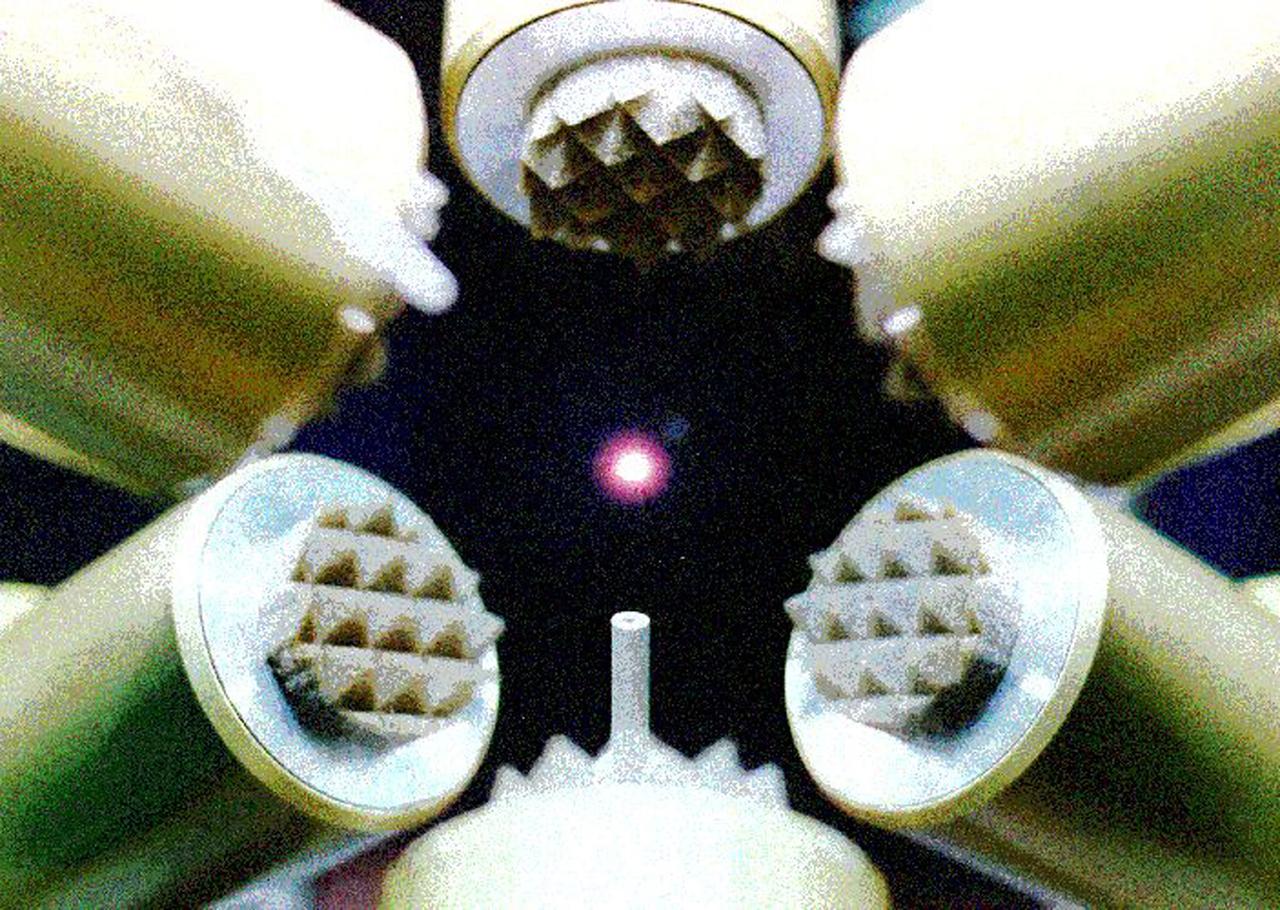
A 3 mm-diameter droplet of aluminum oxide, heated to 2371 deg. C (4,300 deg. F), is suspended in midair by six acoustic transducers. A gas jet (from the nozzle below the drop) helps position the drop for study, and a 500-watt laser melts the sample. Glasses made from aluminum oxide are highly promising for optical transmission and other properties. They are also highly reactive when molten. Containerless processing allows studies of how to form amorphous (glassy) rather than crystalline metal oxides. Credit: Bill Jellison, Containerless Research, Inc.

iss041e096097 (10/23/2014) — Photo documentation of the Electromagnetic Levitator (EML) in the Columbus module of the International Space Station (ISS). The EML multi-user facility is designed for containerless materials processing in space.
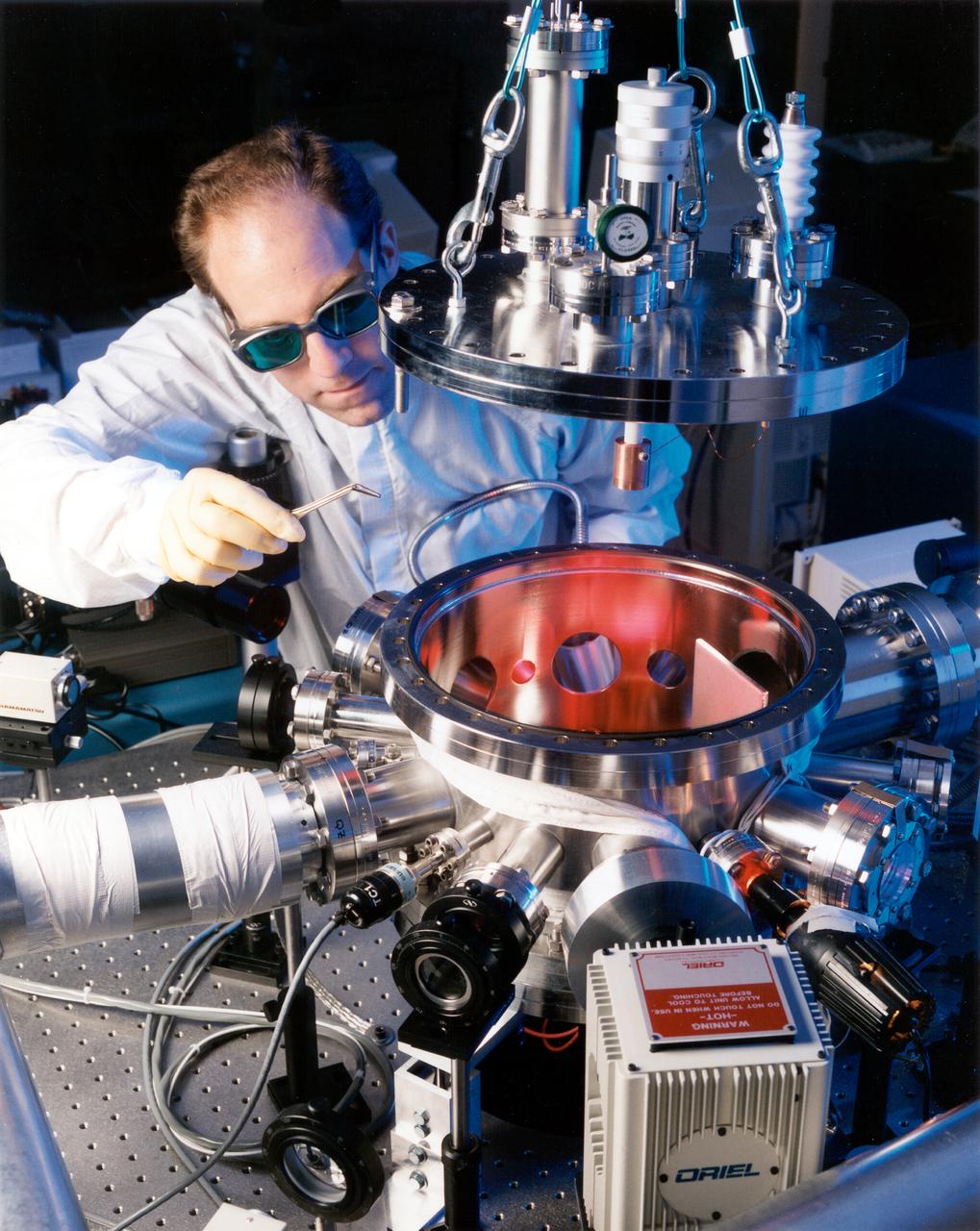
Dr. Rulison of Space System LORAl working with the Electrostatic Levitation (ESL) prior to the donation. Space System/LORAL donated the electrostatic containerless processing system to NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The official hand over took place in July 1998.
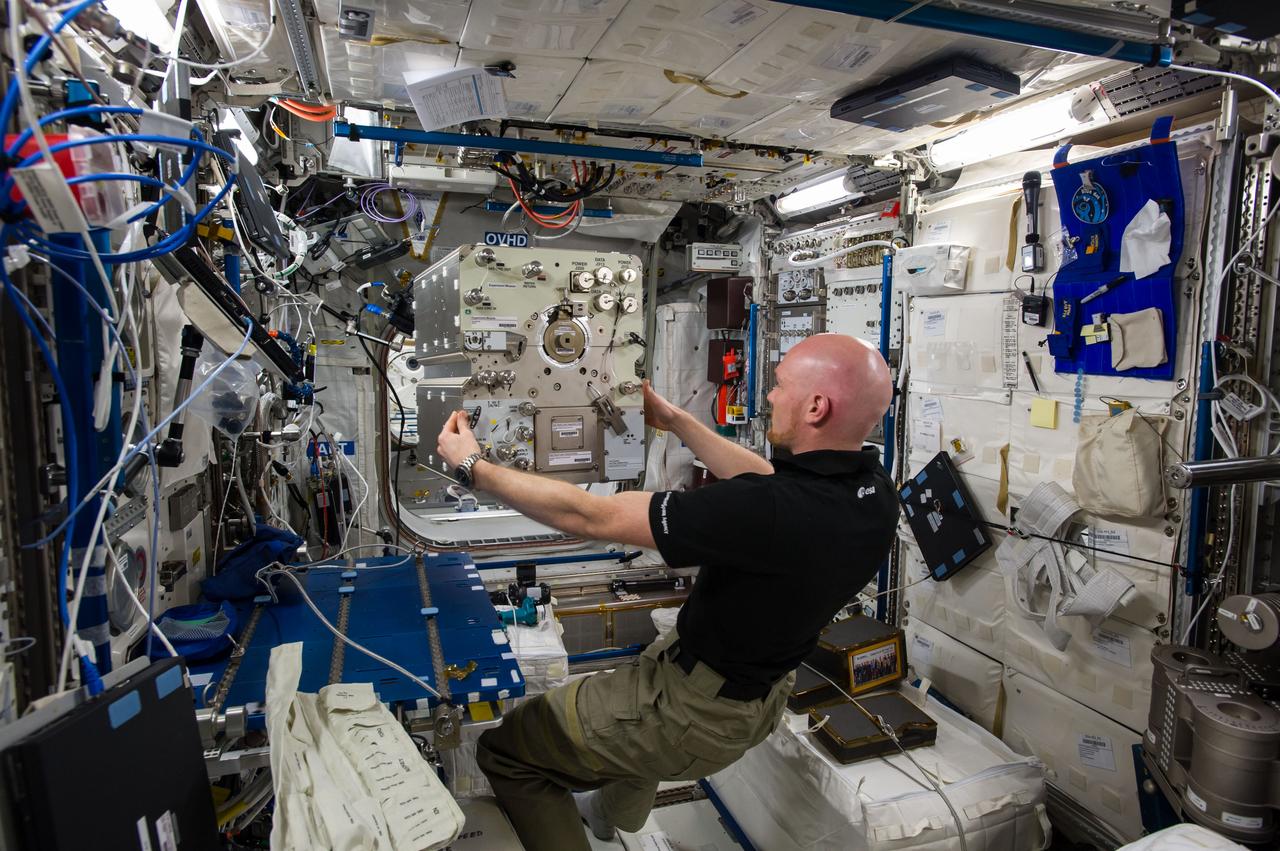

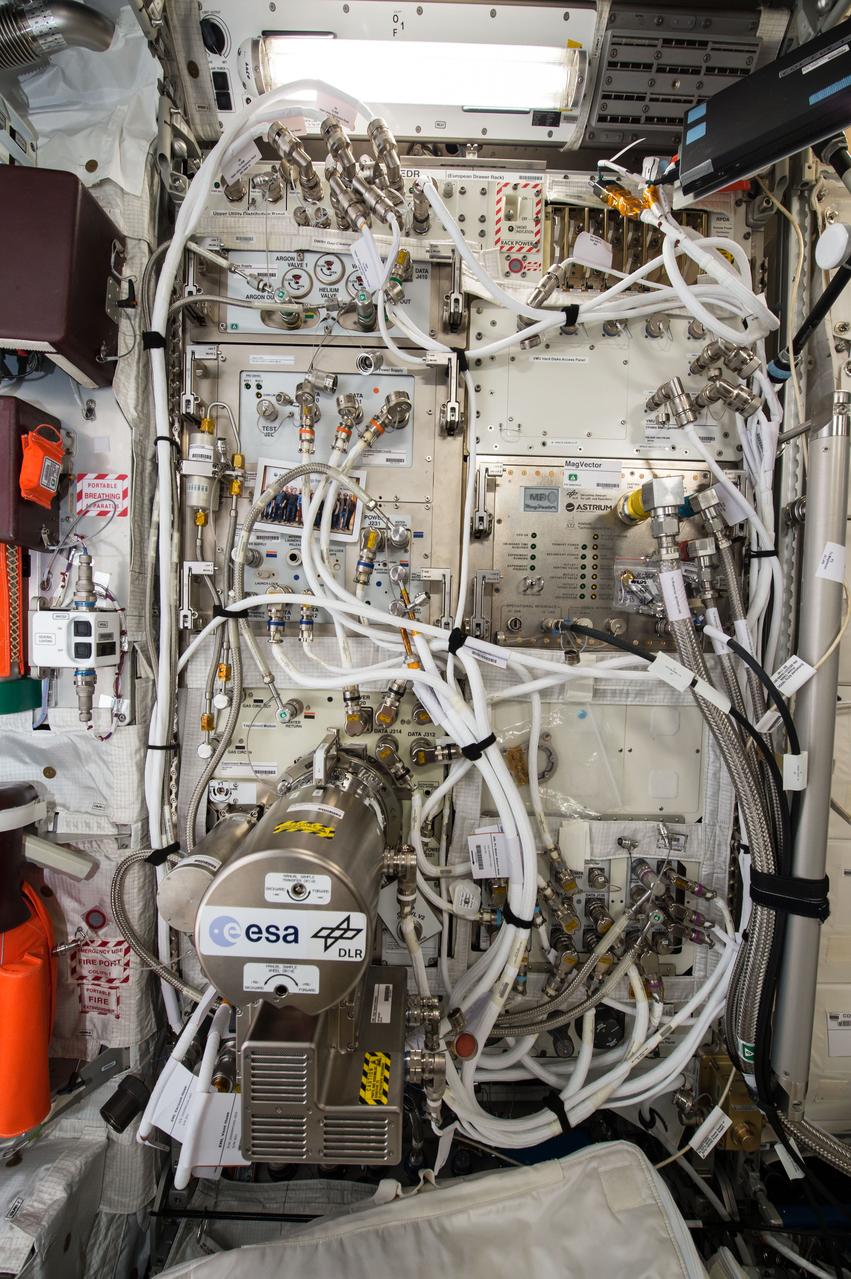
iss040e108044 (8/21/2014) — European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alexander Gerst, is shown in the Columbus module of the International Space Station (ISS) during the installation of the Electromagnetic Levitator (EML). The EML multi-user facility is designed for containerless materials processing in space.
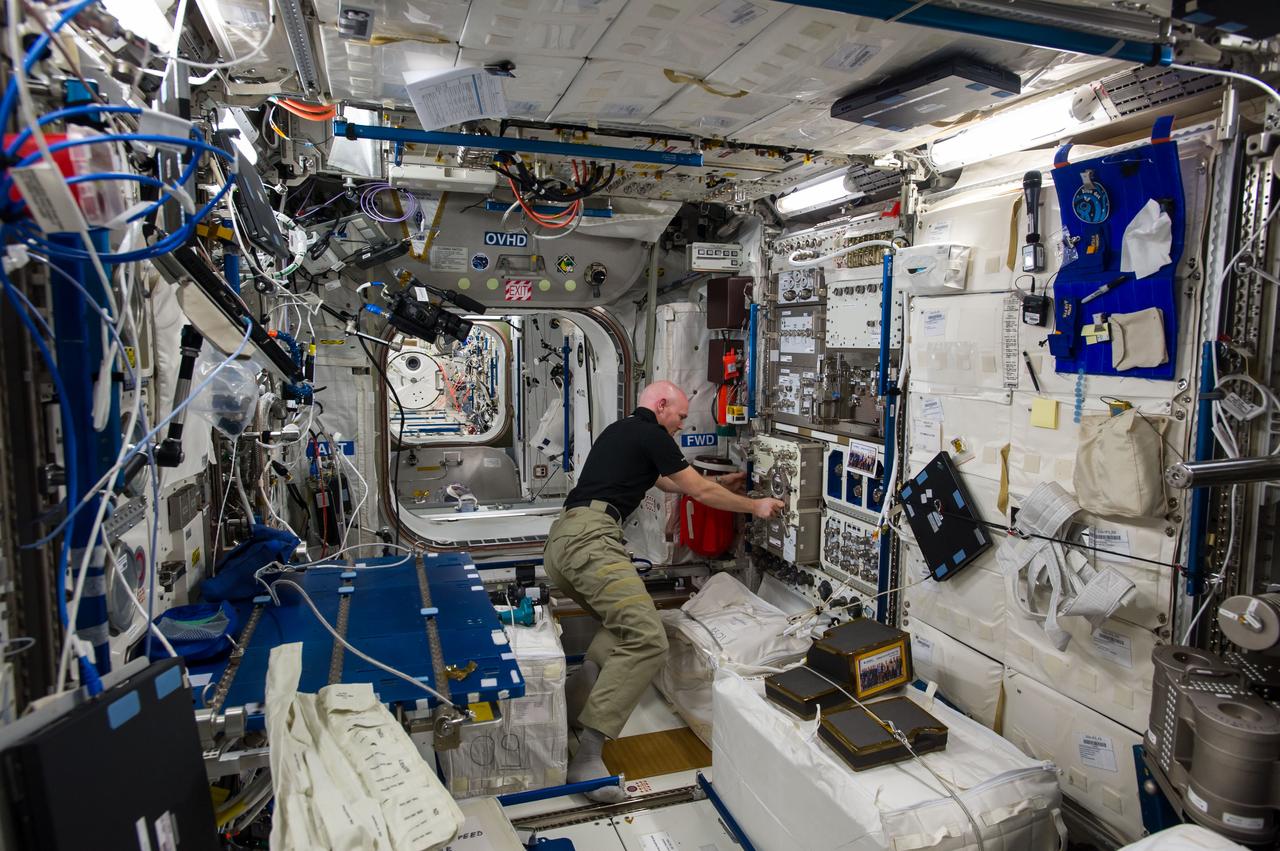

iss040e108050 (8/21/2014) — European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alexander Gerst, is shown in the Columbus module of the International Space Station (ISS) during the installation of the Electromagnetic Levitator (EML). The EML multi-user facility is designed for containerless materials processing in space.
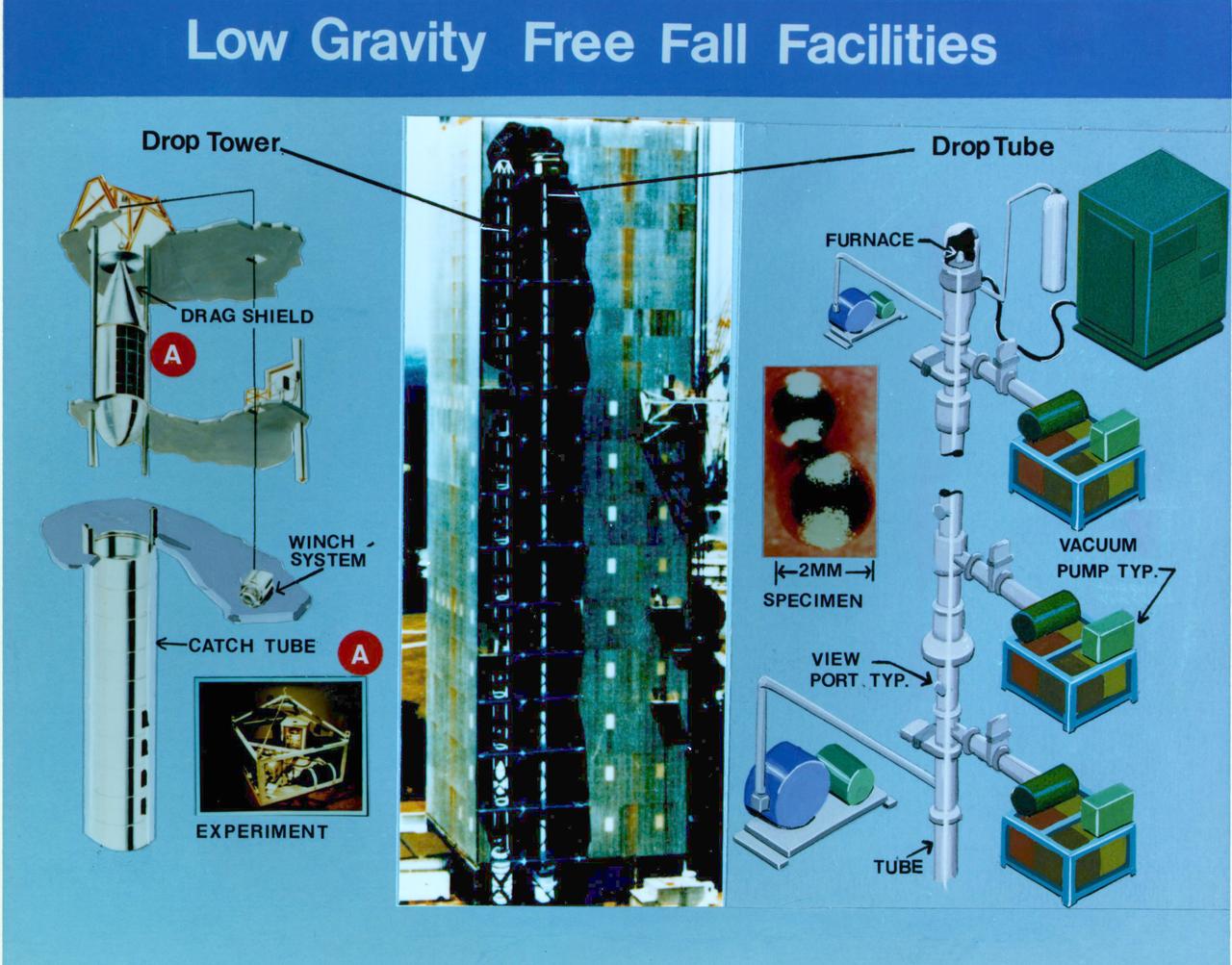
Composite of Marshall Space Flight Center's Low-Gravity Free Fall Facilities.These facilities include a 100-meter drop tower and a 100-meter drop tube. The drop tower simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.2 seconds for containerless processing experiments, immiscible fluids and materials research, pre-flight hardware design test and flight experiment simulation. The drop tube simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.6 seconds and is used extensively for ground-based microgravity convection research in which extremely small samples are studied. The facility can provide deep undercooling for containerless processing experiments that require materials to remain in a liquid phase when cooled below the normal solidification temperature.
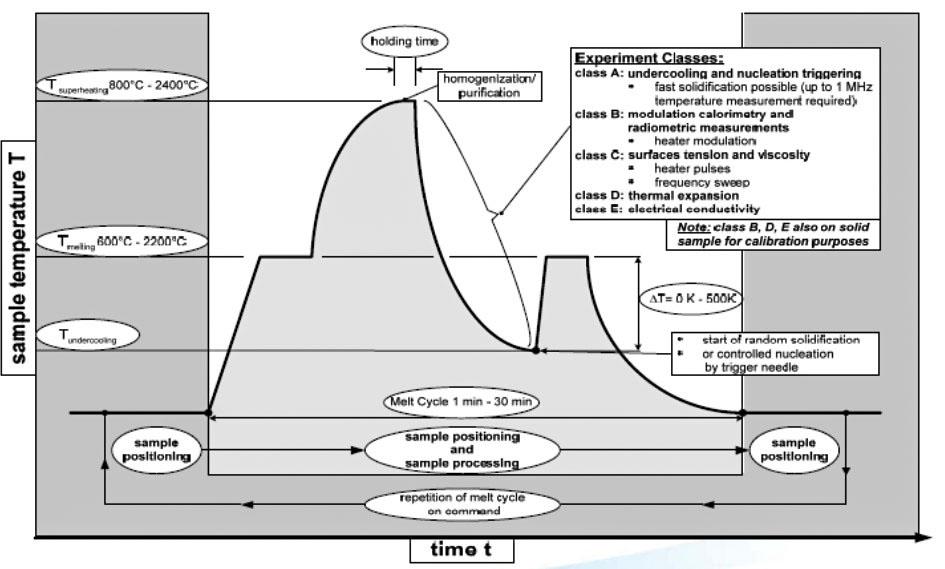
jsc2021e029751 (7/15/2021) --- A diagram showing the the Process cycle of the Electromagnetic Levitator (EML) - Batch 3 of samples. EML is a multi-user facility that provides containerless melting and solidification of electrically conductive, spherical samples, under ultra-high vacuum and/or high gas-purity conditions. Heating and positioning of the sample is achieved by electromagnetic fields generated by a coil system. Batch 3 is a new Sample Chamber to be mounted to the EML process chamber, bringing 18 new samples
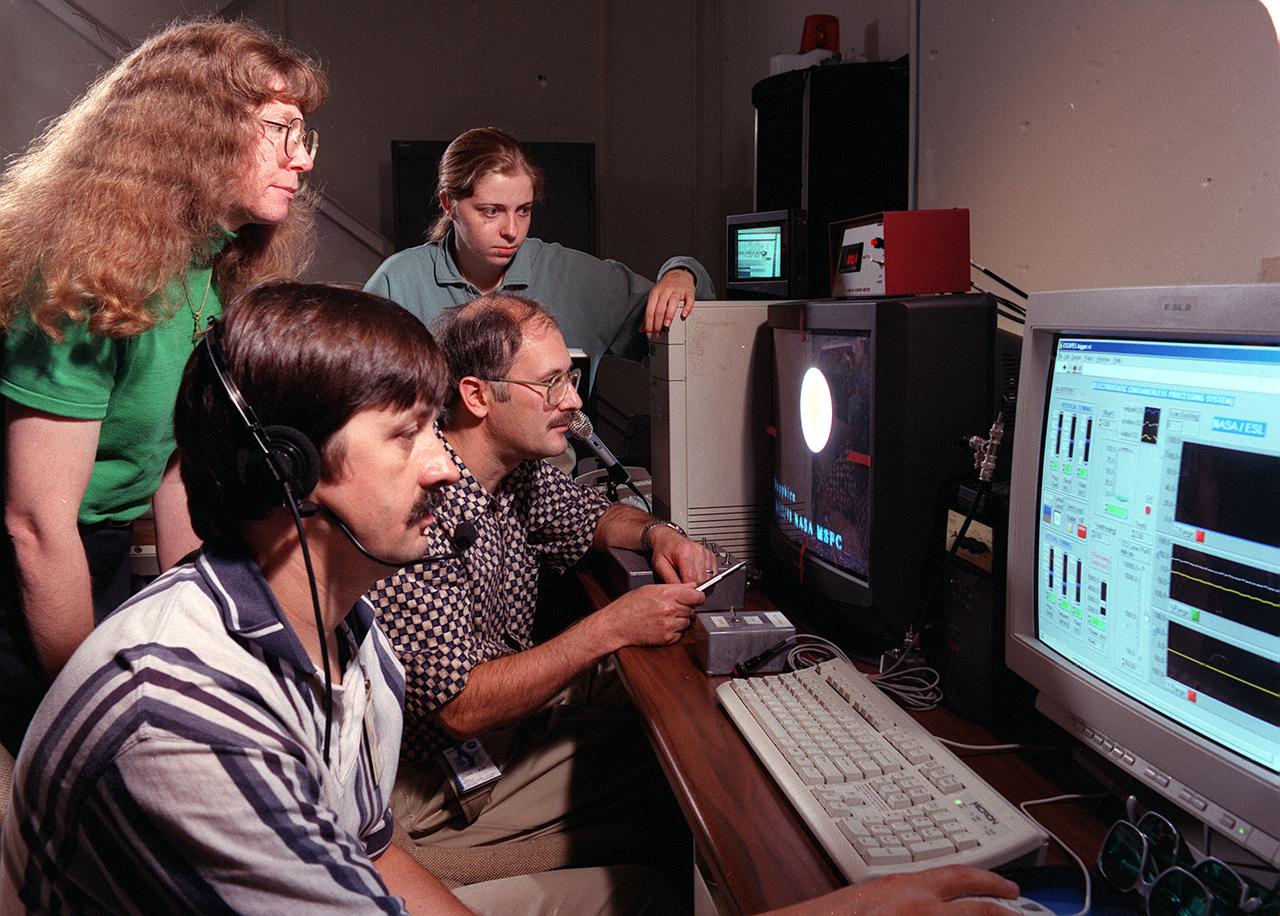

Dr. Jan Rogers (left) and Larry Savage (foreground) of the Science Directorate at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) are joined by Dr. Richard Weber (center) and April Hixon of Containerless Research Inc. of Evanston, Ill., in conducting an experiment run of the Electrostatic Levitator (ESL) using insulating materials. Materials researchers use unique capabilities of the facility to levitate and study the properties of various materials important in manufacturing processes.

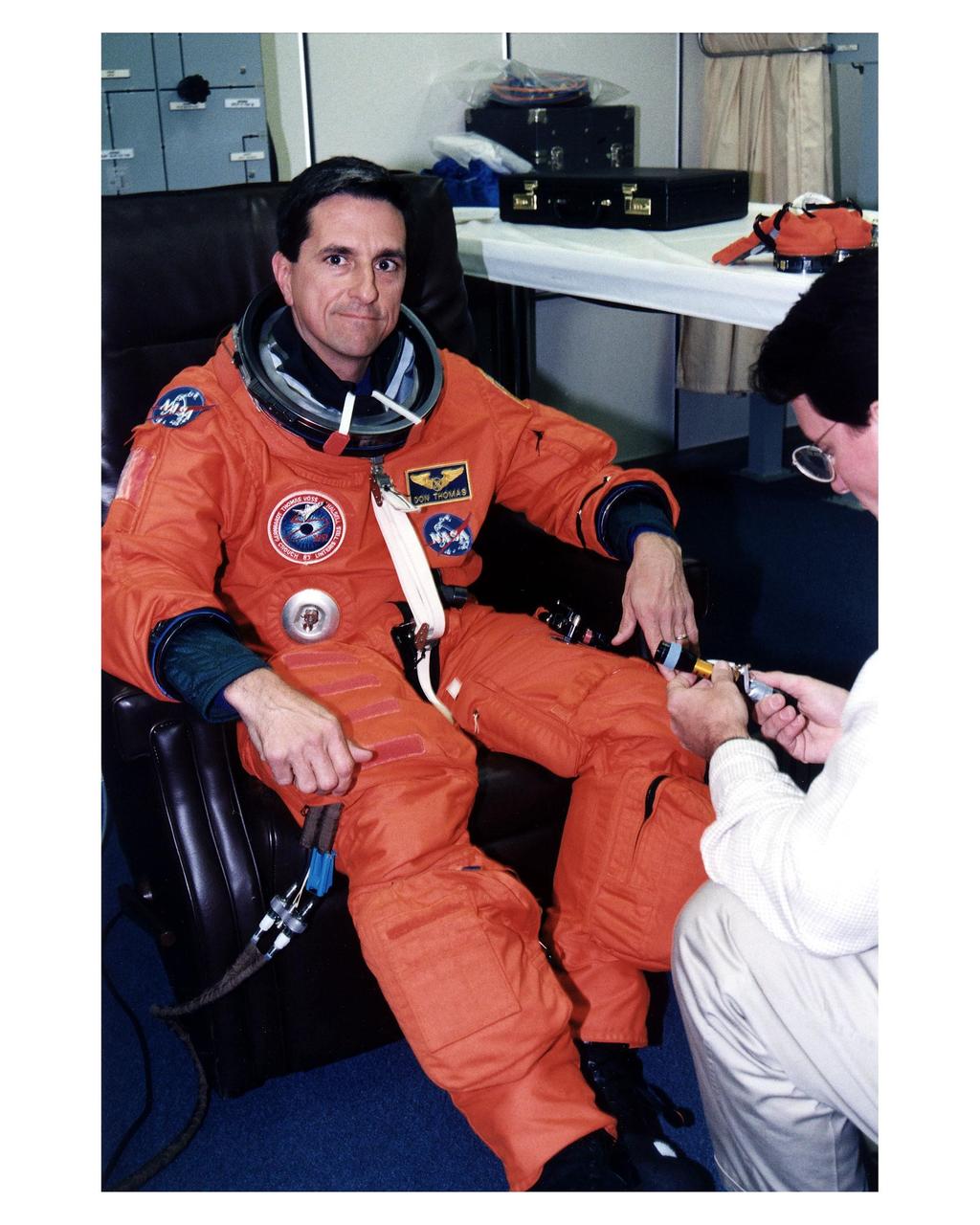
STS-94 Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas prepares to enter the Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Pad 39A in preparation for launch. He has flown on STS-83, STS-70 and STS-65. He holds a doctorate in materials science and has been the Principal Investigator for a Space Shuttle crystal growth experiment. Because of his background in materials science, Thomas will be concentrating his efforts during the Red shift on the five experiments in this discipline in the Large Isothermal Furnace. He also will work on the ten materials science investigations in the Electromagnetic Containerless Processing Facility and four that will be measuring the effects of microgravity and motion in the orbiter on the experiments. Thomas and six fellow crew members will lift off during a launch window that opens at 1:50 p.m. EDT, July 1. The launch window will open 47 minutes early to improve the opportunity to lift off before Florida summer rain showers reach the space center

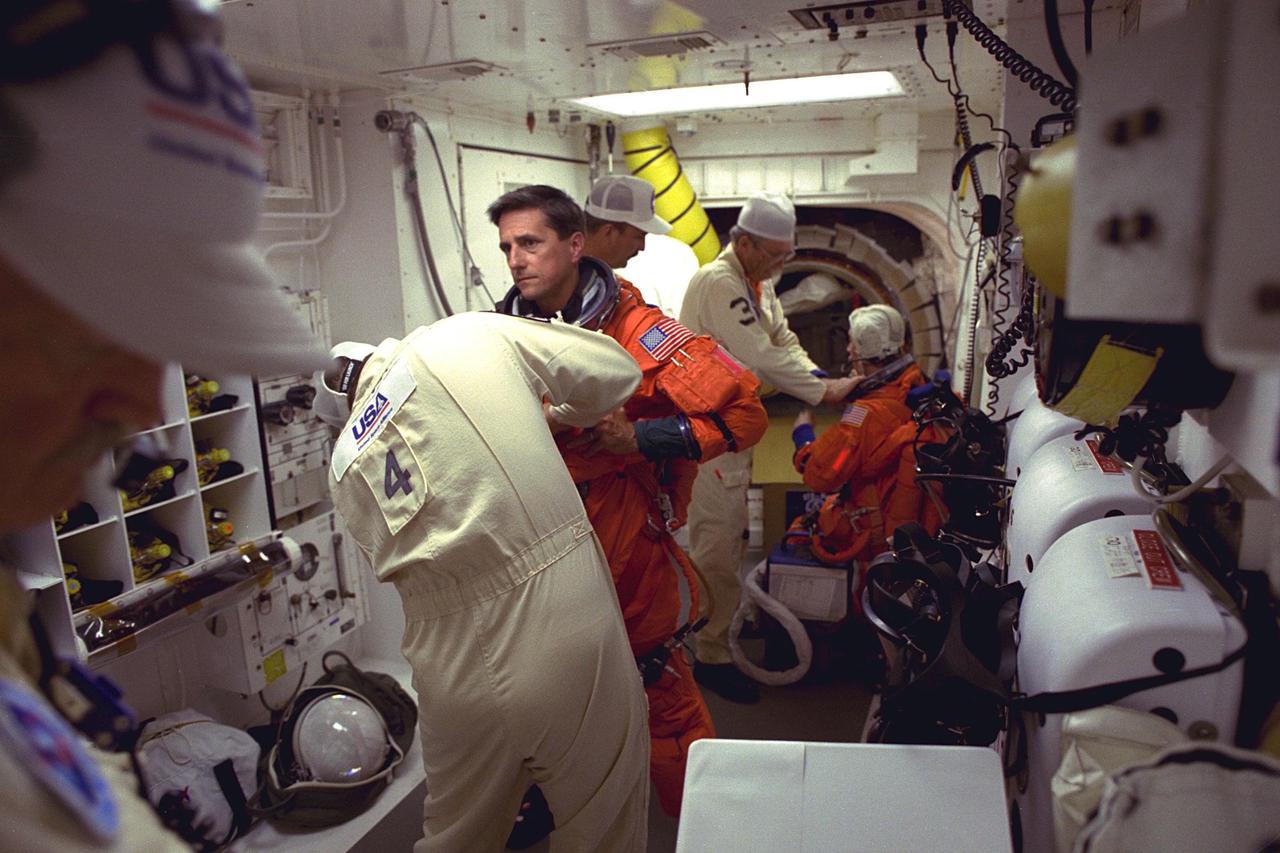
STS-83 Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas is assisted into his launch/entry suit in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building. He has flown on both STS-70 and STS-65. He holds a doctorate in materials science and has been the Principal Investigator for a Space Shuttle crystal growth experiment. Because of his background in materials science, Thomas will be concentrating his efforts during the Red shift on the five experiments in this discipline in the large Isothermal Furnace. He also will work on the ten materials science investigations in the Electromagnetic Containerless Processing Facility and four that will be measuring the effects of microgravity and motion in the orbiter on the experiments. Thomas and six fellow crew members will shortly depart the O&C and head for Launch Pad 39A, where the Space Shuttle Columbia will lift off during a launch window that opens at 2:00 pm EST, April 4
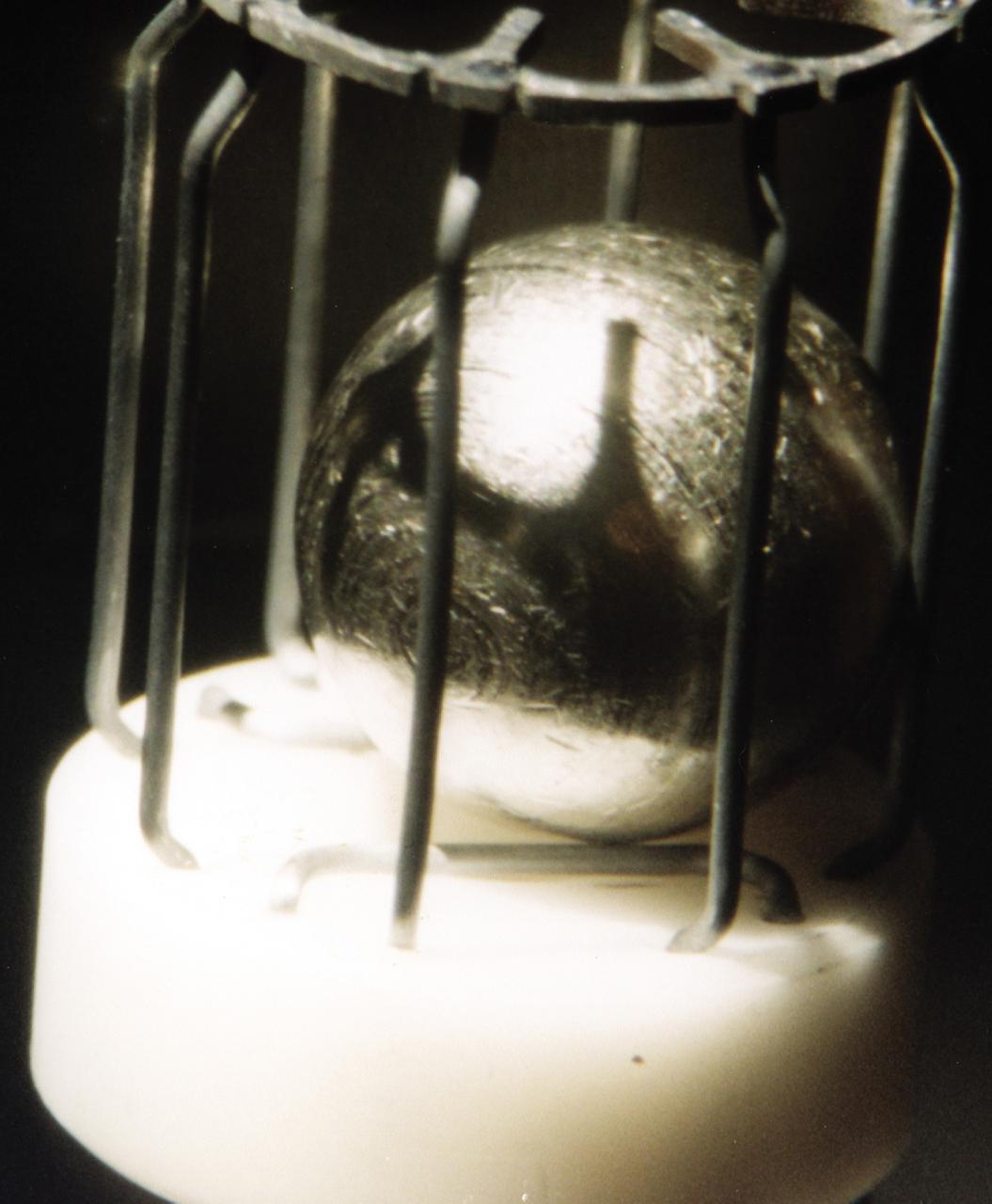
This metal sample, which is approximately 1 cm in diameter, is typical of the metals that were studied using the German designed electromagnetic containerless processing facility. The series of experiments that use this device is known as TEMPUS which is the acronym that stands for the German Tiegelfreies Elektromanetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit. Most of the TEMPUS experiments focused on various aspects of undercooling liquid metal and alloys. Undercooling is the process of melting a material and then cooling it to a temperature that is below its normal freezing or solidification point. The TEMPUS experiments that used the metal cages as shown in the photograph, often studied bulk metallic glass, a solid material with no crystalline structures. We study metals and alloys not only to build things in space, but to improve things that are made on Earth. Metals and alloys are everywhere around us; in our automobiles, in the engines of aircraft, in our power-plants, and elsewhere. Despite their presence in everyday life, there are many scientific aspects of metals that we do not understand.
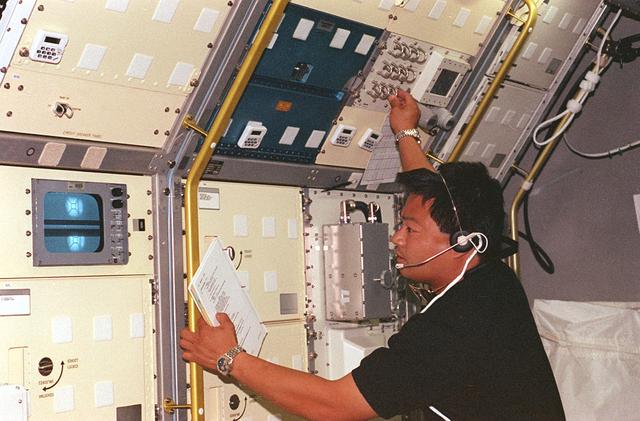

TEMPUS, an electromagnetic levitation facility that allows containerless processing of metallic samples in microgravity, first flew on the IML-2 Spacelab mission. The principle of electromagnetic levitation is used commonly in ground-based experiments to melt and then cool metallic melts below their freezing points without solidification occurring. The TEMPUS operation is controlled by its own microprocessor system; although commands may be sent remotely from the ground and real time adjustments may be made by the crew. Two video cameras, a two-color pyrometer for measuring sample temperatures, and a fast infrared detector for monitoring solidification spikes, will be mounted to the process chamber to facilitate observation and analysis. In addition, a dedicated high-resolution video camera can be attached to the TEMPUS to measure the sample volume precisely.
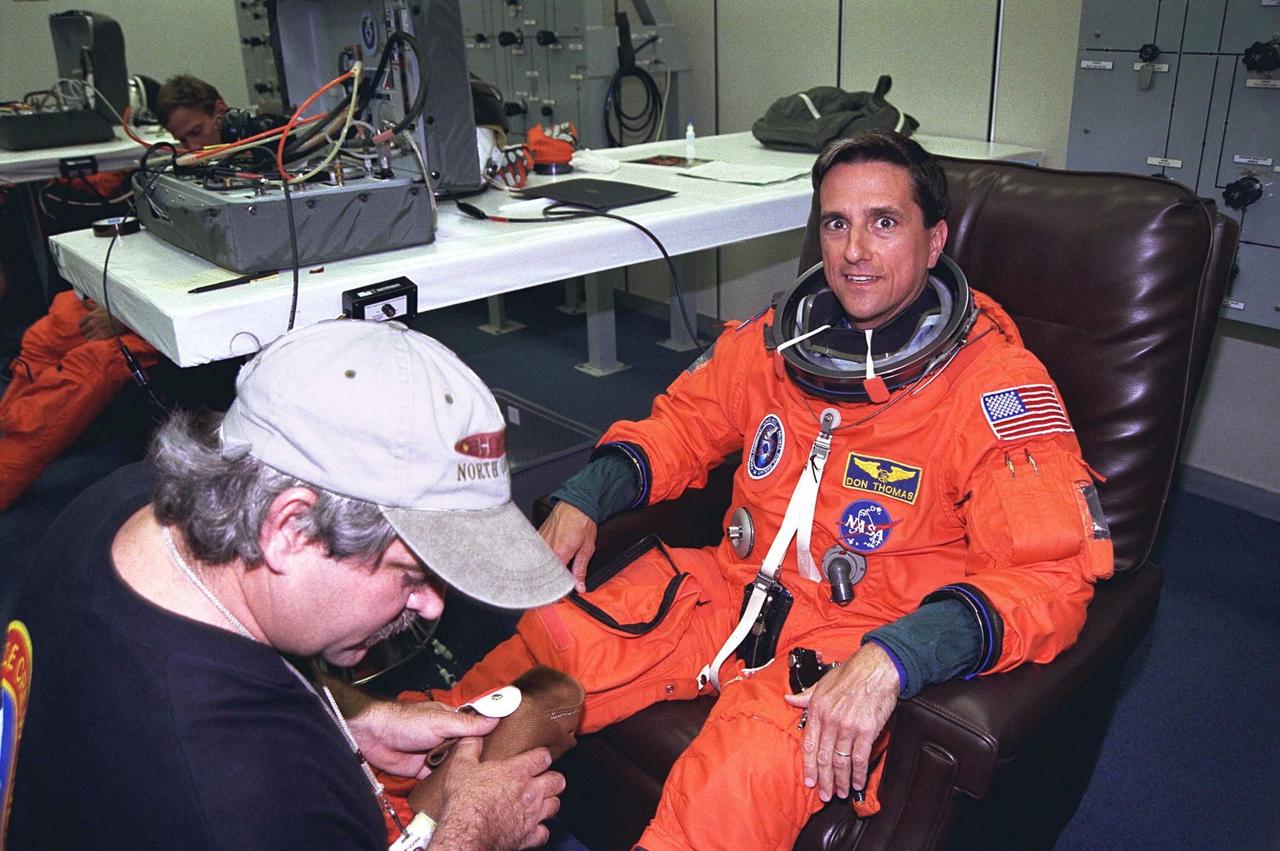

STS-94 Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas smiles as a suit technician helps him into his launch/entry suit in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building. He has flown on STS-83, STS-70 and STS-65. He holds a doctorate in materials science and has been the Principal Investigator for a Space Shuttle crystal growth experiment. Because of his background in materials science, Thomas will be concentrating his efforts during the Red shift on the five experiments in this discipline in the Large Isothermal Furnace. He also will work on the ten materials science investigations in the Electromagnetic Containerless Processing Facility and four that will be measuring the effects of microgravity and motion in the orbiter on the experiments. Thomas and six fellow crew members will shortly depart the O&C and head for Launch Pad 39A, where the Space Shuttle Columbia will lift off during a launch window that opens at 1:50 p.m. EDT, July 1. The launch window was opened 47 minutes early to improve the opportunity to lift off before Florida summer rain showers reached the space center
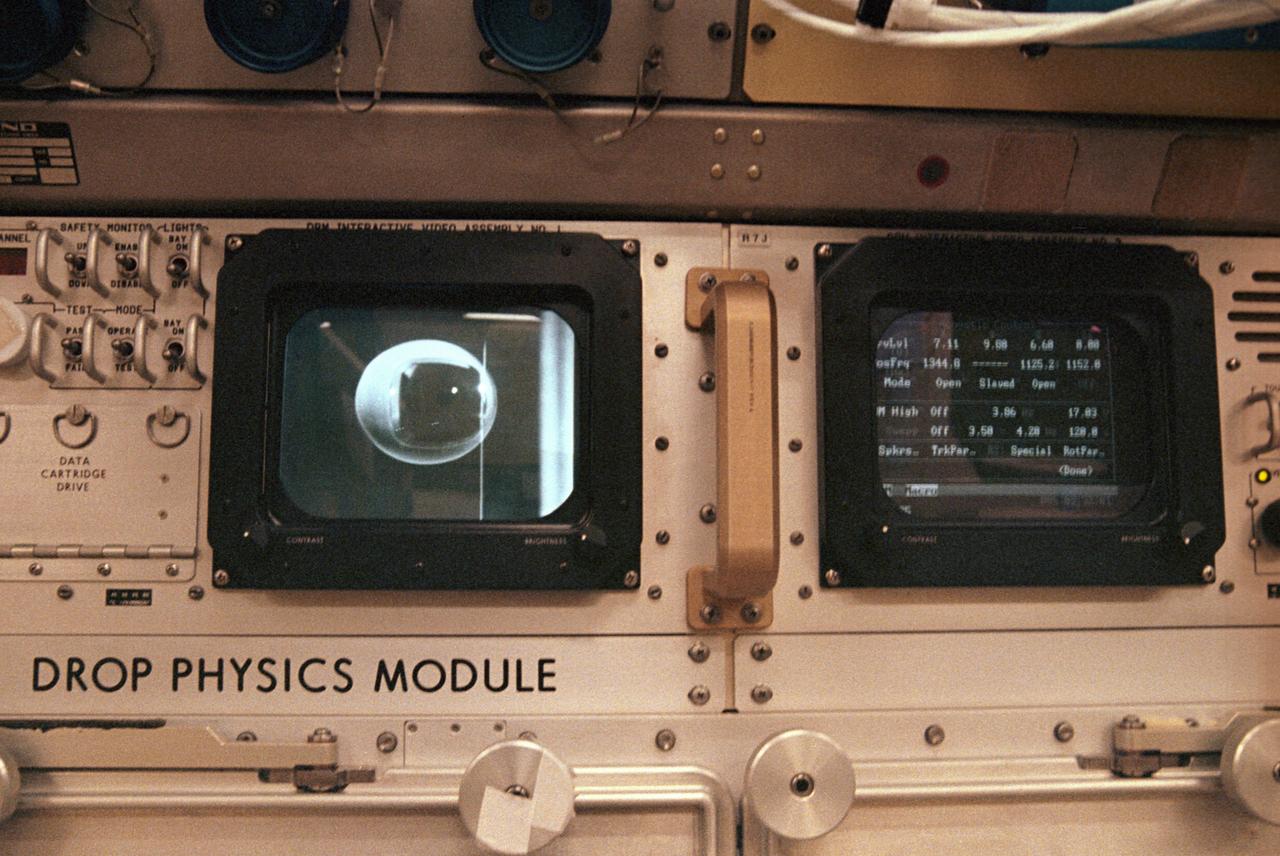
The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs that provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightlessness environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This is a close-up view of the Drop Physics Module (DPM) in the USML science laboratory. The DPM was dedicated to the detailed study of the dynamics of fluid drops in microgravity: their equilibrium shapes, the dynamics of their flows, and their stable and chaotic behaviors. It also demonstrated a technique known as containerless processing. The DPM and microgravity combine to remove the effects of the container, such as chemical contamination and shape, on the sample being studied. Sound waves, generating acoustic forces, were used to suspend a sample in microgravity and to hold a sample of free drops away from the walls of the experiment chamber, which isolated the sample from potentially harmful external influences. The DPM gave scientists the opportunity to test theories of classical fluid physics, which have not been confirmed by experiments conducted on Earth. This image is a close-up view of the DPM. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992, and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.