![In many ways, Mars bears remarkable similarities to Earth, but in some ways it is drastically different. Scientists often use Earth as an example, or analog, to help us to understand the geologic history of the Red Planet. As we continue to study Mars, it is vitally important to remember in what ways it differs from Earth. One very apparent way, readily observed from orbit, has to do with its preservation of numerous craters of all sizes, which are densest in its Southern hemisphere. Earth has comparatively little preserved craters -- about 1,000 to 1,500 times fewer -- due to very active geologic processes, especially involving water. When it comes to impact craters, there are some things that can no longer be observed on Earth, but can be observed on Mars. This color composite shows one such example. It covers a portion of the northern central peak of an unnamed, 20-kilometer crater that contains abundant fragmental bedrock called "breccia." The geological relationships here suggest that these breccias include ones formed by the host crater, and others formed from numerous impacts in the distant past. Because there are fewer craters preserved on Earth, terrestrial central uplifts do not expose bedrock formed by previous craters. It may have been the case in the past, but such craters were destroyed over geologic time. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.9 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28 centimeters (11 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 82 centimeters (32 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21455](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21455/PIA21455~medium.jpg)
In many ways, Mars bears remarkable similarities to Earth, but in some ways it is drastically different. Scientists often use Earth as an example, or analog, to help us to understand the geologic history of the Red Planet. As we continue to study Mars, it is vitally important to remember in what ways it differs from Earth. One very apparent way, readily observed from orbit, has to do with its preservation of numerous craters of all sizes, which are densest in its Southern hemisphere. Earth has comparatively little preserved craters -- about 1,000 to 1,500 times fewer -- due to very active geologic processes, especially involving water. When it comes to impact craters, there are some things that can no longer be observed on Earth, but can be observed on Mars. This color composite shows one such example. It covers a portion of the northern central peak of an unnamed, 20-kilometer crater that contains abundant fragmental bedrock called "breccia." The geological relationships here suggest that these breccias include ones formed by the host crater, and others formed from numerous impacts in the distant past. Because there are fewer craters preserved on Earth, terrestrial central uplifts do not expose bedrock formed by previous craters. It may have been the case in the past, but such craters were destroyed over geologic time. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.9 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28 centimeters (11 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 82 centimeters (32 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21455
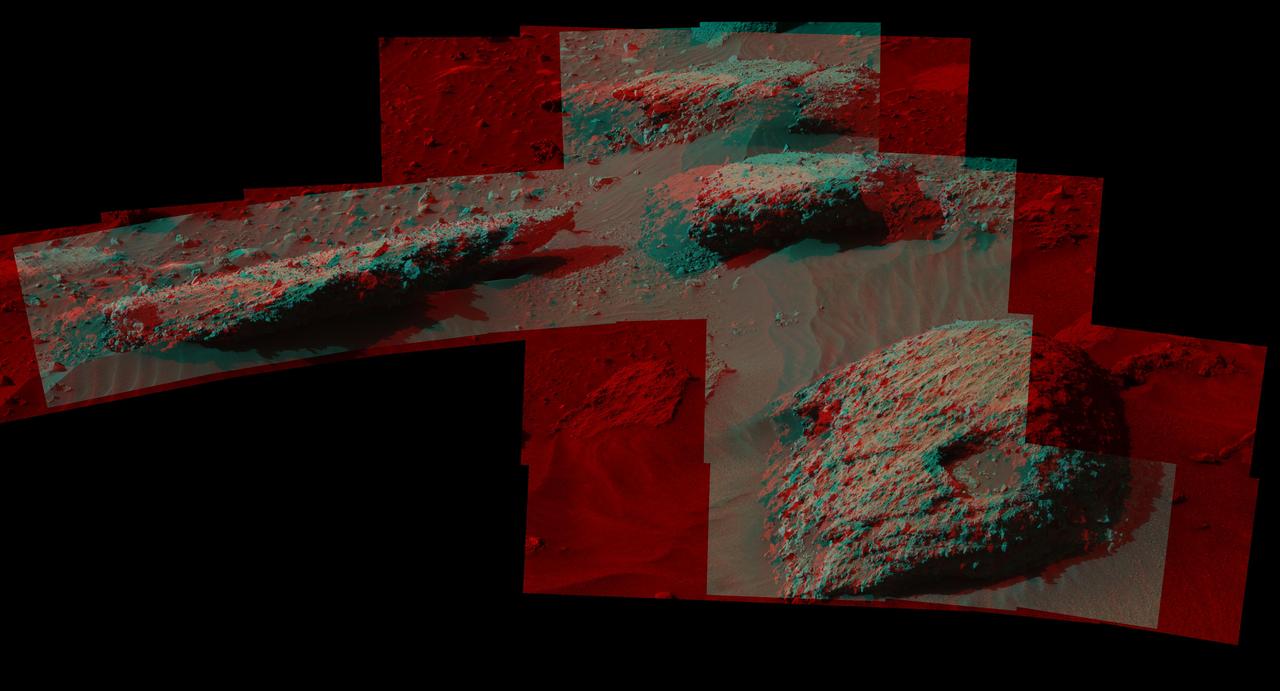

This stereo scene from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars Rover shows boulders composed, in part, of pebble-size (0.2 to 2.6 inches, or 0.5 to 6.5 centimeters across) and larger rock fragments. The size and shape of the fragments provide clues to the origins of these boulders. This image is an anaglyph that appears three dimensional when viewed through red-blue glasses with the red lens on the left. The separate right-eye and left-eye views combined into the stereo version are Figure 1 and Figure 2. Mastcam's right-eye camera has a telephoto lens, with focal length of 100 millimeters. The left-eye camera provides a wider view, with a 34-millimeter lens. These images were taken on July 22, 2016, during the 1,408th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. For scale, the relatively flat rock at left is about 5 feet (1.5 meters) across. The rock in the foreground at right is informally named "Balombo." The group of boulders is at a site called "Bimbe." The Curiosity team chose to drive the rover to Bimbe to further understand patches of boulders first identified from orbit and seen occasionally on the rover's traverse. The boulders at Bimbe consist of multiple rock types. Some include pieces, or "clasts," of smaller, older rock cemented together, called breccias or conglomerates. The shapes of the inclusion clasts -- whether they are rounded or sharp-edged -- may indicate how far the clasts were transported, and by what processes. Breccias have more angular clasts, while conglomerates have more rounded clasts. As is clear by looking at these boulders, they contain both angular and rounded clasts, leading to some uncertainty about how they formed. Conglomerate rocks such as "Hottah" were inspected near Curiosity's landing site and interpreted as part of an ancient streambed. Breccias are generally formed by consolidation of fragments under pressure. On Mars such pressure might come from crater-forming impact, or by deep burial and exhumation. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20836
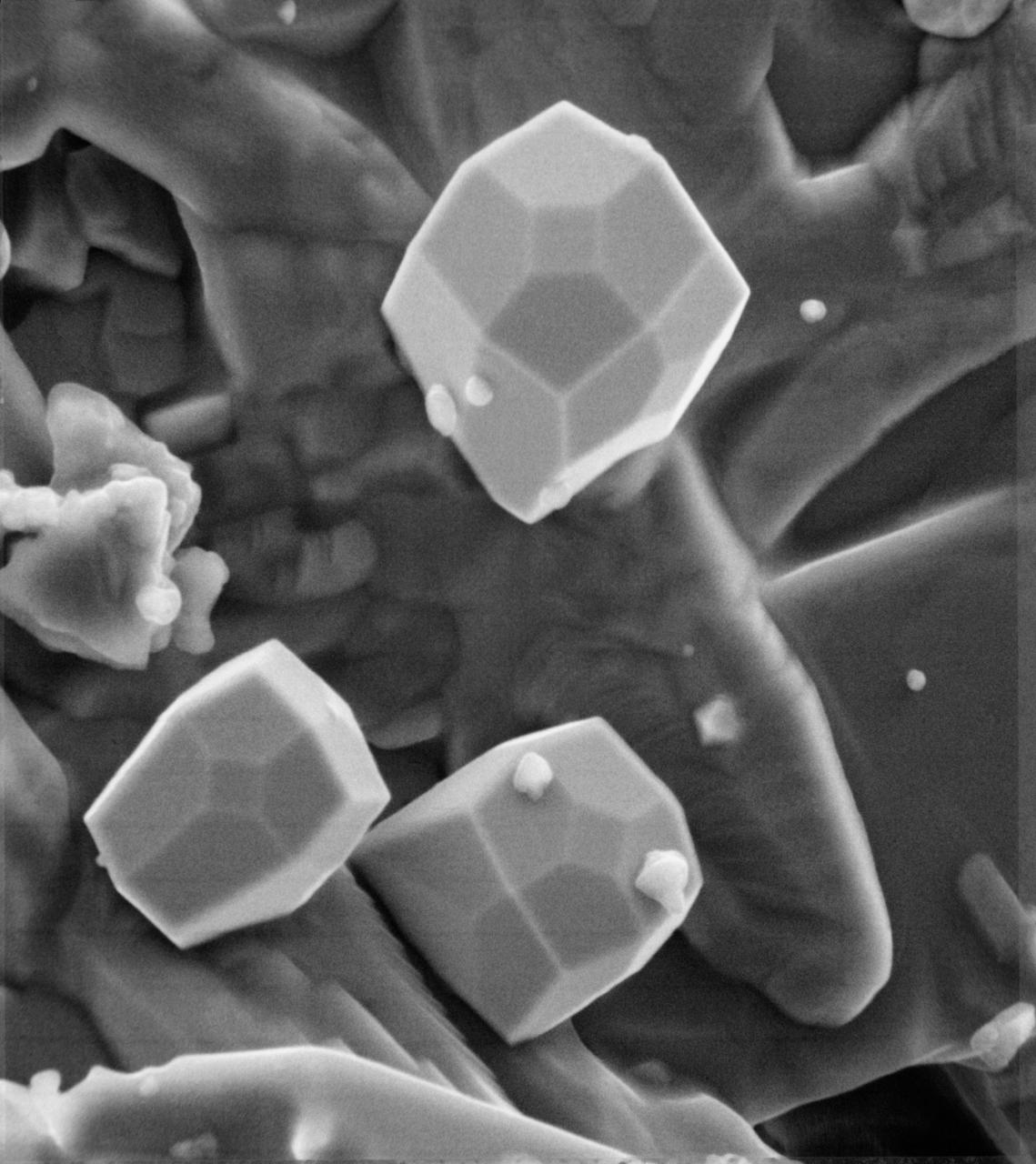

A scanning electron microscope photograph of iron crystals which grow in a small vug or cavity in a recrystallized breccia (fragmented rock) from the Apollo 15 Hadley-Apennino lunar landing site. The largest crystal is three microns across. Perfectly developed crystals such as these indicate slow formation from a hot vapor as the rock was cooling. The crystals are resting on an interlocking lattice of pyroxene (calsium-magnesium-iron silicate).
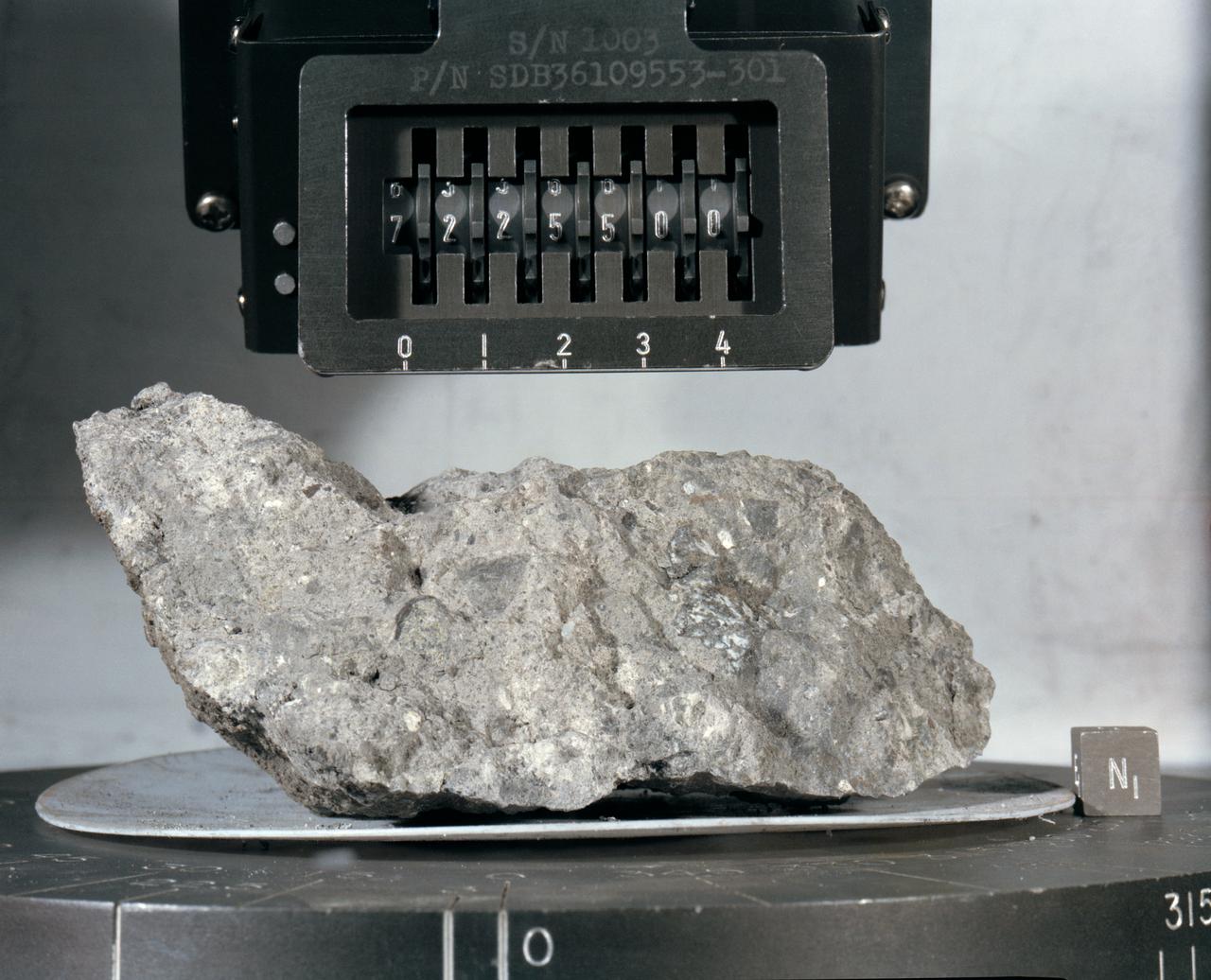

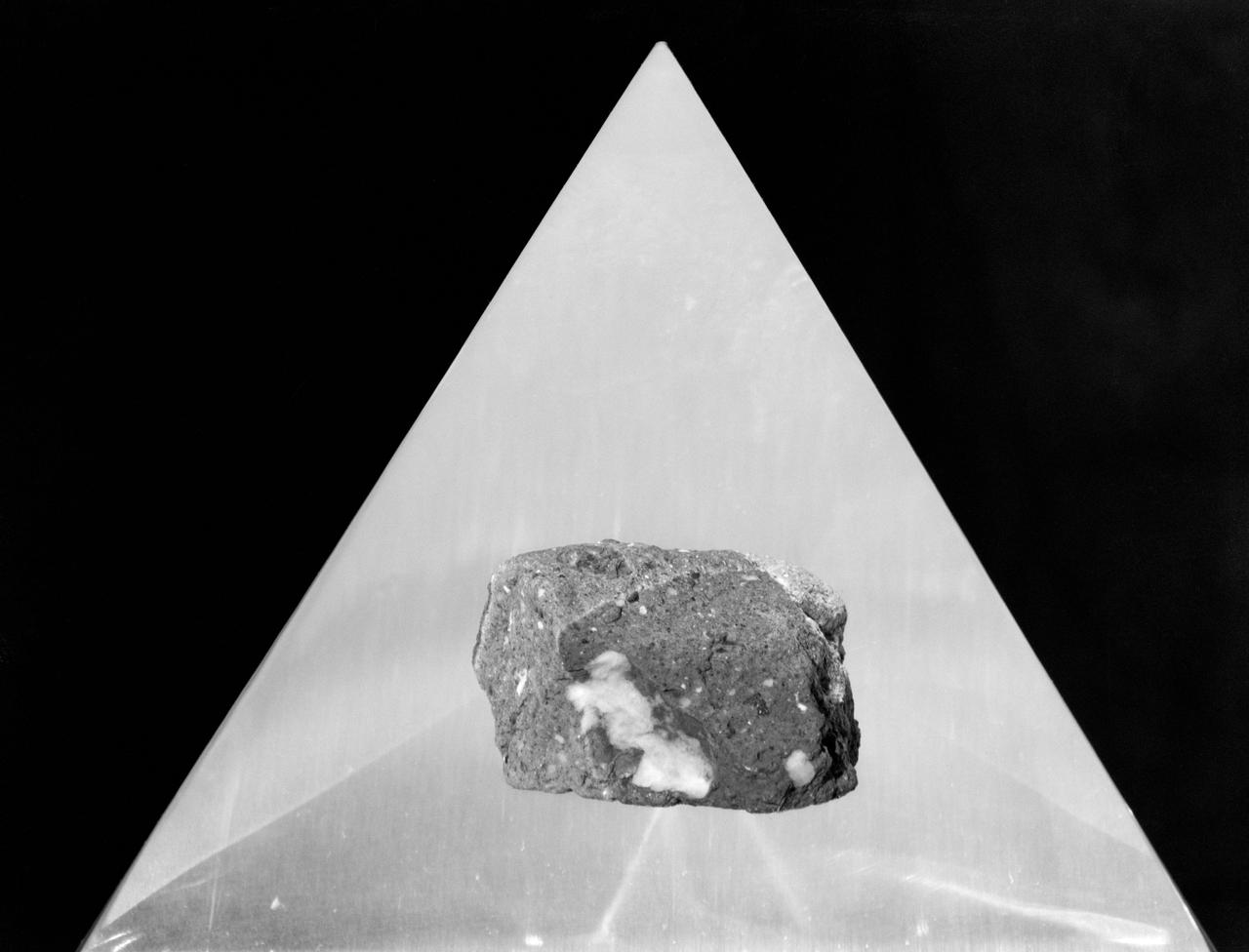
S73-16007 (December 1972) --- A "mug shot" of Apollo 17 lunar sample no. 72255 which was brought back from the lunar surface by the final team of Apollo astronauts. The rock weighs 461.2 grams and measures 2.5 x 9 x 10.5 centimeters. The light grey breccia is sub-rounded on all faces except the top and north sides.

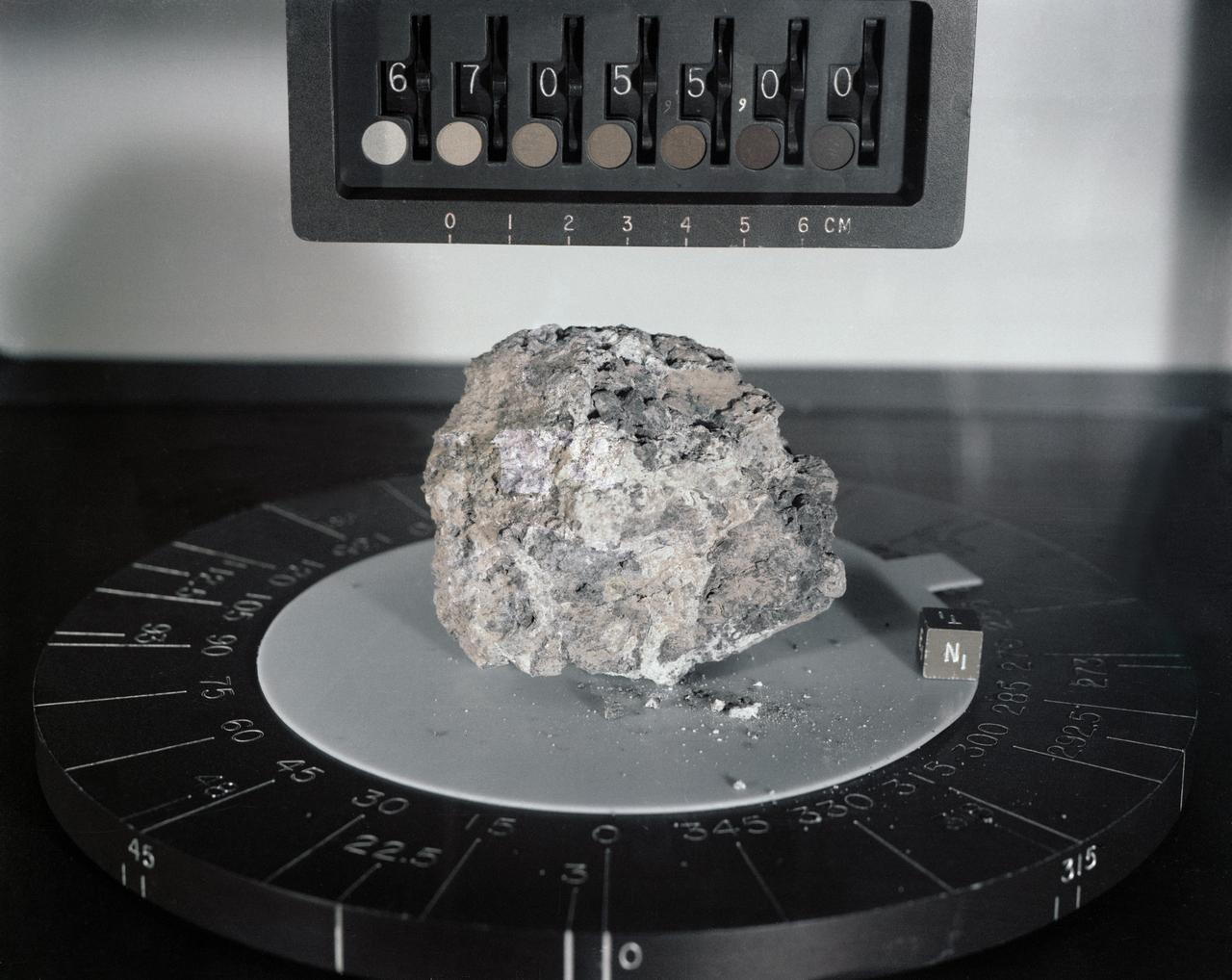
Generic: 14318. Mission: Apollo 14. Station: H. Landmark: NORTH BOULDER FIELD. BagNumber: Bag 1038. OriginalWeight: 600.2. SuperClass: Breccia. SubClass: Regolith. Category: ROCK. Classifications: VMB. Description: Vitric Matrix Breccia. Ipidesc: Breccia sample 14318 was collected from the regolith near the south end of North Boulder Field at Station H during the second EVA. It was returned in weigh bag 1038. Sample 14318 is one of the specimens chosen for study by the Imbrium Consortium, who received 14318,0. A complete set of matched thin sections, across the entire specimen was made by the Consortium (1976); This sample is a very coherent, gray, polymict breccia consisting of light gray clasts in a medium gray matrix. Classification 1: BRECCIA.
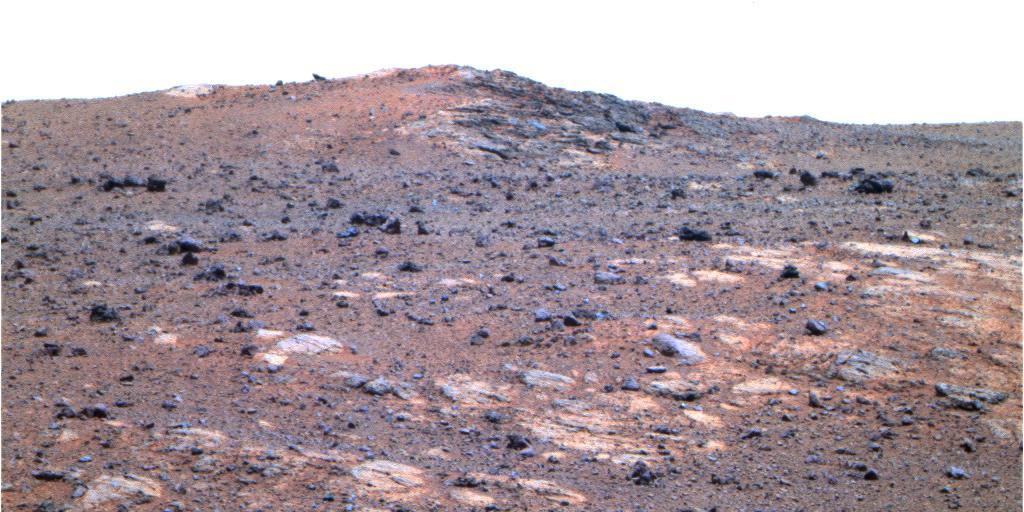

The feature informally named Shoemaker Ridge in the Cape York segment of the western rim of Endeavour Crater includes outcrops that are likely impact breccias as seen by NASA rover Opportunity.
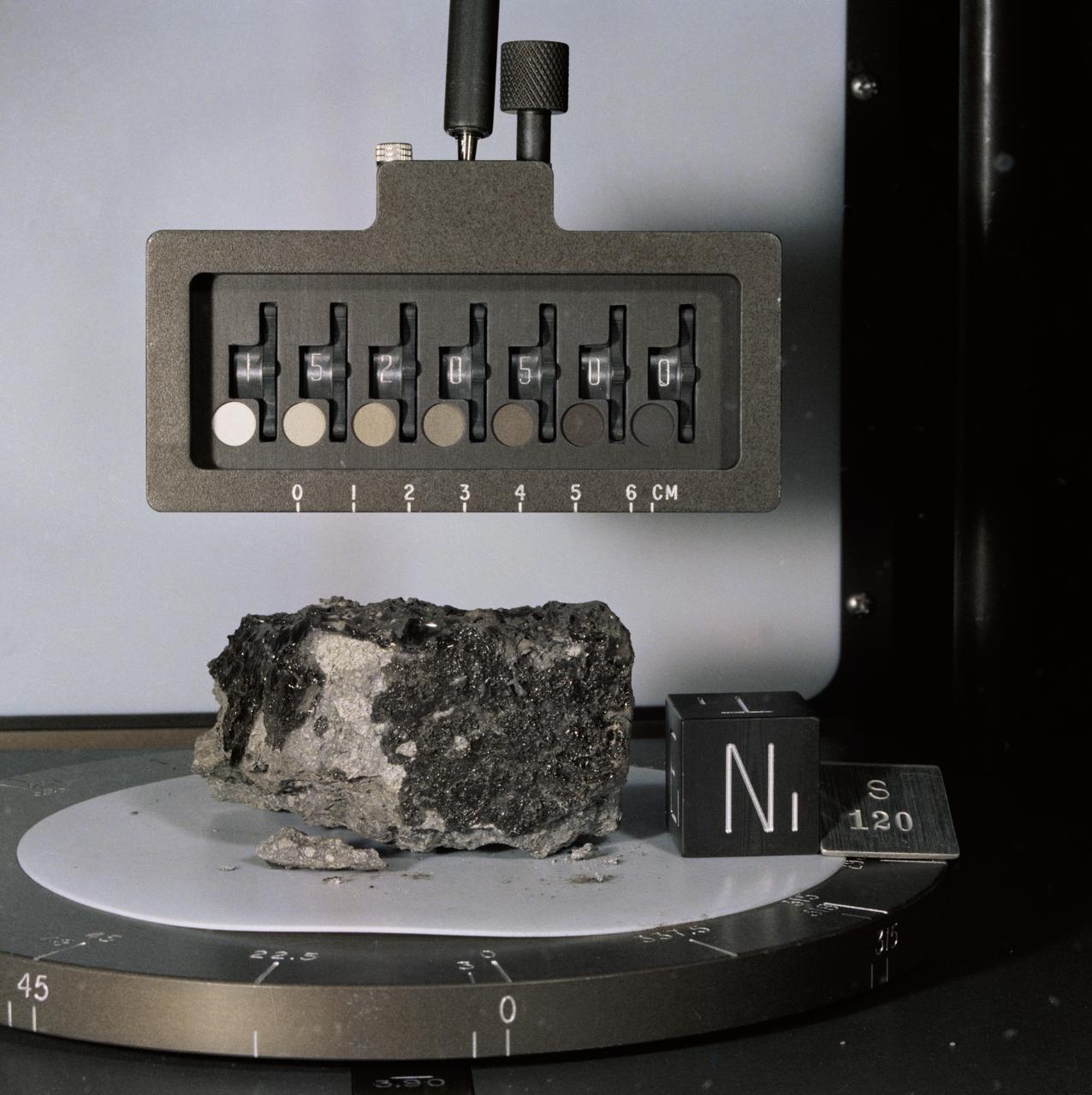
Generic: 15205. Mission: Apollo 15. Station: 2. Landmark: ST. GEORGE CRATER. BagNumber: SCB 1 161. OrignalWeight: 337.3. SuperClass: Breccia. SubClass: Regolith. Category: ROCK . Classifications: Glass-coated. Description: Glass-coated. Classificaiton 1: BRECCIA.
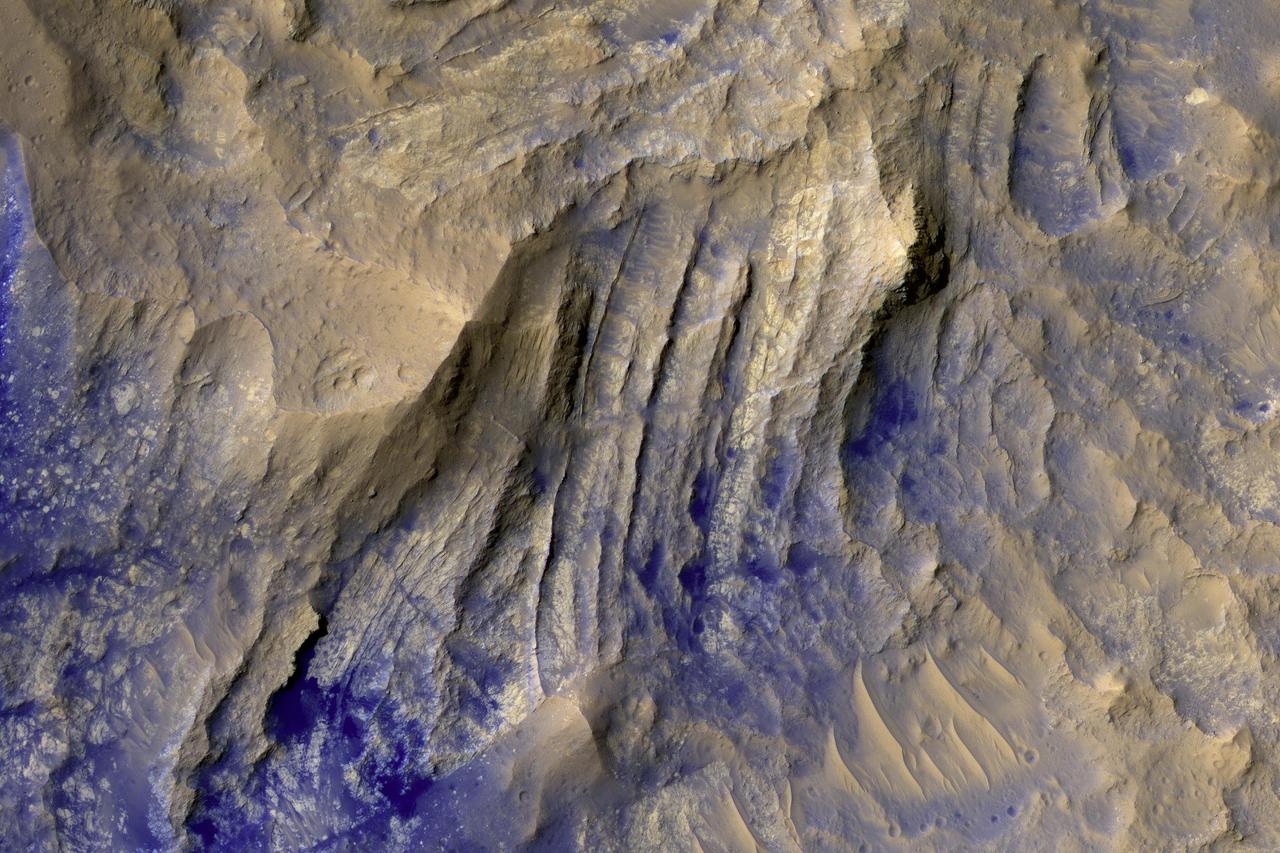

The layered bedrock in this image was brought from several kilometers of depth during the formation of this 44 kilometer wide crater in the volcanic plains of Lunae Planum. As these layers were exhumed and brought to nearly vertical orientations, faulting and fracturing occurred and breccia dikes formed. Breccias are rocks consisting of angular and sharp fragments, and a dike is a fracture that has been widened by forces pulling apart the rock while simultaneously filling it with rocky materials. Breccia dikes are a common feature in terrestrial craters and can now be recognized in brilliant preservation on Mars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12178
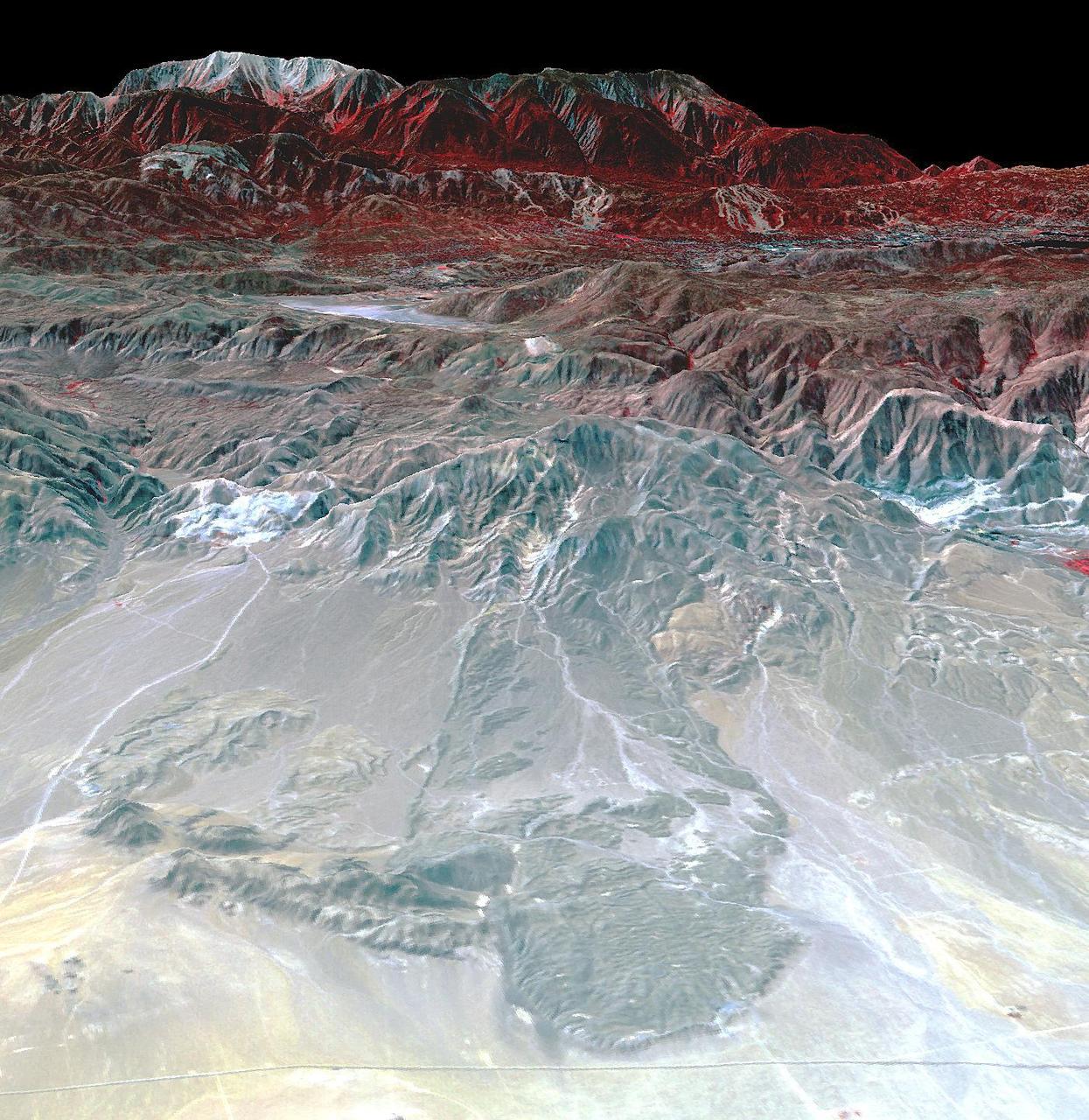

The Blackhawk landslide, Lucerne Valley, California, is a lobe of marble breccia, 10 to 30 m thick, 3 km wide, and nearly 8 km long. Geologic evidence shows that the rockslide came down the gently inclined slope as a nearly monolithic sheet moving more than 100 km per hour. The accepted hypothesis is that the slide was lubricated by a layer of compressed air. At least two earlier similar but smaller rockslides have occurred in the area. The south-looking perspective view image was acquired on September 22, 2014, and is located at 34.4 degrees north, 116.7 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21008

S75-23543 (April 1972) --- This Apollo 16 lunar sample (moon rock) was collected by astronaut John W. Young, commander of the mission, about 15 meters southwest of the landing site. This rock weighs 128 grams when returned to Earth. The sample is a polymict breccia. This rock, like all lunar highland breccias, is very old, about 3,900,000,000 years older than 99.99% of all Earth surface rocks, according to scientists. Scientific research is being conducted on the balance of this sample at NASA's Johnson Space Center and at other research centers in the United States and certain foreign nations under a continuing program of investigation involving lunar samples collected during the Apollo program.
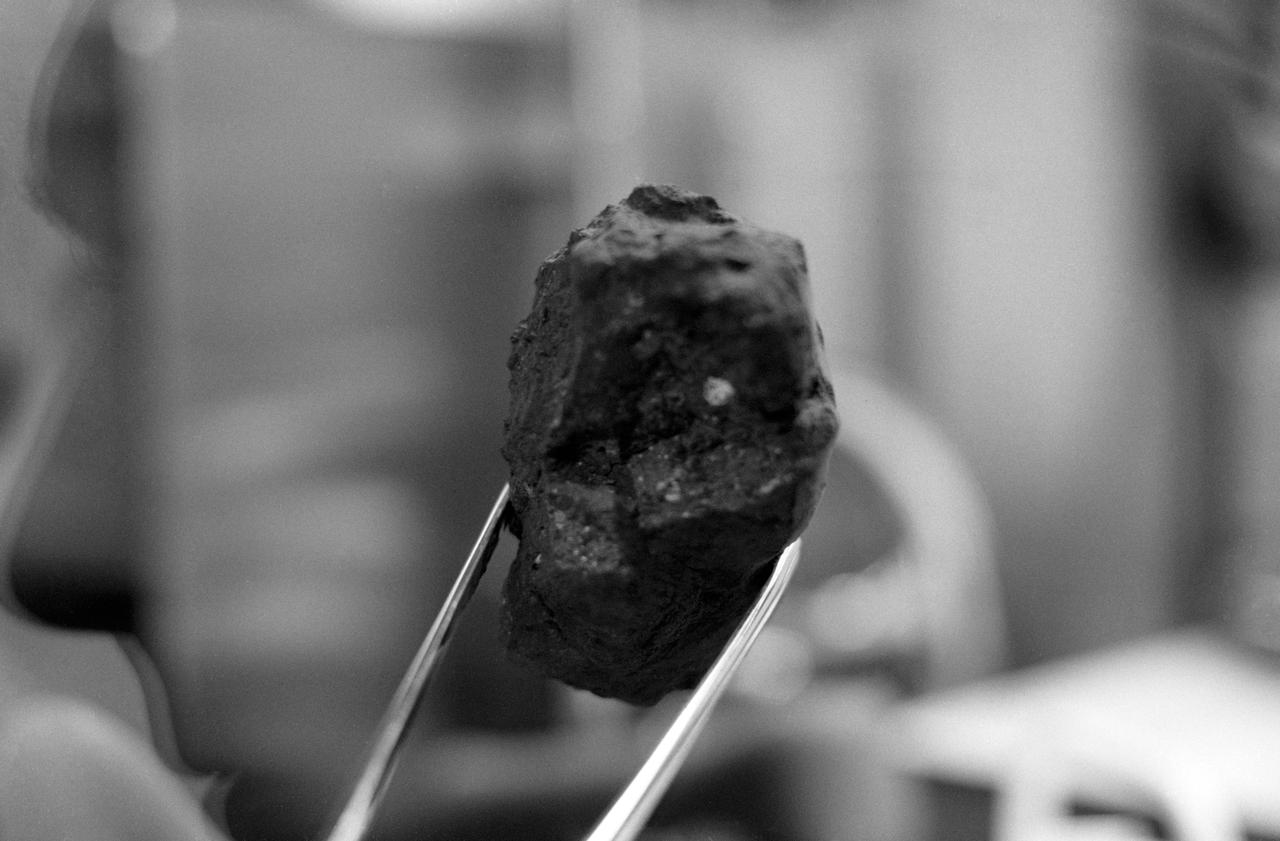

S69-60487 (1 Dec. 1969) --- A close-up view of one of the rocks brought back to Earth from the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The rock is under examination in the Physical-Chemical Test Laboratory in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL), Building 37, MSC. This rock is one of two breccia found in the contingency collection gathered by astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean during their stay on the lunar surface. The breccia rocks, common in the collection of Apollo 11 lunar samples, have been rare in examinations of the Apollo 12 samples thus far.
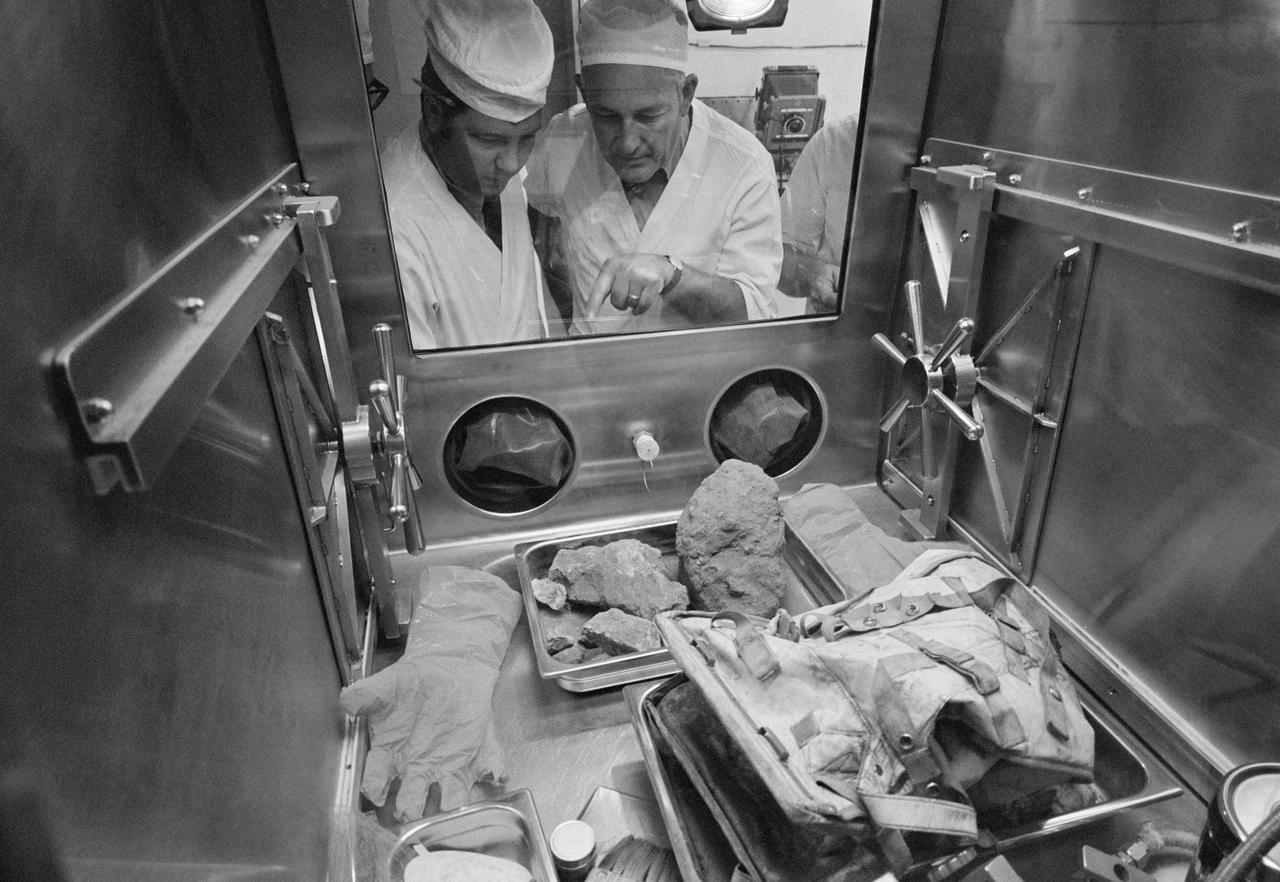
S72-38465 (19 May 1972) --- In an isolated area of the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory, engineer David White (left) and University of Texas geologist/professor William Muehlberger look at a "special" rock brought back from the moon recently by the Apollo 16 astronauts. Lunar sample 61016, better known as "Big Muley," is a large breccia sample, the largest moon rock returned by any Apollo crew, which is named after Muehlberger, the Apollo 16 field geology team leader. Photo credit: NASA

S72-36949 (April 1972) --- A black and white breccia from the rim of North Ray Crater. Its white, feldspar-rich, fine grained matrix is very friable. A variety of different rock types are observed as inclusions. They range in size from several centimeters to less than 1mm. Note also the presence white, feldspar-rich inclusions.
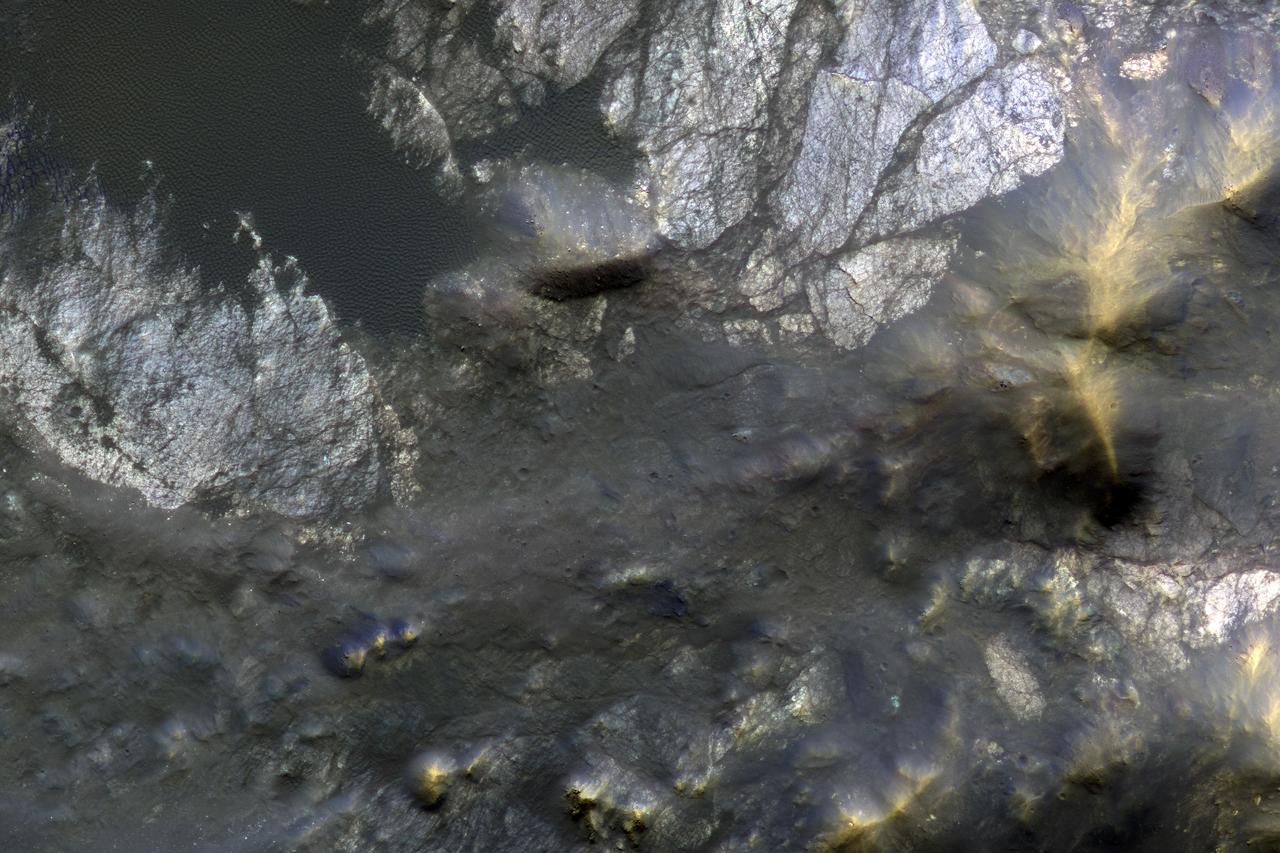

Roadside bedrock outcrops are all too familiar for many who have taken a long road trip through mountainous areas on Earth. Martian craters provide what tectonic mountain building and man's TNT cannot: crater-exposed bedrock outcrops. Although crater and valley walls offer us roadside-like outcrops from just below the Martian surface, their geometry is not always conducive to orbital views. On the other hand, a crater central peak -- a collection of mountainous rocks that have been brought up from depth, but also rotated and jumbled during the cratering process -- produce some of the most spectacular views of bedrock from orbit. This color composite cutout shows an example of such bedrock that may originate from as deep as 2 miles beneath the surface. The bedrock at this scale is does not appear to be layered or made up of grains, but has a massive appearance riddled with cross-cutting fractures, some of which have been filled by dark materials and rock fragments (impact melt and breccias) generated by the impact event. A close inspection of the image shows that these light-toned bedrock blocks are partially to fully covered by sand dunes and coated with impact melt bearing breccia flows. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12291
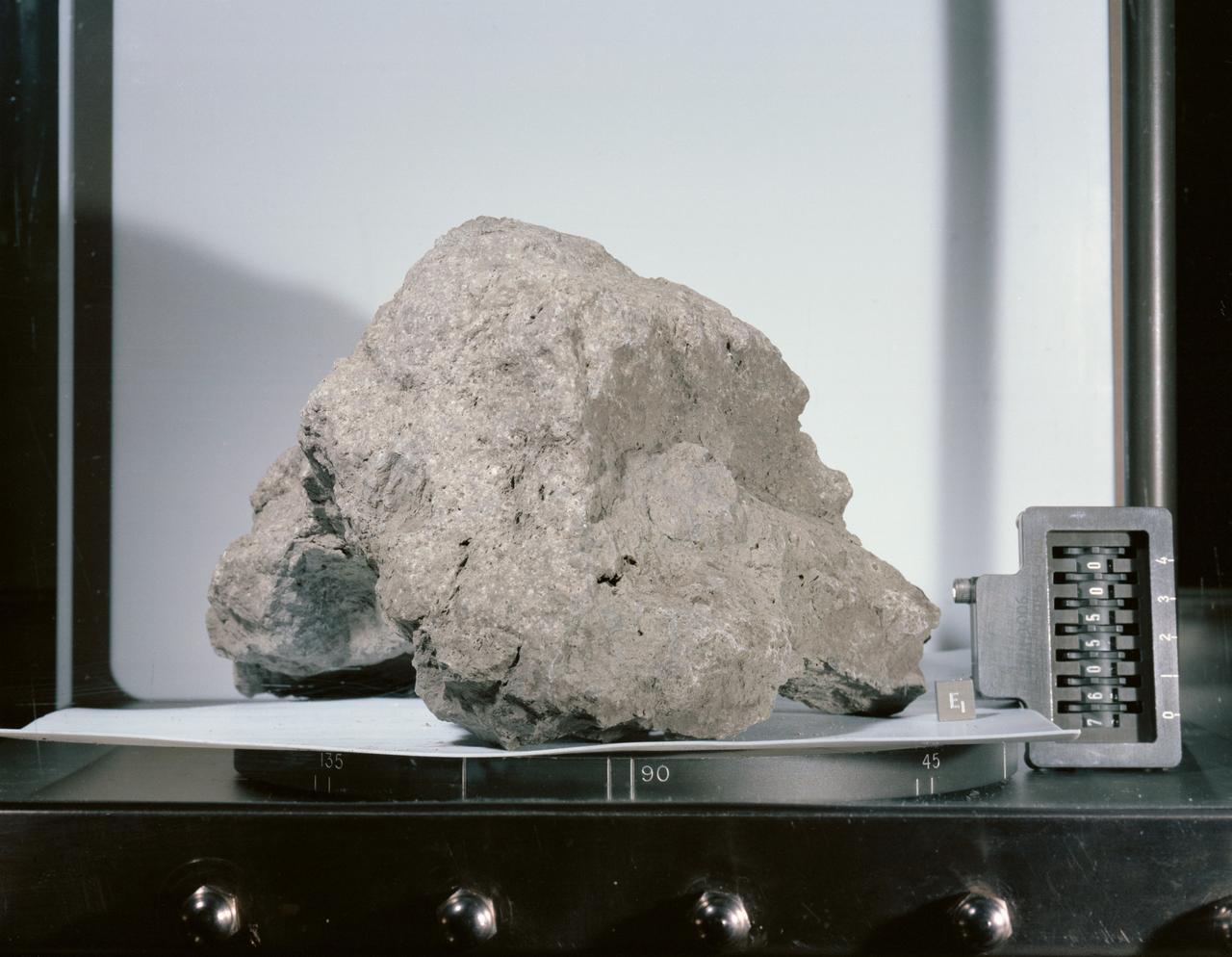

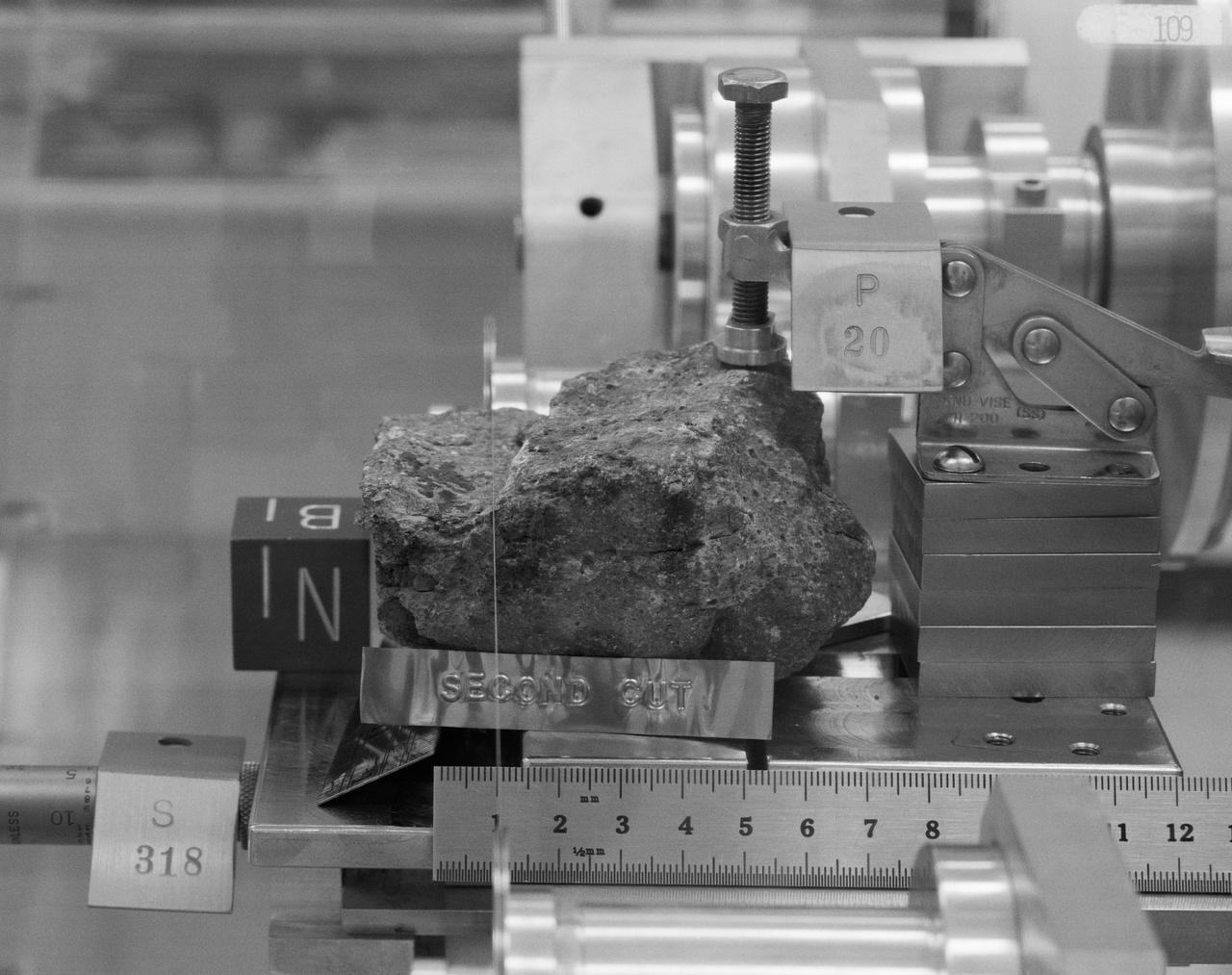
S73-15713 (January 1973) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar rock sample No. 76055 being studied and analyzed in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. This tan-gray irregular, rounded breccia was among many lunar samples brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crew. The rock measures 18 x 20 x 25 centimeters (7.09 x 7.87 x 9.84 inches) and weighs 6,389 grams (14.2554 pounds). The rock was collected from the south side of the lunar roving vehicle while the Apollo 17 astronauts were at Station 7 (base of North Massif).
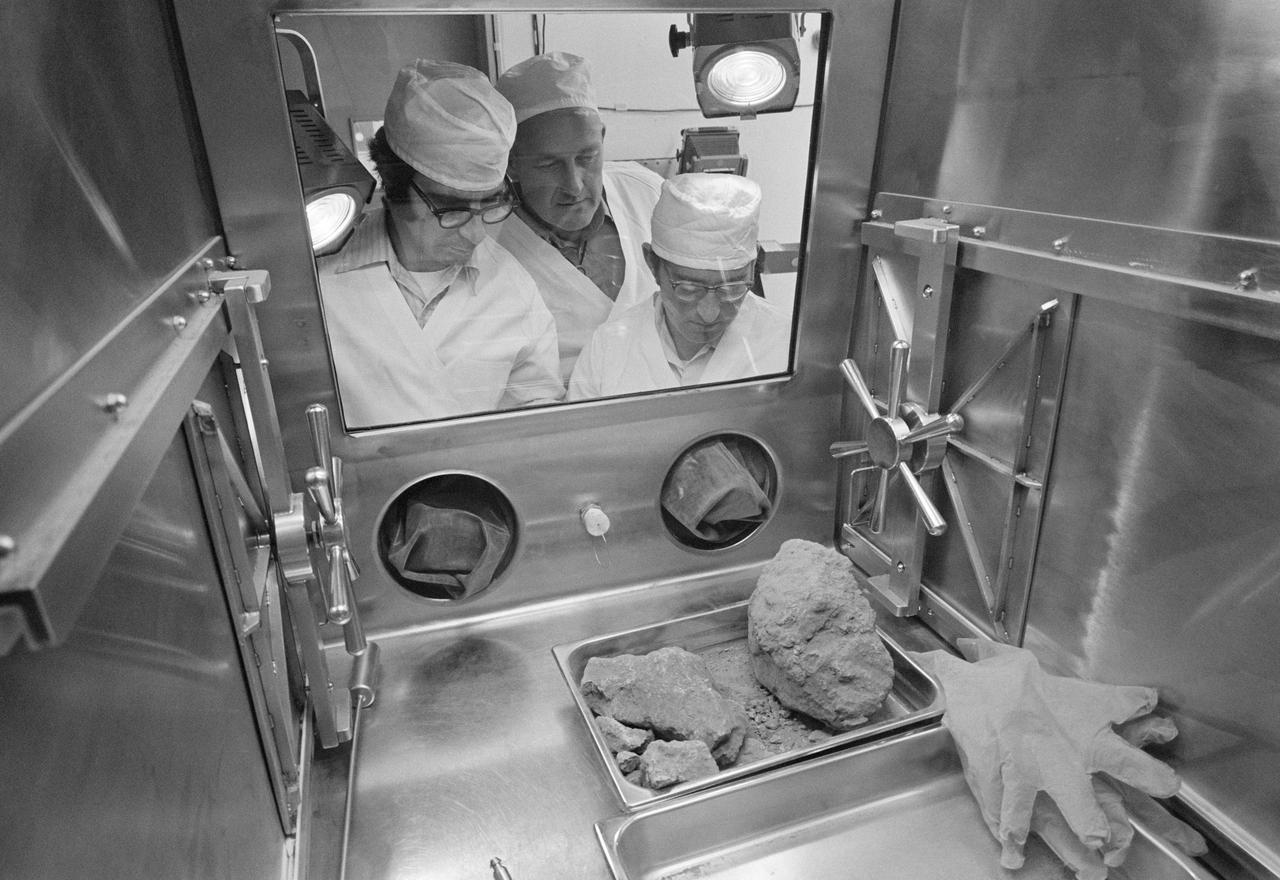

S72-38463 (19 May 1972) --- In an isolated area of the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory, geologists Don Morrison (left) and Fred Horz flank University of Texas geologist/professor William (Bill) Muehlberger as the three look at a "special" rock brought back from the moon recently by the Apollo 16 astronauts. Lunar sample 61016, better known as "Big Muley," is a large breccia sample, the largest moon rock returned by any Apollo crew, which is named after Muehlberger, the Apollo 16 field geology team leader. Photo credit: NASA
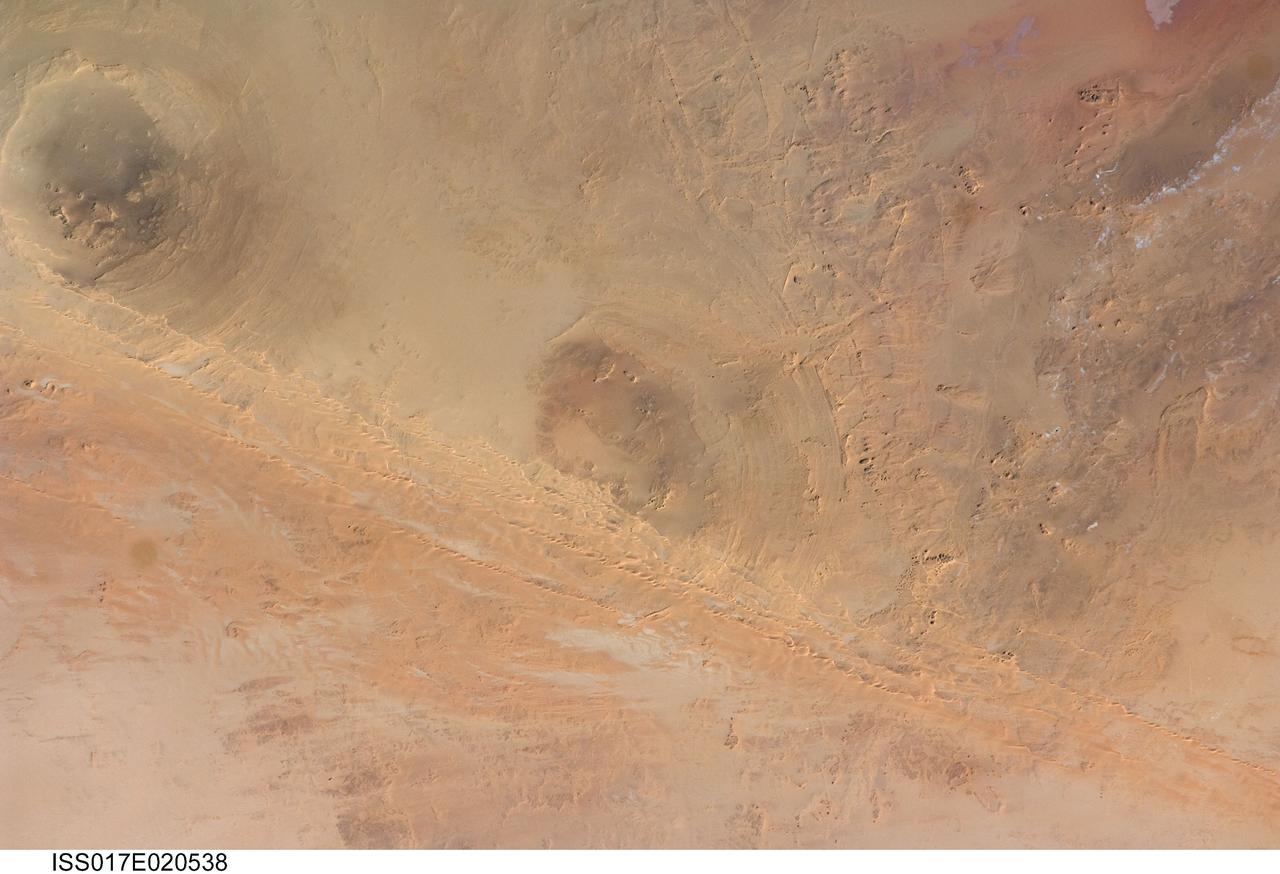

ISS017-E-020538 (21 Oct. 2008) --- Arkenu Craters 1 and 2 in Libya are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station. Geologists often study features on Earth, such as impact craters, to gain insight into processes that occur on other planets. On Earth, more than 150 impact craters have been identified on the continents, but only a few of these are classified as double impact craters. One such example, the Arkenu Craters in northern Africa, is shown in this image. Arkenu 1 and 2 are double impact structures located in eastern Libya (22.04 degrees north latitude and 23.45 degrees east longitude) in the Sahara desert, with diameters of approximately 6.8 kilometers and 10.3 kilometers, respectively. The craters are unusual in that they both exhibit concentric annular ridge structures (gray circles in the image indicate the position of the outermost visible ridges). In many terrestrial complex craters these features are highly eroded and no longer visible. While the circular structure of these features had been noted, the impact origin hypothesis was strengthened in December 2003 when a field team observed shatter cones -- conical-shaped features in rocks created by the high shock pressures generated during impact. Large outcrops of impact breccias -- a jumble of rock fragments generated at the impact site that are now cemented together into an identifiable rock layer -- were also observed by the field team. Two impactors, each approximately 500 meters in diameter, are thought to have created the craters. According to scientists, the age of the impact event has been dated as occurring less than 140 million years ago. While the presence of shatter cones and impact breccias is generally considered to be strong evidence for meteor impact, some scientists now question the interpretation of these features observed at the Arkenu structures and suggest that they were caused by erosive and volcanic processes. At present, both craters are being crossed by linear dunes extending northeast-southwest -- the superposition of the dunes across the annular ridges indicates that they are much younger than the craters.
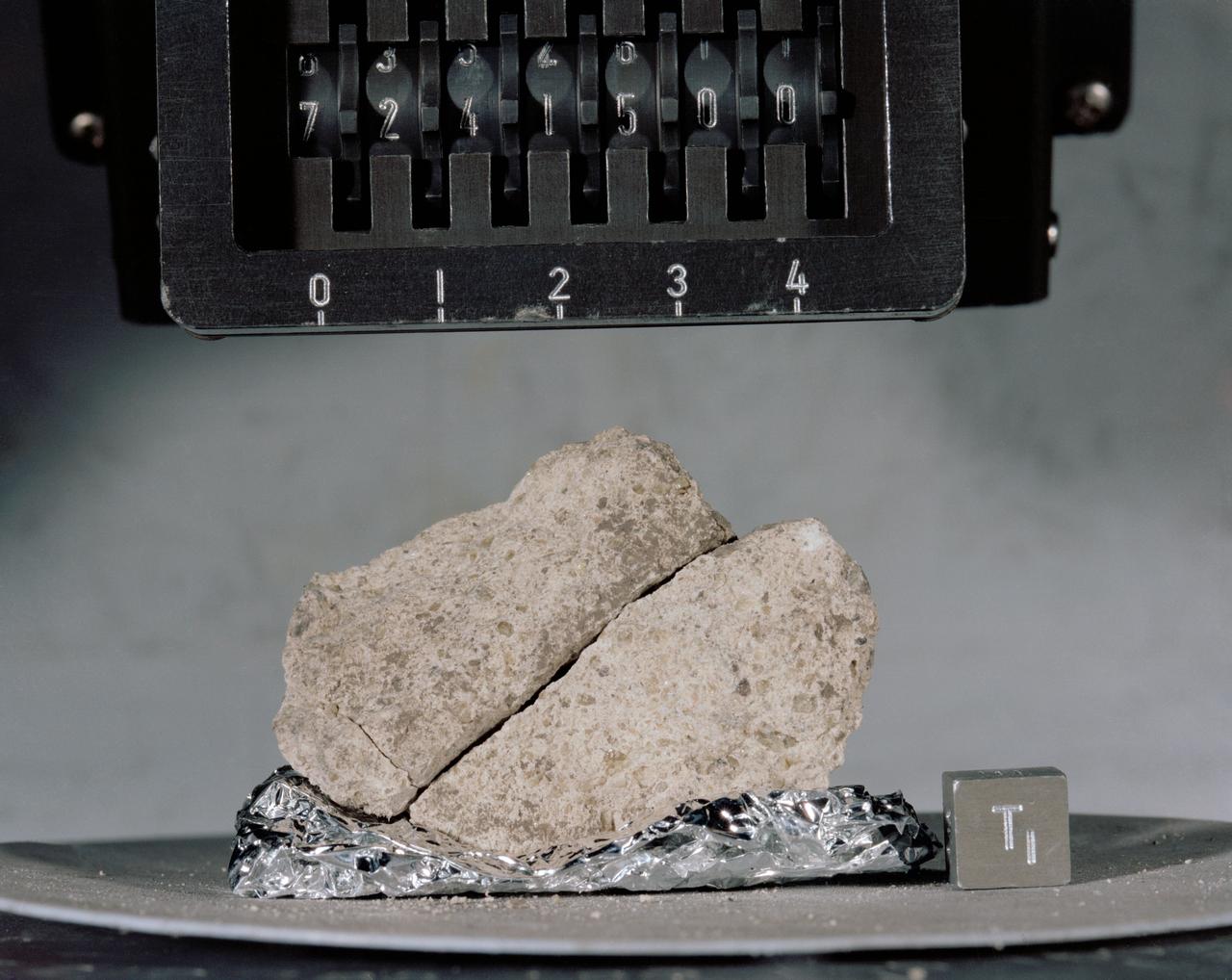

S73-16199 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CREDIT: The view was photographed by Karl Mills, Scientific Photo Arts, Berkeley, California.
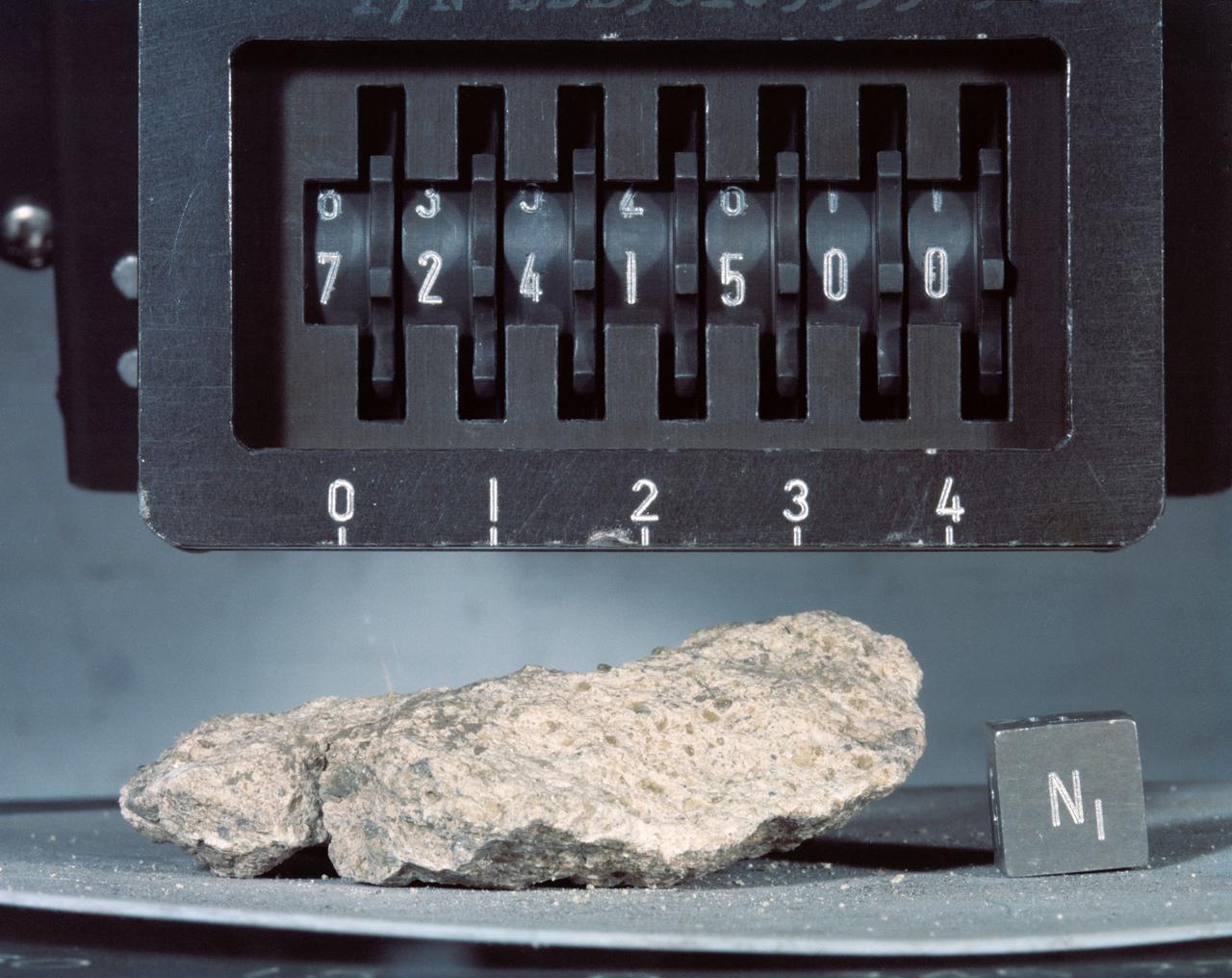

S73-16198 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA).

This HiRISE image shows the central pit feature of an approximately 20-kilometer diameter complex crater in located at 304.480 degrees east, -11.860 degrees south, just north of the Valles Marineris. Here we can observe a partial ring of light-toned, massive and fractured bedrock, which has been exposed by the impact-forming event, and via subsequent erosion that typically obscure the bedrock of complex central features. Features such as this one are of particular interest as they provide scientists with numerous exposures of bedrock that can be readily observed from orbit and originate from the deep Martian subsurface. Unlike on Earth, plate tectonics do not appear to be active on Mars. Thus, much of the Martian subsurface is not directly observable through uplift, erosion and exposure of mountain chains, which provide the majority of bedrock exposures on Earth. Exposures of subsurface materials generated by these features provides us with some of the only "windows" into the subsurface geology. This makes the study of impact craters an invaluable source of information when trying to understand, not only the impact process, but also the composition and history of Mars. Although much of what we see here is composed of massive and fractured bedrock, there are zones of rock fragmentation, called "brecciation." These fragmented rocks (a.k.a., breccias) are best viewed in the eastern portion of the central pit, which was captured in a previous HiRISE image. Additionally, we see some occurrences of impact melt-bearing deposits that surround and coat the bedrock exposed within the central pit. Several dunes are on the surface throughout the central pit and surrounding crater floor. The mechanisms behind the formation of central features, particularly central pits, are not completely understood. Geologic mapping of these circumferential "mega" blocks of bedrock indicate radial and concentric fracturing that is consistent with deformation through uplift. The exposed bedrock shows well-expressed lineament features that are likely fractures and faults formed during the uplift process. Studies of the bedrock, and such structures in this image, allows us better to understand the formative events and physical processes responsible for their formation. Current research suggests that their formation is the result of some component of uplift followed by collapse. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21205

ISS016-E-031056 (3 March 2008) --- Cananea Copper Mine, Sonora, Mexico is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 16 crewmember on the International Space Station. One of the largest open-pit copper mines in the world, the Cananea mine produced over 164,000 tons of copper in 2006. The mine is located approximately 40 kilometers south of the border between the USA (Arizona) and Mexico (Sonora). Copper and gold ores at Cananea are found in a porphyry copper deposit, a geological structure formed by crystal-rich magma moving upwards through pre-existing rock layers. A porphyry - an igneous rock with large crystals in a fine-grained matrix -- is formed as the magma cools and crystallizes. While crystallization is occurring, hot fluids can circulate through the magma and surrounding rocks via fractures. This hydrothermal alteration of the rocks typically forms copper-bearing and other minerals. Much of the Cananea mine's ore is concentrated in breccia pipes -- mineralized rod or chimney-shaped bodies that contain broken rock fragments. The active, two-kilometers-in-diameter Colorada Pit (top right) is recognizable in this image by the concentric steps or benches cut around its perimeter. These benches allow for access into the pit for extraction of ore and waste materials. Water (black) is visible filling the bottom of the pit, and several other basins in the surrounding area. The city of Cananea -- marked by its street grid -- is located to the northeast of the mine workings. A leachate reservoir is located to the east of the mine (lower left) for removal and evaporation of water pumped from the mine workings -- the bluish-white coloration of deposits near the reservoir suggests the high mineral content of the leachate. A worker strike halted mine operations in 2007.
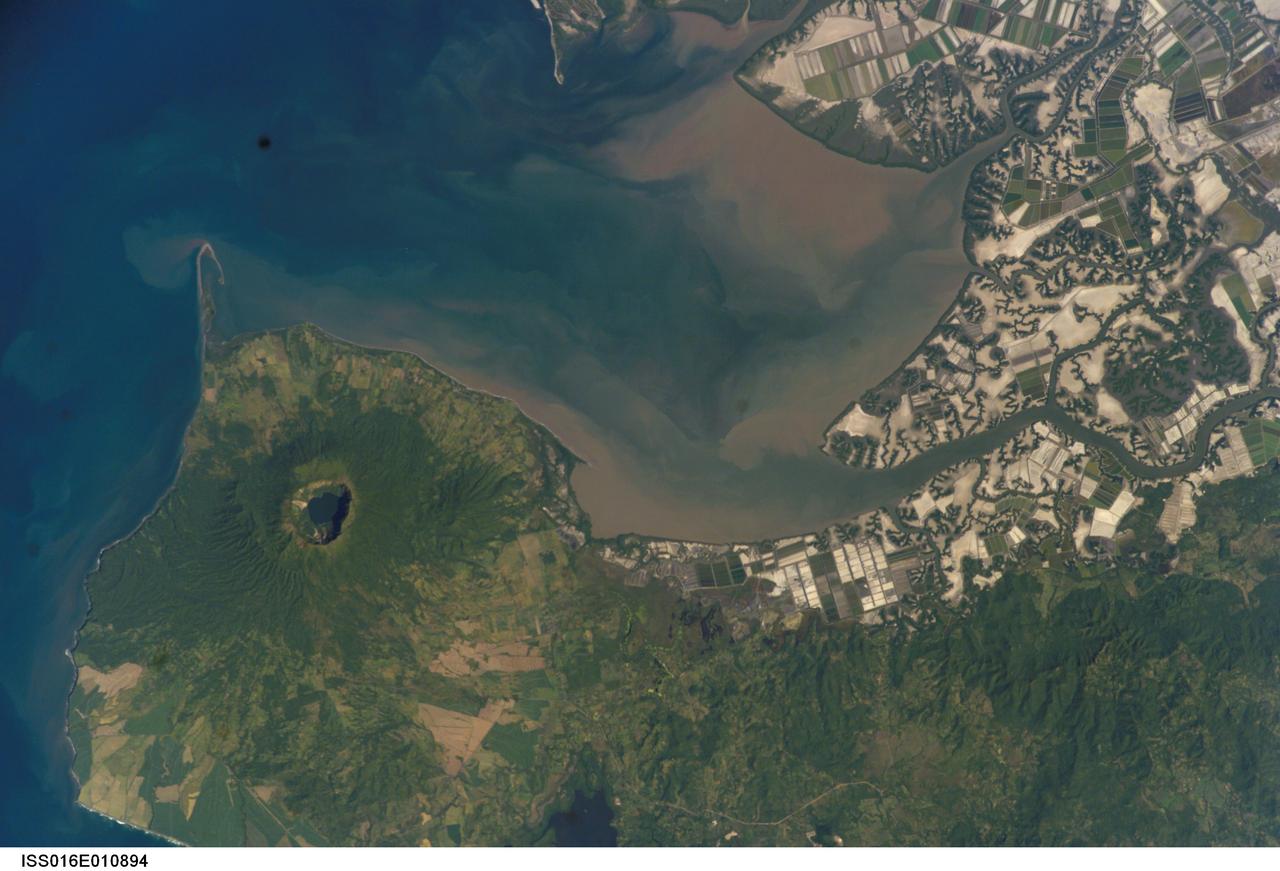

ISS016-E-010894 (17 Nov. 2007) --- Cosiguina Volcano, Nicaragua is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 16 crewmember on the International Space Station. Three Central American countries (El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua) include coastline along the Gulf of Fonseca that opens into the Pacific Ocean. The southern boundary of the Gulf is a peninsula formed by the Cosiguina volcano illustrated in this view. Cosiguina is a stratovolcano, typically tall cone-shaped structures formed by alternating layers of solidified lava and volcanic rocks (ash, pyroclastic flows, breccias) produced by explosive eruptions. The summit crater is filled with a lake (Laguna Cosiguina). The volcano last erupted in 1859, but its most famous activity occurred in 1835 when it produced the largest historical eruption in Nicaragua. Ash from the 1835 eruption has been found in Mexico, Costa Rica, and Jamaica. The volcano has been quiet since 1859, only an instant in terms of geological time. An earthquake swarm was measured near Cosiguina in 2002, indicating that tectonic forces are still active in the region although the volcano is somewhat isolated from the line of more recently active Central American volcanoes to the northwest and southeast. Intermittently observed gas bubbles in Laguna Cosiguina, and a hot spring along the eastern flank of the volcano are the only indicators of hydrothermal activity at the volcano. The fairly uniform vegetation cover (green) on the volcano's sides also attest to a general lack of gas emissions or "hot spots" on the 872 meter high cone, according to NASA scientists who study the photos downlinked from the orbital outpost.