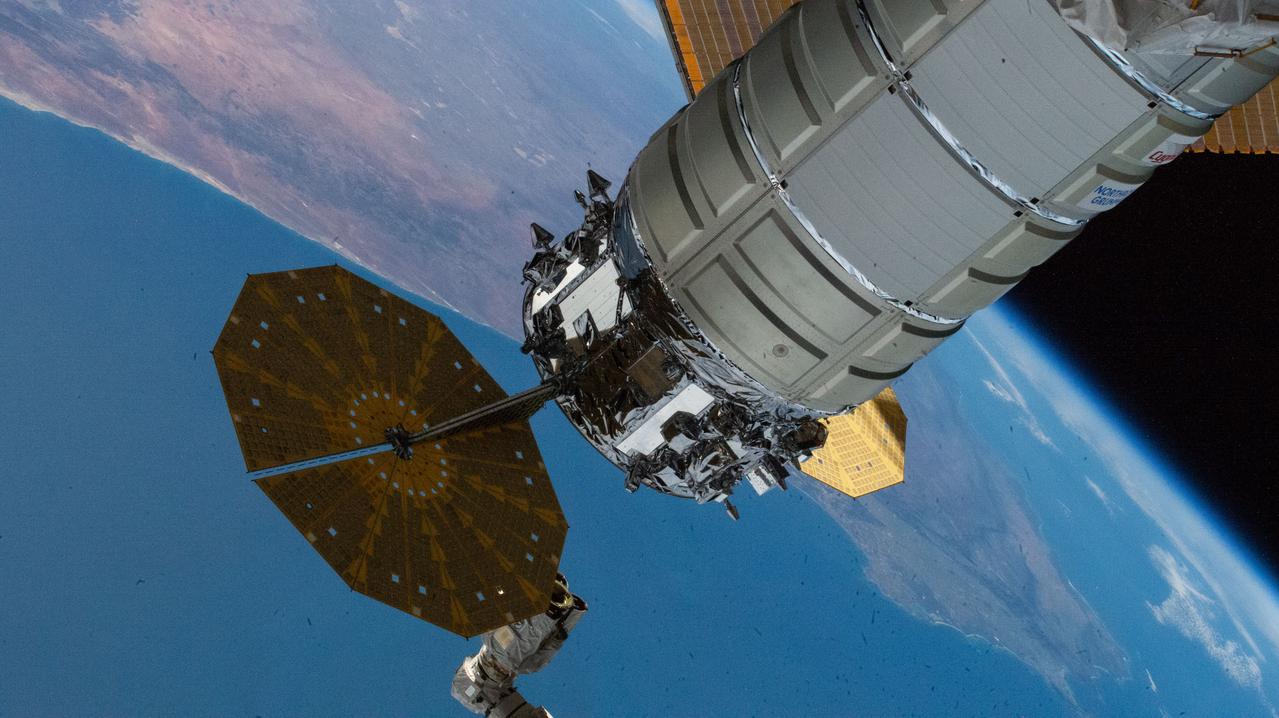

iss073e0768303 (Sept. 25, 2025) --- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus XL cargo craft is pictured installed to the Unity module's Earth-facing port as the International Space Station orbited 262 miles above the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of South Africa.
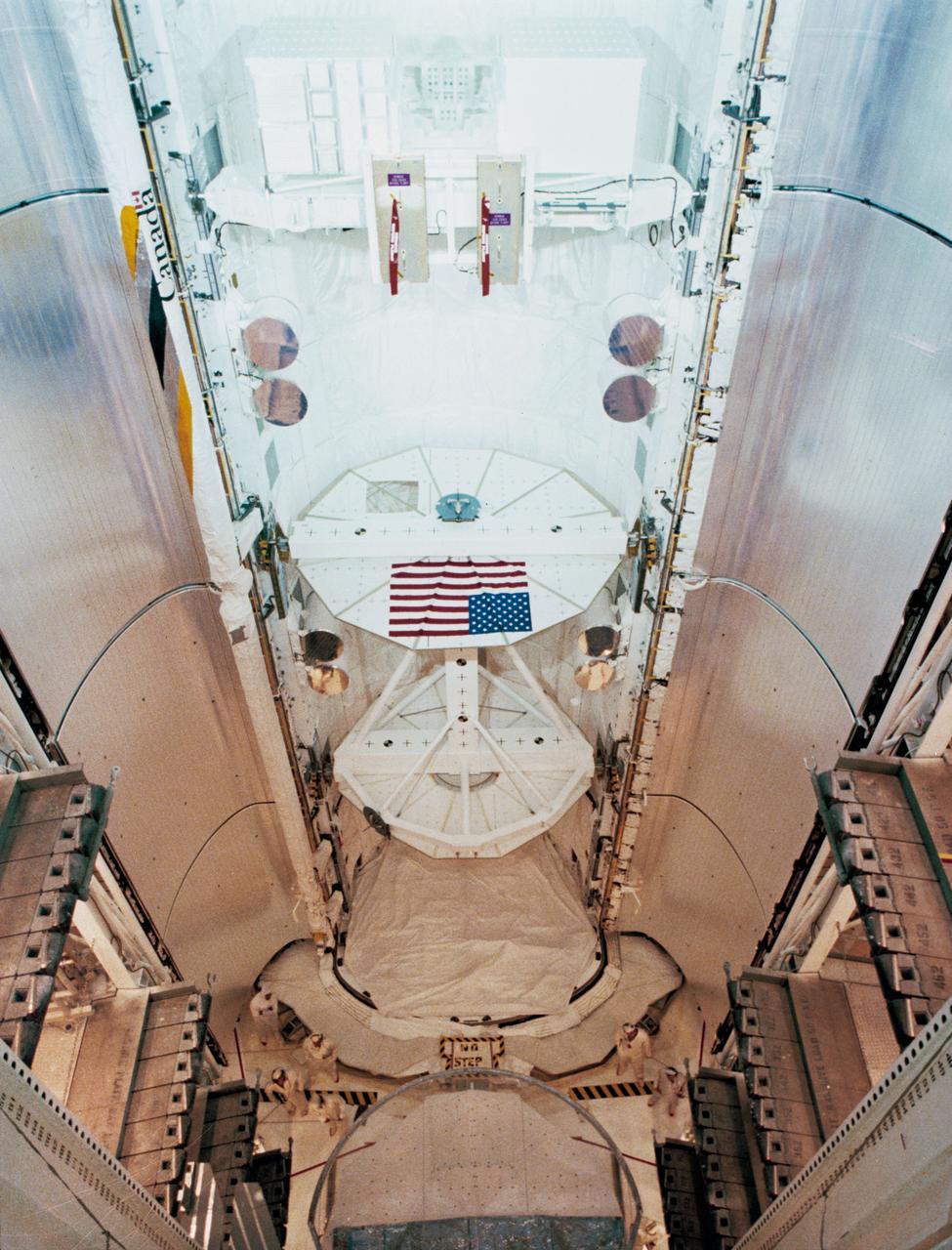

View of the Payload Flight Test Article (PFTA) installed into Challenger's cargo bay in the Payload Changeout Room at Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The American flag is visible on one side of the PFTA in the cargo bay. The Kennedy Space Center alternative photo number is KSC-108-83PC-566.
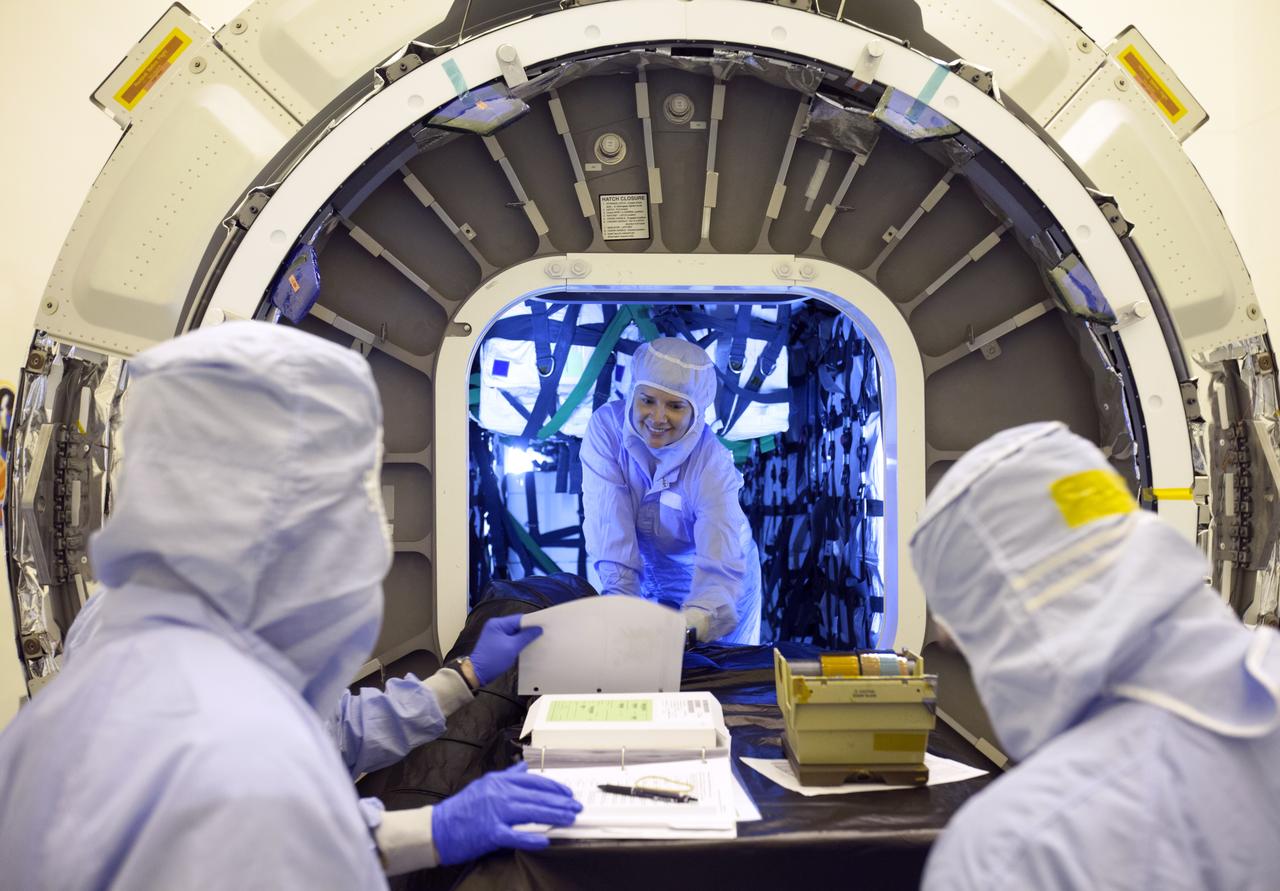

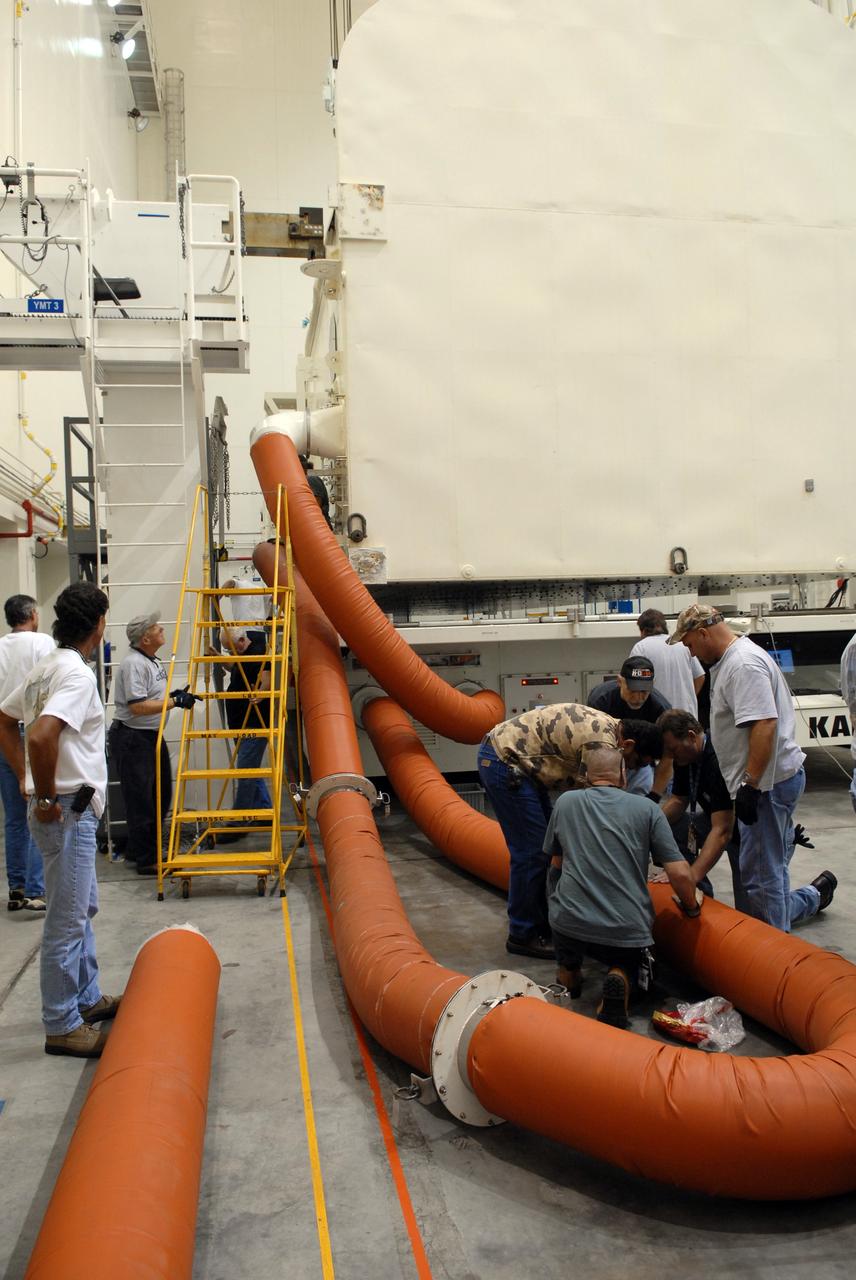
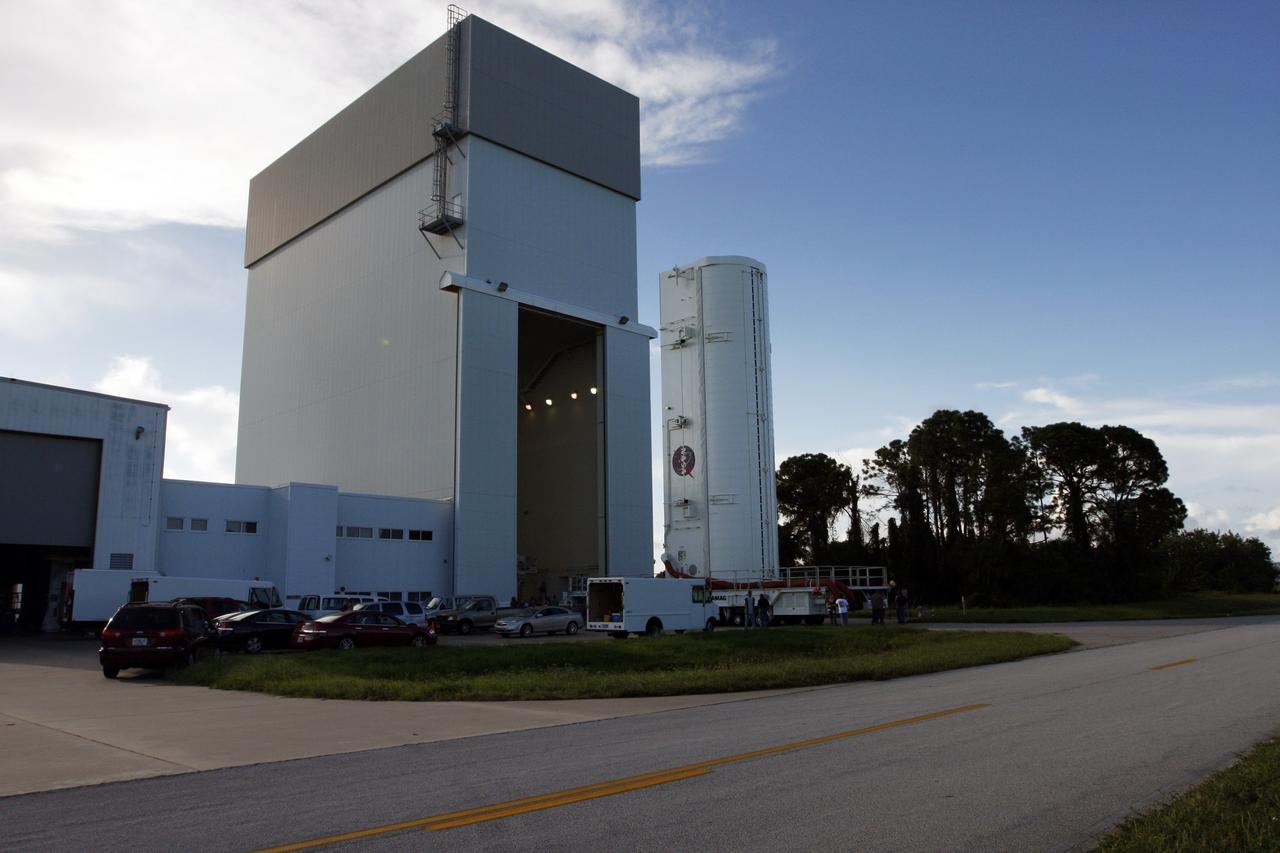
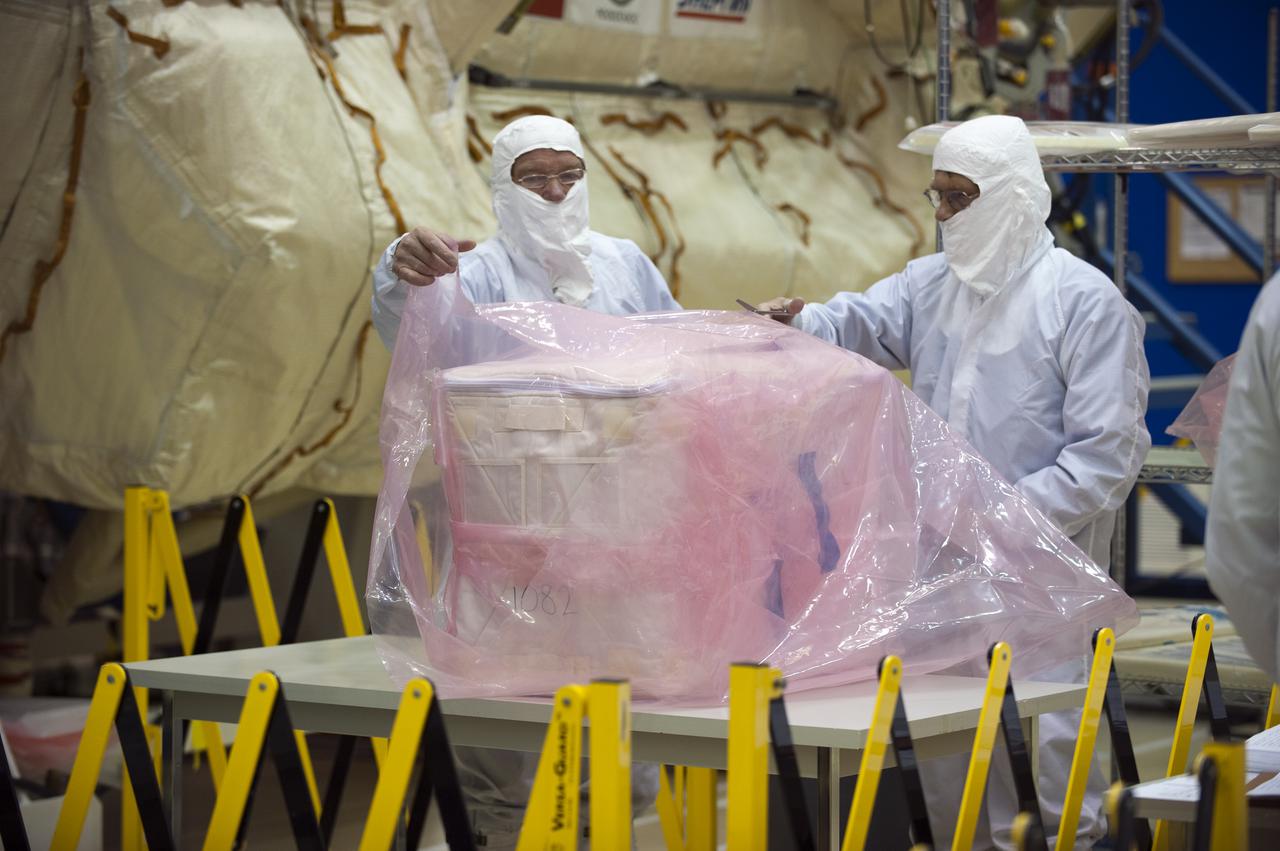
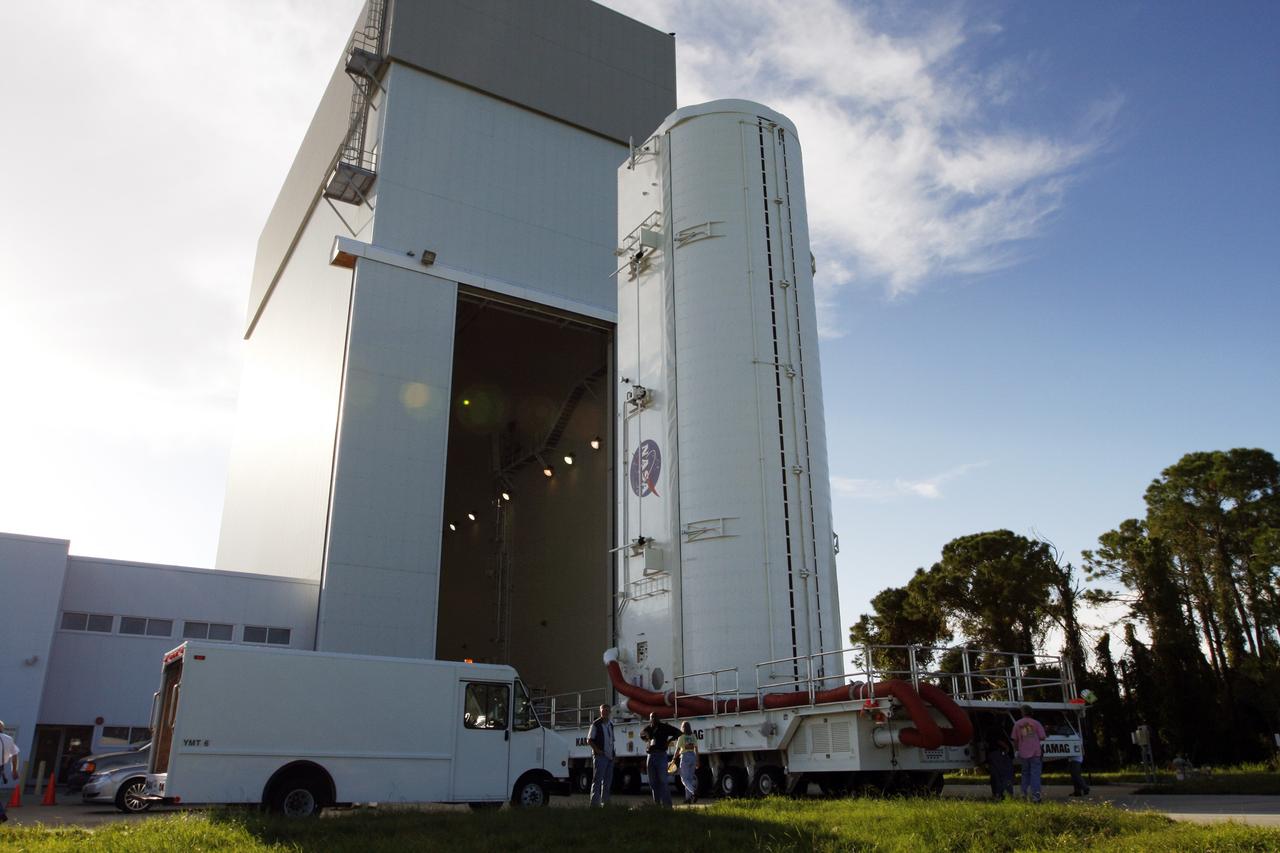
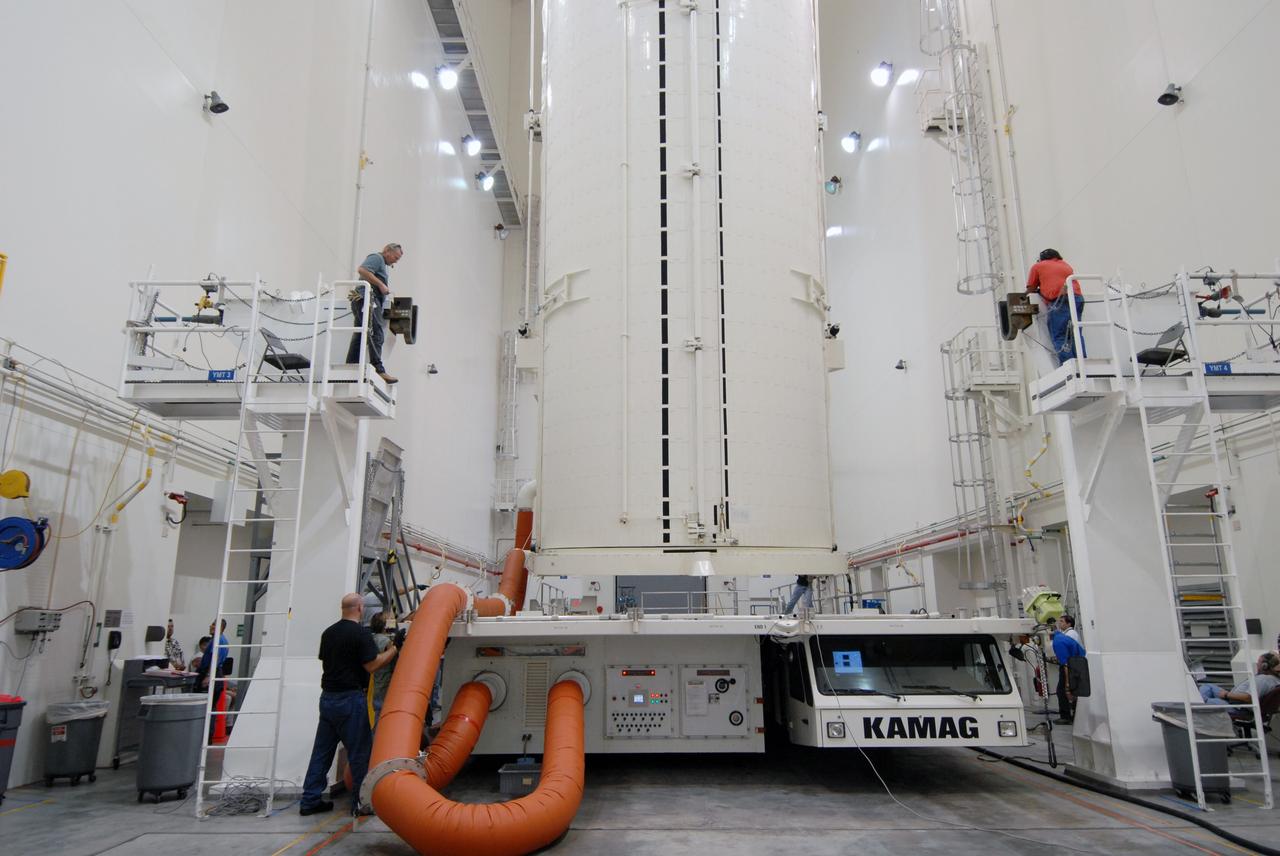
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway for late cargo installation in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway for final cargo installation in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than March 21, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
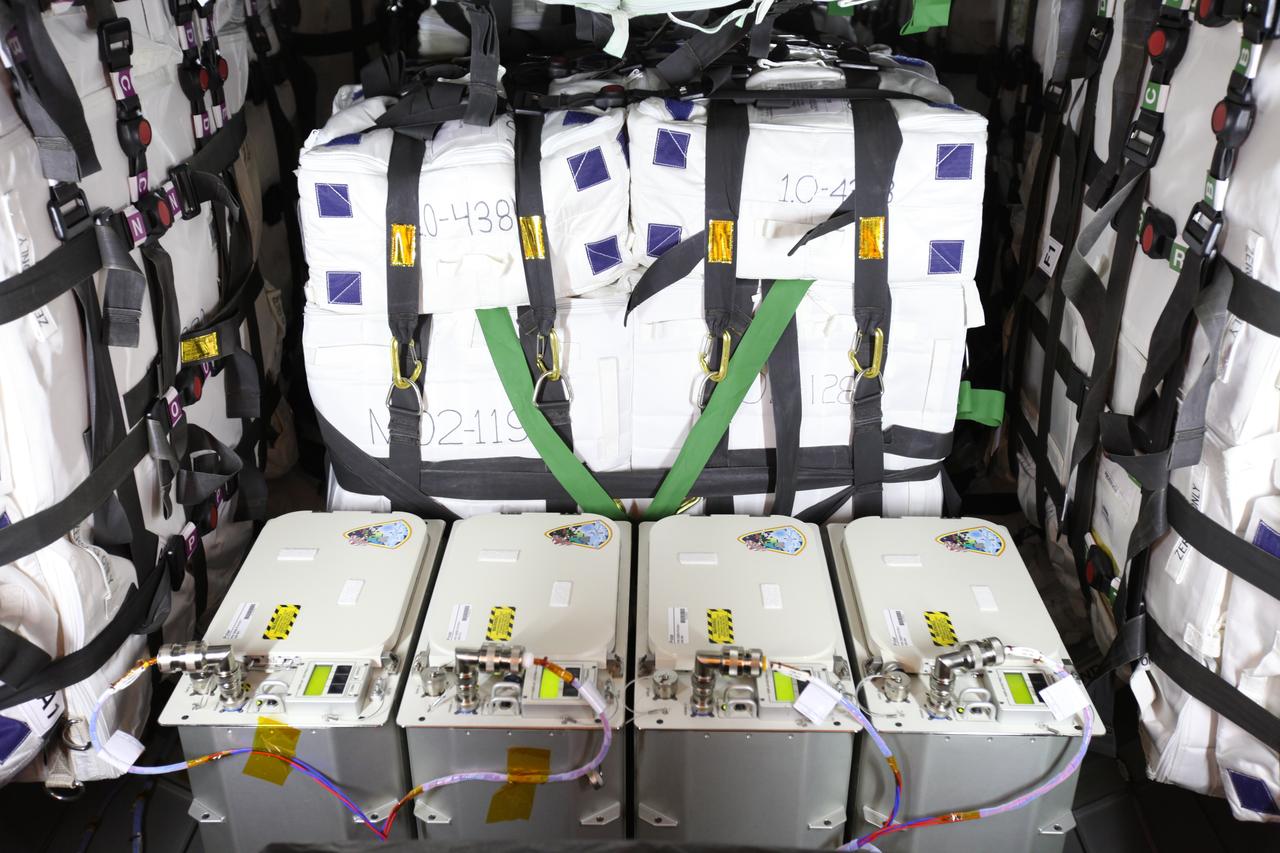

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians have completed installation of the final cargo and power in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than March 21, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
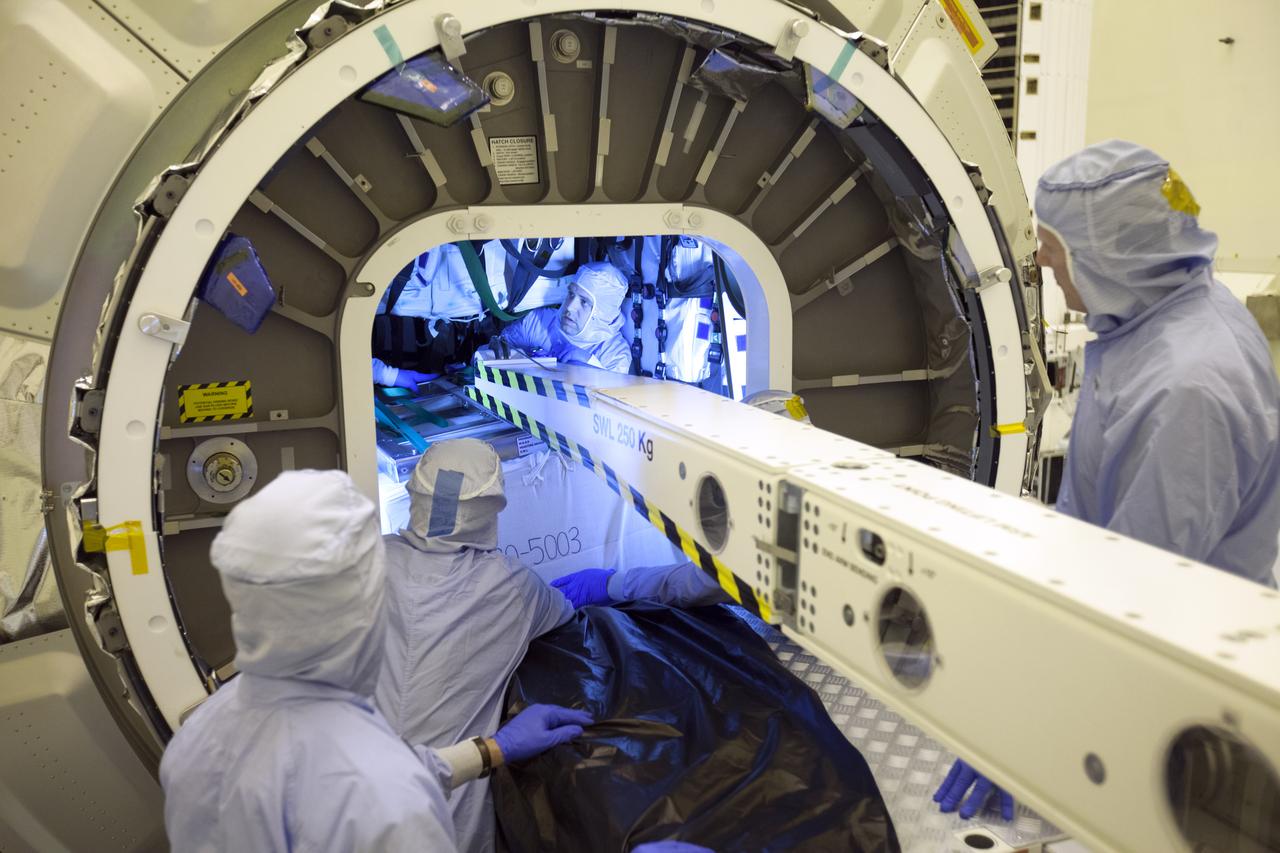

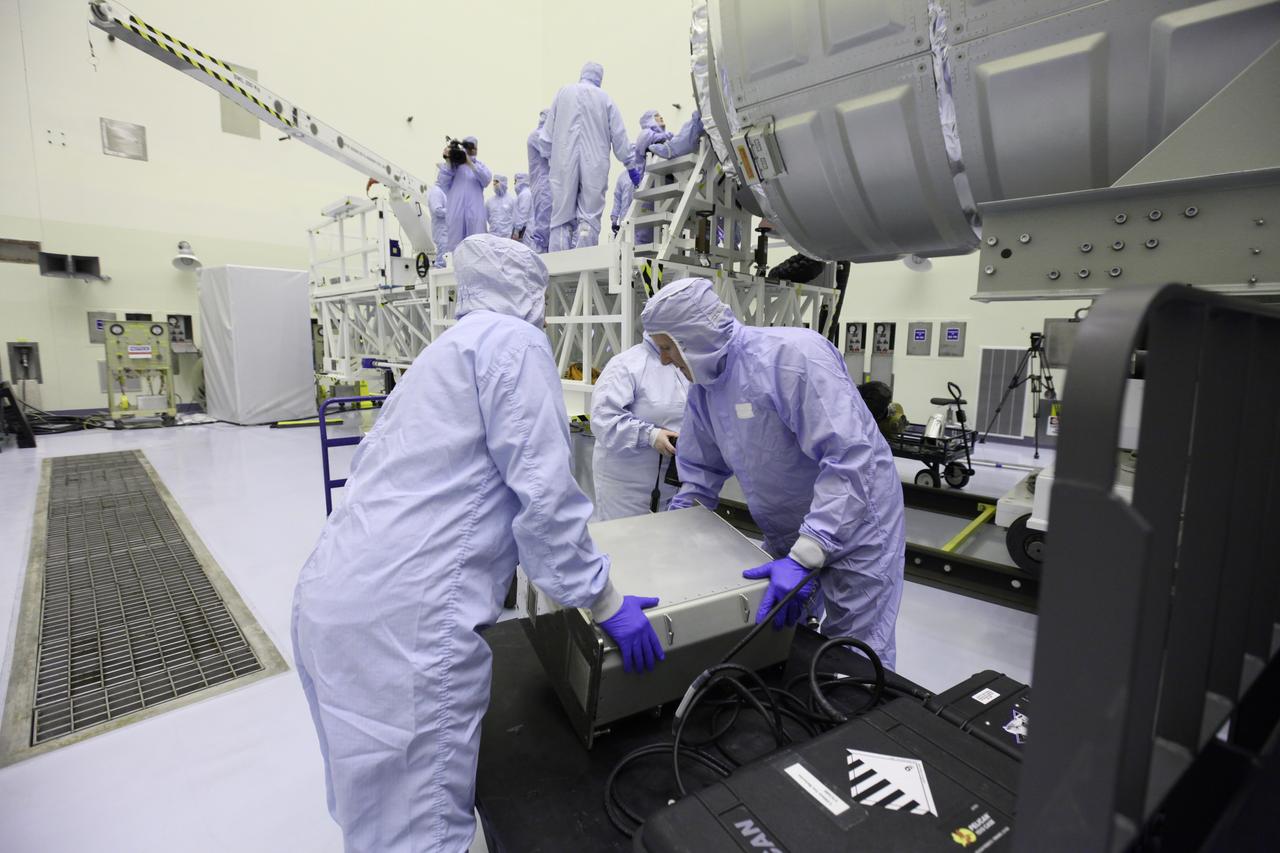
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians use a special mechanism to assist with late cargo installation in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
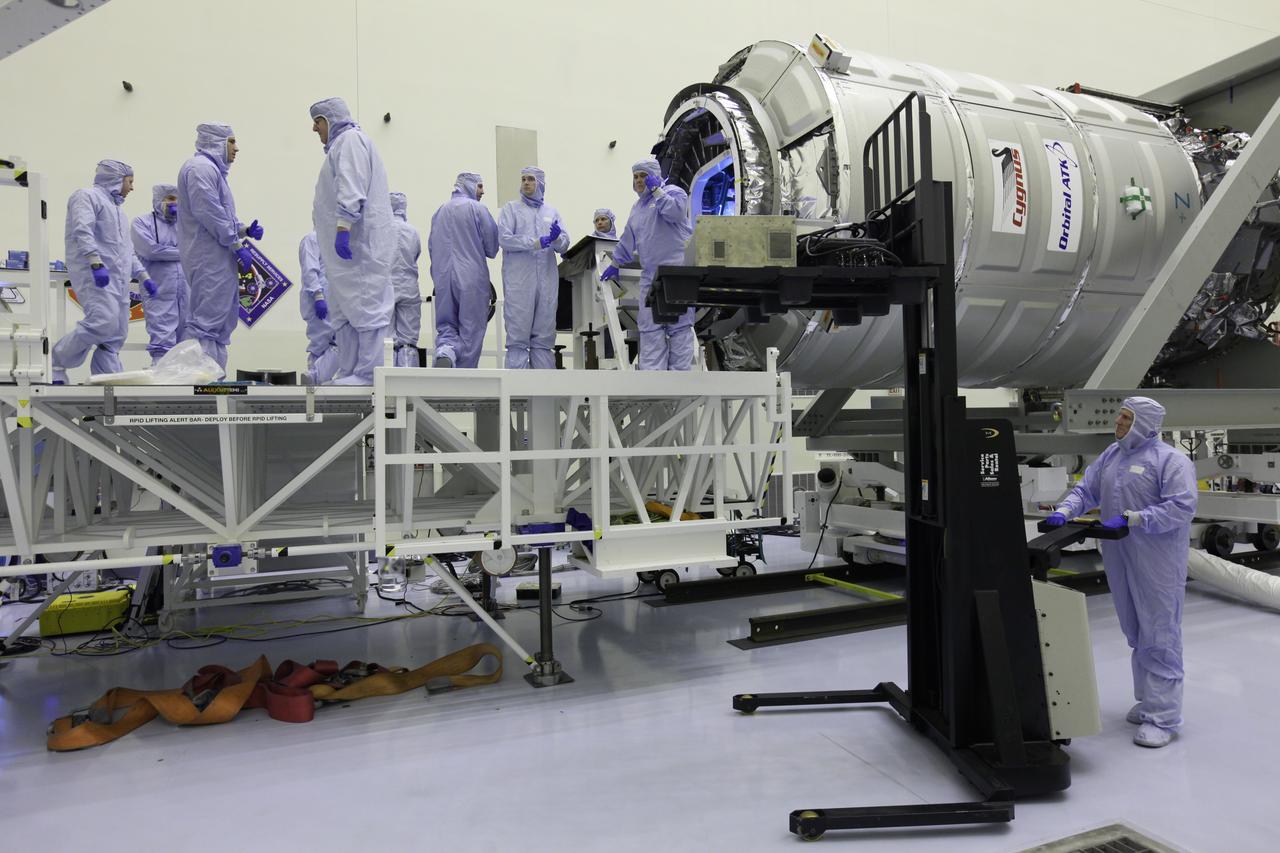

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare payloads for final cargo installation in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than March 21, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin late cargo installation in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
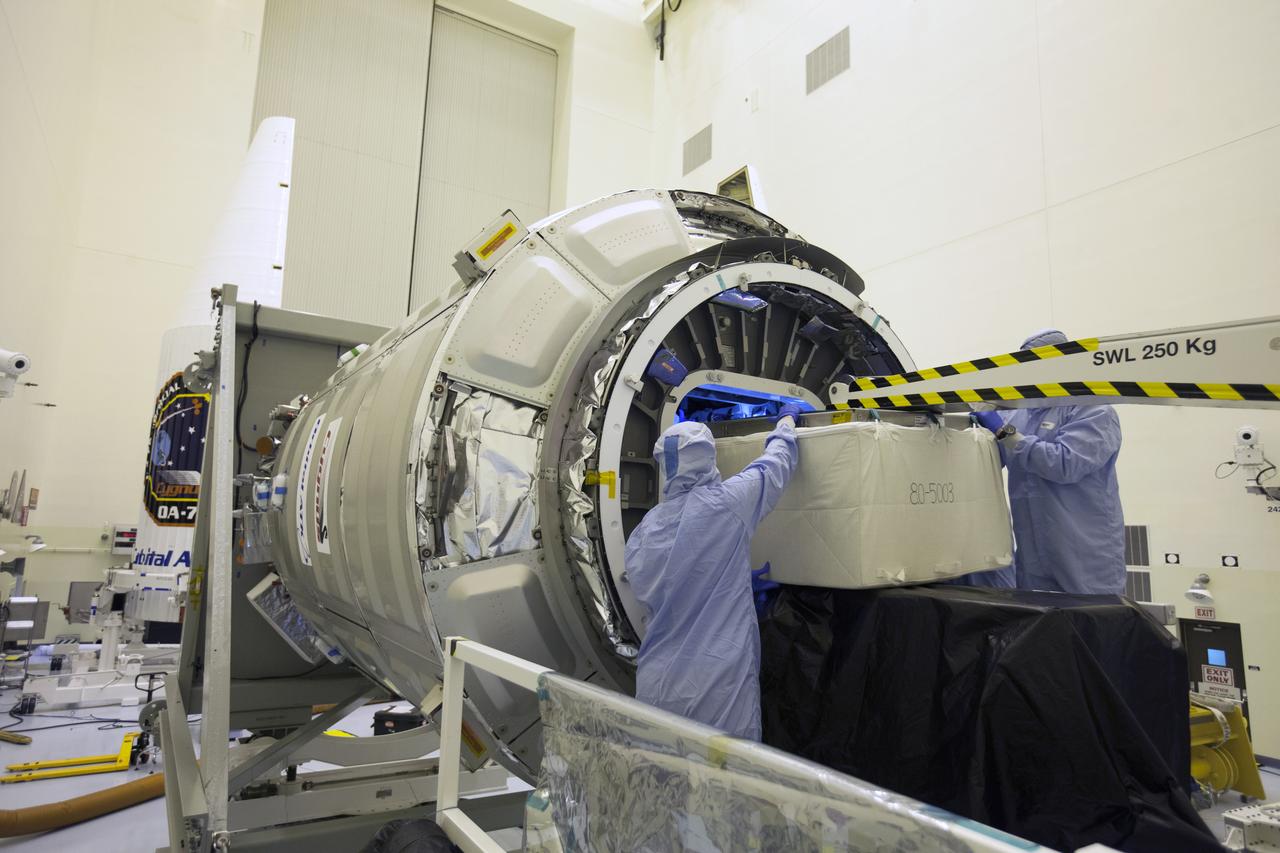

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians use a special mechanism to assist with late cargo installation in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
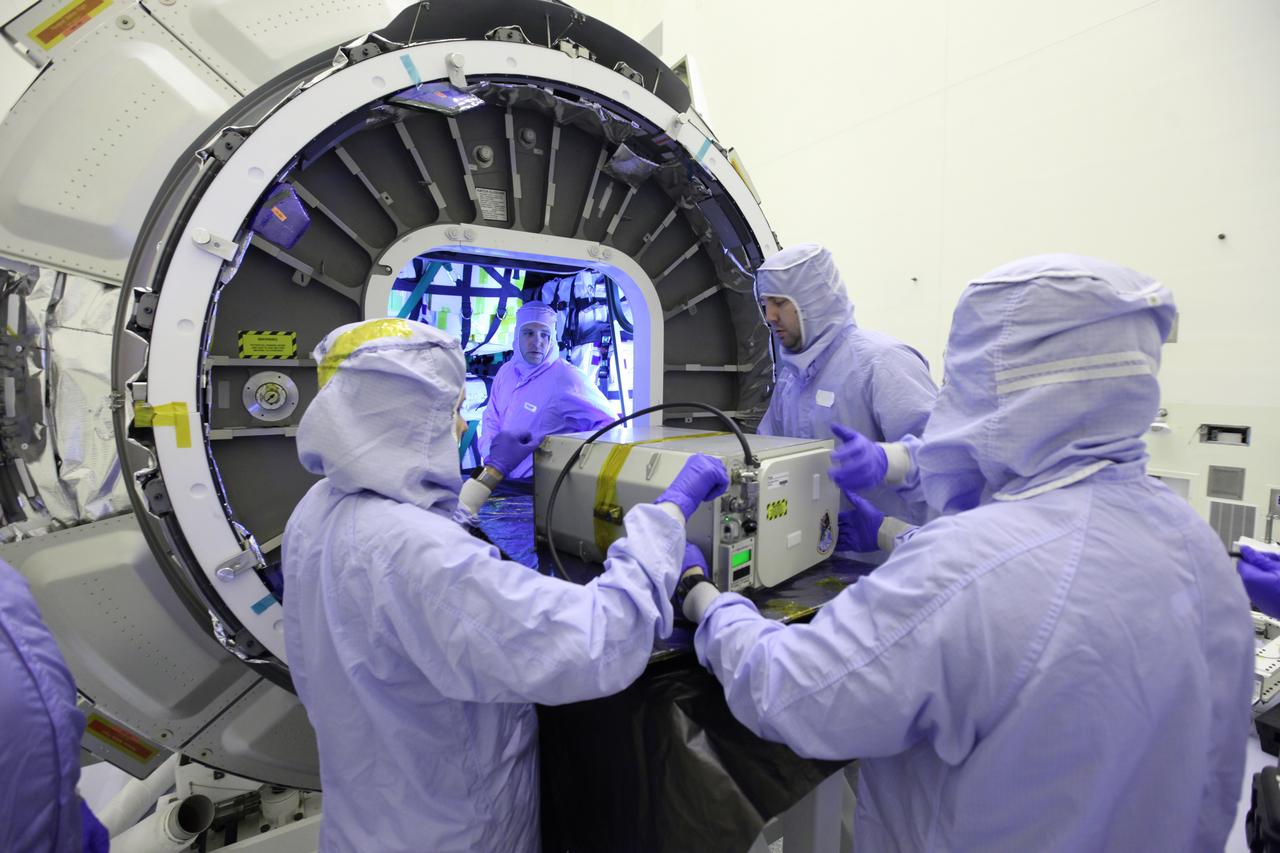

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians perform final cargo installation in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than March 21, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
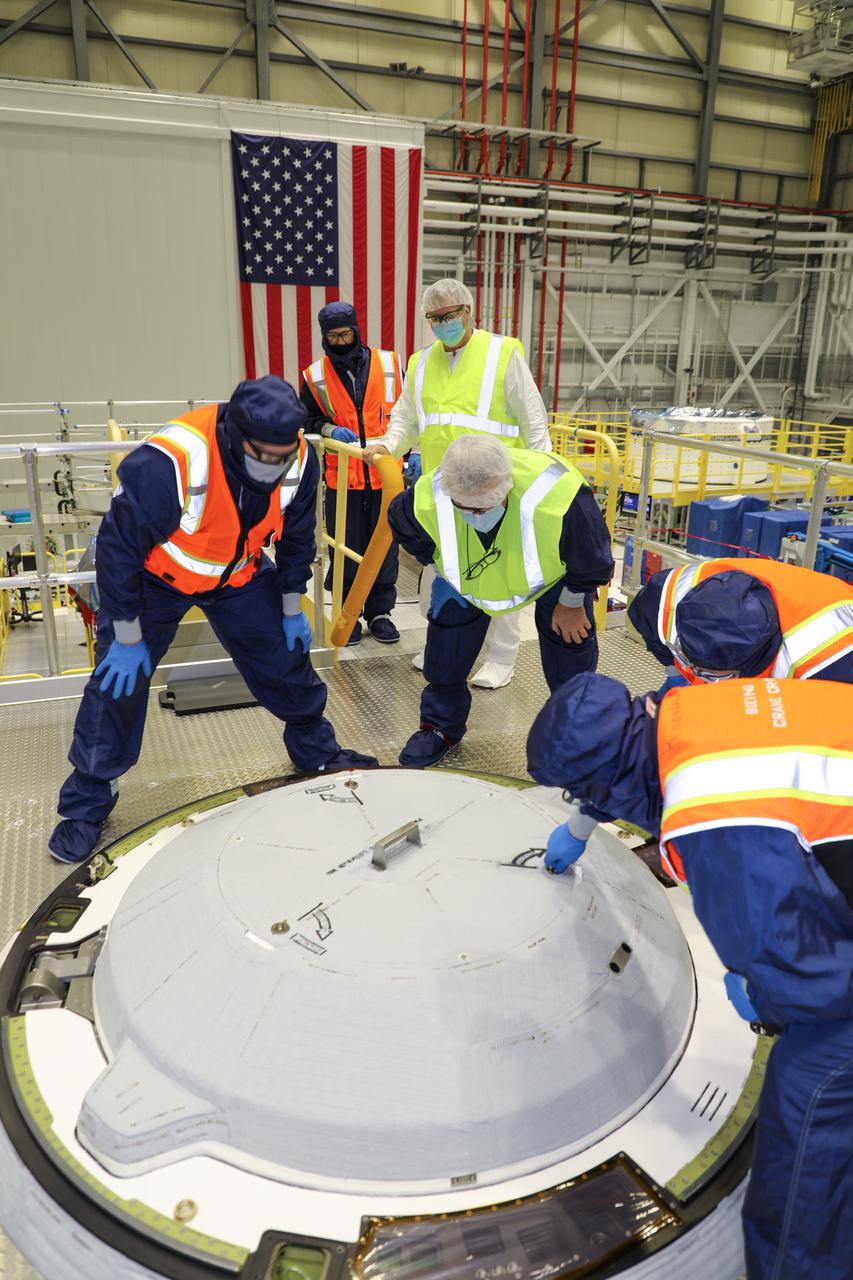

Technicians work on the NASA Docking System (NDS) hatch installation in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 2, 2021. The NDS cover was installed on Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The cover is designed to protect the components that connect the spacecraft to the International Space Station.
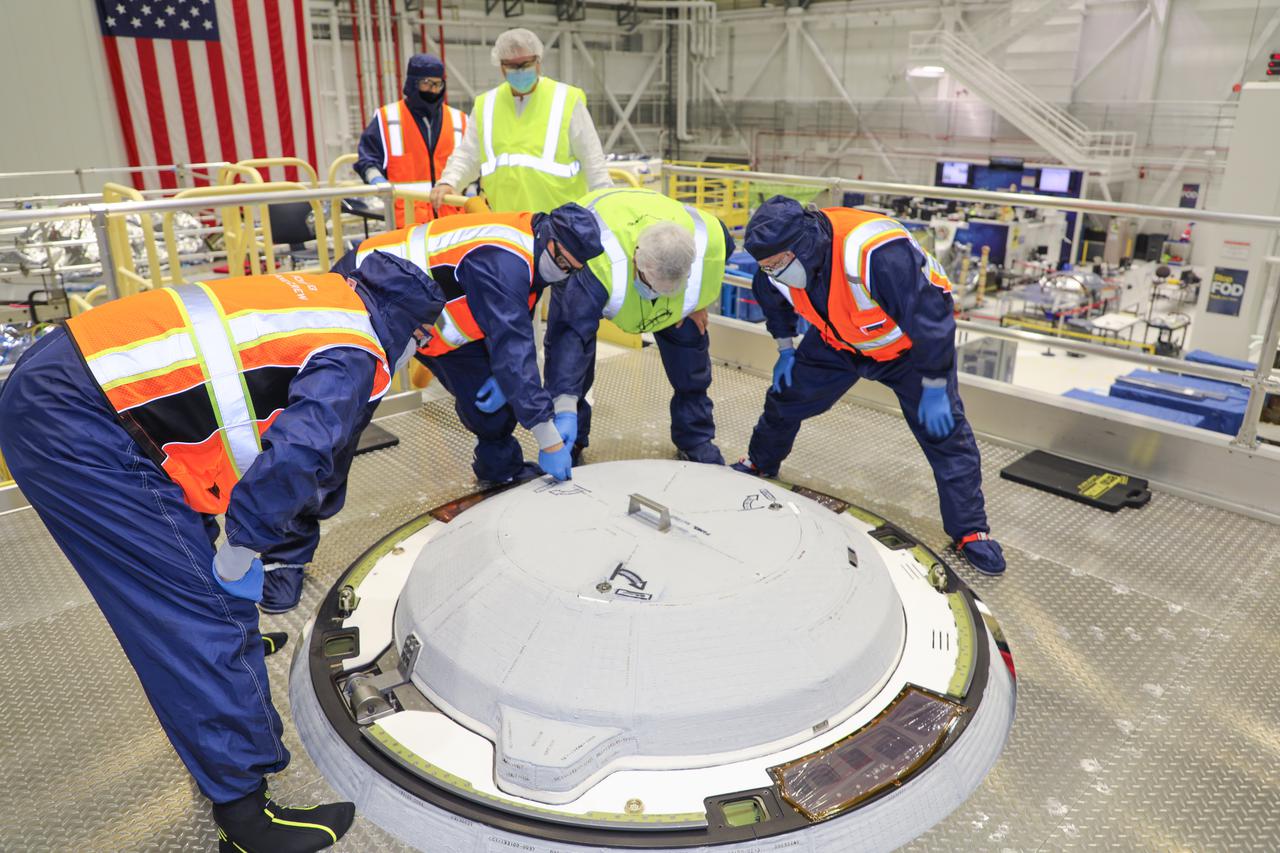

Technicians work on the NASA Docking System (NDS) cover hatch installation in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 2, 2021. The NDS cover was installed on Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The cover is designed to protect the components that connect the spacecraft to the International Space Station.
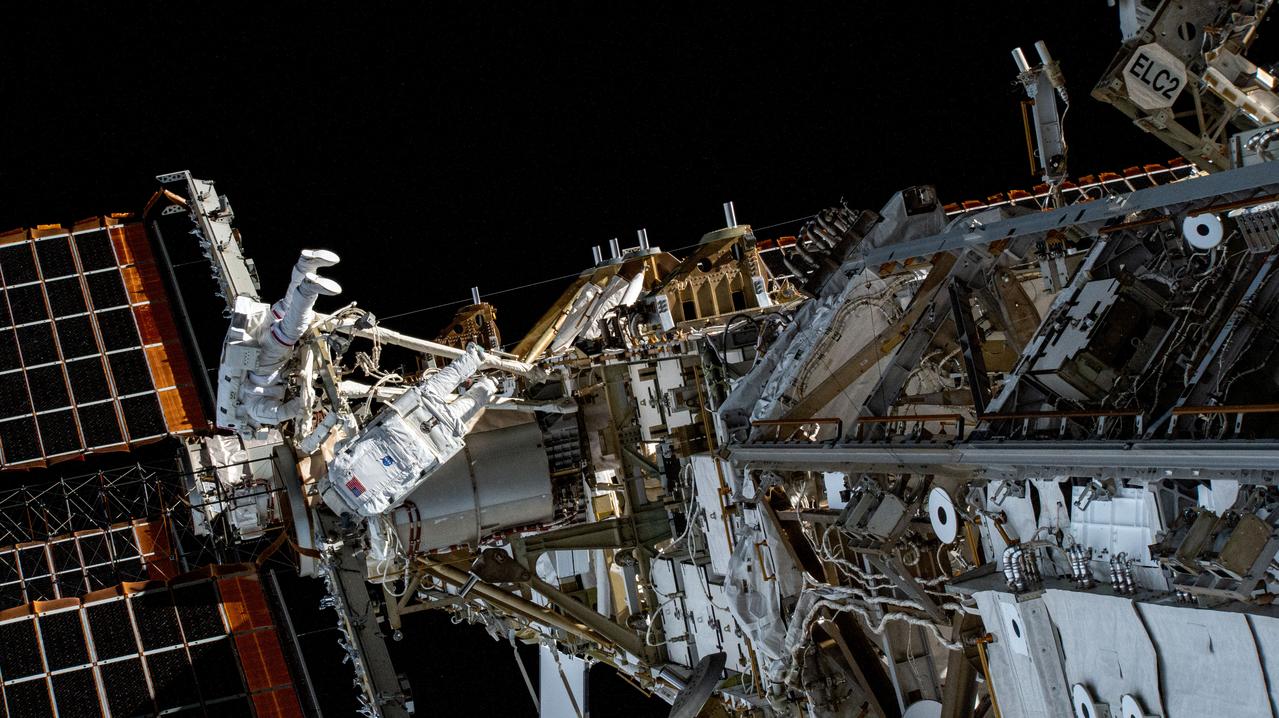

iss069e005734 (April 28, 2023) --- NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen and UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut Sultan Alneyadi are pictured in their Extravehicular Mobility Units, or spacesuits, on the International Space Station's starboard truss structure during a spacewalk. The duo would spend seven hours and one minute in the vacuum of space routing cables and installing insulation readying the orbital outpost for its next set of roll-out solar arrays due to be installed after their delivery on the next SpaceX Dragon cargo mission.
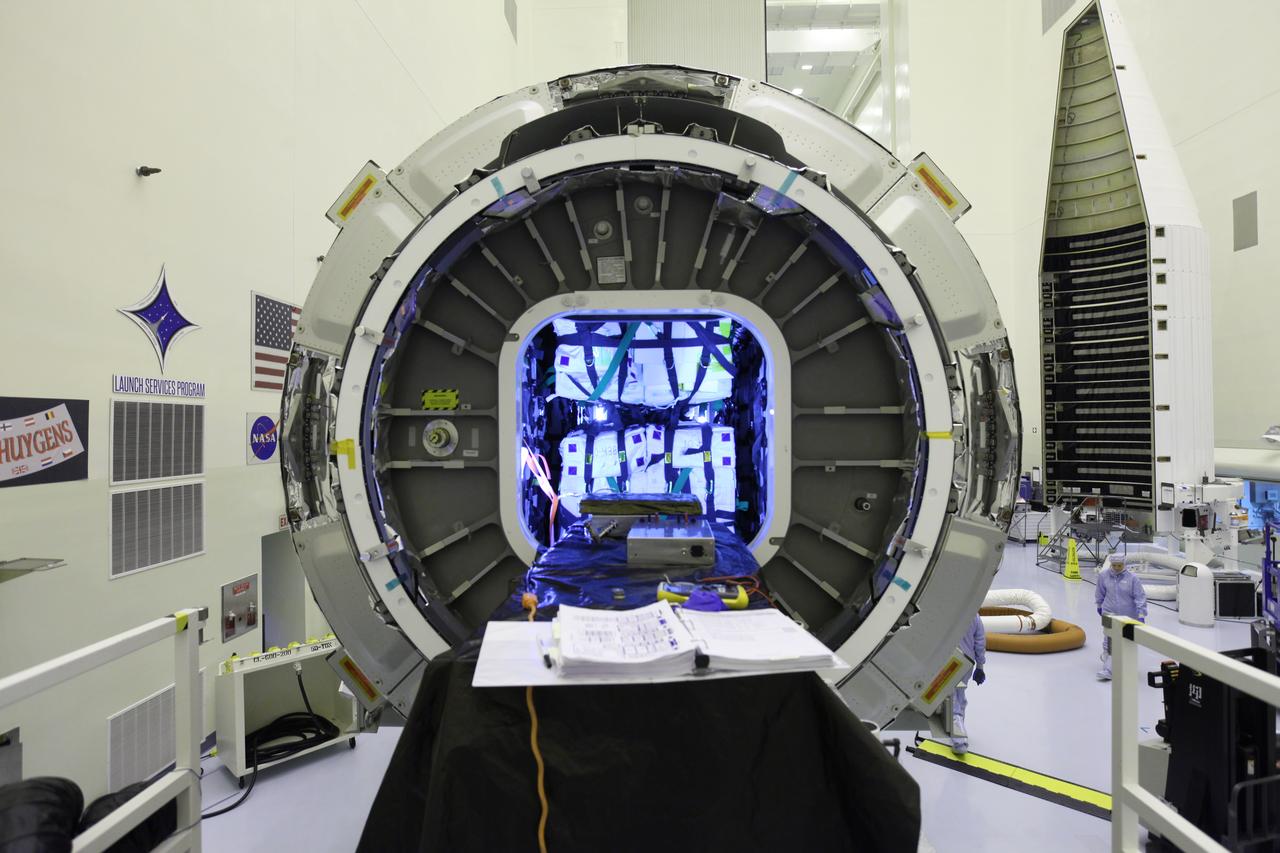

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway for final stowage of powered cargo in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
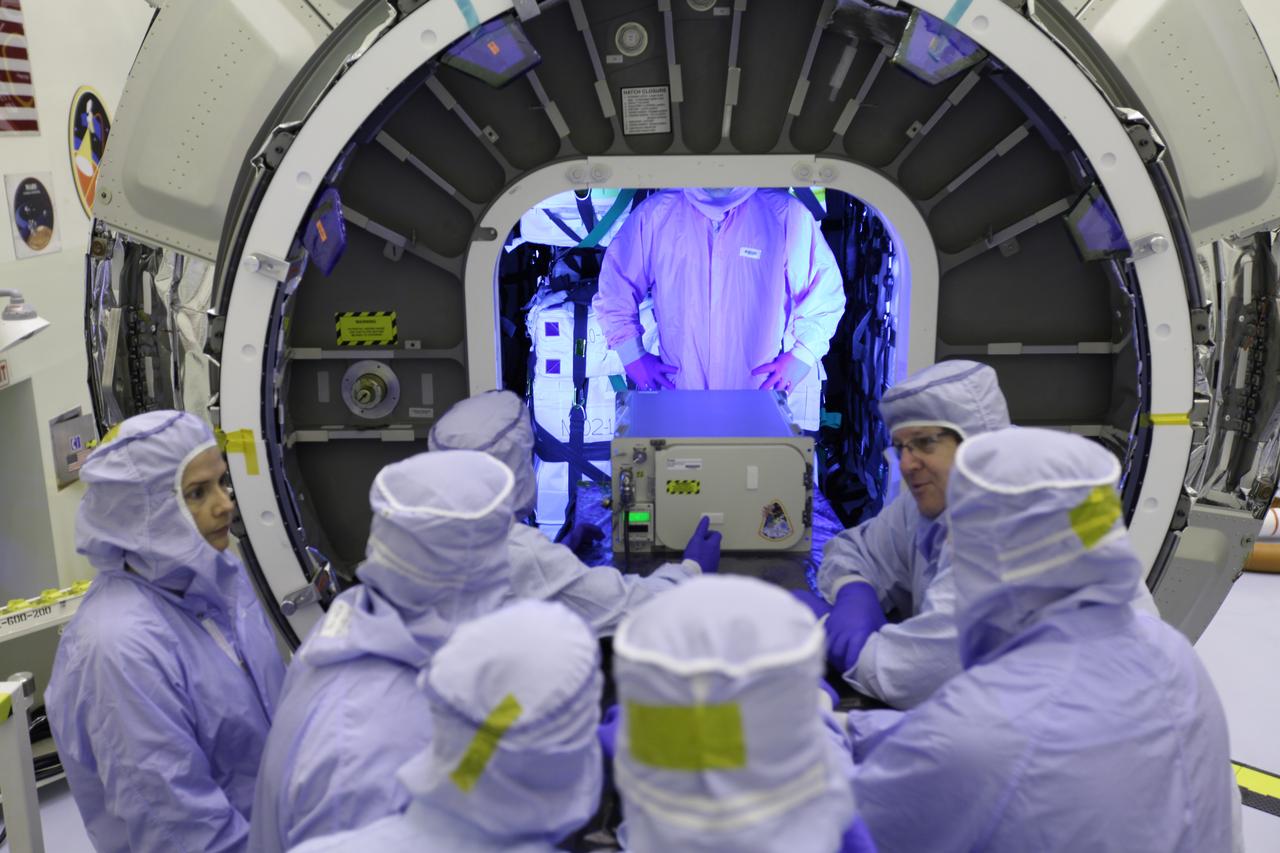

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians load a powered cargo unit into the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module during final stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
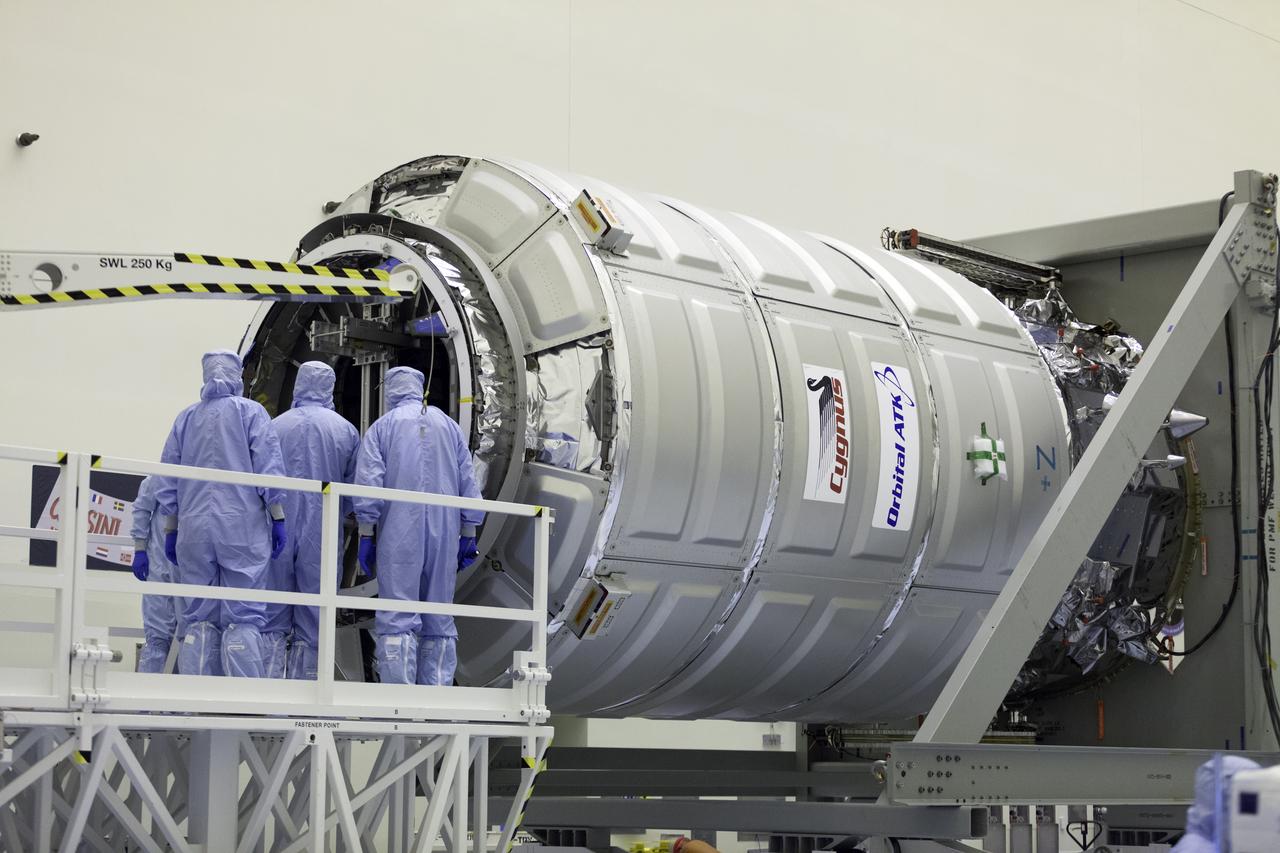

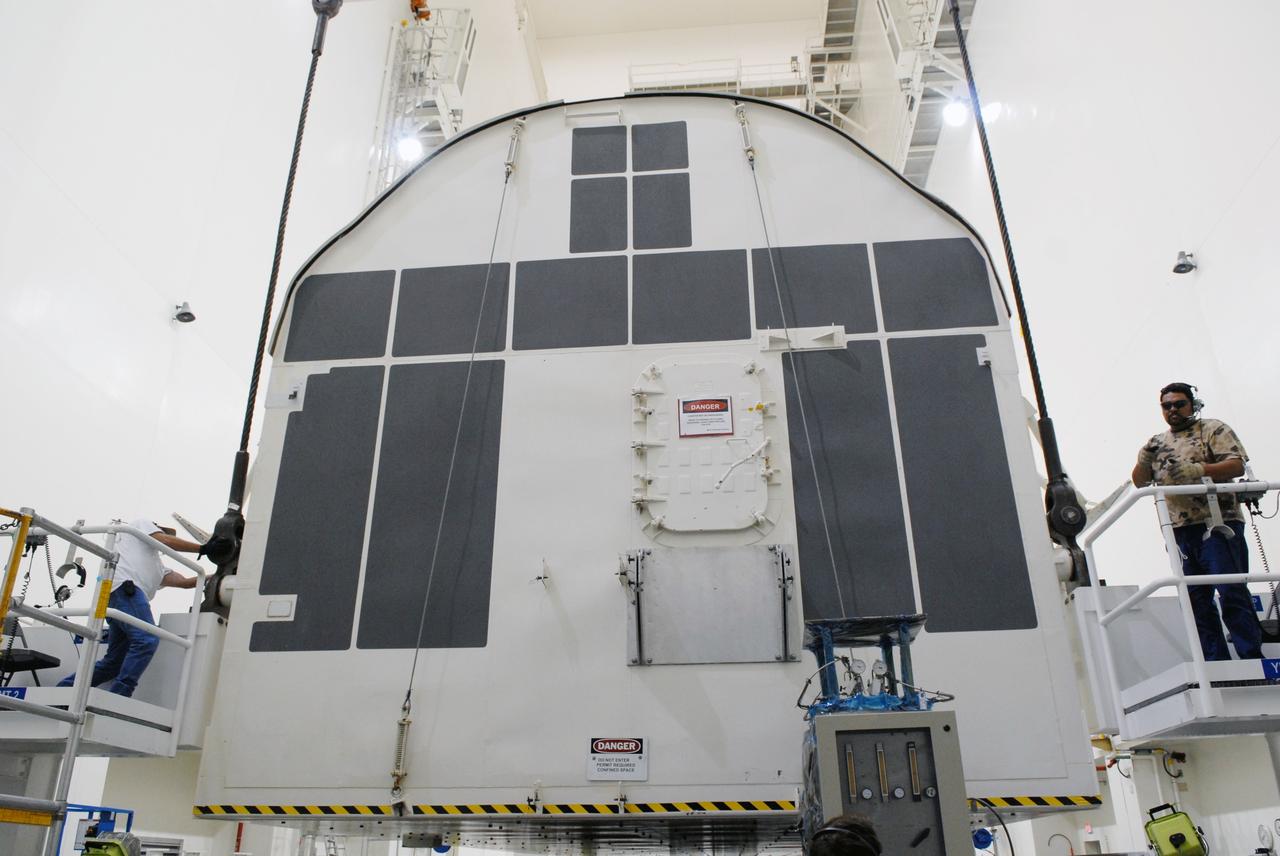
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians have opened the hatch on the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module to prepare for late stowage of supplies and hardware. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians are opening the hatch on the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module to prepare for late stowage of supplies and hardware. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
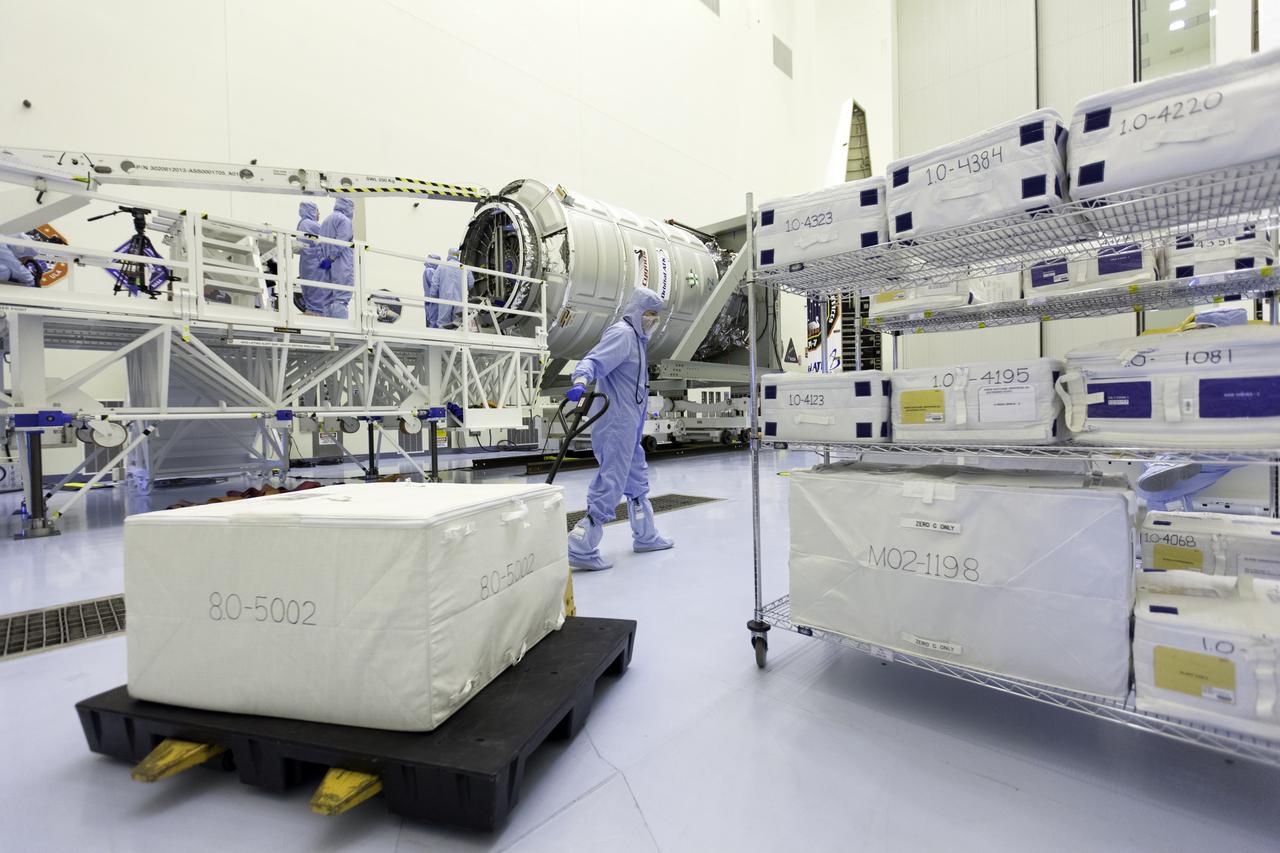

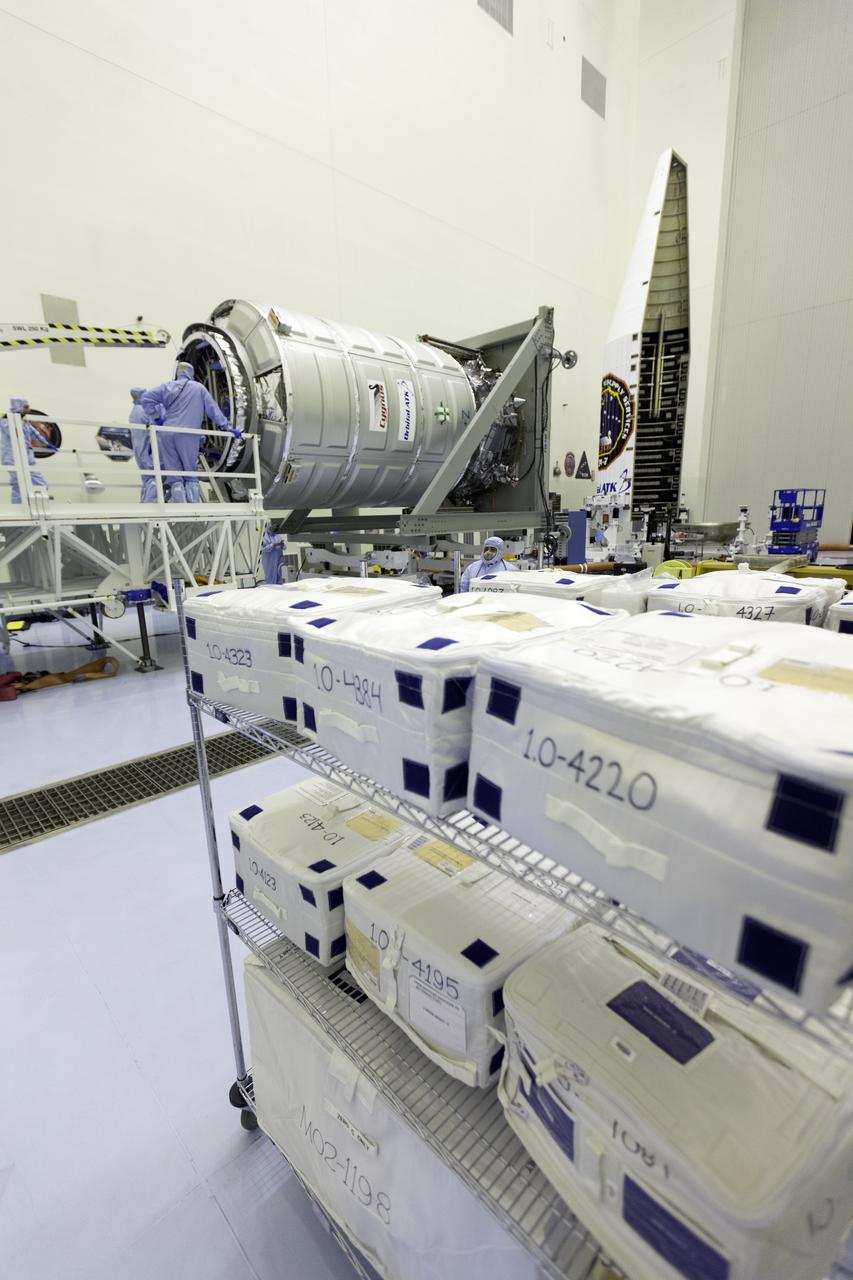
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cargo has arrived for late loading in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
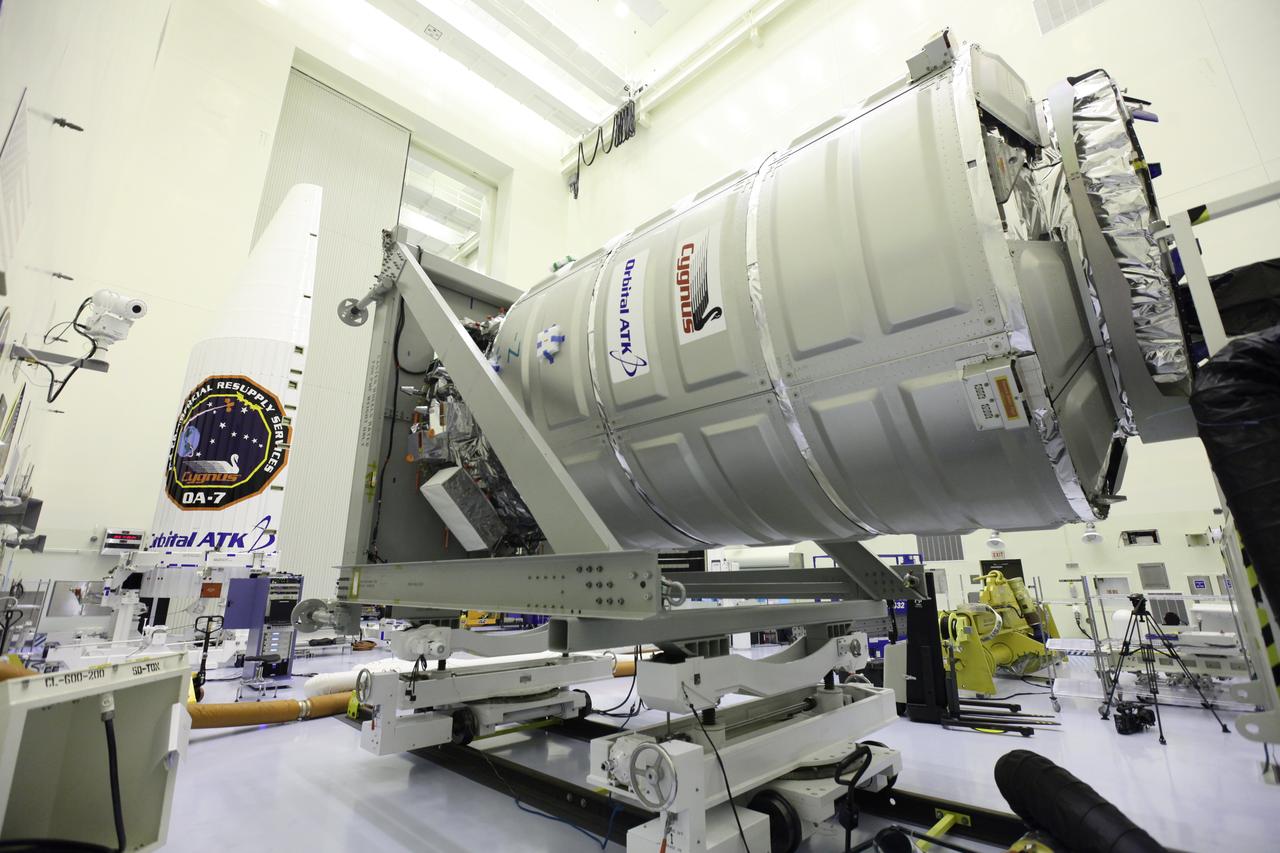

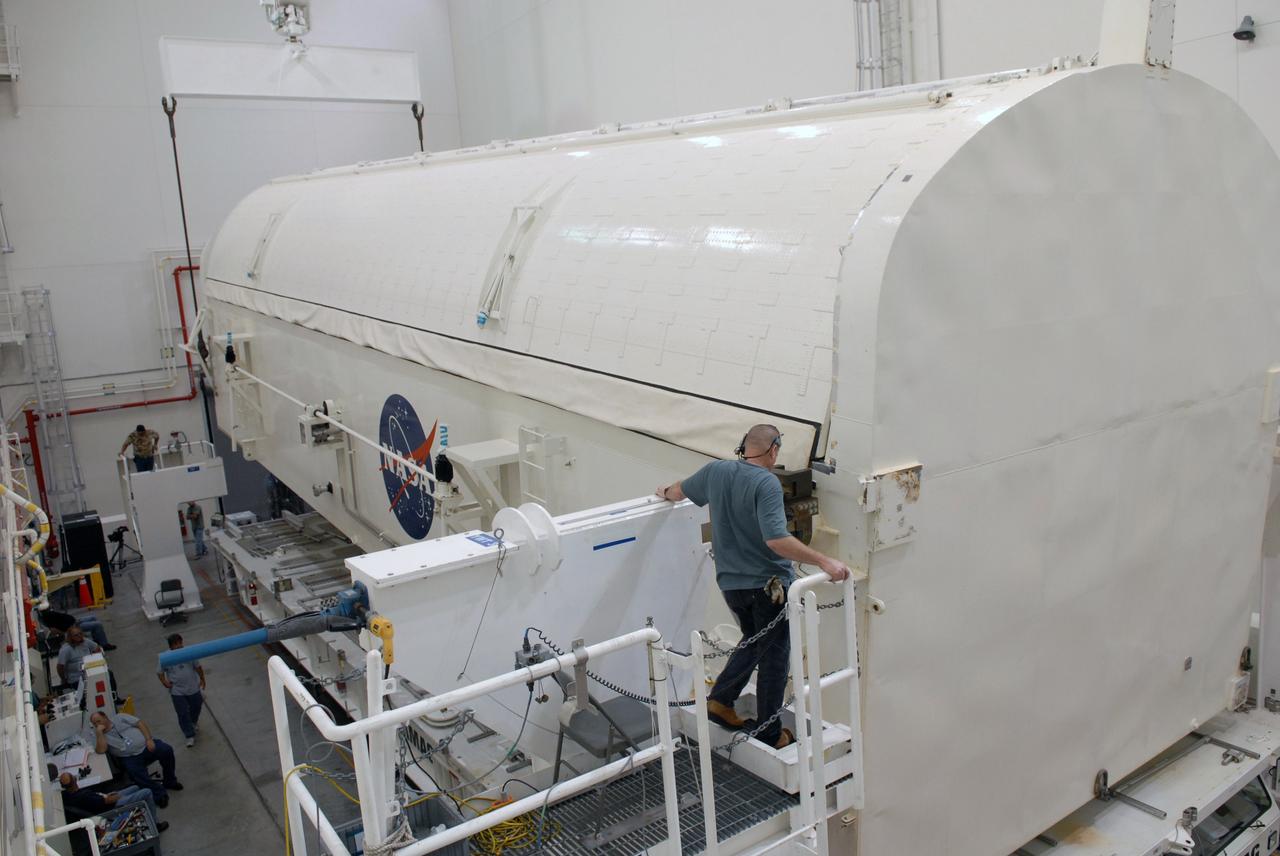
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is tilted to the horizontal position to prepare for final stowage of powered cargo. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians are opening the hatch on the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module to prepare for late stowage of supplies and hardware. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
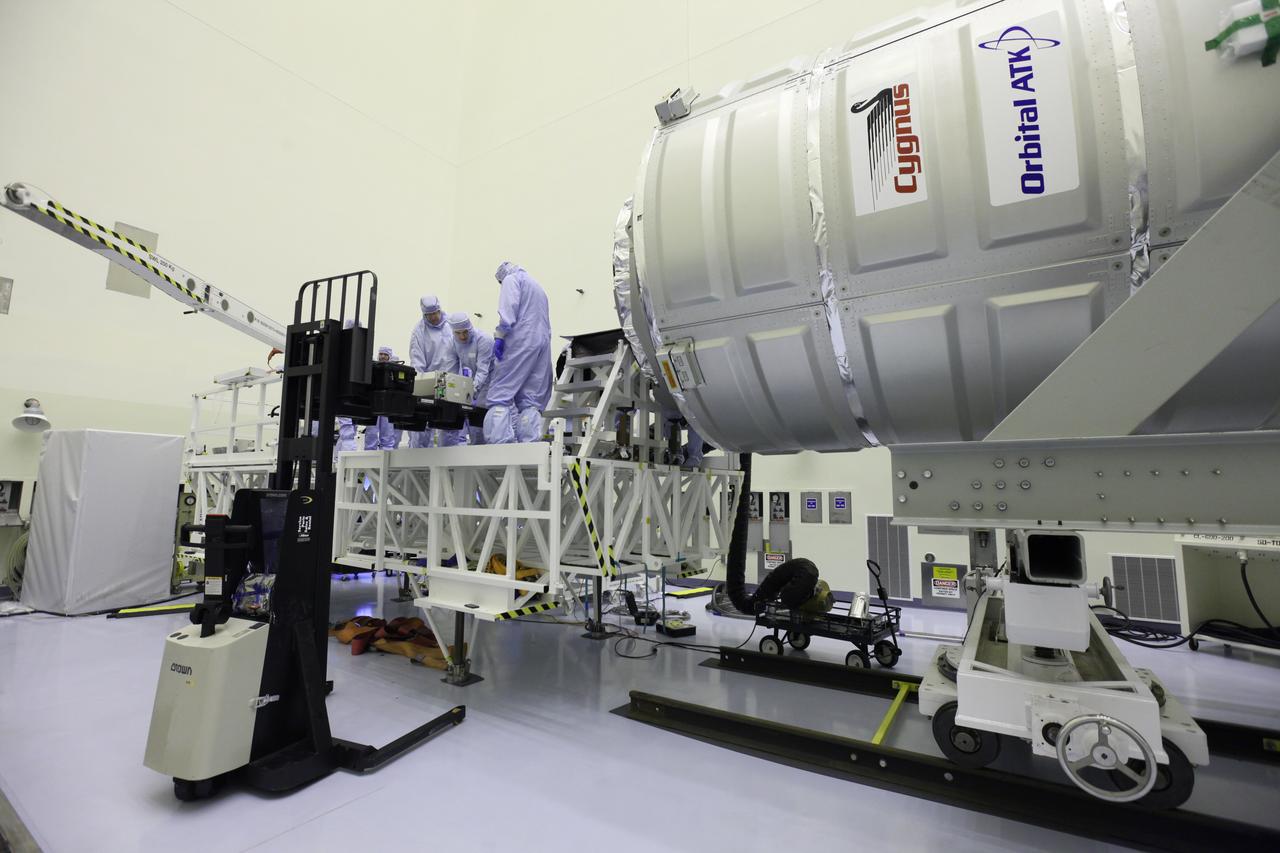

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a powered cargo unit for late stowage in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
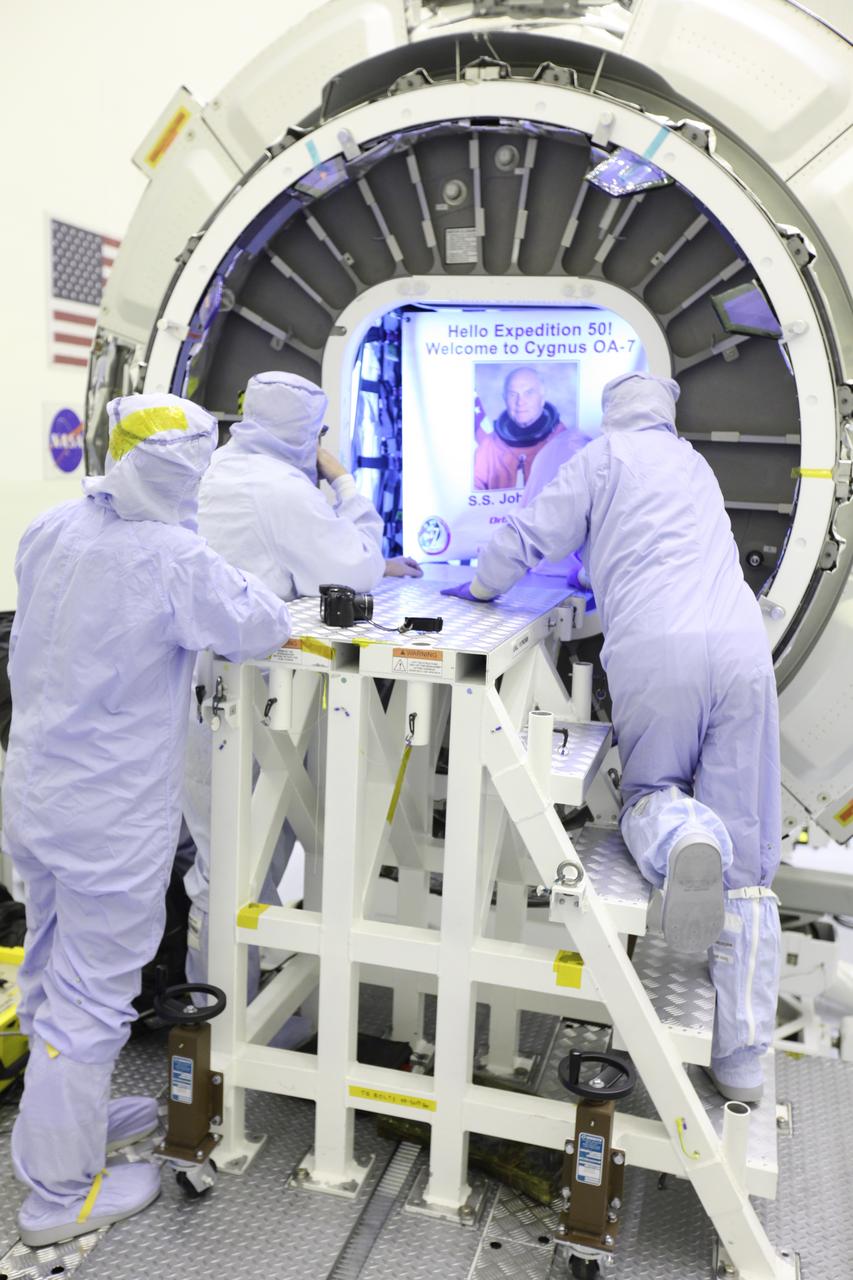

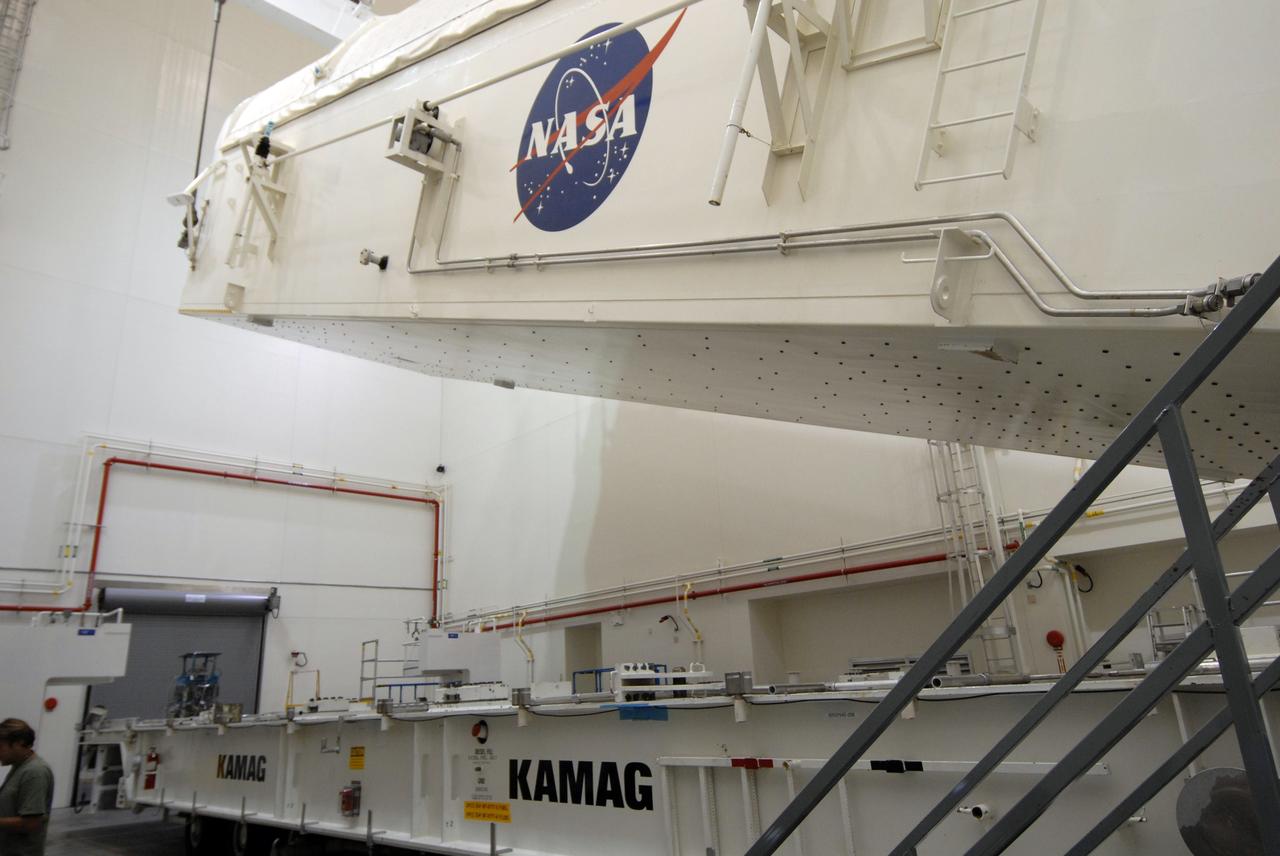
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians attach the John Glenn banner to inside the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Cygnus cargo module has been renamed the S.S. John Glenn to honor the late former Project Mercury and space shuttle astronaut. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than March 21, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
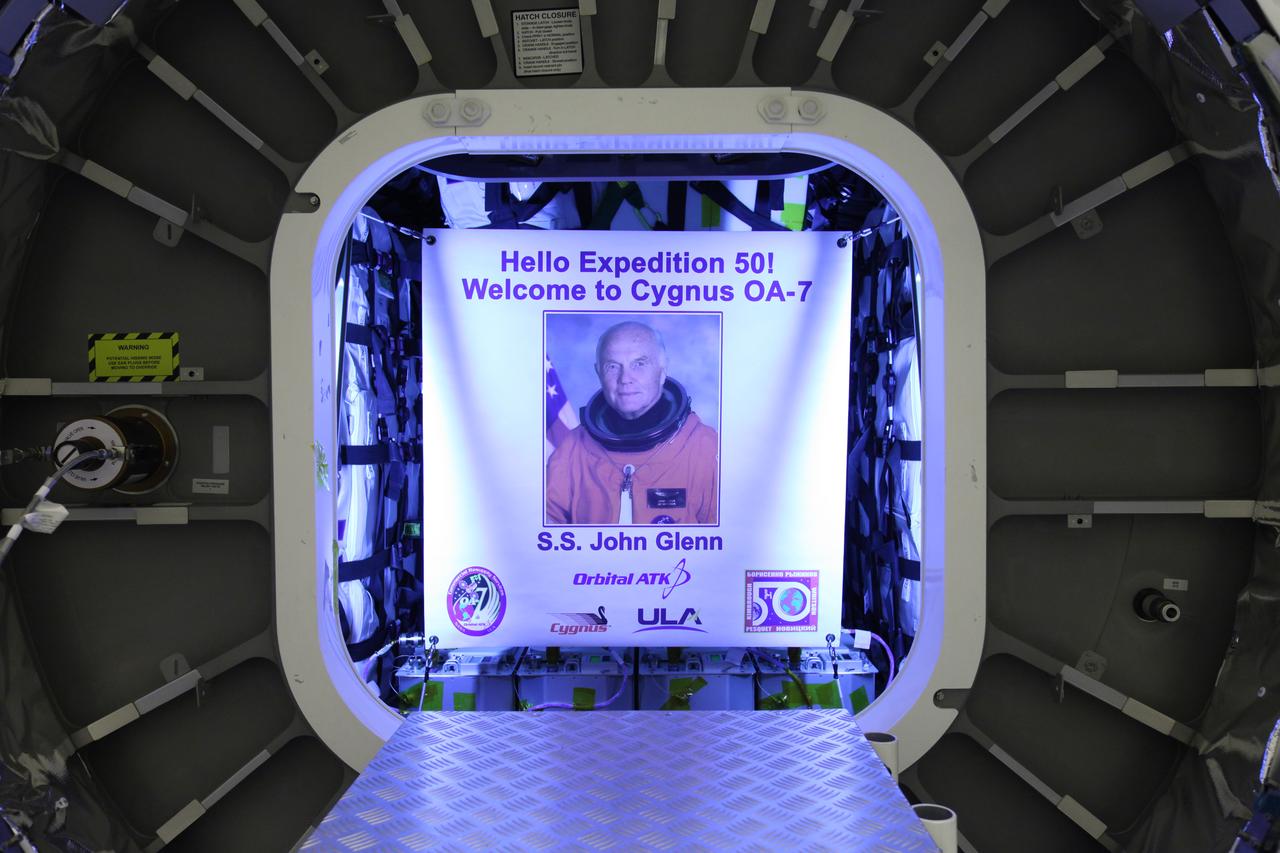

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the John Glenn banner is attached inside the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Cygnus cargo module has been renamed the S.S. John Glenn to honor the late former Project Mercury and space shuttle astronaut. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than March 21, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
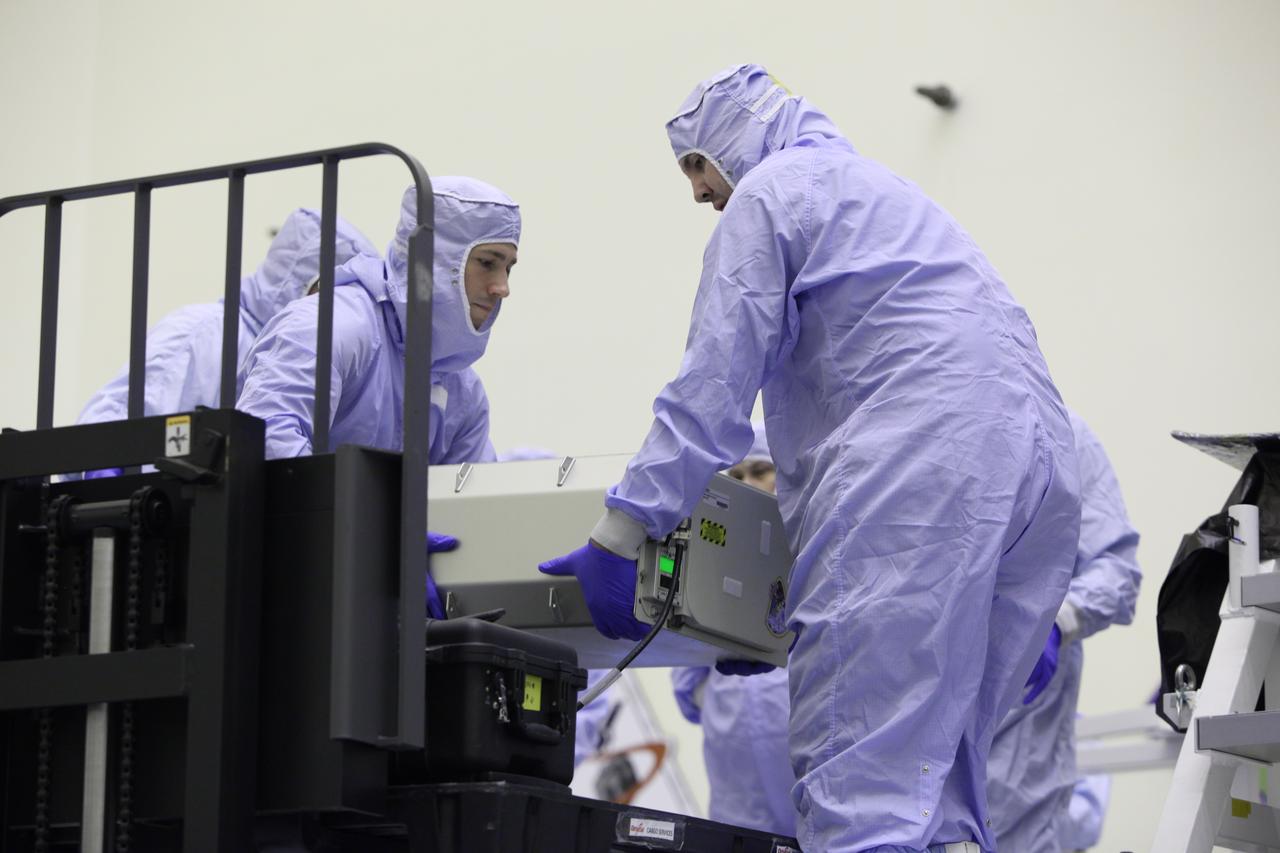

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a powered cargo unit for late stowage in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
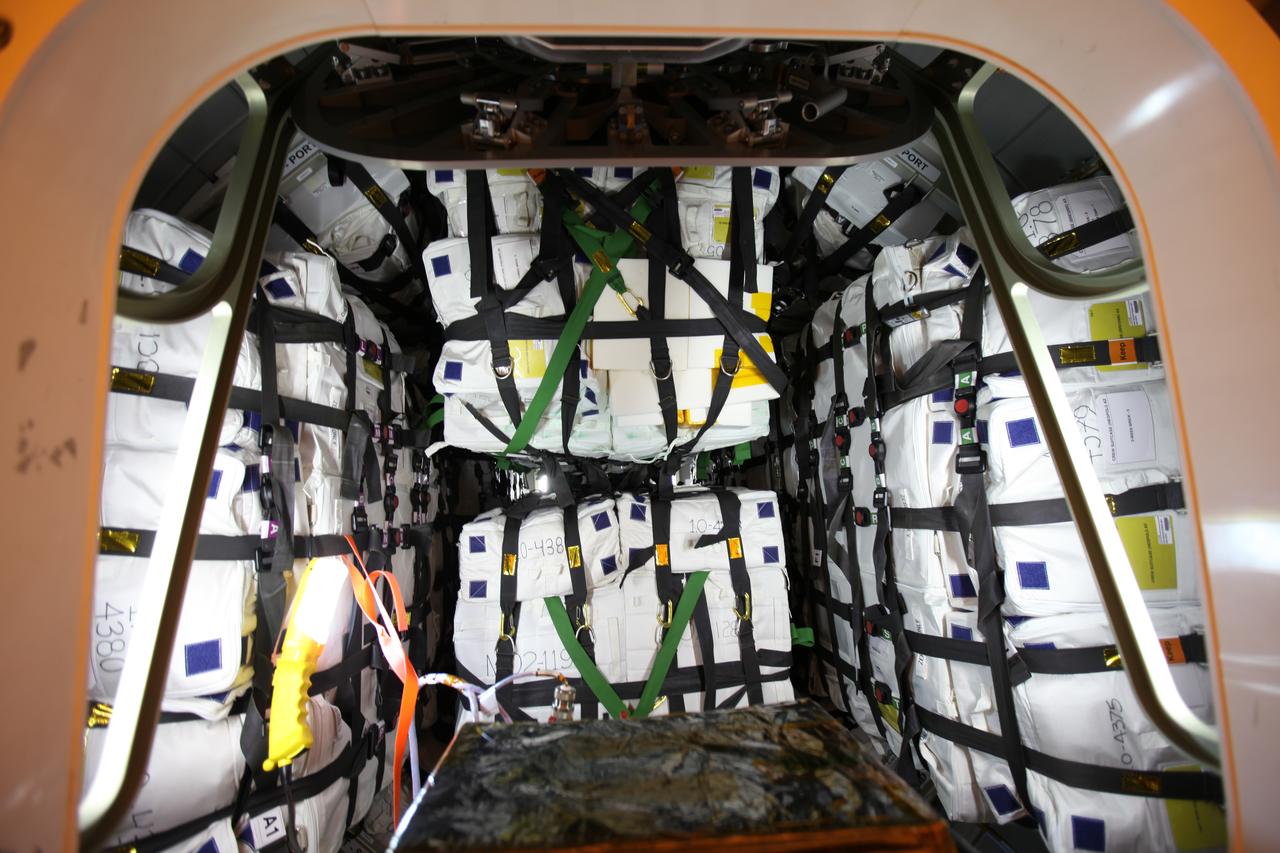

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the hatch on the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is open for final stowage of powered cargo. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
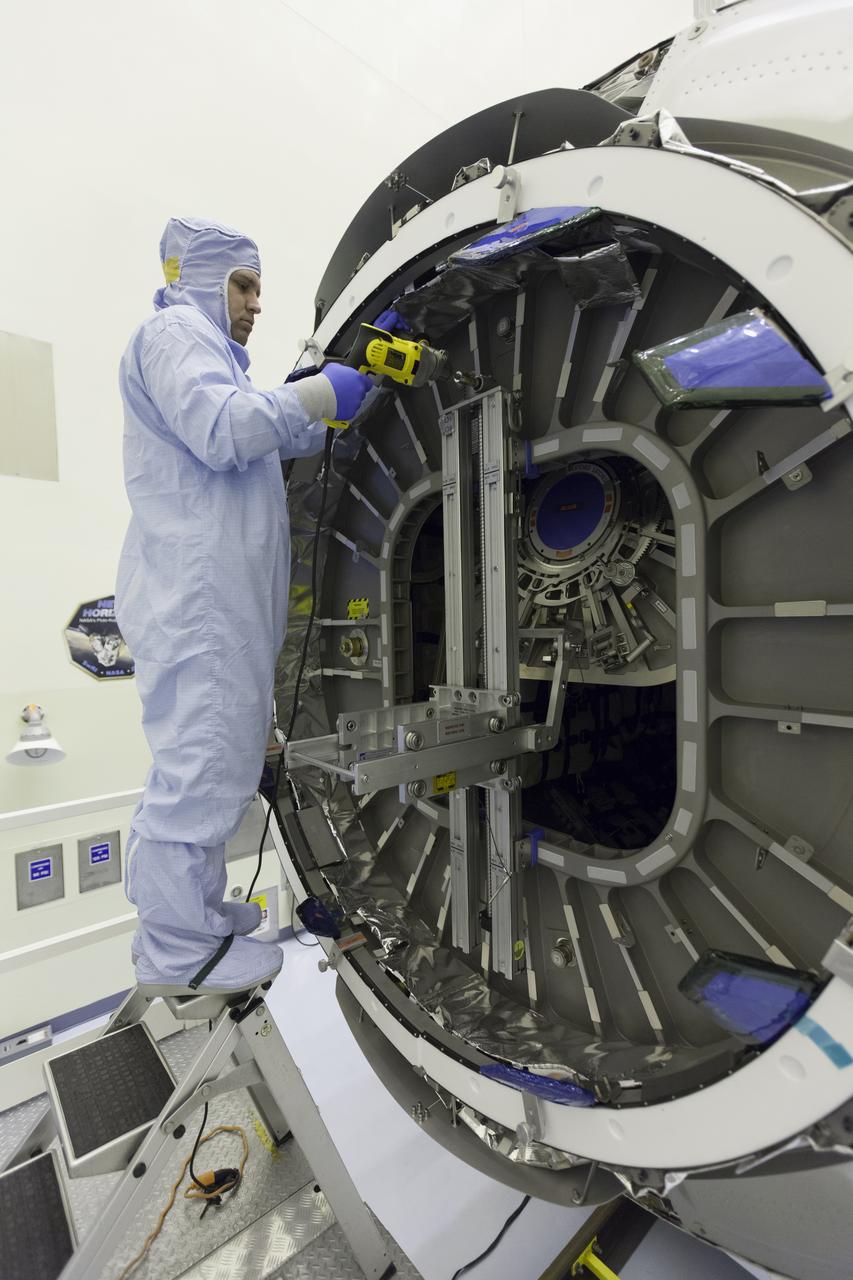

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician open the hatch on the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module to prepare for late stowage of supplies and hardware. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
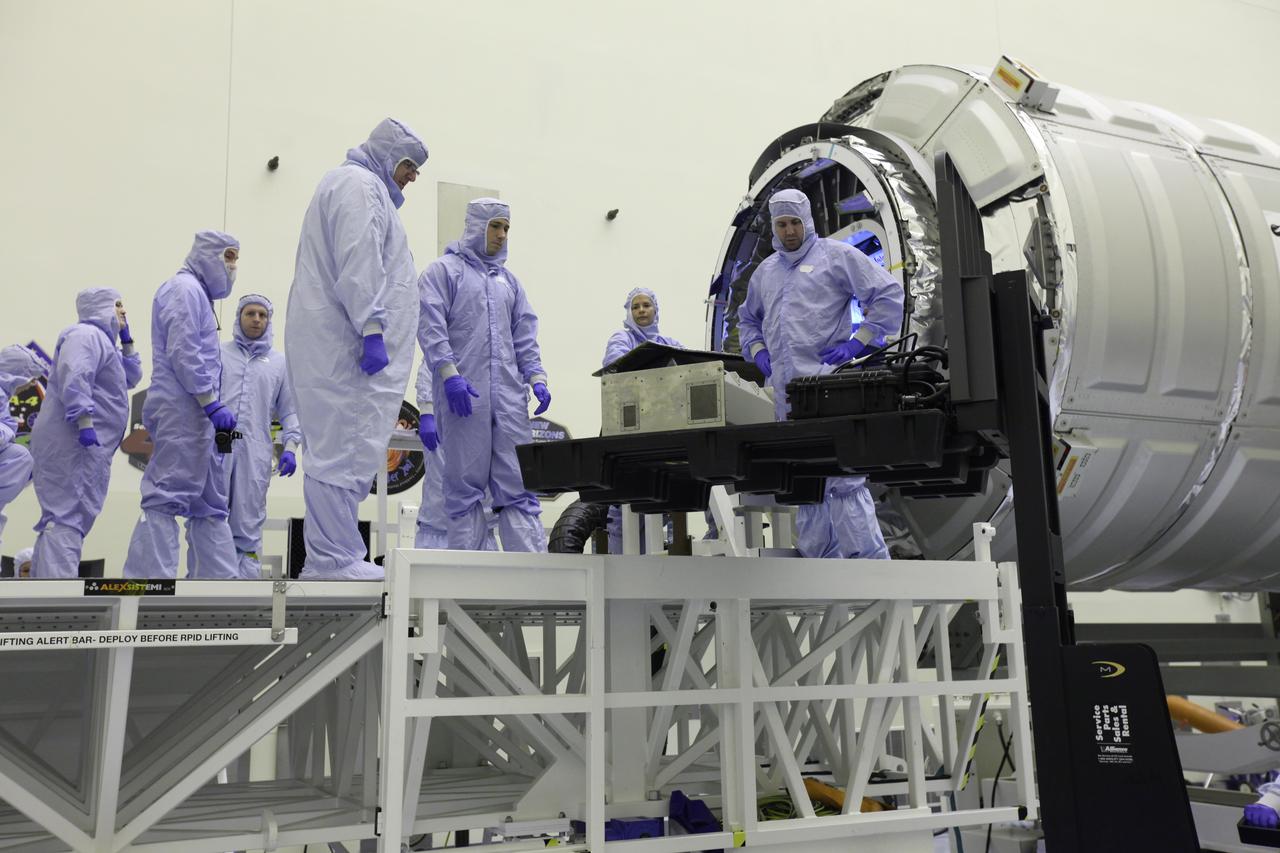

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a powered cargo unit for late stowage in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
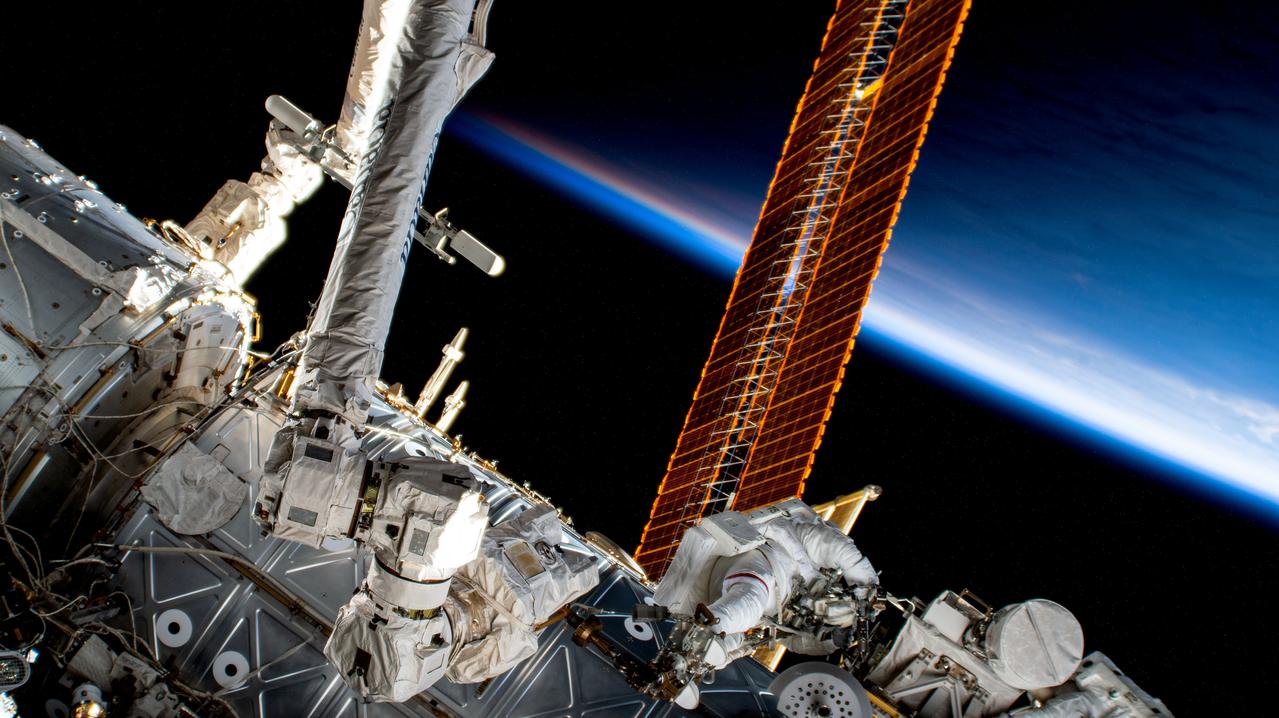

iss069e005732 (April 28, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen is pictured in his Extravehicular Mobility Unit, or spacesuit, outside the International Space Station during his eighth career spacewalk. He and UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut Sultan Alneyadi (out of frame) would spend seven hours and one minute in the vacuum of space routing cables and installing insulation readying the orbital outpost for its next set of roll-out solar arrays due to be installed after their delivery on the next SpaceX Dragon cargo mission.
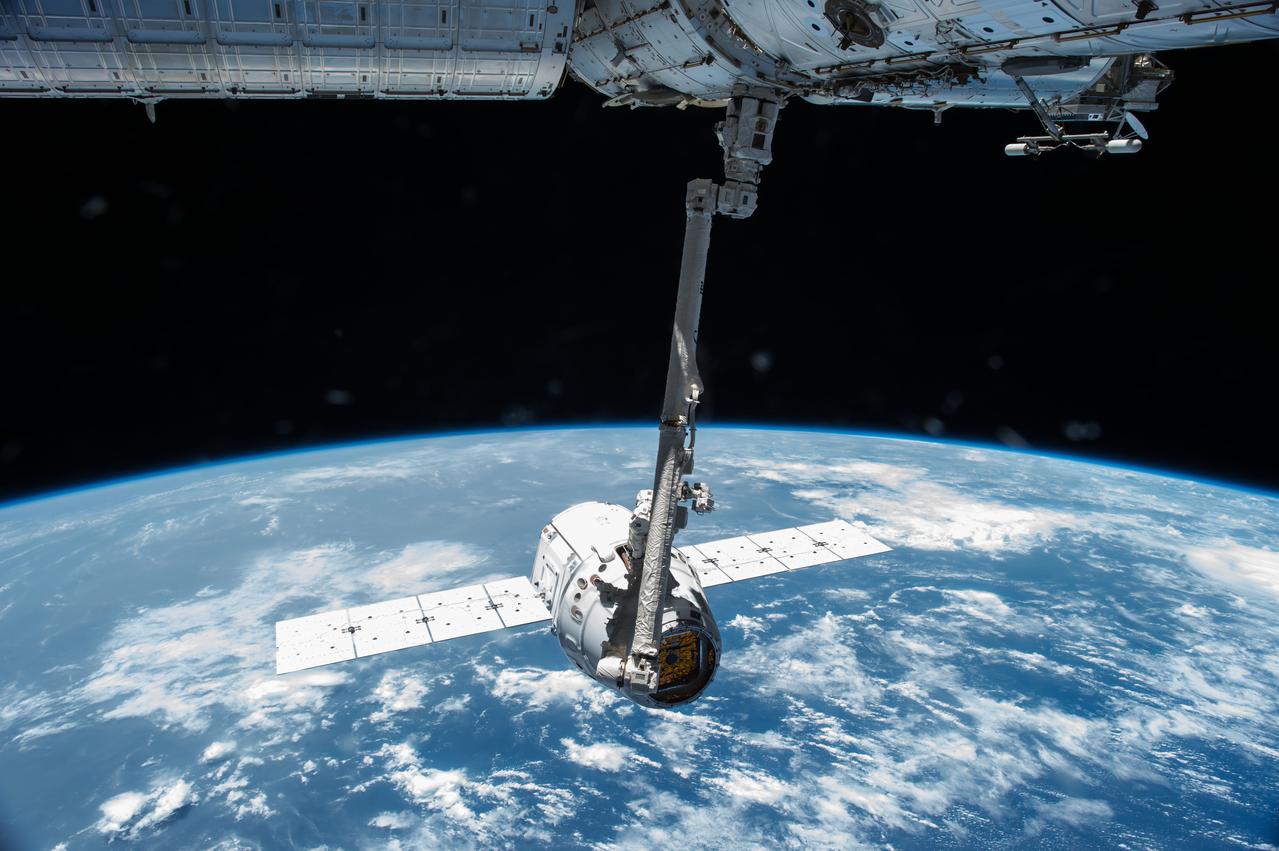

ISS043E124426 (04/17/2015) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm grapples the SpaceX Dragon CRS-6 cargo spacecraft before attaching it to the International Space Station. Robotics officers at Mission Control Houston installed the vehicle to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module. Emptied of its cargo Dragon is set to return to Earth on May 21.
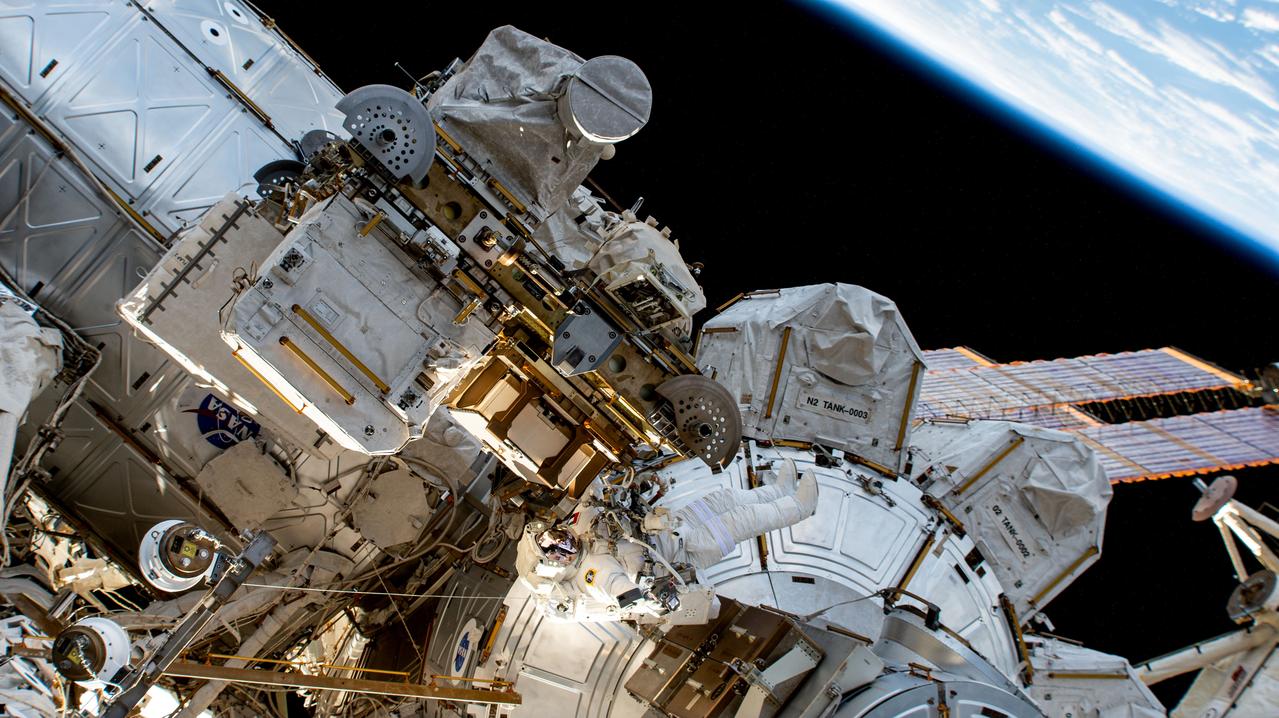

iss069e005729 (April 28, 2023) --- UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Sultan Alneyadi is pictured in his Extravehicular Mobility Unit, or spacesuit, outside the International Space Station's Quest airlock during his first spacewalk. He and NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen (out of frame) would spend seven hours and one minute in the vacuum of space routing cables and installing insulation readying the orbital outpost for its next set of roll-out solar arrays due to be installed after their delivery on the next SpaceX Dragon cargo mission.
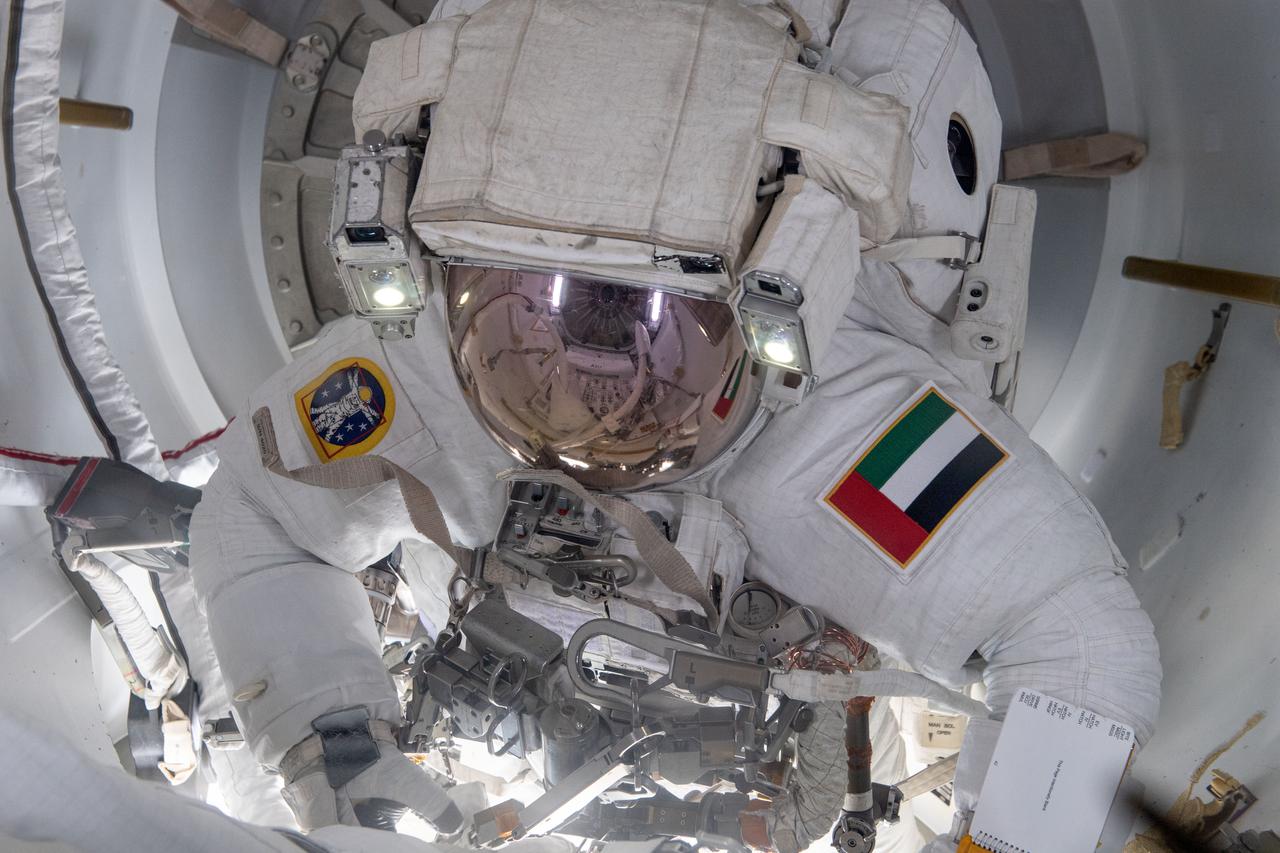

iss069e005717 (April 28, 2023) --- UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Sultan Alneyadi is pictured in his Extravehicular Mobility Unit, or spacesuit, preparing to exit the International Space Station's Quest airlock and begin his first spacewalk. He and NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen (out of frame) would spend seven hours and one minute in the vacuum of space routing cables and installing insulation readying the orbital outpost for its next set of roll-out solar arrays due to be installed after their delivery on the next SpaceX Dragon cargo mission.
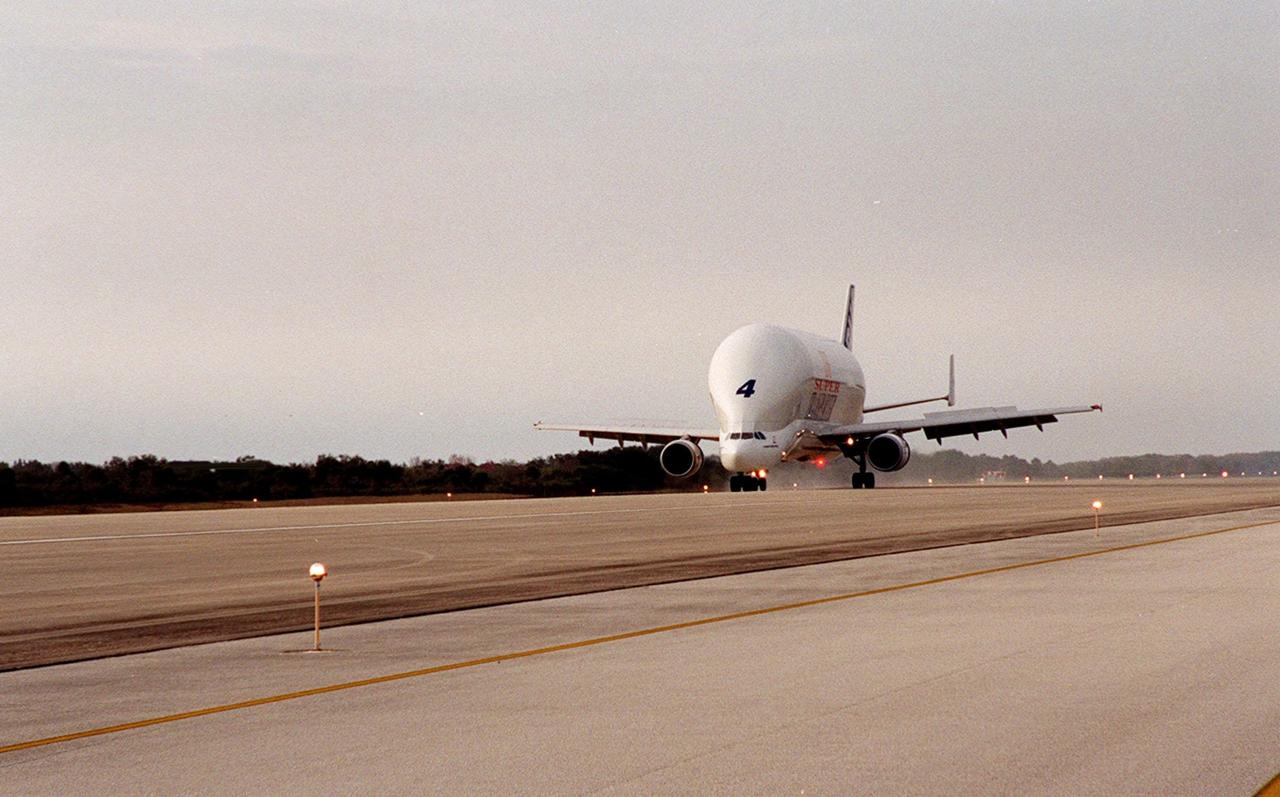

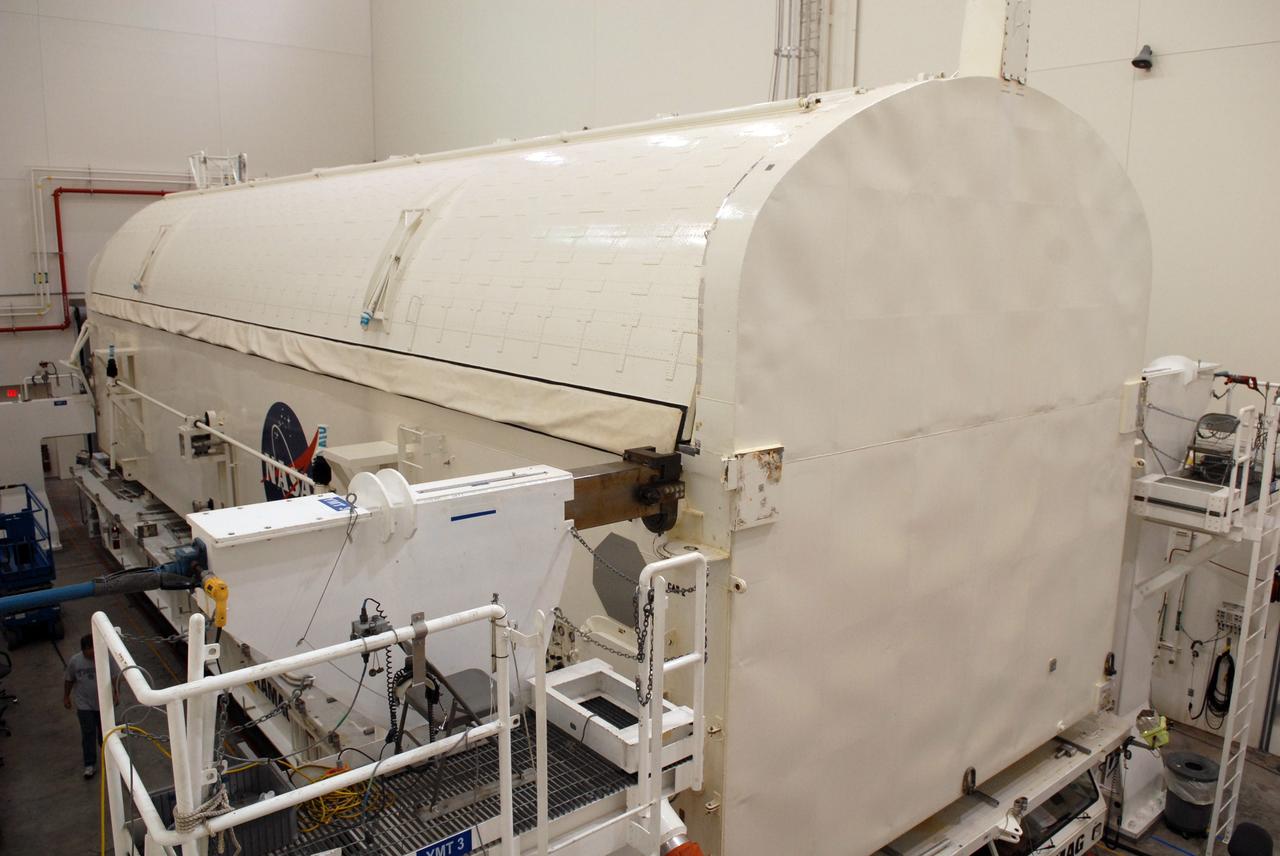
An Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane, The Super Transporter, arrives at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. Its cargo is the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, the third of three for the International Space Station. The module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
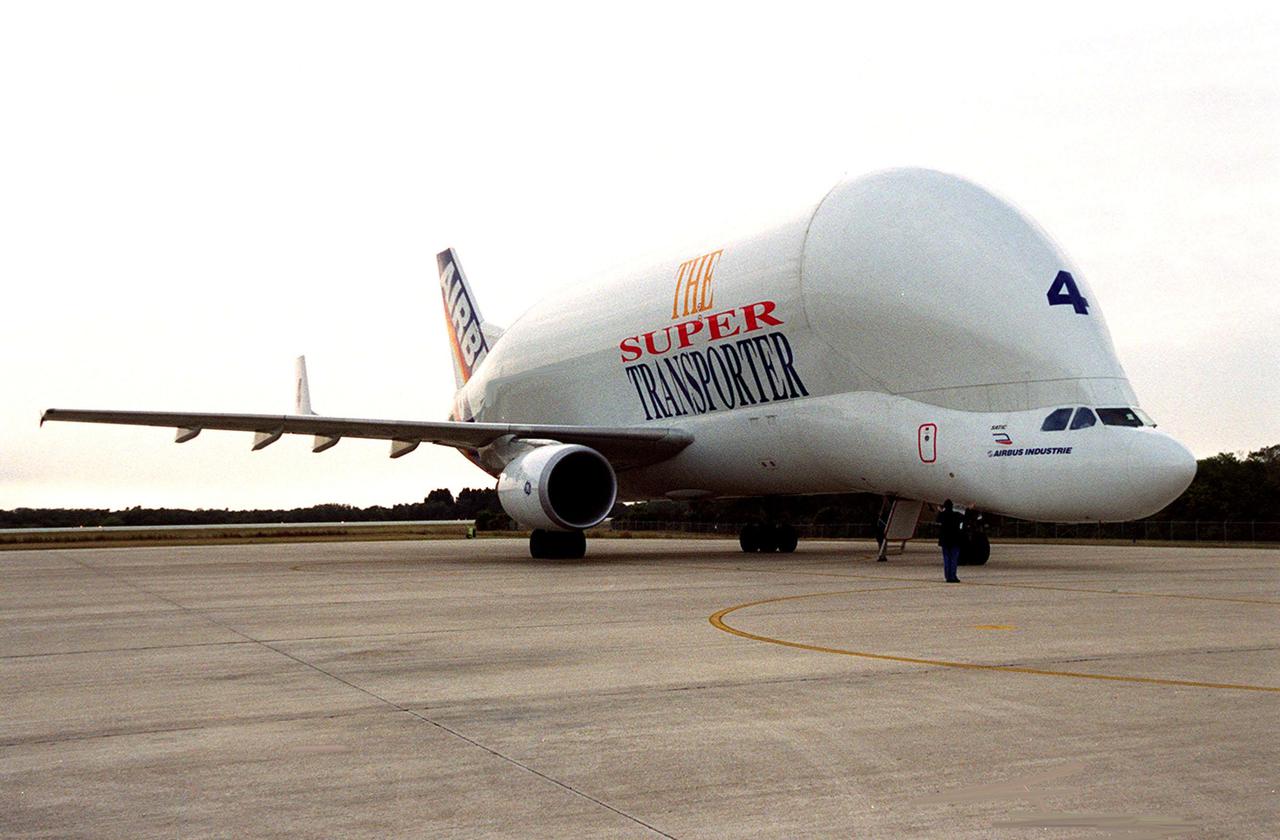

An Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane, The Super Transporter, taxis onto the parking apron at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Its cargo, from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy, is the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, the third of three for the International Space Station. The module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
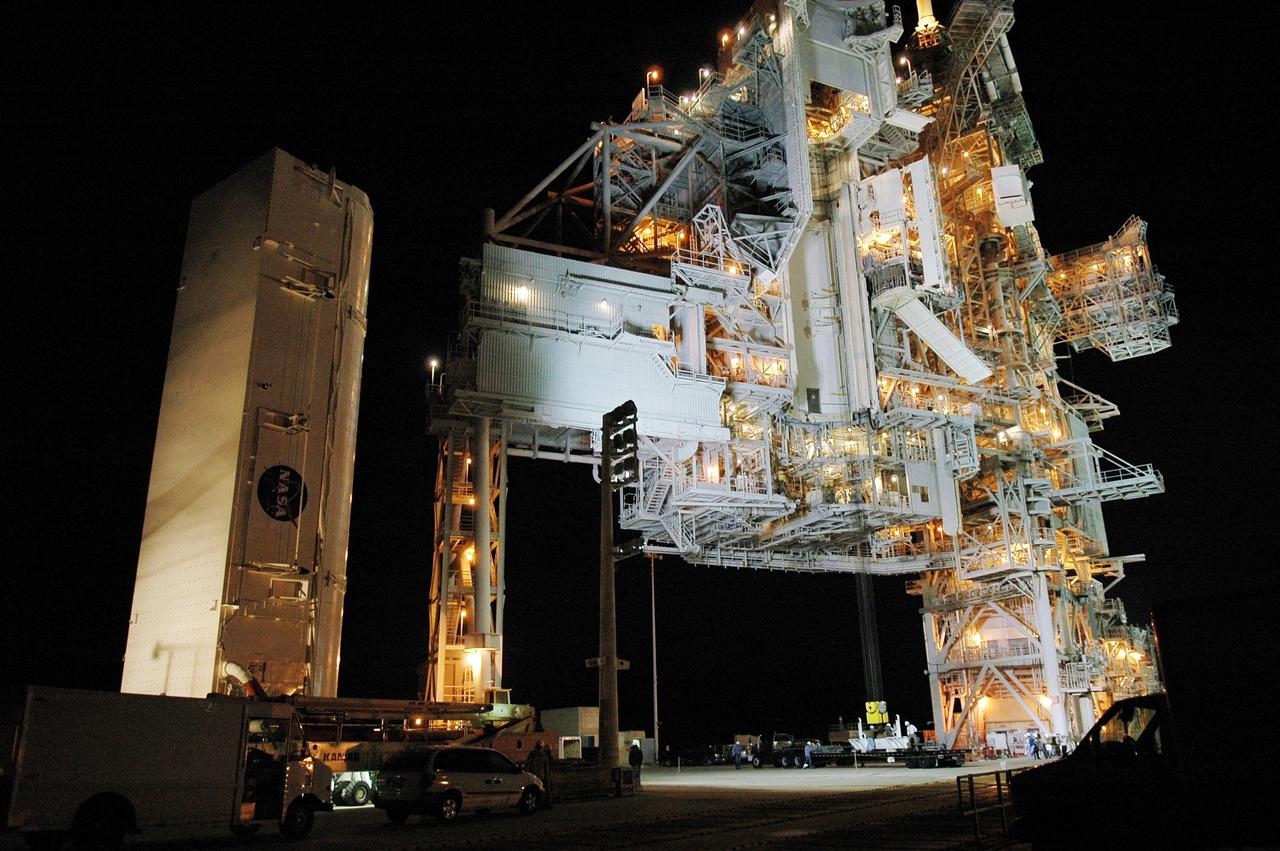
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister transporter and canister approach the rotating service structure (RSS) on Launch Pad 39B. Inside the canister are the SPACEHAB module and the port 5 truss segment for mission STS-116. They will be moved into the payload changeout room (PCR) on the RSS and transferred into Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay once the vehicle has rolled out to the pad. The PCR is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the RSS that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the orbiter payload bay. Seals around the mating surface of the PCR fit against the orbiter and allow the opening of the payload bay or canister doors and removal of the cargo without exposure to outside air and contaminants. A clean-air purge in the PCR maintains environmental control during PCR cargo operations. Cargo is removed from the payload canister and installed vertically in the orbiter by the payload ground handling mechanism (PGHM). Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
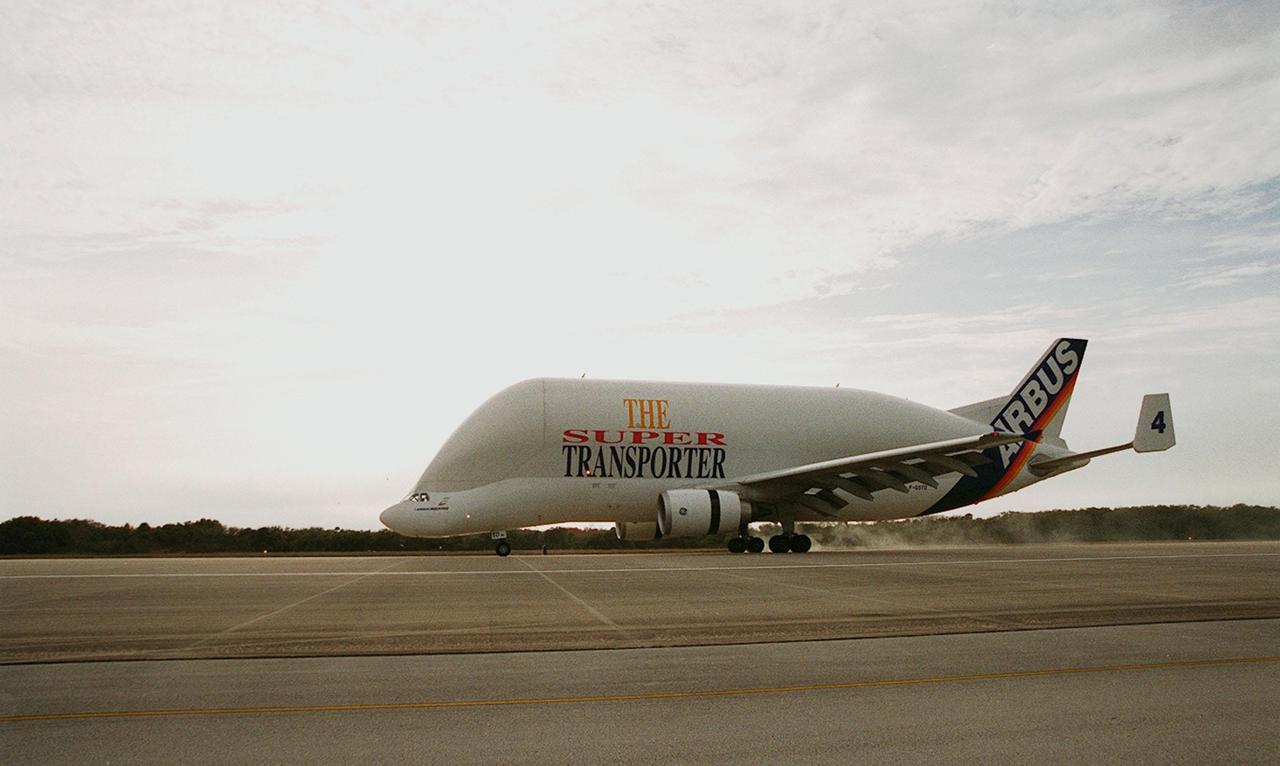

An Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane, The Super Transporter, lands at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Its cargo, from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy, is the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, the third of three for the International Space Station. The module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
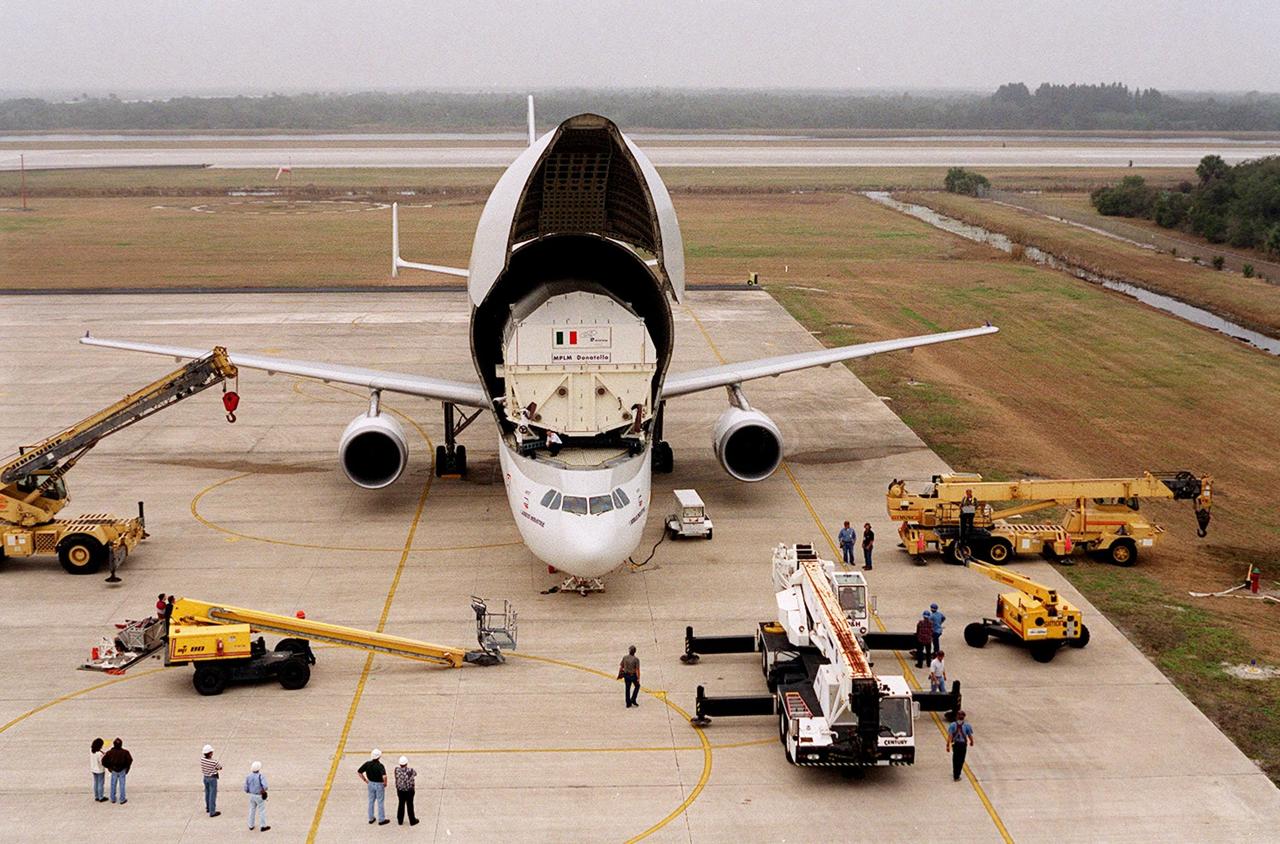

At the KSC <a href="../../subjects/slf.htm"> Shuttle Landing Facility</a>, an Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane opens to reveal its cargo, the Italian Space Agency’s <a href="../../subjects/mplm.htm"> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module</a> Donatello, from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the <a href="../../subjects/sspf.htm"> Space Station Processing Facility</a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
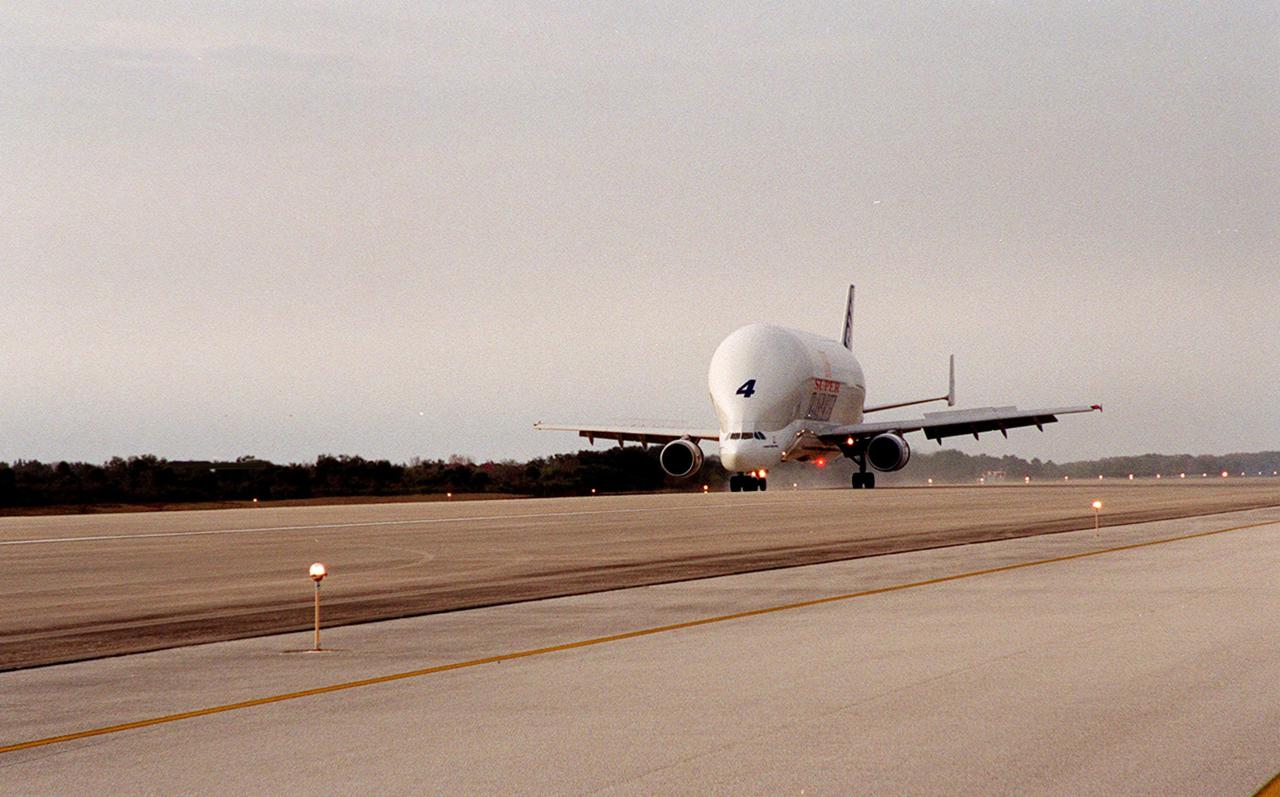

An Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane, The Super Transporter, arrives at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. Its cargo is the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, the third of three for the International Space Station. The module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
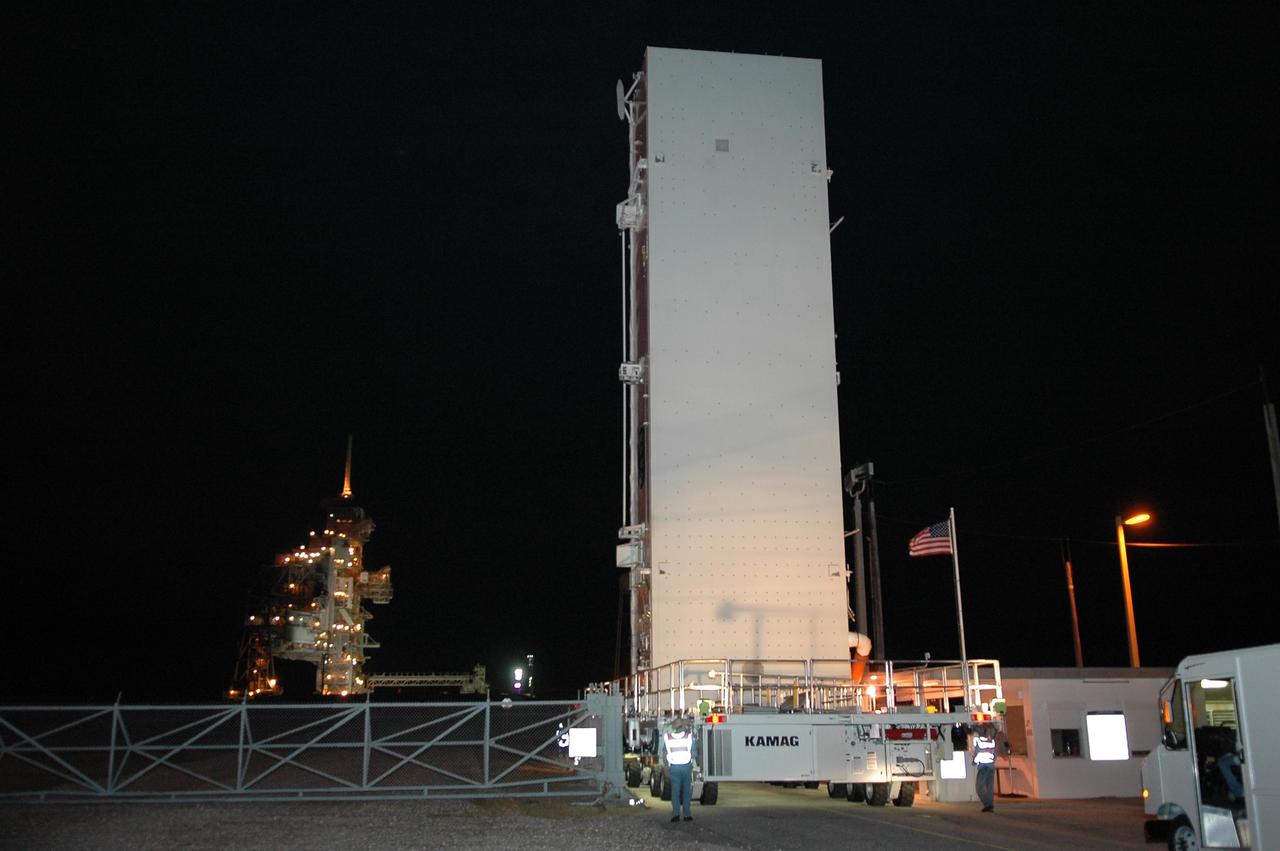

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister transporter and canister arrive at the gate to Launch Pad 39B. Inside the canister are the SPACEHAB module and the port 5 truss segment for mission STS-116. They will be moved into the payload changeout room (PCR) at the pad and transferred into Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay once the vehicle has rolled out to the pad. The PCR is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the RSS that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the orbiter payload bay. Seals around the mating surface of the PCR fit against the orbiter and allow the opening of the payload bay or canister doors and removal of the cargo without exposure to outside air and contaminants. A clean-air purge in the PCR maintains environmental control during PCR cargo operations. Cargo is removed from the payload canister and installed vertically in the orbiter by the payload ground handling mechanism (PGHM). Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
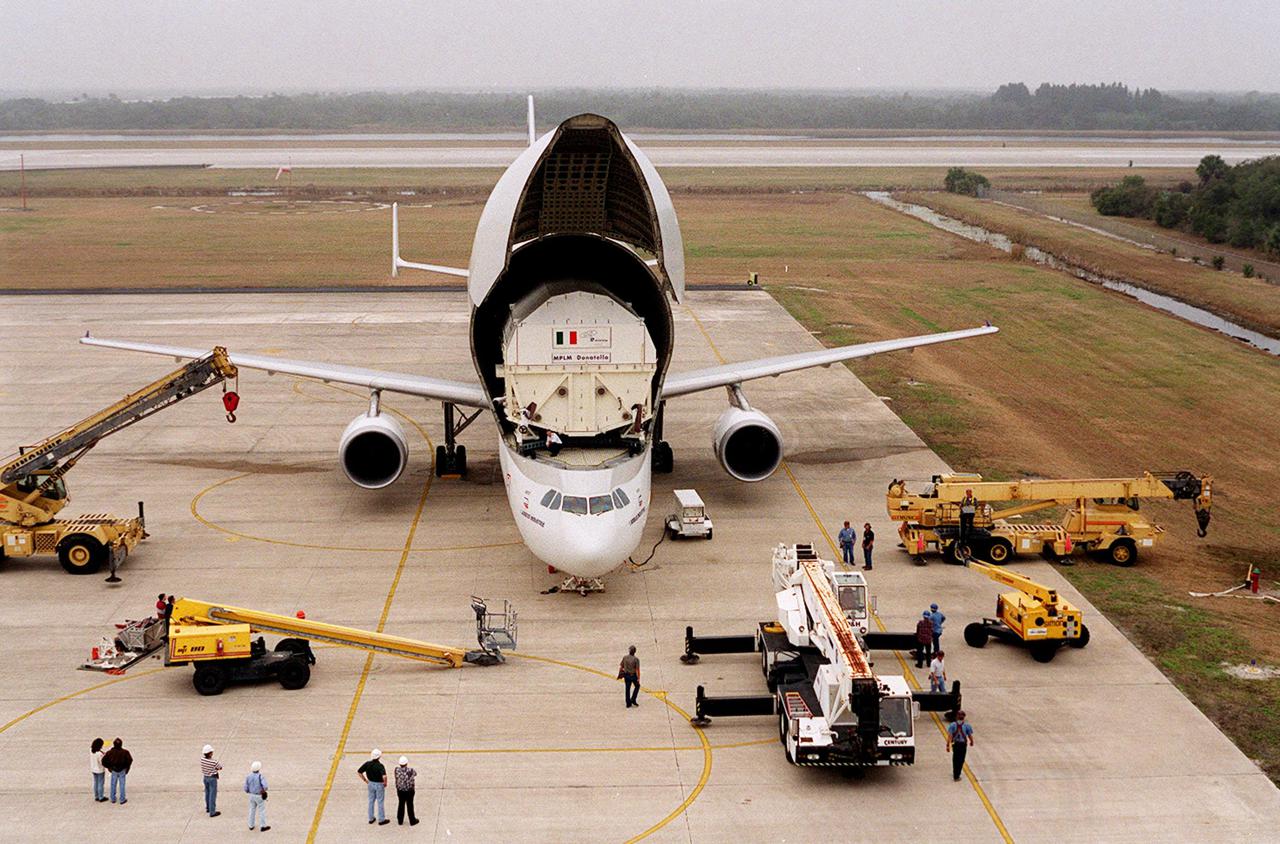

At the KSC <a href='.._.._subjects_slf.htm'> Shuttle Landing Facility<_a>, an Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane opens to reveal its cargo, the Italian Space Agency’s <a href='.._.._subjects_mplm.htm'> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module<_a> Donatello, from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the <a href='.._.._subjects_sspf.htm'> Space Station Processing Facility<_a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
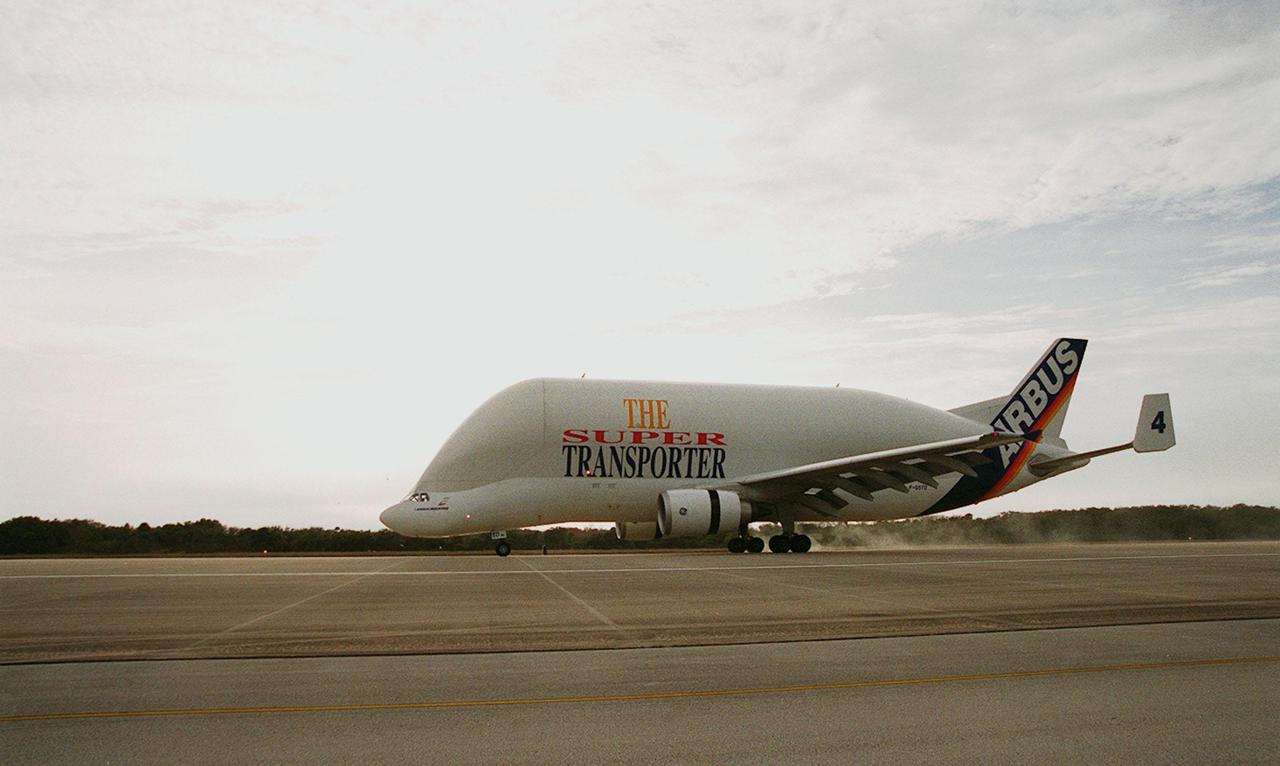

An Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane, The Super Transporter, lands at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Its cargo, from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy, is the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, the third of three for the International Space Station. The module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
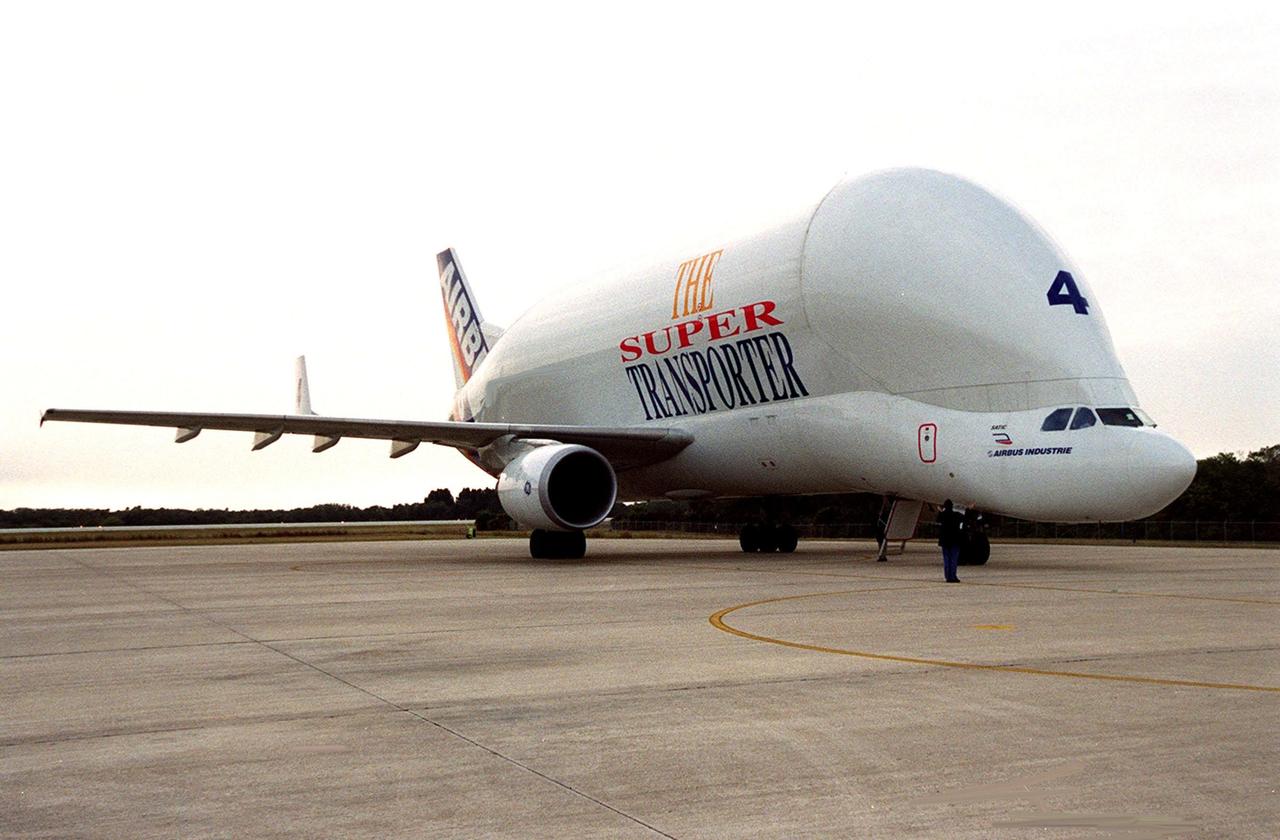

An Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane, The Super Transporter, taxis onto the parking apron at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Its cargo, from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy, is the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, the third of three for the International Space Station. The module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
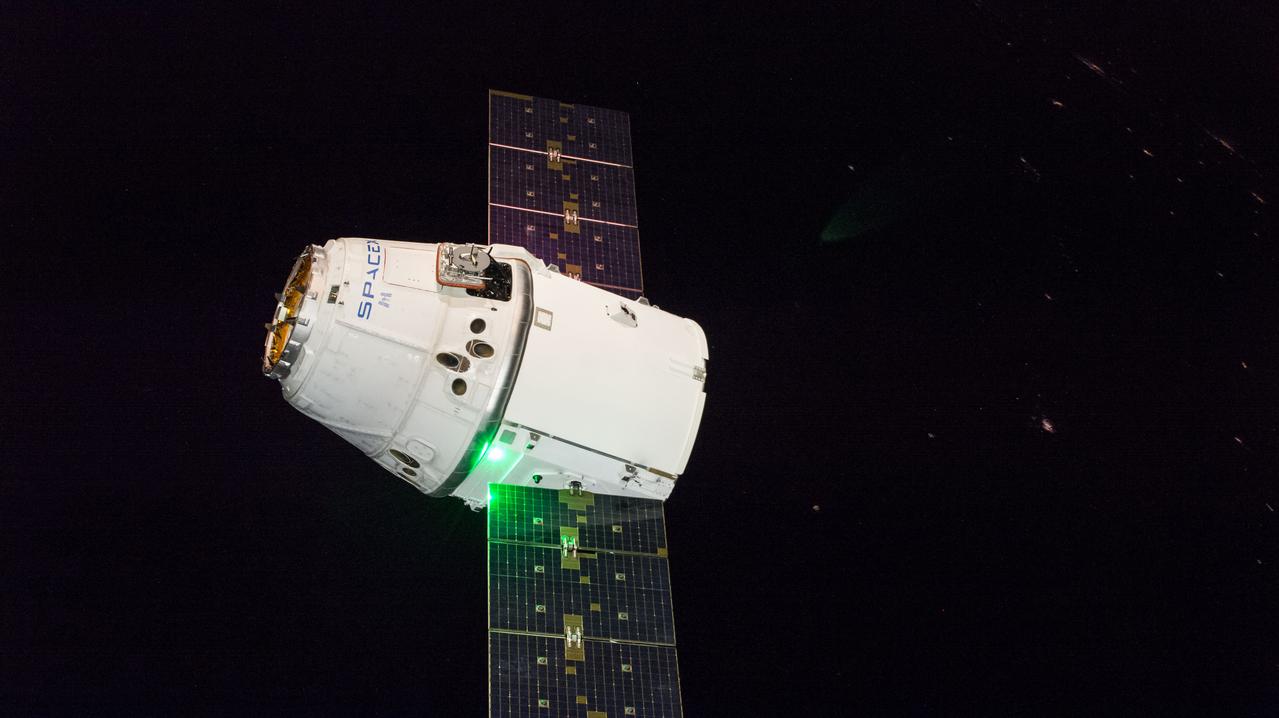

iss057e115431 (Dec. 8, 2018) --- The SpaceX Dragon cargo craft slowly approaches the International Space Station. Astronauts Alexander Gerst and Serena Auñón-Chancellor were monitoring Dragon from inside the cupola and preparing to slowly reach out and grapple the cargo craft with the Canadarm2 robotic arm. Dragon, packed with over 5,600 pounds of cargo, completed a three-day trip to the International Space Station that began with a launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and ended with its installation and hatch opening on the Harmony module..
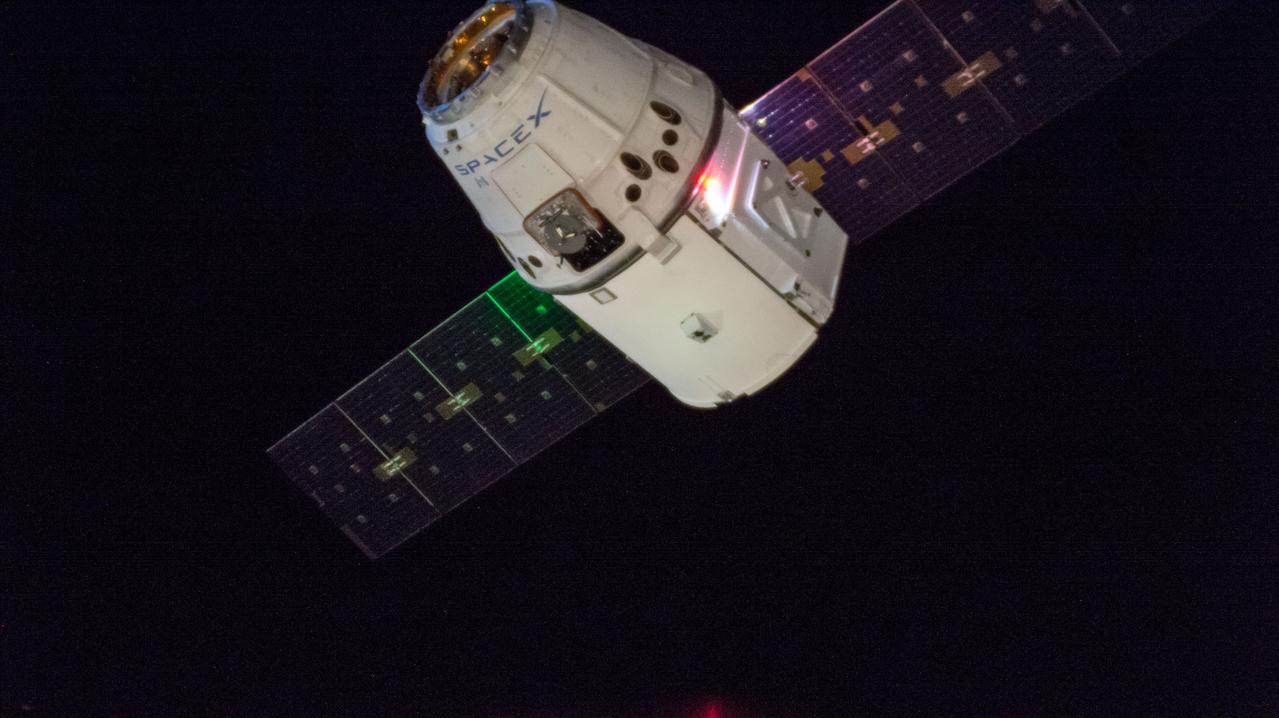

iss057e115424 (Dec. 8, 2018) --- The SpaceX Dragon cargo craft slowly approaches the International Space Station. Astronauts Alexander Gerst and Serena Auñón-Chancellor were monitoring Dragon from inside the cupola and preparing to slowly reach out and grapple the cargo craft with the Canadarm2 robotic arm. Dragon, packed with over 5,600 pounds of cargo, completed a three-day trip to the International Space Station that began with a launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and ended with its installation and hatch opening on the Harmony module..
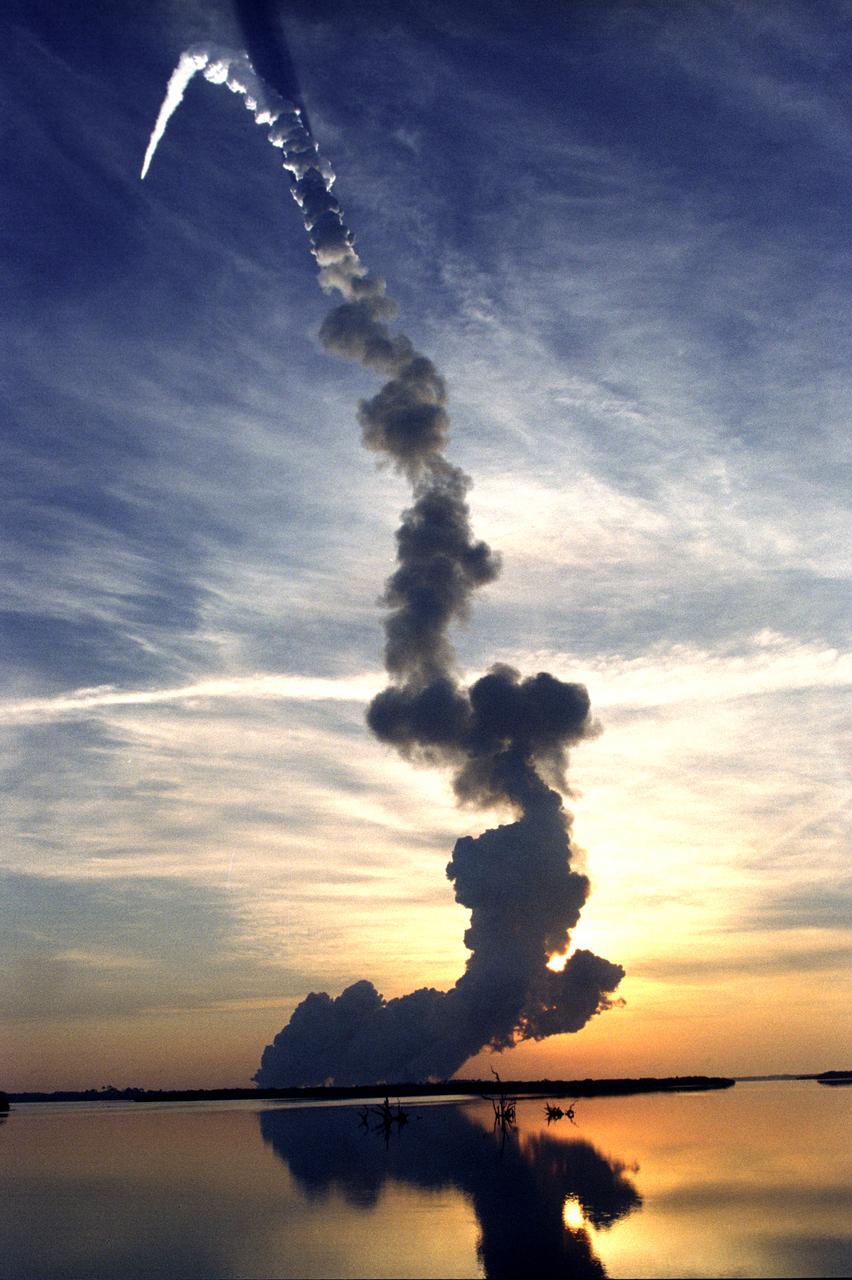

This spectacular photo is of the May 27, 1999 liftoff of the Orbiter Discovery (STS-96). The STS-96 mission, of almost 10 days, was the second International Space Station (ISS) assembly and resupply flight and the first flight to dock with the station. The crew installed foot restraints and the Russian built crane, STRELA. The Shuttle's SPACEHAB double module carried internal and resupply cargo for station outfitting and the Russian cargo crane was carried aboard the shuttle in the integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC).
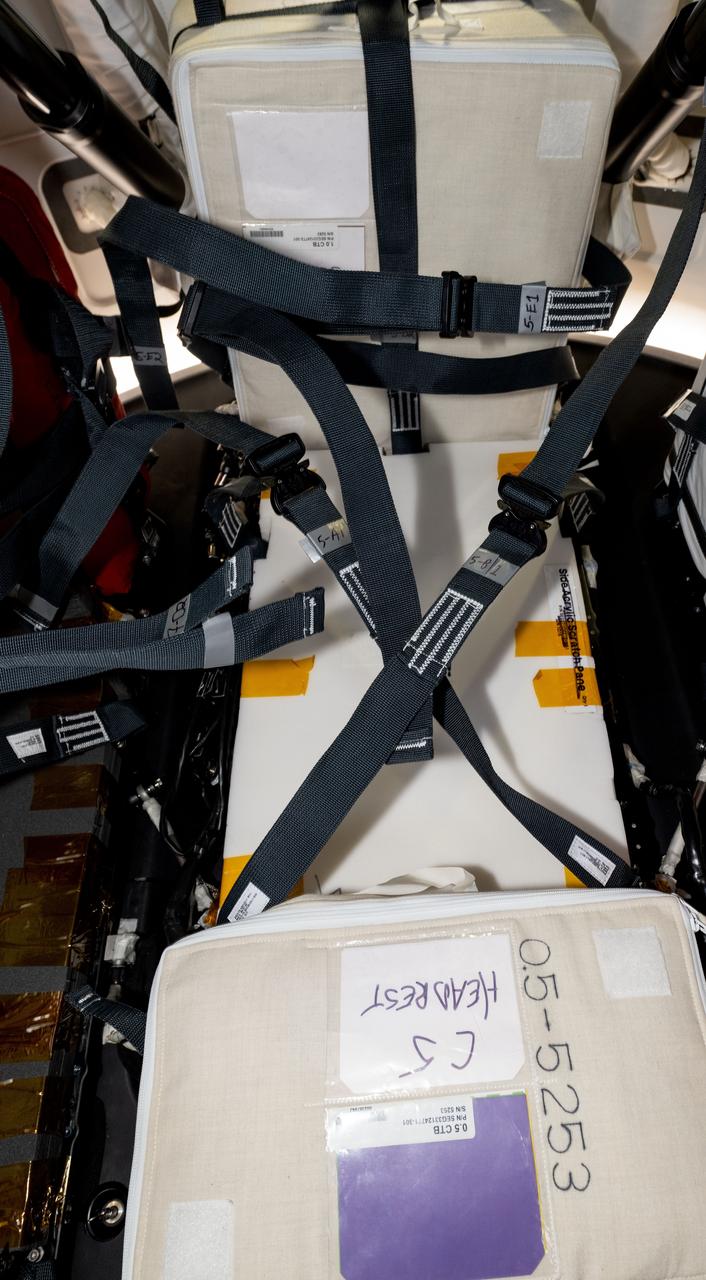

This image shows one of the temporary seat structures built and installed on the Crew-8 Dragon in cargo pallet locations C7 and C5 using foam, straps, and other station soft goods such as cushions.
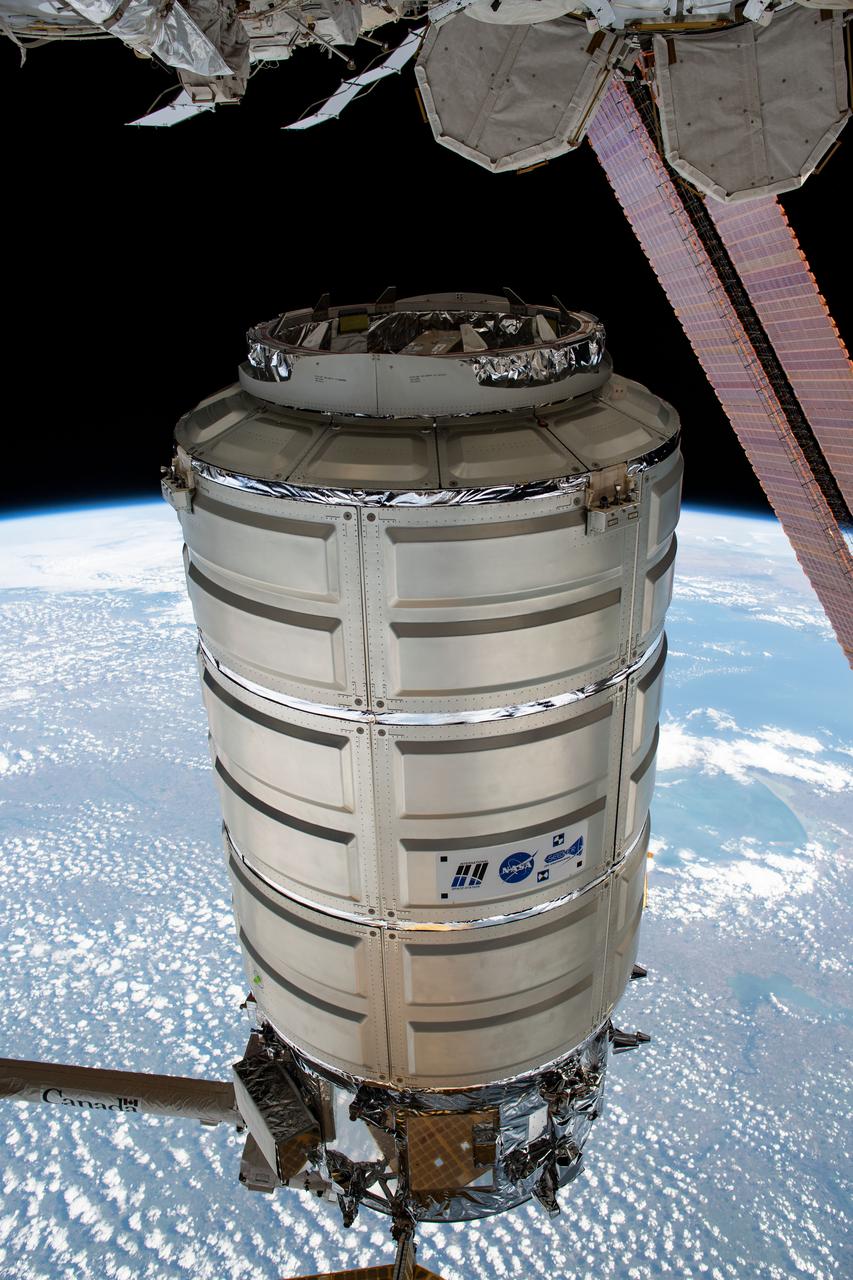

iss060e022965 (Aug. 6, 2019) --- The Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm following its detachment from the Unity module where it was installed for 109 days of cargo transfer operations.
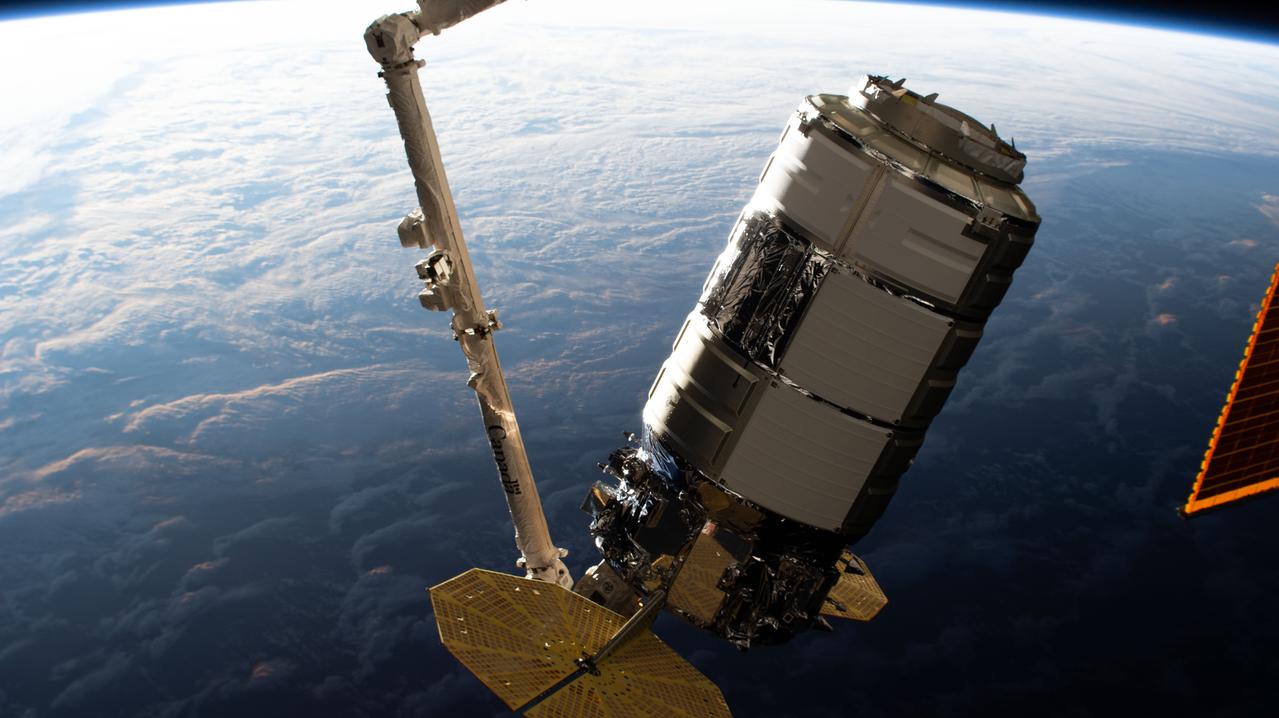

iss063e101638 (Oct. 5, 2020) --- The Northrop Grumman Cygnus space freighter is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm as mission controllers remotely guide the cargo vehicle to its installation point on the International Space Station's Unity module.
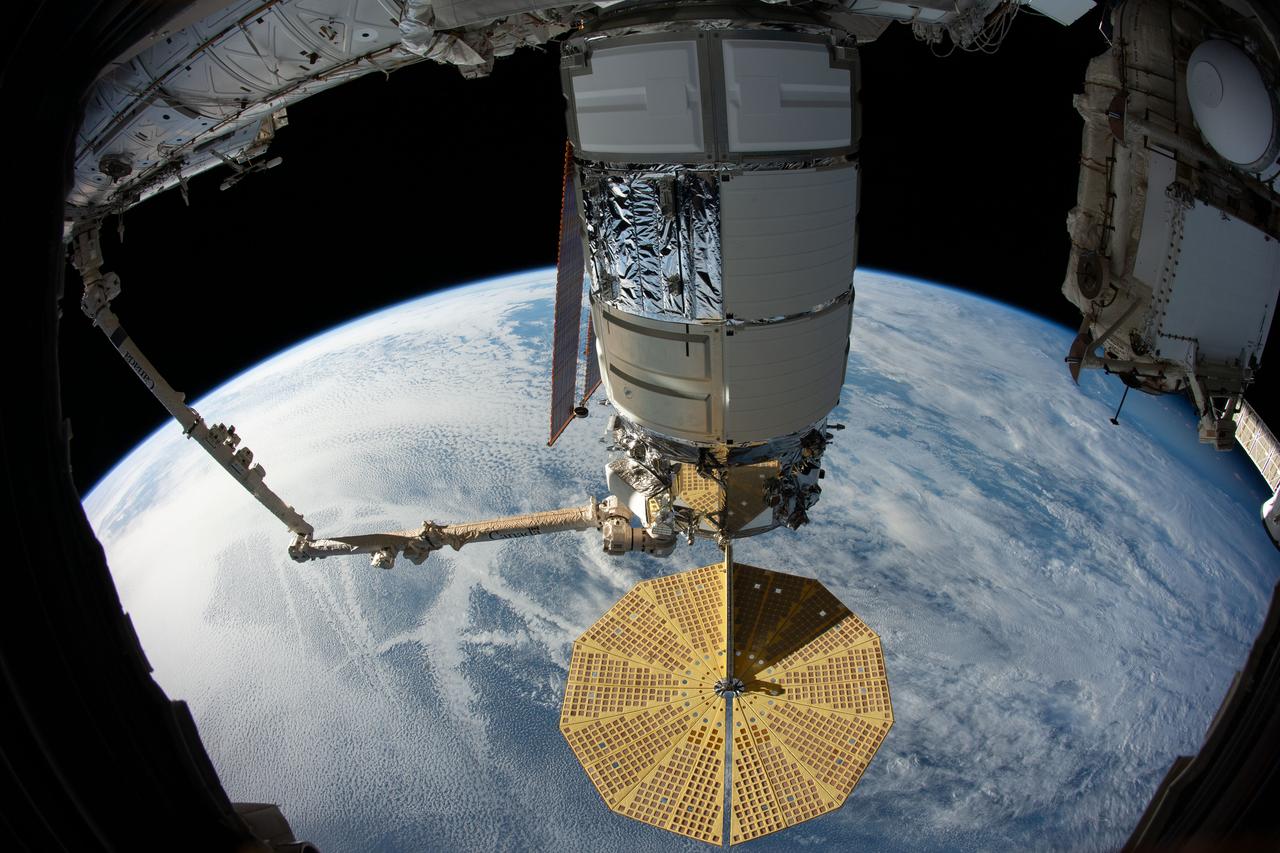

iss061e028414 (Nov. 4, 2019) --- The U.S. Cygnus space freighter from Northrop Grumman is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm as it was installed to the Unity module for 70 days of cargo transfers.
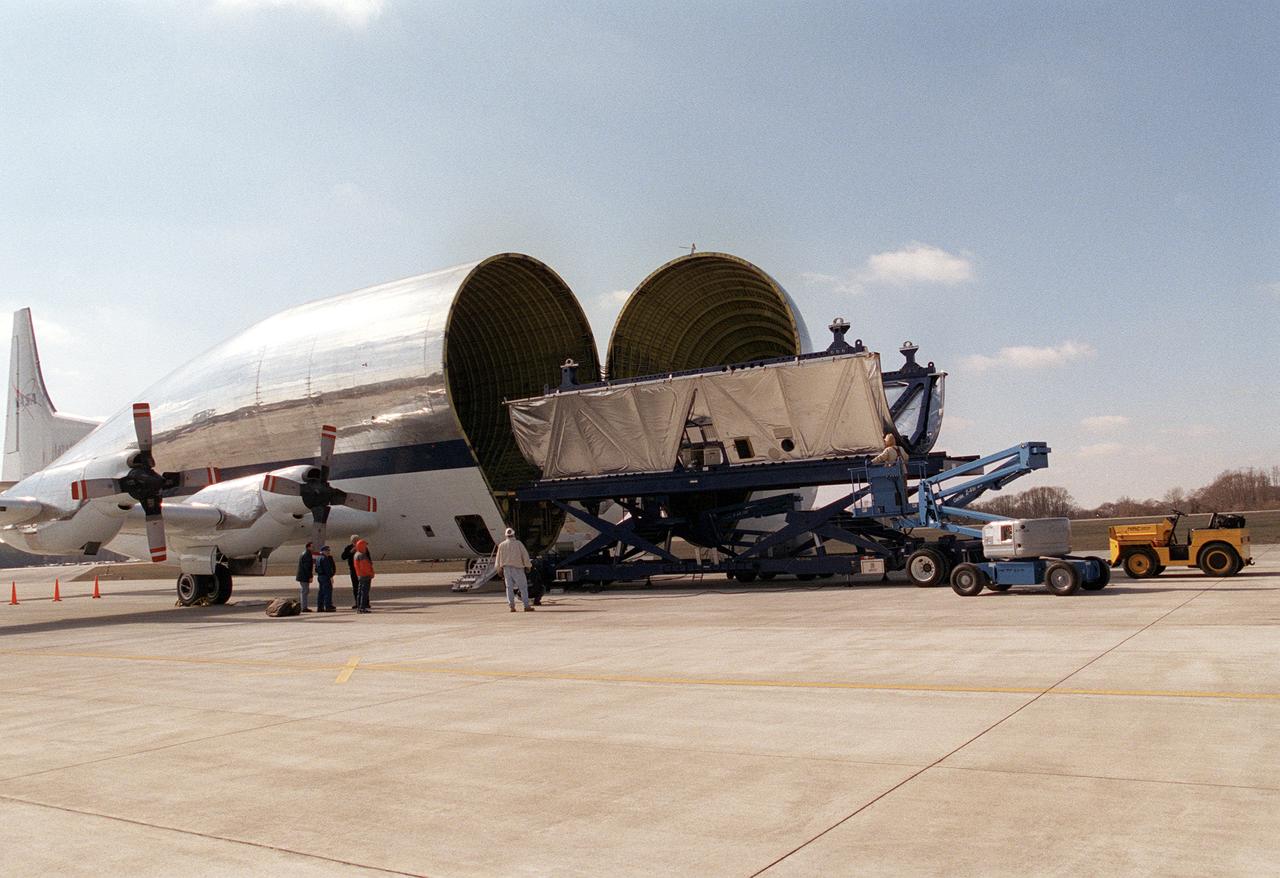

A section of the International Space Station truss assembly arrived at the Marshall Space Flight Center on NASA's Super Guppy cargo plane for structural and design testing as well as installation of critical flight hardware.
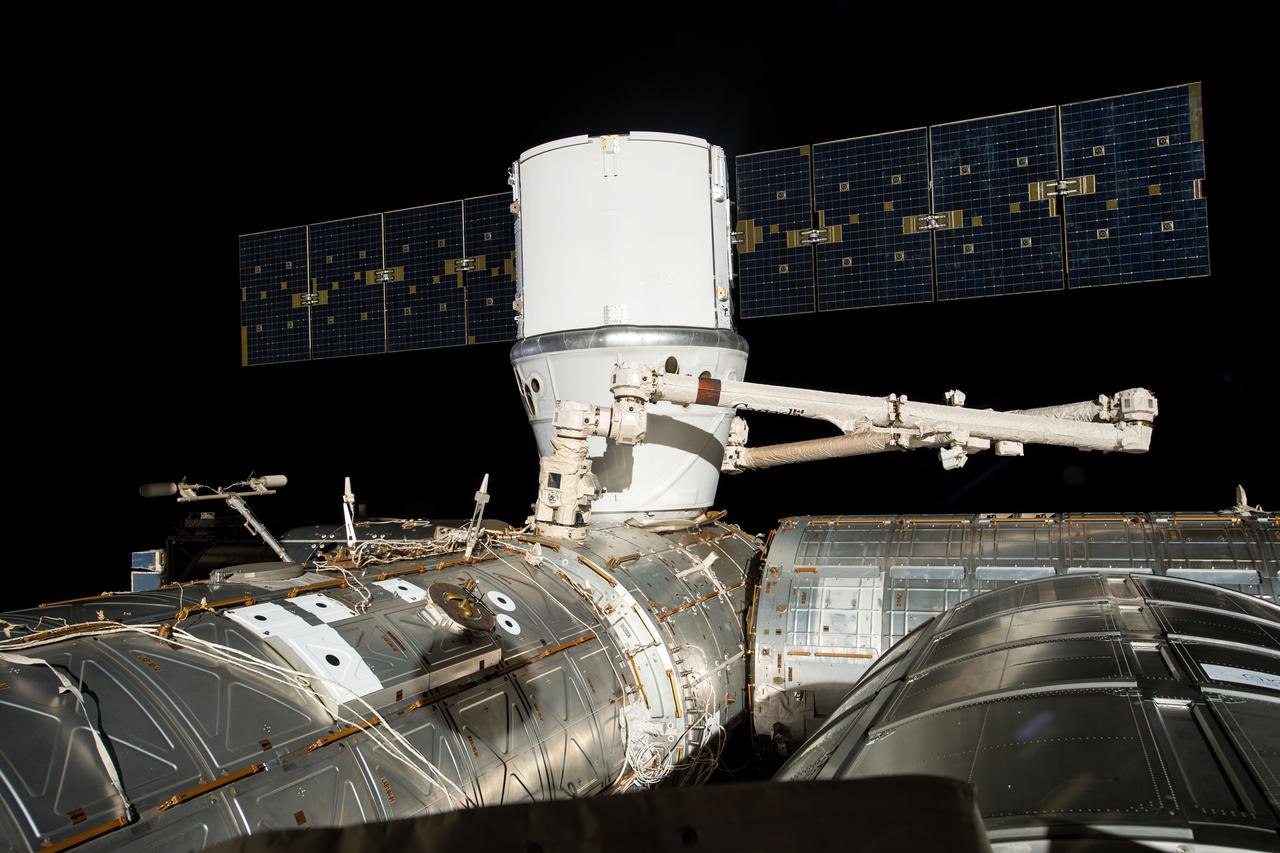

iss059e051334 (May 6, 2019) --- The SpaceX Dragon cargo craft is installed to the Harmony module's Earth-facing port a few hours after it was captured by astronauts David Saint-Jacques and Nick Hague with the Canadarm2 robotic arm.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is in the Canister Rotation Facility where it will be lifted to a vertical position. The canister transporter will then carry the canister and its cargo to Launch Pad 39A. The cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

The lid is off the shipping container with the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello inside. It sits on a transporter inside the Space Station Processing Facility. In the SSPF, Donatello will undergo processing by the payload test team, including integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo. Donatello will be launched on mission STS-130, currently planned for September 2004
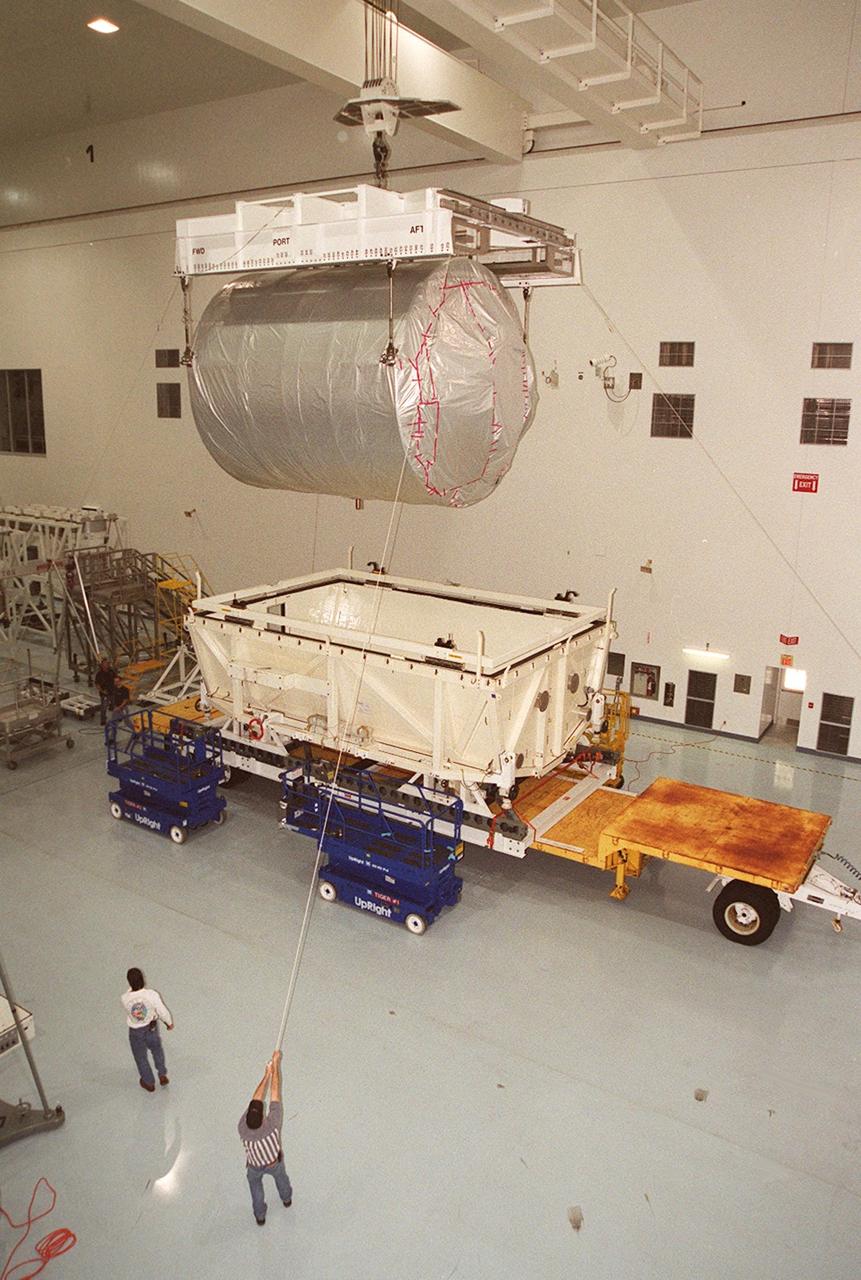

In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers help guide the overhead crane as it lifts the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello out of the shipping container. In the SSPF, Donatello will undergo processing by the payload test team, including integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo. Donatello will be launched on mission STS-130, currently planned for September 2004

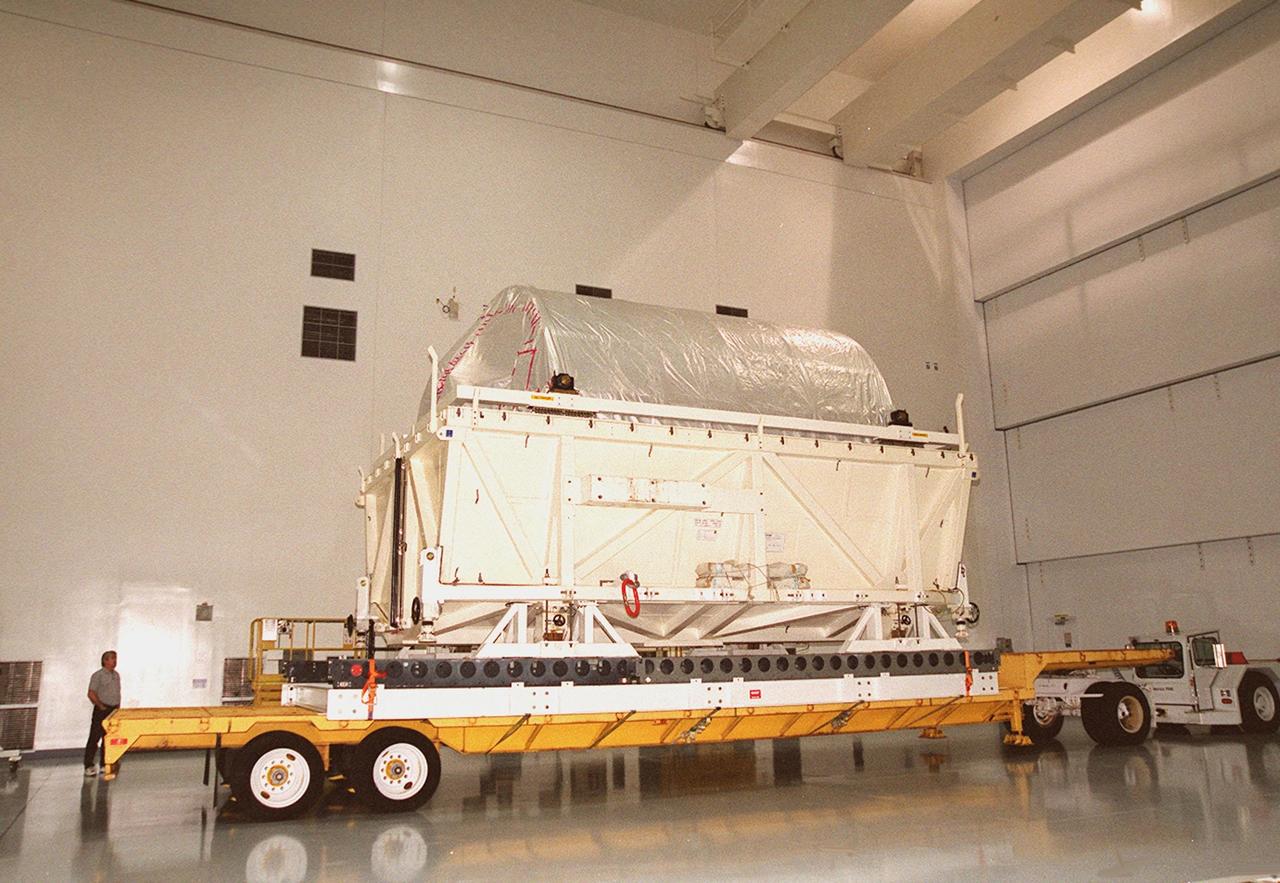
At the Shuttle Landing Facility, workers watch as cranes lower the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello onto a flat bed for transport to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
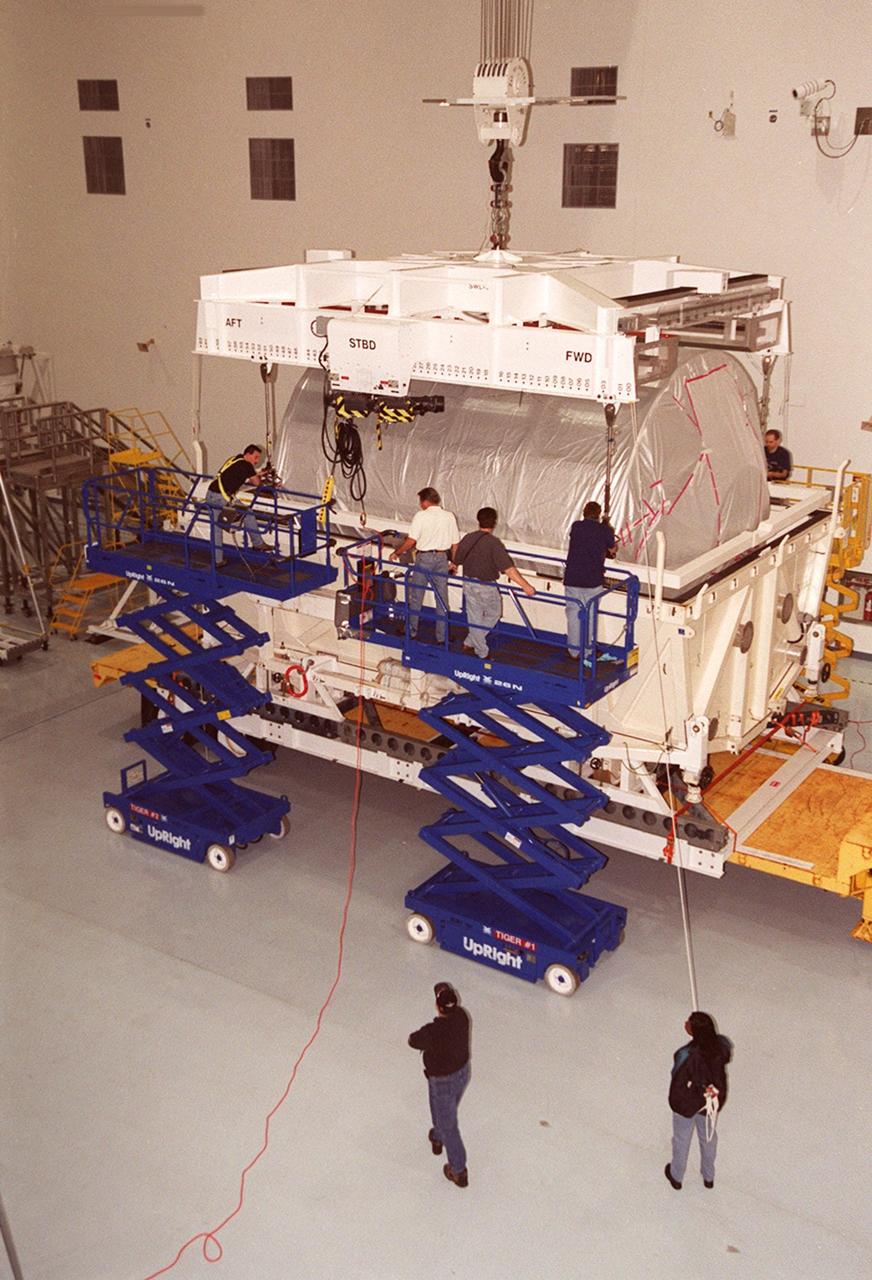
Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility attach an overhead crane to the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello to lift it out of the shipping container. In the SSPF, Donatello will undergo processing by the payload test team, including integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo. Donatello will be launched on mission STS-130, currently planned for September 2004
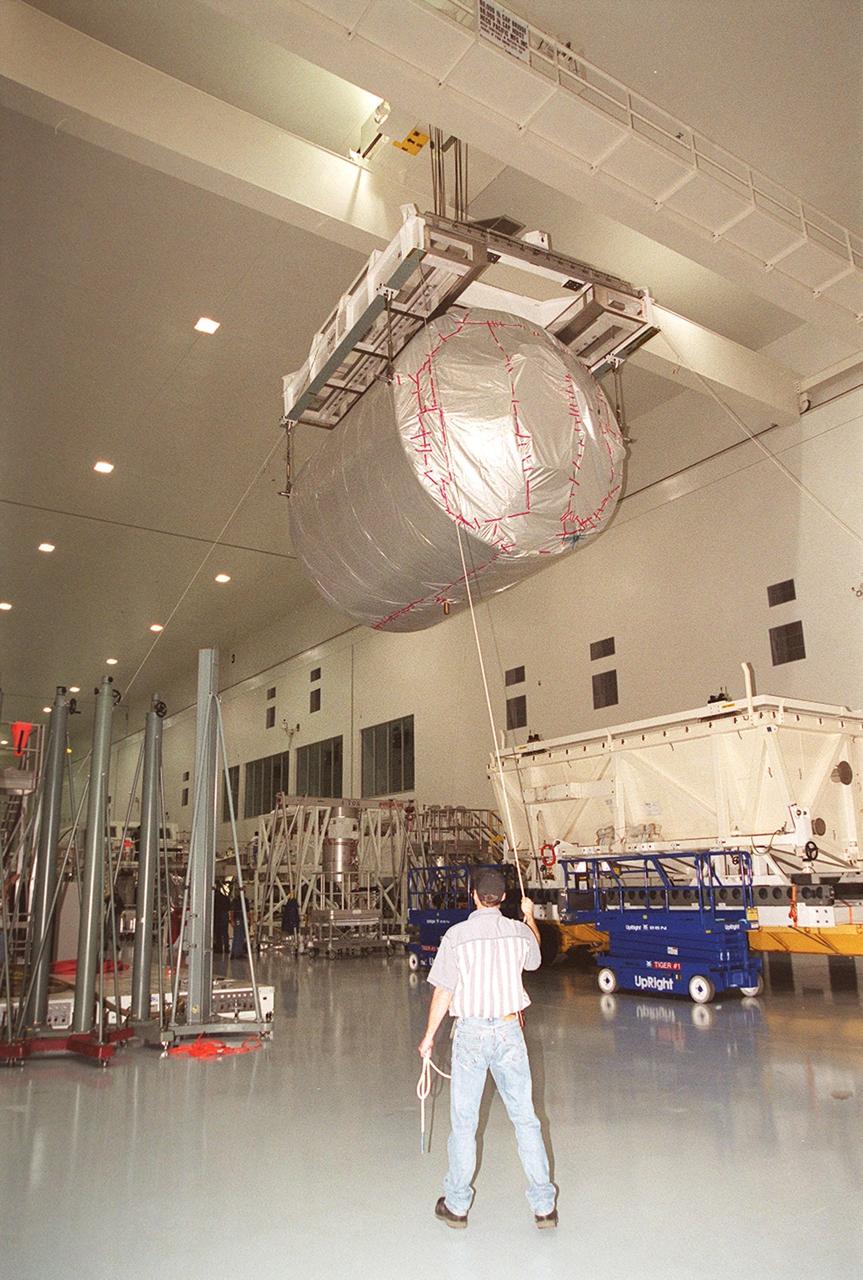

In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers help guide the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello as it moves the length of the SSPF toward a workstand. In the SSPF, Donatello will undergo processing by the payload test team, including integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo. Donatello will be launched on mission STS-130, currently planned for September 2004
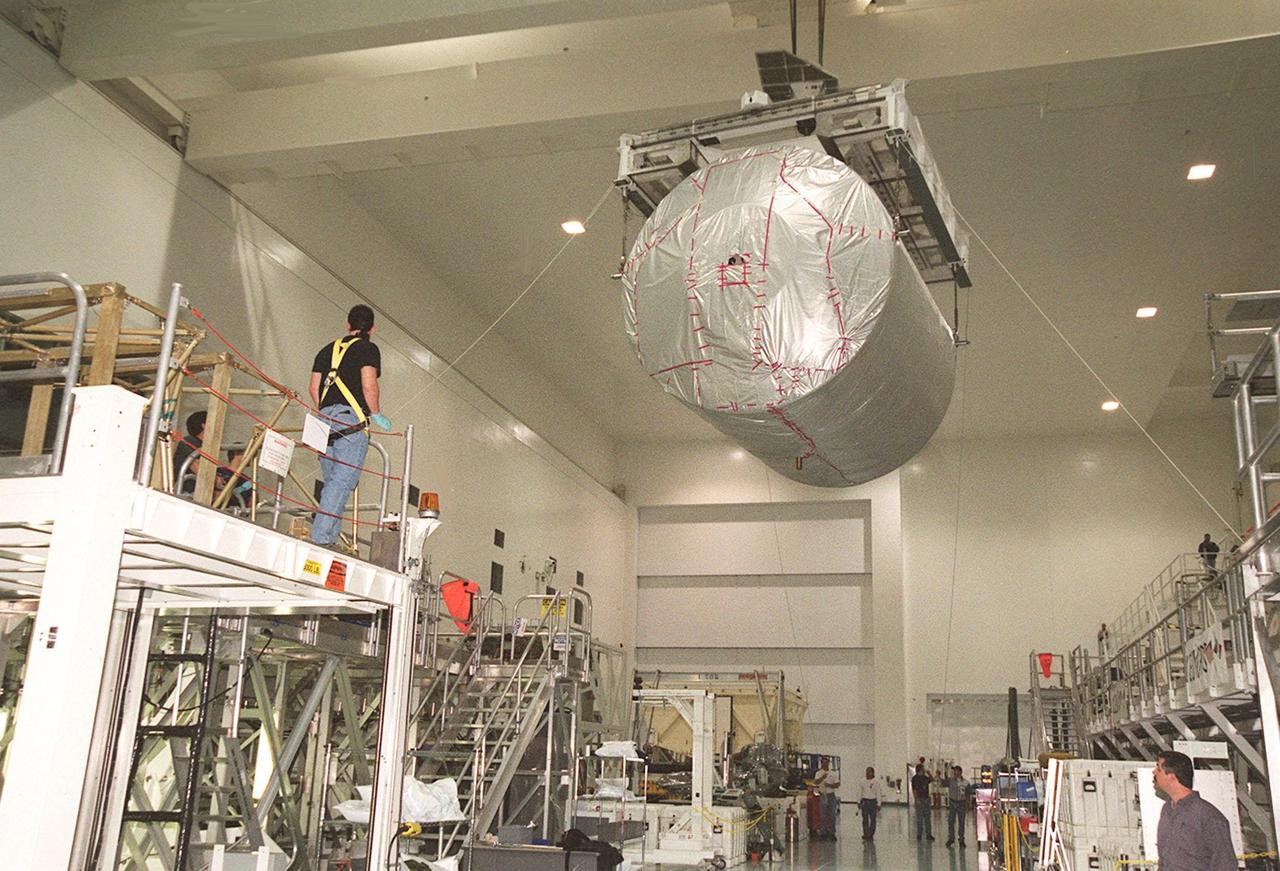

In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers wait for the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello, suspended by an overhead crane, to move onto a workstand. In the SSPF, Donatello will undergo processing by the payload test team, including integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo. Donatello will be launched on mission STS-130, currently planned for September 2004
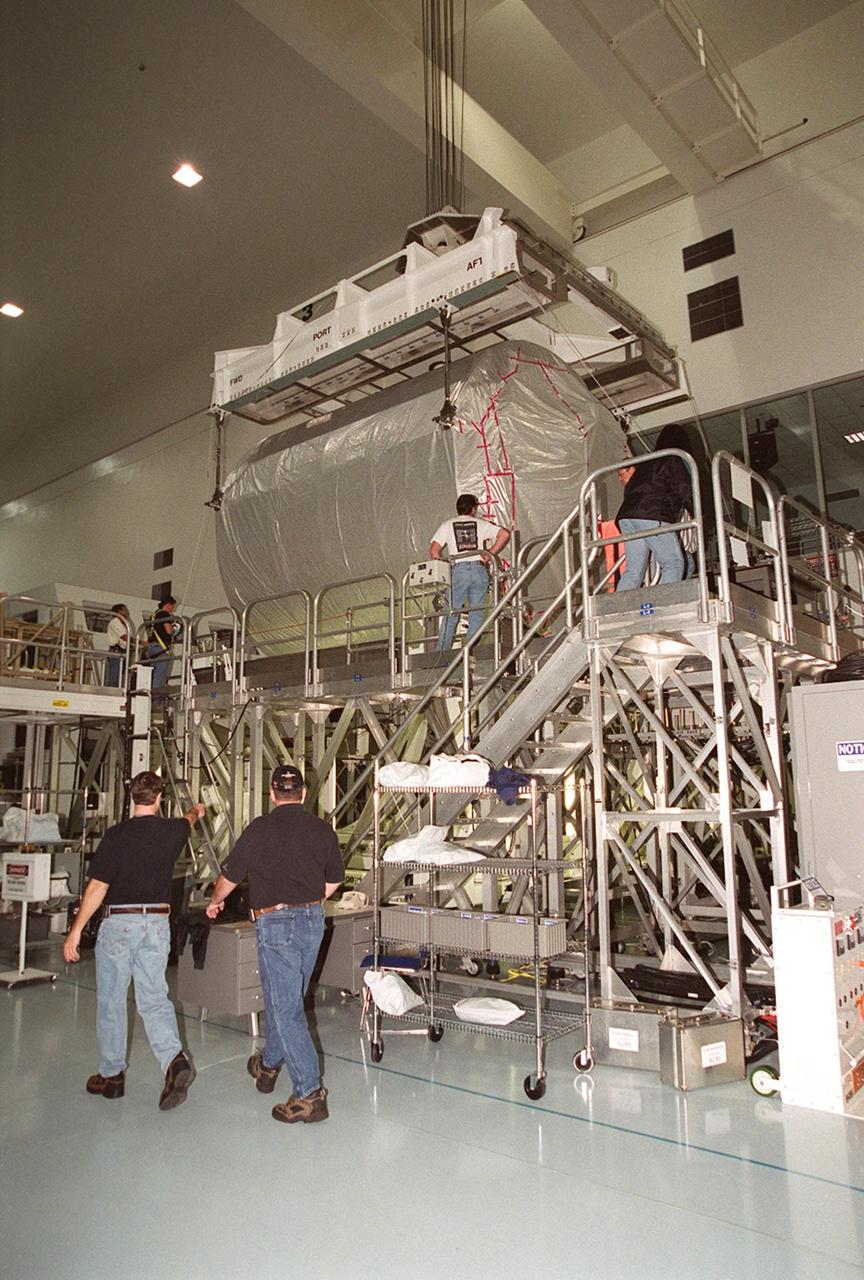

An overhead crane lowers the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello onto a workstand. In the SSPF, Donatello will undergo processing by the payload test team, including integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo. Donatello will be launched on mission STS-130, currently planned for September 2004
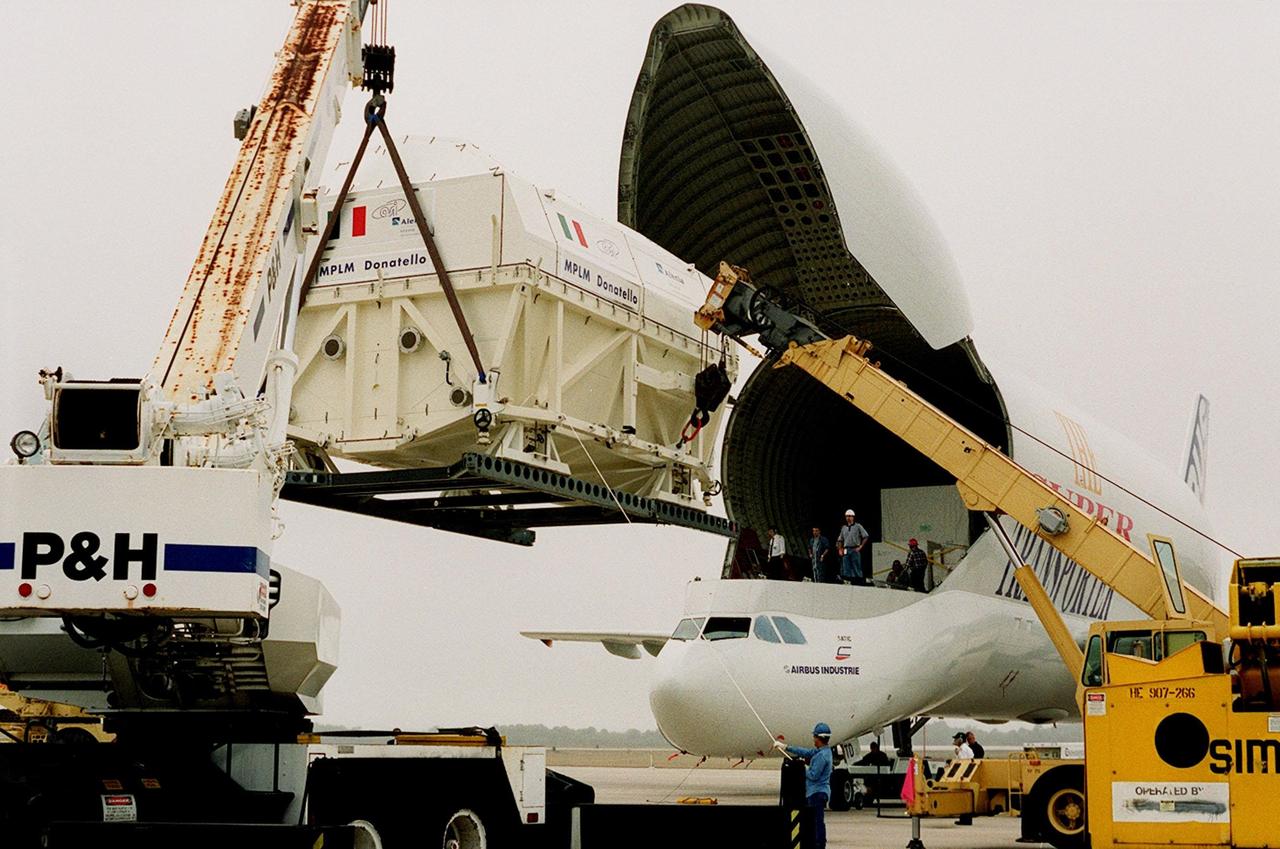

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, cranes help offload the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello from the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be moved on a transporter to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
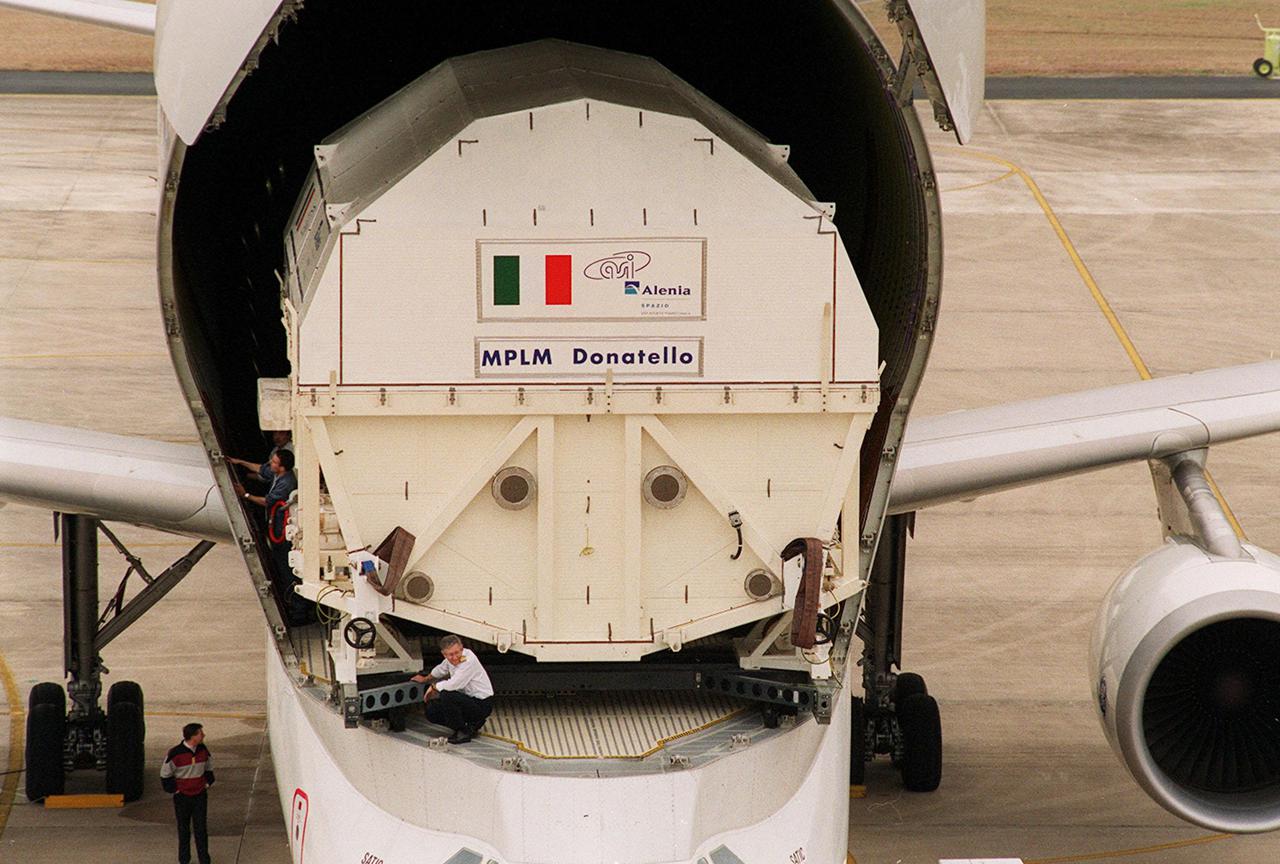

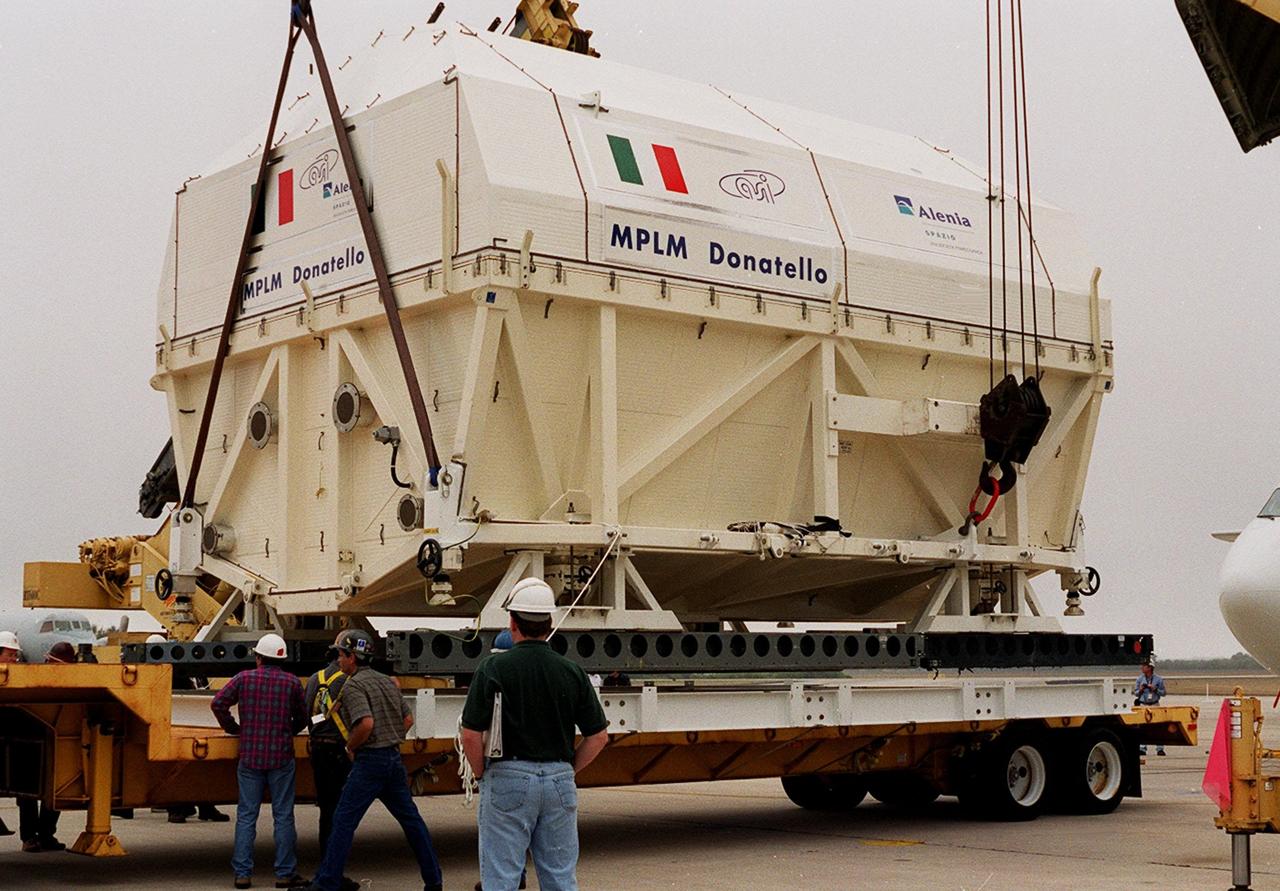
At the KSC <a href='.._.._subjects_slf.htm'> Shuttle Landing Facility<_a>, the Italian Space Agency’s <a href='.._.._subjects_mplm.htm'> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello<_a> begins rolling out of the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane that brought it from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the <a href='.._.._subjects_sspf.htm'> Space Station Processing Facility<_a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo

At the KSC <a href='.._.._subjects_slf.htm'> Shuttle Landing Facility<_a>, the Italian Space Agency’s <a href='.._.._subjects_mplm.htm'> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module<_a> Donatello rolls out of the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane that brought it from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the <a href='.._.._subjects_sspf.htm'> Space Station Processing Facility<_a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
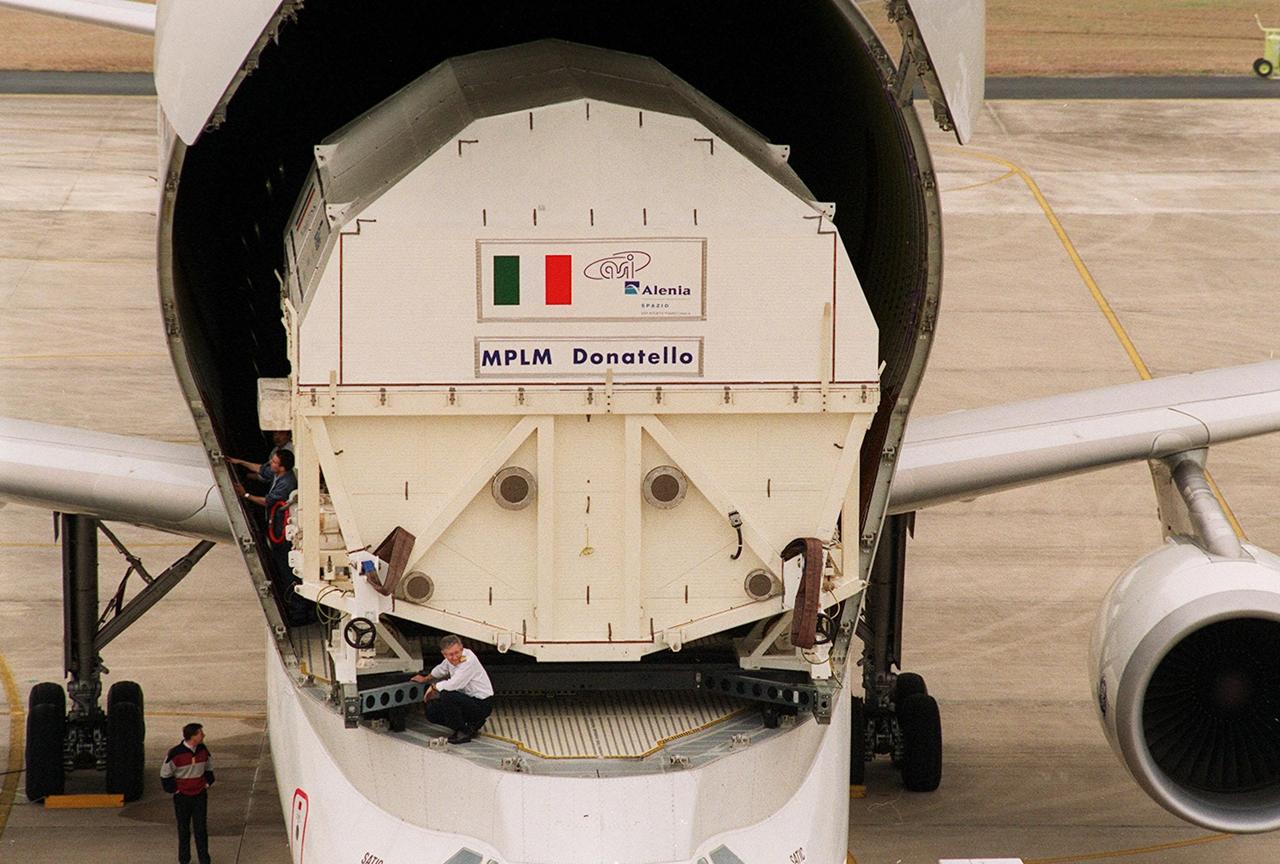

At the KSC <a href="../../subjects/slf.htm"> Shuttle Landing Facility</a>, the Italian Space Agency’s <a href="../../subjects/mplm.htm"> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello</a> begins rolling out of the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane that brought it from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the <a href="../../subjects/sspf.htm"> Space Station Processing Facility</a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
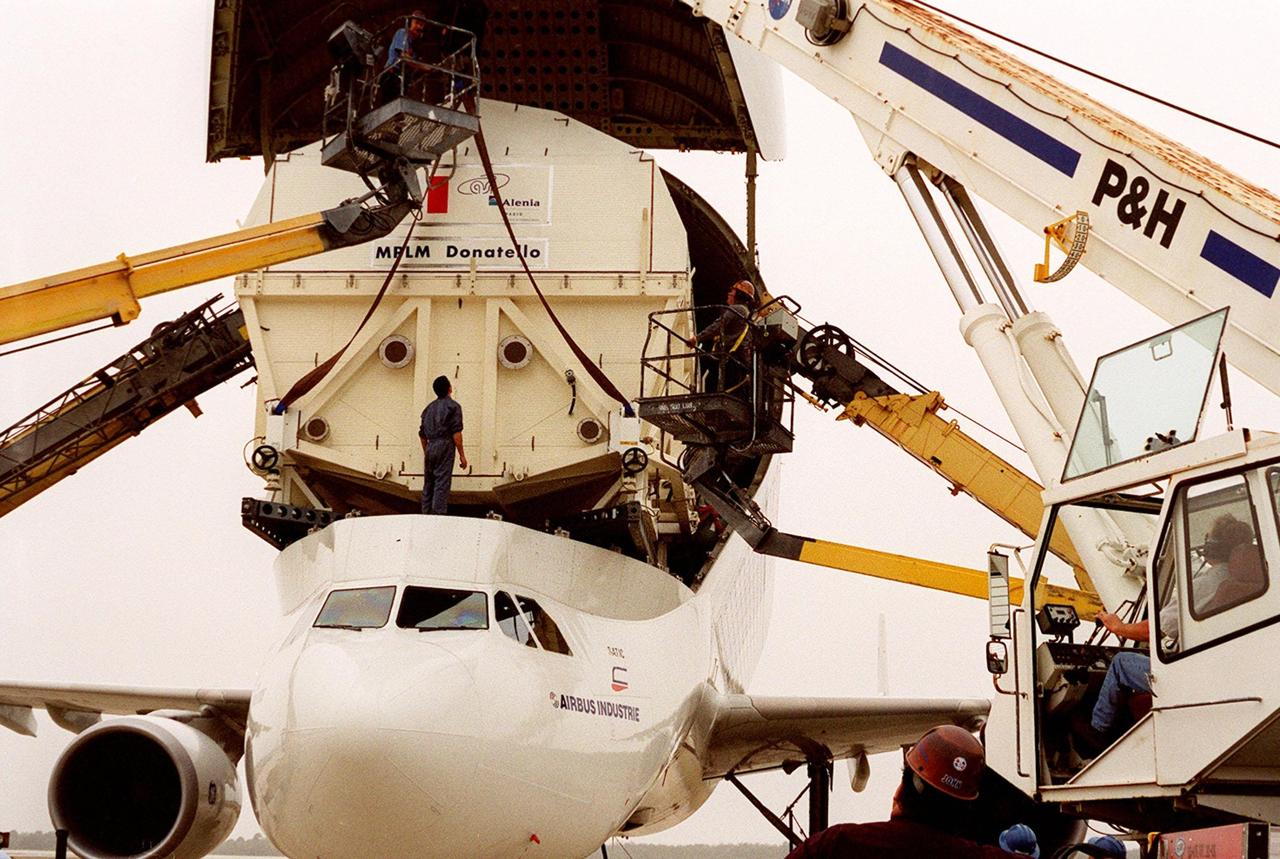

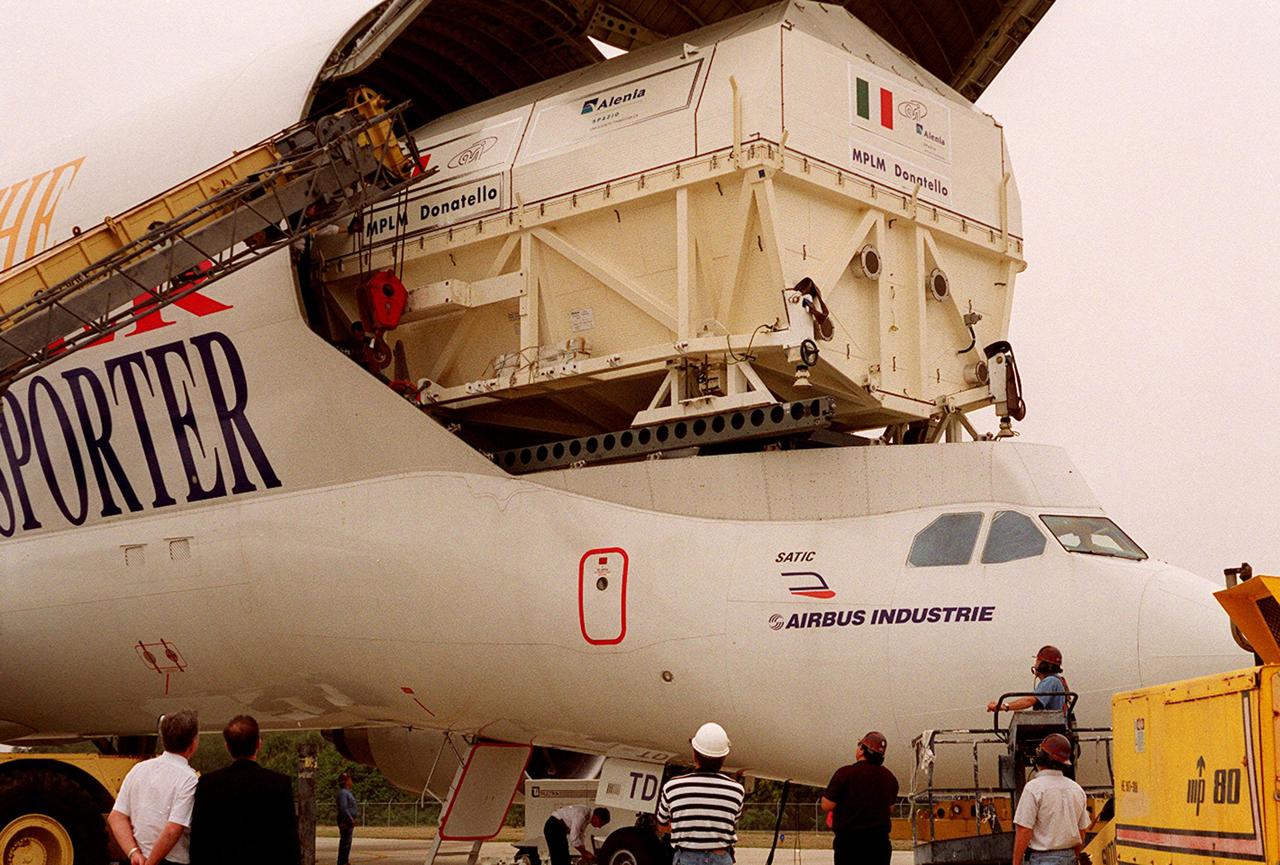
At the <a href="../../subjects/slf.htm"> Shuttle Landing Facility</a>, cranes are poised to help offload the Italian Space Agency’s <a href="../../subjects/mplm.htm"> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module</a> Donatello from the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane that brought it from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the <a href="../../subjects/iss.htm"> International Space Station</a>, the module will be transported to the <a href="../../subjects/sspf.htm"> Space Station Processing Facility</a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
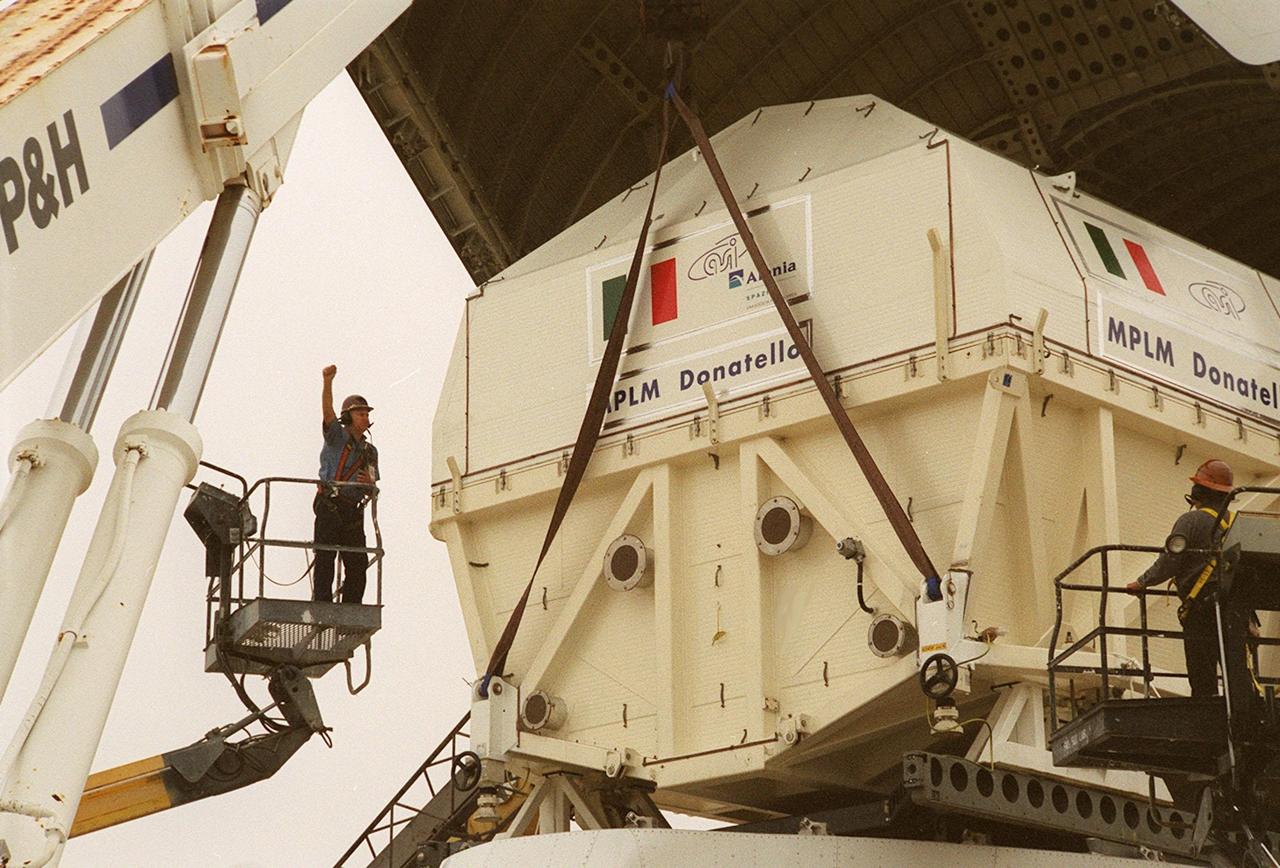

At the <a href="../../subjects/slf.htm"> Shuttle Landing Facility</a>, workers in cherry pickers (left and right) help direct the offloading of the Italian Space Agency’s <a href="../../subjects/mplm.htm"> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module</a> Donatello from the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane that brought it from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the <a href="../../subjects/sspf.htm"> Space Station Processing Facility</a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
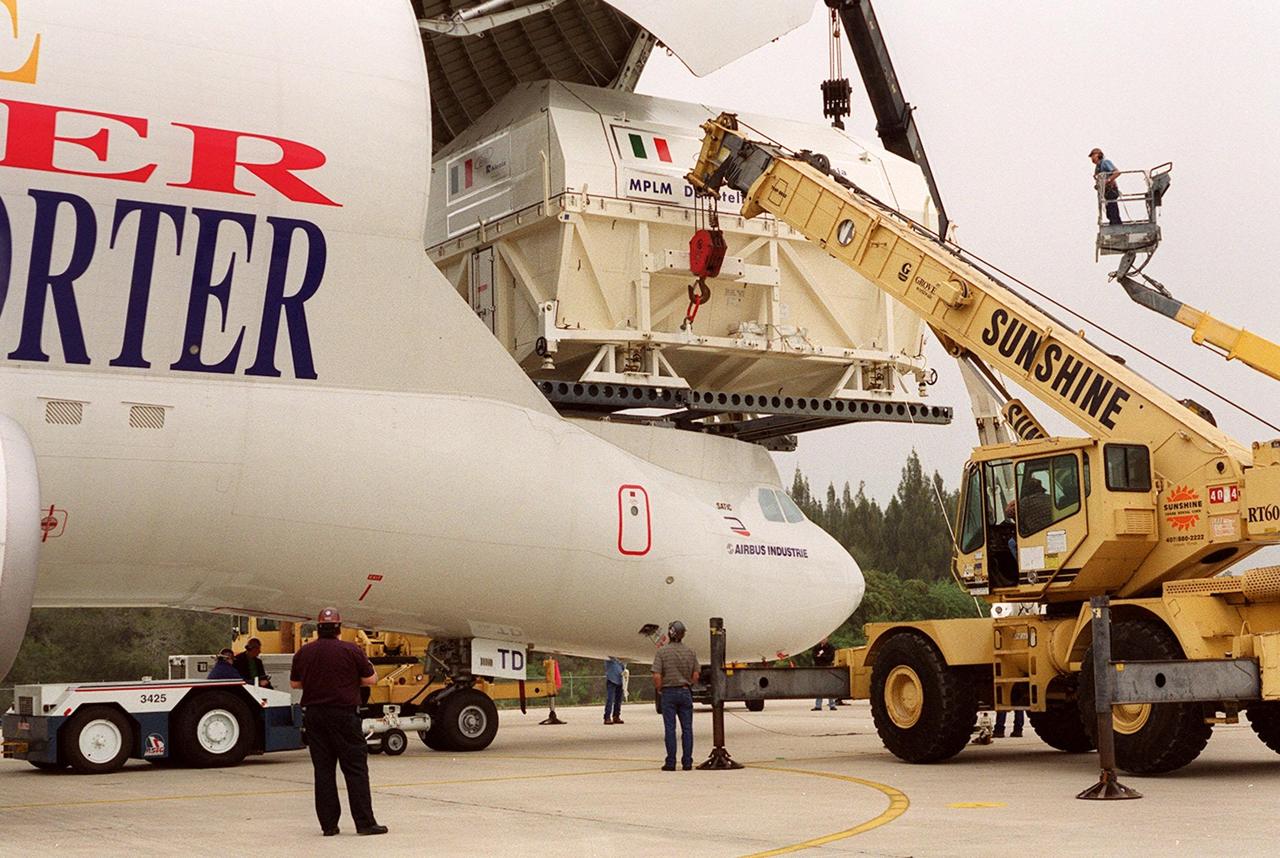

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, workers in cherry pickers (right) help guide offloading of the Italian Space Agency’s Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello from the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane that brought it from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
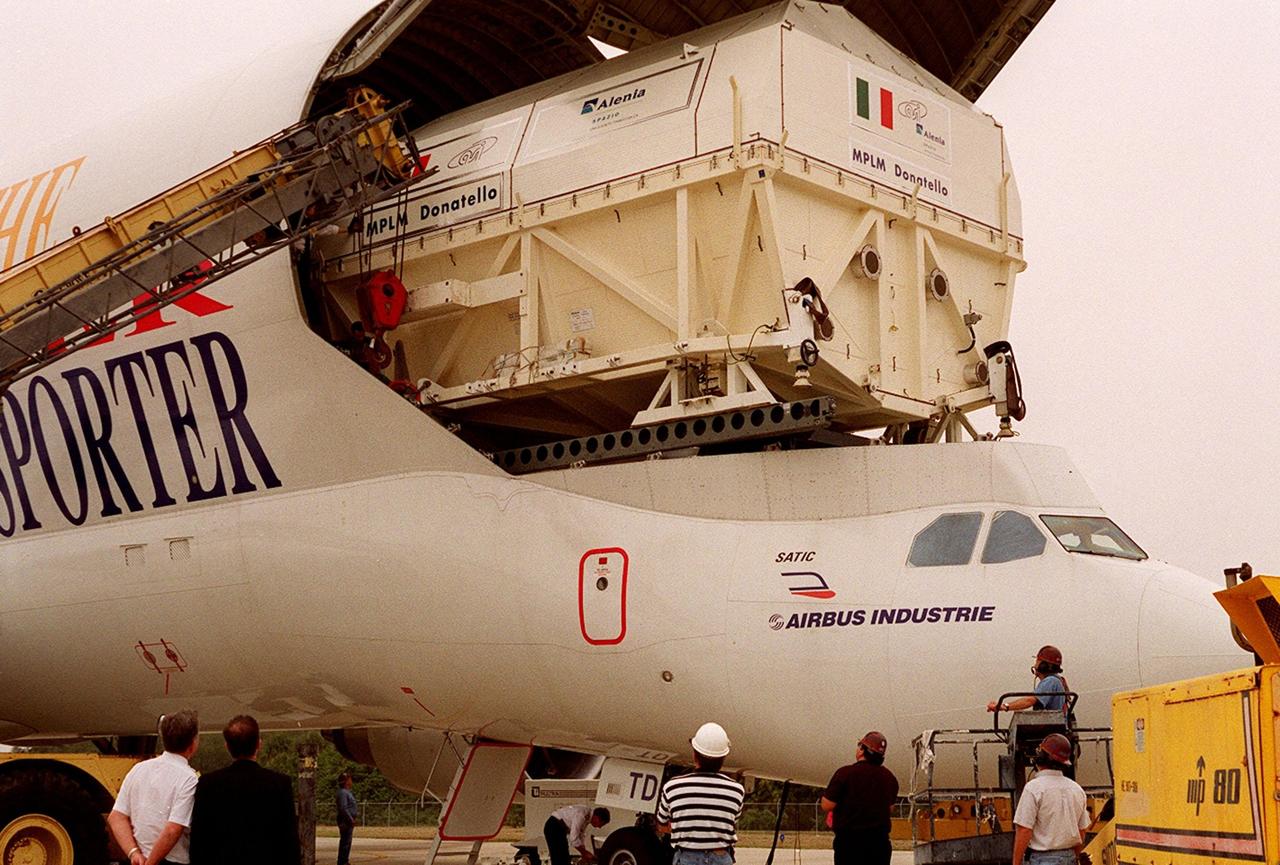

At the KSC <a href="../../subjects/slf.htm"> Shuttle Landing Facility</a>, the Italian Space Agency’s <a href="../../subjects/mplm.htm"> Multi-Purpose Logistics Module</a> Donatello rolls out of the Airbus “Beluga” air cargo plane that brought it from the factory of Alenia Aerospazio in Turin, Italy. The third of three for the International Space Station, the module will be transported to the <a href="../../subjects/sspf.htm"> Space Station Processing Facility</a> for processing. Among the activities for the payload test team are integrated electrical tests with other Station elements in the SSPF, leak tests, electrical and software compatibility tests with the Space Shuttle (using the Cargo Integrated Test equipment) and an Interface Verification Test once the module is installed in the Space Shuttle’s payload bay at the launch pad. The most significant mechanical task to be performed on Donatello in the SSPF is the installation and outfitting of the racks for carrying the various experiments and cargo
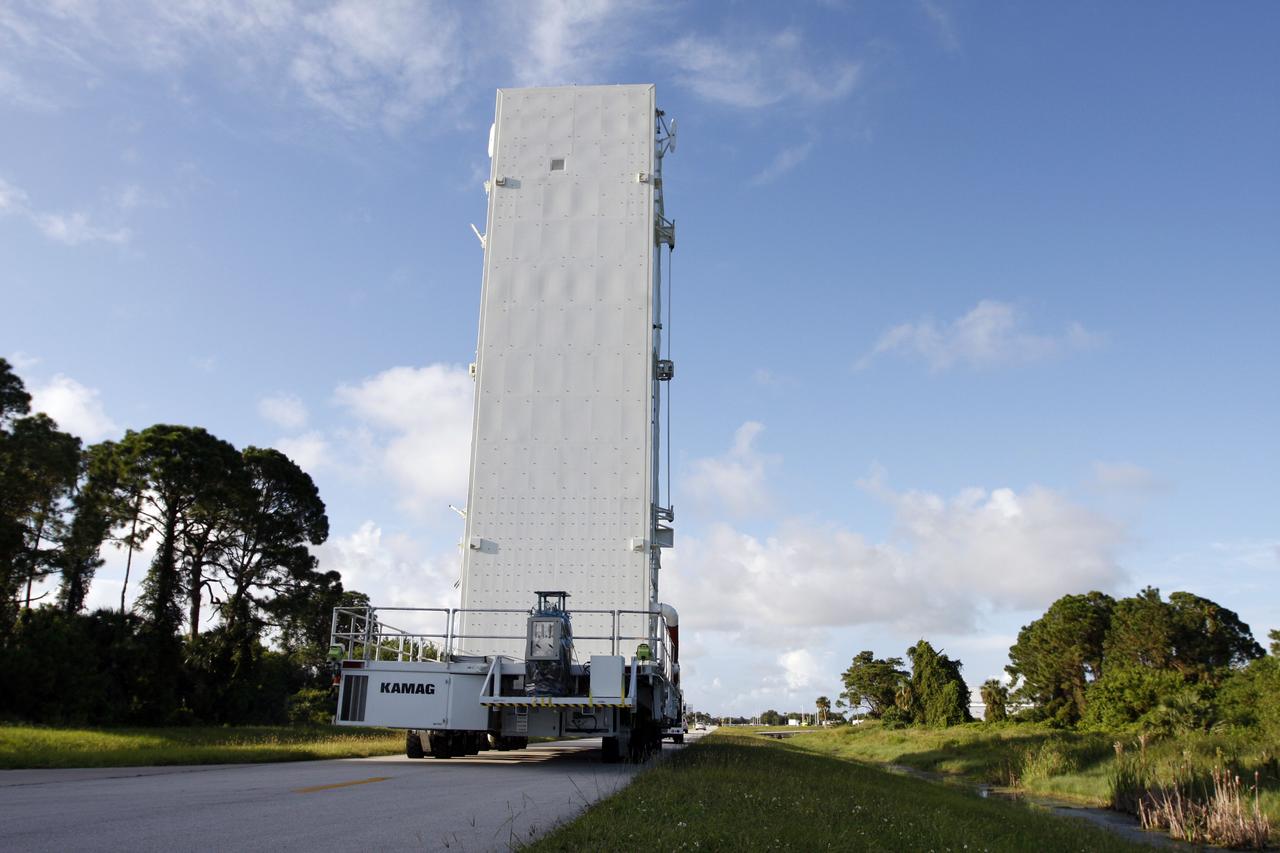

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister makes its way from the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Launch Pad 39A. It carries a cargo of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
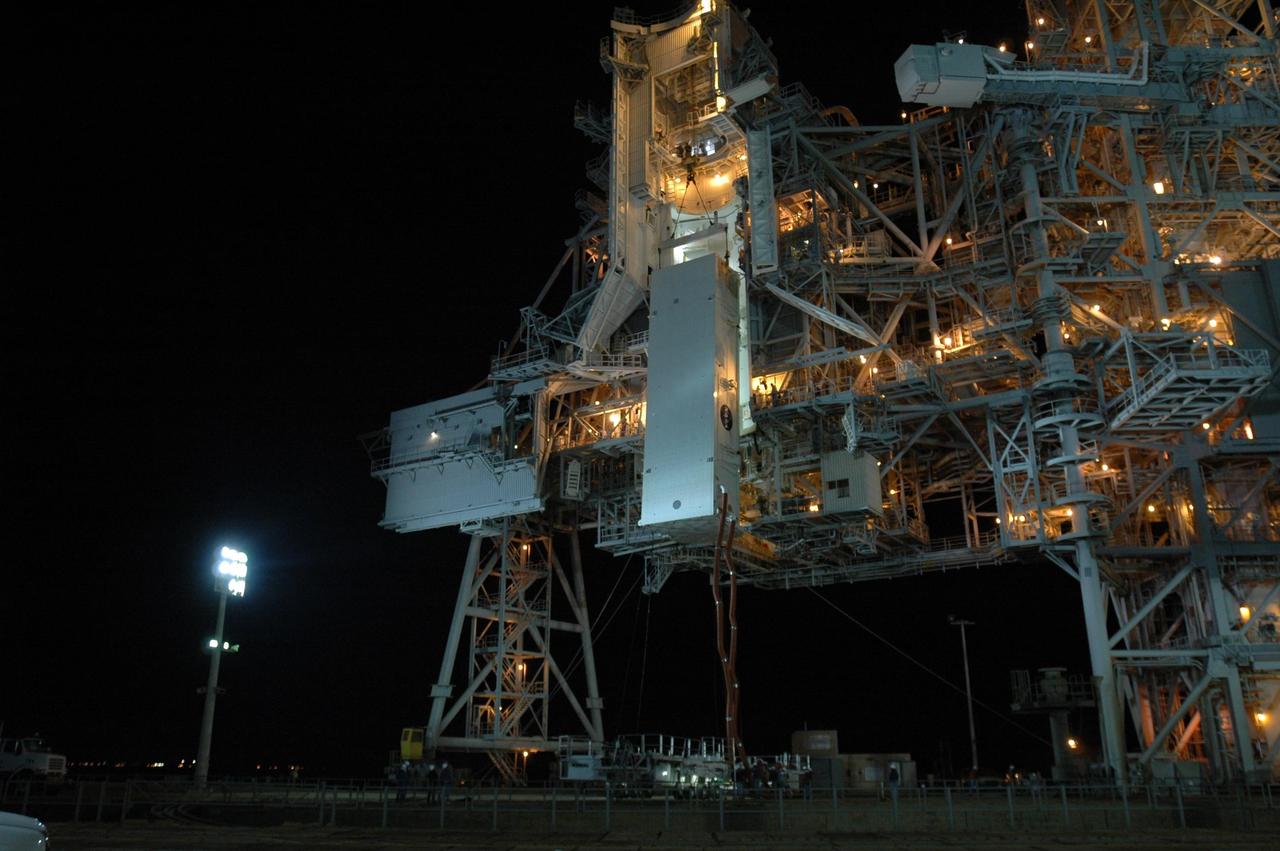

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister containing the Columbus Laboratory module and integrated cargo carrier-lite is lifted up toward the payload changeout room on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Once in place, the canister will be opened and the cargo transferred inside the payload changeout room. The payload will be installed in space shuttle Atlantis' payload bay.The canister contains the Columbus Lab module and integrated cargo carrier-lite payloads for space shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-122. Atlantis is targeted to launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is in the Canister Rotation Facility where it will be lifted to a vertical position. Workers check the umbilical lines that keep a controlled environment in the canister. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers check cable fittings that will lift the payload canister to a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister moves out of the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida heading for Launch Pad 39A. It carries a cargo of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
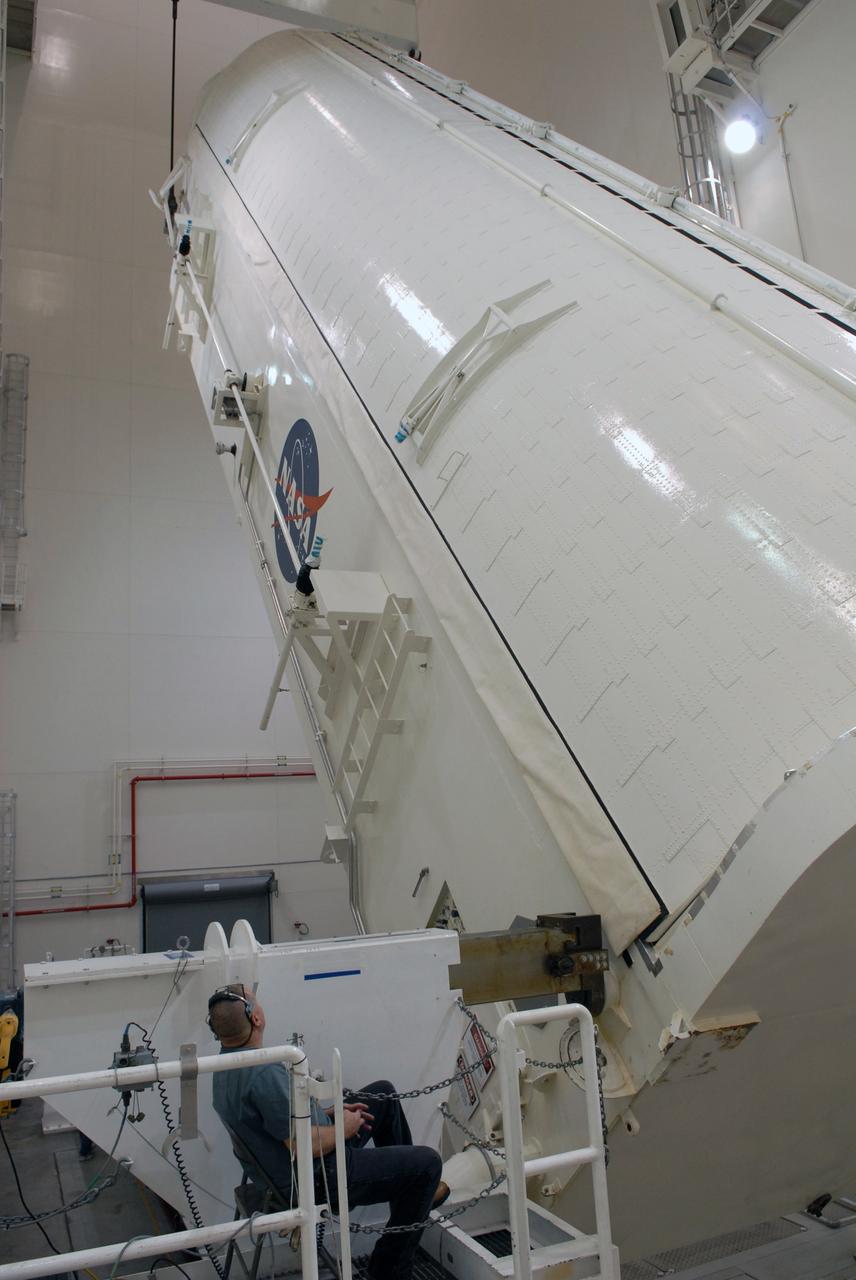

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is lifted toward a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
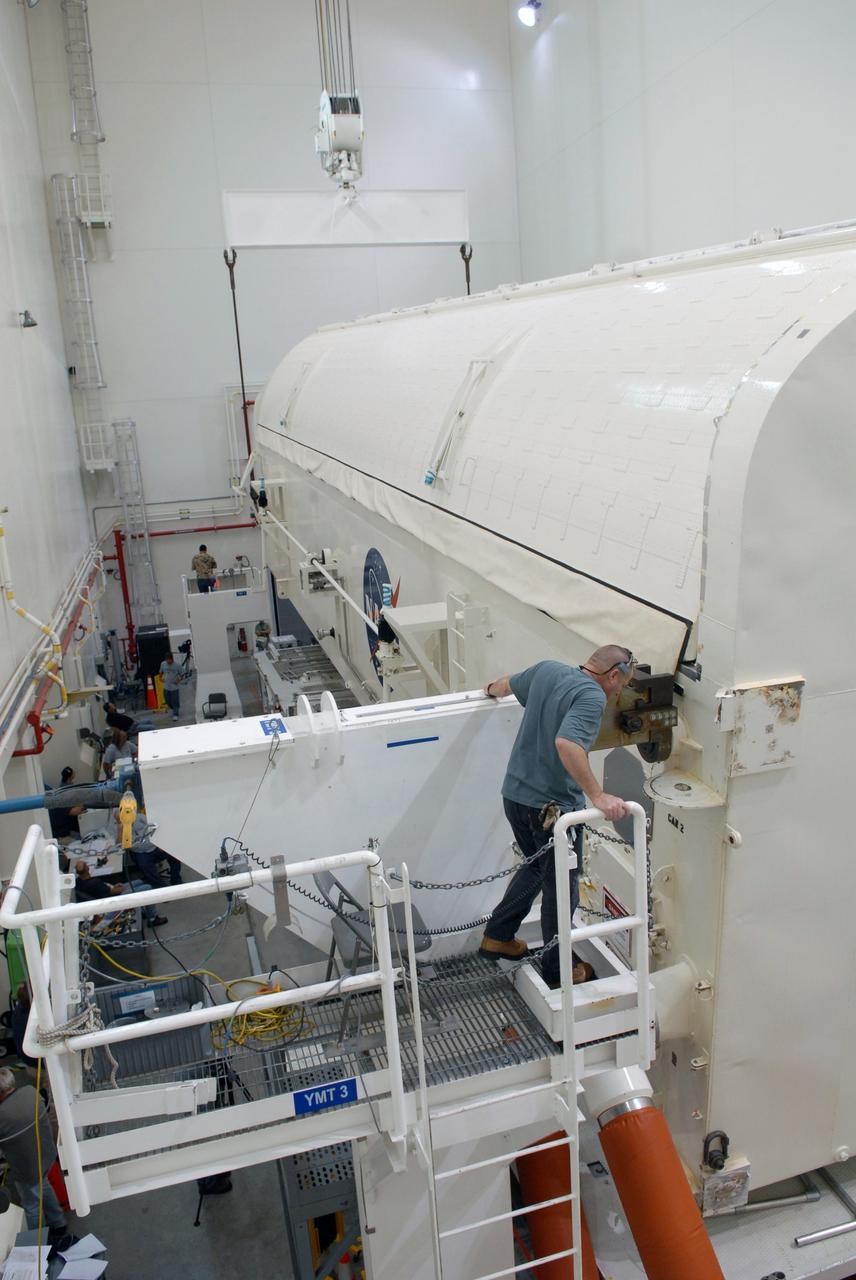

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers get ready to lift the payload canister to a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
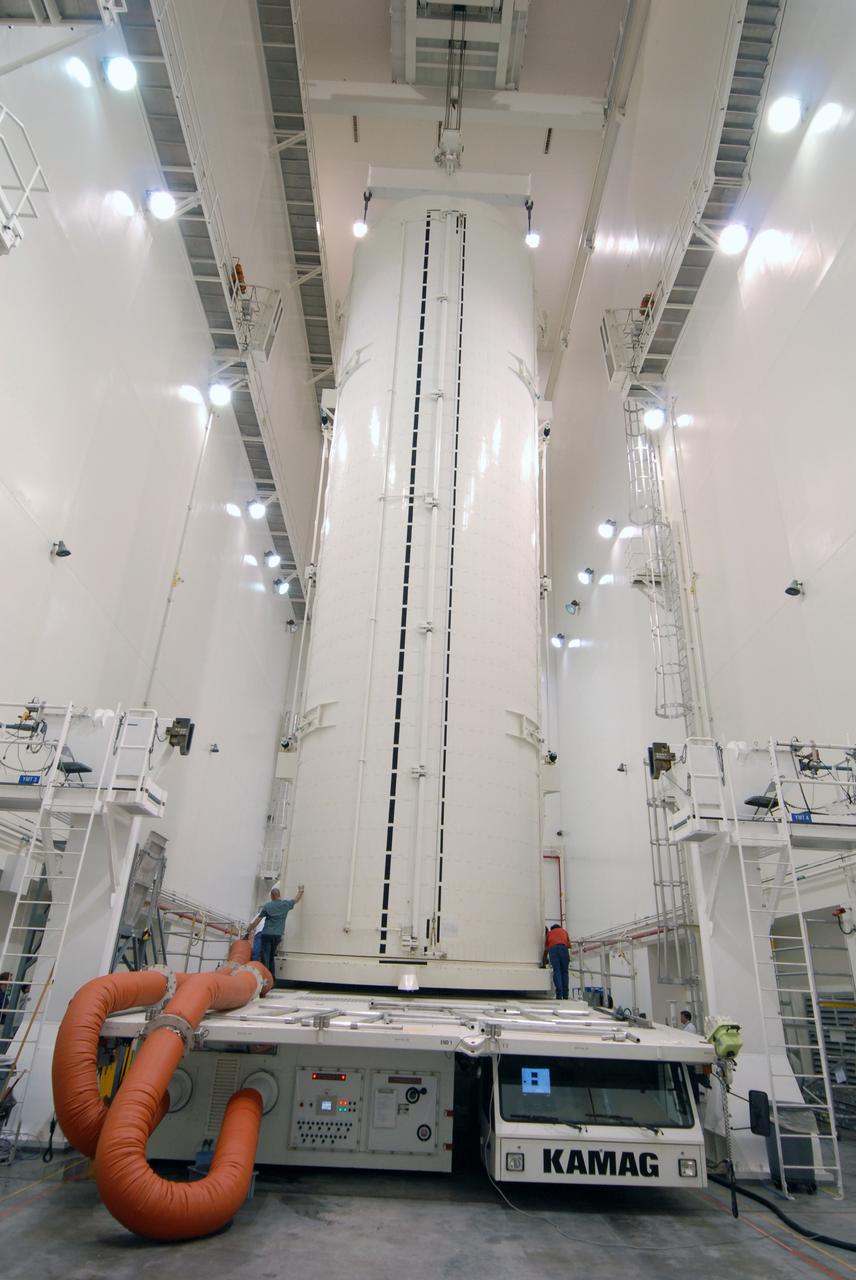

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is in a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
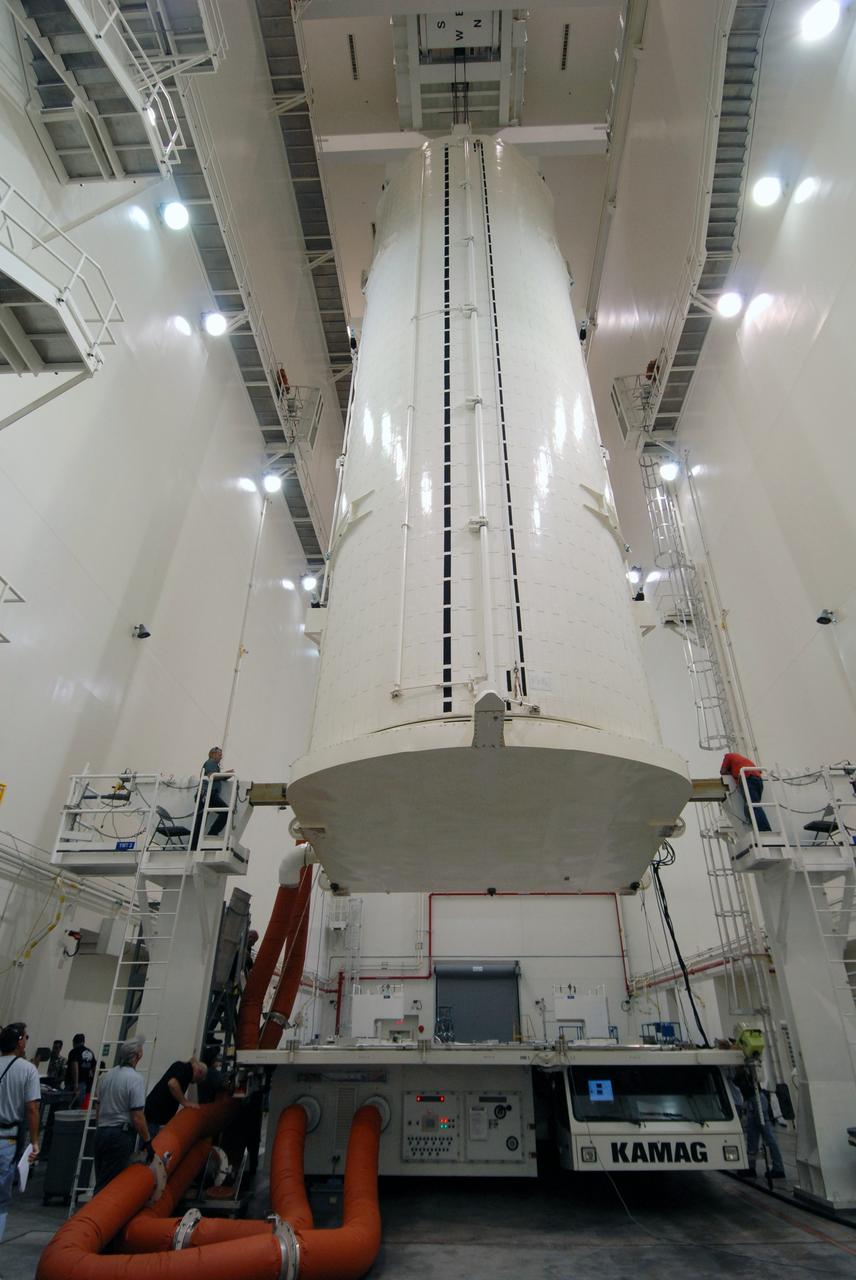

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is lifted to a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is lifted toward a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On its way to Launch Pad 39A, the payload canister passes the Vehicle Assembly Building and Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The canister carries a cargo of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers check the umbilical lines that keep a controlled environment in the payload canister. The canister will be lifted to a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers get ready to lift the payload canister to a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is lifted toward a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Astrotech payload processing facility at Port Canaveral, Fla., supplies and other cargo are prepared for installation in the Russian-built Mini-Research Module, or MRM, in the background. The six-member crew of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-132 mission will deliver an Integrated Cargo Carrier and the MRM to the International Space Station. The second in a series of new pressurized components for Russia, the MRM will be permanently attached to the bottom port of the Zarya module. The MRM also will carry U.S. pressurized cargo. STS-132 is the 34th mission to the station and the 132nd space shuttle mission. Launch is targeted for May 14. For information on the STS-132 mission, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister moves out of the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida heading for Launch Pad 39A. It carries a cargo of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister is in a vertical position for the trip to Launch Pad 39A. The canister’s cargo consists of four carriers holding various equipment for the STS-125 mission aboard space shuttle Atlantis to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. At the pad, the cargo will be moved into the Payload Changeout Room. The changeout room is the enclosed, environmentally controlled portion of the rotating service structure that supports cargo delivery to the pad and subsequent vertical installation into the shuttle’s payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
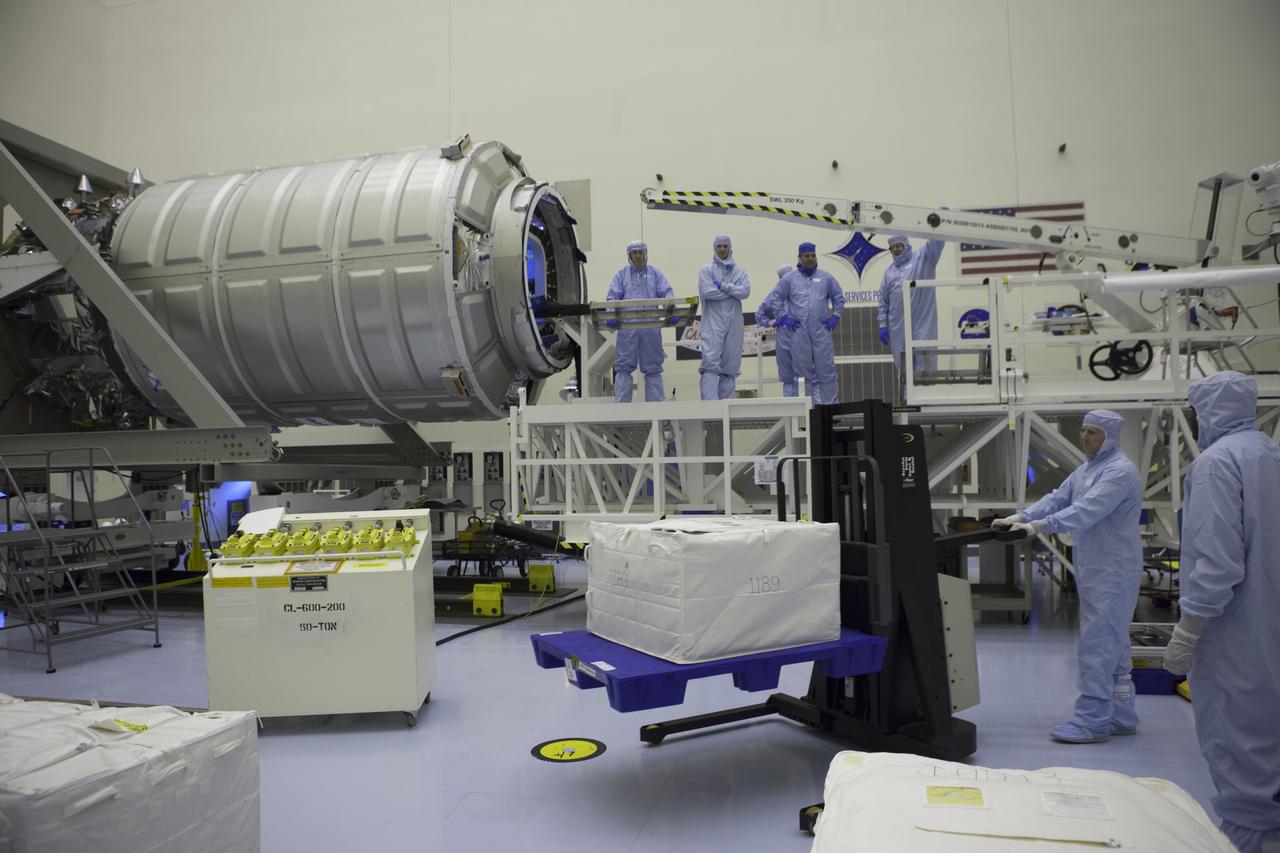

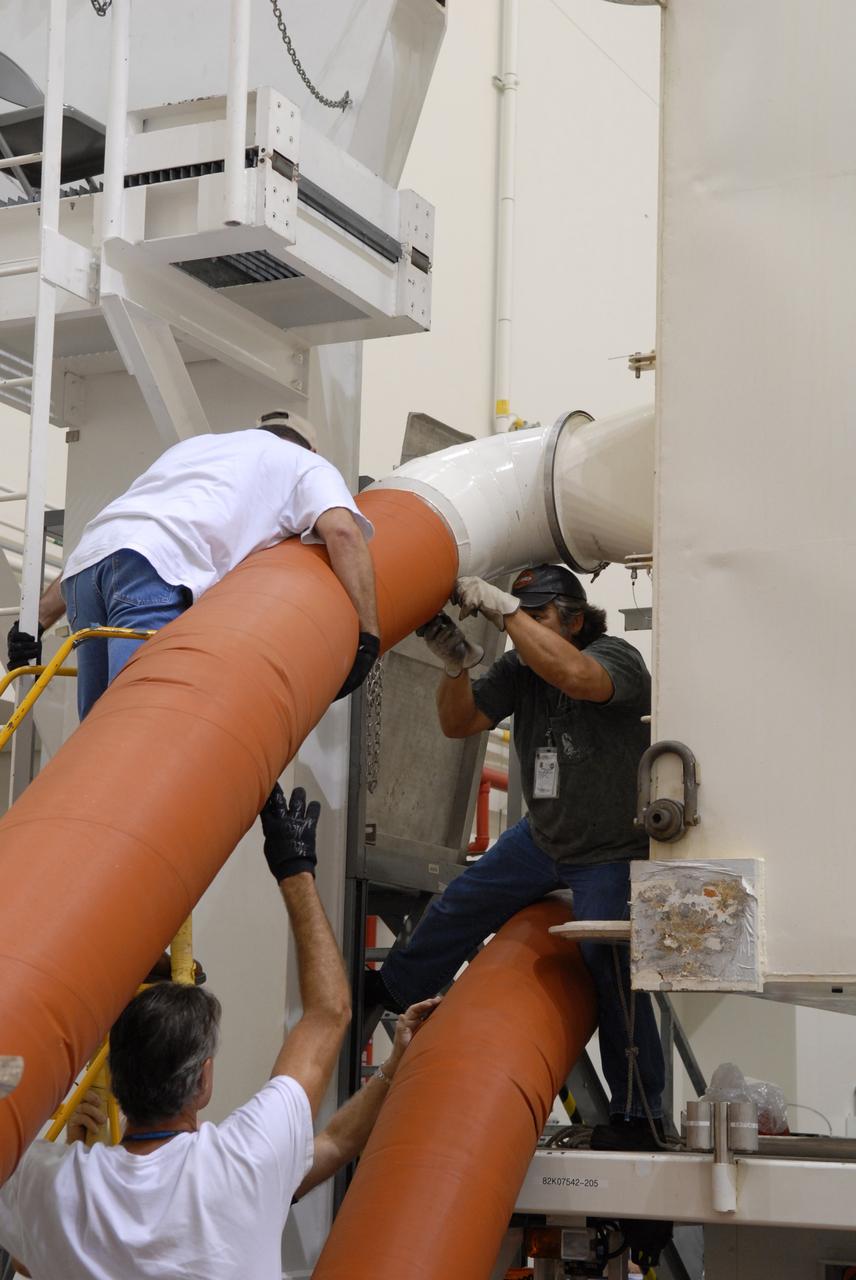
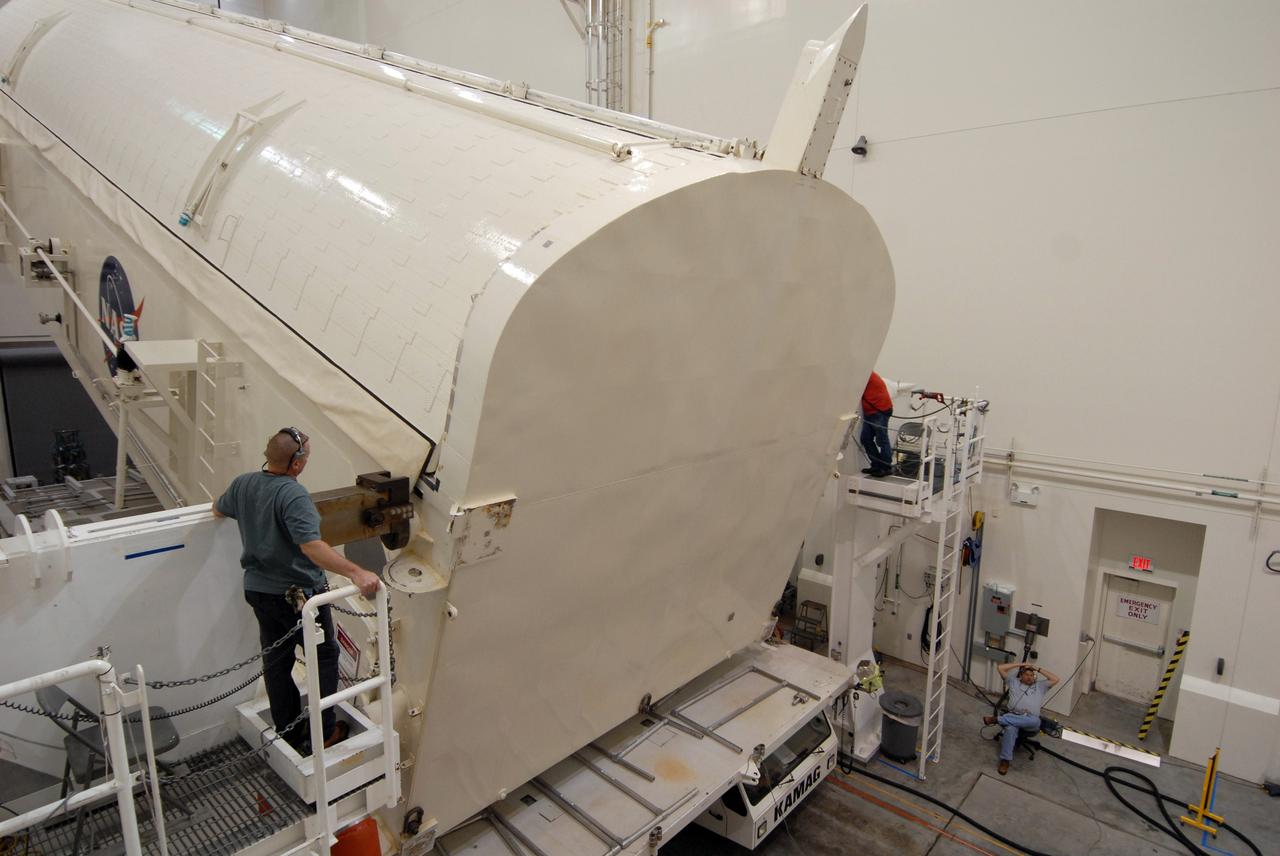
Technicians are positioned at the hatch of the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module as a forklift moves a cargo package into position for installation into the spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22
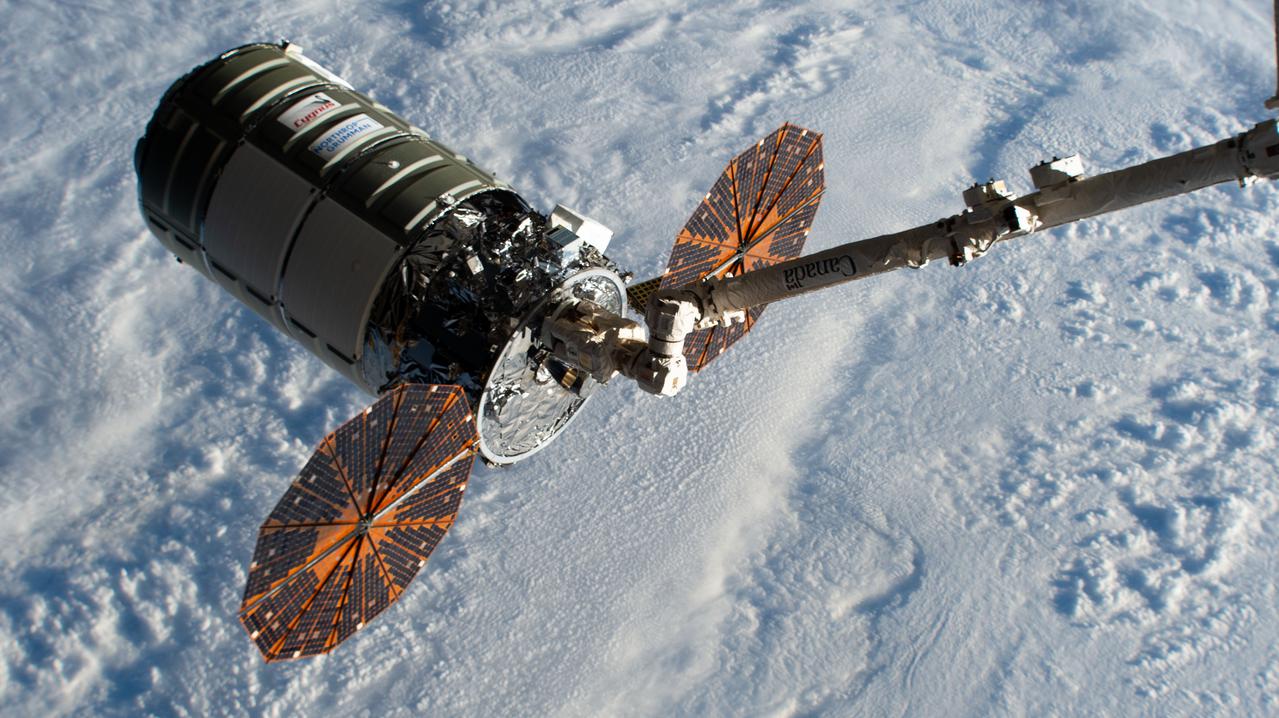

iss066e147592 (Feb. 21, 2022) --- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus space freighter is pictured in the grip of the Canadarm2 robotic arm moments after NASA astronaut Raja Chari commanded it to capture the U.S. cargo craft. Robotics controllers on the ground would take over shortly afterward and remotely guide the Canadarm2 with Cygnus attached and install it to the Unity module to begin three months of cargo operations. This is Northrop Grumman’s 17th contracted resupply mission under the second Commercial Resupply Services contract with NASA.
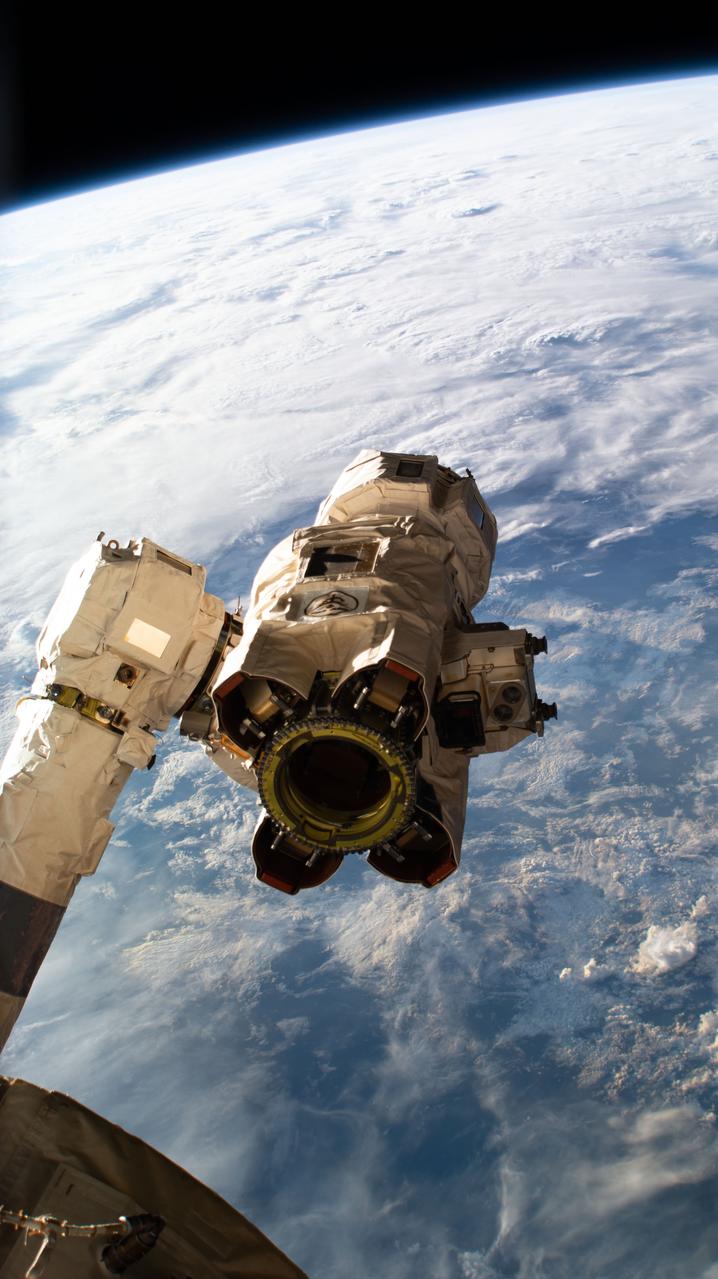

iss067e043497 (May 13, 2022) --- The Leading End Effector (LEE) is the portion of the Canadarm2 robotic arm that captures visiting cargo craft such as Northrop Grumman's Cygnus space freighter when commanded by an astronaut aboard the International Space Station. Mission controllers on the ground then take over and remotely guide the Canadarm2, with the captured cargo craft in the LEE's grip, and carefully install the vehicle to common berthing mechanisms on the orbiting lab.
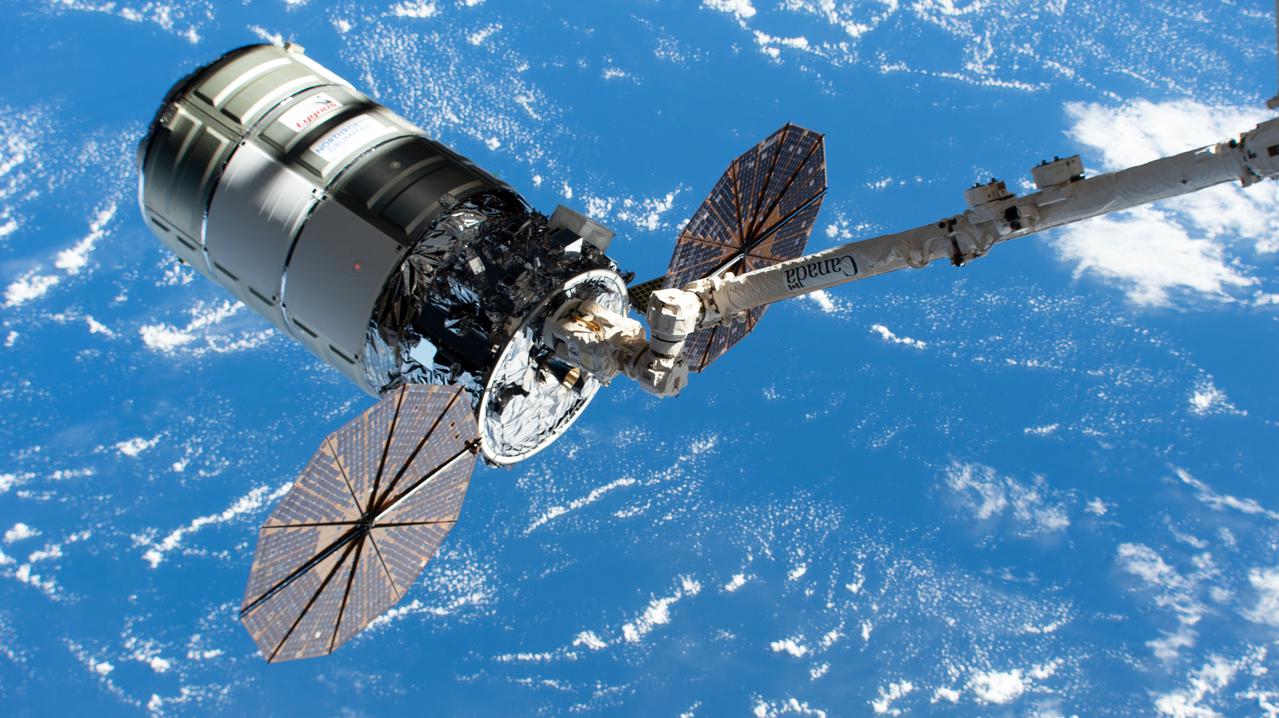

iss066e147590 (Feb. 21, 2022) --- Northrop Grumman's Cygnus space freighter is pictured in the grip of the Canadarm2 robotic arm moments after NASA astronaut Raja Chari commanded it to capture the U.S. cargo craft. Robotics controllers on the ground would take over shortly afterward and remotely guide the Canadarm2 with Cygnus attached and install it to the Unity module to begin three months of cargo operations. This is Northrop Grumman’s 17th contracted resupply mission under the second Commercial Resupply Services contract with NASA.
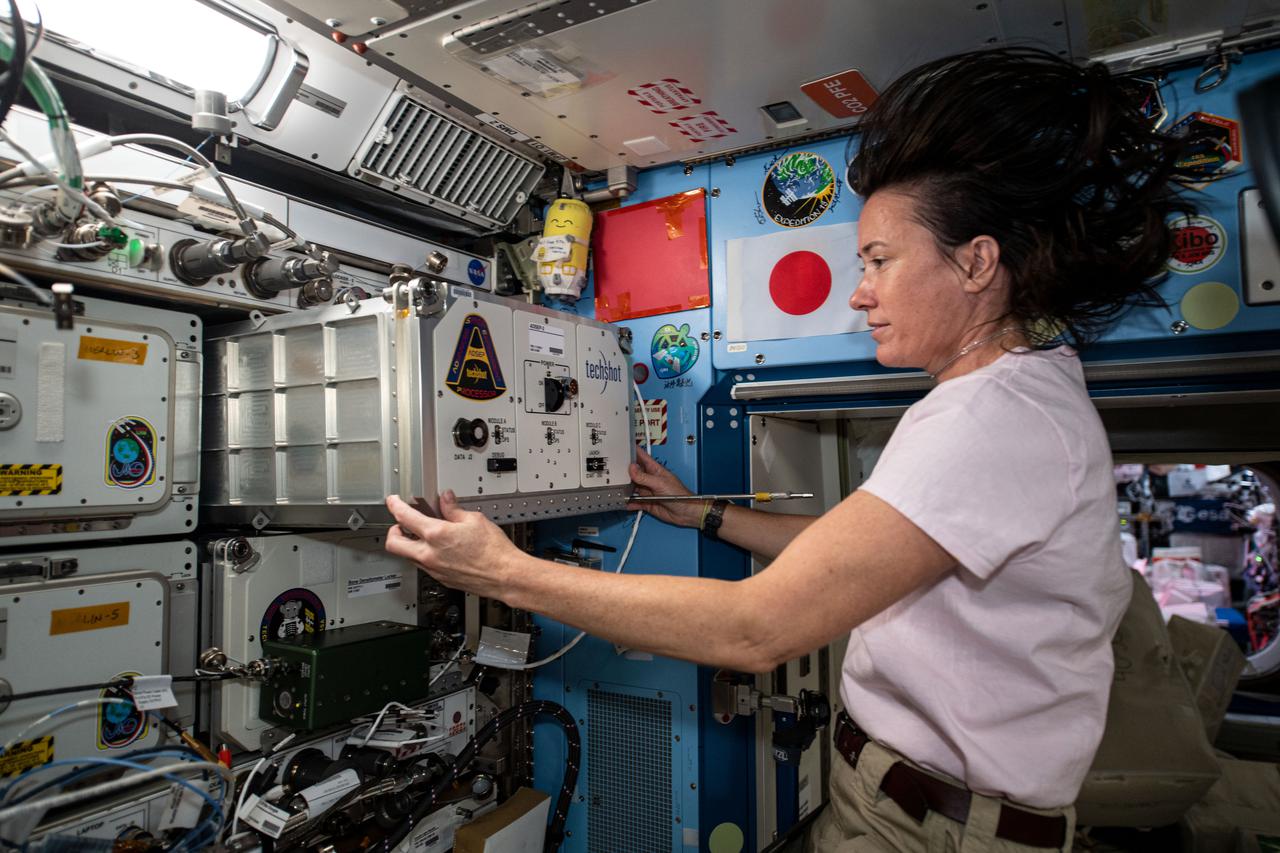

iss065e093499 (June 7, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur installs a new research device, recently delivered aboard the SpaceX Cargo Dragon vehicle, inside the Kibo laboratory module. Known as the ADSEP-2, or Advanced Space Experiment Processor-2, the science facility supports observations of biological or physical samples and can also be operated aboard the Cargo Dragon and Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply ships.
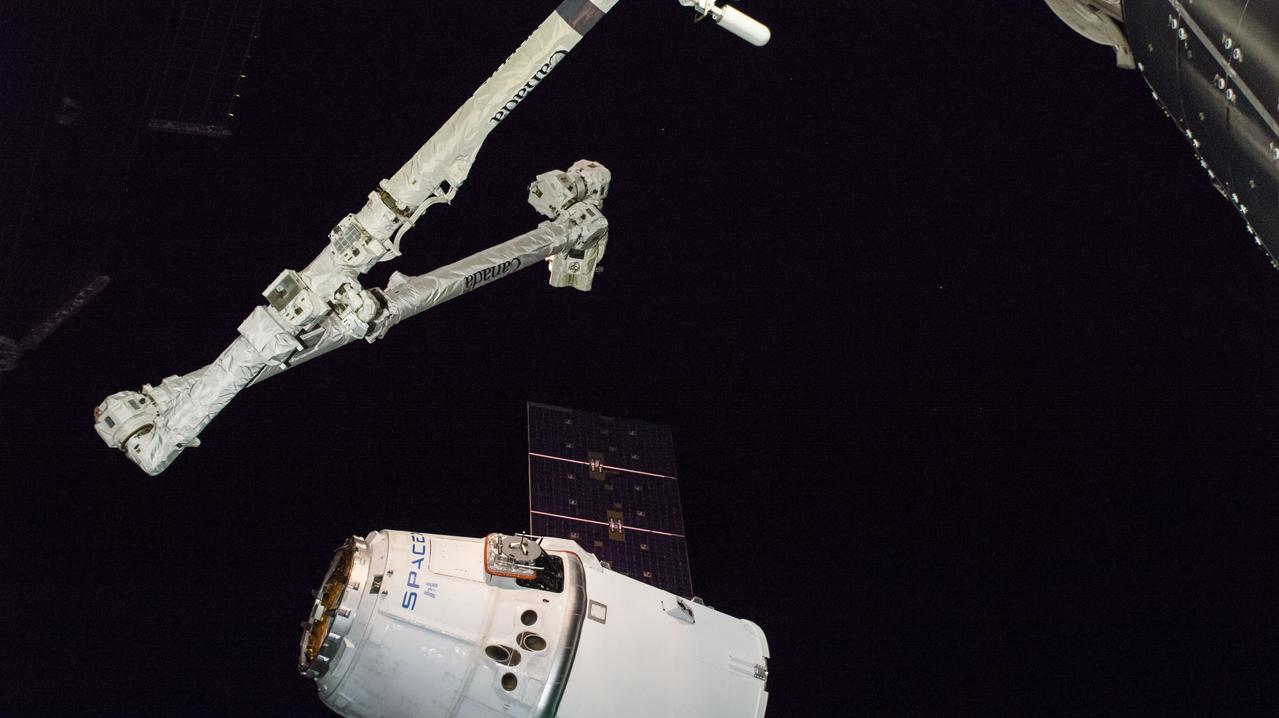

iss057e115434 (Dec. 8, 2018) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm, operated by astronauts Alexander Gerst and Serena Auñón-Chancellor, slowly reaches out to grapple the SpaceX Dragon cargo craft. Dragon, packed with over 5,600 pounds of cargo, completed a three-day trip to the International Space Station that began with a launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and ended with its installation and hatch opening on the Harmony module..
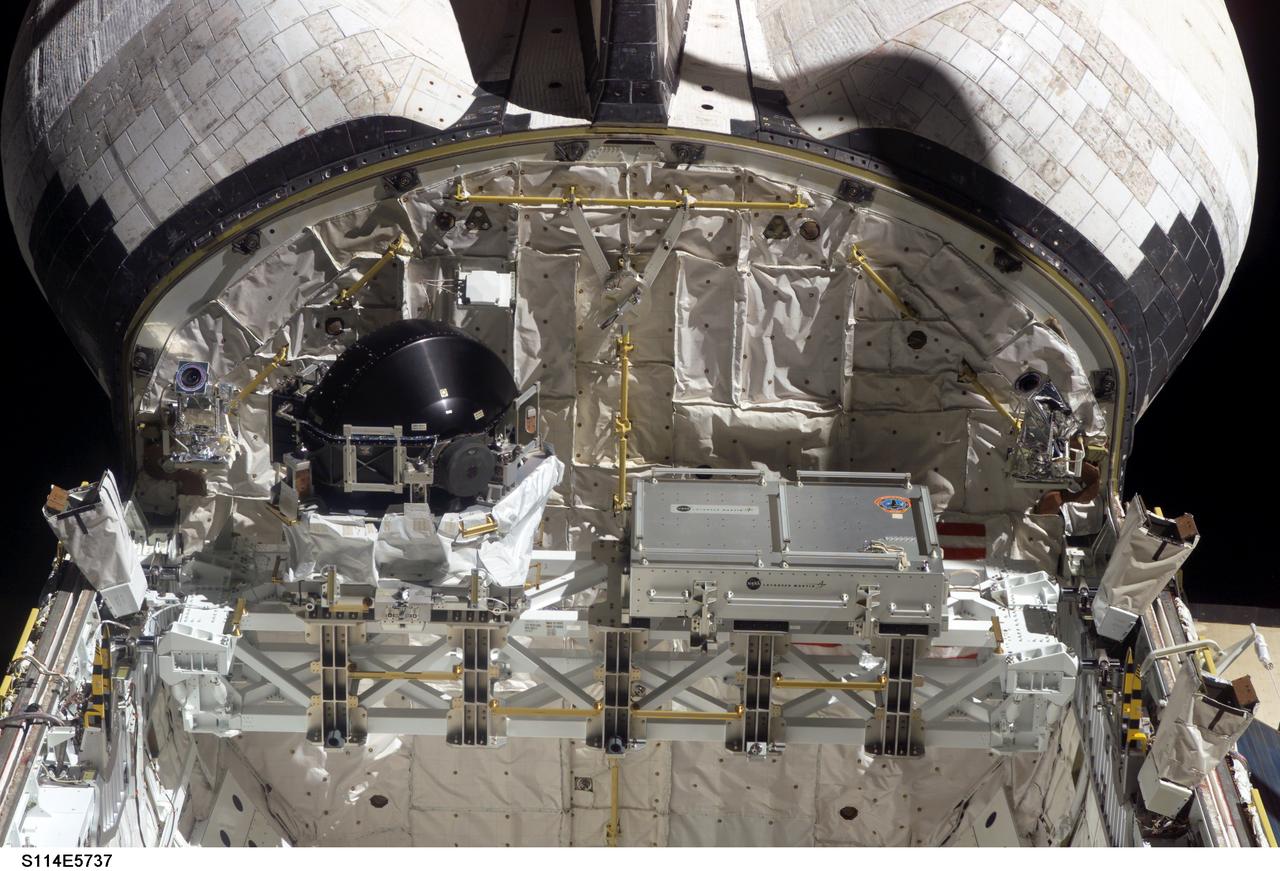

S114-E-5737 (29 July 2005) --- This high angle view of the aft end of Discovery's cargo bay in Earth orbit was taken from the International Space Station to which the Space Shuttle was docked at the time. The control moment gyro (CMG) replacement article, to be installed on an upcoming space walk, is on the left side of the frame.
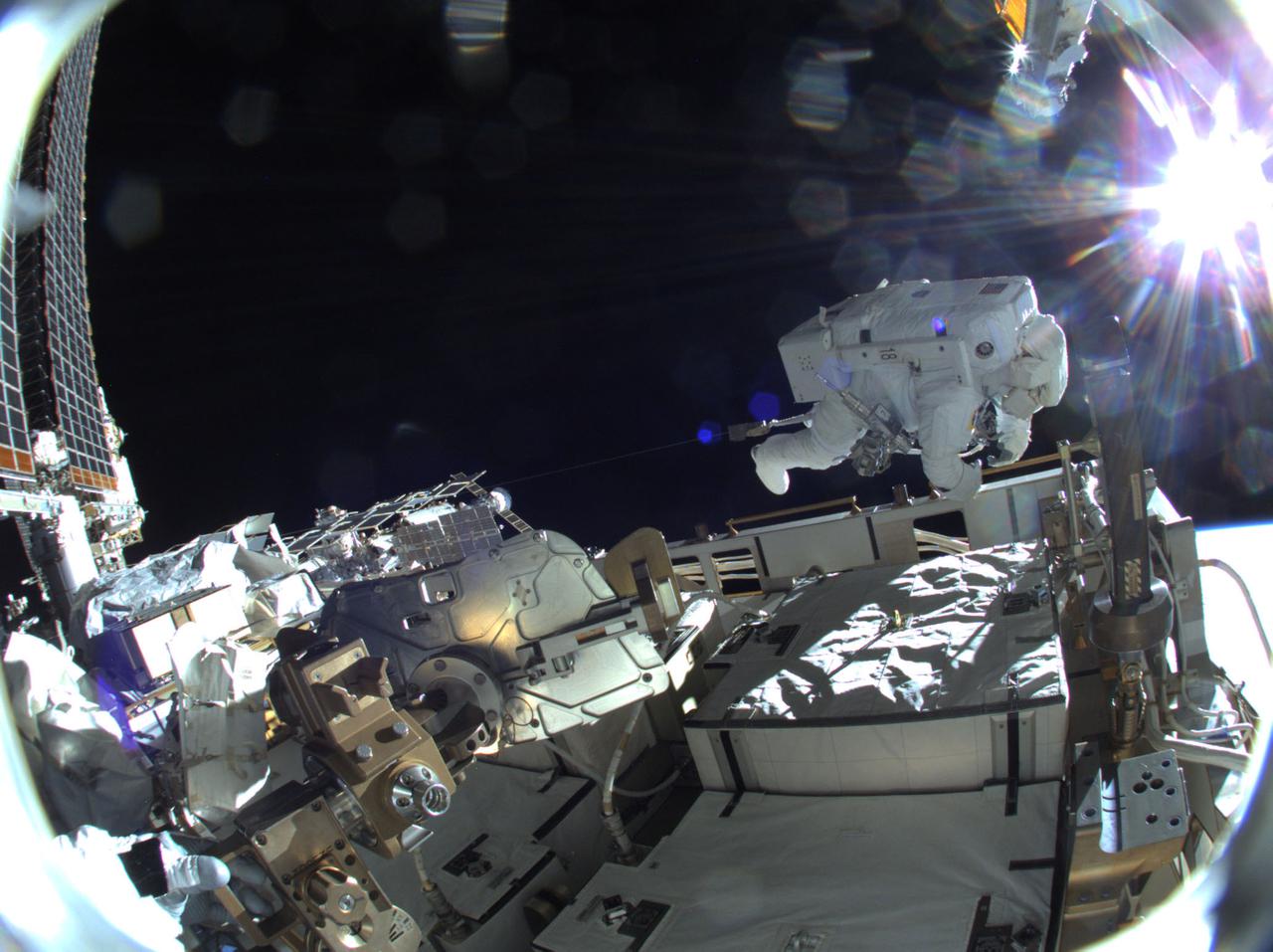

iss064e040058 (March 5, 2021) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Soichi Noguchi is pictured during a spacewalk to install solar array modification kits to ready the International Space Station for newer, more powerful solar arrays being delivered on upcoming SpaceX Dragon cargo missions.
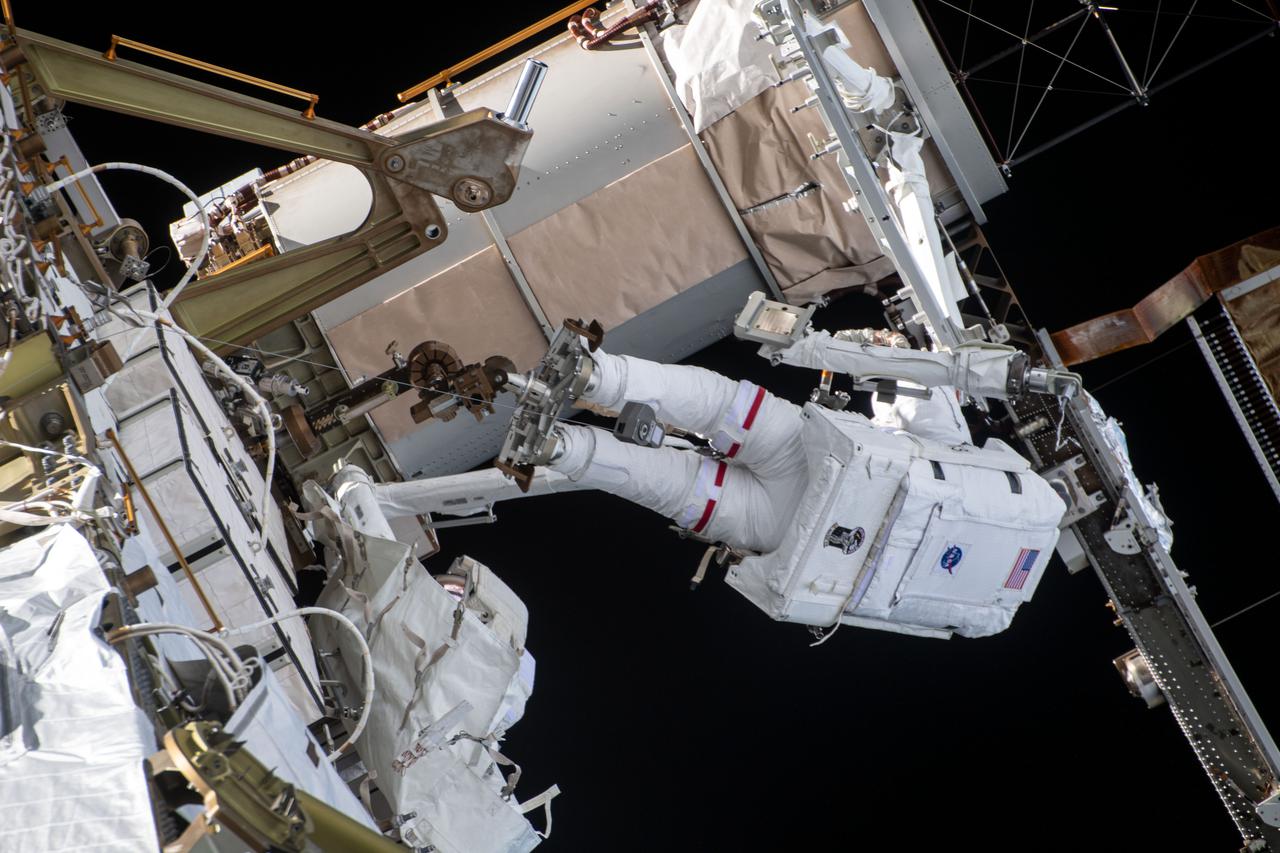

iss064e039827 (March 5, 2021) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins (at top) is pictured during a spacewalk to install solar array modification kits to ready the International Space Station for newer, more powerful solar arrays being delivered on upcoming SpaceX Dragon cargo missions.
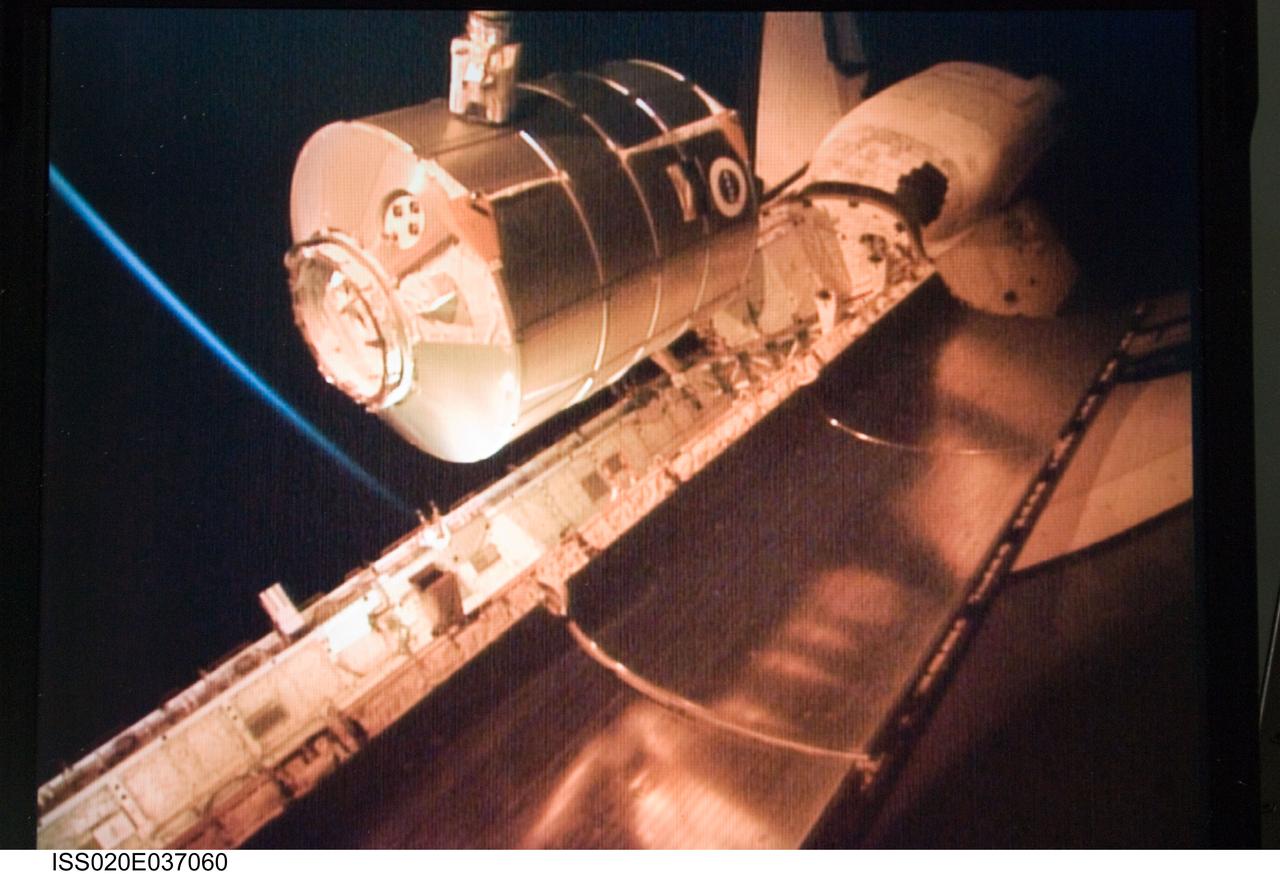
ISS020-E-037060 (31 Aug. 2009) --- Viewed from a computer monitor, the International Space Station’s robotic Canadarm2 unberths the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module from Space Shuttle Discovery’s (STS-128) cargo bay for installation on the nadir port of the station’s Harmony node.
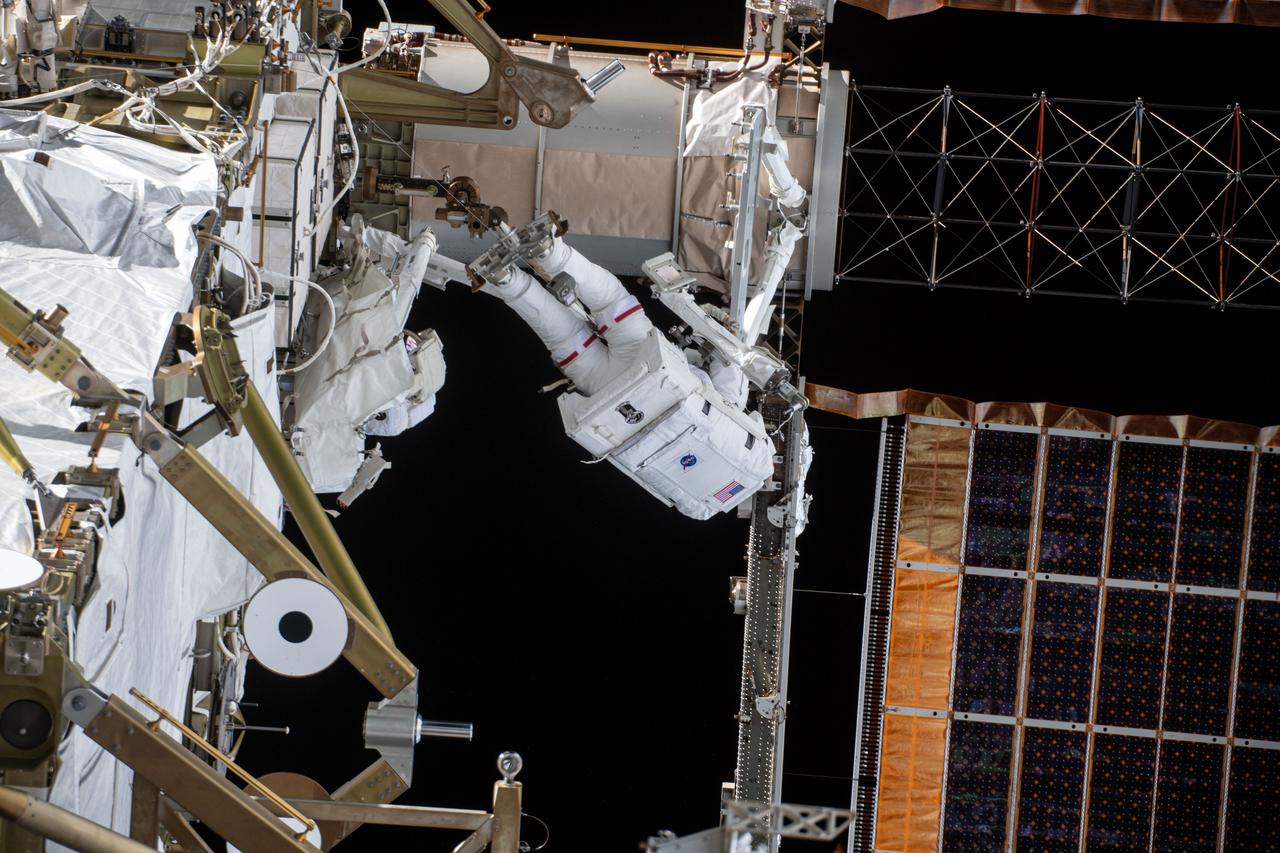

iss064e039836 (March 5, 2021) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is pictured during a spacewalk to install solar array modification kits to ready the International Space Station for newer, more powerful solar arrays being delivered on upcoming SpaceX Dragon cargo missions.
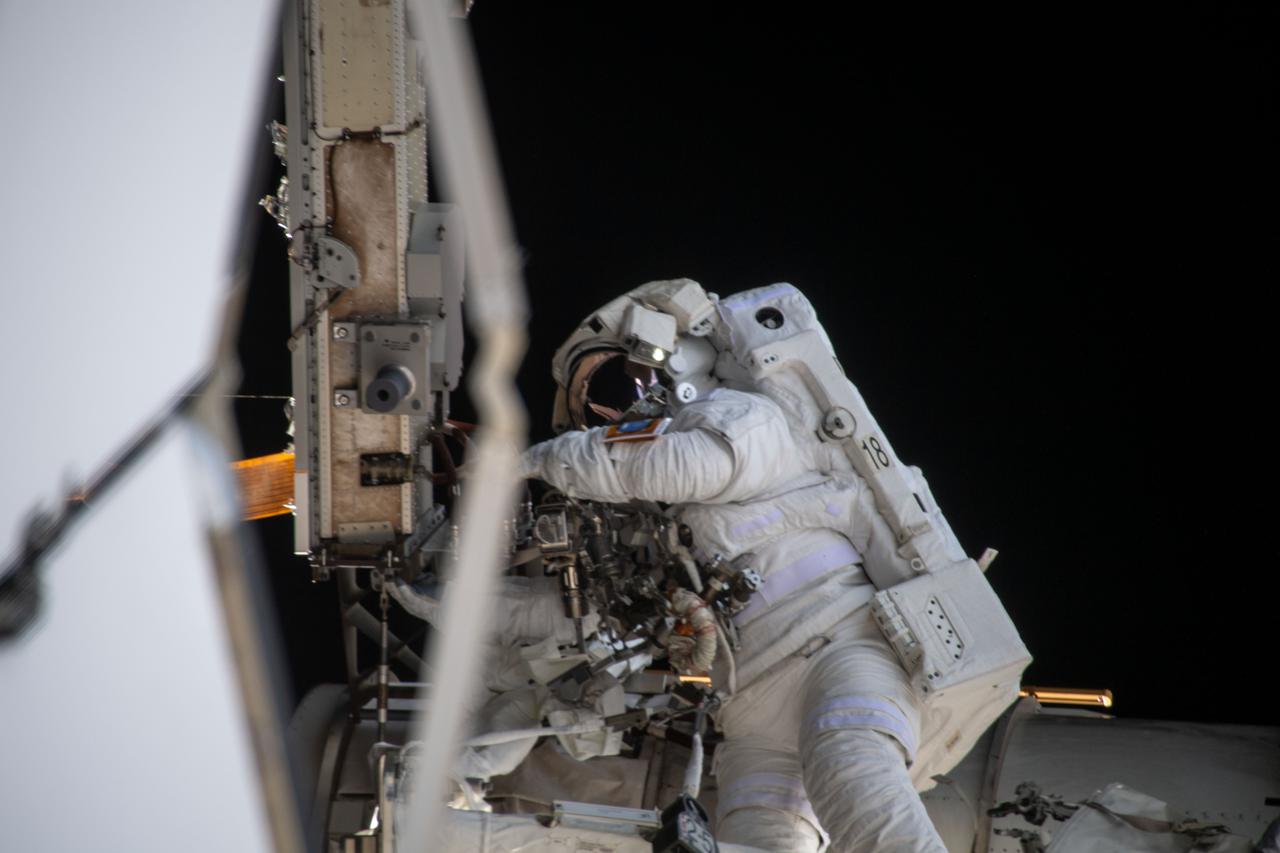

iss064e039894 (March 5, 2021) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Soichi Noguchi is pictured during a spacewalk to install solar array modification kits to ready the International Space Station for newer, more powerful solar arrays being delivered on upcoming SpaceX Dragon cargo missions.
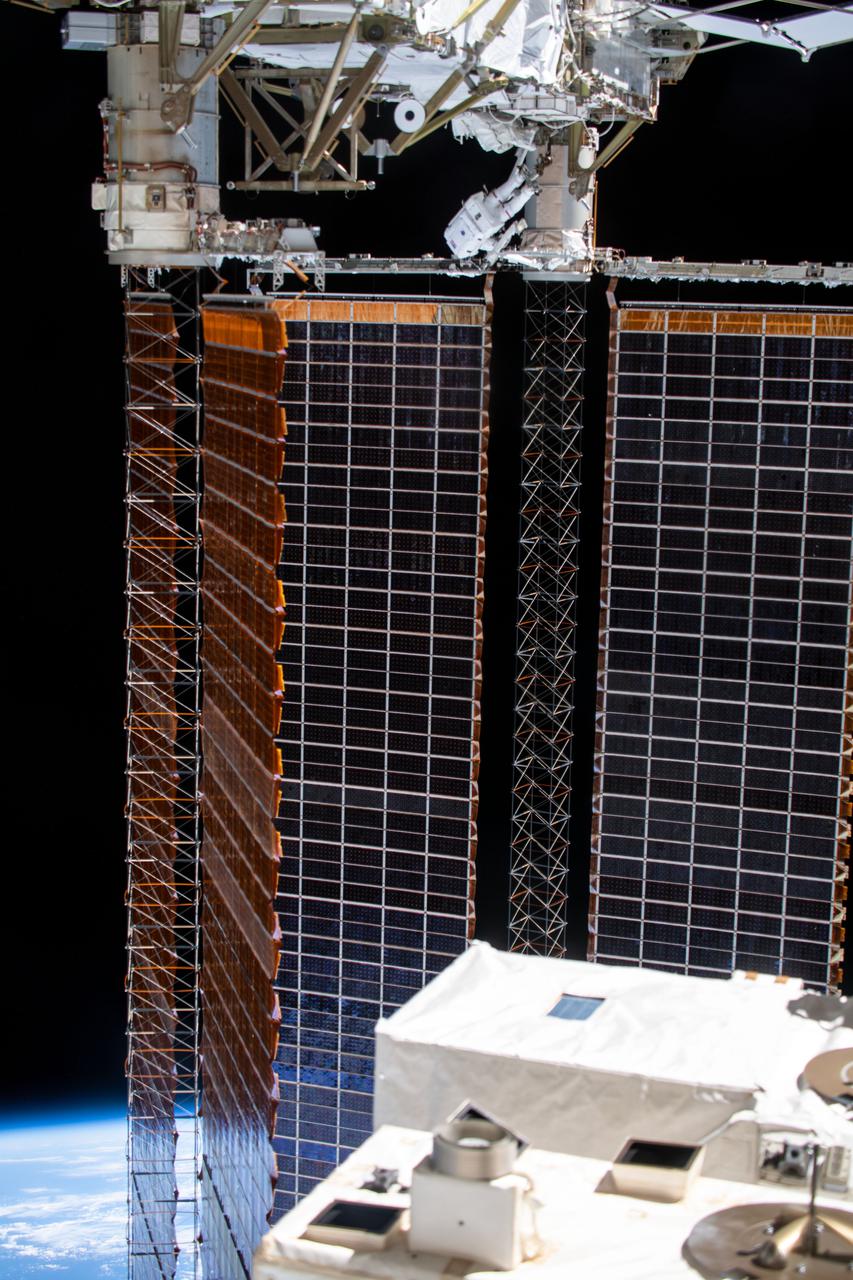

iss064e039832 (March 5, 2021) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins (at top) is pictured during a spacewalk to install solar array modification kits to ready the International Space Station for newer, more powerful solar arrays being delivered on upcoming SpaceX Dragon cargo missions.
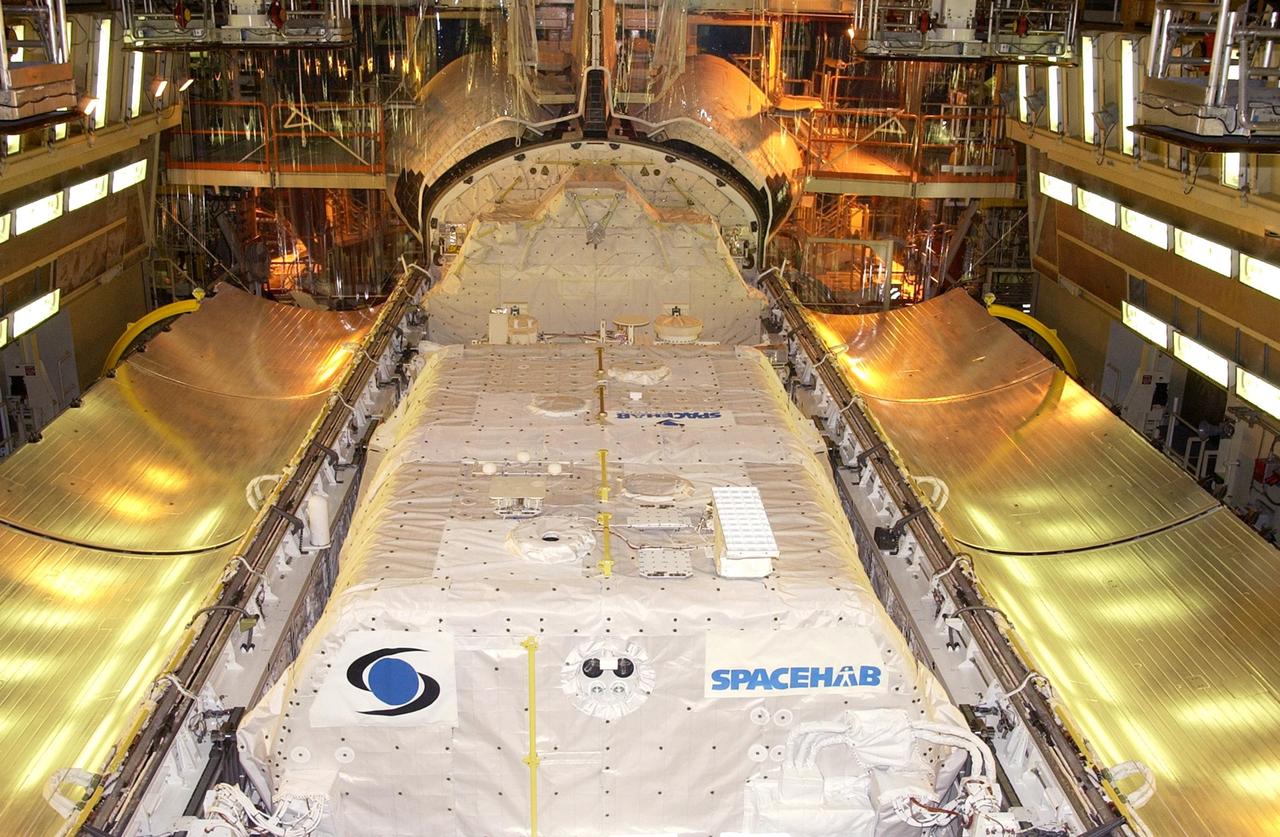

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With its SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM) and other cargo installed, Columbia's payload bay doors are ready to be closed for mission STS-107. A research mission, STS-107 is scheduled for launch July 19, 2001
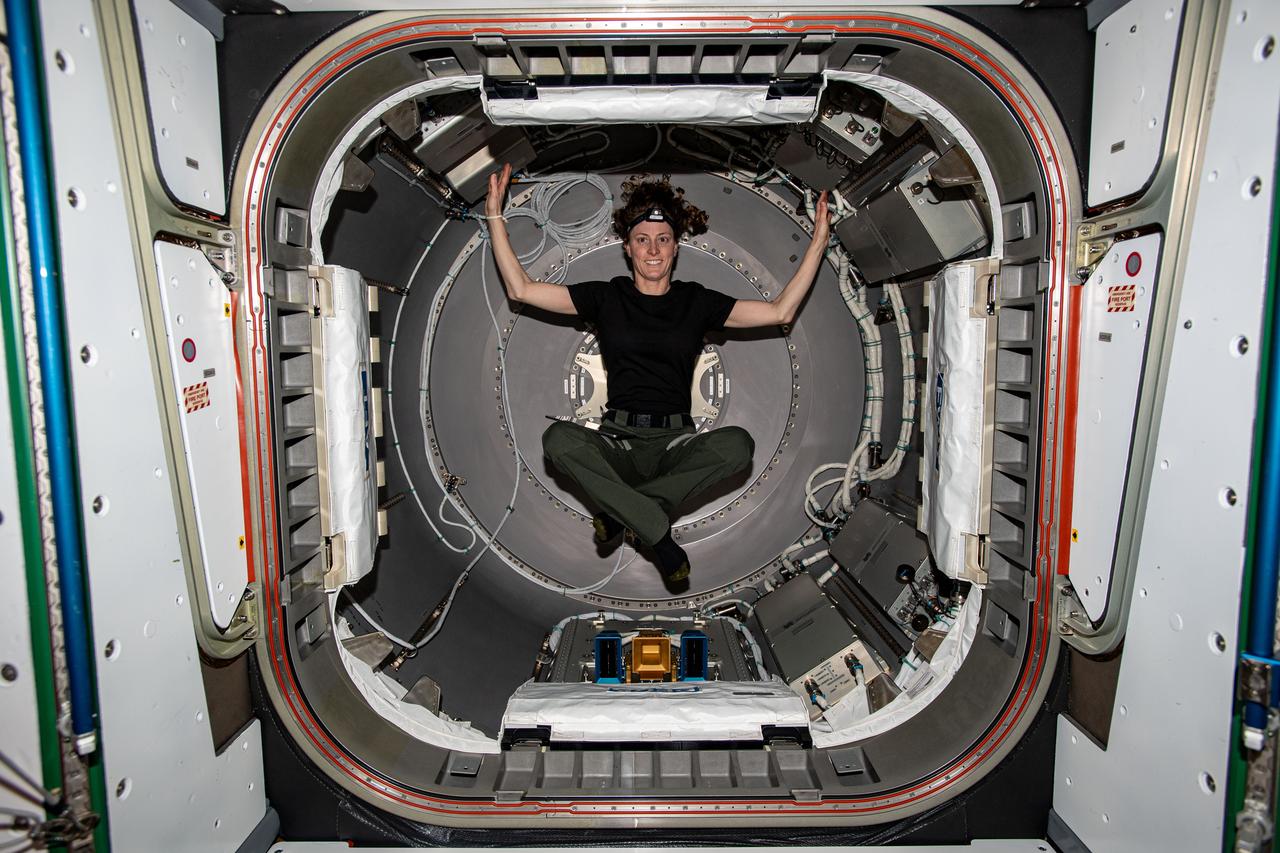

iss070e102747 (Feb. 26, 2024) --- Expedition 70 Flight Engineer and NASA astronaut Loral O'Hara is photographed inside the NanoRacks Bishop airlock. Bishop can be uninstalled from its home on the Tranquility module for portable operations. It can also be used to stow cargo and extract or install payloads.
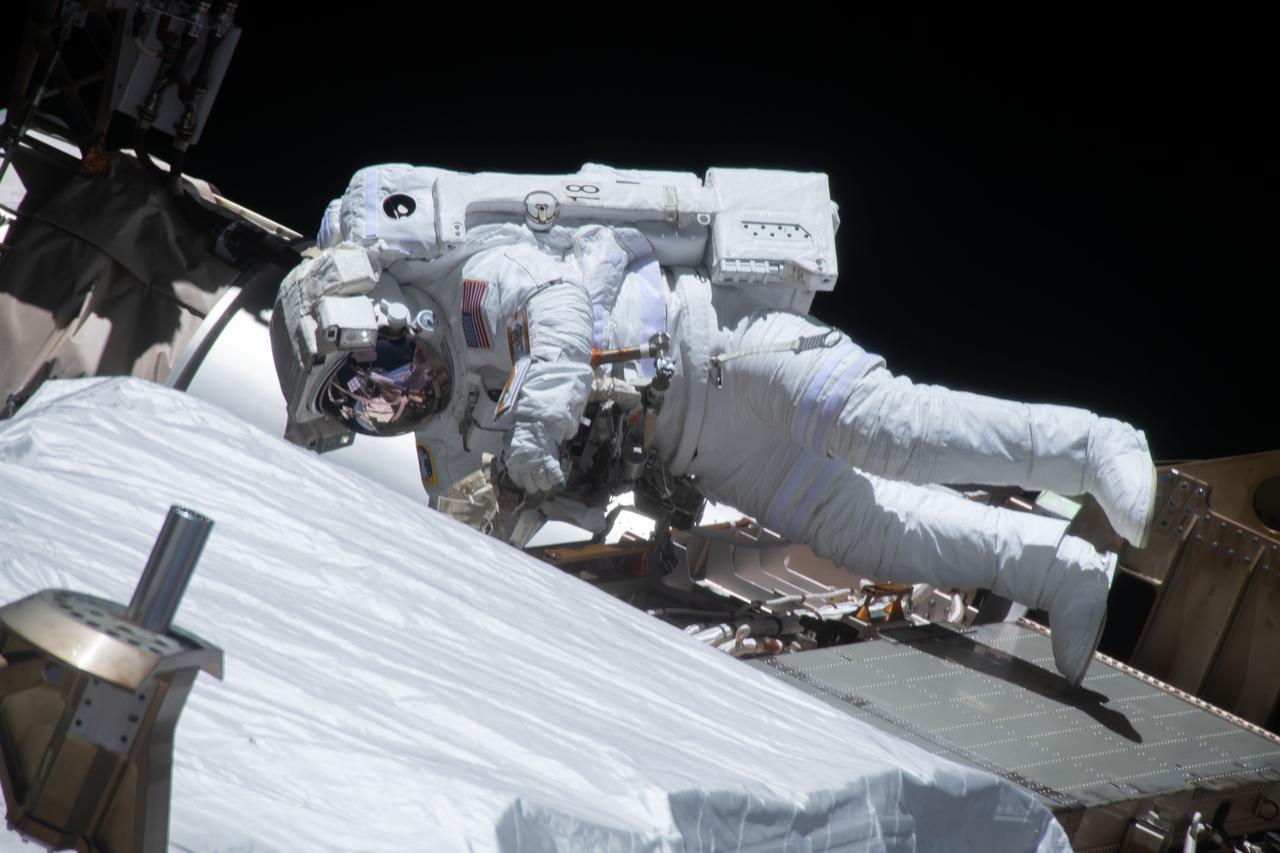

iss064e038332 (Feb. 28, 2021) --- NASA astronaut Victor Glover is pictured during a spacewalk to install solar array modification kits on the International Space Station. The maintenance work will support new, more powerful solar arrays that will be delivered on upcoming SpaceX Dragon cargo missions.
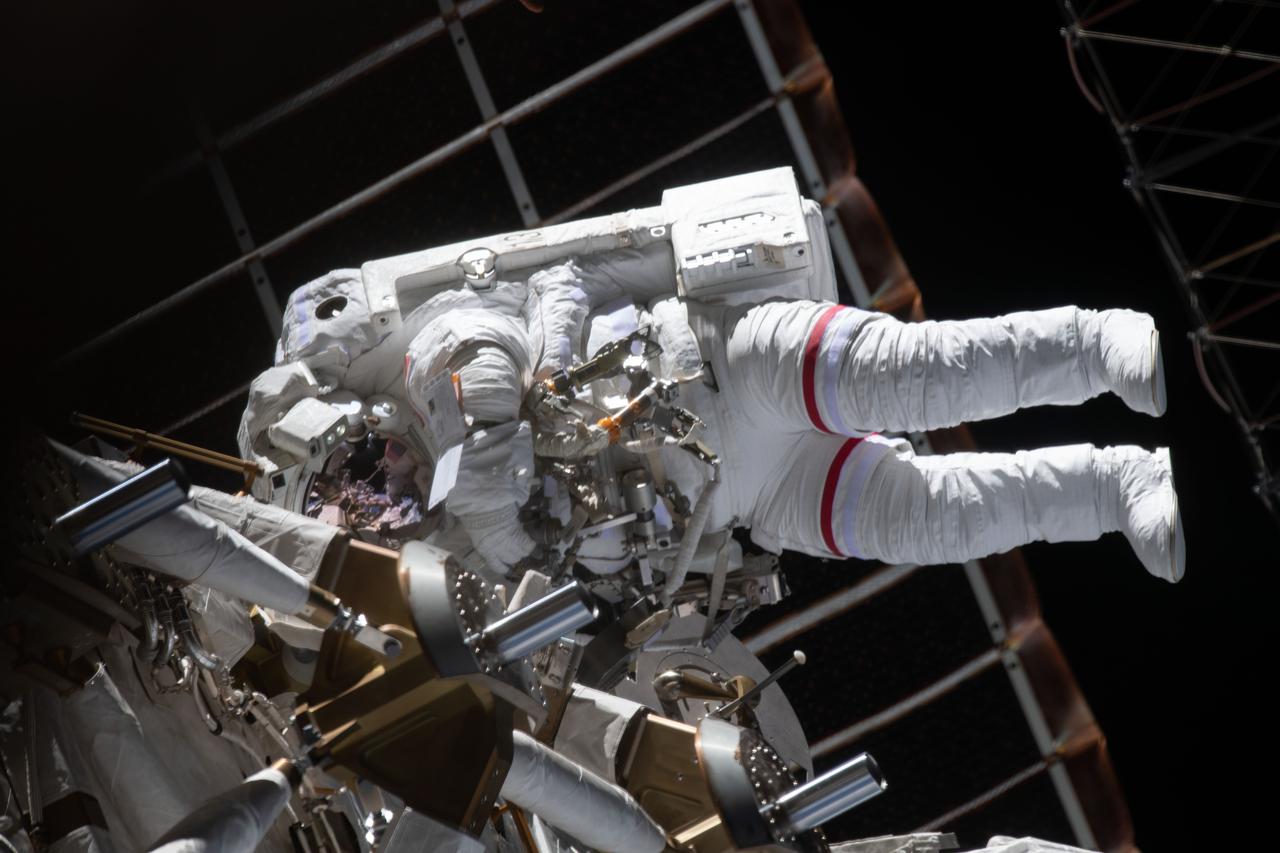

iss064e038485 (Feb. 28, 2021) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is pictured during a spacewalk to install solar array modification kits on the International Space Station. The maintenance work will support new, more powerful solar arrays that will be delivered on upcoming SpaceX Dragon cargo missions.