
On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
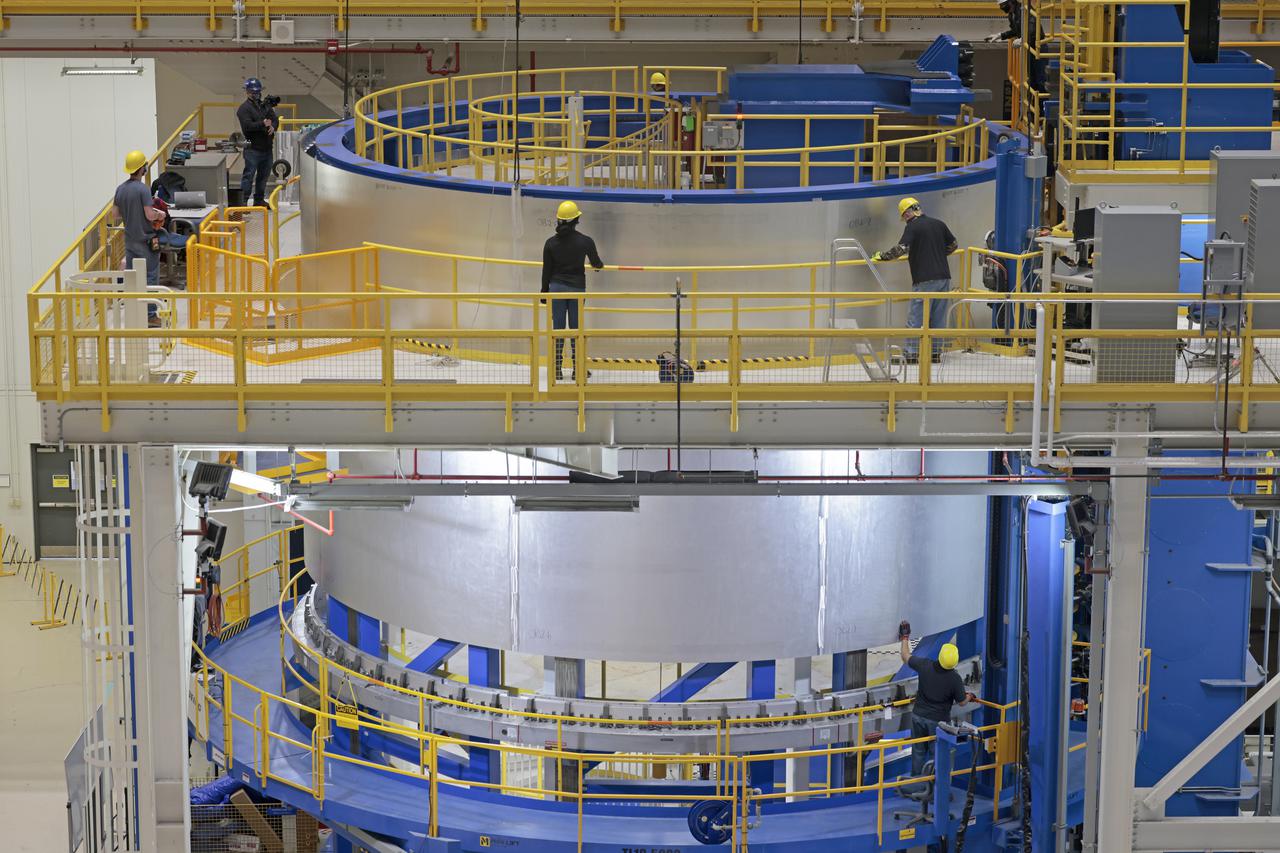

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
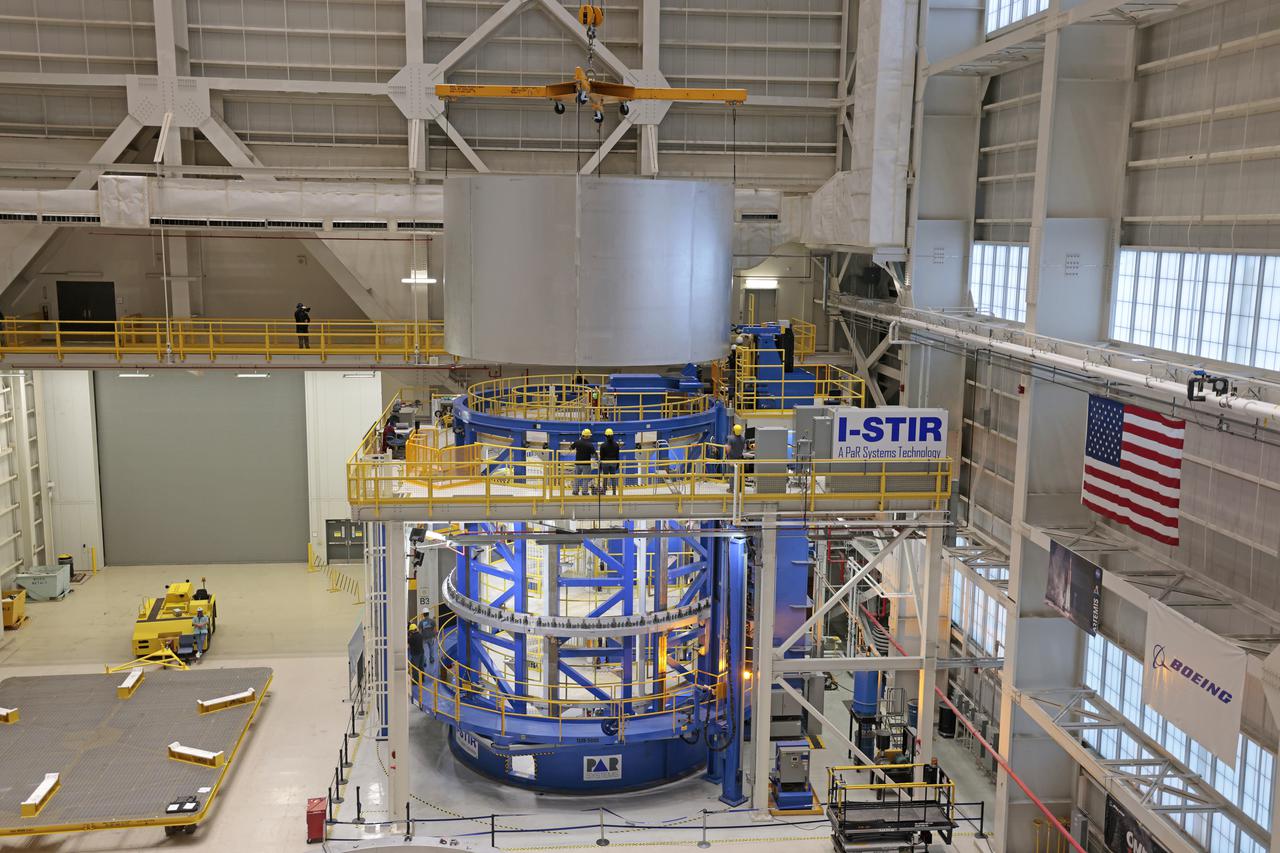

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
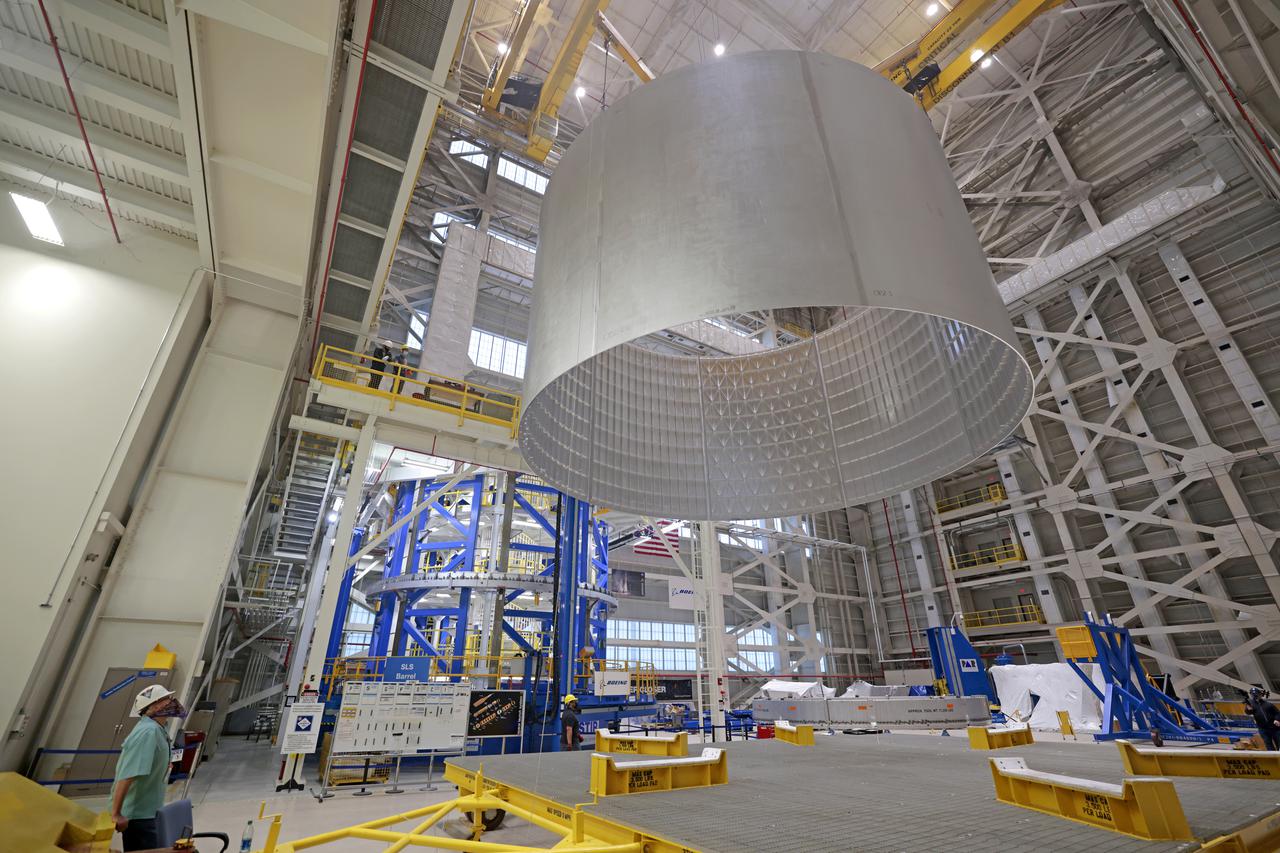

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
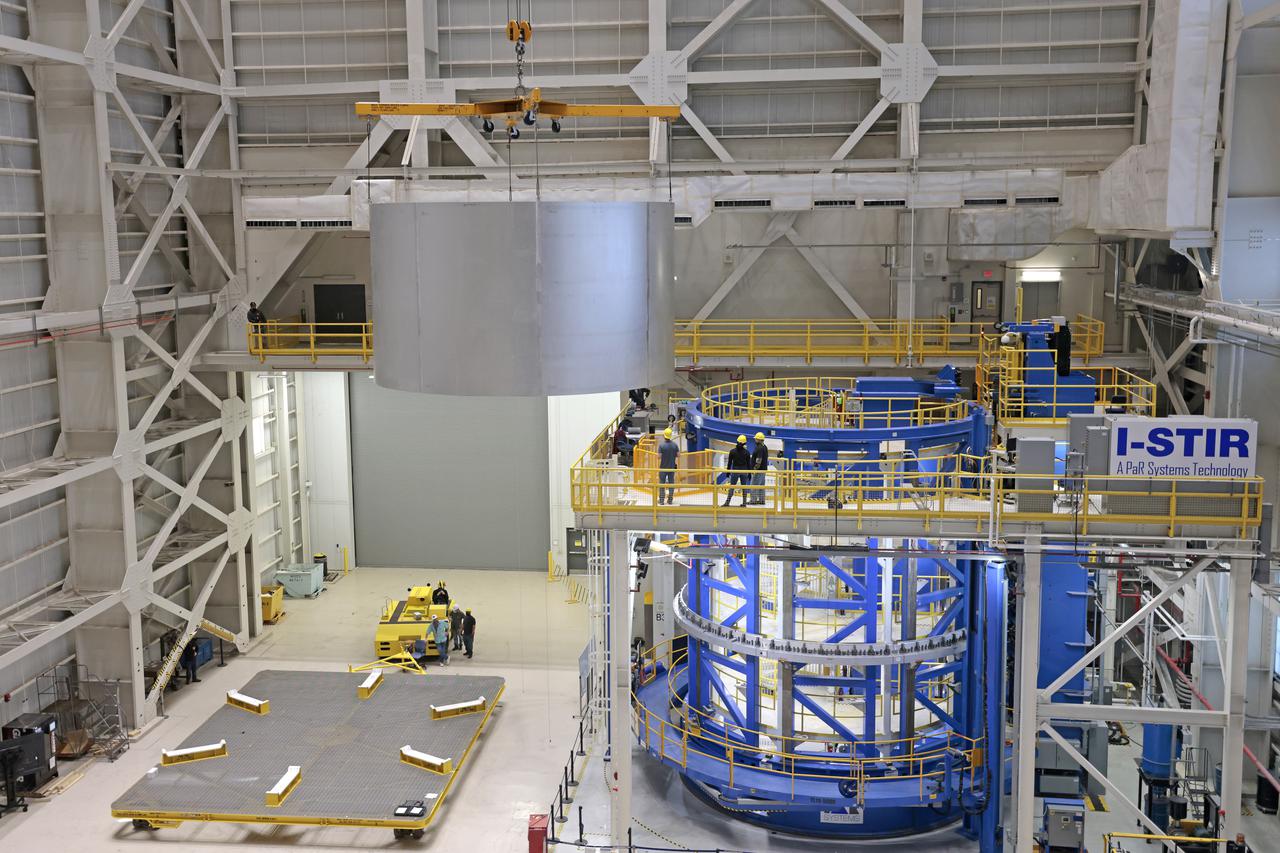

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
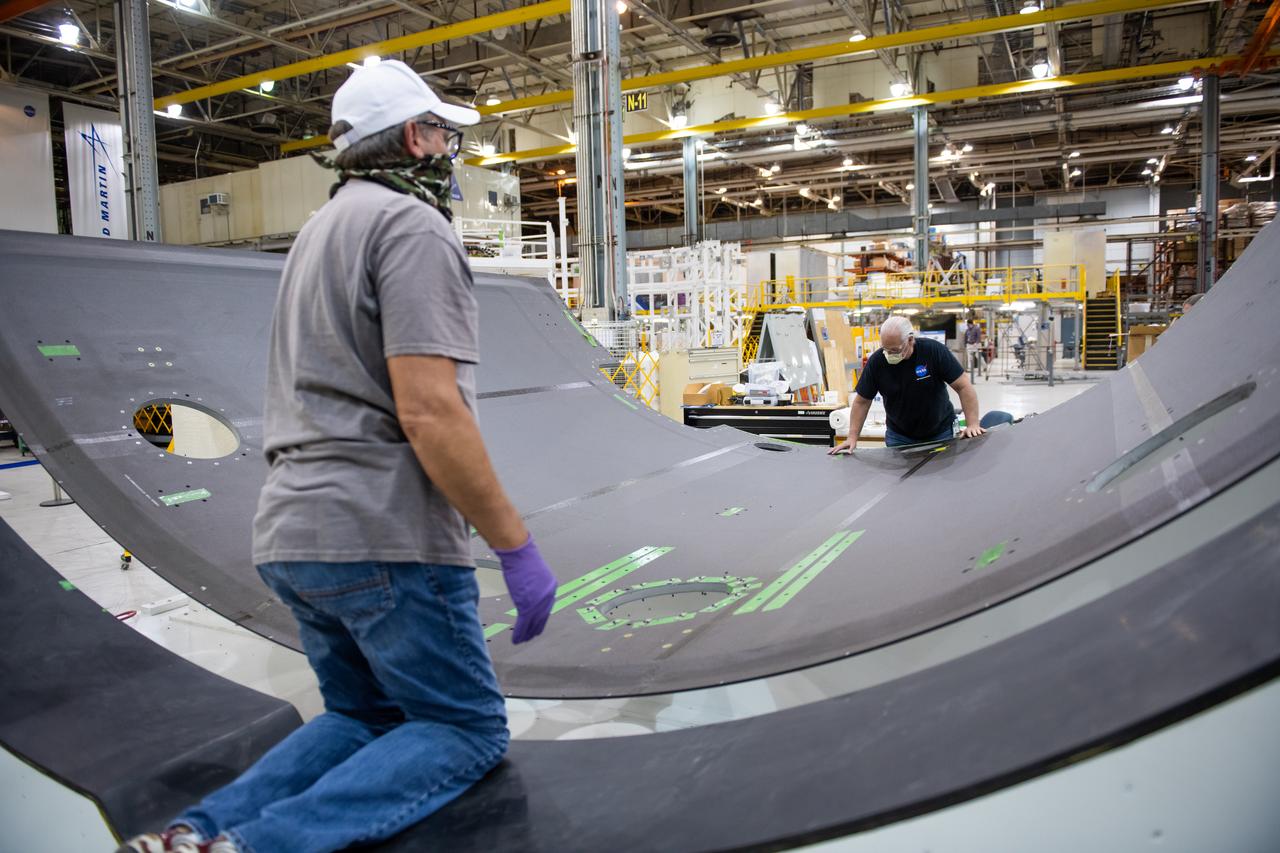

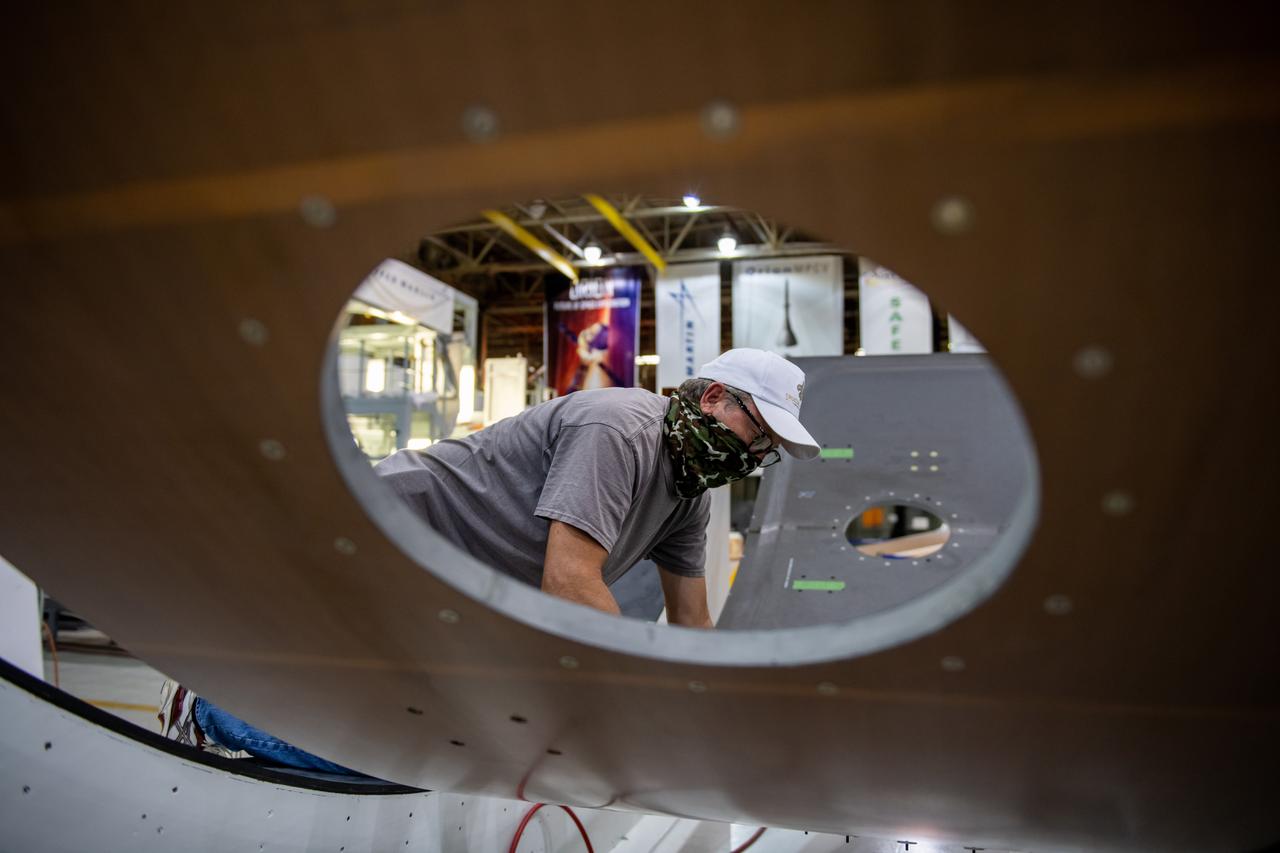
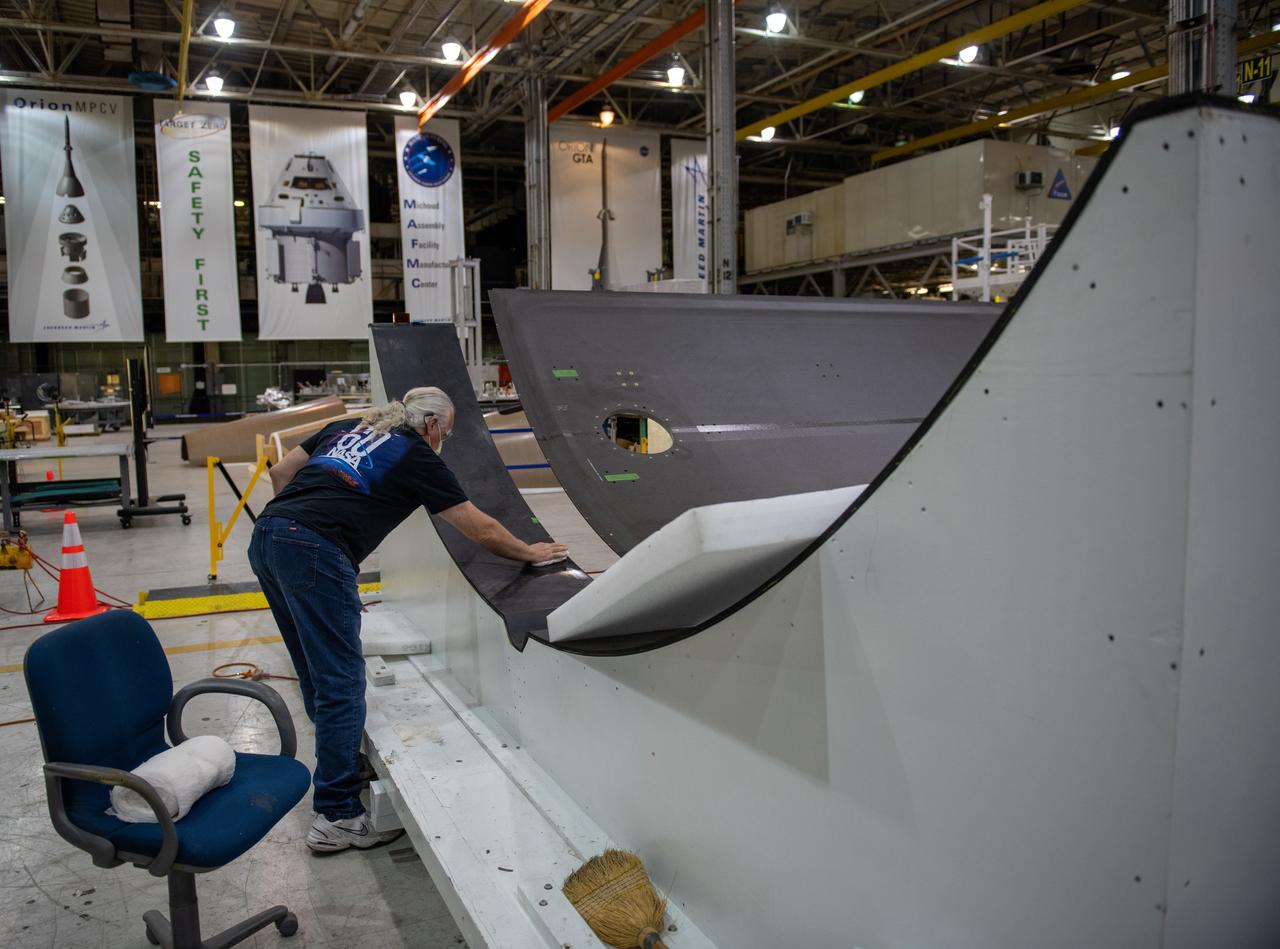
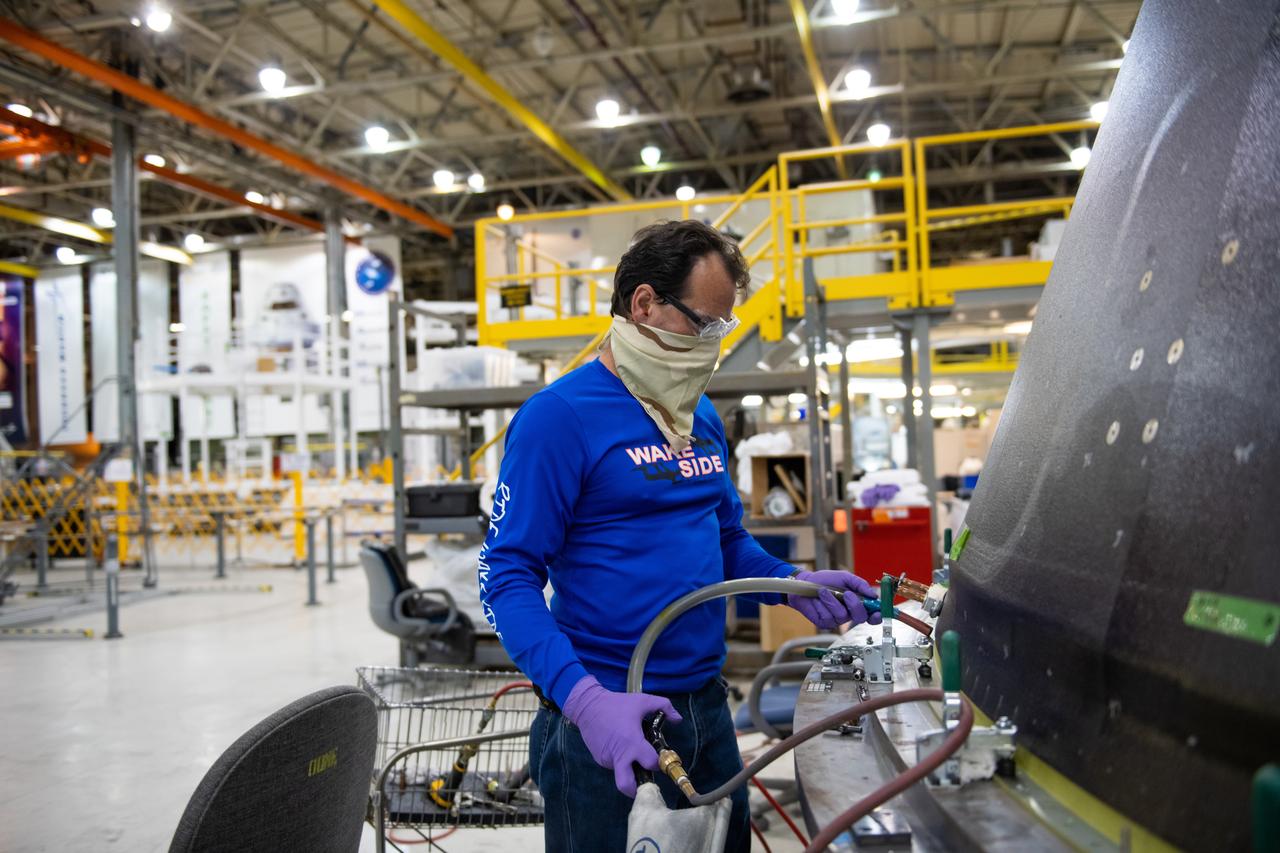
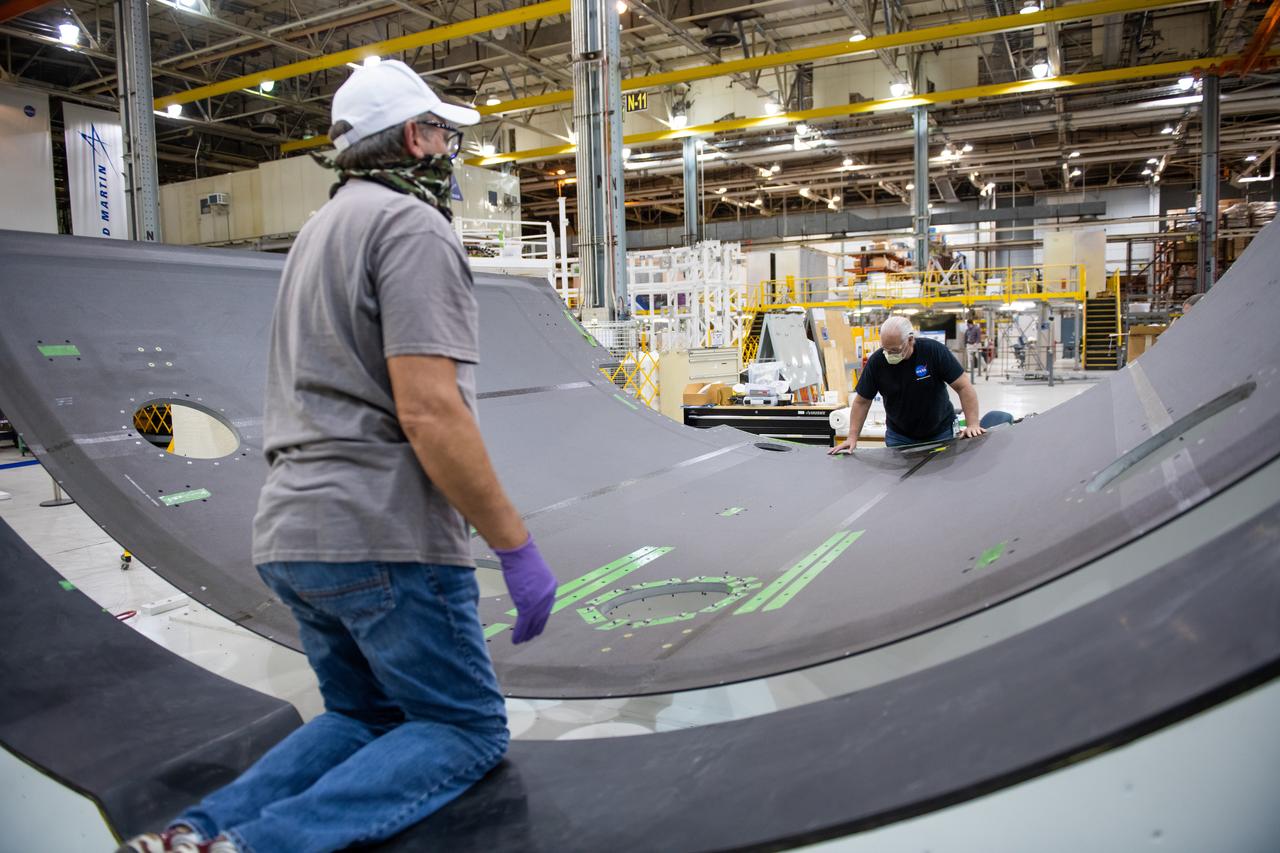
Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
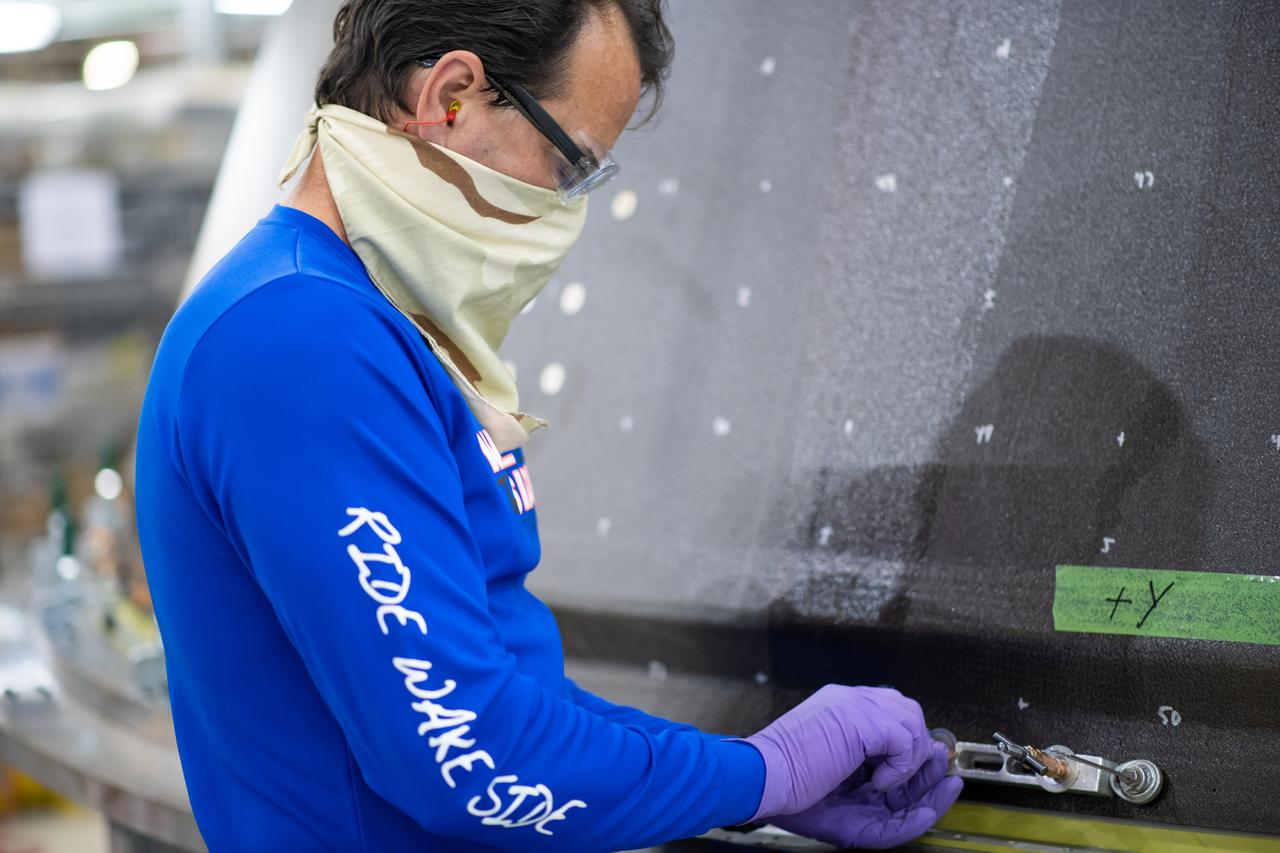

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
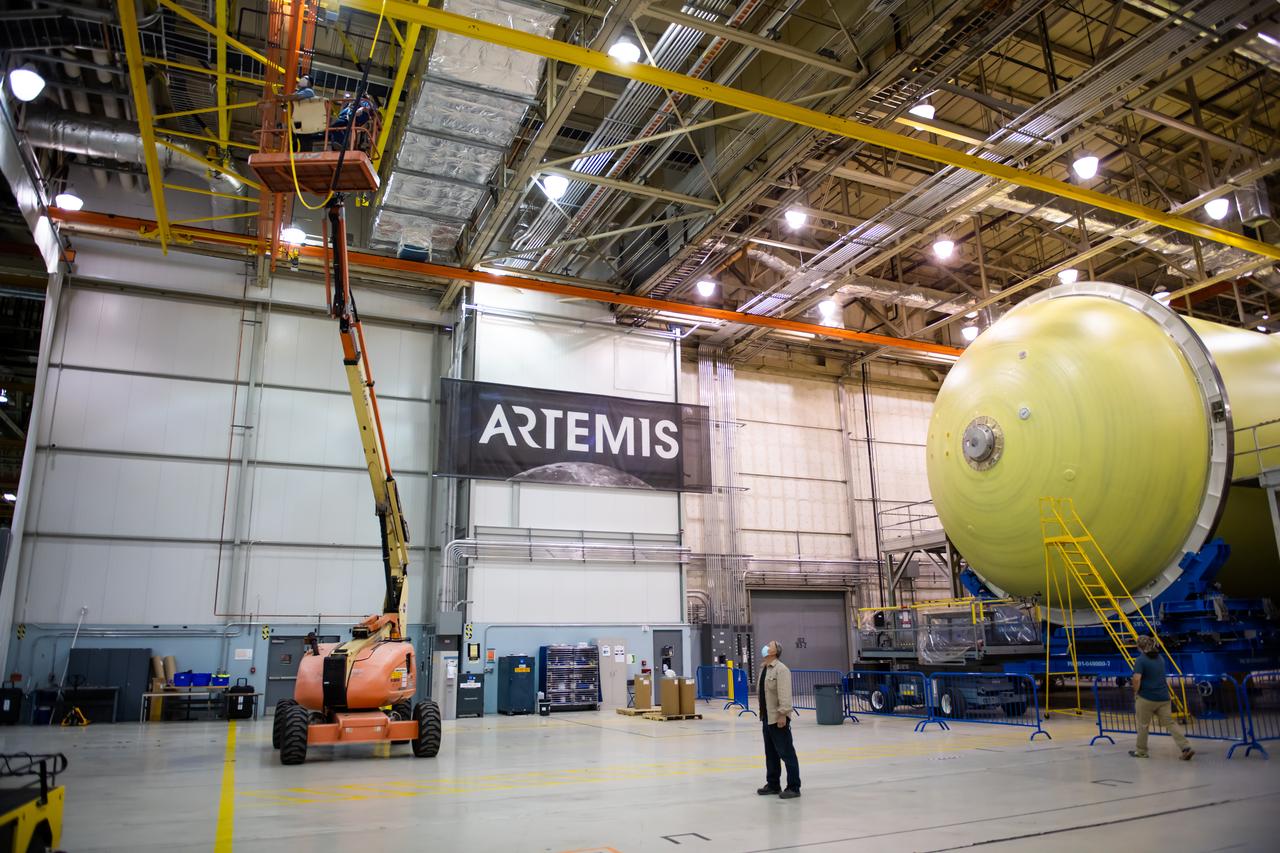

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
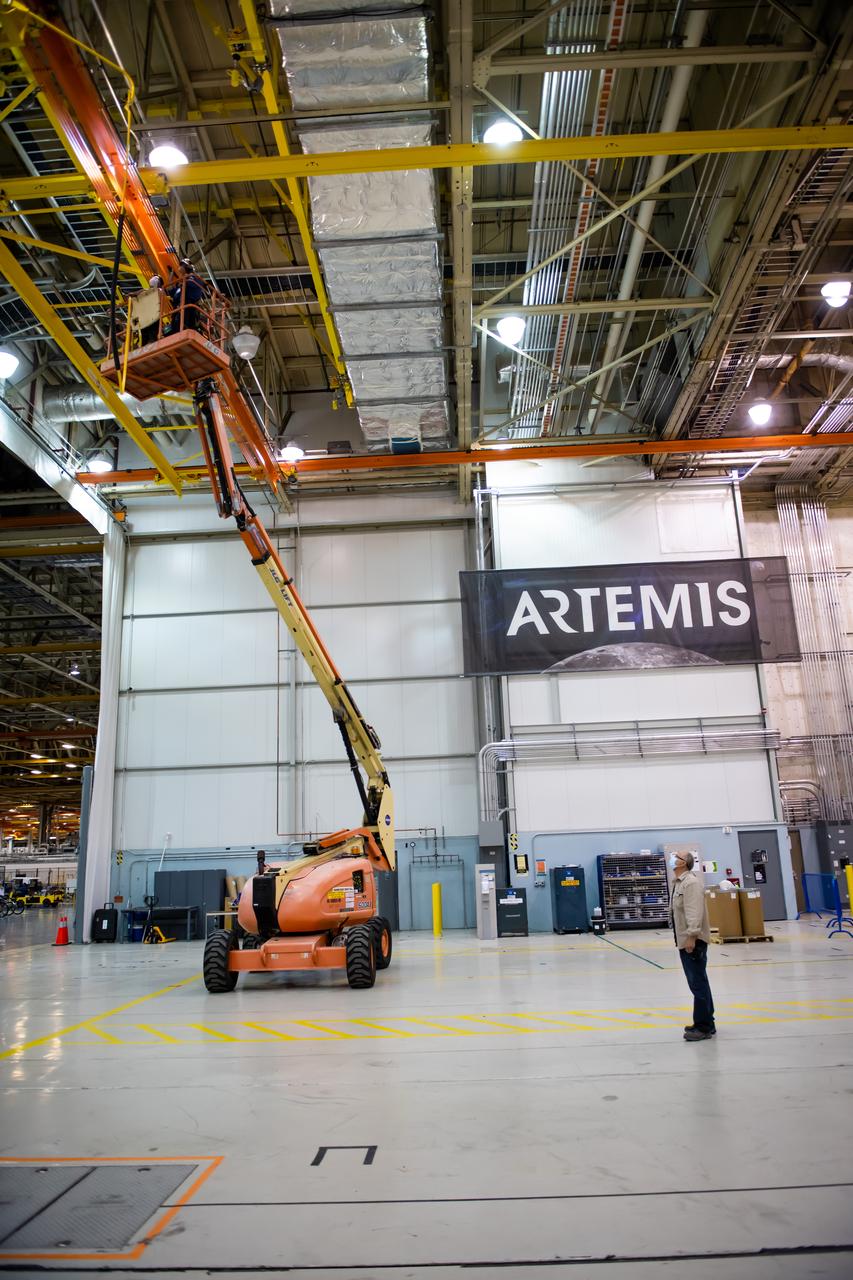

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
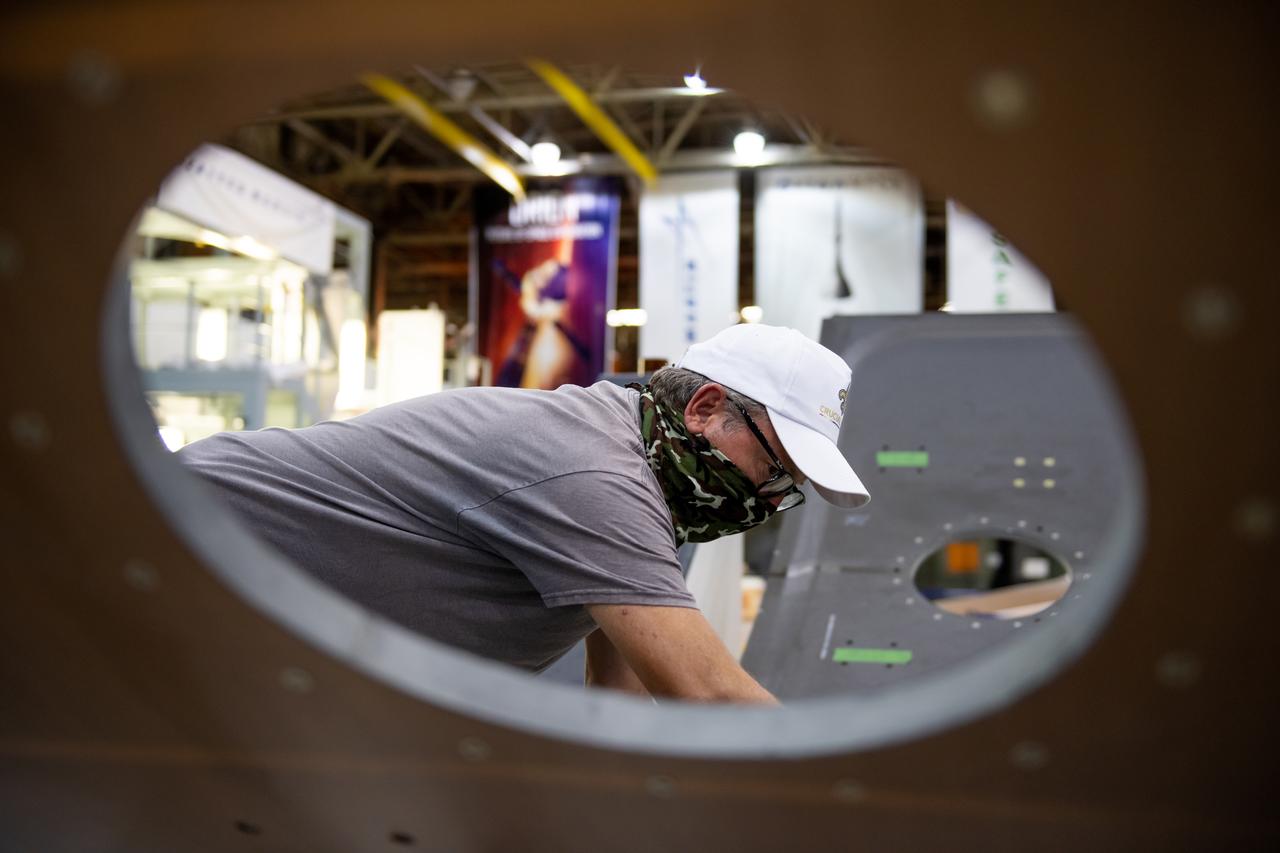

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
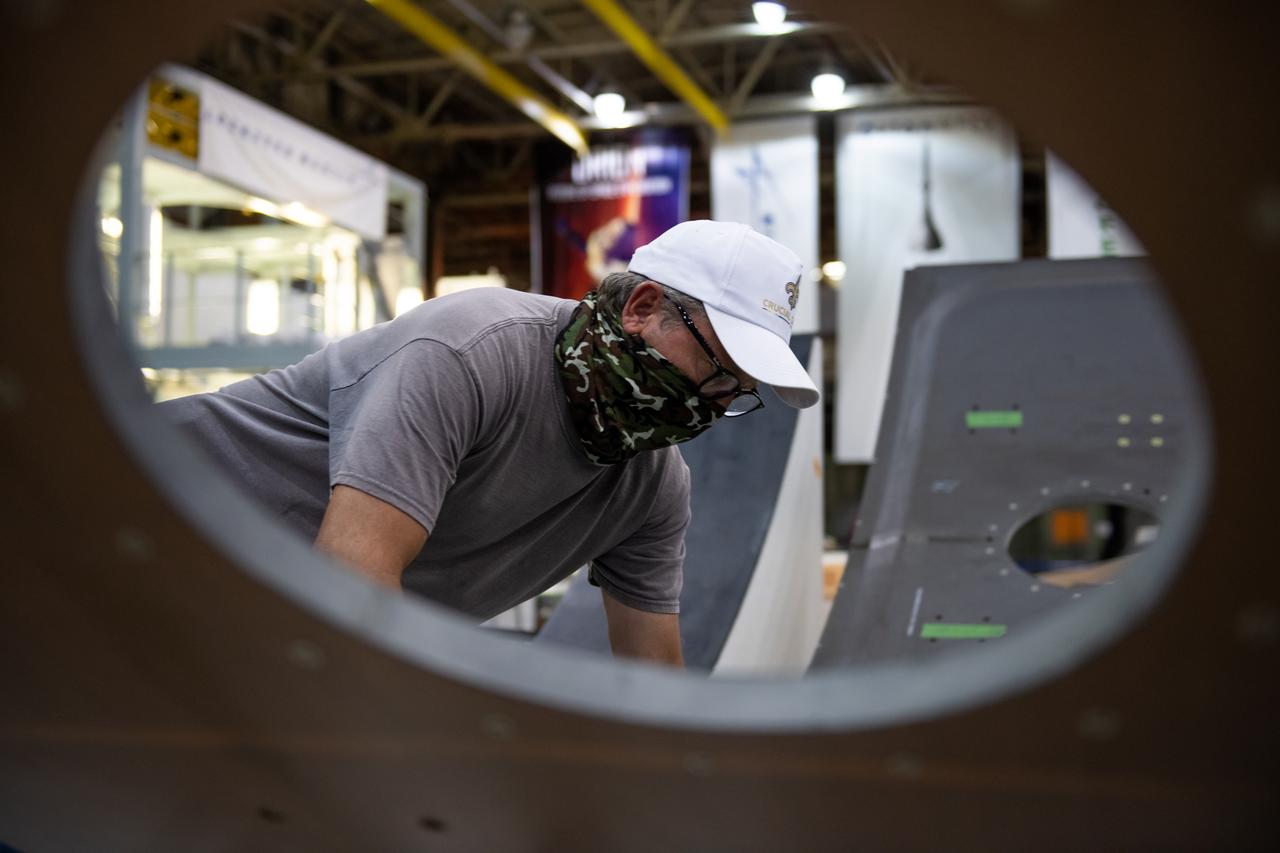

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
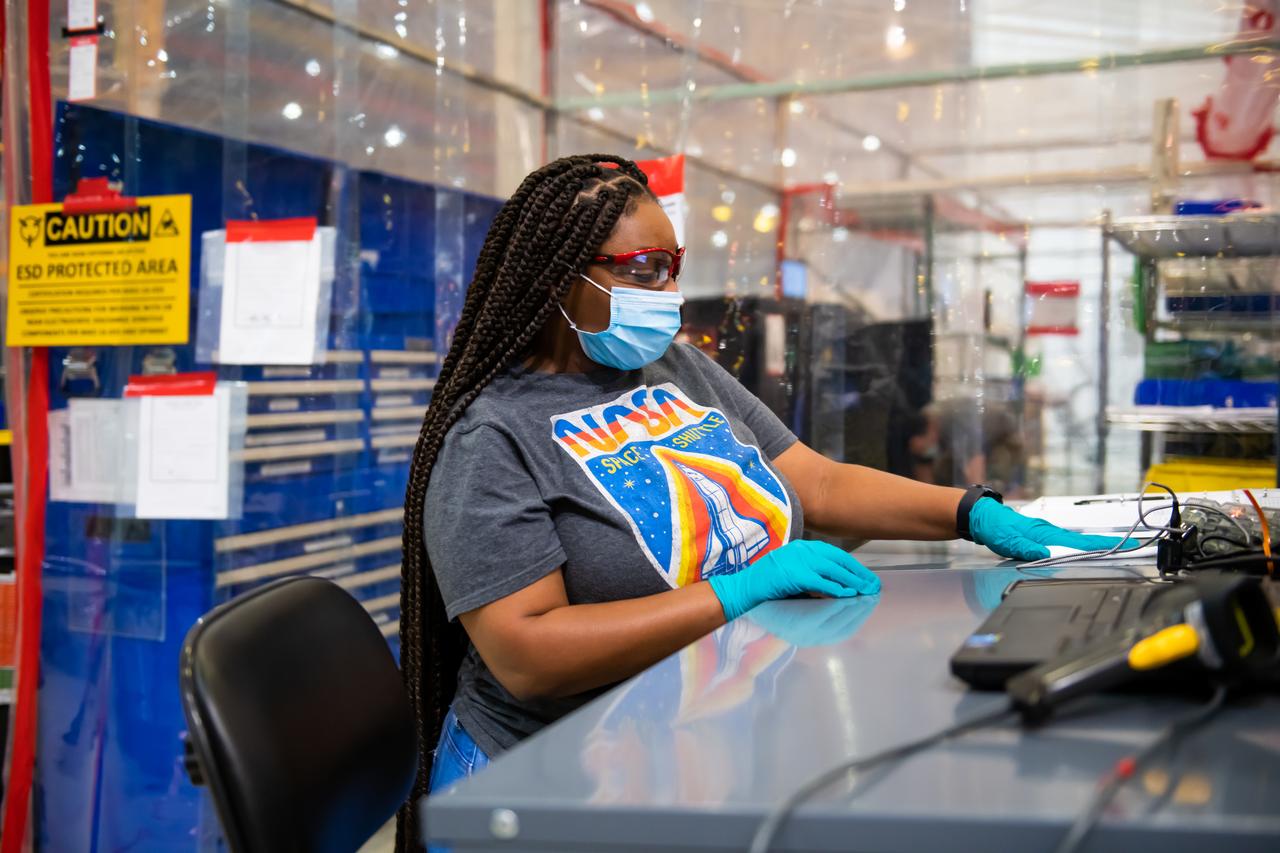

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
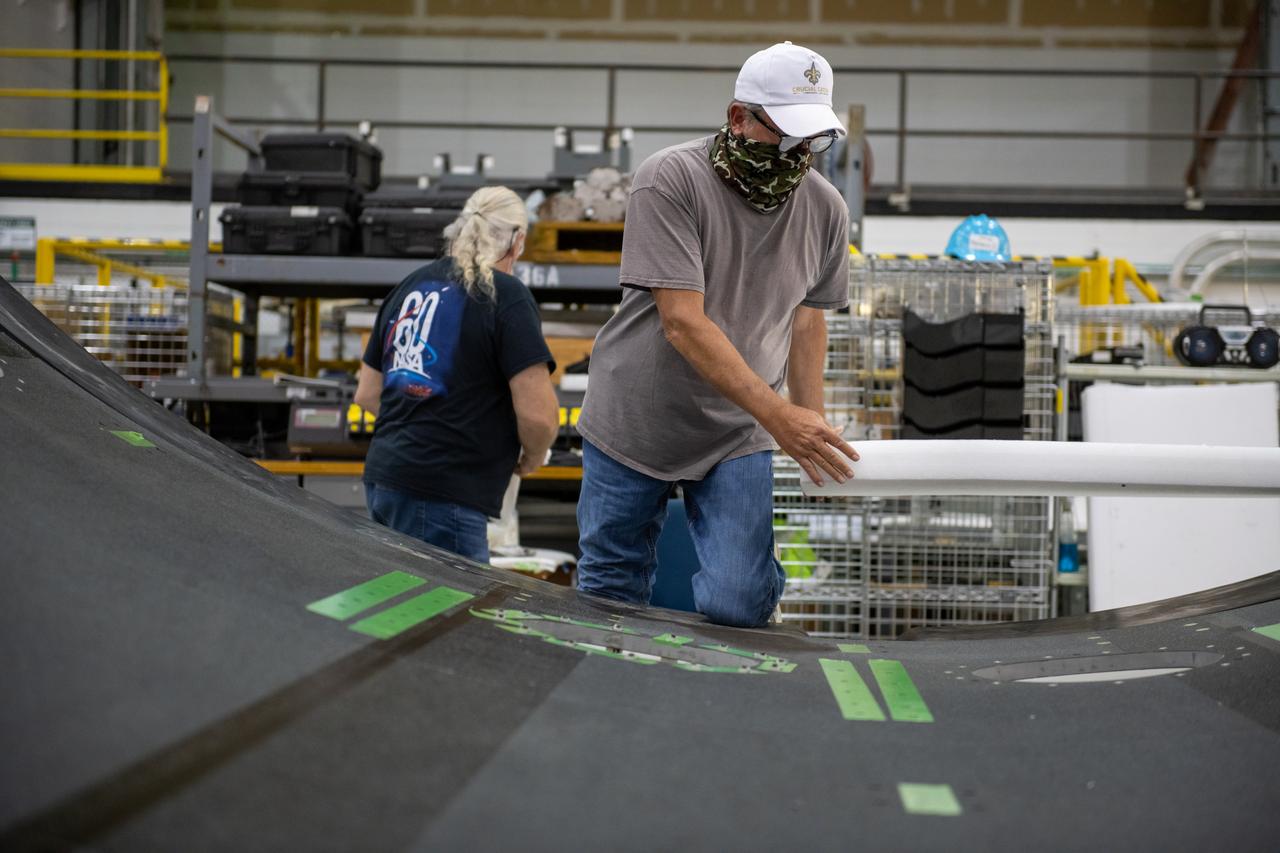

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
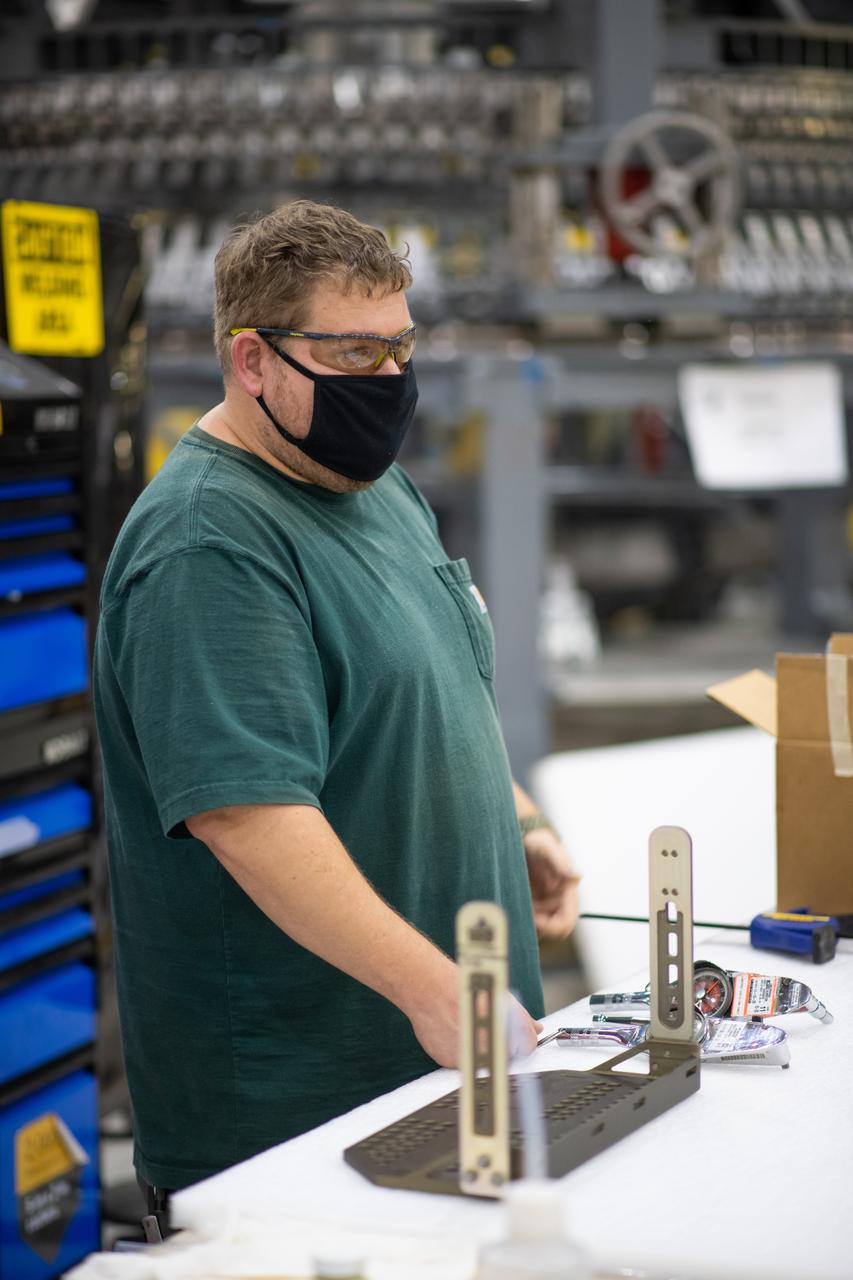

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
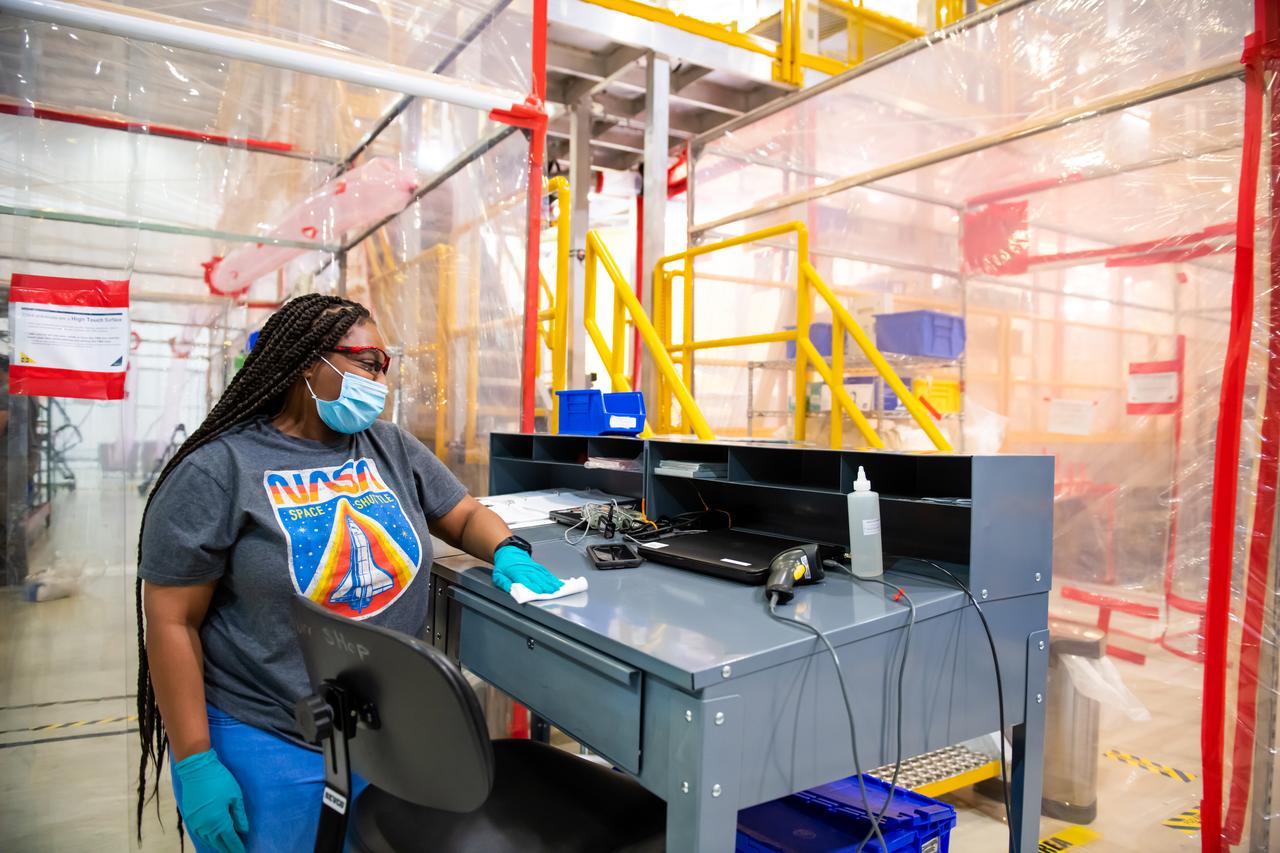

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
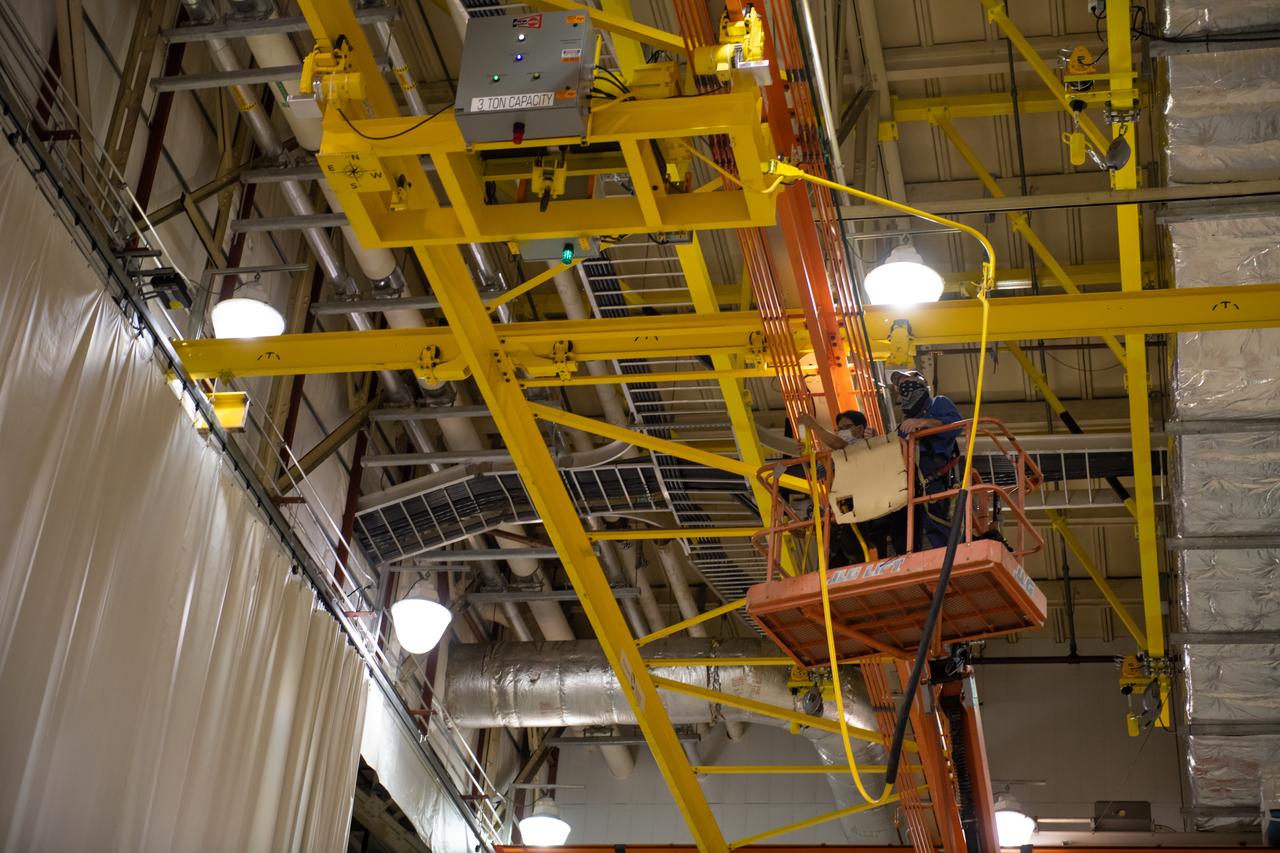

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
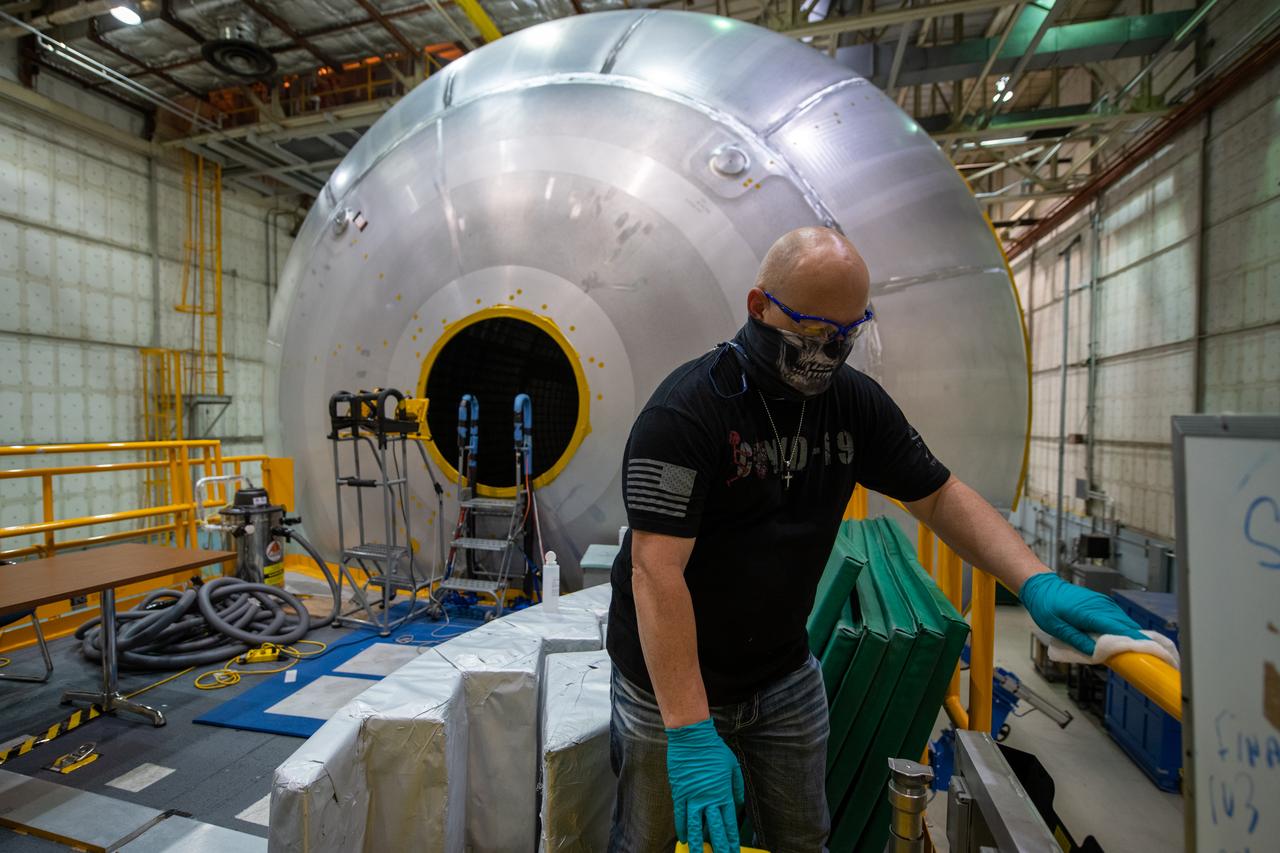

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
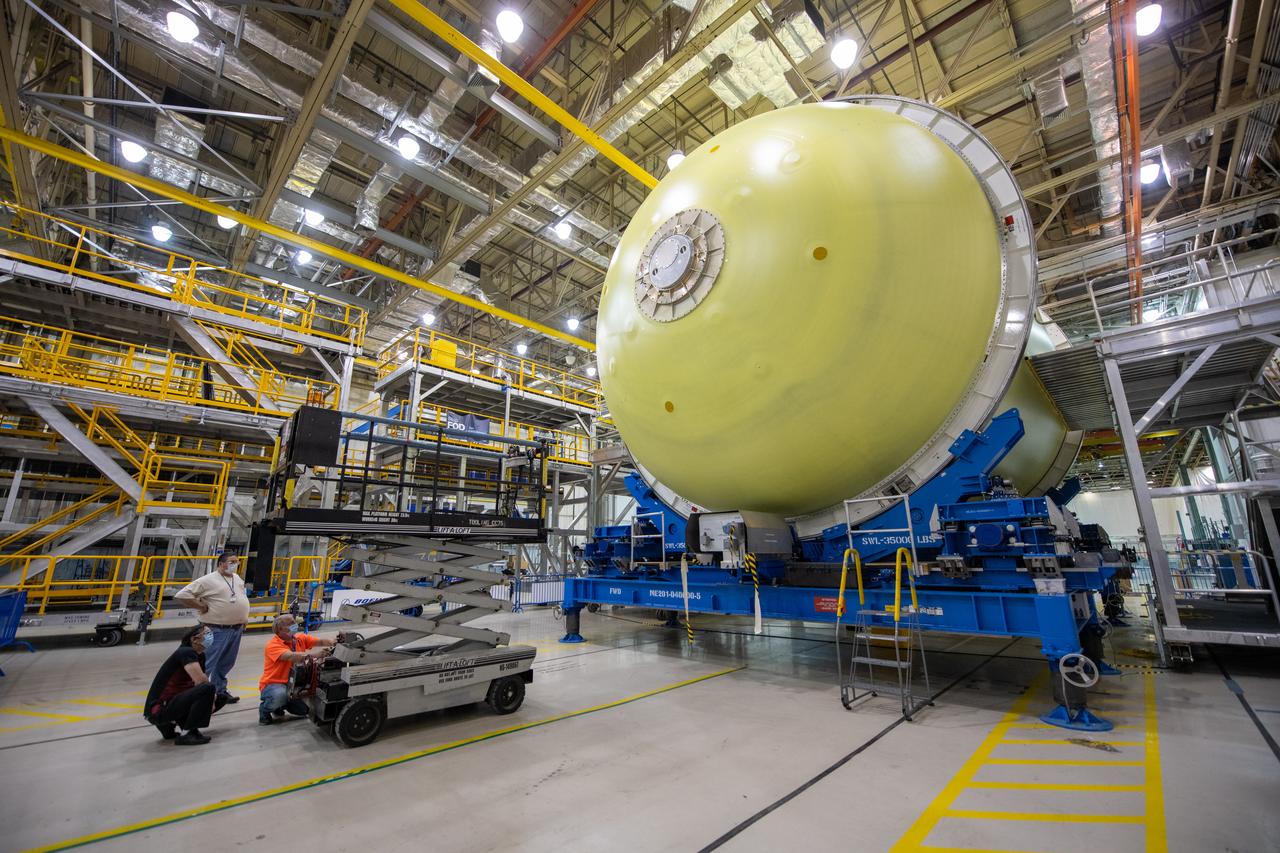

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
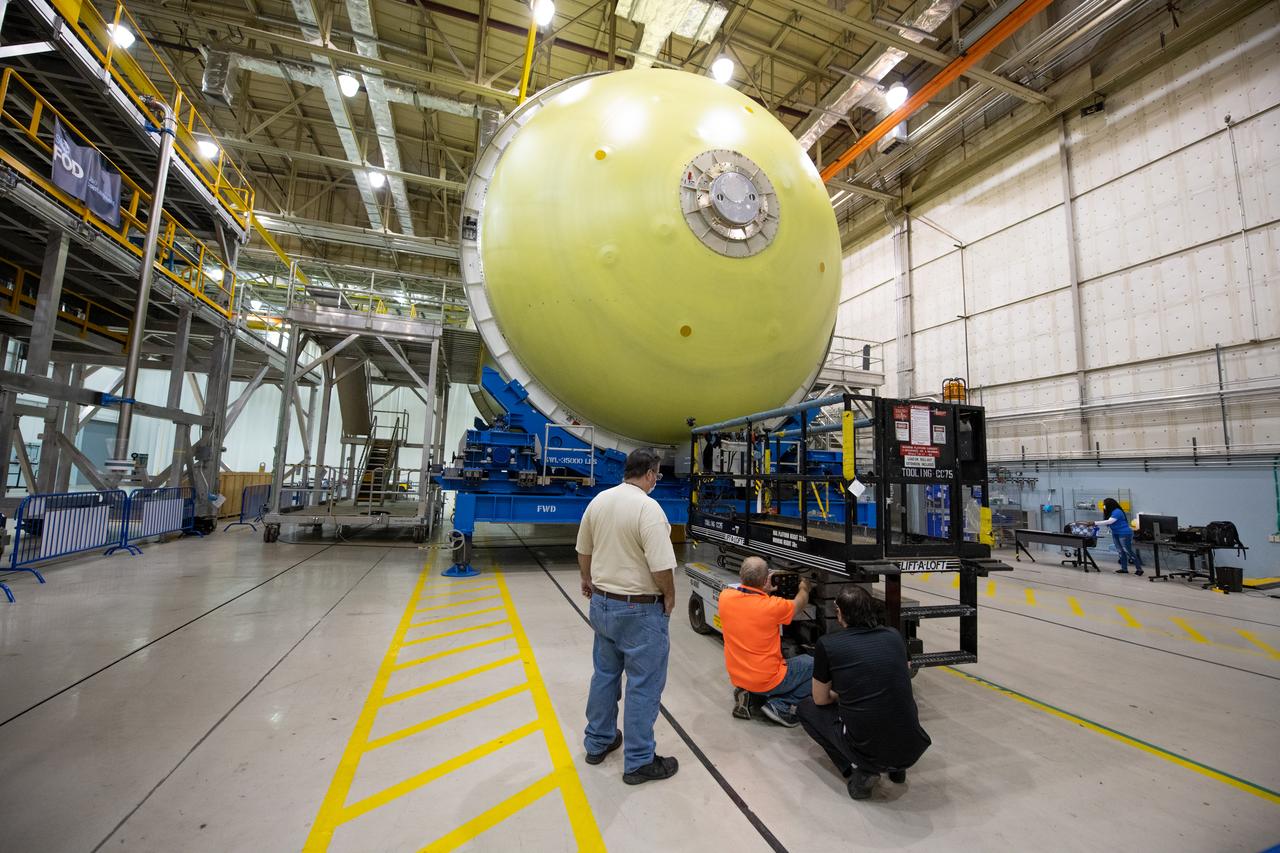

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
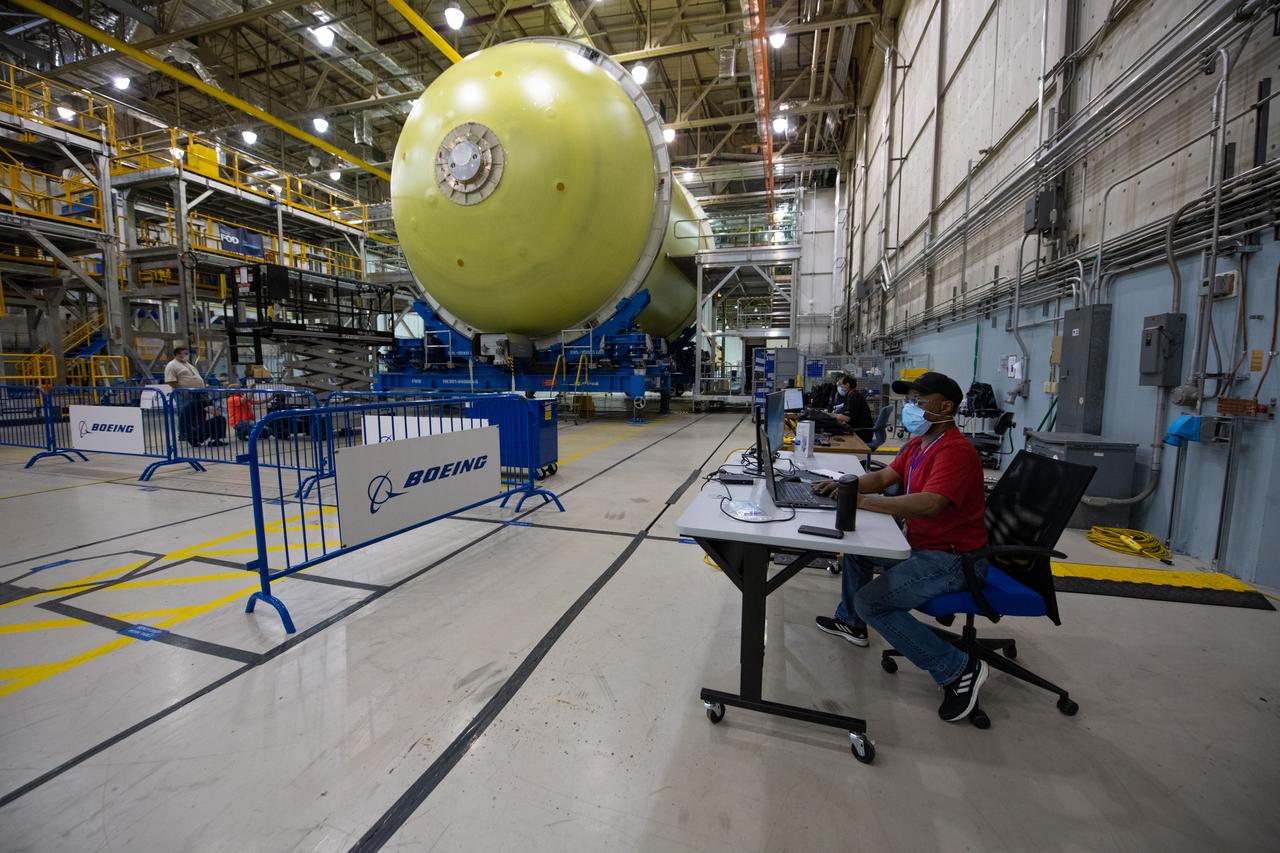

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
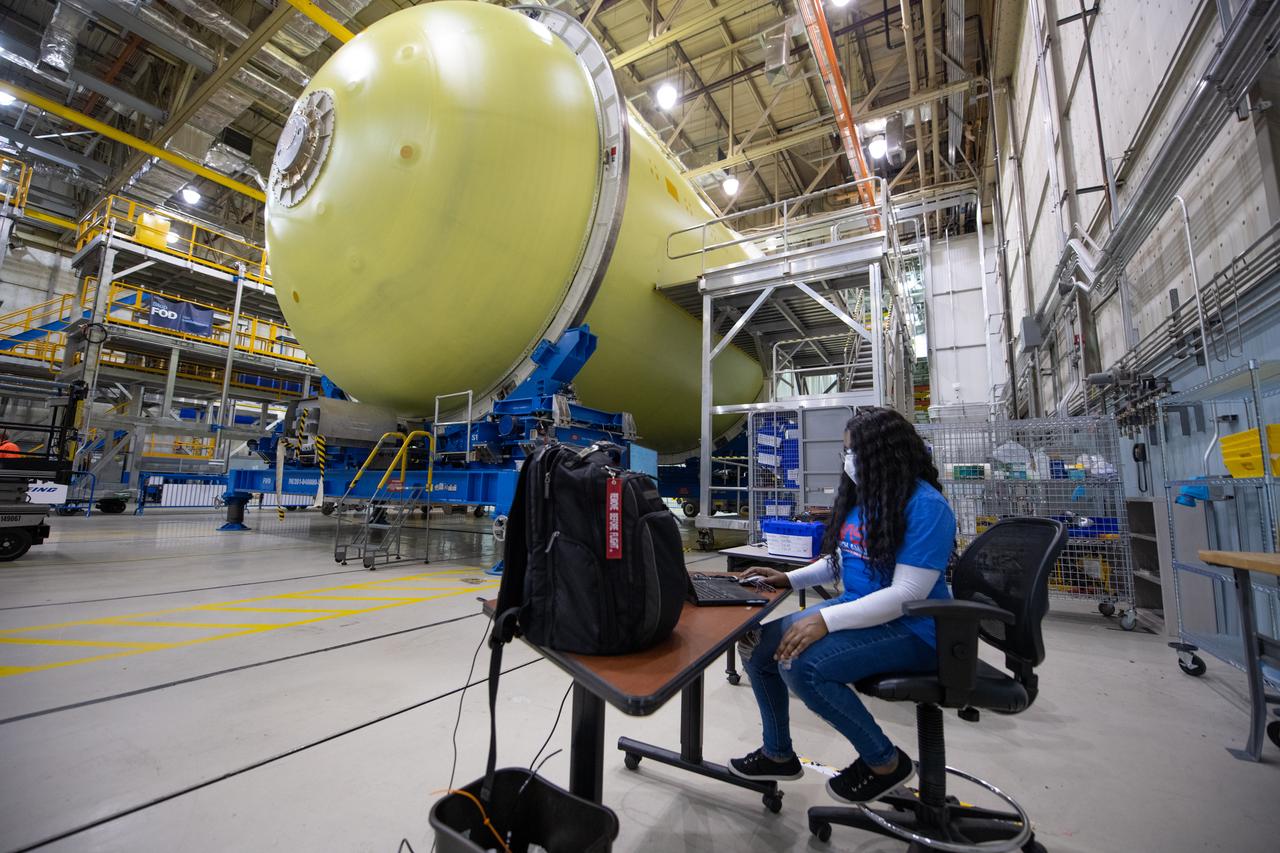

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
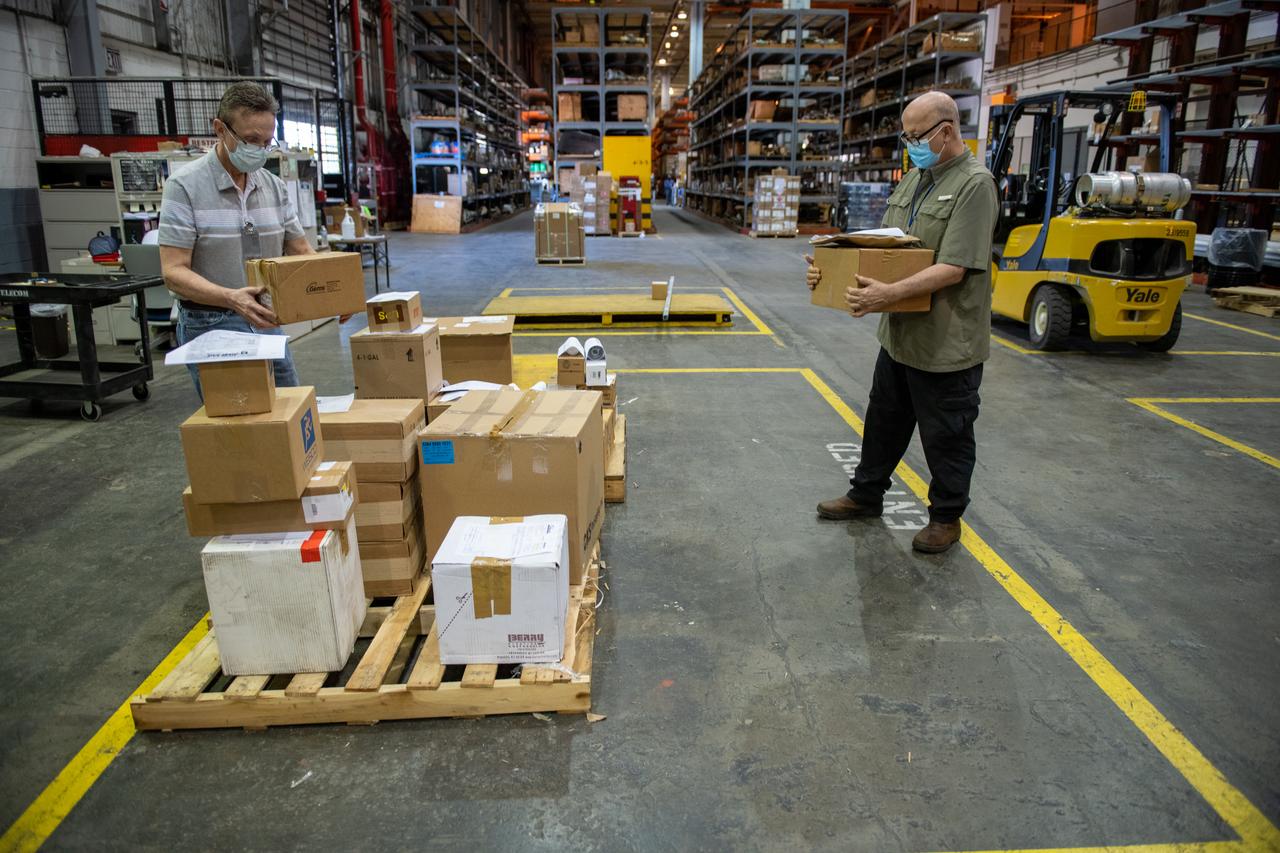

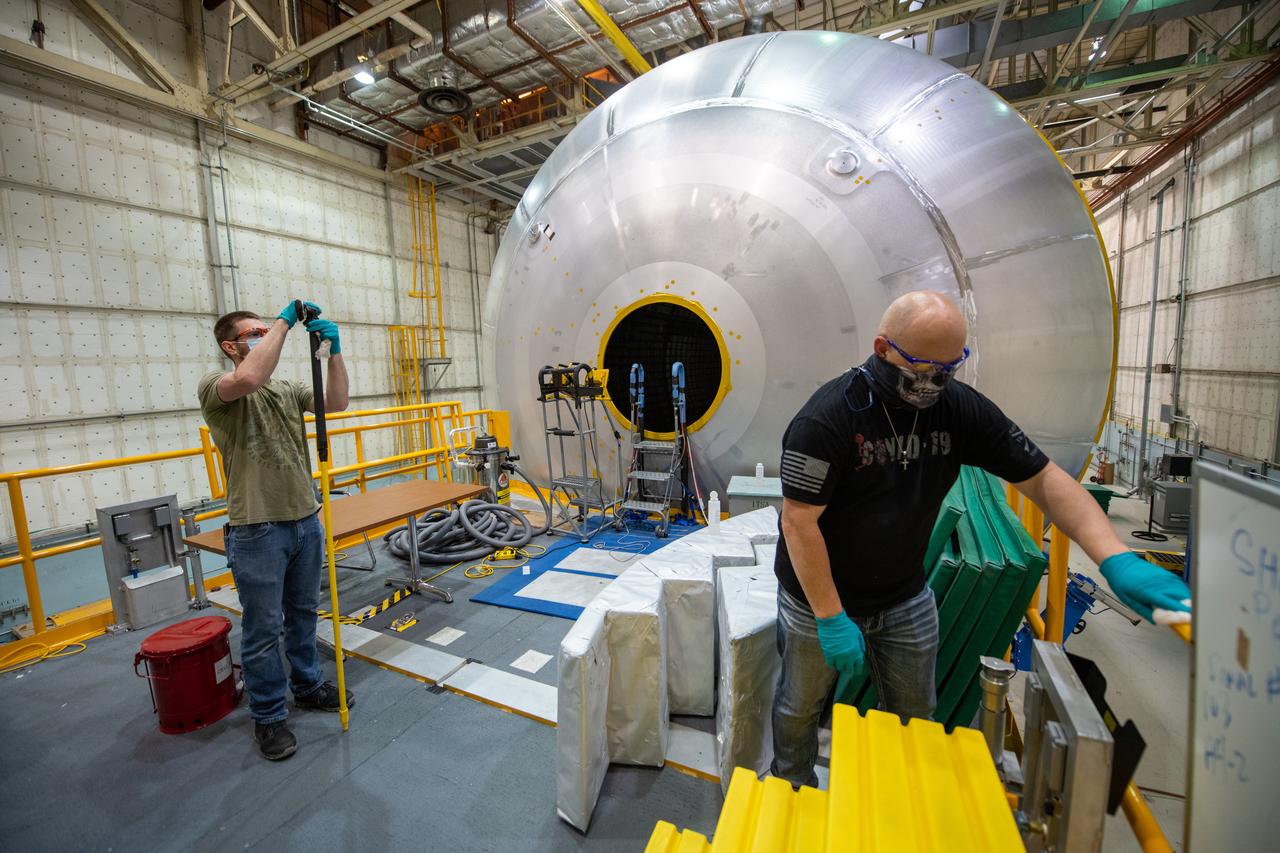
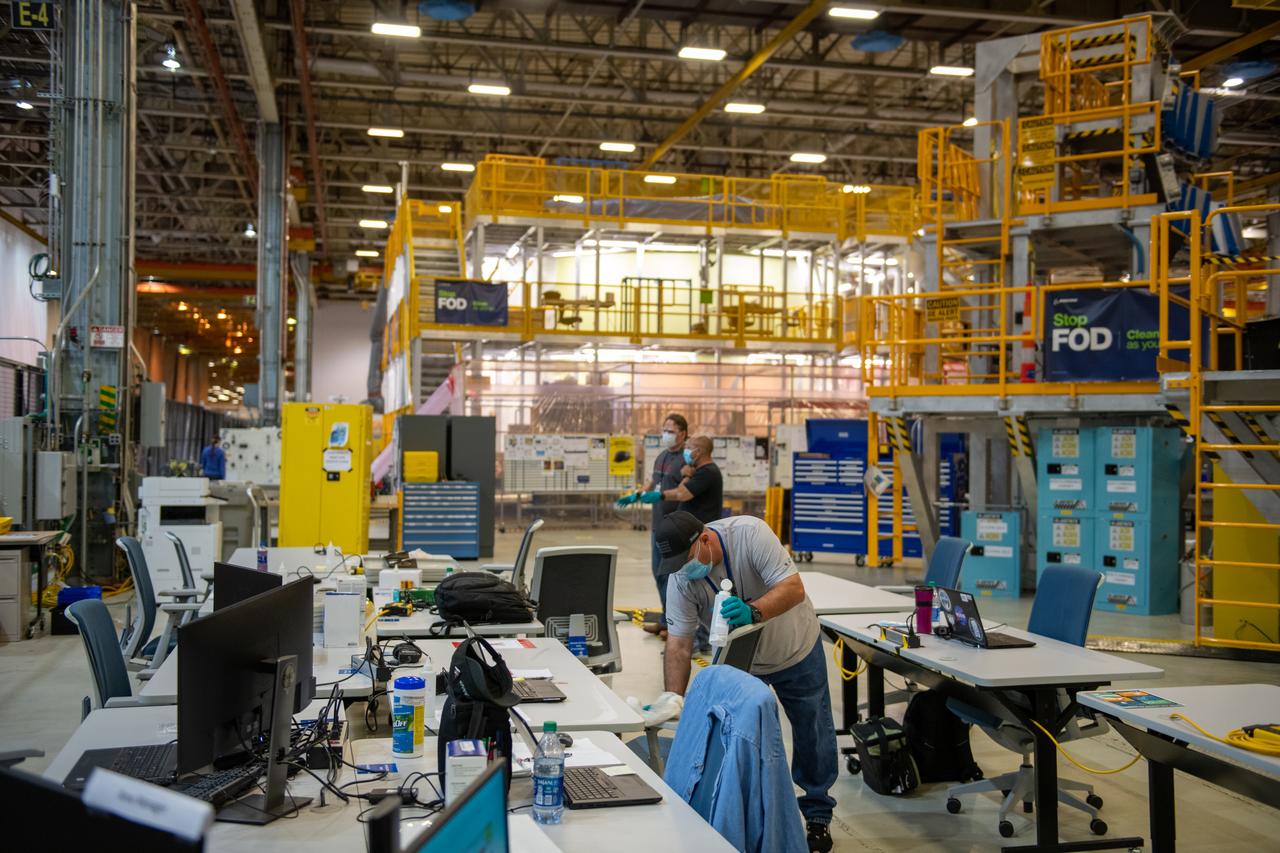
This photo includes two employees wearing personal protective gear in the shipping and receiving area of Michoud Assembly Facility during the Stage 3 transition of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Wearing a facemask is mandatory for common areas where social distancing is difficult to achieve. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Employees at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans will slowly and methodically resume Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion Spacecraft production and assembly activities at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
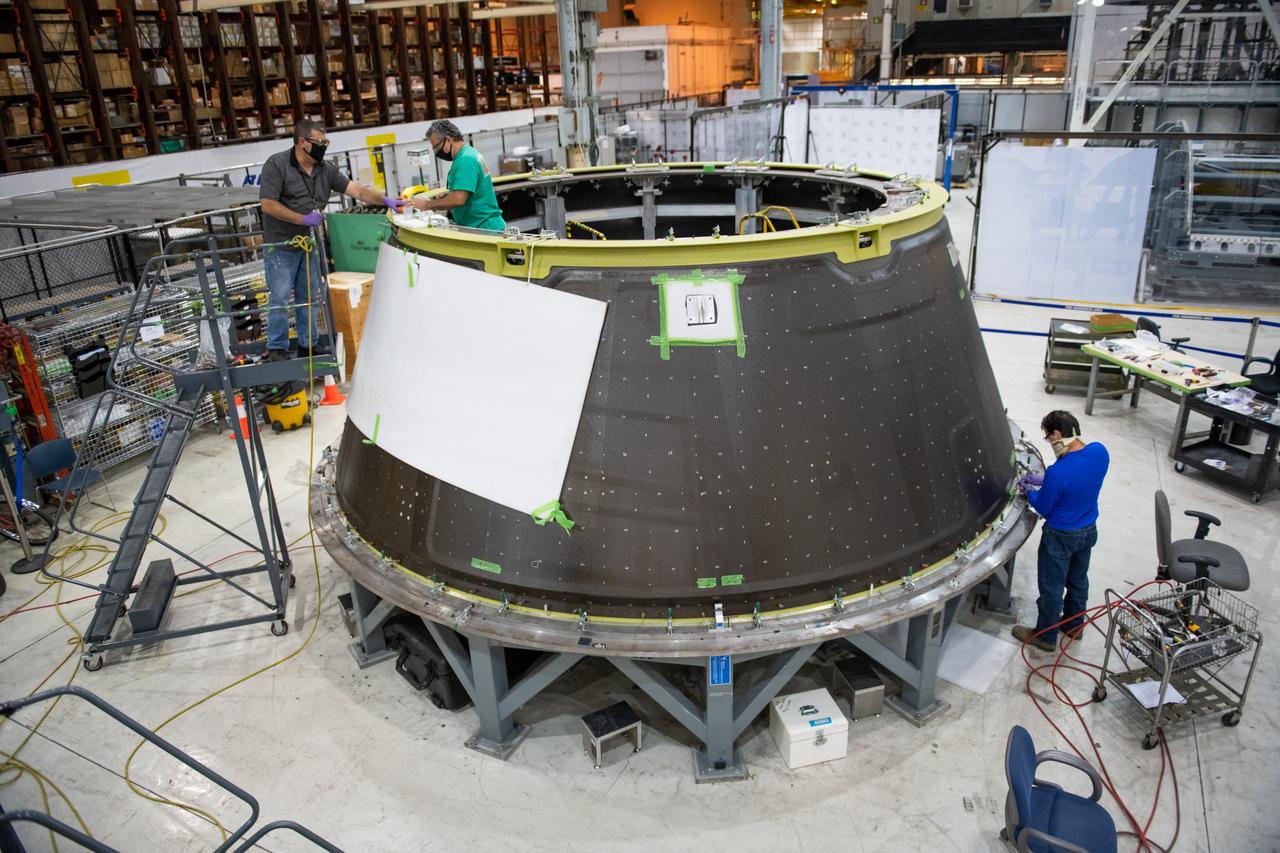

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
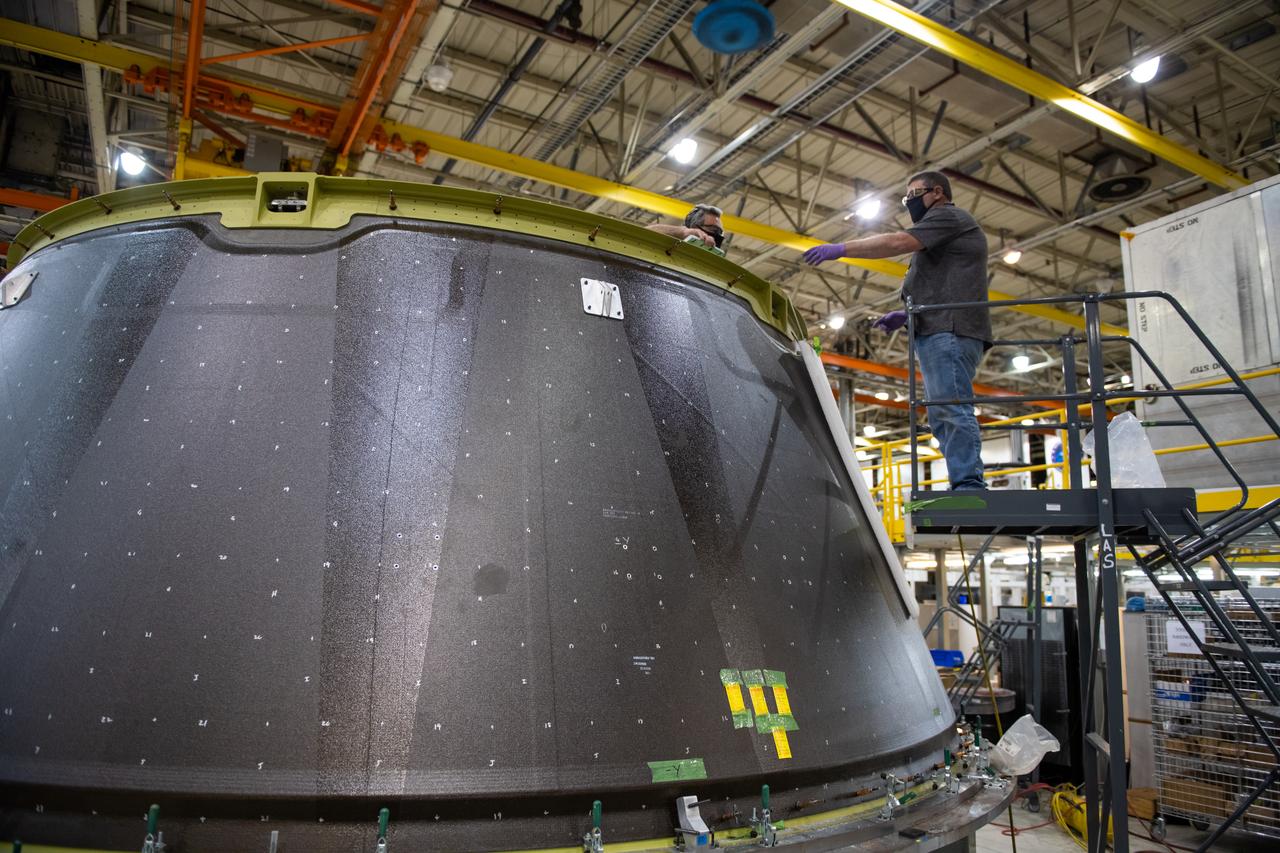

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
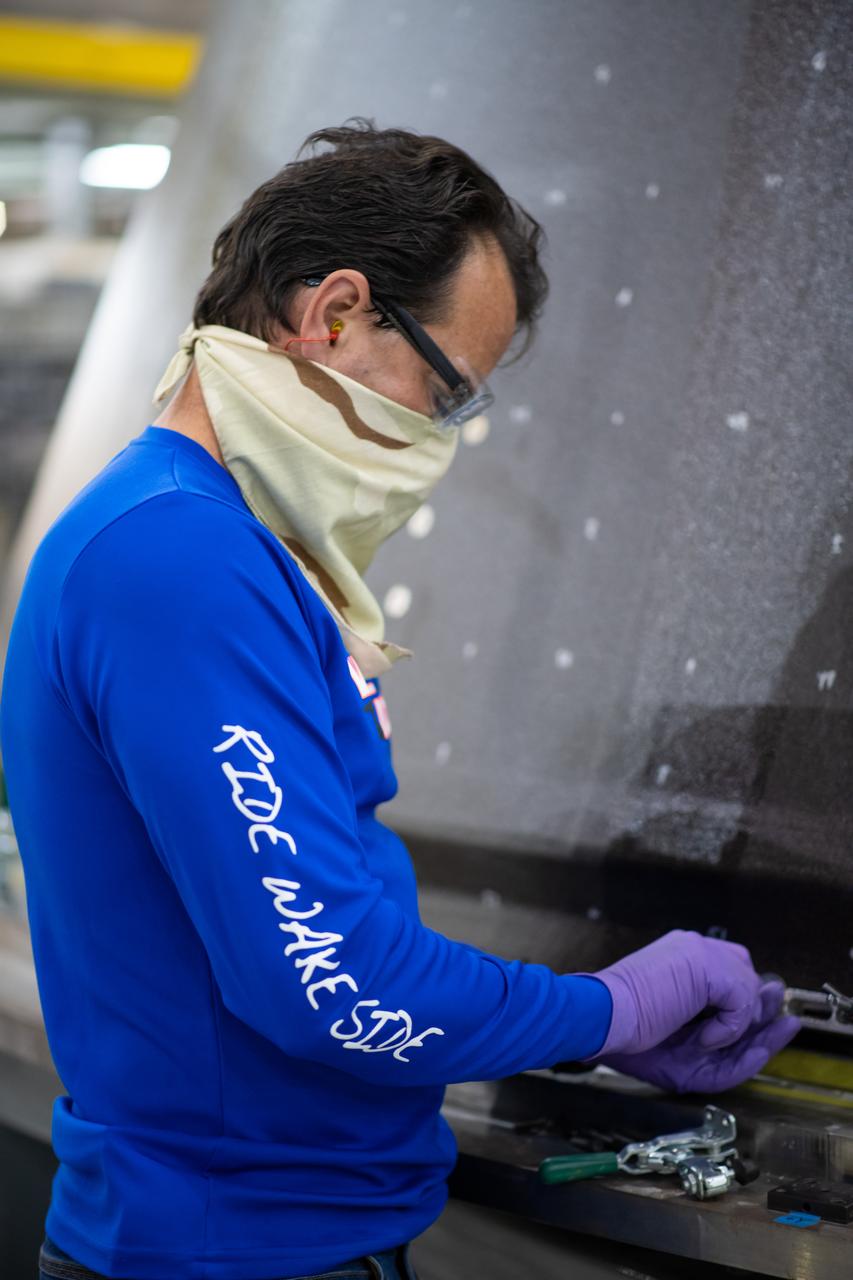

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
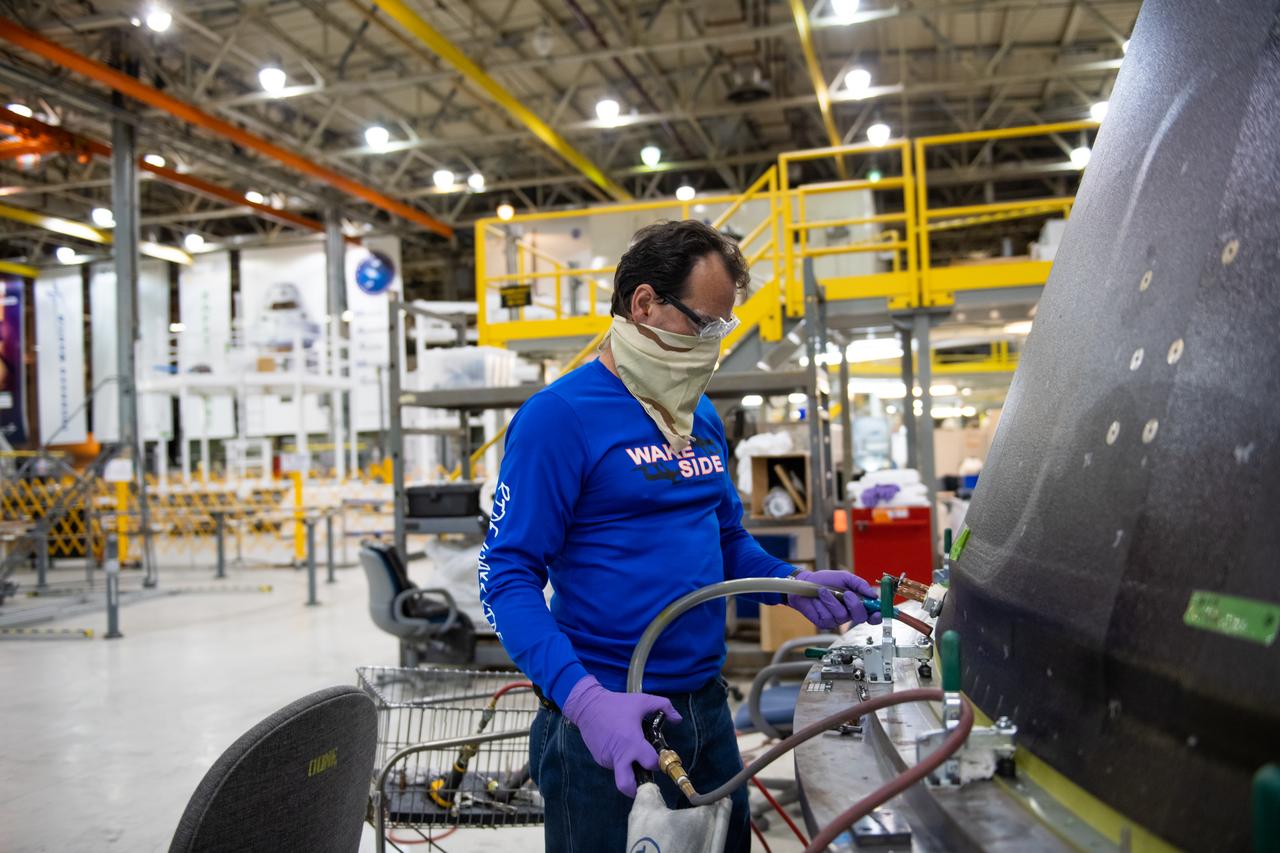

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
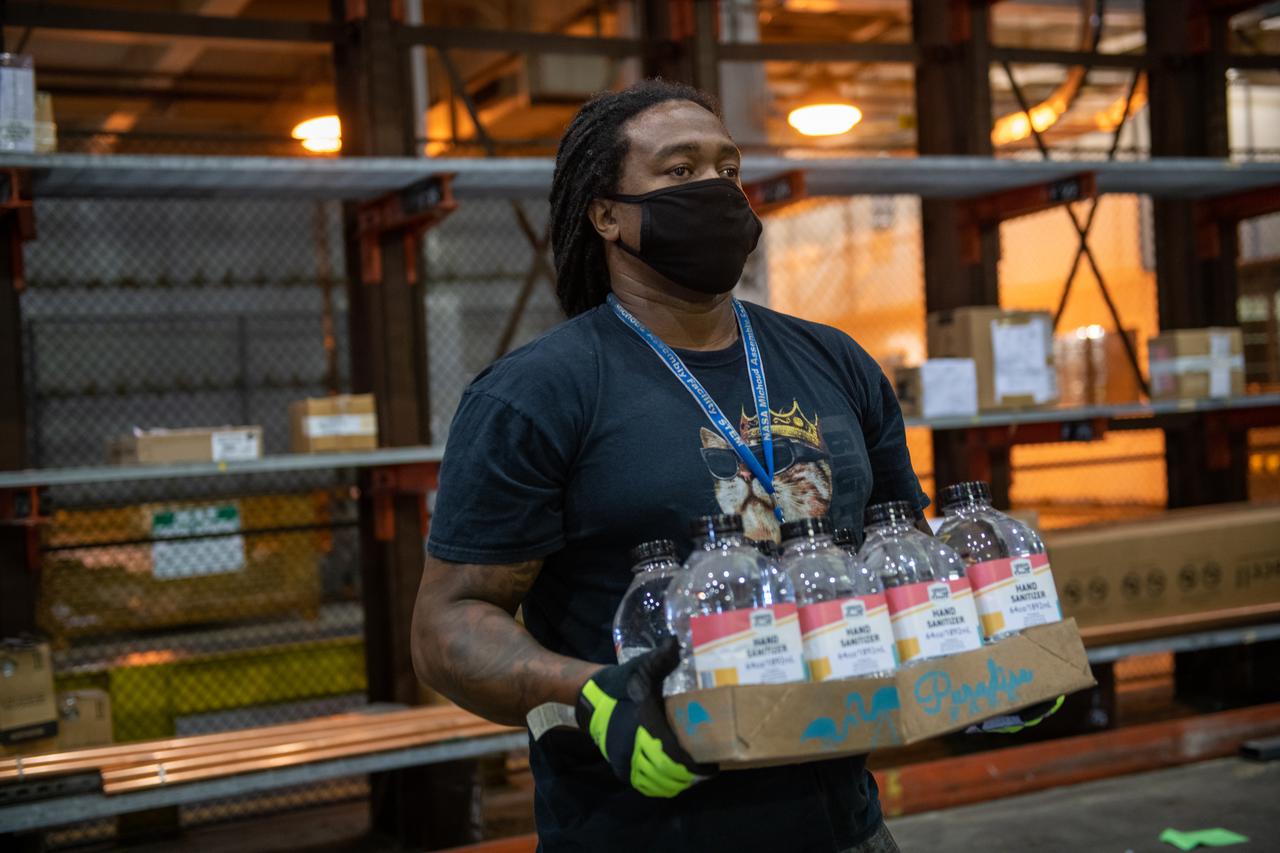

This photo includes two employees wearing personal protective gear in the shipping and receiving area of Michoud Assembly Facility during the Stage 3 transition of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Wearing a facemask is mandatory for common areas where social distancing is difficult to achieve. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Employees at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans will slowly and methodically resume Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion Spacecraft production and assembly activities at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
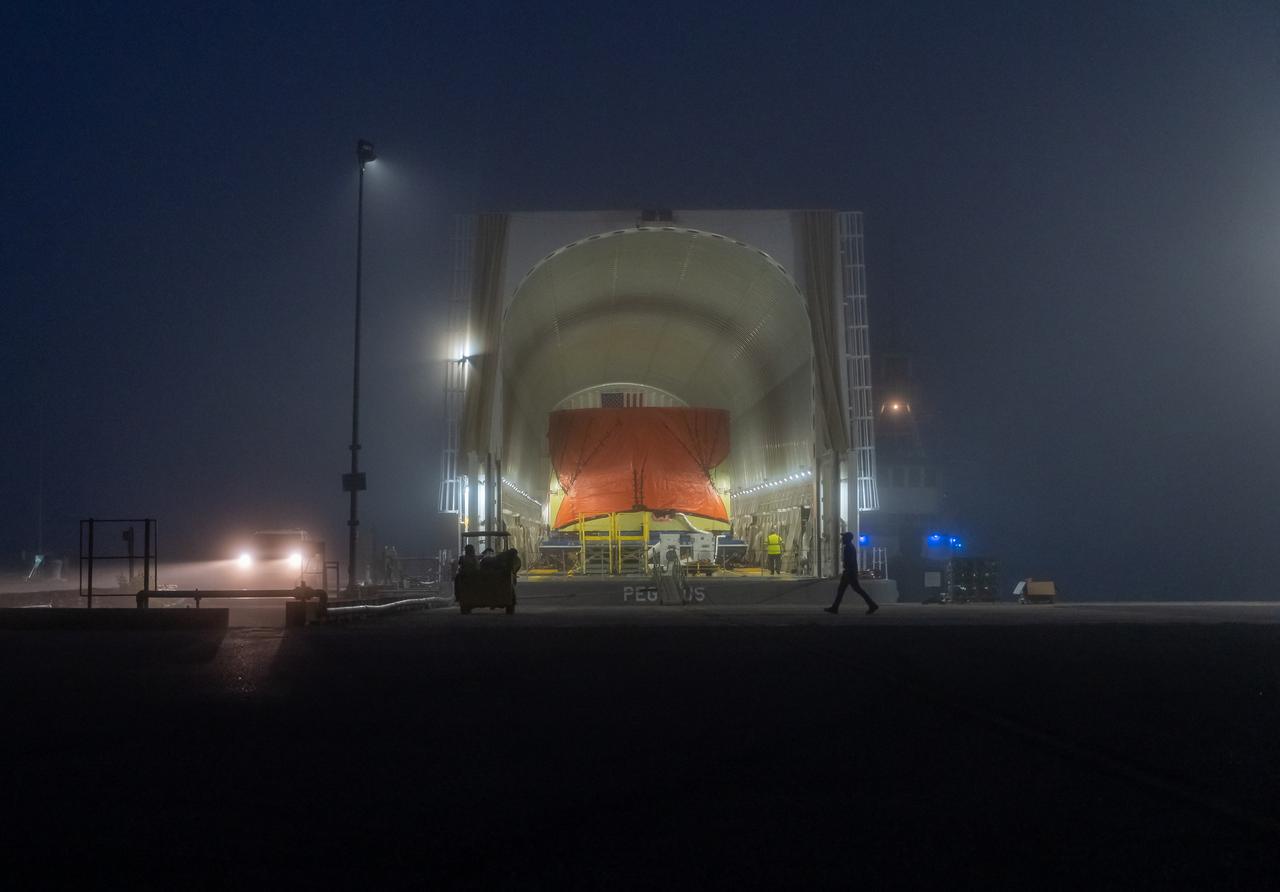

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration.
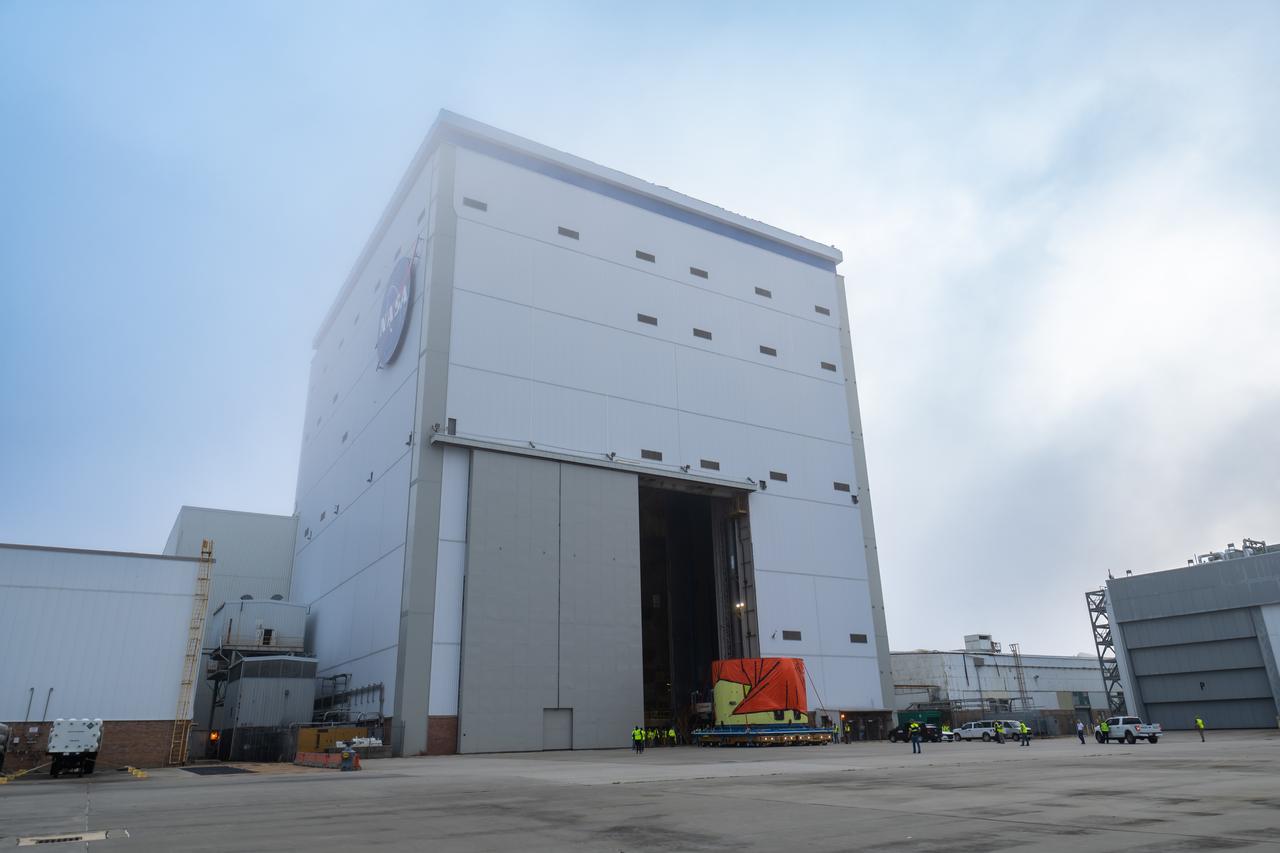

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration.
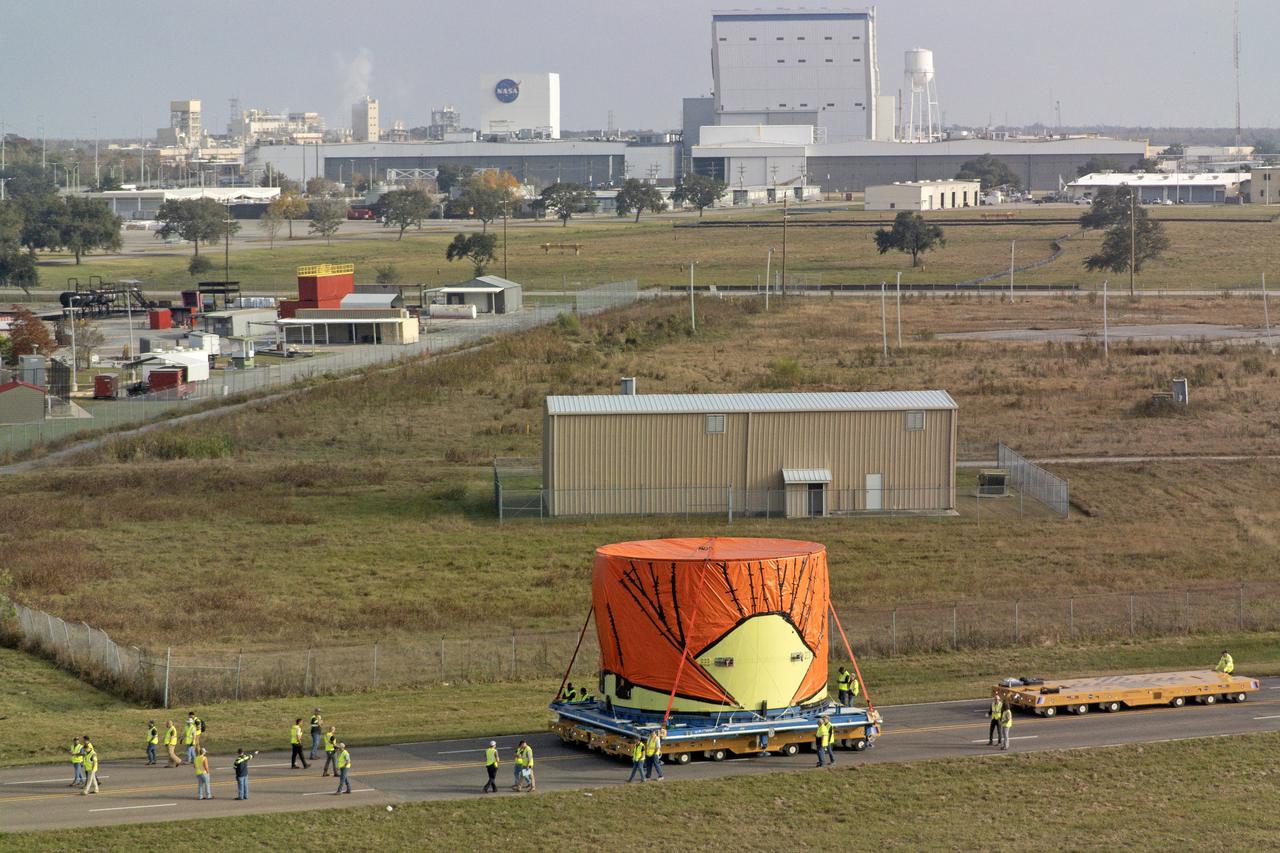

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge on Sunday, December 4, 2022. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
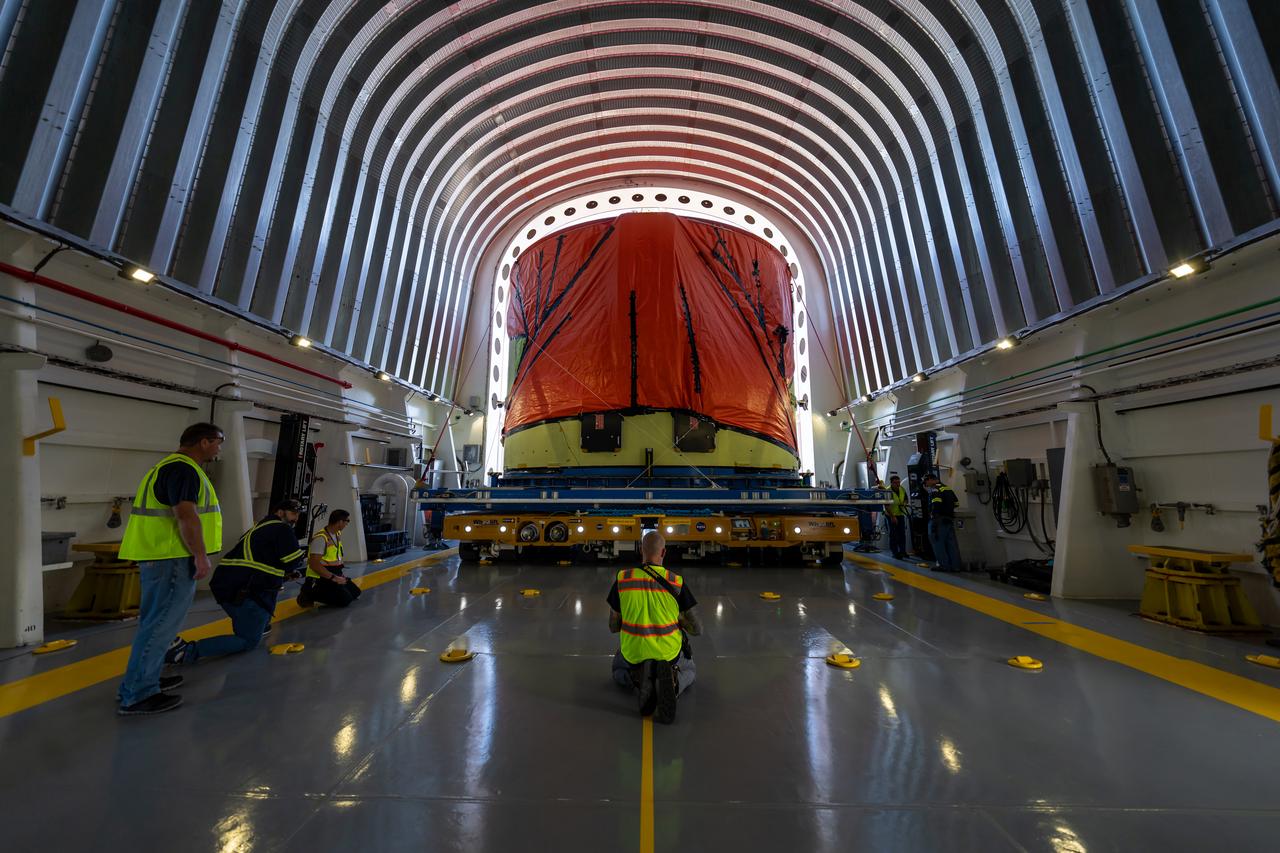

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration.
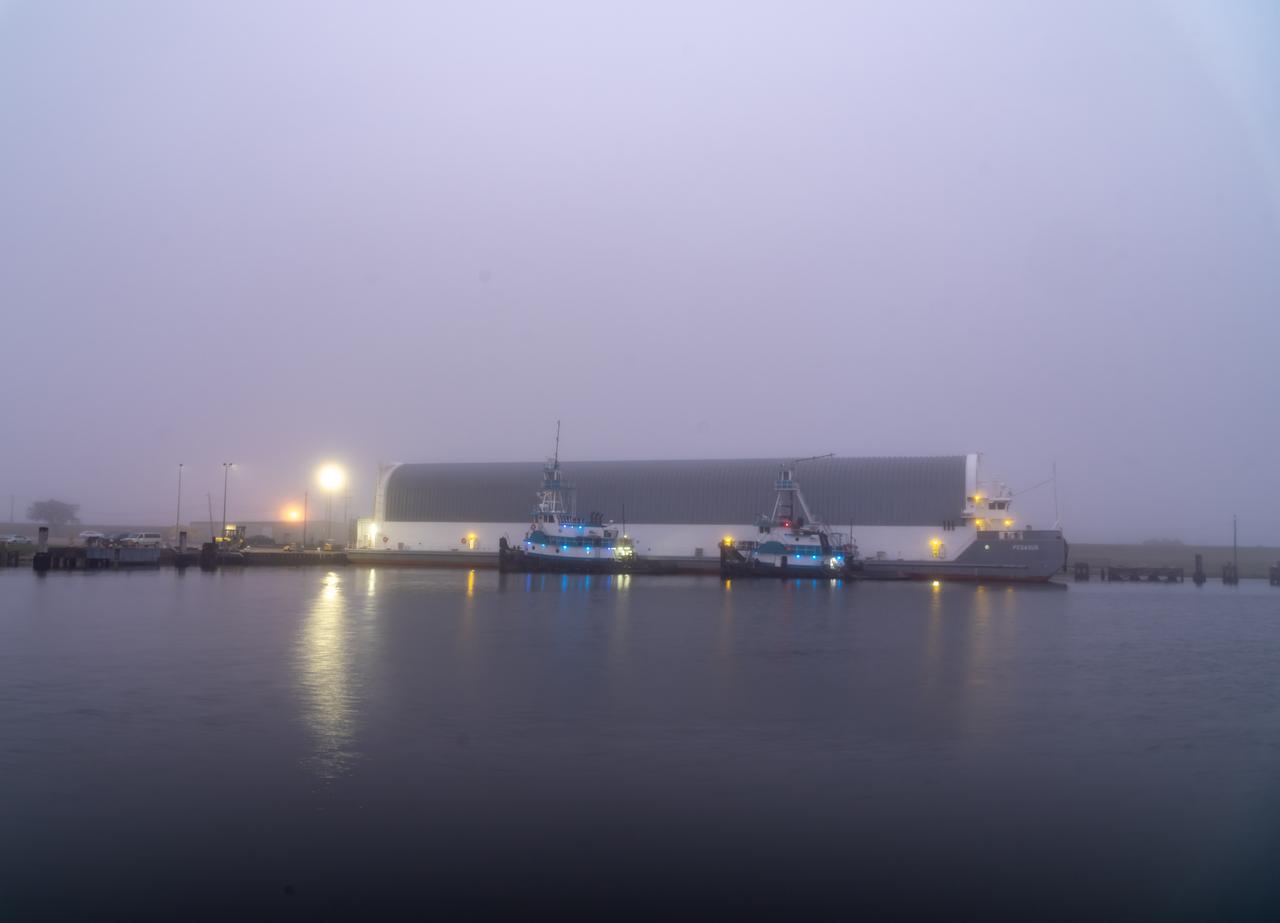

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration.
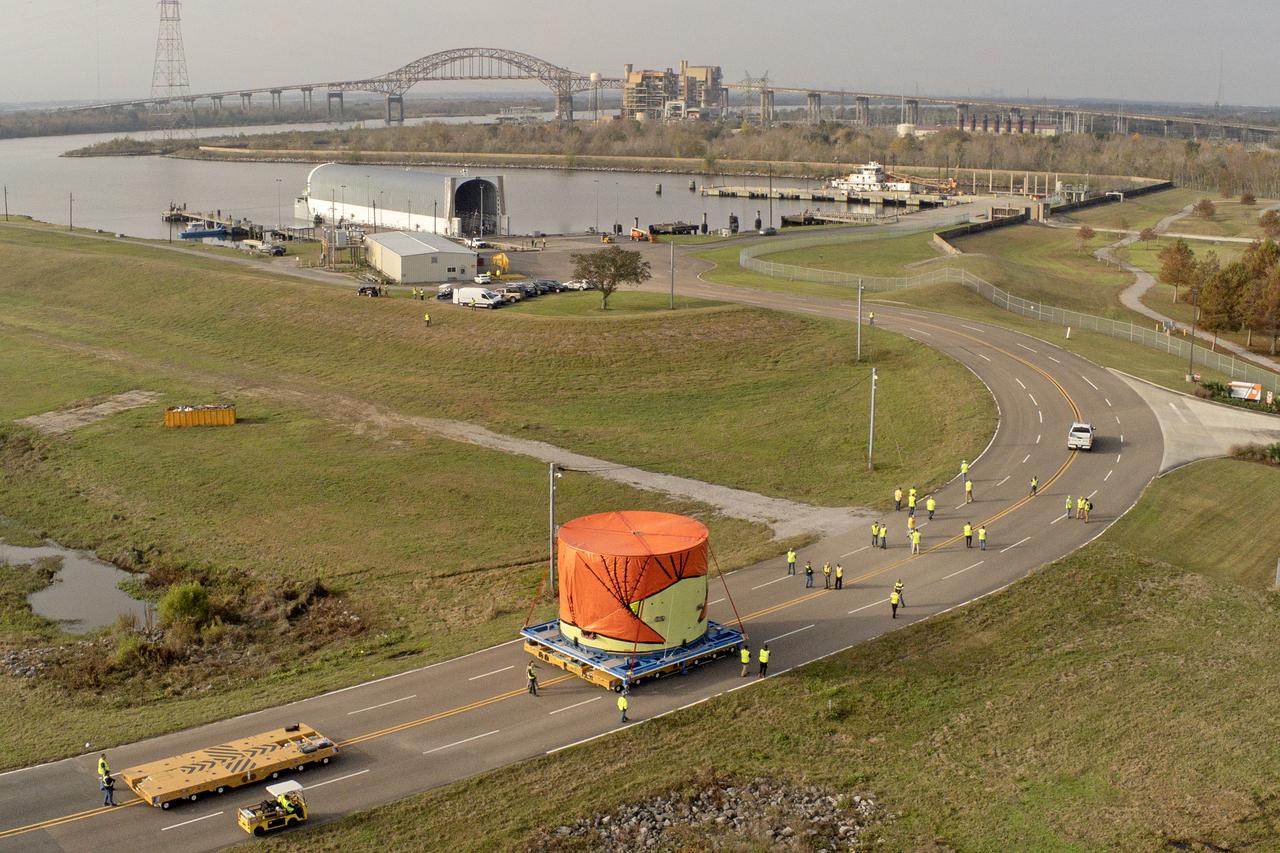

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge on Sunday, December 4, 2022. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
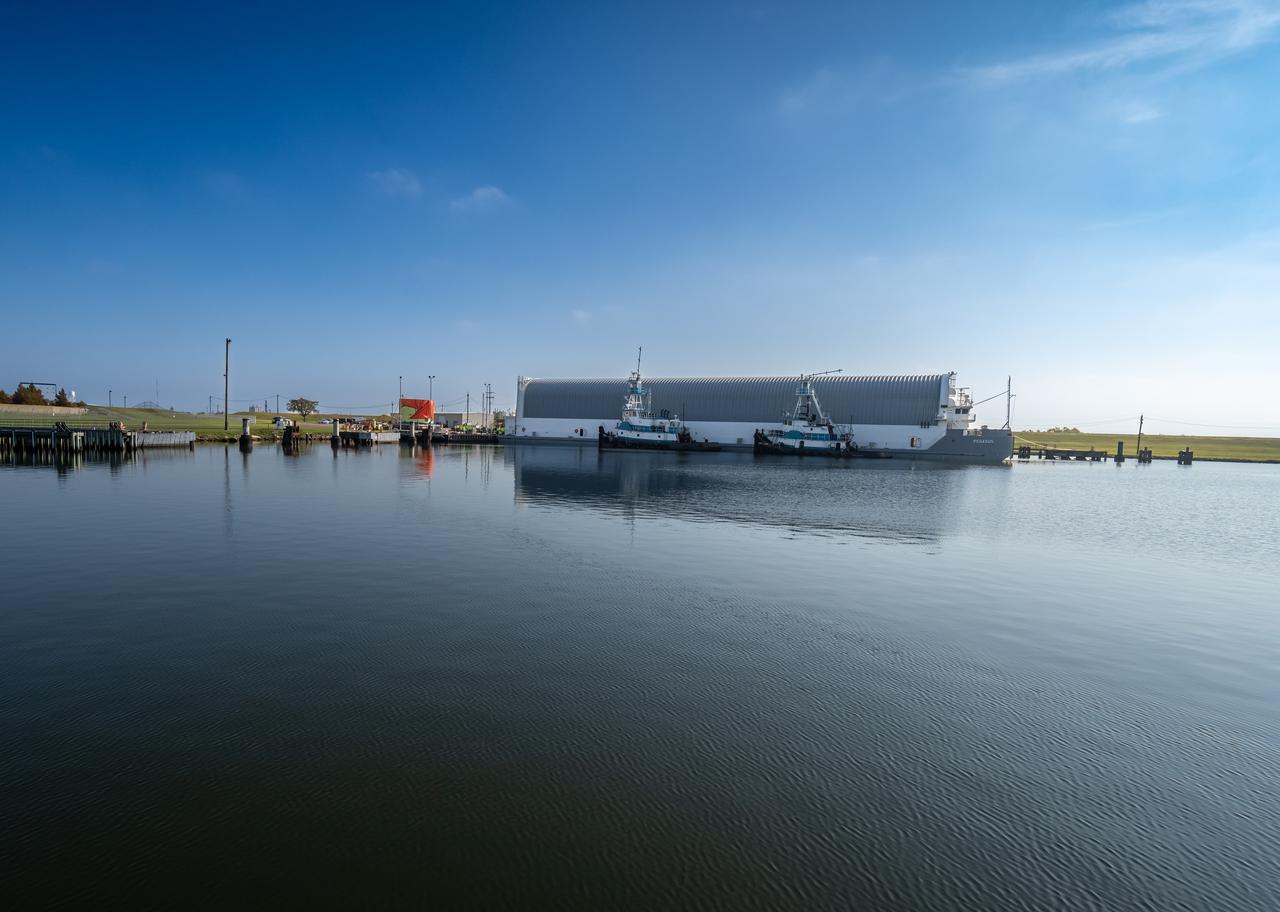

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration.
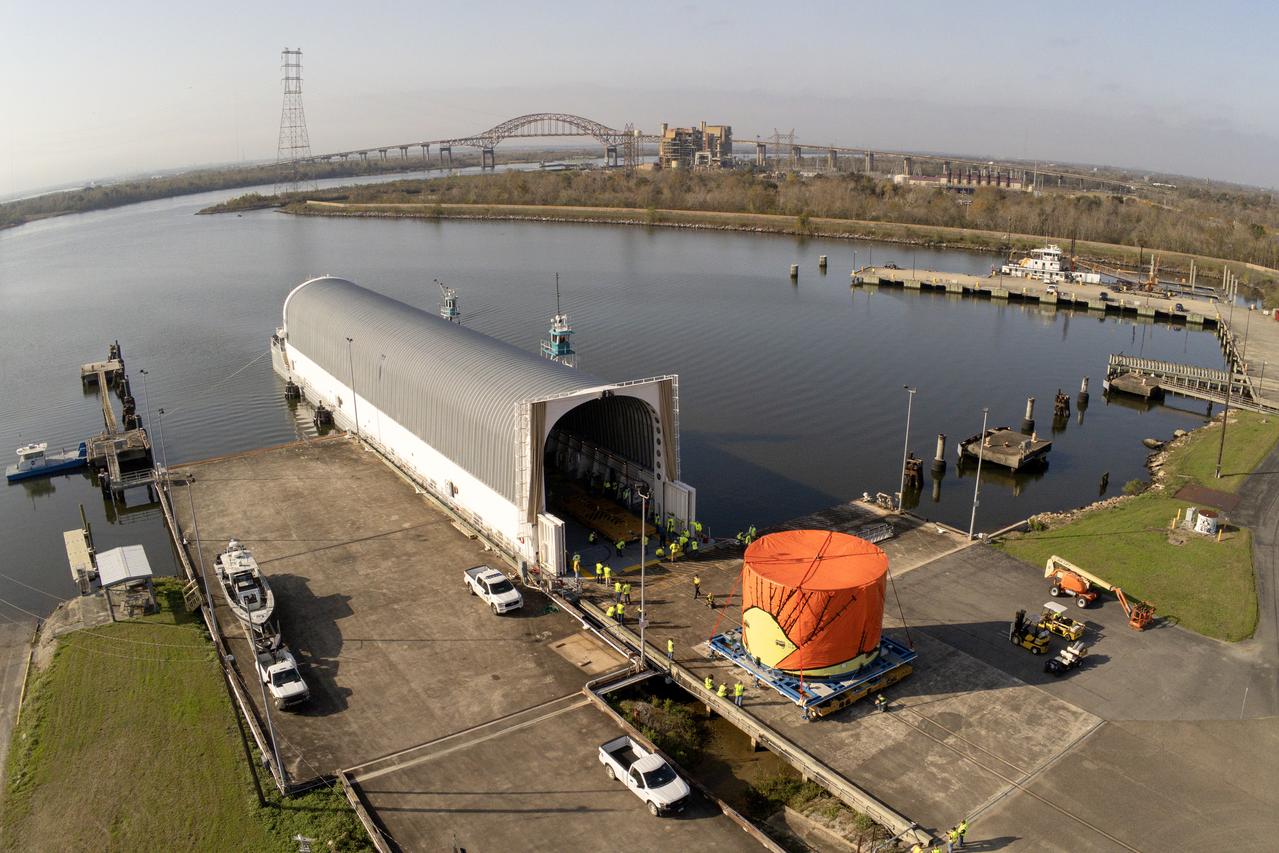

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge on Sunday, December 4, 2022. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

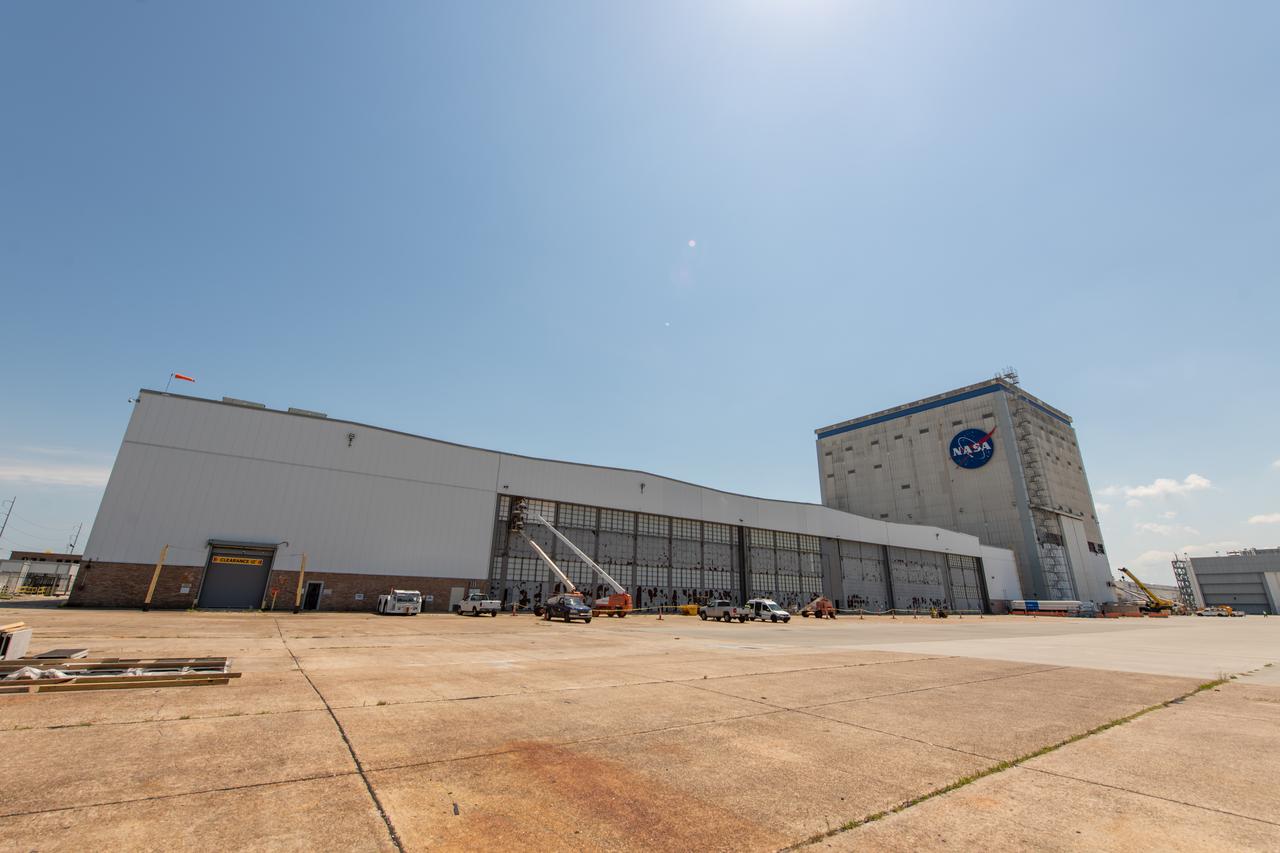
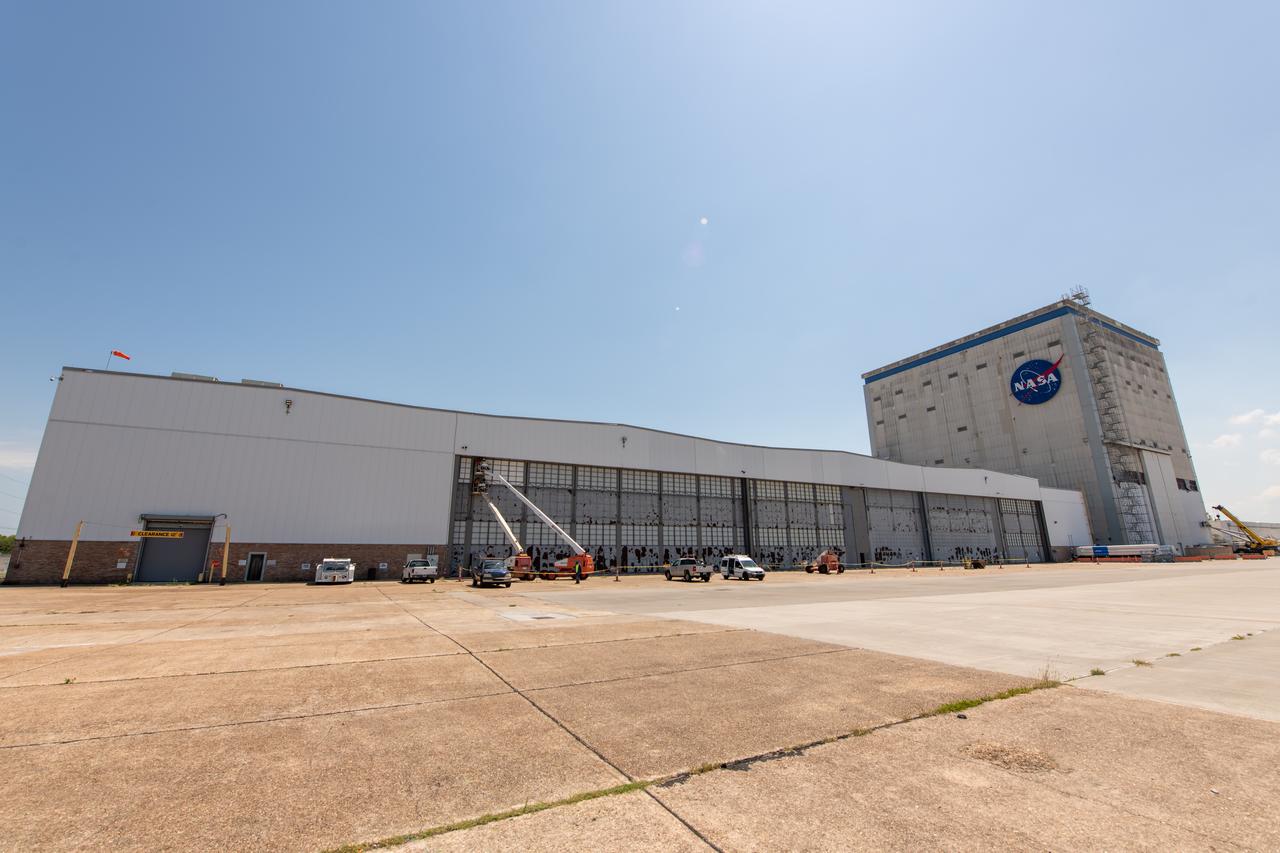
This photo includes two employees wearing personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Every team member who goes on-site brings their own cloth face covering and wears it when social distancing is not possible, such as in a shared vehicle when working inside the large factory. Michoud Assembly Facility is made up of multiple buildings, the largest of which is more than 38 acres under one roof. Wearing a facemask is mandatory for common areas where social distancing is difficult to achieve. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
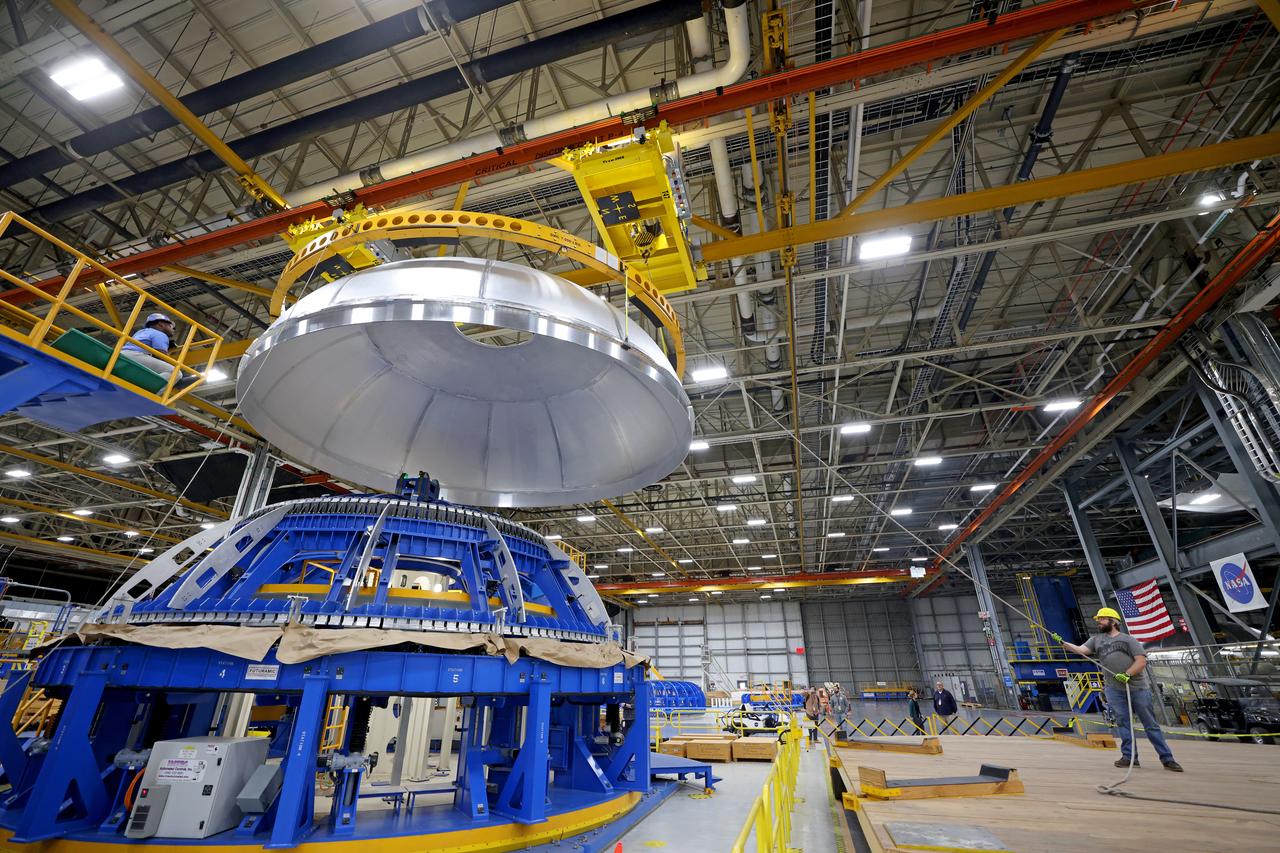

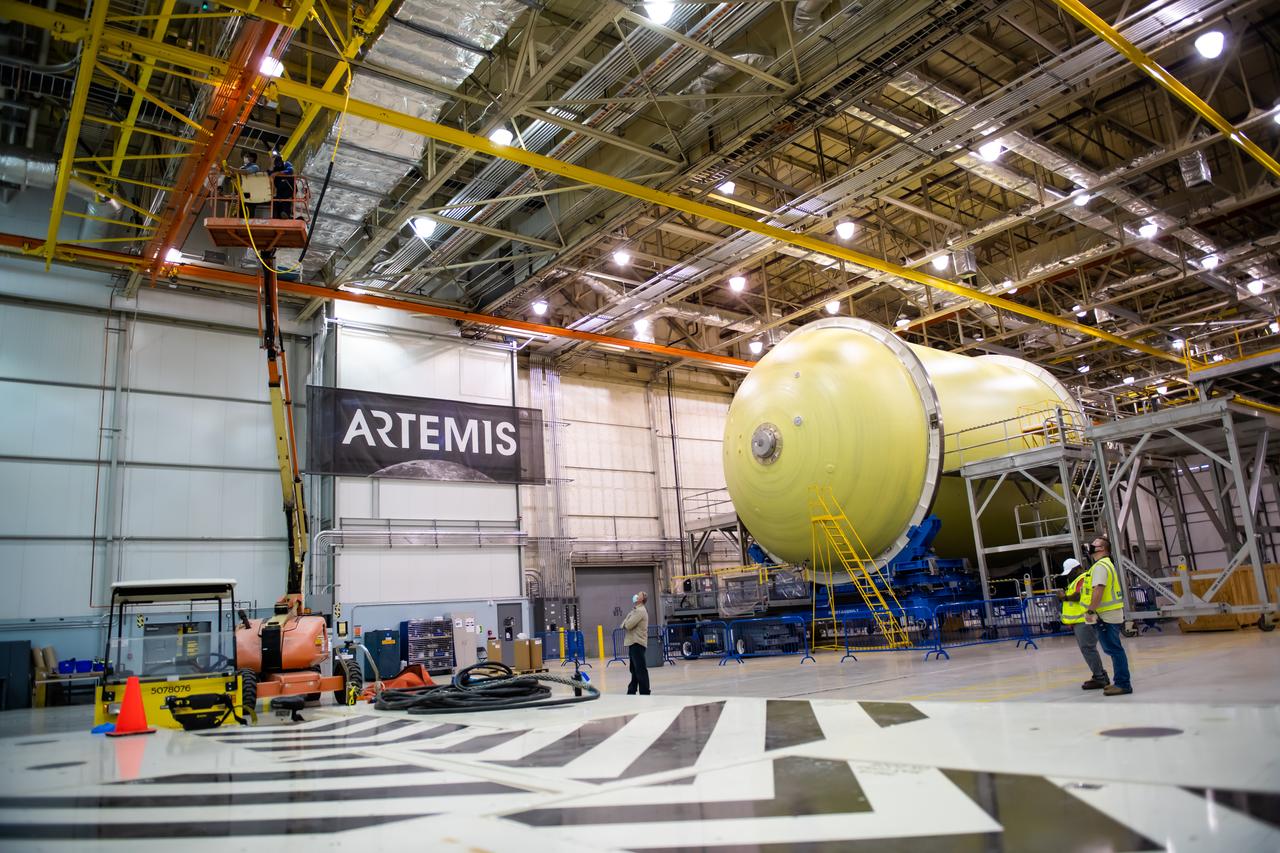
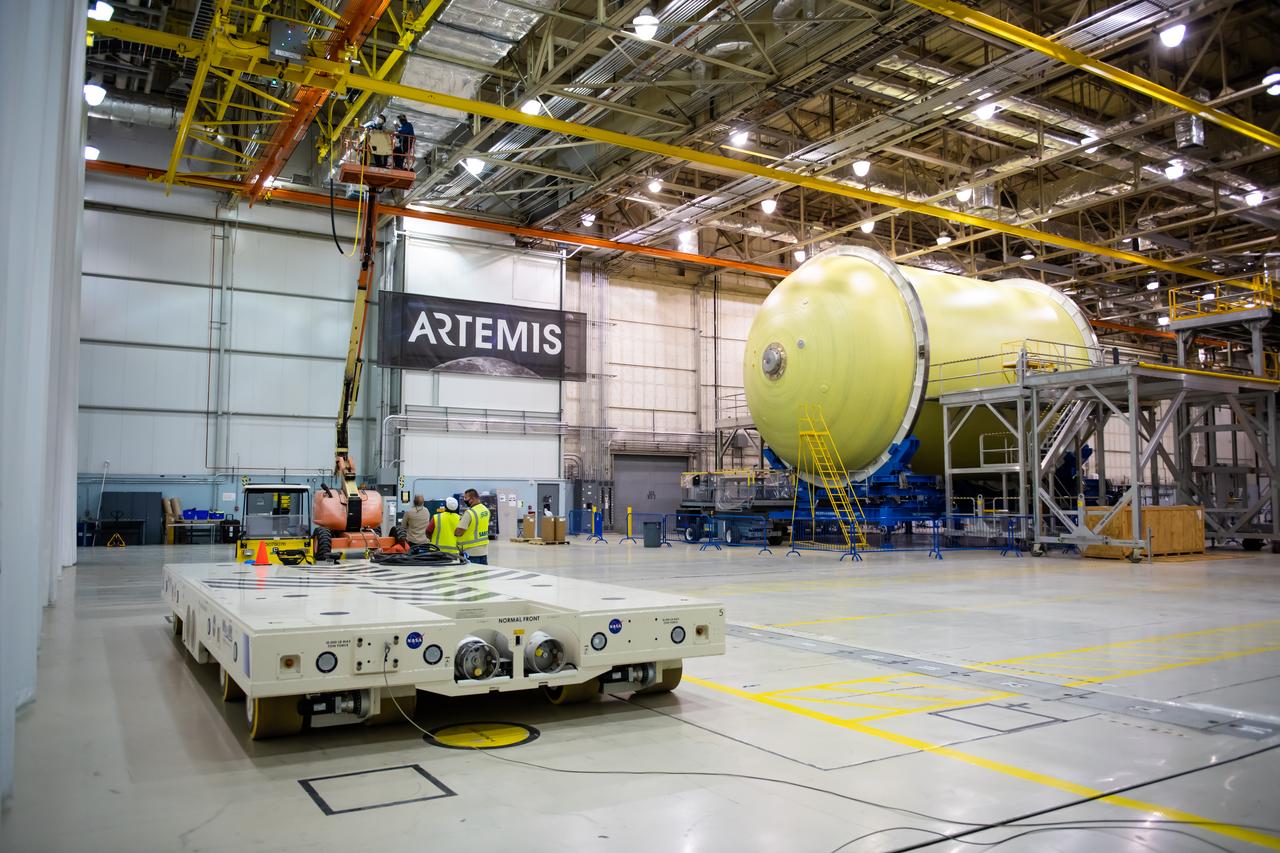
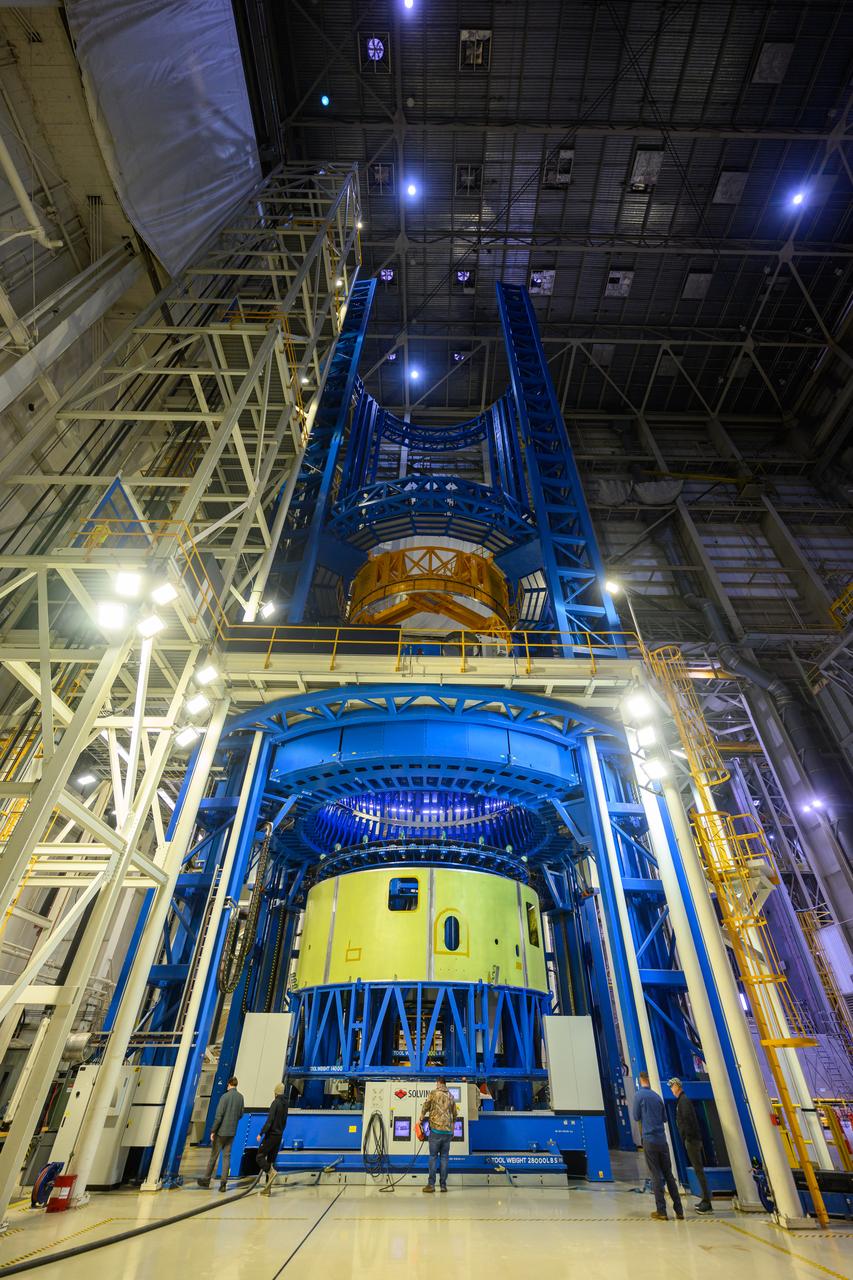
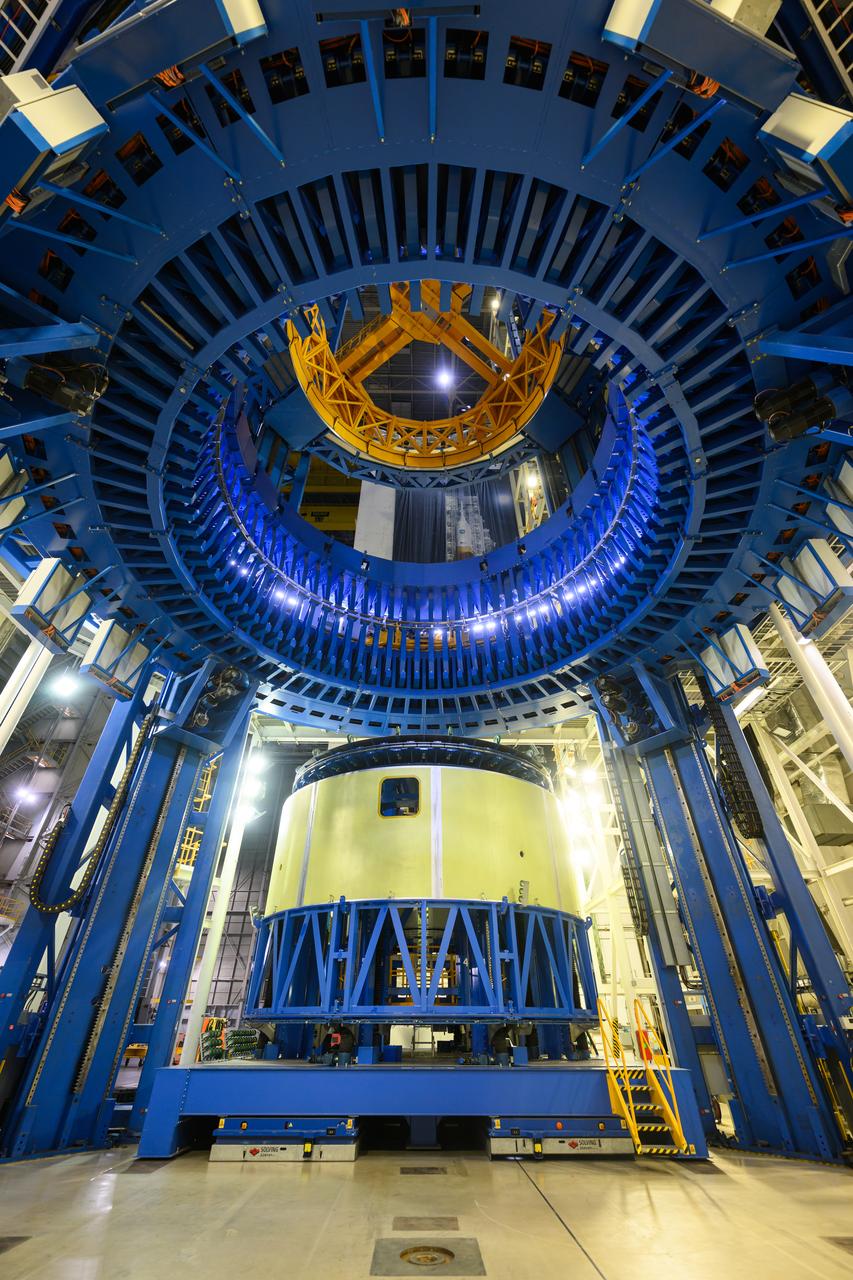
This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
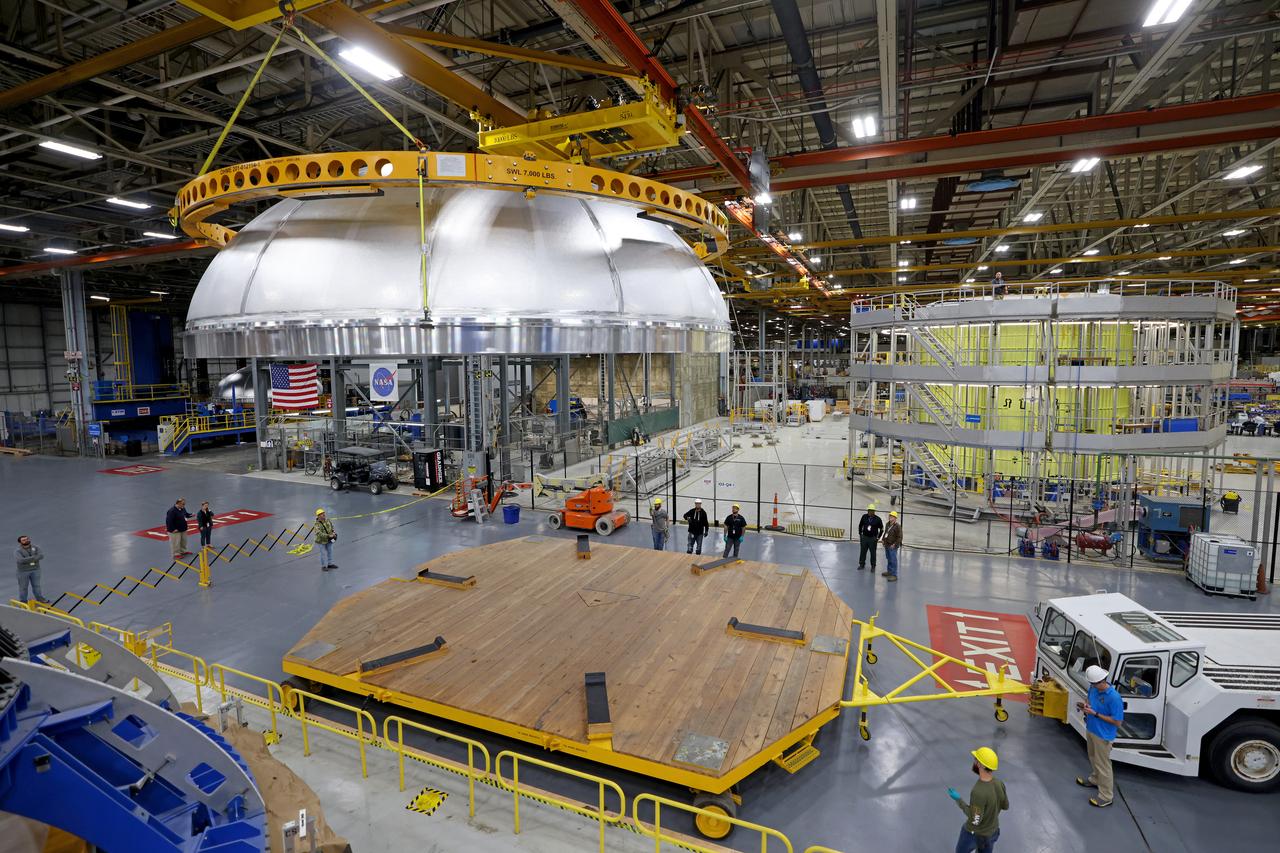

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
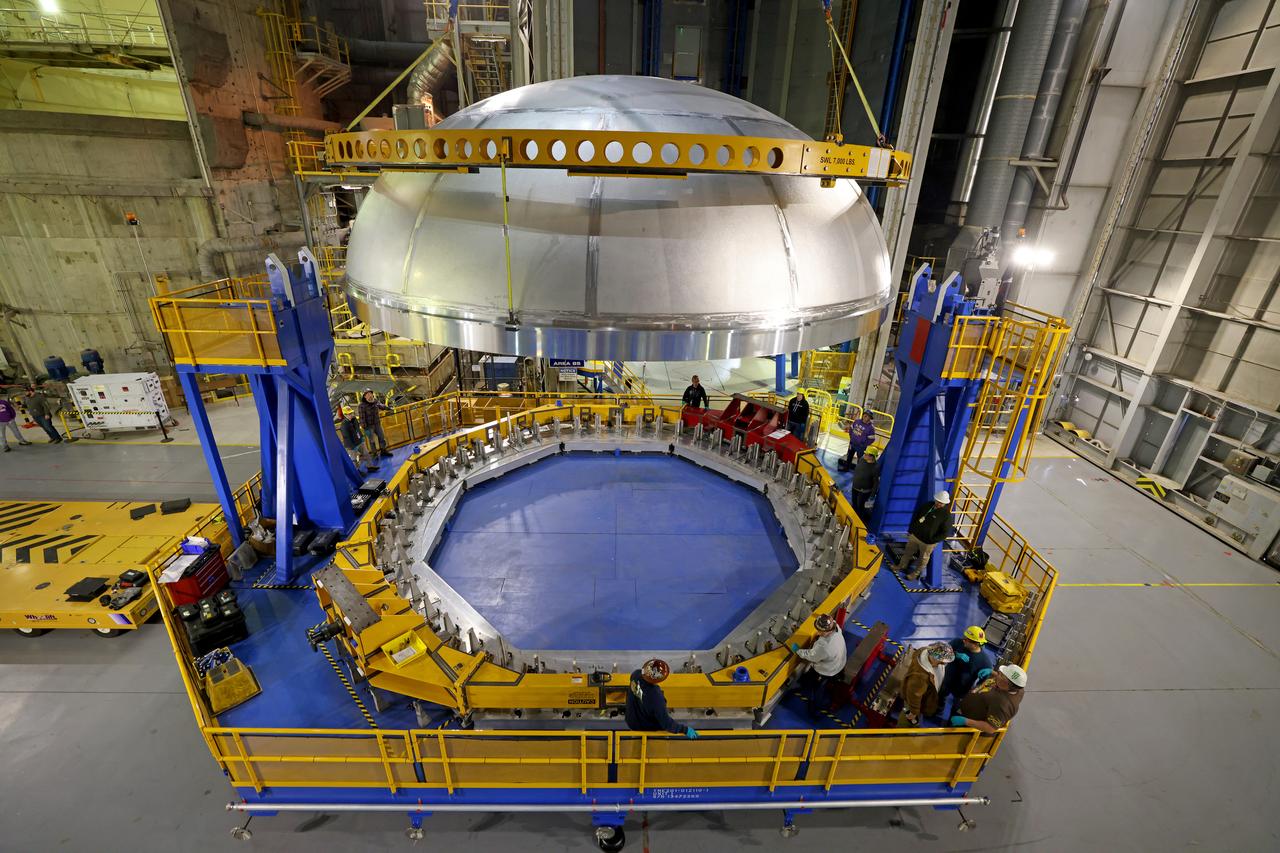

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 6. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
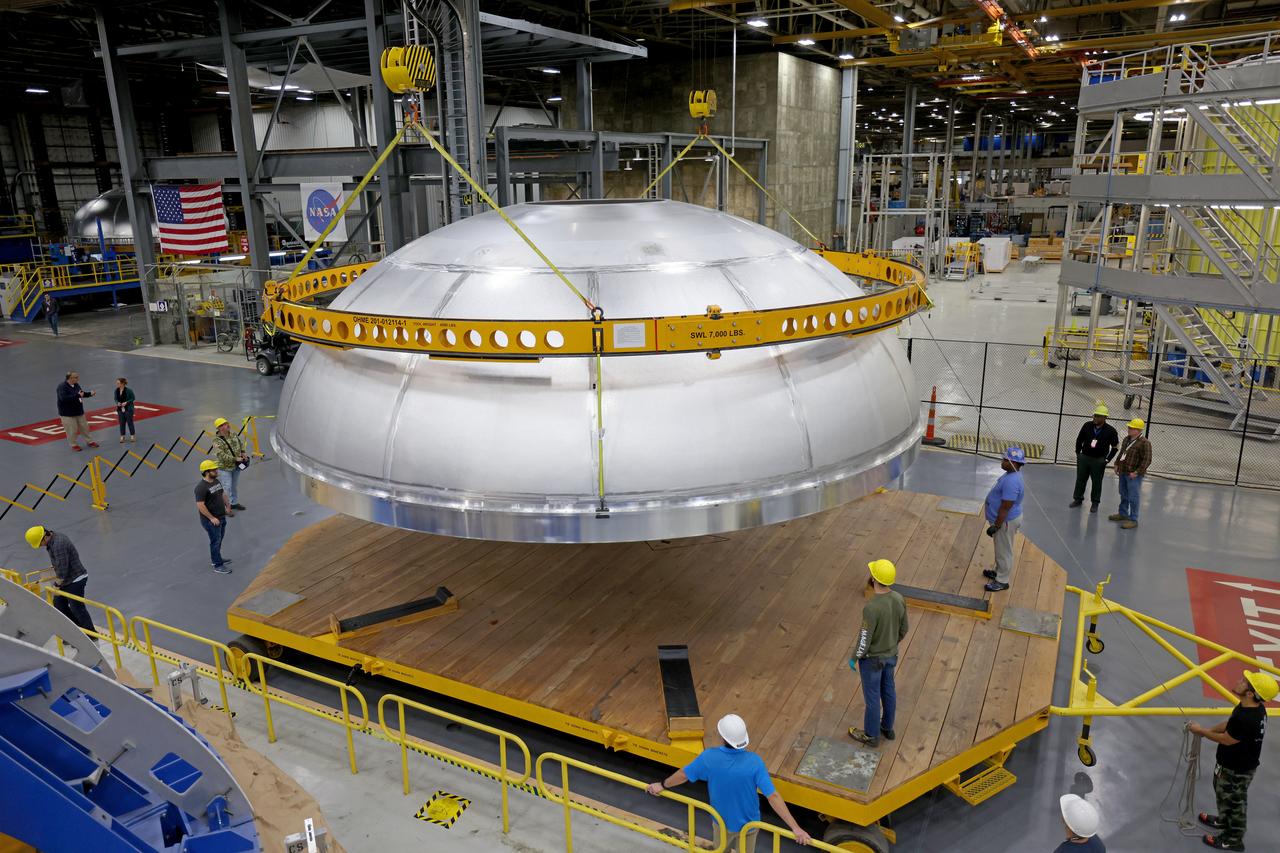

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
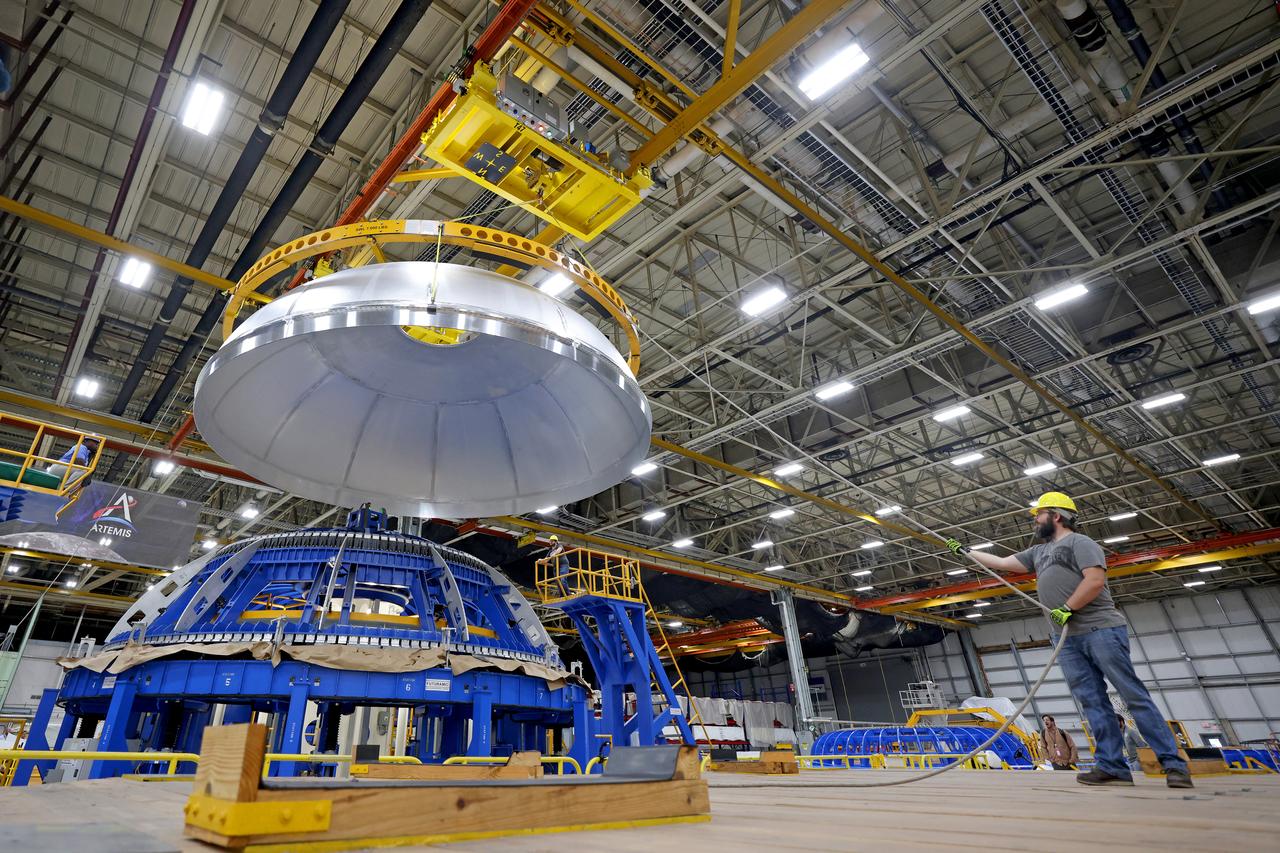

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
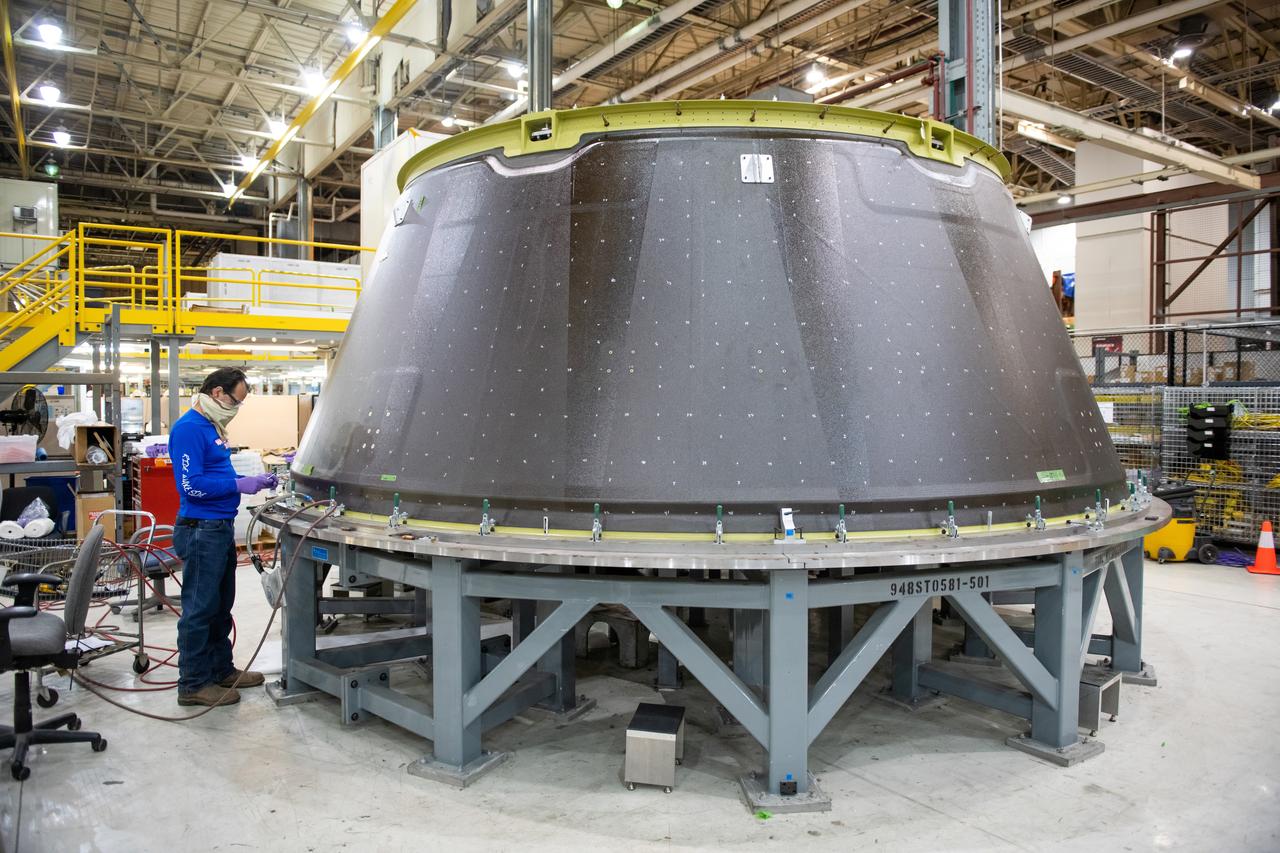

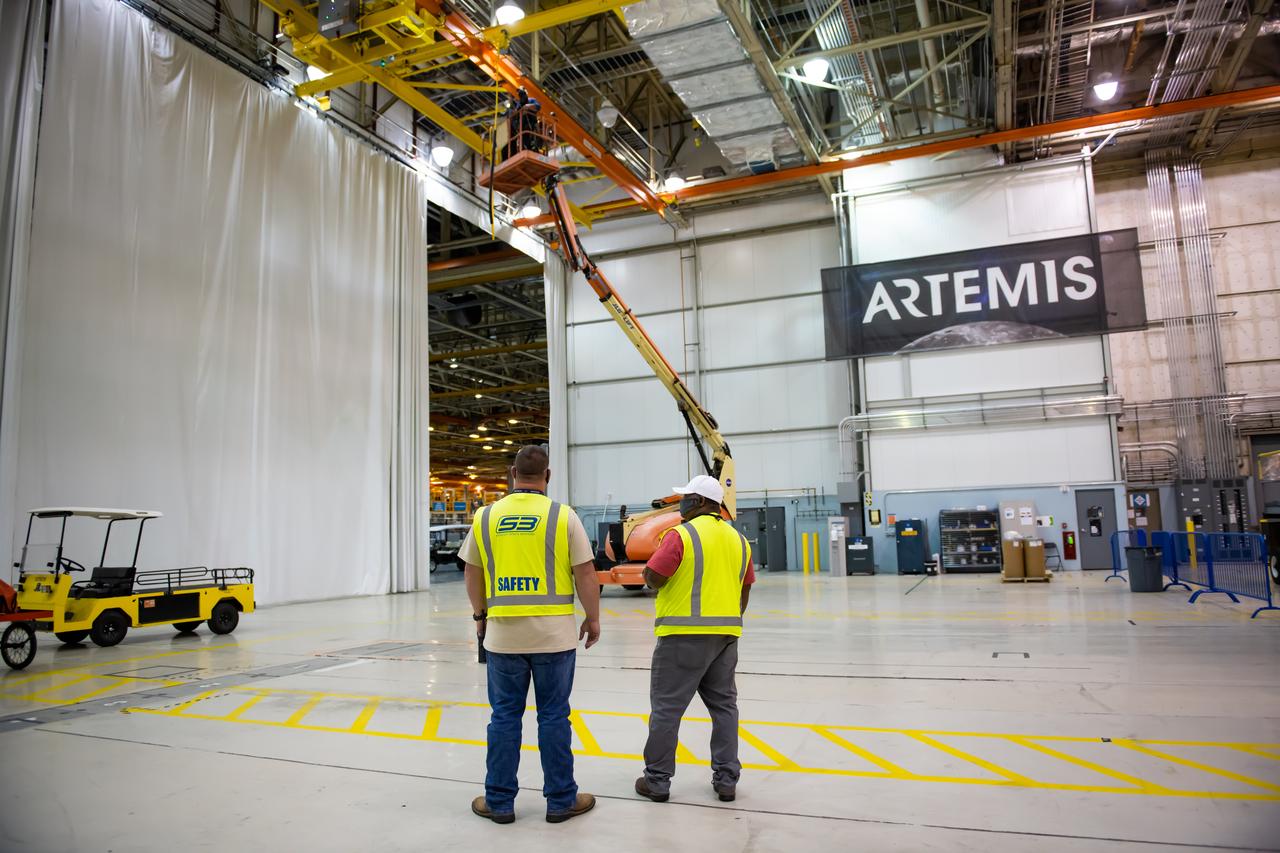
This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.
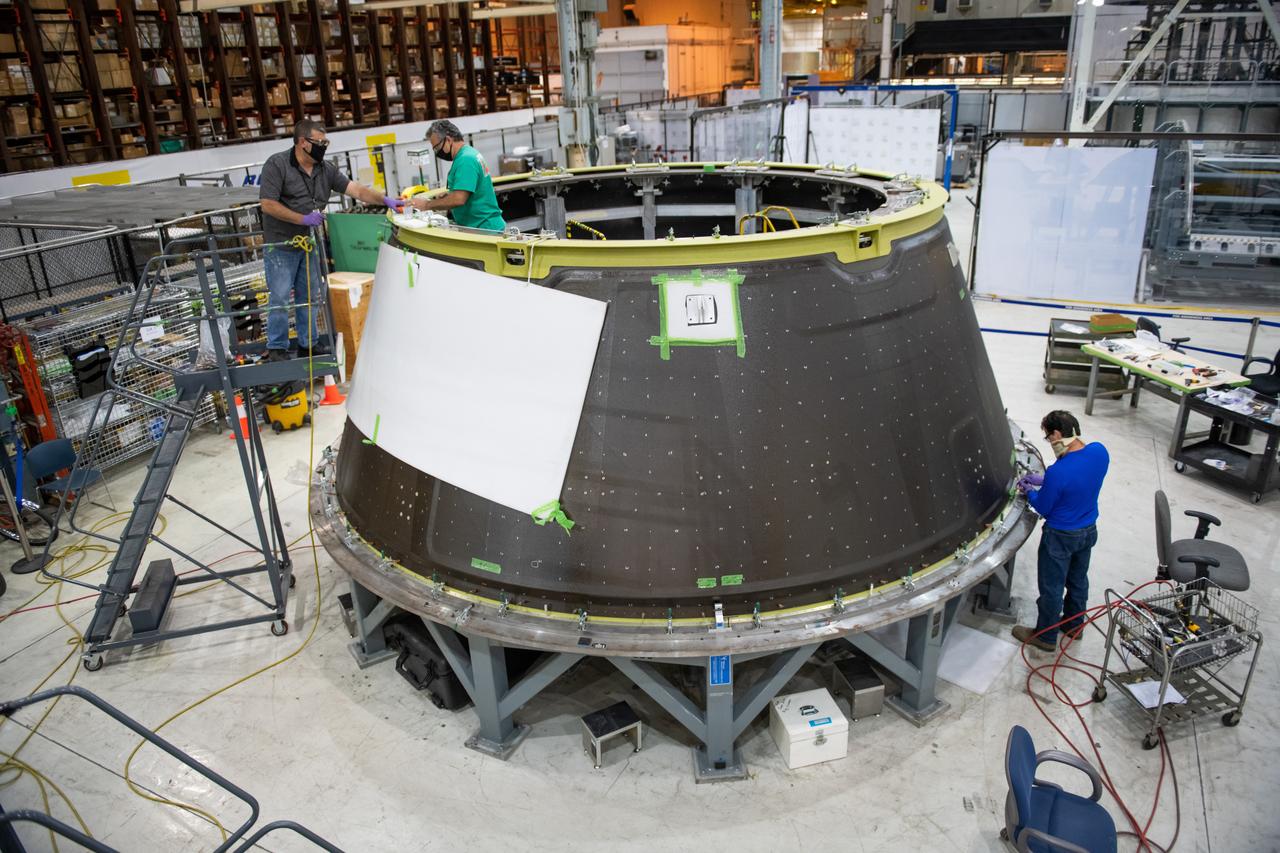

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.
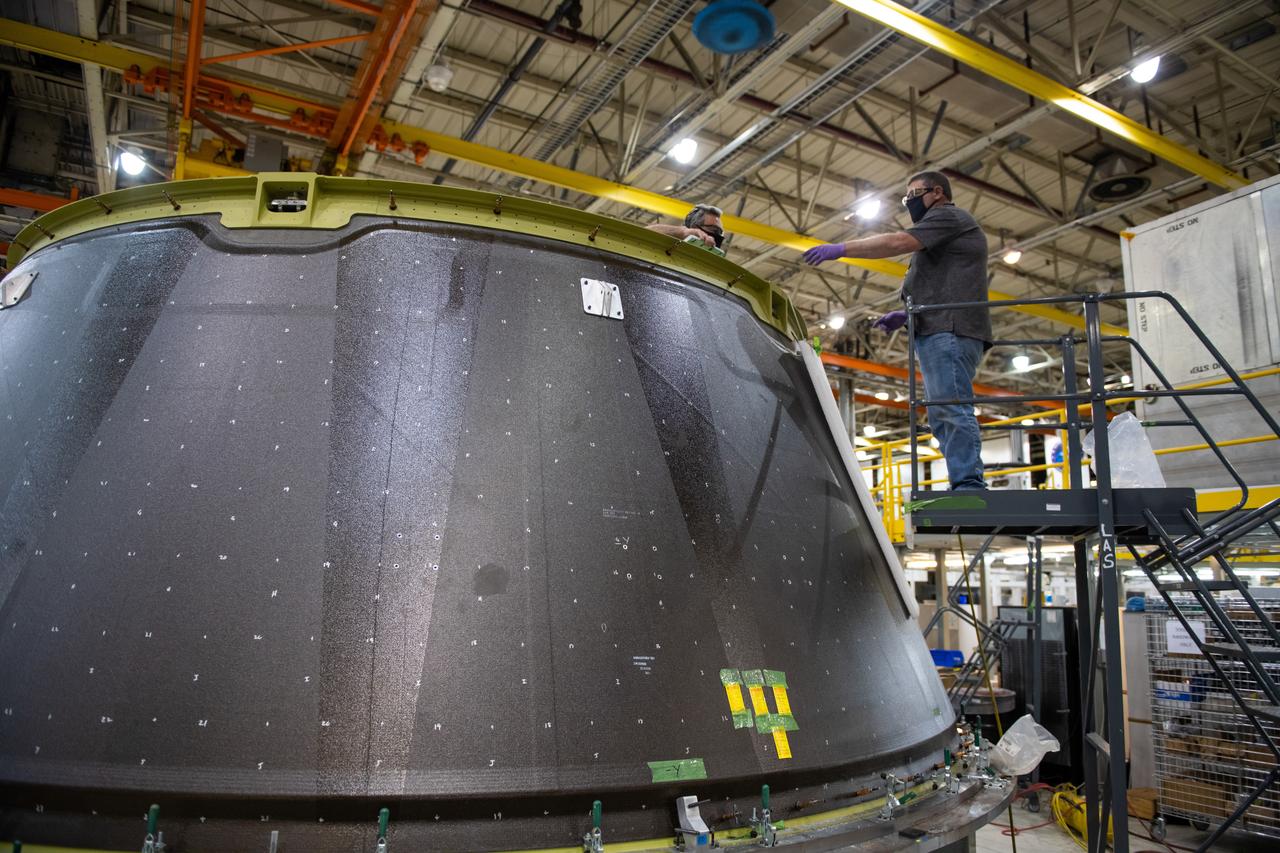

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.
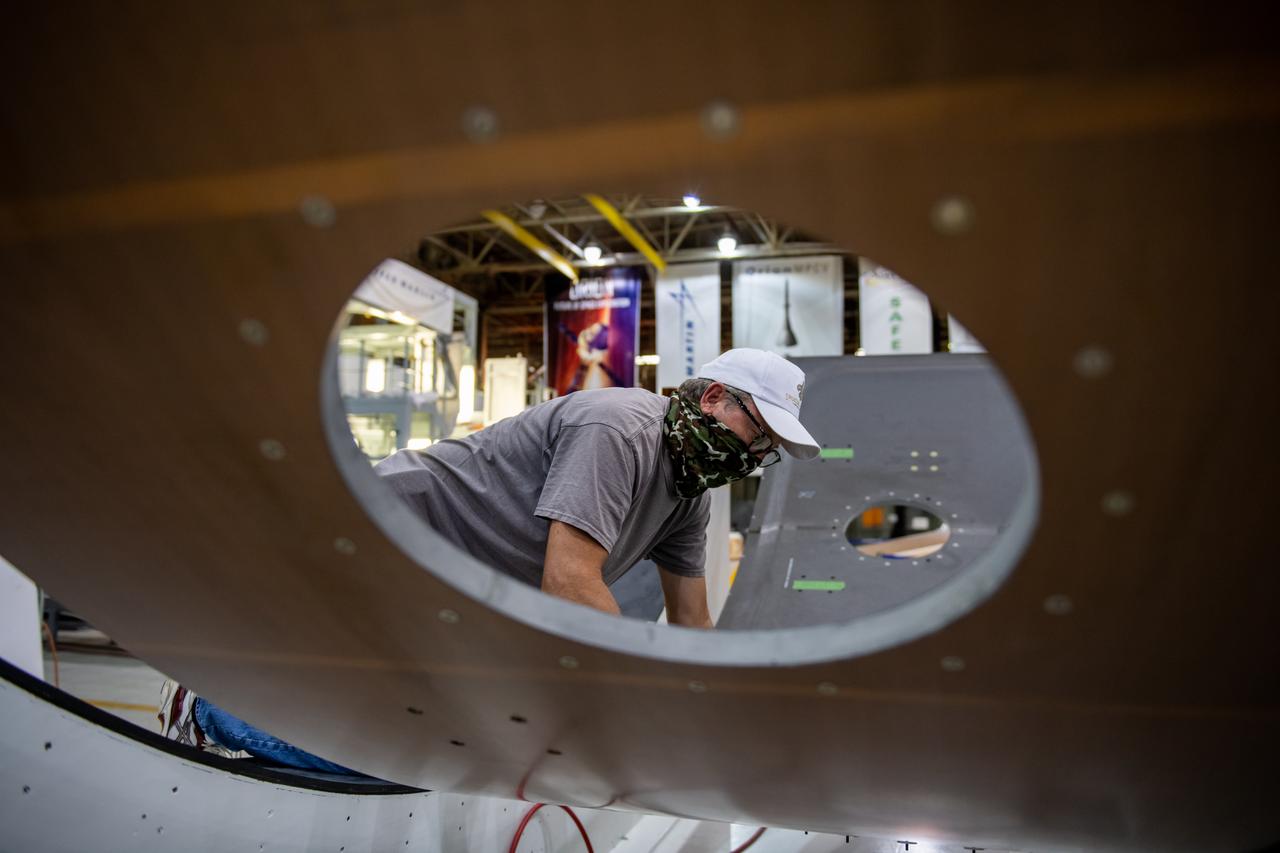
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
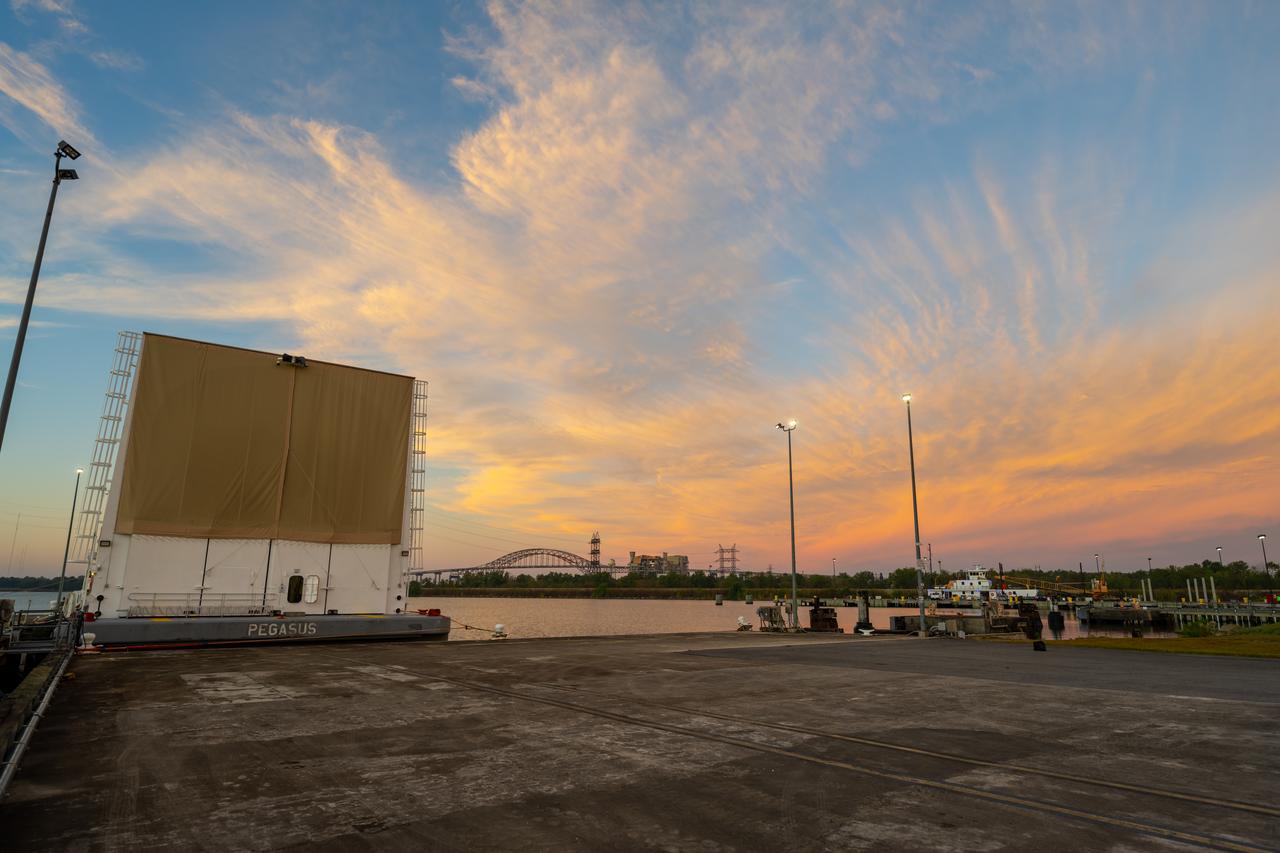

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jared Lyons)
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
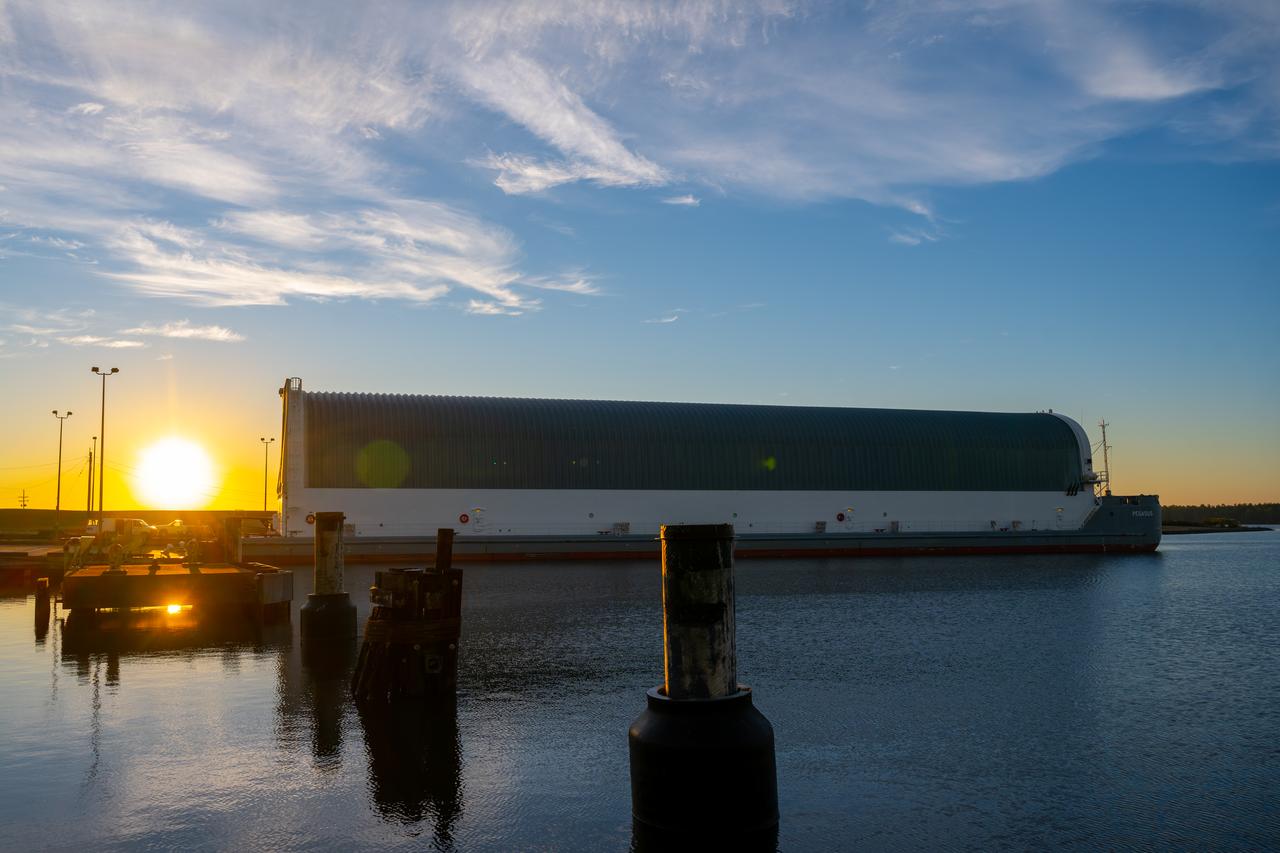

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jared Lyons)
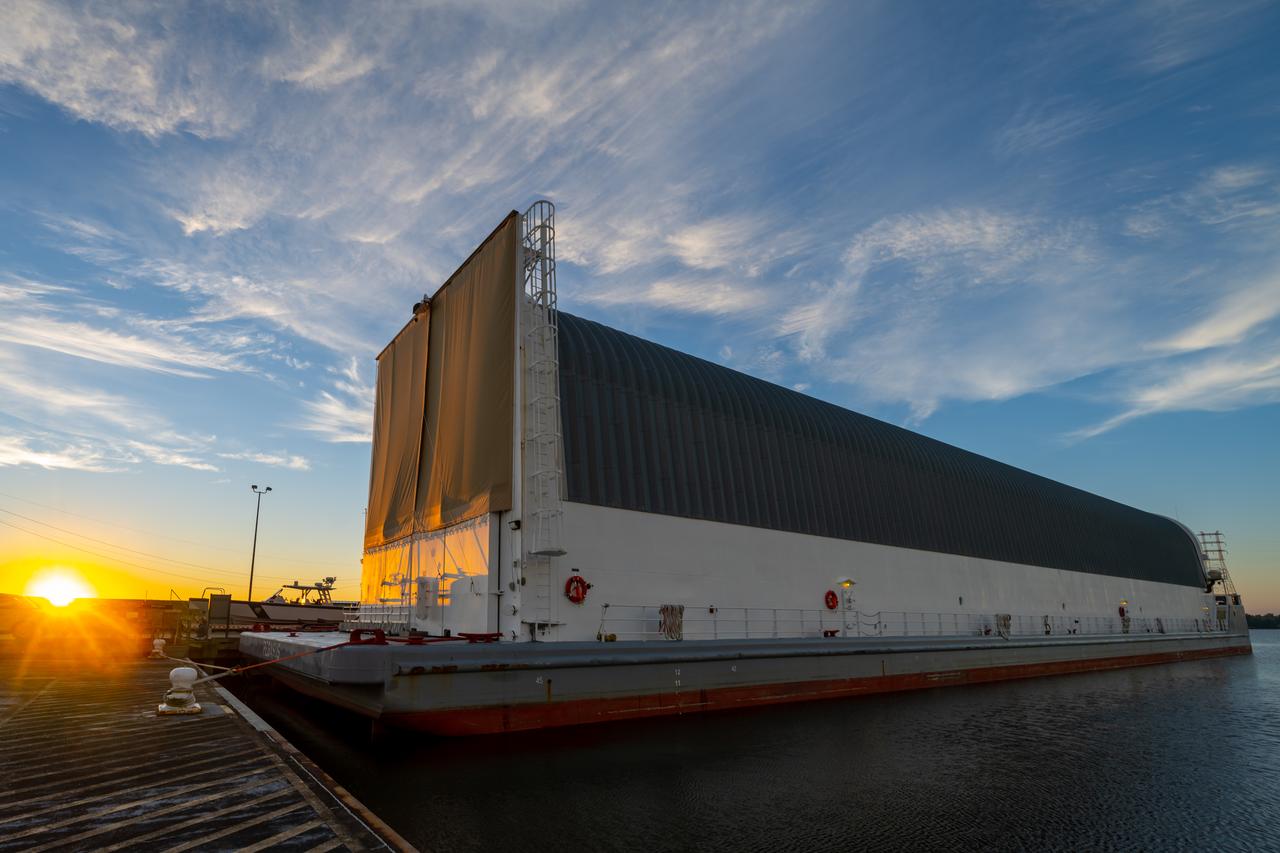

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jared Lyons)

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
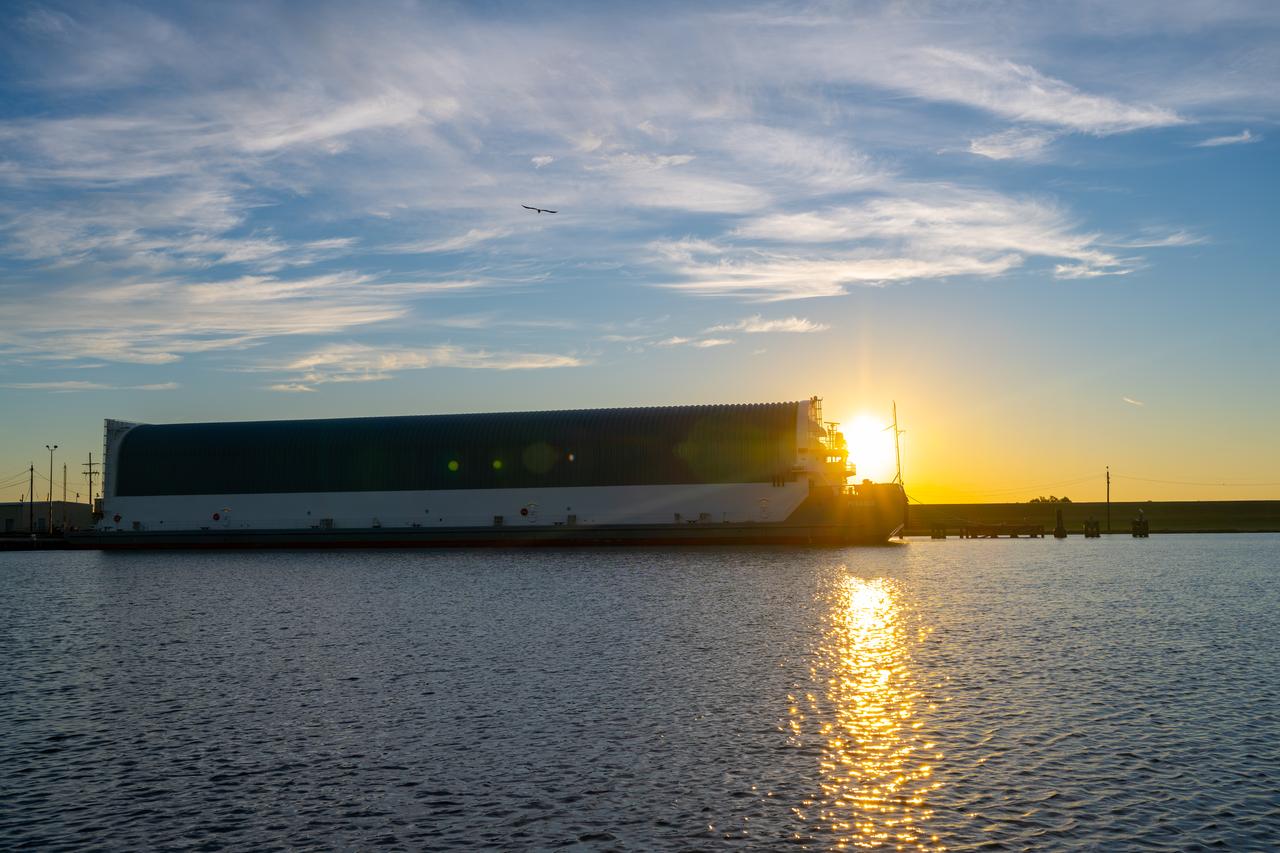

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jared Lyons)
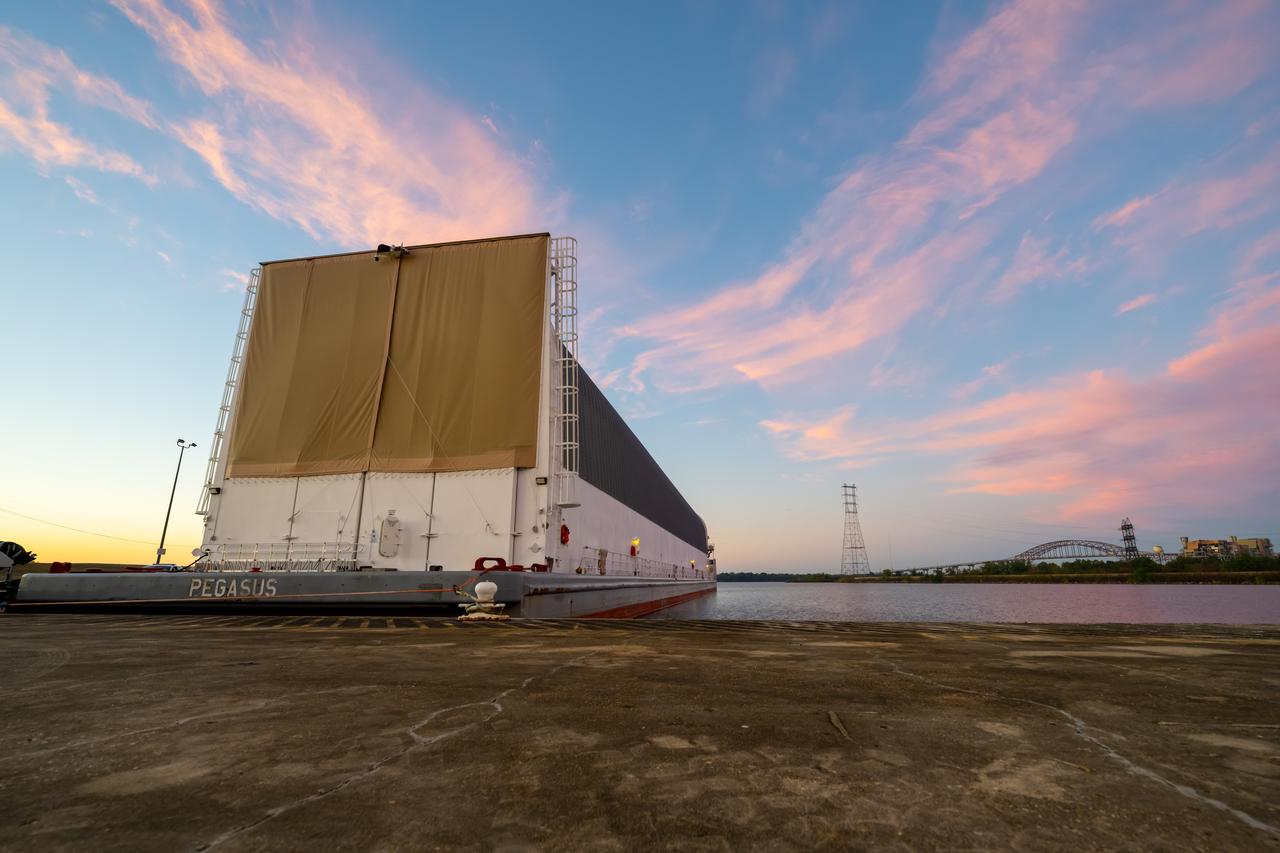

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the engine section flight hardware to the agency’s Pegasus barge Sunday, Dec. 4. The barge will ferry the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis III to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once there, teams at Kennedy will finish outfitting the engine section, which comprises the tail-end of the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, before integrating it to the rest of the stage. Beginning with production for Artemis III, NASA and core stage lead contractor Boeing will use Michoud, where the SLS core stages are currently manufactured, to produce and outfit the core stage’s five elements, and available space at Kennedy for final assembly and integration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jared Lyons)
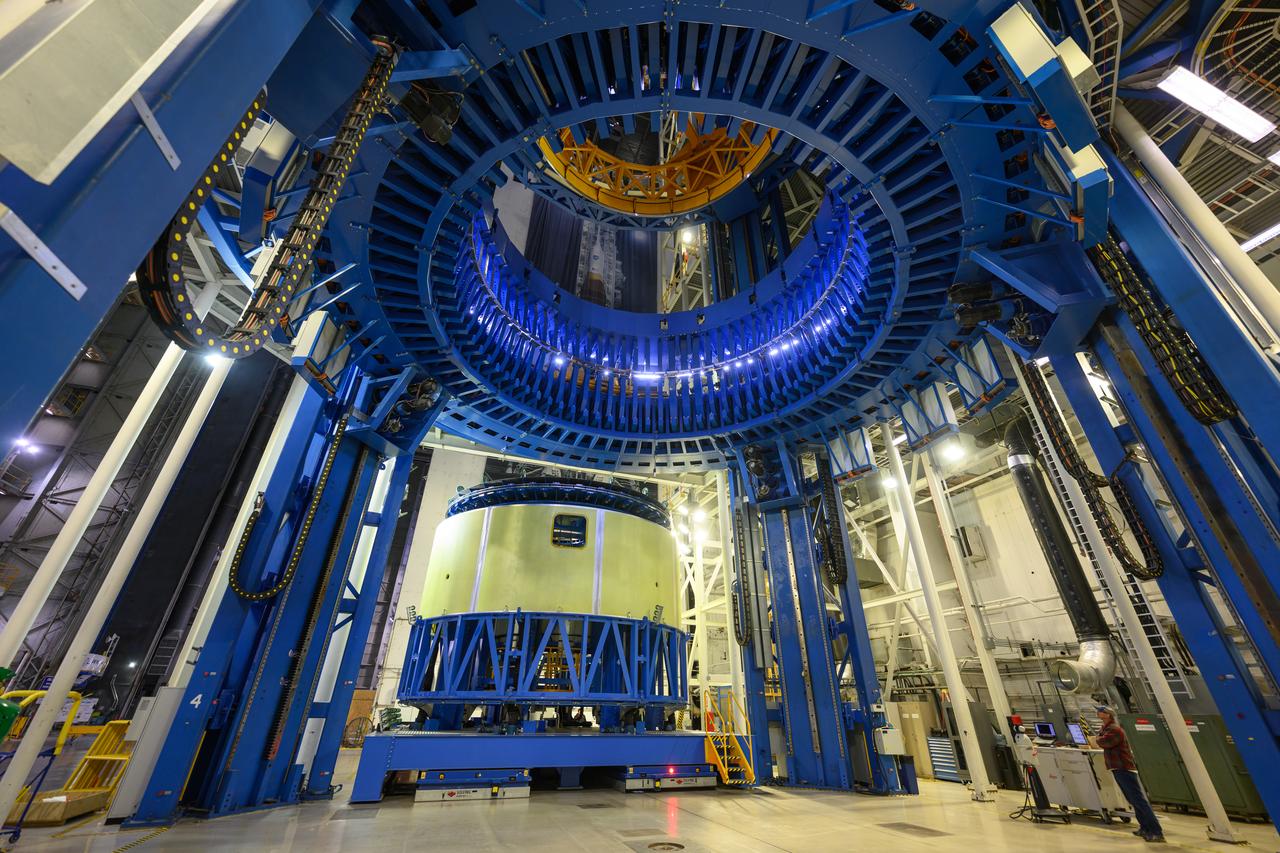

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

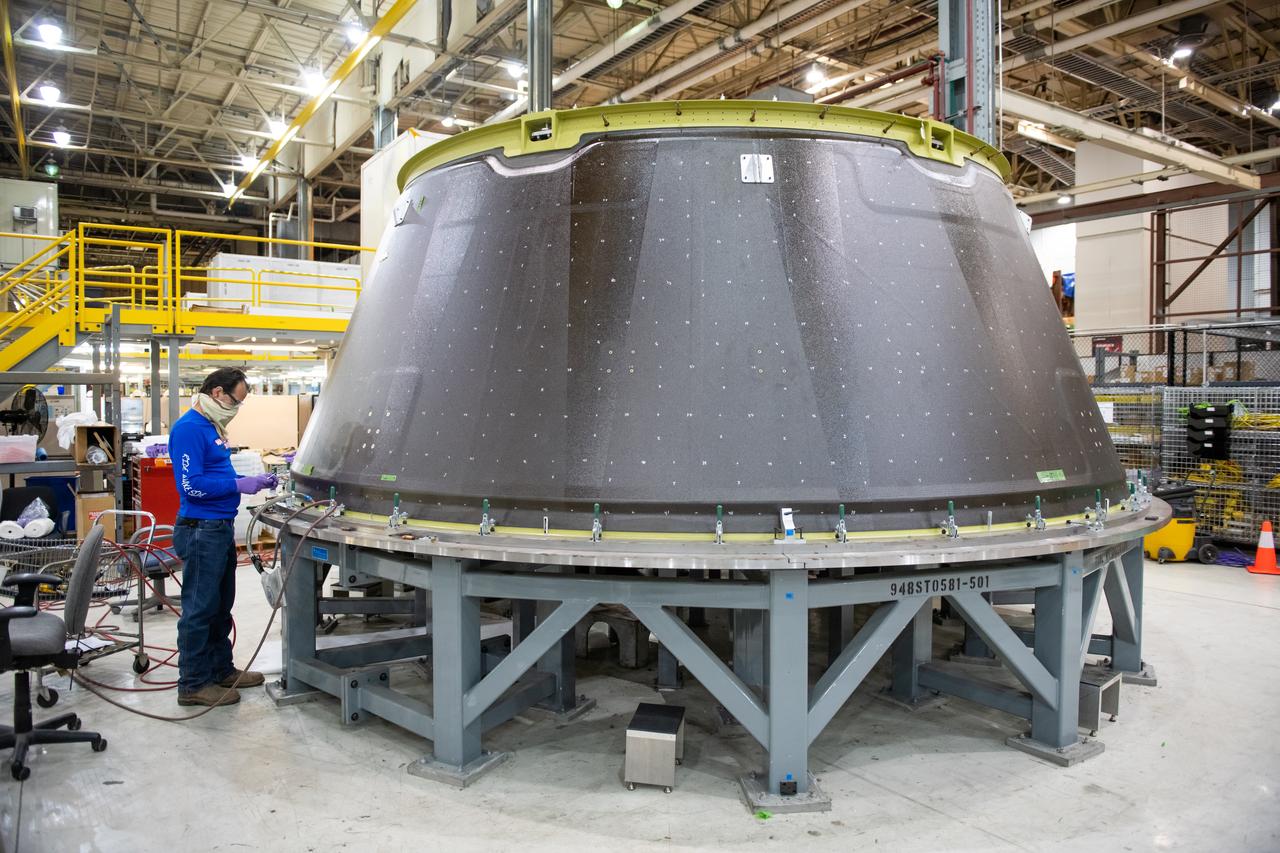
These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
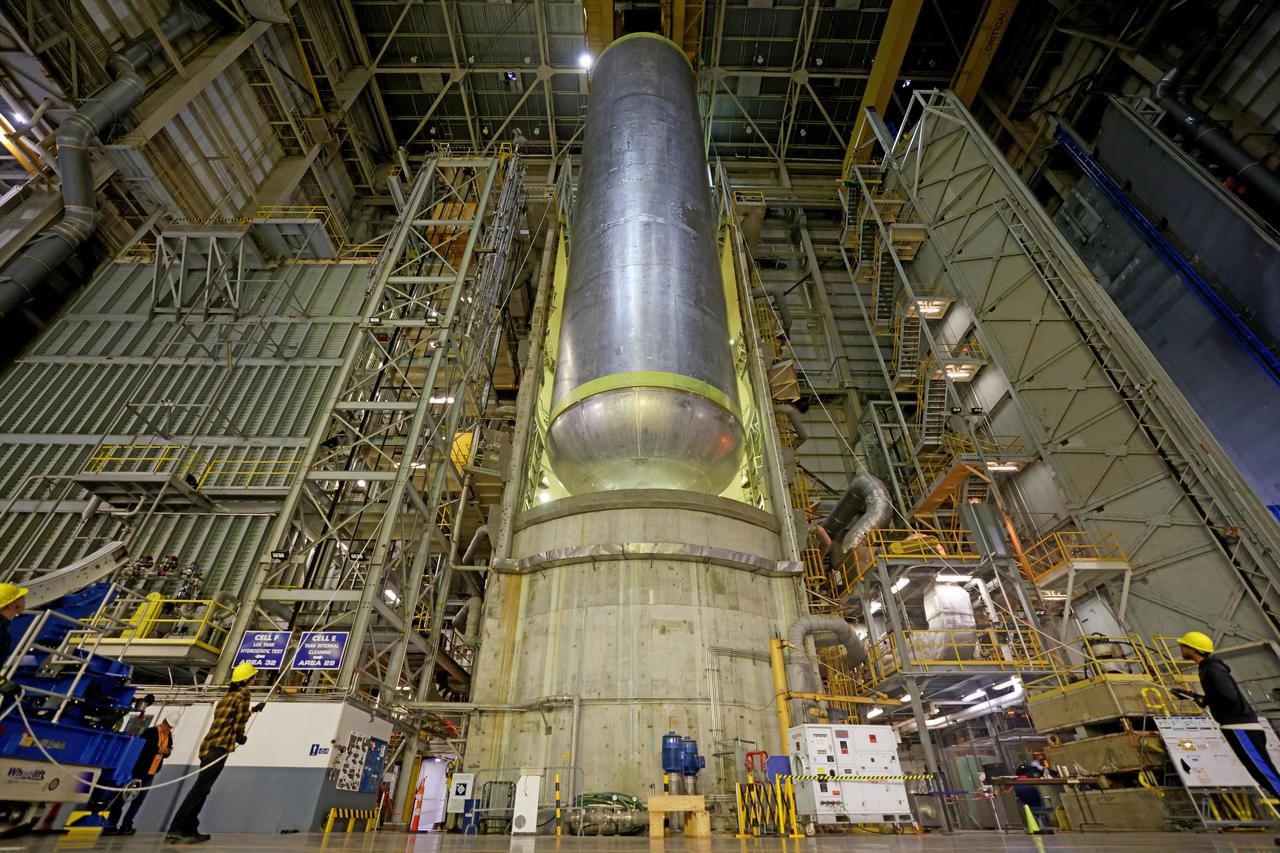

These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
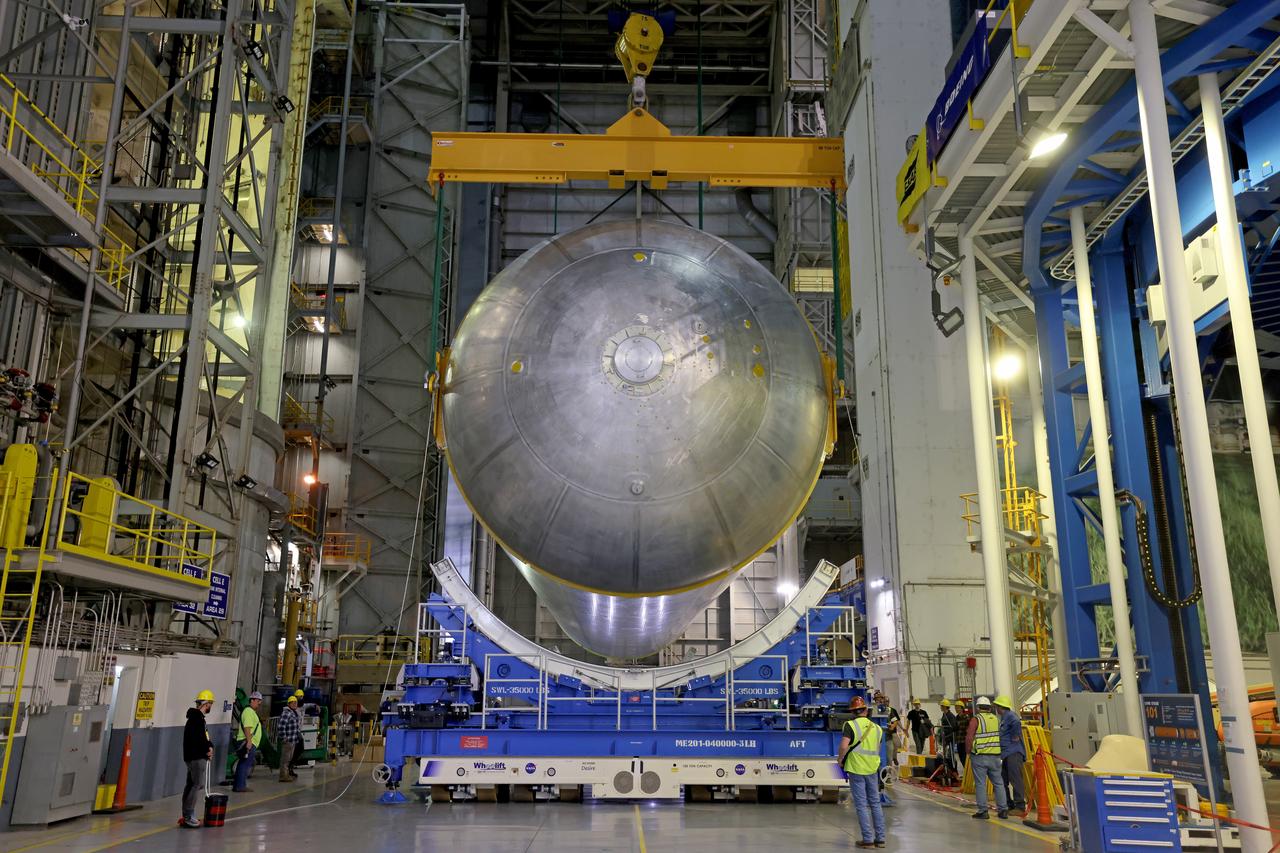

These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
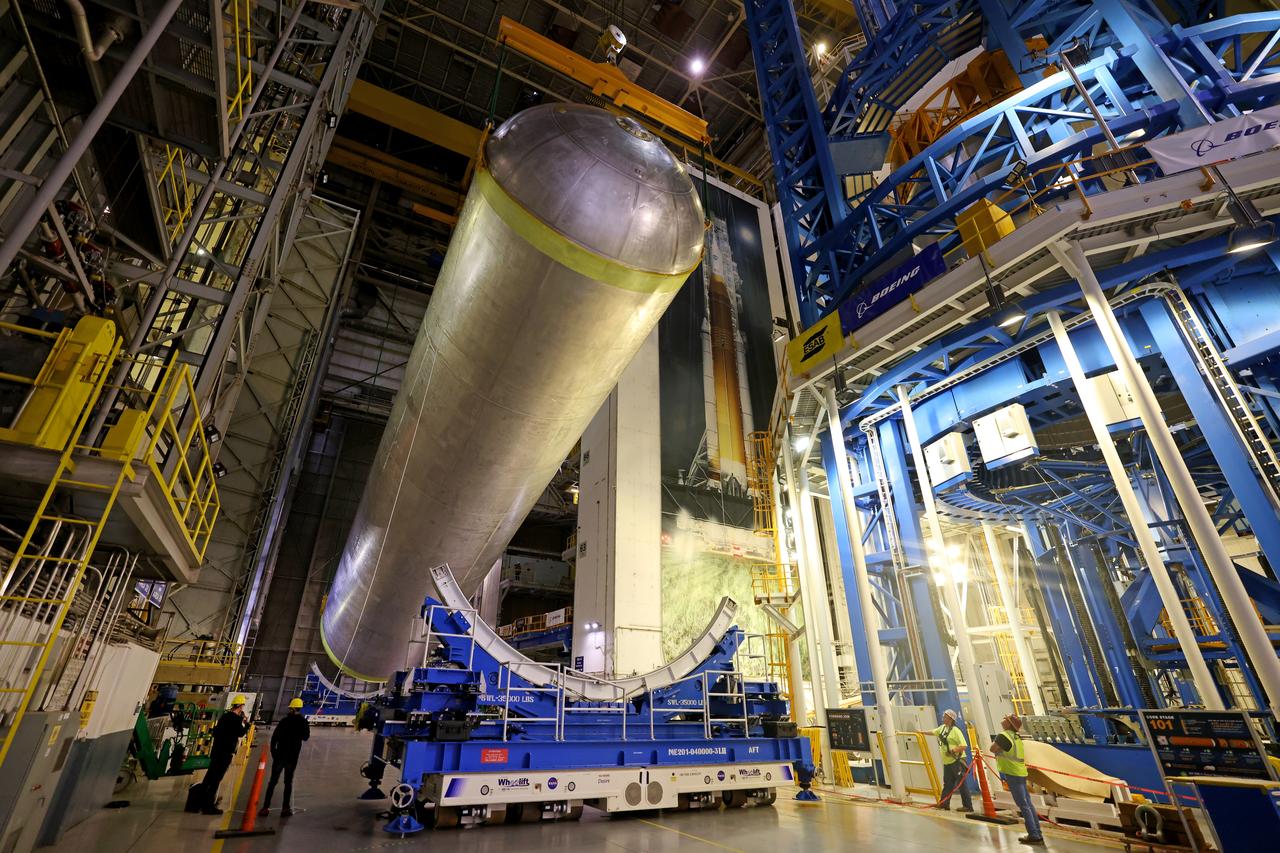

These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

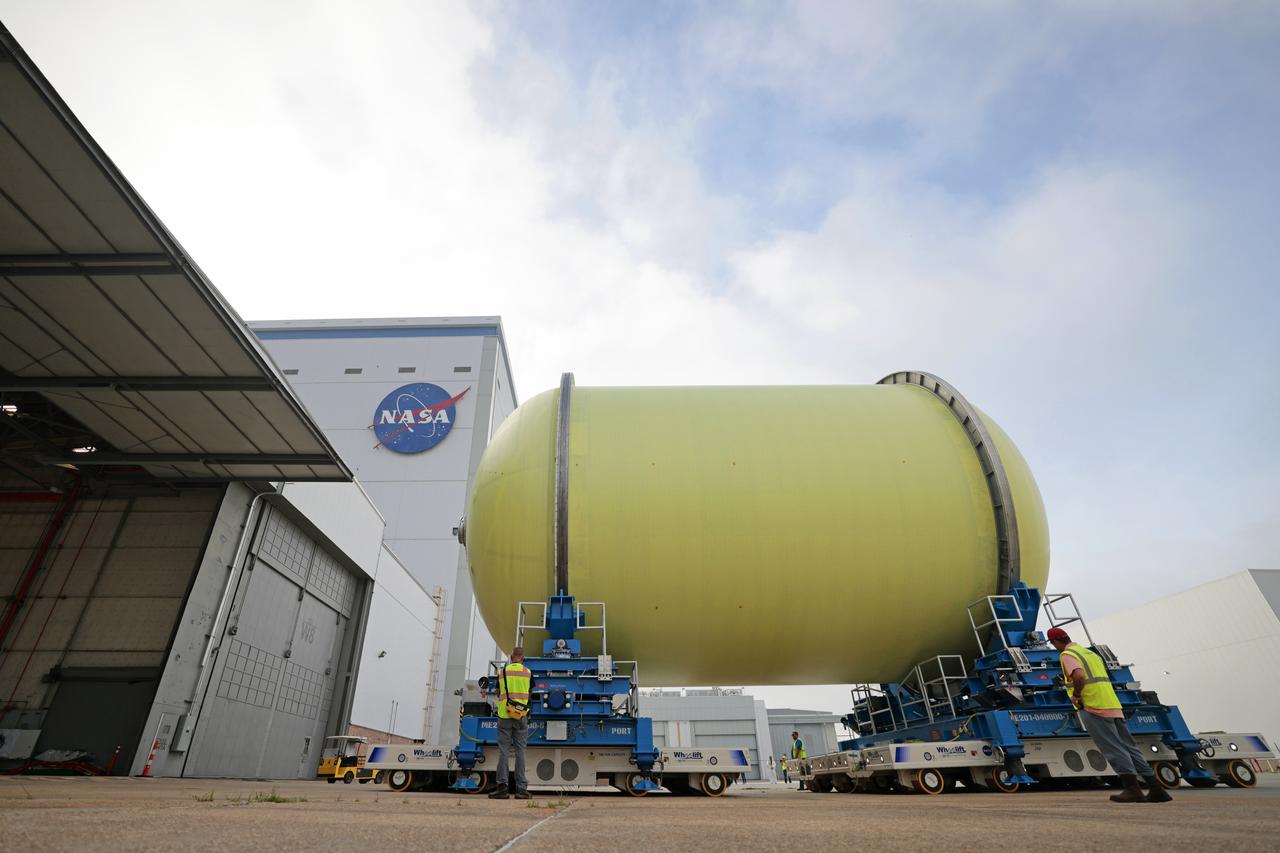
Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
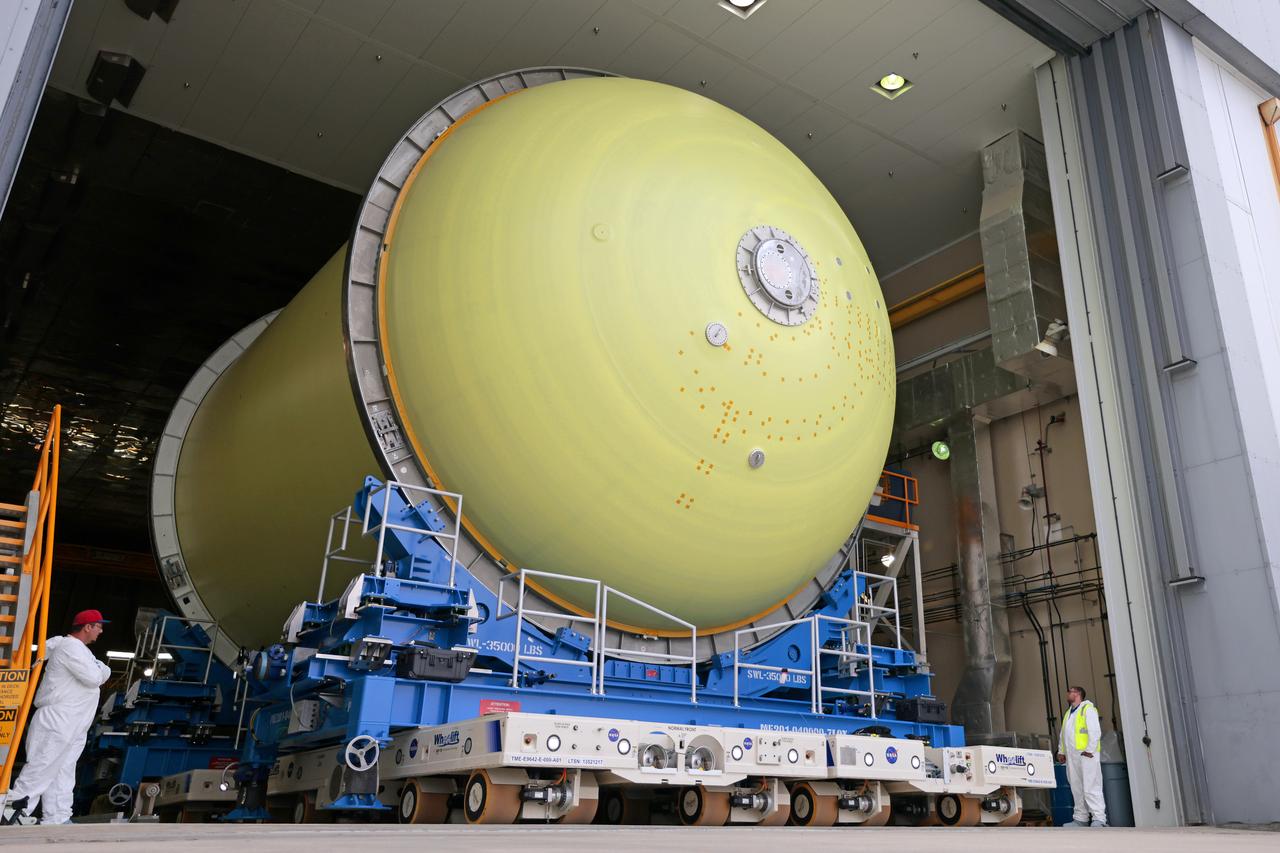

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
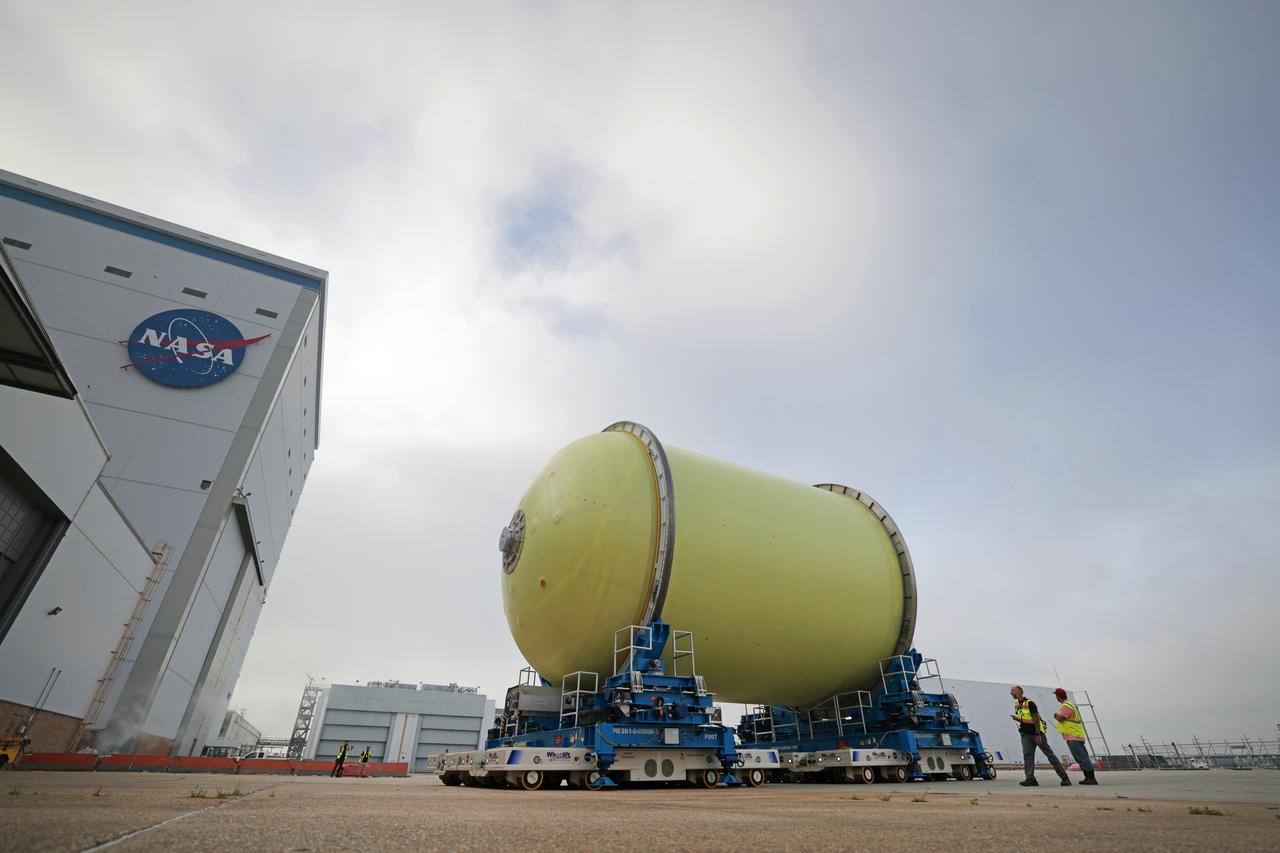

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
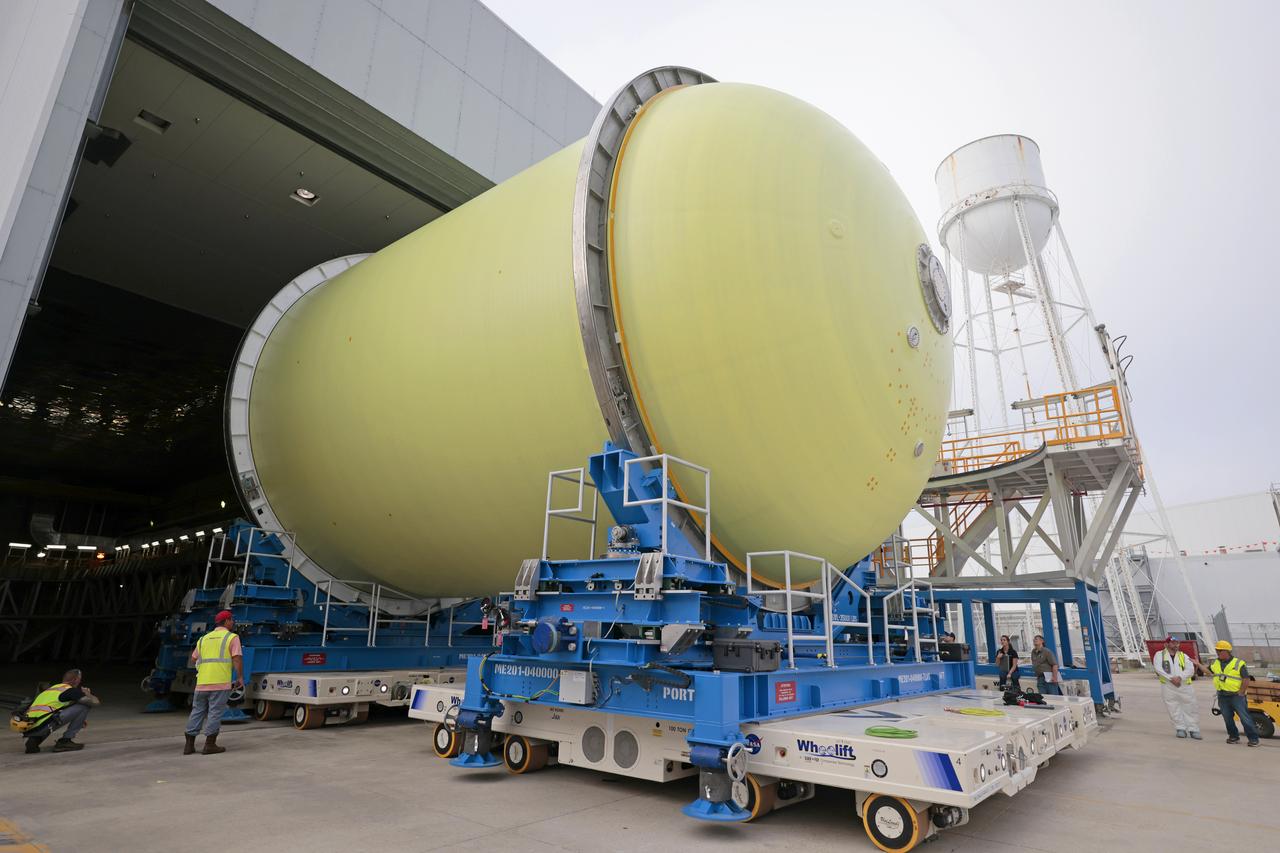

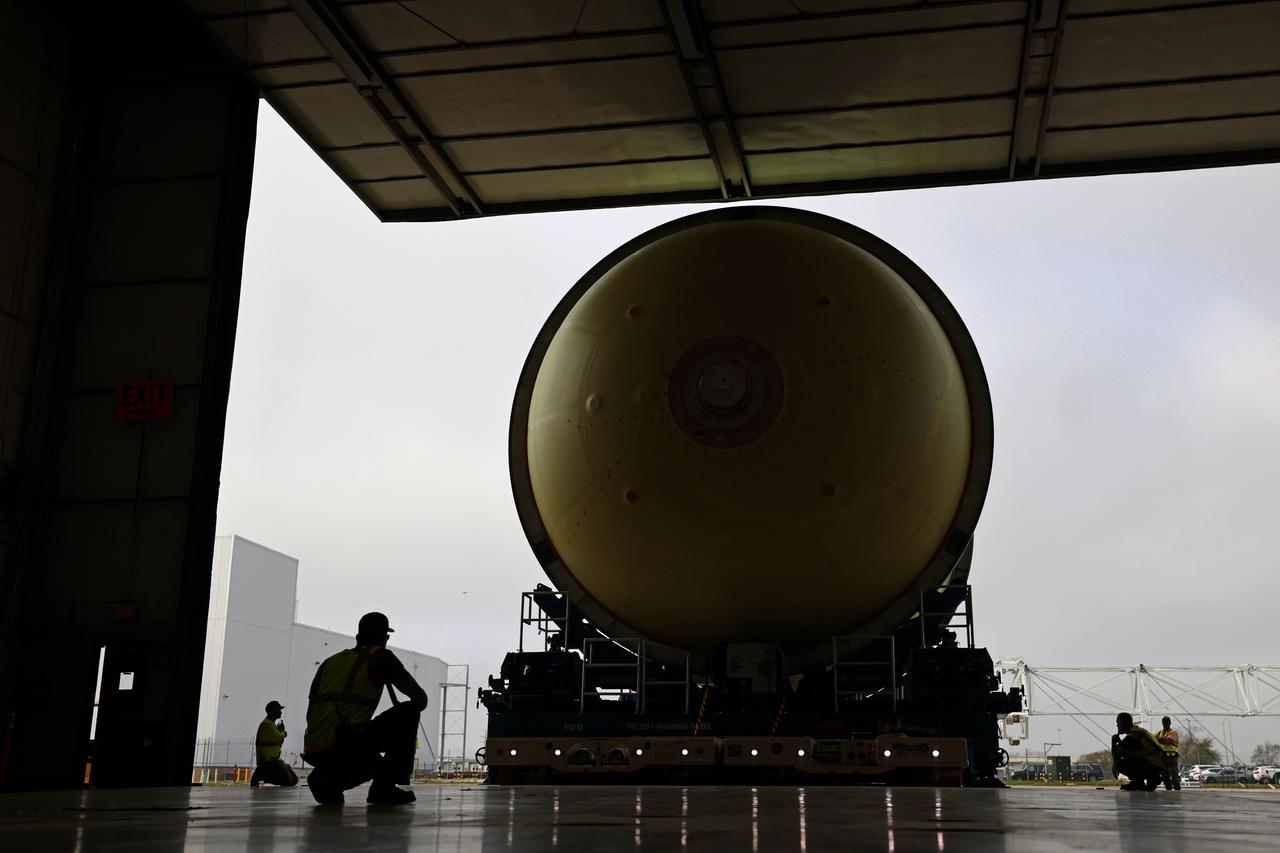
Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
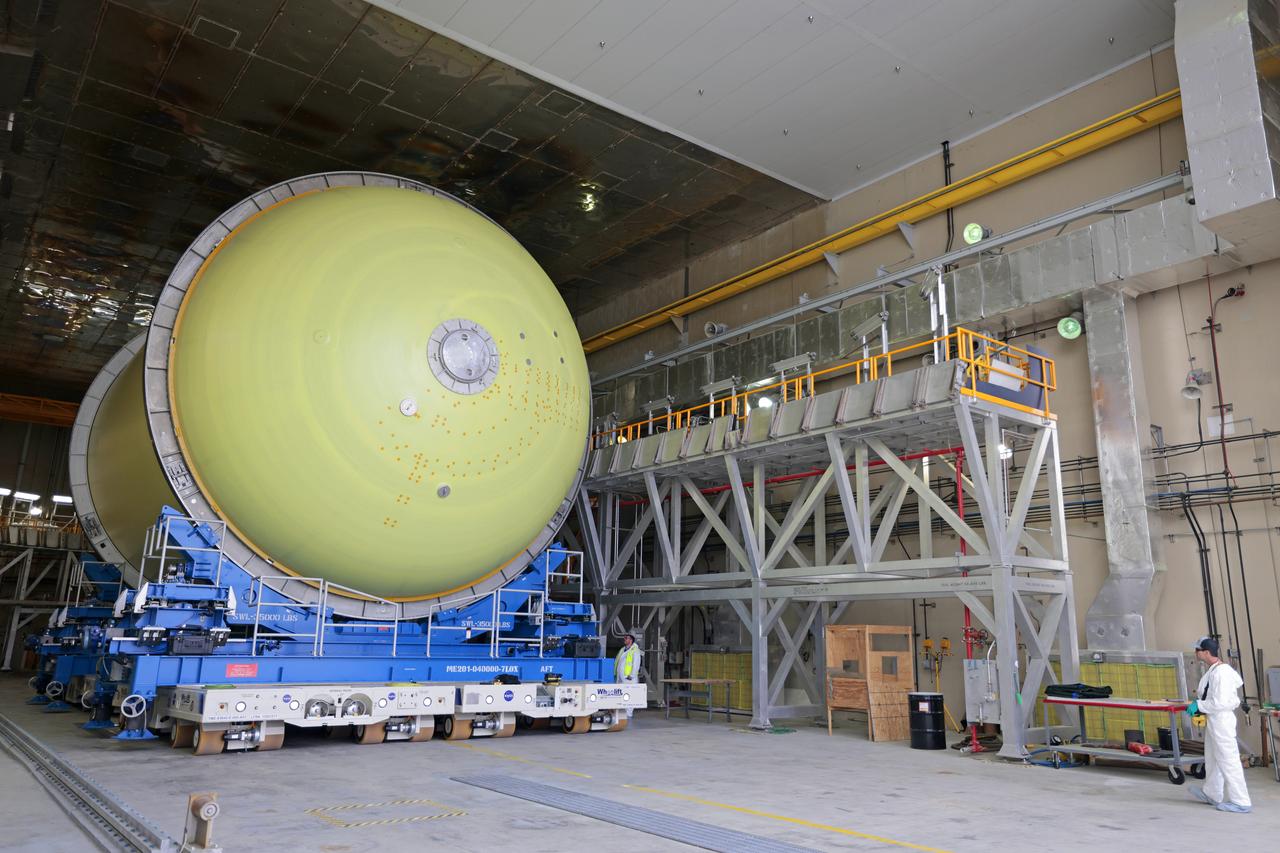

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
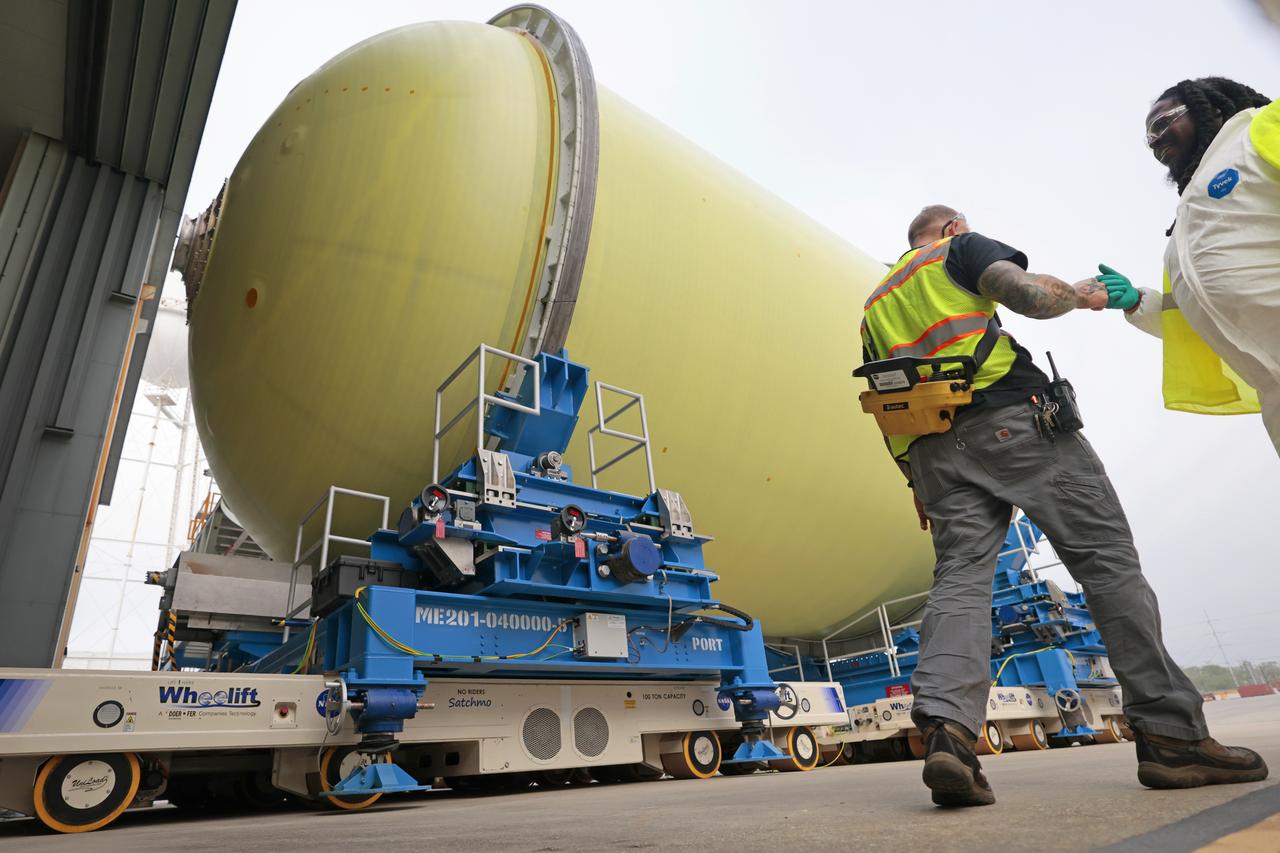

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
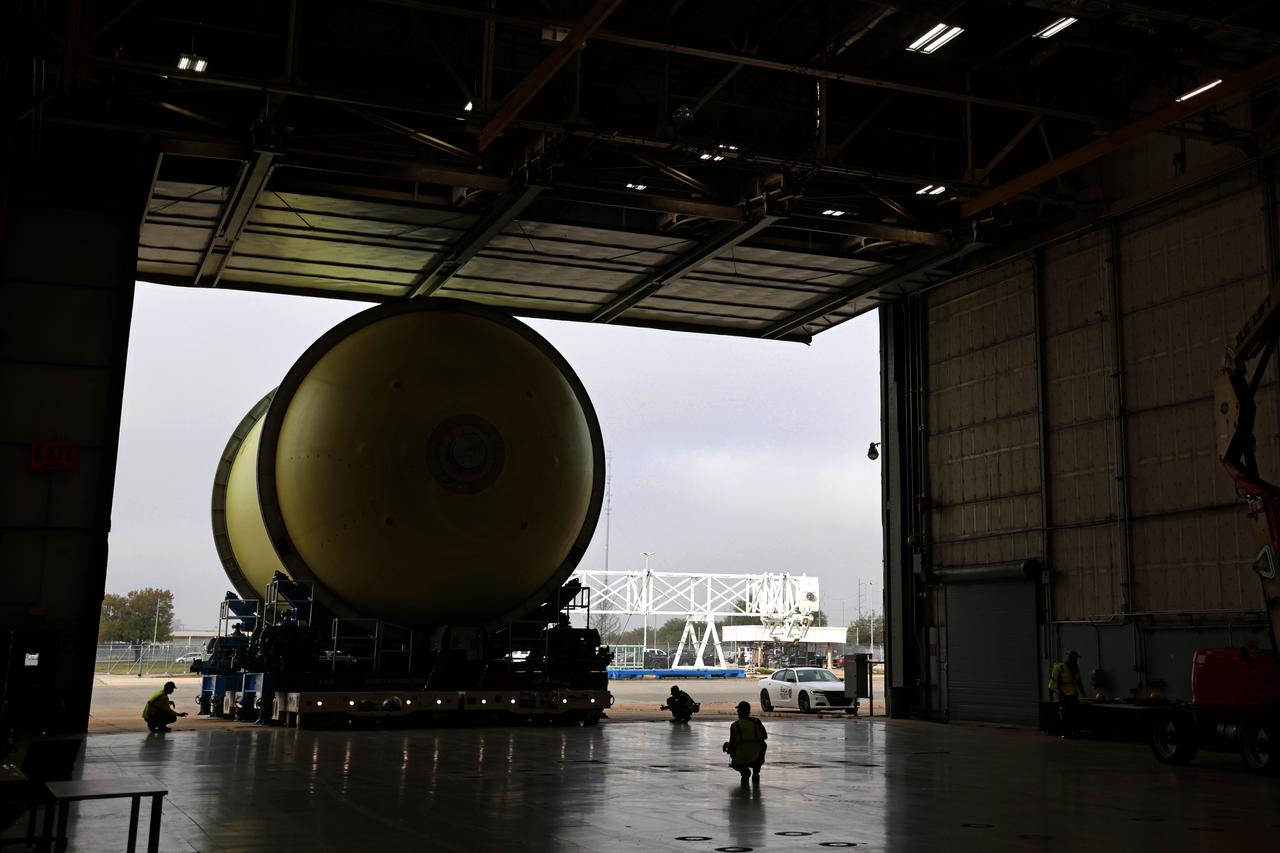

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
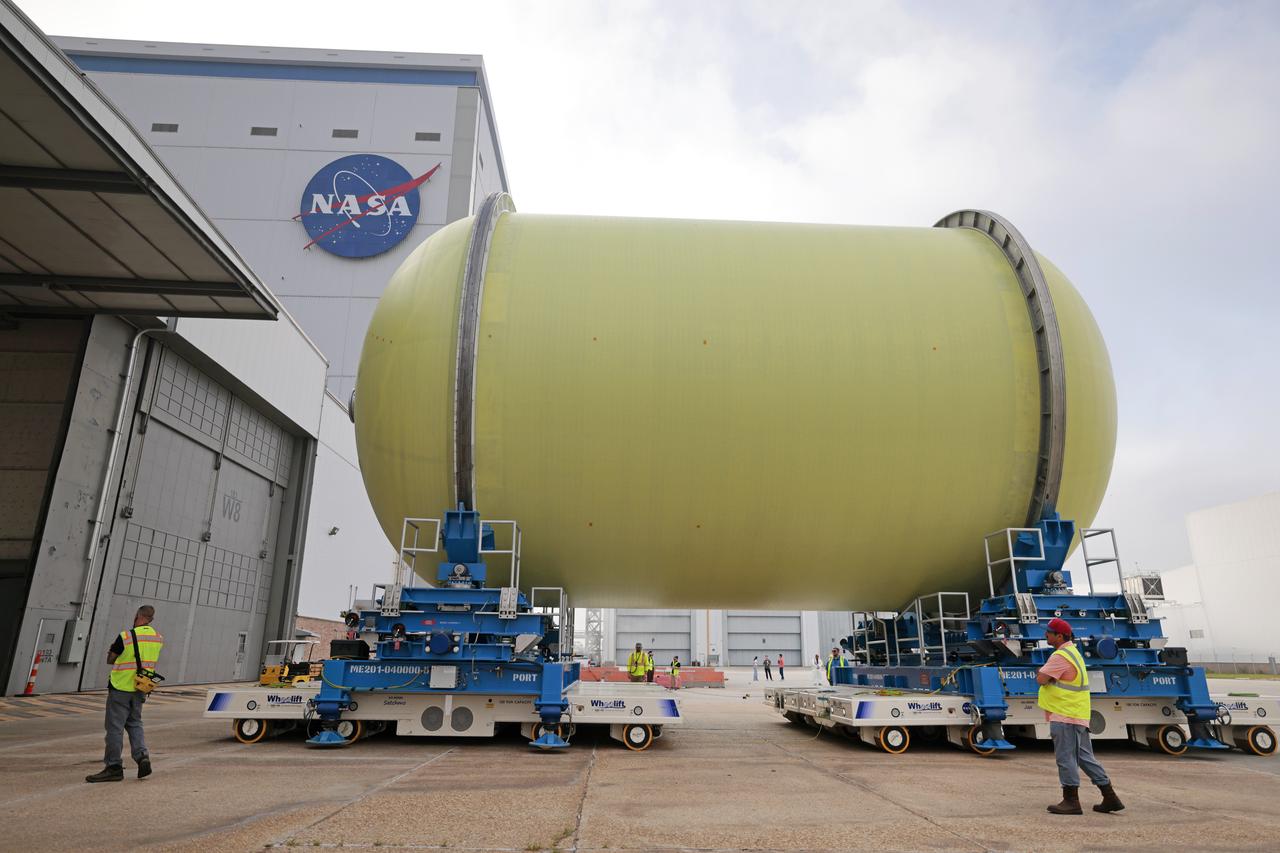

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
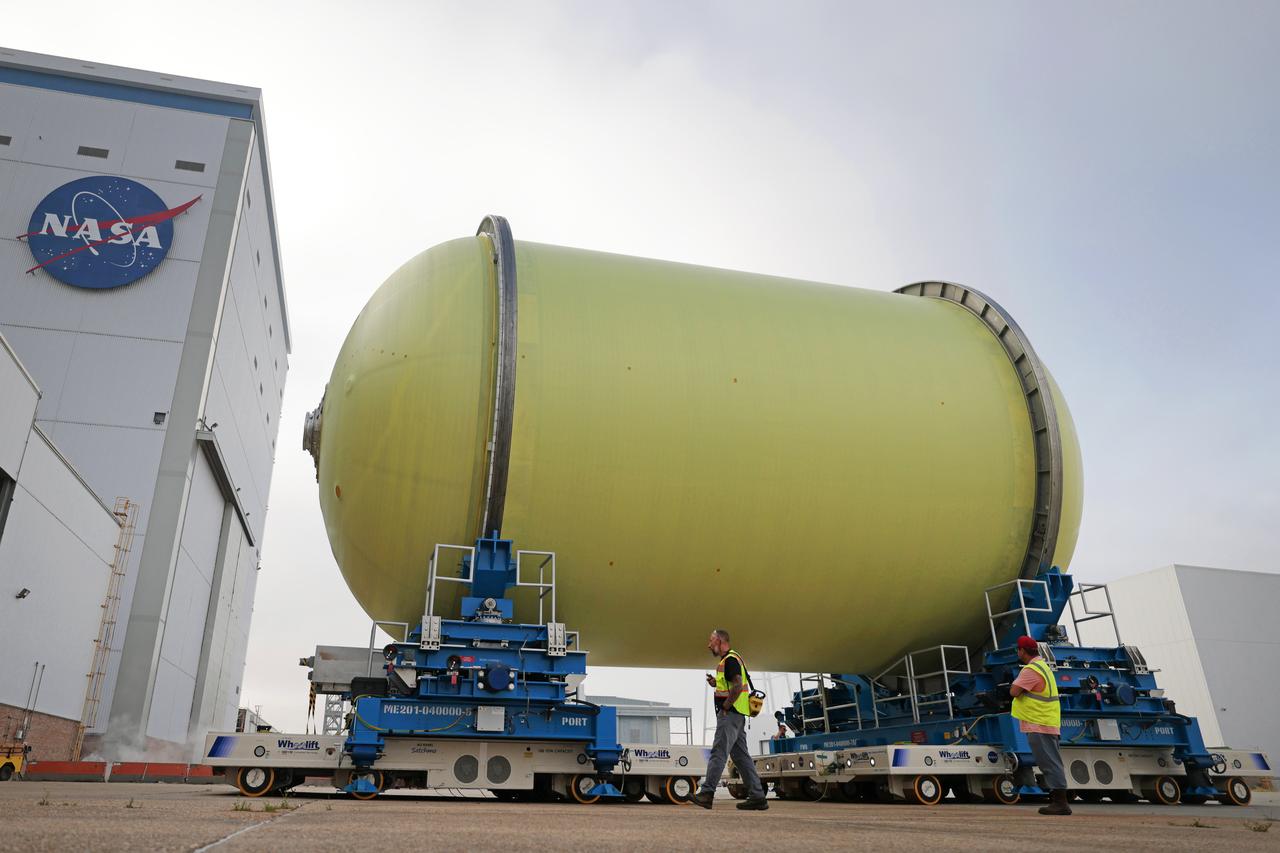

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
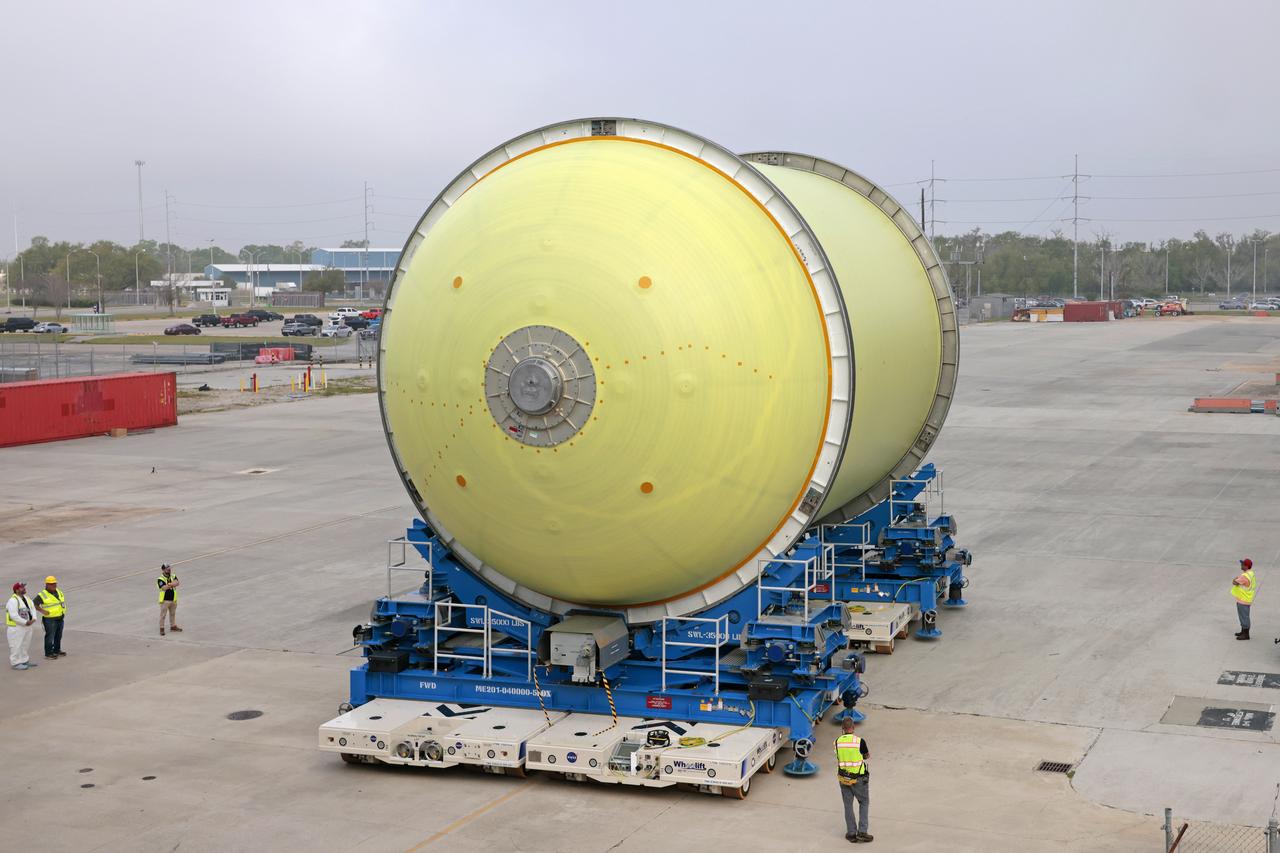

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
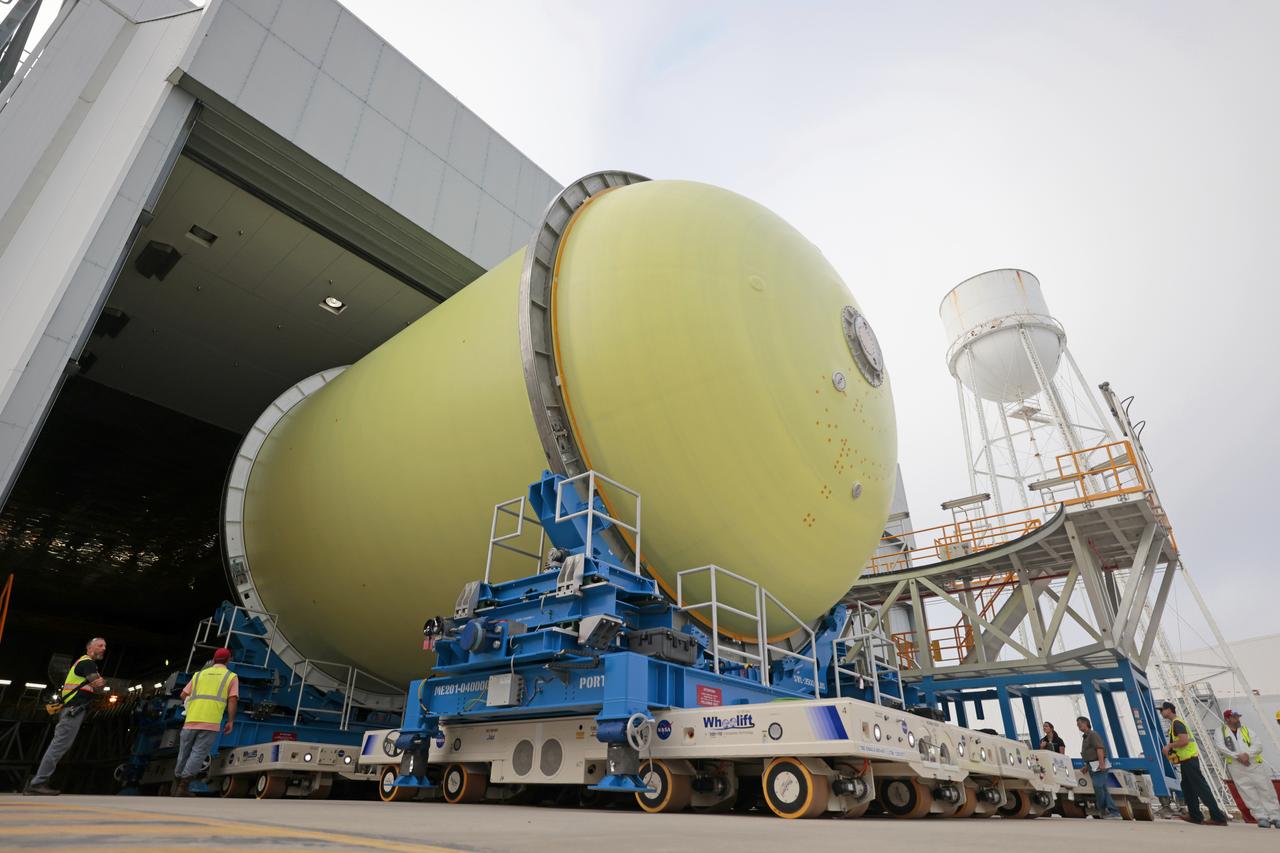

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
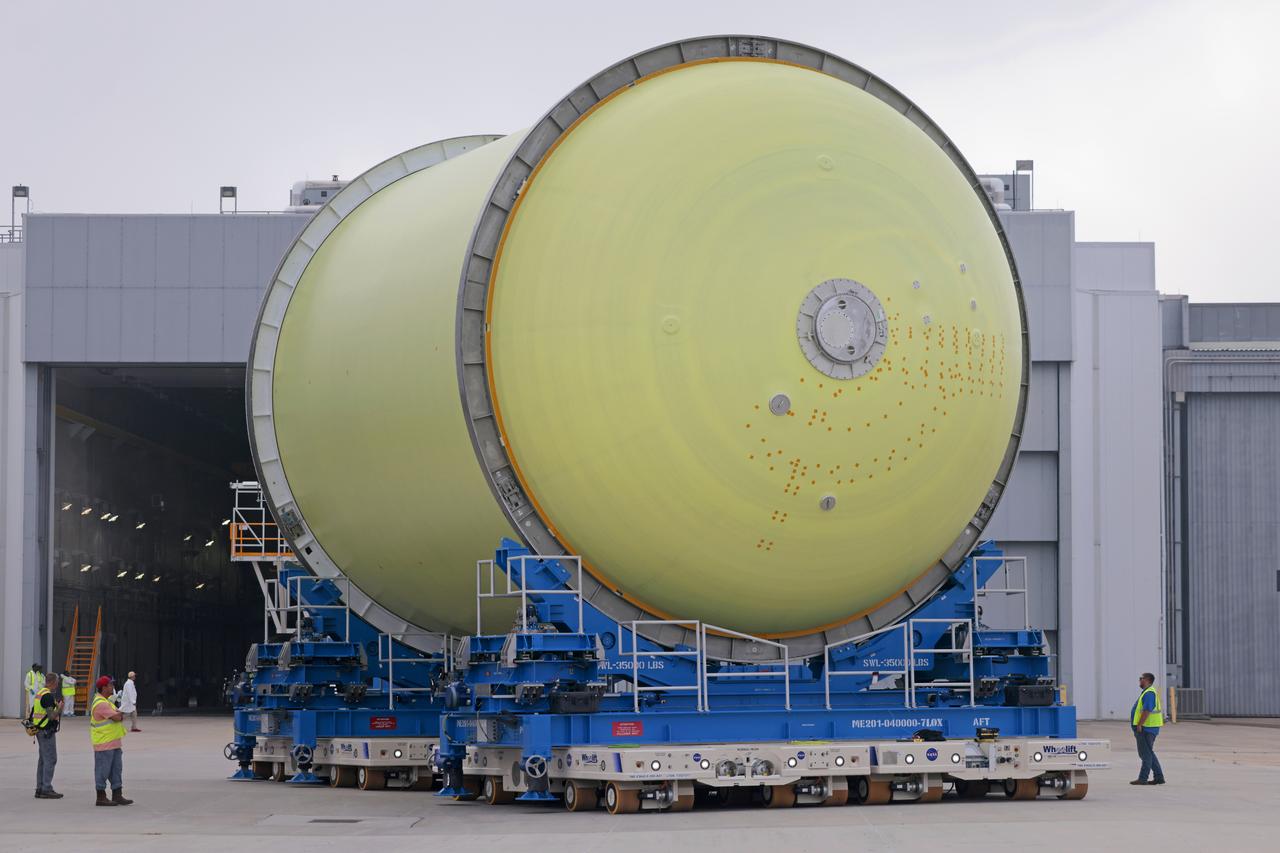

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
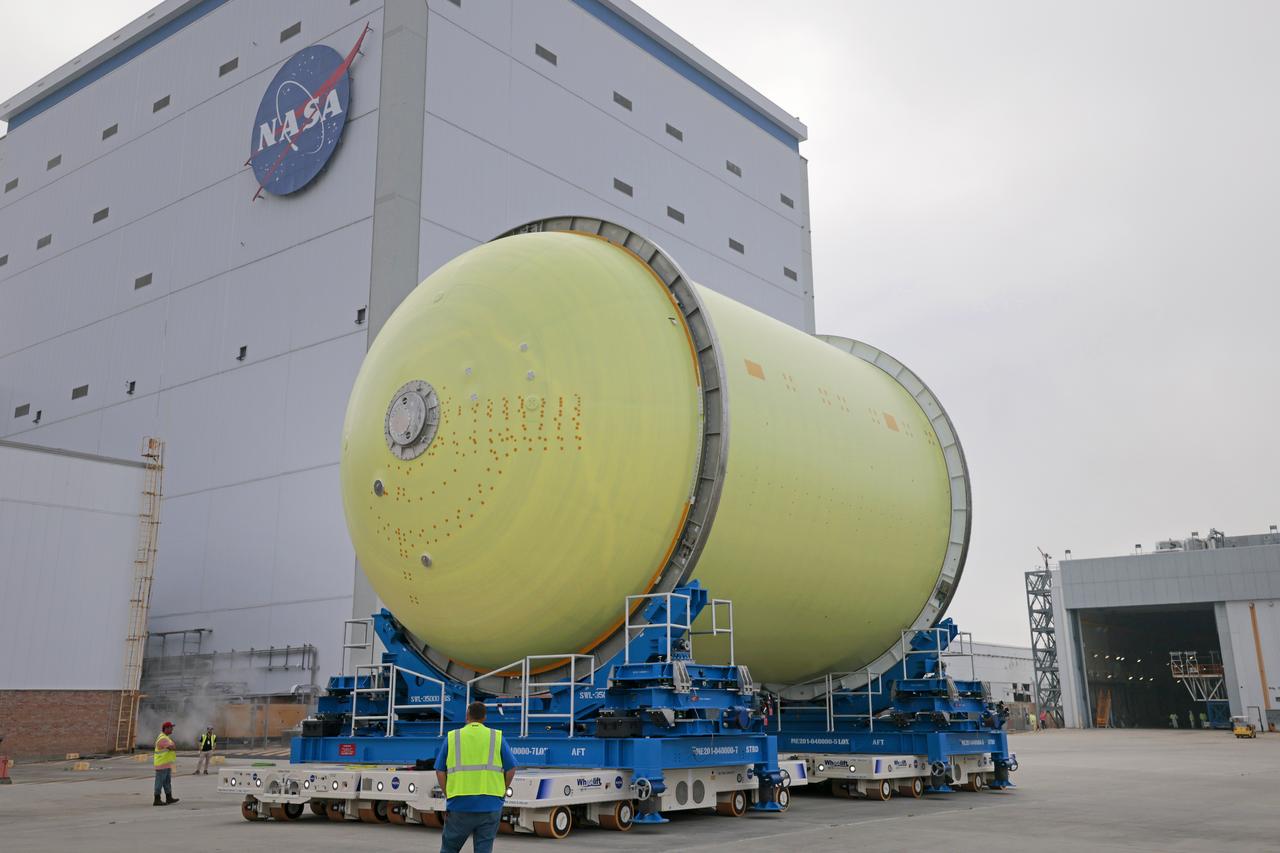

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
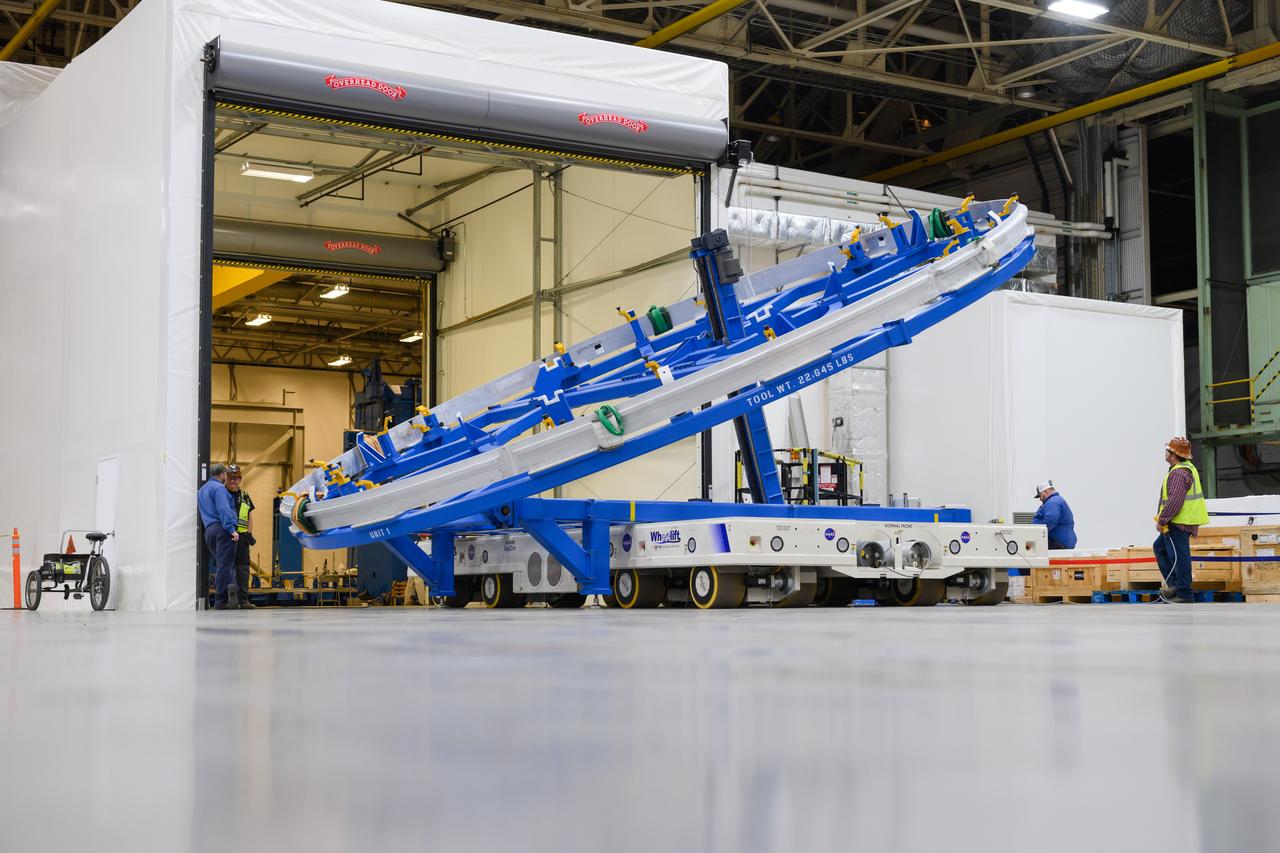

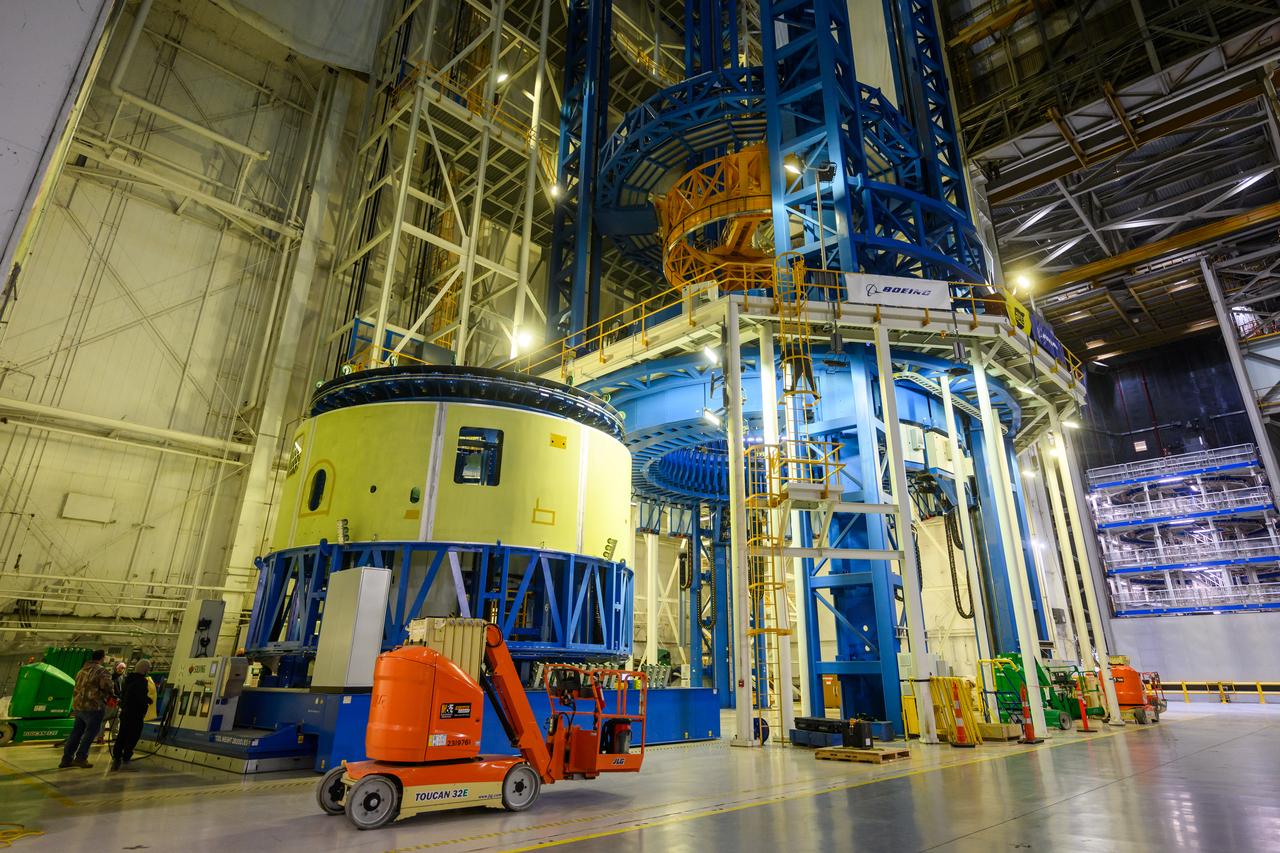
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
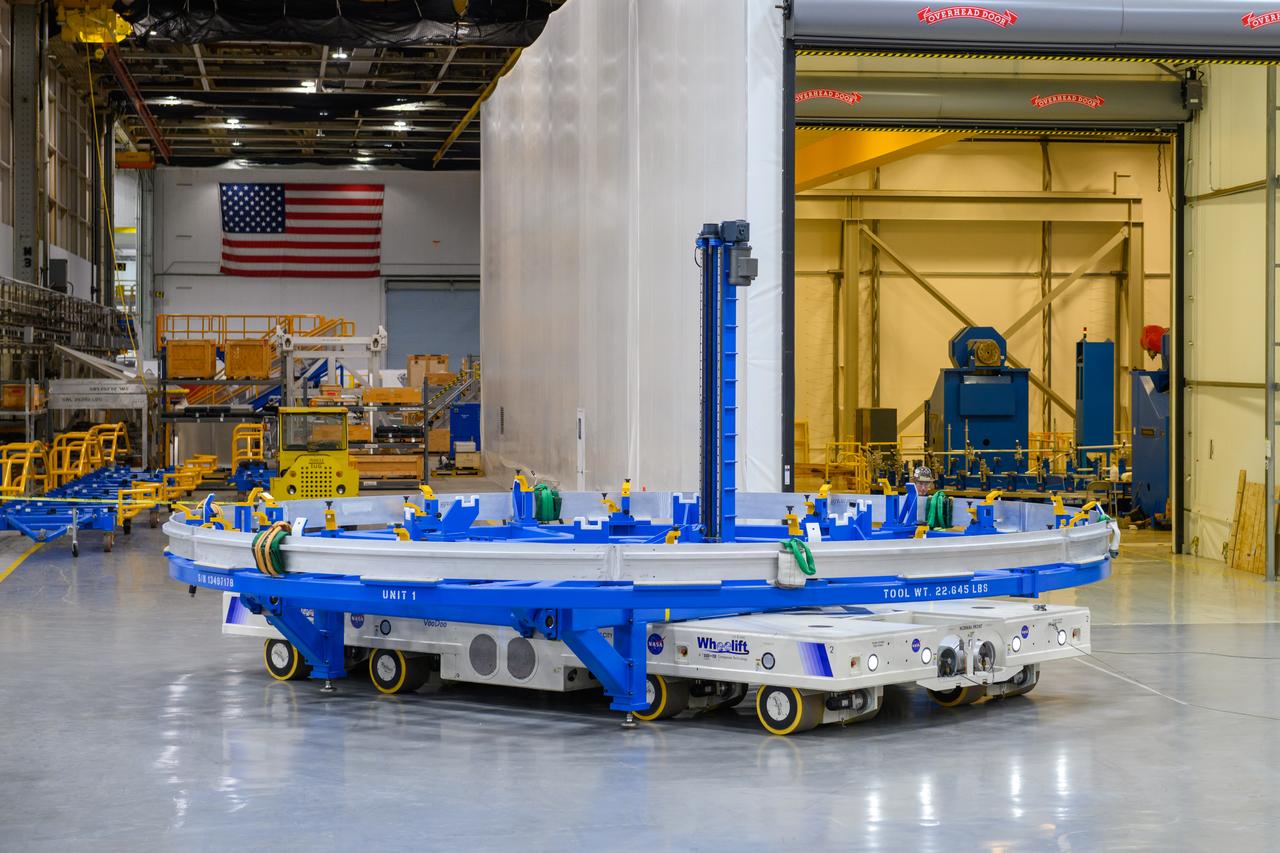

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
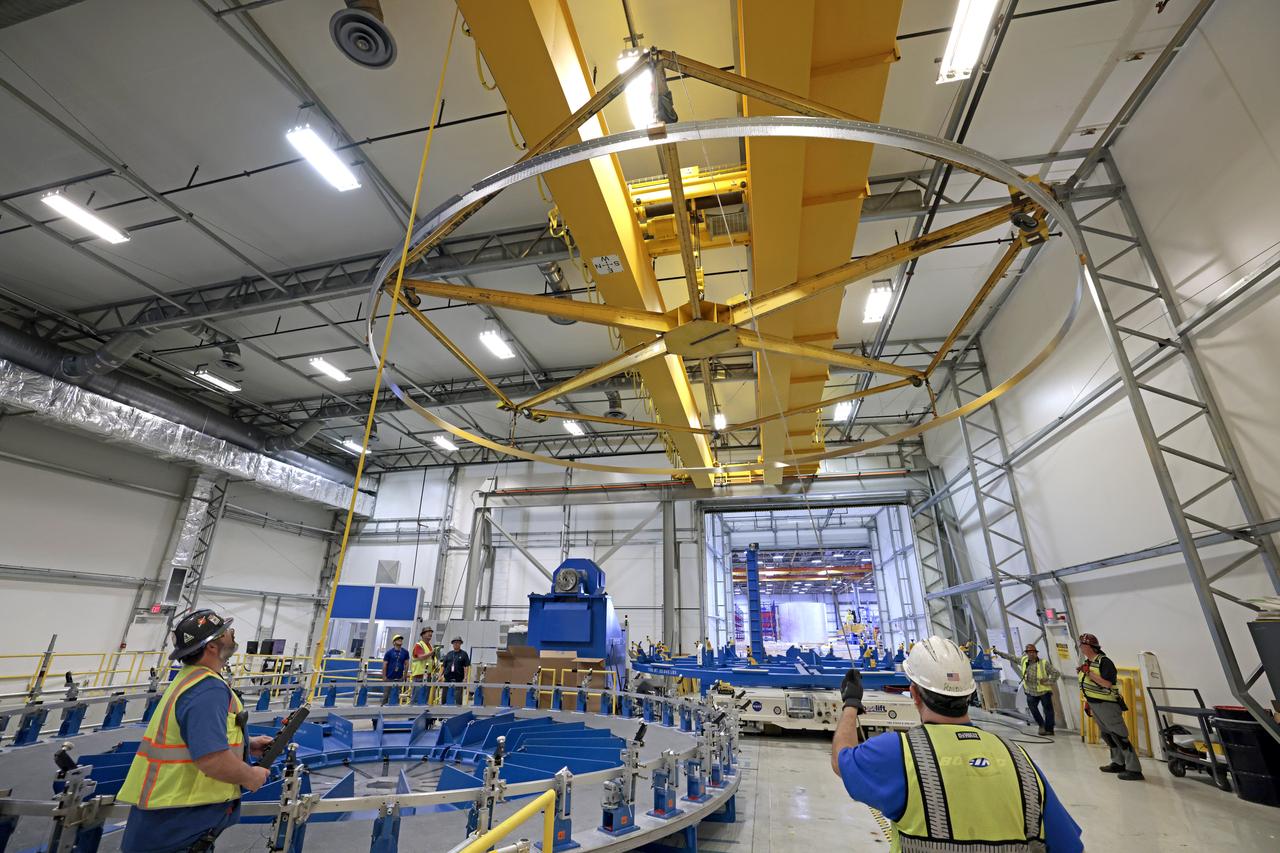

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
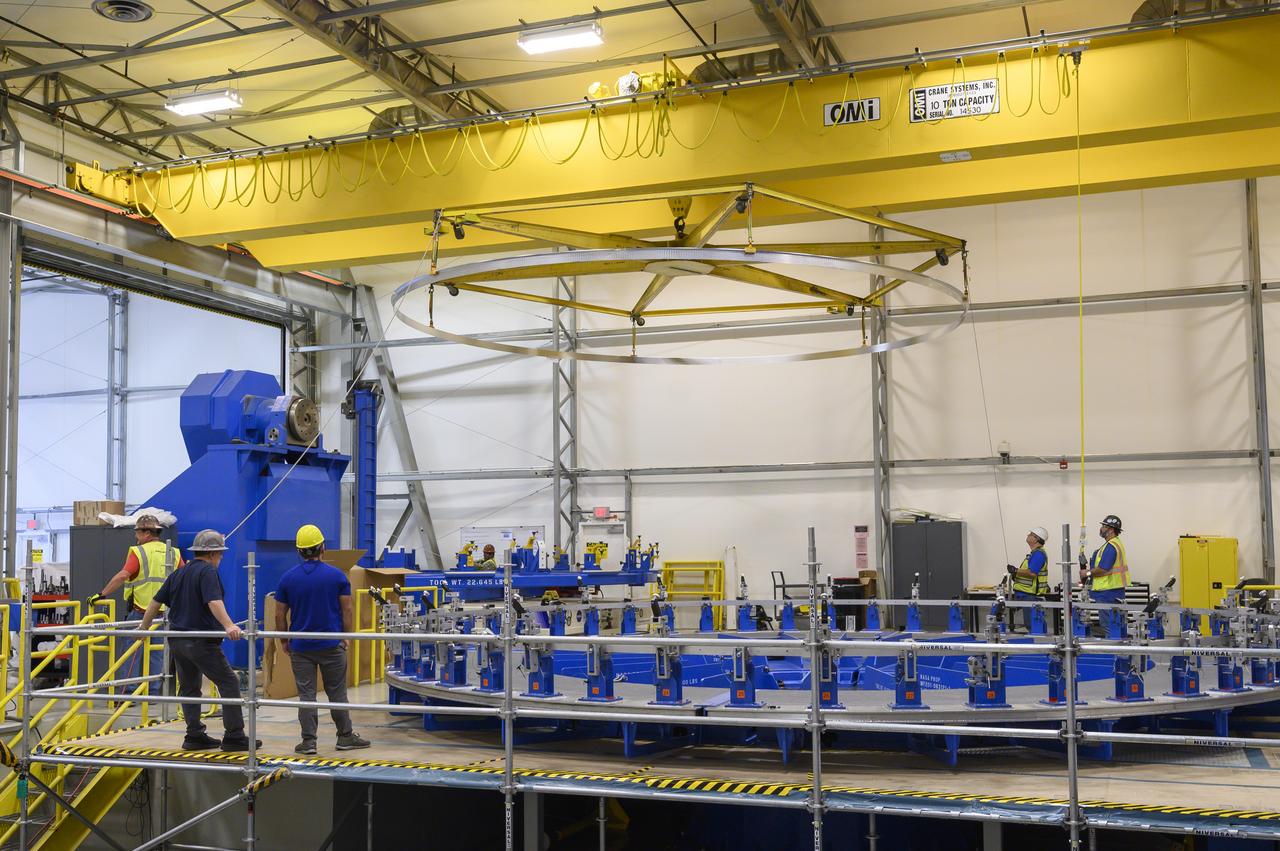

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
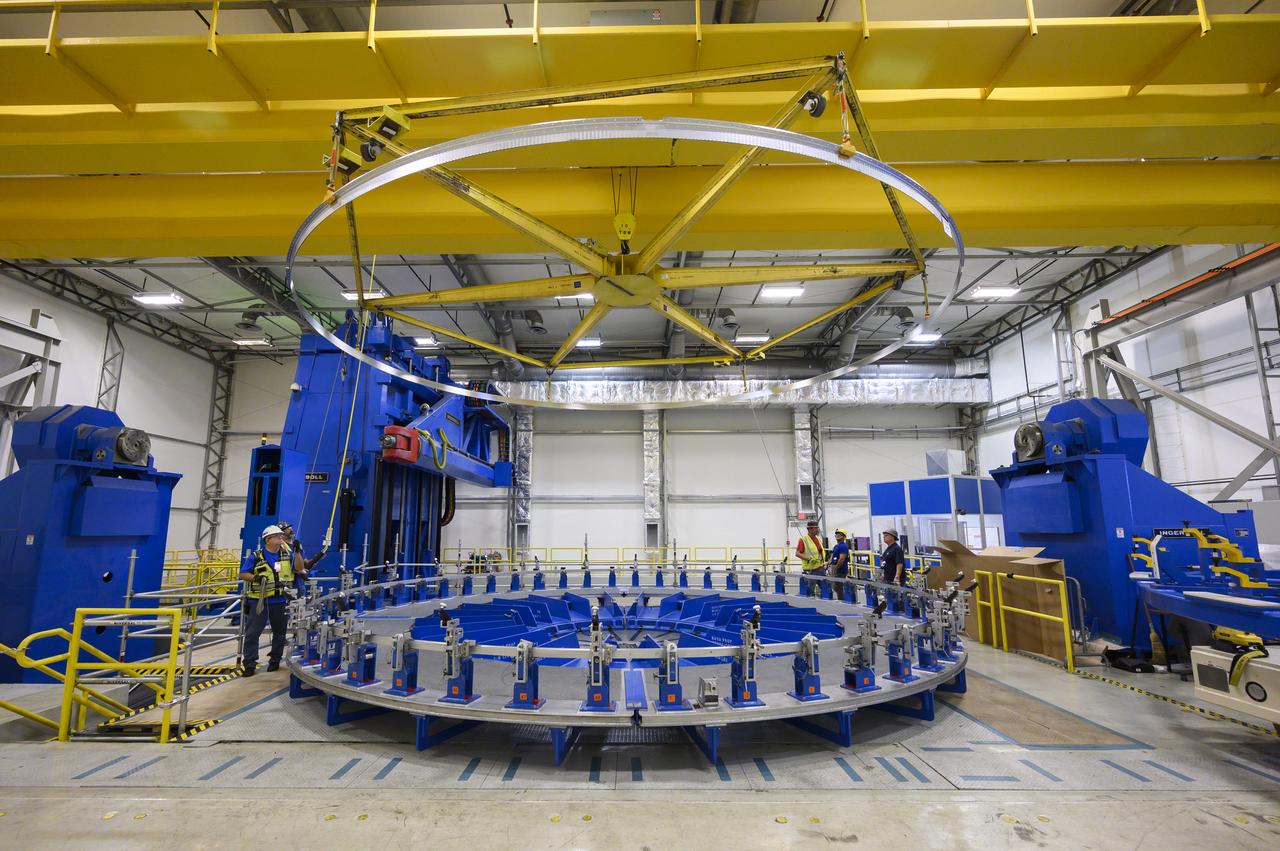

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift a ring for the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to move it to another location in the 43-acre factory for further inspection and production. Flight hardware of the SLS EUS, a more powerful in-space propulsion stage beginning with Artemis IV, is in early production at Michoud. The rings make up the barrel sections for the flight hardware. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Block 1 configuration of SLS. It has larger propellant tanks and four RL10 engines, enabling SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with crew. NASA and Boeing, the SLS lead contractor for the core stage and EUS, are currently manufacturing stages for Artemis II, III, IV, and V at the factory. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.