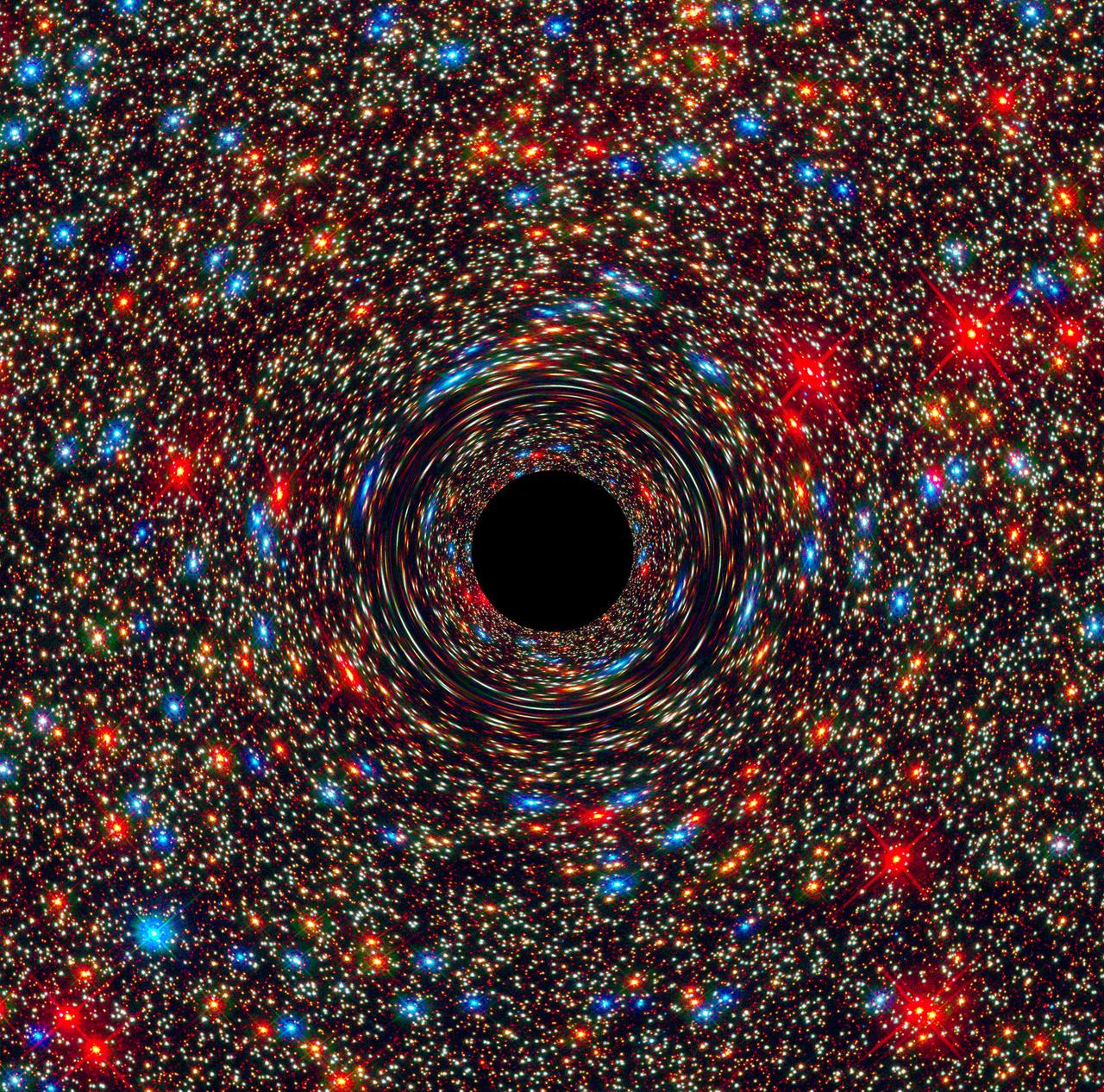

This computer-simulated image shows a supermassive black hole at the core of a galaxy. The black region in the center represents the black hole’s event horizon, where no light can escape the massive object’s gravitational grip. The black hole’s powerful gravity distorts space around it like a funhouse mirror. Light from background stars is stretched and smeared as the stars skim by the black hole. Credits: NASA, ESA, and D. Coe, J. Anderson, and R. van der Marel (STScI) More info: Astronomers have uncovered a near-record breaking supermassive black hole, weighing 17 billion suns, in an unlikely place: in the center of a galaxy in a sparsely populated area of the universe. The observations, made by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the Gemini Telescope in Hawaii, may indicate that these monster objects may be more common than once thought. Until now, the biggest supermassive black holes – those roughly 10 billion times the mass of our sun – have been found at the cores of very large galaxies in regions of the universe packed with other large galaxies. In fact, the current record holder tips the scale at 21 billion suns and resides in the crowded Coma galaxy cluster that consists of over 1,000 galaxies.

This graphic shows the computer simulation of a black hole from start to finish. Plasma is falling slowly toward the black hole in a (at the upper left). The plasma has a magnetic field, shown by the white lines. It picks up speed as it falls toward the hole in b (at the upper right), c (lower left) and d (lower right). However, the rotating black hole twists up space itself (and the magnetic field lines) and ejects electromagnetic power along the north and south poles above the black hole. The red and white color shows the immense electromagnetic power output, which eventually will pick up particles and form squirting jets. This simulation was conducted using supercomputers at Japan's National Institute for Fusion Science. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04206

This artist's concept shows a black hole with an accretion disk -- a flat structure of material orbiting the black hole -- and a jet of hot gas, called plasma. Using NASA's NuSTAR space telescope and a fast camera called ULTRACAM on the William Herschel Observatory in La Palma, Spain, scientists have been able to measure the distance that particles in jets travel before they "turn on" and become bright sources of light. This distance is called the "acceleration zone." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22085

The blue dots in this field of galaxies, known as the COSMOS field, show galaxies that contain supermassive black holes emitting high-energy X-rays. The black holes were detected by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Array, or NuSTAR, which spotted 32 such black holes in this field and has observed hundreds across the whole sky so far. The other colored dots are galaxies that host black holes emitting lower-energy X-rays, and were spotted by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra data show X-rays with energies between 0.5 to 7 kiloelectron volts, while NuSTAR data show X-rays between 8 to 24 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20865

Black Holes in Caloris

This animation shows the events that serve as the basis of an astrophysics technique called "echo mapping," also known as reverberation mapping. At center is a supermassive black hole surrounded by a disk of material called an accretion disk. As the disk gets brighter it sometimes even releases short flares of visible light. Blue arrows show the light from this flash traveling away from the black hole, both toward an observer on Earth and toward an enormous, doughnut-shaped structure (called a torus) made of dust. The light gets absorbed, causing the dust to heat up and release infrared light. This brightening of the dust is a direct response to — or, one might, say an "echo" — of the changes happening in the disk. Red arrows show this light traveling away from the galaxy, in the same direction as the initial flash of visible light. Thus an observer would see the visible light first, and (with the right equipment) the infrared light later. Astronomers have previously proposed using echo mapping as a means of measuring distances to cosmic objects. If scientists can observe both the initial flare of visible light and the subsequent infrared brightening in the dust, they could in theory use that information to measure the disk's luminosity, which could then be used to measure the distance to that galaxy by comparing it to the galaxy's brightness as seen from Earth. The temperature in the part of the disk closest to the black hole can reach tens of thousands of degrees but decreases with distance. When it reaches about 2,200 degrees Fahrenheit (1,200 Celsius), it is cool enough for dust to form. The more luminous the disk, the farther away from it the dust forms and the longer it takes light from the disk to reach the dust and produce the "echo." The distance from the accretion disk to the inside of the dust doughnut can be billions or trillions of miles. Even light, traveling at 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second, can take months or years to cross it. NASA's Near Earth Object Wide Field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE), previously named WISE, surveys the entire sky about once every six months and is on track to complete 16 such surveys by the end of 2020, providing astronomers with repeated opportunities to observe galaxies and look for signs of those light echoes. A study using data from WISE measured the luminosity of over 500 black hole accretion disks using echo mapping, but the subsequent distance measurements lacked precision compared to other distance measuring techniques. Additional data and an improved understanding of dust torus dynamics could improve those measurements. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23866

When two black holes collide, they release massive amounts of energy in the form of gravitational waves that last a fraction of a second and can be "heard" throughout the universe - if you have the right instruments. Today we learned that the #LIGO project heard the telltale chirp of black holes colliding, fulfilling Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. NASA's LISA mission will look for direct evidence of gravitational waves. <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/23ZbqoE" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/23ZbqoE</a> This video illustrates what that collision might look like.

On June 15, NASA's Swift caught the onset of a rare X-ray outburst from a stellar-mass black hole in the binary system V404 Cygni. Astronomers around the world are watching the event. In this system, a stream of gas from a star much like the sun flows toward a 10 solar mass black hole. Instead of spiraling toward the black hole, the gas accumulates in an accretion disk around it. Every couple of decades, the disk switches into a state that sends the gas rushing inward, starting a new outburst. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-missions-monitor-a-waking-black-hole" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-missions-monitor-a-waki...</a> Credits: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Download this video in HD formats from NASA Goddard's Scientific Visualization Studio <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/details.cgi?aid=11110" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/details.cgi?aid=11110</a>

An artist's concept of a tidal disruption event (TDE) that happens when a star passes fatally close to a supermassive black hole, which reacts by launching a relativistic jet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22355

The beautiful spiral galaxy visible in the center of the image is known as RX J1140.1+0307, a galaxy in the Virgo constellation imaged by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, and it presents an interesting puzzle. At first glance, this galaxy appears to be a normal spiral galaxy, much like the Milky Way, but first appearances can be deceptive! The Milky Way galaxy, like most large galaxies, has a supermassive black hole at its center, but some galaxies are centered on lighter, intermediate-mass black holes. RX J1140.1+0307 is such a galaxy — in fact, it is centered on one of the lowest black hole masses known in any luminous galactic core. What puzzles scientists about this particular galaxy is that the calculations don’t add up. With such a relatively low mass for the central black hole, models for the emission from the object cannot explain the observed spectrum. There must be other mechanisms at play in the interactions between the inner and outer parts of the accretion disk surrounding the black hole. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This computer-simulated image shows a supermassive black hole at the core of a galaxy. The black region in the center represents the black hole’s event horizon, where no light can escape the massive object’s gravitational grip. The black hole’s powerful gravity distorts space around it like a funhouse mirror. Light from background stars is stretched and smeared as the stars skim by the black hole. Credits: NASA, ESA, and D. Coe, J. Anderson, and R. van der Marel (STScI) More info: Astronomers have uncovered a near-record breaking supermassive black hole, weighing 17 billion suns, in an unlikely place: in the center of a galaxy in a sparsely populated area of the universe. The observations, made by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the Gemini Telescope in Hawaii, may indicate that these monster objects may be more common than once thought. Until now, the biggest supermassive black holes – those roughly 10 billion times the mass of our sun – have been found at the cores of very large galaxies in regions of the universe packed with other large galaxies. In fact, the current record holder tips the scale at 21 billion suns and resides in the crowded Coma galaxy cluster that consists of over 1,000 galaxies. More: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/behemoth-black-hole-found-in-an-unlikely-place" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/behemoth-black-hole-fou...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A disk of hot gas swirls around a black hole in this illustration. Some of the gas came from a star that was pulled apart by the black hole, forming the long stream of hot gas on the right, feeding into the disk. These events are formally known as tidal disruption events, or TDEs. It can take just a matter or weeks or months from the destruction of the star to the formation of the disk. The gas gets hotter the closer it gets to the black hole, but the hottest material can be found above the black hole. This hottest material is cloud of plasma (gas atoms with their electrons stripped away) known as a corona. Most TDEs that result in the formation of a corona also produce jets of material that spew into space away from the black hole at its poles. A TDE called AT2021ehb is the first confirmed example of a corona forming without jets in a tidal disruption event. The observation of AT2021ehb makes it possible for scientists to study the formation of jets and coronae separately. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25440

A range of supermassive black holes lights up this new image from NASA NuSTAR. All of the dots are active black holes tucked inside the hearts of galaxies, with colors representing different energies of X-ray light.

This animation shows two massive black holes in the OJ 287 galaxy. The smaller black hole orbits the larger one, which remains stationary in the animation and is surrounded by a disk of gas. When the smaller black hole crashes through the disk, it produces a flare brighter than 1 trillion stars. But the smaller black hole's orbit is elongated and moving relative to the disk, causing the flares to occur irregularly. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23687

This artist concept shows a galaxy with a supermassive black hole at its core. The black hole is shooting out jets of radio waves.

These two data plots from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope show a primitive supermassive black hole top compared to a typical one; usually, dust tori are missing and only gas disks are observed in primitive black holes.

Nearly all black holes come in one of two sizes: stellar mass black holes that weigh up to a few dozen times the mass of our sun or supermassive black holes ranging from a million to several billion times the sun’s mass. Astronomers believe that medium-sized black holes between these two extremes exist, but evidence has been hard to come by, with roughly a half-dozen candidates described so far. A team led by astronomers at the University of Maryland and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center has found evidence for a new intermediate-mass black hole about 5,000 times the mass of the sun. The discovery adds one more candidate to the list of potential medium-sized black holes, while strengthening the case that these objects do exist. The team reported its findings in the September 21, 2015 online edition of Astrophysical Journal Letters. This image, taken with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope, shows the central region of galaxy NGC1313. This galaxy is home to the ultraluminous X-ray source NCG1313X-1, which astronomers have now determined to be an intermediate-mass black hole candidate. NGC1313 is 50,000 light-years across and lies about 14 million light-years from the Milky Way in the southern constellation Reticulum. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/astronomers-identify-a-new-mid-size-black-hole" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/astronomers-identify-a-new-m...</a> Image credit: European Southern Observatory #nasagoddard #blackhole #space <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The real monster black hole is revealed in this image from NASA Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array of colliding galaxies Arp 299.

This artist conception illustrates one of the most primitive supermassive black holes known central black dot at the core of a young, star-rich galaxy.

This cartoon shows how magnetic waves, called Alfvén S-waves, propagate outward from the base of black hole jets. The jet is a flow of charged particles, called a plasma, which is launched by a black hole. The jet has a helical magnetic field (yellow coil) permeating the plasma. The waves then travel along the jet, in the direction of the plasma flow, but at a velocity determined by both the jet's magnetic properties and the plasma flow speed. The BL Lac jet examined in a new study is several light-years long, and the wave speed is about 98 percent the speed of light. Fast-moving magnetic waves emanating from a distant supermassive black hole undulate like a whip whose handle is being shaken by a giant hand, according to a study using data from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory's Very Long Baseline Array. Scientists used this instrument to explore the galaxy/black hole system known as BL Lacertae (BL Lac) in high resolution. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19822

This is an illustration of a supermassive black hole, weighing as much as 21 million suns, located in the middle of the ultradense galaxy M60-UCD1. The dwarf galaxy is so dense that millions of stars fill the sky as seen by an imaginary visitor. Because no light can escape from the black hole, it appears simply in silhouette against the starry background. The black hole's intense gravitational field warps the light of the background stars to form ring-like images just outside the dark edges of the black hole's event horizon. Combined observations by the Hubble Space Telescope and Gemini North telescope determined the presence of the black hole inside such a small and dense galaxy. More info: Astronomers using data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and ground observation have found an unlikely object in an improbable place -- a monster black hole lurking inside one of the tiniest galaxies ever known. The black hole is five times the mass of the one at the center of our Milky Way galaxy. It is inside one of the densest galaxies known to date -- the M60-UCD1 dwarf galaxy that crams 140 million stars within a diameter of about 300 light-years, which is only 1/500th of our galaxy’s diameter. If you lived inside this dwarf galaxy, the night sky would dazzle with at least 1 million stars visible to the naked eye. Our nighttime sky as seen from Earth’s surface shows 4,000 stars. The finding implies there are many other compact galaxies in the universe that contain supermassive black holes. The observation also suggests dwarf galaxies may actually be the stripped remnants of larger galaxies that were torn apart during collisions with other galaxies rather than small islands of stars born in isolation. “We don’t know of any other way you could make a black hole so big in an object this small,” said University of Utah astronomer Anil Seth, lead author of an international study of the dwarf galaxy published in Thursday’s issue of the journal Nature. Seth’s team of astronomers used the Hubble Space Telescope and the Gemini North 8-meter optical and infrared telescope on Hawaii’s Mauna Kea to observe M60-UCD1 and measure the black hole’s mass. The sharp Hubble images provide information about the galaxy’s diameter and stellar density. Gemini measures the stellar motions as affected by the black hole’s pull. These data are used to calculate the mass of the black hole. Black holes are gravitationally collapsed, ultra-compact objects that have a gravitational pull so strong that even light cannot escape. Supermassive black holes -- those with the mass of at least one million stars like our sun -- are thought to be at the centers of many galaxies. The black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy has the mass of four million suns. As heavy as that is, it is less than 0.01 percent of the Milky Way’s total mass. By comparison, the supermassive black hole at the center of M60-UCD1, which has the mass of 21 million suns, is a stunning 15 percent of the small galaxy’s total mass. “That is pretty amazing, given that the Milky Way is 500 times larger and more than 1,000 times heavier than the dwarf galaxy M60-UCD1,” Seth said. One explanation is that M60-UCD1 was once a large galaxy containing 10 billion stars, but then it passed very close to the center of an even larger galaxy, M60, and in that process all the stars and dark matter in the outer part of the galaxy were torn away and became part of M60. The team believes that M60-UCD1 may eventually be pulled to fully merge with M60, which has its own monster black hole that weighs a whopping 4.5 billion solar masses, or more than 1,000 times bigger than the black hole in our galaxy. When that happens, the black holes in both galaxies also likely will merge. Both galaxies are 50 million light-years away. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington. For images and more information about Hubble, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This artist concept illustrates a supermassive black hole with millions to billions times the mass of our sun. Supermassive black holes are enormously dense objects buried at the hearts of galaxies.

Scientists measure the spin rates of supermassive black holes by spreading the X-ray light into different colors. The light comes from accretion disks that swirl around black holes, as shown in both of the artist concepts.

This artist concept illustrates what the flaring black hole called GX 339-4 might look like. Infrared observations from NASA WISE reveal the best information yet on the chaotic and extreme environments of this black hole jets.

Top: An illustration of NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, in orbit. The unique school bus-long mast allows NuSTAR to focus high energy X-rays. Lower-left: A color image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope of one of the nine galaxies targeted by NuSTAR in search of hidden black holes. Bottom-right: An artist's illustration of a supermassive black hole, actively feasting on its surroundings. The central black hole is hidden from direct view by a thick layer of encircling gas and dust. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19348

This three-dimensional illustration shows how the rotating space around a black hole twists up the magnetic field in the plasma falling toward the black hole. The black sphere at the center of the figure is the black hole itself. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04207

This two-panel illustration shows a black hole surrounded by a disk of gas, before and after the disk is partially dispersed. In the left panel, the ball of white light above the black hole is the black hole corona, a collection of ultra-hot gas particles that forms as gas from the disk falls into the black hole. The streak of debris falling toward the disk is what remains of a star that was torn apart by the black hole's gravity. The right panel shows the black hole after the debris from the star has dispersed some of the gas in the disk, causing the corona to disappear. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23864

Chandra X-Ray Observatory provided this composite X-ray (blue and green) and optical (red) image of the active galaxy NGC 1068 showing gas blowing away in a high-speed wind from the vicinity of a central supermassive black hole. Regions of intense star formation in the irner spiral arms of the galaxy are highlighted by both optical and x-ray emissions. A doughnut shaped cloud of cool gas and dust surrounding the black hole, known as the torus, appears as the elongated white spot . It has has a mass of about 5 million suns and is estimated to extend from within a few light years of the black hole out to about 300 light years.

This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: : <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11530" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11530</a>

Some 290 million years ago, a star much like the sun wandered too close to the central black hole of its galaxy. Intense tides tore the star apart, which produced an eruption of optical, ultraviolet and X-ray light that first reached Earth in 2014. Now, a team of scientists using observations from NASA's Swift satellite have mapped out how and where these different wavelengths were produced in the event, named ASASSN-14li, as the shattered star's debris circled the black hole. "We discovered brightness changes in X-rays that occurred about a month after similar changes were observed in visible and UV light," said Dheeraj Pasham, an astrophysicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and the lead researcher of the study. "We think this means the optical and UV emission arose far from the black hole, where elliptical streams of orbiting matter crashed into each other." Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2nLmSoa" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2nLmSoa</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Herschel Space Observatory has shown that galaxies with the most powerful, active, supermassive black holes at their cores produce fewer stars than galaxies with less active black holes in this artist concept.

This artist concept shows a supermassive black hole at the center of a remote galaxy digesting the remnants of a star.

This false-color image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows a distant galaxy yellow that houses a quasar, a super-massive black hole circled by a ring, or torus, of gas and dust.

Magenta spots in this image from NASA NuSTAR show two black holes in the Circinus galaxy, located 13 million light-years from Earth in the Circinus constellation.

NASA NuSTAR will be able to identify individual black holes making up the diffuse X-ray glow, also called the X-ray background. At bottom right is a simulated view of what NuSTAR will see.

The magenta spots in this image from NASA NuSTAR show two black holes in the spiral galaxy called NGC 1313, or the Topsy Turvy galaxy, located about 13 million light-years away in the Reticulum constellation.

This computer-simulated image shows gas from a tidally shredded star falling into a black hole. Astronomers observed the flare in ultraviolet light using NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer.

NASA Spitzer and Chandra space telescopes have uncovered a long-lost population of active supermassive black holes, or quasars located deep in the bellies of distant, massive galaxies circled in blue.

This artist's impression depicts the accretion disc surrounding a black hole, in which the inner region of the disc precesses. "Precession" means that the orbit of material surrounding the black hole changes orientation around the central object. In these three views, the precessing inner disc shines high-energy radiation that strikes the matter in the surrounding accretion disc. This causes the iron atoms in that disc to emit X-rays, depicted as the glow on the accretion disc to the right (in view a), to the front (in view b) and to the left (in view c) (see Figure 1). In a study published in July 2016, astronomers used data from ESA's XMM-Newton X-ray Observatory and NASA's NuSTAR telescope to measure this "wobble" in X-ray emission from excited iron atoms. Scientists interpreted this as evidence for the Lense-Thirring effect -- a name for the precession phenomenon -- in the strong gravitational field of a black hole. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20697

Every second a star somewhere out in the universe explodes as a supernova. But some extremely massive stars go out with a whimper instead of a bang. When they do, they can collapse under the crushing tug of gravity and vanish out of sight, only to leave behind a black hole. The doomed star N6946-BH1 was 25 times as massive as our sun. It began to brighten weakly in 2009. But, by 2015, it appeared to have winked out of existence. By a careful process of elimination, based on observations by the Large Binocular Telescope and NASA's Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, researchers eventually concluded that the star must have become a black hole. This may be the fate for extremely massive stars in the universe. This illustration shows the final stages in the life of a supermassive star that fails to explode as a supernova, but instead implodes to form a black hole. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21466

A 2 week observation through the optic eye of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory revealed this sturning explosion occurring in the super massive black hole at the Milky Way's center, known as Sagittarius A or Sgr A*. Huge lobes of 20-million degree Centigrade gas ( red loops in image) flank both sides of the black hole and extend over dozens of light years indicating that enormous explosions occurred several times over the last 10 thousand years. Weighing in at 3-million times the mass of the sun, the Sgr A* is a starved black hole, possibly because explosive events in the past have cleared much of the gas around it.

SCI2017_0007: Artist illustration of the thick ring of dust that can obscure the energetic processes that occur near the supermassive black hole of an active galactic nuclei. The SOFIA studies suggest that the dust distribution is about 30 percent smaller than previously thought. Credit: NASA/SOFIA/Lynette Cook

This new false-colored image from NASA Hubble, Chandra and Spitzer space telescopes shows a giant jet of particles that has been shot out from the vicinity of a type of supermassive black hole called a quasar.

This zoomed-in view of a portion of the all-sky survey from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer shows a collection of quasar candidates shown in yellow circles. Quasars are supermassive black holes feeding off gas and dust.

This plot of data from two space telescopes, NASA NuSTAR and ESA XMM-Newton determines for the first time the shape of ultra-fast winds from supermassive black holes, or quasars.

This plot of data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope indicates that a flat, spiral galaxy called NGC 3621 has a feeding, supermassive black hole lurking within it.

This infographic explains a popular theory of active supermassive black holes, referred to as the unified model -- and how new data from NASA WISE, is at conflict with the model.

Tidal disruption event Every galaxy has a black hole at its center. Usually they are quiet, without gas accretions, like the one in our Milky Way. But if a star creeps too close to the black hole, the gravitational tides can rip away the star’s gaseous matter. Like water spinning around a drain, the gas swirls into a disk around the black hole at such speeds that it heats to millions of degrees. As an inner ring of gas spins into the black hole, gas particles shoot outward from the black hole’s polar regions. Like bullets shot from a rifle, they zoom through the jets at velocities close to the speed of light. Astronomers using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope observed correlations between supermassive black holes and an event similar to tidal disruption, pictured above in the Centaurus A galaxy. Certain galaxies have shining centers, illuminated by heated gas circling around a supermassive black hole. Matter escapes where it can, forming two jets of plasma moving near the speed of light. To learn more about the relationship between galaxies and the black holes at their cores, go to NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/</a> -------------------------------- Original caption: A team of astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope found an unambiguous link between the presence of supermassive black holes that power high-speed, radio-signal-emitting jets and the merger history of their host galaxies. Almost all galaxies with the jets were found to be merging with another galaxy, or to have done so recently. Credit: NASA/ESA/STScI <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A supermassive black hole is depicted in this artist's concept, surrounded by a swirling disk of material falling onto it. The purplish ball of light above the black hole, a feature called the corona, contains highly energetic particles that generate X-ray light. If you could view the corona with your eyes, it would appear nearly invisible since we can't see its X-ray light. The corona gathers inward (left), becoming brighter, before shooting away from the black hole (middle and right). Astronomers don't know why the coronas shift, but they have learned that this process leads to a brightening of X-ray light that can be observed by telescopes. Normally, before a black hole's corona shifts, there is already an effect at work called relativistic boosting. As X-ray light from the corona reflects off the black hole's surrounding disk of material -- which is traveling near half the speed of light -- the X-ray light becomes brightened, as seen on the left side of the illustration. This boosting occurs on the side of the disk where the material is traveling toward us. The opposite effect, a dimming of the X-ray light, occurs on the other side of the disk moving away from us. Another form of relativistic boosting happens when the corona shoots away from the black hole, and later collapses. Its X-ray light is also brightened as the corona travels toward us at very fast speeds, leading to X-ray flares. In 2014, NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, and Swift space telescopes witnessed an X-flare from the supermassive black hole in a distant galaxy called Markarian 335. The observations allowed astronomers to link a shifting corona to an X-ray flare for the first time. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20051

Peering more than 10 billion light-years into the distance, WISE has found tens of millions of actively feeding supermassive lack holes across the full sky. The orange circles highlight those that the telescope identified in a small patch of sky; the two zoomed-in images came from the Hubble Space Telescope. WISE easily sees these monsters because their powerful, accreting black holes warm the dust, causing it to glow in infrared light. The blue circles indicate black holes that were detected using visible-light imagers. In most, that light is blocked by dust. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23588

NASA image release May 20, 2011 <b>To see a really cool video related to this image go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5740451675/in/photostream">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5740451675/in/photostream</a></b> This composite of visible, microwave (orange) and X-ray (blue) data reveals the jets and radio-emitting lobes emanating from Centaurus A's central black hole. Credit: ESO/WFI (visible); MPIfR/ESO/APEX/A.Weiss et al. (microwave); NASA/CXC/CfA/R.Kraft et al. (X-ray) To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/radio-particle-jets.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/radio-particle-jets...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

Black holes are tremendous objects whose immense gravity can distort and twist space-time, the fabric that shapes our universe as this chart from NASA NuSTAR and ESA XMM-Newton telescope illustrates.

This data plot captured by NASA Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, shows X-ray light streaming from regions near a supermassive black hole known as Markarian 335.

A growing black hole, called a quasar, is seen at the center of a faraway galaxy in this artist concept. Astronomers using NASA Spitzer and Chandra space telescopes discovered swarms of similar quasars hiding in dusty galaxies in the distant universe.

Supermassive black holes at the cores of galaxies blast radiation and ultra-fast winds outward, as illustrated in this artist conception based on NASA NuSTAR and ESA XMM-Newton telescopes.

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

With its all-sky infrared survey, NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, has identified millions of quasar candidates. Quasars are supermassive black holes with masses millions to billions times greater than our sun.

NASA NuSTAR has captured these first, focused views of the supermassive black hole at the heart of our Milky Way galaxy in high-energy X-ray light.

NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, helped lead astronomers to what appears to be a new example of a dancing black hole duo.

This illustration shows a glowing stream of material from a star as it is being devoured by a supermassive black hole in a tidal disruption flare. When a star passes within a certain distance of a black hole -- close enough to be gravitationally disrupted -- the stellar material gets stretched and compressed as it falls into the black hole. In the process of being accreted, the gas heats up and creates a lot of optical and ultraviolet light, which destroys nearby dust but merely heats dust further out. The farther dust that is heated emits a large amount of infrared light. In recent years, a few dozen such flares have been discovered, but they are not well understood. Astronomers gained new insights into tidal disruption flares thanks to data from NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE). Studies using WISE data characterized tidal disruption flares by studying how surrounding dust absorbs and re-emits their light, like echoes. This approach allowed scientists to measure the energy of flares from stellar tidal disruption events more precisely than ever before. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20027

This chart illustrates relative masses of super-dense cosmic objects, ranging from white dwarfs to supermassive black holes encased in the cores of most galaxies. The first three dead stars left all form when stars more massive than our sun explode.

The spiral galaxy NGC 3627, located about 30 million light years from Earth as seen by four NASA telescopes; inset shows the central region, which contains a bright X-ray source that is likely powered by material falling onto a supermassive black hole.

Observations from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope provide strong evidence that the slender, bulgeless galaxies can, like their chubbier counterparts, harbor supermassive black holes at their cores in this artist concept.

This diagram illustrates research from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer showing that black holes once they reach a critical size can put the brakes on new star formation in elliptical galaxies.

NASA image release September 29, 2011 This image of the distant active galaxy Markarian 509 was taken in April 2007 with the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 2. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/turbulent-black-hole.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/turbulent-black...</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, G. Kriss (STScI), and J. de Plaa (SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research); Acknowledgment: B. Peterson (Ohio State University) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release May 20, 2011 <b>To see a really cool video related to this image go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5740451675/in/photostream">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5740451675/in/photostream</a></b> The giant elliptical galaxy NGC 5128 is the radio source known as Centaurus A. Vast radio-emitting lobes (shown as orange in this optical/radio composite) extend nearly a million light-years from the galaxy. Credit: Capella Observatory (optical), with radio data from Ilana Feain, Tim Cornwell, and Ron Ekers (CSIRO/ATNF), R. Morganti (ASTRON), and N. Junkes (MPIfR). To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/radio-particle-jets.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/radio-particle-jets...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

An image of the galaxy Arp299B, which is undergoing a merging process with Arp299A (the galaxy to the left), captured by NASA's Hubble space telescope. The inset features an artist's illustration of a tidal disruption event (TDE), which occurs when a star passes fatally close to a supermassive black hole. A TDE was recently observed near the center of Arp299B. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22356

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians complete a second fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians perform a fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians perform a fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to do a fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to do a fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians complete a second fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians perform a fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Pegasus XL launch vehicle awaits a fillet and wing fit check. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to complete a second fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians complete a second fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians complete a second fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to complete a second fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to complete a second fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to do a fillet and wing fit check on the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus rocket will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) into space. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be flown on the Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 carrier aircraft to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit science.nasa.gov/missions/nustar/. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

This artist concept shows a feeding, or active, supermassive black hole with a jet streaming outward at nearly the speed of light. Such active black holes are often found at the hearts of elliptical galaxies.

These images, taken by NASA black-hole hunter, NuSTAR, are the first, focused high-energy X-ray views of the area surrounding the supermassive black hole, called Sagittarius A*, at the center of our galaxy.

This image from NASA WISE spacecraft shows a blazar, a voracious supermassive black hole inside a galaxy with a jet that happens to be pointed right toward Earth. Active black holes are often found at the hearts of elliptical galaxies.

This artist concept depicts a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy. NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer found evidence that black holes once they grow to a critical size stifle the formation of new stars in elliptical galaxies.

This image of the suspected Black Hole, Cygnus X-1, was the first object seen by the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2/Einstein Observatory. According to the theories to date, one concept of a black hole is a star, perhaps 10 times more massive than the Sun, that has entered the last stages of stelar evolution. There is an explosion triggered by nuclear reactions after which the star's outer shell of lighter elements and gases is blown away into space and the heavier elements in the stellar core begin to collapse upon themselves. Once this collapse begins, the inexorable force of gravity continues to compact the material until it becomes so dense it is squeezed into a mere point and nothing can escape from its extreme gravitational field, not even light. The HEAO-2, the first imaging and largest x-ray telescope built to date, was capable of producing actual photographs of x-ray objects. Shortly after launch, the HEAO-2 was nicknamed the Einstein Observatory by its scientific experimenters in honor of the centernial of the birth of Albert Einstein, whose concepts of relativity and gravitation have influenced much of modern astrophysics, particularly x-ray astronomy.

Artist concept illustrates a quasar, or feeding black hole, similar to APM 08279+5255, where astronomers discovered huge amounts of water vapor. Gas and dust likely form a torus around the central black hole, with clouds of charged gas above and below.
This Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) image is a spectrum of a black hole, which is similar to the colorful spectrum of sunlight produced by a prism. The x-rays of interest are shown here recorded in bright stripes that run rightward and leftward from the center of the image. These x-rays are sorted precisely according to their energy with the highest-energy x-rays near the center of the image and the lower-energy x-rays farther out. The spectrum was obtained by using the Low Energy Transmission Grating (LETG), which intercepts x-rays and changes their direction by the amounts that depend sensitively on the x-ray energy. The assembly holds 540 gold transmission gratings. When in place behind the mirrors, the gratings intercept the x-rays reflected from the telescope. The bright spot at the center is due to a fraction of the x-ray radiation that is not deflected by the LETG. The spokes that intersect the central spot and the faint diagonal rays that flank the spectrum itself are artifacts due to the structure that supports the LETG grating elements. (Photo credit: NASA Cfa/J. McClintock et al)

This artist concept shows NASA NuSTAR mission orbiting Earth. NuSTAR will hunt for hidden black holes and other exotic cosmic objects.

Black-hole-powered galaxies called blazars are the most common sources detected by NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. As matter falls toward the supermassive black hole at the galaxy's center, some of it is accelerated outward at nearly the speed of light along jets pointed in opposite directions. When one of the jets happens to be aimed in the direction of Earth, as illustrated here, the galaxy appears especially bright and is classified as a blazar. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20912
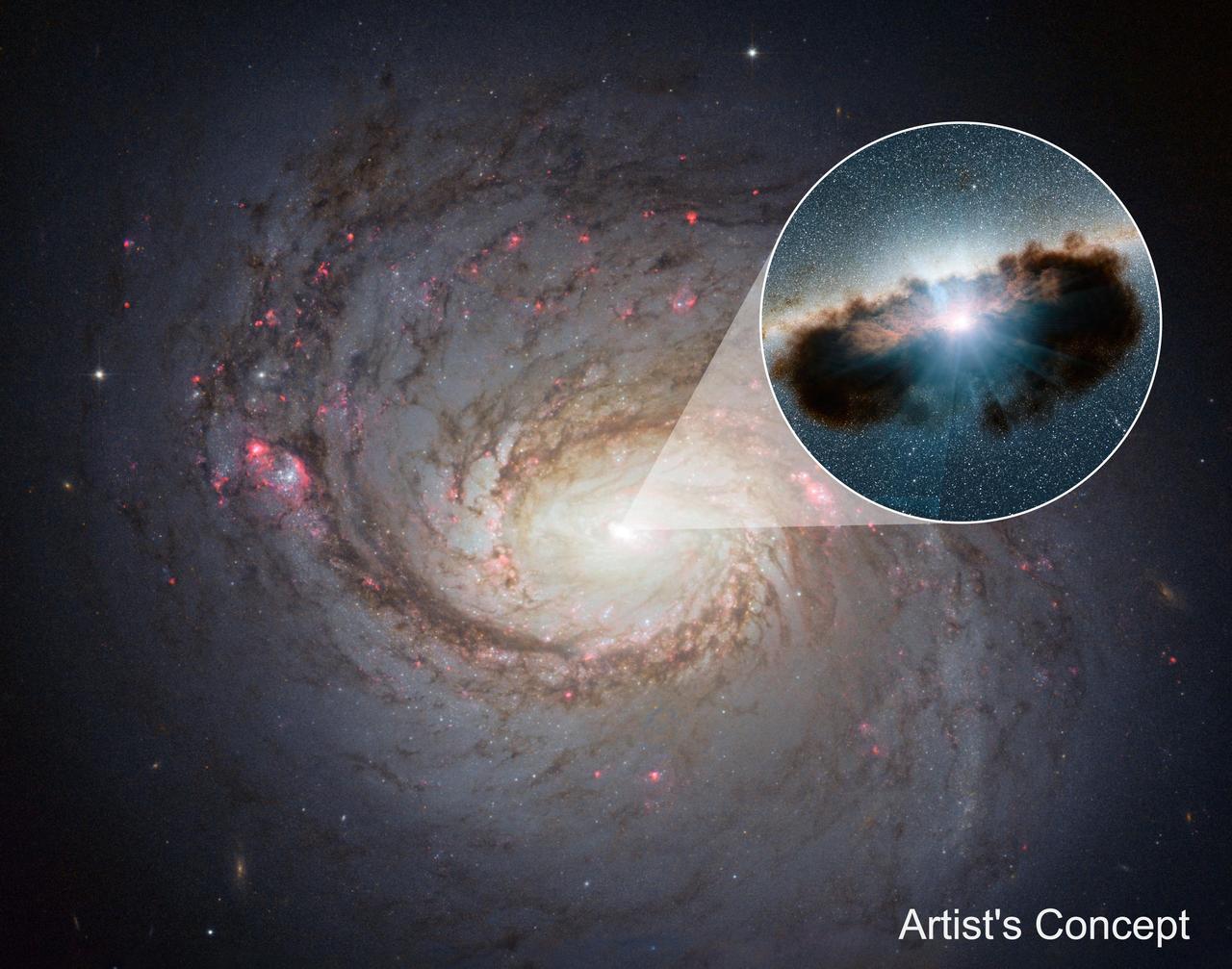
Galaxy NGC 1068 can be seen in close-up in this view from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. NuSTAR's high-energy X-rays eyes were able to obtain the best view yet into the hidden lair of the galaxy's central, supermassive black hole. This active black hole -- shown as an illustration in the zoomed-in inset -- is one of the most obscured known, meaning that it is surrounded by extremely thick clouds of gas and dust. The NuSTAR data revealed that the torus of gas and dust surrounding the black hole, also referred to as a doughnut, is more clumpy than previously thought. doughnuts around active, supermassive black holes were originally proposed in the mid-1980s to be smooth entities. More recently, researchers have been finding that doughnuts are not so smooth but have lumps. NuSTAR's latest finding shows that this is true for even the thickest of doughnuts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20058
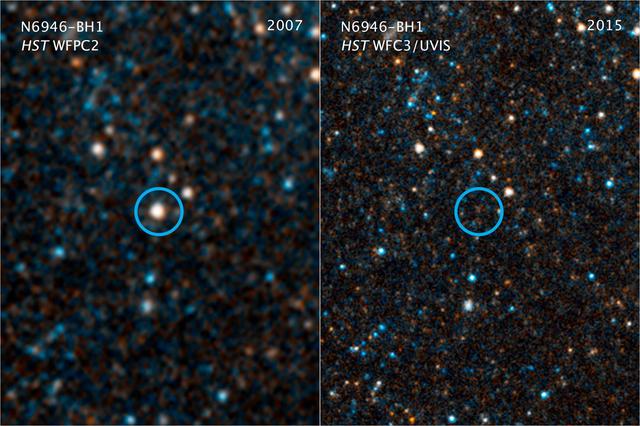

This pair of visible-light and near-infrared photos from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows the giant star N6946-BH1 before and after it vanished out of sight by imploding to form a black hole. The left image shows the star, which is 25 times the mass of our sun, as it looked in 2007. In 2009, the star shot up in brightness to become over 1 million times more luminous than our sun for several months. But then it seemed to vanish, as seen in the right panel image from 2015. A small amount of infrared light has been detected from where the star used to be. This radiation probably comes from debris falling onto a black hole. The black hole is located 22 million light-years away in the spiral galaxy NGC 6946. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21467
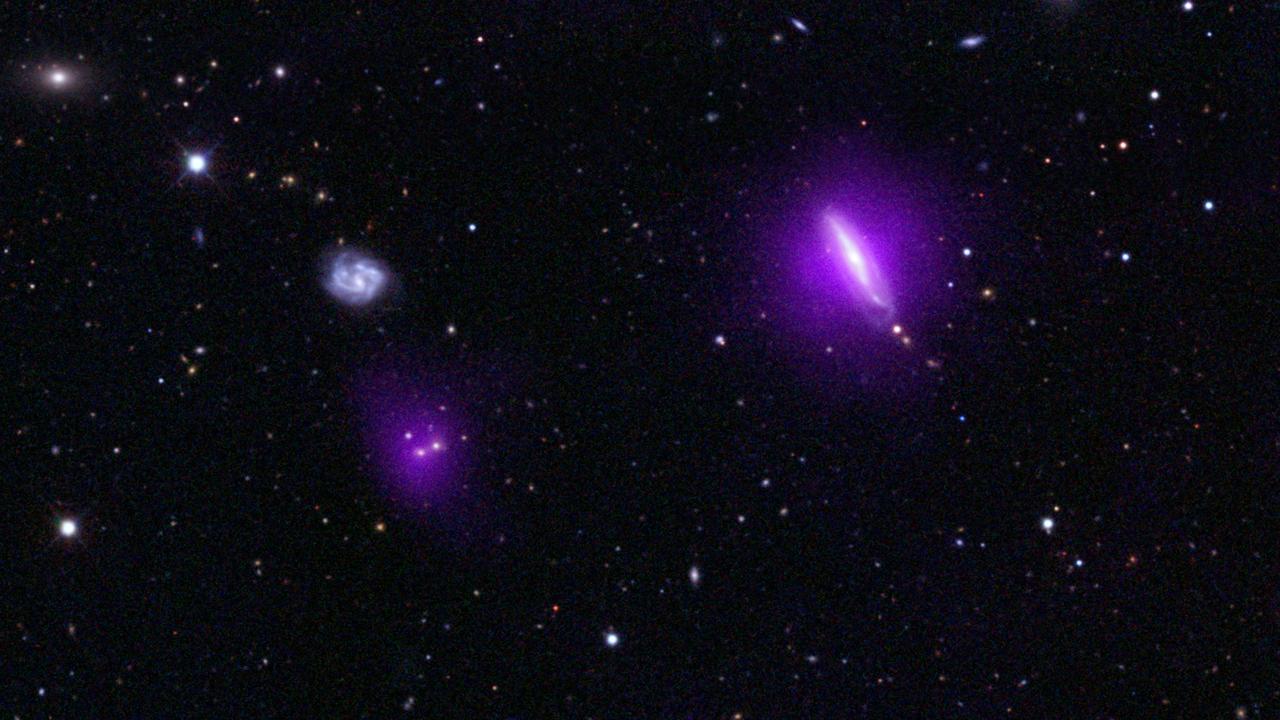

NASA NuSTAR serendipitous discovery in this field lies to the left of a galaxy, called IC751, at which the telescope originally intended to look.
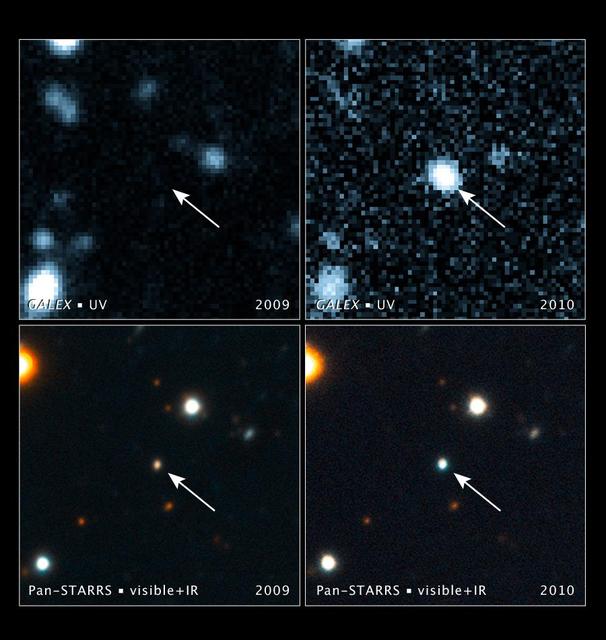

These images, taken with NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer and the Pan-STARRS1 telescope in Hawaii, show a brightening inside a galaxy caused by a flare from its nucleus. The arrow in each image points to the galaxy.

This artist concept illustrates the frenzied activity at the core of our Milky Way galaxy. The galactic center hosts a supermassive black hole in the region known as Sagittarius A*, or Sgr A*, with a mass of about four million times that of our sun.
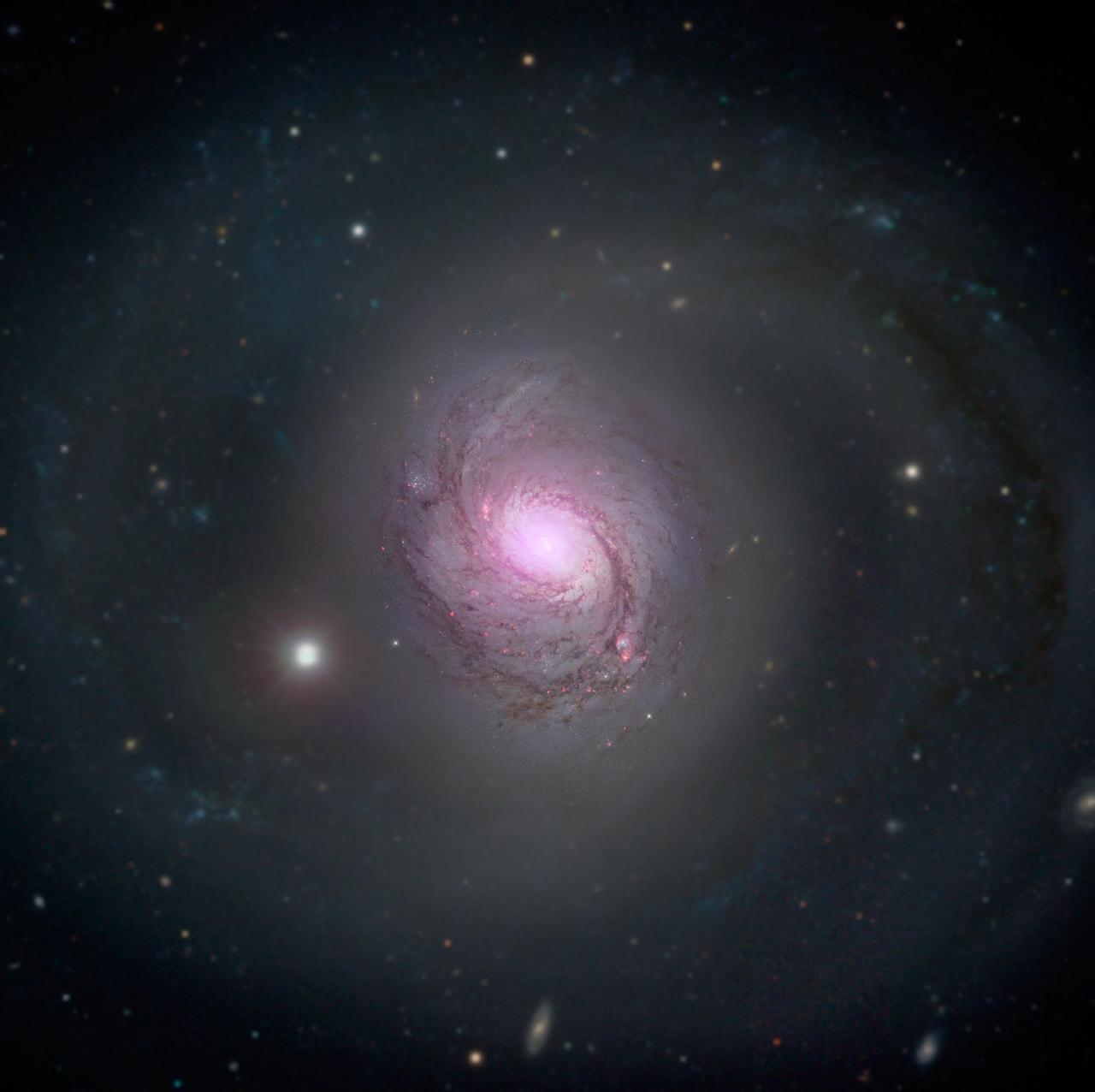

Galaxy NGC 1068 is shown in visible light and X-rays in this composite image. High-energy X-rays (magenta) captured by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, are overlaid on visible-light images from both NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The X-ray light is coming from an active supermassive black hole, also known as a quasar, in the center of the galaxy. This supermassive black hole has been extensively studied due to its relatively close proximity to our galaxy. NGC 1068 is about 47 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus. The supermassive black hole is also one of the most obscured known, blanketed by thick clouds of gas and dust. NuSTAR's high-energy X-ray view is the first to penetrate the walls of this black hole's hidden lair. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20057