
A cover, called a “spider” is attached to the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for NASA’s Artemis II mission inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Oct. 28, 2024. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems will use a crane to attach to the spider cover to raise the core stage vertically. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs prepare to lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage and transfer it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust at launch, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch the Artemis I mission. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

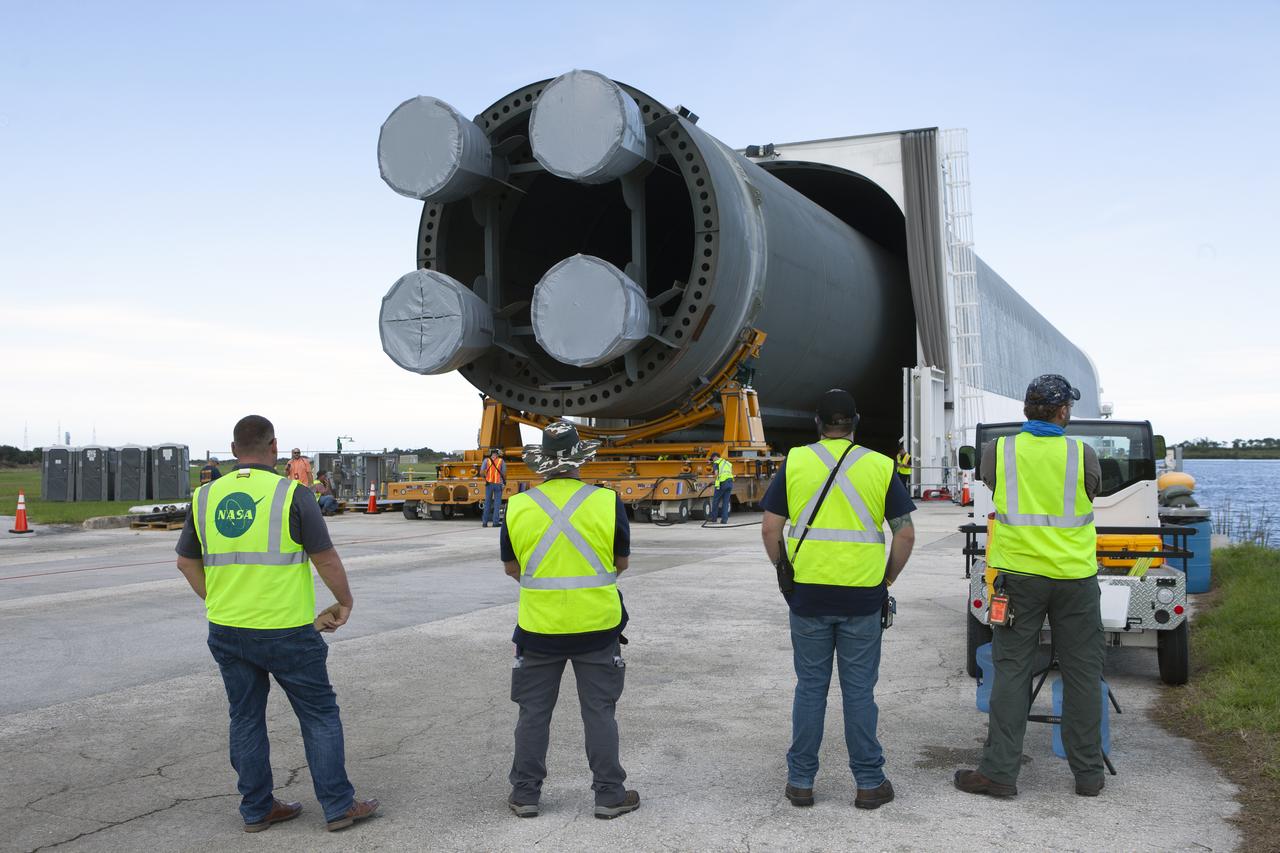
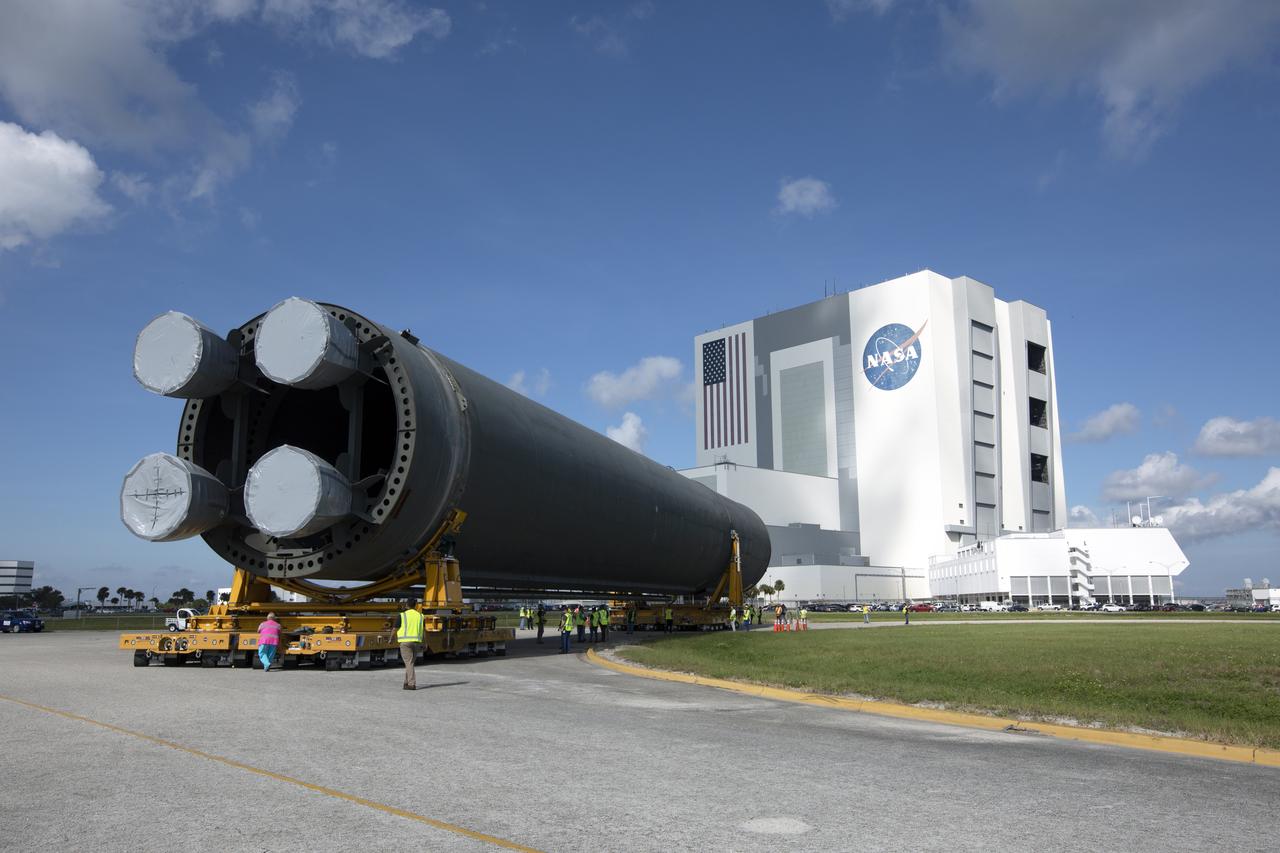
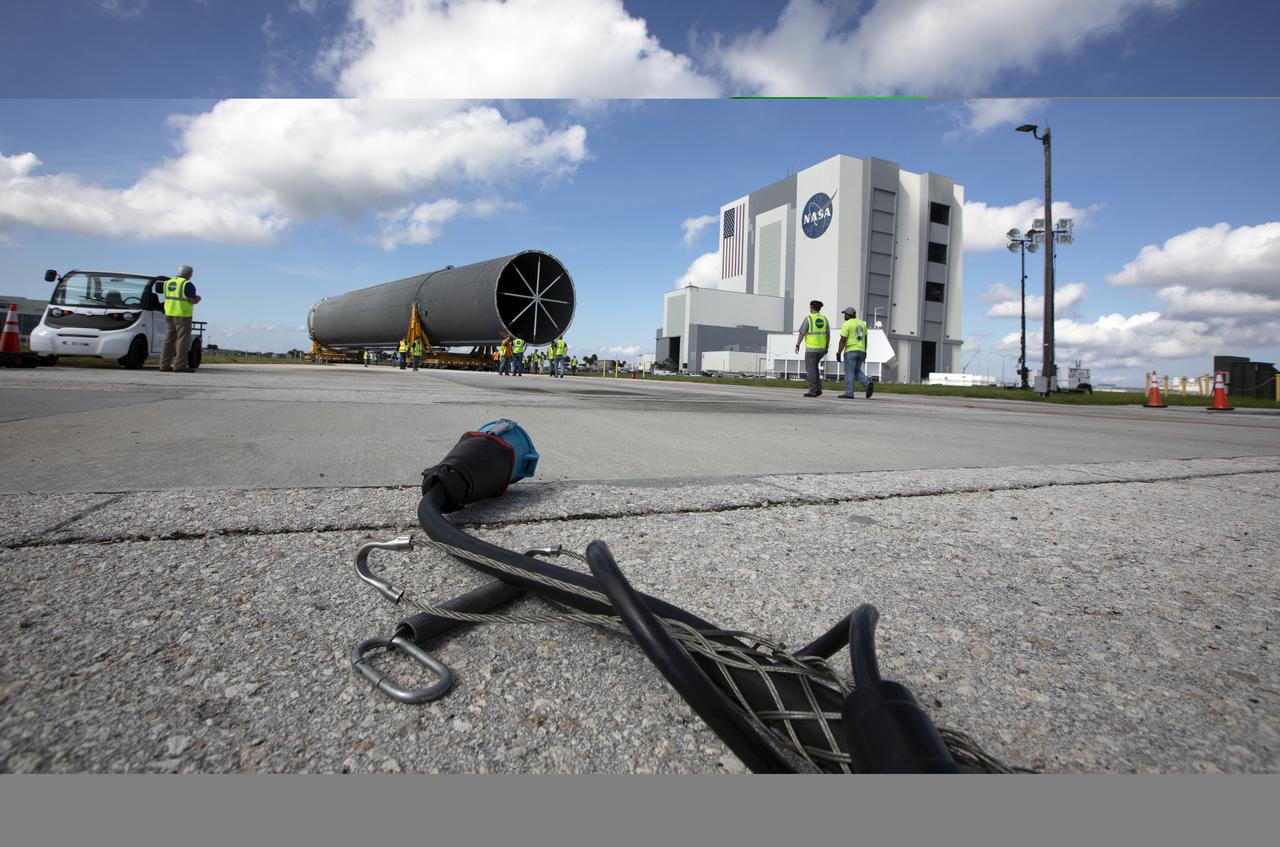
Teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems transport the engine section of the agency’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) core stage from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the core stage engine section housing the four RS-25 engines from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024. The engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
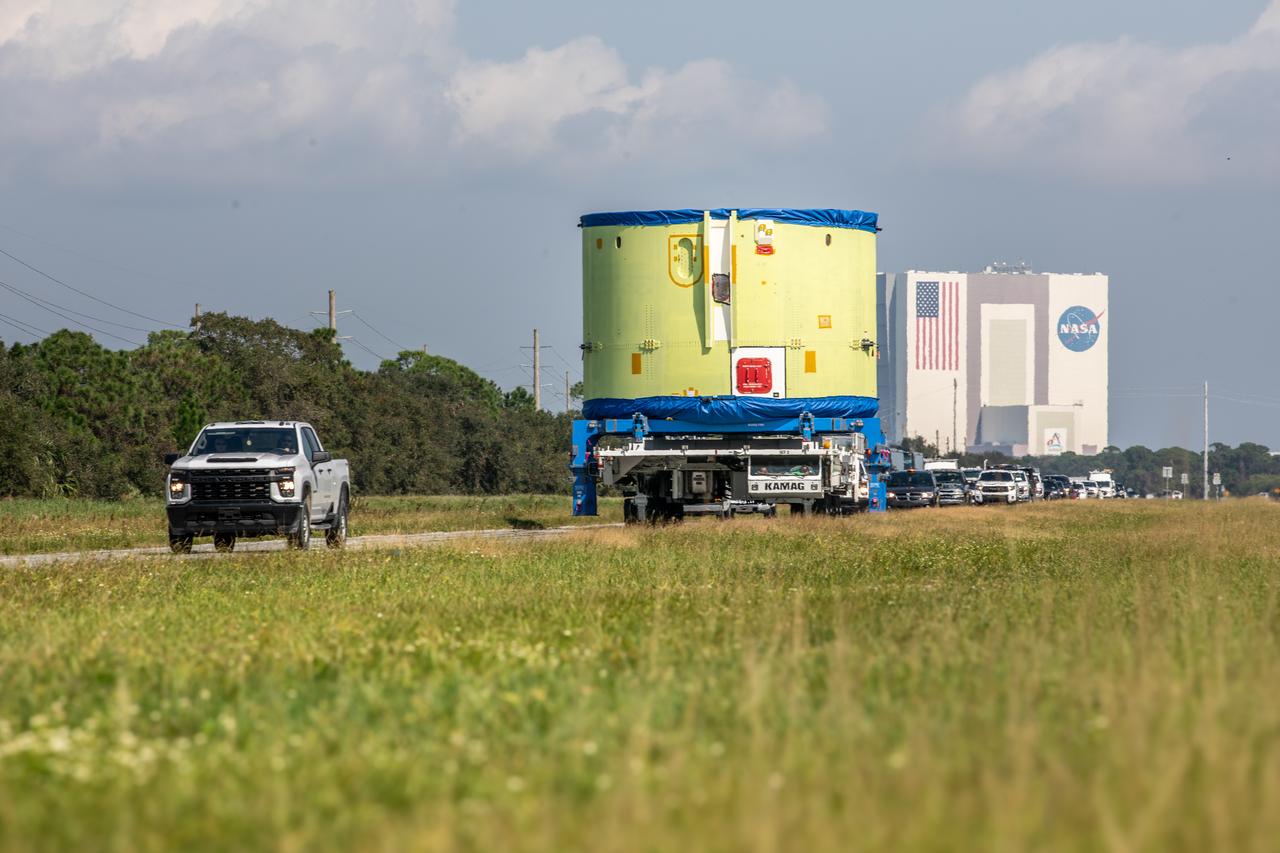

Teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems transport the engine section of the agency’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) core stage from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the core stage engine section housing the four RS-25 engines from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024. The engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
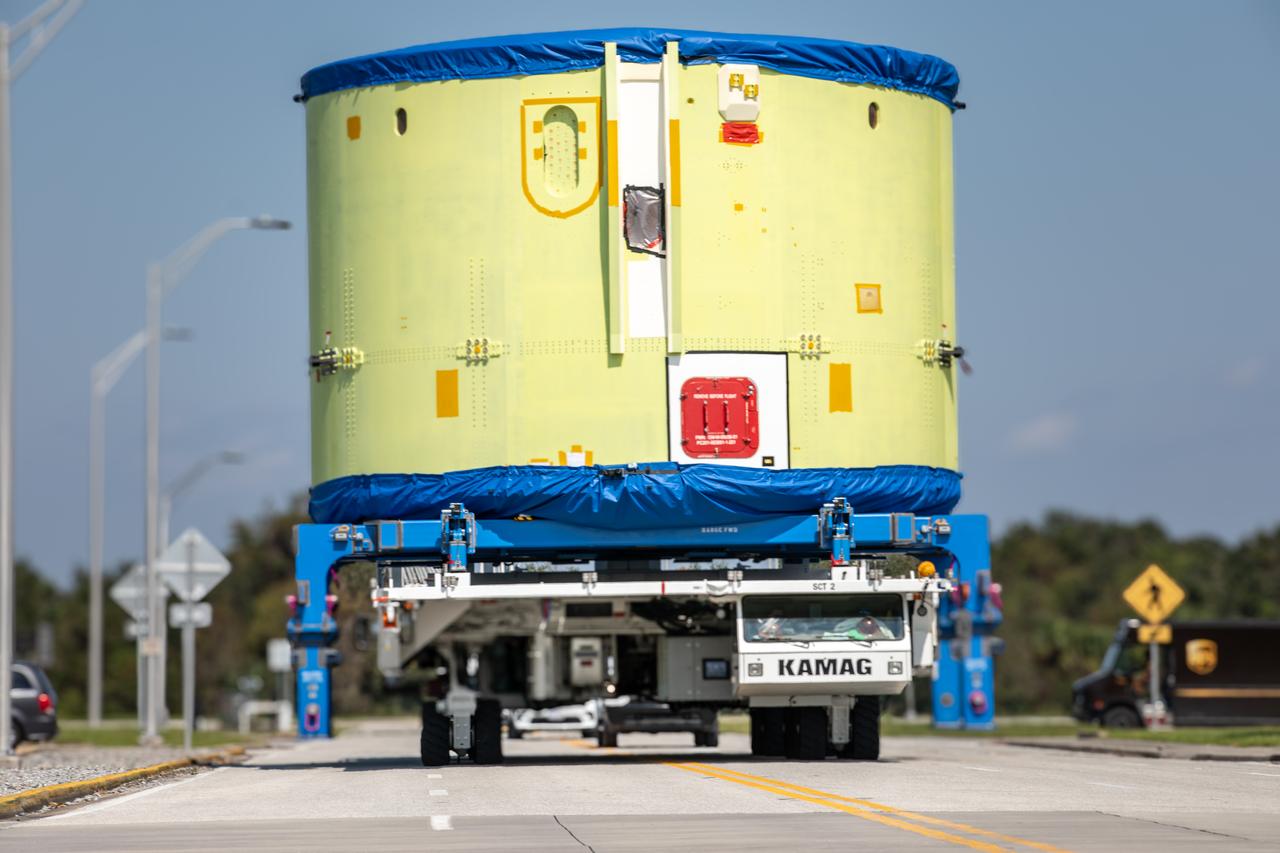

Teams from NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems transport the engine section of the agency’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) core stage from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the core stage engine section housing the four RS-25 engines from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024. The engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
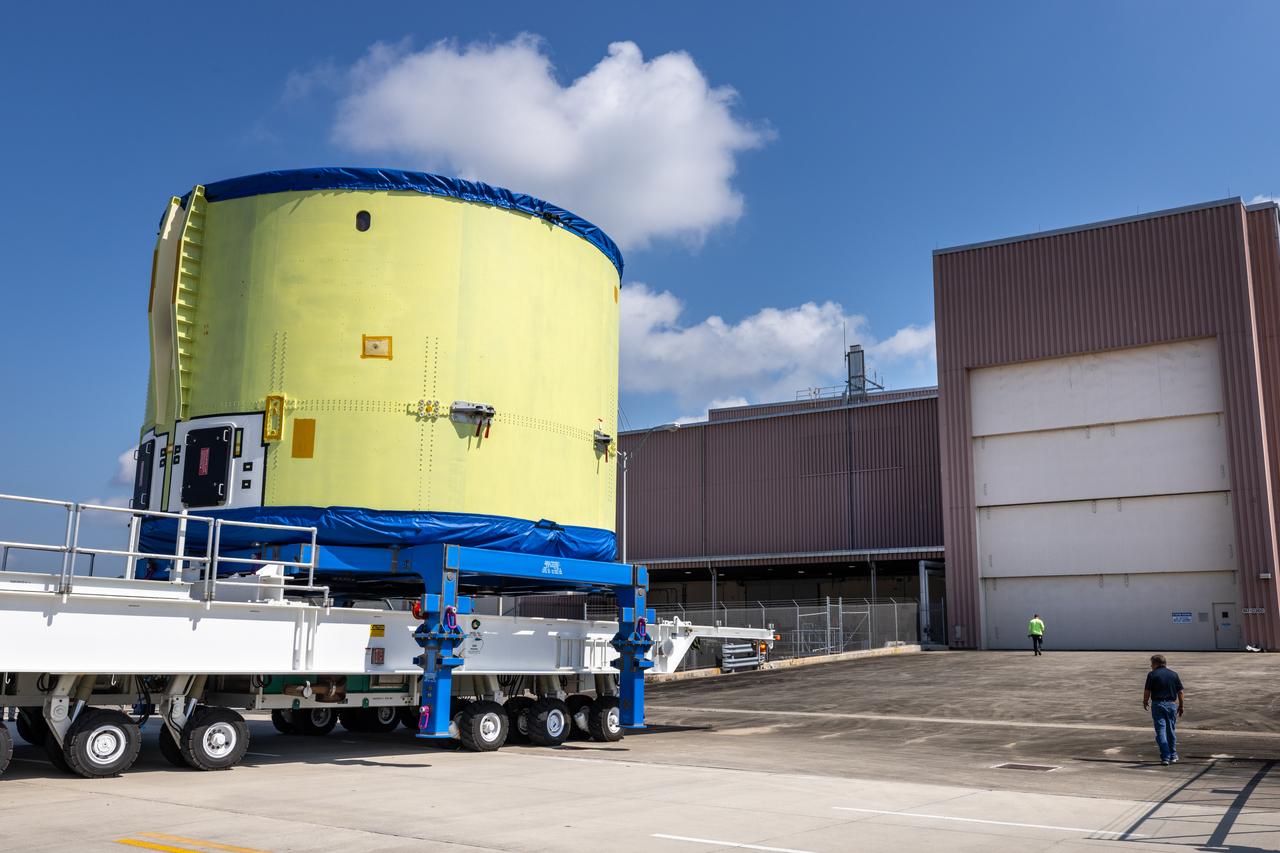

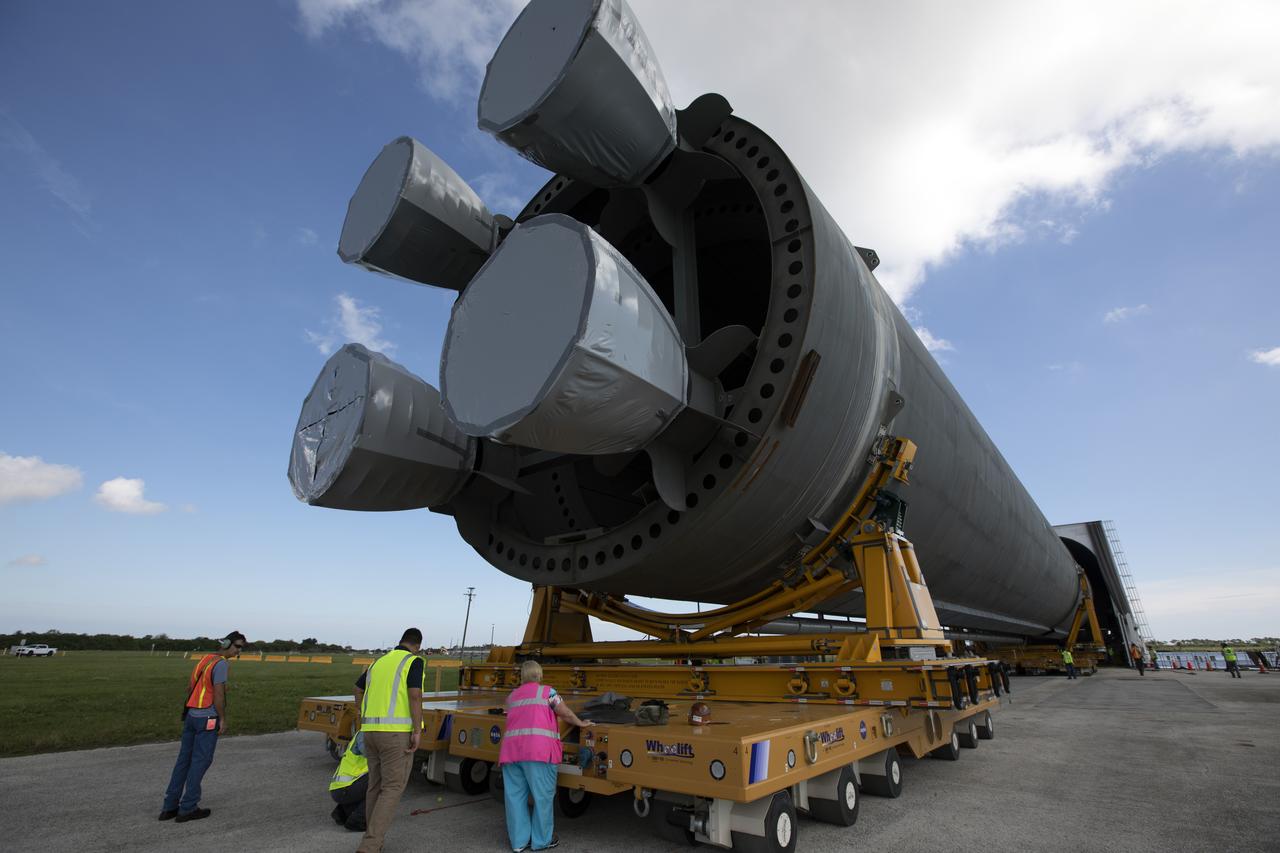
The engine section of NASA’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) core stage arrives at the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Oct. 15, 2024, after being transported from the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building. NASA’s Pegasus barge delivered the core stage engine section housing the four RS-25 engines from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana to NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Sept. 5, 2024. The engine section is one the most complex and intricate parts of the rocket stage that will help power the Artemis missions to the Moon.
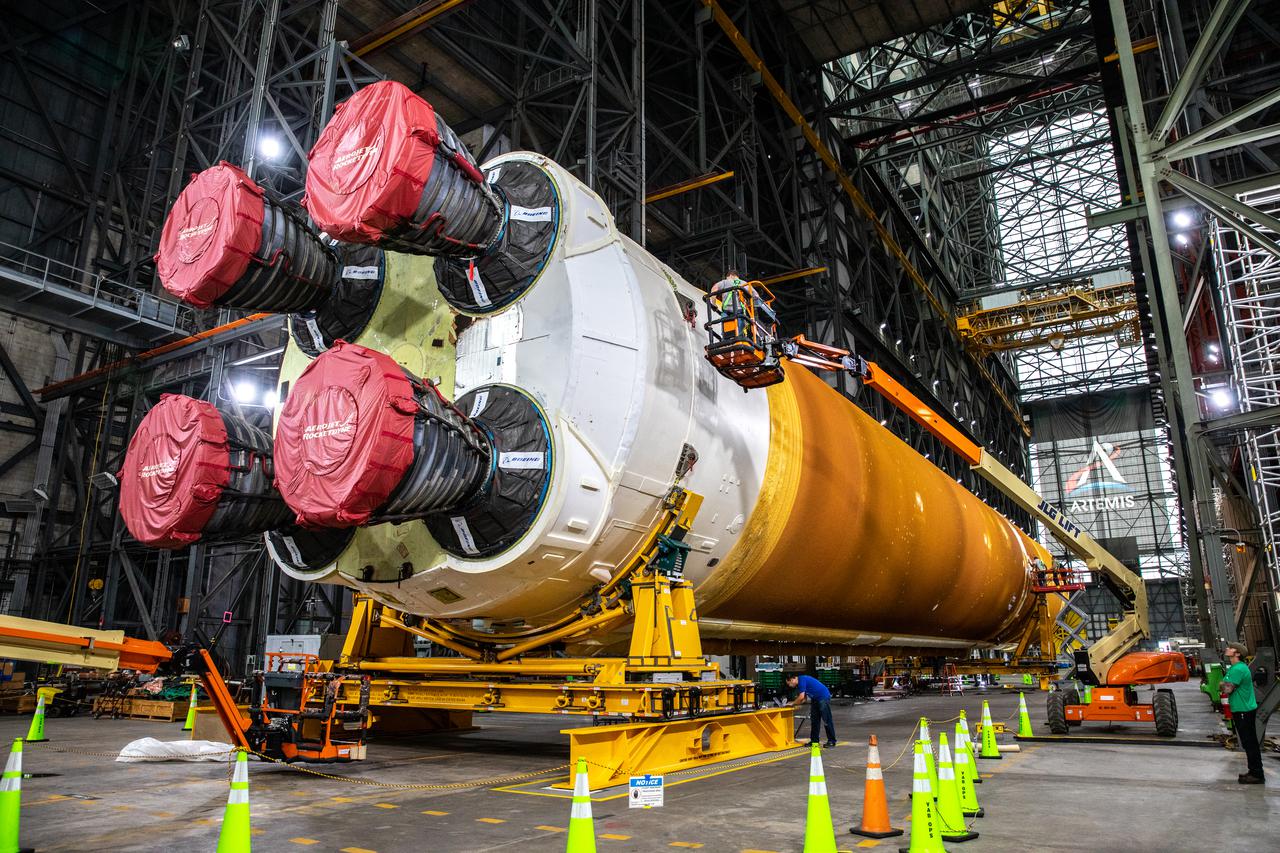

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 4, 2021. Teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to lift the 188,000-pound core stage and place it on the mobile launcher in between the two solid rocket boosters in High Bay 3 of the VAB. The core stage alone will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust at launch, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch the Artemis I mission. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
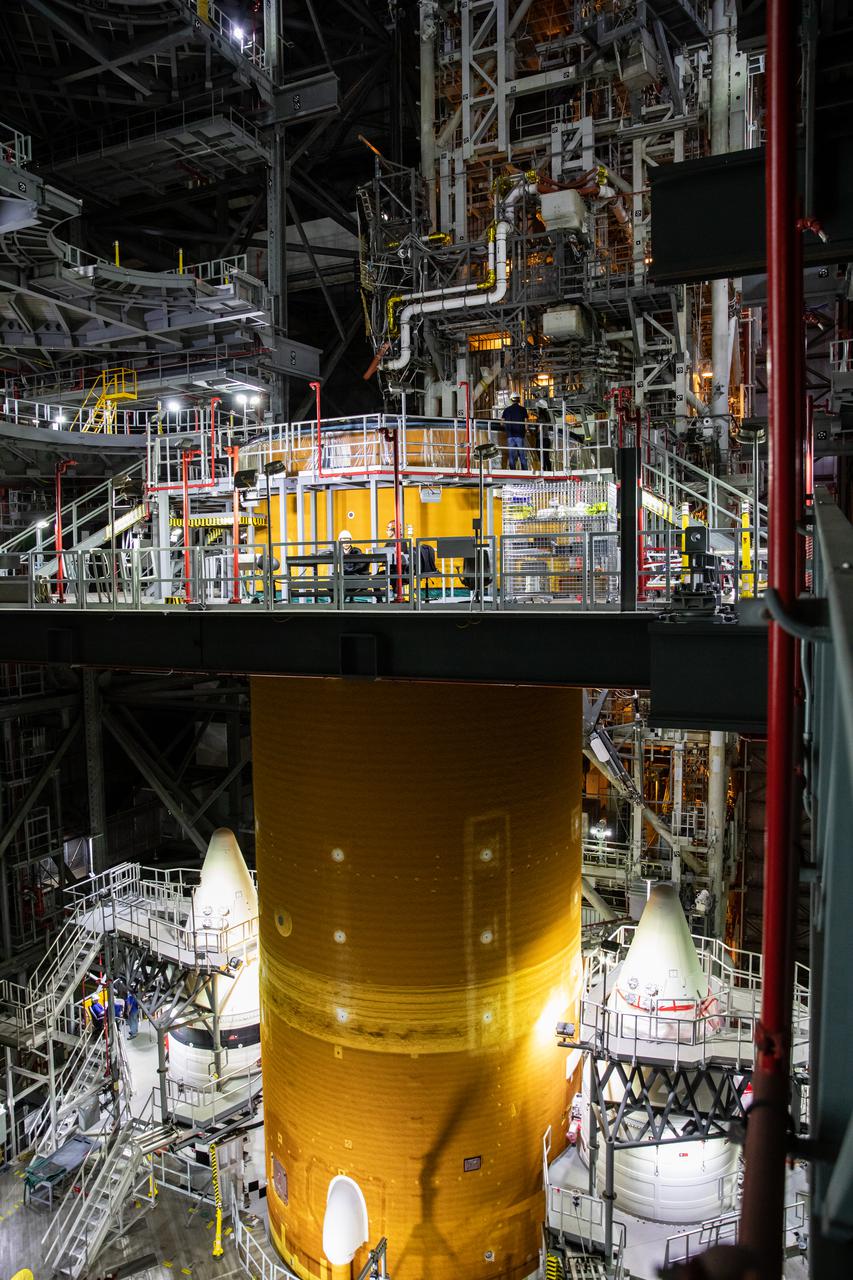

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen atop the mobile launcher inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 15, 2021. Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lifted and lowered the core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, placing it in between the twin solid rocket boosters. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
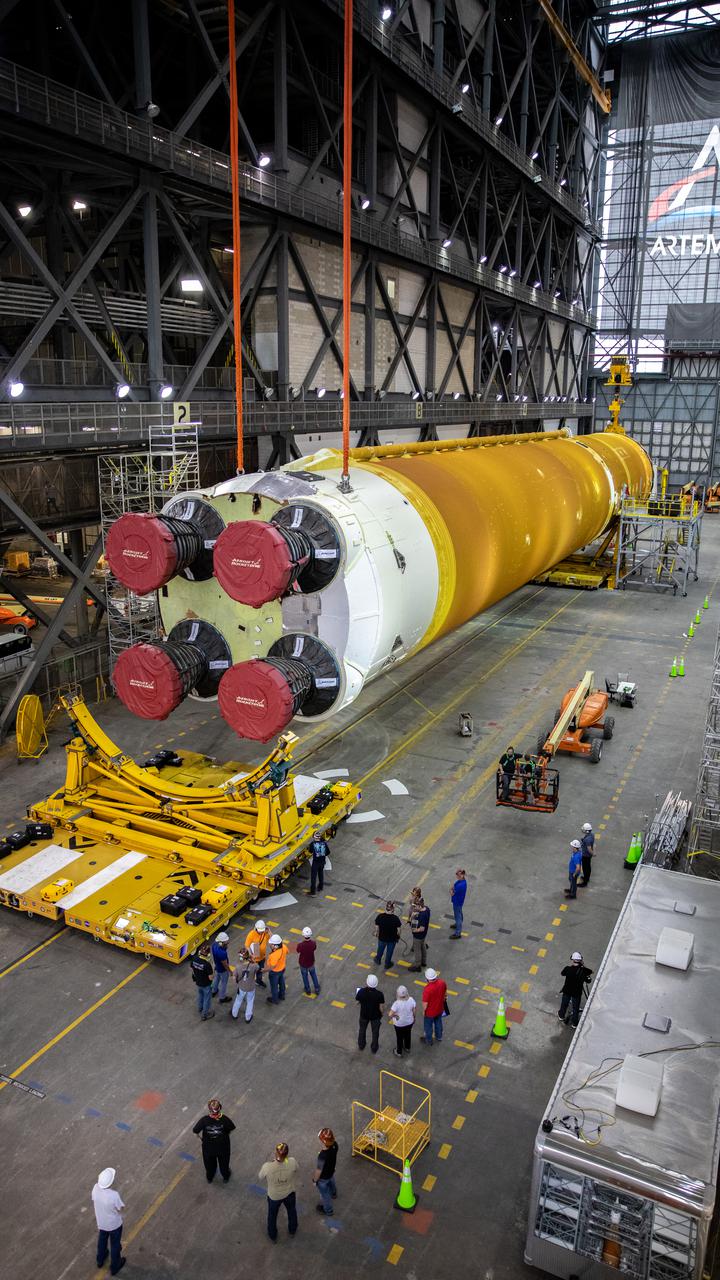

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. Teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to lift the 188,000-pound core stage and place it on the mobile launcher in between the two solid rocket boosters in High Bay 3 of the VAB. The core stage alone will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust at launch, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch the Artemis I mission. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
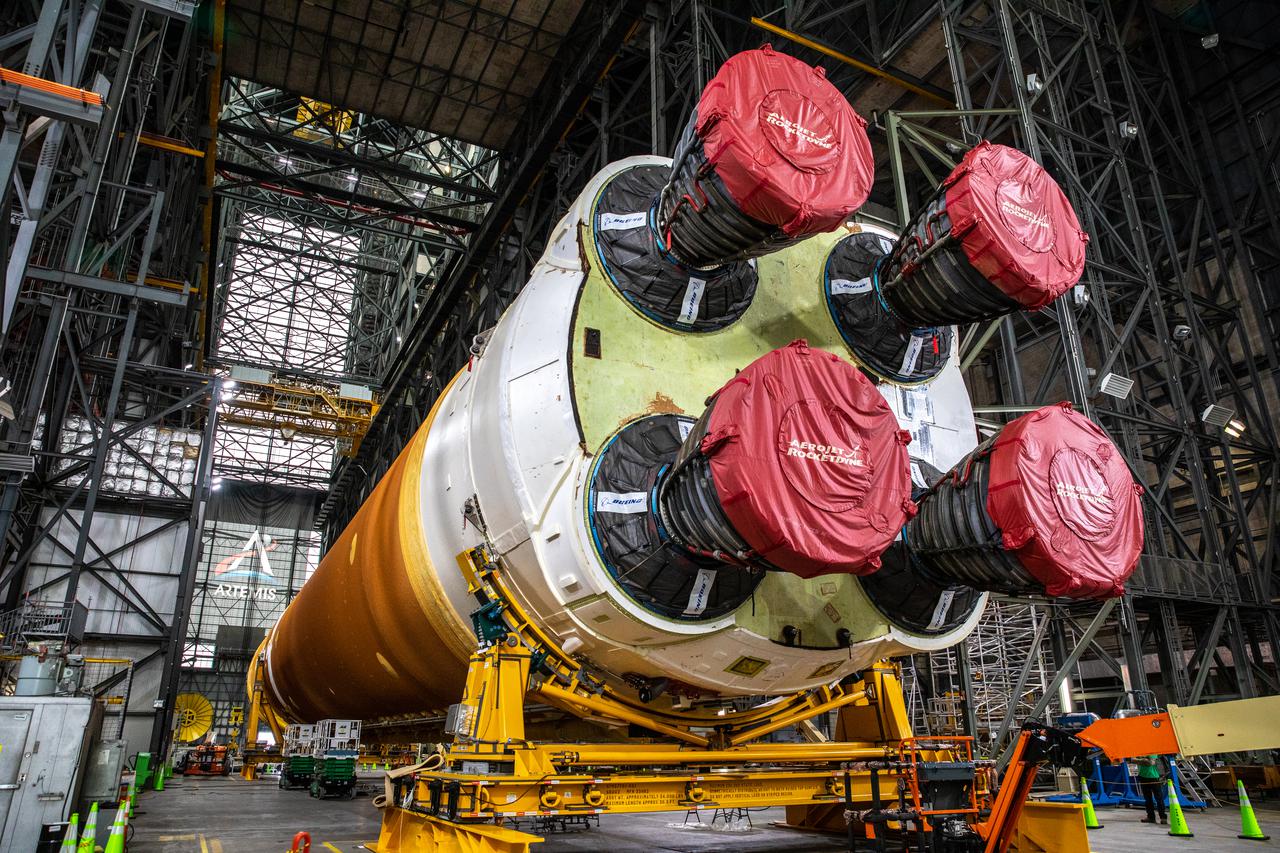

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 4, 2021. Teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to lift the 188,000-pound core stage and place it on the mobile launcher in between the two solid rocket boosters in High Bay 3 of the VAB. The core stage alone will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust at launch, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch the Artemis I mission. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen atop the mobile launcher inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lifted and lowered the core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, placing it in between the twin solid rocket boosters. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
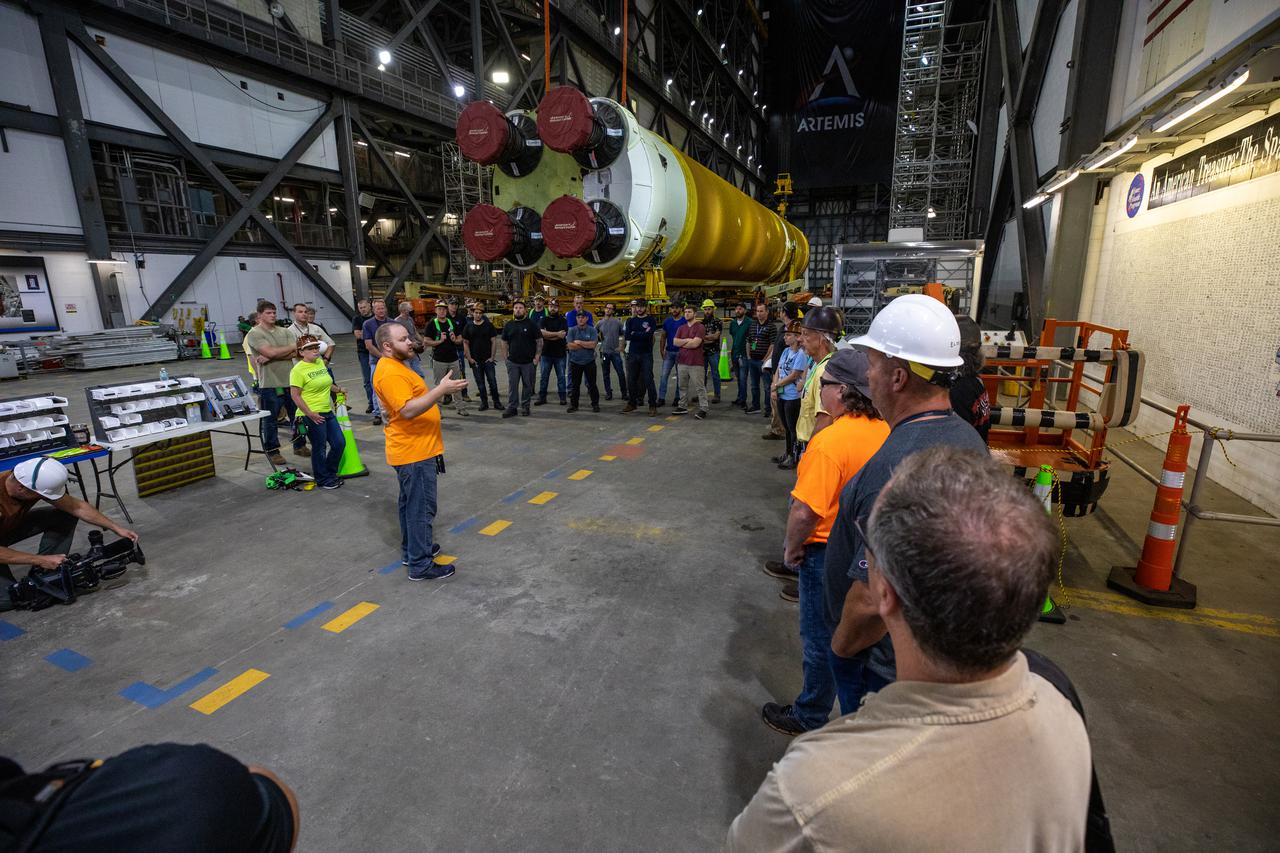

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 9, 2021. Teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to lift the 188,000-pound core stage, which is the largest part of the rocket, and place it on the mobile launcher in between the two solid rocket boosters in High Bay 3 of the VAB. The core stage alone, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
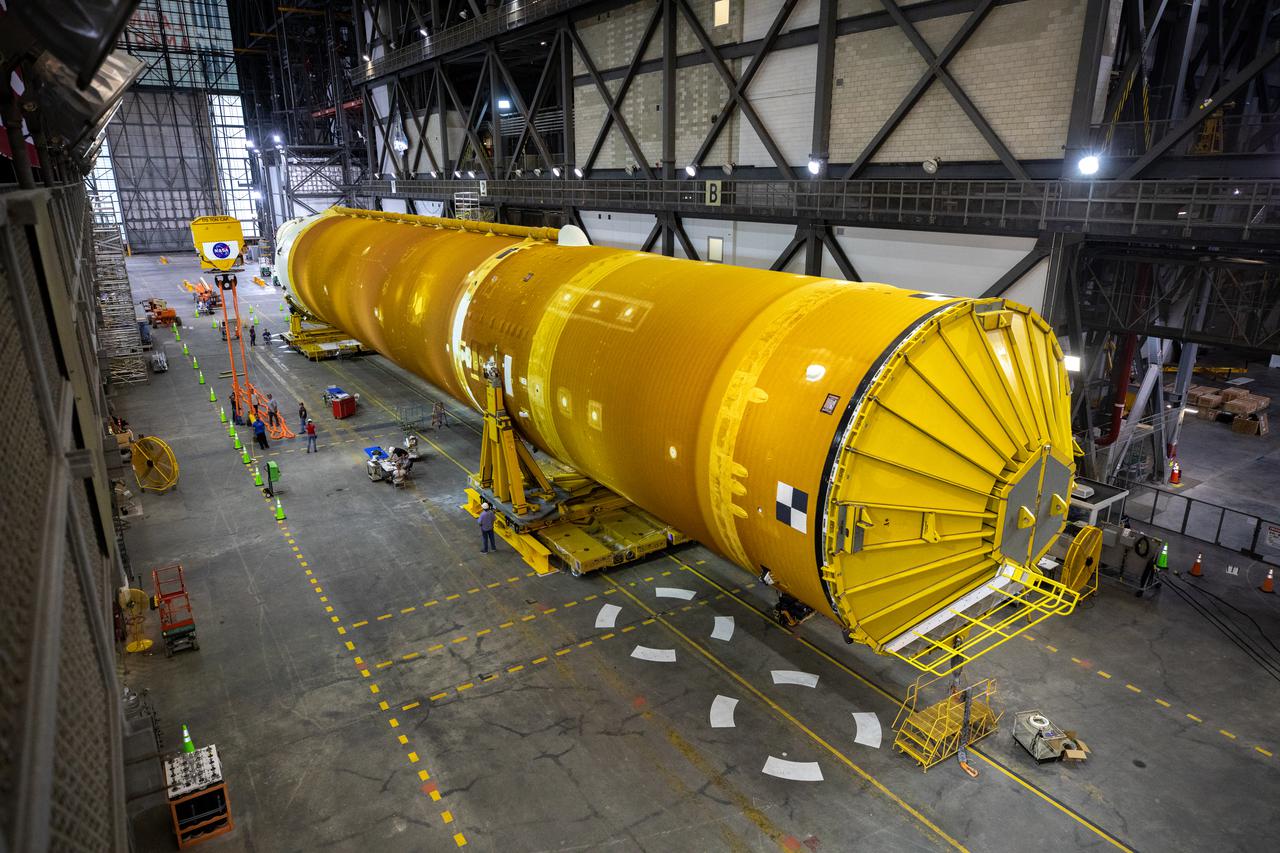

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 9, 2021. Teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to lift the 188,000-pound core stage, which is the largest part of the rocket, and place it on the mobile launcher in between the two solid rocket boosters in High Bay 3 of the VAB. The core stage alone, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
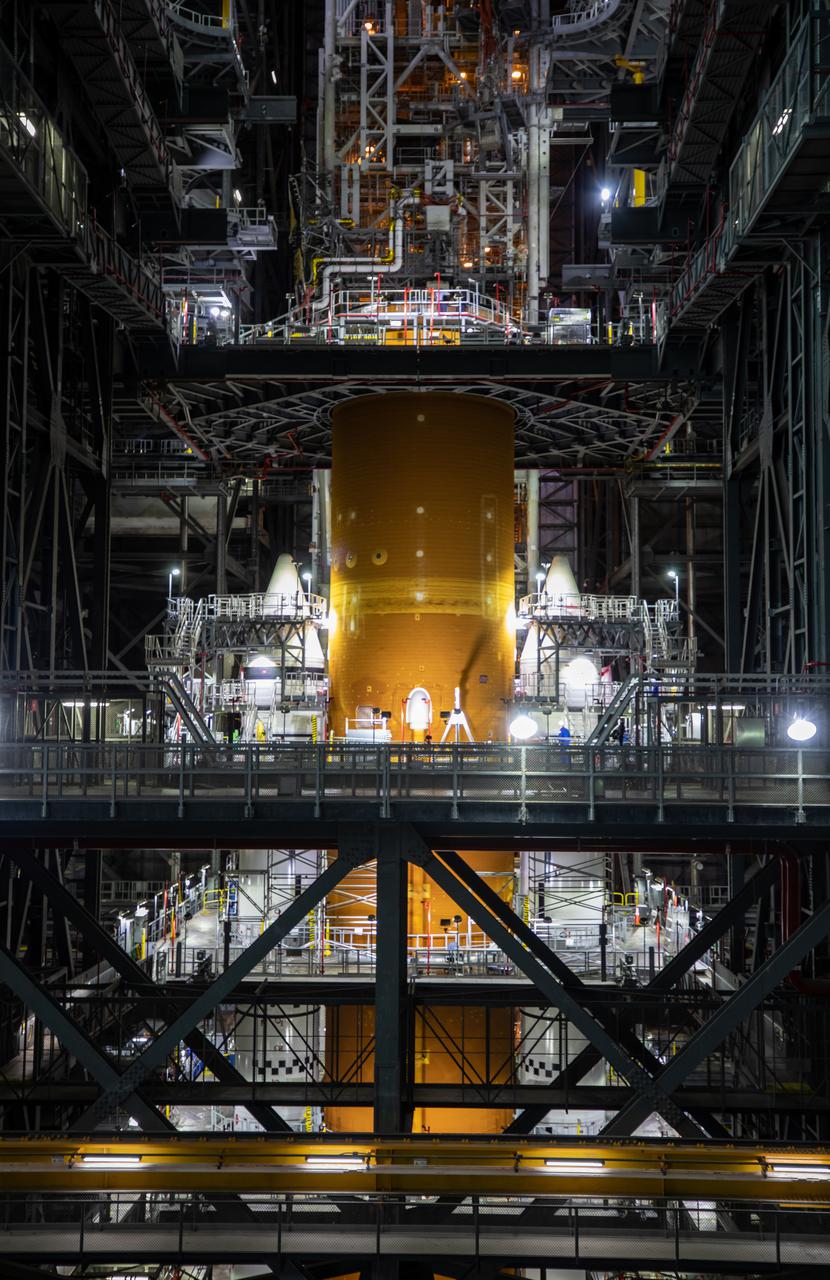

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen atop the mobile launcher inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 15, 2021. Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lifted and lowered the core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, placing it in between the twin solid rocket boosters. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
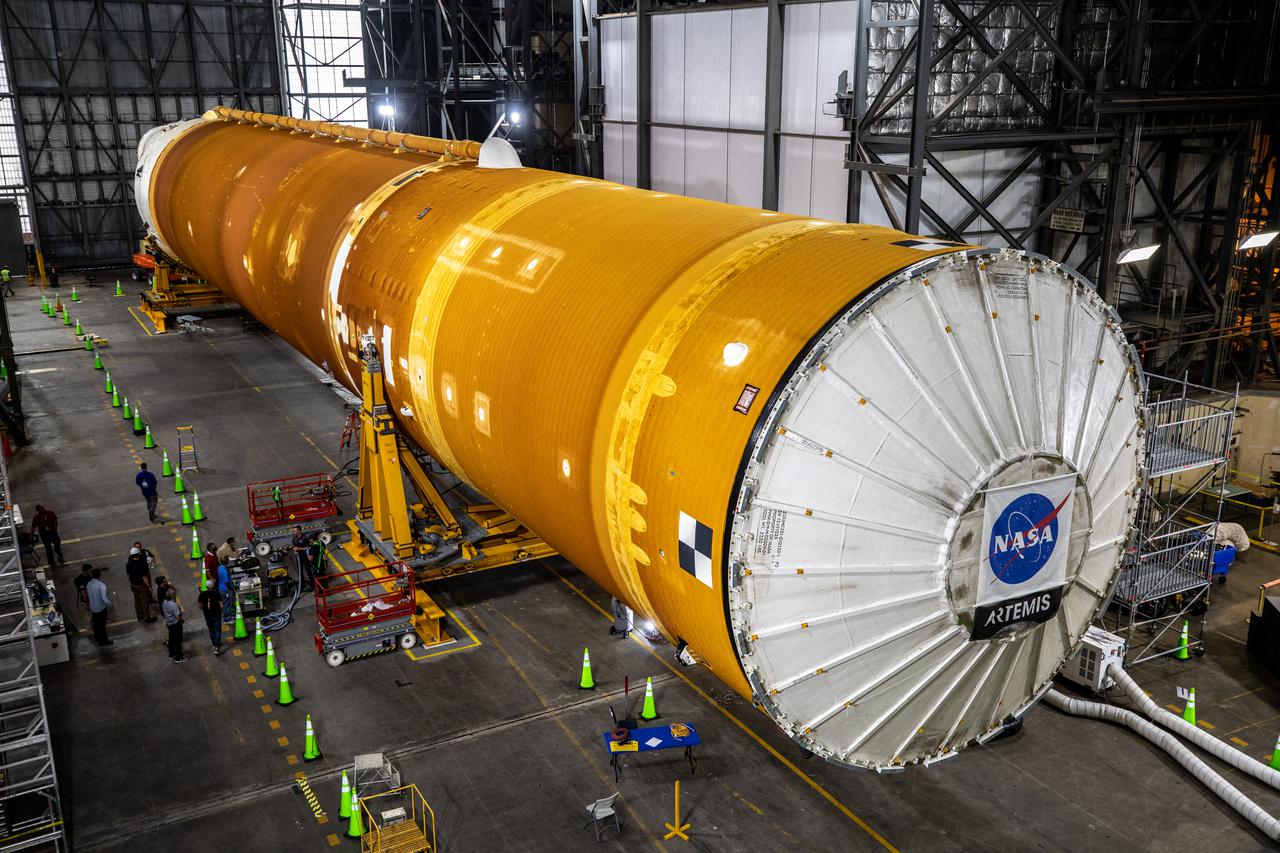

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 4, 2021. Teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to lift the 188,000-pound core stage and place it on the mobile launcher in between the two solid rocket boosters in High Bay 3 of the VAB. The core stage alone will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust at launch, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch the Artemis I mission. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
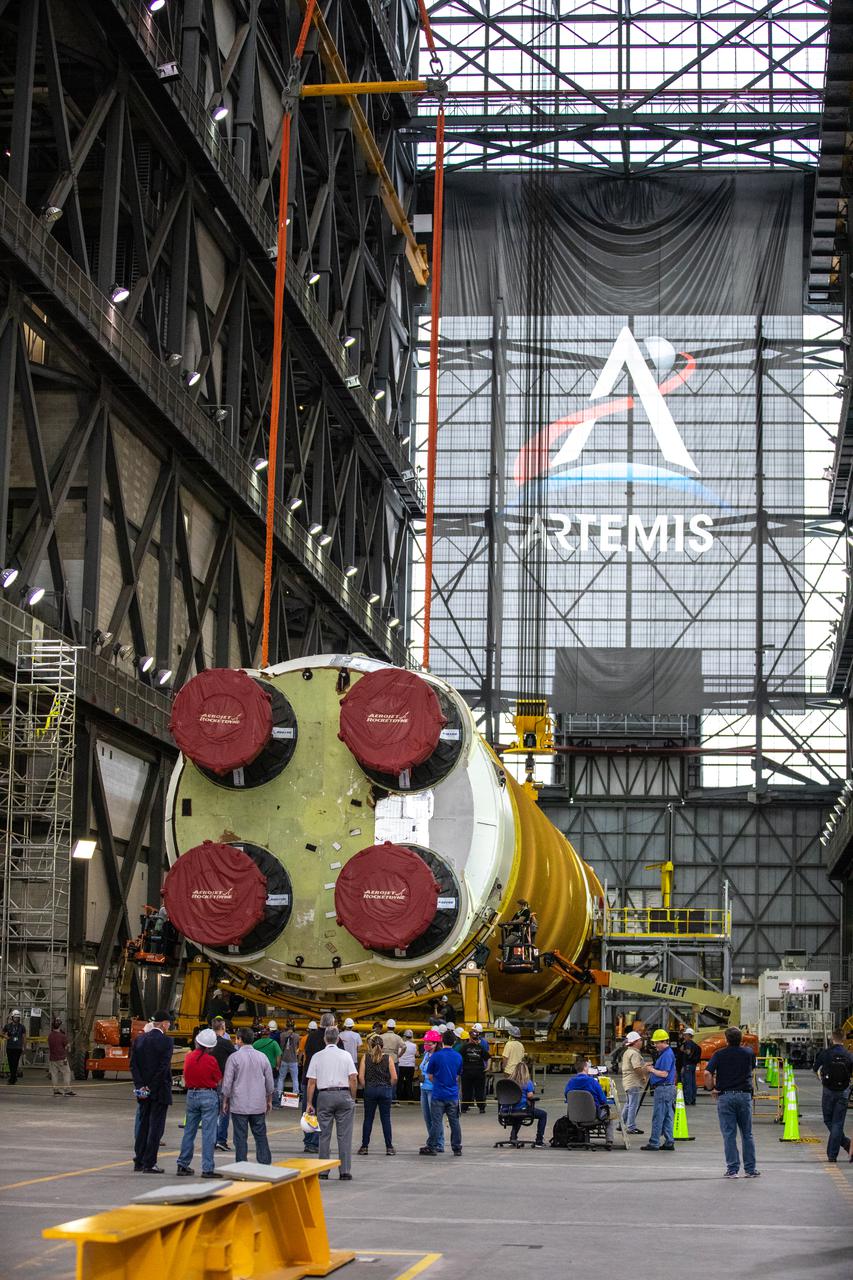

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage is seen in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. Teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to lift the 188,000-pound core stage and place it on the mobile launcher in between the two solid rocket boosters in High Bay 3 of the VAB. The core stage alone will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust at launch, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch the Artemis I mission. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
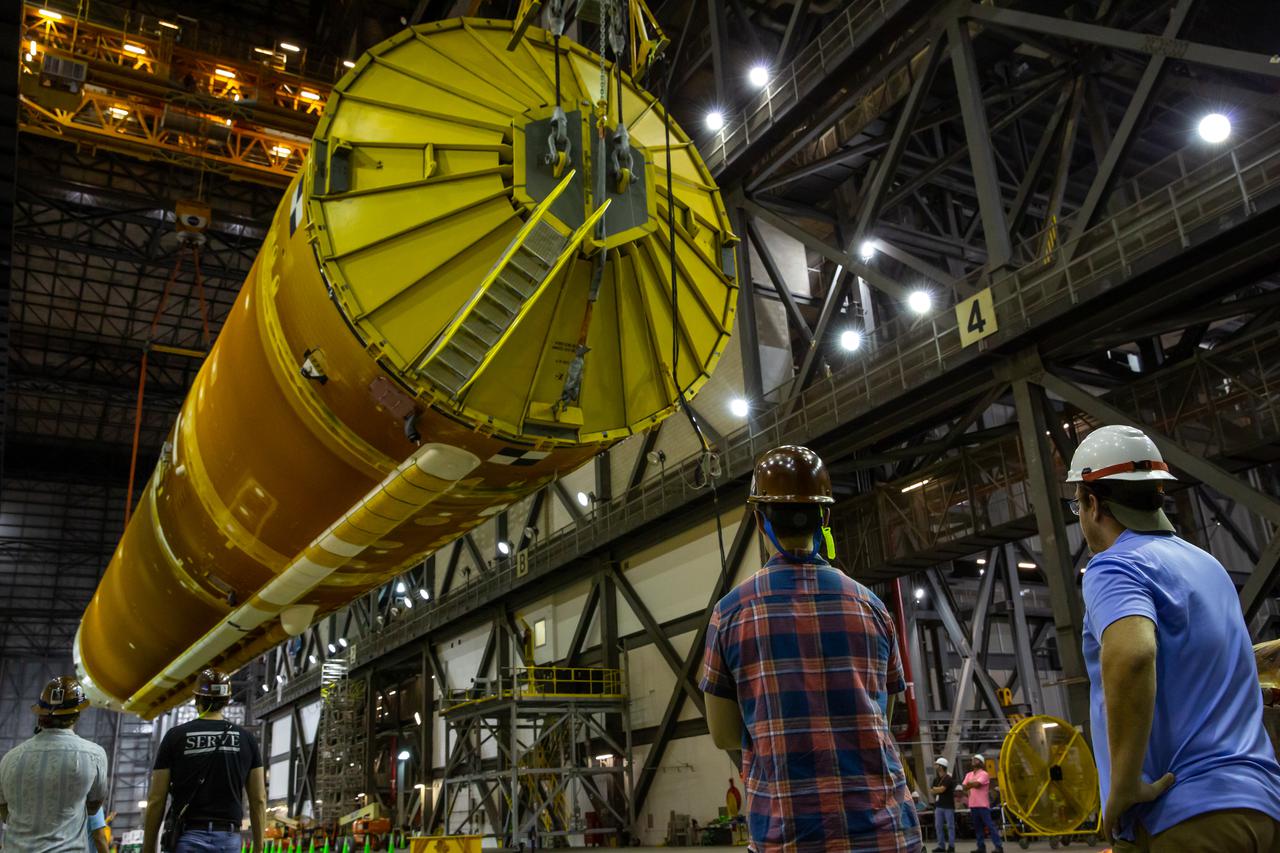

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
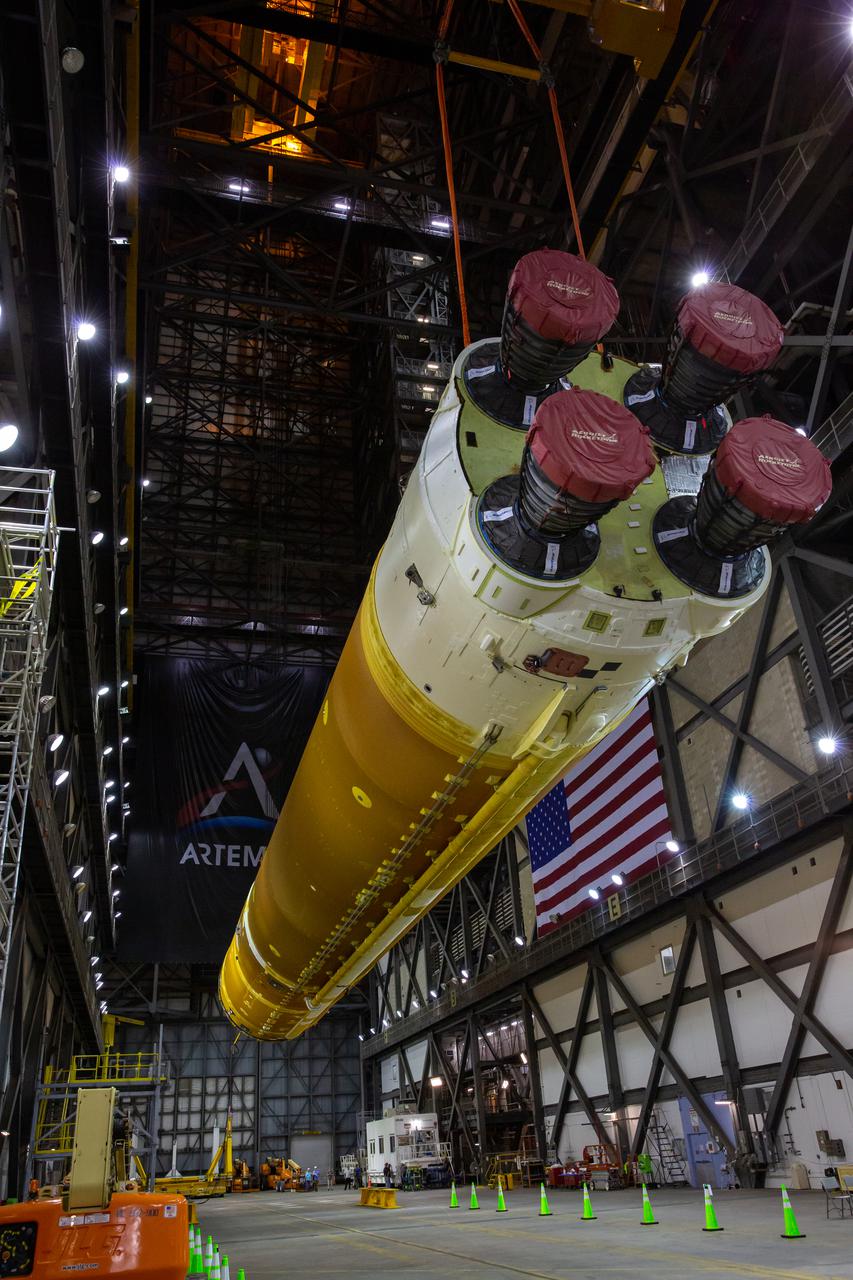

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
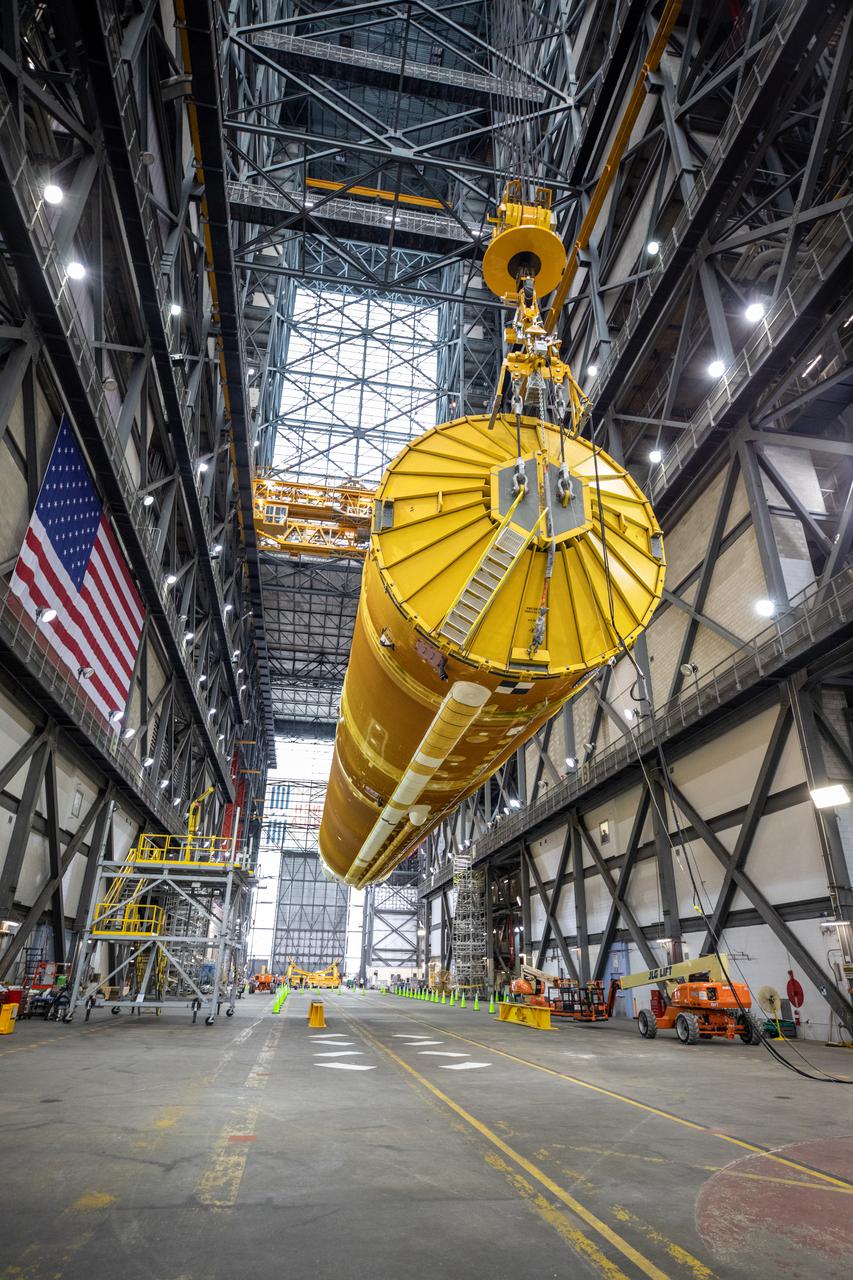

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs rotate the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – into a vertical position in preparation for its move to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
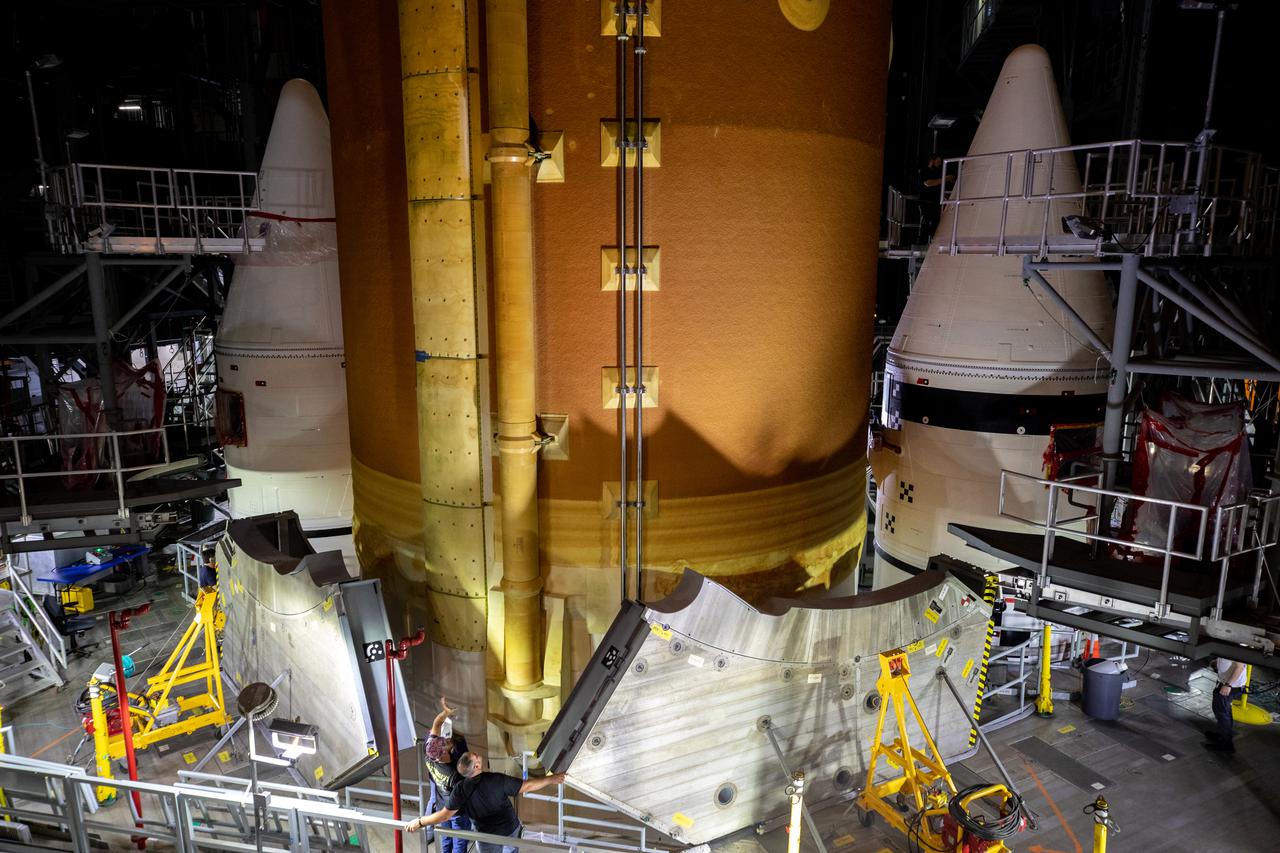

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
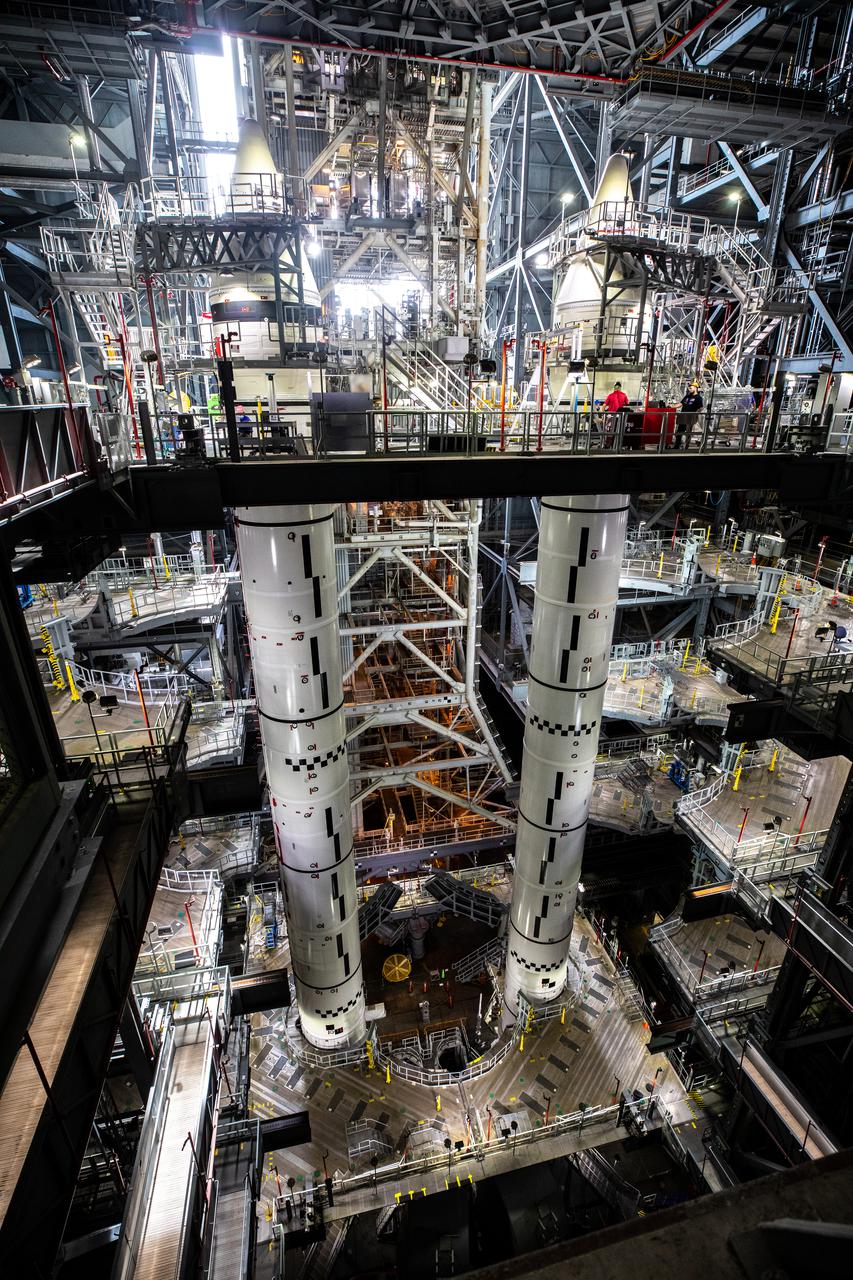

The fully stacked twin solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket are seen on top of the mobile launcher inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 4, 2021. Now that booster stacking is complete, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to integrate the massive core stage, which arrived at Kennedy in April 2020, with the boosters inside the VAB. The 188,000-pound core stage alone will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust at launch, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch the Artemis I mission. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
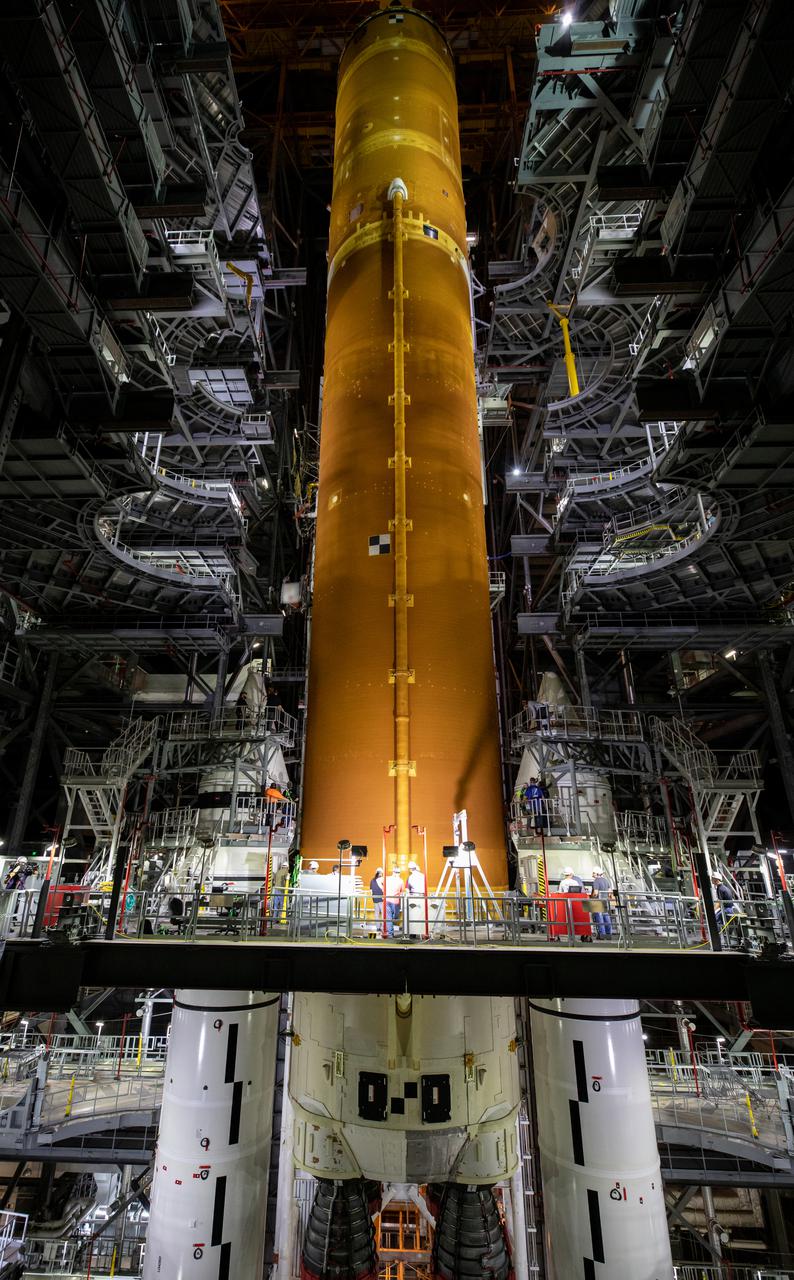

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
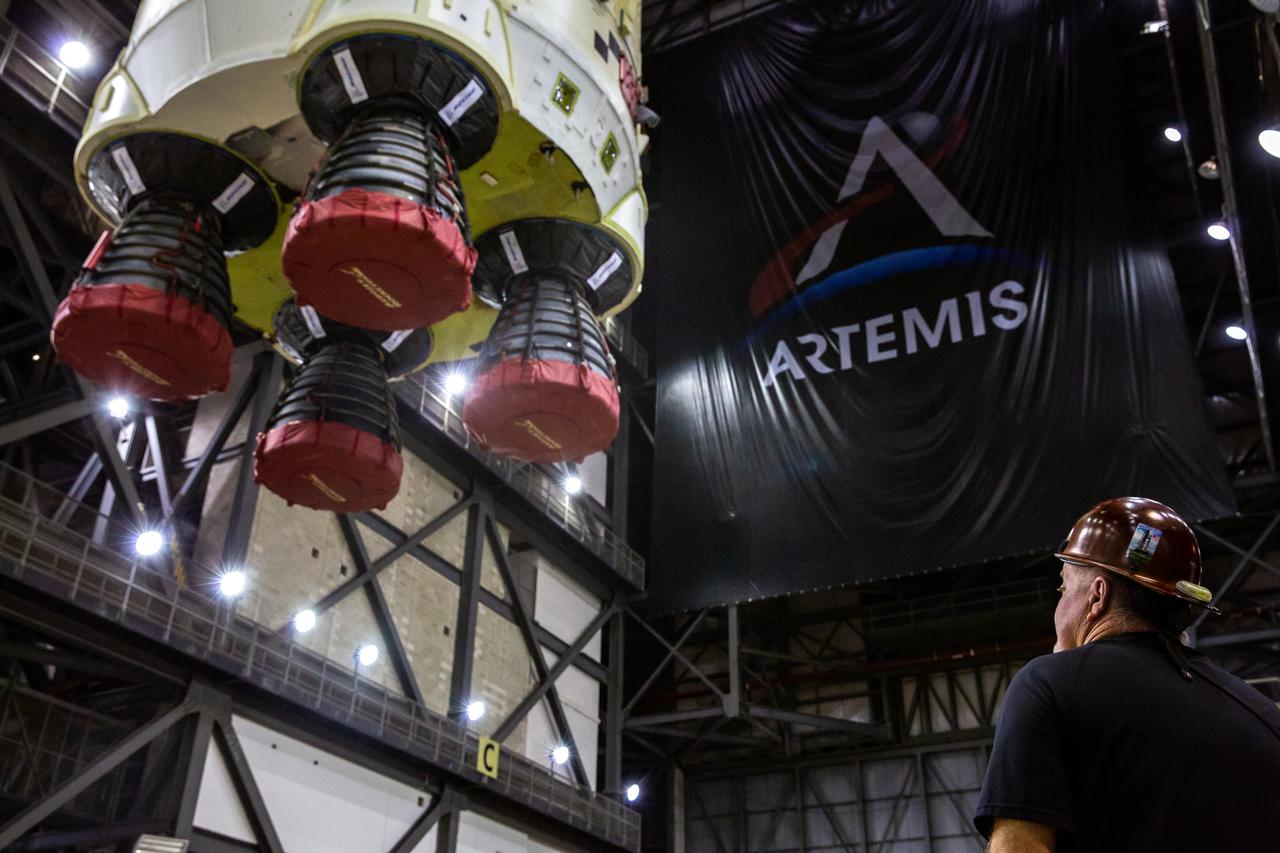

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
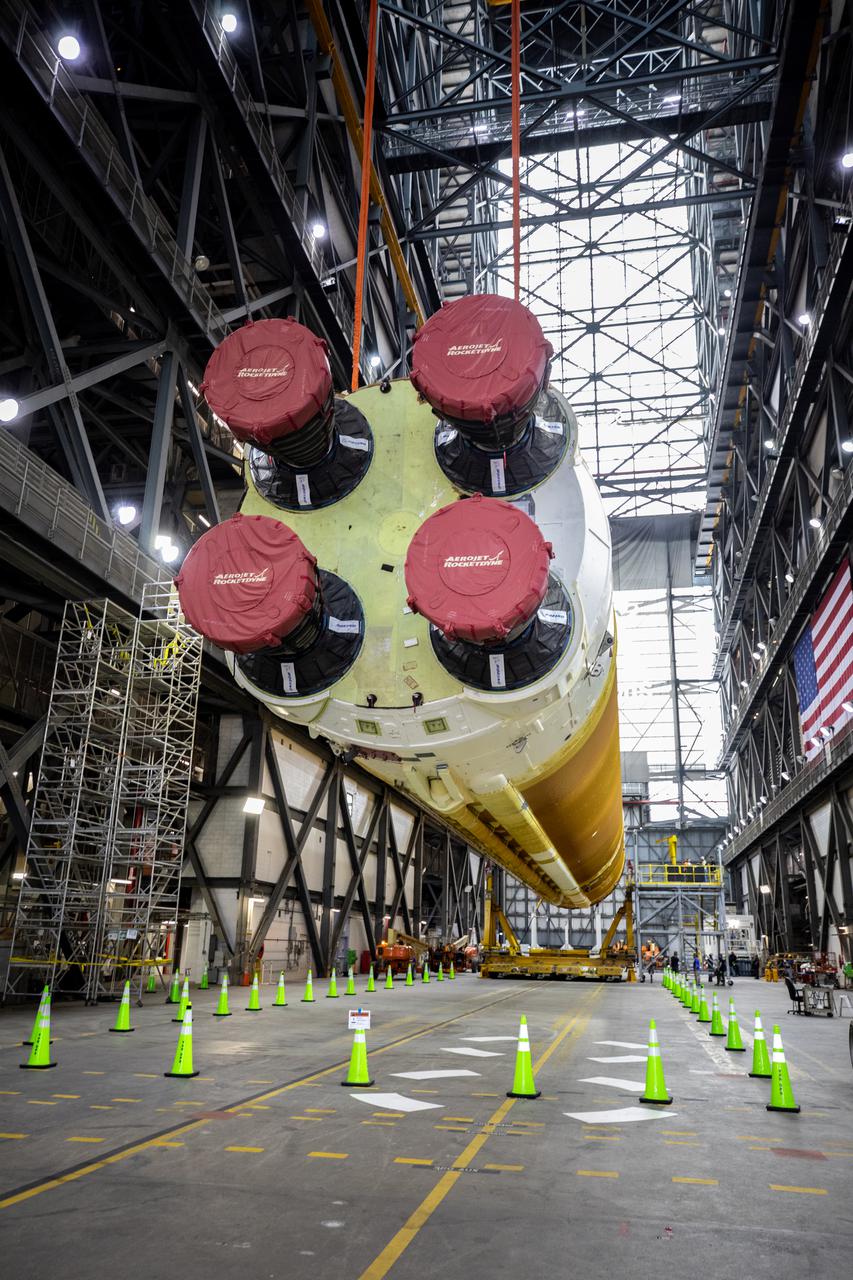

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
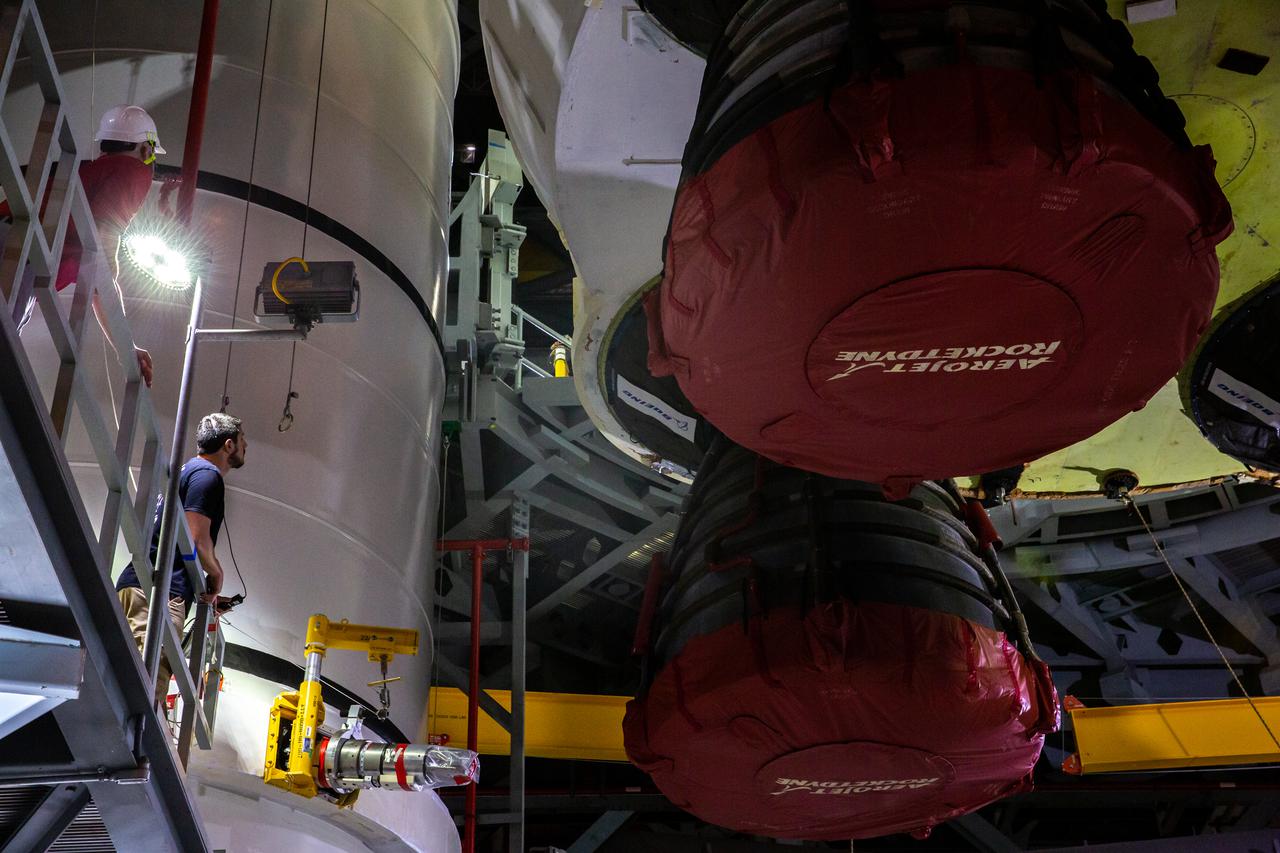

Seen here is a close-up view of the Space Launch System’s (SLS) RS-25 engines as teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lower the core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
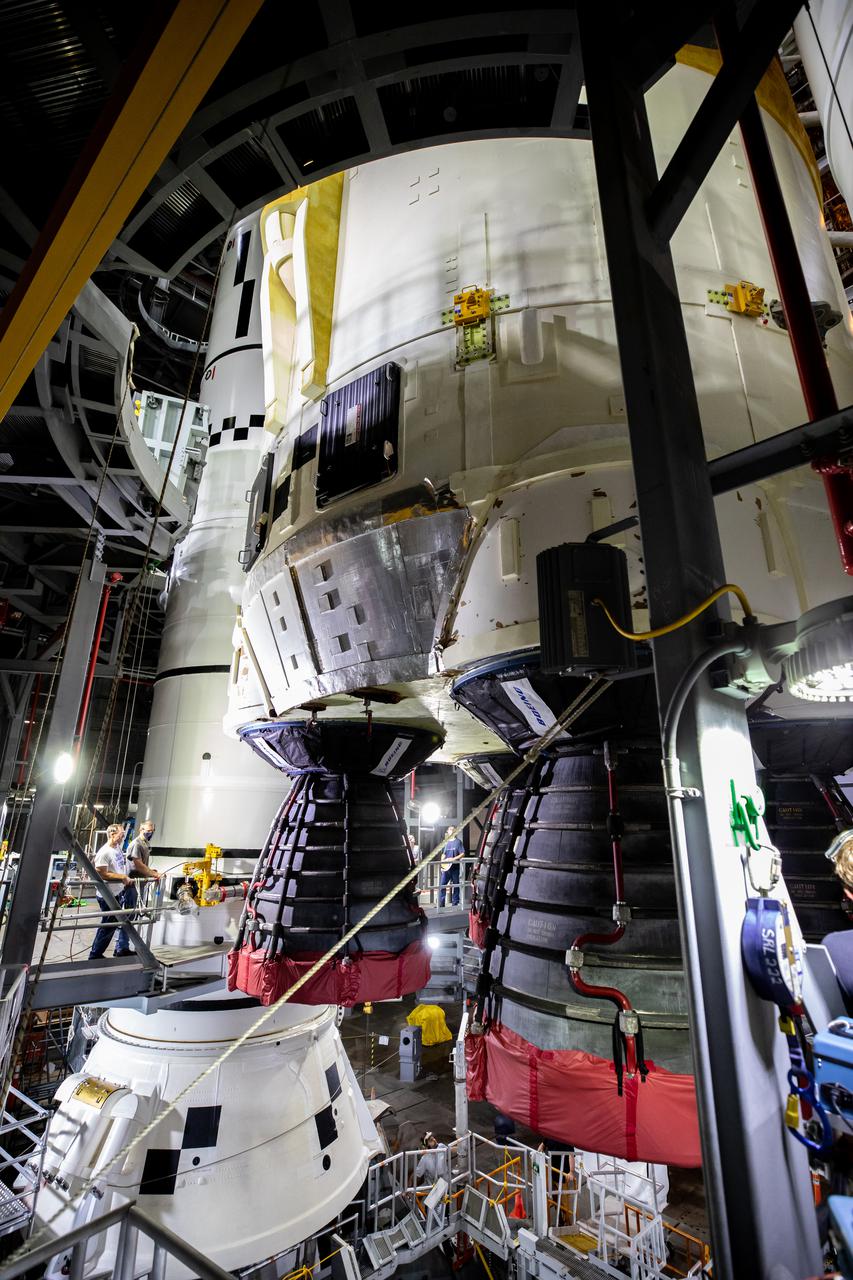

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
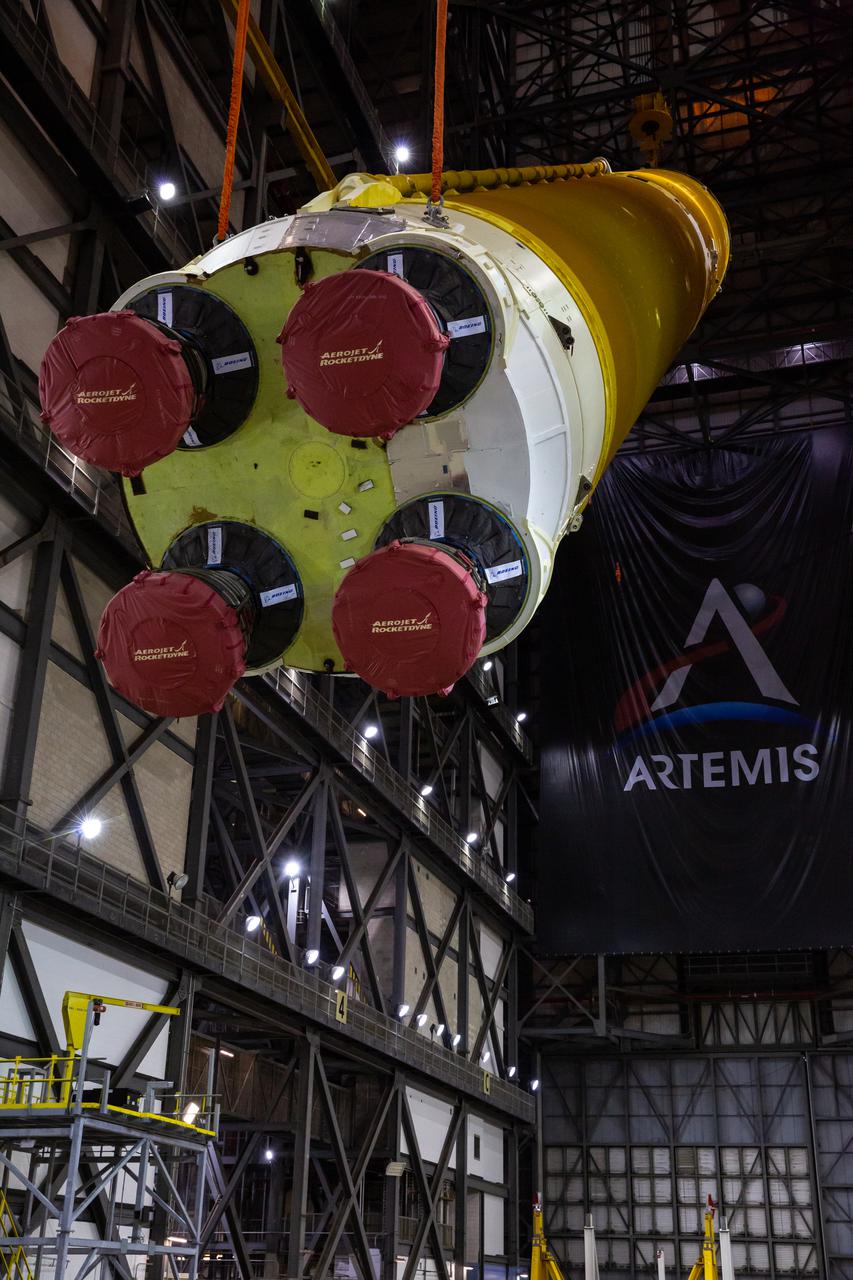

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs begin to rotate the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – into a vertical position in preparation for its move to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
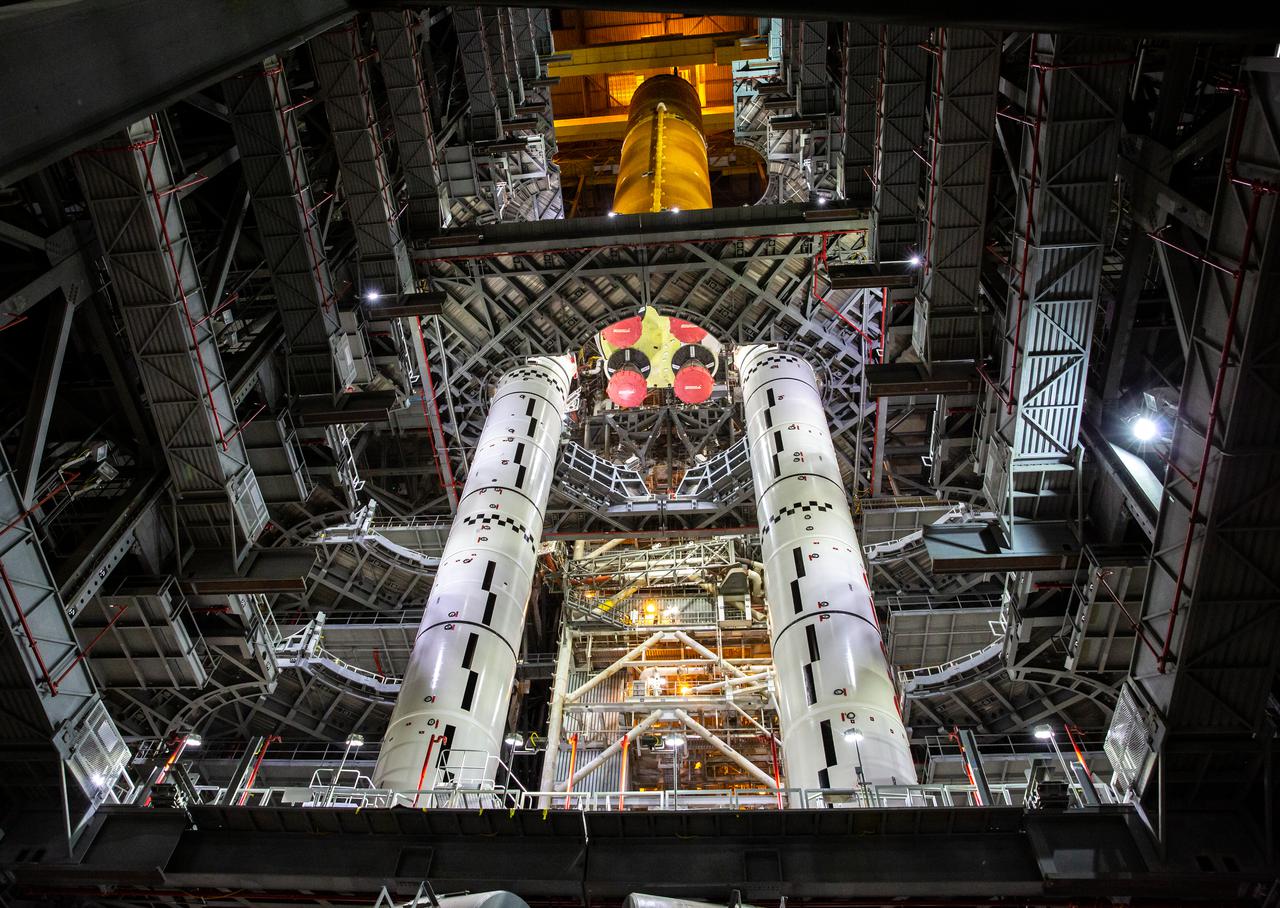

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
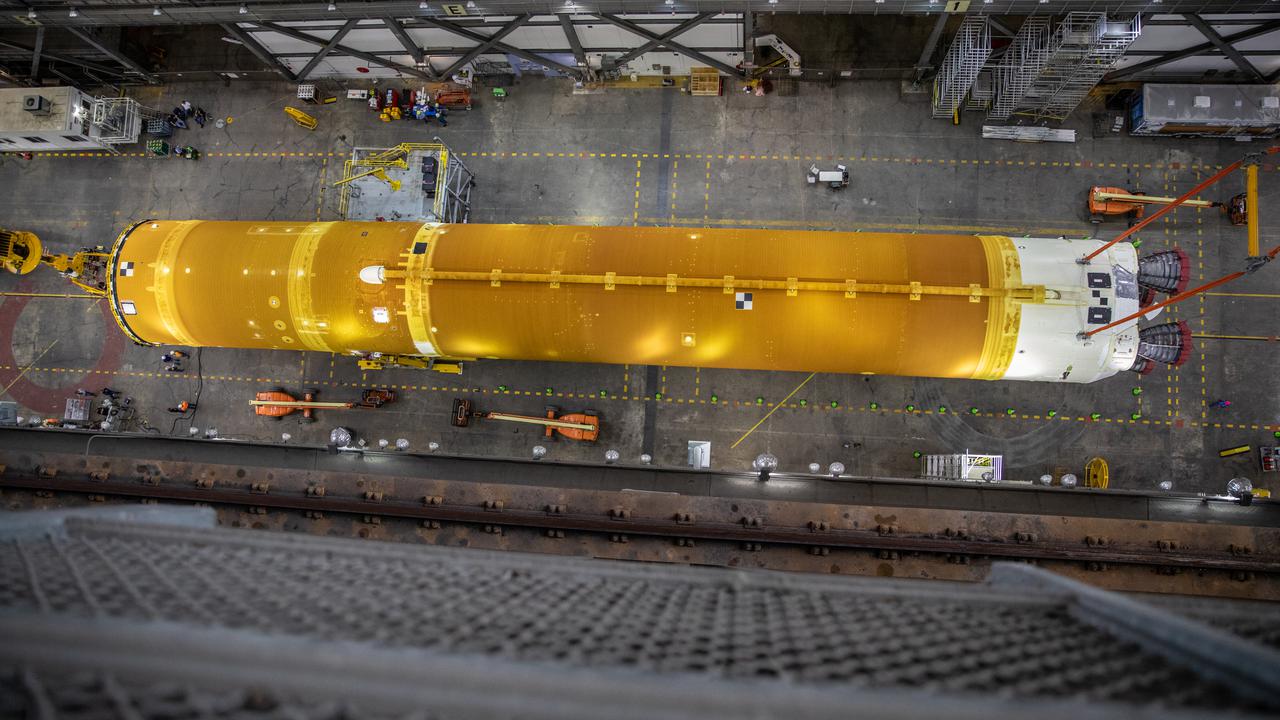

In this aerial view, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
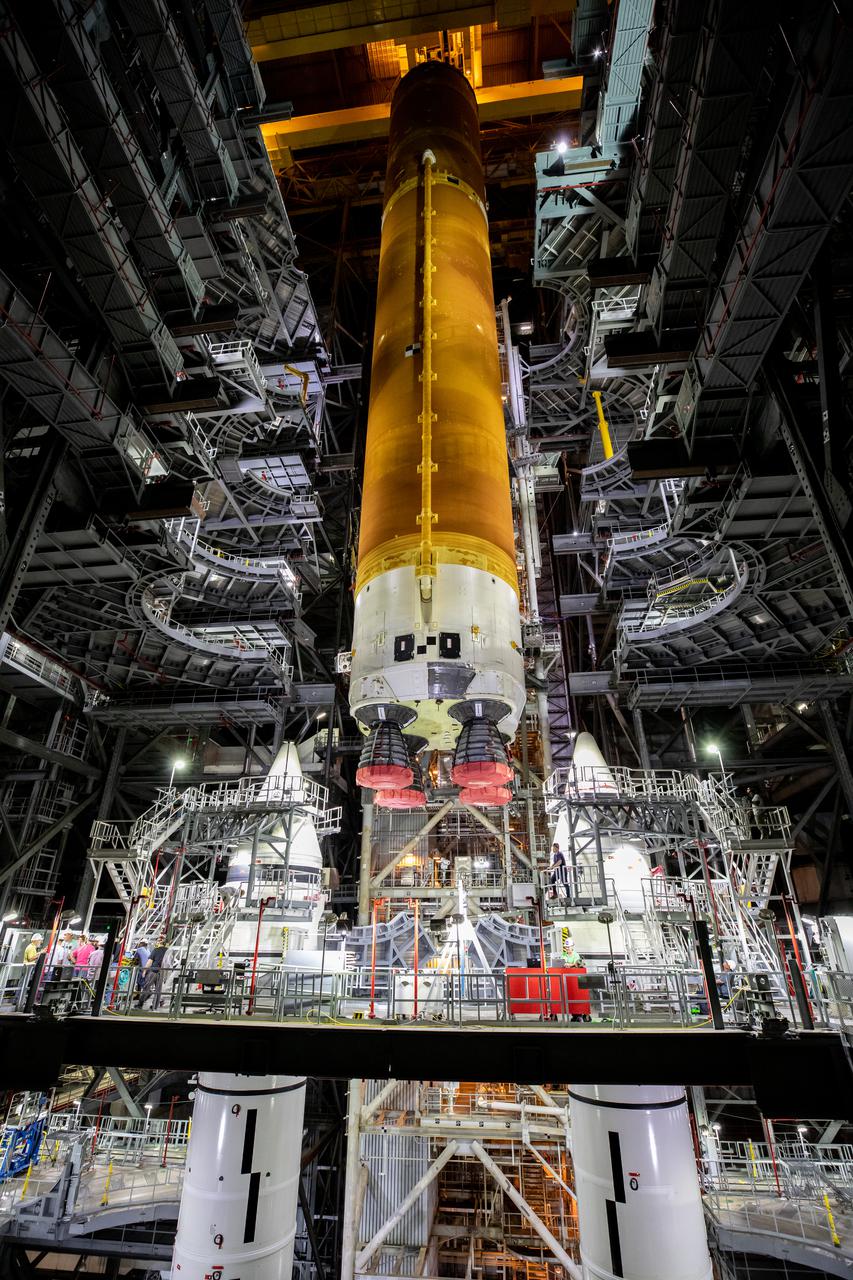

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs prepare to lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
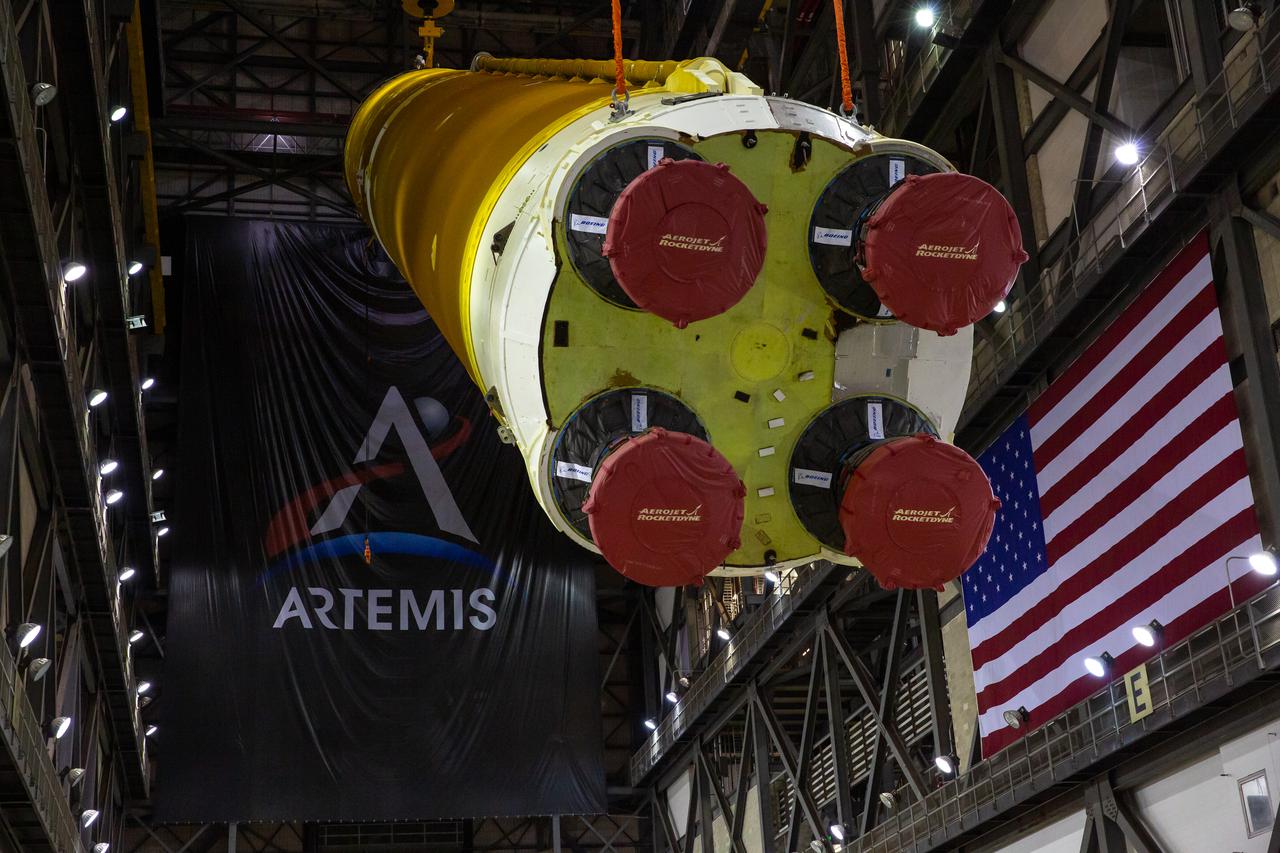

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs begin to rotate the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – into a vertical position in preparation for its move to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
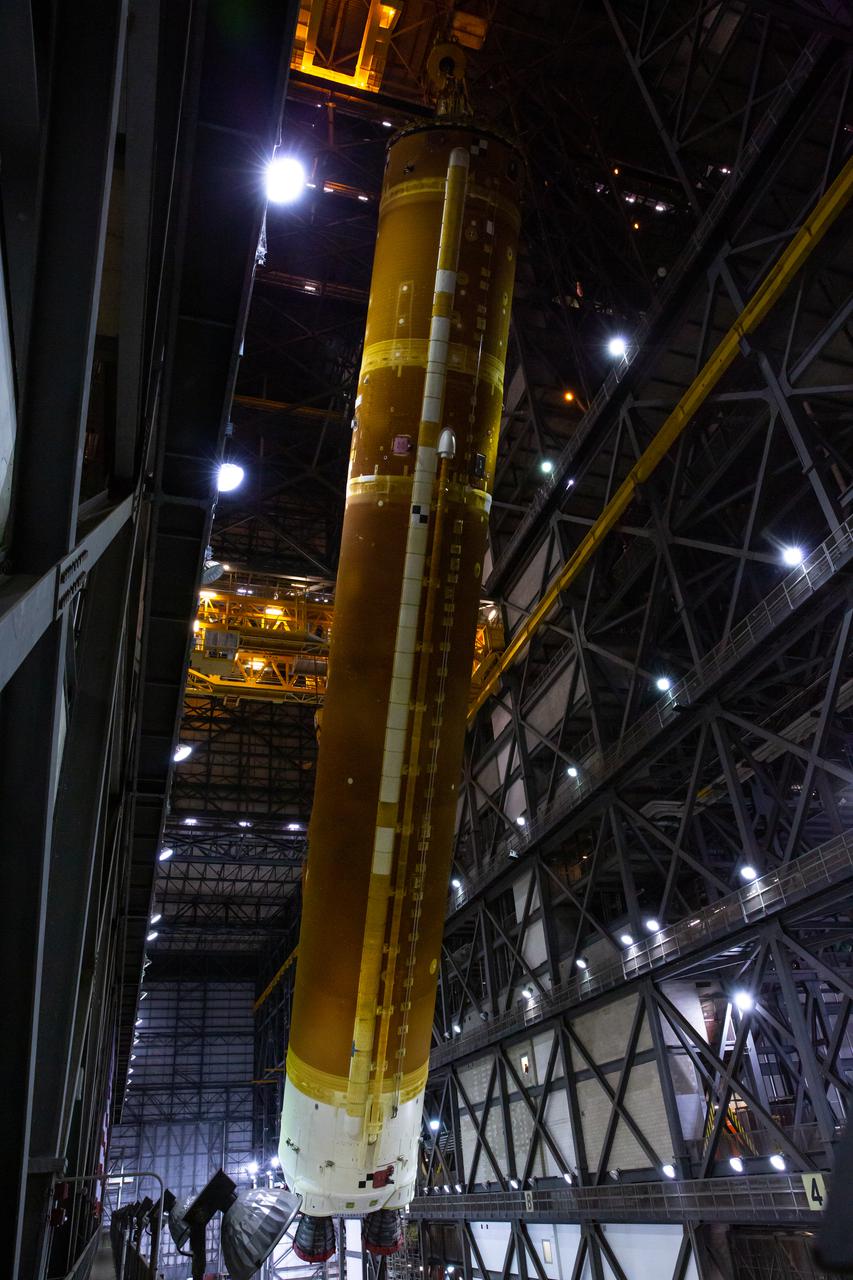

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs rotate the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – into a vertical position in preparation for its move to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
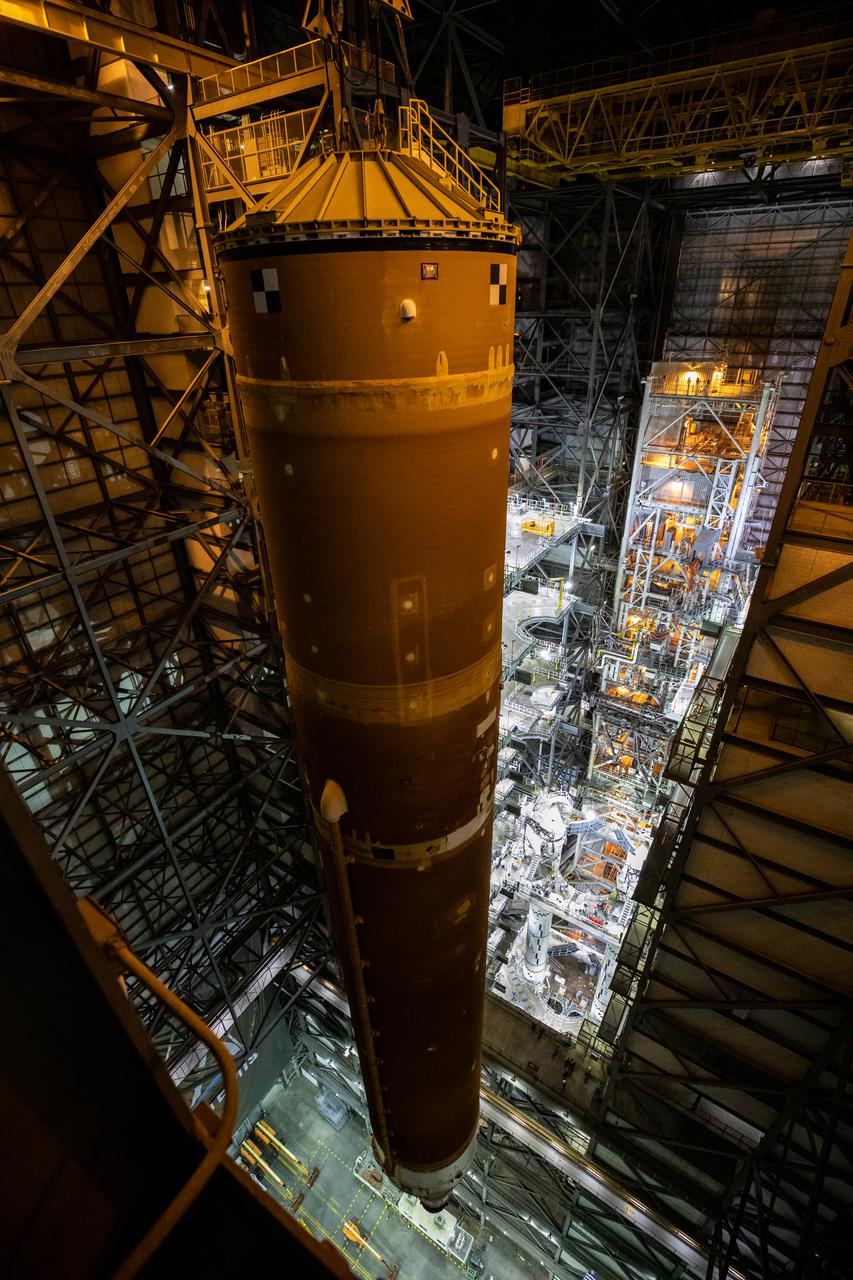

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
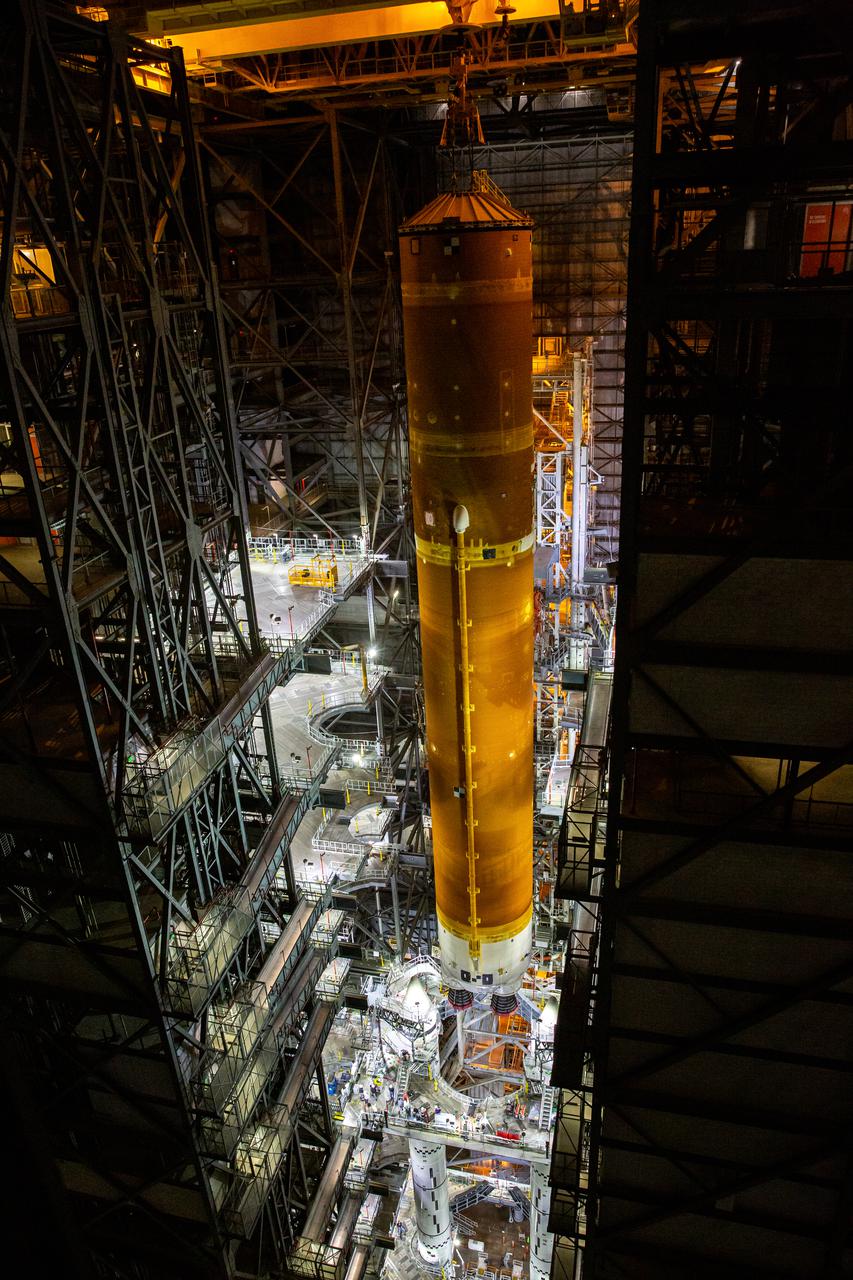

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs prepare to lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
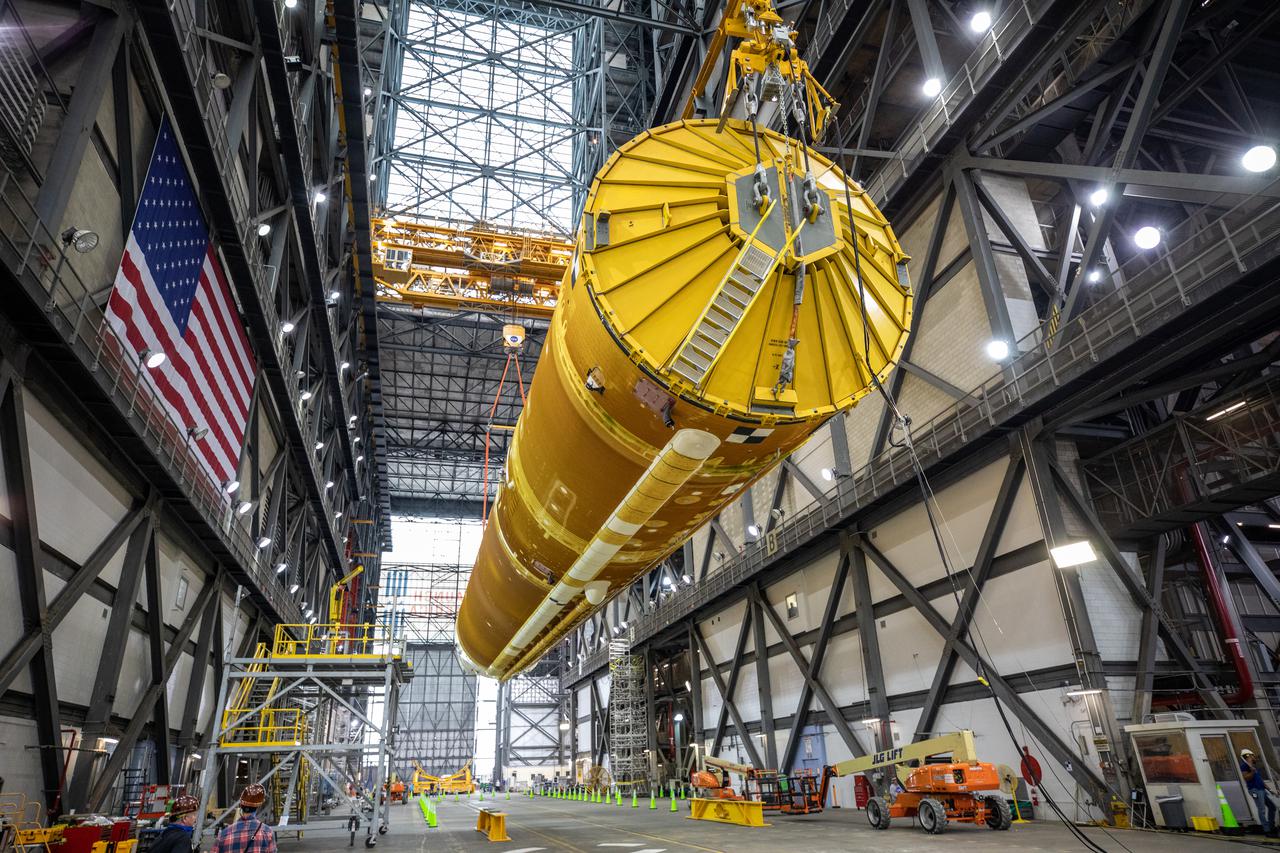

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
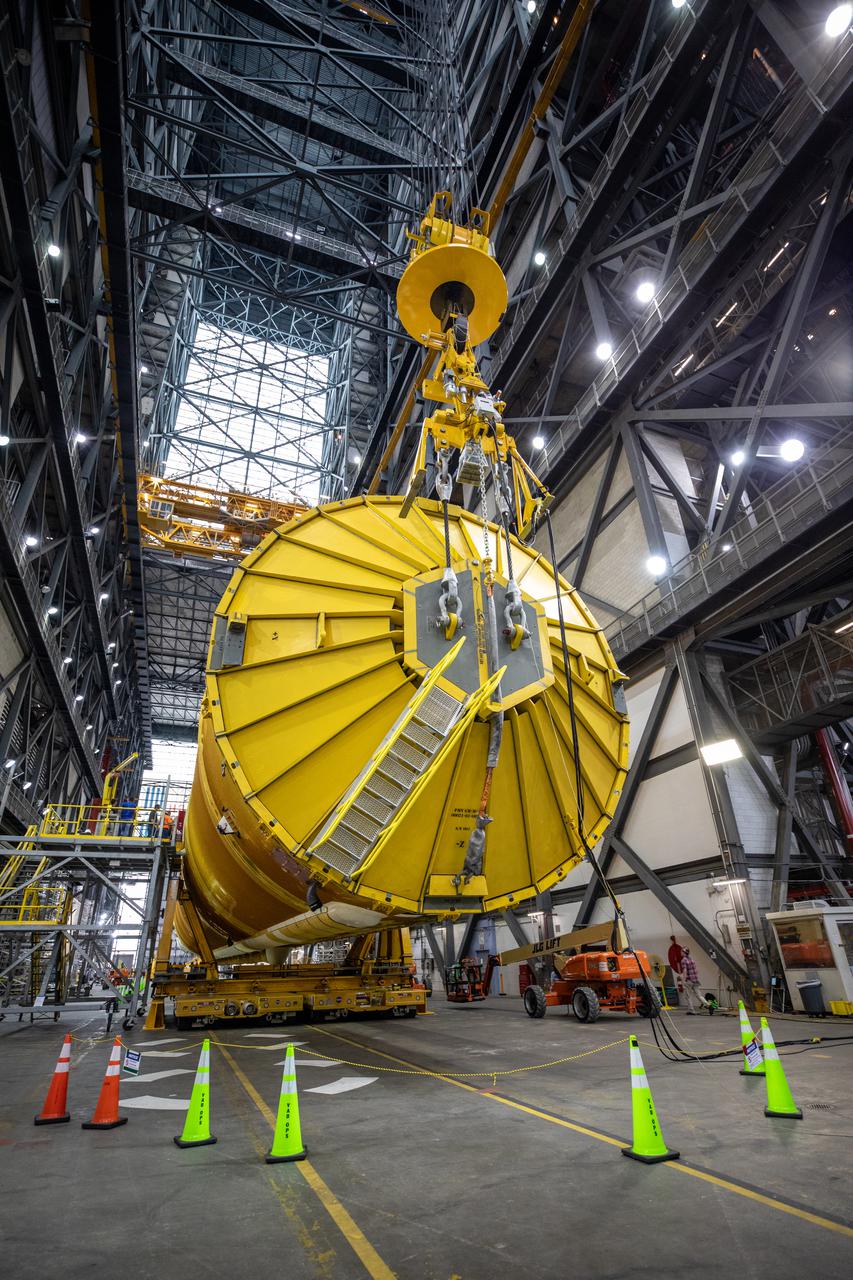

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs prepare to lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage and transfer it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, which is the largest part of the rocket, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
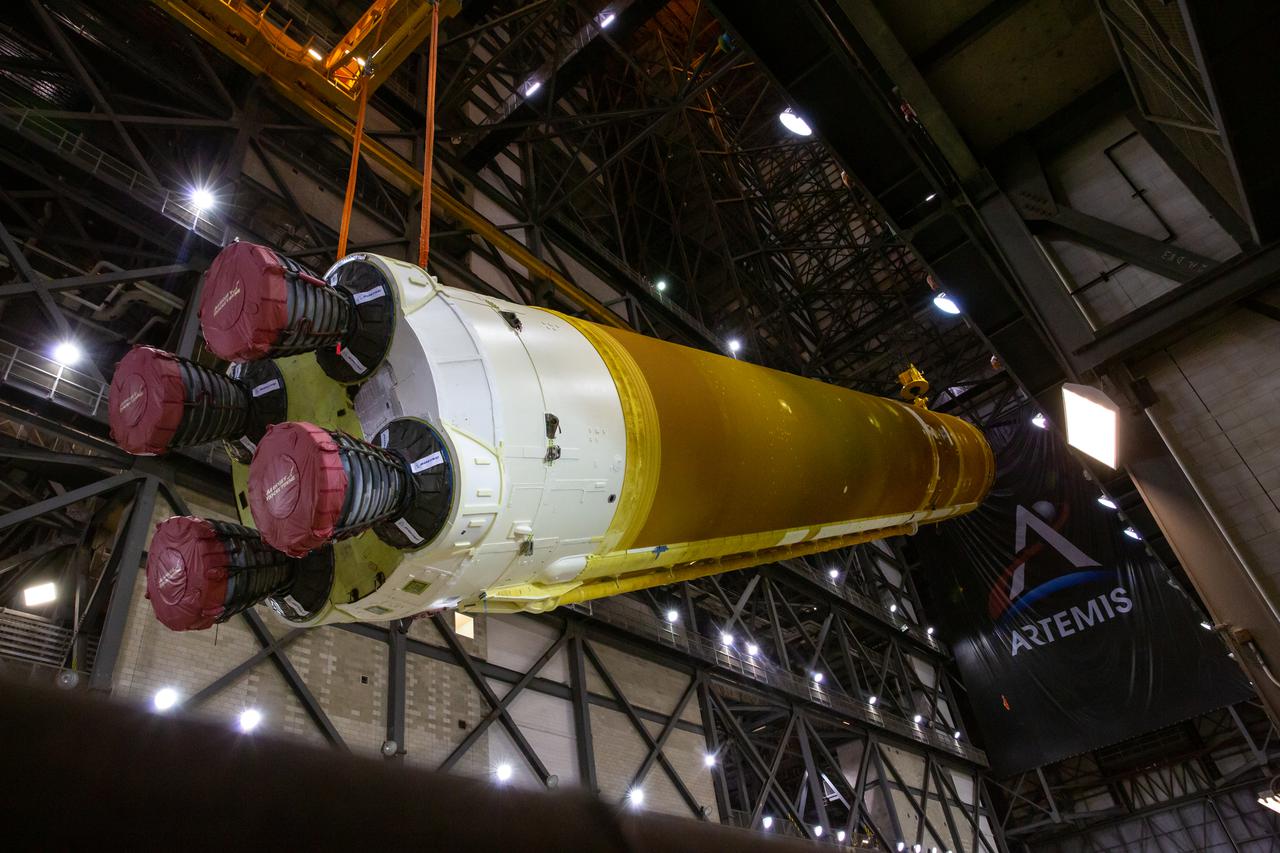

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs begin to rotate the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – into a vertical position in preparation for its move to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.

The fully stacked twin solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket are seen on top of the mobile launcher inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 9, 2021. Now that booster stacking is complete inside the VAB, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs are preparing to integrate the boosters with largest part of the SLS rocket, the massive 212-foot core stage, which arrived at Kennedy in April 2020. The 188,000-pound core stage alone will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
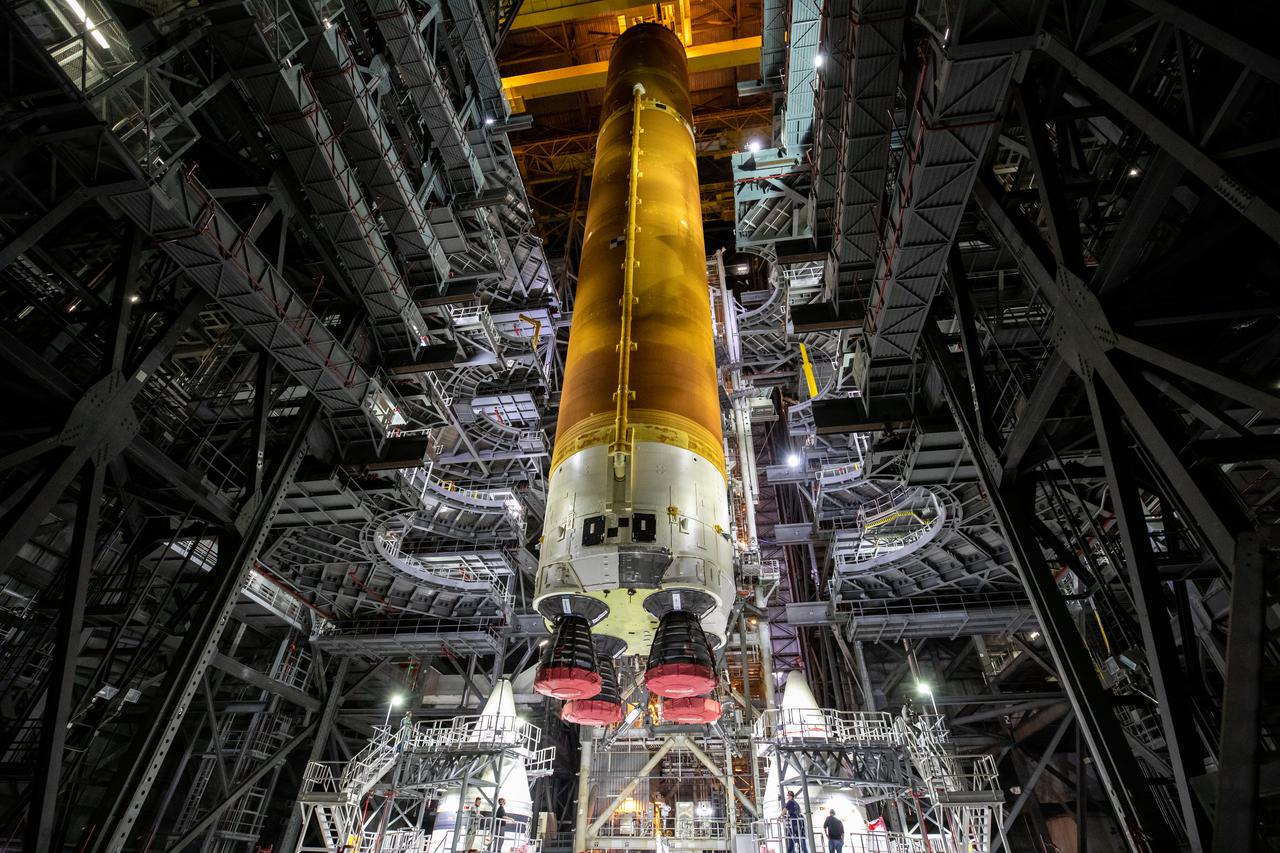

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs prepare to lower the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
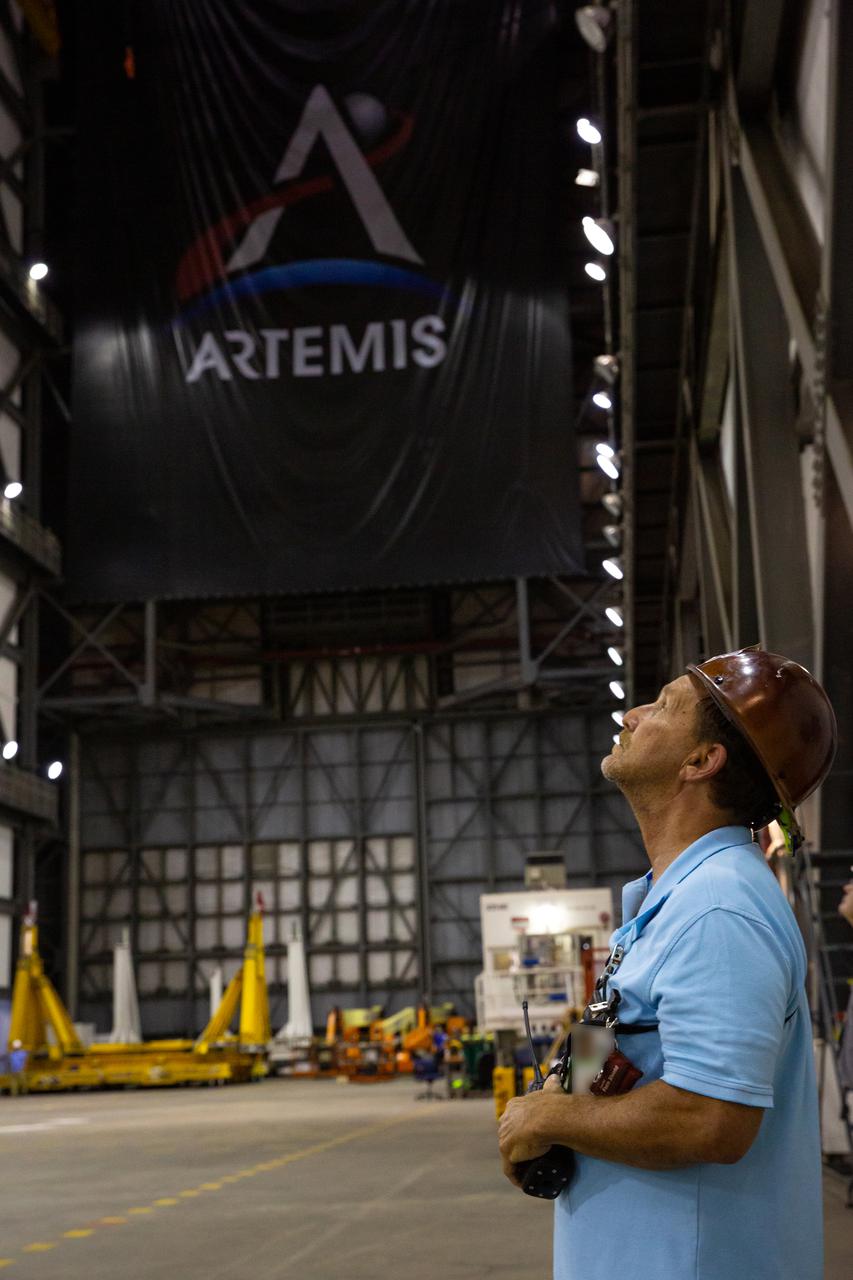

A Kennedy Space Center employee monitors operations as teams with the agency’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
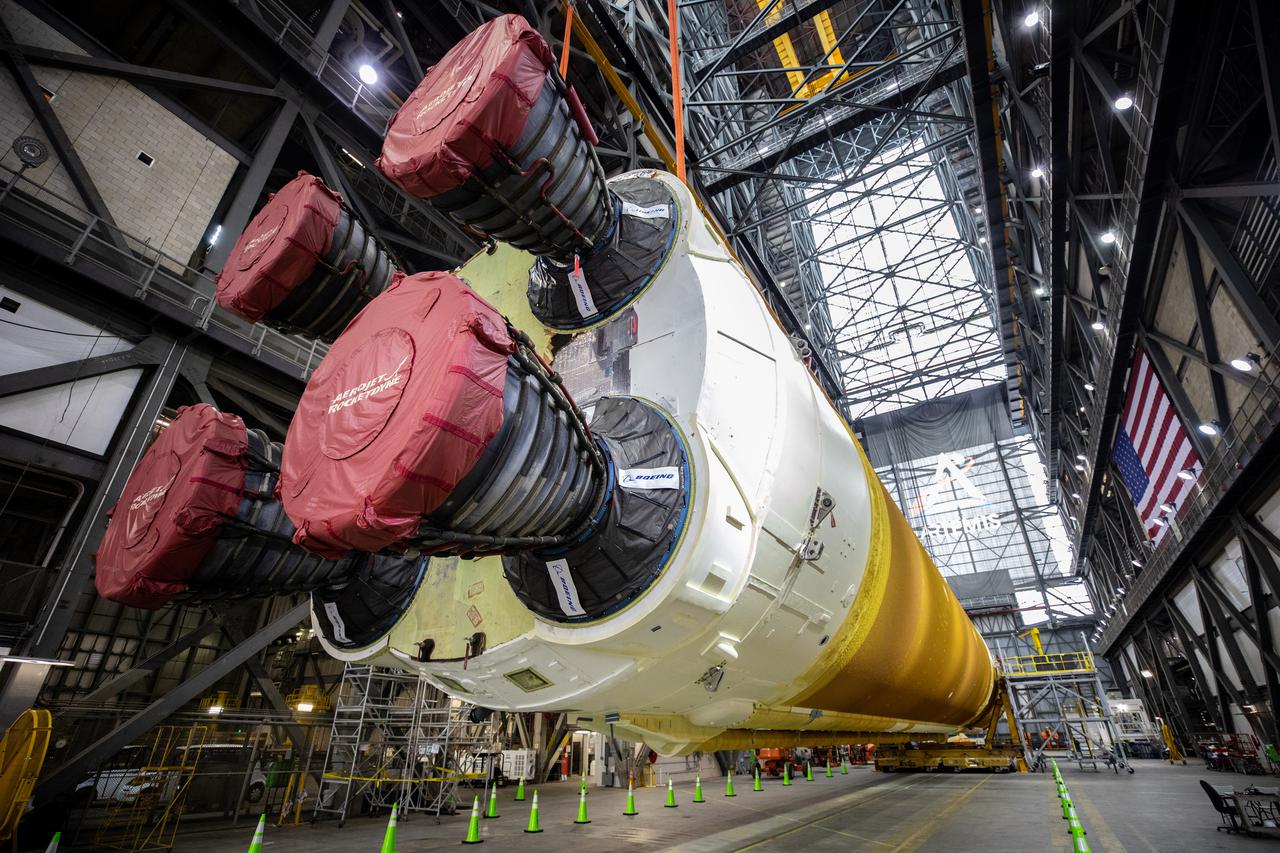

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lift the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – and prepare to move it over to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
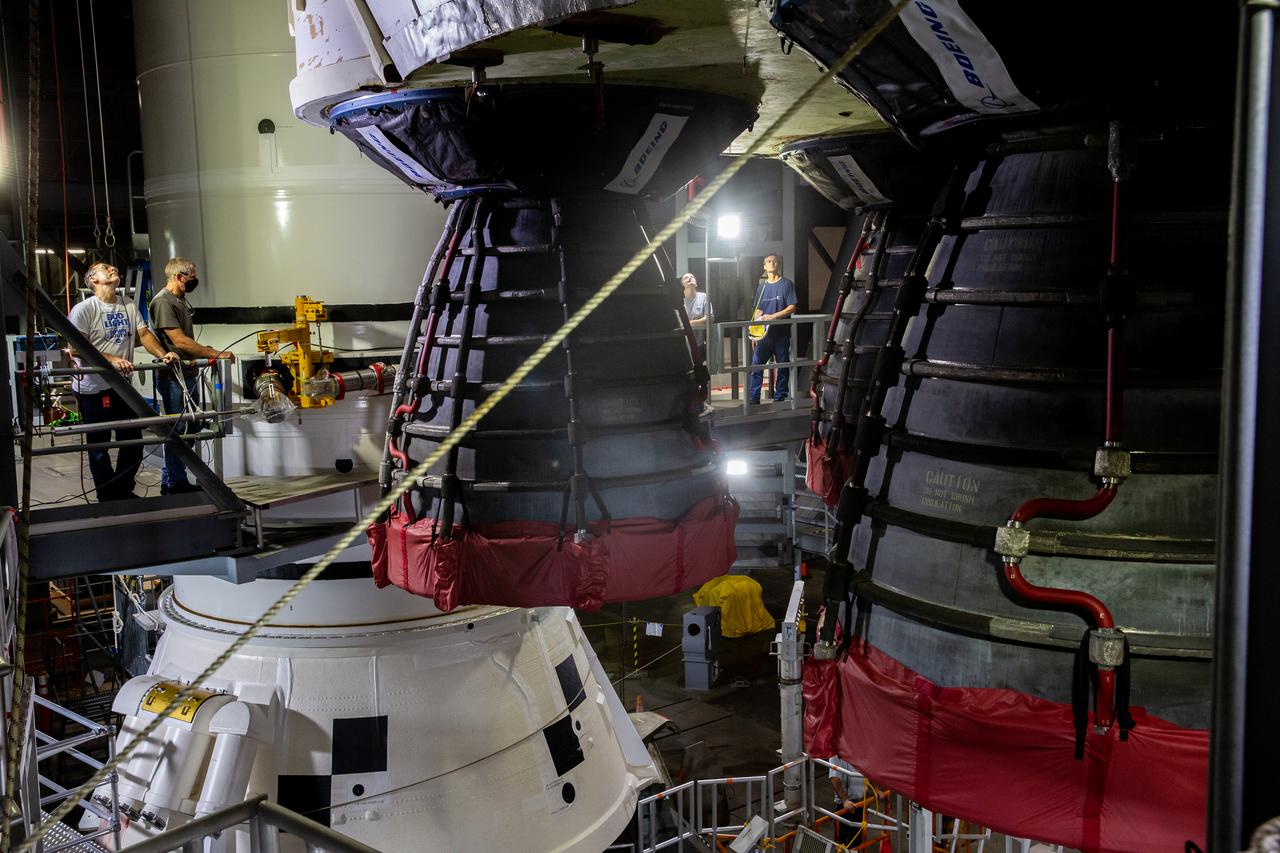

Seen here is a close-up view of the Space Launch System’s (SLS) RS-25 engines as teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs lower the core stage – the largest part of the rocket – onto the mobile launcher, in between the twin solid rocket boosters, inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 12, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
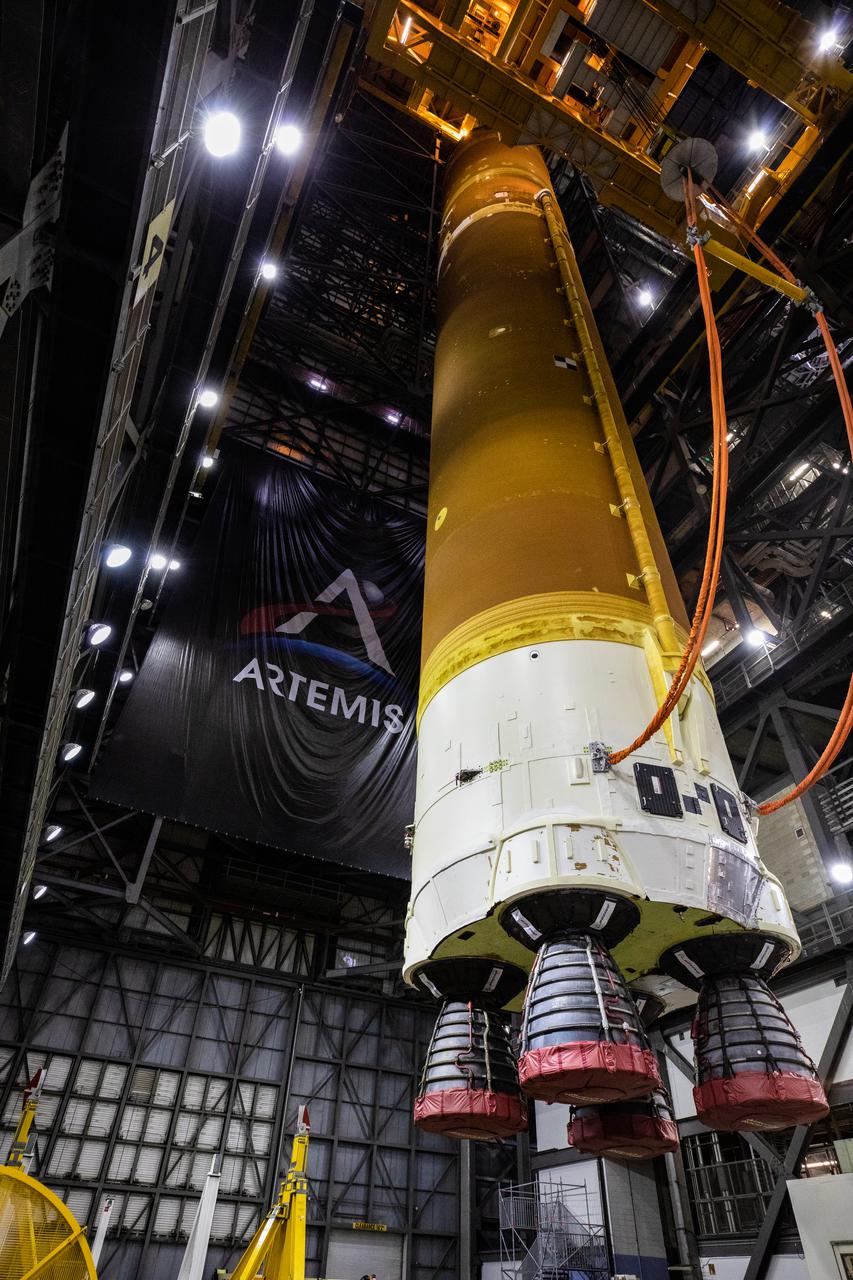

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs rotate the Space Launch System (SLS) core stage – the largest part of the rocket – into a vertical position in preparation for its move to High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be placed atop the mobile launcher in between the twin solid rocket boosters, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 11, 2021. The 188,000-pound core stage, with its four RS-25 engines, will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust during launch and ascent, and coupled with the boosters, will provide more than 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send the Artemis I mission to space. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, as well as establish a sustainable presence on the lunar surface in preparation for human missions to Mars.
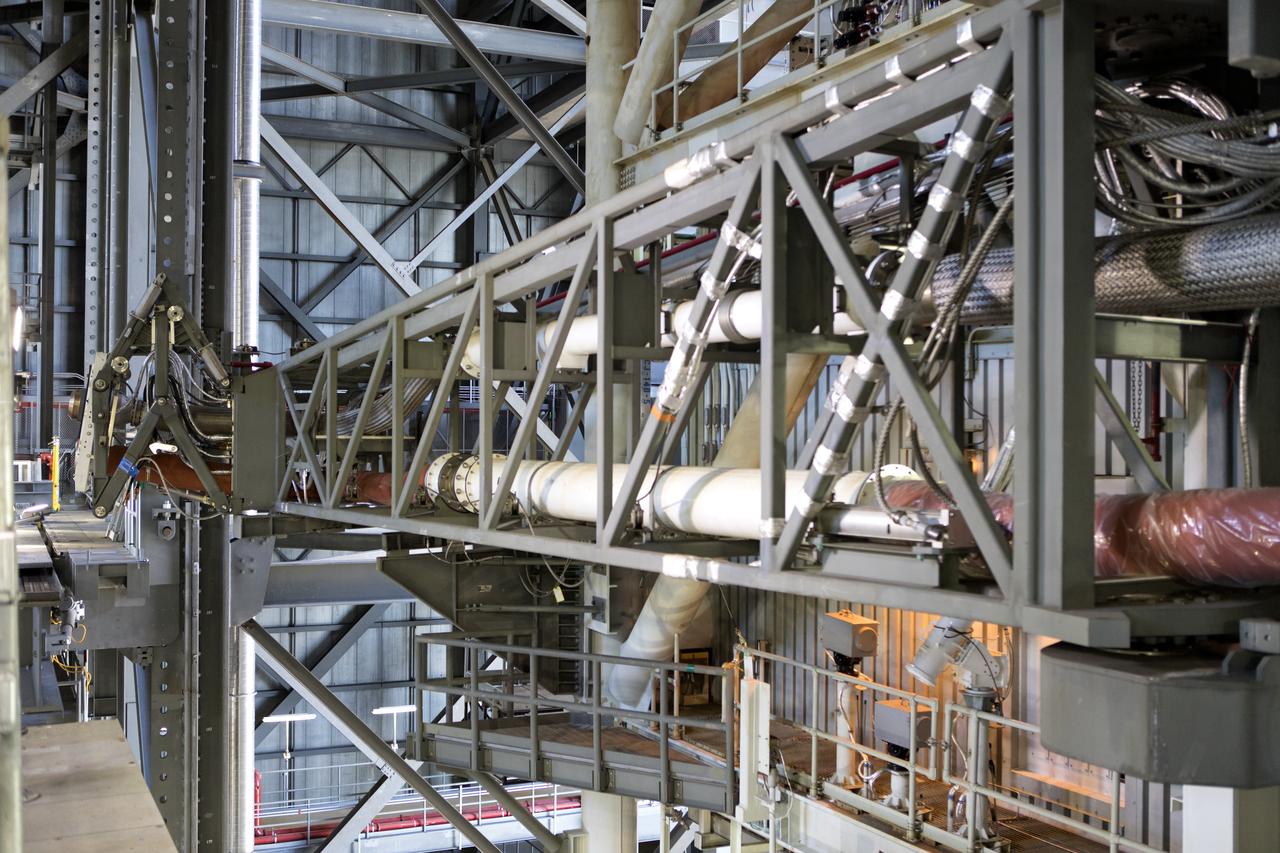

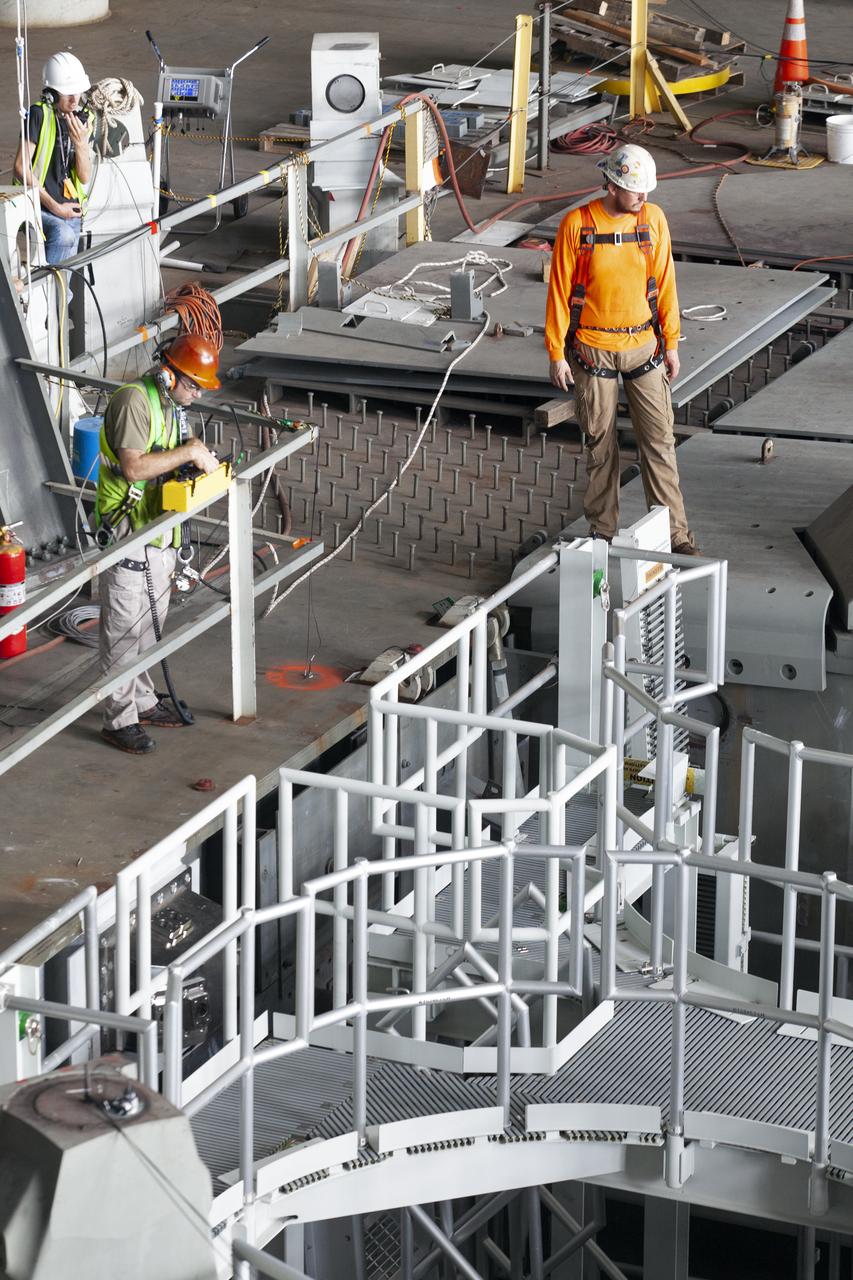
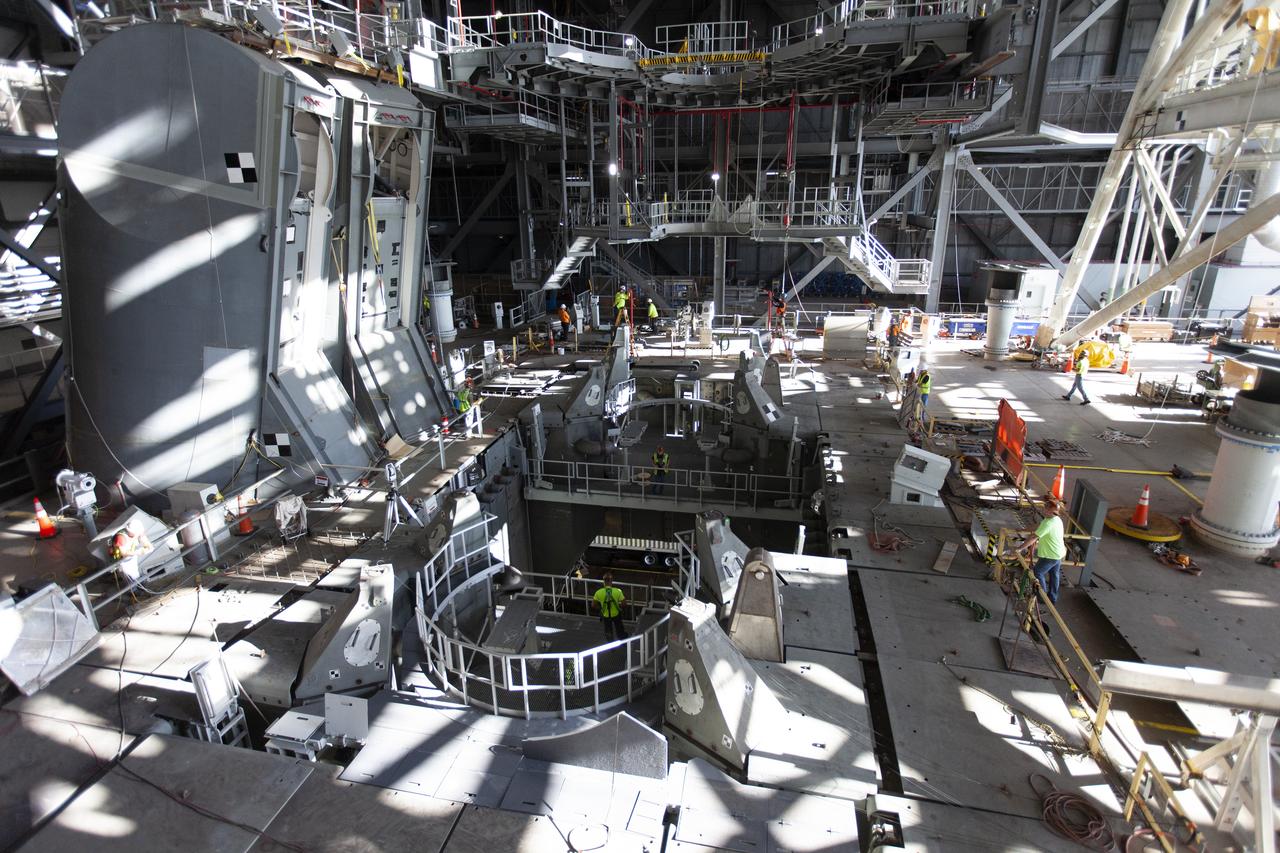
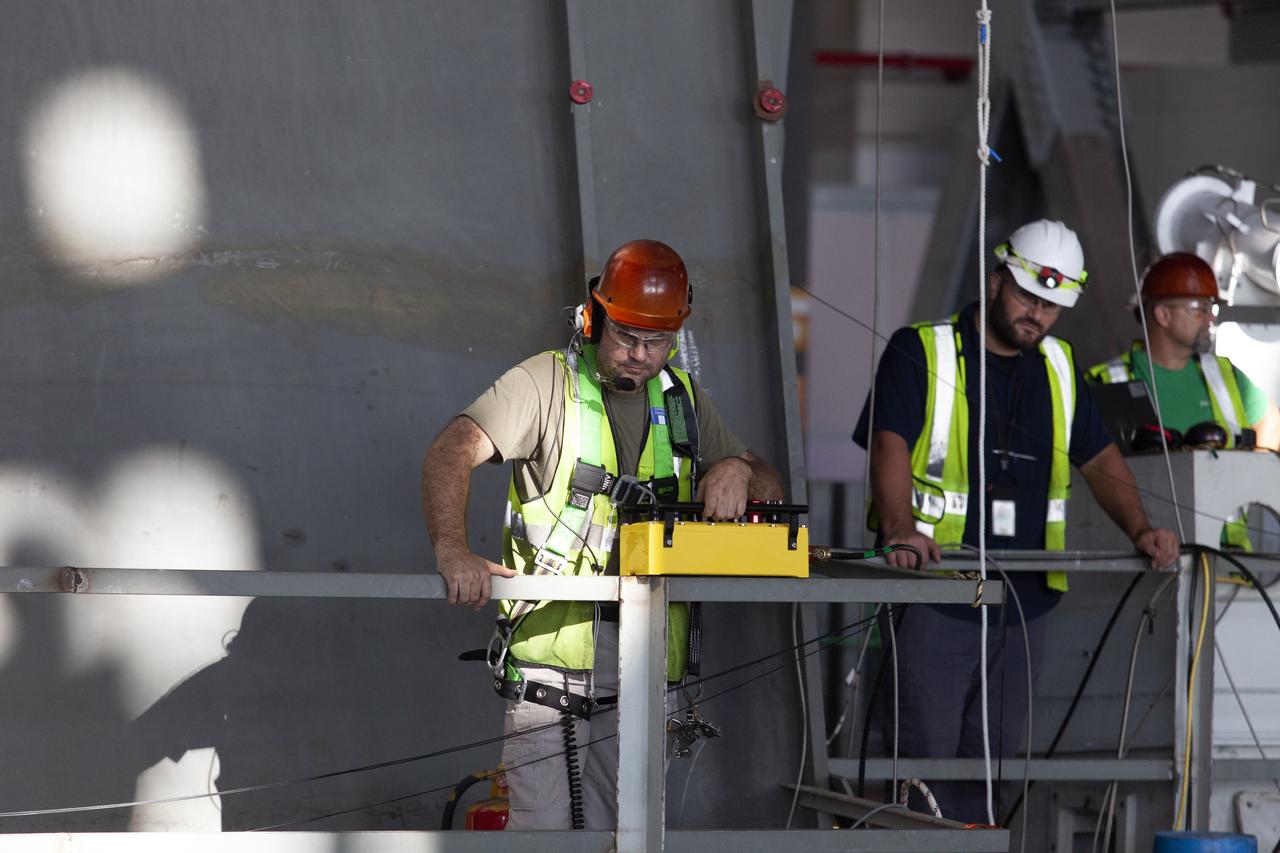
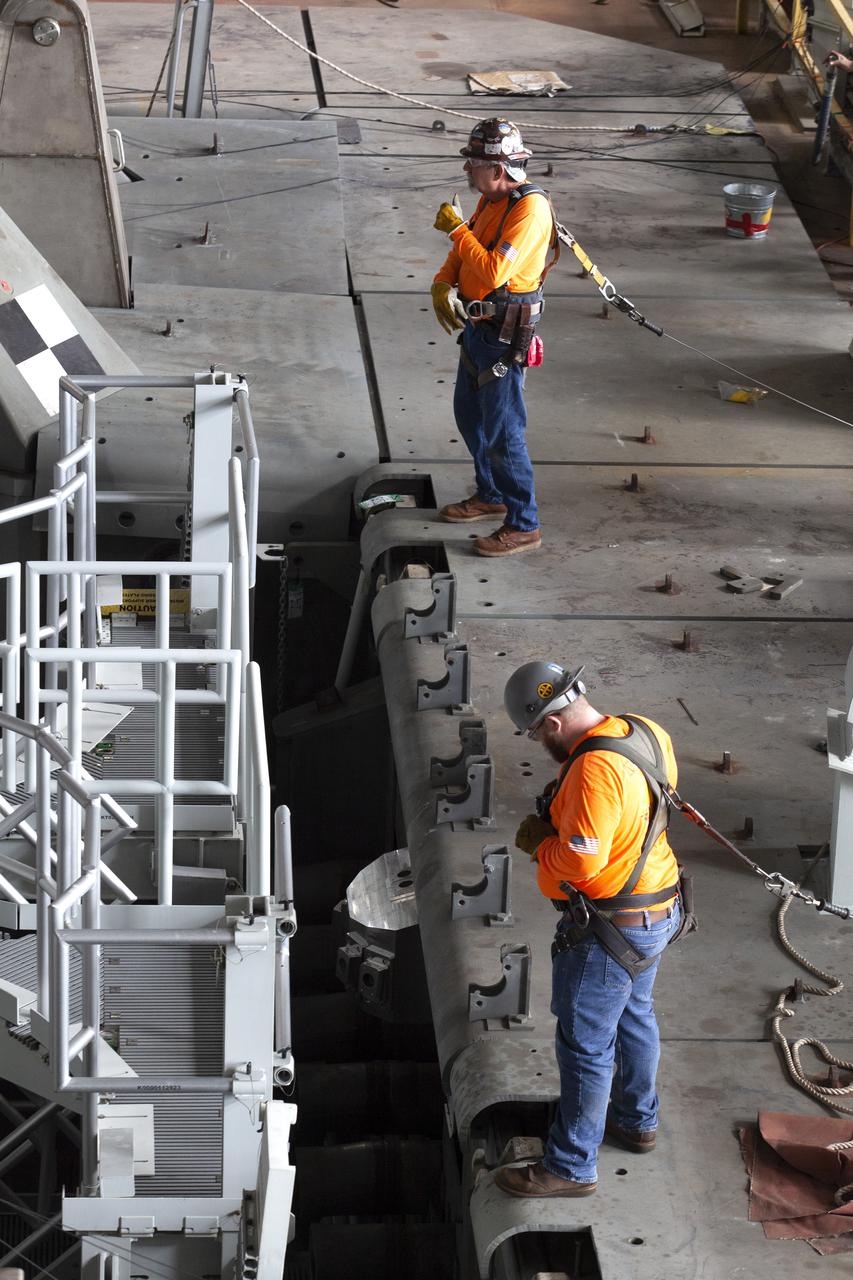
Preparations are underway to perform a preliminary swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Exploration Ground Systems Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
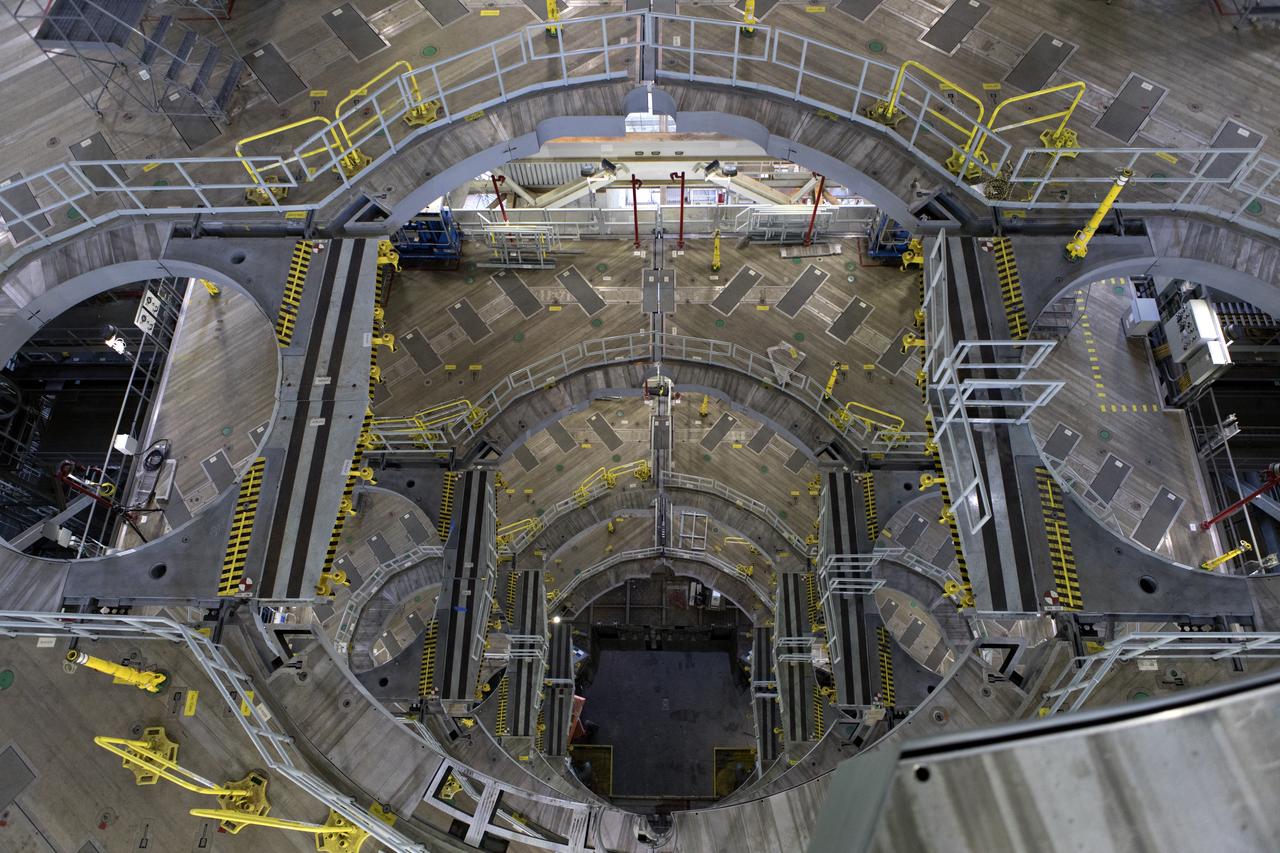

A view of the new work platforms in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Preparations are underway to perform an initial swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.
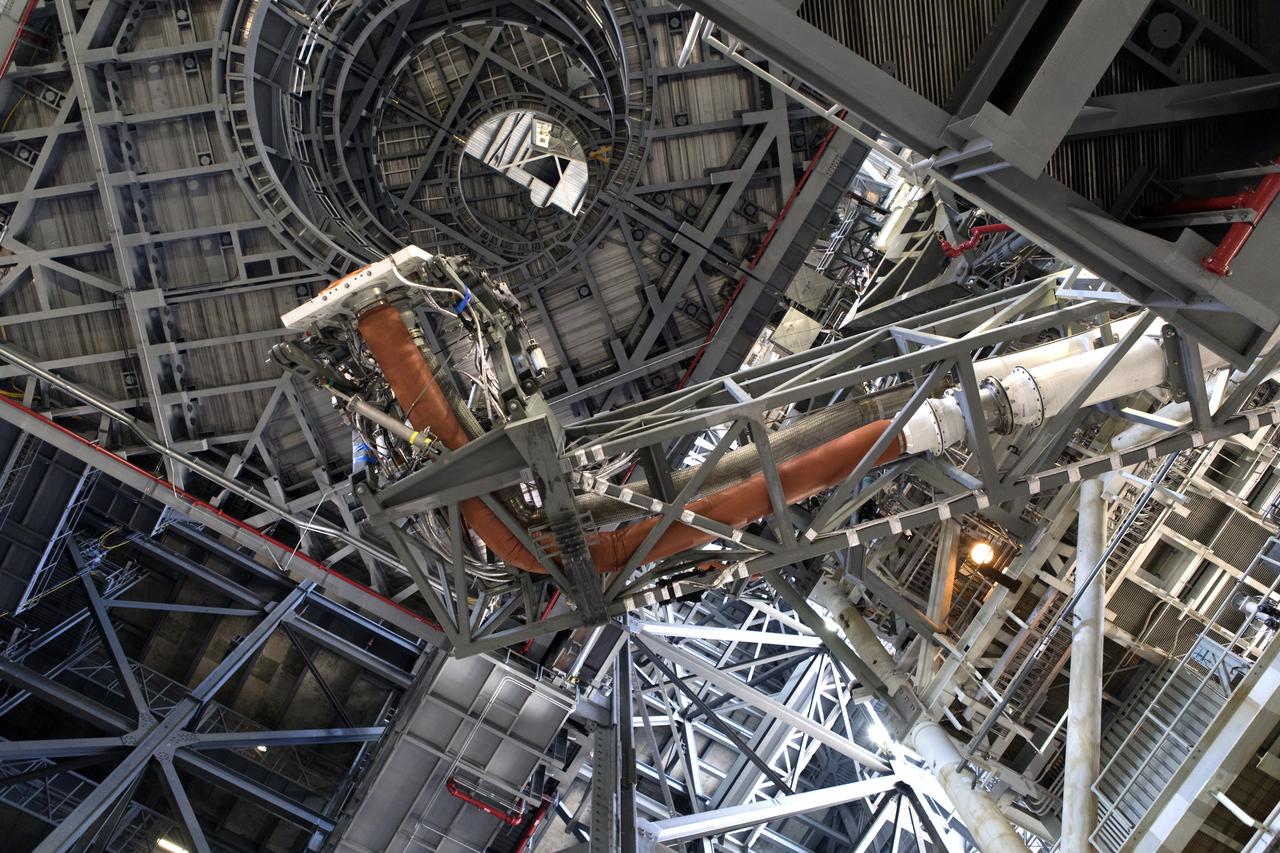

In this view looking up in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a preliminary swing test is being performed on the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on Feb. 22, 2019. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.
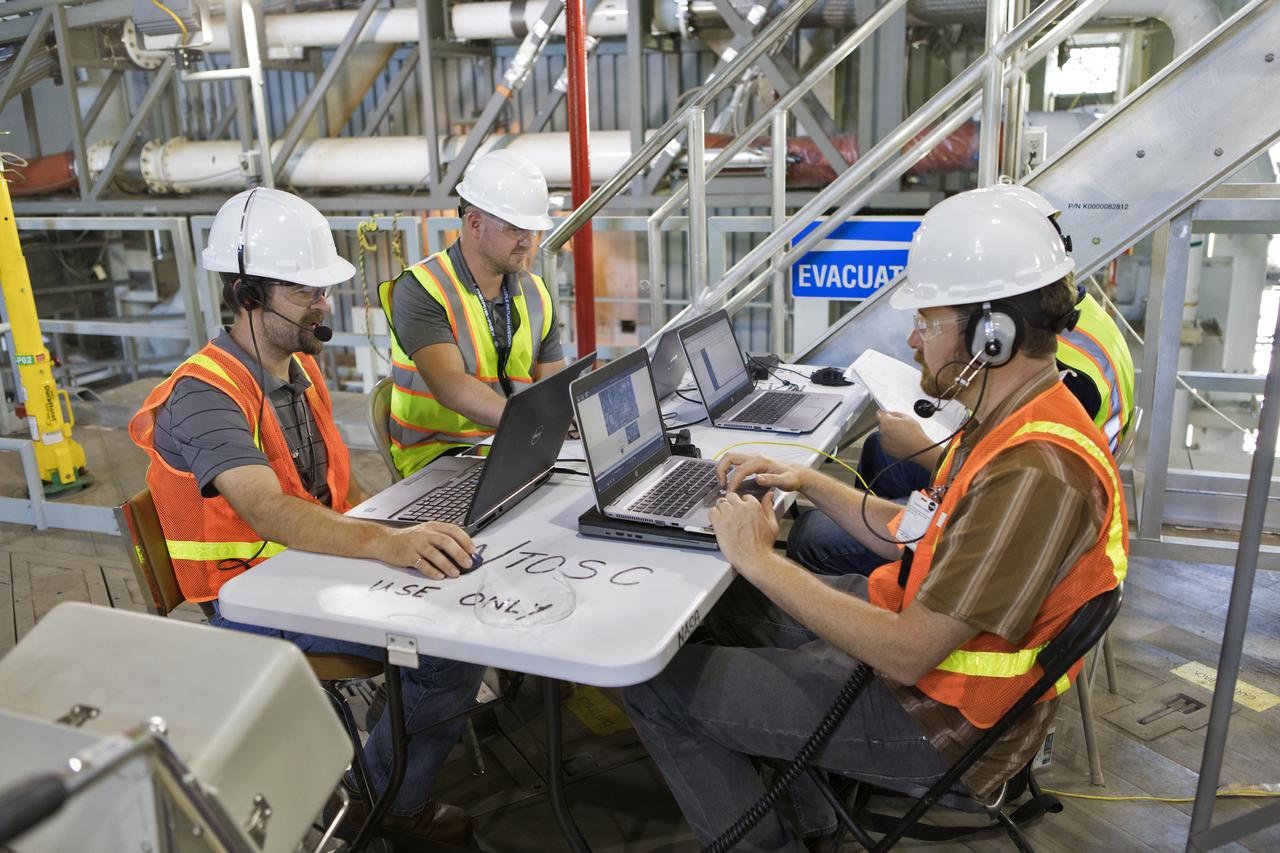

Technicians and engineers with Jacobs on the Test and Operations Support Contract, prepare for a swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.
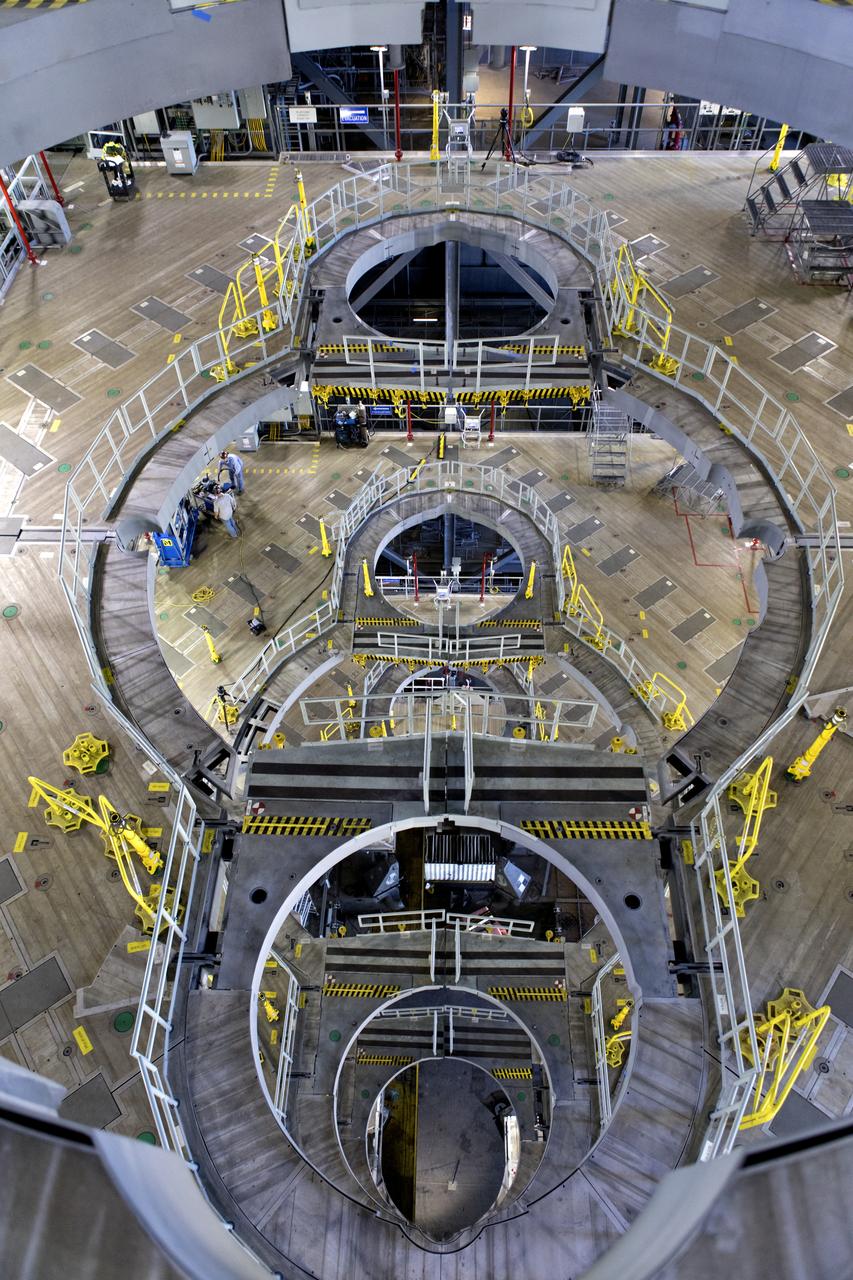

A view from above of new work platforms in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Preparations are underway to perform an initial swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
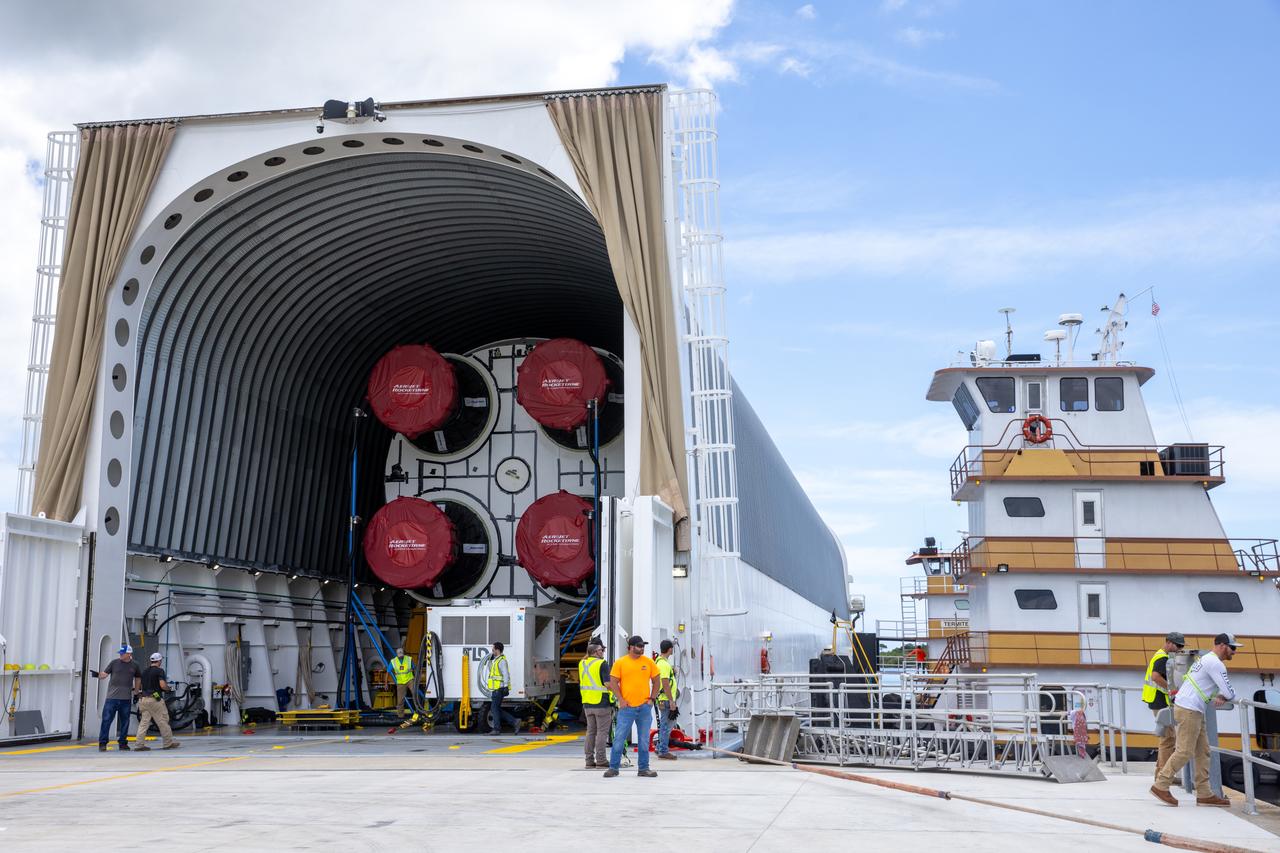

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
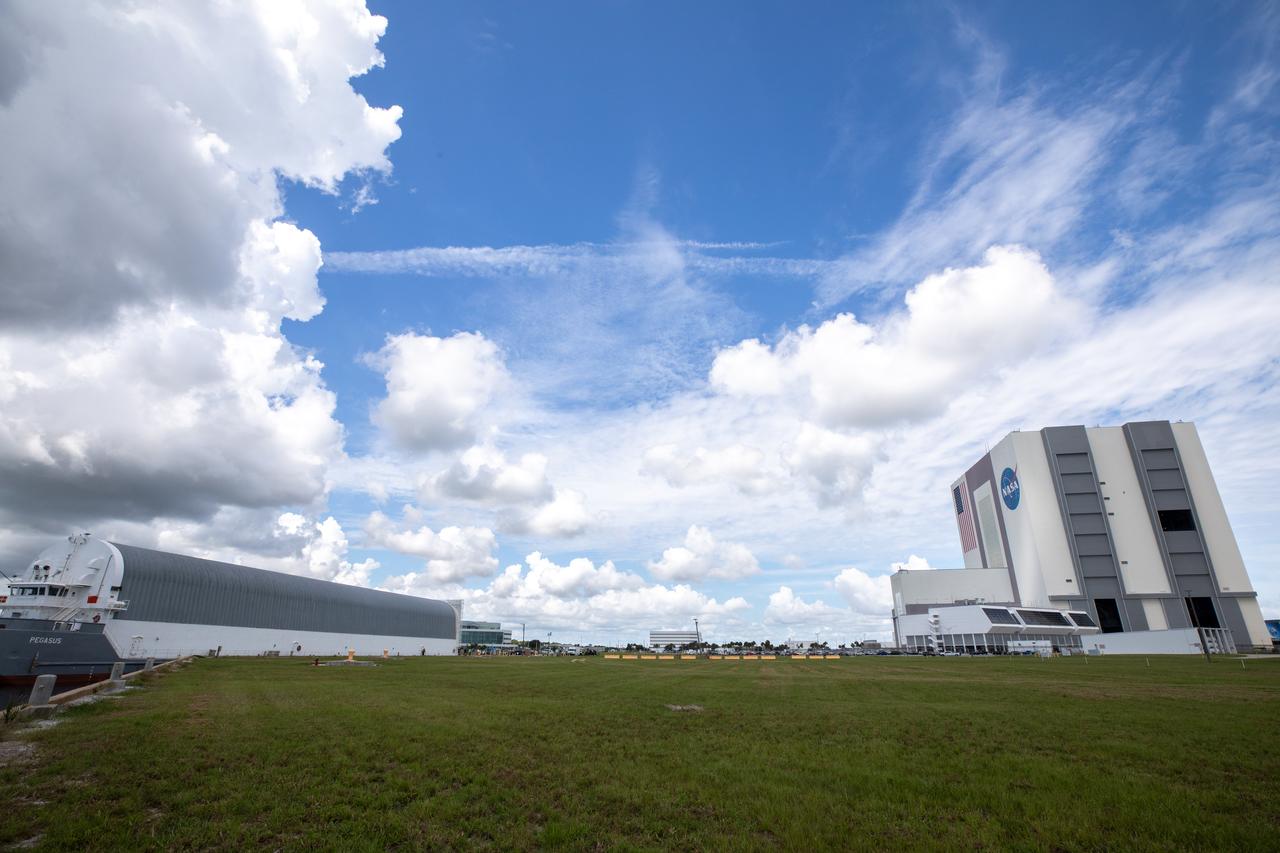

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
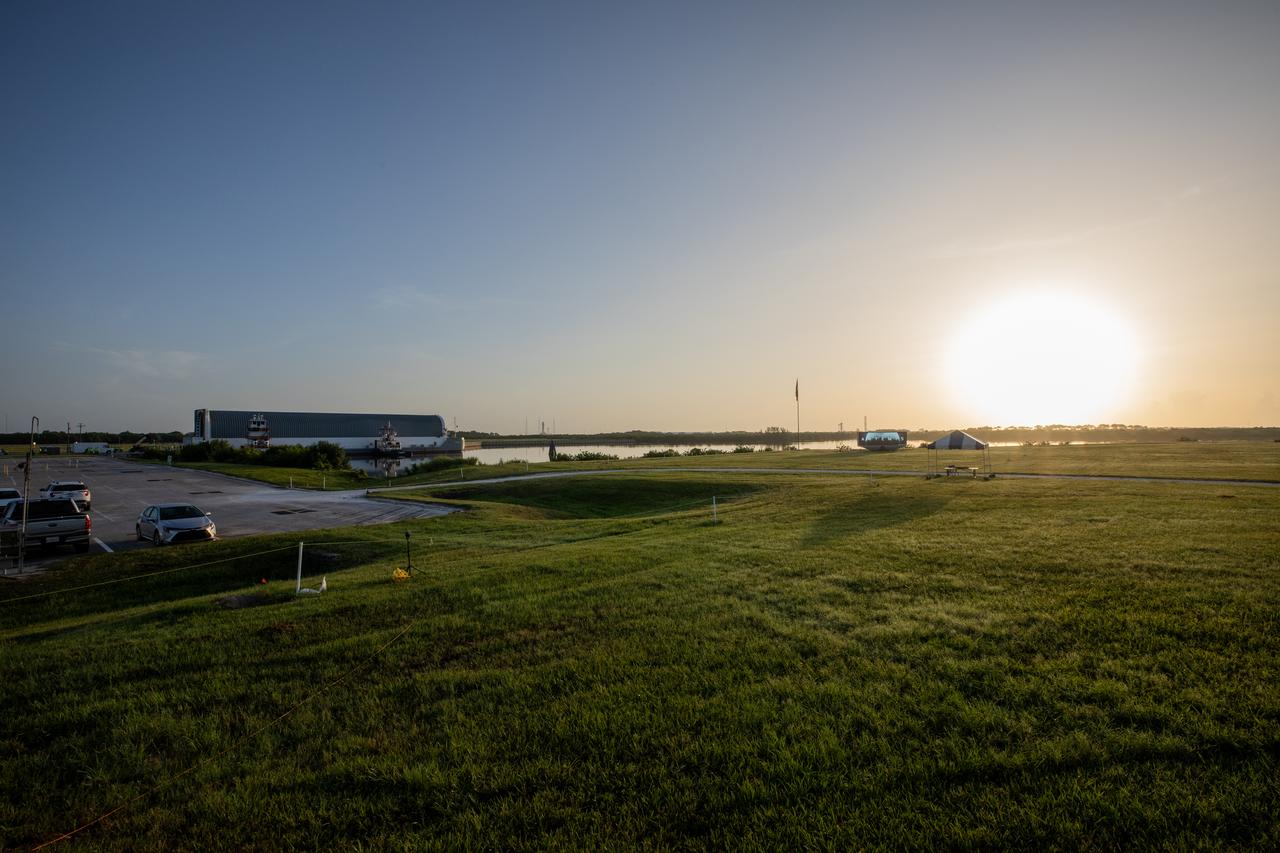

The sun rises over NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Wednesday, July 24, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
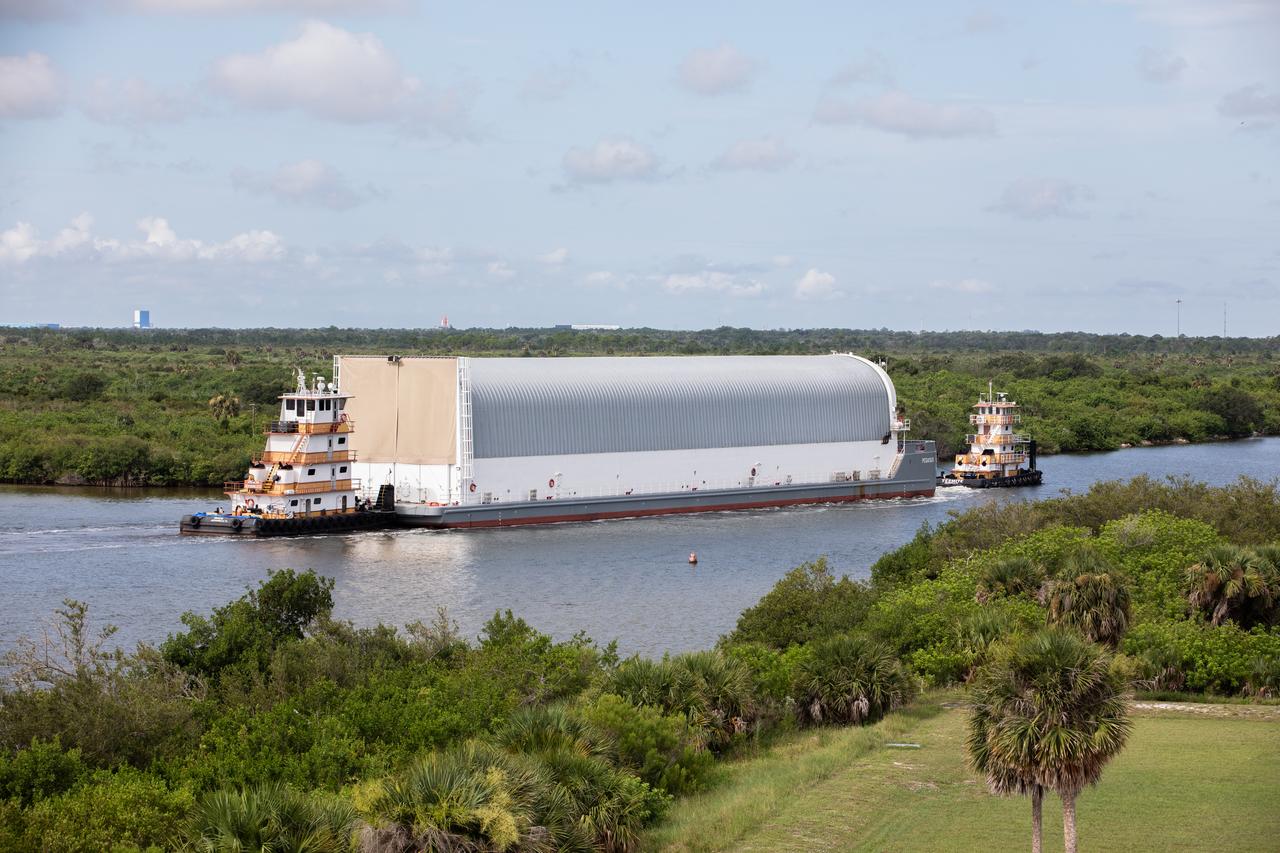

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
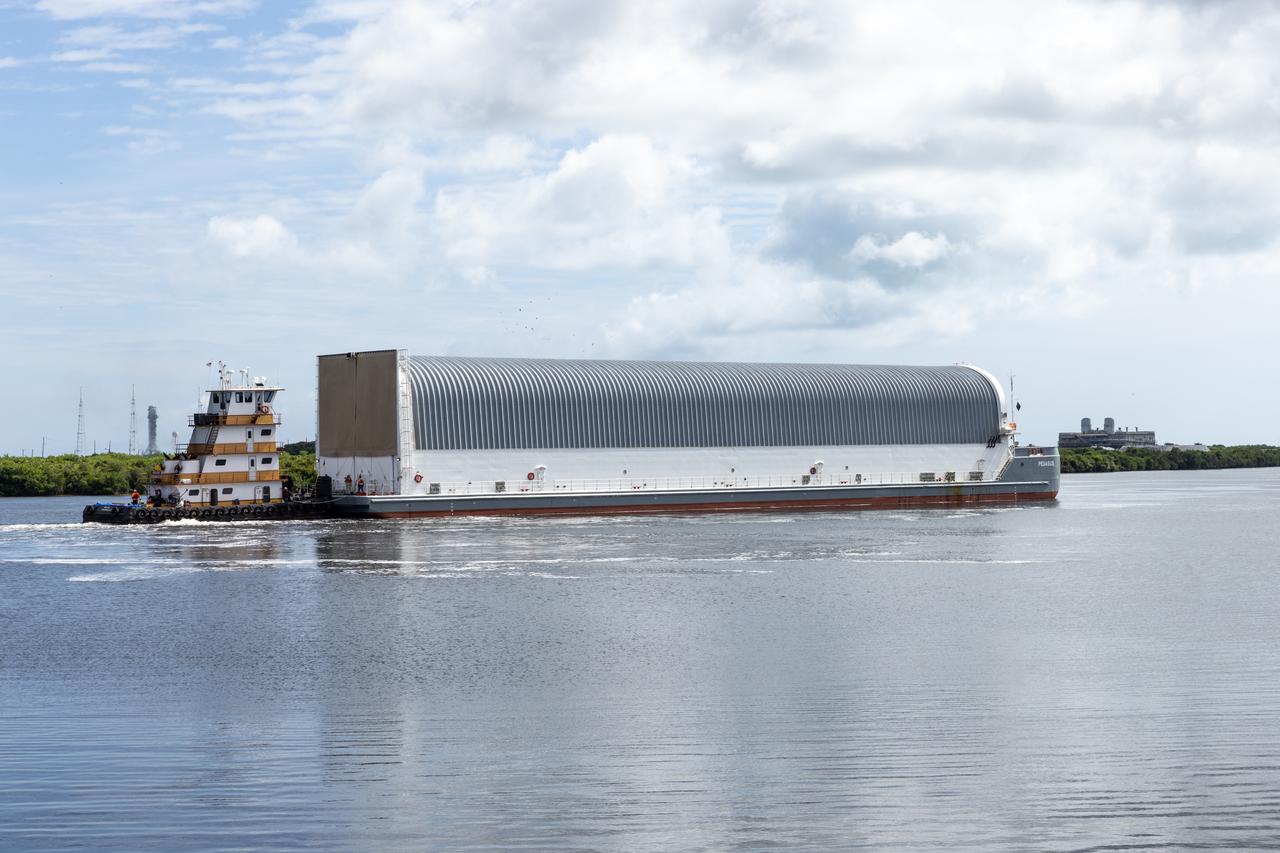

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
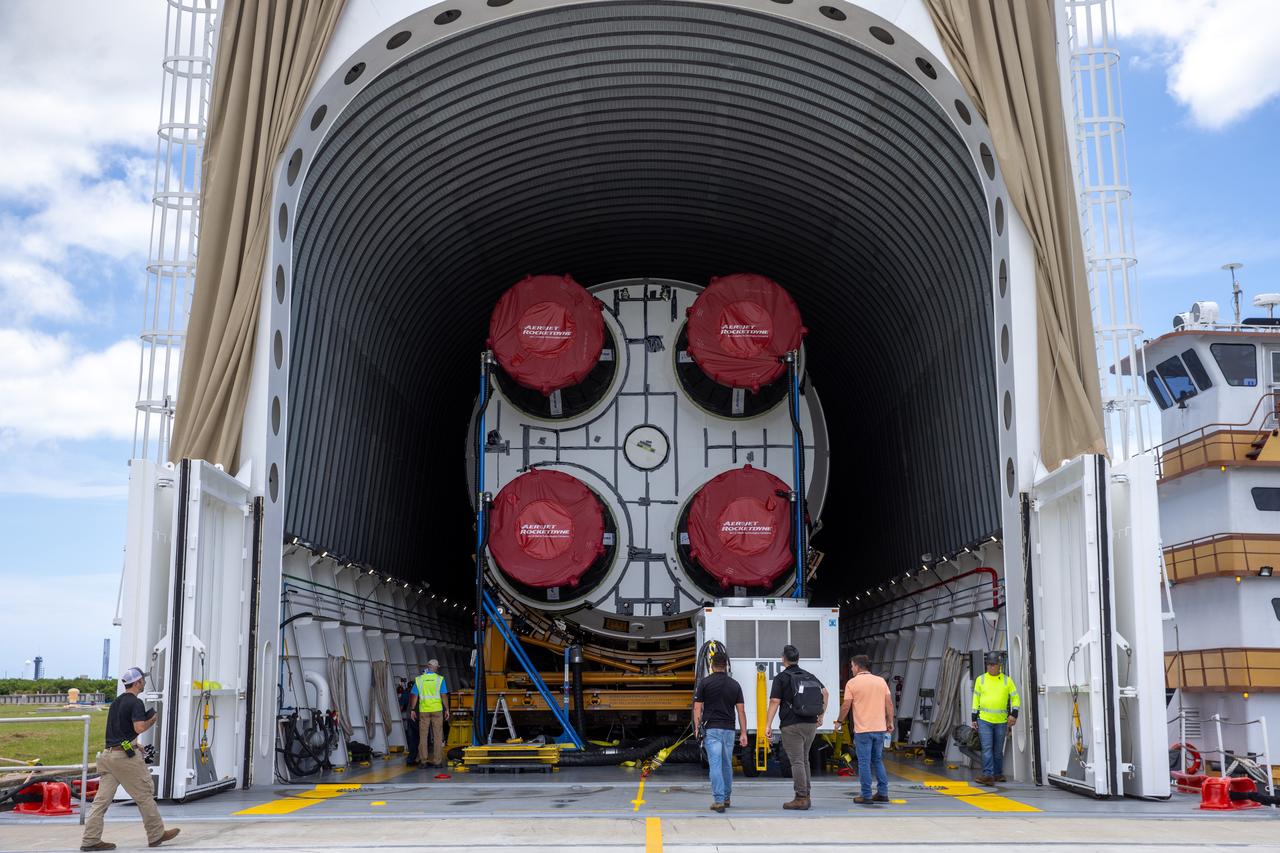

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
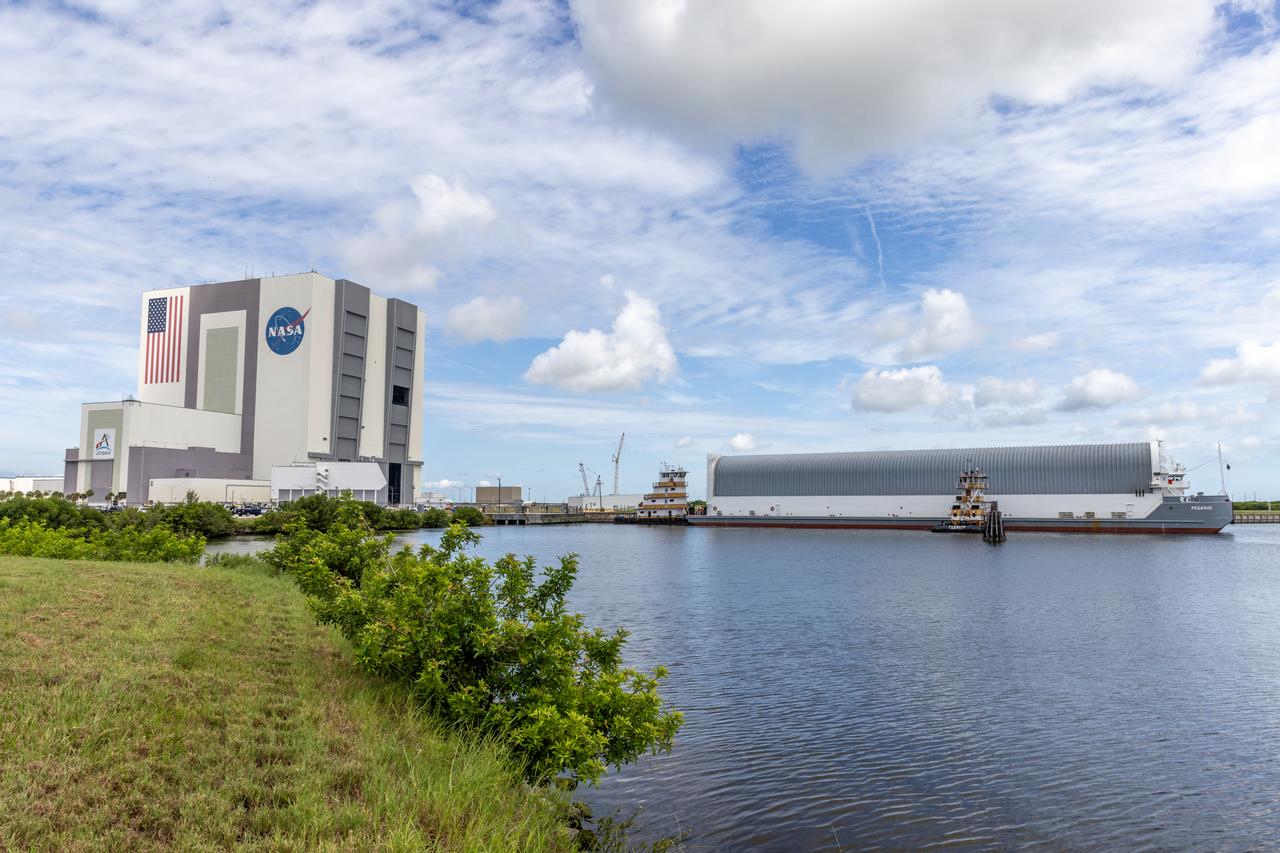

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
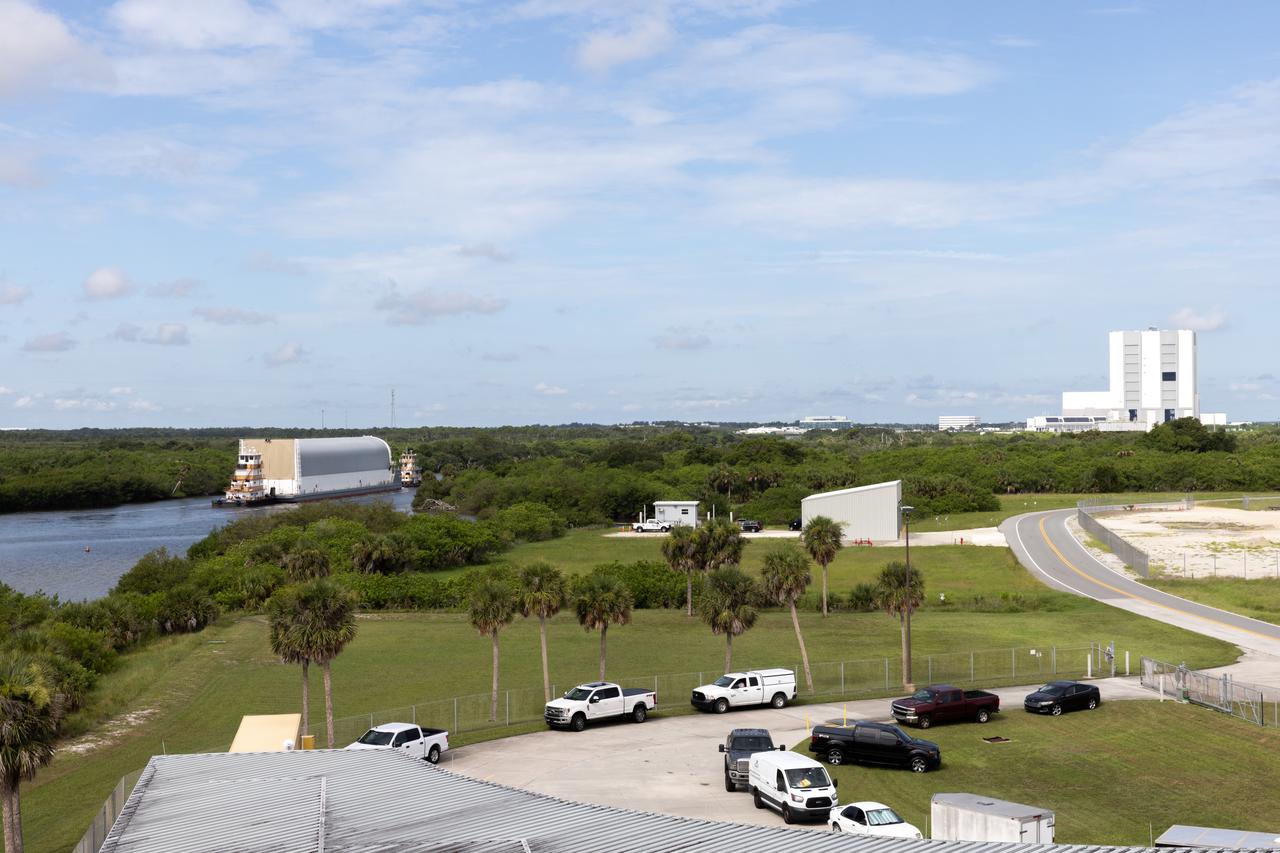

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the agency’s massive SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, arrives at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Complex 39 turn basin wharf in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, after journeying from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The core stage is the next piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at the spaceport and will be offloaded and moved to NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration ahead of the Artemis II launch.
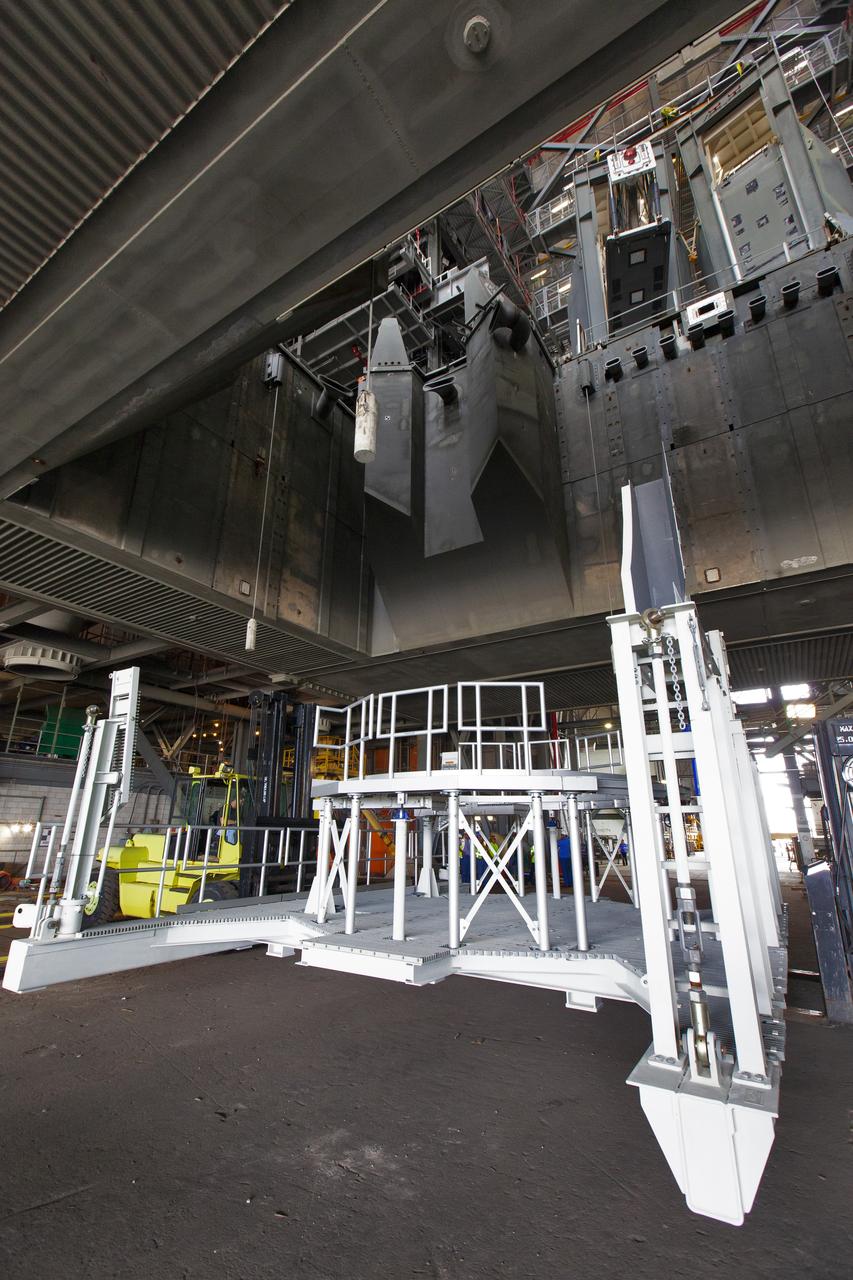

The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket arrives in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
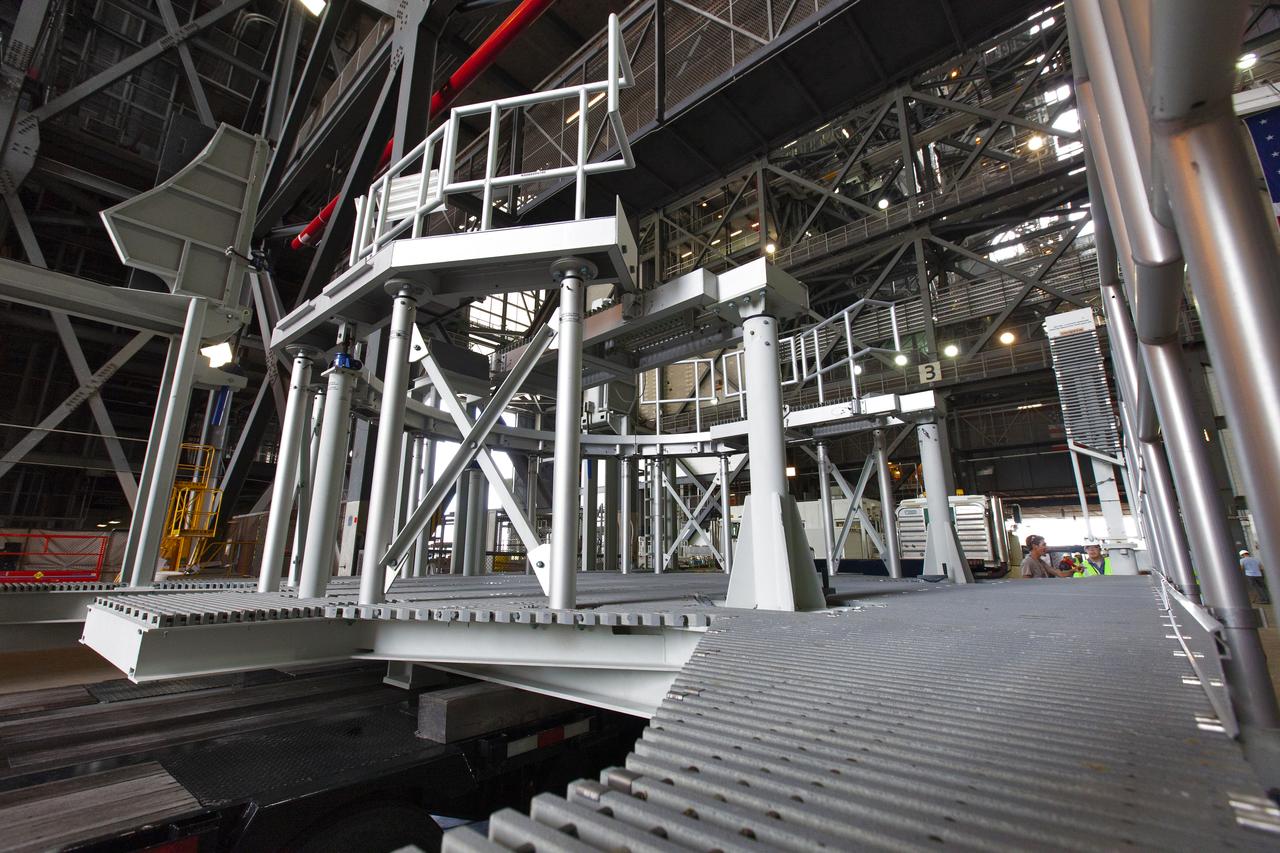

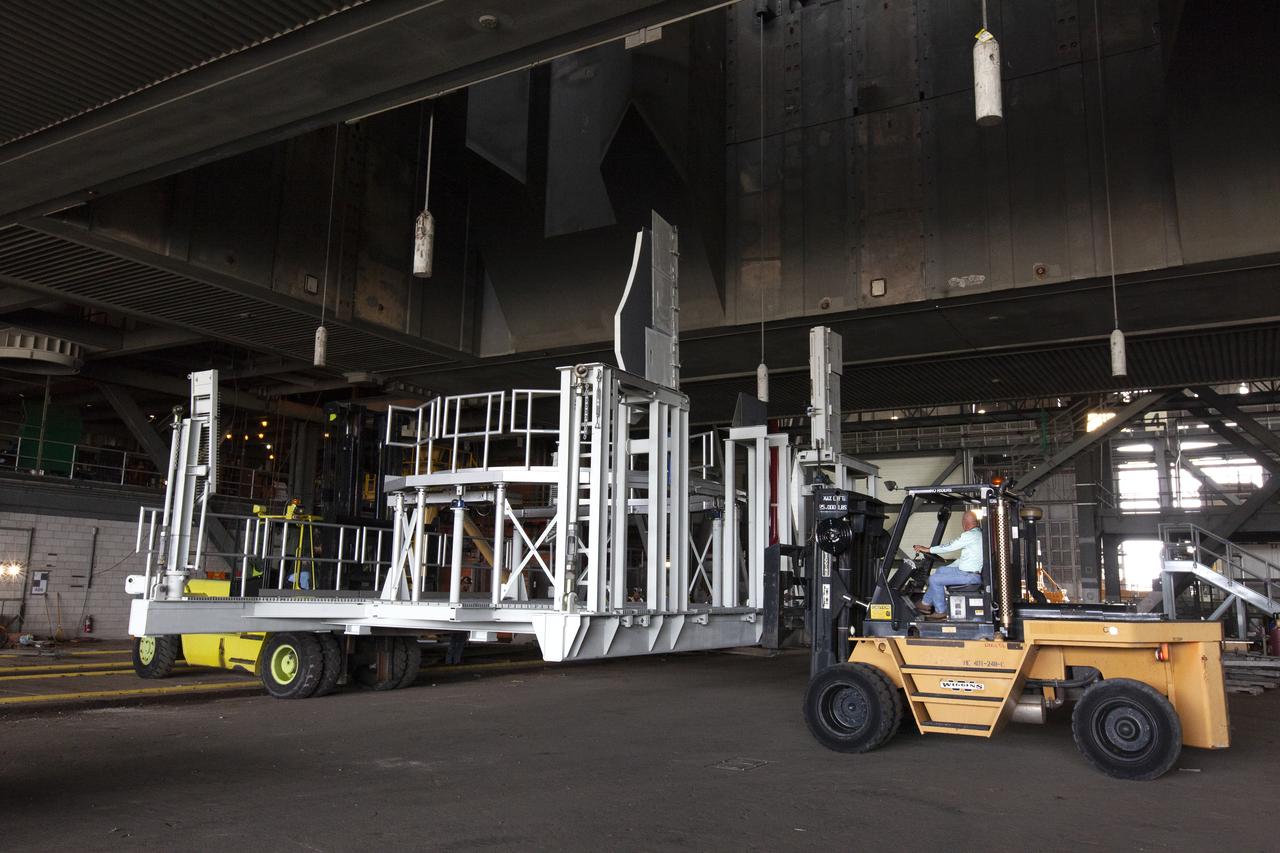
The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is moved beneath the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is moved beneath the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket arrives in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
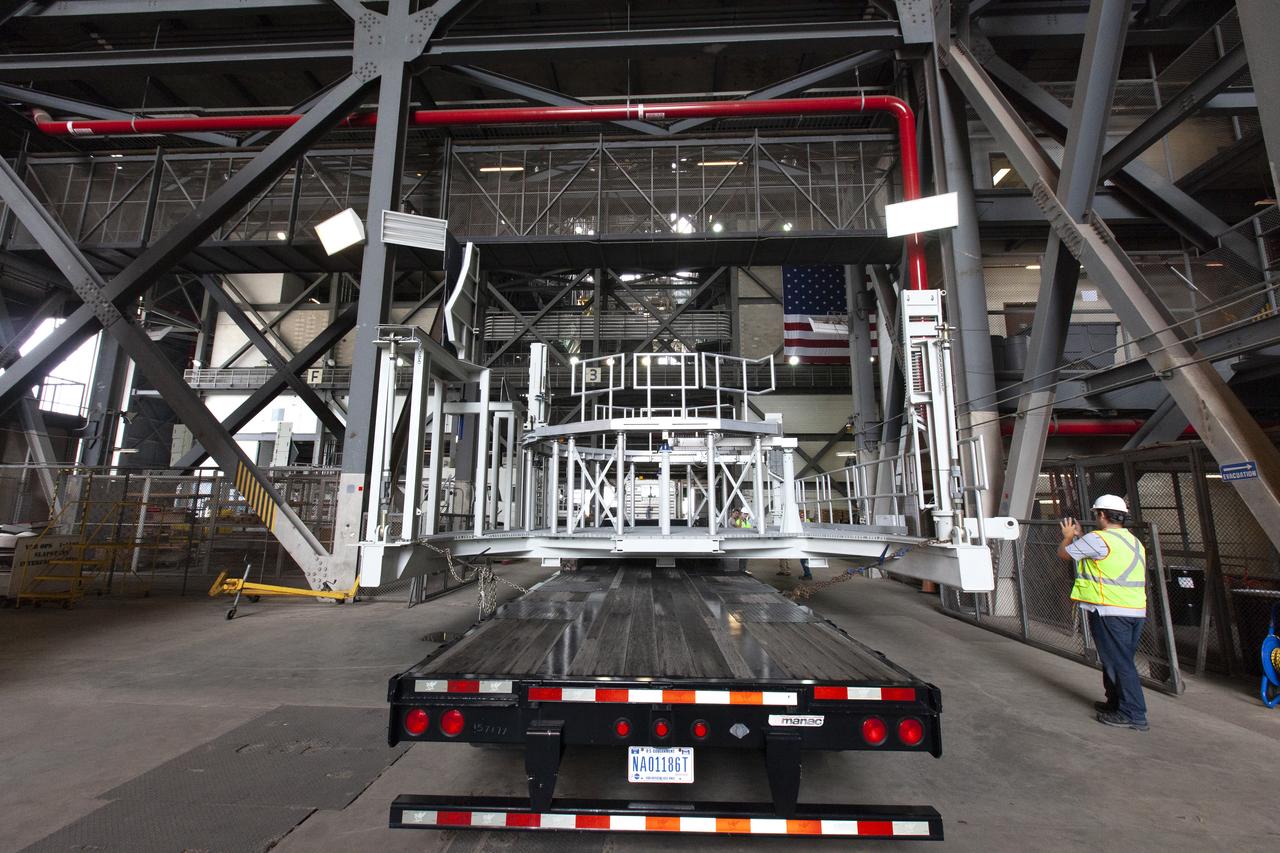

The engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket arrives in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
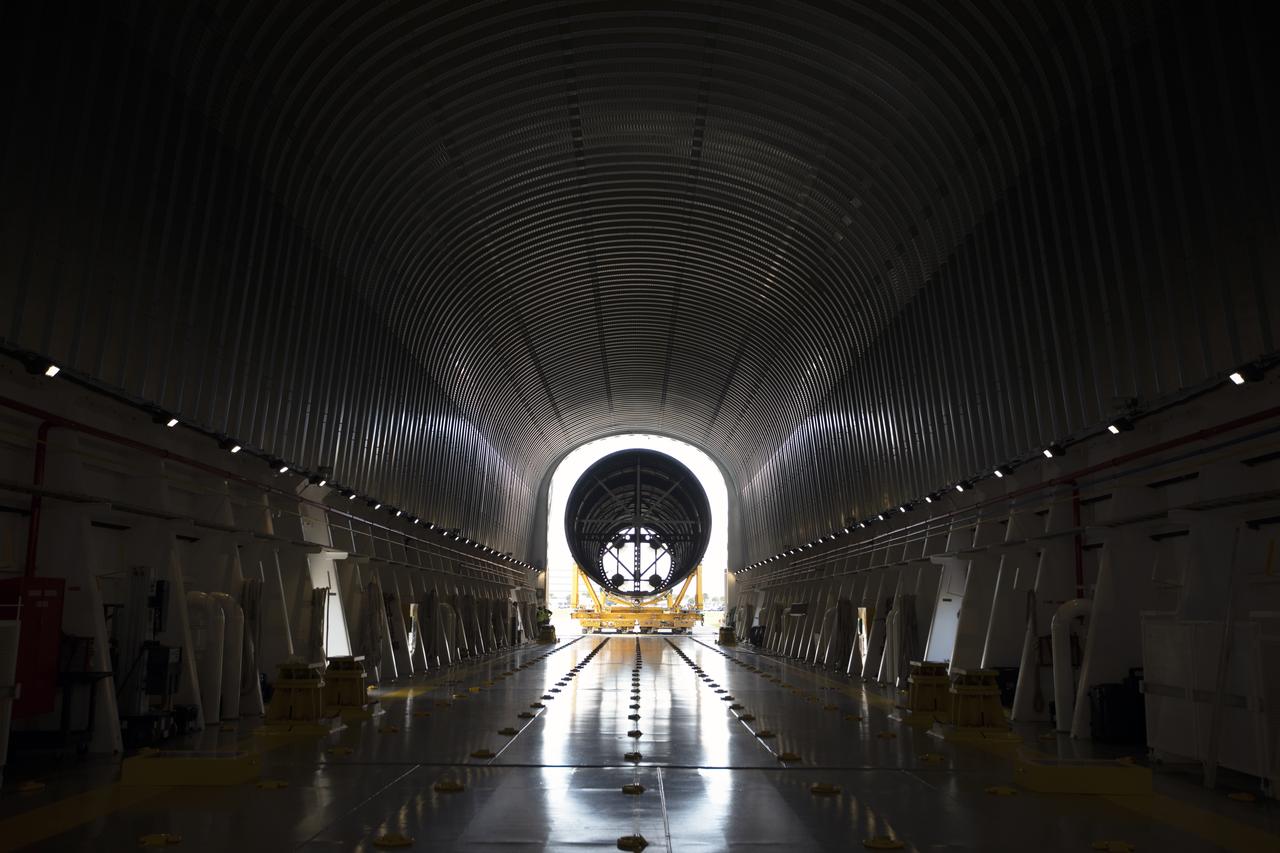

A view of the inside of the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is moved inside the barge on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
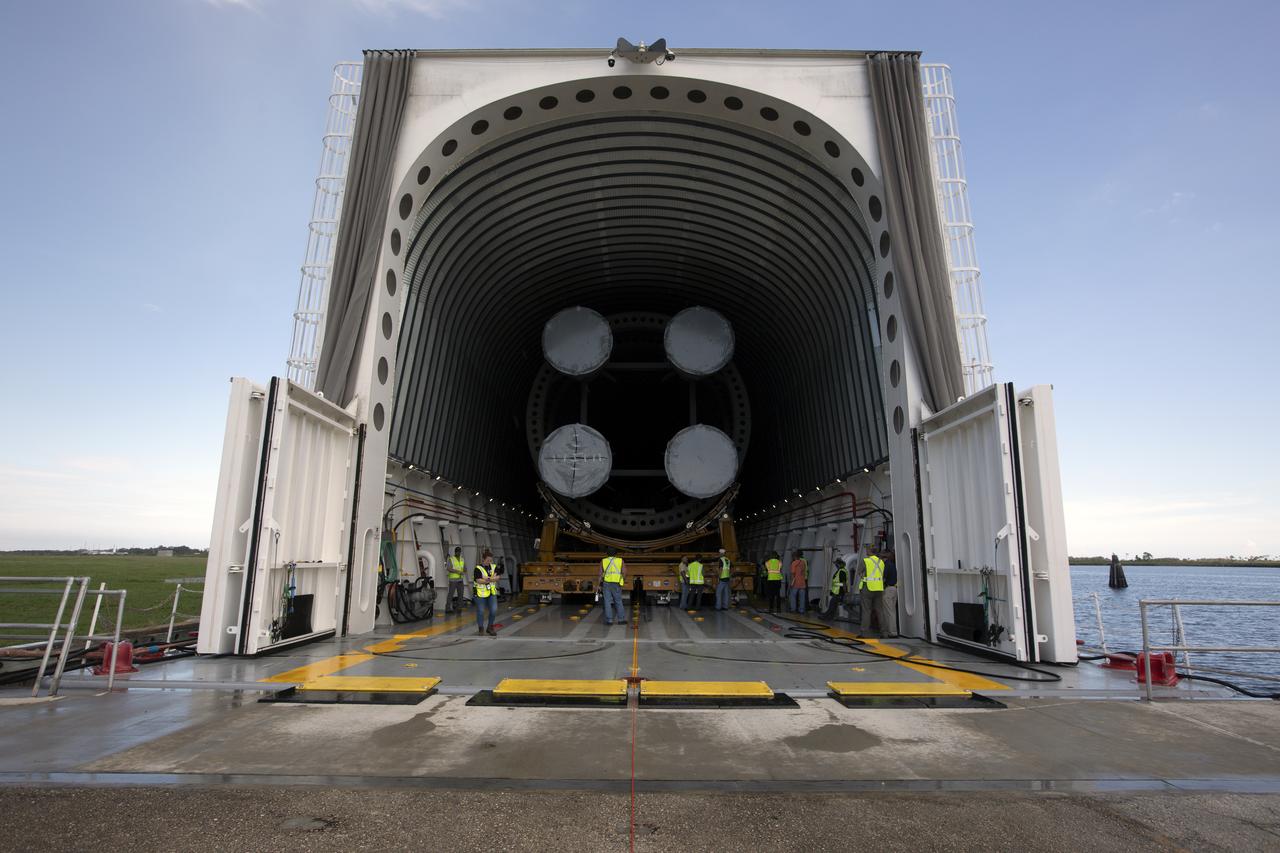

NASA and Jacobs workers assist as the 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is moved inside the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
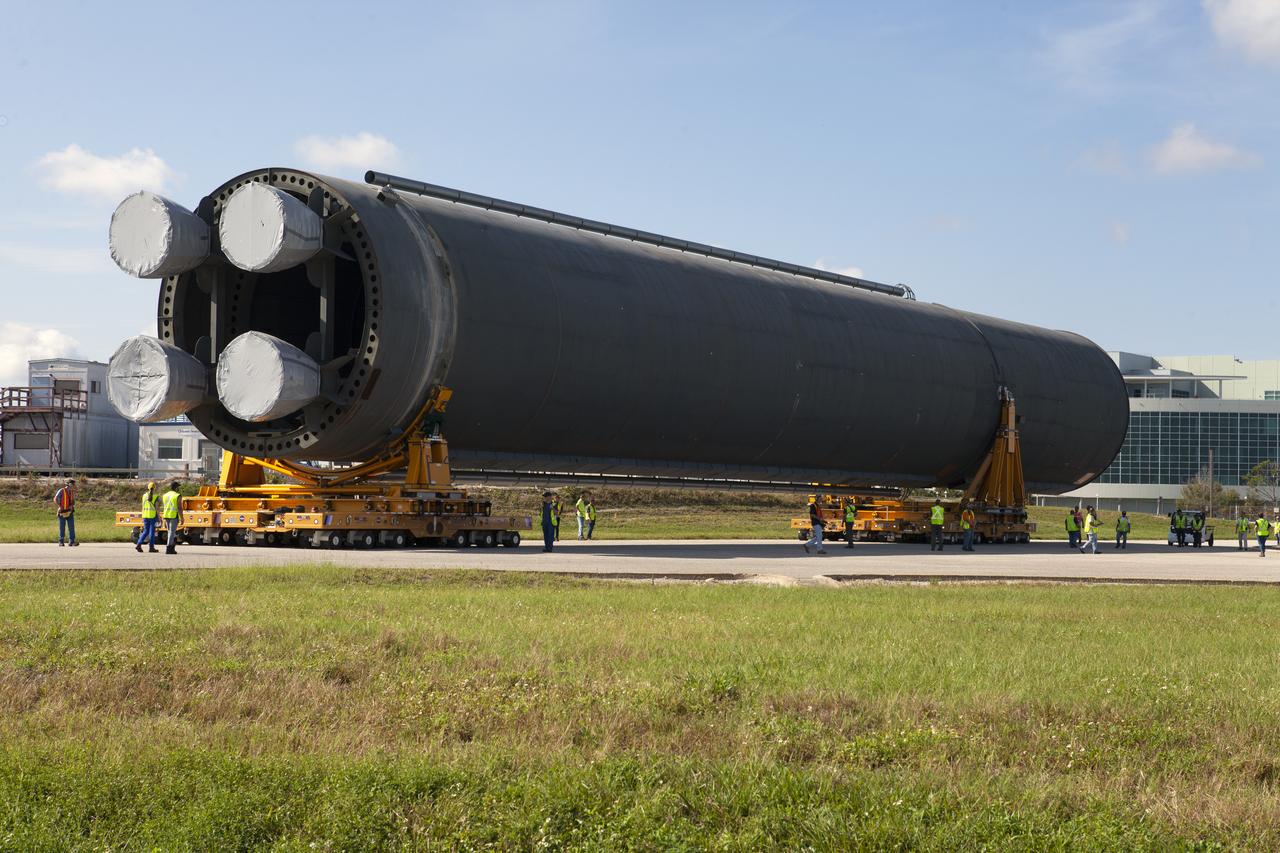

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is being transported back to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
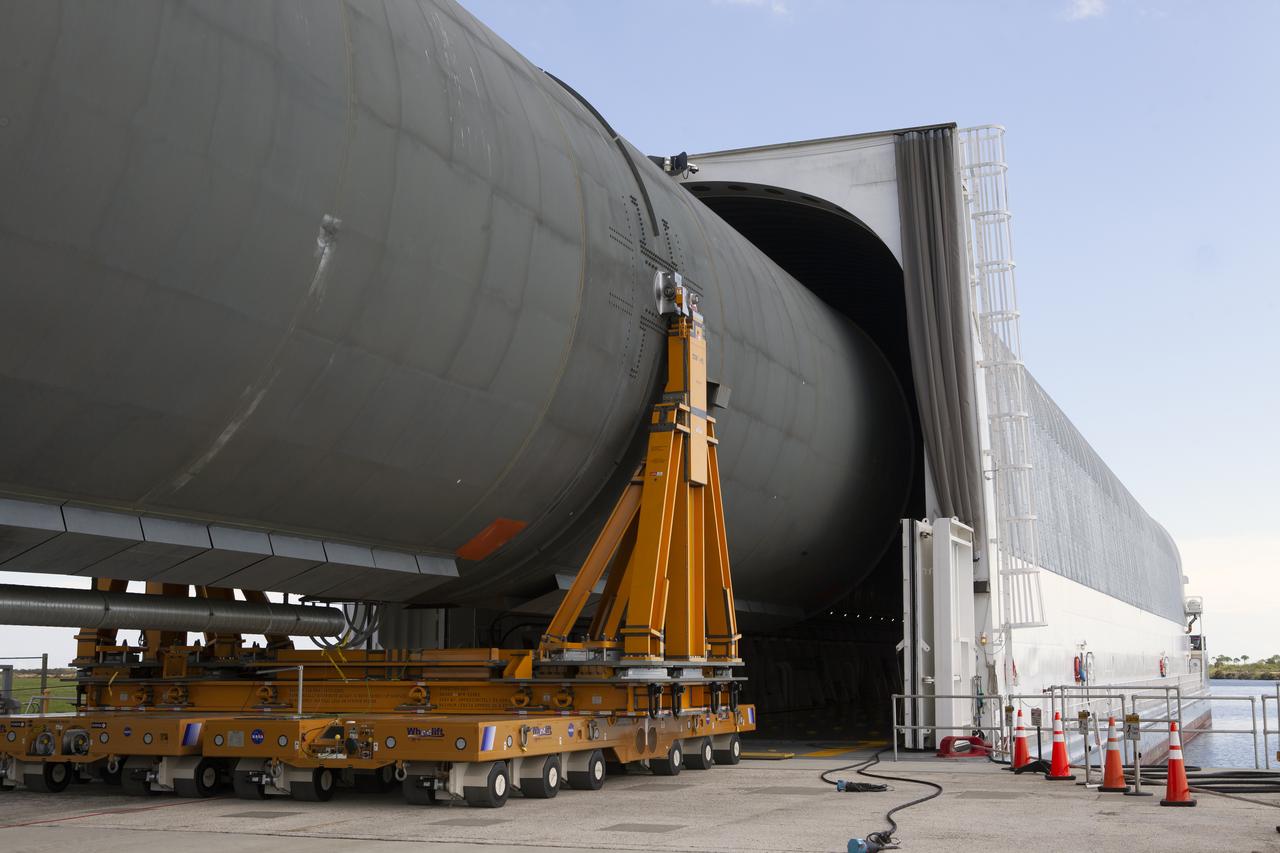

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is moved inside the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
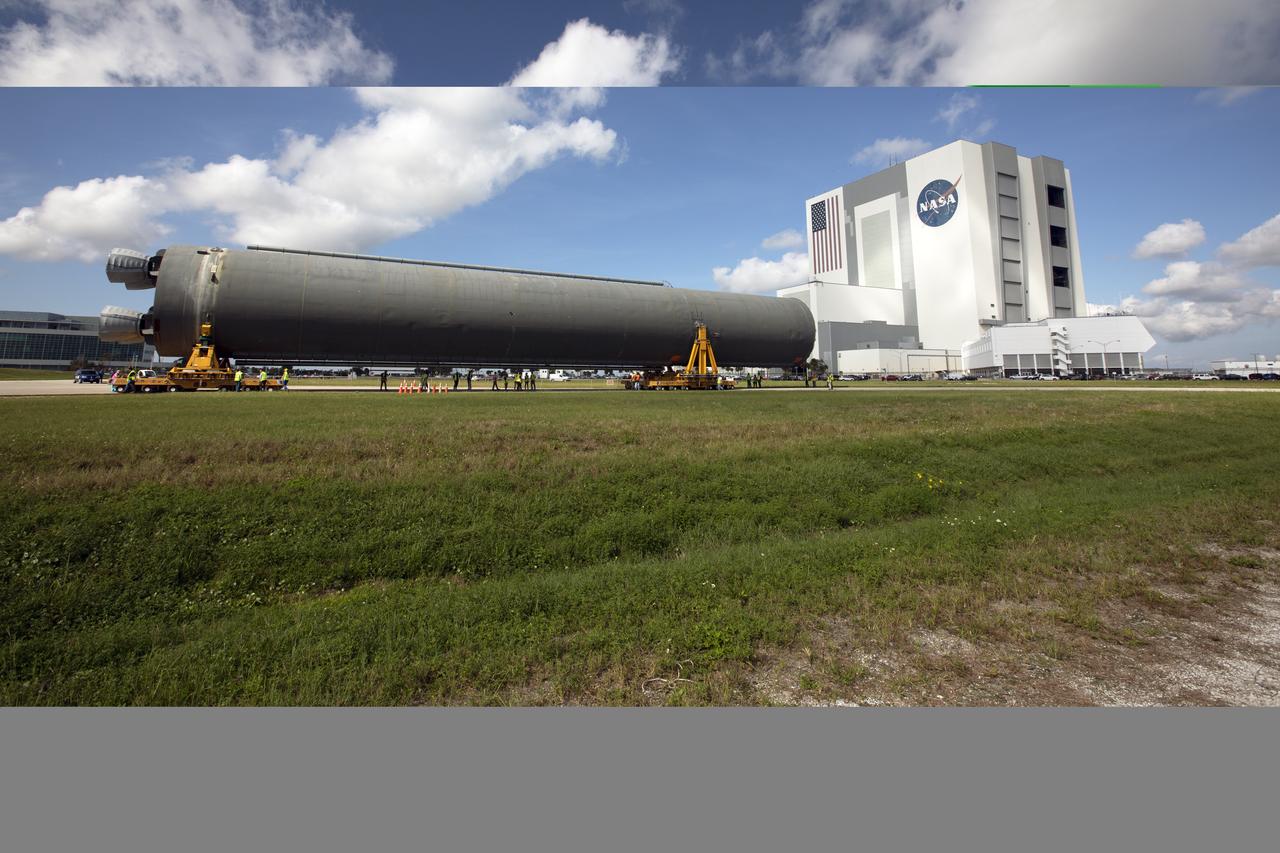

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is being transported back to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.

NASA and Jacobs workers watch as the 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is moved inside the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is being transported back to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder nears the entrance ramp to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder nears the entrance ramp to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
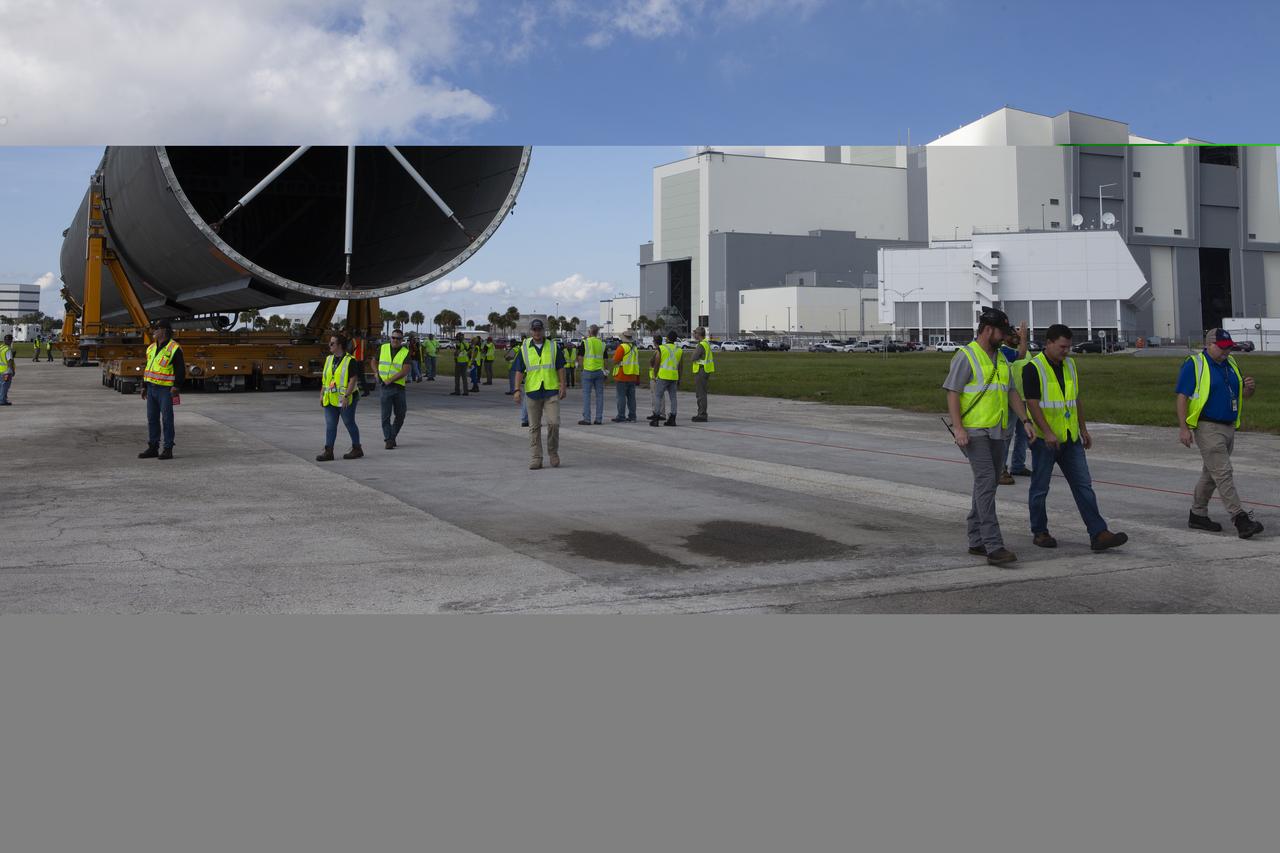

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is being transported back to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
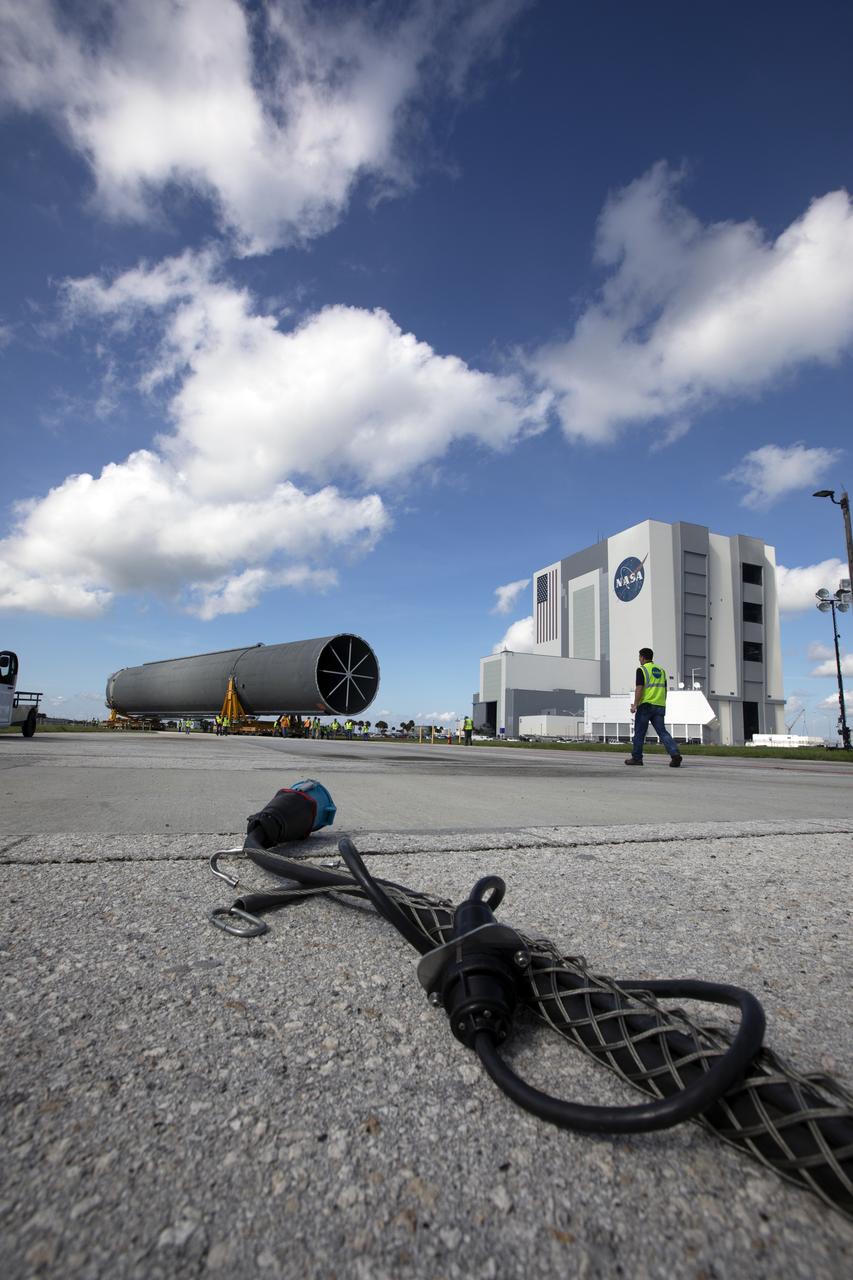

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder nears the entrance ramp to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
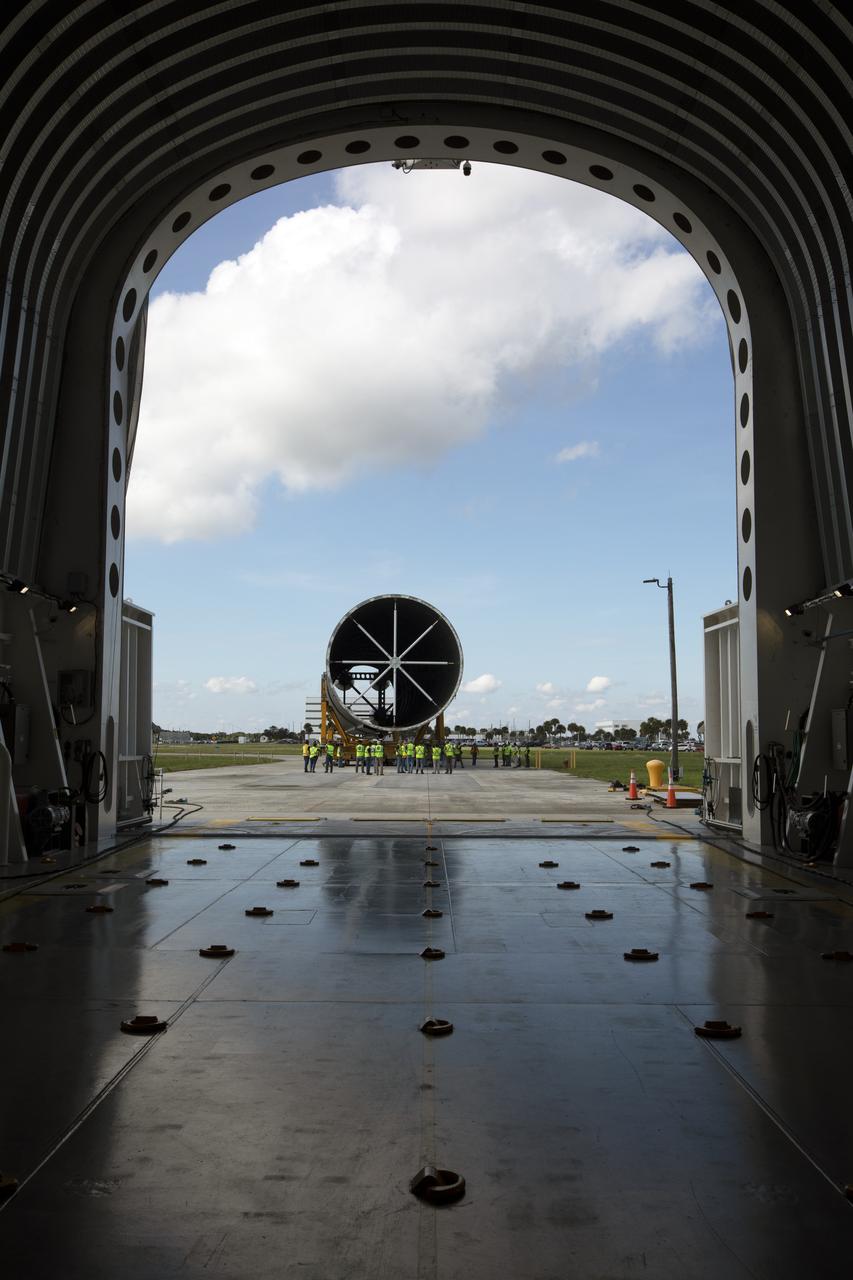

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder nears the entrance ramp to the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
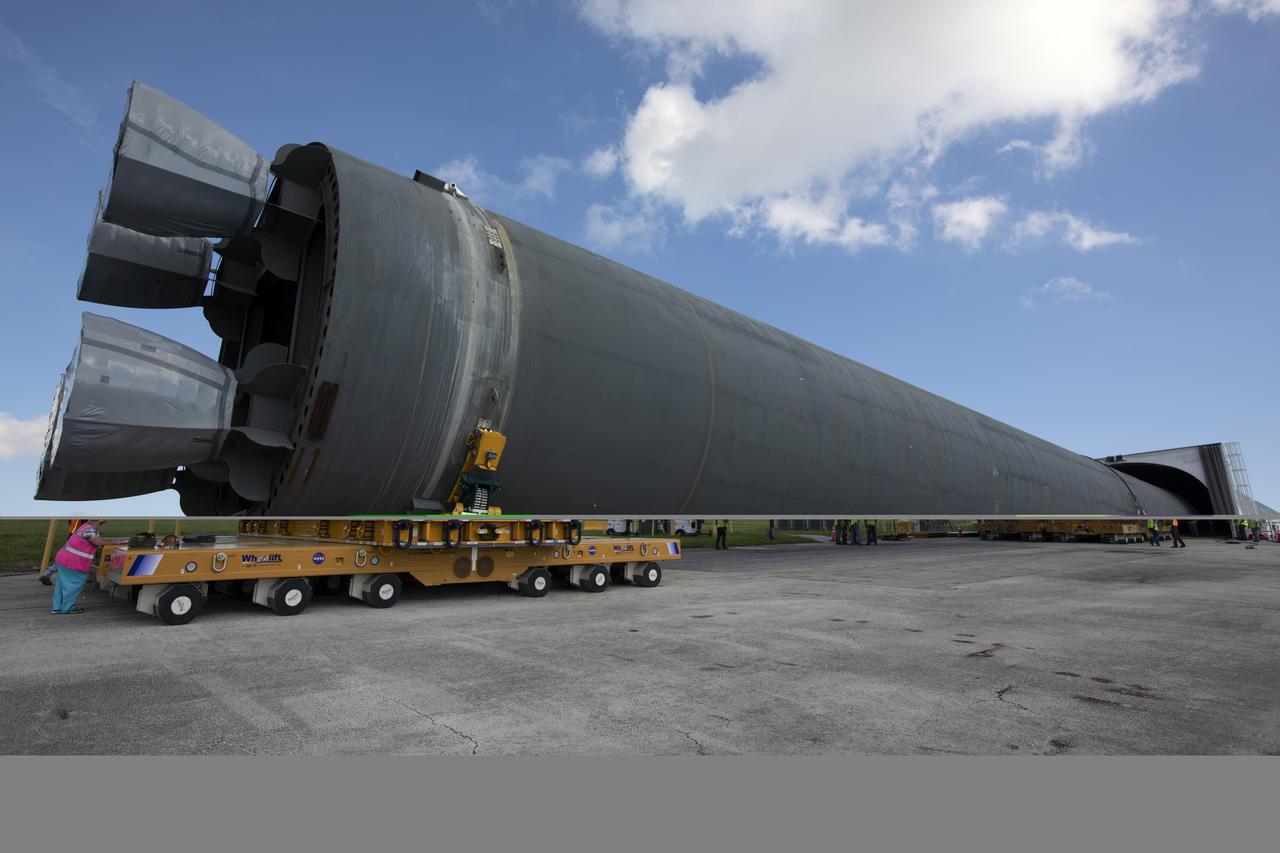

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is moved inside the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2019. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
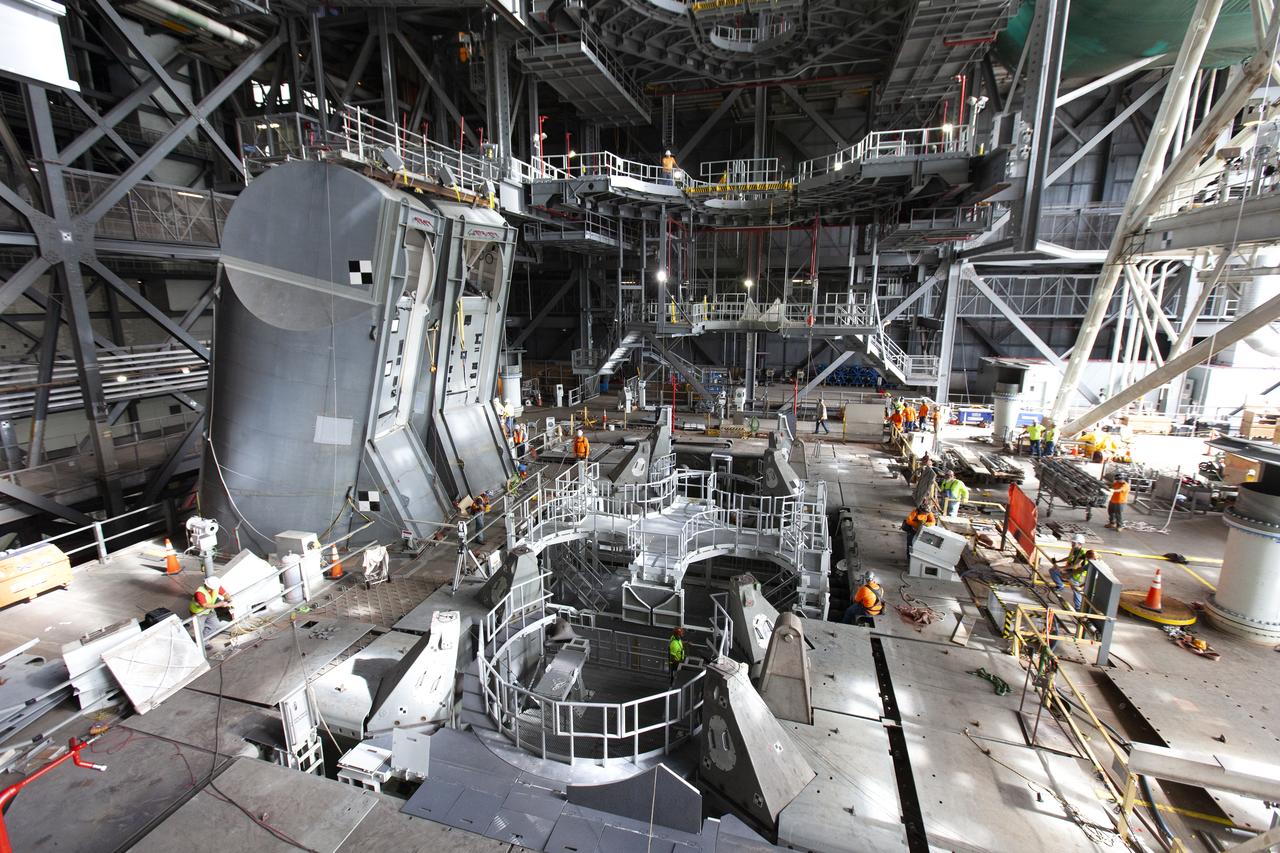
Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. In view at left are the two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals. They will provide liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen fluid lines and electrical cable connections to the SLS core stage engine section. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
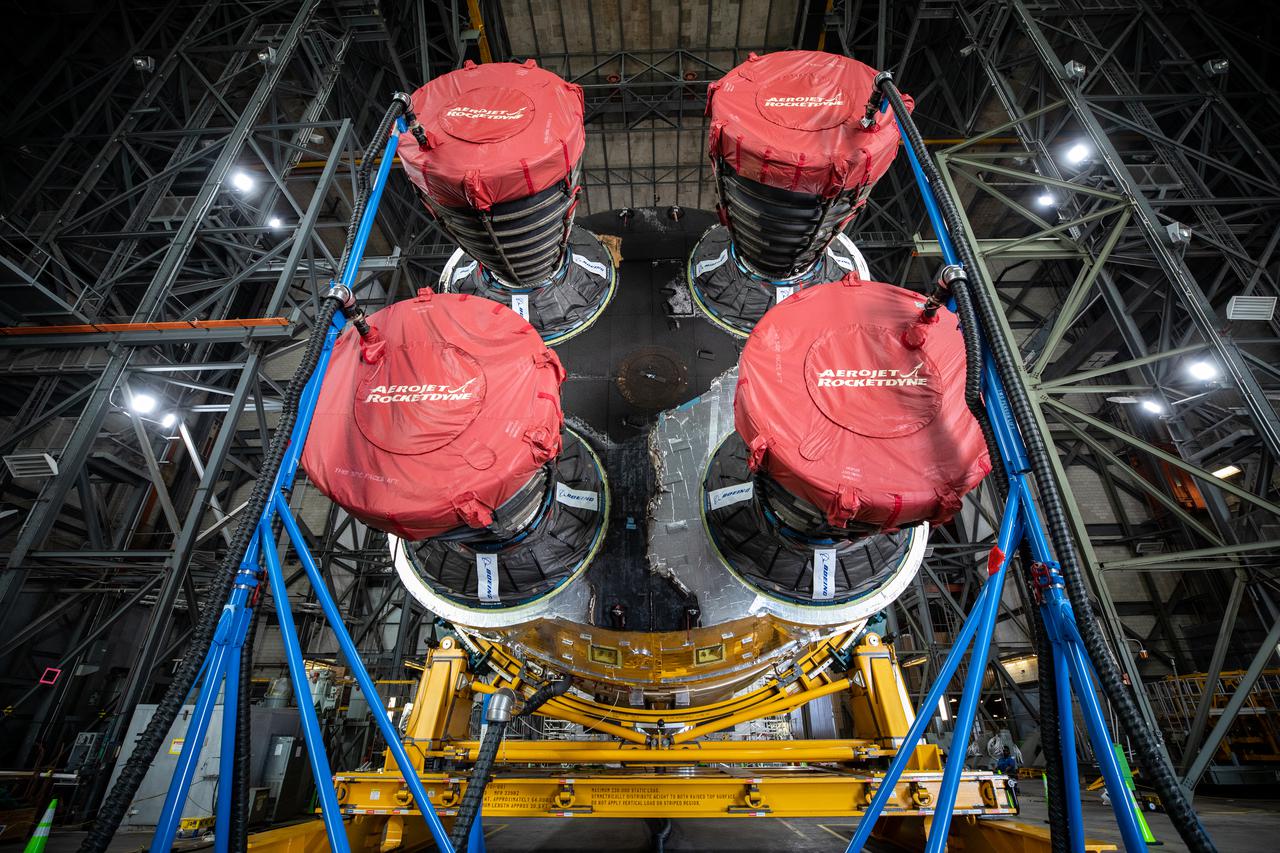

The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage for NASA’s Artemis I mission is in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 5, 2021. In view are the core stage’s four RS-25 engines in protective covers. Teams from the center’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will perform checkouts ahead of integrating the massive rocket stage with the twin solid rocket boosters, Orion spacecraft, and additional flight hardware ahead of the Artemis I launch. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of SLS and Orion and will pave the way for landing the first woman and first person of color on the lunar surface. It will be a proving ground for deep space exploration, leading the agency’s efforts under the Artemis program for a sustainable presence on the Moon and preparing for human missions to Mars.
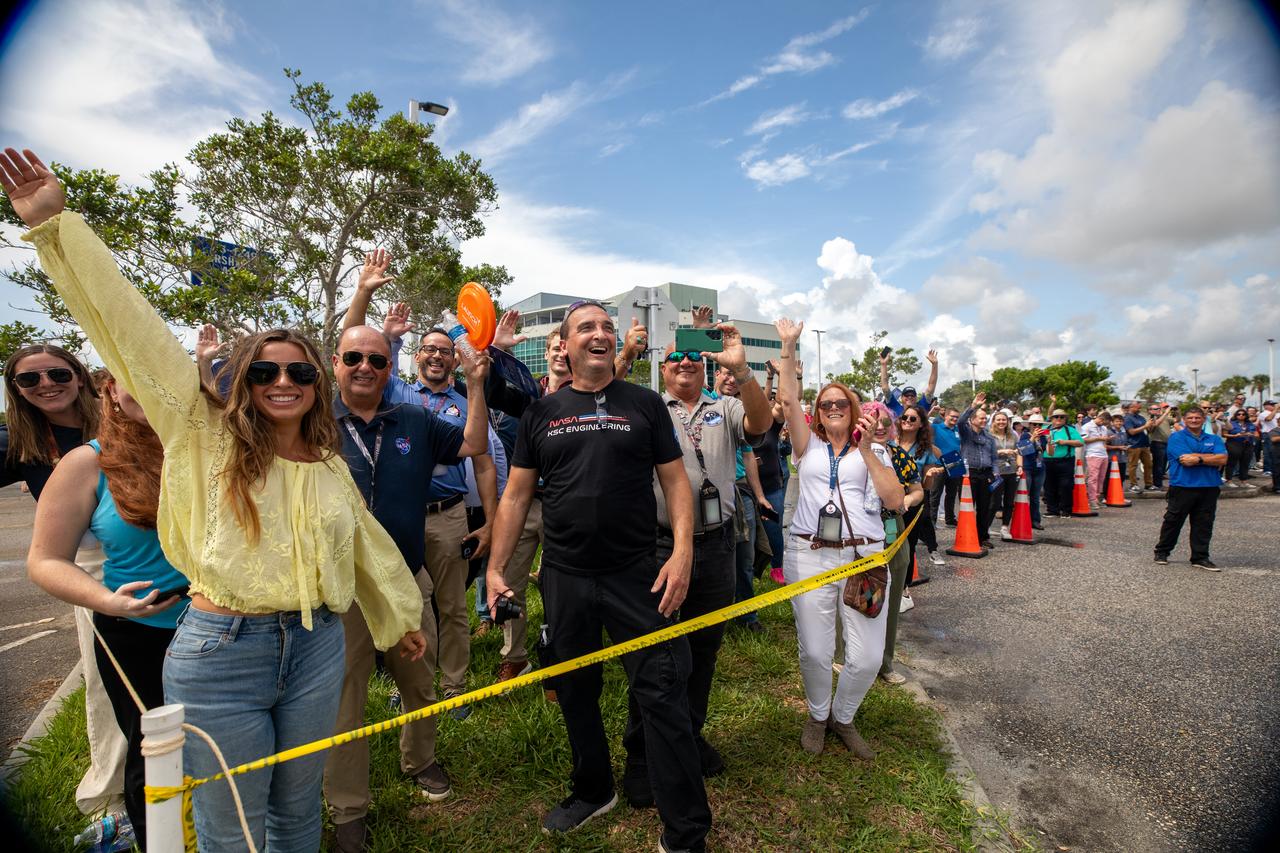

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
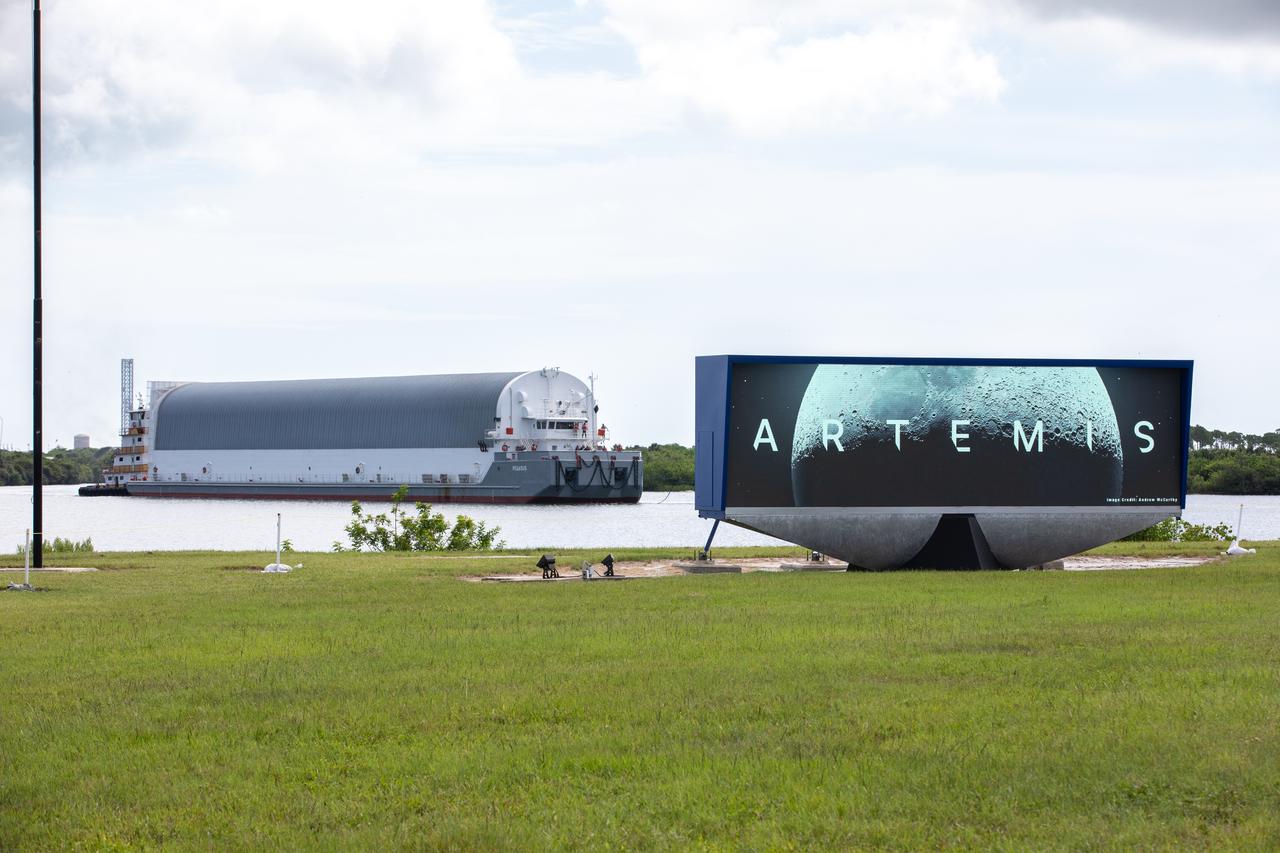
Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
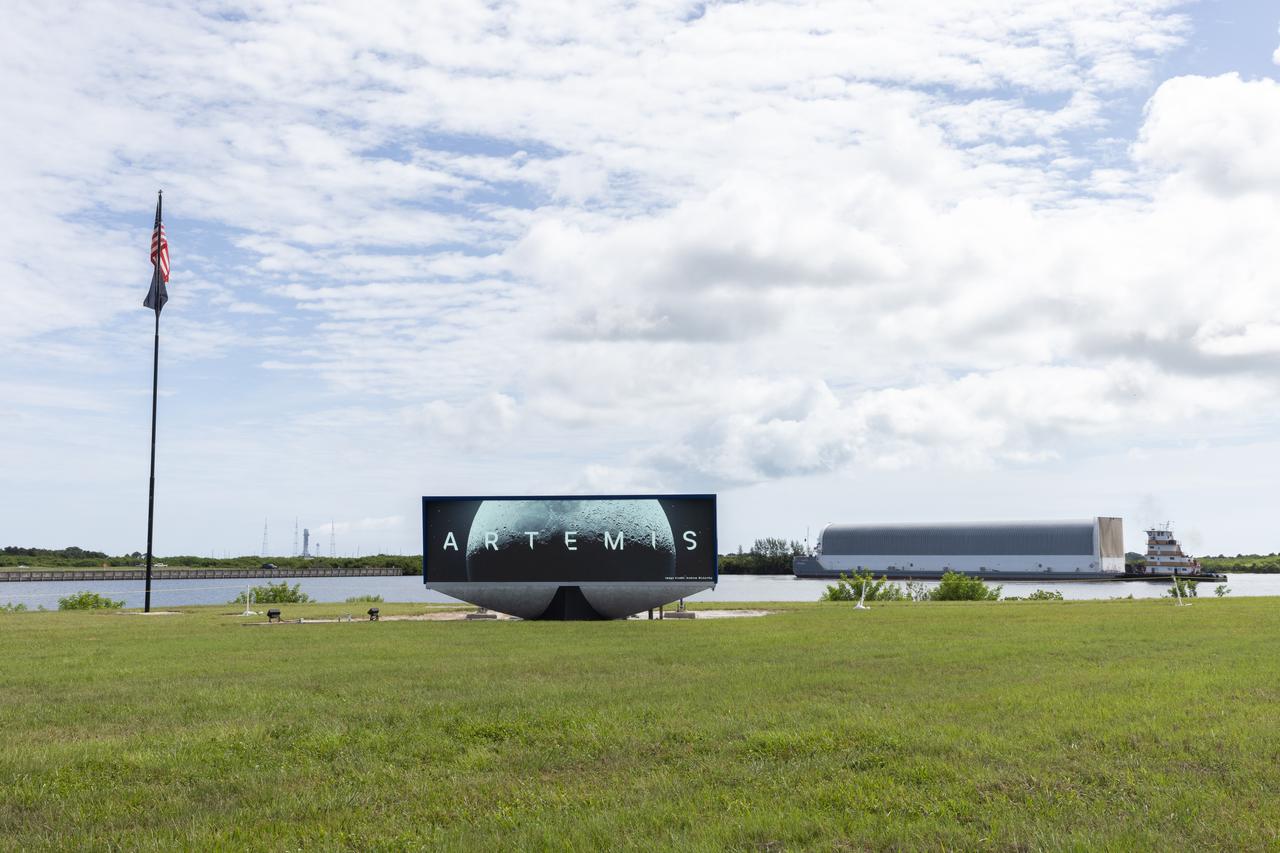

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
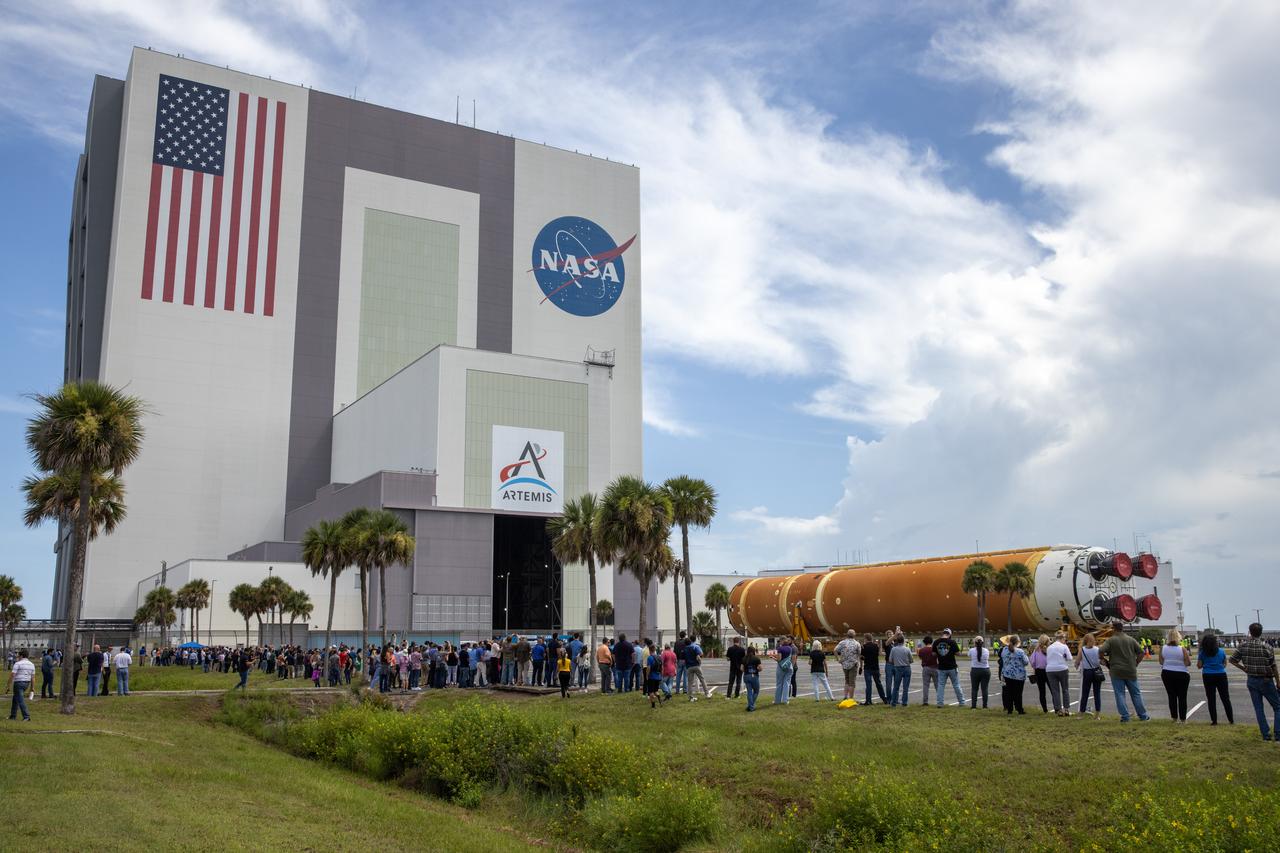

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
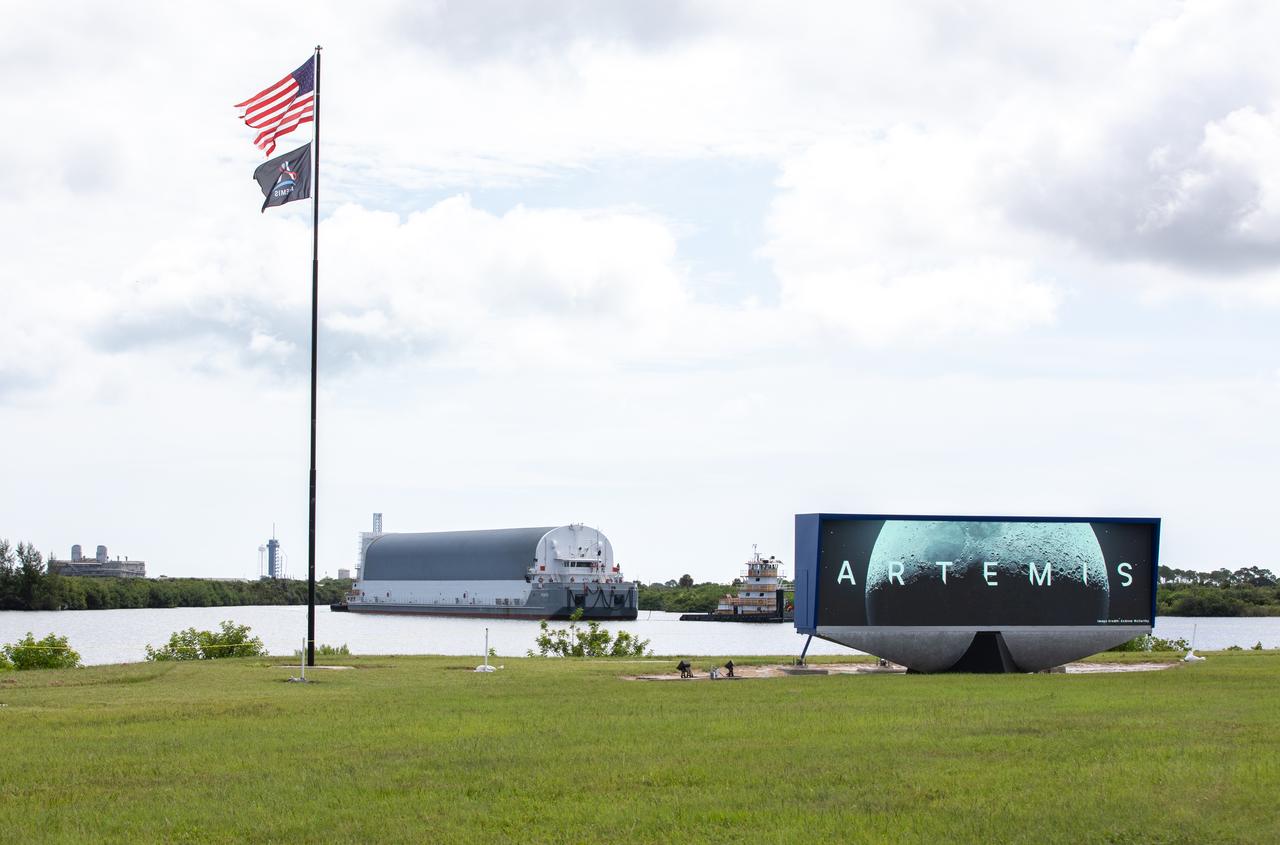

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with NASA's Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
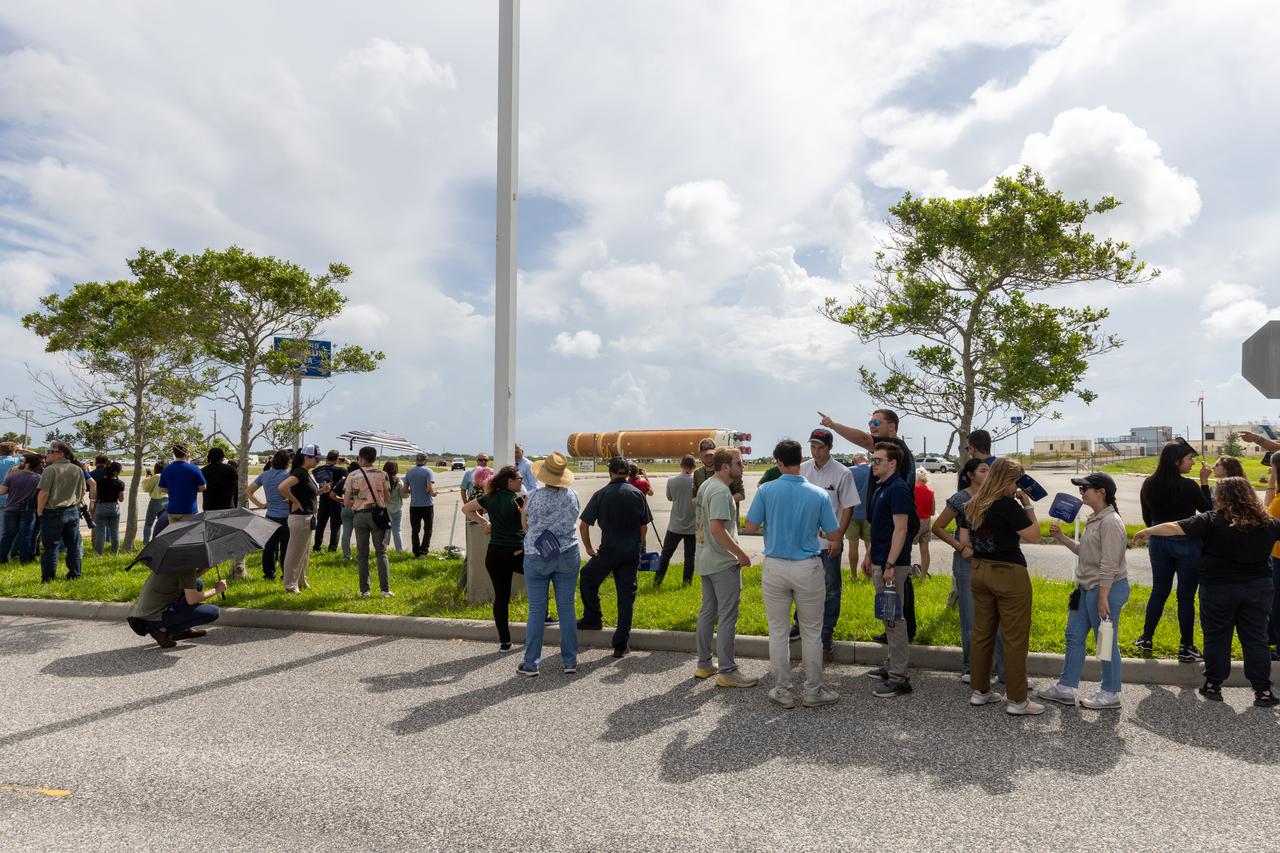

Employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) transport the agency’s powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Wednesday, July 24, 2024. The 212-foot-long rocket stage completed its journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus barge the previous day. Once inside, SLS will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
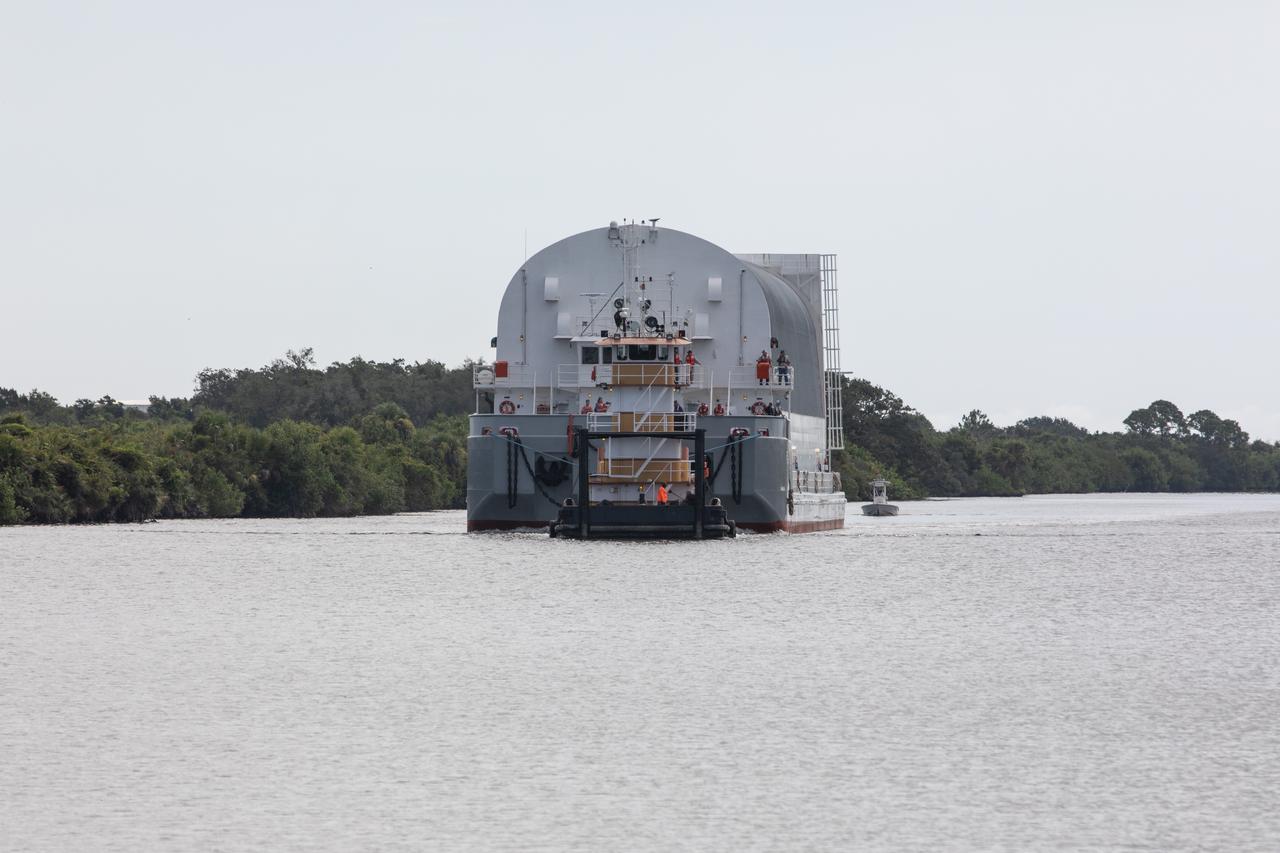

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with NASA's Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.

Behind the iconic countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Pegasus barge completes its 900-mile journey from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans carrying the powerful SLS (Space Launch System) core stage on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) will offload the rocket stage and transfer it to the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building to prepare it for integration atop the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis II launch.
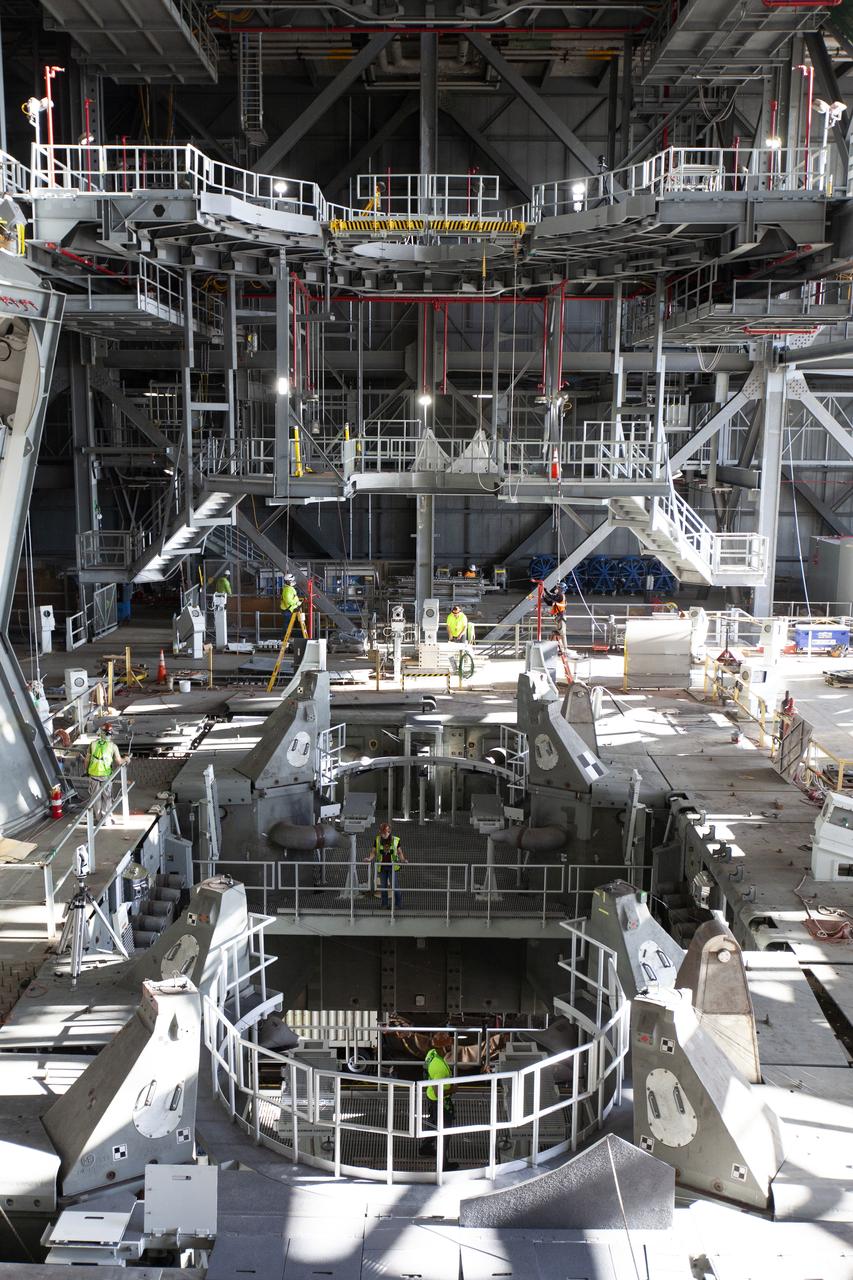

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

Workers with Bragg Crane and Rigging prepare for the lift of the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
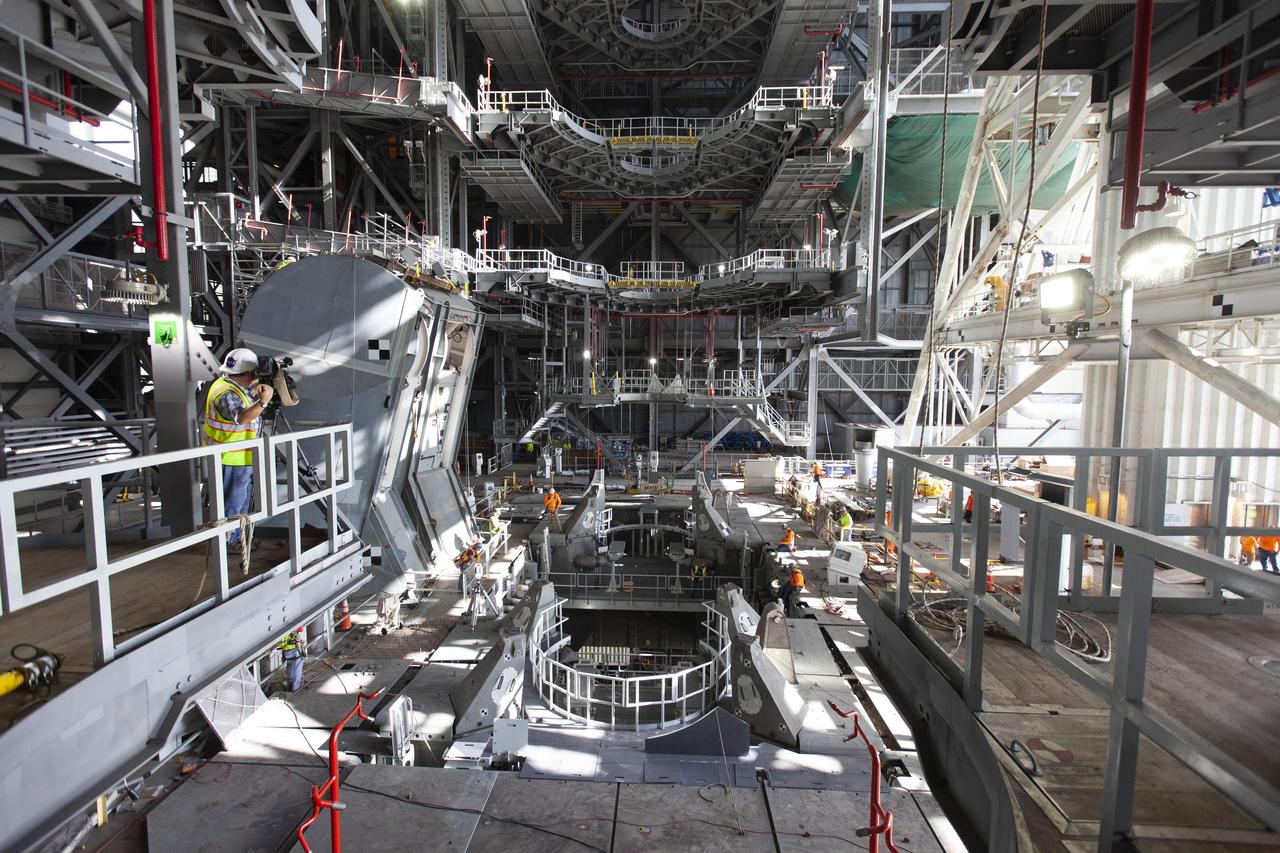
Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is lifted up in the center of the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

Jacobs TOSC workers prepare for the lift of the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.

Workers with Bragg Crane and Rigging prepare to assist with the lift of the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the mobile (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
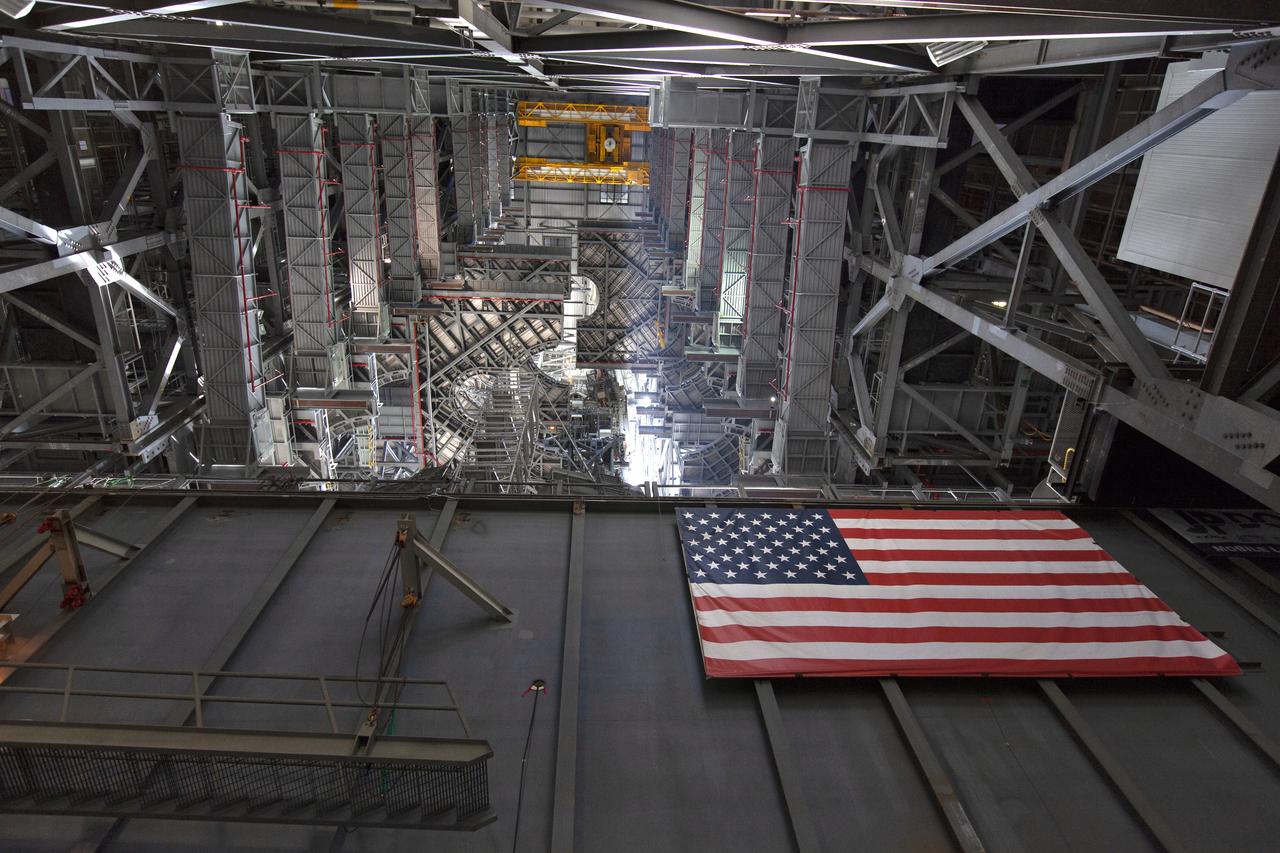

A view looking up at the mobile launcher (ML) in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 18, 2019. Work is underway to lift the engine service platform that will provide access to the core stage of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in the center of the ML. The large work platform is designed to provide unrestricted access to the RS-25 engines on the SLS core stage from the ML. The service platform will be used for Artemis 1 and subsequent missions. For Artemis 1, the Orion spacecraft will launch atop the SLS rocket from Launch Pad 39B and begin an approximately three-week mission that will send Orion thousands of miles beyond the Moon. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing work on the ML.
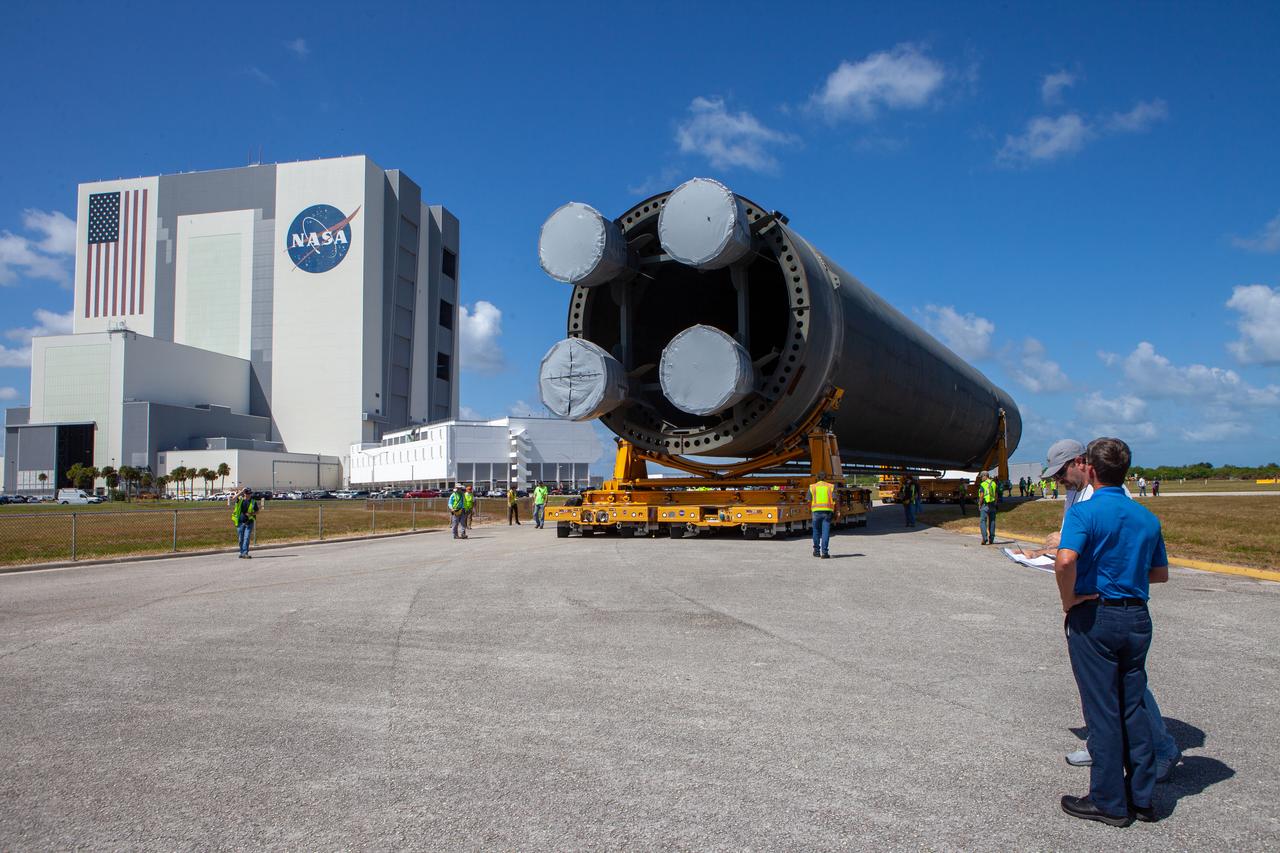

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder has been offloaded from NASA’s Pegasus Barge at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Oct. 1, 2019. It is slowly being backed up so that it is in the correct configuration for the move forward to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The upgraded 310-foot-long barge arrived Sept. 27, 2019, ferrying the SLS core stage pathfinder, a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It will be used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy for approximately one month before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
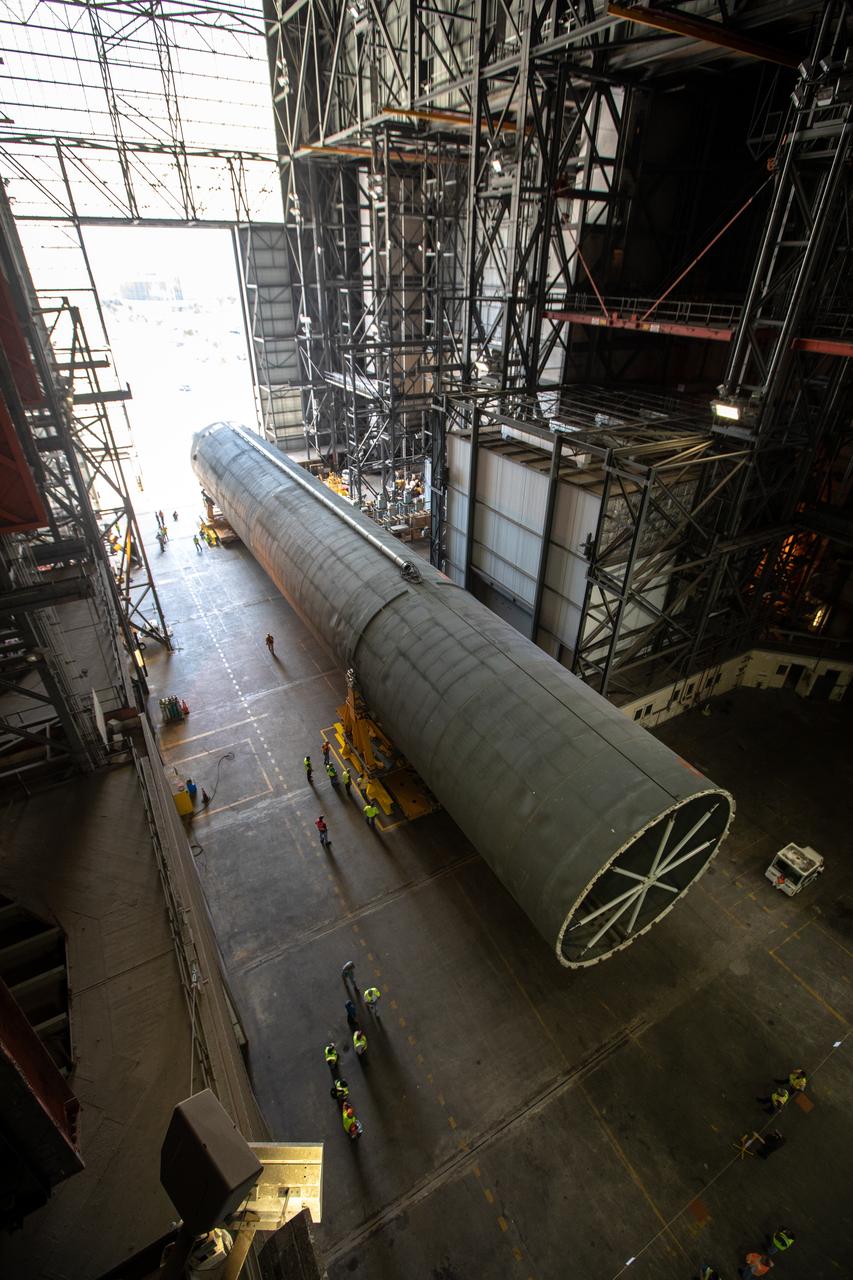

The 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is inside the low bay of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. NASA's Pegasus Barge arrived at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 30, 2019, making its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The upgraded 310-foot-long barge arrived Sept. 27, 2019, ferrying the SLS core stage pathfinder, a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. The pathfinder will be used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy for approximately one month before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
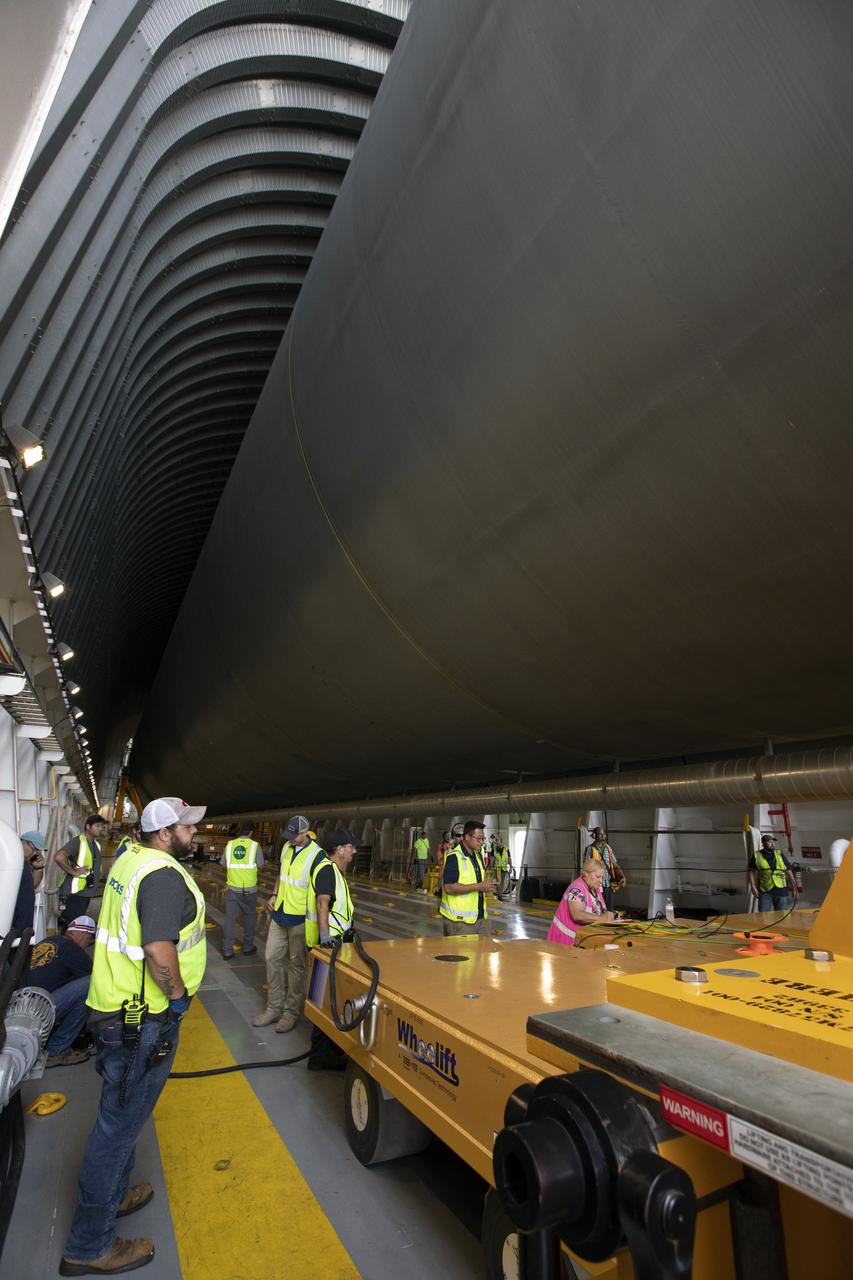

Inside the Pegasus barge at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf, NASA and Jacobs workers assist as the 212-foot-long Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage pathfinder is moved inside the barge on Oct. 28, 2019 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage pathfinder is a full-scale mock-up of the rocket's core stage. It was used by the Exploration Ground Systems Program and their contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder was at Kennedy for about a month. It will make the trek back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.