
Complete Makeover
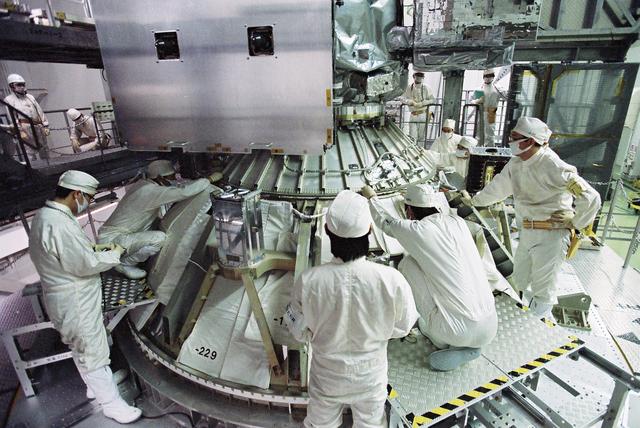

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
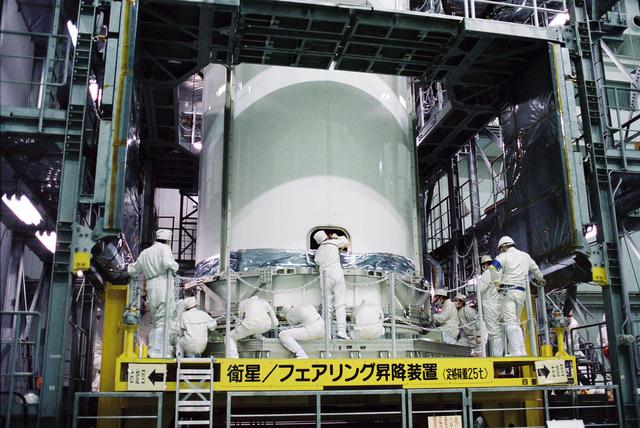

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
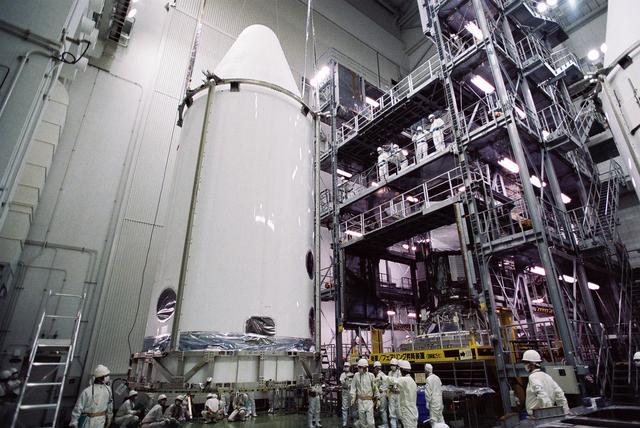

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
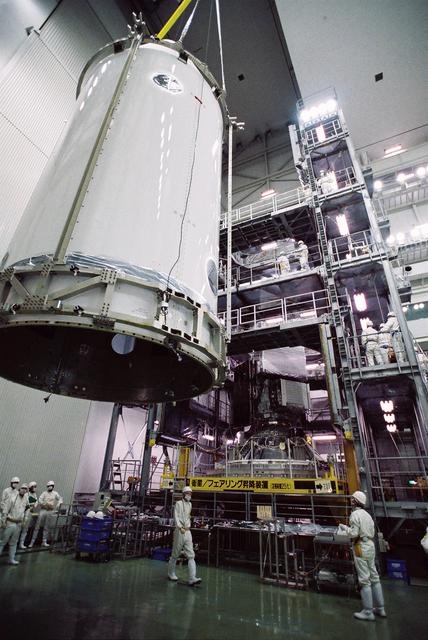

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
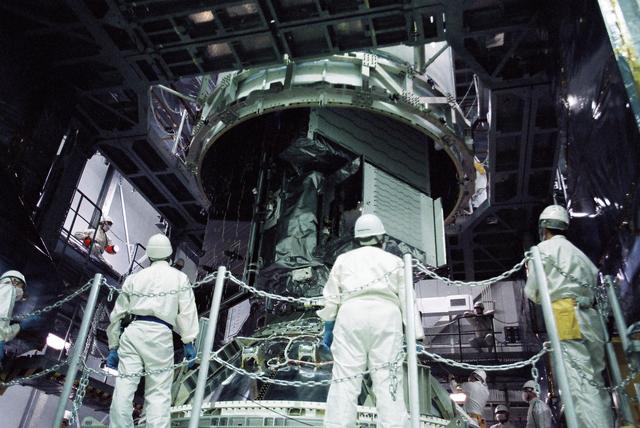

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
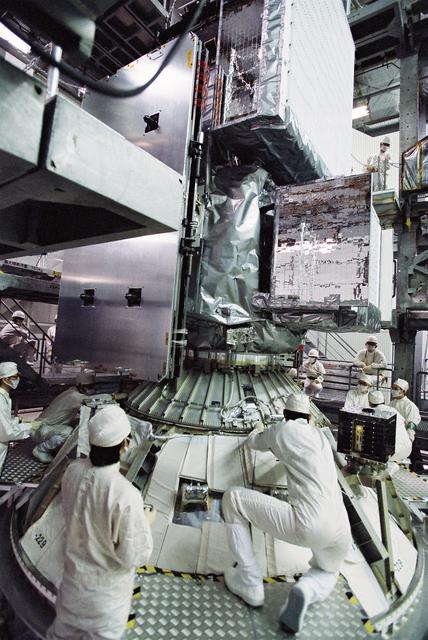

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
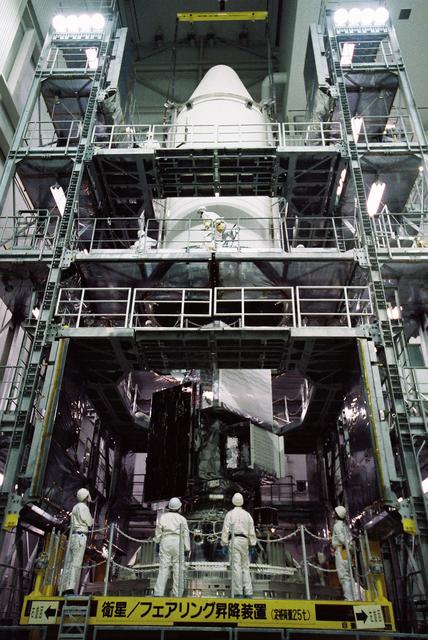

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
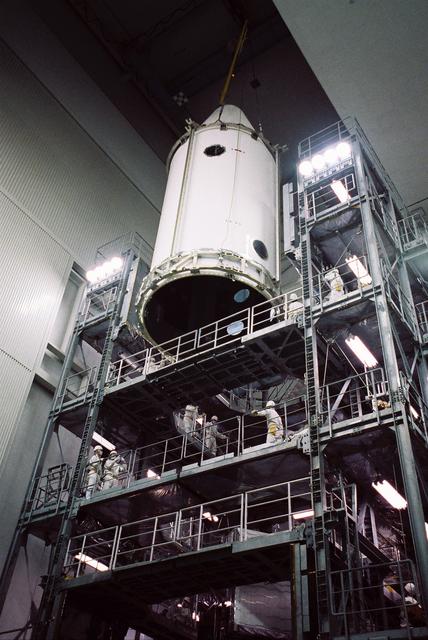

GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The Core Observatory will link data from a constellation of current and planned satellites to produce next-generation global measurements of rainfall and snowfall from space. On Feb. 11, the Core Observatory was moved into the spacecraft fairing assembly building and into the Encapsulation Hall. Final inspections and preparations were completed for the installation into the fairing, which began on Feb 13. The fairing is the part of the rocket that will contain the spacecraft at the top of the H-IIA rocket. The encapsulation process for the H-IIA is very different than for most U.S. rockets. For U.S. rockets, the fairing is usually in two pieces that close around the payload like a clamshell. To install the GPM Core Observatory into the fairing of the H-IIA rocket, first the Core Observatory and the Payload Attach Fitting (PAF) are set up in scaffolding in the Encapsulation Hall. Then, the fairing is lifted above and lowered onto the fitting. When only a few feet remain above the final position, stanchions support the fairing while technicians go inside to complete the electrical connections. When this is completed, they remove the stanchions and lower the fairing to its final position, where it is bolted in place. The GPM mission is the first coordinated international satellite network to provide near real-time observations of rain and snow every three hours anywhere on the globe. The GPM Core Observatory anchors this network by providing observations on all types of precipitation. The observatory's data acts as the measuring stick by which partner observations can be combined into a unified data set. The data will be used by scientists to study climate change, freshwater resources, floods and droughts, and hurricane formation and tracking. Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
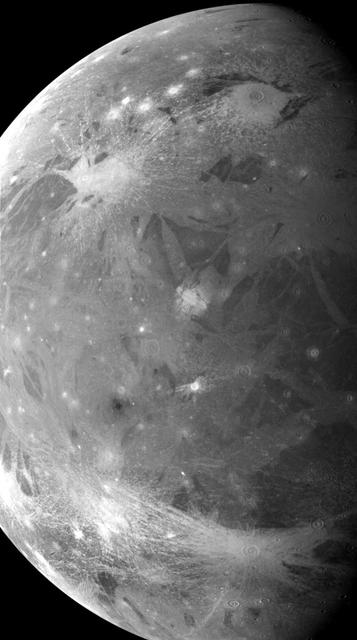
Completing a Global Map of Ganymede
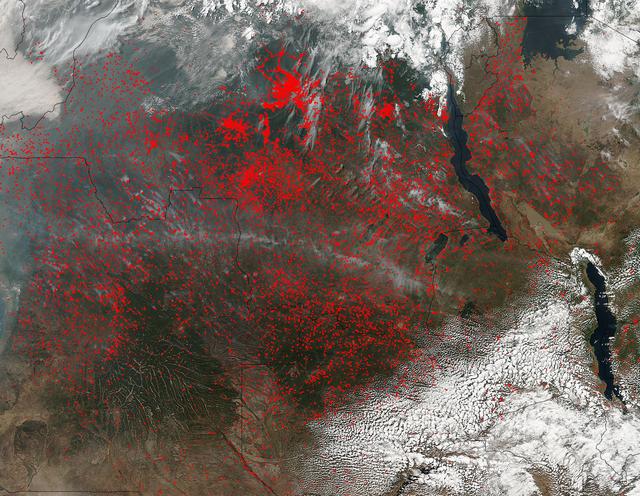
NASA’s Suomi NPP satellite detected thousands of fires burning in central Africa on July 11, 2016. The fires are represented by the multitudes of red dots. Most of the fires burn in grass or cropland. The location, widespread nature, and number of fires suggest that these fires were deliberately set to manage land. Places where traditional plots of open land is not available because the vegetation in the area is dense are the places where "slash and burn" agriculture is practiced most often. These regions include parts of Africa, northern South America, and Southeast Asia, where an abundance of grasslands and rainforests are found. Although most parts of the world outlaw this type of agriculture due to the fact that the smoke from these (or any) fires is a health hazard, the method of agriculture continues because it is the easiest and lowest cost solution to clearing fields for next year's crops. The Suomi NPP satellite is a joint mission between NASA, NOAA and the U.S. Department of Defense. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team.
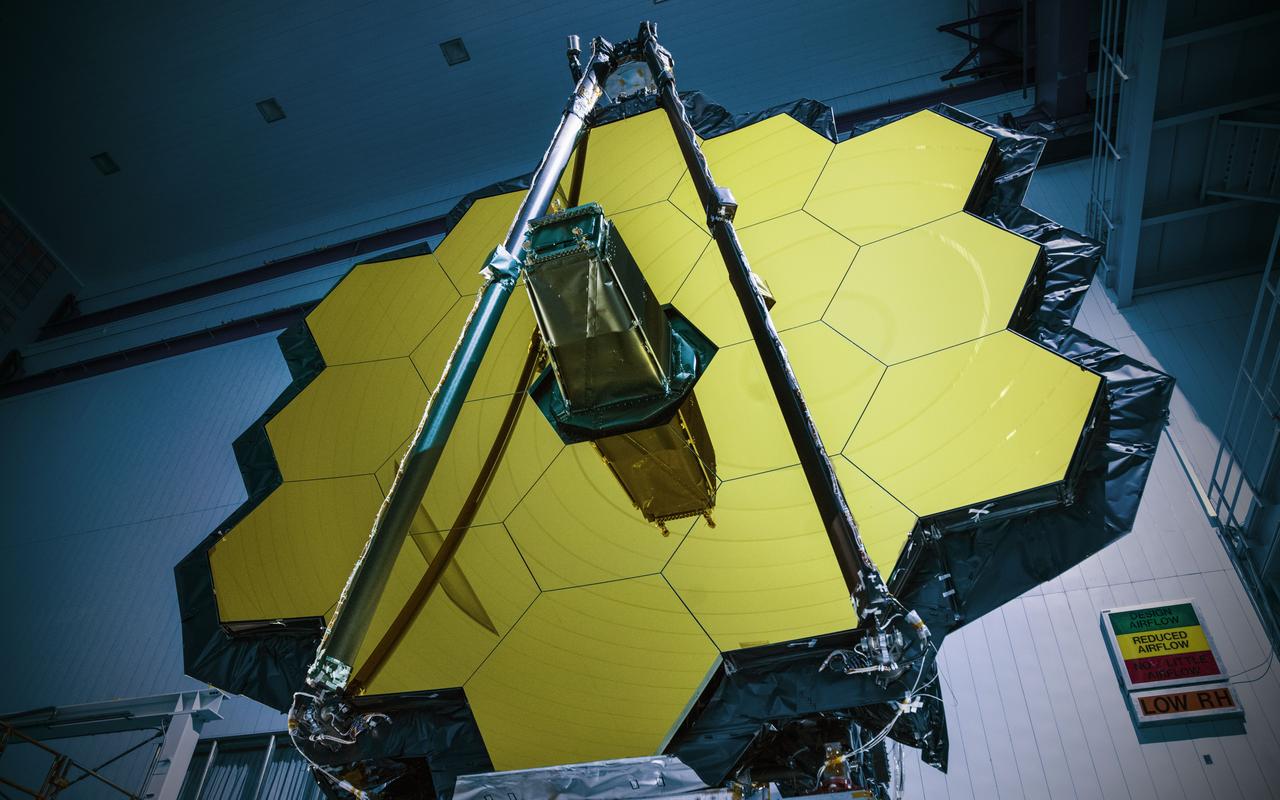

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has successfully passed the center of curvature test, an important optical measurement of Webb’s fully assembled primary mirror prior to cryogenic testing, and the last test held at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, before the spacecraft is shipped to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston for more testing. After undergoing rigorous environmental tests simulating the stresses of its rocket launch, the Webb telescope team at Goddard analyzed the results from this critical optical test and compared it to the pre-test measurements. The team concluded that the mirrors passed the test with the optical system unscathed. “The Webb telescope is about to embark on its next step in reaching the stars as it has successfully completed its integration and testing at Goddard. It has taken a tremendous team of talented individuals to get to this point from all across NASA, our industry and international partners, and academia,” said Bill Ochs, NASA’s Webb telescope project manager. “It is also a sad time as we say goodbye to the Webb Telescope at Goddard, but are excited to begin cryogenic testing at Johnson.” Rocket launches create high levels of vibration and noise that rattle spacecraft and telescopes. At Goddard, engineers tested the Webb telescope in vibration and acoustics test facilities that simulate the launch environment to ensure that functionality is not impaired by the rigorous ride on a rocket into space. Before and after these environmental tests took place, optical engineers set up an interferometer, the main device used to measure the shape of the Webb telescope’s mirror. An interferometer gets its name from the process of recording and measuring the ripple patterns that result when different beams of light mix and their waves combine or “interfere.” Waves of visible light are less than a thousandth of a millimeter long and optics on the Webb telescope need to be shaped and aligned even more accurately than that to work correctly. Making measurements of the mirror shape and position by lasers prevents physical contact and damage (scratches to the mirror). So, scientists use wavelengths of light to make tiny measurements. By measuring light reflected off the optics using an interferometer, they are able to measure extremely small changes in shape or position that may occur after exposing the mirror to a simulated launch or temperatures that simulate the subfreezing environment of space. During a test conducted by a team from Goddard, Ball Aerospace of Boulder, Colorado, and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, temperature and humidity conditions in the clean room were kept incredibly stable to minimize fluctuations in the sensitive optical measurements over time. Even so, tiny vibrations are ever-present in the clean room that cause jitter during measurements, so the interferometer is a “high-speed” one, taking 5,000 “frames” every second, which is a faster rate than the background vibrations themselves. This allows engineers to subtract out jitter and get good, clean results on any changes to the mirror's shape. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR</a> NASA’s Webb Telescope Completes Goddard Testing
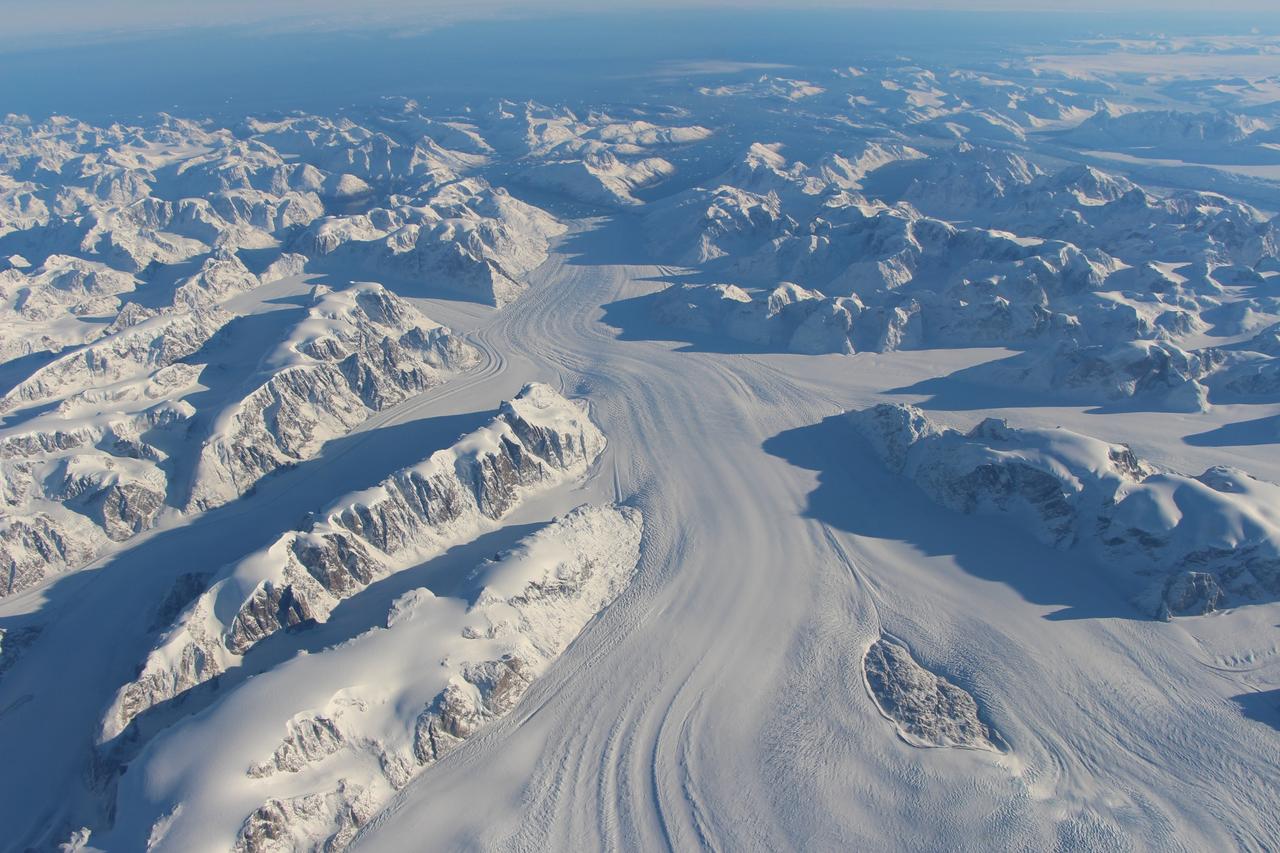

Heimdal Glacier in southern Greenland, in an image captured on Oct. 13, 2015, from NASA Langley Research Center's Falcon 20 aircraft flying 33,000 feet above mean sea level. NASA’s Operation IceBridge, an airborne survey of polar ice, recently finalized two overlapping campaigns at both of Earth’s poles. Down south, the mission observed a big drop in the height of two glaciers situated in the Antarctic Peninsula, while in the north it collected much needed measurements of the status of land and sea ice at the end of the Arctic summer melt season. This was the first time in its seven years of operations that IceBridge carried out parallel flights in the Arctic and Antarctic. Every year, the mission flies to the Arctic in the spring and to Antarctica in the fall to keep collect an uninterrupted record of yearly changes in the height of polar ice. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-s-operation-icebridge-completes-twin-polar-campaigns" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-s-operation-icebridge-c...</a> Credits: NASA/Goddard/John Sonntag <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
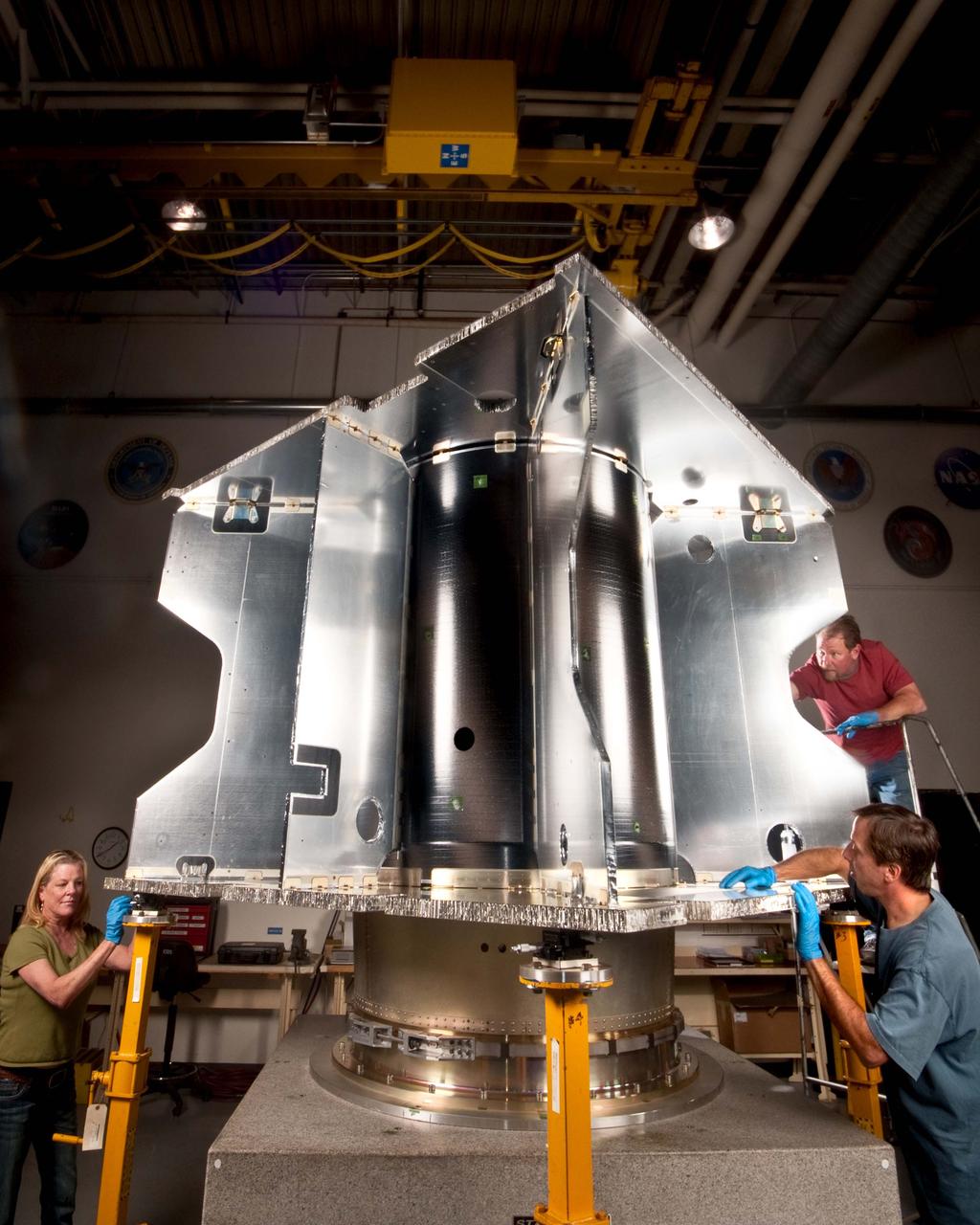

NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) mission has reached a new milestone. Lockheed Martin has completed building the primary structure of the MAVEN spacecraft at its Space Systems Company facility near Denver. The MAVEN spacecraft is scheduled to launch in November 2013 and will be the first mission devoted to understanding the Martian upper atmosphere. The mission's principal investigator is Bruce Jakosky from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado. In the photo taken on Sept. 8, technicians from Lockheed Martin are inspecting the MAVEN primary structure following its recent completion at the company’s Composites Lab. The primary structure is cube shaped at 7.5 feet x 7.5 feet x 6.5 feet high (2.3 meters x 2.3 meters x 2 meters high). Built out of composite panels comprised of aluminum honeycomb sandwiched between graphite composite face sheets and attached to one another with metal fittings, the entire structure only weighs 275 pounds (125 kilograms). At the center of the structure is the 4.25 feet (1.3 meters) diameter core cylinder that encloses the hydrazine propellant tank and serves as the primary vertical load-bearing structure. The large tank will hold approximately 3,615 pounds (1640 kilograms) of fuel. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/news/maven-structure.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/news/maven-structure.html</a> Credit: Lockheed Martin <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
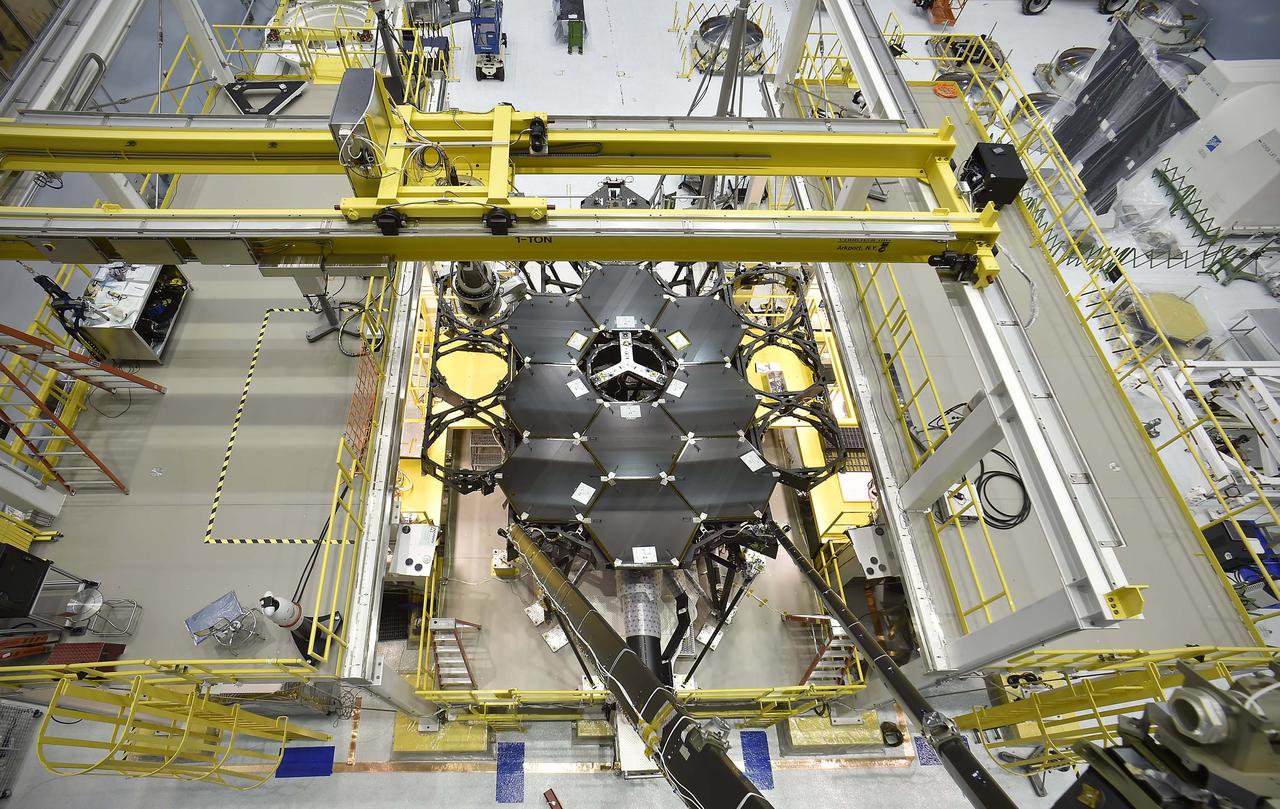
Inside NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center's massive clean room in Greenbelt, Maryland, the ninth flight mirror was installed onto the telescope structure with a robotic arm. This marks the halfway completion point for the James Webb Space Telescope's segmented primary mirror. Engineers worked tirelessly to install the ninth primary flight mirror onto the telescope structure. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW</a>
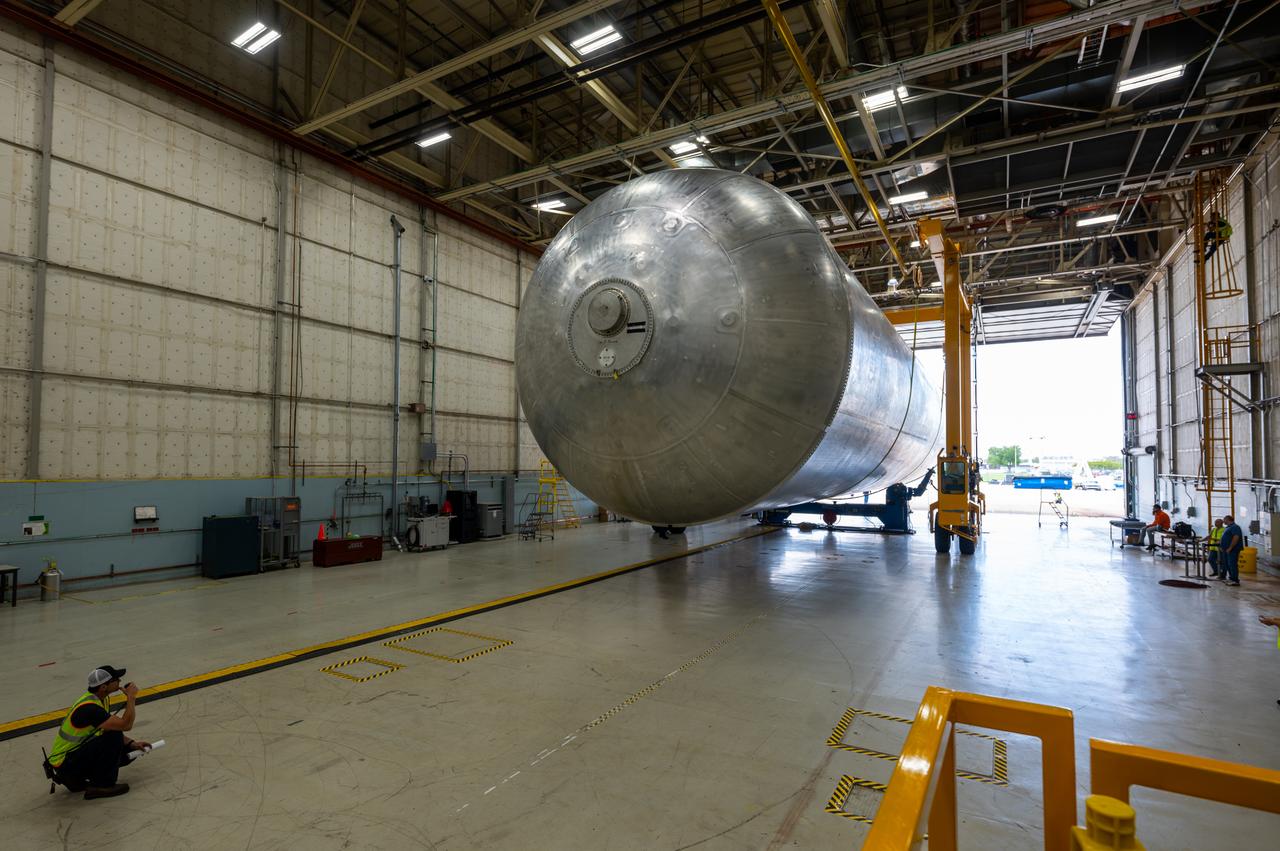

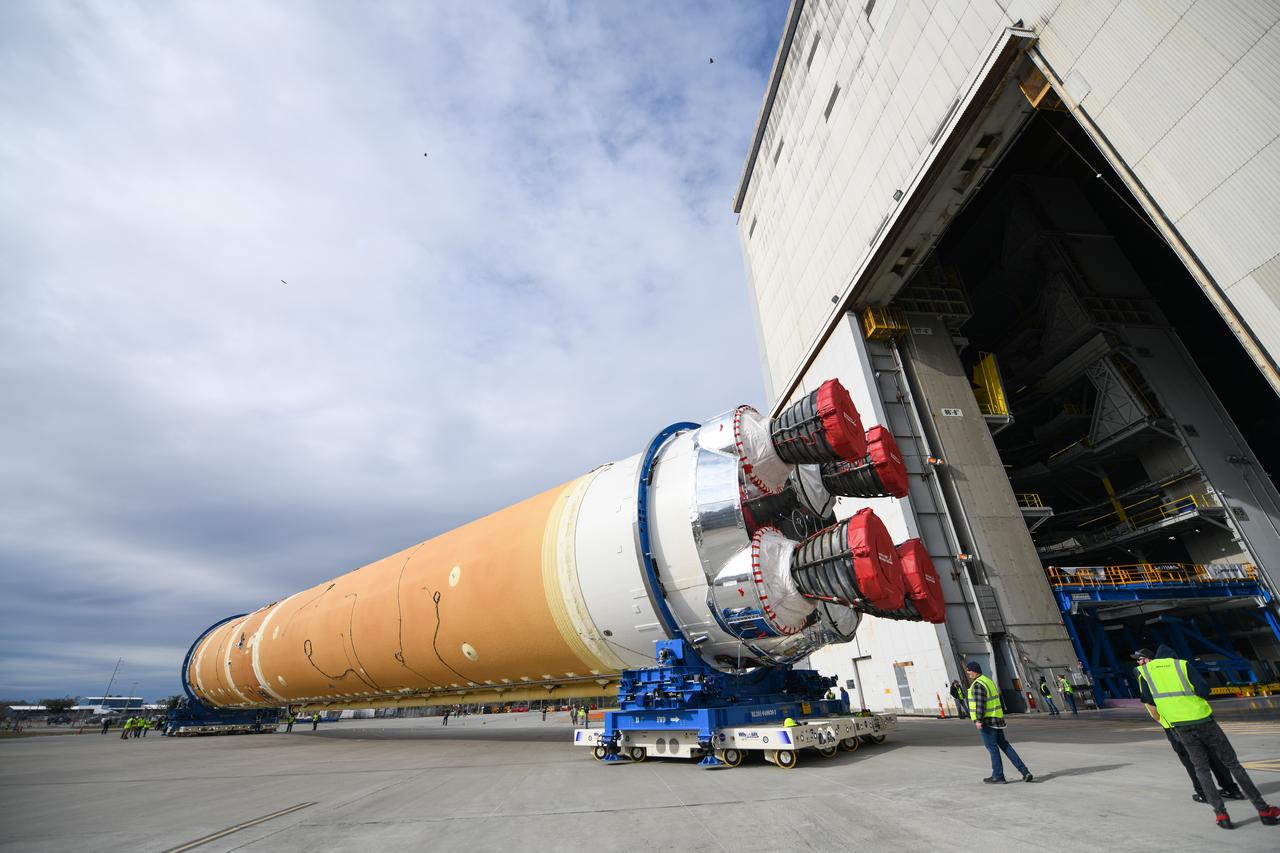
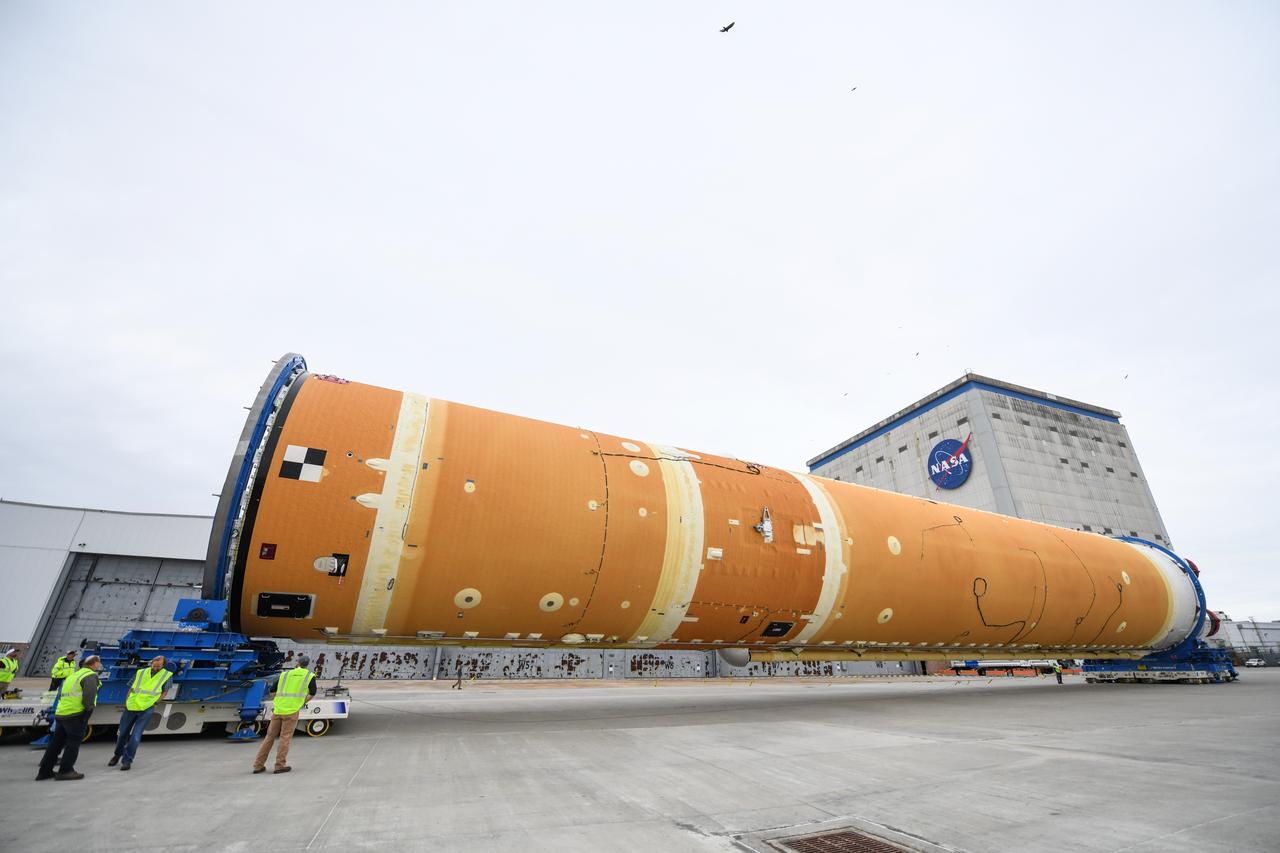
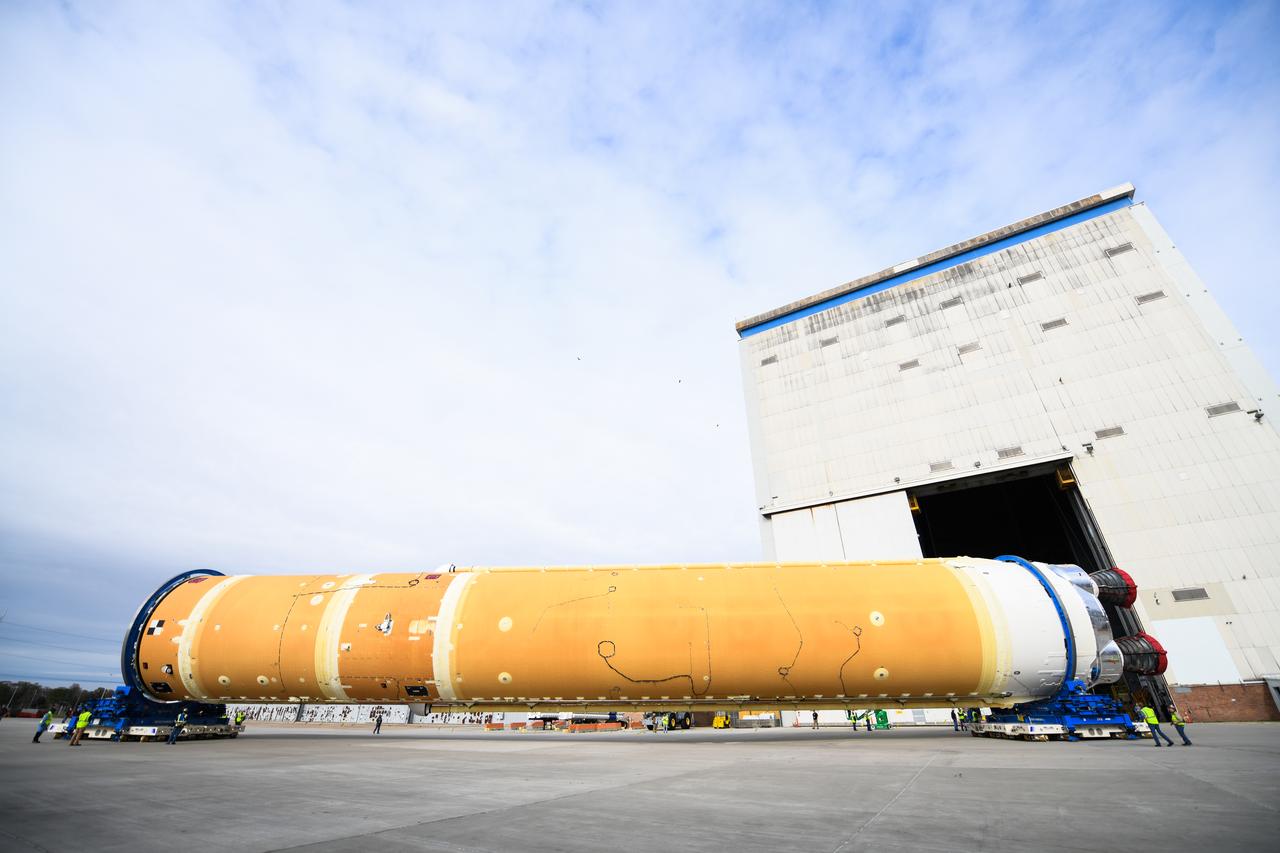
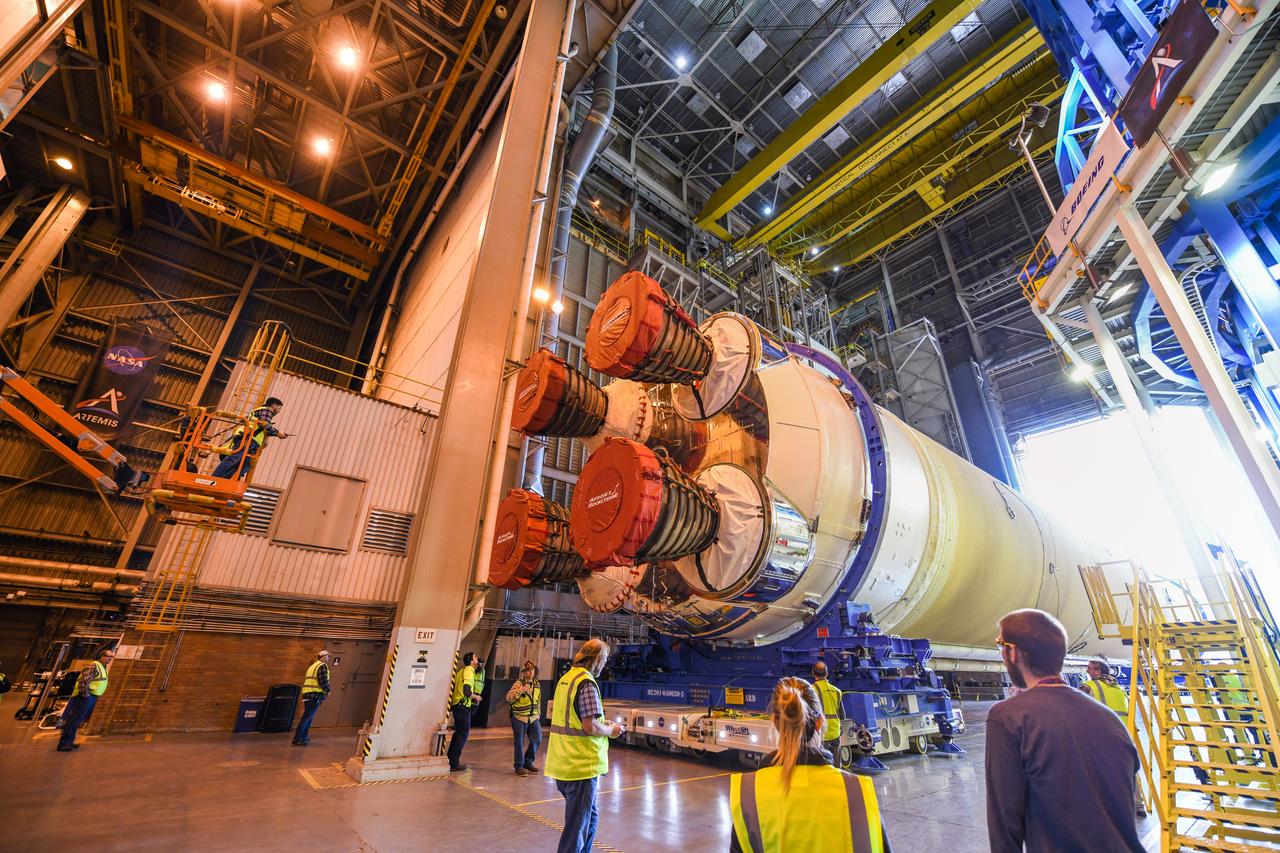
The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
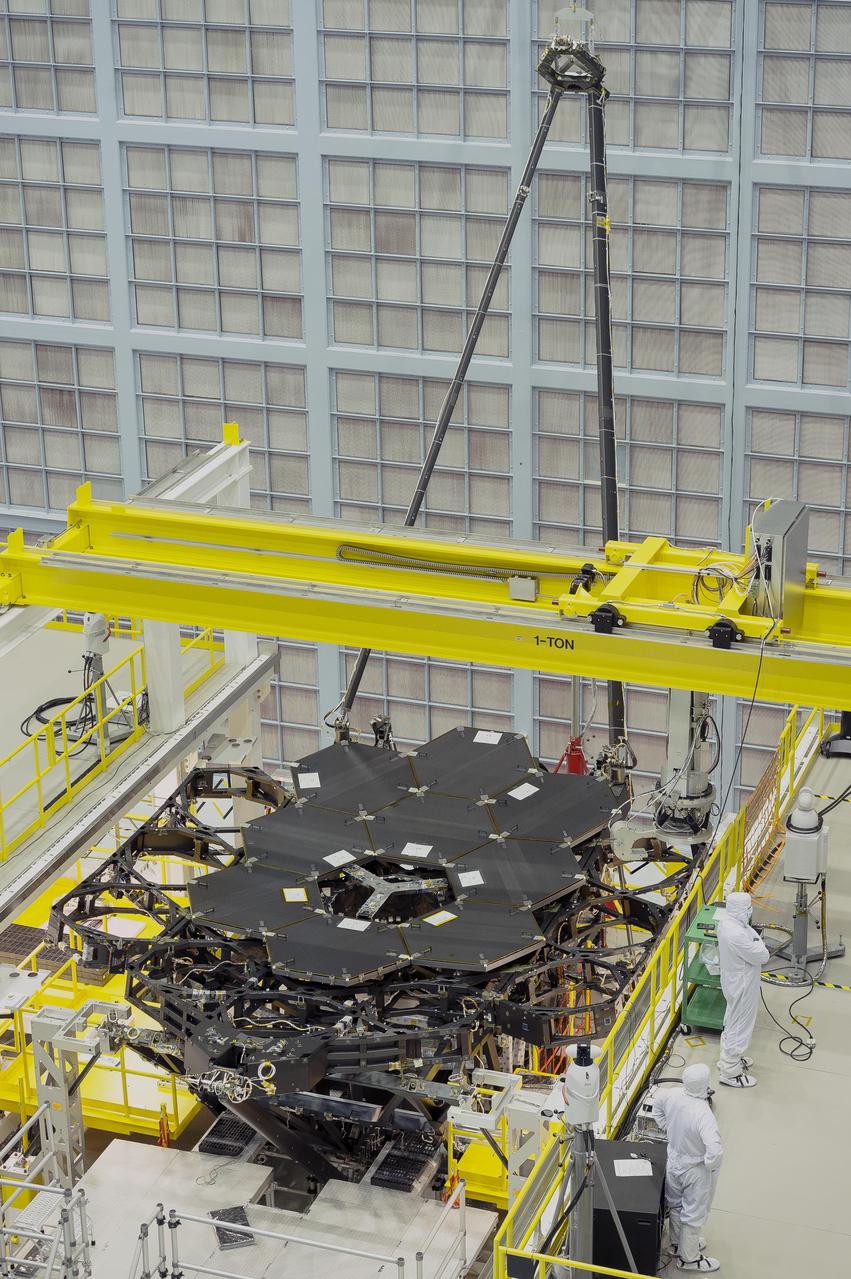
Inside NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center's massive clean room in Greenbelt, Maryland, the ninth flight mirror was installed onto the telescope structure with a robotic arm. This marks the halfway completion point for the James Webb Space Telescope's segmented primary mirror. Nine of the James Webb Space Telescope's 18 primary flight mirrors have been installed on the telescope structure. This marks the halfway point in the James Webb Space Telescope's primary mirror installation. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW</a>
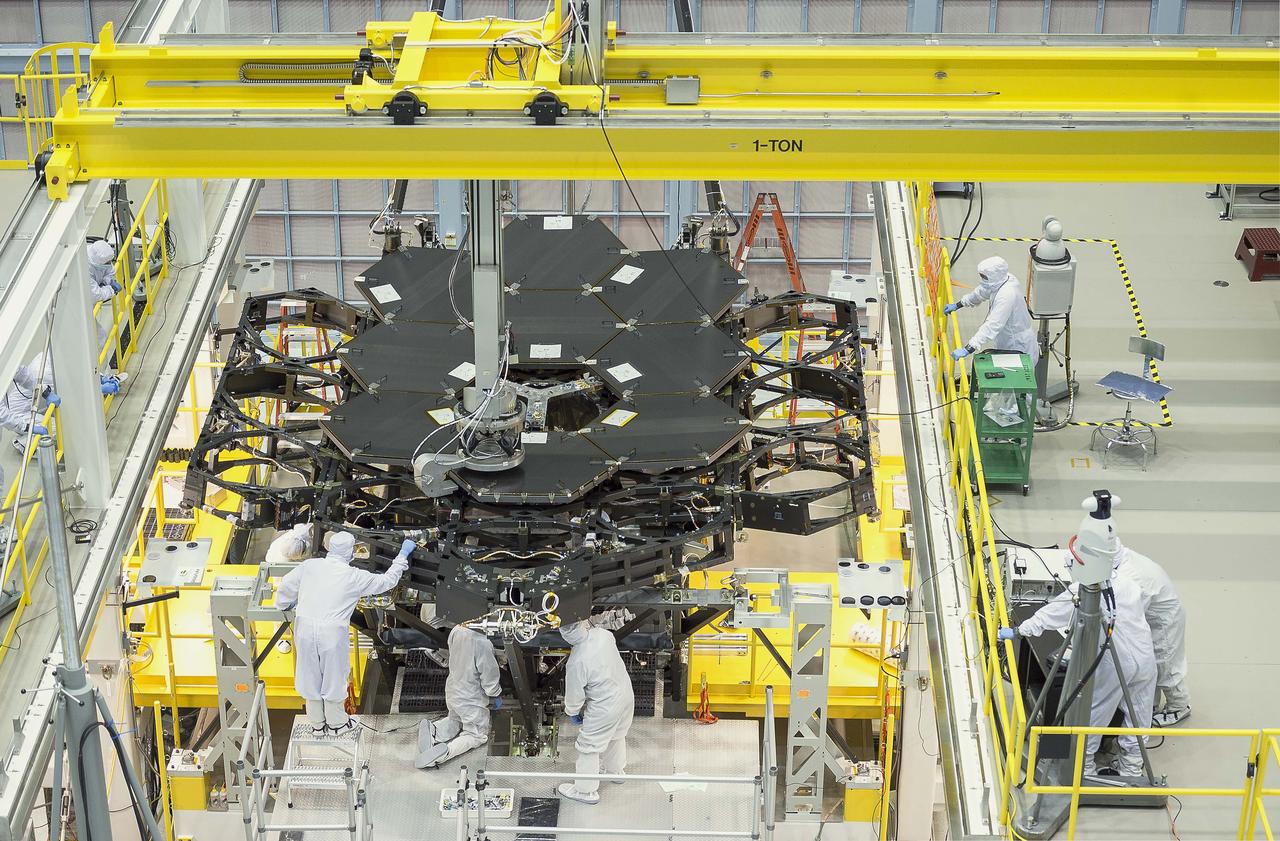
Inside NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center's massive clean room in Greenbelt, Maryland, the ninth flight mirror was installed onto the telescope structure with a robotic arm. This marks the halfway completion point for the James Webb Space Telescope's segmented primary mirror. This rare overhead shot of the James Webb Space Telescope shows the nine primary flight mirrors installed on the telescope structure in a clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Credits: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW</a>
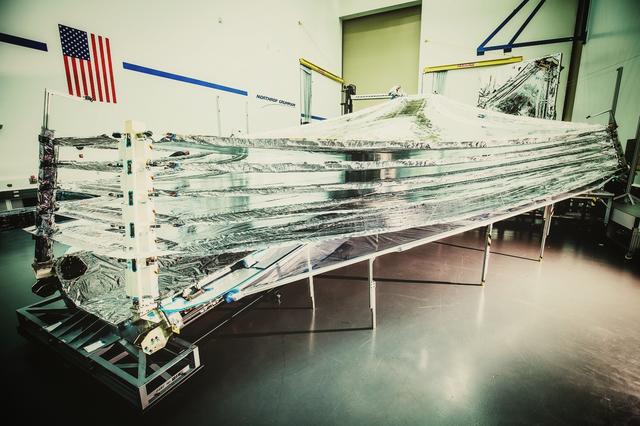

The last of the five sunshield layers responsible for protecting the optics and instruments of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is now complete. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2erZV41" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2erZV41</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Hubble Provides Complete View of Jupiter Auroras
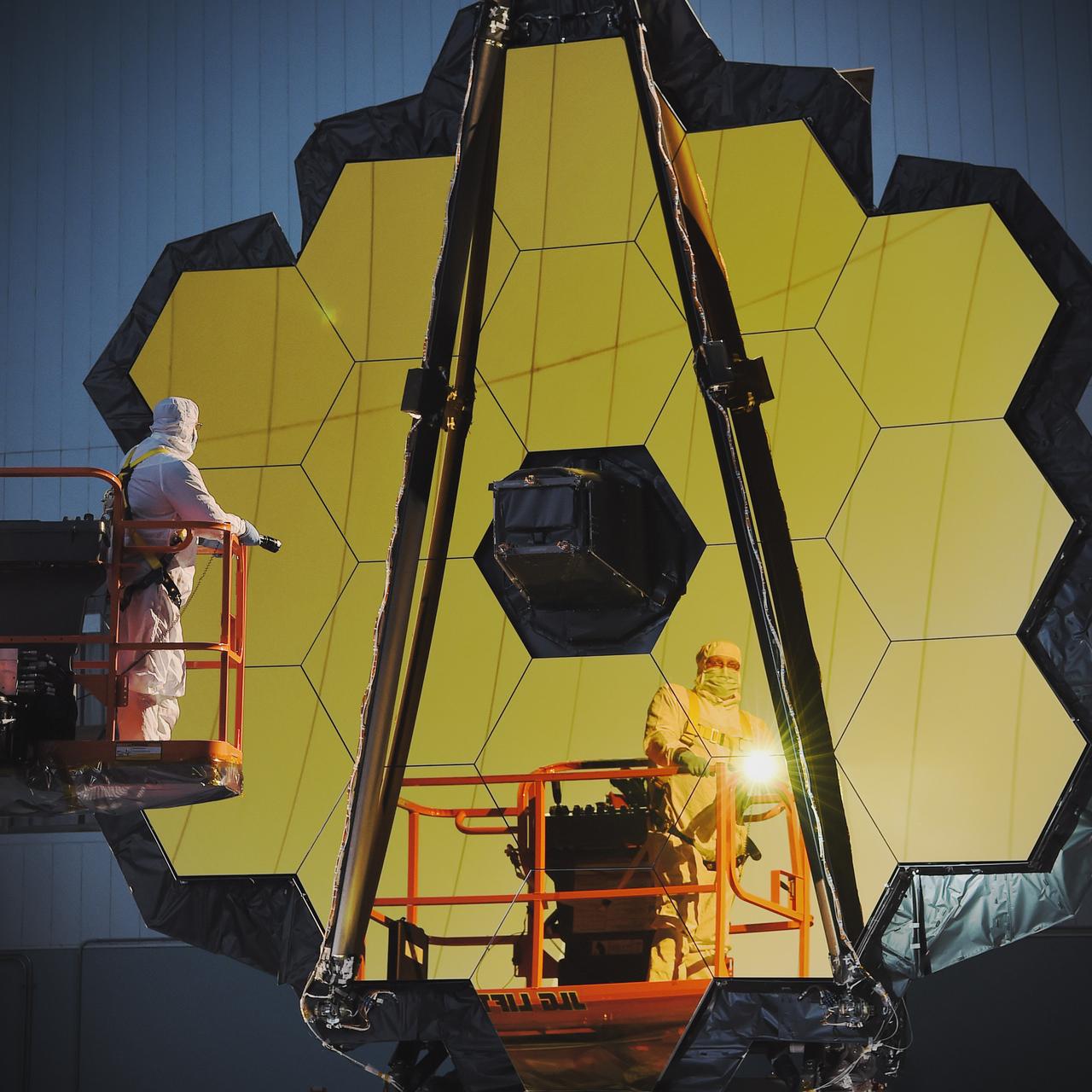

Engineers and technicians working on the James Webb Space Telescope successfully completed the first important optical measurement of Webb’s fully assembled primary mirror, called a Center of Curvature test. Taking a “before” optical measurement of the telescope’s deployed mirror is crucial before the telescope goes into several stages of rigorous mechanical testing. These tests will simulate the violent sound and vibration environments the telescope will experience inside its rocket on its way out into space. This environment is one of the most stressful structurally and could alter the shape and alignment of Webb’s primary mirror, which could degrade or, in the worst case, ruin its performance. Webb has been designed and constructed to withstand its launch environment, but it must be tested to verify that it will indeed survive and not change in any unexpected way. Making the same optical measurements both before and after simulated launch environment testing and comparing the results is fundamental to Webb’s development, assuring that it will work in space. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2enIgwP" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2enIgwP</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
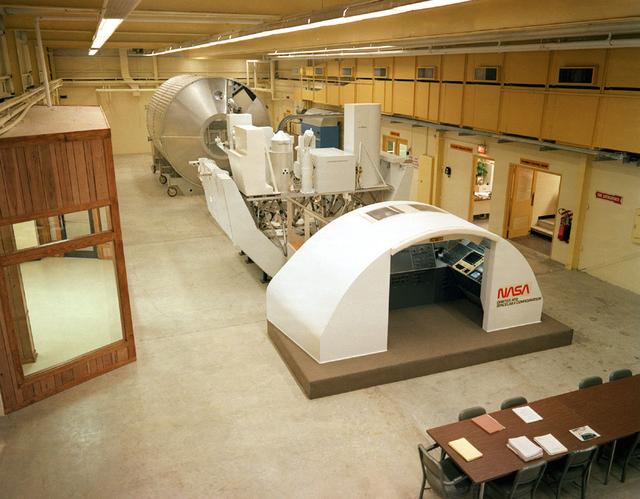

A mockup of the Spacelab II configuration was built at Marshall's Completed Payload Crew Training Complex (PCTC) located at Building 4612.
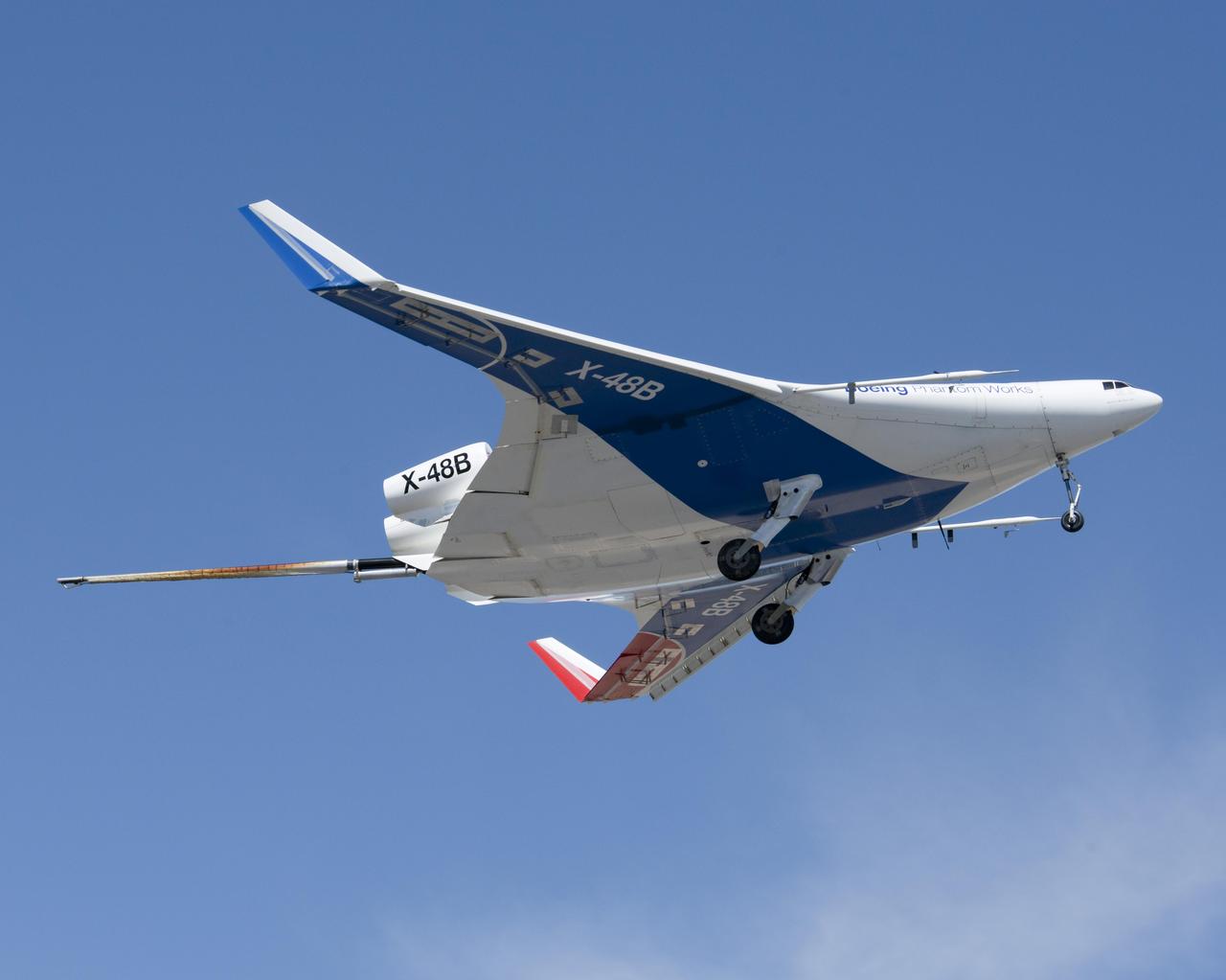

A joint NASA/Boeing team completed the first phase of flight tests on the unique X-48B Blended Wing Body aircraft at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, CA. The team completed the 80th and last flight of the project's first phase on March 19, 2010.
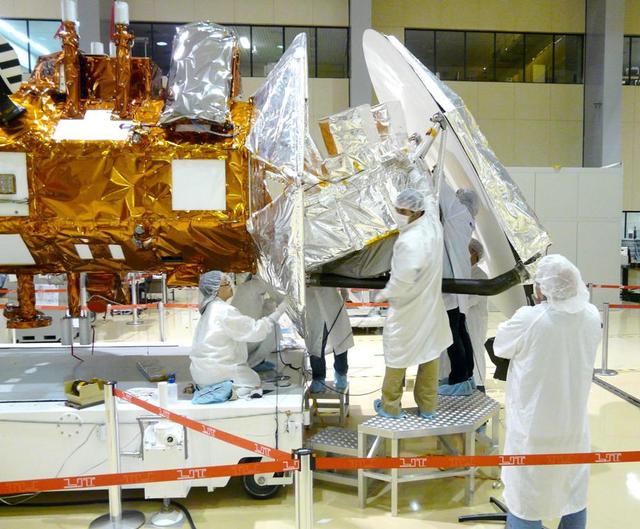

NASA Aquarius instrument thermal blanketing is completed and inspected. In addition, all external surfaces of the satellite are cleaned and inspected with white light to uncover any visible debris.
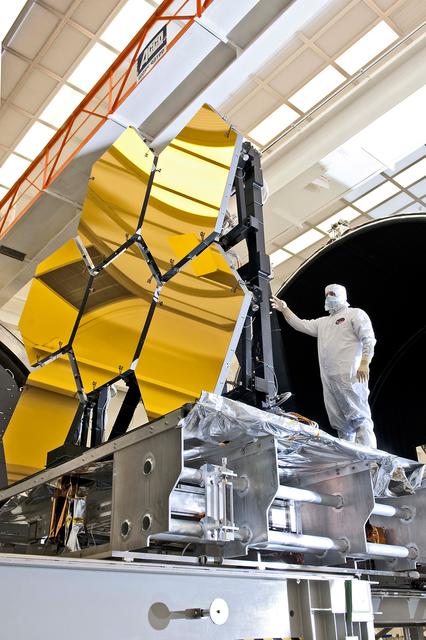

The first six flight ready James Webb Space Telescope's primary mirror segments are prepped to begin final cryogenic testing at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-mirror-coating.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-mirror-coati...</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
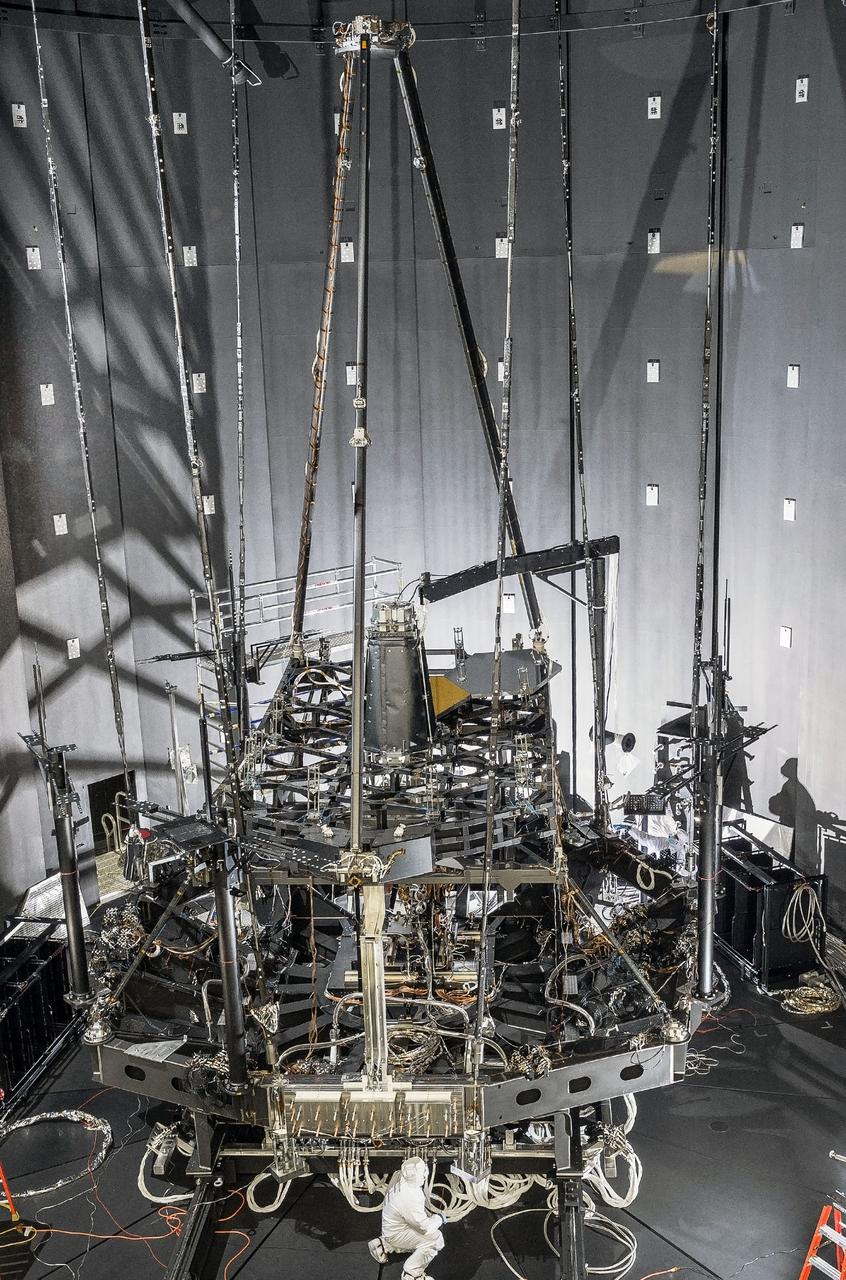

Testing is crucial part of NASA's success on Earth and in space. So, as the actual flight components of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope come together, engineers are testing the non-flight equipment to ensure that tests on the real Webb telescope later goes safely and according to plan. Recently, the "pathfinder telescope," or just “Pathfinder,” completed its first super-cold optical test that resulted in many first-of-a-kind demonstrations. "This test is the first dry-run of the equipment and procedures we will use to conduct an end-to-end optical test of the flight telescope and instruments," said Mark Clampin, Webb telescope Observatory Project Scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. "It provides confidence that once the flight telescope is ready, we are fully prepared for a successful test of the flight hardware." The Pathfinder is a non-flight replica of the Webb telescope’s center section backplane, or “backbone,” that includes mirrors. The flight backplane comes in three segments, a center section and two wing-like parts, all of which will support large hexagonal mirrors on the Webb telescope. The pathfinder only consists of the center part of the backplane. However, during the test, it held two full size spare primary mirror segments and a full size spare secondary mirror to demonstrate the ability to optically test and align the telescope at the planned operating temperatures of -400 degrees Fahrenheit (-240 Celsius). Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasas-webb-pathfinder-telescope-successfully-completes-first-super-cold-optical-test" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasas-webb-pathfinder-telesc...</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
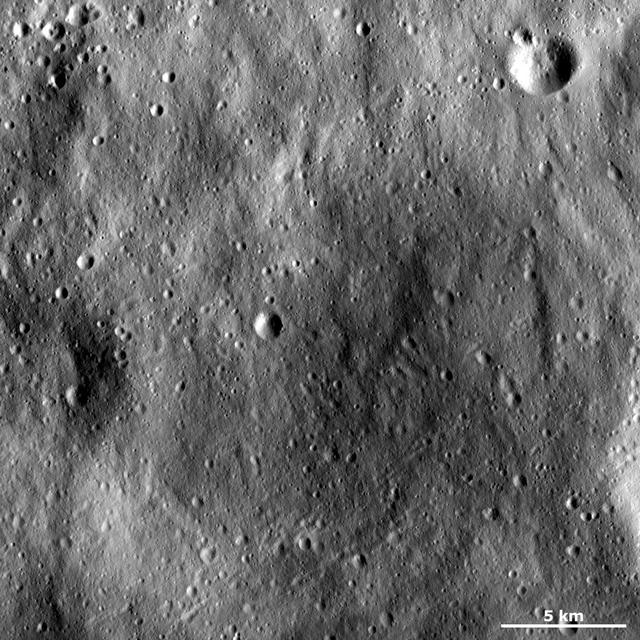

This image of asteroid Vesta from NASA Dawn spacecraft shows an old, very degraded crater that is almost completely filled with regolith. Regolith is the fine-grained material that covers most of Vesta surface.
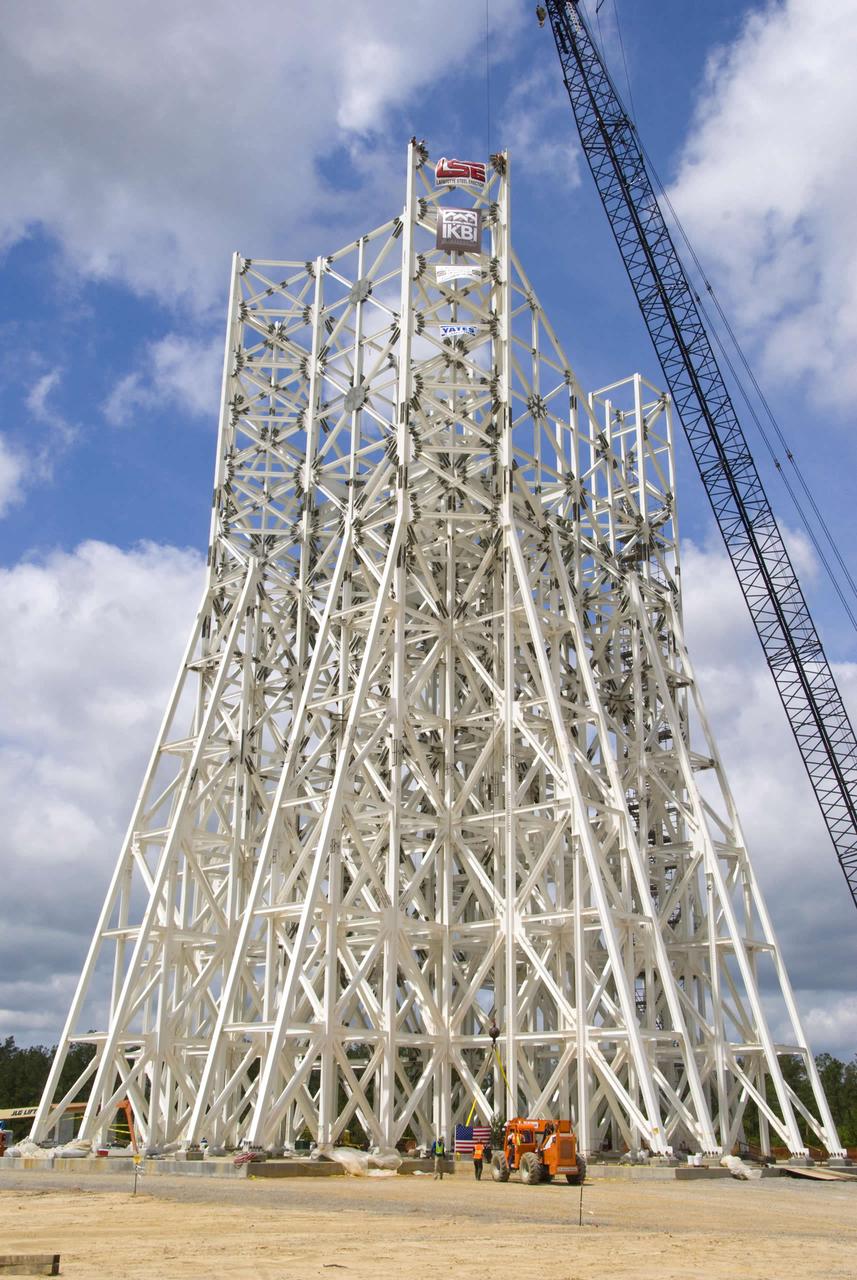

Stennis Space Center engineers celebrated a key milestone in construction of the A-3 Test Stand on April 9 - completion of structural steel work. Workers with Lafayette (La.) Steel Erector Inc. placed the last structural steel beam atop the stand during a noon ceremony attended by more than 100 workers and guests.
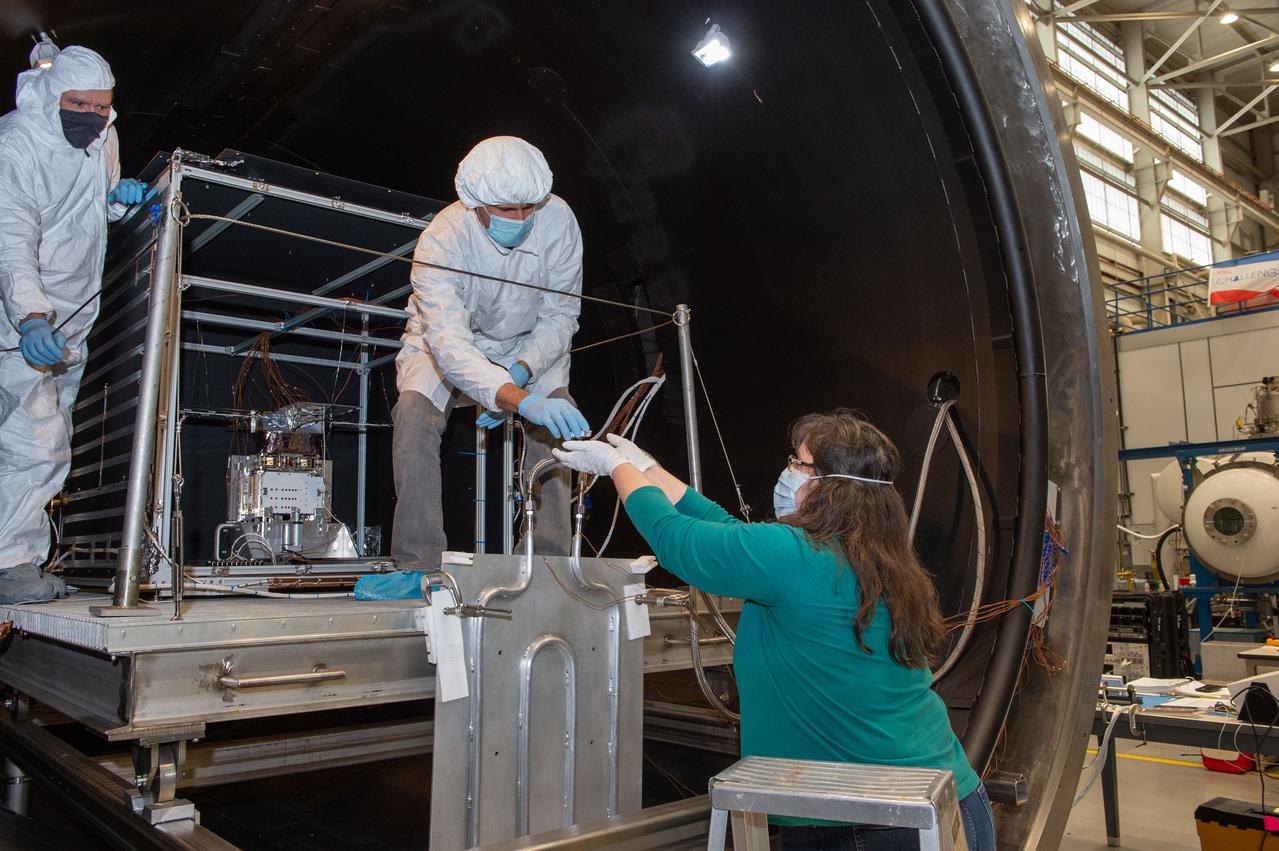

Miria Finckenor collects Optical Witness Samples and swab samples for analysis to verify that the NEA Scout thermal vacuum bake-out is complete and the chamber is clean.
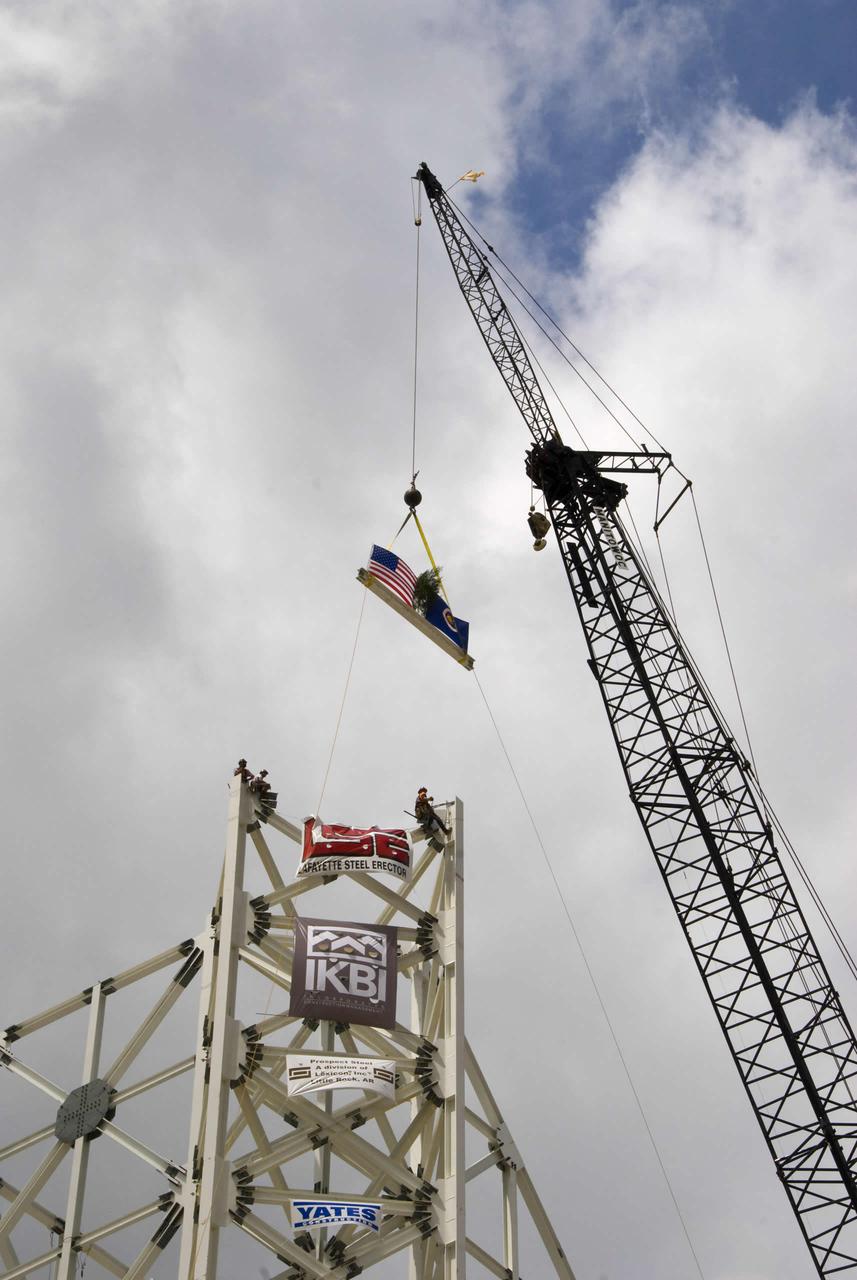

The final structural steel beam, bearing flags and the names of project workers, is hoisted and fastened into place atop the A-3 Test Stand.
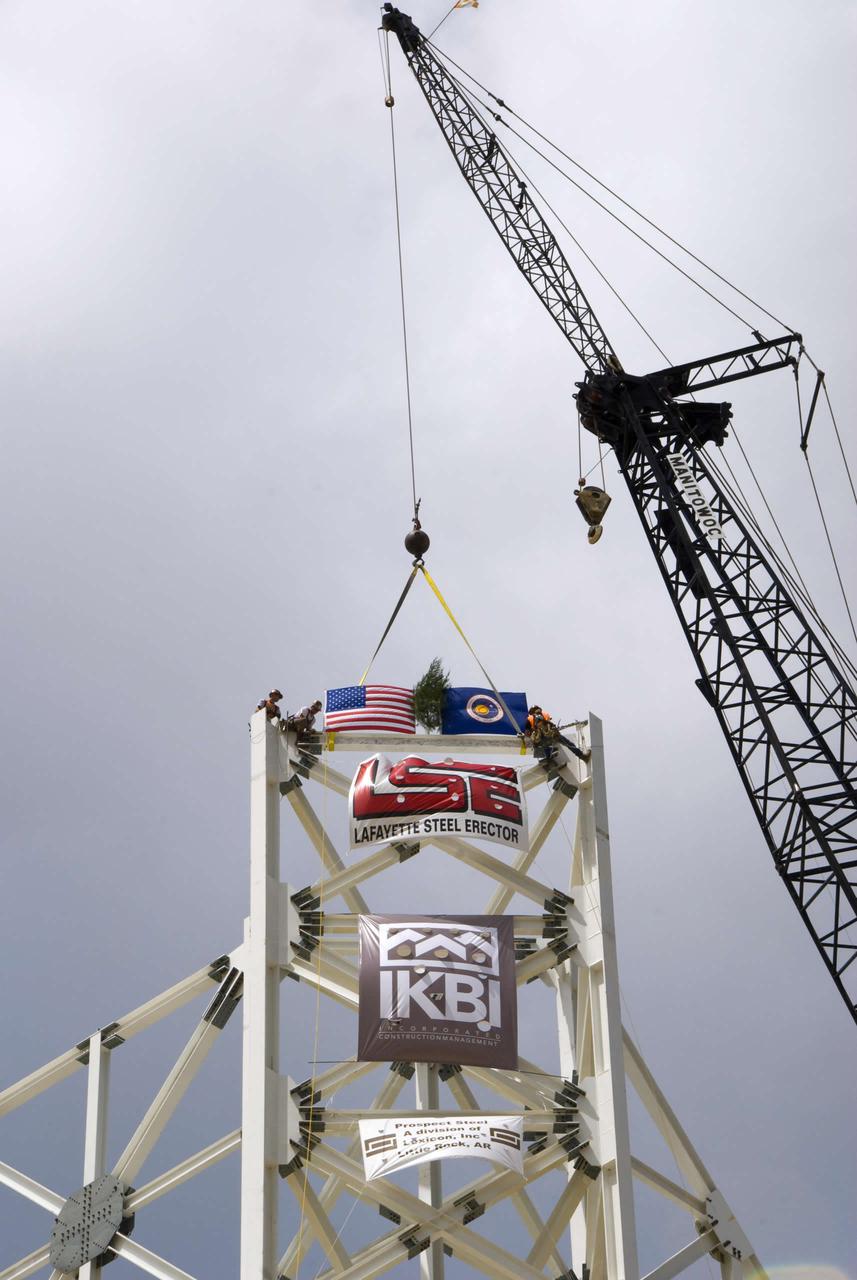

The final structural steel beam, bearing flags and the names of project workers, is hoisted and fastened into place atop the A-3 Test Stand.
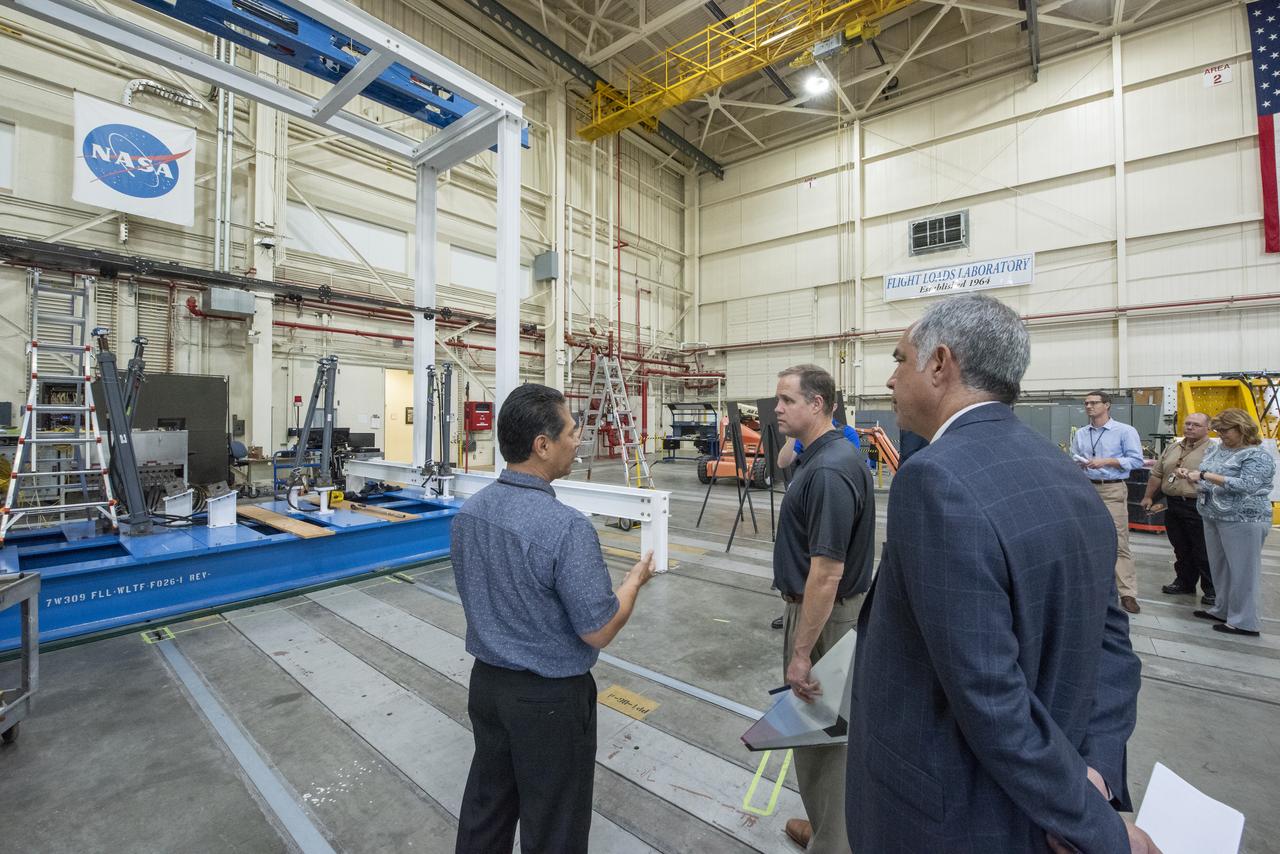

NASA Administrator Bridenstine talks with Armstrong's Larry Hudson about the capabilities of the Flight Loads Lab to conduct mechanical-load and thermal studies of structural components and complete flight vehicles.
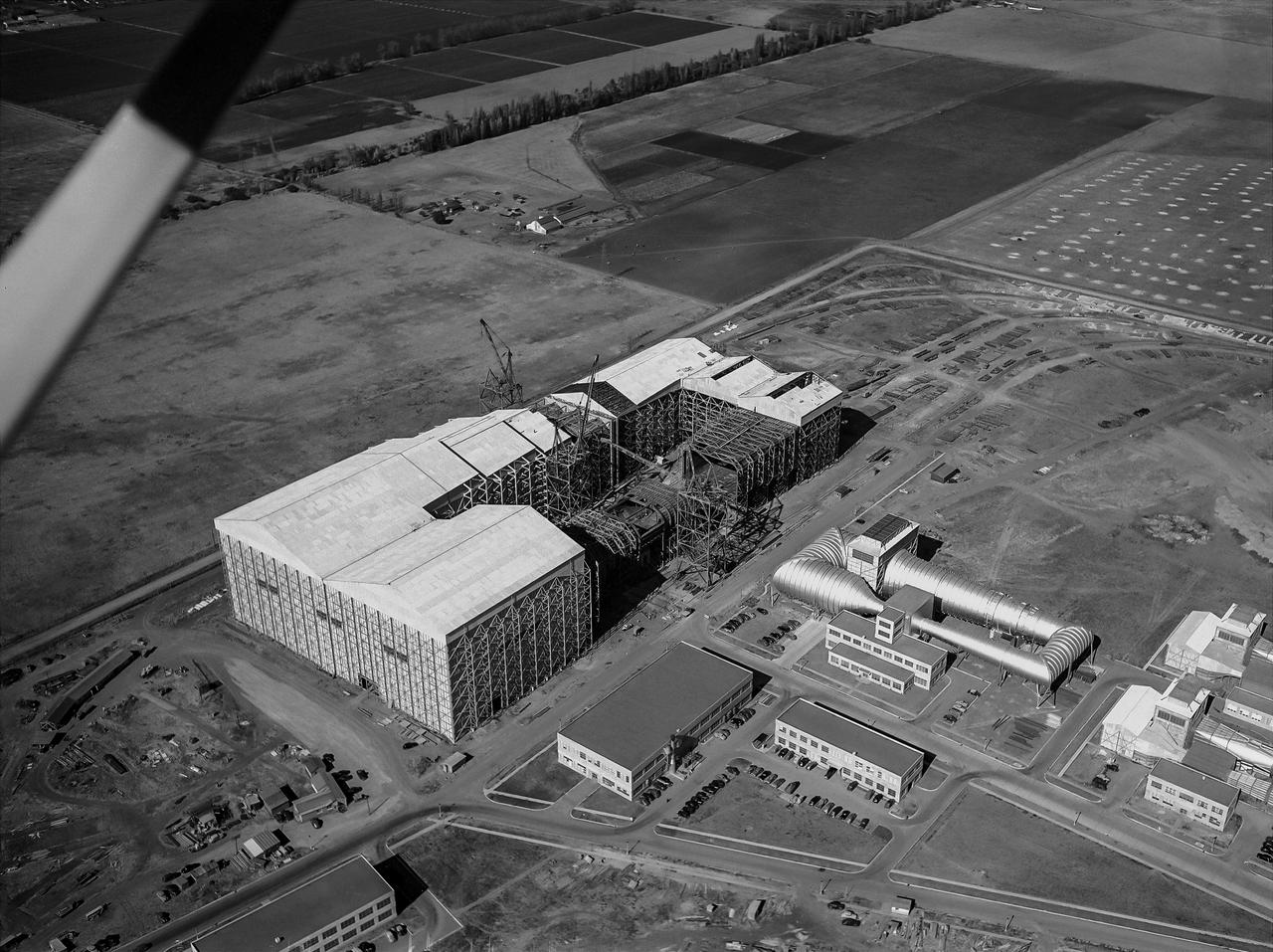

Aerial view looking North West of the nearly completed 40 x 80 foot wind tunnel. Drive and test section exposed. The facility covered 8 acres, and the air circuit was just over 1/2 mile long (2700 feet).

jsc2025e044727 (5/12/2025) --- Image of complete SEED payload, includes space-qualified lens, Image Sensor, and POBC. Space Test Program – Houston 10 – Space Edge Experiments and Demonstrations (STP-H10-SEED) tests hardware to deliver near-real time actionable information using machine learning algorithms. Results could validate the low size, weight, and power of this commercial off-the-shelf edge processing hardware for various applications. Image courtesy of NOVI LLC.
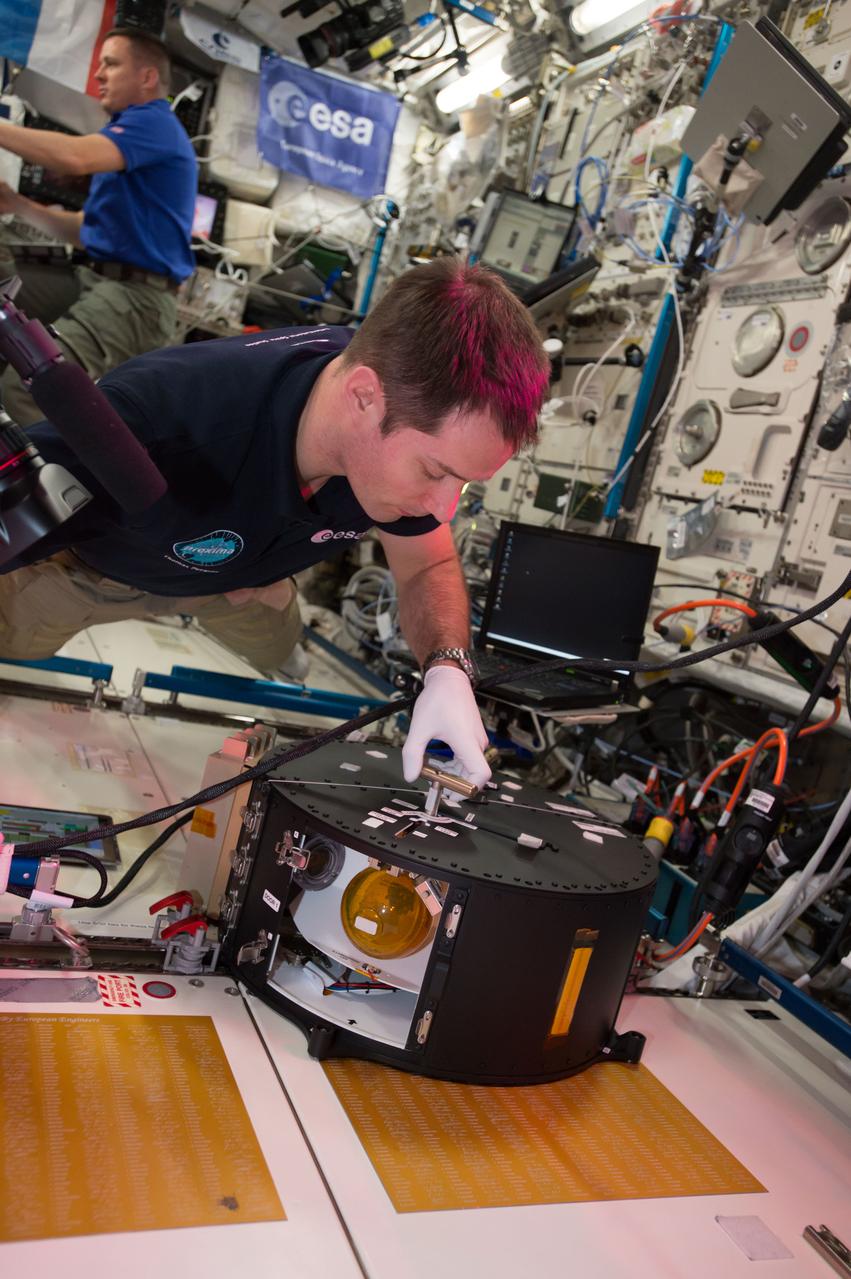

iss051e036148 (5/3/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet works with Fluid Dynamics in Space (FLUIDICS) hardware during the completion of experiment runs. FE Jack Fischer is visible in the background. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory. The FLUIDICS investigation evaluates the Center of Mass (CoM) position regarding a temperature gradient on a representation of a fuel tank. The observation of capillary wave turbulence on the surface of a fluid layer in a low-gravity environment can provide insights into measuring the existing volume in a sphere.
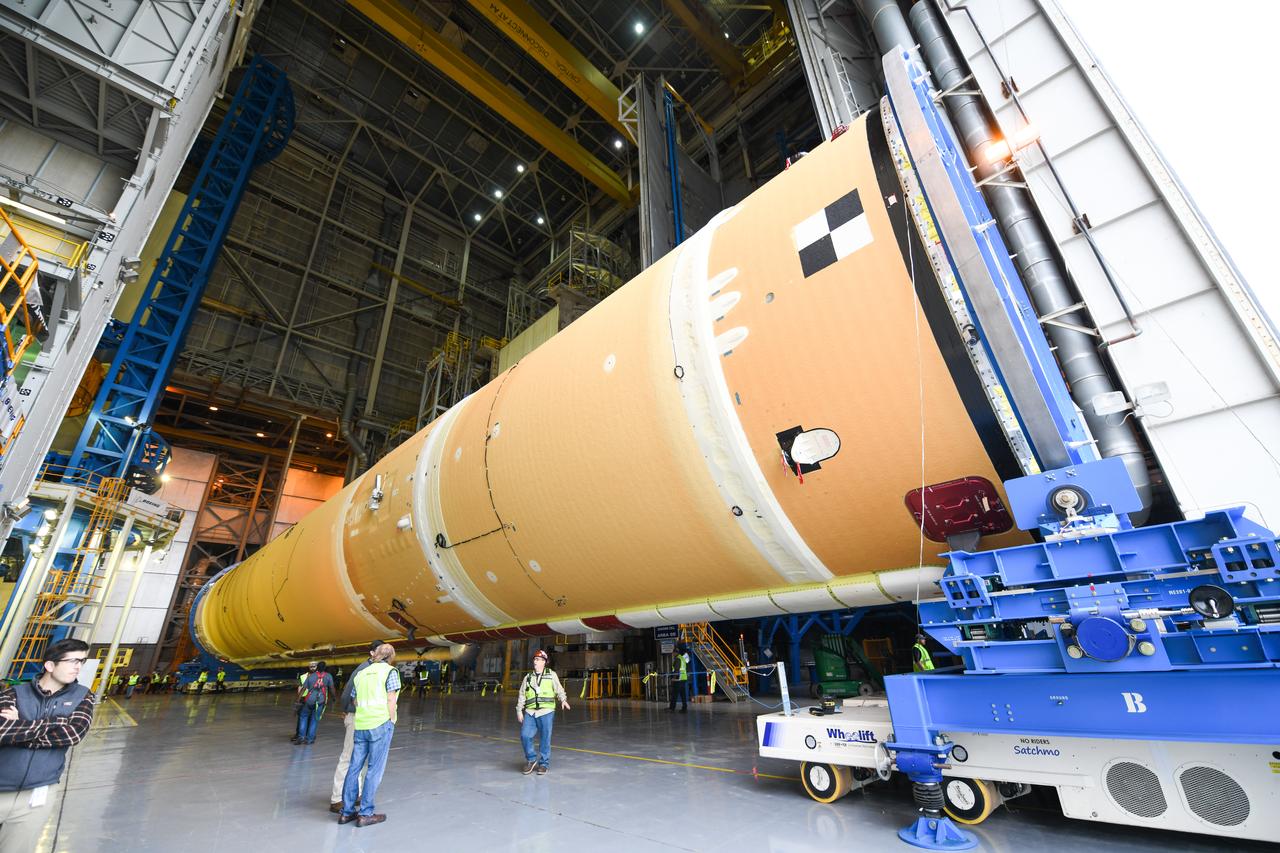

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
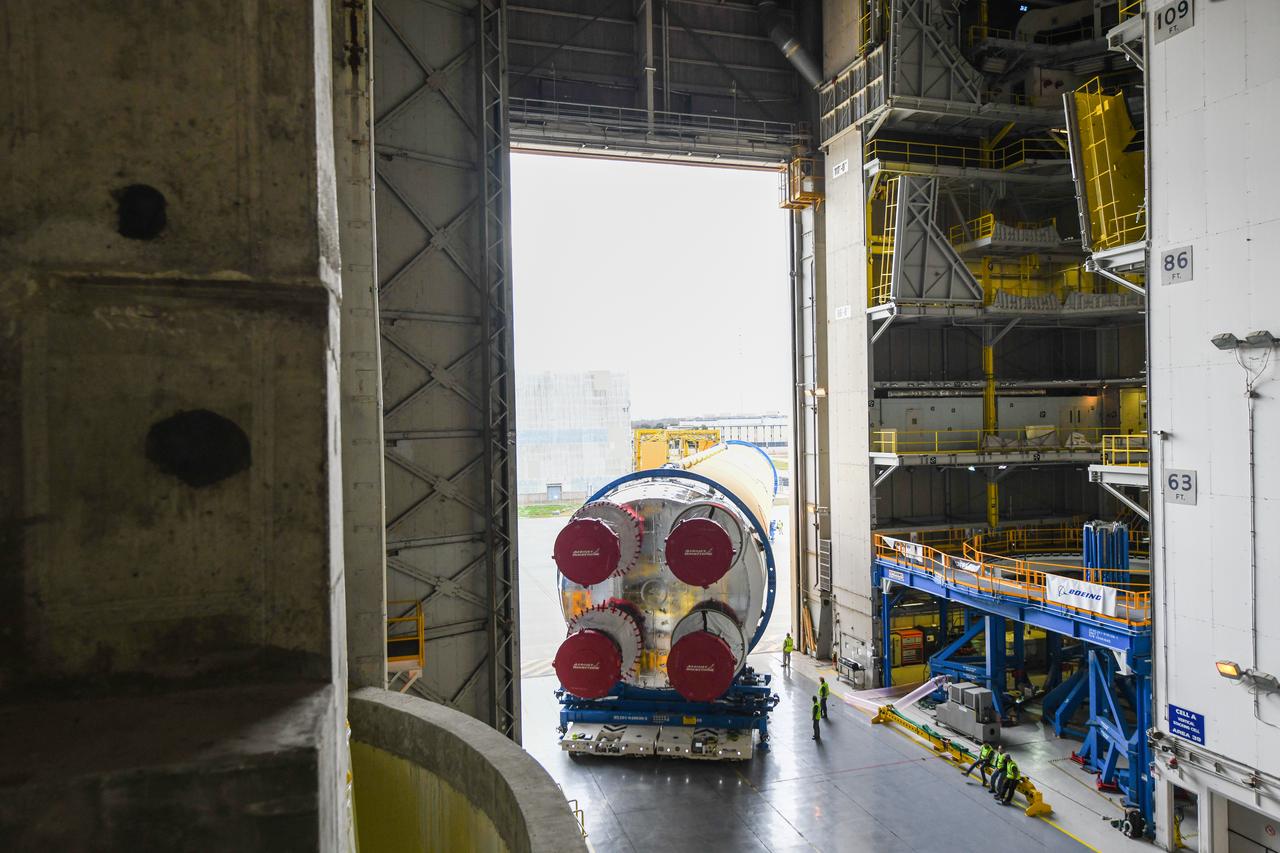

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
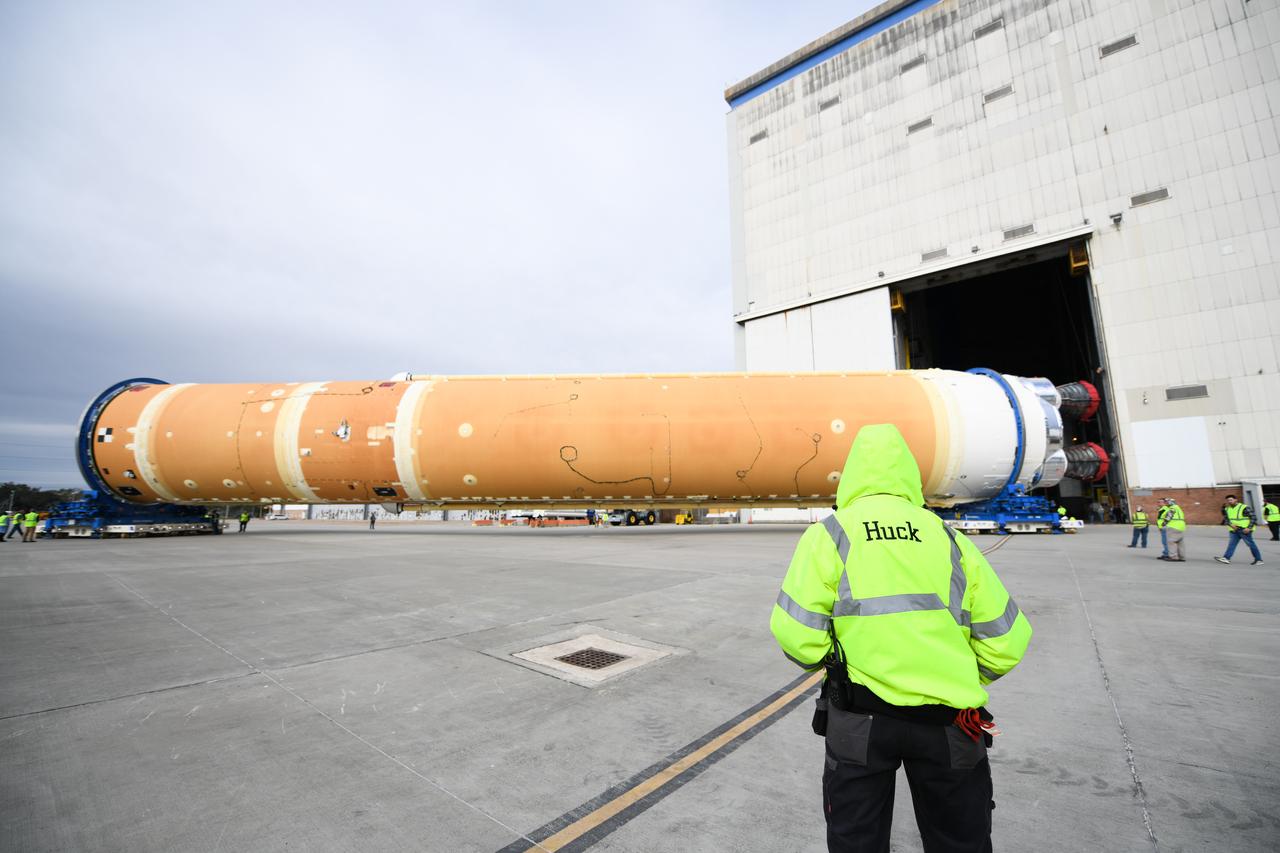

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
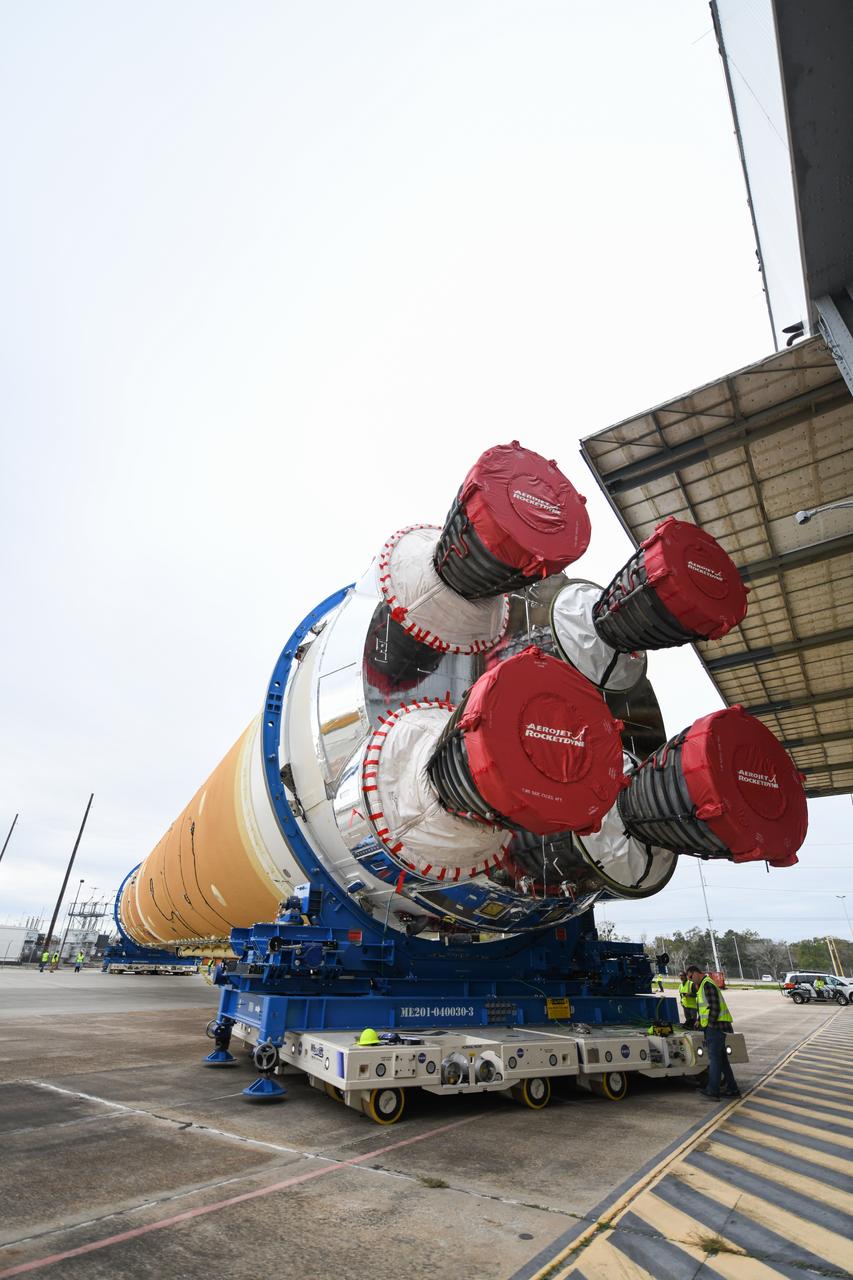

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
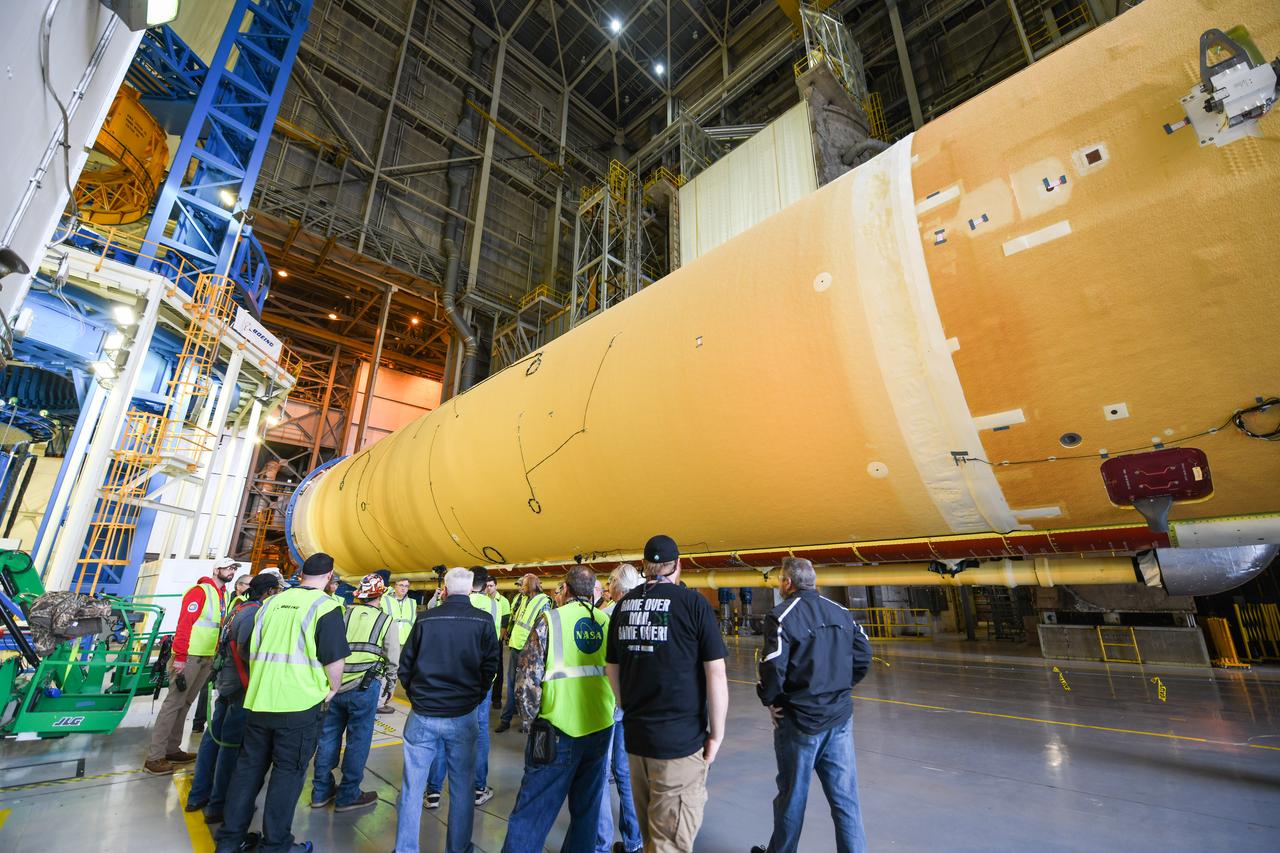

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
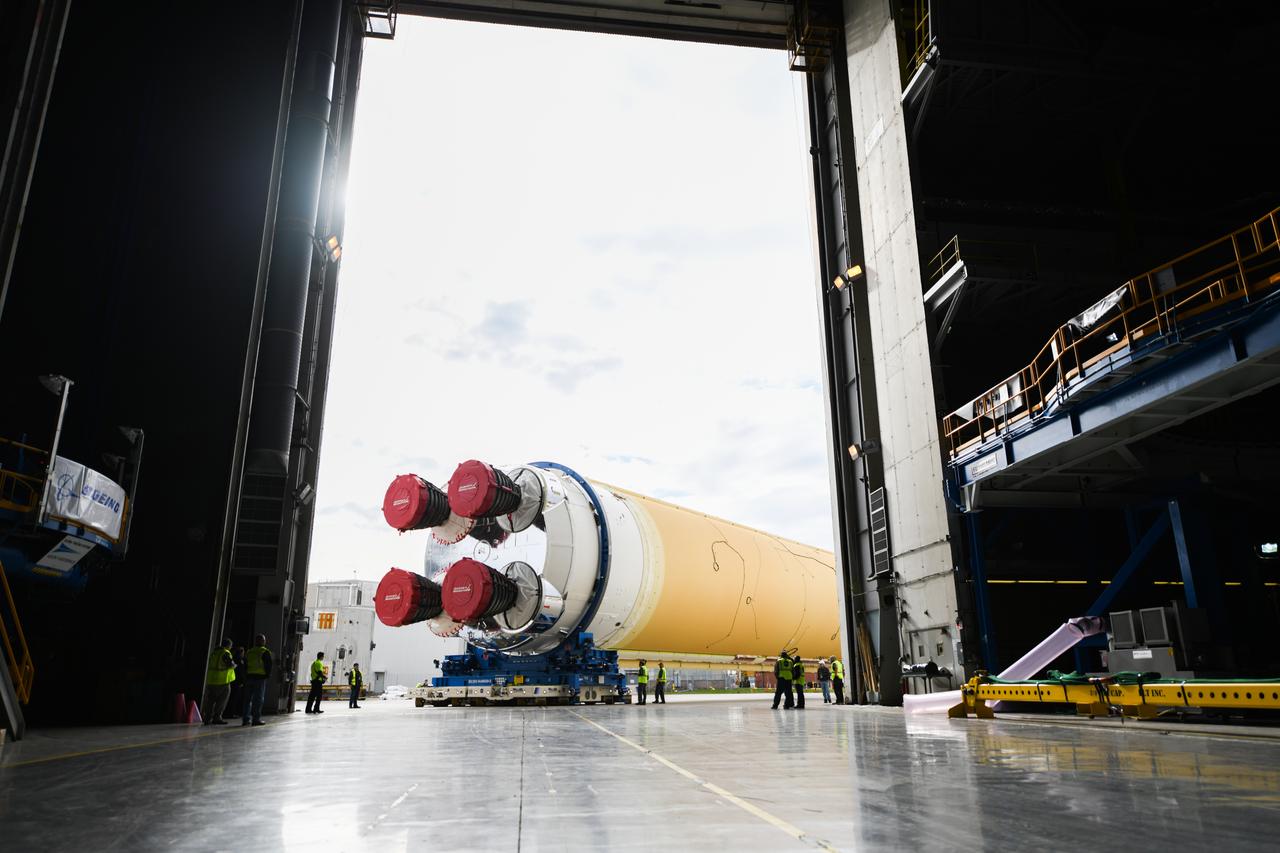

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
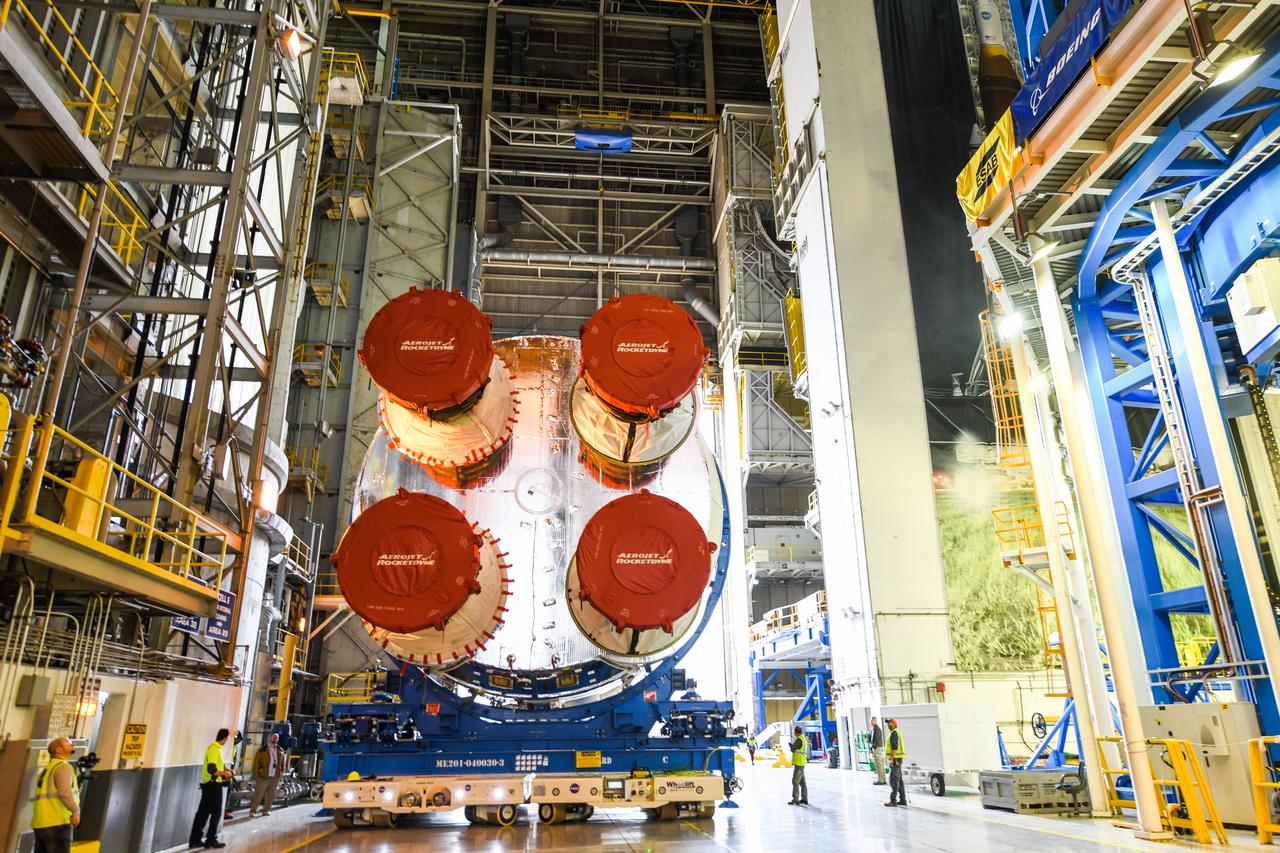
These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
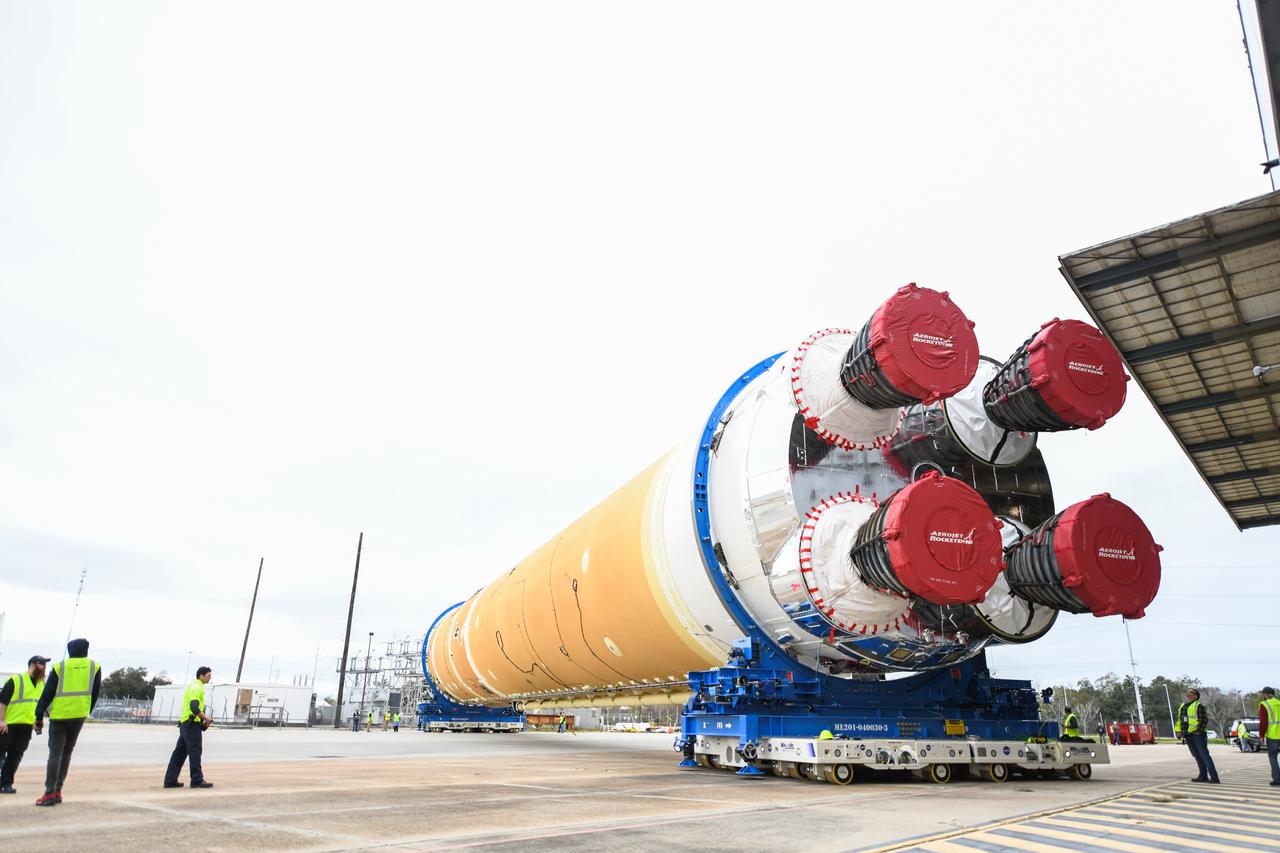

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
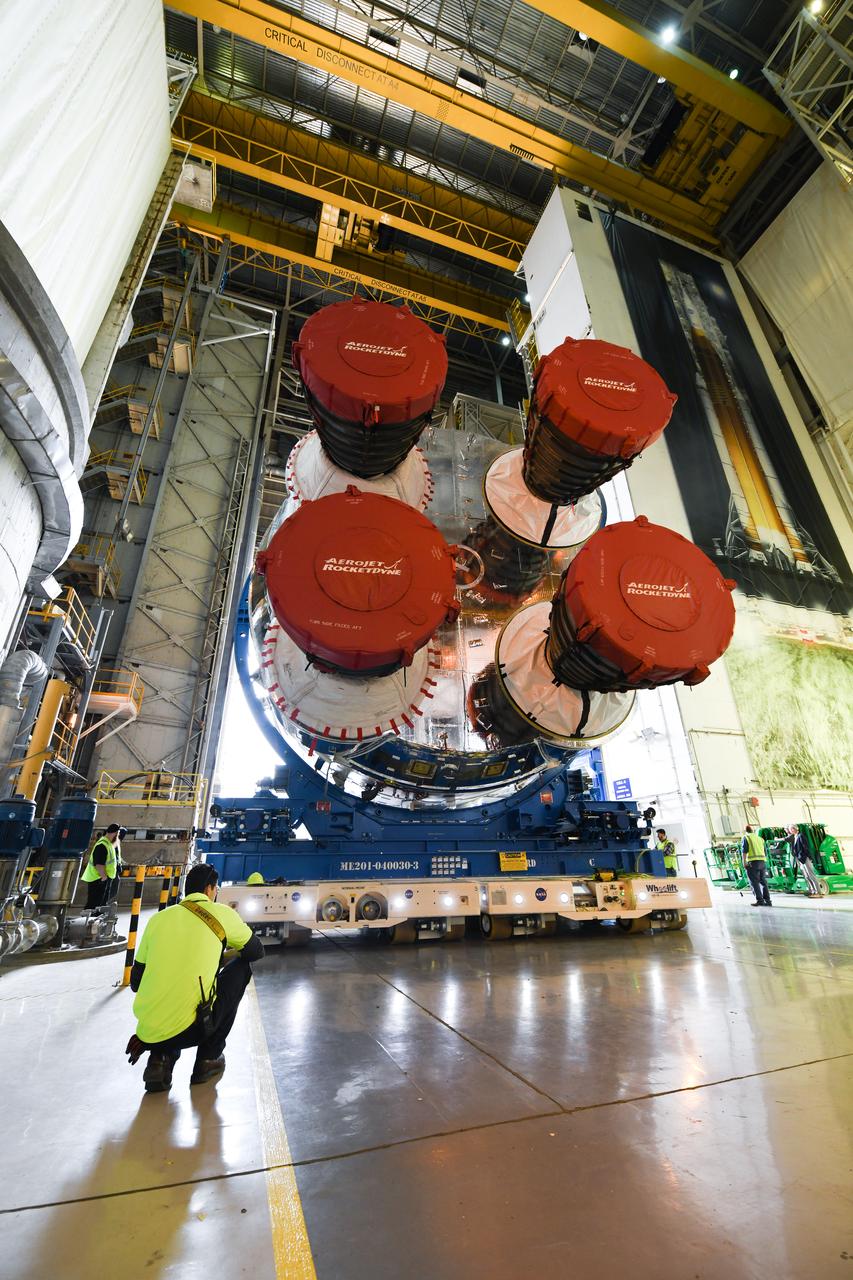

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
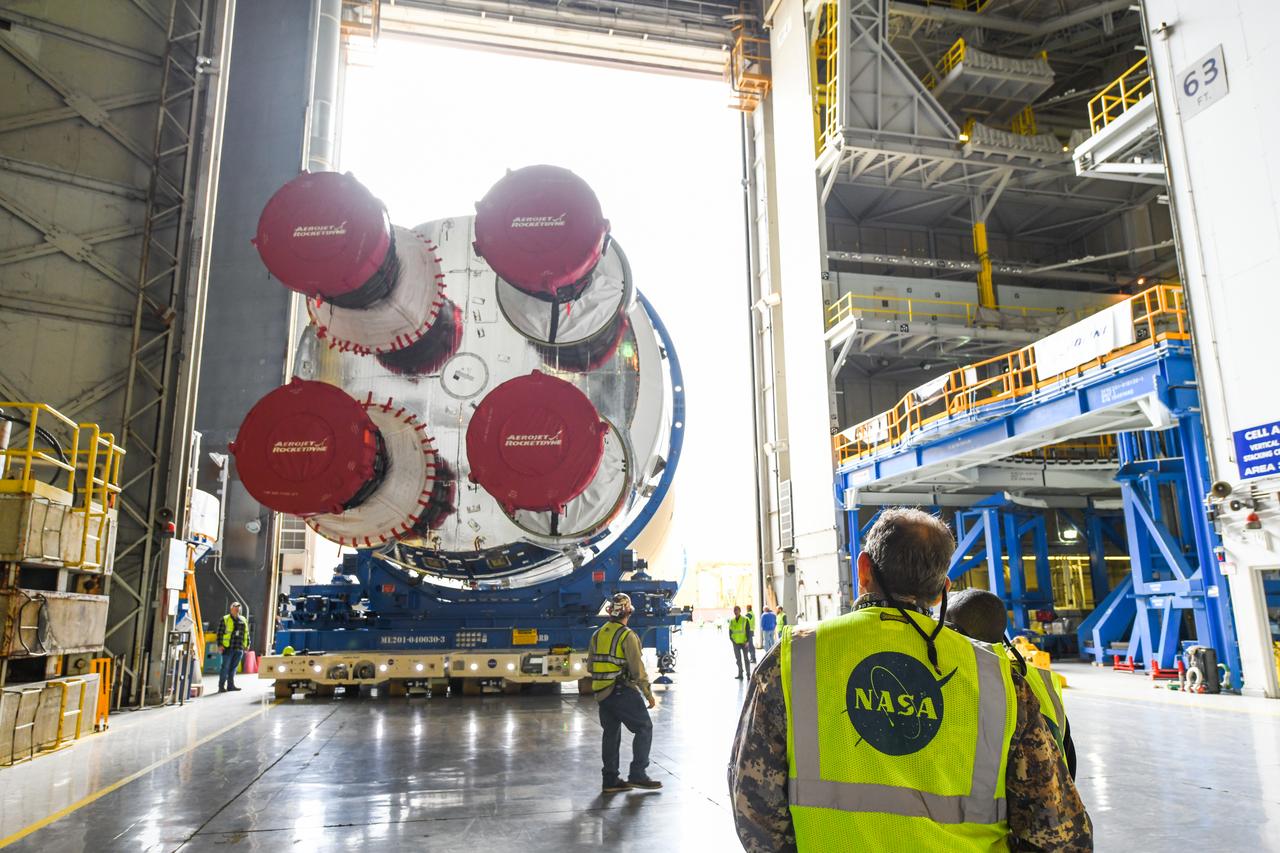

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
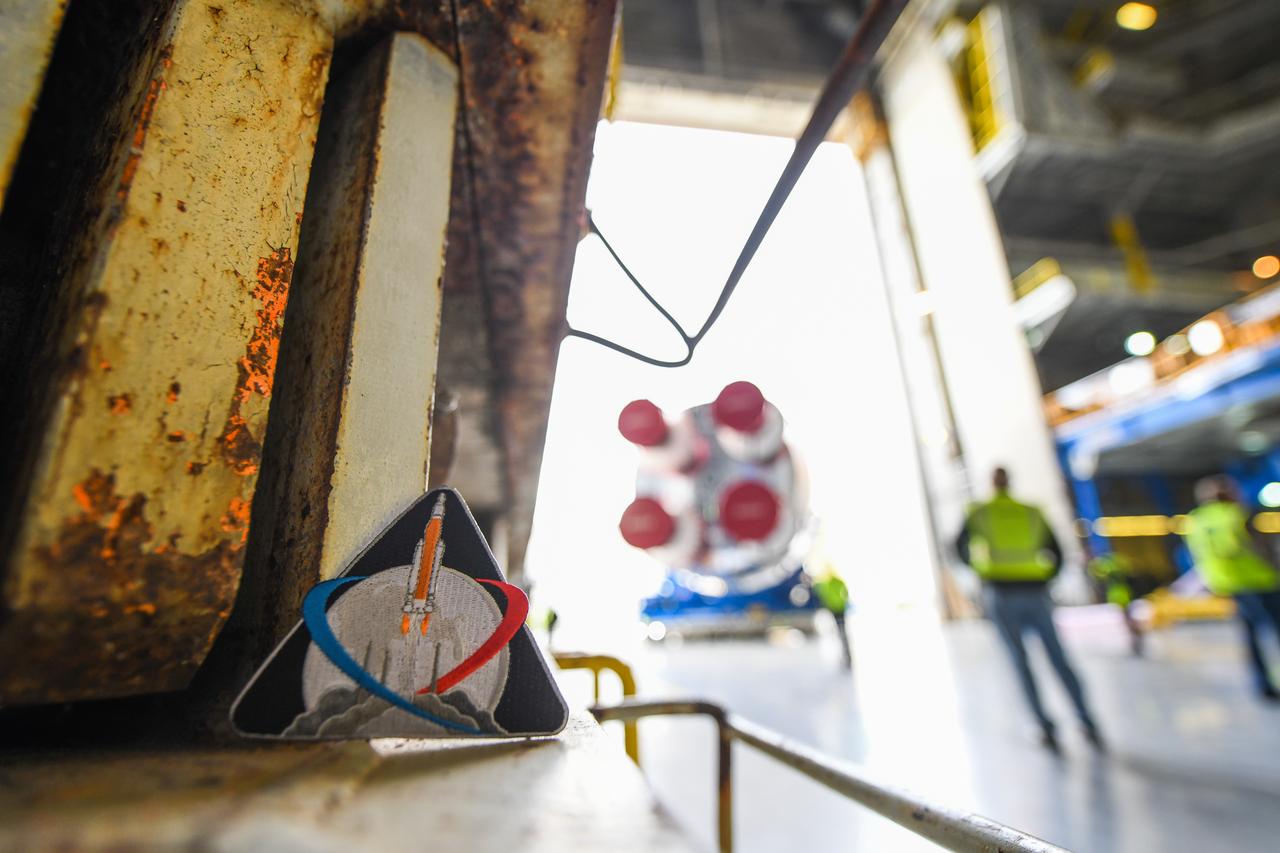

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
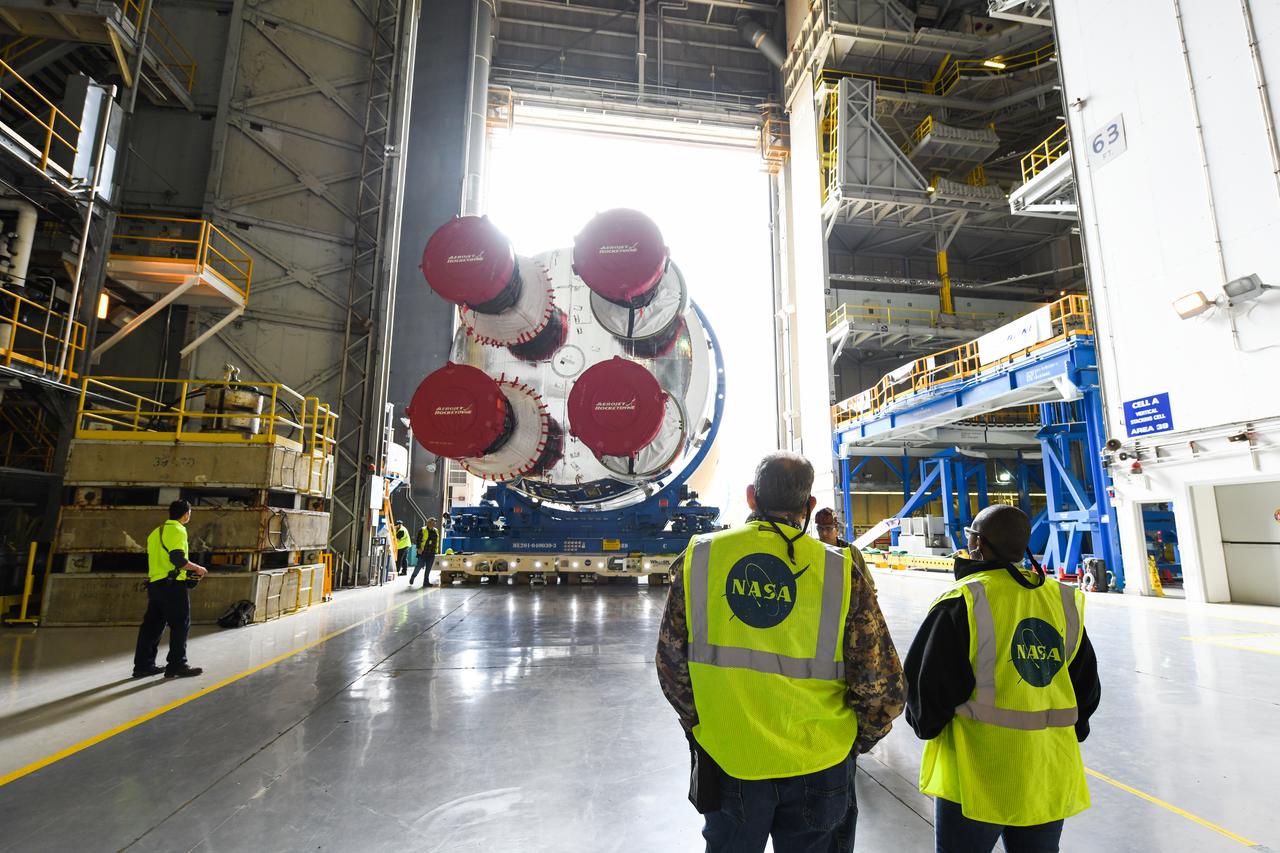

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
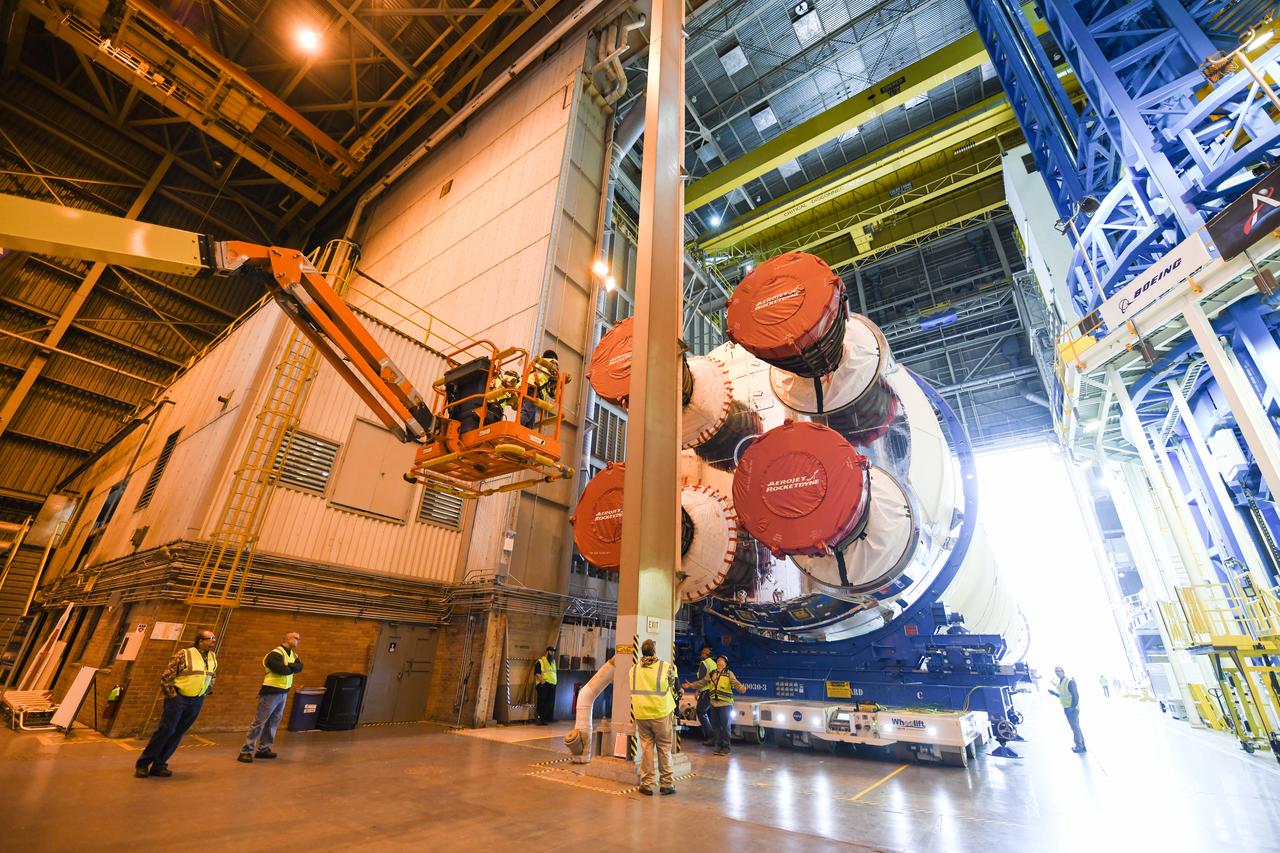

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
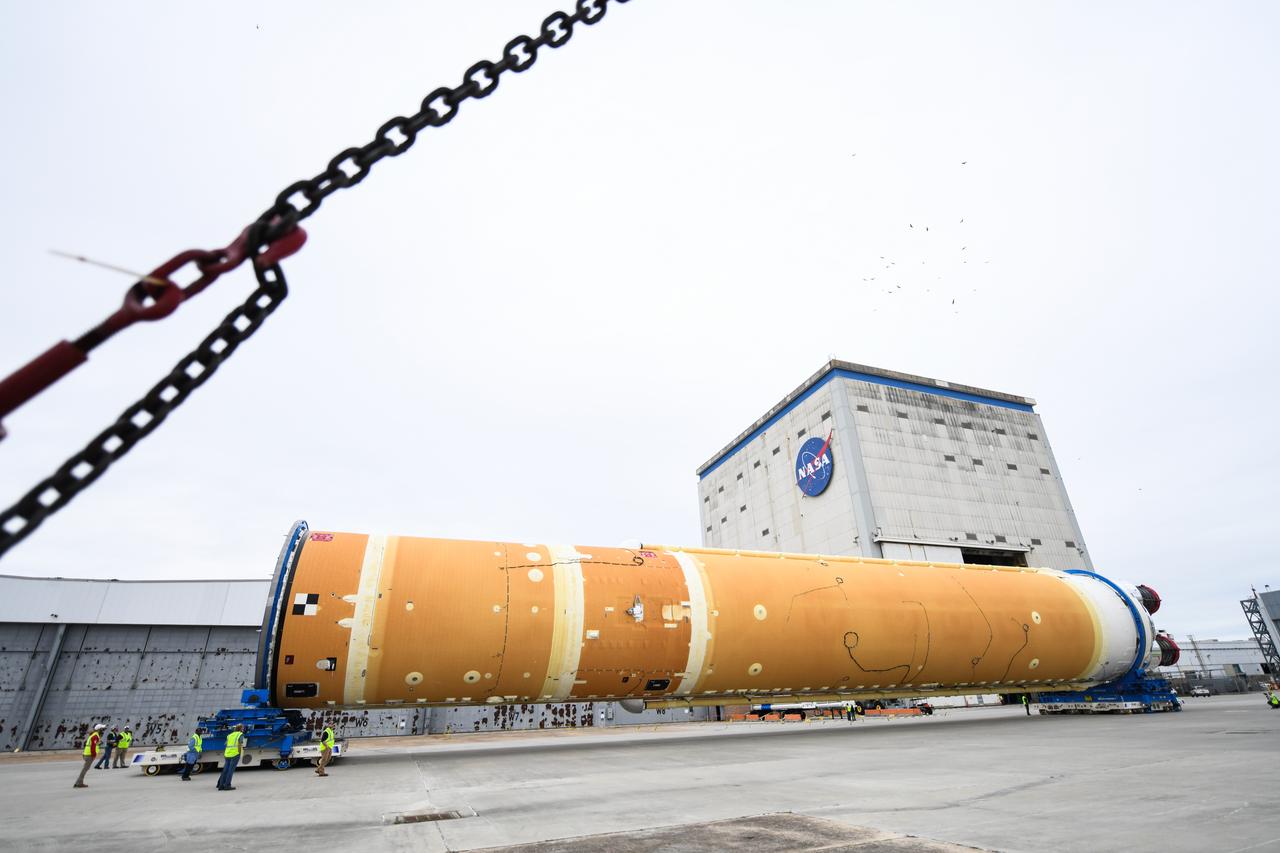

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
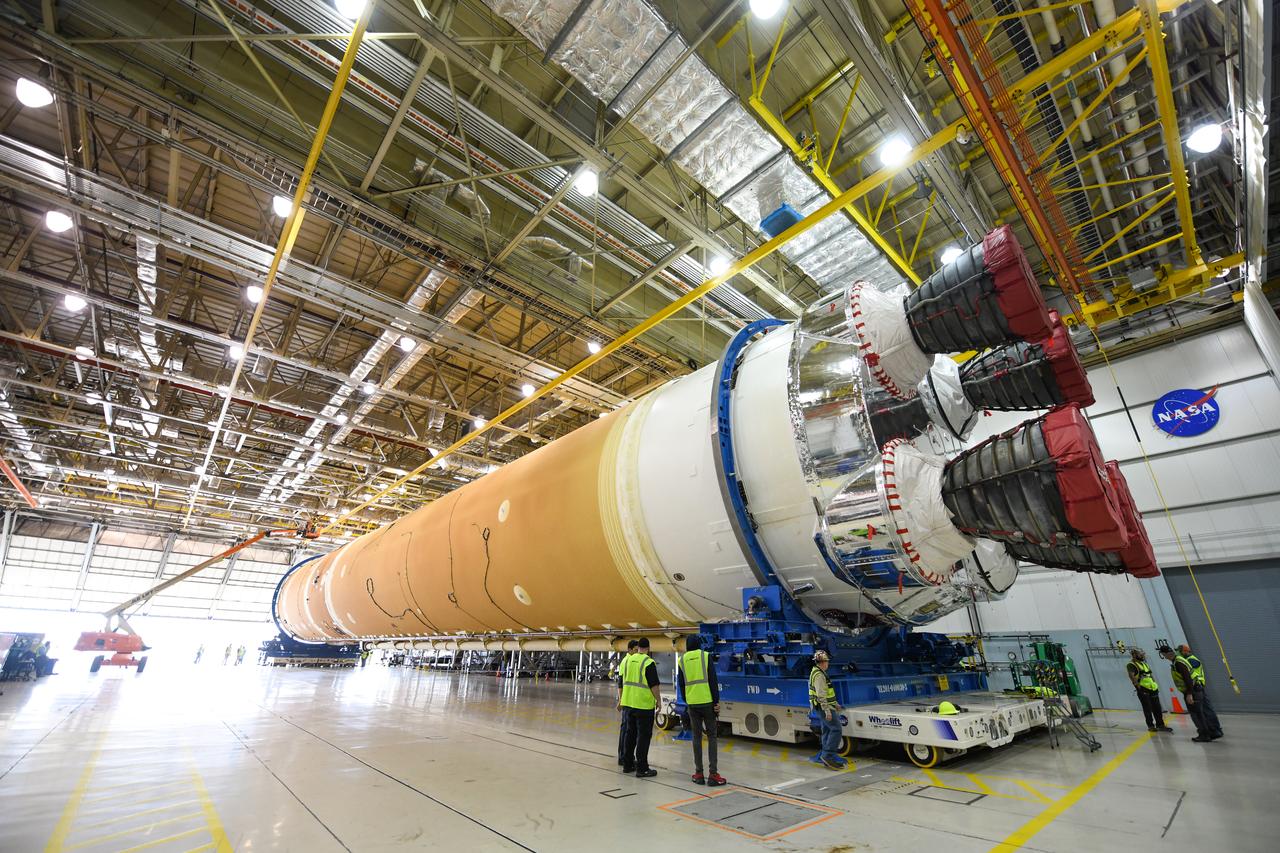

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
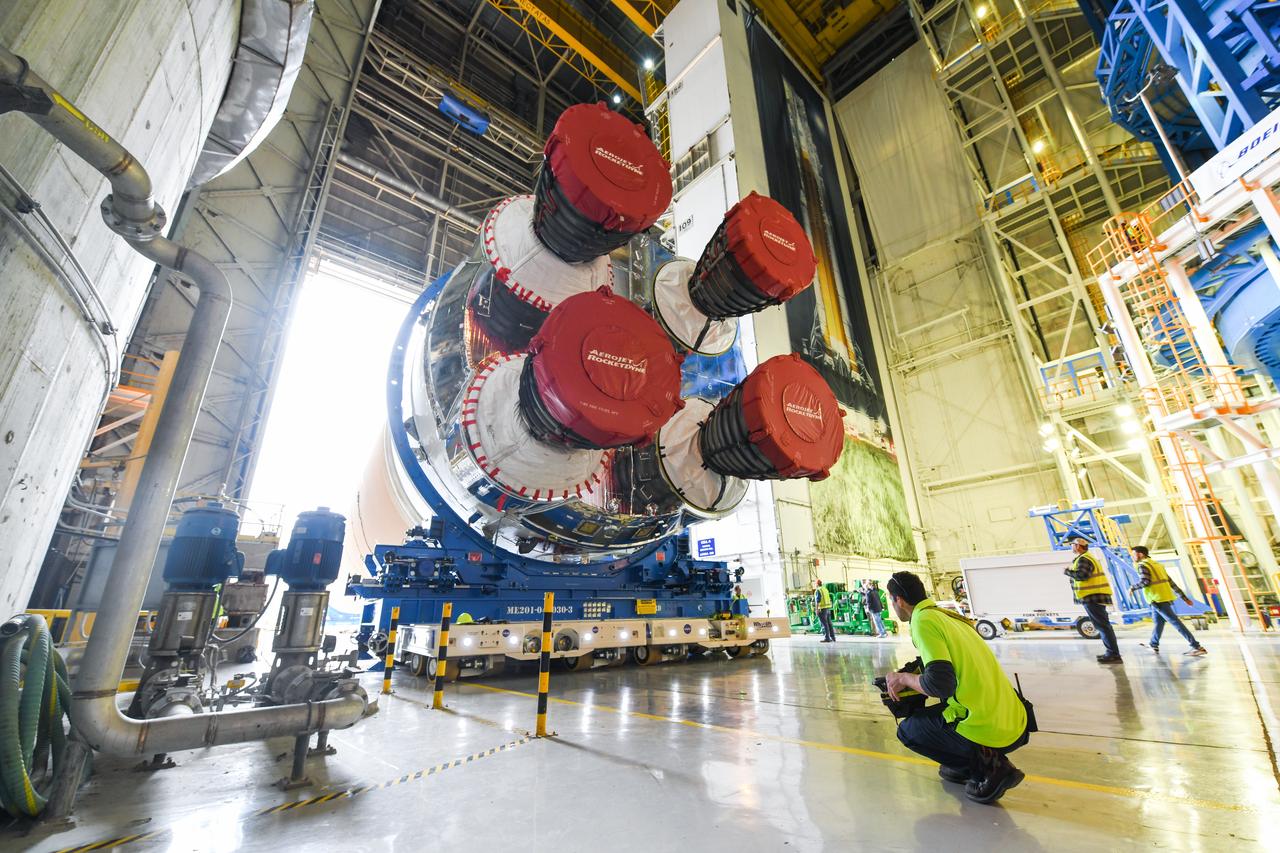

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
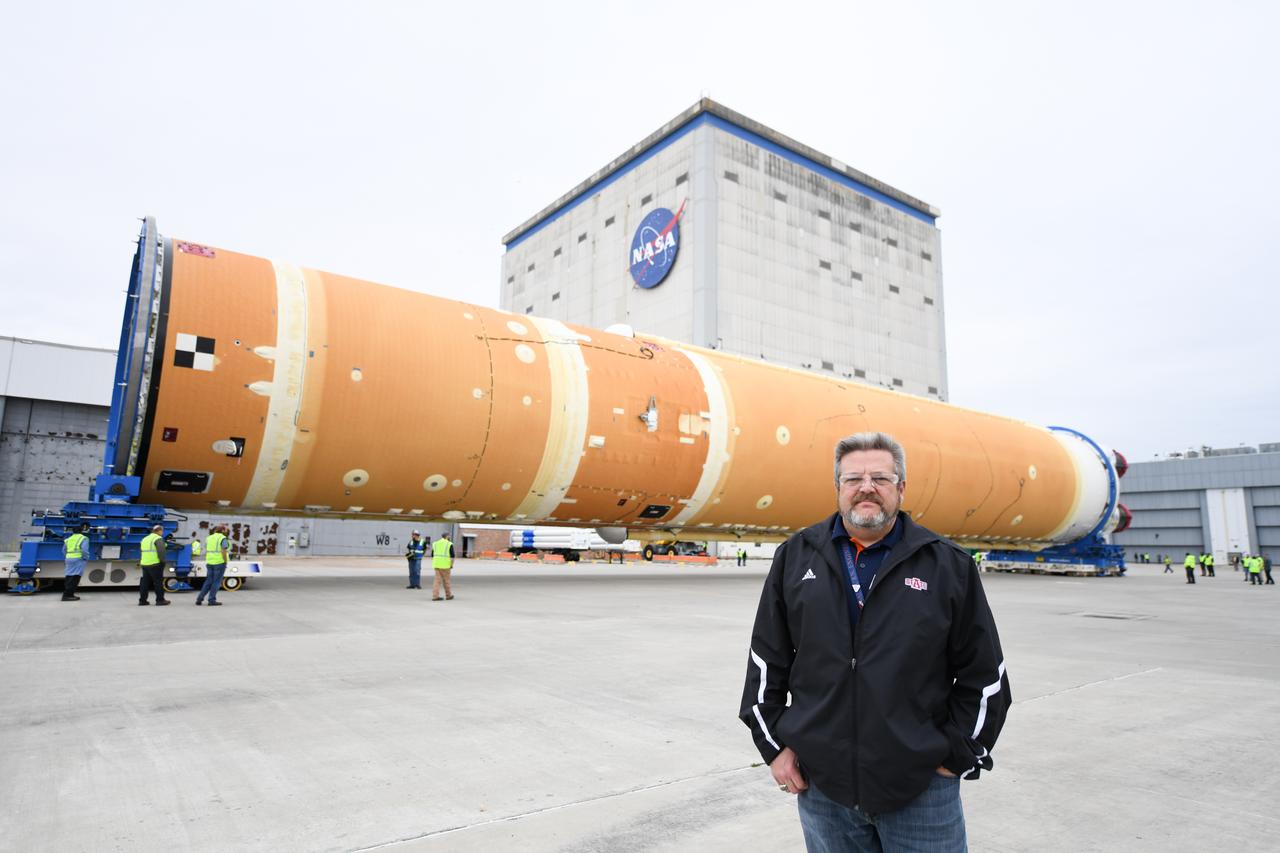

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
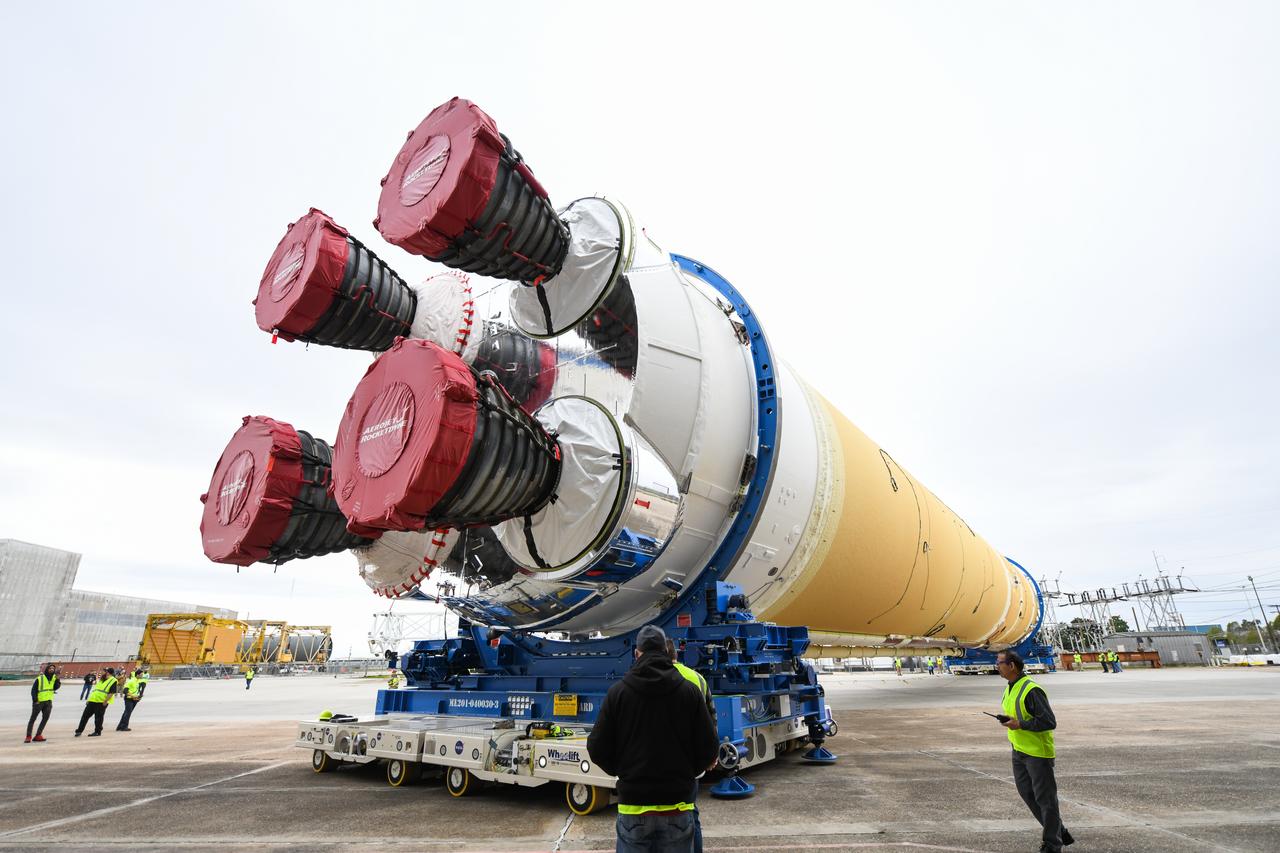

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
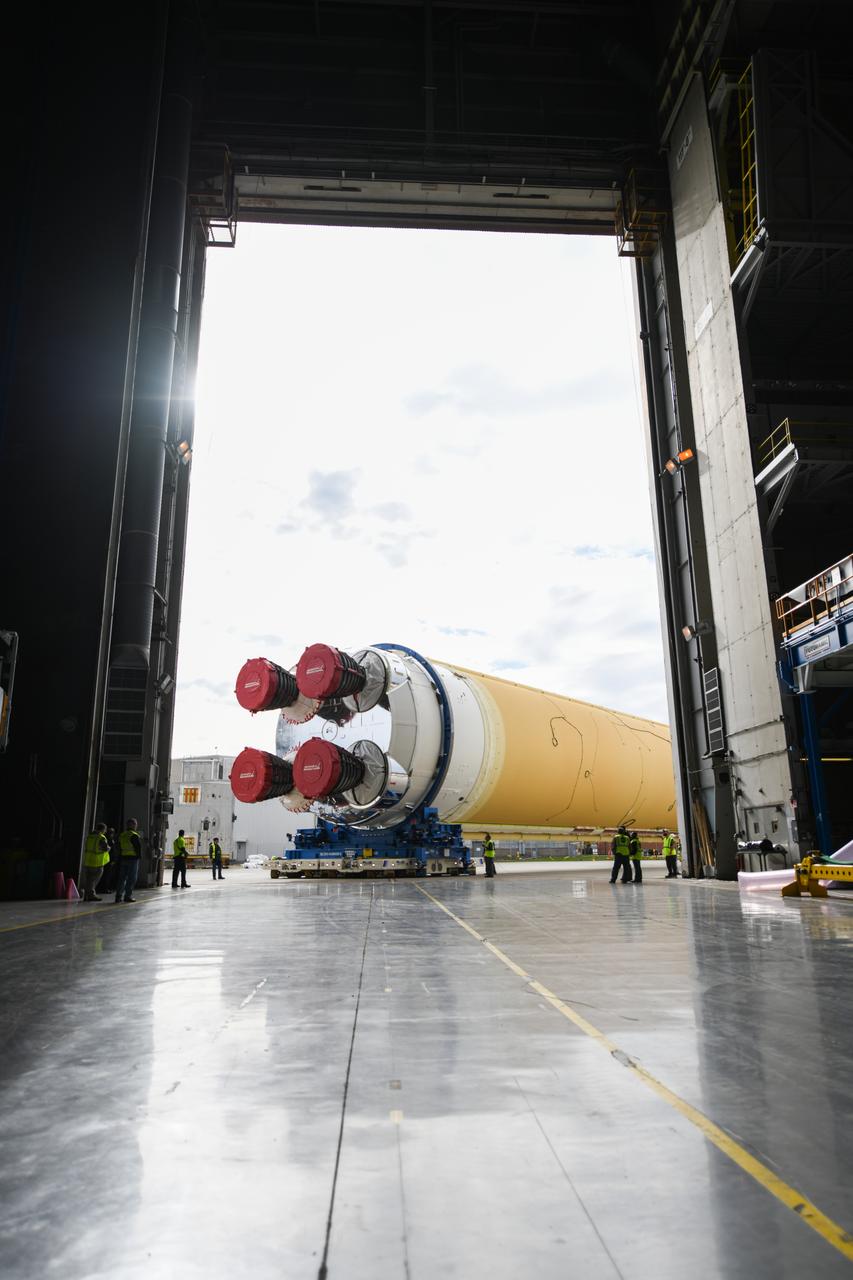

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
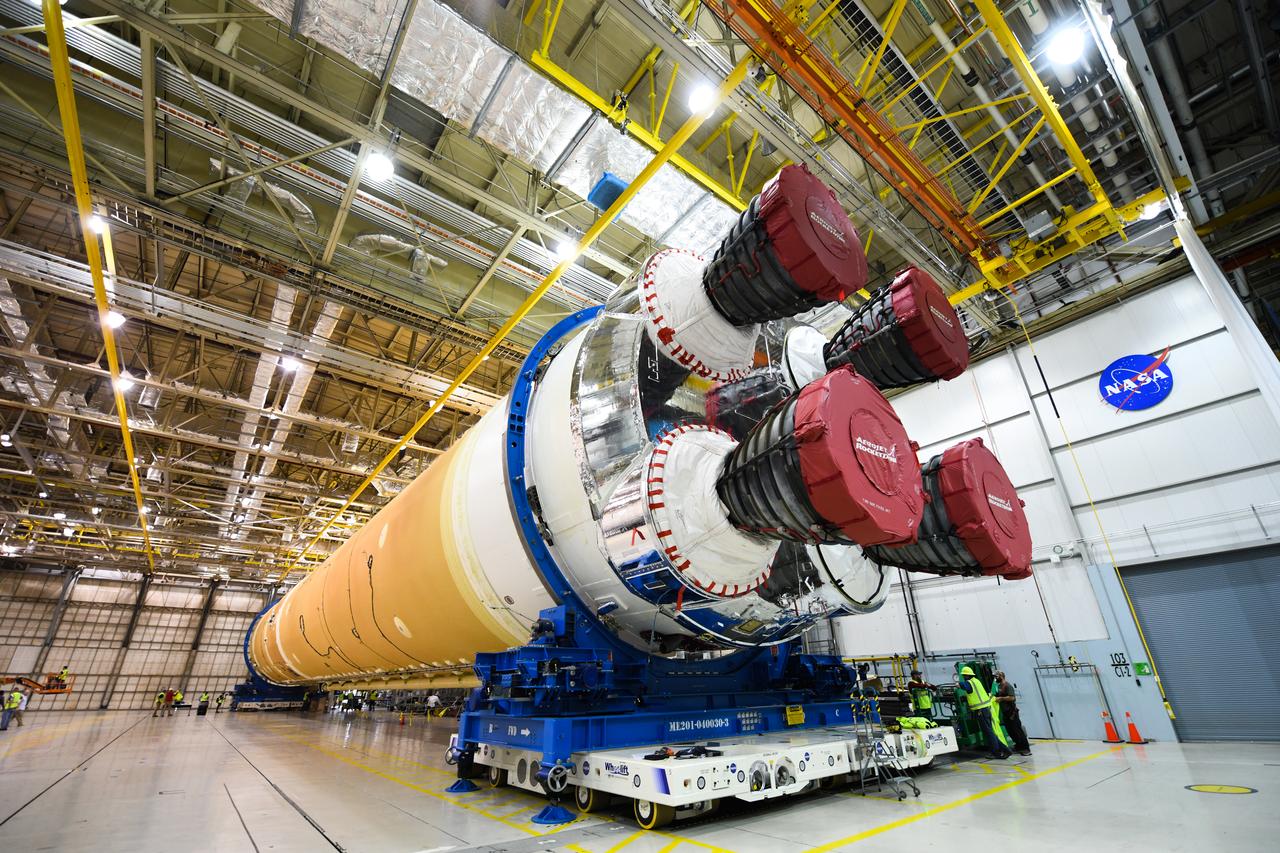

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
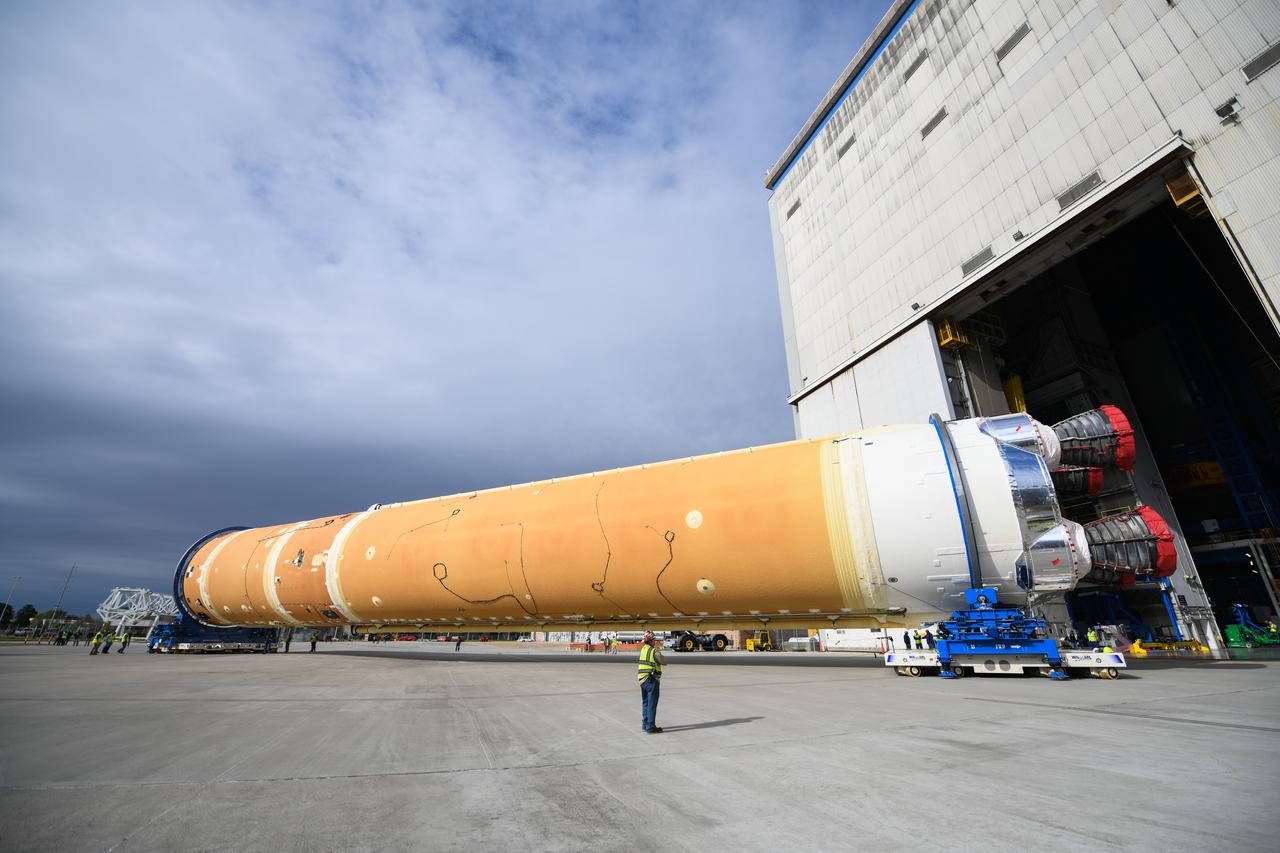

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
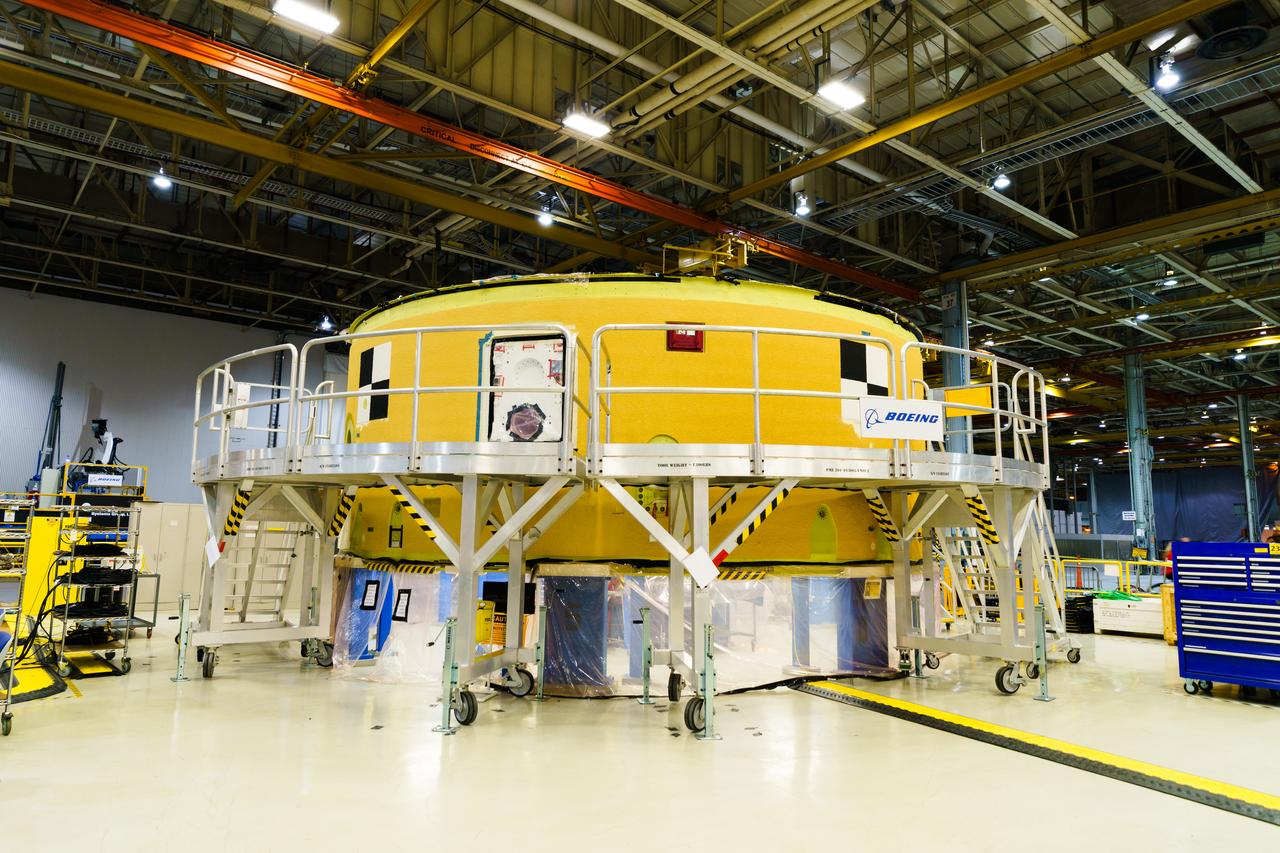

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
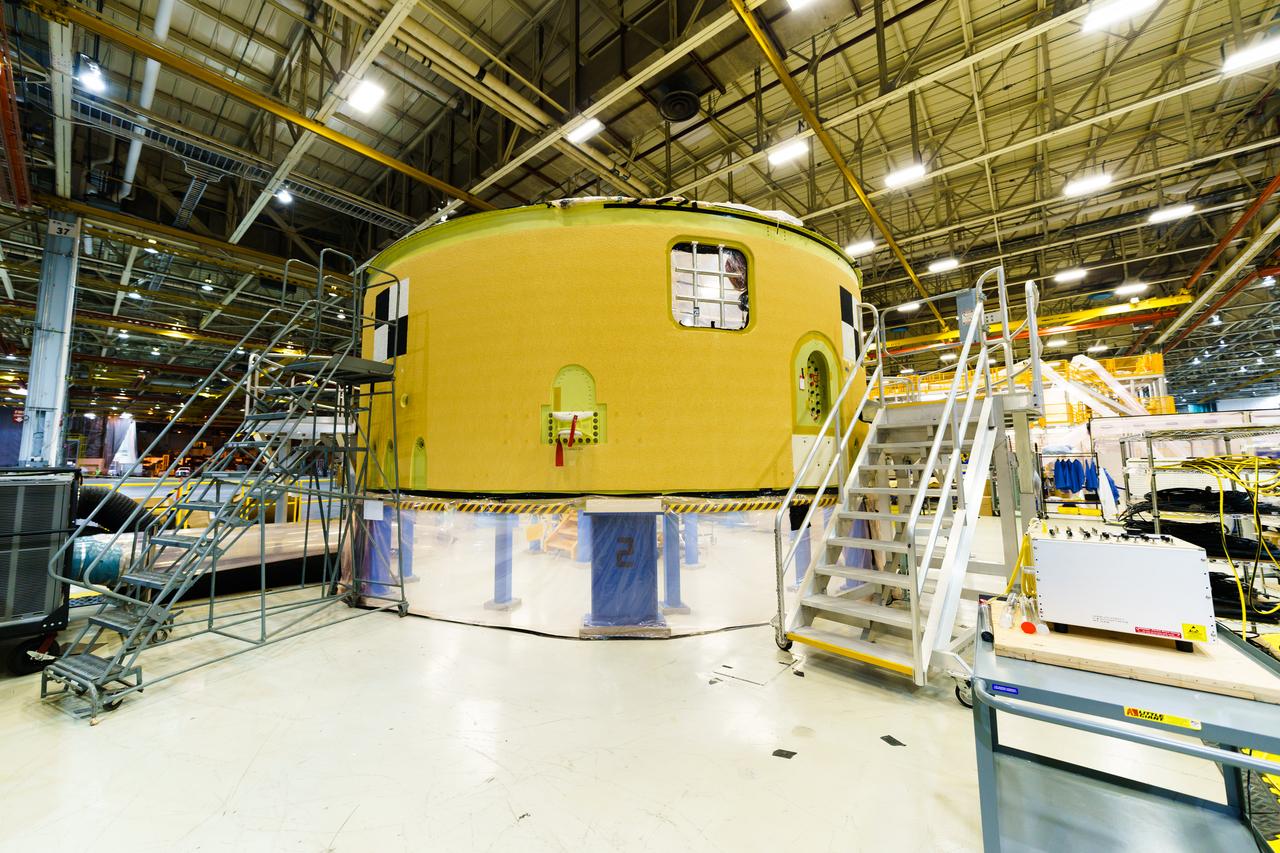

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
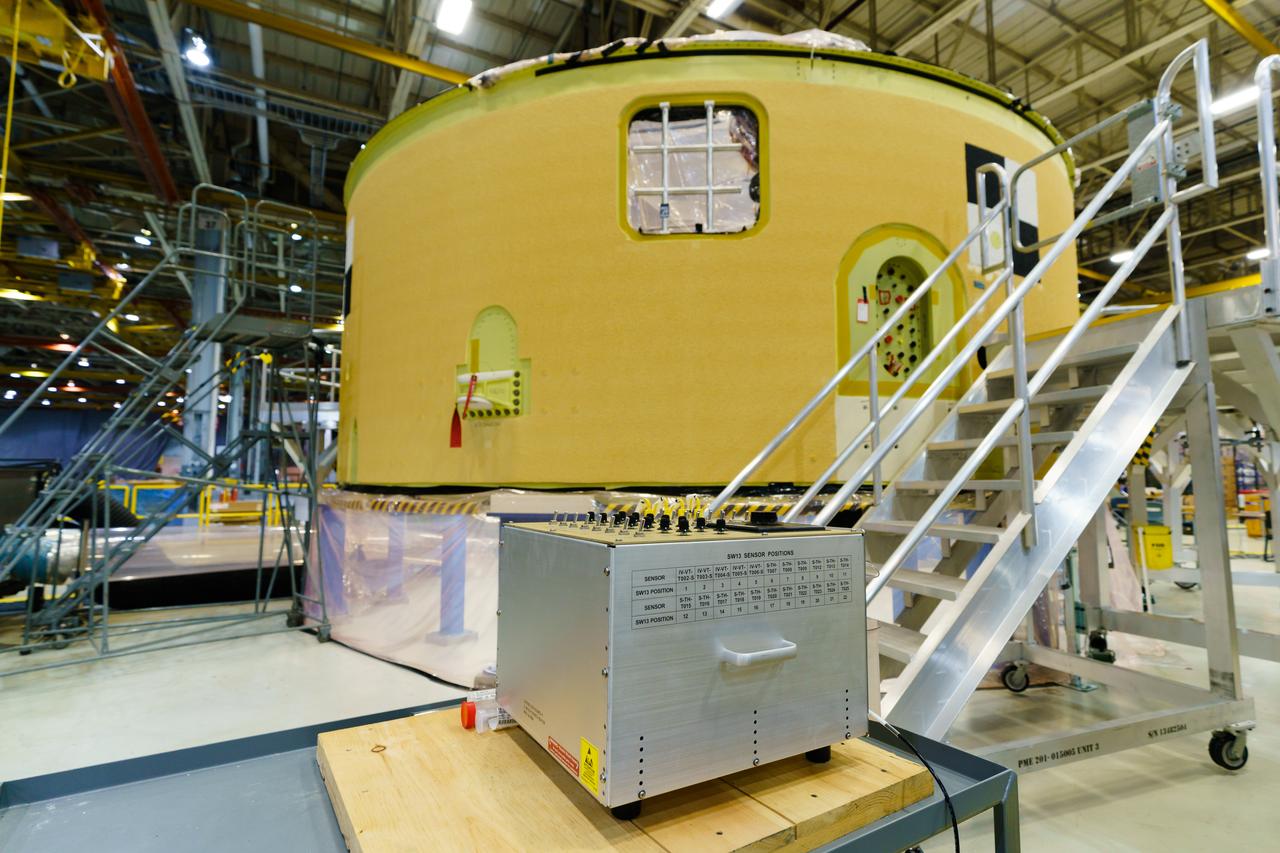

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
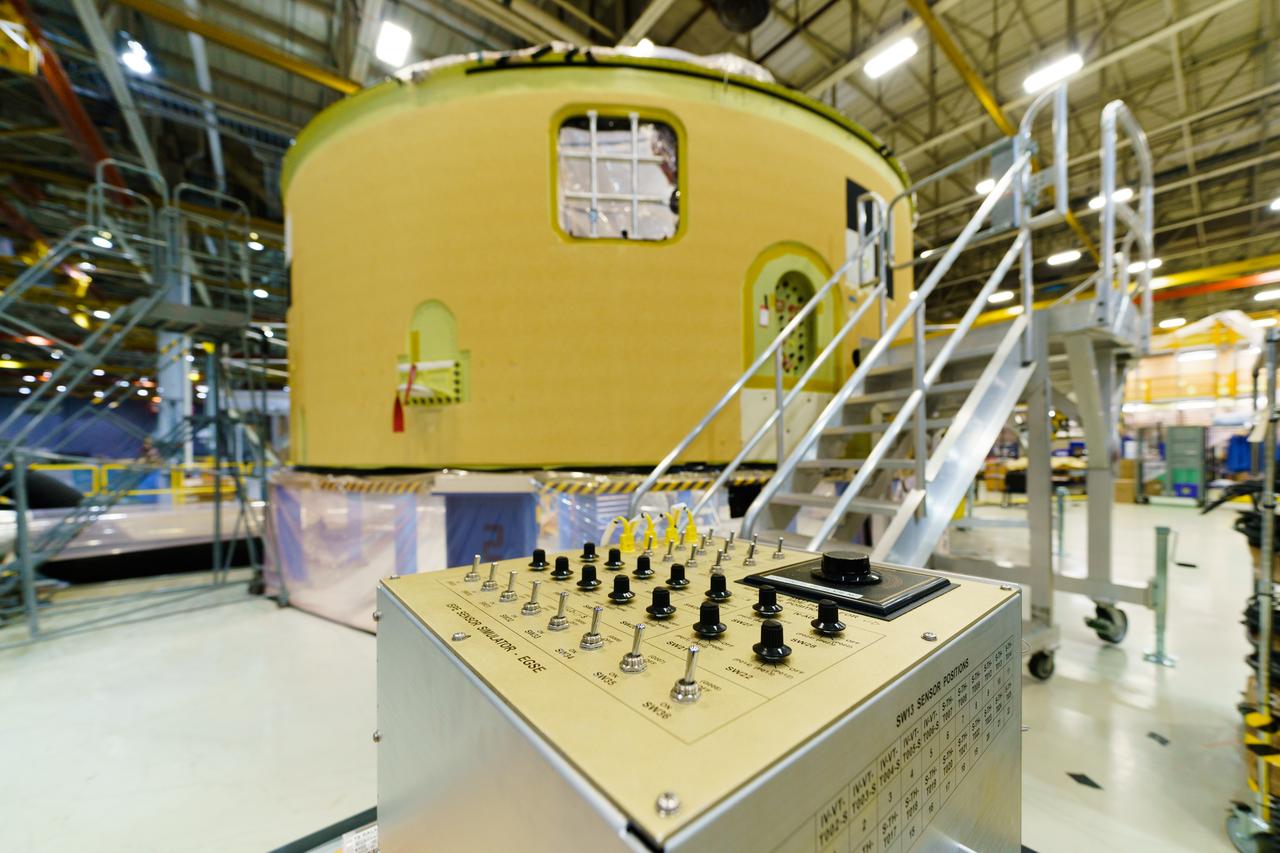

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
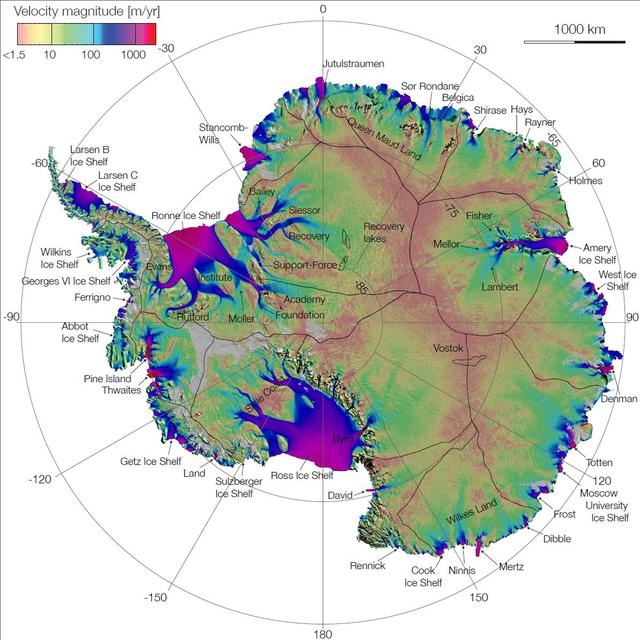
This image is the first complete map of the speed and direction of ice flow in Antartica. The thick black lines delineate major ice divides. Subglacial lakes in Antarctica interior are also outlined in black.
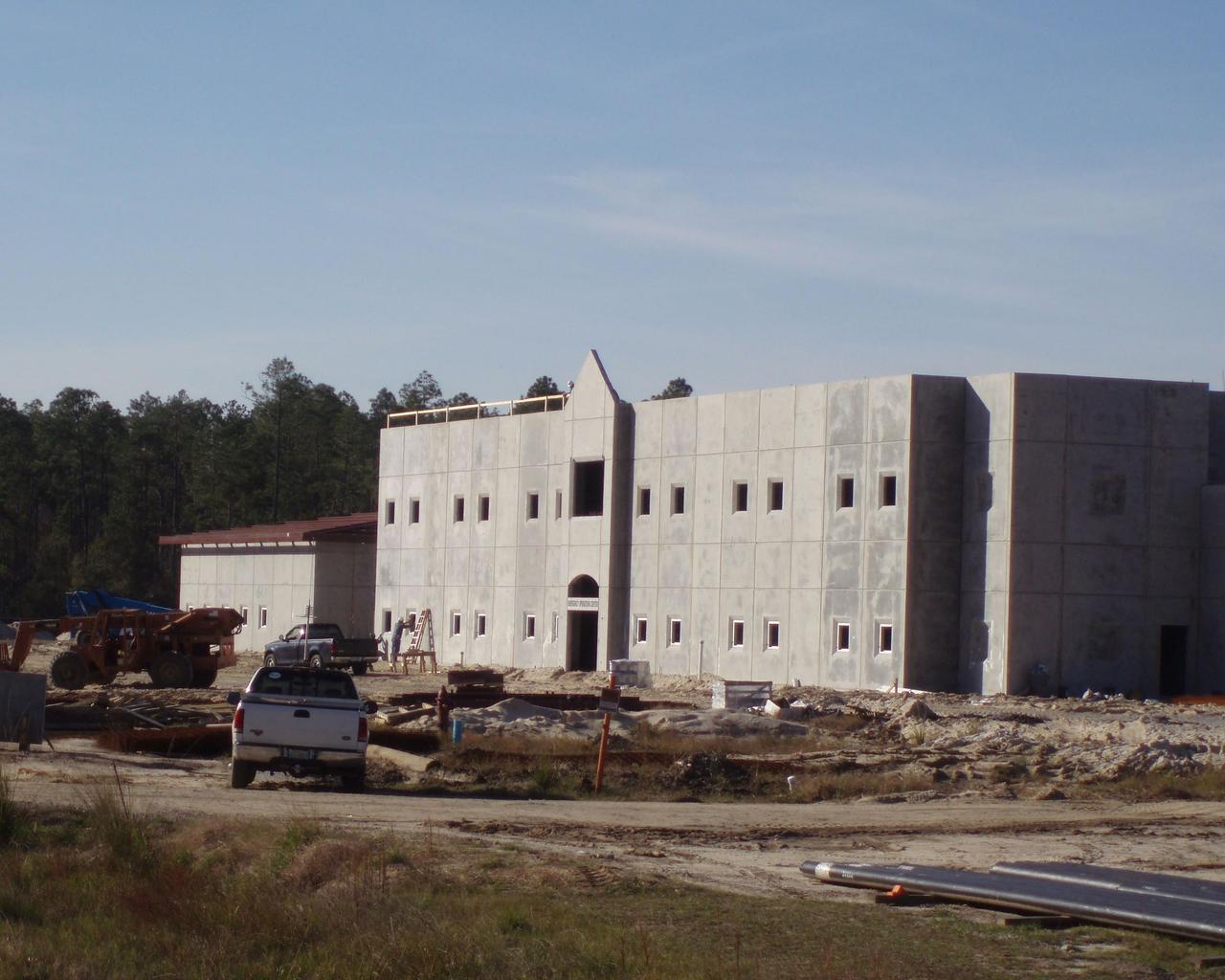

Work on Stennis Space Center's new Emergency Operations Center is progressing on schedule, according to Robert Perkins, construction manager with Jacobs Technology. At the turn of the New Year, construction contractors had completed the pervious paving for the north and west parking lots. Part of the facility's `green' design, pervious paving allows water to pass through and be absorbed directly into the ground below, preventing erosion from runoff. Through January, workers concentrated on installing the roof, sprinkler piping and overhead cable trays for electrical and communication lines. The next step will be interior work, erecting wallboard and installing electrical equipment. Perkins said NASA seeks to earn a Silver LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) Rating for the project's environmentally-friendly and sustainable design, construction and operation. The facility has a projected completion date of February 2009.
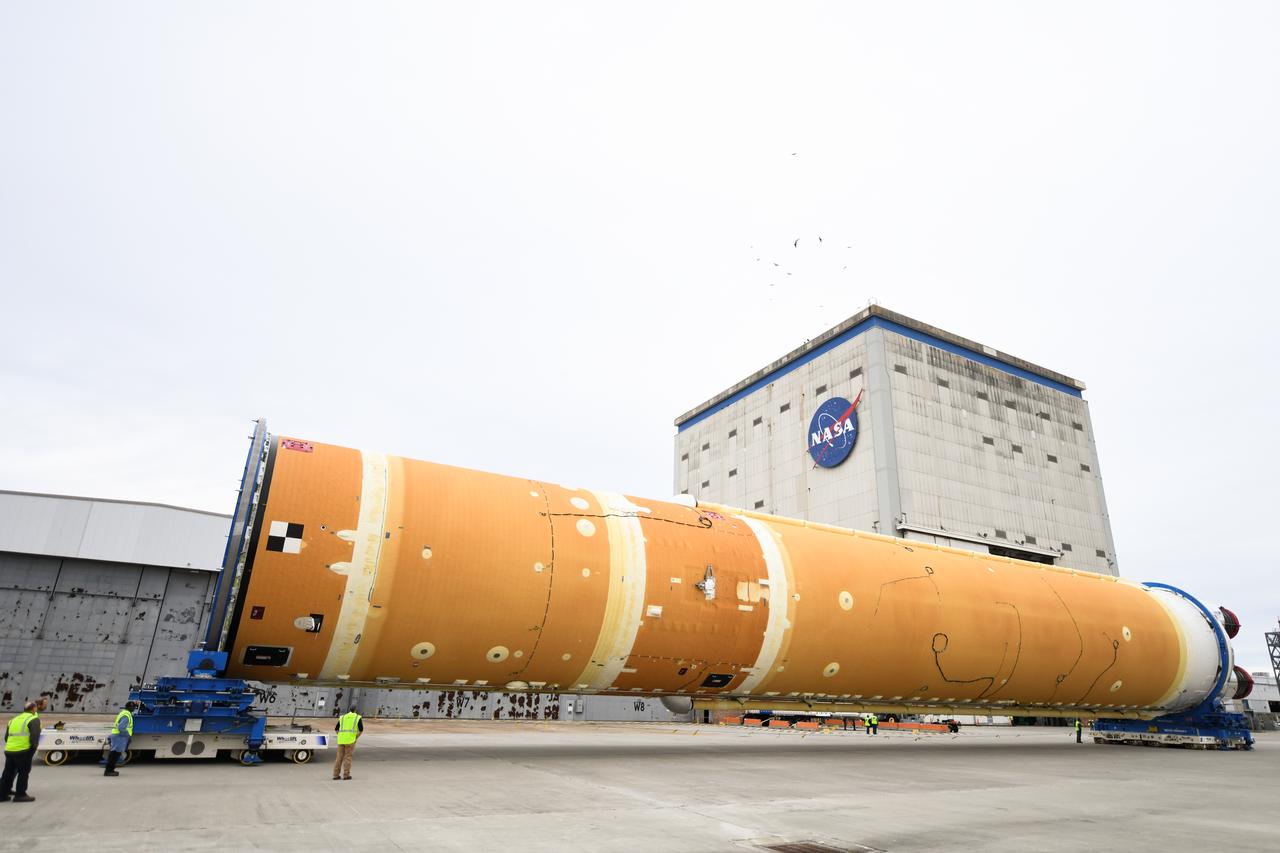

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

A view of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) with a vibrant NASA logo, referred to as the meatball, and American Flag at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 27, 2020. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, began repainting the meatball and flag on the iconic facility in May and recently completed the project. The VAB was last painted in 2007, when repairs where completed after Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne tore 845 panels off the building in 2004. It took over 500 gallons of paint to repaint the 209’ X 110’ flag and the 110’ X 132’ meatball.

Seen on Oct. 27, 2020, is the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) with a vibrant NASA logo, referred to as the meatball, and American Flag at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, began repainting the meatball and flag on the iconic facility in May and recently completed the project. The VAB was last painted in 2007, when repairs where completed after Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne tore 845 panels off the building in 2004. It took over 500 gallons of paint to repaint the 209’ X 110’ flag and the 110’ X 132’ meatball.

A view of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) with a vibrant NASA logo, referred to as the meatball, and American Flag at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 27, 2020. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, began repainting the meatball and flag on the iconic facility in May and recently completed the project. The VAB was last painted in 2007, when repairs where completed after Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne tore 845 panels off the building in 2004. It took over 500 gallons of paint to repaint the 209’ X 110’ flag and the 110’ X 132’ meatball.

A ground-level view of a vibrant NASA logo, referred to as the meatball, and American Flag on the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 27, 2020. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, began repainting the meatball and flag on the iconic facility in May and recently completed the project. The VAB was last painted in 2007, when repairs where completed after Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne tore 845 panels off the building in 2004. It took over 500 gallons of paint to repaint the 209’ X 110’ flag and the 110’ X 132’ meatball.

A ground-level view of a vibrant NASA logo, referred to as the meatball, and American Flag on the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 27, 2020. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, began repainting the meatball and flag on the iconic facility in May and recently completed the project. The VAB was last painted in 2007, when repairs where completed after Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne tore 845 panels off the building in 2004. It took over 500 gallons of paint to repaint the 209’ X 110’ flag and the 110’ X 132’ meatball.

Seen on Oct. 27, 2020, is the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) with a vibrant NASA logo, referred to as the meatball, and American Flag at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, began repainting the meatball and flag on the iconic facility in May and recently completed the project. The VAB was last painted in 2007, when repairs where completed after Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne tore 845 panels off the building in 2004. It took over 500 gallons of paint to repaint the 209’ X 110’ flag and the 110’ X 132’ meatball.
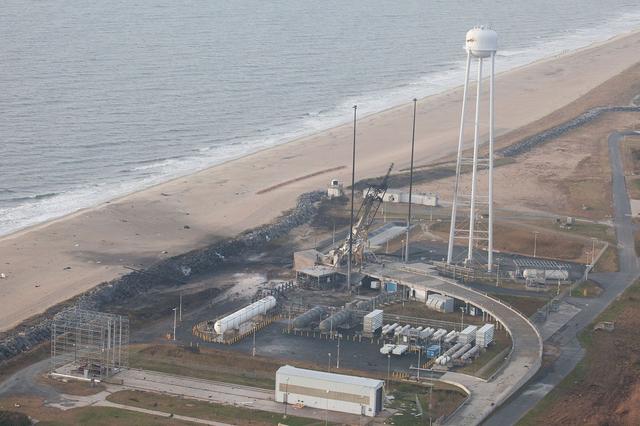

An aerial view of the Wallops Island launch facilities taken by the Wallops Incident Response Team Oct. 29 following the failed launch attempt of Orbital Science Corp.'s Antares rocket Oct. 28. Credit: NASA/Terry Zaperach --- The Wallops Incident Response Team completed today an initial assessment of Wallops Island, Virginia, following the catastrophic failure of Orbital Science Corp.’s Antares rocket shortly after liftoff at 6:22 p.m. EDT Tuesday, Oct. 28, from Pad 0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. “I want to praise the launch team, range safety, all of our emergency responders and those who provided mutual aid and support on a highly-professional response that ensured the safety of our most important resource -- our people,” said Bill Wrobel, Wallops director. “In the coming days and weeks ahead, we'll continue to assess the damage on the island and begin the process of moving forward to restore our space launch capabilities. There's no doubt in my mind that we will rebound stronger than ever.” The initial assessment is a cursory look; it will take many more weeks to further understand and analyze the full extent of the effects of the event. A number of support buildings in the immediate area have broken windows and imploded doors. A sounding rocket launcher adjacent to the pad, and buildings nearest the pad, suffered the most severe damage. At Pad 0A the initial assessment showed damage to the transporter erector launcher and lightning suppression rods, as well as debris around the pad. The Wallops team also met with a group of state and local officials, including the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality, the Virginia Department of Emergency Management, the Virginia Marine Police, and the U.S. Coast Guard. The Wallops environmental team also is conducting assessments at the site. Preliminary observations are that the environmental effects of the launch failure were largely contained within the southern third of Wallops Island, in the area immediately adjacent to the pad. Immediately after the incident, the Wallops’ industrial hygienist collected air samples at the Wallops mainland area, the Highway 175 causeway, and on Chincoteague Island. No hazardous substances were detected at the sampled locations. Additional air, soil and water samples will be collected from the incident area as well as at control sites for comparative analysis. The Coast Guard and Virginia Marine Resources Commission reported today they have not observed any obvious signs of water pollution, such as oil sheens. Furthermore, initial assessments have not revealed any obvious impacts to fish or wildlife resources. The Incident Response Team continues to monitor and assess. Following the initial assessment, the response team will open the area of Wallops Island, north of the island flagpole opposite of the launch pad location, to allow the U.S. Navy to return back to work. Anyone who finds debris or damage to their property in the vicinity of the launch mishap is cautioned to stay away from it and call the Incident Response Team at 757-824-1295. Further updates on the situation and the progress of the ongoing investigation will be available at: <a href="http://www.orbital.com" rel="nofollow">www.orbital.com</a> and <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/orbital" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/orbital</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

STS-128 cake-cutting celebrating the completion of mission training.
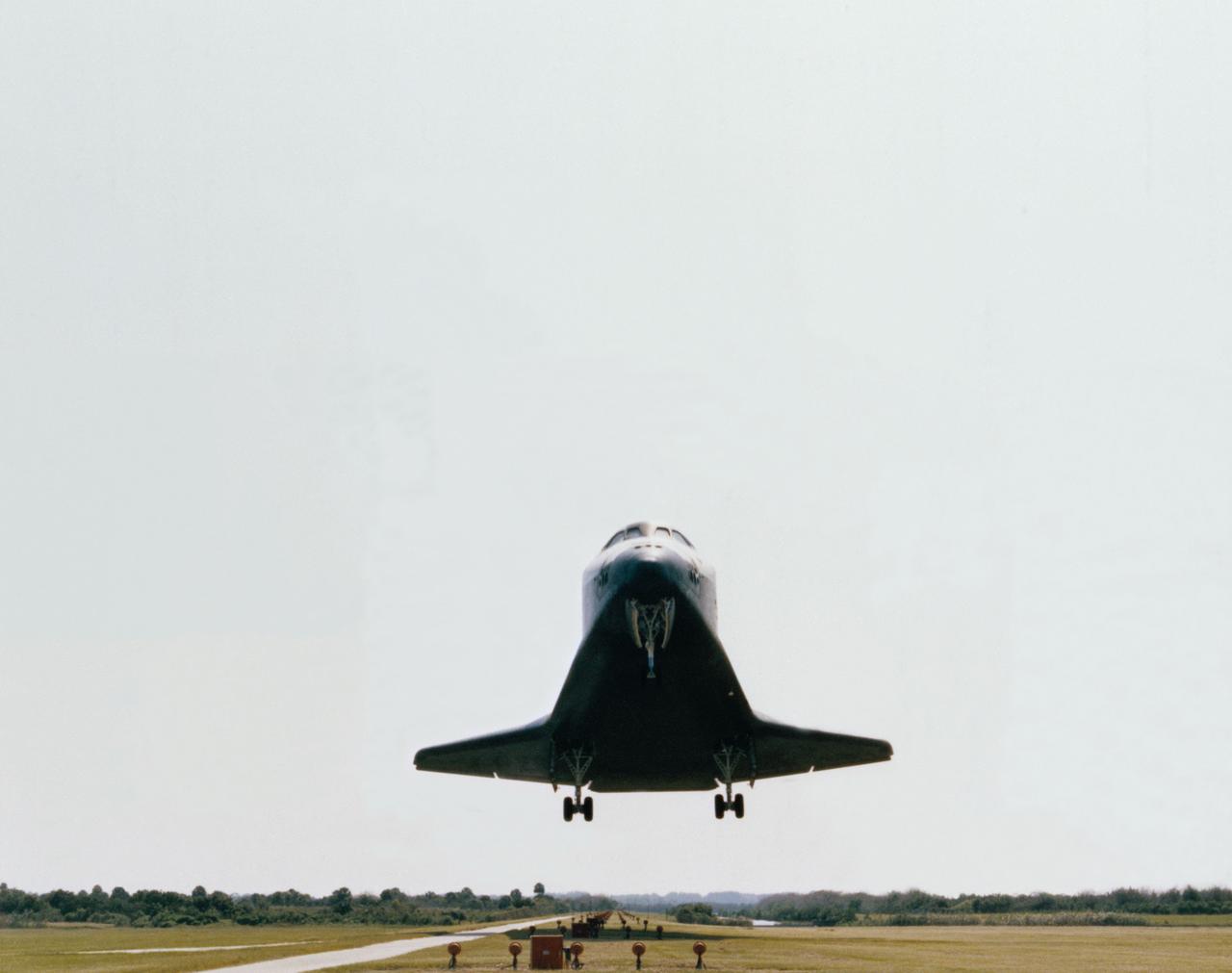

Landing of Orbiter Challenger at KSC completion of 41G Mission. Views closeup front view of the Orbiter approaching the runway, its landing gear extended in preparation for touchdown. The KSC Alternative Photo Number is 108-KSC-84PC-639. KSC, FL
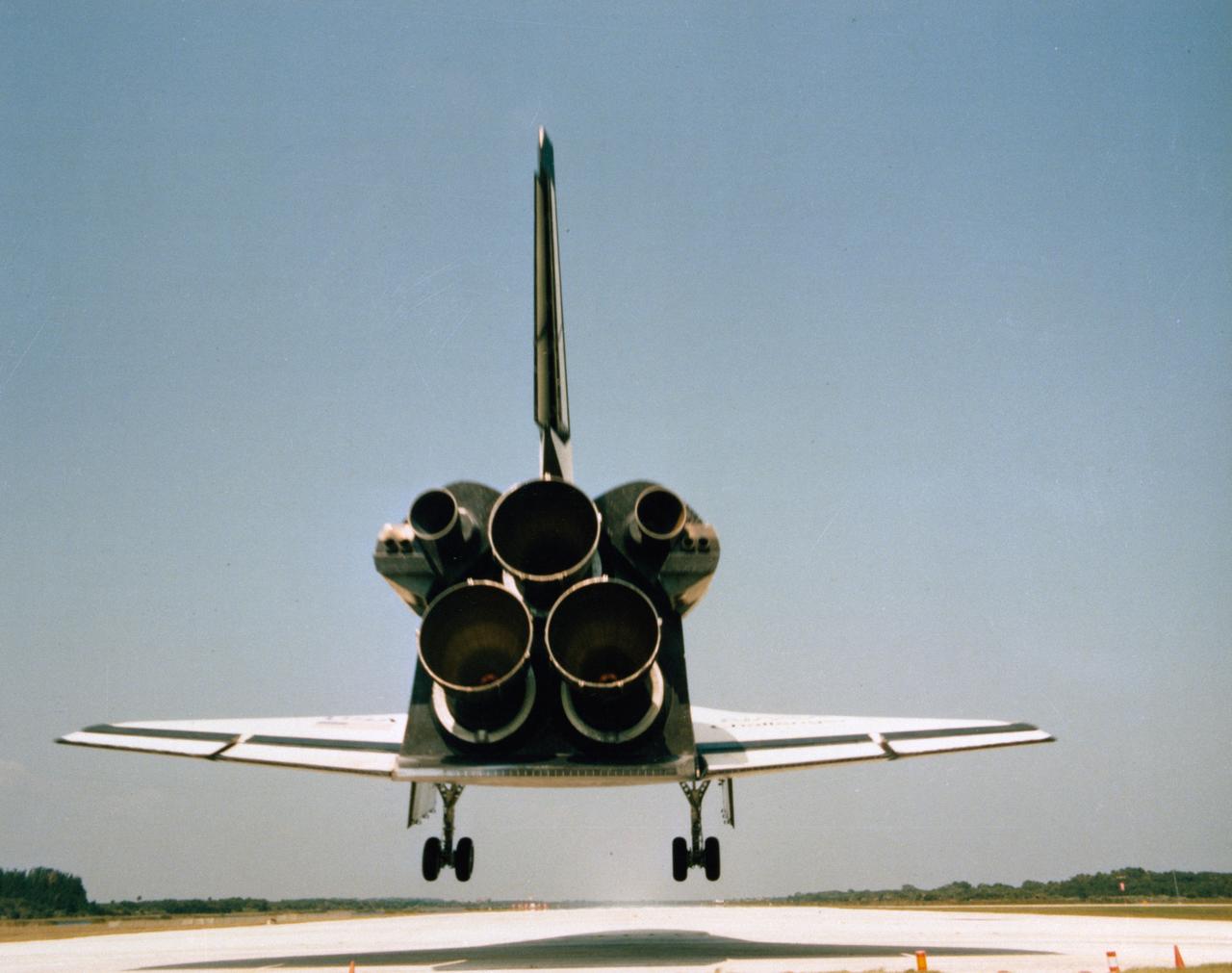

Landing of Orbiter Challenger at KSC at completion of 41G mission. View of the rear of the Orbiter as it approaches the runway with its landing gear extended. The main engines are clearly visible. The KSC Alternative Photo Number is 108-KSC-84PC-654 (43896). KSC, FL

Members of the assembly, test, launch, and operations team for NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) project pose in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Jan. 26, 2024, with three lunar rovers after their completion. Bound for the Moon, CADRE is a technology demonstration designed to show that a group of robotic spacecraft can work together as a team to accomplish tasks and record data autonomously – without explicit commands from mission controllers on Earth. Seen behind the rovers are hardware elements that will be mounted on the lunar lander aboard which CADRE will arrive at the Moon: the situational awareness camera assembly (SACA), one of the deployers that will lower the rovers onto the lunar surface, and the base station with which the rovers will communicate via mesh network radios. Back row, from left: Wei Chen Wilson Yeh, Mark White, Nathan Cheek, Baylor de los Reyes, Jacqueline Sly, Blair Emanuel, Josh Miller, Jonathan Tan, Sawyer Brooks, Libby Boroson, Leroy Montalvo, Tonya Beatty, Bert Turney, George Dupas, Leo Ortiz, and Nelson Serrano. Front row, from left: Kristopher Sherril, Coleman Richdale, Russell Smith, Daniel Esguerra, Will Raff, Justin Schachter, and Clara Nguyen. Shown on the cellphone held by Smith are absent ATLO team members Ara Kourchians, Molly Shelton, and Randy Ballat. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26165

NASA’s Sustainable Flight Demonstrator project completed wind tunnel tests on a Boeing-built X-66 full-span model during a 13-week campaign between January and March 2025. The tests were completed in the 11-Foot Transonic Unitary Plan Facility at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley. The model underwent tests in expected flight conditions to obtain engineering data to help improve the aircraft’s design and flight simulators.
The surface of Mars is completely hidden from view by clouds
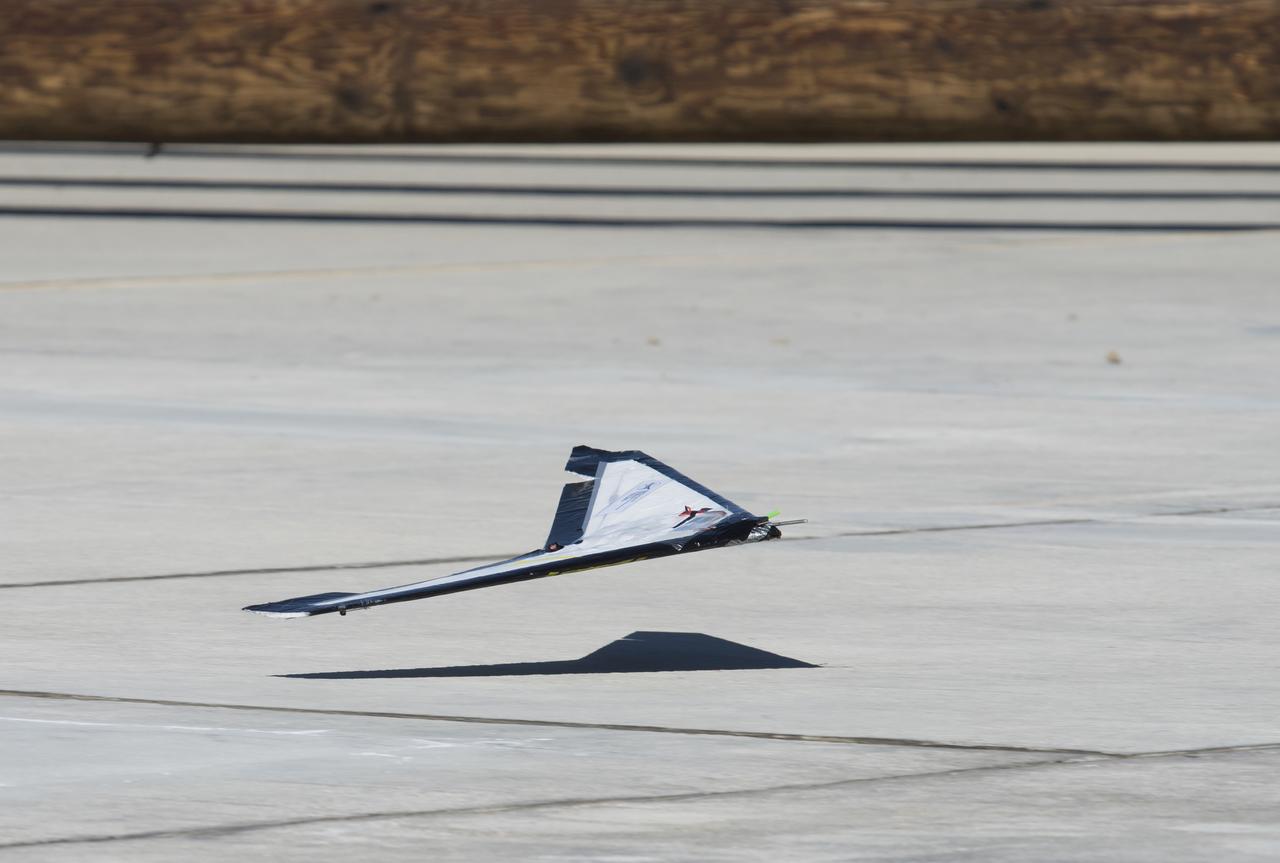

The Prandtl-M completes a successful research flight.
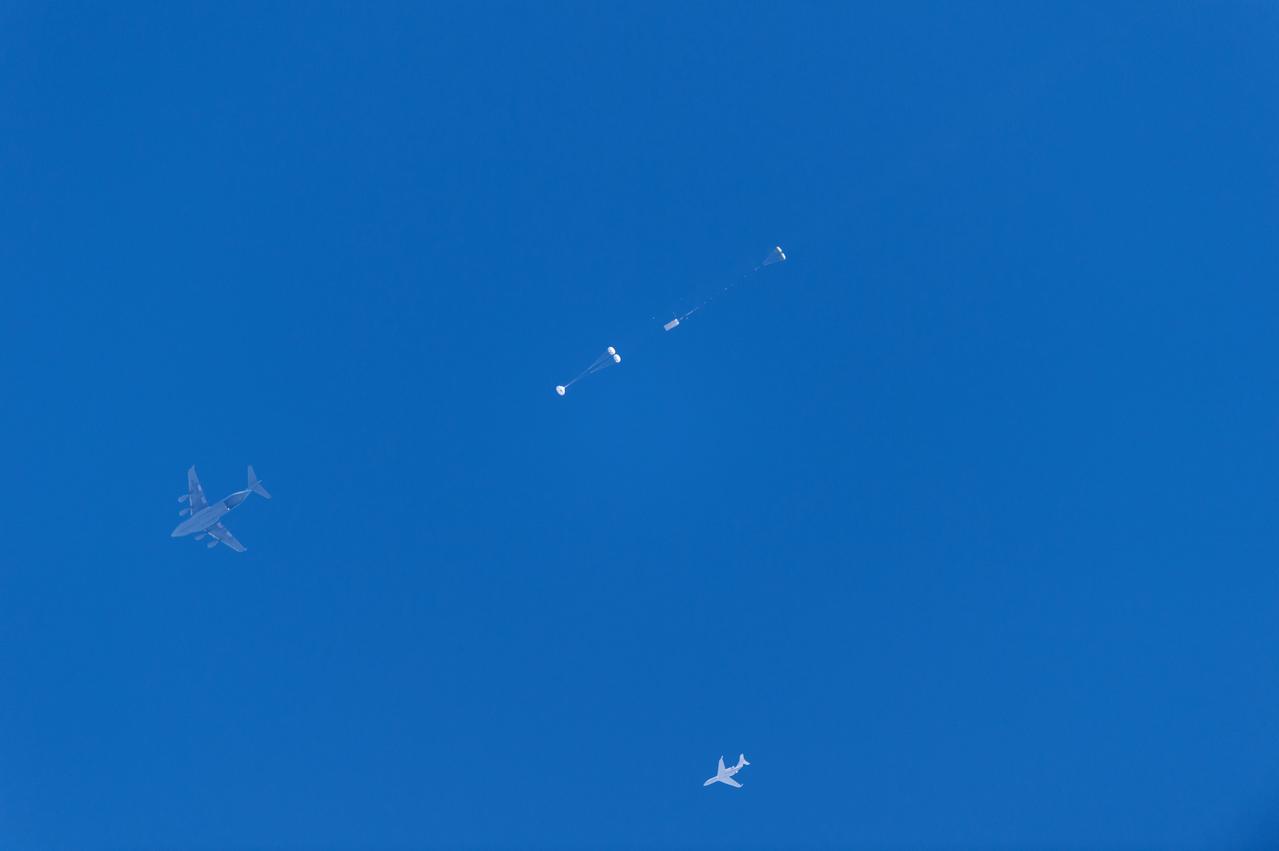

NASA has completes the final test to qualify Orion’s parachute system for flights with astronauts, checking off an important milestone on the path to send humans on missions to the Moon and beyond on Sept. 12, 2018...Over the course of eight tests at the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona, engineers have evaluated the performance of Orion’s parachute system during normal landing sequences as well as several failure scenarios and a variety of potential aerodynamic conditions to ensure astronauts can return safely from deep space missions.

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, is stacked on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The stacking of Orion on top of the SLS completes assembly for the Artemis I flight test. Teams will begin conducting a series of verification tests ahead of rolling out to Launch Complex 39B for the Wet Dress Rehearsal.
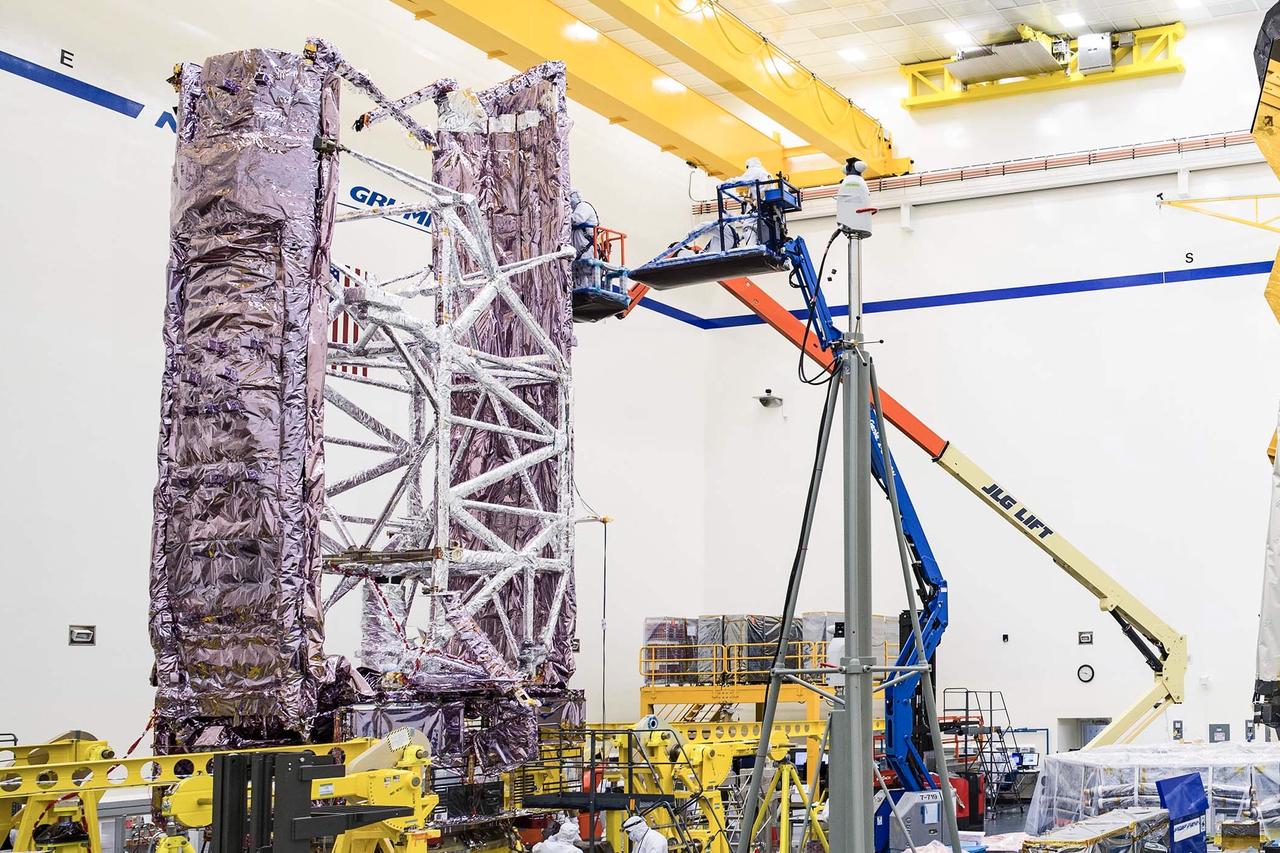

The James Webb Space Telescope’s spacecraft element just prior to being transported to nearby acoustic, and vibration test facilities at Northrop Grumman in Redondo Beach, California. Credits: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Chris Gunn more info: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2019/nasa-s-webb-is-sound-after-completing-critical-milestones
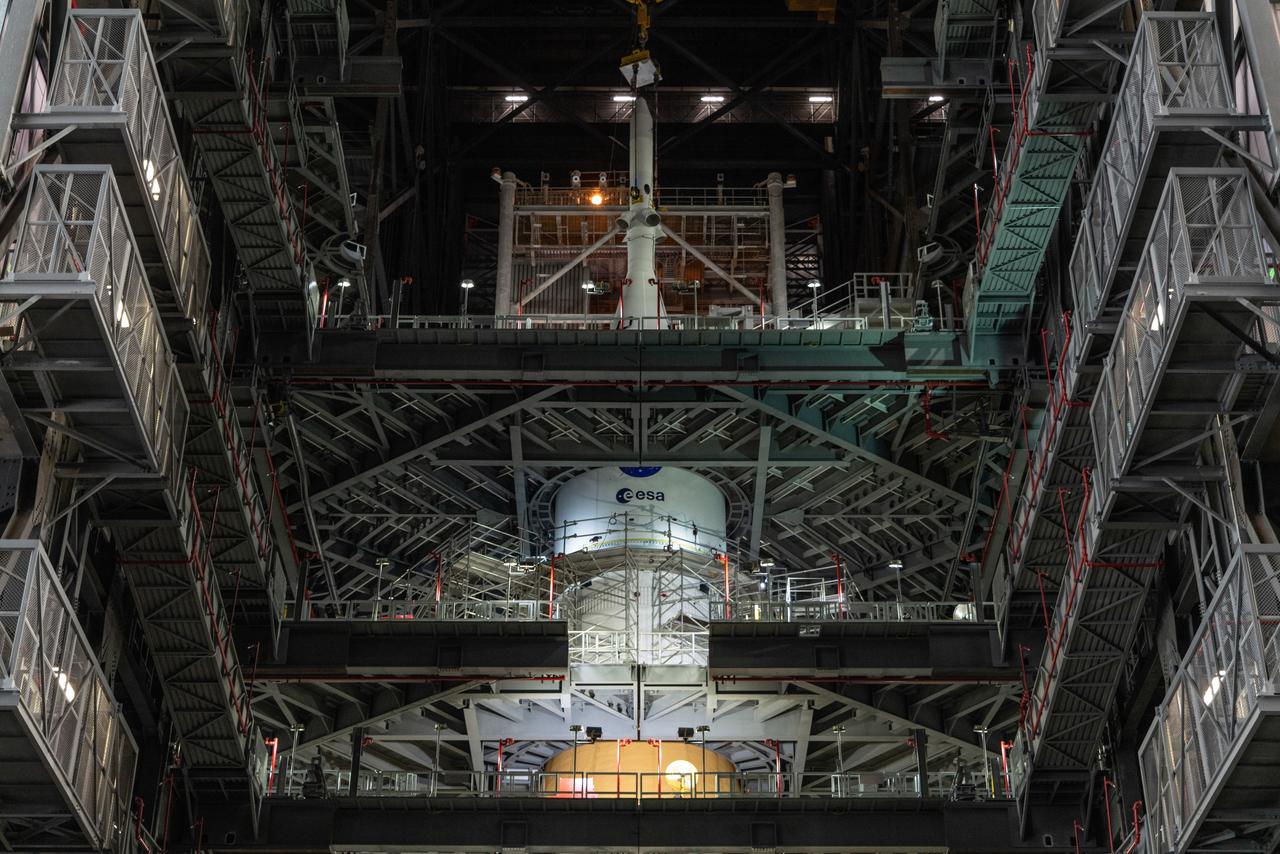

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, is stacked on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The stacking of Orion on top of the SLS completes assembly for the Artemis I flight test. Teams will begin conducting a series of verification tests ahead of rolling out to Launch Complex 39B for the Wet Dress Rehearsal.

Construction is complete on the main flame deflector in the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flame deflector will safely deflect the plume exhaust from NASA's Space Launch System rocket during launch. It will divert the rocket's exhaust, pressure and intense heat to the north at liftoff. The Exploration Ground Systems Program at Kennedy is refurbishing the pad to support the launch of the SLS rocket and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, and helping to transform the space center into a multi-user spaceport.
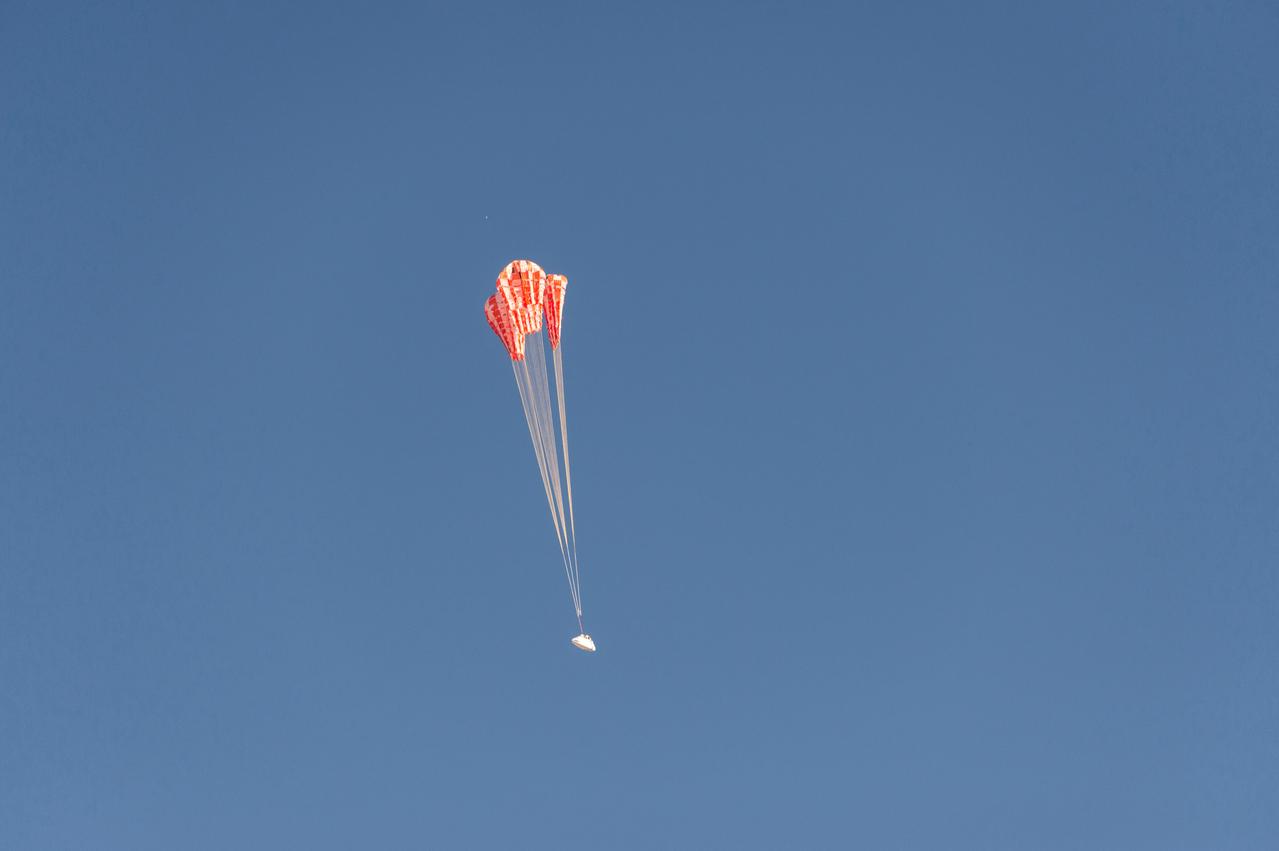

NASA has completes the final test to qualify Orion’s parachute system for flights with astronauts, checking off an important milestone on the path to send humans on missions to the Moon and beyond on Sept. 12, 2018...Over the course of eight tests at the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona, engineers have evaluated the performance of Orion’s parachute system during normal landing sequences as well as several failure scenarios and a variety of potential aerodynamic conditions to ensure astronauts can return safely from deep space missions.
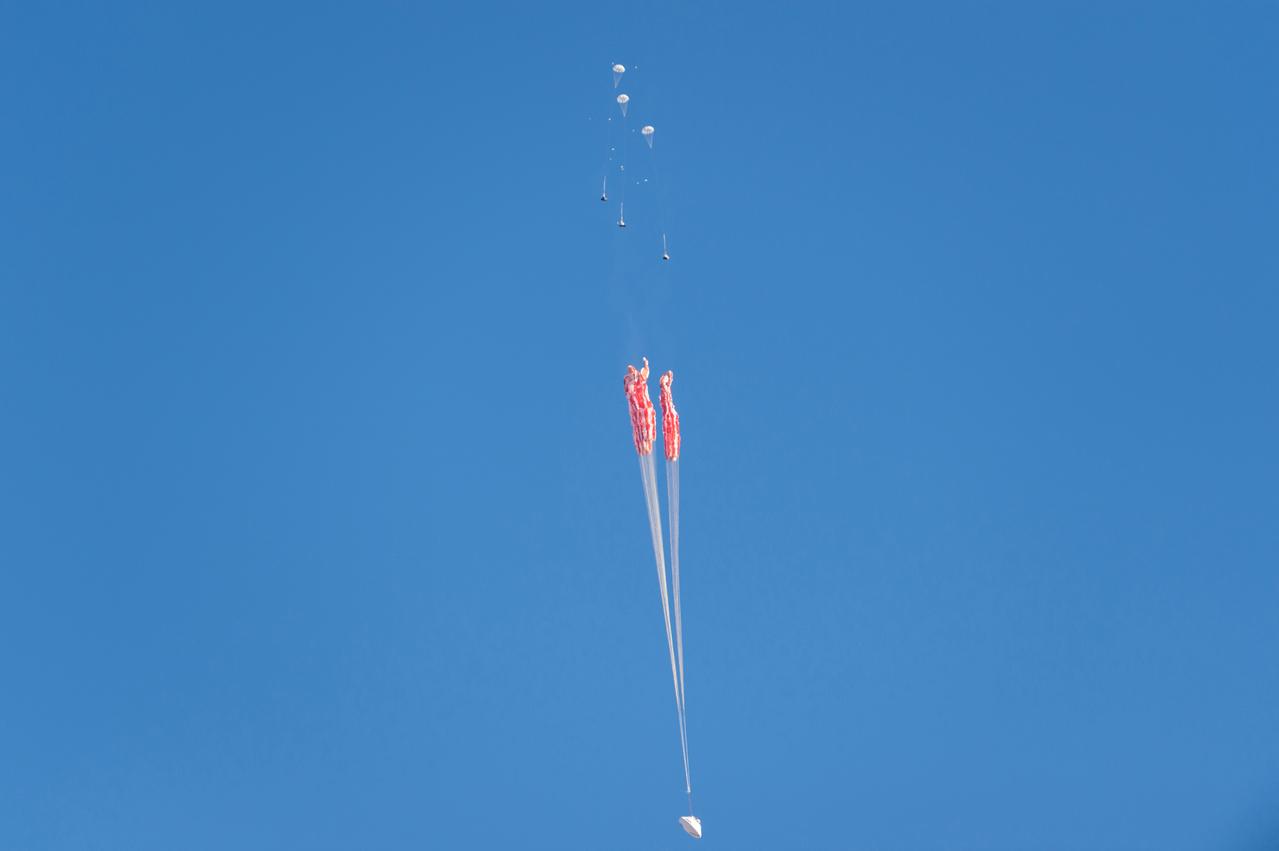

NASA has completes the final test to qualify Orion’s parachute system for flights with astronauts, checking off an important milestone on the path to send humans on missions to the Moon and beyond on Sept. 12, 2018...Over the course of eight tests at the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona, engineers have evaluated the performance of Orion’s parachute system during normal landing sequences as well as several failure scenarios and a variety of potential aerodynamic conditions to ensure astronauts can return safely from deep space missions.
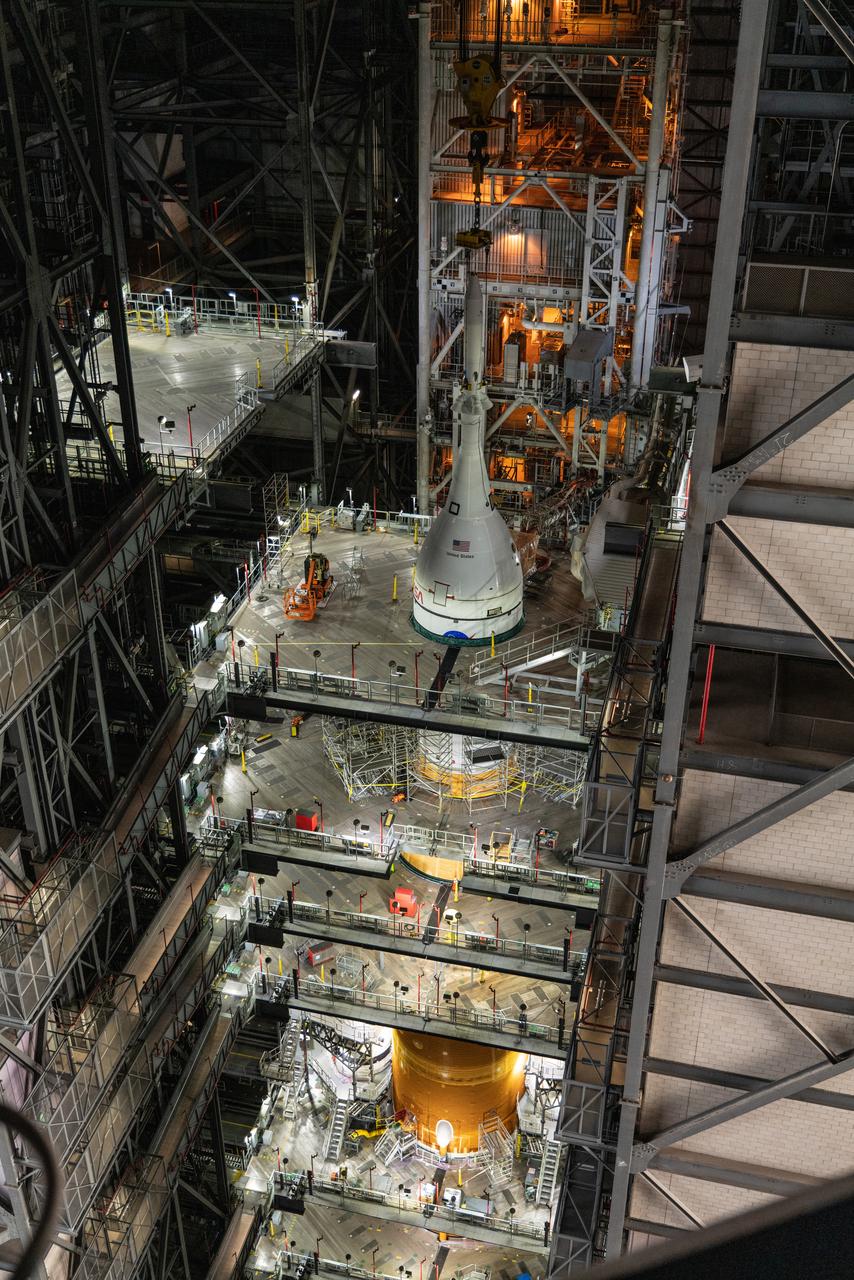

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, is stacked on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The stacking of Orion on top of the SLS completes assembly for the Artemis I flight test. Teams will begin conducting a series of verification tests ahead of rolling out to Launch Complex 39B for the Wet Dress Rehearsal.
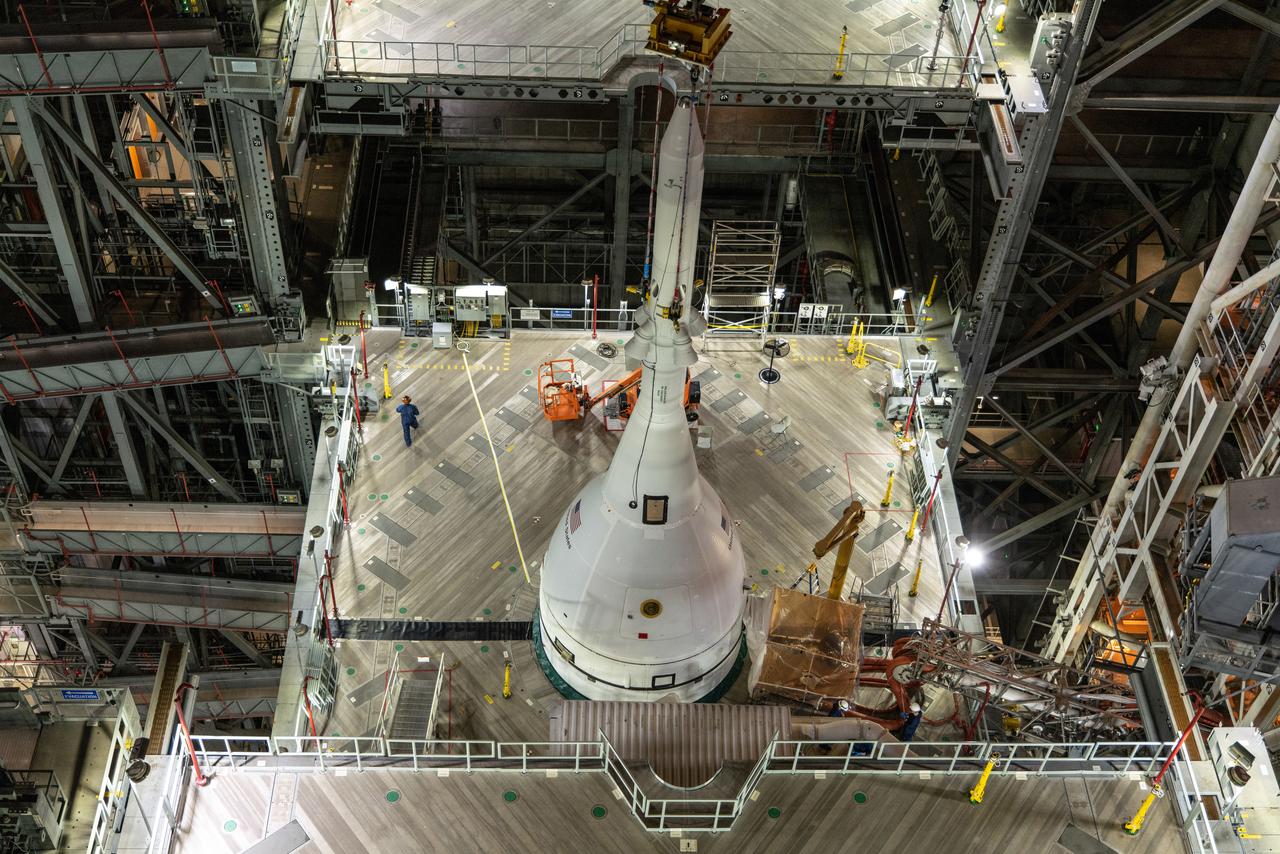

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, is stacked on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The stacking of Orion on top of the SLS completes assembly for the Artemis I flight test. Teams will begin conducting a series of verification tests ahead of rolling out to Launch Complex 39B for the Wet Dress Rehearsal.

Flight Research Inc.’s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter lands on a helipad at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021 at the completion of an urban air mobility scenario. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project conducted a second phase of research called build II. This helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to study aspects of a future air taxi mission.
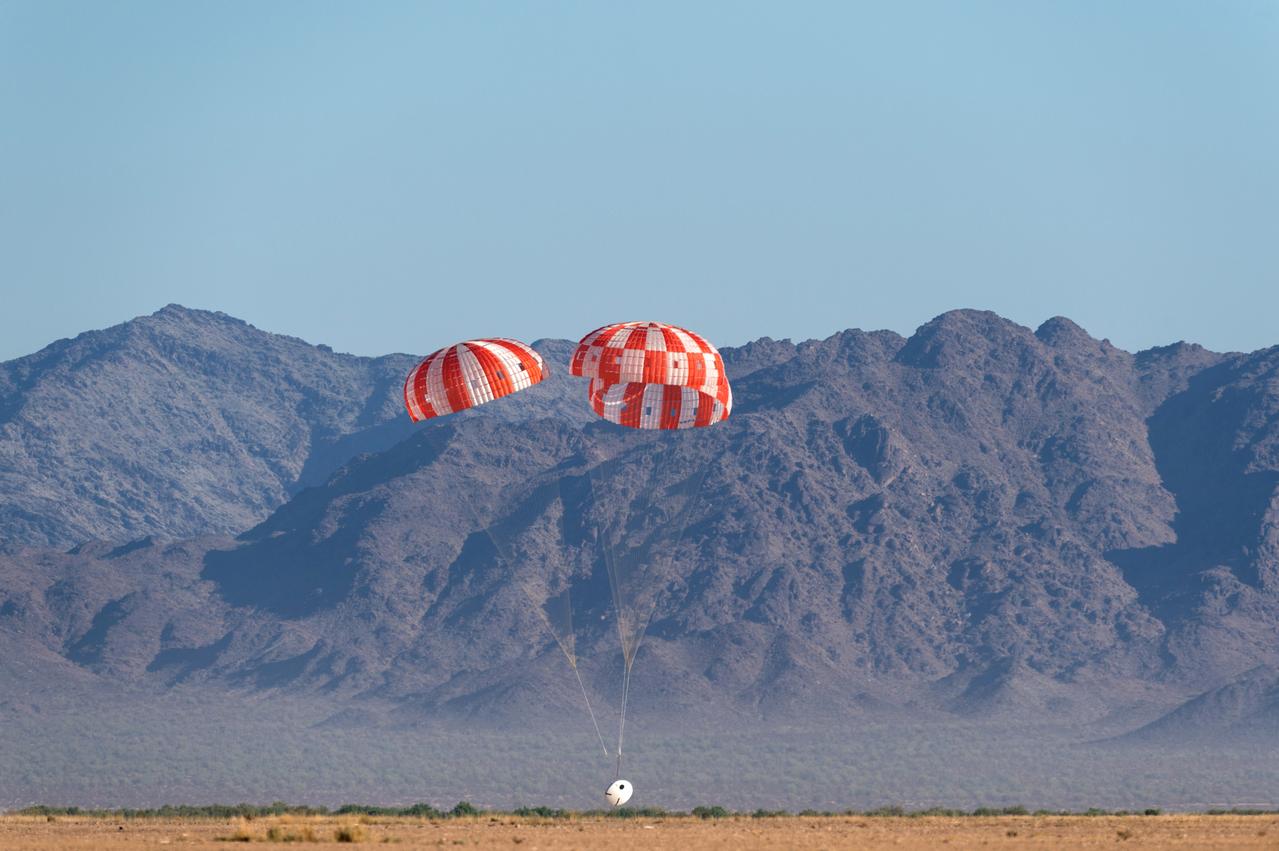

NASA has completes the final test to qualify Orion’s parachute system for flights with astronauts, checking off an important milestone on the path to send humans on missions to the Moon and beyond on Sept. 12, 2018...Over the course of eight tests at the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona, engineers have evaluated the performance of Orion’s parachute system during normal landing sequences as well as several failure scenarios and a variety of potential aerodynamic conditions to ensure astronauts can return safely from deep space missions.
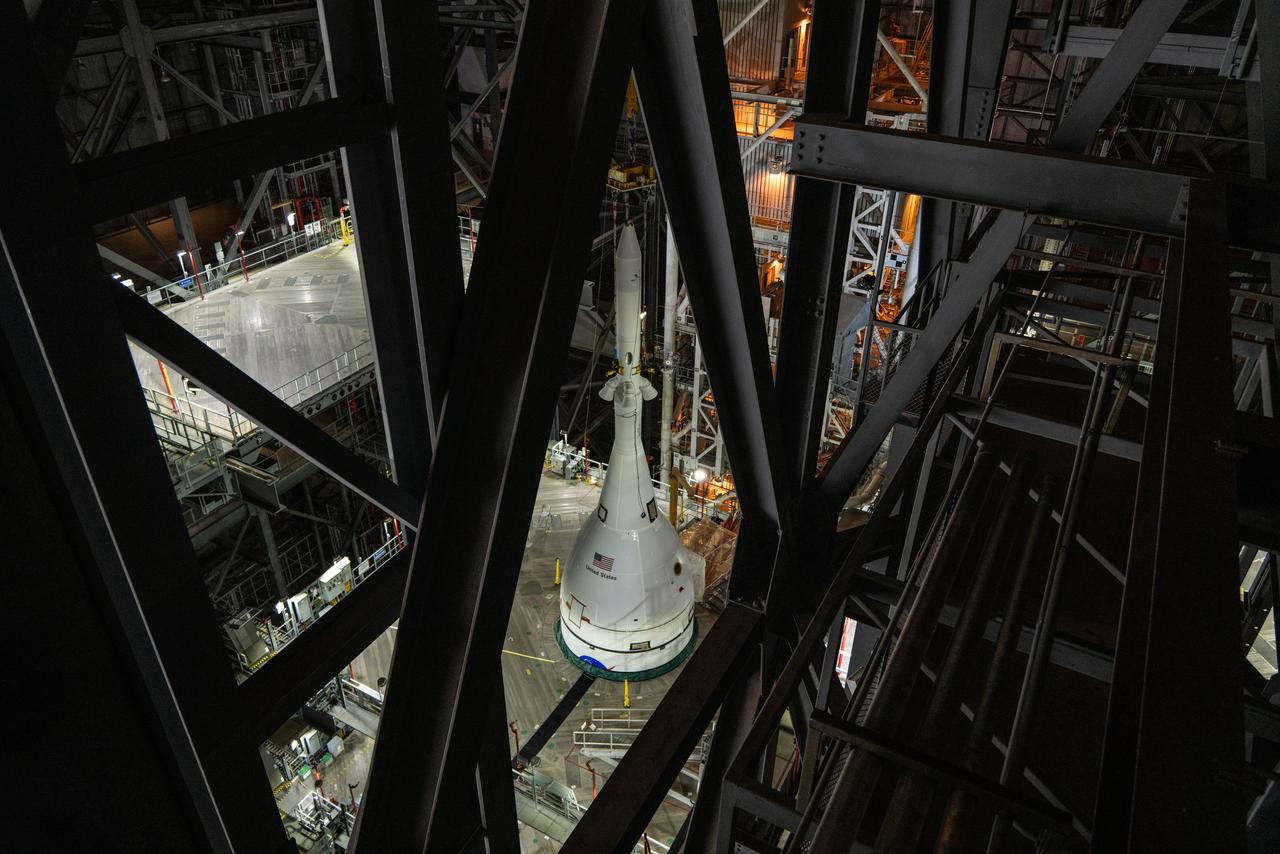

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, is stacked on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The stacking of Orion on top of the SLS completes assembly for the Artemis I flight test. Teams will begin conducting a series of verification tests ahead of rolling out to Launch Complex 39B for the Wet Dress Rehearsal.
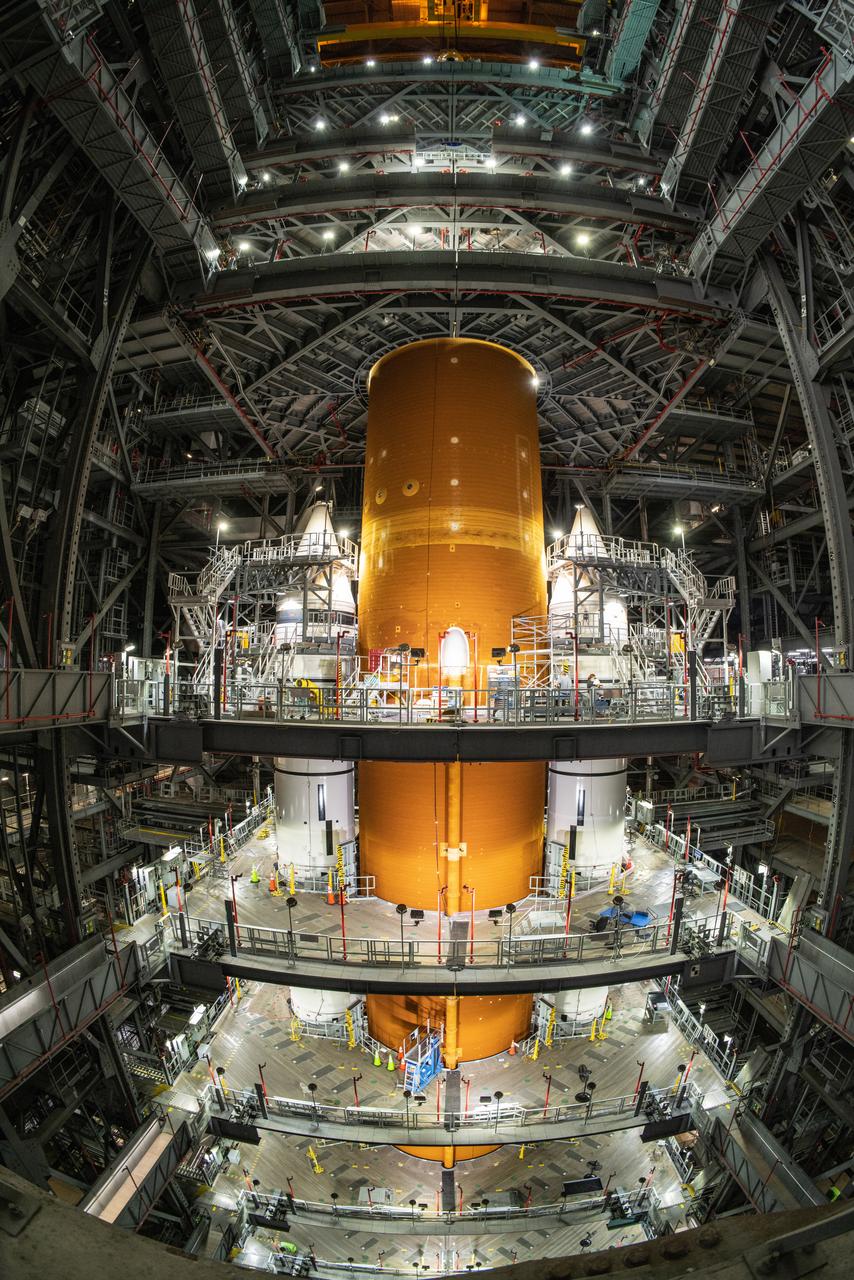

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, is stacked on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The stacking of Orion on top of the SLS completes assembly for the Artemis I flight test. Teams will begin conducting a series of verification tests ahead of rolling out to Launch Complex 39B for the Wet Dress Rehearsal.
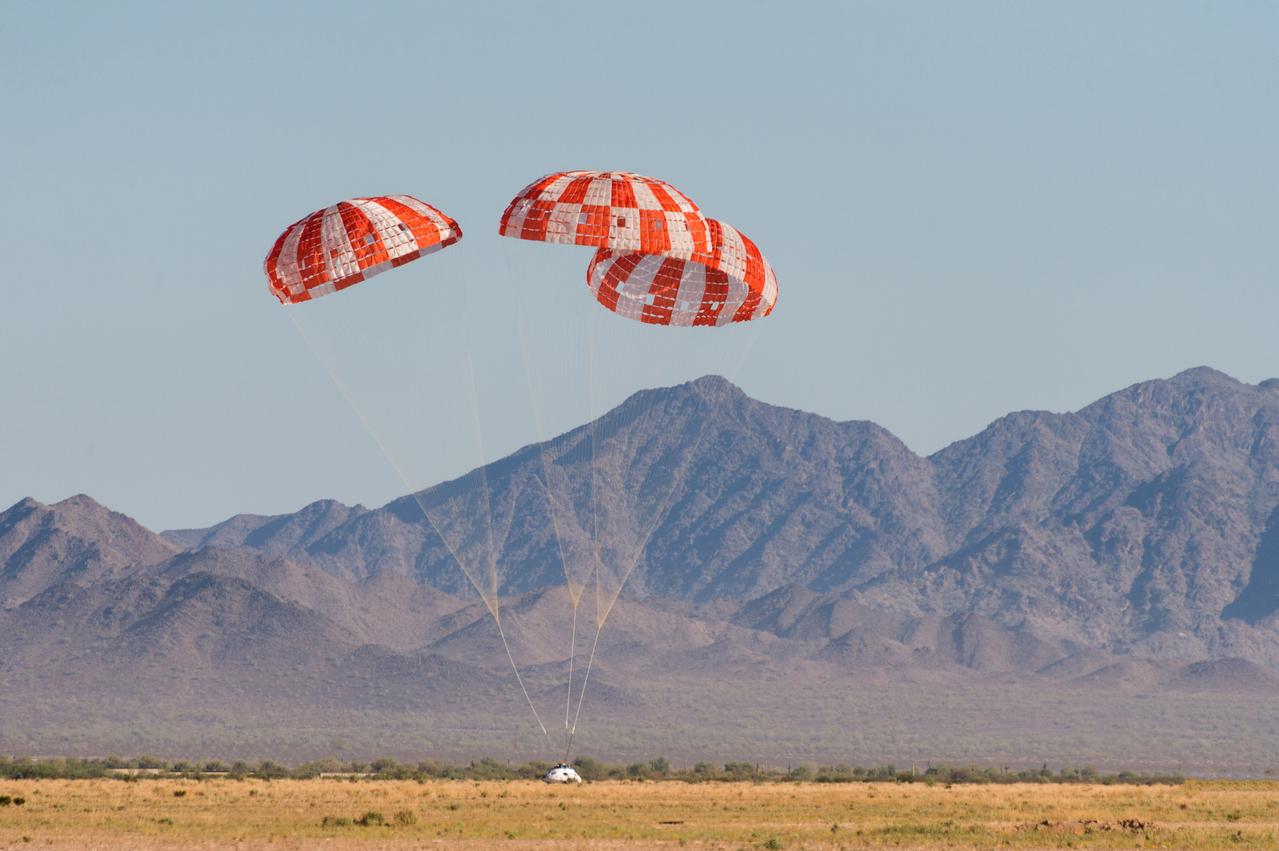

NASA has completes the final test to qualify Orion’s parachute system for flights with astronauts, checking off an important milestone on the path to send humans on missions to the Moon and beyond on Sept. 12, 2018...Over the course of eight tests at the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona, engineers have evaluated the performance of Orion’s parachute system during normal landing sequences as well as several failure scenarios and a variety of potential aerodynamic conditions to ensure astronauts can return safely from deep space missions.
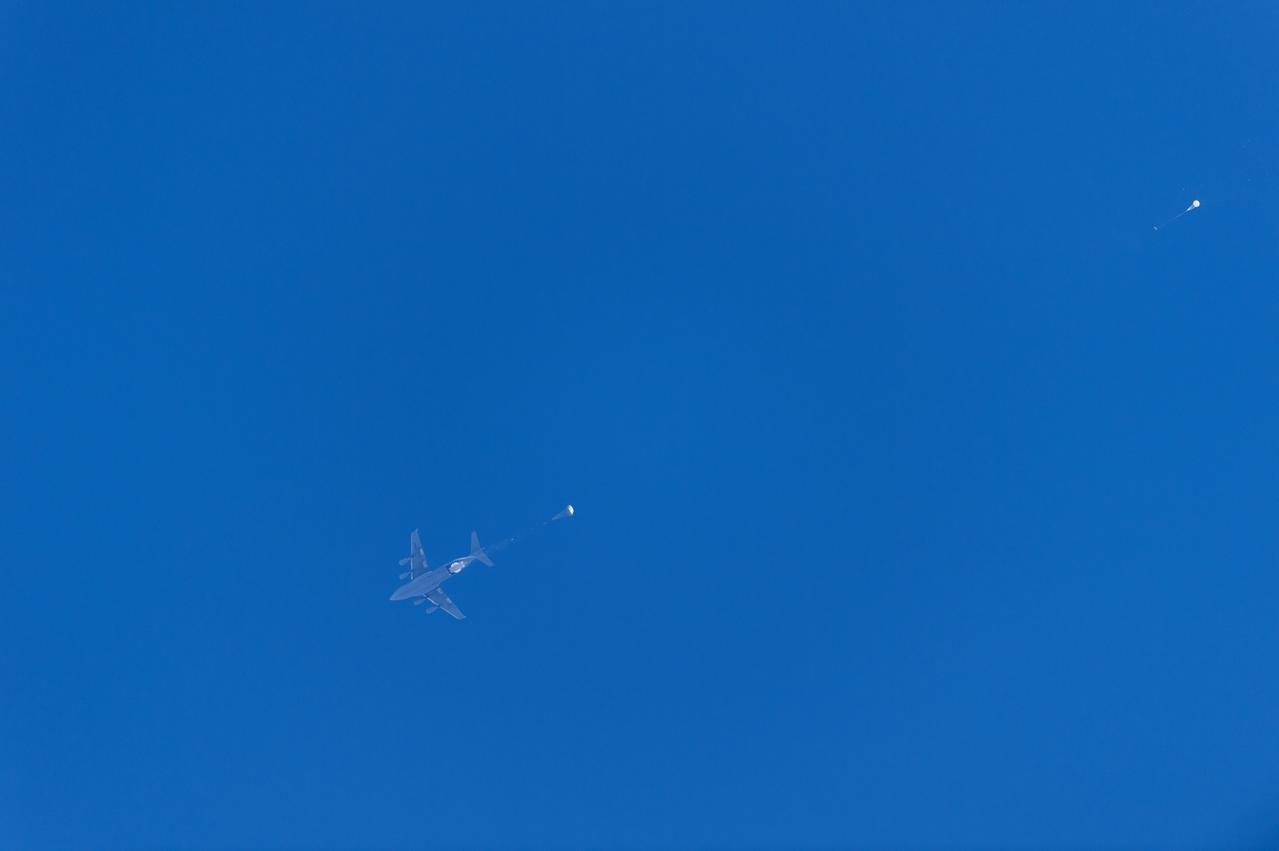

NASA has completes the final test to qualify Orion’s parachute system for flights with astronauts, checking off an important milestone on the path to send humans on missions to the Moon and beyond on Sept. 12, 2018...Over the course of eight tests at the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona, engineers have evaluated the performance of Orion’s parachute system during normal landing sequences as well as several failure scenarios and a variety of potential aerodynamic conditions to ensure astronauts can return safely from deep space missions.
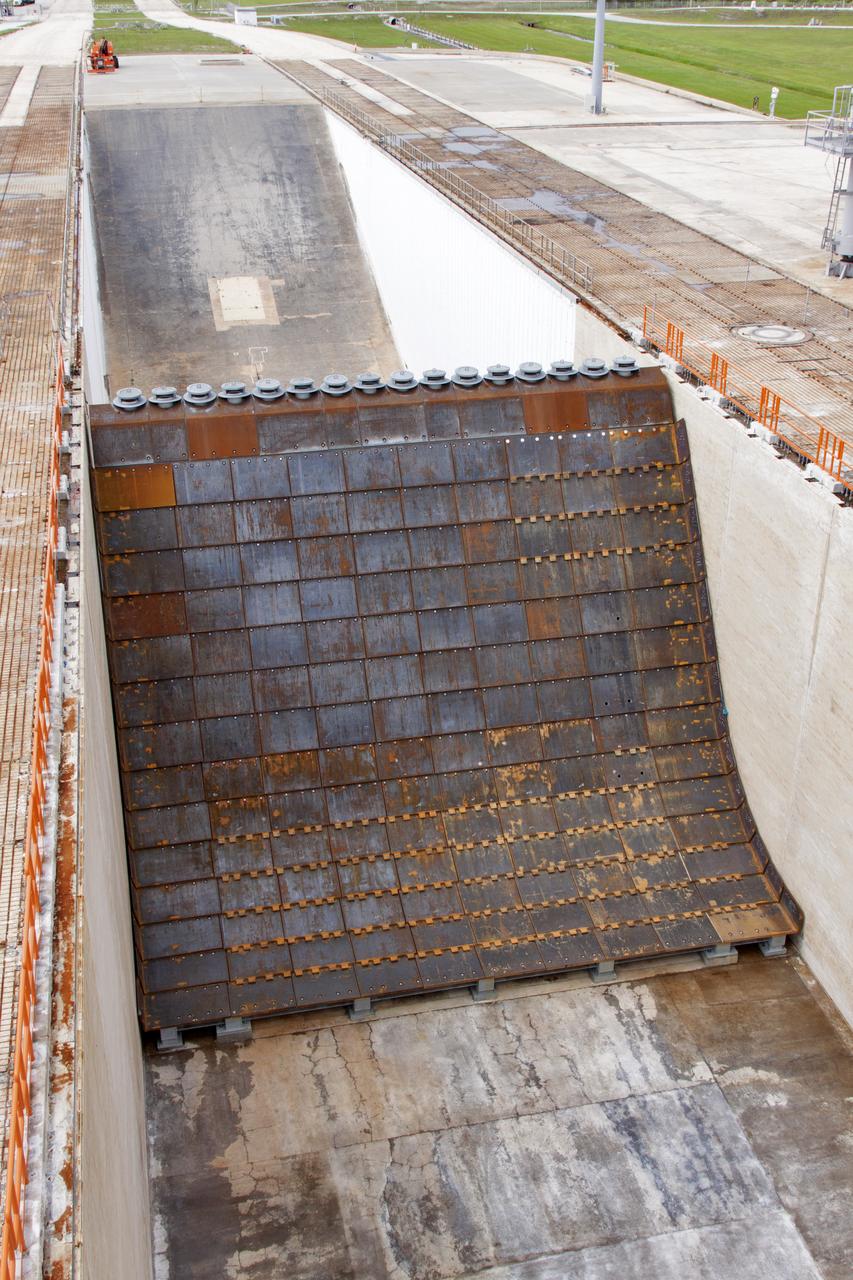

Construction is complete on the main flame deflector in the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flame deflector will safely deflect the plume exhaust from NASA's Space Launch System rocket during launch. It will divert the rocket's exhaust, pressure and intense heat to the north at liftoff. The Exploration Ground Systems Program at Kennedy is refurbishing the pad to support the launch of the SLS rocket and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, and helping to transform the space center into a multi-user spaceport.
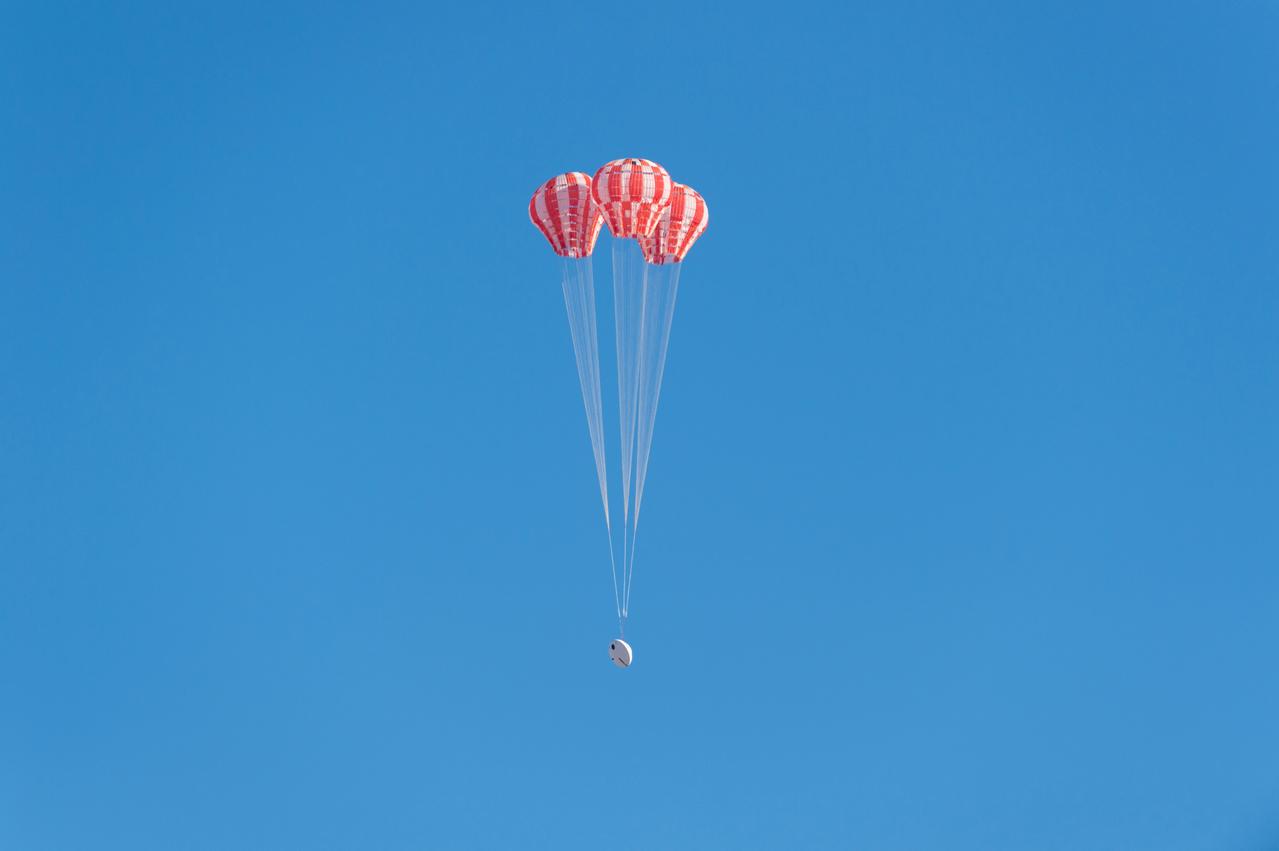

NASA has completes the final test to qualify Orion’s parachute system for flights with astronauts, checking off an important milestone on the path to send humans on missions to the Moon and beyond on Sept. 12, 2018...Over the course of eight tests at the U.S. Army’s Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona, engineers have evaluated the performance of Orion’s parachute system during normal landing sequences as well as several failure scenarios and a variety of potential aerodynamic conditions to ensure astronauts can return safely from deep space missions.