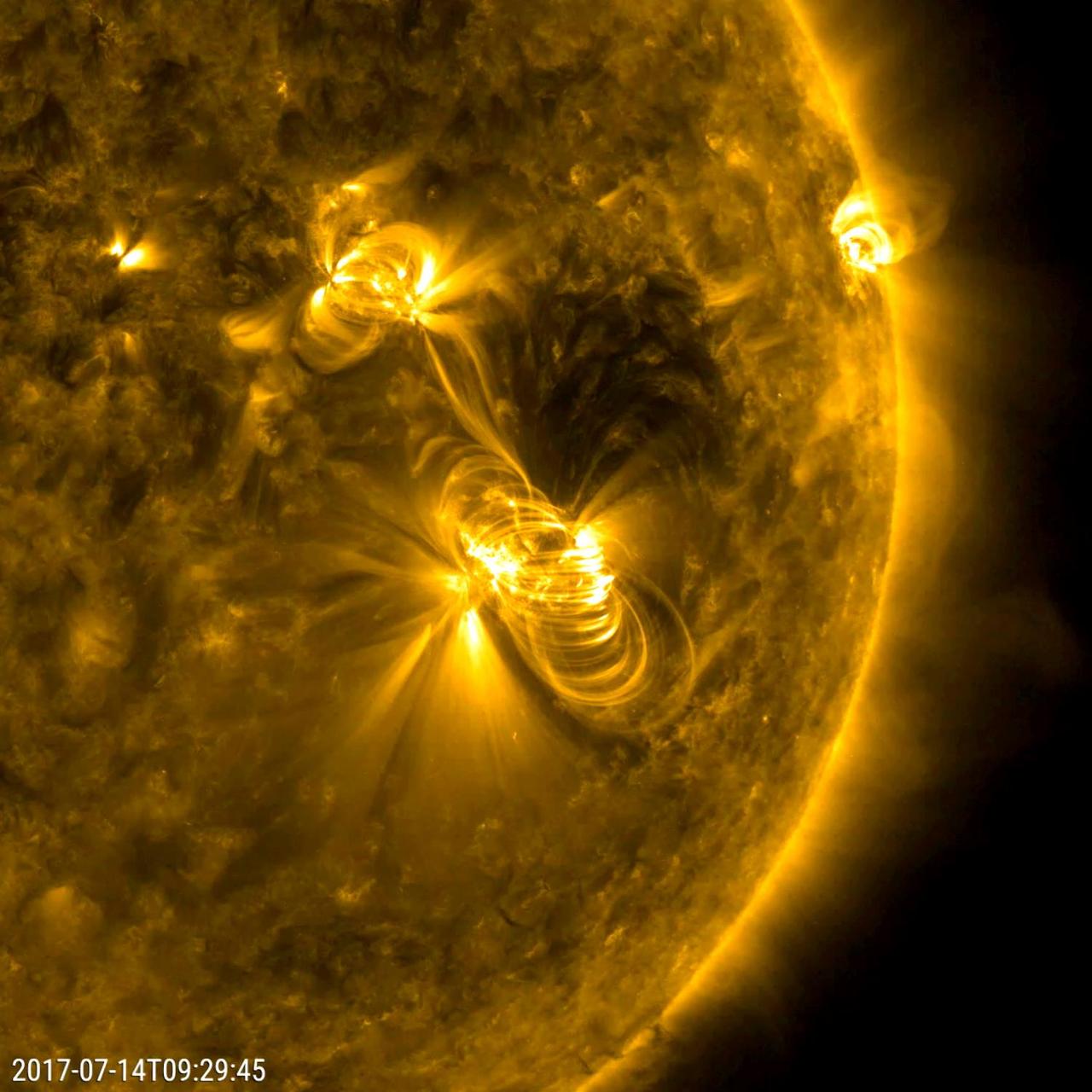

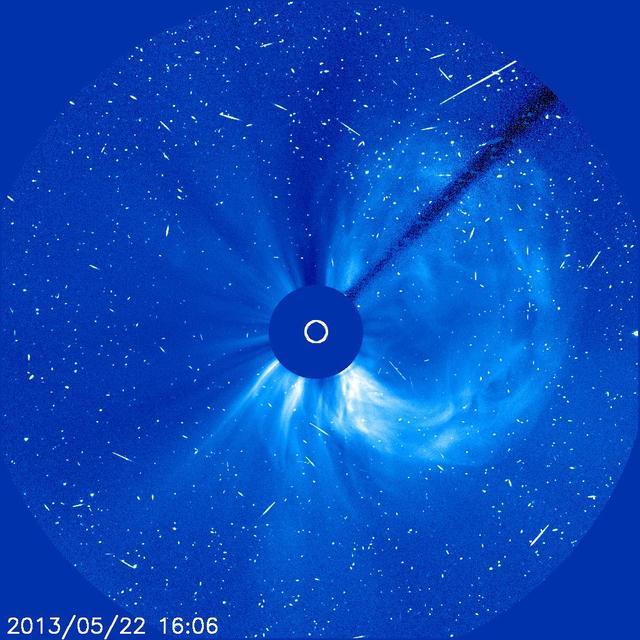
A flare medium-sized (M2) flare and a coronal mass ejection erupted from the same, large active region (July 14, 2017). The flare lasted almost two hours, quite a long duration. Coronagraphs on the SOHO spacecraft show a substantial cloud of charged particles blasting into space just after the blast. The coils arcing over this active region are particles spiraling along magnetic field lines, which were reorganizing themselves after the magnetic field was disrupted by the blast. Images were taken in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21836

The sun shot out a small coronal mass ejection that was also associated with a small flare (Jan. 22, 2018). The video, which covers about 5 hours, shows the burst of plasma as the magnetic loops break apart. Immediately the magnetic fields brighten intensely and begin to reorganize themselves in coils above the active region. The images were taken in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Videos are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22184
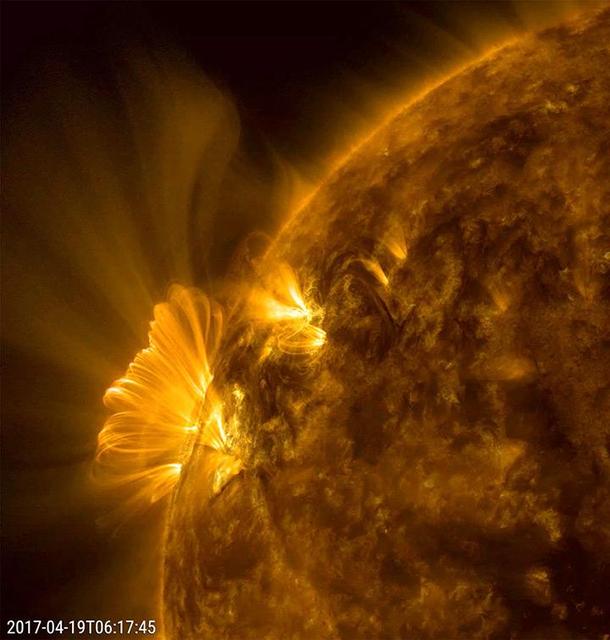

An active region that had just rotated into view blasted out a coronal mass ejection, which was immediately followed by a bright series of post-coronal loops seeking to reorganize that region's magnetic field (April 19, 2017). We have observed this phenomenon numerous times, but this one was one of the longest and clearest sequences we have seen in years. The bright loops are actually charged particles spinning along the magnetic field lines. The action was captured in a combination of two wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light over a period of about 20 hours. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21598
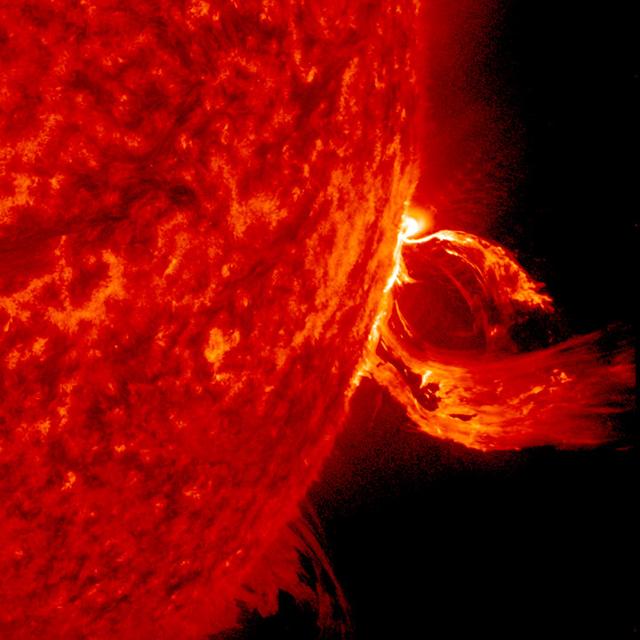

A substantial coronal mass ejection, or CME, blew out from side of the Sun, giving us a great view of the event in profile (June 17-18, 2015). NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory caught the action in the 304 Angstrom wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. The video clip covers about four hours of the event. While some of the plasma falls back into the Sun, a look at the coronagraph on SOHO shows a large cloud of particles heading into space. Credit: NASA/Goddard//SDO
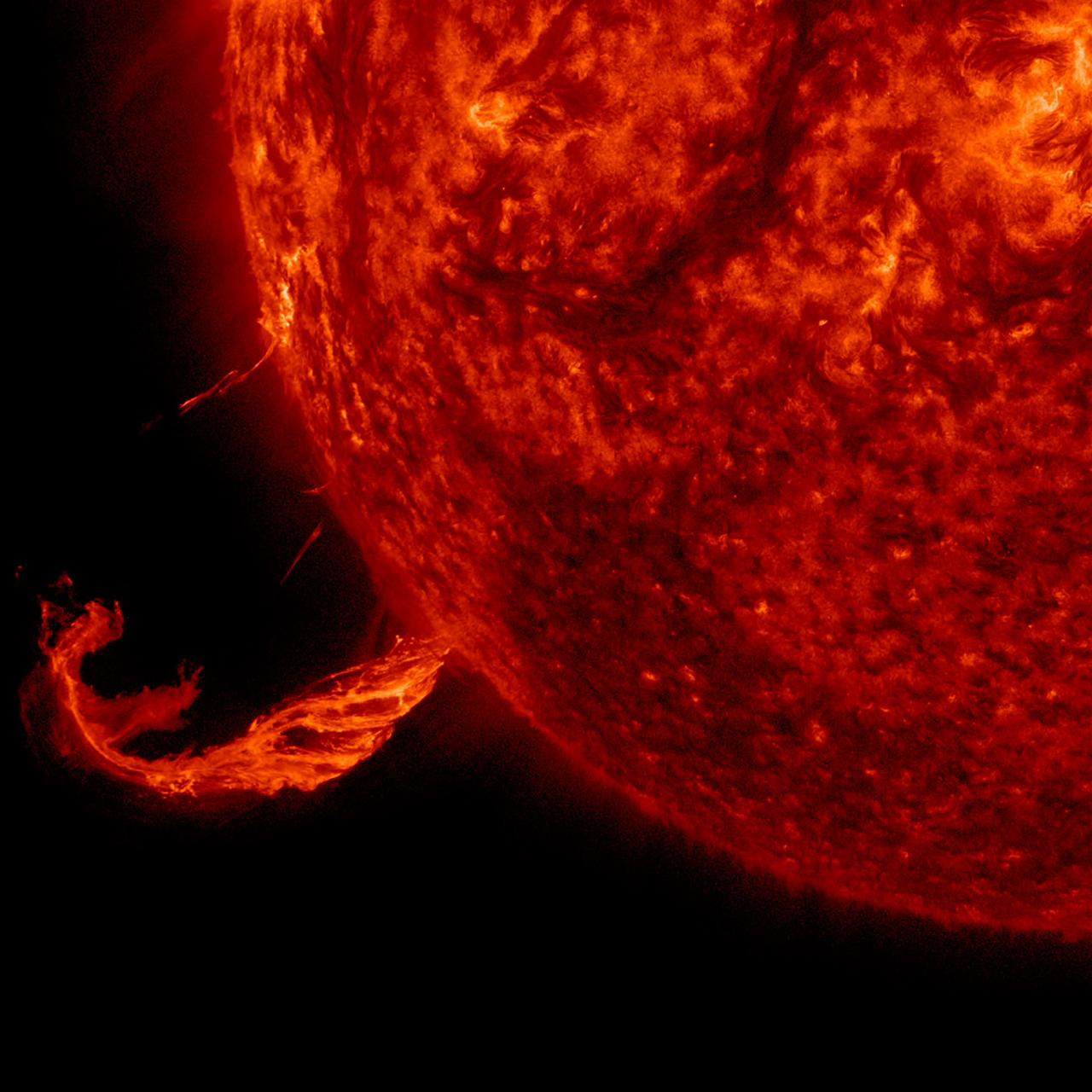
The Sun blew out a coronal mass ejection along with part of a solar filament over a three-hour period (Feb. 24, 2015). While some of the strands fell back into the Sun, a substantial part raced into space in a bright cloud of particles (as observed by the SOHO spacecraft). The activity was captured in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Because this occurred way over near the edge of the Sun, it was unlikely to have any effect on Earth. Credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory
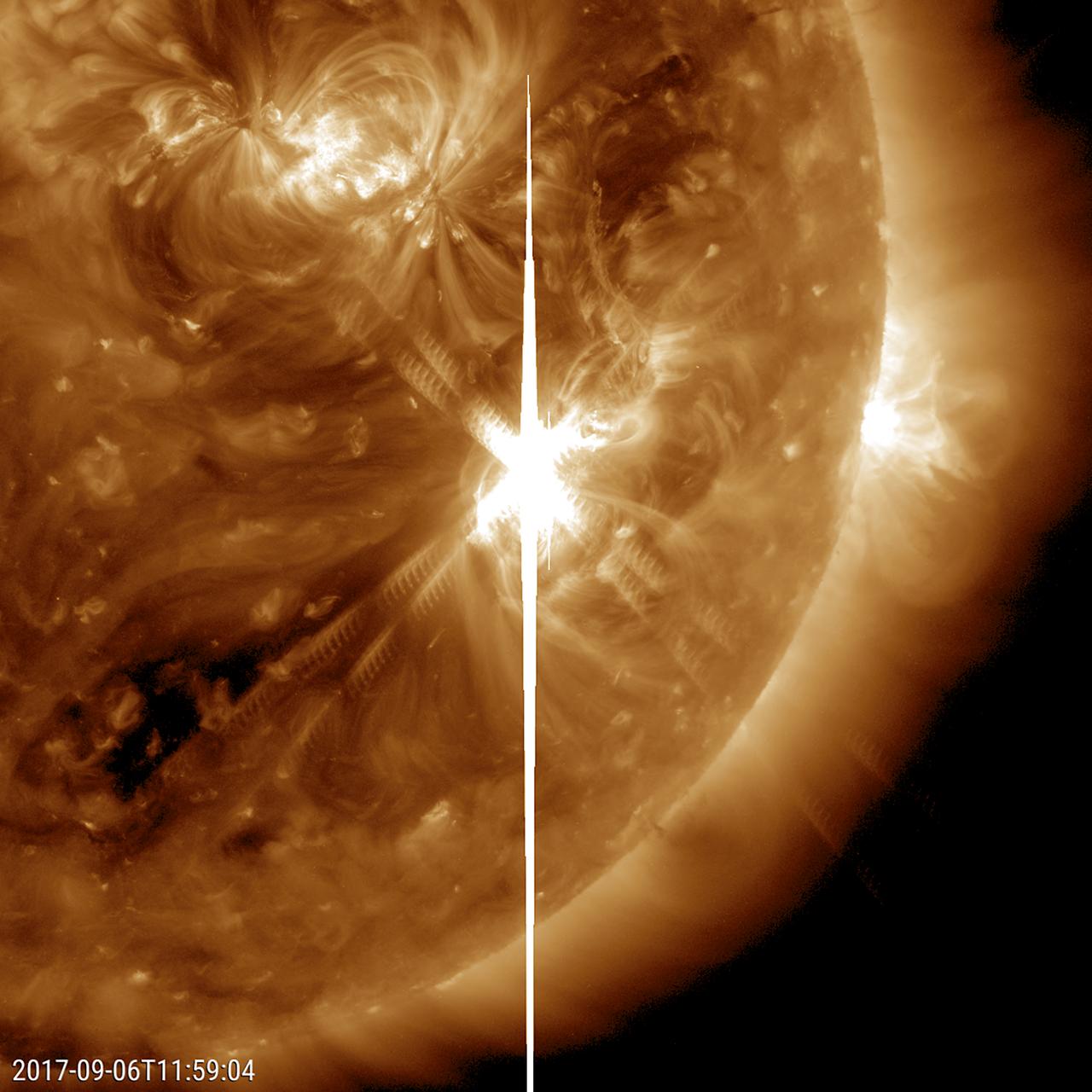
A large sunspot was the source of a powerful solar flare (an X 9.3) and a coronal mass ejection (Sept. 6, 2017). The flare was the largest solar flare of the last decade. For one thing, it created a strong shortwave radio blackout over Europe, Africa and the Atlantic Ocean. Sunspot 2673 has been also the source of several other smaller to medium-sized solar flares over the past few days. Data from the SOHO spacecraft shows the large cloud of particles blasting into space just after the flare. Note: the bright vertical line and the other rays with barred lines are aberrations in our instruments caused by the bright flash of the flare. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21949
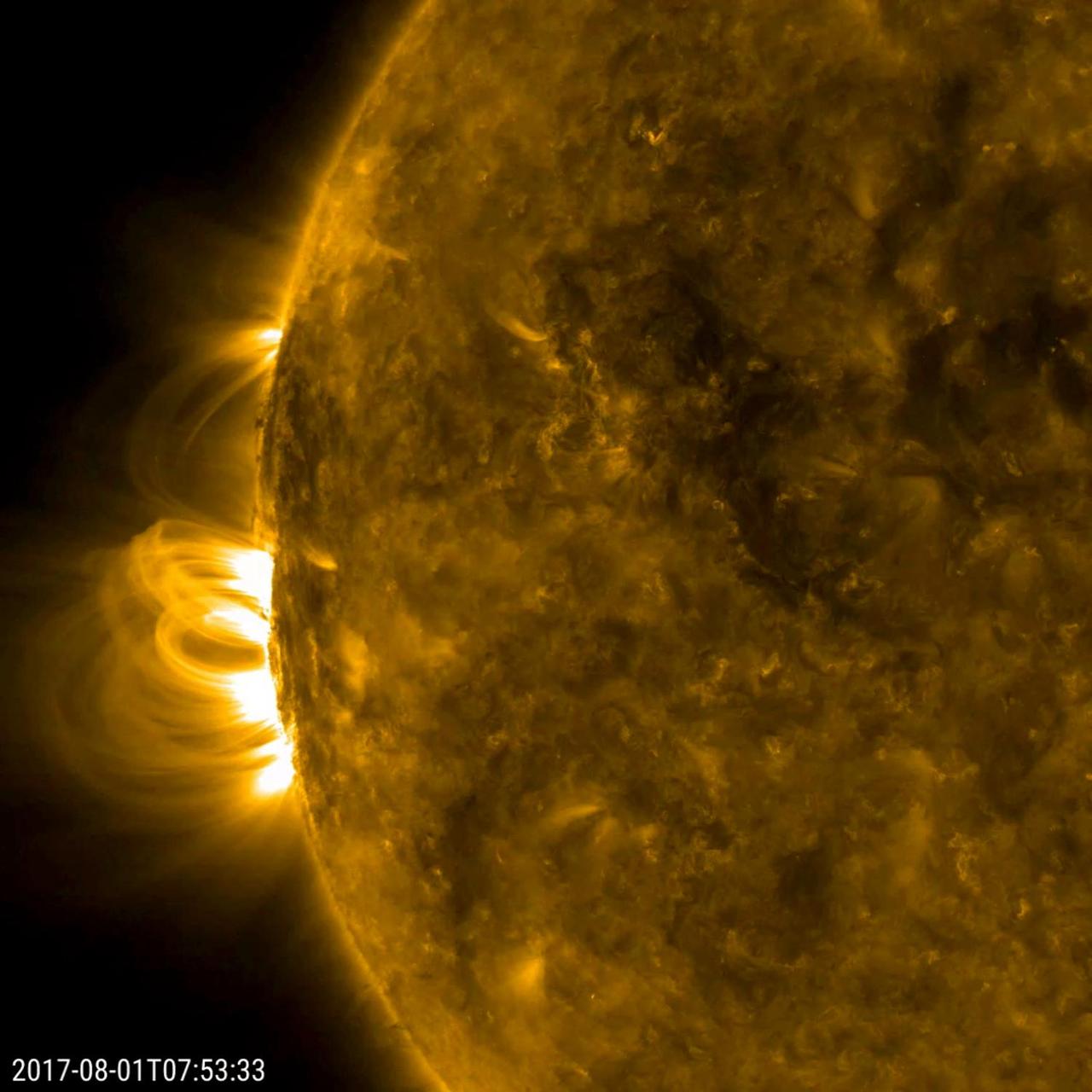
The large sunspot (called AR2665) that rotated out of view about two weeks ago has returned (Aug. 1-2, 2017). Though much reduced in size, it did blast a good-sized coronal mass ejection about a week ago on the far side of the sun. Sunspots can last from days to months, so for it to return again is not an unusual event. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21873
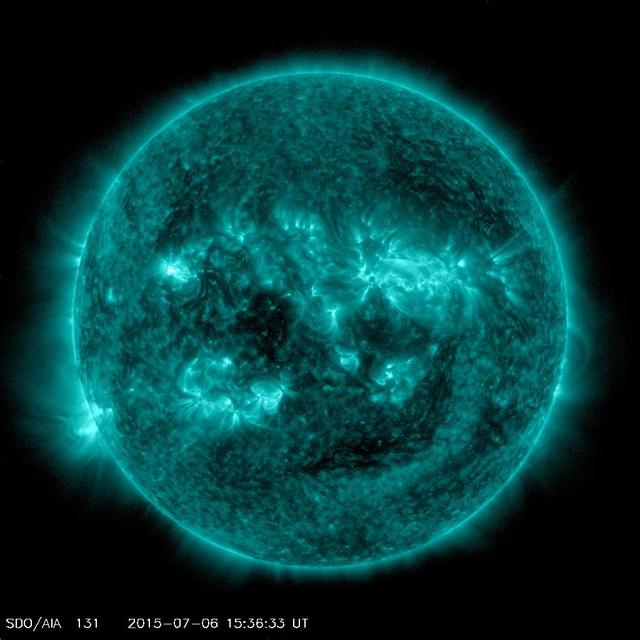
An eruption from the surface of the sun is conspicuous in the lower left portion of this July 6, 2015, image from NASA's Earth-orbiting Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It originates from a location on the surface where NASA's Curiosity Mars rover had been tracking a sunspot in late June and early July. This image was taken by the Atmosphere Imaging Assembly on SDO using the instrument's 131-Angstrom wavelength channel, which is sensitive to hot solar flares. The sun completes a rotation about once a month -- faster near its equator than near its poles. This summer, Mars has a view of the opposite side of the sun from what's facing Earth. Images from Curiosity tracking a southern-hemisphere sunspot until it rotated out of view during the July 4 weekend are in an animation at PIA19801. This location on the sun rotated into position to be seen from Earth a few days later. The eruption visible in this image was linked to a coronal mass ejection observed by SDO and NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory. The coronal mass ejection affected interplanetary space weather, as shown at http://go.nasa.gov/1JSXLF3. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19680
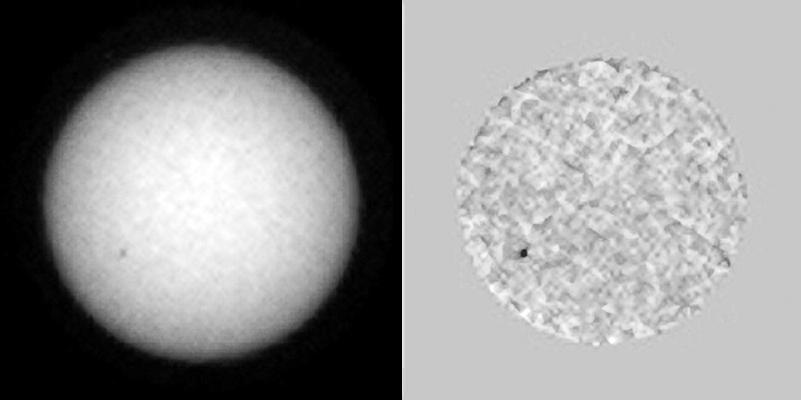
This single frame from a sequence of images shows sunspots as viewed by NASA Curiosity Mars rover from June 27 to July 8, 2015; the rover was in position to see the opposite side of the sun from the side facing Earth during this period. One sunspot seen in this series emerged while under Curiosity's view, subsequently rotated out of view over the July 4 weekend. That sunspot's location showed up a few days later observable from Earth's point of view as an area of solar eruptions and source of a coronal mass ejection. The coronal mass ejection affected interplanetary space weather, though not in Earth's direction. The images were taken by the right-eye camera of Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam), which has a 100-millimeter telephoto lens. The view on the left of each pair in this sequence has little processing other than calibration and putting north toward the top of each frame. The view on the right of each pair has been enhanced to make sunspots more visible. The apparent granularity throughout these enhanced images is an artifact of this processing. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19801

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., engineers move one of the two STEREO spacecraft to a workstand for installation of the solar arrays. Under black protective wrap on the left is the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians perform final internal alignment verification of the Heliospheric Imager (HI) instrument prior to closing for flight. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians perform a final cleaning of the Heliospheric Imager (HI) instrument prior to closing for flight. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians close the door on the Heliospheric Imager (HI) assembly for flight. The top cover hinges open on-orbit. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians perform a final cleaning of the Heliospheric Imager (HI) instrument prior to closing for flight. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
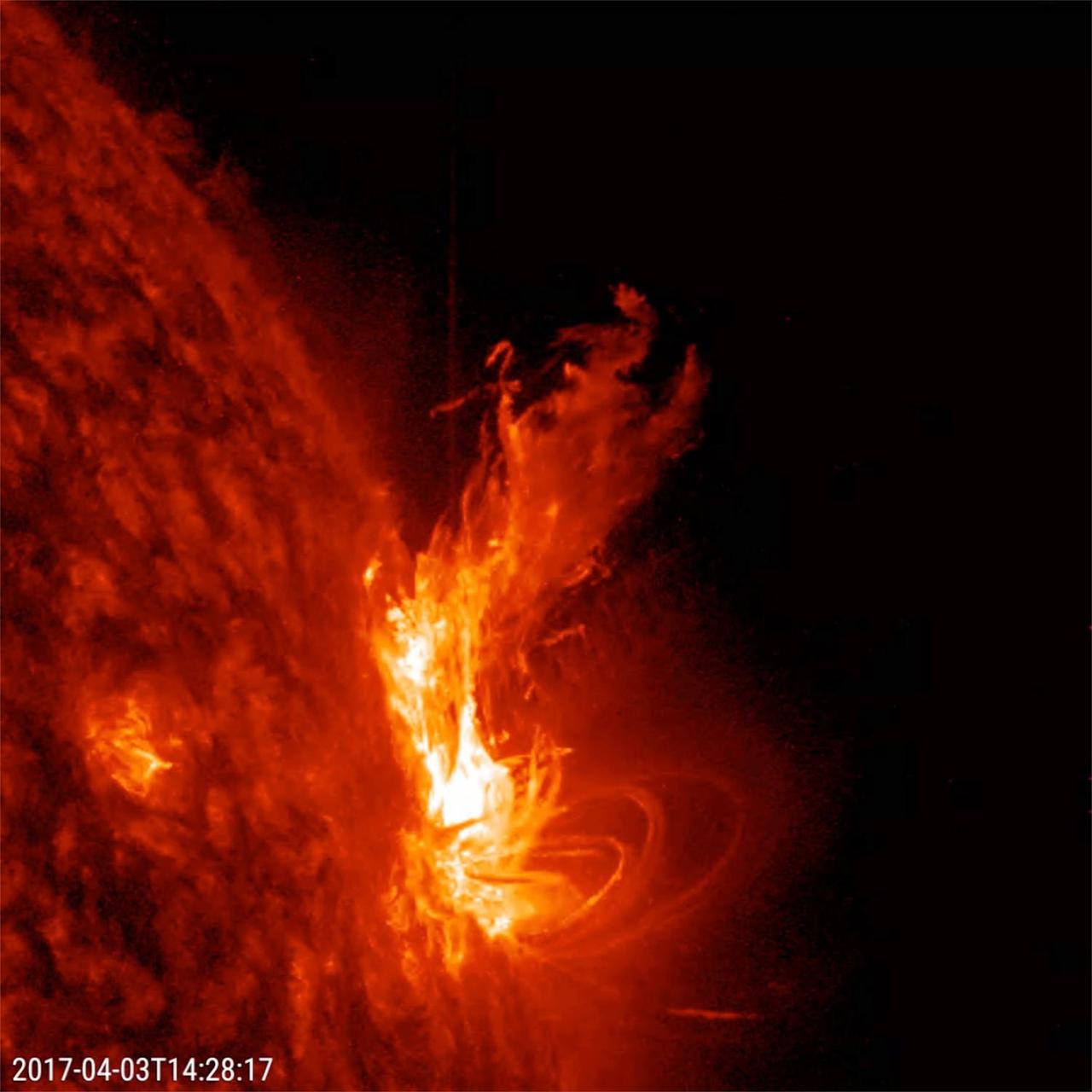

An active region at the sun's edge produced several M5-class (medium sized) flares over a ten-hour period (Apr. 3, 2017). The most dramatic flare occurs about half way through the video clip, when it shoots up a bright towering plume of plasma. These were the strongest flares of the year so far. Some coronal mass ejections (which hurled clouds of plasma into space) were also associated with some of these flares. The images were taken in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21584
A solar flare associated with the coronal mass ejection seen in this image generated a flurry of fast-moving solar protons. As each one hits the CCD camera on SOHO, it produces a brief snow-like speckle in the image. Credit: NASA/SOHO CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This LASCO C2 image, taken 8 January 2002, shows a widely spreading coronal mass ejection (CME) as it blasts more than a billion tons of matter out into space at millions of kilometers per hour. The C2 image was turned 90 degrees so that the blast seems to be pointing down. An EIT 304 Angstrom image from a different day was enlarged and superimposed on the C2 image so that it filled the occulting disk for effect. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (SDO AIA 131 and 171 difference blended image of flux ropes during CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b>

Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (SDO AIA 131 and 171 difference blended image of flux ropes during CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b>
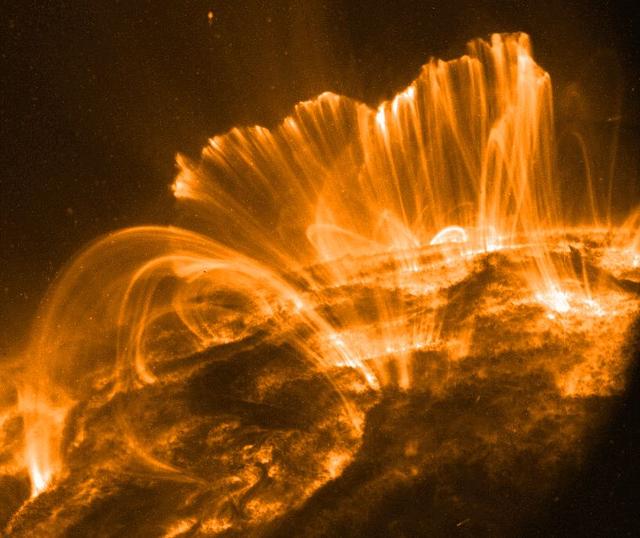

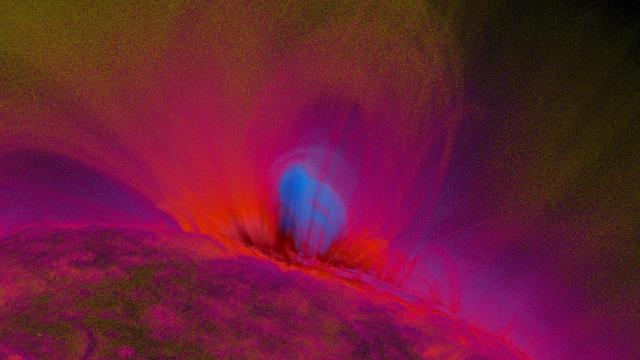
Explanation: In this picture, the Sun's surface is quite dark. A frame from a movie recorded on November 9th by the orbiting TRACE telescope, it shows coronal loops lofted over a solar active region. Glowing brightly in extreme ultraviolet light, the hot plasma entrained above the Sun along arching magnetic fields is cooling and raining back down on the solar surface. Hours earlier, on November 8th, astronomers had watched this particular active region produce a not so spectacular solar flare. Still, the M-class flare spewed forth an intense storm of particles, suddenly showering satellites near the Earth with high energy protons. The flare event was also associated with a large coronal mass ejection, a massive cloud of material which impacted our fair planet's magnetic field about 31 hours later. The result ... a strong geomagnetic storm. Credit: NASA/GSFC/TRACE To learn more go to: <a href="http://nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/trace" rel="nofollow">nasascience.nasa.gov/missions/trace</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
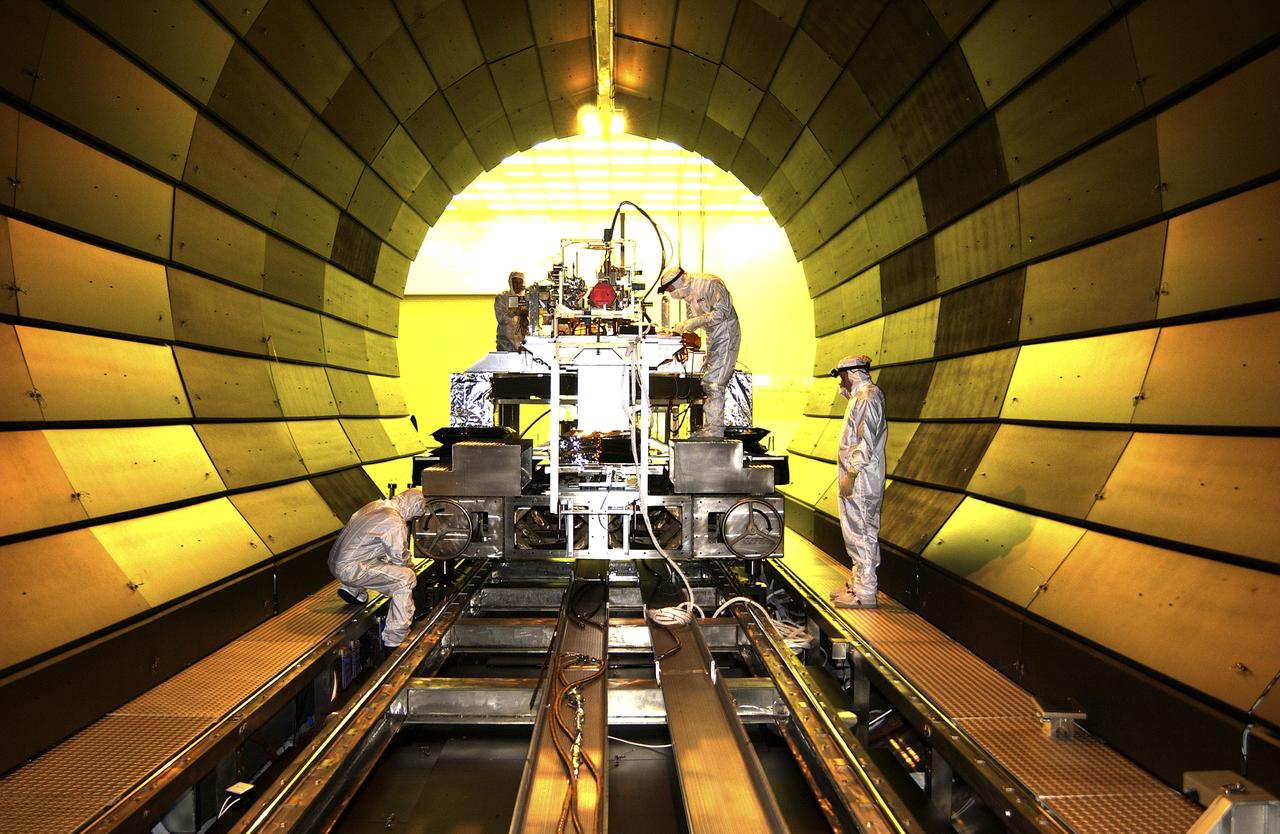

This photograph depicts the Solar X-Ray Imager (SXI) being installed in the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) vacuum chamber for testing at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The XRCF vacuum chamber simulates a space environment with low temperature and pressure. The x-ray images from SXI on the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-12 (GOES-12) will be used by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and U.S. Air Force to forecast the intensity and speed of solar disturbances that could destroy satellite electronics or disrupt long-distance radio communications. The SXI will observe solar flares, coronal mass ejections, coronal holes, and active regions in the x-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These features are the dominant sources of disturbances in space weather. The imager instrument consists of a telescope assembly with a 6.3-inch (16-centimeter) diameter grazing incidence mirror and a detector system. The imager was developed, tested, and calibrated by MSFC, in conjunction with the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and U.S. Air Force.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., engineers install a solar array to one of the two STEREO spacecraft. The dish in front is a high gain antenna. Under black protective wrap at right is the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. The long silver cylinder in the front, at right of the antenna, is the In situ Measurements of Particles and CME Transients, known as IMPACT, boom. The red protective covers are removed before flight. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., engineers install a solar array to one of the two STEREO spacecraft. The dish in front is the high gain antenna. Under black protective wrap at right is the Heliospheric Imager instrument, part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. The long silver cylinder in the front, at right of the antenna, is the In situ Measurements of Particles and CME Transients, known as IMPACT, boom. The red protective covers are removed before flight. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., engineers install a solar array to one of the two STEREO spacecraft. The dish in front is a high gain antenna. Under black protective wrap at right is the Heliospheric Imager instrument, part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. The long silver cylinder in the front, at right of the antenna, is the In situ Measurements of Particles and CME Transients, known as IMPACT, boom. The red protective covers are removed before flight. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., engineers have completed installing the solar array on STEREO spacecraft "A." The panel displaying the "A" is a protective cover on the solar array to protect it during ground processing. The dish in front is a high gain antenna. Under black protective wrap at right is the Heliospheric Imager instrument, part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. The long silver cylinder in the front, at right of the antenna, is the In situ Measurements of Particles and CME Transients, known as IMPACT, boom. The red protective covers are removed before flight. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
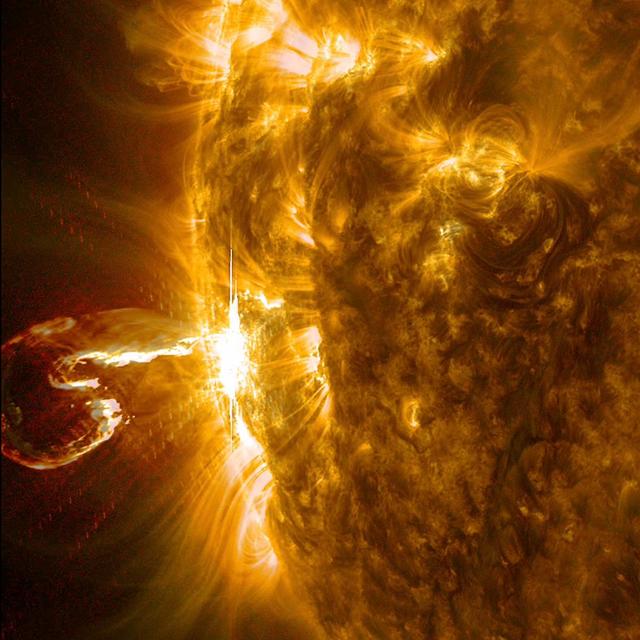

An active region at the edge of the Sun blew out an X4 flare (one of the largest of the solar cycle) and a coronal mass ejection on Feb. 25, 2014. The still image of the ejected plasma (taken at 00:45 UT) shows it curled like a shrimp, but this eruption was no shrimp: it was powerful. The images seen here are a combination of two wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light (171 and 304 Angstroms). The video clip covers about three hours of activity. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Solar Dynamics Observatory <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
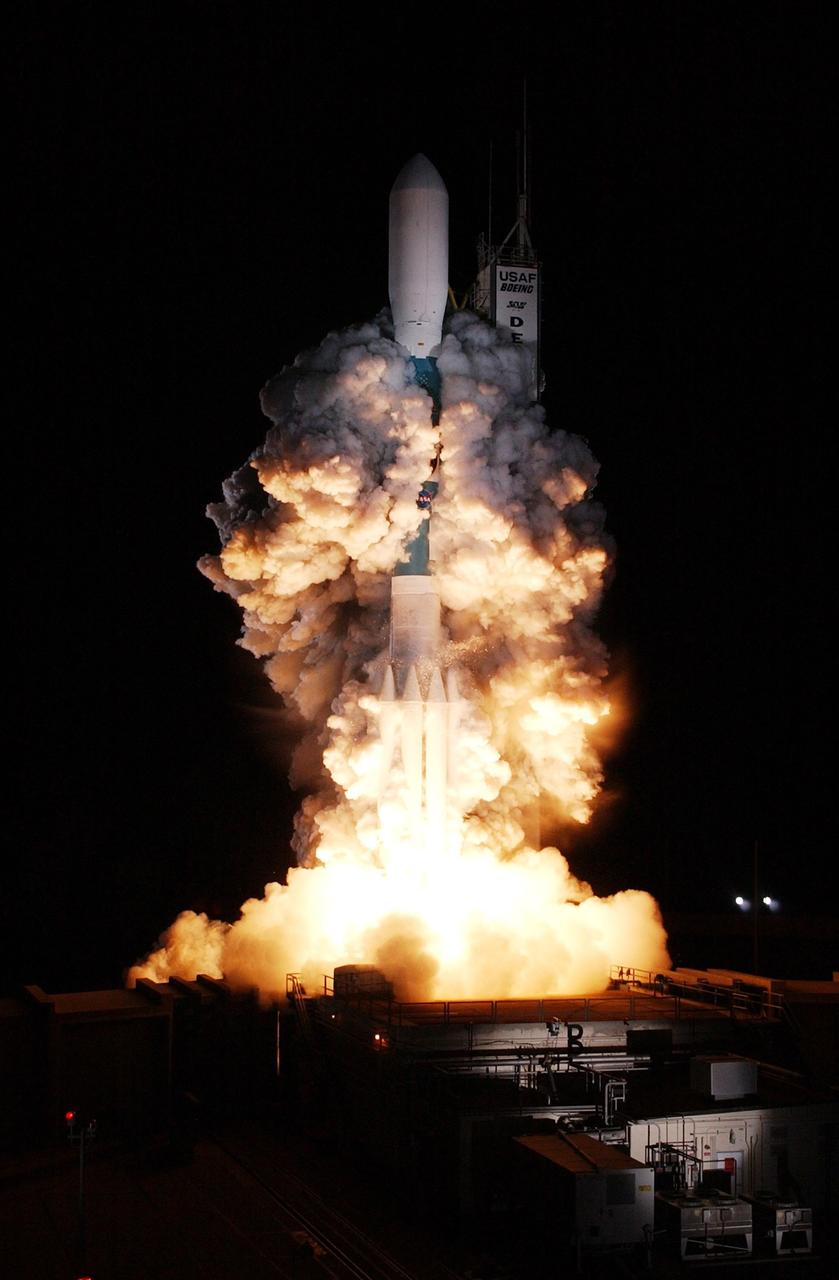

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just after liftoff, clouds of smoke billow up and around the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
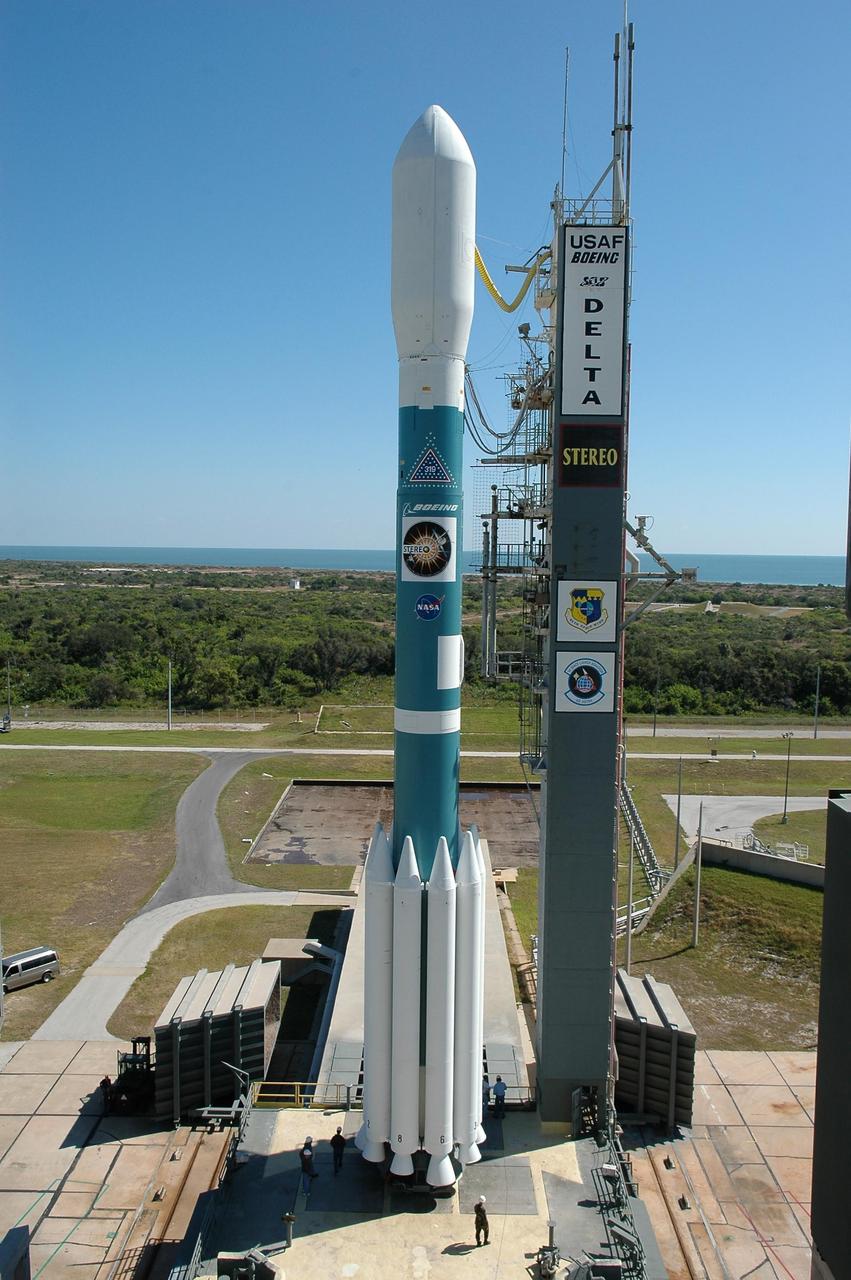

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After the mobile service tower has rolled away, the Delta II rocket with the STEREO spacecraft at top stands alone next to the launch gantry. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
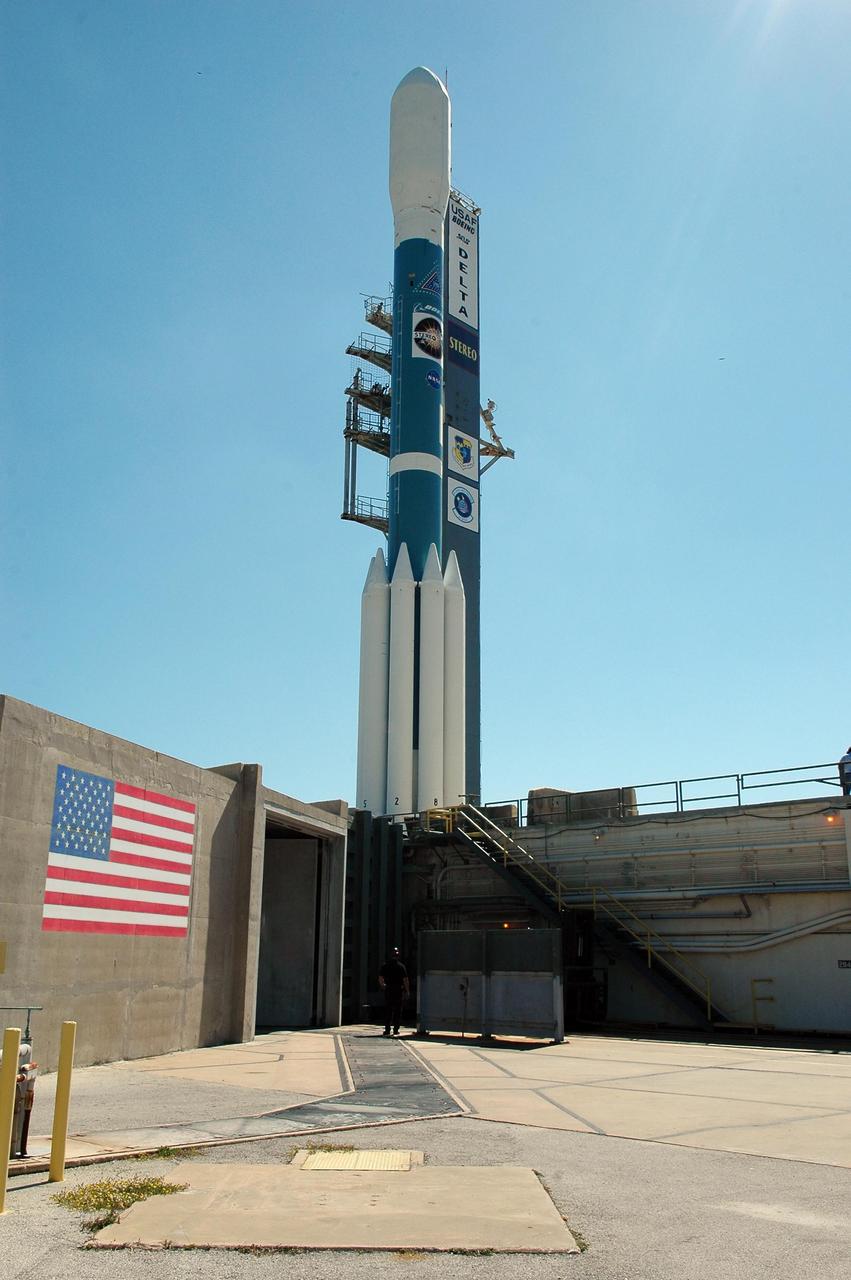

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II rocket with the STEREO spacecraft at top stands next to the launch gantry, ready for liftoff. Launch is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25.STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
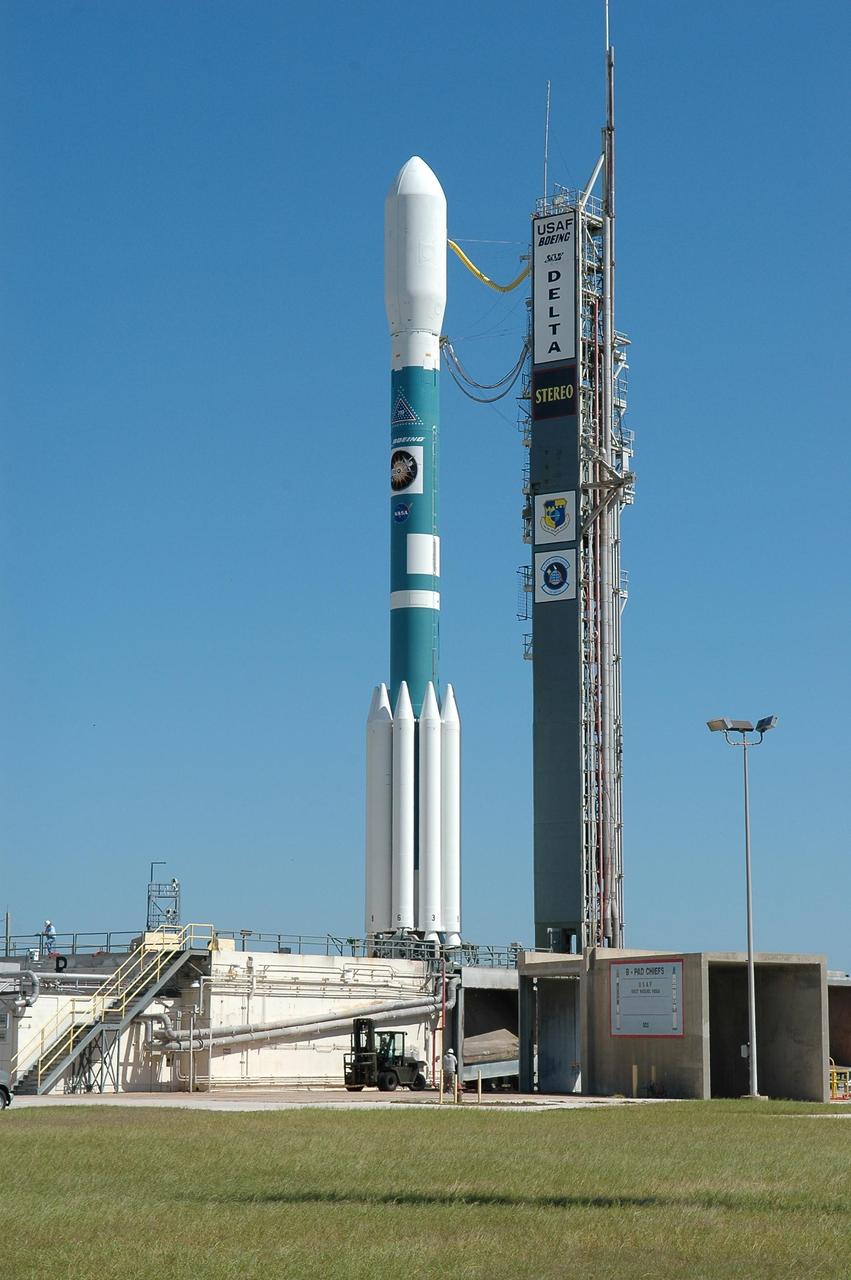

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II rocket with the STEREO spacecraft at top stands next to the launch gantry, ready for liftoff. Launch is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
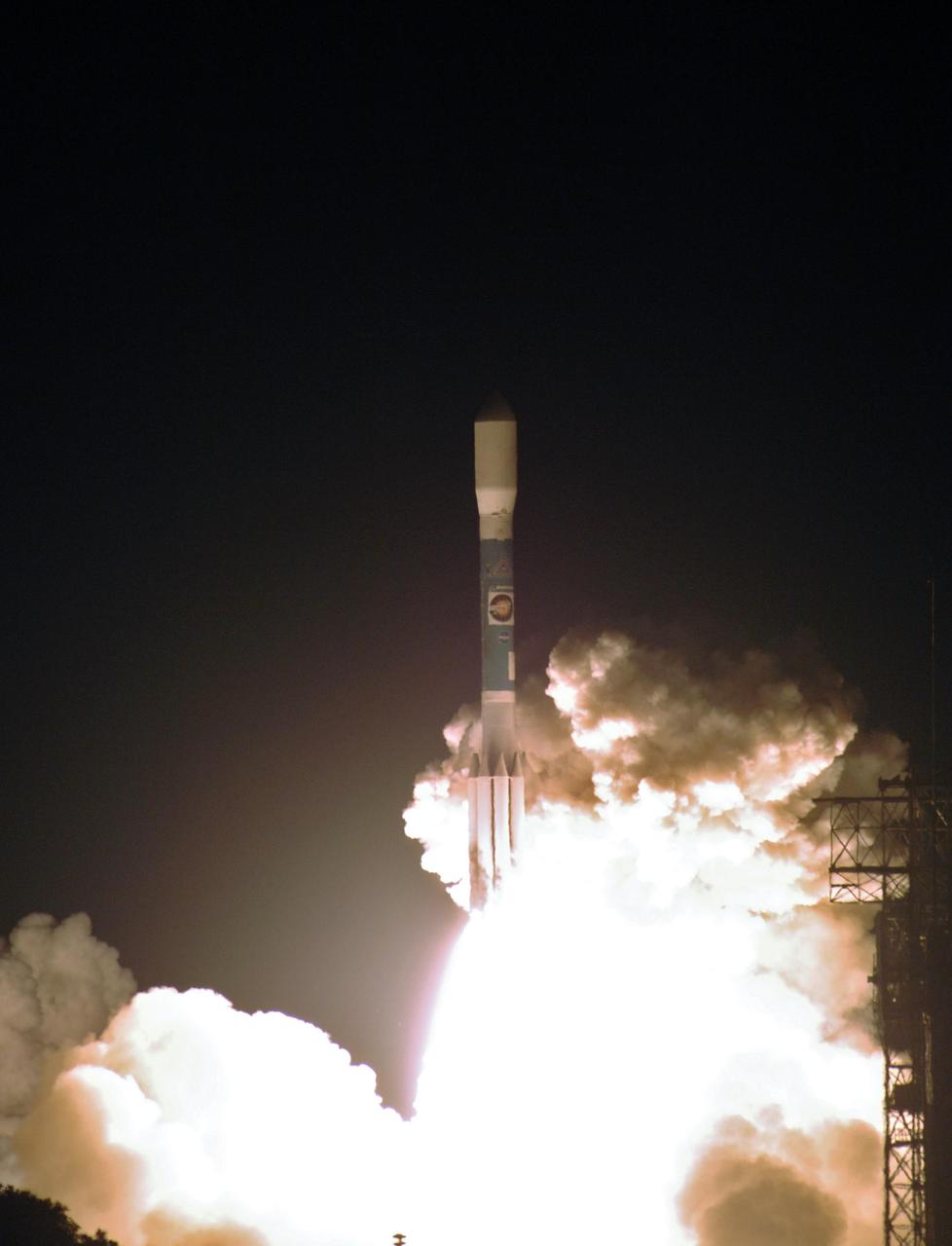

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II launch vehicle carrying the STEREO spacecraft hurtles through the smoke and steam after liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Liftoff was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
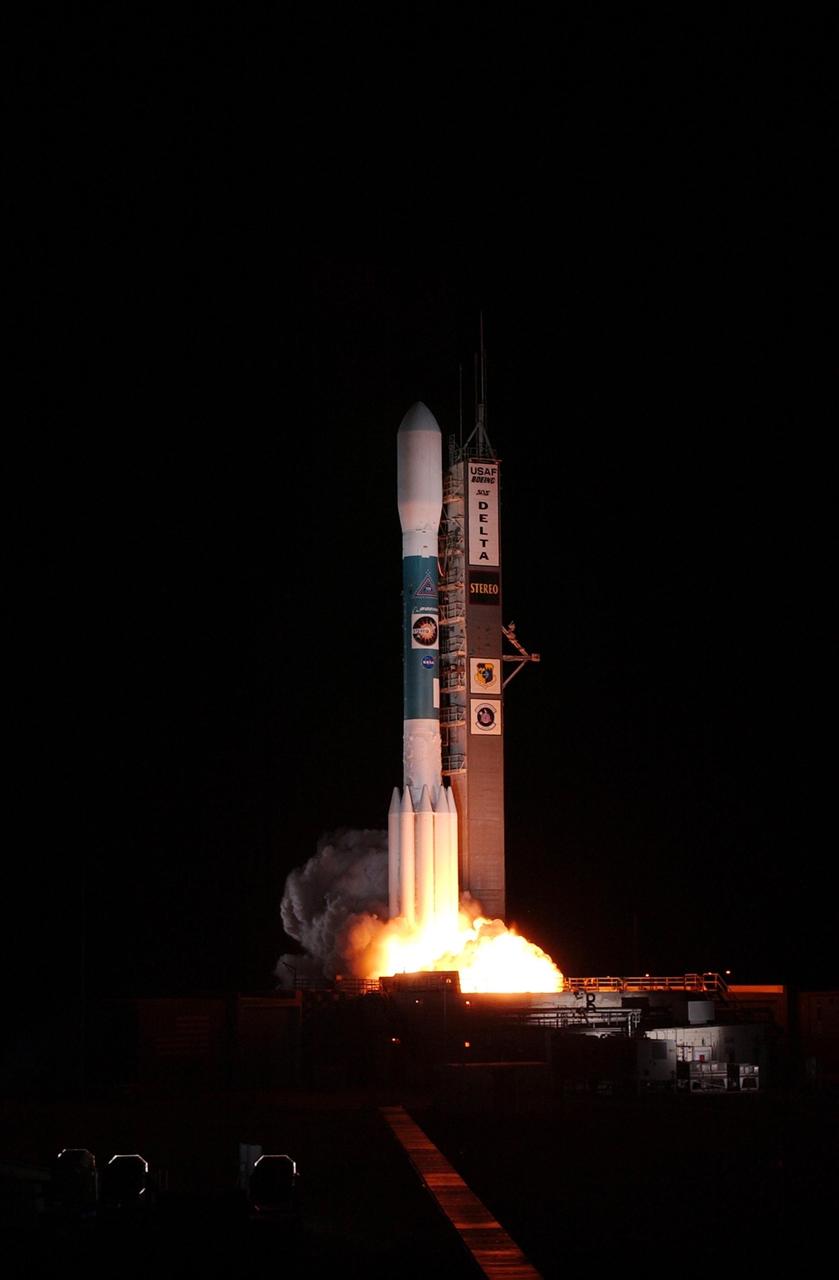

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At liftoff, clouds of smoke spread beneath the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
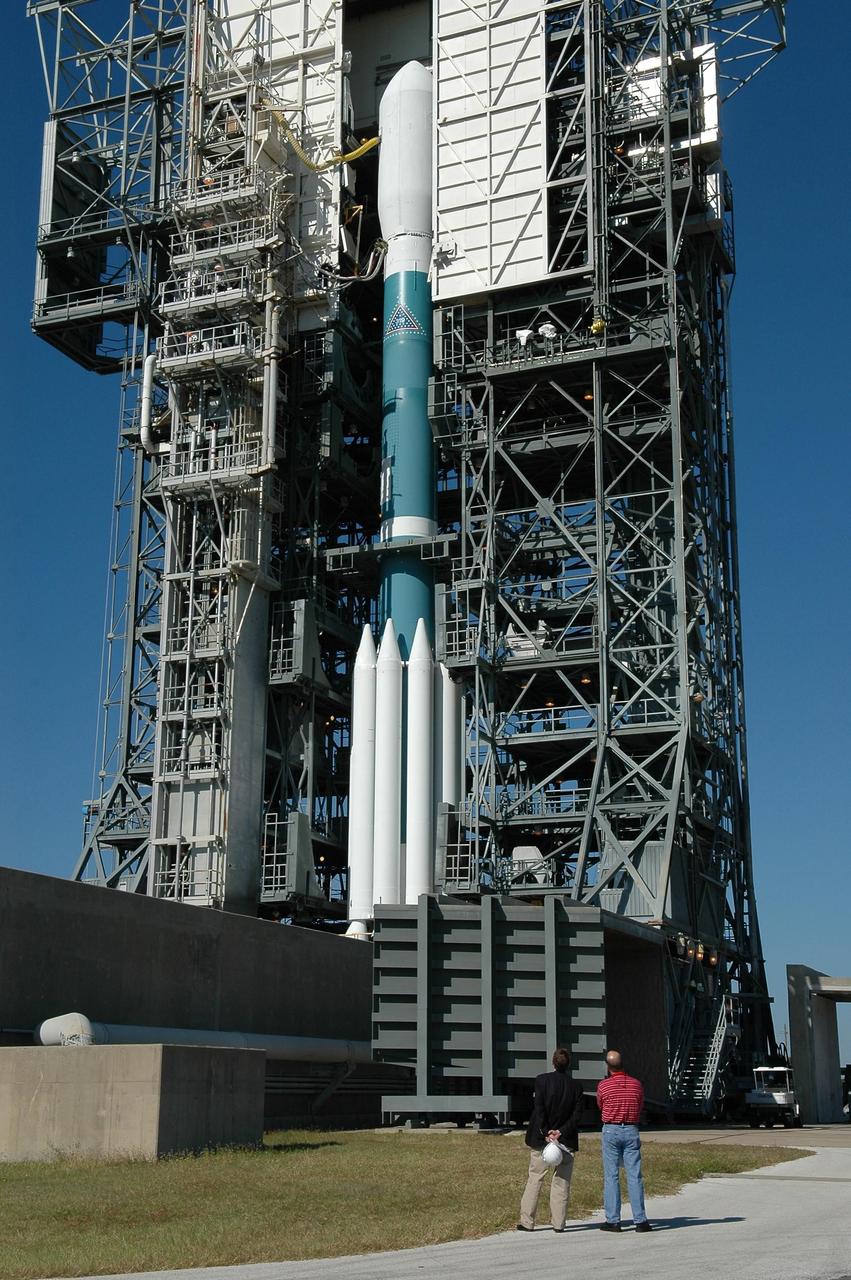

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The mobile service tower begins to roll away from the STEREO spacecraft aboard the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for launch. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Captured in the water of the Banana River, the brilliant light from the Delta II carrying the STEREO spacecraft lights up the night sky. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
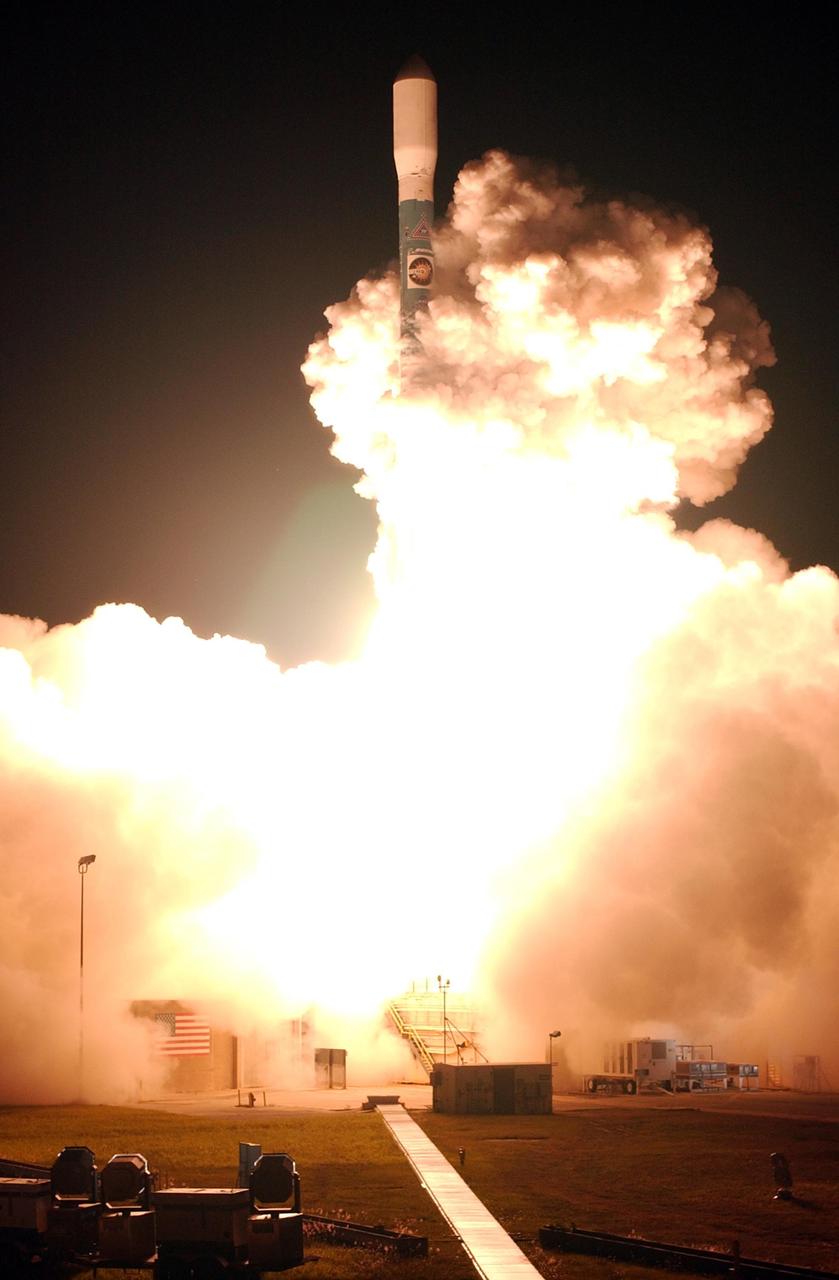

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top streaks through the smoke as it climbs to orbit. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
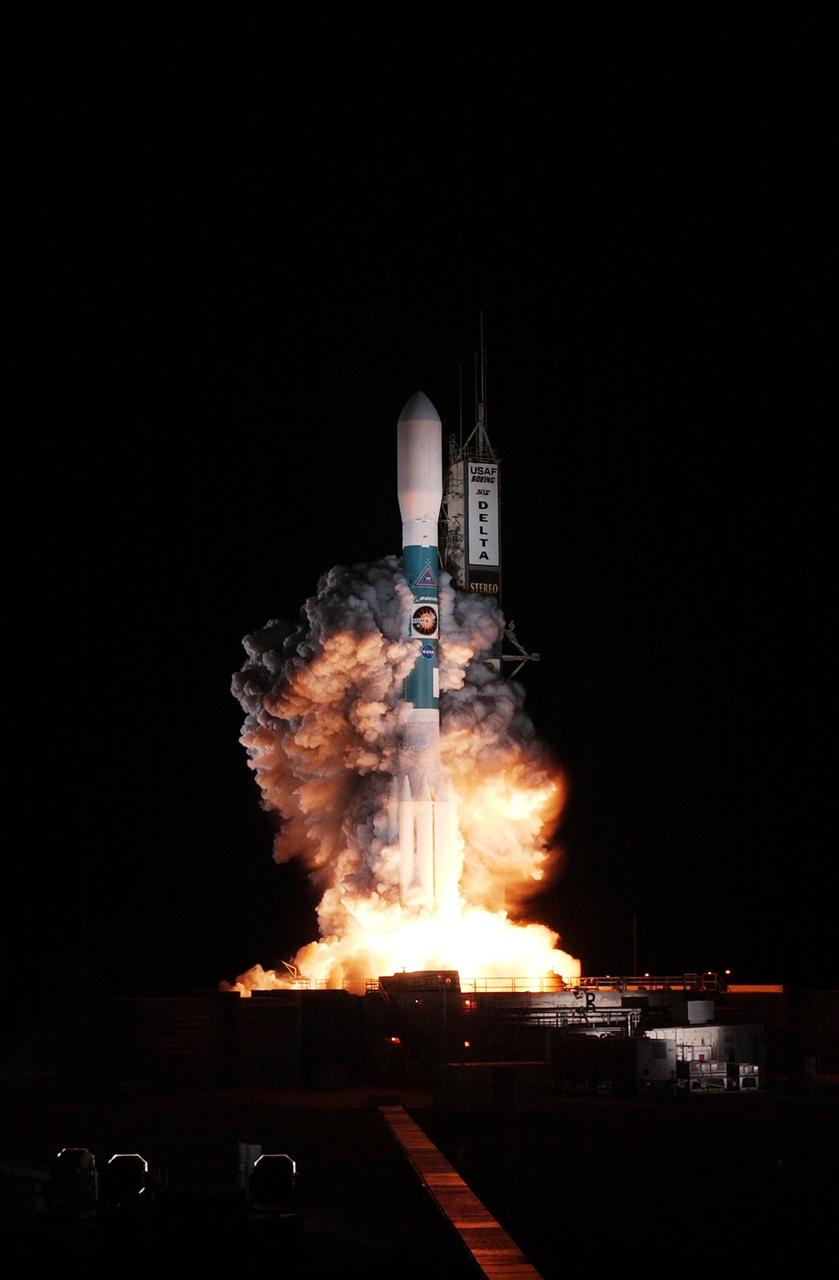

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just after liftoff, clouds of smoke billow up and around the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Banana River reflects the brilliant launch of the Delta II carrying the STEREO spacecraft. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
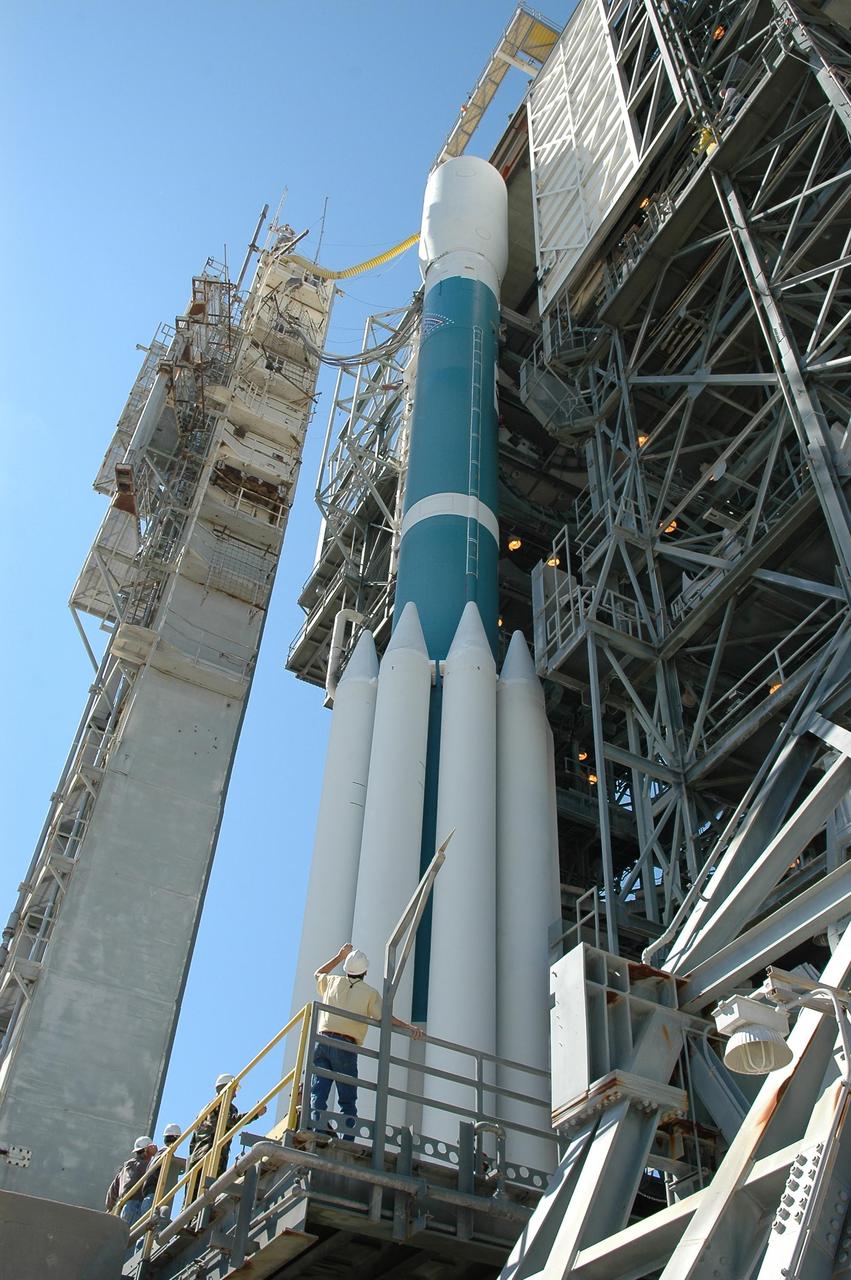

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The mobile service tower (right) begins to roll away from the STEREO spacecraft aboard the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for launch. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at liftoff, clouds of smoke and steam rise around the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
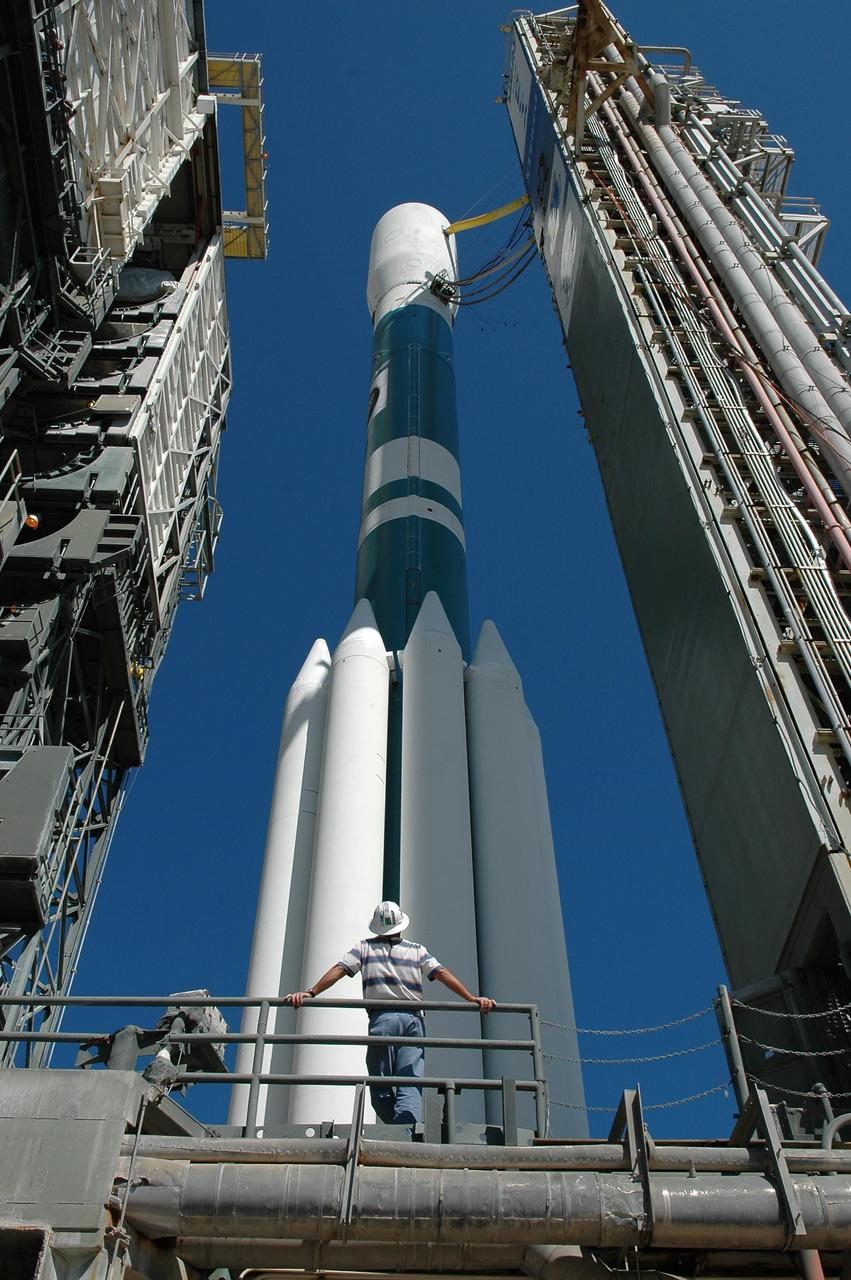

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The mobile service tower (left) rolls away from the STEREO spacecraft aboard the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for launch. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
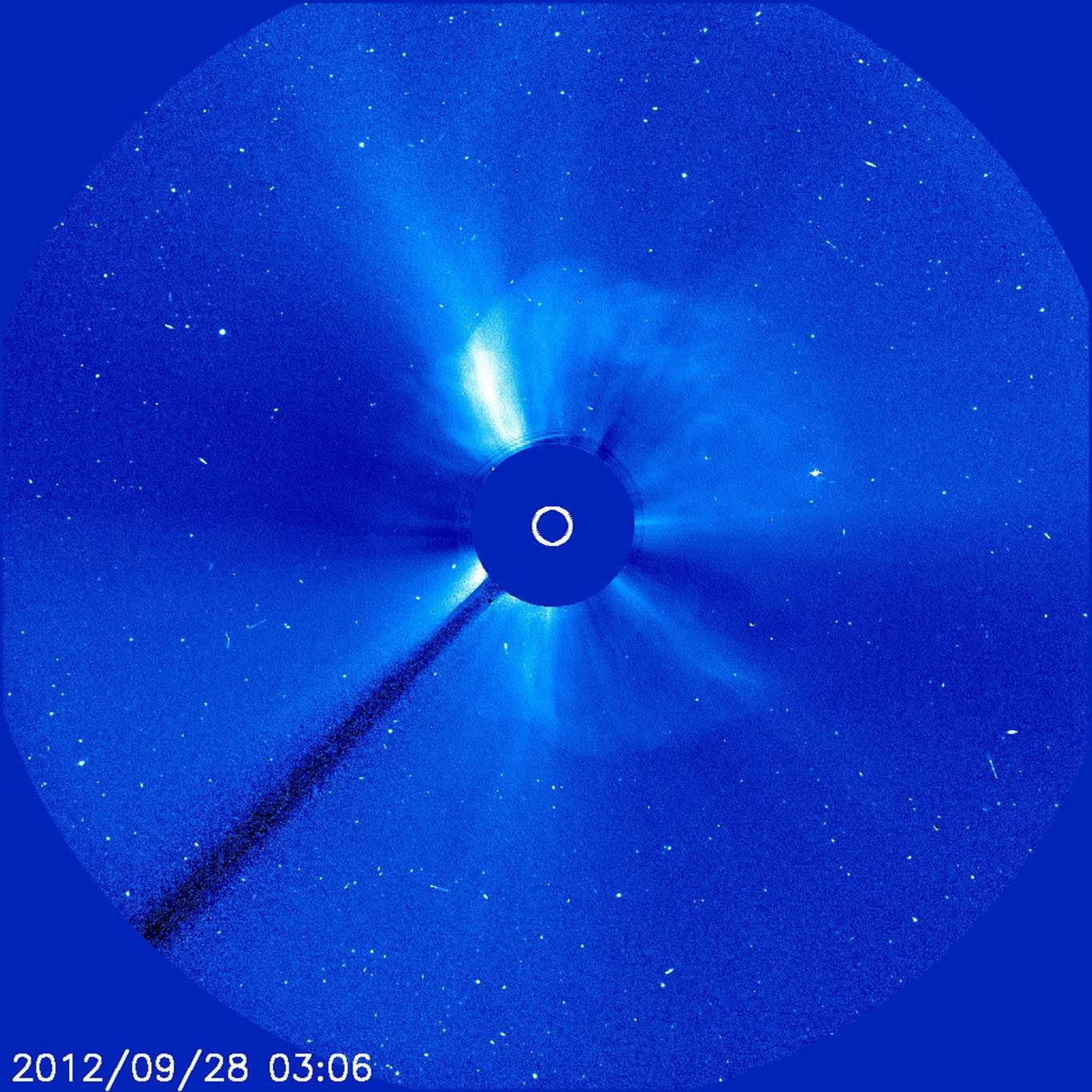
A giant cloud appears to expand outward from the sun in all directions in this image from Sept. 28, 2012, which is called a halo CME. This kind of image occurs when a CME moves toward Earth – as here – or directly away from it. Credit: ESA/NASA/SOHO CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
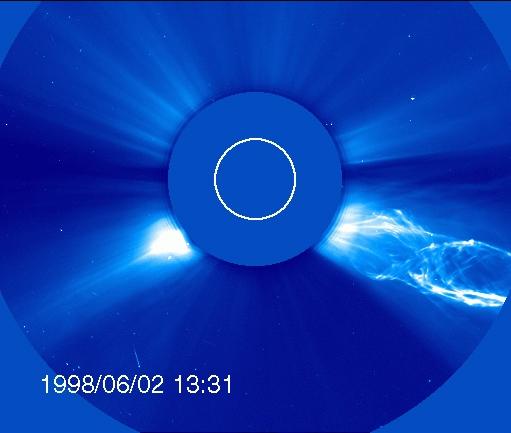
OHO captured this image of a CME from the side – but the structure looks much different from the classic light bulb CME. The filament of material bursting off the sun has a helical magnetic structure, which is unraveling like a piece of yarn during the eruption. Credit: ESA/NASA/SOHO..---..CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

STEREO witnessed the March 5, 2013, CME from the side of the sun – Earth is far to the left of this picture. While the SOHO images show a halo CME, STEREO shows the CME clearly moving away from Earth. Credit: NASA/STEREO --- CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
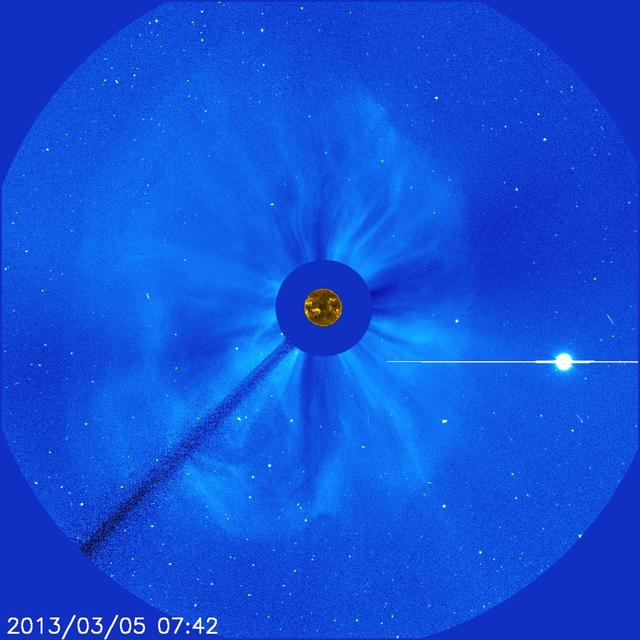
There's no way to tell from this SOHO image whether the halo CME on March 5, 2013, originated from the front or far of the sun. But the STEREO spacecraft were watching the sun from the sides and showed it was from the far side. The bright planet is Venus. Credit: NASA/SOHO CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
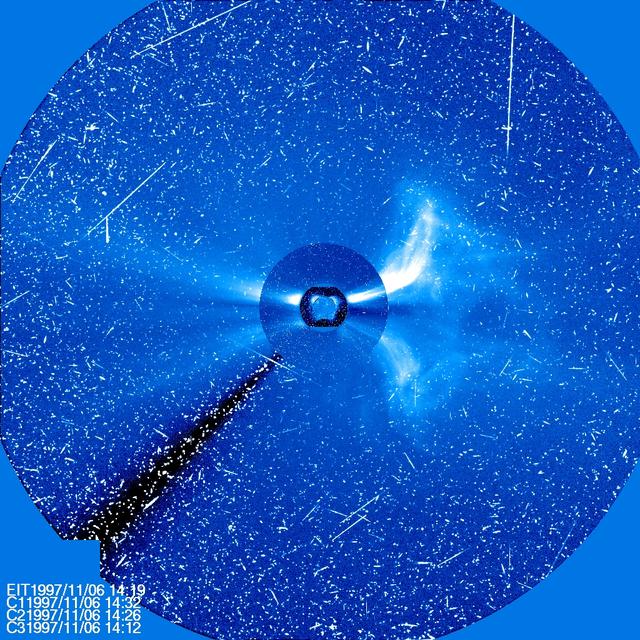
Four different instruments on SOHO show a large CME on Nov. 6, 1997. The sun is at the center, with three coronagraph images of different sizes around it. The streaks of white light are from protons hitting the SOHO cameras producing a snowy effect typical of a significant flare. ..Credit: NASA/SOHO..---..CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
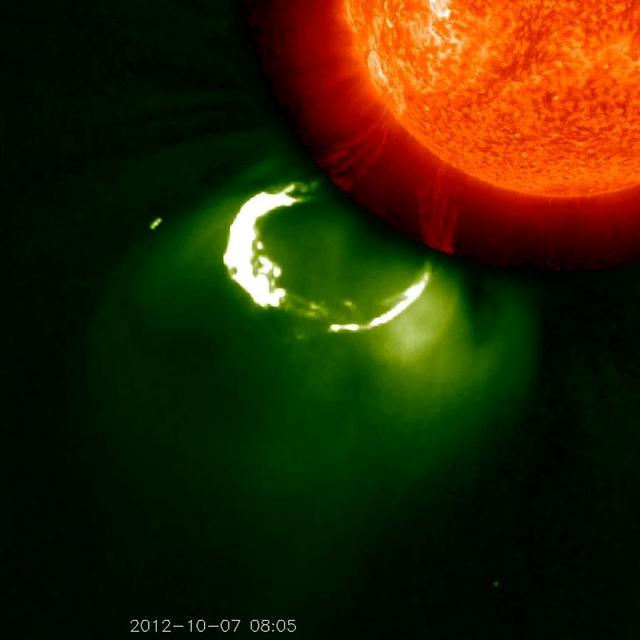

This CME image from Oct. 7, 2012, captured by two instruments on STEREO, shows the eruption from its base out into space. The base of the CME near the sun is seen in extreme ultraviolet light emitted directly from the solar material; the growing loop is seen in visible light. Credit: NASA/STEREO CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
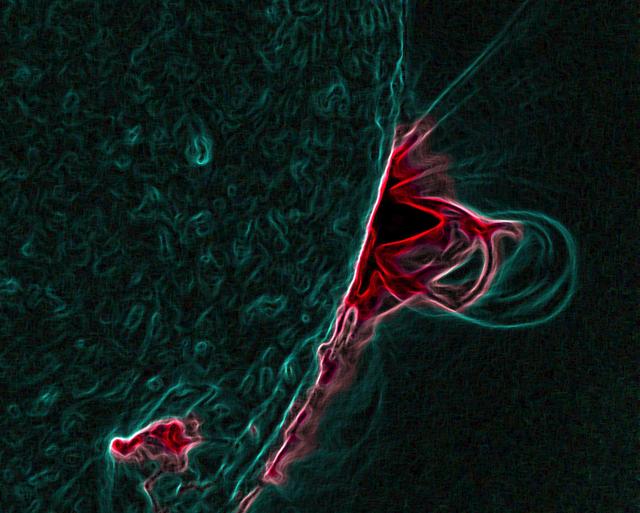
Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory on July 18, 2012. It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: This image from June 20, 2013, at 11:15 p.m. EDT shows the bright light of a solar flare on the left side of the sun and an eruption of solar material shooting through the sun’s atmosphere, called a prominence eruption. Shortly thereafter, this same region of the sun sent a coronal mass ejection out into space. --- On June 20, 2013, at 11:24 p.m., the sun erupted with an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection or CME, a solar phenomenon that can send billions of tons of particles into space that can reach Earth one to three days later. These particles cannot travel through the atmosphere to harm humans on Earth, but they can affect electronic systems in satellites and on the ground. Experimental NASA research models, based on observations from NASA’s Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory and ESA/NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory show that the CME left the sun at speeds of around 1350 miles per second, which is a fast speed for CMEs. Earth-directed CMEs can cause a space weather phenomenon called a geomagnetic storm, which occurs when they funnel energy into Earth's magnetic envelope, the magnetosphere, for an extended period of time. The CME’s magnetic fields peel back the outermost layers of Earth's fields changing their very shape. Magnetic storms can degrade communication signals and cause unexpected electrical surges in power grids. They also can cause aurora. Storms are rare during solar minimum, but as the sun’s activity ramps up every 11 years toward solar maximum – currently expected in late 2013 -- large storms occur several times per year. In the past, geomagnetic storms caused by CMEs of this strength and direction have usually been mild. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14OxuEe" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14OxuEe</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
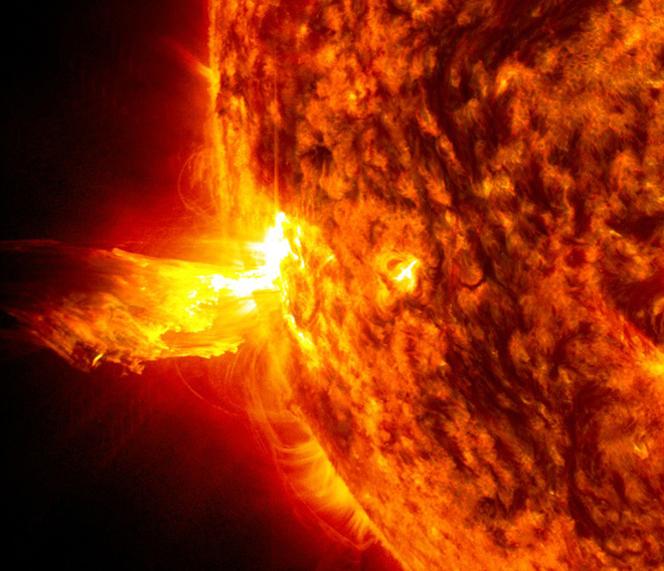

Caption: This image from June 20, 2013, at 11:15 p.m. EDT shows the bright light of a solar flare on the left side of the sun and an eruption of solar material shooting through the sun’s atmosphere, called a prominence eruption. Shortly thereafter, this same region of the sun sent a coronal mass ejection out into space. --- On June 20, 2013, at 11:24 p.m., the sun erupted with an Earth-directed coronal mass ejection or CME, a solar phenomenon that can send billions of tons of particles into space that can reach Earth one to three days later. These particles cannot travel through the atmosphere to harm humans on Earth, but they can affect electronic systems in satellites and on the ground. Experimental NASA research models, based on observations from NASA’s Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory and ESA/NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory show that the CME left the sun at speeds of around 1350 miles per second, which is a fast speed for CMEs. Earth-directed CMEs can cause a space weather phenomenon called a geomagnetic storm, which occurs when they funnel energy into Earth's magnetic envelope, the magnetosphere, for an extended period of time. The CME’s magnetic fields peel back the outermost layers of Earth's fields changing their very shape. Magnetic storms can degrade communication signals and cause unexpected electrical surges in power grids. They also can cause aurora. Storms are rare during solar minimum, but as the sun’s activity ramps up every 11 years toward solar maximum – currently expected in late 2013 -- large storms occur several times per year. In the past, geomagnetic storms caused by CMEs of this strength and direction have usually been mild. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
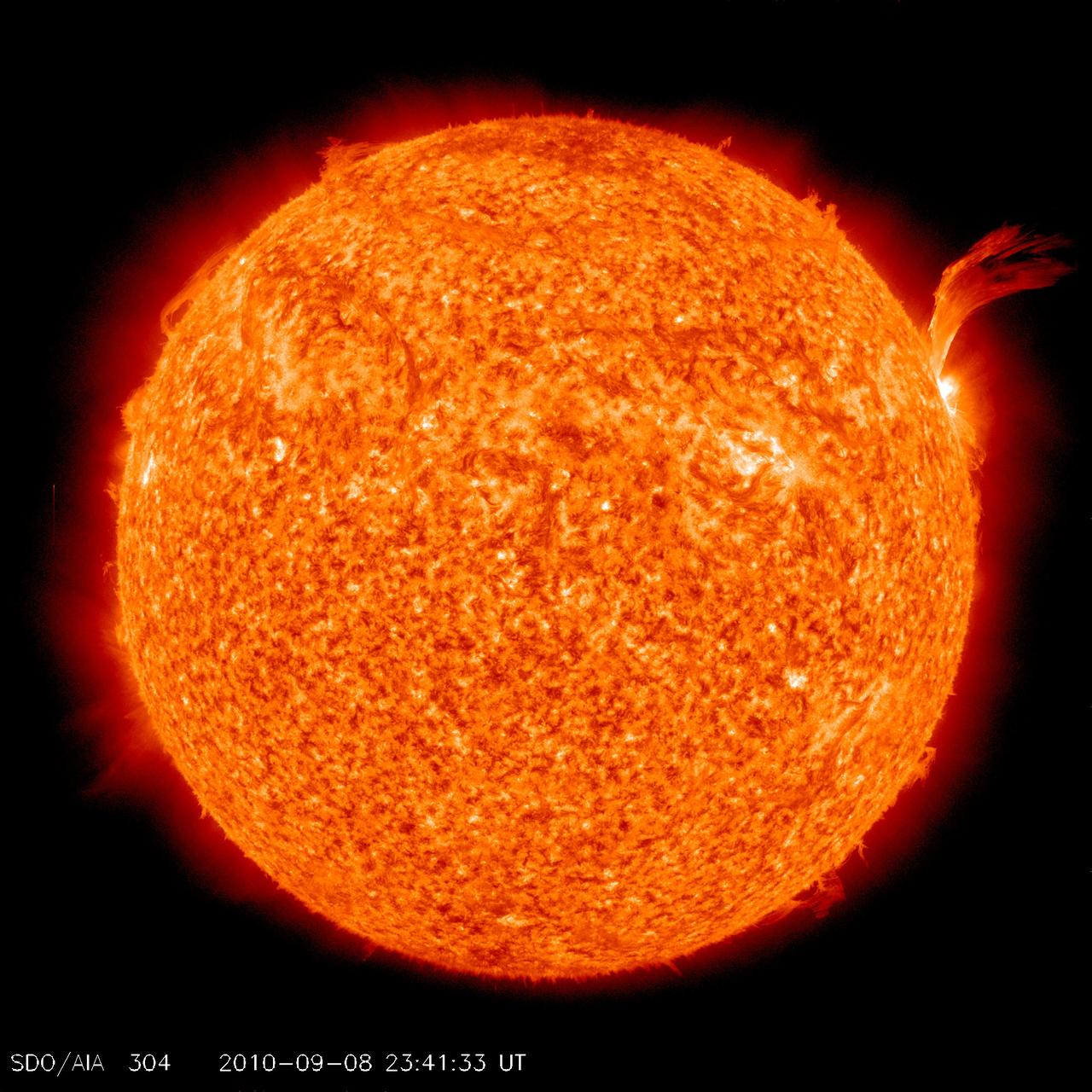

NASA image release Sept 9, 2010 Just as sunspot 1105 was turning away from Earth on Sept. 8, the active region erupted, producing a solar flare and a fantastic prominence. The eruption also hurled a bright coronal mass ejection into space. The eruption was not directed toward any planets. To see a detail go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974263471/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974263471/</a> View the video here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090</a> This is a snapshot of the prominence. Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
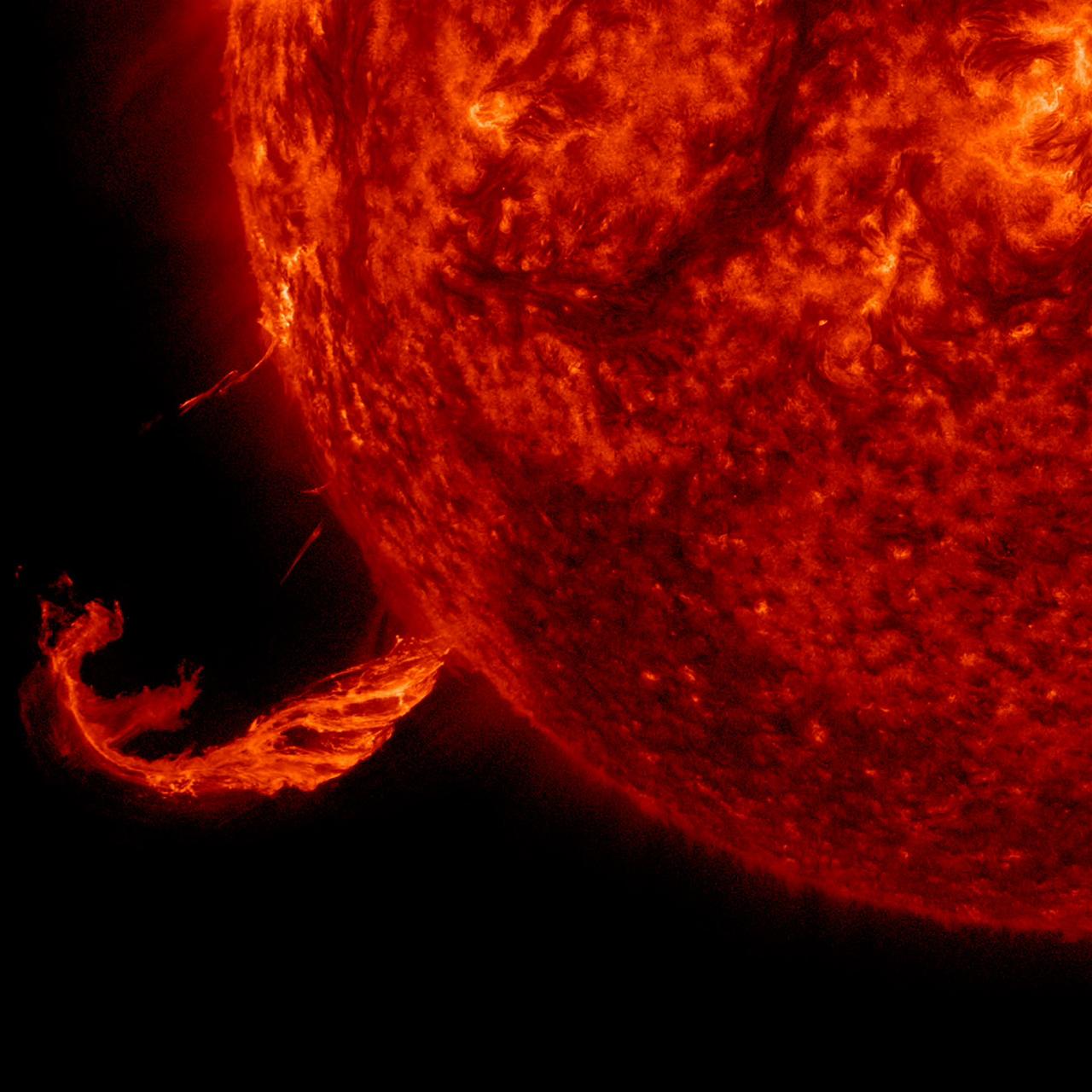
The Sun blew out a coronal mass ejection along with part of a solar filament over a three-hour period (Feb. 24, 2015). While some of the strands fell back into the Sun, a substantial part raced into space in a bright cloud of particles (as observed by the SOHO spacecraft). The activity was captured in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Because this occurred way over near the edge of the Sun, it was unlikely to have any effect on Earth. Credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
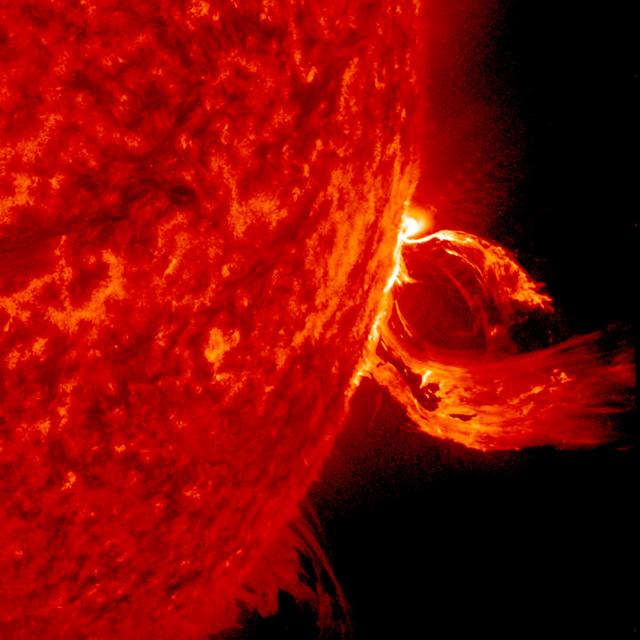

A substantial coronal mass ejection, or CME, blew out from side of the Sun, giving us a great view of the event in profile (June 17-18, 2015). NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory caught the action in the 304 Angstrom wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. The video clip covers about four hours of the event. While some of the plasma falls back into the Sun, a look at the coronagraph on SOHO shows a large cloud of particles heading into space. Credit: NASA/Goddard//SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The largest solar flare ever recorded occurred at 4:51 p.m. EDT, on Monday, April 2, 2001. as Observed by the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) satellite. Solar flares, among the solar systems mightiest eruptions, are tremendous explosions in the atmosphere of the Sun capable of releasing as much energy as a billion megatons of TNT. Caused by the sudden release of magnetic energy, in just a few seconds, solar flares can accelerate solar particles to very high velocities, almost to the speed of light, and heat solar material to tens of millions of degrees. The recent explosion from the active region near the sun's northwest limb hurled a coronal mass ejection into space at a whopping speed of roughly 7.2 million kilometers per hour. Luckily, the flare was not aimed directly towards Earth. Second to the most severe R5 classification of radio blackout, this flare produced an R4 blackout as rated by the NOAA SEC. This classification measures the disruption in radio communications. Launched December 2, 1995 atop an ATLAS-IIAS expendable launch vehicle, the SOHO is a cooperative effort involving NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). (Image courtesy NASA Goddard SOHO Project office)
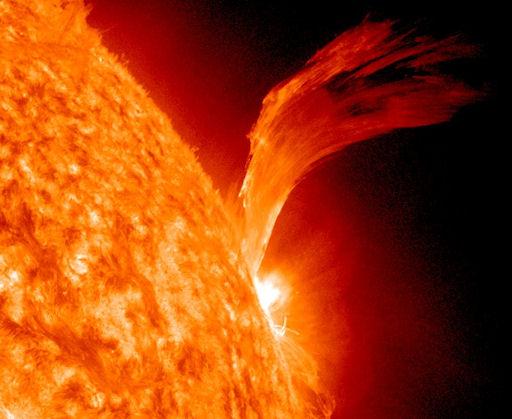

NASA image release Sept 9, 2010 Just as sunspot 1105 was turning away from Earth on Sept. 8, the active region erupted, producing a solar flare and a fantastic prominence. The eruption also hurled a bright coronal mass ejection into space. The eruption was not directed toward any planets. View the video here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090</a> To see a full disk view go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4975115754/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4975115754/</a> This is a snapshot of the prominence. Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
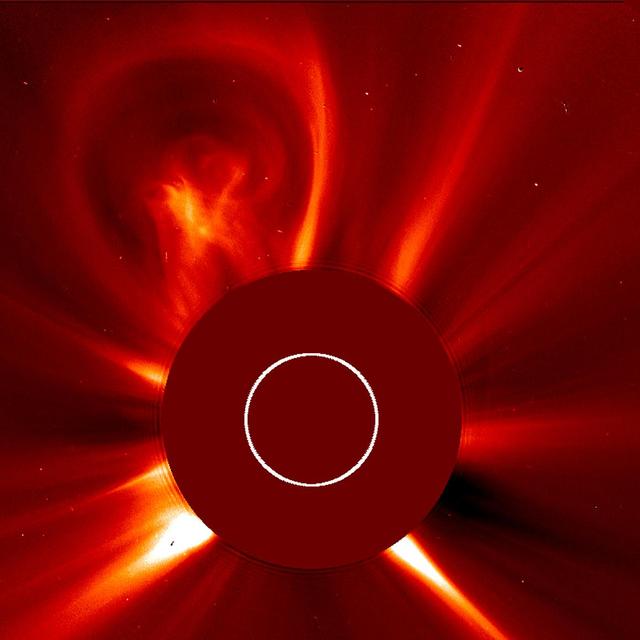
The first of a series of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) over three days (Aug. 20-22), this bulbous CME certainly resembles a light bulb. It has the thin outer edge and a bright, glowing core at its center. CMEs are often bulbous, but it has been years since we have seen one with the elements (pun intended) of a light bulb. The frames were taken by SOHO's LASCO C3 instrument. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are monitoring the explosive potential of magnetic areas of the Sun. This effort could someday lead to better prediction of severe space weather, a phenomenon that occurs when blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, the magnetic storm wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. The researchers from MSFC and NSSTC's solar physics group develop instruments for measuring magnetic fields on the Sun. With these instruments, the group studies the origin, structure, and evolution of the solar magnetic field and the impact it has on Earth's space environment. This photograph shows the Solar Vector Magnetograph and Dr. Mona Hagyard of MSFC, the director of the observatory who leads the development, operation and research program of the Solar Vector Magnetograph.

Using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are monitoring the explosive potential of magnetic areas of the Sun. This effort could someday lead to better prediction of severe space weather, a phenomenon that occurs when blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, magnetic storms wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. Photographed are a group of contributing researchers in front of the Solar Vector Magnetograph at MSFC. The researchers are part of NSSTC's solar physics group, which develops instruments for measuring magnetic fields on the Sun. With these instruments, the group studies the origin, structure, and evolution of the solar magnetic fields and the impact they have on Earth's space environment.

Captured March 12, 2010 The SOHO spacecraft captured a very bright, sungrazing comet as it rocketed towards the Sun (Mar. 12, 2010) and was vaporized. This comet is arguably the brightest comet that SOHO has observed since Comet McNaught in early 2007. The comet is believed to belong to the Kreutz family of comets that broke up from a much larger comet many hundreds of years ago. They are known to orbit close to the Sun. A coronal mass ejection (CME) burst away from the Sun during the bright comet’s approach. Interestingly, a much smaller comet that preceded this one can be seen about half a day earlier on just about the identical route. And another pair of small comets followed the same track into the Sun after the bright one. Such a string of comets has never been witnessed before by SOHO. SOHO's C3 coronagraph instrument blocks out the Sun with an occulting disk; the white circle represents the size of the Sun. The planet Mercury can also be seen moving from left to right just beneath the Sun. To learn more and to download the video and still images go here: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/pickoftheweek/old/15mar2010/" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/pickoftheweek/old/15mar2010/</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO

On August 31, 2012 a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into space at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The coronal mass ejection, or CME, traveled at over 900 miles per second. The CME did not travel directly toward Earth, but did connect with Earth's magnetic environment, or magnetosphere, causing aurora to appear on the night of Monday, September 3. This is a a lighten blended version of the 304 and 171 angstrom wavelengths. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
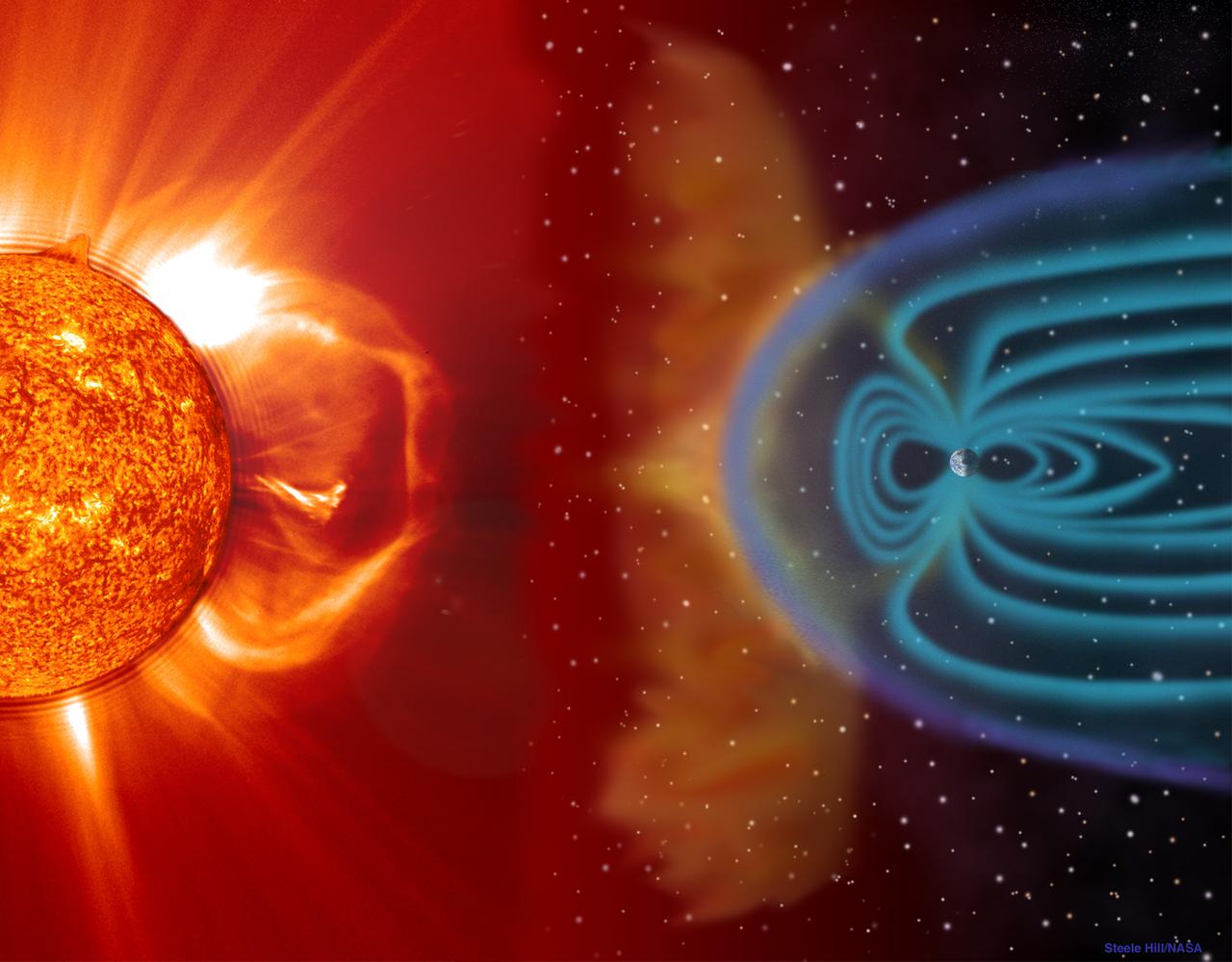
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and university scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are watching the Sun in an effort to better predict space weather - blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun that impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. Filled by charged particles trapped in the Earth's magnetic field, the spherical comet-shaped magnetosphere extends out 40,000 miles from Earth's surface in the sunward direction and more in other directions. This image illustrates the Sun-Earth cornection. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, magnetic storms wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. By using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at MSFC, scientists are learning what signs to look for as indicators of potential severe space weather.
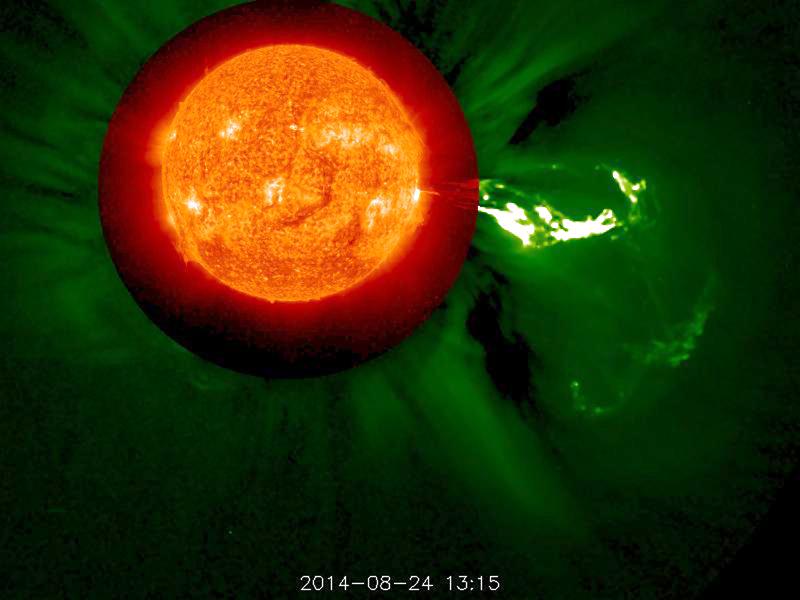

STEREO (Behind) captured this magnificent coronal mass ejection (associated with an M-class flare) that flung a long stream of plasma into space (Aug. 24, 2014). We have combined a view of the Sun in extreme UV light with a broader visible light view of the Sun's corona. It is interesting to note that a lot of the plasma, lacking sufficient kinetic energy to break free from the Sun's gravity, was pulled back into the Sun. Credit: NASA/STEREO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

An aurora in Whitehorse Yukon Canada that appeared in the sky in the early hours of Oct. 1, 2012 due to the effects of a coronal mass ejection (CME) that erupted from the sun three days earlier. Image Courtesy of Joseph Bradley to read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sunearth/news/News092812-cme.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sunearth/news/News092812-cme.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
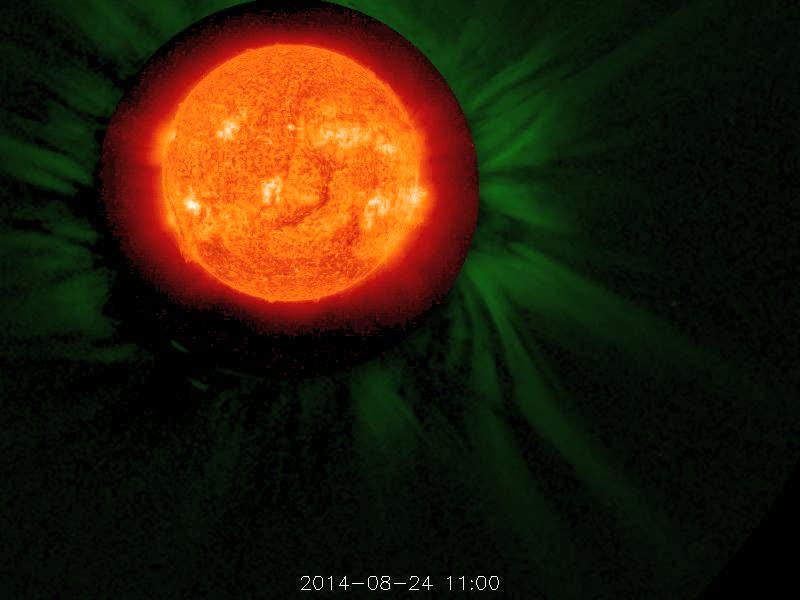

STEREO (Behind) captured this magnificent coronal mass ejection (associated with an M-class flare) that flung a long stream of plasma into space (Aug. 24, 2014). We have combined a view of the Sun in extreme UV light with a broader visible light view of the Sun's corona. It is interesting to note that a lot of the plasma, lacking sufficient kinetic energy to break free from the Sun's gravity, was pulled back into the Sun. Credit: NASA/STEREO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
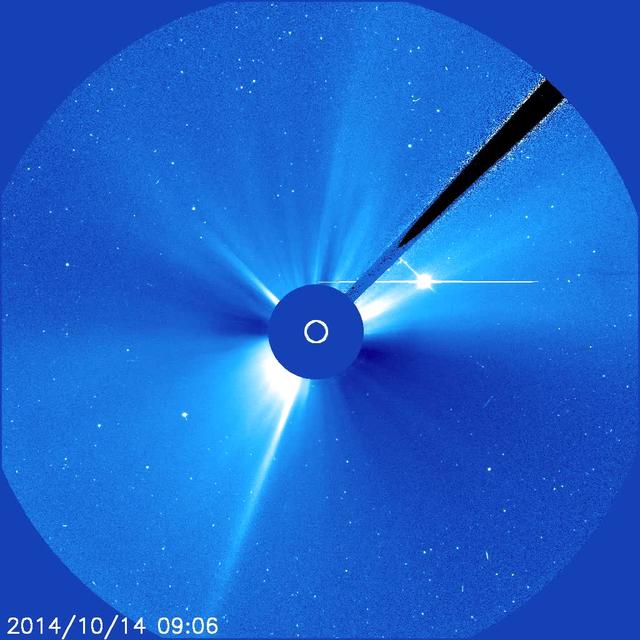

The Sun blew out a powerful coronal mass ejection (CME) from just around the edge of the Sun (Oct. 14, 2014). The particle cloud expanded around all the Sun in a rough circle, hence the name 'halo' CME. This event was also associated with a fairly strong flare. The active region that was the source of these events is just rotating into view. Then, we can better observe its size and structure. The bright object to the right and just above the Sun is Venus now on the far side of the Sun. Credit: NASA/ESA/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

<b>To view a video of the Gradient Sun go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8103212817">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8103212817</a></b> Looking at a particularly beautiful image of the sun helps show how the lines between science and art can sometimes blur. But there is more to the connection between the two disciplines: science and art techniques are often quite similar, indeed one may inform the other or be improved based on lessons from the other arena. One such case is a technique known as a "gradient filter" – recognizable to many people as an option available on a photo-editing program. Gradients are, in fact, a mathematical description that highlights the places of greatest physical change in space. A gradient filter, in turn, enhances places of contrast, making them all the more obviously different, a useful tool when adjusting photos. Scientists, too, use gradient filters to enhance contrast, using them to accentuate fine structures that might otherwise be lost in the background noise. On the sun, for example, scientists wish to study a phenomenon known as coronal loops, which are giant arcs of solar material constrained to travel along that particular path by the magnetic fields in the sun's atmosphere. Observations of the loops, which can be more or less tangled and complex during different phases of the sun's 11-year activity cycle, can help researchers understand what's happening with the sun's complex magnetic fields, fields that can also power great eruptions on the sun such as solar flares or coronal mass ejections. The still here shows an unfiltered image from the sun next to one that has been processed using a gradient filter. Note how the coronal loops are sharp and defined, making them all the more easy to study. On the other hand, gradients also make great art. NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center To download this video go to: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11112" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11112</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (Blended 131 Angstrom and 171 Angstrom images of July 19, 2012 flare and CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
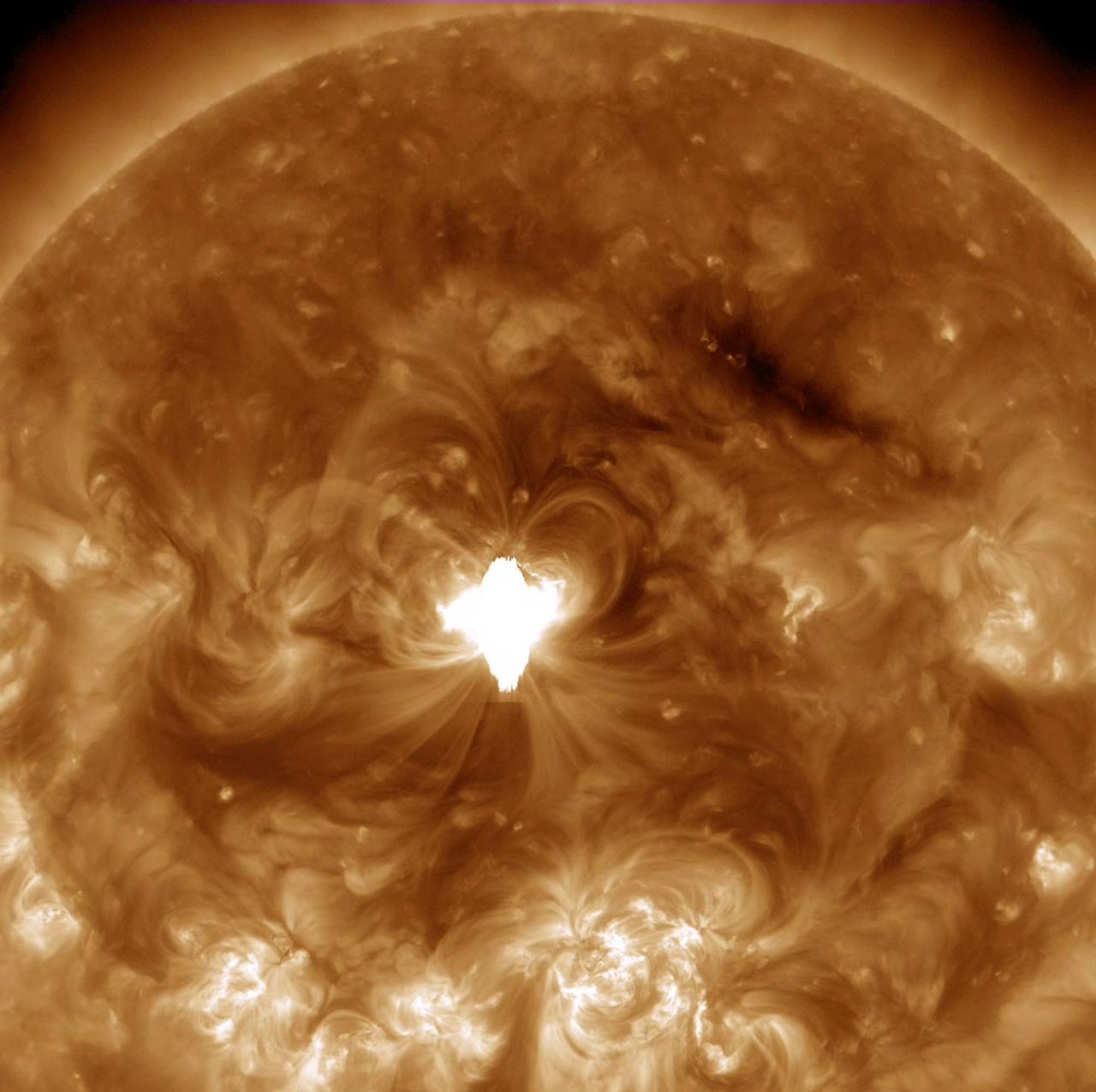
An active region just about squarely facing Earth erupted with an X 1.6 flare (largest class) as well as a coronal mass ejection on Sept. 10, 2014. The flare lasted longer than usual and sent out a burst of radiation into space. The movie shows the bright, flickering flare and the ensuing coils of magnetic loops over a period of about five hours. A darker wave of material was also propelled across part of the Sun's surface. Images were taken in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
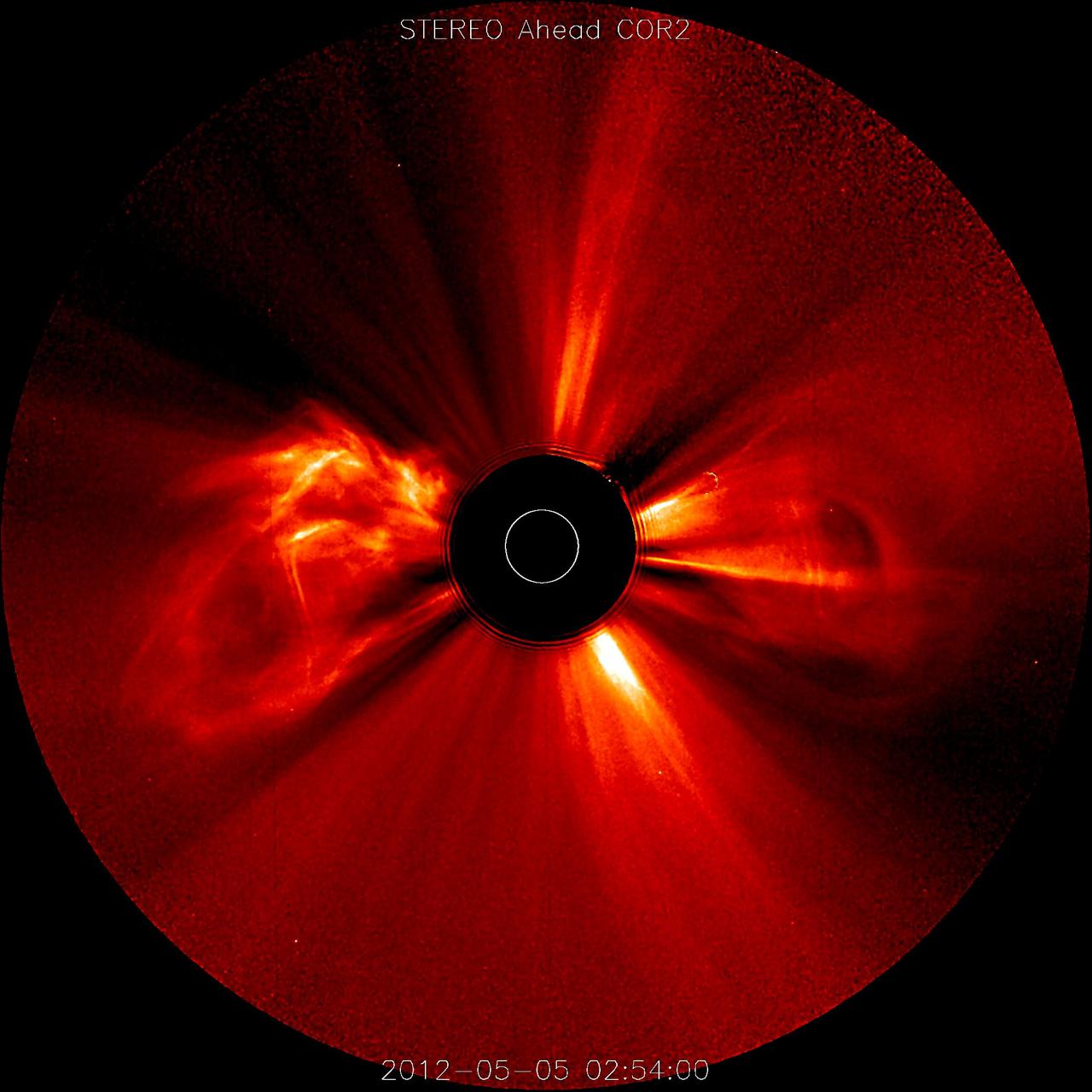
Nearly a dozen coronal mass ejections in less than four days (May 3-6, 2012) may serve as a reminder that the Sun is approaching its period of maximum activity, expected to peak next year. STEREO (Ahead) from its position over 100 degrees ahead of Earth, captured several major eruptions, with most of them heading way to the right (i.e., away from Earth). In these coronagraph images the Sun is represented by the white circle. The black occulting disk blocks out the Sun and some of the corona so that we can see the faint structures beyond that. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
The Sun blew out a coronal mass ejection along with part of a solar filament over a three-hour period (Feb. 24, 2015). While some of the strands fell back into the Sun, a substantial part raced into space in a bright cloud of particles (as observed by the SOHO spacecraft). The activity was captured in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Because this occurred way over near the edge of the Sun, it was unlikely to have any effect on Earth. Download high res/video file: <a href="http://sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/potw/item/603" rel="nofollow">sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/potw/item/603</a> Credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
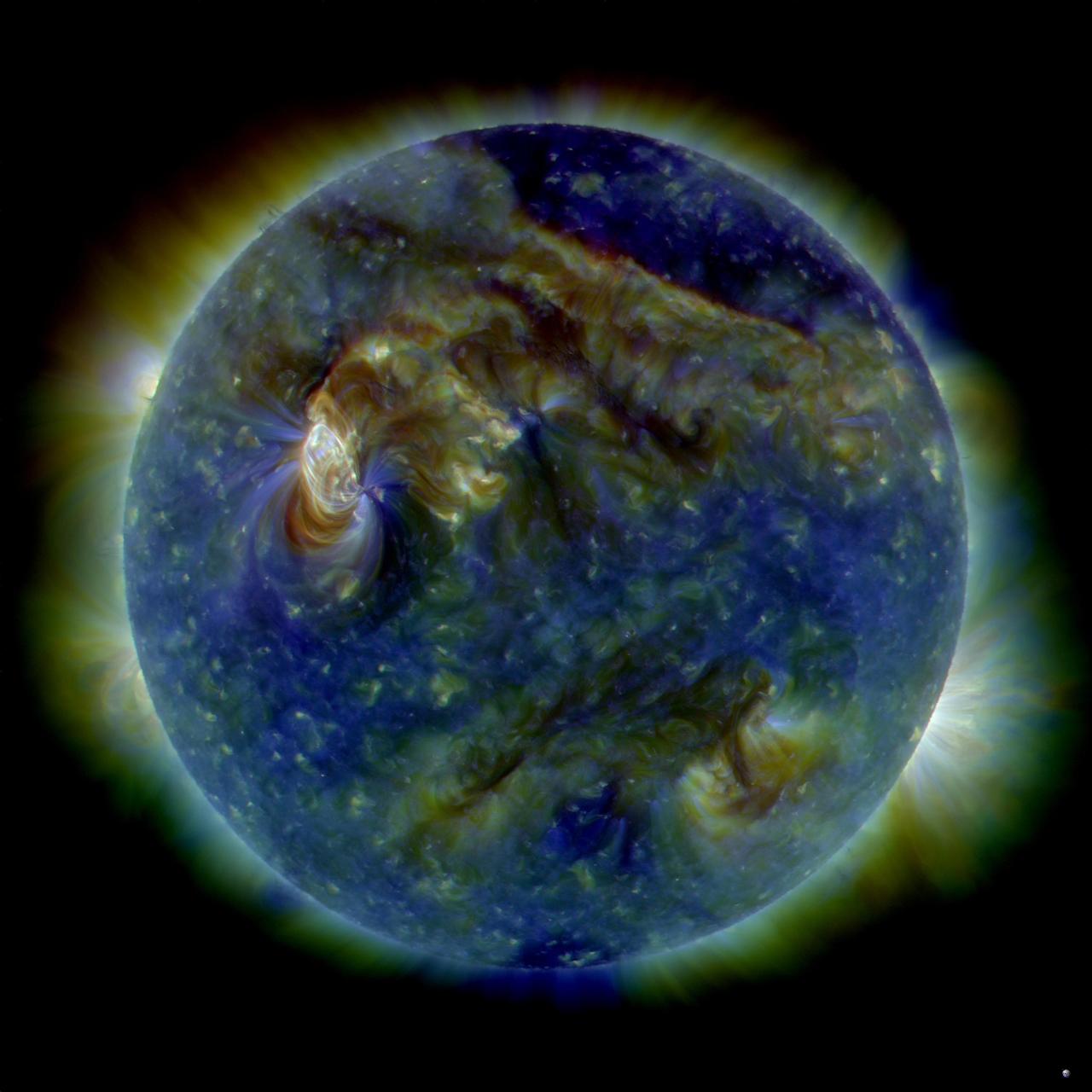
NASA image release August 6, 2010 On August 1, 2010, almost the entire Earth-facing side of the sun erupted in a tumult of activity. This image from the Solar Dynamics Observatory of the news-making solar event on August 1 shows the C3-class solar flare (white area on upper left), a solar tsunami (wave-like structure, upper right), multiple filaments of magnetism lifting off the stellar surface, large-scale shaking of the solar corona, radio bursts, a coronal mass ejection and more. This multi-wavelength extreme ultraviolet snapshot from the Solar Dynamics Observatory shows the sun's northern hemisphere in mid-eruption. Different colors in the image represent different gas temperatures. Earth's magnetic field is still reverberating from the solar flare impact on August 3, 2010, which sparked aurorae as far south as Wisconsin and Iowa in the United States. Analysts believe a second solar flare is following behind the first flare and could re-energize the fading geomagnetic storm and spark a new round of Northern Lights. Credit: NASA/SDO/AIA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b> </b></b>

NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory caught this image of an eruption on the side of the sun on June 18, 2015. The eruption ultimately escaped the sun, growing into a substantial coronal mass ejection, or CME — a giant cloud of solar material traveling through space. This imagery is shown in the 304 Angstrom wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, a wavelength that highlights material in the low parts of the sun’s atmosphere and that is typically colorized in red. The video clip covers about four hours of the event. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO Download: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11908" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11908</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A coronal mass ejection (CME) erupted from just around the edge of the sun on May 1, 2013, in a gigantic rolling wave. CMEs can shoot over a billion tons of particles into space at over a million miles per hour. This CME occurred on the sun’s limb and is not headed toward Earth. The video (seen here: <a href="http://bit.ly/103whUl" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/103whUl</a>), taken in extreme ultraviolet light by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), covers about two and a half hours. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
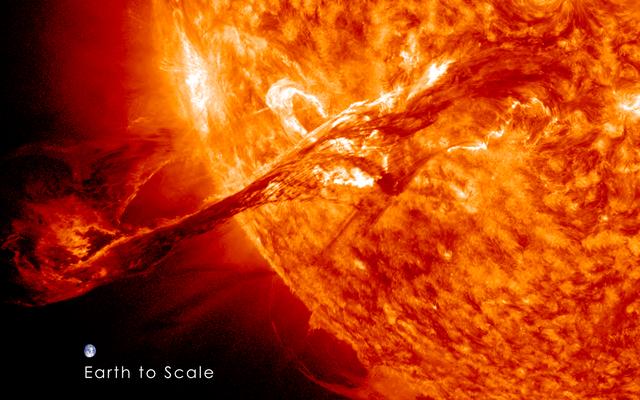

On August 31, 2012 a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into space at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The coronal mass ejection, or CME, traveled at over 900 miles per second. The CME did not travel directly toward Earth, but did connect with Earth's magnetic environment, or magnetosphere, causing aurora to appear on the night of Monday, September 3. The image above includes an image of Earth to show the size of the CME compared to the size of Earth. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
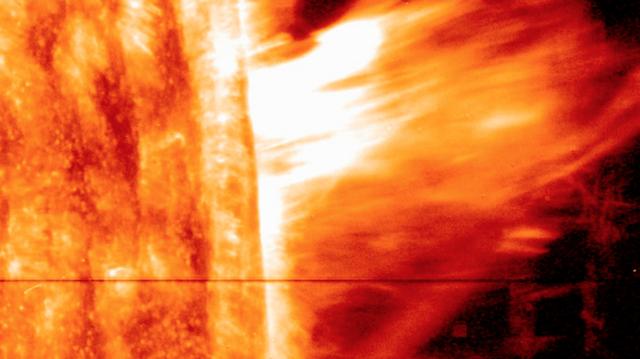
Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
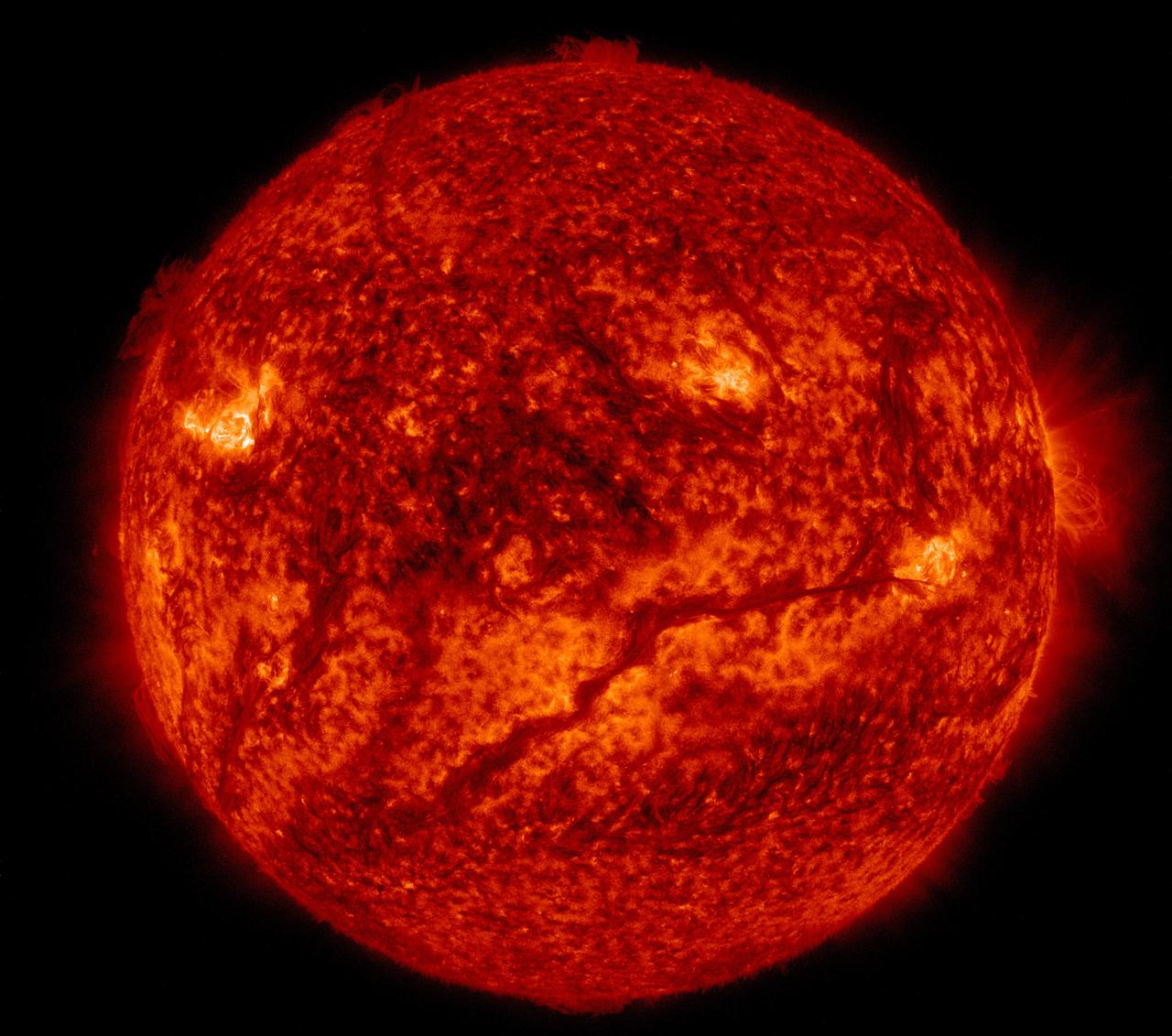
A dark line snaked across the lower half of the sun on Feb.10, 2015, as seen in this image from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. SDO shows colder material as dark and hotter material as light, so the line is, in fact, an enormous swatch of colder material hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona. Stretched out, that line – or solar filament as scientists call it – would be more than 533,000 miles long. That is longer than 67 Earths lined up in a row. Filaments can float sedately for days before disappearing. Sometimes they also erupt out into space, releasing solar material in a shower that either rains back down or escapes out into space, becoming a moving cloud known as a coronal mass ejection, or CME. SDO captured images of the filament in numerous wavelengths, each of which helps highlight material of different temperatures on the sun. By looking at such features in different wavelengths and temperatures, scientists learn more about what causes these structures, as well as what catalyzes their occasional eruptions. For more on SDO, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/sdo" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/sdo</a> Karen C. Fox NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
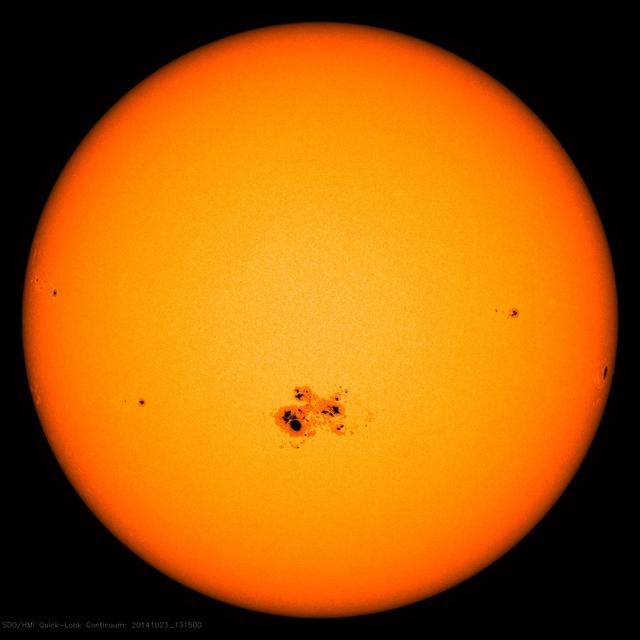
On Oct. 18, 2014, a sunspot rotated over the left side of the sun, and soon grew to be the largest active region seen in the current solar cycle, which began in 2008. Currently, the sunspot is almost 80,000 miles across -- ten Earth's could be laid across its diameter. Sunspots point to relatively cooler areas on the sun with intense and complex magnetic fields poking out through the sun's surface. Such areas can be the source of solar eruptions such as flares or coronal mass ejections. So far, this active region – labeled AR 12192 -- has produced several significant solar flares: an X-class flare on Oct. 19, an M-class flare on Oct. 21, and an X-class flare on Oct. 22, 2014. The largest sunspot on record occurred in 1947 and was almost three times as large as the current one. Active regions are more common at the moment as we are in what's called solar maximum, which is the peak of the sun's activity, occurring approximately every 11 years. Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
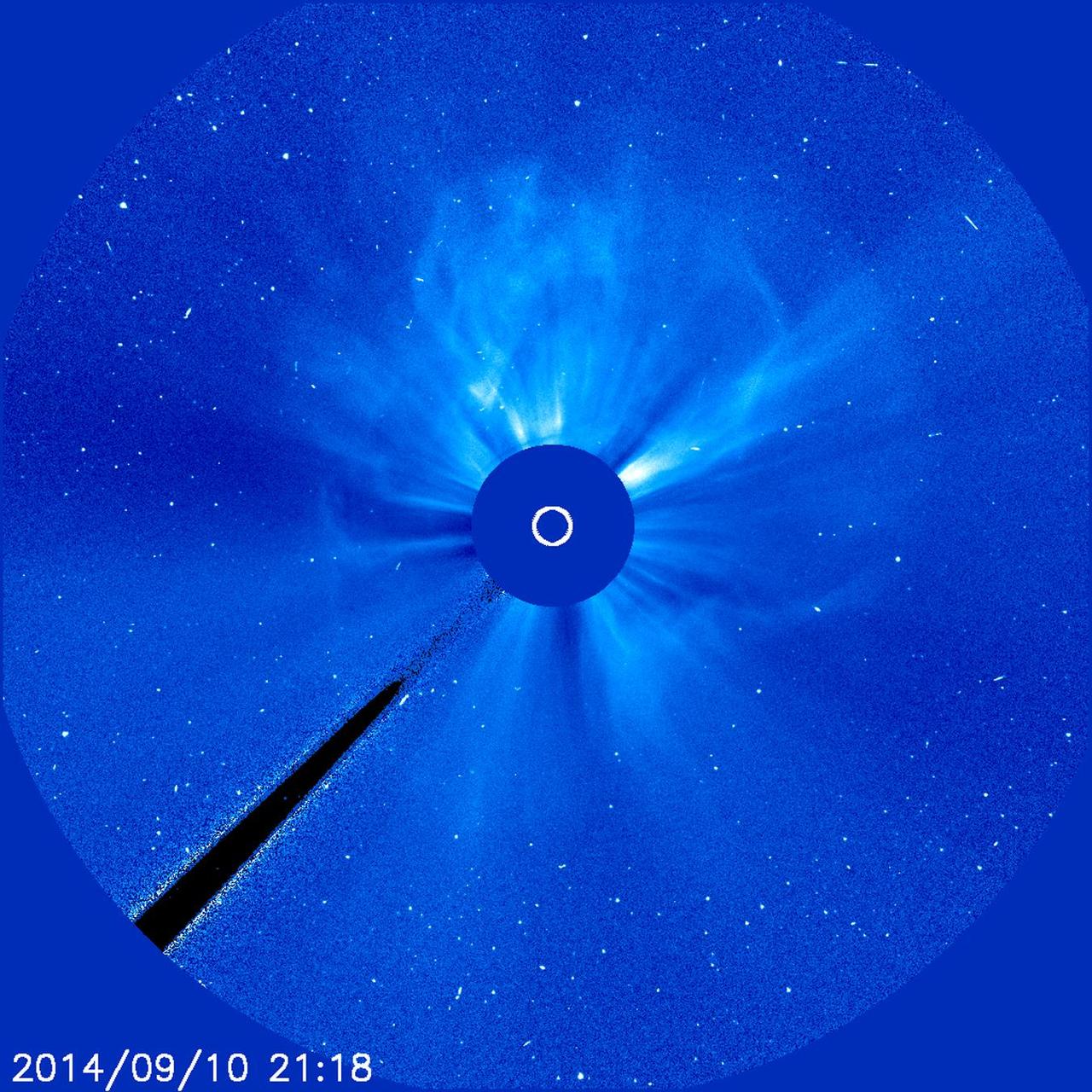
An active region just about squarely facing Earth erupted with an X 1.6 flare (largest class) as well as a coronal mass ejection (CME) on Sept. 10-11, 2014. This event featured both a long flare decay time and a storm of electrically charged, energetic particles. The particles can be seen as bright white specks scattering across the frames. The coronagraph movie shows the cloud of particles expanding in all directions as if it were creating a halo around the Sun. Data shows that the CME was heading towards Earth that could generate strong aurora displays several days later. In coronagraph images the Sun (represented by the small white circle in the center) is blocked by an occulting disk so that we can observe faint features in the corona and beyond. Credit: NASA/ESA/Goddard/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
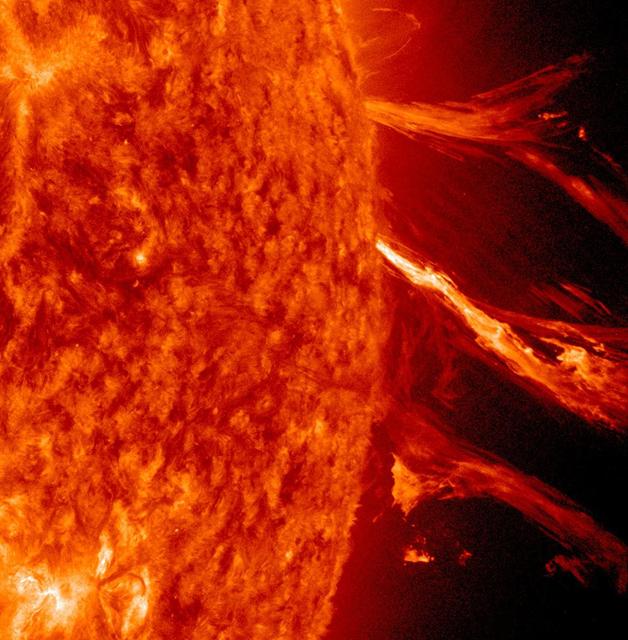

NASA image captured January 2, 2012 To view a video of this event go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/6648724193">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/6648724193</a> The Sun erupted with a good-sized solar flare and a coronal mass ejection (CME) on its far-side beyond the view of SDO, but the resulting strands of particle clouds as seen in extreme ultraviolet light still made for quite a show that lasted about three hours (Jan. 2, 2011). Note how a portion of the strands fall back to the Sun. It appears the force of the blast was unable, for some portion of the material, to overcome the pull of the Sun's magnetic fields. This blast was not directed at Earth. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
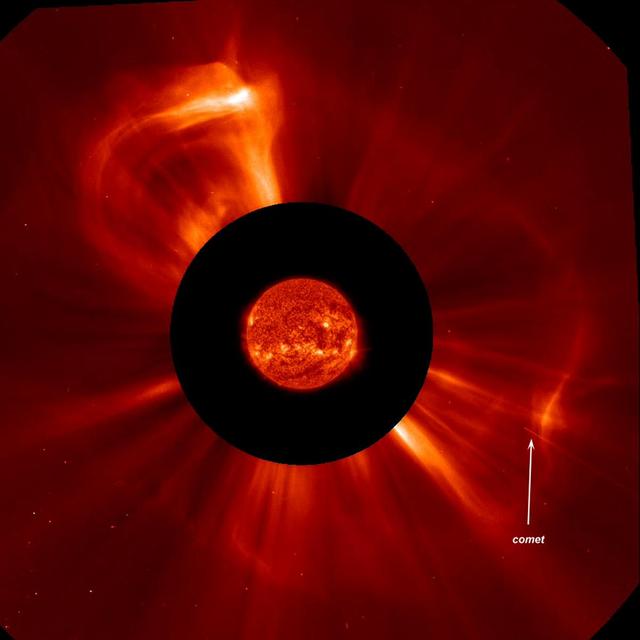
A small comet was streaking towards the Sun when the Sun blew out a "halo" coronal mass ejection (CME) Aug. 19-20, 2013). The CME originated from the far side of the Sun and did not have any interaction with the comet. The comet, only perhaps 30 meters across, was not seen after it went out of view, likely disintegrated by the heat and radiation from the Sun. We call this a "full halo" CME since the front edge of the CME is expanding in all directions around the Sun like a halo. The images were taken by SOHO's coronagraphs in which a disk (red) blocks the Sun and some of the area around it so we can see faint structures beyond that. Here we superimposed the Sun from NASA's SDO. The movie covers about five hours of activity and can be seen here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/9601034896/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/9601034896/</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
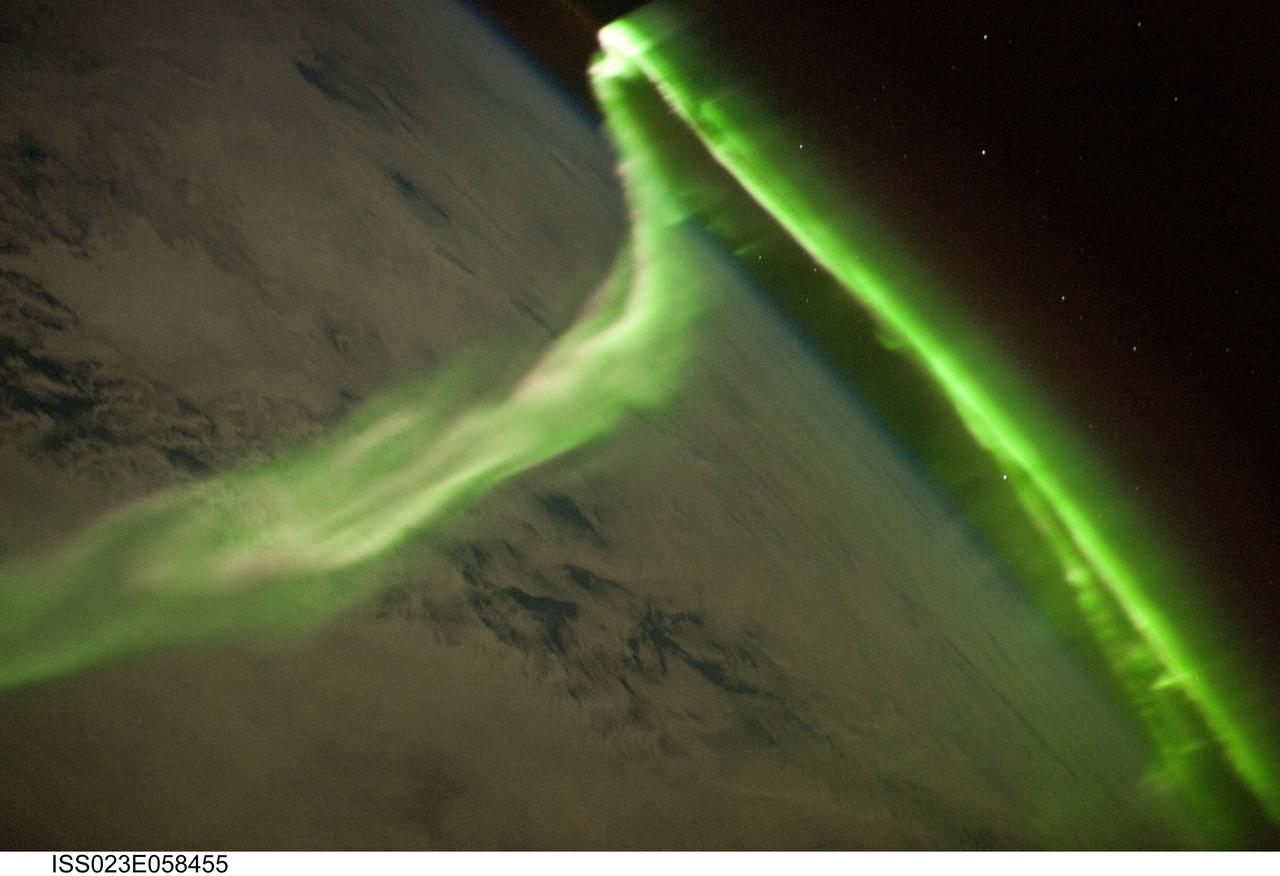

ISS023-E-058455 (29 May 2010) --- Aurora Australis is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 23 crew member on the International Space Station. Among the views of Earth afforded crew members aboard the ISS, surely one of the most spectacular is of the aurora. These ever-shifting displays of colored ribbons, curtains, rays, and spots are most visible near the North (Aurora Borealis) and South (Aurora Australis) Poles as charged particles streaming from the sun (the solar wind) interact with Earth’s magnetic field, resulting in collisions with atoms of oxygen and nitrogen in the upper atmosphere. The atoms are excited by these collisions, and typically emit photons as a means of returning to their original energy state. The photons form the aurora that we see. The most commonly observed color of aurora is green, caused by photons (light) emitted by excited oxygen atoms at wavelengths centered at 0.558 micrometers, or millionths of a meter. Visible light is reflected from healthy (green) plant leaves at approximately the same wavelength. Red auroras are generated by light emitted at a longer wavelength (0.630 micrometers), and other colors such as blue and purple are also sometimes observed. While auroras are generally only visible close to the poles, severe magnetic storms impacting Earth’s magnetic field can shift them towards the equator. This striking aurora image was taken during a geomagnetic storm that was most likely caused by a coronal mass ejection from the sun on May 24, 2010. The ISS was located over the Southern Indian Ocean at an altitude of 350 kilometers, with the observer most likely looking towards Antarctica (not visible) and the South Pole. The aurora has a sinuous ribbon shape that separates into discrete spots near the lower right corner of the image. While the dominant coloration of the aurora is green, there are faint suggestions of red photon emission as well (light fuscia tones at center left). Dense cloud cover is dimly visible below the aurora. The curvature of Earth’s horizon, or limb, is clearly visible as is the faint blue line of the upper atmosphere directly above at top center. Several stars appear as bright pinpoints against the blackness of space at top right.
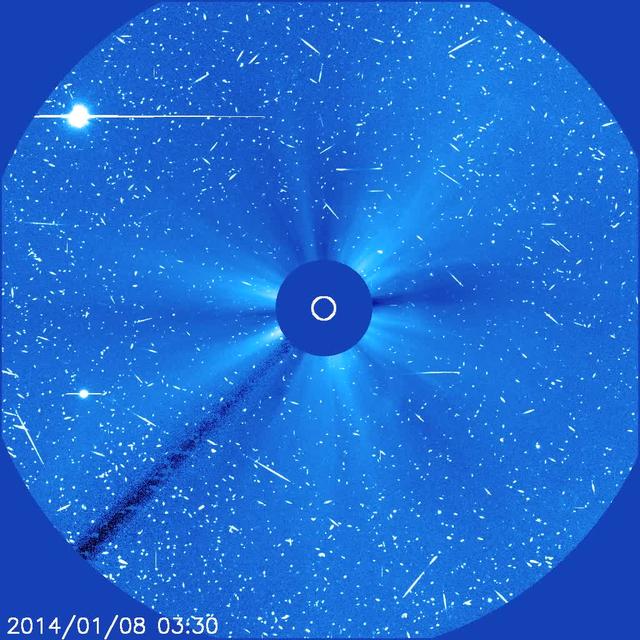
A solar magnetic active region containing the largest sunspot group of the last 10 years unleashed a large (X1.2) flare when it was facing right towards Earth. The flare was associated with a bright coronal mass ejection that emerges from the lower right (Jan. 7-8, 2014). A fast moving cloud of high-energy particles produced in the flare and at the CME front began striking the SOHO spacecraft imagers, creating the "snow" effect that went on for more than a day. SOHO is a million miles sunwards of Earth, and outside the earth's protective magnetosphere. In these coronagraph images the Sun is represented by the white circle and is blocked by an occulting disk, so we can observe fainter structures in the Sun's corona. Venus (upper left) enters the field of view during the video clip, while Mercury (lower left) is just about to leave the file of view. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

With its C2 coronagraph instrument, NASA's satellite SOHO captured a blossoming coronal mass ejection (CME) as it roared into space from the right side of the Sun (Dec. 28, 2013). SOHO also produces running difference images and movies of the Sun's corona in which the difference between one image and the next (taken about 10 minutes apart) is highlighted. This technique strongly emphasizes the changes that occurred. Here we have taken a single white light frame and shift it back and forth with a running difference image taken at the same time to illustrate the effect. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
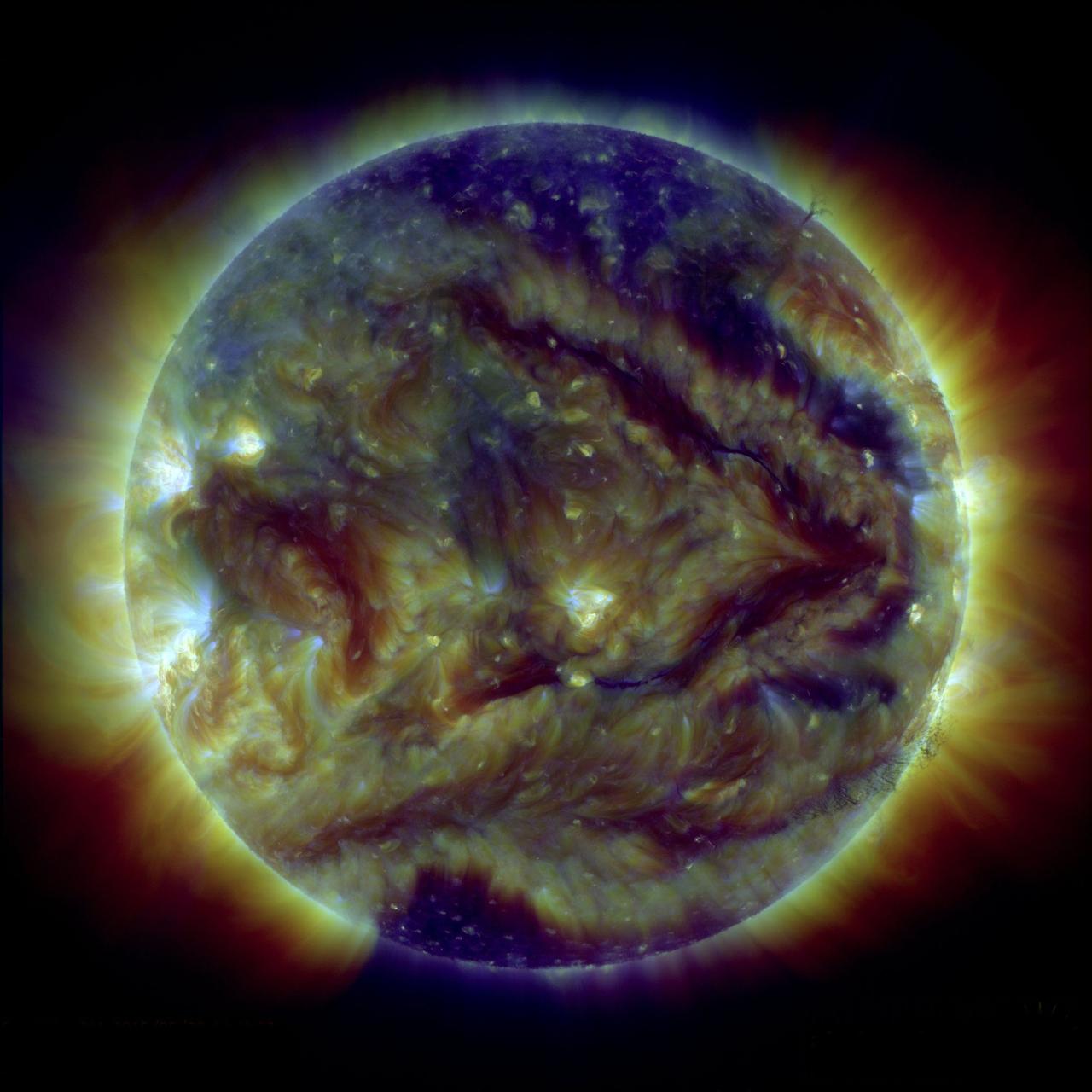
A pair of giant filaments on the face of the sun have formed what appears to be an enormous arrow. If straightened out, each filament would be about as long as the sun’s diameter, 1 million miles long. Filaments are cooler clouds of solar material suspended above the sun's surface by powerful magnetic forces. Filaments can float for days without much change, though they can also erupt, releasing solar material in a shower that either rains back down or escapes out into space, becoming a moving cloud known as a coronal mass ejection, or CME. This image was captured on May 28, 2015, in combined wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which observes the sun 24 hours a day. Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
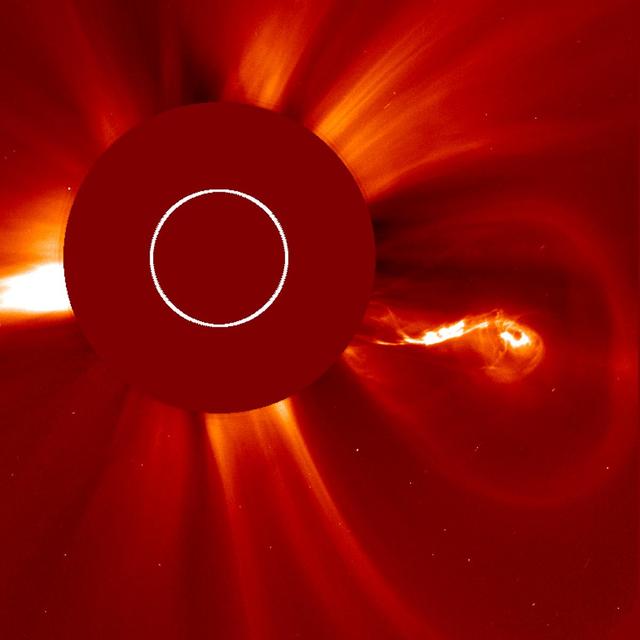

The Sun blasted out five coronal mass ejections (CMEs) over about two days (Feb. 26-28, 2013) and each one had quite a different shape and structure, seen here in a video <a href="http://bit.ly/Za8Aso" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/Za8Aso</a>. The most interesting one (seen above) blew out to the right with a bright, elongated center, likely part of a solar filament, that maintained its curly-Q shape as it expanded out of view. The images were taken by SOHO LASCO C2 coronagraph. The Sun is represented by the white circle and the red disk blocks out the Sun and part of the corona. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
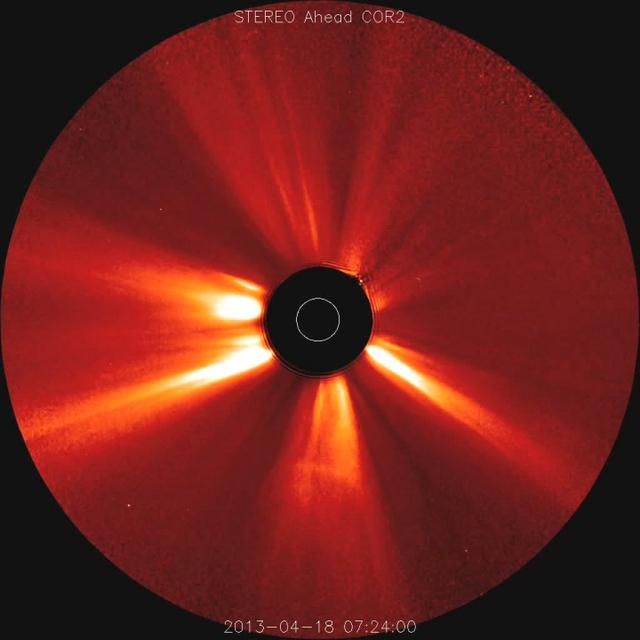

Coronal mass ejections were popping out from the Sun at a pace of two per day on average (Apr. 18-23, 2013). We counted ten CMEs for the five days, but some of the eruptions were complex and difficult to differentiate from one another. Almost all of them blew particles out to the left, most of them probably originating from the same active region. These were taken by the STEREO (Ahead) spacecraft?s coronagraph, in which the black disk blocks the Sun (represented by the white circle) so that we can observe the fainter features beyond it. Credit: NASA/Goddard/STEREO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Overnight on October 4-5, 2012, a mass of energetic particles from the atmosphere of the Sun were flung out into space, a phenomenon known as a coronal mass ejection. Three days later, the storm from the Sun stirred up the magnetic field around Earth and produced gorgeous displays of northern lights. NASA satellites track such storms from their origin to their crossing of interplanetary space to their arrival in the atmosphere of Earth. Using the “day-night band” (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite acquired this view of the aurora borealis early on the morning of October 8, 2012. The northern lights stretch across Canada’s Quebec and Ontario provinces in the image, and are part of the auroral oval that expanded to middle latitudes because of a geomagnetic storm. The DNB sensor detects dim light signals such as auroras, airglow, gas flares, city lights, and reflected moonlight. In the case of the image above, the sensor detected the visible light emissions as energetic particles rained down from Earth’s magnetosphere and into the gases of the upper atmosphere. The images are similar to those collected by the Operational Linescan System flown on U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites for the past three decades. “When I first saw images like this as a graduate student, I was immediately struck by the fluid dynamic characteristics of the aurora,” said Tom Moore, a space physicist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. “Viewing the aurora in this way makes it immediately clear that space weather is an interaction of fluids from the Sun with those of the Earth's upper atmosphere. The electrodynamics make for important differences between plasmas and ordinary fluids, but familiar behaviors (for example, waves and vortices) are still very apparent. It makes me wonder at the ability of apparently empty space to behave like a fluid.” Auroras typically occur when solar flares and coronal mass ejections—or even an active solar wind stream—disturb and distort the magnetosphere, the cocoon of space protected by Earth’s magnetic field. The collision of solar particles and pressure into our planet’s magnetosphere accelerates particles trapped in the space around Earth (such as in the radiation belts). Those particles are sent crashing down into Earth’s upper atmosphere—at altitudes of 100 to 400 kilometers (60 to 250 miles)—where they excite oxygen and nitrogen molecules and release photons of light. The results are rays, sheets, and curtains of dancing light in the sky. Auroras are a beautiful expression of the connection between Sun and Earth, but not all of the connections are benign. Auroras are connected to geomagnetic storms, which can distort radio communications (particularly high frequencies), disrupt electric power systems on the ground, and give slight but detectable doses of radiation to flight crews and passengers on high-latitude airplane flights and on spacecraft. The advantage of images like those from VIIRS and DMSP is resolution, according to space physicist Patrick Newell of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. “You can see very fine detail in the aurora because of the low altitude and the high resolution of the camera,” he said. Most aurora scientists prefer to use images from missions dedicated to aurora studies (such as Polar, IMAGE, and ground-based imagers), which can offer many more images of a storm (rather than one per orbit) and can allow researchers to calculate the energy moving through the atmosphere. There are no science satellites flying right now that provide such a view, though astronauts regularly photograph and film auroras from the International Space Station. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) and the University of Wisconsin's Community Satellite Processing Package. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
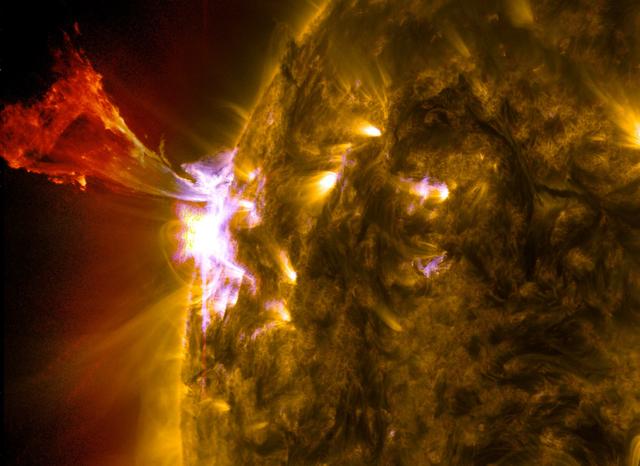
Caption: A burst of solar material leaps off the left side of the sun in what’s known as a prominence eruption. This image combines three images from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured on May 3, 2013, at 1:45 pm EDT, just as an M-class solar flare from the same region was subsiding. The images include light from the 131, 171 and 304 Angstrom wavelengths. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO --- The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 1:32 pm EDT on May 3, 2013. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This disrupts the radio signals for as long as the flare is ongoing, and the radio blackout for this flare has already subsided. This flare is classified as an M5.7 class flare. M-class flares are the weakest flares that can still cause some space weather effects near Earth. Increased numbers of flares are quite common at the moment, since the sun's normal 11-year activity cycle is ramping up toward solar maximum, which is expected in late 2013. Updates will be provided as they are available on the flare and whether there was an associated coronal mass ejection (CME), another solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and affect electronic systems in satellites and on Earth. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: A burst of solar material leaps off the left side of the sun in what’s known as a prominence eruption. This image combines three images from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured on May 3, 2013, at 1:45 pm EDT, just as an M-class solar flare from the same region was subsiding. The images include light from the 131, 171 and 304 Angstrom wavelengths. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO --- The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 1:32 pm EDT on May 3, 2013. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This disrupts the radio signals for as long as the flare is ongoing, and the radio blackout for this flare has already subsided. This flare is classified as an M5.7 class flare. M-class flares are the weakest flares that can still cause some space weather effects near Earth. Increased numbers of flares are quite common at the moment, since the sun's normal 11-year activity cycle is ramping up toward solar maximum, which is expected in late 2013. Updates will be provided as they are available on the flare and whether there was an associated coronal mass ejection (CME), another solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and affect electronic systems in satellites and on Earth. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Solar Flare Extremely energetic objects permeate the universe. But close to home, the sun produces its own dazzling lightshow, producing the largest explosions in our solar system and driving powerful solar storms.. When solar activity contorts and realigns the sun’s magnetic fields, vast amounts of energy can be driven into space. This phenomenon can create a sudden flash of light—a solar flare. Flares typically last a few minutes and unleash energies equivalent to millions of hydrogen bombs. The above picture features a filament eruption on the sun, accompanied by solar flares. To learn more about solar flares, go to NASA’s SDO mission: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/sdo" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/sdo</a> --------------------------------- Original caption: <b>Click here to view an image showing the size of this CME compared to the size of Earth: <a href="http://bit.ly/RkYr7z" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/RkYr7z</a> </b> On August 31, 2012 a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into space at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The coronal mass ejection, or CME, traveled at over 900 miles per second. The CME did not travel directly toward Earth, but did connect with Earth's magnetic environment, or magnetosphere, causing aurora to appear on the night of Monday, September 3. Pictured here is a lighten blended version of the 304 and 171 angstrom wavelengths. Cropped Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
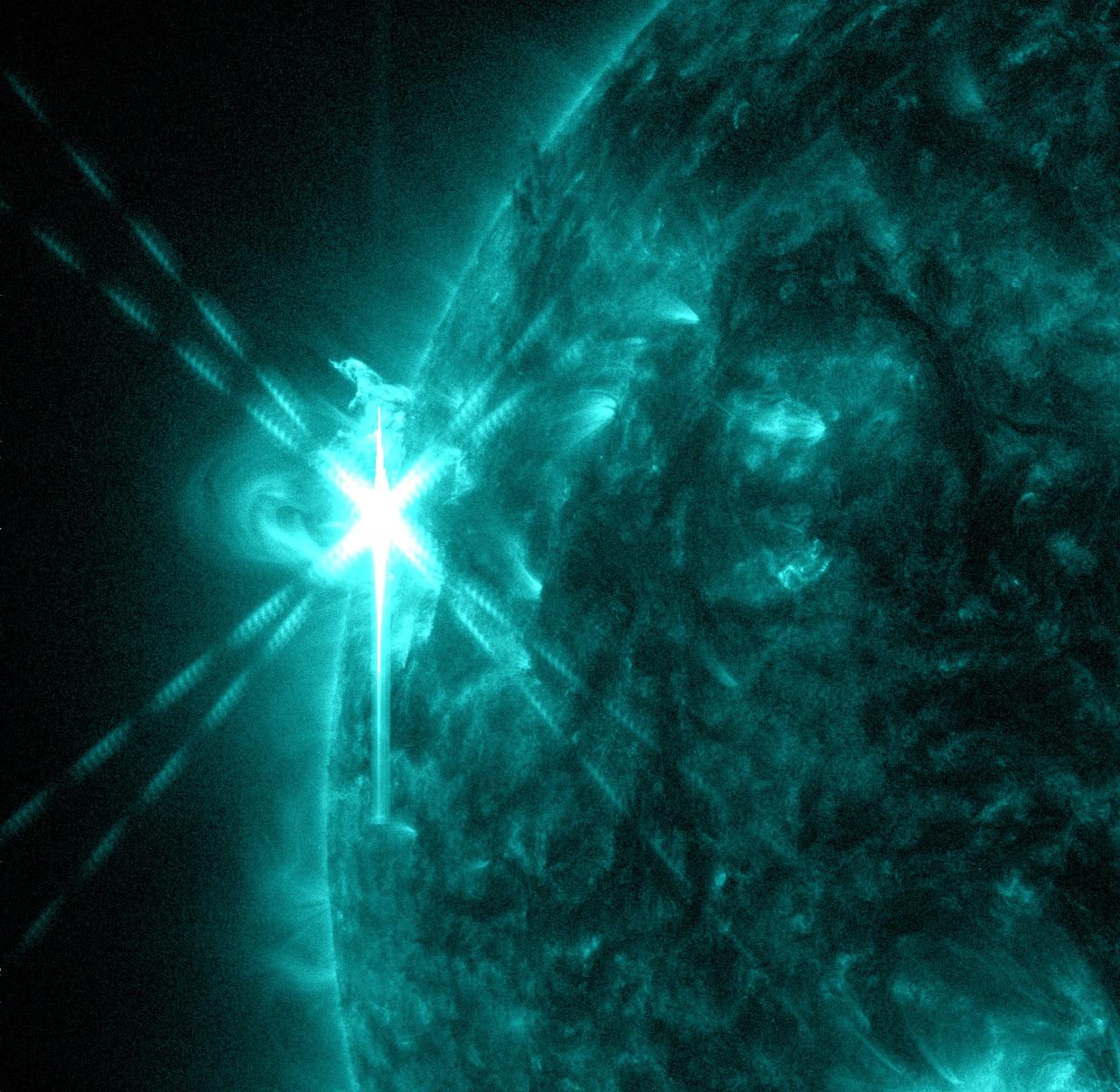
Caption: NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) captured this image of an M5.7 class flare on May 3, 2013 at 1:30 p.m. EDT. This image shows light in the 131 Angstrom wavelength, a wavelength of light that can show material at the very hot temperatures of a solar flare and that is typically colorized in teal. Caption: NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) captured this image of an M5.7 class flare on May 3, 2013 at 1:30 p.m. EDT. This image shows light in the 131 Angstrom wavelength, a wavelength of light that can show material at the very hot temperatures of a solar flare and that is typically colorized in teal. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO --- The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 1:32 pm EDT on May 3, 2013. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This disrupts the radio signals for as long as the flare is ongoing, and the radio blackout for this flare has already subsided. This flare is classified as an M5.7 class flare. M-class flares are the weakest flares that can still cause some space weather effects near Earth. Increased numbers of flares are quite common at the moment, since the sun's normal 11-year activity cycle is ramping up toward solar maximum, which is expected in late 2013. Updates will be provided as they are available on the flare and whether there was an associated coronal mass ejection (CME), another solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and affect electronic systems in satellites and on Earth. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
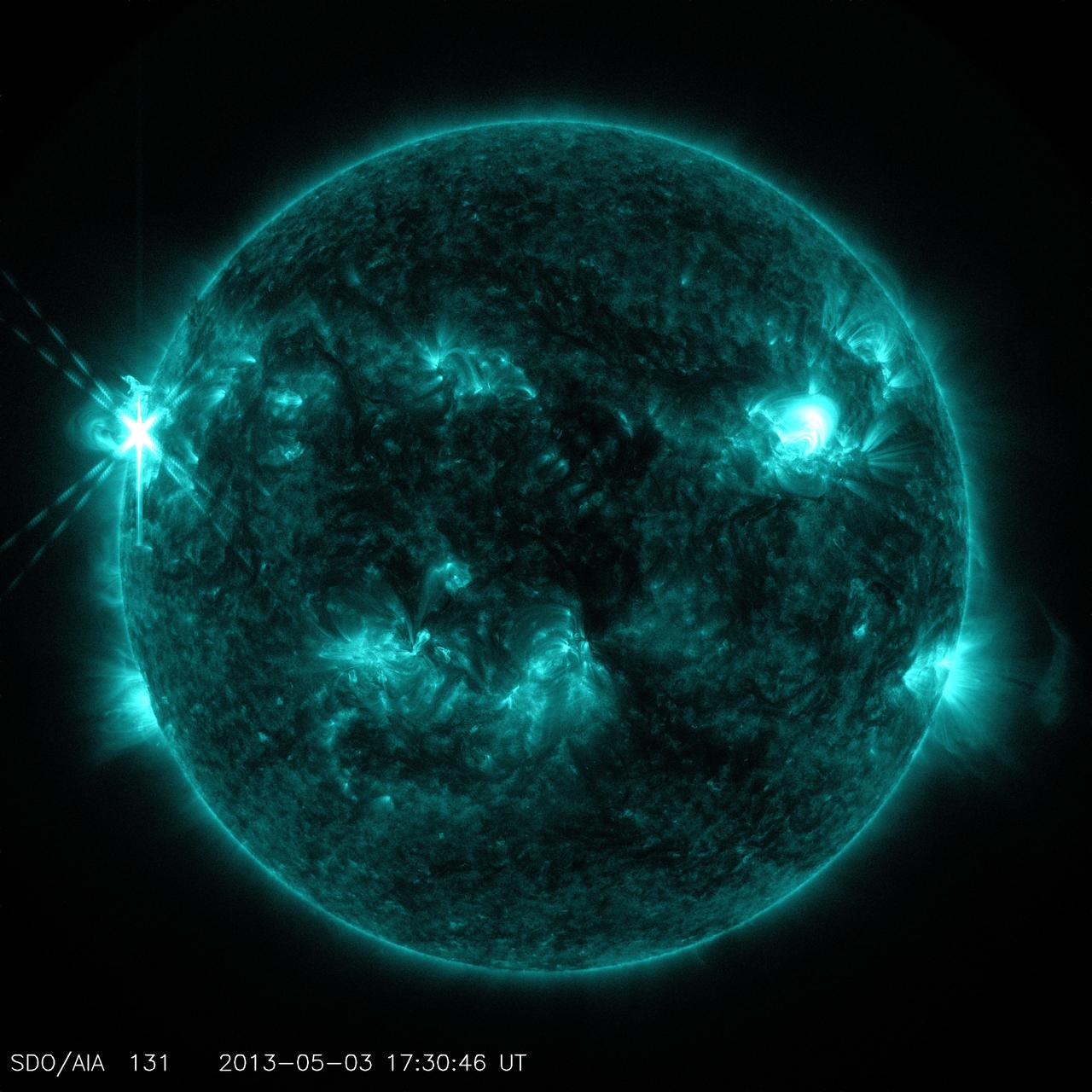
Caption: NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) captured this image of an M5.7 class flare on May 3, 2013 at 1:30 p.m. EDT. This image shows light in the 131 Angstrom wavelength, a wavelength of light that can show material at the very hot temperatures of a solar flare and that is typically colorized in teal. Caption: NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) captured this image of an M5.7 class flare on May 3, 2013 at 1:30 p.m. EDT. This image shows light in the 131 Angstrom wavelength, a wavelength of light that can show material at the very hot temperatures of a solar flare and that is typically colorized in teal. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO --- The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 1:32 pm EDT on May 3, 2013. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This disrupts the radio signals for as long as the flare is ongoing, and the radio blackout for this flare has already subsided. This flare is classified as an M5.7 class flare. M-class flares are the weakest flares that can still cause some space weather effects near Earth. Increased numbers of flares are quite common at the moment, since the sun's normal 11-year activity cycle is ramping up toward solar maximum, which is expected in late 2013. Updates will be provided as they are available on the flare and whether there was an associated coronal mass ejection (CME), another solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and affect electronic systems in satellites and on Earth. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Geomagnetic Storms Sometimes during the solar magnetic events, solar explosions hurl clouds of magnetized particles into space. Traveling more than a million miles per hour, these coronal mass ejections, or CMEs, made up of hot material called plasma take up to three days to reach Earth. Spacecraft and satellites in the path of CMEs can experience glitches as these plasma clouds pass by. In near-Earth space, magnetic reconnection incites explosions of energy driving charged solar particles to collide with atoms in Earth’s upper atmosphere. We see these collisions near Earth’s polar regions as the aurora. The prevalence of specific gases in the atmosphere determines the color of the aurora. For example, if charged particles strike oxygen atoms, the aurora will appear green. Excited nitrogen closer to 60 miles above Earth’s surface will produce a blood red color. Three spacecraft from NASA’s Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms (THEMIS) mission, observe these outbursts known as substorms. Substorms can intensify aurora’s near Earth’s poles. To learn more about the aurora, go to NASA’s THEMIS mission: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/themis/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/themis/main/index.html</a> ---------- Original caption: How about a little something green for St. Patrick's Day? "St. Patrick's Aurora" was taken at Donnelly Creek, Alaska at 1:30 am, March 17, 2015 by our good friend Sebastian Saarloos! You can see more images from Sebastian here: <a href="http://www.facebook.com/SebastianSaarloos" rel="nofollow">www.facebook.com/SebastianSaarloos</a> Credit: Sebastian Saarloos <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Using the “day-night band” (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite acquired this view of the aurora borealis on March 18, 2015. The northern lights stretch across Canada’s Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, Nunavut, and Newfoundland provinces in the image, and are part of the auroral oval that expanded to middle latitudes because of a geomagnetic storm on March 17, 2015. The DNB sensor detects dim light signals such as auroras, airglow, gas flares, city lights, and reflected moonlight. In the case of the image above, the sensor detected the visible light emissions as energetic particles rained down from Earth’s magnetosphere and into the gases of the upper atmosphere. The images are similar to those collected by the Operational Linescan System flown on U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites for the past three decades. Auroras typically occur when solar flares and coronal mass ejections—or even an active solar wind stream—disturb and distort the magnetosphere, the cocoon of space protected by Earth’s magnetic field. The collision of solar particles and pressure into our planet’s magnetosphere accelerates particles trapped in the space around Earth (such as in the radiation belts). Those particles are sent crashing down into Earth’s upper atmosphere—at altitudes of 100 to 400 kilometers (60 to 250 miles)—where they excite oxygen and nitrogen molecules and release photons of light. The results are rays, sheets, and curtains of dancing light in the sky. Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=85556&eocn=home&eoci=nh" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=8555...</a> NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen, using VIIRS day-night band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz and Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
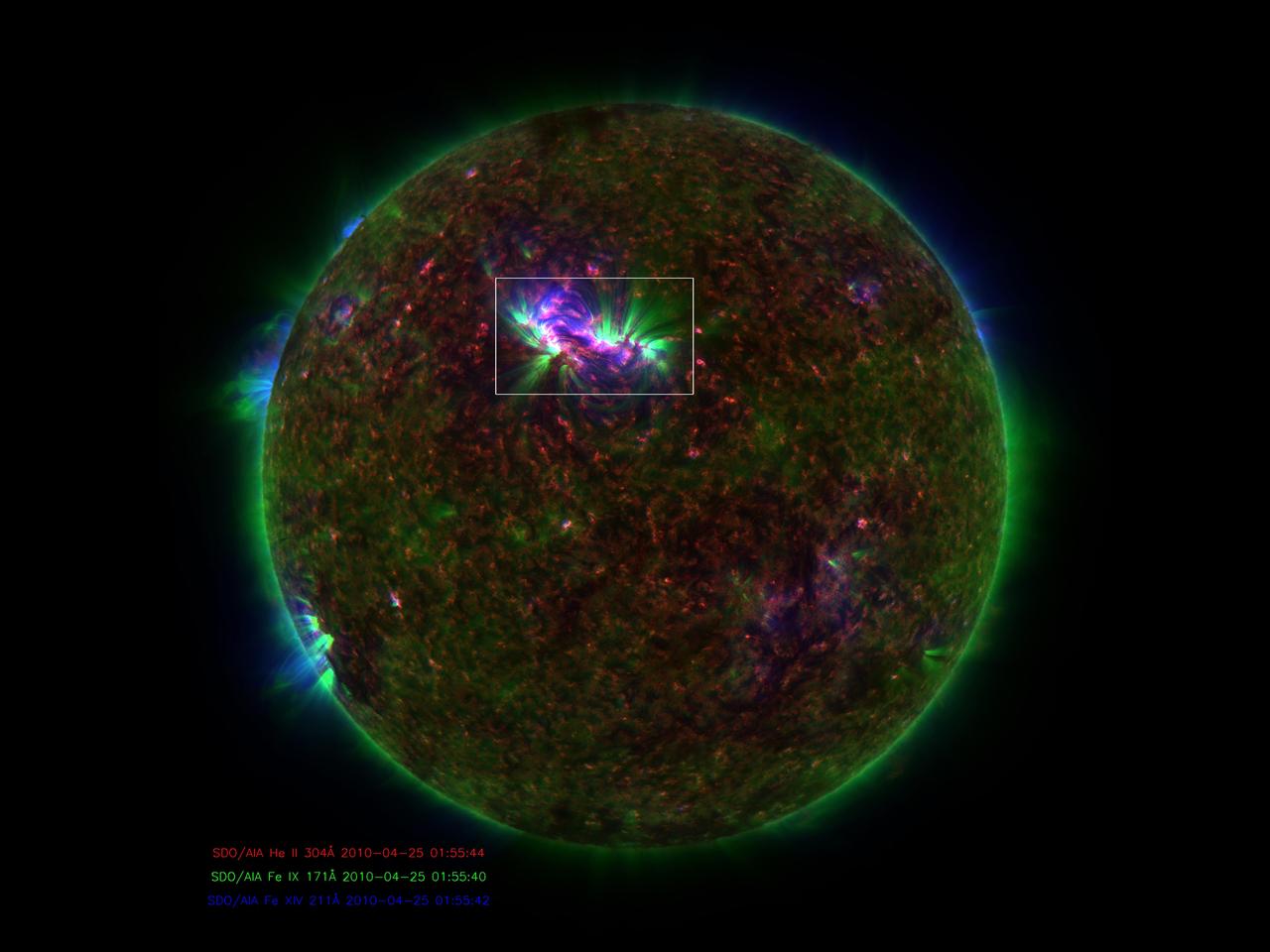
NASA image release January 6, 2010 Caption: Spicules on the sun, as observed by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. These bursts of gas jet off the surface of the sun at 150,000 miles per hour and contain gas that reaches temperatures over a million degrees. GREENBELT, Md. -- Observations from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Japanese satellite Hinode show that some gas in the giant, fountain-like jets in the sun's atmosphere known as spicules can reach temperatures of millions of degrees. The finding offers a possible new framework for how the sun's high atmosphere gets so much hotter than the surface of the sun. What makes the high atmosphere, or corona, so hot – over a million degrees, compared to the sun surface's 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit -- remains a poorly understood aspect of the sun's complicated space weather system. That weather system can reach Earth, causing auroral lights and, if strong enough, disrupting Earth's communications and power systems. Understanding such phenomena, therefore, is an important step towards better protecting our satellites and power grids. "The traditional view is that all the heating happens higher up in the corona," says Dean Pesnell, who is SDO's project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "The suggestion in this paper is that cool gas is being ejected from the sun's surface in spicules and getting heated on its way to the corona." Spicules were first named in the 1940s, but were hard to study in detail until recently, says Bart De Pontieu of Lockheed Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory, Palo Alto, Calif. who is the lead author on a paper on this subject in the January 7, 2011 issue of Science magazine. In visible light, spicules can be seen to send large masses of so-called plasma – the electromagnetic gas that surrounds the sun – up through the lower solar atmosphere or photosphere. The amount of material sent up is stunning, some 100 times as much as streams away from the sun in the solar wind towards the edges of the solar system. But nobody knew if they contained hot gas. "Heating of spicules to the necessary hot temperatures has never been observed, so their role in coronal heating had been dismissed as unlikely," says De Pontieu. Now, De Pontieu's team -- which included researchers at Lockheed Martin, the High Altitude Observatory of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Colorado and the University of Oslo, Norway -- was able to combine images from SDO and Hinode to produce a more complete picture of the gas inside these gigantic fountains. The scientists found that a large fraction of the gas is heated to a hundred thousand degrees, while a small fraction is heated to millions of degrees. Time-lapsed images show that this material spews up into the corona, with most falling back down towards the surface of the sun. However, the small fraction of the gas that is heated to millions of degrees does not immediately return to the surface. Given the large number of spicules on the Sun, and the amount of material in the spicules, the scientists believe that if even some of that super hot plasma stays aloft it would make a contribution to coronal heating. Astrophysicist Jonathan Cirtain, who is the U.S. project scientist for Hinode at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., says that incorporating such new information helps address an important question that reaches far beyond the sun. "This breakthrough in our understanding of the mechanisms which transfer energy from the solar photosphere to the corona addresses one of the most compelling questions in stellar astrophysics: How is the atmosphere of a star heated?" he says. "This is a fantastic discovery, and demonstrates the muscle of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, comprised of numerous instruments on multiple observatories." Hinode is the second mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program, the goal of which is to improve understanding of fundamental solar and space physics processes. The mission is led by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The collaborative mission includes the U.S., the United Kingdom, Norway and Europe. NASA Marshall manages Hinode U.S. science operations and oversaw development of the scientific instrumentation provided for the mission by NASA, academia and industry. The Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center is the lead U.S. investigator for the Solar Optical Telescope on Hinode. SDO is the first mission in a NASA science program called Living With a Star, the goal of which is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to address those aspects of the sun-Earth system that directly affect our lives and society. NASA Goddard built, operates, and manages the SDO spacecraft for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules...</a> Credit: NASA Goddard/SDO/AIA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>