
NASA Glenn Research Pilot Jim Demers flies the T-34C Mentor aircraft. When NASA scientists study Great Lakes algal blooms, Demers is one of the pilots at the controls.
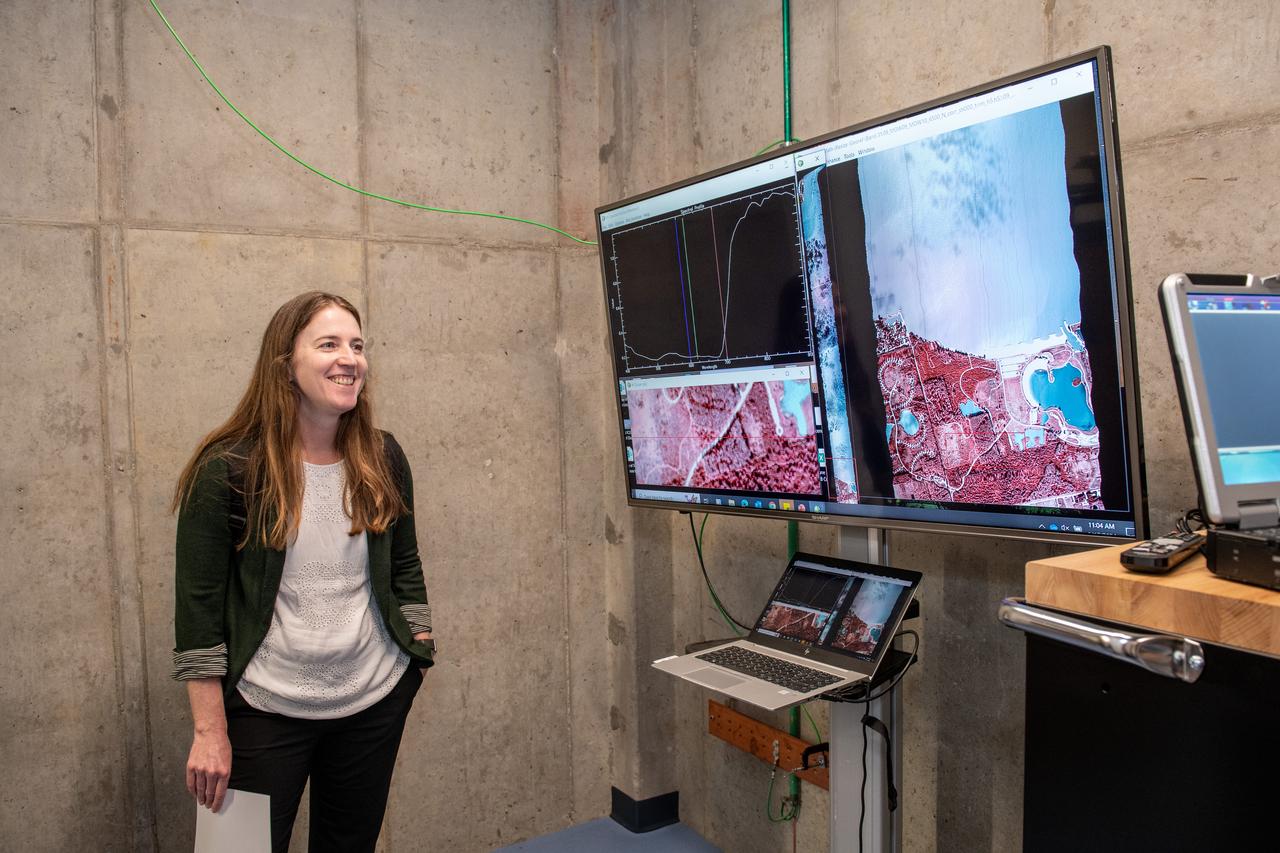

Dr. Katherine Calvin listens to a harmful algal bloom presentation on June 17, 2024. NASA Glenn Research Center conducts aerial remote sensing of harmful algal blooms to warn water filtration plants to enact more stringent filtering when harmful blooms are present. Aerial remote sensing is advantageous to satellite remote sensing that is limited by factors of resolution, on demand performance, cloud cover, and upgrades to instrumentation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
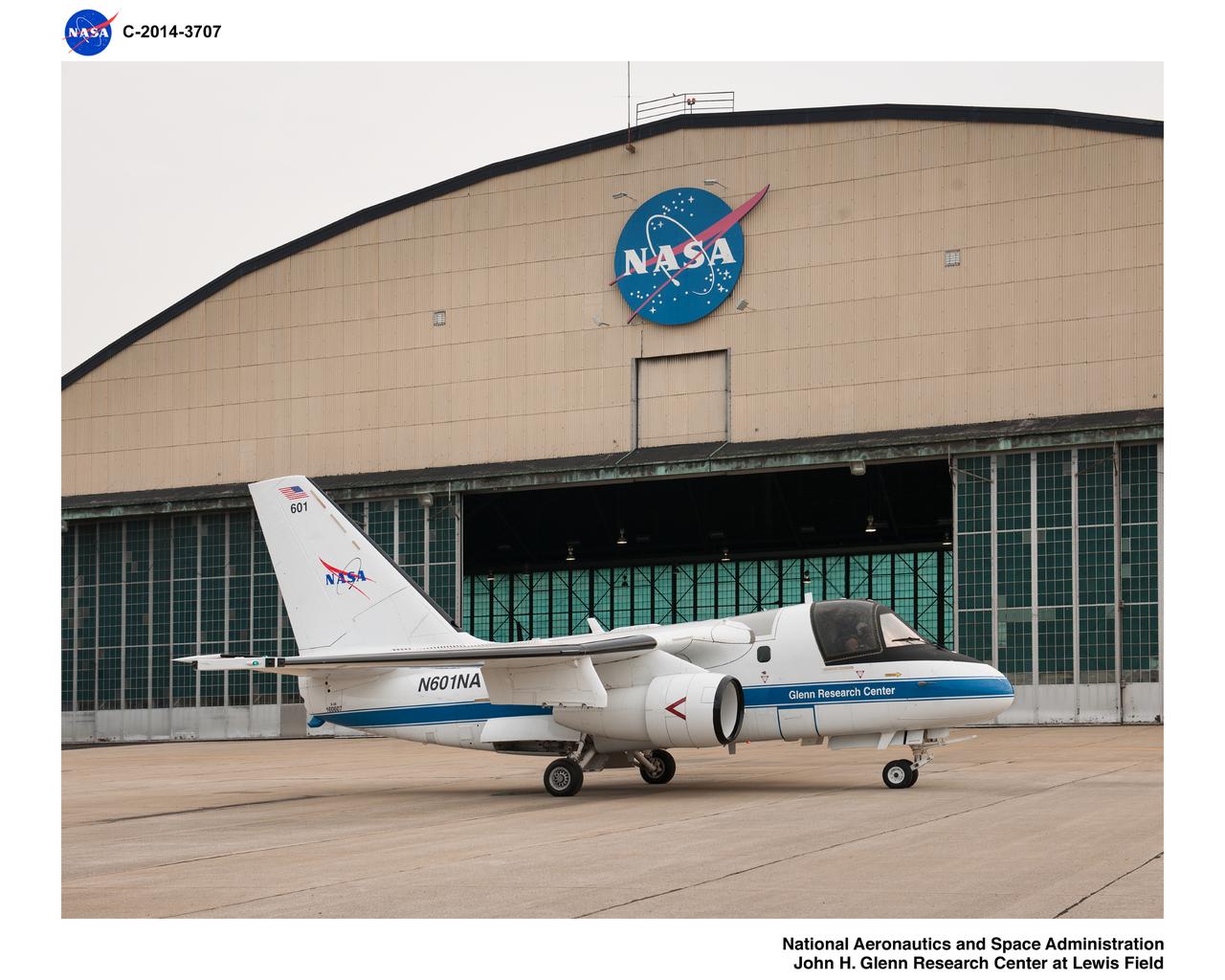

Pre-Flight Check Out of Lockheed Martin S-3B Viking Aircraft #N601NA in preparation for the Lake Erie Algal Bloom Flight Campaign
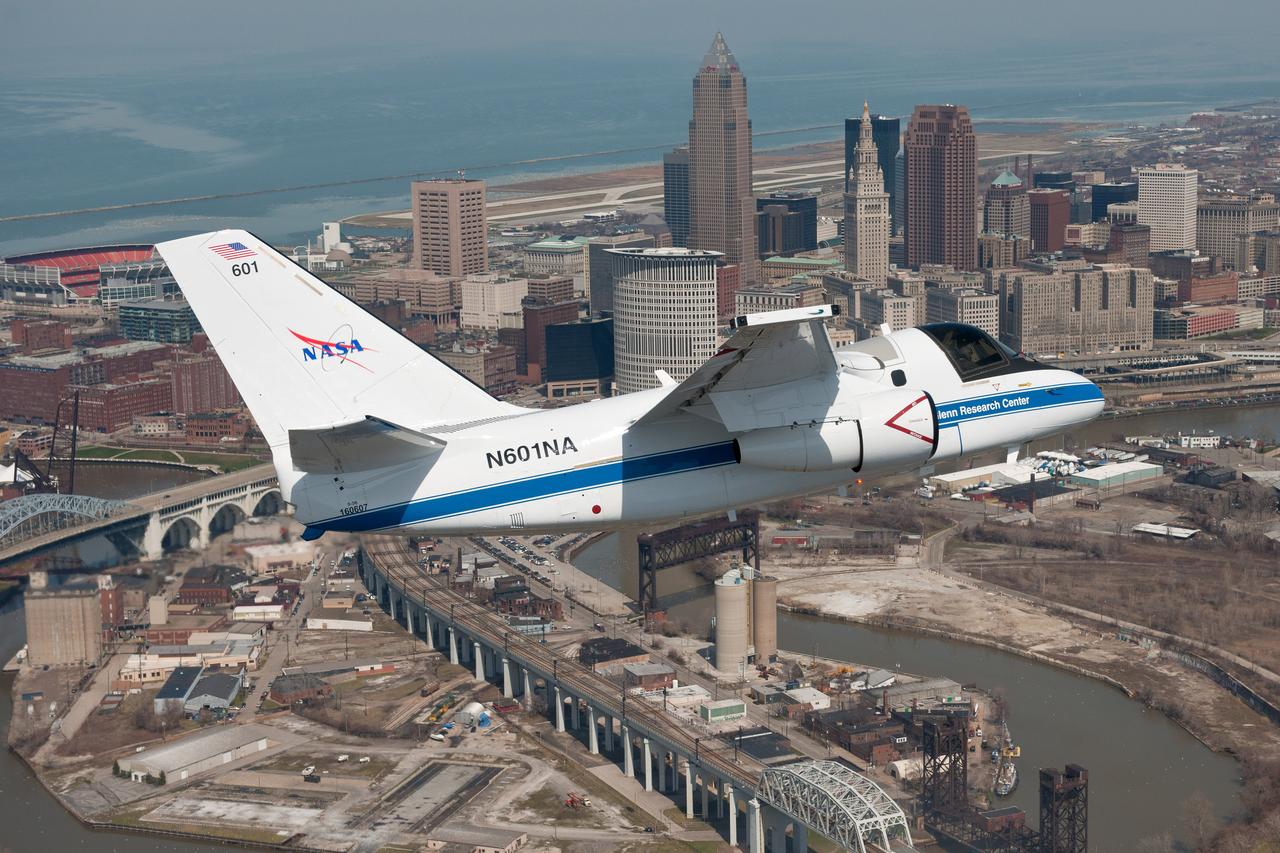

This photo shows NASA Glenn’s S-3 Viking Aircraft flying over downtown Cleveland, Ohio. The S-3 continues to conduct important research including regular flights over Lake Erie and other waterways to image algal blooms that have plagued the area’s waters.
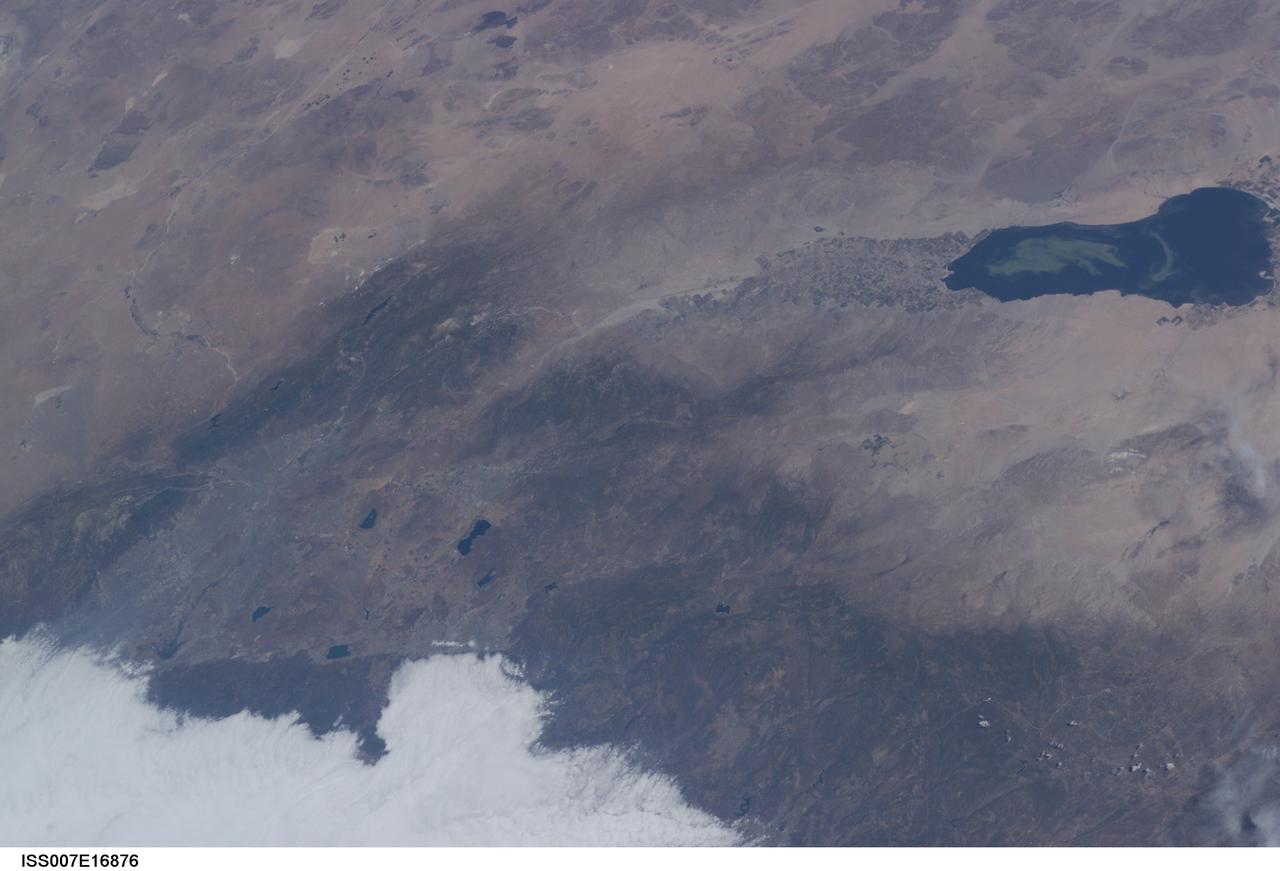

ISS007-E-16876 (9 October 2003) --- This view featuring the Salton Sea was taken by an Expedition 7 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS). This wide image shows a portion of drought-stricken southern California, including the urban sprawl of San Bernardino and Riverside, the agricultural development of the Imperial Valley and the Salton Sea sporting a huge swirl, speculated to be an algal bloom. The coastal region is obscured by fog.
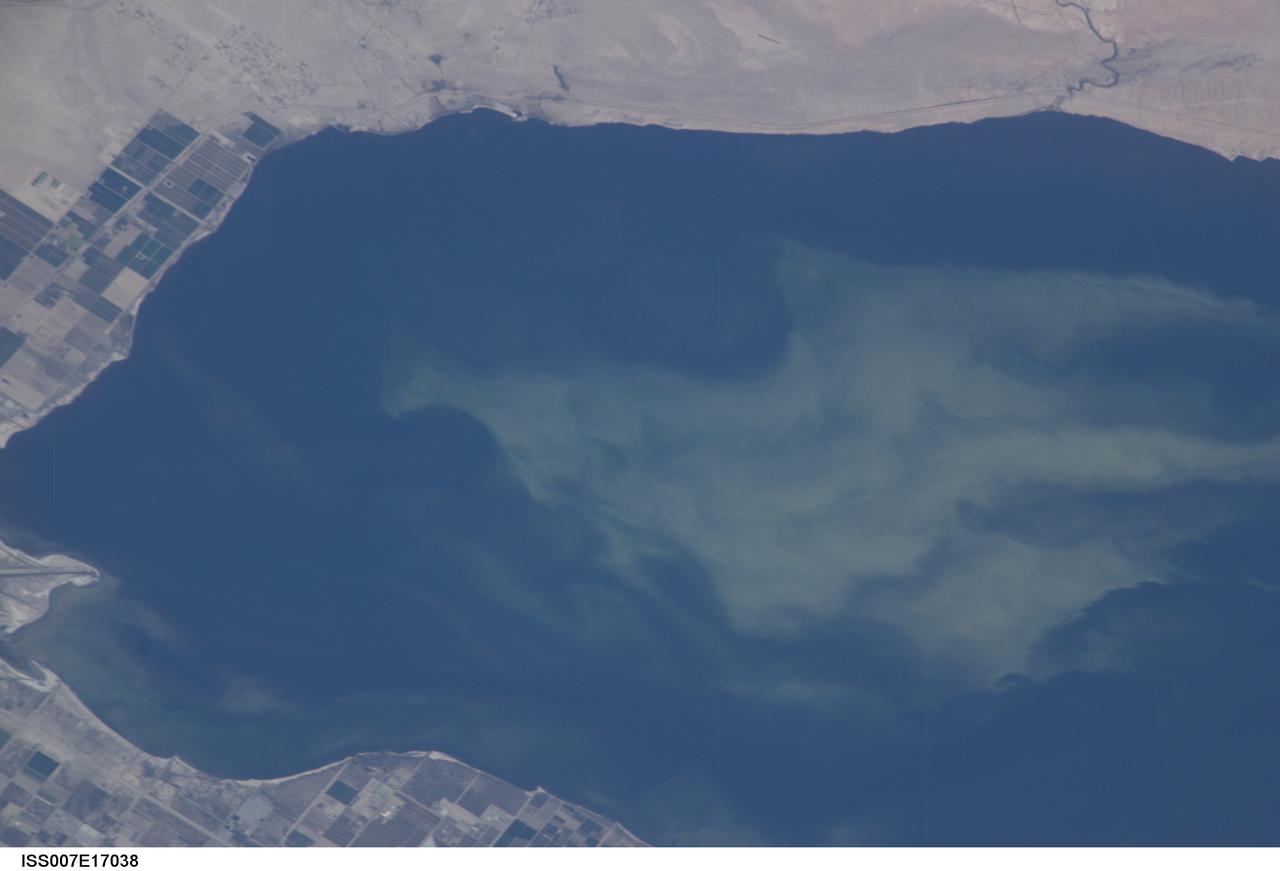

ISS007-E-17038 (11 October 2003) --- This view featuring a close-up of the Salton Sea was taken by an Expedition 7 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The image provides detail of the structure of the algal bloom. These blooms continue to be a problem for the Salton Sea. They are caused by high concentrations of nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorous, which drain into the basin from the agricultural run-off. As the algae die and decompose, oxygen levels in the sea drop, causing fish kills and hazardous condition for other wildlife.
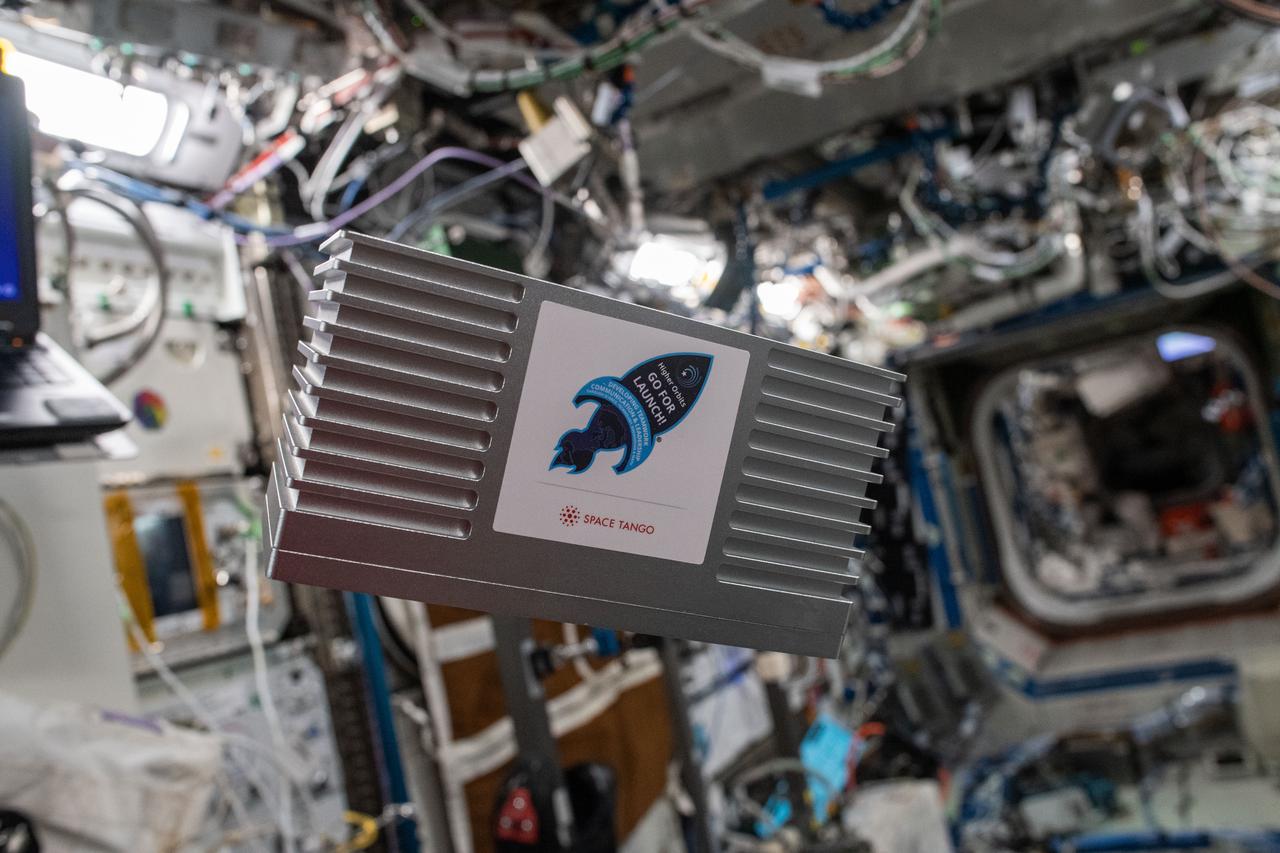
iss067e000376 (3/31/2022) --- A Higher Orbits Double Cube aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Effects of Microgravity on Oxygen Output Regarding Chlorella vulgaris (Oxygen Production in Algae) investigates how microgravity affects the oxygen output of an algal species. Results could improve understanding of microgravity’s effects on the process of photosynthesis and development of photosynthetic organisms, which could contribute to design of oxygen production systems for future space travel.
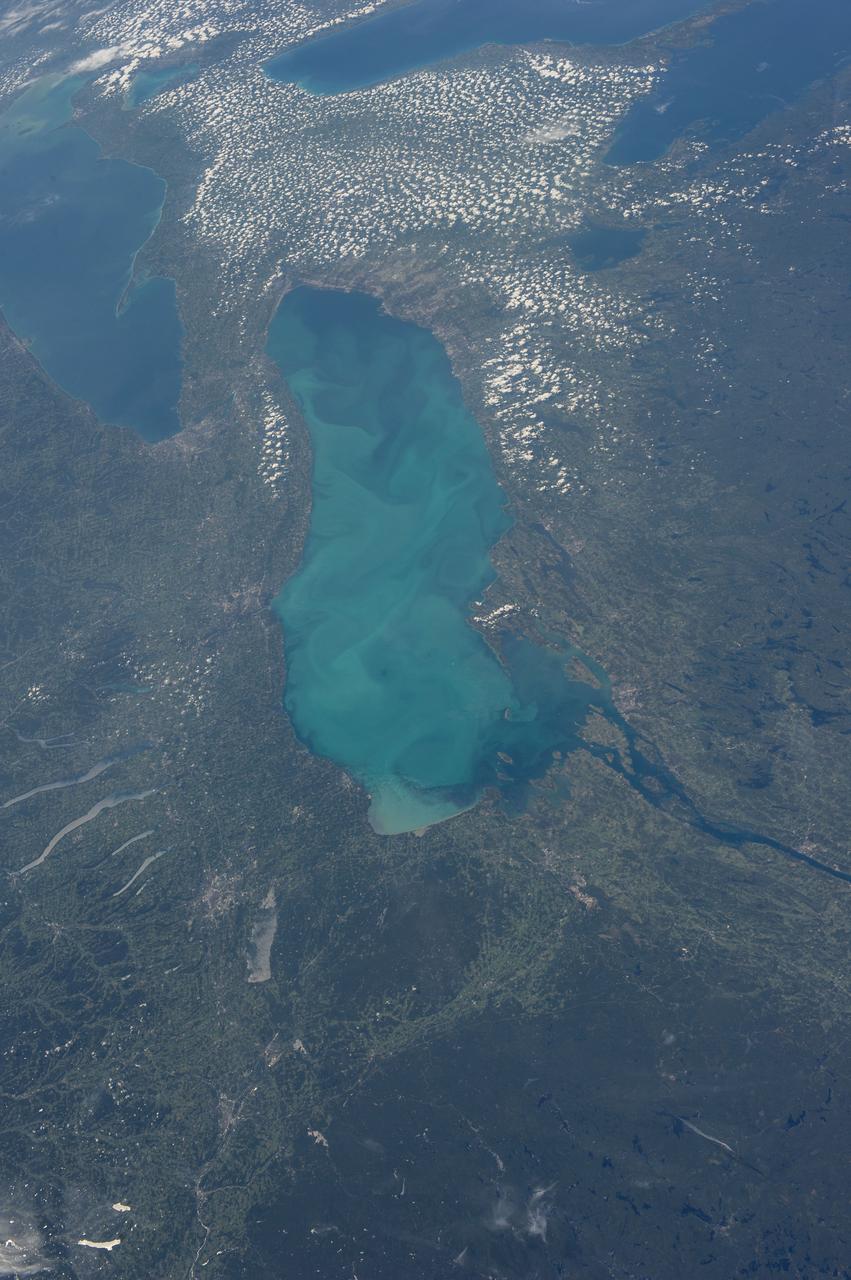

ISS036-E-035635 (24 Aug. 2013) --- Plankton bloom and Lake Ontario are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 36 crew member on the International Space Station. This photograph highlights a late summer plankton bloom visible throughout much of Lake Ontario (one of the Great Lakes, together with Michigan, Superior, Erie, and Huron). Cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae, can reach such large concentrations that they color the water to such an extent that the change is visible from orbit. Harmful algal blooms, or HABs, have been observed in all of the Great Lakes – particularly Lake Erie - and are associated with a variety of causative factors including changes in precipitation; drought; invasive species (quagga, zebra mussels, Asian carp); nutrient loading from runoff and sewage (nitrogen and phosphorus); and warmer average temperatures. In addition to reduced water quality and human health concerns, algal blooms can also lead to hypoxia (reduction of oxygen in the bottom waters) that kills large numbers of fish and other aquatic life. Lake Ontario, like the other Great Lakes Erie, Huron, and Superior is roughly divided between the USA and Canada. The USA side of Lake Ontario has its shoreline along the state of New York, while its Canadian shoreline lies within the province of Ontario. The city of Kingston, Ontario, is visible near the Saint Lawrence River outflow from the lake. Several other landscape features of New York State are visible in the image, including the Finger Lakes region to the west of Syracuse, NY (upper left). To the northeast of Syracuse, the dark wooded slopes of the Adirondack Mountains are visible at lower right. Patchy white cloud cover obscures much of the land surface to the west of Lake Ontario.
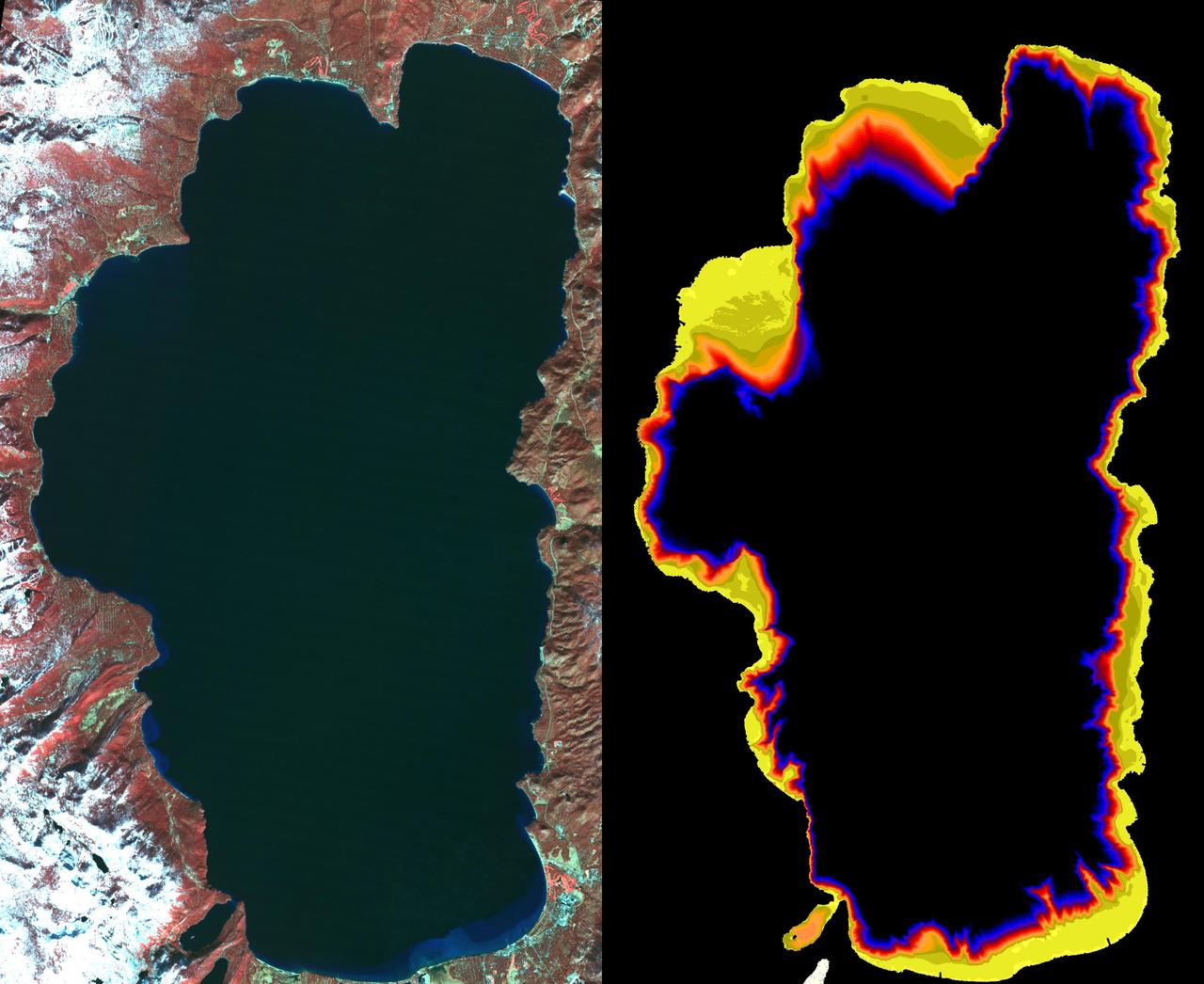

Images from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer aboard NASA's Terra satellite, launched in 1999, illustrate the state of gradually decreasing water clarity at Lake Tahoe, one of the clearest lakes in the world. The images are available at: http://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/default.htm. In the image on the left, acquired in November 2000, vegetation can be seen in red. The image on the right, acquired at the same time by a different spectral band of the instrument, is color-coded to show the bottom of the lake around the shoreline. Where the data are black, the bottom cannot be seen. Scientists monitoring the lake's water clarity from boat measurements obtained since 1965 have discovered that the lake along the California-Nevada border has lost more than one foot of visibility each year, according to the Lake Tahoe Watershed Assessment, a review of scientific information about the lake undertaken at the request of President Clinton and published in February 2000. The most likely causes are increases in algal growth, sediment washed in from surrounding areas and urban growth and development. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03854
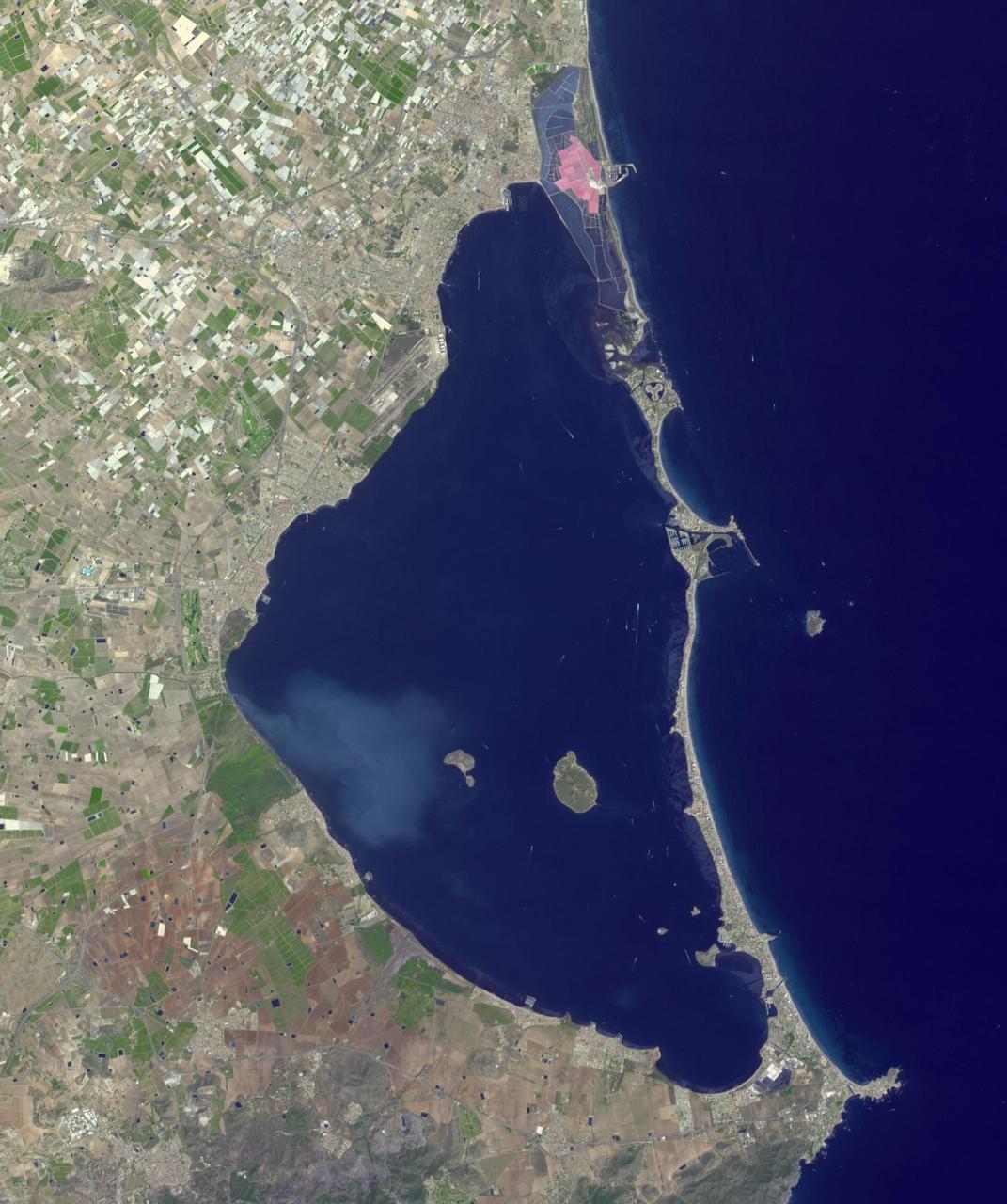

Mar Menor, in southeast Spain, is Europe's largest coastal saltwater lagoon. For the past 40 years, Mar Menor has faced severe contamination from agricultural runoff, leading to large algal blooms, and ecological degradation. Now, major restoration and prevention programs are in place to restore the lagoon, and try to reverse the damage. The image was acquired August 24, 2023, covers an area of 22.6 by 27.4 km, and is located at 37.7 degrees north, 0.8 degrees west. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of about 50 to 300 feet (15 to 90 meters), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and data products. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26009
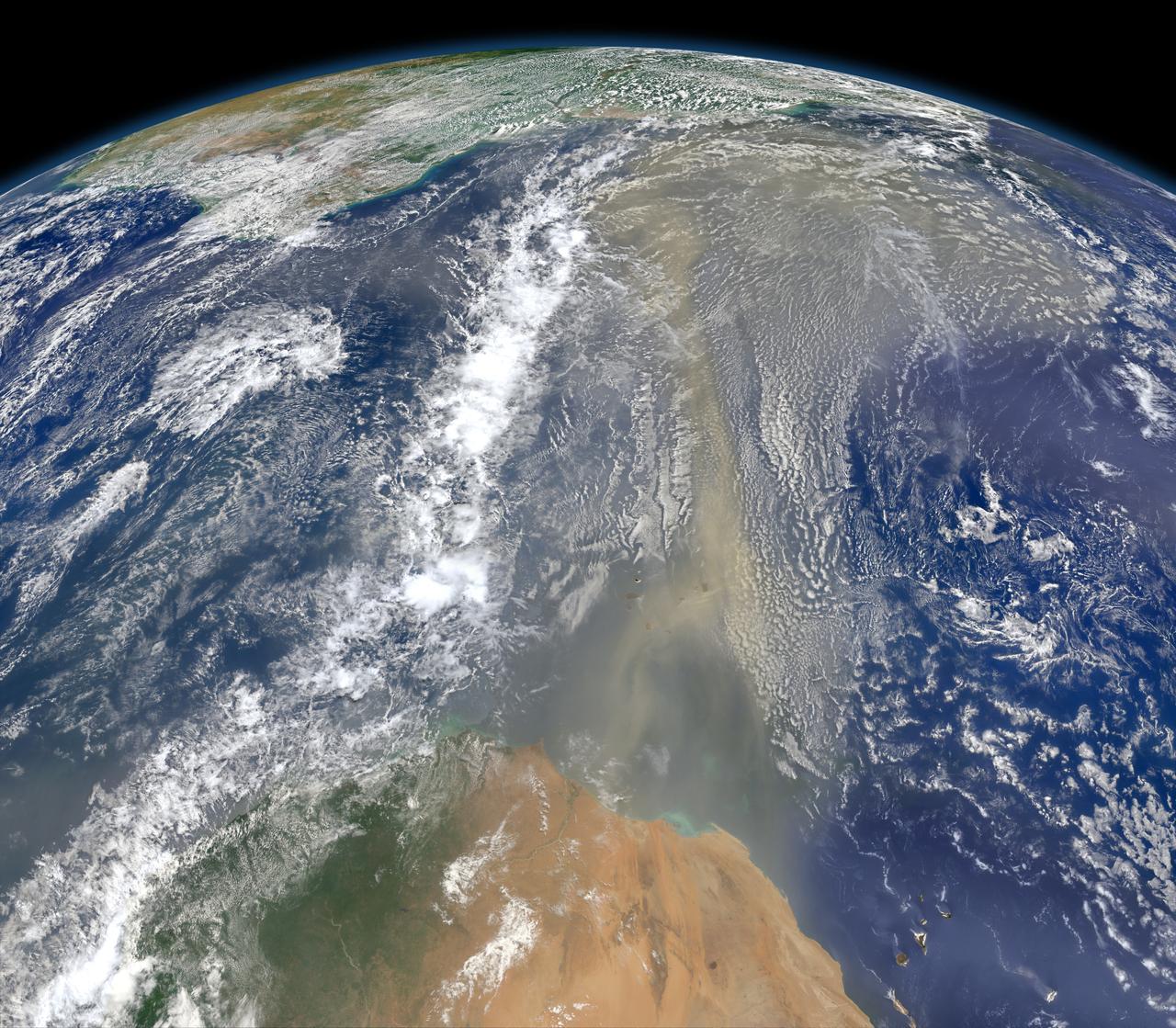
A piece of Africa—actually lots of them—began to arrive in the Americas in June 2014. On June 23, a lengthy river of dust from western Africa began to push across the Atlantic Ocean on easterly winds. A week later, the influx of dust was affecting air quality as far away as the southeastern United States. This composite image, made with data from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on Suomi NPP, shows dust heading west toward South America and the Gulf of Mexico on June 25, 2014. The dust flowed roughly parallel to a line of clouds in the intertropical convergence zone, an area near the equator where the trade winds come together and rain and clouds are common. In imagery captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), the dust appeared to be streaming from Mauritania, Senegal, and Western Sahara, though some of it may have originated in countries farther to the east. Saharan dust has a range of impacts on ecosystems downwind. Each year, dust events like the one pictured here deliver about 40 million tons of dust from the Sahara to the Amazon River Basin. The minerals in the dust replenish nutrients in rainforest soils, which are continually depleted by drenching, tropical rains. Research focused on peat soils in the Everglades show that African dust has been arriving regularly in South Florida for thousands of years as well. In some instances, the impacts are harmful. Infusion of Saharan dust, for instance, can have a negative impact on air quality in the Americas. And scientists have linked African dust to outbreaks of certain types of toxic algal blooms in the Gulf of Mexico and southern Florida. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1snkzmS" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1snkzmS</a> NASA images by Norman Kuring, NASA’s Ocean Color web. Caption by Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
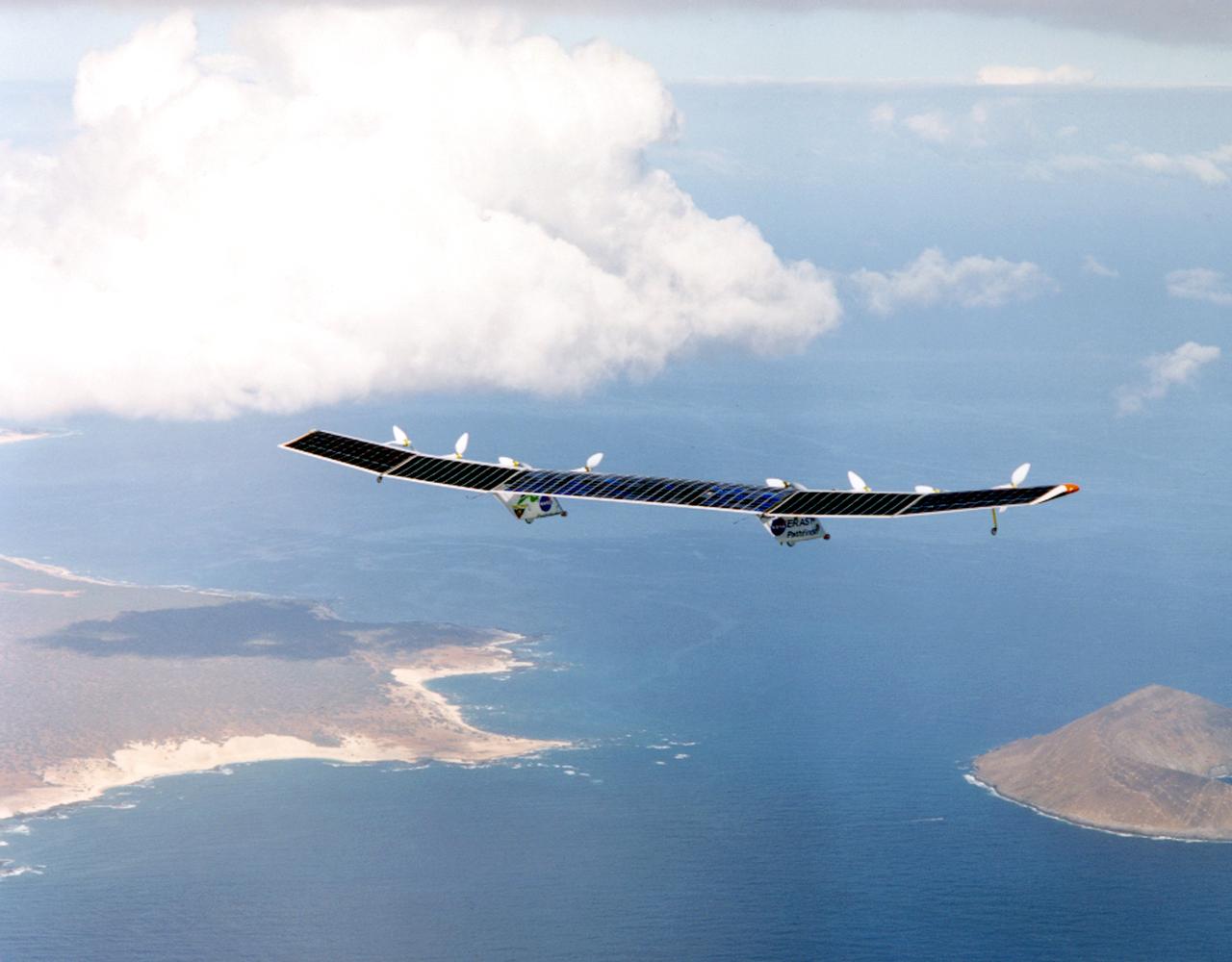

Pathfinder-Plus on flight over Hawaiian Islands, with N'ihau and Lehua in the background.
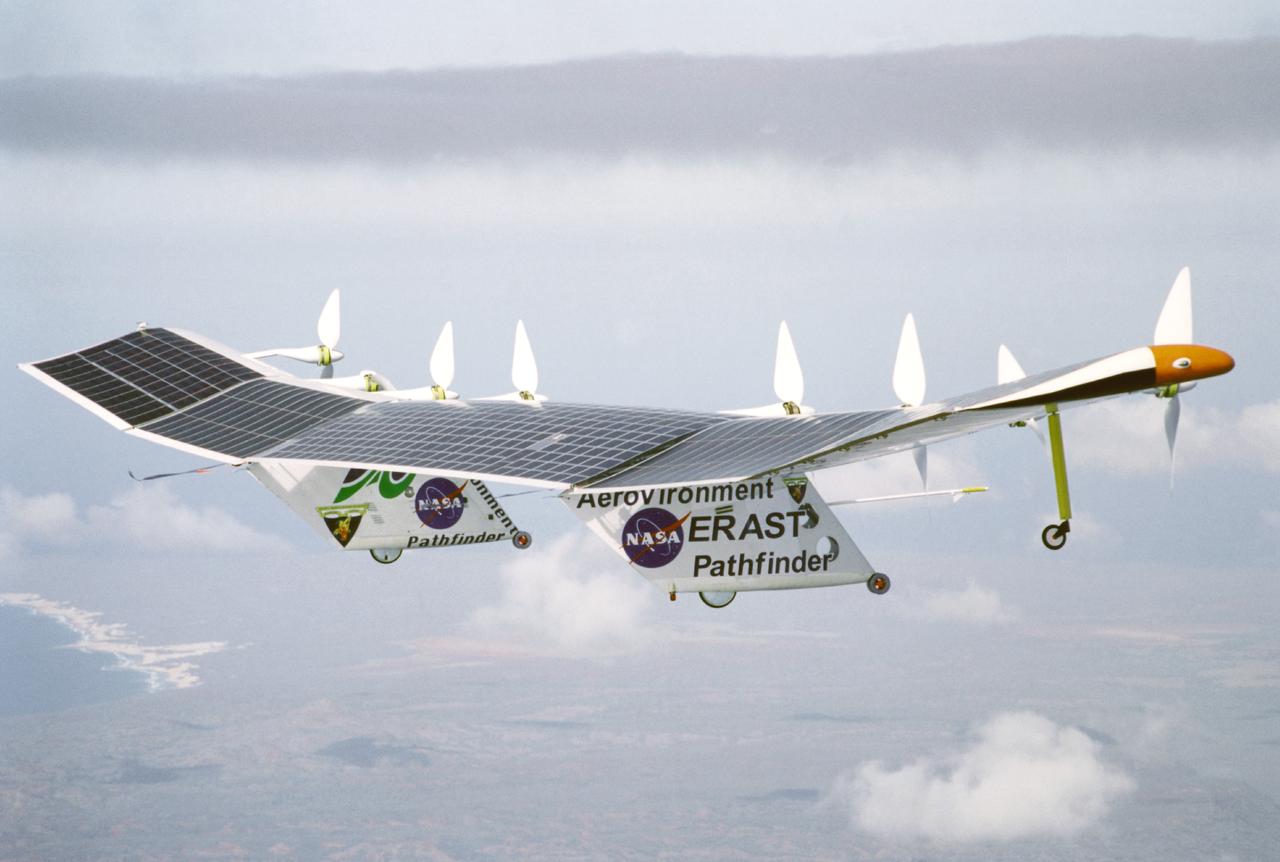

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in 1998.

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight in 1998 over Hawaiian waters.
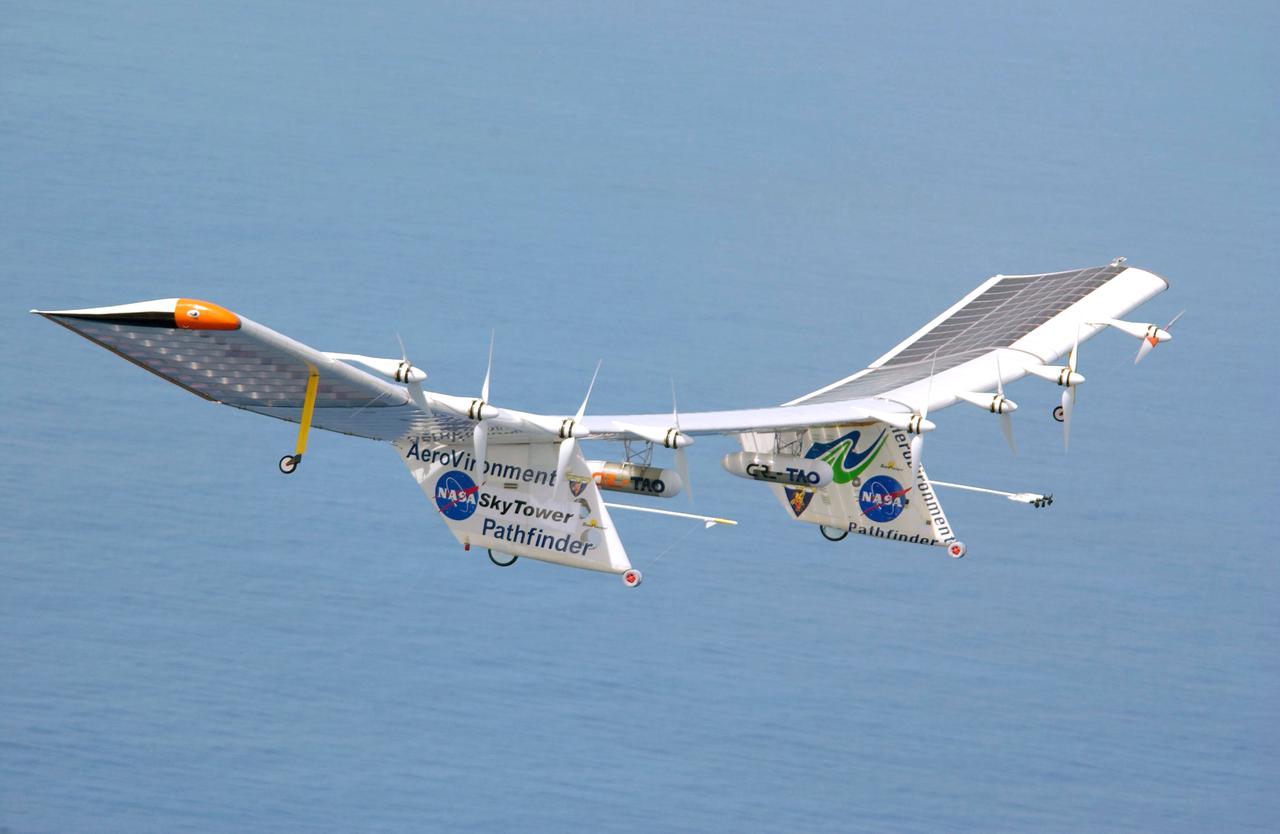

Pathfinder-Plus flight in Hawaii June 2002
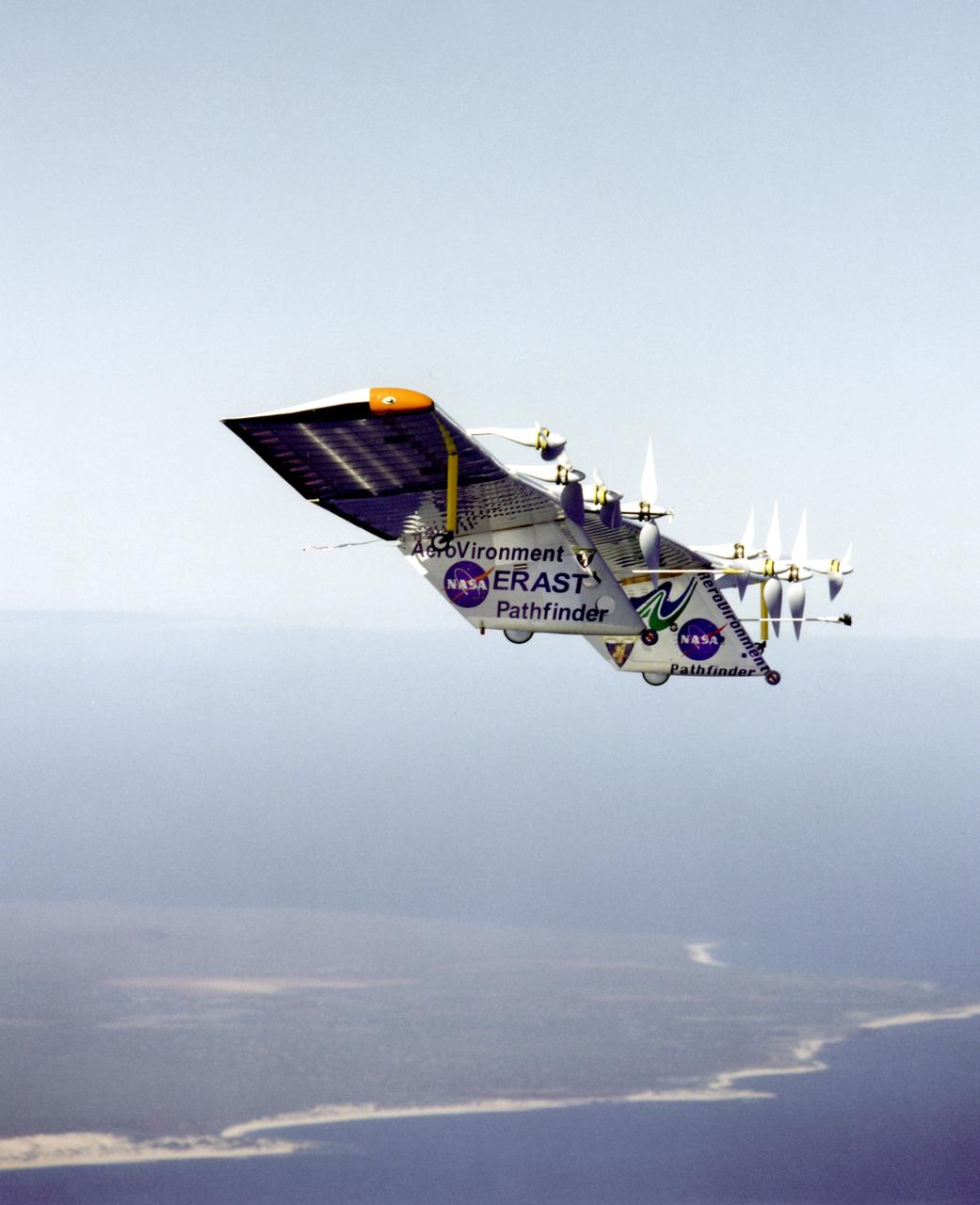

Pathfinder-Plus flying over the Hawaiian Islands in 1998 with Ni'ihau Island in the background.
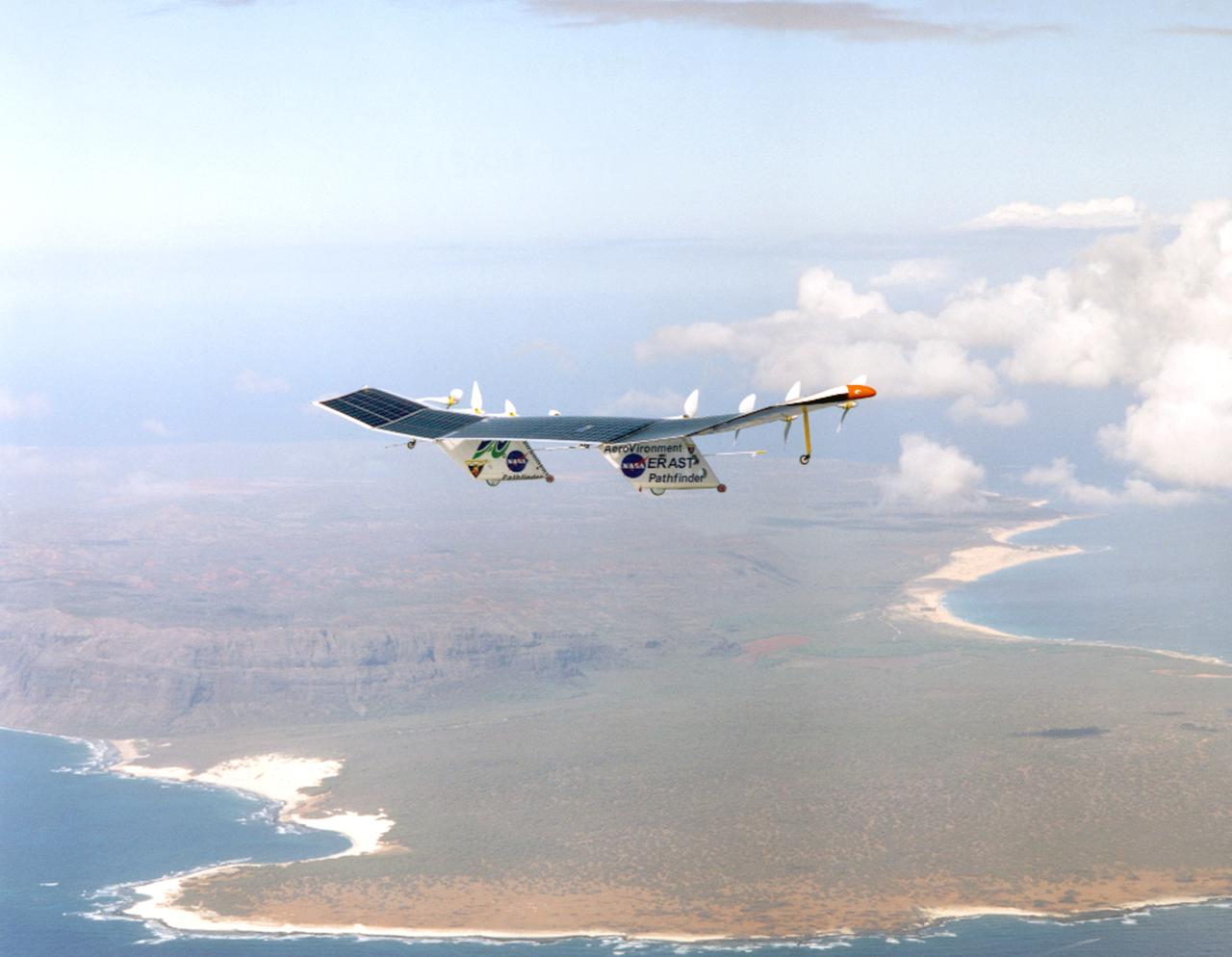

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight with the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in the background.
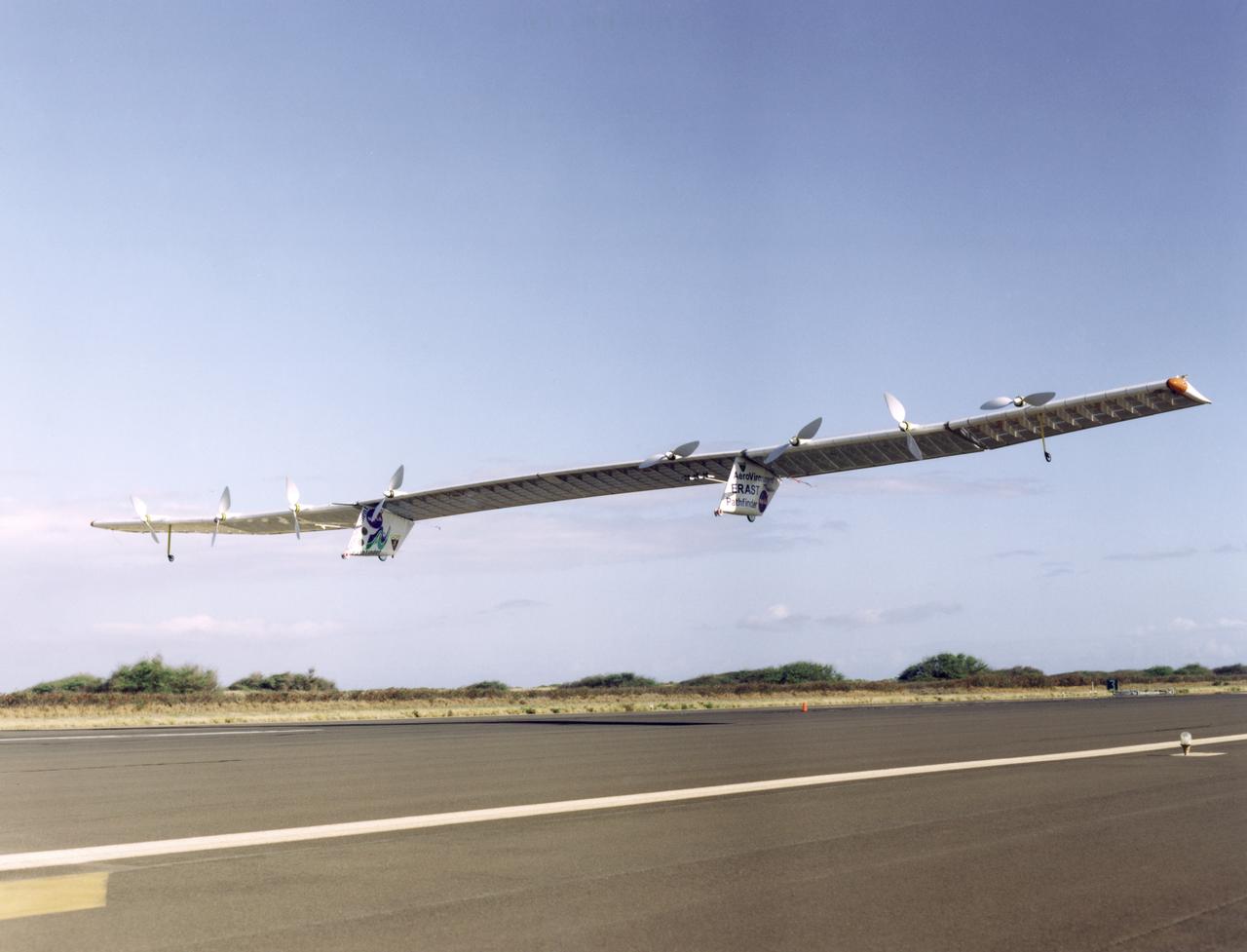

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over Hawaii in 1998.
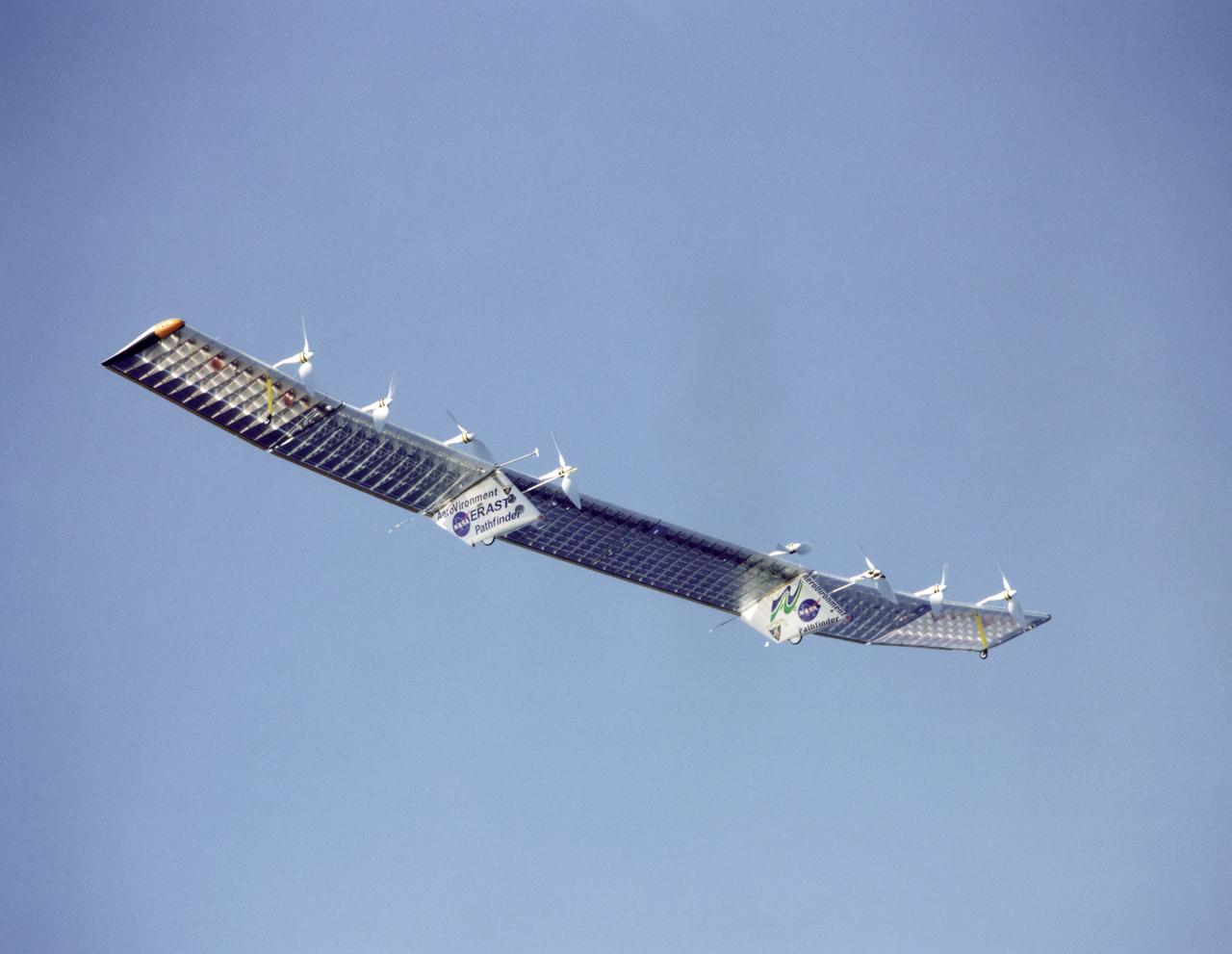

Pathfinder-Plus on flight over Hawaii.
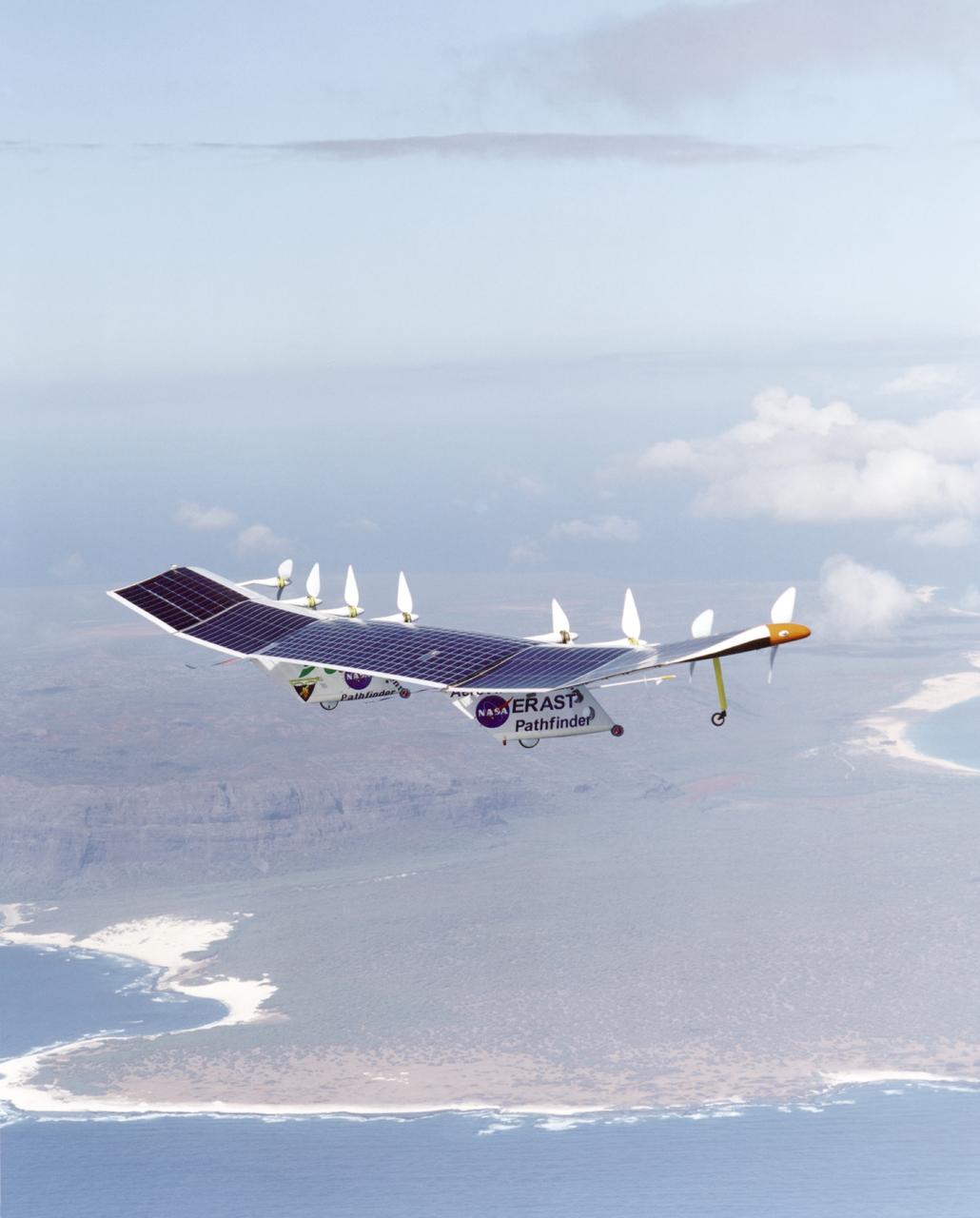

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in 1998.
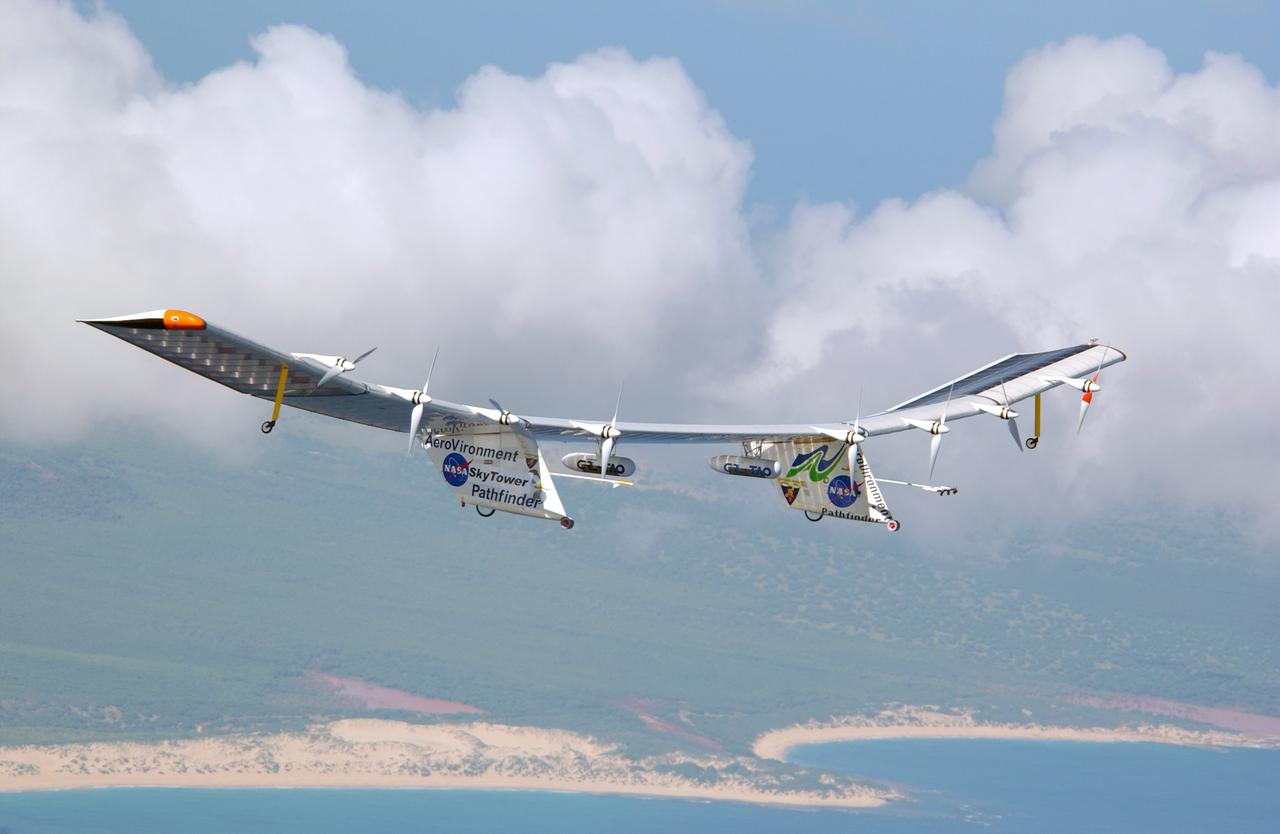

Pathfinder-Plus flight in Hawaii June 2002
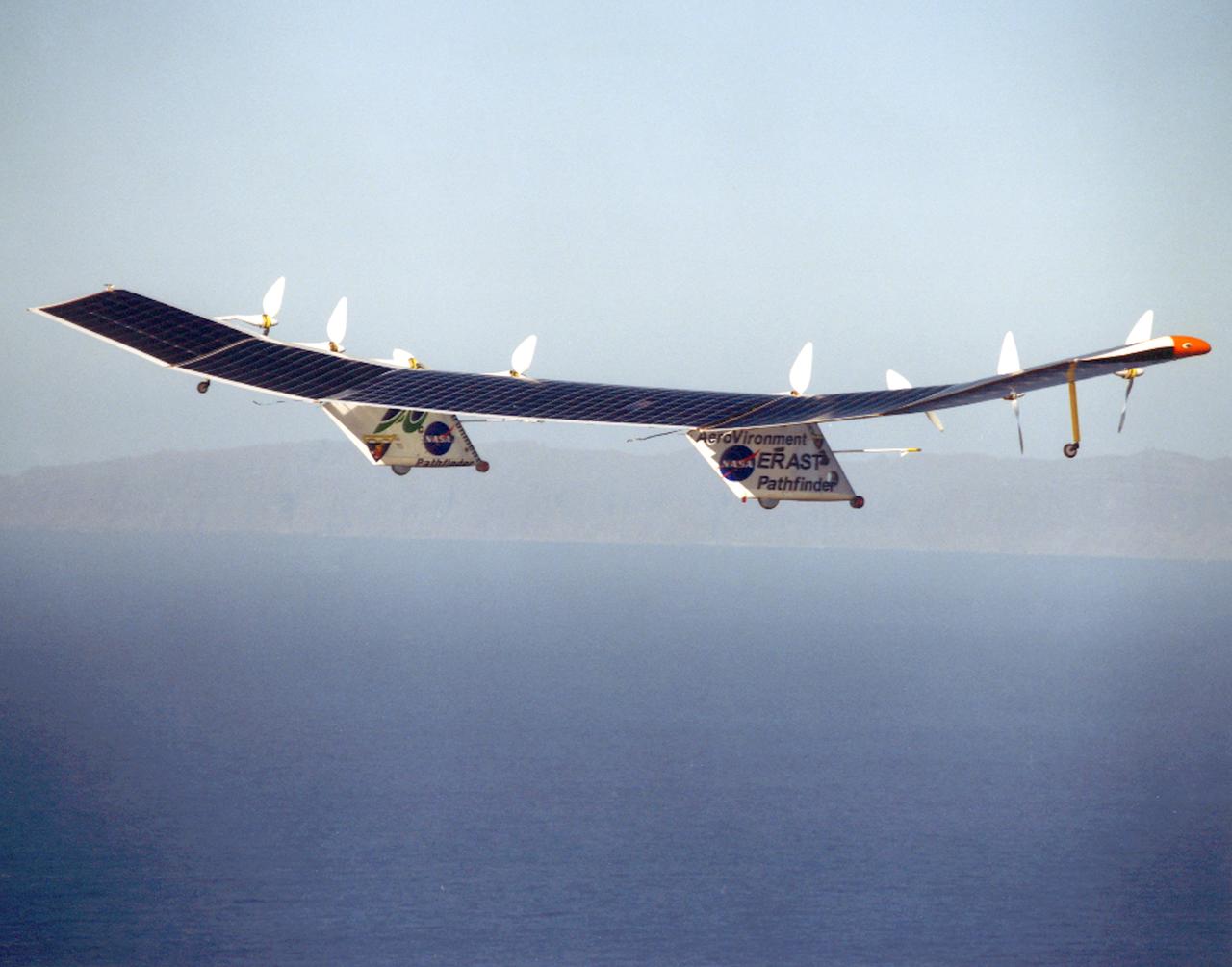

Pathfinder-Plus on flight over Hawaiian Islands in 1998.

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in 1998.
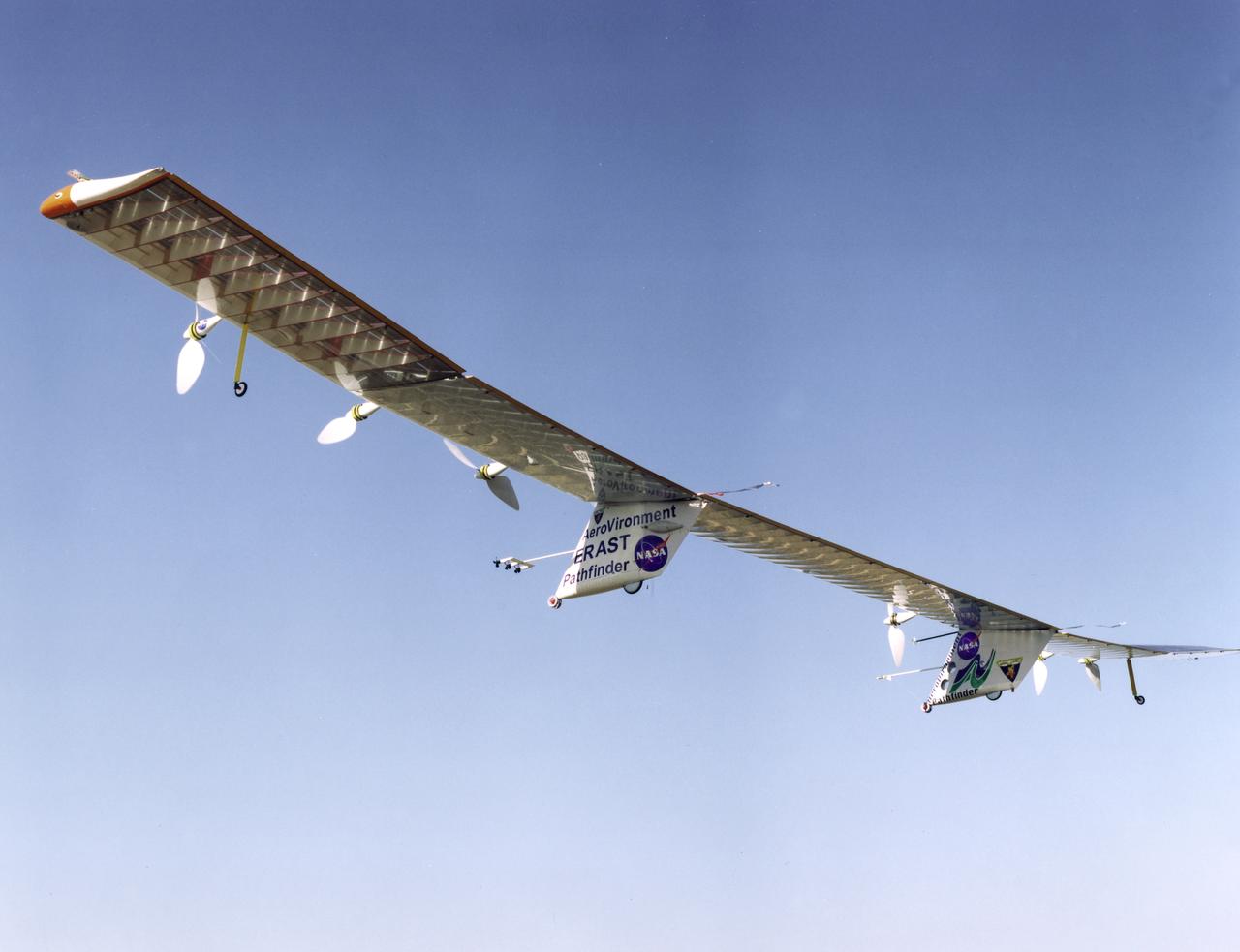

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over Hawaii in 1998.