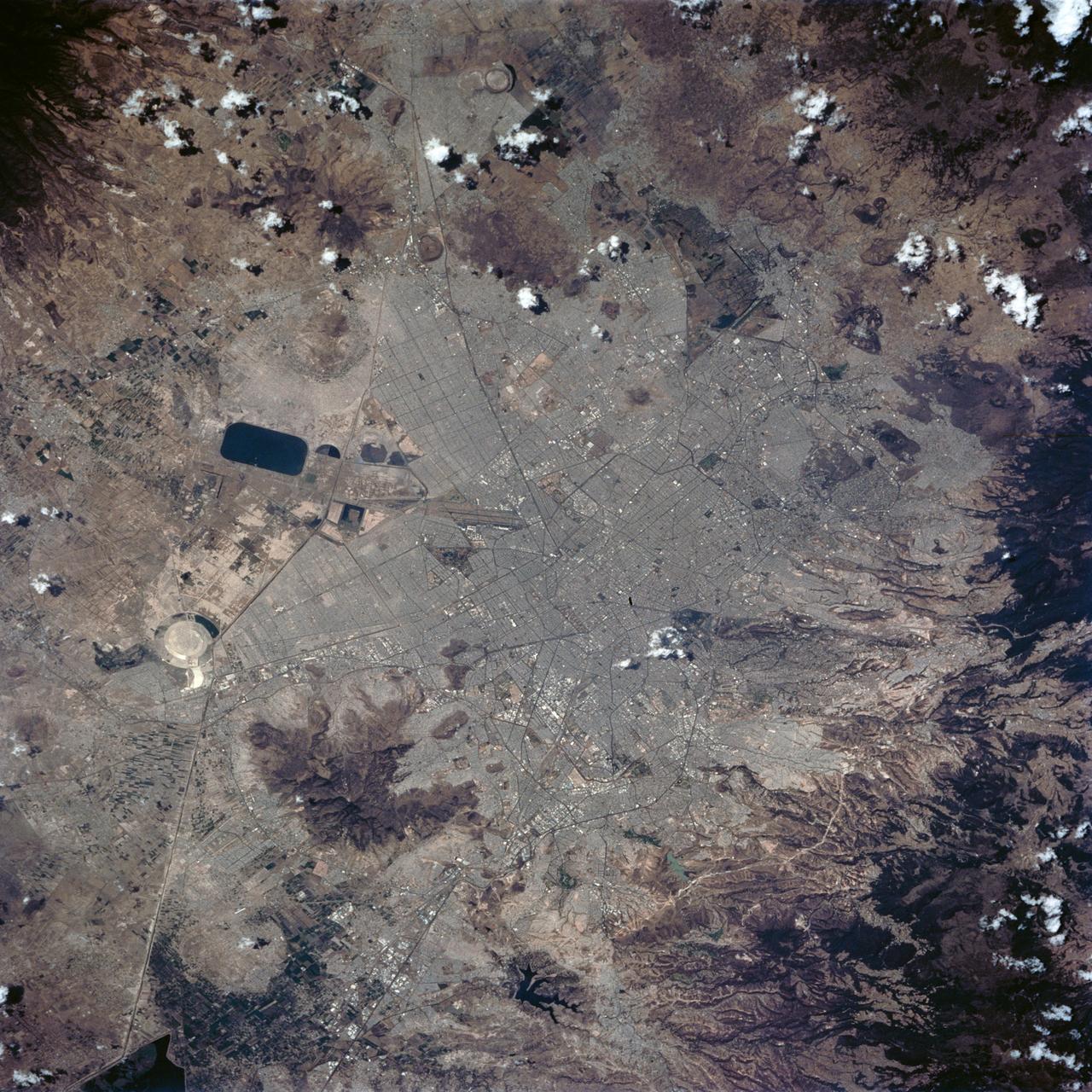

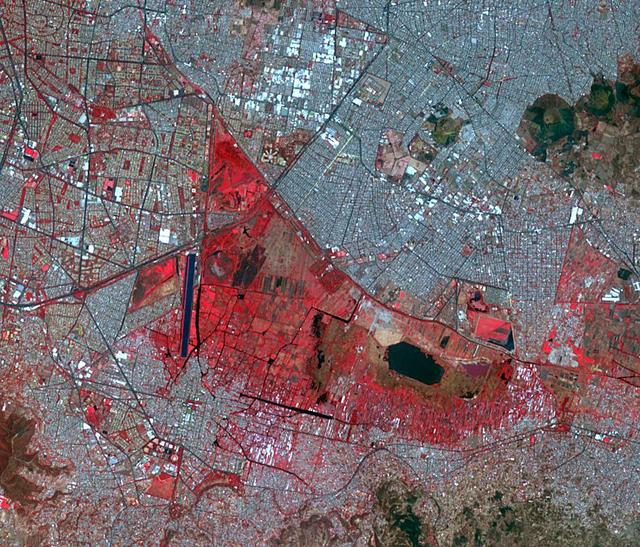
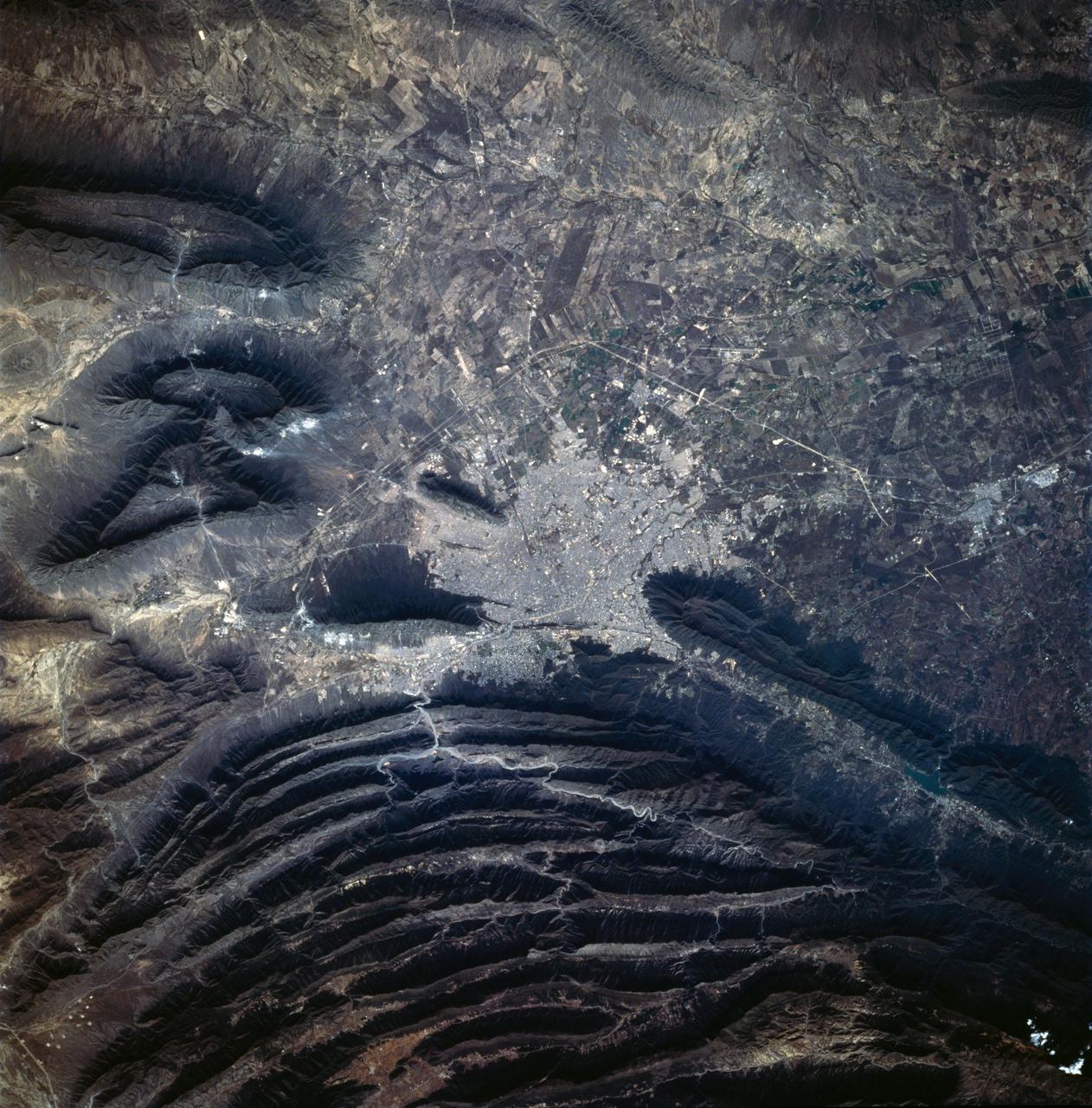
STS062-84-028 (4-18 March 1994) --- According to NASA scientists this image is the clearest photo of Mexico City taken from United States manned spacecraft. North is to the upper right. Mexico City sits in a basin surrounded by large volcanoes. The restricted atmospheric circulation in the basin, coupled with the inevitable air emissions produced by a city of 20 million people has created a critical air pollution problem for the city. In most photographs of the region, Mexico City is obscured by haze. Scientists feel the clear atmosphere in this photograph may be due, in part, to the stringent air emission restrictions now in place. The clarity of the photograph allows many key cultural features to be identified, including all of the major boulevards, the horse track (western part of the city), the university (south of the city), and the museum areas. Large, man-made ponds east of the city also stand out.
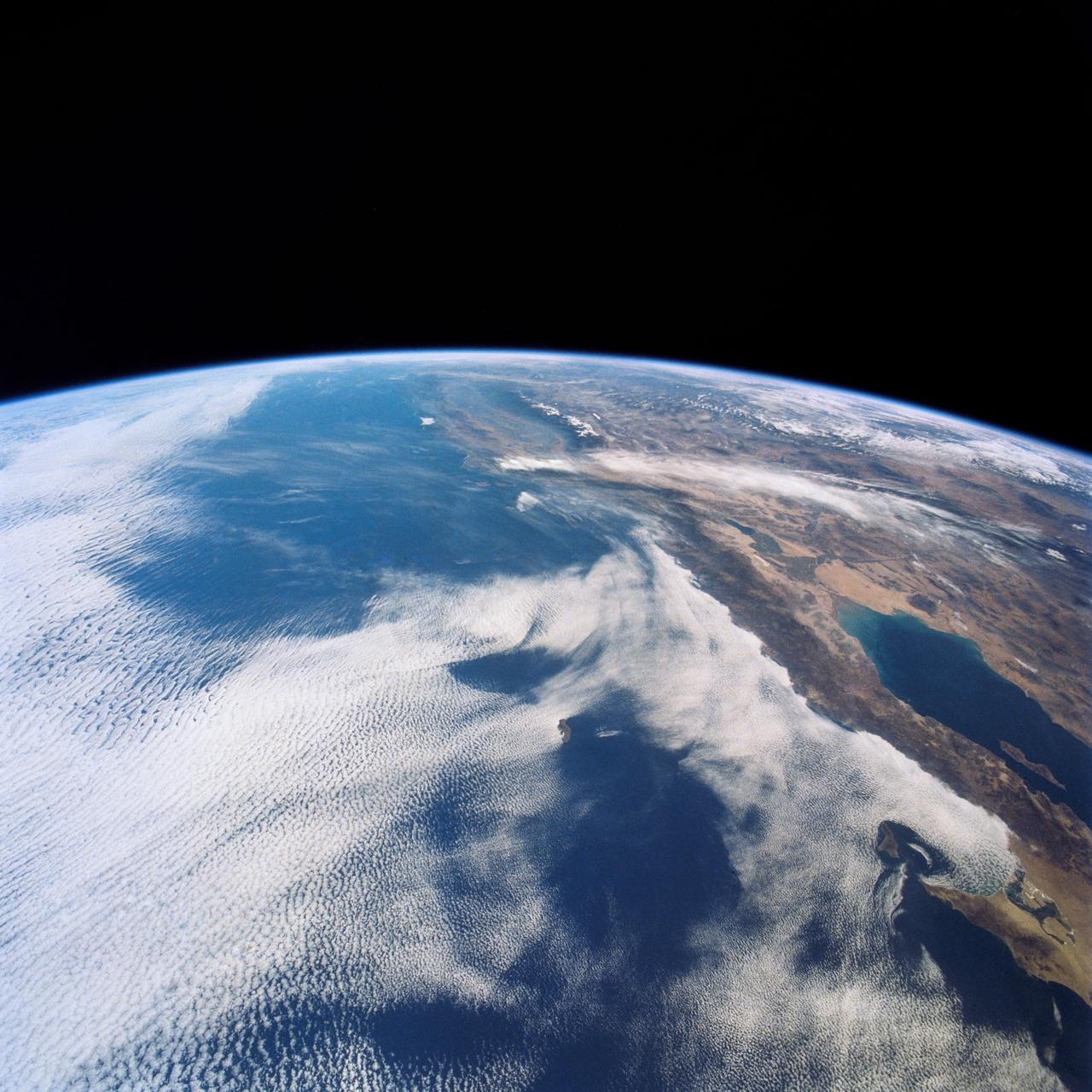

This view shows the west coast of the United States and Mexico (32.5N, 118.0W) and gives an indication of the range of view from orbital altitude. The visual range of this particular scene is from Skammon's Lagoon on Baja to the northern tip of California's Central Valley and Sierra Nevada, a range of over 15 degrees of latitude. Coastal fog drapes over southern California and northern Baja California. White Sands, New Mexico is at far right center.
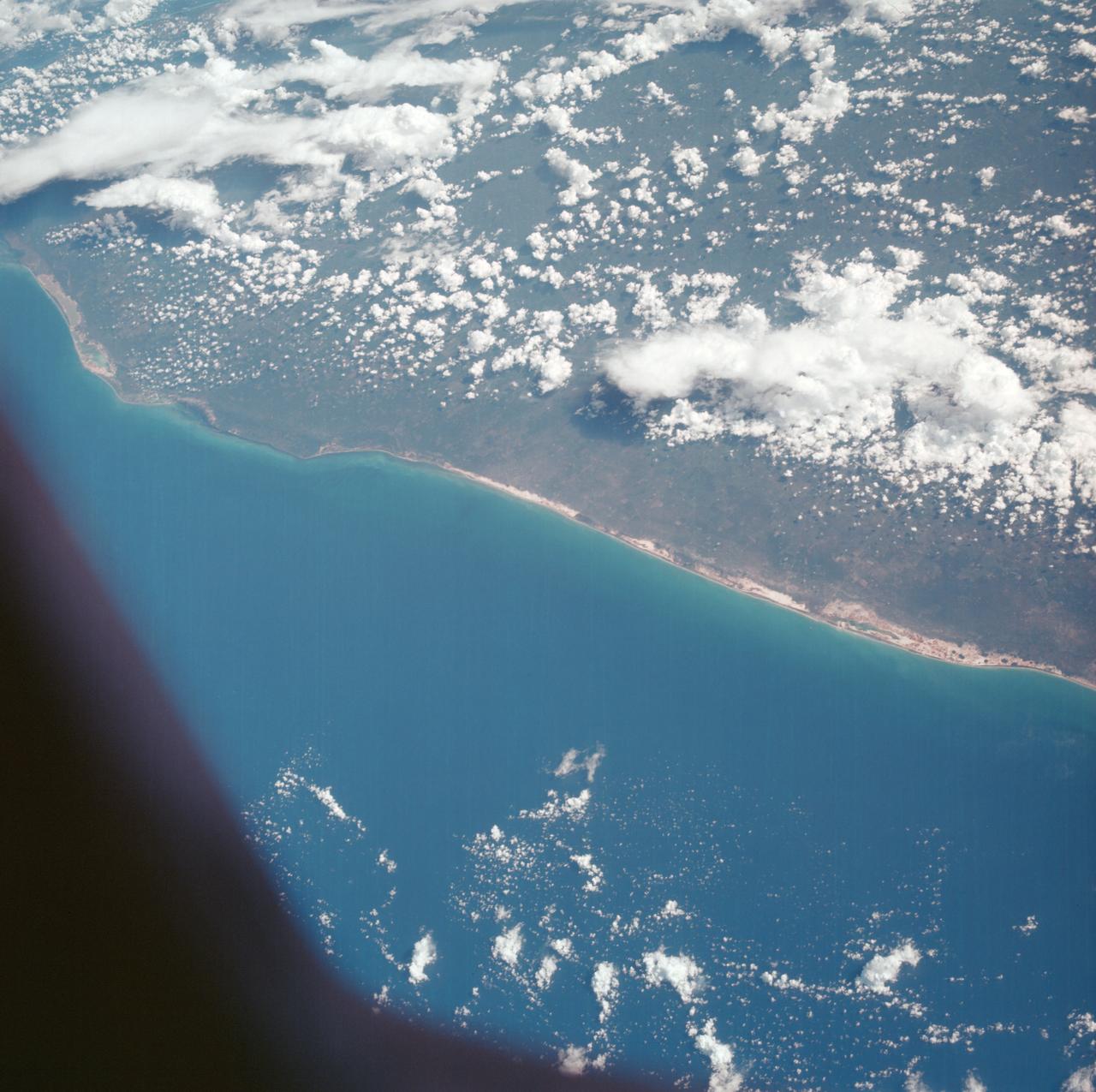

AS07-05-1635 (13 Oct. 1968) --- Gulf of Mexico, coast of Yucatan, Mexico, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 33rd revolution of Earth. Note road leading to city of Merida which is under cloud cover. Photographed from an altitude of 123 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 52 hours and 37 minutes.
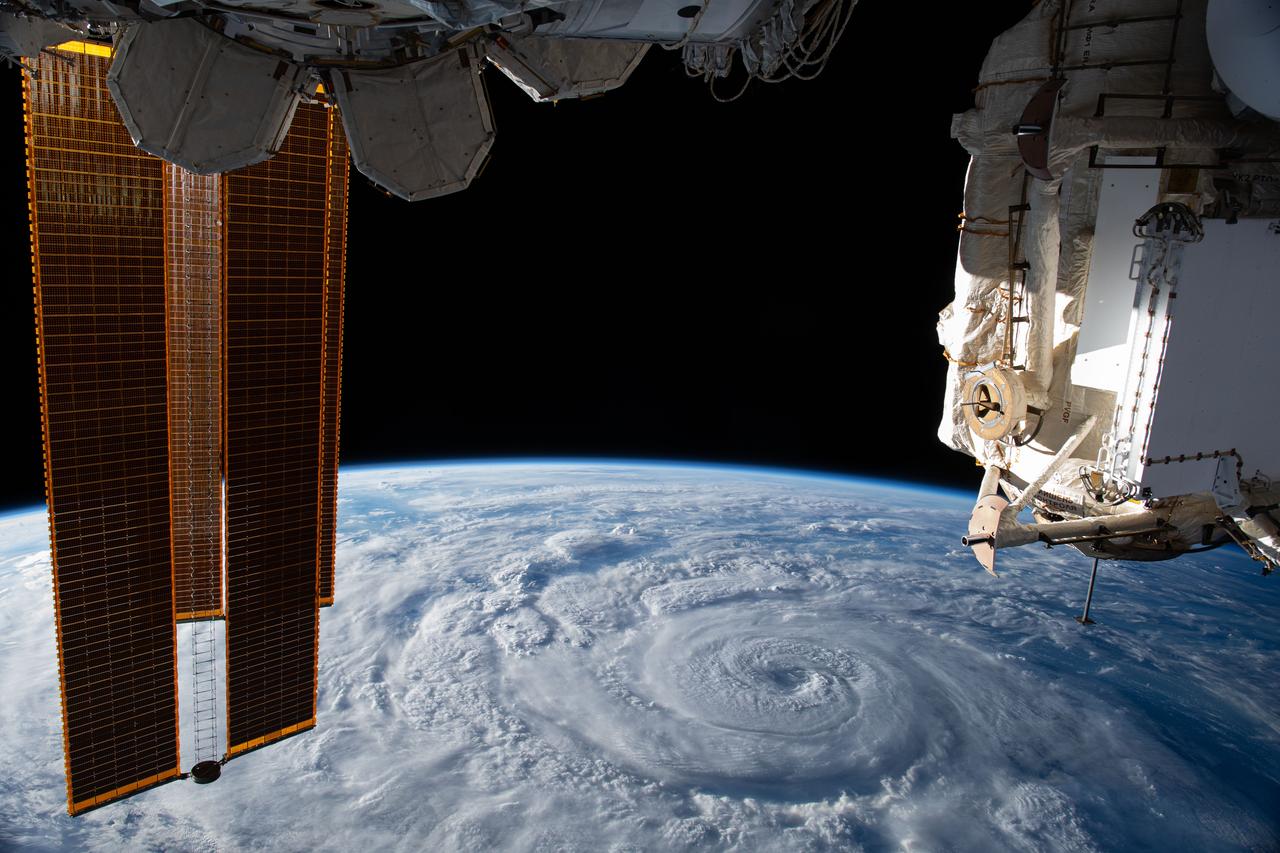

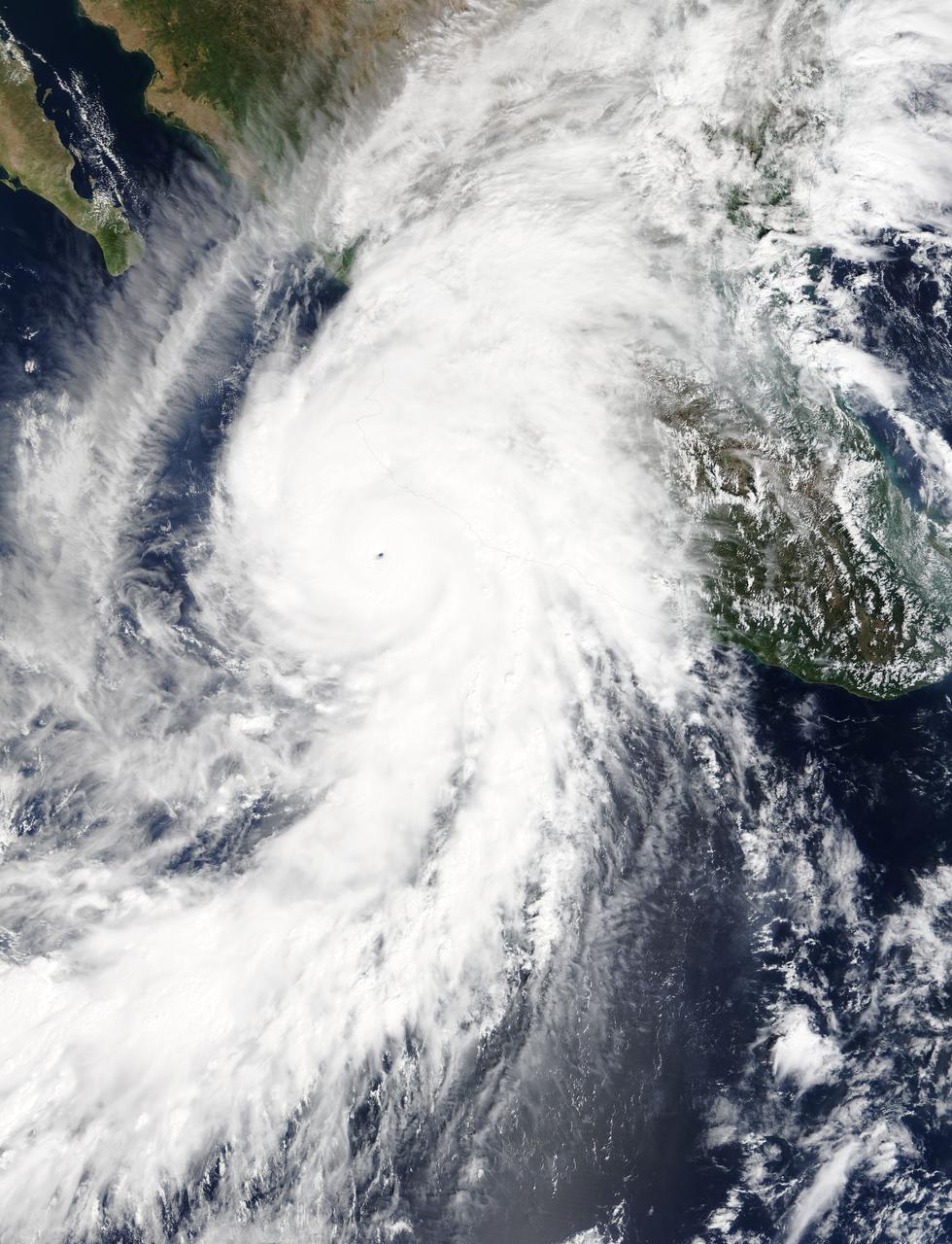
iss063e074380 (Aug. 19, 2020) --- Hurricane Genevieve is pictured off the Pacific coast of Mexico from the International Space Station.
Twenty-eight kilometers south of Mexico City are the Floating Gardens of Xochimilco. These man-made island-farms are the last vestiges of a massive 14th-Century land reclamation project of the Aztec Empire that continues to feed the people of Mexico City even today. The chinampas are artificially constructed, long, narrow strips of land in the ancient Lake Xochimilco. The image was acquired April 27, 2019, covers an area of 13.5 by 11.5 km, and is located at 19.3 degrees north, 99.1 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25555
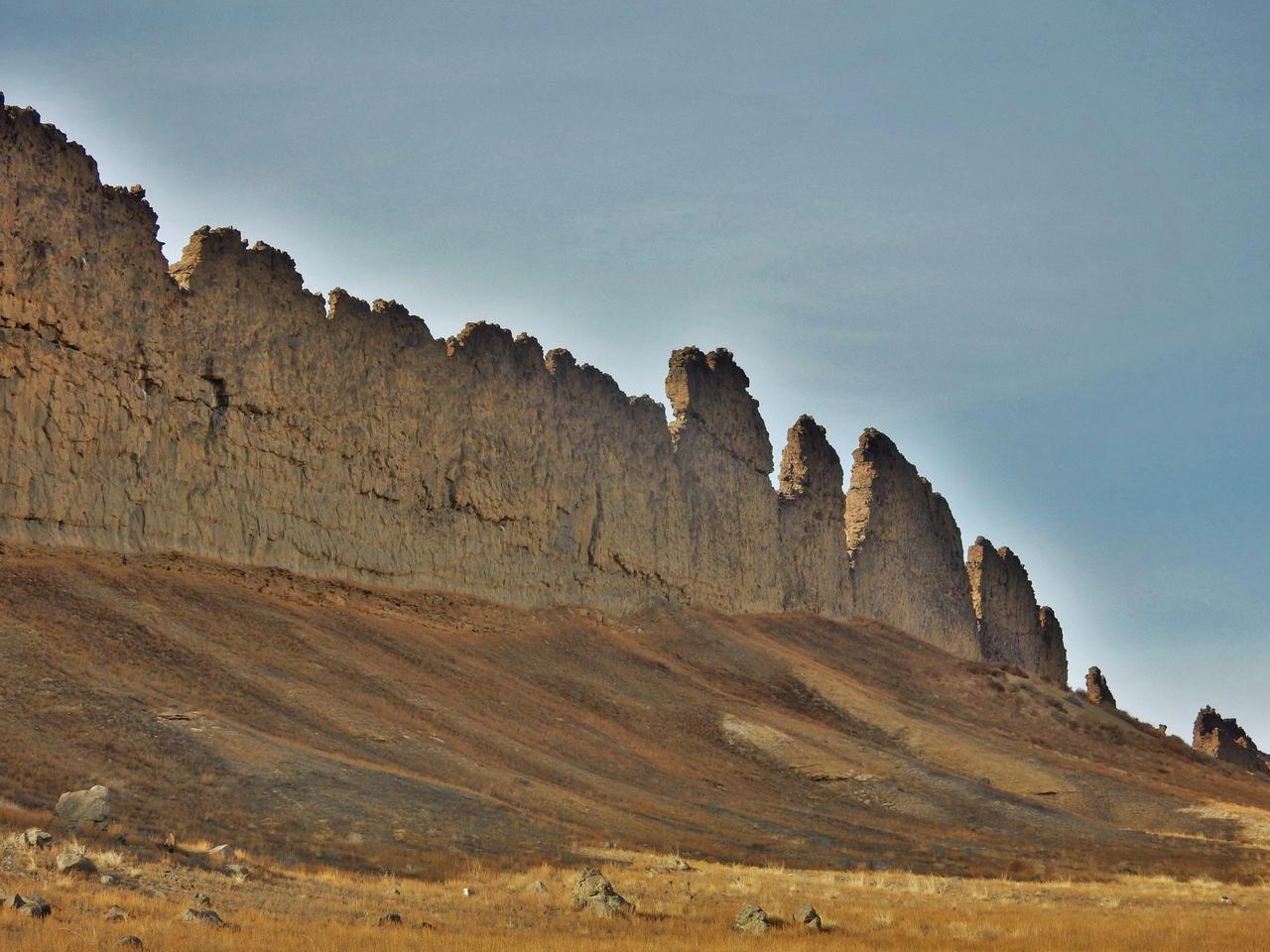

This photograph from northwestern New Mexico shows a ridge roughly 30 feet about 10 meters tall that formed from lava filling an underground fracture then resisting erosion better than the material around it did. The dike extends from a volcanic peak (out of view here) called Shiprock in English and Tsé Bit'a'í, meaning "rock with wings," in the Navajo language. It offers an Earth analog for some larger hardened-lava walls on Mars http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21266
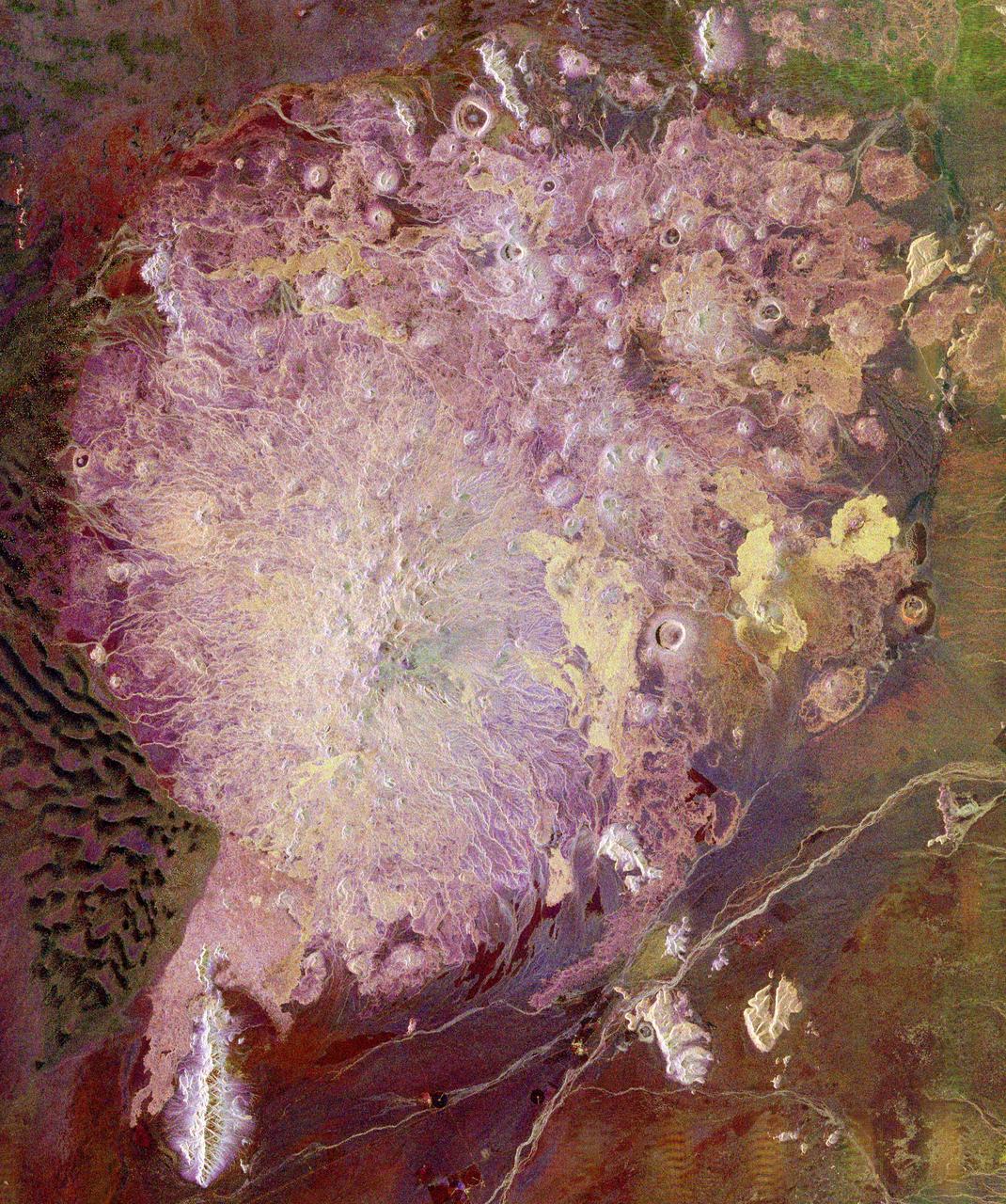

This spaceborne radar image shows the Pinacate Volcanic Field in the state of Sonora, Mexico, about 150 kilometers 93 miles southeast of Yuma, Arizona. The United States/Mexico border runs across the upper right corner of the image.
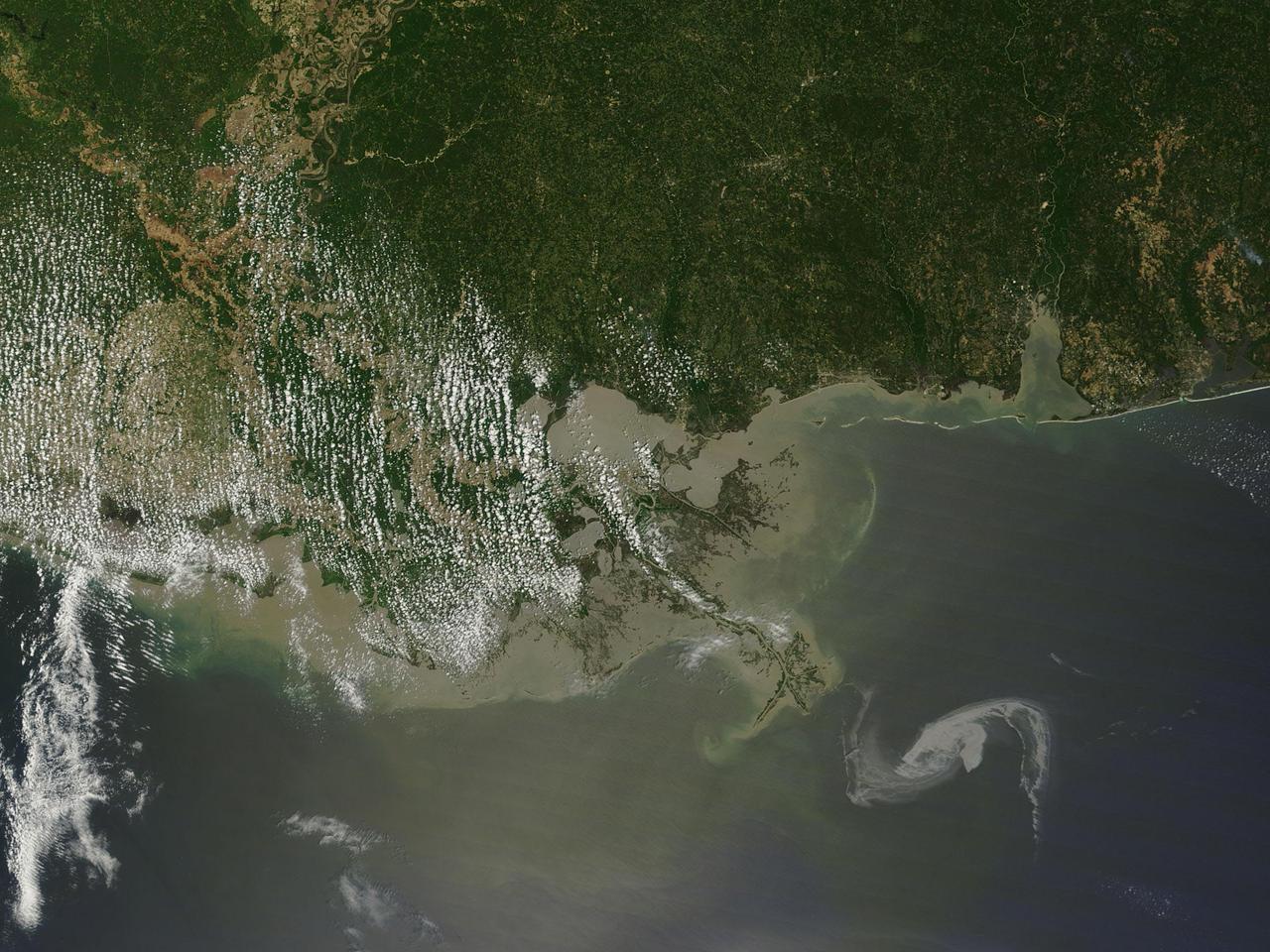

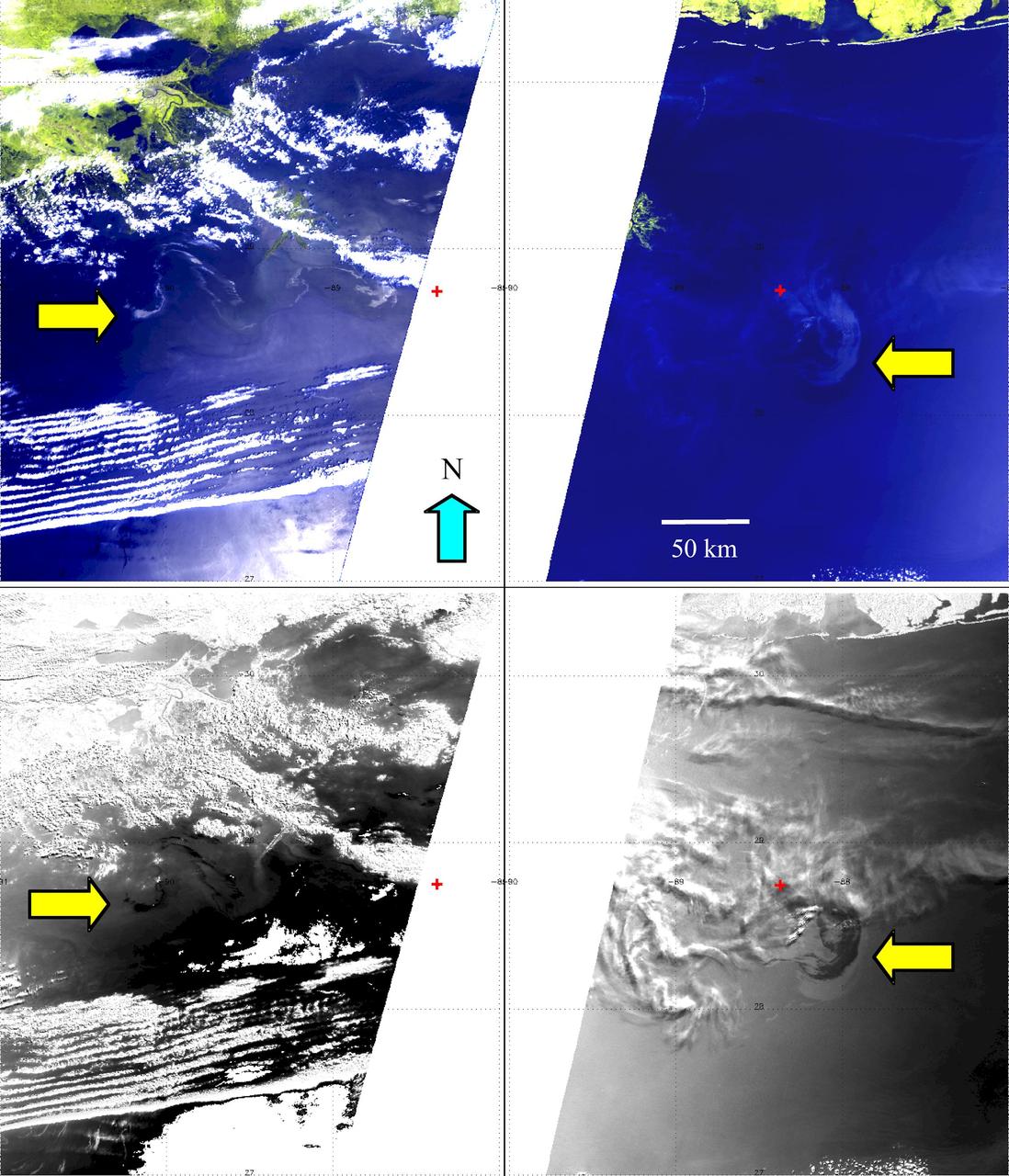
2010/119 - 04/29 at 16 :48 UTC Oil slick in the Gulf of Mexico (Input Direct Broadcast data courtesy Direct Readout Lab, NASA/GSFC) Satellite: Terra NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team To learn more about MODIS go to: <a href="http://rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?latest" rel="nofollow">rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?latest</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

On May 2, 2002, numerous fires in southern Mexico sent smoke drifting northward over the Gulf of Mexico. These views from NASA Terra satellite illustrate the smoke extent over parts of the Gulf and the southern Mexican states of Tabasco, Campeche and Ch

On Oct. 23 at 17:30 UTC (1:30 p.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite saw Hurricane Patricia moving over Mexico. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
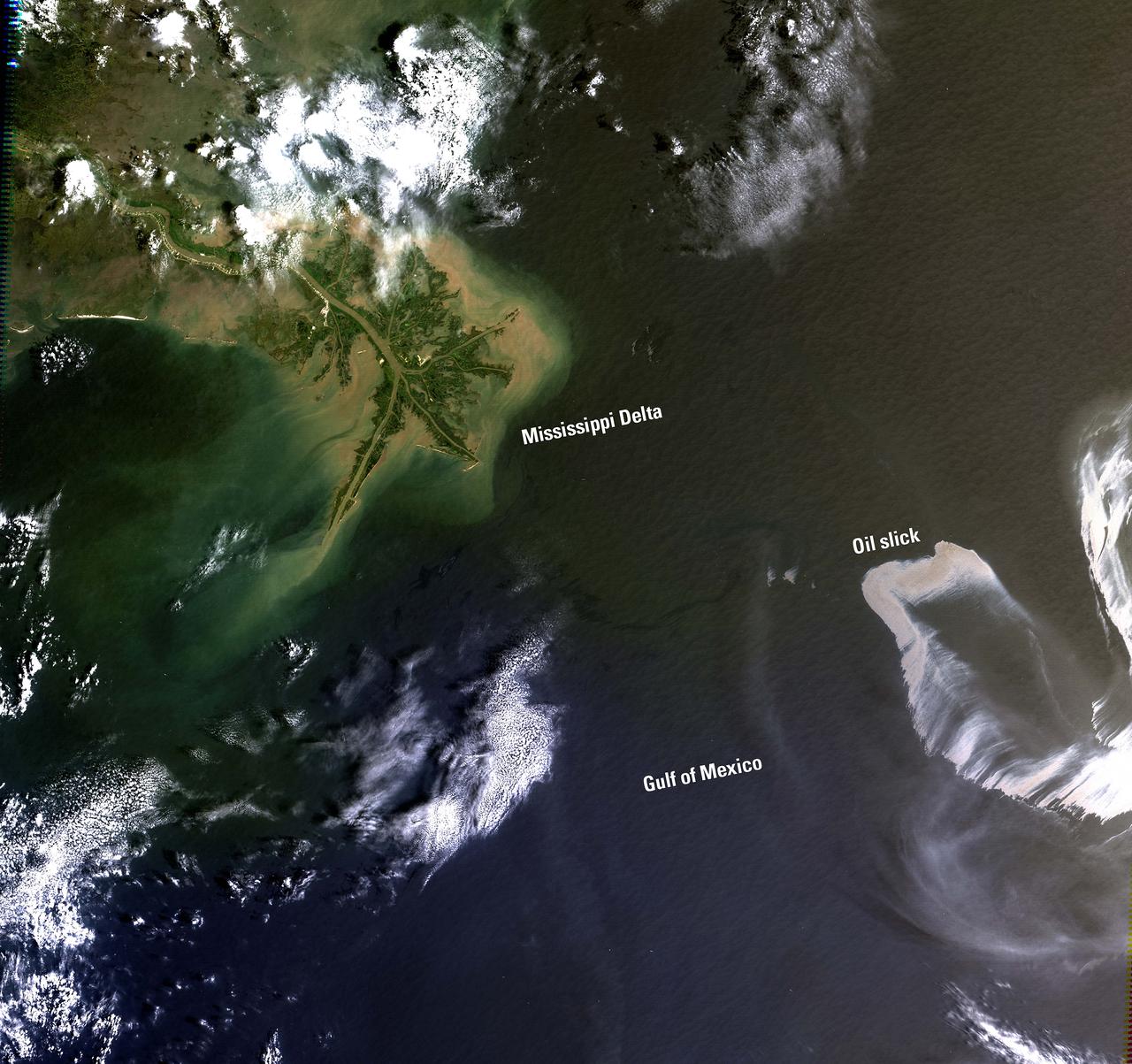
On April 20, 2010, an explosion at an oil well in the Gulf of Mexico resulted in a major oil spill. Since then, emergency response efforts have been underway to contain the growing oil slick before it reaches the southern coast of the United States. Landsat imagery, acquired by the U.S. Geological Survey on May 1 shows the extent of the oil slick. The Landsat data are being used to monitor the extent and movement of the slick. Location: LA, USA Date Taken: May 1 2010 Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

Evidence of a recent flash flood can be seen in the form of light brown sediment that flowed down gullies and mountain sides forming ponds of debris over agricultural areas in the broad valley near the town of Parras (26.5N, 102.5W). This part of Mexico has extensive vineyards, orchards and both dry land and irrigated agriculture. Based on the photo, it appears that flash flood waters damaged some 300 square miles of property in this area alone.

AS07-05-1652 (13 Oct. 1968) --- Pacific coast area of southwestern Mexico, State of Guerrero, from Acapulco to Tecoanapa, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 34th revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of 125 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 54 hours and 10 minutes. Much cloud cover in area.
This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the city of Tequila, Mexico. Its red volcanic soil surrounding Tequila is particularly well suited to the growing of blue agave, and more than 300 million plants are harvested each year.

SL4-142-4548 (27 Jan. 1974) --- An oblique view of northwestern Mexico, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen. The camera used was a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad, with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome film. This photograph was taken on a sweep down the coast to document the fault patterns of southern California and northwest Mexico. SL4-142-4532 gives an excellent overview of the entire region. The specific reason for this picture was an attempt to see if the Agua Blanca Fault in Baja California extends to the east toward the Gulf of California. Several attempts were made by the Skylab 4 crew to visually detect such an extension, but none was found. The report was that the fault disappeared into an area of sand and heavily eroded material that obscured any feature that might be present deeper. This area of sand and loose material is the light-colored area in the center of Baja at the extreme north part of the photograph. In addition to this geology the Pinacate volcanic field in Sonora, the sand dunes in Sonora, and the sediment flow patterns of the Colorado River entering the Gulf are additional areas of study utilizing this photograph. Photo credit: NASA

This image taken by the MAHLI camera shows a sample of basaltic rock from a lava flow in New Mexico serves as a calibration target carried on the front of NASA Mars rover Curiosity for the rover Canadian-made APXS instrument.
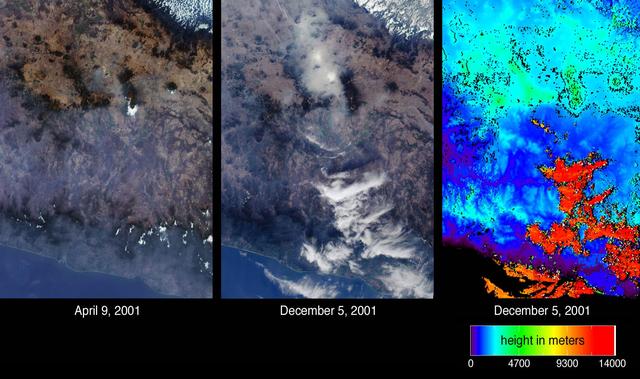
Mexico City has one of the world most serious air pollution problems. These images from NASA Terra satellite were captured on April 9 and December 5, 2001.
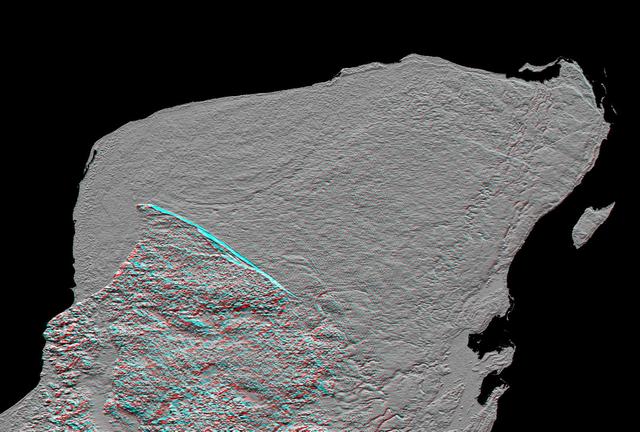
This anaglyph of Mexico Yucatan Peninsula was generated from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission data, and shows a subtle but distinctive indication of the Chicxulub impact crater. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
NASA Terra spacecraft captured this image of the growing oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico on May 1, 2010. On April 20, 2010, an explosion destroyed the Deepwater Horizon oil platform operating offshore in the Gulf of Mexico.
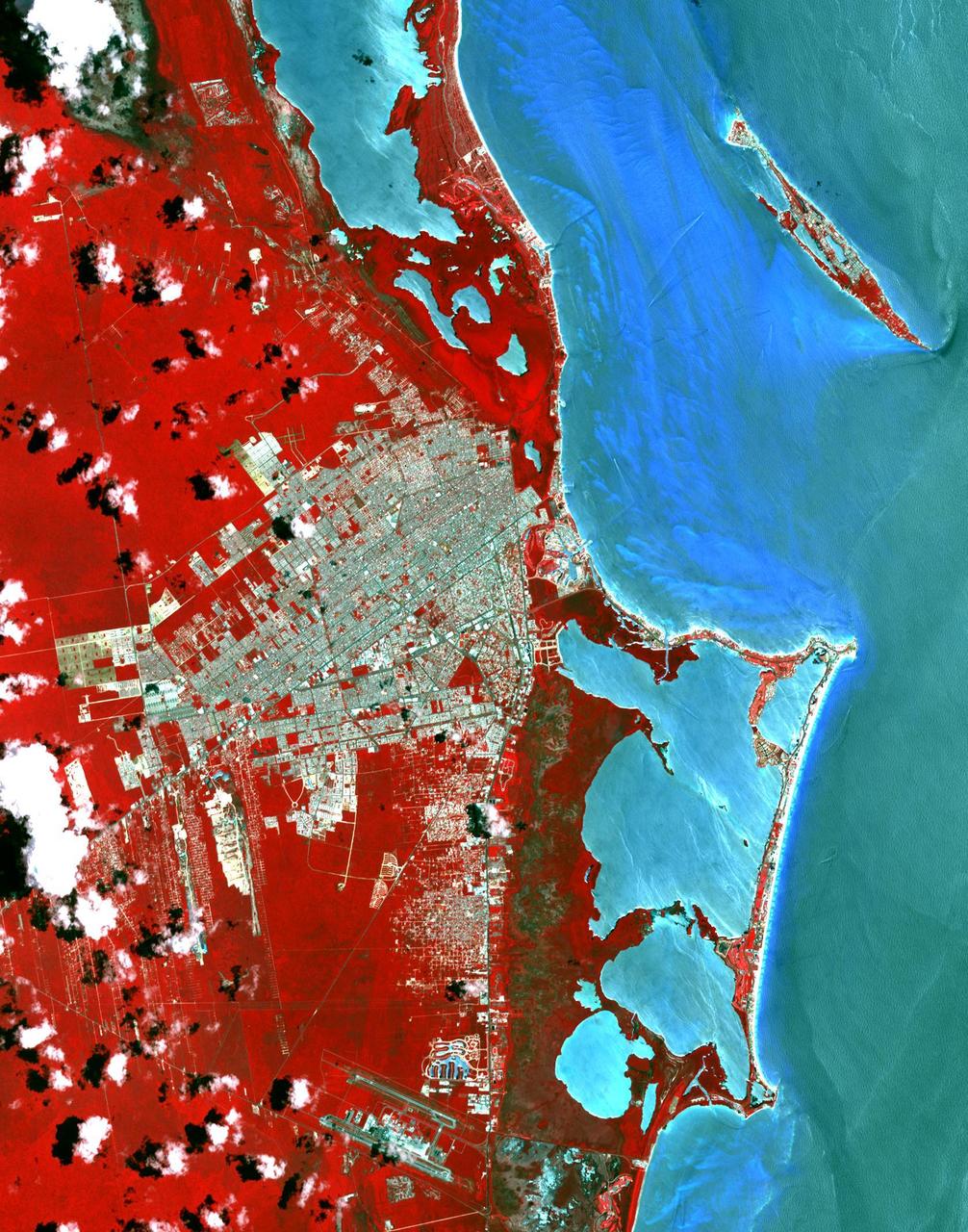

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows Cancun, a resort city on the east side of Mexico Yucatan Peninsula. In 1970, the population was 120 people. The city began as a tourism project in 1974. Since then, it has undergone a comprehensive transformation from being a fisherman's island surrounded by virgin forest and undiscovered shores to being one of the two most well-known Mexican resorts, along with Acapulco. In 1990 the city had grown to 167,000 inhabitants, and by 2014 to 723,000 inhabitants. These two images show the area on March 28, 1985, acquired by Landsat; and May 14, 2014, acquired by ASTER. The images cover an area of 25 x 36 km, and are located at 21.1 degrees north, 86.8 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20086
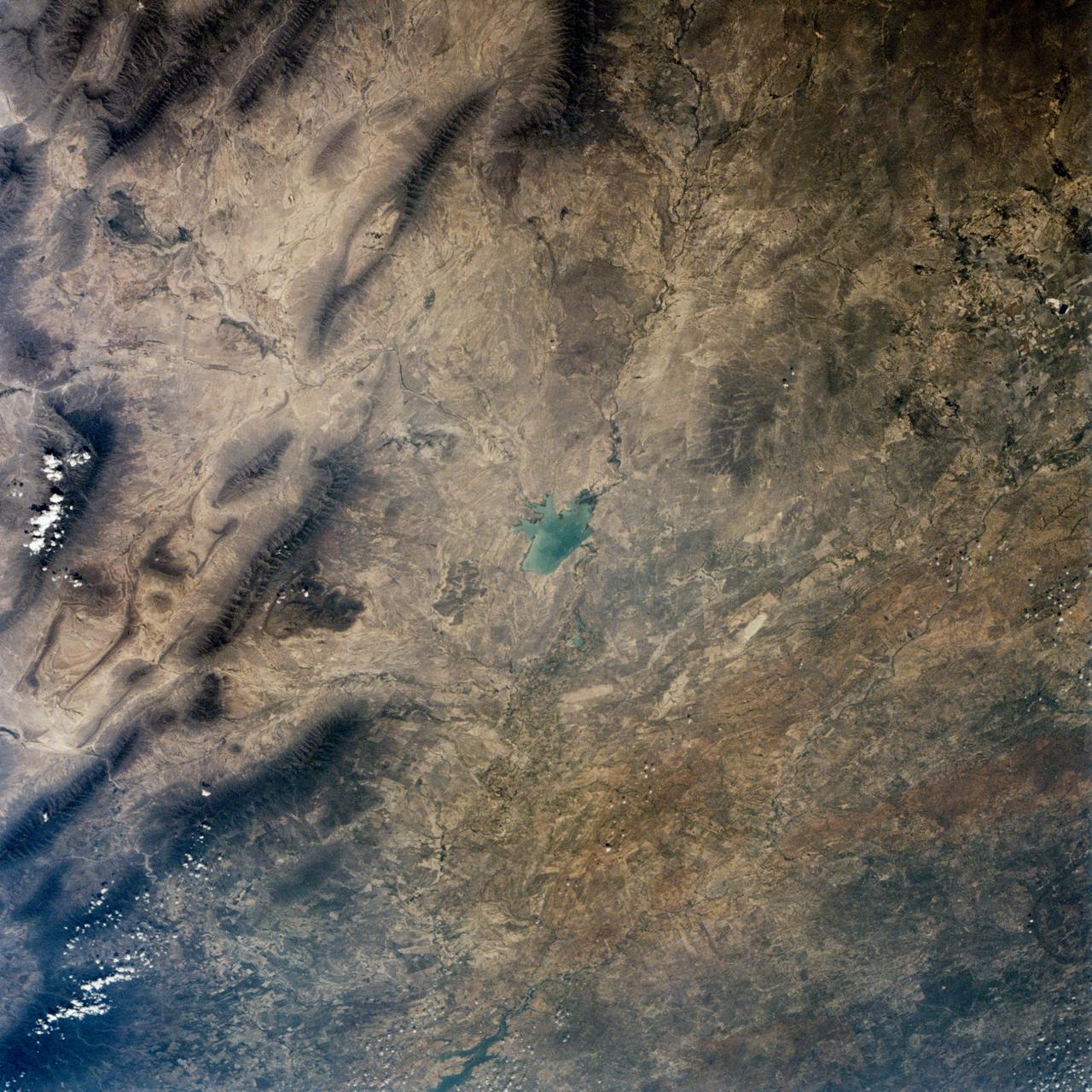

This is a single scene from a pair (frames 021 & 024) to study the effects of polarized light in Earth Observations. One scene was exposed with vertically polarized light, the other, horizontally. The subject in this study, is a lake behind Presa (dam) Don Martin (27.5N, 100.5W) on thge edge of the Rio Grande Plain near it's boundry with the Sierra Madre Oriental in Coahuila, Mexico.
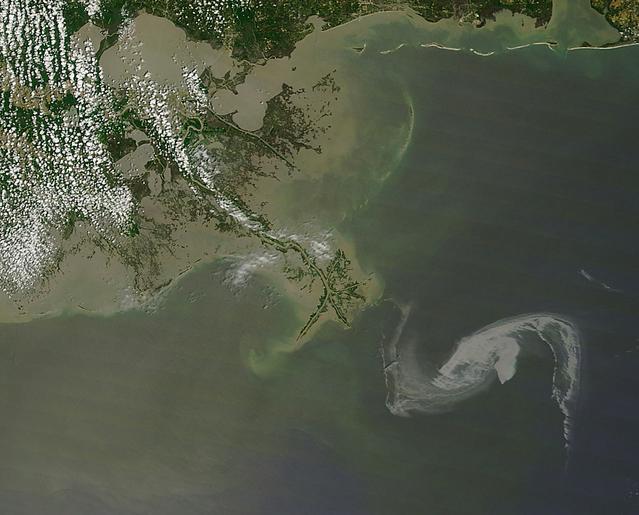

2010/119 - 04/29 at 16 :48 UTC Oil slick in the Gulf of Mexico To see a full view of this image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4563296541/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4563296541/</a> (Input Direct Broadcast data courtesy Direct Readout Lab, NASA/GSFC) Satellite: Terra NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team To learn more about MODIS go to: <a href="http://rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?latest" rel="nofollow">rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?latest</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
NASA image acquired Sept 6, 2010 at 16 :45 UTC Tropical Storm Hermine (10L) in the Gulf of Mexico Satellite: Terra Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2010/h2010_Hermine.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2010/h2010...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
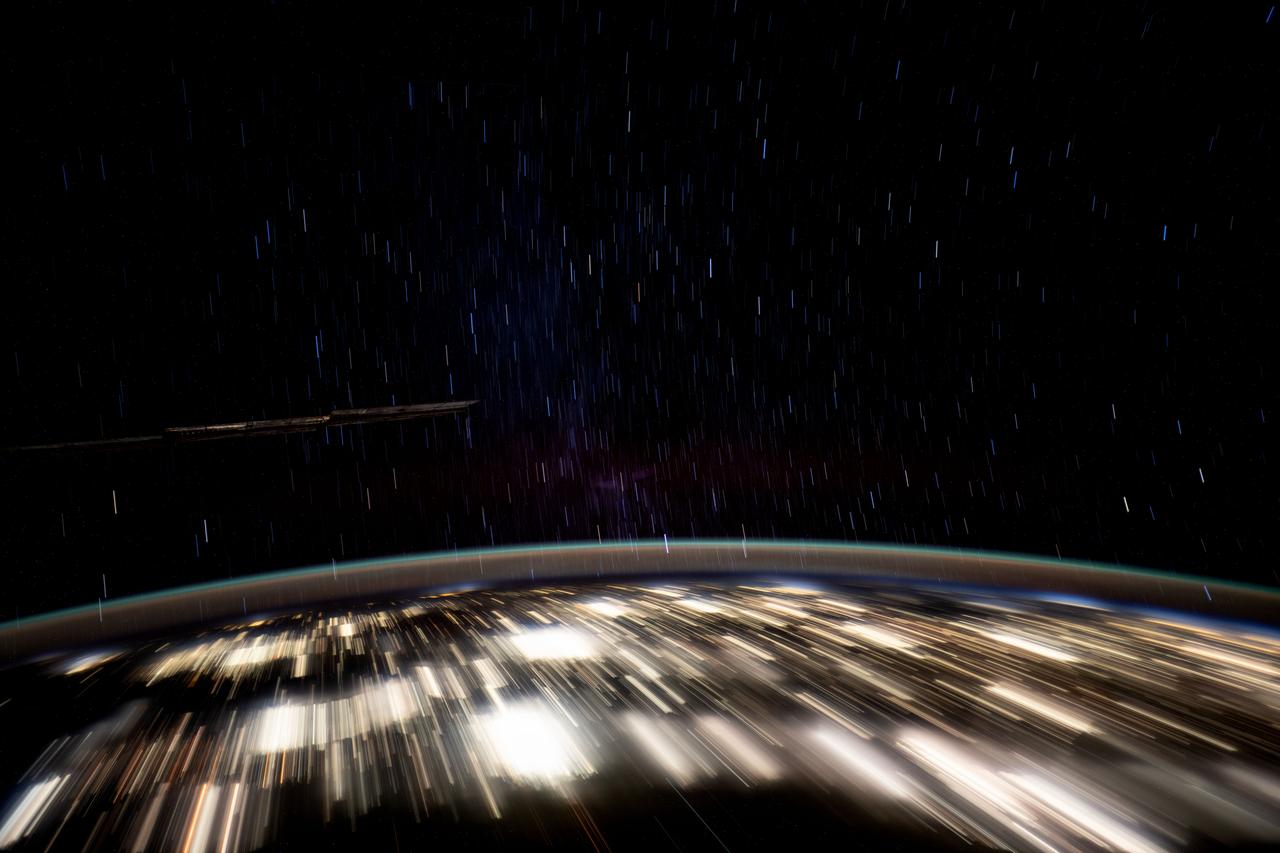

iss072e518202 (Jan. 23, 2025) --- This long-duration photograph highlights the city lights of Mexico's Yucatan peninsula, Earth's atmospheric glow, and star trails above taken from the International Space Station as it orbited 258 miles above.

STS060-83-041 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The large city of Monterrey, in northeastern Mexico, was founded at the edge between the Sierra Madre Oriental and the Rio Grande Embayment portion of the Gulf Coastal Plain. This location is analogous to the Fall Line along the United States eastern seaboard, but instead of lying along a stream at the head of navigation, Monterrey lies at the boundary between a well-watered mountain range and a semi-arid plain where irrigation is often necessary for successful agriculture. The mountains themselves are formed from folded limestone and shale beds; to the south of the city, beds are crumpled into tight folds. Around and north of the city, more open folds gradually give way to nearly flat-lying beds of the coastal plain. Because of the water and other resources such as shale and limestone to quarry and burn for cement, Monterrey early became a thriving industrial center. It is now one of Mexico's largest cities with a population of approximately 5 million. According to NASA geologists, the STS-60 photography of this area is the best that has been acquired during the past 32 years of space photography by the United States. Monterrey remains an area of high interest for future photography in order to assess the impact of urbanization in this area.

AS07-07-1877 (17 Oct. 1968) --- Hurricane Gladys, Gulf of Mexico, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 91st revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 99 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 144 hours and 27 minutes.
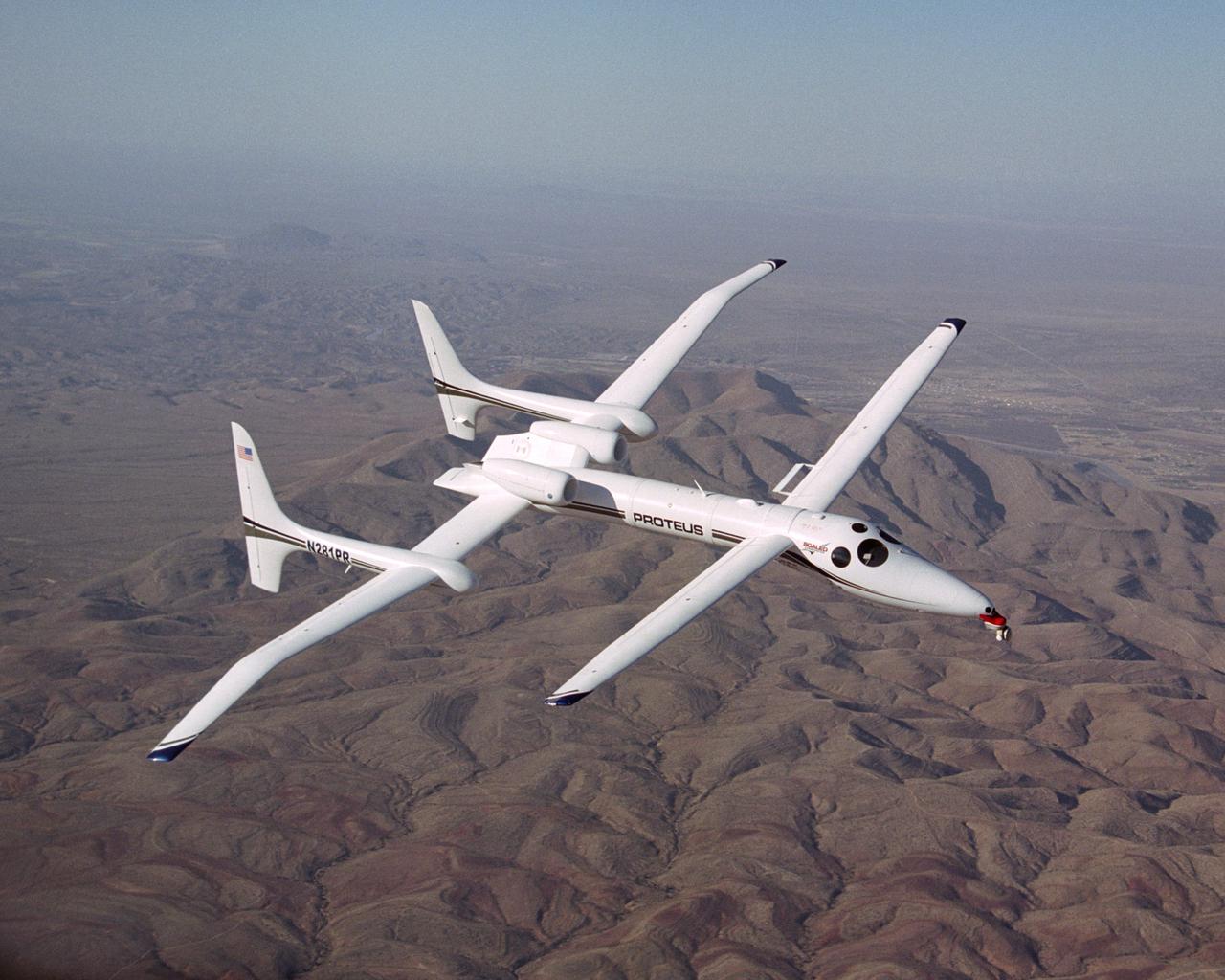

Proteus in flight over mountains near Las Cruces, New Mexico.
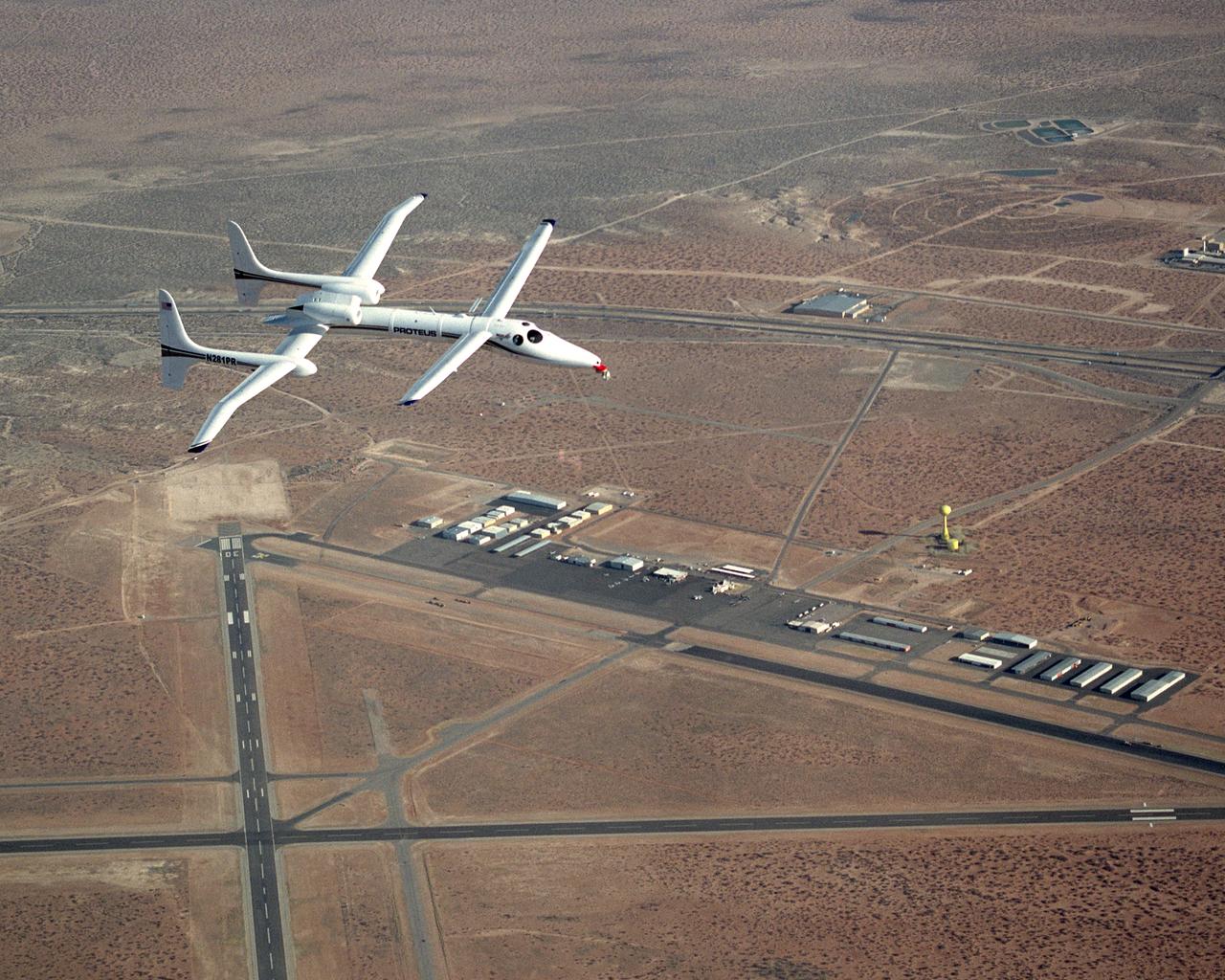

Proteus aircraft over Las Cruces International Airport in New Mexico.
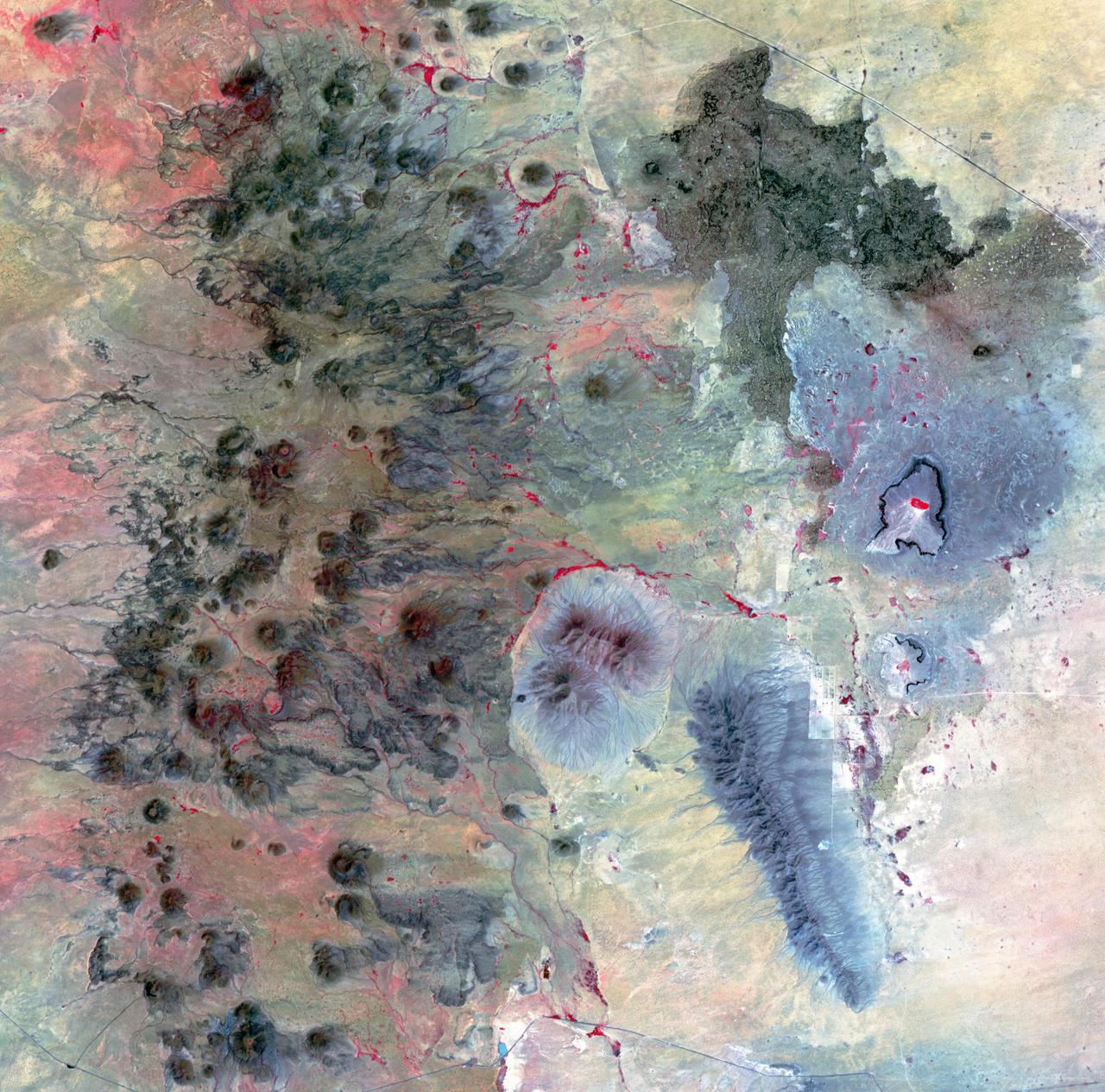

The Potrillo volcanic field is located on the Rio Grande Rift in southern New Mexico. Different kinds of volcanism form distinct landforms. The western part is composed of hundreds of cinder cones and flows. The eastern side has a small shield volcano with many tube-fed lava flows and two large maar craters, formed by the explosive interaction of magma with ground water. The age of the field is between 1 million to 20,000 years old. The image was acquired August 26, 2002, covers an area of 36 by 36.4 kilometers, and is located at 32 degrees north, 107.1 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23065

S66-54565 (14 Sept. 1966) --- Central portion of Florida, Gulf of Mexico to Atlantic Ocean, Cape Kennedy is at left center of photo, as seen from the Gemini-11 spacecraft during its 29th revolution of Earth. Photo lacks detail due to low sun angle. Sunglint on lakes is visible. Photo credit: NASA
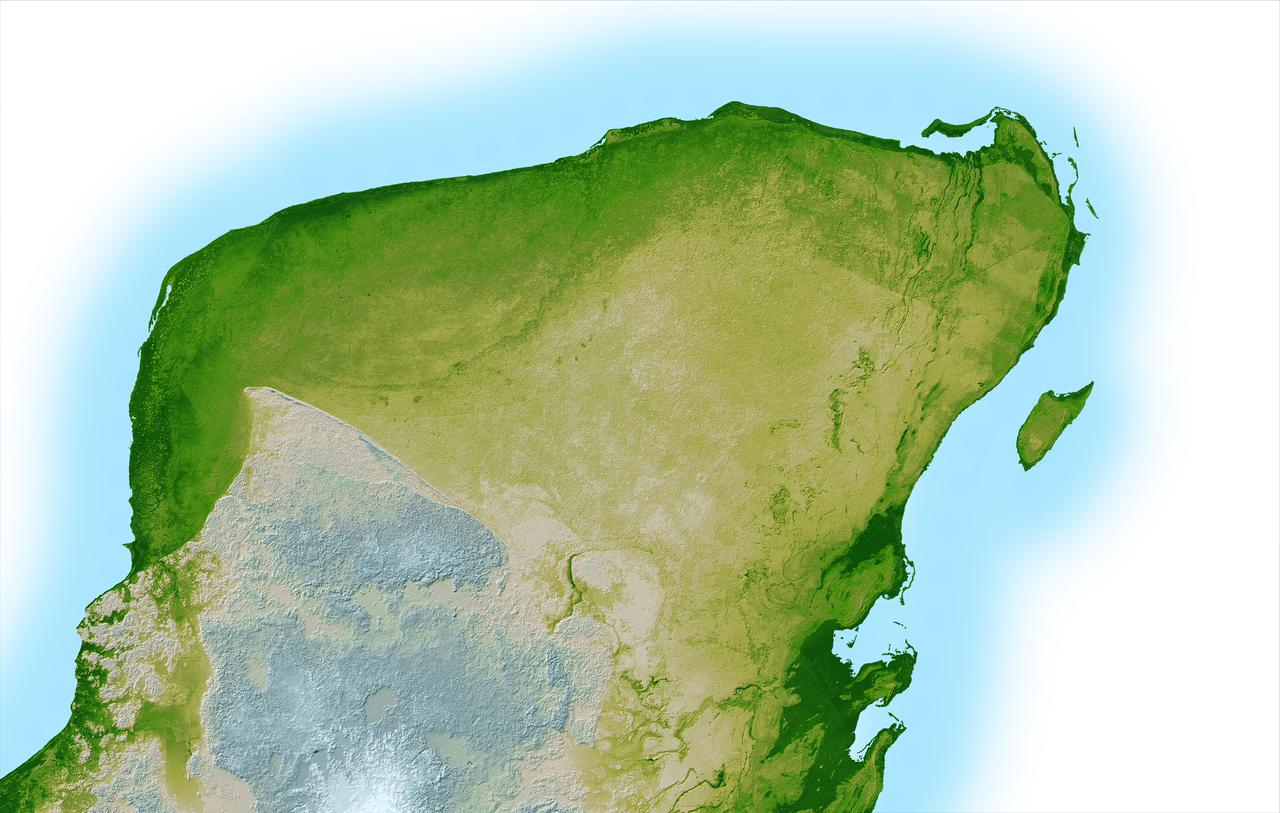
This shaded relief image of Mexico Yucatan Peninsula show a subtle, but unmistakable, indication of the Chicxulub impact crater. Most scientists now agree that this impact was the cause of the Cretatious-Tertiary Extinction.

This image from NASA Terra satellite was acquired on May 1, 2010. The red symbol indicates the approximate position of the Deepwater Horizon platform and the source of the oil slick which resulted in a significant oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico.
This image, from NASA Terra spacecraft, was acquired May 1, 2010. An explosion destroyed the Deepwater Horizon oil platform operating in the offshore in Gulf of Mexico on April 20, 2010.
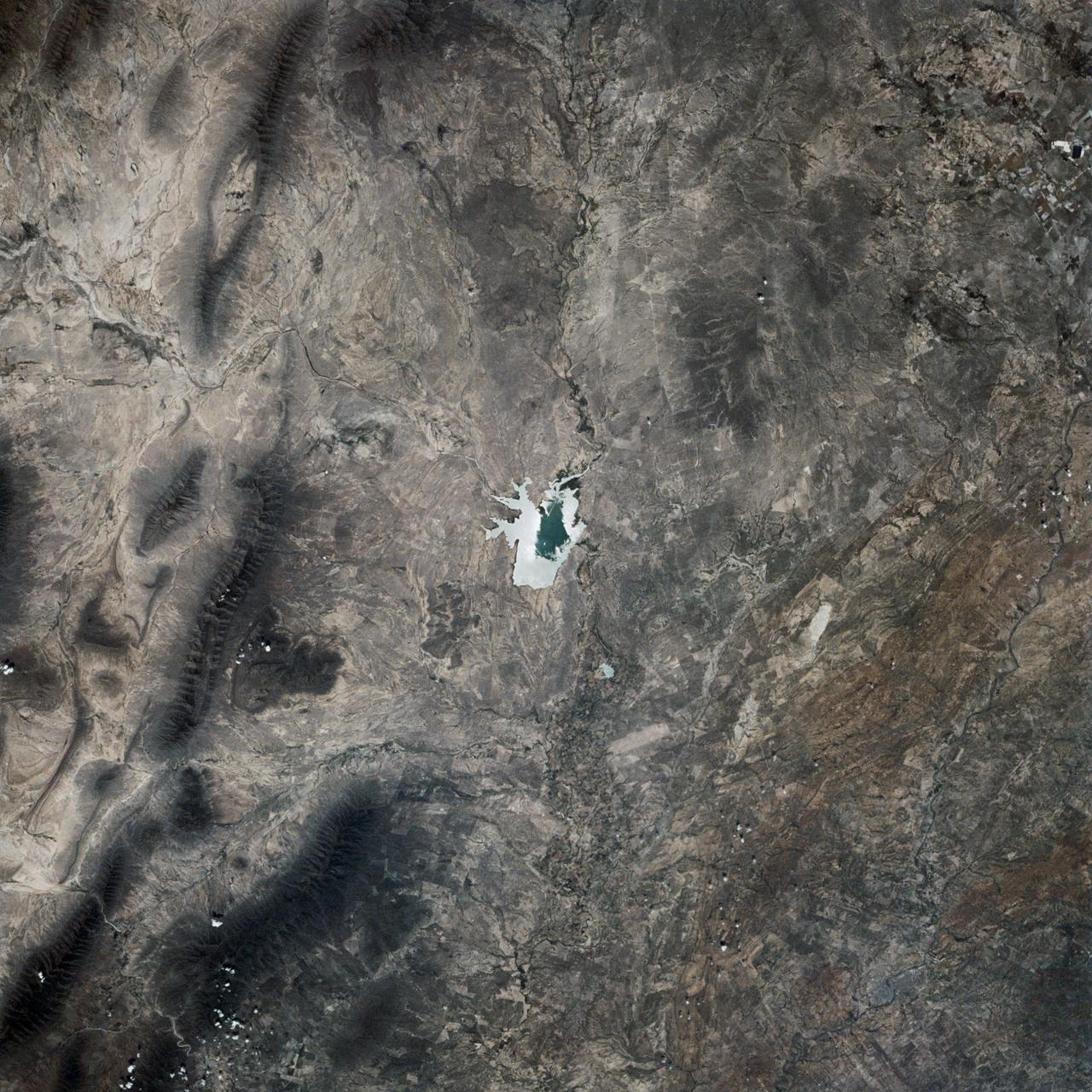

This is a single scene from a pair (frames 021 & 024) to study the effects of polarized light in Earth Observations. One scene was exposed with vertically polarized light, the other, horizontally. The subject in this study, is a lake behind Presa (dam) Don Martin (27.5N, 100.5W) on the edge of the Rio Grande Plain near it's boundry with the Sierra Madre Orientral in Coahuila, Mexico.
This image captured by NASA Terra spacecraft is an enhanced true color image of the Gulf of Mexico as it passed over the Deepwater Horizon oil slick on May 10, 2010.

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft is seen as it lands with NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer aboard, in the Gulf of Mexico, off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
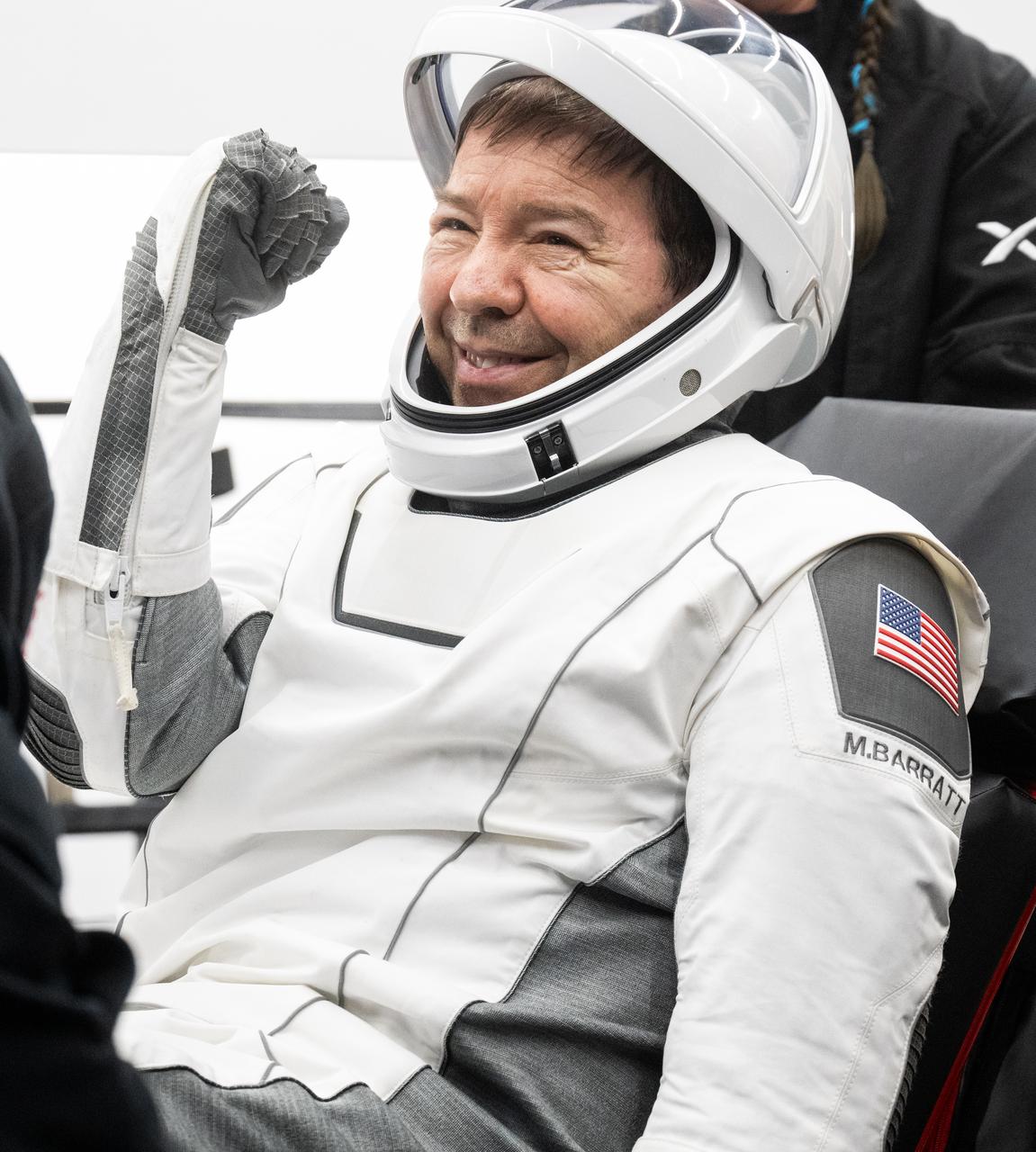

NASA astronaut Michael Barratt helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after he, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick, Jeanette Epps, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexander Grebenkin landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Friday, Oct. 25, 2024. Dominick, Barratt, Epps, Grebenkin are returning after seven-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
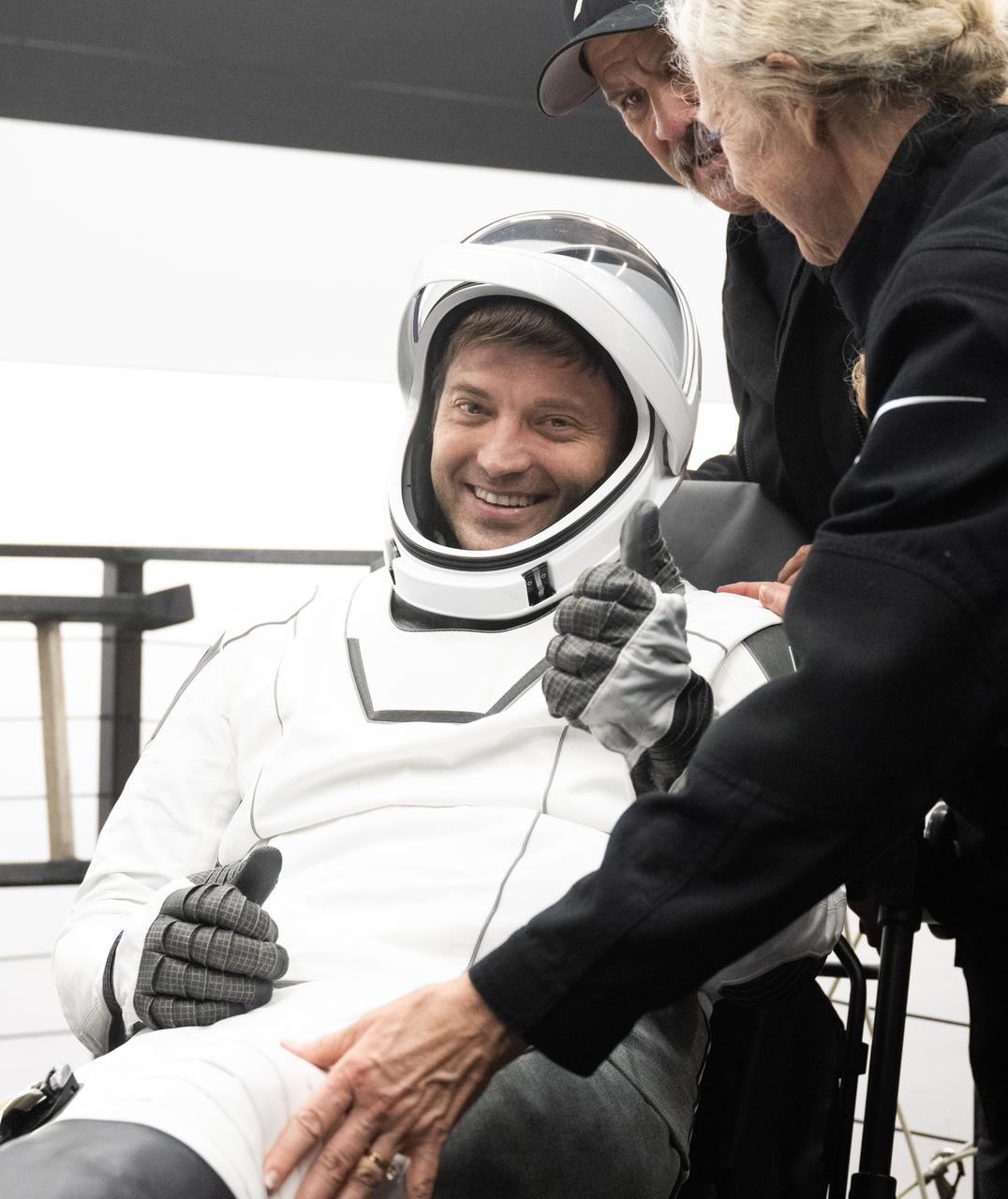

NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick is helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after he, NASA astronauts Michael Barratt, Jeanette Epps, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexander Grebenkin landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Friday, Oct. 25, 2024. Dominick, Barratt, Epps, Grebenkin are returning after seven-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
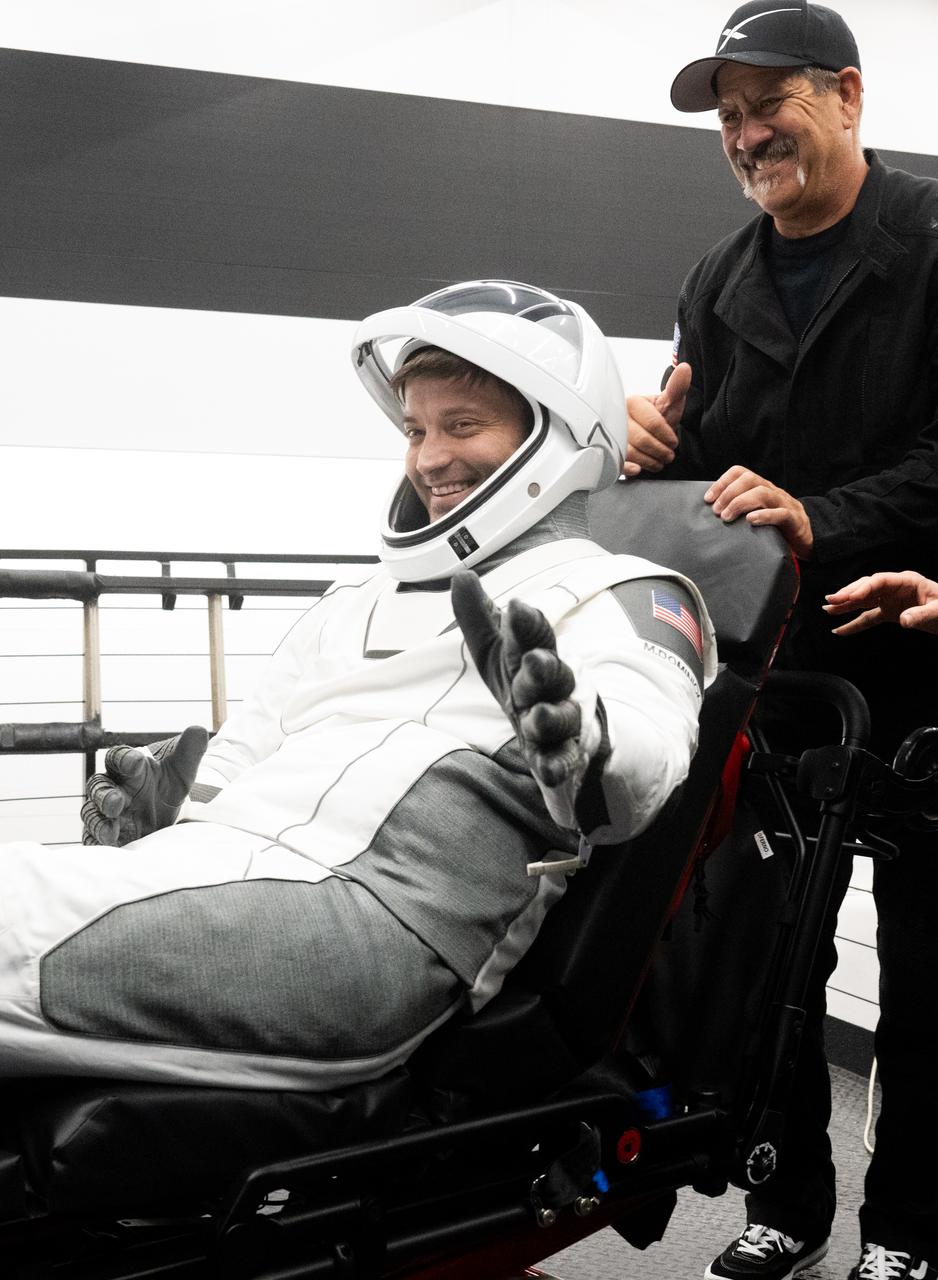

NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick is helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after he, NASA astronauts Michael Barratt, Jeanette Epps, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexander Grebenkin landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Friday, Oct. 25, 2024. Dominick, Barratt, Epps, Grebenkin are returning after seven-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
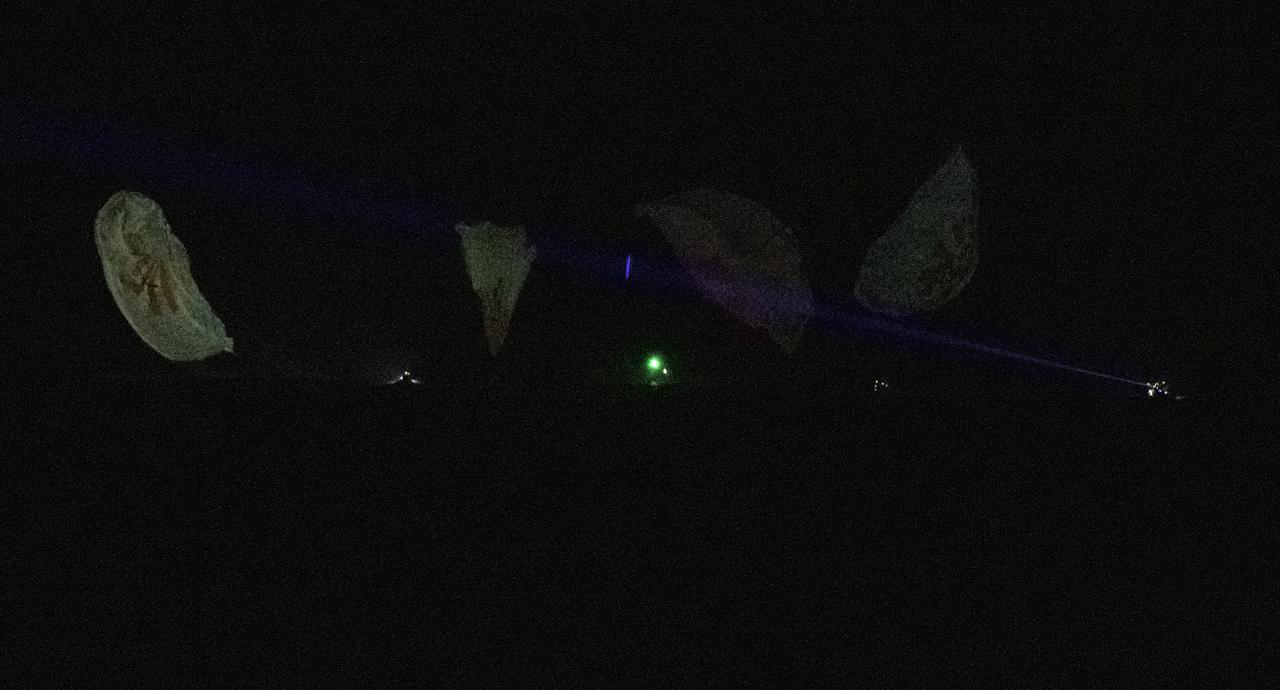

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft is seen as it lands with NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer aboard, in the Gulf of Mexico, off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft is seen as it lands with NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer aboard, in the Gulf of Mexico, off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexander Grebenkin is helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after he, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick, Michael Barratt, and Jeanette Epps landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Friday, Oct. 25, 2024. Dominick, Barratt, Epps, Grebenkin are returning after seven-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA astronaut Jeanette Epps is helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endeavour spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after she, NASA astronaut Matthew Dominick, Michael Barratt, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexander Grebenkin landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Friday, Oct. 25, 2024. Dominick, Barratt, Epps, Grebenkin are returning after seven-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
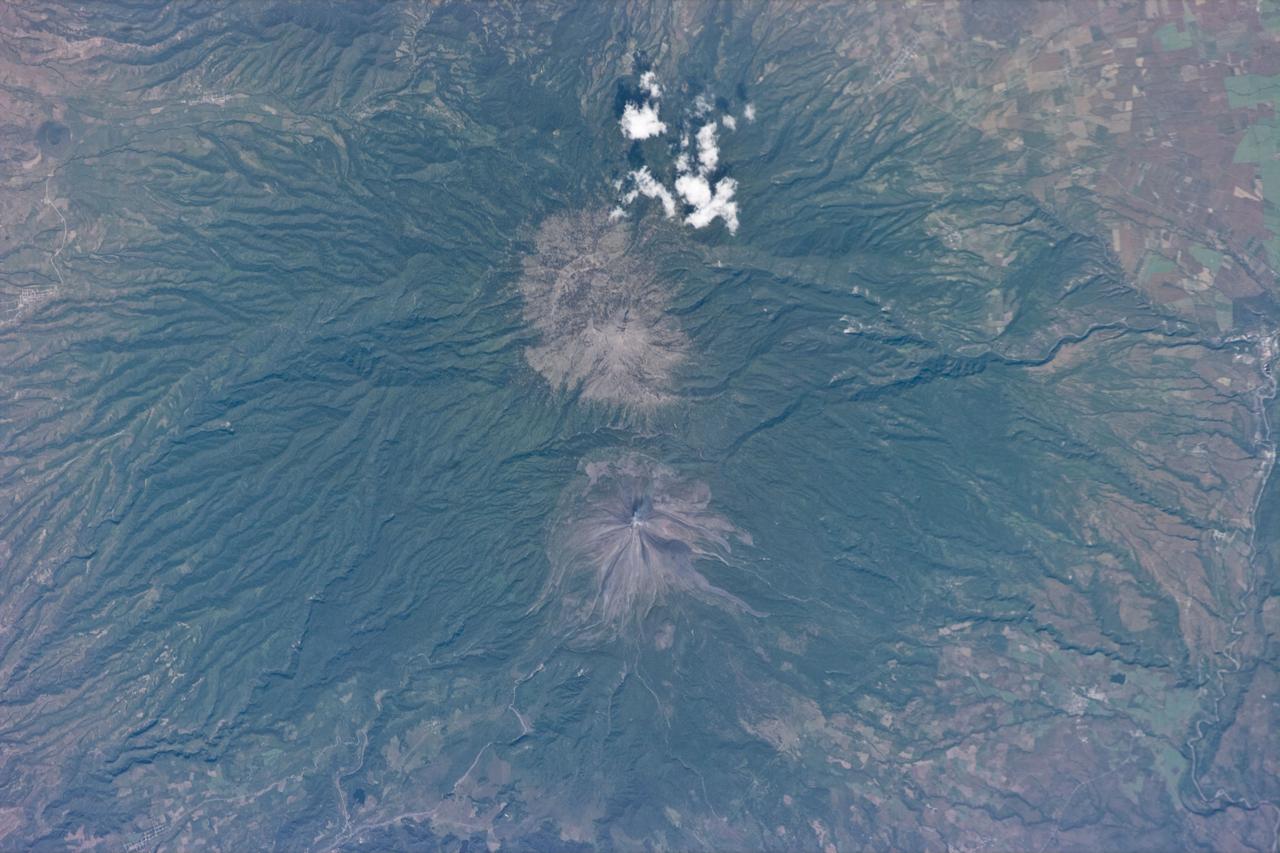

STS073-E-5274 (3 Nov. 1995) --- Colima was photographed with a color Electronic Still Camera (ESC) onboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia. The volcano lies due south of Guadalajara and Lake Chapala. It is considered to be one of Mexico's most active and most dangerous volcanoes, lying not far from heavily populated areas.
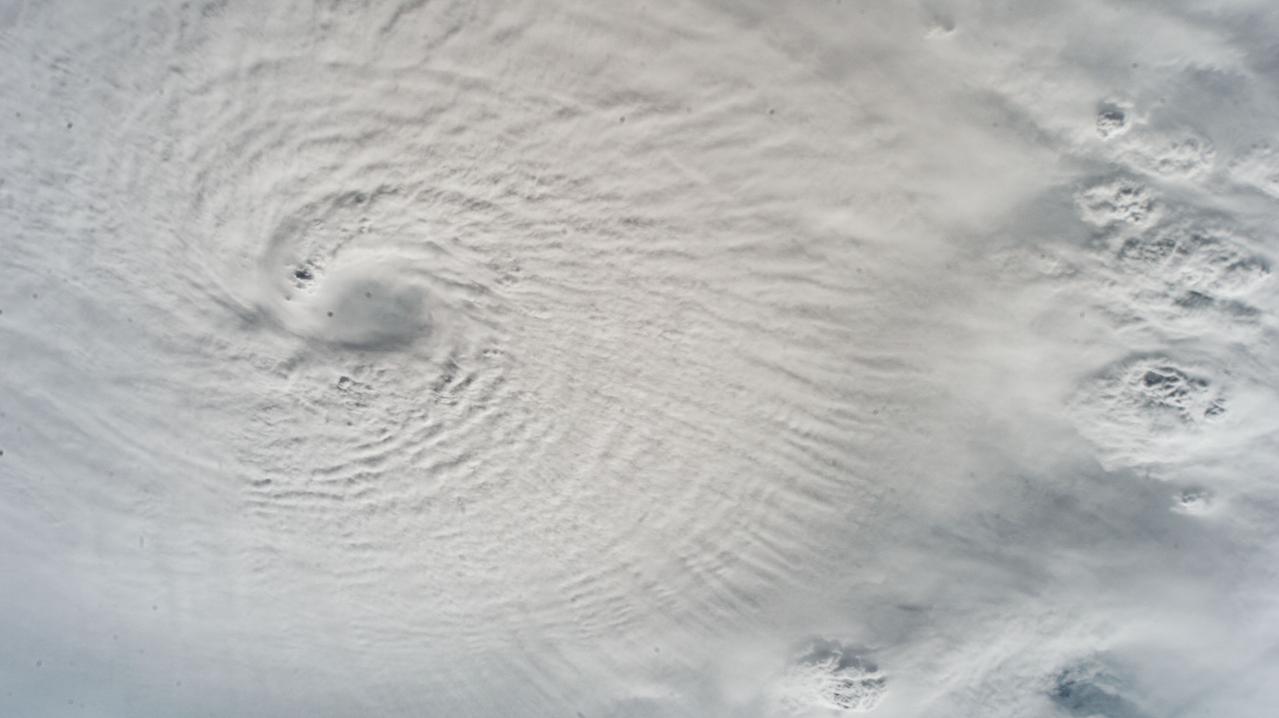

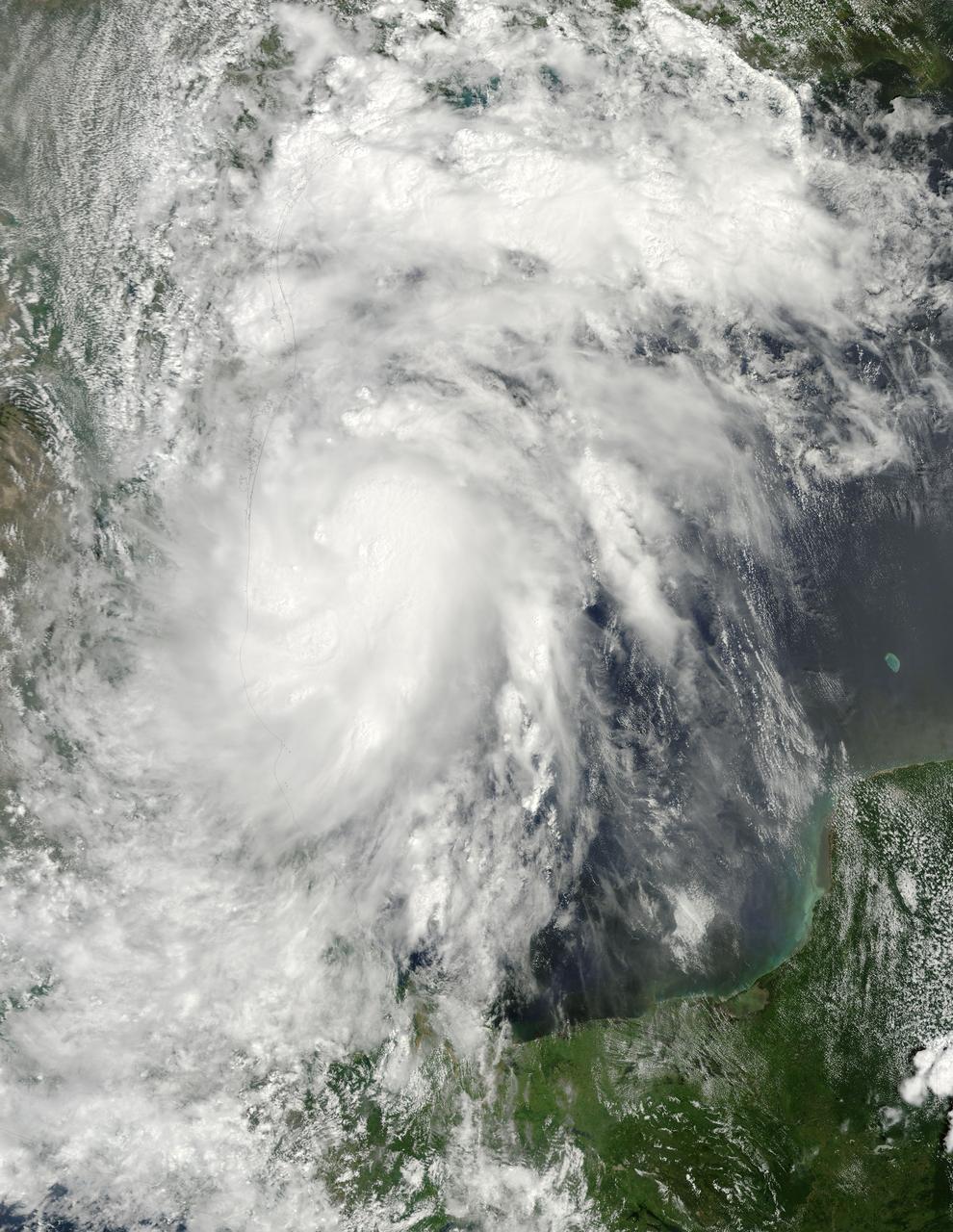
iss072e029017 (Oct. 7, 2024) --- While orbiting 257 miles above the Gulf of Mexico, an external camera on the International Space Station captured this image of Hurricane Milton, a Category 5 storm packing winds of 175 miles an hour at the time of this photograph, and its well-defined eye.
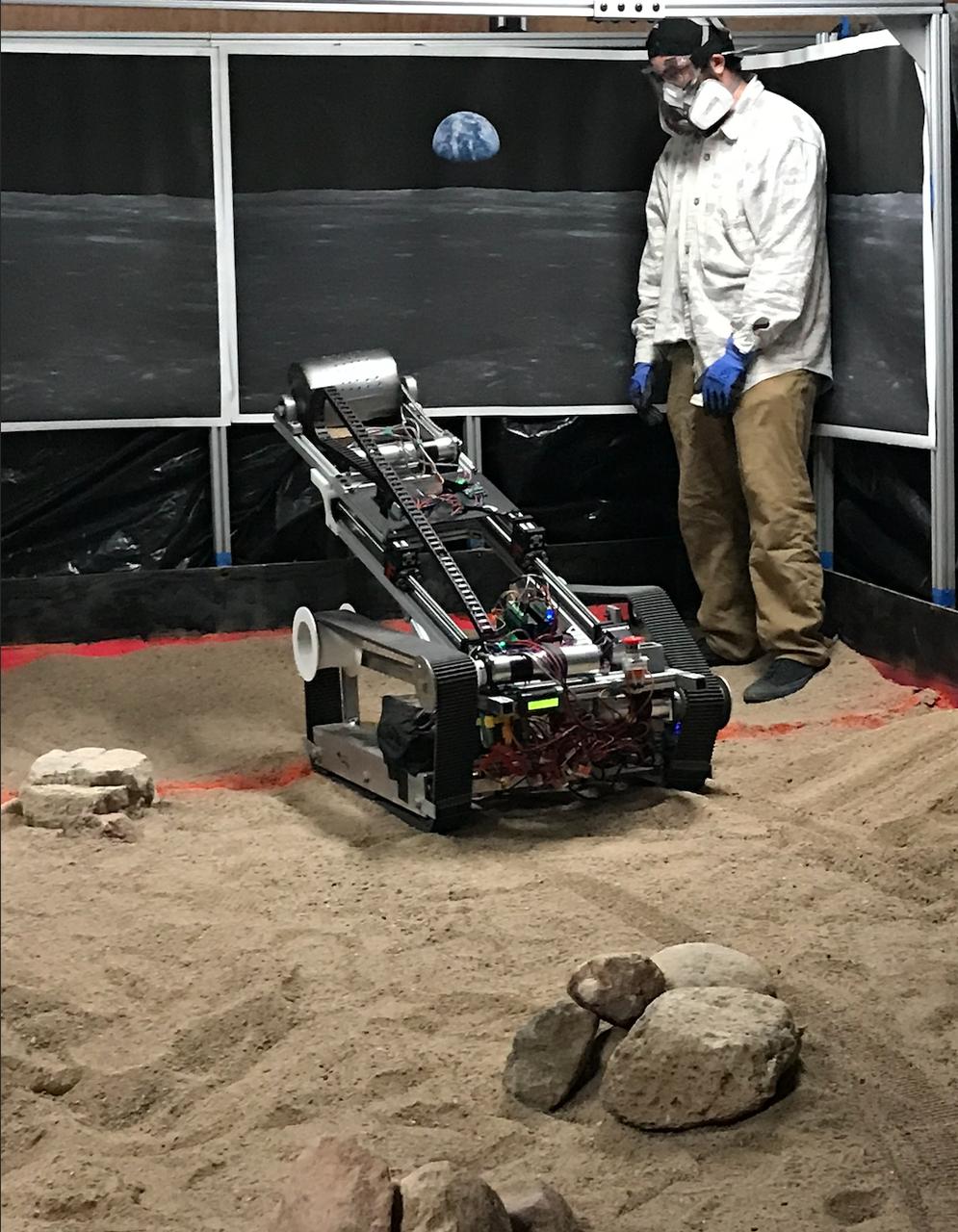

The New Mexico College of Mining and Technology robotic miner takes its first dig in the school’s mining arena. More than 40 teams from around the U.S. participated in NASA’s Lunabotics competition, which challenges collegiate teams to design and built remote-controlled robots under constraints similar to those the agency will face as it returns to the lunar surface through Artemis. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
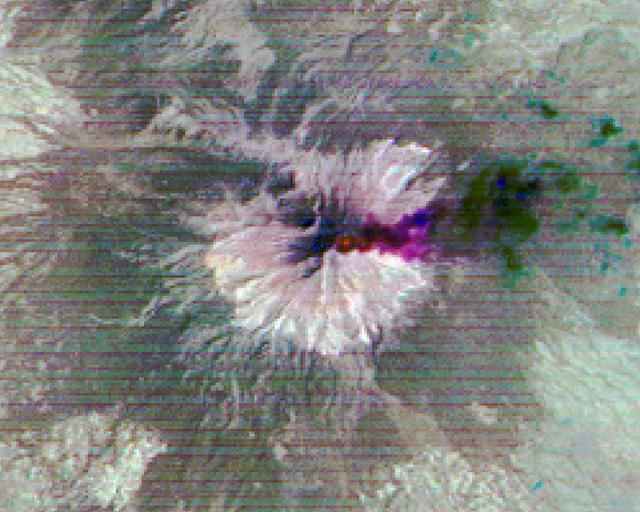

Popocatepetl, Mexico's most active volcano, erupted on February 23, sending blocks and bombs down the volcano's flanks, and emitting an ash column 1 km above the summit. Two days later, an ash cloud was still seen coming from the volcano. The thermal infrared color composite reveals a hot spot (red) at the summit crater. The dark red color near the vent of the east-blowing ash cloud suggests that its composition is dominantly ash material; further downwind, the color changes to purple, suggesting that some of the ash particles may be ice-covered. The images were acquired February 25, 2020, cover an area of 18 by 22.5 km, and are located at 19 degrees north, 98.6 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23680
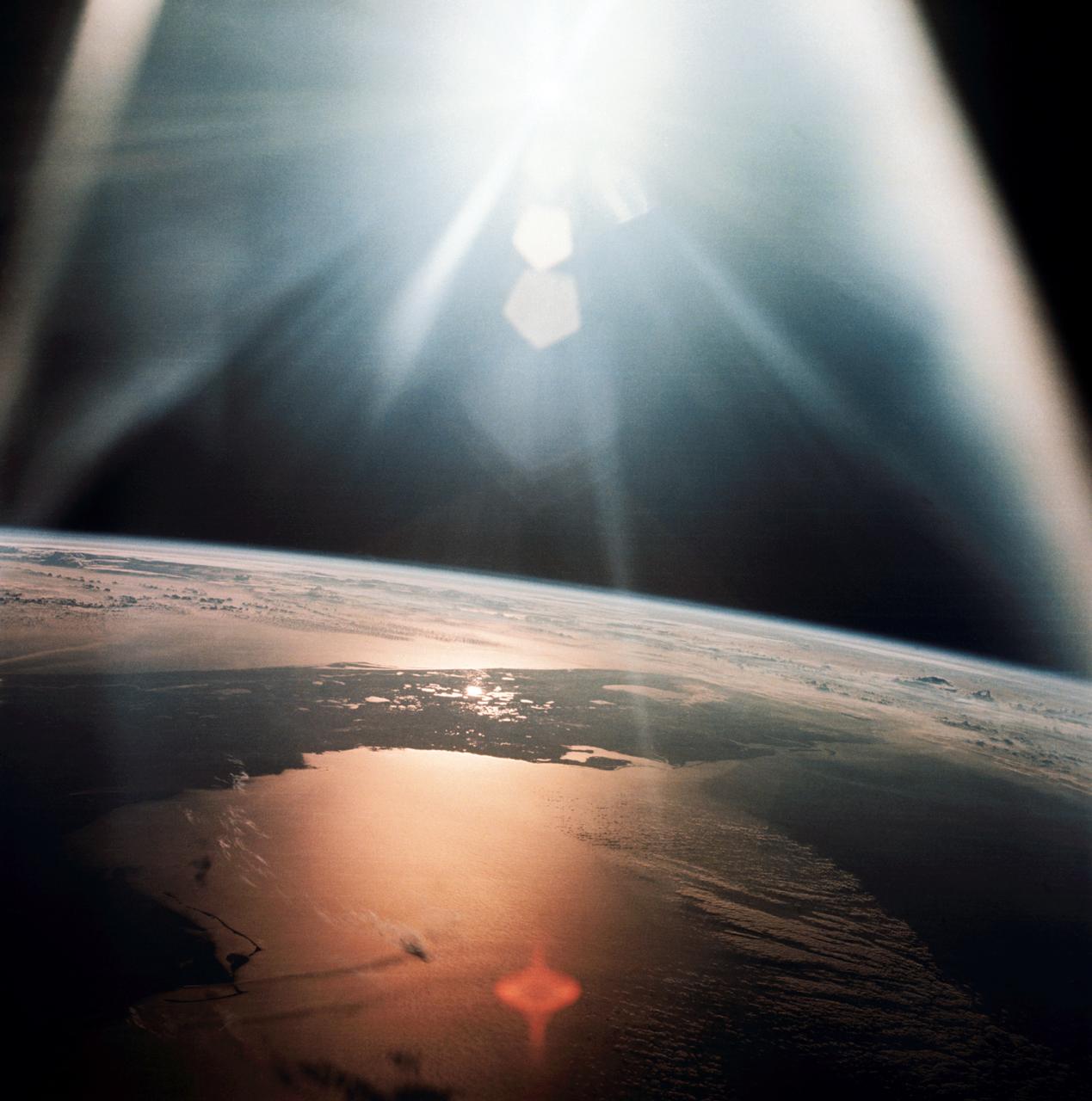

AS07-08-1933 (20 Oct. 1968) --- The morning sun reflects on the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft at an altitude of 120 nautical miles above Earth. Most of Florida peninsula appears as a dark silhouette. This photograph was made during the spacecraft's 134th revolution of Earth, some 213 hours and 19 minutes after liftoff.
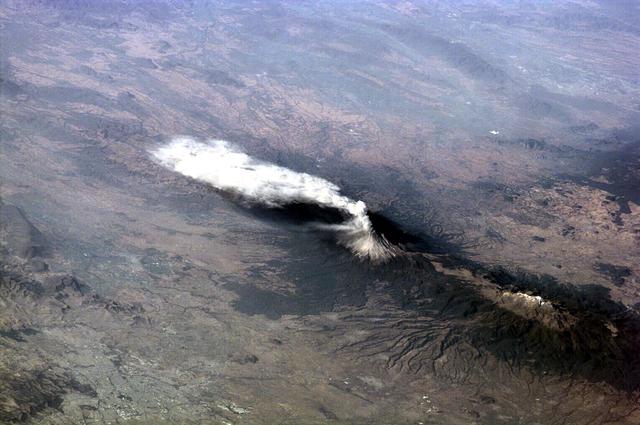

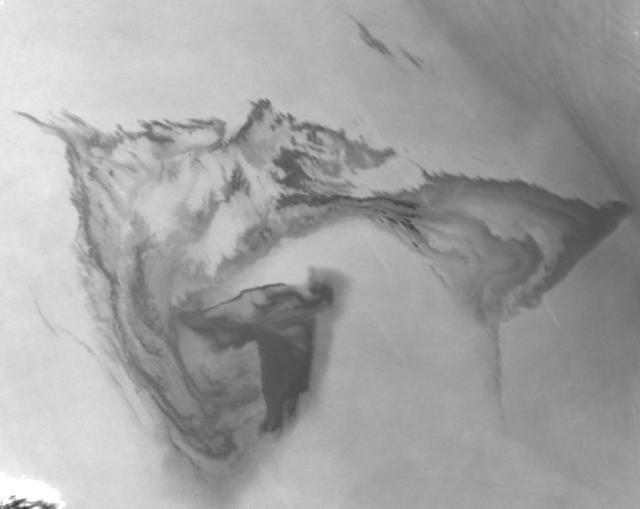
ISS01-E-5316 (23 January 2001) -- Popocatépetl, or Popo, the active volcano located about 70 kilometers southeast of Mexico City, sends a plume south on January 23, 2001. The Expedition One crew onboard the International Space Station (ISS) observed and recorded this image with a digital still camera as it orbited to the northeast of the volcano. Popo has been frequently active for six years. On this day, the eruption plume reportedly rose to more than 9 kilometers above sea level (for reference, Popo's summit elevation is 5426 meters). Note the smaller ash plume below the main plume. The perspective from the ISS allowed the crew members this unique three dimensional view. Popo is situated between two large population centers: Mexico City (more than 18 million people, and just out of this image at right) and Puebla (about 1.2 million people), partially visible at lower left.

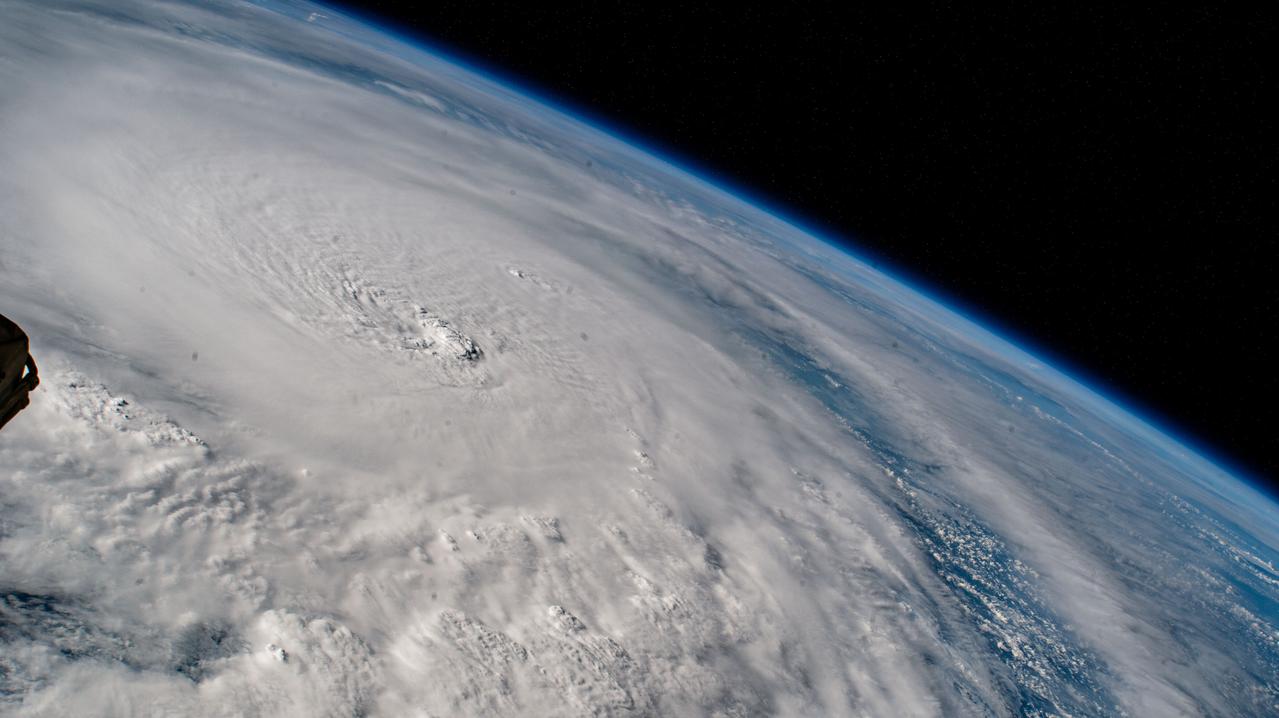
iss072e029295 (Oct. 8, 2024) --- Hurricane Milton, a Category 5 storm at the time of this photograph, is pictured in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Yucatan Peninsula from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above.

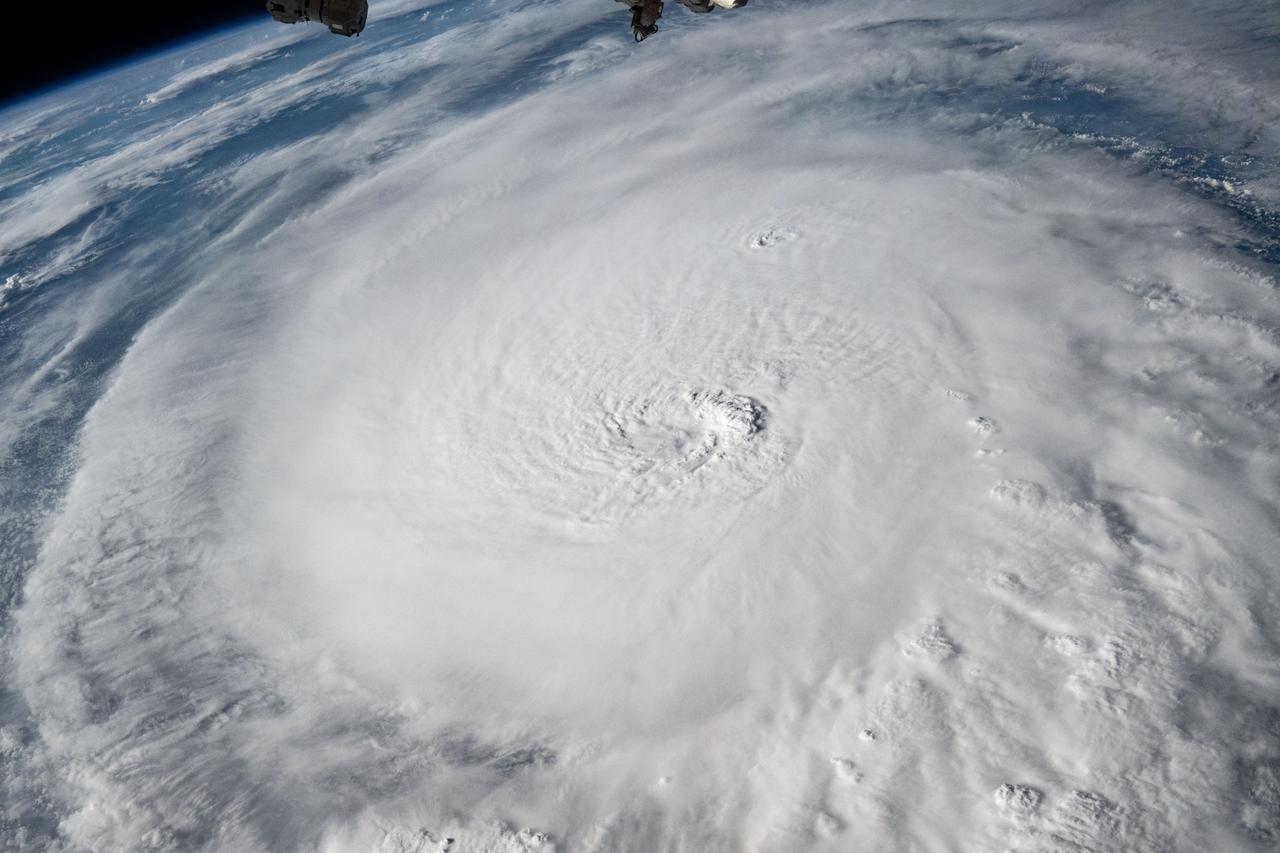
iss072e029488 (Oct. 8, 2024) --- Hurricane Milton, a Category 4 storm at the time of this photograph, is pictured in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Yucatan Peninsula from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above.

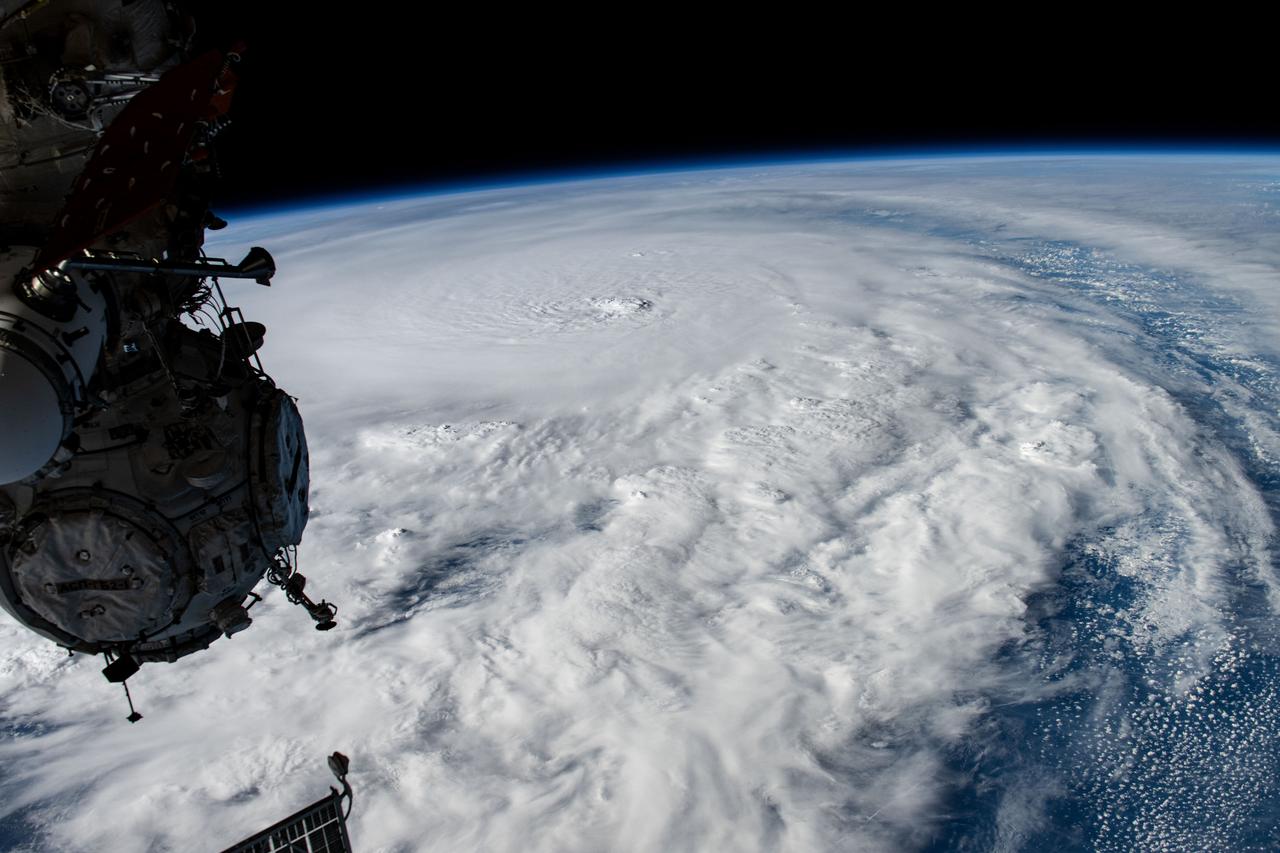
iss072e029135 (Oct. 8, 2024) --- Hurricane Milton, a Category 5 storm at the time of this photograph, is pictured in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Yucatan Peninsula from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above.

iss072e029445 (Oct. 8, 2024) --- Hurricane Milton, a Category 5 storm at the time of this photograph, is pictured in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Yucatan Peninsula from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above.
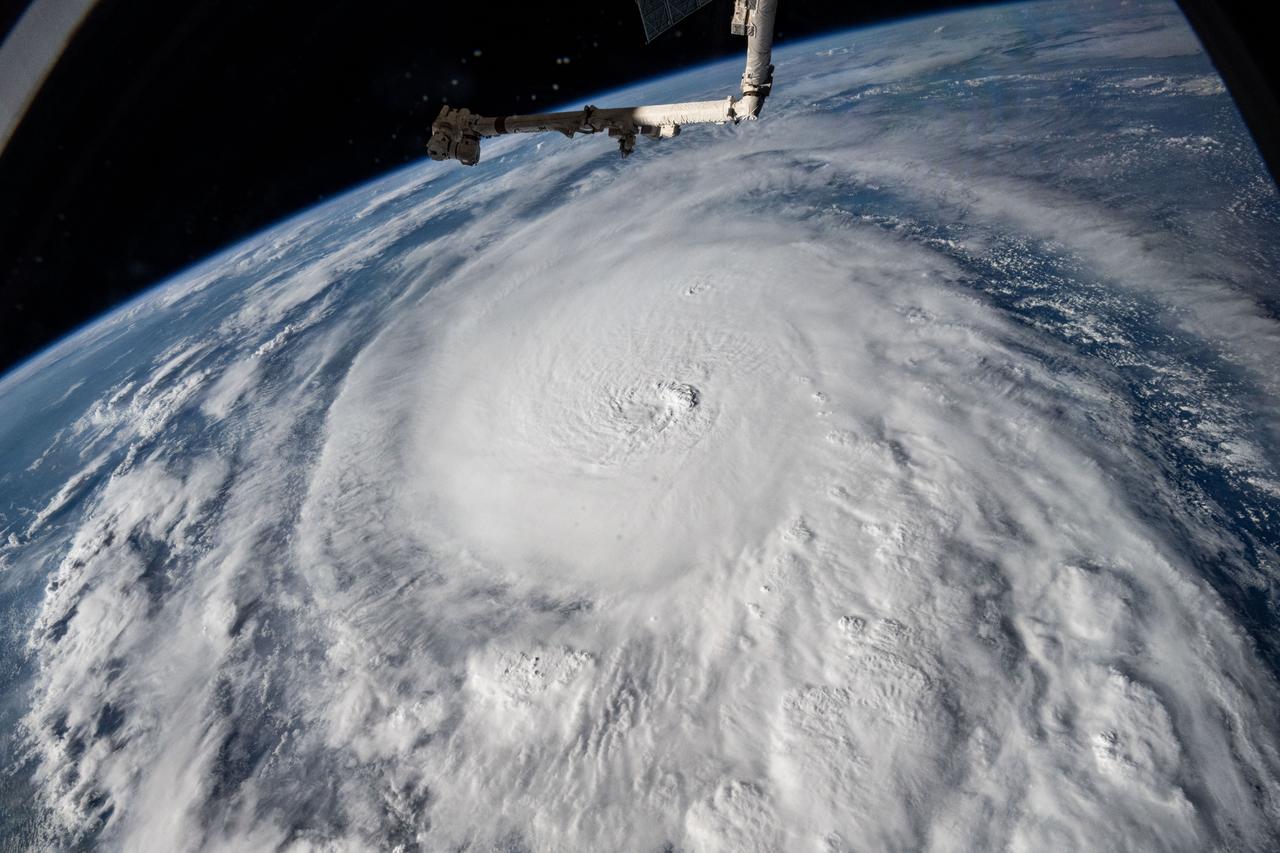

iss072e029127 (Oct. 8, 2024) --- Hurricane Milton, a Category 5 storm at the time of this photograph, is pictured in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Yucatan Peninsula from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above.

iss072e029487 (Oct. 8, 2024) --- Hurricane Milton, a Category 4 storm at the time of this photograph, is pictured in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Yucatan Peninsula from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above.
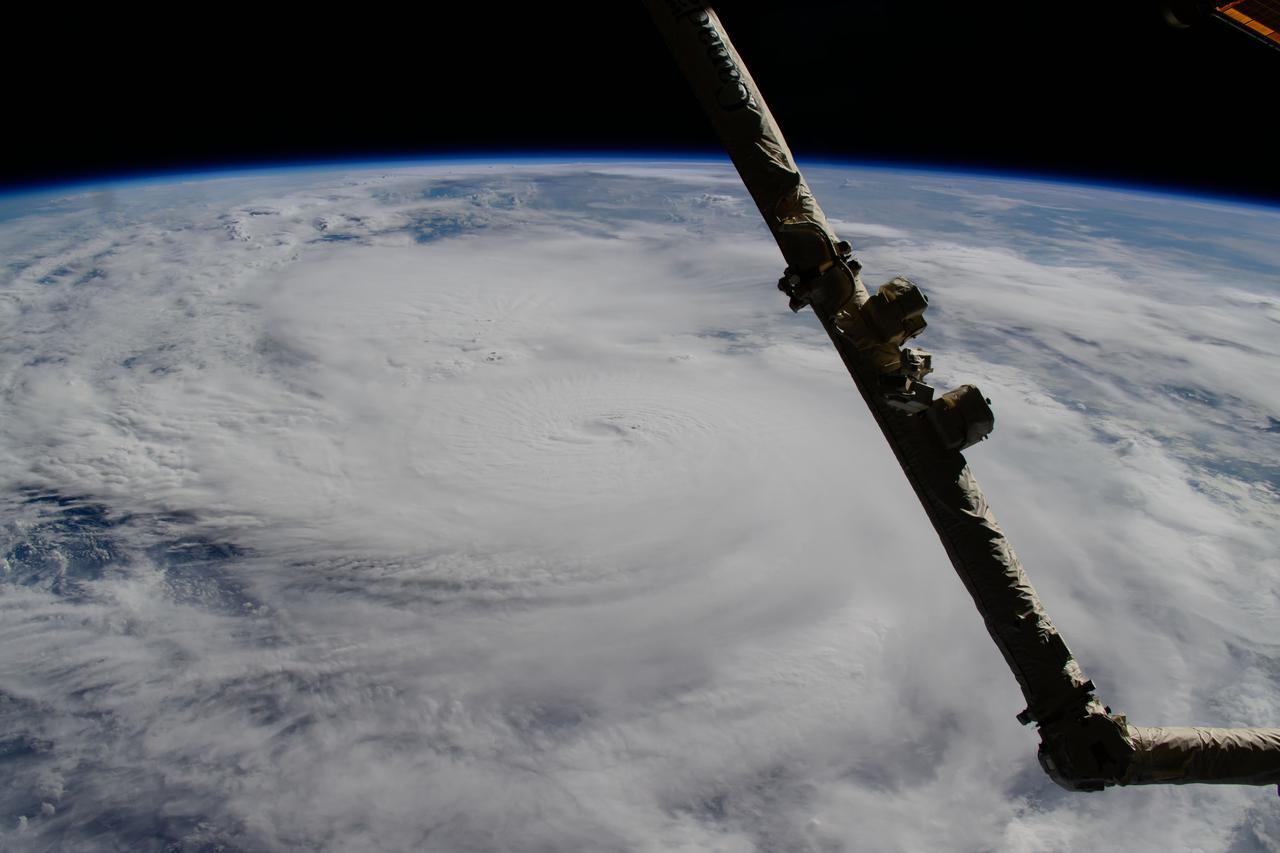

iss072e014652 (Oct. 7, 2024) --- Hurricane Milton, a Category 4 storm at the time of this photograph, is pictured in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Yucatan Peninsula from the International Space Station as it orbited 257 miles above.
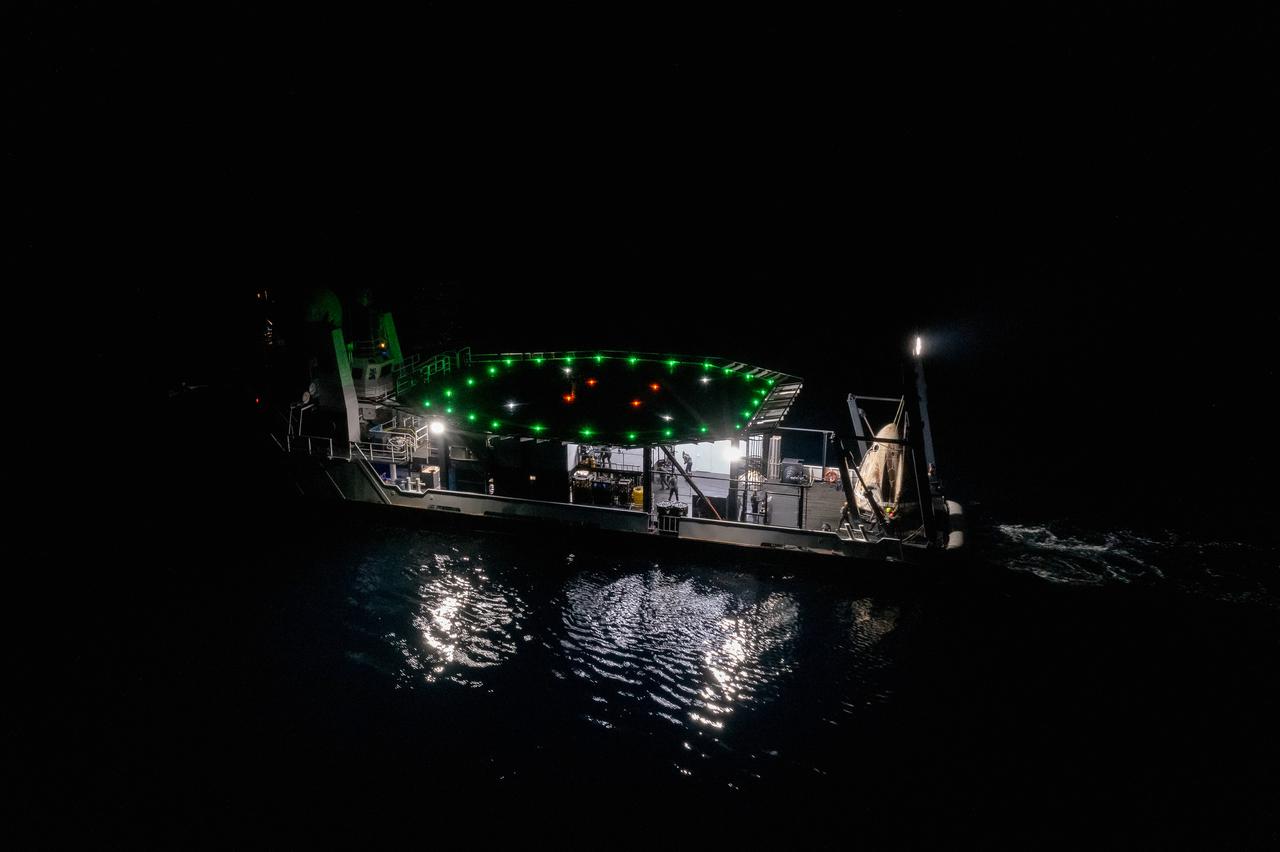

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience splashed down in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, in Florida, at 2:56 a.m. EDT on May 2, 2021. Astronauts Michael Hopkins, Victor Glover, and Shannon Walker of NASA, and Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) completed Crew-1, the first crew rotation mission to the International Space Station in partnership with NASA as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Teams on the Go Navigator recovery ship, including two fast boats, work to secure and hoist Crew Dragon onto the main deck of the recovery ship with the astronauts inside.
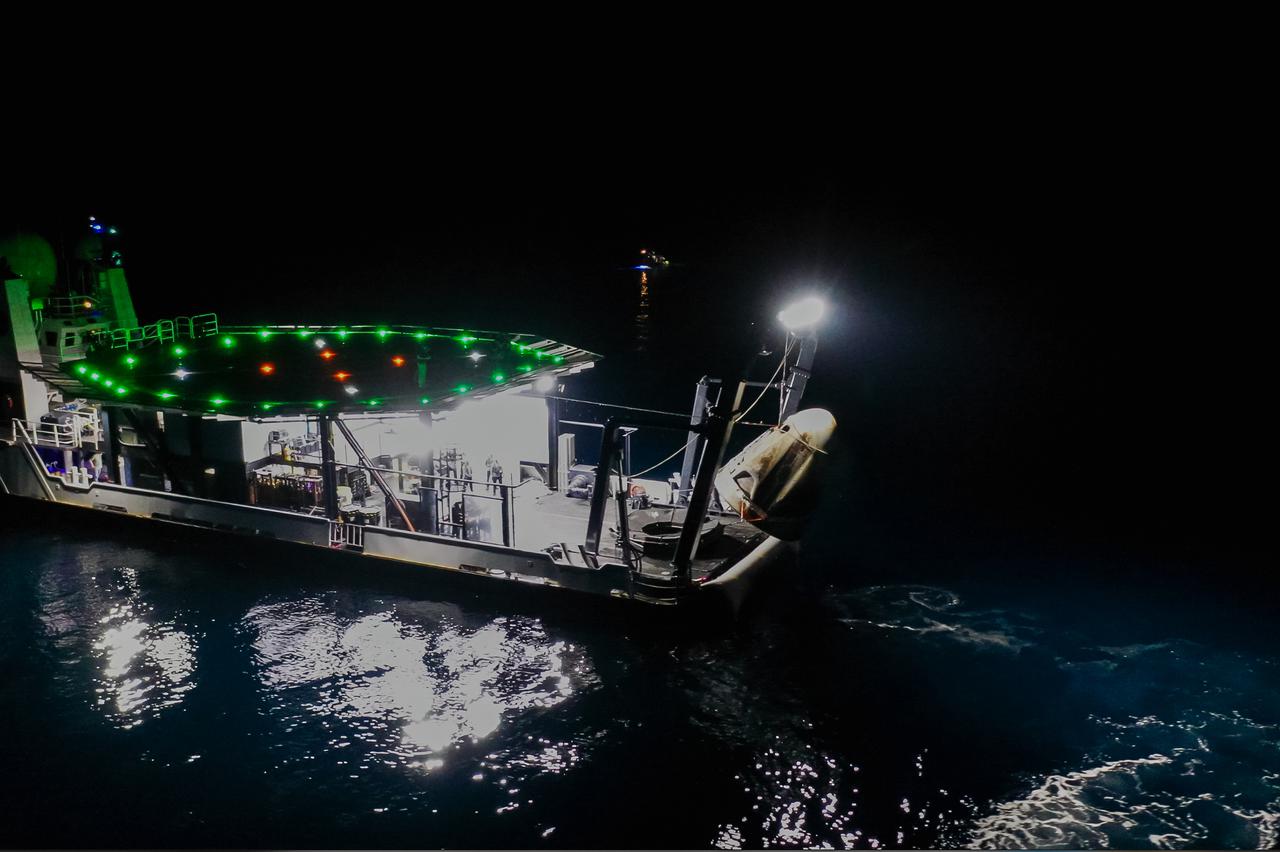

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience splashed down in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, in Florida, at 2:56 a.m. EDT on May 2, 2021. Astronauts Michael Hopkins, Victor Glover, and Shannon Walker of NASA, and Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) completed Crew-1, the first crew rotation mission to the International Space Station in partnership with NASA as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Teams on the Go Navigator recovery ship, including two fast boats, work to secure and hoist Crew Dragon onto the main deck of the recovery ship with the astronauts inside.
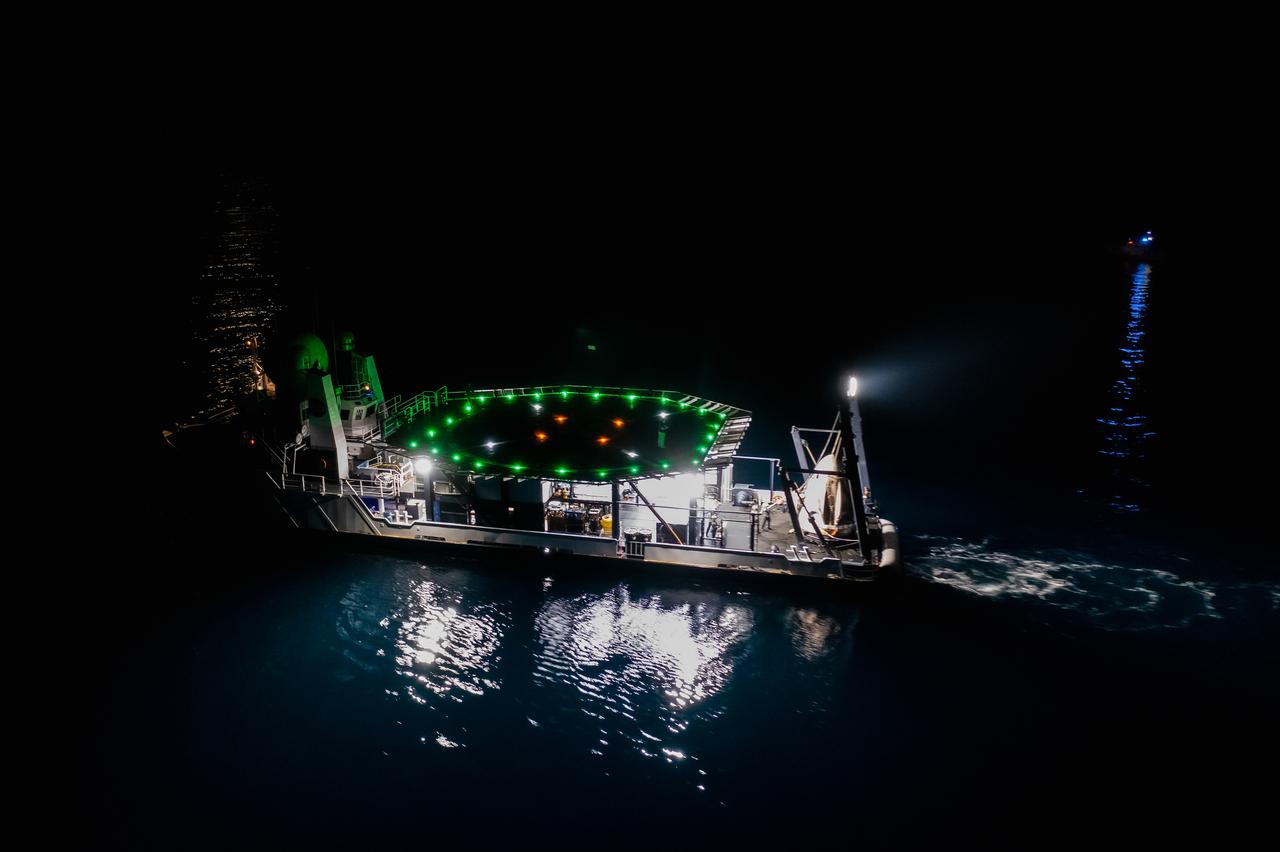

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience splashed down in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, in Florida, at 2:56 a.m. EDT on May 2, 2021. Astronauts Michael Hopkins, Victor Glover, and Shannon Walker of NASA, and Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) completed Crew-1, the first crew rotation mission to the International Space Station in partnership with NASA as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Teams on the Go Navigator recovery ship, including two fast boats, work to secure and hoist Crew Dragon onto the main deck of the recovery ship with the astronauts inside.
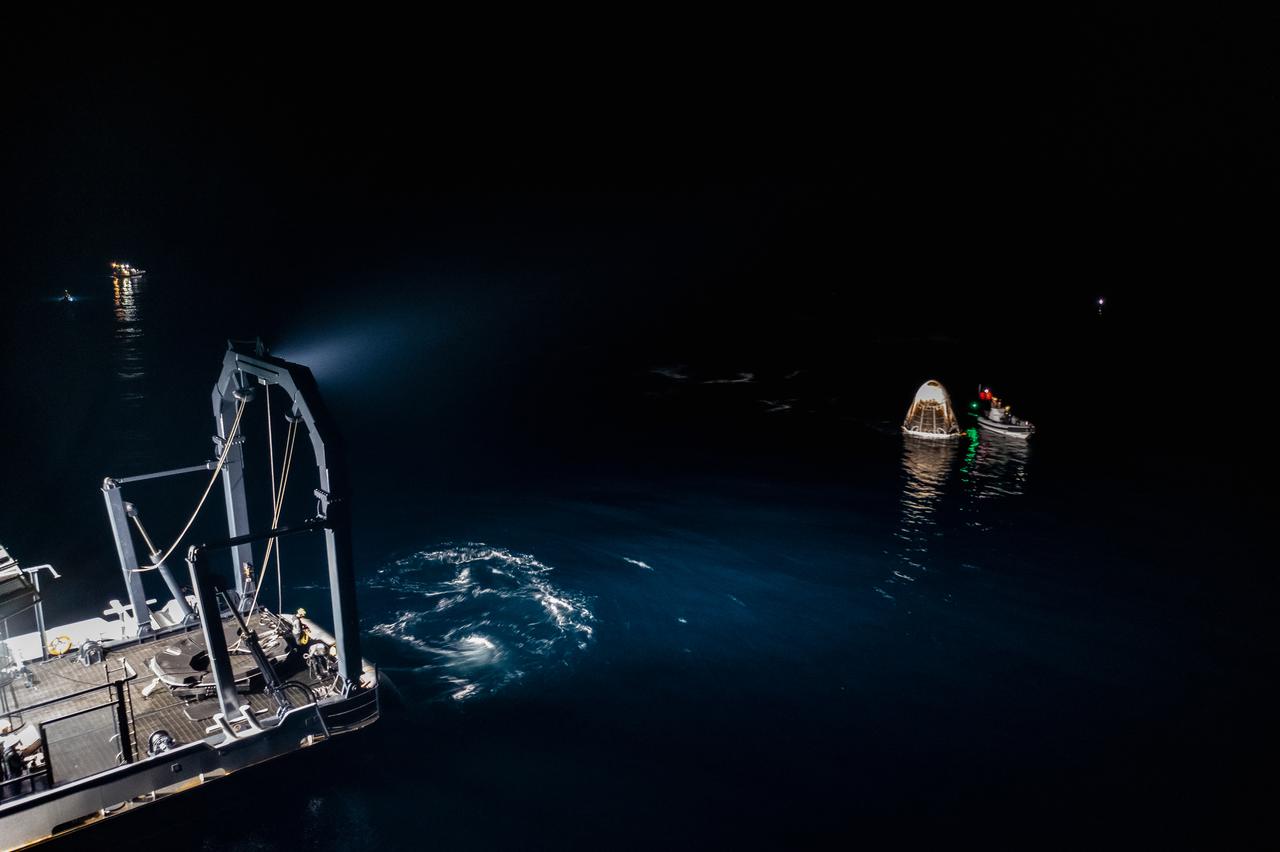

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience splashes down in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, in Florida, at 2:56 a.m. EDT on May 2, 2021. Astronauts Michael Hopkins, Victor Glover, and Shannon Walker of NASA, and Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) completed Crew-1, the first crew rotation mission to the International Space Station in partnership with NASA as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. At left is SpaceX’s Go Navigator recovery ship. Crew Dragon will be secured and then hoisted onto the main deck of the recovery ship with the astronauts inside.
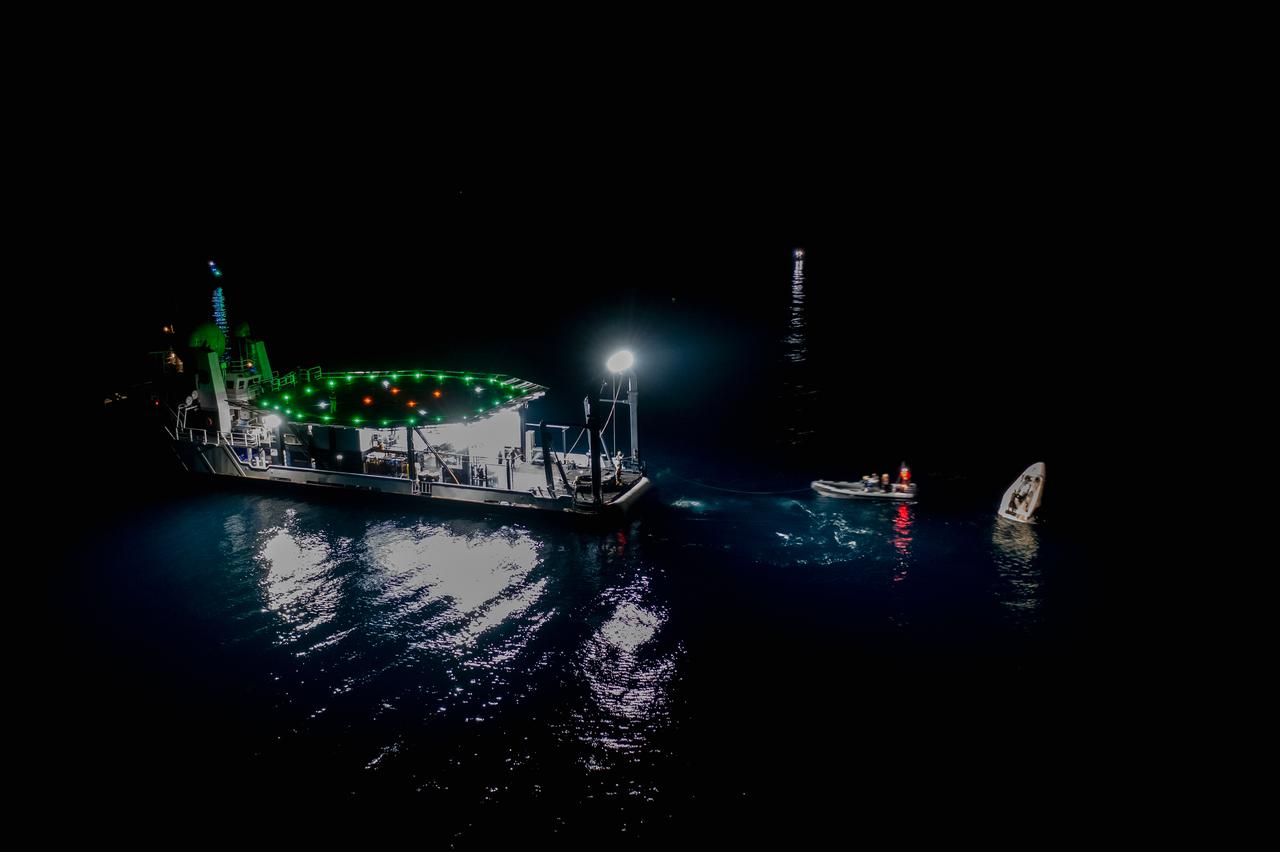

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience splashes down in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, in Florida, at 2:56 a.m. EDT on May 2, 2021. Astronauts Michael Hopkins, Victor Glover, and Shannon Walker of NASA, and Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) completed Crew-1, the first crew rotation mission to the International Space Station in partnership with NASA as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. At left is SpaceX’s Go Navigator recovery ship. Teams on two fast boats and Go Navigator will secure Crew Dragon to be hoisted onto the main deck of the recovery ship with the astronauts inside.
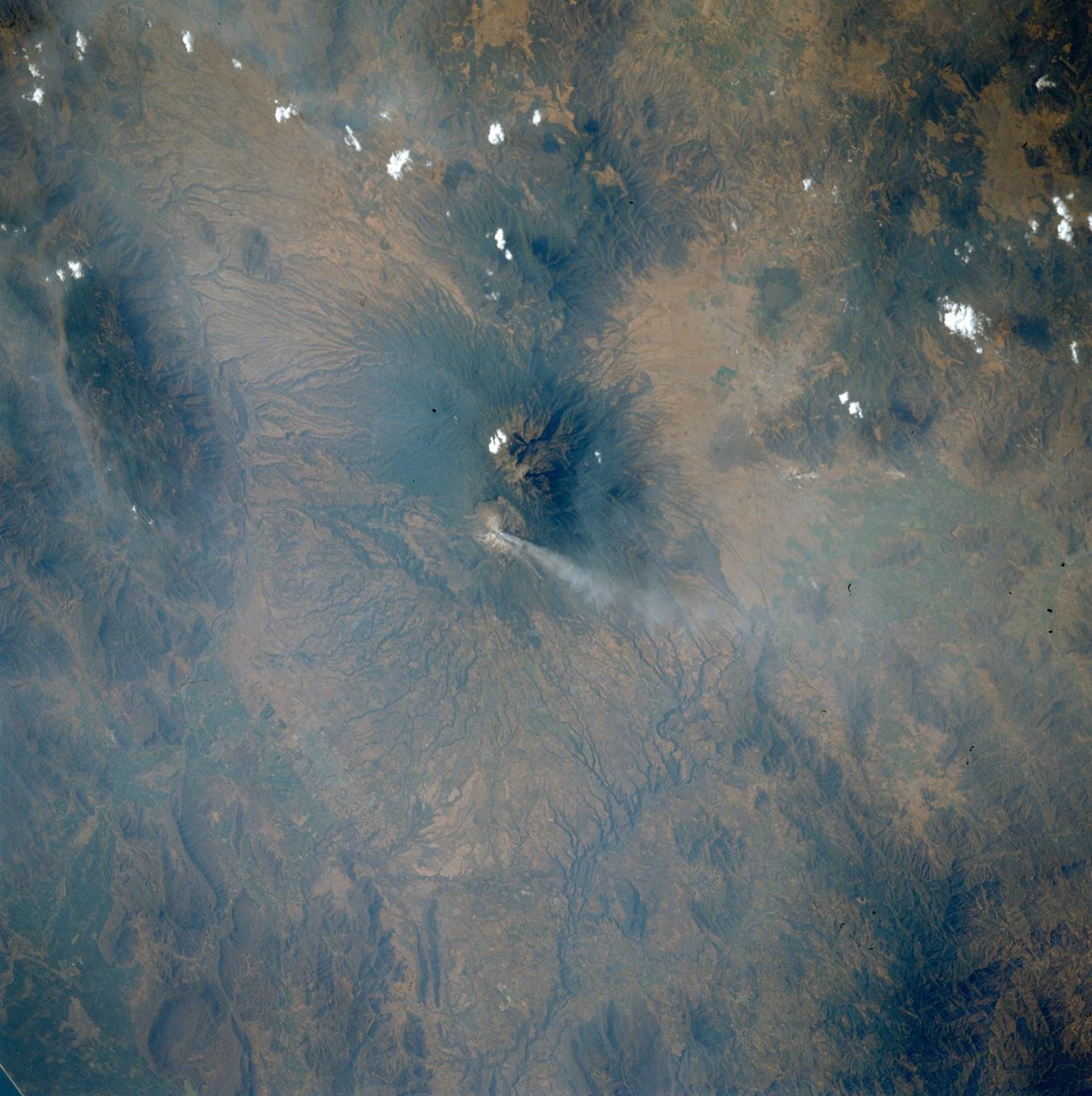

STS039-75-101 (28 April-6 May 1991) --- Spending over eight days in Earth orbit, the STS-39 crew was able to return with photographic coverage of highly variegated geographic scenery, including a number of volcanoes such as Mexico's Colima. Located south of Guadalajara, Colima is Mexico's most active volcano. The current activity started in the first part of March 1991 with avalanches occurring, followed by lava extrusion and ash emission. Colima is captured here in action. The steam plume drifts eastward from the 13,325 ft. summit. Scars from recent landslides can be seen on the southwest flank of the summit.
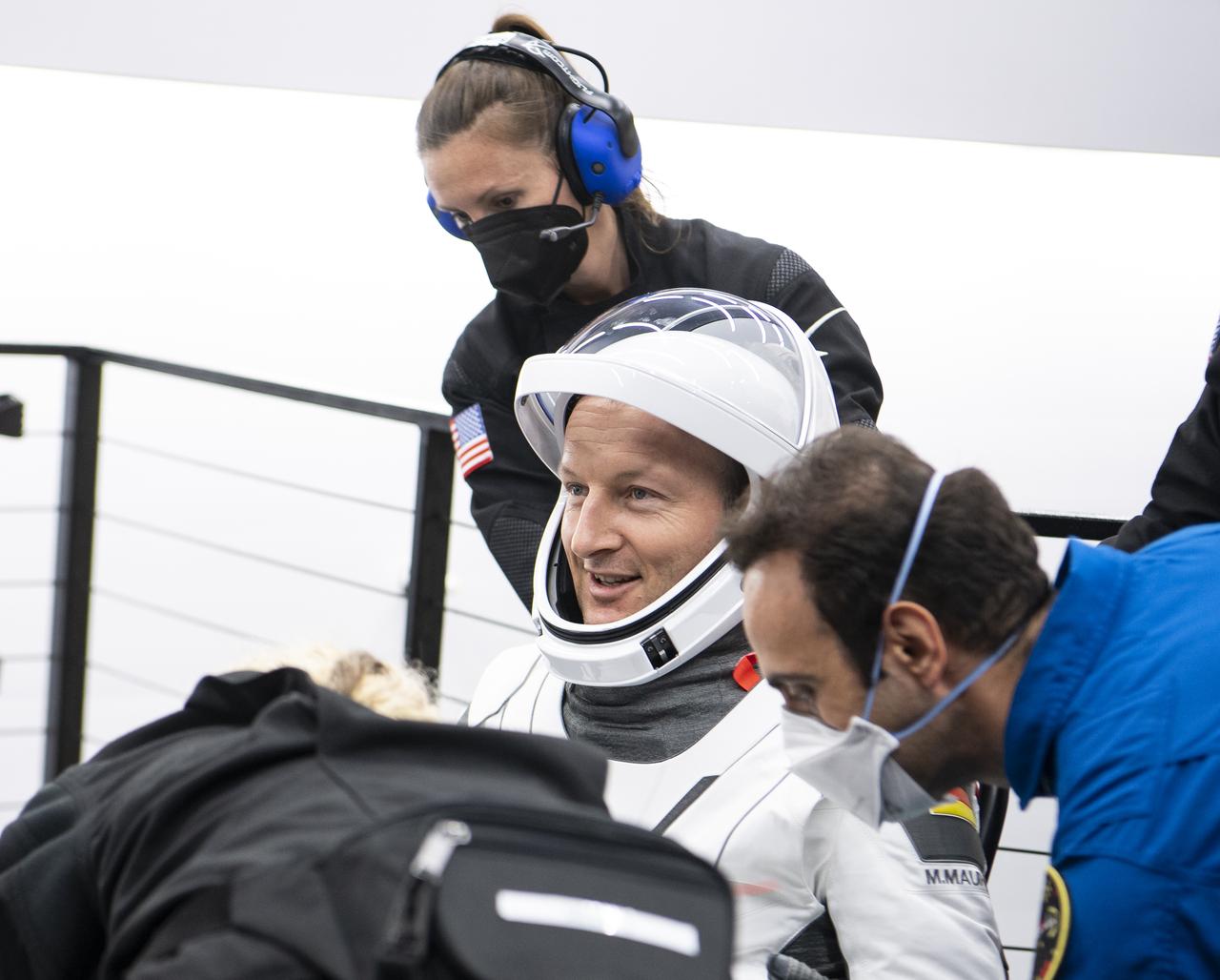

ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer is helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX Shannon recovery ship after he and NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron, and Tom Marshburn, landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
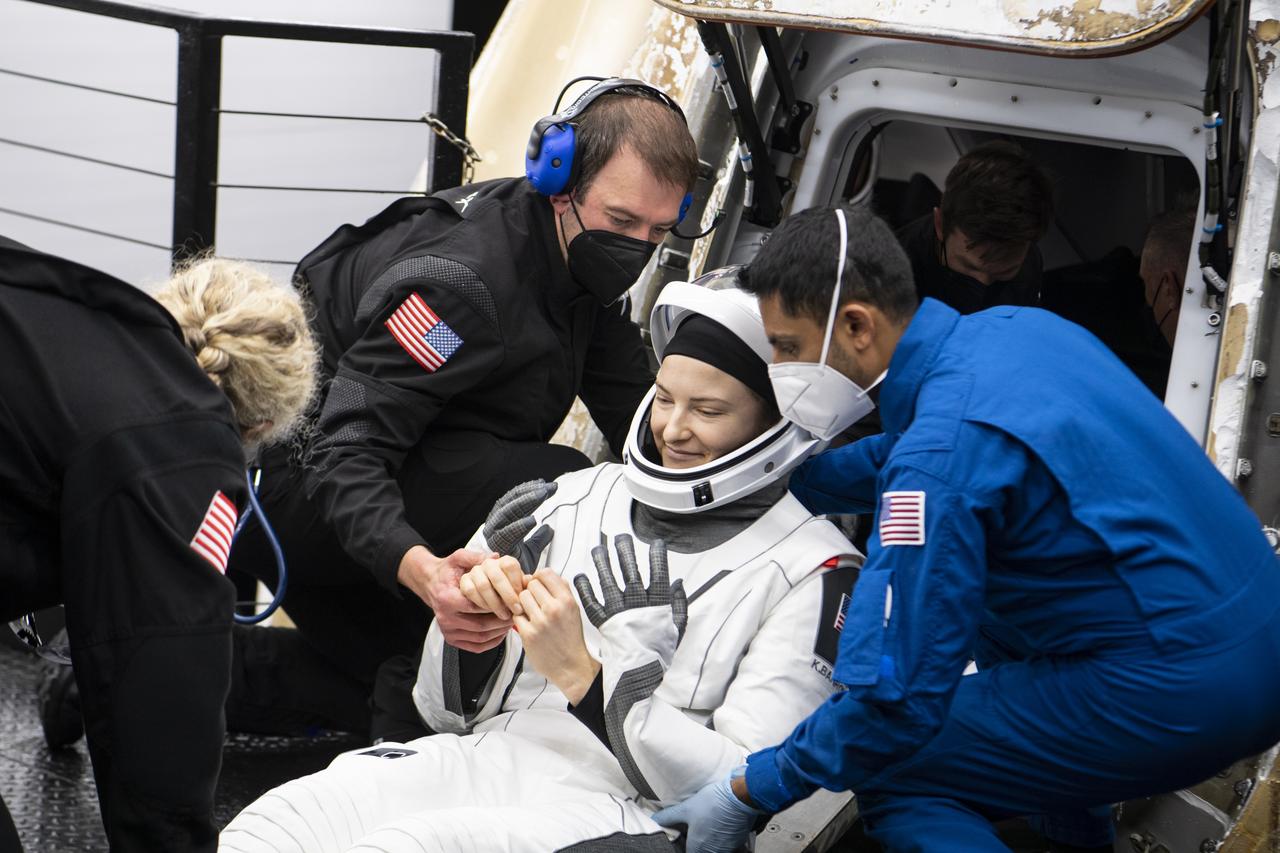

NASA astronaut Kayla Barron is helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX Shannon recovery ship after she and NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Tom Marshburn, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
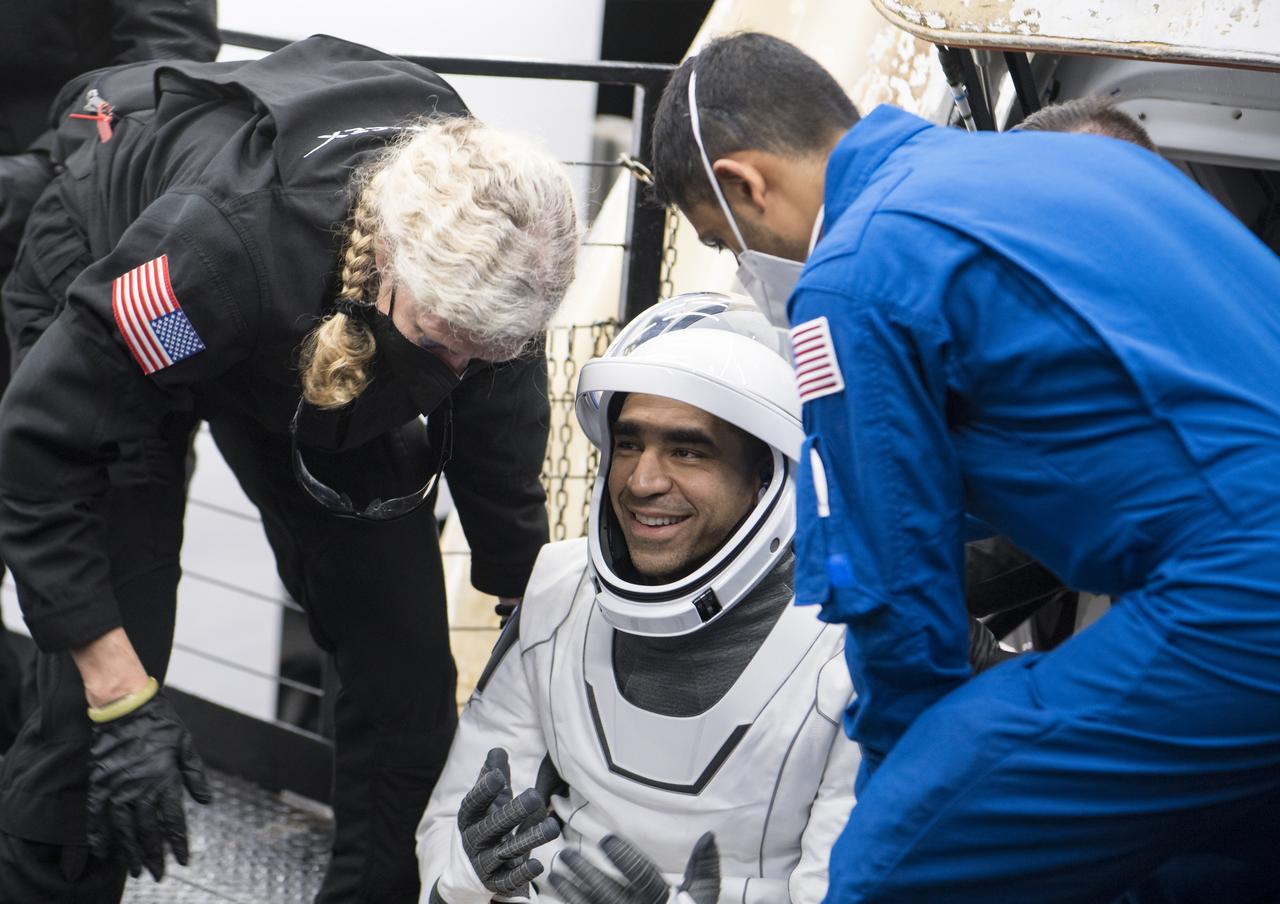

NASA astronaut Raja Chari is helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX Shannon recovery ship after he and NASA astronauts Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
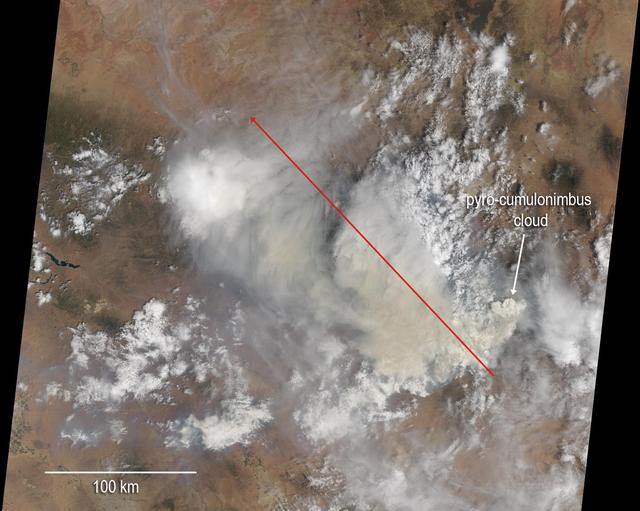
NASA Terra spacecraft passed over the Silver Fire in western New Mexico on June 7, 2013. It has since consumed more than 137,000 acres of timber in a rugged area of the Gila National Forest that has not seen large fires for nearly a century.
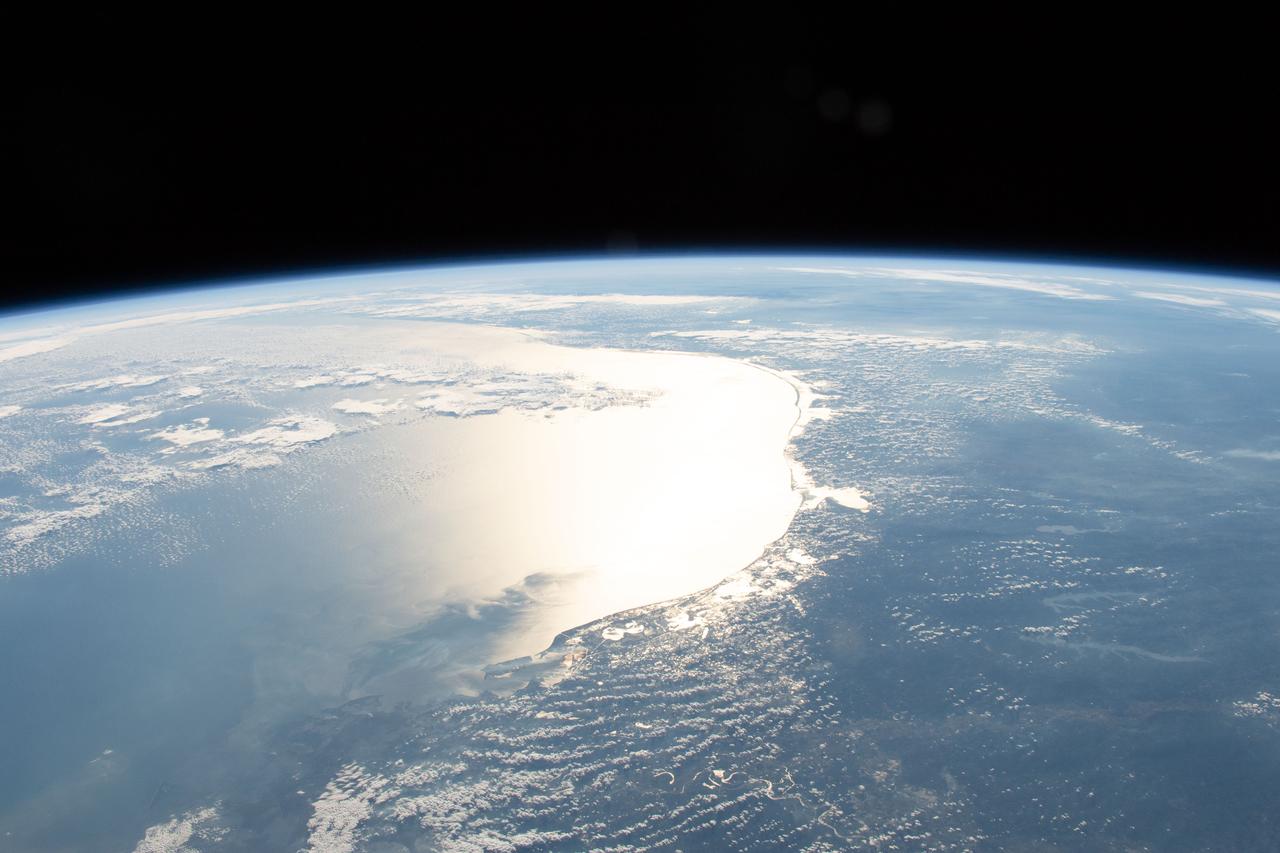

iss058e005915 (Jan. 27, 2019) --- The Sun's glint reflects off the Gulf of Mexico and outlines the coasts of Texas and Louisiana. The International Space Station was orbiting 254 miles above Louisiana when an Expedition 58 crew member photographed the Gulf coast including Matagorda Bay, Galvestion Bay and Sabine Lake.

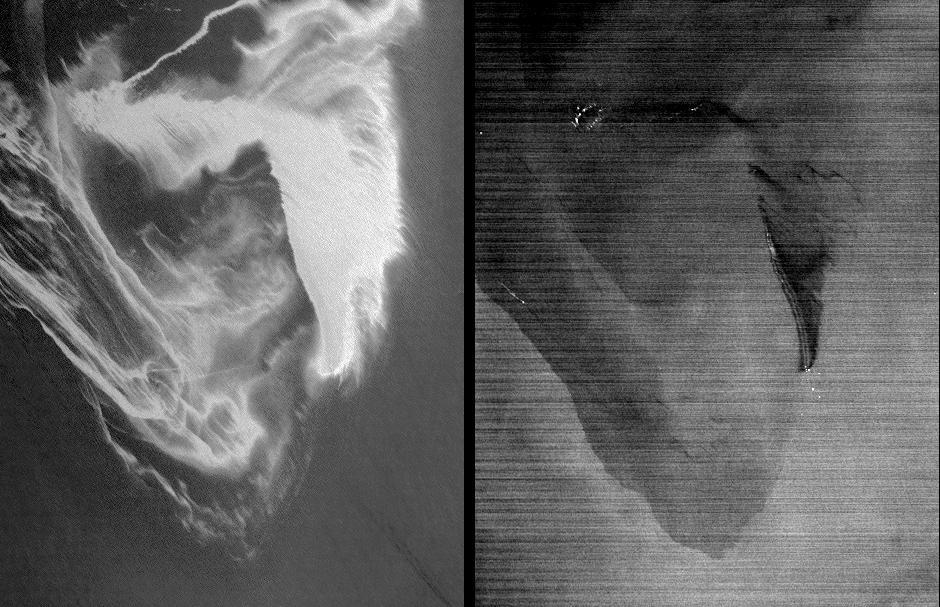
This radar image from NASA Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar UAVSAR shows the deformed Earth caused by a 7.2 earthquake in Mexico state of Baja California in 2010.
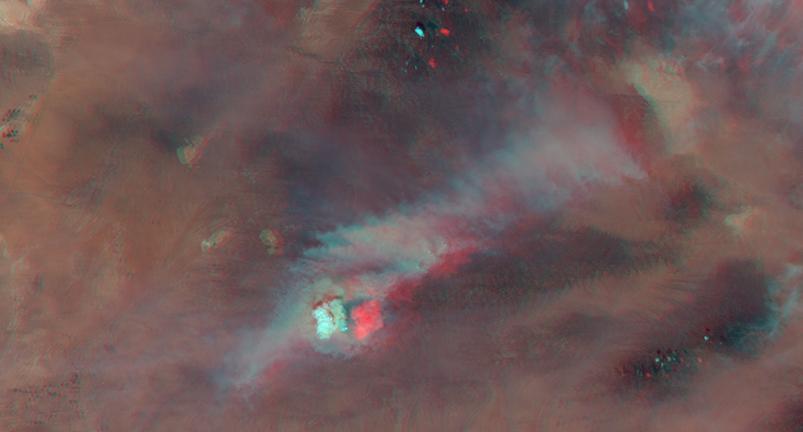

NASA Terra satellite passed over the Silver Fire in New Mexico June 12, 2013. By combining information from different MISR cameras, scientists have produced a 3D image of the smoke plume associated with the Silver Fire.

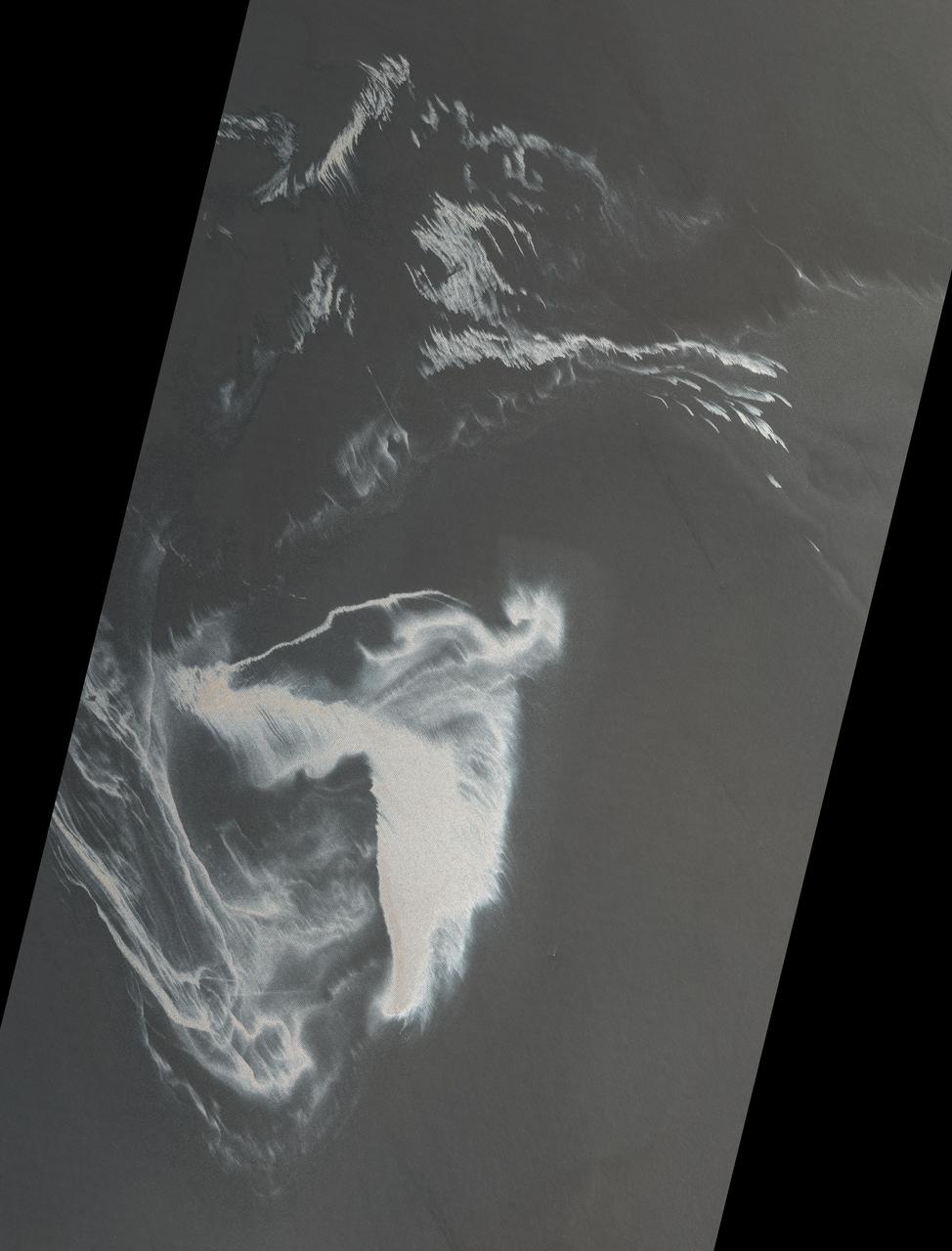
NASA Terra spacecraft captured this image of the growing oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico on May 7, 2010. The thickest parts of the oil spill appear as dark grey, filamentous masses in the southern part of the image, extending off of the bottom.
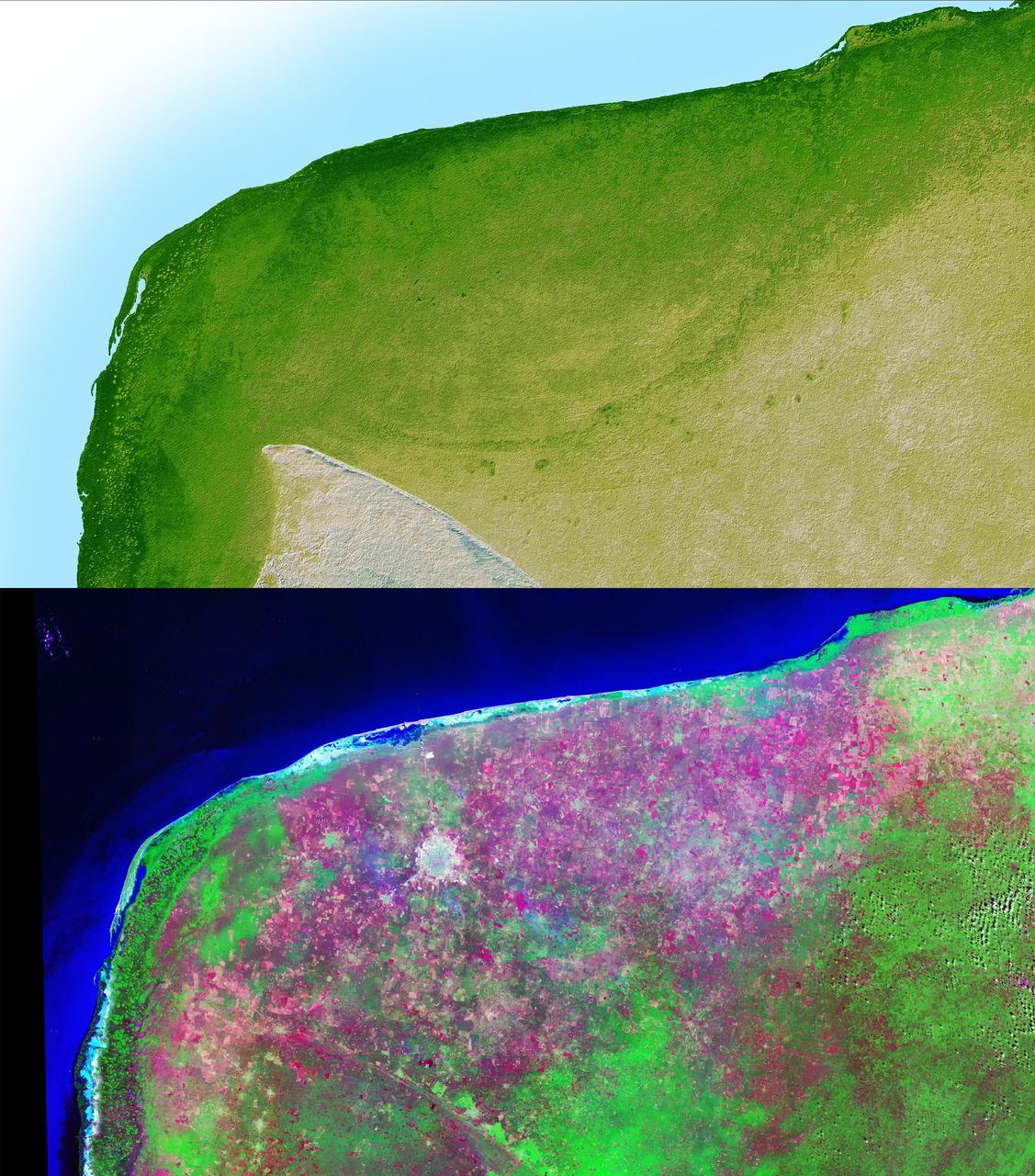
The top picture is a shaded relief image of the northwest corner of Mexico Yucatan Peninsula generated from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM data, and shows a subtle, but unmistakable, indication of the Chicxulub impact crater.
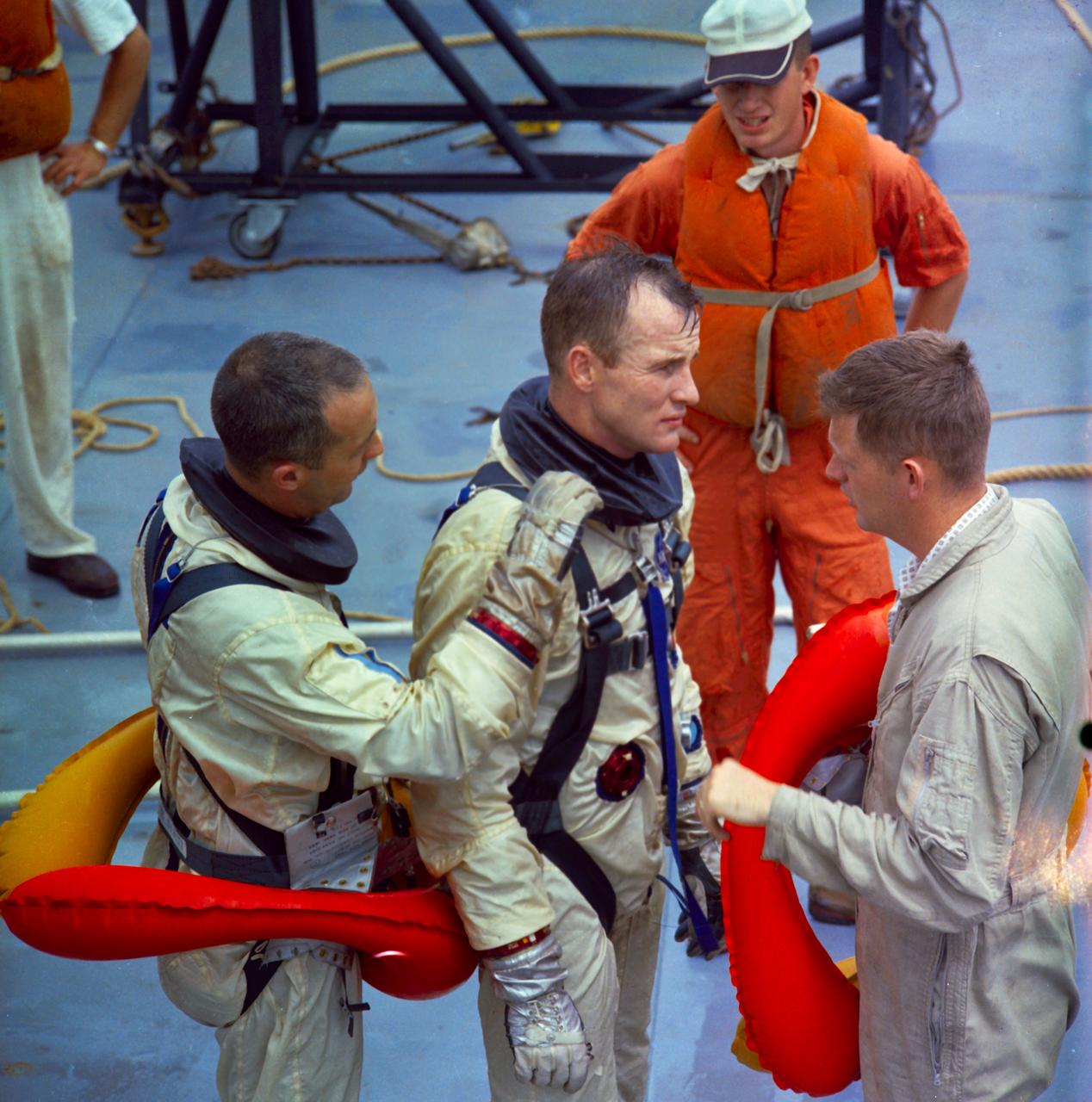

S65-22655 (14 April 1965) --- The Gemini-Titan 4 prime crew is shown aboard the NASA Motor Vessel Retriever in the Gulf of Mexico suiting up for water egress training. Astronaut James A. McDivitt (left) is the command pilot, and astronaut Edward H. White II is the pilot.
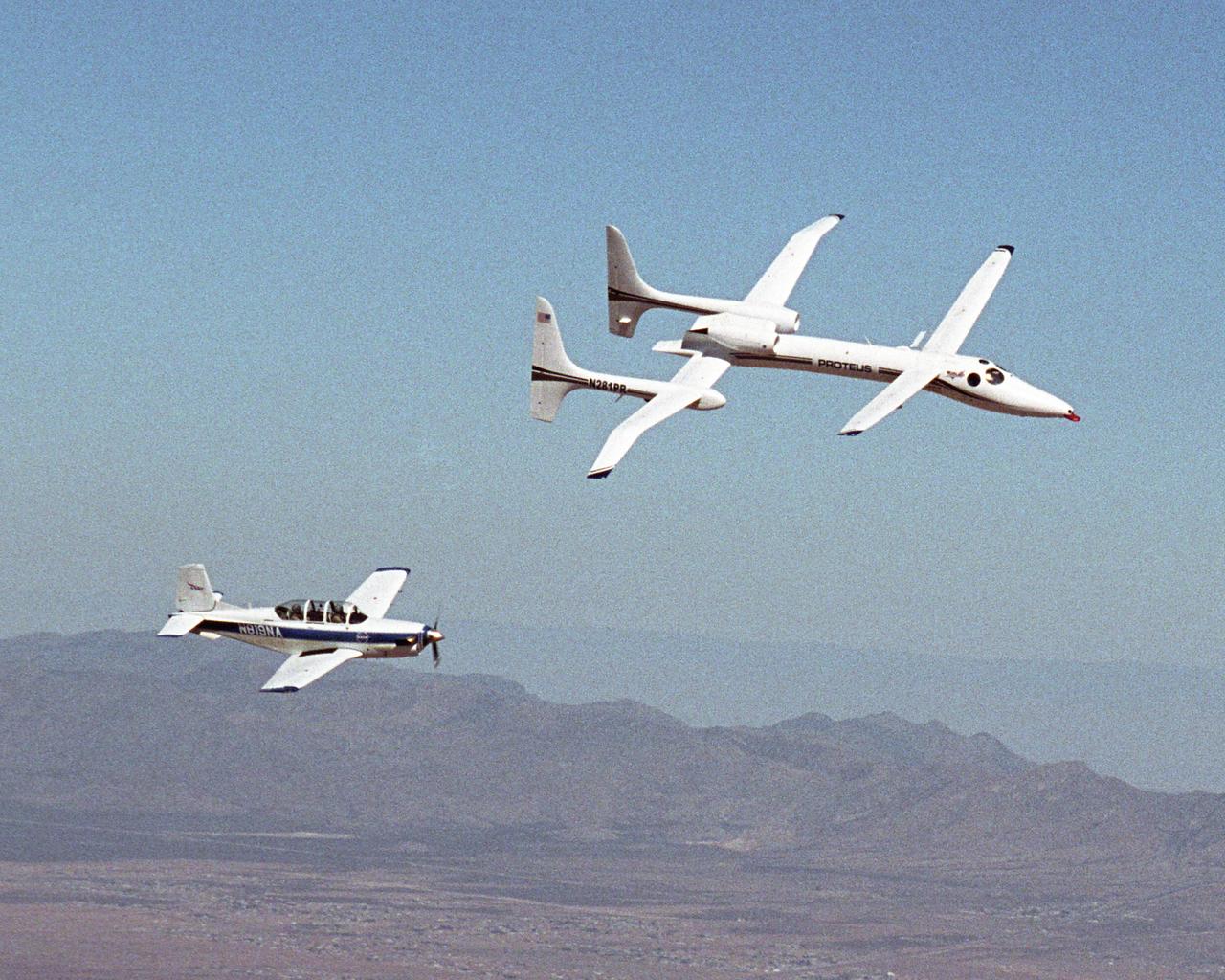

The Proteus aircraft and NASA Dryden's T-34 in flight over Las Cruces, New Mexico.

Dr. Lee Silver (pointing foregroung), California Institute of Technology, calls a geological feature near Taos, New Mexico, to the attention of Apollo 16 prime and backup crewmen during a geological field trip. The crewmen, from left to right, are Astronauts Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; Fred W. Haise Jr., backup commander; Edgar D. Mitchell, backup Lunar Module pilot; and John W. Young, commander.

The Naica mine in Chihuahua, Mexico, with its enormous gypsum crystals, may well be called the "Queen of the Giant Crystals localities." Though the Naica mine is no show mine, but still a working lead-zinc mine hosted in layered limestones, the first of several crystal caves was discovered in 1910. This "Cave of the Swords" contained extraordinary large sword-like selenite (gypsum) crystals up to 2 m long. In 2000 another crystal cave system was discovered at 300 m depth, even more spectacular than the original cave. Inside were free growing gypsum crystals up to 12 m long and 2 m in diameter. The ASTER image uses SWIR bands 4, 6, and 8 in RGB. Limestone is displayed in yellow-green colors, vegetation is red. The image was acquired February 16, 2004, covers an area of 26 x 23.5 km, and is located near 27.8 degrees north latitude, 105.5 degrees west longitude. The photo of crystals was taken from: http://www.thatcrystalsite.com/. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10615
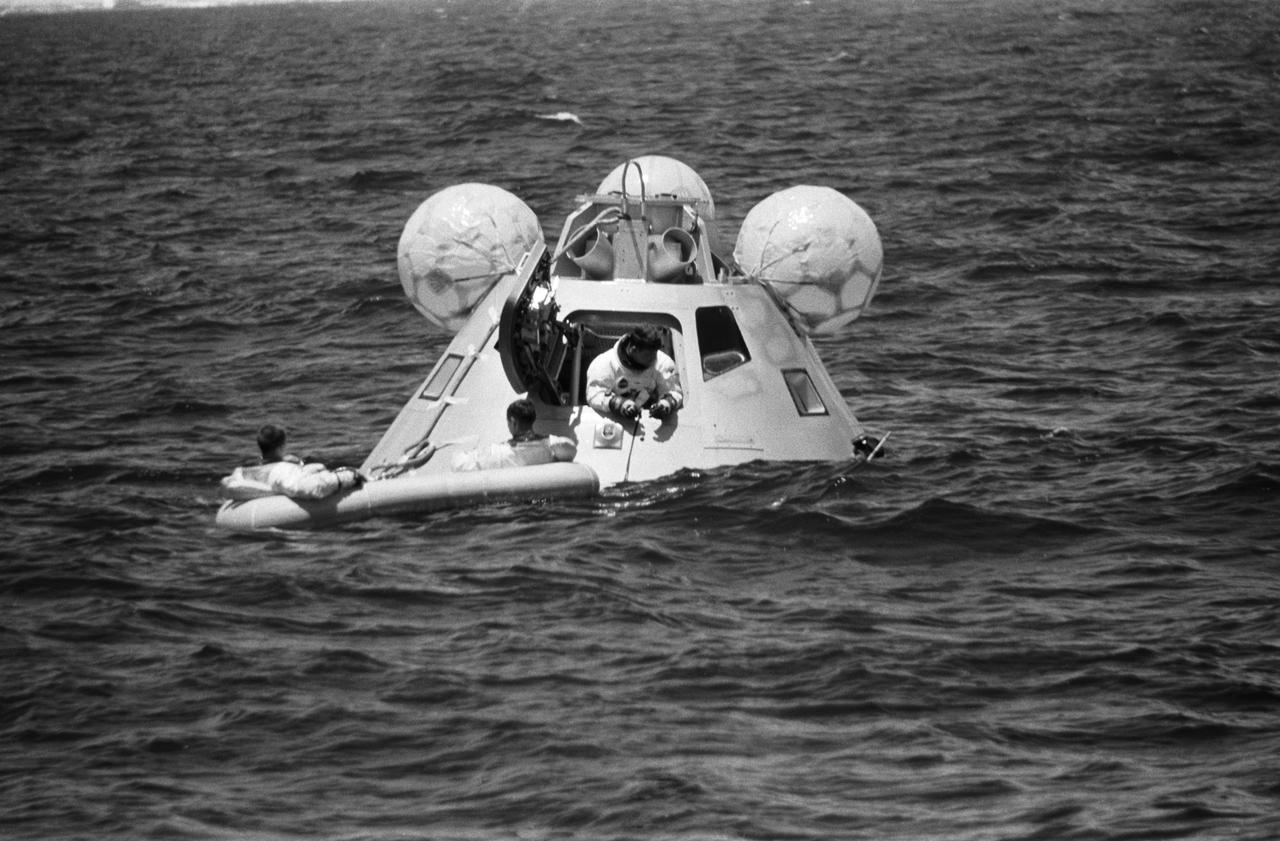

S68-42197 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo space mission, Apollo 7, participates in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. In hatch of the Apollo egress trainer (command module) is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. Sitting in life raft are astronauts Walter Cunningham (on left) and Donn F. Eisele. A team of MSC swimmers assisted with the training exercise. The inflated bags were used to upright the trainer prior to egress.
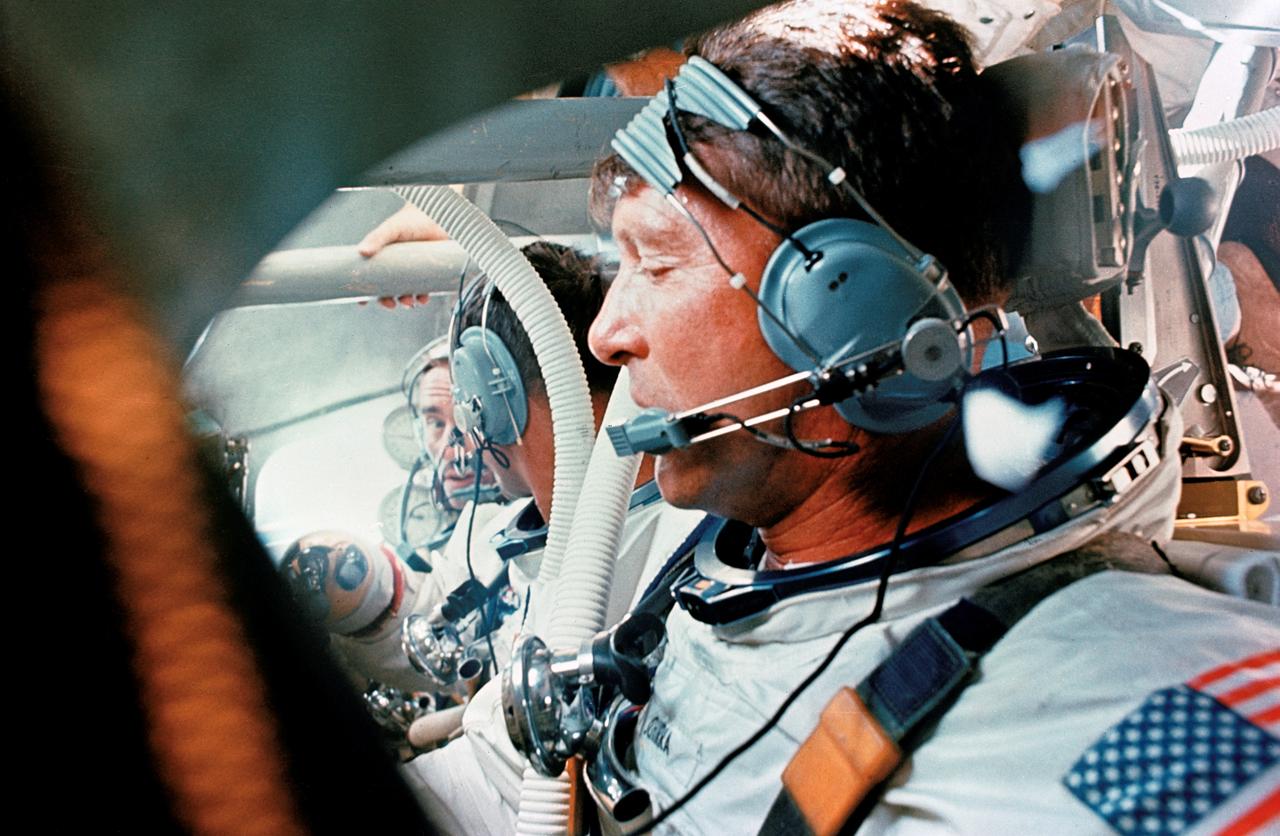

S68-46604 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo mission (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) is seen in Apollo Command Module Boilerplate 1102 during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. In foreground is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr., in center is astronaut Donn F. Eisele, and in background is astronaut Walter Cunningham.
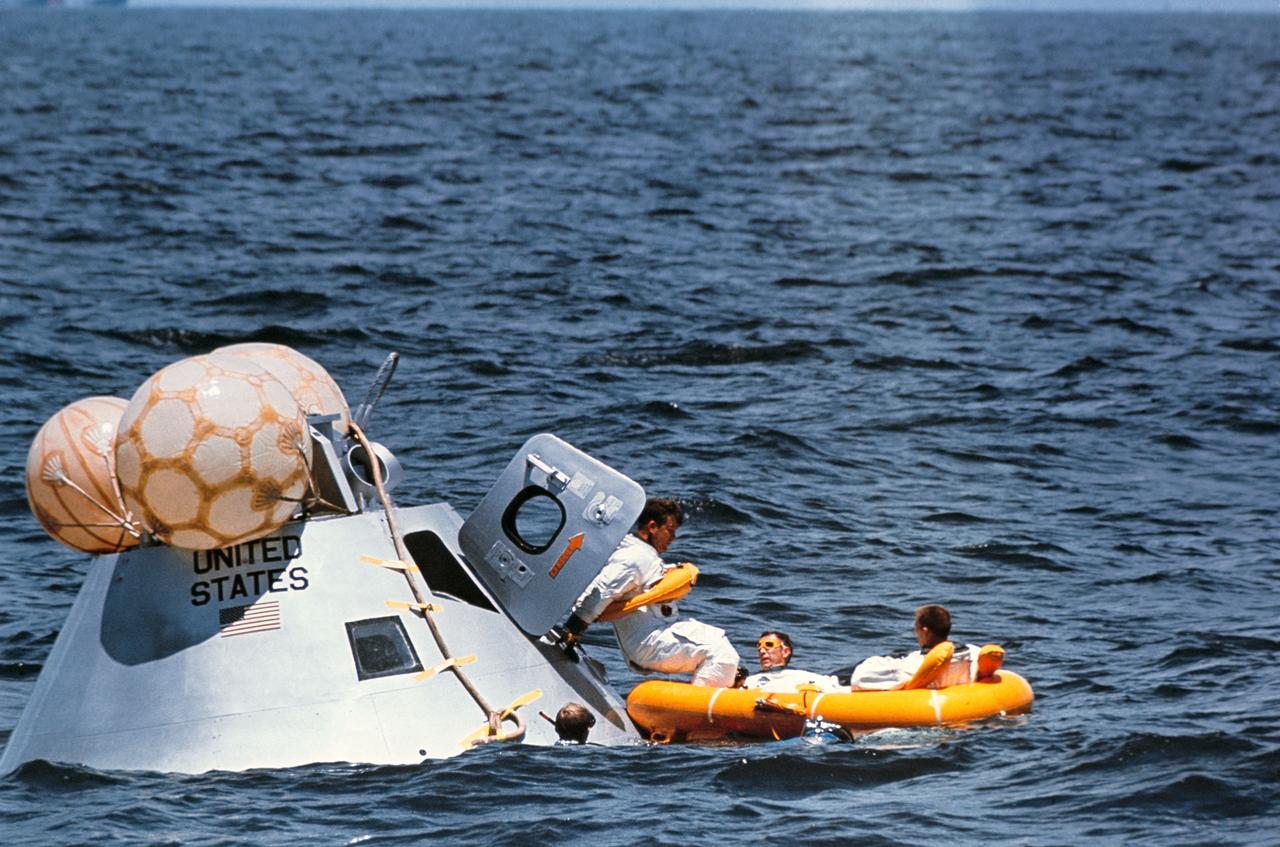

S68-46605 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo mission (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) participates in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Left to right, are astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr. (stepping into life raft), Donn F. Eisele, and Walter Cunningham. They have just egressed Apollo Command Module Boilerplate 1102, and are awaiting helicopter pickup. Inflated bags were used to upright the boilerplate. MSC swimmers assisted in the training exercise.
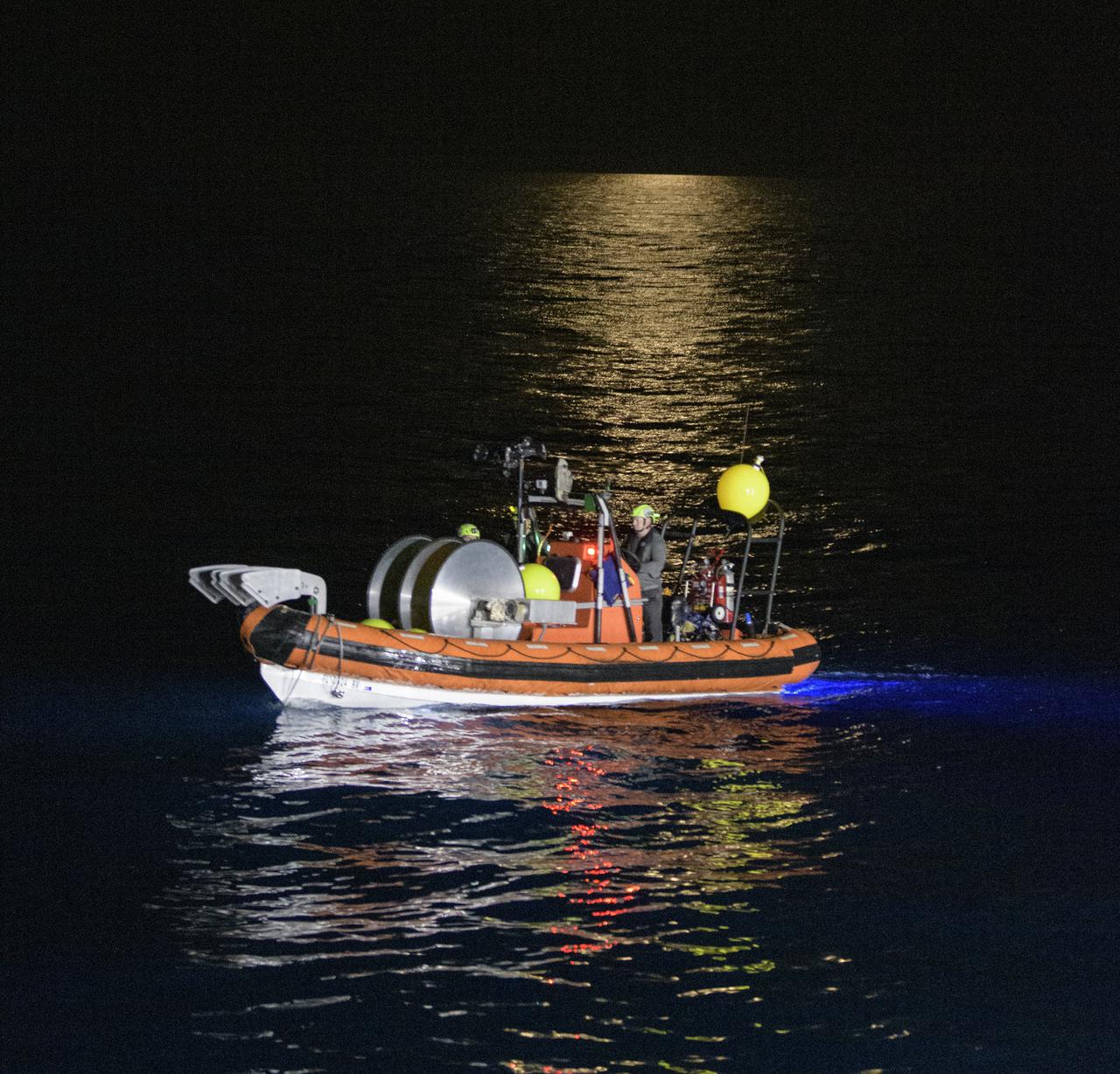

SpaceX support teams deploy in fast boats off the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship as they prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Sunday, May 2, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
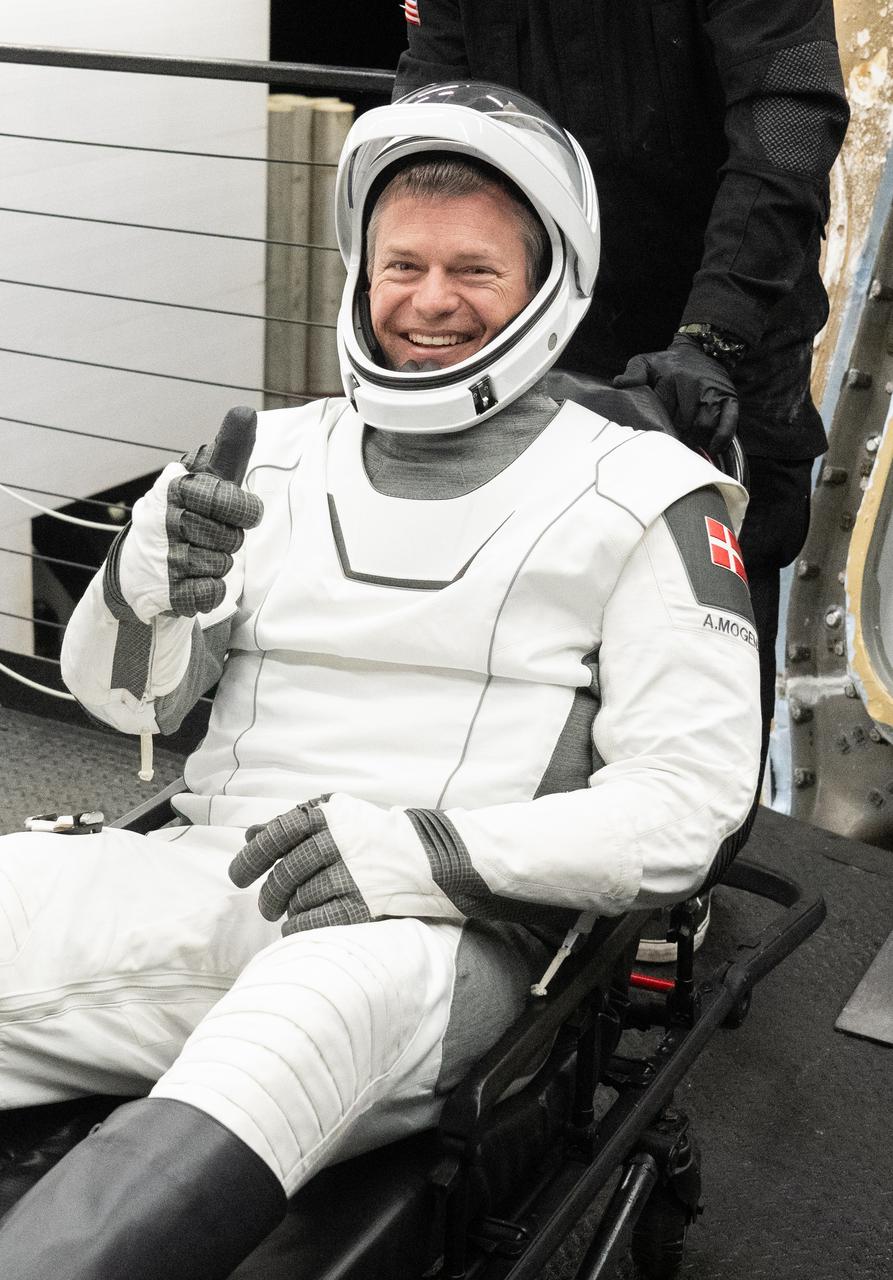

ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen is helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after he, NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Satoshi Furukawa, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Tuesday, March 12, 2024. Moghbeli, Mogensen, Furukawa, and Borisov are returning after nearly six-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
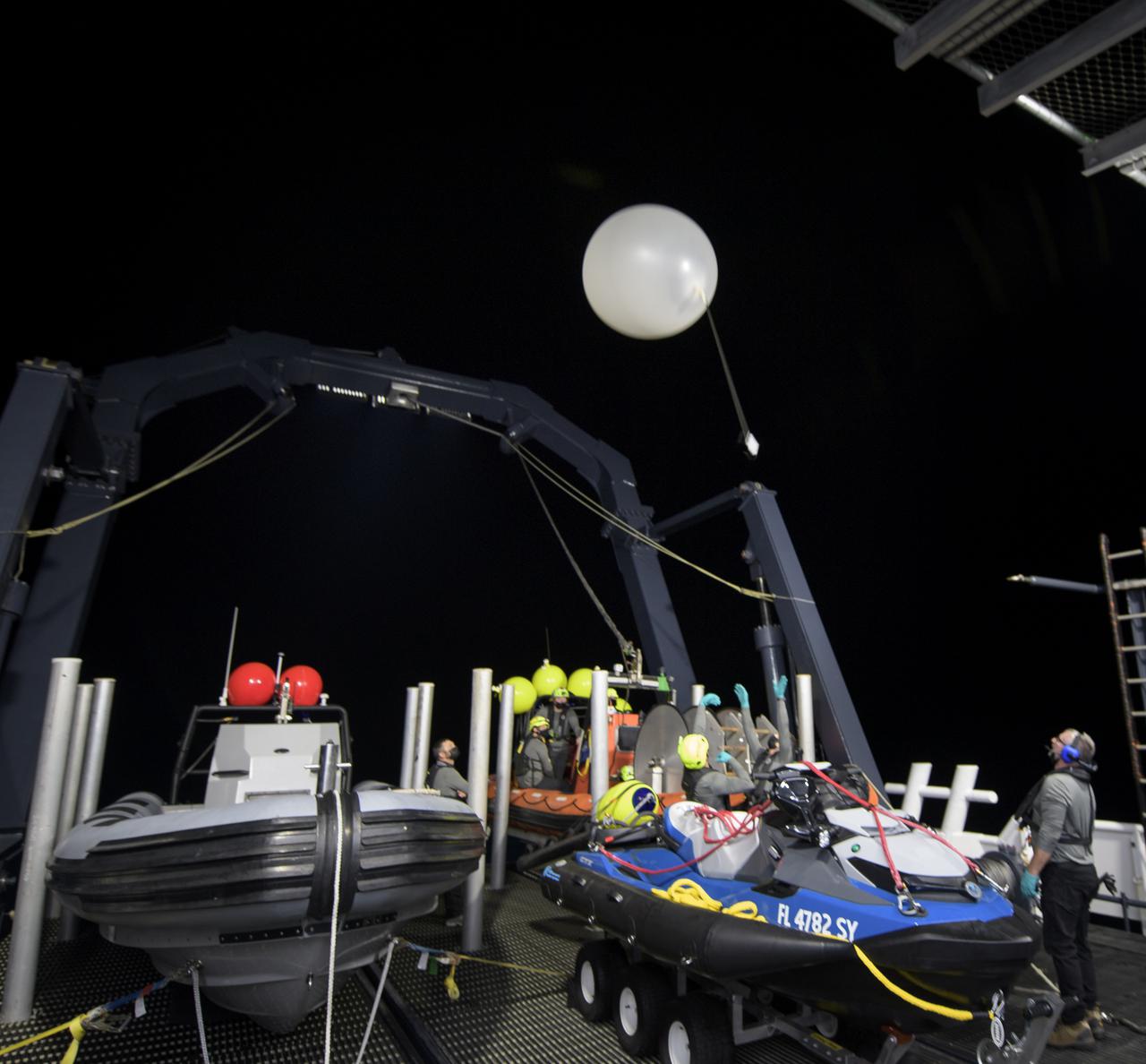

SpaceX support teams onboard the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery launch a weather balloon ahead of the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
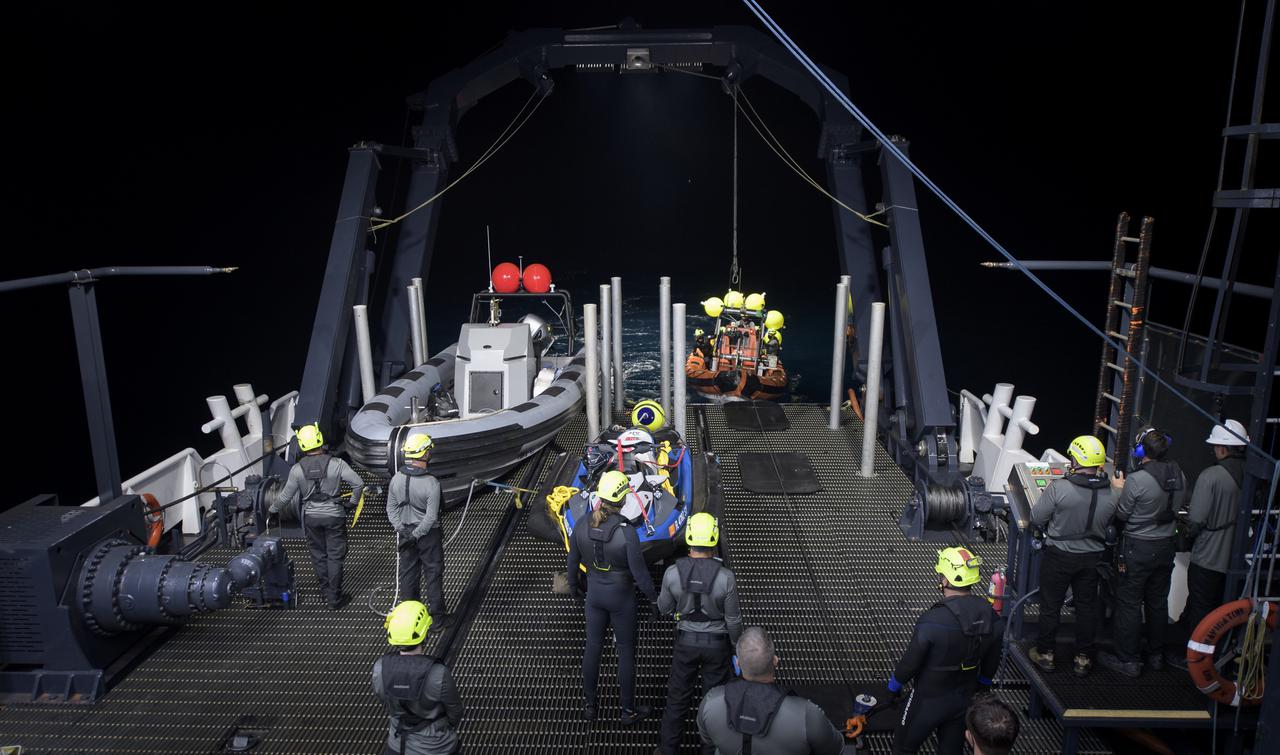

NASA and SpaceX support teams onboard the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
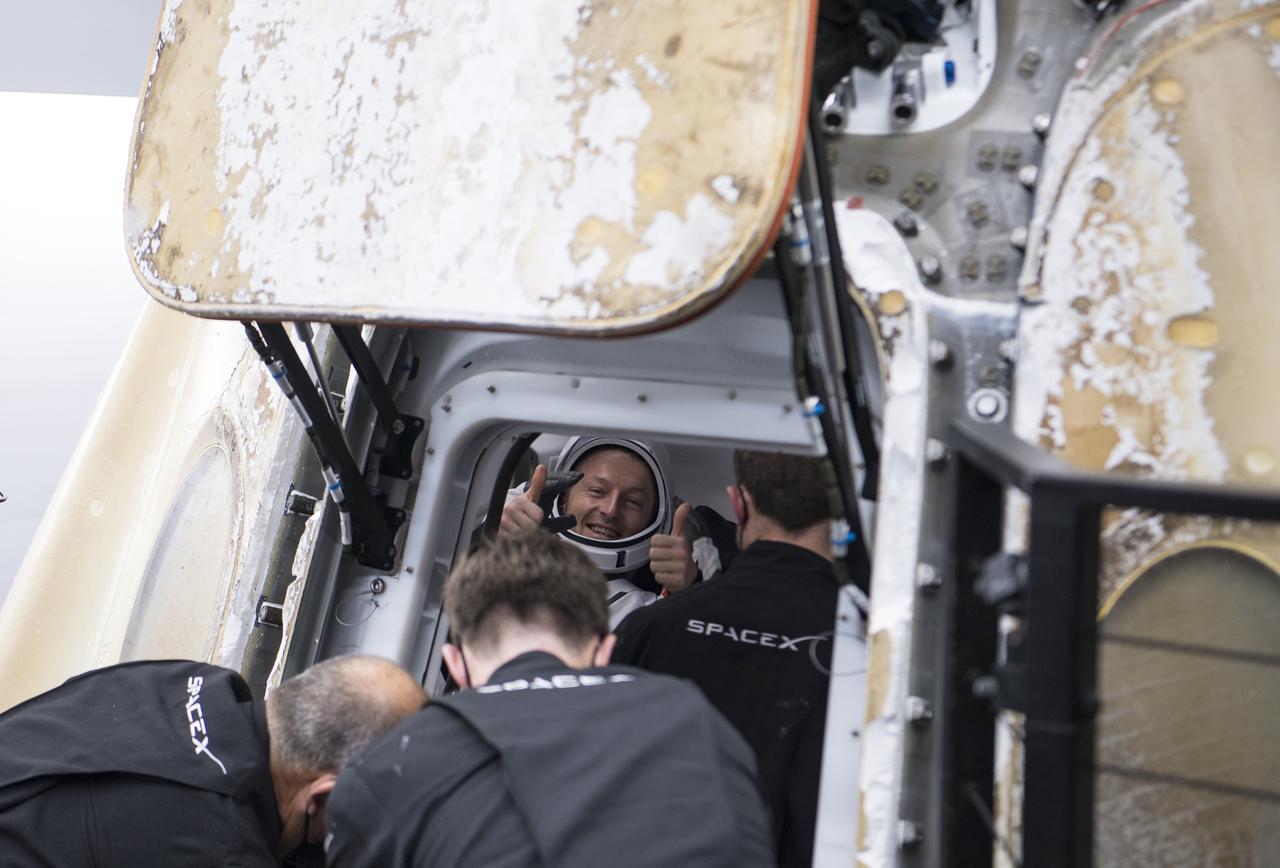

ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer gives a thumbs as he waits to be helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX Shannon recovery ship after he and NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The night sky off the bow of the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship is seen in this one second exposure photograph as NASA and SpaceX support teams prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
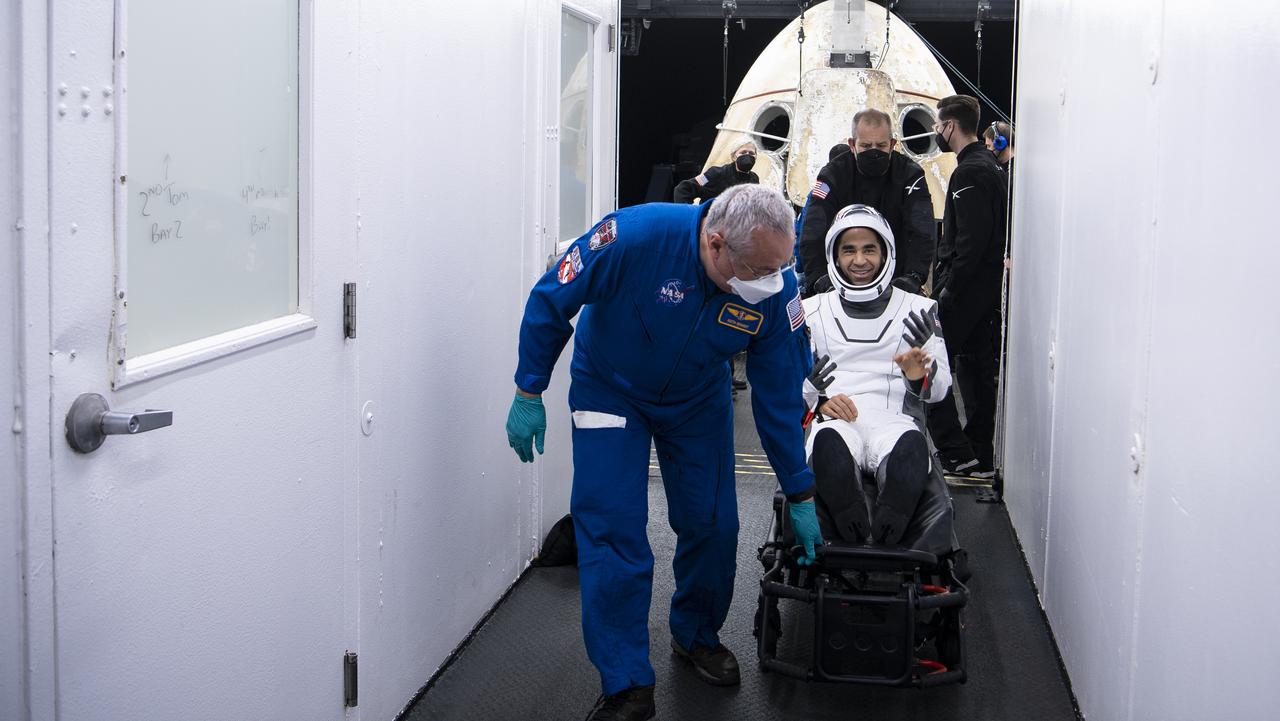

NASA astronaut Raja Chari greets friends after being helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX Shannon recovery ship after he and NASA astronauts Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
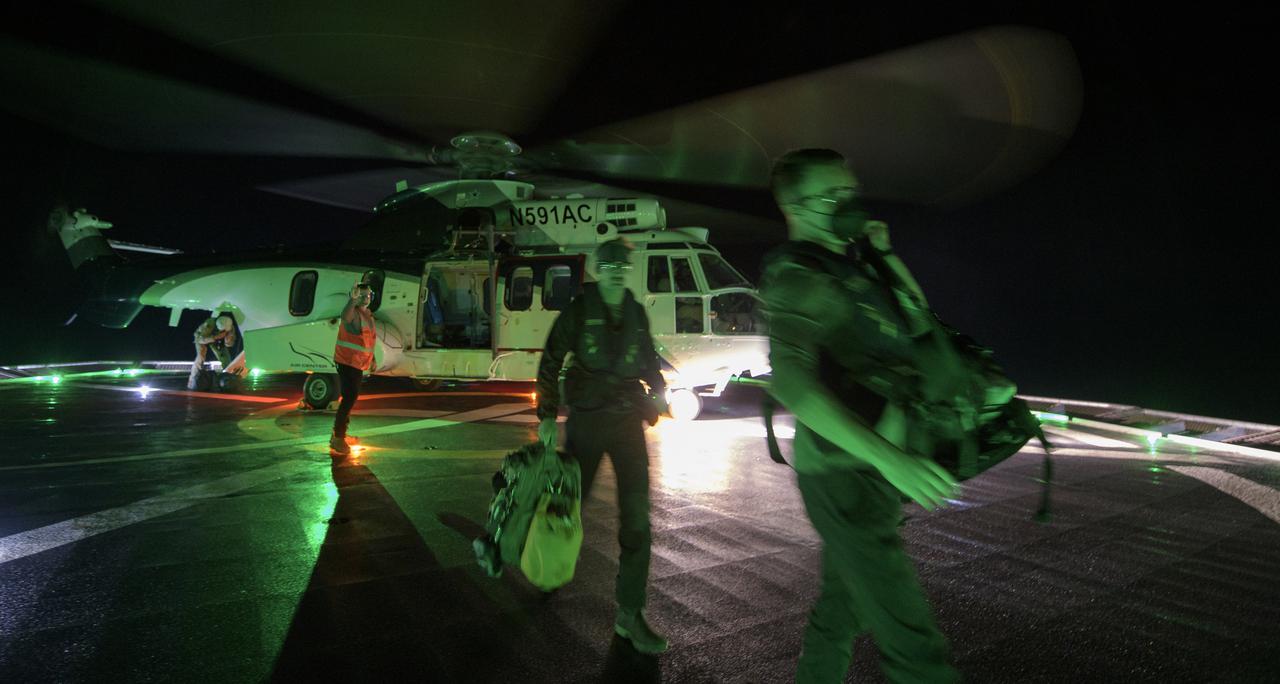

NASA and SpaceX support teams arrive via helicopter to the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship in order to prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour spacecraft is seen as it lands with NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Megan McArthur, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Aki Hoshide, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Thomas Pesquet aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Monday, Nov. 8, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-2 mission is the second operational mission of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
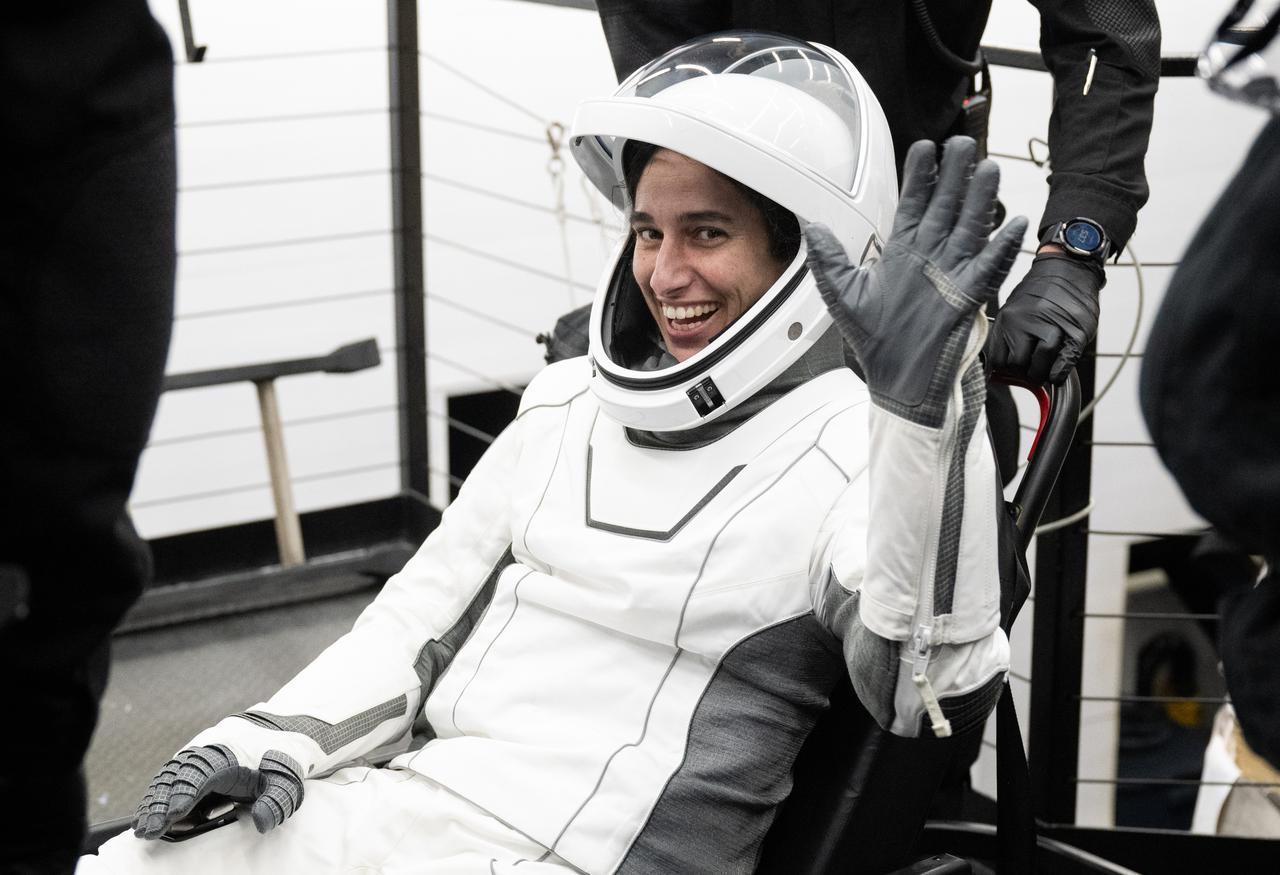

NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after she, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Tuesday, March 12, 2024. Moghbeli, Mogensen, Furukawa, and Borisov are returning after nearly six-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
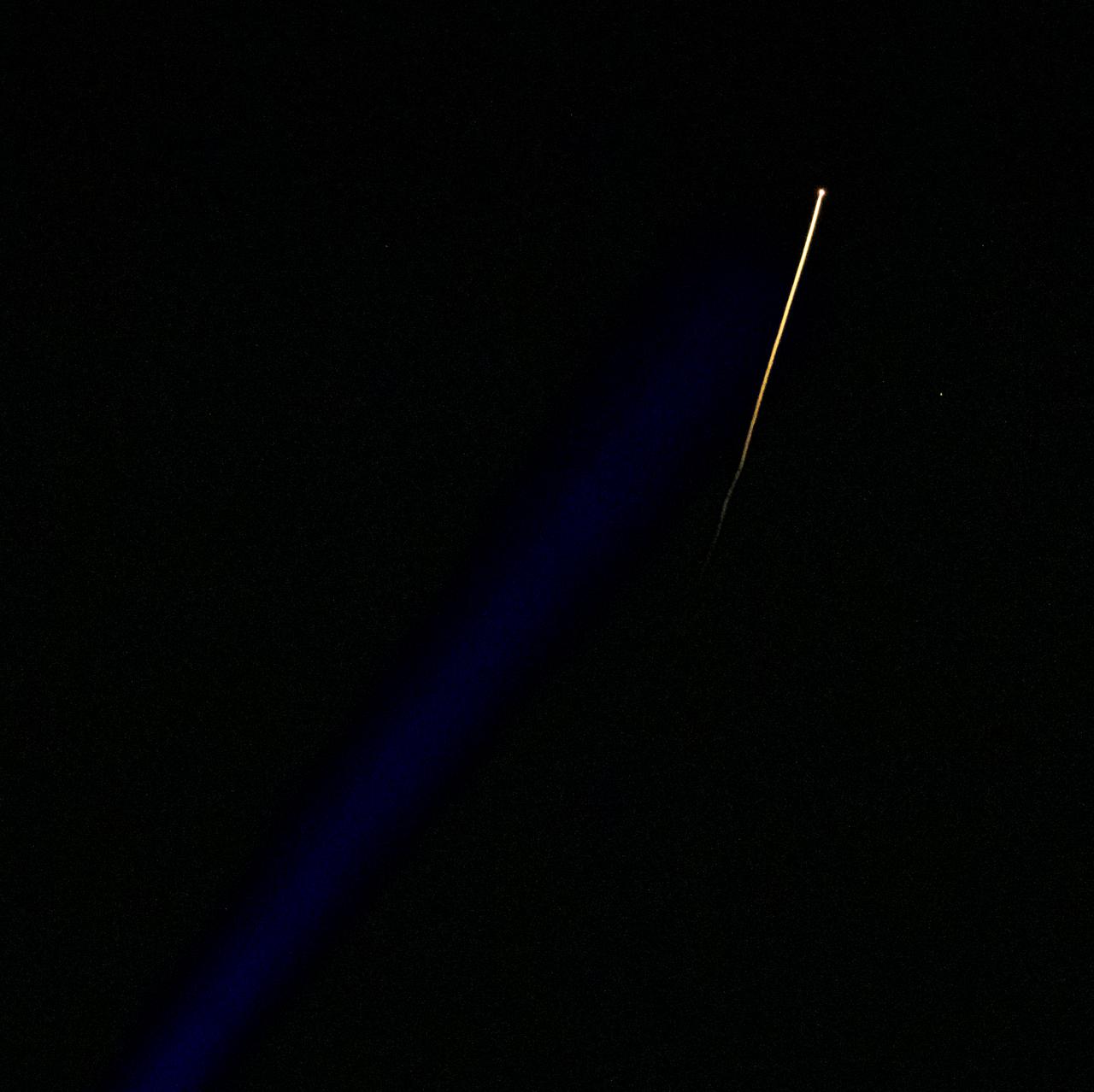

The SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour spacecraft is seen as it lands with NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Megan McArthur, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Aki Hoshide, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Thomas Pesquet aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Monday, Nov. 8, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-2 mission is the second operational mission of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
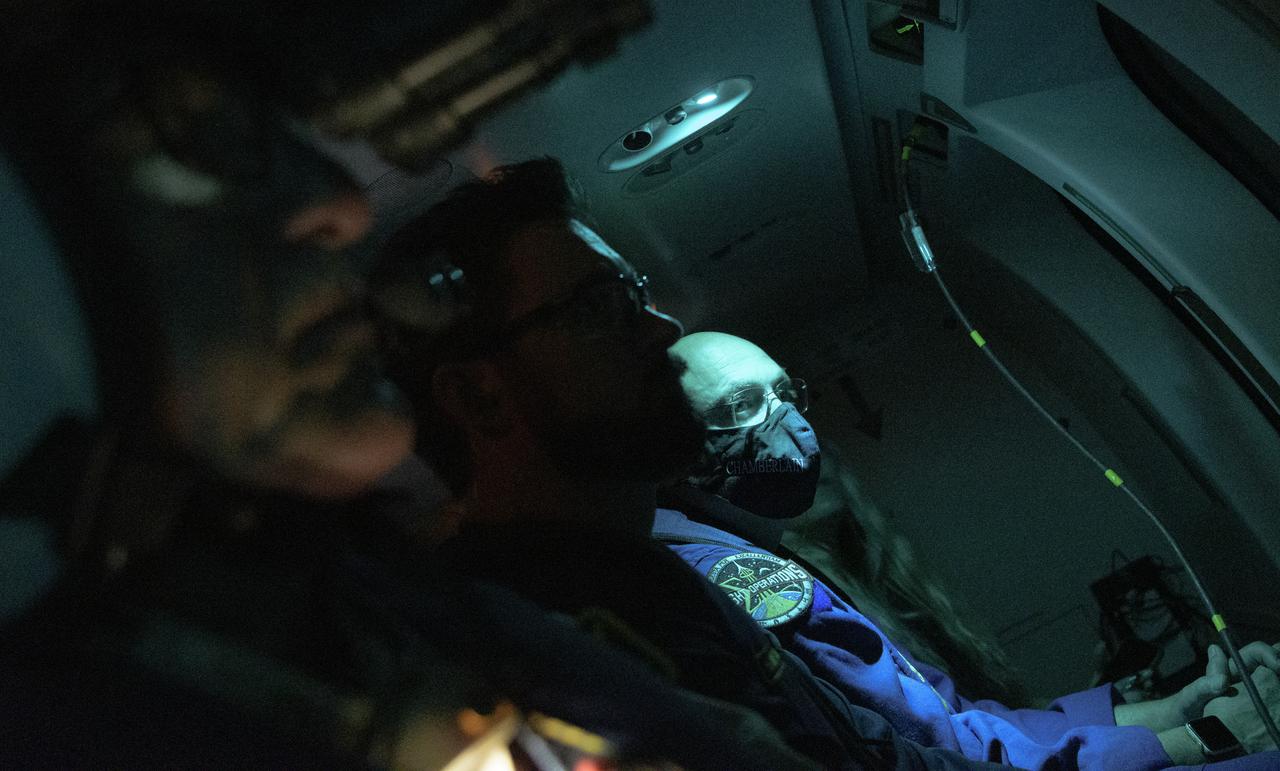

NASA Flight Surgeon Blake Chamberlain and other NASA and SpaceX support teams helicopter out to the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship to prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
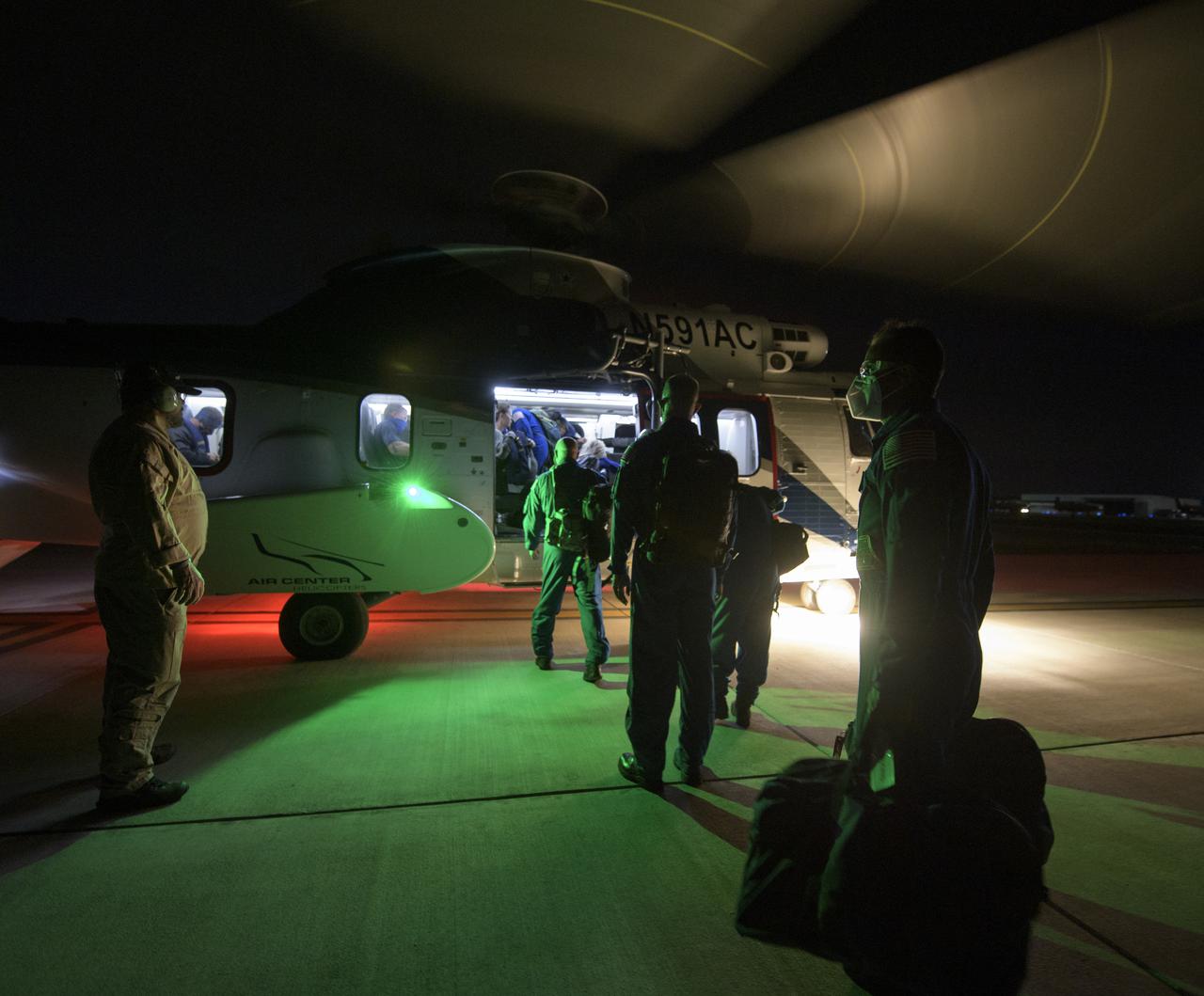

NASA and SpaceX support teams depart from Pensacola, Florida via helicopter to the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship to prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
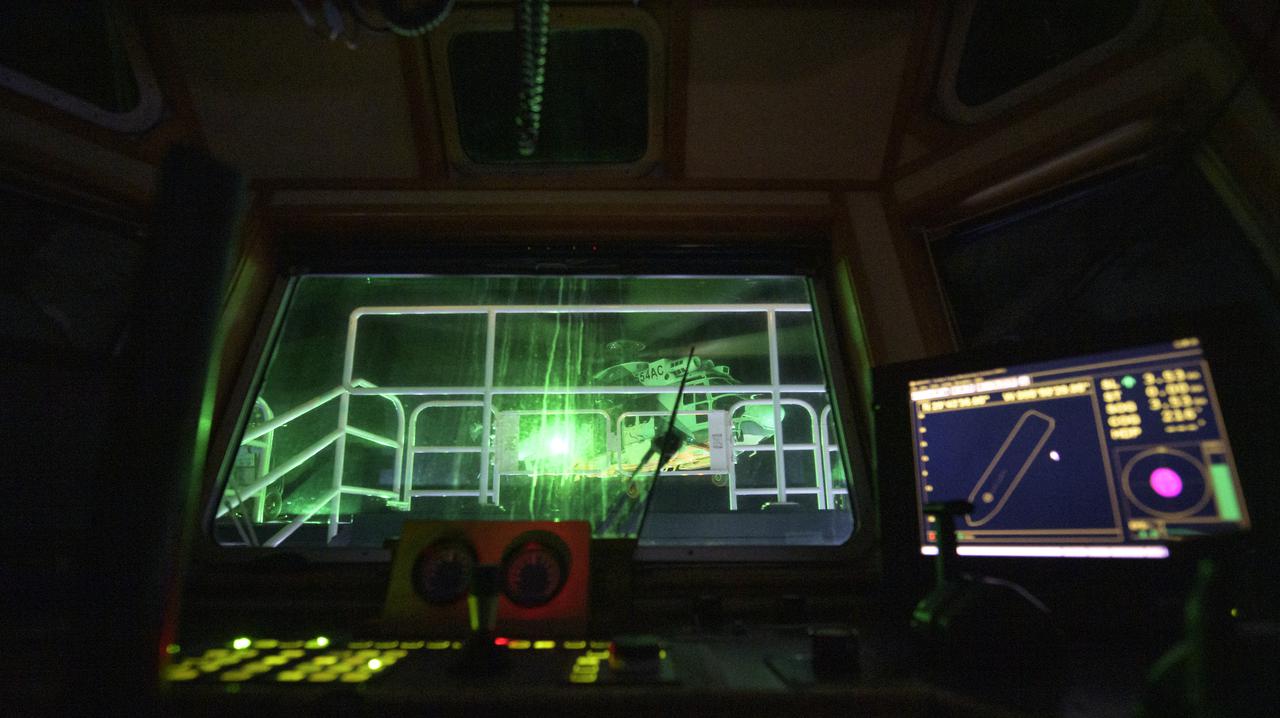

NASA and SpaceX support teams arrive via helicopter to the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship in order to prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
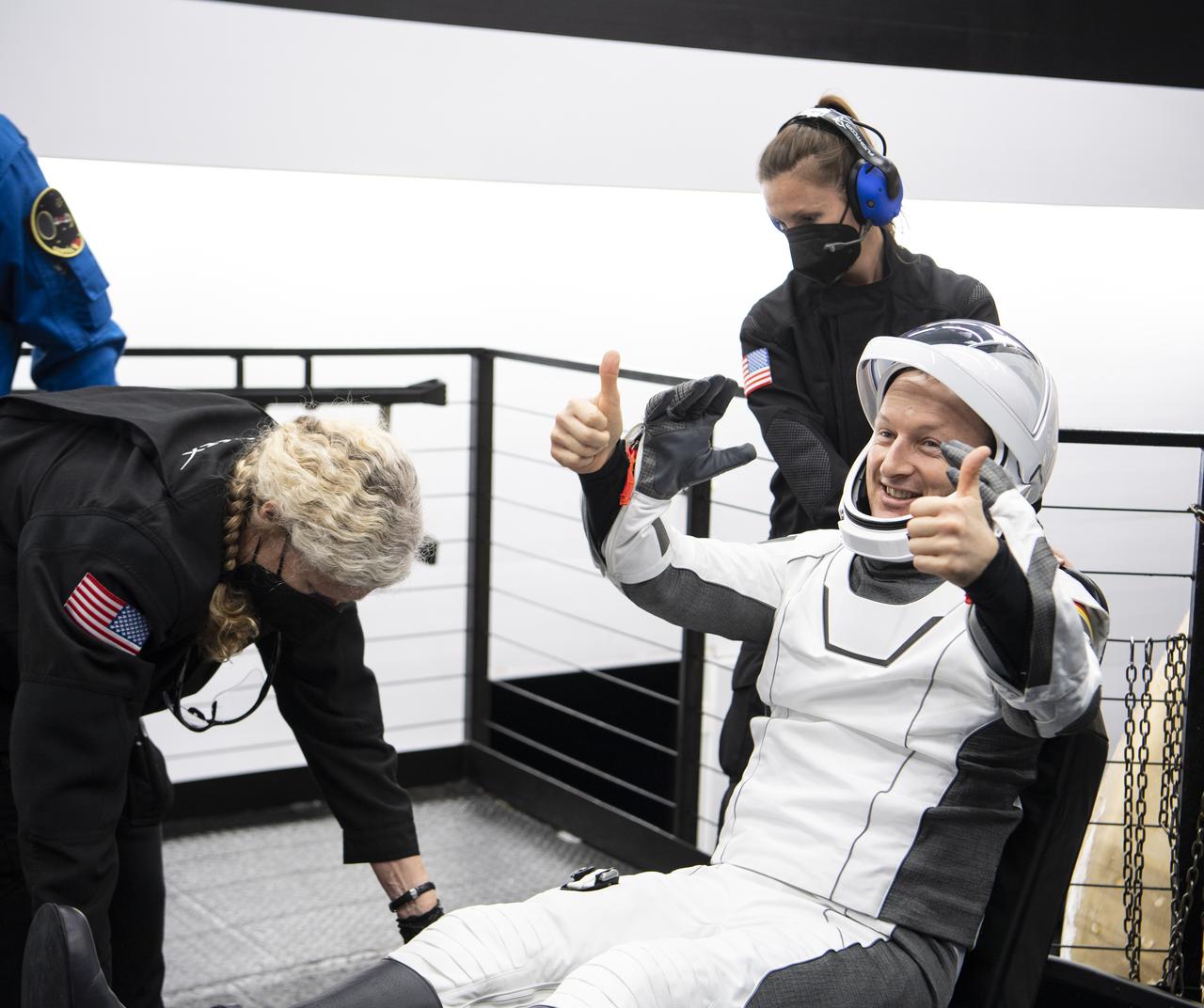

ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer gives a thumbs up after being helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX Shannon recovery ship after he and NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA astronaut Raja Chari greets friends after being helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX Shannon recovery ship after he and NASA astronauts Kayla Barron, Tom Marshburn, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Tampa, Florida, Friday, May 6, 2022. Maurer, Marshburn, Chari, and Barron are returning after 177 days in space as part of Expeditions 66 and 67 onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
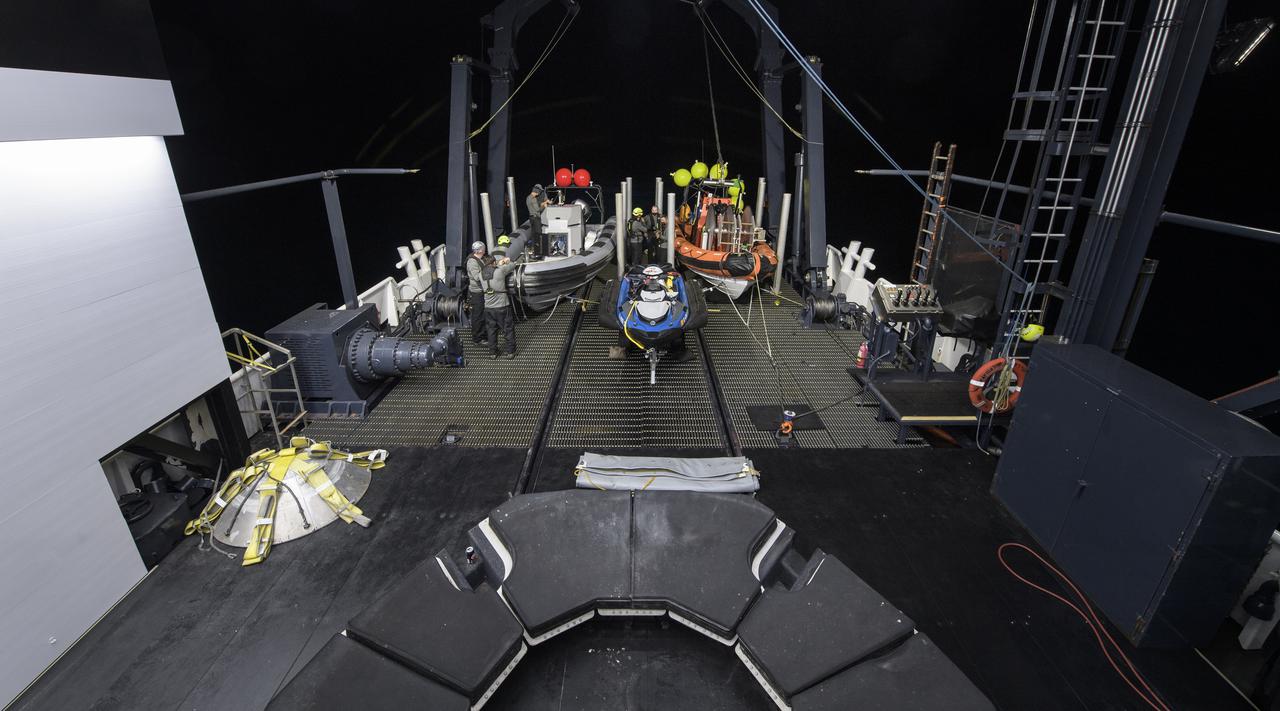

NASA and SpaceX support teams onboard the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship prepare for the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

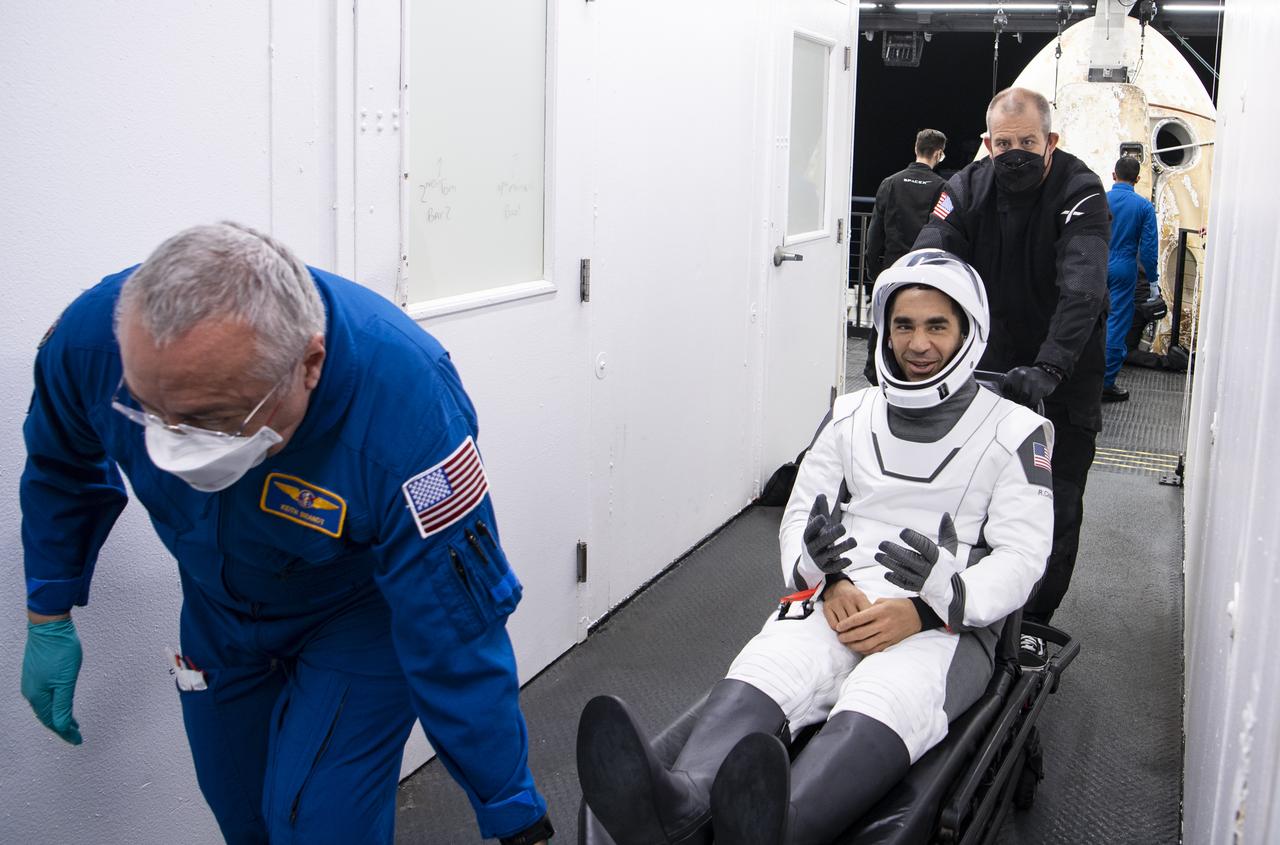
Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov is seen inside an elevator on the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN that will take him up to a waiting helicopter to fly to Pensacola, Florida along with NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa a few hours after they landed in the SpaceX Dragon Endurance spacecraft in the Gulf of Mexico of the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Tuesday, March 12, 2024. Moghbeli, Mogensen, Furukawa, and Borisov are returning after nearly six-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
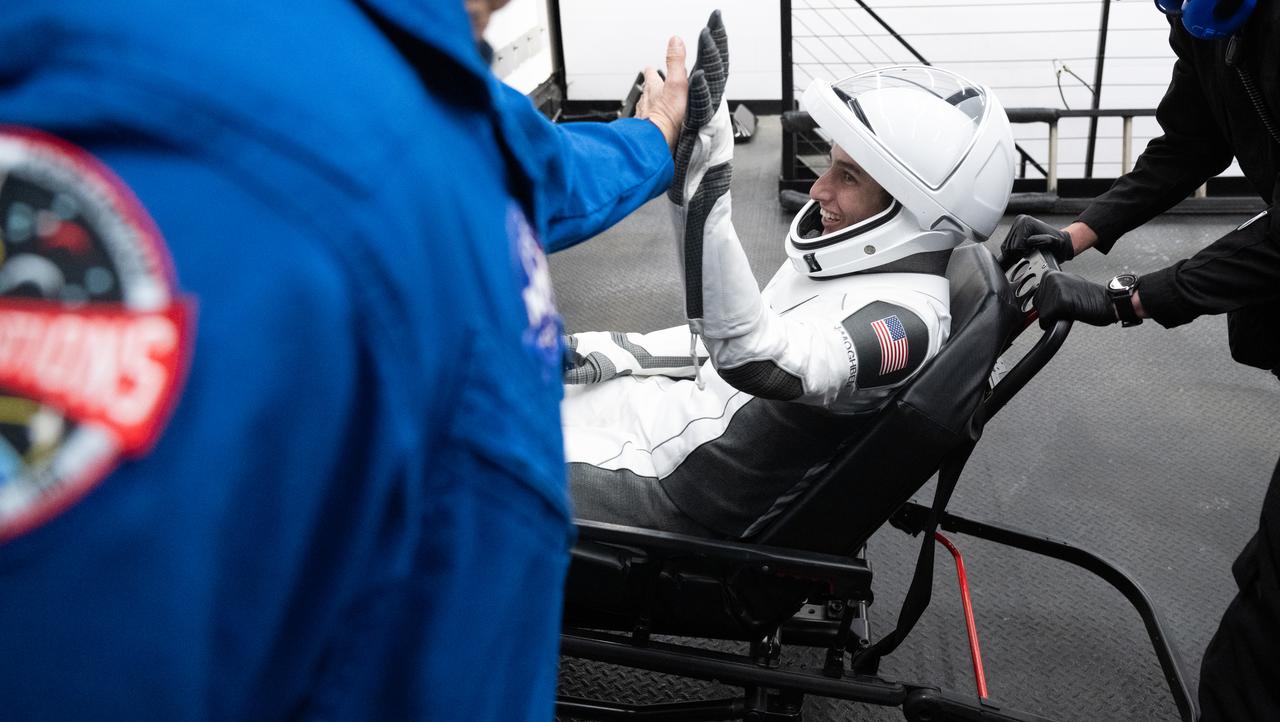

NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli high fives NASA astronaut Eric Boe, Crew Recovery Coordinator, after being helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after she, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Tuesday, March 12, 2024. Moghbeli, Mogensen, Furukawa, and Borisov are returning after nearly six-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
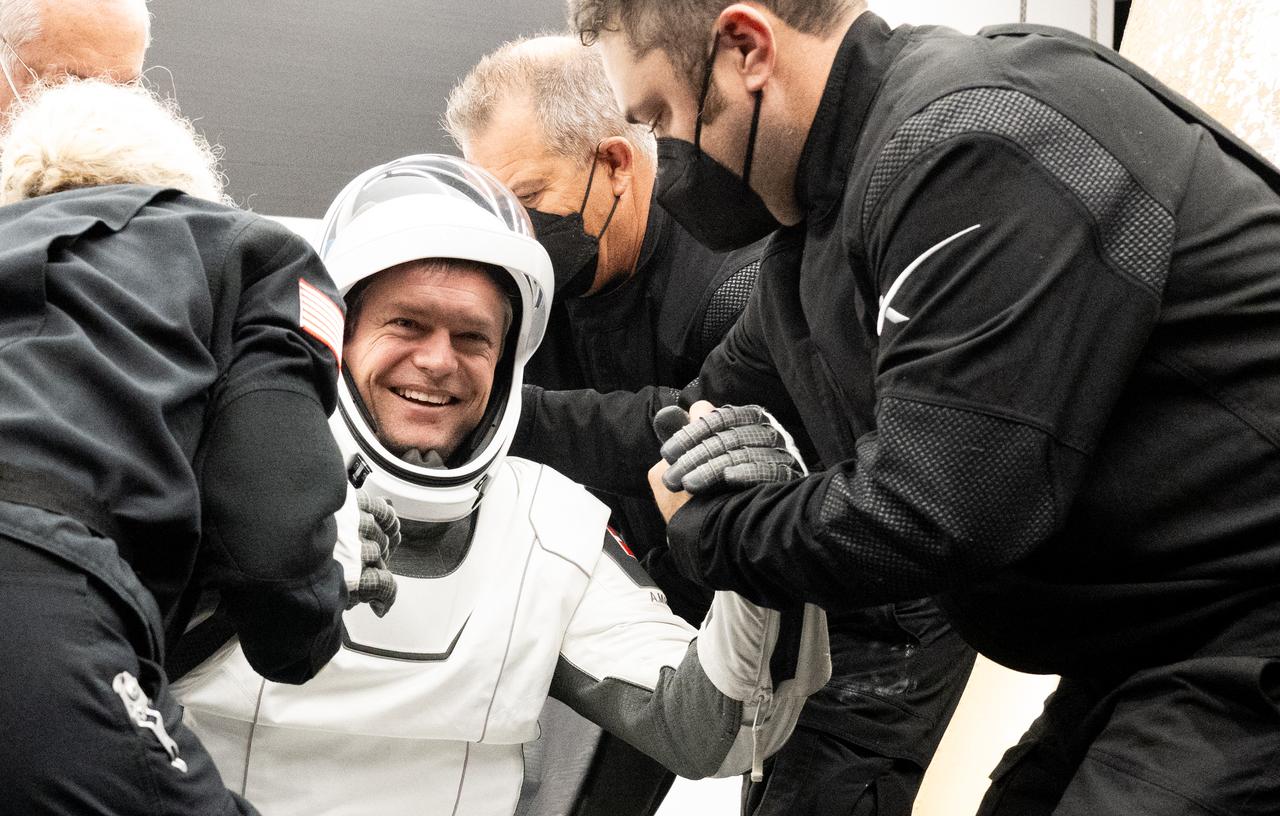

ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen is helped out of the SpaceX Dragon Endurance spacecraft onboard the SpaceX recovery ship MEGAN after he, NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Satoshi Furukawa, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Tuesday, March 12, 2024. Moghbeli, Mogensen, Furukawa, and Borisov are returning after nearly six-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

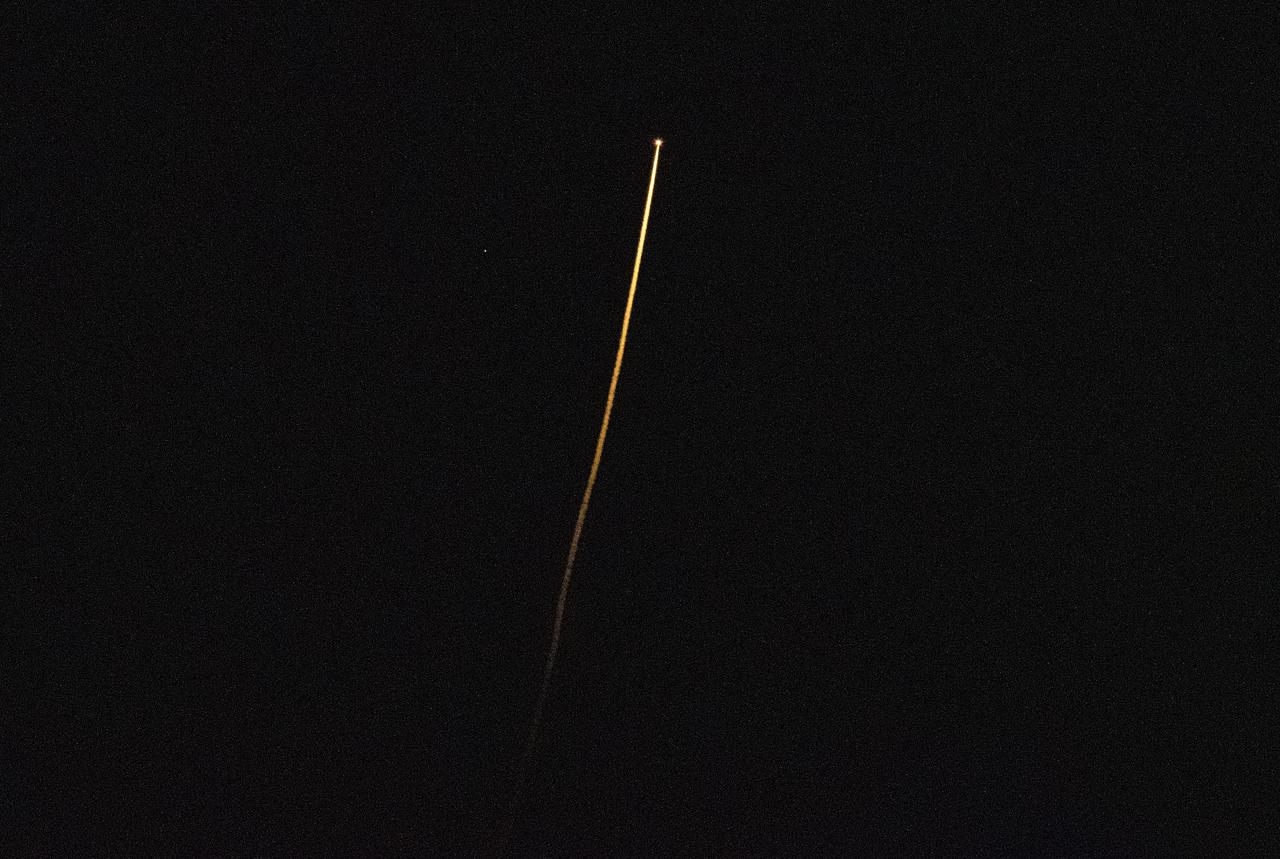
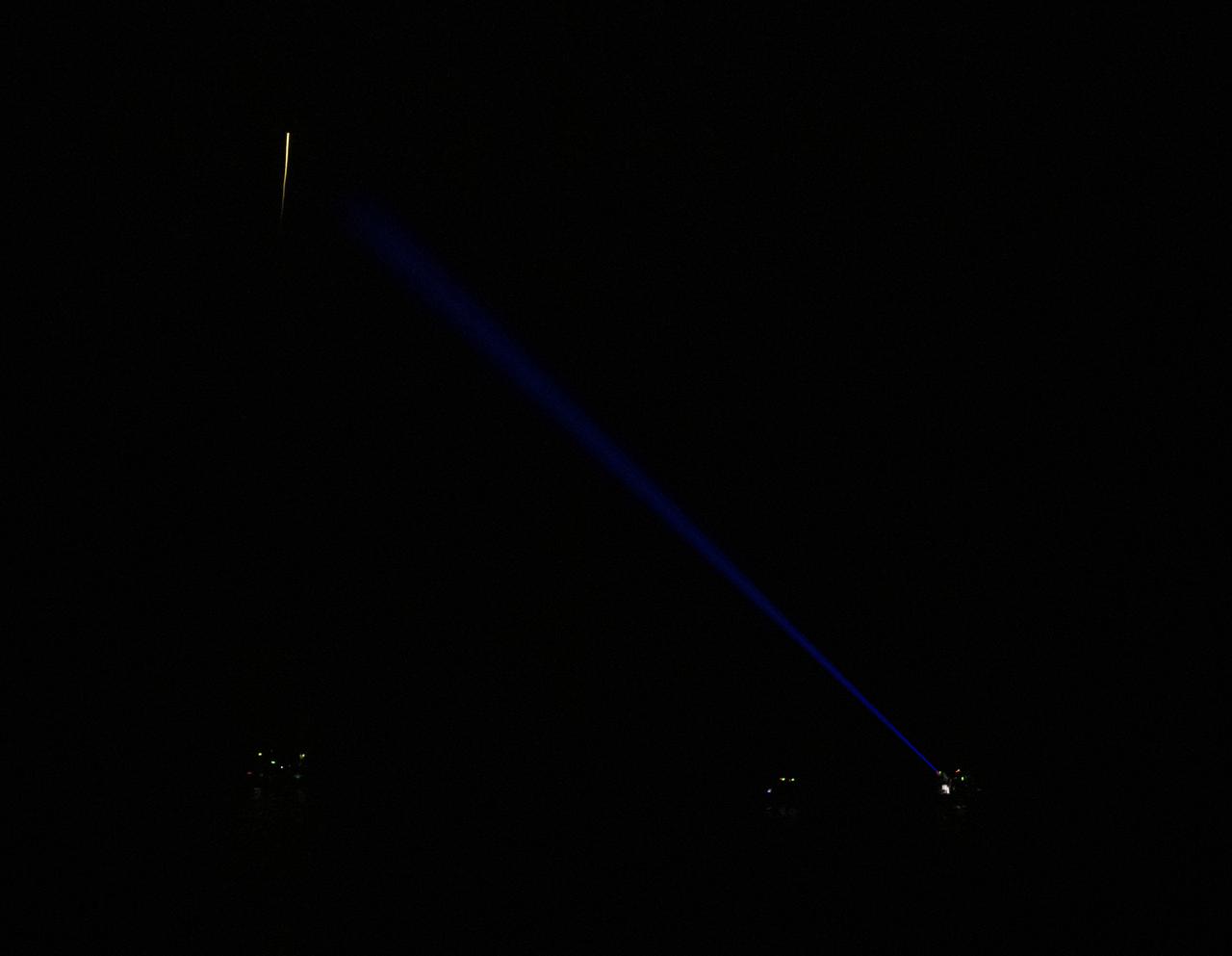
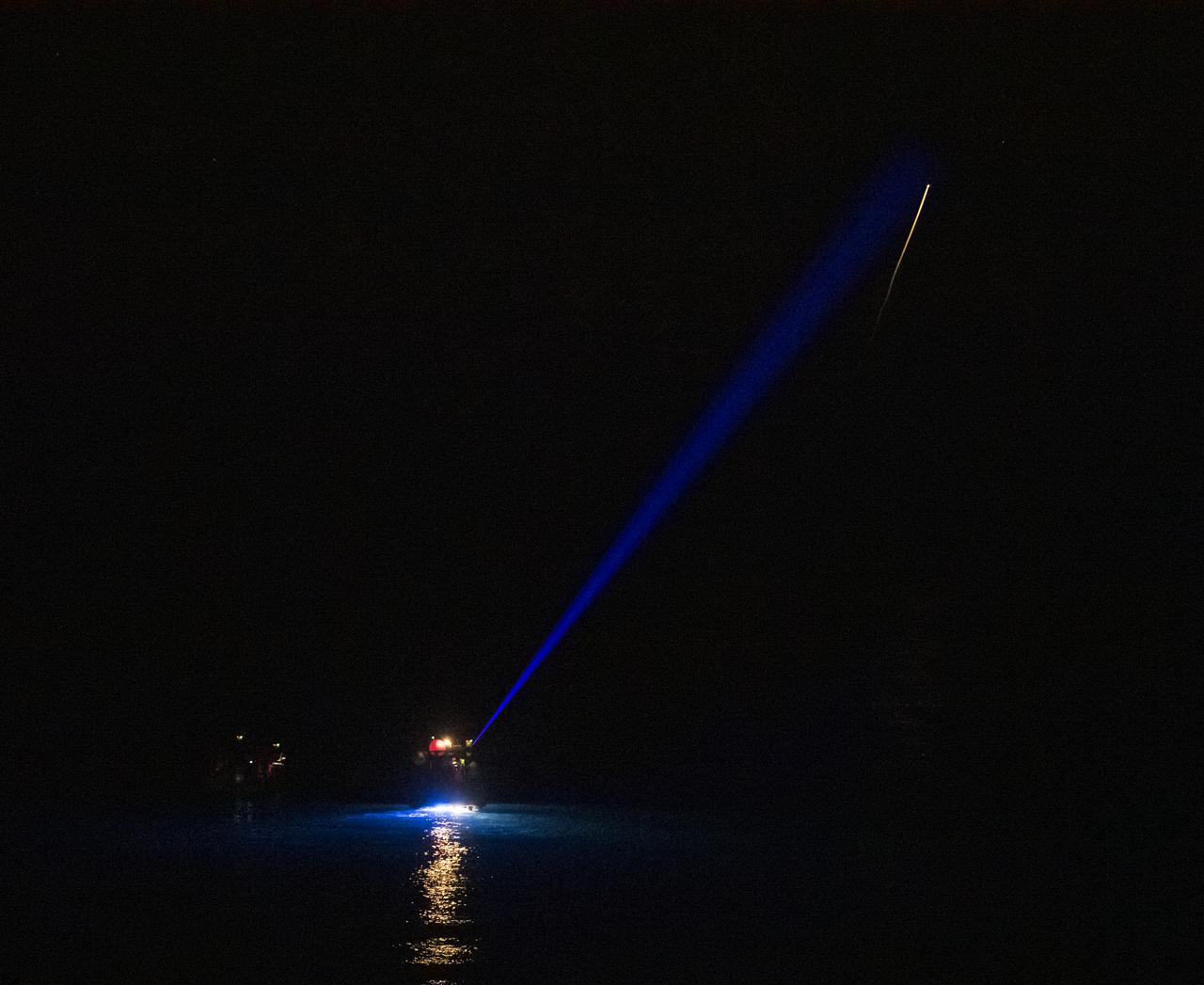
The SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft is seen in the distance as it lands with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Sunday, May 2, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission was the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Note - this image noise is a result of using a very high sensitivity setting in the camera in a very dark situation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
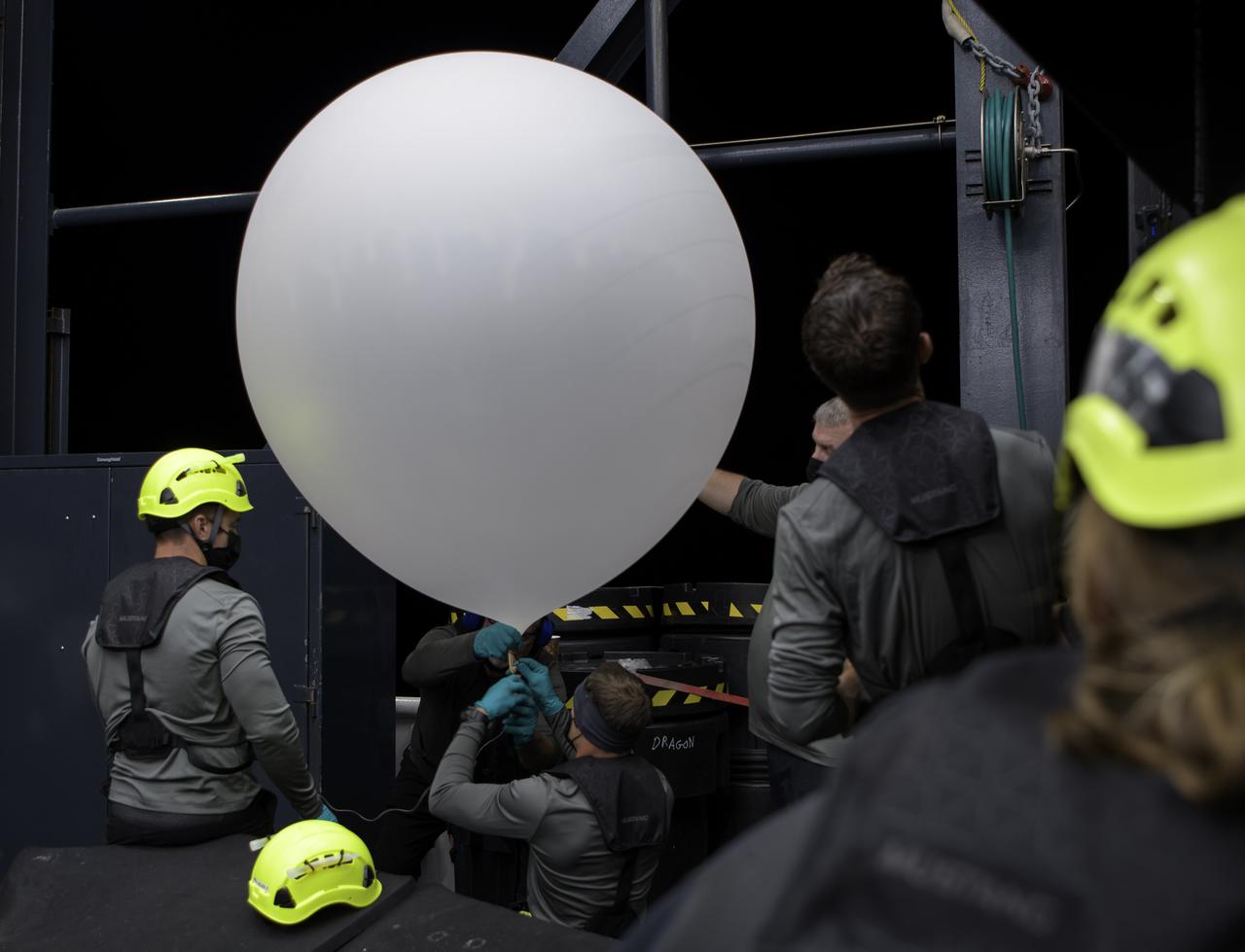

SpaceX support teams onboard the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship prepare to launch a weather balloon ahead of the landing of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Resilience spacecraft with NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Shannon Walker, and Victor Glover, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi aboard in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Panama City, Florida, Saturday, May 1, 2021. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotation flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket with astronauts to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)