Dawn cartoon character, part of Dawn Mission Art series. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19381

51D-09-014 (12-19 April 1985) --- U.S. Senator E. J. (Jake) Garn (left), payload specialist; and Karol J. Bobko, mission commander, show a copy of a cartoon from the Doonesbury strip of Garry Trudeau. The senator had been the subject of a series of Trudeau's creations prior to 51-D. The single enlarged panel is autographed by the crewmembers.
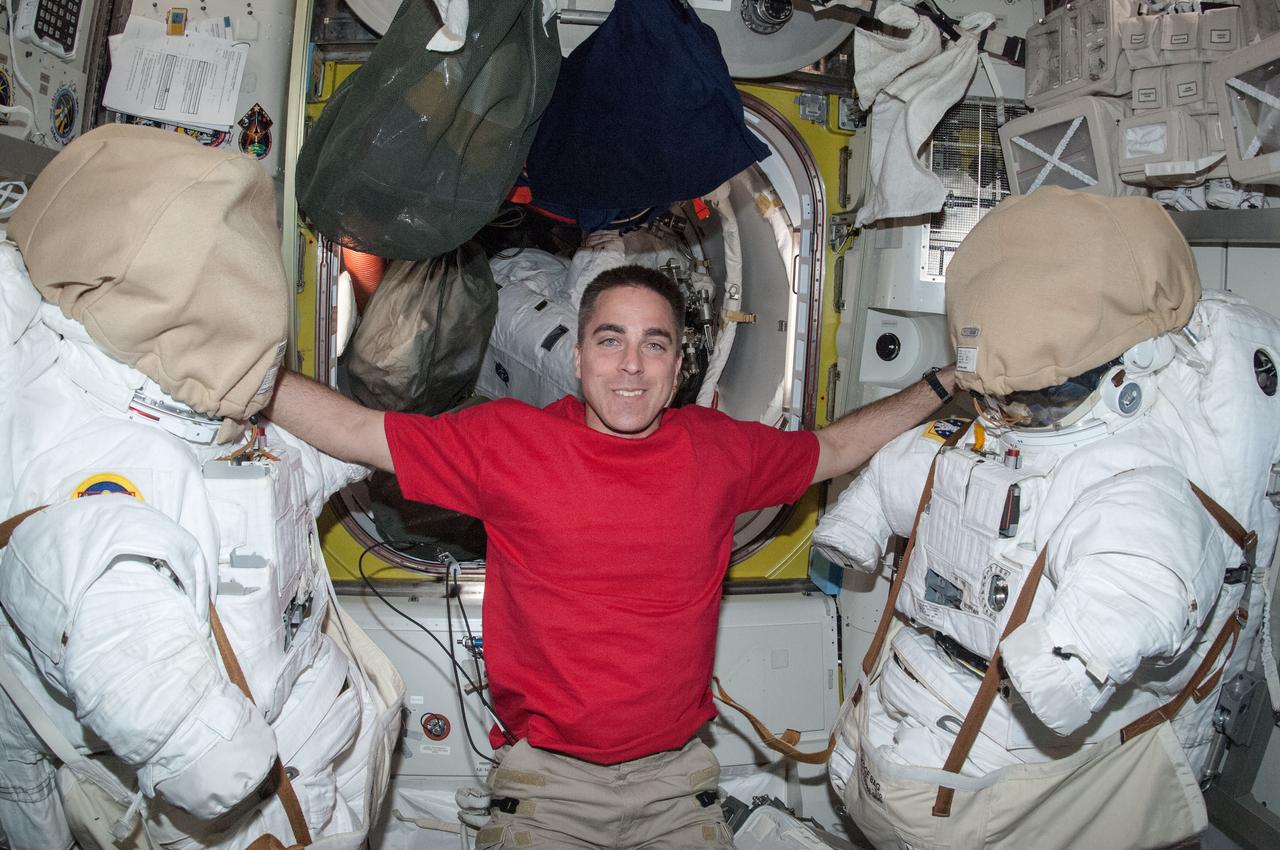

ISS035-E-017762 (10 April 2013) --- In the Quest Airlock of the Earth-orbiting International Space Station, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy "hangs out" with two creatures that look like characters in a Saturday morning cartoon. Actually the "creatures" are two NASA space suits called extravehicular mobility units or EMU.
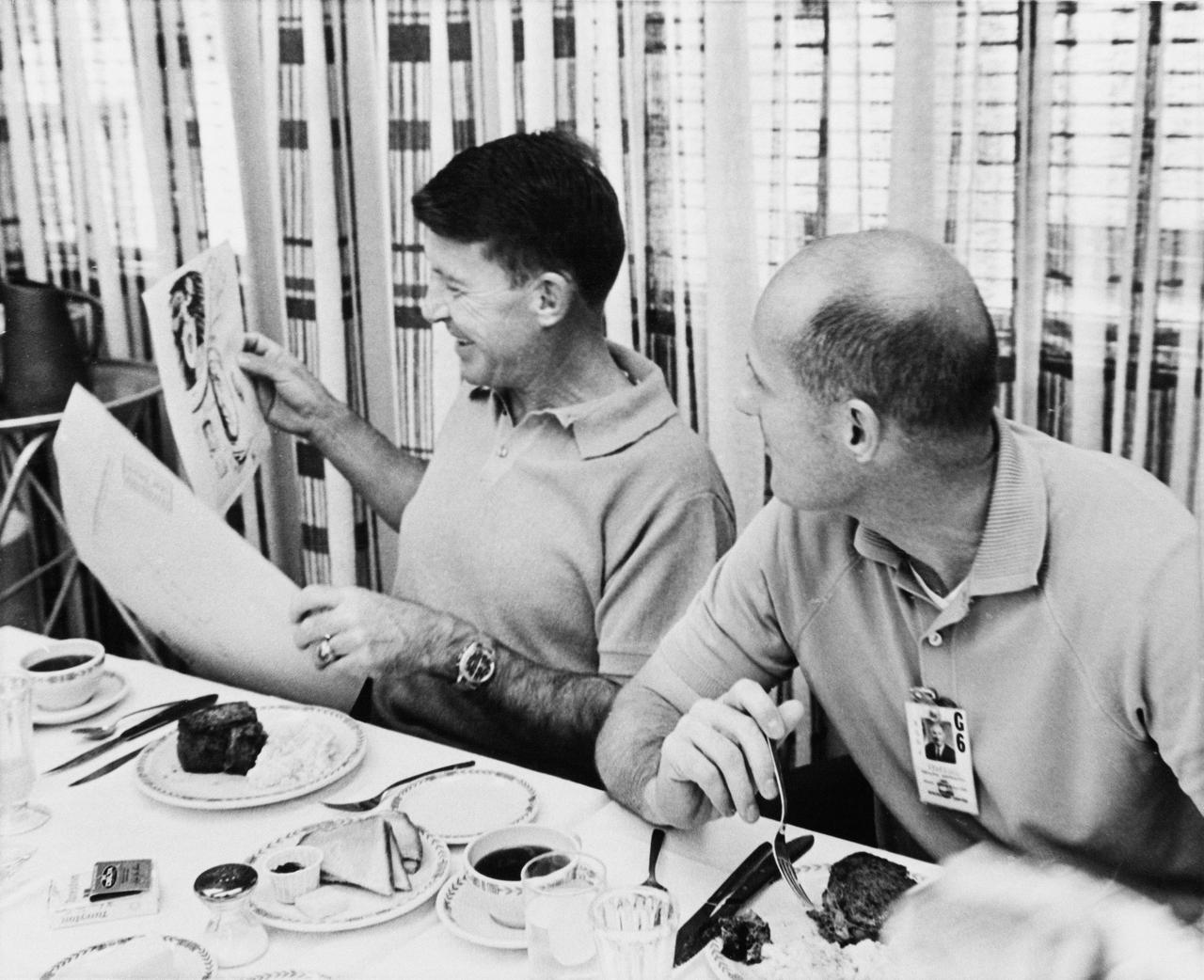

S65-56159 (15 Dec. 1965) --- Astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr. (left), command pilot, and Thomas P. Stafford, pilot, look at a cartoon presented to them by the other astronauts on the morning of the scheduled Gemini-6 launch. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
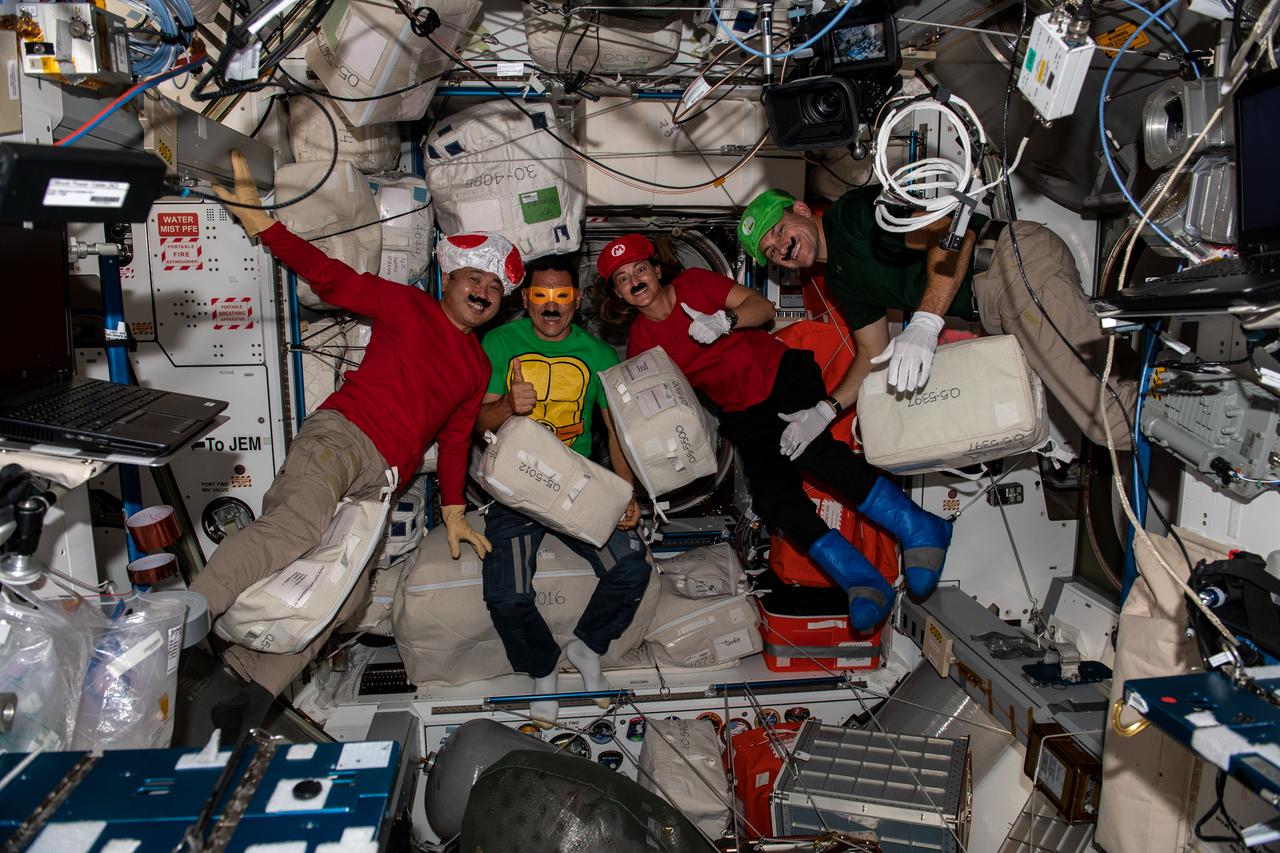

iss068e020276 (Oct. 31, 2022) --- Four Expedition 68 Flight Engineers dress up as popular video game and cartoon characters to celebrate Halloween fun aboard the International Space Station. From left are, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata with NASA astronauts Frank Rubio, Nicole Mann, and Josh Cassada.
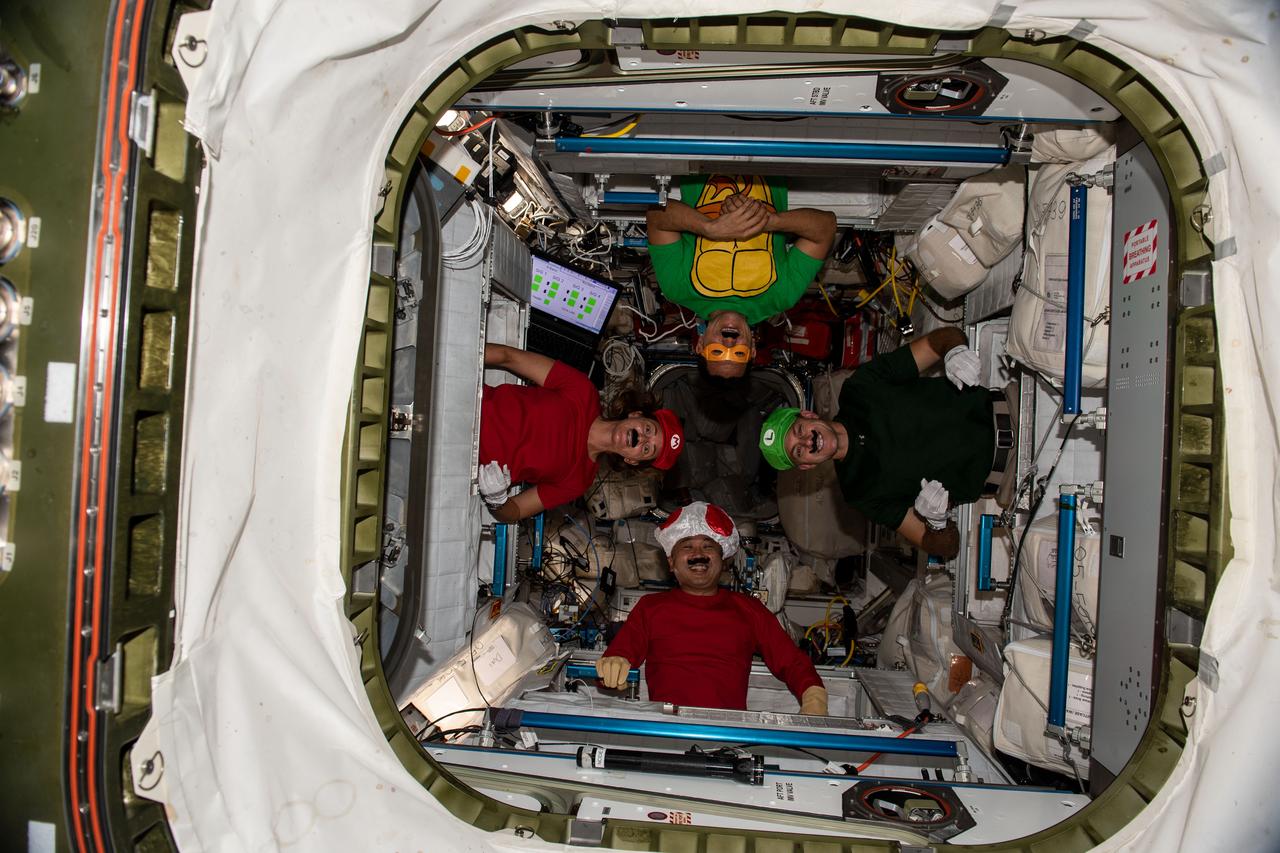

iss068e020320 (Oct. 31, 2022) --- Four Expedition 68 Flight Engineers dress up as popular video game and cartoon characters to celebrate Halloween fun aboard the International Space Station. Clockwise from left are, NASA astronauts Nicole Mann, Frank Rubio, and Josh Cassada with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata.
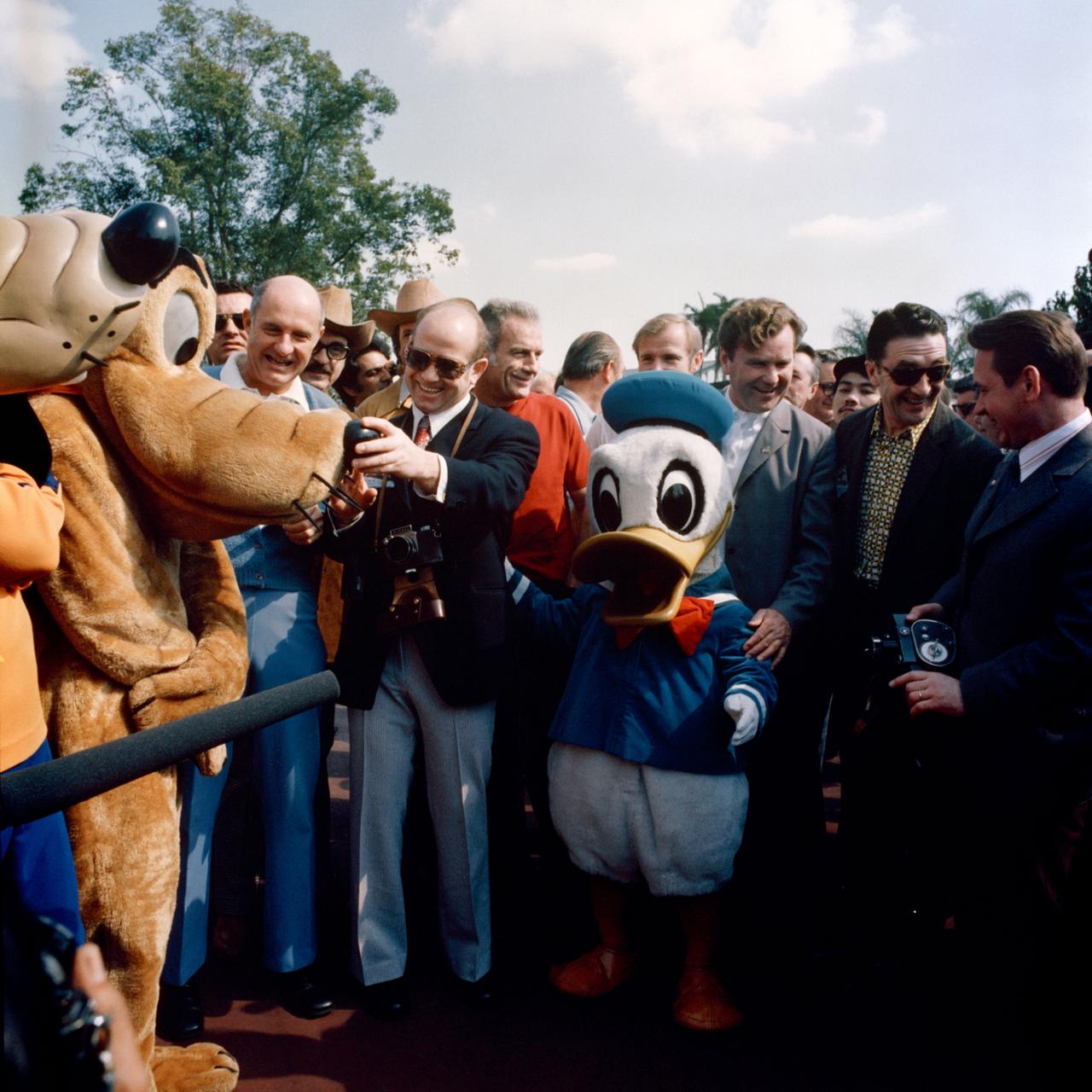

S75-24114 (8-10 Feb. 1975) --- Two Walt Disney comic cartoon characters, Donald Duck and Pluto, were on hand to greet a group of Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) crewmen on their arrival at Disney World near Orlando. From left, are interpreter K. S. Samofal, interpreter Nicholas Timacheff, cosmonaut Vladimir A. Shatalov, astronaut Vance D. Brand, astronaut Donald K. Slayton, cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov (squeezing Pluto's nose) and astronaut Thomas P. Stafford. The astronauts and cosmonauts were in Florida for a three-day inspection tour of NASA's Kennedy Space Center where they looked over ASTP launch facilities and flight hardware.

This cartoon shows how magnetic waves, called Alfvén S-waves, propagate outward from the base of black hole jets. The jet is a flow of charged particles, called a plasma, which is launched by a black hole. The jet has a helical magnetic field (yellow coil) permeating the plasma. The waves then travel along the jet, in the direction of the plasma flow, but at a velocity determined by both the jet's magnetic properties and the plasma flow speed. The BL Lac jet examined in a new study is several light-years long, and the wave speed is about 98 percent the speed of light. Fast-moving magnetic waves emanating from a distant supermassive black hole undulate like a whip whose handle is being shaken by a giant hand, according to a study using data from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory's Very Long Baseline Array. Scientists used this instrument to explore the galaxy/black hole system known as BL Lacertae (BL Lac) in high resolution. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19822

This intriguing, almost cartoon-like terrain is composed of coalescing pits and smooth-topped mesas, forming part of what is known as the Residual South Polar Cap (RSPC) of Mars. The RSPC is a permanent deposit of carbon dioxide (dry) ice that is several kilometers thick and overlies a much larger water ice cap. This part of the RSPC lies at an elevation of about 6.5 kilometers. The mesas are several kilometers long while the pits range in diameter up to several hundred meters. The dark regions surrounding the mesas are thought to be exposed water ice. This image was taken during southern summer when the brighter-appearing dry ice cap sublimates (evaporates directly from ice to vapor) exposing the darker, underlying water ice cap. Understanding the seasonal and yearly volumes of carbon dioxide exchange between the surface and the atmosphere provides important insights into Mars' climate. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24463

S75-28504 (17 July 1975) --- The American ASTP crewmen search the skies for the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft in this humorous artwork by cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov. Astronauts Vance D. Brand, Donald K. Slayton and Thomas P. Stafford (left to right) sit astride the Apollo spacecraft and Docking Module ready to lasso Soyuz. The cartoon humorously depicts the approaching historic event of an American spacecraft rendezvousing and docking in Earth orbit with a USSR spacecraft, scheduled today (July 17, 1975). Aboard Soyuz are Leonov, crew commander, and his fellow cosmonaut, Valeriy N. Kubasov. Stafford is the Apollo crew commander. The U.S. and USSR crewmen will visit each other's spacecraft while the Apollo and Soyuz are docked in Earth orbit for two days. Leonov, an accomplished artist, specializes in paintings on space subjects. He has a number of paintings on public exhibit in his native land.
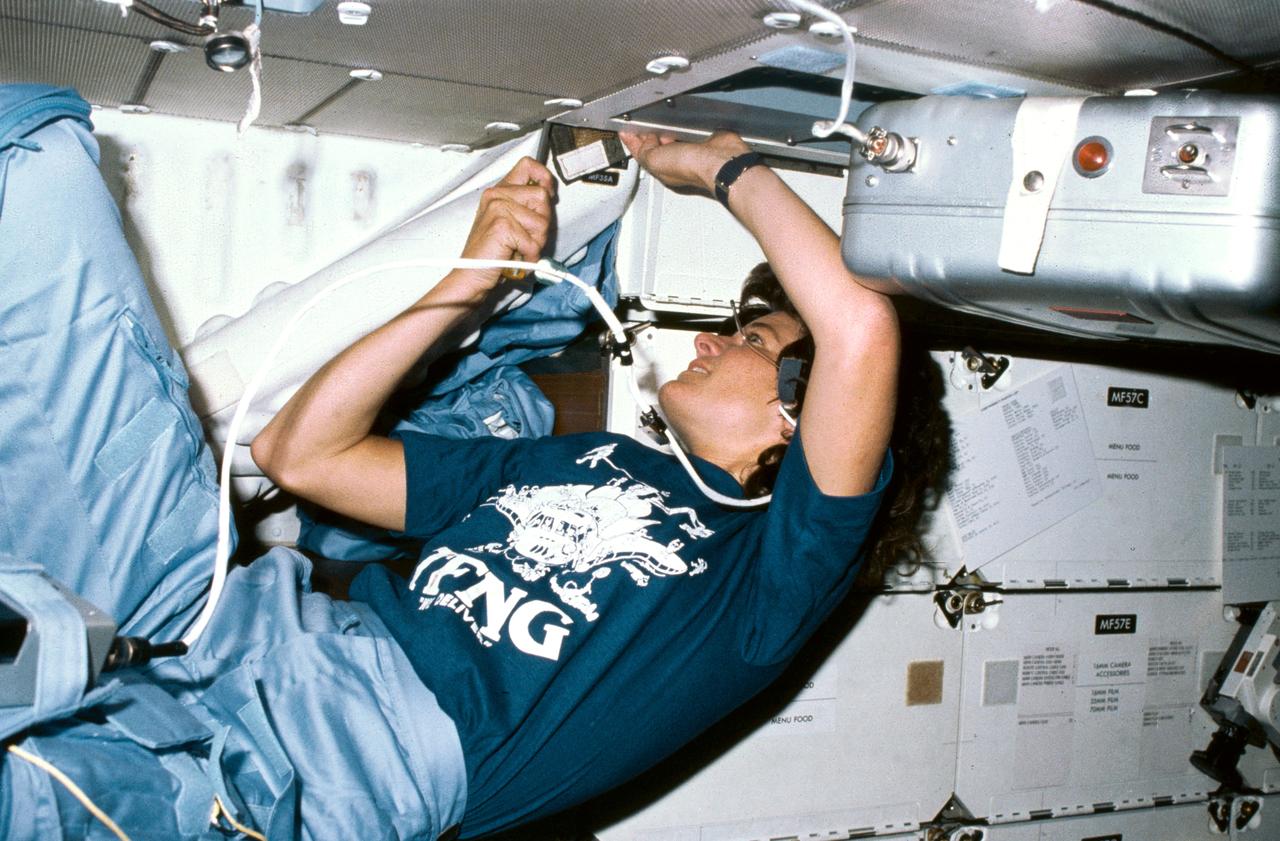

S83-35768 (18-24 June 1983) --- Astronaut Sally K. Ride, mission specialist for STS-7, uses a screw driver in order to clean out an air filtering system in the mid-deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger. Dr. Ride's constant wear garment bears some extras -- a cartoon of 35 busy astronauts around a Space Shuttle and the acronym TFNG, below which is written, "We deliver!" TFNG stands for thirty-five new guys, referring to the 1978 class of astronaut candidates (ASCAN) from which Dr. Ride and three of her crew members hail. The tiny two-word declarative in white lettering refers to the successful deployment of two communications satellites. This photograph was made with a 35mm camera.
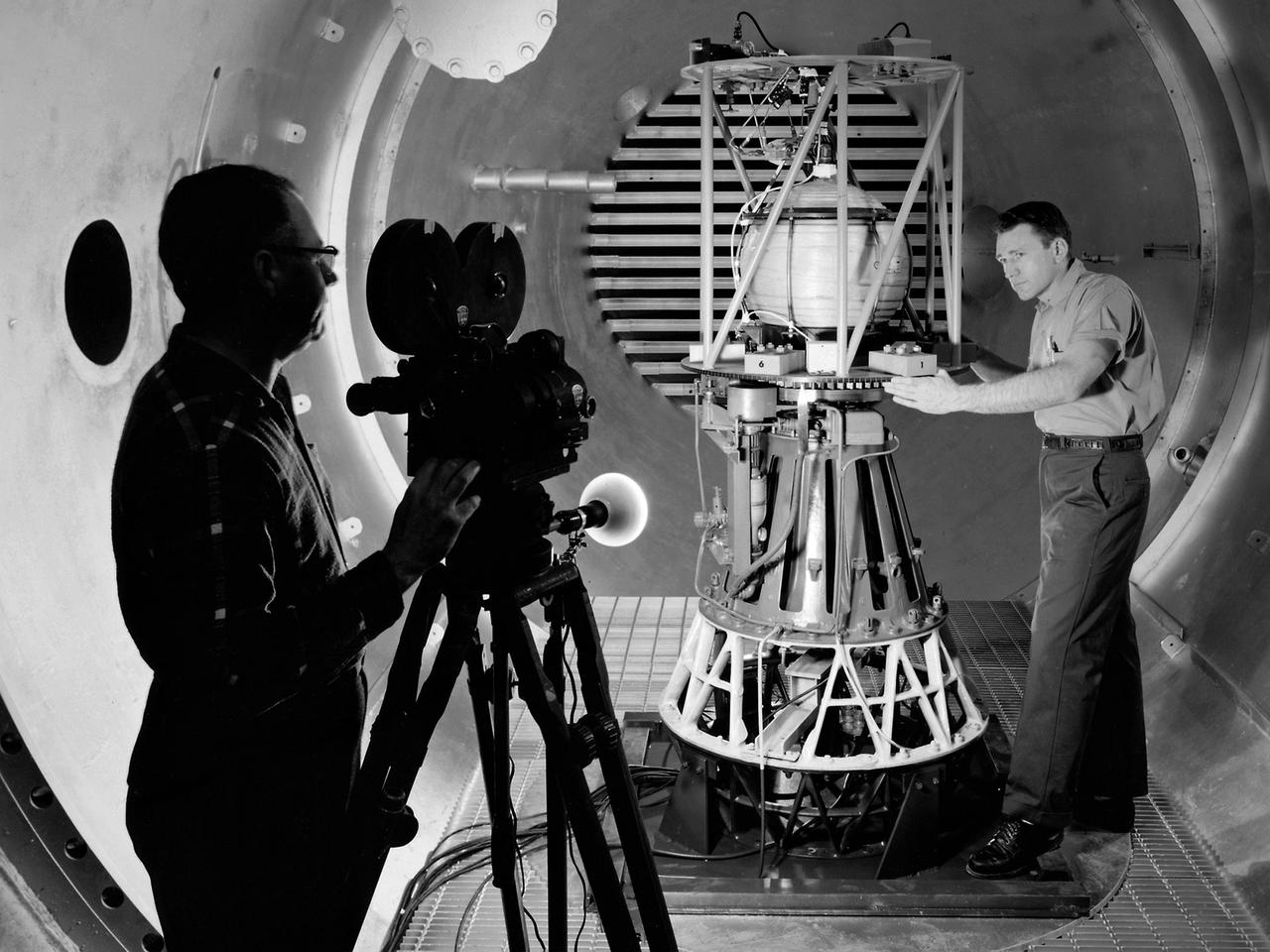

Mechanic Howard Wine inspects the setup of a spin isolator in Cell 2 of the Propulsion Systems Laboratory at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Photographer Al Jecko filmed the proceedings. This test was unique in that the chamber’s altitude system was used, but not its inlet air flow. The test was in preparation for an upcoming launch of modified liquid hydrogen propellant tank on a sounding rocket. This Weightlessness Analysis Sounding Probe (WASP) was part of Lewis investigation into methods for controlling partially filled liquid hydrogen fuel tanks during flight. Second-stage rockets, the Centaur in particular, were designed to stop their engines and coast, then restart them when needed. During this coast period, the propellant often shifted inside the tank. This movement could throw the rocket off course or result in the sloshing of fuel away from the fuel pump. Wine was one of only three journeymen mechanics at Lewis when he was hired in January 1954. He spent his first decade in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory and was soon named a section head. Wine went on to serve as Assistant Division Chief and later served as an assistant to the director. Jecko joined the center in 1947 as a photographer and artist. He studied at the Cleveland School or Art and was known for his cartoon drawing. He worked at the center for 26 years.
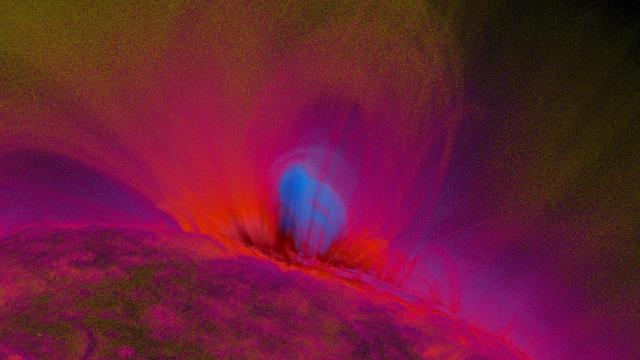
Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (SDO AIA 131 and 171 difference blended image of flux ropes during CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b>

Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (SDO AIA 131 and 171 difference blended image of flux ropes during CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b>
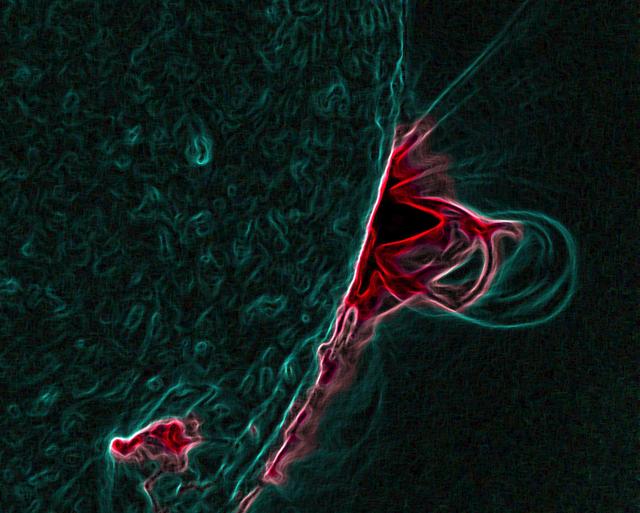
Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory on July 18, 2012. It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (Blended 131 Angstrom and 171 Angstrom images of July 19, 2012 flare and CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>