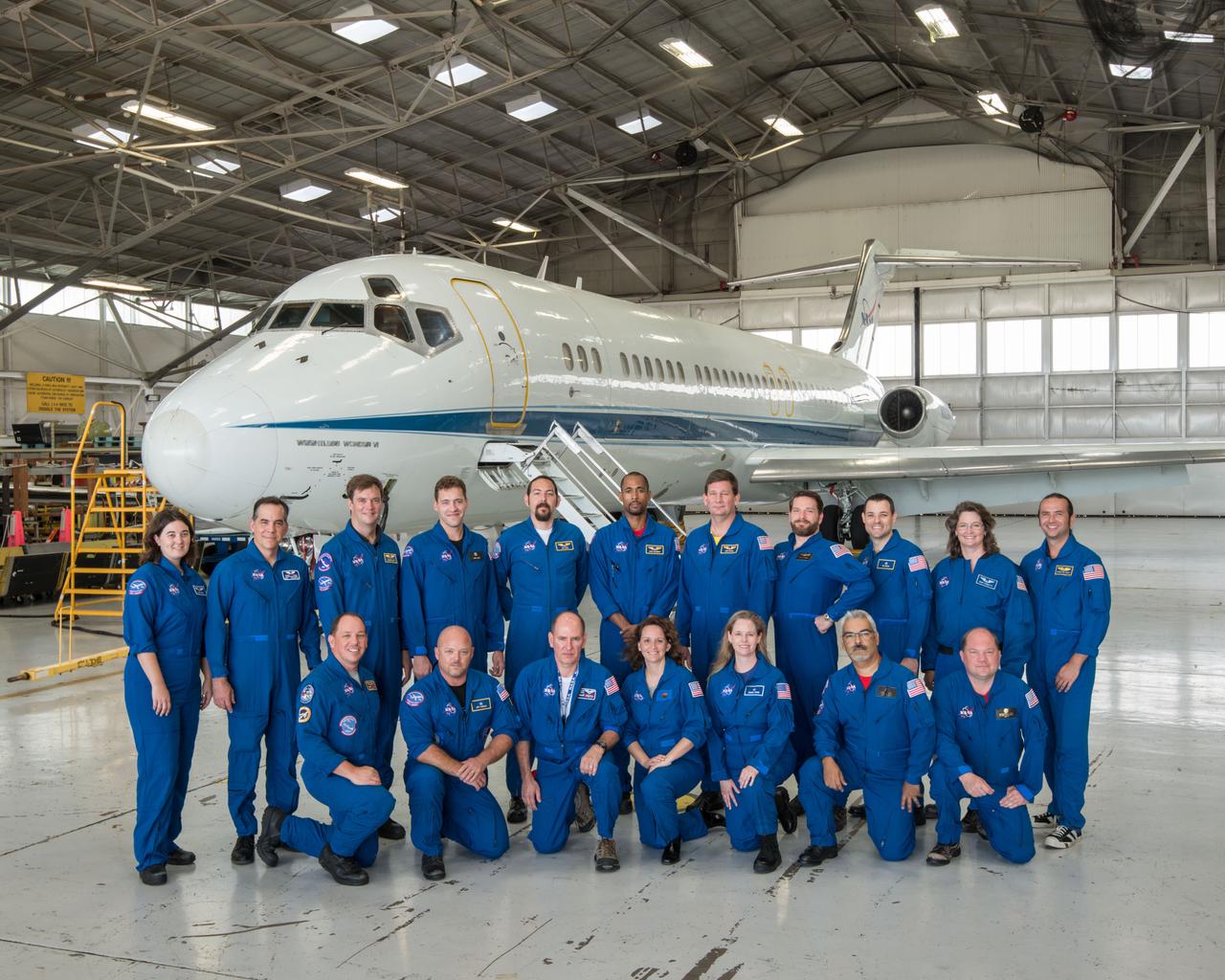

Group photo representating past and present Multi-Media Services (MMS) photographer and videographers that have supported Zero-G Reduced Gravity Office operations throughout the year prior to the programs final flight on August 29, 2014. Photo Date: August 18, 2014. Location: Ellington Field - Hangar 990. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
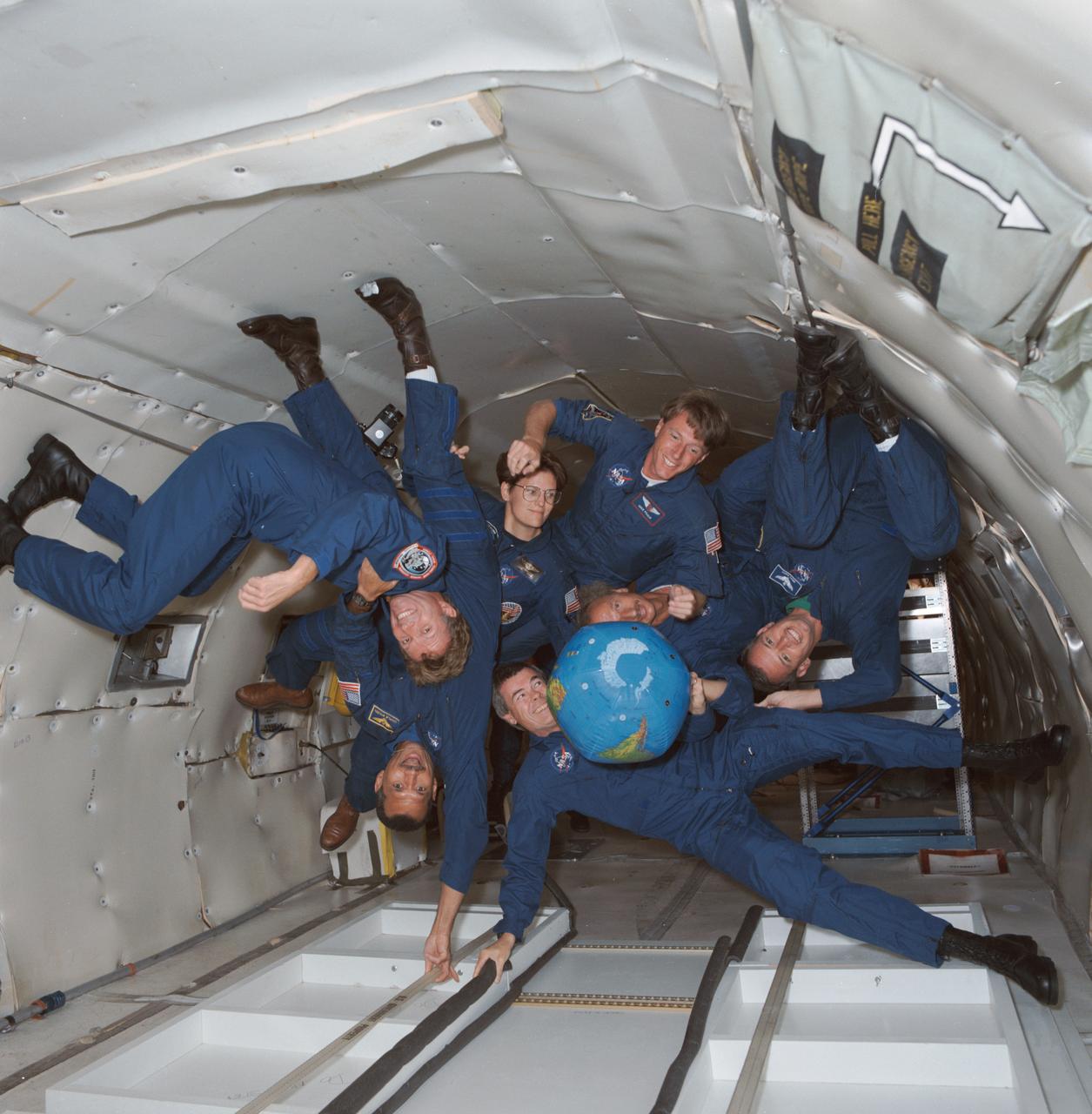

S91-44453 (21 Aug 1991) --- The crew of STS-45 is already training for its March 1992 mission, including stints on the KC-135 zero-gravity-simulating aircraft. Shown with an inflatable globe are, clockwise from the top, C. Michael Foale, mission specialist; Dirk Frimout, payload specialist; Brian Duffy, pilot; Charles R. (Rick) Chappell, backup payload specialist; Charles F. Bolden, mission commander; Byron K. Lichtenberg, payload specialist; and Kathryn D. Sullivan, payload commander.
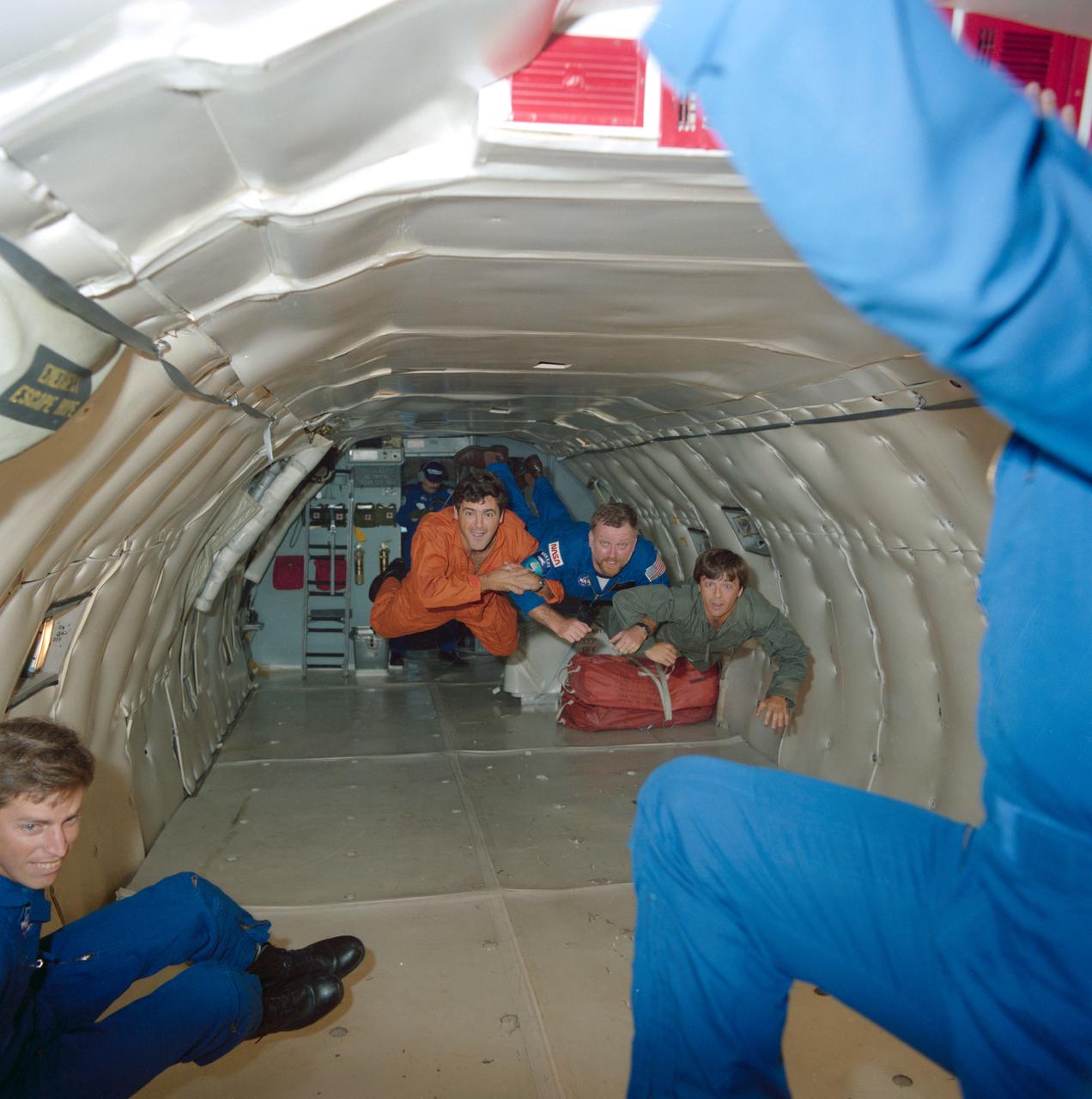

S84-40538 (24 Aug 1984) --- Two 41-G payload specialists and a backup for one of them appear to be at home in zero gravity in this scene photographed aboard a KC-135 "Zero gravity" aircraft flying one of its weightlessness opportunity parabolas. Paul D. Scully-Power, a civilian oceanographer with the U.S. Navey, is flanked by Marc Garneau (left) and Robert Thirsk, both representing the National Research Council of Canada. Thirsk is back up payload specialist for Garneau.
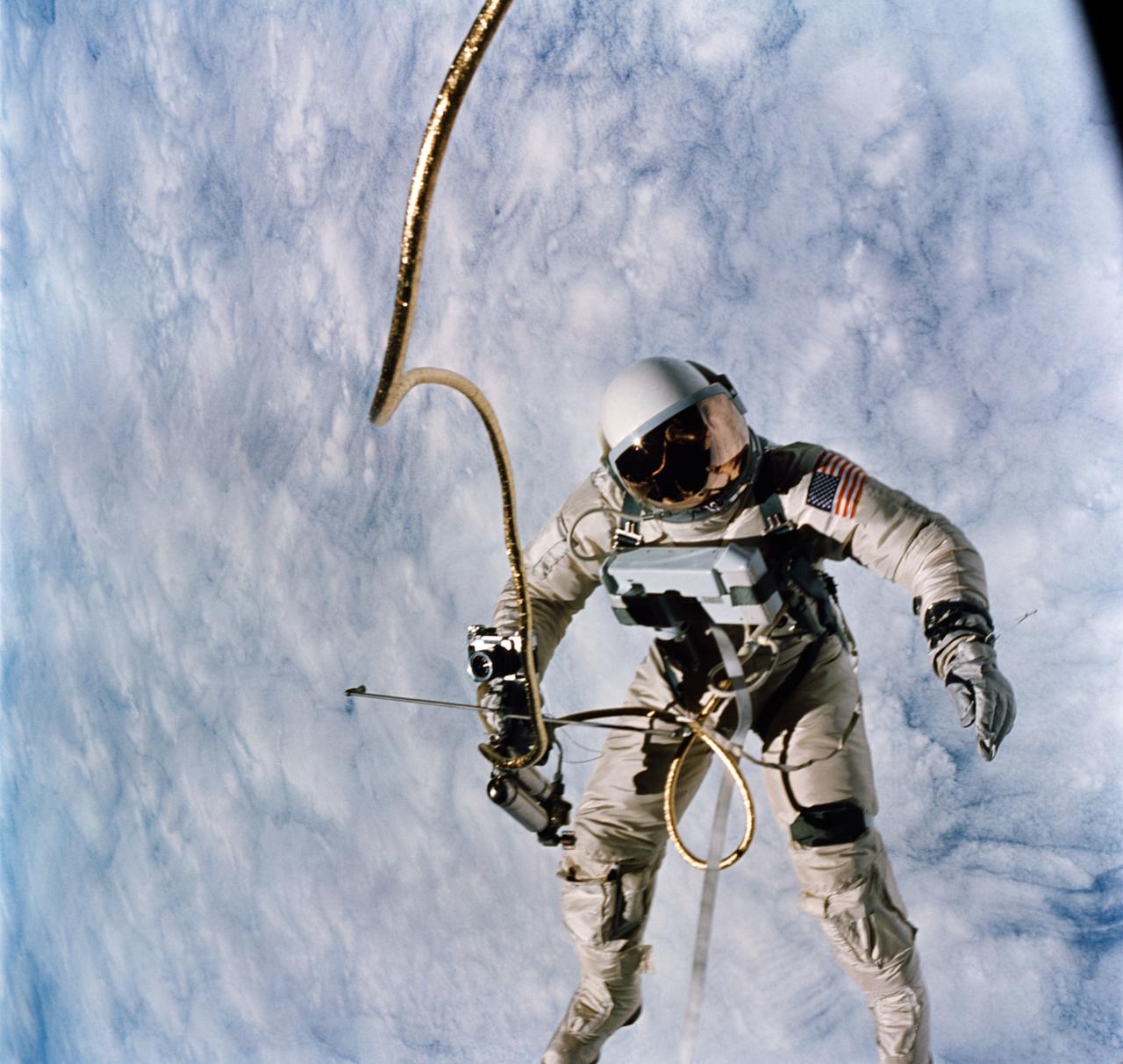

S65-30427 (3 June 1965) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 (GT-4) spaceflight, floats in the zero-gravity of space during the third revolution of the GT-4 spacecraft. White wears a specially designed spacesuit. His face is shaded by a gold-plated visor to protect him from unfiltered rays of the sun. In his right hand he carries a Hand-Held Self-Maneuvering Unit (HHSMU) that gives him control over his movements in space. White also wears an emergency oxygen chest pack; and he carries a camera mounted on the HHSMU for taking pictures of the sky, Earth and the GT-4 spacecraft. He is secured to the spacecraft by a 25-feet umbilical line and a 23-feet tether line. Both lines are wrapped together in gold tape to form one cord. Astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot, remained inside the spacecraft during the extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronaut Edward H. White II died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.
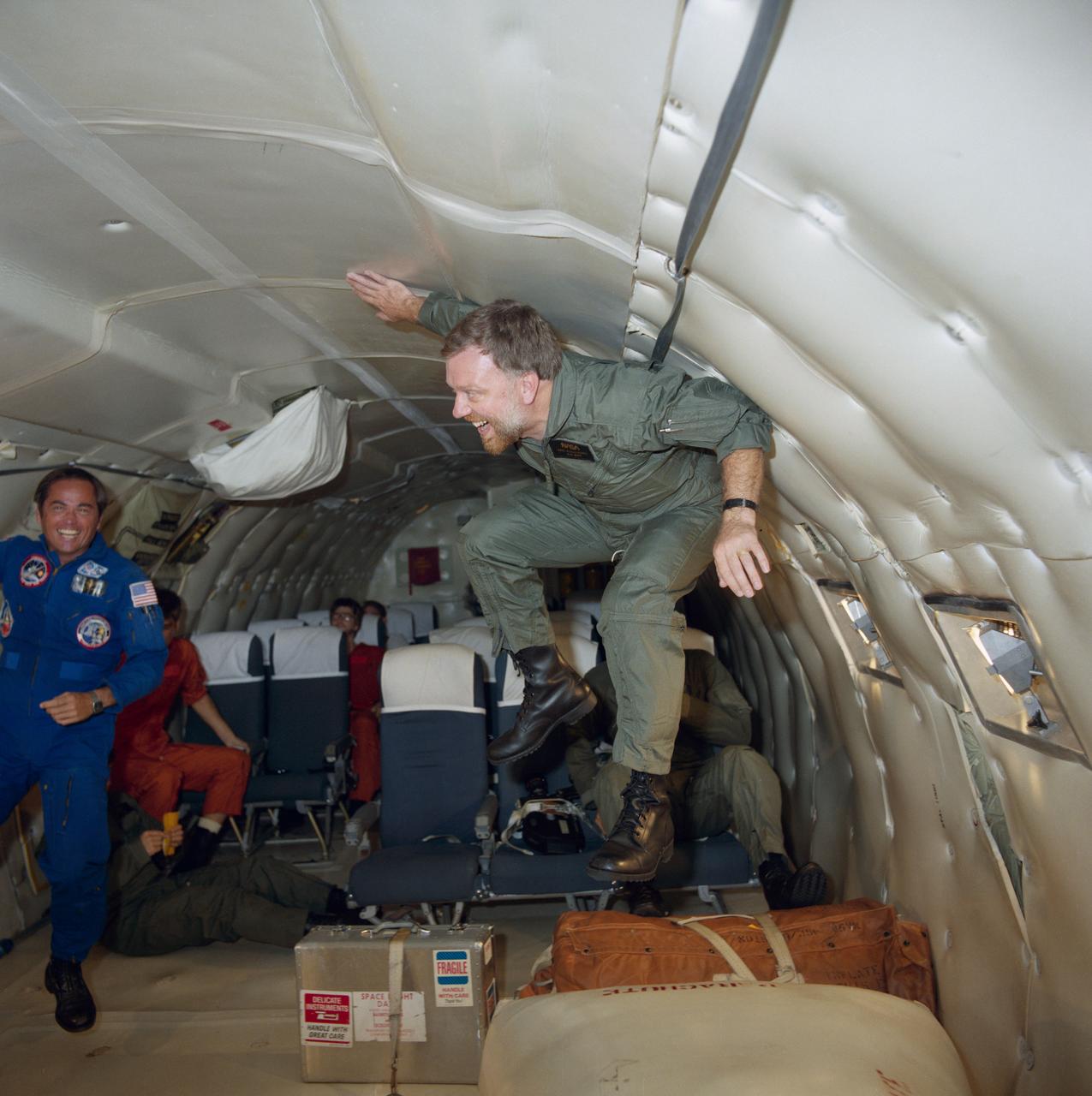

S84-37536 (18 July 1984) --- Astronaut Robert L. Crippen, left, 41-G crew commander watches as one of his fellow crewmembers gets an introduction to weightlessness aboard a KC-135, "zero-gravity" aircraft. Paul D. Scully-Power is the crew member literally floating here in the brief period of micro-gravity. Scully-Power, an oceanographer with the U.S. Navy, and Marc Garneau (partially visible in chair behind the floating Scully-Power)are payload specialists for 41-G. Garneau represents the National Research Council (Canada).

SL4-150-5074 (February 1974) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot for the Skylab 4 mission, demonstrates the effects of zero-gravity as he sails through airlock module hatch. Photo credit: NASA

Astronaut Gerald P. Carr, commander for the Skylab 4 mission, demonstrates the effects of zero-gravity as he floats in the forward dome area of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab space station while in Earth orbit.
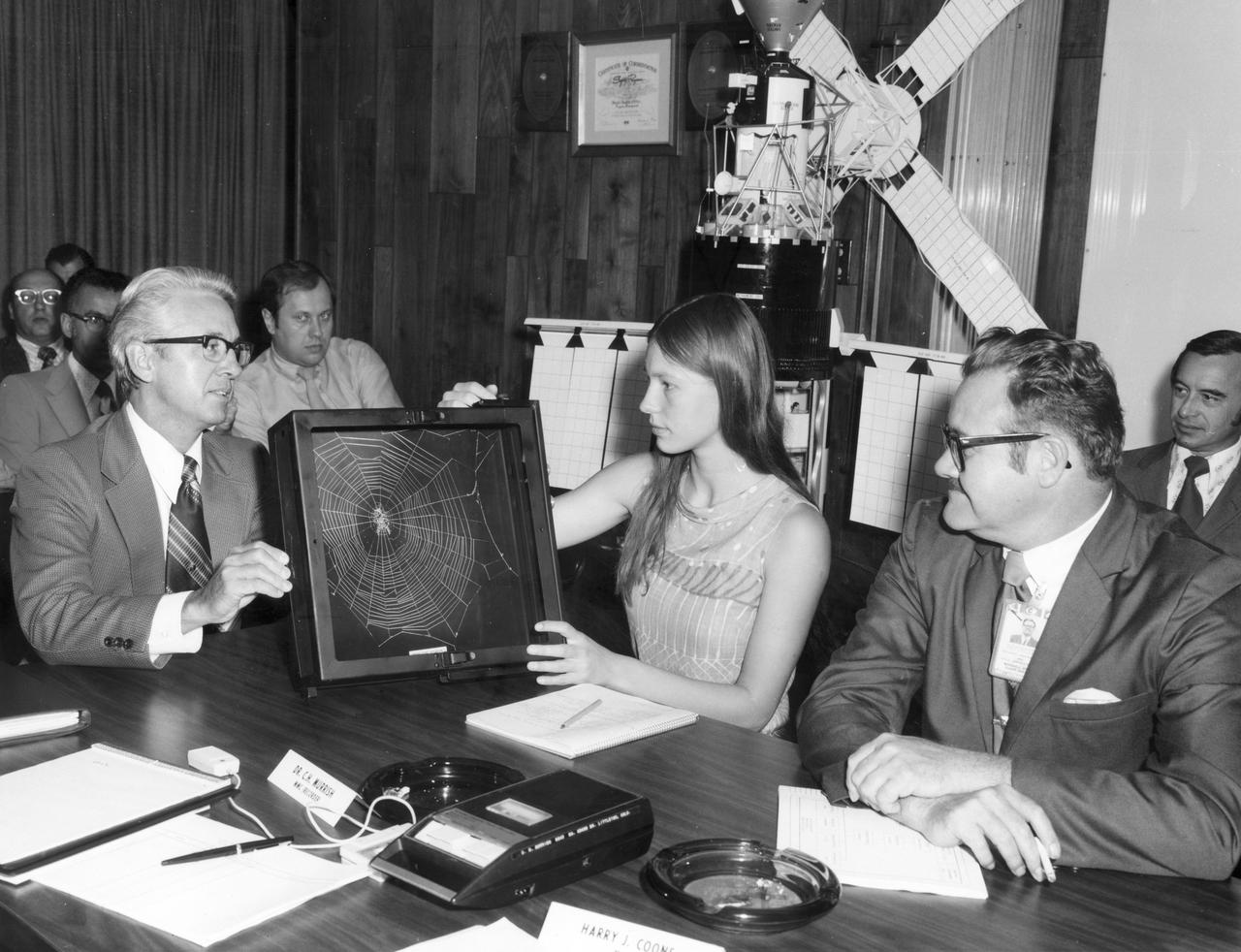

Lexington, Massachusetts high school student, Judith Miles, discusses her proposed Skylab experiment with Keith Demorest (right) and Henry Floyd, both of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In her experiment, called the “Web Formation in Zero Gravity”, called for spiders to be released into a box and their actions recorded to determine how well they adapt to the absence of gravity. Spiders are known to adapt quickly to other changes in the environment but nothing was known of their ability to adapt to weightlessness. At the same time spiders were weaving webs in Earth orbit, similar spiders were spinning webs in identical boxes on Earth under full gravity conditions. Miles was among the 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab Mission. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of equipment.
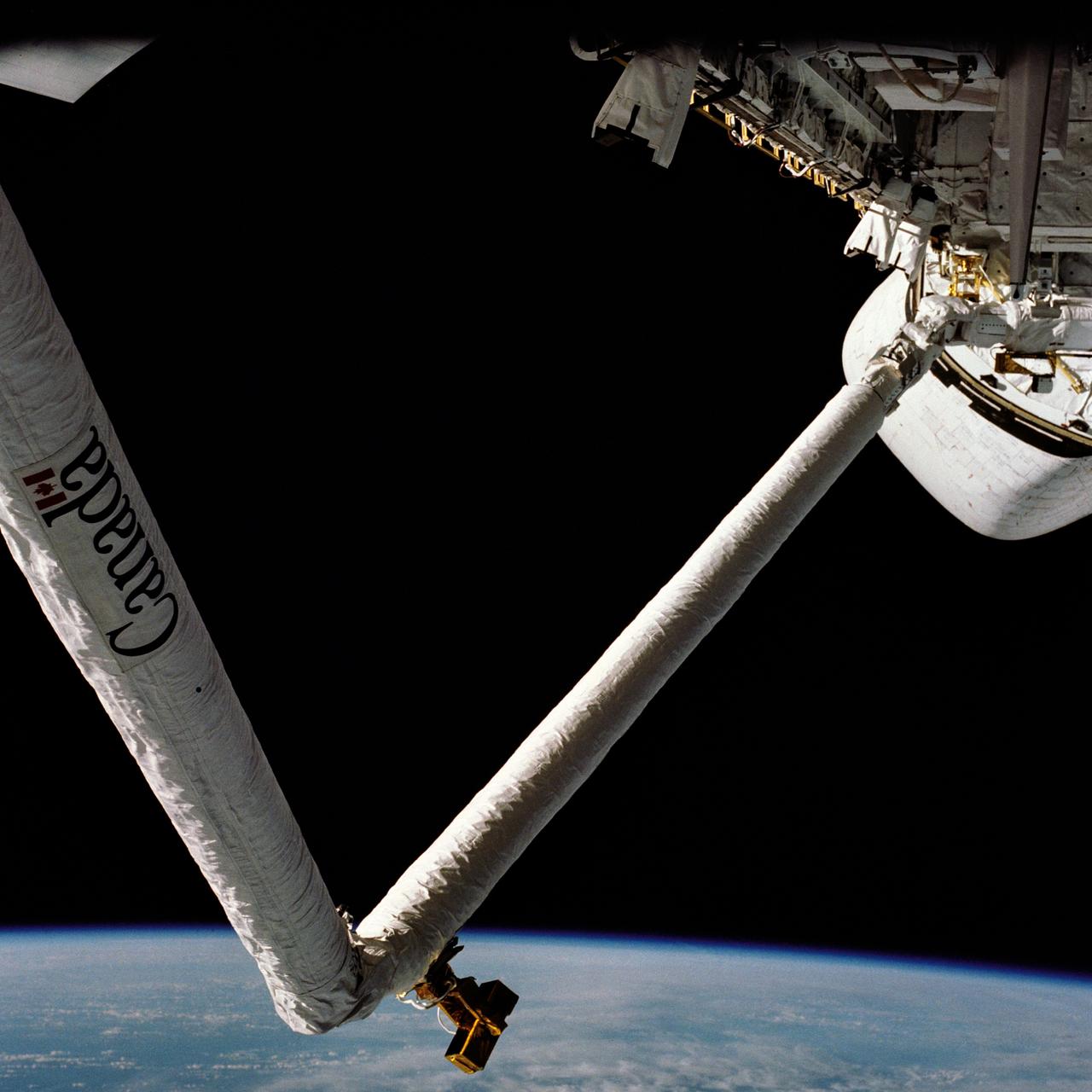

STS002-13-226 (13 Nov. 1981) --- Backdropped against Earth's horizon and the darkness of space, the space shuttle Columbia's remote manipulator system (RMS) gets its first workout in zero-gravity during the STS-2 mission. A television camera is mounted near the elbow and another is partially visible near the wrist of the RMS. Photo credit: NASA
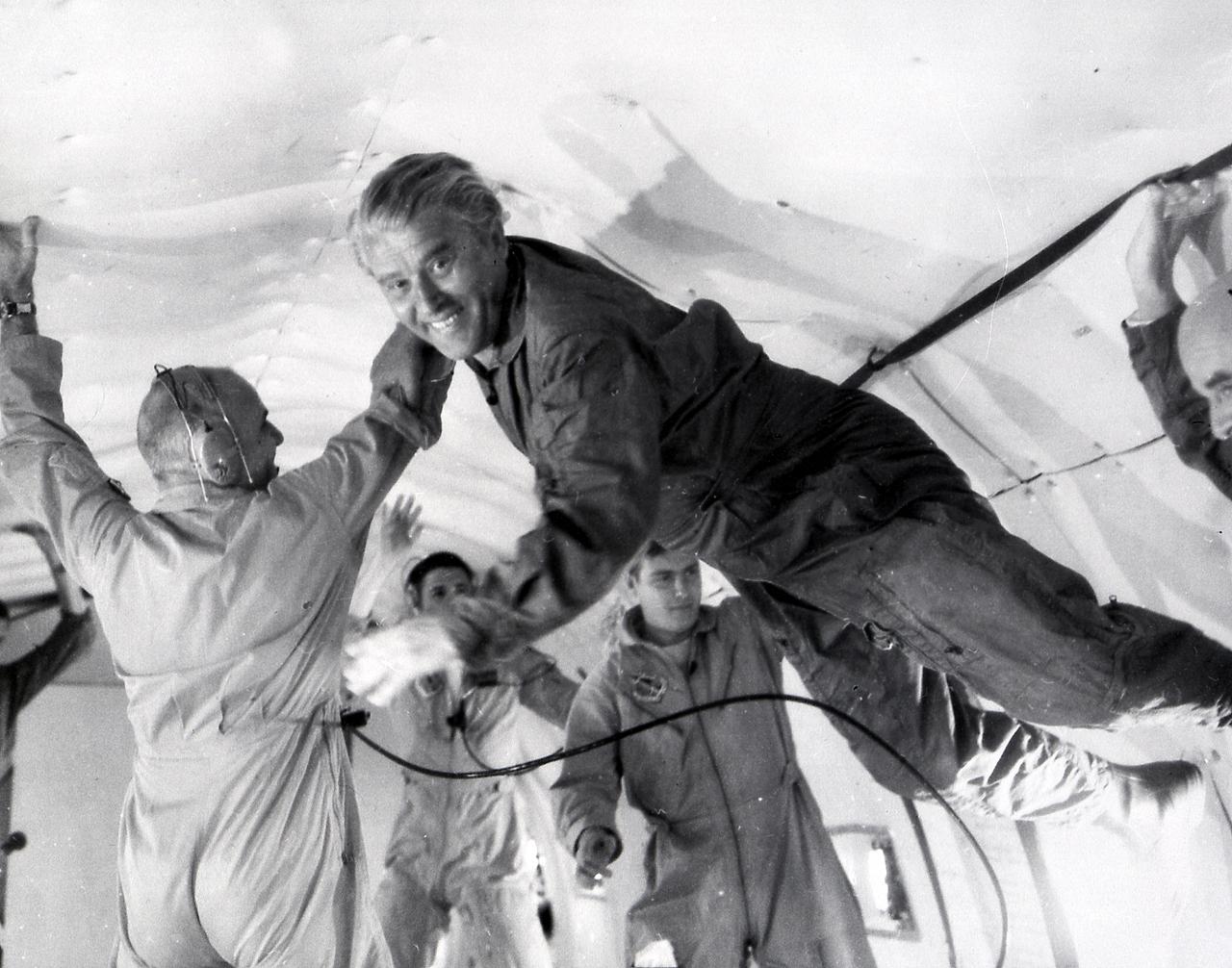

Dr. von Braun inside the KC-135 in flight. The KC-135 provide NASA's Reduced-Gravity Program the unique weightlessness or zero-g environment of space flight for testing and training of human and hardware reactions. The recent version, KC-135A, is a specially modified turbojet transport which flies parabolic arcs to produce weightlessness periods of 20 to 25 seconds and its cargo bay test area is approximately 60 feet long, 10 feet wide, and 7 feet high.
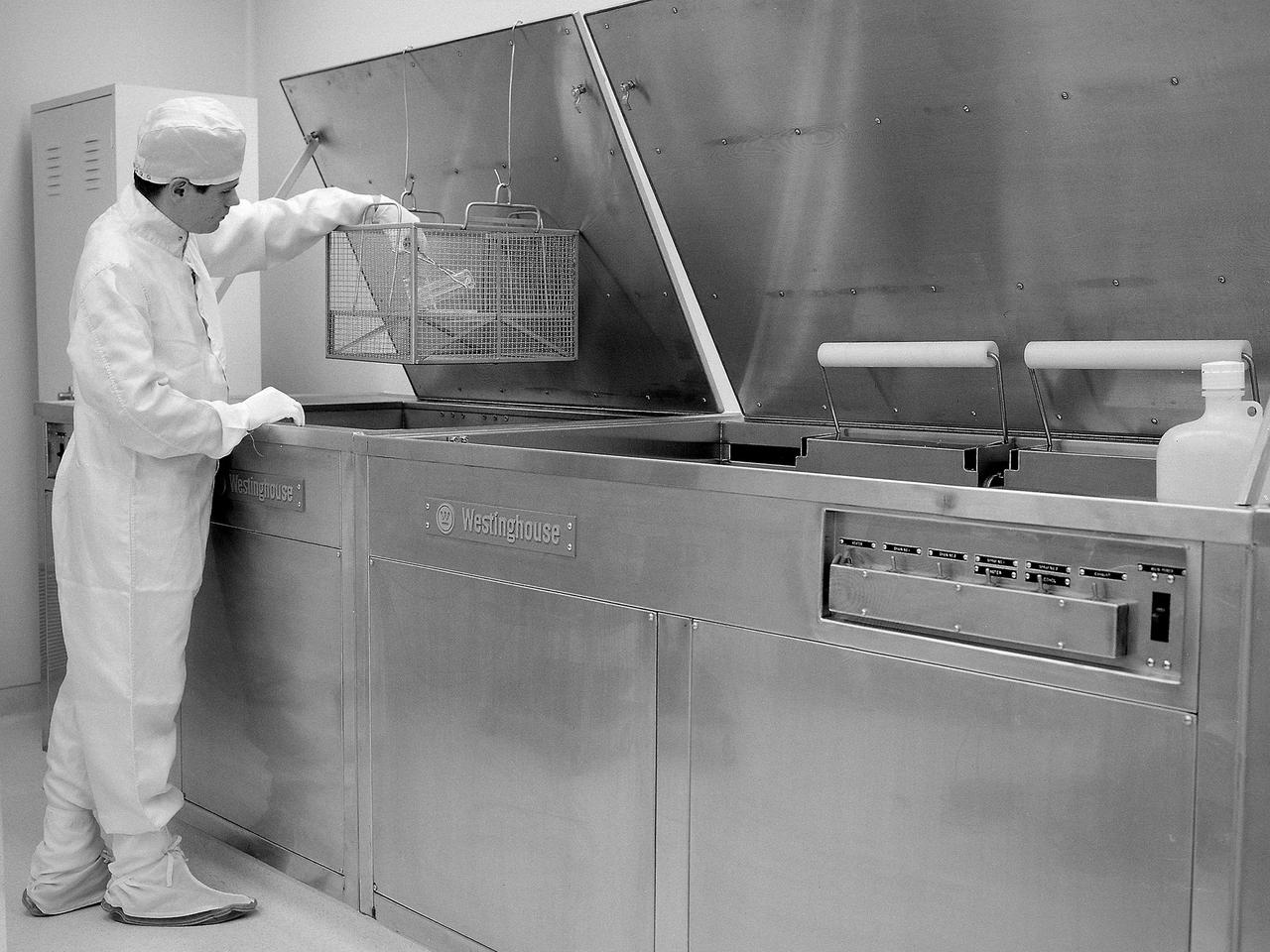

A technician prepares a test sample in the Zero Gravity Research Facility clean room at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Zero Gravity Research Facility contained a drop tower which provided five seconds of microgravity during freefall in its 450-foot deep vacuum chamber. The facility has been used for a variety of studies relating to the behavior of fluids and flames in microgravity. During normal operations, a cylindrical 3-foot diameter and 11-foot long vehicle was used to house the experiments, instrumentation, and high speed cameras. The 4.5-foot long and 1.5-foot wide rectangular vehicle, seen in this photograph, was used less frequently. A 3-foot diameter orb was used for the special ten-second drops in which the package was pneumatically shot to the top of the tower then dropped. The facility also contained a control room, shop offices, tool and equipment rooms, and this clean room. The 242.5-foot long and 19.5-foot wide clean room was equipped with specialized cleaning equipment. In the 1960s the room was rated as a class 10,000 clean room, but I was capable of meeting the class 100 requirements. The room included a fume hood, ultrasonic cleaner, and a laminar flow station which operated as a class 100 environment. The environment in the clean room was maintained at 71° F and a relative humidity of 45- percent.
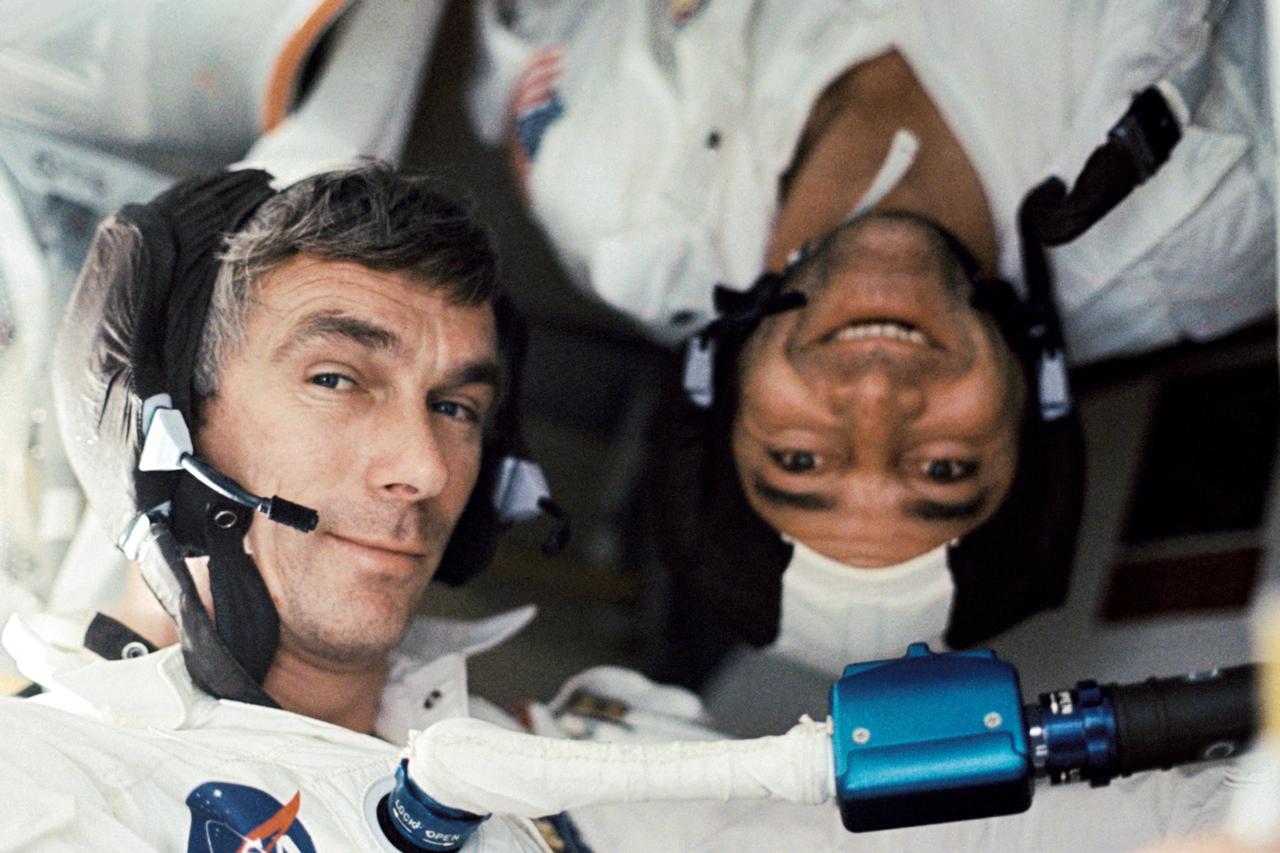

AS17-162-24053 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot, took this photograph of his two fellow crew men under zero-gravity conditions aboard the Apollo 17 spacecraft during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. That is astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander, who is seemingly "right side up." Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, appears to be "upside down." While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
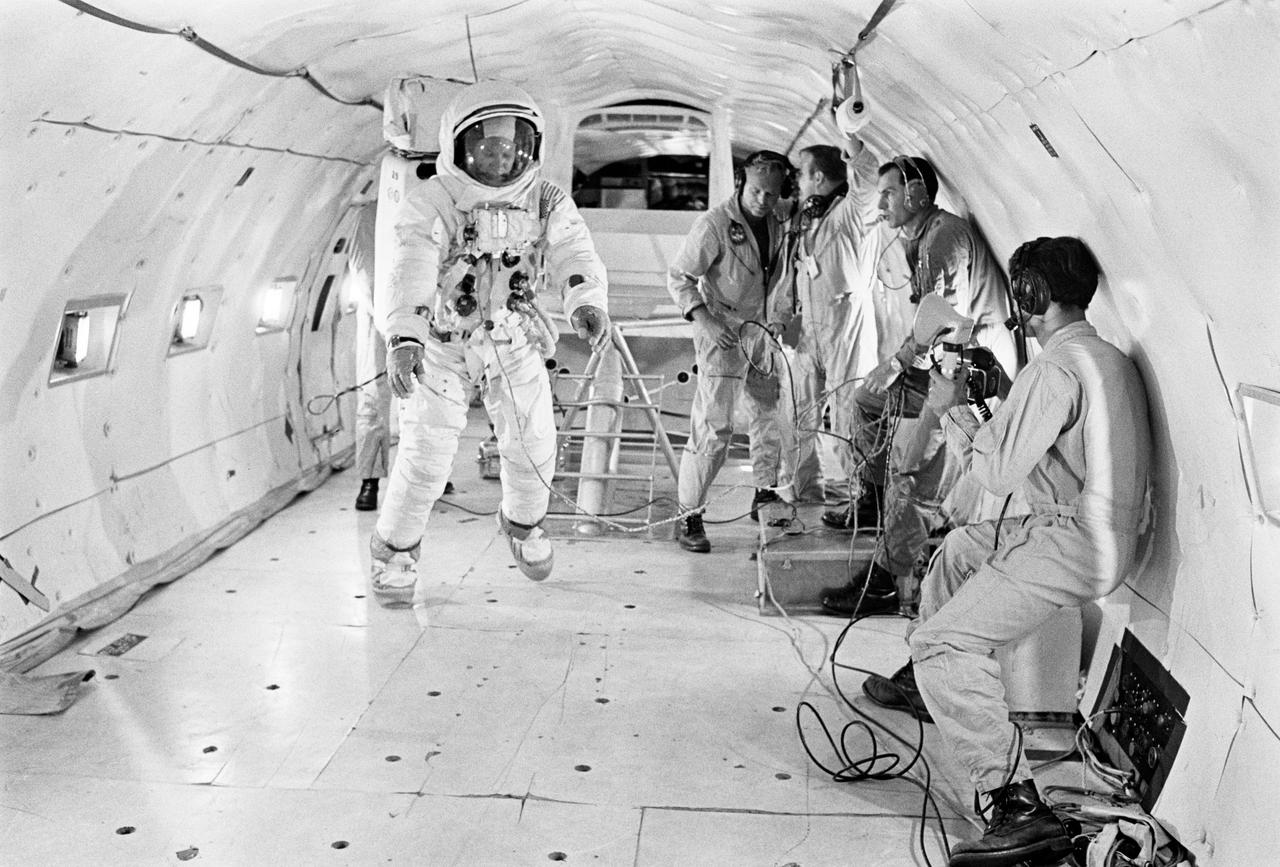

S69-39269 (10 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, undergoes zero-gravity training aboard a U.S. Air Force KC-135 jet aircraft from nearby Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. Aldrin is wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), the type of equipment which he will wear on the lunar surface.
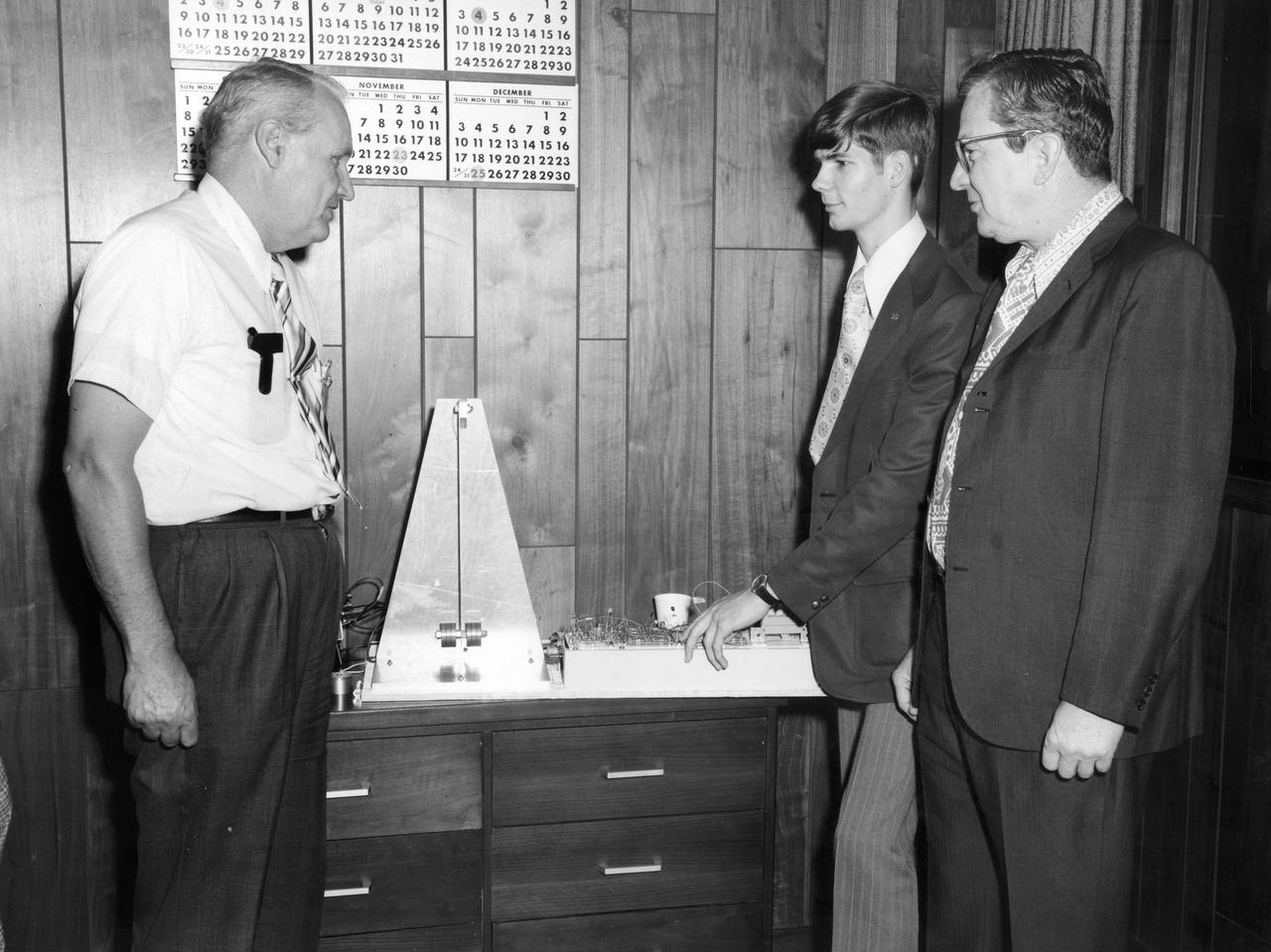

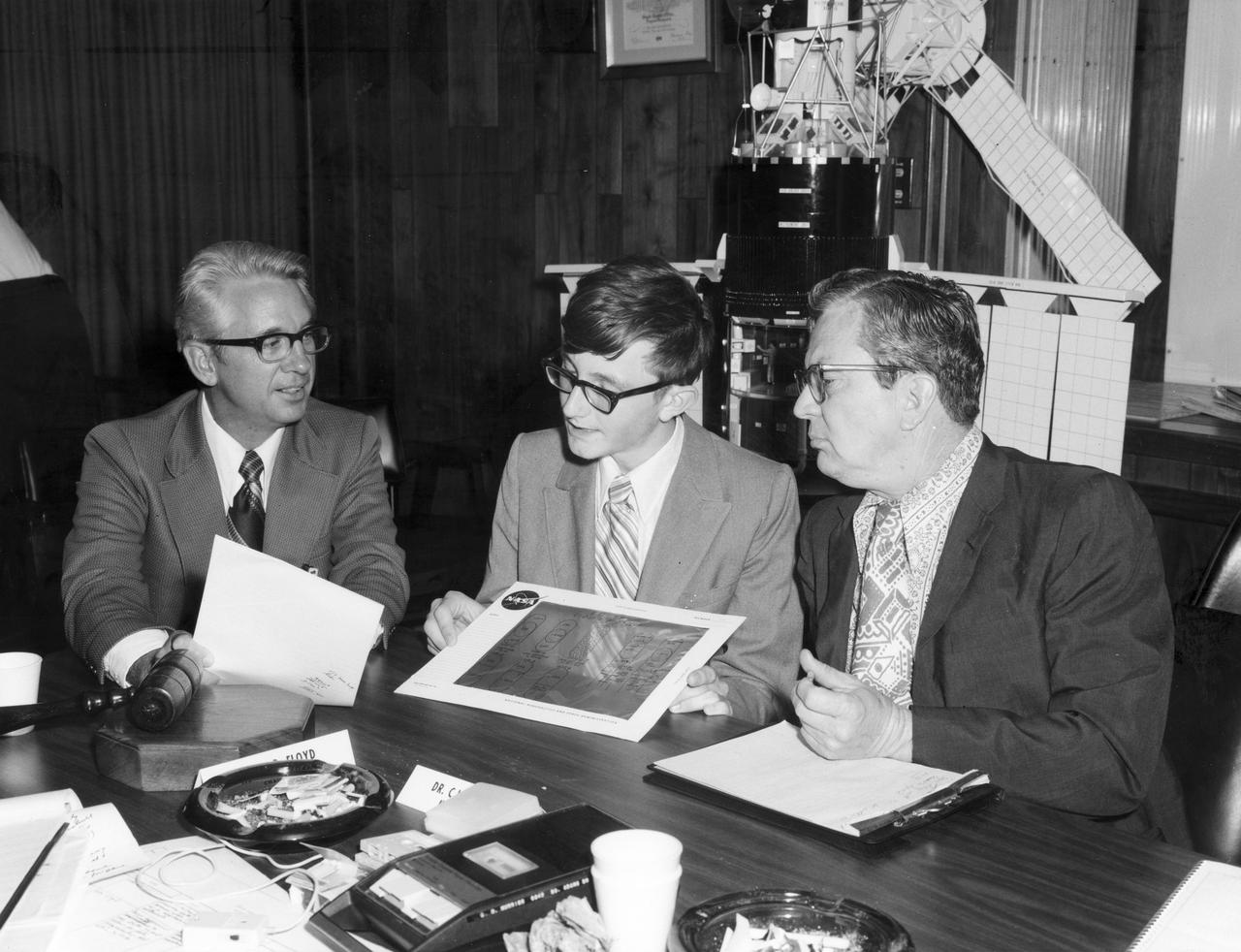
Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse, discussed his proposed Skylab experiment with Dr. Robert Head (right) and Gene Greshman of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. The electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of equipment, such as that of Converse’s experiment.
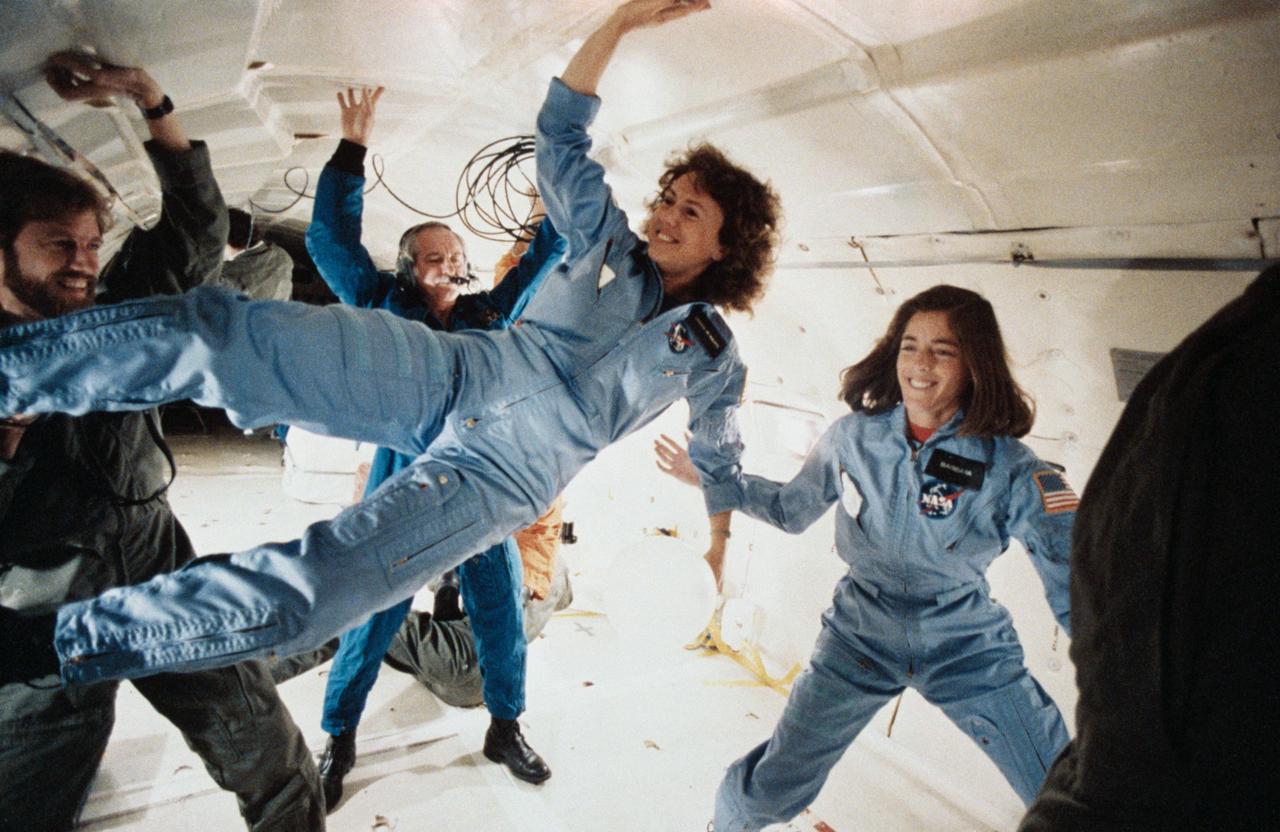

S86-25191 (for release January 1986) --- The two representatives of the Teacher-in-Space Project continue their training program at the Johnson Space Center with an additional flight aboard NASA?s KC-135 ?zero gravity? aircraft. Sharon Christa McAuliffe, left, is prime crew payload specialist, and Barbara R. Morgan is in training as backup payload specialist. The photo was taken by Keith Meyers of New York Times. Photo credit: NASA
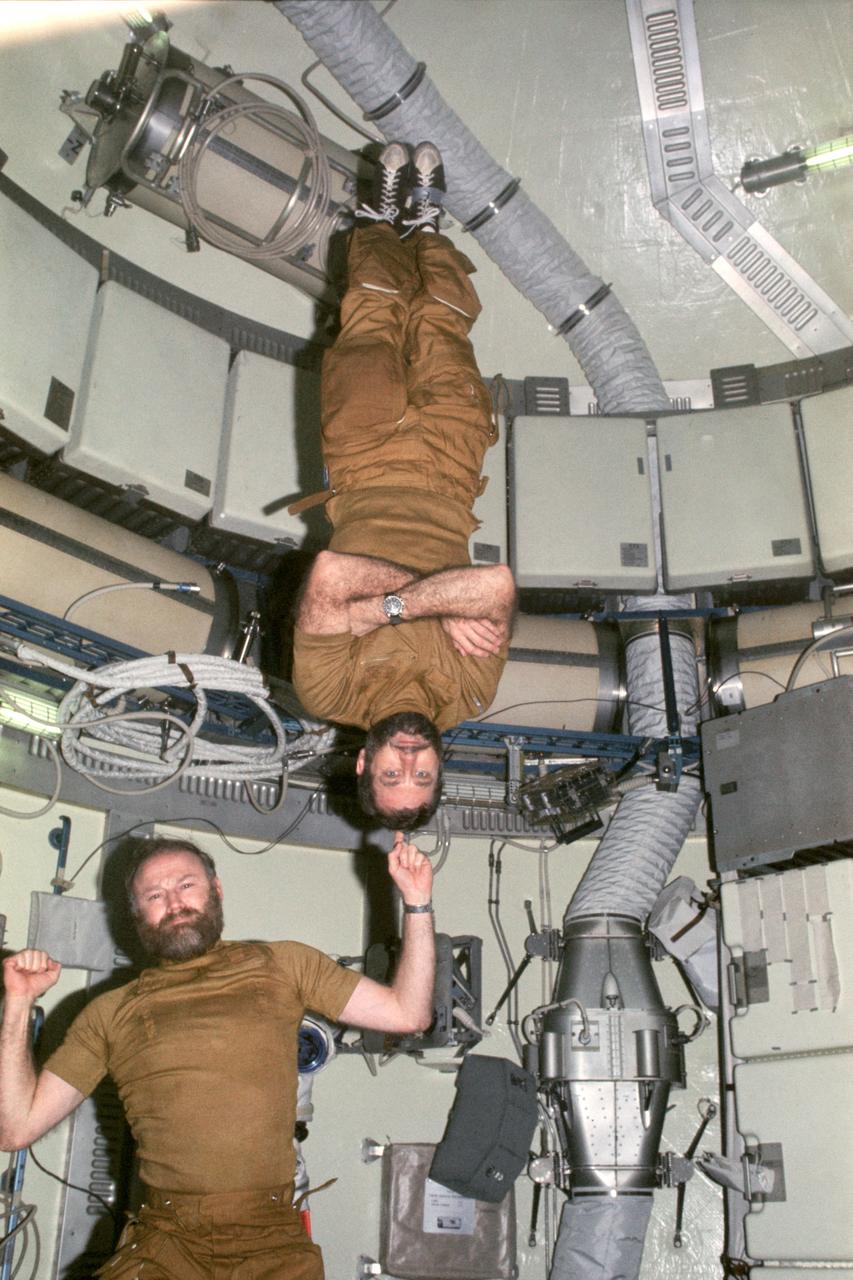

SL4-150-5080 (16 Nov. 1973-8 Feb. 1974) --- Two of the three Skylab 4 (third manning) astronauts exhibit the "magic" that can be accomplished in the weightlessness of space. Astronaut Gerald D. Carr, mission commander, uses his index finger to suspend astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot, in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The two "wizards" completed almost three months aboard the Earth-orbiting Skylab space station, plenty of time to grow these full beards. The photograph was taken with a 35mm camera by astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot. Photo credit: NASA
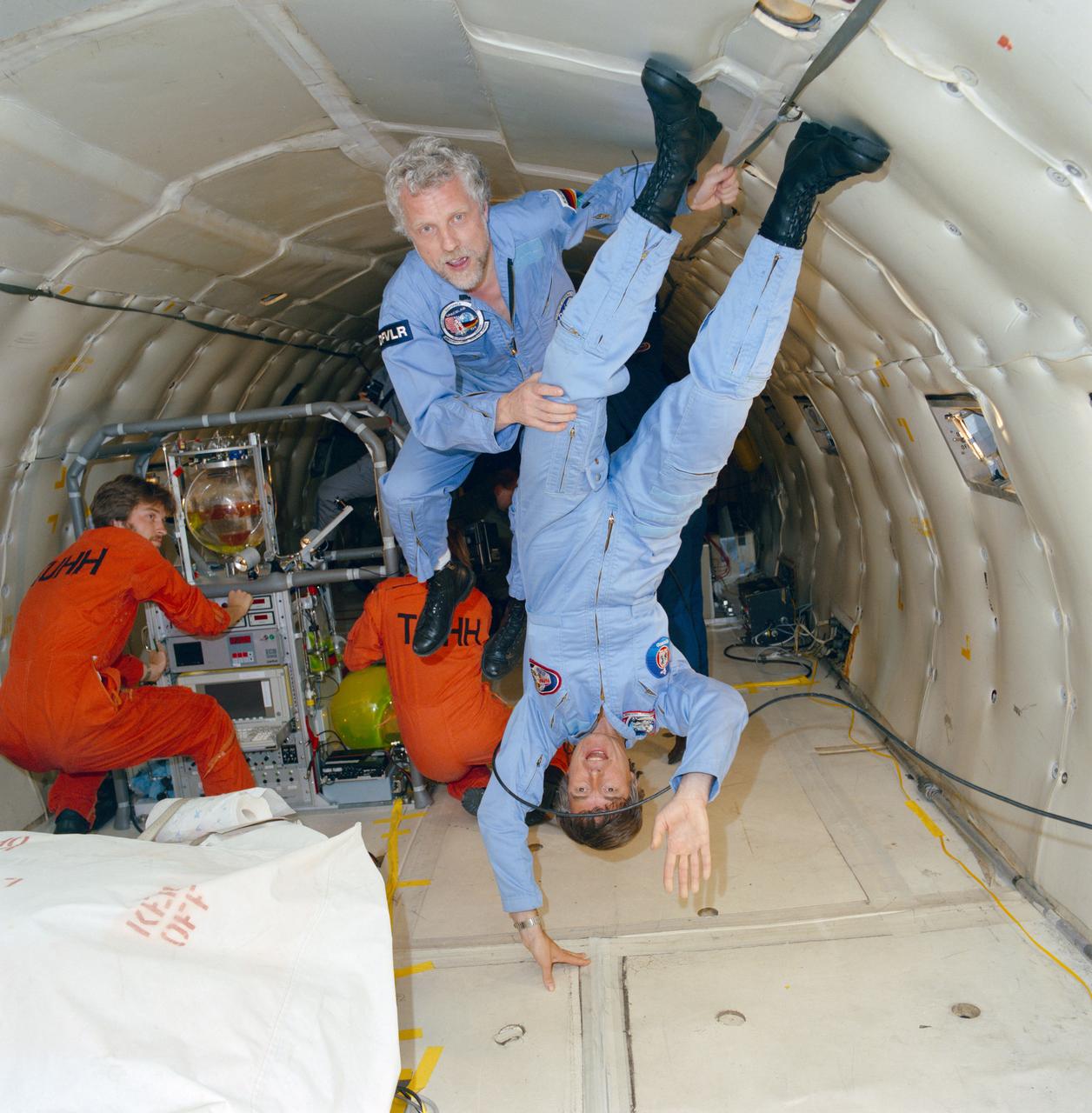

S88-37966 (2 Oct 1988) --- European Space Agency payload specialists Ulf Merbold (STS-42, right) and Reinhold Furrer (STS 61-A) get the "feel" of zero-gravity aboard NASA's KC-135 aircraft over the Gulf of Mexico.
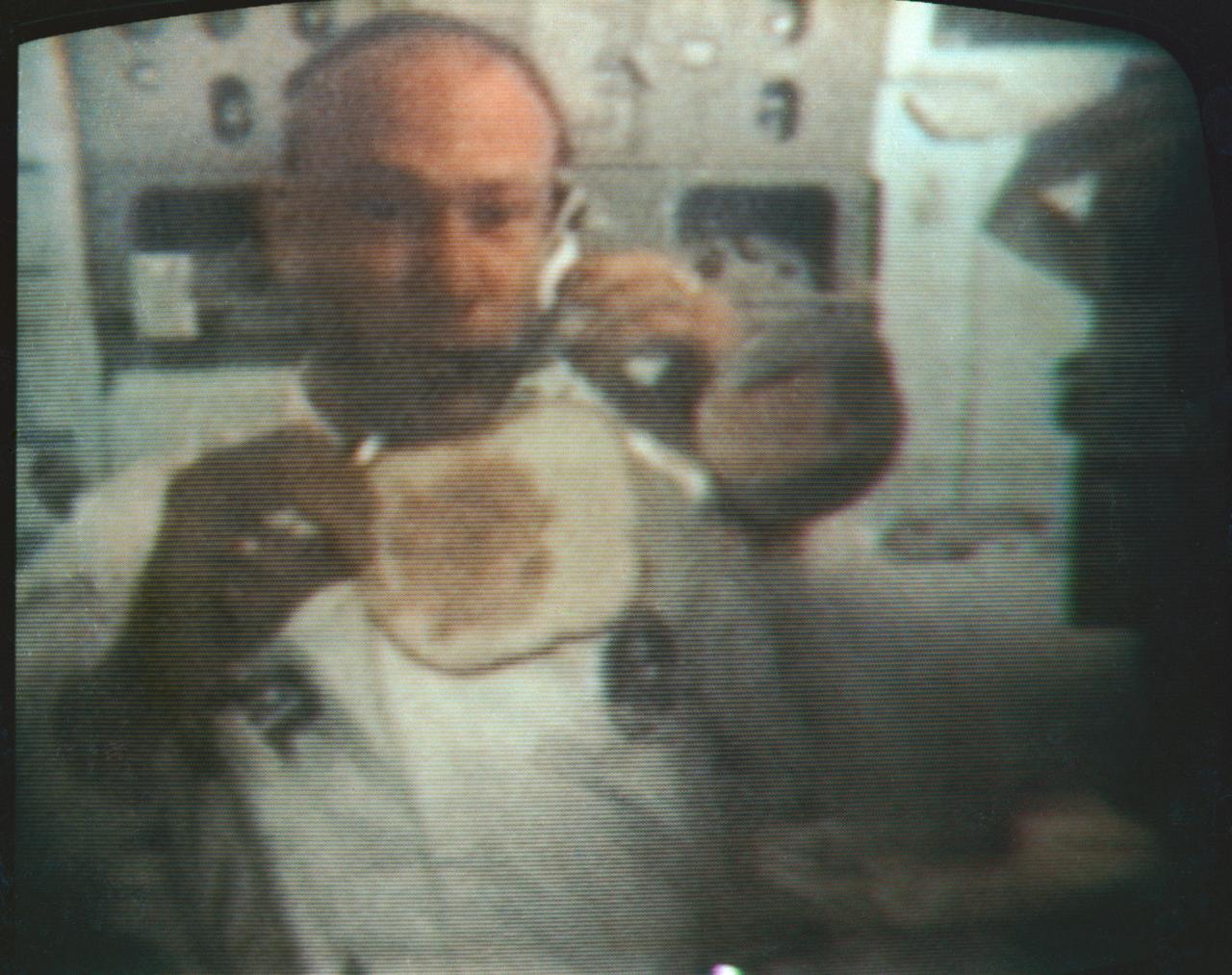

S69-39724 (22 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Apollo 11 lunar module pilot, performs for his Earth-bound television audience, in this color reproduction taken from a TV transmission, from the Apollo 11 spacecraft during its trans-Earth journey home from the moon. Aldrin illustrates how to make a sandwich under zero-gravity conditions. When this picture was made, Apollo 11 was approximately 137,000 nautical miles from Earth, traveling at a speed of about 4,300 feet per second. Also, aboard the spacecraft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; and Michael Collins, command module pilot.
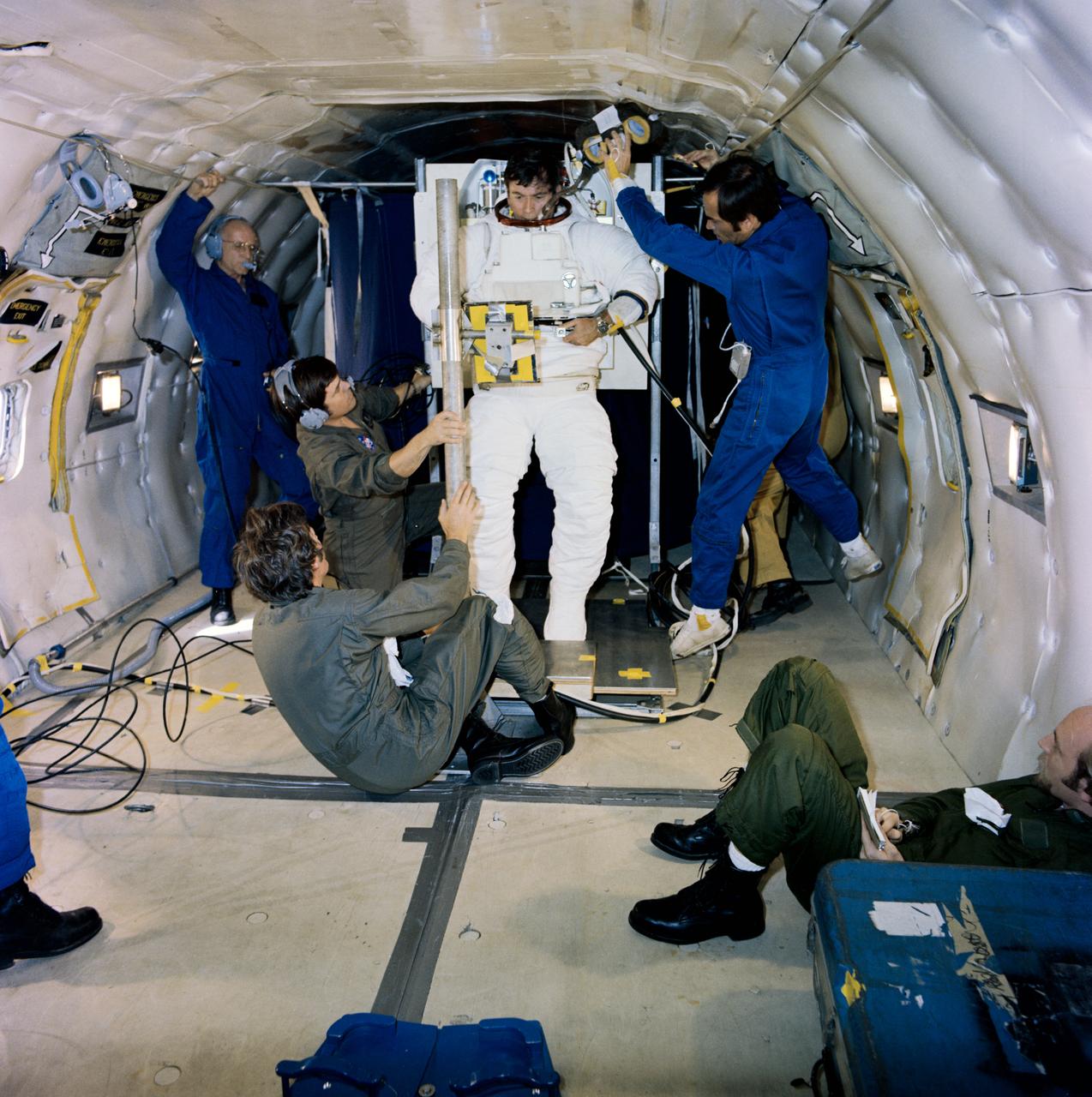

S79-30347 (31 March 1979) --- Taking advantage of a brief period of zero-gravity afforded aboard a KC-135 flying a parabolic curve, the flight crew of the first space shuttle orbital flight test (STS-1) goes through a spacesuit donning exercise. Astronaut John W. Young has just entered the hard-material torso of the shuttle spacesuit by approaching it from below. He is assisted by astronaut Robert L. Crippen. The torso is held in place by a special stand here, simulating the function provided by the airlock wall aboard the actual shuttle craft. The life support system is mated to the torso on Earth and remains so during the flight, requiring this type of donning and doffing exercise. Note Crippen?s suit is the type to be used for intravehicular activity in the shirt sleeve environment to be afforded aboard shuttle. The suit worn by Young is for extravehicular activity (EVA). Young will be STS-1 commander and Crippen, pilot. They will man the space shuttle orbiter 102 Columbia. Photo credit: NASA
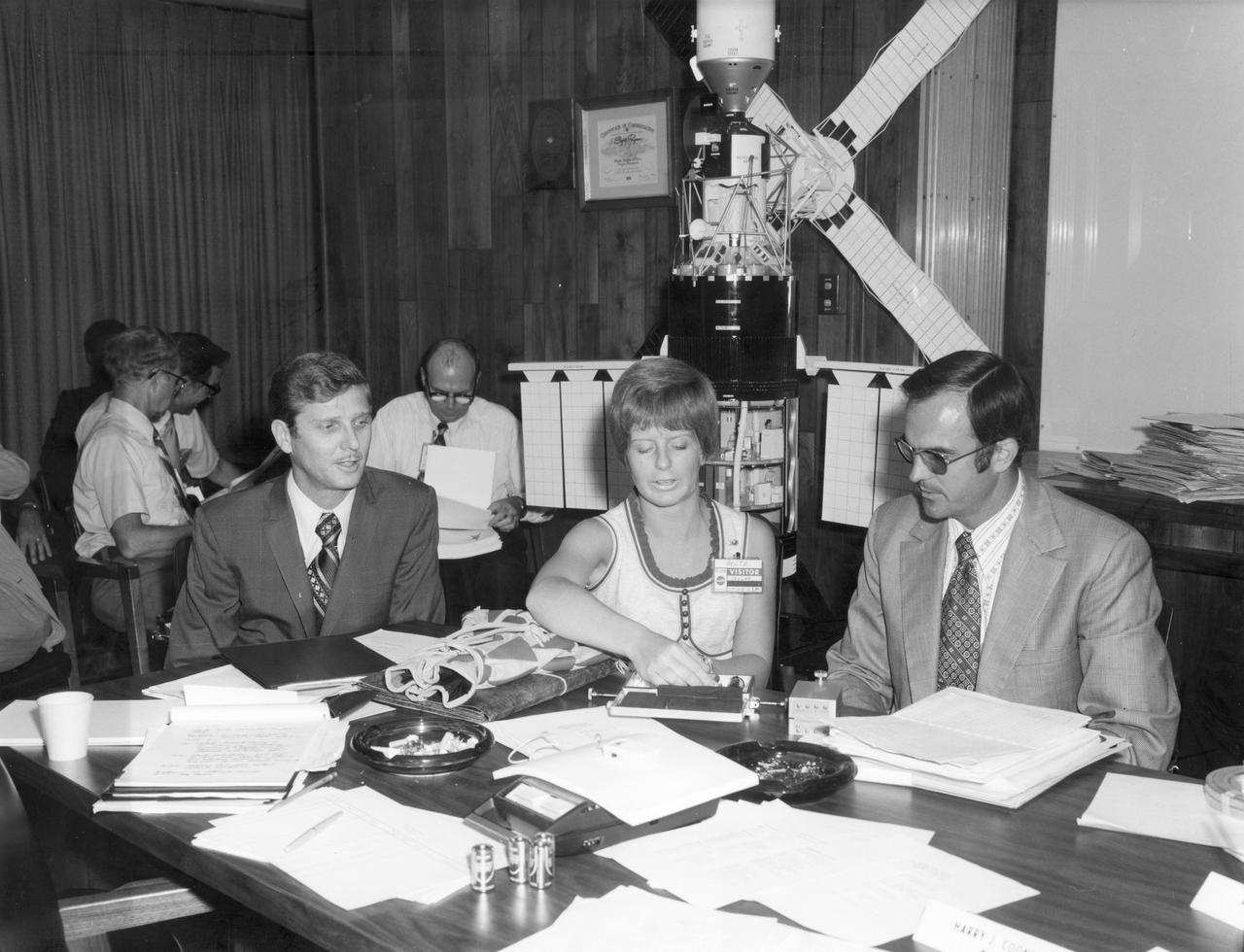

Miss Cheryl Peltz, high school student from Littleton, Colorado, discusses her “Cytoplasmic Streaming in Zero Gravity” experiment with Ed Armstrong (left) of the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center, and her advisor Charles Cothran (right) of the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). She was one of the 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab Mission. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of equipment, of which Miss Peltz’s was one.
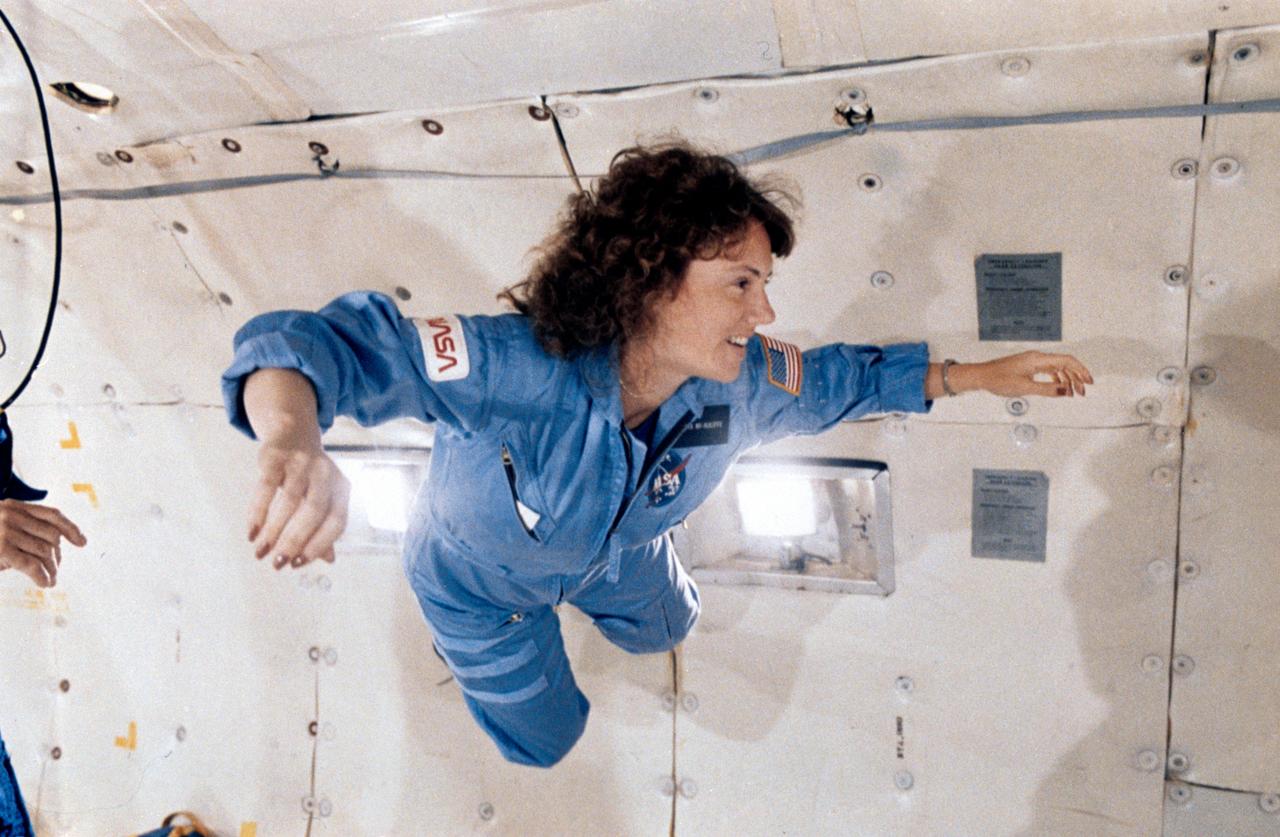

S86-25196 (January 1986) --- Sharon Christa McAuliffe, STS-51L citizen observer/payload specialist, gets a preview of microgravity during a special flight aboard NASA?s KC-135 ?zero gravity? aircraft. McAuliffe will represent the Teacher-in-Space Project aboard the space shuttle Challenger when it launches later this month. This photograph was taken by Keith Meyers of the New York Times. EDITOR?S NOTE: The STS-51L crew members lost their lives in the space shuttle Challenger accident moments after launch on Jan. 28, 1986 from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Photo credit: NASA
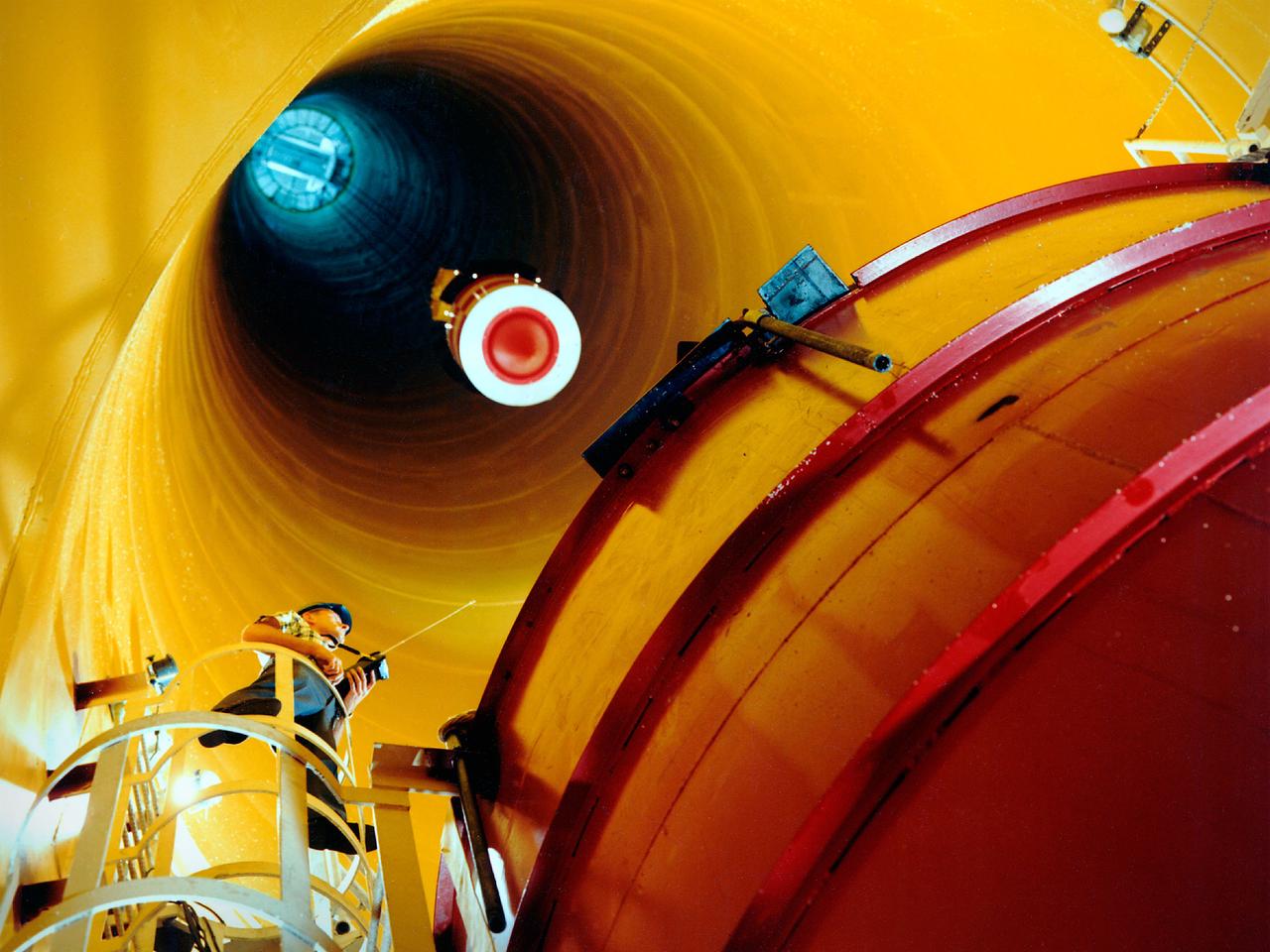

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis researchers had been studying the behavior of liquid in microgravity for several years using ballistic rocket flights, aircraft flying series of parabolas, and in the 2.2-Second Drop Tower. It was easier to control experiments and repeat tests based on almost instantaneous test results in the Zero Gravity Research Facility than missiles or aircraft. It also more than doubled the microgravity time of the original drop tower. The experiments were enclosed in a large experiment package that was suspended inside the chamber. A vacuum was introduced to the chamber before the package was released. The test equipment allowed researchers to film and take measurements of the experiment as it was falling. The 2500‐pound package was slowed by special Styrofoam‐like pellets in a decelerator cart. An experiment, traveling 176 feet per second, was stopped in about 15 feet of deceleration material. The facility’s designers struggled to determine the correct type of deceleration pellets to use. For several years Lewis engineers tested various samples from manufacturers. The final selection was not made until the facility’s completion in May 1966, just before the facility made its public debut at the 1966 Inspection of the Center.
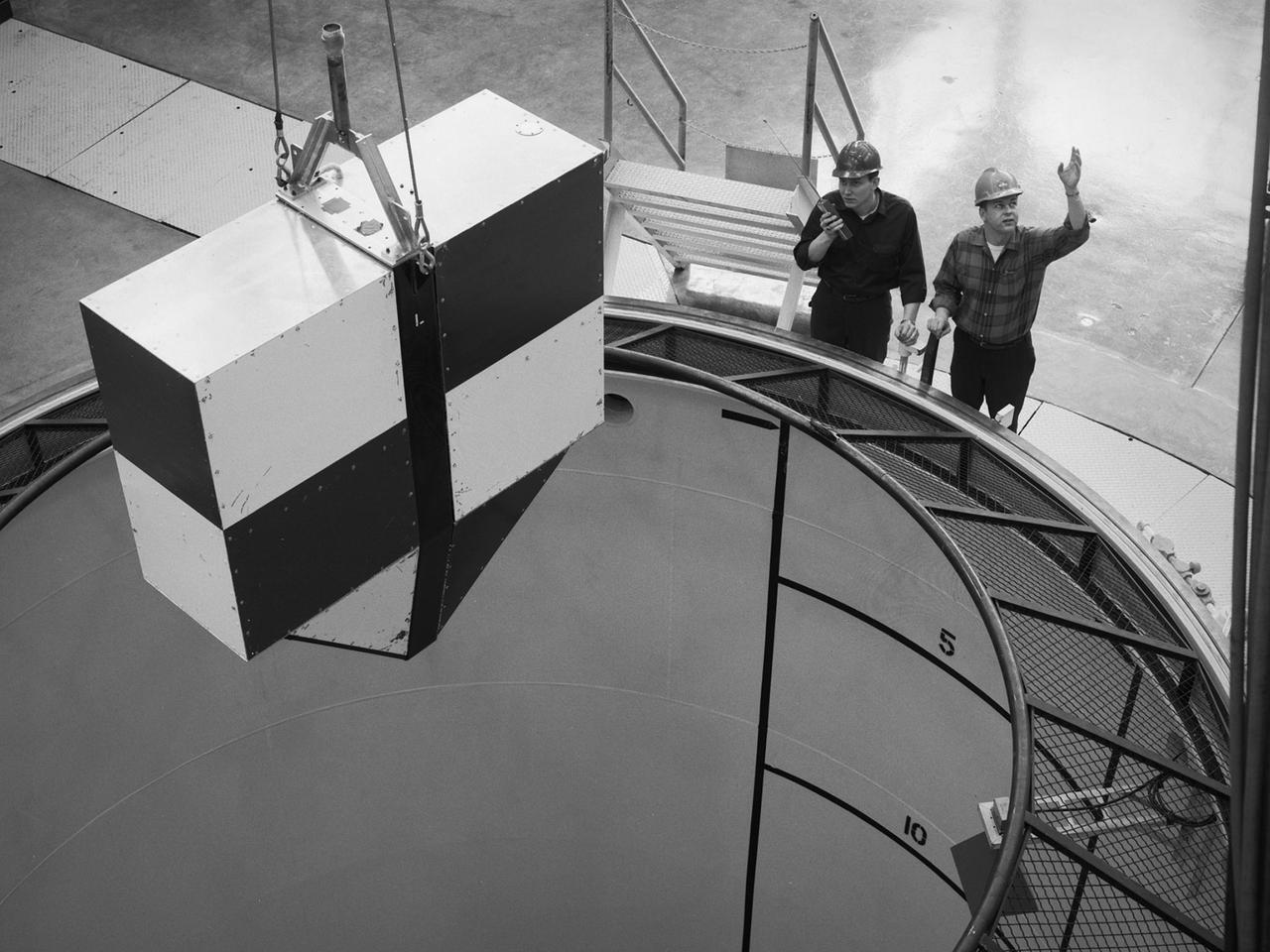
A rectangular drop test vehicle perched above 450-foot shaft at the Zero Gravity Research Facility at NASA Lewis Research Center. The drop tower was designed to provide five seconds of microgravity during a normal drop, but had a pneumatic gun that could quickly propel the vehicle to the top of the shaft prior to its drop, thus providing ten seconds of microgravity. The shaft contained a steel-lined vacuum chamber 20 feet in diameter and 469 feet deep. The package was stopped at the bottom of the pit by a 15-foot deep deceleration cart filled with polystyrene pellets. During normal operations, a cylindrical 3-foot diameter and 11-foot long vehicle was used to house the experiments, instrumentation, and high speed cameras. The 4.5-foot long and 1.5-foot wide rectangular vehicle, seen in this photograph, was used less frequently. A 3-foot diameter orb was used for the ten second drops. After the test vehicle was prepared it was suspended above the shaft from the top of the chamber. A lid was used to seal the top of the chamber. The vacuum system reduced the pressure levels inside the chamber. The bolt holding the vehicle was then sheared and the vehicle plummeted into the deceleration cart.
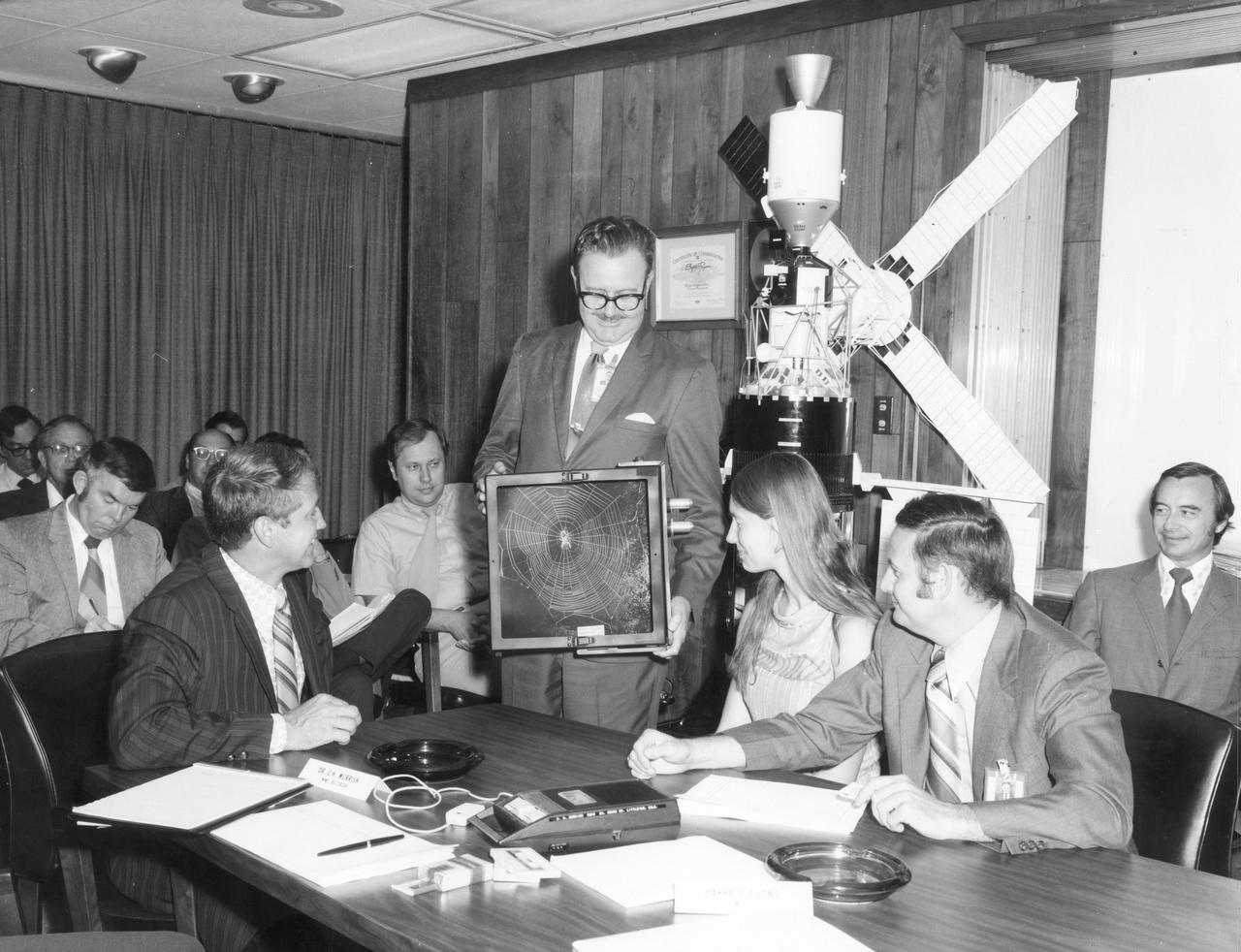

Lexington, Massachusetts high school student, Judith Miles, discusses her proposed Skylab experiment with engineers and scientists during a design review of the experiment equipment. At left is Ron Pavlue of Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC), holding a box is Keith Demorest of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Right of Miles is Dr. Raymond Gause, also of MSFC, who is Miles’ scientific advisor. In her experiment, called the “Web Formation in Zero Gravity”, spiders were released into a box and their actions recorded to determine how well they adapt to the absence of gravity. Spiders are known to adapt quickly to other changes in the environment but nothing was known of their ability to adapt to weightlessness. At the same time spiders were weaving webs in Earth orbit, similar spiders were spinning webs in identical boxes on Earth under full gravity conditions. Miles was among the 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of equipment.
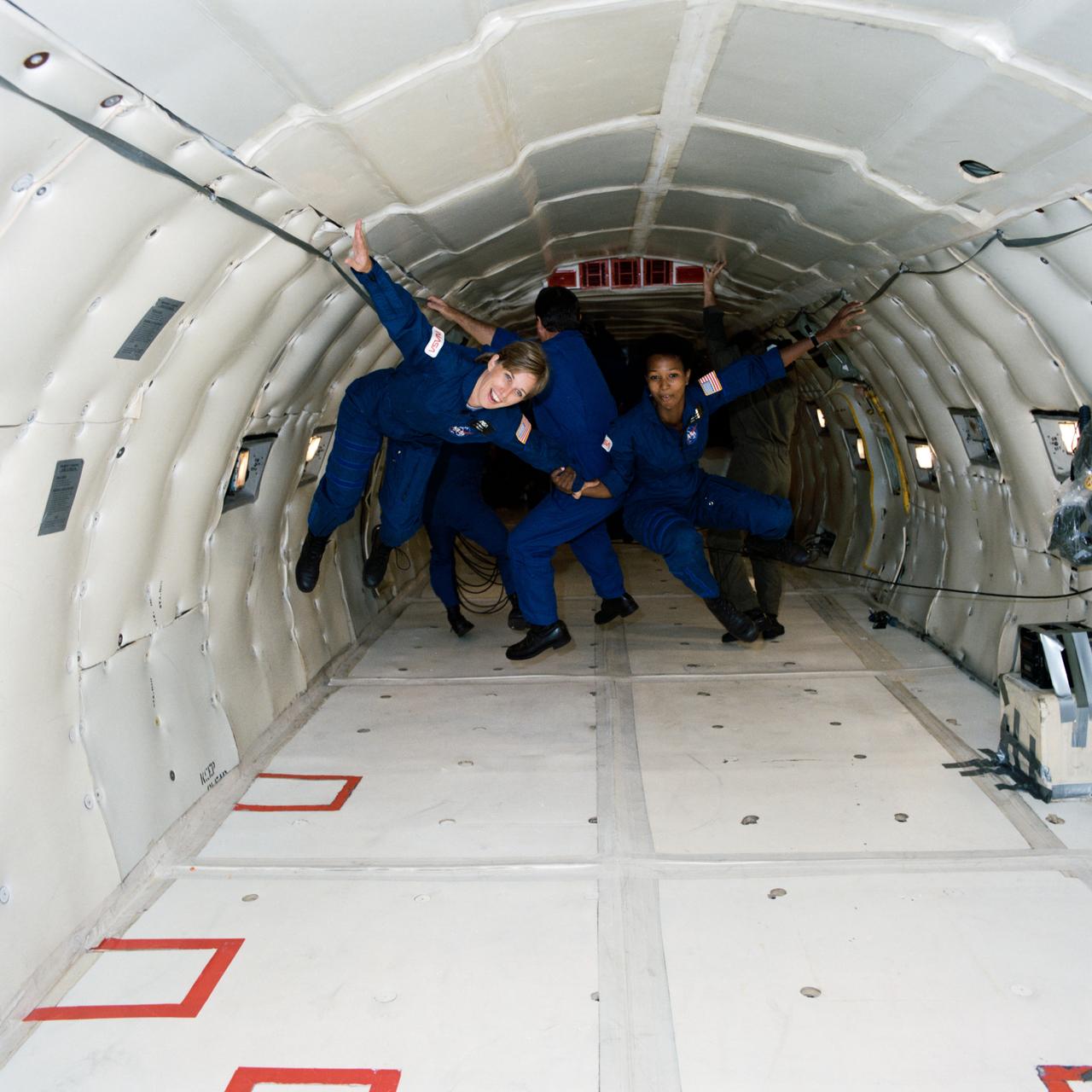

S87-44950 --- Group 12, 1987 Astronaut Class, candidates (ASCANs) N. Jan Davis (left) and Mae C. Jemison freefloat during the seconds of microgravity created aboard the KC-135 NASA 930 aircraft's parabolic flight. Davis and Jemison, two of the recently-named ASCANs, were taking a familiarization flight aboard the KC-135 "zero gravity" aircraft. Photo credit: NASA
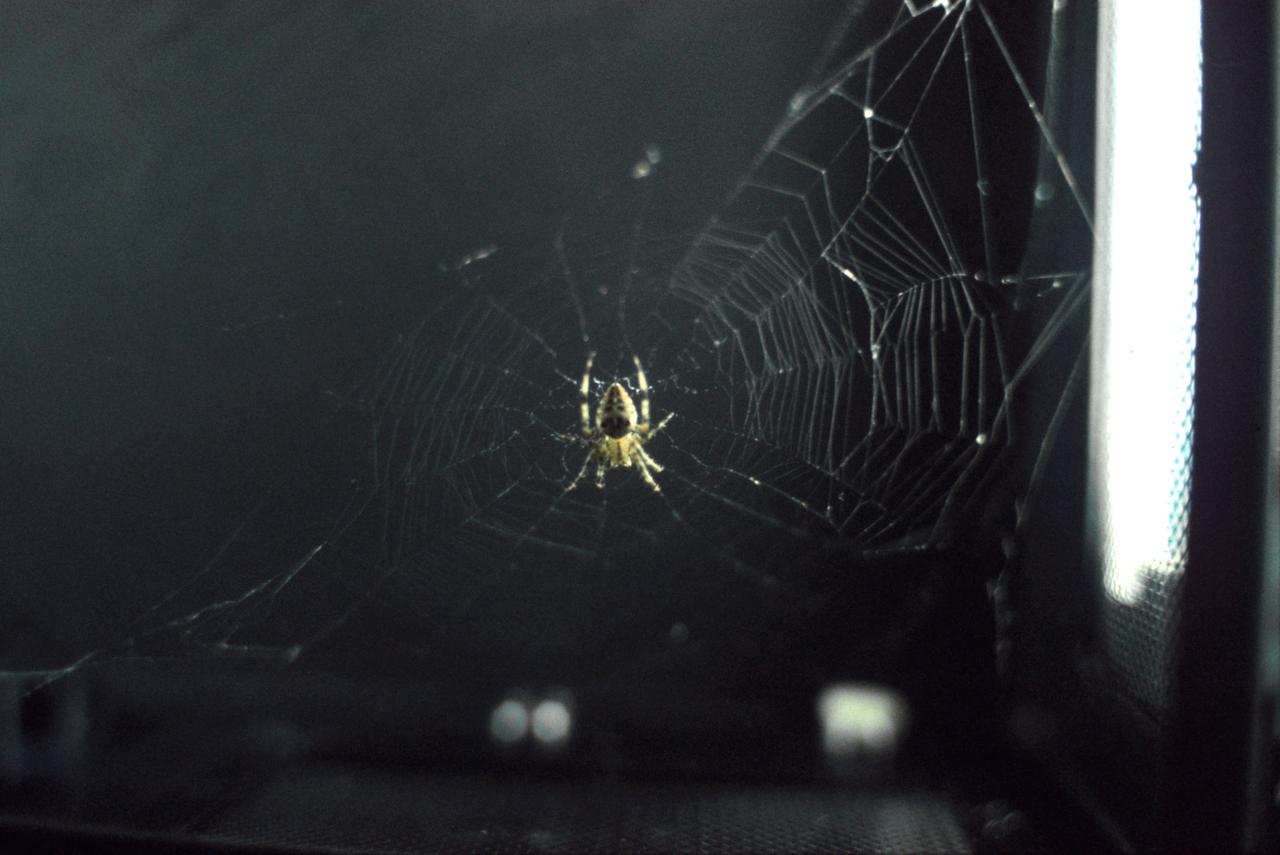

SL3-108-1307 (July-September 1973) --- A close-up view of Arabella, one of the two Skylab 3 common cross spiders "Araneus diadematus," and the web it had spun in the zero-gravity of space aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a hand-held 35mm Nikon camera. During the 59-day Skylab 3 mission the two spiders, Arabella and Anita, were housed in an enclosure onto which a motion picture and a still camera were attempts to build a web in the weightless environment. The spider experiment (ED52) was one of 25 experiments selected for Skylab by NASA from more than 3,400 experiment proposals submitted by high school students throughout the nation. ED52 was submitted by 17-year-old Judith S. Miles of Lexington, Massachusetts. Anita died during the last week of the mission. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27262 (1 June 1973) --- The three Skylab 2 crewmen give a demonstration on the effects of weightlessness in the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz are crouched in a fast-start stance to race around the dome area of the OWS forward compartment. The astronauts had ease of motion and good maneuverability in the zero-gravity of space. Photo credit: NASA
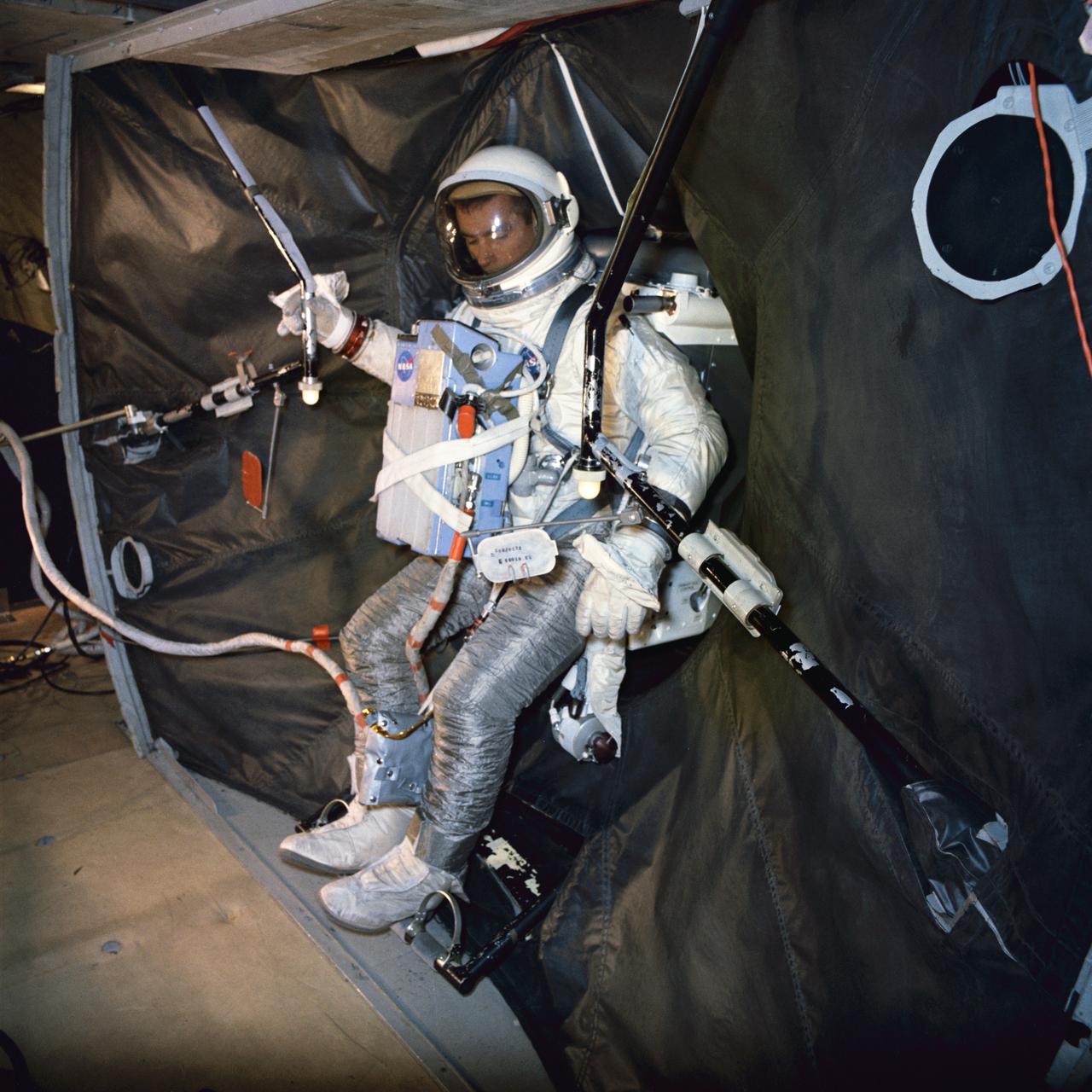

S66-31665 (3 May 1966) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, pilot of the Gemini-9 spaceflight, participates in extravehicular training under zero-gravity conditions aboard a KC-135 aircraft. Here, he is donning the Astronaut Maneuvering Unit (AMU) backpack after egressing a Gemini mock-up. The AMU backpack is mounted in the adapter equipment section of the mock-up. Cernan wears an extravehicular activity (EVA) life support system chest pack. Cernan will use the AMU during his scheduled EVA on the Gemini-9 mission. The KC-135 flew a parabolic curve to create the weightlessness condition for training purposes. Photo credit: NASA

Zero Gravity Research Facility
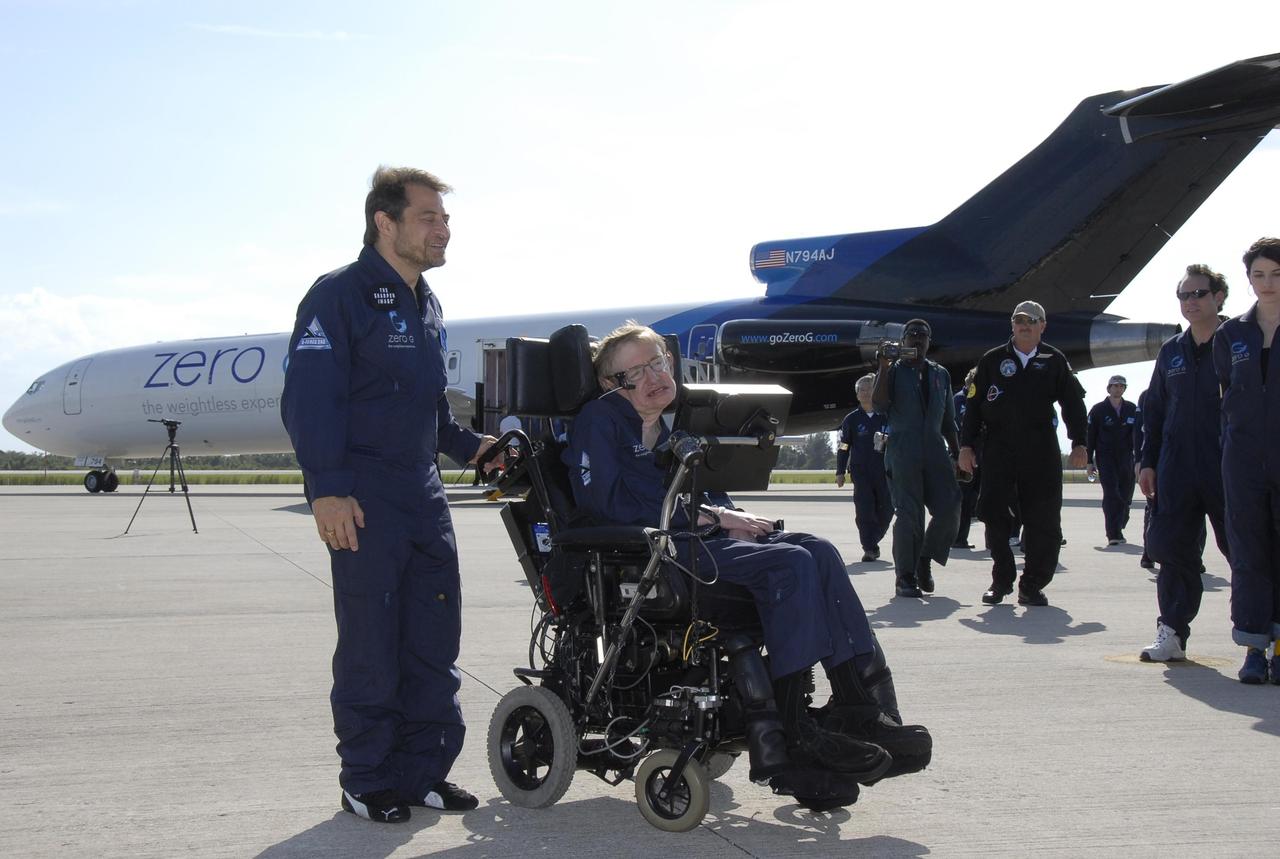

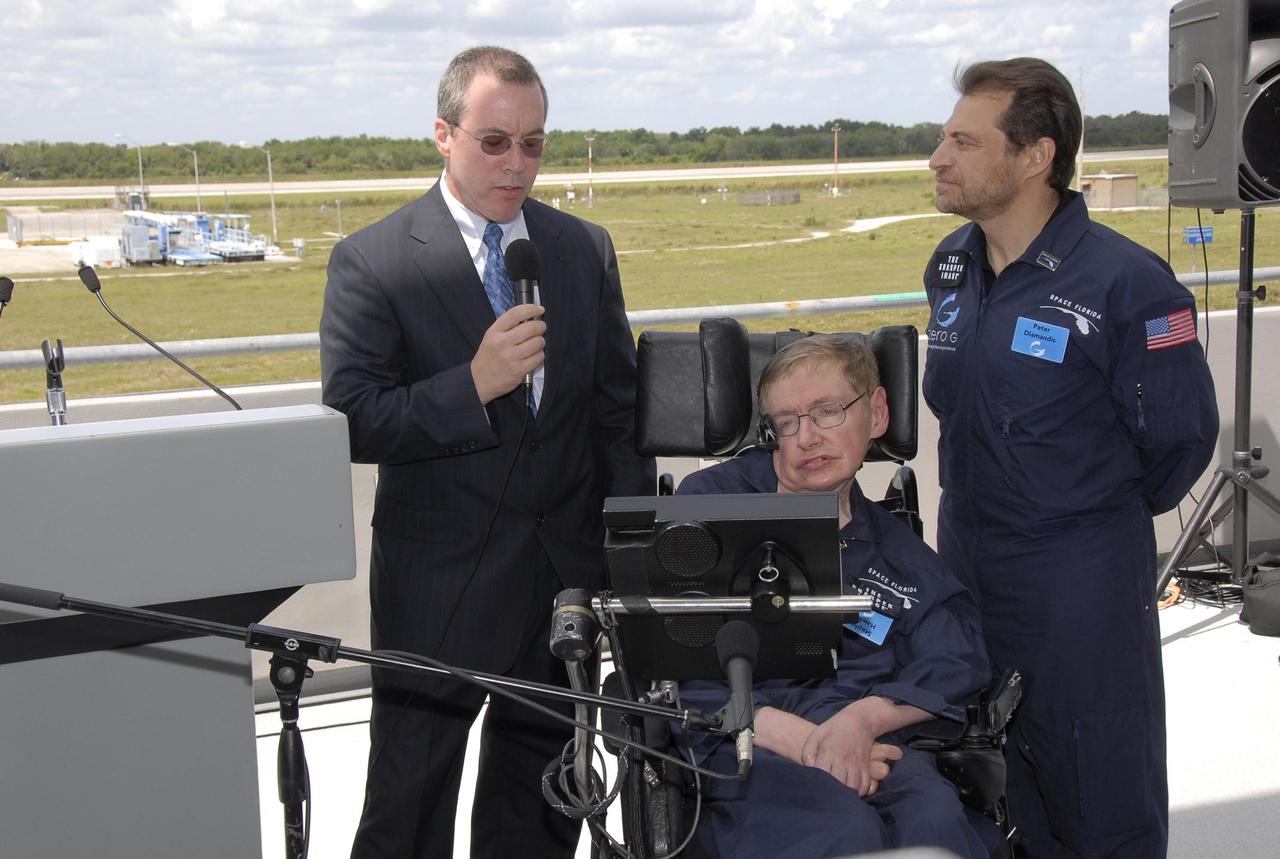
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Peter Diamandis (left), founder of the Zero Gravity Corp., and noted physicist Stephen Hawking move away from Zero G's modified Boeing 727 on the runway at the Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility. Hawking enjoyed his first zero gravity flight provided by Zero G. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
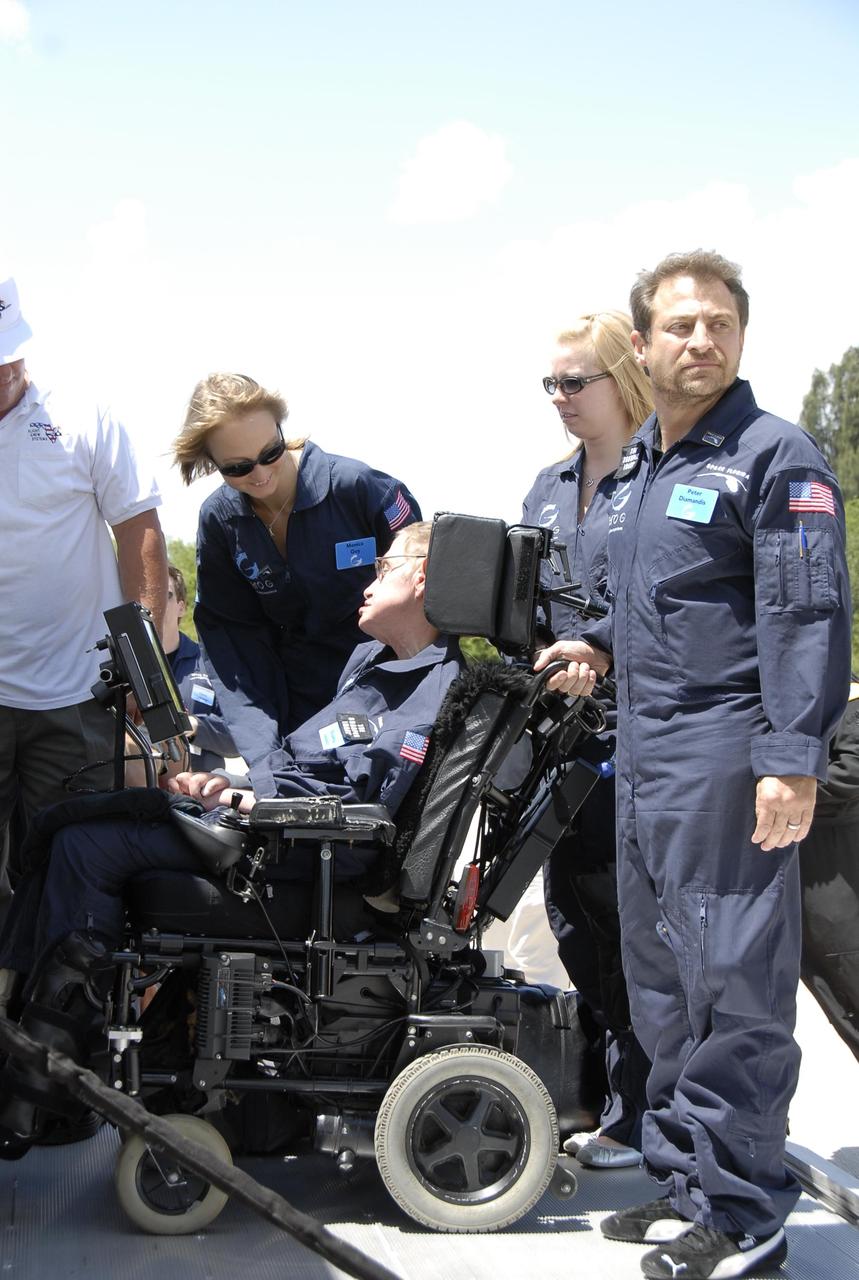

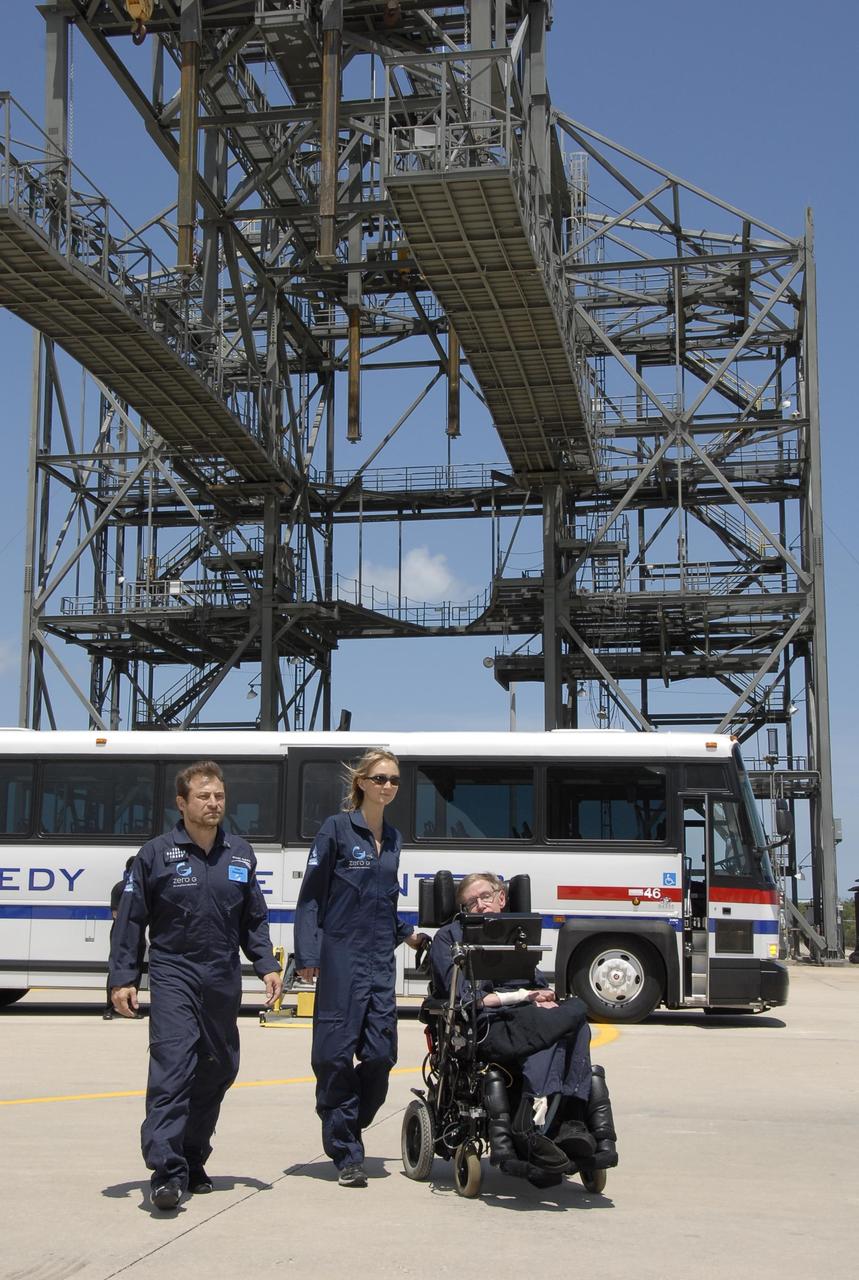
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, noted physicist Stephen Hawking, in the wheelchair, is ready to get onboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp. for his first zero-gravity flight. Zero Gravity Corp. is a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. At right is Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. Behind Hawking is Nicola O'Brien, a nurse practitioner who is Hawking's aide. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
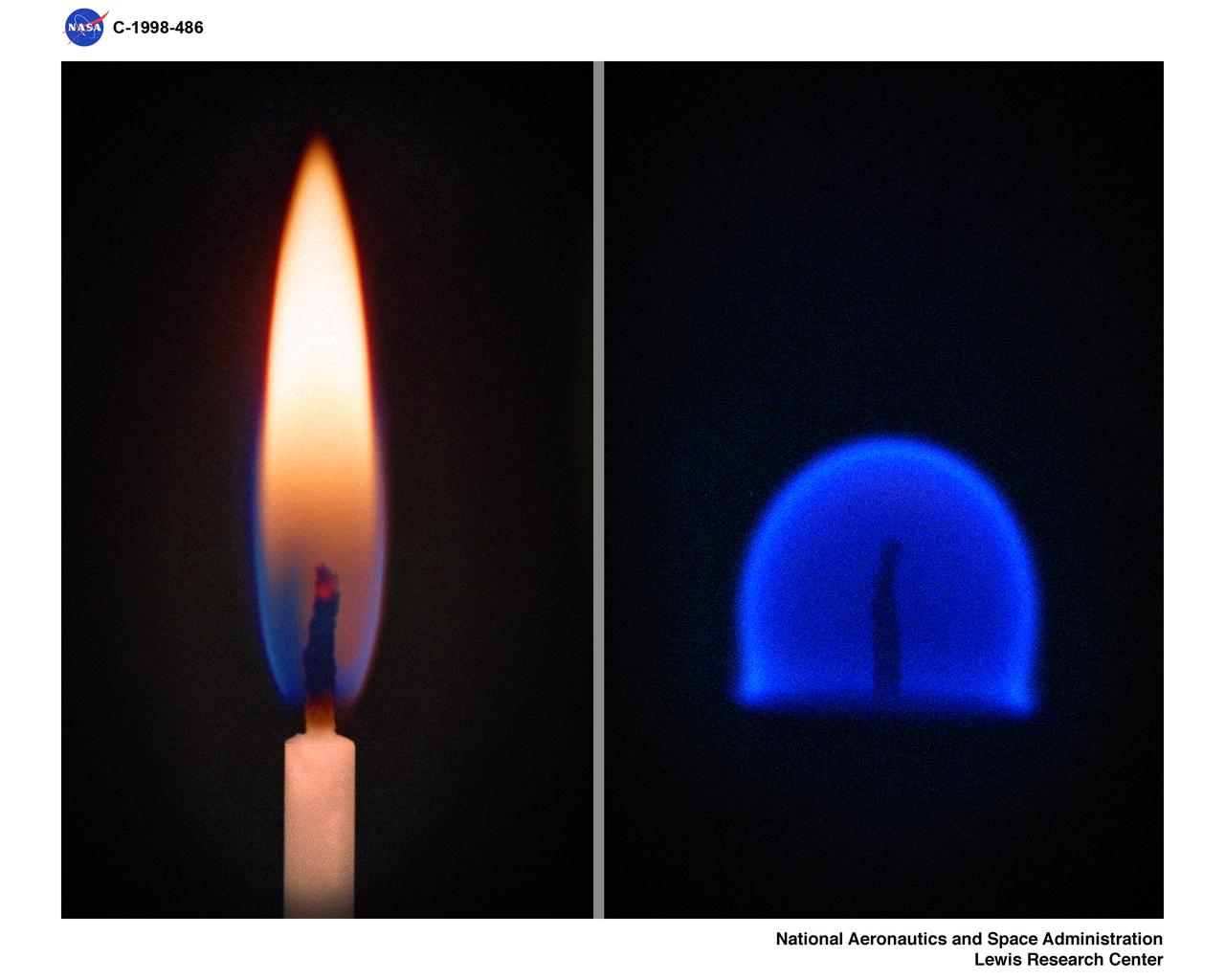

CANDLE FLAME NORMAL 1-G ONE GRAVITY AND MICROGRAVITY 0-G ZERO GRAVITY COMPARISON
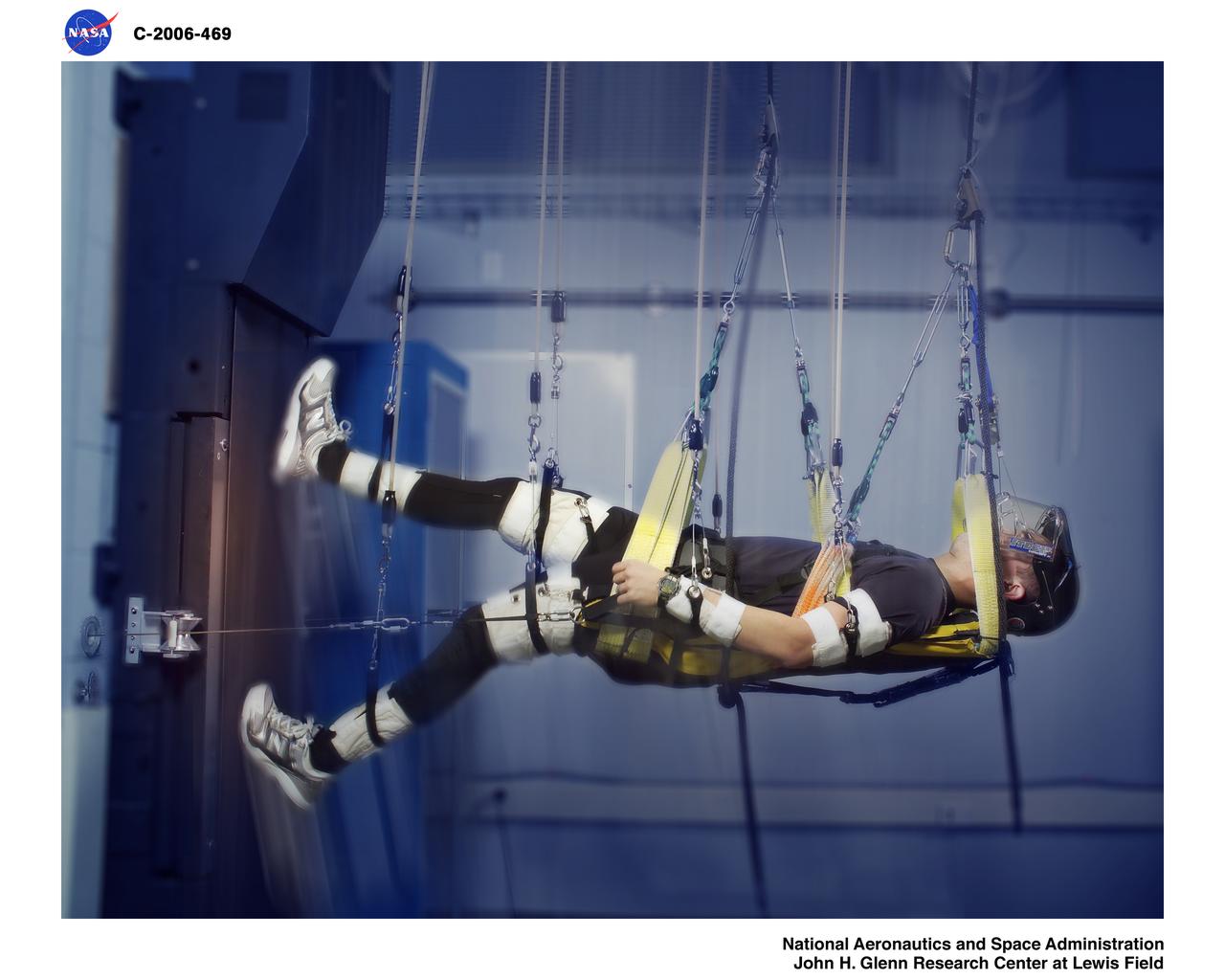

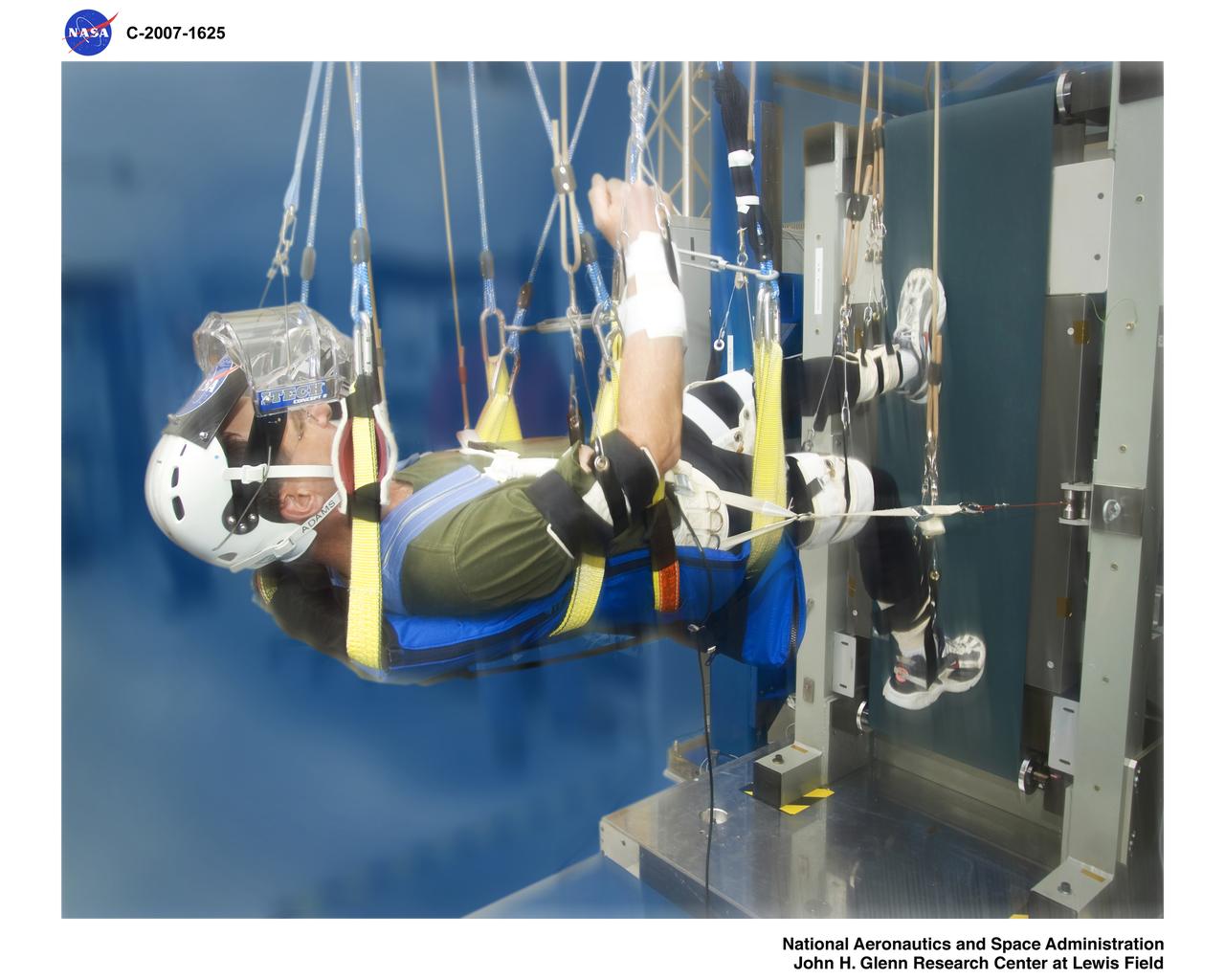
Zero Gravity Locomotion Simulator (ZLS) (0-g)
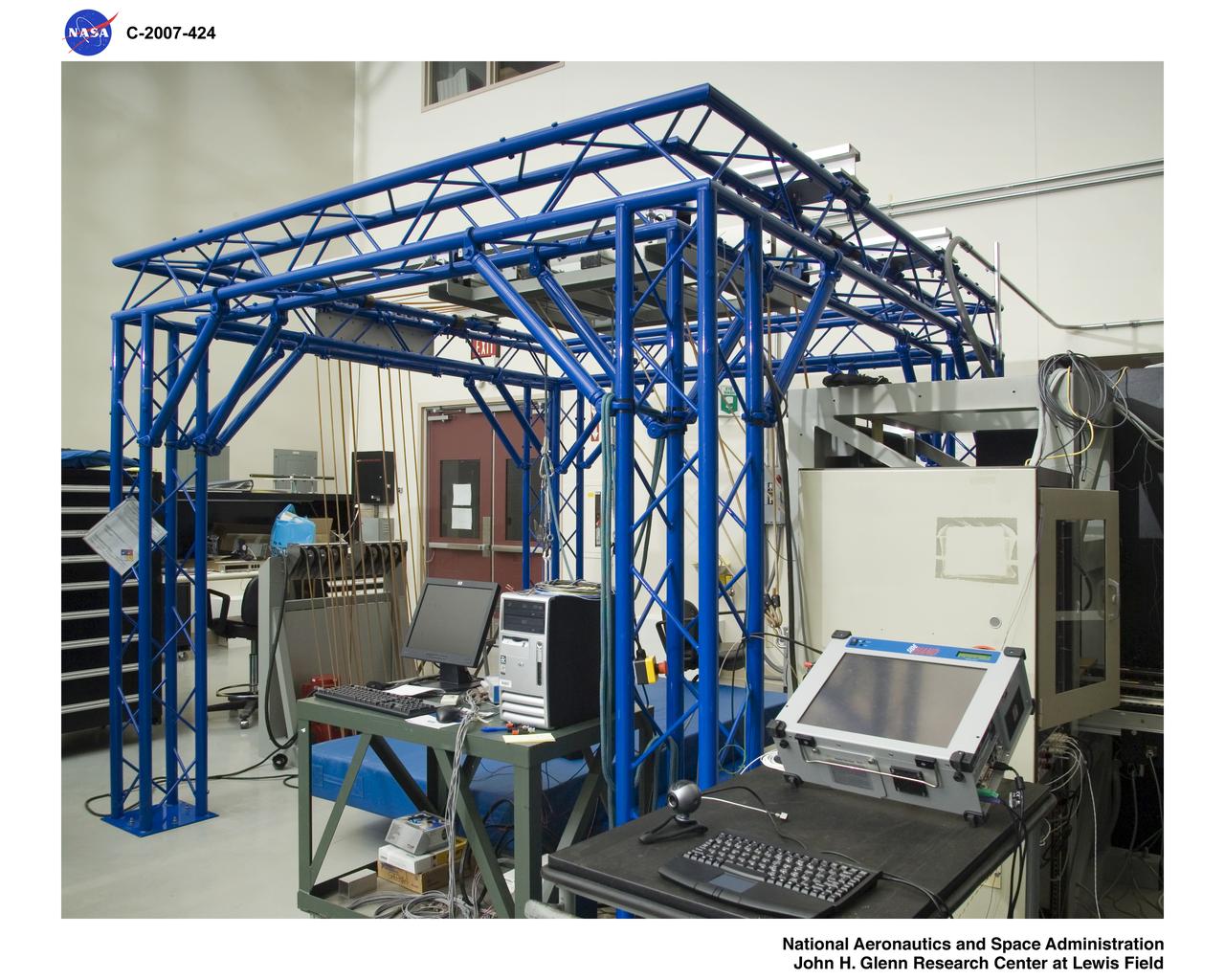

Stand alone Zero gravity Locomotion Simulator (sZLS)
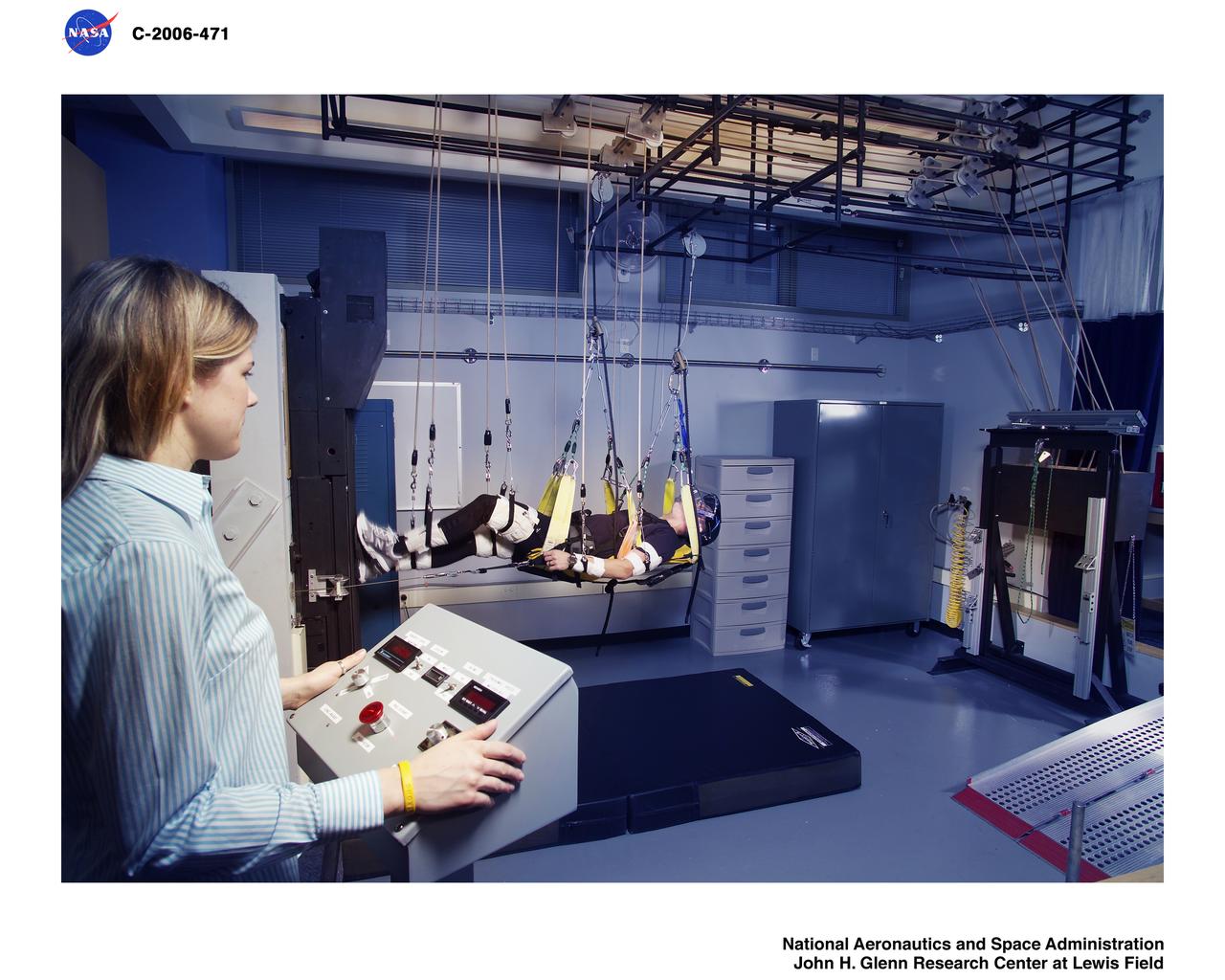

Zero Gravity Locomotion Simulator (ZLS) (0-g)

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse (left), and Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), check out the equipment to be used in conducting the student’s experiment aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. An electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC two months earlier where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

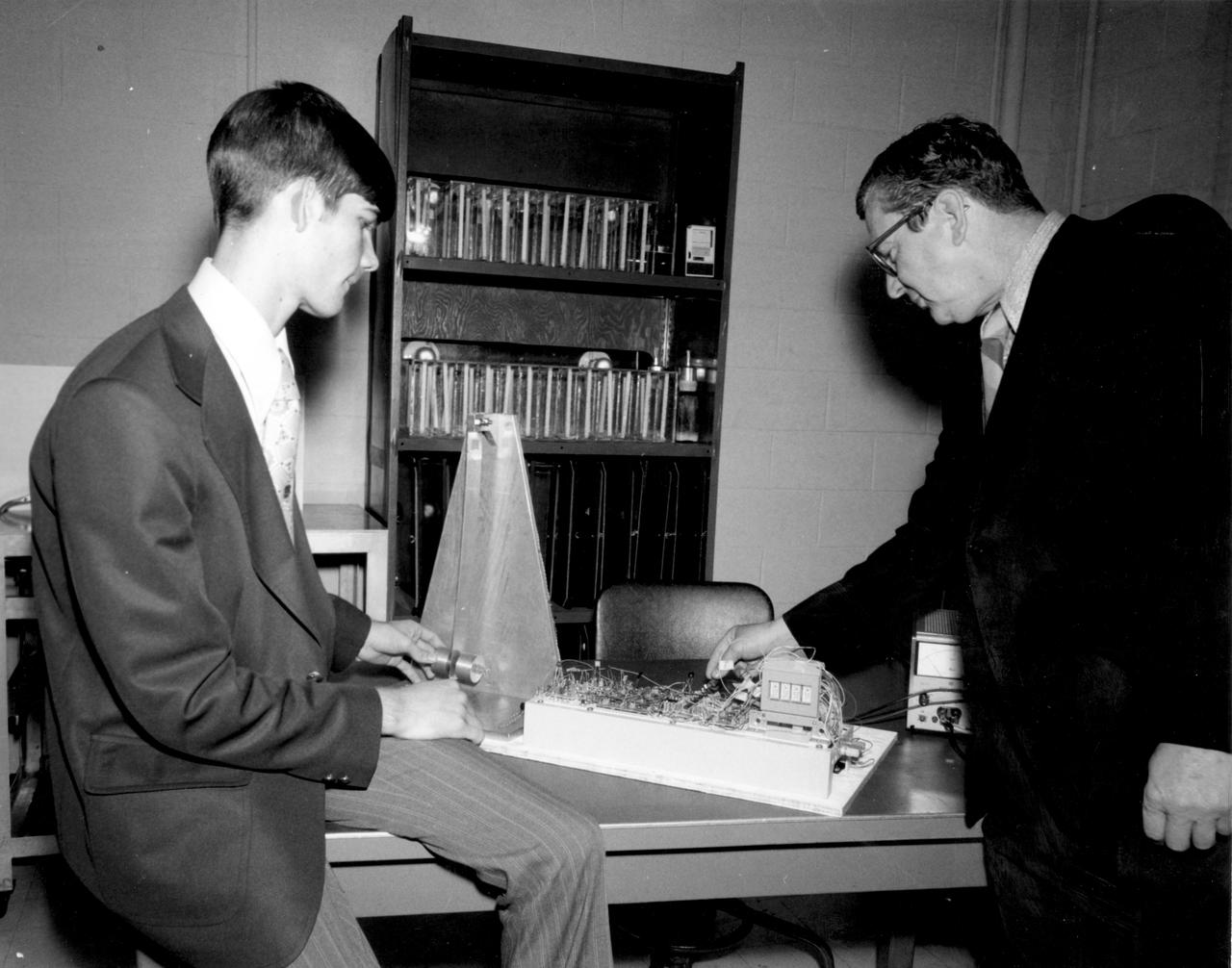
Youngstown, Ohio high school student, W. Brian Dunlap (center), discusses with Dr. Robert Head (right), and Henry Floyd, both of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), his experiment to be performed aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Wave Motion Trough A Liquid in Zero Gravity” used a container attached to the end of a leaf spring which was oscillated at specific rates using two thickness differentiated types of liquids. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. The equipment for the experiments was manufactured at MSFC.
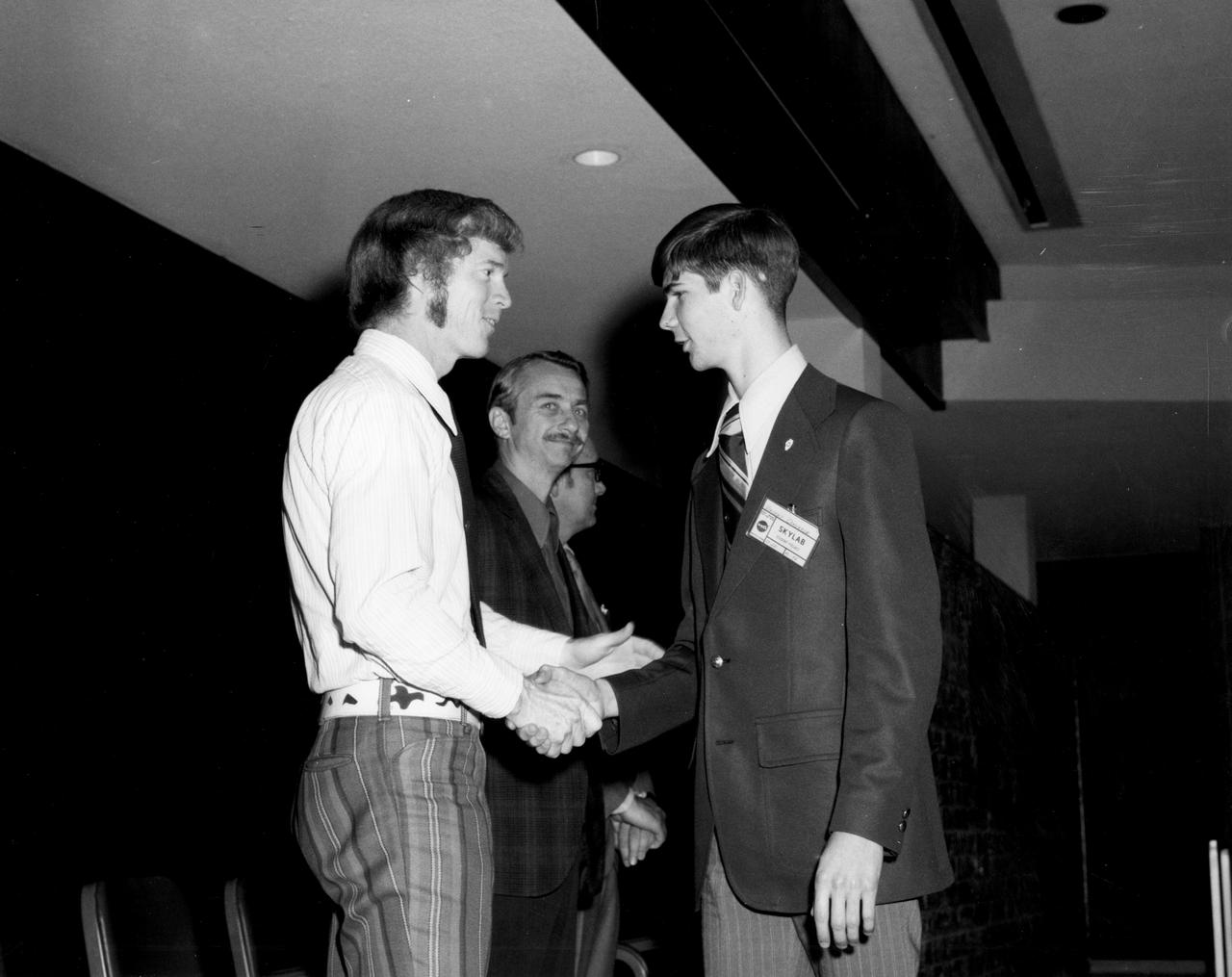

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse (right), is greeted by astronauts Russell L. Schweickart and Owen K. Garriott during a tour of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. An electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipme
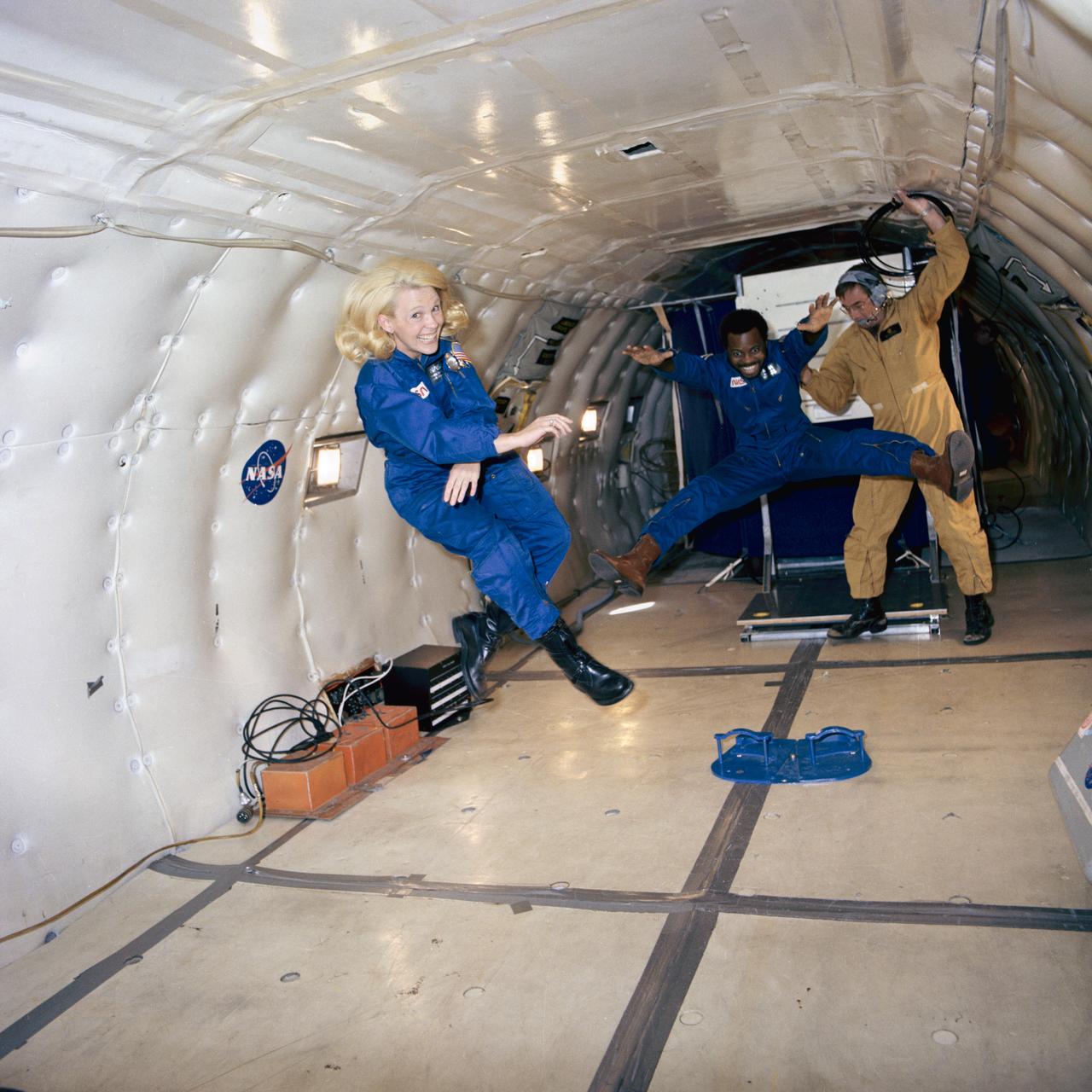

Zero-gravity experiments in KC-135 conducted by John Young, Robert L. Crippen, Joseph Kerwin, and Margaret Seddon. 1. Kerwin, Joseph - Zero-G 2. Seddon, Margaret - Zero-G 3. Young, John - Zero-G 4. Aircraft - KC-135
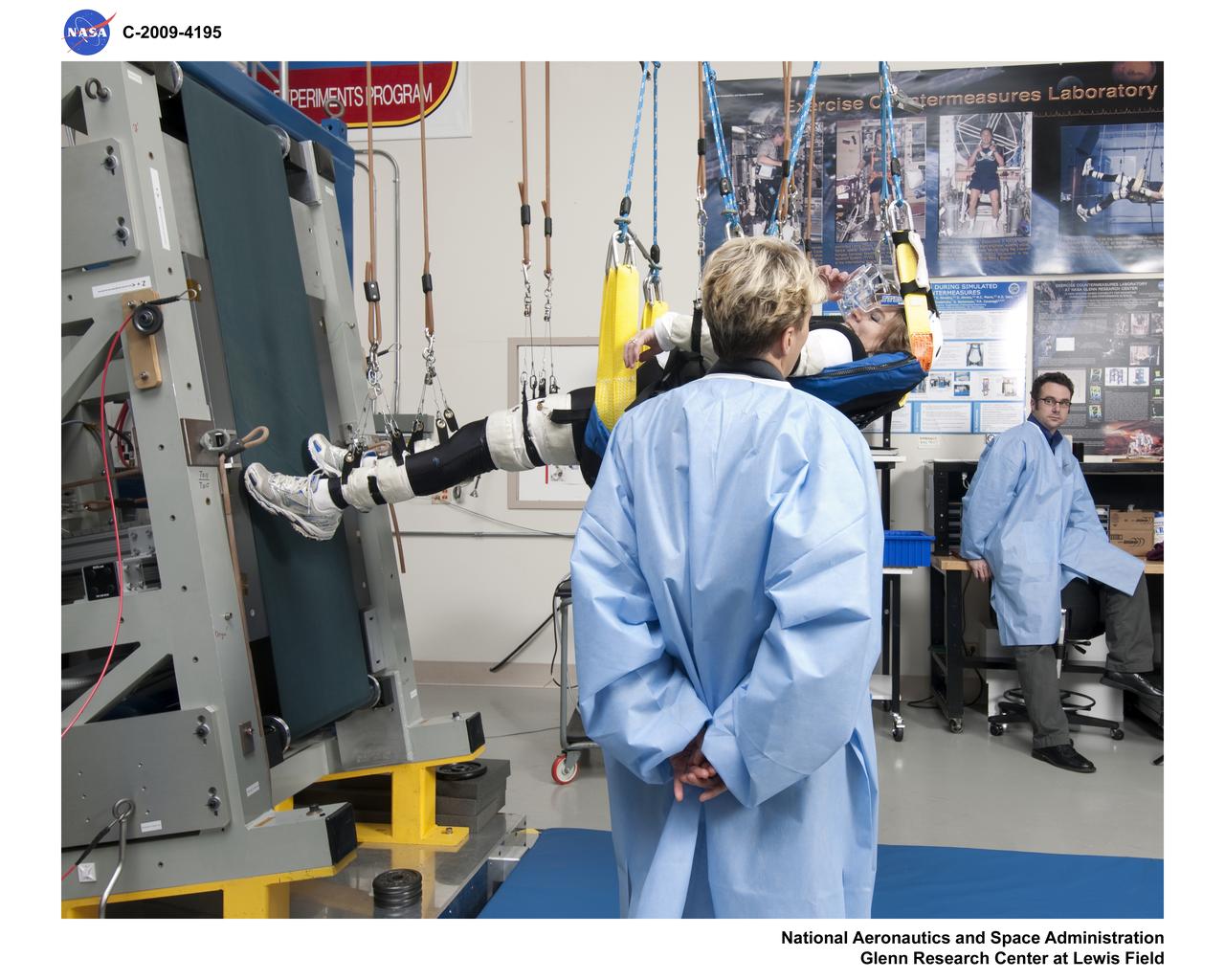

Enhanced Zero-gravity Locomotion Simulator, eZLS in the Lunar Configuration

Physical Sciences and Biomedical Technologies in Space - Enhanced Zero Gravity Locomotion (eZLS)

Enhanced Zero-gravity Locomotion Simulator, eZLS in the Lunar Configuration
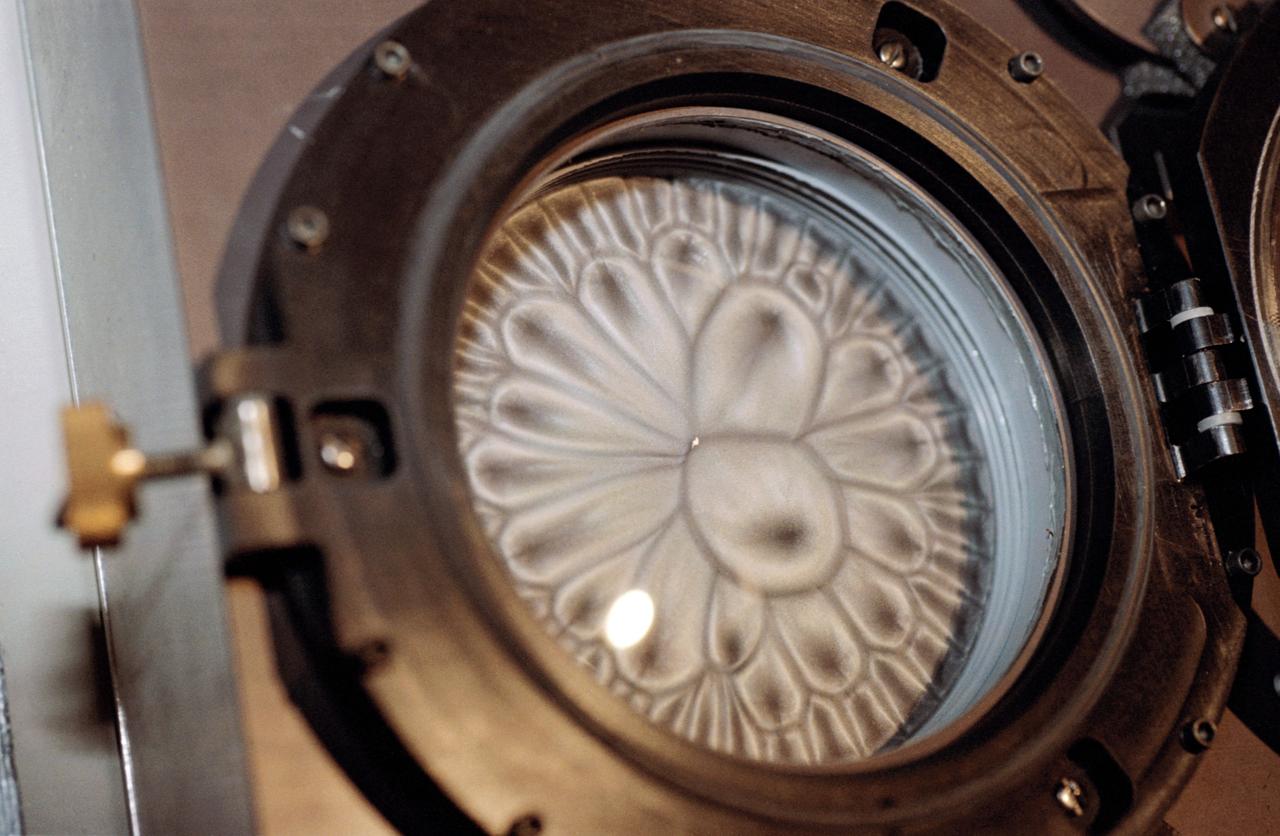
STS-42 closeup view shows Student Experiment 81-09 (SE 81-09), Convection in Zero Gravity experiment, with radial pattern caused by convection induced by heating an oil and aluminum powder mixture in the weightlessness of space. While the STS-42 crewmembers activated the Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSIP) experiment on Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, middeck, Scott Thomas, the student who designed the experiment, was able to observe the procedures via downlinked television (TV) in JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC). Thomas, now a physics doctoral student at the University of Texas, came up with the experiment while he participated in the SSIP as a student at Richland High School in Johnstown, Pennsylvia.
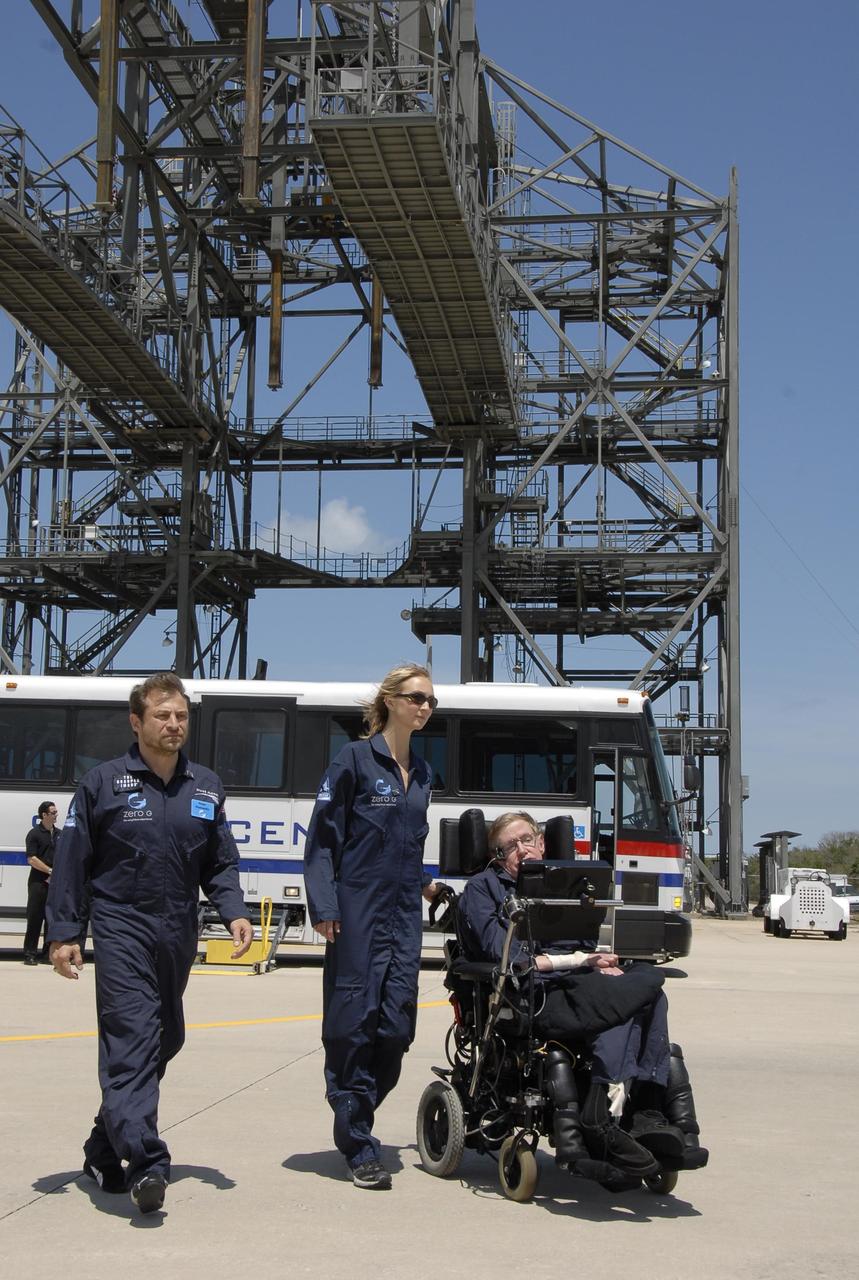

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, noted physicist Stephen Hawking, in the wheelchair, arrives at the runway for his first zero-gravity flight. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp., a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. At left is Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. At center is Nicola O'Brien, a nurse practitioner who is Hawking's aide. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
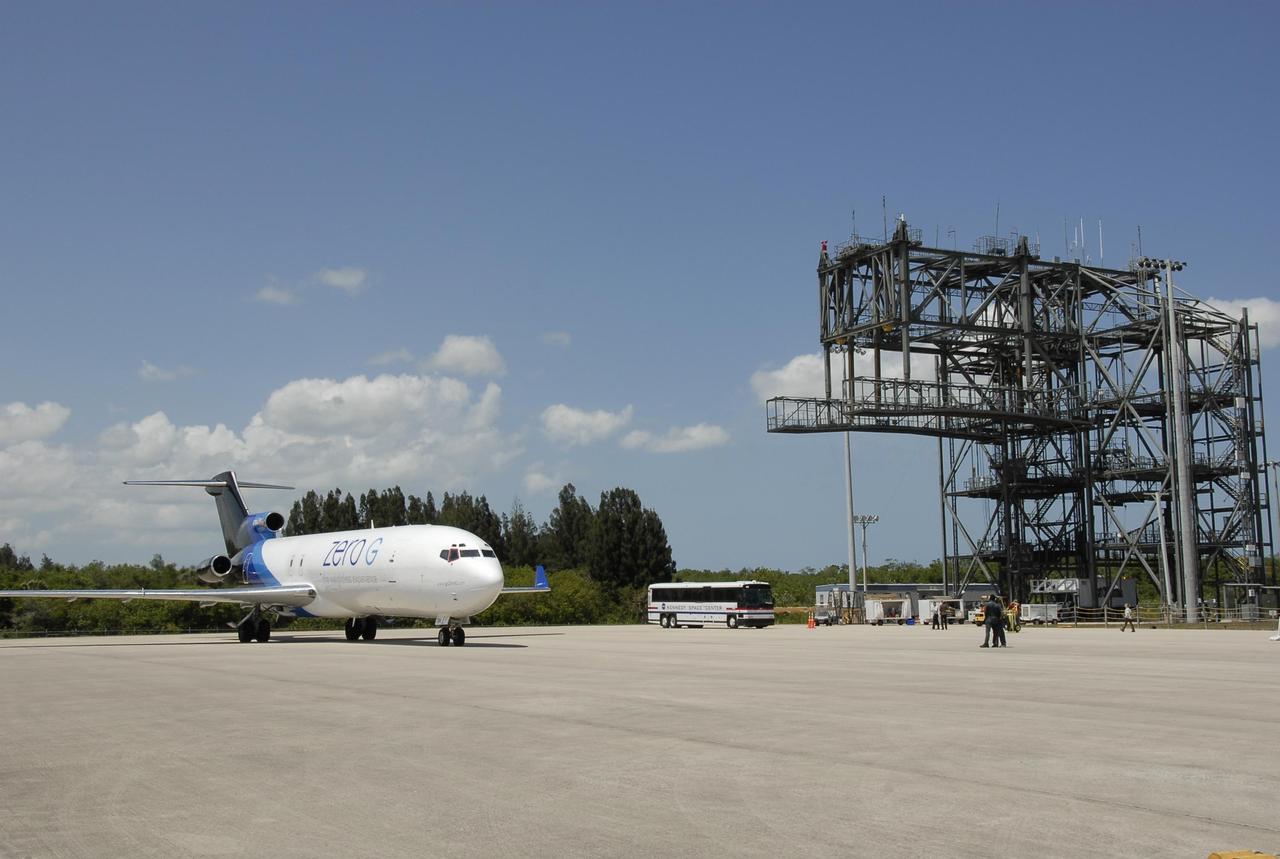

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp. is ready to take off with its well-known passenger, physicist Stephen Hawking. Zero Gravity Corp. is a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. Hawking will be making his first zero-gravity flight. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, noted physicist Stephen Hawking, in the wheelchair, arrives at the runway for his first zero-gravity flight. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp., a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. At left is Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. At center is Nicola O'Brien, a nurse practitioner who is Hawking's aide. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
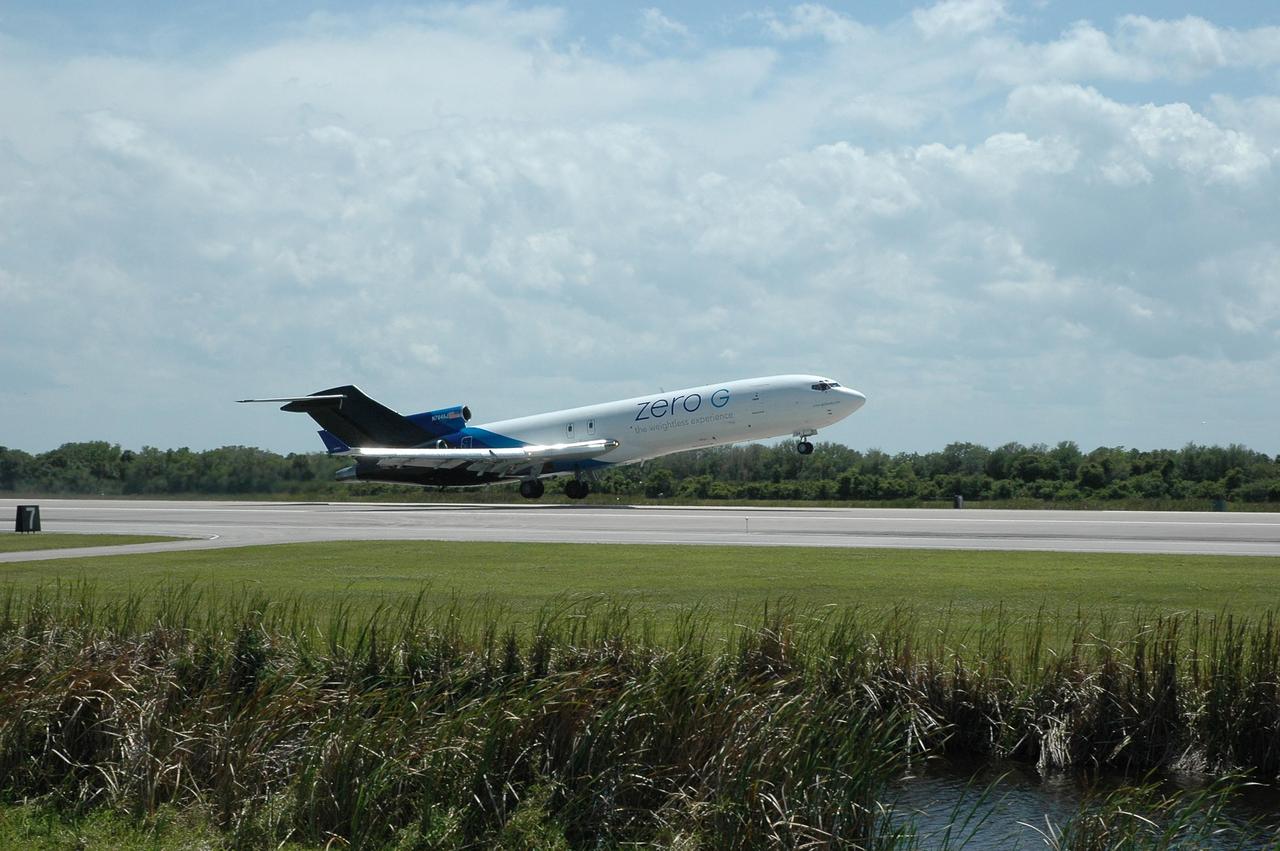

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp. takes off with its well-known passenger, physicist Stephen Hawking. Zero Gravity Corp. is a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. Hawking will be making his first zero-gravity flight. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, Space Florida president Steve Kohler (left) talks to the media about physicist Stephen Hawking's (in the wheelchair) first zero-gravity flight. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp., a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. At right is Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
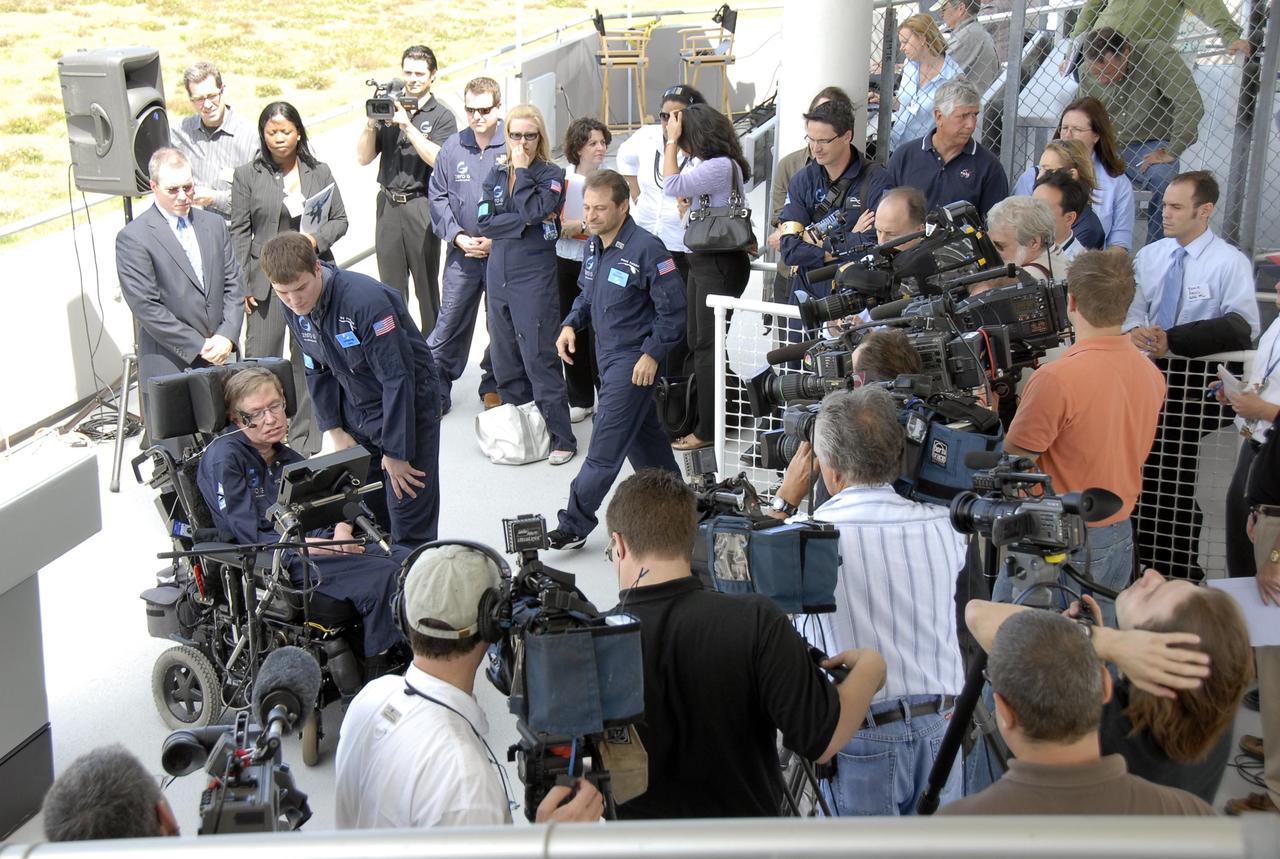

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The media surround noted wheelchair-bound physicist Stephen Hawking after his arrival at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility for his first zero-gravity flight. Behind Hawking, at left, is Space Florida president Steve Kohler. In the center, striding toward Hawking, is Zero Gravity Corp. founder Peter Diamandis. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity, a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
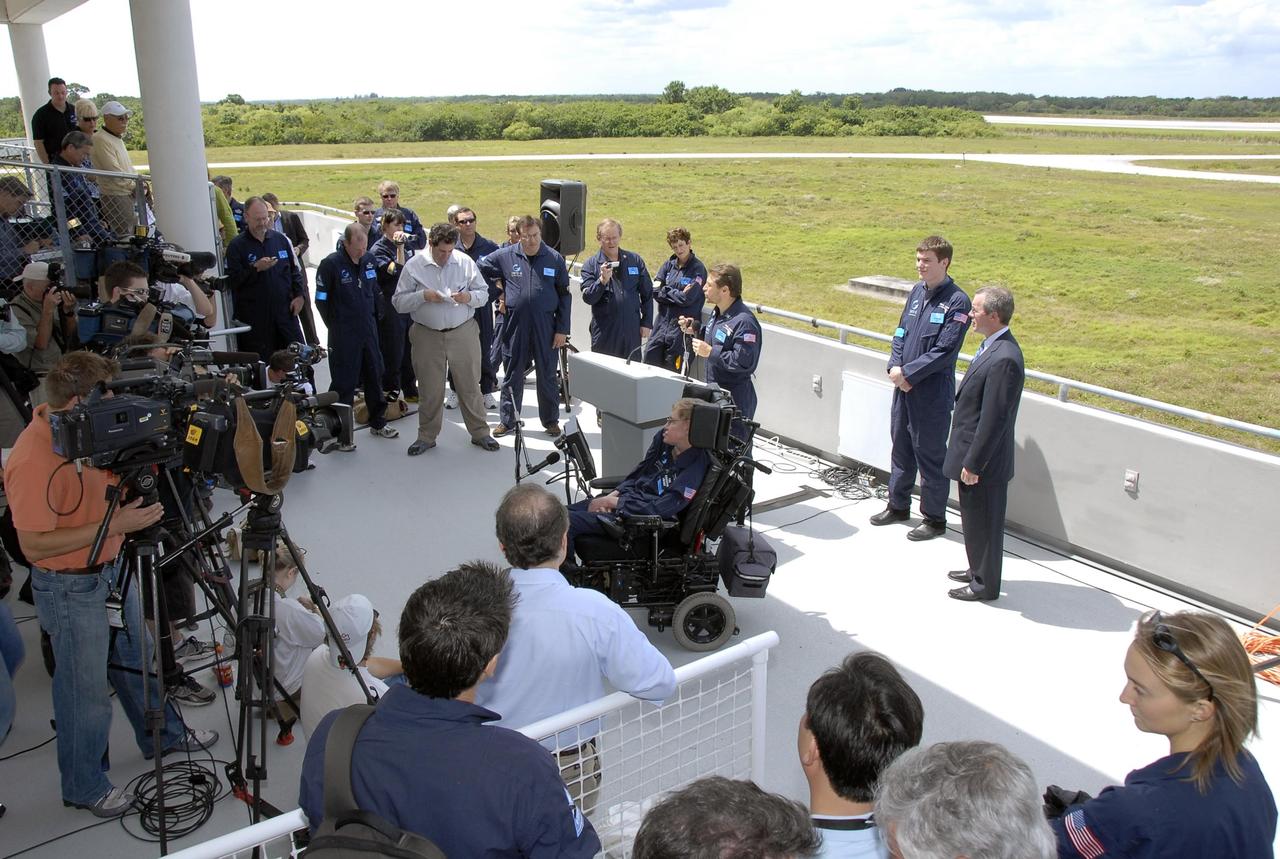

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp., talks to the media about physicist Stephen Hawking's (in the wheelchair) first zero-gravity flight. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp., a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
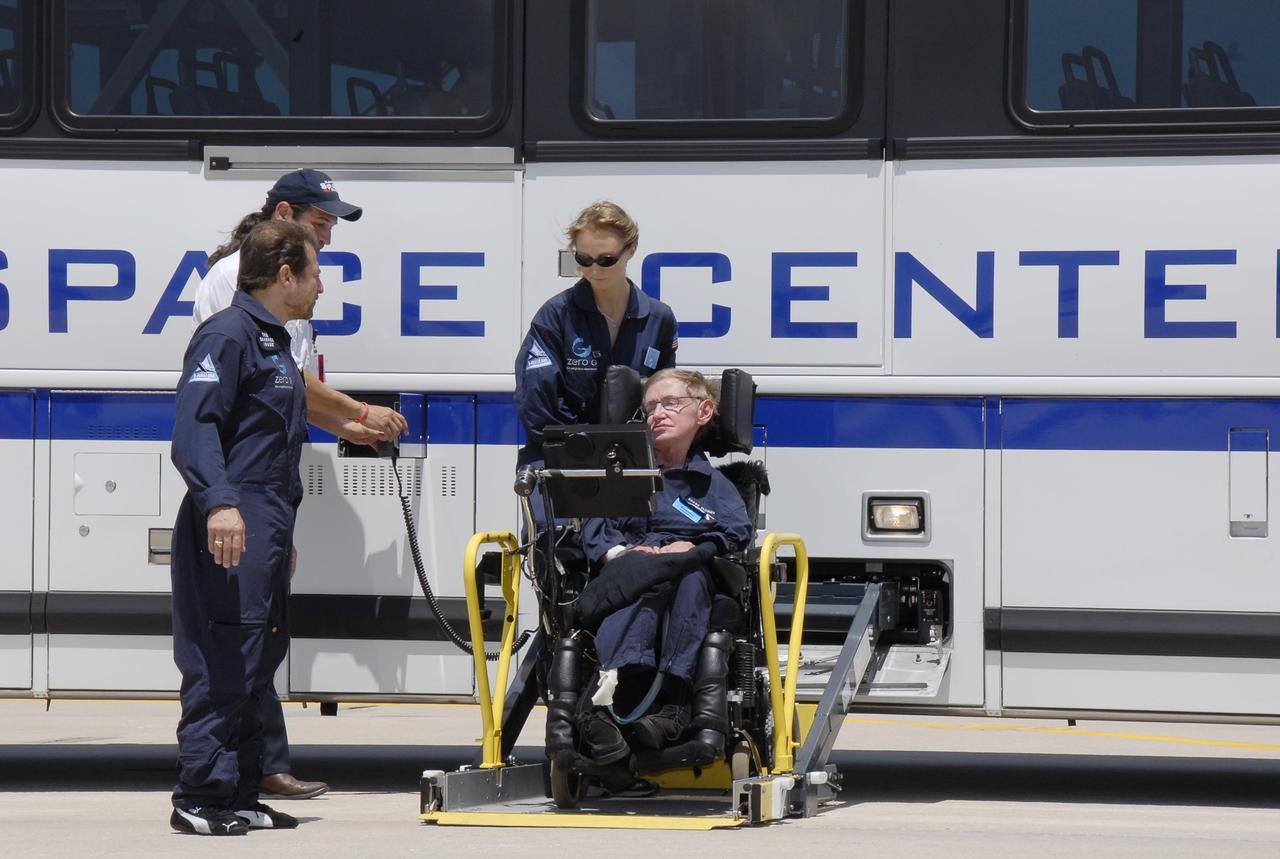

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility, noted physicist Stephen Hawking, in the wheelchair, arrives at the runway for his first zero-gravity flight. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp., a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. At left is Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. Behind Hawking is Nicola O'Brien, a nurse practitioner who is Hawking's aide. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
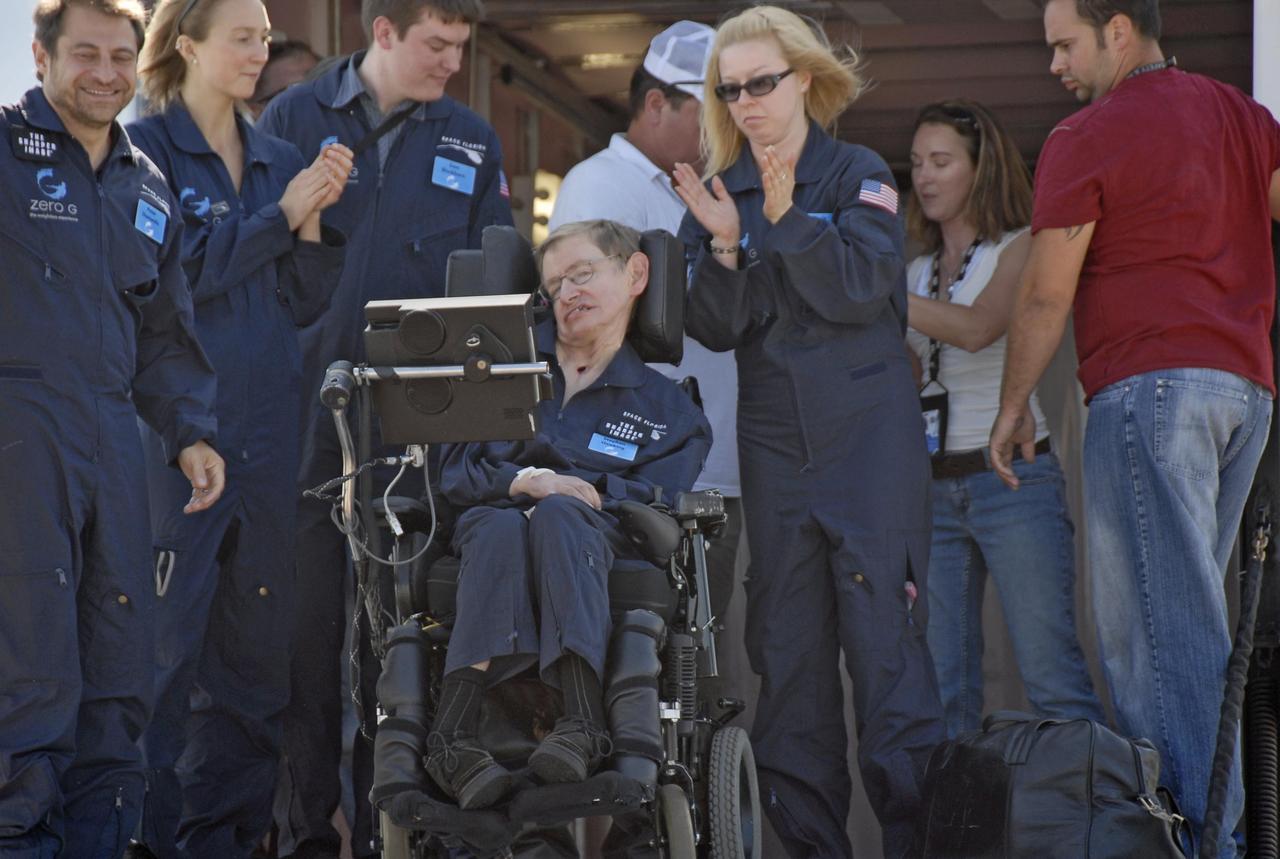

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Noted physicist Stephen Hawking (center) returns to the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility after a zero gravity flight. At far left is Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. that provided the flight aboard its modified Boeing 727. Hawking suffers from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also known as Lou Gehrig's disease). At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
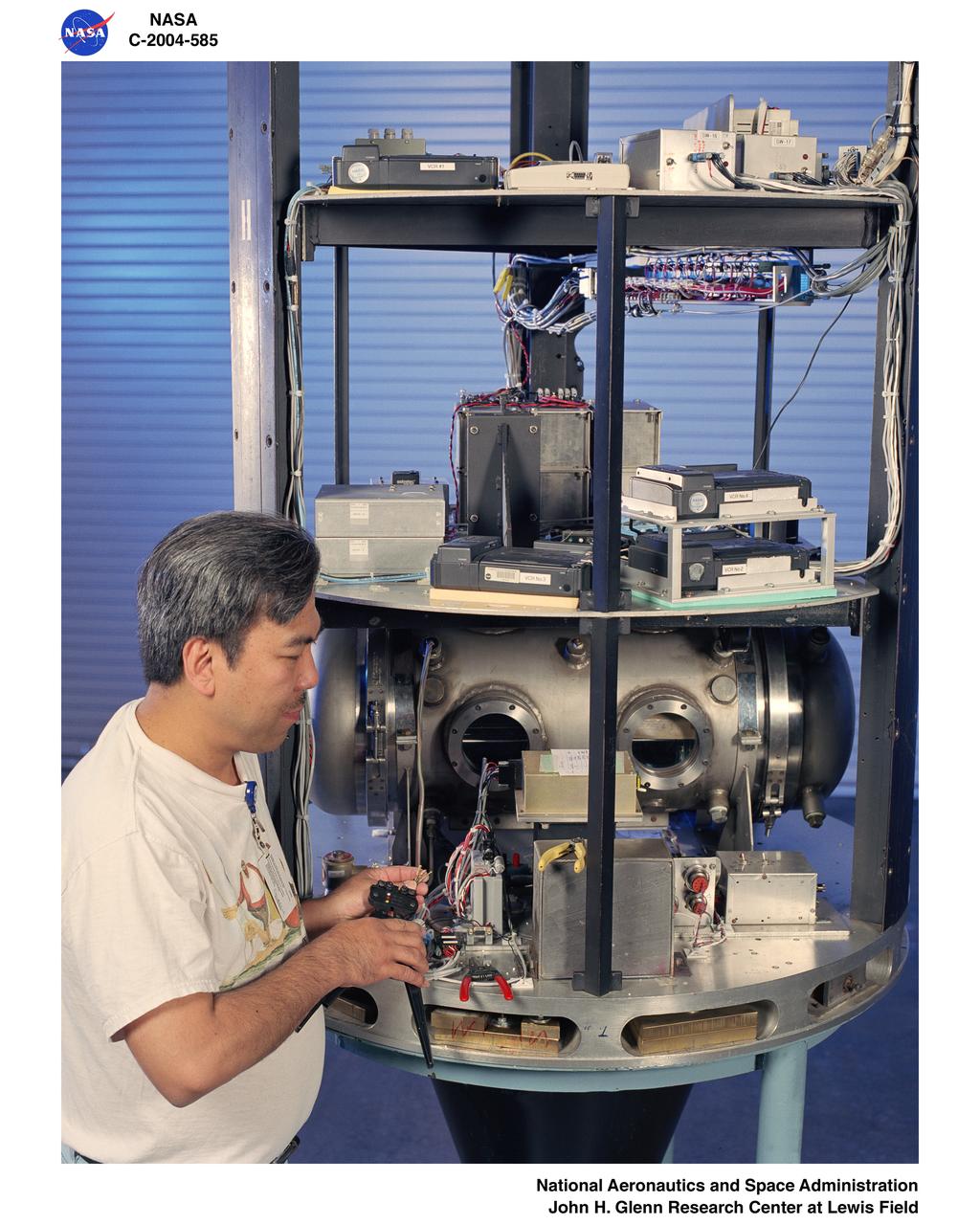

An electronics technician makes adjustments to the experiment on the ÒHÓ drop vehicle at the Zero Gravity Research Facility.
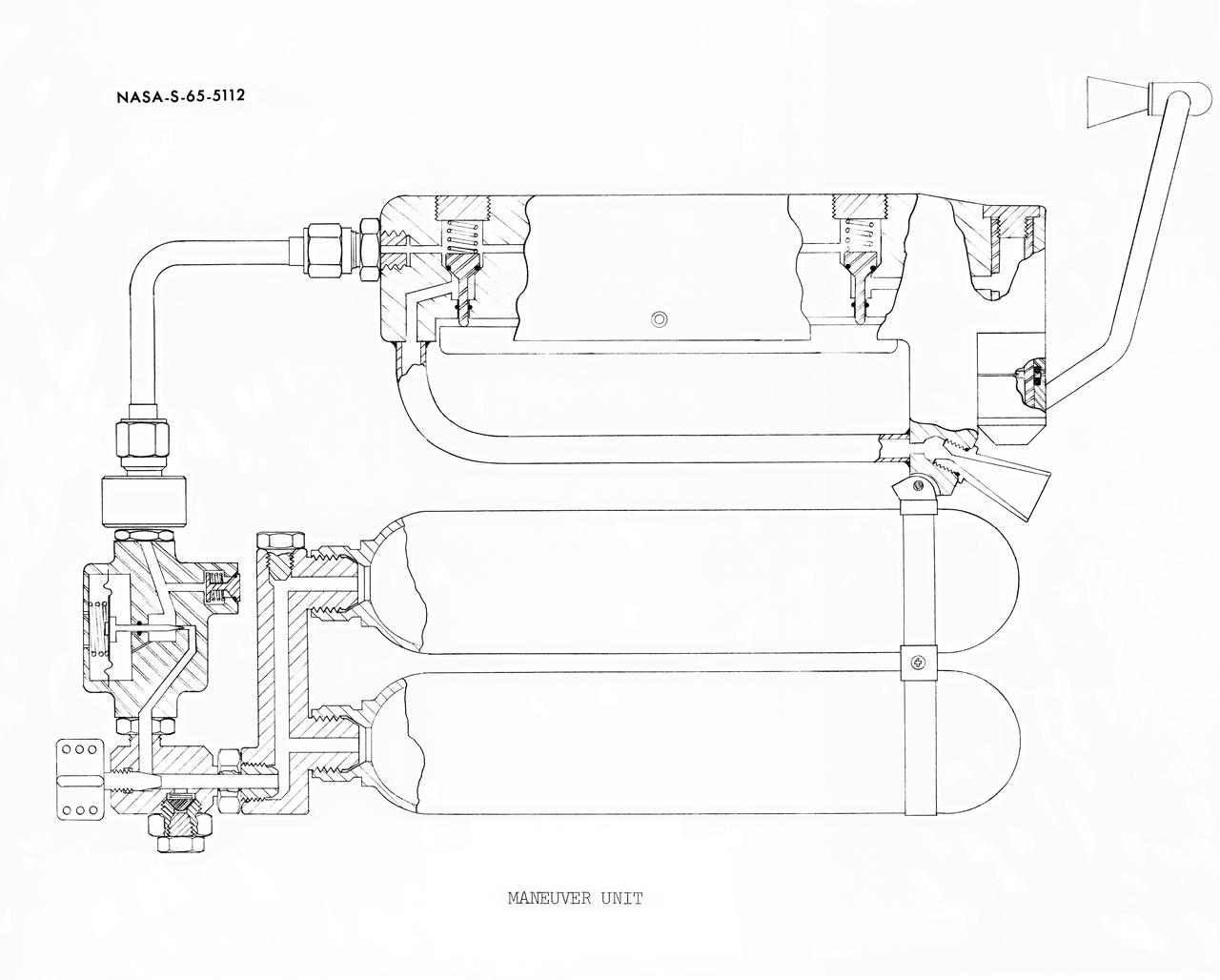
S65-05112 (30 May 1965) --- Cutaway engineering drawing showing some of the features of the zero-gravity integral propulsion unit.
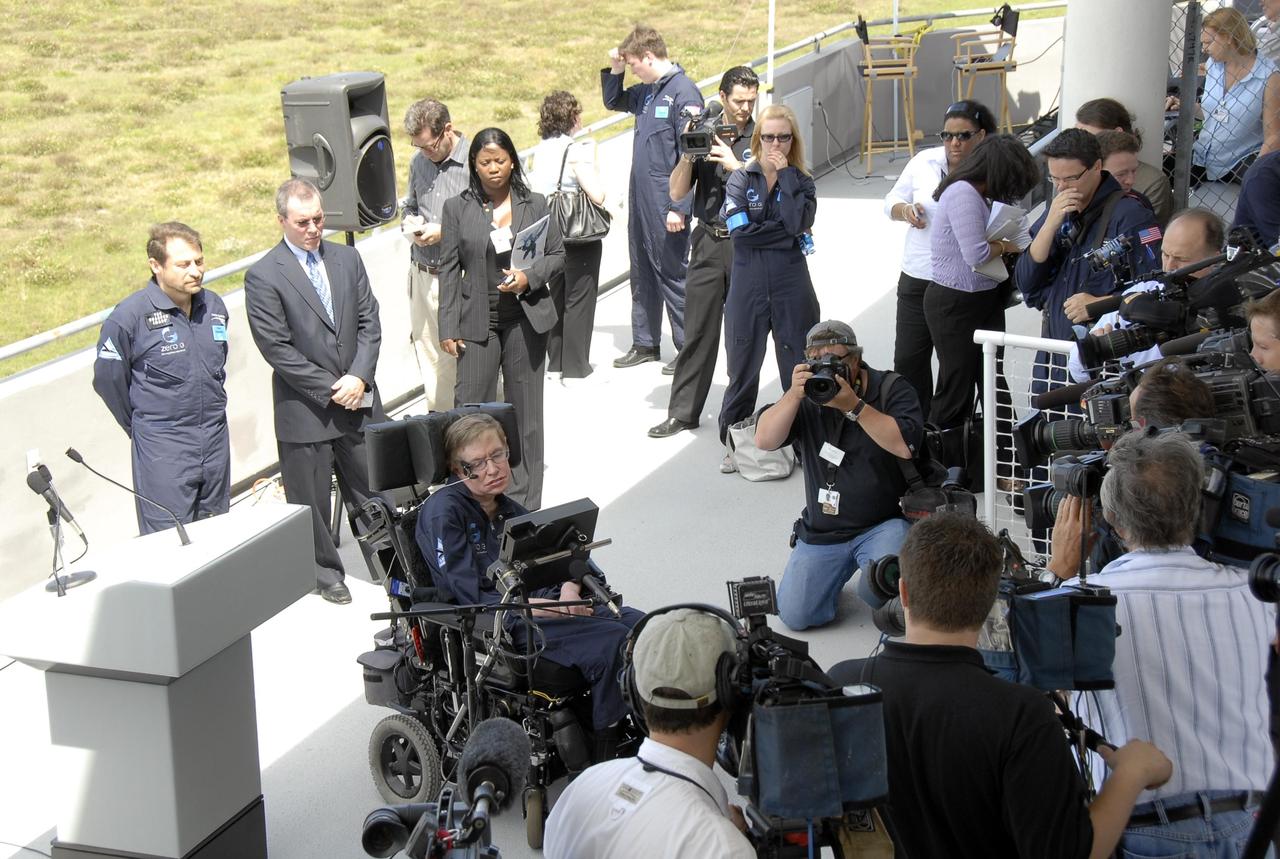

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The media surround noted wheelchair-bound physicist Stephen Hawking after his arrival at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility for his first zero-gravity flight. Behind Hawking, at left, are Zero Gravity Corporation founder Peter Diamandis and Space Florida president Steve Kohler. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero G, a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
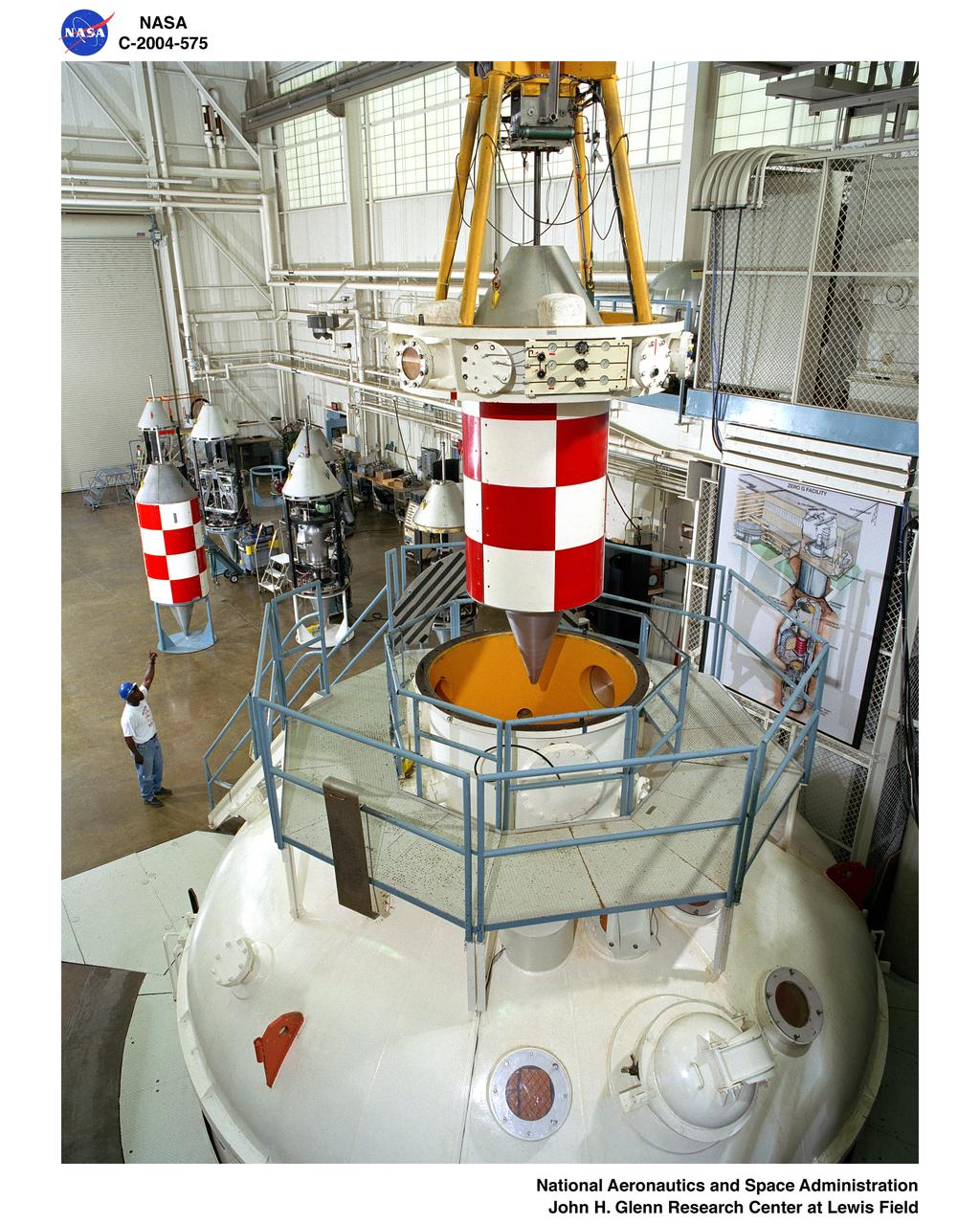

Mezzanine view of the drop vehicle and release mechanism being positioned over the vacuum chamber with a technician signaling the crane operator in the Zero Gravity Research Facility.
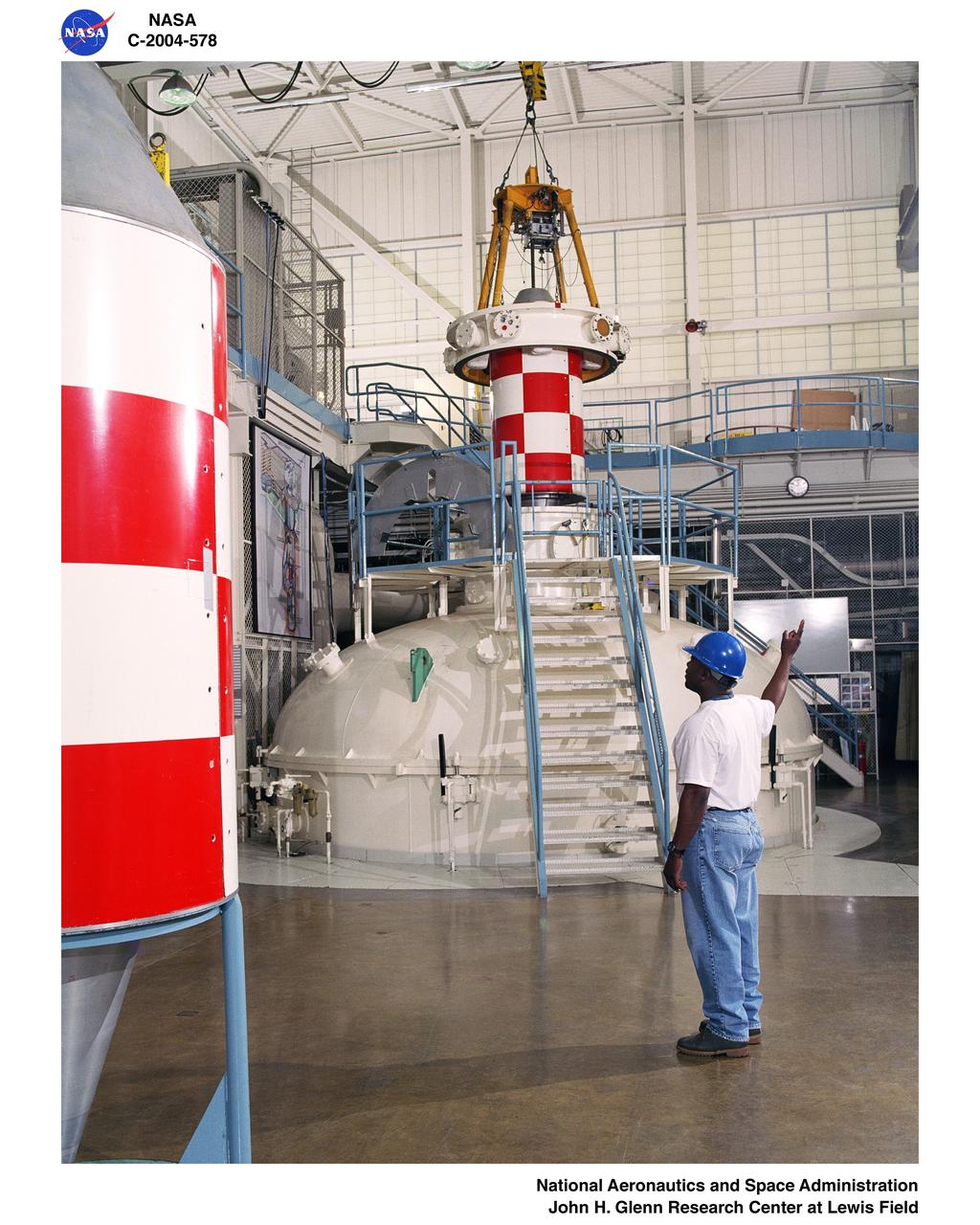

Floor view of drop vehicle and release mechanism being positioned over the vacuum chamber with a technician signaling the crane operator – Zero Gravity Research Facility.

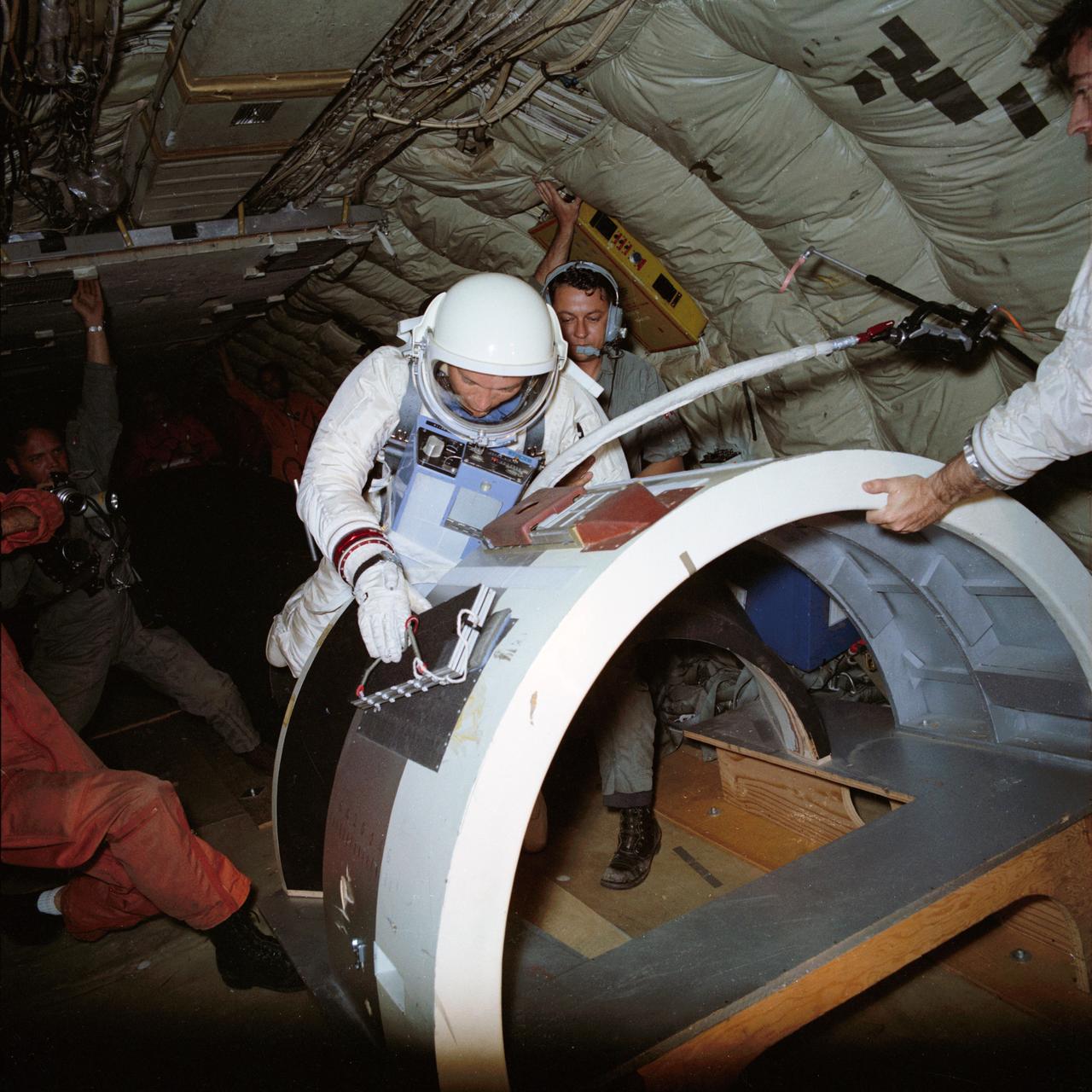
S66-54938 (29 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, prepares to take a rest position during underwater zero-gravity training. His feet are secured to a mock-up of the adapter section of the spacecraft by a special foot plate. The underwater environment closely simulates the zero-gravity condition found in space. Photo credit: NASA

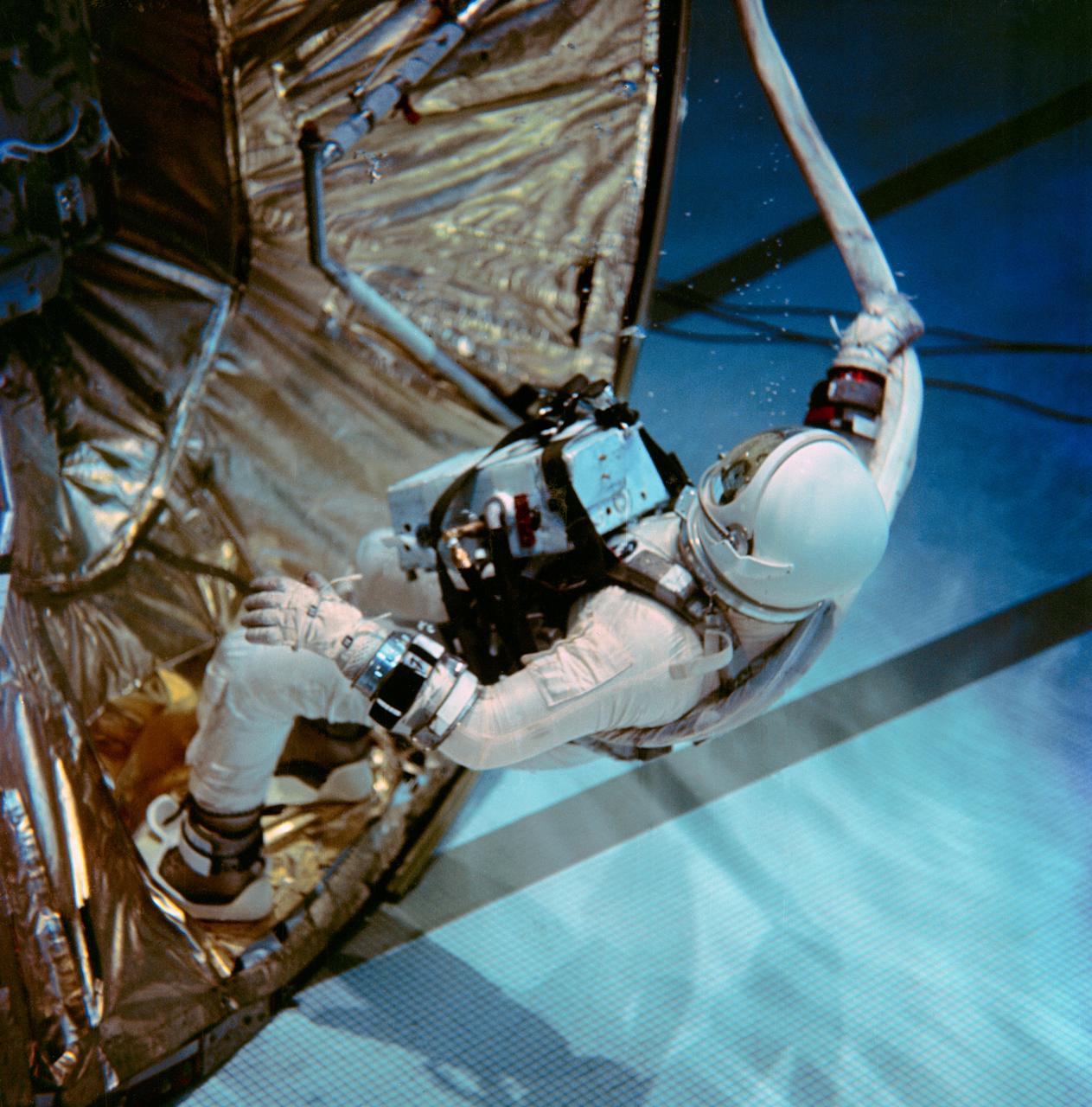
S66-54935 (29 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, practices extravehicular work tasks during underwater zero-gravity training. He works on the docking collar of the Agena Target Docking Vehicle mock-up using hand-holds to secure himself to the vehicle. The underwater environment closely simulates the zero-gravity condition found in space. Photo credit: NASA

S66-40098 (17 June 1966) --- Astronaut Michael Collins, prime crew pilot of the Gemini-10 spaceflight, undergoes zero-gravity (weightlessness) training aboard an Air Force KC-135 aircraft. He practices with micrometeorite experiment-type equipment. The KC-135 flew a parabolic curve to create the zero-gravity condition. This training is in preparation for Collins' Gemini-10 extravehicular activity. Photo credit: NASA

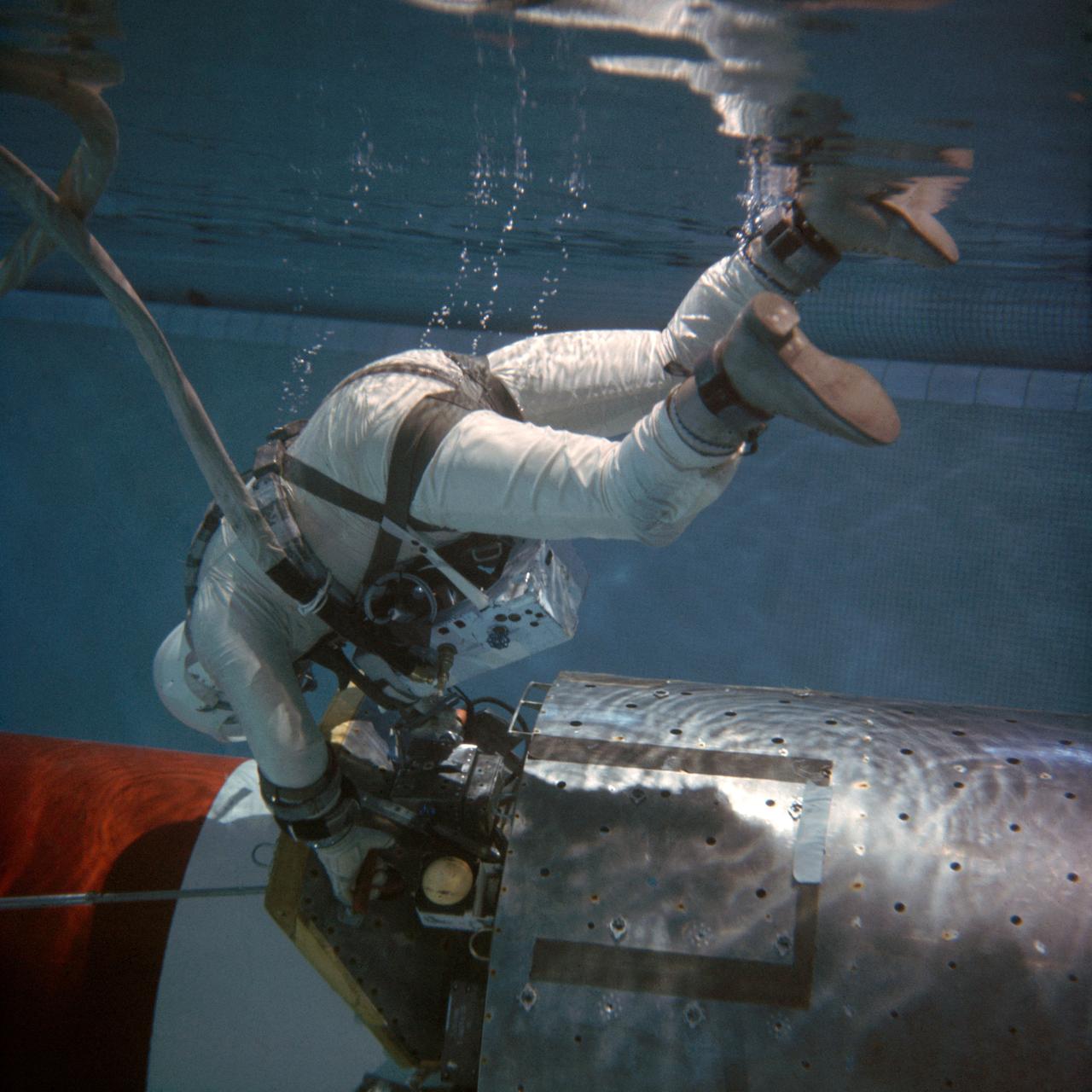
S66-54939 (29 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, practices work tasks during underwater zero-gravity training. He is placing his feet into a special foot plate in an adapter section of the spacecraft. The foot plate will help secure him to the spacecraft during extravehicular activity (EVA). The underwater environment closely simulates the zero-gravity condition found in space. Photo credit: NASA

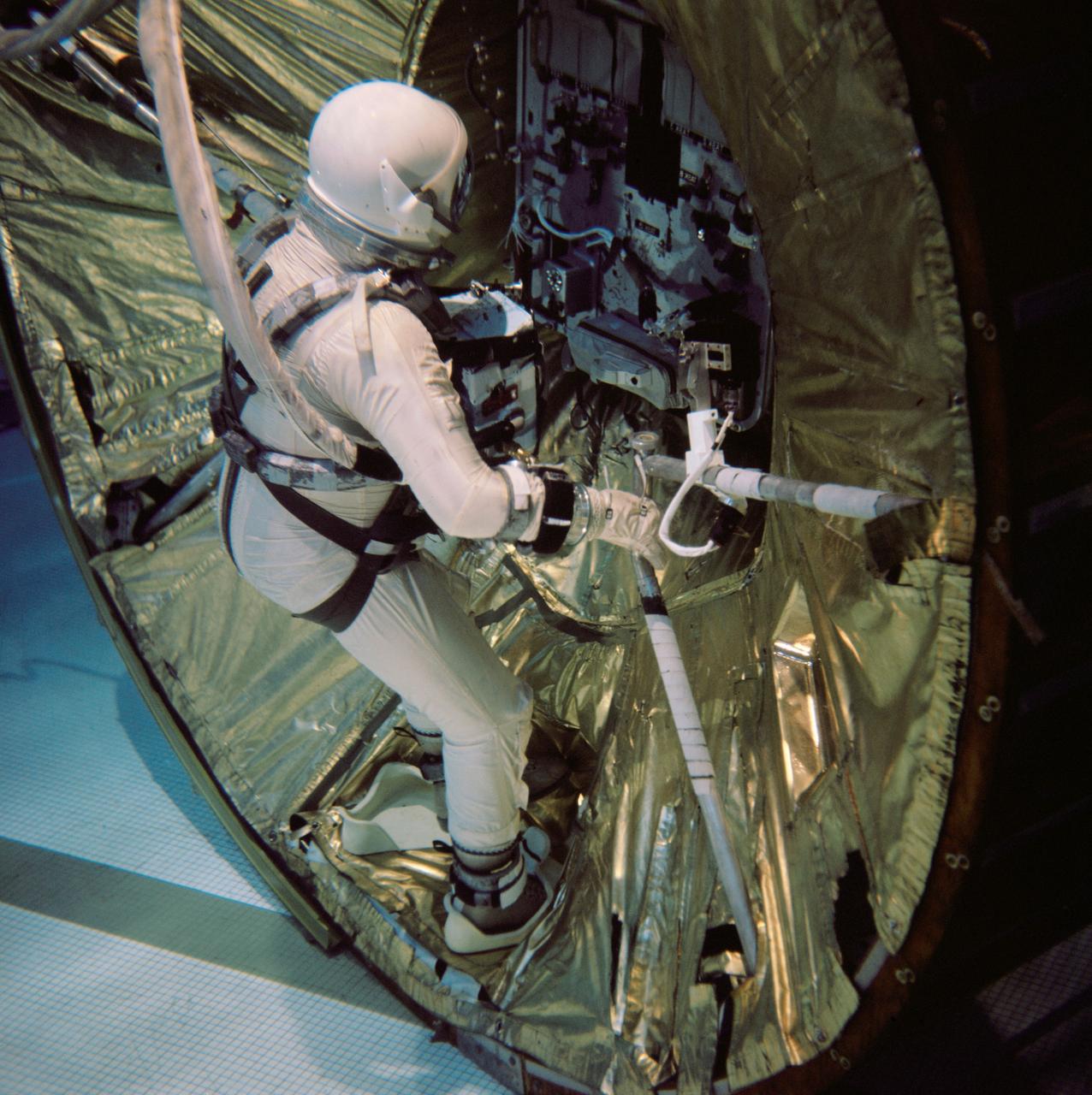
S66-54937 (29 Oct. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, practices egress procedures from a mock-up of his spacecraft during underwater zero-gravity training. He holds a telescoping handrail in his left hand which he will use to move from the spacecraft to the Agena Target Docking Vehicle. The underwater environment closely simulates the zero-gravity condition found in space. Photo credit: NASA
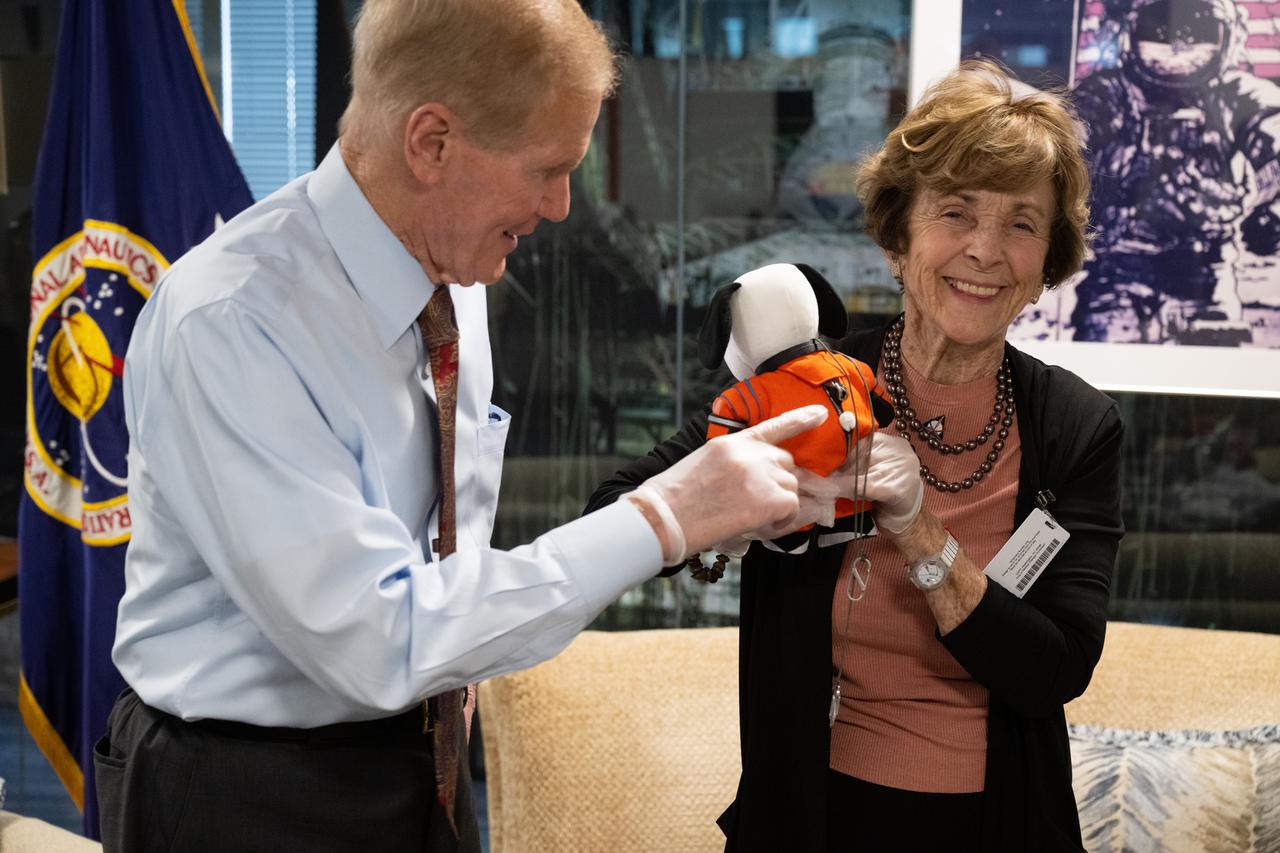

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, is seen with Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, right, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, during a visit to the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
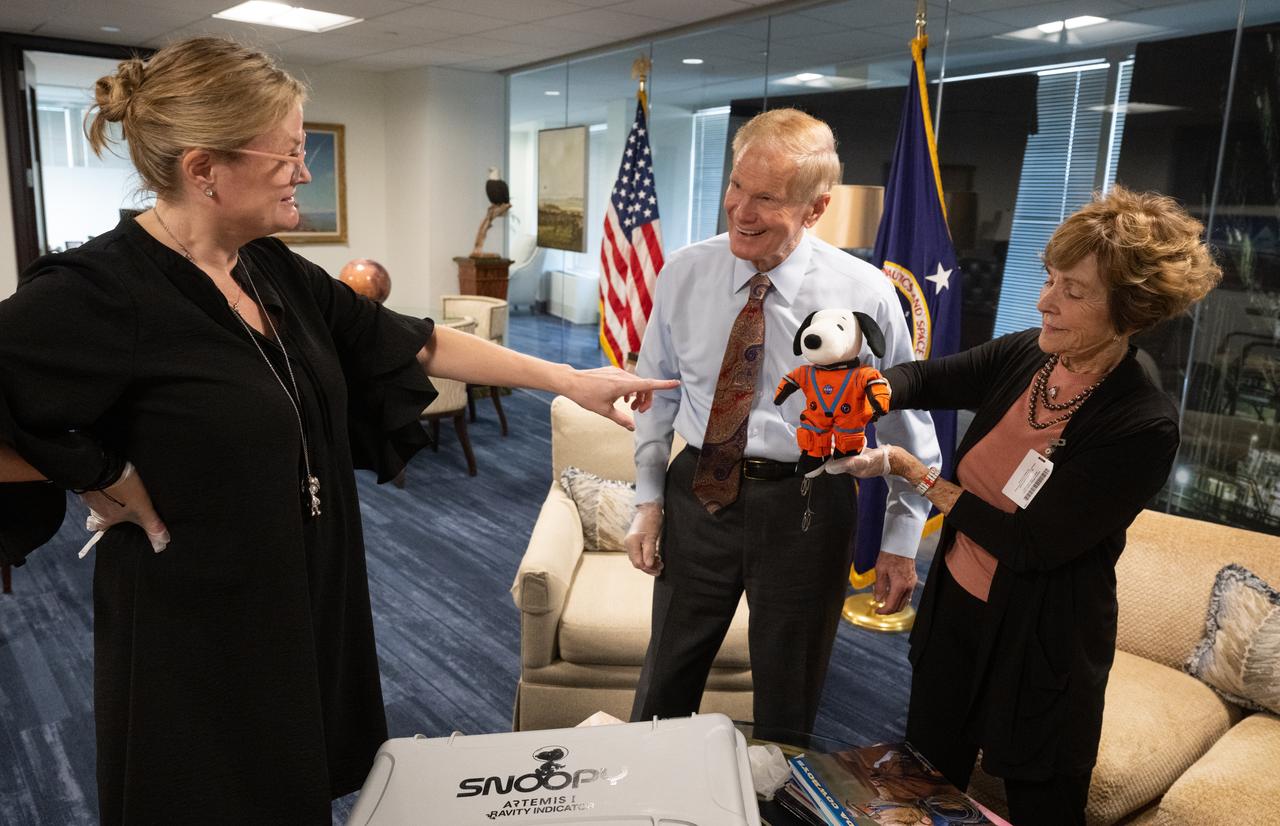

Melissa Menta, executive vice president at Peanuts Worldwide, left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, center, and Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, left, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, are seen, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, during a visit to the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — Noted physicist Stephen Hawking greets the media after his arrival at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility for his first zero-gravity flight. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp., a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Noted physicist Stephen Hawking (center) returns to the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility after a zero gravity flight. At his side is Nicola O'Brien, a nurse practitioner who is Hawking's aide. At far left on the truck's tail gate is Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. that provided the flight aboard its modified Boeing 727. Hawking suffers from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also known as Lou Gehrig's disease). At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
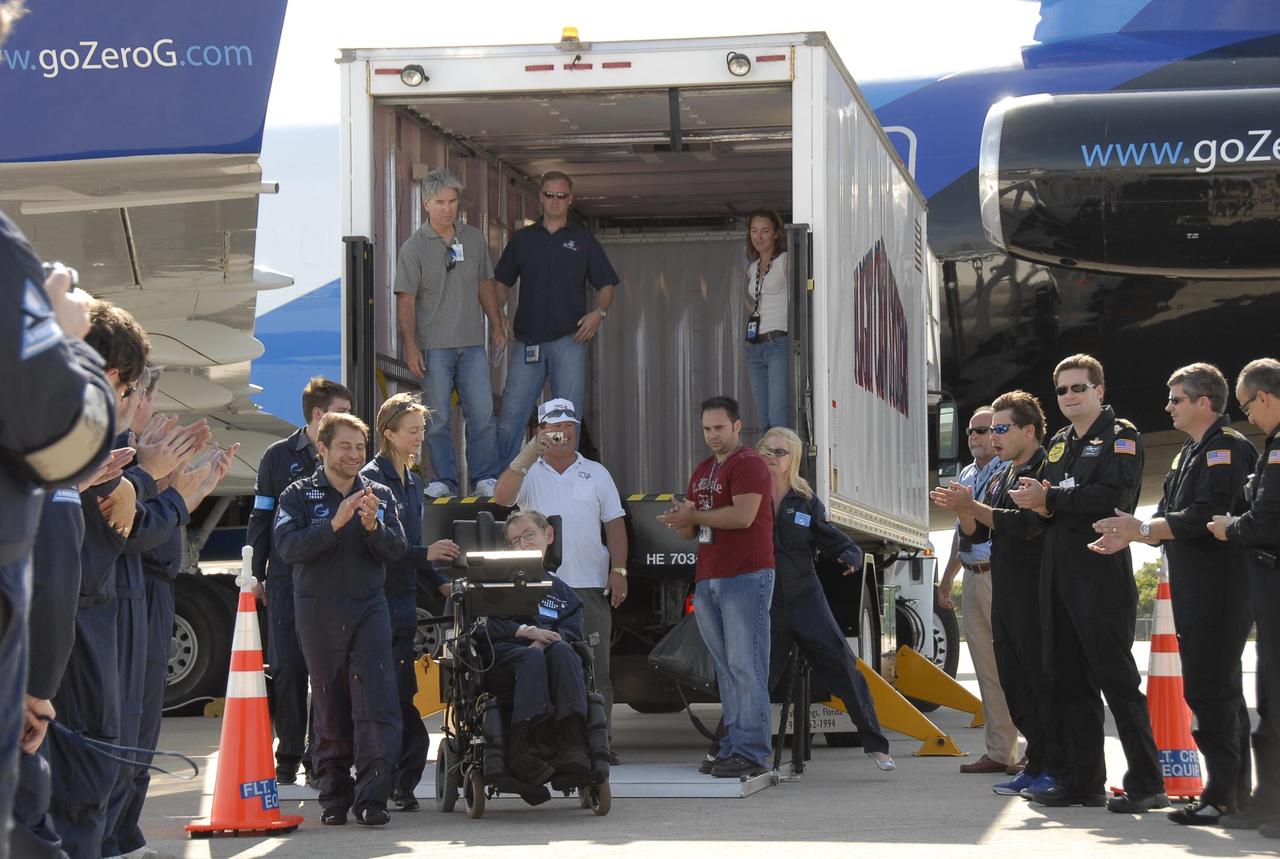

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Well-wishers greet noted physicist Stephen Hawking (in the wheelchair) at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility after a zero gravity flight. Next to him at left are Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. that provided the flight aboard its modified Boeing 727, and Nicola O'Brien, a nurse practitioner who is Hawking's aide. Hawking suffers from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also known as Lou Gehrig's disease). At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
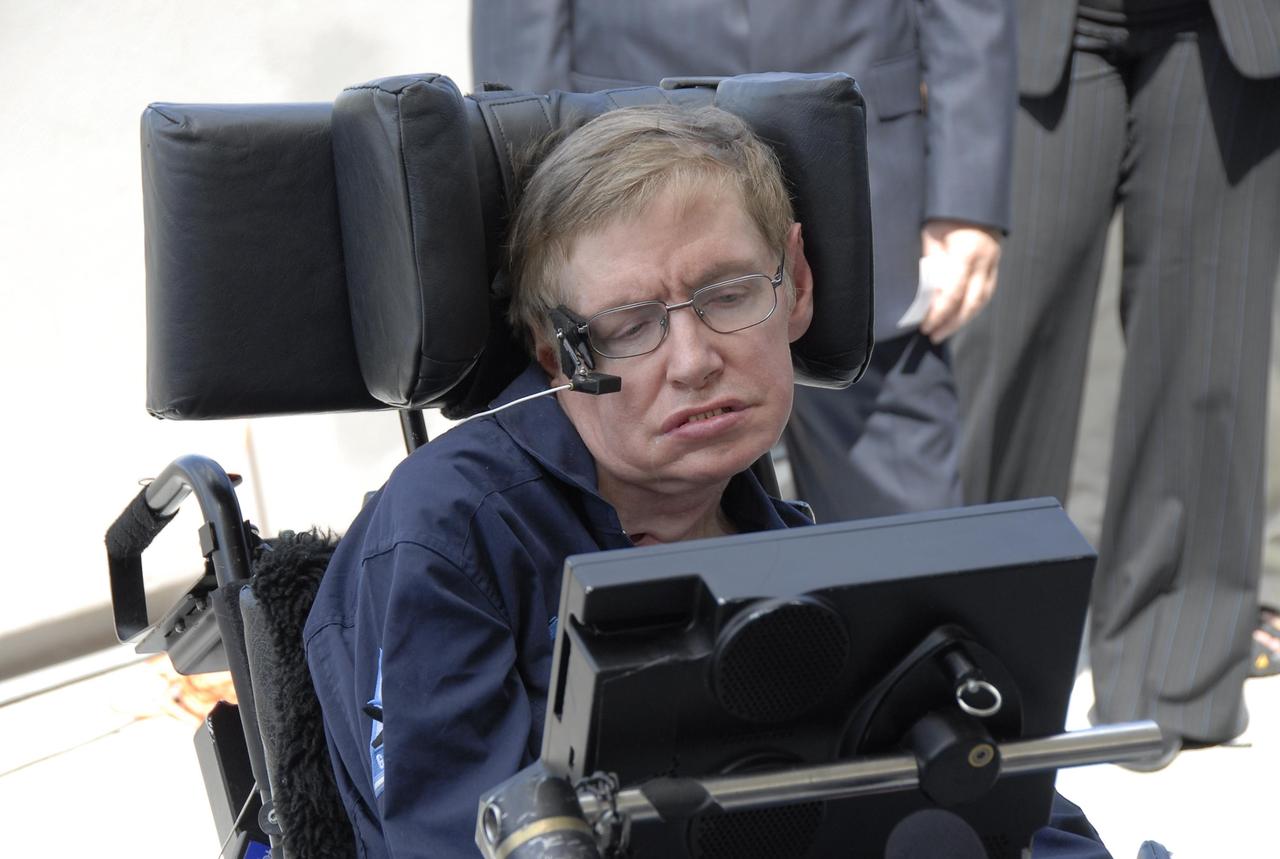

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Noted physicist Stephen Hawking arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility for his first zero-gravity flight. The flight will be aboard a modified Boeing 727 aircraft owned by Zero Gravity Corp., a commercial company licensed to provide the public with weightless flight experiences. Hawking developed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease in the 1960s, a type of motor neuron disease which would cost him the loss of almost all neuromuscular control. At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
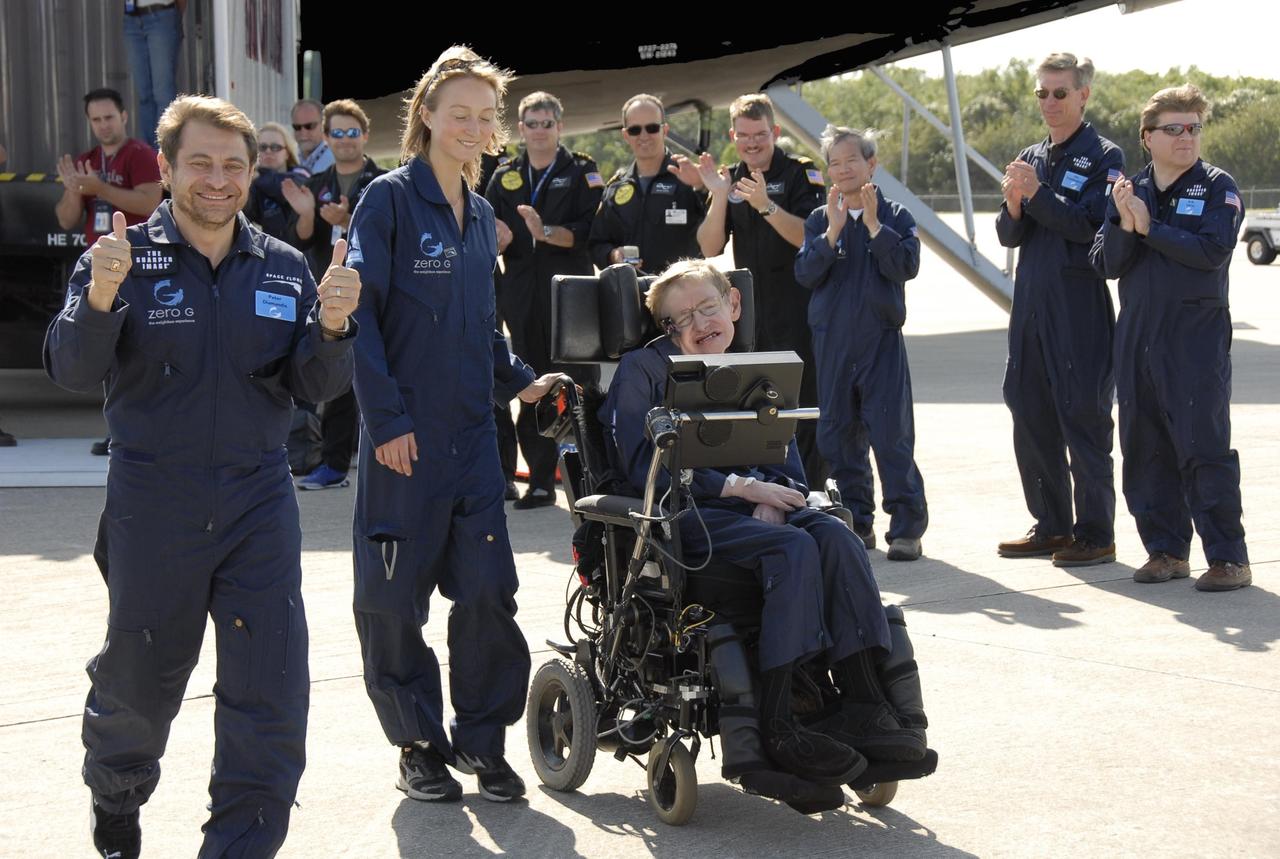

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Well-wishers greet noted physicist Stephen Hawking (in the wheelchair) at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility after a zero gravity flight. Next to him at left are Peter Diamandis, founder of the Zero Gravity Corp. that provided the flight aboard its modified Boeing 727, and Nicola O'Brien, a nurse practitioner who is Hawking's aide. Hawking suffers from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also known as Lou Gehrig's disease). At the celebration of his 65th birthday on January 8 this year, Hawking announced his plans for a zero-gravity flight to prepare for a sub-orbital space flight in 2009 on Virgin Galactic's space service. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
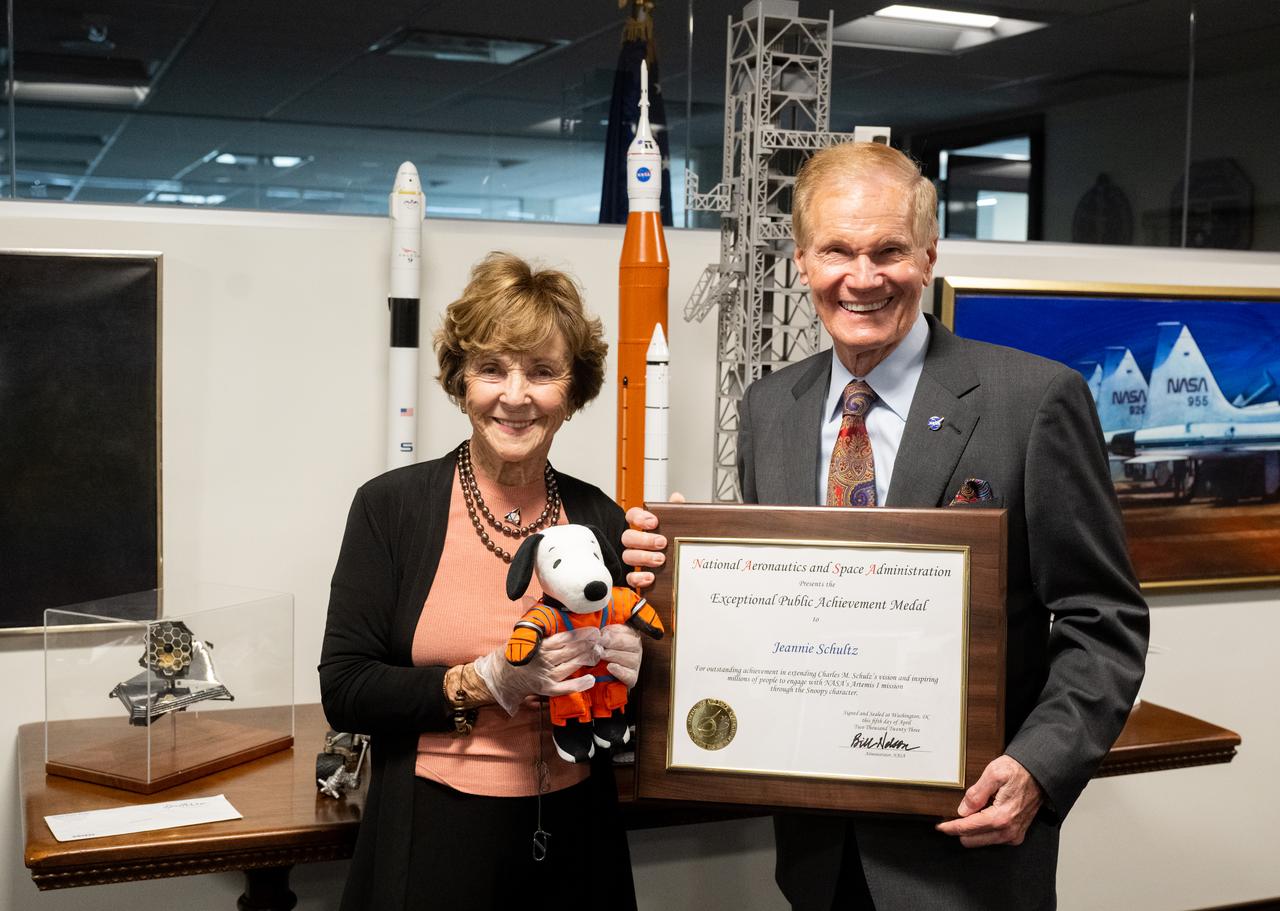

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, and Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, left, pose for a picture with the NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal plaque, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz was awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
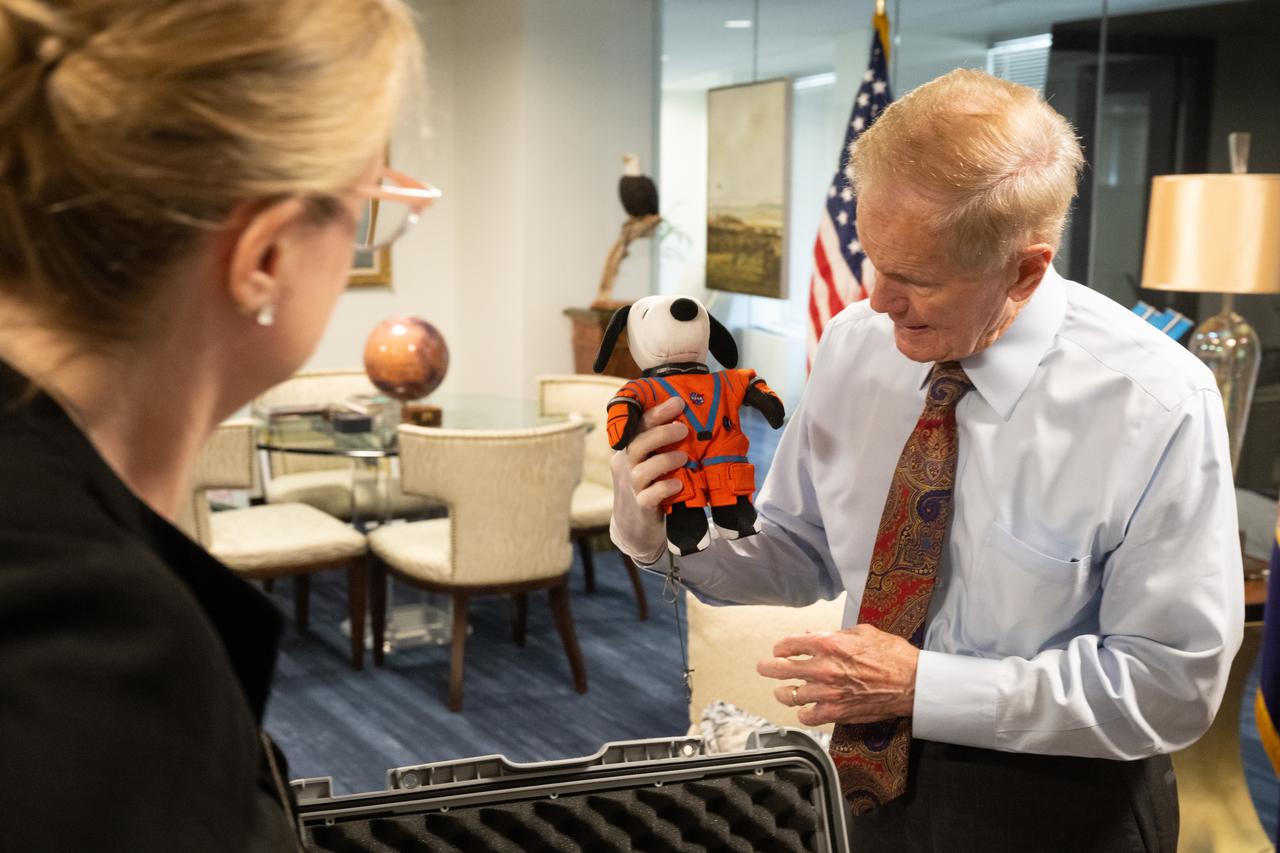

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, is seen during a visit with Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
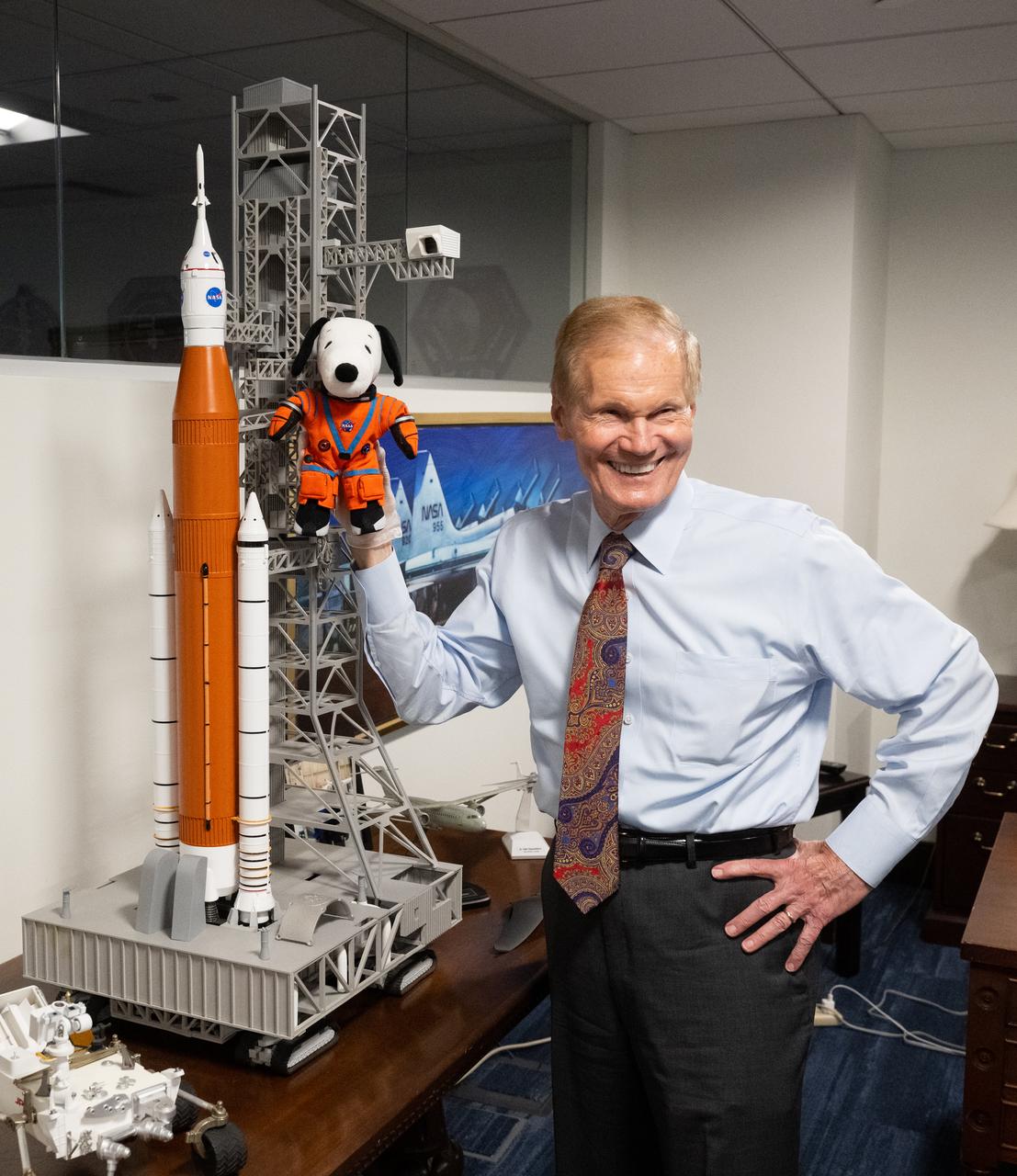

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, is seen during a visit with Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
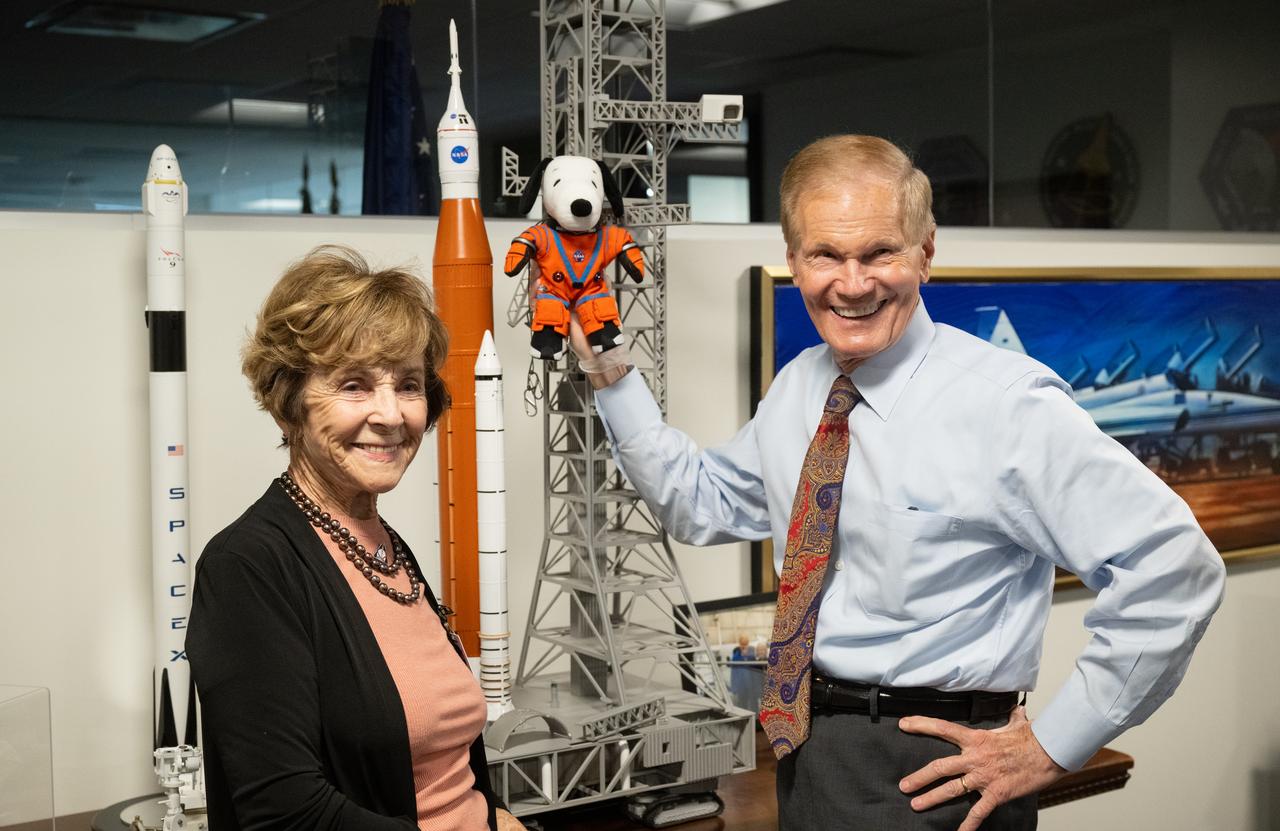

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, is seen with Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, left, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, during a visit to the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
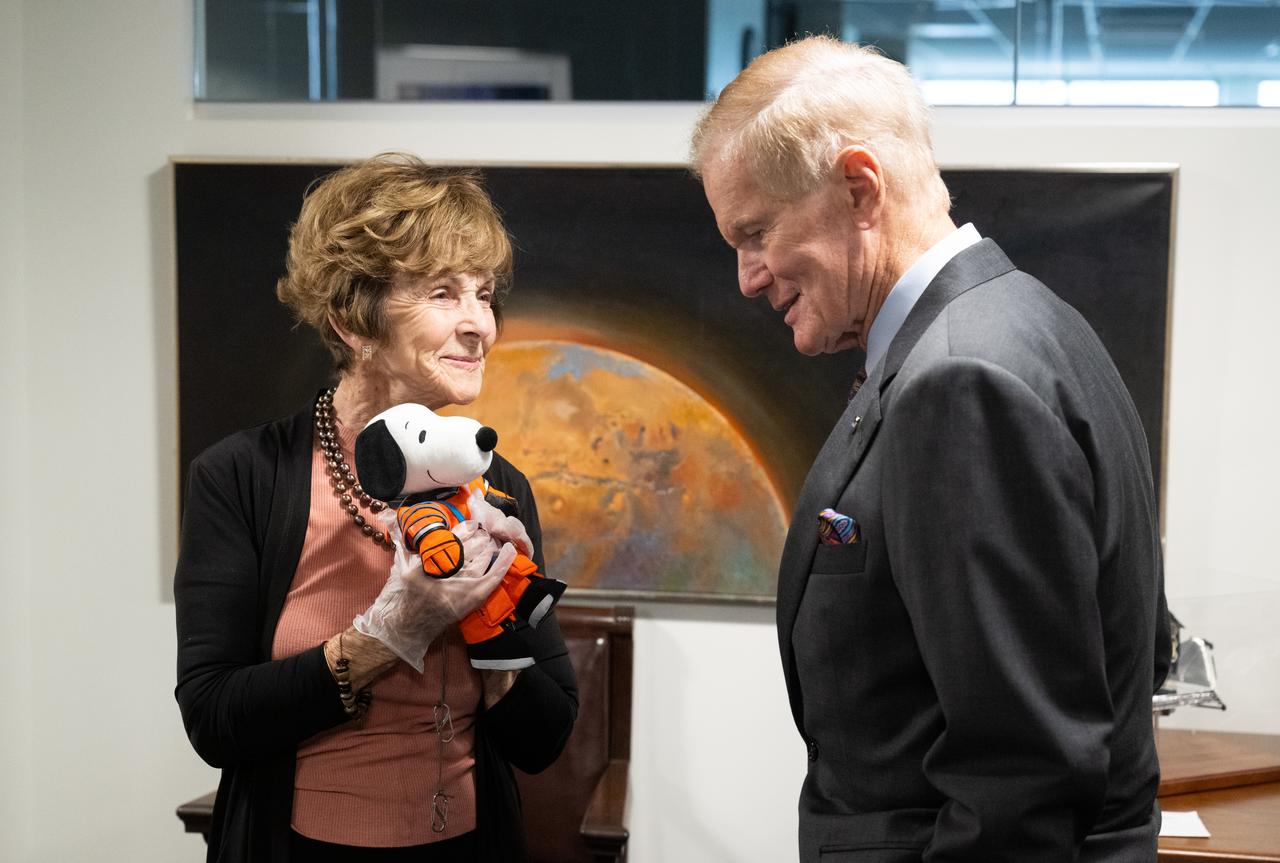

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, is seen with Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, left, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, during a visit to the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
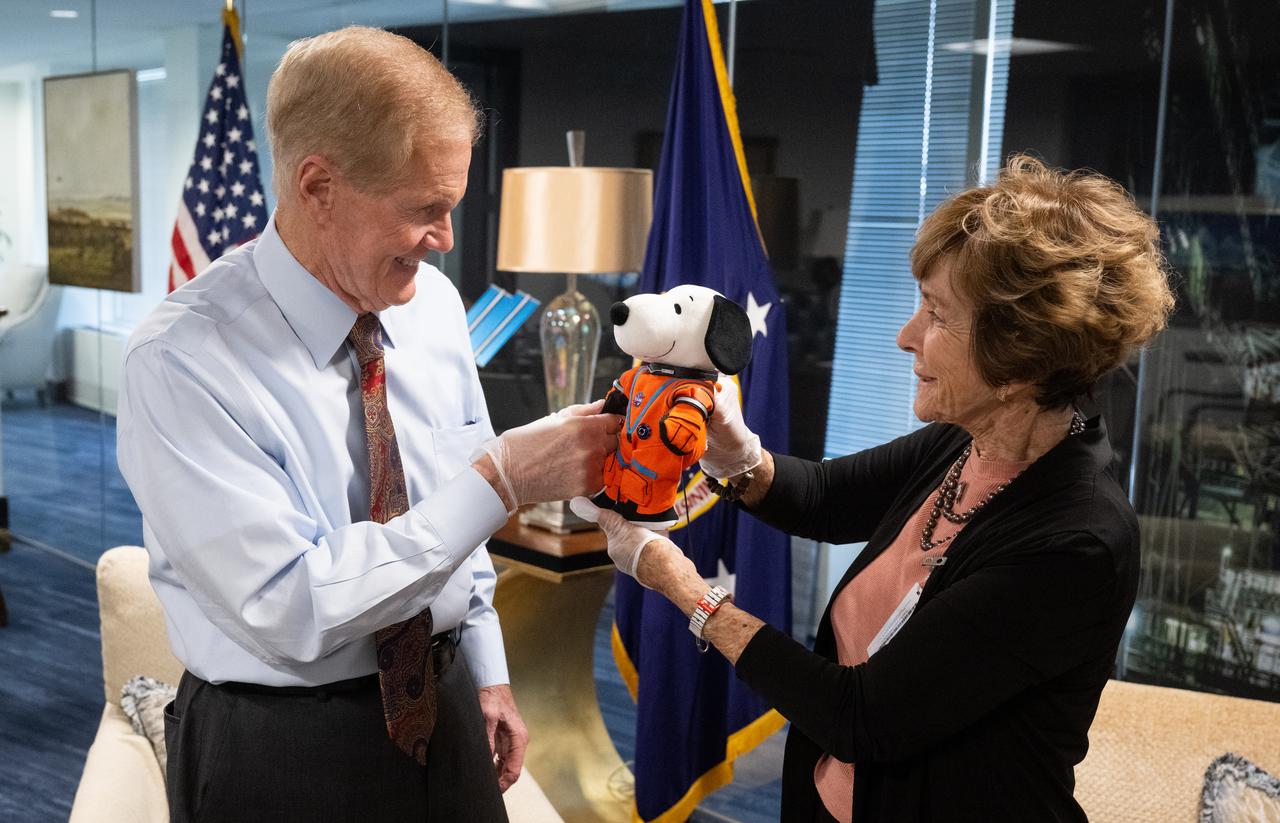

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, is seen with Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, right, holding the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, during a visit to the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an “Our Blue Planet” concert at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
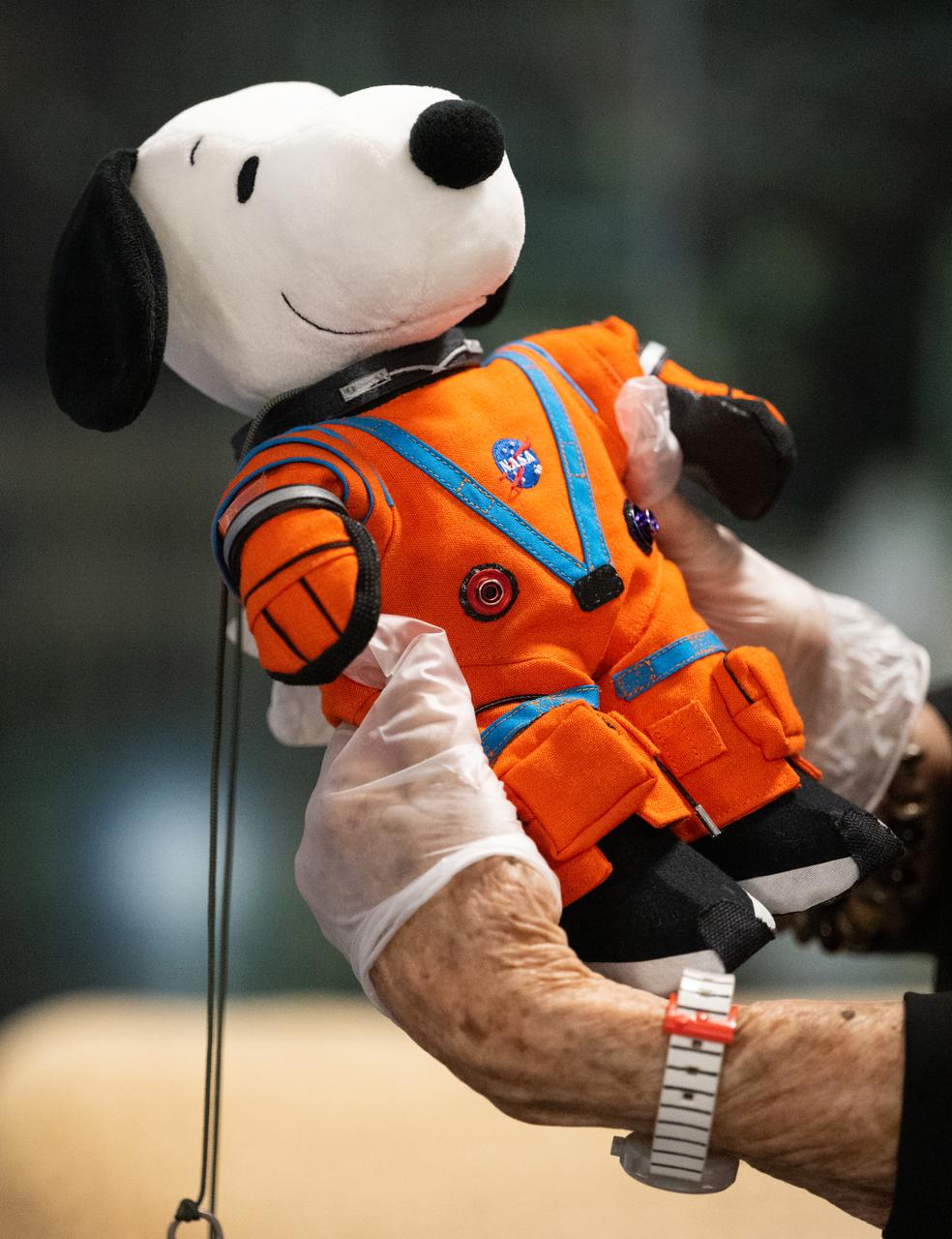

Jeannie Schulz, widow of Peanuts gang creator Charles M. Schulz, holds the Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator, Wednesday, April 5, 2023, during visit to the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Schulz was awarded a NASA Exceptional Achievement Medal by Administrator Nelson at an Our Blue Planet concert at the Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts. Snoopy rode along as the zero gravity indicator on NASA’s Artemis I mission as part of a partnership with the agency and continues to help NASA inspire kids of all ages to follow along with Artemis missions. As part of the visit, Schulz showed the flown Artemis I Snoopy zero gravity indicator before it goes to its final home for display at the Schulz Museum in Santa Rosa, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
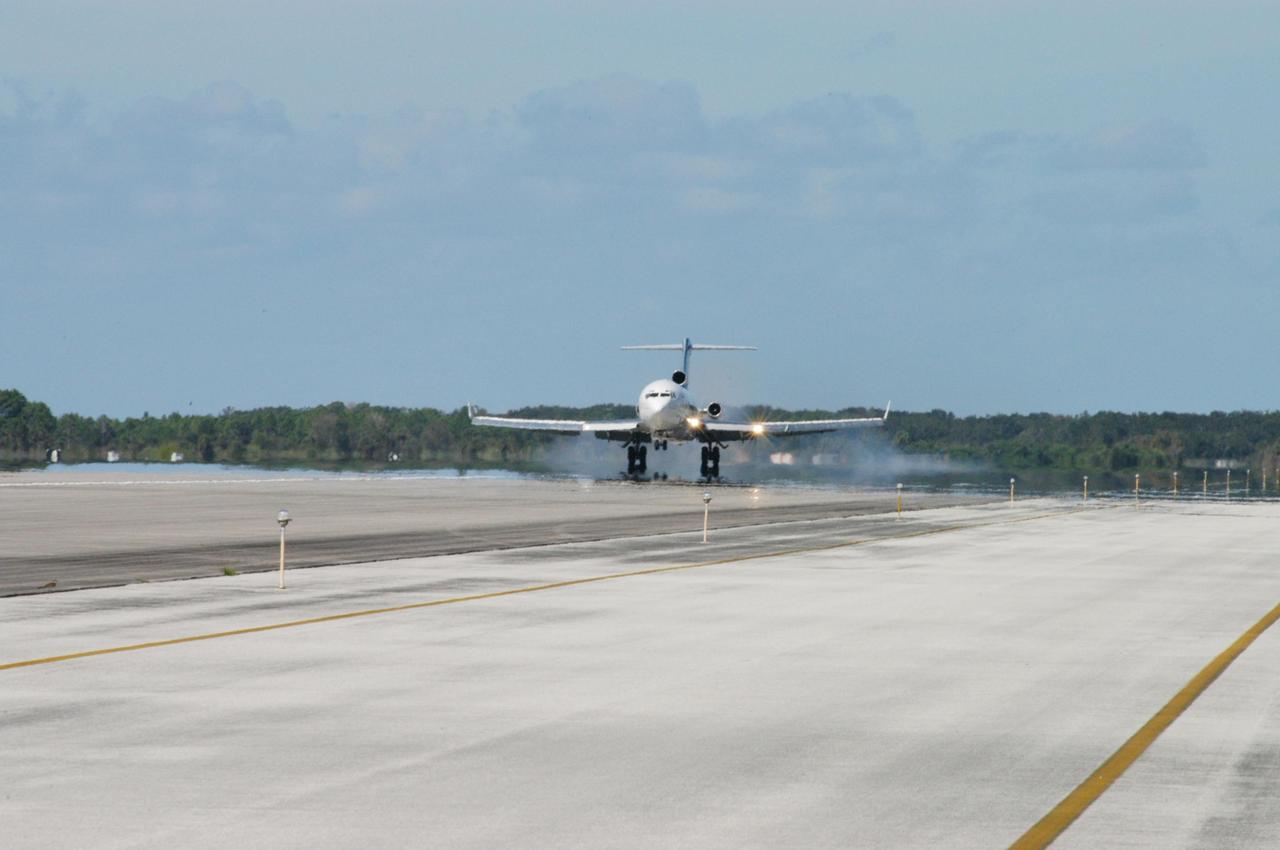

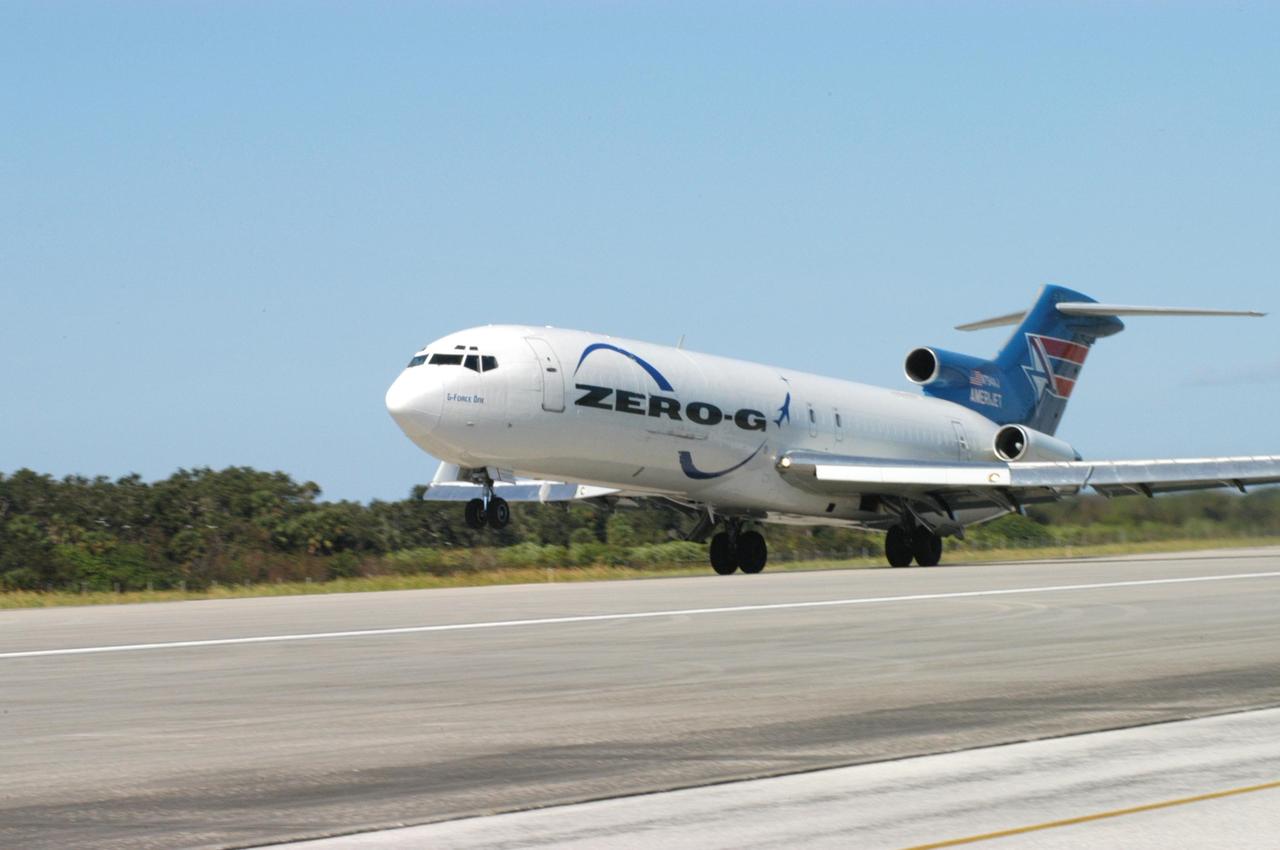
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., lands after taking a group of passengers for demonstration. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. This group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., lands after taking a group of passengers for demonstration. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. This group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
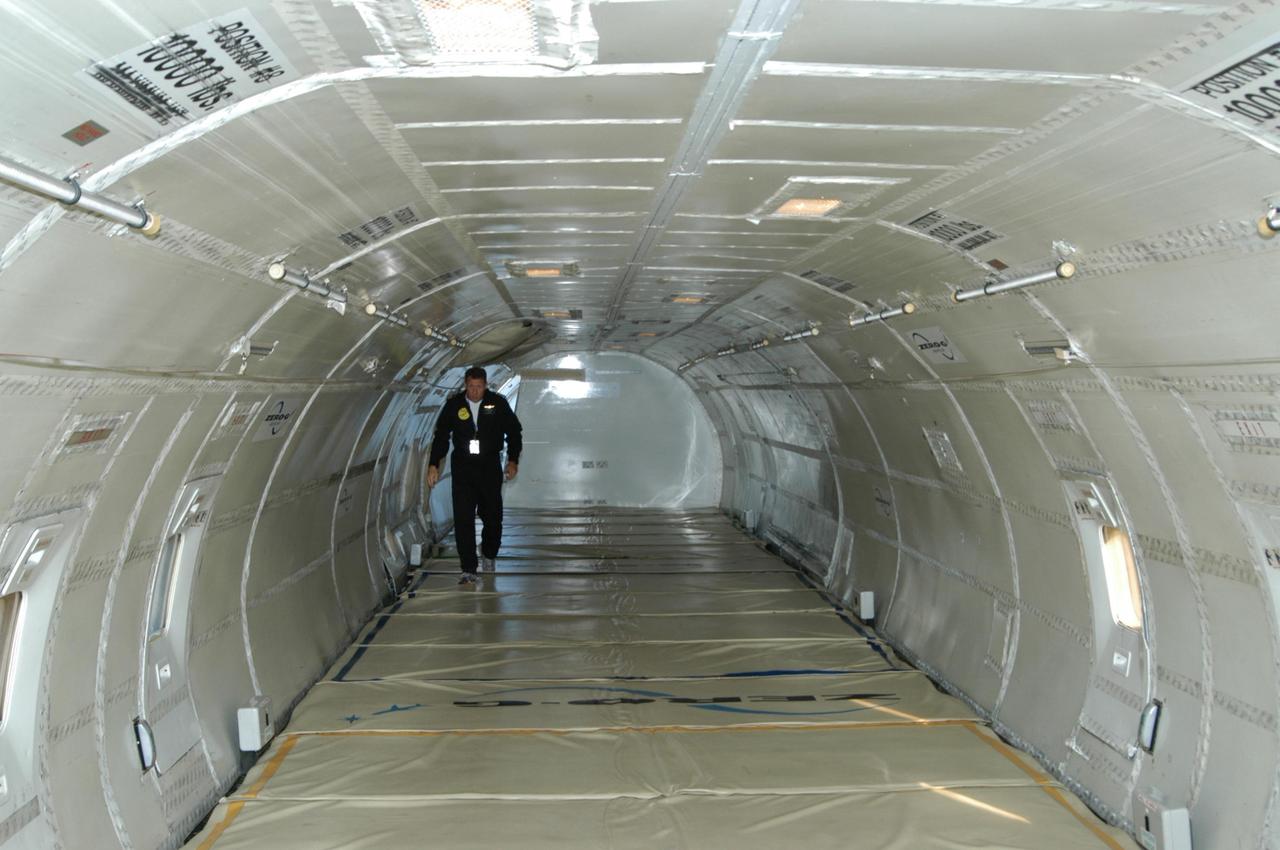

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A view inside the Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. A group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.

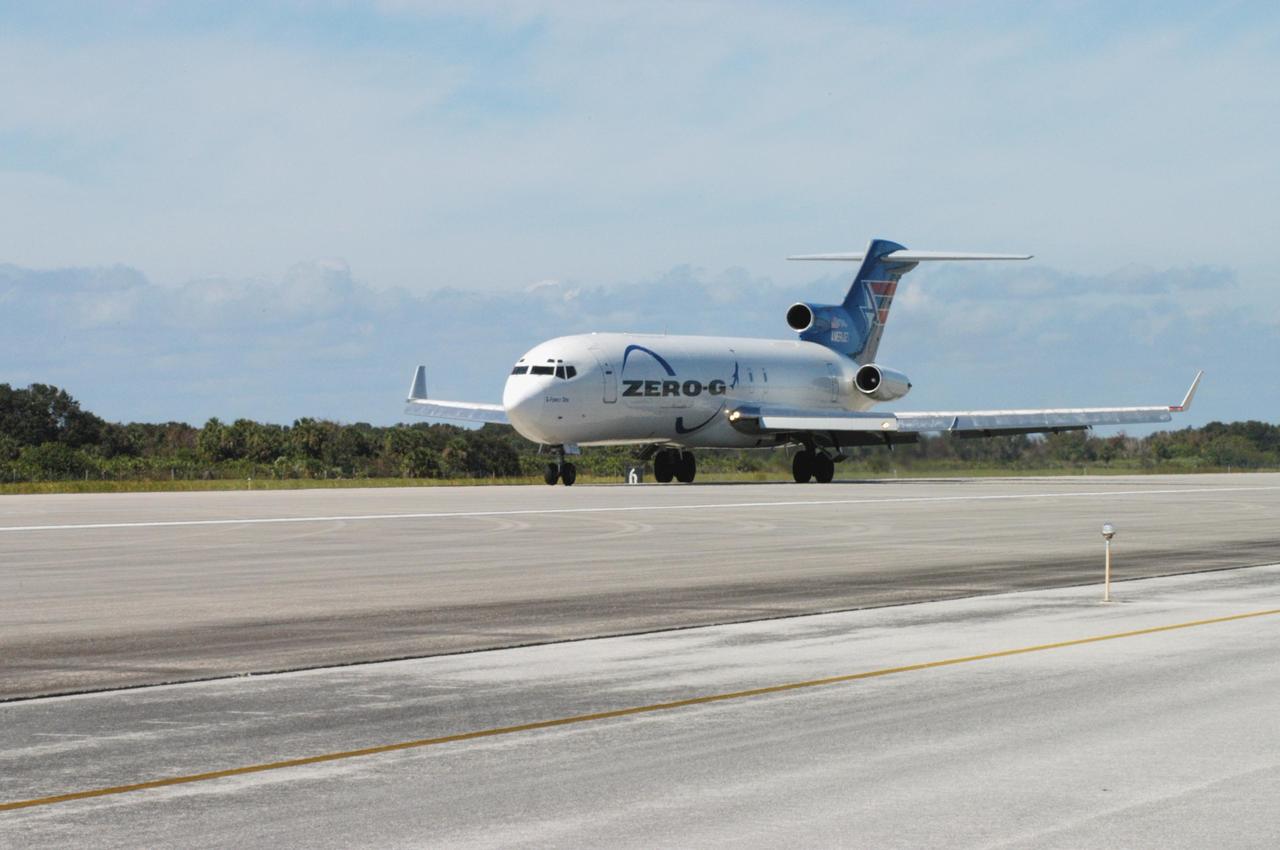
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., waits for its passengers. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. A group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.

Astronaut Joe H. Engle, STS-2 commander, practices donning and doffing his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) in the weightless environment afforded aboard a KC-135 "zero-gravity" aircraft.
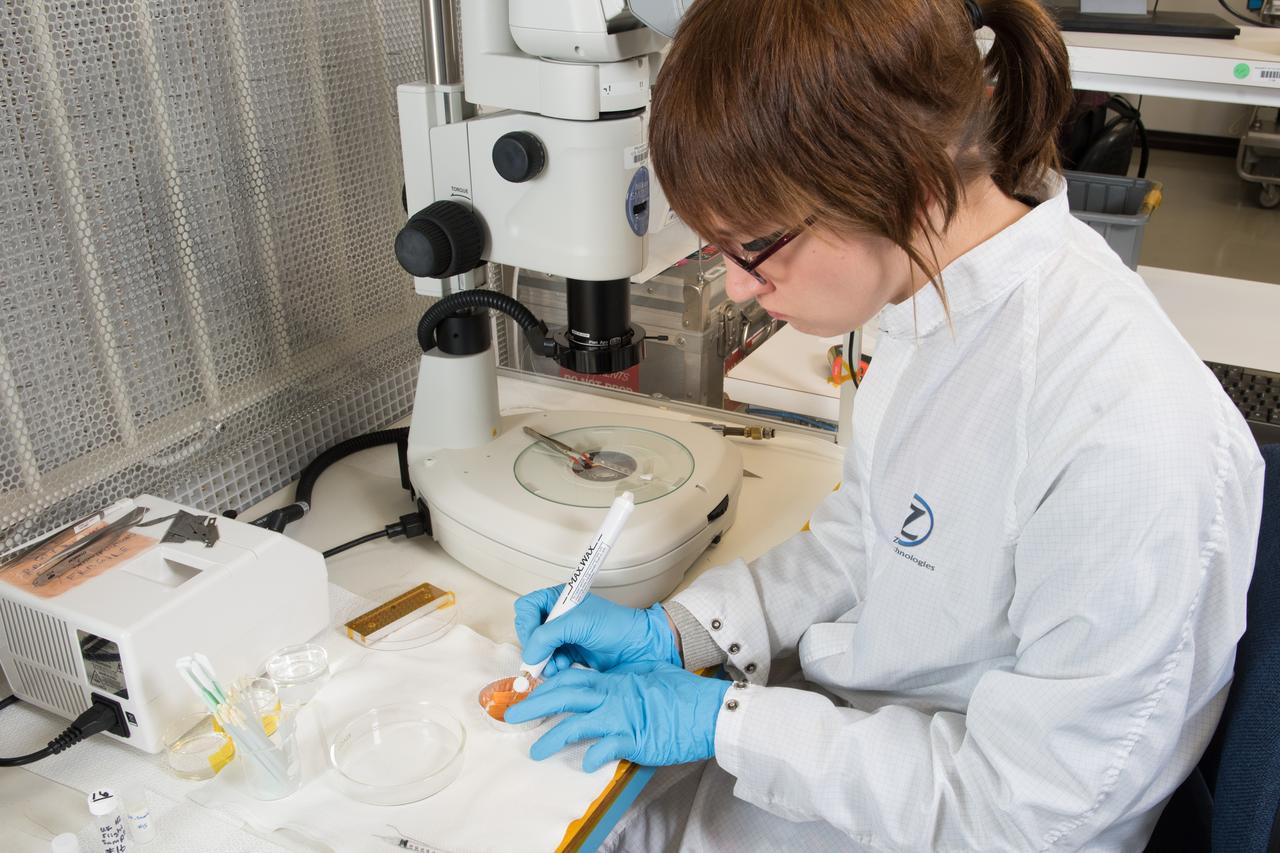

NASA (Zin Technologies) engineer prepares Advanced Colloid Experiment Heated-2 samples that will be analyzed aboard the International Space Station using the zero-gravity Light Microscopy Module, LMM in the Fluids Integrated Rack, FIR
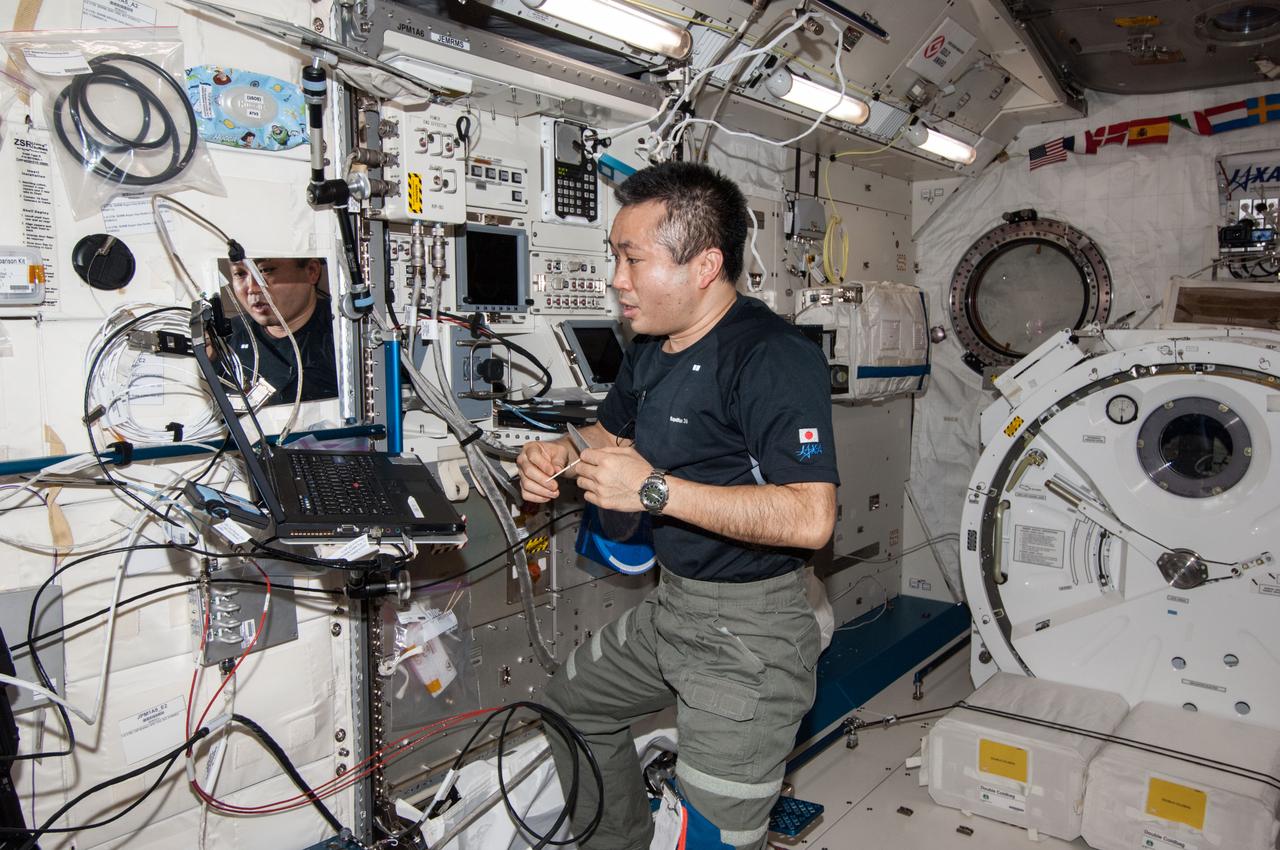

ISS038-E-031382 (14 Jan. 2014) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 38 flight engineer, works at the Zero-Gravity Stowage Rack (ZSR) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
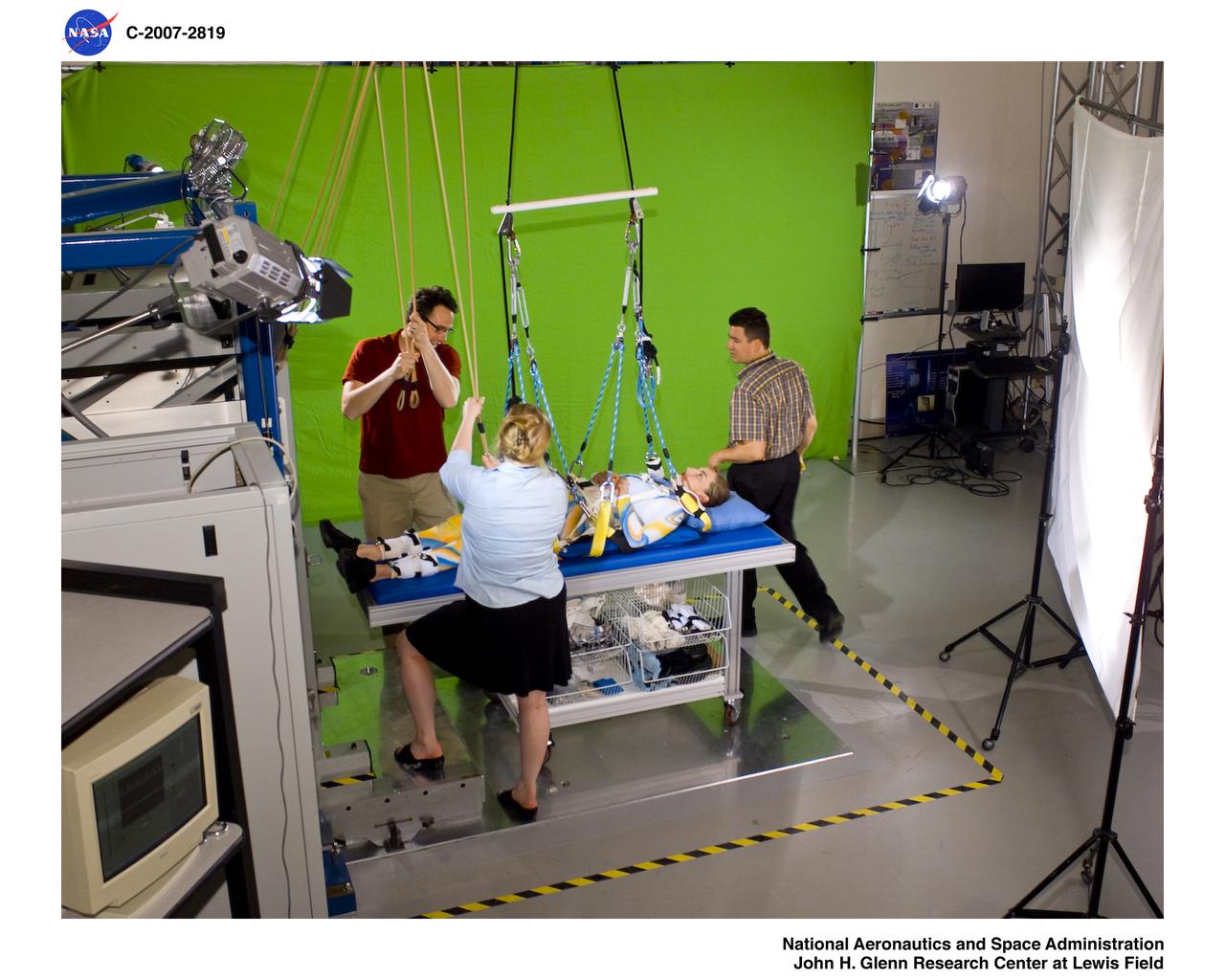

Members of Glen's Exercise Countermeasures Lab work to prepare dancer Sarah Morrison in the Enhanced Zero-gravity Locomotion Simulator for a choreographed video performance entitled "Walking on Other Worlds" produced for IngenuityFest 2007
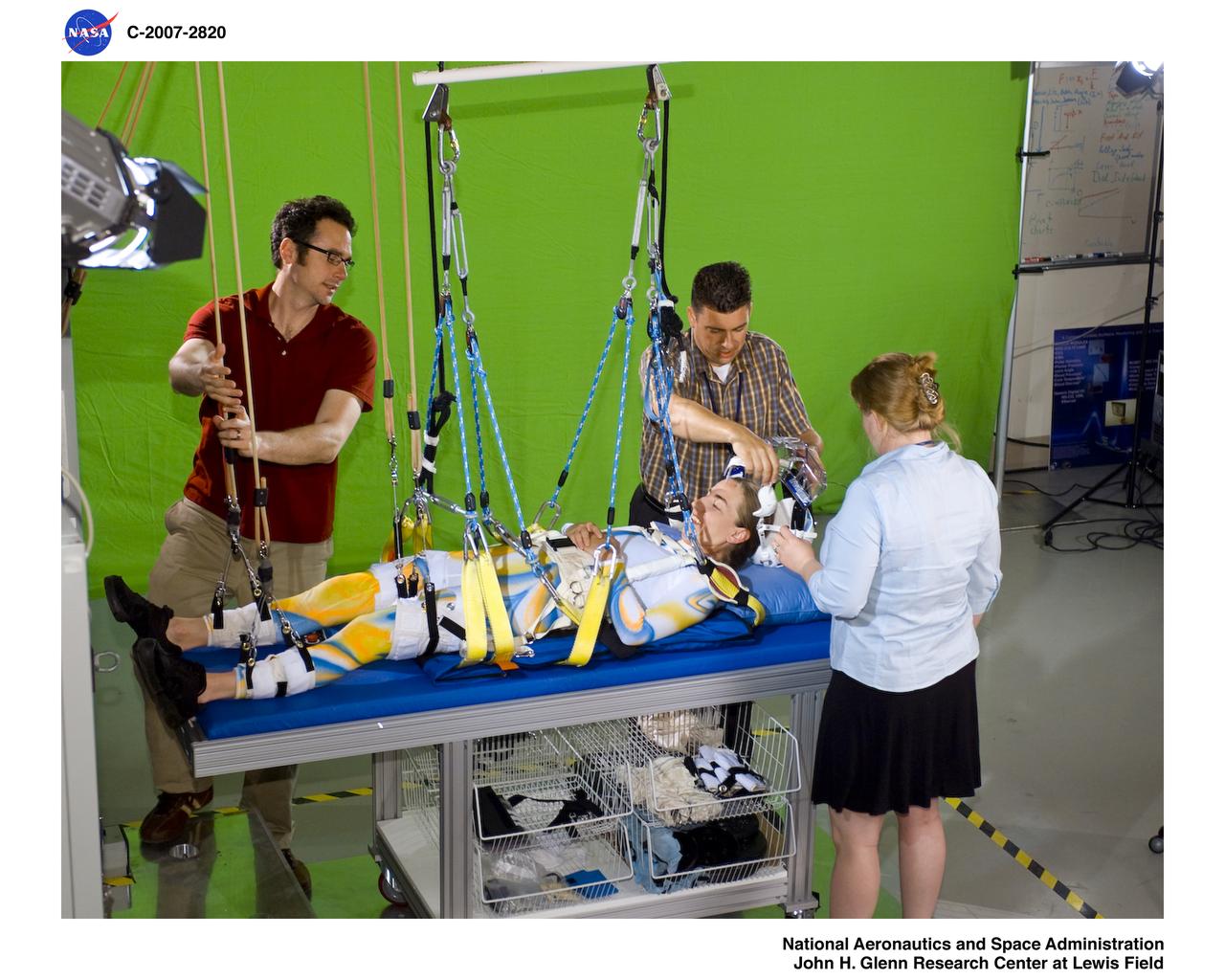

Members of Glen's Exercise Countermeasures Lab work to prepare dancer Sarah Morrison in the Enhanced Zero-gravity Locomotion Simulator for a choreographed video performance entitled "Walking on Other Worlds" produced for IngenuityFest 2007
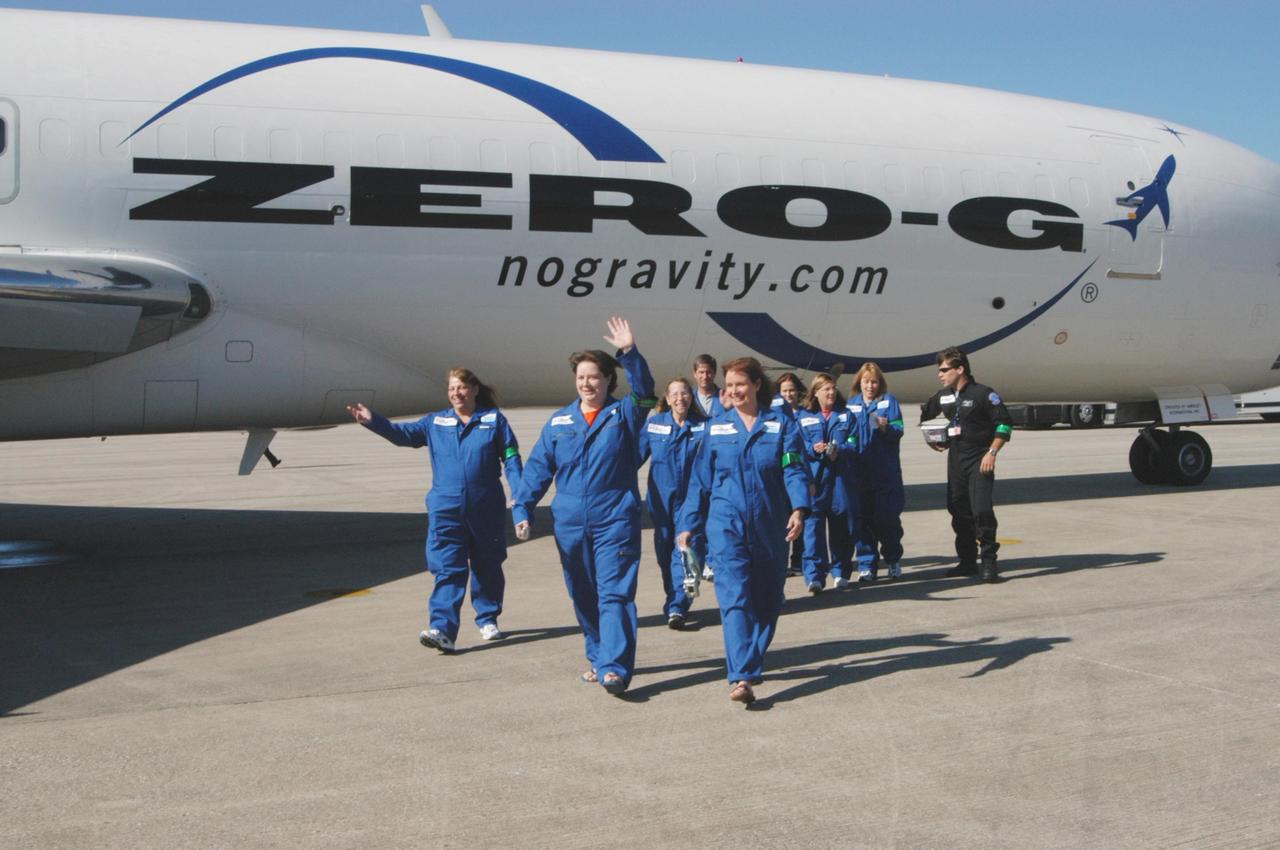

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first group of passengers to fly on the ZERO-G aircraft are eager to get started. The Boeing 727-200 aircraft is used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
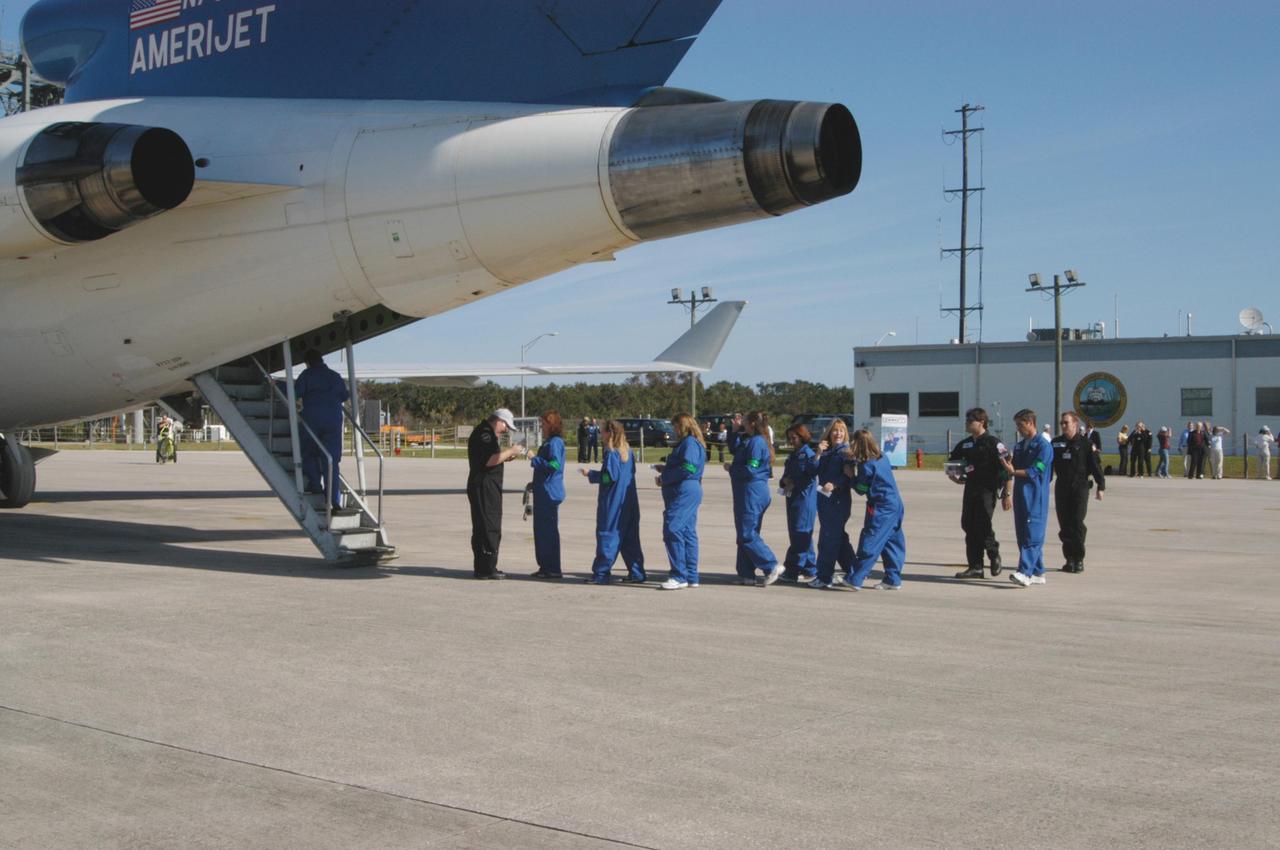

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The first group of passengers to fly on the ZERO-G aircraft line up. The Boeing 727-200 aircraft is used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
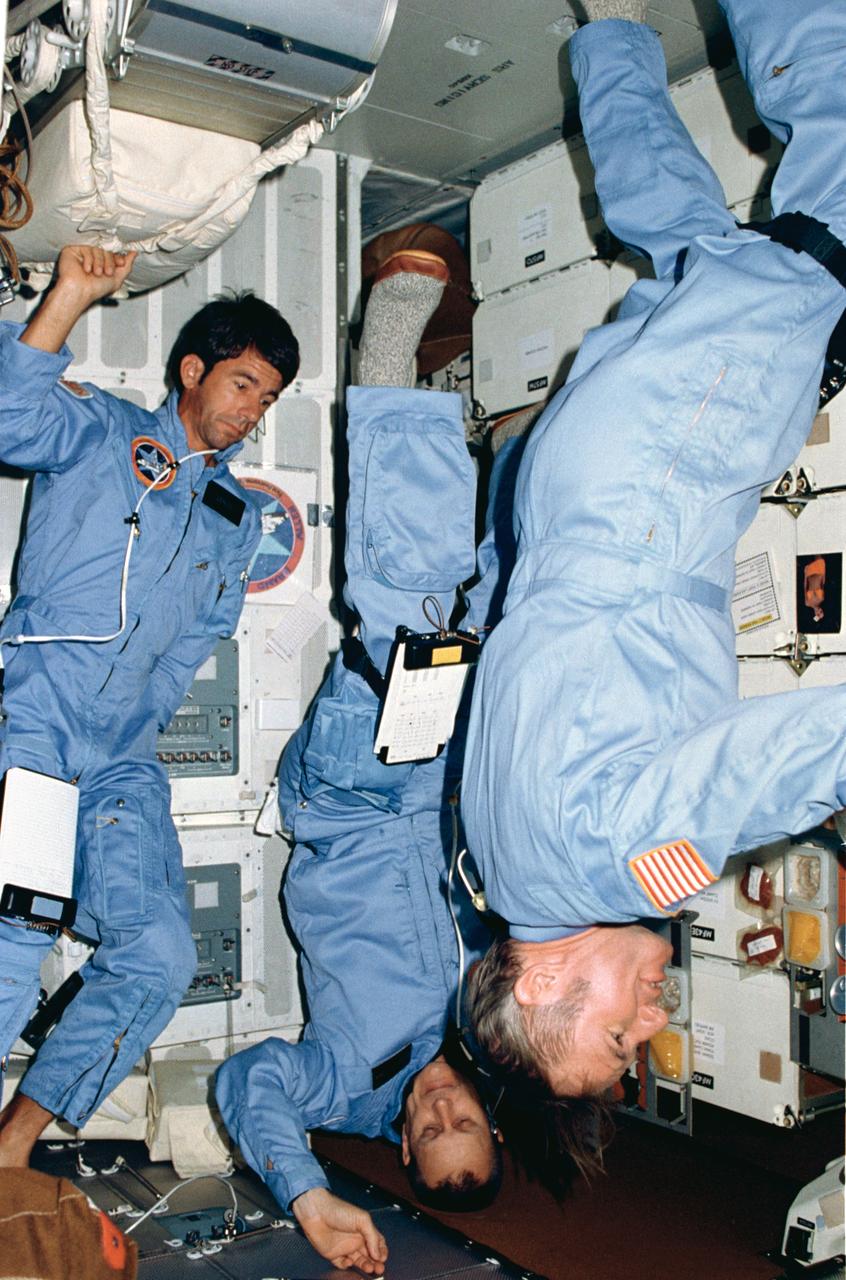

STS005-04-124 (14 Nov. 1982) --- Three members of the four-man STS-5 crew demonstrate the zero-gravity environment aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia. Astronaut Vance D. Brand, mission commander, holds a fairly typical Earth-bound pose, but crewmates, astronauts Robert F. Overmyer (center), pilot, and Dr. William B. Lenoir, mission specialist, perform body movements that could only be accomplished in zero-gravity. Dr. Joseph P. Allen IV, the flight’s other mission specialist, exposed this frame with a 35mm handheld camera. The four astronauts were in the middeck area of their reusable spacecraft when this photograph was made. Photo credit: NASA
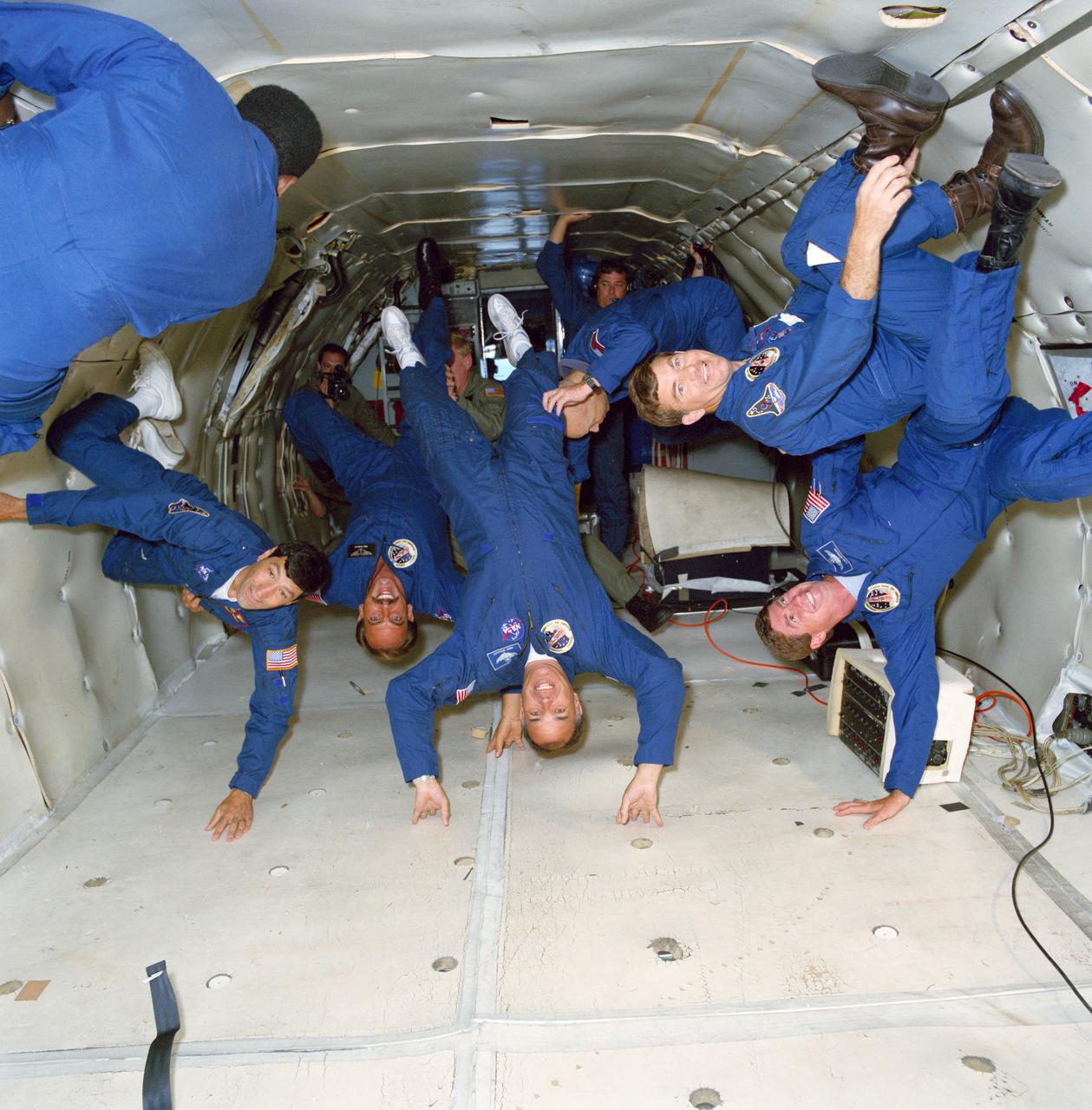

S91-38355 (28 May 1991) --- Seen floating about the vacant spaces of the Johnson Space Center's KC-135 "zero-gravity" aircraft are the six crewmembers for the STS 44 mission. Left to right are Terence T. Henricks, James S. Voss, F. Story Musgrave (partially obscured), Frederick D. Gregory, Thomas J. Hennen and Mario Runco Jr. Gregory is mission commander. Hennen is payload specialist for this flight, dedicated to the Department of Defense. The flight served as a refresher and a preview of the experience of weightlessness, as the special aircraft flew a series of parabolas which provided short sessions of zero-gravity.
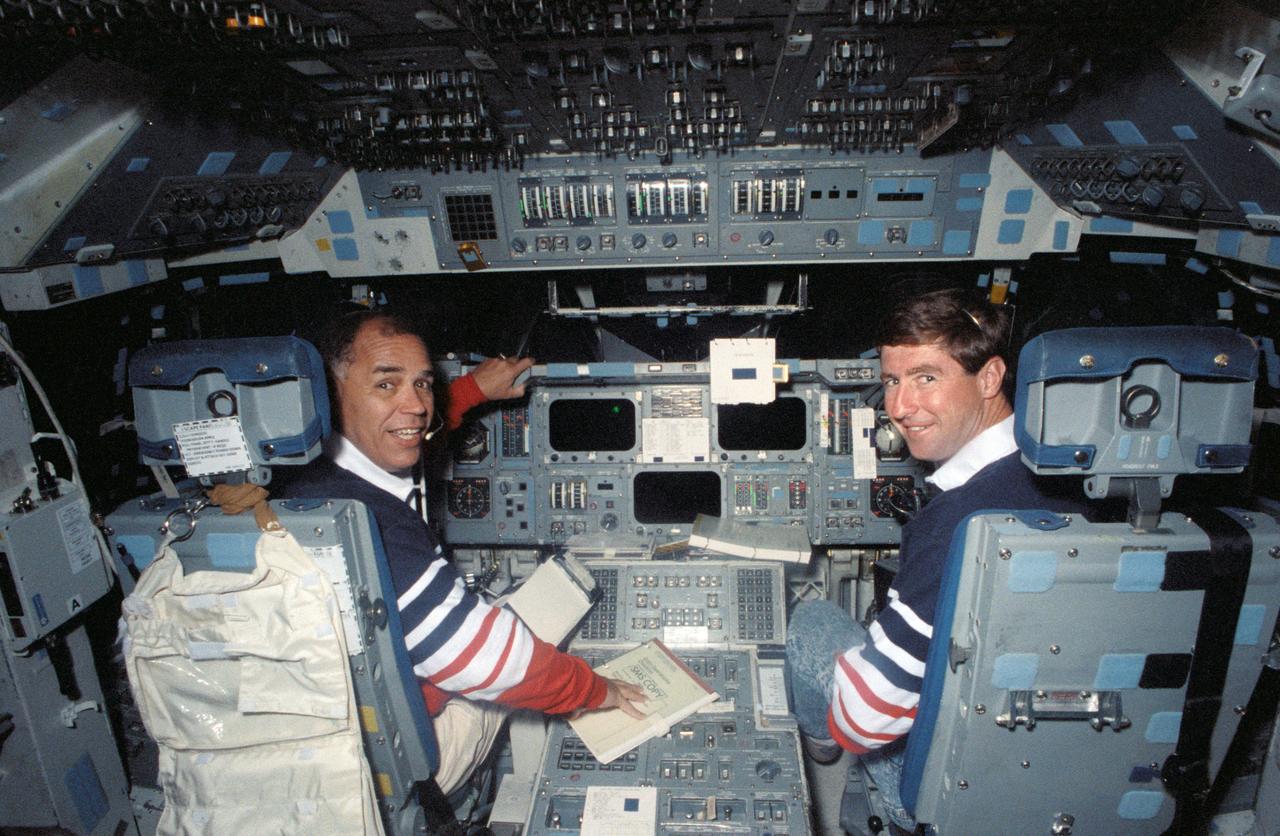

S91-38355 (28 May 1991) --- Seen floating about the vacant spaces of the Johnson Space Center's KC-135 "zero-gravity" aircraft are the six crewmembers for the STS 44 mission. Left to right are Terence T. Henricks, James S. Voss, F. Story Musgrave (partially obscured), Frederick D. Gregory, Thomas J. Hennen and Mario Runco Jr. Gregory is mission commander. Hennen is payload specialist for this flight, dedicated to the Department of Defense. The flight served as a refresher and a preview of the experience of weightlessness, as the special aircraft flew a series of parabolas which provided short sessions of zero-gravity.
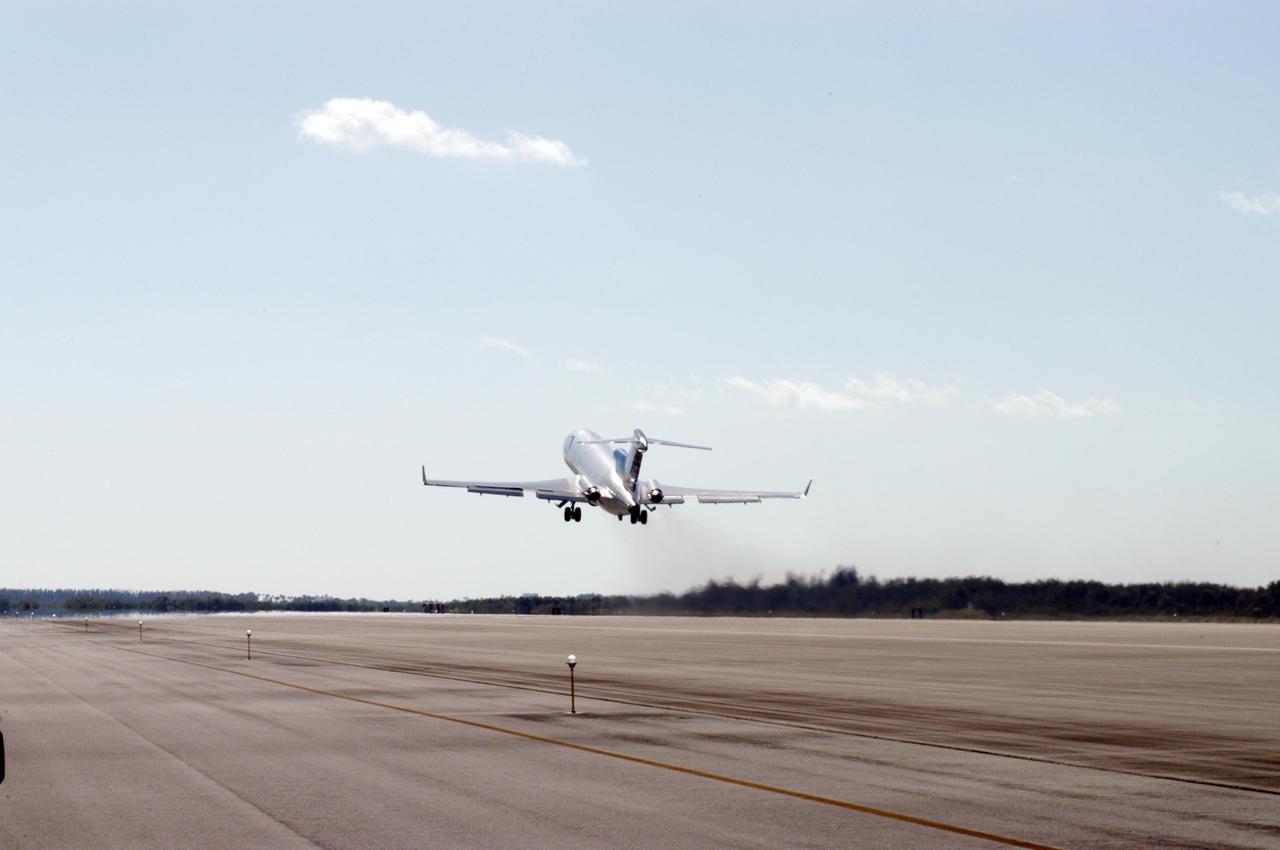

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., is airborne from Kennedy Space Center’s shuttle landing facility. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla., takes off from Kennedy Space Center’s shuttle landing facility. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The group of passengers, called "Flyers," were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.
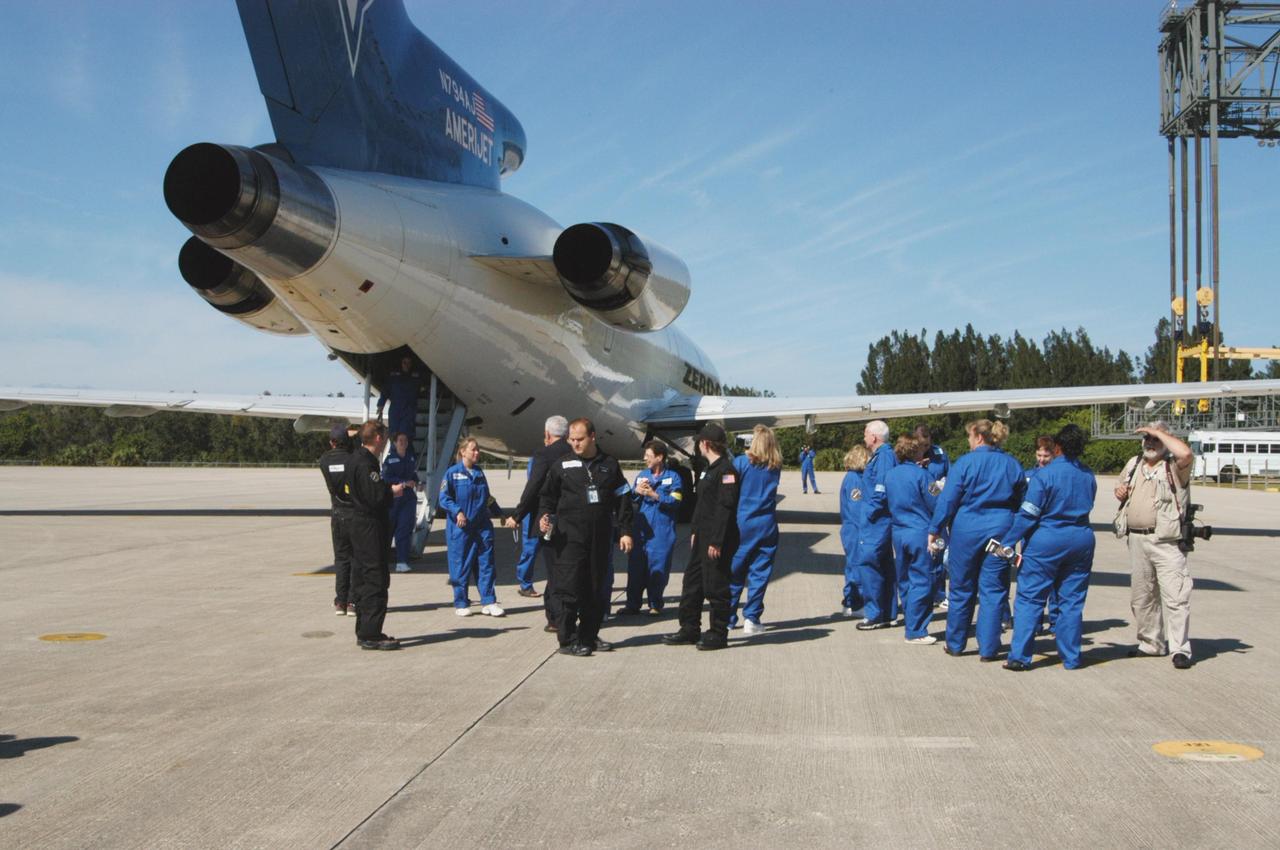

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Passengers known as “Flyers” disembark at Kennedy Space Center’s shuttle landing facility from a Boeing 727-200 aircraft used for weightless flights by Zero Gravity Corporation, known as ZERO-G, of Fort Lauderdale, Fla. NASA and ZERO-G demonstrated Nov. 5 the expanded access to and use of the space shuttle's runway and landing facility at Kennedy Space Center for non-NASA activities. The “Flyers” were predominantly teachers who performed simple microgravity experiments they can share with their students back in the classroom.