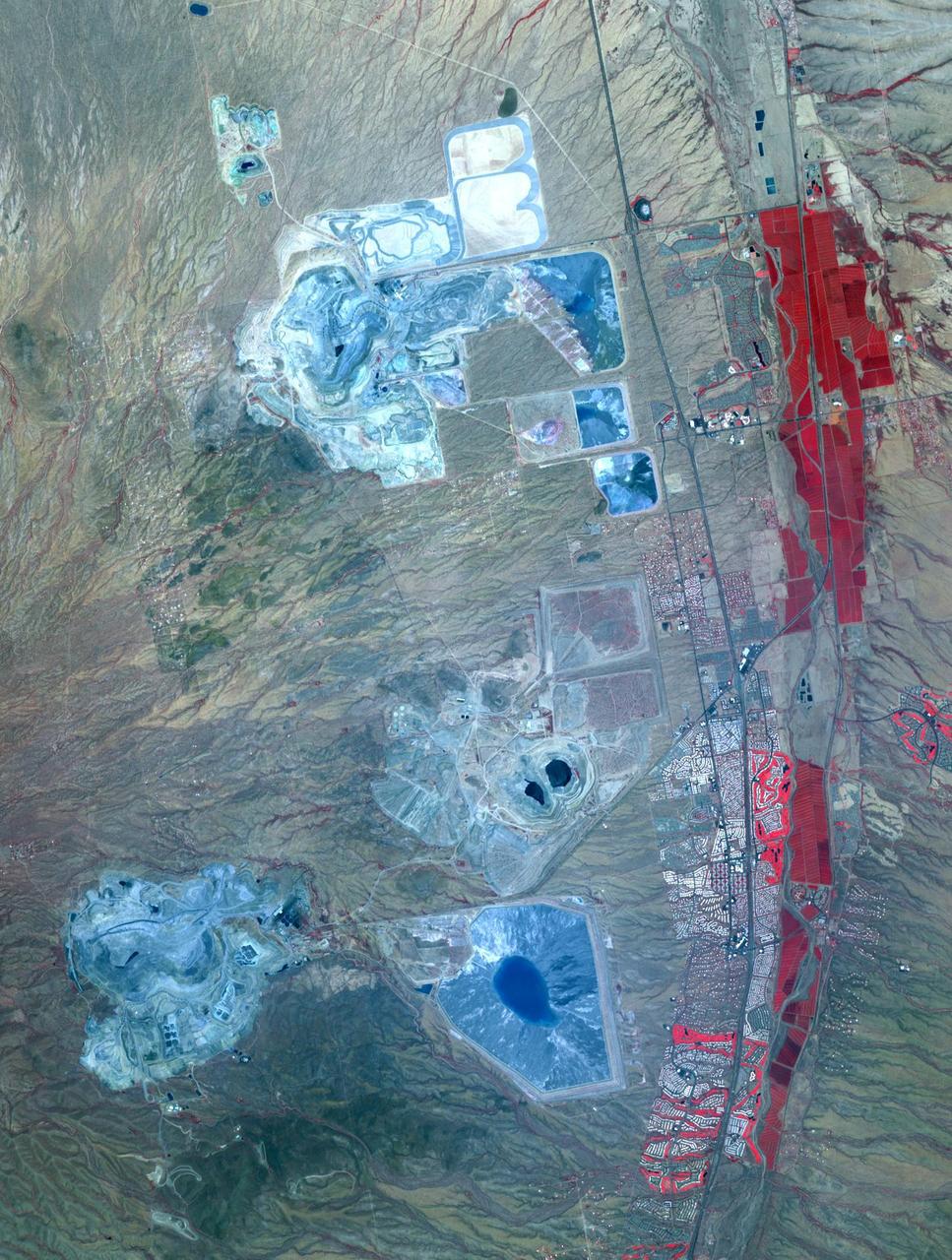

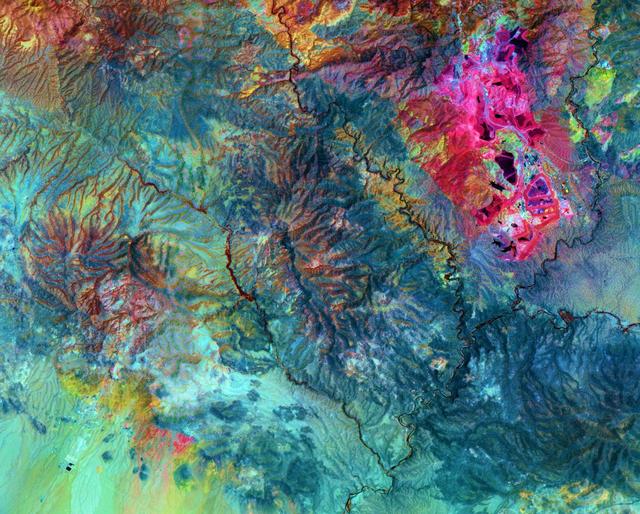
Arizona produces 60% of the total copper mined in the US; in 2007, 750,000 tons of copper came out of the state. One of the major mining districts is located about 30 km south of Tucson. Starting around 1950, open-pit mining replaced underground operations, and the ASARCO-Mission complex, Twin Buttes, and Sierrita mines became large open pit operations. Accompanying copper mineralization, silver, molybdenum, zinc, lead and gold are extracted. In addition to the pits themselves, enormous leach ponds and tailings piles surround the pits. The image was acquired May 31, 2012, covers an area of 22 by 28 km, and is located at 31.9 degrees north, 111 degrees west. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and data products. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are: monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. The U.S. science team is located at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. The Terra mission is part of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. More information about ASTER is available at <a href="http://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
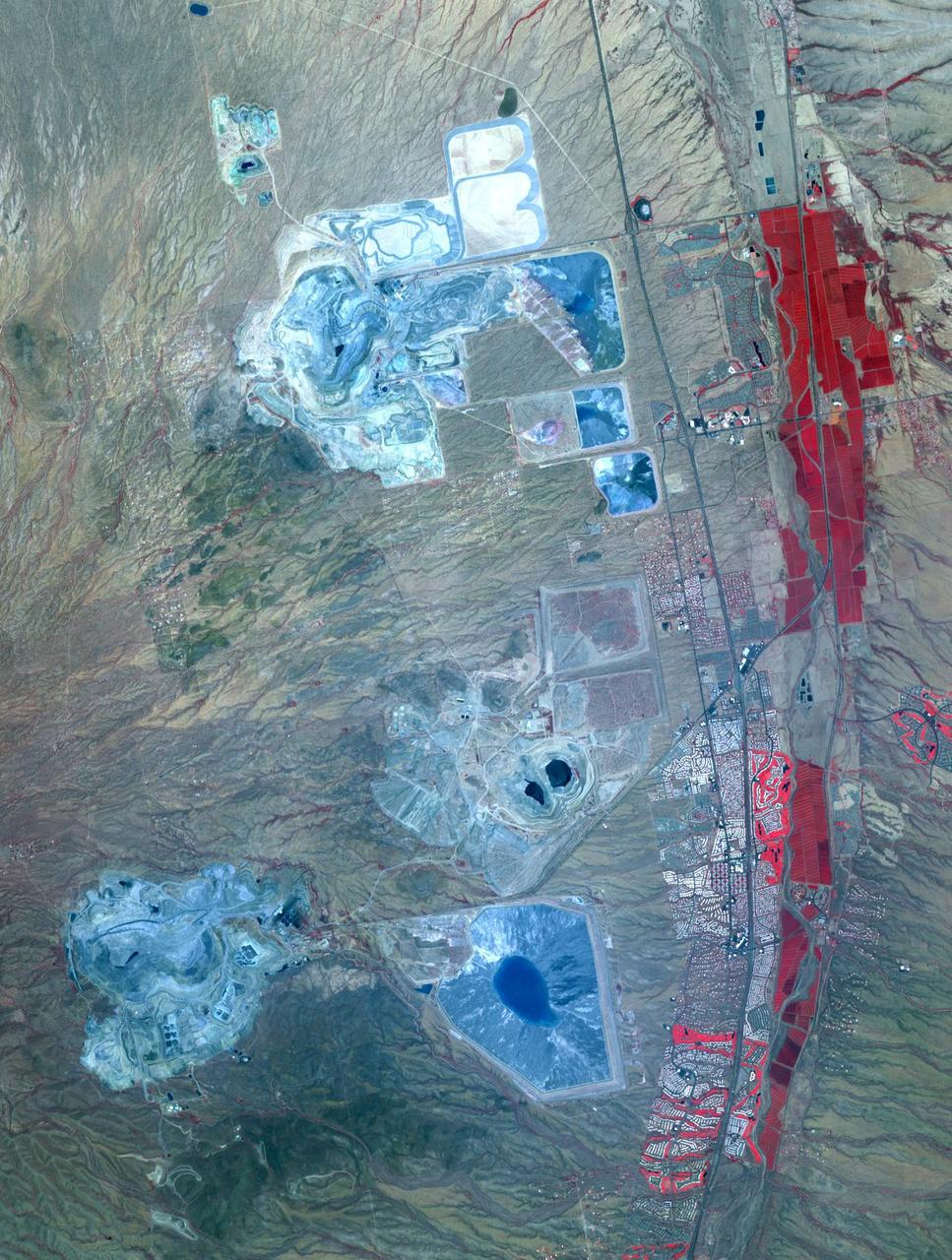

This image acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft shows Arizona, Calif., which produces 60% of the total copper mined in the United States.
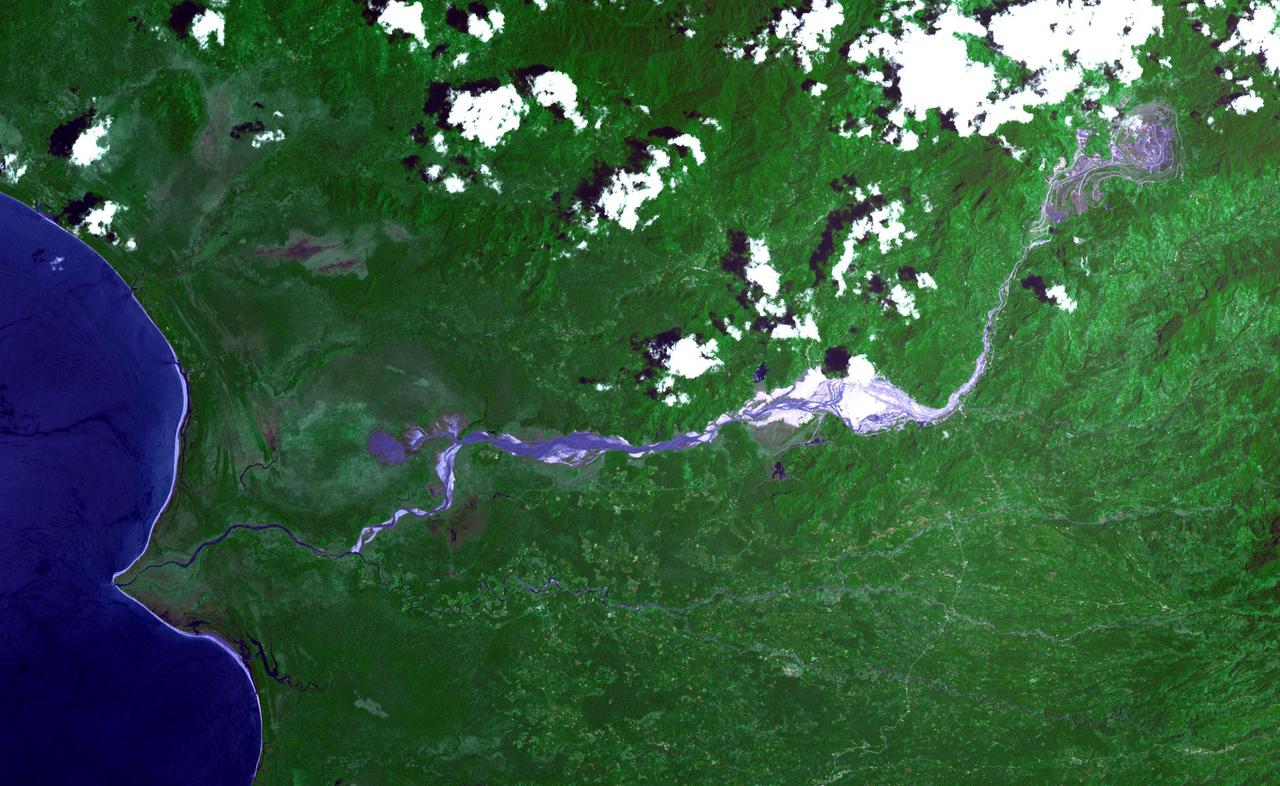

The Panguna copper ore deposit was discovered in 1969 in the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, Papua New Guinea. It has one of the largest reserves in the world, with 1 billion tons of copper and 12 million ounces of gold. In 1989 the then world's largest open pit copper-gold mine closed as a result of conflict between the mine owners and traditional land owners over the profits. The mine owners were also accused of poisoning the entire length of the Jaba River. The image was acquired November 12, 2013, covers an area of 24 by 39 kilometers, and is located at 6.3 degrees south, 155.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23338
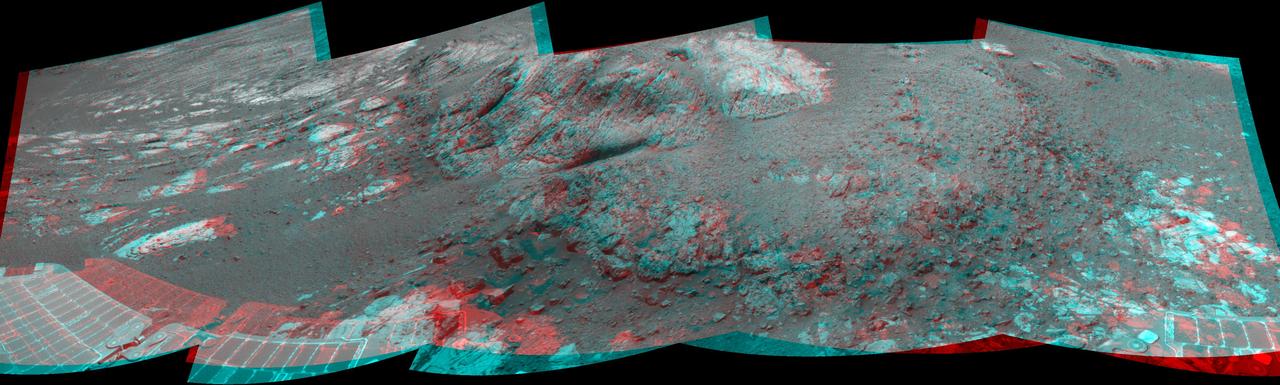
This 180-degree 3-D mosaic of images from the navigation camera on the NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows the rover close to the outcrop called Copper Cliff, which is in the center of this scene.

This 180-degree mosaic of images from the navigation camera on the NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows the rover close to the outcrop called Copper Cliff, which is in the center of this scene.

EXPLODING WIRE GUN, BLDG 4205, WITH BACKING BLOCK, BARREL, COPPER RIBBON WITH WIRE
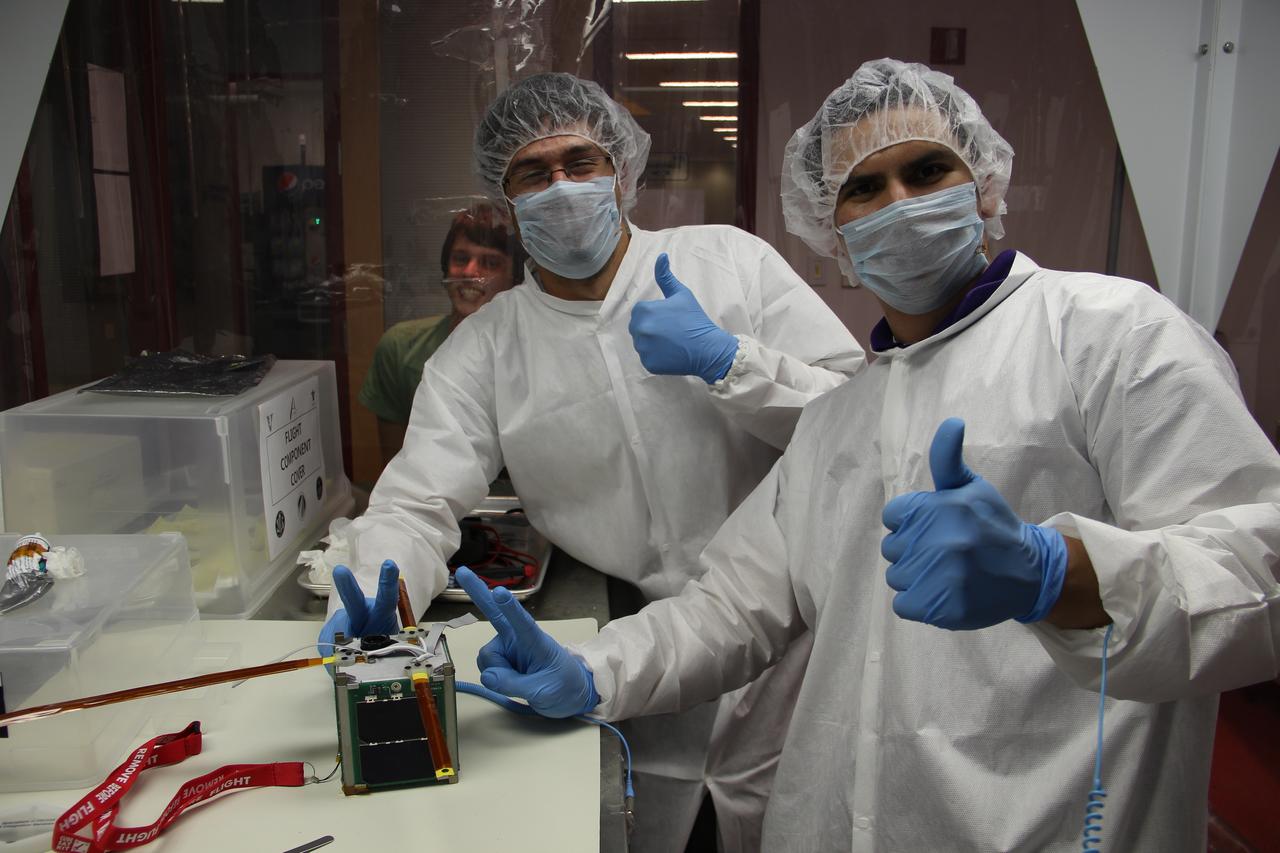

The Close Orbiting Propellant Plume Elemental Recognition (COPPER) was developed by students from St. Louis University as a technology demonstration mission whose objective is to test the suitability of a commercially-available compact uncooled microbolometer (tiny infrared camera) array for scientific imagery of Earth in the long-wave infrared range (LWIR, 7-13 microns). Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa IV mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force-led Operationally Responsive Space (ORS-3) Mission on November 19, 2013.

This image from NASA Terra satellite shows the Morenci open-pit copper mine in southeast Arizona, North America leading producer of copper.
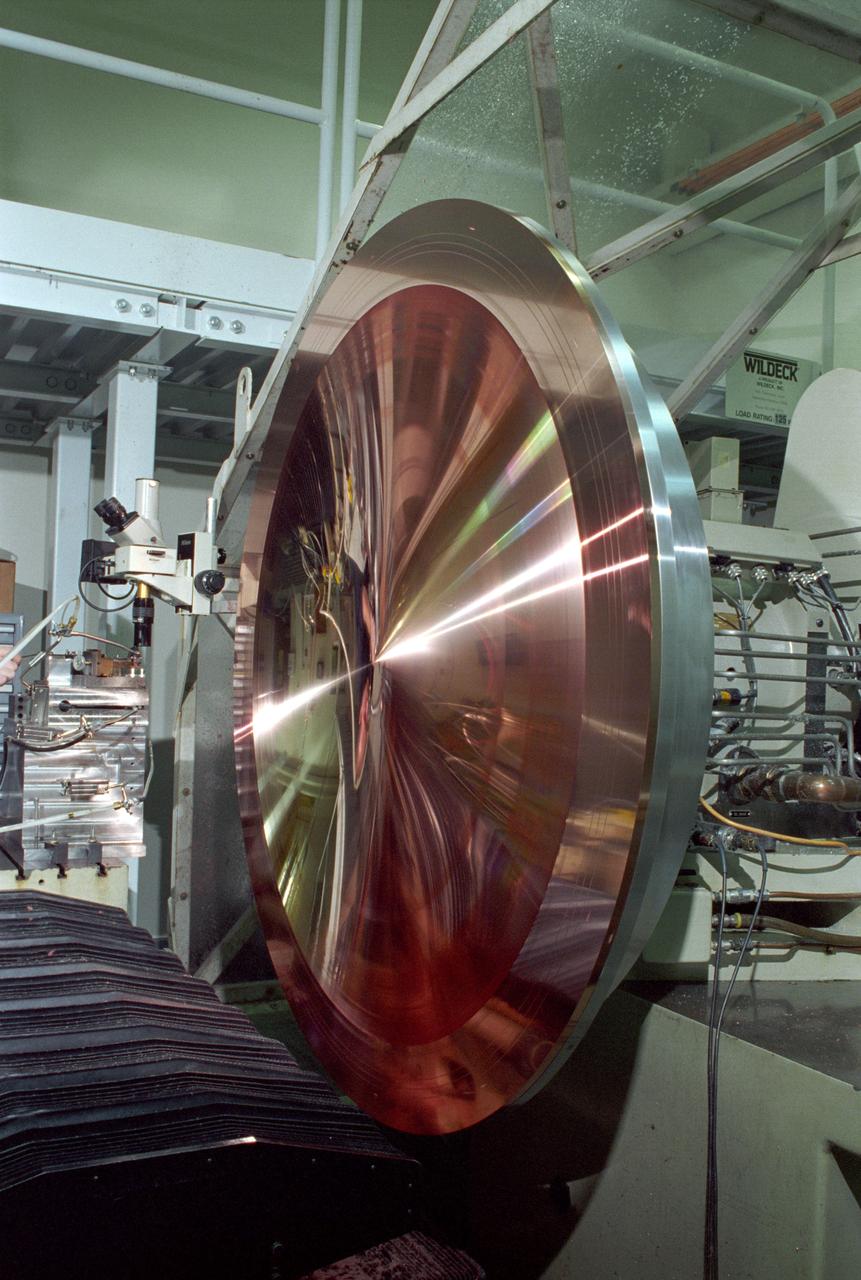
This king-size copper disk, manufactured at the Space Optics Manufacturing and Technology Center (SOMTC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), is a special mold for making high resolution monitor screens. This master mold will be used to make several other molds, each capable of forming hundreds of screens that have a type of lens called a Fresnel lens. Weighing much less than conventional optics, Fresnel lenses have multiple concentric grooves, each formed to a precise angle, that together create the curvature needed to focus and project images. MSFC leads NASA's space optics manufacturing technology development as a technology leader for diamond turning. The machine used to manufacture this mold is among many one-of-a-kind pieces of equipment of MSFC's SOMTC.
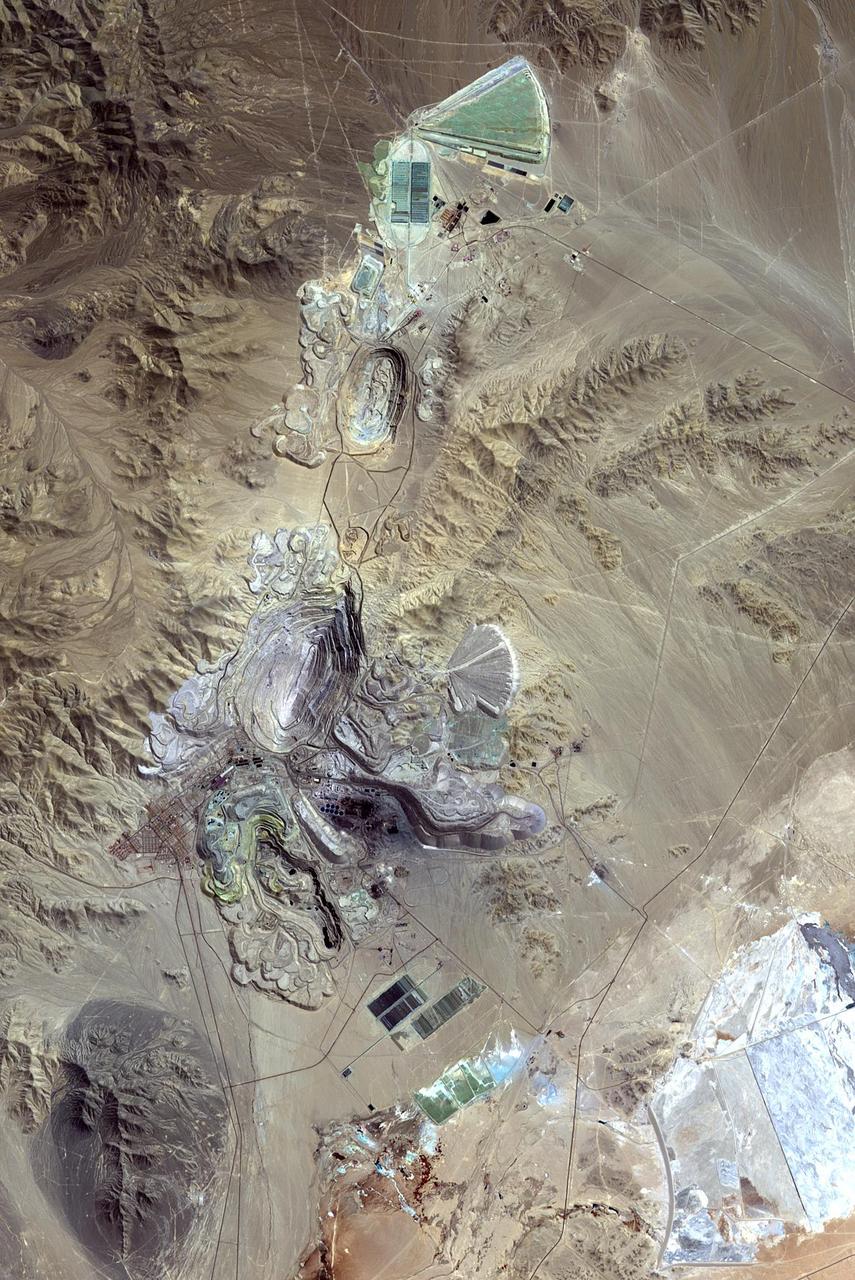

Chuquicamata, in Chile's Atacama Desert, is the largest open pit copper mine in the world, by excavated volume. The copper deposits were first exploited in pre-Hispanic times. Open pit mining began in the early 20th century when a method was developed to work low grade oxidized copper ores. The image was acquired September 2, 2007, covers an area of 19.5 by 29.3 km, and is located at 22.1 degrees south, 68.9 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20973
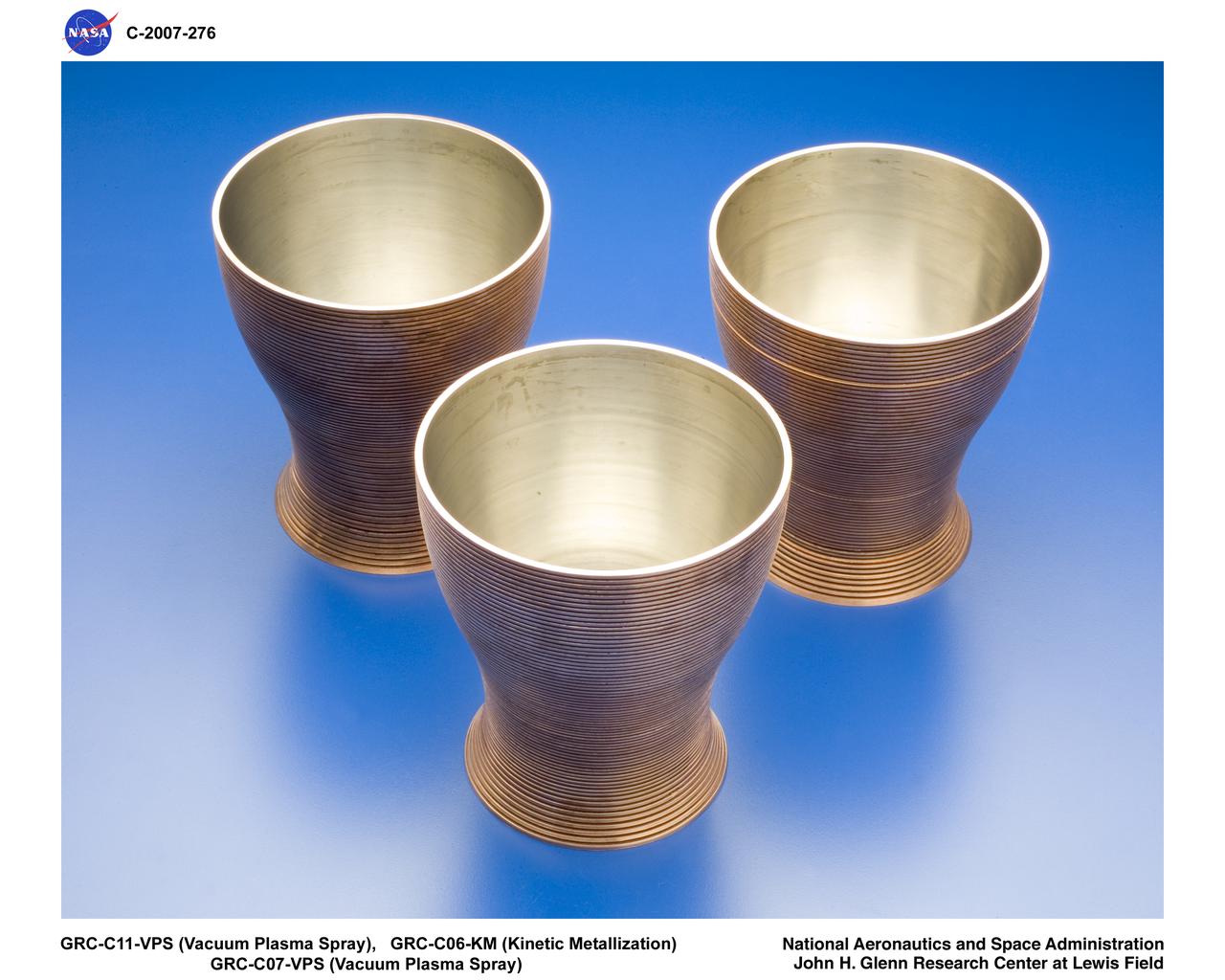

Machined Copper CGR-84 Thrusters
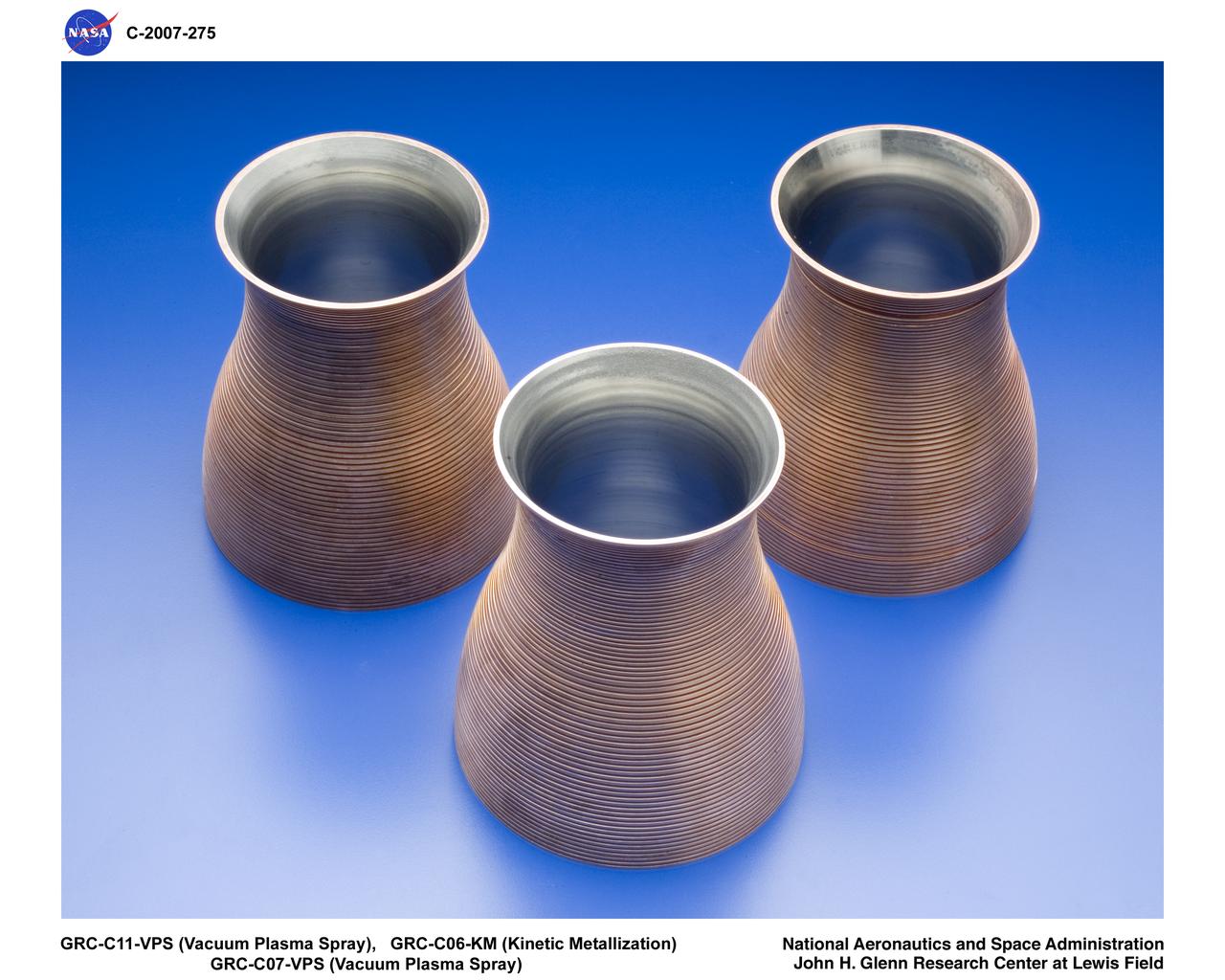

Machined Copper CGR-84 Thrusters
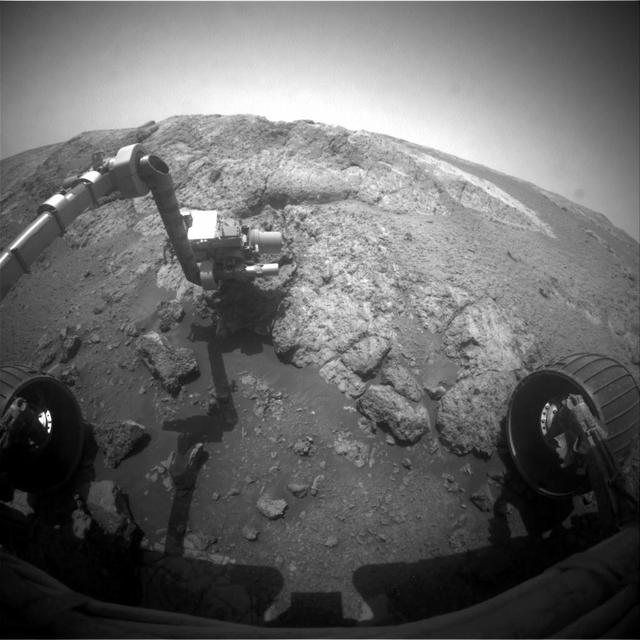

This image from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows the rover arm extended for examination of a target called Onaping at the base of an outcrop called Copper Cliff in the Matijevic Hill area of the west rim of Endeavour Crater.

This nadir camera view was captured by NASA Terra spacecraft around Kruger National Park in NE South Africa. The bright white feature is the Palabora Copper Mine, and the water body near upper right is Lake Massingir in Mozambique.
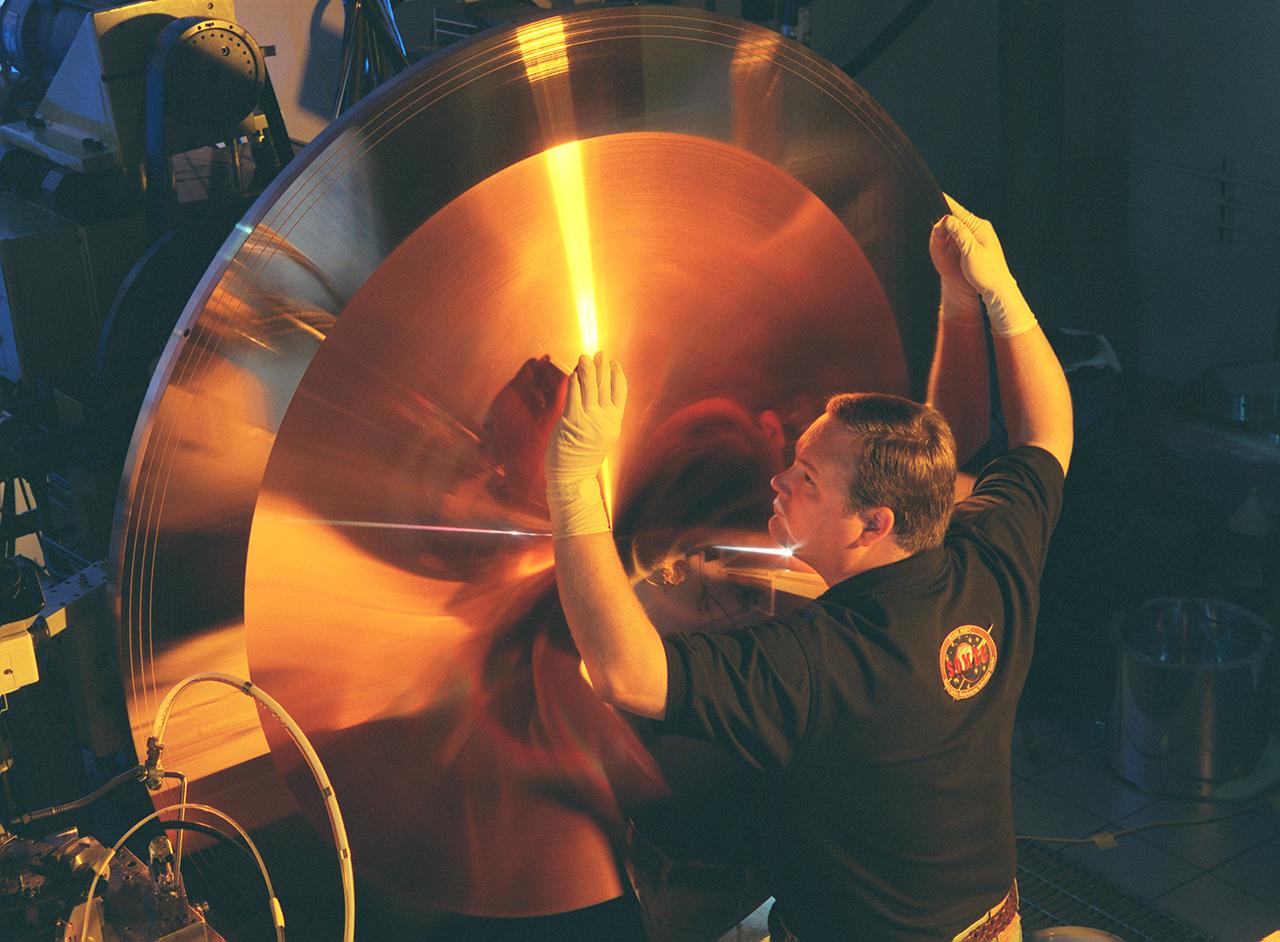

This photograph shows Wes Brown, Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) lead diamond tuner, an expert in the science of using diamond-tipped tools to cut metal, inspecting the mold's physical characteristics to ensure the uniformity of its more than 6,000 grooves. This king-size copper disk, manufactured at the Space Optics Manufacturing and Technology Center (SOMTC) at MSFC, is a special mold for making high resolution monitor screens. This master mold will be used to make several other molds, each capable of forming hundreds of screens that have a type of lens called a fresnel lens. Weighing much less than conventional optics, fresnel lenses have multiple concentric grooves, each formed to a precise angle, that together create the curvature needed to focus and project images. The MSFC leads NASA's space optics manufacturing technology development as a technology leader for diamond turning. The machine used to manufacture this mold is among many one-of-a-kind pieces of equipment of MSFC's SOMTC.

ISS022-E-026137 (14 Jan. 2010) --- Open Pit Mines in southern Arizona are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. The State of Arizona is the United States? largest producer of the metal copper, primarily mined from ore bodies known as porphyry copper deposits. Copper is a good conductor of electricity and heat, and is a vital element of virtually all of our electronic devices and components. A porphyry copper deposit is a geological structure formed by crystal-rich magma moving upwards through pre-existing rock layers. As the magma cools and crystallizes, it forms an igneous rock with large crystals embedded in a fine-grained matrix, known as porphyry. Hot fluids circulate through the magma and surrounding rocks via fractures, depositing copper-bearing and other minerals in characteristic spatial patterns that signal the nature of the ore body to a geologist. The most common approach to extracting metal-bearing ore from a porphyry copper deposit is by open-pit mining. For more details, please refer to http://earth.jsc.nasa.gov/EarthObservatory/OpenPitMinesSouthernArizona.htm.
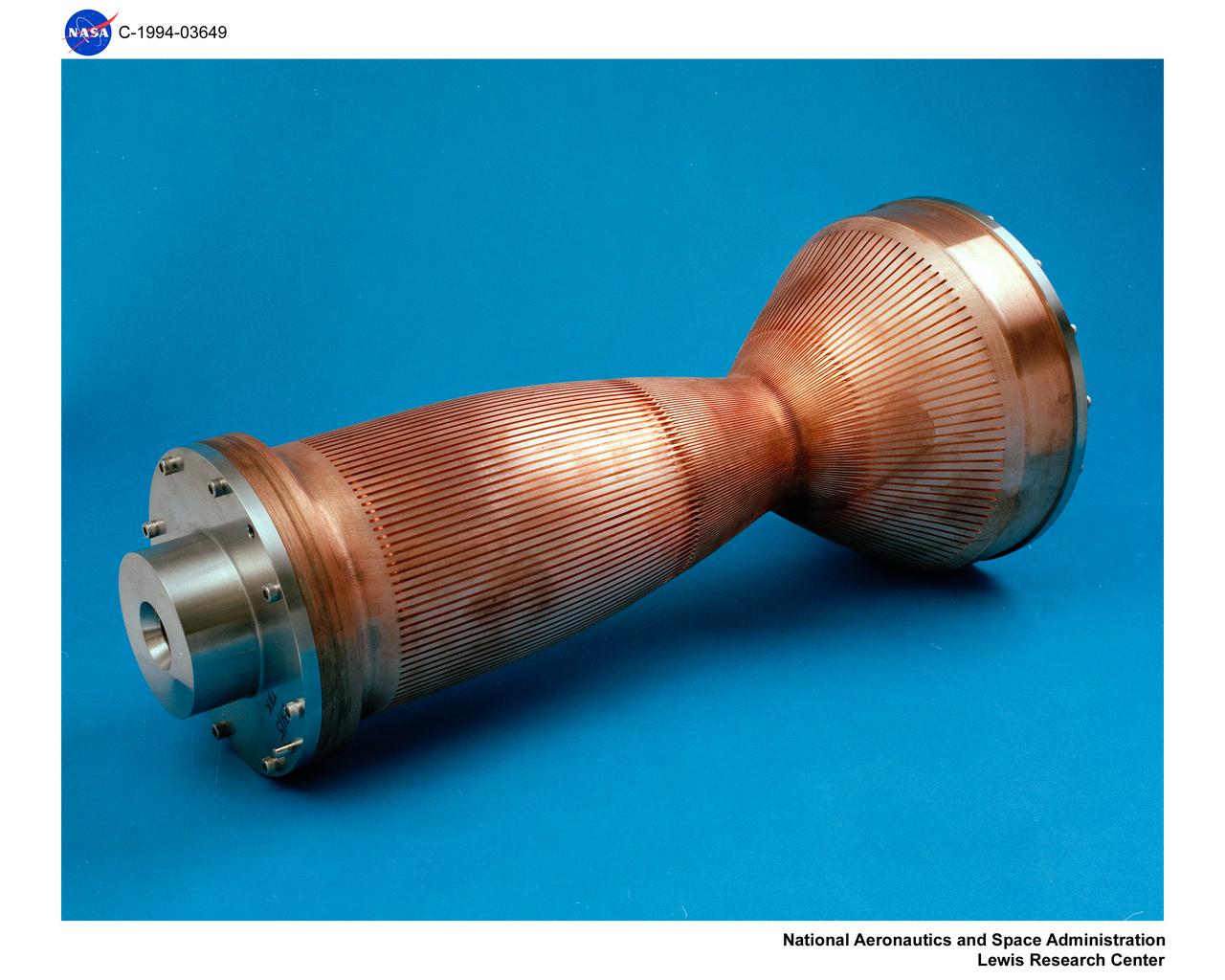

COPPER INNER LINER FOR HIGH ASPECT RATIO LH2 COOLED ENGINE
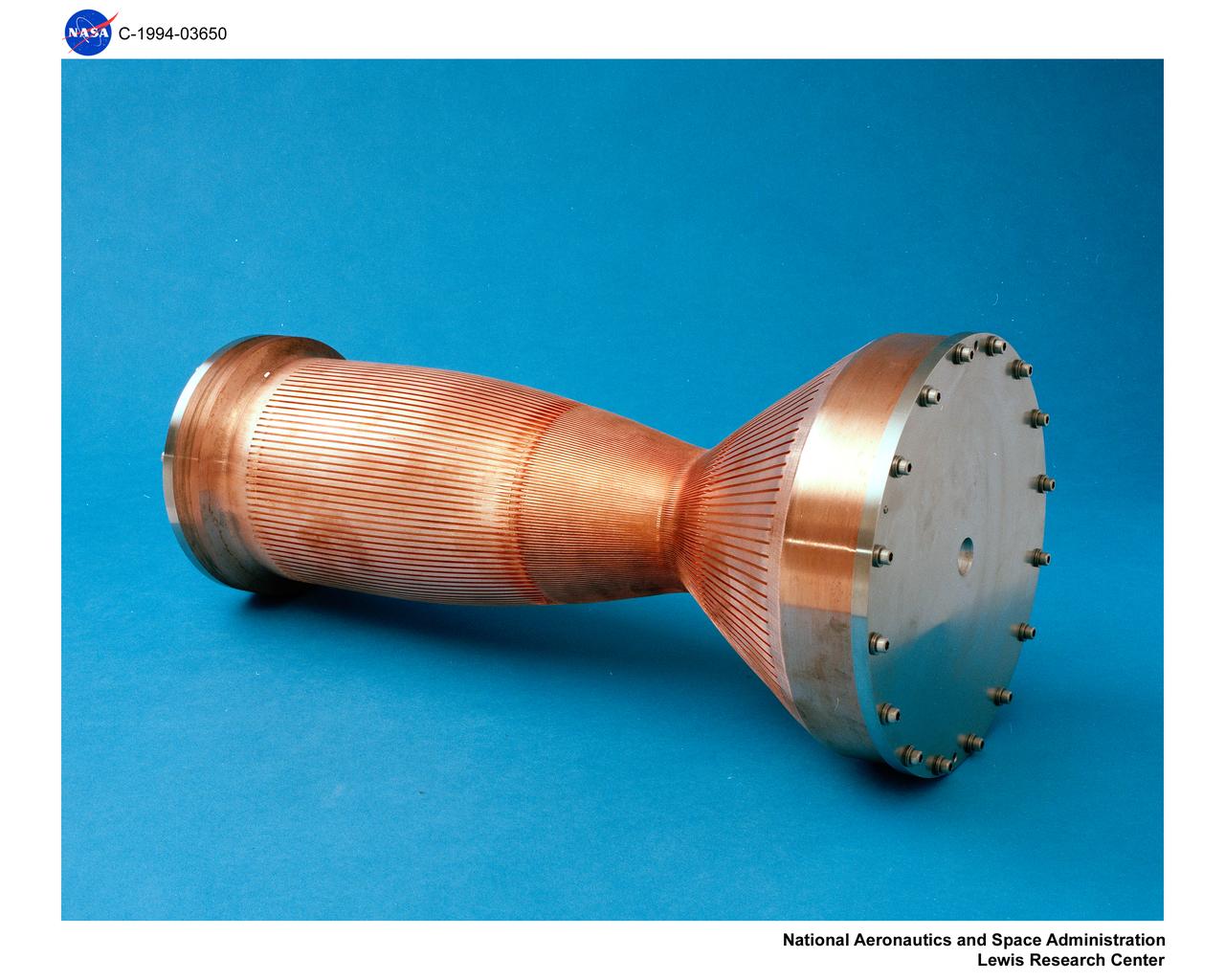

COPPER INNER LINER FOR HIGH ASPECT RATIO LH2 COOLED ENGINE
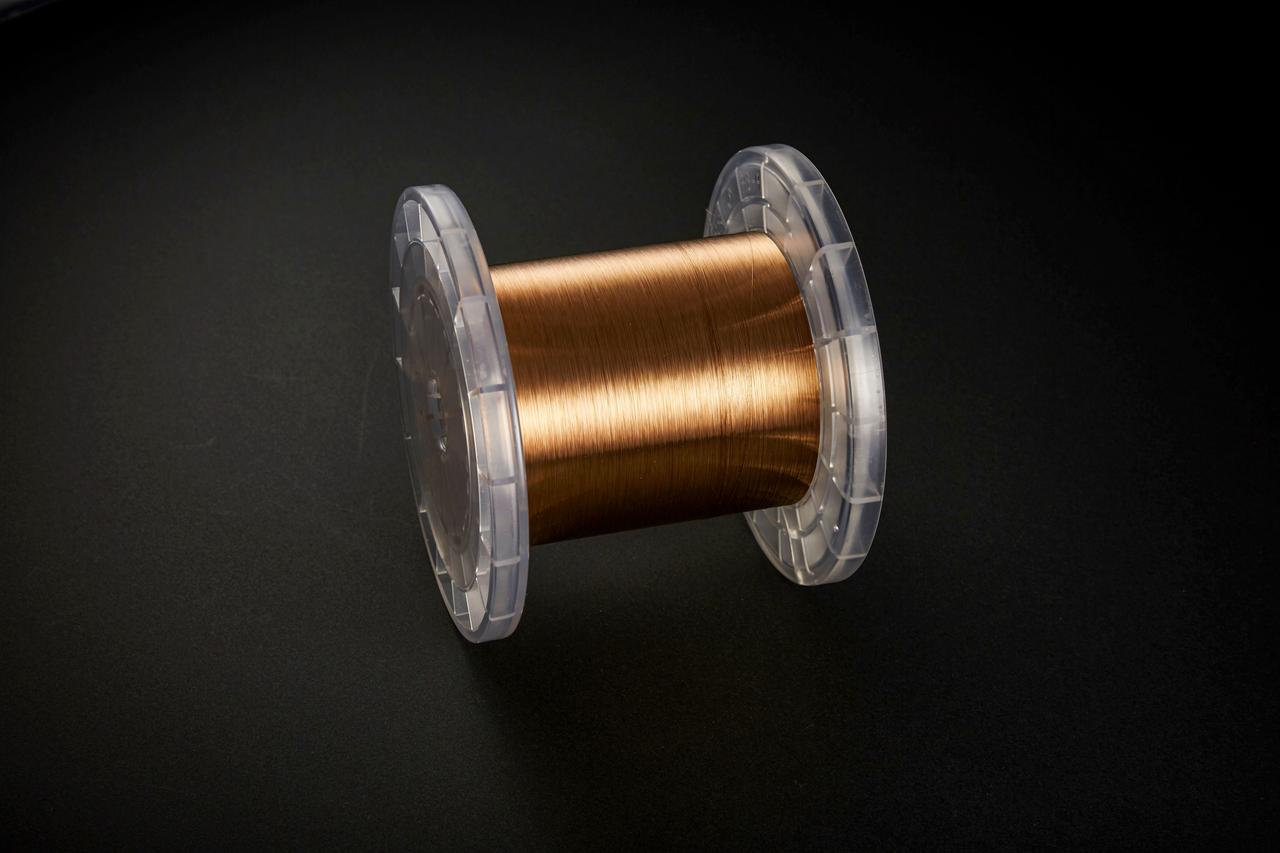

jsc2020e040942 (4/18/2015) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..
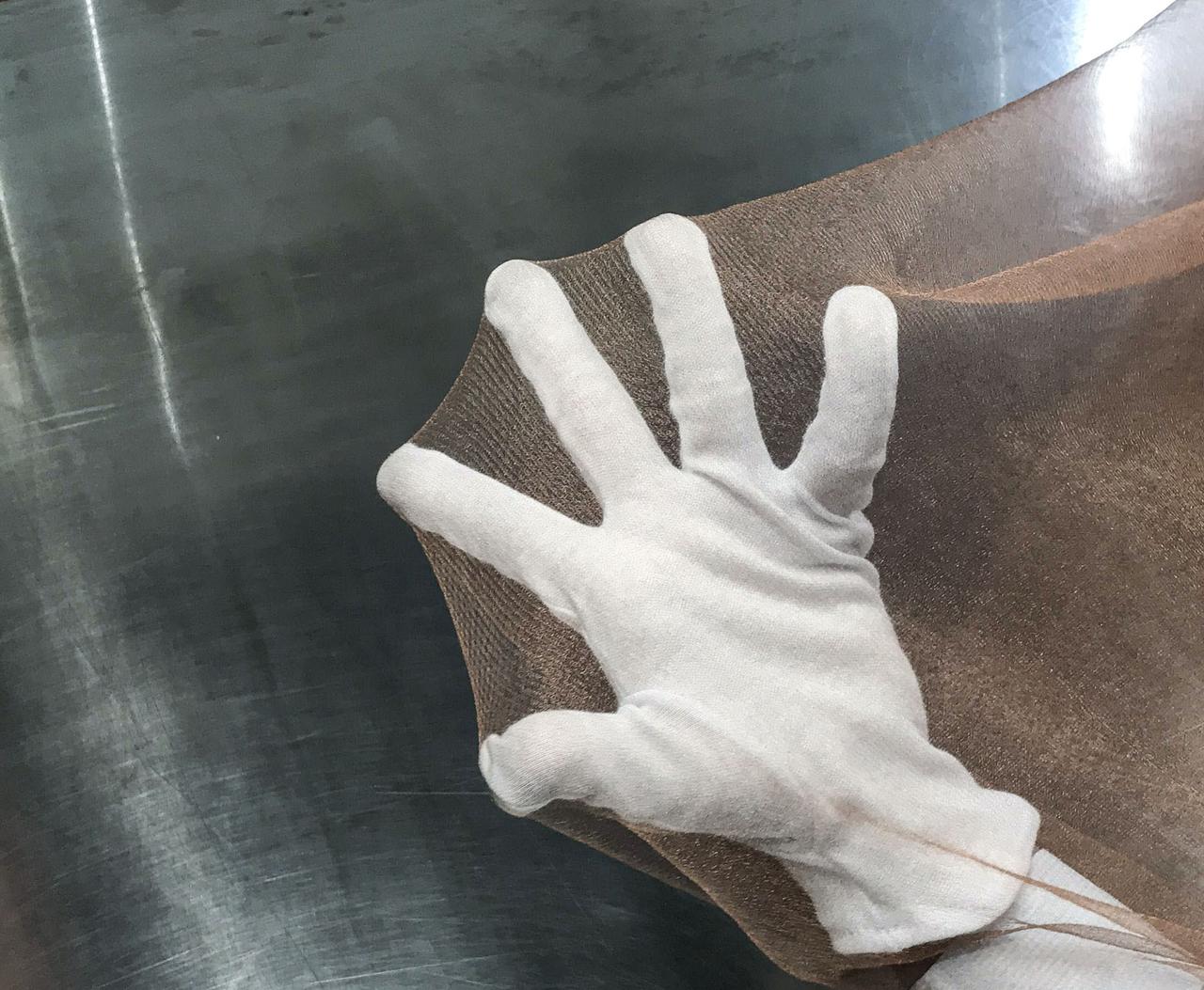

jsc2020e040945 (7/10/2020) --- Copper zirconium antenna metal mesh. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..
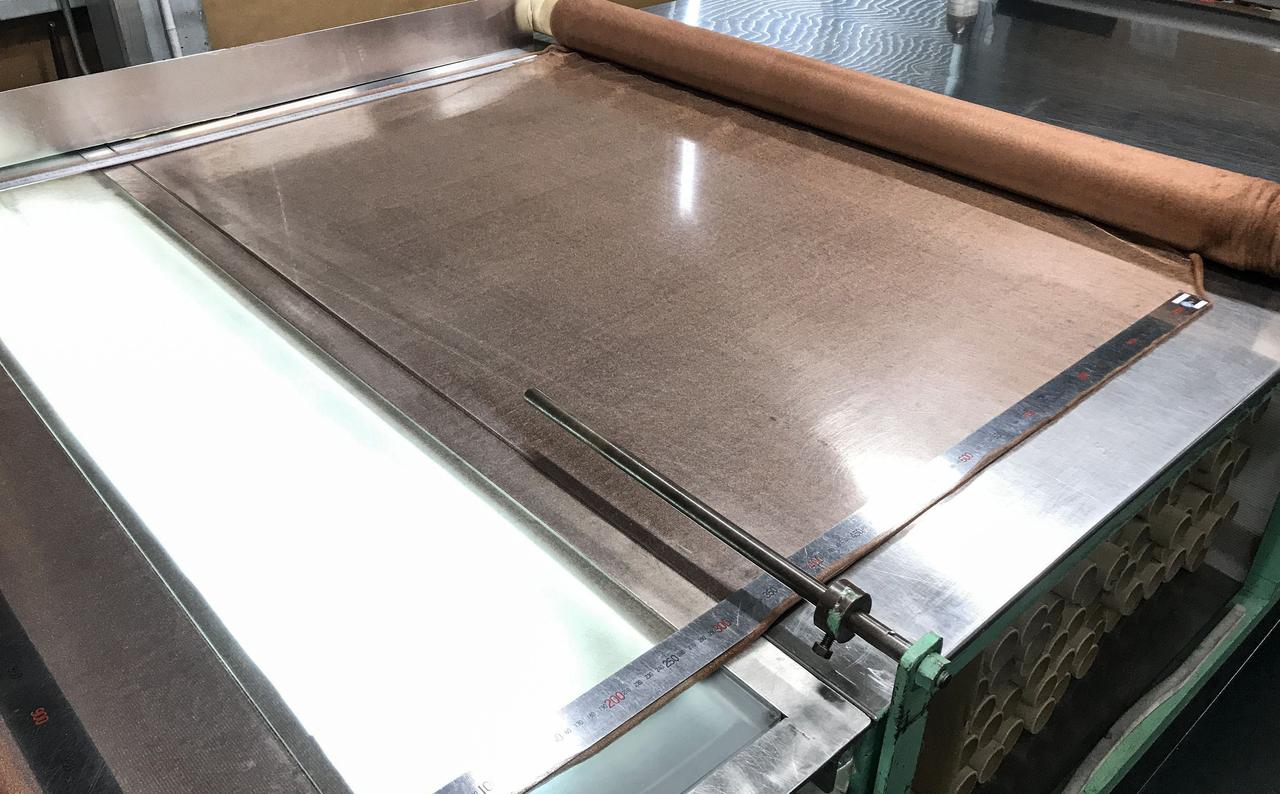

jsc2020e040944 (7/8/2020) --- Copper zirconium antenna metal mesh. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..

jsc2020e040941 (9/3/2018) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire being produced. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..

jsc2020e040940 (9/3/2018) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire being produced. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..
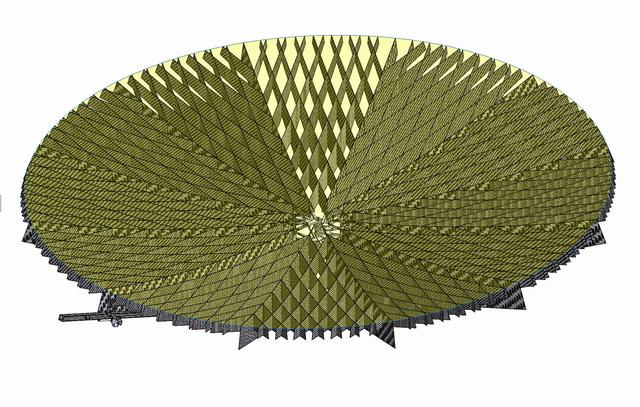
jsc2020e040943 (9/10/2020) --- An example of a copper zirconium antenna metal mesh on a deployable reflector. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: Technosolver Corporation, JAXA.

ISS013-E-63766 (2 Aug. 2006) --- Berkeley Pit and Butte, Montana are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. The city of Butte, Montana has long been a center of mining activity. Underground mining of copper began in Butte in the 1870s, and by 1901 underground workings had extended to the groundwater table. Thus began the creation of an intricate complex of underground drains and pumps to lower the groundwater level and continue the extraction of copper. Water extracted from the mines was so rich in dissolved copper sulfate that it was also "mined" (by chemical precipitation) for the copper it contained. In 1955, the Anaconda Copper Mining Company began open-pit mining for copper in what is now know as the Berkeley Pit (dark oblong area in center). The mine took advantage of the existing subterranean drainage and pump network to lower groundwater until 1982, when the new owner ARCO suspended operations at the mine. The groundwater level swiftly rose, and today water in the Pit is more than 900 feet deep. Many features of the mine workings are visible in this image such as the many terraced levels and access roadways of the open mine pits (gray and tan sculptured surfaces). A large gray tailings pile of waste rock and an adjacent tailings pond are visible to the north of the Berkeley Pit. Color changes in the tailings pond are due primarily to changing water depth. The Berkeley Pit is listed as a federal Superfund site due to its highly acidic water, which contains high concentrations of metals such as copper and zinc. The Berkeley Pit receives groundwater flowing through the surrounding bedrock and acts as a "terminal pit" or sink for these heavy metal-laden waters. Ongoing efforts include regulation of water flow into the pit to reduce filling of the Pit and potential release of contaminated water into local aquifers or surface streams.

Our robotic emissary, flying high above Saturn, captured this view of an alien copper-colored ring world. The overexposed planet has deliberately been removed to show the unlit rings alone, seen from an elevation of 60 degrees
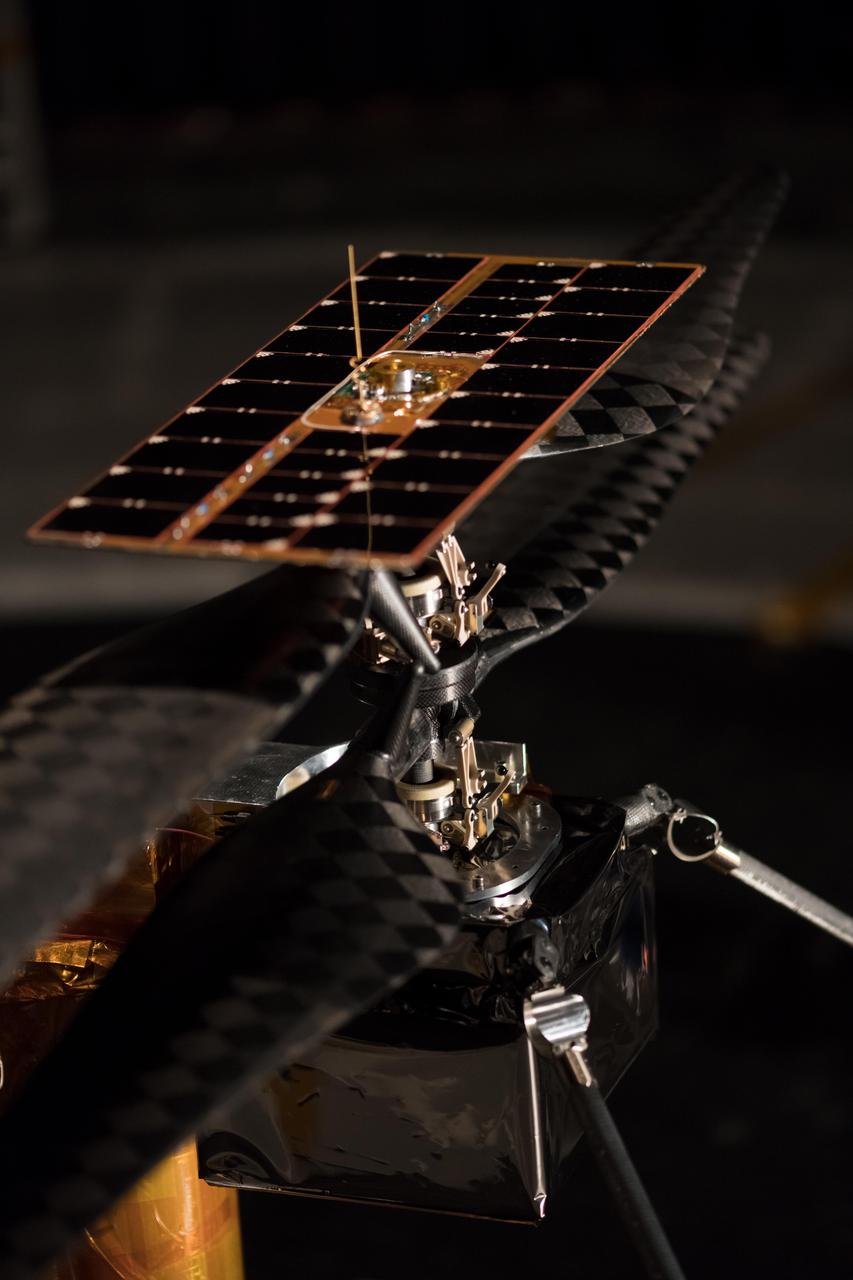
More than 1,500 individual pieces of carbon fiber, flight-grade aluminum, silicon, copper, foil and foam go into a Mars Helicopter. This image of the Flight Model (the actual vehicle going to the Red Planet), was taken on Feb. 1, 2019 when the helicopter was inside the Space Simulator, a 25-foot (7.62 meter) wide vacuum chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23158

ISS022-E-008282 (9 Dec. 2009) --- One of the world?s leading copper mines, Escondida, in the Atacama Desert of Chile, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. The copper mining industry is a major part of the Chilean economy. The mine is located 170 kilometers southeast of Chile?s port city of Antofagasta, in the hyper arid northern Atacama Desert at an elevation of 3,050 meters (approximately 10,000 feet) above sea level. Escondida produces mainly copper concentrates; assisted by gravity, the concentrates are piped as slurry down to the smaller port of Coloso just south of Antofagasta where they are dewatered for shipping. The photograph features a large light tan and gray waste or ?spoil? materials impoundment area (center) of the mine complex. The copper-bearing waste, which is a large proportion of the material excavated from open pits to the north (not in frame), is poured into the impoundment area as a liquid (green region at photo?s center), and dries to the lighter-toned spoil seen in the image. The spoil is held behind a retaining dam, just a little more than one kilometer in length, visible as a straight line at lower left. ?Escondida? means ?hidden? in Spanish, and refers to the fact that the copper ore body was buried beneath hundreds of meters of barren rock and had to be located by a laborious drilling program following a geologic trend established from other copper occurrences.

ISS016-E-031056 (3 March 2008) --- Cananea Copper Mine, Sonora, Mexico is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 16 crewmember on the International Space Station. One of the largest open-pit copper mines in the world, the Cananea mine produced over 164,000 tons of copper in 2006. The mine is located approximately 40 kilometers south of the border between the USA (Arizona) and Mexico (Sonora). Copper and gold ores at Cananea are found in a porphyry copper deposit, a geological structure formed by crystal-rich magma moving upwards through pre-existing rock layers. A porphyry - an igneous rock with large crystals in a fine-grained matrix -- is formed as the magma cools and crystallizes. While crystallization is occurring, hot fluids can circulate through the magma and surrounding rocks via fractures. This hydrothermal alteration of the rocks typically forms copper-bearing and other minerals. Much of the Cananea mine's ore is concentrated in breccia pipes -- mineralized rod or chimney-shaped bodies that contain broken rock fragments. The active, two-kilometers-in-diameter Colorada Pit (top right) is recognizable in this image by the concentric steps or benches cut around its perimeter. These benches allow for access into the pit for extraction of ore and waste materials. Water (black) is visible filling the bottom of the pit, and several other basins in the surrounding area. The city of Cananea -- marked by its street grid -- is located to the northeast of the mine workings. A leachate reservoir is located to the east of the mine (lower left) for removal and evaporation of water pumped from the mine workings -- the bluish-white coloration of deposits near the reservoir suggests the high mineral content of the leachate. A worker strike halted mine operations in 2007.
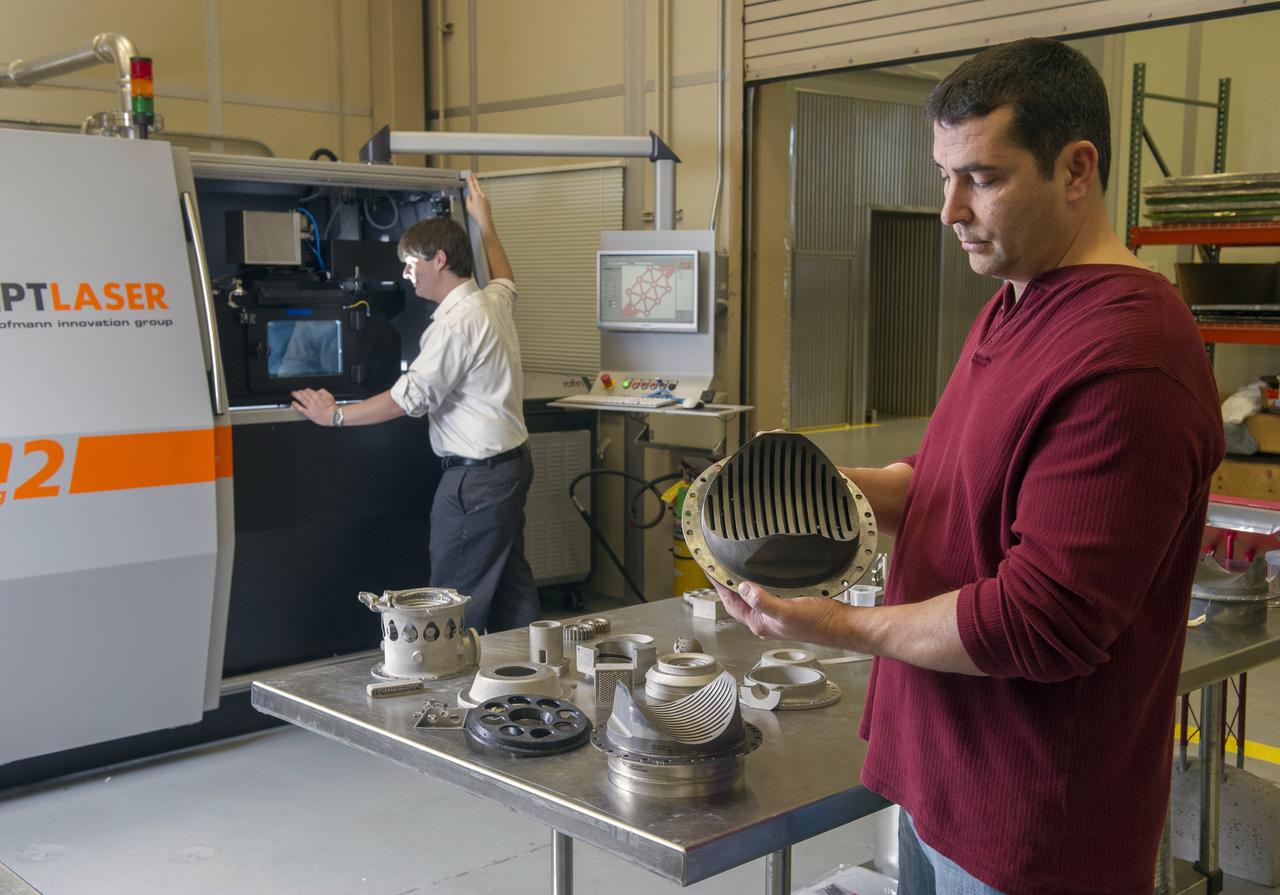

ZACK JONES AND JIM LYDON OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S M2 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M2 IS CURRENTLY DEDICATED TO ADVANCED COPPER MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT FOR THE LOW COST UPPER STAGE PROGRAM.
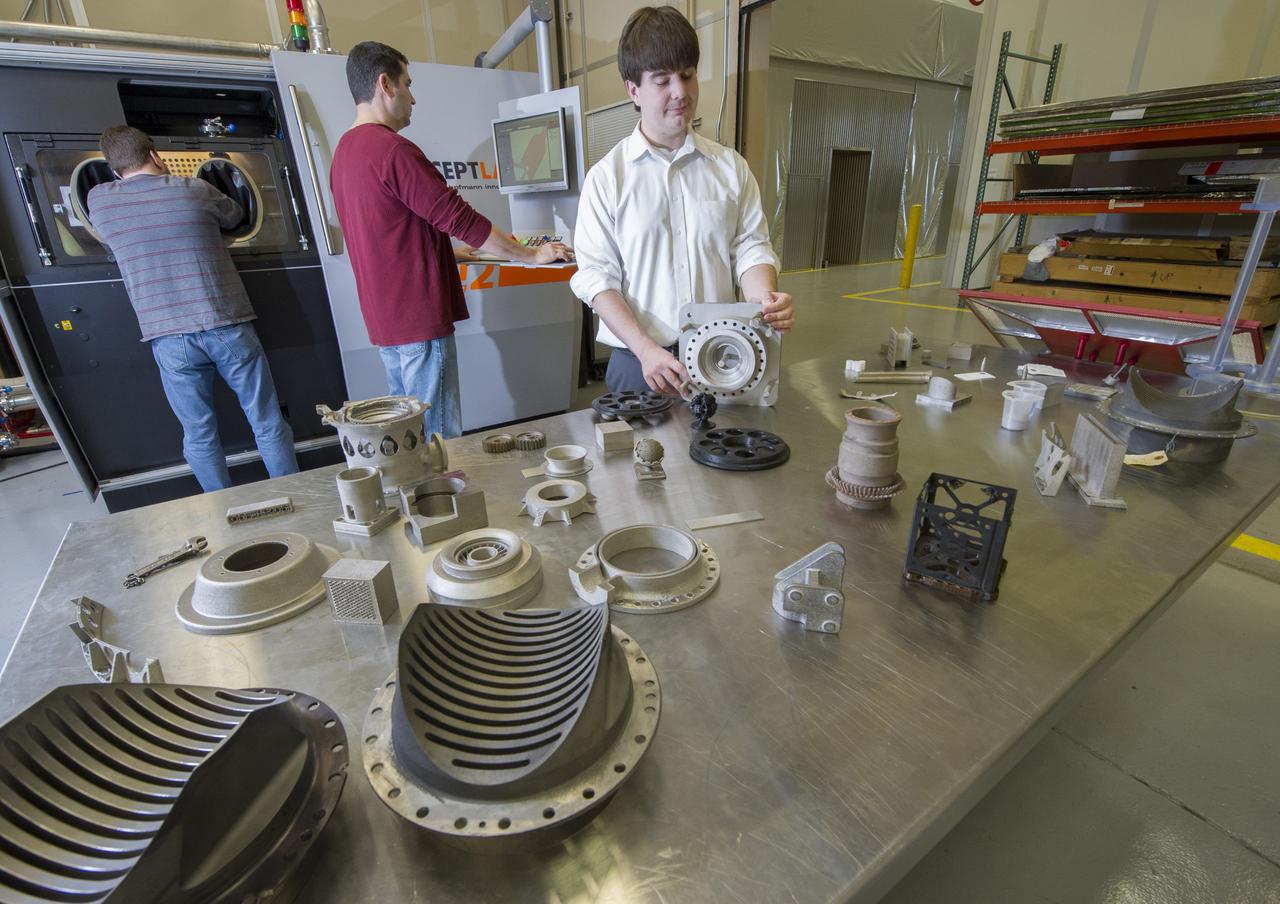

QUINCY BEAN, JIM LYDON, AND ZACK JONES OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S M2 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M2 IS CURRENTLY DEDICATED TO ADVANCED COPPER MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT FOR THE LOW COST UPPER STAGE PROGRAM.
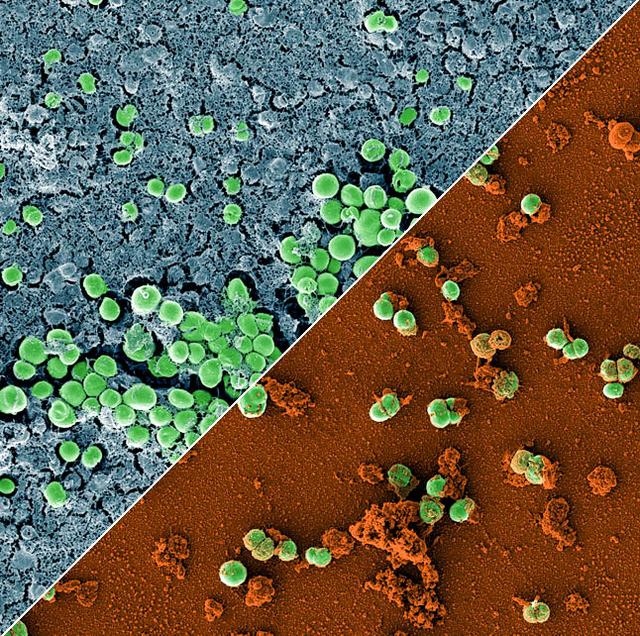
jsc2023e010179 (2/28/2023) --- This image is a composition of two scanning electron microscopic images of the bacterium Staphylococcus capitis on stainless steel versus antimicrobial copper. The image was colored to visualize the bacterial cells (green) either embedded in a biofilm matrix (blue), or covered with copper particles (red/orange). The ESA-Biofilms investigation studies bacterial biofilm formation and antimicrobial properties of different metal surfaces under spaceflight conditions in altered gravity. Both images were taken as part of the preflight experiments for ESA-Biofilms. Image courtesy of DLR, CC BY-NC-ND 3.0.
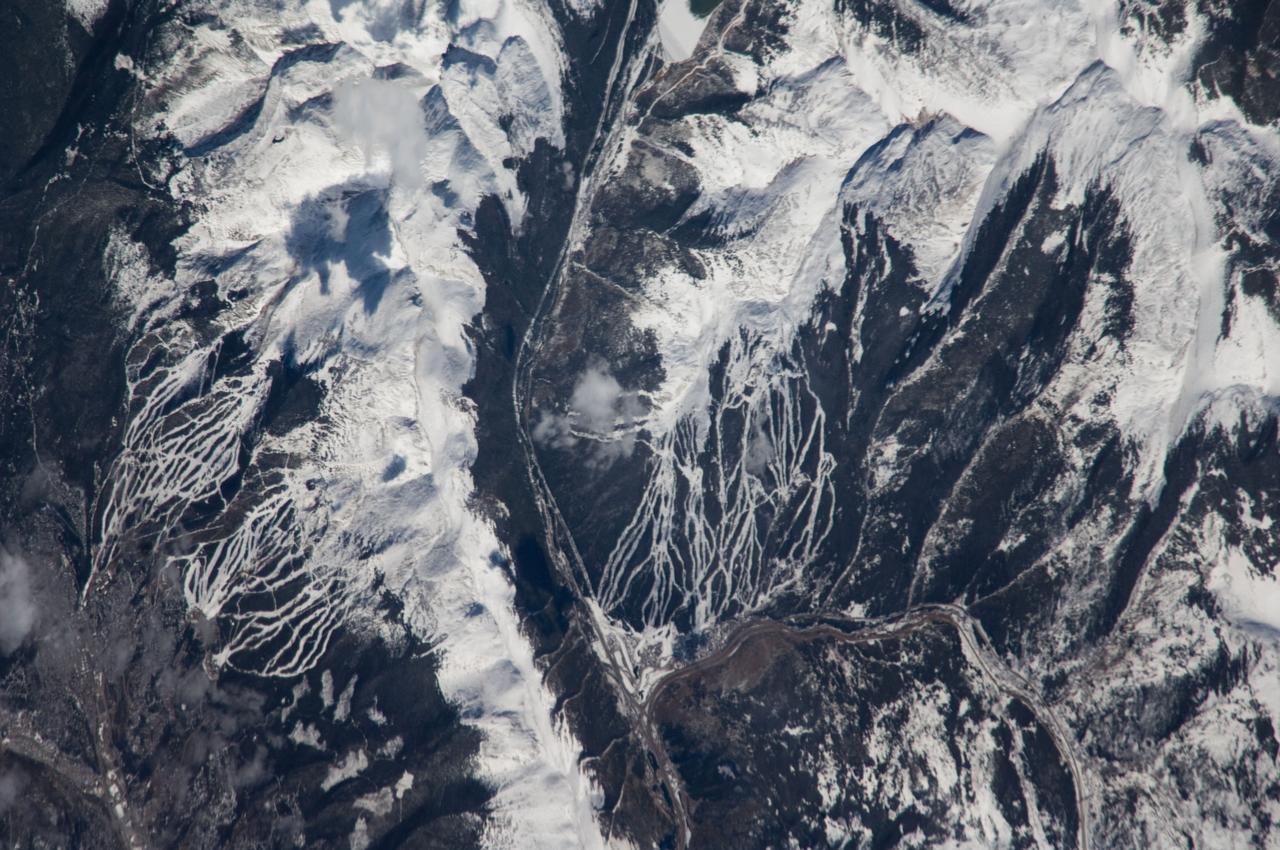

ISS018-E-005353 (24 Oct. 2008) --- Breckenridge and Copper Mountain ski slopes, Colorado are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 18 crewmember on the International Space Station. Located in a section of the Rocky Mountains which extend through central Colorado, Tenmile Range and Copper Mountain provide the ideal location and landscape for popular winter sports. In this view, the Breckenridge and Copper Mountain ski areas are clearly visible as the snow covered ski runs stand out among the surrounding darker forest. Tenmile Range has mountain peaks that are named Peaks 1 through Peaks 10. The Breckenridge ski area use Peaks 7 through Peaks 10 which range from 12,631 feet (3,850 meters) to 13,615 feet (4,150 meters) high. Tenmile Canyon is a north northeast-trending fault-controlled valley running nearly 3,000 feet (914.4 meters) deep that serves as the boundaries for Tenmile Creek running through the center of the photo. The snow-covered peaks clearly delineate the tree line at an elevation of around 11,000 feet (3,350 meters). In the winter, this area's annual average snowfall ranges between 284 inches (7.21 meters) at Copper Mountain to 300 inches (7.62 meters) a year at Breckenridge. Before recreation became the main industry, miners were attracted to the area in the mid-1800's following discoveries of gold, silver, lead, and zinc. The towns of Breckenridge and Wheeler Junction (at the base of Copper Mountain ski area) were born out of the surge to settle the West during the Pike's Peak Gold Rush. While this image records snow on the peaks of Tenmile Range, the months of October and November 2008 saw little accumulation of snow pack in the area of Breckenridge. The situation changed in early December 2008 however, when more snow fell in eight days than in the preceding two months. The late, but significant, snowfall boosted the snow pack back to expected levels for this time of year.
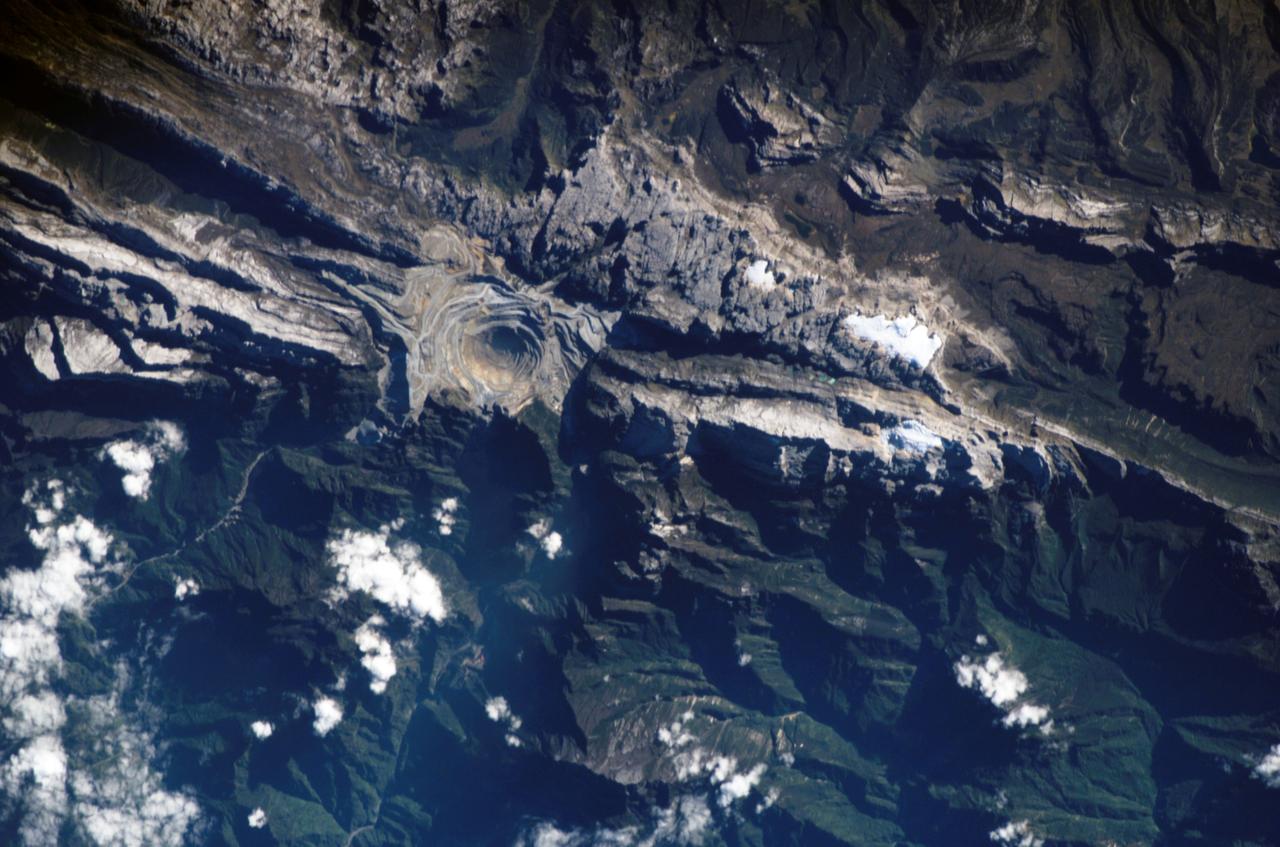

ISS011-E-09620 (26 June 2005) --- Grasberg Mine, Indonesia is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 11 crewmember on the International Space Station. Located in the Sudirman Mountains of the Irian Jaya province of Indonesia, the Grasberg complex (also known as the Freeport Mine) is one of the largest gold and copper mining operations in the world. The Sudirman Mountains form the western portion of the Maoke Range that extend across Irian Jaya from west to the east-southeast. According to scientists, these ranges were formed by ongoing collision of the northward-moving Australian and westward-moving Pacific tectonic plates. Intrusion of hot magma into sedimentary rock layers during uplift of the mountains resulted in the formation of copper- and gold-bearing ore bodies. Rich copper ore bodies were discovered in the area in 1936, and the Grasberg gold-bearing ore bodies were discovered in 1988. This image illustrates the approximately 4 kilometers-wide open-pit portion of the mine complex; there are also extensive underground mine workings. Access roads for trucks hauling ore and waste rock are visible along the sides of the pit.
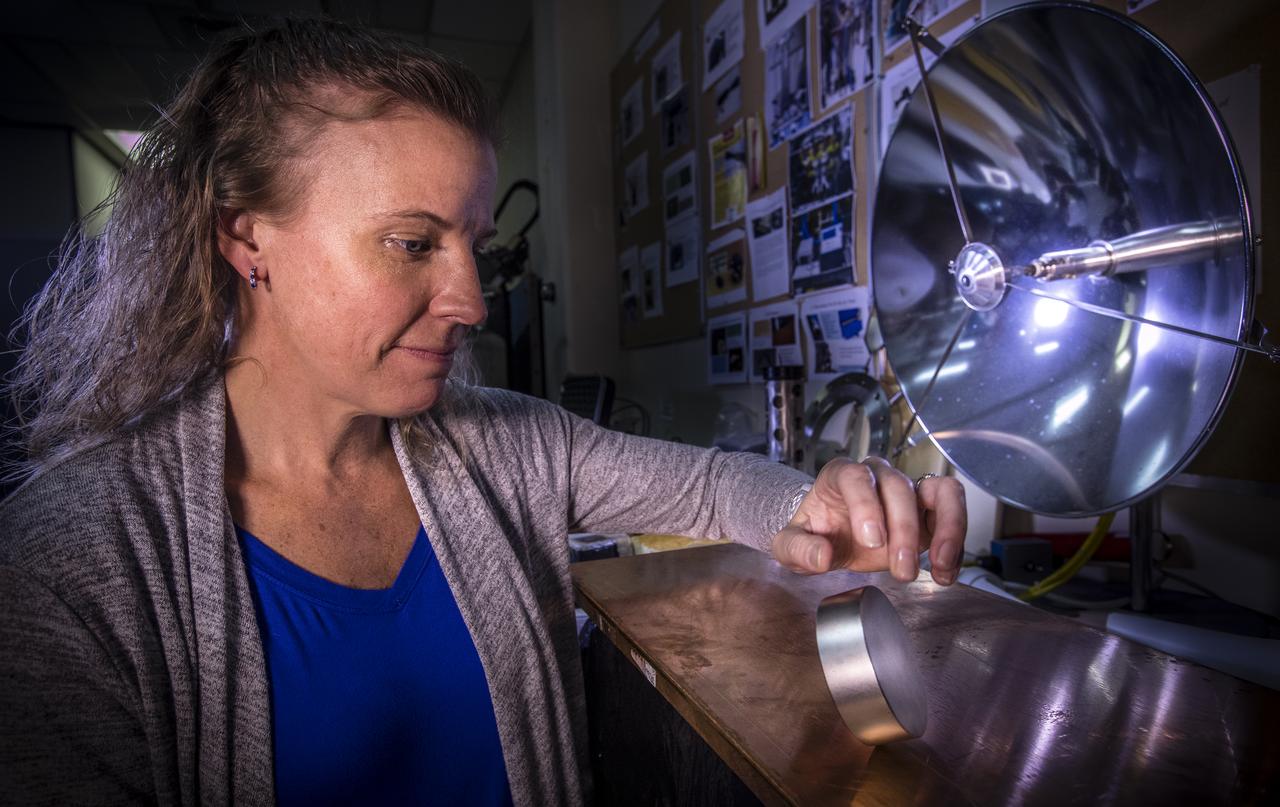

Principal investigator, Dr. Janine Captain, demonstrates the effects of moving a magnet against metal in the Applied Physics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 12, 2018. When dropped or tipped over on a plate of copper, the magnet decelerates and slowly touches down on the plate visually demonstrating the physics of the magnetic field.
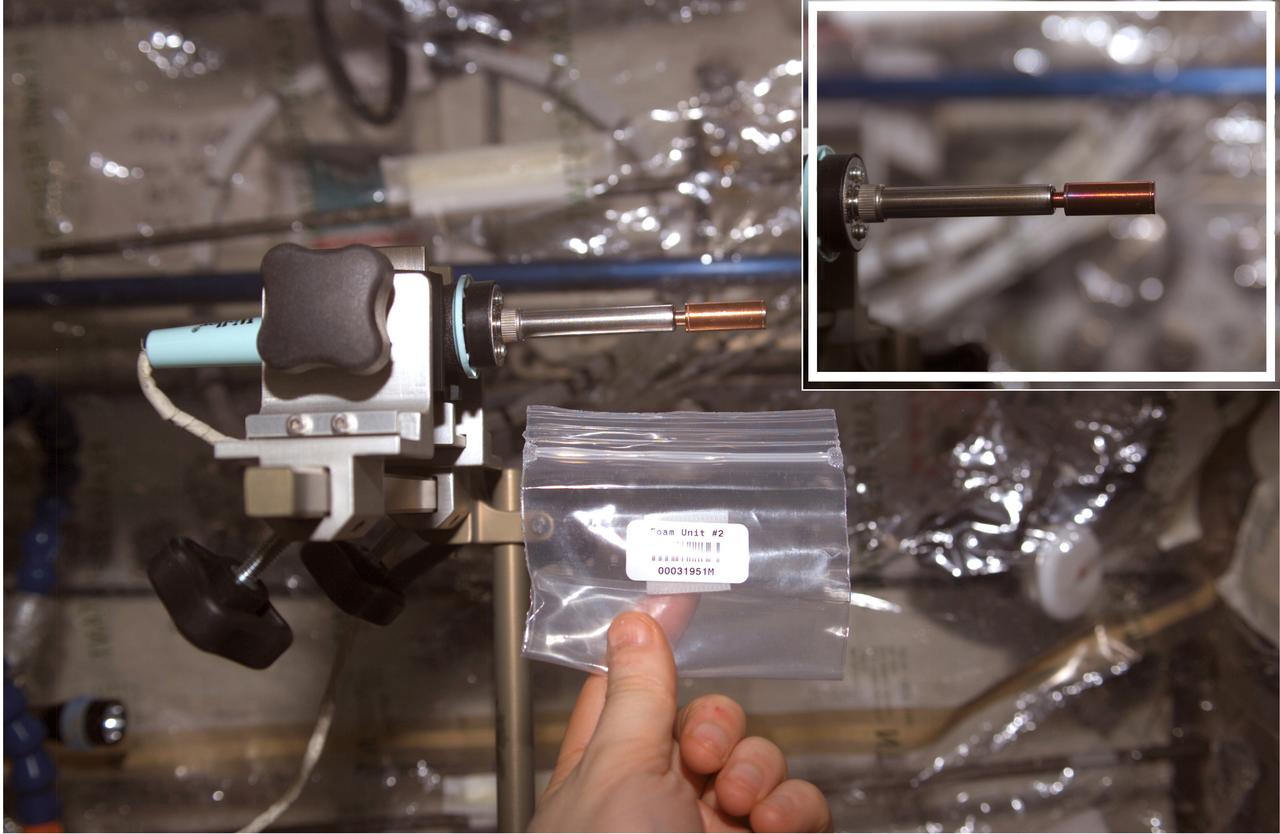
This soldering iron has an evacuated copper capsule at the tip that contains a pellet of Bulk Metallic Glass (BMG) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Prior to flight, researchers sealed a pellet of bulk metallic glass mixed with microscopic gas-generating particles into the copper ampoule under vacuum. Once heated in space, such as in this photograph, the particles generated gas and the BMG becomes a viscous liquid. The released gas made the sample foam within the capsule where each microscopic particle formed a gas-filled pore within the foam. The inset image shows the oxidation of the sample after several minutes of applying heat. Although hidden within the brass sleeve, the sample retained the foam shape when cooled, because the viscosity increased during cooling until it was solid.
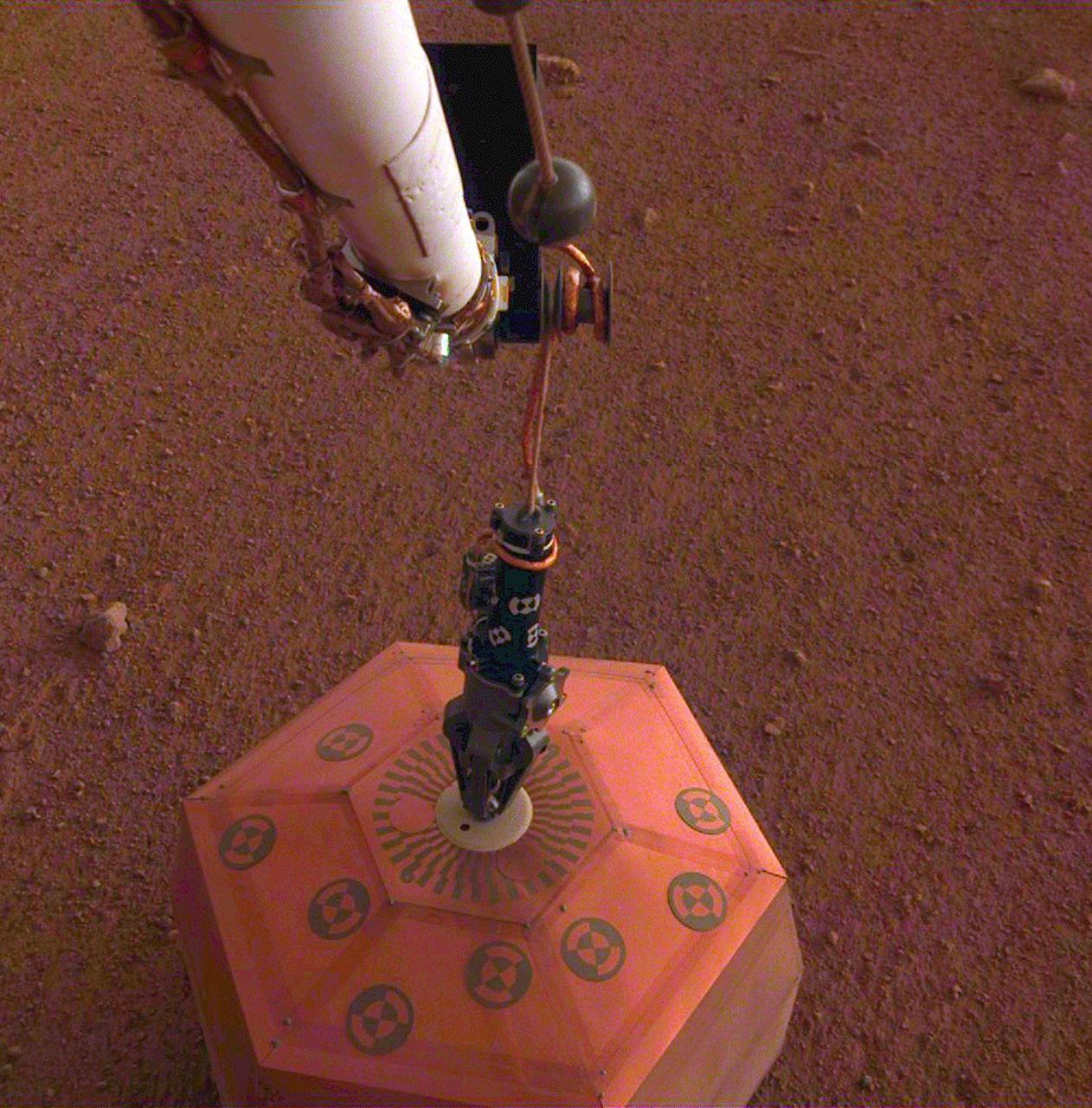
This set of images shows NASA's InSight lander deploying its first instrument onto the surface of Mars, completing a major mission milestone. InSight's robotic arm is white, with a black, handlike grapple at the end. The grapple is holding onto the copper-colored seismometer. The color-calibrated image was taken on Dec. 19, 2018, around dusk on Mars, with InSight's Instrument Deployment Camera (IDC), which is on the lander's robotic arm. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22977
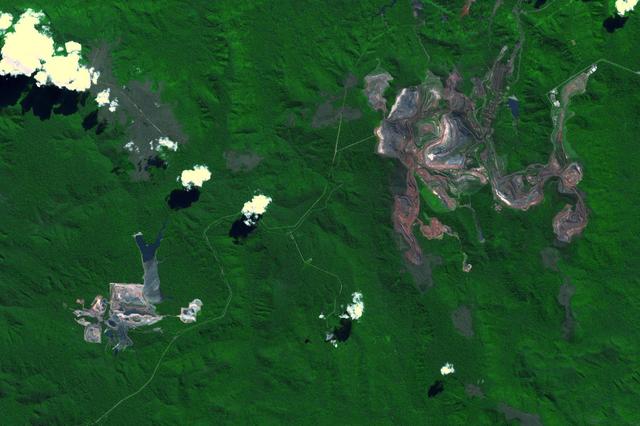

The Carajas Mine is the largest open-pit iron ore mine in the world. It is located in the state of Para, northern Brazil. The mine is estimated to contain over 7 billion tons of iron ore, plus gold, manganese, bauxite, copper and nickel. Ore is loaded into rail cars, and shipped to the Atlantic port city of Sao Luis over 250 kilometers away. The image was acquired June 19, 2017, covers an area of 18 by 27 kilometers, and is located at 6.1 degrees south, 50.2 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22861
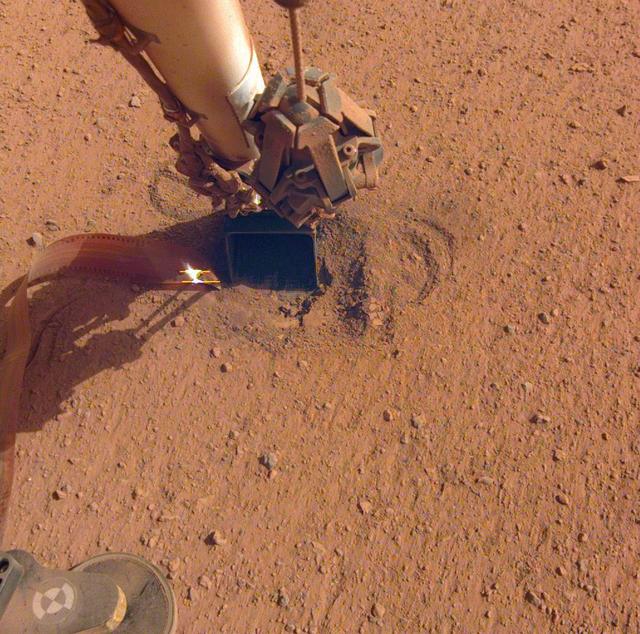

NASA's InSight lander retracted its robotic arm on Oct. 3, 2020, revealing the spot where the self-digging "mole" is attempting to burrow into the planet's surface. Attached to the mole is the copper-colored ribbon, which is laden with temperature sensors designed to measure the heat flow within Mars. In the months to come, the scoop seen on the end of the arm will be used to scrape and tamp down soil on top of the mole, in hopes of helping it dig. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24098

ISS007-E-15222 (22 September 2003) --- This view in southern Peru, photographed by an Expedition 7 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS), features the Toquepala copper mine, a steep sided and stepped open-pit mine. Mid-afternoon sunlight of the arid slopes of the central Andes Mountains provides an accent to the mine contours. At the surface the open pit is 6.5 kilometers across and it descends more than 3000 meters into the earth. A dark line on the wall of the pit is the main access road to the bottom.
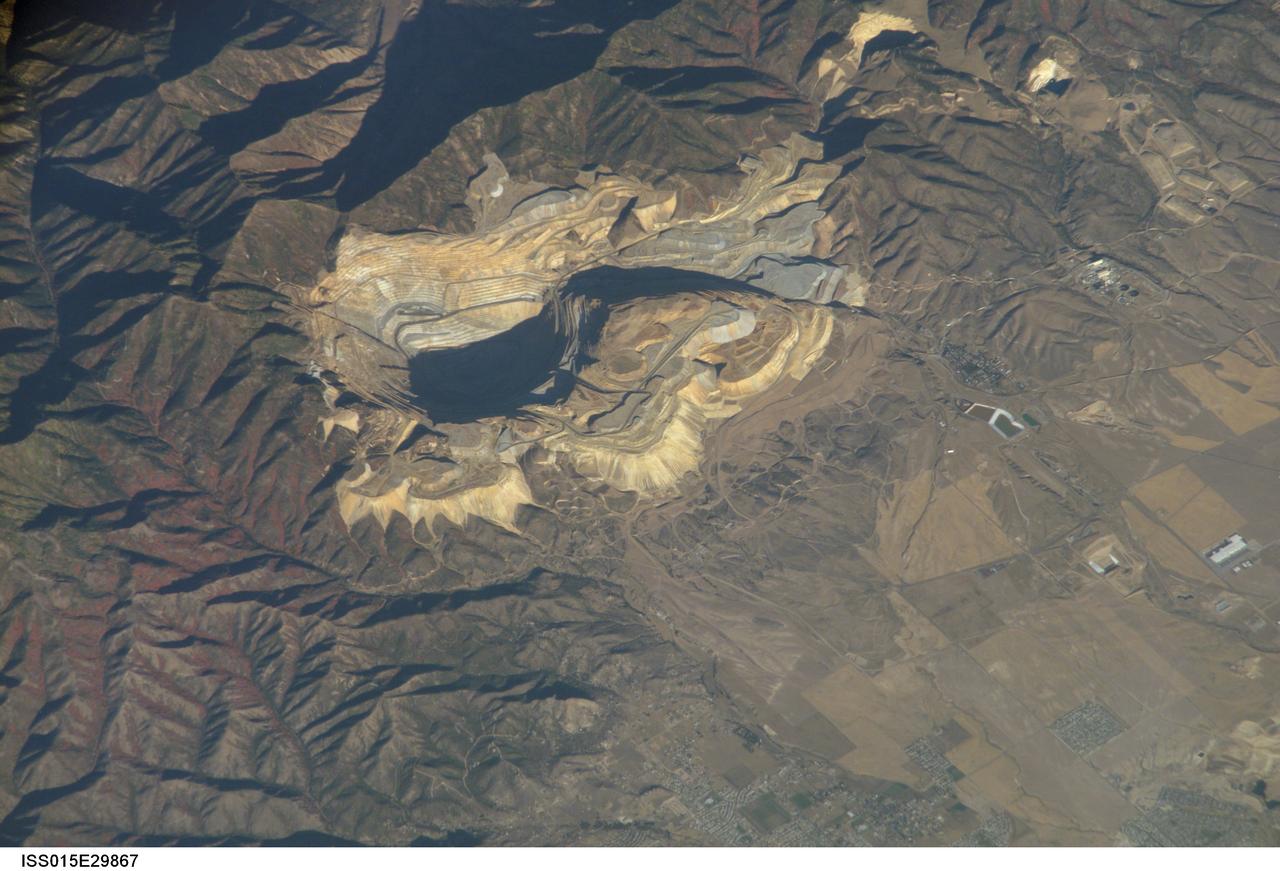
ISS015-E-29867 (20 Sept. 2007) --- Bingham Canyon Mine, Utah is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. The Bingham Canyon Mine (center) located approximately 32 kilometers to the southeast of Salt Lake City, UT is one of the largest open-pit mines in the world, measuring over 4 kilometers wide and 1,200 meters deep. The mine exploits a porphyry copper, a type of geological structure formed by crystal-rich magma moving upwards through pre-existing rock layers. As the magma cools and crystallizes (forming an igneous rock with large crystals in a fine-grained matrix, known as a porphyry), hot fluids circulate through the magma and surrounding rocks via fractures. This process of hydrothermal alteration typically forms copper-bearing and other minerals in spatial patterns that a geologist recognizes as a potential porphyry copper deposit. Parallel benches (stepped terraces), visible along the western pit face (center left), range from 16 to 25 meters high - these provide access for equipment to work the rock face, as well as maintaining stability of the sloping pit walls. A dark, larger roadway is also visible directly below the benches. Brown to gray, flat topped hills of gangue (waste rock) surround the pit, and are thrown into sharp relief by shadows and the oblique viewing angle of this image. Leachate reservoirs associated with ore processing are visible to the south of the city of Bingham Canyon, UT (right).
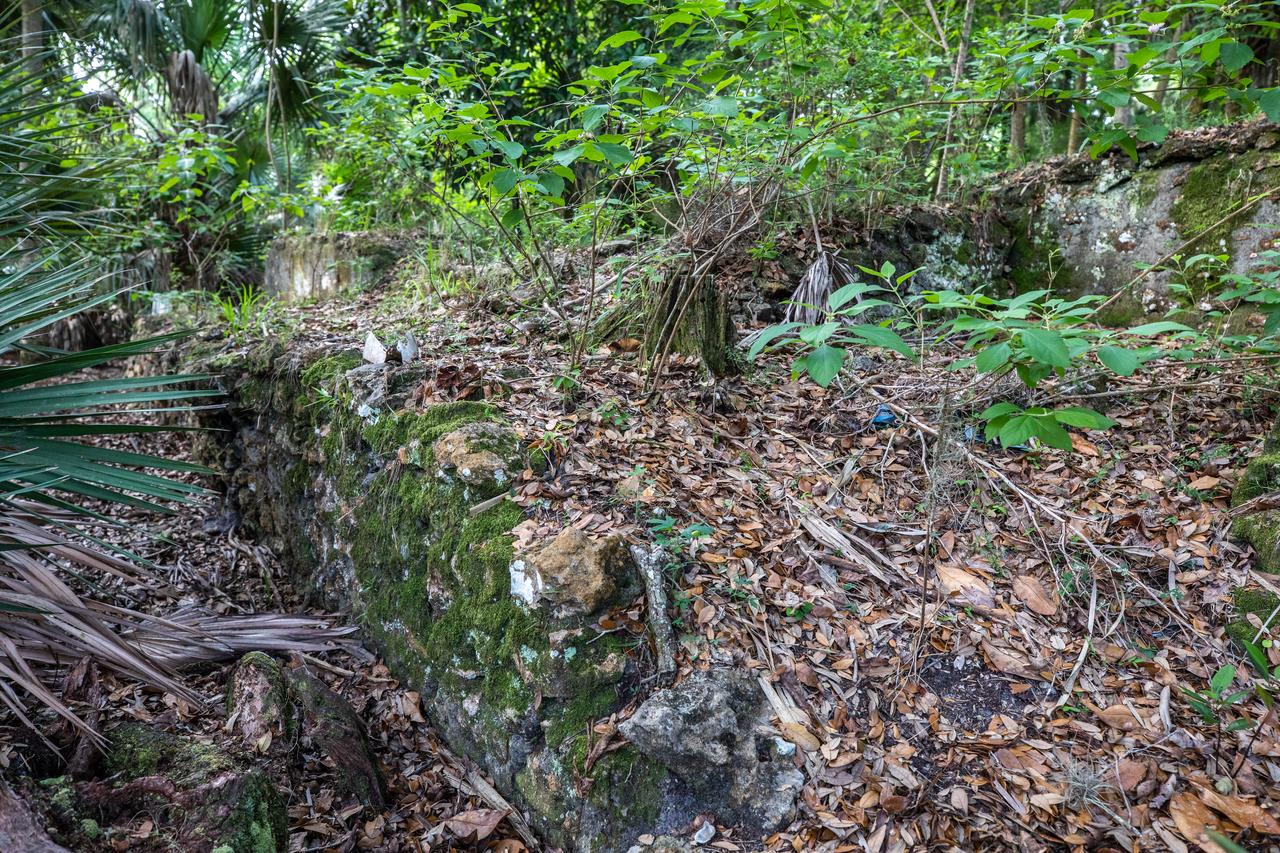

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
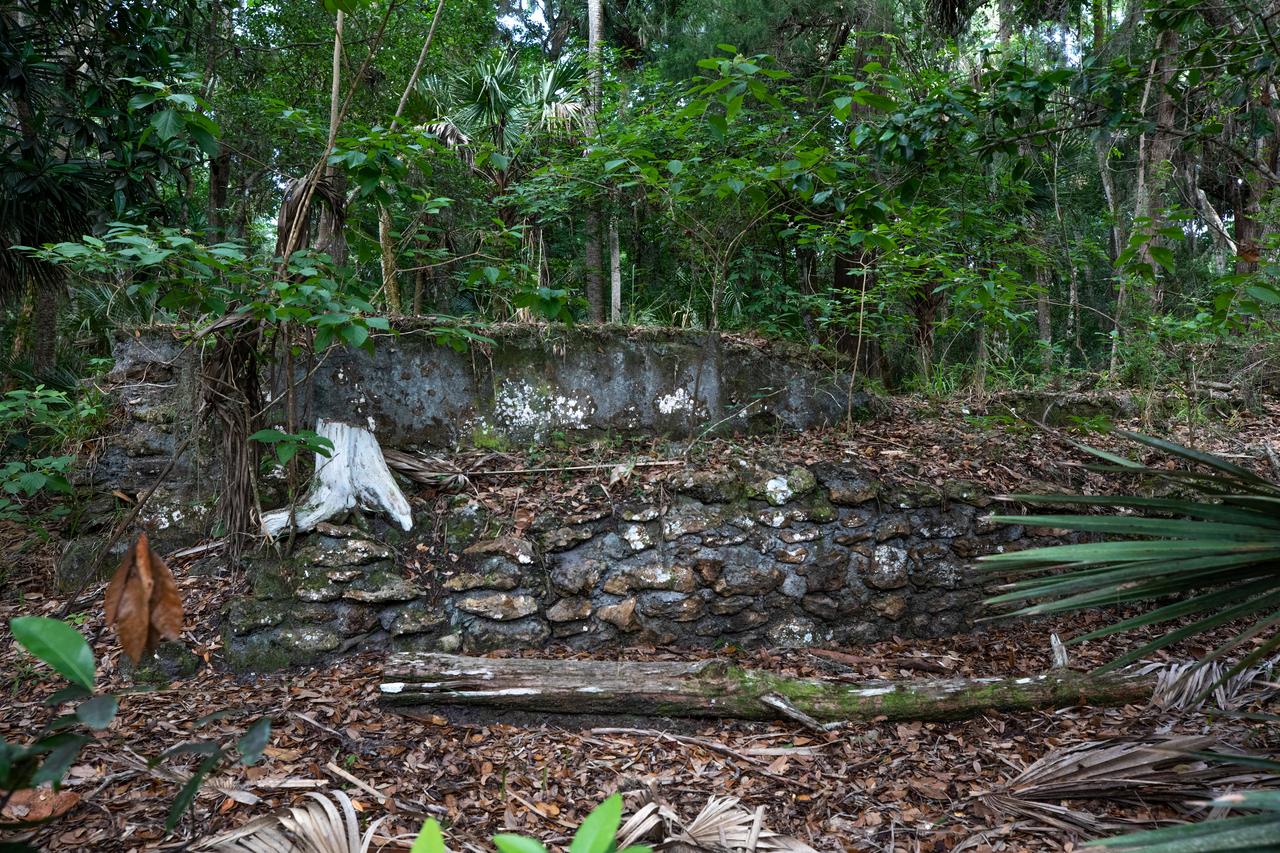

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.

The dart and associated launching system was developed by engineers at MSFC to collect a sample of the aluminum oxide particles during the static fire testing of the Shuttle's solid rocket motor. The dart is launched through the exhaust and recovered post test. The particles are collected on sticky copper tapes affixed to a cylindrical shaft in the dart. A protective sleeve draws over the tape after the sample is collected to prevent contamination. The sample is analyzed under a scarning electron microscope under high magnification and a particle size distribution is determined. This size distribution is input into the analytical model to predict the radiative heating rates from the motor exhaust. Good prediction models are essential to optimizing the development of the thermal protection system for the Shuttle.

jsc2021e037879 (8/24/2021) --- A preflight view of the Touching Surfaces investigation hardware. The Touch Array (136 mm x 45 mm x 8 mm). Housing : Aluminum (EN-AW 7075 T7351). (Panel A) Nine metallic test surfaces: 3 x steel, copper, brass (from left to right) – with no greater than 3 ?m and less than 3 ?m laser structure (from top to bottom); (Panel B) in each Touch Array two 3 printed humidity detectors are mounted. Image Courtesy DLR
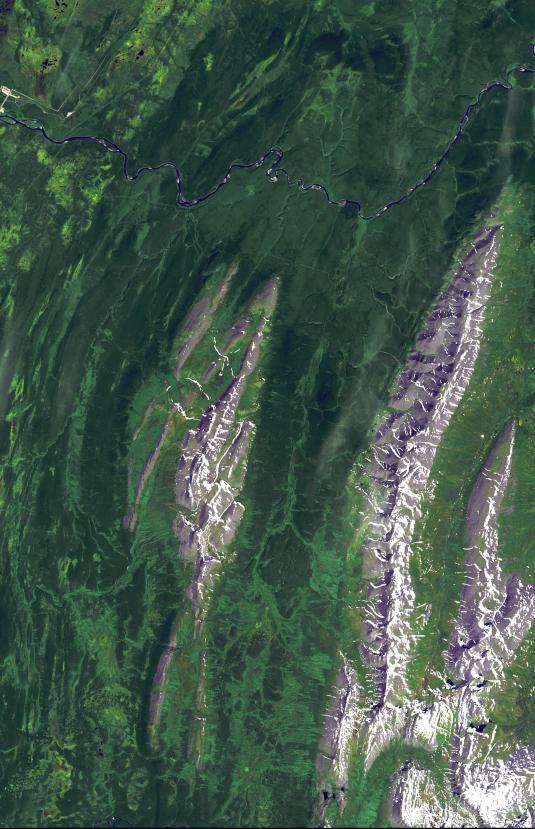

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the Ural Mountains, which run 2500 km north-south through western Russia, and form the boundary between Europe and Asia. Since the 17th century, the mountains were exploited for their deposits of iron, copper, gold, coal, oil, mica and gemstones. The Urals are among the world's oldest existing mountain ranges, having been formed about 275 million years ago due to the collision of the Laurussia supercontinent with the continent of Kazakhstania. The image was acquired July 13, 2011, covers an area of 39 by 62 km, and is located near 65.5 degrees north, 59.9 degrees east. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19795
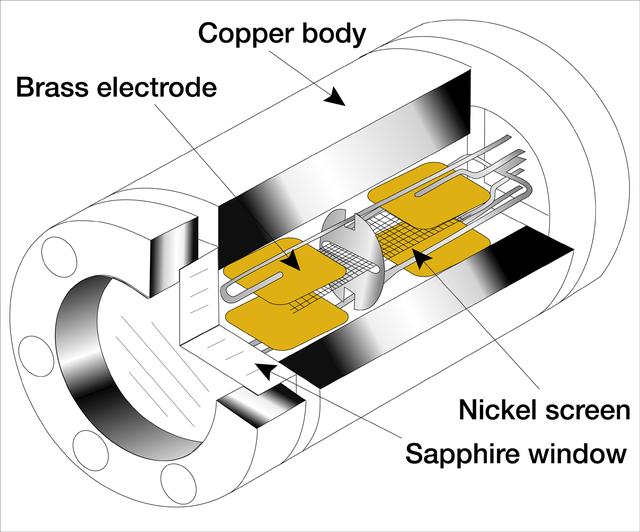
The Critical Viscosity of Xenon Experiment (CVX-2) on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2002 will measure the viscous behavior of xenon, a heavy inert gas used in flash lamps and ion rocket engines, at its critical point. The sample cell at the heart of CVX-2 will sit inside a thermostat providing three layers of insulation. The cell itself comprises a copper body that conducts heat efficiently and smoothes out thermal variations that that would destroy the xenon's uniformity. Inside the cell, the oscillating screen viscometer element is supported between two pairs of electrodes that deflect the screen and then measure screen motion.
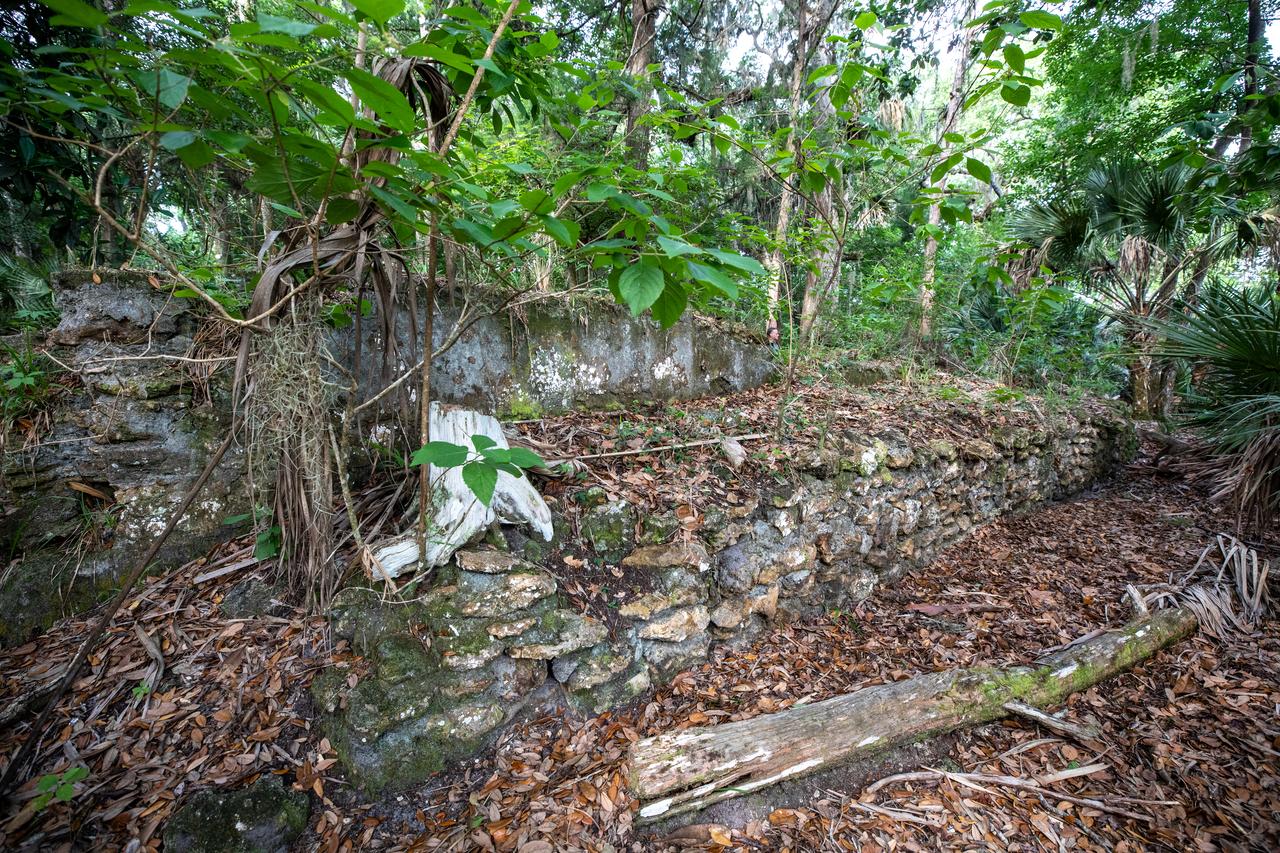

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
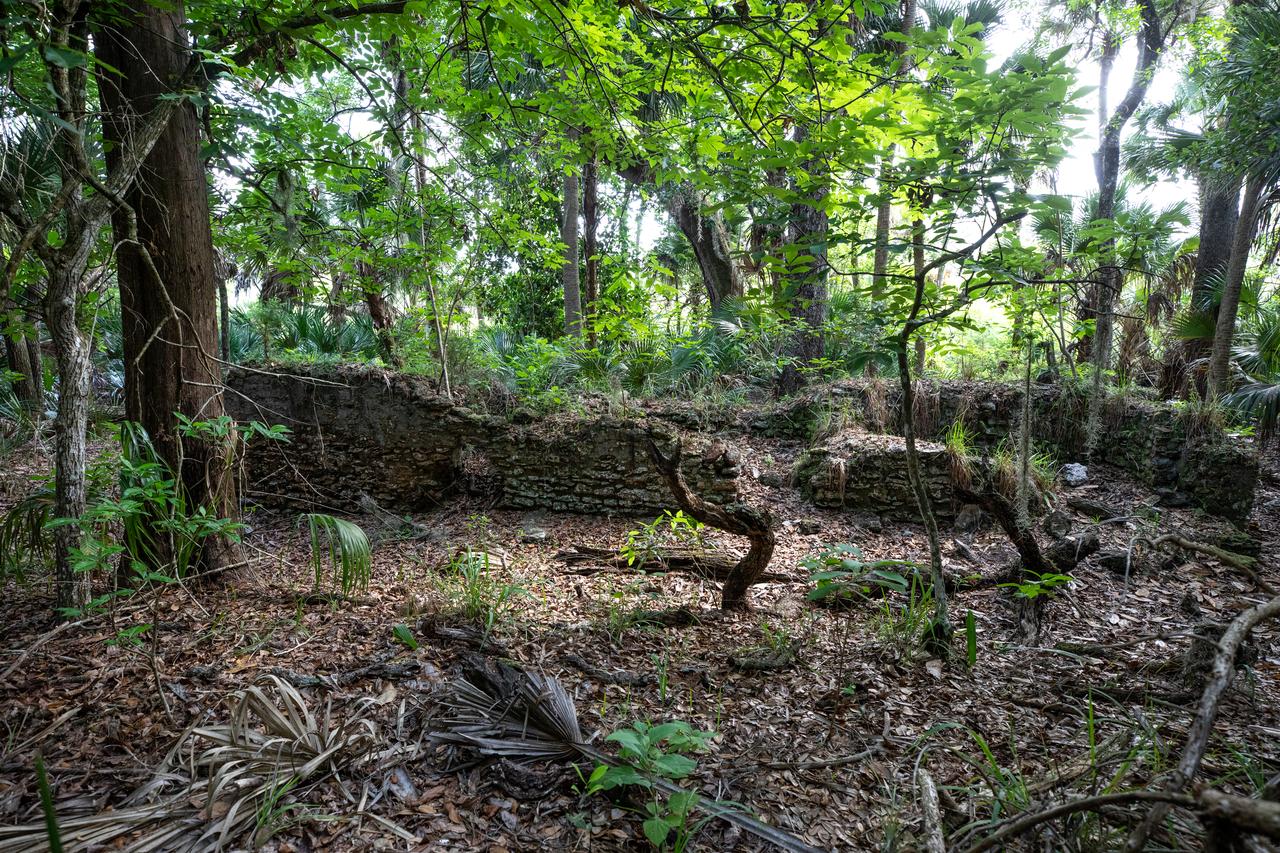

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
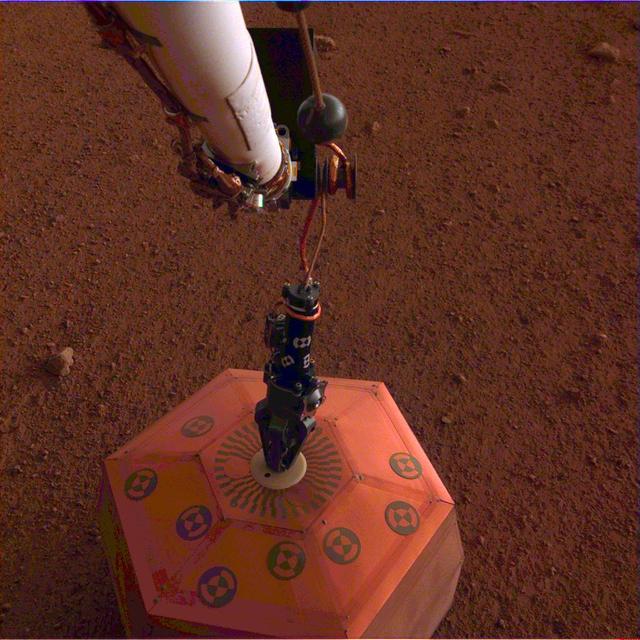
NASA's InSight lander placed its seismometer onto Mars on Dec. 19, 2018. This was the first time a seismometer had ever been placed onto the surface of another planet. The seismometer is the copper-colored object in this image, which was taken around Martian dusk. The seismometer, called Seismic Explorations for Interior Structure (SEIS), will measure seismic waves caused by marsquakes, meteorite strikes and other phenomena. Watching how these waves travel through Mars' interior will let scientists study how the planet's crust, mantle and core are layered. It will also reveal more about how all rocky bodies are formed, including Earth and its Moon. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22956
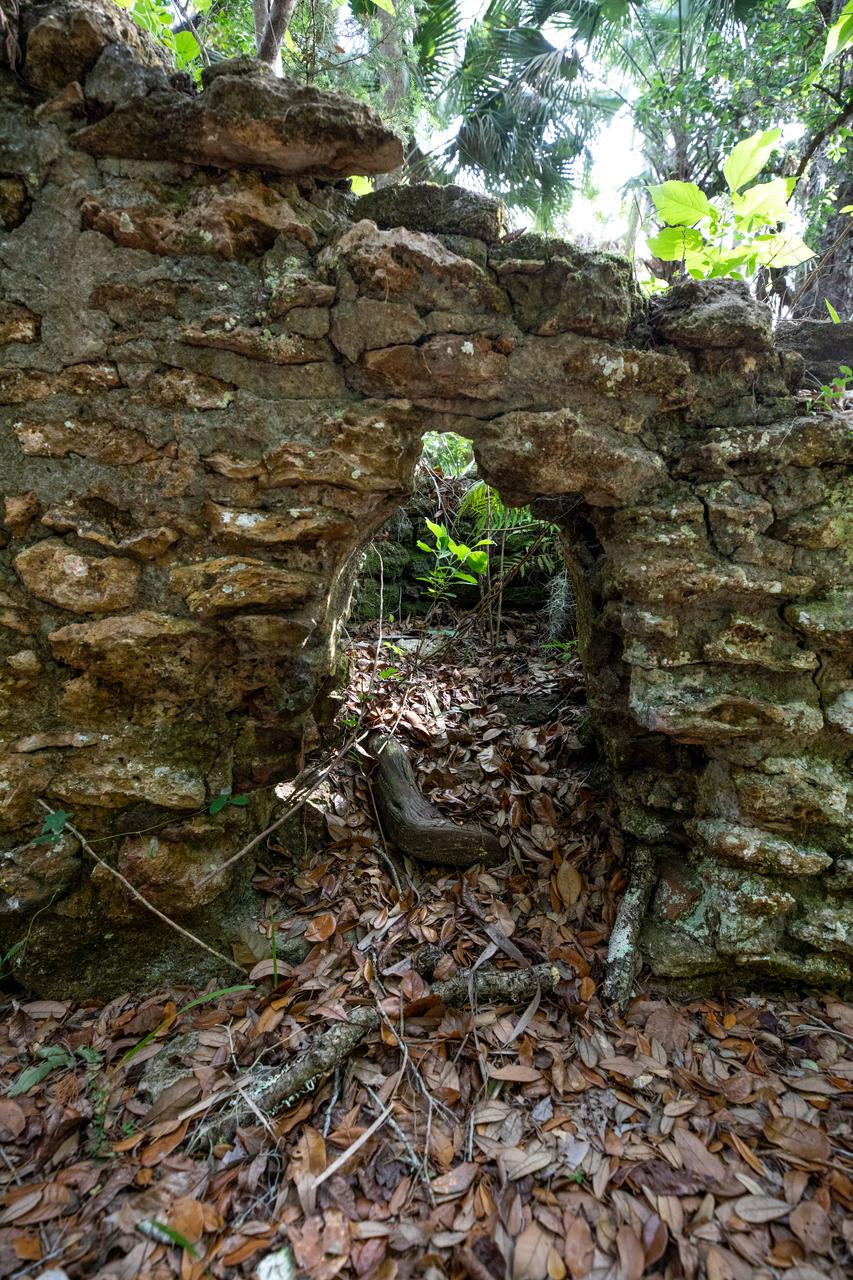

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
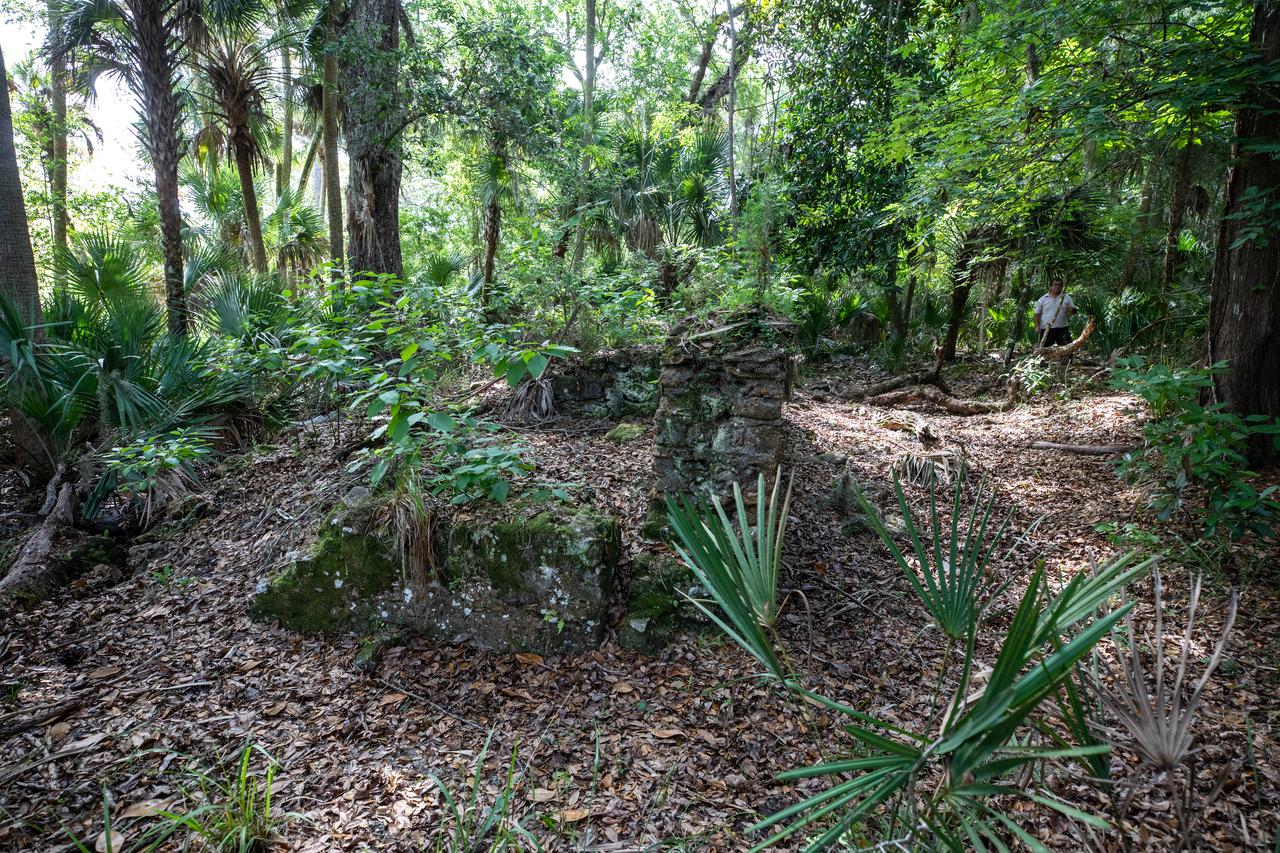

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
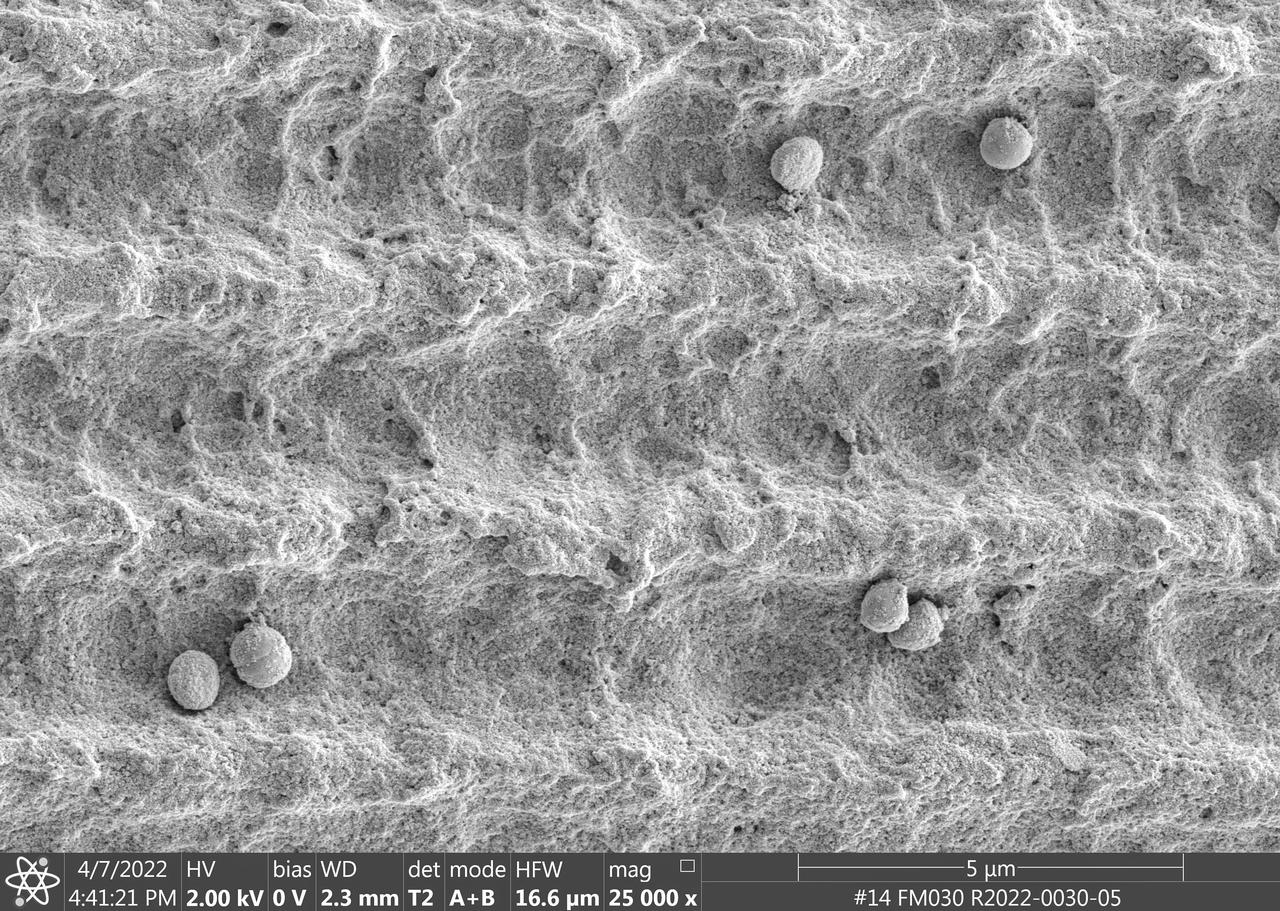

jsc2023e010177 (4/7/2022) --- This image is a scanning electron microscopic image of one of the ESA-Biofilms sample plates from the first launch to the ISS. The sample plate in this image is made of copper, which naturally has antimicrobial properties. This surface has a 3 µm laser structure engraved to the surface which improves antimicrobial efficacy. On the surface, only few cells of the bacterial species Staphylococcus capitis are attached. The cells appear small and are not actively dividing. The ESA-Biofilms investigation studies bacterial biofilm formation and antimicrobial properties of different metal surfaces under spaceflight conditions in altered gravity. Image courtesy of DLR, CC BY-NC-ND 3.0.
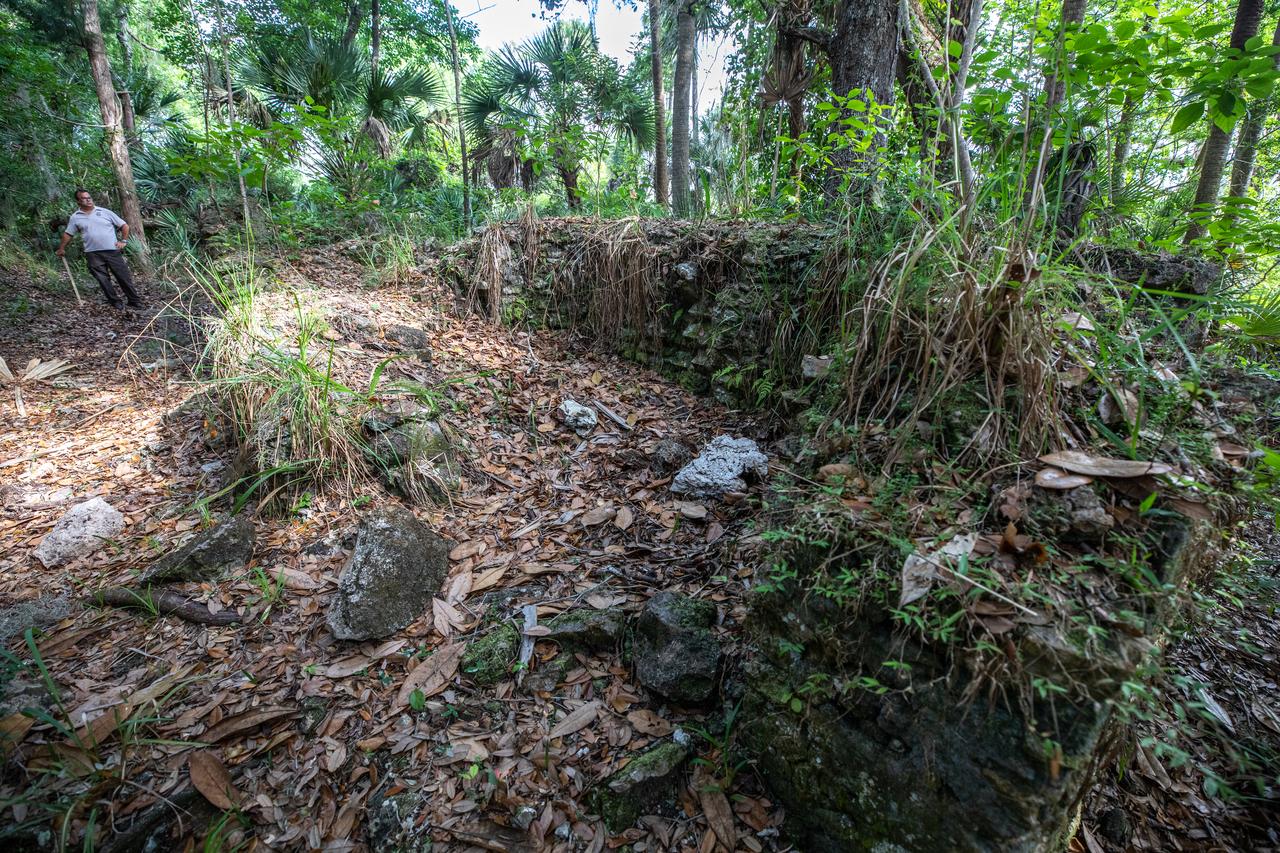

Michael Legare, of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, stands near the archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
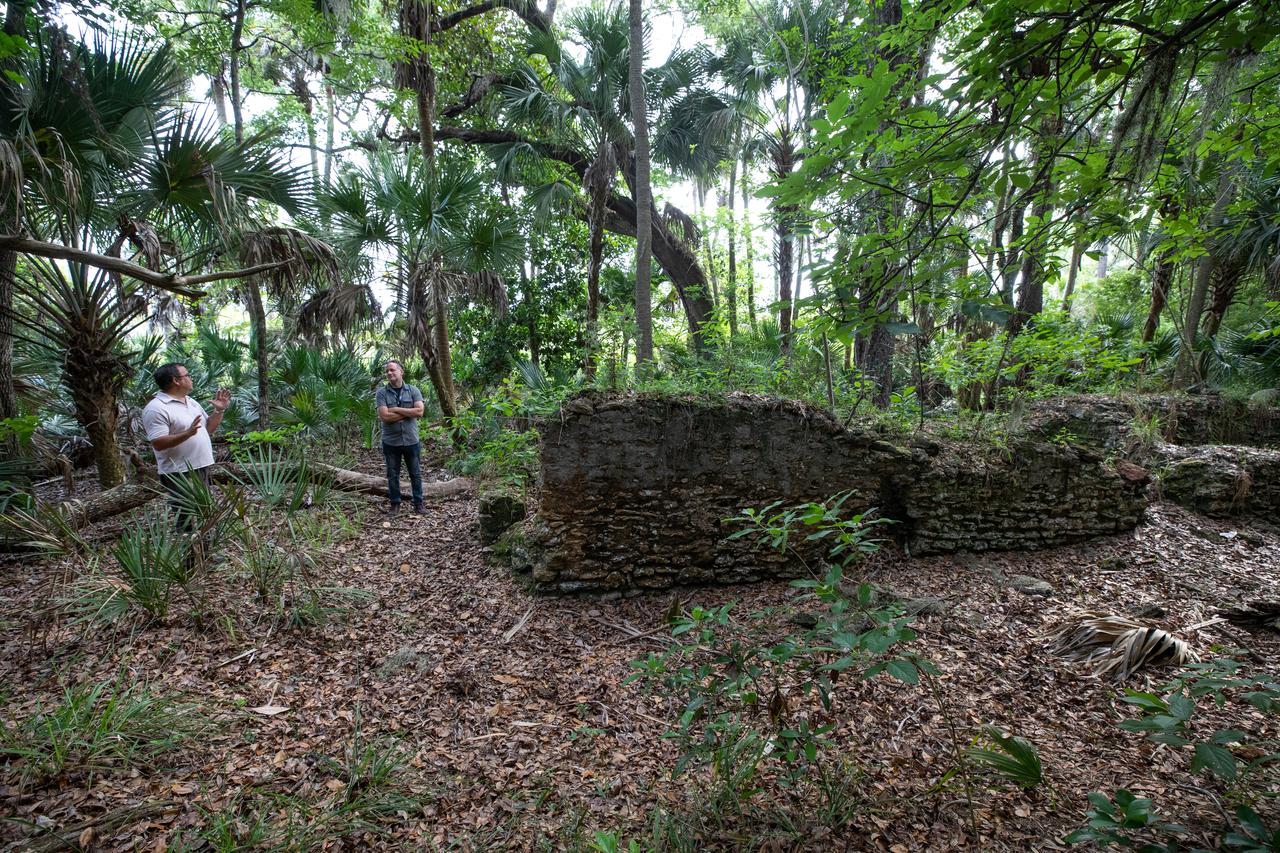

Members of U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and NASA Communications visit the archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
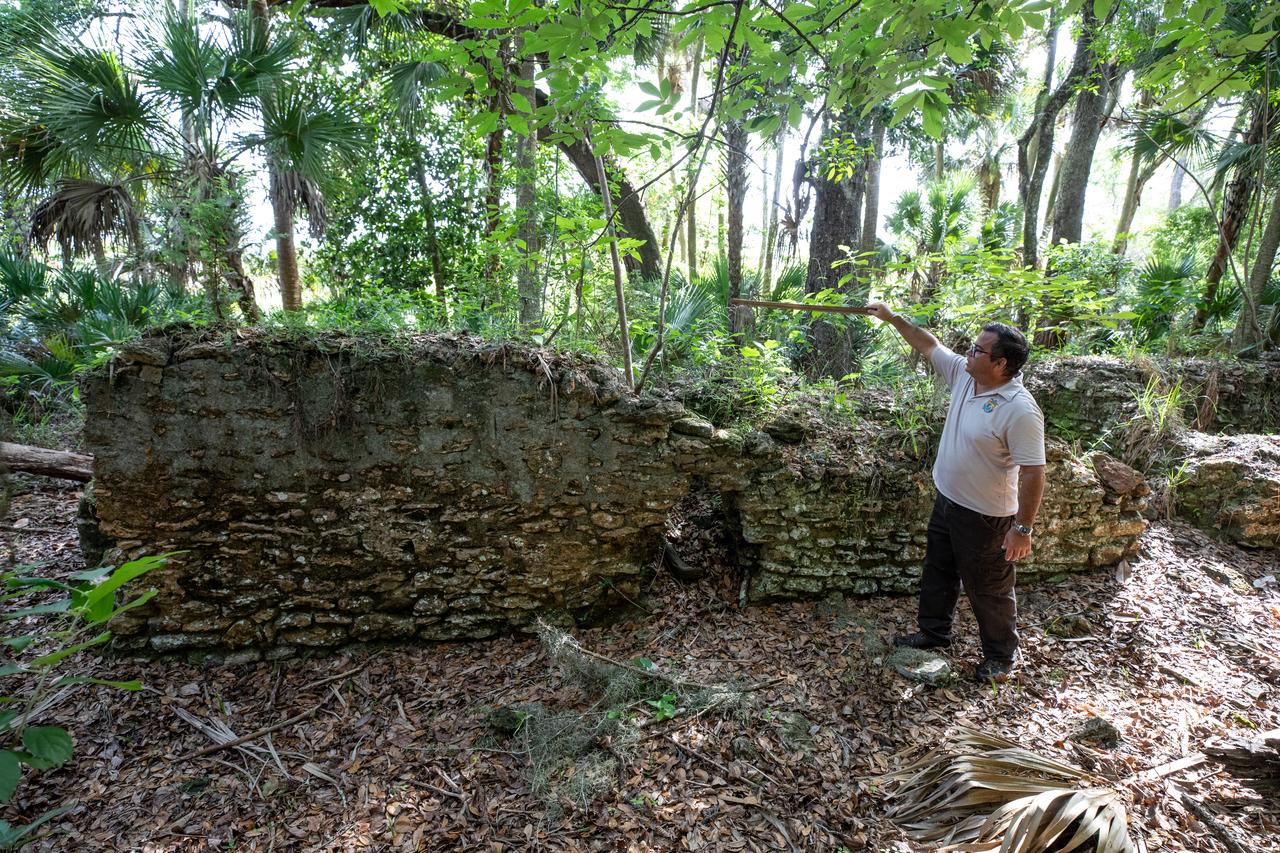

Near the archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michael Legare, of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, recreates the original wall height of the structure on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
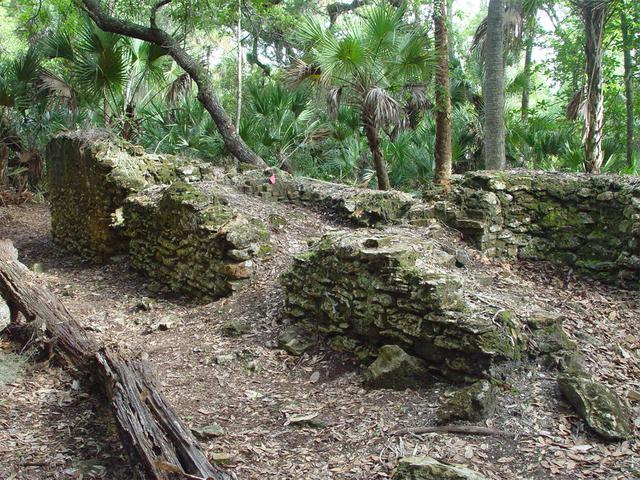

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar factory are revealed through the oak hammock on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 2008. The sugar factory structure, or sugar train, was built from fieldstone and is where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. In interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA, and with the assistance of volunteers from the Indian River Anthropological Society, and historic preservation offices of Brevard and Volusia counties, approximately 200 shovel tests and 20 excavation units were completed in three areas of the plantation complex from 2008 to 2009.
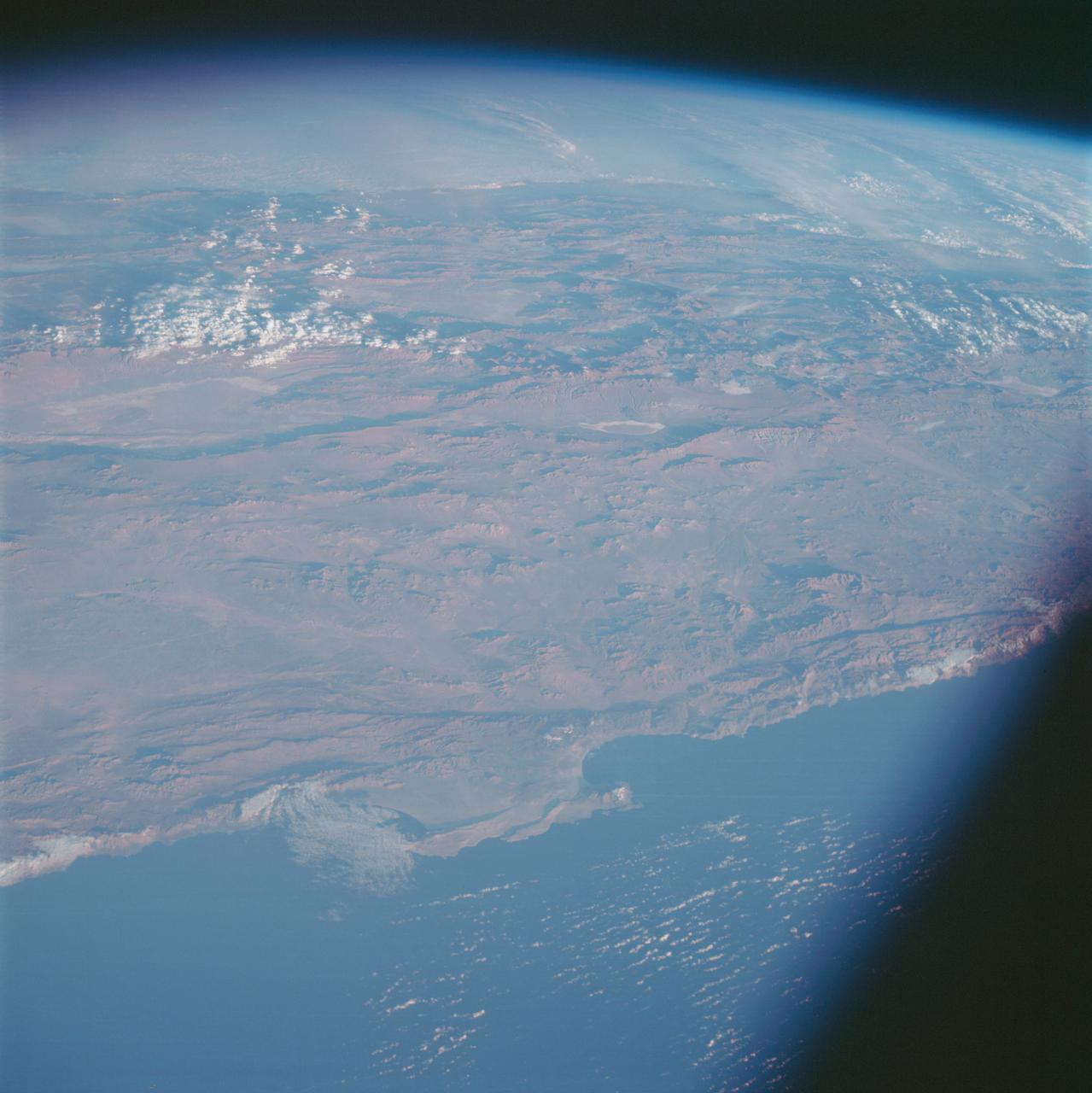

AS07-07-1826 (17 Oct. 1968) --- This view of South America was photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 81st revolution of Earth from an altitude of 120 nautical miles. The port city of Antofagasta, Chile, is located in the half-moon shaped bay in the lower left portion of the picture. Beyond the coast is the Andean peak of Llullaillaco Volcano which rises 22,000 feet above sea level. At left center is the Chuquicamata copper mines located near Coloma. At the center of the photo, behind the large salt lake and atop a 19,000 foot high volcano, the countries of Bolivia, Argentina, and Chile meet at a common point. Below the clouds in the upper portion of the photo are the Great Plains known as the Gran Chaco.
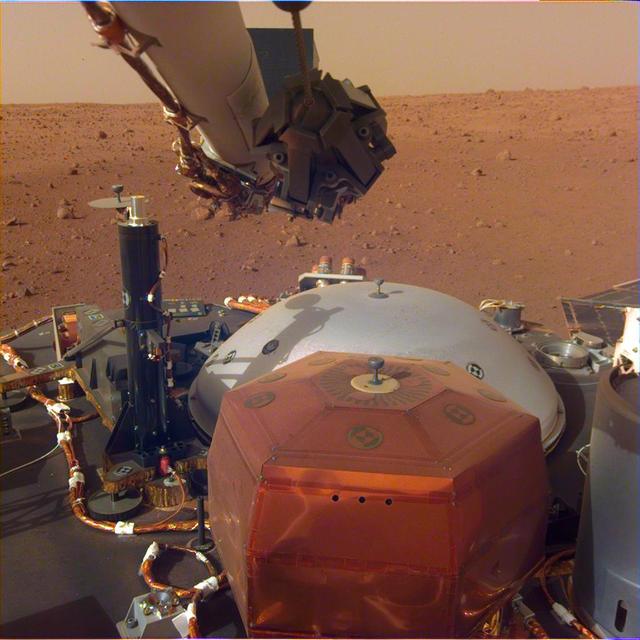

This image from InSight's robotic-arm mounted Instrument Deployment Camera shows the instruments on the spacecraft's deck, with the Martian surface of Elysium Planitia in the background. The color-calibrated picture was acquired on Dec. 4, 2018 (Sol 8). In the foreground, a copper-colored hexagonal cover protects the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure instrument (SEIS), a seismometer that will measure marsquakes. The gray dome behind SEIS is the wind and thermal shield, which will be placed over SEIS. To the left is a black cylindrical instrument, the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Probe (HP3). HP3 will drill up to 16 feet (5 meters) below the Martian surface, measuring heat released from the interior of the planet. Above the deck is InSight's robotic arm, with the stowed grapple directly facing the camera. To the right can be seen a small portion of one of the two solar panels that help power InSight and part of the UHF communication antenna. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22871
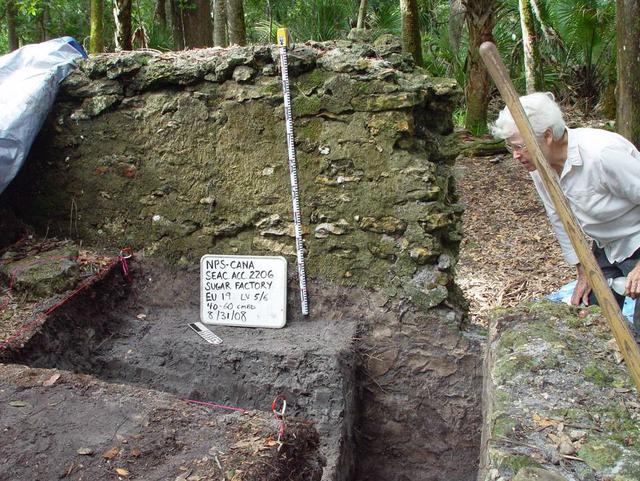

Preservationist Dot Moore views the ruins of Elliot Plantation sugar factory during an excavation in 2008 on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The sugar factory structure, or sugar train, was built from fieldstone and is where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. In interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA, and with the assistance of volunteers from the Indian River Anthropological Society, and historic preservation offices of Brevard and Volusia counties, approximately 200 shovel tests and 20 excavation units were completed in three areas of the plantation complex from 2008 to 2009.
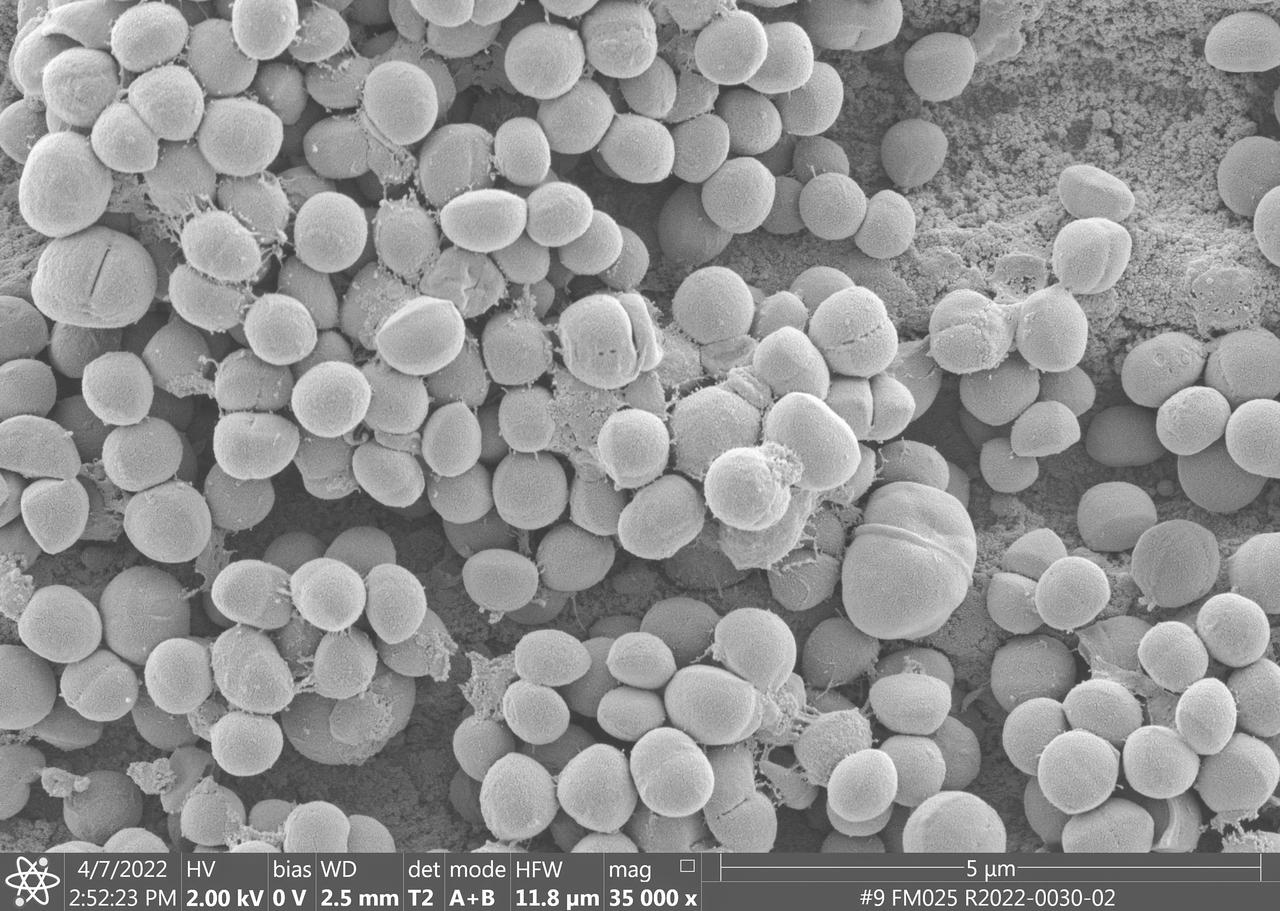

jsc2023e010178 (4/7/2022) --- This image taken by a scanning electron microscope shows one of the ESA-Biofilms sample plates from its first launch to the International Space Station. The sample plate in this image is made of stainless steel, which is the reference surface in the experiment since it has no antimicrobial properties. This surface also has a 3 µm laser structure engraved to the surface as control. In contrast to the copper surface, there are many Staphylococcus capitis cells attached to the steel surface that are actively dividing and starting to from components of a biofilm matrix. The ESA-Biofilms investigation studies bacterial biofilm formation and antimicrobial properties of different metal surfaces under spaceflight conditions in altered gravity. Image courtesy of DLR, CC BY-NC-ND 3.0.
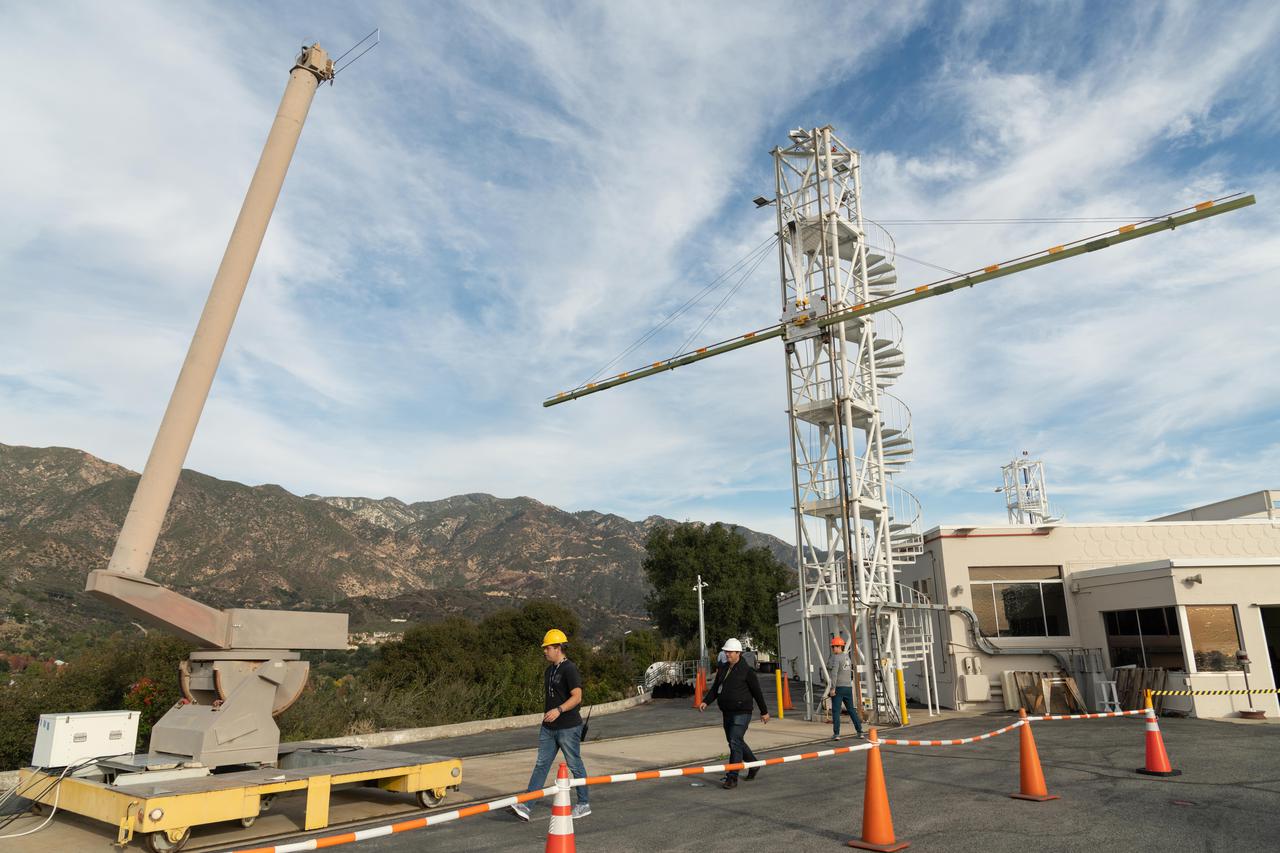

Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California test an engineering model of a high-frequency (HF) radar antenna that makes up part of NASA's Europa Clipper radar instrument on Dec. 17, 2019. The antenna is a 59-foot-long (18-meter-long) narrow copper tube held straight by several cables and a cross bar on the tower at right. In space, the copper tube will stick out straight on its own, but in Earth's gravity, the antenna requires supports to keep it straight for testing. The mobile tower at left holds a model of the VHF (very high-frequency) antenna so that engineers could measure the amount of energy coupled from one antenna to the other. Europa Clipper's radar instrument is called Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface, or REASON. As the spacecraft orbits Jupiter and surveys its icy moon Europa, REASON will use HF and VHF radio signals to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) into the icy shell that covers Europa. The radio waves will bounce off subsurface features and return to the spacecraft to create images of the ice layers' internal structure. REASON will help scientists look for the moon's suspected ocean, measure ice thickness, and better understand the icy shell's interior. The instrument will also study the elevation, properties, and roughness of Europa's surface, and will prowl Europa's upper atmosphere for signs of plume activity. The antennae were built for NASA by Heliospace Corporation in Berkeley, California, and the University of Texas at Austin is the lead institution for REASON. The testing was conducted at JPL's Mesa Antenna Measurement Facility, which sits on a high plateau. With an internal global ocean twice the size of Earth's oceans combined, Europa may have the potential to harbor life. The Europa Clipper orbiter will swoop around Jupiter on an elliptical path, dipping close to the moon on each flyby to collect data. Understanding Europa's habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet. Europa Clipper is aiming for a launch readiness date of 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24323
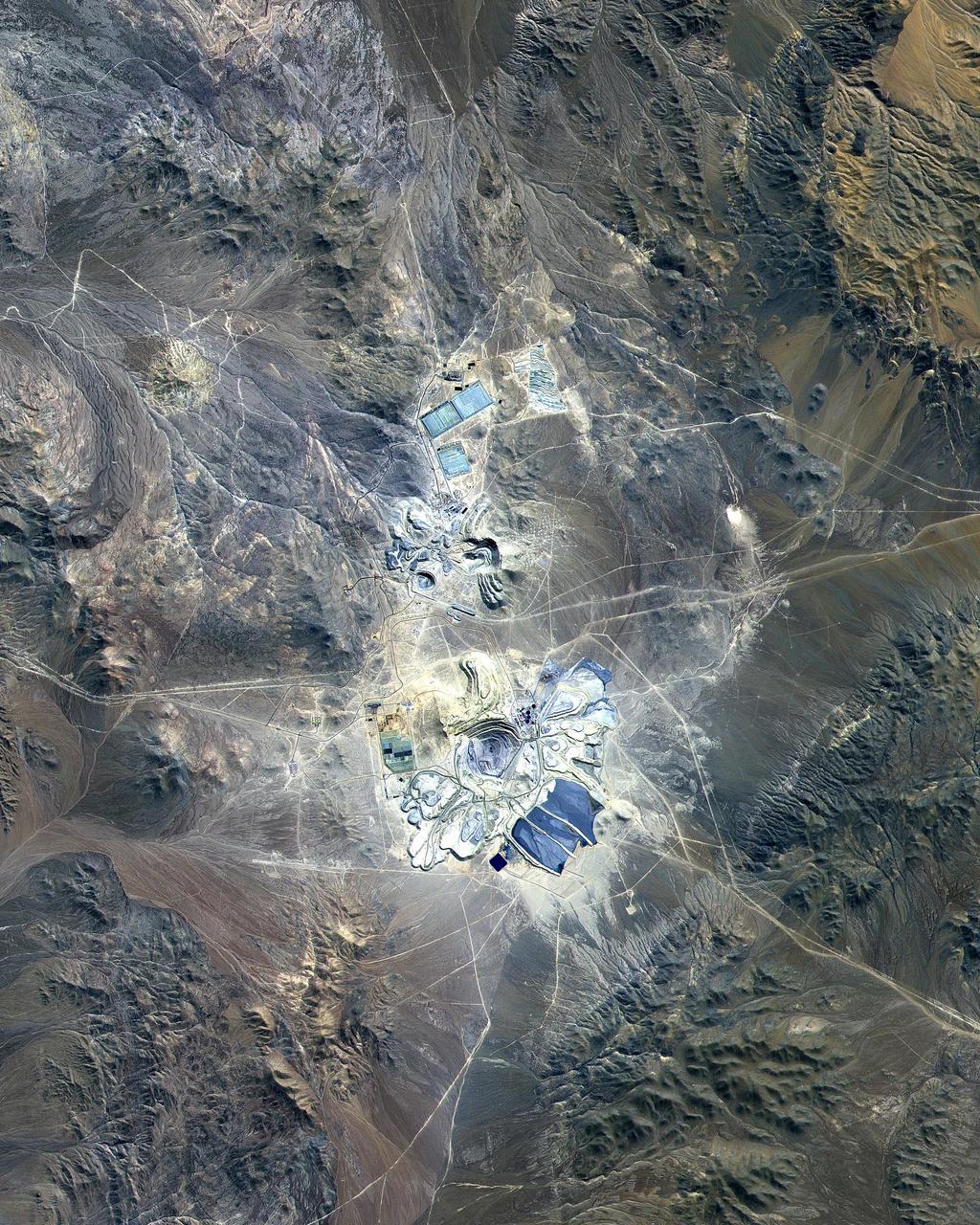

This ASTER image covers 30 by 37 km in the Atacama Desert, Chile and was acquired on April 23, 2000. The Escondida Cu-Au-Ag open-pit mine is at an elevation of 3050 m, and came on stream in 1990. Current capacity is 127,000 tons/day of ore; in 1999 production totaled 827,000 tons of copper, 150,000 ounces of gold and 3.53 million ounces of silver. Primary concentration of the ore is done on-site; the concentrate is then sent to the coast for further processing through a 170 km long, 9 pipe. Escondida is related geologically to three porphyry bodies intruded along the Chilean West Fissure Fault System. A high grade supergene cap overlies primary sulfide ore. This image is a conventional 3-2-1 RGB composite. Figure 1 displays SWIR bands 4-6-8 in RGB, and highlights lithologic and alteration differences of surface units. The image is located at 24.3 degrees south latitude and 69.1 degrees west longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11090

ISS011-E-12401 (10 July 2005) --- Gulf of Finland is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 11 crew member on the international space station. This strongly oblique view shows the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in the sunglint of late afternoon. The image was taken from the station when the position of the craft lay north of the Caspian Sea, approximately 2,500 kilometers to the southeast on the Russia–Kazakhstan border. The Neva River appears in sunglint, connecting Lake Ladoga to the gulf. Although not visible, St. Petersburg—the home town of Sergei Krikalev, space station commander when this picture was taken—lies on the Neva River delta. In this view taken with a powerful 400 millimeter lens, sunglint even reveals the causeways to Kotlin Island in the gulf—including some of the details of their construction. Oblique views reveal marked layers of gray haze generated by air pollution, a common sight over Western Europe. Pollution also renders the bright glint areas a copper color.
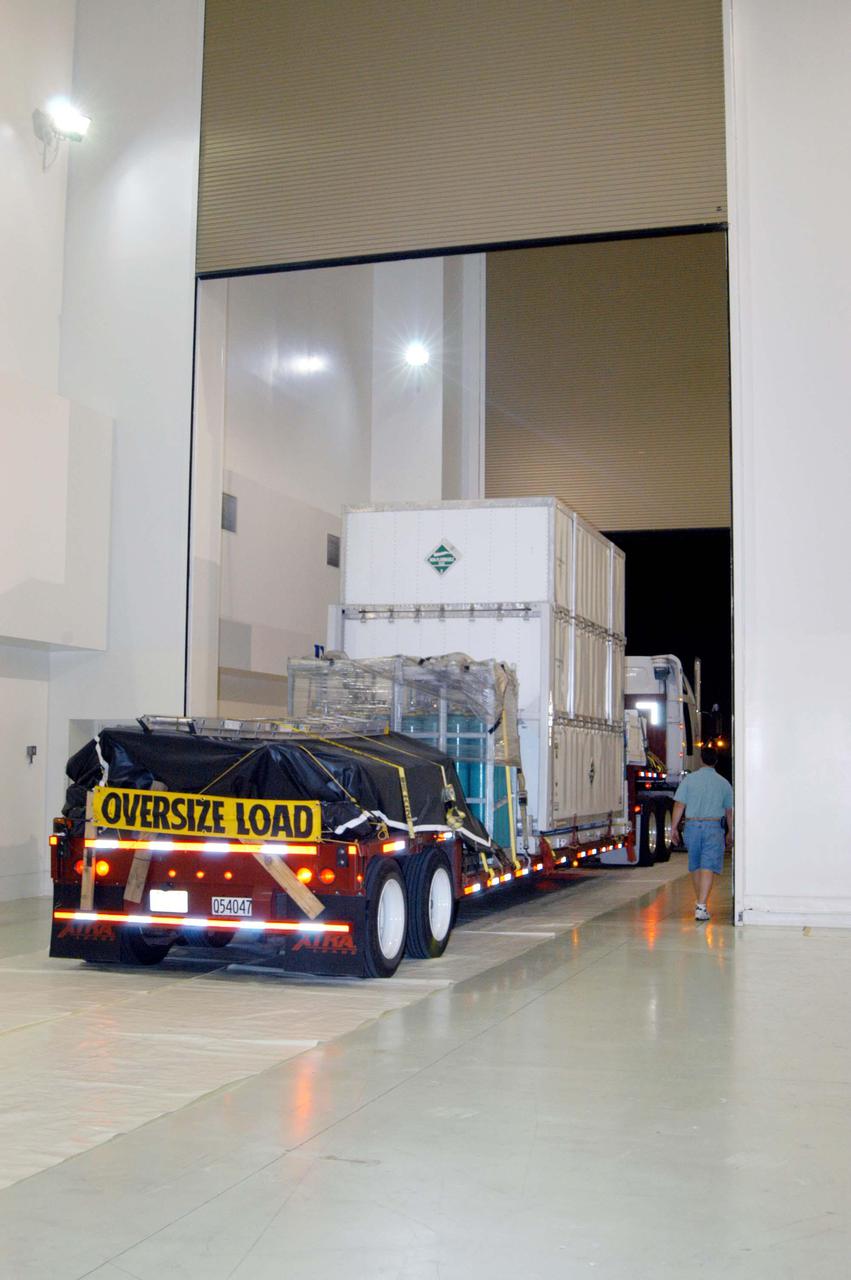

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The truck carrying the NASA Discovery Mission Deep Impact spacecraft backs into the facility at Astrotech Space Operations near Kennedy Space Center. The spacecraft was transported from Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. in Boulder, Colo. Deep Impact is designed to launch a copper projectile into the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth. When this 820-pound “impactor” hits the surface of the comet at nearly 23,000 miles per hour, the 3- by 3-foot projectile will create a crater hundreds of feet in size. Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch Dec. 30, 2004, aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla.
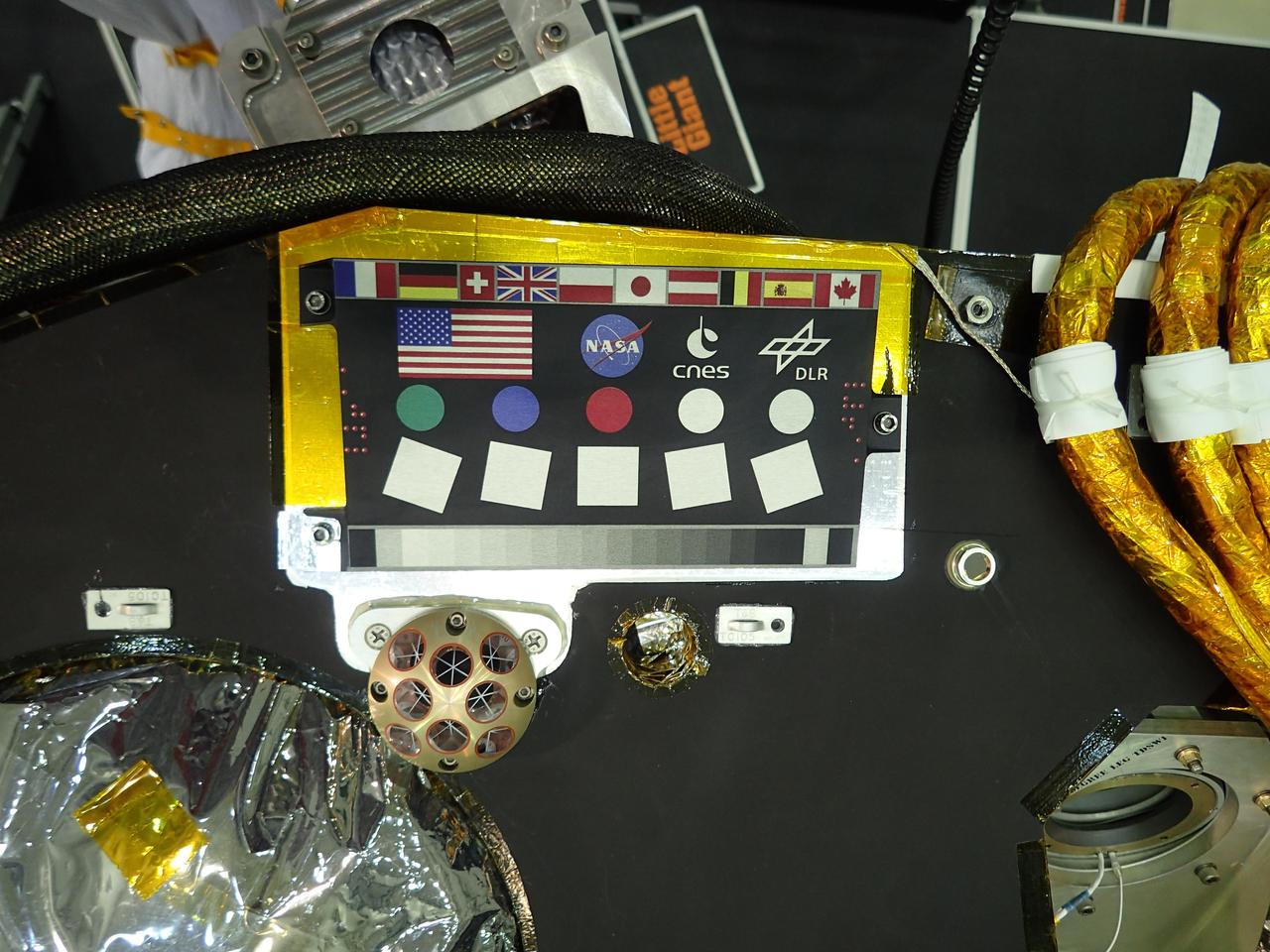

A camera calibration target sits on the deck of the NASA's InSight lander, adorned with the flags of the countries participating in the mission. The target, which will be viewed by InSight's cameras, provides a variety of colors and shapes to help calibrate the lander's cameras. It also shows off international flags representing the agencies, institutions and participating scientists of the mission as of late 2014 (since that time, Italy has contributed an experiment). In the second row are the United States flag and the logos of NASA, the French space agency CNES, which provided InSight's seismometer; and the German Aerospace Center DLR, which provided InSight's heat flow probe. Below the target in the photo is an Italian experiment called the Laser Retroreflector for InSight (LaRRI). LaRRI is the small, copper-colored dome covered with circles just below the calibration target; it won't actually play a role in InSight's mission. The national space agency of Italy (ASI, for Agenzia Spaziale Italiana) provided LaRRI to be used by a possible future Mars orbiter mission with a laser altimeter making extremely precise measurements of the lander's location for fundamental physics studies and precision cartography. A microchip bearing the names of nearly a million members of the public is visible in this image to the right of the calibration target. A second microchip with more than a million additional names was added after this photo was taken. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22540
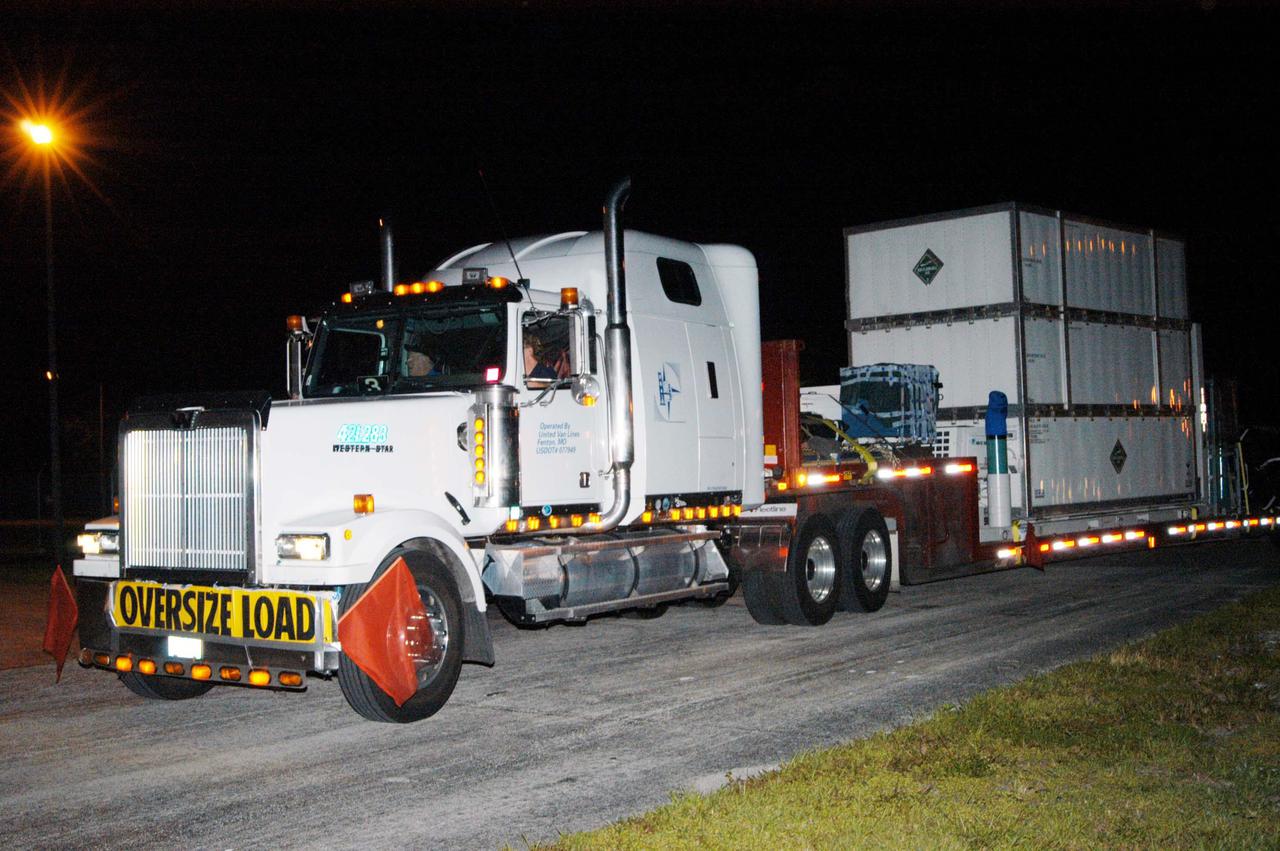

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The NASA Discovery Mission Deep Impact spacecraft arrives via truck from Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. in Boulder, Colo. It is being taken to Astrotech Space Operations near Kennedy Space Center. Deep Impact is designed to launch a copper projectile into the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth. When this 820-pound “impactor” hits the surface of the comet at nearly 23,000 miles per hour, the 3- by 3-foot projectile will create a crater hundreds of feet in size. Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch Dec. 30, 2004, aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla.
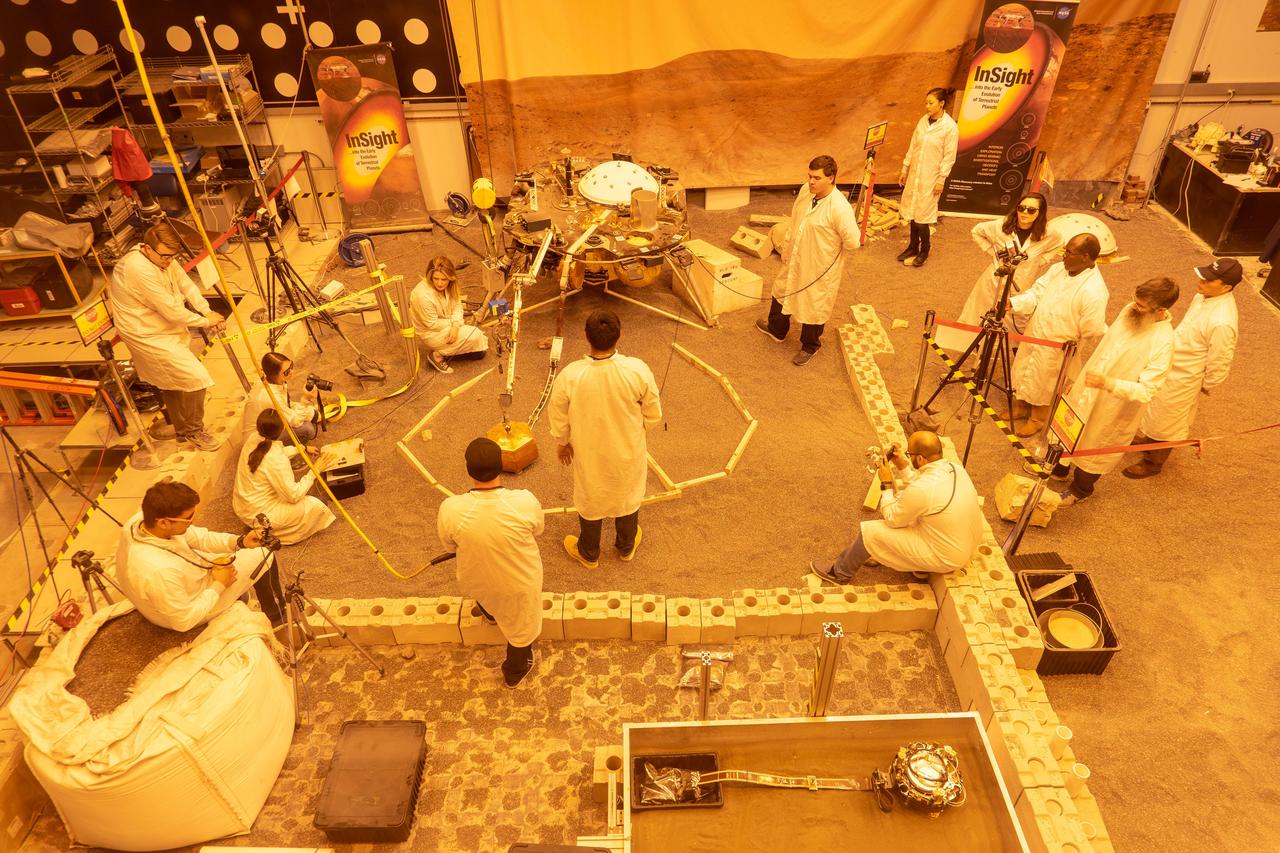

Engineers practice deploying InSight's instruments in a lab at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Several of them are wearing sunglasses to block the bright yellow lights in the test space, which mimic sunlight as it appears on Mars. The yellow lights are used to test cameras which are the same as those used by InSight on Mars. The entire lab space in the center of the image has been sculpted to mimic the terrain in front of the lander on Mars, creating more reliable test conditions. The area in the center of the image is the "workspace" where the lander's instruments can be set down; wood blocks have been laid down to mark the perimeter of these areas. Rocks have been chosen to match the size, shape and location of those in front of InSight on Mars. In the center of the image is a model of the lander's copper-colored seismometer; at the bottom-right is a second model of the seismometer used for a different kind of testing. In the lower left corner of the image is a bag of crushed granite, which is used in this lab to simulate Martian sand. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22744

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The truck carrying the NASA Discovery Mission Deep Impact spacecraft arrives from Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. in Boulder, Colo. It is being taken to Astrotech Space Operations near Kennedy Space Center. Deep Impact is designed to launch a copper projectile into the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth. When this 820-pound “impactor” hits the surface of the comet at nearly 23,000 miles per hour, the 3- by 3-foot projectile will create a crater hundreds of feet in size. Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch Dec. 30, 2004, aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla.
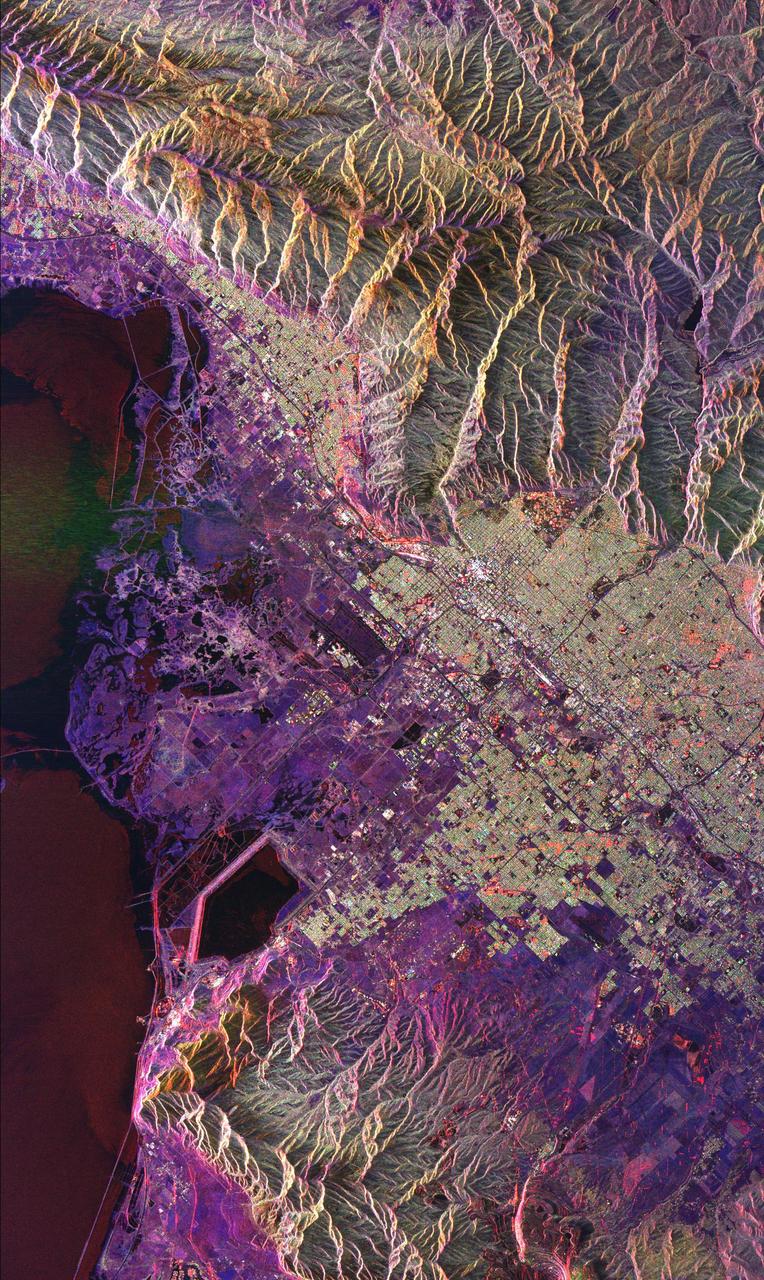

This radar image of Salt Lake City, Utah, illustrates the different land use patterns that are present in the Utah Valley. Salt Lake City lies between the shores of the Great Salt Lake (the dark area on the left side of the image) and the Wasatch Front Range (the mountains in the upper half of the image). The Salt Lake City area is of great interest to urban planners because of the combination of lake, valley and alpine environments that coexist in the region. Much of the southern shore of the Great Salt Lake is a waterfowl management area. The green grid pattern in the right center of the image is Salt Lake City and its surrounding communities. The Salt Lake City airport is visible as the brown rectangle near the center of the image. Interstate Highway 15 runs from the middle right edge to the upper left of the image. The bright white patch east of Interstate 15 is the downtown area, including Temple Square and the state capitol. The University of Utah campus is the yellowish area that lies at the base of the mountains, east of Temple Square. The large reservoir in the lower left center is a mine tailings pond. The semi-circular feature in the mountains at the bottom edge of the image is the Kennecott Copper Mine. The area shown is 60 kilometers by 40 kilometers (37 miles by 25 miles) and is centered at 40.6 degrees north latitude, 112.0 degrees west longitude. North is toward the upper left. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on April 10, 1994. The colors in this image represent the following radar channels and polarizations: red is L-band, horizontally transmitted and received; green is L-band, horizontally transmitted and vertically received; and blue is C-band, horizontally transmitted and vertically received. SIR-C/X-SAR, a joint mission of the German, Italian and United States space agencies, is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth program. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01798
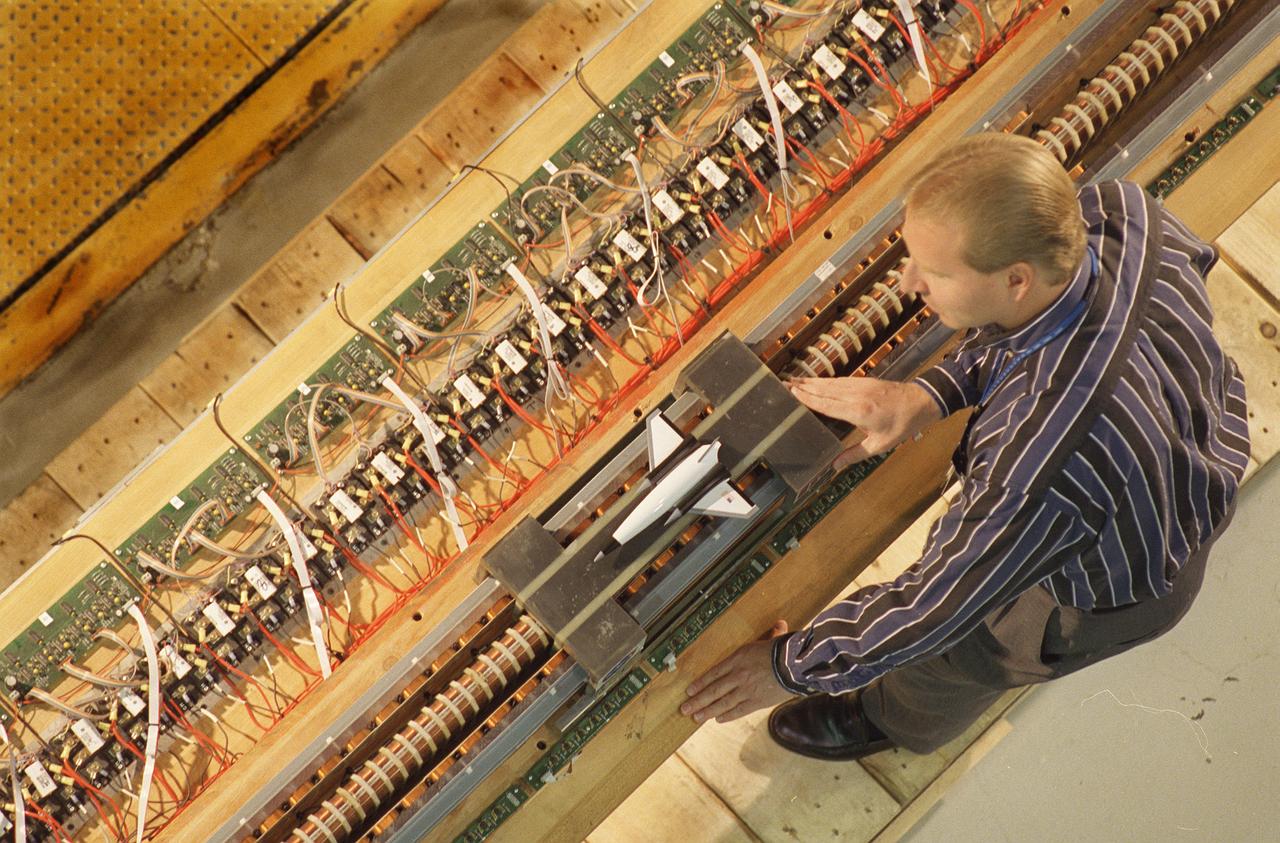

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC’s) Advanced Space Transportation Program has developed the Magnetic Launch Assist System, formerly known as the Magnetic Levitation (MagLev) technology that could give a space vehicle a running start to break free from Earth’s gravity. A Magnetic Launch Assist system would use magnetic fields to levitate and accelerate a vehicle along a track at speeds up to 600 mph. The vehicle would shift to rocket engines for launch into orbit. Similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would electromagnetically propel a space vehicle along the track. The tabletop experimental track for the system shown in this photograph is 44-feet long, with 22-feet of powered acceleration and 22-feet of passive braking. A 10-pound carrier with permanent magnets on its sides swiftly glides by copper coils, producing a levitation force. The track uses a linear synchronous motor, which means the track is synchronized to turn the coils on just before the carrier comes in contact with them, and off once the carrier passes. Sensors are positioned on the side of the track to determine the carrier’s position so the appropriate drive coils can be energized. MSFC engineers have conducted tests on the indoor track and a 50-foot outdoor track. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
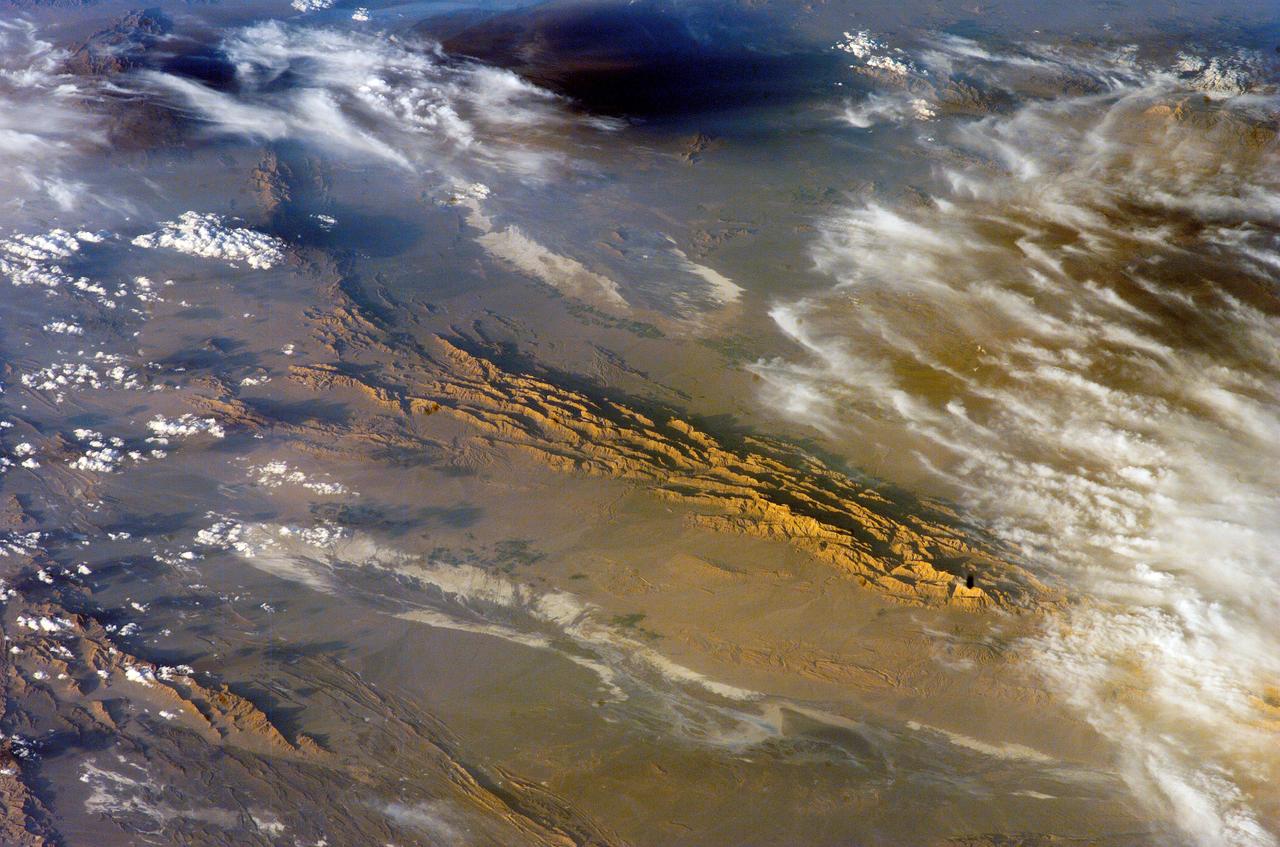

ISS012-E-18779 (28 Feb. 2006) --- Winter in the Dasht-e-Lut Desert, eastern Iran is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 12 crew member on the International Space Station. The image takes advantage of the low angle of illumination to reveal linear geological structures of the Iranian mountain range bordering the western edge of the basin known as Dasht-e-Lut. The range rises 1818 meters (6000 feet) above sea level and lies 750 kilometers (466 miles) north of the Persian Gulf. The convoluted appearance results from erosion of folded and faulted rocks – softer rocks erode away quickly, leaving more resistant rock to form linear ridges perpendicular to the direction of compression. While not a major oil producing region like the Zagros Fold Belt to the southwest, the mountains of east-central Iran contain economically important deposits of copper and other metals. Little vegetation is visible from space in the arid interior basin of the Dasht-e-Lut. Iran is climatically part of the Afro-Asian belt of deserts that stretch from the Cape Verde islands off West Africa all the way to Mongolia near Beijing. The patchy, elongated, light-colored feature in the foreground (parallel to the mountain range) is the northernmost of the Dasht dry lakes that stretch southward 300 kilometers (186 miles). High country is the source of precipitation-derived water in all near-tropical deserts. Agricultural fields (small dark patches in the image) that depend on this precipitation are located down slope near the margin of the dry, salty soils of the lake.
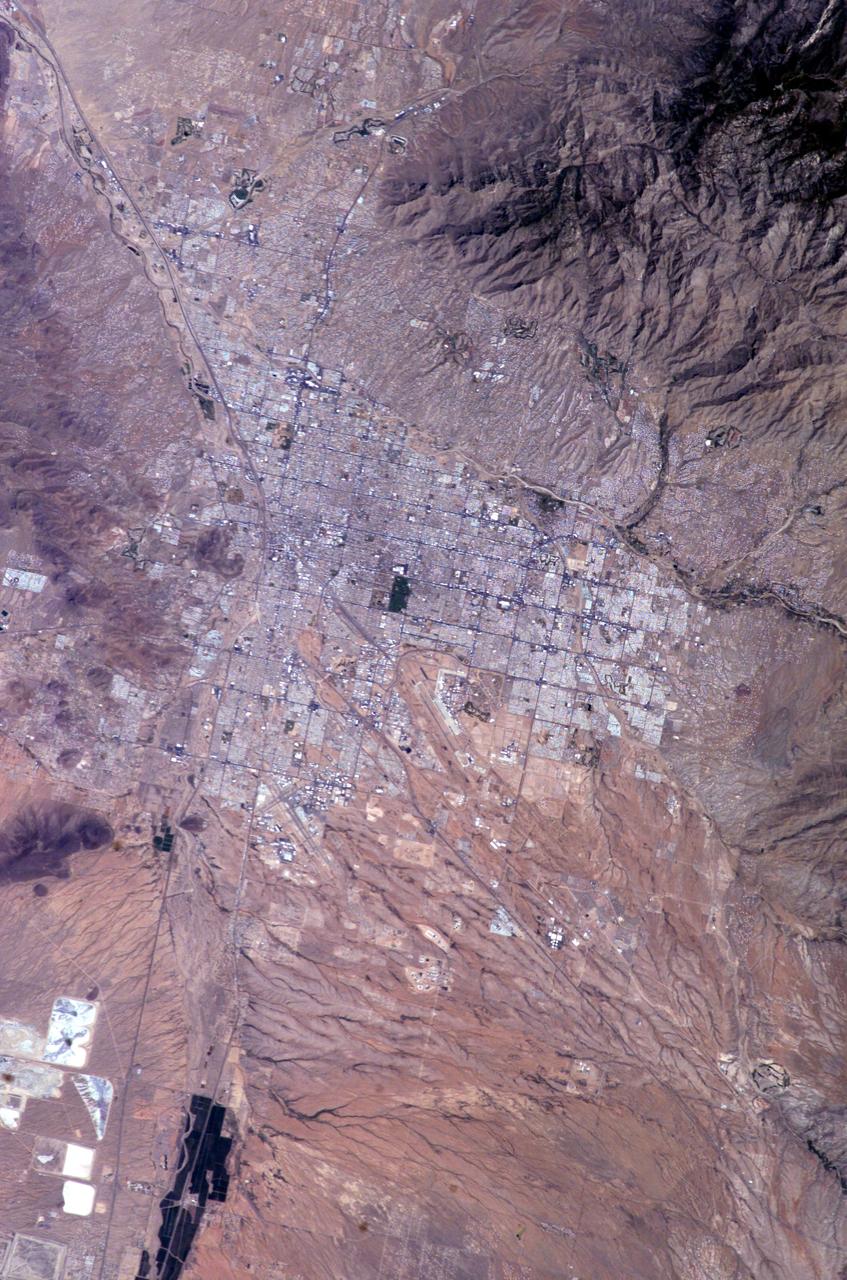

ISS009-E-10382 (7 June 2004) --- Tucson, Arizona is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 9 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). Tucson lies between the forested Catalina Mountains and the Tucson Mountains (dark reddish brown at left). The typical western North American cityscape is a pattern of regular north-south aligned rectangles outlined by major streets set one mile apart. Tucson’s Randolph golf course is the large rectangular dark zone in the image center. The striking contrast between the golf course and its surroundings is due to dense grass cover maintained by frequent watering. The rectangular grid pattern disappears in the small streets of the original city center, situated along the Santa Cruz River (enters the view lower left and exits in the top left corner). Newer and less densely built-up neighborhoods in the foothills of the Catalina Mountains are designed to incorporate natural landscape features, and retain major washes with natural vegetation. This portion of the cityscape seen from space is consequently quite different from the main city grid. The foothills afford views of the city to the south and the mountains to the north and are major areas of development. Large white dots within the urban grid are the reflective rooftops of shopping malls. Tucson enjoys an important position along several major crossroads. Interstate highway I-10, which connects southern California to Florida, appears as a straight line running parallel with the Santa Cruz River northwest from Tucson in the direction of Phoenix. The I-10 traverses a well-marked alluvial fan that extends from the Santa Rita Mountains to the southeast (fine drainage pattern lower center) and exits the view lower right. Highway I-19 is the straight line (lower left) leading south from the city center, between the Santa Cruz River and rectangular spoil heaps of nearby copper mines. The I-19 connects Tucson with Nogales on the Mexican border.
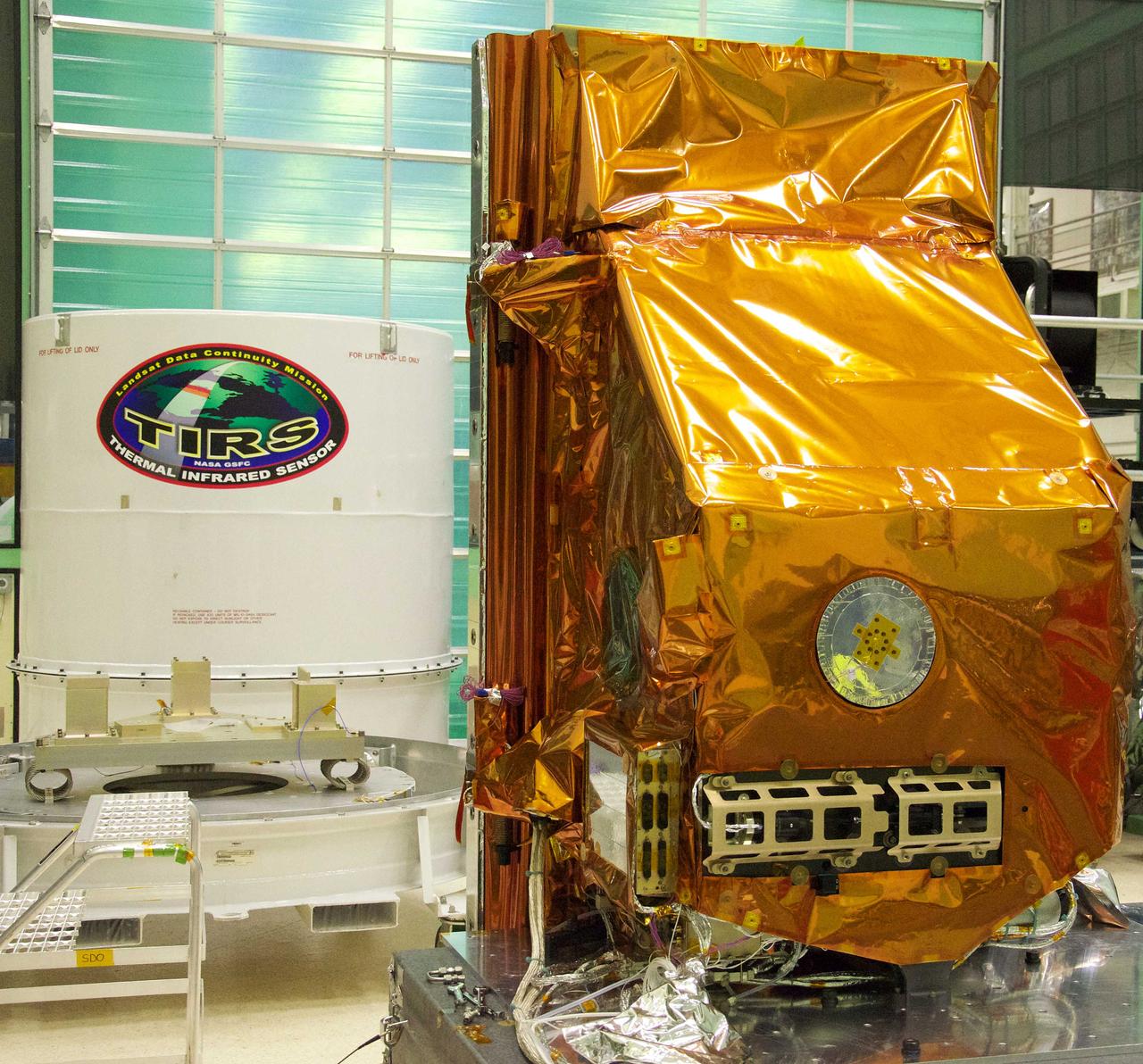

The TIRS instrument in the foreground with its shipping container waits in the background. The copper-color of TIRS is due to the gold-colored foil that coats the Multi-Layer Insulation blankets. The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) will fly on the next Landsat satellite, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM). TIRS was built on an accelerated schedule at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. and will now be integrated into the LDCM spacecraft at Orbital Science Corp. in Gilbert, Ariz. The Landsat Program is a series of Earth observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat satellites have been consistently gathering data about our planet since 1972. They continue to improve and expand this unparalleled record of Earth's changing landscapes for the benefit of all. For more information on Landsat, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/landsat" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/landsat</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
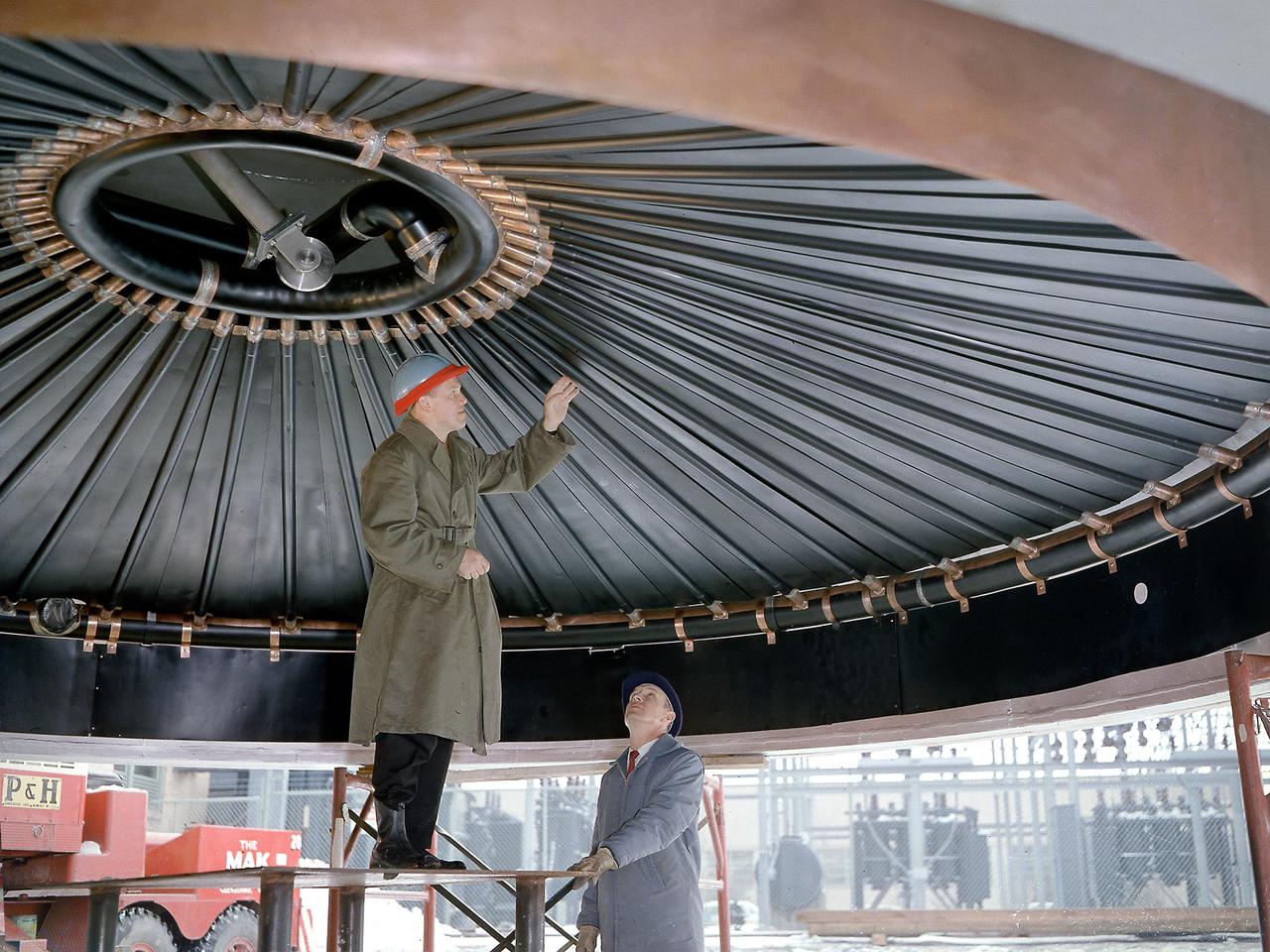

Engineers at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center inspect the nitrogen baffle in the interior of the 22.5-foot diameter dome at the Space Power Chambers. In 1961 NASA Lewis management decided to convert the Altitude Wind Tunnel into two large test chambers and renamed the facility the Space Power Chambers. The conversion, which took over two years, included removing the tunnel’s drive fan, exhaust scoop, and turning vanes from the east end and inserting bulkheads to seal off the new chambers within the tunnel. The eastern section of the tunnel became a vacuum chamber capable of simulating 100 miles altitude. In 1962 NASA management decided to use the new vacuum chamber exclusively to study the second-stage rocket. This required significant modifications to the new tank and extensive test equipment to create a space environment. The Lewis test engineers sought to subject the Centaur to long durations in conditions that would replicate those encountered during its missions in space. The chamber was already capable of creating the vacuum of space, but the test engineers also wanted to simulate the cryogenic temperatures and solar radiation found in space. Six panels of 500-watt tungsten-iodine lamps were arranged around the Centaur to simulate the effect of the Sun’s heat. A large copper cold wall with its interior coated with heat-absorbing black paint was created specifically for these tests and assembled around the Centaur. The 42-foot-high wall had vertical ribs filled with liquid nitrogen which produced the low temperatures.

ISS025-E-005538 (30 Sept. 2010) --- The Great Dyke of Zimbabwe, Africa is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 25 crew member on the International Space Station. The Great Dyke of Zimbabwe is a prominent geological feature that extends for over 550 kilometers, varying from 3-12 kilometers in width across the center of the country northeast – southwest; the southern end of the Dyke is illustrated in this view. The Dyke (or Dike in American English) is a layered mafic intrusion of igneous, metal-bearing rock that has been dated using uranium-lead isotopes to approximately 2.5 billion years in age, according to scientists. It intrudes even older rocks of the African craton, or core of oldest rocks forming the continent; in cross section, the Great Dyke looks somewhat triangular or keel-shaped suggesting to geologists that it rose along deep faults associated with extension of the African crust. Layered mafic intrusions are usually associated with economically important metals such as chromium, nickel, copper, platinum, titanium, iron, vanadium and tin. Chromium, in the form of the mineral chromite and platinum are particularly abundant in the Great Dyke and actively mined. Younger faults have offset sections of the Dyke along its length – two of the most obvious faults in the image are indicated, with arrows showing the relative directions of offset relative to the main trend of the intrusion. While the Great Dyke and its metal ores are products of geologic processes operating in the deep past, more recent events have also left their mark on the landscape as illustrated by two large fire burn scars which are visible at top center.
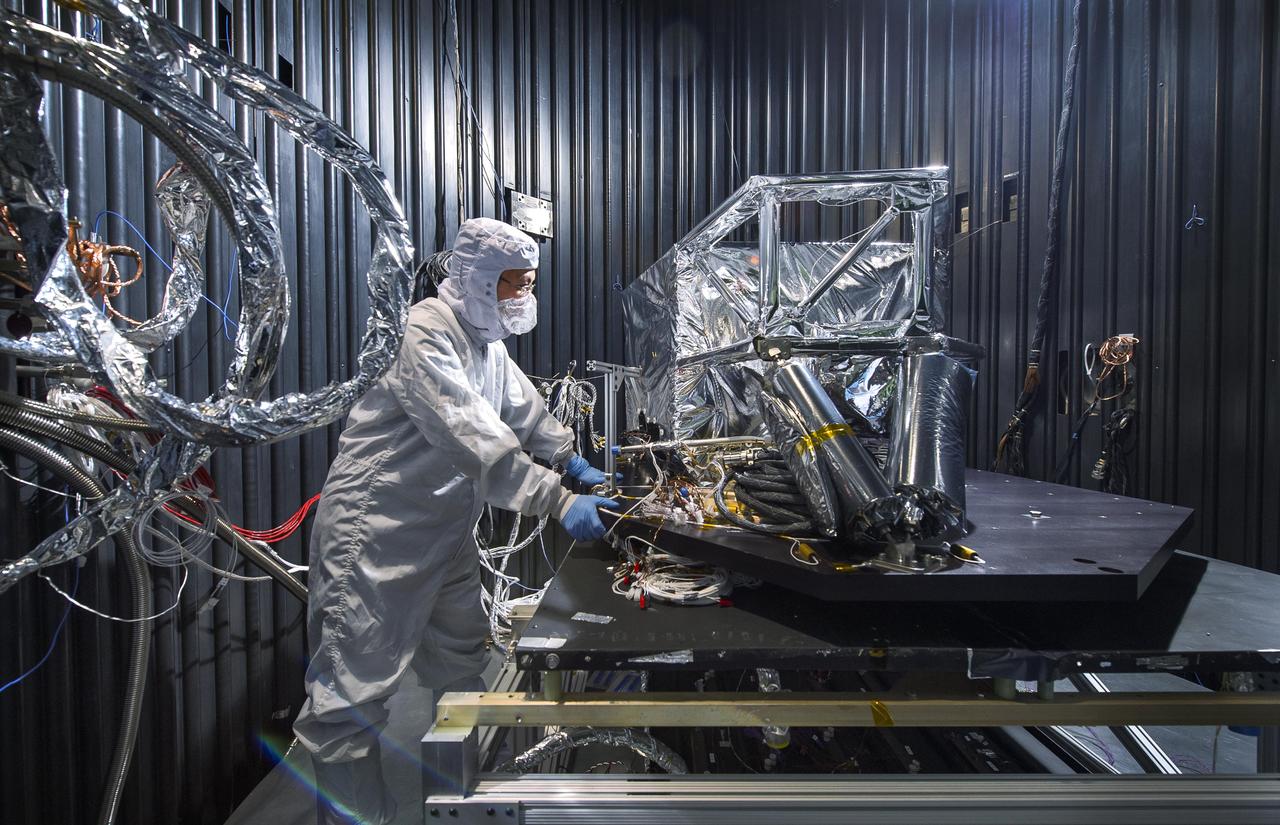

NASA engineer Acey Herrera recently checked out copper test wires inside the thermal shield of the Mid-Infrared Instrument, known as MIRI, that will fly aboard NASA's James Webb Space Telescope. The shield is designed to protect the vital MIRI instrument from excess heat. At the time of the photo, the thermal shield was about to go through rigorous environmental testing to ensure it can perform properly in the extreme cold temperatures that it will encounter in space. Herrera is working in a thermal vacuum chamber at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. As the MIRI shield lead, Herrera along with a thermal engineer and cryo-engineer verify that the shield is ready for testing. On the Webb telescope, the pioneering camera and spectrometer that comprise the MIRI instrument sit inside the Integrated Science Instrument Module flight structure, that holds Webb's four instruments and their electronic systems during launch and operations. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/15I0wrS" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/15I0wrS</a> Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
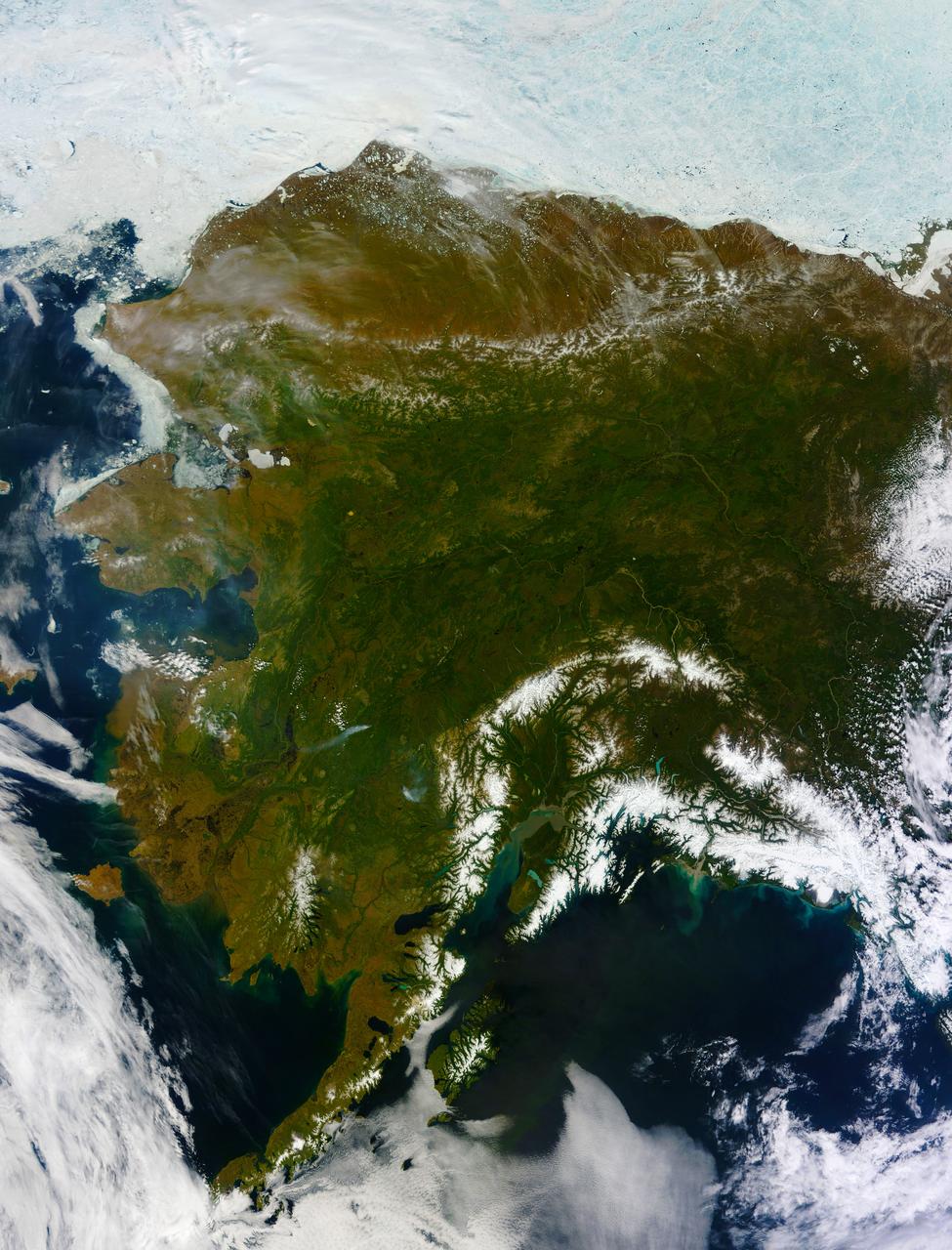

On most days, relentless rivers of clouds wash over Alaska, obscuring most of the state’s 6,640 miles (10,690 kilometers) of coastline and 586,000 square miles (1,518,000 square kilometers) of land. The south coast of Alaska even has the dubious distinction of being the cloudiest region of the United States, with some locations averaging more than 340 cloudy days per year. That was certainly not the case on June 17, 2013, the date that the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this rare, nearly cloud-free view of the state. The absence of clouds exposed a striking tapestry of water, ice, land, forests, and even wildfires. Snow-covered mountains such as the Alaska Range and Chugach Mountains were visible in southern Alaska, while the arc of mountains that make up the Brooks Range dominated the northern part of the state. The Yukon River—the longest in Alaska and the third longest in the United States—wound its way through the green boreal forests that inhabit the interior of the state. Plumes of sediment and glacial dust poured into the Gulf of Alaska from the Copper River. And Iliamna Lake, the largest in Alaska, was ice free. The same ridge of high pressure that cleared Alaska’s skies also brought stifling temperatures to many areas accustomed to chilly June days. Talkeetna, a town about 100 miles north of Anchorage, saw temperatures reach 96°F (36°C) on June 17. Other towns in southern Alaska set all-time record highs, including Cordova, Valez, and Seward. The high temperatures also helped fuel wildfires and hastened the breakup of sea ice in the Chukchi Sea. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Terra - MODIS More info: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/102MAEj" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/102MAEj</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
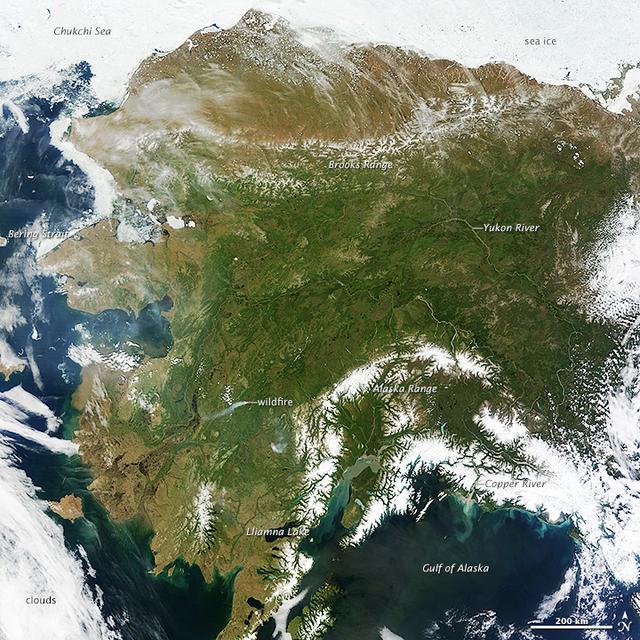
On most days, relentless rivers of clouds wash over Alaska, obscuring most of the state’s 6,640 miles (10,690 kilometers) of coastline and 586,000 square miles (1,518,000 square kilometers) of land. The south coast of Alaska even has the dubious distinction of being the cloudiest region of the United States, with some locations averaging more than 340 cloudy days per year. That was certainly not the case on June 17, 2013, the date that the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this rare, nearly cloud-free view of the state. The absence of clouds exposed a striking tapestry of water, ice, land, forests, and even wildfires. Snow-covered mountains such as the Alaska Range and Chugach Mountains were visible in southern Alaska, while the arc of mountains that make up the Brooks Range dominated the northern part of the state. The Yukon River—the longest in Alaska and the third longest in the United States—wound its way through the green boreal forests that inhabit the interior of the state. Plumes of sediment and glacial dust poured into the Gulf of Alaska from the Copper River. And Iliamna Lake, the largest in Alaska, was ice free. The same ridge of high pressure that cleared Alaska’s skies also brought stifling temperatures to many areas accustomed to chilly June days. Talkeetna, a town about 100 miles north of Anchorage, saw temperatures reach 96°F (36°C) on June 17. Other towns in southern Alaska set all-time record highs, including Cordova, Valez, and Seward. The high temperatures also helped fuel wildfires and hastened the breakup of sea ice in the Chukchi Sea. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Terra - MODIS More info: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/102MAEj" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/102MAEj</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>