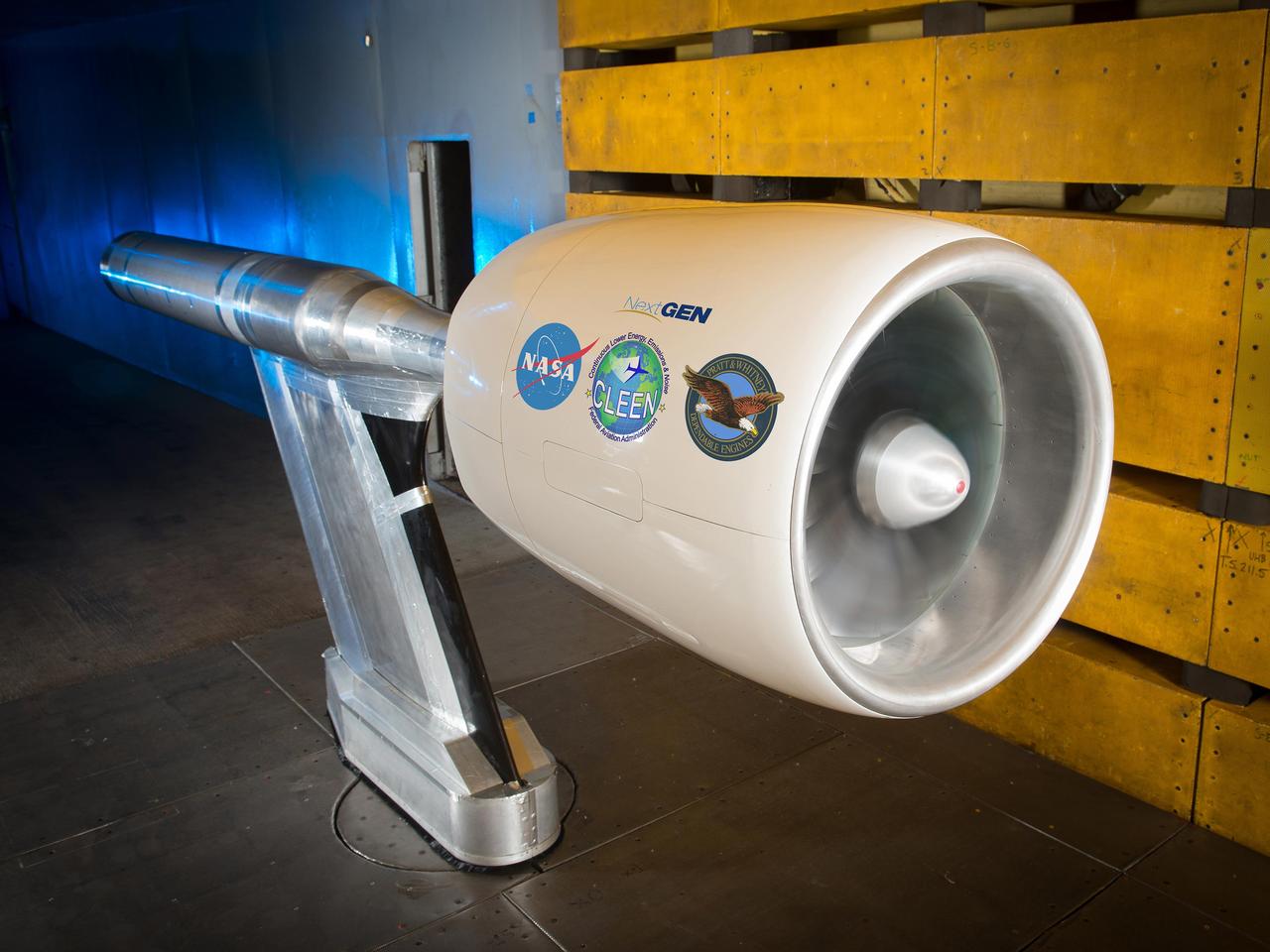

NASA’s Environmentally Responsible Aviation Project, in collaboration with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and Pratt & Whitney, completed testing of an Ultra High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Model in the 9’ x 15’ Low Speed Wind Tunnel at NASA Glenn Research Center. The fan model is representative of the next generation of efficient and quiet Ultra High Bypass Ratio Turbofan Engine designs.
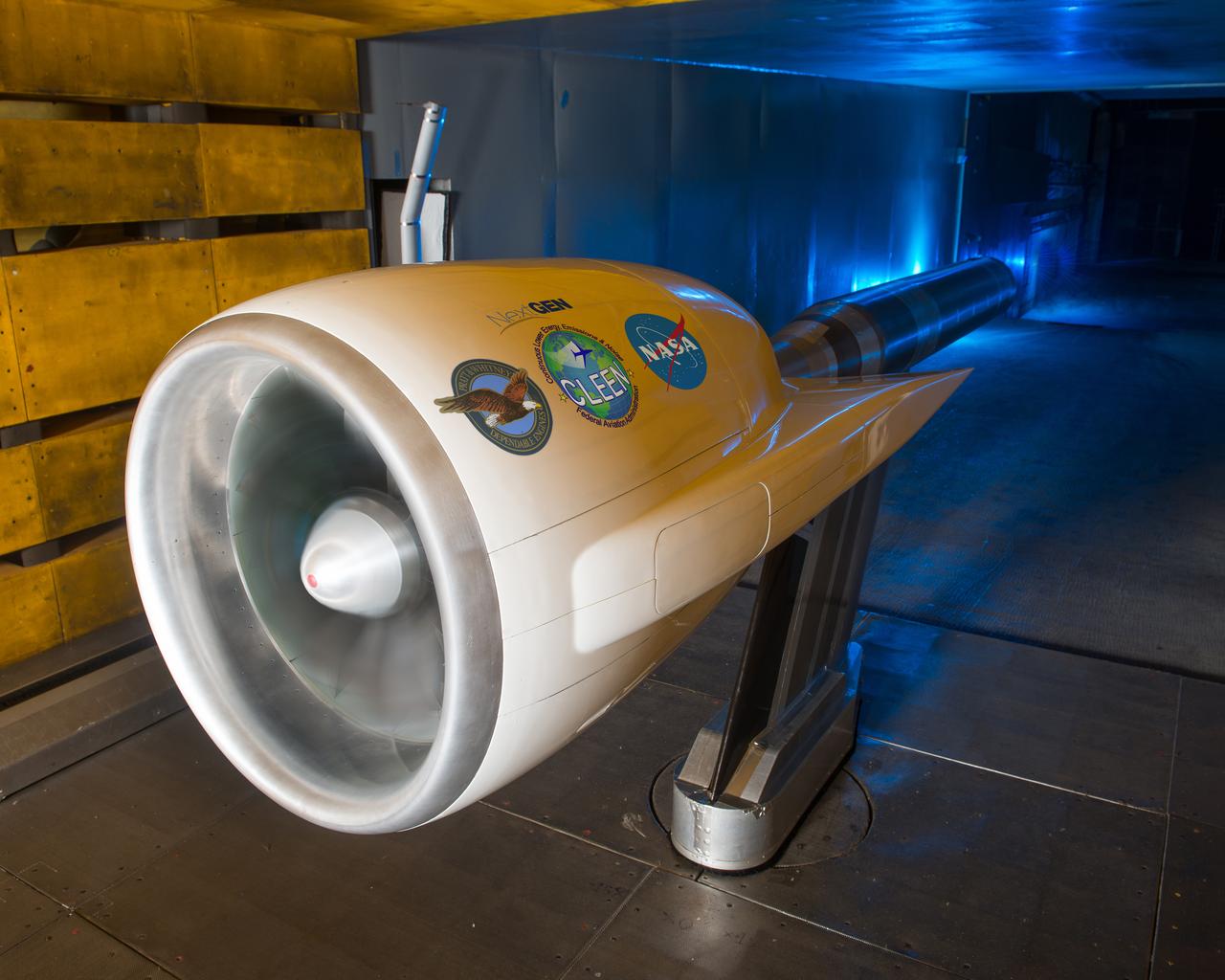
Ultra High Bypass Integrated System Test Testing of an Ultra High Bypass Ratio Turbofan model in the 9-by 15-Foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel. Pratt & Whitney designed the experimental engine to meet new efficiency and noise reduction targets for commercial aircraft set by NASA and the Federal Aviation Administration. The 9-by 15 tests analyzed two noise reduction technologies.
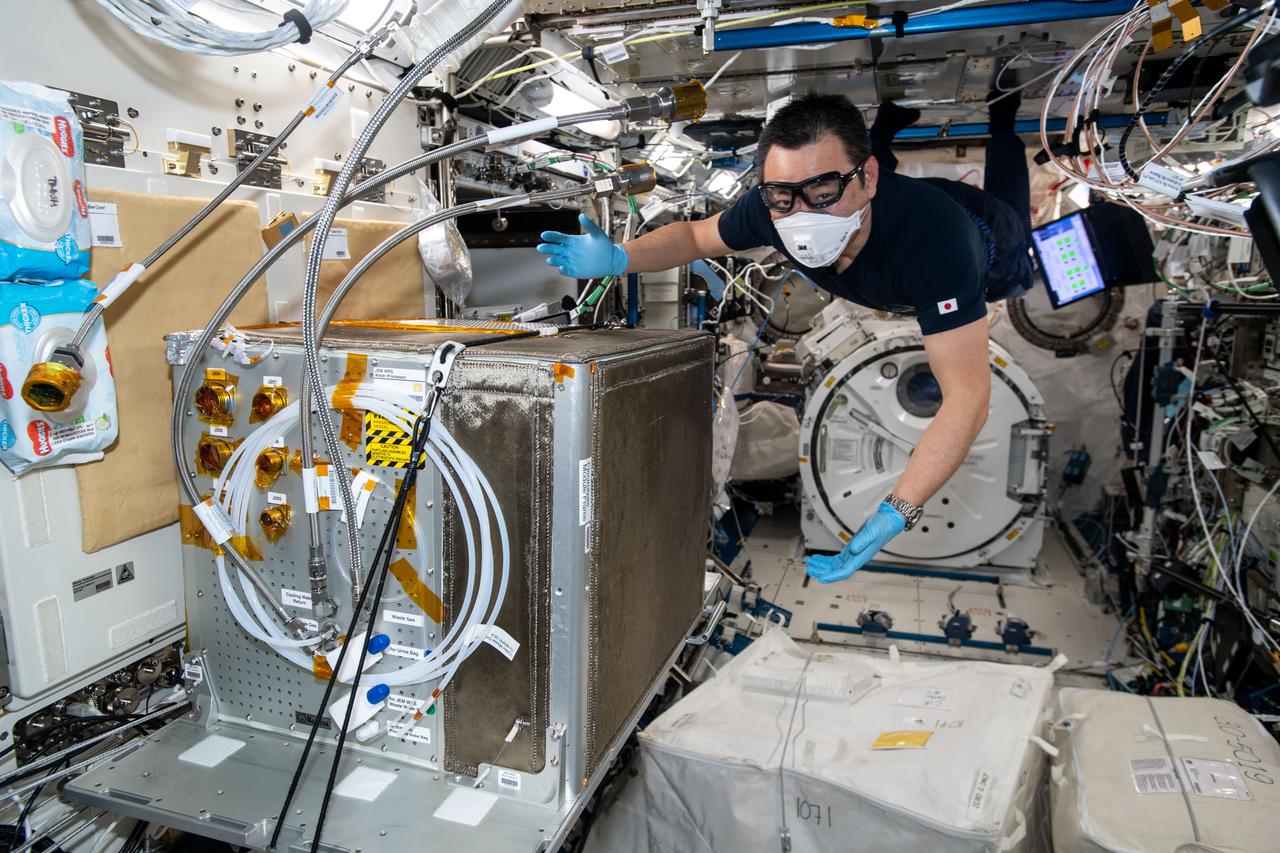

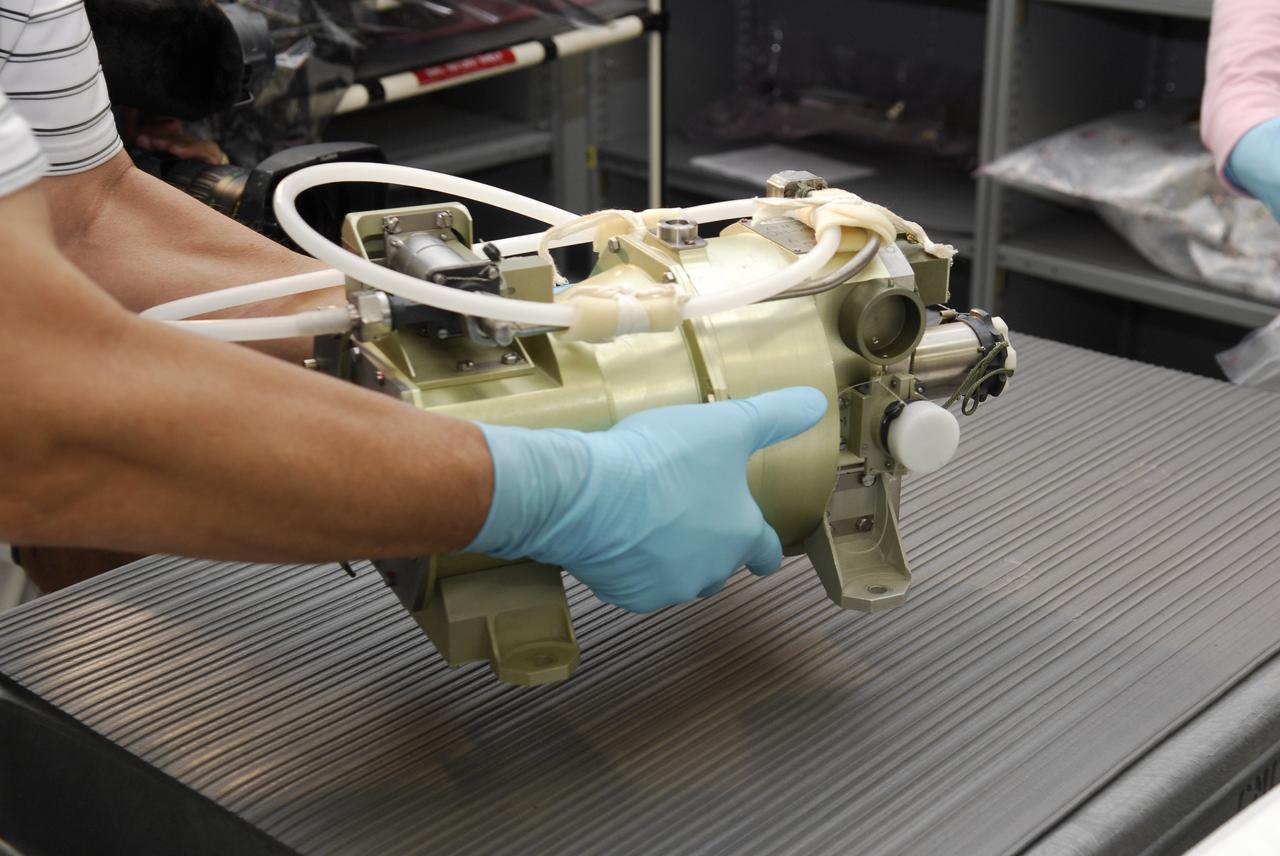
iss065e333421 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.
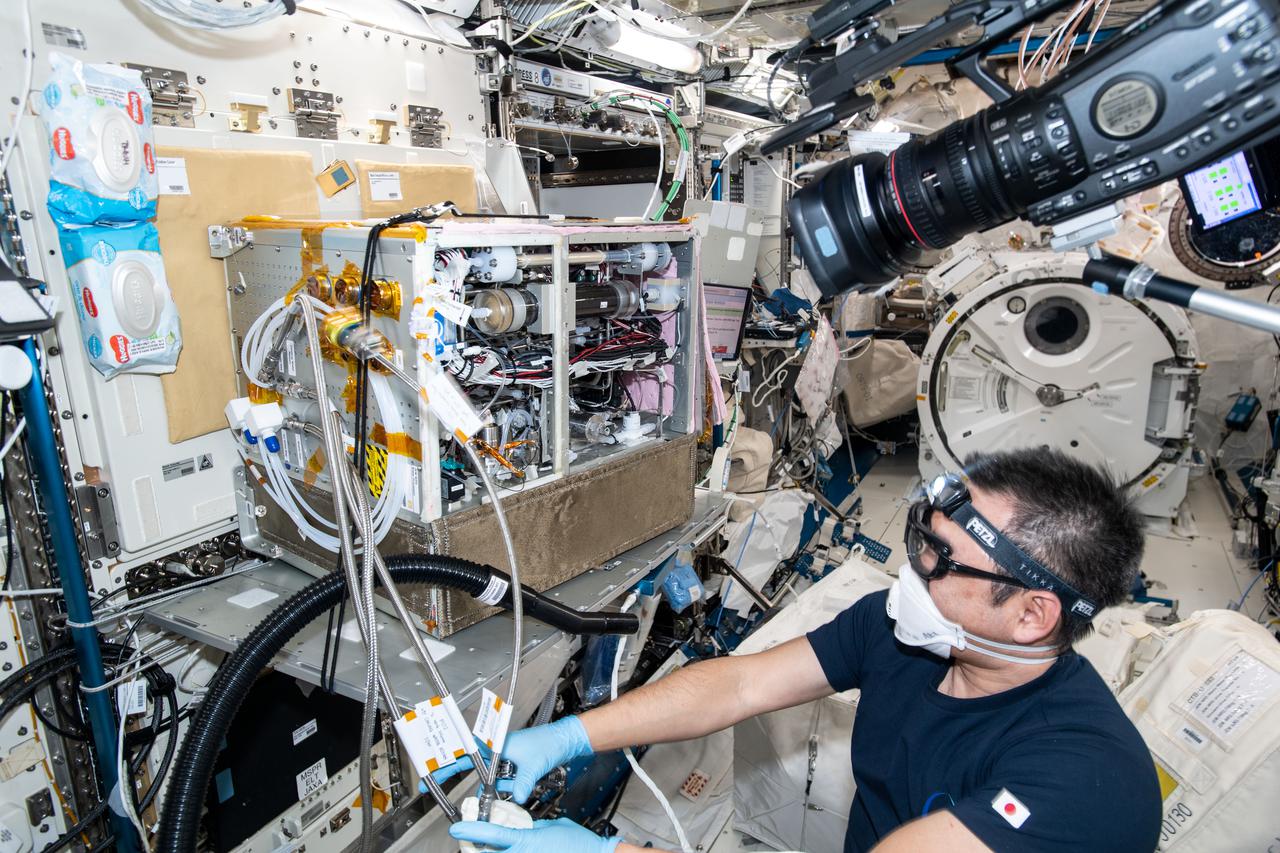

iss065e333427 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.
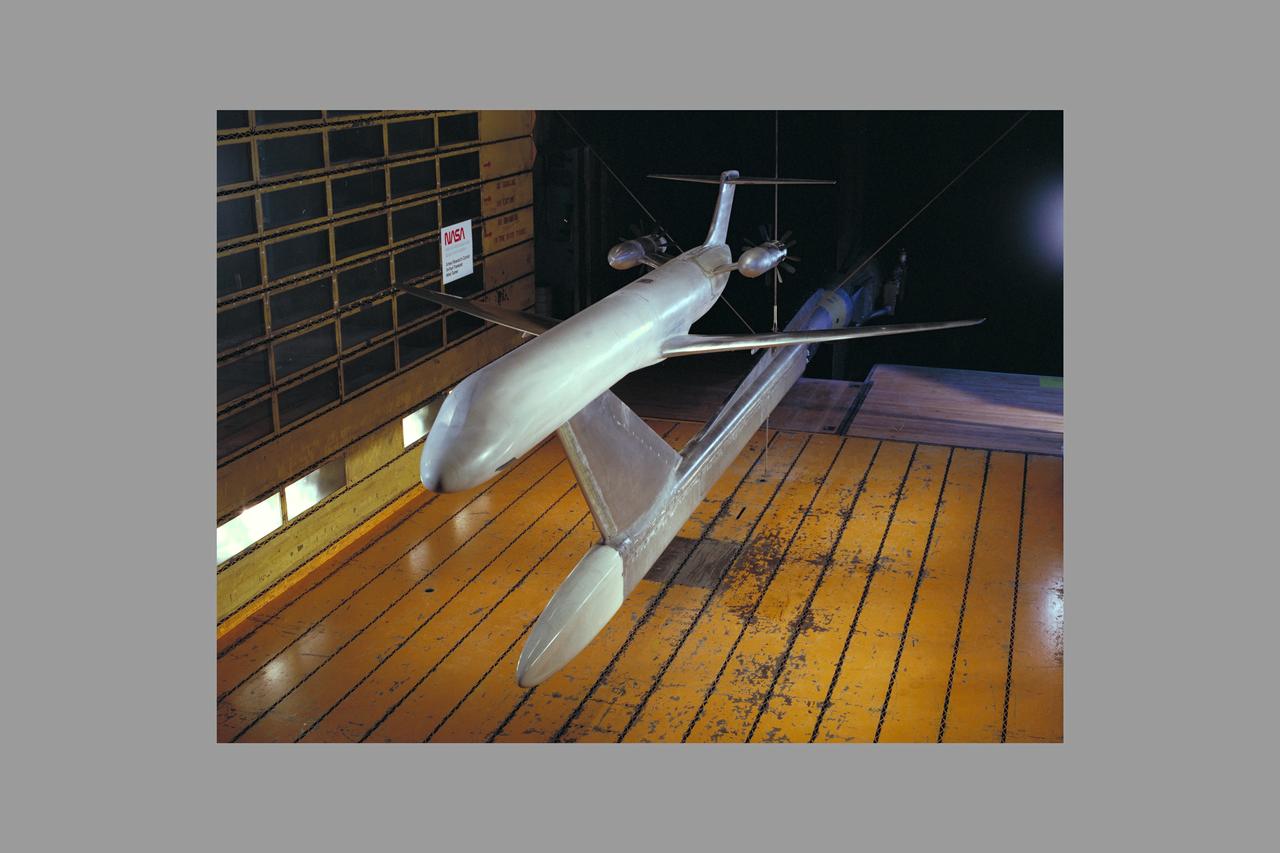

McDonnell Douglas Hub (Ultra-High Bypass) Model and SAAB Wake Rake Test 14ft W.T. Test-060-1-14, Turbo Fan Configuration
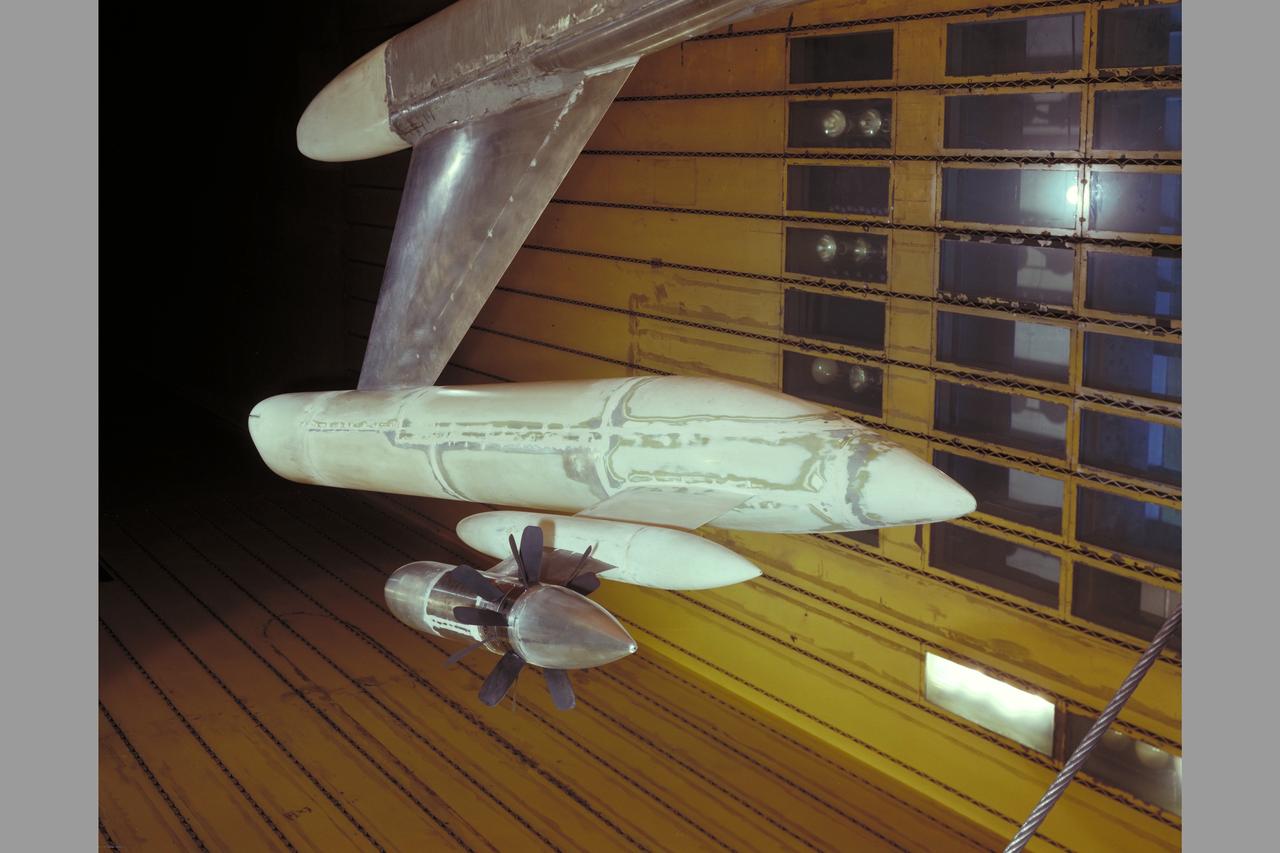
McDonnell Douglas Hub (Ultra-High Bypass) Model and SAAB Wake Rake Test 14ft W.T. Test-060-1-14, Turbo Fan Configuration
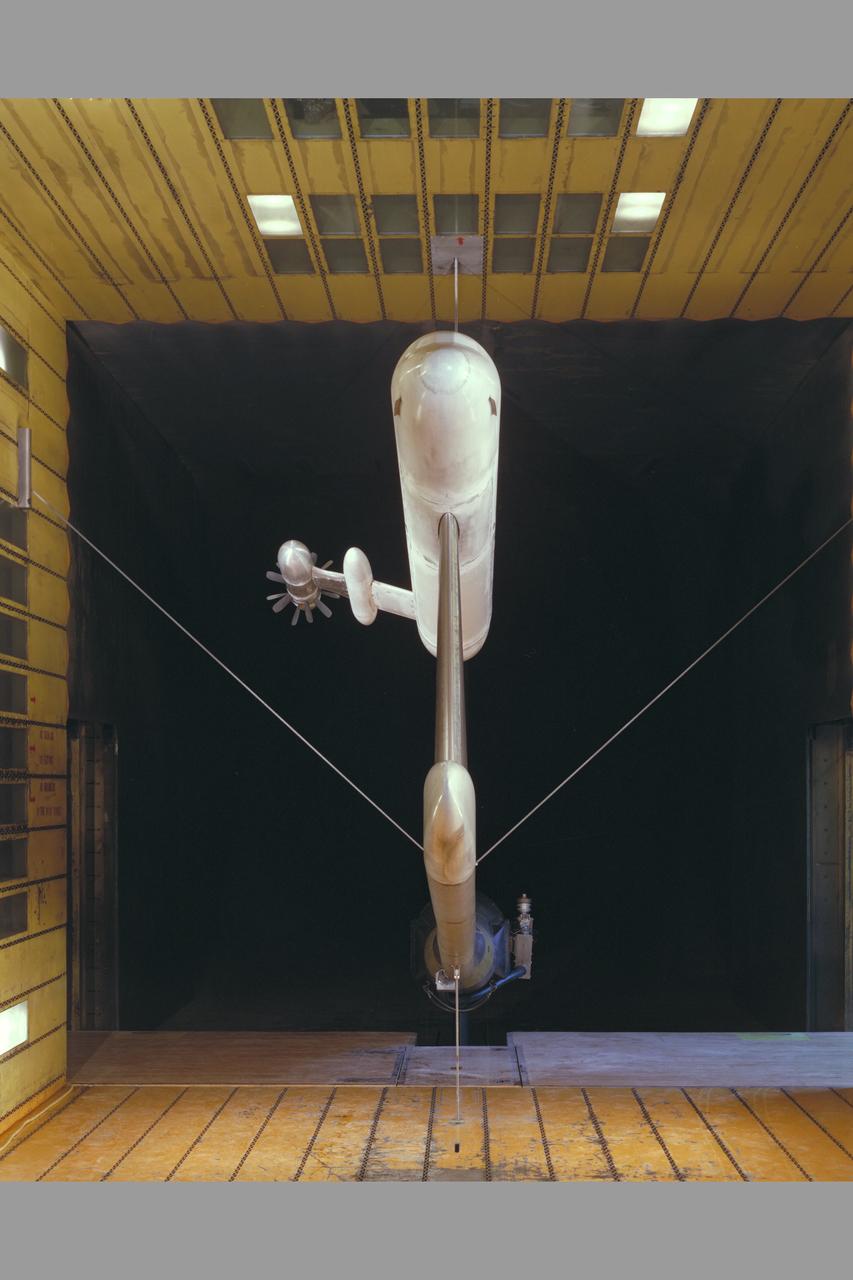

McDonnell Douglas Hub (Ultra-High Bypass) Model and SAAB Wake Rake Test 14ft W.T. Test-060-1-14, Turbo Fan Configuration
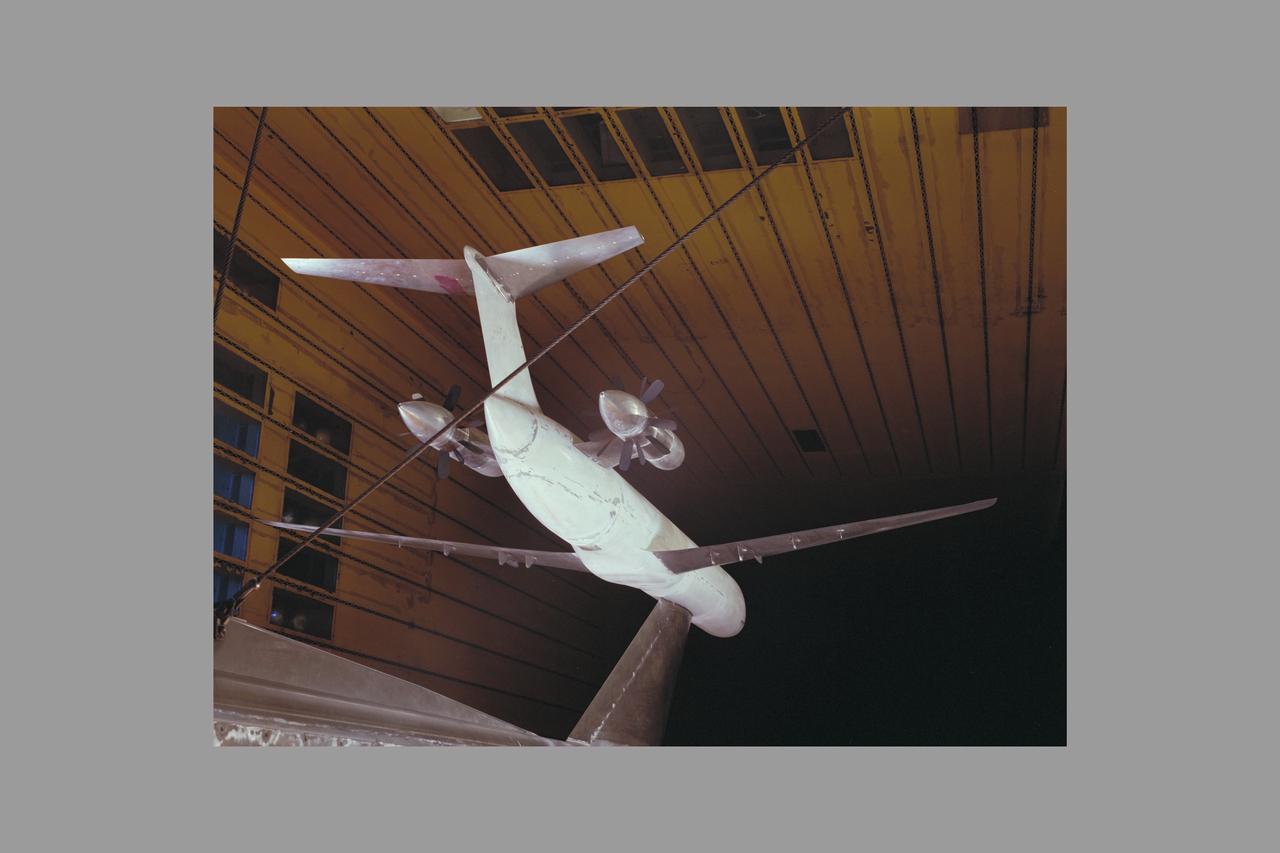

McDonnell Douglas Hub (Ultra-High Bypass) Model and SAAB Wake Rake Test 14ft W.T. Test-060-1-14, Turbo Fan Configuration
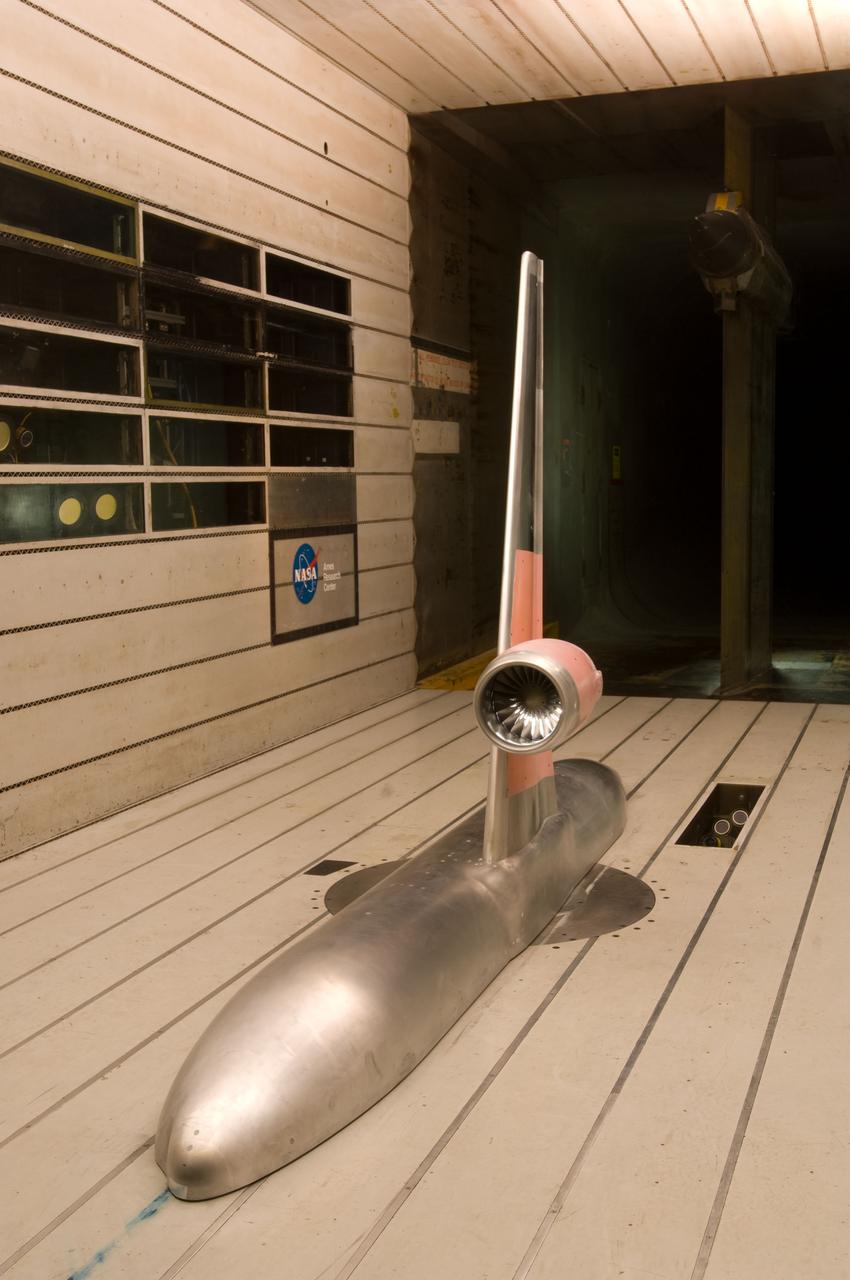

Next-Generation Aircraft, Pratt and Whitney Ultra-High Bypass Integration test at NASA Ames 11ft. wind tunnel (test 11-0182) assess the interaction effects of a scaled Pratt & Whitney geared turbofan on a Boeing 737-800 fuselage in an effort to use emerging technologies to make next-generation airliners quieter, more fuel efficient and lower on emissions. (printed in Aviation Week & Space Technology April 8, 2011 issue)
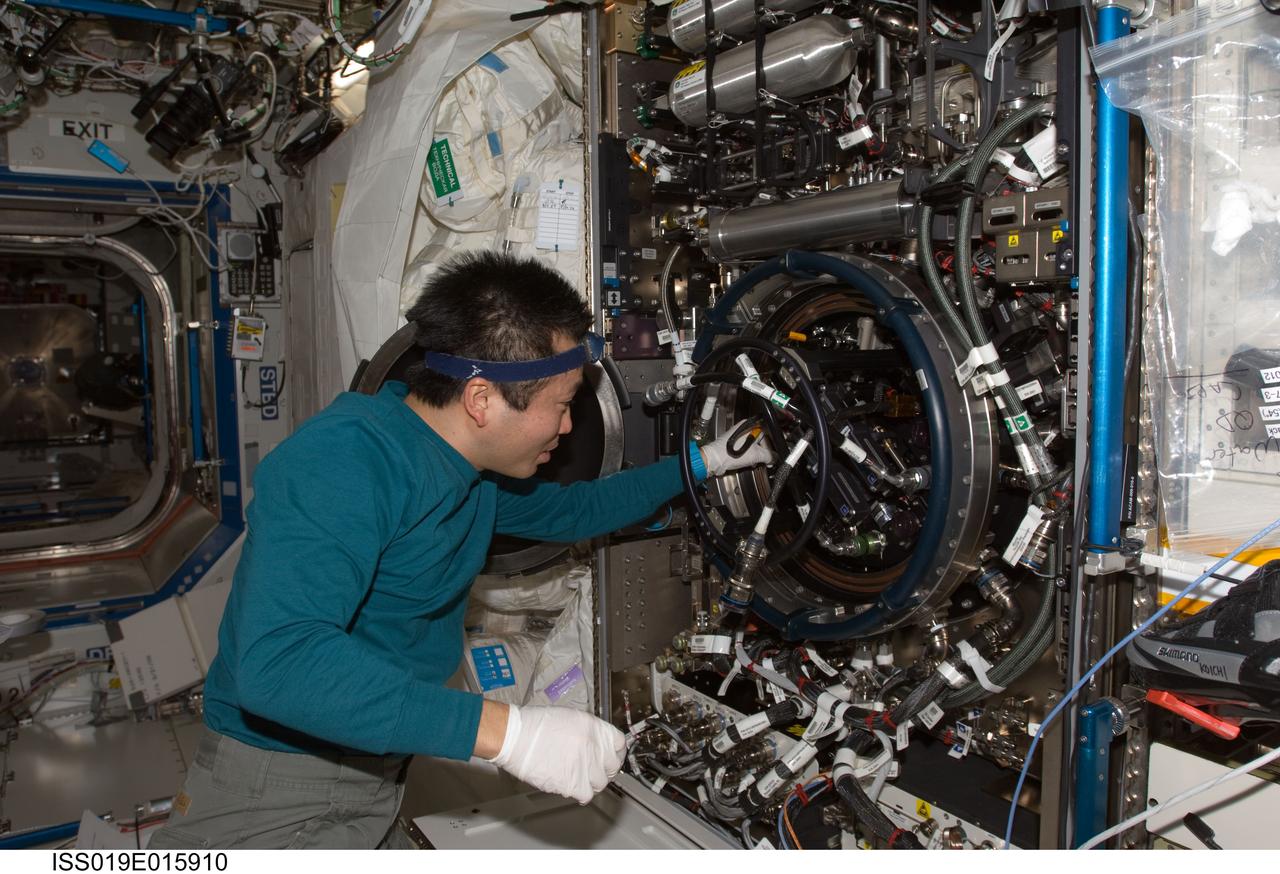

ISS019-E-015910(12 May 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, works on the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. Wakata removed and replaced one fuel reservoir, which required temporary opening the front end cap and removing the fuel supply bypass Quick Disconnect (QD).
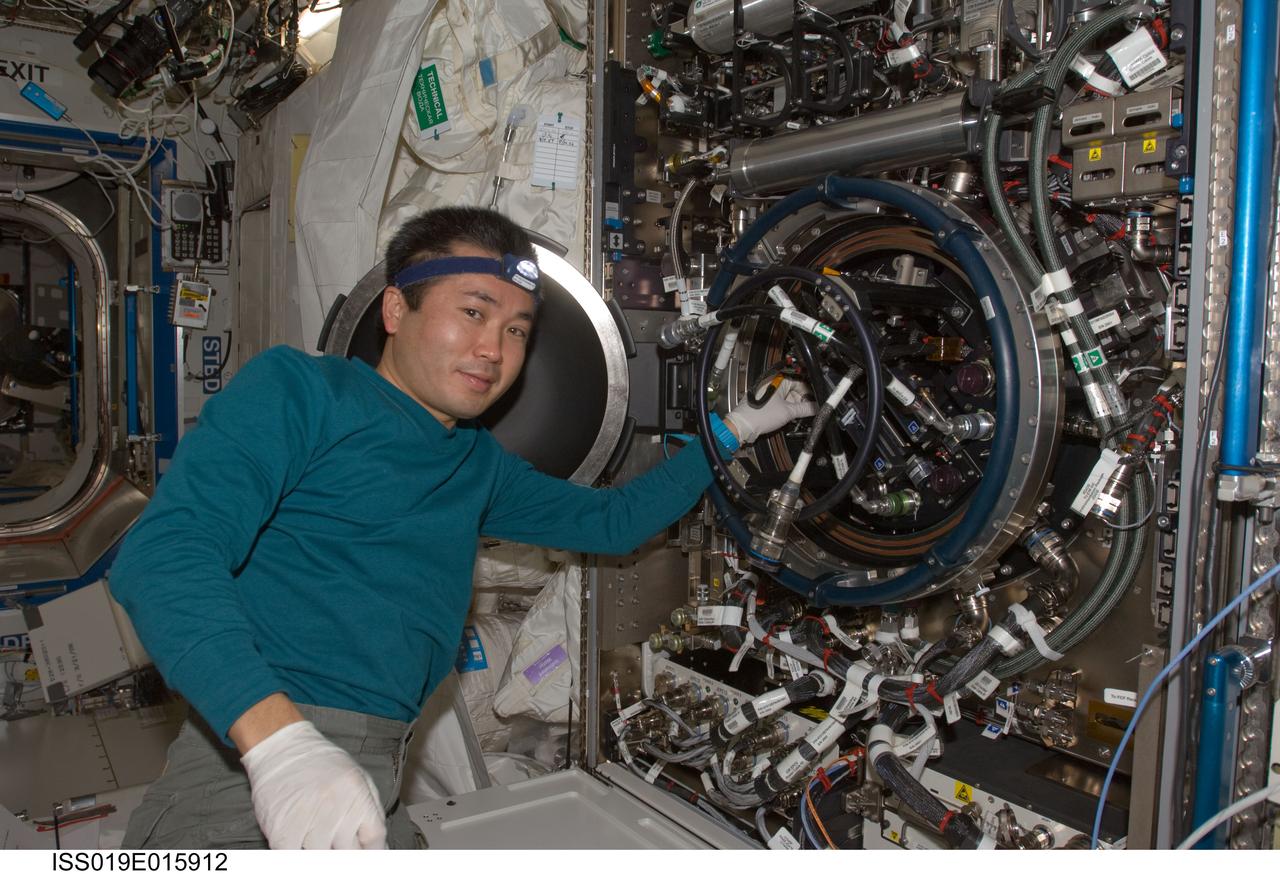

ISS019-E-015912 (12 May 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, works on the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. Wakata removed and replaced one fuel reservoir, which required temporary opening the front end cap and removing the fuel supply bypass Quick Disconnect (QD).

On June 16, 2020, a test was conducted at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center on a new pointing mode for the observatory. Uploaded to the spacecraft only days before, the mode allows for a problematic gyroscope (a sensor used to determine which direction and how fast Hubble is turning) to be bypassed when trying to keep the spacecraft steady. Systems manager Morgan Van Arsdall monitors the process while many of her teammates monitor the spacecraft’s subsystems from home. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth
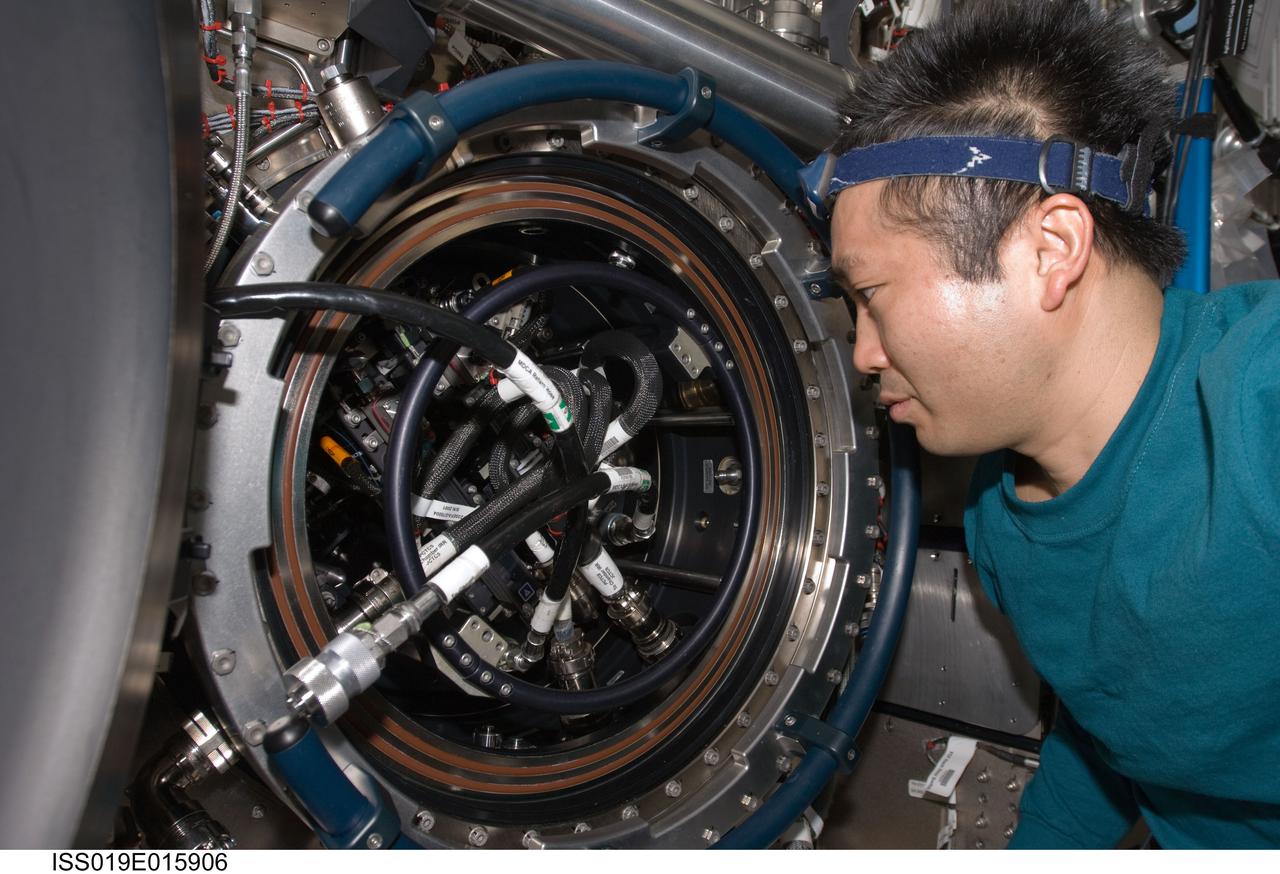
ISS019-E-015906 (12 May 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, works on the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. Wakata removed and replaced one fuel reservoir, which required temporary opening the front end cap and removing the fuel supply bypass Quick Disconnect (QD).
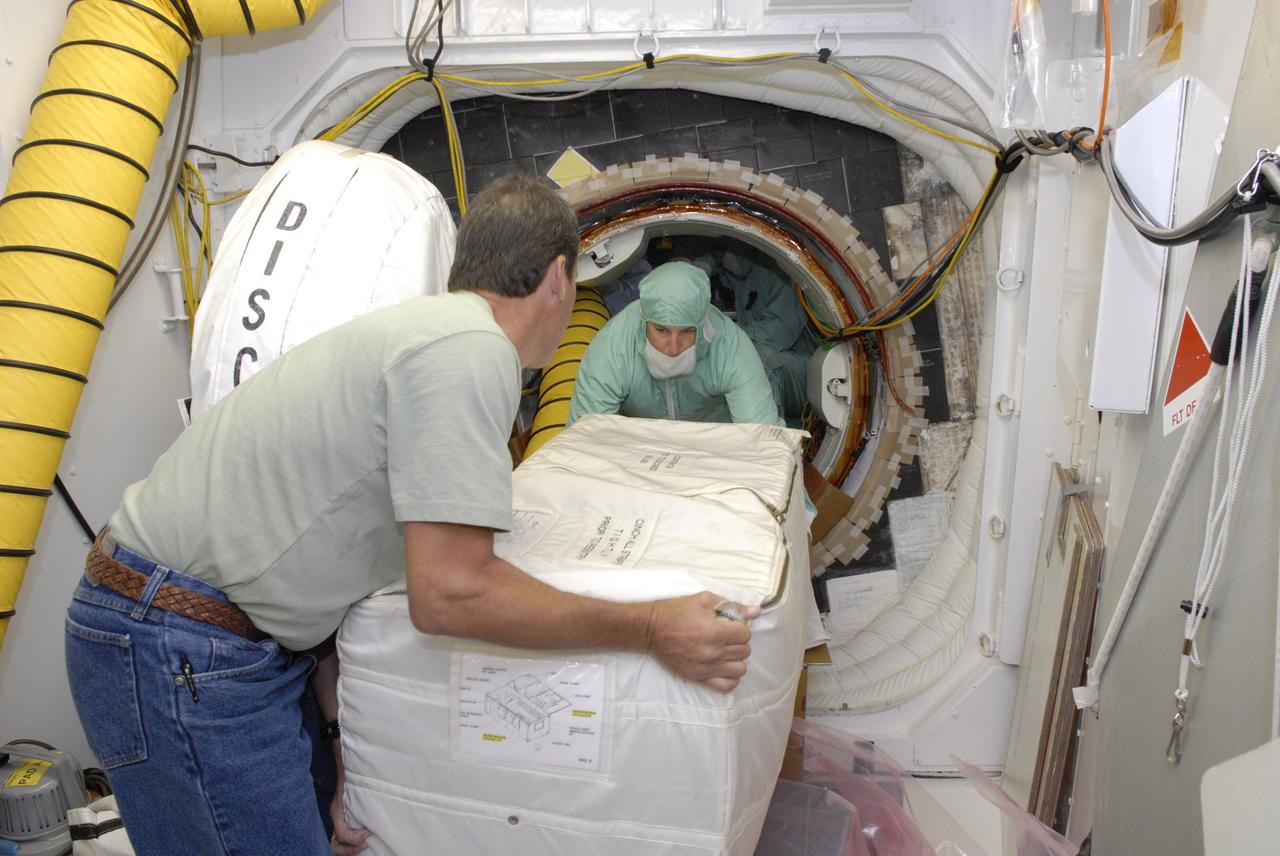

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Launch Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, technicians load replacement parts for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Discovery. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Replacement parts for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station are inspected following their arrival at Kennedy Space Center. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to space shuttle Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Launch Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, technicians load replacement parts for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Discovery. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Launch Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, replacement parts for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station are loaded aboard space shuttle Discovery. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A replacement part for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station is inspected following its arrival at Kennedy Space Center. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to space shuttle Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A technician inspects a replacement part for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station following its arrival at Kennedy Space Center. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to space shuttle Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
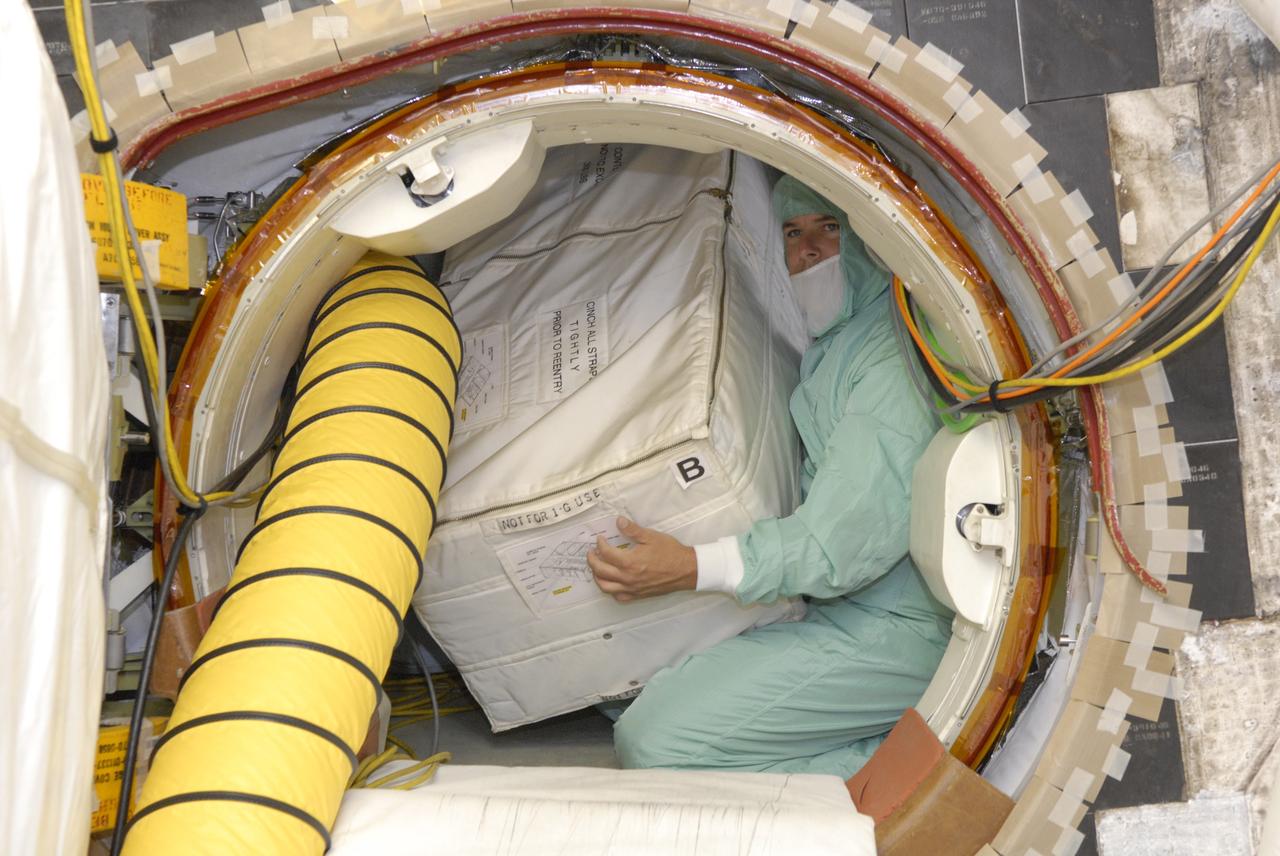

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Launch Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, a technician loads replacement parts for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Discovery. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
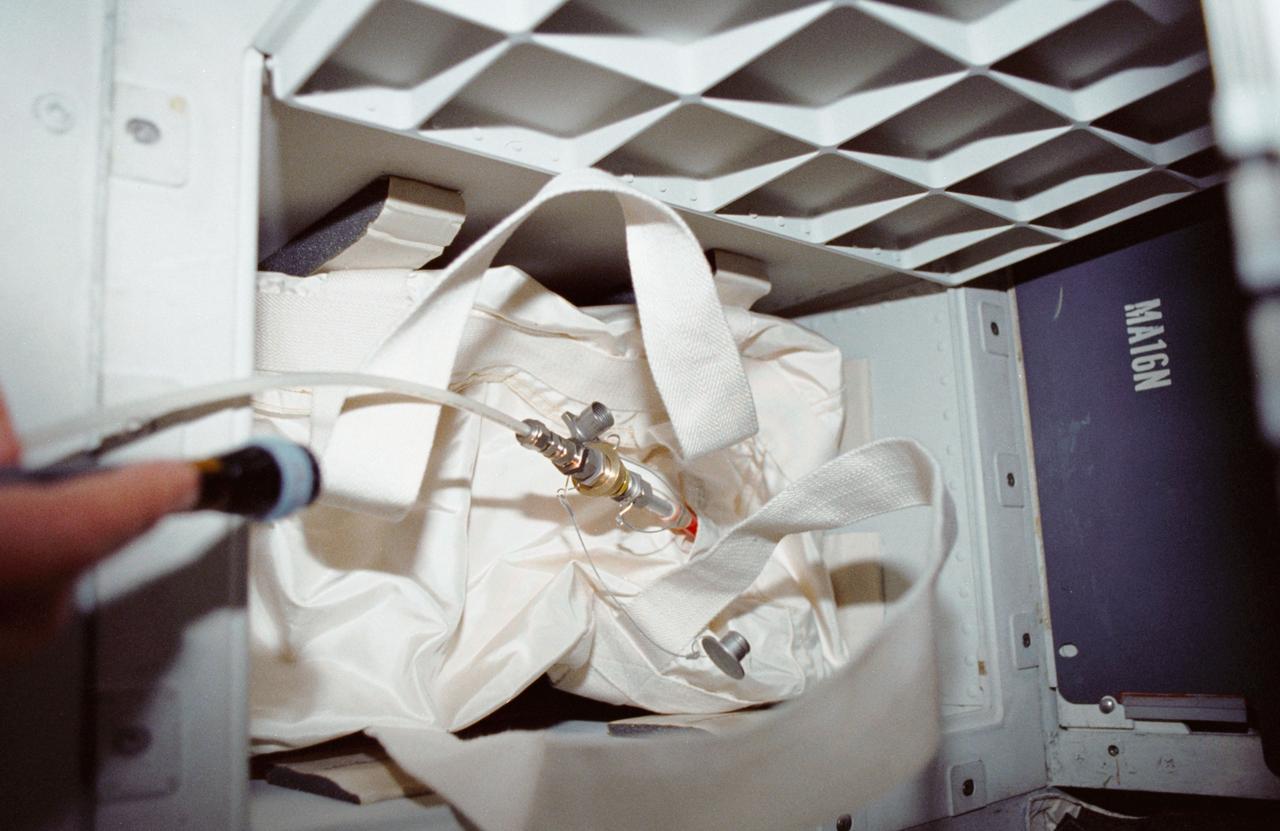

STS035-12-005 (2-10 Dec 1990) --- During STS-35, middeck stowage volume G and a contingency water container (CWC) were utilized to remedy a problem onboard Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102. A hose connecting OV-102's waste water system to the CWC was used in order to bypass a suspected clog in the line from the waste water tank to the exit nozzle. On flight day seven, Pilot Guy S. Gardner carried out an inflight maintenance (IFM) procedure by connecting a spare hose from the line to the container. The CWC is a rubber-lined duffle bag that holds about 95 pounds of water and is used in situations where water cannot be dumped overboard normally.
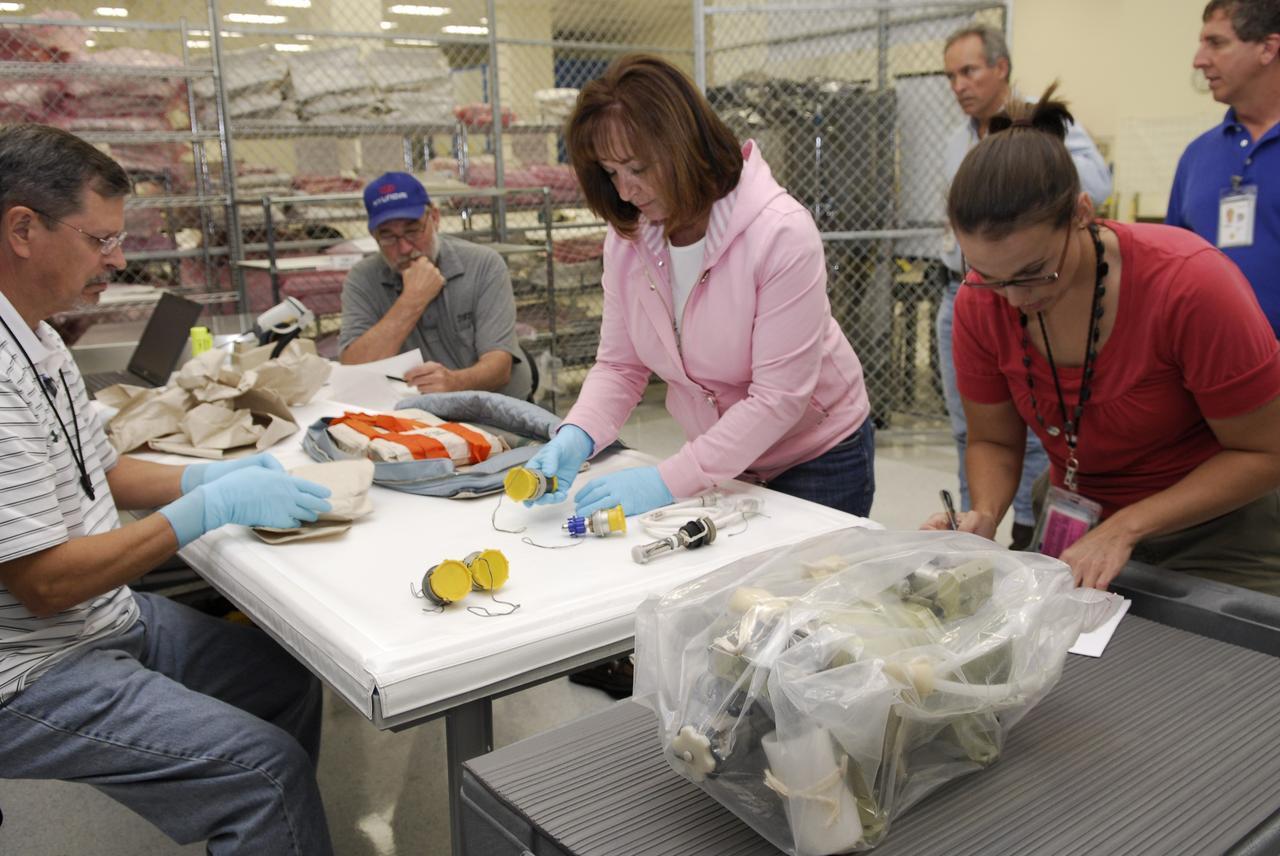

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Replacement parts for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station are inspected following their arrival at Kennedy Space Center. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to space shuttle Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
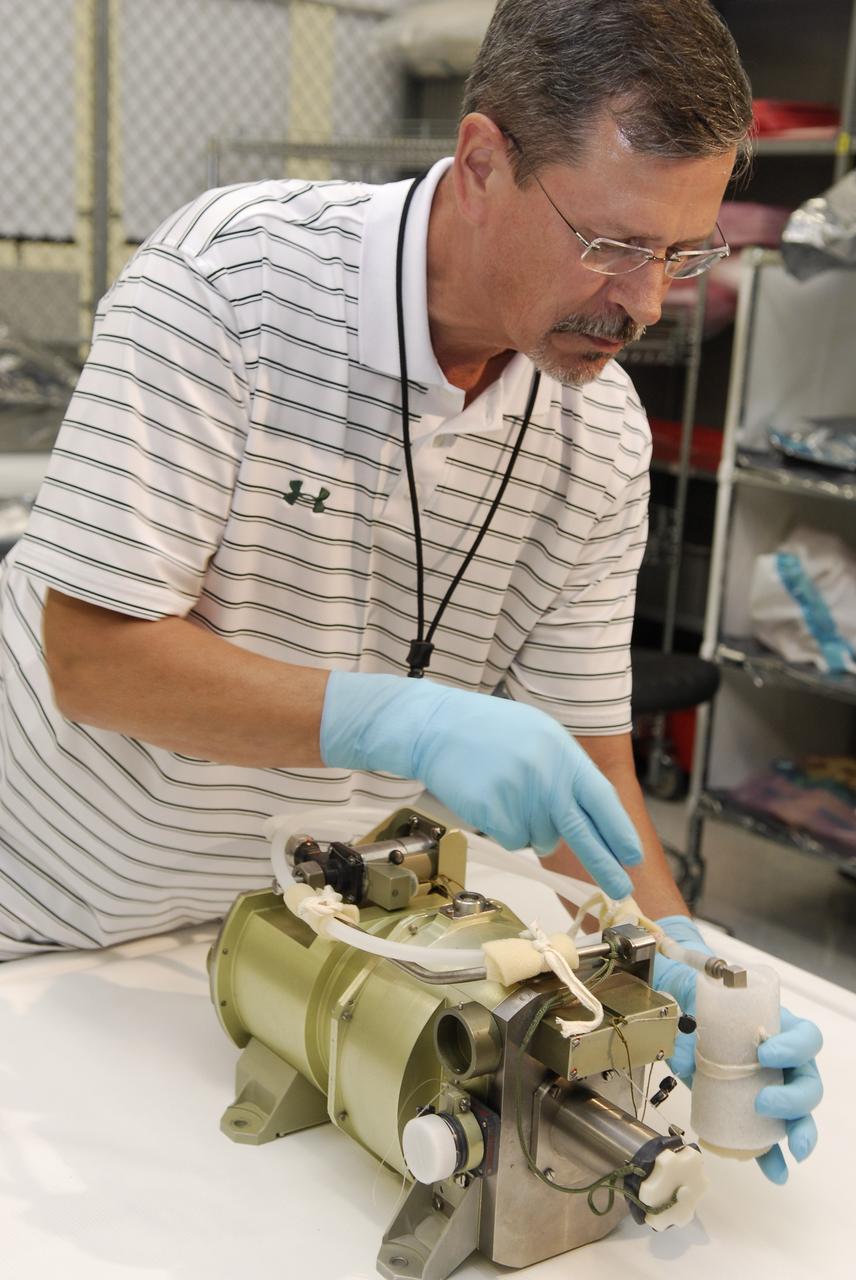

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A technician inspects a replacement part for the Zvezda service module toilet on the International Space Station following its arrival at Kennedy Space Center. The toilet malfunctioned last week and was initially repaired by replacing a microprocessor valve. After the station crew members experienced additional difficulties with the toilet, they were directed to use Soyuz toilet facilities at first and are using the main toilet again after rigging a urine bypass. The spare toilet parts have been added to space shuttle Discovery’s manifest for delivery to the station on the STS-124 mission. On the 14-day mission, Discovery and its crew will deliver the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Japanese Experiment Module – Pressurized Module and the Japanese Remote Manipulator System. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. EDT May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
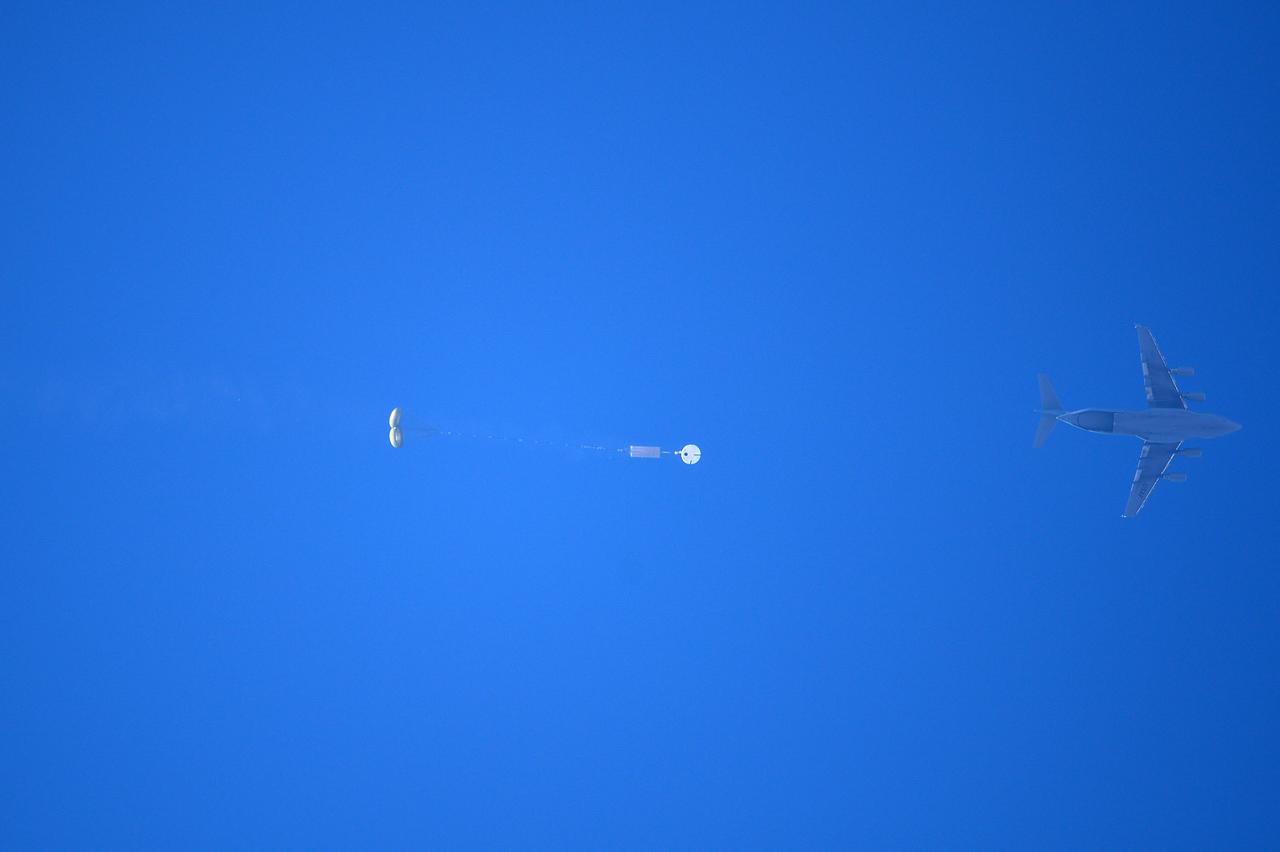

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
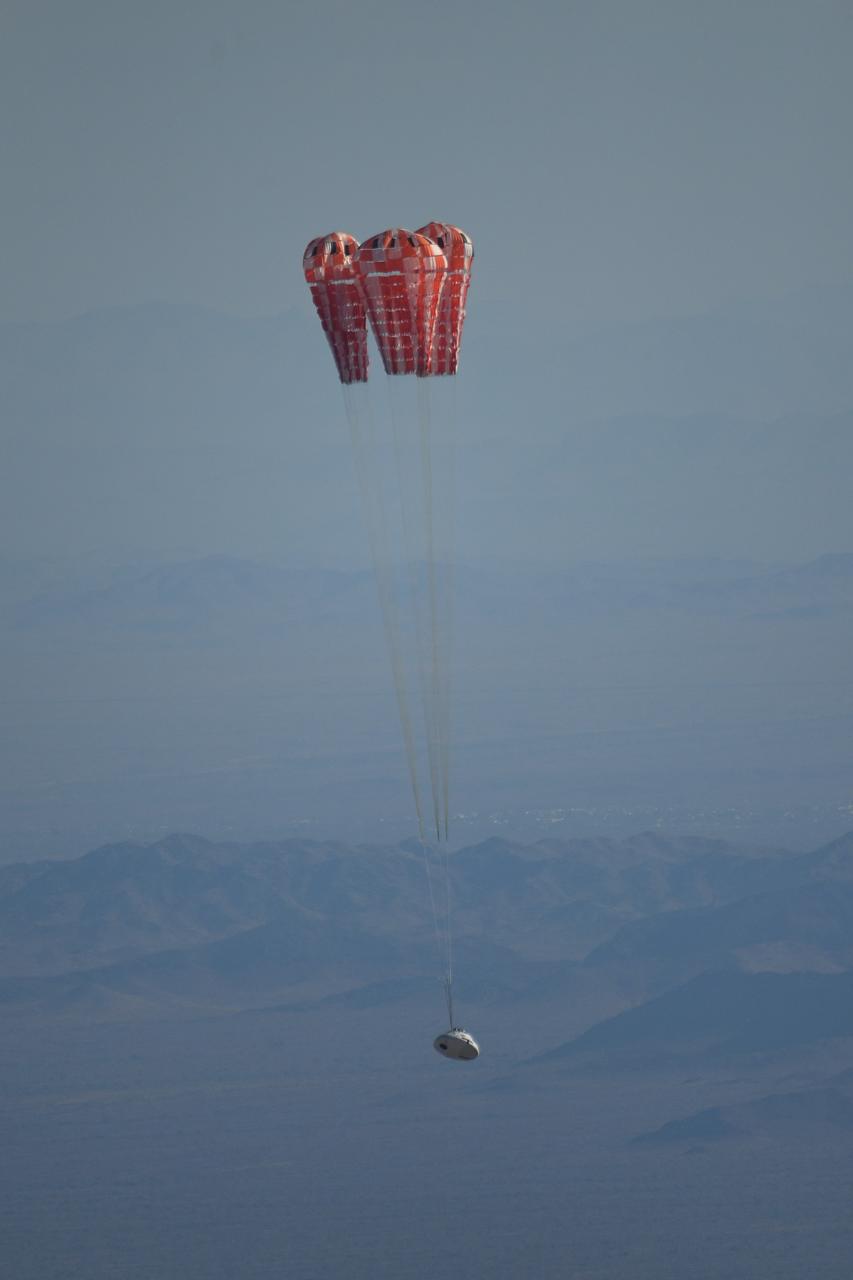

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
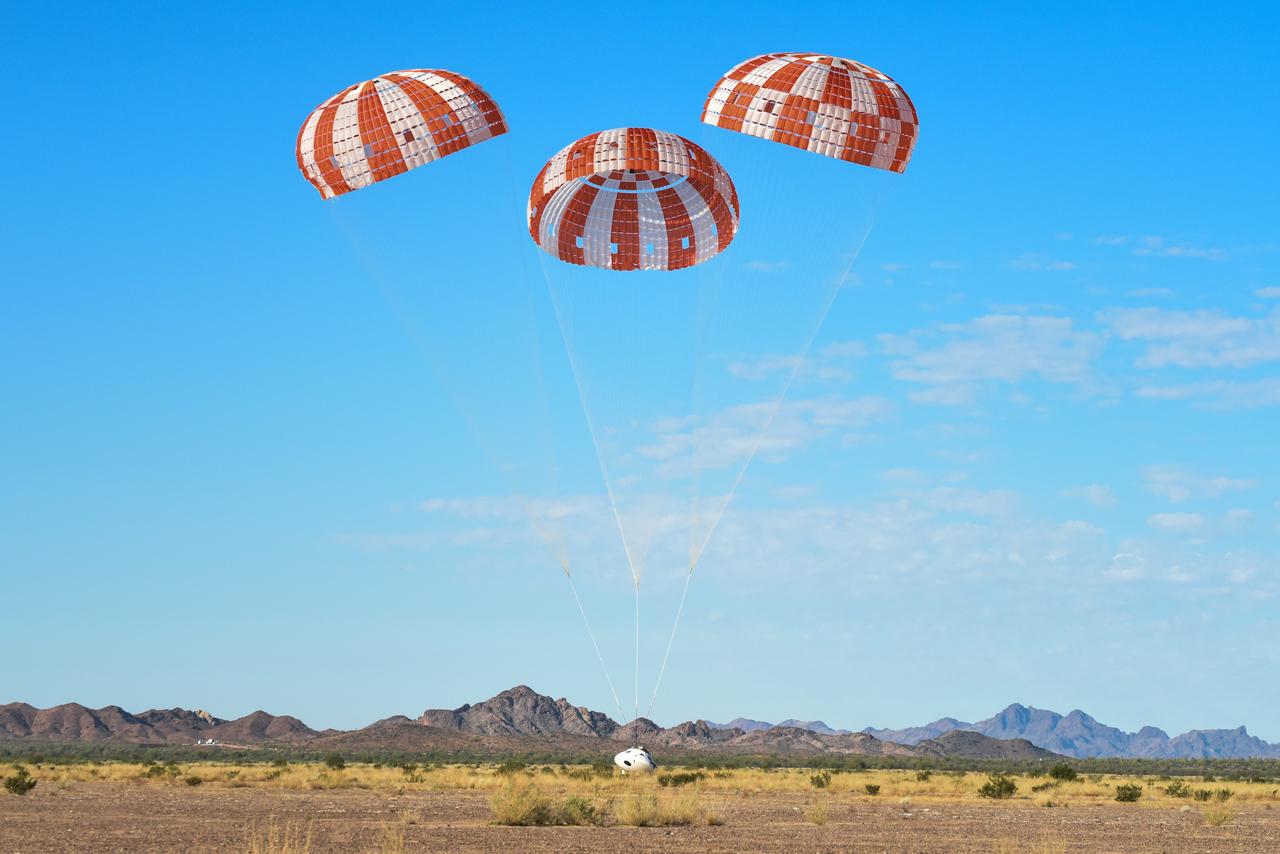

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
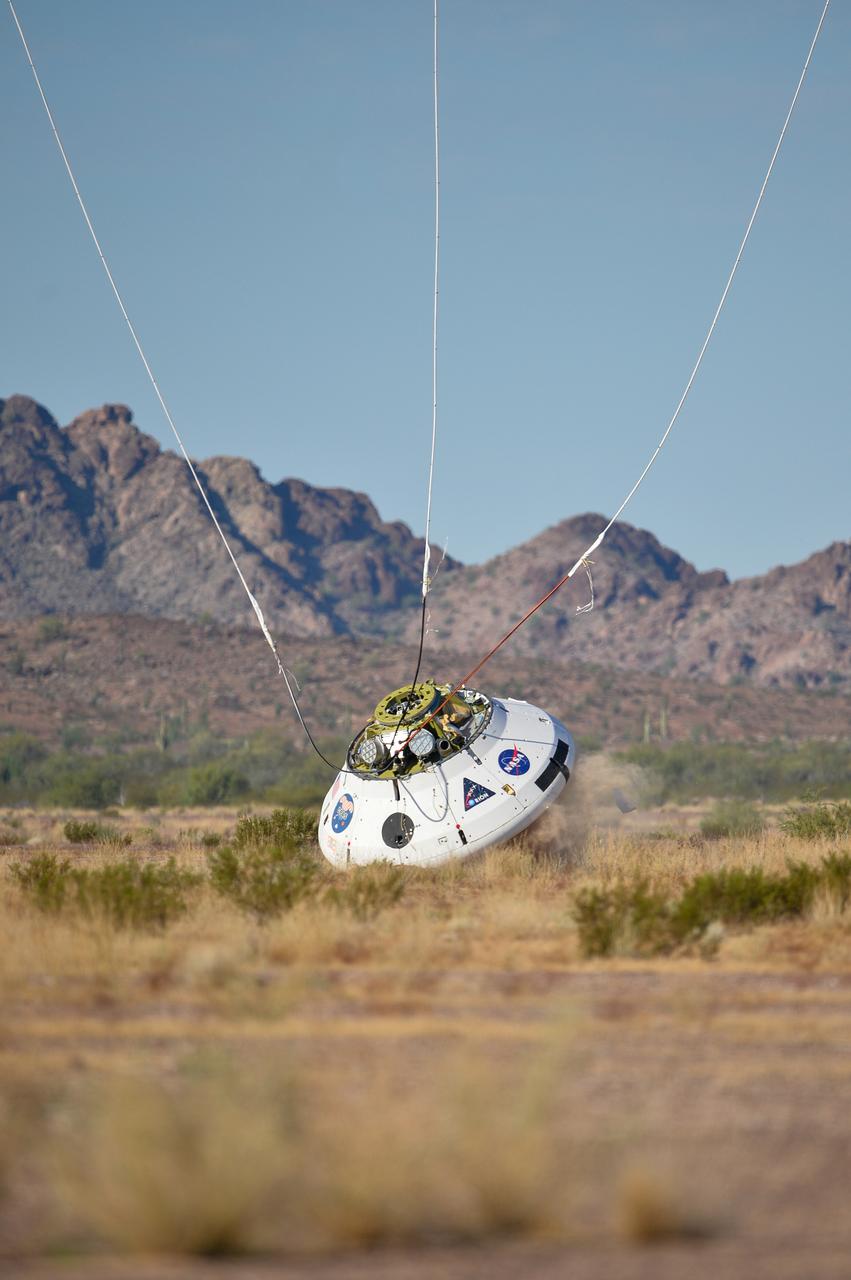

Engineers testing the parachute system for Orion during a Sept. 13, 2017 evaluation at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
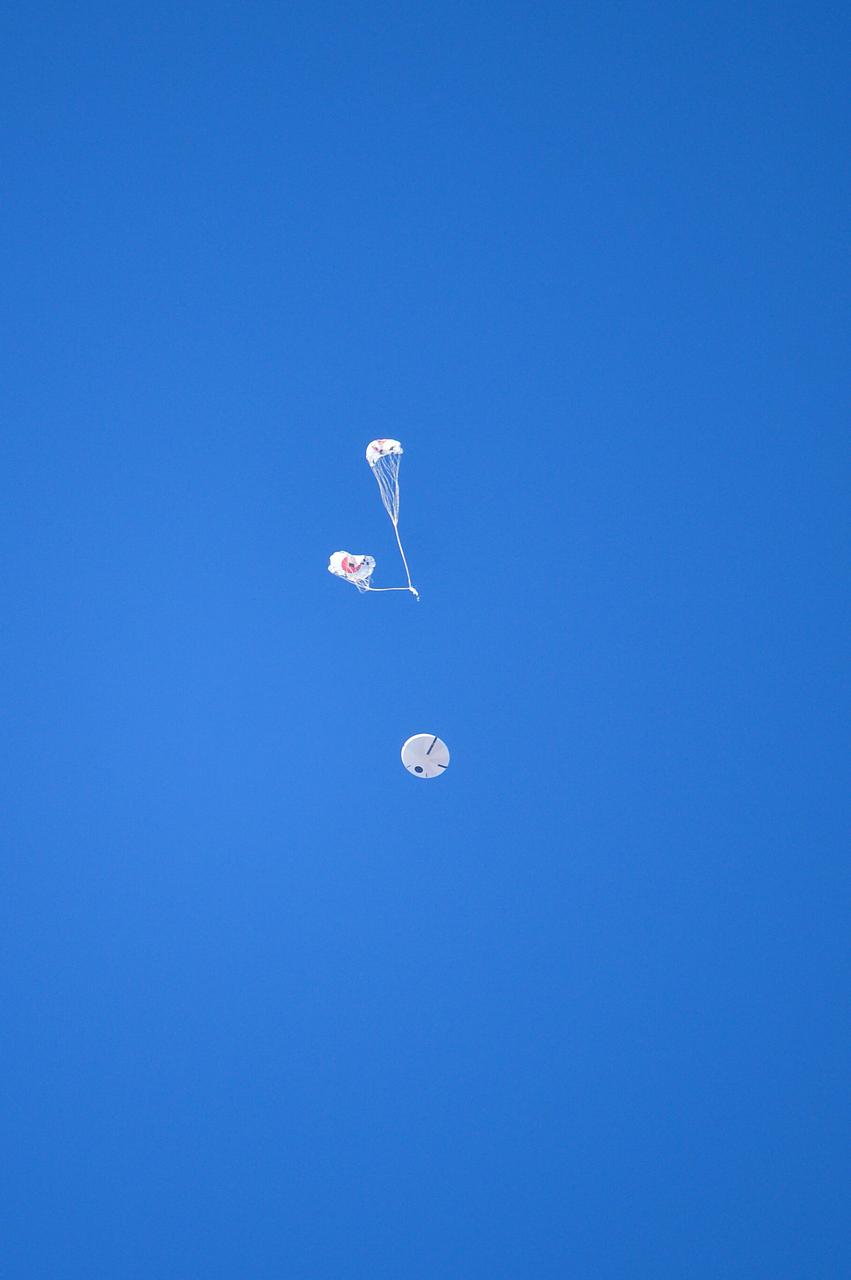

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
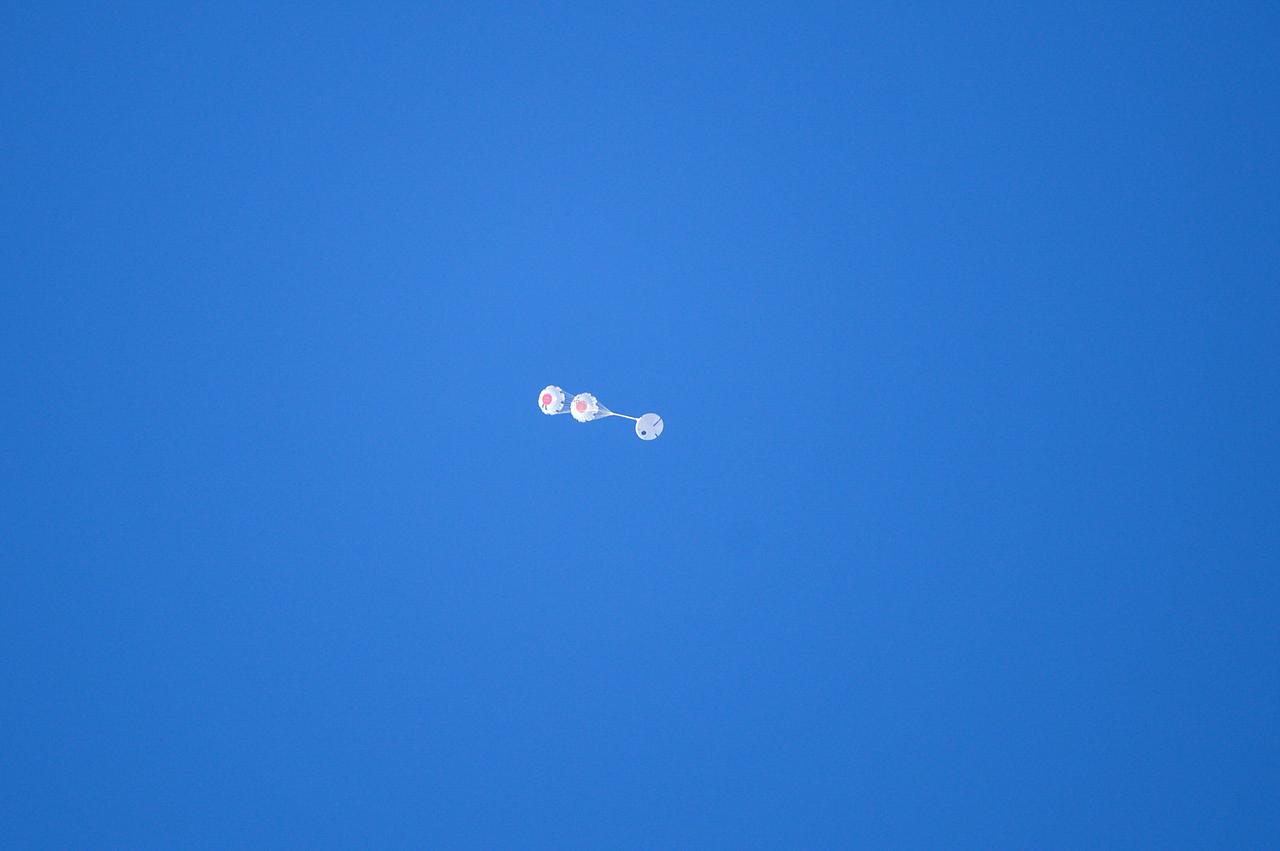

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
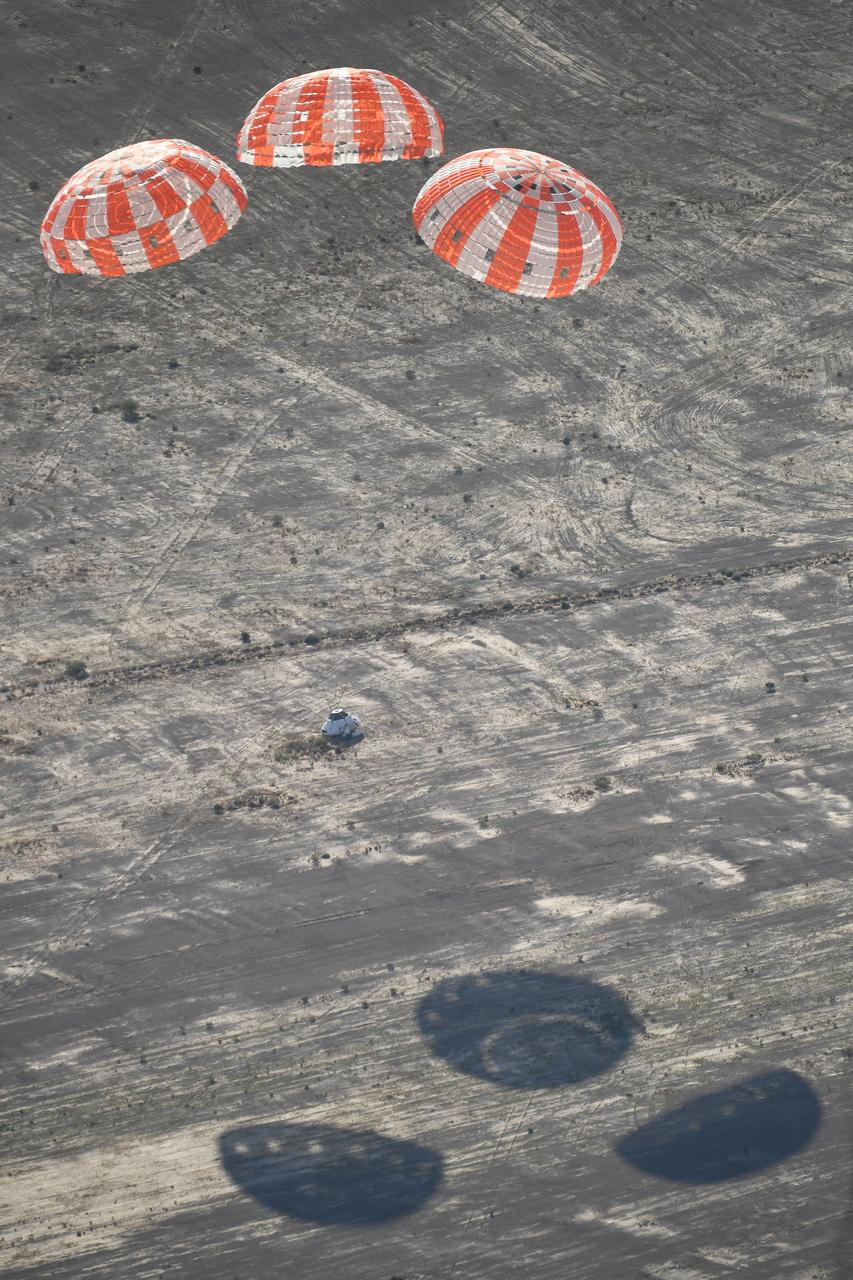

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
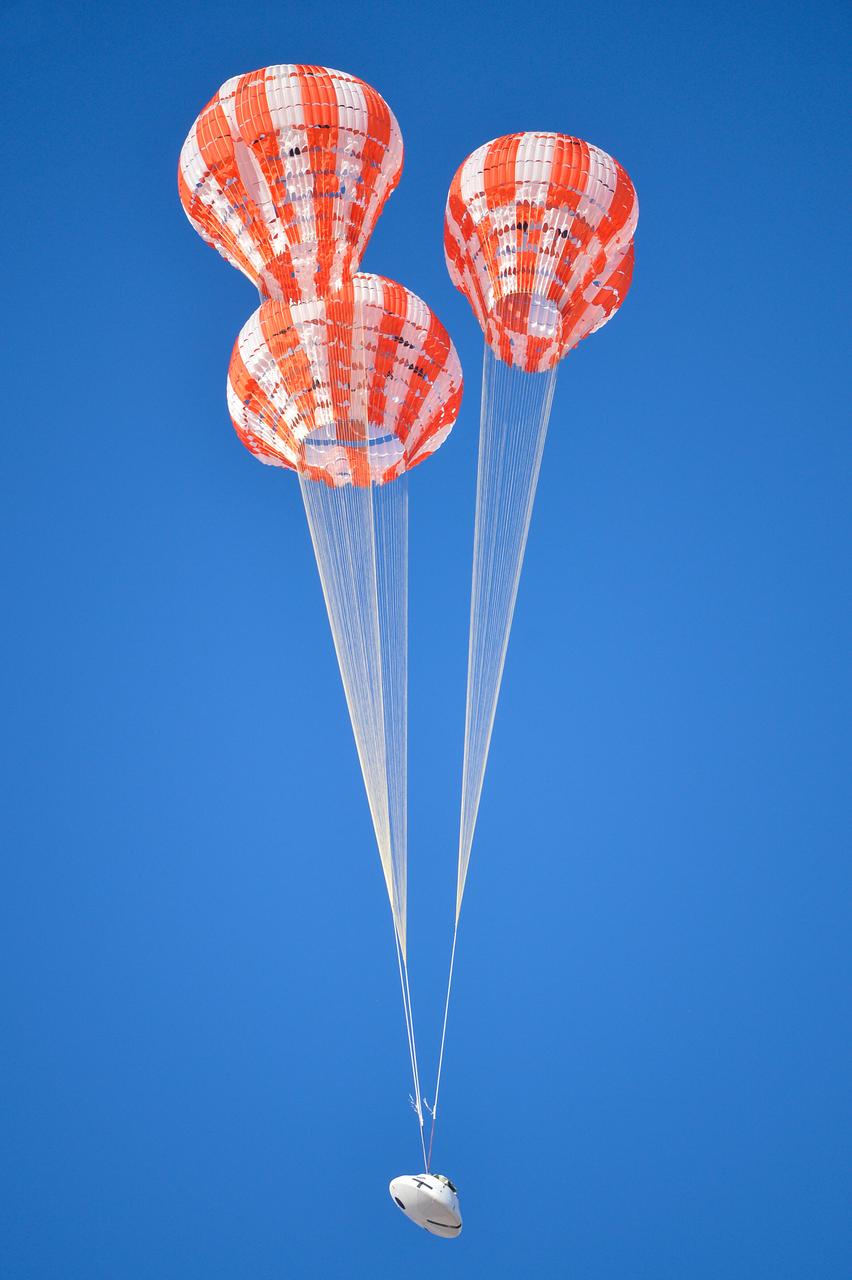

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
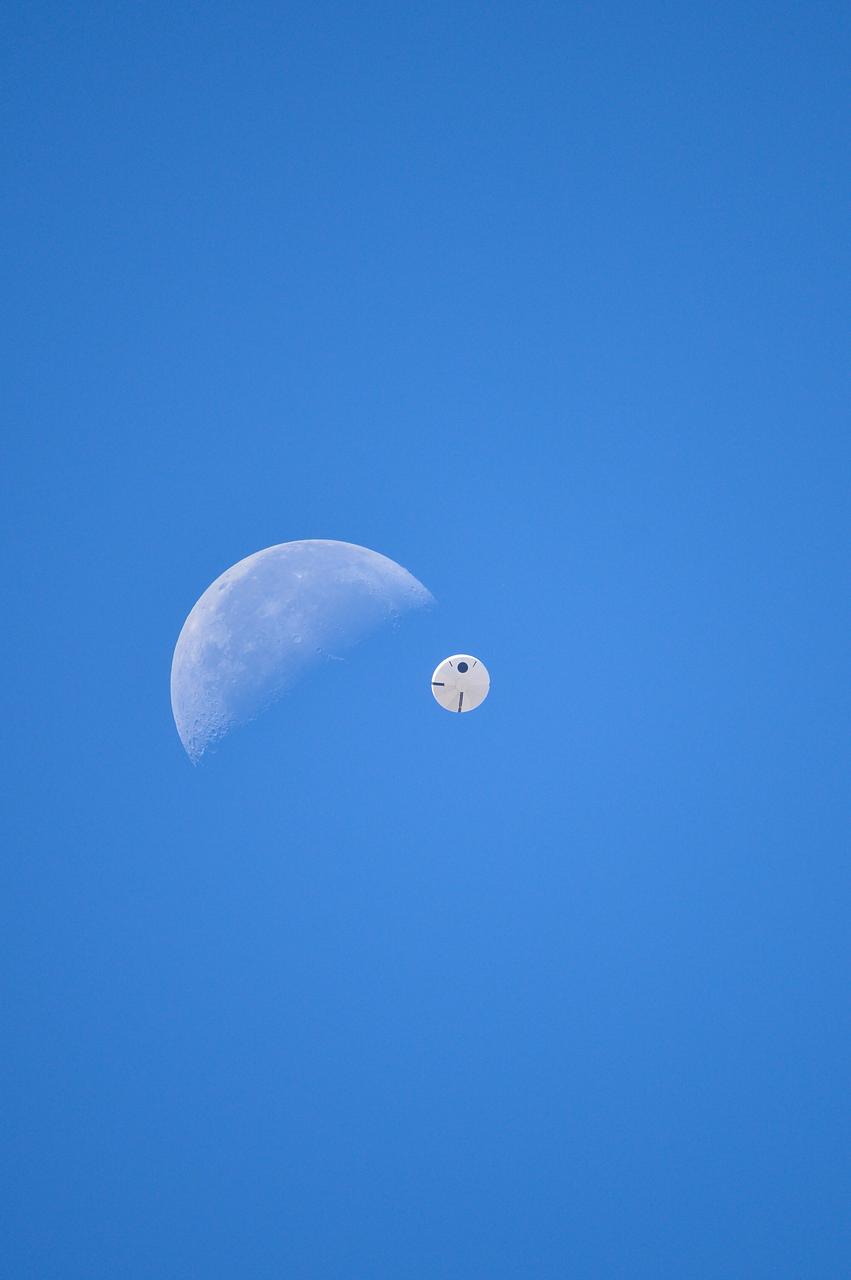

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
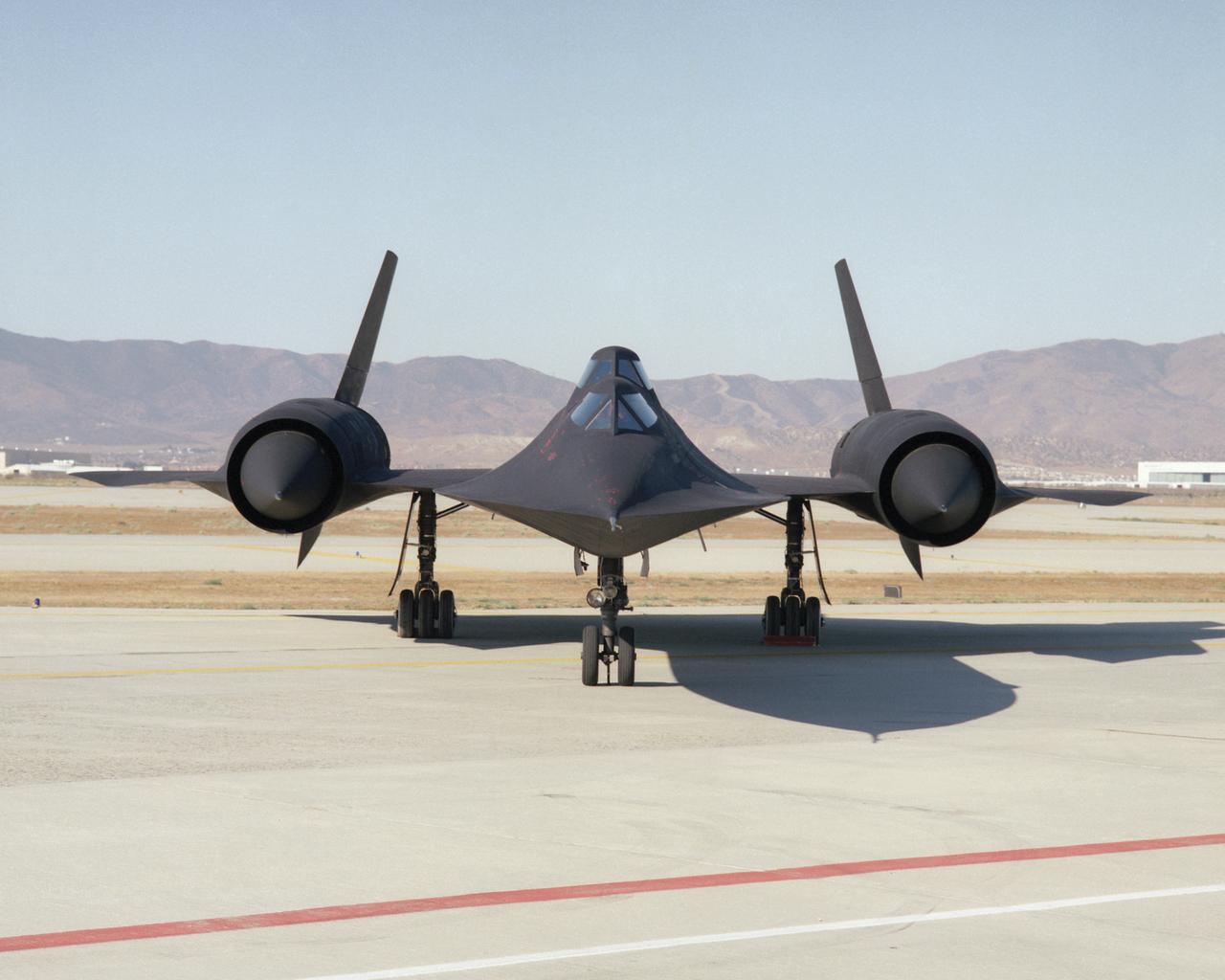

This photo shows a head-on view of NASA's SR-71B, used for pilot proficiency and training, on the ramp at the Air Force's Plant 42 in Palmdale, California, shortly before delivery to the Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later, Dryden Flight Research Center) at Edwards, California. NASA operated two of these unique aircraft, an SR-71A, for high-speed, high altitude research, and this SR- 71B pilot trainer for most of the decade of the 1990s. The "B" model is special because of its raised rear cockpit, which provided a second pilot position so a trainer and an experienced pilot could both see what was going on during flights. The SR-71 was designed and built by the Lockheed Skunk Works, now the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works. Studies have shown that less than 20 percent of the total thrust used to fly at Mach 3 is produced by the basic engine itself. The balance of the total thrust is produced by the unique design of the engine inlet and "moveable spike" system at the front of the engine nacelles, and by the ejector nozzles at the exhaust which burn air compressed in the engine bypass system. Data from the SR-71 high speed research program will be used to aid designers of future supersonic/hypersonic aircraft and propulsion systems, including a high speed civil transport.
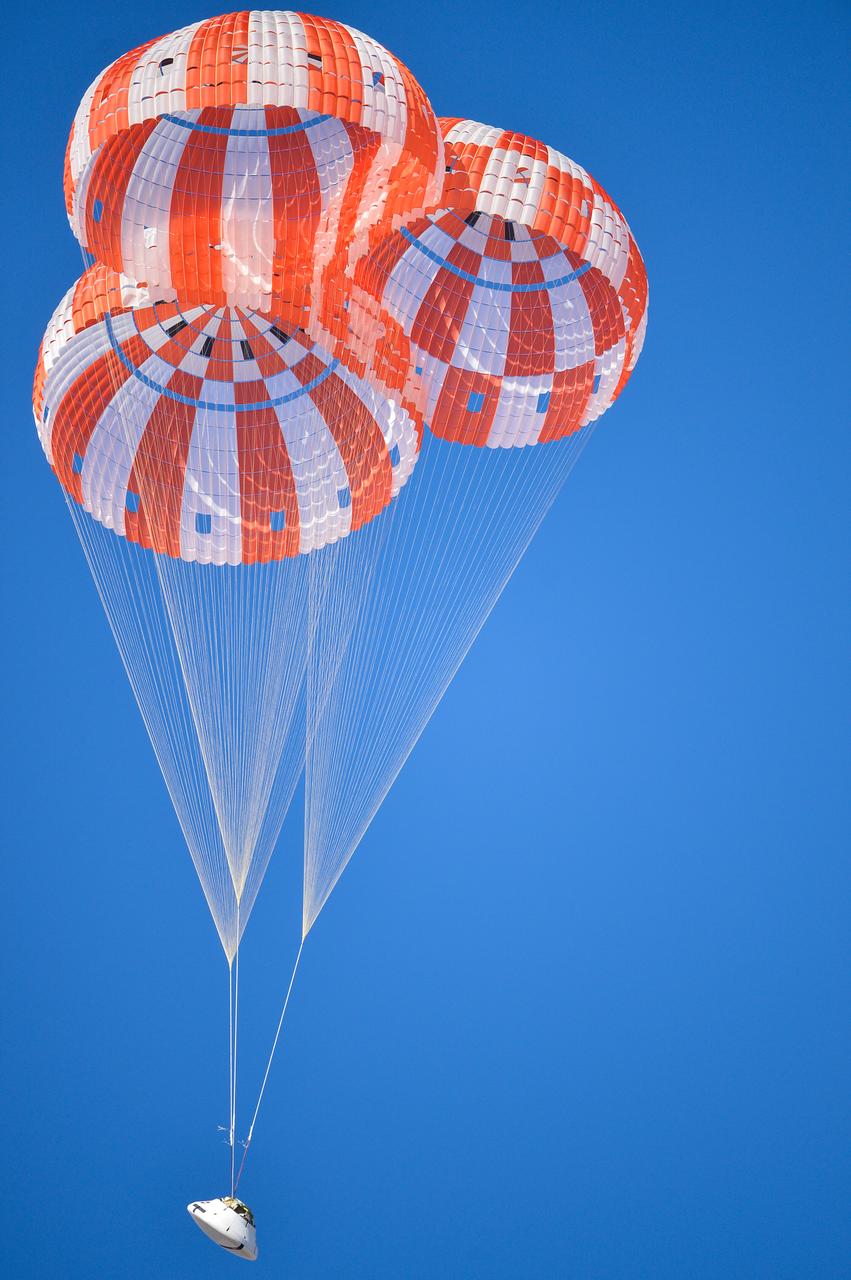

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
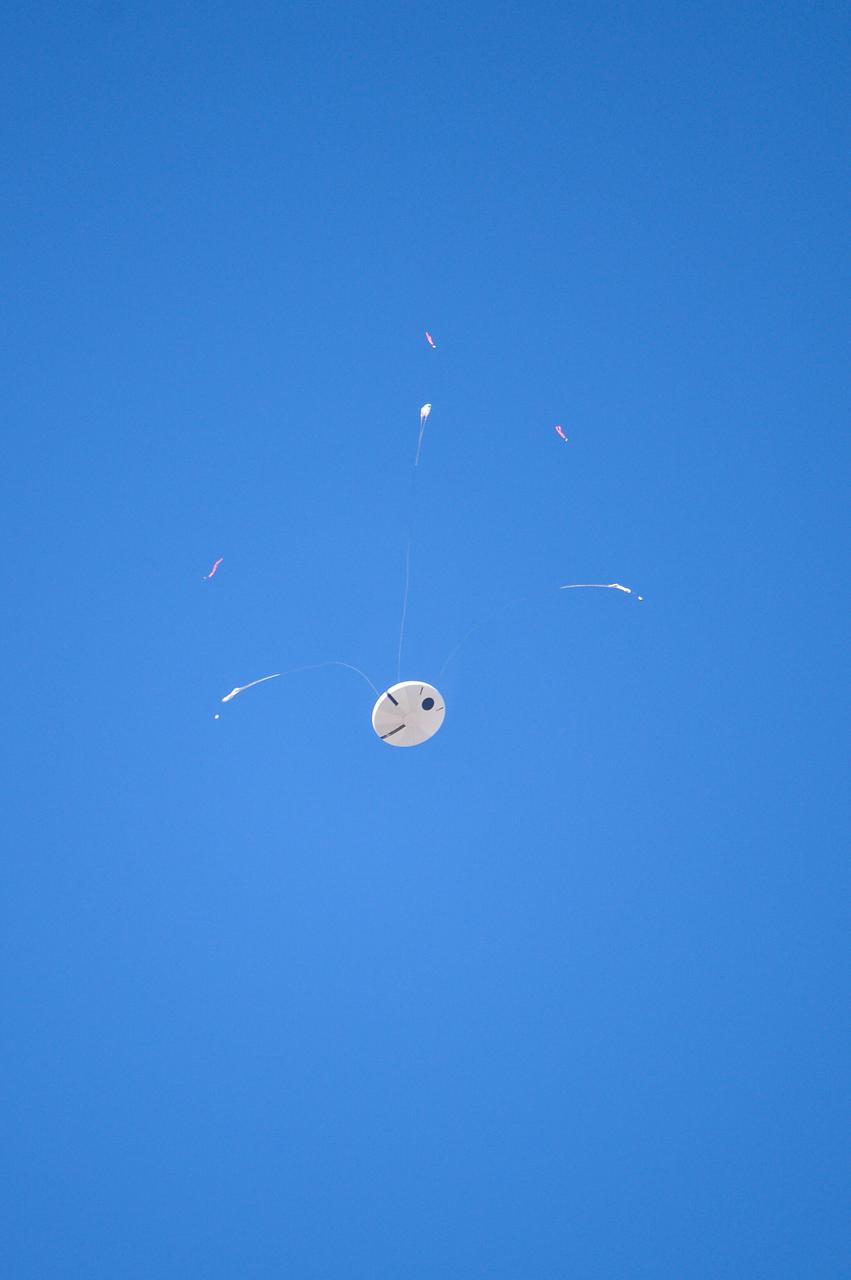

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
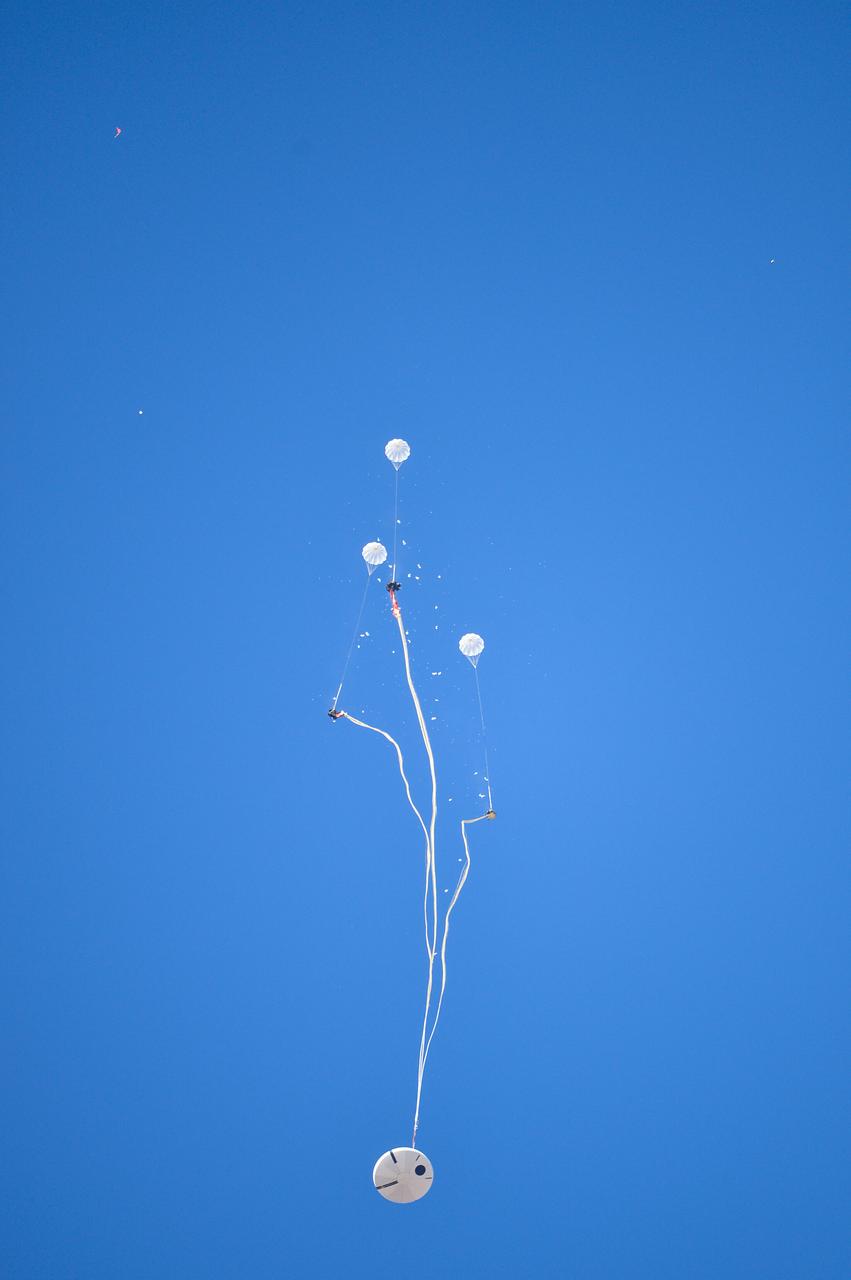

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
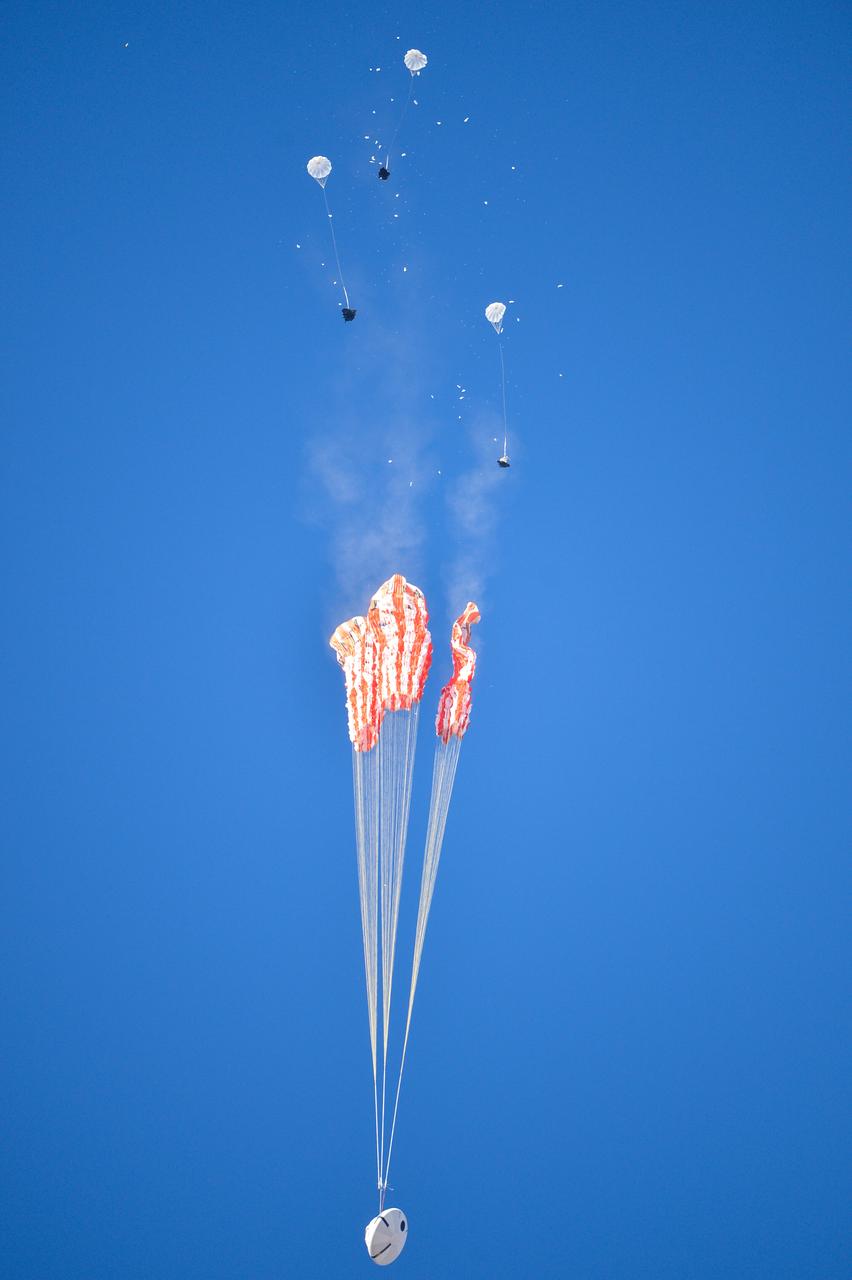

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
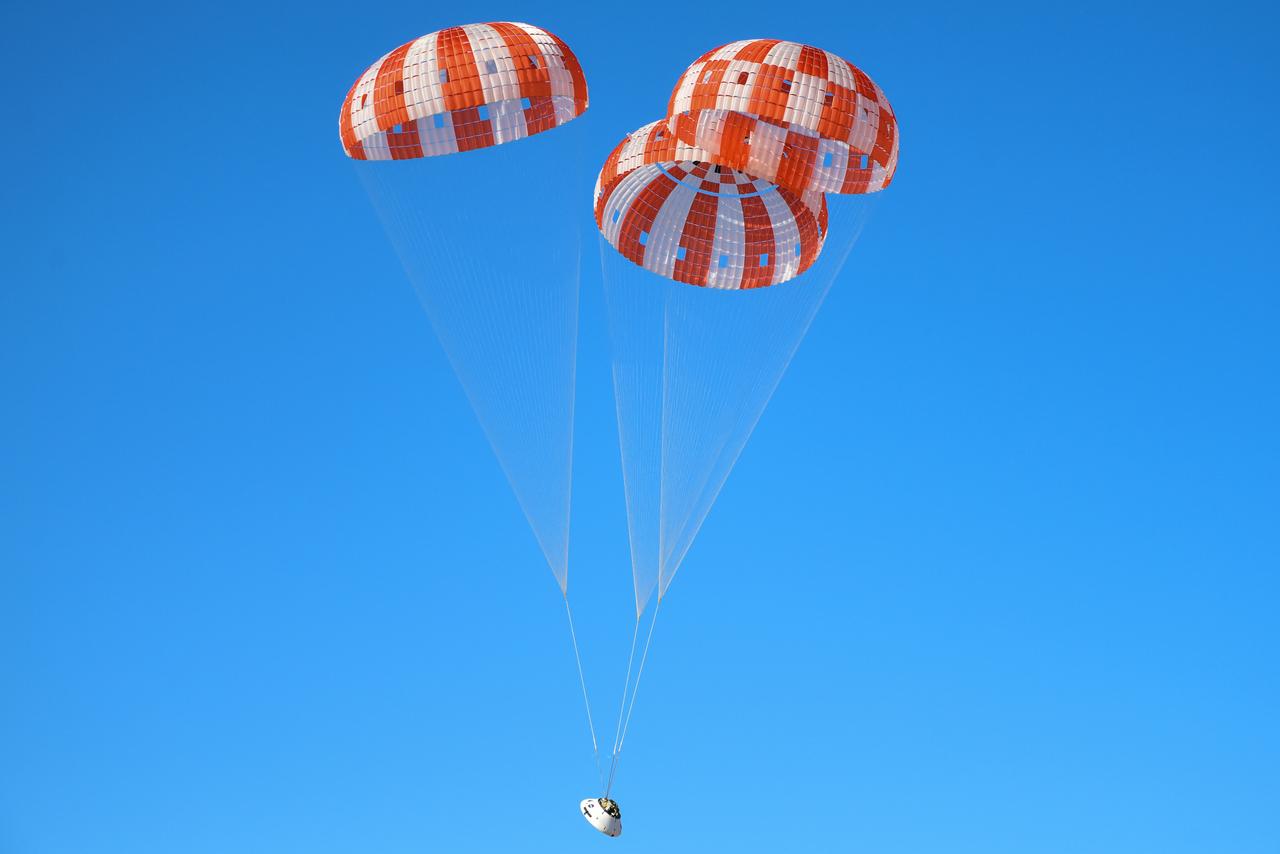

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.

Orion’s three main orange and white parachutes help a representative model of the spacecraft descend through sky above Arizona, where NASA engineers tested the parachute system on Sept. 13, 2017 at the U.S. Army Proving Ground in Yuma. NASA is qualifying Orion’s parachutes for missions with astronauts.. .During this test, engineers replicated a situation in which Orion must abort off the Space Launch System rocket and bypasses part of its normal parachute deployment sequence that typically helps the spacecraft slow down during its descent to Earth after deep space missions. The capsule was dropped out of a C-17 aircraft at more than 4.7 miles in altitude and allowed to free fall for 20 seconds, longer than ever before, to produce high aerodynamic pressure before only its pilot and main parachutes were deployed, testing whether they could perform as expected under extreme loads. Orion’s full parachute system includes 11 total parachutes -- three forward bay cover parachutes and two drogue parachutes, along with three pilot parachutes that help pull out the spacecraft’s three mains.
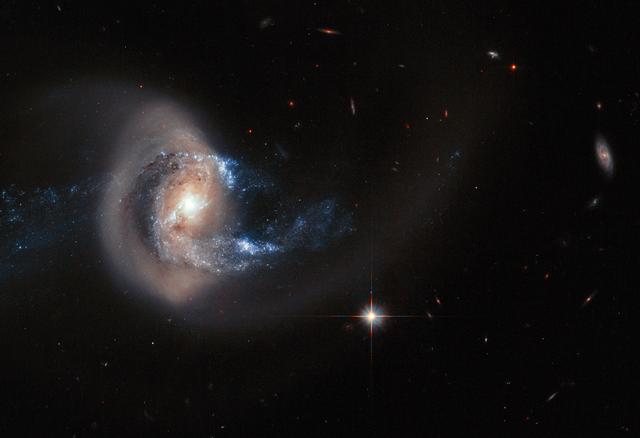

This NASA Hubble Space Telescope photo of NGC 7714 presents an especially striking view of the galaxy's smoke-ring-like structure. The golden loop is made of sun-like stars that have been pulled deep into space, far from the galaxy's center. The galaxy is located approximately 100 million light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Pisces. The universe is full of such galaxies that are gravitationally stretched and pulled and otherwise distorted in gravitational tug-o'-wars with bypassing galaxies. The companion galaxy doing the "taffy pulling" in this case, NGC 7715, lies just out of the field of view in this image. A very faint bridge of stars extends to the unseen companion. The close encounter has compressed interstellar gas to trigger bursts of star formation seen in bright blue arcs extending around NGC 7714's center. The gravitational disruption of NGC 7714 began between 100 million and 200 million years ago, at the epoch when dinosaurs ruled the Earth. The image was taken with the Wide Field Camera 3 and the Advanced Camera for Surveys in October 2011. Credit: NASA and ESA. Acknowledgment: A. Gal-Yam (Weizmann Institute of Science) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Title: W-8 Fan Acoustic Casing Treatment Test on the Source Diagnostic Test Rotor Alone Hardware Program: Advanced Air Vehicles Program (AAVP) Project: Advanced Air Transport Technology (AATT) Sub-project: Aircraft Noise Reduction (ANR) Weekly Highlight: · Acoustic Casing Treatment Testing Completed in the W-8 Single Stage Axial Compressor Facility: Testing of Acoustic Casing Treatments on the Source Diagnostic Test (SDT) rotor alone hardware which had begun in early January was completed on Thursday, February 16th. Four different over-the-rotor acoustic casing treatment concepts were tested along with two baseline configurations. Testing included steady-aerodynamic measurements of fan performance, hotfilm turbulence measurements, and inlet acoustic measurements with an in-duct array. These measurements will be used to assess the aerodynamic and acoustic impact of fan acoustic casing treatments on a high bypass ratio fan at TRL 3. This test was the last of 3 planned tests of potential over-the-rotor acoustic casing treatments. The first treatment test was completed in the Normal Incidence Tube (NIT) at Langley Research Center (LaRC) in Fall 2015 and the second was completed on the Advanced Noise Control Fan (ANCF) in the Aero-Acoustic Propulsion Laboratory (AAPL) in Winter 2016. This work is supported by the Aircraft Noise Reduction (ANR) subproject of the Advanced Air Transport Technology (AATT) Project. (POC: LTV/ Rick Bozak 3-5160)
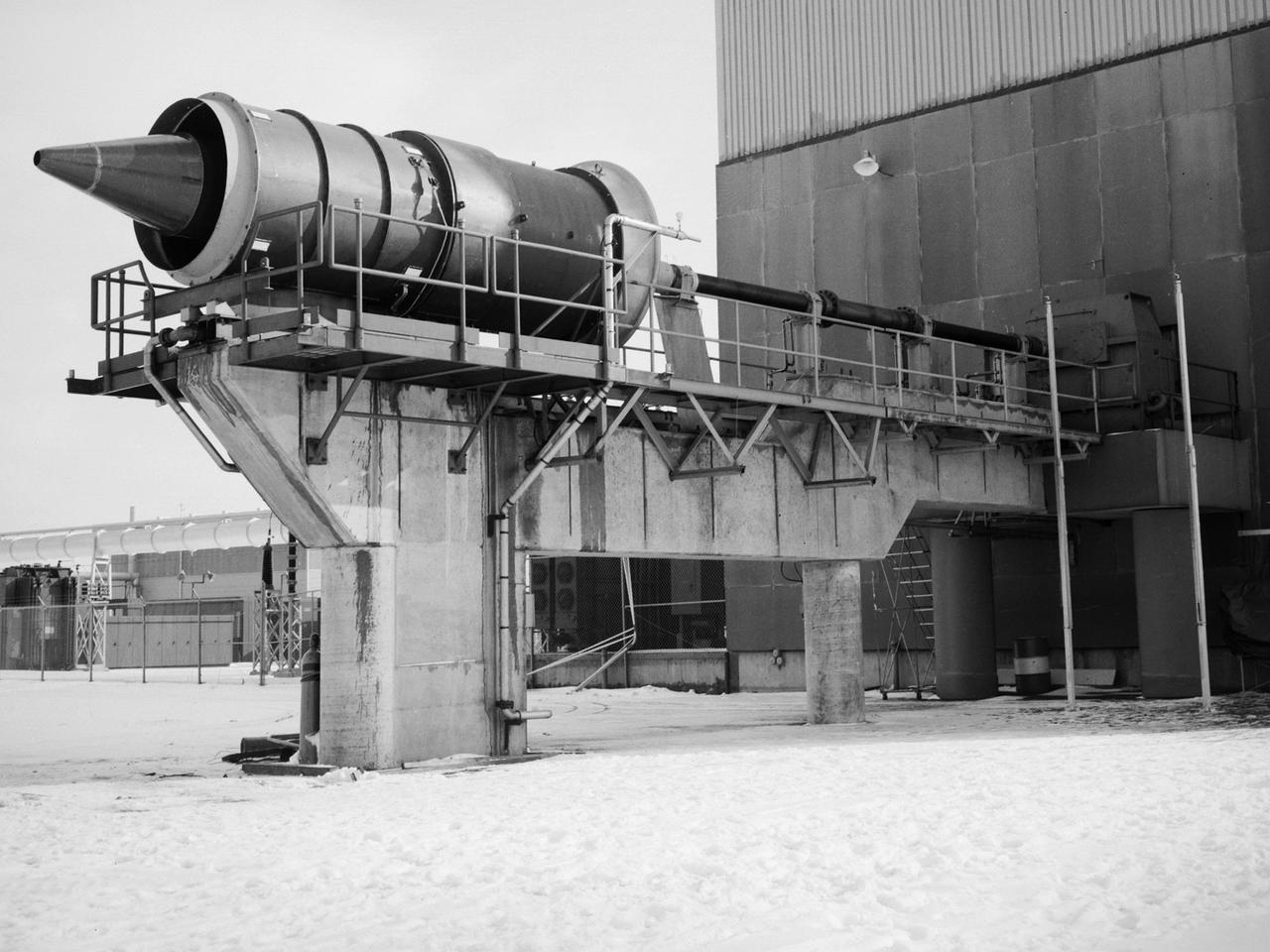

The Fan Noise Test Facility built at the Lewis Research Center to obtain far-field noise data for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and General Electric Quiet Engine Program. The engine incorporated existing noise reduction methods into an engine of similar power to those that propelled the Boeing 707 or McDonnell-Douglas DC-8 airliner. The new the low-bypass ratio turbofan engines of the 1960s were inherently quieter than their turbojet counterparts, researchers had a better grasp of the noise generation problem, and new acoustic technologies had emerged. Lewis contracted General Electric in 1969 to build and aerodynamically test three experimental engines with 72-inch diameter fans. The engines were then brought to Lewis and tested with an acoustically treated nacelle. This Fan Noise Test Facility was built off of the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel’s Main Compressor and Drive Building. Lewis researchers were able to isolate the fan’s noise during these initial tests by removing the core of the engine. The Lewis test rig drove engines to takeoff tip speeds of 1160 feet per second. The facility was later used to test a series of full-scale model fans and fan noise suppressors to be used with the quiet engine. NASA researchers predicted low-speed single-stage fans without inlet guide vanes and with large spacing between rotors and stators would be quieter. General Electric modified a TF39 turbofan engine by removing the the outer protion of the fan and spacing the blade rows of the inner portion. The tests revealed that the untreated version of the engine generated less noise than was anticipated, and the acoustically treated nacelle substantially reduced engine noise.