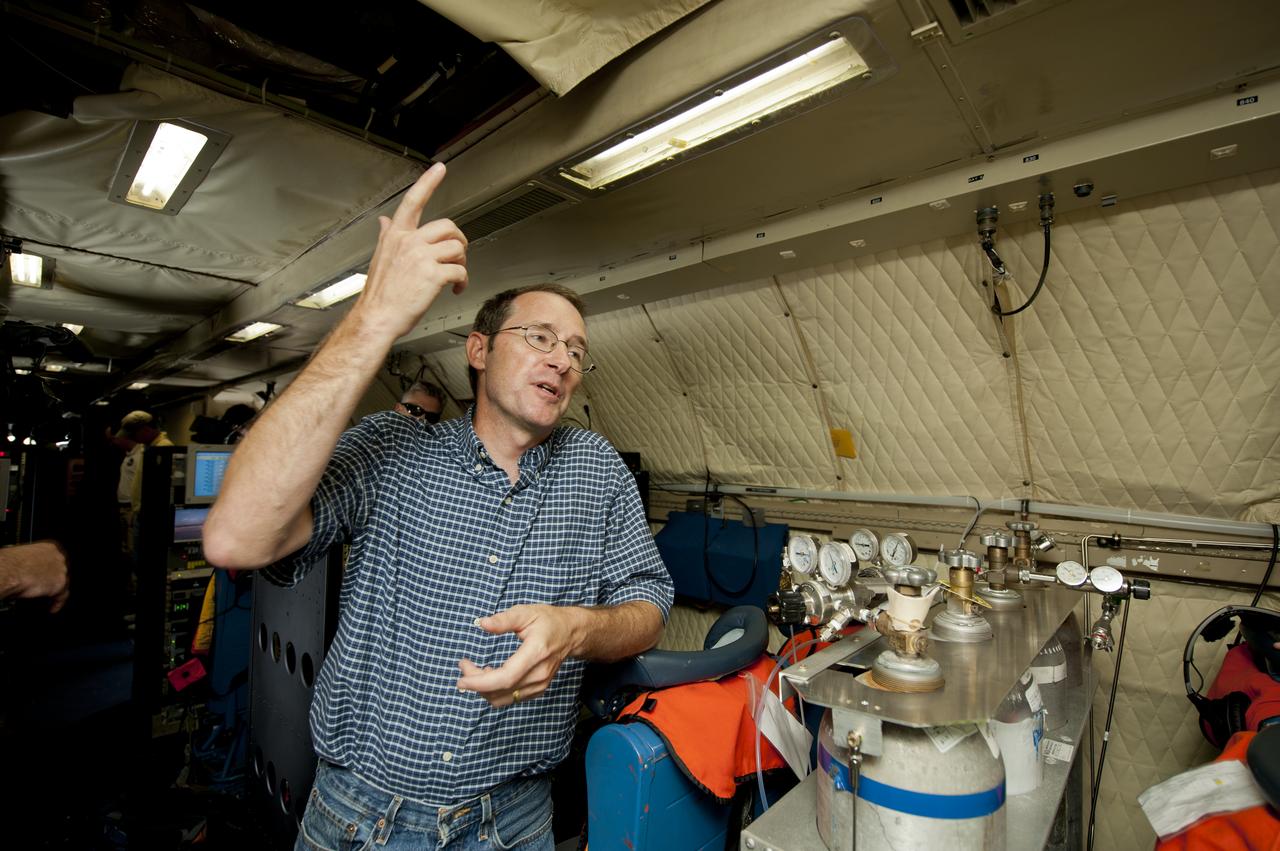

James Crawford, principal investigator and scientist based at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., talks about the DISCOVER-AQ project on board the P-3B NASA research aircraft at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
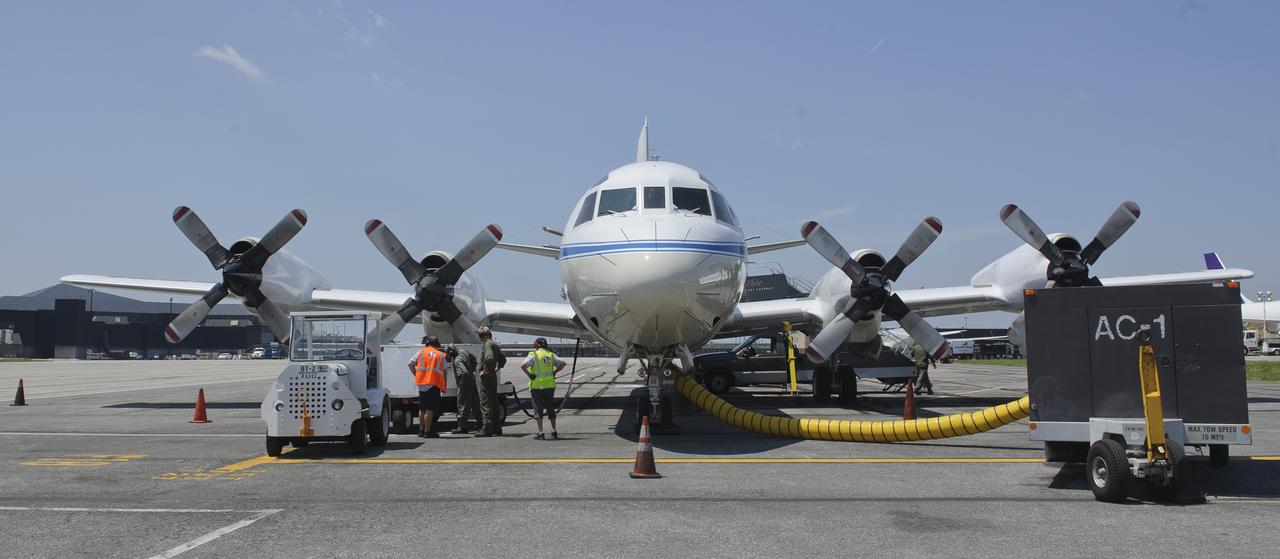

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
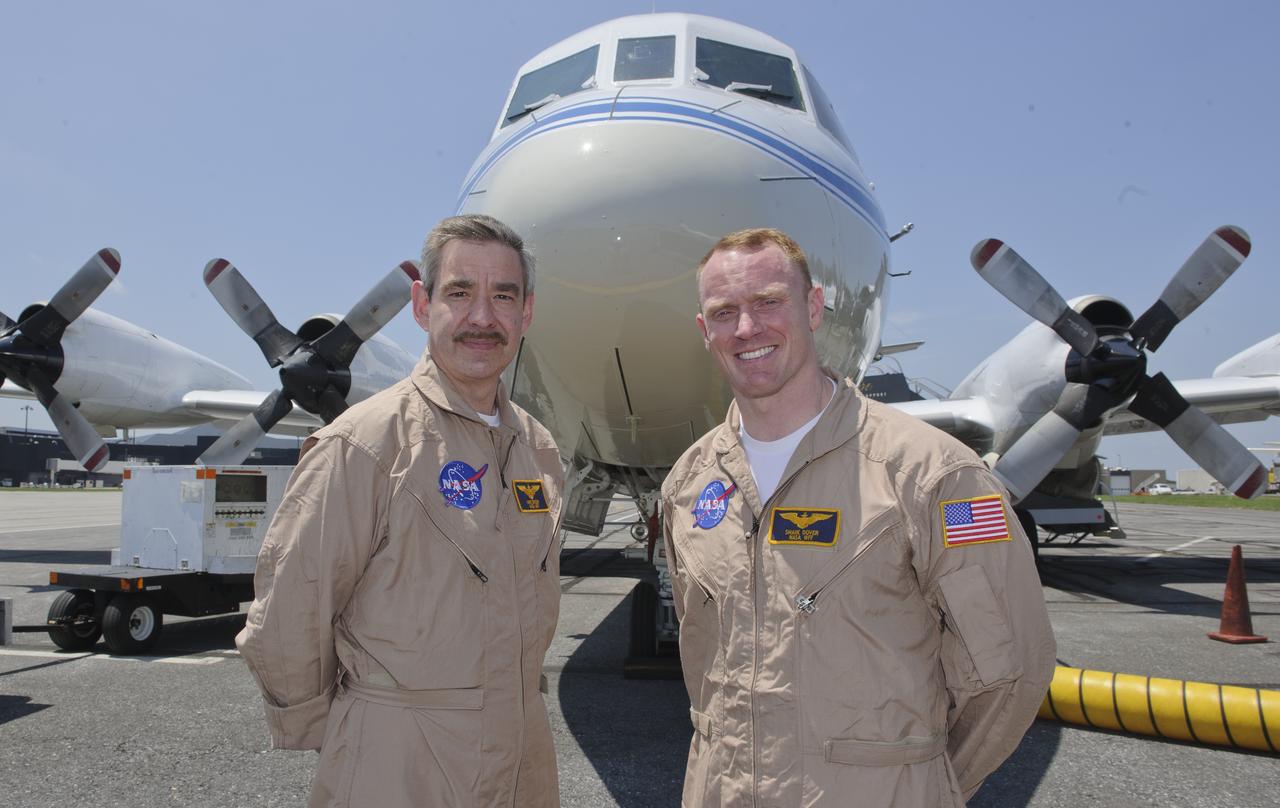

WFF Pilots Mike Singer, left, and Shane Dover stand in front of the 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
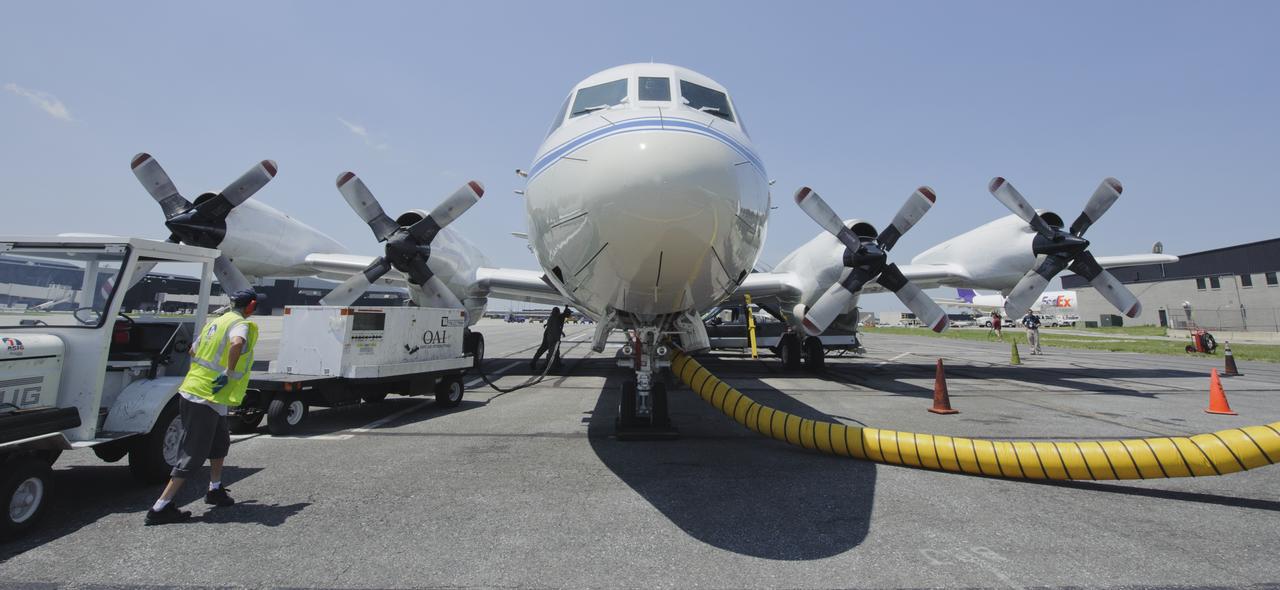

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
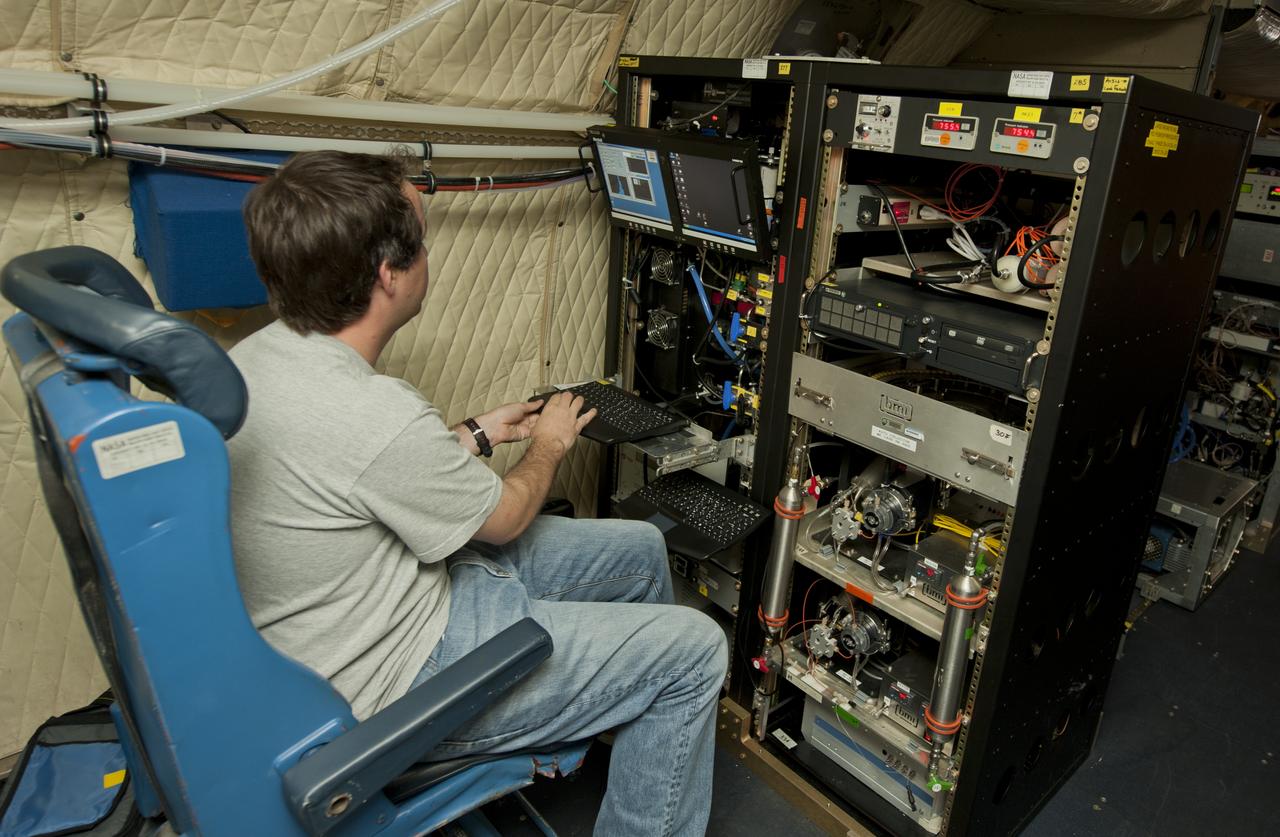

An unidentified researcher works aboard the P-3B NASA research aircraft at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
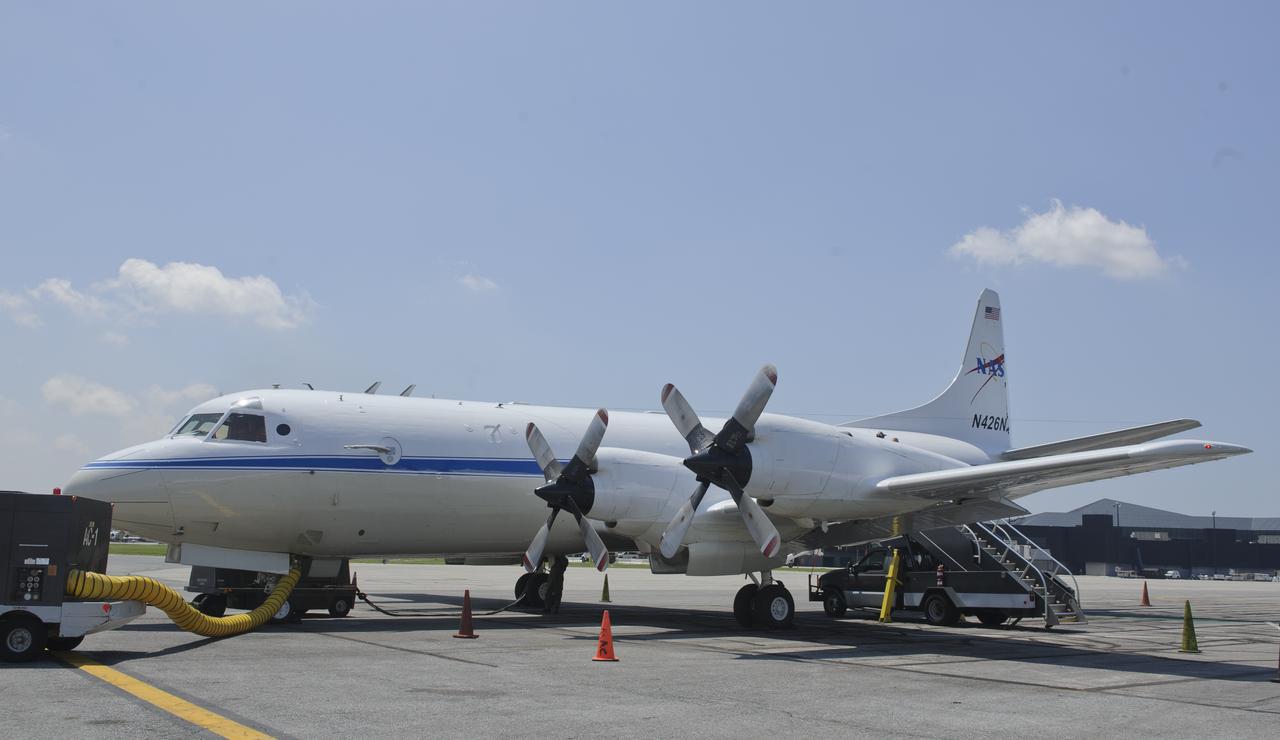

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Pilots Shane Dover, left, and Mike Singer are seen on the flight deck of the P-3B NASA research aircraft at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
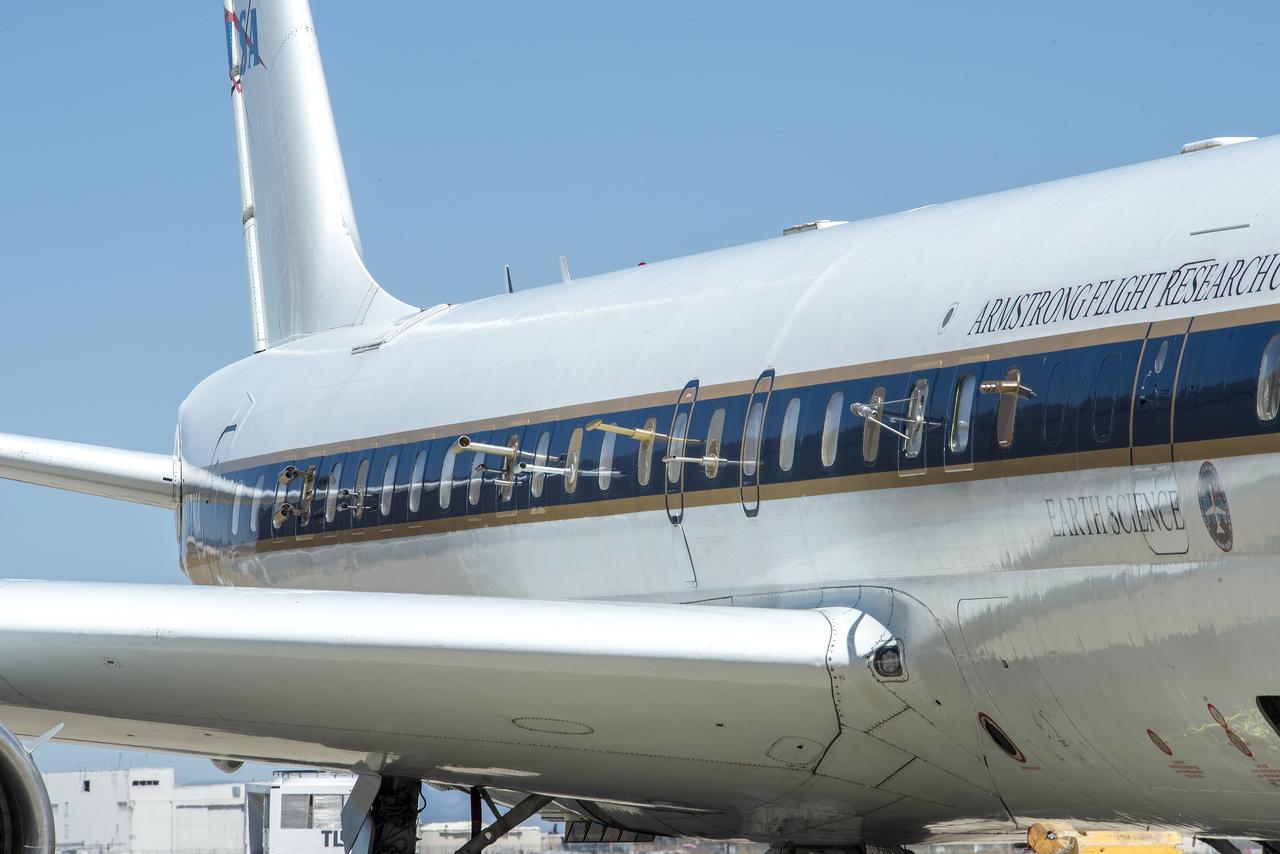

NASA’s DC-8 flying laboratory carried the Fire Influence on Regional to Global Environments and Air Quality, or FIREX-AQ, science team and a suite of state-of-the-art instrumentation to observe different components of fire smoke in varying altitudes and weather. The aircraft is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
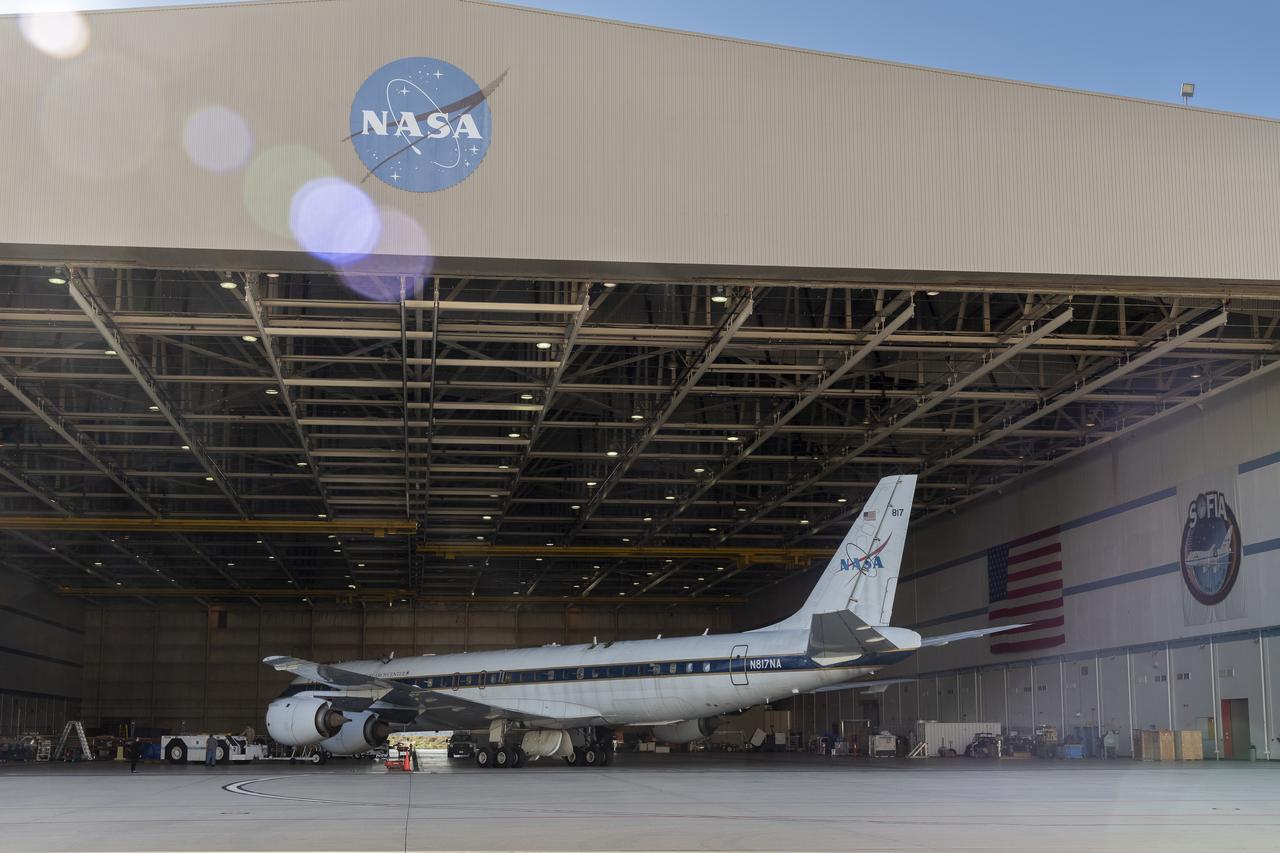

The DC-8 aircraft returns to the hangar at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, after completing its final mission supporting Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).
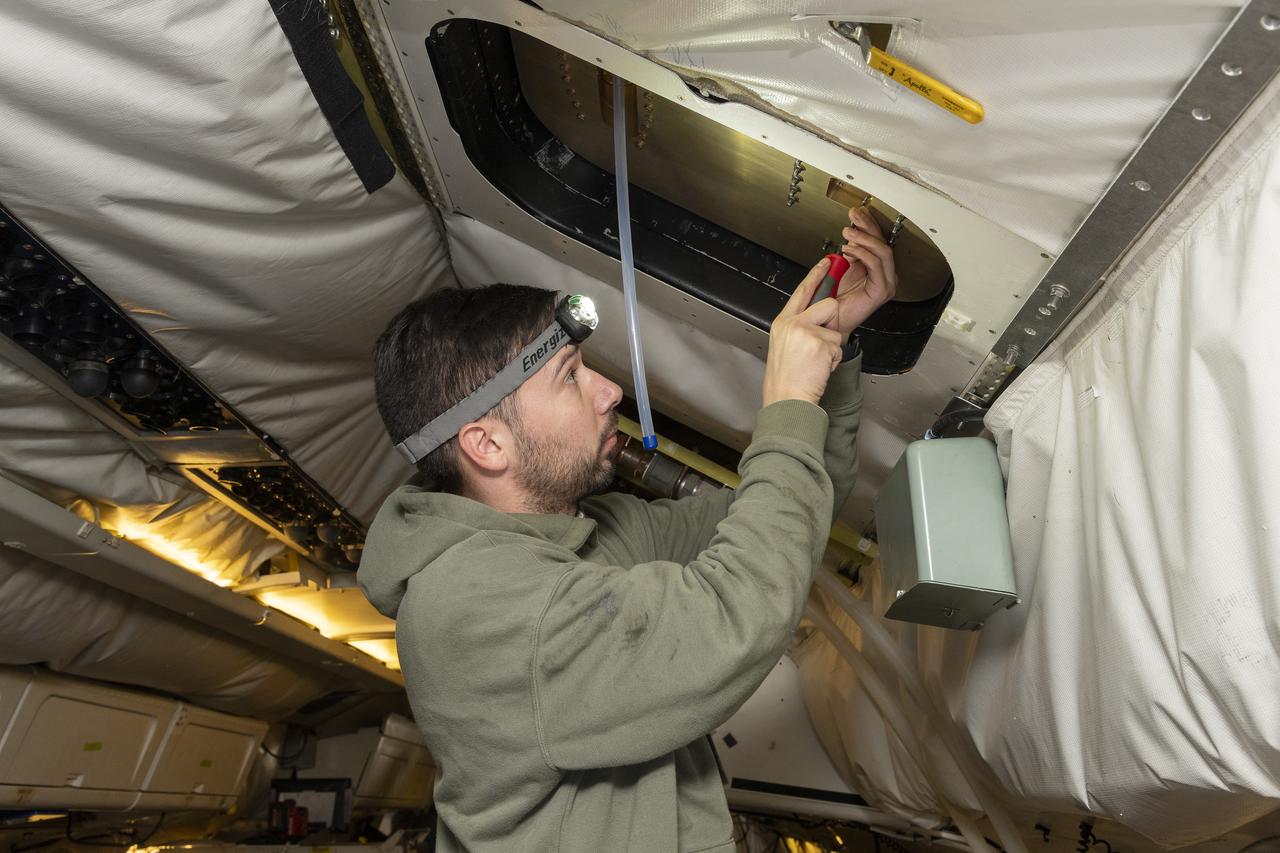

Isac Mata, engineering technician at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center, attends to the interior of the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
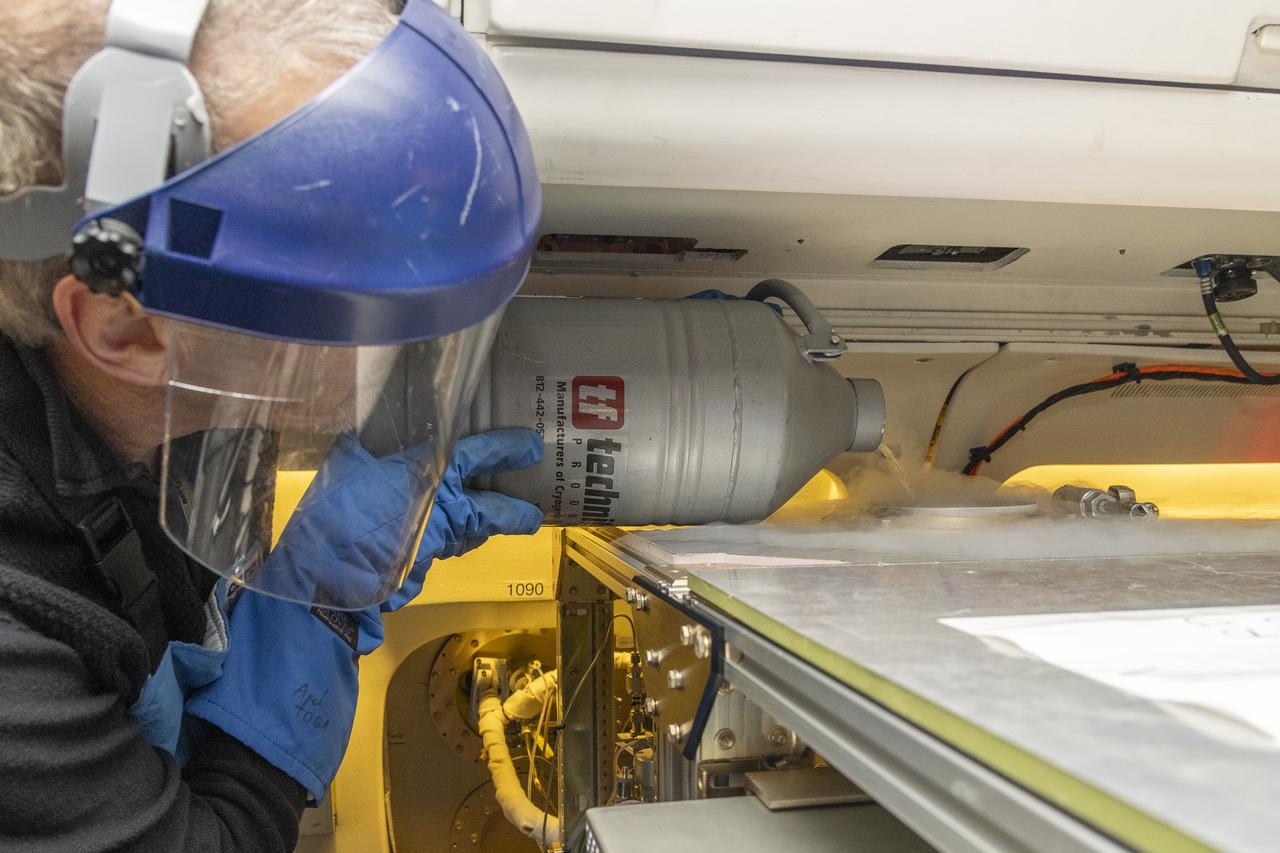

Alan Hills fills liquid nitrogen in the Trace Organic Gas Analyzer (TOGA) instrument onboard the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. This instrument measures volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
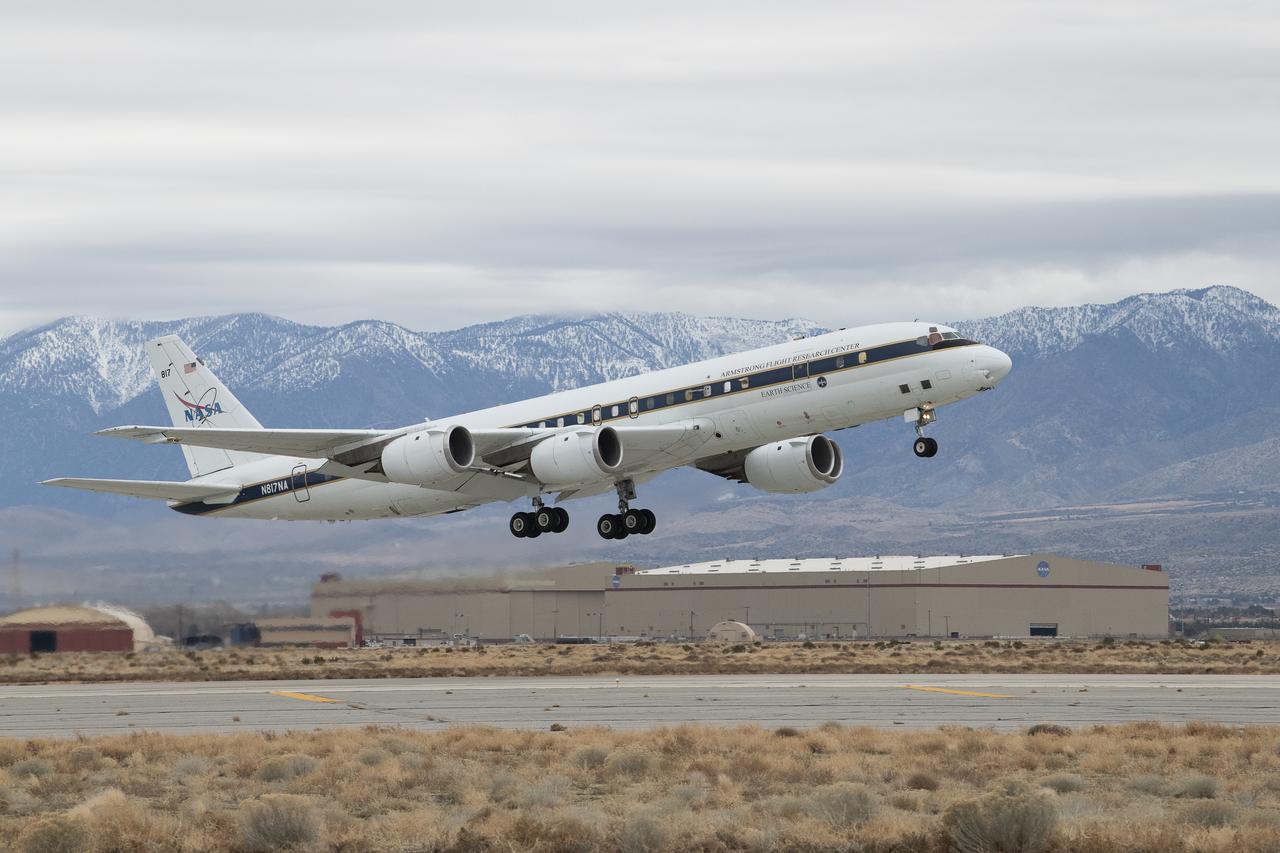

DC-8 aircraft conducts test flights at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
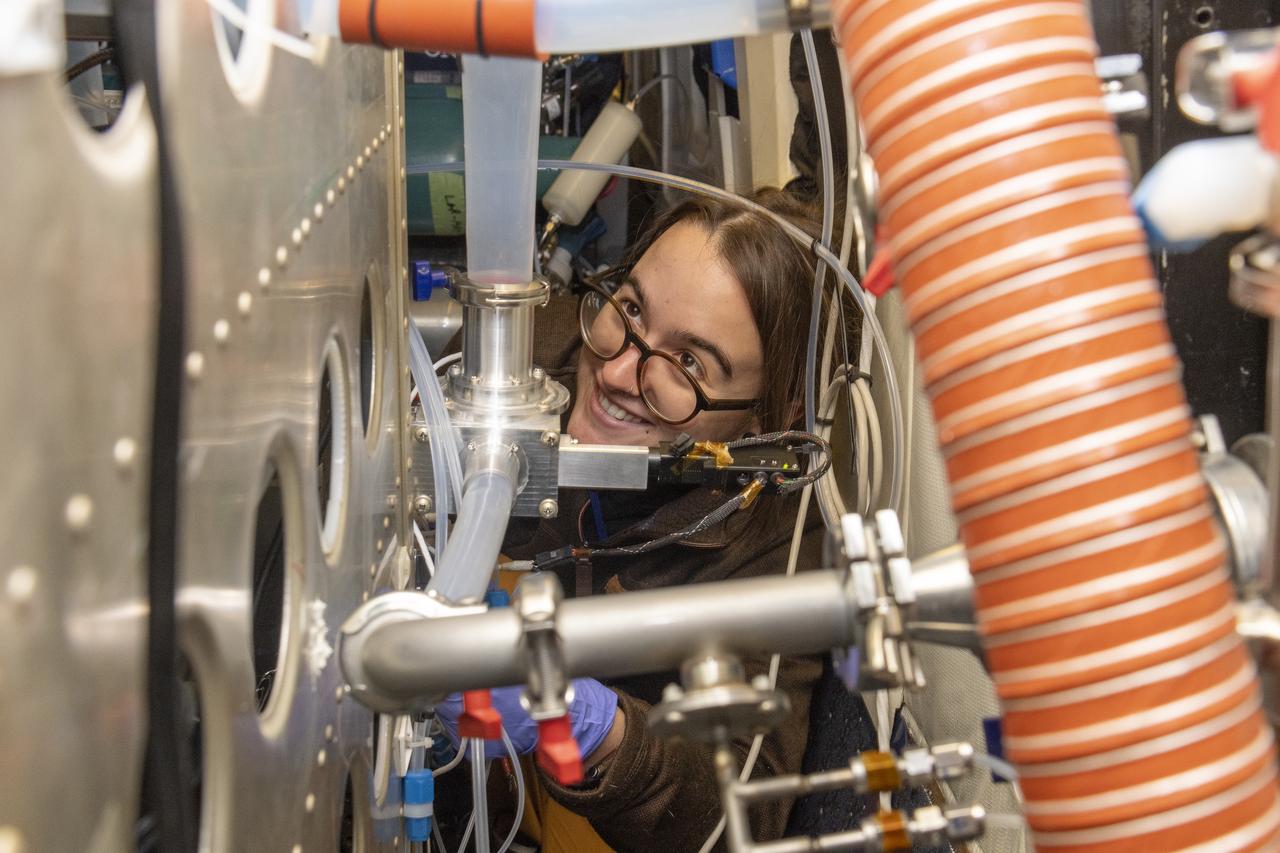
Kat Ball, Chemical Engineering Ph.D candidate at Caltech, attends to the Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer (CIMS) rack onboard the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
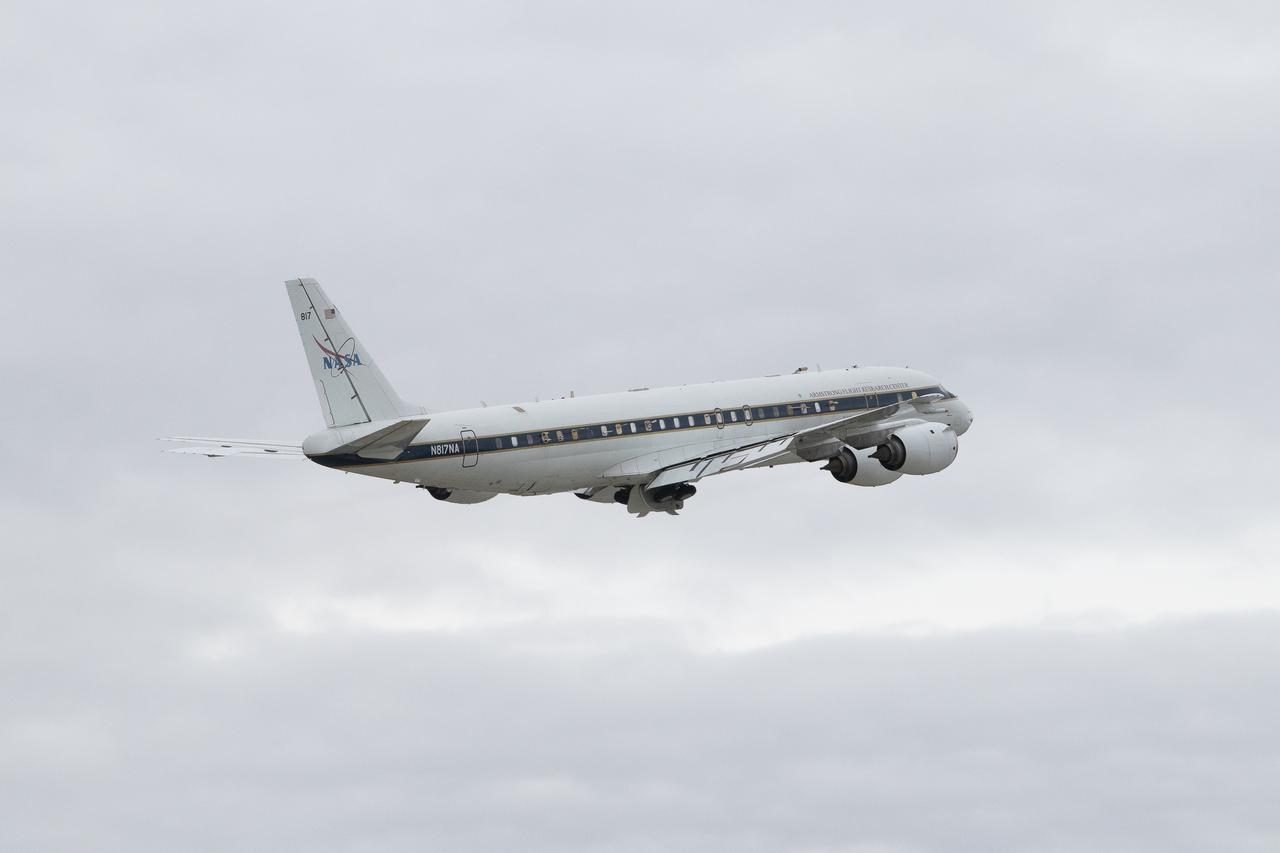

DC-8 aircraft conducts test flights at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
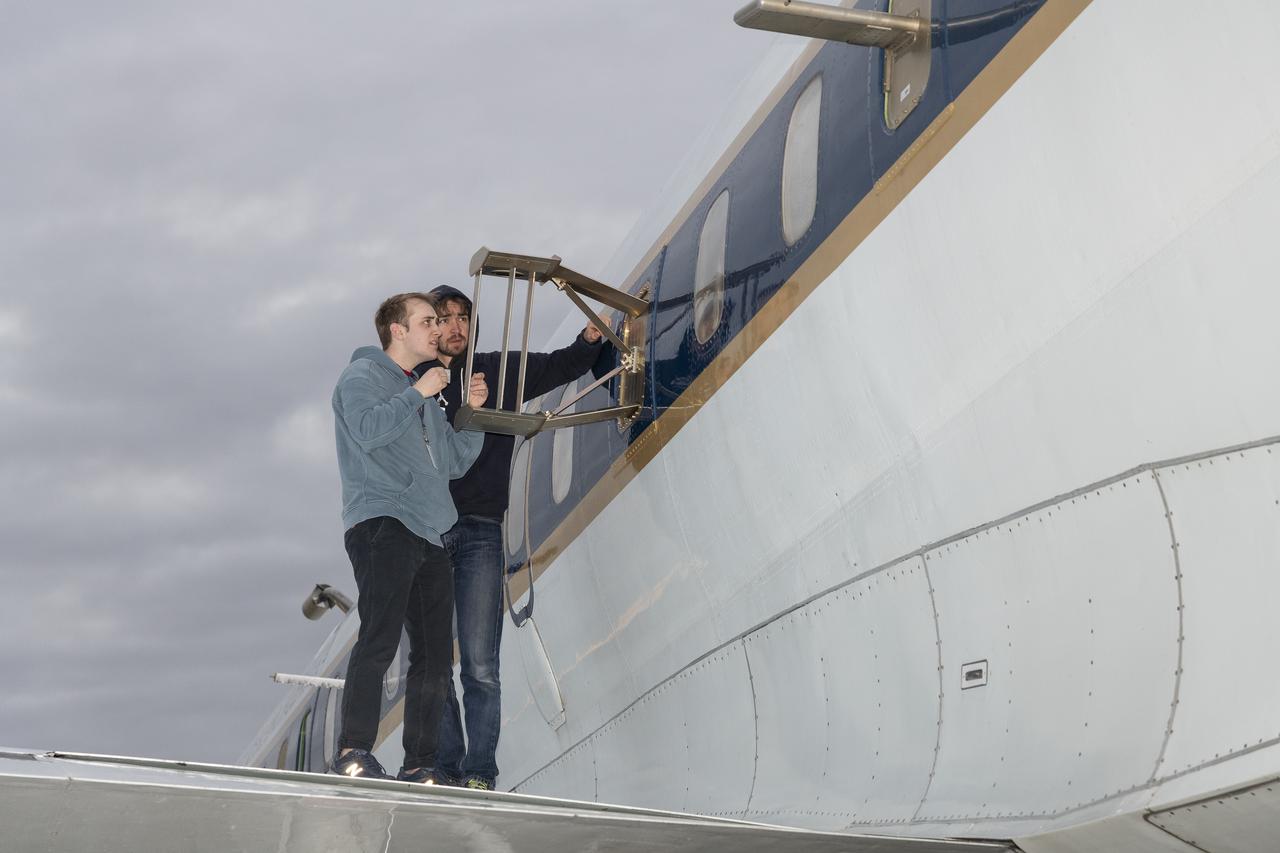

Scientists Ryan Boyd (left) and Vladislav Sevostianov (right) attend to the Optical Payload for Lasercomm Science (OPALS) instrument on the exterior the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners

NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Director Brad Flick smiles as members of the DC-8 team gather and exchange congratulations after the aircraft and crew return to NASA Armstrong’s Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).

From left, Wayne Ringelberg, chief pilot at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, is welcomed by Michael Thomson, director of NASA Armstrong’s Science Mission Directorate, and Kirsten Boogaard, NASA’s DC-8 project manager, after the DC-8 aircraft and crew return to NASA Armstrong’s Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).
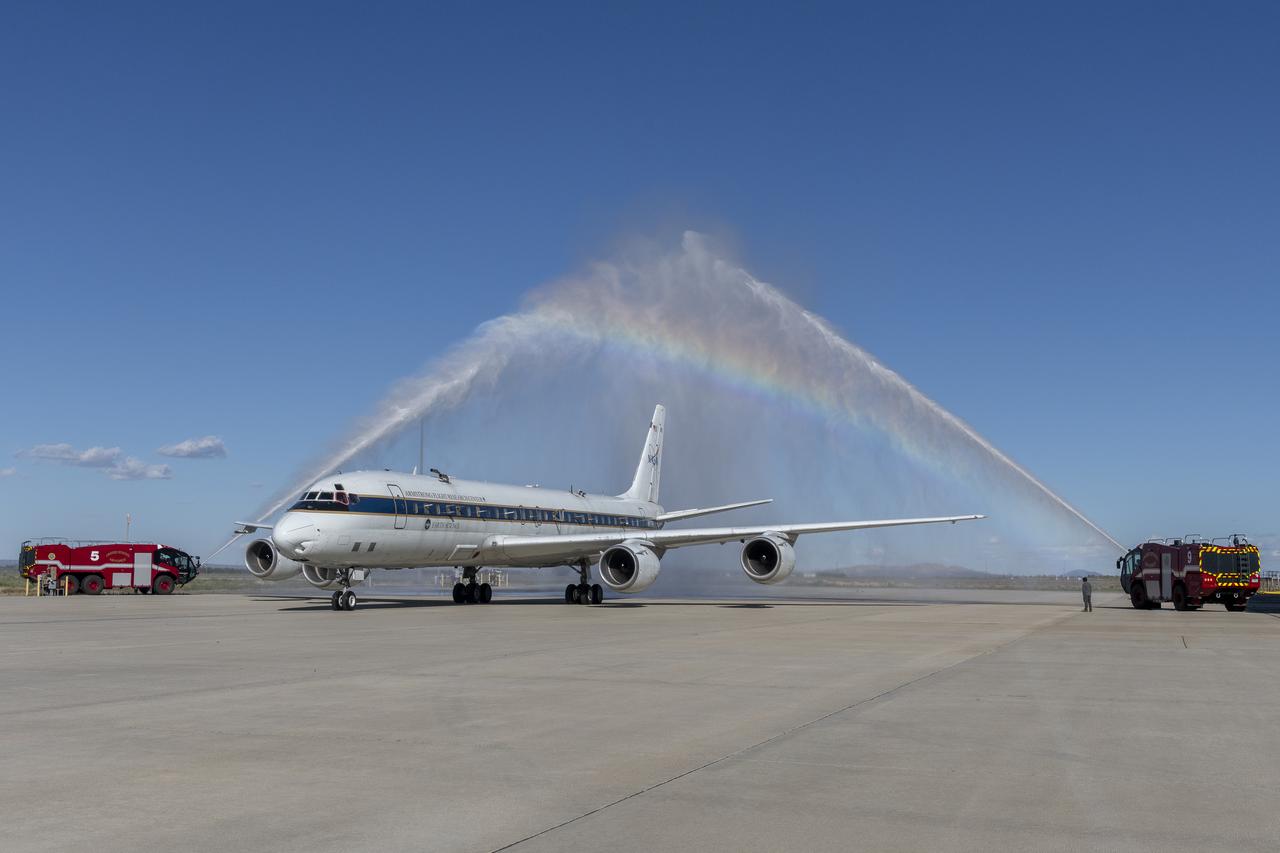

The DC-8 aircraft returned to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, after completing its final mission supporting Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ). The aircraft and crew were welcomed back with a celebratory water salute by the U.S. Air Force Plant 42 Fire Department.
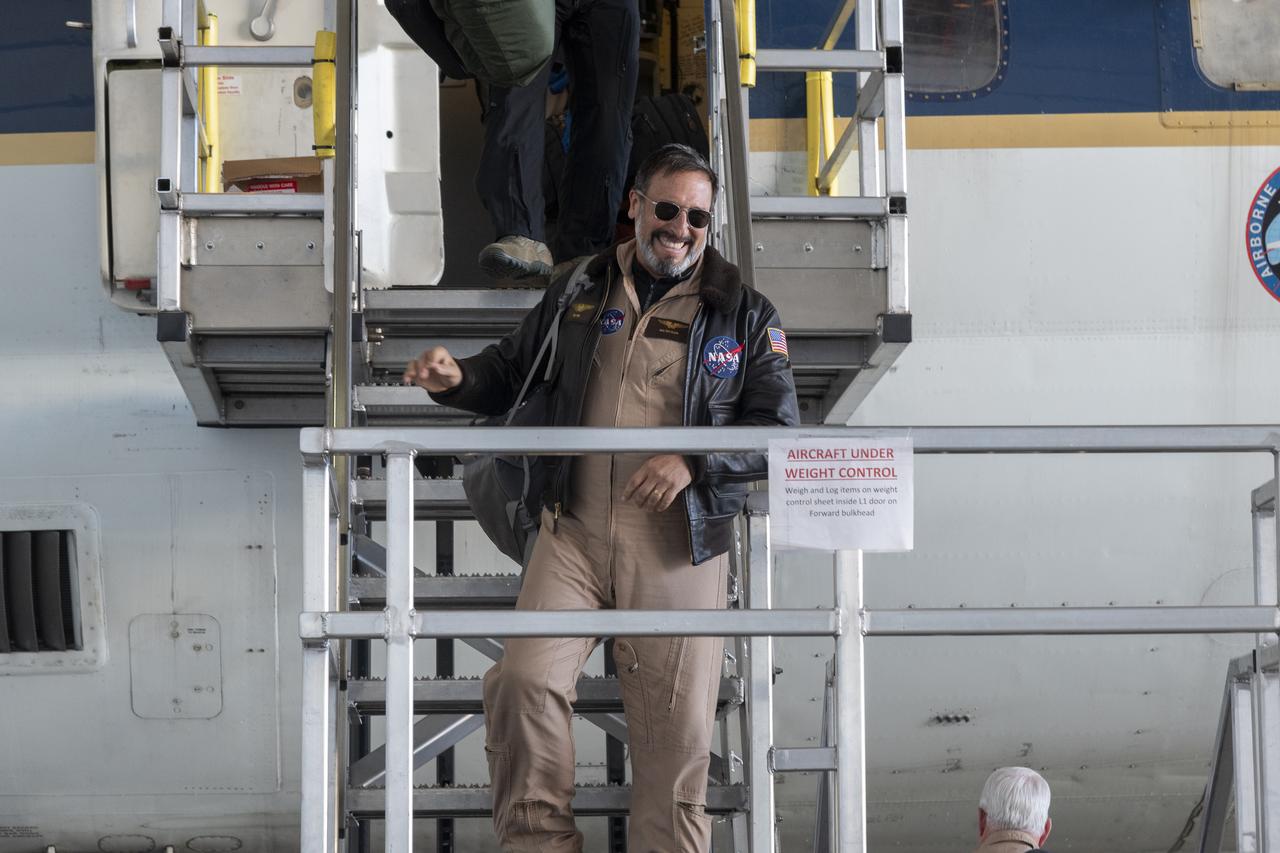

Walter Klein, DC-8 navigator, exits the aircraft cabin and is welcomed with applause from a supportive team after the DC-8 aircraft and crew return to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).

NASA DC-8 crew members Nickelle “Nicki” Reid, operations engineer, left, and Isac Mata, engineer technician, exchange in a heartfelt hug after the DC-8 aircraft and crew return to NASA Armstrong’s Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ). Smiling in the background is Michael Thomson, director of NASA Armstrong’s Science Mission Directorate.
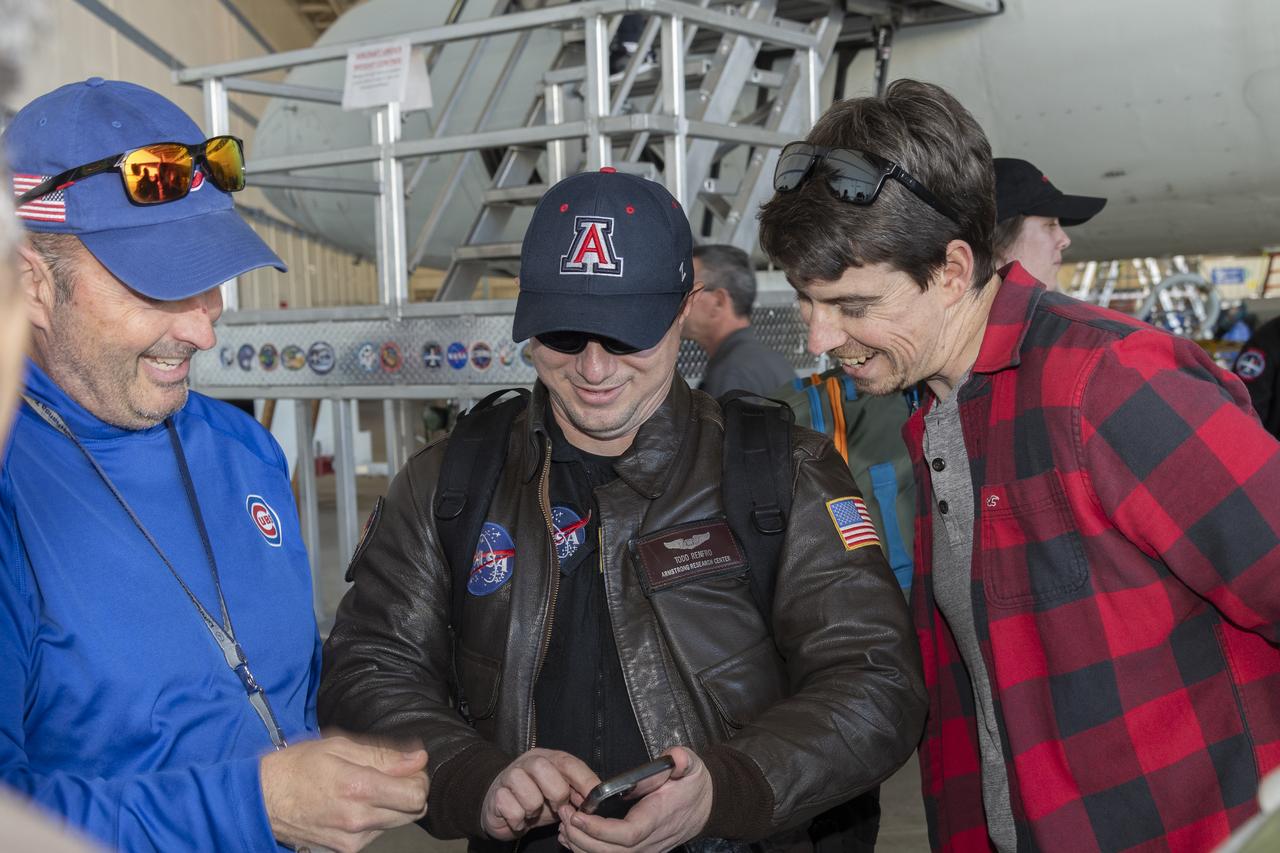

From left, Andy Barry, DC-8 pilot; Todd Renfro, flight navigator; and Adam Devalon, flight engineer, share smiles after the DC-8 aircraft and crew return to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).
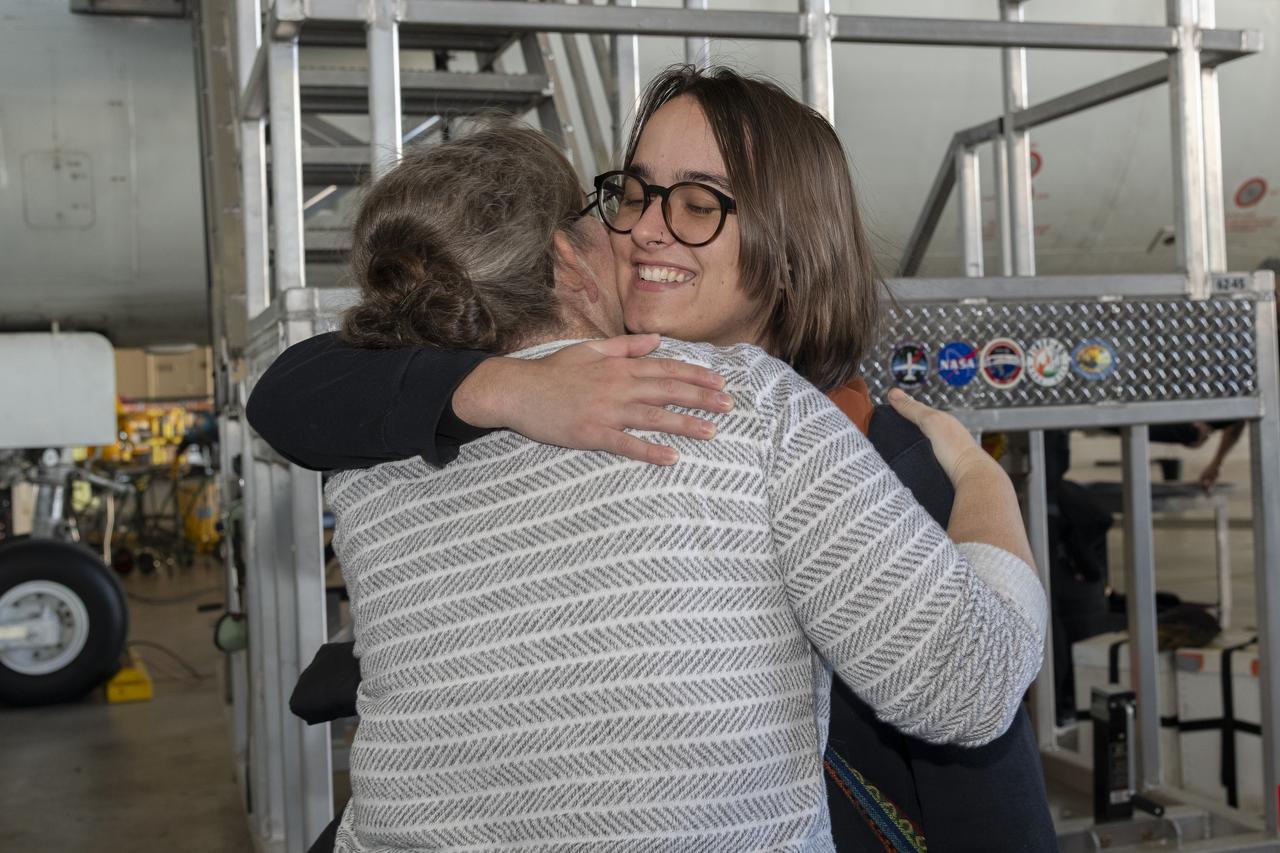

NASA’s DC-8 operations engineer, Nickelle “Nicki” Reid, left, embraces Katherine Ball, chemical engineering Ph.D. candidate at California Institute of Technology, after the DC-8 aircraft and crew return to NASA Armstrong’s Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).
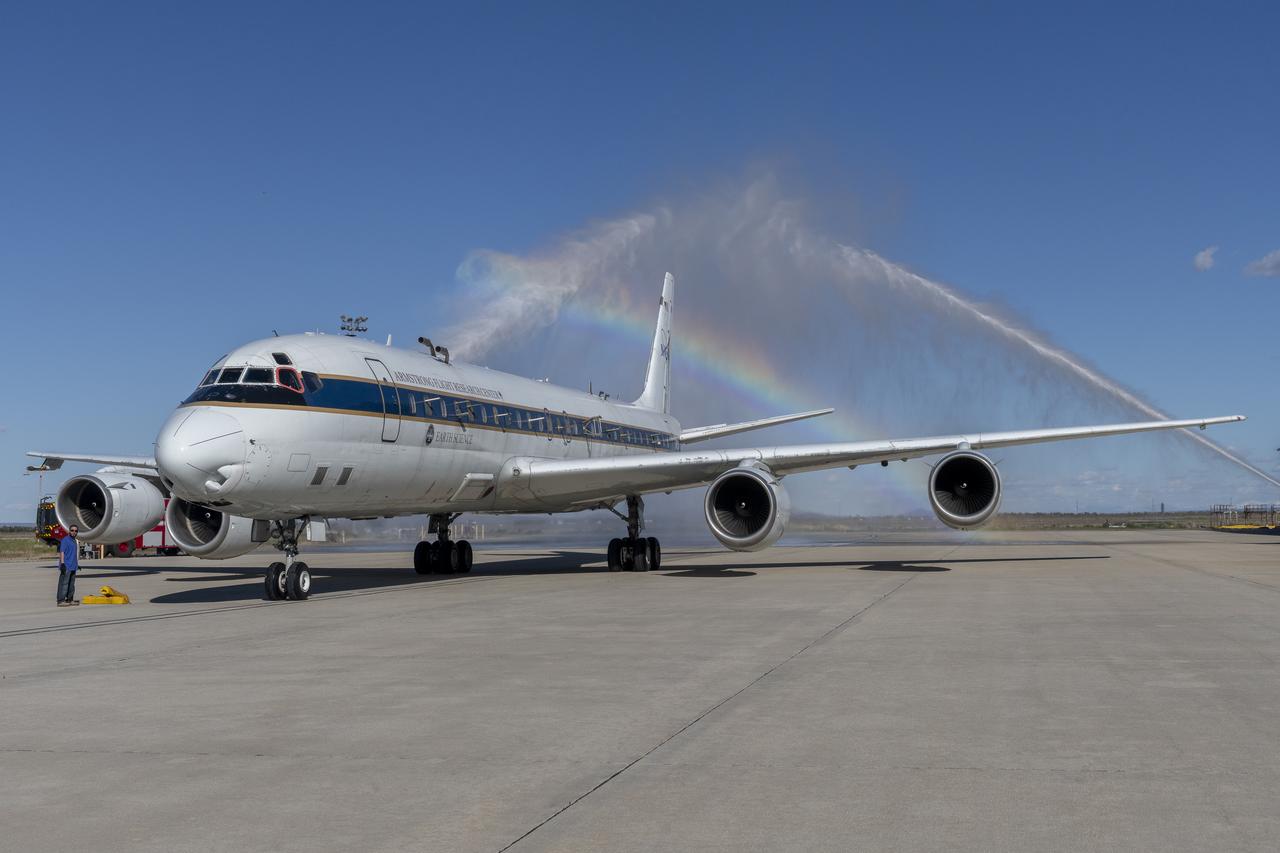

The DC-8 aircraft returned to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, after completing its final mission supporting Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ). The aircraft and crew were welcomed back with a celebratory water salute by the U.S. Air Force Plant 42 Fire Department.
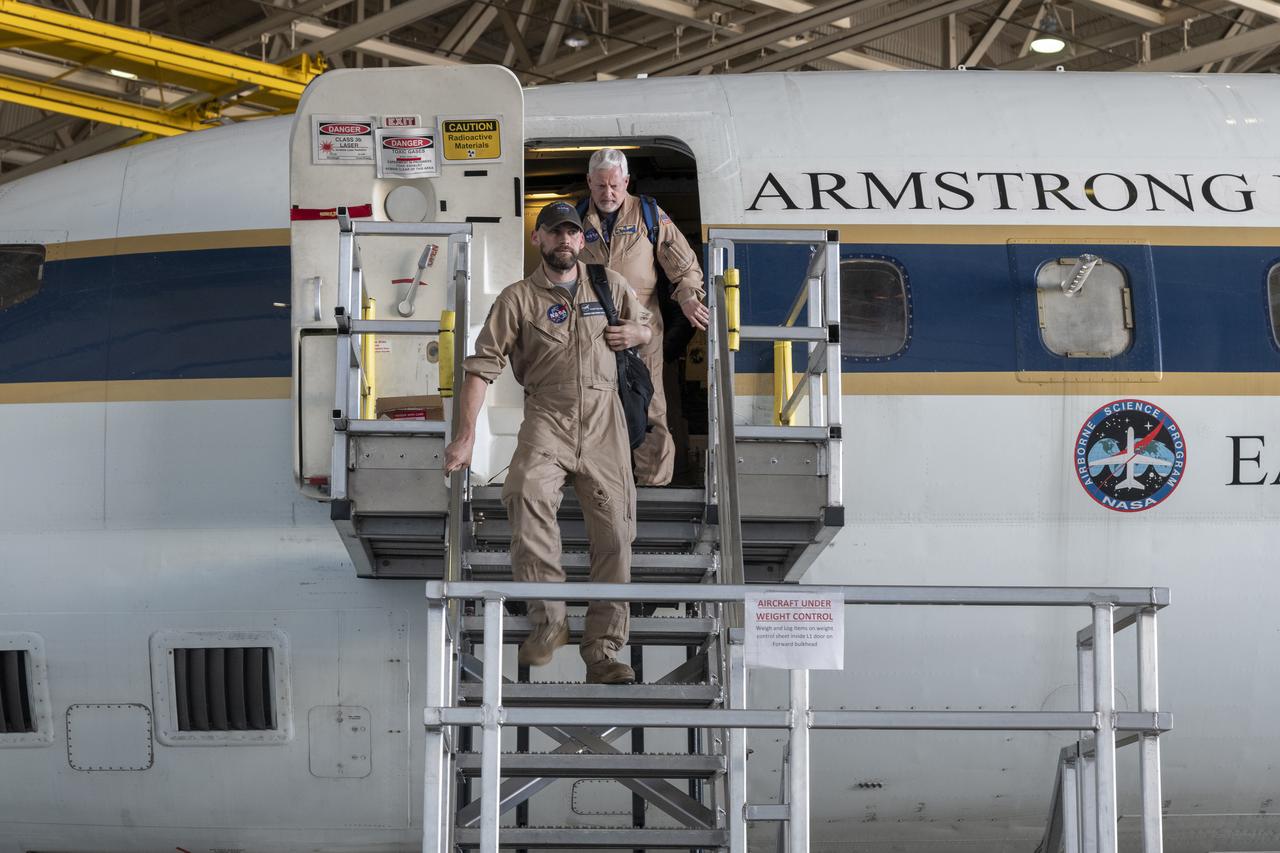

Kelly Jellison, avionics lead, and Tim Sandon, flight engineer, exit the DC-8 aircraft cabin and are welcomed with applause from a supportive team after the DC-8 aircraft and crew return to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).
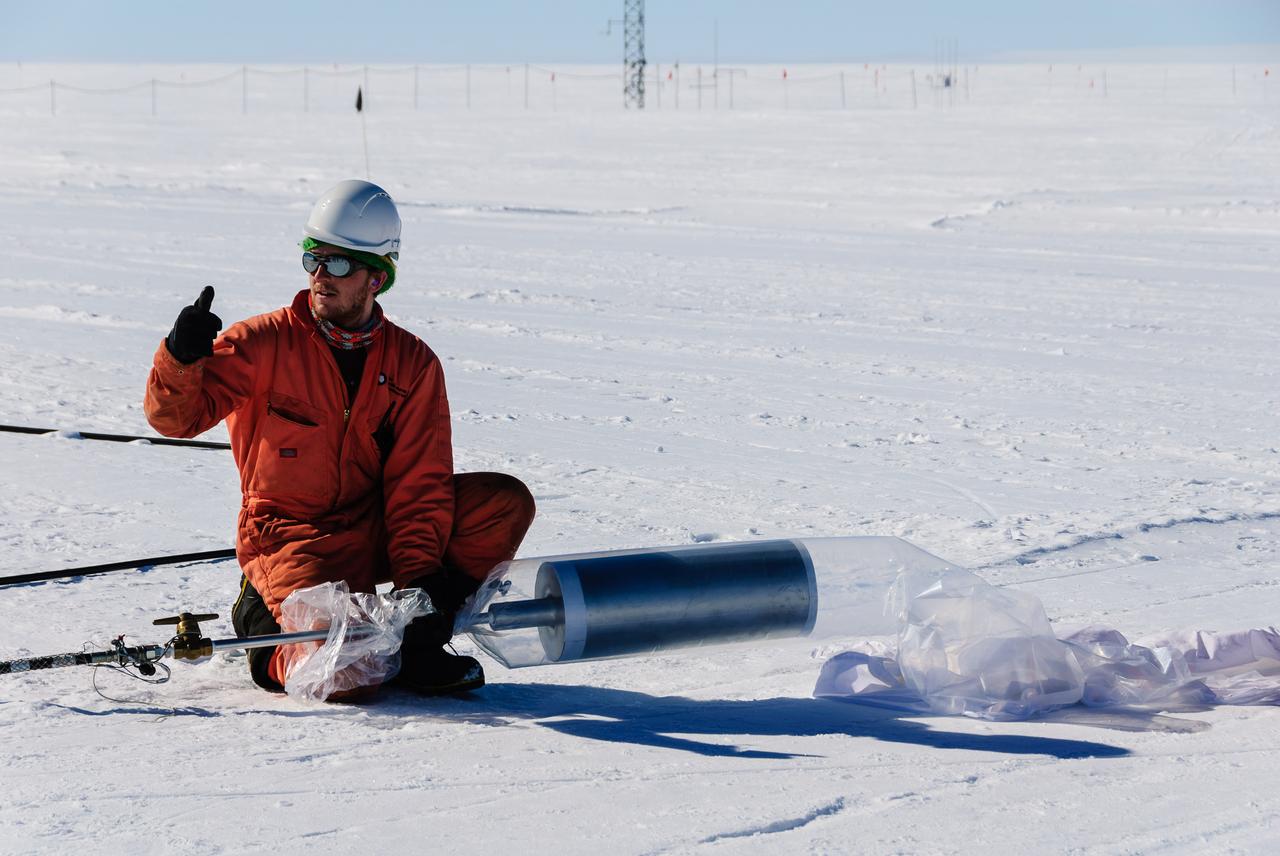

The Halley station team members assisted the BARREL team with the launches. Here, one gives the thumbs up to start inflating a BARREL balloon. Credit: NASA/Goddard/BARREL/M. Krzysztofowicz Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/nasas-barrel-returns-successful-from-antarctica/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/nasas-barrel-returns-successful-from...</a> -- Three months, 20 balloons, and one very successful campaign. The team for NASA's BARREL – short for Balloon Array for Radiation belt Relativistic Electron Losses -- mission returned from Antarctica in March 2014. BARREL's job is to help unravel the mysterious Van Allen belts, two gigantic donuts of radiation that surround Earth, which can shrink and swell in response to incoming energy and particles from the sun and sometimes expose satellites to harsh radiation. While in Antarctica, the team launched 20 balloons carrying instruments that sense charged particles that are scattered into the atmosphere from the belts, spiraling down the magnetic fields near the South Pole. Each balloon traveled around the pole for up to three weeks. The team will coordinate the BARREL data with observations from NASA's two Van Allen Probes to better understand how occurrences in the belts relate to bursts of particles funneling down toward Earth. BARREL team members will be on hand at the USA Science and Engineering Festival in DC on April 26 and 27, 2014 for the exhibit Space Balloons: Exploring the Extremes of Space Weather. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
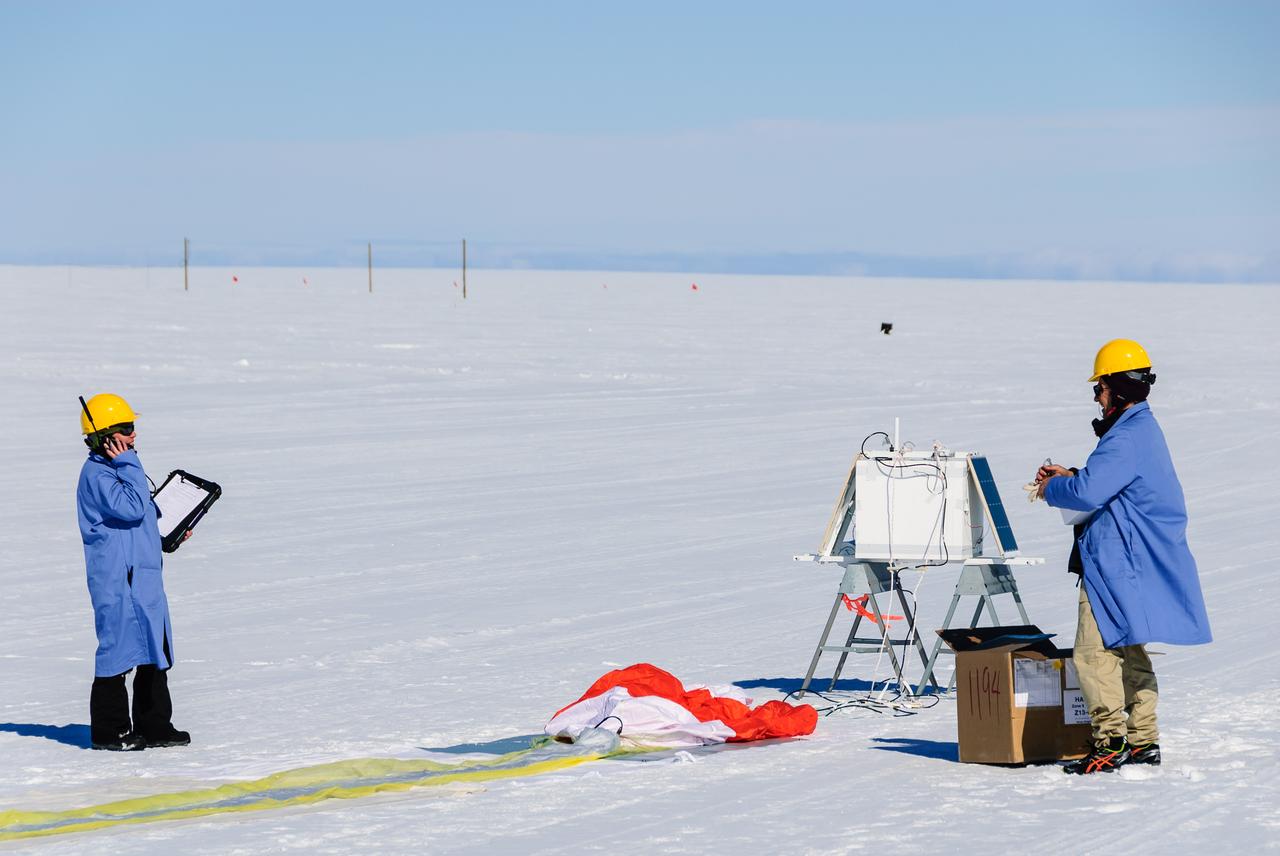

Researchers communicate with the BARREL ground station during preparations for launch. The white box in the background is the science payload and the orange and white parachute can be seen on the ground in front of it. On the left is BARREL Principal Investigator Robyn Millan of Dartmouth College in Hanover, N.H.; on the right is BARREL Co-Investigator Michael McCarthy of the University of Washington in Seattle. Credit: NASA/Goddard/BARREL/M. Krzysztofowicz Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasas-barrel-returns-successful-from-antarctica" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasas-barrel-returns-success...</a> -- Three months, 20 balloons, and one very successful campaign. The team for NASA's BARREL – short for Balloon Array for Radiation belt Relativistic Electron Losses -- mission returned from Antarctica in March 2014. BARREL's job is to help unravel the mysterious Van Allen belts, two gigantic donuts of radiation that surround Earth, which can shrink and swell in response to incoming energy and particles from the sun and sometimes expose satellites to harsh radiation. While in Antarctica, the team launched 20 balloons carrying instruments that sense charged particles that are scattered into the atmosphere from the belts, spiraling down the magnetic fields near the South Pole. Each balloon traveled around the pole for up to three weeks. The team will coordinate the BARREL data with observations from NASA's two Van Allen Probes to better understand how occurrences in the belts relate to bursts of particles funneling down toward Earth. BARREL team members will be on hand at the USA Science and Engineering Festival in DC on April 26 and 27, 2014 for the exhibit Space Balloons: Exploring the Extremes of Space Weather. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>