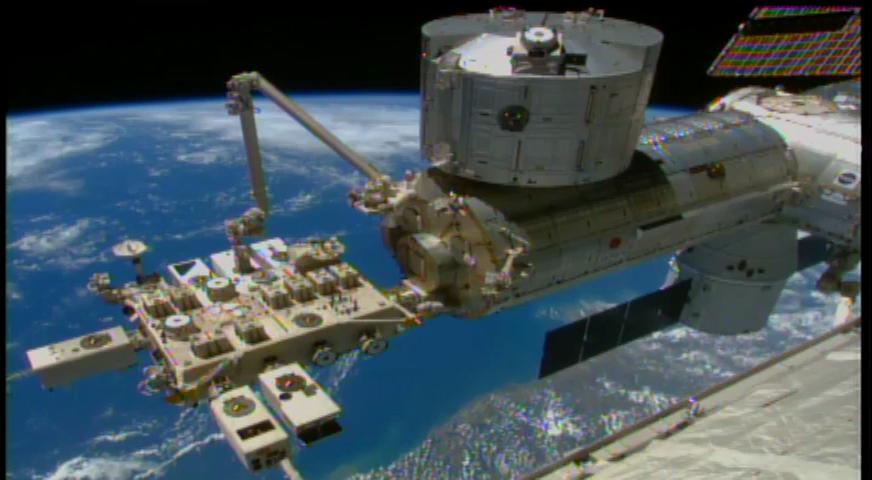

On Jan. 22, 2015, robotic flight controllers successfully installed NASA’s Cloud Aerosol Transport System (CATS) onboard the International Space Station. CATS will collect data about clouds, volcanic ash plumes and tiny airborne particles that can help improve our understanding of aerosol and cloud interactions, and improve the accuracy of climate change models. CATS had been mounted inside the SpaceX Dragon cargo craft’s unpressurized trunk since it docked at the station on Jan. 12. Ground controllers at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, used one of the space station’s robotic arms, called the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, to extract the instrument from the capsule. The NASA-controlled arm passed the instrument to a second robotic arm— like passing a baton in a relay race. This second arm, called the Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System, is controlled by the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency. The Japanese-controlled arm installed the instrument to the Space Station’s Japanese Experiment Module, making CATS the first NASA-developed payload to fly on the Japanese module. CATS is a lidar remote-sensing instrument designed to last from six months to three years. It is specifically intended to demonstrate a low-cost, streamlined approach to developing science payloads on the space station. CATS launched aboard the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft on Jan. 10 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. To learn more about the impact of CATS data, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/cats/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/cats/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Cat Eye

Cat Scratches

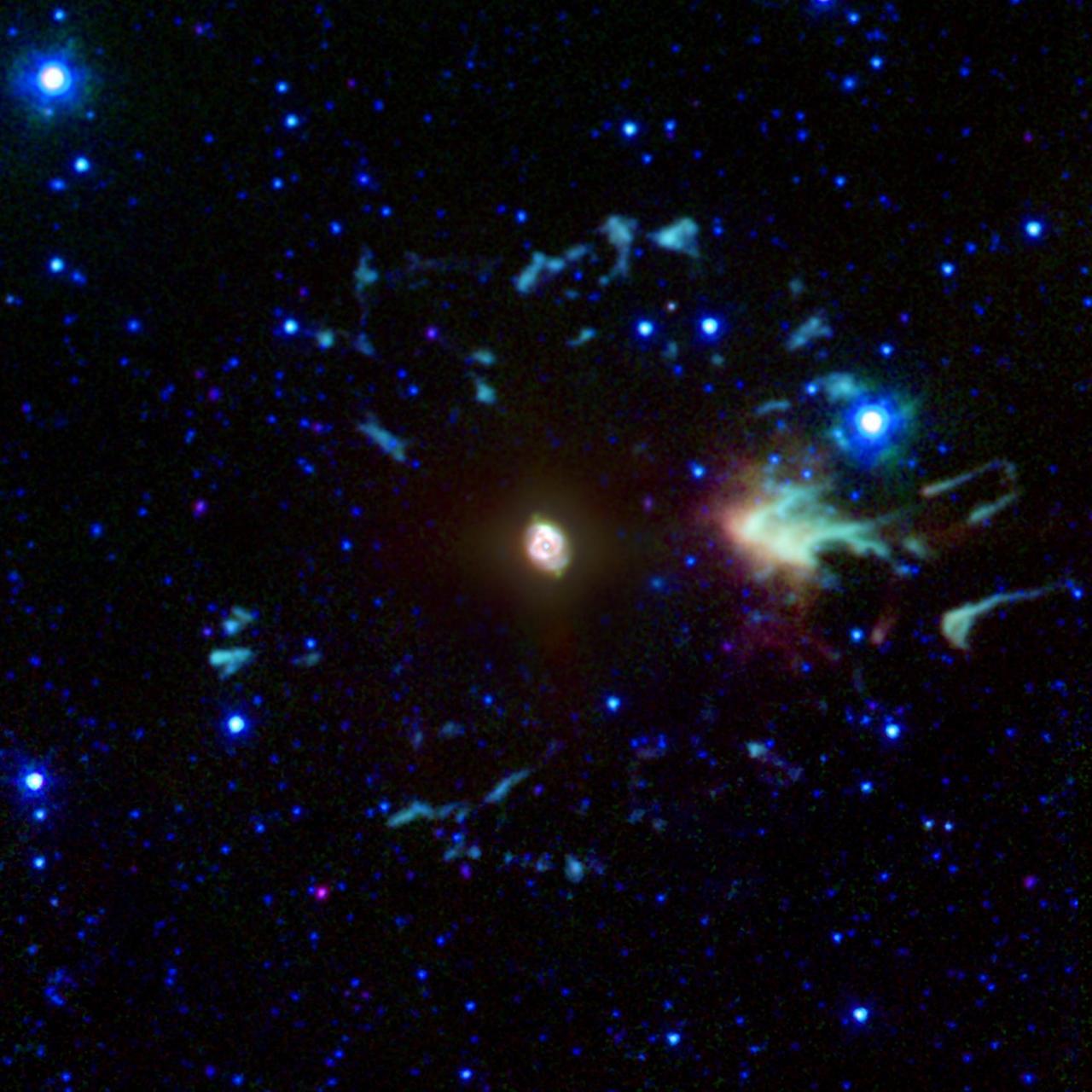
Nebula? No, It the Cat Eye Crater!
Black Cat on Titan

Cloud Aerosol Transport System (CATS) leaves Goddard building 33 for shipment to Space X for installation at the International Space Station

Cat Eye Rings and Peek-a-boo Shadows

The Cat's Eye Nebula, one of the first planetary nebulae discovered, also has one of the most complex forms known to this kind of nebula. Eleven rings, or shells, of gas make up the Cat's Eye. The full beauty of the Cat's Eye Nebula is revealed in this detailed view from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The image from Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) shows a bull's eye pattern of eleven or even more concentric rings, or shells, around the Cat's Eye. Each 'ring' is actually the edge of a spherical bubble seen projected onto the sky -- that's why it appears bright along its outer edge. Observations suggest the star ejected its mass in a series of pulses at 1,500-year intervals. These convulsions created dust shells, each of which contain as much mass as all of the planets in our solar system combined (still only one percent of the Sun's mass). These concentric shells make a layered, onion-skin structure around the dying star. The view from Hubble is like seeing an onion cut in half, where each skin layer is discernible. The bull's-eye patterns seen around planetary nebulae come as a surprise to astronomers because they had no expectation that episodes of mass loss at the end of stellar lives would repeat every 1,500 years. Several explanations have been proposed, including cycles of magnetic activity somewhat similar to our own Sun's sunspot cycle, the action of companion stars orbiting around the dying star, and stellar pulsations. Another school of thought is that the material is ejected smoothly from the star, and the rings are created later on due to formation of waves in the outflowing material. Credit: NASA, ESA, HEIC, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: R. Corradi (Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes, Spain) and Z. Tsvetanov (NASA) The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute conducts Hubble science operations. Goddard is responsible for HST project management, including mission and science operations, servicing missions, and all associated development activities. To learn more about the Hubble Space Telescope go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

iss049e006037 (Sep. 17, 2016) --- Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS) mounted on the Japanese Experiment Module's Exposed Facility (JEM-EF). The CATS investigation uses a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) system to measure the location, composition and distribution of pollution, dust, smoke, aerosols and other particulates in the atmosphere. CATS is used to study the atmospheric constituents that impact global climate. By gaining a better understanding of cloud and aerosol coverage, scientists can create a better model of the Earth's climate feedback processes.
Bright, high altitude clouds, like those imaged here, often appear more filamentary or streak-like than clouds imaged at slightly deeper levels in Saturn atmosphere. This view also shows one of the many cat eye vortices.
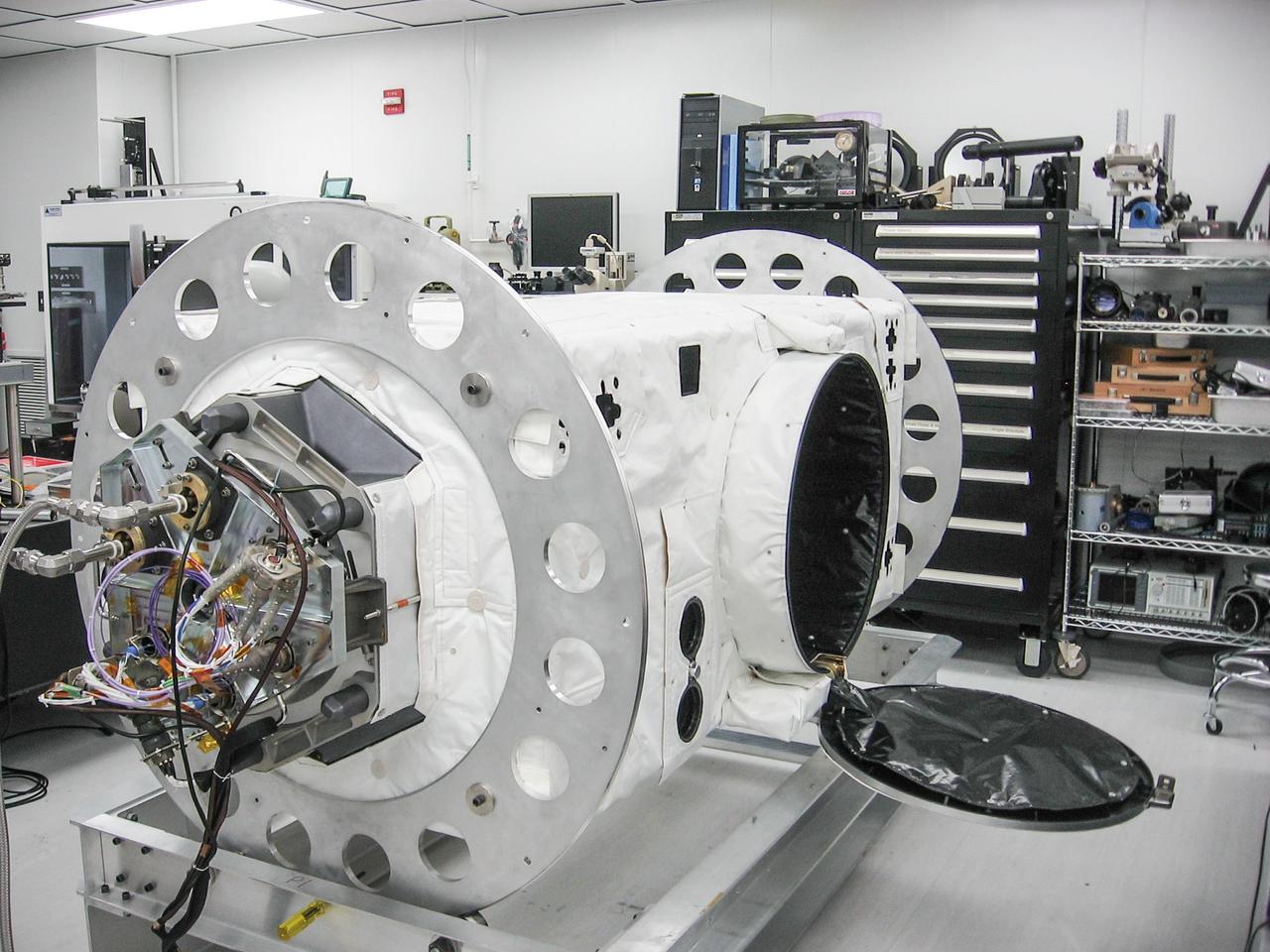
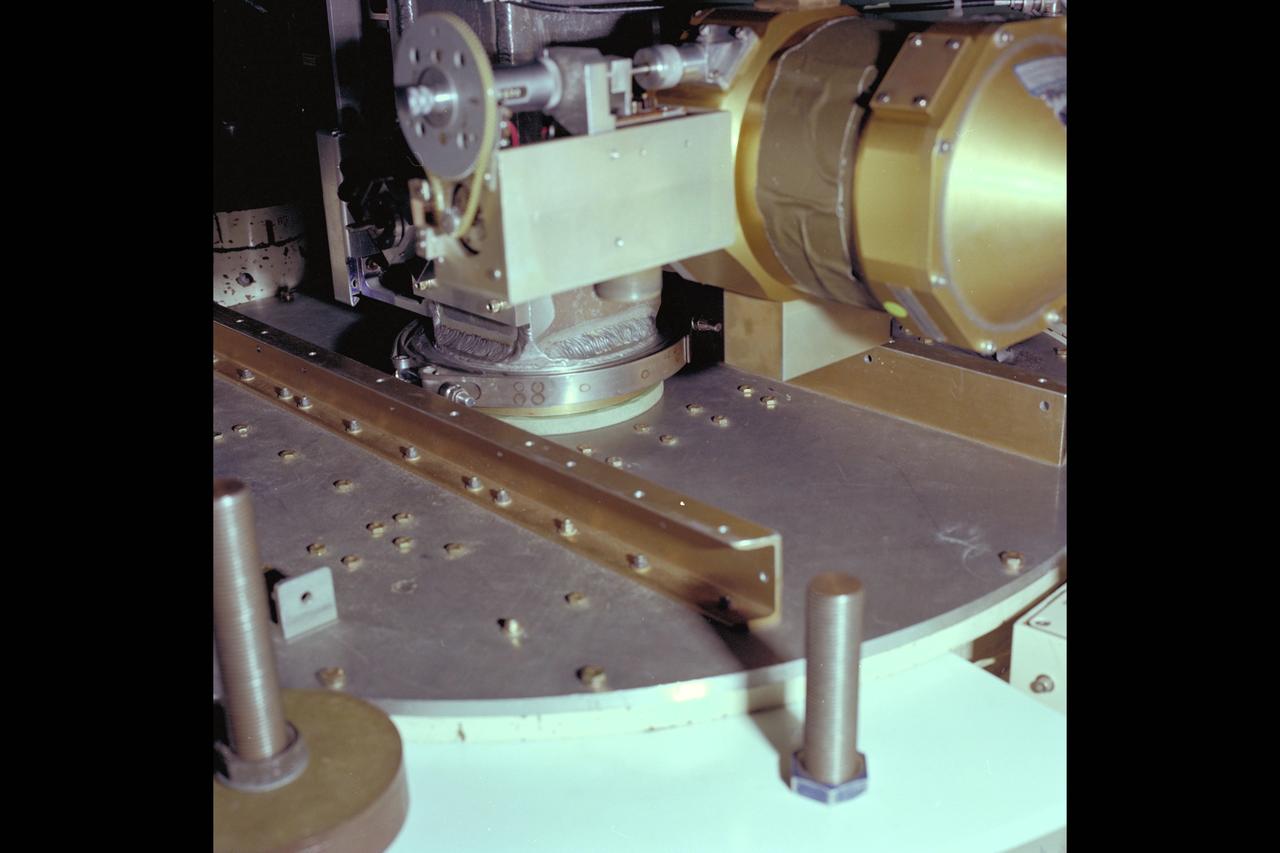
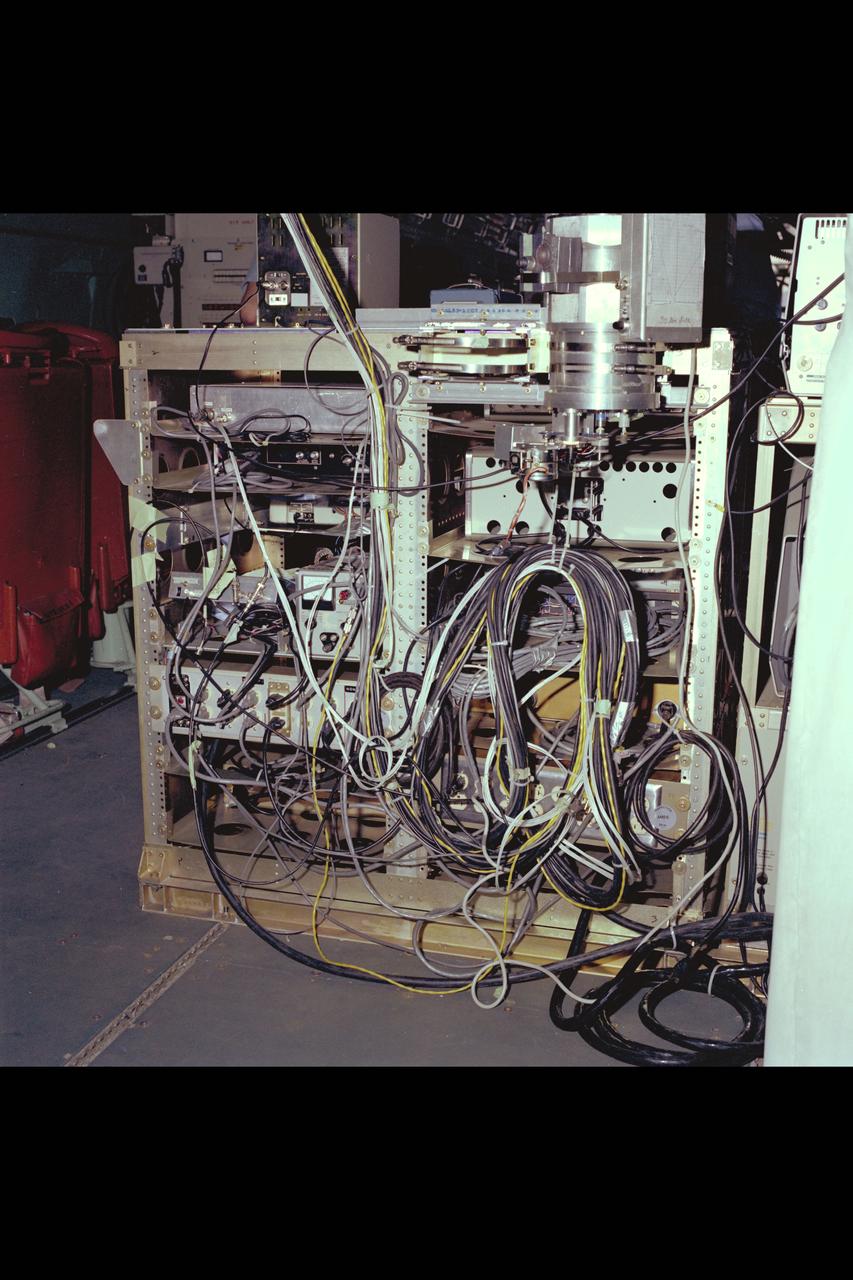
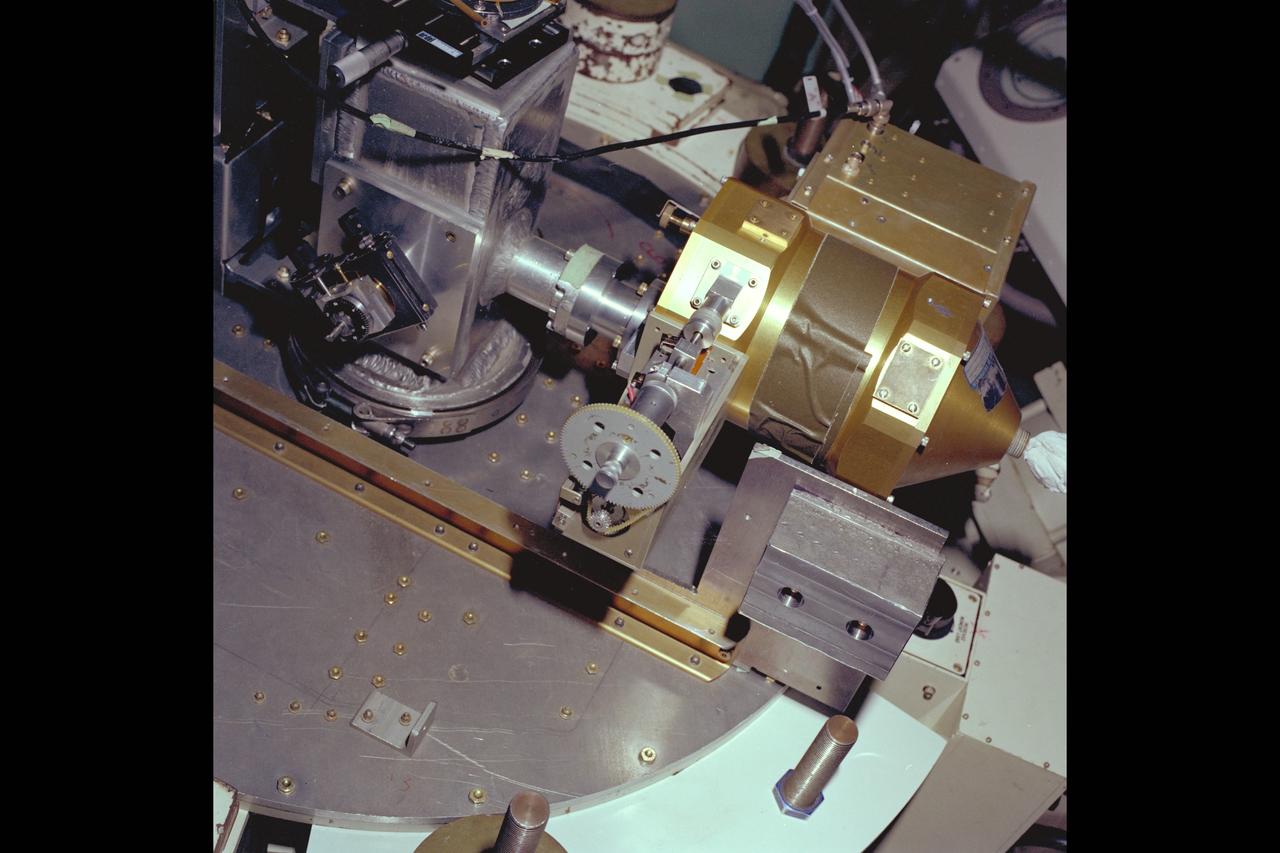
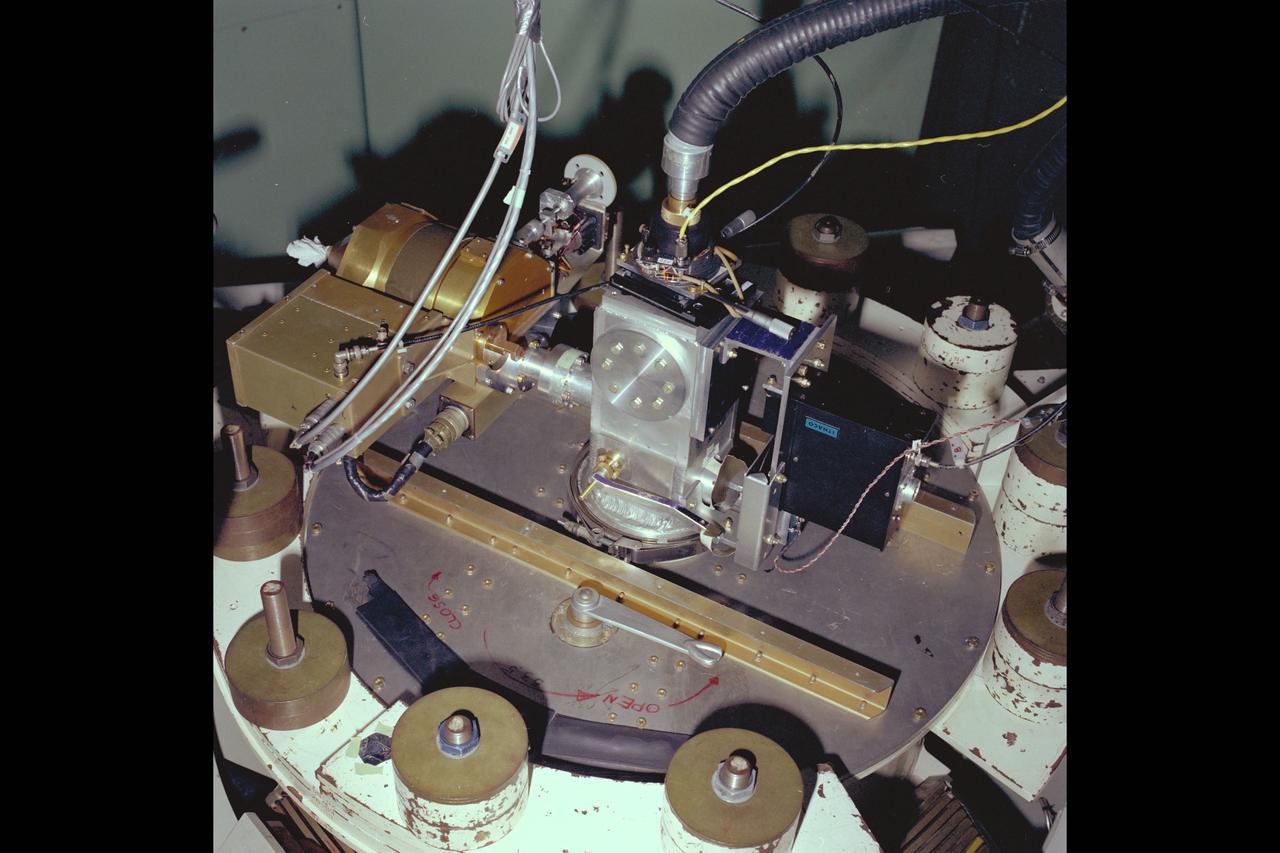
jsc2013e090265 (Sep. 26, 2013) --- Cloud Aerosol Transport System (CATS) at NASA's Johnson Space Center undergoing payload fit-check and Support Equipment Installation (SEI). The CATS investigation uses a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) system to measure the location, composition and distribution of pollution, dust, smoke, aerosols and other particulates in the atmosphere. CATS is used to study the atmospheric constituents that impact global climate. By gaining a better understanding of cloud and aerosol coverage, scientists can create a better model of the Earth's climate feedback processes.
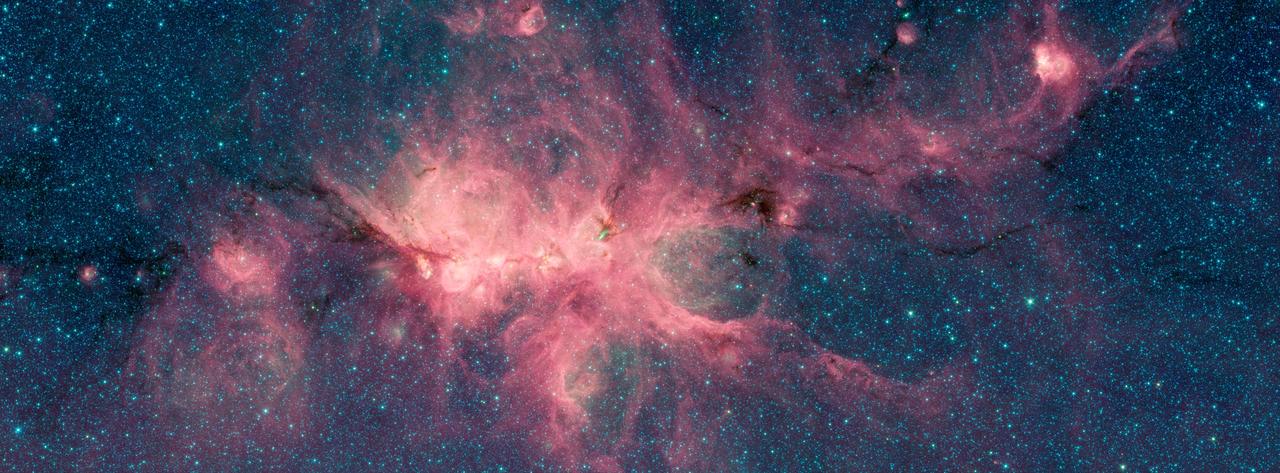

The Cat's Paw Nebula, imaged here by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, is a star-forming region inside the Milky Way Galaxy and is located in the constellation Scorpius. Its distance from Earth is estimated to be between 1.3 kiloparsecs (about 4,200 light years) to 1.7 kiloparsecs (about 5,500 light years). The image was taken as part of the Galactic Legacy Infrared Midplane Survey Extraordinaire (GLIMPSE), a survey of the Milky Way Galaxy. It was taken using Spitzer's Infrared Array Camera (IRAC). The colors correspond with wavelengths of 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (green), and 8 microns (red). The bright, cloudlike band running left to right across the image shows the presence of gas and dust that can collapse to form new stars. The black filaments running through the nebula are particularly dense regions of gas and dust. The entire star-forming region is thought to be between 24 and 27 parsecs (80-90 light years) across. New stars may heat up the pressurized gas surrounding them causing the gas to expand and form "bubbles." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22567
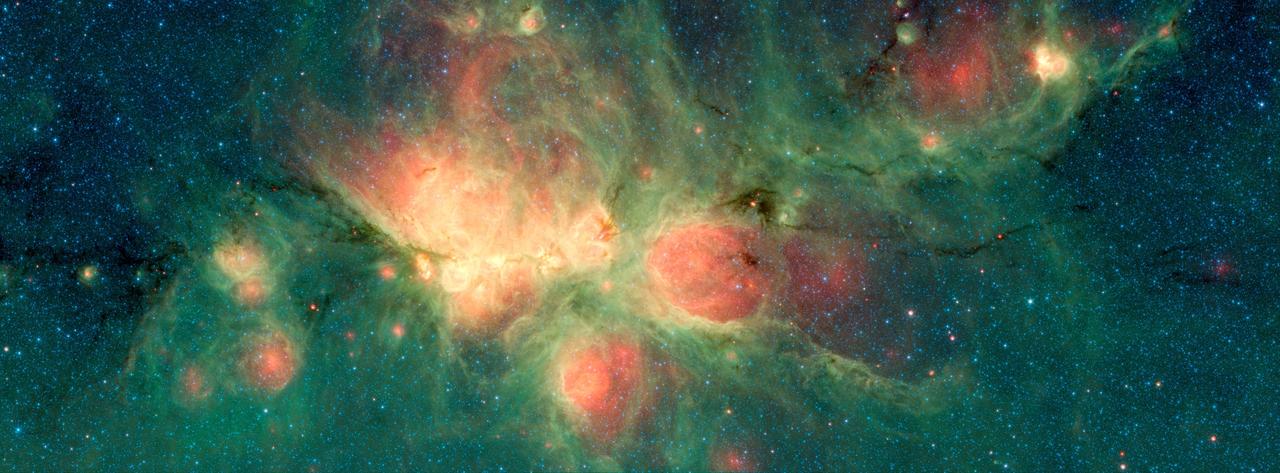

The Cat's Paw Nebula, imaged here by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, lies inside the Milky Way Galaxy and is located in the constellation Scorpius. Its distance from Earth is estimated to be between 1.3 kiloparsecs (about 4,200 light years) to 1.7 kiloparsecs (about 5,500 light years). The bright, cloudlike band running left to right across the image shows the presence of gas and dust that can collapse to form new stars. The black filaments running through the nebula are particularly dense regions of gas and dust. The entire star-forming region is thought to be between 24 and 27 parsecs (80-90 light years) across. The stars that form inside the nebula heat up the pressurized gas surrounding them, such that the gas may expand and form "bubbles", which appear red in this image. Asymmetric bubbles may "burst," creating U-shaped features. The green areas show regions where radiation from hot stars collided with large molecules and small dust grains called "polycyclic aromatic hydocarbons" (PAHs), causing them to fluoresce. This image was compiled using data from two Spitzer instruments, the Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) and the Multiband Imaging Photometer (MIPS). The colors correspond with wavelengths of 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (cyan), 8 microns (green) and 24 microns (red). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22568
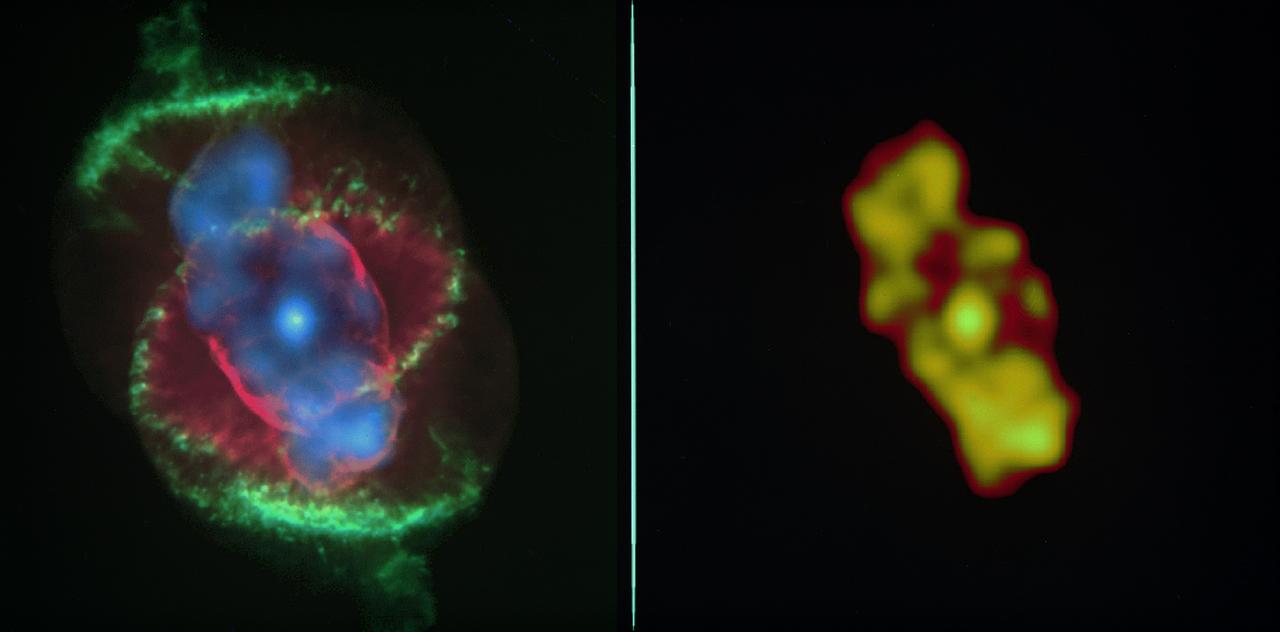
Left image: The x-ray data from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) has revealed a bright central star surrounded by a cloud of multimillion-degree gas in the planetary nebula known as the Cat's Eye. This CXO image, where the intensity of the x-ray emission is correlated to the brightness of the orange coloring, captures the expulsion of material from a star that is expected to collapse into a white dwarf in a few million years. The intensity of x-rays from the central star was unexpected, and it is the first time astronomers have seen such x-ray emission from the central star of a planetary nebula. Right image: An image of Cat's Eye taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). By comparing the CXO data with that from the HST, researchers are able to see where the hotter, x-ray emitting gas appears in relation to the cooler material seen in optical wavelengths by the HST. The CXO team found that the chemical abundance in the region of hot gas (its x-ray intensity is shown in purple) was not like those in the wind from the central star and different from the outer cooler material (the red and green structures.) Although still incredibly energetic and hot enough to radiate x-rays, CXO shows the hot gas to be somewhat cooler than scientists would have expected for such a system. CXO image credit: (NASA/UIUC/Y. Chu et al.) HST image credit: (NASA/HST)
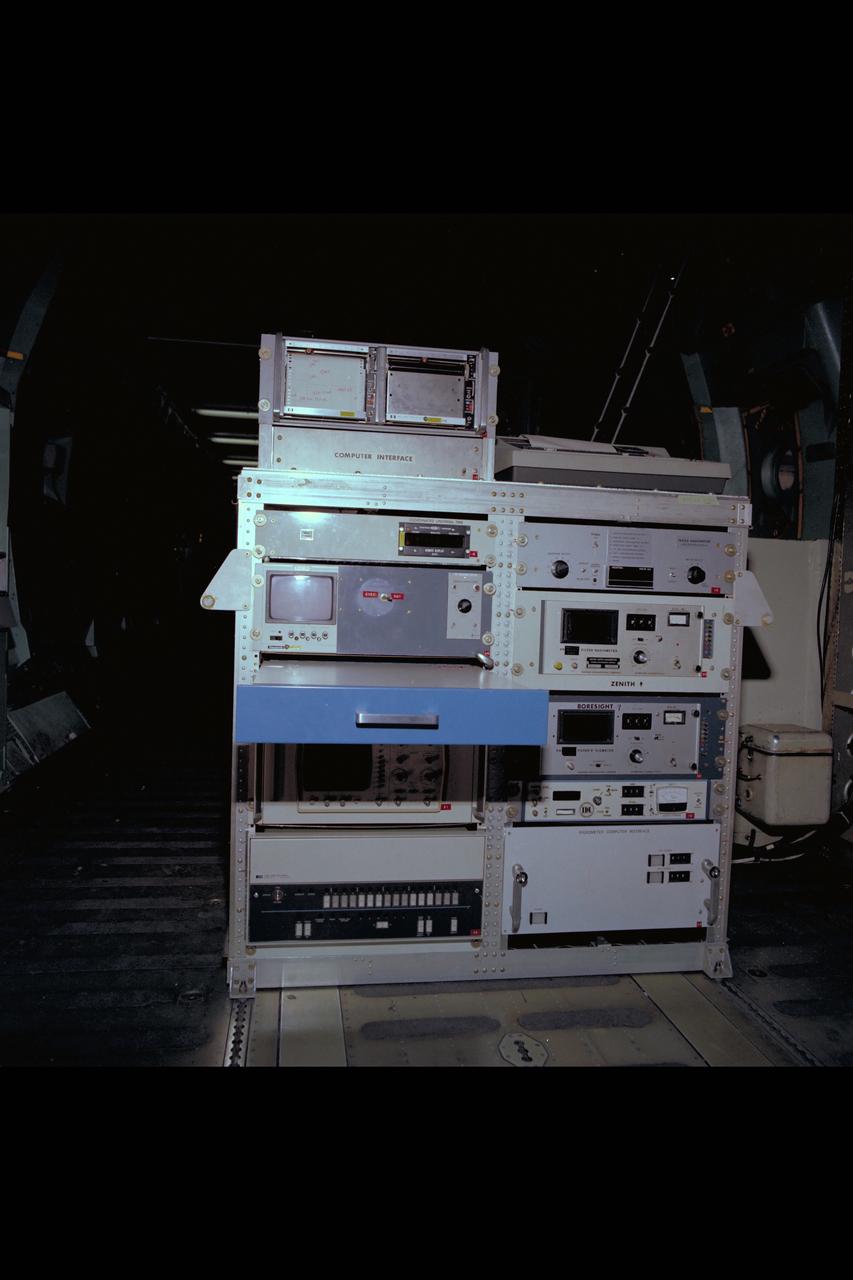
C-141 KAO: CAT experiment

C-141 KAO: CAT equipment
C-141 KAO: CAT equipment
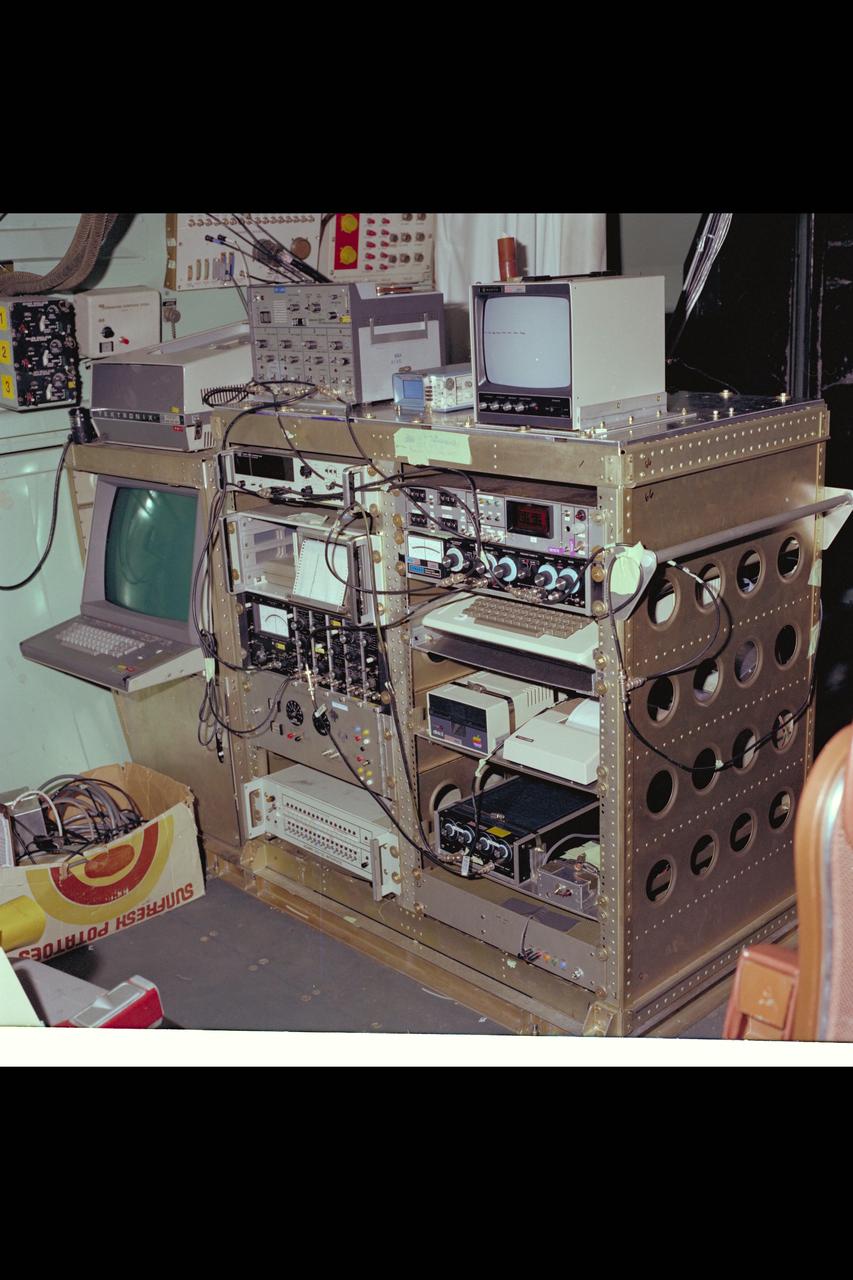

C-141 KAO: CAT equipment
C-141 KAO: CAT experiement

C-141 KAO: CAT Experiment
C-141 KAO: CAT Experiment
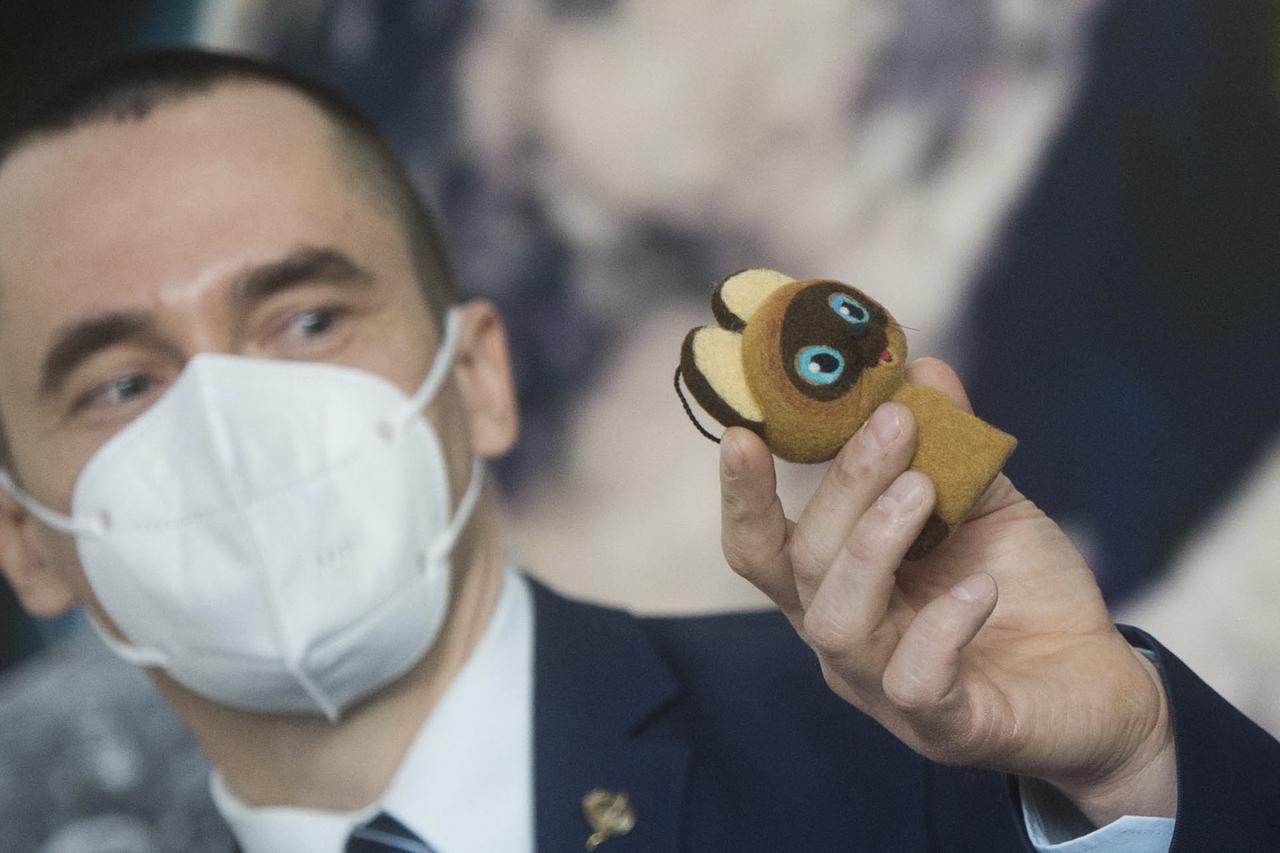

Expedition 65 prime crew member Oleg Novitskiy of Roscosmos, holds up a toy cat that will be used in the Soyuz capsule to help indicate the start of weightlessness after leaving the Earth’s atmosphere, Wednesday, March 24, 2021 at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center (GCTC) in Star City, Russia. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
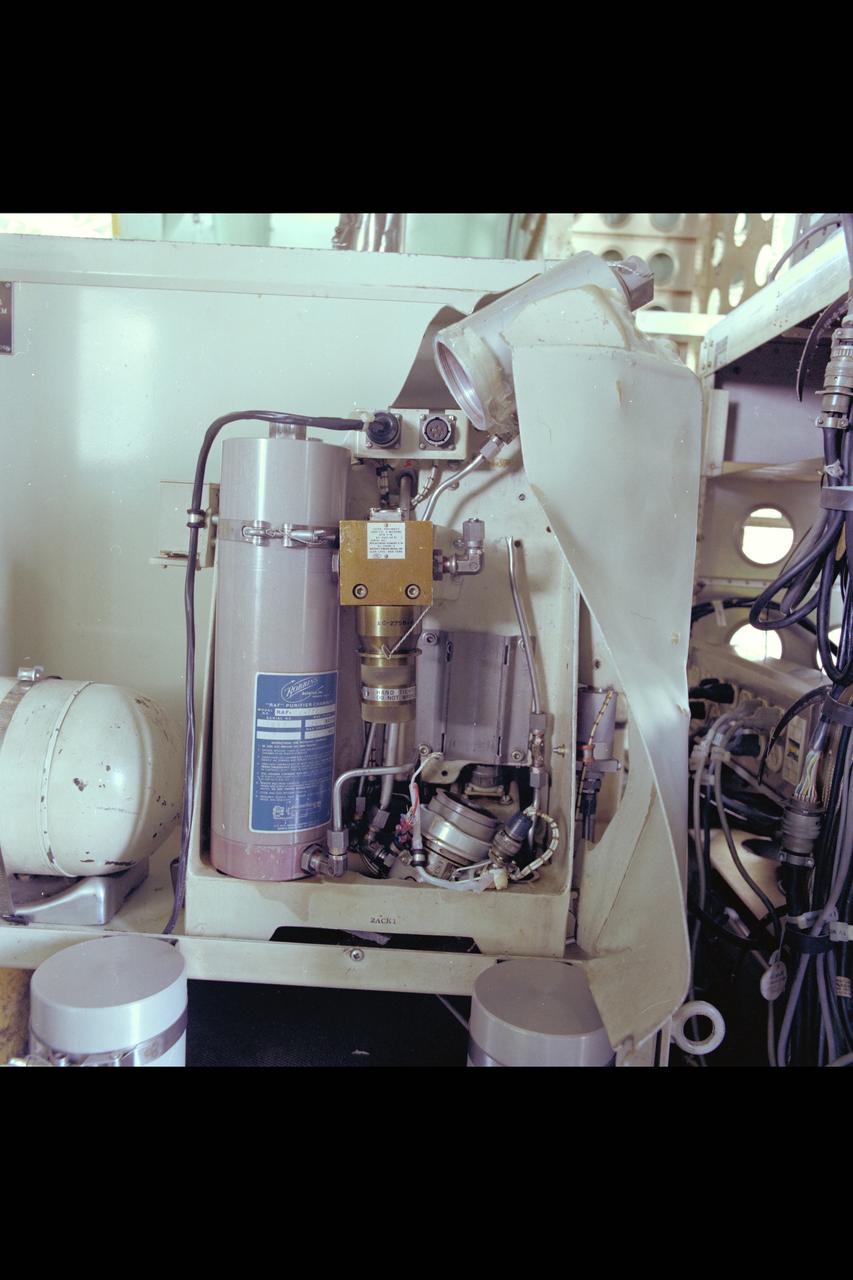

C-141 KAO: CAT experiment - compressor damage

C-141 KAO: CAT experiment - Damage Compressor
C-141 KAO: CAT experiment - Damage Compressor
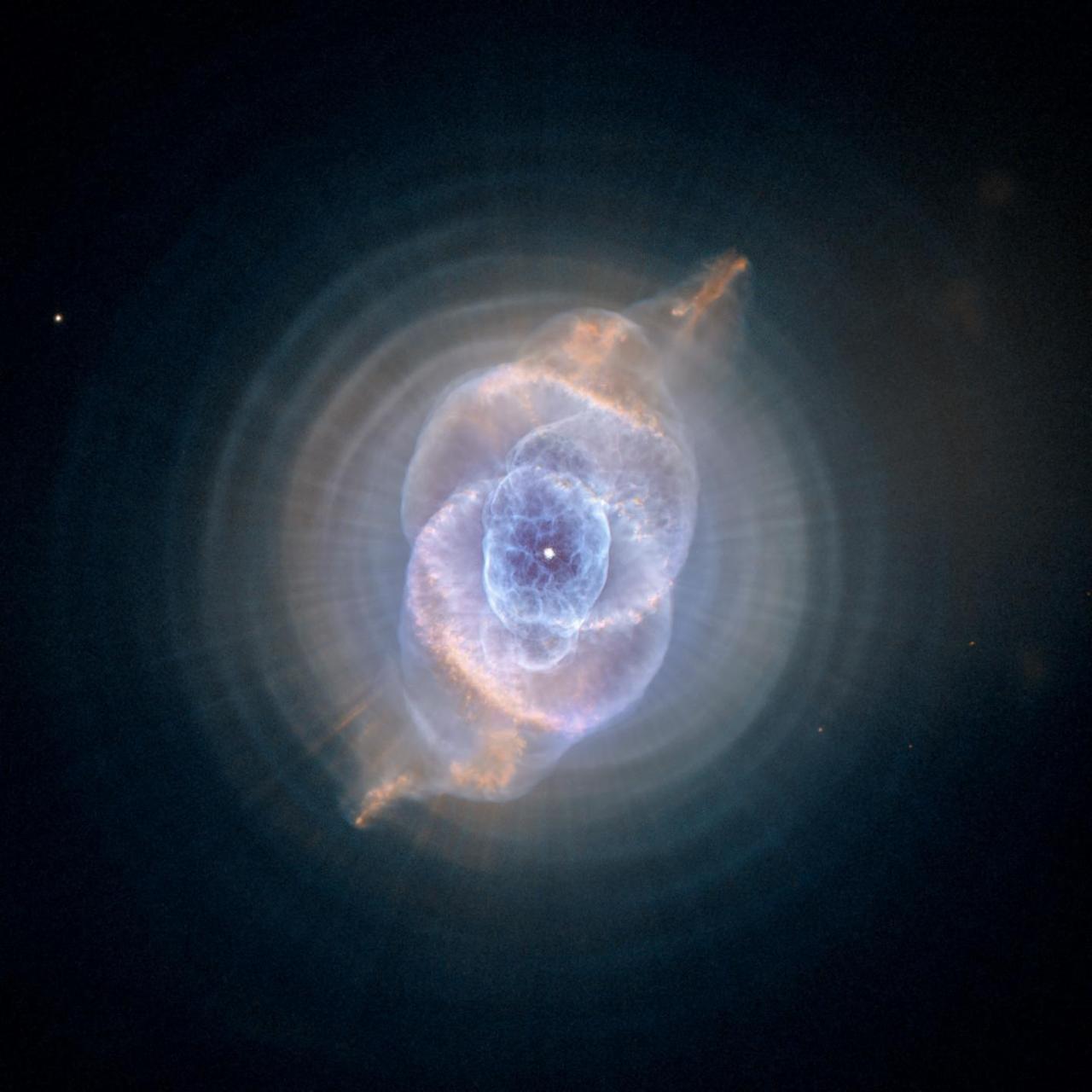

This detailed view of NGC 6543, the Cat Eye Nebula, from NASA Hubble Space Telescope includes intricate structures, including concentric gas shells, jets of high-speed gas, and unusual shock-induced knots of gas.
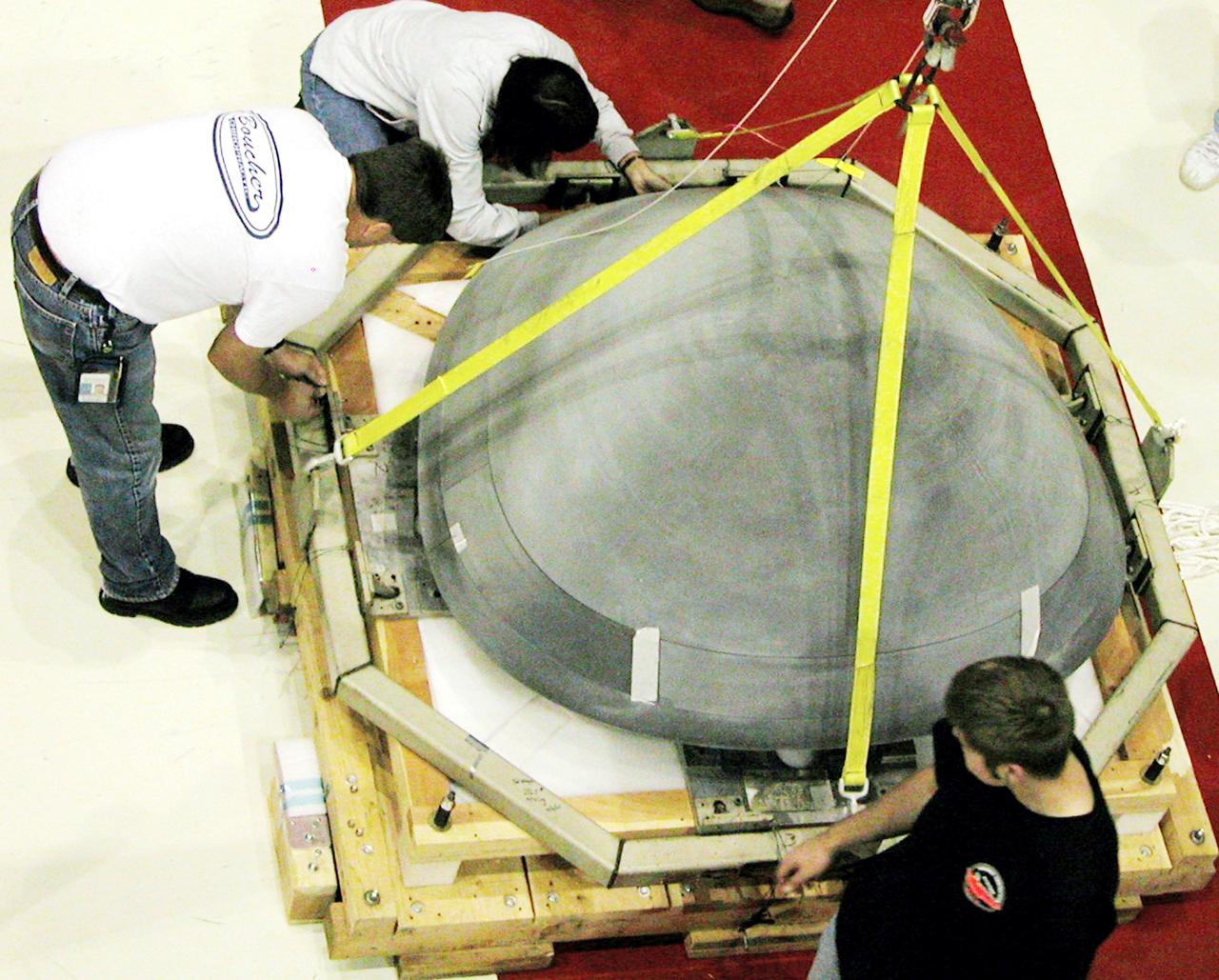

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap from Atlantis is secured on a shipping pallet. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap from Atlantis is lowered toward a shipping pallet. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.

C-141 KAO: Dr Fred Witteborn and Ames Science Team onbaord for CAT experiment
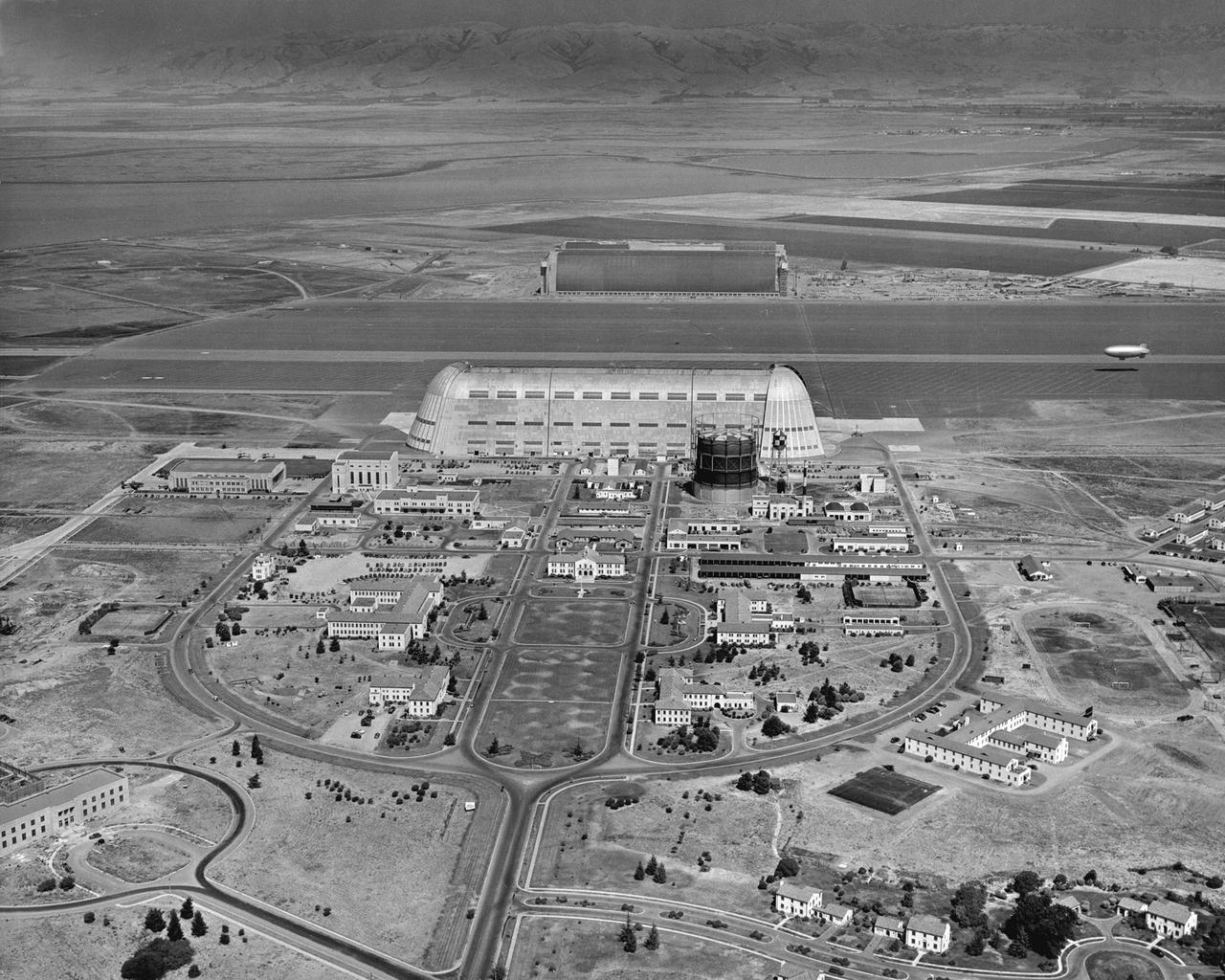

Navy NAS Sunnyvale, Moffett Field, Cat Altitude 1500ft E.S. East from front gate toward Shenandoah Plaza and Hangar One

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency leaders spoke to members of the news media on the Cloud-Aerosol Transport System. CATS will monitor cloud and aerosol coverage that directly impacts global climate. Participants included Matthew McGill, CATS principal investigator at Goddard. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
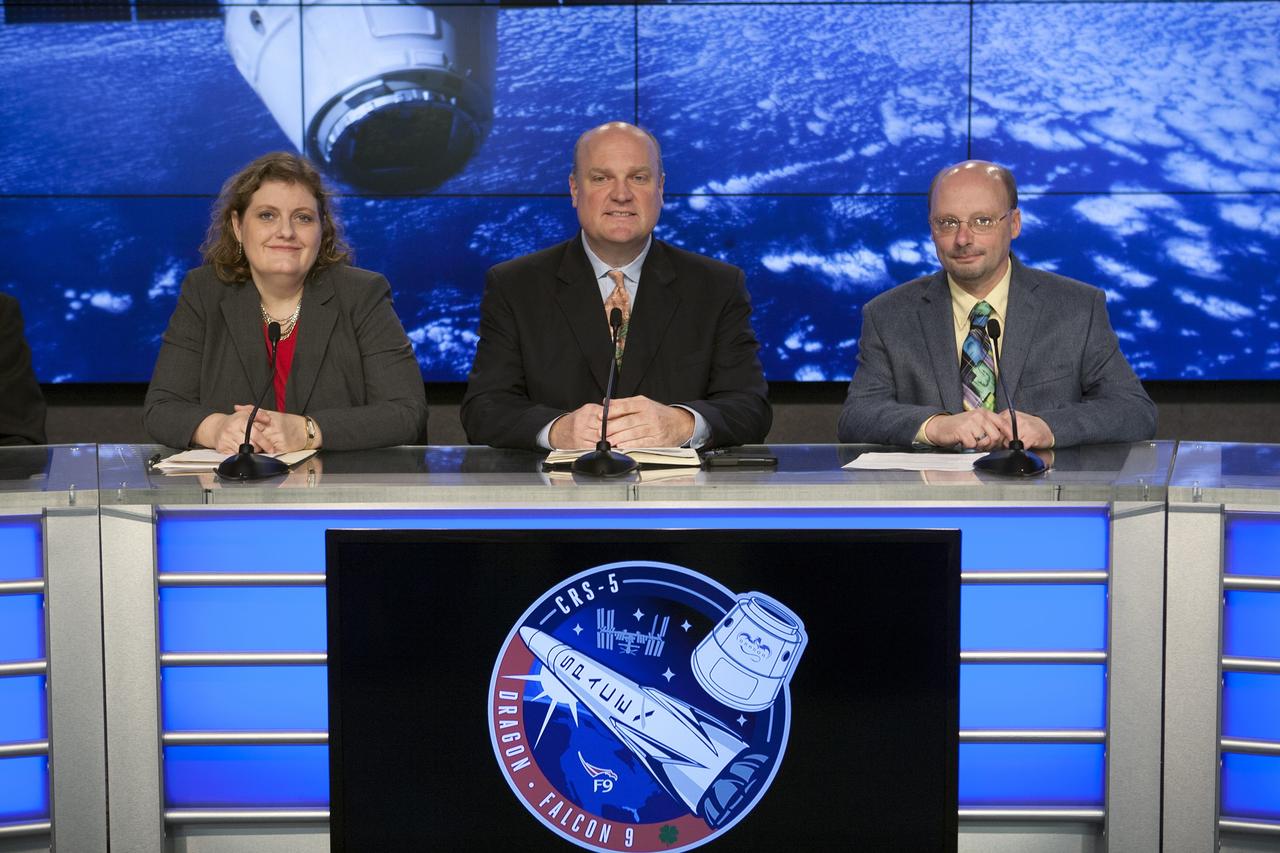

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency leaders spoke to members of the news media on the Cloud-Aerosol Transport System. CATS will monitor cloud and aerosol coverage that directly impacts global climate. From left are: Julie Robinson, ISS Program chief scientist at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, Robert Swap, program scientist at NASA Headquarters' Earth Science Division, and Matthew McGill, CATS principal investigator at Goddard. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope captured the Cat’s Eye nebula, or NGC 6543, is a well-studied example of a planetary nebula. Such objects are the glowing remnants of dust and gas expelled from moderate-sized stars during their last stages of life.

Matt McGill, Andrew Kopchock and John Yorks with Cloud Aerosol Transport System (CATS) as it leaves Goddard building 33 for shipment to Space X for installation at the International Space Station
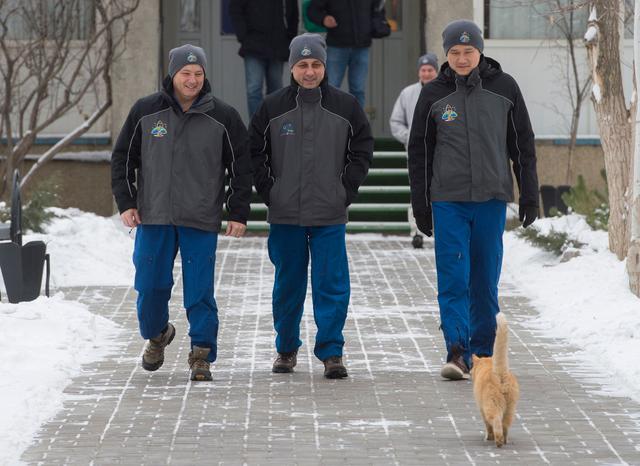

jsc2017e137336 - At their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 54-55 prime crewmembers Scott Tingle of NASA (left), Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos, center) and Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA, right) are greeted by a kitty cat Dec. 11 as they take a stroll around the grounds of the complex. Minus the kitty cat, they will launch Dec. 17 on the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome for a five month mission on the International Space Station...Andrey Shelepin / Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency leaders spoke to members of the news media on the Cloud-Aerosol Transport System. CATS will monitor cloud and aerosol coverage that directly impacts global climate. From left are: Mike Curie of NASA Public Affairs, Julie Robinson, ISS Program chief scientist at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, Robert Swap, program scientist at NASA Headquarters' Earth Science Division, and Matthew McGill, CATS principal investigator at Goddard. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
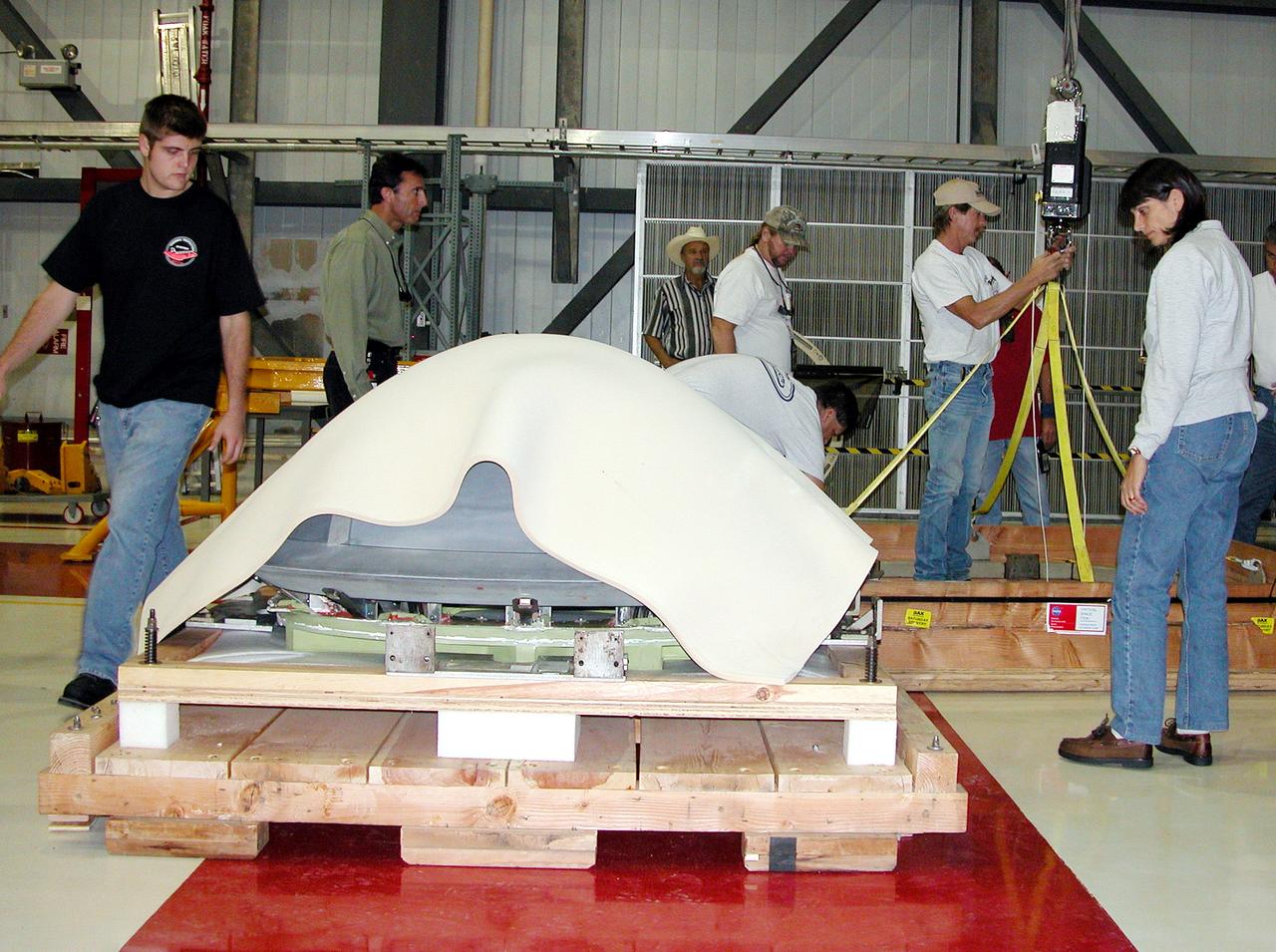

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, packing material is placed over the nose cap that was removed from Atlantis. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.
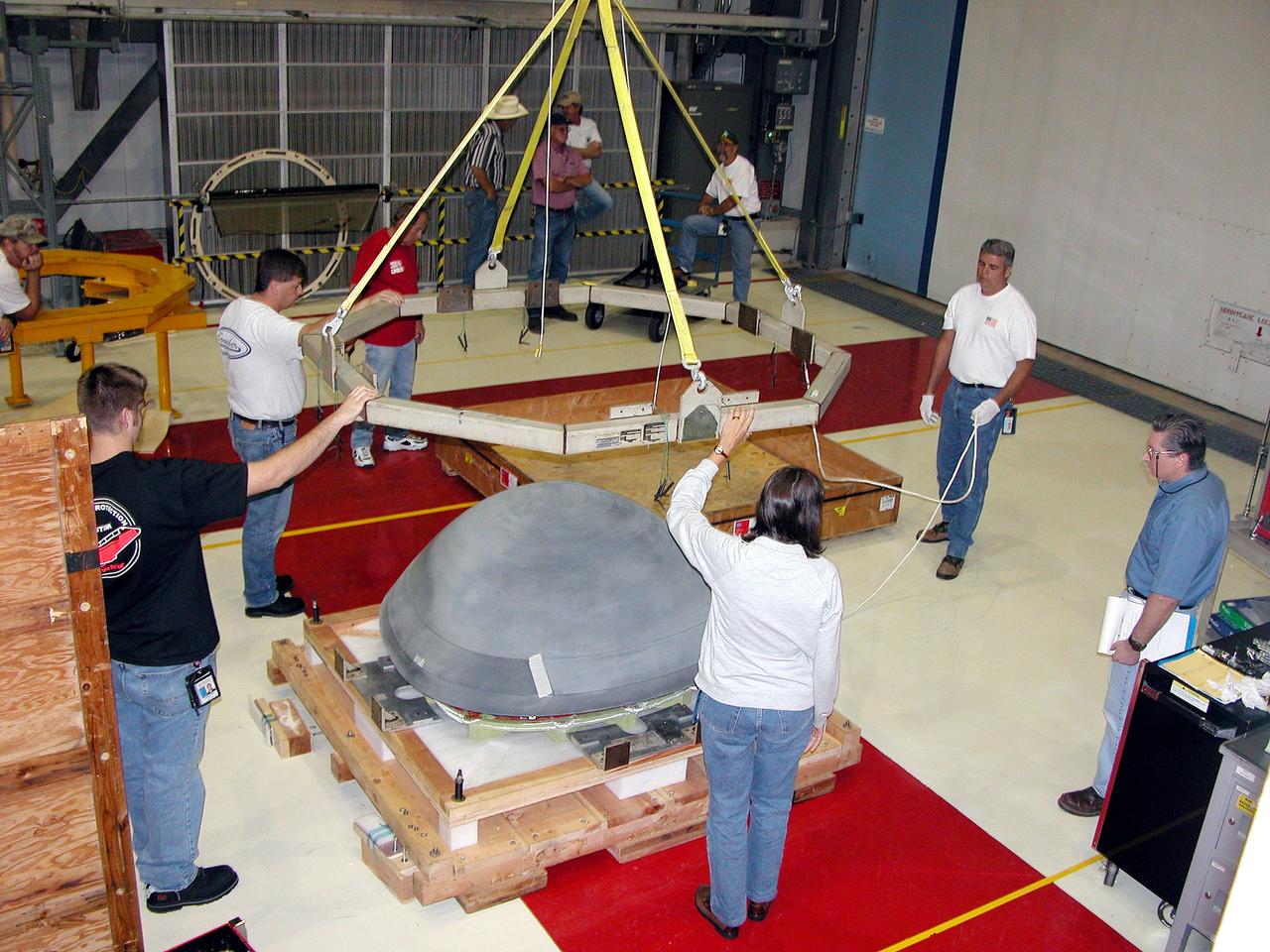

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers remove the overhead crane from the nose cap that was removed from Atlantis. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.
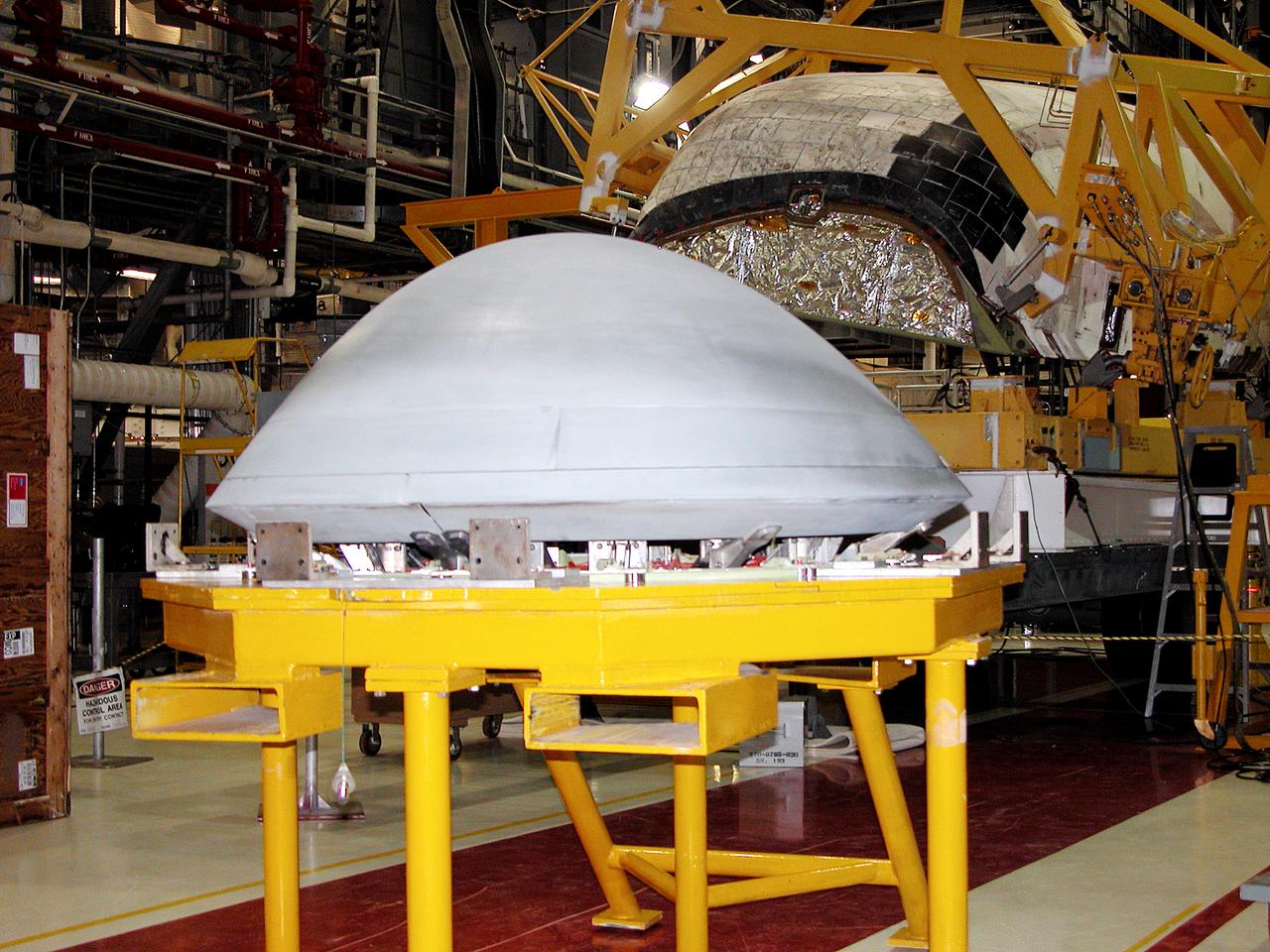

In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the nose cap (foreground) removed from Atlantis (behind) waits to be shipped to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.
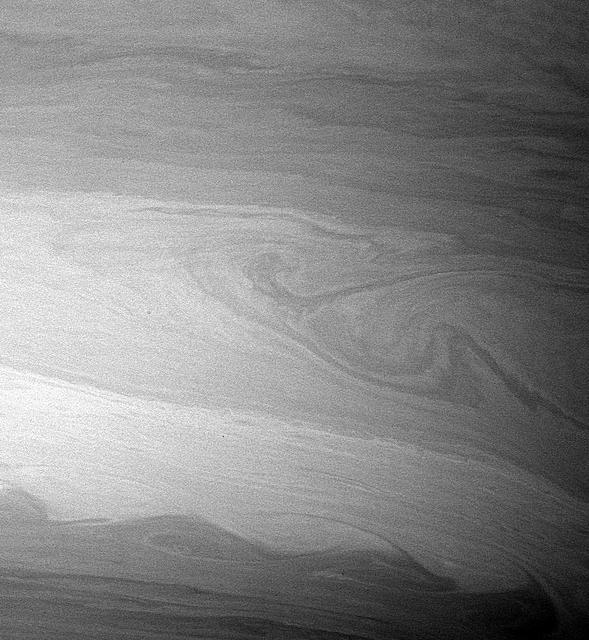

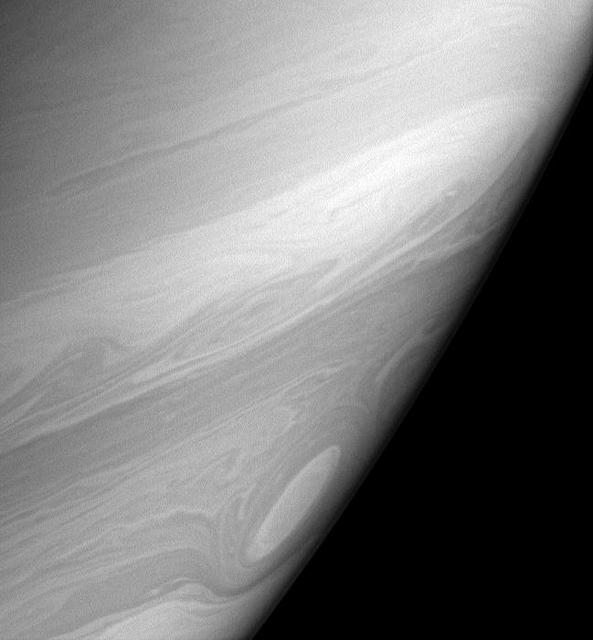
During its time in orbit, Cassini has spotted many beautiful cat's eye-shaped patterns like the ones visible here. These patterns occur in places where the winds and the atmospheric density at one latitude are different from those at another latitude. The opposing east-west flowing cloud bands are the dominant patterns seen here and elsewhere in Saturn's atmosphere. Contrast in the image was enhanced to aid the visibility of atmospheric features. The image was taken with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on Aug. 20, 2005. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07600

ISS026-E-033193 (10 March 2011) --- Cat Island, Commonwealth of the Bahamas, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member on the International Space Station. Cat Island is one of 29 islands, 661 cays, and 2,387 islets that form the Commonwealth of the Bahamas. Mount Alvernia, the highest point in the Bahamas at an elevation of approximately 63 meters above sea level, is located on the southeastern part of the island. Like most other islands in the Bahamas, Cat Island is located on a large depositional platform that is composed mainly of carbonate sediments and surrounding reefs. The approximately 77-kilometers-long island is the part of the platform continuously exposed above the water surface; this allows for soil development (brown to tan areas) and establishment of vegetation (green areas) to occur. Shallow water to the west-southwest of the island appears bright blue in this photograph (center) in contrast to the deeper ocean waters to the north, east, and south. The ocean surface near the southeastern half of the island has a slight grey tinge; this is due to sunglint, or light reflecting off of the water surface backs towards the observer onboard the space station. Small white cumulus clouds obscure some parts of the island. Named San Salvador prior to 1925, the island has been put forward as a candidate for Christopher Columbus’ first landfall in the Americas. Cat Island is inhabited, and had a total population of 1,647 in 2000 according to the Department of Statistics of the Bahamas. The smaller island of Little San Salvador to the west is privately owned and used as a port of call for cruise ships.

Expedition 65 prime crew member Oleg Novitskiy of Roscosmos, holds up a toy cat that will be used in the Soyuz capsule to help indicate the start of weightlessness after leaving the Earth’s atmosphere, Wednesday, March 24, 2021 at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center (GCTC) in Star City, Russia. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Irina Spector)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency leaders spoke to members of the news media on the Cloud-Aerosol Transport System. CATS will monitor cloud and aerosol coverage that directly impacts global climate. Participants included Julie Robinson, ISS Program chief scientist at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency leaders spoke to members of the news media on the Cloud-Aerosol Transport System. CATS will monitor cloud and aerosol coverage that directly impacts global climate. Participants included Robert Swap, program scientist at NASA Headquarters' Earth Science Division. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
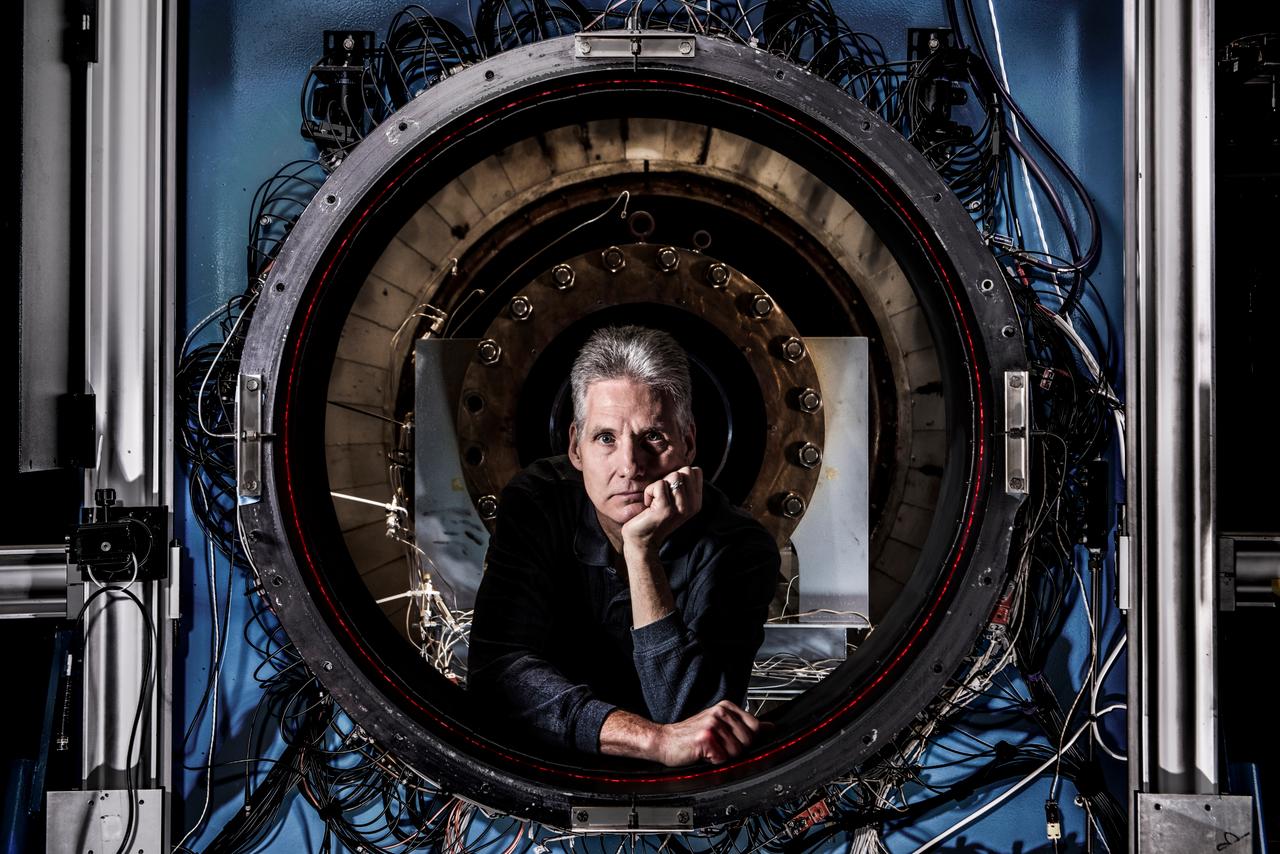

How do you measure a cloud? Tim Bencic does it with lasers. The NASA Glenn engineer invented a tomography system for our Propulsion Systems Lab to help understand the dangers of ice crystal icing on airplanes. Bencic’s system, affectionally called “Tim-ography” is like a CAT Scan. The laser light within its circular geometry bounces off the surface of ice particles in the cloud and fiber optic detectors map out its properties. This tool is helping NASA’s researchers make aircraft safer in challenging weather conditions.
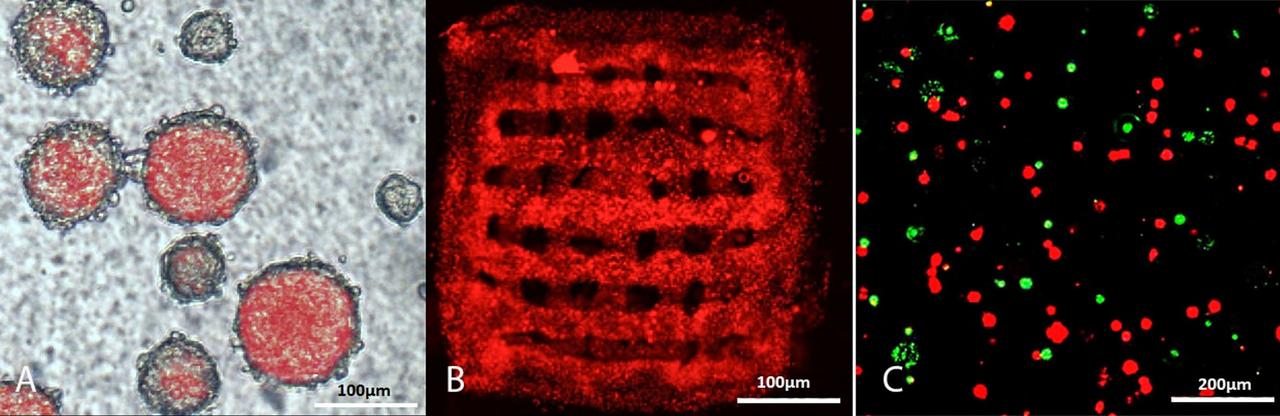
jsc2024e006078 (1/18/2024) --- A = Free floating BC neurospheres, produced from 11 days mouse embryo, expressing red fluorescent protein under actin promoter; B = 3D-printed BC neurospheres in gelatin scaffold 3 days after printing; C = BC neuropsheres survival after Maser15 microgravity exposure (NucGreen™ Dead 488 ReadyProbes (Invitrogen, Cat# R37109) staining for green dead BC neuropsheres, and live BC neurospheres imaged in red without staining). Credit: Uppsala University, Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology
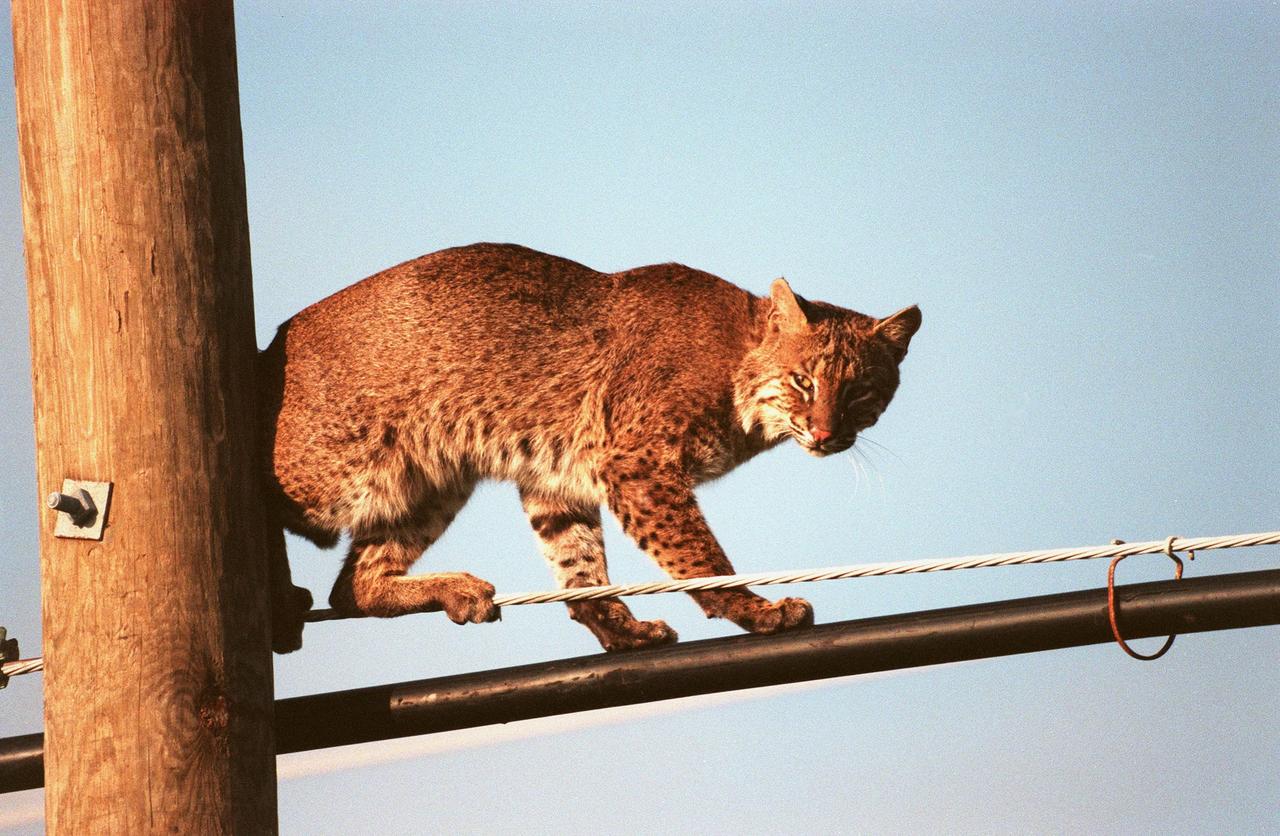

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A young, male bobcat balances gingerly on telephone pole cables next to the south-bound lane of Kennedy Parkway. The cat is nocturnal and is seldom observed during the day unless scared from its daytime shelter in the grass or beneath a shrub. Usually found in broken sections of heavily wooded or brushy country, bobcats are reported as common in scrub strand and roadside or weedy grass habitats at KSC. The bobcat is known to inhabit mangrove habitats and will readily swim across small bodies of water. The bobcat occurs across southern Canada then south over the entire United States, except for the midwestern corn belt, to southern Mexico. It is the last large mammalian predator remaining on KSC. The Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which is located on Kennedy Space Center property, is home to many species of wild animals, including the bobcat.
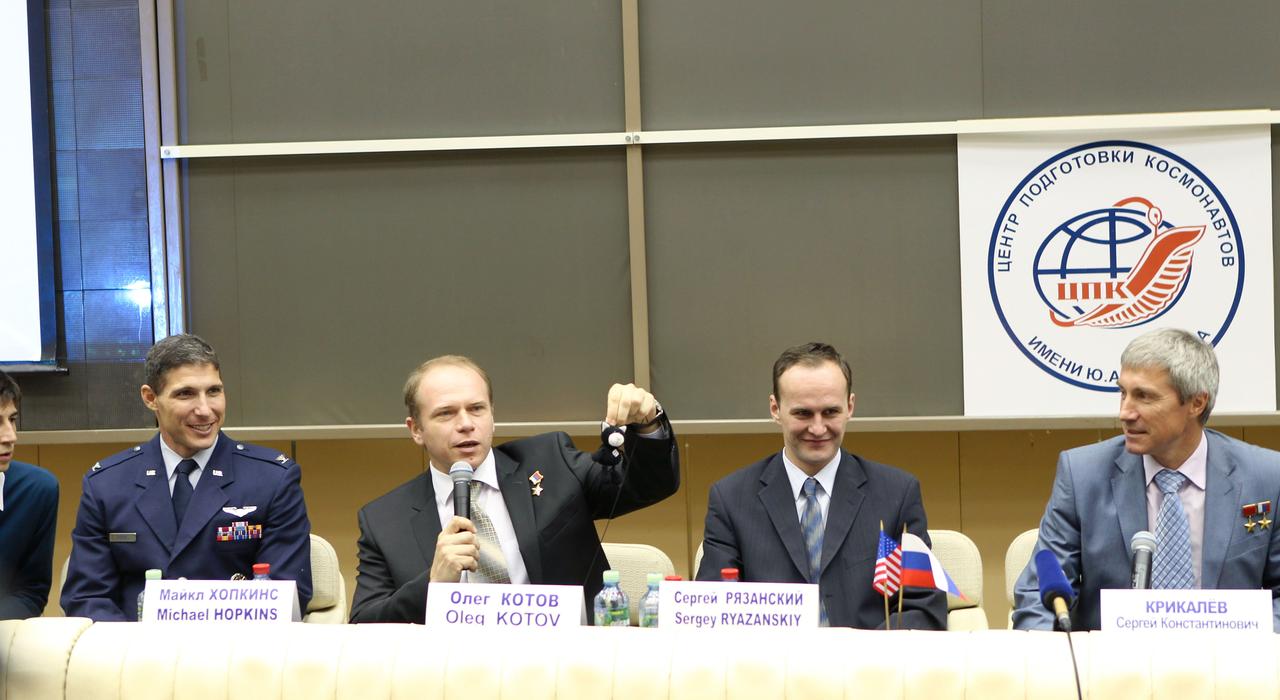

At the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City, Russia, Expedition 37/38 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kotov (second from left) holds a toy cat mascot during a pre-launch news conference Sept. 6 as his crewmates, Flight Engineer Michael Hopkins of NASA (far left) and Flight Engineer Sergey Ryazanskiy (second from the right) look on. Also participating in the news conference was the head of the Cosmonaut Training Center, Sergei Krikalev (far right). The mascot will be mounted inside the crew’s Soyuz TMA-10M spacecraft over Kotov’s head as a “zero-g indicator” once the crew launches. Their launch to the International Space Station is set for Sept. 26, Kazakh time, from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. NASA/Stephanie Stoll
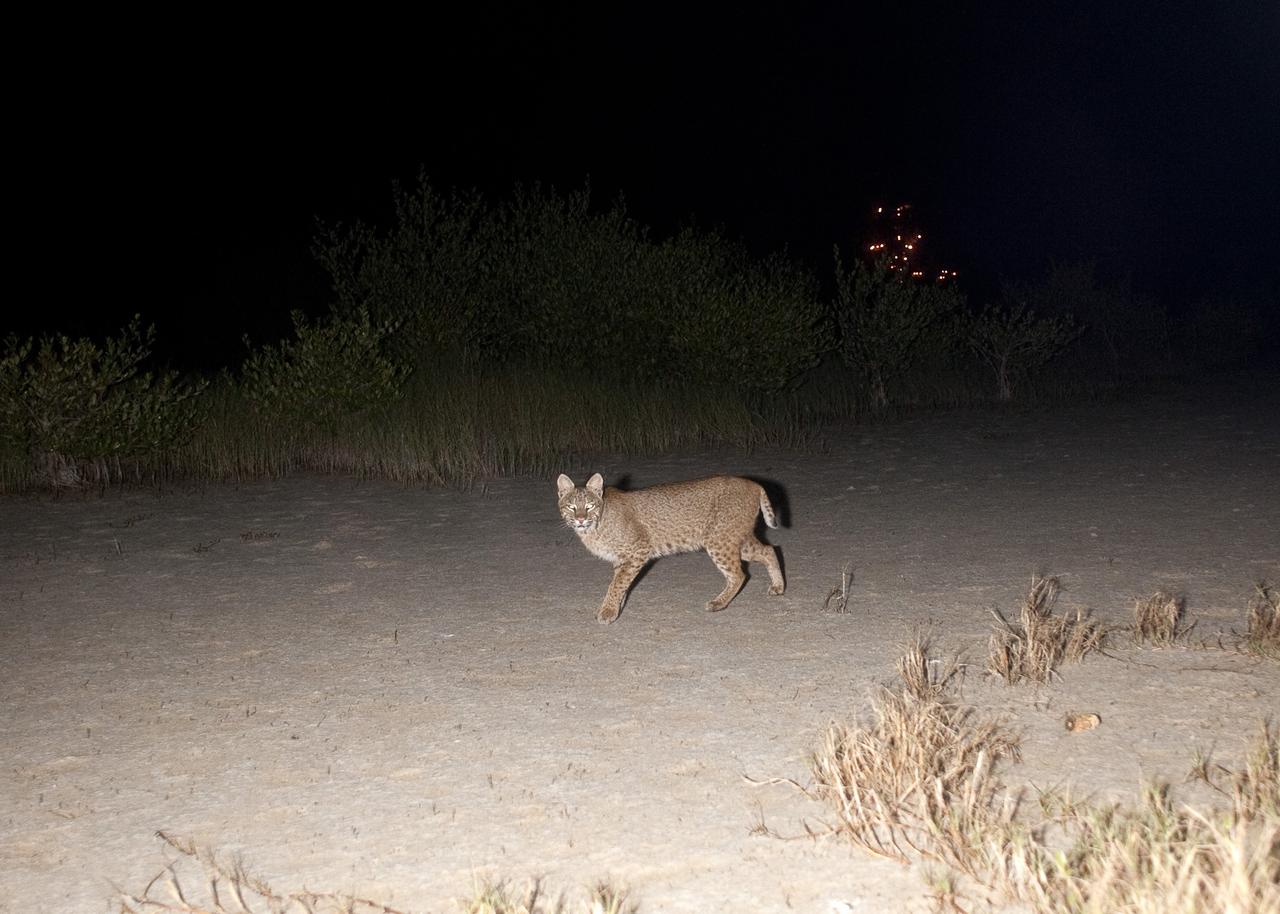

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Gotcha! A bobcat out on a nocturnal stroll triggers a motion-activated remote camera set up for this purpose at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cat is seldom observed during the day unless scared from its daytime shelter. It is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. In the background are the lights on Launch Pad 39A. Kennedy and the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge mutually reside on 140,000 acres on central Florida’s east coast. The area’s coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks provide habitats for more than 1,500 species of plants and animals, including about 331 species of birds. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray
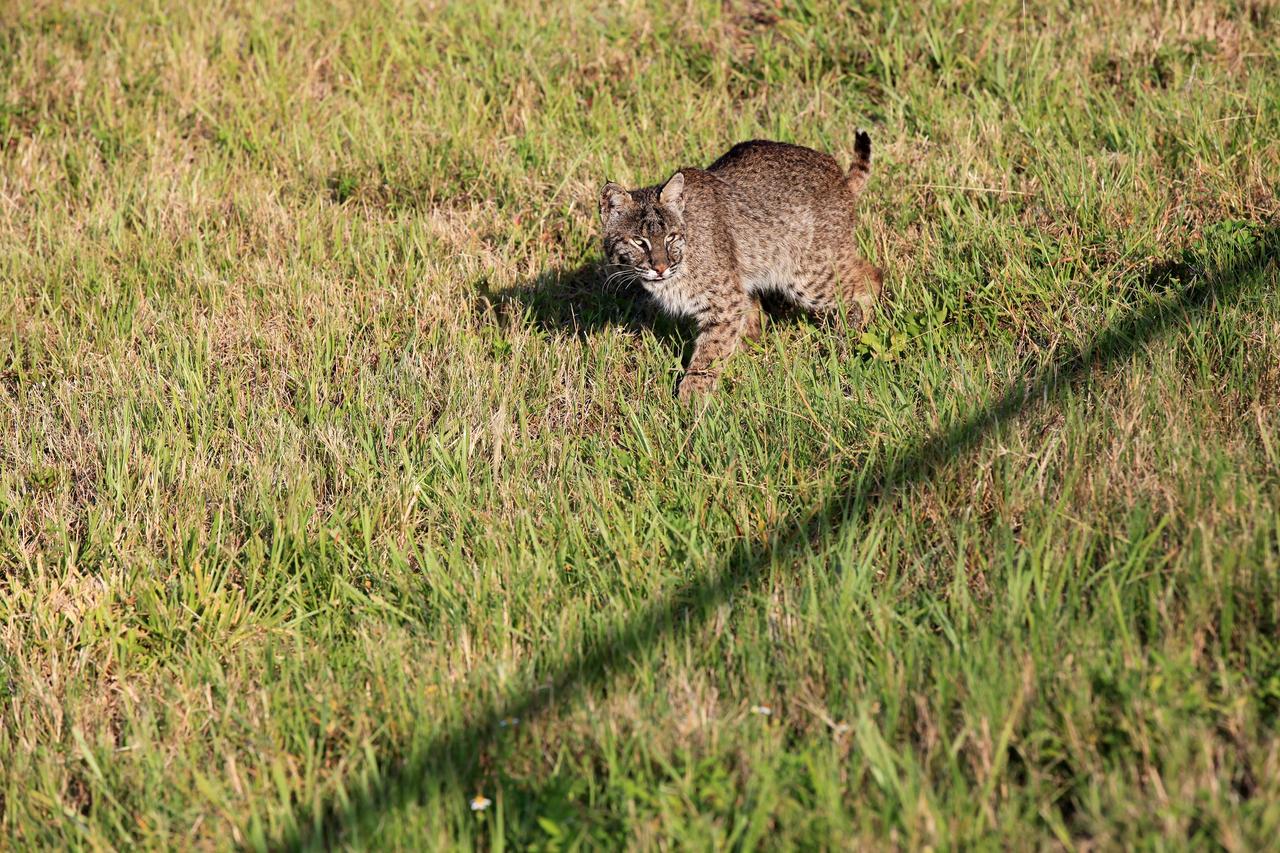

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A bobcat is startled to be discovered near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center, the only launch site for crewed missions from U.S. soil, coexists with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which encompasses 140,000 acres. The cat is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. The refuge provides a wide variety of habitats, including coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks, and is a sanctuary for more than 1,500 species of plants and animals, including more than 330 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. For additional information about the refuge, visit http://www.fws.gov/merrittisland. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
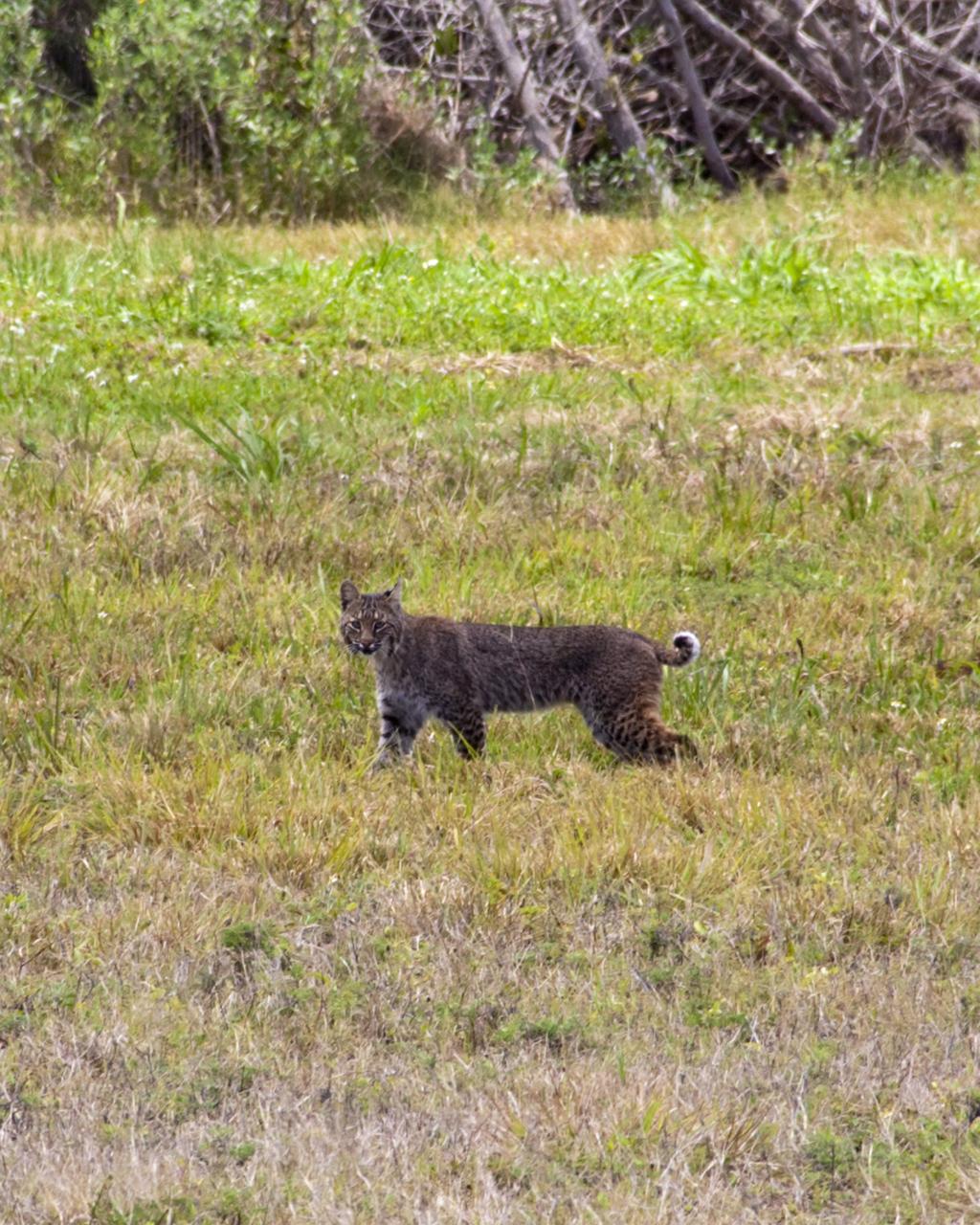

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A bobcat on the causeway between NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida pauses to check out the photographer who chanced upon it during the hunt for its next meal. The cat is seldom observed during the day unless scared from its daytime shelter. It is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. Kennedy and the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge mutually reside on 140,000 acres on central Florida’s east coast. The area’s coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks provide habitats for more than 1,000 species of plants and animals, including about 331 species of birds. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
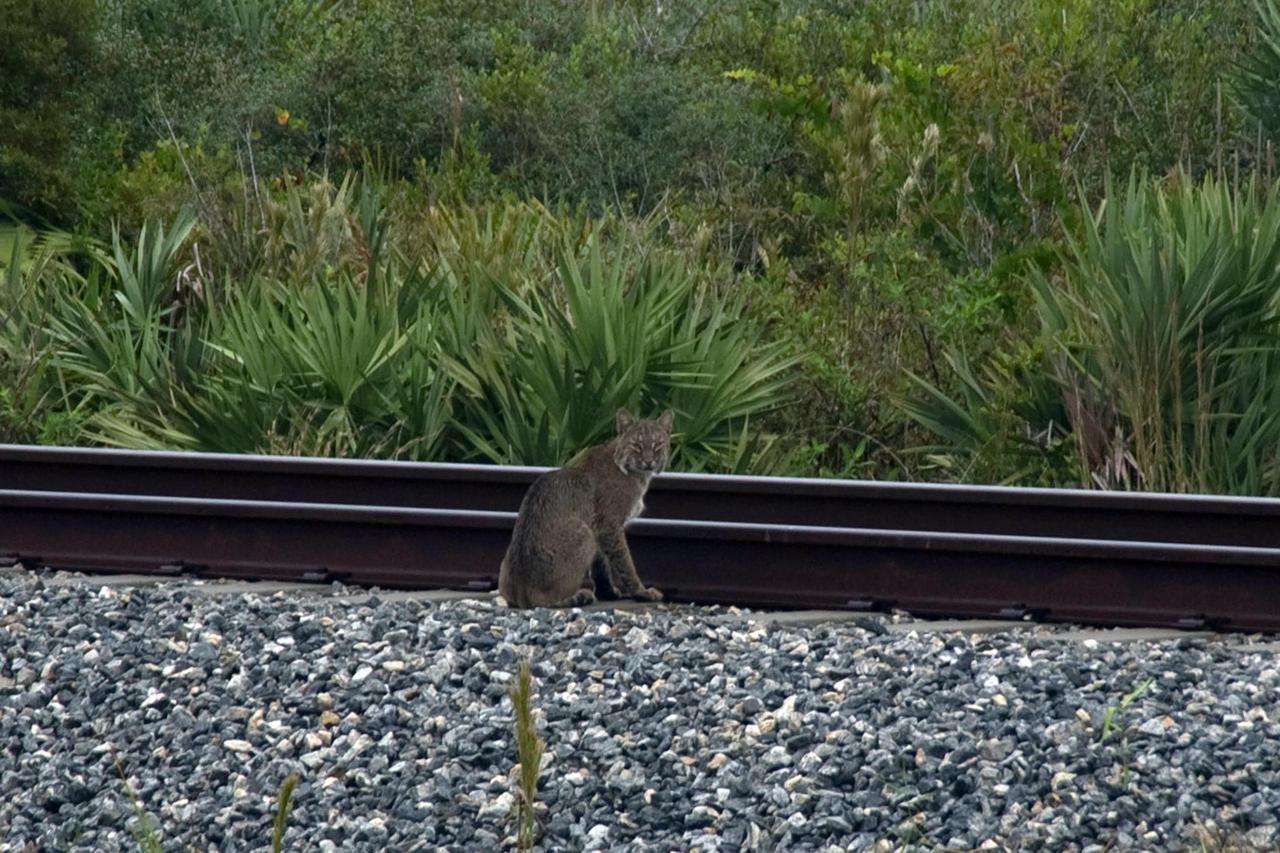

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A rare view of a bobcat, spotted near the NASA Railroad tracks on a mid-morning. The bobcat is a solitary and territorial predator mammal. They are mostly nocturnal and solitary, but will travel long distances for a mate. Not as big as a panther, but about the size of a medium-sized dog, male and female bobcats average 39 inches and 36 inches in length, and 24 pounds and 15 pounds in weight, respectively. They are most easily identified by their short tails which are about 5.5 inches long. Their fur, which is short, soft and dense, ranges from light tan to reddish or yellowish brown and markings vary from tabby stripes to spotting. They swim more than other native cats. The backs of their ears are white with a black outline. Their underparts are generally white. Bobcats can most likely be found in every county in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph
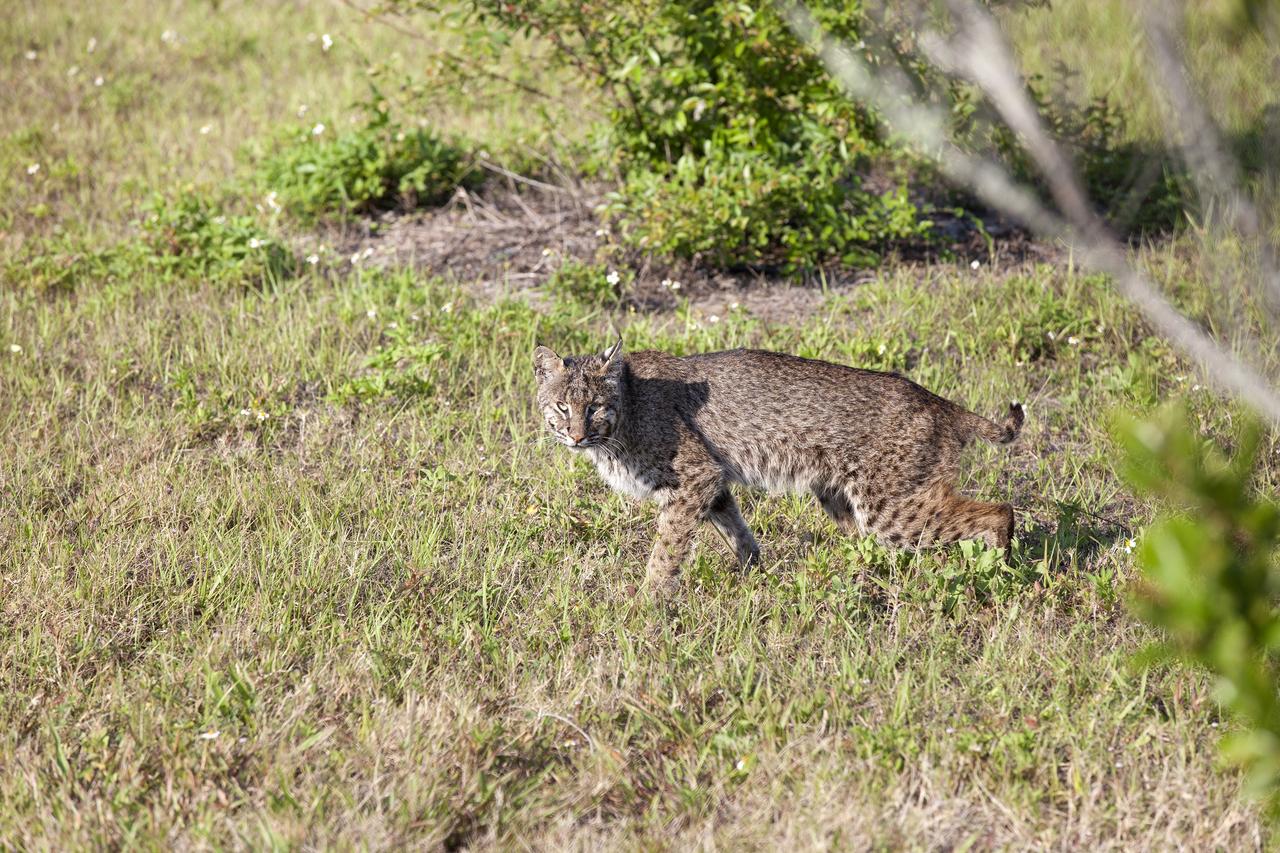

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A bobcat prowls through the grass near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center, the only launch site for crewed missions from U.S. soil, coexists with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which encompasses 140,000 acres. The cat is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. The refuge provides a wide variety of habitats, including coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks, and is a sanctuary for more than 1,500 species of plants and animals, including more than 330 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. For additional information about the refuge, visit http://www.fws.gov/merrittisland. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
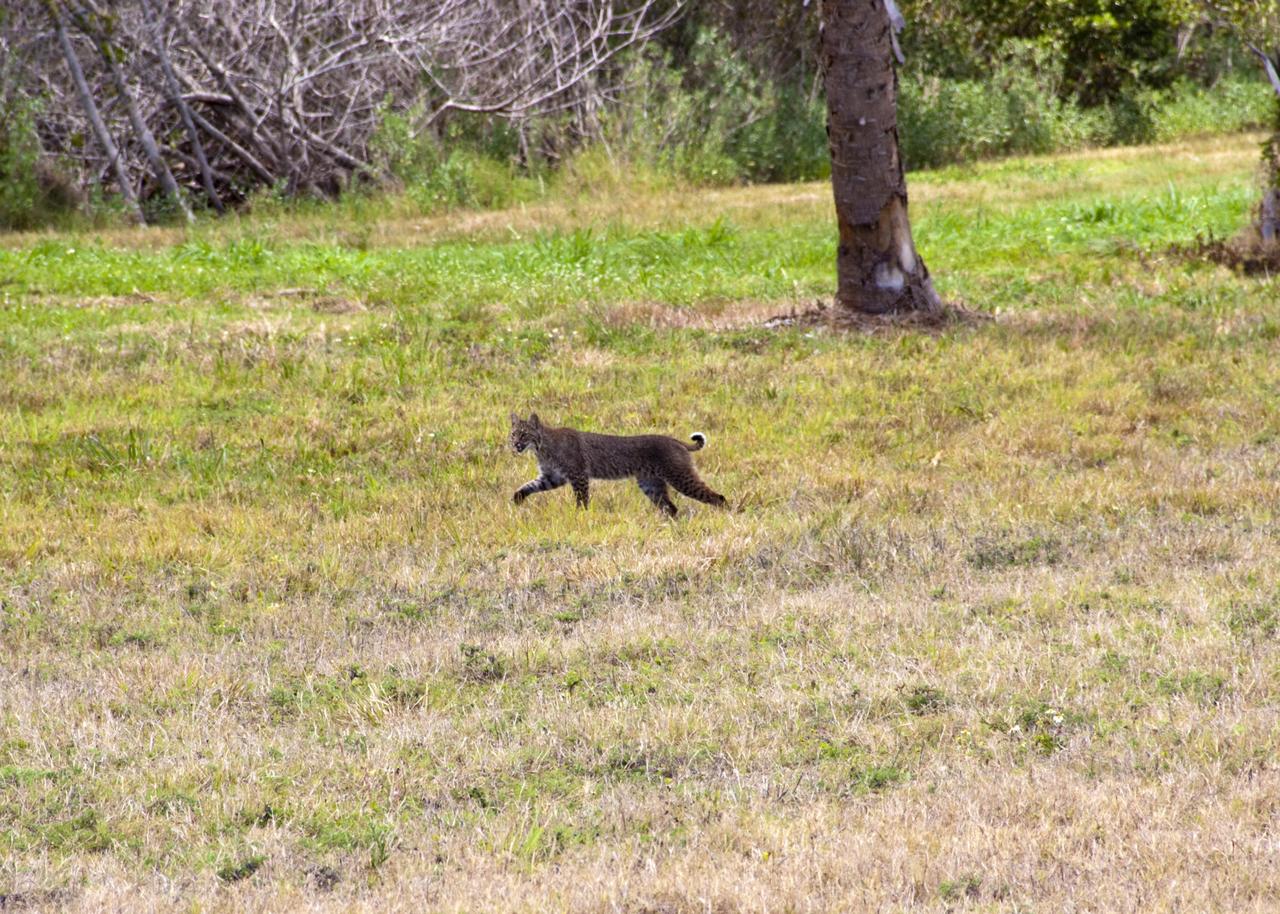

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A bobcat strolls across the causeway between NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, oblivious to everything but the hunt for its next meal. The cat is seldom observed during the day unless scared from its daytime shelter. It is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. Kennedy and the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge mutually reside on 140,000 acres on central Florida’s east coast. The area’s coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks provide habitats for more than 1,000 species of plants and animals, including about 331 species of birds. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
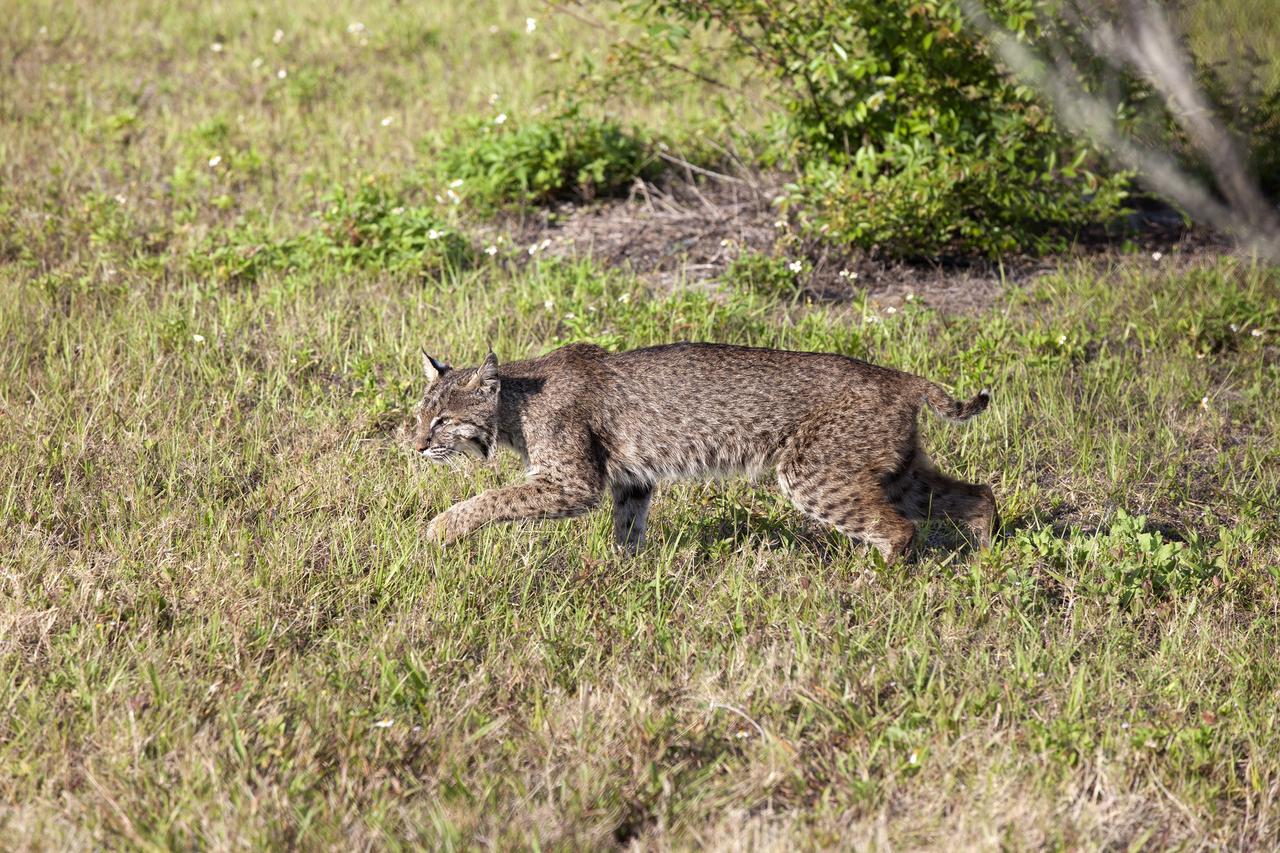

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A bobcat retreats from the limelight near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center, the only launch site for crewed missions from U.S. soil, coexists with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which encompasses 140,000 acres. The cat is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. The refuge provides a wide variety of habitats, including coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks, and is a sanctuary for more than 1,500 species of plants and animals, including more than 330 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. For additional information about the refuge, visit http://www.fws.gov/merrittisland. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
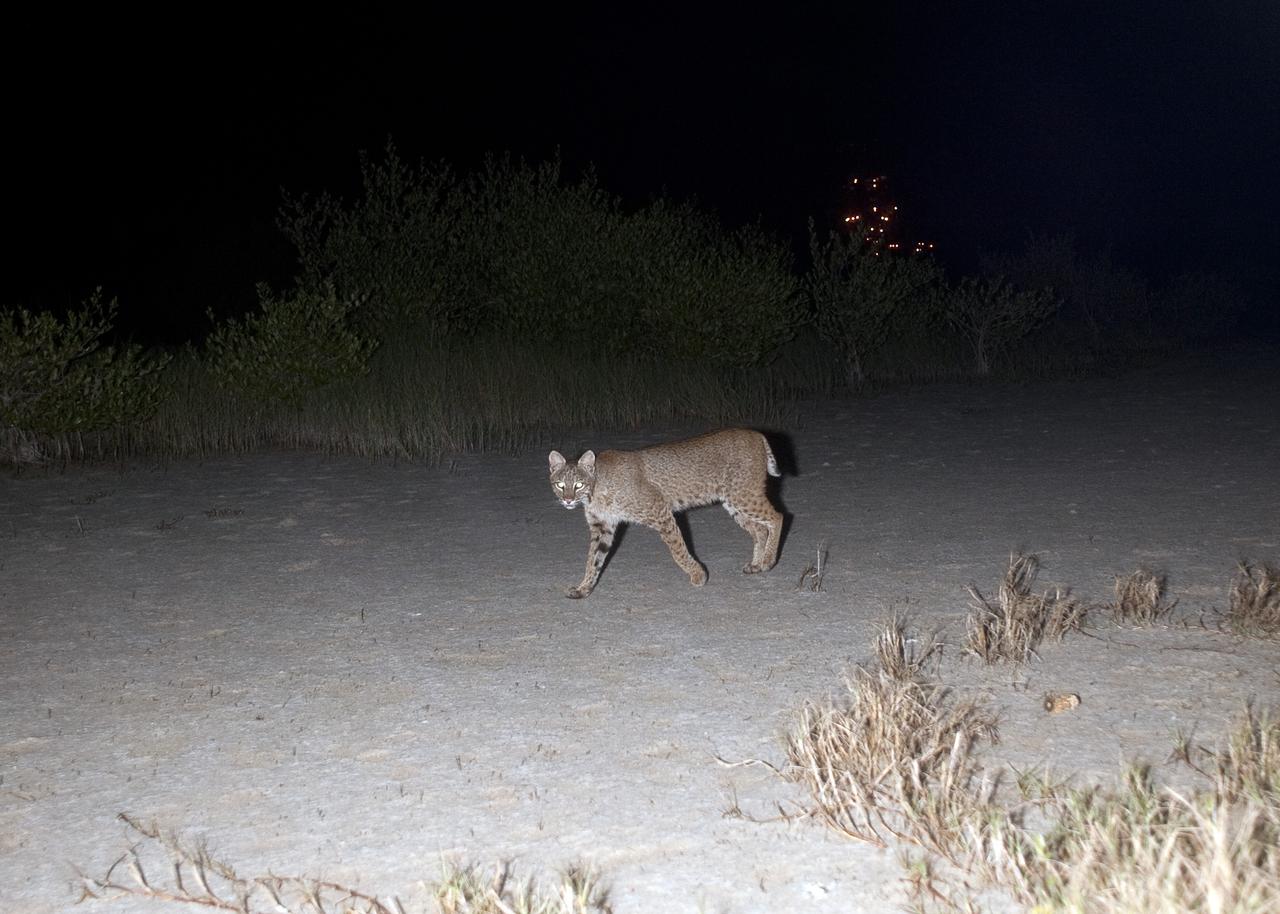

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Out on a nocturnal stroll, a bobcat triggers a motion-activated remote camera set up for this purpose at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cat is seldom observed during the day unless scared from its daytime shelter. It is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. In the background are the lights on Launch Pad 39A. Kennedy and the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge mutually reside on 140,000 acres on central Florida’s east coast. The area’s coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks provide habitats for more than 1,500 species of plants and animals, including about 331 species of birds. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray
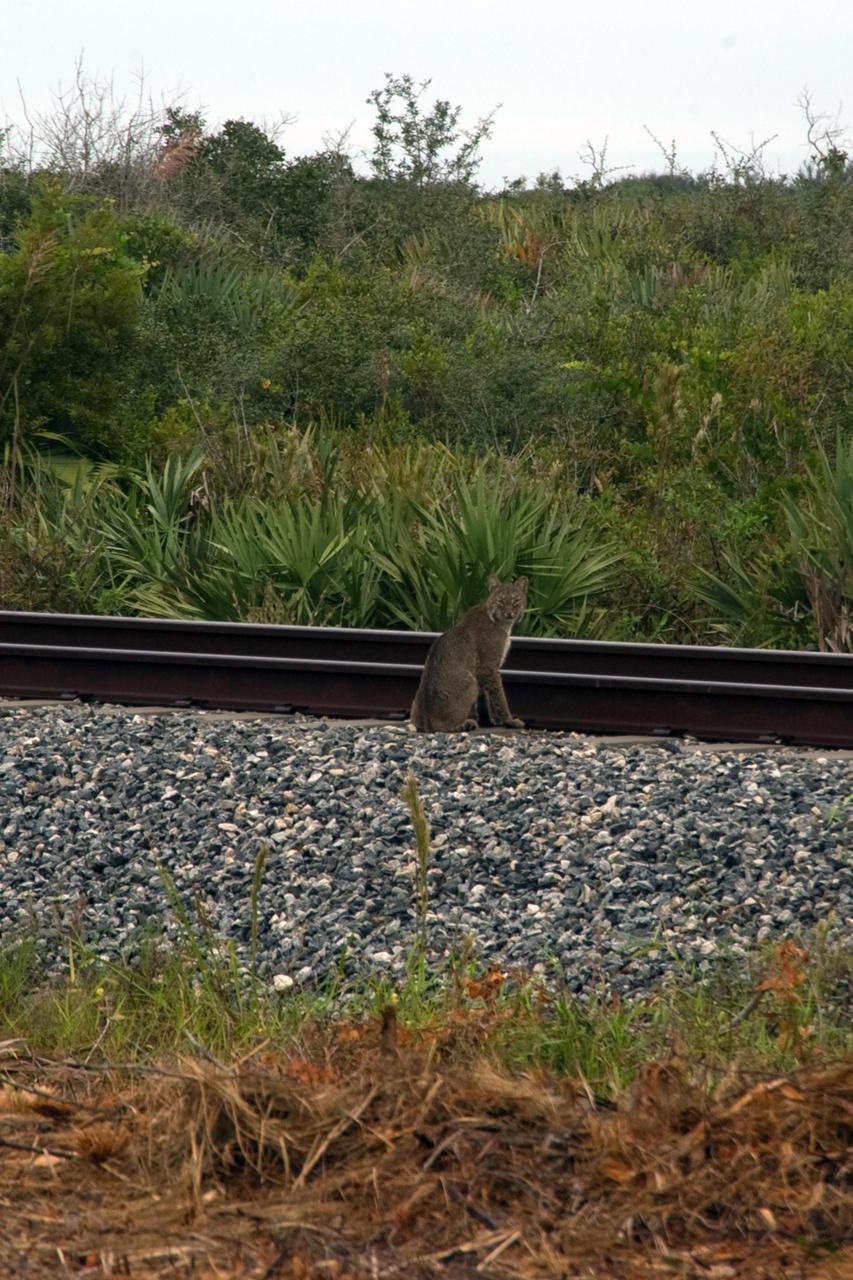

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A rare view of a bobcat, spotted near the NASA Railroad tracks on a mid-morning. The bobcat is a solitary and territorial predator mammal. They are mostly nocturnal and solitary, but will travel long distances for a mate. Not as big as a panther, but about the size of a medium-sized dog, male and female bobcats average 39 inches and 36 inches in length, and 24 pounds and 15 pounds in weight, respectively. They are most easily identified by their short tails which are about 5.5 inches long. Their fur, which is short, soft and dense, ranges from light tan to reddish or yellowish brown and markings vary from tabby stripes to spotting. They swim more than other native cats. The backs of their ears are white with a black outline. Their underparts are generally white. Bobcats can most likely be found in every county in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph
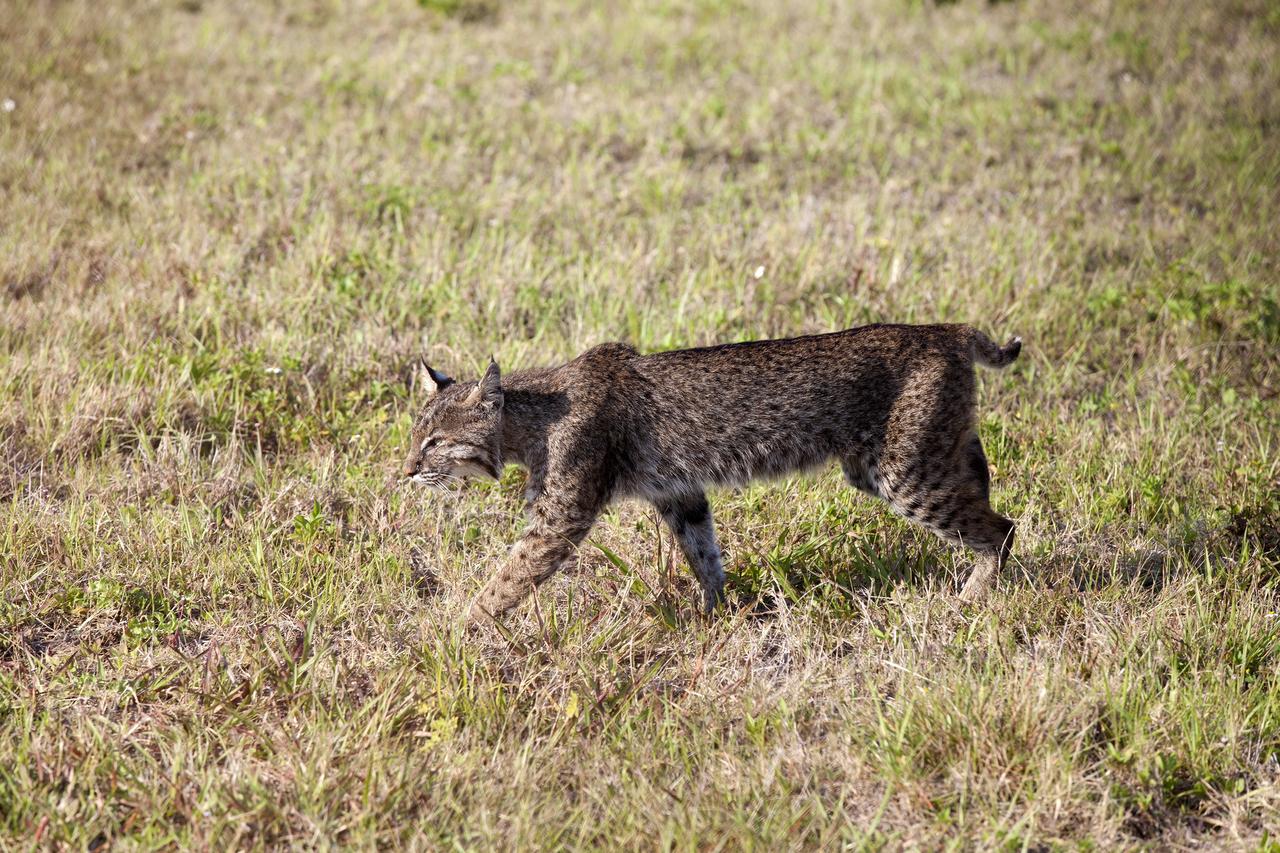

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A bobcat continues on its way past the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center, the only launch site for crewed missions from U.S. soil, coexists with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which encompasses 140,000 acres. The cat is the last large mammalian predator remaining on the center. The refuge provides a wide variety of habitats, including coastal dunes, saltwater estuaries and marshes, freshwater impoundments, scrub, pine flatwoods, and hardwood hammocks, and is a sanctuary for more than 1,500 species of plants and animals, including more than 330 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. For additional information about the refuge, visit http://www.fws.gov/merrittisland. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
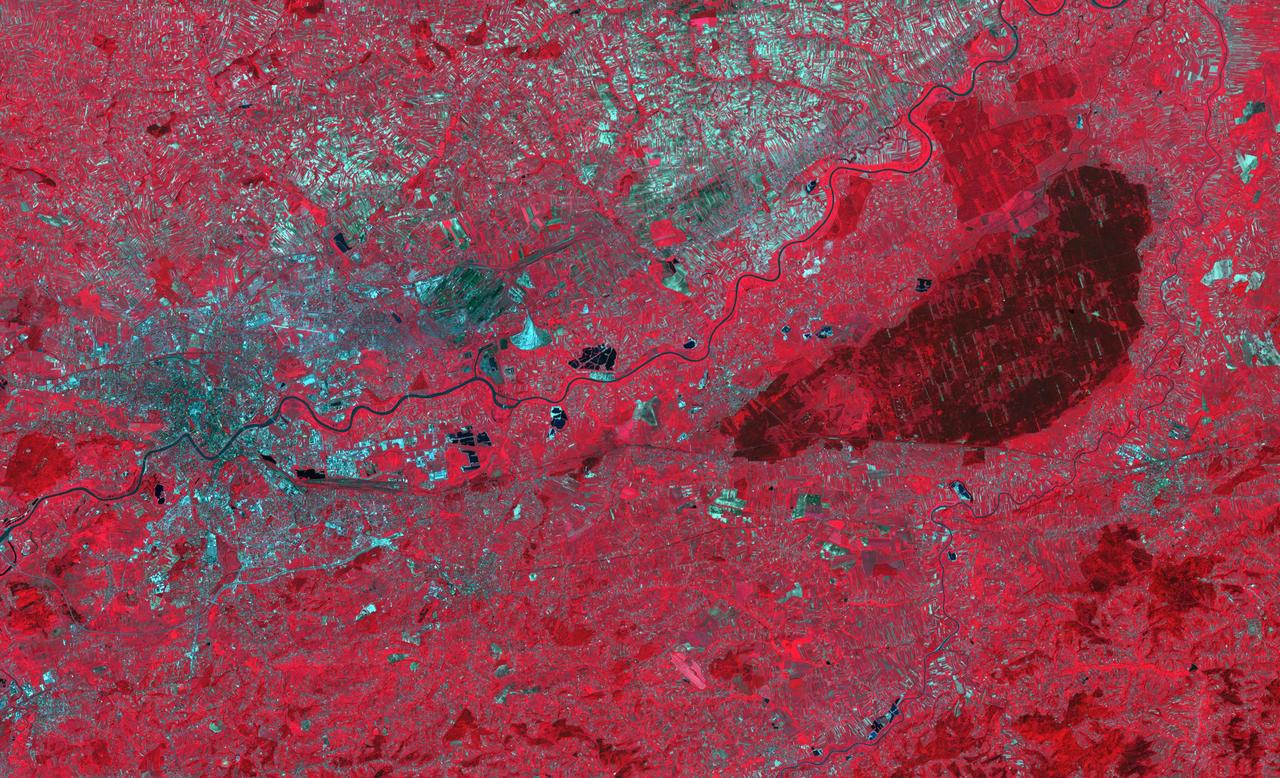

The Niepolmice Forest in Poland consists of six nature reserves, providing sanctuary for such threatened animals as lynx, wild cats and European Bison. Because of its proximity to Krakow, the old capital of Poland (left side of image), the forest (right side of image, dark red area) was a hunting ground for Polish Royalty beginning in the 13th century. The image was acquired May 25, 2003, covers an area of 29.5 by 48.5 km, and is located at 50 degrees north, 20.4 degrees east. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of about 50 to 300 feet (15 to 90 meters), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and data products. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23678
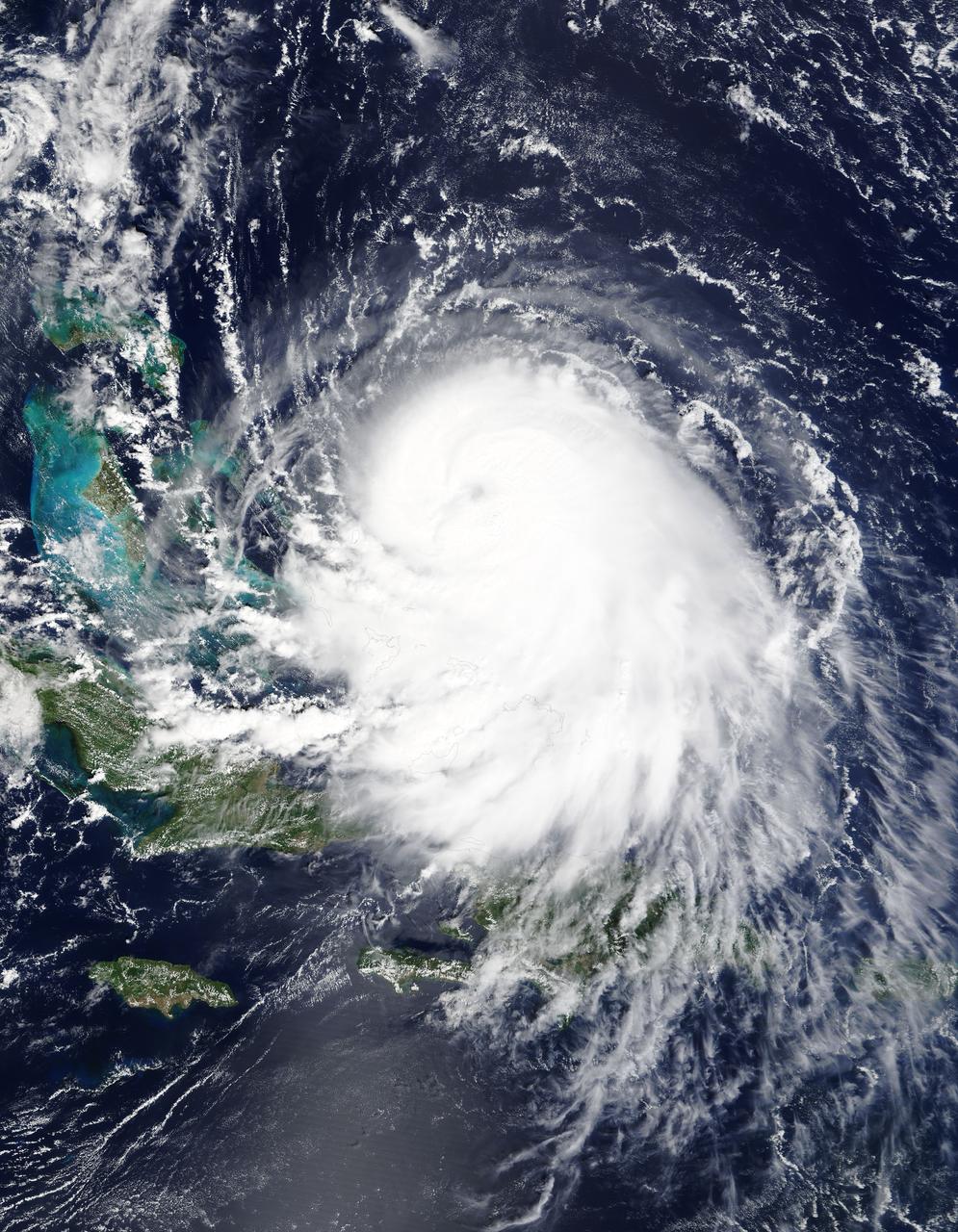

The MODIS instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured Hurricane Joaquin off the Bahamas at 15:45 UTC (11:45 a.m. EDT) on September 30, 2015. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on Wednesday, September 30, 2015 the center of Hurricane Joaquin was located near latitude 24.7 North, longitude 72.6 West. That puts the center of Joaquin about 215 miles (345 km) east-northeast of the Central Bahamas. Joaquin became a tropical storm Monday evening (EDT), September 29 when it was midway between the Bahamas and Bermuda. By 8 a.m. EDT on September 30, it strengthened into a hurricane and has become the third hurricane of the Atlantic Hurricane season. On September 30, the National Hurricane Center issued a Hurricane Warning for the central Bahamas including Cat Island, the Exumas, Long Island, Rum Cay, and San Salvador. A Hurricane Watch is in effect for the northwestern Bahamas including the Abacos, Berry Islands, Bimini, Eleuthera, Grand Bahama Island, and New Providence, but excluding Andros Island. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
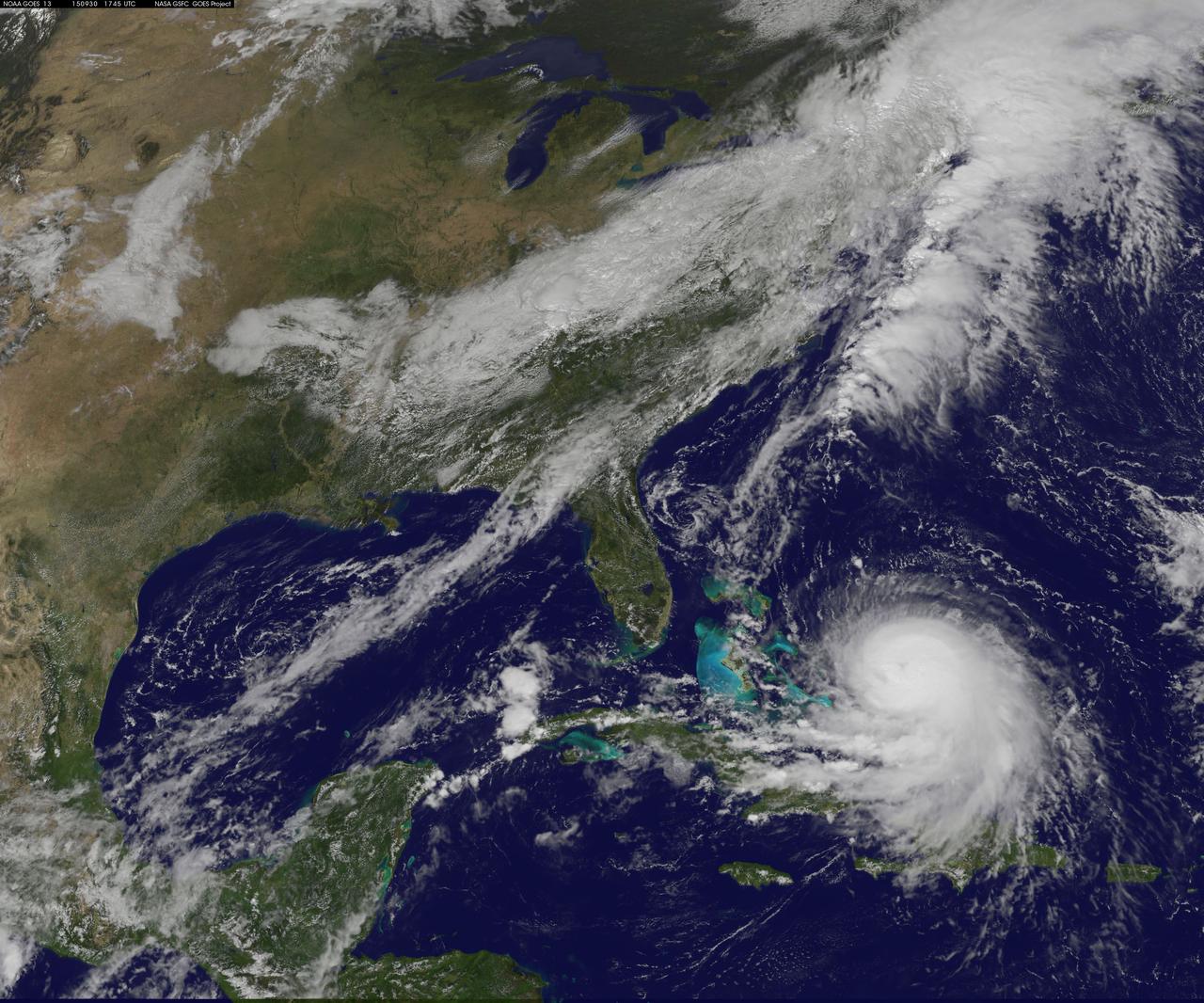
NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this visible image of Hurricane Joaquin east of the Bahamas on Sept. 30 at 1745 UTC (1:45 p.m. EDT). Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on Wednesday, September 30, 2015 the center of Hurricane Joaquin was located near latitude 24.7 North, longitude 72.6 West. That puts the center of Joaquin about 215 miles (345 km) east-northeast of the Central Bahamas. Joaquin became a tropical storm Monday evening (EDT), September 29 when it was midway between the Bahamas and Bermuda. By 8 a.m. EDT on September 30, it strengthened into a hurricane and has become the third hurricane of the Atlantic Hurricane season. On September 30, the National Hurricane Center issued a Hurricane Warning for the central Bahamas including Cat Island, the Exumas, Long Island, Rum Cay, and San Salvador. A Hurricane Watch is in effect for the northwestern Bahamas including the Abacos, Berry Islands, Bimini, Eleuthera, Grand Bahama Island, and New Providence, but excluding Andros Island. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this visible image of Hurricane Joaquin east of the Bahamas on Sept. 30 at 1745 UTC (1:45 p.m. EDT). Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on Wednesday, September 30, 2015 the center of Hurricane Joaquin was located near latitude 24.7 North, longitude 72.6 West. That puts the center of Joaquin about 215 miles (345 km) east-northeast of the Central Bahamas. Joaquin became a tropical storm Monday evening (EDT), September 29 when it was midway between the Bahamas and Bermuda. By 8 a.m. EDT on September 30, it strengthened into a hurricane and has become the third hurricane of the Atlantic Hurricane season. On September 30, the National Hurricane Center issued a Hurricane Warning for the central Bahamas including Cat Island, the Exumas, Long Island, Rum Cay, and San Salvador. A Hurricane Watch is in effect for the northwestern Bahamas including the Abacos, Berry Islands, Bimini, Eleuthera, Grand Bahama Island, and New Providence, but excluding Andros Island. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
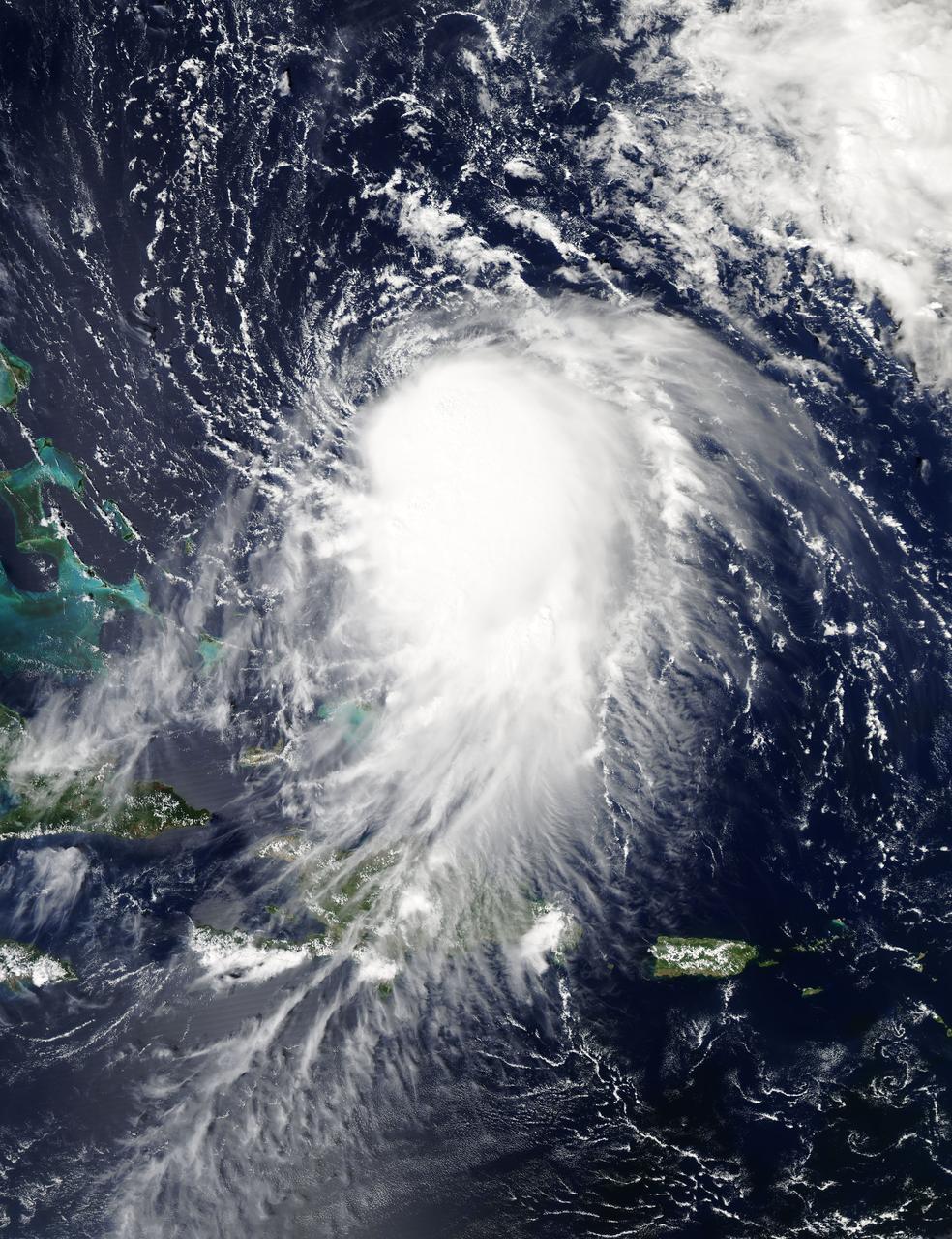

NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image of Joaquin near the Bahamas on Sept. 29 at 18:10 UTC (2:10 p.m. EDT). Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on Wednesday, September 30, 2015 the center of Hurricane Joaquin was located near latitude 24.7 North, longitude 72.6 West. That puts the center of Joaquin about 215 miles (345 km) east-northeast of the Central Bahamas. Joaquin became a tropical storm Monday evening (EDT), September 29 when it was midway between the Bahamas and Bermuda. By 8 a.m. EDT on September 30, it strengthened into a hurricane and has become the third hurricane of the Atlantic Hurricane season. On September 30, the National Hurricane Center issued a Hurricane Warning for the central Bahamas including Cat Island, the Exumas, Long Island, Rum Cay, and San Salvador. A Hurricane Watch is in effect for the northwestern Bahamas including the Abacos, Berry Islands, Bimini, Eleuthera, Grand Bahama Island, and New Providence, but excluding Andros Island. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
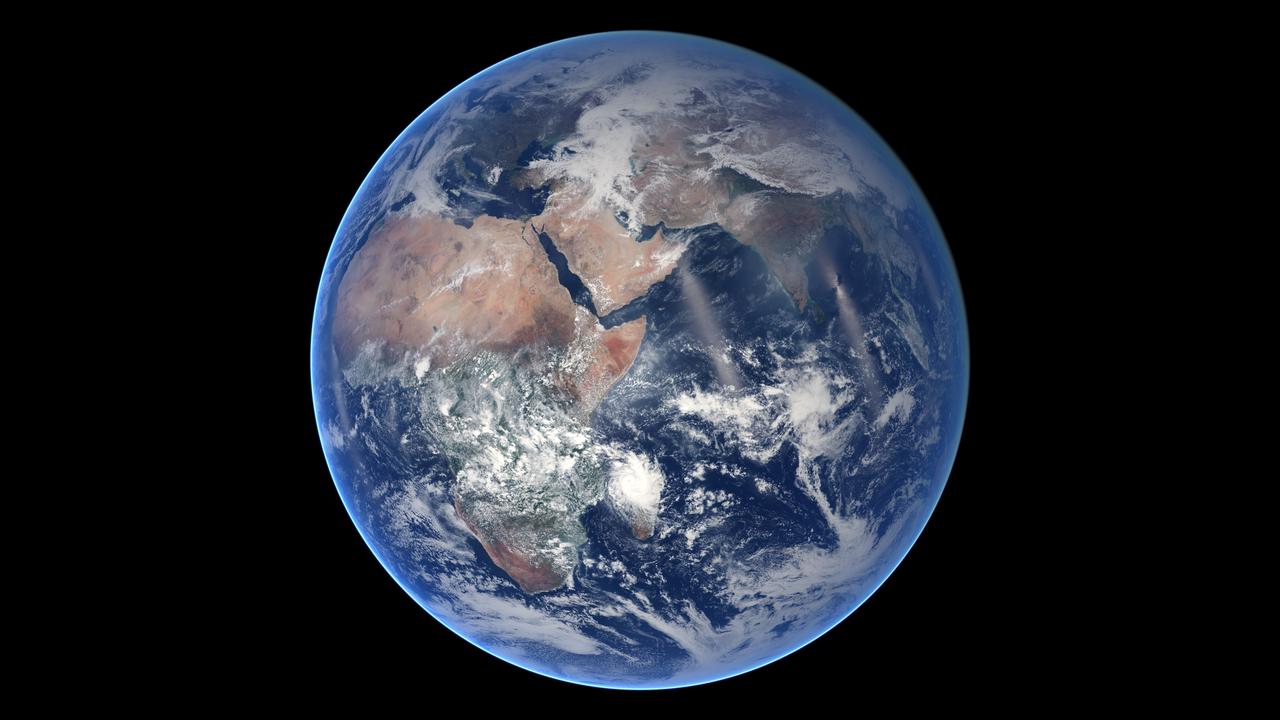

Of all the planets NASA has explored, none have matched the dynamic complexity of our own. Earth is constantly changing, and NASA are working constantly to explore and understand the planet on scales from local to global. Though Earth science has been a key part of NASA’s mission since the agency was founded in 1958, this year has been one of the peaks. Two new Earth-observing satellites have already been launched and put to work: the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) and the Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2 (OCO-2). Three more missions are set to take off in the next six months: the wind-measuring ISS-RapidScat, the ISS Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS), and the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP). And research planes have been flying over polar ice, hurricanes, boreal forests, and pollution plumes. All of these new efforts complement an existing fleet of Earth-observing satellites. In visible light and many invisible wavelengths, NASA and its science partners are observing the entire planet every day. The image above was captured on March 30, 2014, by the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite. The composite image of the eastern hemisphere was compiled from eight orbits of the satellite and ten imaging channels, then stitched together to blend the edges of each satellite pass. Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84214&eocn=home&eoci=iotd_title" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84214&eocn...</a> NASA Earth Observatory image by Robert Simmon, using Suomi NPP VIIRS imagery from NOAA's Environmental Visualization Laboratory. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, NOAA and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The Hubble Space Telescope has spotted a UFO — well, the UFO Galaxy, to be precise. NGC 2683 is a spiral galaxy seen almost edge-on, giving it the shape of a classic science fiction spaceship. This is why the astronomers at the Astronaut Memorial Planetarium and Observatory gave it this attention-grabbing nickname. While a bird’s eye view lets us see the detailed structure of a galaxy (such as this Hubble image of a barred spiral), a side-on view has its own perks. In particular, it gives astronomers a great opportunity to see the delicate dusty lanes of the spiral arms silhouetted against the golden haze of the galaxy’s core. In addition, brilliant clusters of young blue stars shine scattered throughout the disc, mapping the galaxy’s star-forming regions. Perhaps surprisingly, side-on views of galaxies like this one do not prevent astronomers from deducing their structures. Studies of the properties of the light coming from NGC 2683 suggest that this is a barred spiral galaxy, even though the angle we see it at does not let us see this directly. NGC 2683, discovered on 5 February 1788 by the famous astronomer William Herschel, lies in the Northern constellation of Lynx. A constellation named not because of its resemblance to the feline animal, but because it is fairly faint, requiring the “sensitive eyes of a cat” to discern it. And when you manage to get a look at it, you’ll find treasures like this, making it well worth the effort. This image is produced from two adjacent fields observed in visible and infrared light by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. A narrow strip which appears slightly blurred and crosses most the image horizontally is a result of a gap between Hubble’s detectors. This strip has been patched using images from observations of the galaxy made by ground-based telescopes, which show significantly less detail. The field of view is approximately 6.5 by 3.3 arcminutes. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
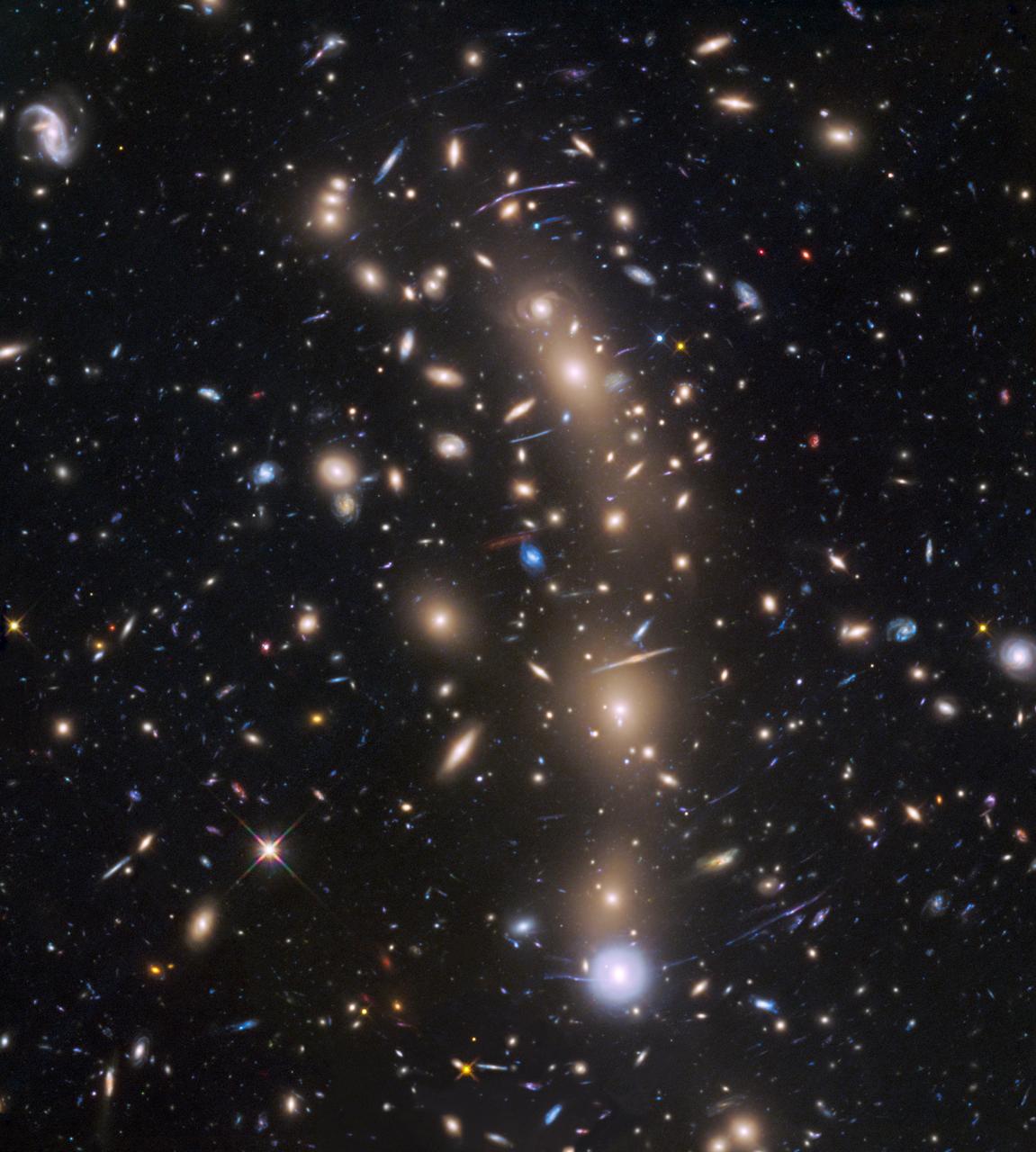

This is a Hubble Space Telescope view of a very massive cluster of galaxies, MACS J0416.1-2403, located roughly 4 billion light-years away and weighing as much as a million billion suns. The cluster's immense gravitational field magnifies the image of galaxies far behind it, in a phenomenon called gravitational lensing. The inset is an image of an extremely faint and distant galaxy that existed only 400 million years after the big bang. It was discovered by Hubble and NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. The gravitational lens makes the galaxy appear 20 times brighter than normal. The galaxy is comparable in size to the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a diminutive satellite galaxy of our Milky Way. It is rapidly making stars at a rate ten times faster than the LMC. This might be the growing core of what was to eventually evolve into a full-sized galaxy. The research team has nicknamed the object Tayna, which means "first-born" in Aymara, a language spoken in the Andes and Altiplano regions of South America. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20054