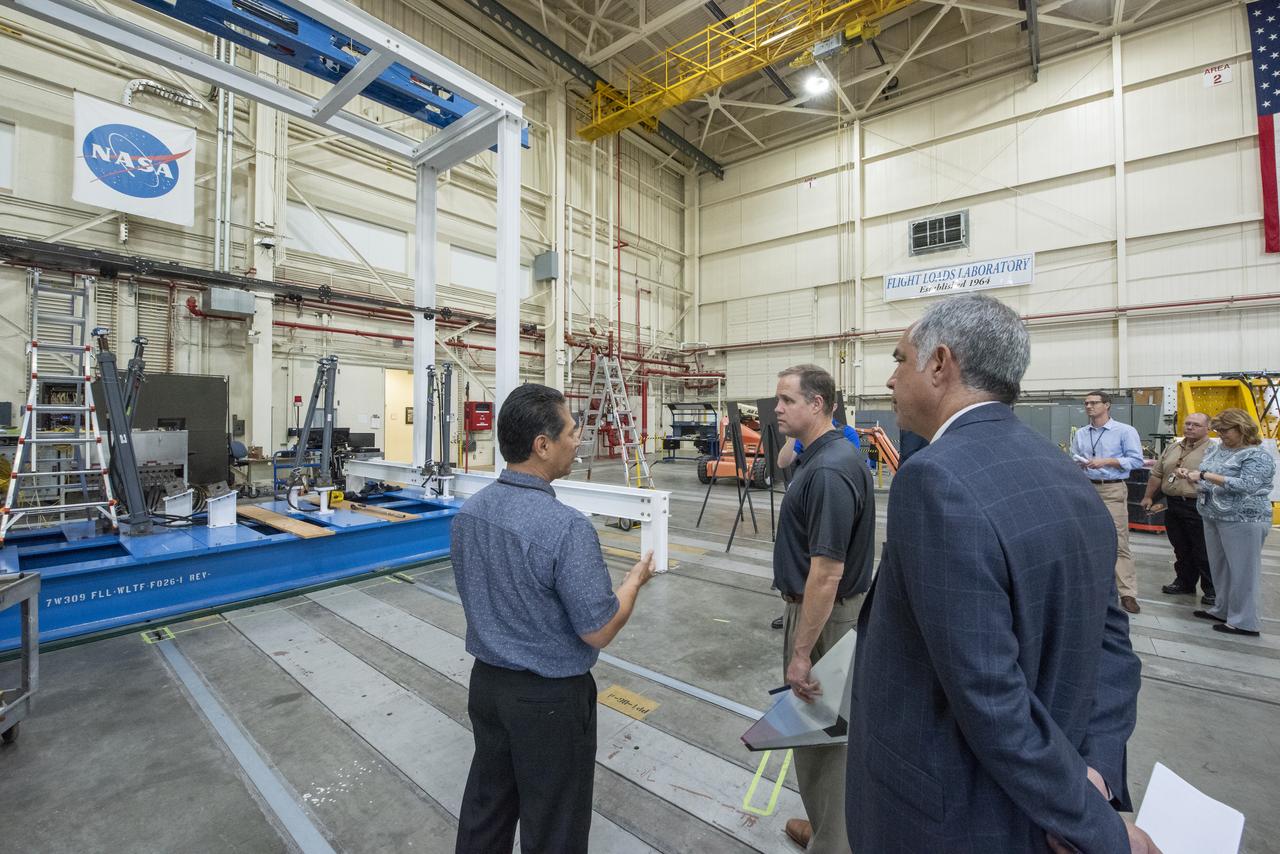

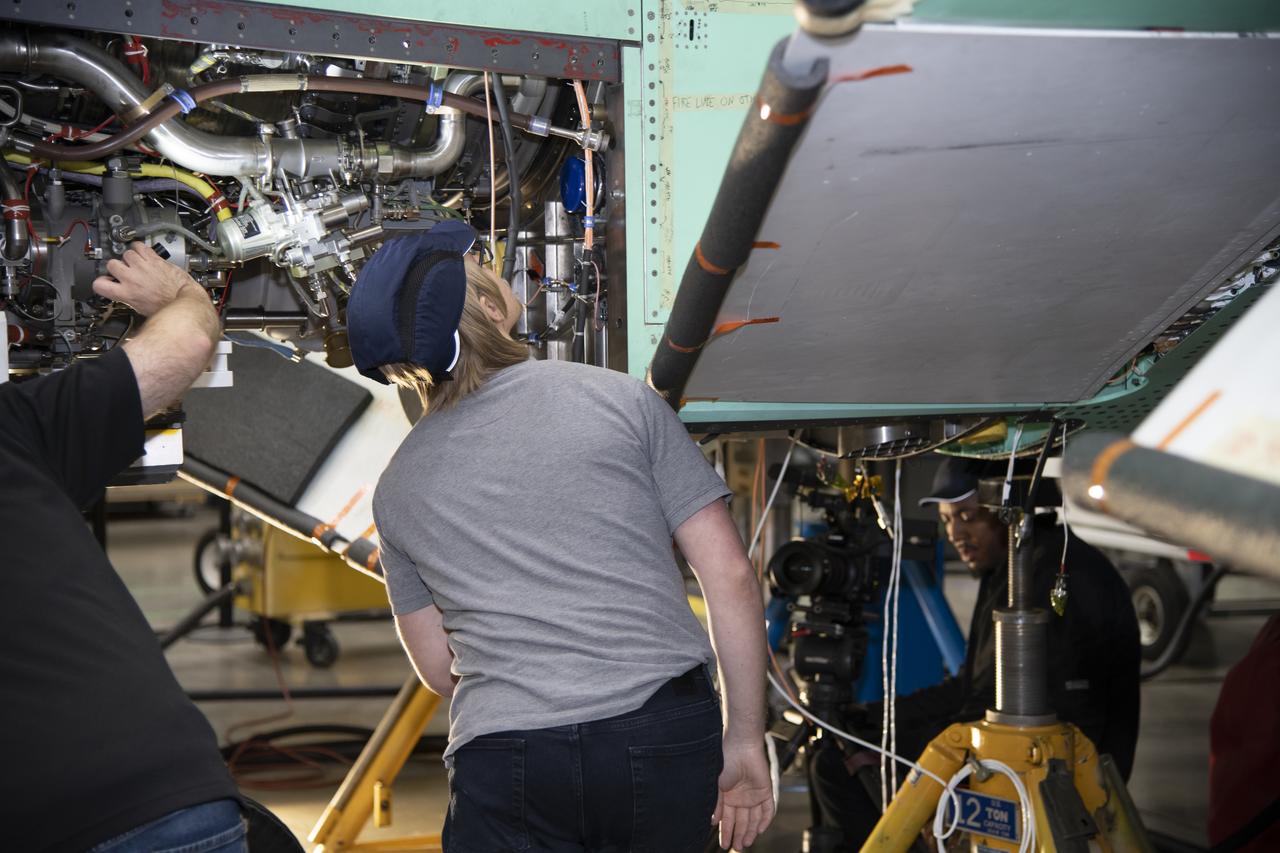
NASA Administrator Bridenstine talks with Armstrong's Larry Hudson about the capabilities of the Flight Loads Lab to conduct mechanical-load and thermal studies of structural components and complete flight vehicles.
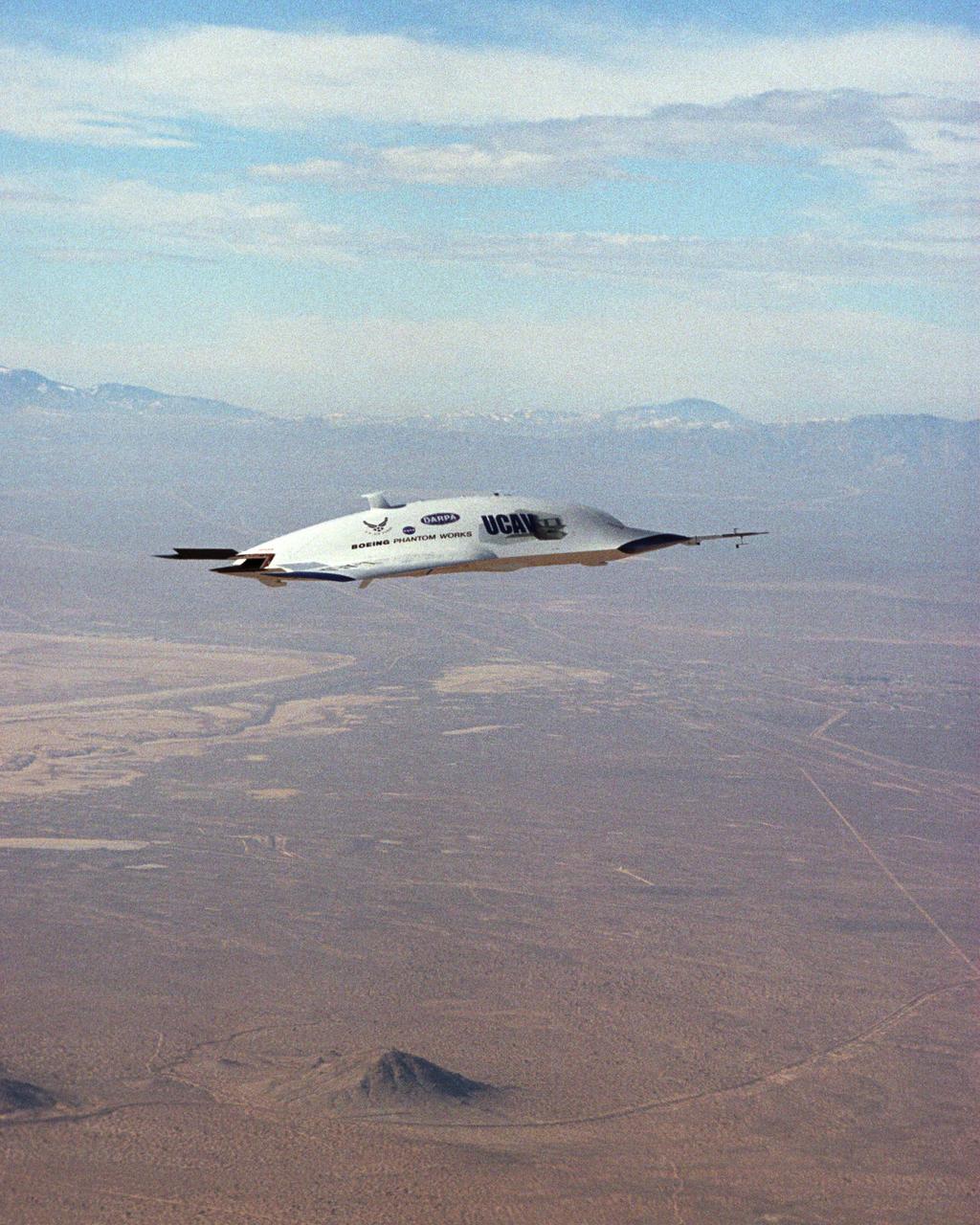

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
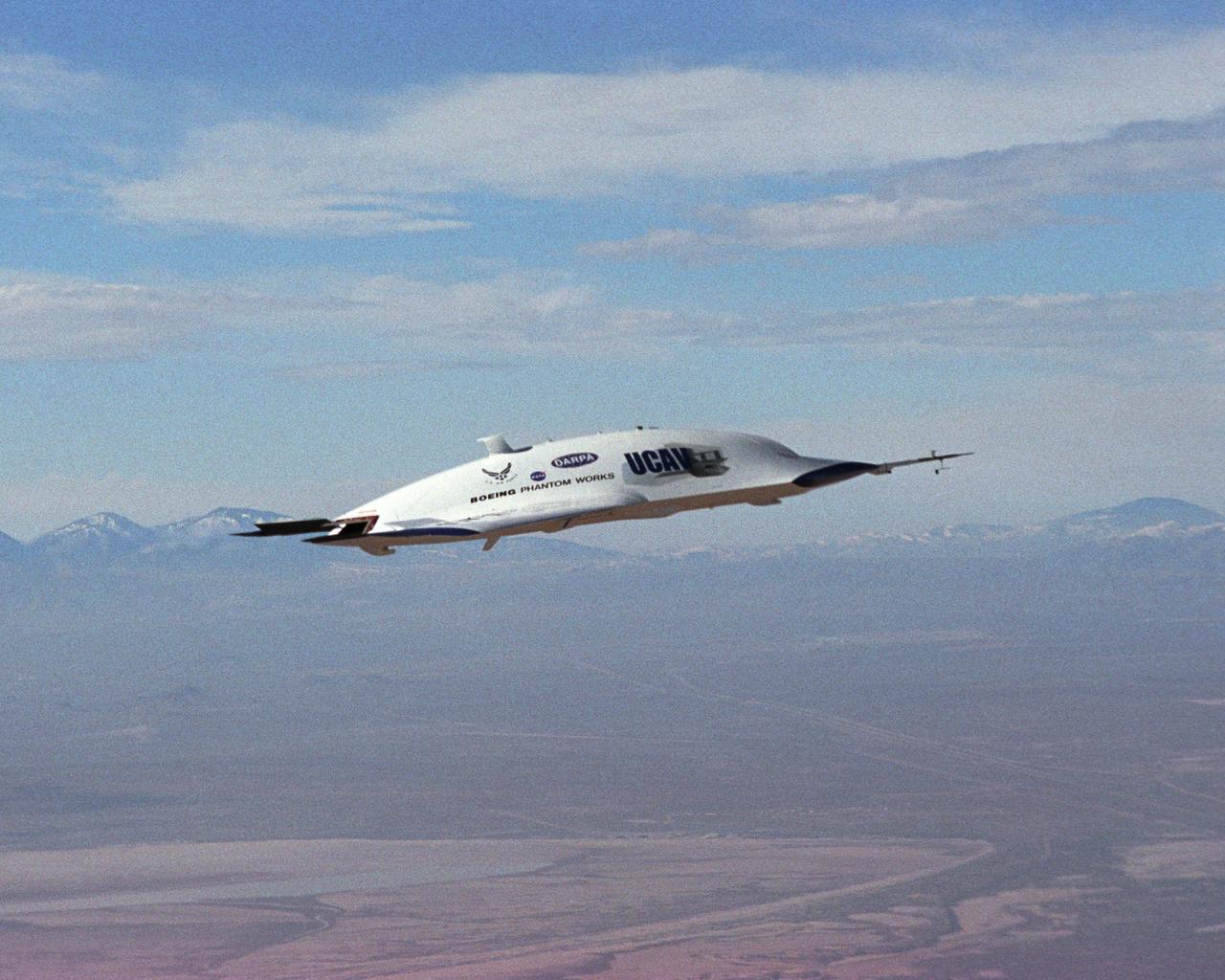

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
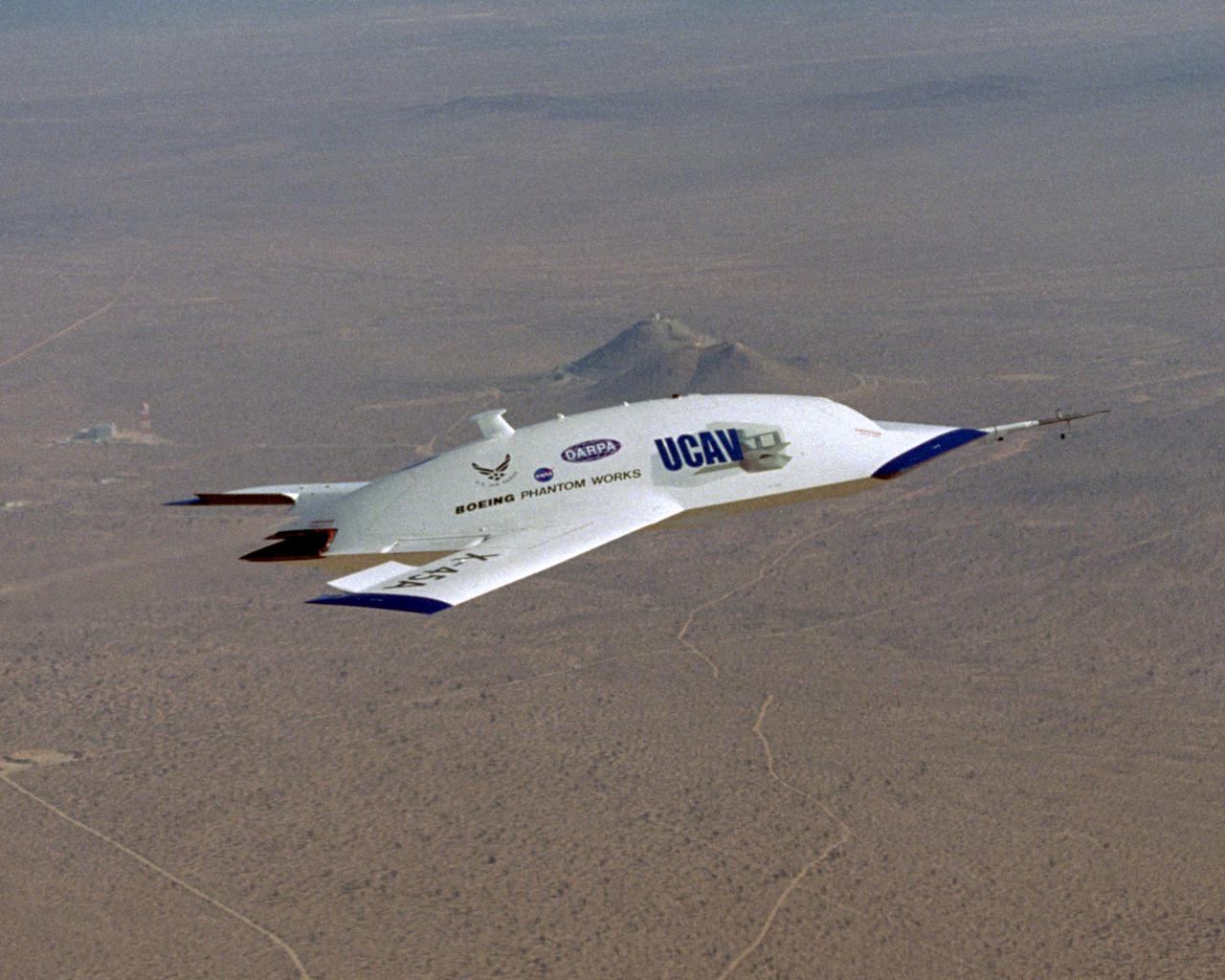

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
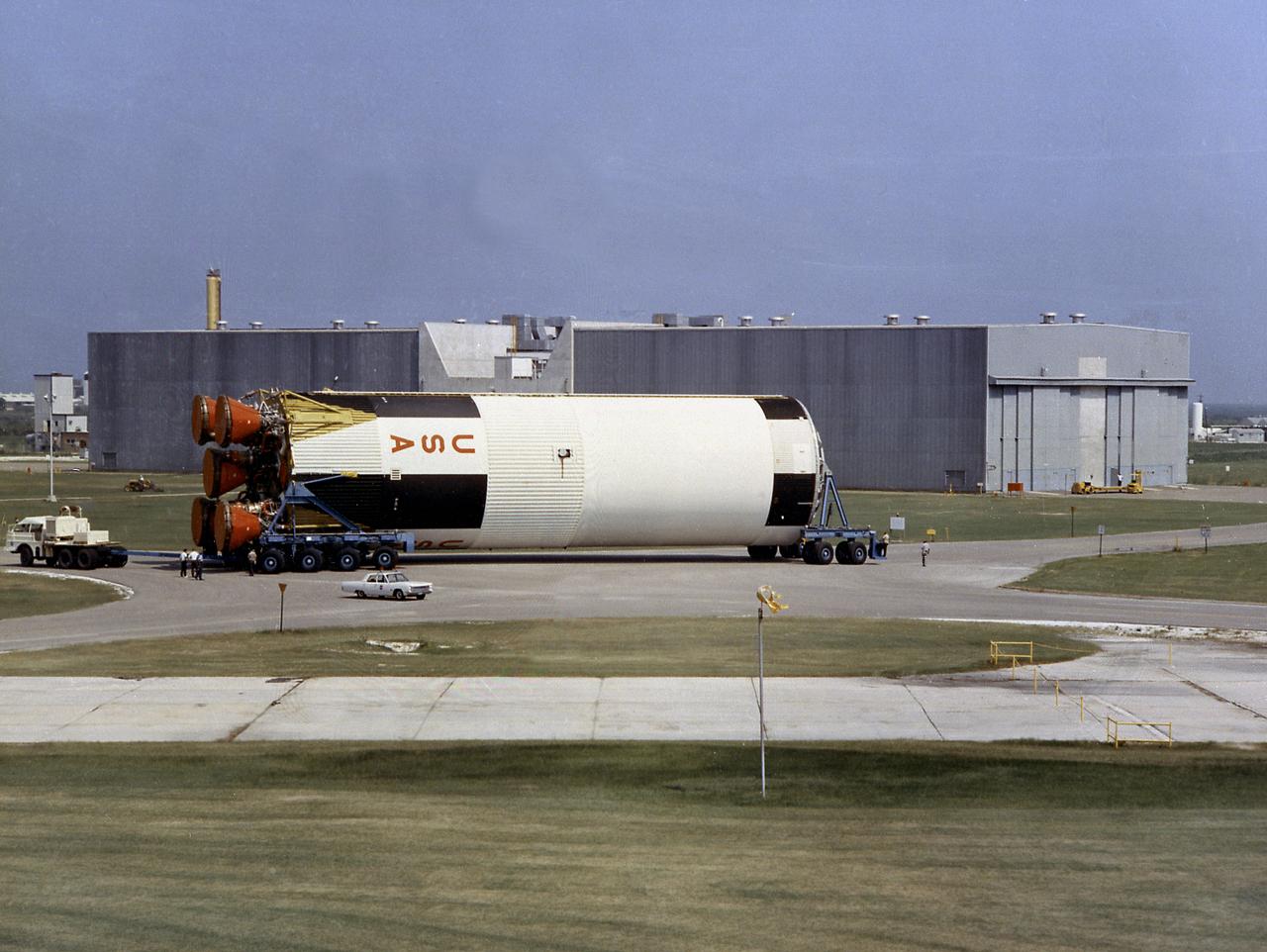

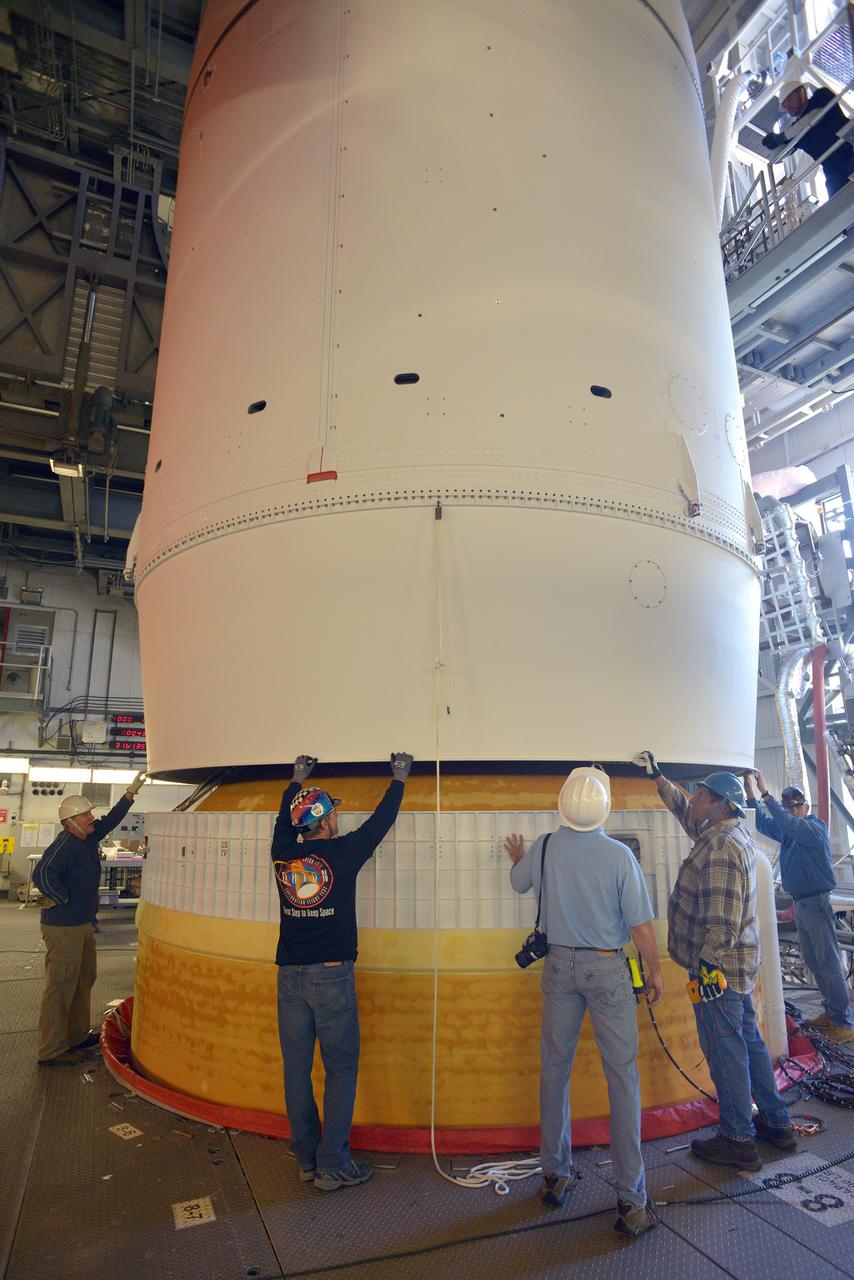
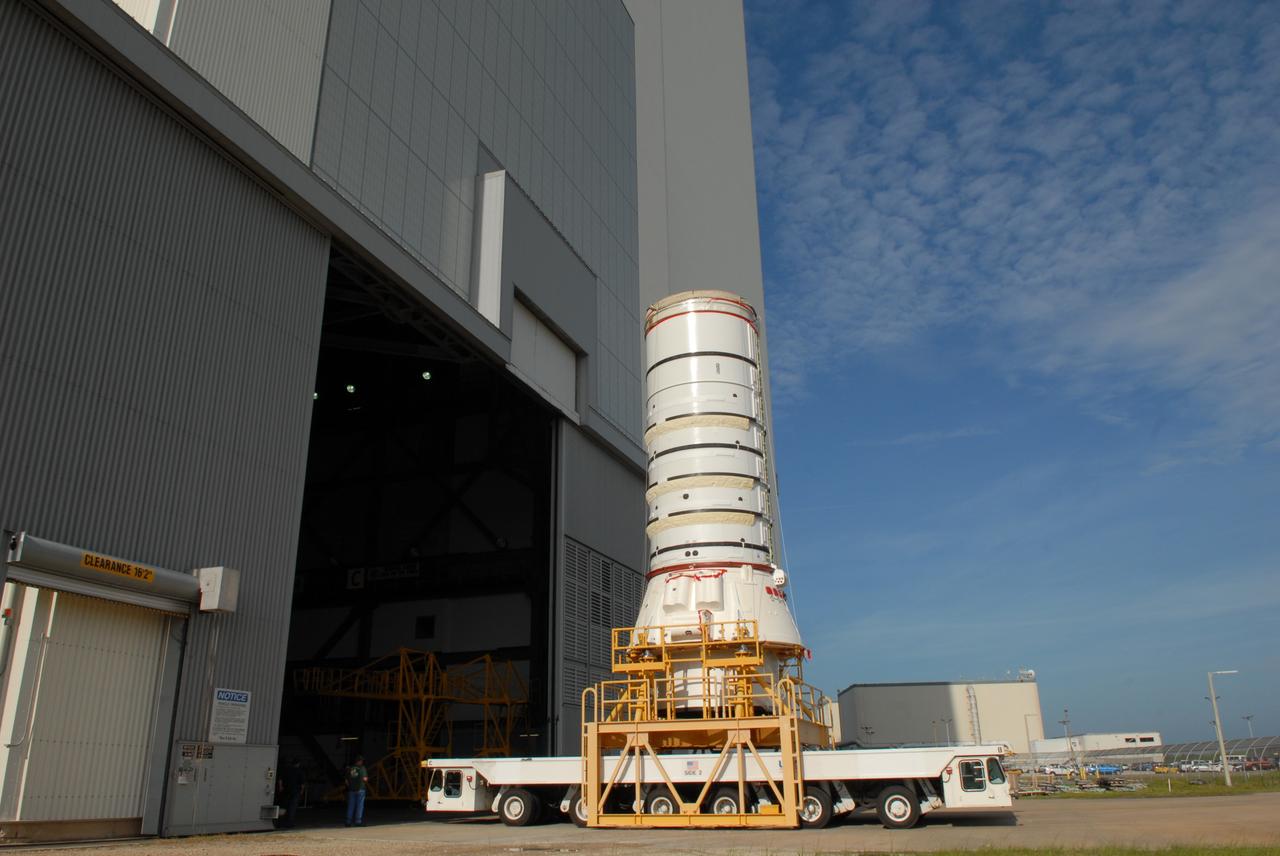
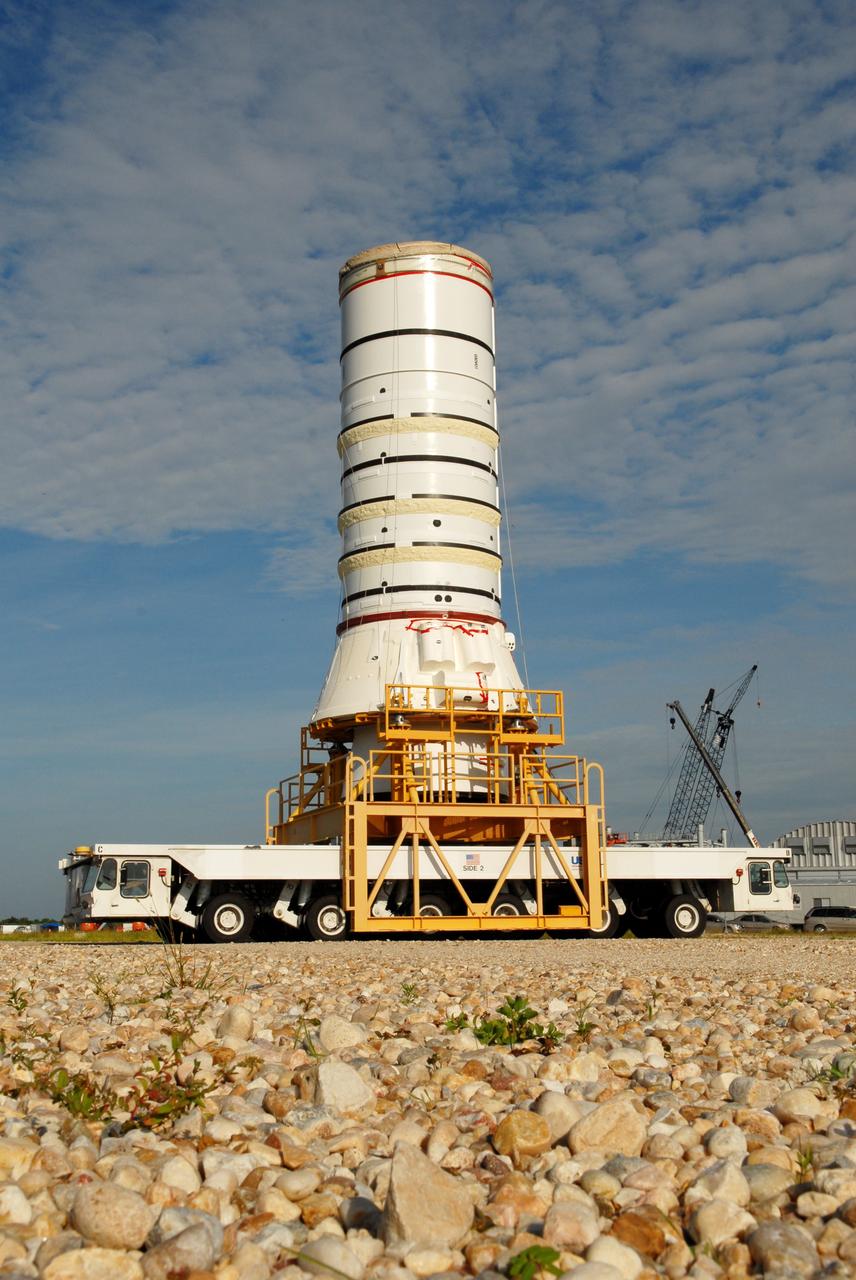
This photograph shows a completed S-IC flight stage being transferred from the vehicle assembly building to the stage test building at the Michoud Assembly Facility.

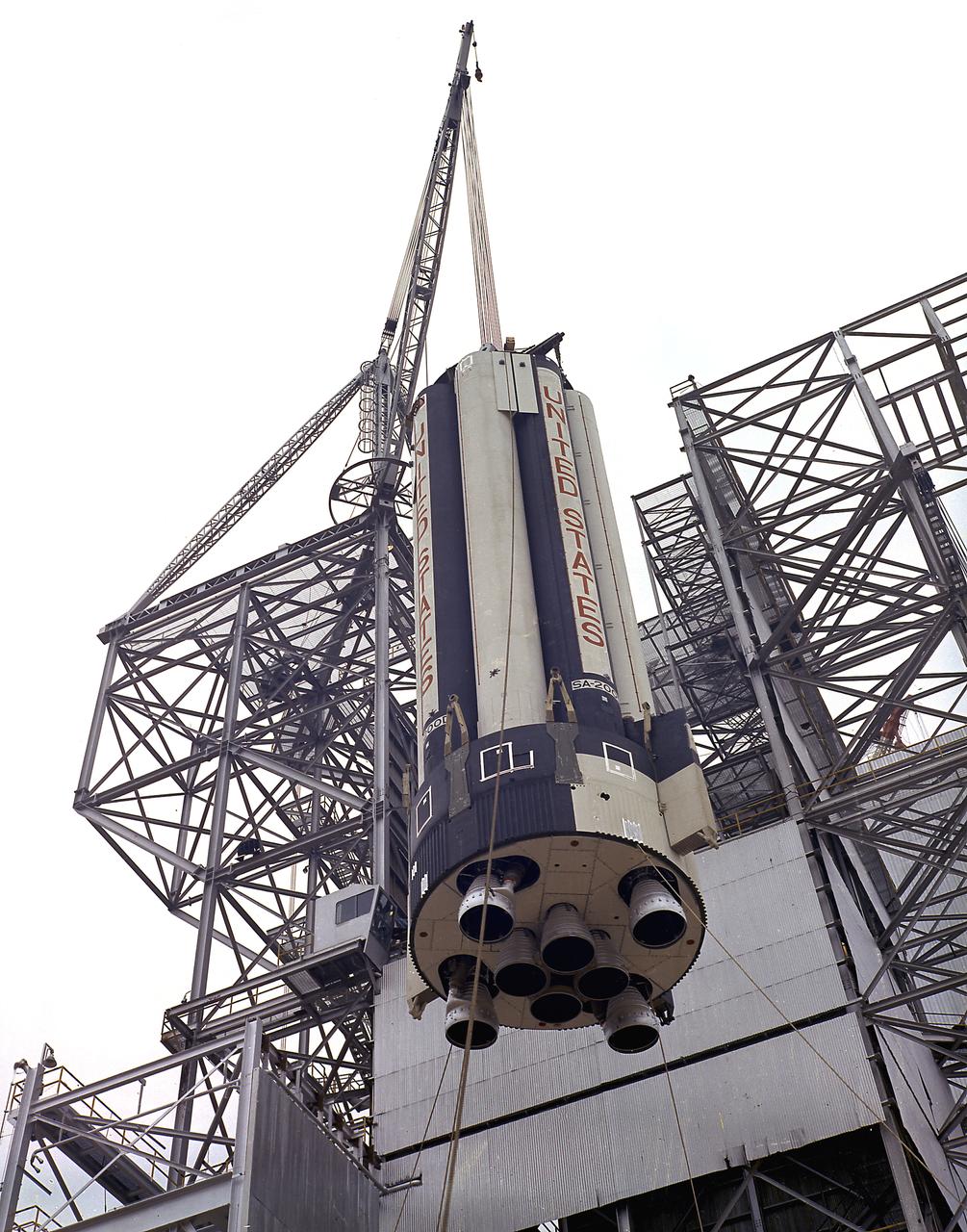
This photograph depicts the Saturn V vehicle (SA-501) for the Apollo 4 mission in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). After the completion of the assembly operation, the work platform was retracted and the vehicle was readied to rollout from the VAB to the launch pad. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
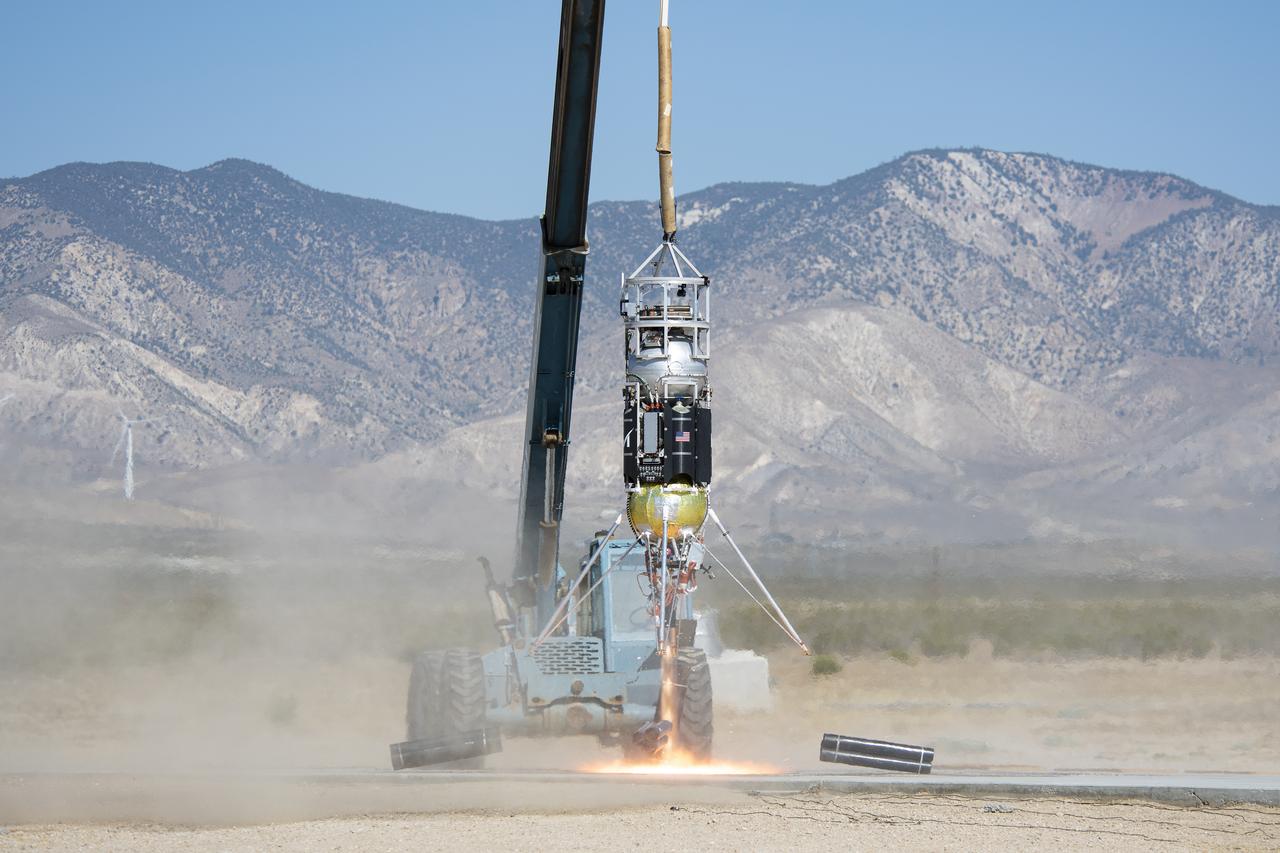

Masten Space Systems’ Xodiac lander completes a tethered flight test at the Mojave Air & Space Port. Xodiac is one of several suborbital vehicles used to flight test NASA-sponsored technologies supported by the agency’s Flight Opportunities program.
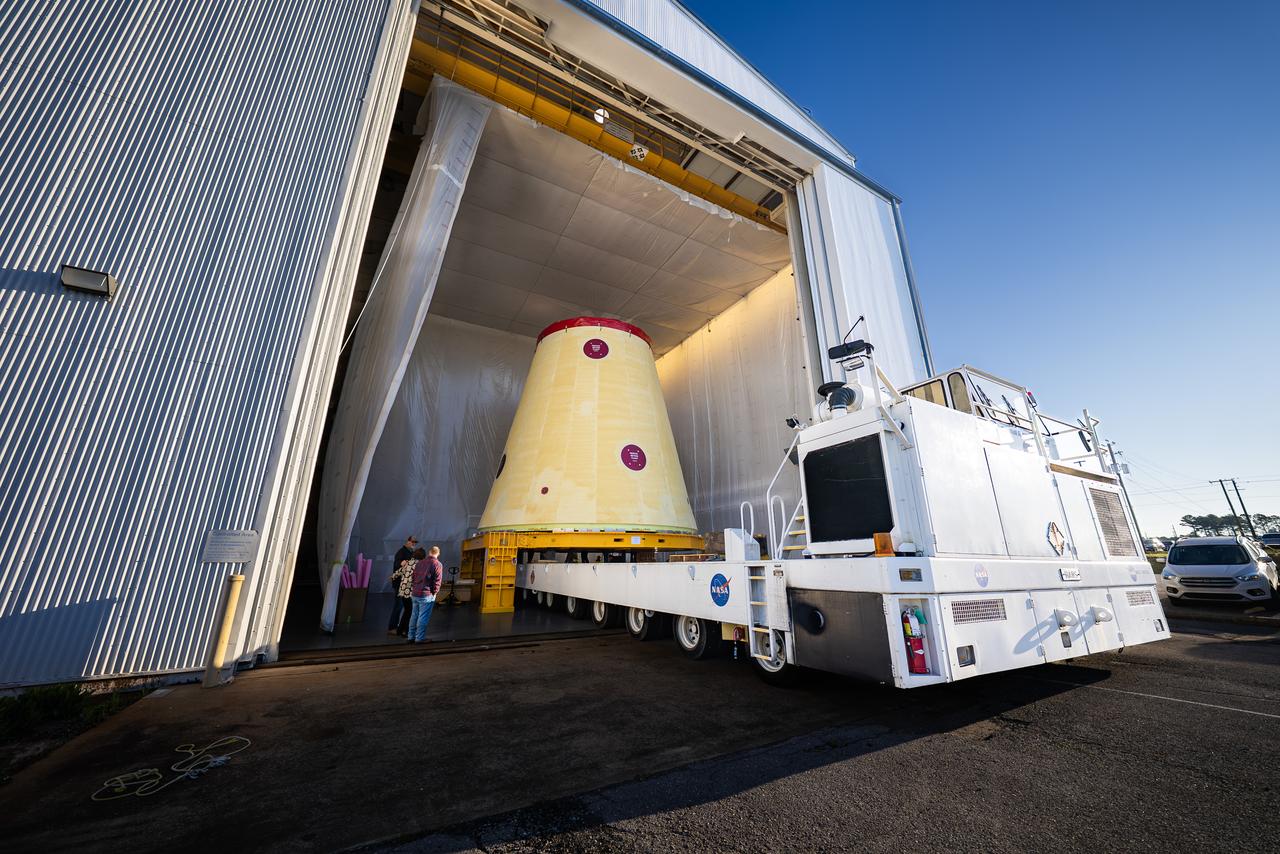

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
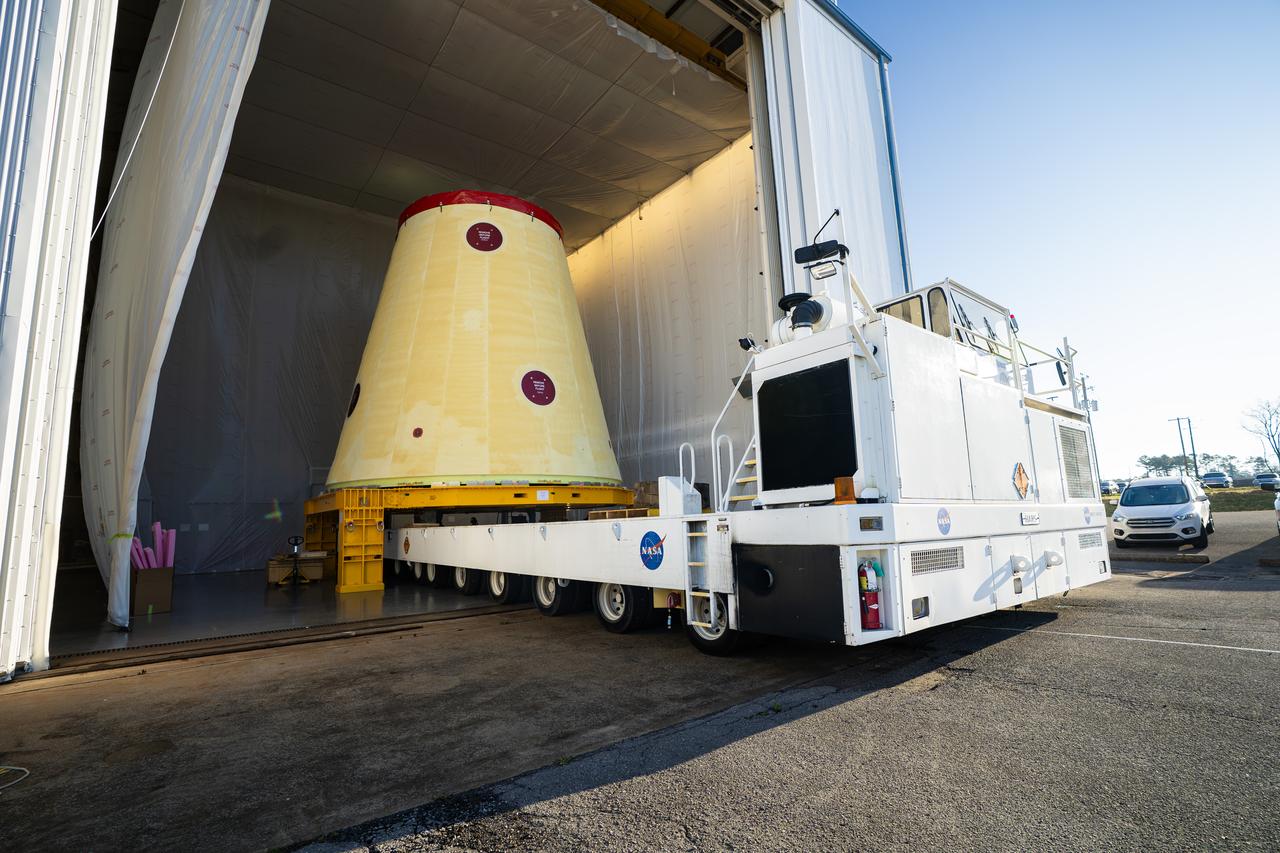

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
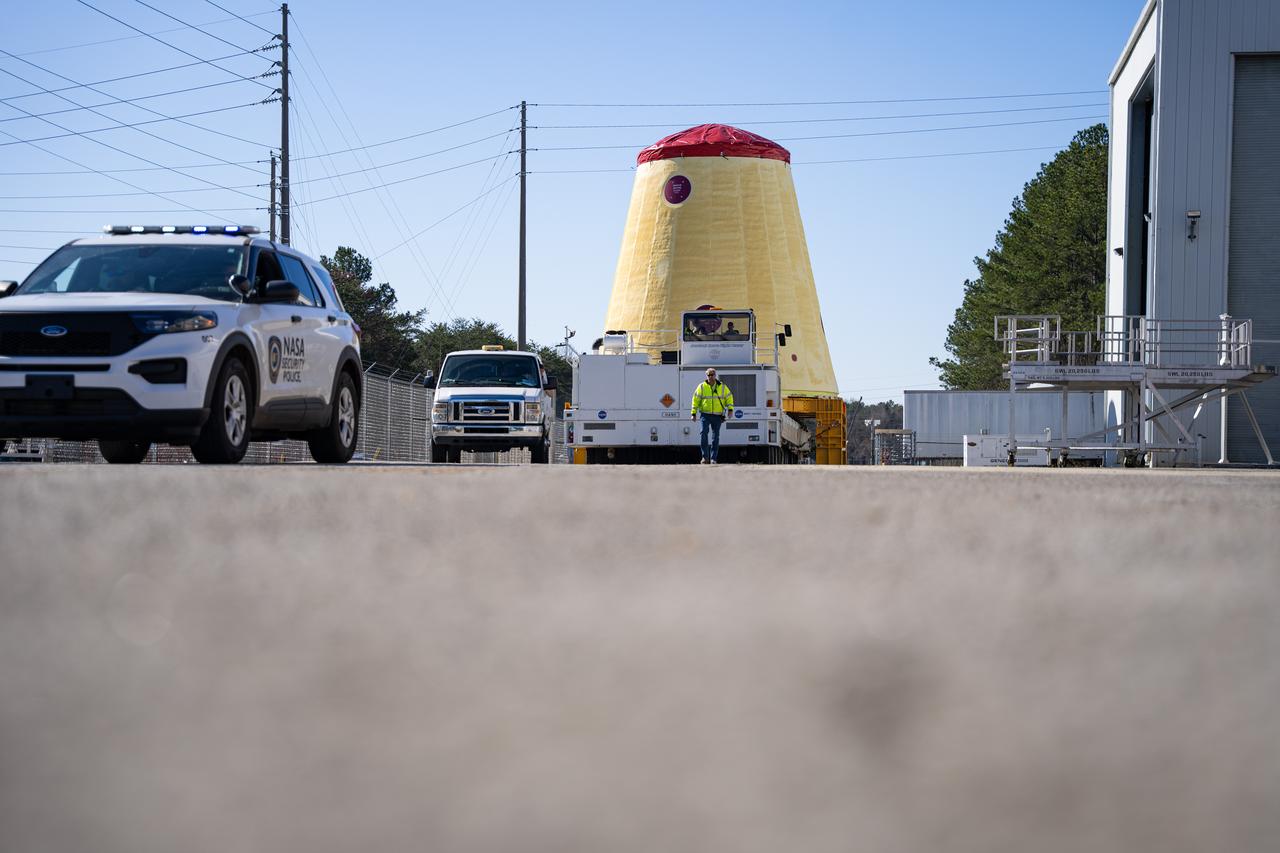

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708, where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
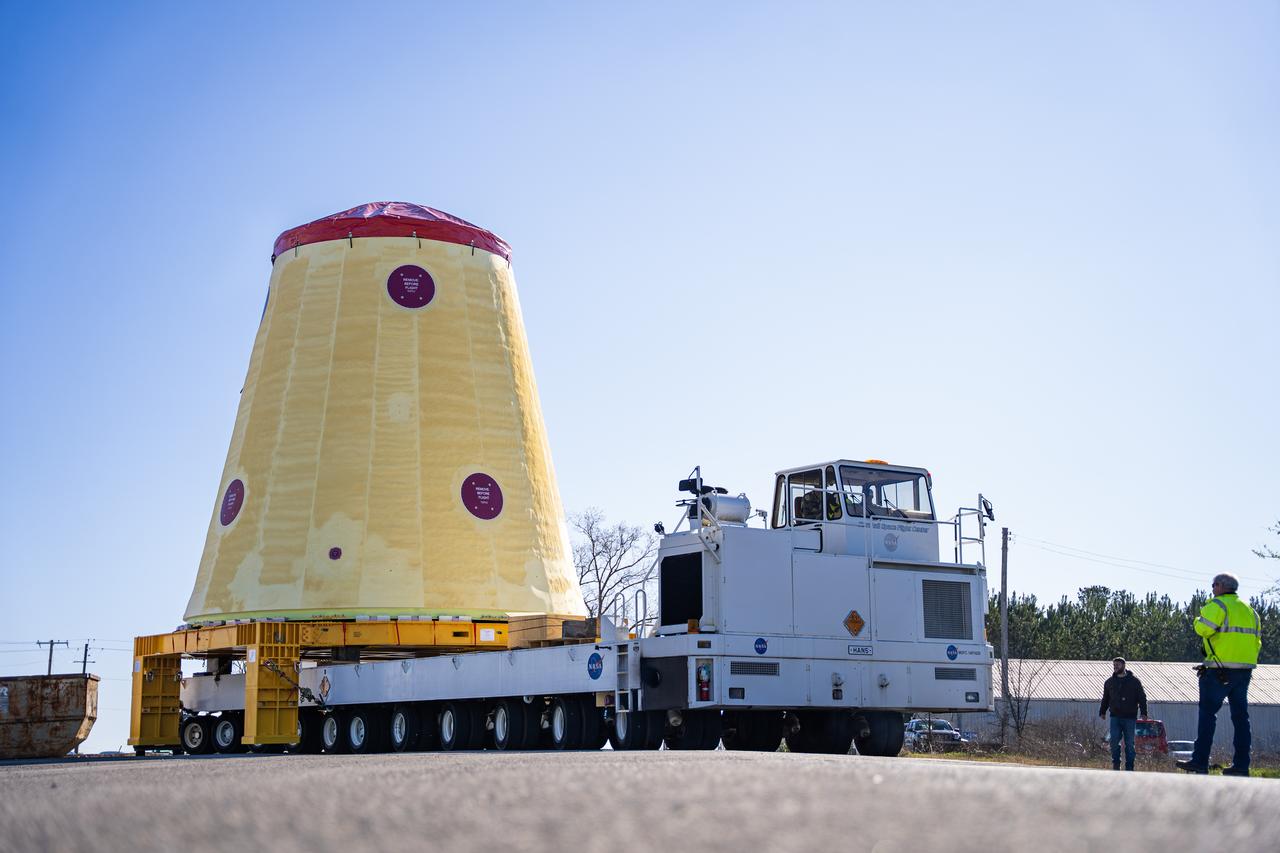

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.

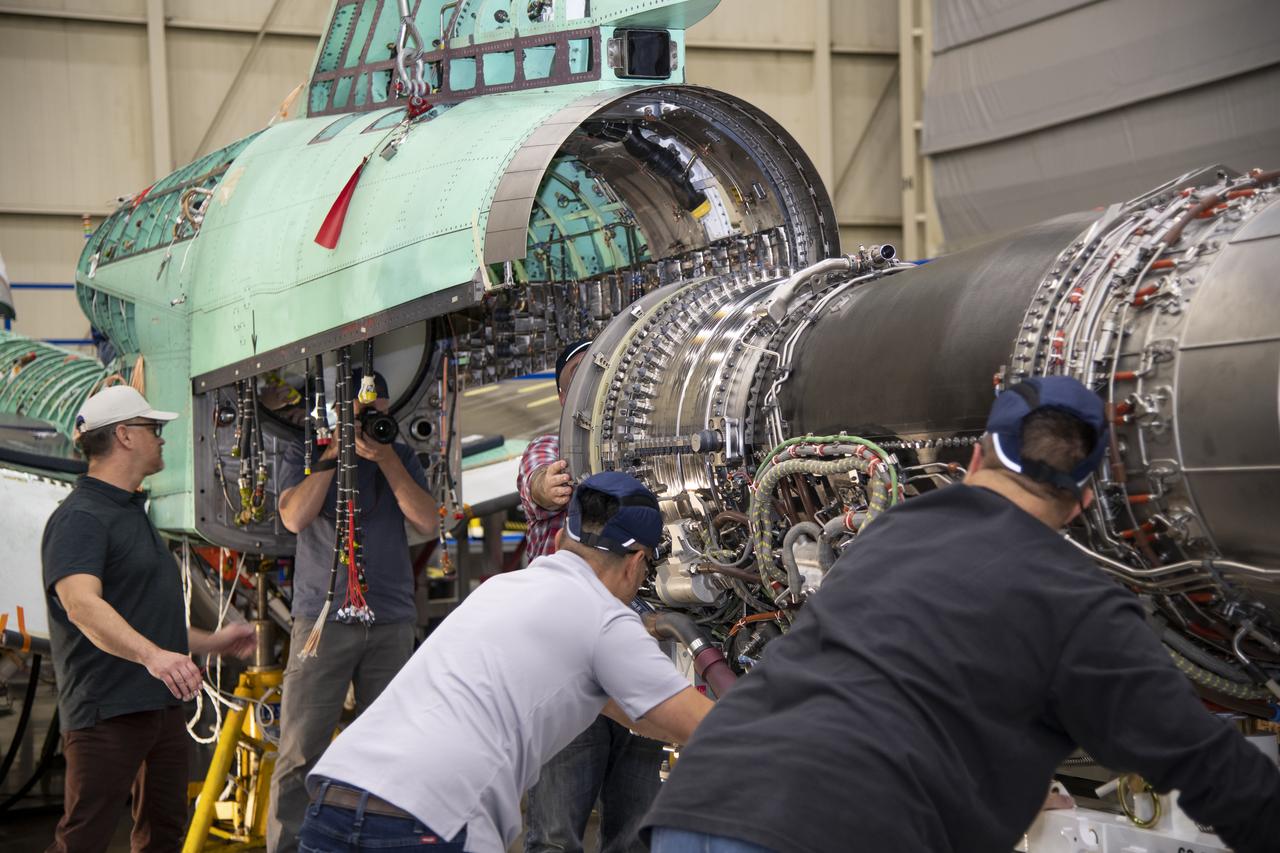
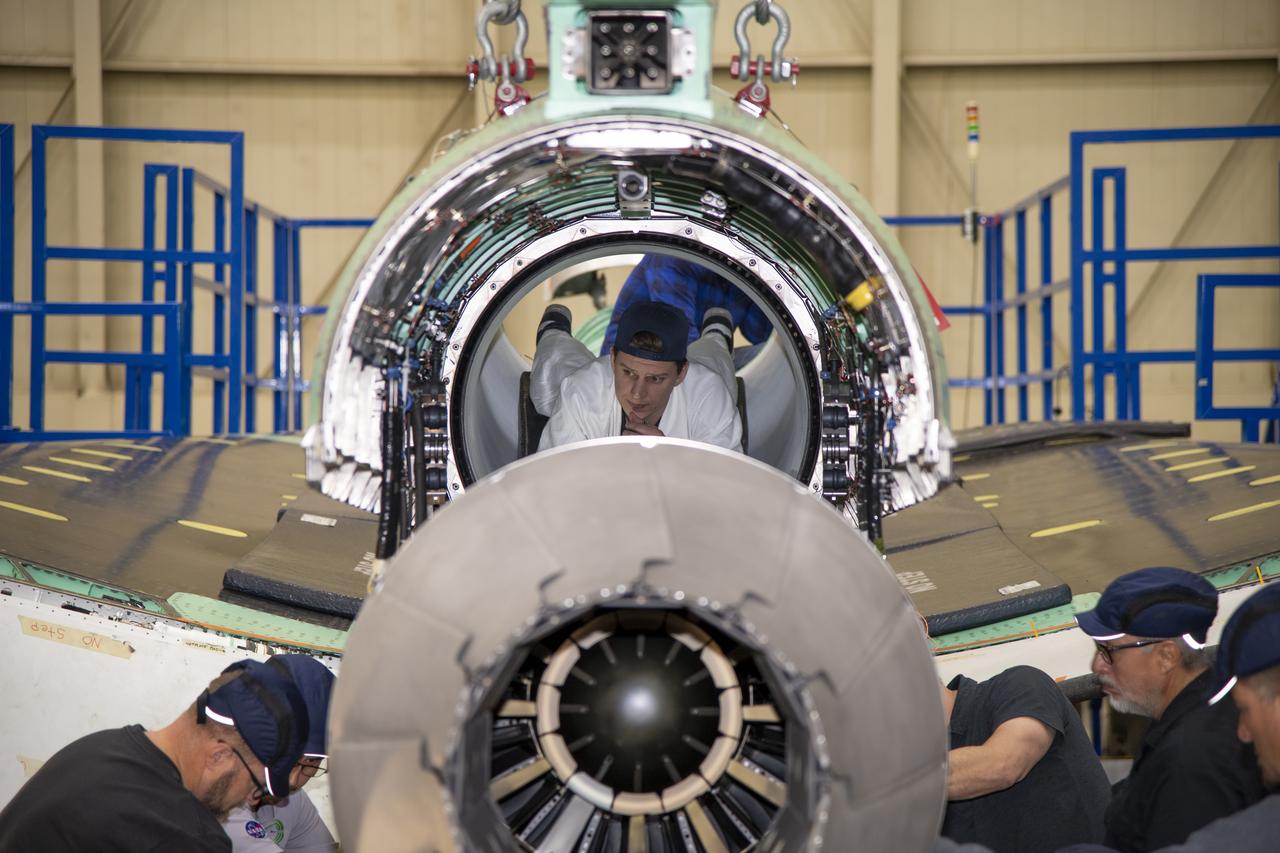
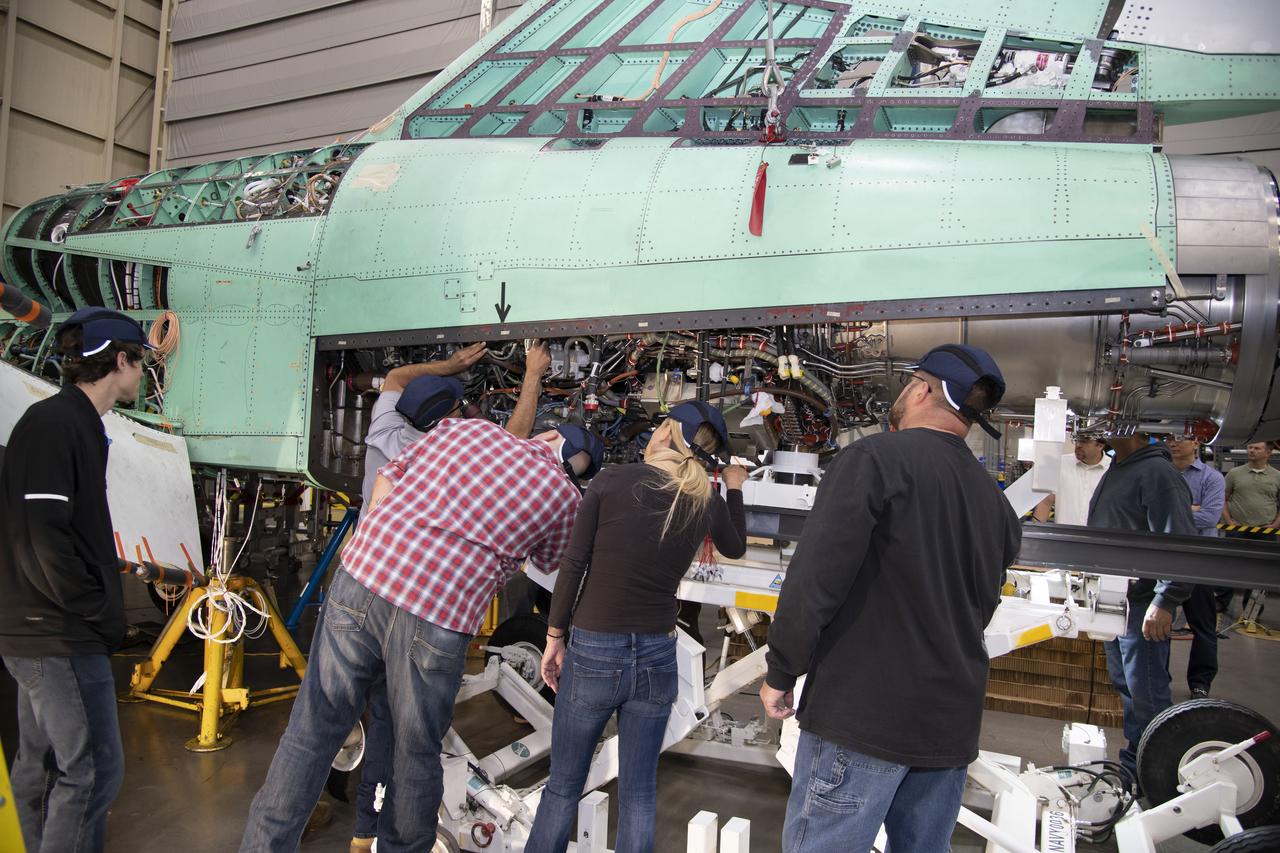
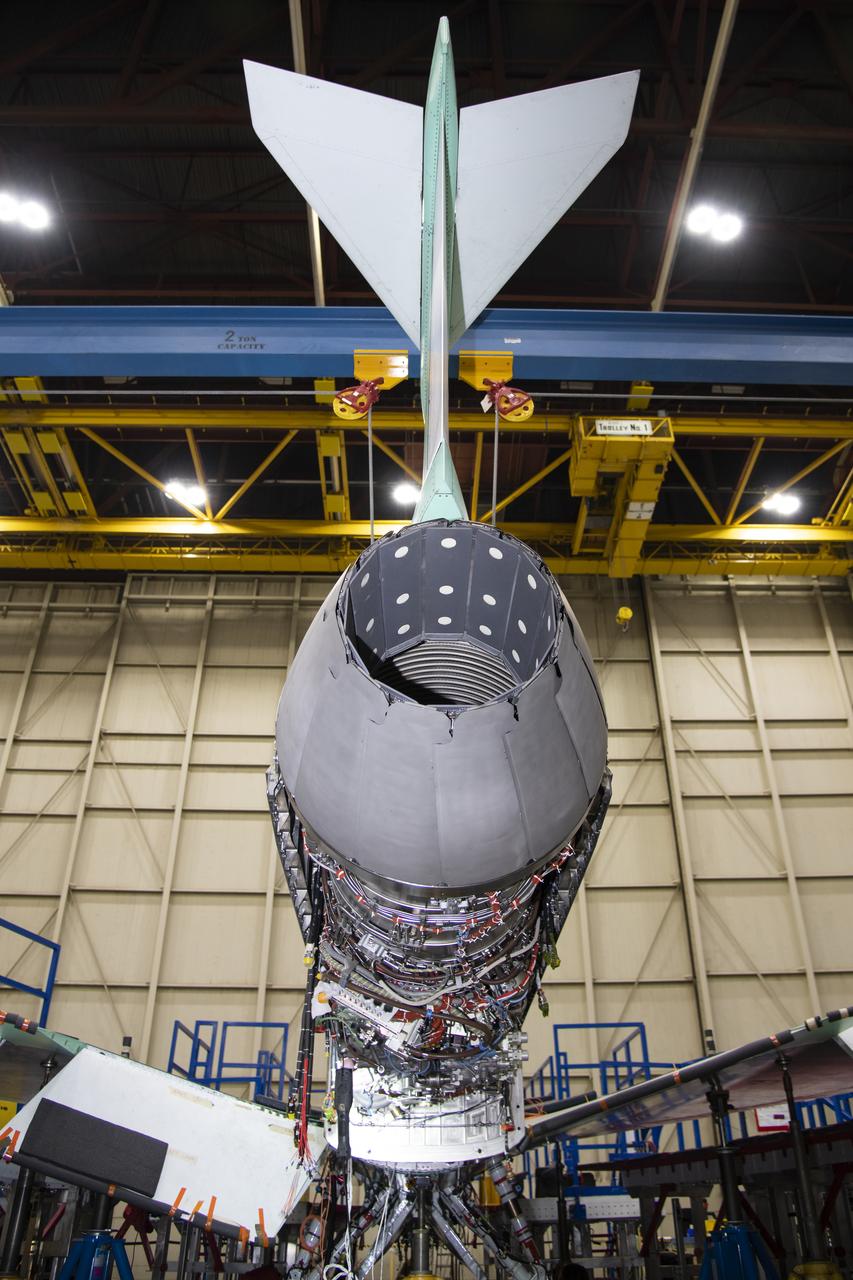
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
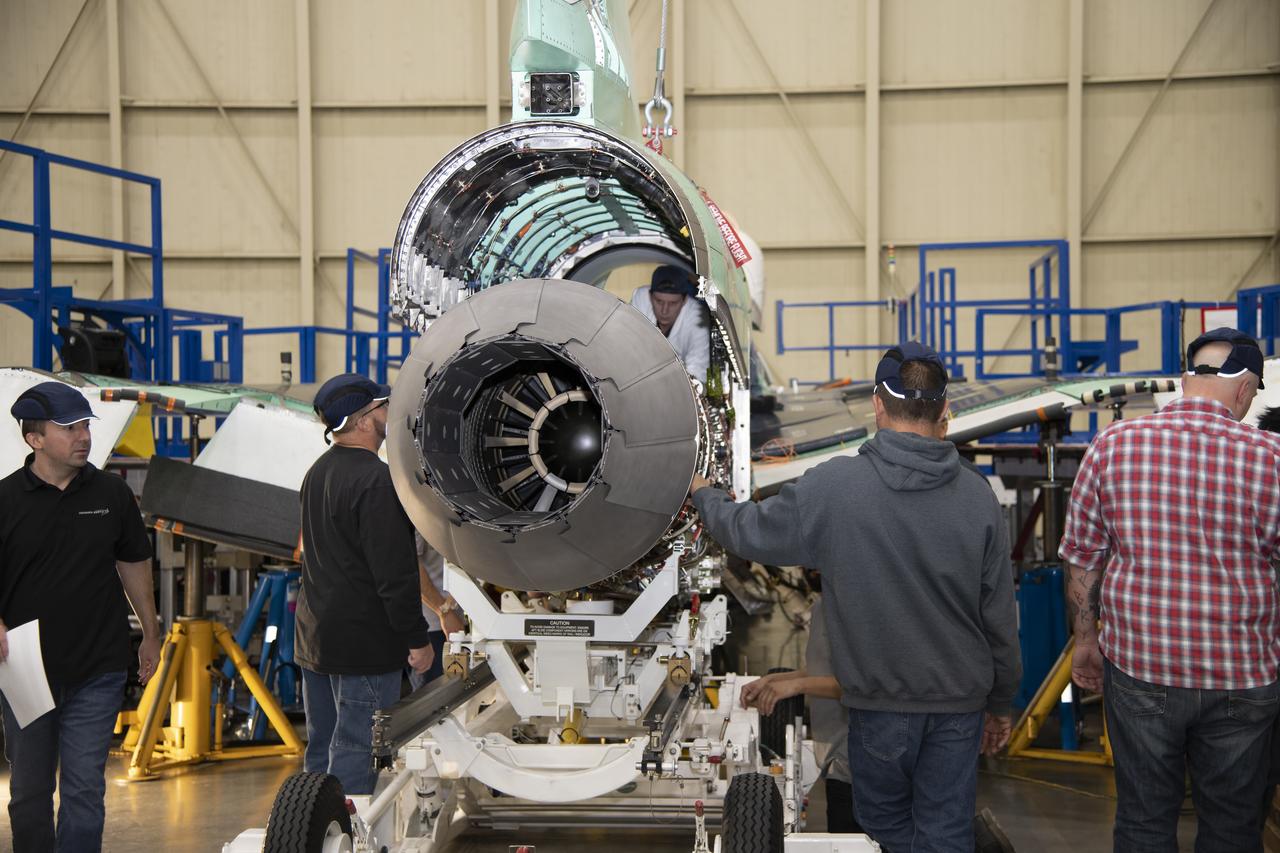

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
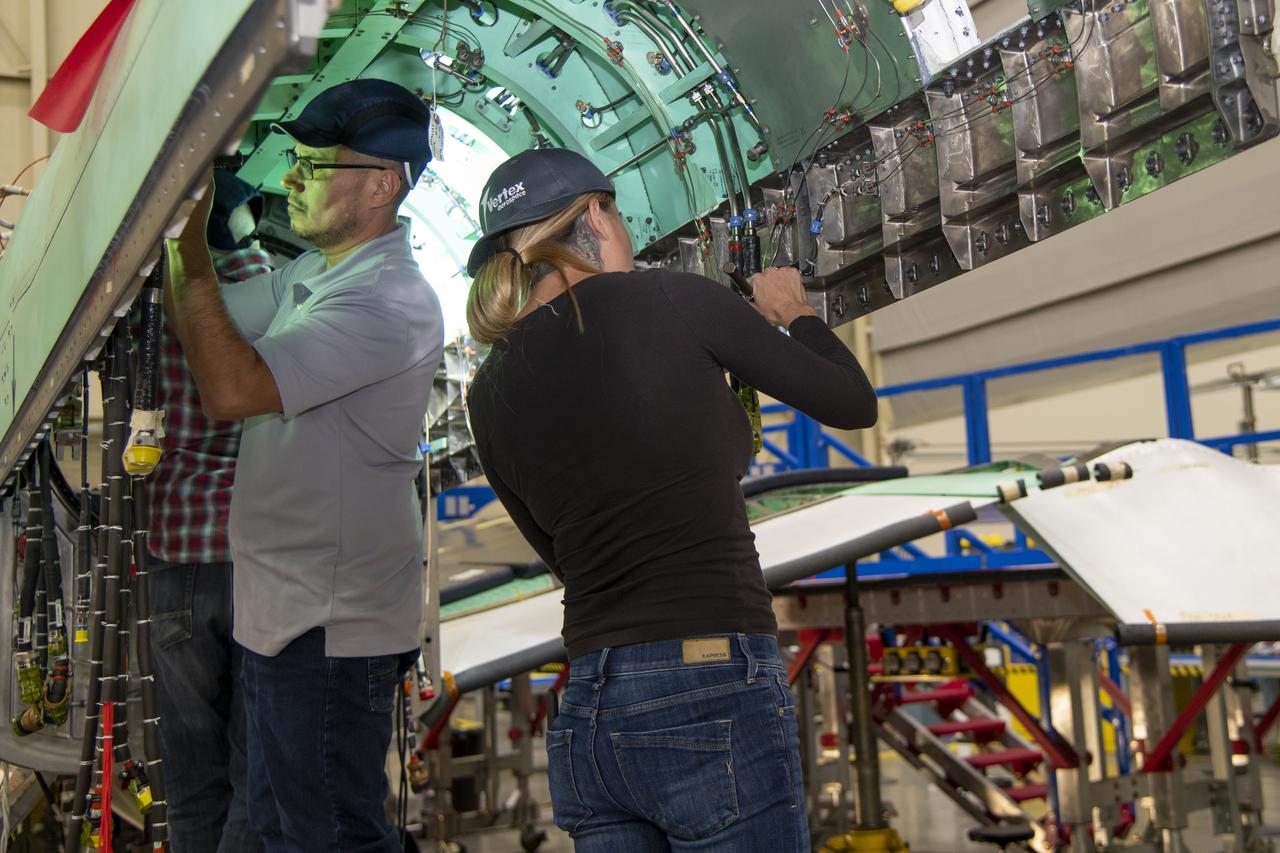

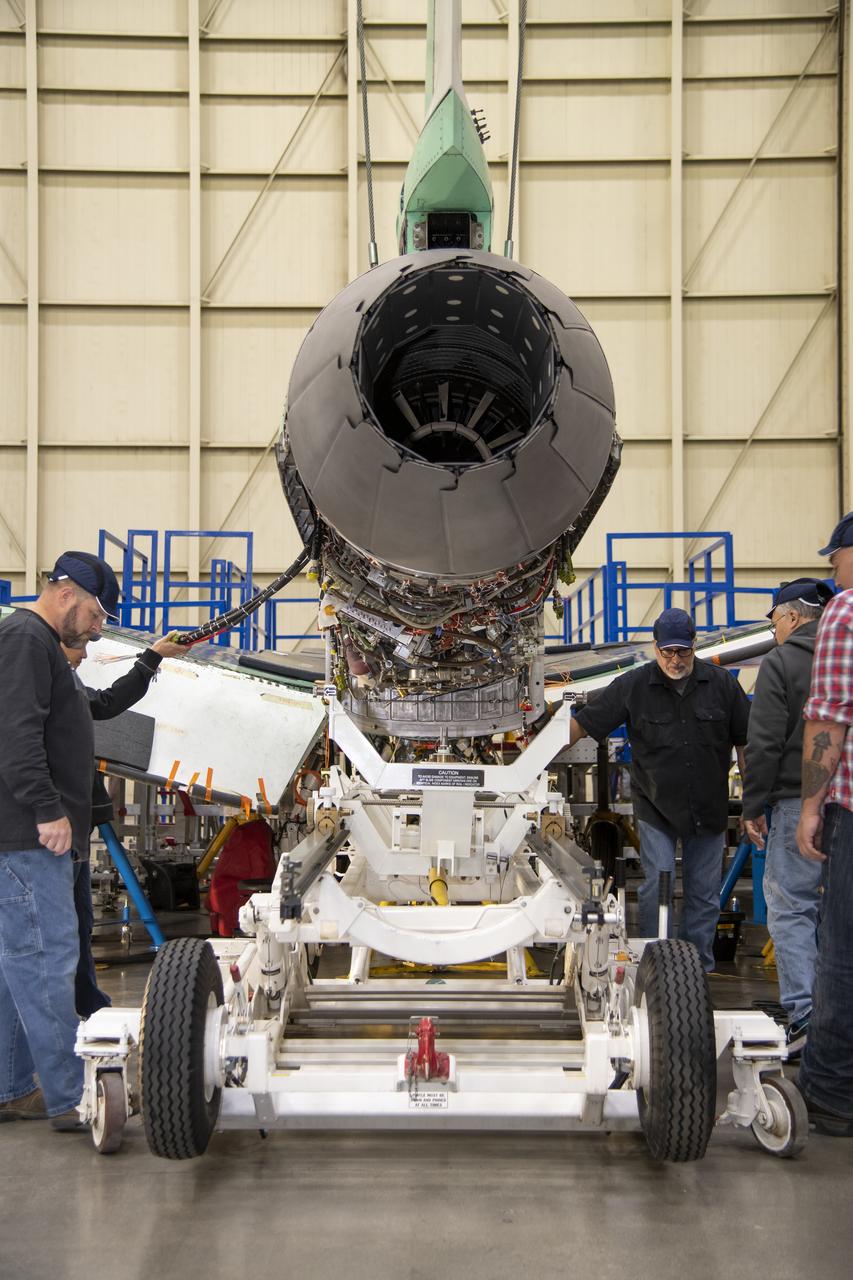
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
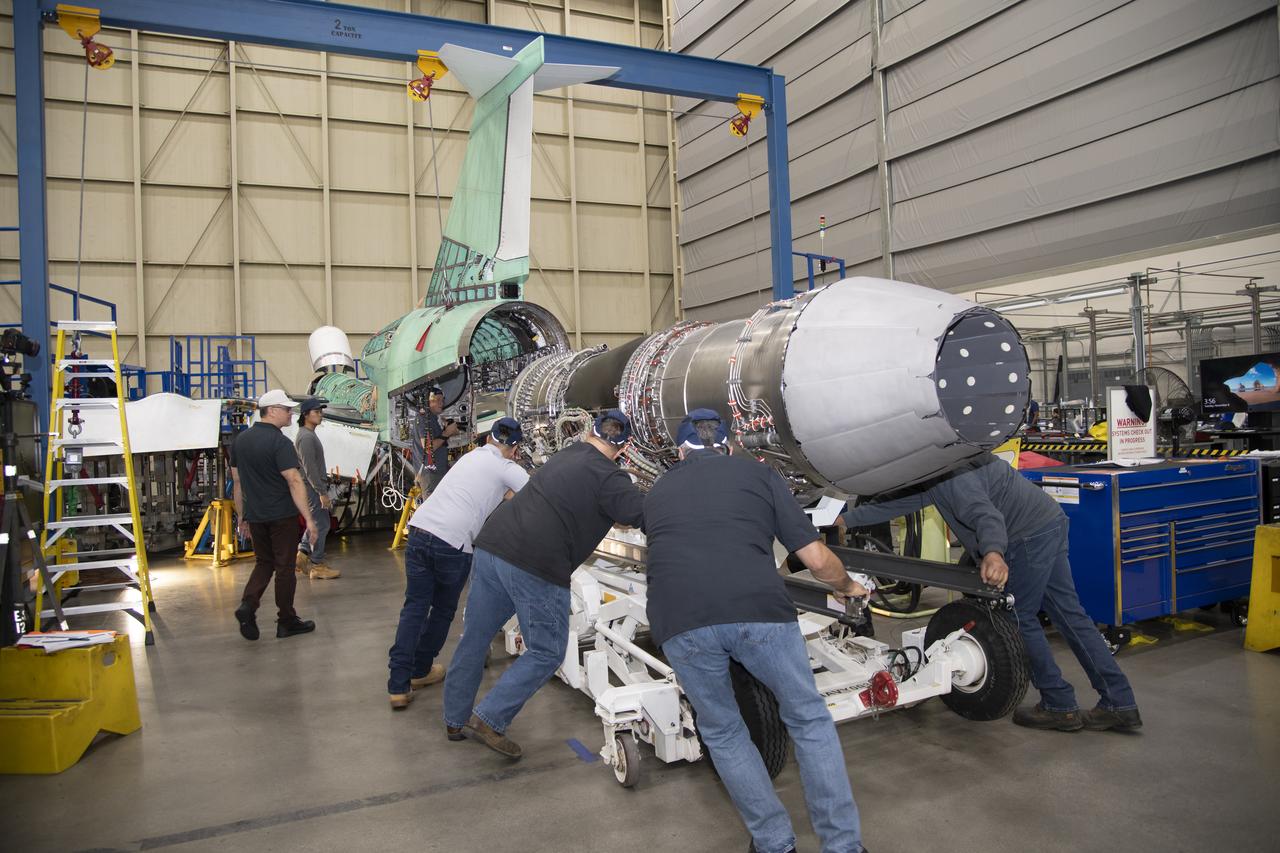

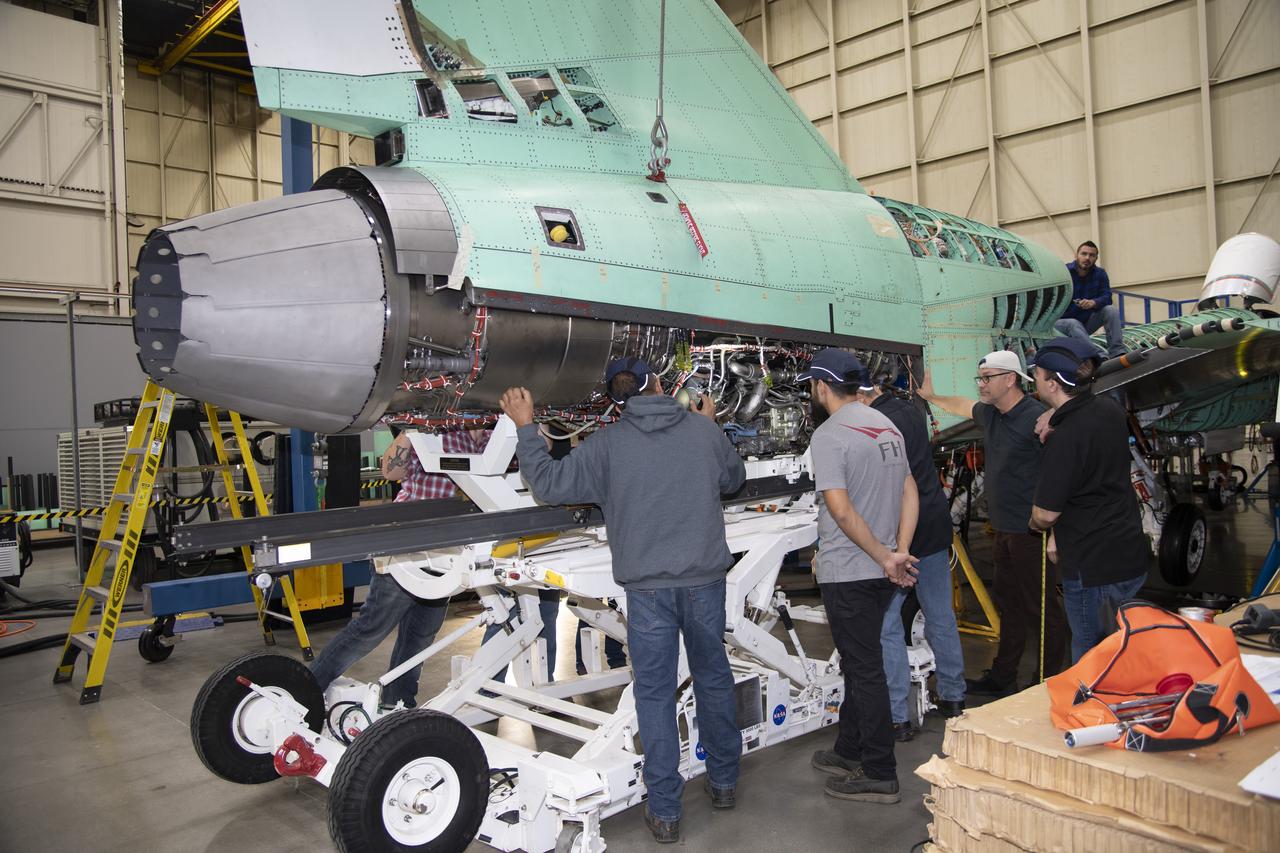
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
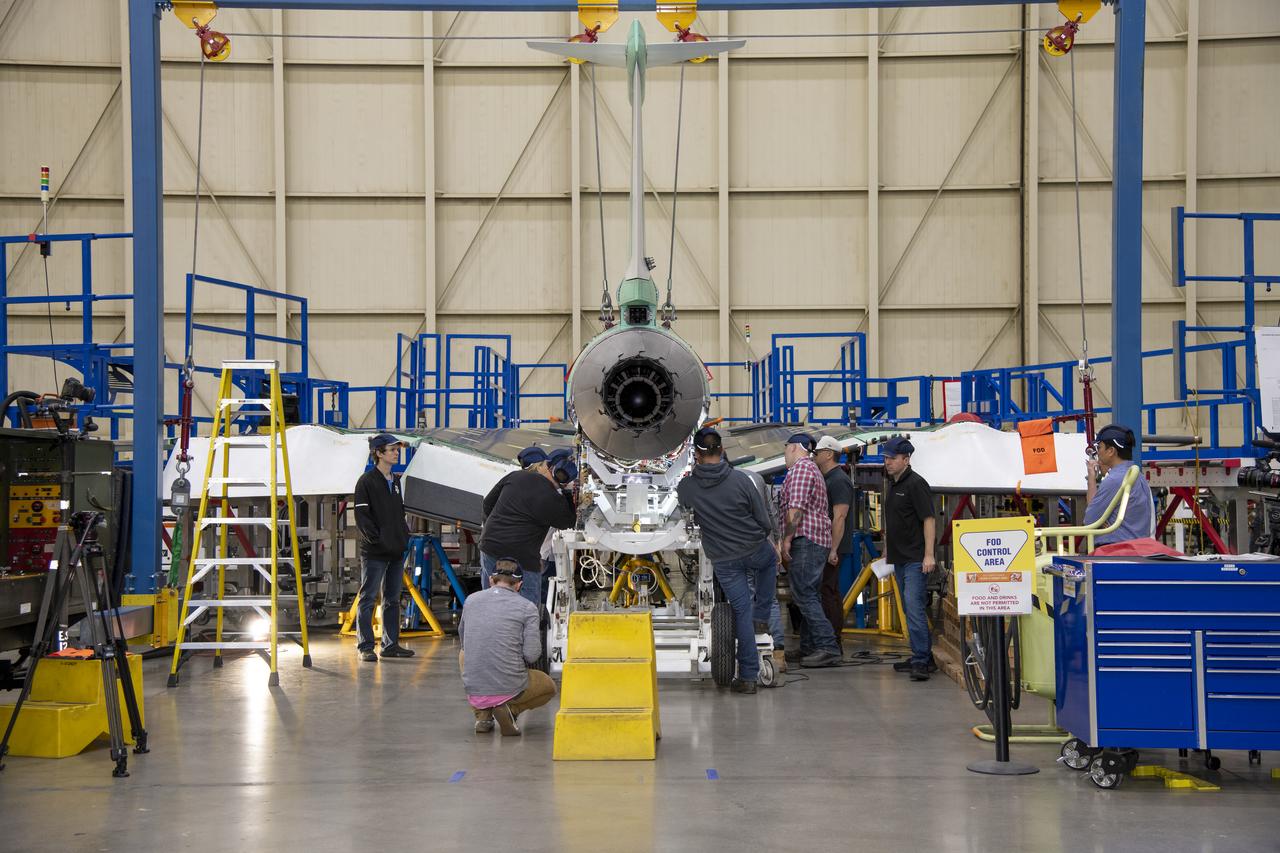

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

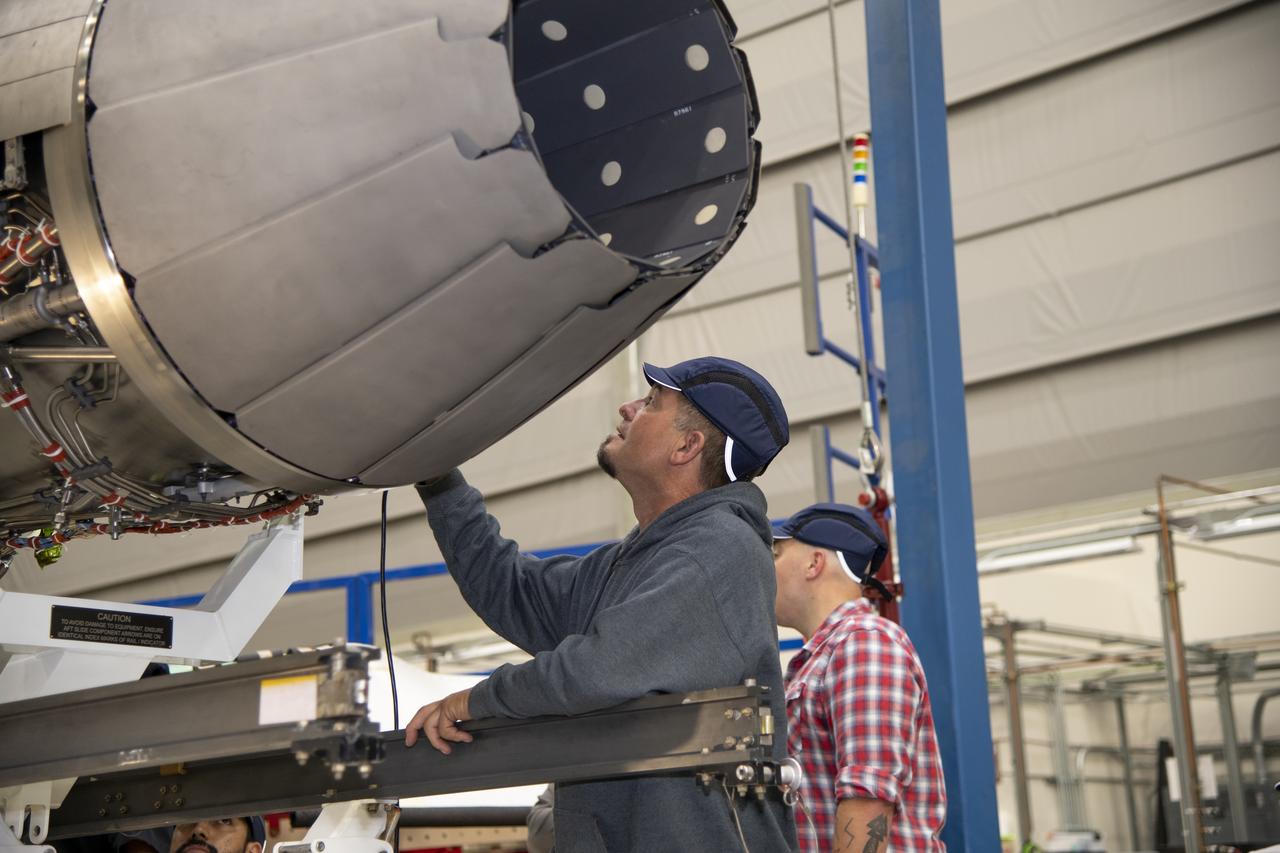
The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

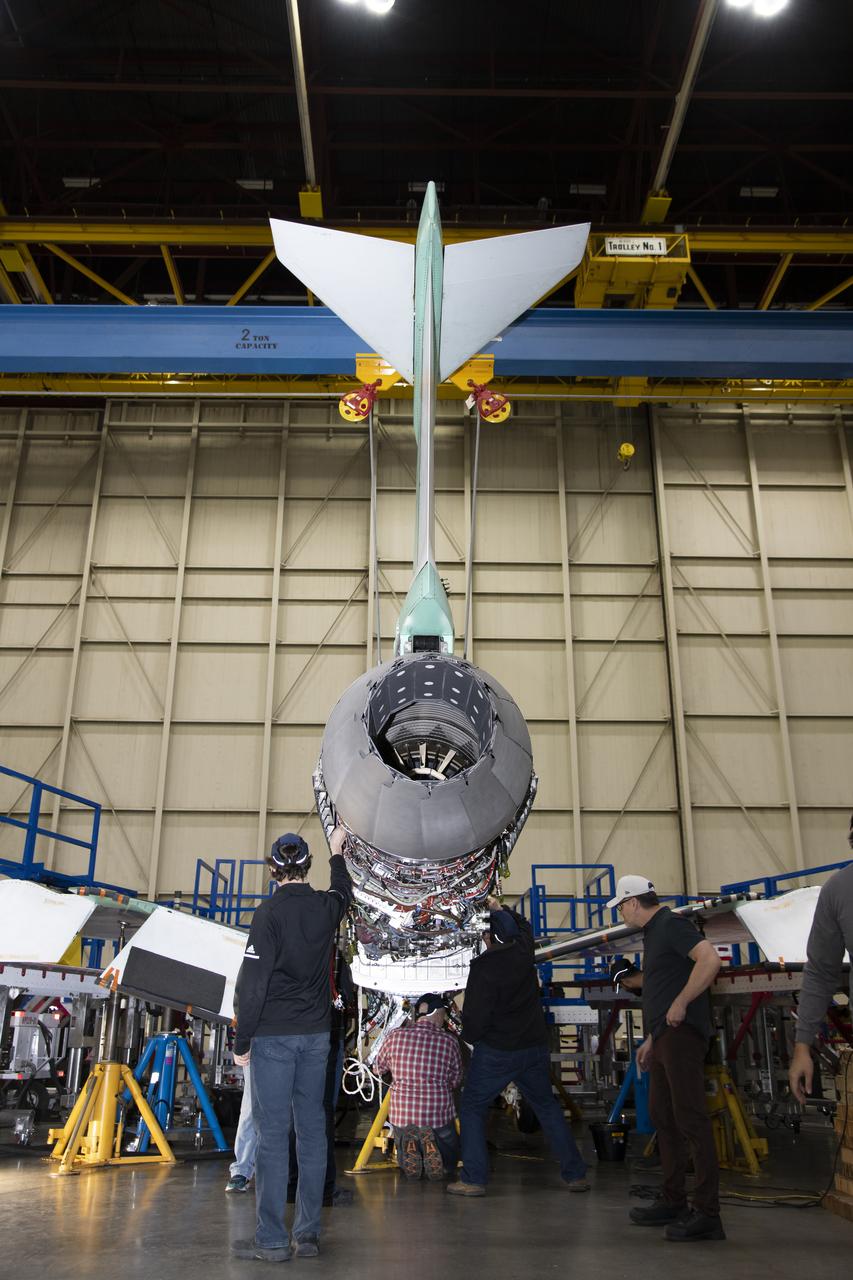
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
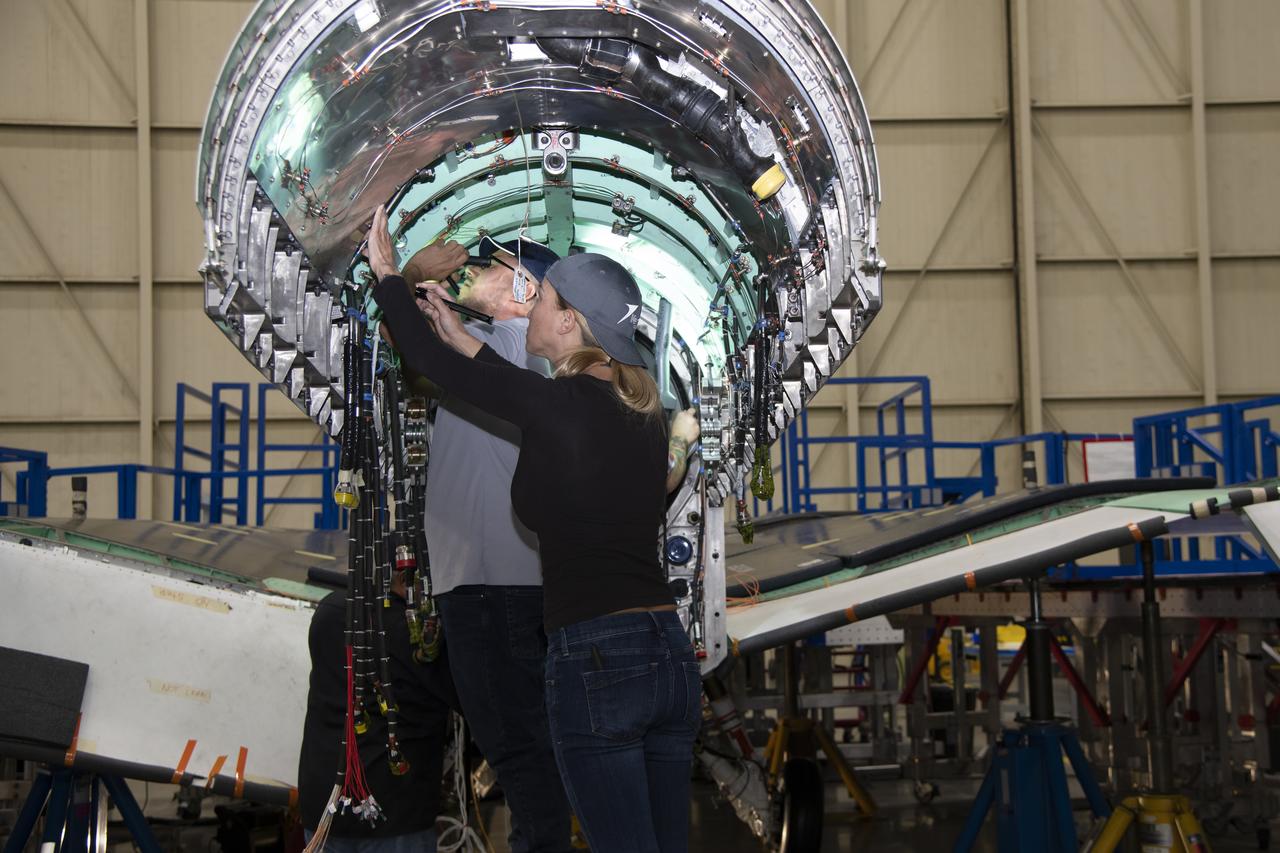

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
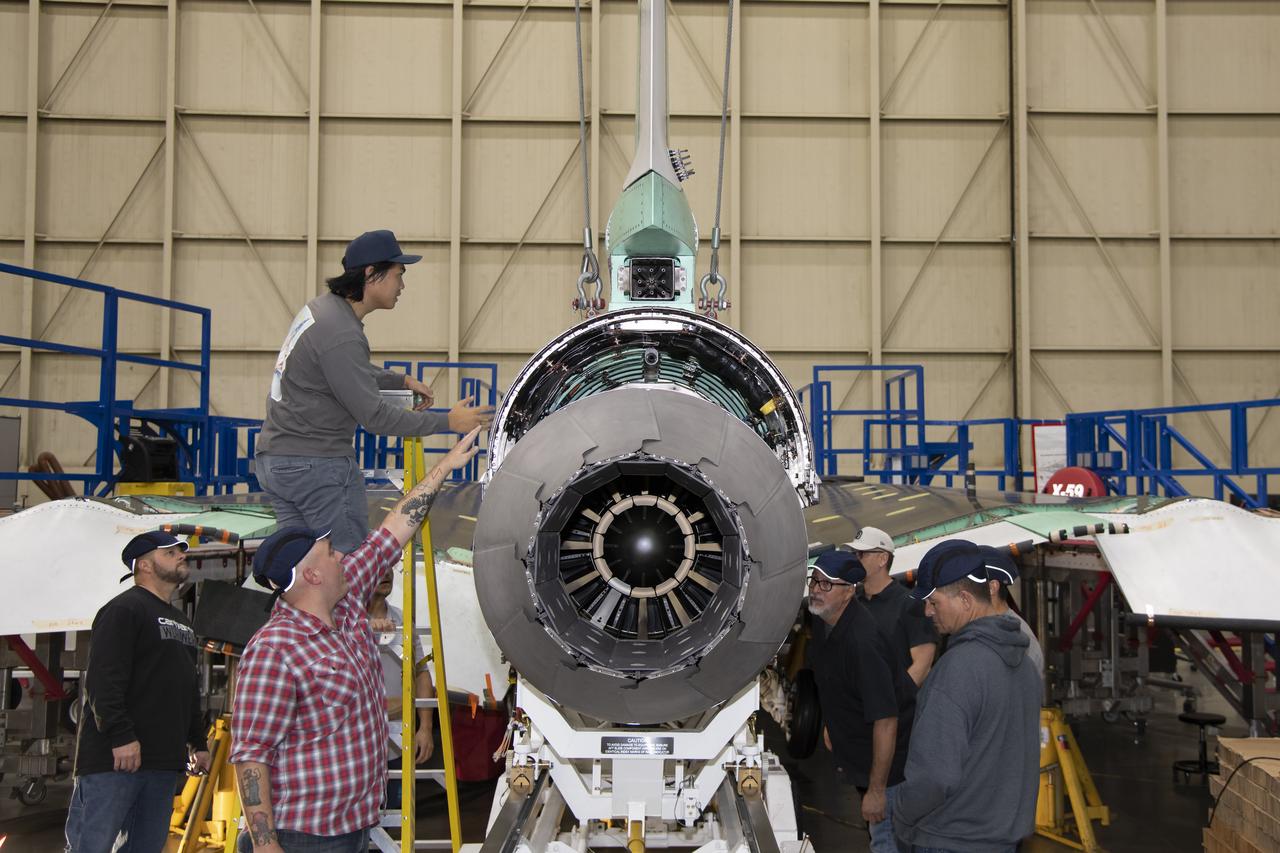

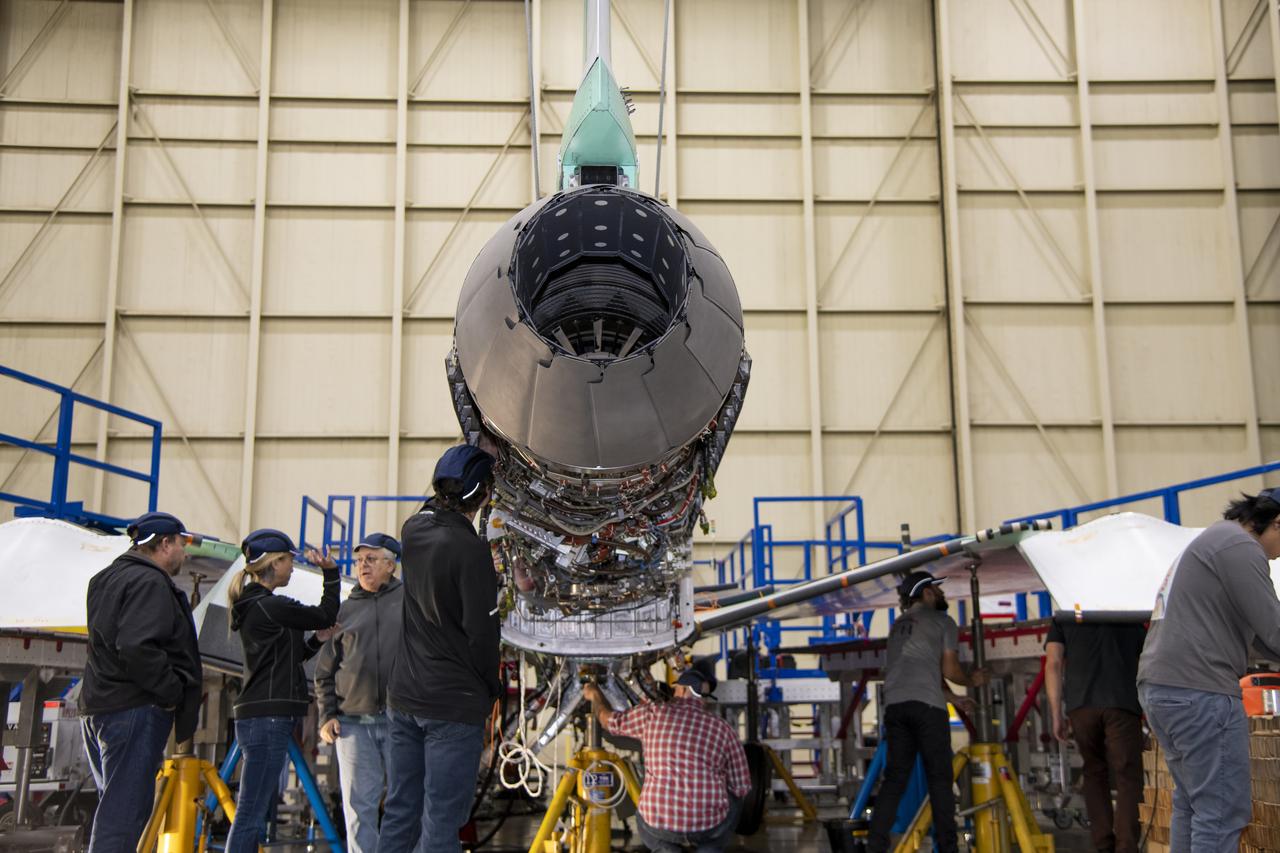
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
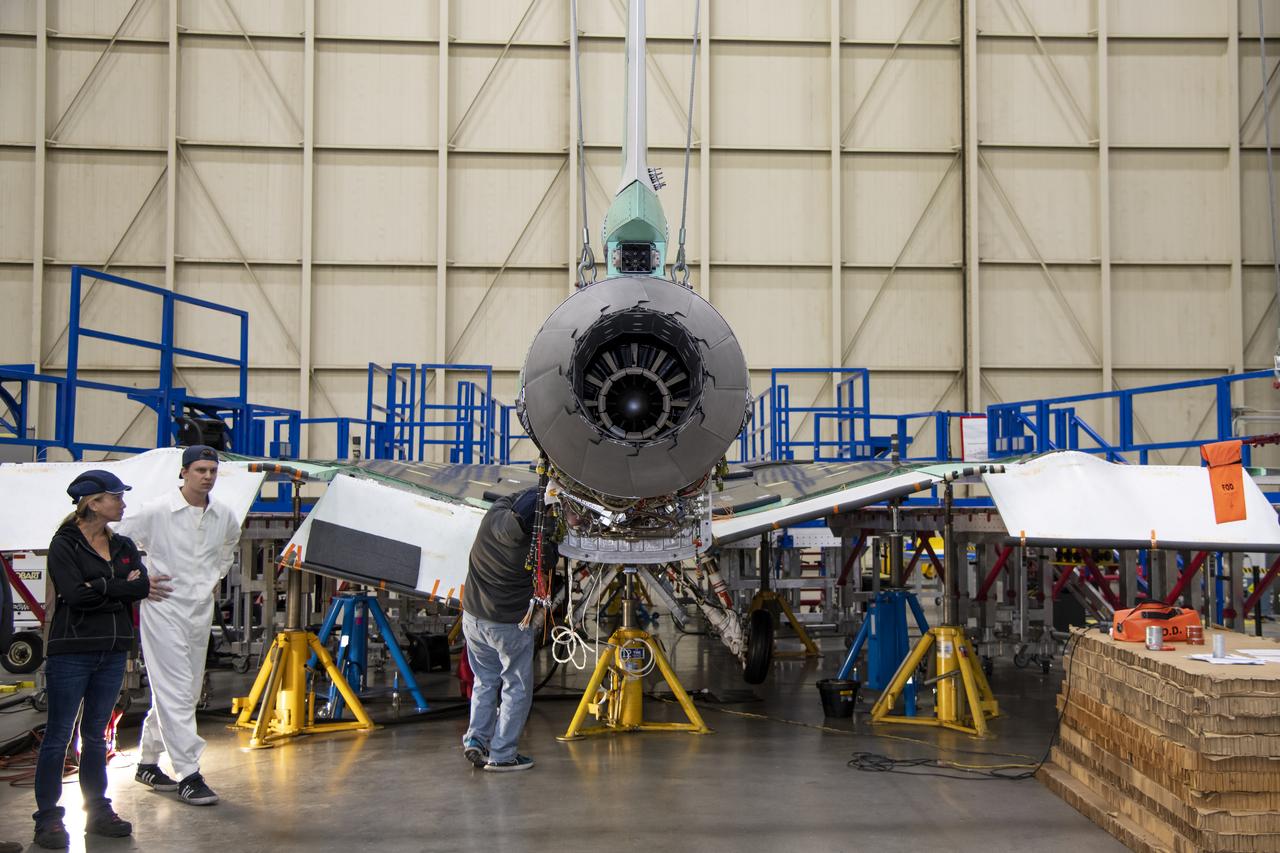

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
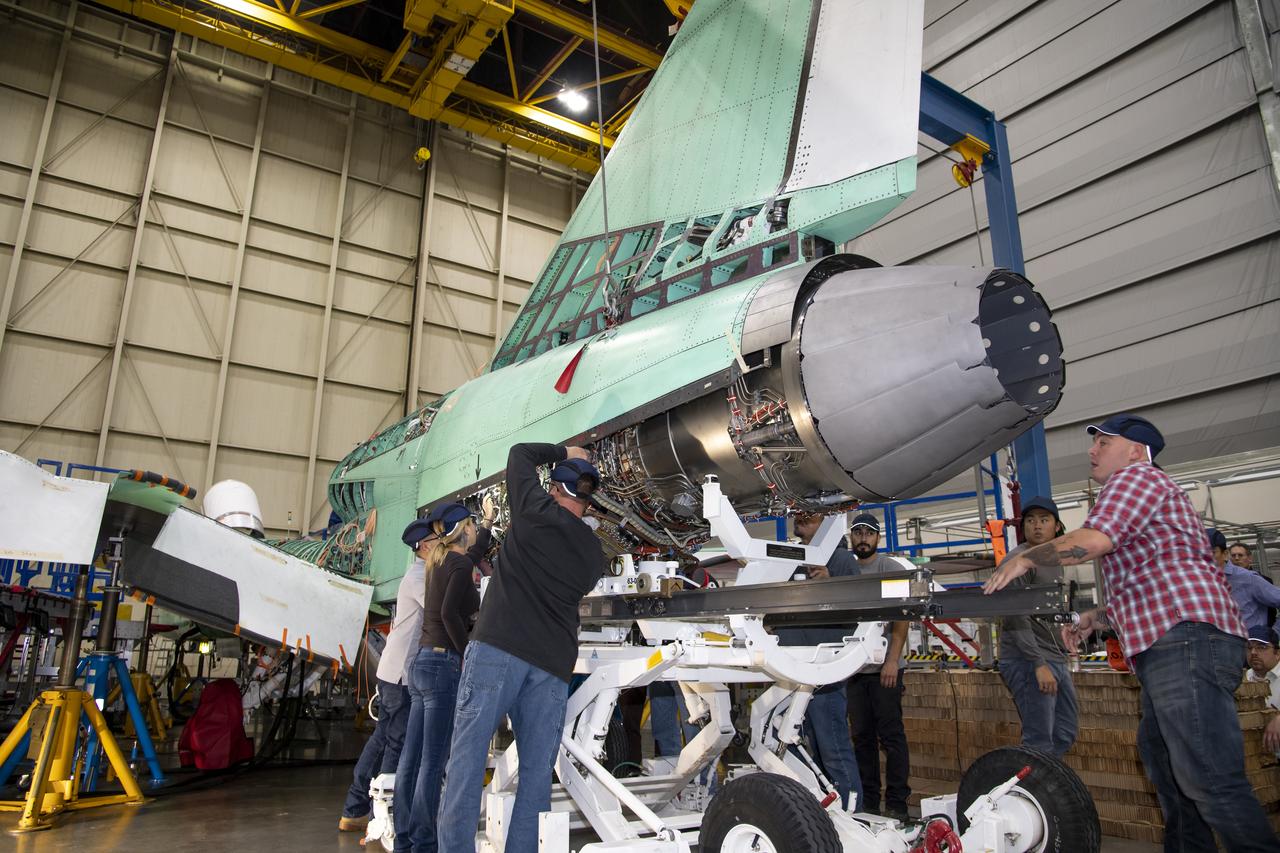

The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
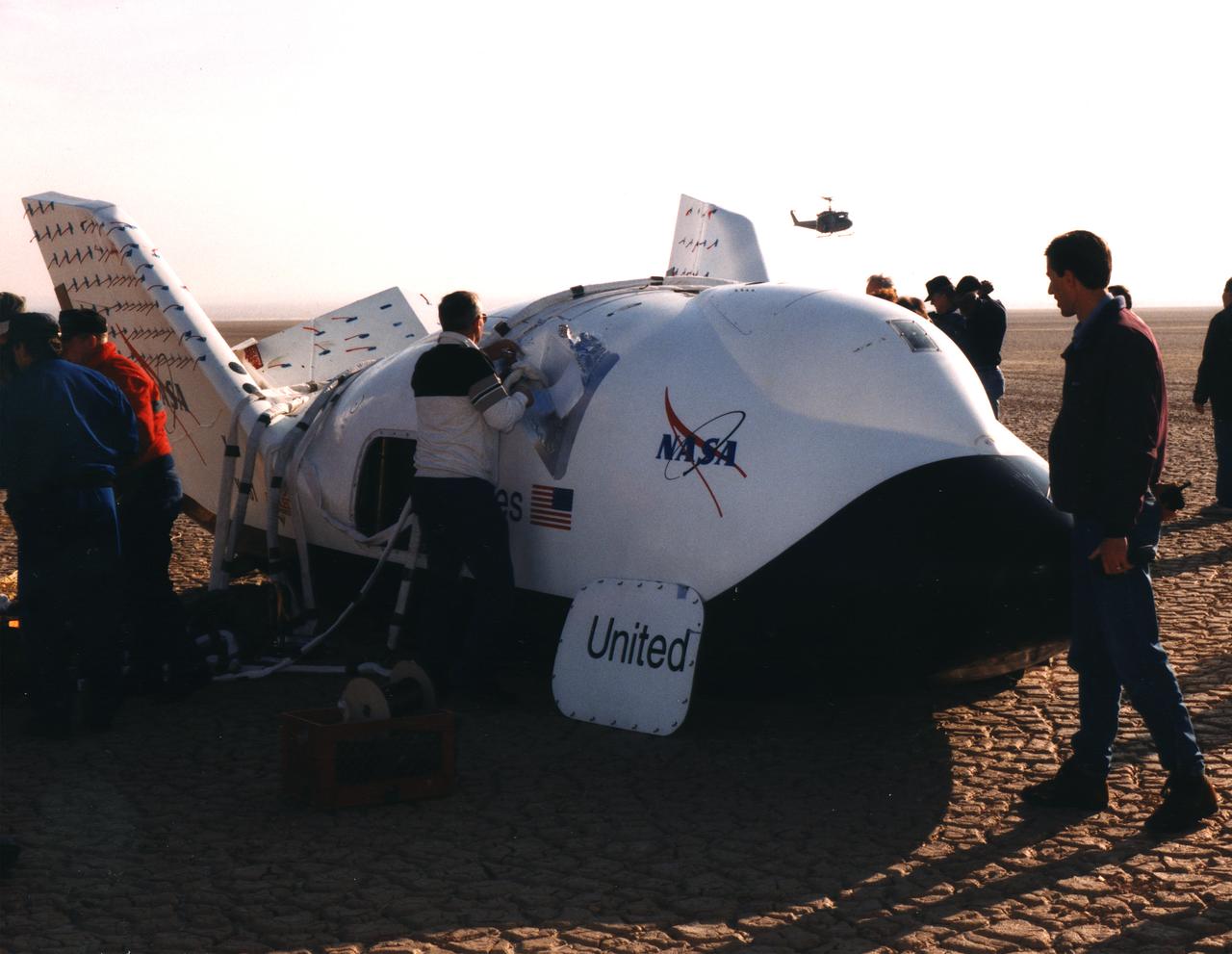

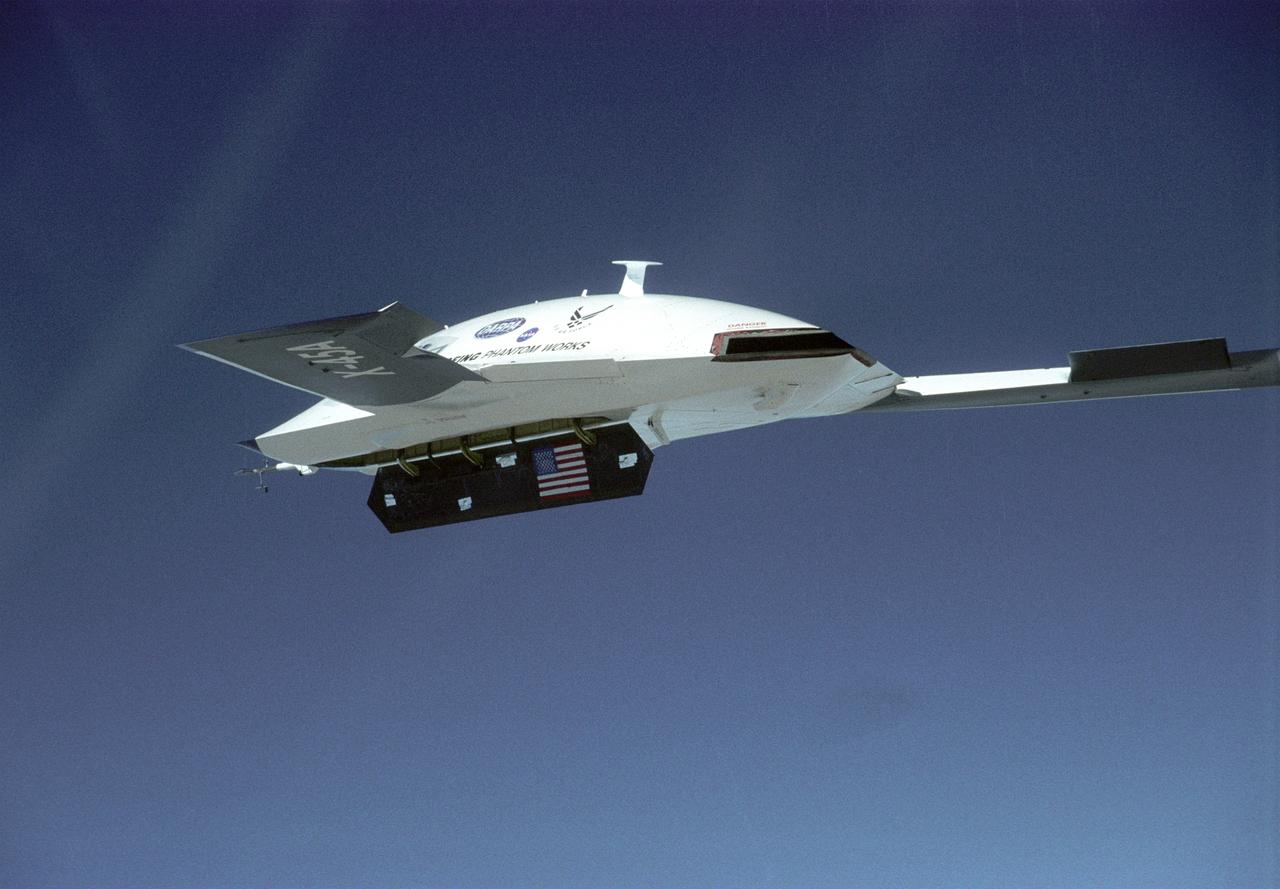
NASA's X-38, a prototype of a Crew Return Vehicle (CRV) resting on the lakebed near the Dryden Flight Research Center after the completion of its second free flight. The X-38 was launched from NASA Dryden's B-52 Mothership on Saturday, February 6, 1999, from an altitude of approximately 23,000 feet.
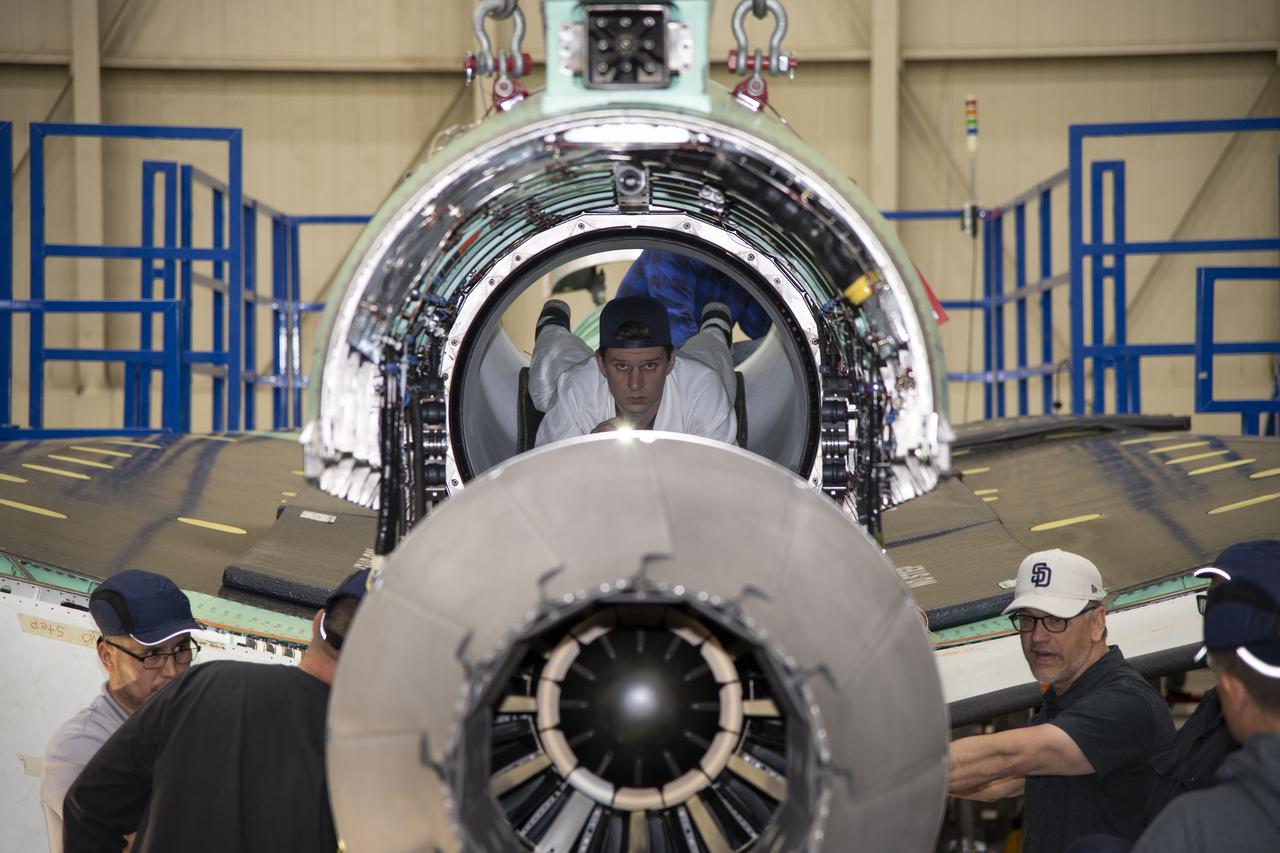

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
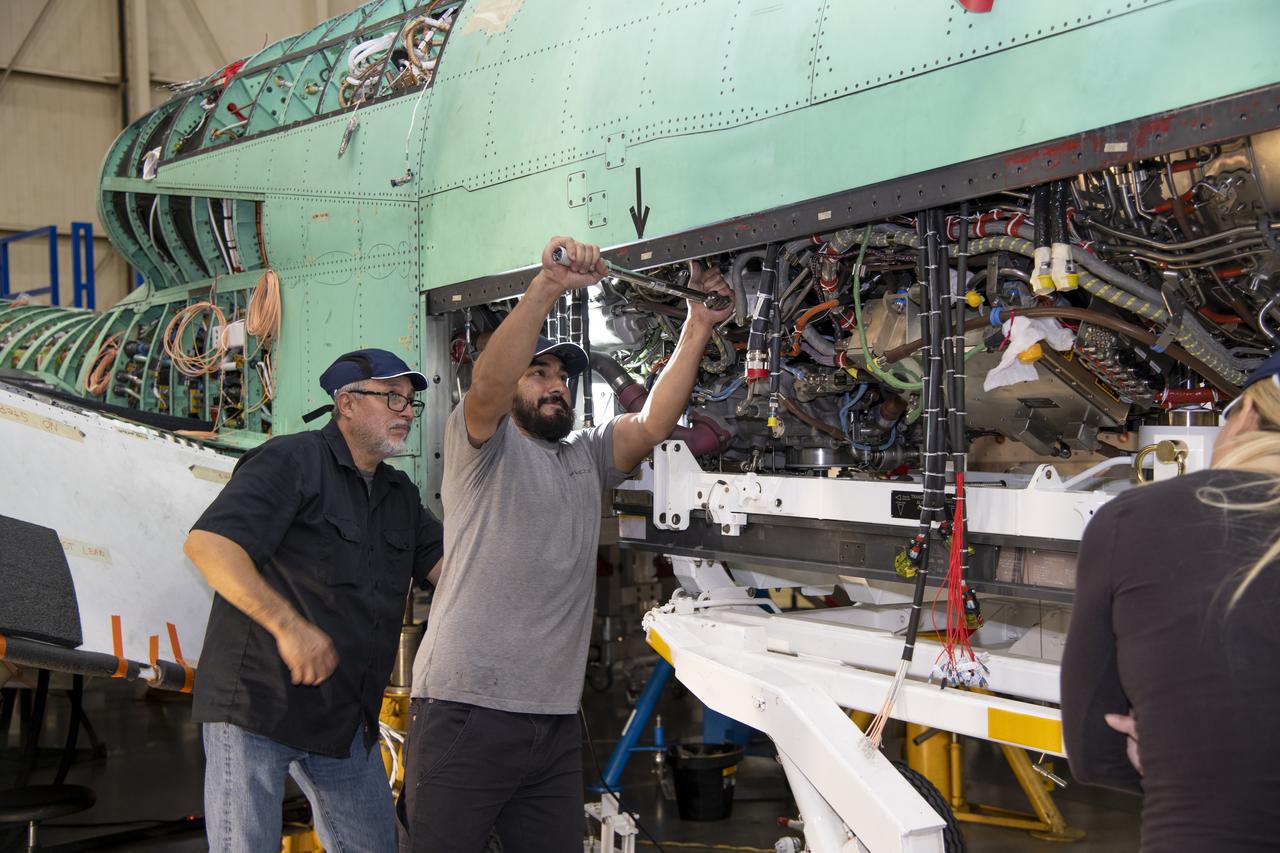

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
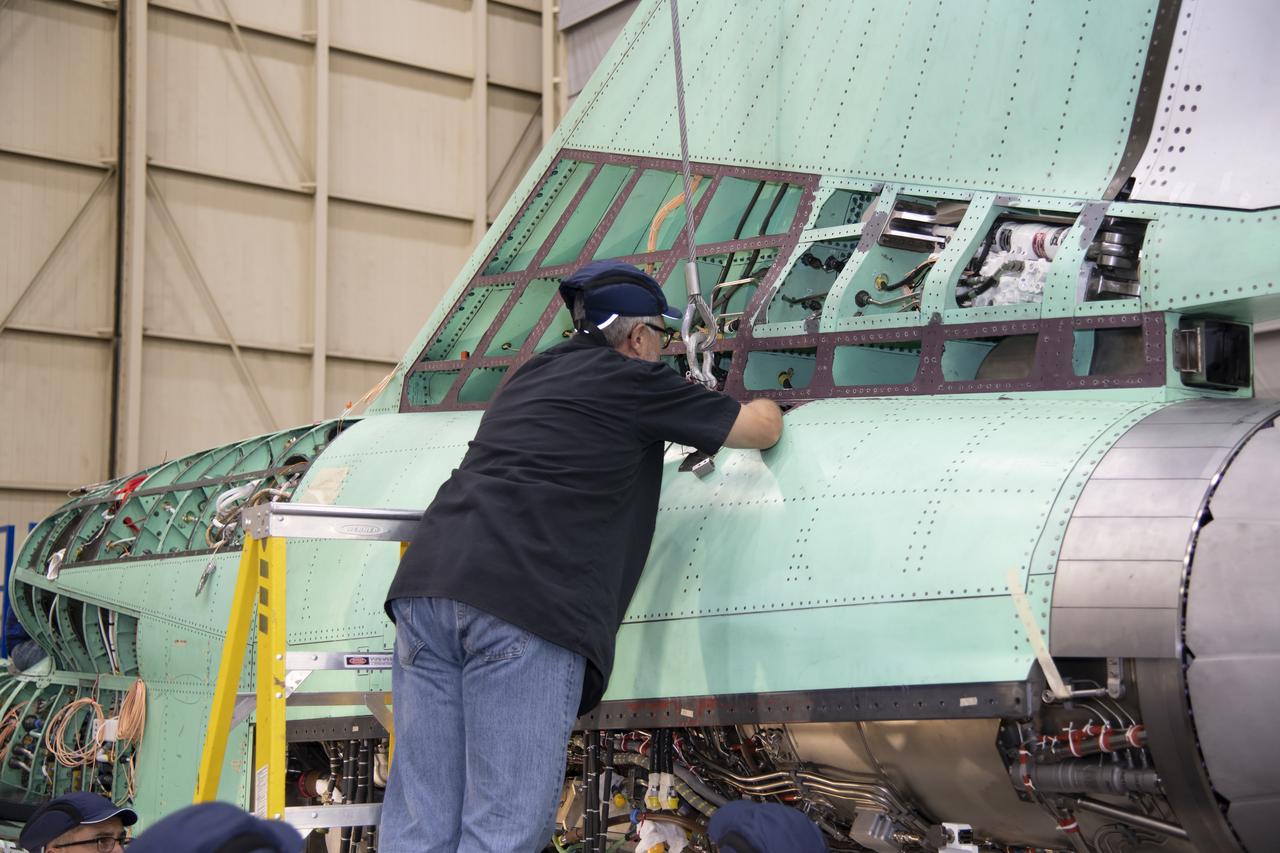

The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA's quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft's journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
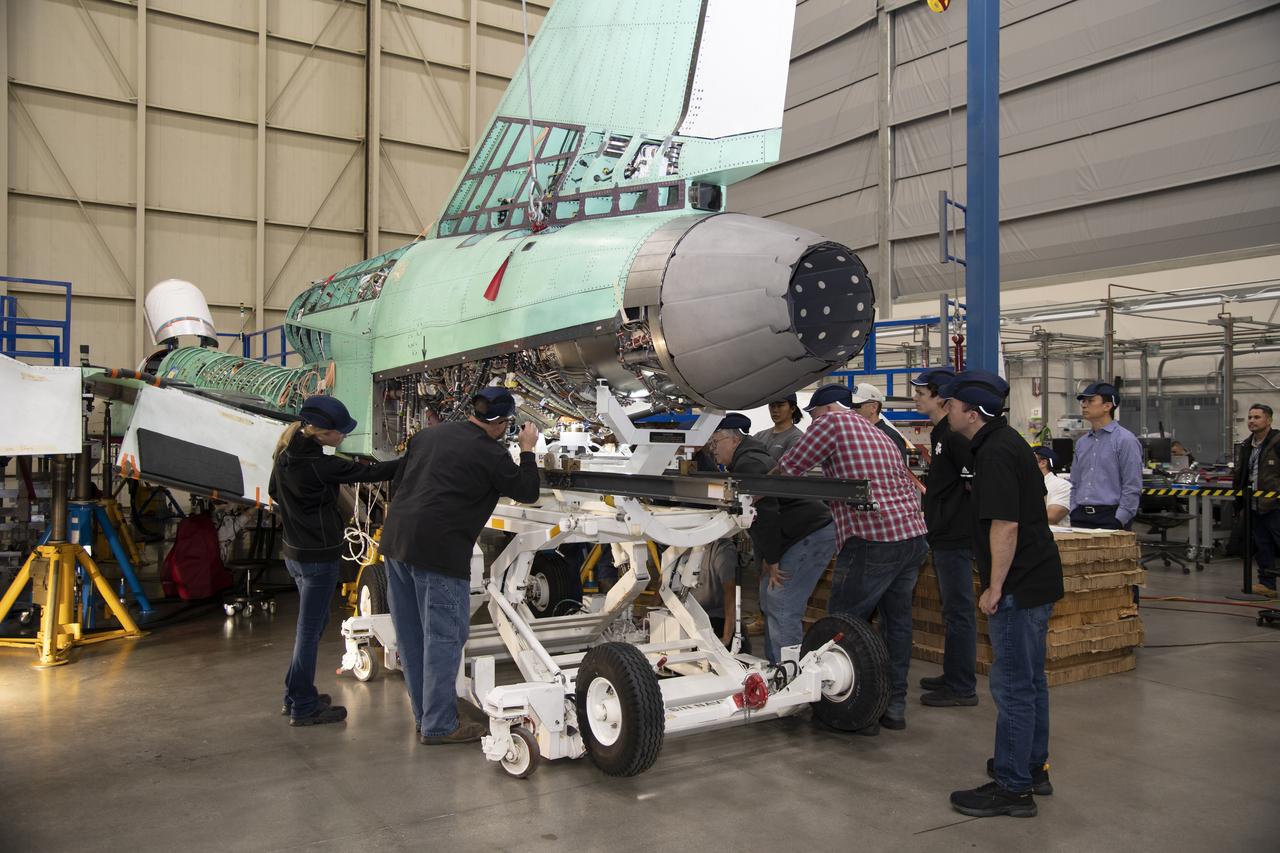

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
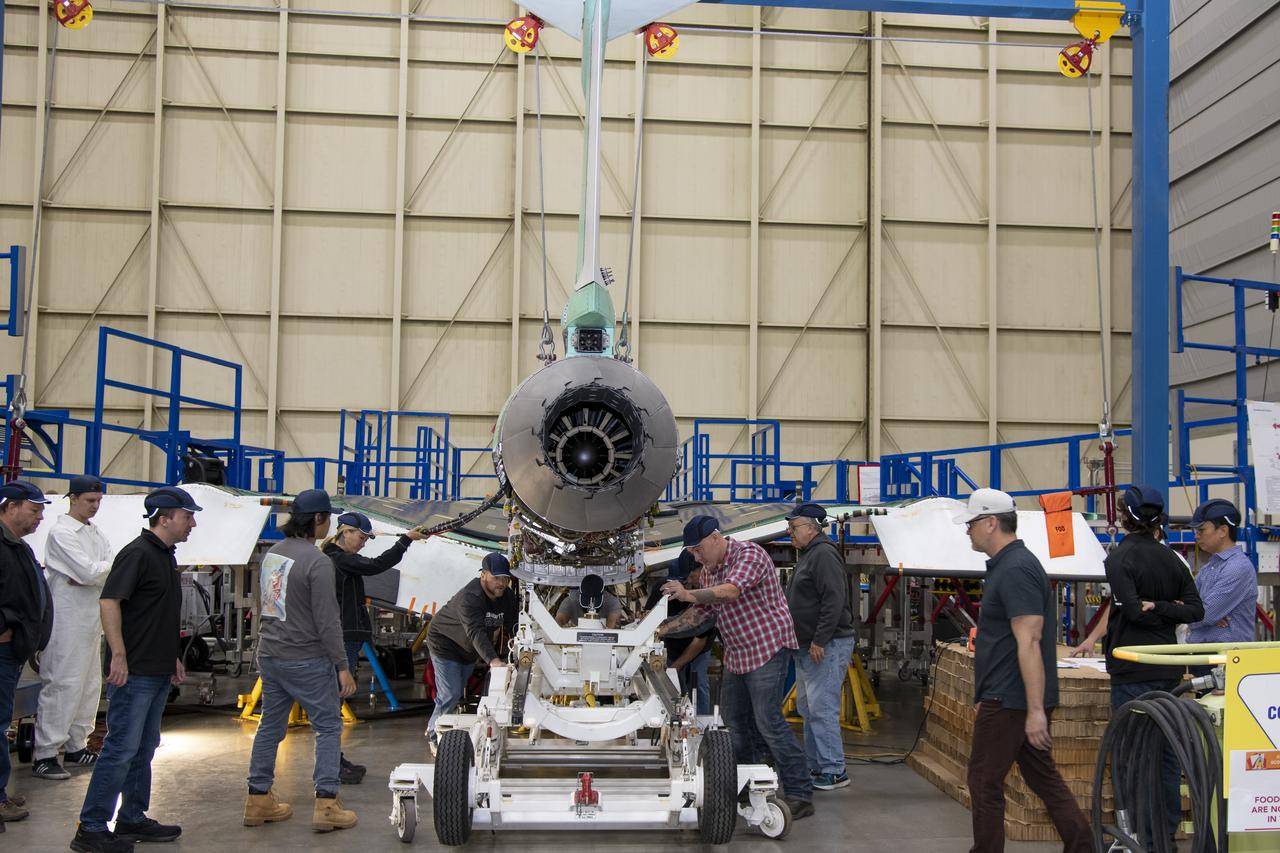

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
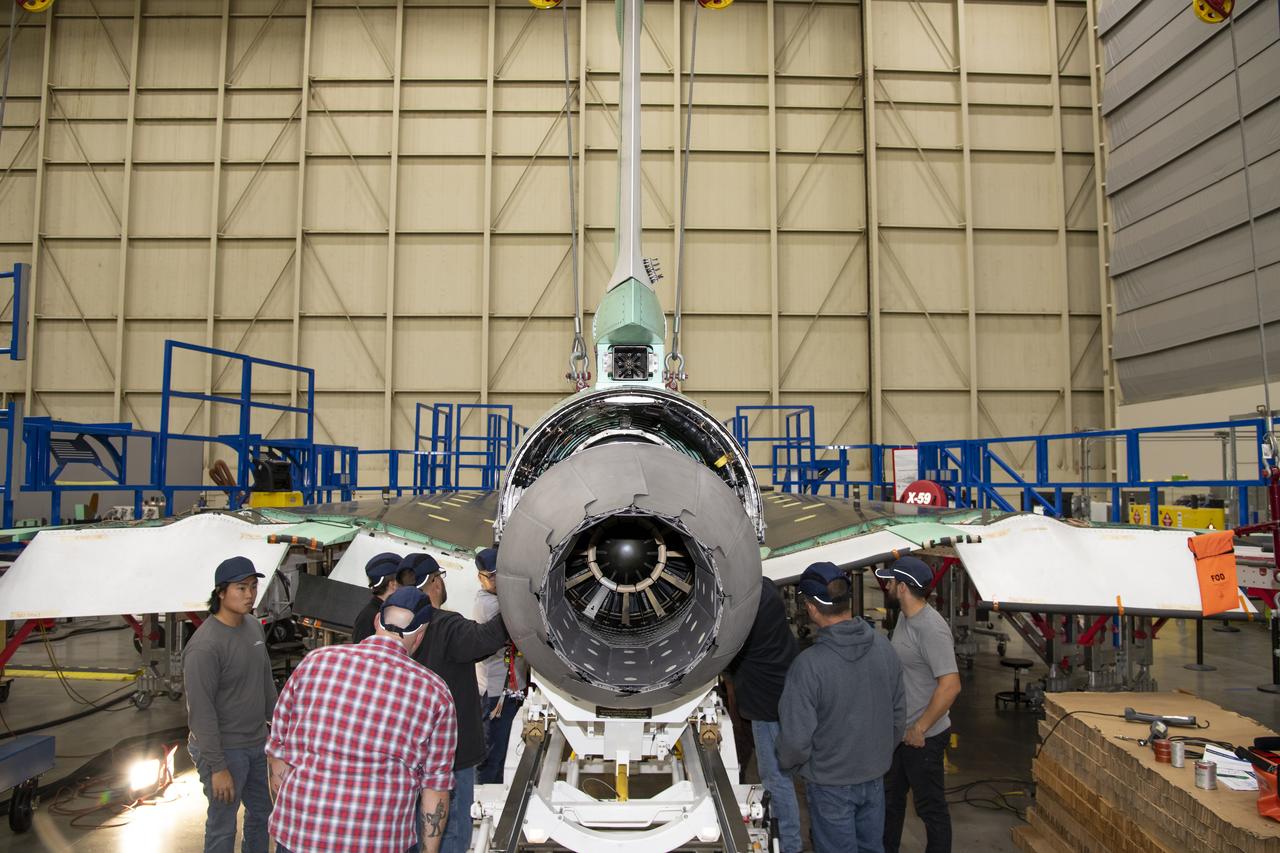

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
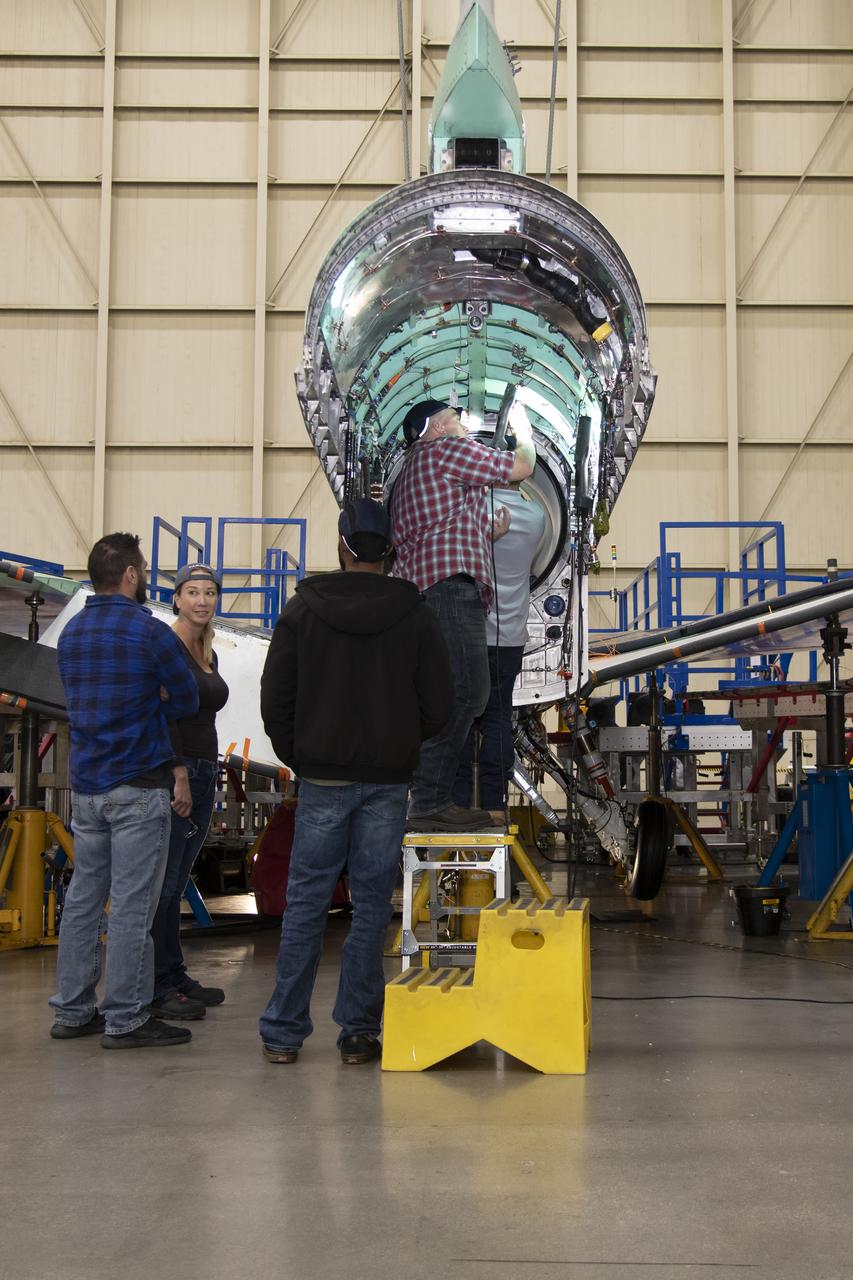

The engine that will power NASA’s quiet supersonic X-59 in flight is installed, marking a major milestone in the experimental aircraft’s journey toward first flight. The installation of the F414-GE-100 engine at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility brings the vehicle close to the completion of its assembly.
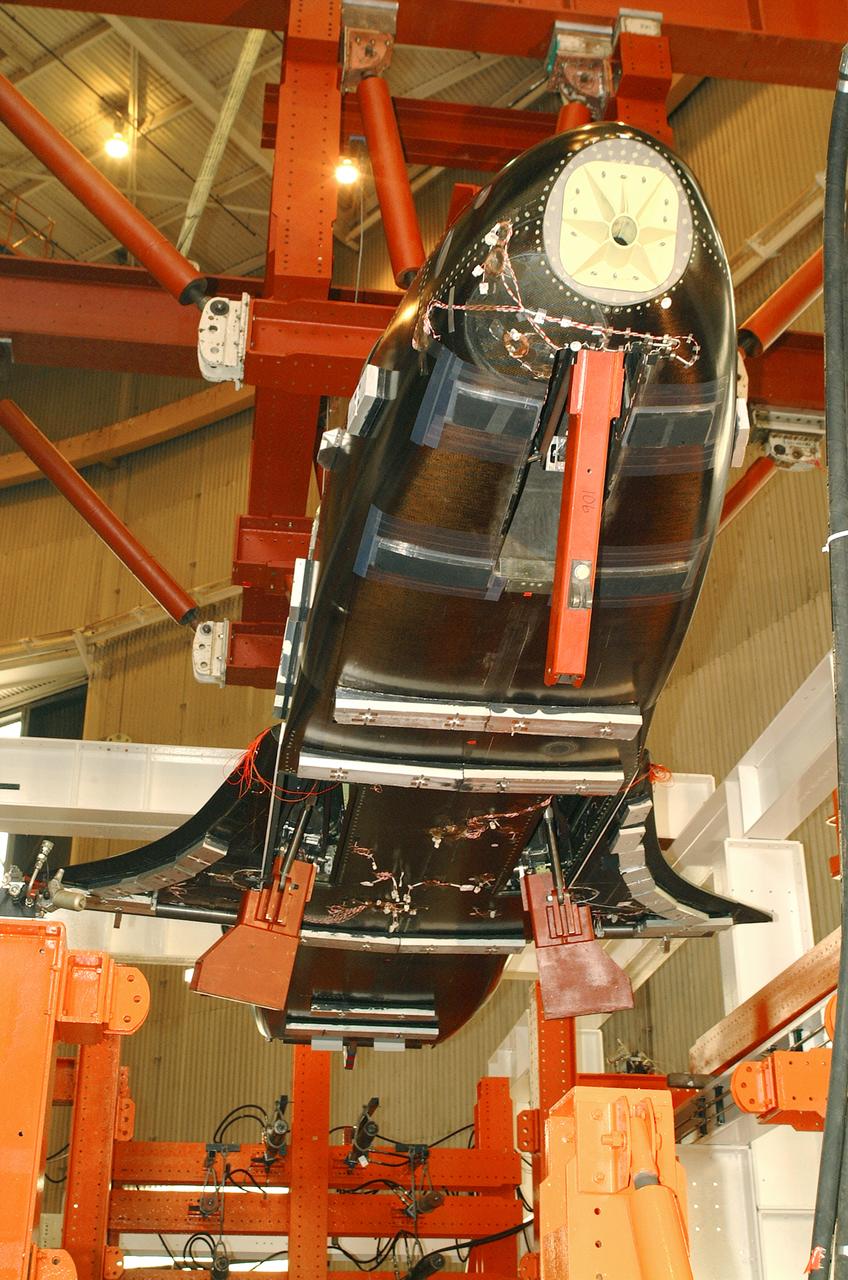

NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle is installed is a structural facility at Boeing's Huntington Beach, California plant. Tests, completed in July, were conducted to verify the structural integrity of the vehicle in preparation for atmospheric flight tests. Atmospheric flight tests of the Approach and Landing Test Vehicle are scheduled for 2004 and flight tests of the Orbital Vehicle are scheduled for 2006. The X-37 experimental launch vehicle is roughly 27.5 feet (8.3 meters) long and 15 feet (4.5 meters) in wingspan. It's experiment bay is 7 feet (2.1 meters) long and 4 feet (1.2 meters) in diameter. Designed to operate in both the orbital and reentry phases of flight, the X-37 will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000.00 per pound. The X-37 program is managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
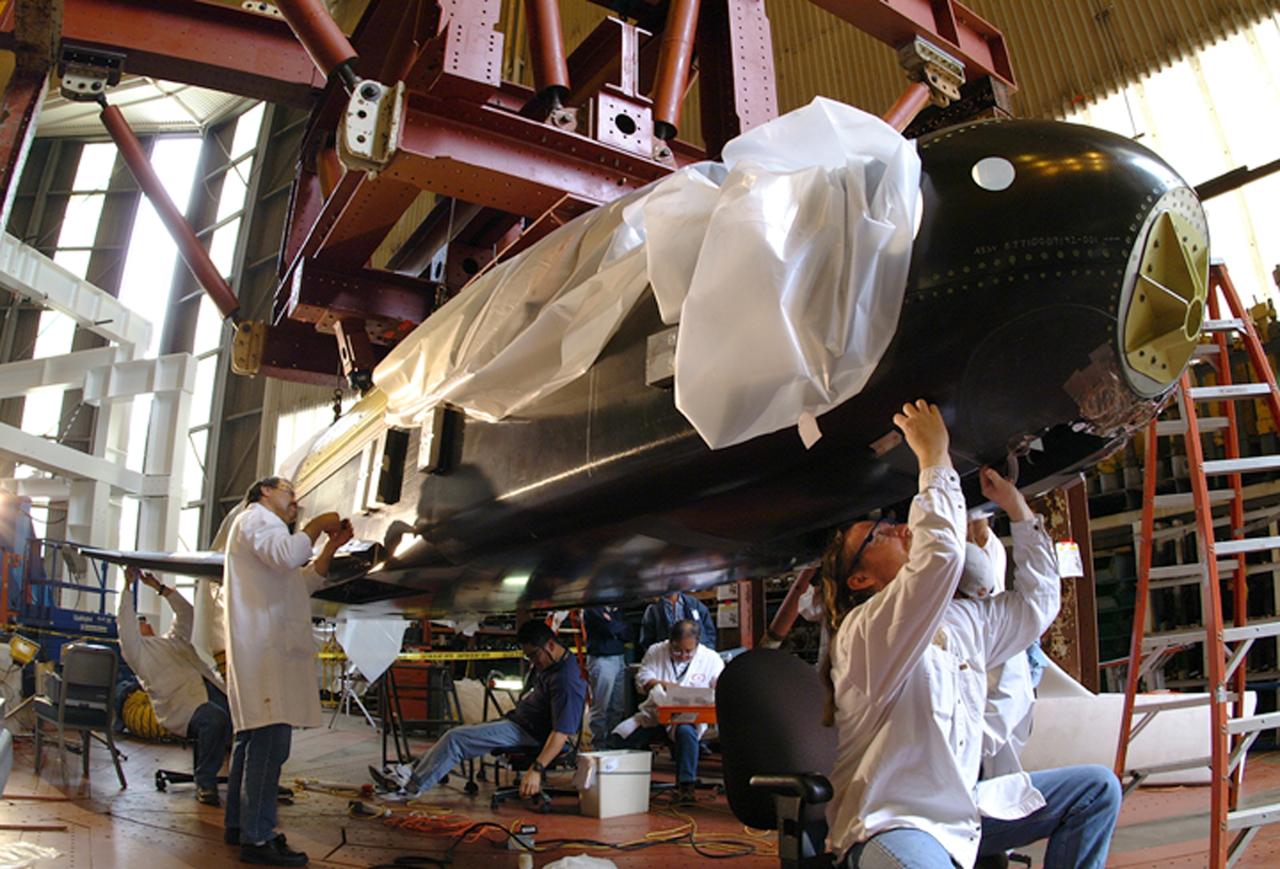

NASA's X-37 Approach and Landing Test Vehicle is installed is a structural facility at Boeing's Huntington Beach, California plant, where technicians make adjustments to composite panels. Tests, completed in July, were conducted to verify the structural integrity of the vehicle in preparation for atmospheric flight tests. Atmospheric flight tests of the Approach and Landing Test Vehicle are scheduled for 2004 and flight tests of the Orbital Vehicle are scheduled for 2006. The X-37 experimental launch vehicle is roughly 27.5 feet (8.3 meters) long and 15 feet (4.5 meters) in wingspan. It's experiment bay is 7 feet (2.1 meters) long and 4 feet (1.2 meters) in diameter. Designed to operate in both the orbital and reentry phases of flight, the X-37 will increase both safety and reliability, while reducing launch costs from $10,000 per pound to $1,000.00 per pound. The X-37 program is managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
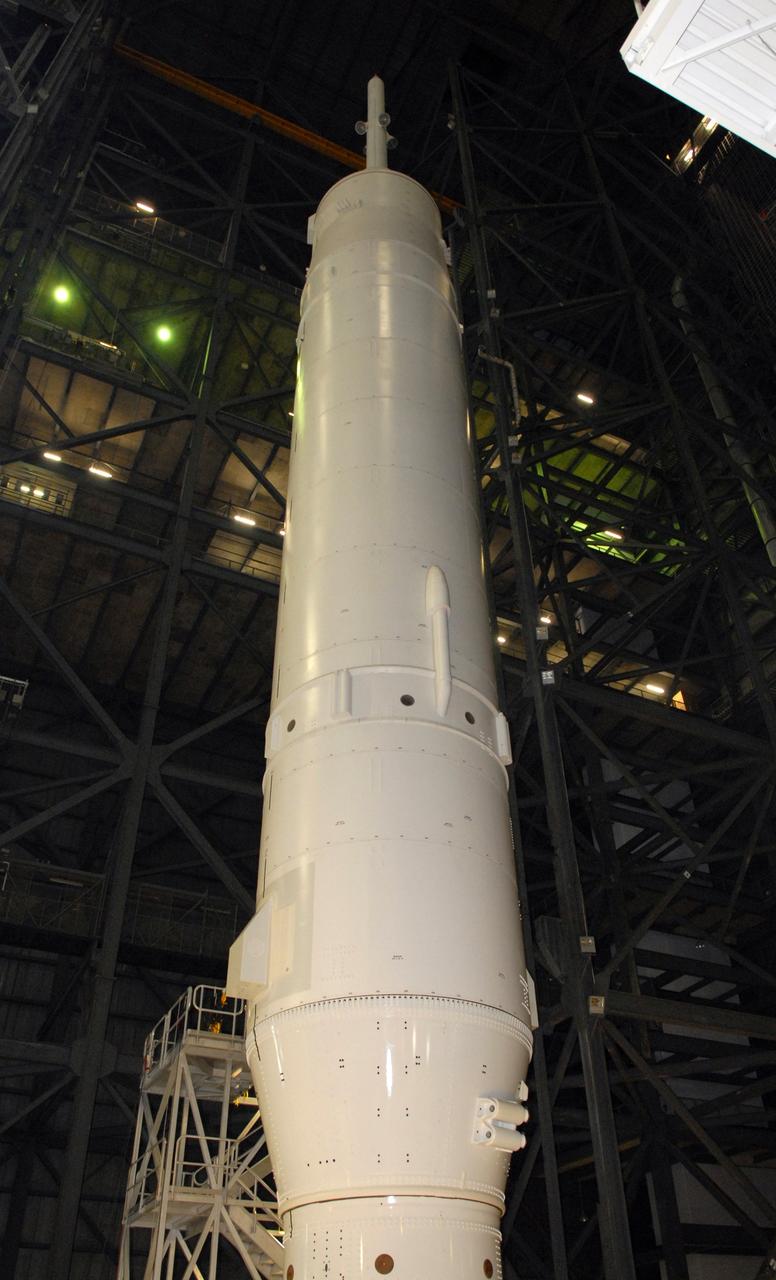

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Processing of the Ares I-X vehicle nears completion in the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Rollout to Launch Pad 39B is targeted for Oct. 19. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system designed to carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/constellation/ares/flighttests/aresIx/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
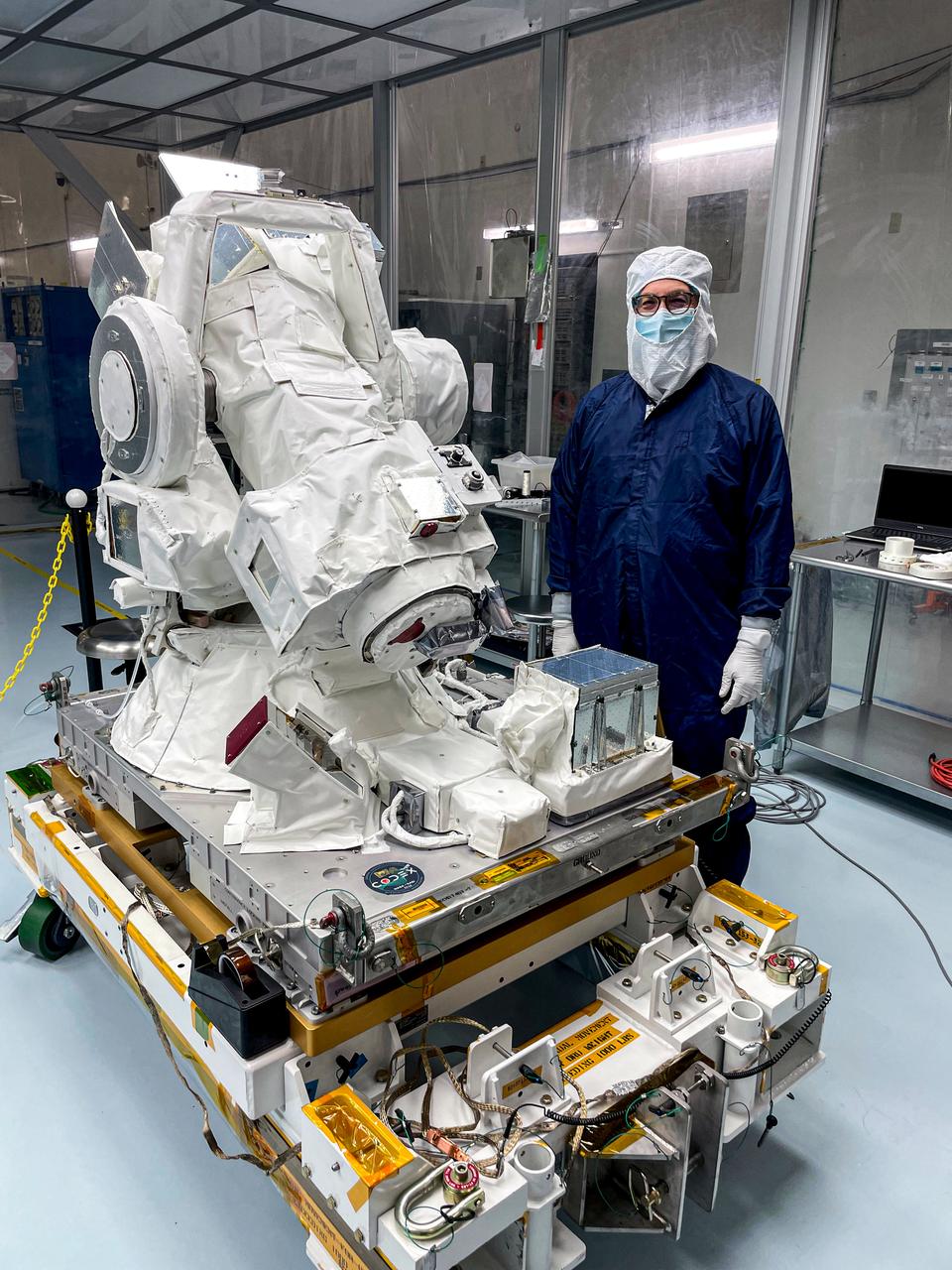

jsc2024e061953 (8/6/2024) --- Jeff Newmark, principal investigator for COronal Diagnostic EXperiment (CODEX), stands with the instrument at the Kennedy Space Flight Center Space Station Processing Facility. CODEX successfully completed all testing at the site and is awaiting integration into the launch vehicle. Credit: CODEX team / NASA
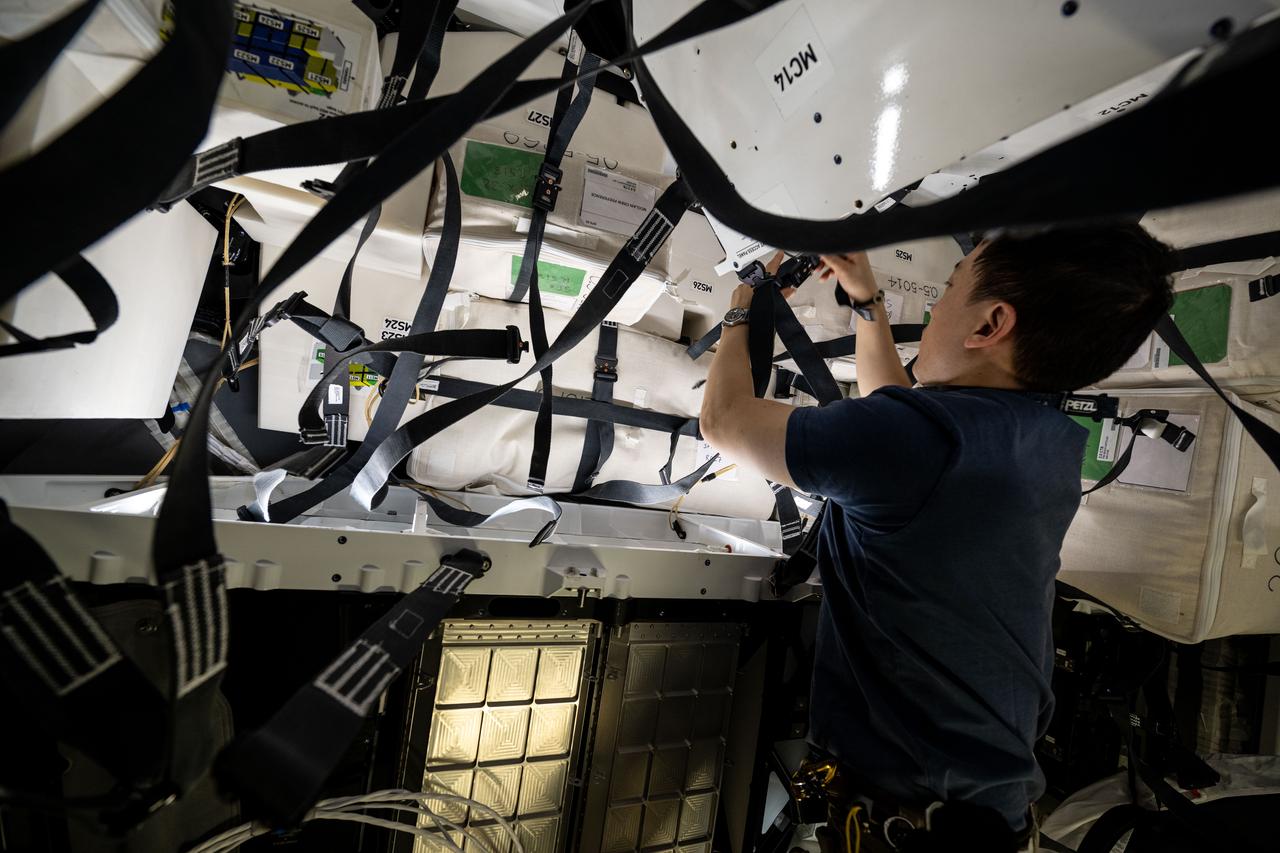

iss073e0071396 (May 15, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim works inside the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft readying the vehicle to be packed with completed science experiments, time-critical research samples, and International Space Station hardware before its departure.
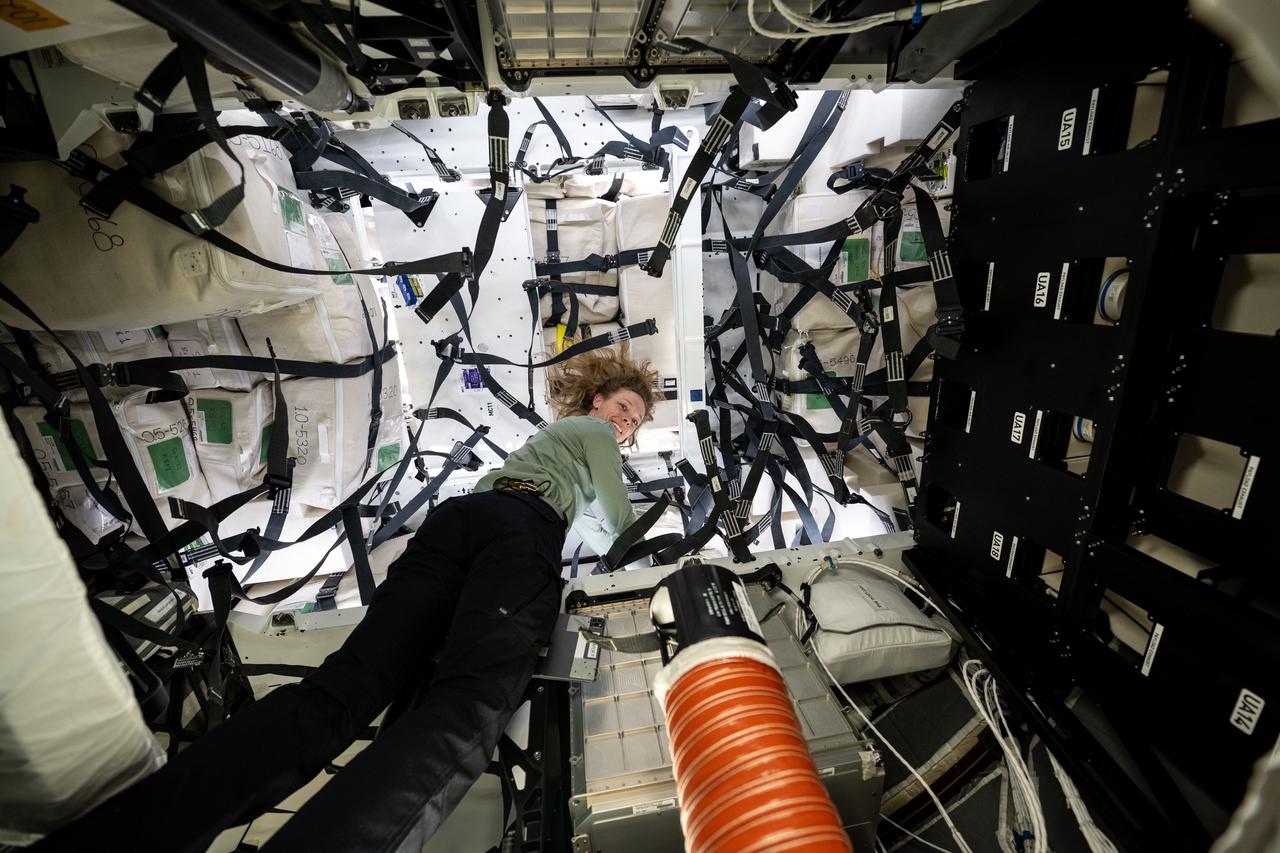

iss073e0071511 (May 15, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers works inside the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft readying the vehicle to be packed with completed science experiments, time-critical research samples, and International Space Station hardware before its departure.
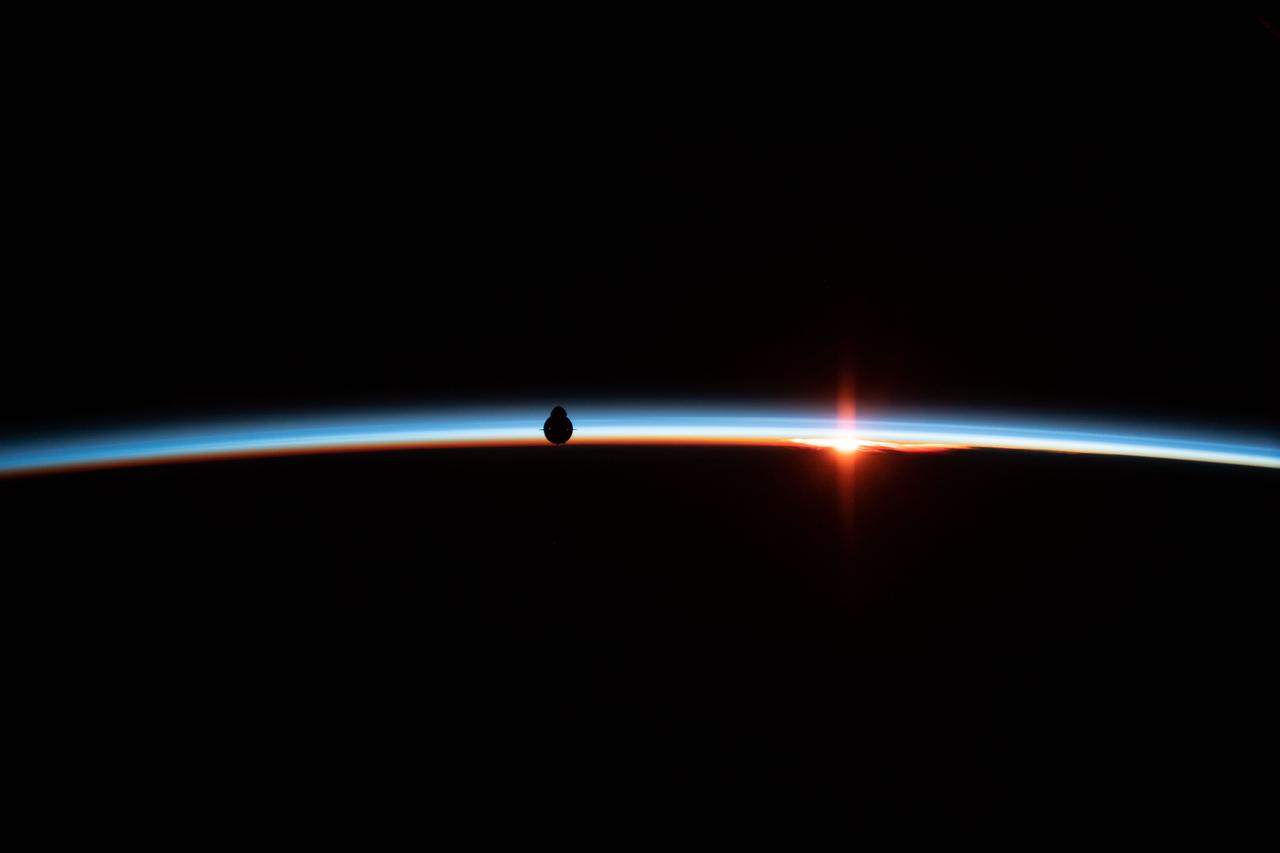

iss058e027197 (March 4, 2019) --- The uncrewed SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft is silhouetted against the Earth's horizon during Demo-1, the first flight of NASA's Commercial Crew Program to the International Space Station. The vehicle ultimately docked to the station's Harmony module after completing several successful demonstrations during approach.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vehicle Assembly Building, the mating of upper and lower segments of the starboard Solid Rocket Booster is complete. The SRB is being stacked for Return to Flight mission STS-114 on Space Shuttle Discovery to the International Space Station. Discovery is scheduled for a launch planning window of May 12 to June 3, 2005.
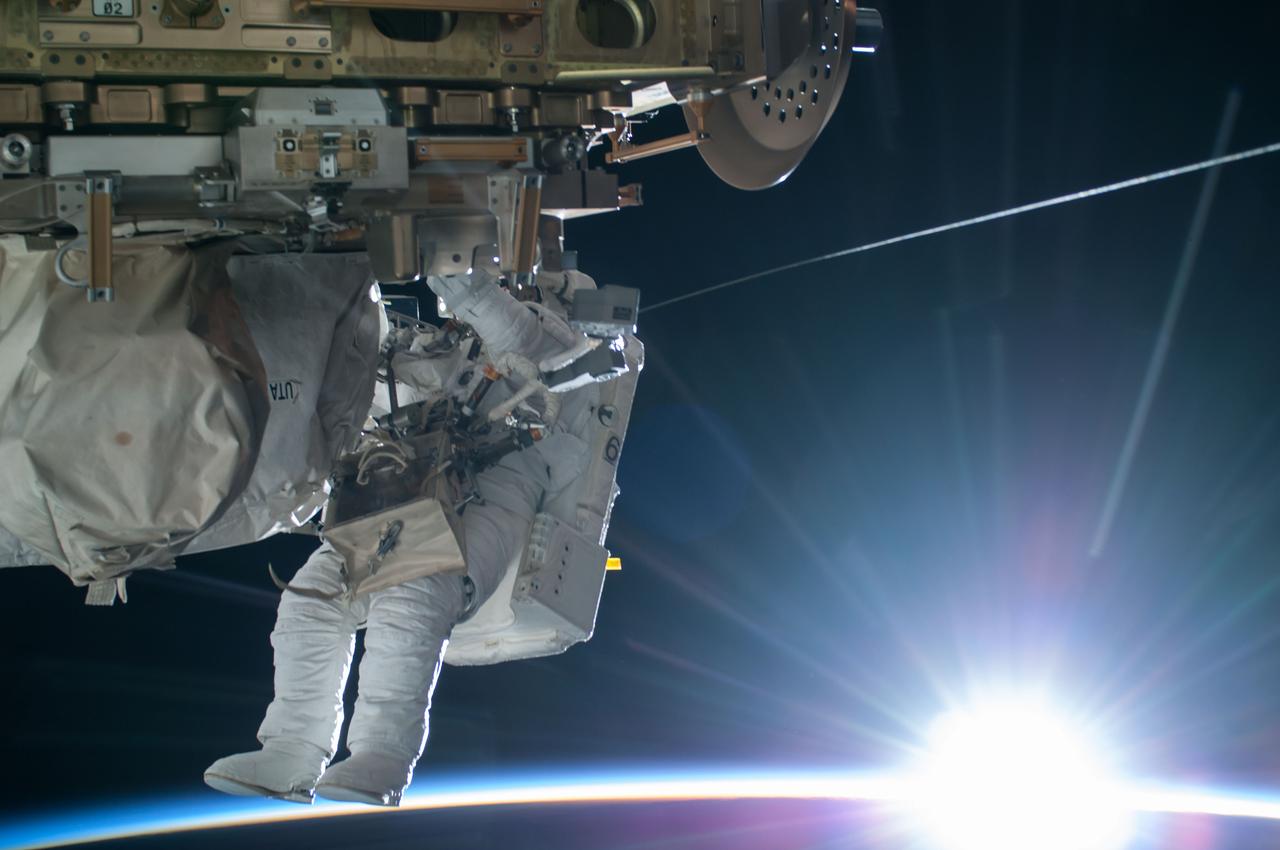

ISS042E283203 (02/21/2015) – NASA astronaut Terry Virts Flight Engineer of Expedition 42 on the International Space Station is seen working to complete a cable routing task while the sun begins to peak over the Earth’s horizon on Feb. 21 2015. Virts and fellow astronaut Barry “Butch” Wilmore completed a 6-hour, 41-minute spacewalk routing more than 300 feet of cable as part of a reconfiguration of the station to enable U.S. commercial crew vehicles under development to dock to the space station in the coming years.
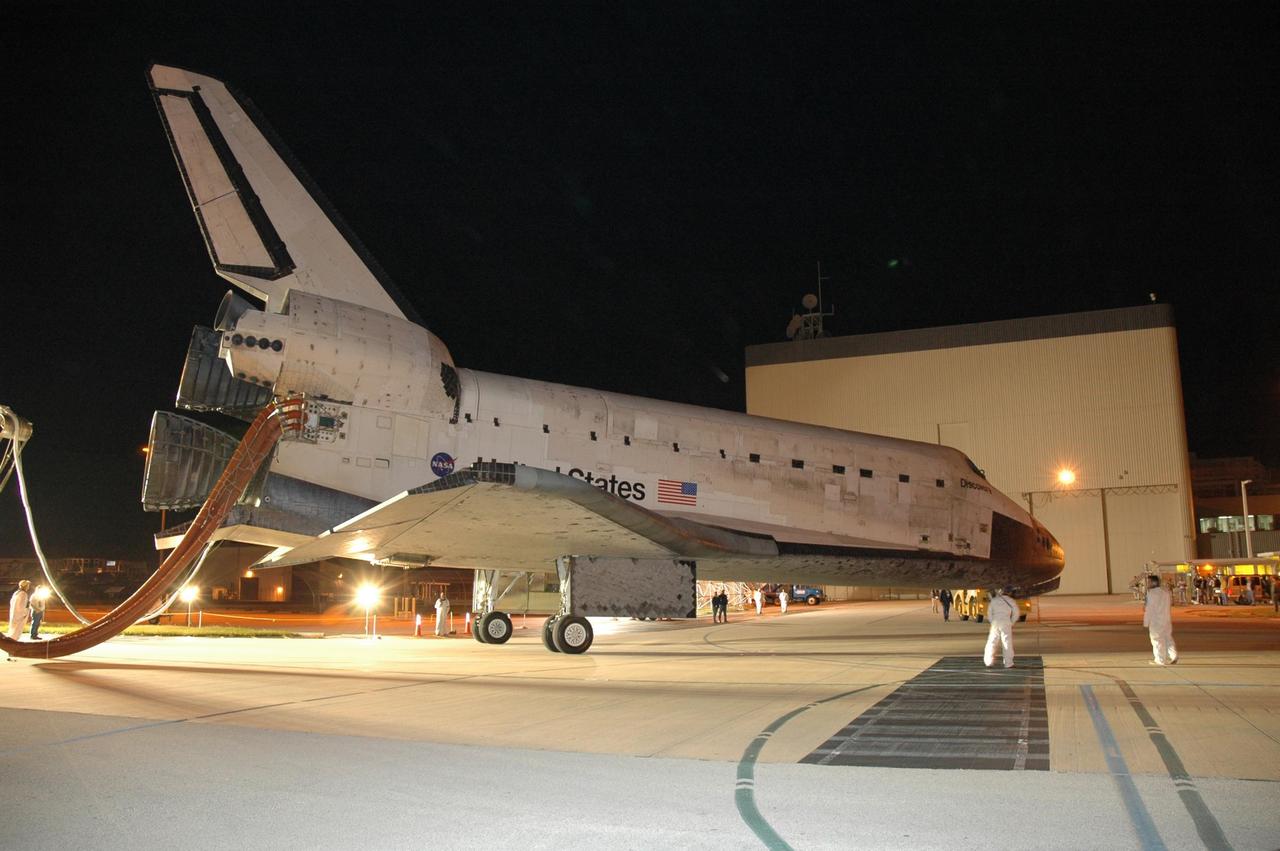

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The space shuttle Discovery nears the Orbital Processing Facility, or OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. Towing normally begins within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments is required on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
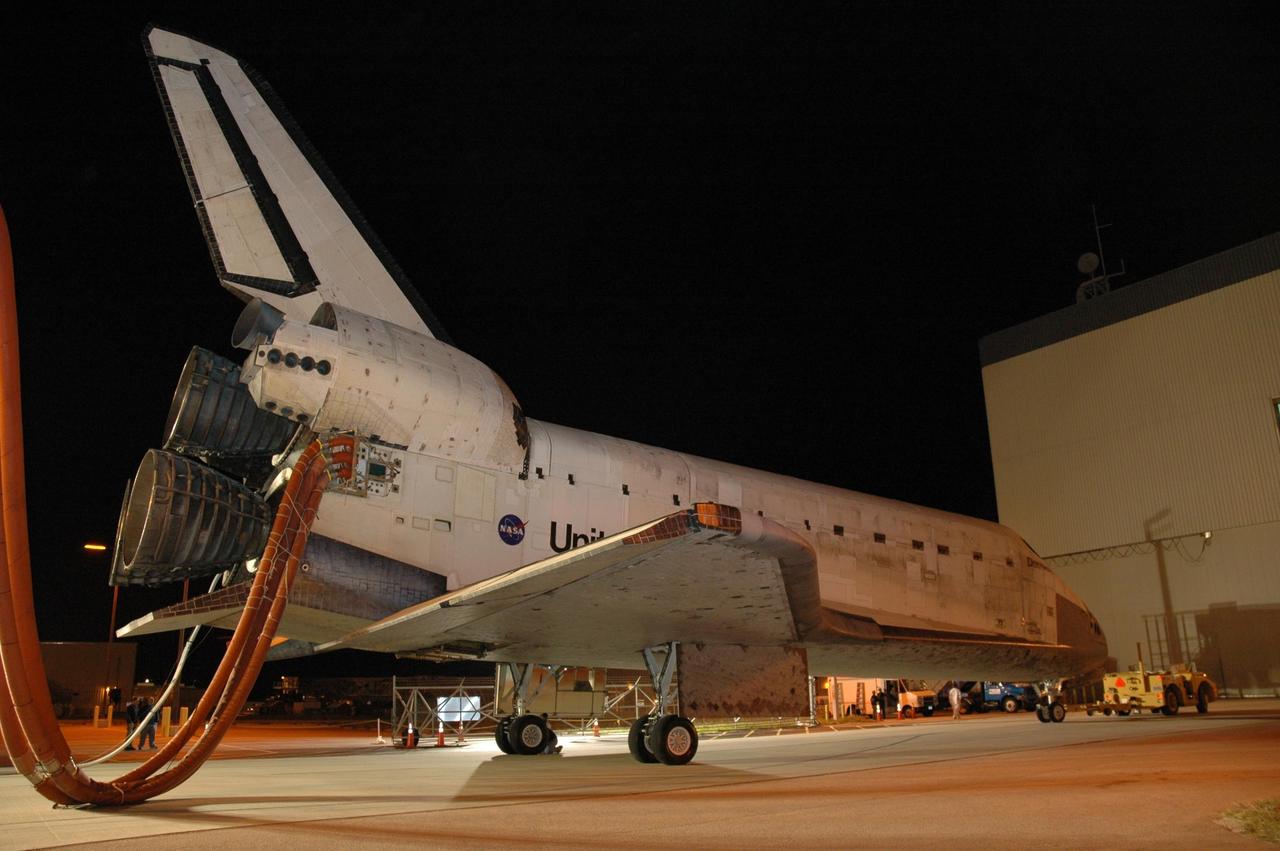

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The space shuttle Discovery nears the Orbital Processing Facility, or OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. Towing normally begins within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments is required on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
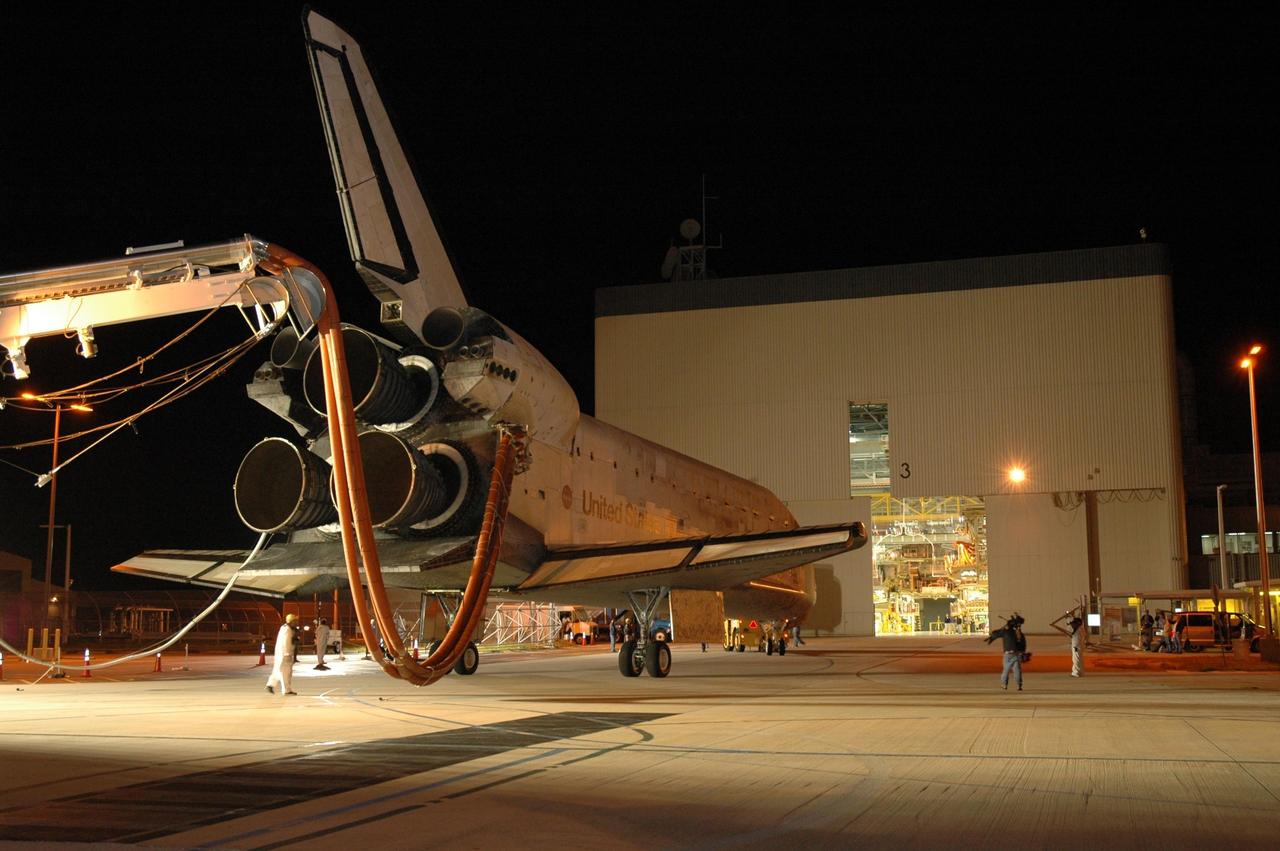

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The space shuttle Discovery nears the Orbital Processing Facility, or OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. Towing normally begins within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments is required on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
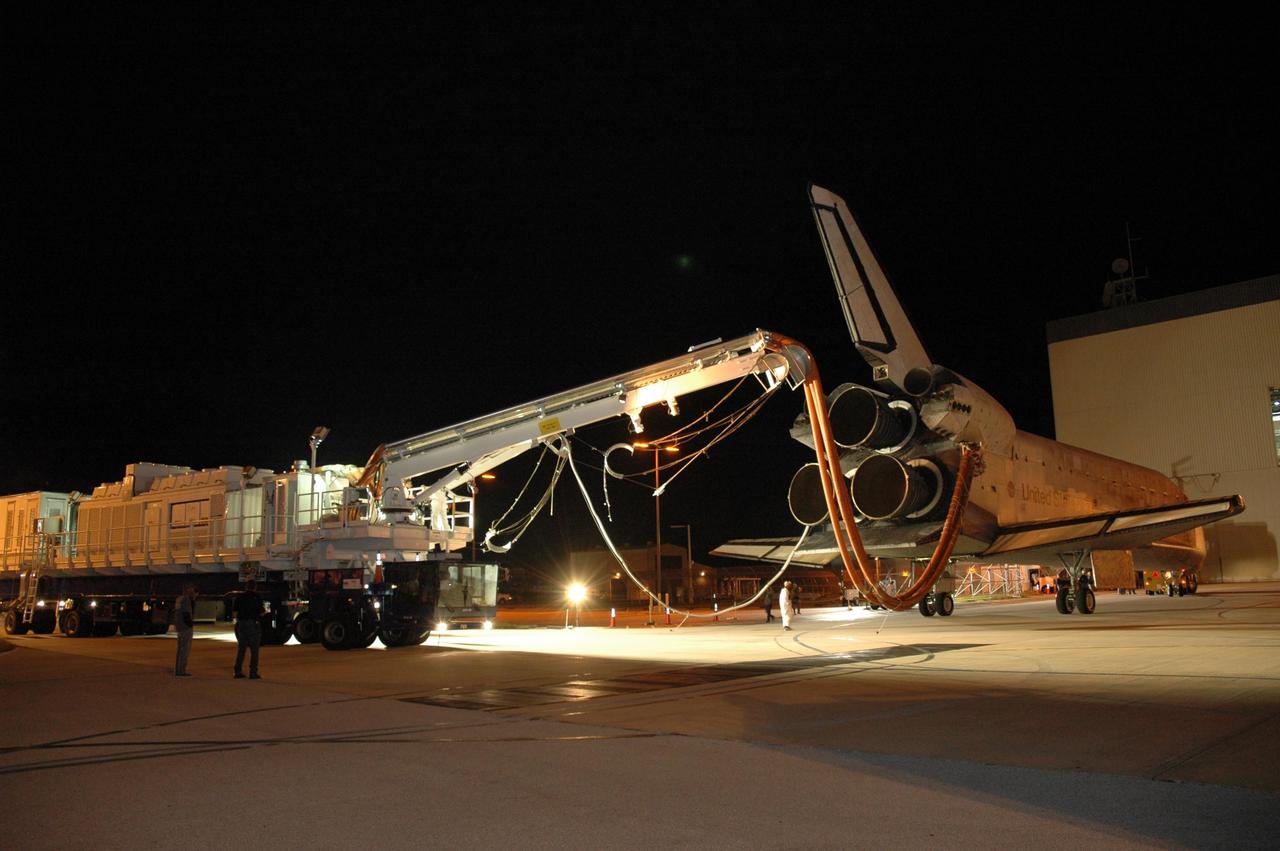

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The space shuttle Discovery nears the Orbital Processing Facility, or OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. Towing normally begins within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments is required on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a tractor tow vehicle is backed up to space shuttle Discovery. Towing normally begins approximately within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments require an additional period on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. The tractor tow vehicle will pull Discovery along a two-mile tow-way to the Orbiter Processing Facility, or OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. The tow vehicle is very much like the typical towing units used for large aircraft, but it is equipped with a special towing bar designed specifically for the orbiter. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a tractor tow vehicle is backed up to space shuttle Discovery. Towing normally begins approximately within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments require an additional period on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. The tractor tow vehicle will pull Discovery along a two-mile tow-way to the Orbiter Processing Facility, or OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. The tow vehicle is very much like the typical towing units used for large aircraft, but it is equipped with a special towing bar designed specifically for the orbiter. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a tractor tow vehicle is backed up to space shuttle Discovery. Towing normally begins approximately within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments require an additional period on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. The tractor tow vehicle will pull Discovery along a two-mile tow-way to the Orbiter Processing Facility, or OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. The tow vehicle is very much like the typical towing units used for large aircraft, but it is equipped with a special towing bar designed specifically for the orbiter. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
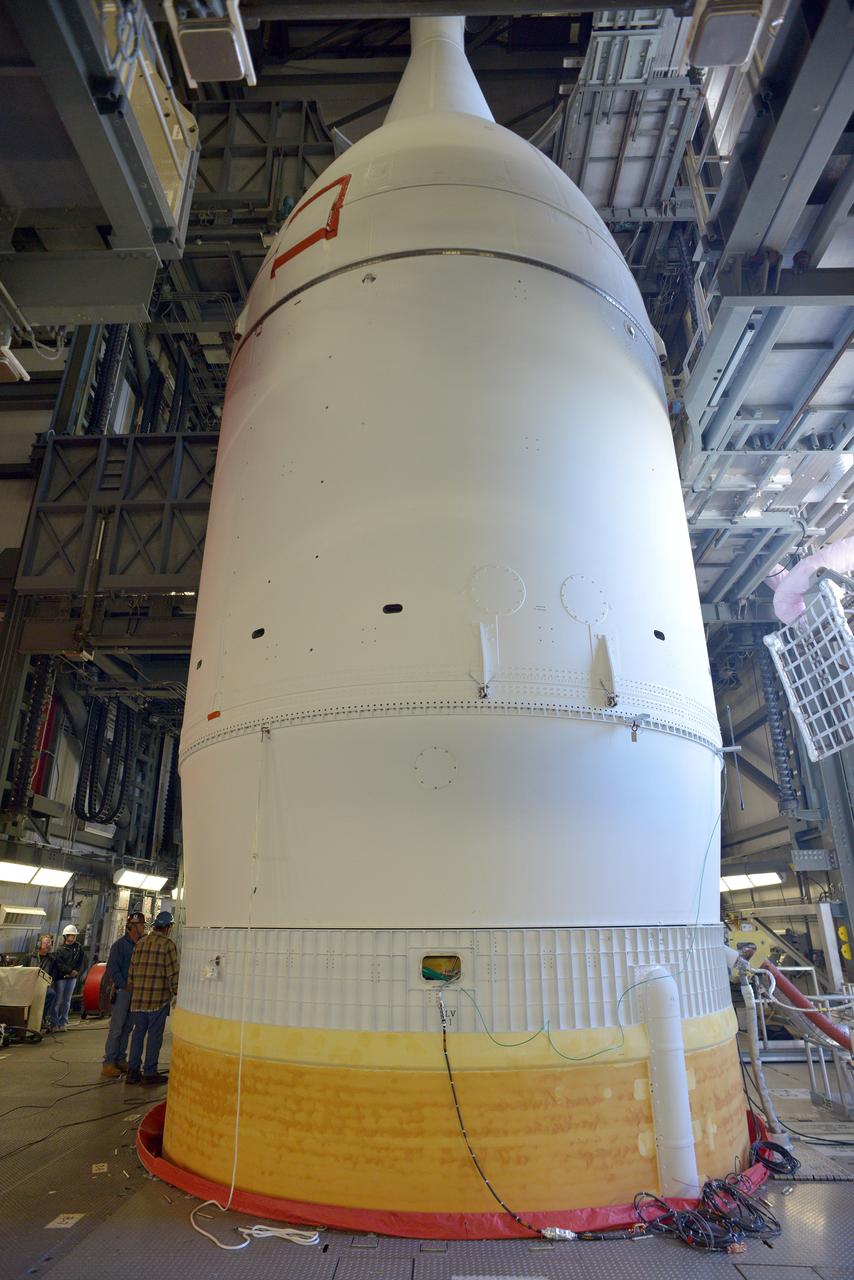

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
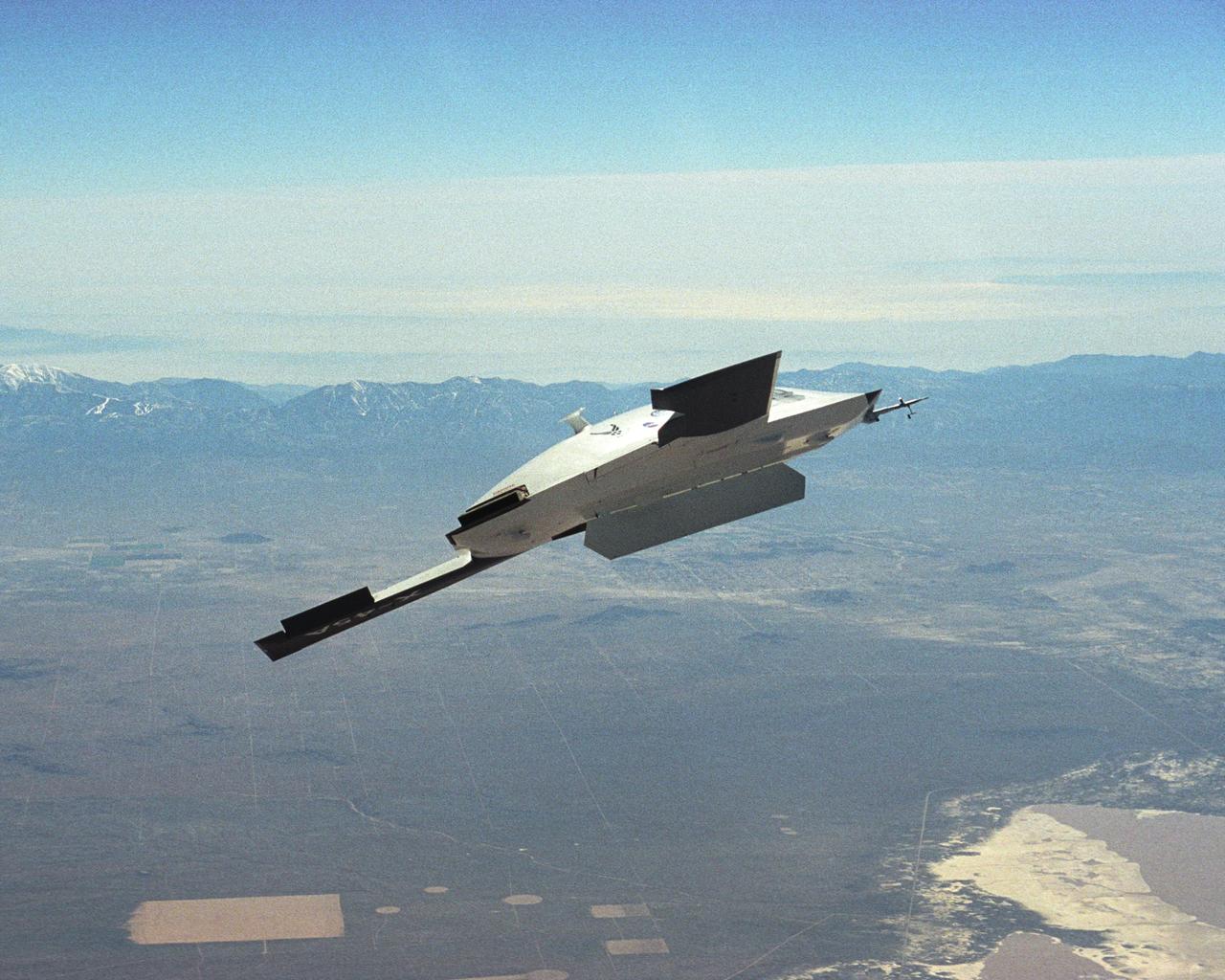

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
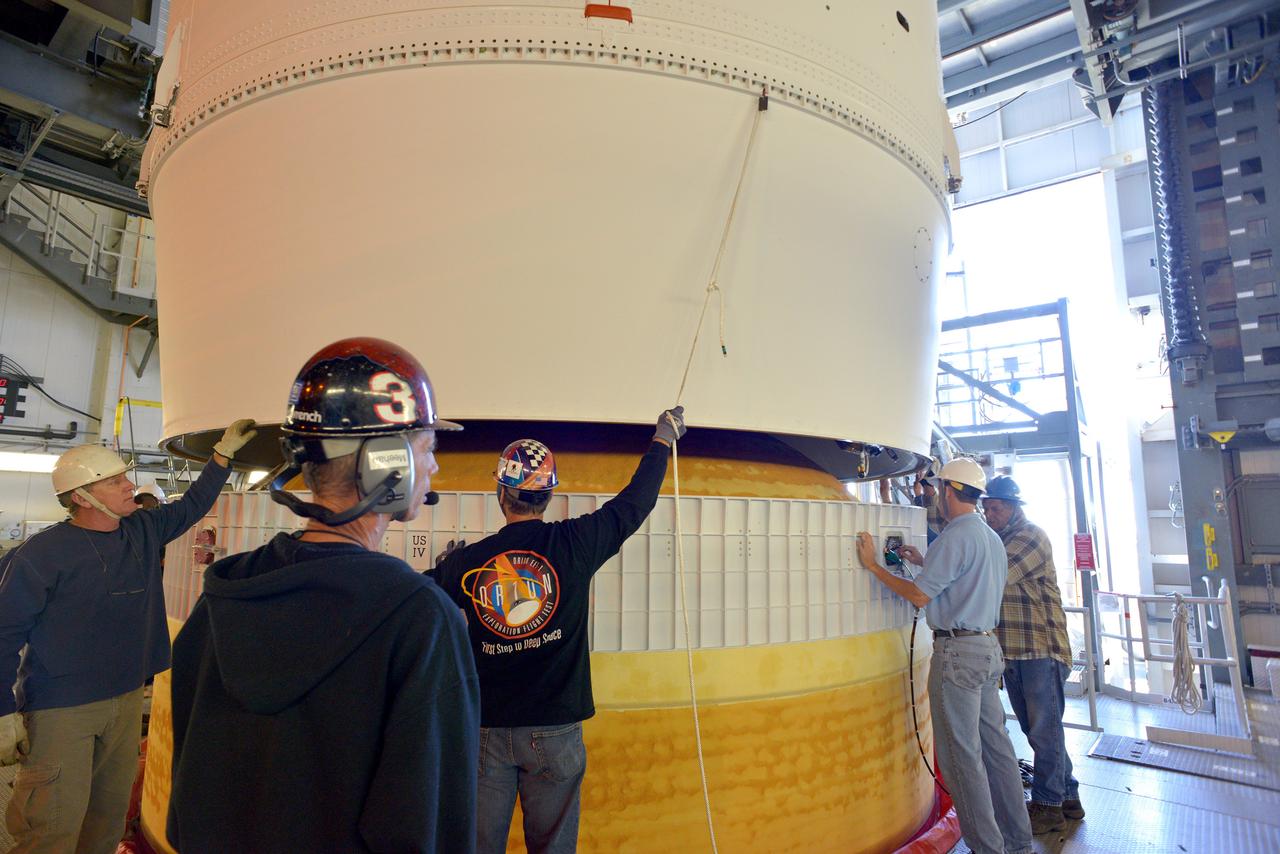

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
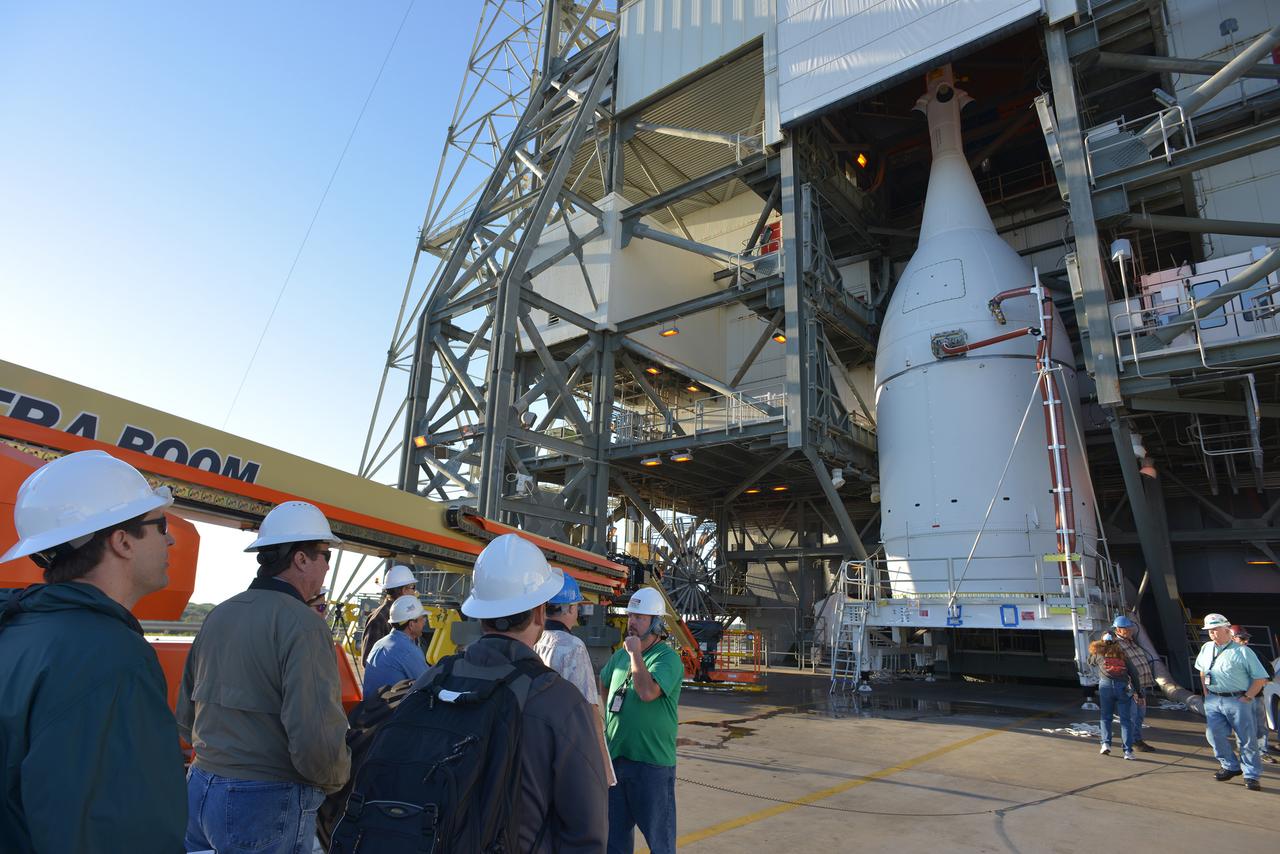

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
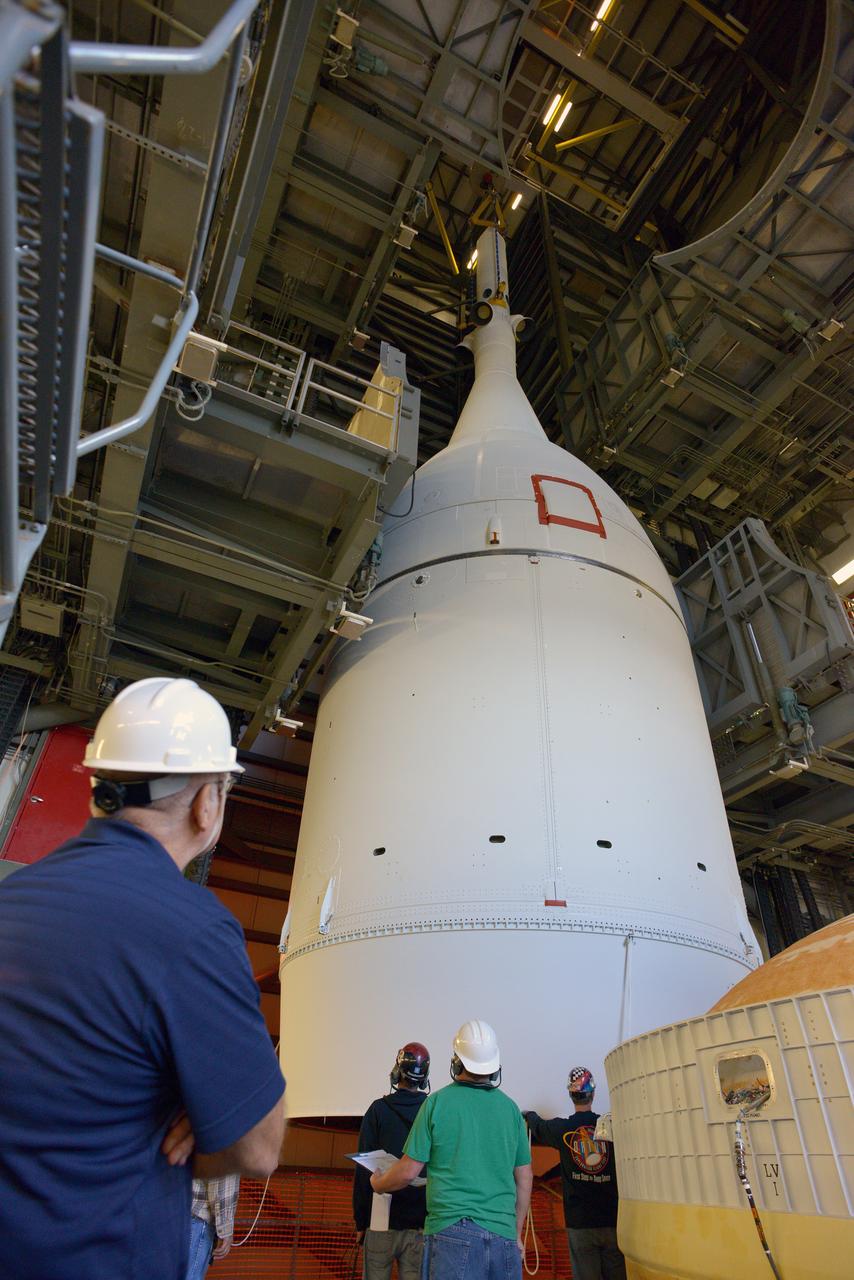

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
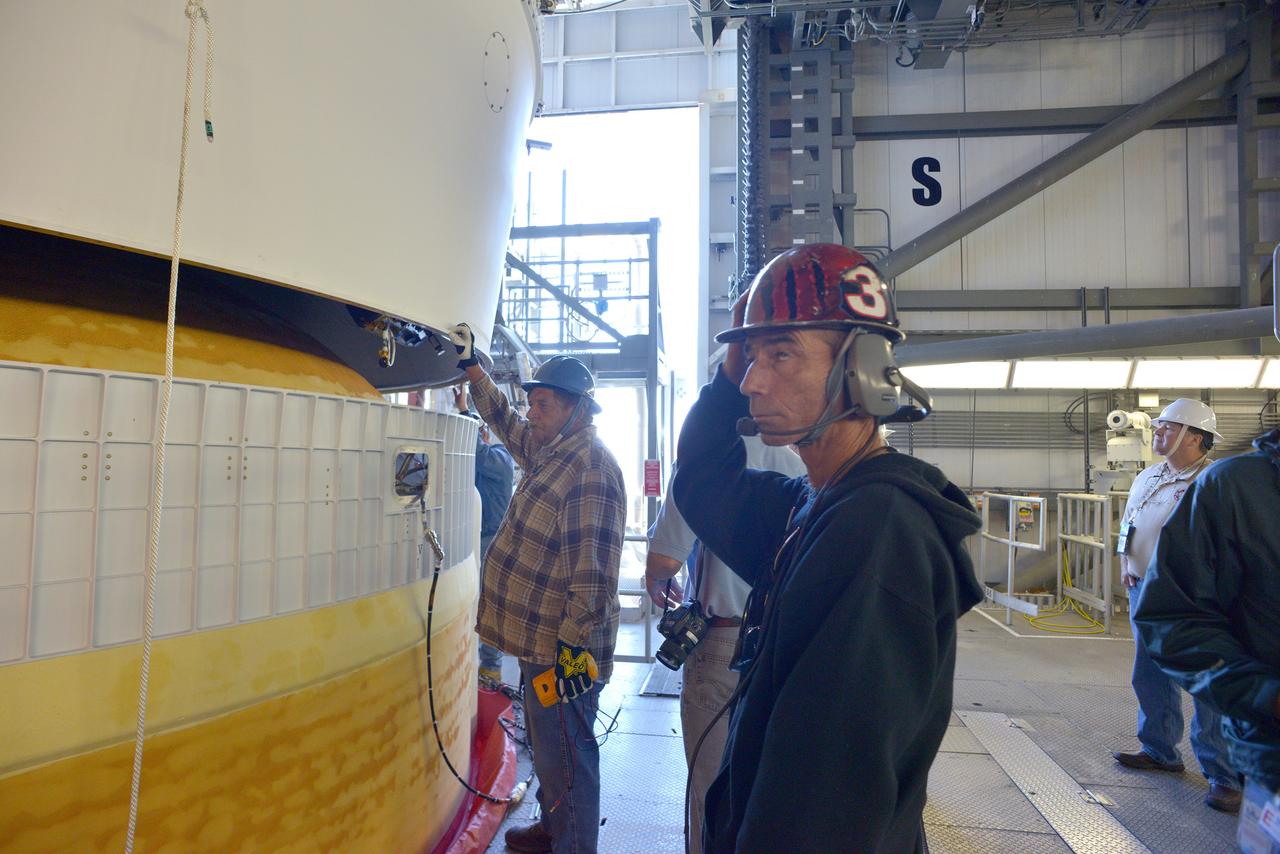

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
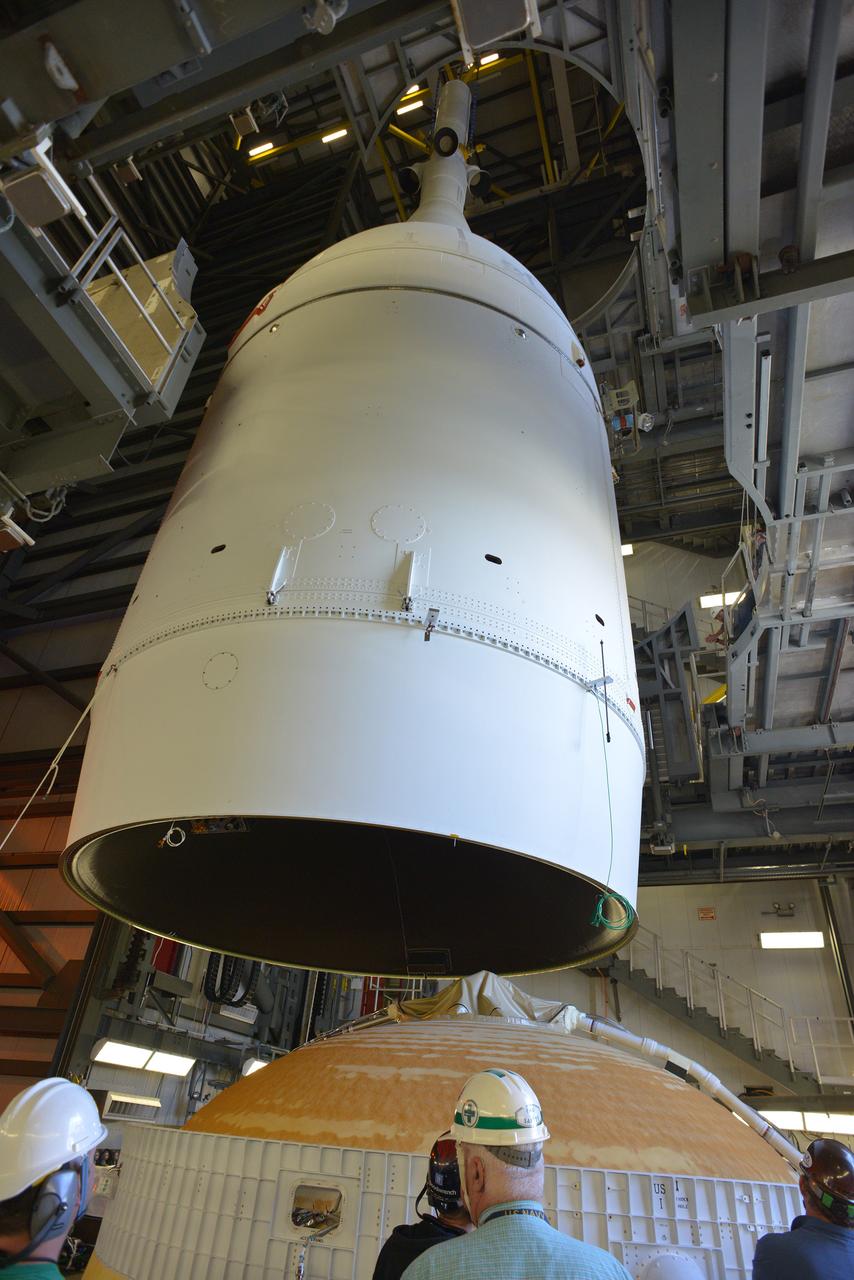

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
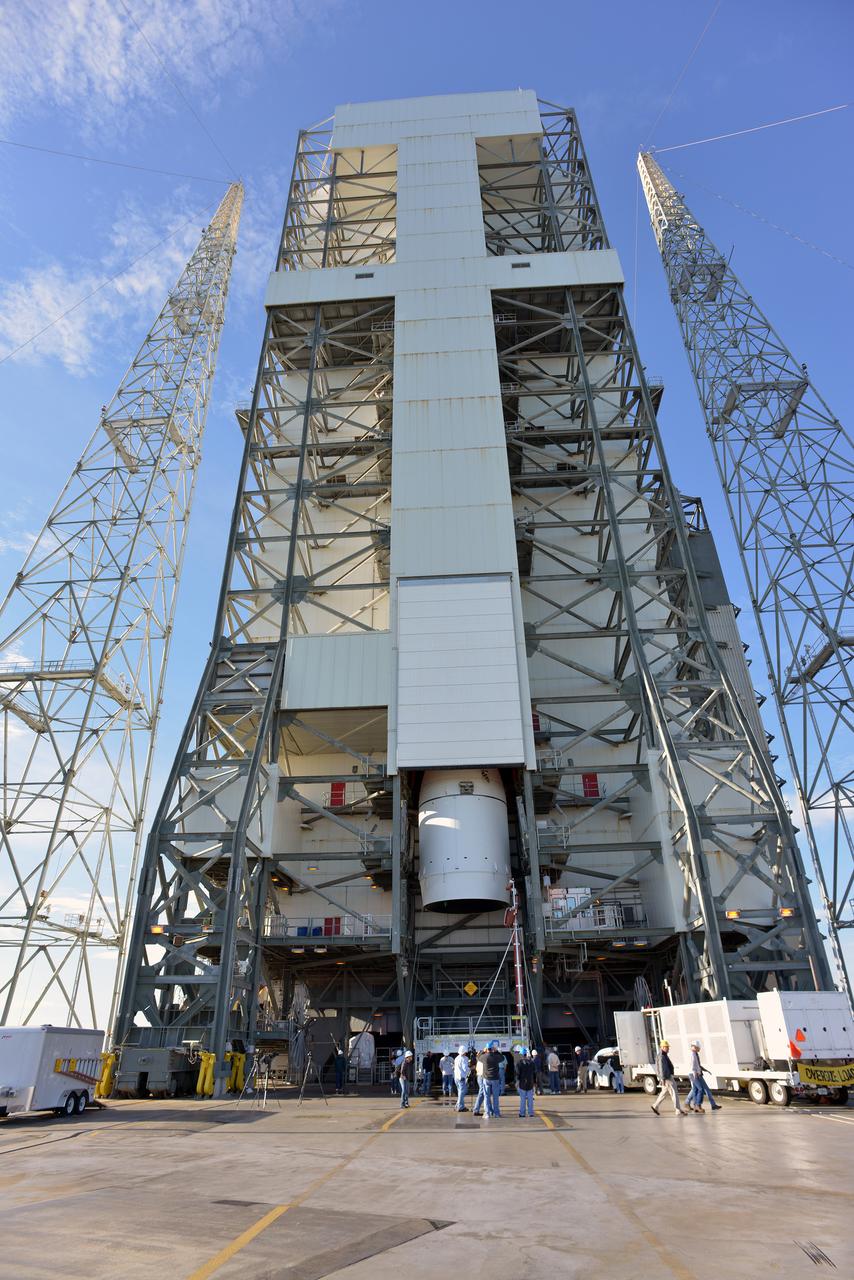

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
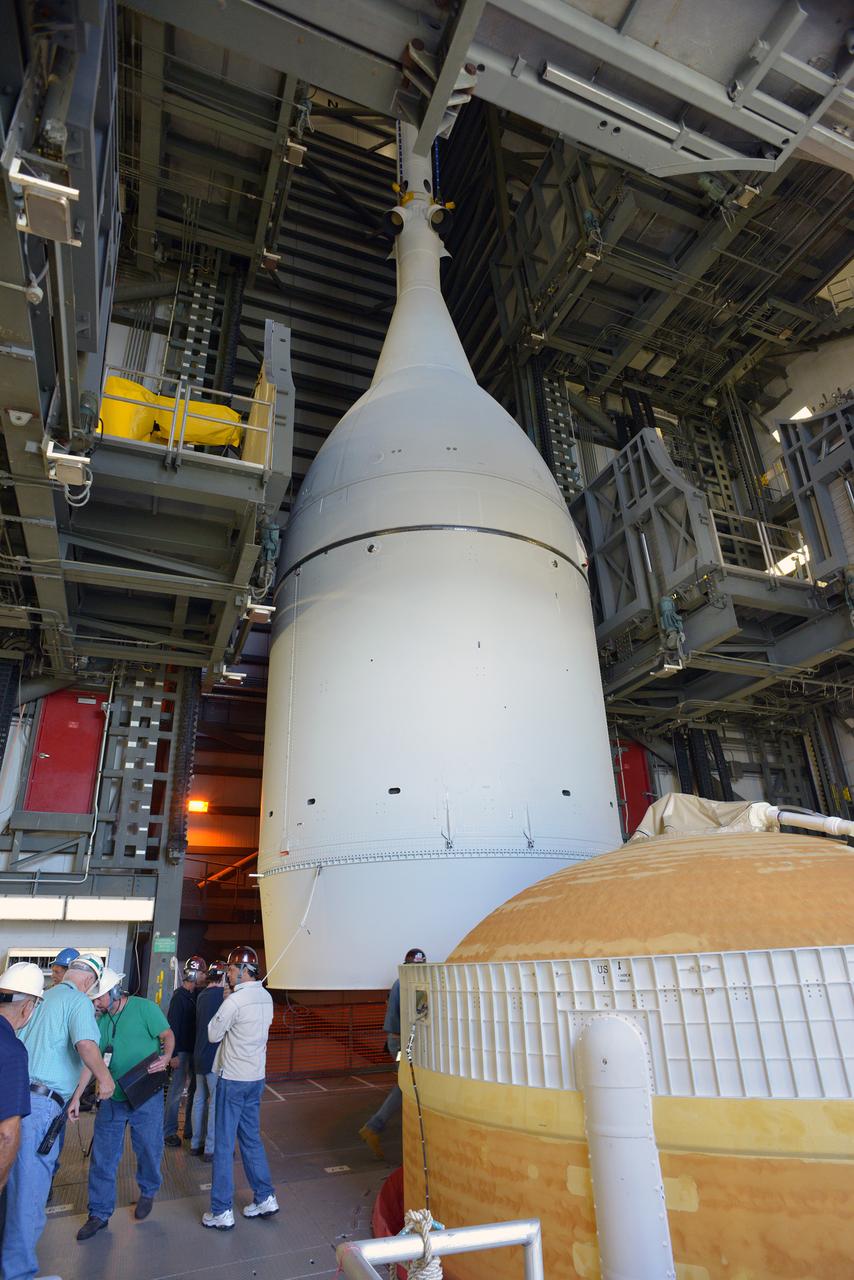

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
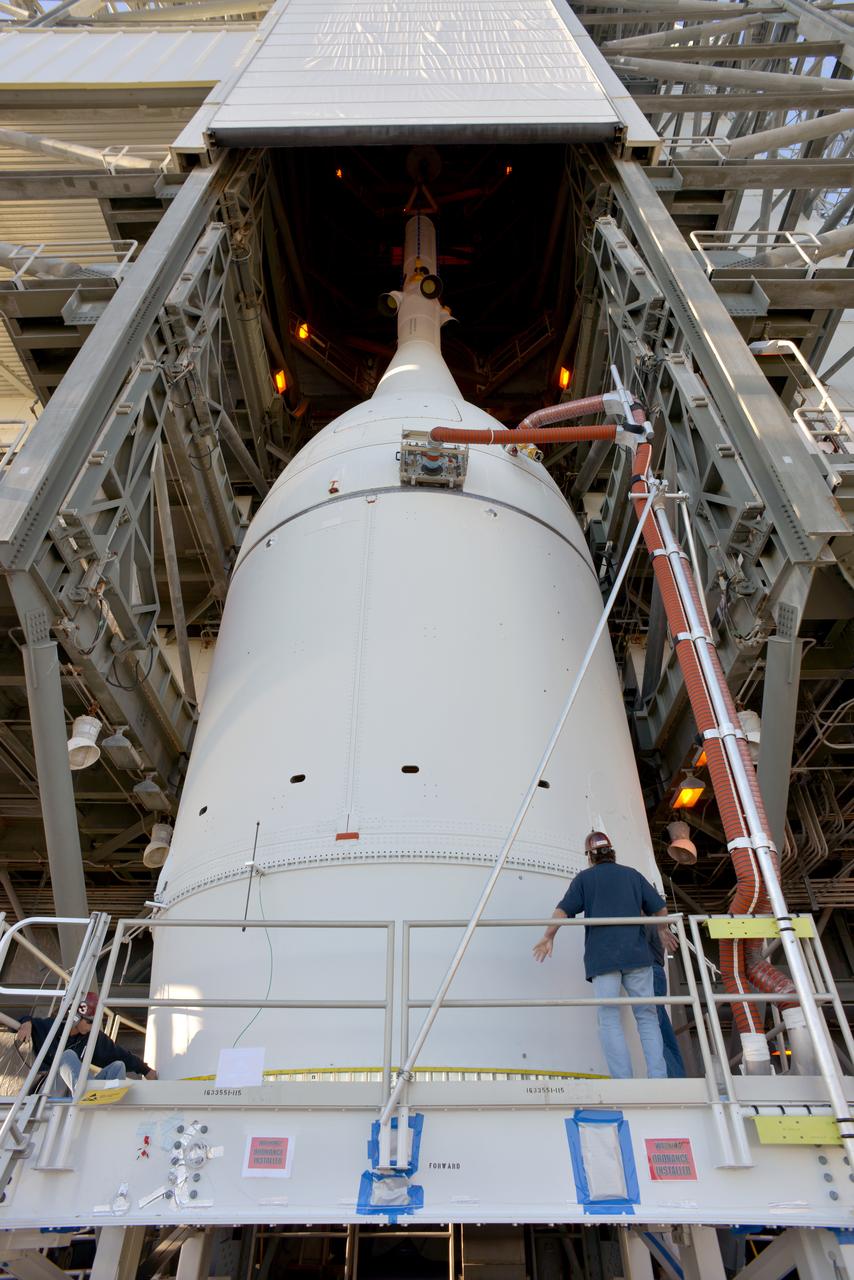

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
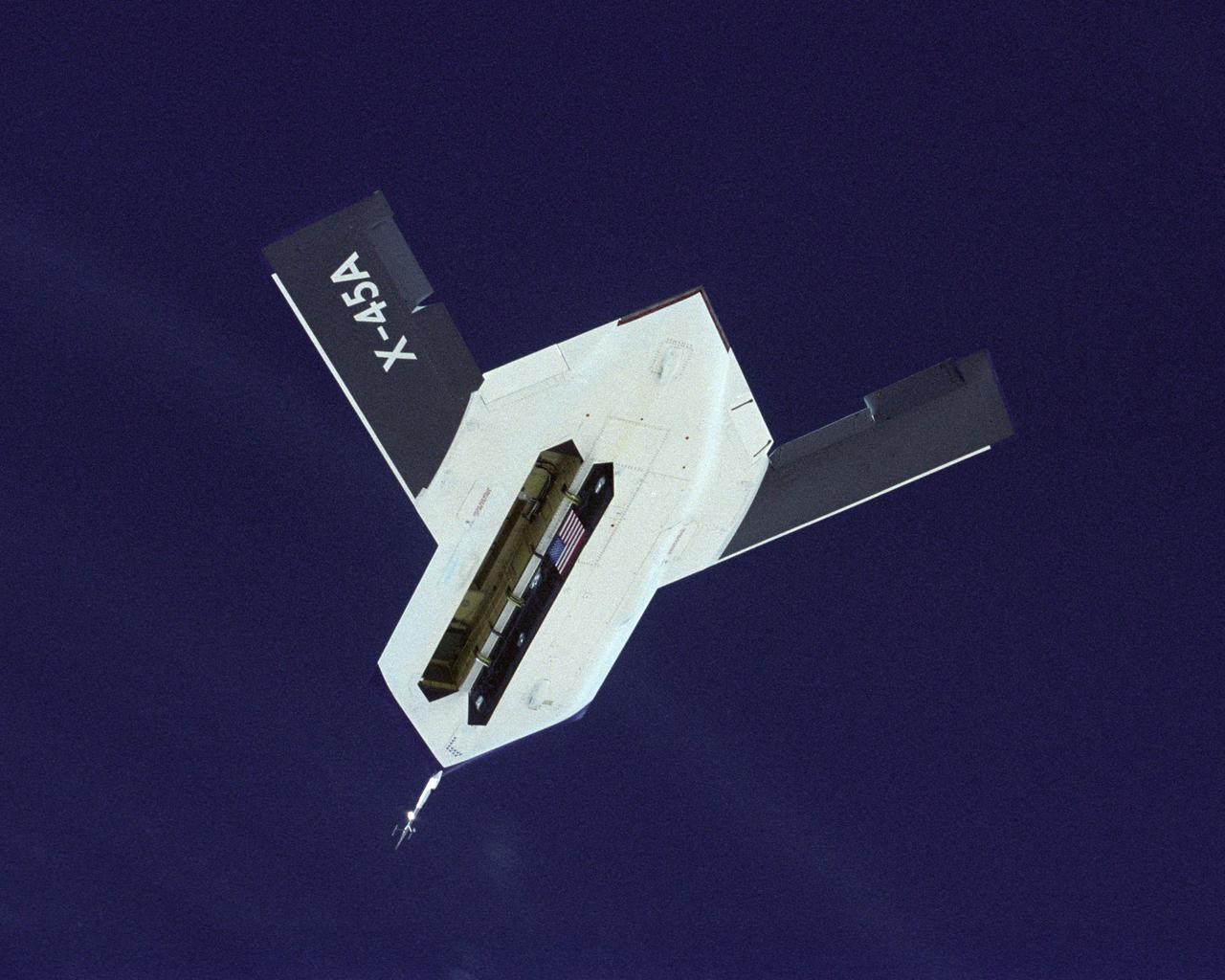
The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
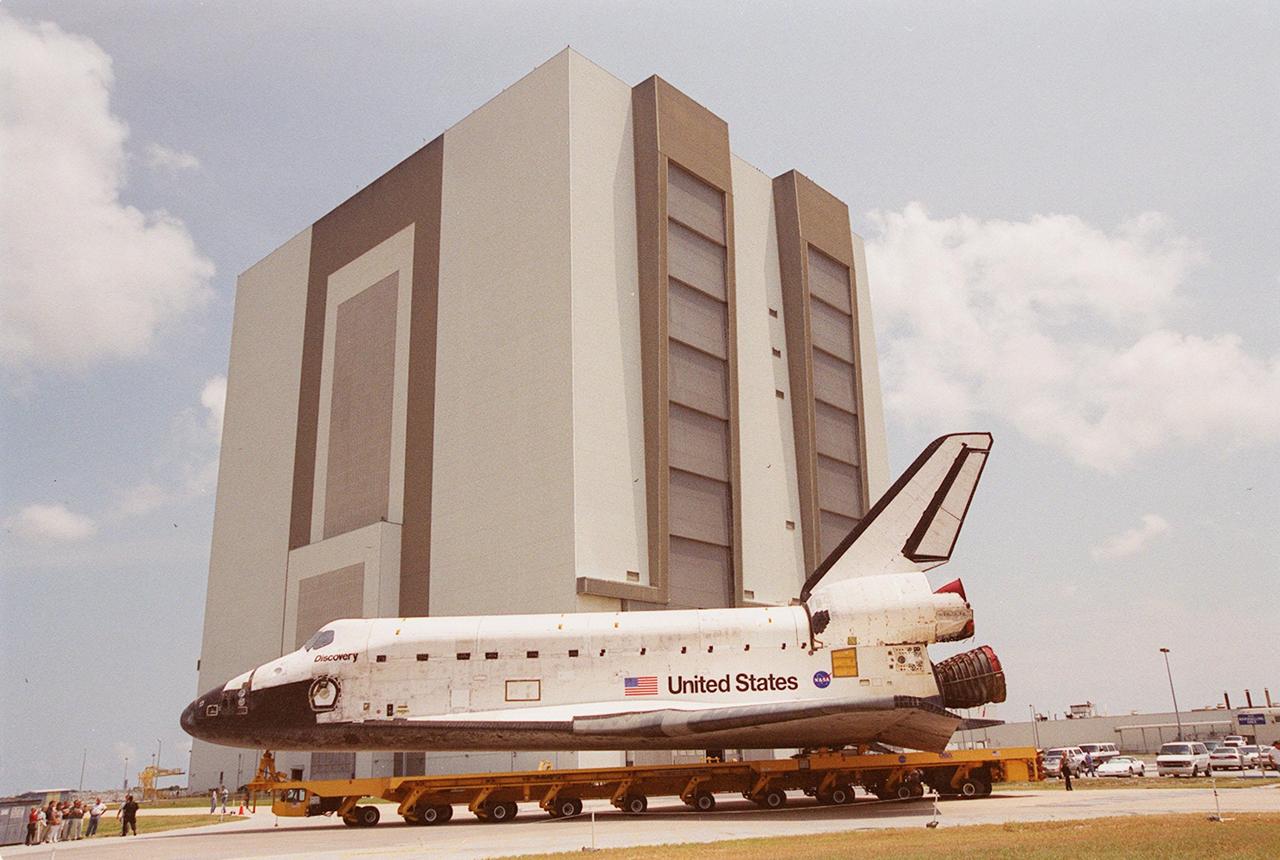

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Discovery rolls past the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) bay 3 where ongoing payload and ground processing assessments will be completed. Managers will then determine when to roll the orbiter to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking with the external tank and solid rocket boosters, and when to roll out to Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:30 p.m. EDT on mission STS-92, which will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
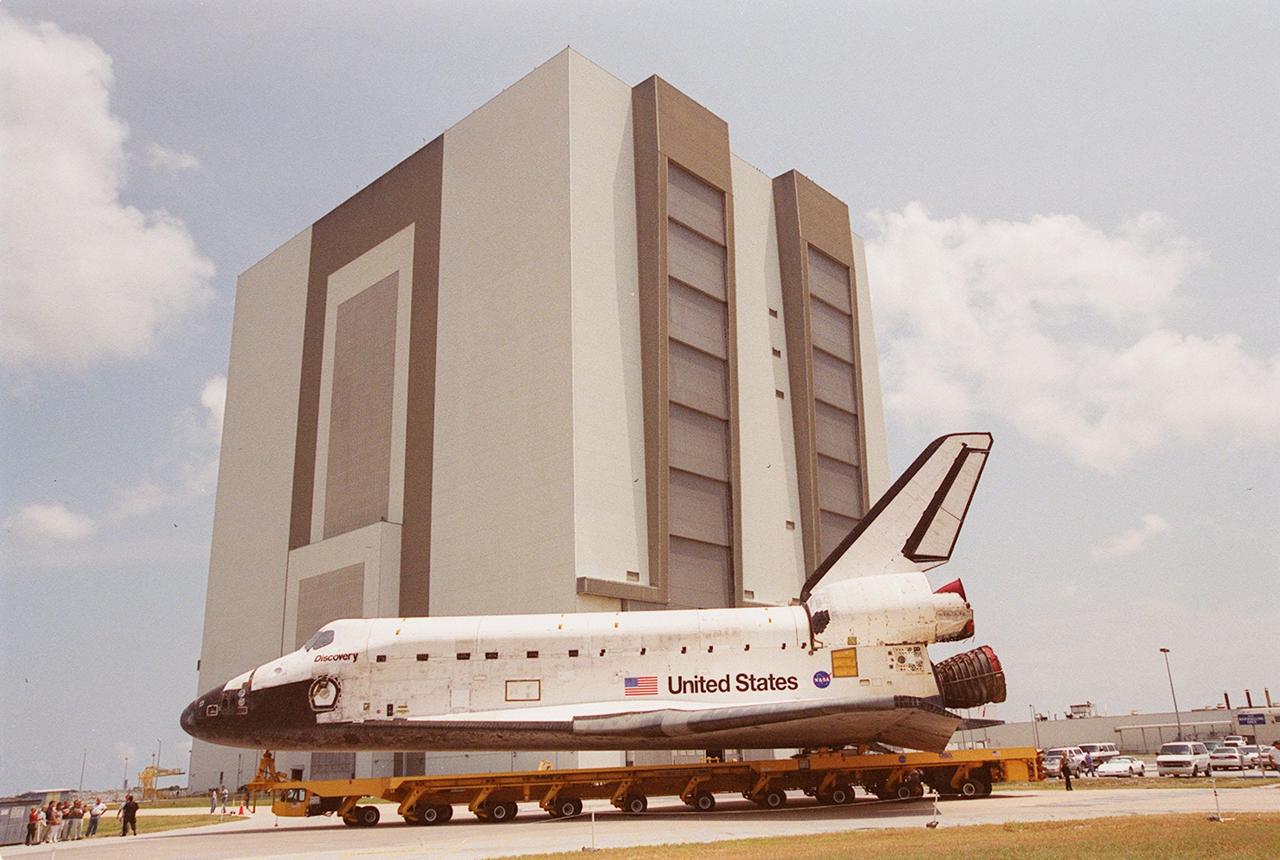

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Discovery rolls past the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) bay 3 where ongoing payload and ground processing assessments will be completed. Managers will then determine when to roll the orbiter to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking with the external tank and solid rocket boosters, and when to roll out to Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 at 9:30 p.m. EDT on mission STS-92, which will be the 100th flight in the Shuttle program
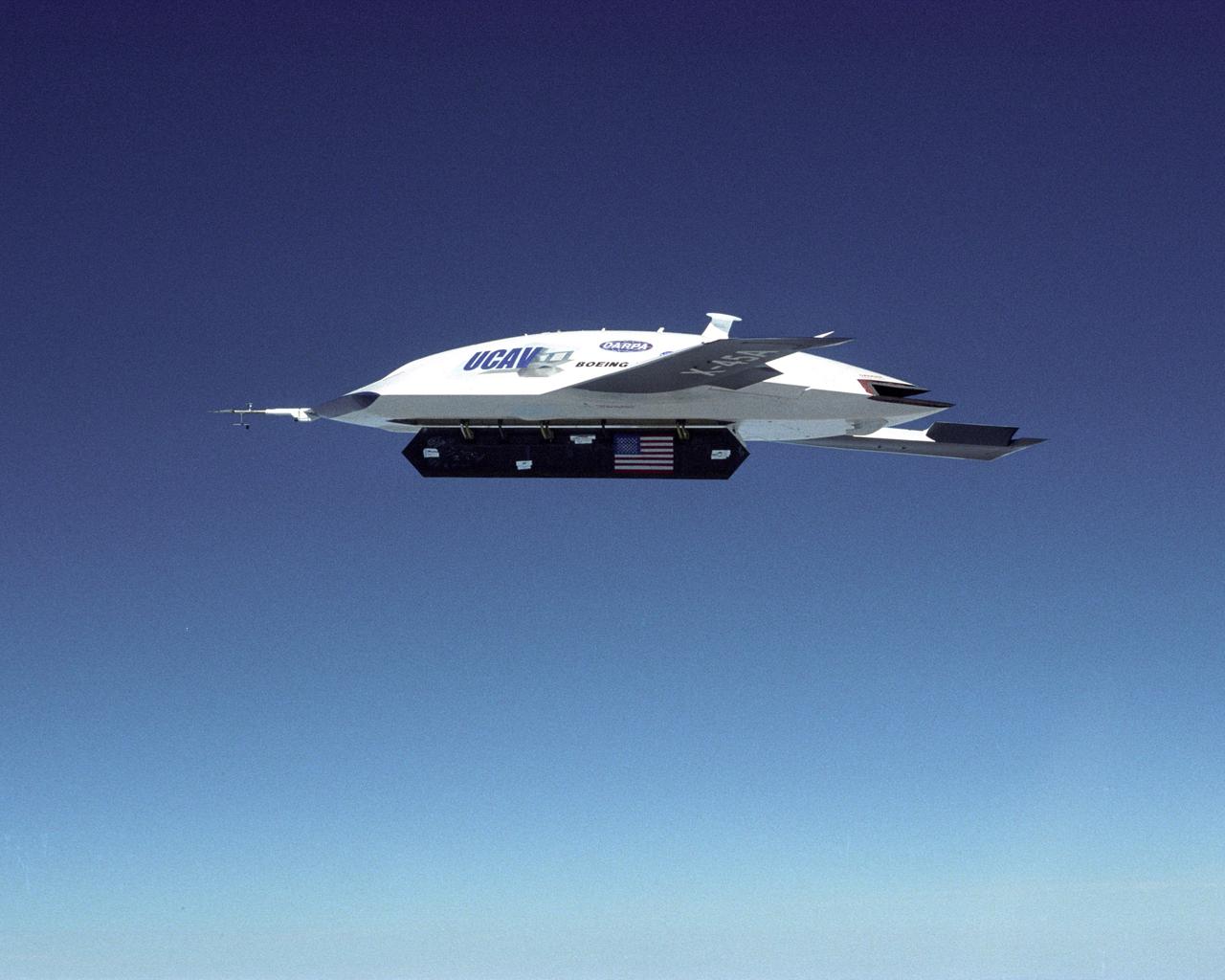

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
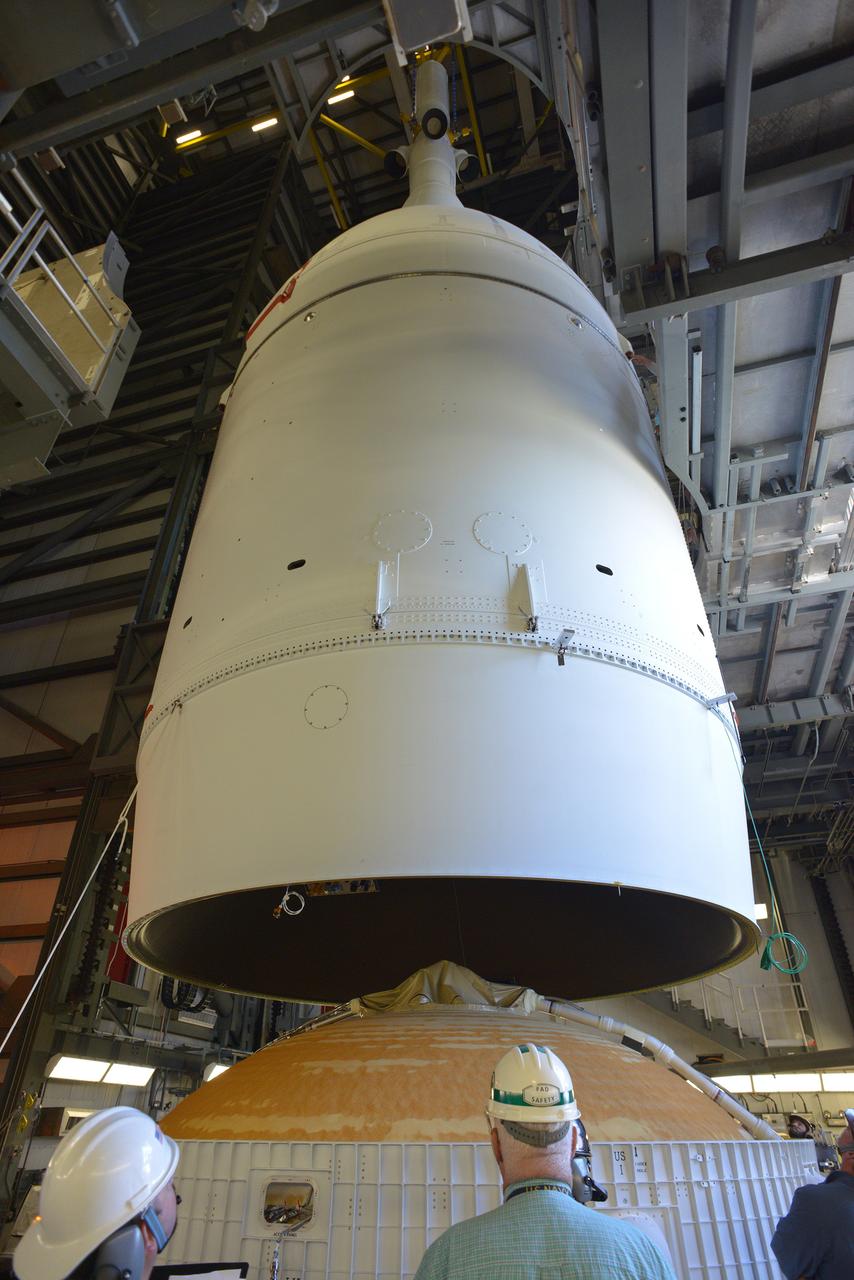

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
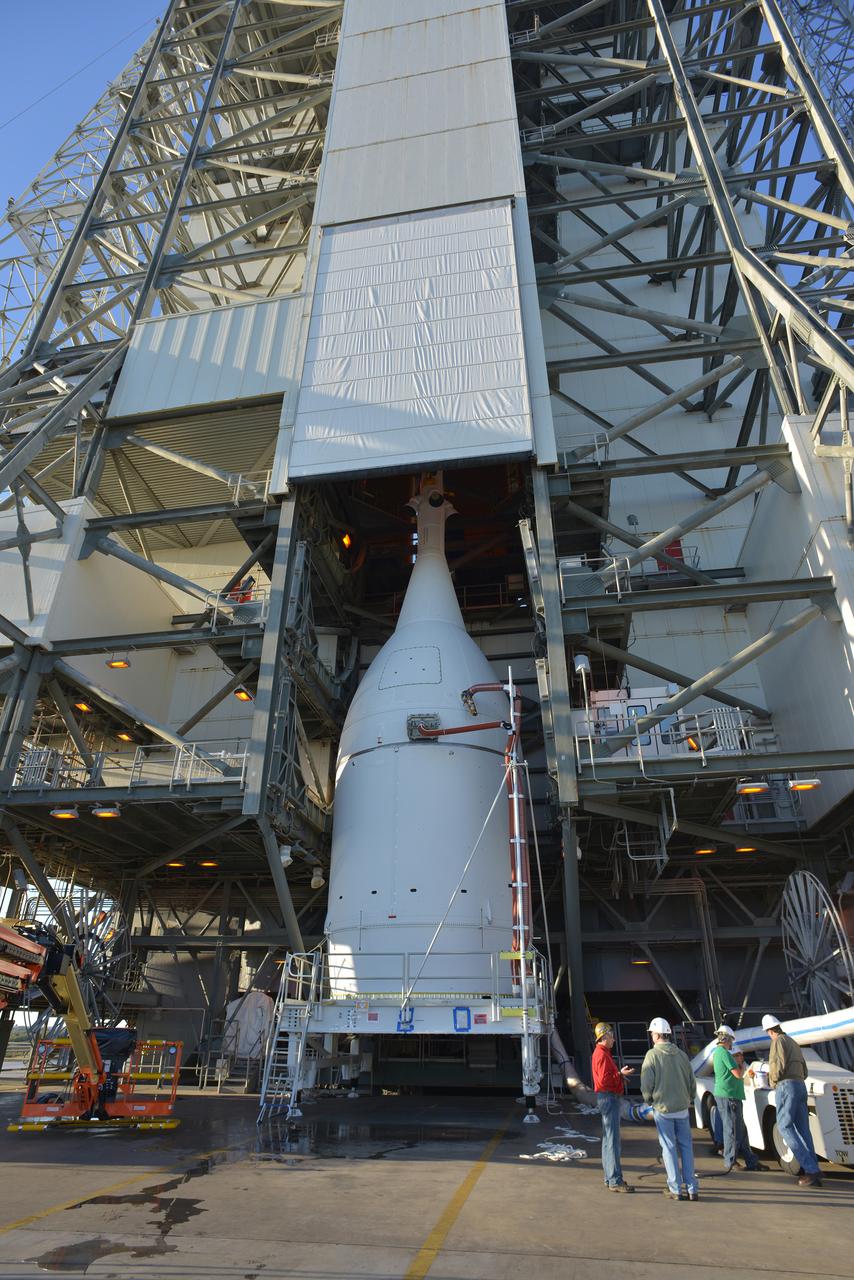

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
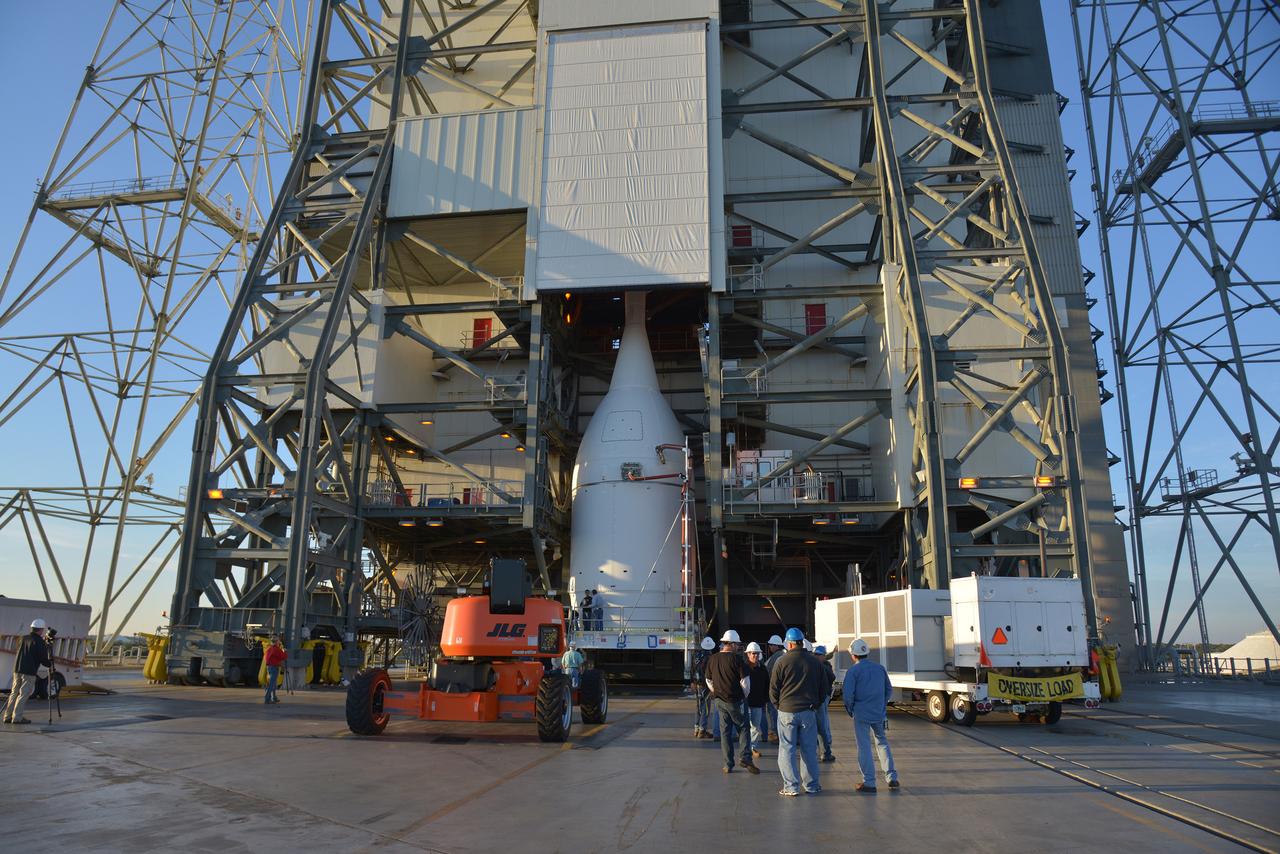

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
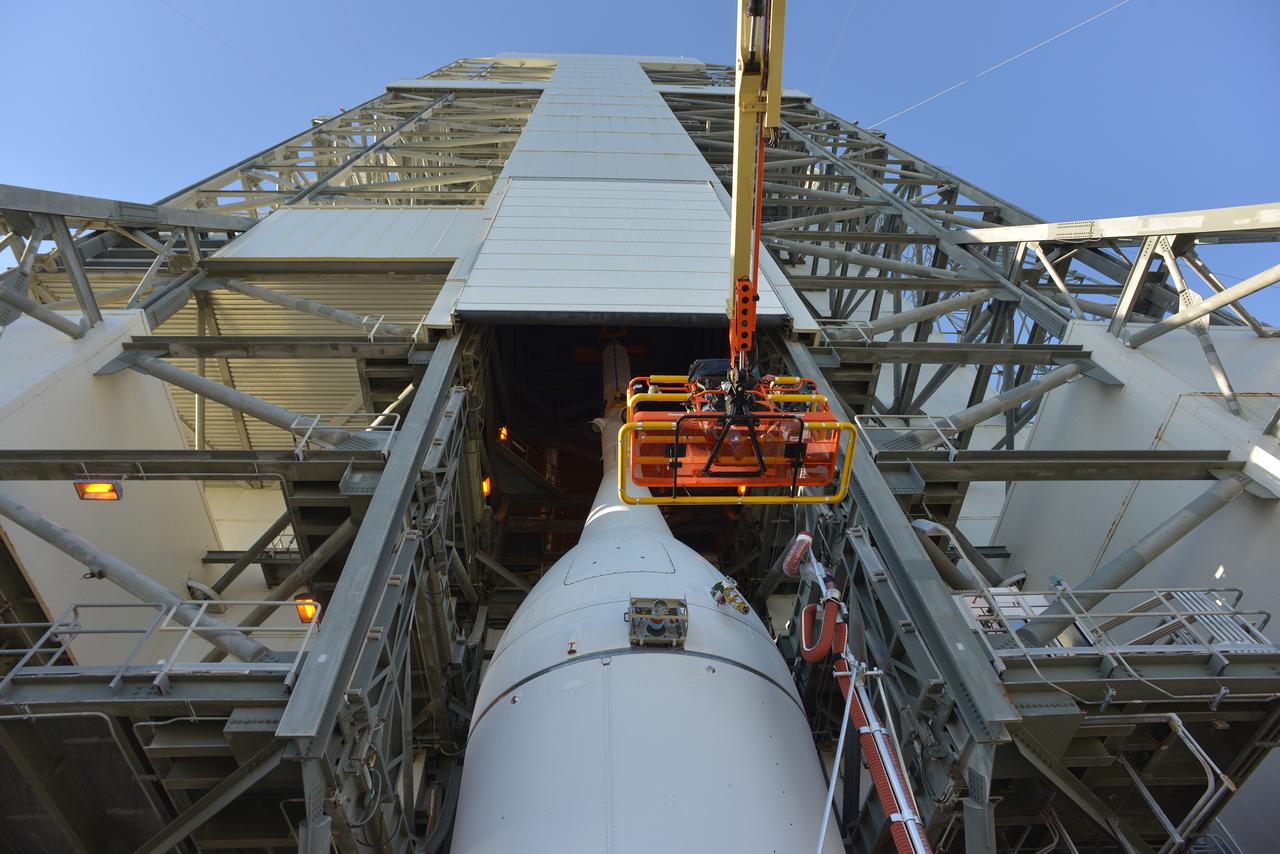

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
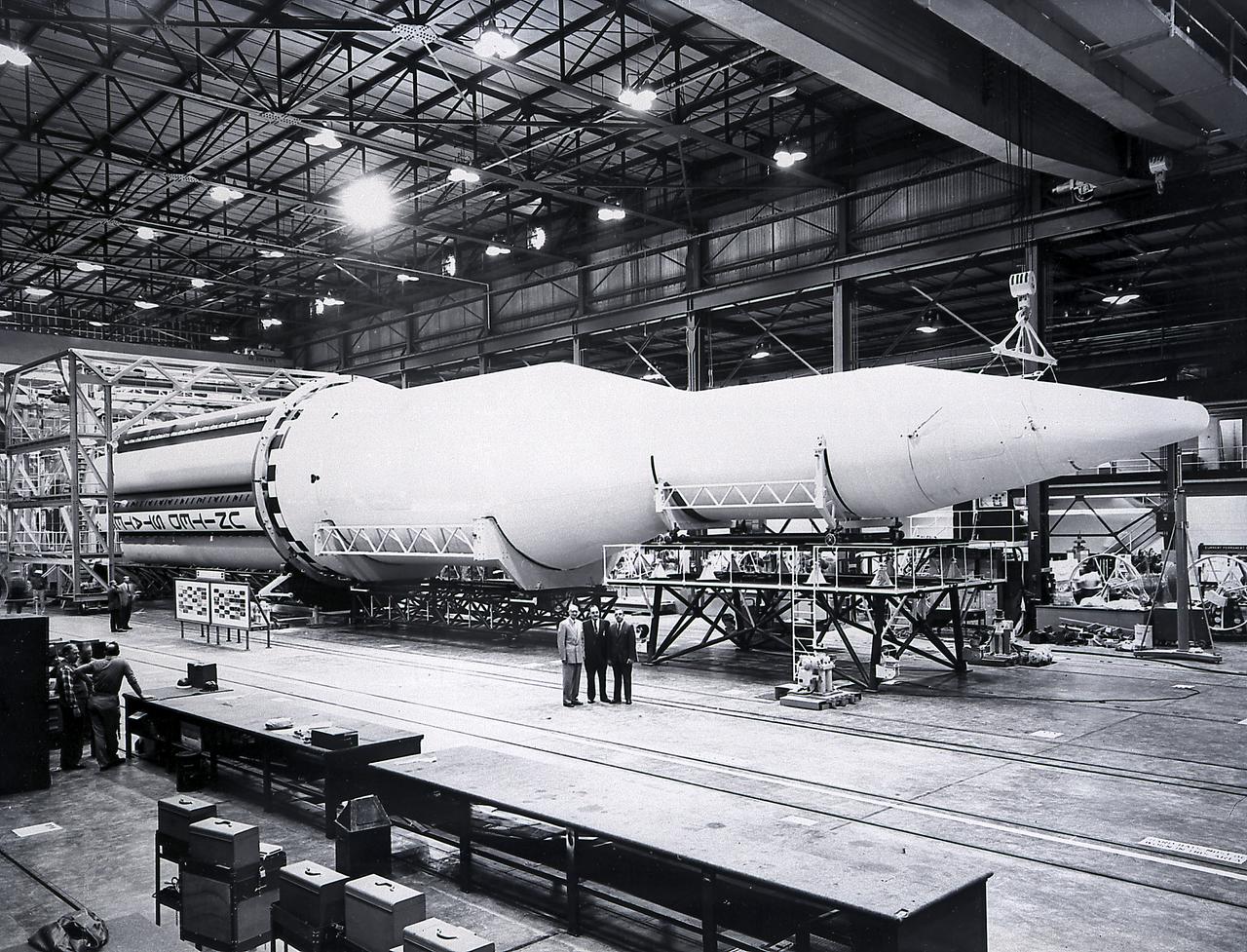

A completed Saturn I launch vehicle in the Fabrication and Assembly Engineering Division at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The Saturn I launch vehicle is composed of an S-I first stage or booster (rear), powered by eight H-1 engines having a thrust of 1,500,000 pounds, followed by a dummy S-IV second stage with six RL-10 engine, with a total thrust of 90,000 pounds.
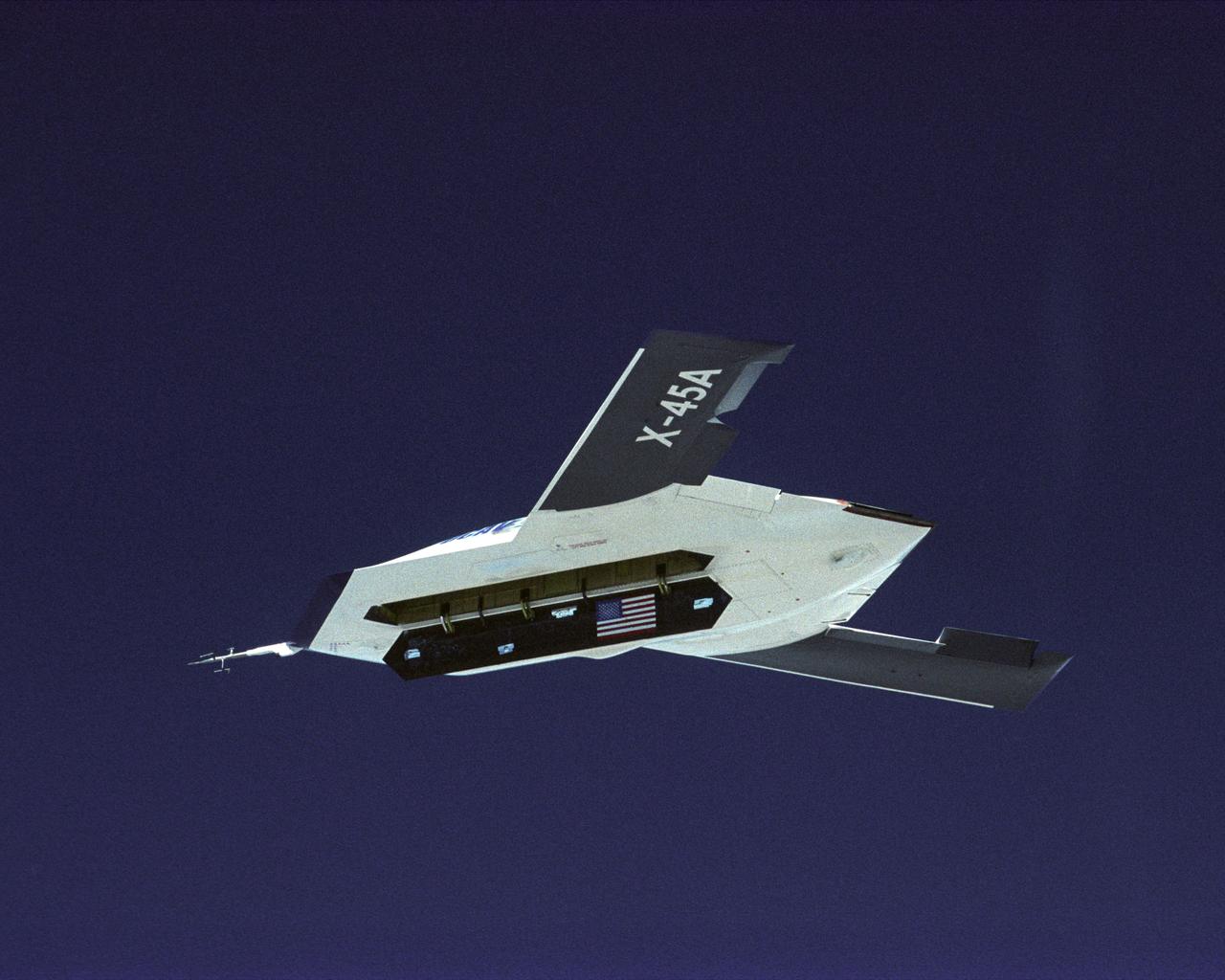

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
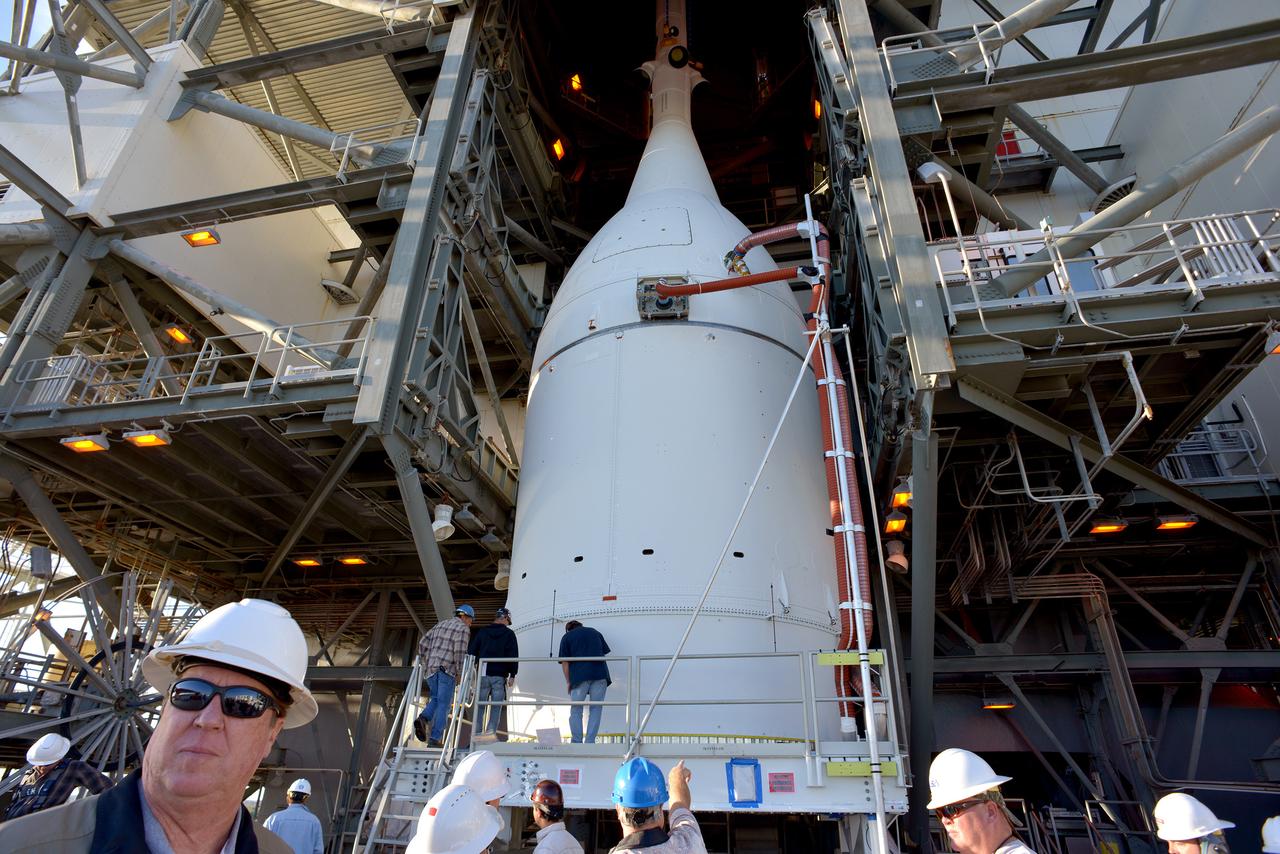

The Orion spacecraft was lifted on top of the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at ULA's Launch Complex 37 on Nov. 12, 2014. Over the next few days the Lockheed Martin/ULA team will work to complete the connections between Orion and the launch vehicle in preparation for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1). Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
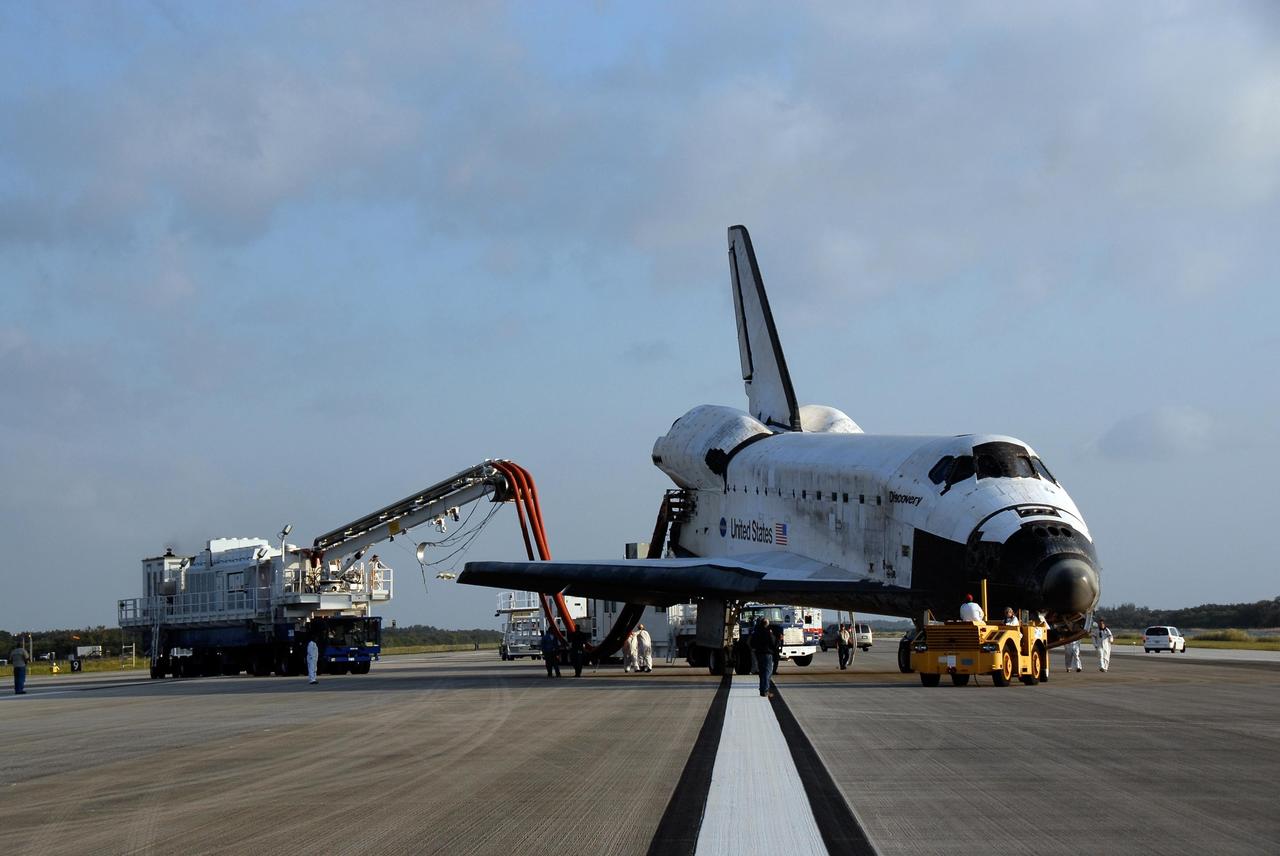

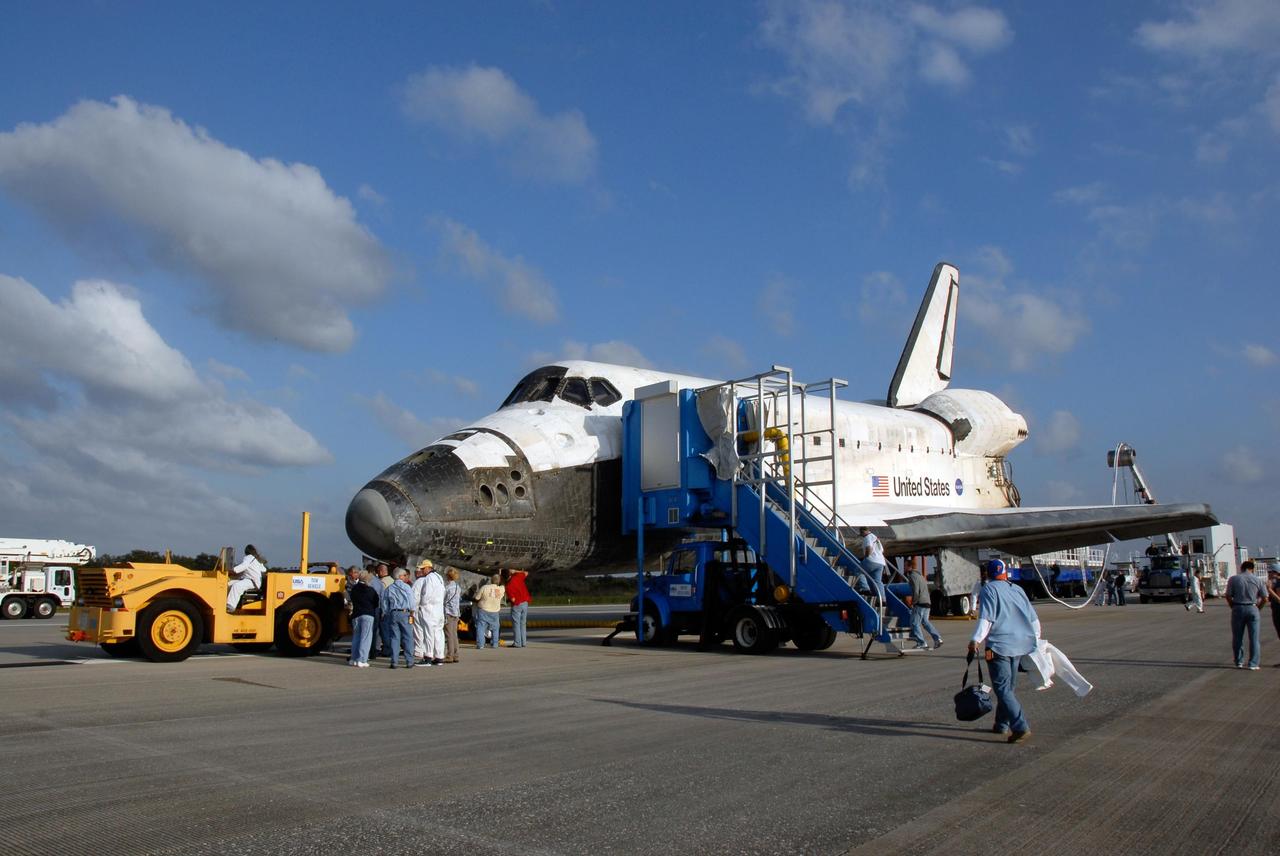
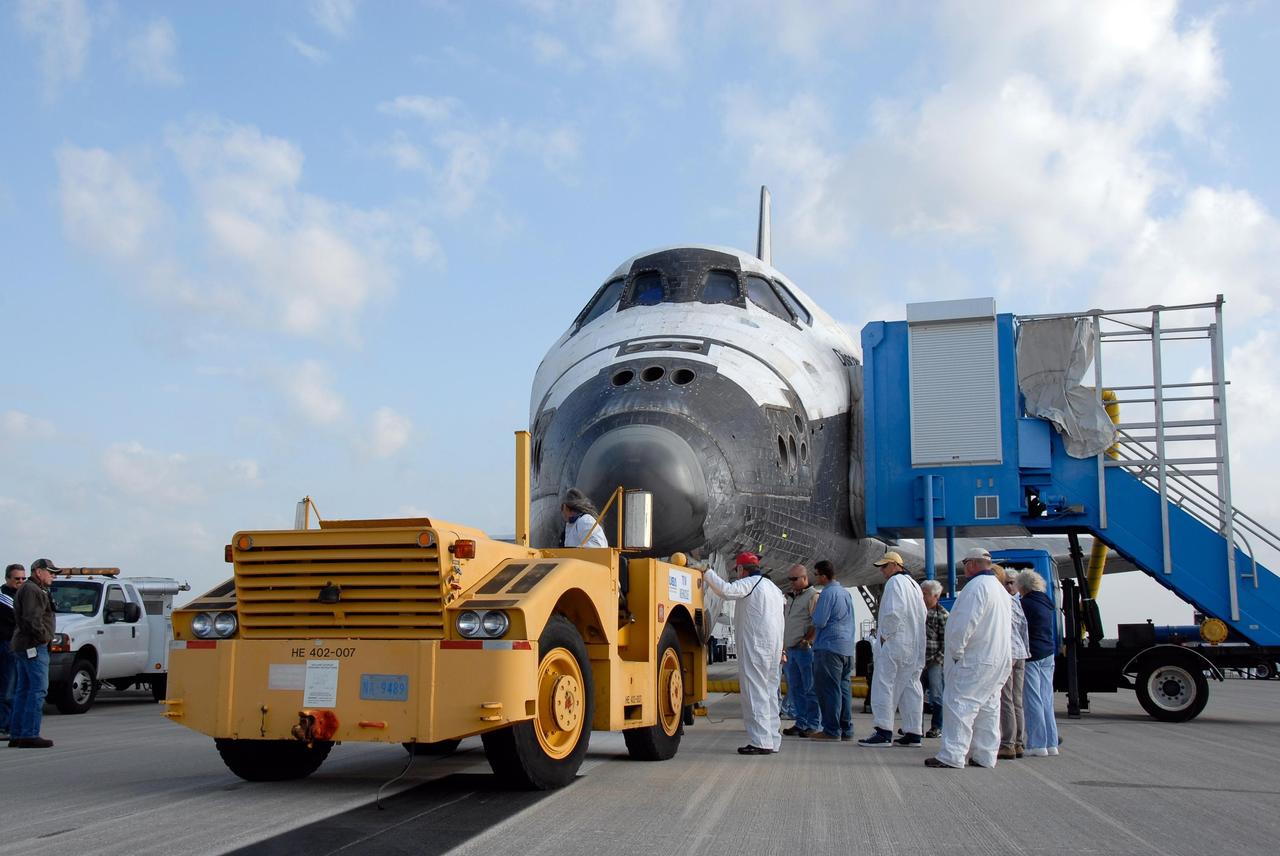
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Discovery is ready for towing to the Orbiter Processing Facility, or OPF. Towing normally begins approximately within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments require an additional period on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. The tractor tow vehicle will pull Discovery along a two-mile tow-way to the OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. The tow vehicle is very much like the typical towing units used for large aircraft, but it is equipped with a special towing bar designed specifically for the orbiter. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
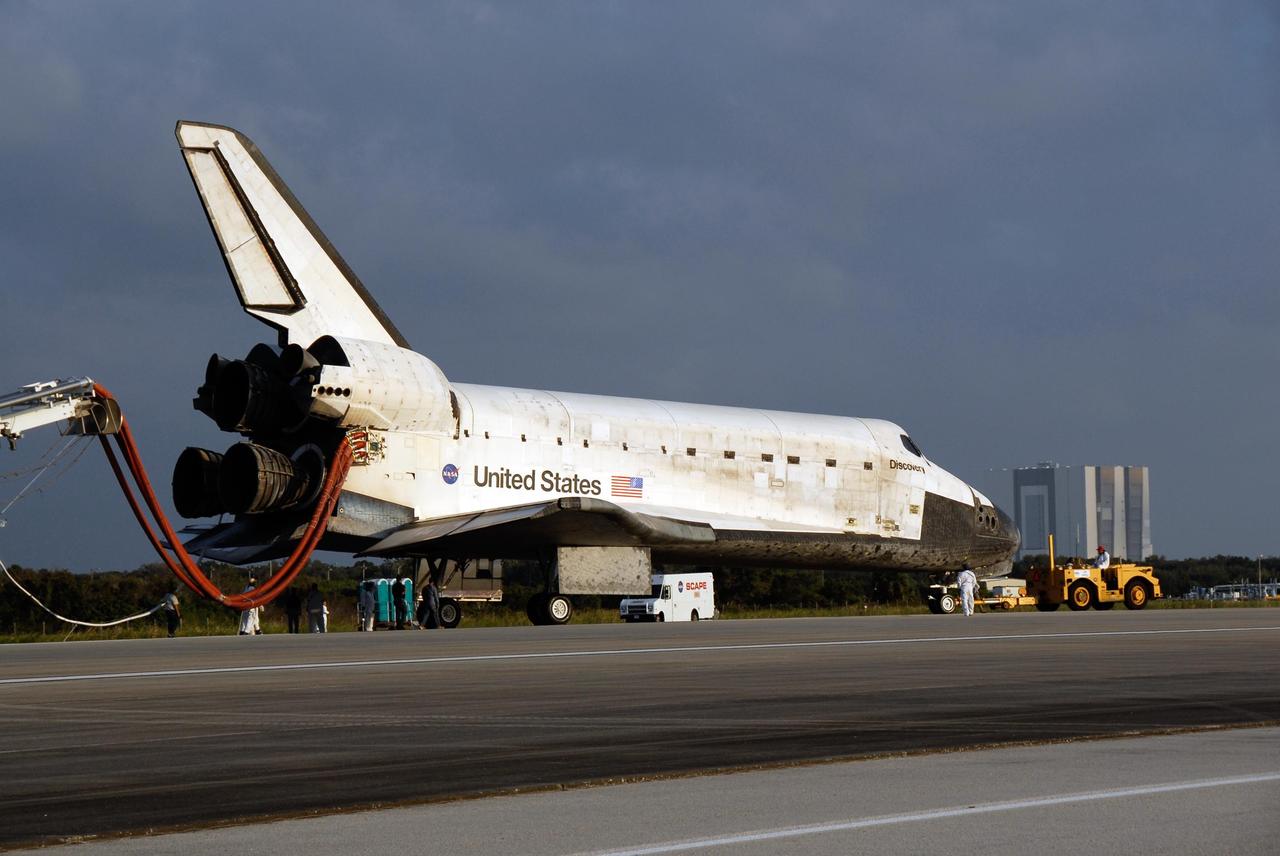

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Discovery is towed to the Orbiter Processing Facility, or OPF. Towing normally begins approximately within four hours after landing and is completed within six hours unless removal of time-sensitive experiments requires an additional period on the runway. Umbilicals are attached to purge the vehicle of any possible residual explosive or toxic fumes. The tractor tow vehicle will pull Discovery along a two-mile tow-way to the OPF, where processing Discovery for another flight begins. The tow vehicle is very much like the typical towing units used for large aircraft, but it is equipped with a special towing bar designed specifically for the orbiter. In the OPF, turnaround processing procedures on Discovery will include various post-flight deservicing and maintenance functions, which are carried out in parallel with payload removal and the installation of equipment needed for the next mission. Before post-flight deservicing can continue beyond initial safing operations, certain vehicle systems must be mechanically secured and access platforms installed. Discovery completed mission STS-120 with an on-time landing at 1:01 p.m. EST. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
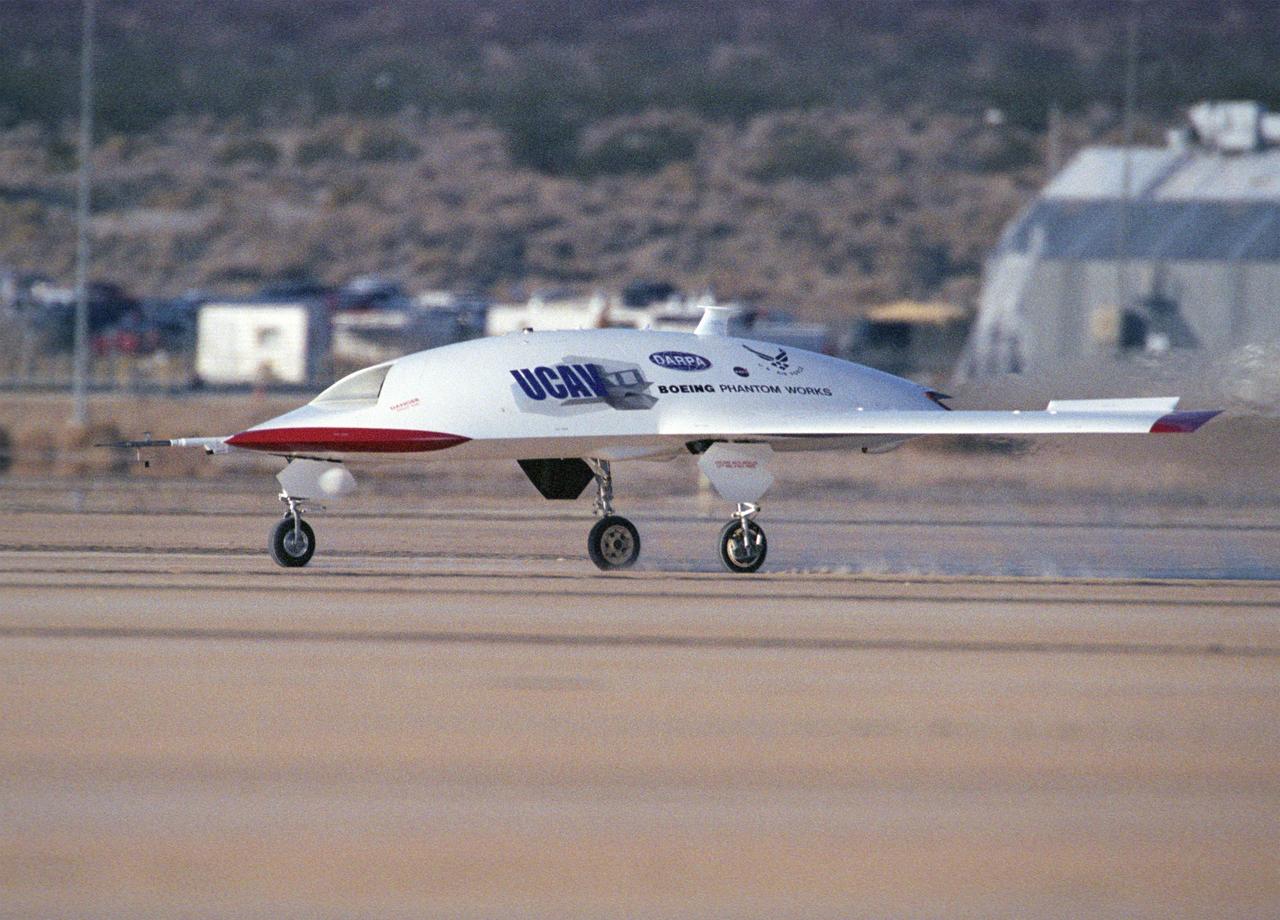

The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.

The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.

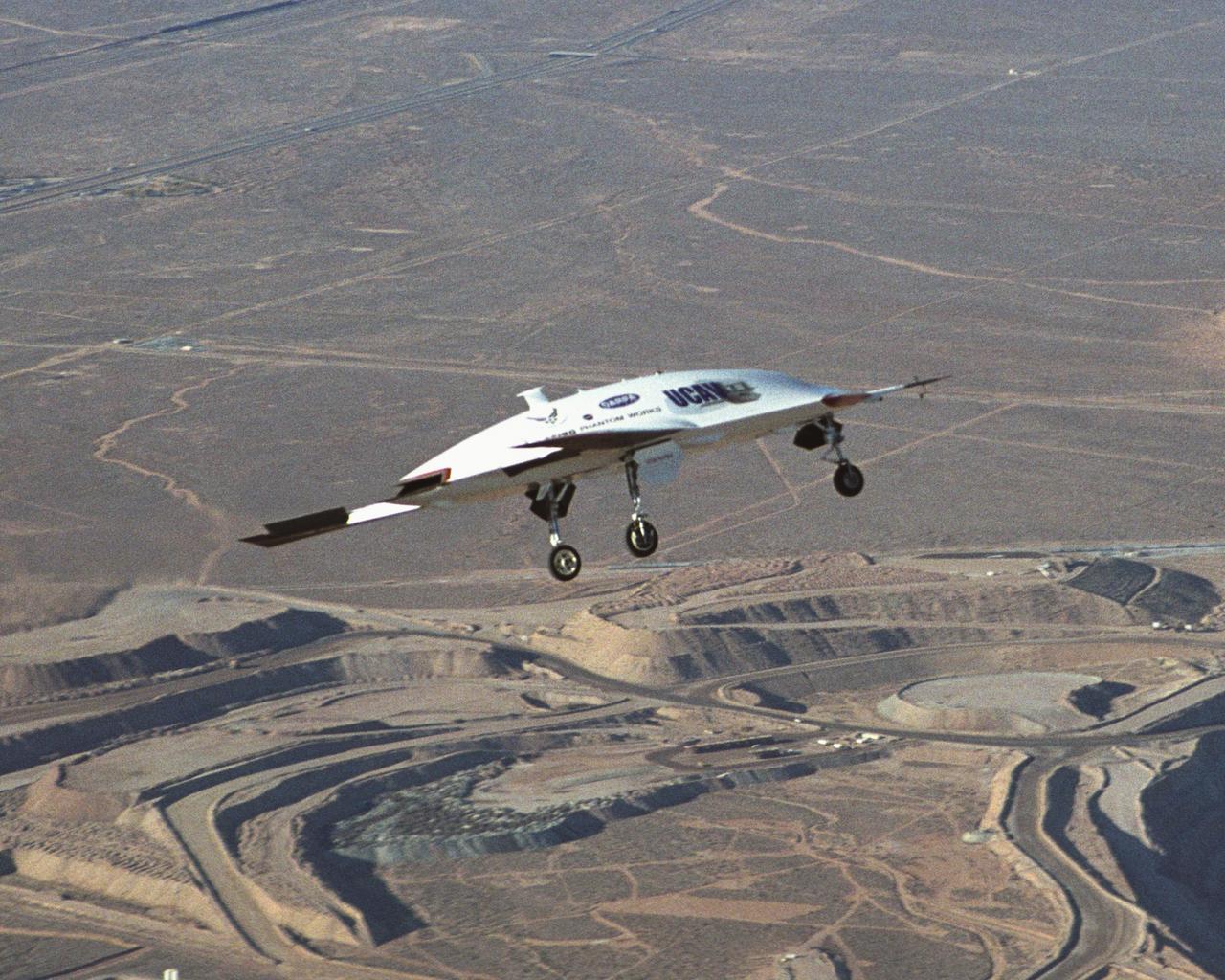
The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
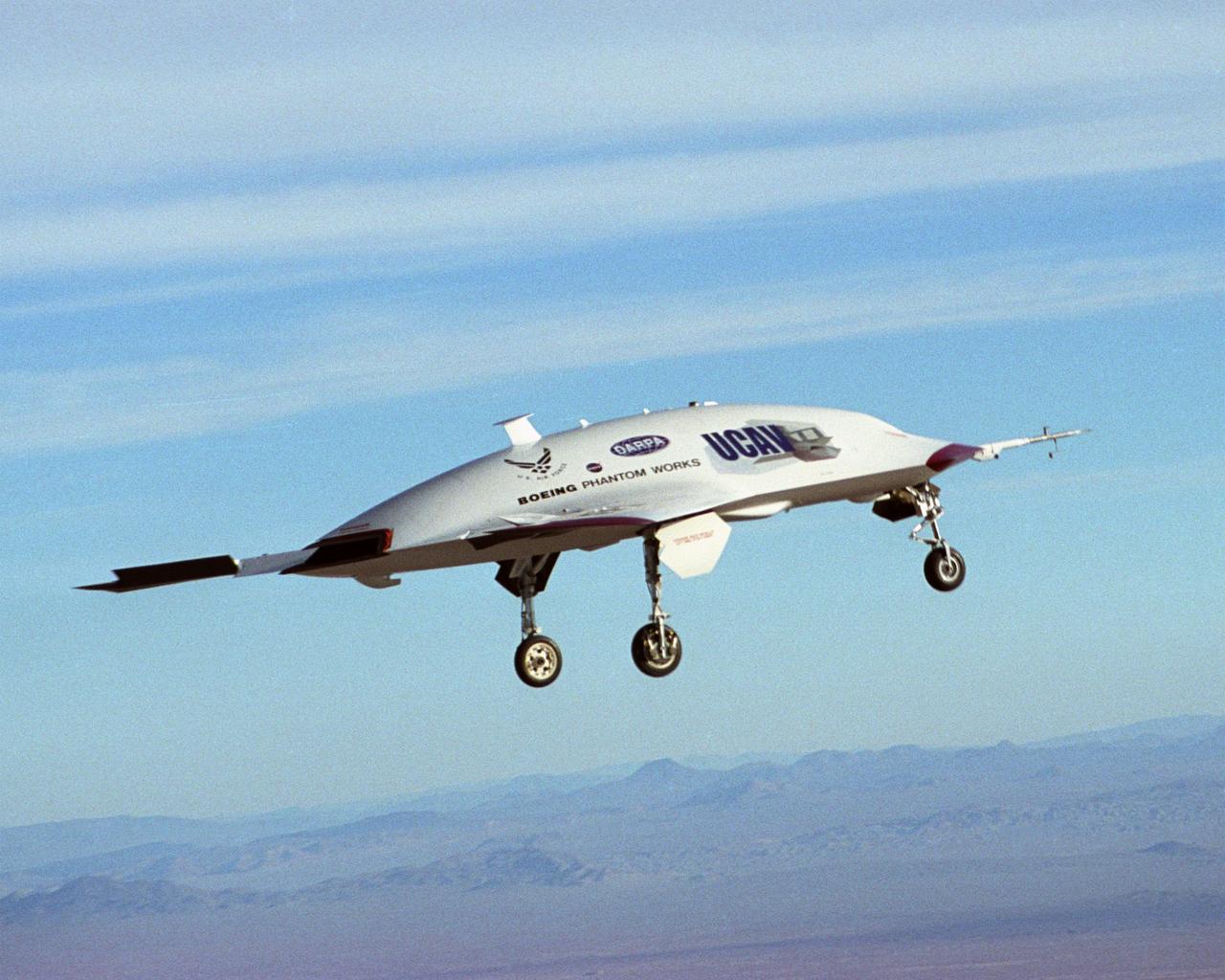

The second X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its first flight on November 21, 2002, after taking off from a dry lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards Air Force Base, California. X-45A vehicle two flew for approximately 30 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7500 feet. This flight validated the functionality of the UCAV flight software on the second air vehicle. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
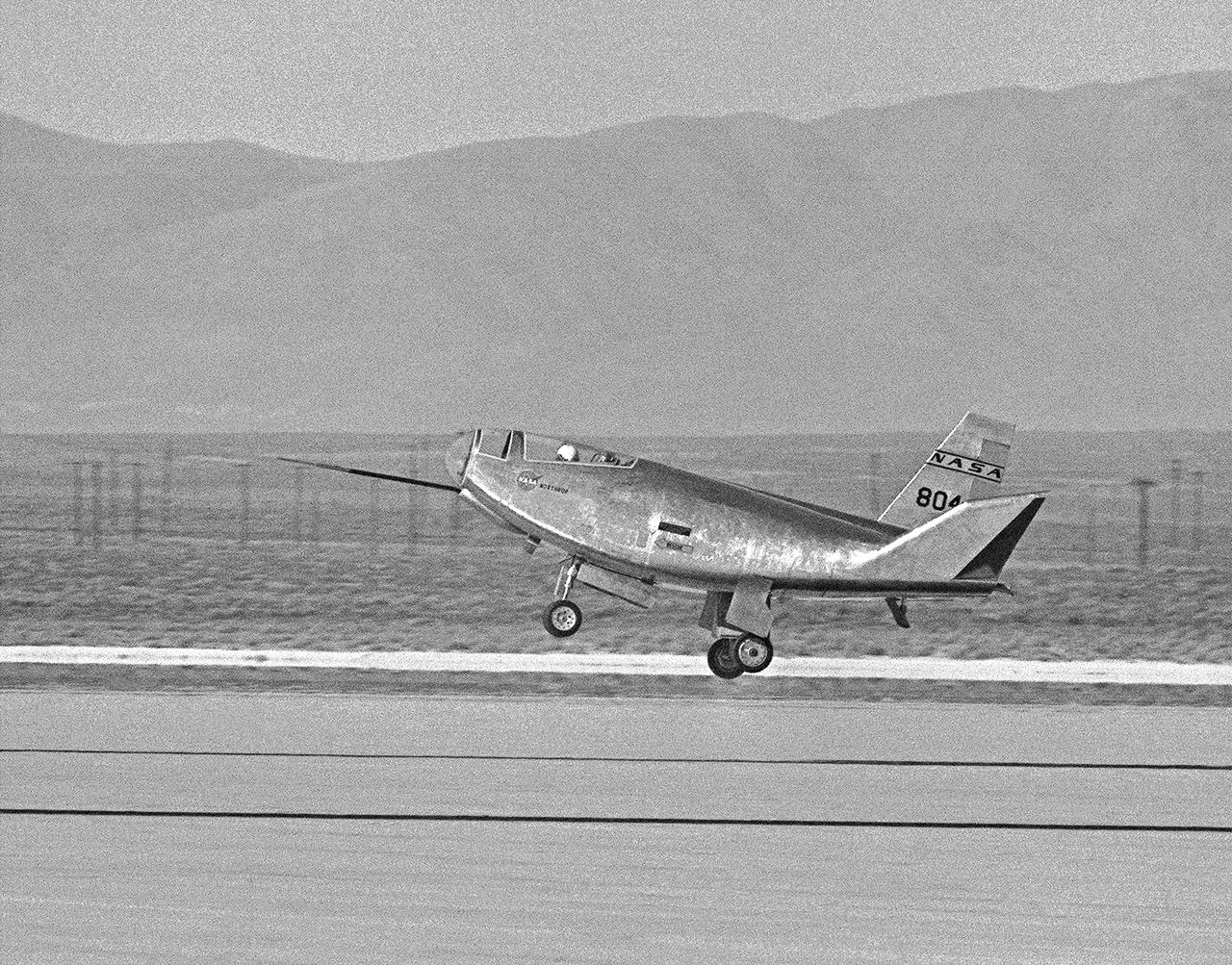

The HL-10 Lifting Body completes its first research flight with a landing on Rogers Dry Lake. Due to control problems, pilot Bruce Peterson had to land at a higher speed than originally planned in order to keep the vehicle under control. The actual touchdown speed was about 280 knots. This was 30 knots above the speed called for in the flight plan. The HL-10's first flight had lasted 3 minutes and 9 seconds.
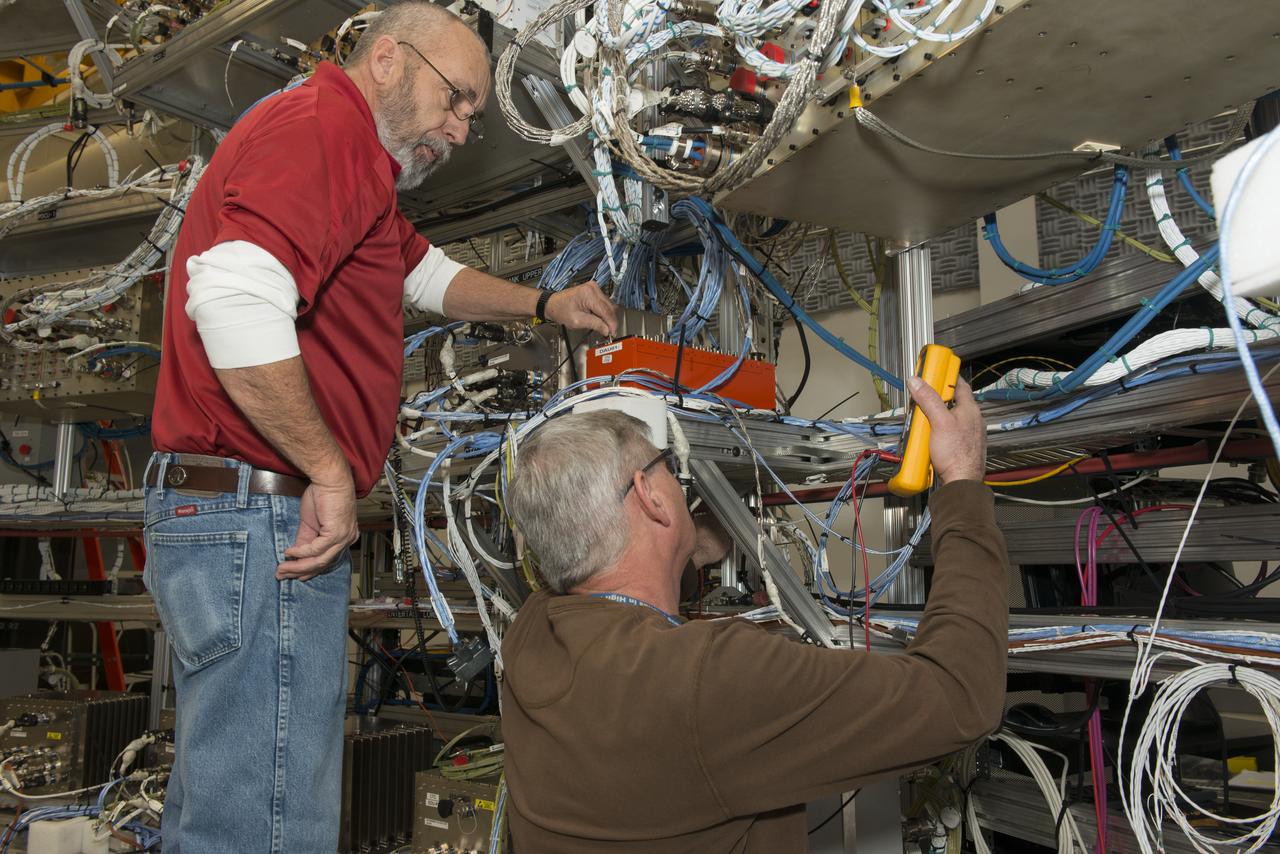

From left, Wayne Arrington, a Boeing Company technician, and Steve Presti, a mechanical technician at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., install Developmental Flight Instrumentation Data Acquisition Units in Marshall's Systems Integration and Test Facility. The units are part of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) core stage avionics, which will guide the biggest, most powerful rocket in history to deep space missions. When completed, the core stage will be more than 200 feet tall and store cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen that will feed the vehicle's RS-25 engines. The hardware, software and operating systems for the SLS are arranged in flight configuration in the facility for testing. The new Data Acquisition Units will monitor vehicle behavior in flight -- like acceleration, thermal environments, shock and vibration. That data will then be used to validate previous ground tests and analyses models that were used in the development of the SLS vehicle.
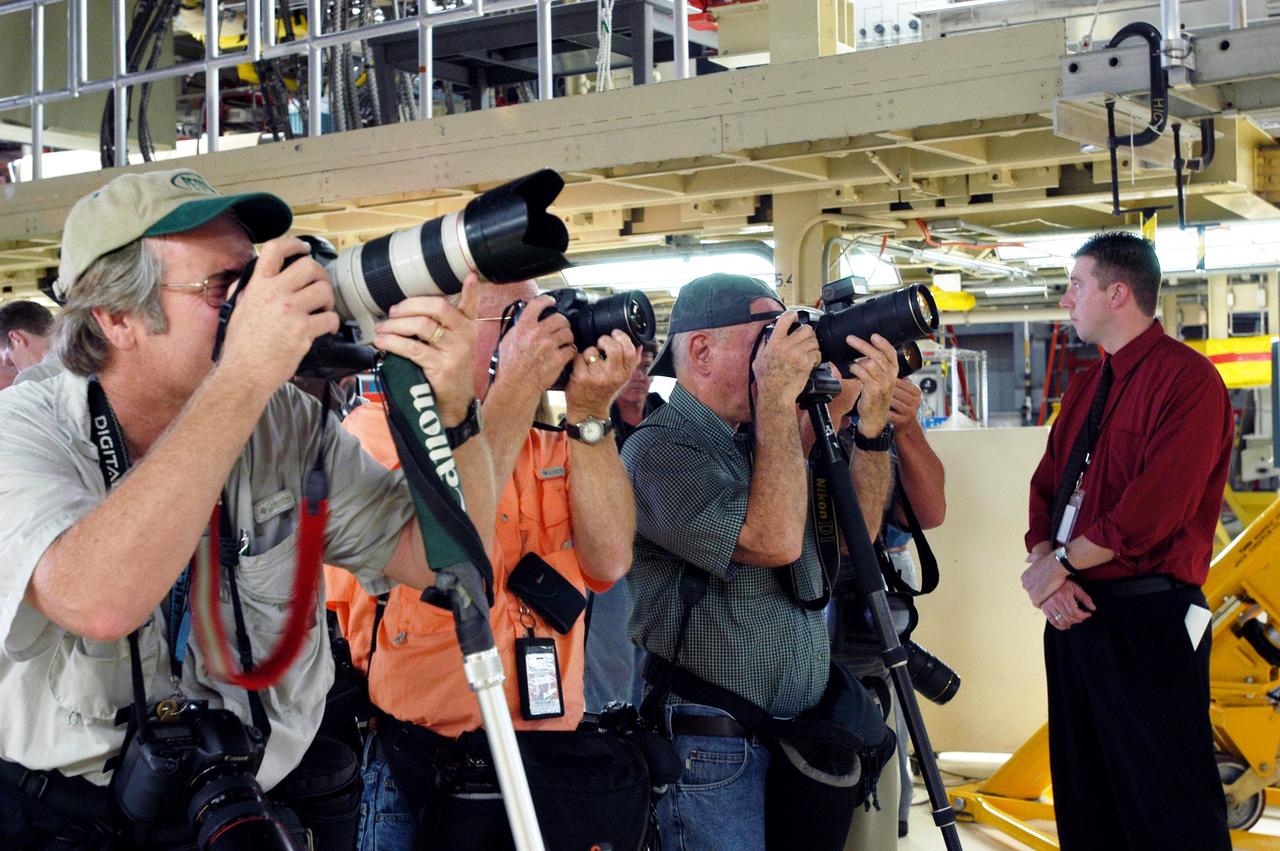

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Media tour the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) housing the Space Shuttle Discovery at KSC. During this event, they received the latest information on Discovery’s processing and viewed workers preparing the vehicle for its safe return to flight scheduled for a launch planning window of March 2005. Kicking off the activities at the Press Site Auditorium, technical experts led two workshops addressing Reinforced Carbon-Carbon and vehicle instrumentation. Later, reporters toured the OPF to see work in progress on Discovery, including reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the Shuttle's wing leading edge, wiring inspections and instrumentation updates being completed for Return to Flight.
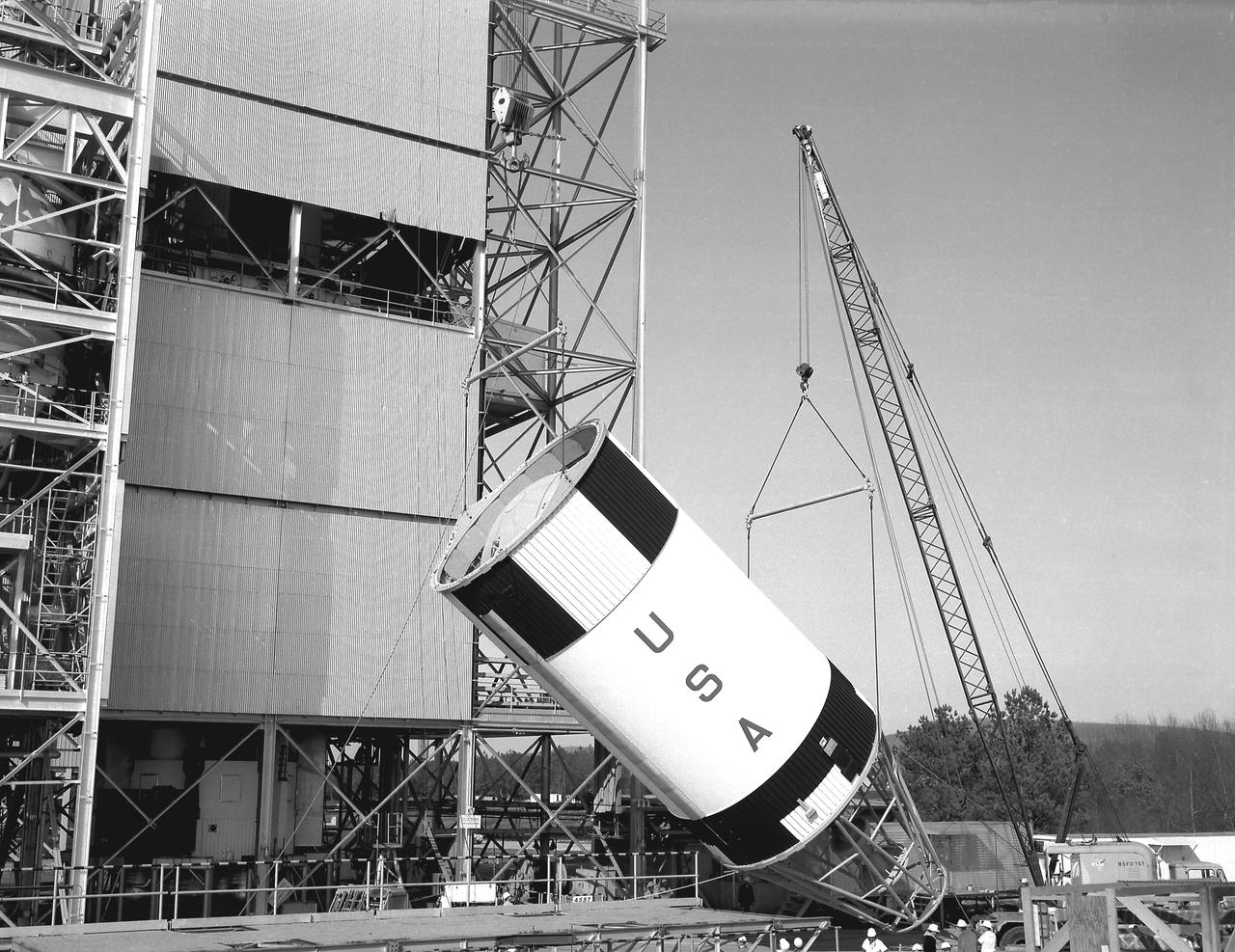

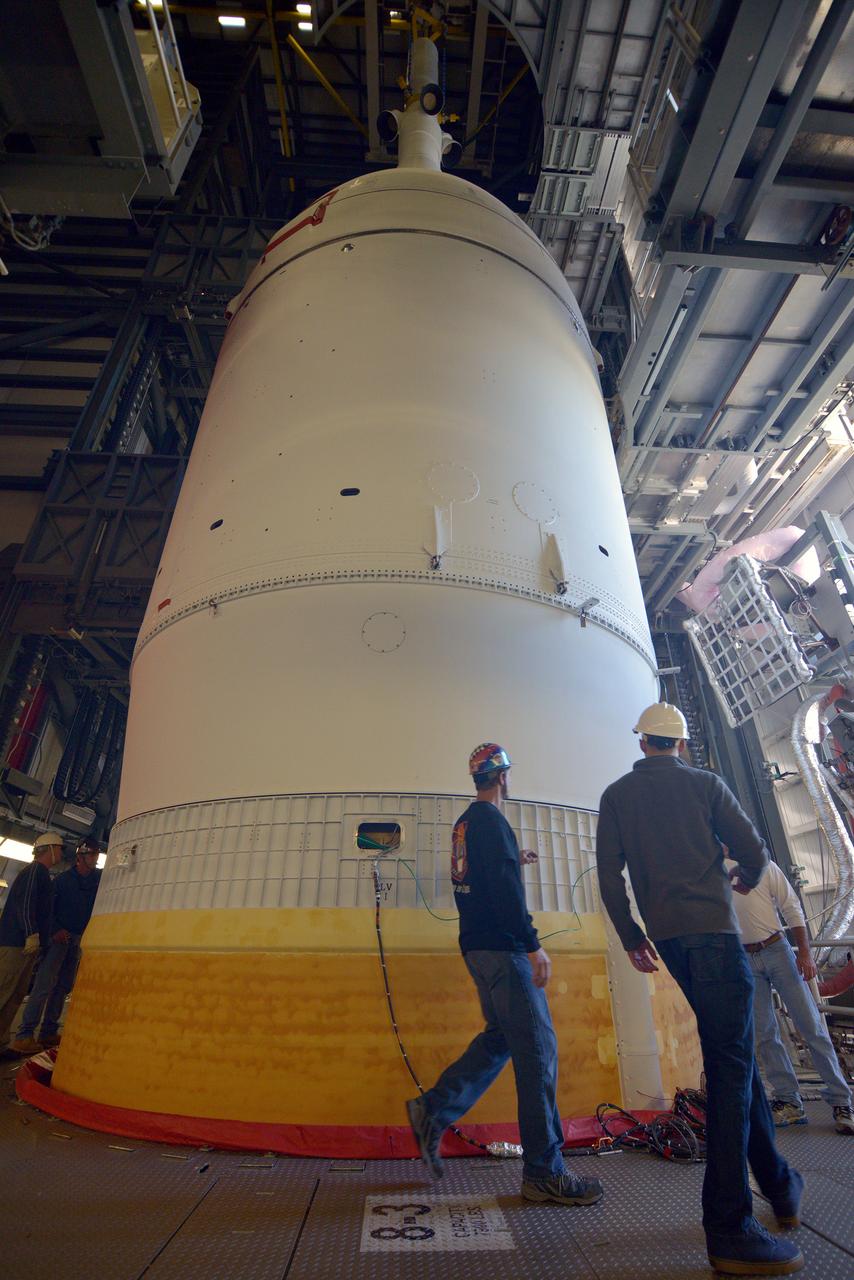
Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) workers hoist a dynamic test version of the S-IVB stage, the Saturn IB launch vehicle's second stage, into the Center's Dynamic Test Stand on January 18, 1965. MSFC Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the launch vehicle's structural soundness. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.

Workers at the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Dynamic Test Stand install S-IB-200D, a dynamic test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage, on January 11, 1965. MSFC Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the launch vehicle's structural soundness. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
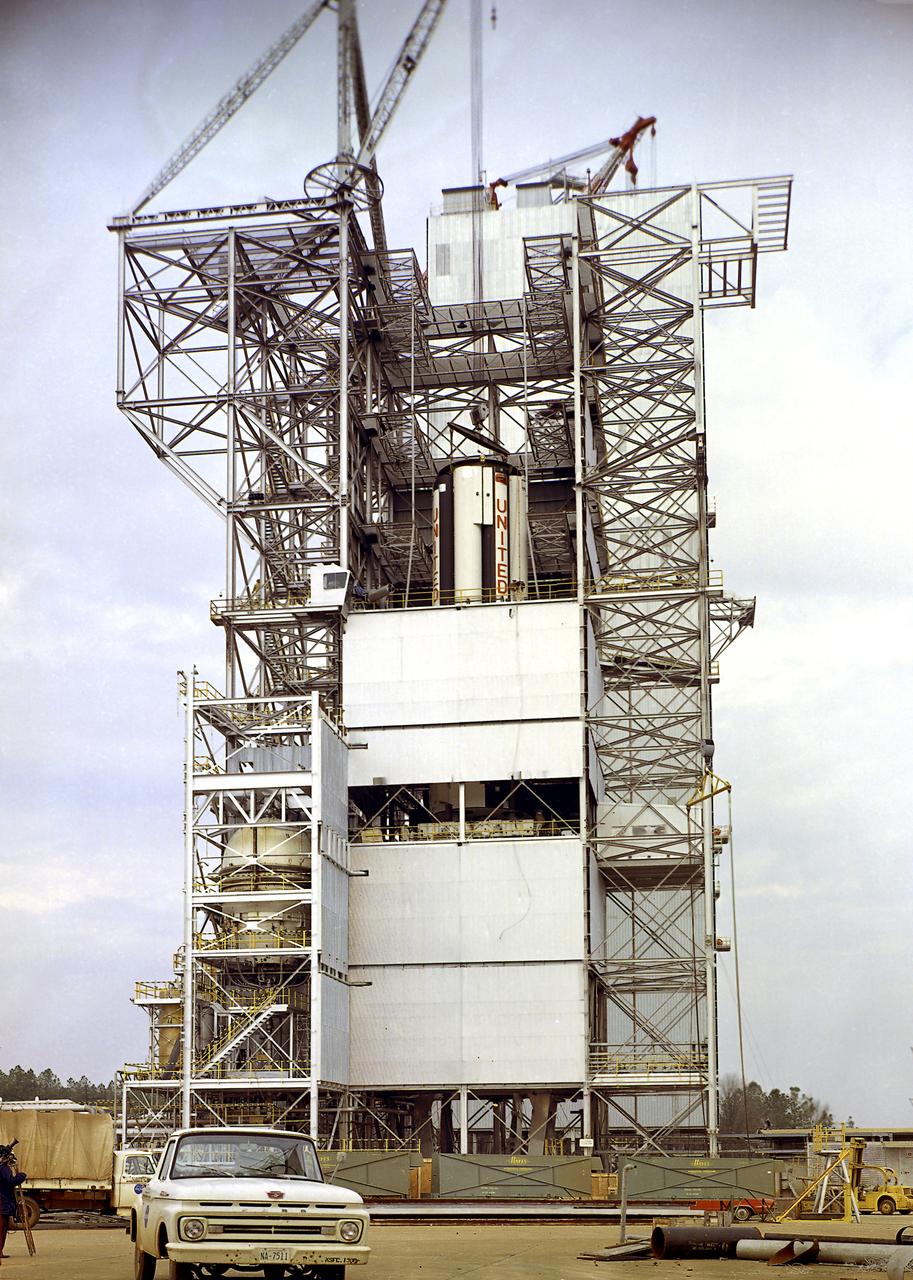
Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) workers lower S-IB-200D, a dynamic test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), into the Center's Dynamic Test Stand on January 12, 1965. Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the structural soundness of the launch vehicle. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine large boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X aft assembly moves toward the door of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside, it will be stacked with other segments to complete the Ares I-X test vehicle. The aft assembly will be the first segment to be stacked on the mobile launch platform in the VAB. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted no earlier than Aug. 30 from Launch Pad 39B. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X aft assembly is being moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. There it will be stacked with other segments to complete the Ares I-X test vehicle. The aft assembly will be the first segment to be stacked on the mobile launch platform in the VAB. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted no earlier than Aug. 30 from Launch Pad 39B. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
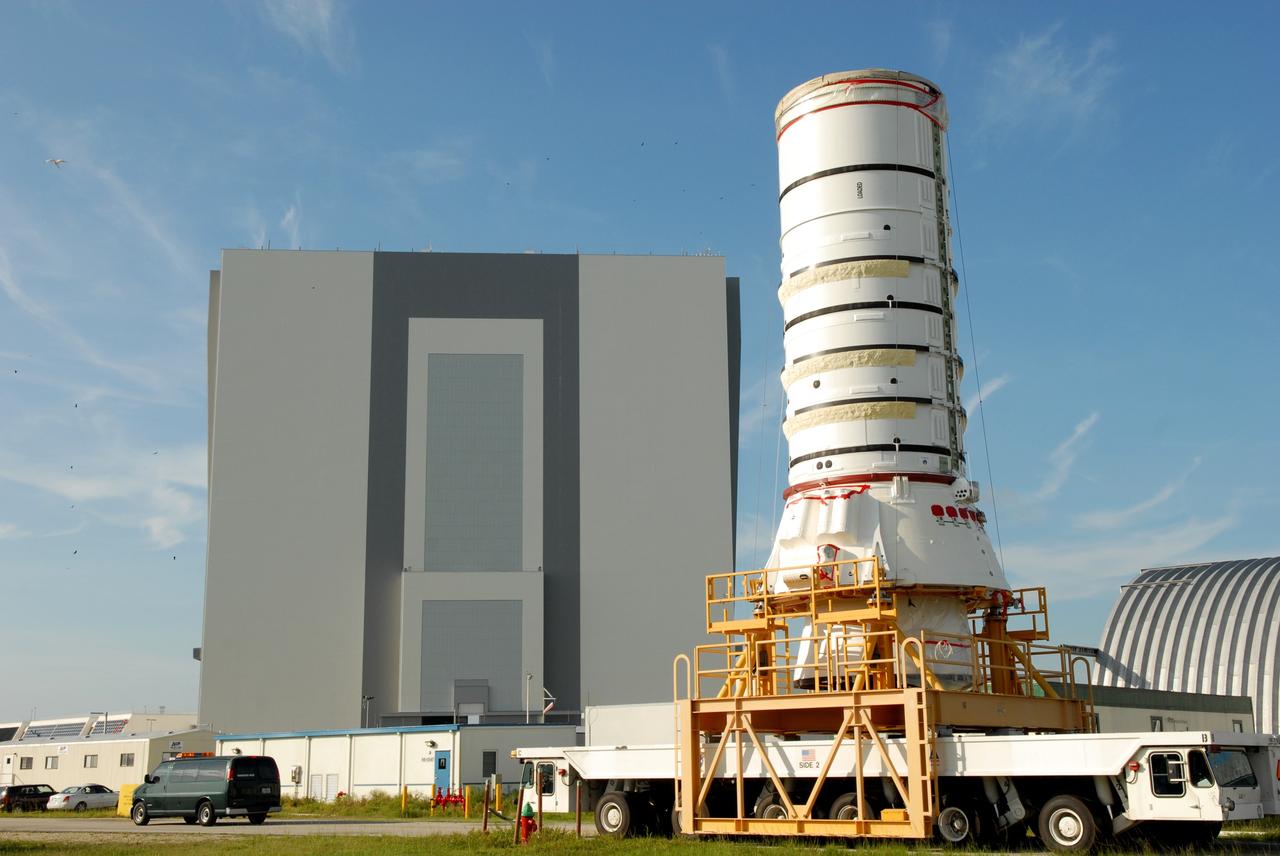

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X aft assembly nears the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It is being moved to the VAB for stacking to complete the Ares I-X test vehicle. The aft assembly will be the first segment to be stacked on the mobile launch platform in the VAB. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted no earlier than Aug. 30 from Launch Pad 39B. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
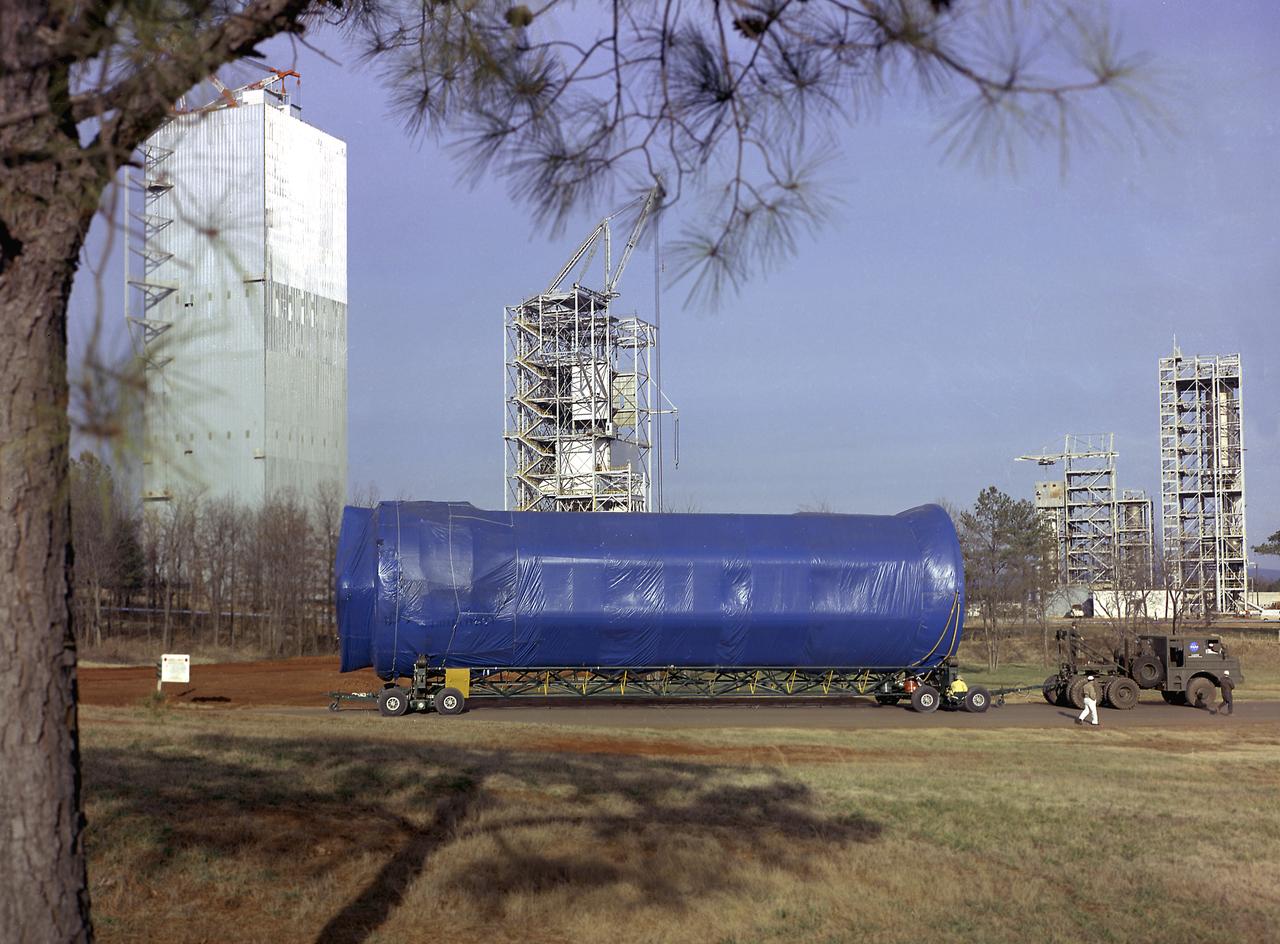

S-IB-200D, a dynamic test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB), makes its way to the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) East Test Area on January 4, 1965. Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the structural soundness of the launch vehicle in the Dynamic Test Stand. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
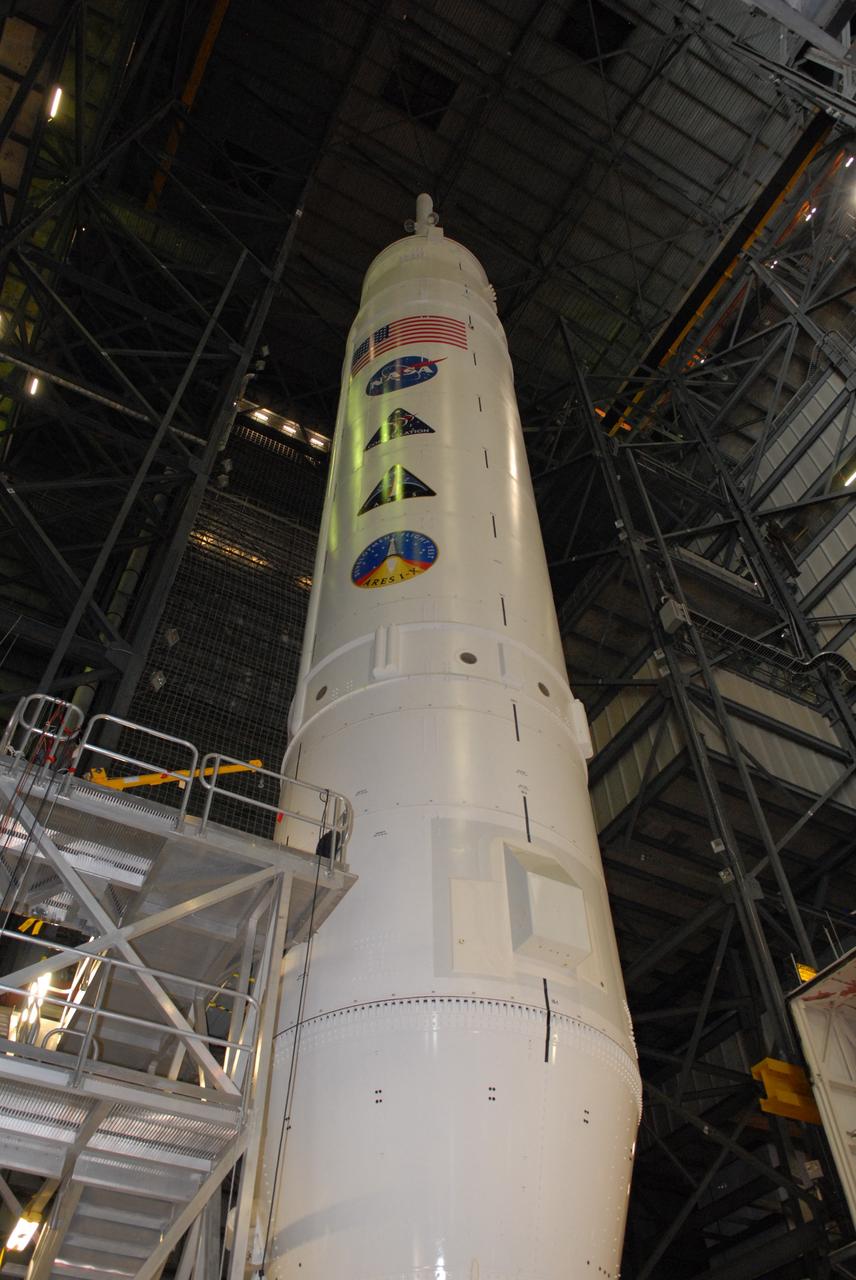

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The United States flag, along with program and NASA decals, stretch the length of the Ares I-X upper stage. Stacking of the vehicle is complete in the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system designed to carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/constellation/ares/flighttests/aresIx/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
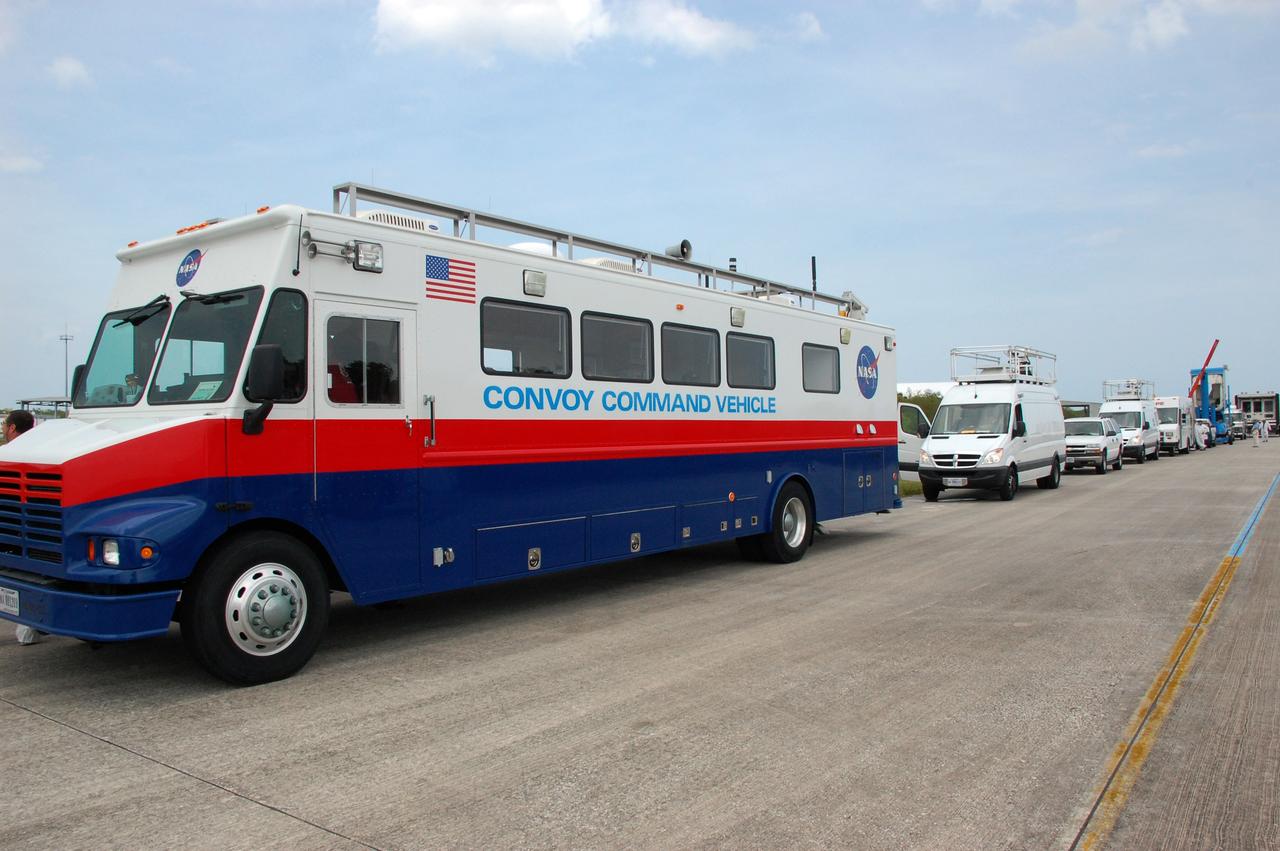

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The landing convoy is lined up on the Shuttle Landing Facility runway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The convoy awaits space shuttle Discovery's landing, after completing itsa 13-day journey of more than 5.3 million miles on the STS-119 mission. At left is the Convoy Command Vehicle which is the command post for the convoy commander. the convoy commander is in communication with the shuttle and all of the landing convoy vehicles during the post-landing operations. The landing convoy's purpose is to safe the vehicle and provide support for the disembarking crew and experiments. The STS-119 flight delivered the space station's fourth and final set of large solar array wings and the S6 truss segment, completing the station's truss, or backbone. The additional electricity provided by the arrays will fully power science experiments and help support six-person station operations in May. The mission was the 28th flight to the station, the 36th flight of Discovery and the 125th in the Space Shuttle Program, as well as the 70th landing at Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky