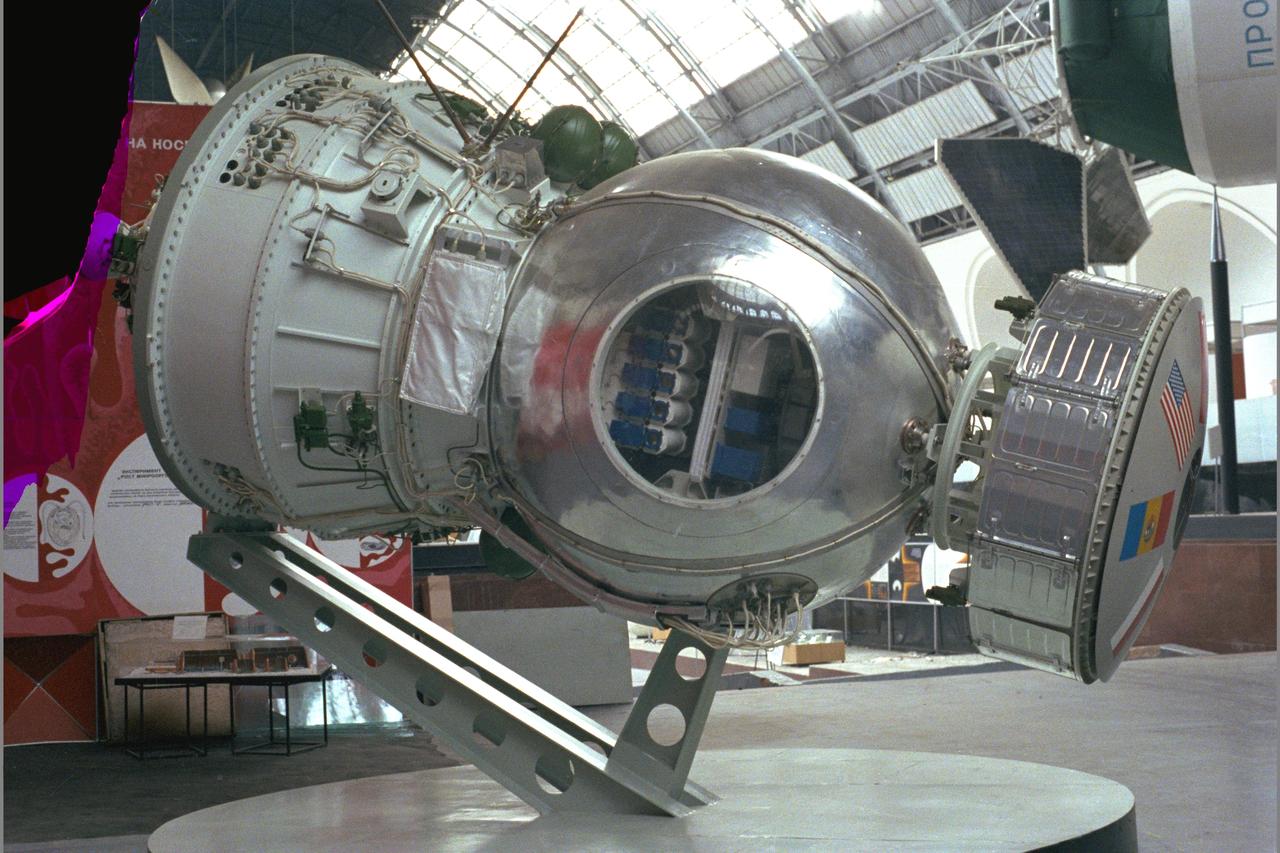
Soviet COSMOS unmanned biosatellite
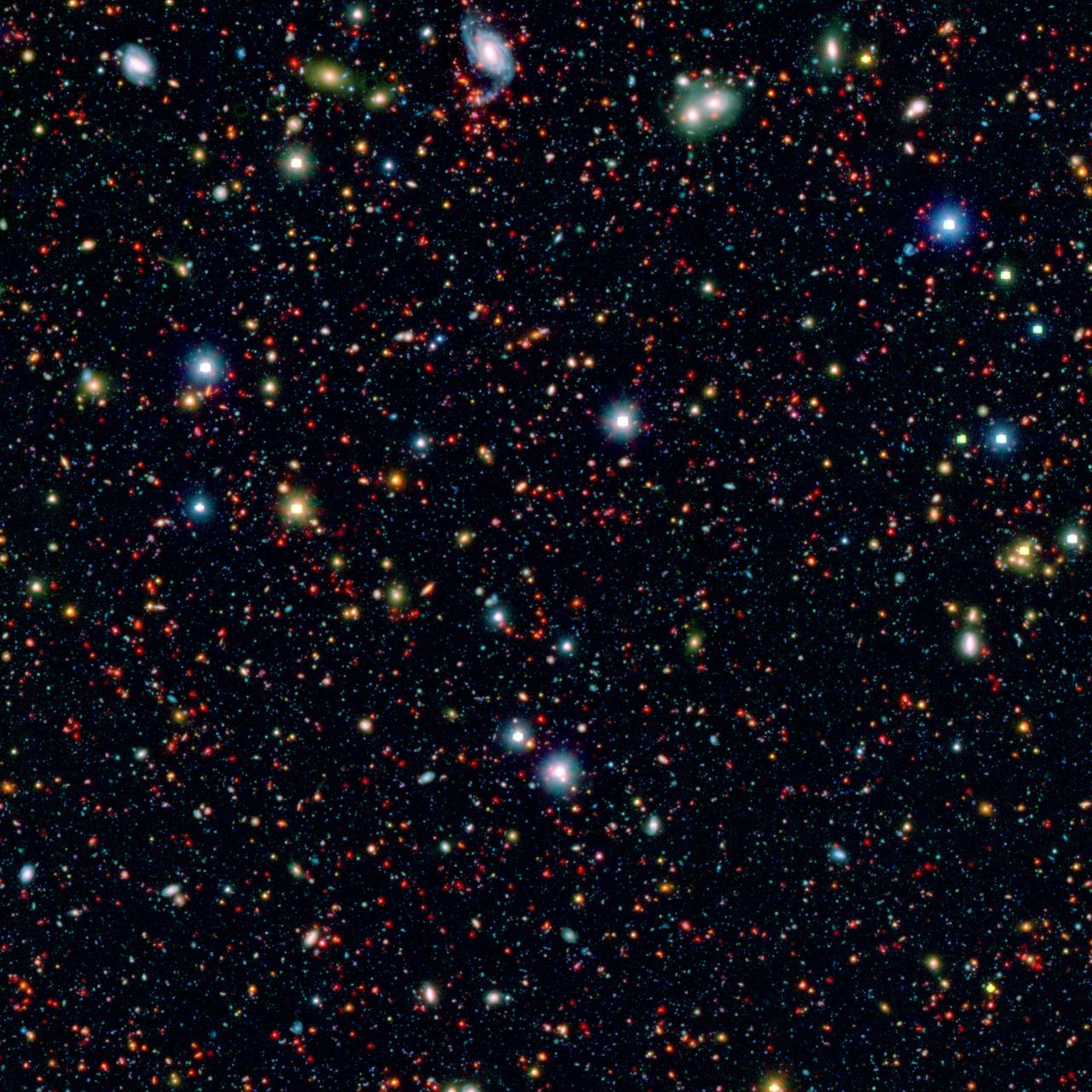

Millions of galaxies populate the patch of sky known as the COSMOS field, short for Cosmic Evolution Survey, a portion of which is shown here. Even the smallest dots in this image are galaxies, some up to 12 billion light-years away.

jsc2025e044835 (9/8/2016) --- Contents flown for the NanoRacks-Crystallization Of Silver Nitrate in Microgravity On a Silver Cathode (NanoRacks-COSMOS). This investigation assesses the 3D structure of silver nitrate crystals formed by electrolysis in microgravity. Image courtesy of Dave Schlichting.
![This new Hubble image showcases a remarkable variety of objects at different distances from us, extending back over halfway to the edge of the observable Universe. The galaxies in this image mostly lie about five billion light-years from Earth but the field also contains other objects, both significantly closer and far more distant. Studies of this region of the sky have shown that many of the objects that appear to lie close together may actually be billions of light-years apart. This is because several groups of galaxies lie along our line of sight, creating something of an optical illusion. Hubble’s cross-section of the Universe is completed by distorted images of galaxies in the very distant background. These objects are sometimes distorted due to a process called gravitational lensing, an extremely valuable technique in astronomy for studying very distant objects [1]. This lensing is caused by the bending of the space-time continuum by massive galaxies lying close to our line of sight to distant objects. One of the lens systems visible here is called CLASS B1608+656, which appears as a small loop in the centre of the image. It features two foreground galaxies distorting and amplifying the light of a distant quasar the known as QSO-160913+653228. The light from this bright disc of matter, which is currently falling into a black hole, has taken nine billion years to reach us — two thirds of the age of the Universe. As well as CLASS B1608+656, astronomers have identified two other gravitational lenses within this image. Two galaxies, dubbed Fred and Ginger by the researchers who studied them, contain enough mass to visibly distort the light from objects behind them. Fred, also known more prosaically as [FMK2006] ACS J160919+6532, lies near the lens galaxies in CLASS B1608+656, while Ginger ([FMK2006] ACS J160910+6532) is markedly closer to us. Despite their different distances from us, both can be seen near to CLASS B1608+656 in the central region of this Hubble image. To capture distant and dim objects like these, Hubble required a long exposure. The image is made up of visible and infrared observations with a total exposure time of 14 hours. More info: <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1408/" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1408/</a> Credit: NASA/ESA/Hubble <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/GSFC_20171208_Archive_e001152/GSFC_20171208_Archive_e001152~medium.jpg)
This new Hubble image showcases a remarkable variety of objects at different distances from us, extending back over halfway to the edge of the observable Universe. The galaxies in this image mostly lie about five billion light-years from Earth but the field also contains other objects, both significantly closer and far more distant. Studies of this region of the sky have shown that many of the objects that appear to lie close together may actually be billions of light-years apart. This is because several groups of galaxies lie along our line of sight, creating something of an optical illusion. Hubble’s cross-section of the Universe is completed by distorted images of galaxies in the very distant background. These objects are sometimes distorted due to a process called gravitational lensing, an extremely valuable technique in astronomy for studying very distant objects [1]. This lensing is caused by the bending of the space-time continuum by massive galaxies lying close to our line of sight to distant objects. One of the lens systems visible here is called CLASS B1608+656, which appears as a small loop in the centre of the image. It features two foreground galaxies distorting and amplifying the light of a distant quasar the known as QSO-160913+653228. The light from this bright disc of matter, which is currently falling into a black hole, has taken nine billion years to reach us — two thirds of the age of the Universe. As well as CLASS B1608+656, astronomers have identified two other gravitational lenses within this image. Two galaxies, dubbed Fred and Ginger by the researchers who studied them, contain enough mass to visibly distort the light from objects behind them. Fred, also known more prosaically as [FMK2006] ACS J160919+6532, lies near the lens galaxies in CLASS B1608+656, while Ginger ([FMK2006] ACS J160910+6532) is markedly closer to us. Despite their different distances from us, both can be seen near to CLASS B1608+656 in the central region of this Hubble image. To capture distant and dim objects like these, Hubble required a long exposure. The image is made up of visible and infrared observations with a total exposure time of 14 hours. More info: <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1408/" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/heic1408/</a> Credit: NASA/ESA/Hubble <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
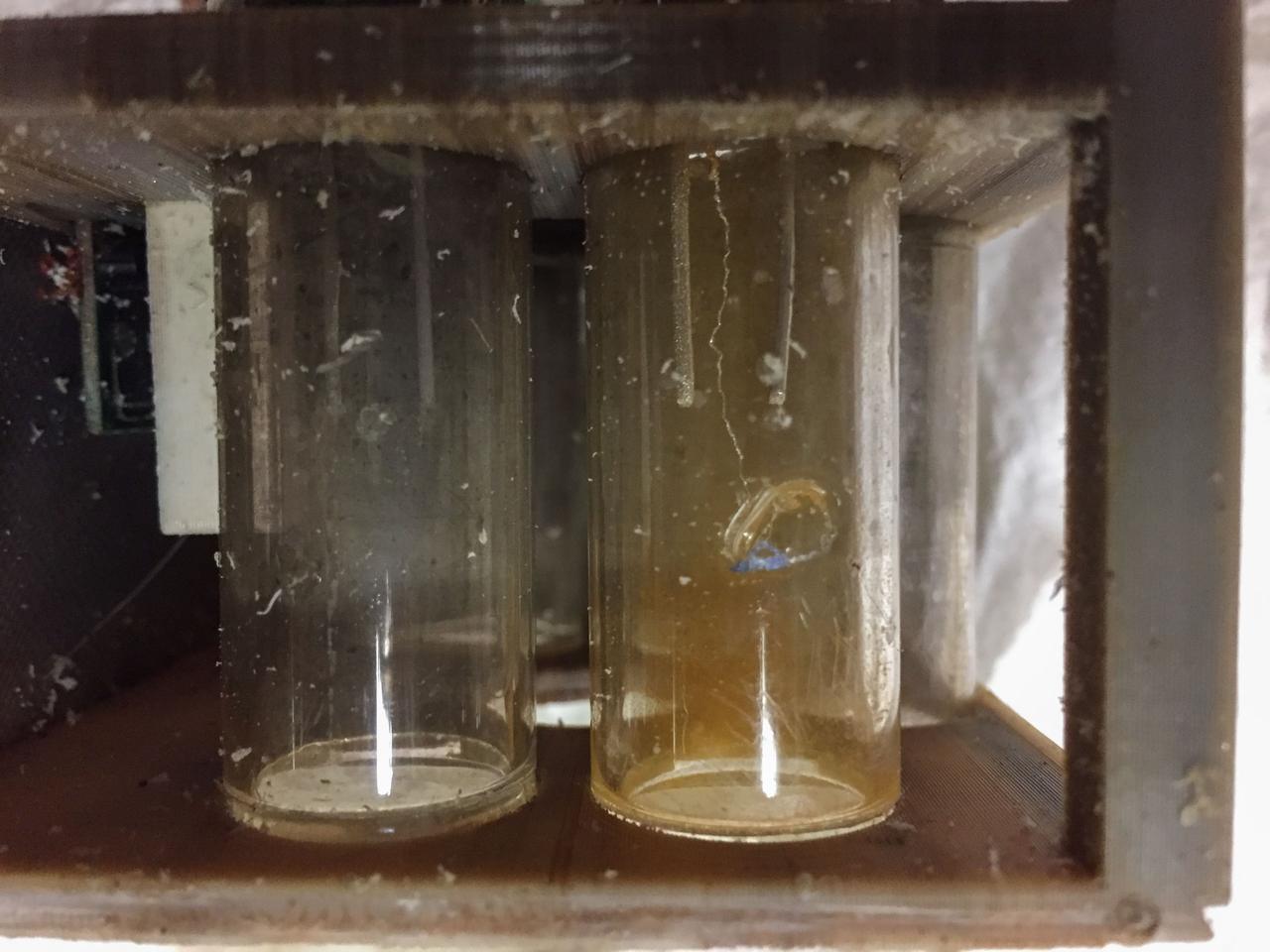

jsc2025e044836 (9/29/2016) --- Silver nitrate crystals grown in microgravity as part of NanoRacks-Crystallization Of Silver Nitrate in Microgravity On a Silver Cathode (NanoRacks-COSMOS). This investigation is designed to assess the 3D structure of silver nitrate crystals formed by electrolysis in microgravity. Results benefit the development of nanoscale electronics, which could be used in spacecraft and instruments on future space missions. Image courtesy of Dave Schlichting.
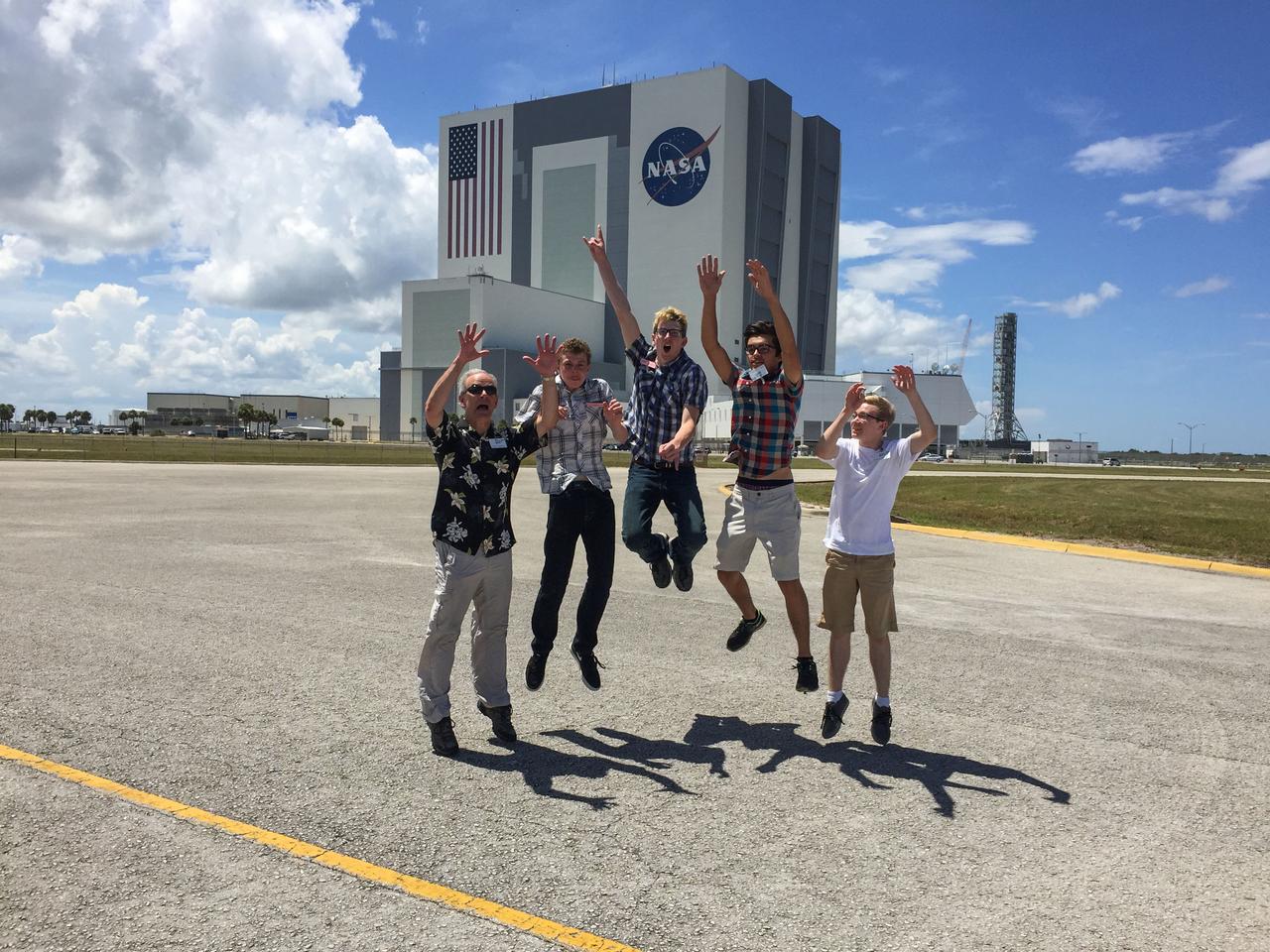

jsc2025e044834 (7/16/2016) --- The NanoRacks-Crystallization Of Silver Nitrate in Microgravity On a Silver Cathode (NanoRacks-COSMOS) research team from Eaglecrest High School in Centennial, Colorado is photographed at Kennedy Space Center on July 18, 2016. This investigation assesses the 3D structure of silver nitrate crystals formed by electrolysis in microgravity. From Left: Dave Schlichting, Gavin Morgenneg, Scott Crowner, Lars Drieth, Ben Sheffer. Image courtesy of Dave Schlichting.

The blue dots in this field of galaxies, known as the COSMOS field, show galaxies that contain supermassive black holes emitting high-energy X-rays. The black holes were detected by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Array, or NuSTAR, which spotted 32 such black holes in this field and has observed hundreds across the whole sky so far. The other colored dots are galaxies that host black holes emitting lower-energy X-rays, and were spotted by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra data show X-rays with energies between 0.5 to 7 kiloelectron volts, while NuSTAR data show X-rays between 8 to 24 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20865
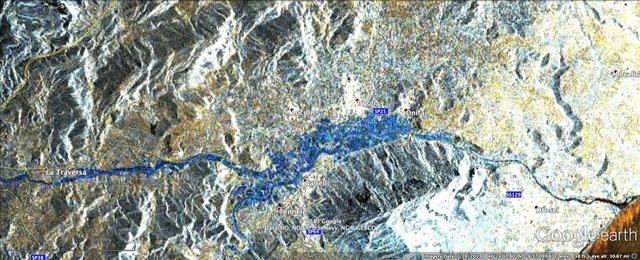
In mid-November 2013, extratropical cyclone Cleopatra brought devastating flooding to the Italian island of Sardinia as shown by the COSMO-SkyMed satellite.
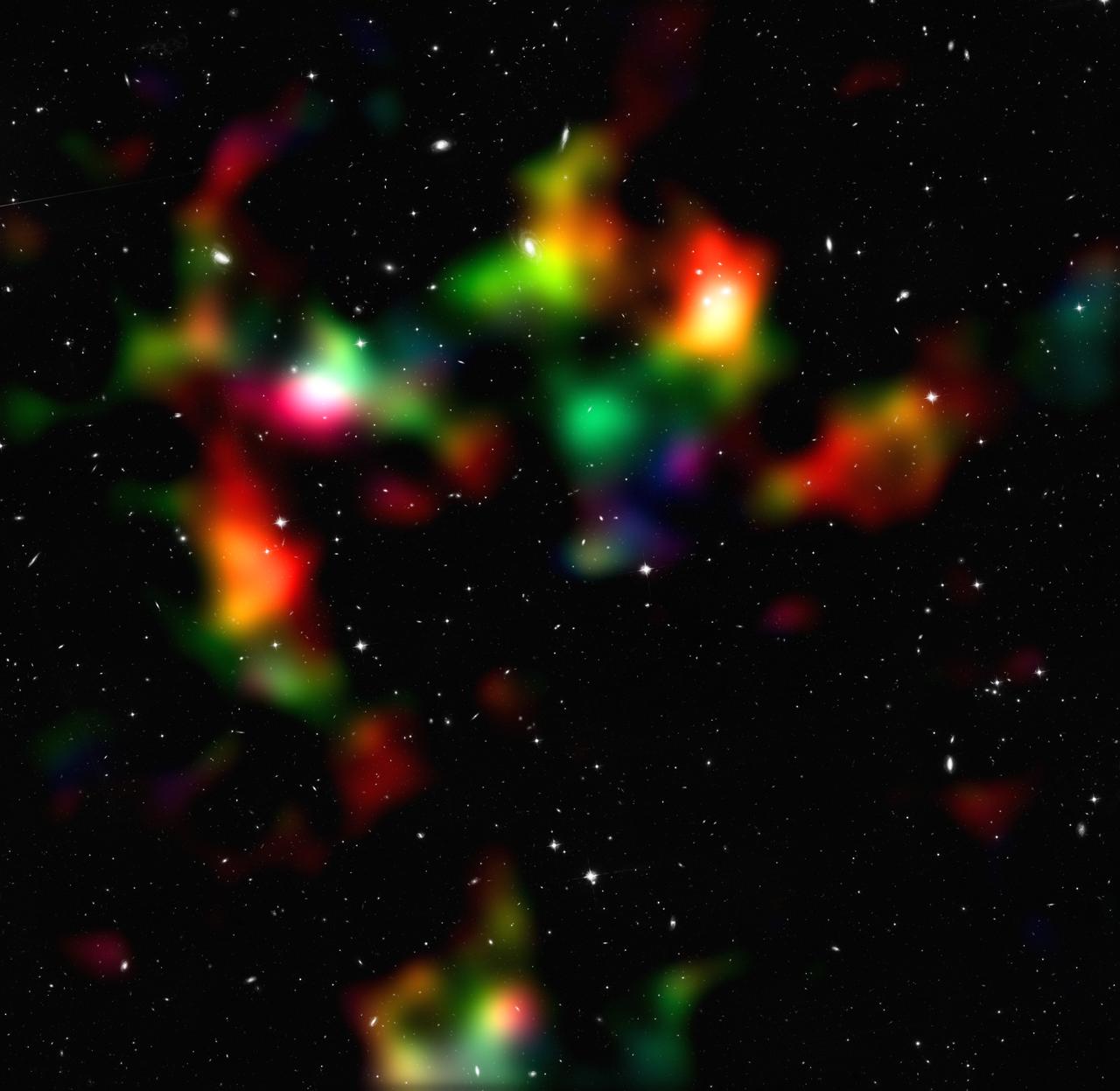

NASA/ESA Hubble Release Date: March 25, 2010 This image shows a smoothed reconstruction of the total (mostly dark) matter distribution in the COSMOS field, created from data taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based telescopes. It was inferred from the weak gravitational lensing distortions that are imprinted onto the shapes of background galaxies. The colour coding indicates the distance of the foreground mass concentrations as gathered from the weak lensing effect. Structures shown in white, cyan, and green are typically closer to us than those indicated in orange and red. To improve the resolution of the map, data from galaxies both with and without redshift information were used. The new study presents the most comprehensive analysis of data from the COSMOS survey. The researchers have, for the first time ever, used Hubble and the natural "weak lenses" in space to characterise the accelerated expansion of the Universe. Credit: NASA, ESA, P. Simon (University of Bonn) and T. Schrabback (Leiden Observatory) To learn more abou this image go to: <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/html/heic1005.html" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/html/heic1005.html</a> For more information about Goddard Space Flight Center go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html</a>

This illustration summarizes the almost 14-billion-year-long history of our universe. It shows the main events that occurred between the initial phase of the cosmos.

NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer observed the star-forming cloud NGC 281 in the constellation of Cassiopeia as it appears to be chomping through the cosmos, earning it the nickname the Pacman nebula.

NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer is a little like the Vincent van Gogh of the infrared sky, providing the world with picturesque images of the cosmos by representing infrared light through color. This image is the nebula NGC 2174.

Astronomers have discovered a massive cluster of young galaxies forming in the distant universe. The growing galactic metropolis is known as COSMOS-AzTEC3. This image was taken Japan Subaru telescope atop Mauna Kea in Hawaii.

This satellite interferometric synthetic aperture radar image using COSMO-SkyMed radar data, depicts the relative deformation of Earth surface at Kilauea between Feb. 11, 2011 and March 7, 2011 two days following the start of the current eruption.
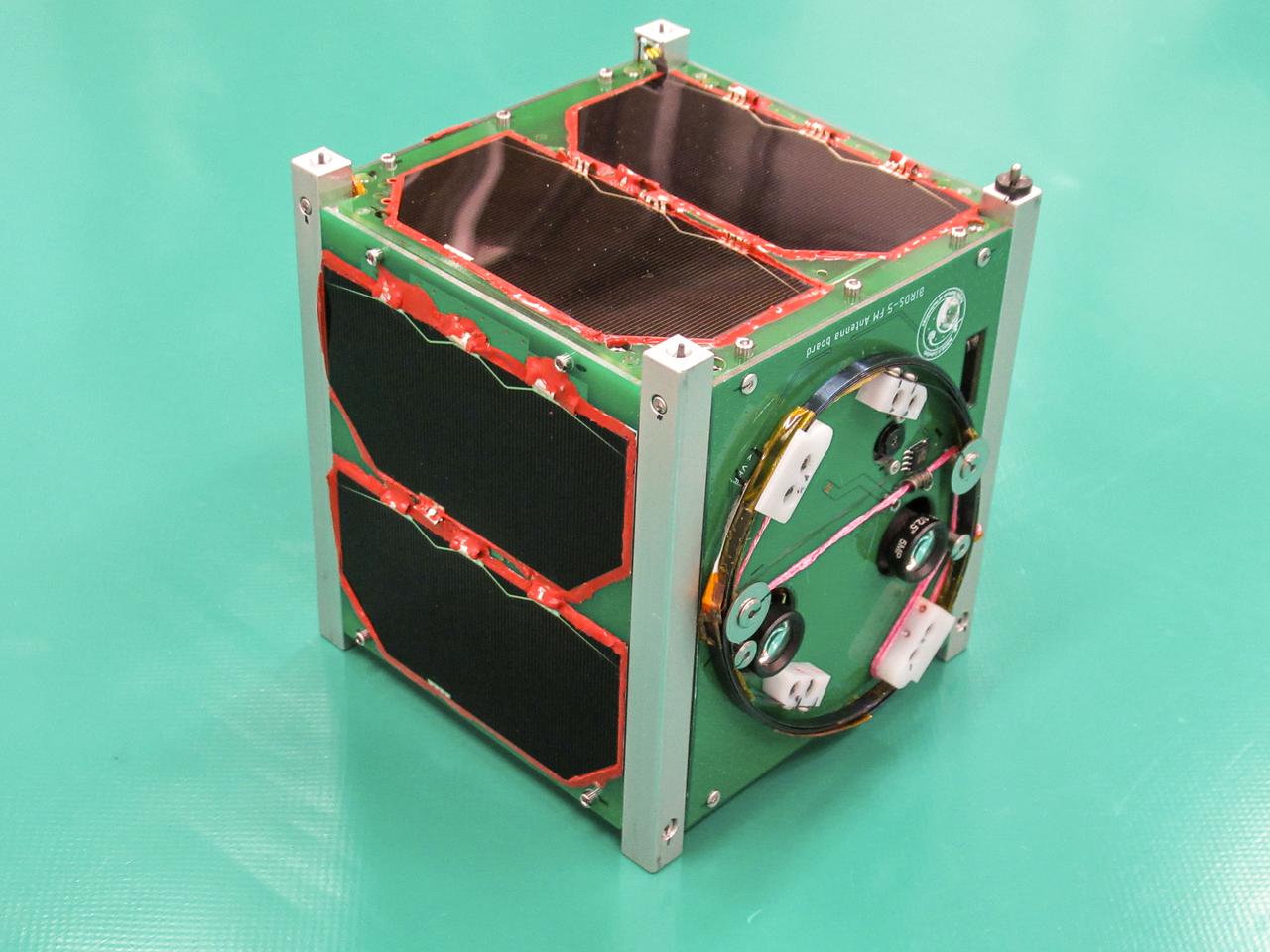

JSC2024E043924 (4/14/2025) --- The CosmoGirl-Sat CubeSat from Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) shows deep blue solar panels at the front of the spacecraft that power three sunken camera lenses (seen on the top of the satellite), amongst a plethora of other subsystems. CosmoGirl-Sat is developed by the Cosmo Women’s Amateur Radio Club, and its primary mission is to transmit imagery to a ground station on Earth. Image courtesy of Cosmo Girls Amateur Radio Club.
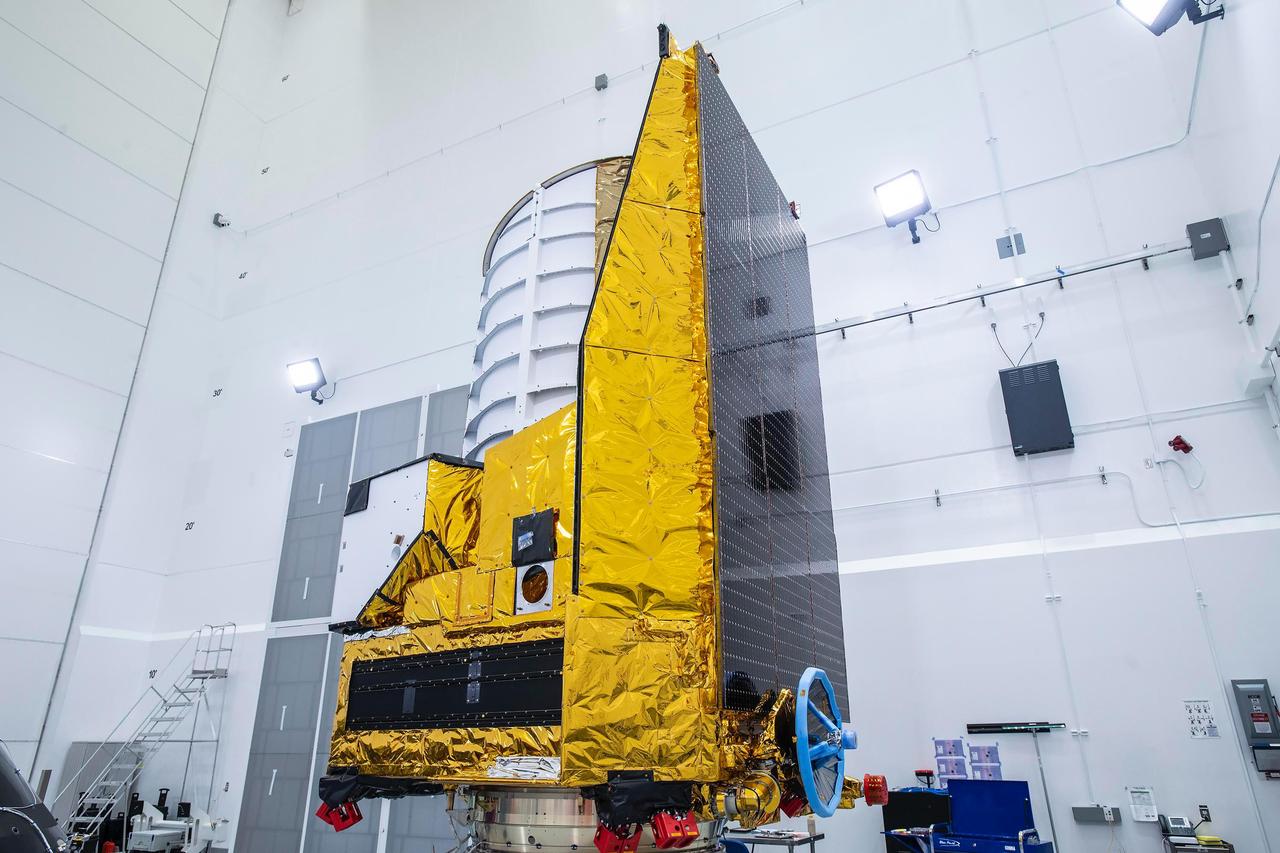

The ESA (European Space Agency) Euclid telescope, with contributions from NASA, is shown here on Friday 23 June, being secured to the adaptor of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket before launch. Black solar panels line the right side of the spacecraft. The telescope will view the cosmos through the top of the white cylinder that sits above the spacecraft's instruments. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25783
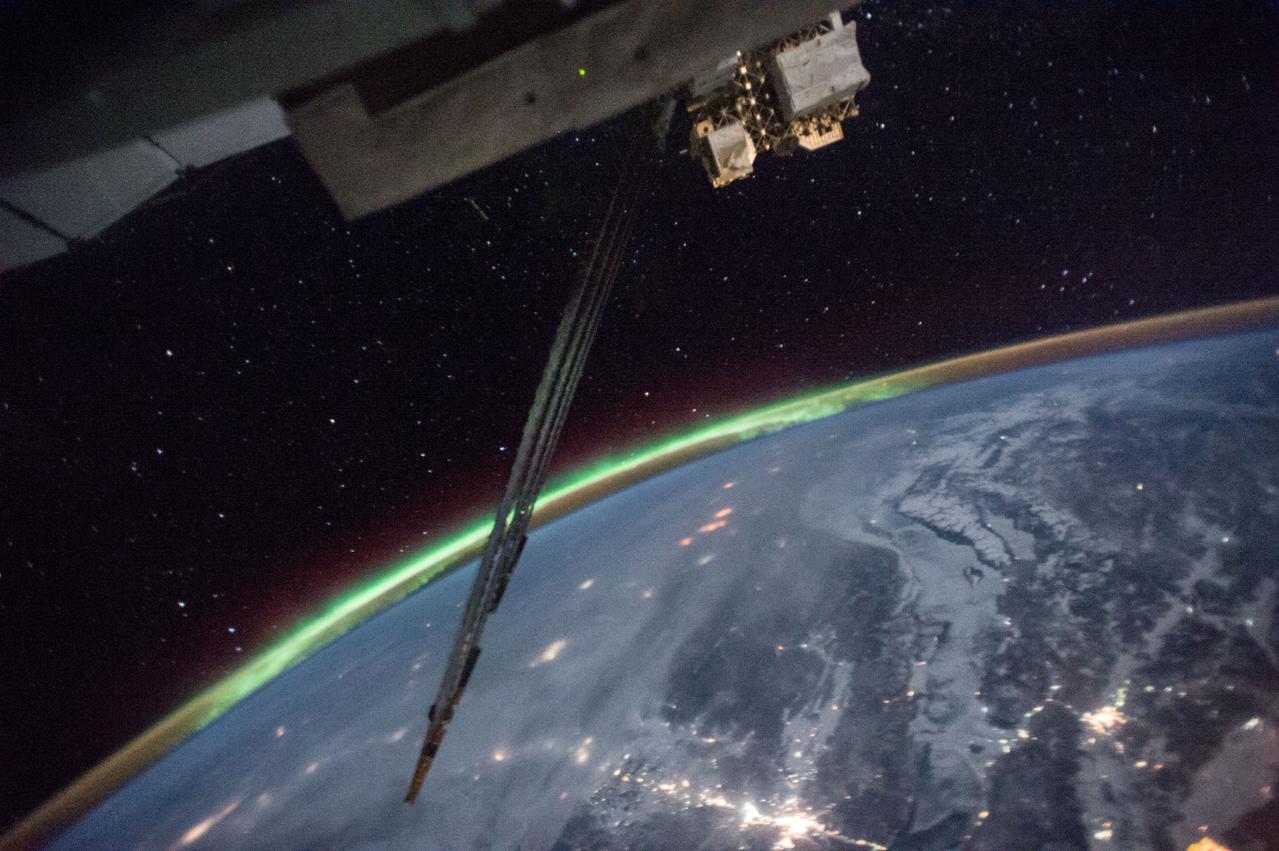

iss050e034428 (01/18/2017) --- This long exposure photo taken from the International Space Station as it orbits around the Earth provides a spectacular view of auroras, sparkling city lights and the stars filling the cosmos beyond.

In archived NASA data, researchers have discovered "super spiral" galaxies that dwarf our own spiral galaxy, the Milky Way, and compete in size and brightness with the largest galaxies in the universe. The unprecedented galaxies have long hidden in plain sight by mimicking the appearance of typical spirals. Three examples of super spirals are presented here in images taken by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The super spiral on the left (Figure 1), catalogued as 2MASX J08542169+0449308, contains two galactic nuclei, instead of just the usual one, and thus looks like two eggs frying in a pan. The central image (Figure 2) shows a super spiral designated 2MASX J16014061+2718161, and it also contains the double nuclei. On the right (Figure 3), a huge galaxy with the moniker SDSS J094700.08+254045.7 stands as one of the biggest and brightest super spirals. The mega-galaxy's starry disk and spiral arms stretch about 320,000 light-years across, or more than three times the breadth of the Milky Way. These double nuclei, which are known to result from the recent merger of two galaxies, could offer a vital hint about the potential origin of super spirals. Researchers speculate that a special merger involving two, gas-rich spiral galaxies could see their pooled gases settle down into a new, larger stellar disk -- presto, a super spiral. The super spirals were discovered using the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database, or NED, an online repository containing information on over 100 million galaxies. NED brings together a wealth of data from many different projects, including ultraviolet light observations from the Galaxy Evolution Explorer, visible light from Sloan Digital Sky Survey, infrared light from the 2-Micron All-Sky Survey, and links to data from other missions such as NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20064

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
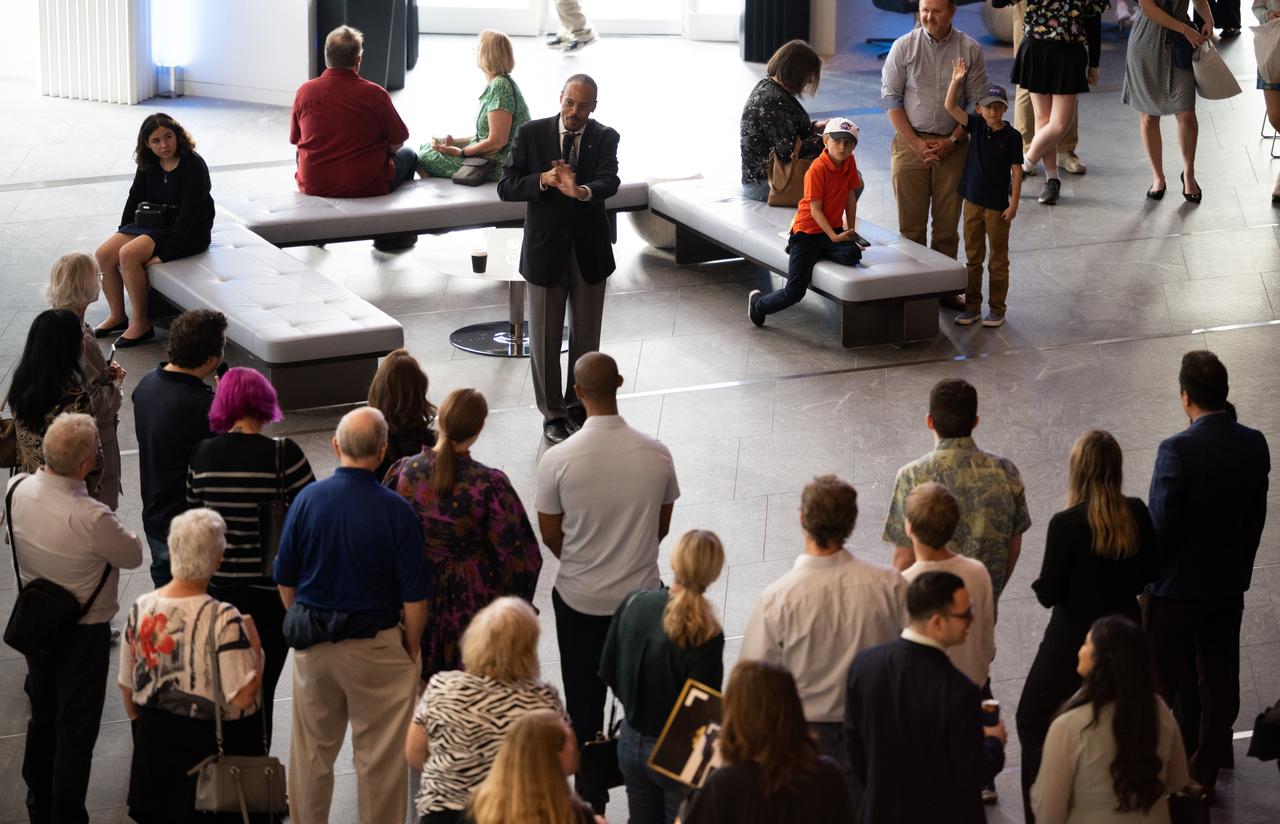

NASA astronaut Alvin Drew answers question prior to the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Return to the Moon: Fanfare to Artemis,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
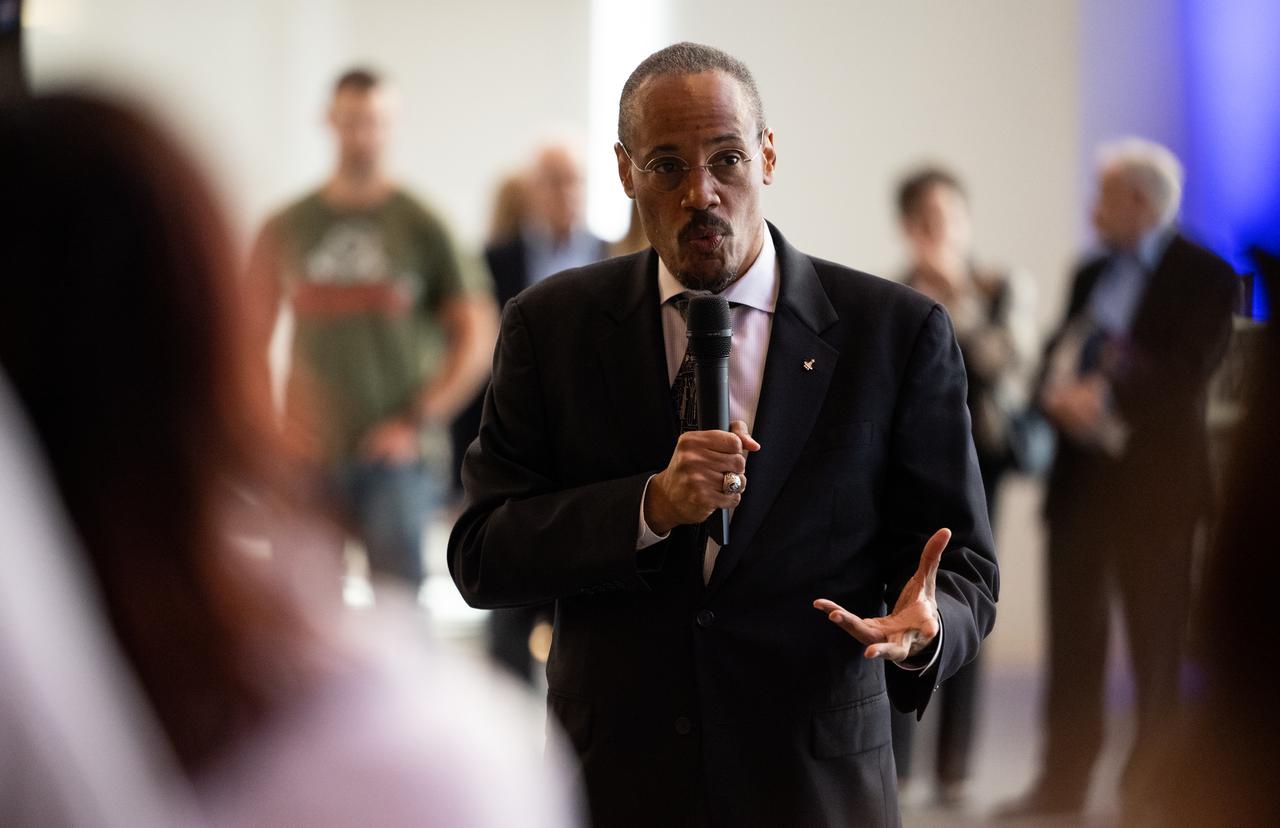

NASA astronaut Alvin Drew answers question prior to the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
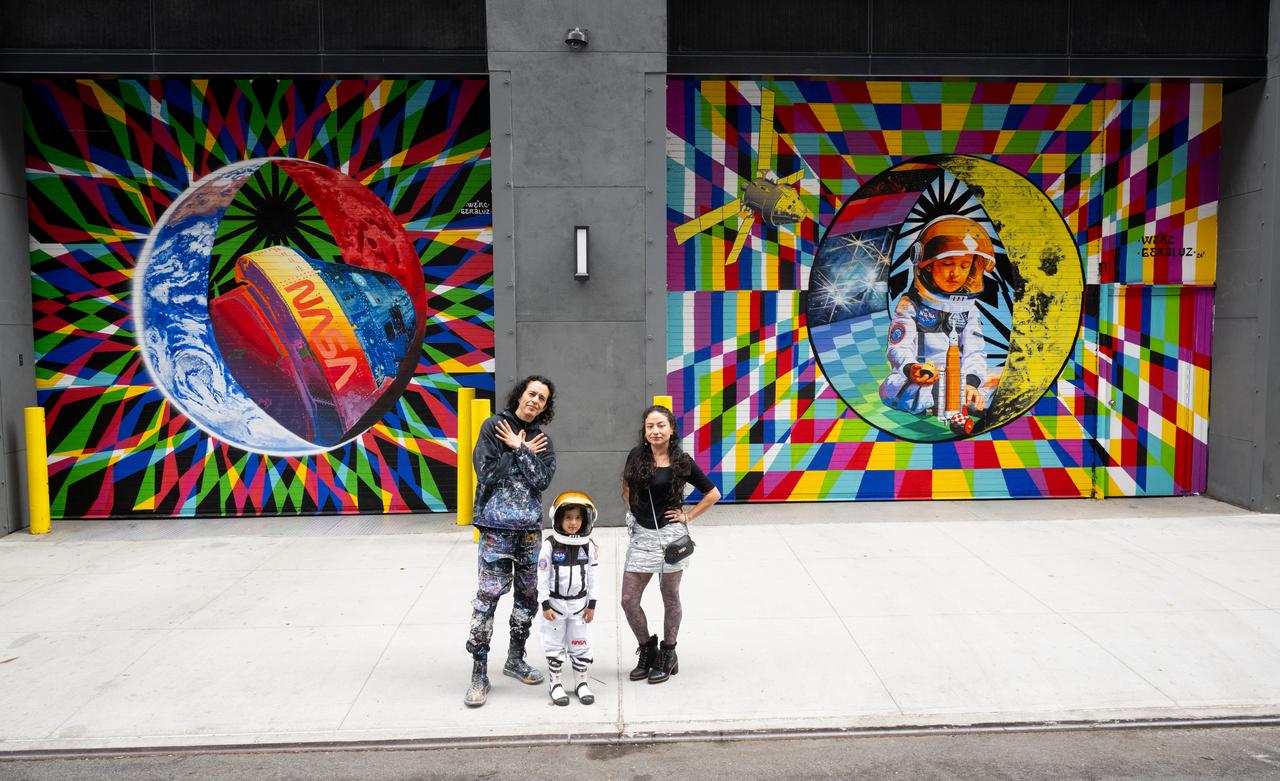

The New York-based artist team Geraluz, left, and WERC, right, and their son Amaru Alvarez, 5, pose for picture with the mural “To the Moon, and Back” by the artist team that was created as part of the reimagined NASA Art Program, Tuesday, September 24, 2024, at 350 Hudson Street in New York City. The murals use geometrical patterns to invite deeper reflection on the exploration, creativity, and connection with the cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
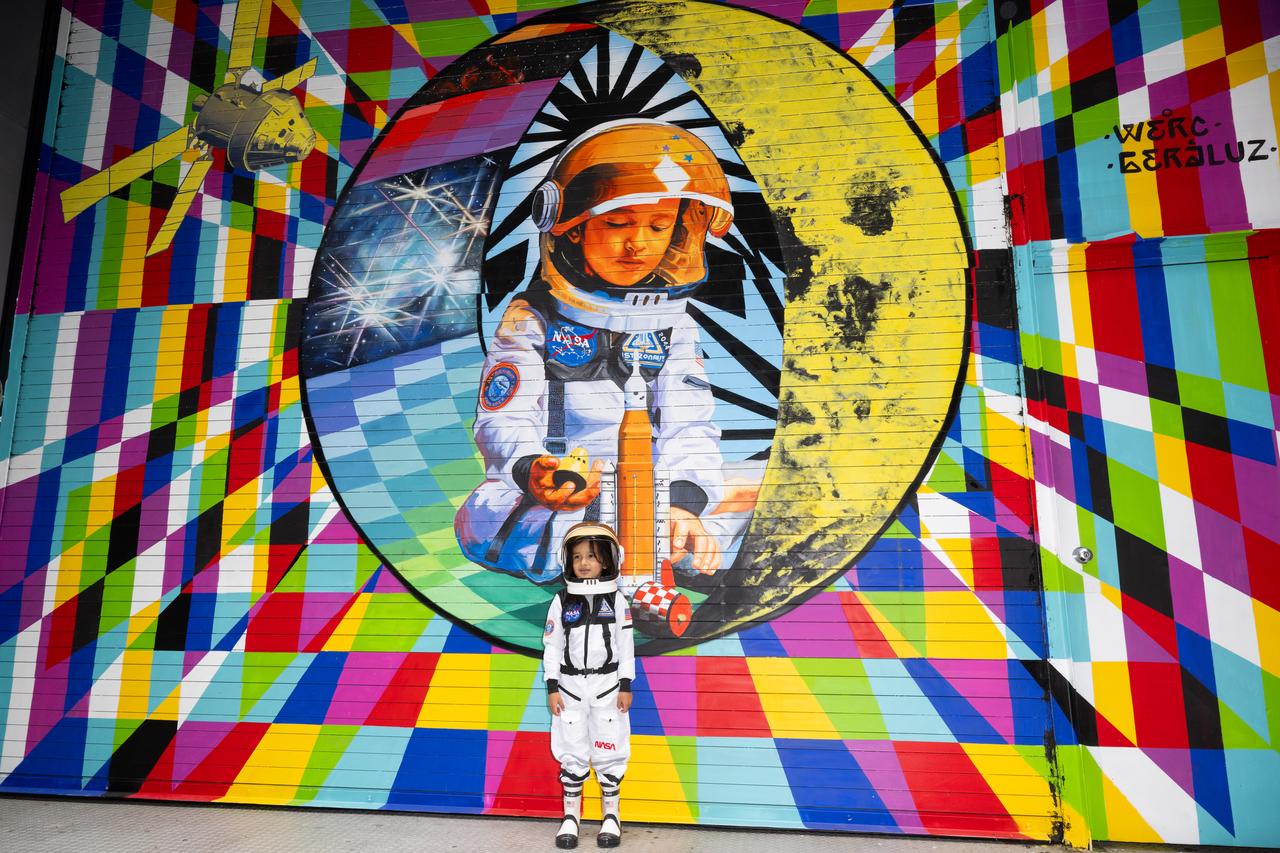

Amaru Alvarez, 5, the son of the artist team Geraluz and WERC and model for the mural, poses for picture with the mural “To the Moon, and Back” by the New York-based artist team that was created as part of the reimagined NASA Art Program, Tuesday, September 24, 2024, at 350 Hudson Street in New York City. The murals use geometrical patterns to invite deeper reflection on the exploration, creativity, and connection with the cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Composer Henry Dehlinger, left, and Maestro Piotr Gajewski, right, are seen with the National Philharmonic following the world premier performance of Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
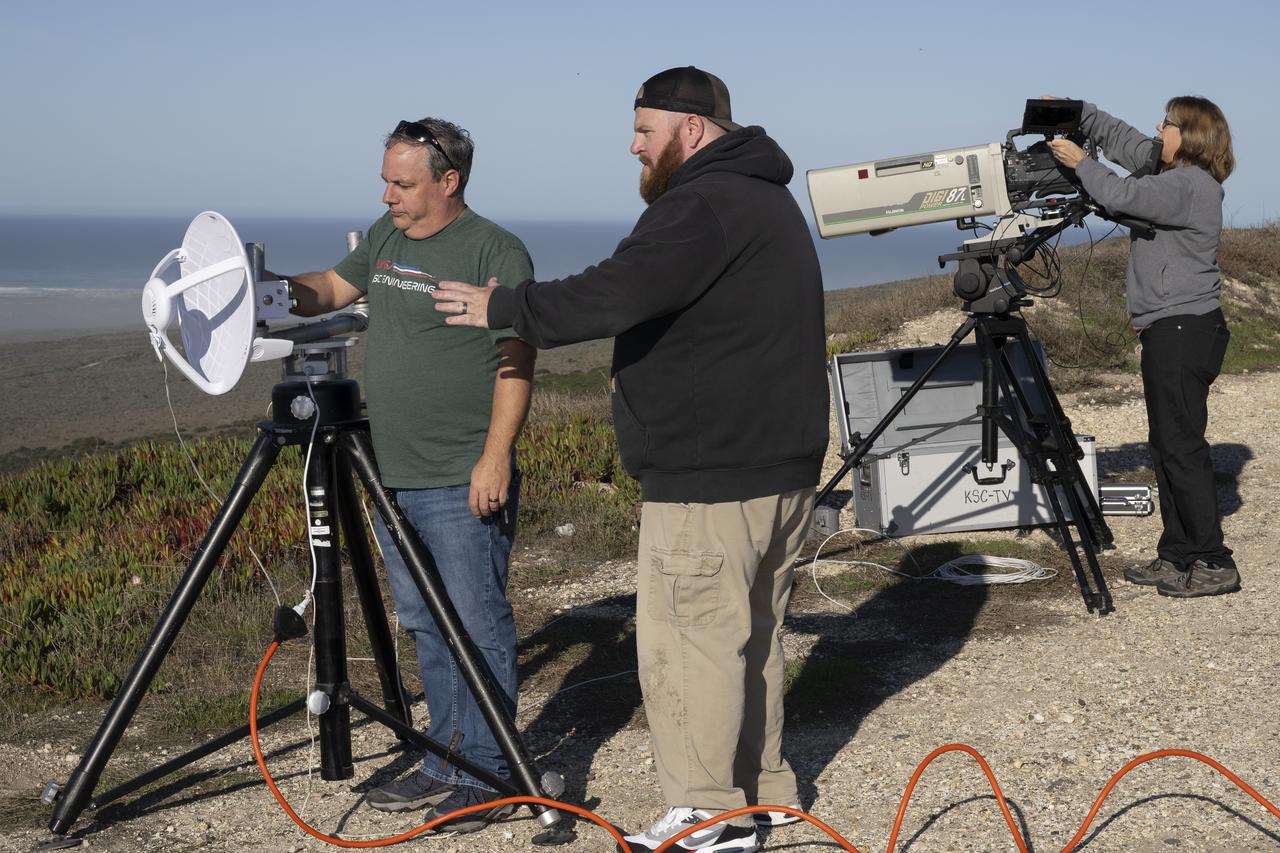

NASA videographer Jacob Shaw and the video team from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, prepare to film the launch of NASA’s SPHEREx mission at Vandenberg Space Force Base. The mission, short for Specto-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer, launched on March 11, 2025, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, continuing NASA’s exploration of the cosmos – and its commitment to visual storytelling.
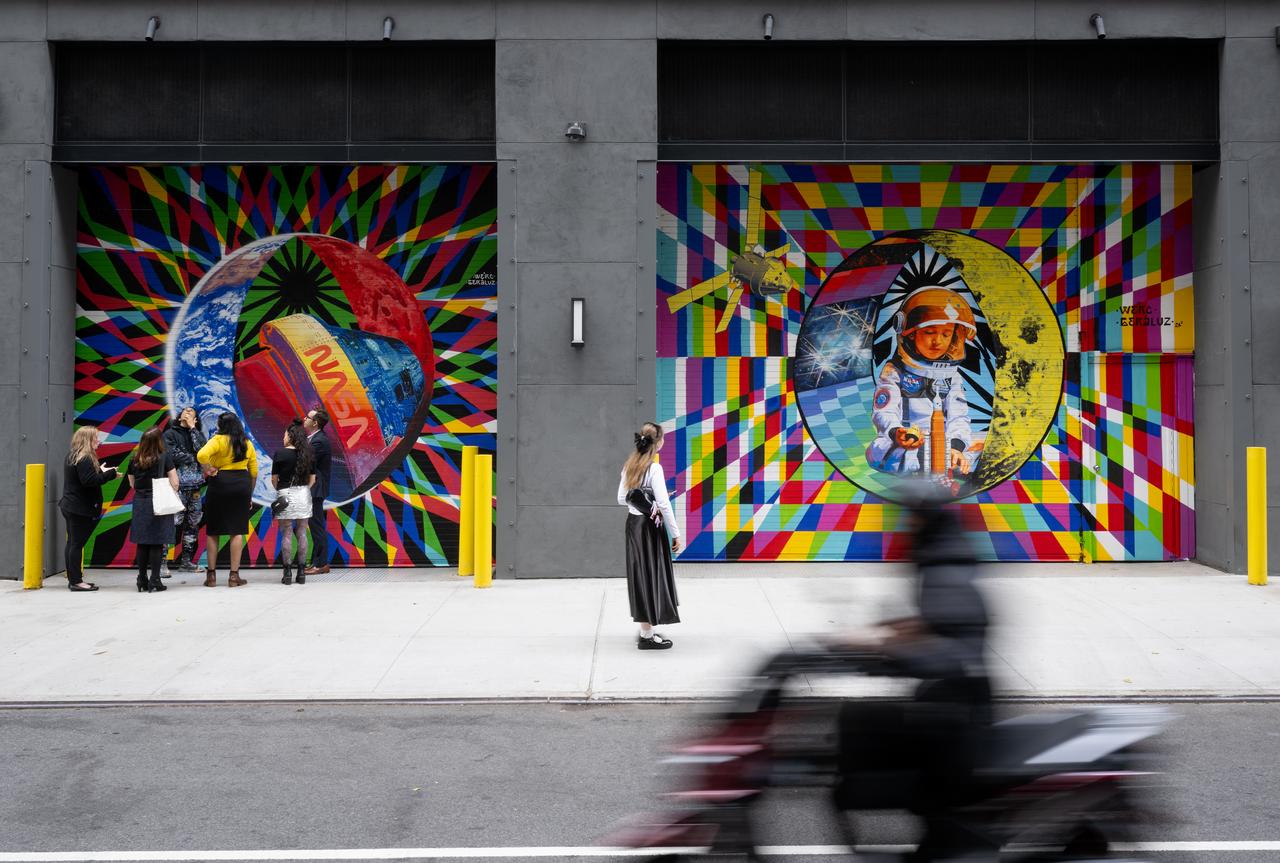

The inaugural murals for the relaunched NASA Art Program appear side-by-side at 350 Hudson Street, Tuesday, Sept. 24, 2024, in New York City. The murals, titled “To the Moon, and Back,” were created by New York-based artist team Geraluz and WERC and use geometrical patterns to invite deeper reflection on the exploration, creativity, and connection with the cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
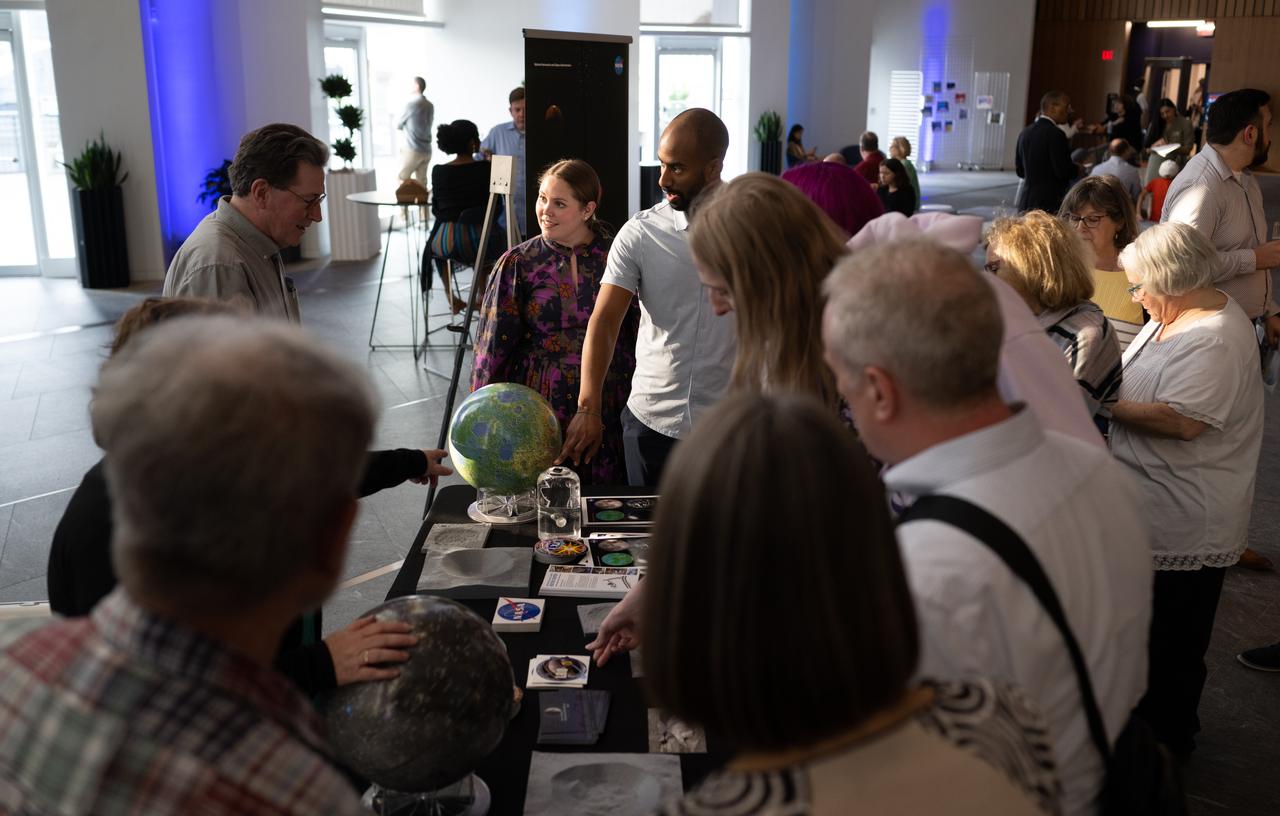

Attendees of the National Philharmonic performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles” view a Moon rock, Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
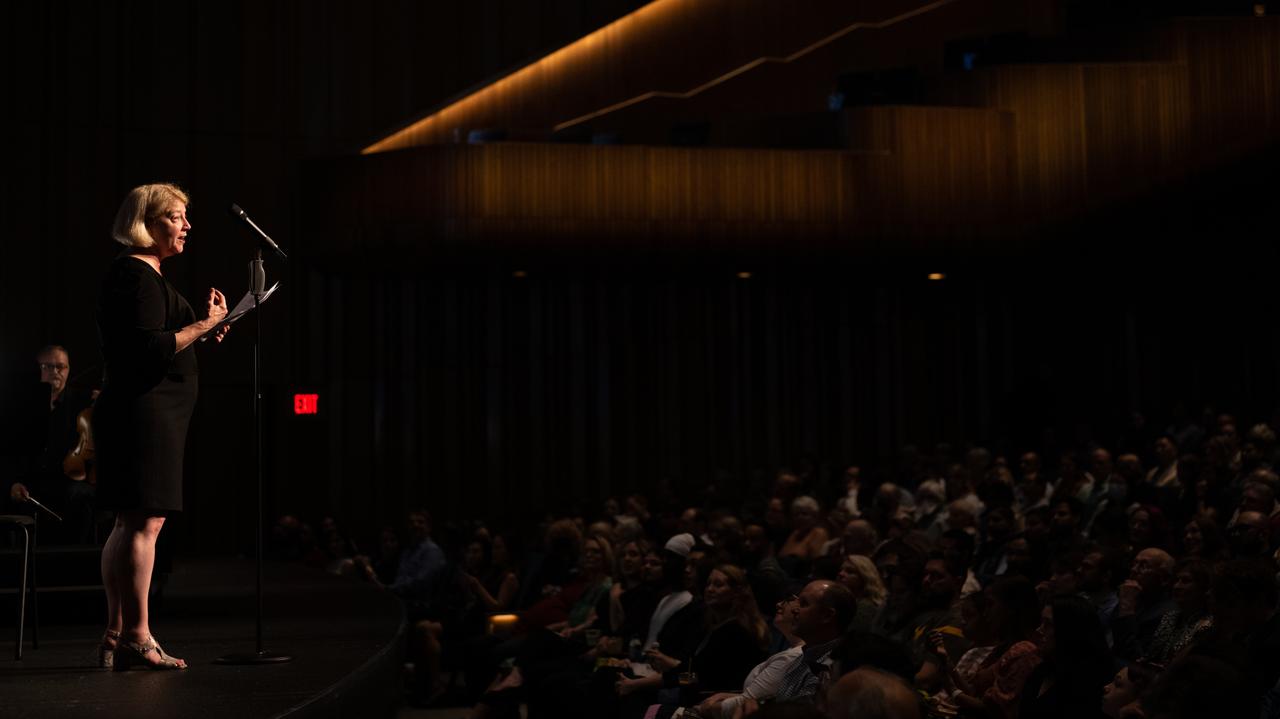

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers remarks prior to the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers remarks prior to the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
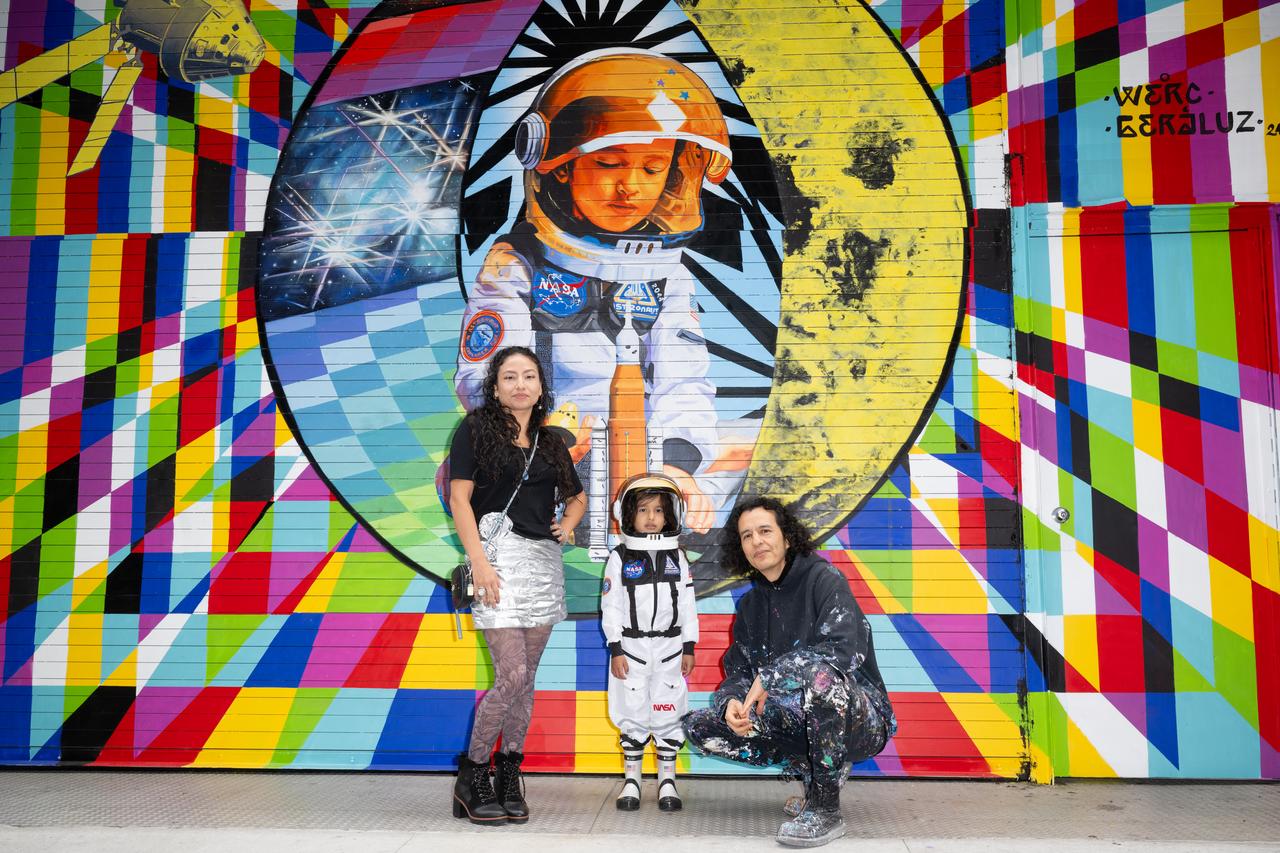

The New York-based artist team Geraluz, left, and WERC, right, and their son Amaru Alvarez, 5, pose for picture with the mural “To the Moon, and Back” by the artist team that was created as part of the reimagined NASA Art Program, Tuesday, September 24, 2024, at 350 Hudson Street in New York City. The murals use geometrical patterns to invite deeper reflection on the exploration, creativity, and connection with the cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
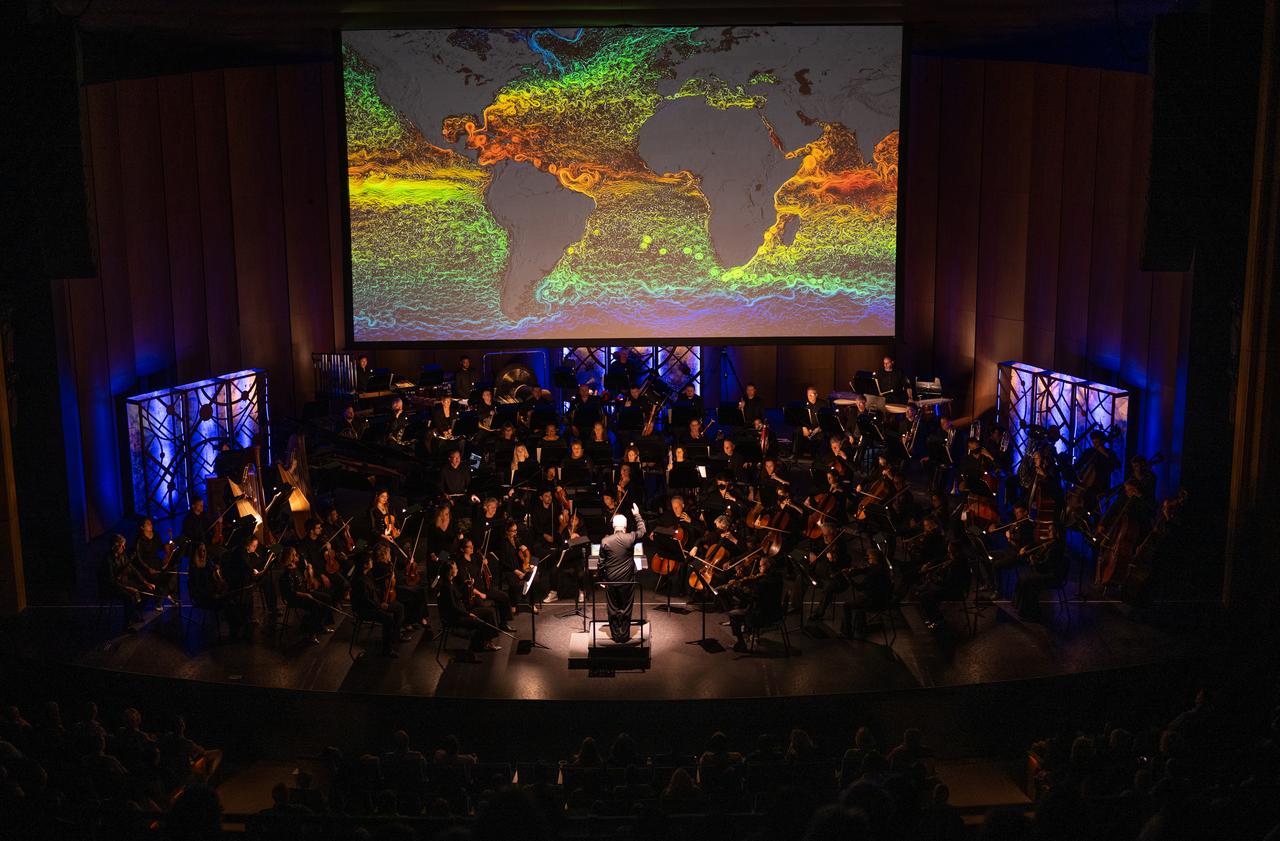

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
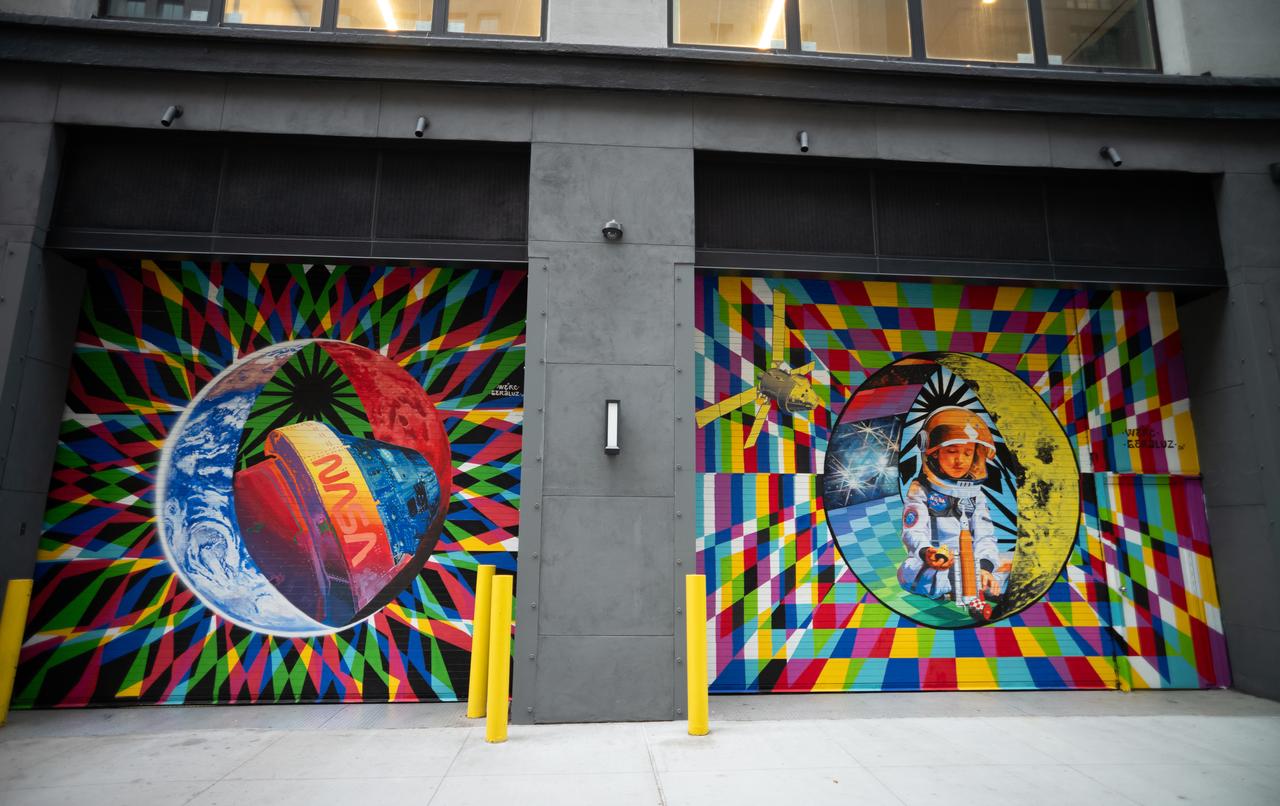

The inaugural murals for the relaunched NASA Art Program appear side-by-side at 350 Hudson Street, Monday, Sept. 23, 2024, in New York City. The murals, titled “To the Moon, and Back,” were created by New York-based artist team Geraluz and WERC and use geometrical patterns to invite deeper reflection on the exploration, creativity, and connection with the cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
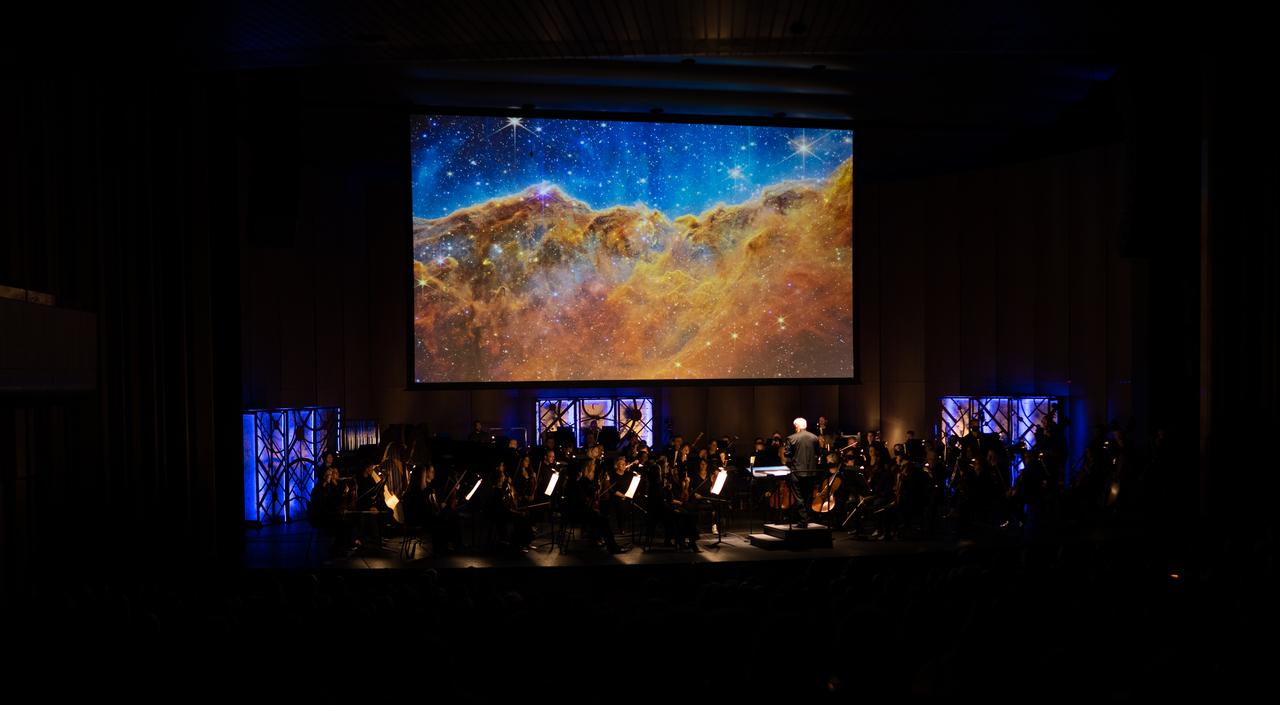

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
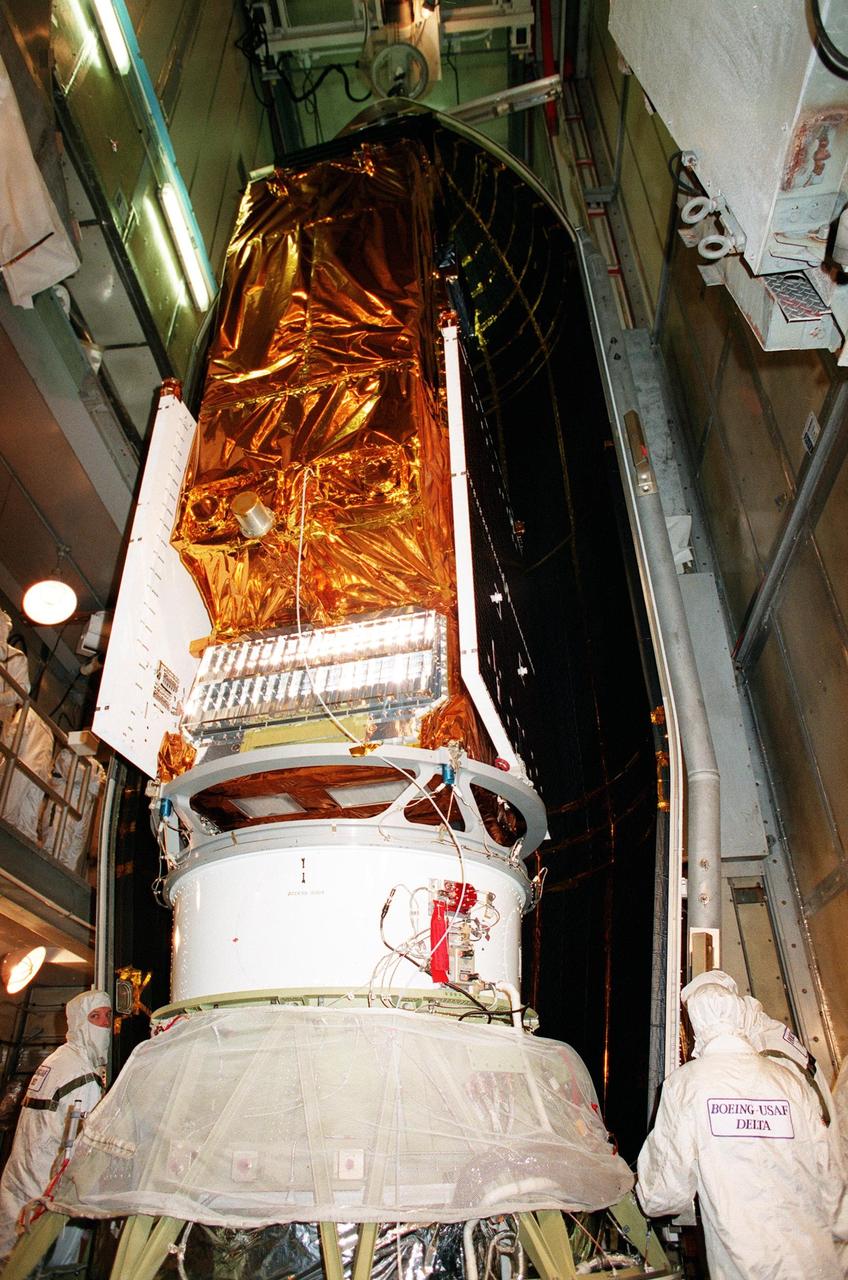

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite (foreground) is partially covered by half of the fairing (behind it) that will protect it during launch. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study those elements to unlock the secrets of how galaxies evolve and to discover what the Universe was like when it was only a few minutes old

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
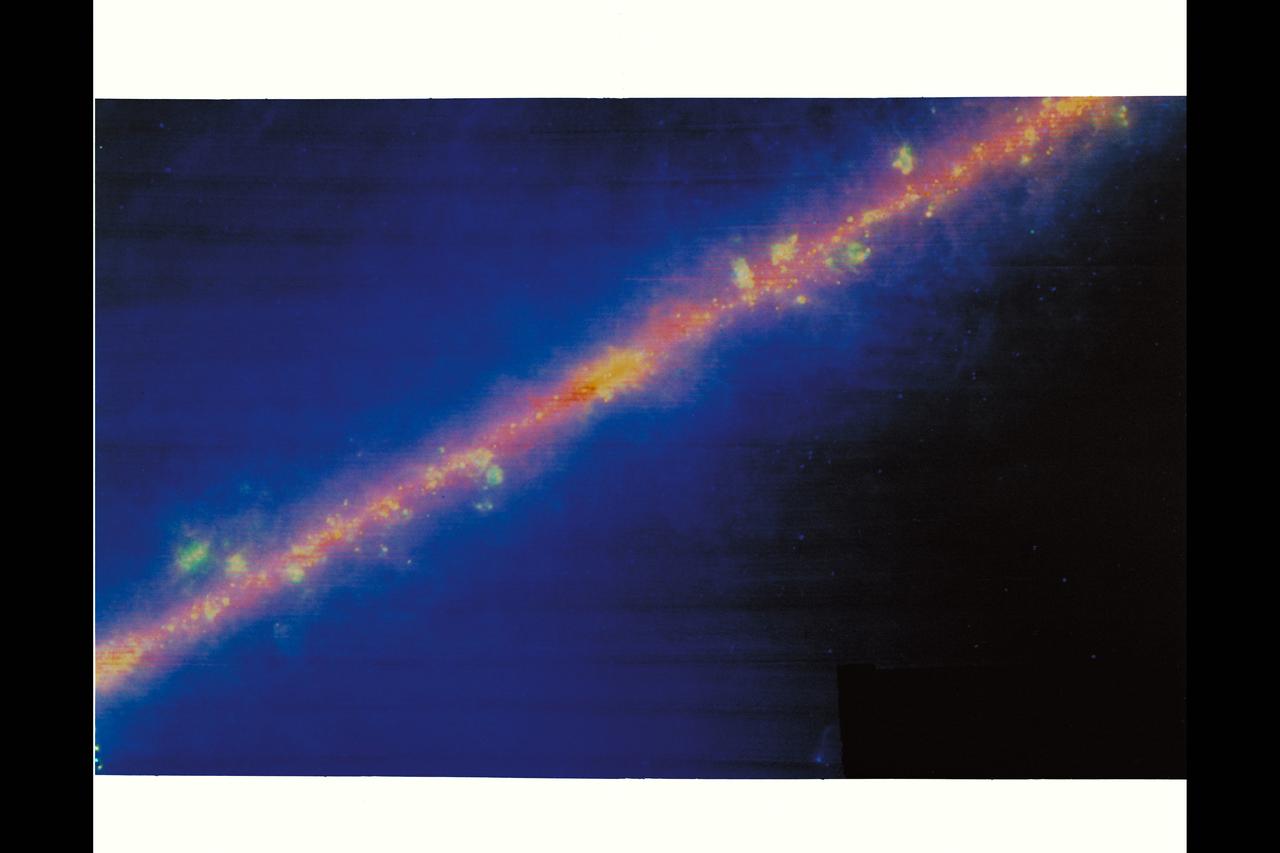

Milky way - The real shape of our galaxy is revealed in this infrared image obtained by IRAS. Infrared light penetrates the dust clouds and shows that the galaxy appears as a thin disk, just like the edge-on spiral galaxies we see throughtout the cosmos. The bulge in the band is the center of the galaxy. The yellow and green knots and blobs scattered along the band are giant clouds of interstellar gas and dust heated by nearby stars.

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers remarks prior to the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
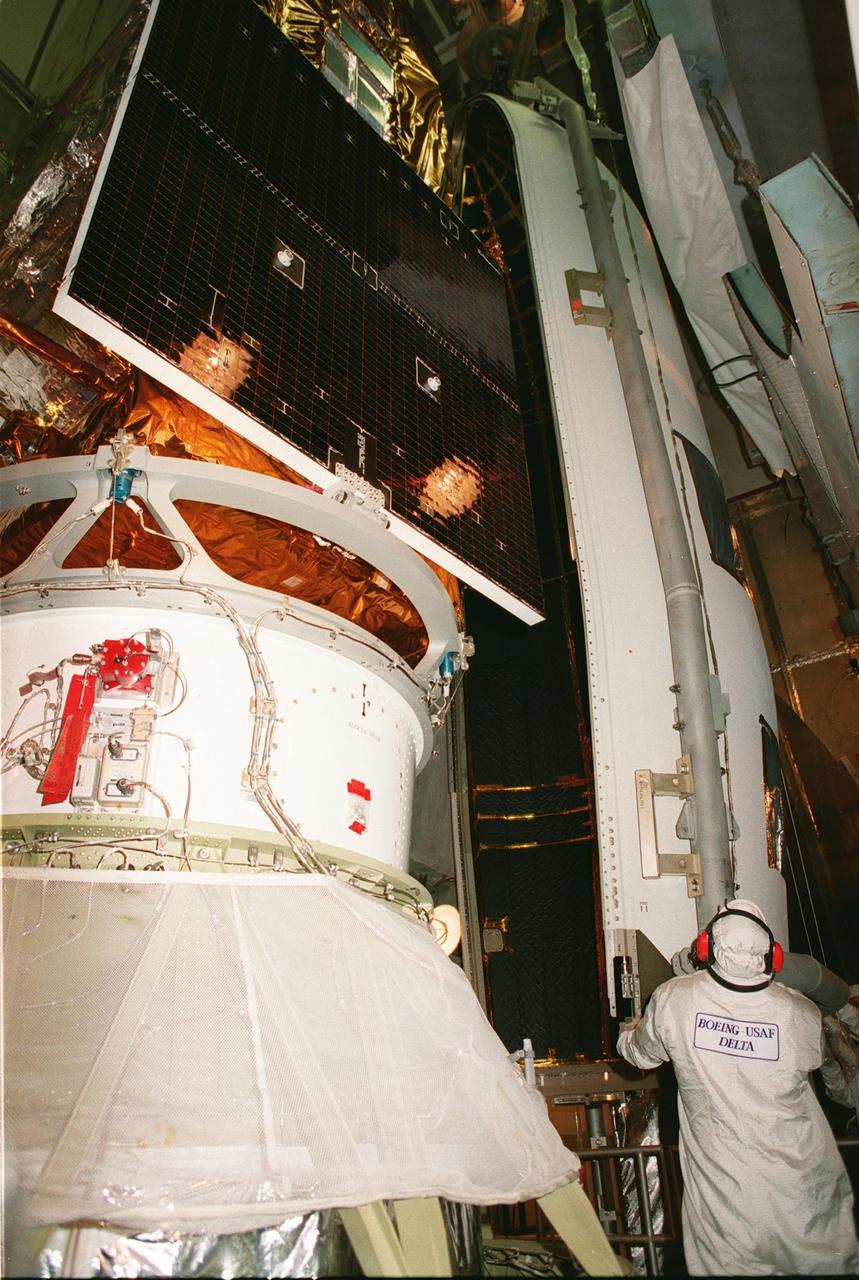

Workers in the launch tower at Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, help guide the first segment of the fairing around NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study those elements to unlock the secrets of how galaxies evolve and to discover what the Universe was like when it was only a few minutes old
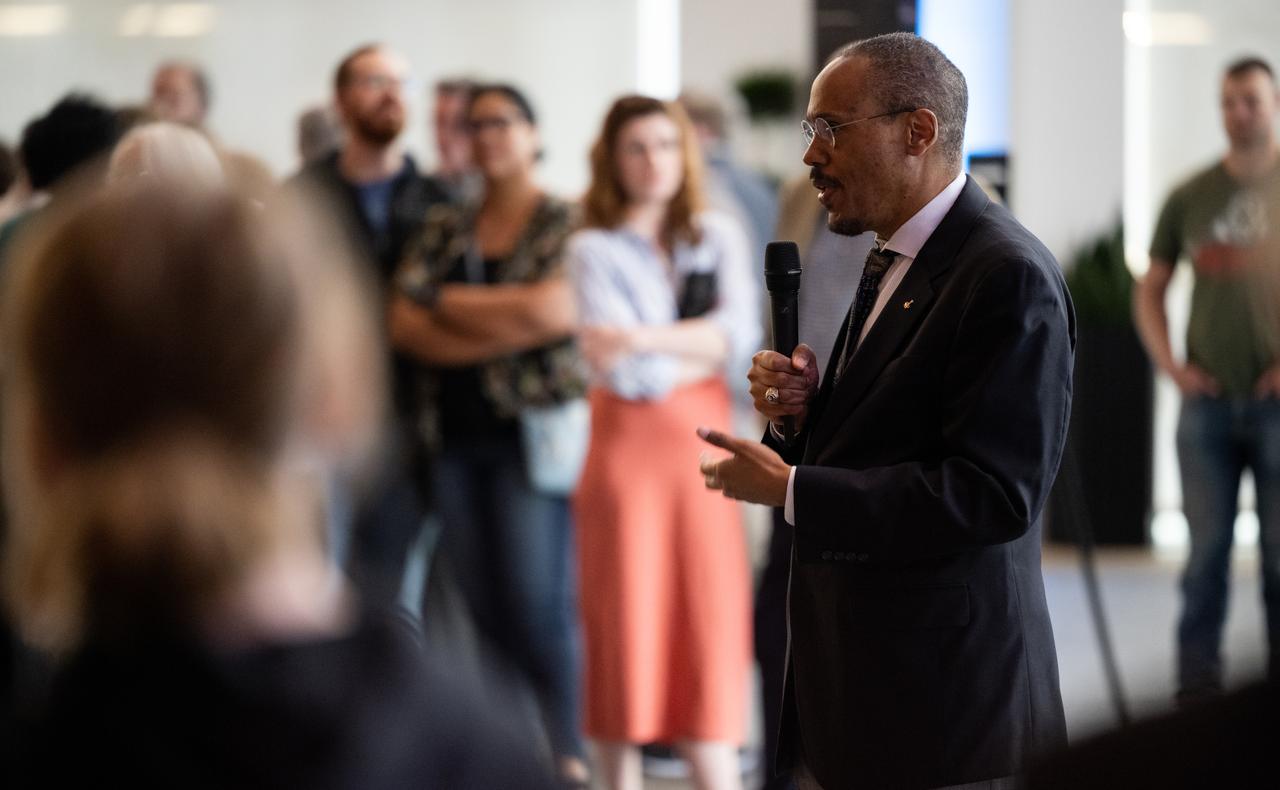

NASA astronaut Alvin Drew answers question prior to the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
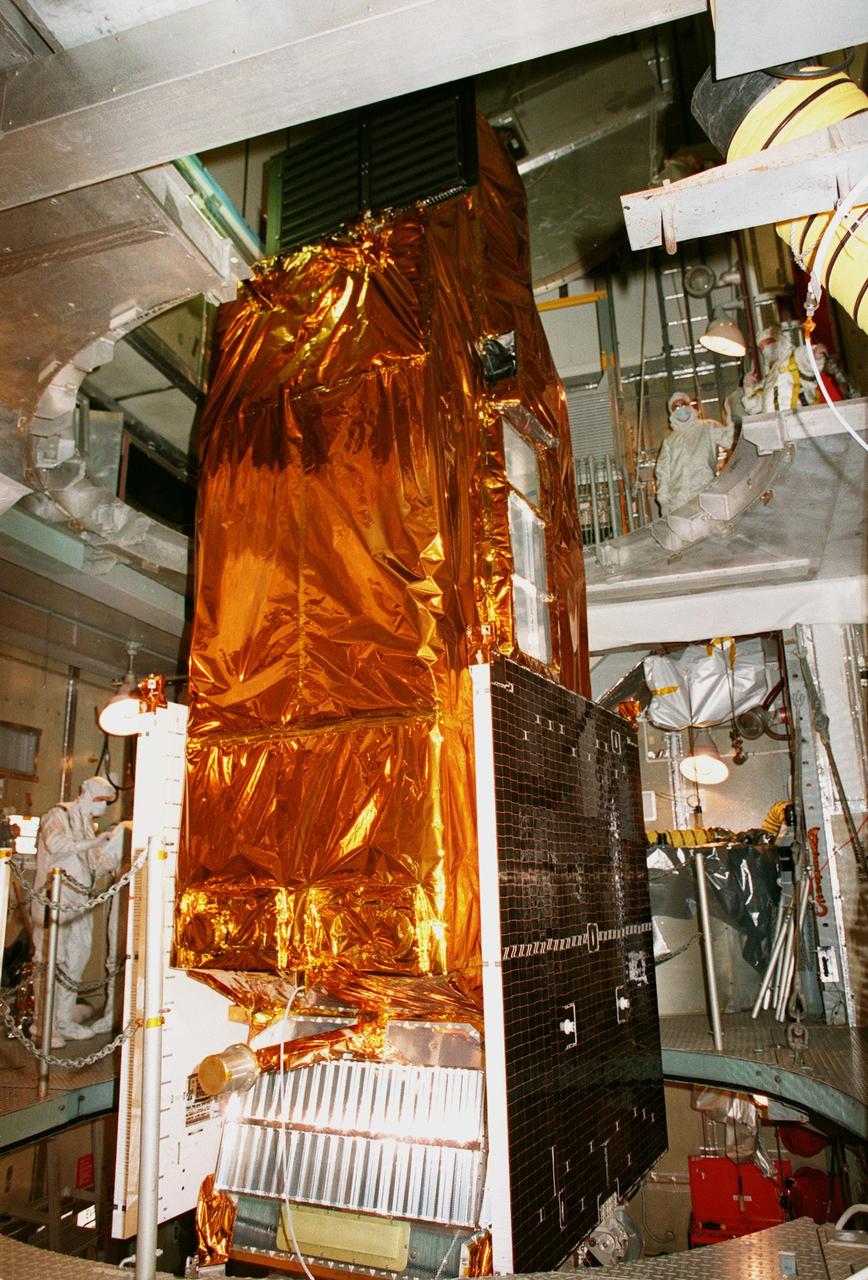

NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite sits ready for the fairing installation at Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
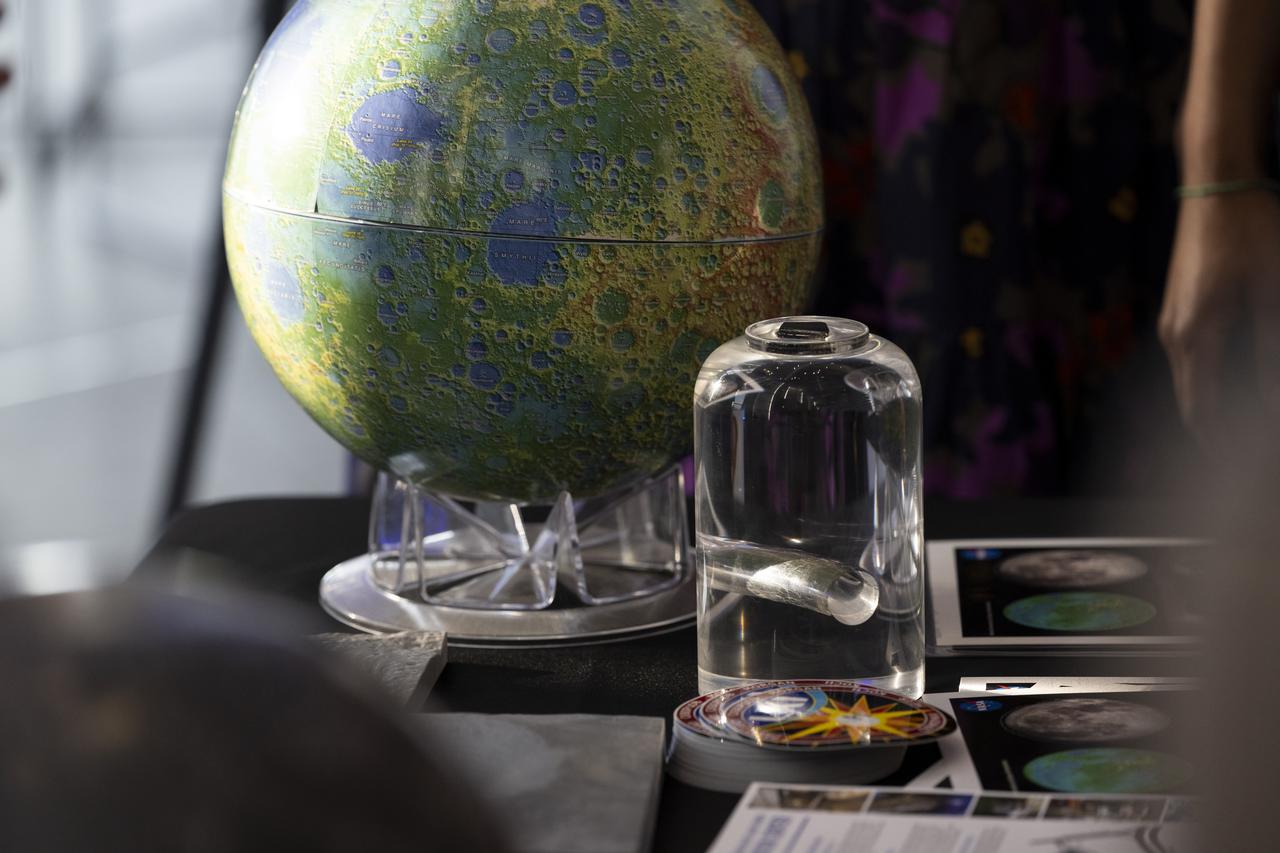

Attendees of the National Philharmonic performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles” view a Moon rock, Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
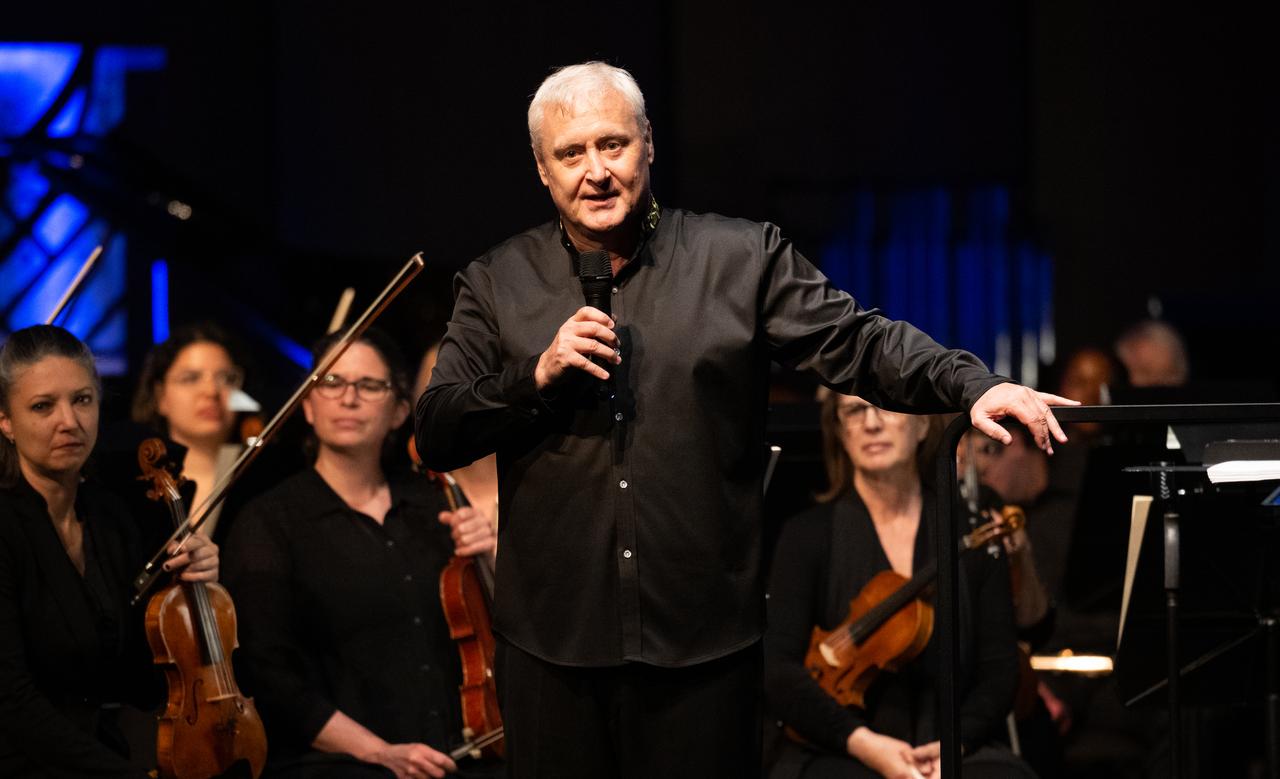

Maestro Piotr Gajewski speaks after conducting the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Maestro Piotr Gajewski conducts the National Philharmonic in the world premier performance of Henry Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
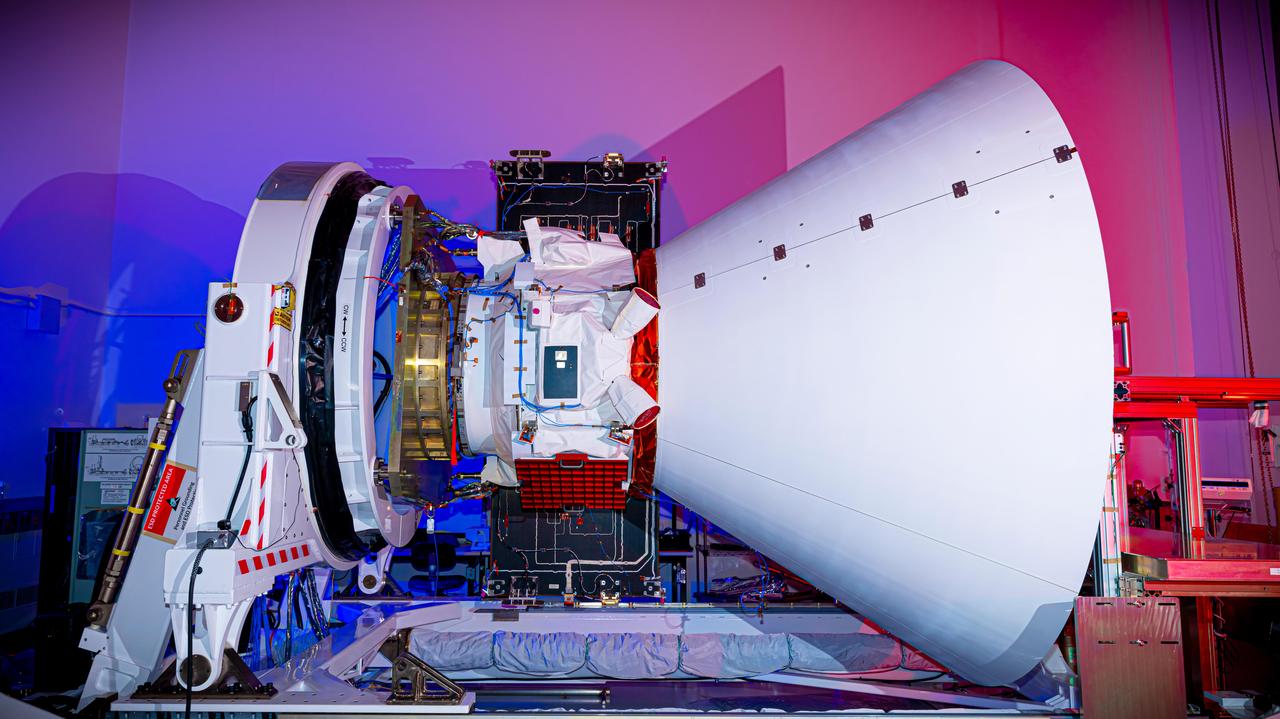
The SPHEREx observatory sits in a clean room after environmental testing at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in late 2024. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26537
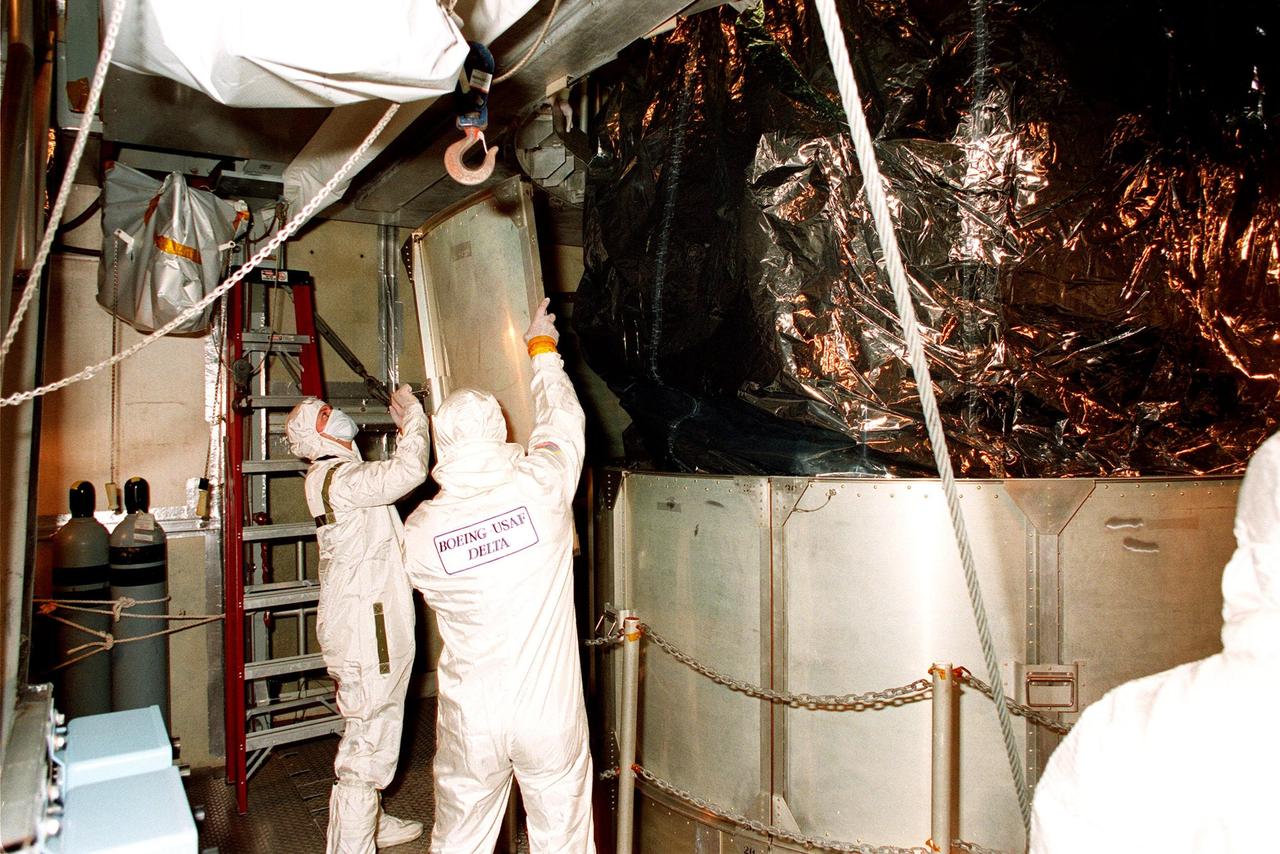

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), workers begin removing the lower sections of the canister surrounding NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe. FUSE is scheduled to be launched from CCAS June 23 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket

NASA's SPHEREx observatory is oriented in a horizontal position, revealing all three layers of photon shields as well as the telescope. This photo was taken at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in April 2024. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26542
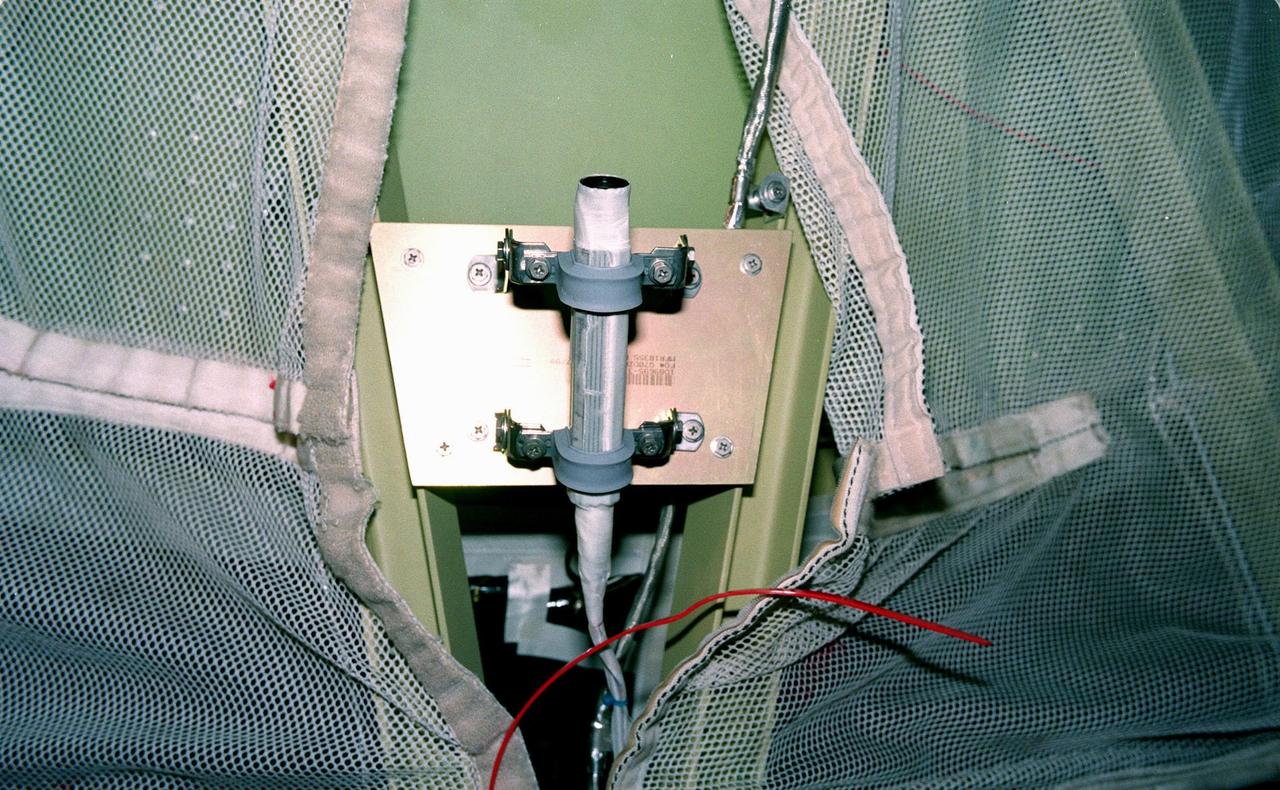
A camera is shown mounted on the second stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket scheduled to launch NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite June 24 from Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. The camera will record the separation of the fairing encircling the satellite, which should occur several minutes after launch. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe
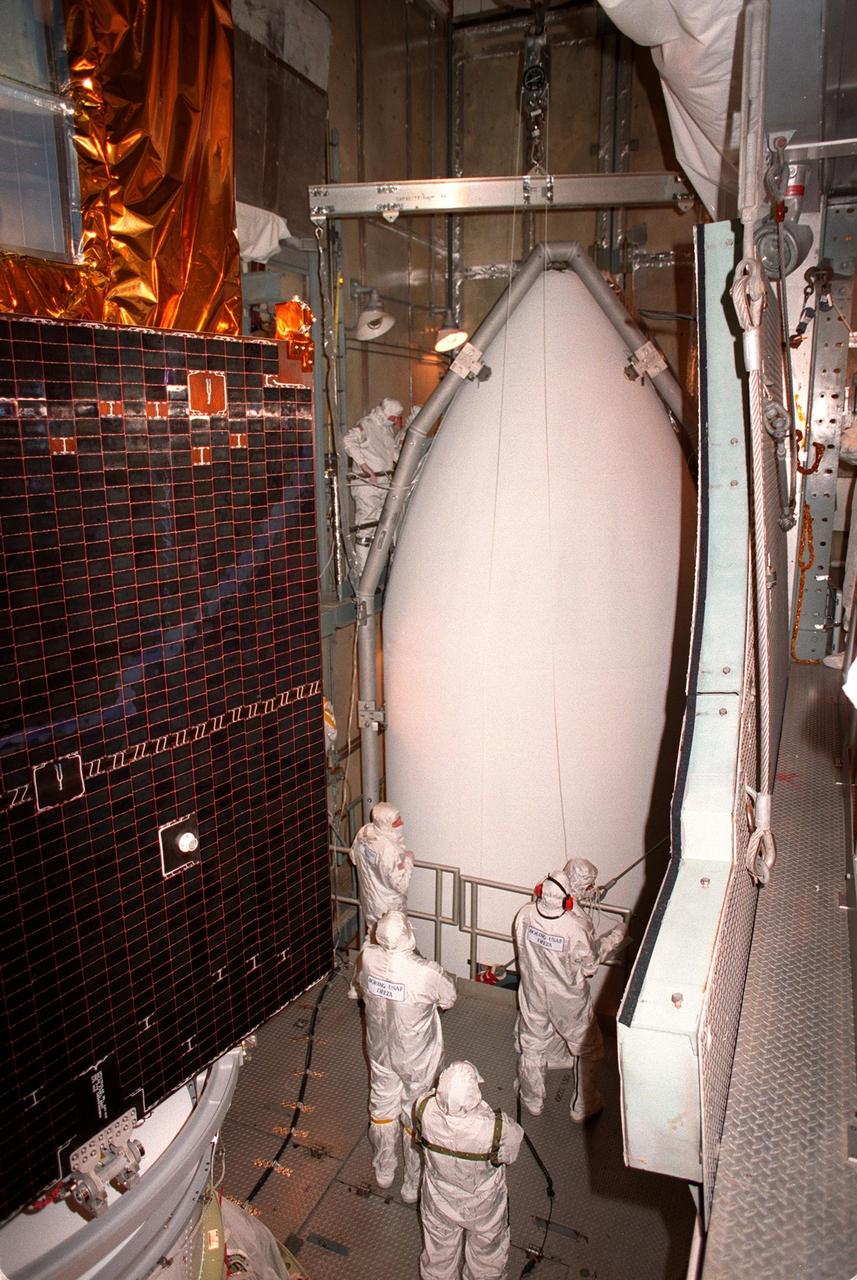

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers oversee the lifting of the fairing (right) into the tower. At left is NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite around which the fairing will be fitted. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe
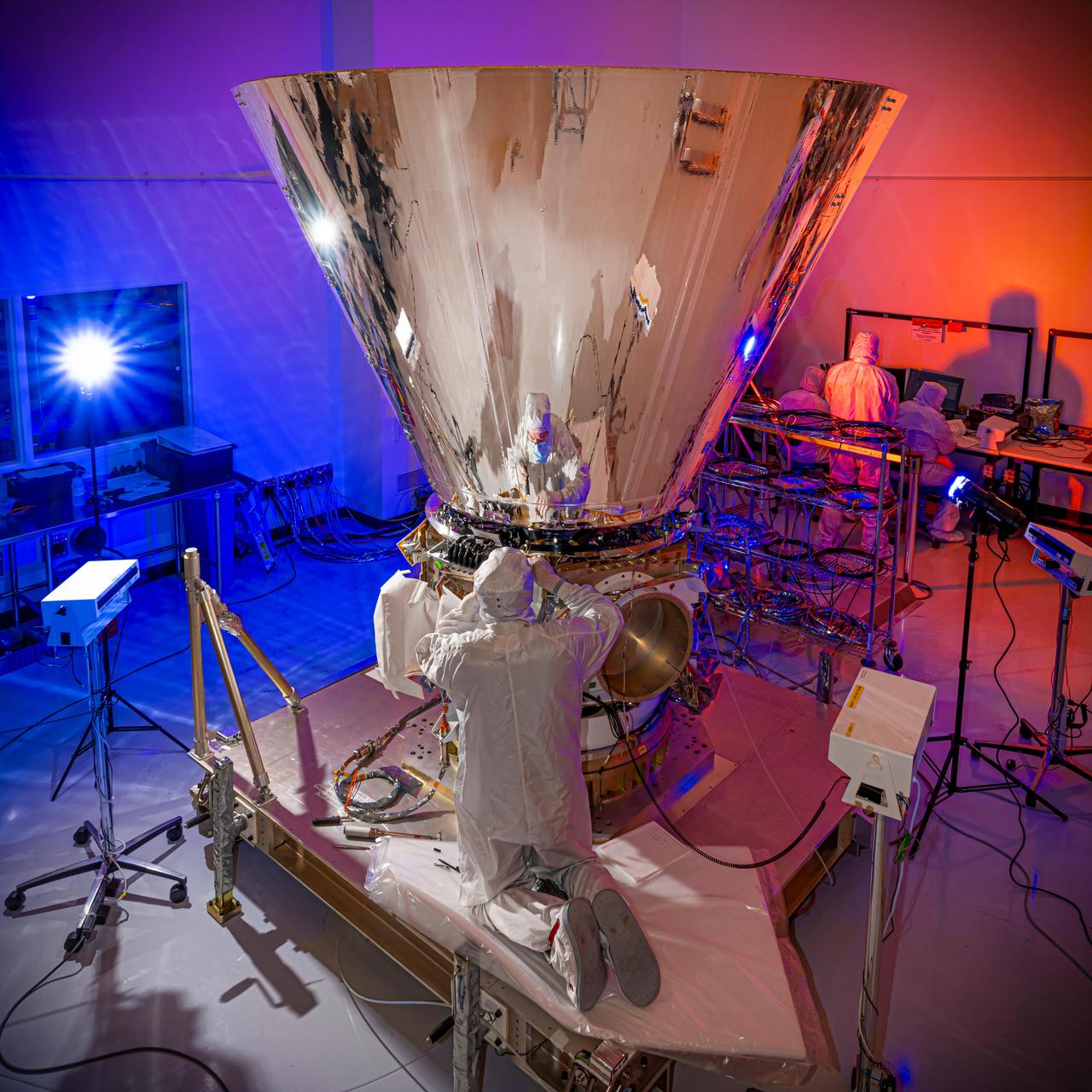

Final assembly of NASA's SPHEREx spacecraft is shown at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in March 2024. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26543
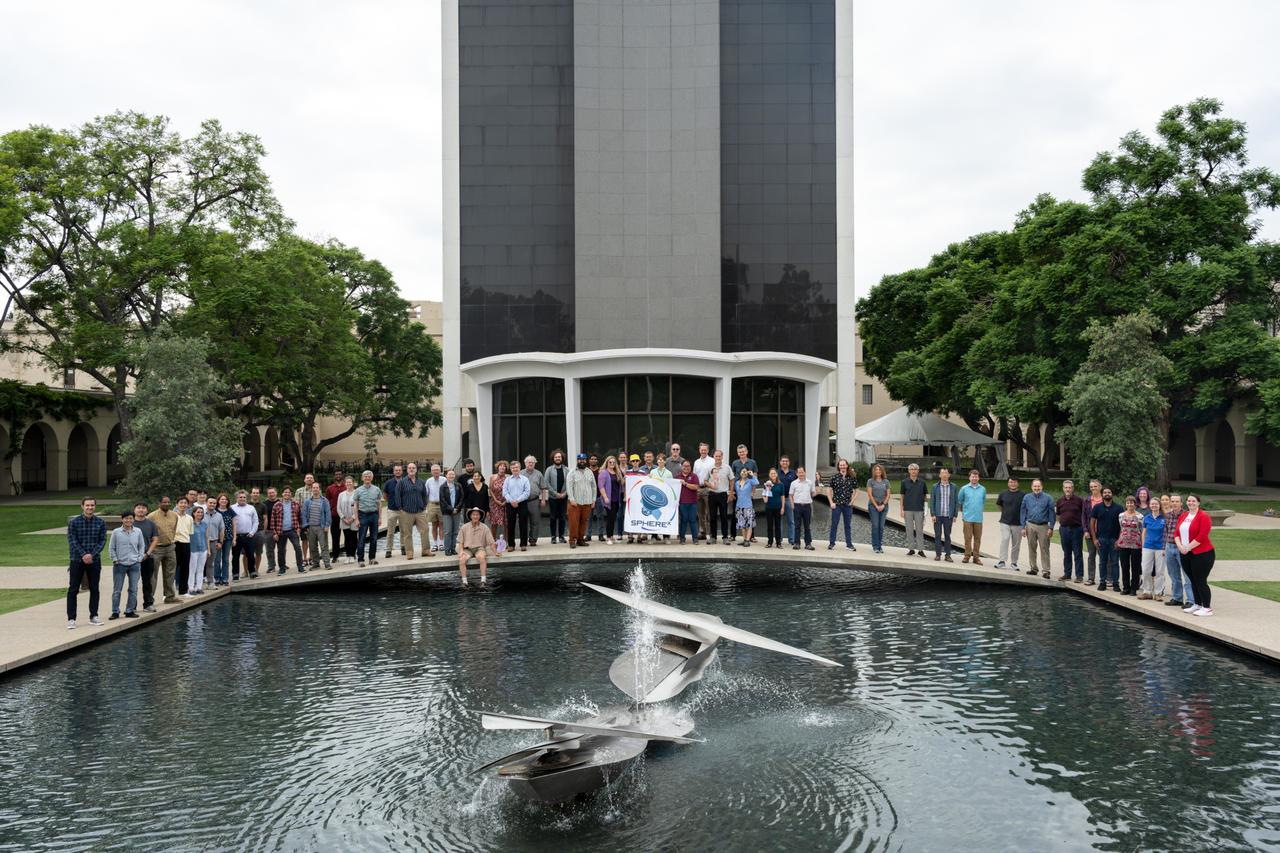

Members of the SPHEREx mission team pose for a photo on the campus of Caltech in Pasadena, California, in October 2023. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26534
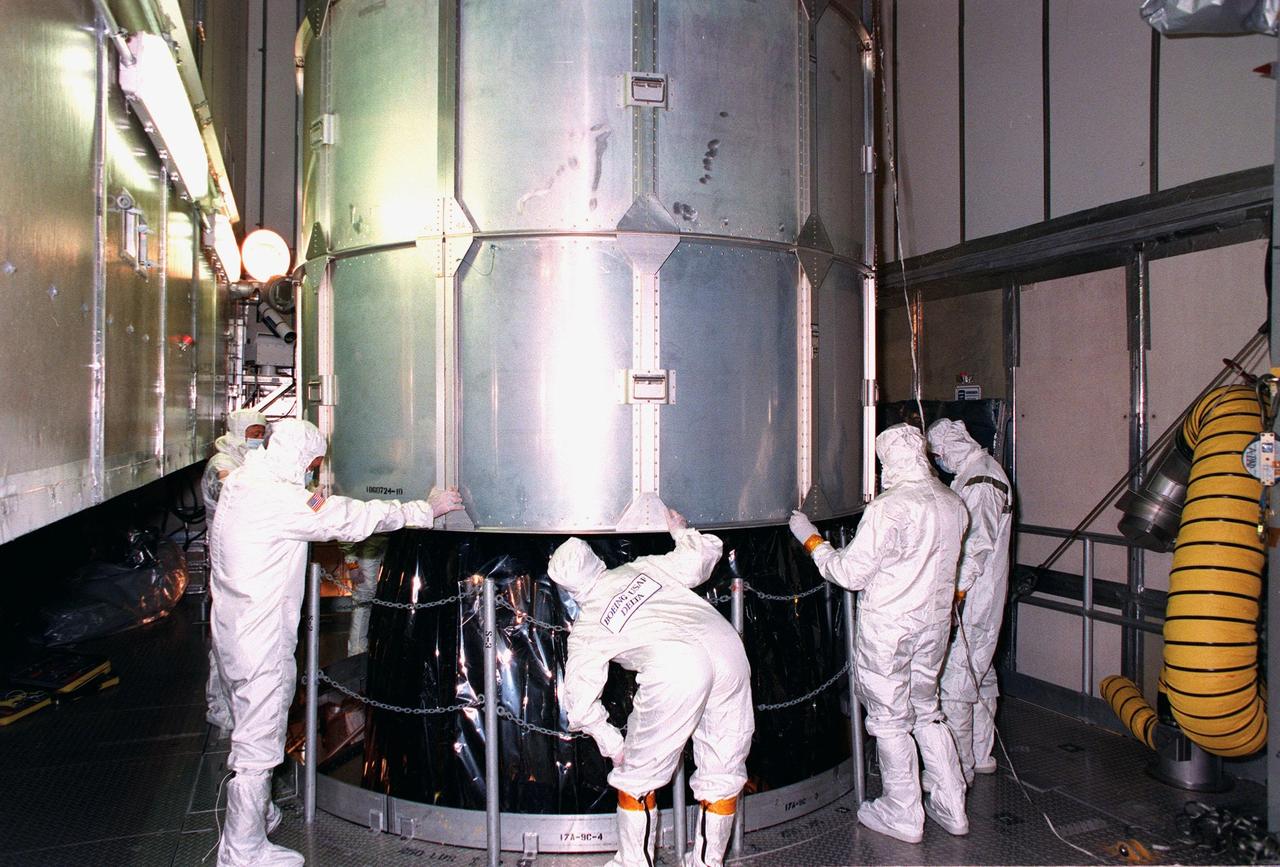

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), workers begin to remove the canister around the top of the NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe. FUSE is scheduled to be launched from CCAS June 23 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket
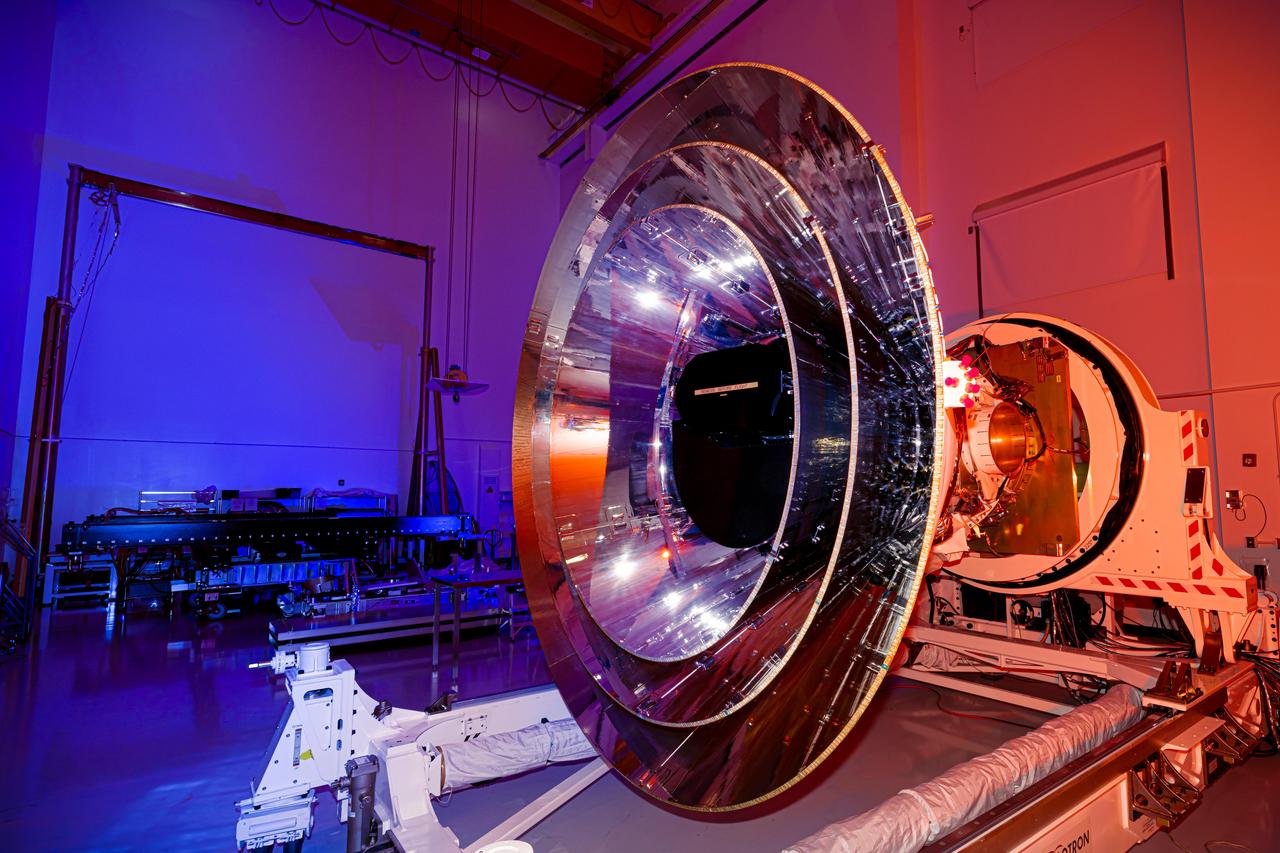
NASA's SPHEREx observatory undergoes integration and testing at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in April 2024. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26538
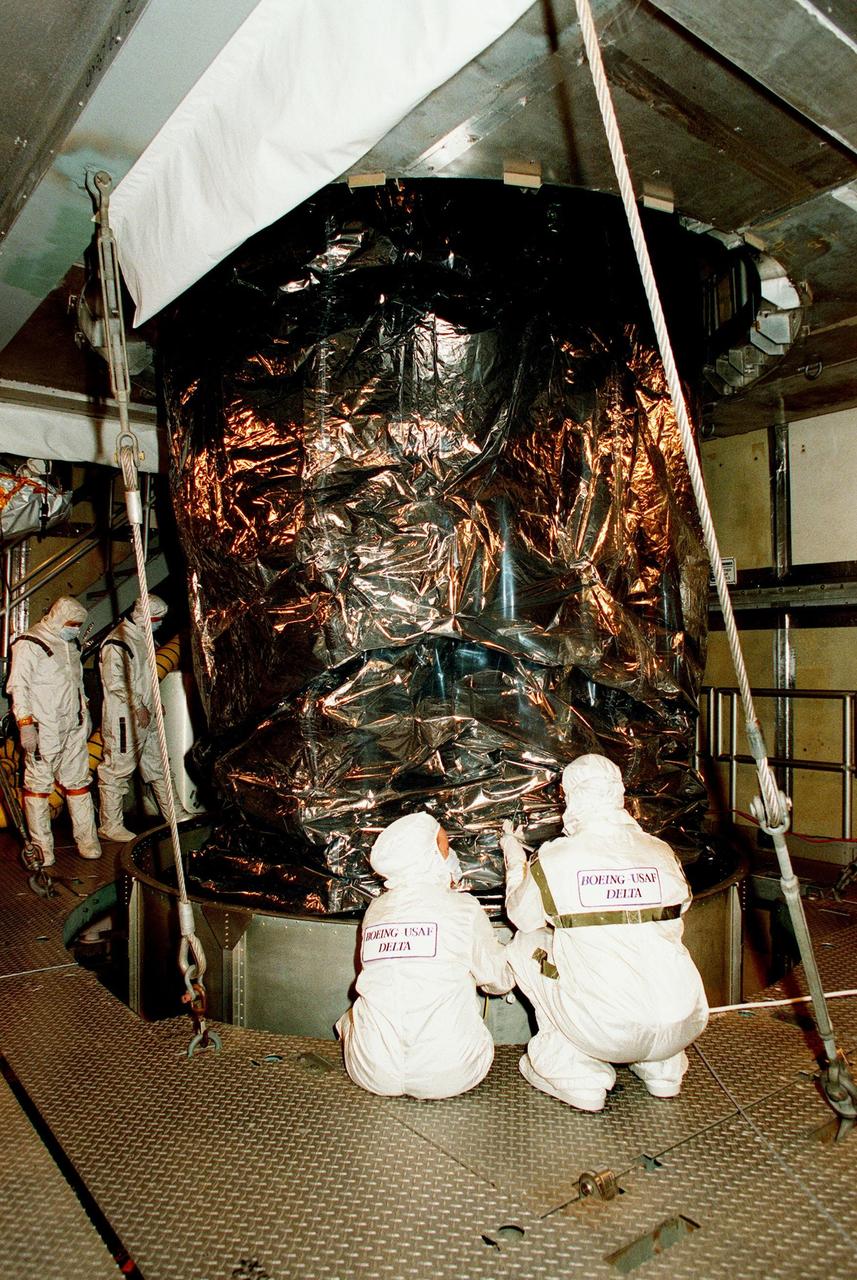

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), workers look over NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite after sections of the canister have been removed. FUSE is scheduled to be launched from CCAS June 23 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe
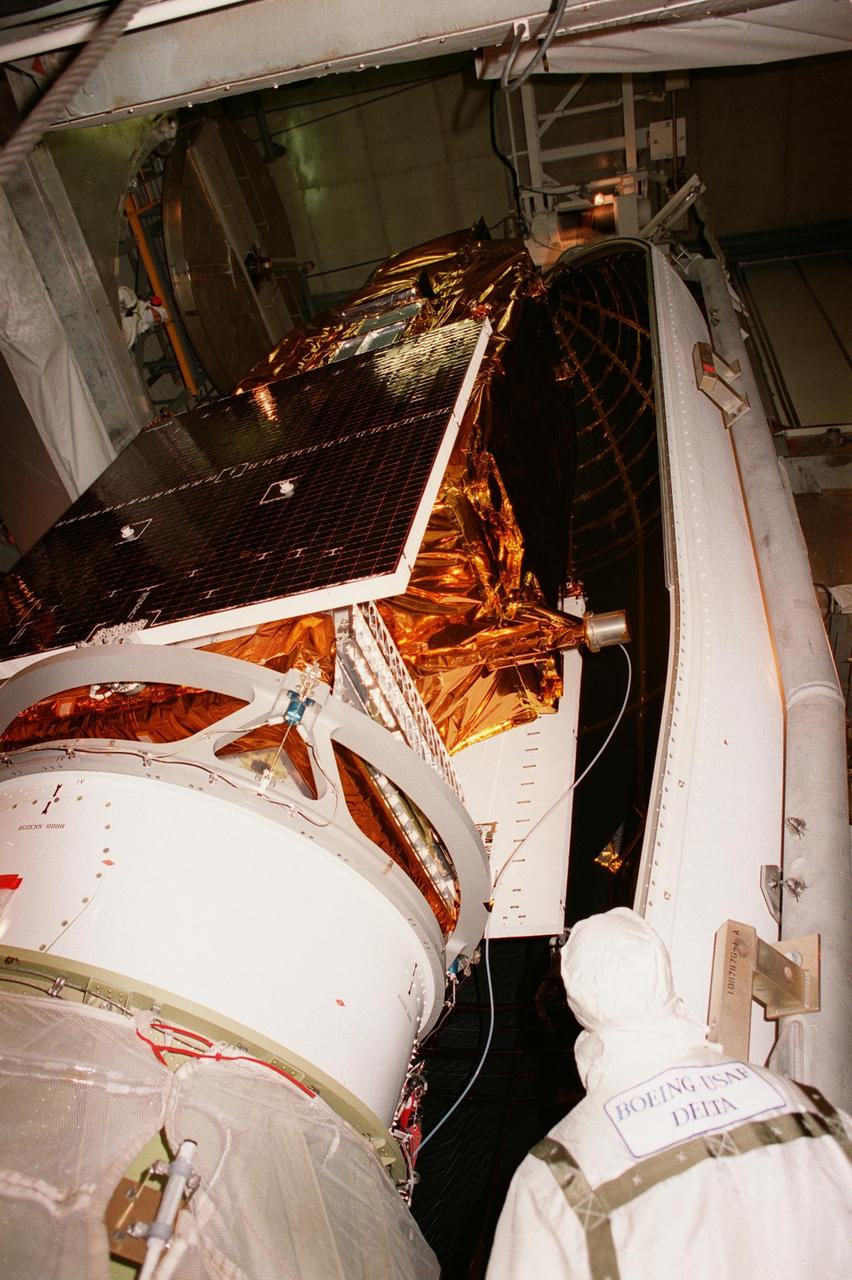

A worker in the launch tower at Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, watches as the first segment of the fairing is maneuvered around NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. At the lower left in the photo can be seen a camera installed on the second stage of the rocket to record the separation of the fairing several minutes after launch. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study those elements to unlock the secrets of how galaxies evolve and to discover what the Universe was like when it was only a few minutes old
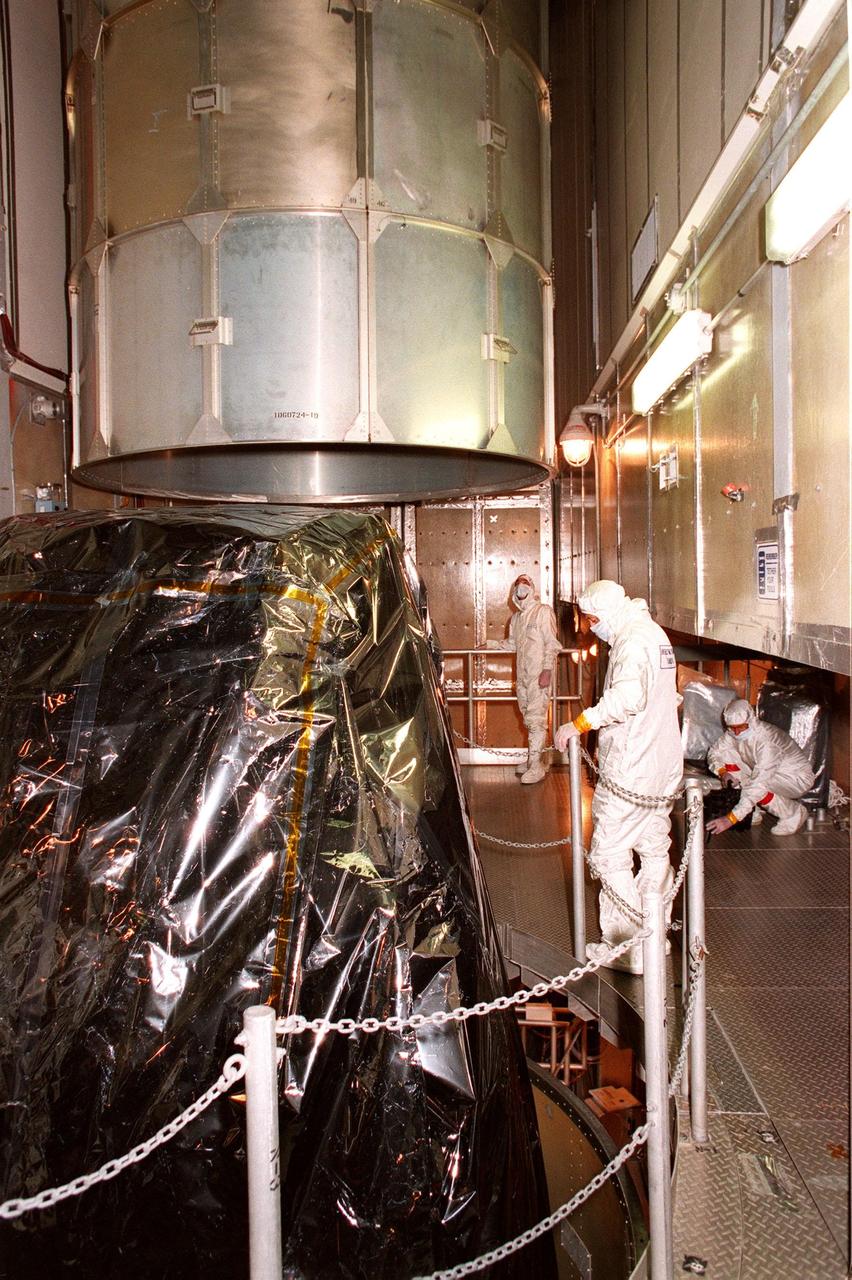

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), workers oversee the removal of the canister from the top of NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe. FUSE is scheduled to be launched from CCAS June 23 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket
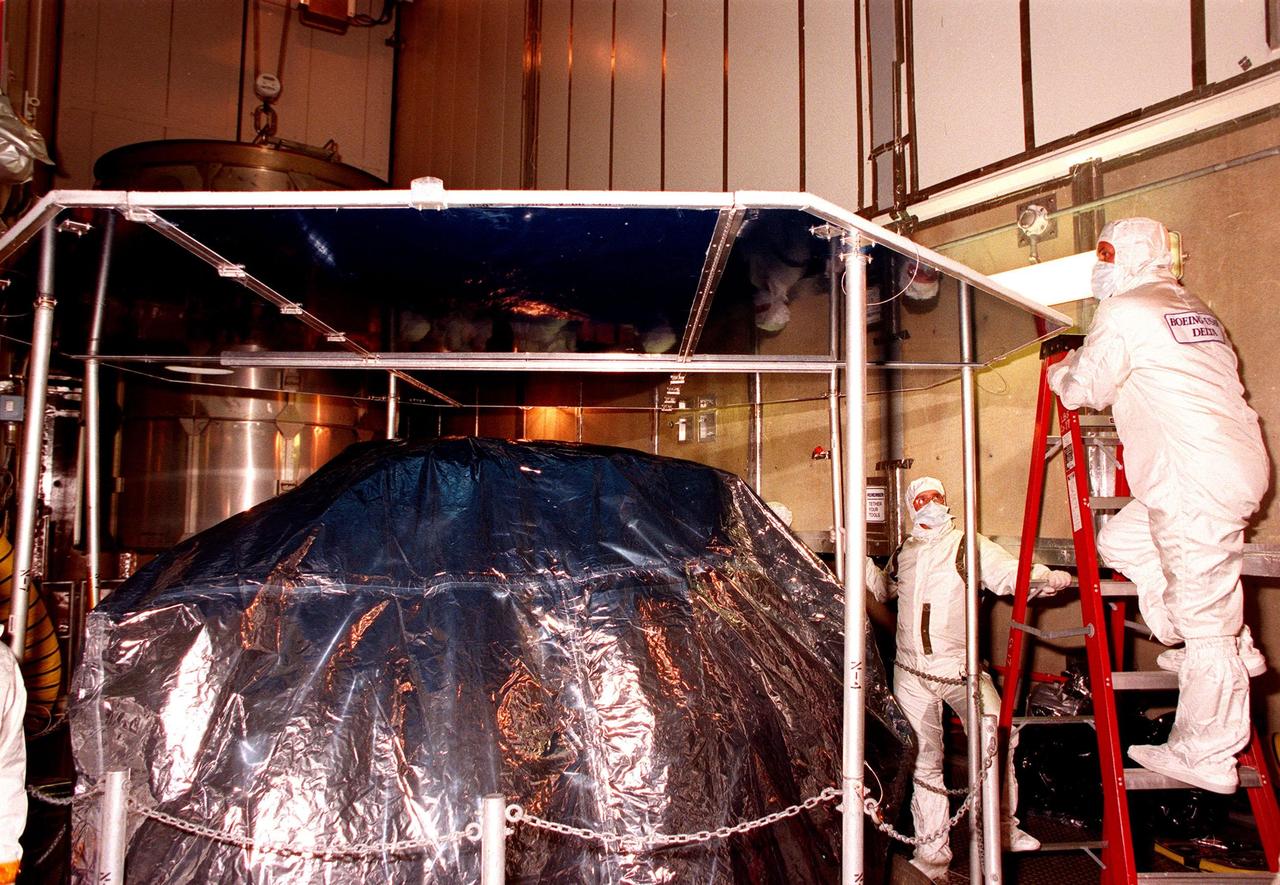

At Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), workers check out the protective cover placed over the top of NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. The satellite is scheduled to be launched from CCAS June 23 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study hydrogen and deuterium to unlock the secrets of how the primordial chemical elements of which all stars, planets and life evolved, were created and distributed since the birth of the universe

The mission insignia for NASA's STS-31 mission features the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in its observing configuration against a background of the universe it will study. The cosmos includes a stylistic depiction of galaxies in recognition of the contribution made by Sir Edwin Hubble to our understanding of the nature of galaxies and the expansion of the universe. The STS-31 crew points out that is it in honor of Hubble's work that this great observatory in space bears his name. The depicted Space Shuttle trails a spectrum symbolic of both the red shift observations that were so important to Hubble's work and new information which will be obtained with the HST. Encircling the art work, designed by the crew, are the names of its members.

Workers in the launch tower at Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, help guide the first segment of the fairing around NASA's Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) satellite. The satellite is scheduled for launch June 24 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. At the lower left can be seen a camera installed on the second stage of the rocket to record the separation of the fairing several minutes after launch. FUSE is designed to scour the cosmos for the fossil record of the origins of the universe hydrogen and deuterium. Scientists will use FUSE to study those elements to unlock the secrets of how galaxies evolve and to discover what the Universe was like when it was only a few minutes old
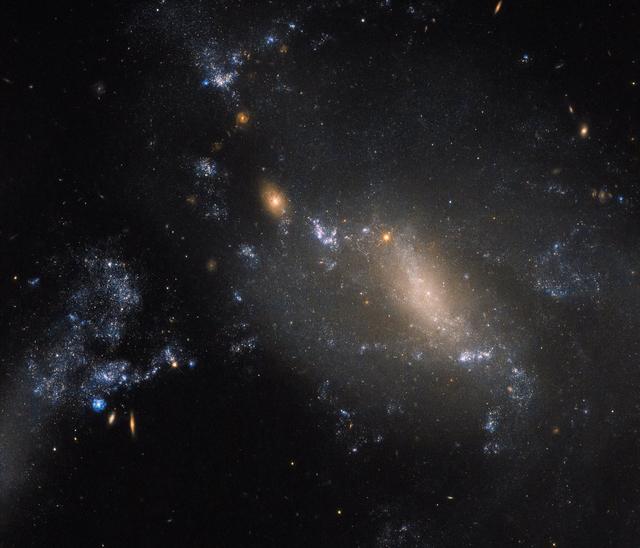

Two galaxies in a cosmic dance defy conventions. 60 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo, the more diffuse and patchy blue glow covering the right side of the frame is known as NGC 3447B, while the smaller clump to the upper left is NGC 3447A. Known together as NGC 3447, we’re unsure what each looked like before they began to tear one another apart. So close that they are strongly influenced and distorted by the gravitational forces between them, the galaxies to twist themselves into the unusual and unique shapes seen here. NGC 3447A appears to display the remnants of a central bar structure and some disrupted spiral arms, both properties characteristic of certain spiral galaxies. Some identify NGC 3447B as a former spiral galaxy, while others categorize it as being an irregular galaxy. Credit: NASA/Hubble <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
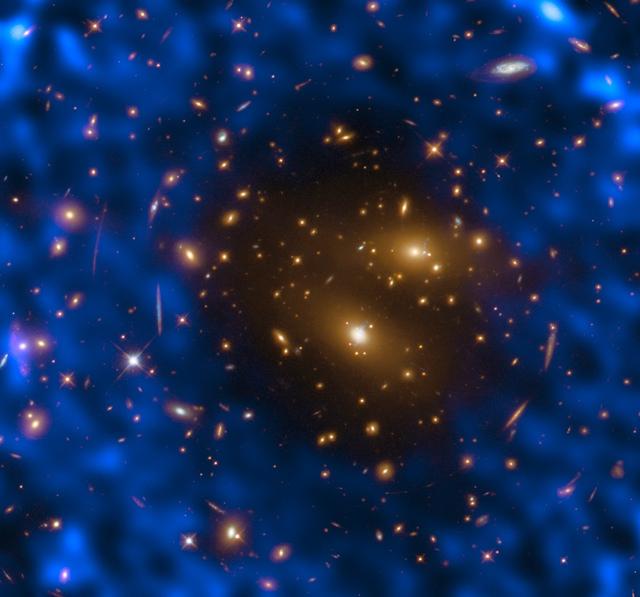

The events surrounding the Big Bang were so cataclysmic that they left an indelible imprint on the fabric of the cosmos. We can detect these scars today by observing the oldest light in the universe. As it was created nearly 14 billion years ago, this light — which exists now as weak microwave radiation and is thus named the cosmic microwave background (CMB) — permeates the entire cosmos, filling it with detectable photons. The CMB can be used to probe the cosmos via something known as the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich (SZ) effect, which was first observed over 30 years ago. We detect the CMB here on Earth when its constituent microwave photons travel to us through space. On their journey to us, they can pass through galaxy clusters that contain high-energy electrons. These electrons give the photons a tiny boost of energy. Detecting these boosted photons through our telescopes is challenging but important — they can help astronomers to understand some of the fundamental properties of the universe, such as the location and distribution of dense galaxy clusters. The NASA/ESA (European Space Agency) Hubble Space Telescope observed one of most massive known galaxy clusters, RX J1347.5–1145, seen in this Picture of the Week, as part of the Cluster Lensing And Supernova survey with Hubble (CLASH). This observation of the cluster, 5 billion light-years from Earth, helped the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile to study the cosmic microwave background using the thermal Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect. The observations made with ALMA are visible as the blue-purple hues. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, T. Kitayama (Toho University, Japan)/ESA/Hubble & NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
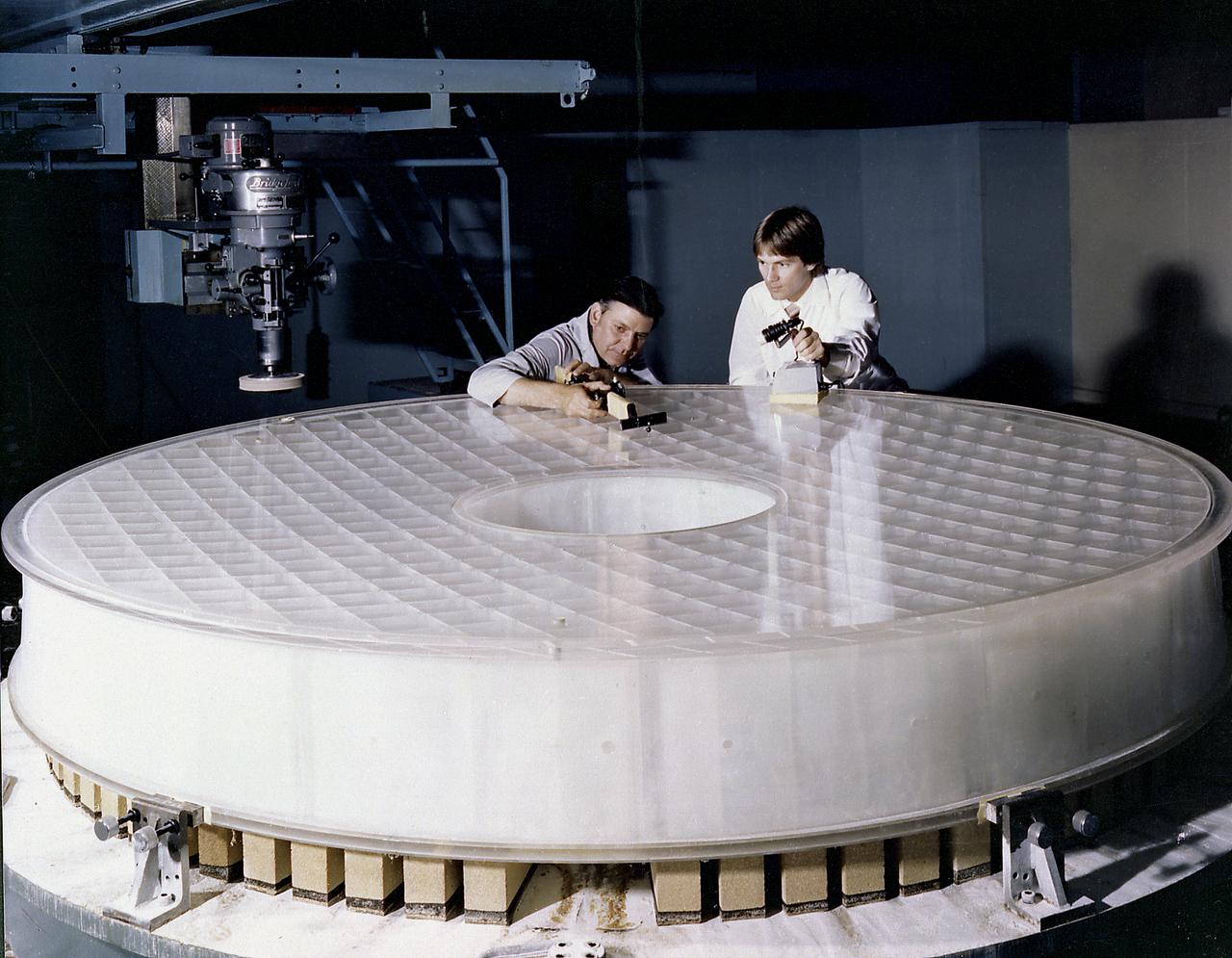

This photograph shows engineers inspecting the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Primary Mirror at the Perkin-Elmer Corporation's large optics fabrication facility. After the 8-foot diameter mirror was ground to shape and polished, the glass surface was coated with a reflective layer of aluminum and a protective layer of magnesium fluoride, 0.1- and 0.025- micrometers thick, respectively. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST and the Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
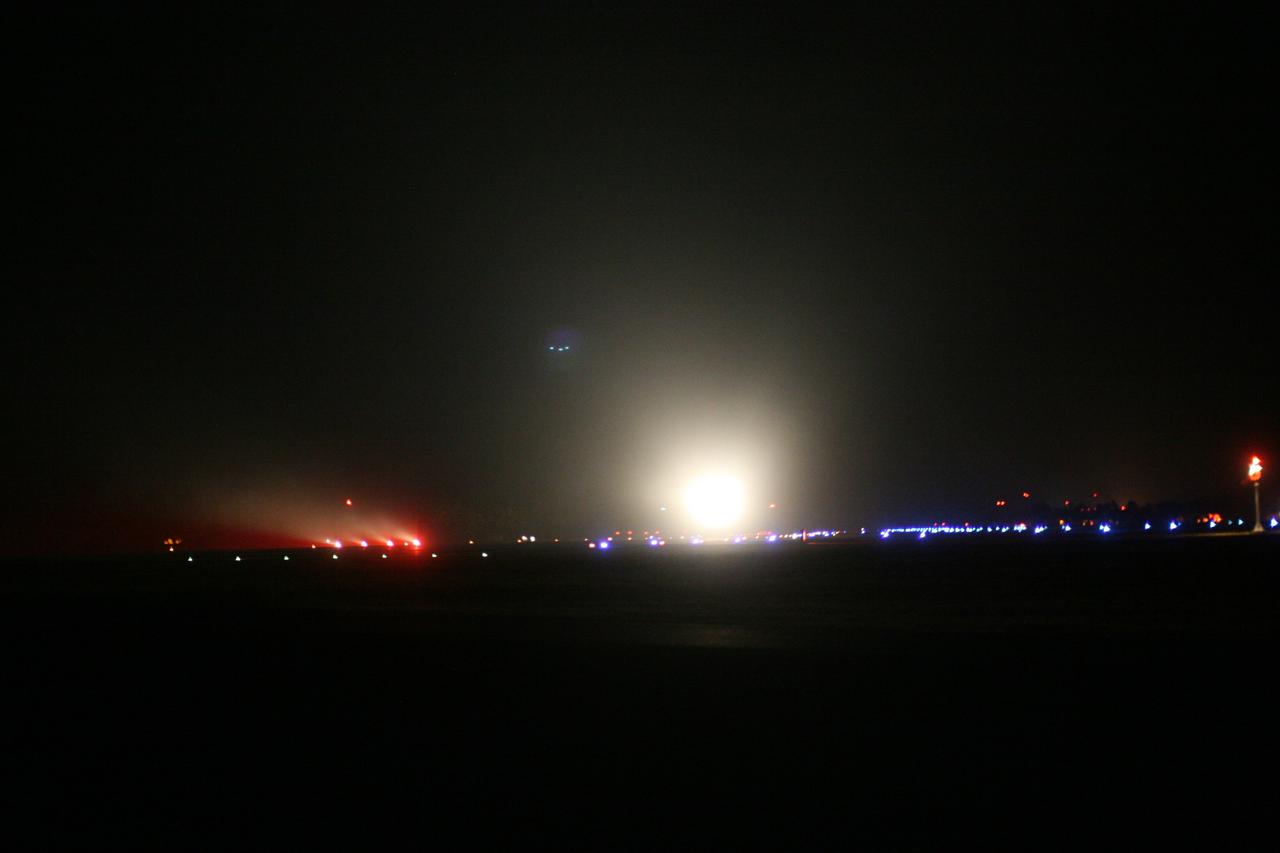

KWAJALEIN ATOLL, Marshall Islands - The lights of Orbital Sciences' L-1011 "Stargazer" aircraft illuminates the night sky as it takes off from the runway at Kwajalein Atoll with the company's Pegasus rocket to launch NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR. The plane left Kwajalein one hour before launch. At 9:00:35 a.m. PDT 12:00:35 p.m. EDT), June 13, 2012, the rocket dropped with the NuSTAR payload 117 nautical miles south of Kwajalein. NuSTAR will use a unique set of “eyes” to see the highest energy X-ray light from the cosmos to reveal black holes lurking in our Milky Way galaxy, as well as those hidden in the hearts of faraway galaxies. Kwajalein is located in the Marshall Islands chain in the Pacific Ocean and is part of the Reagan Test Site and used for launches of NASA, commercial and military missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA
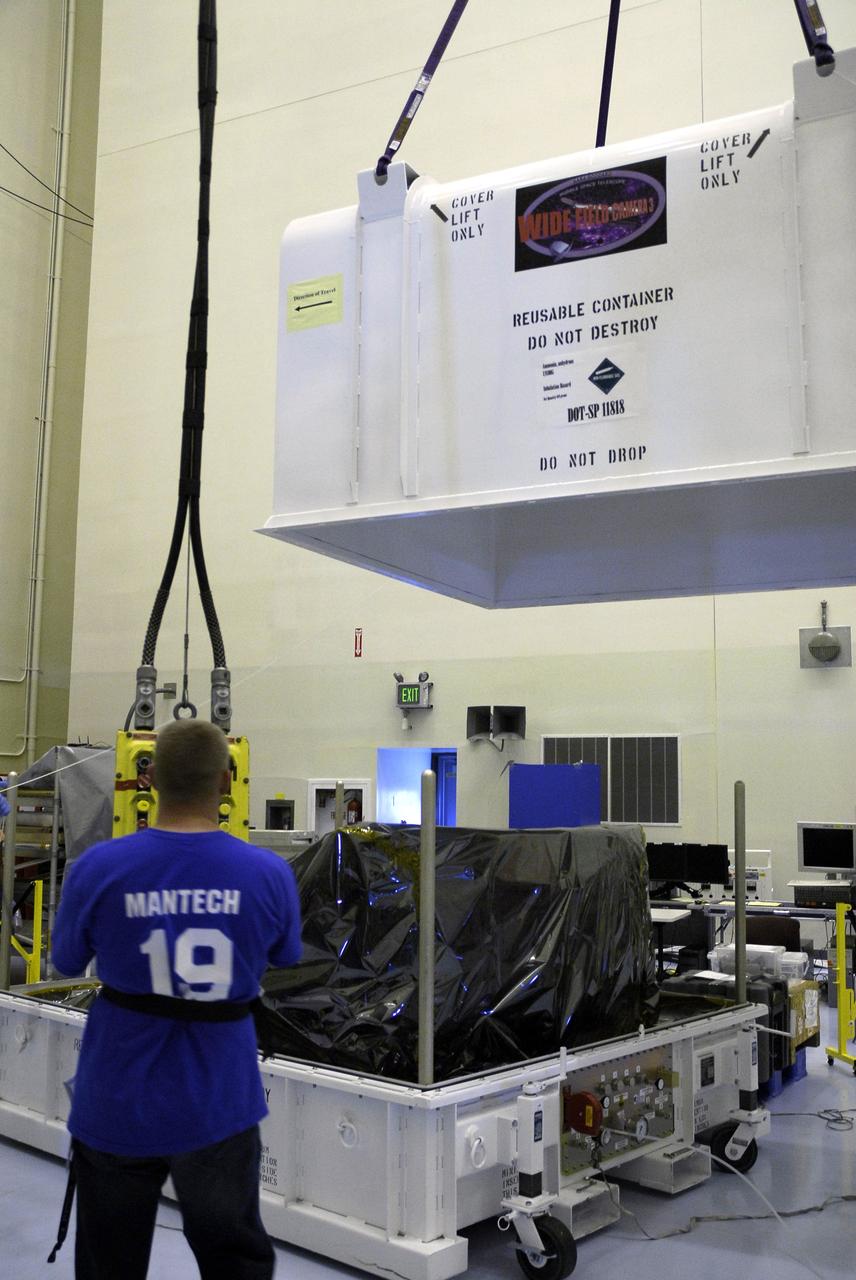

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, shipping container is lifted away from the mobile base. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is ready to be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
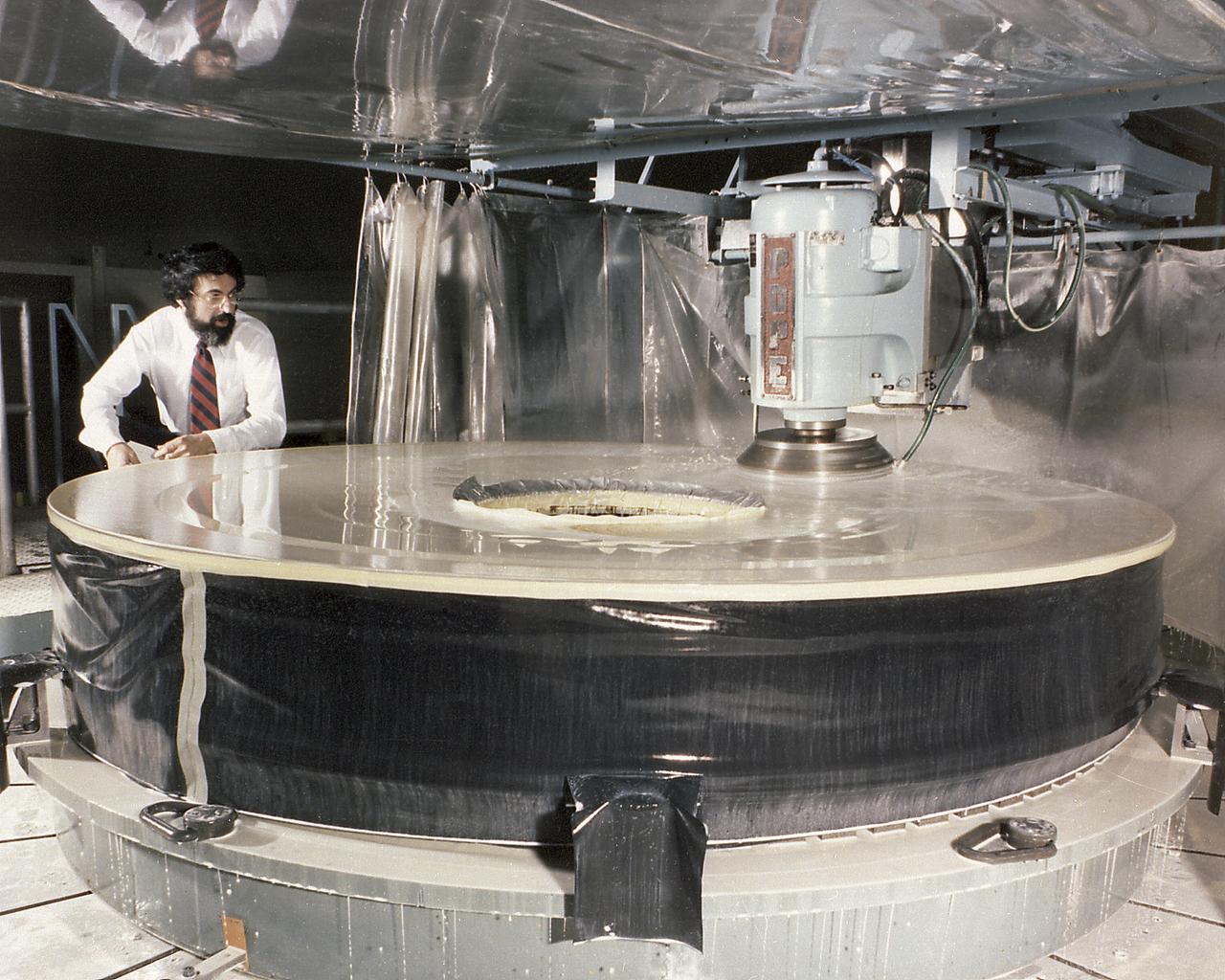

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Primary Mirror being ground at the Perkin-Elmer Corporation's large optics fabrication facility. After the 8-foot diameter mirror was ground to shape and polished, the glass surface was coated with a reflective layer of aluminum and a protective layer of magnesium fluoride, 0.1- and 0.025-micrometers thick, respectively. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST and the Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
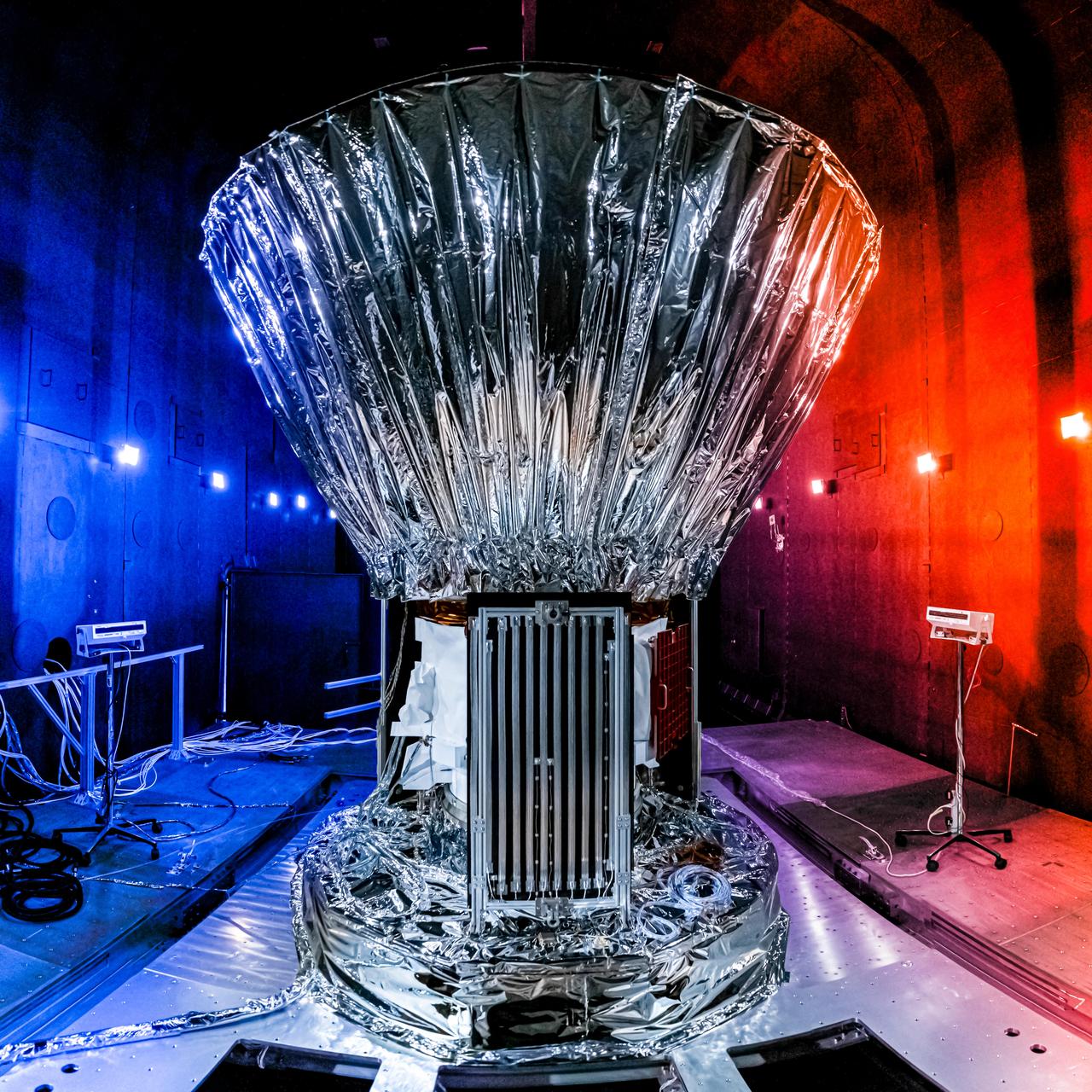

NASA's SPHEREx observatory is installed in the Titan Thermal Vacuum (TVAC) test Chamber at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in June 2024. As part of the test setup, the spacecraft and photon shield are covered in multilayer insulation and blankets and surrounded by ground support equipment. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26541
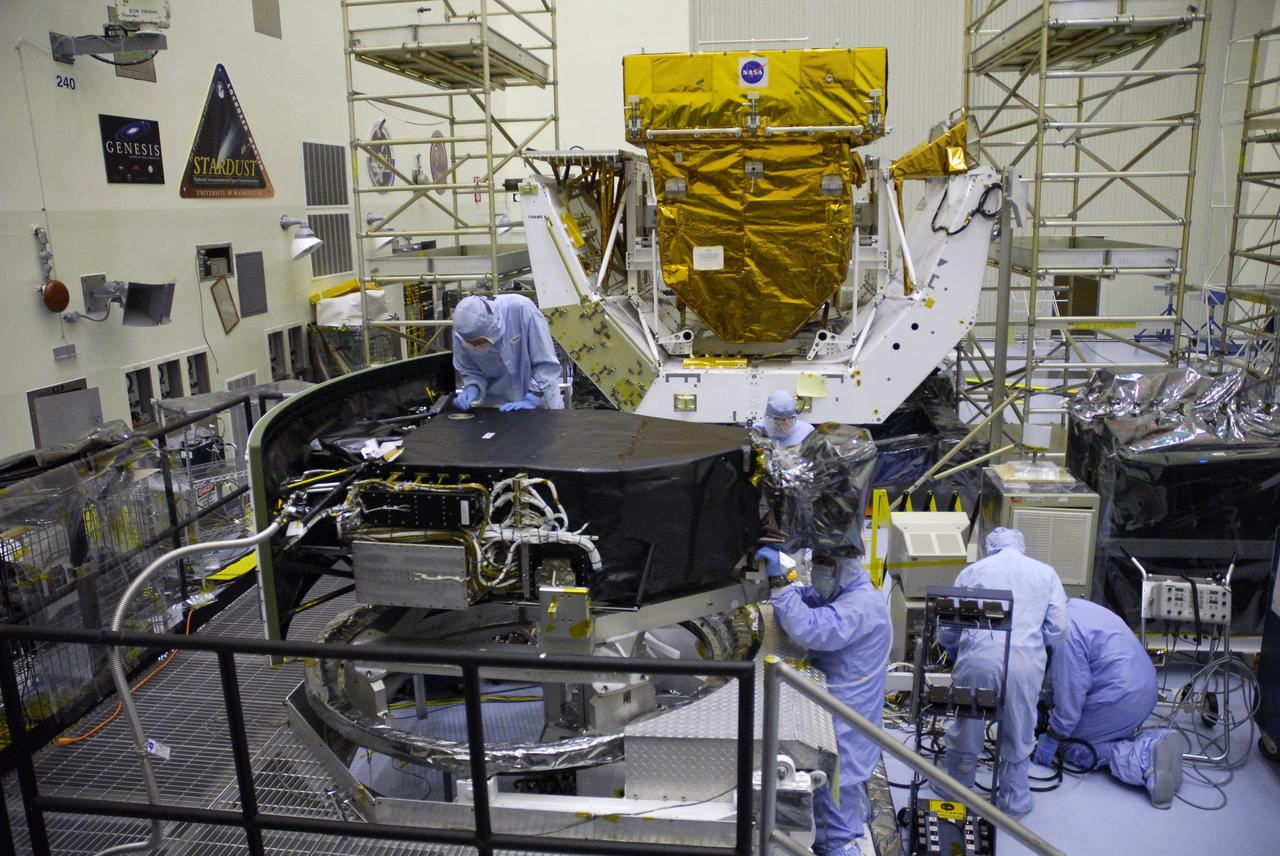

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility complete removal of the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
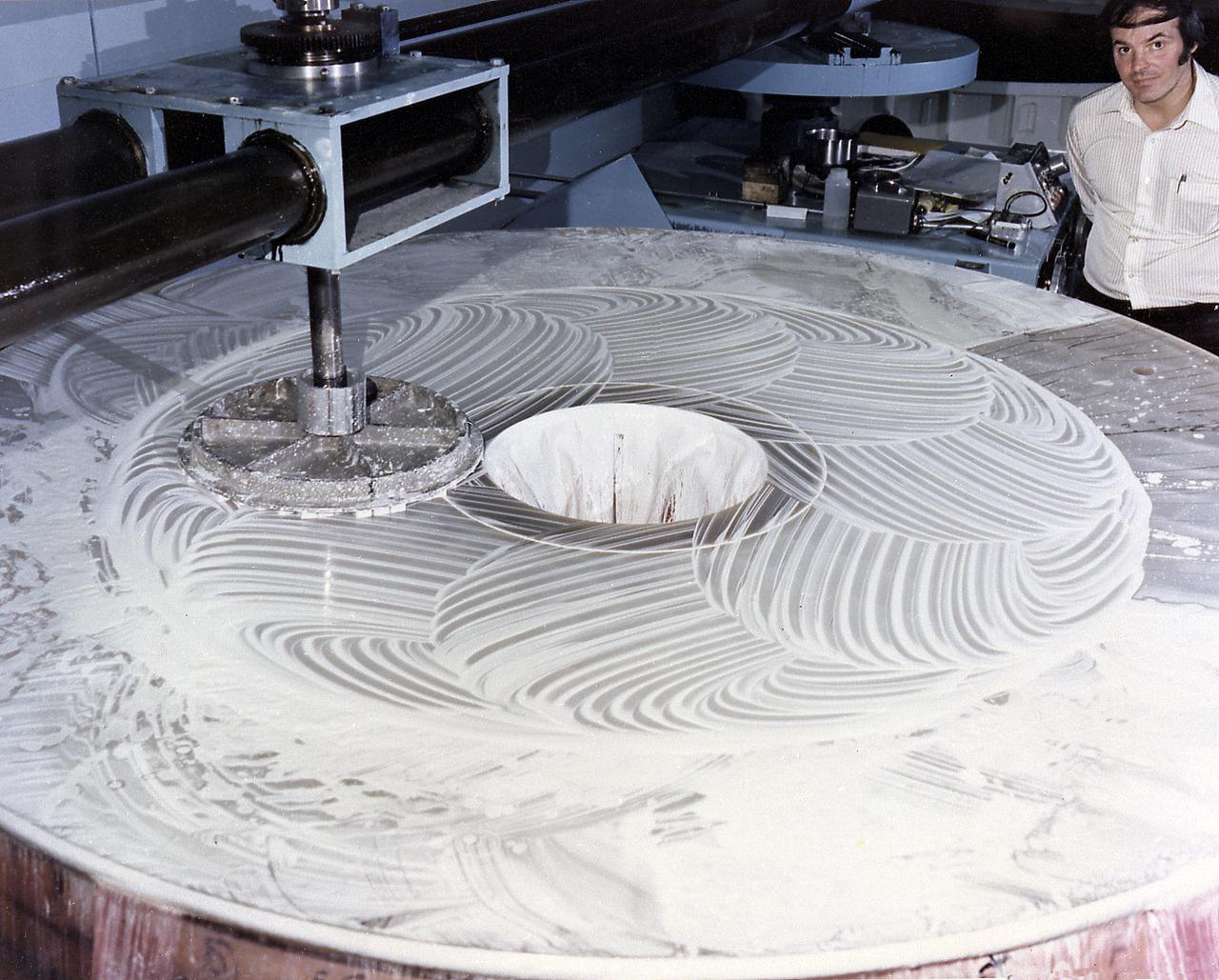

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Primary Mirror being polished at the the Perkin-Elmer Corporation's large optics fabrication facility. After the 8-foot diameter mirror was ground to shape and polished, the glass surface was coated with a reflective layer of aluminum and a protective layer of magnesium fluoride, 0.1- and 0.025-micrometers thick, respectively. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST and the Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
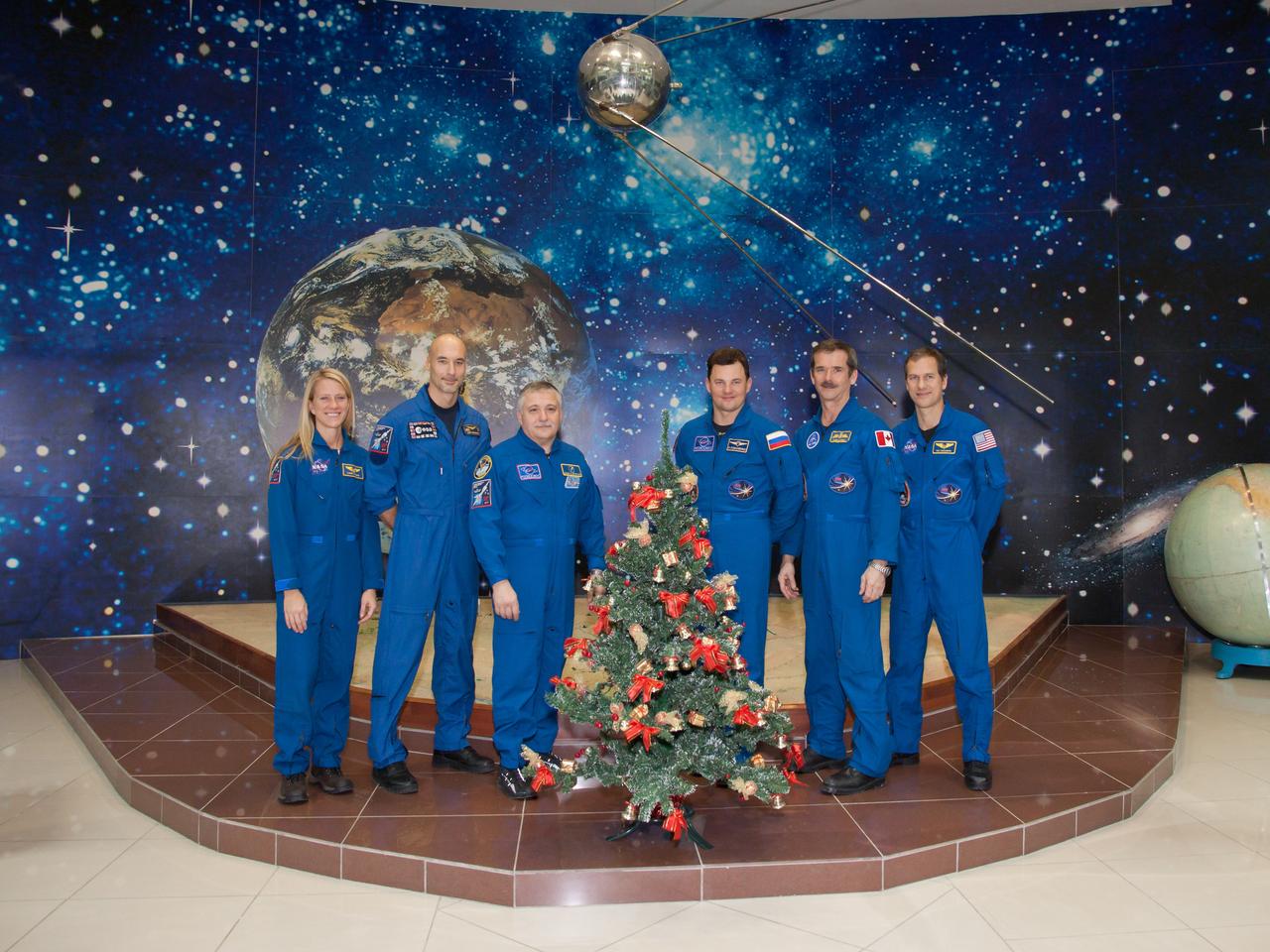

At the Korolev Museum at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, the Expedition 34/35 prime and backup crewmembers reflect the spirit of the holiday season as they pose for pictures in front of a wall mural depicting the cosmos and a model of Sputnik 1, the first satellite launched into orbit in October 1957 during ceremonial activities Dec. 14, 2012. From left to right are backup crewmembers Karen Nyberg of NASA, Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency and Fyodor Yurchikhin and prime crewmembers Soyuz Commander Roman Romanenko, Flight Engineer Chris Hadfield of the Canadian Space Agency and Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn of NASA. Romanenko, Hadfield and Marshburn will launch Dec. 19 on the Soyuz TMA-07M spacecraft for a five-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Victor Zelentsov
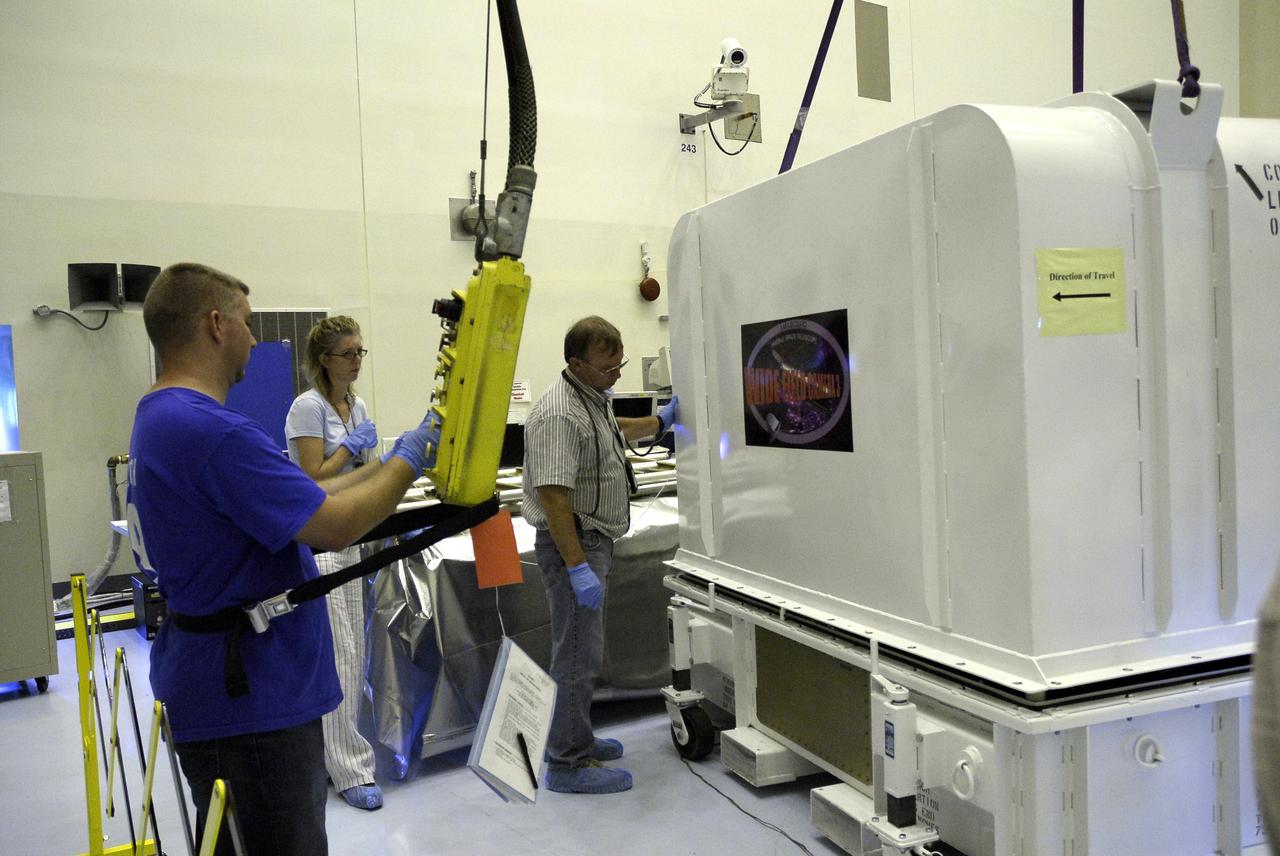
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians begin lifting the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, shipping container. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians monitor the movement of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, as the overhead crane transfers it to a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
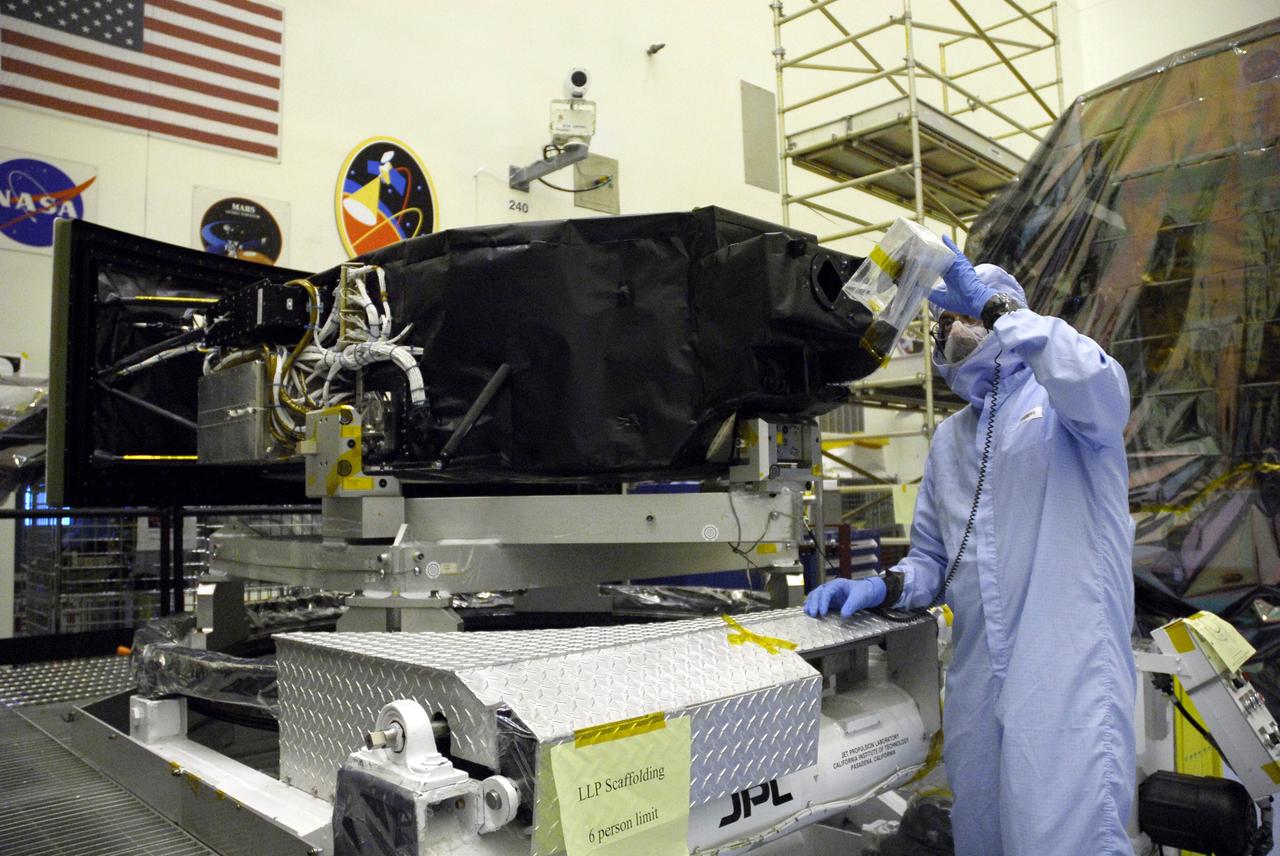

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician checks the pick-off mirror on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, that will be installed on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to Hubble. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
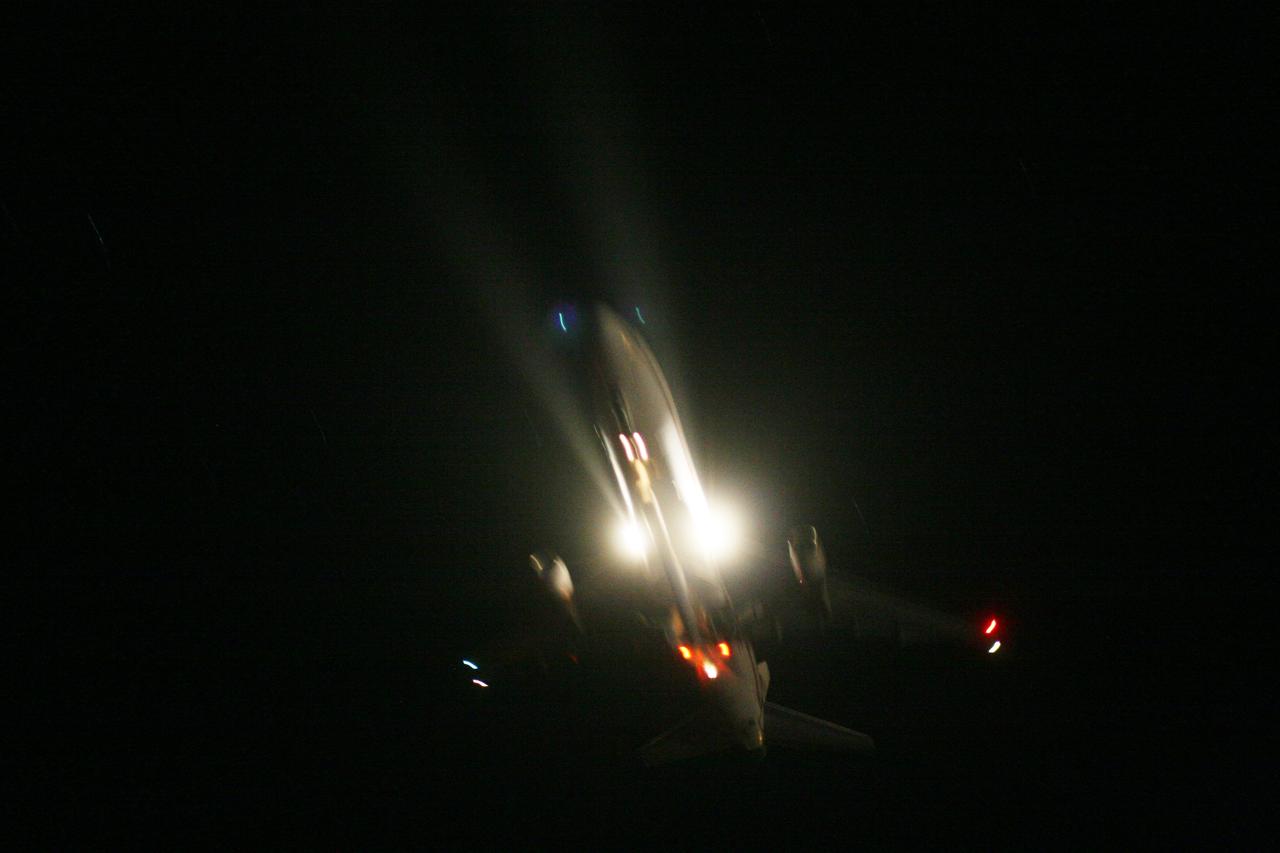

KWAJALEIN ATOLL, Marshall Islands - Orbital Sciences' L-1011 "Stargazer" aircraft takes off from the runway at Kwajalein Atoll with the company's Pegasus rocket to launch NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, payload strapped to the belly of the plane. The plane left Kwajalein one hour before launch. At 9:00:35 a.m. PDT 12:00:35 p.m. EDT), June 13, 2012, the rocket dropped with the NuSTAR payload 117 nautical miles south of Kwajalein. NuSTAR will use a unique set of “eyes” to see the highest energy X-ray light from the cosmos to reveal black holes lurking in our Milky Way galaxy, as well as those hidden in the hearts of faraway galaxies. Kwajalein is located in the Marshall Islands chain in the Pacific Ocean and is part of the Reagan Test Site and used for launches of NASA, commercial and military missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA
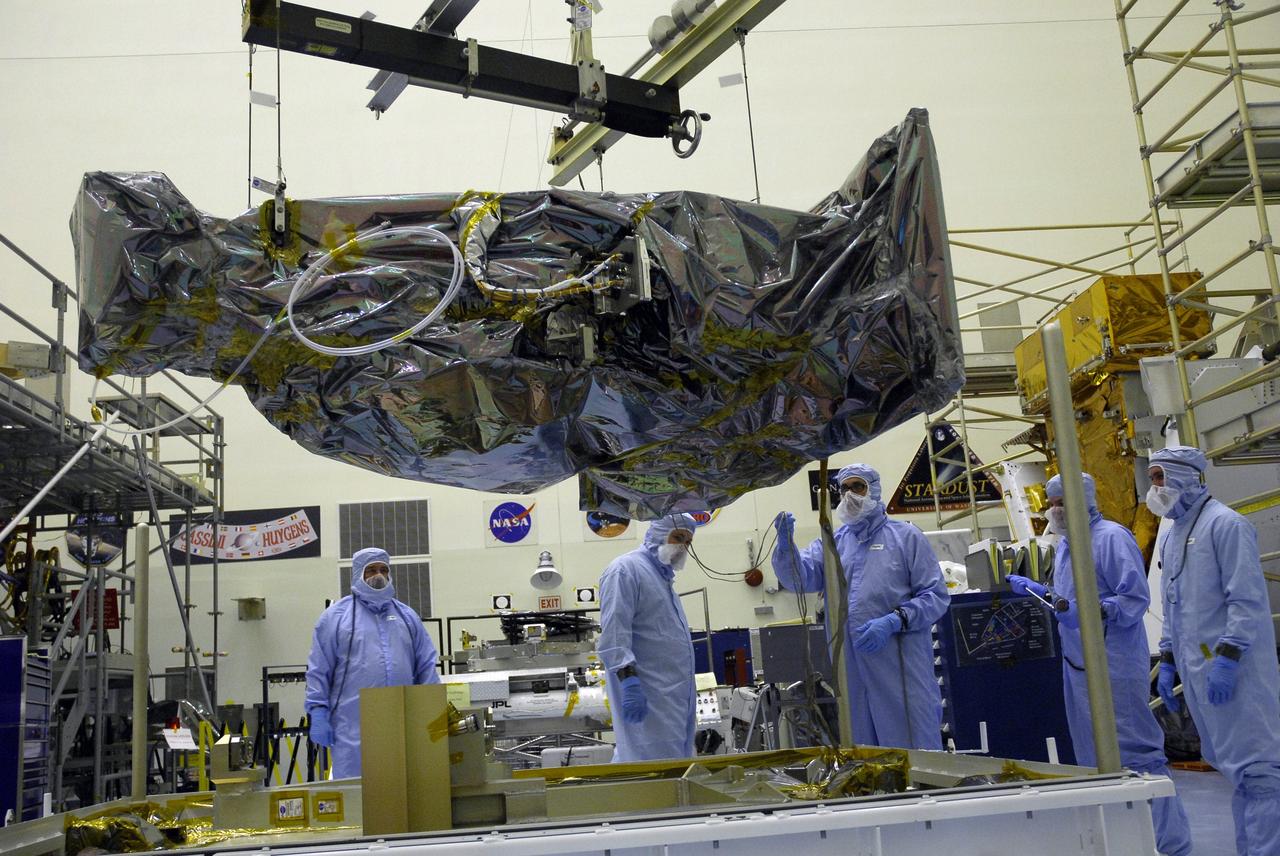

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, from the base of the shipping container. The WFC3 will be transferred to a work stand. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
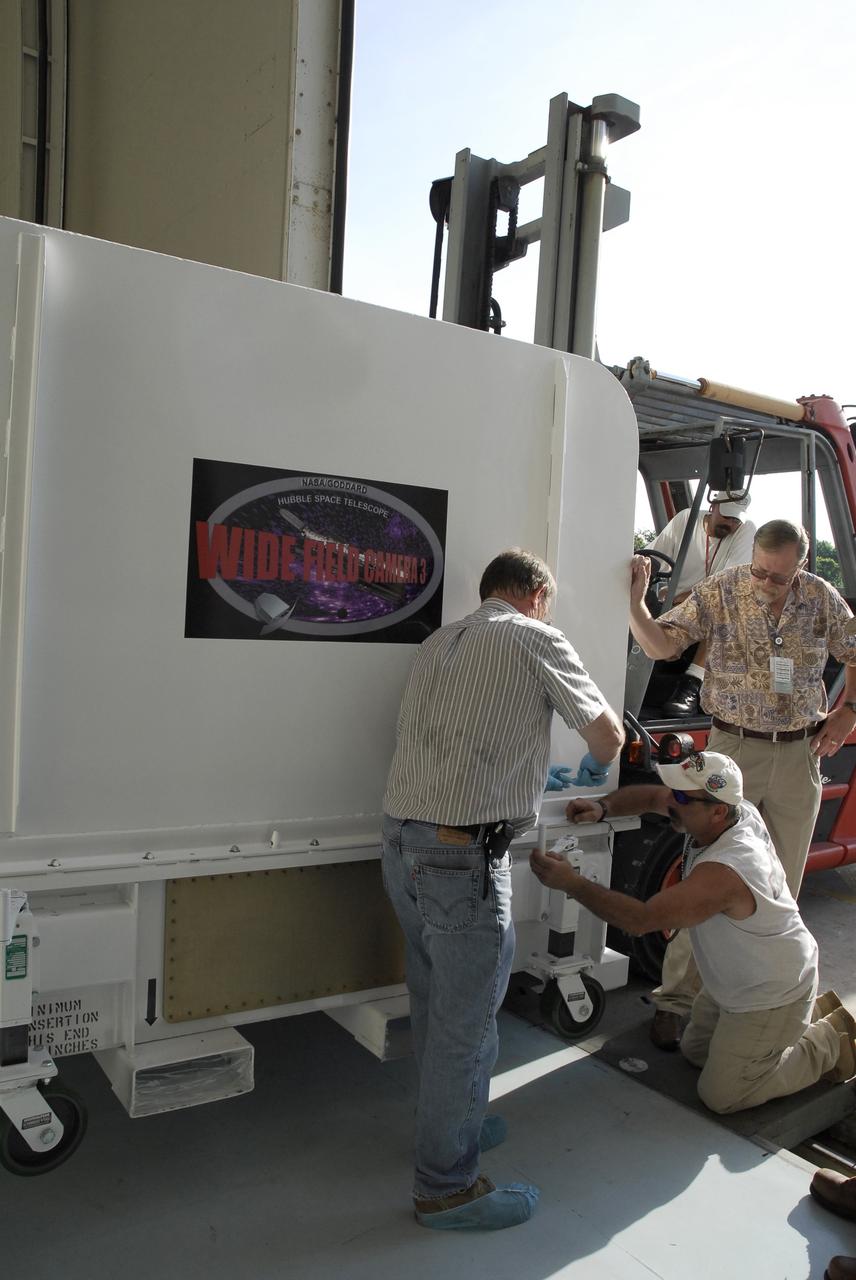

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians unlatch the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3,shipping container before removing it. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
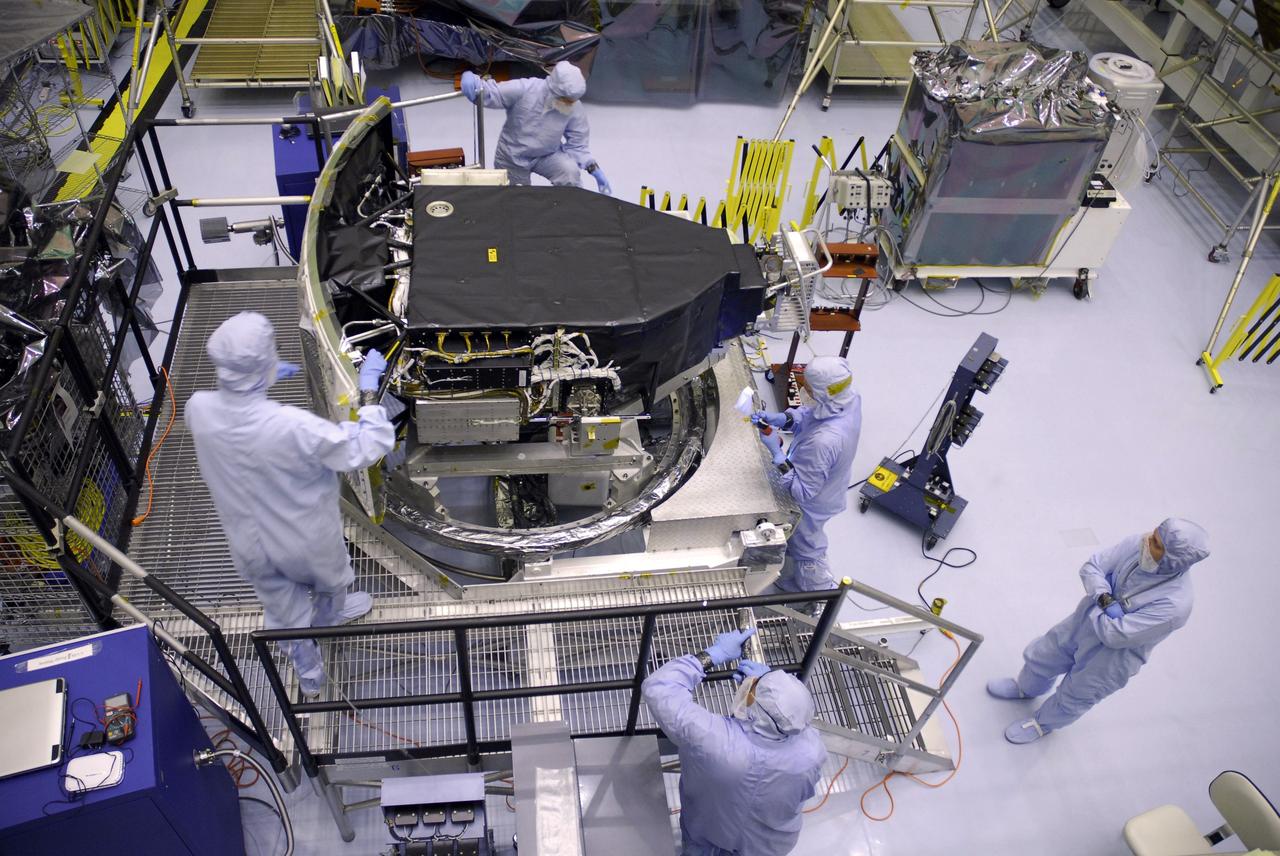

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, after removal of its protective cover. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
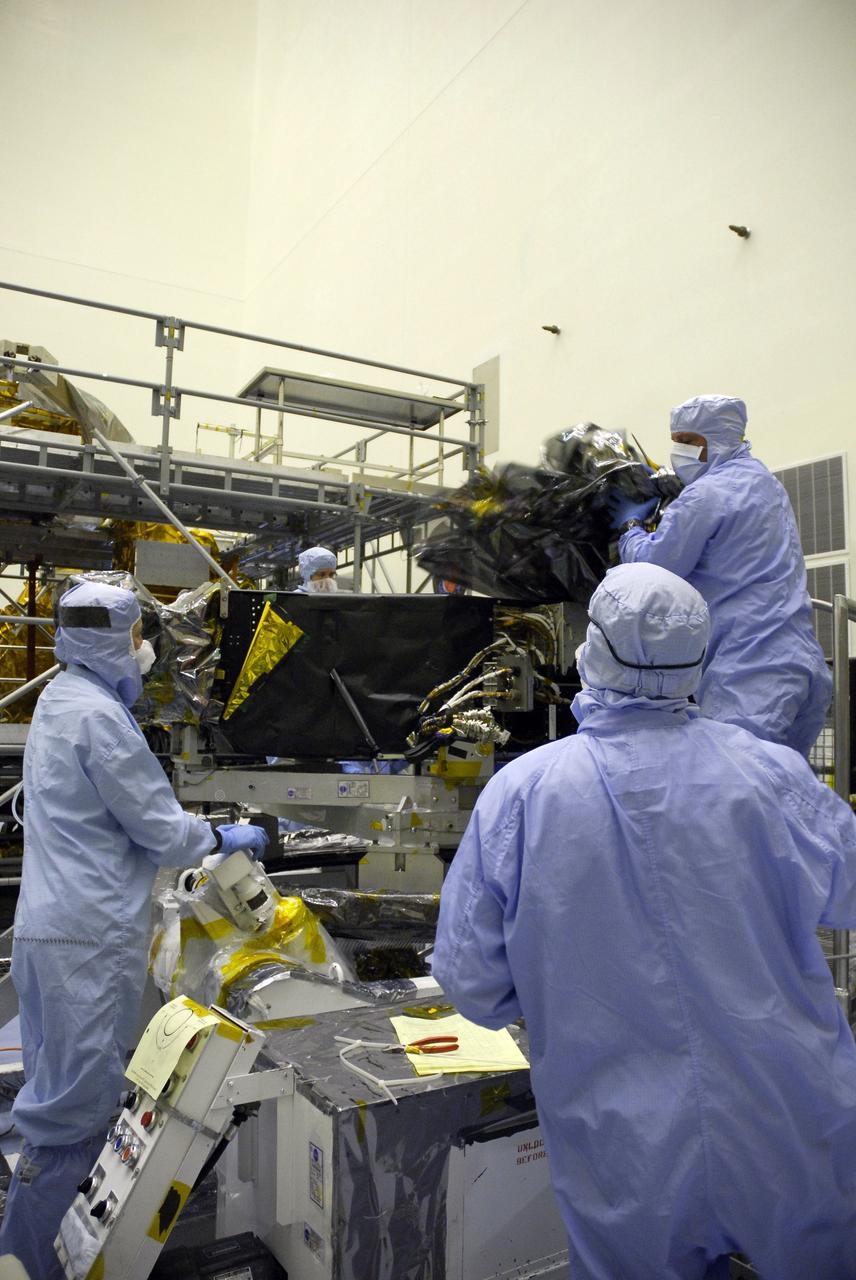

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility begin removing the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
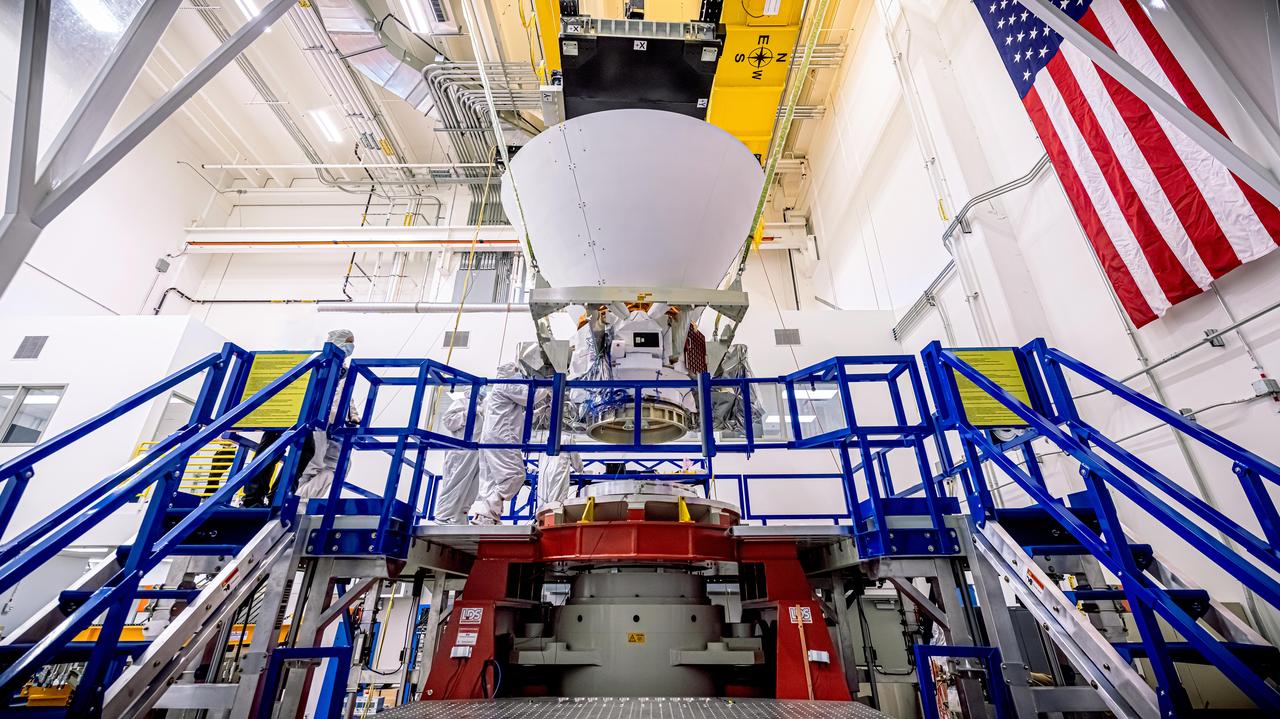

NASA's SPHEREx observatory is lifted and installed onto a vibration table in the Z-axis configuration at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in August 2024. In this test, the spacecraft is subjected to vibrations in all three axes separately. The test was successfully completed Aug. 16, 2024. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26539

The crew patch of STS-73, the second flight of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2), depicts the Space Shuttle Columbia in the vastness of space. In the foreground are the classic regular polyhedrons that were investigated by Plato and later Euclid. The Pythagoreans were also fascinated by the symmetrical three-dimensional objects whose sides are the same regular polygon. The tetrahedron, the cube, the octahedron, and the icosahedron were each associated with the Natural Elements of that time: fire (on this mission represented as combustion science); Earth (crystallography), air and water (fluid physics). An additional icon shown as the infinity symbol was added to further convey the discipline of fluid mechanics. The shape of the emblem represents a fifth polyhedron, a dodecahedron, which the Pythagoreans thought corresponded to a fifth element that represented the cosmos.
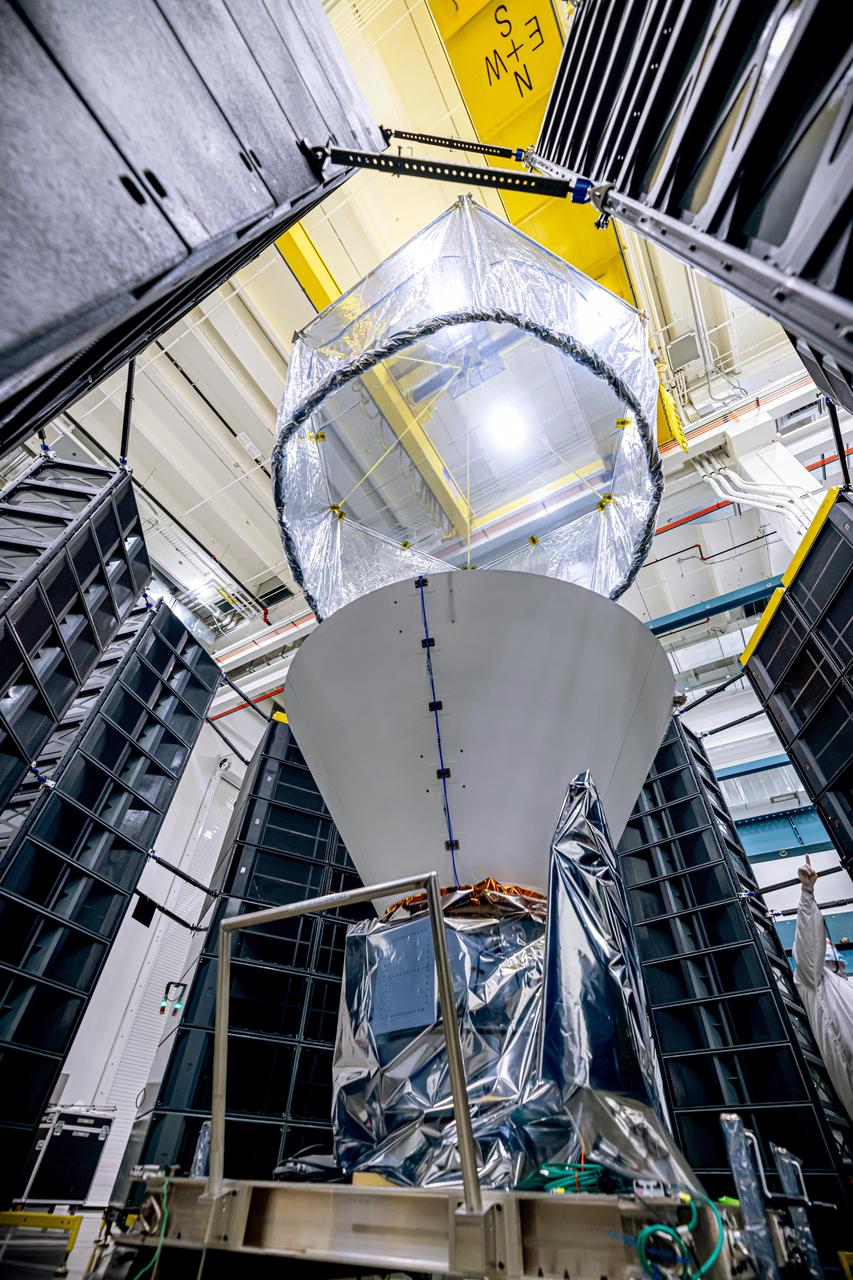

NASA's SPHEREx observatory is installed in the Fiesta Area at BAE Systems in Boulder, Colorado, in July 2024. The observatory is surrounded by speaker stacks used to perform acoustics testing, which subjects the spacecraft to the acoustics loads that it will experience during launch. Short for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer, SPHEREx will create a map of the cosmos like no other. Using a technique called spectroscopy to image the entire sky in 102 wavelengths of infrared light, SPHEREx will gather information about the composition of and distance to millions of galaxies and stars. With this map, scientists will study what happened in the first fraction of a second after the big bang, how galaxies formed and evolved, and the origins of water in planetary systems in our galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26540

Scott Wiessinger, multimedia producer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, left, Wade Sisler, executive producer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, second from left, maestro Piotr Gajewski, second from right, composer Henry Dehlinger, right, are seen as they answer questions following the world premier performance of Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
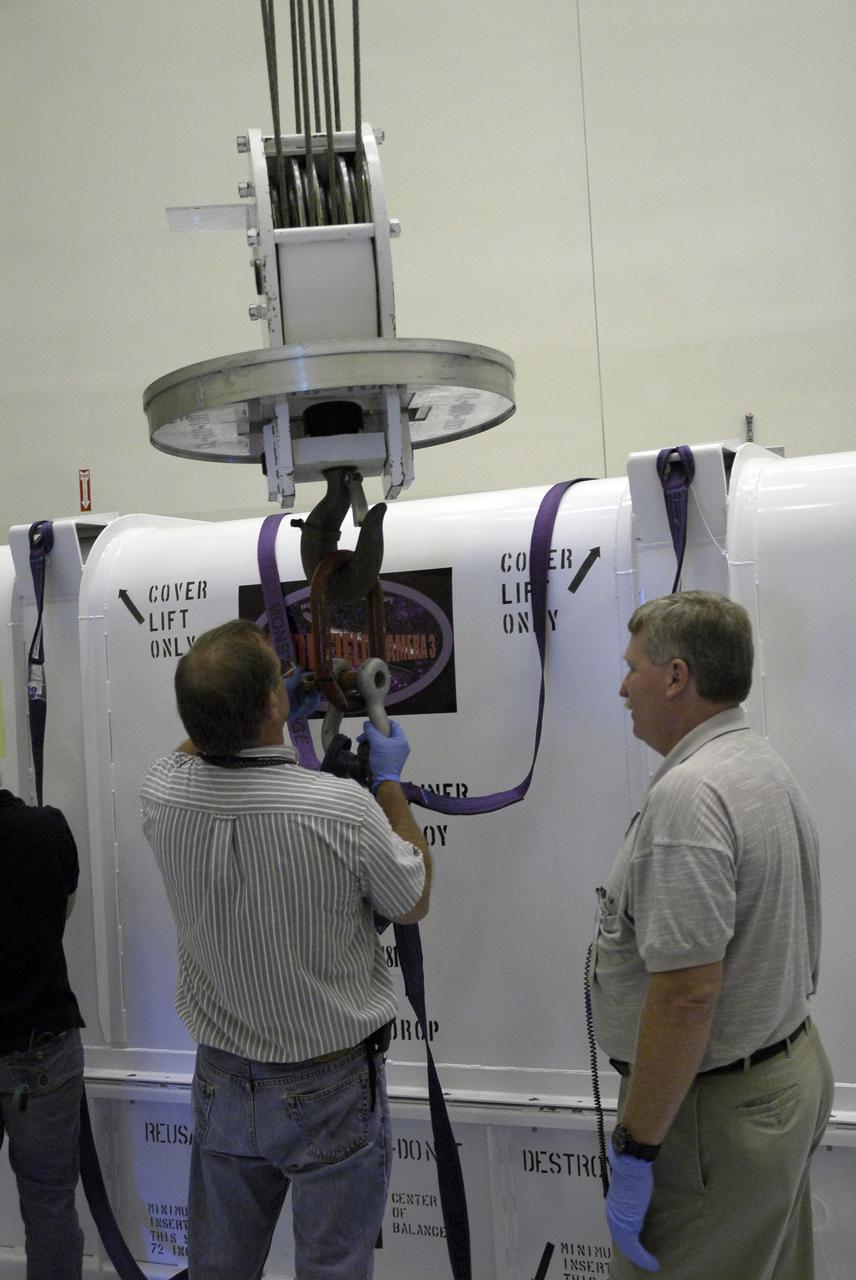

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians attach an overhead crane to the cover of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, shipping container. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
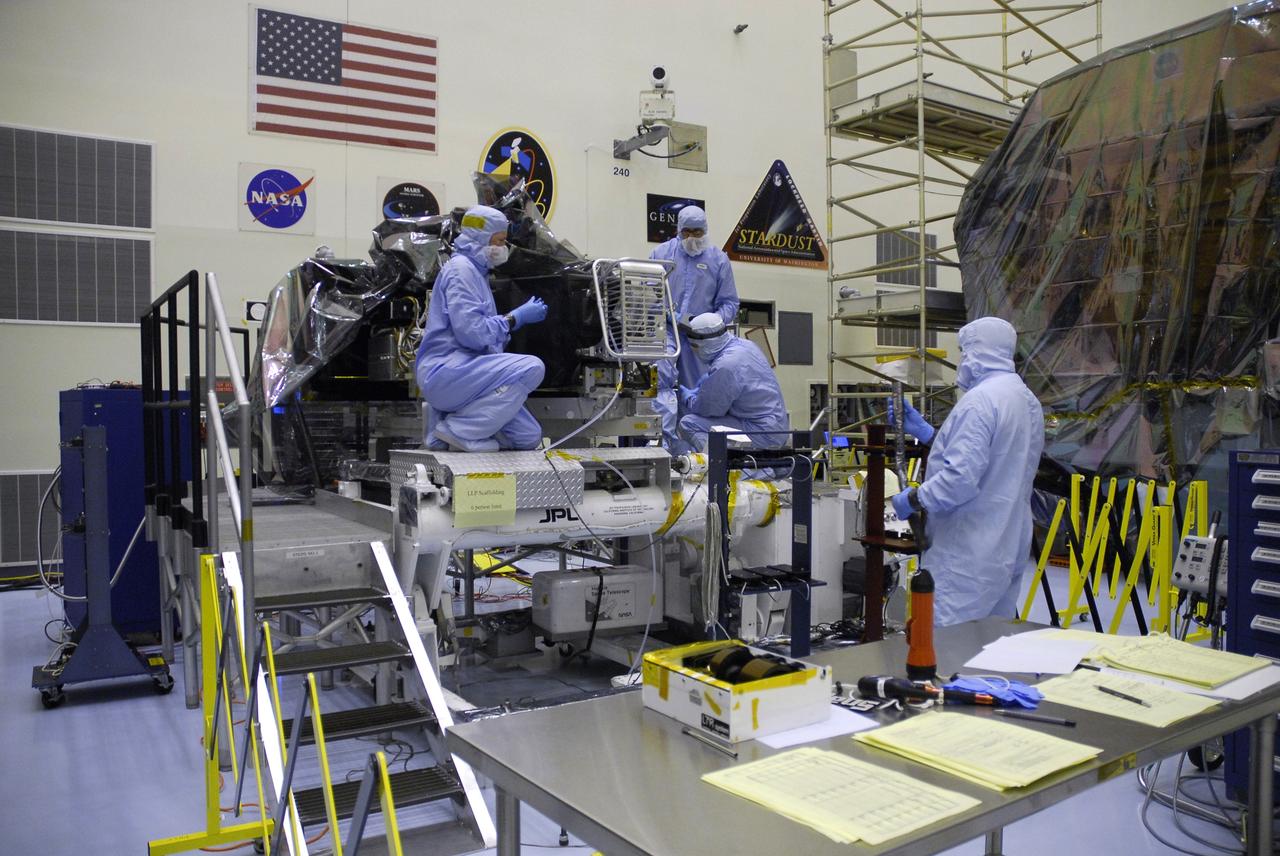

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, after removal of its protective cover. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
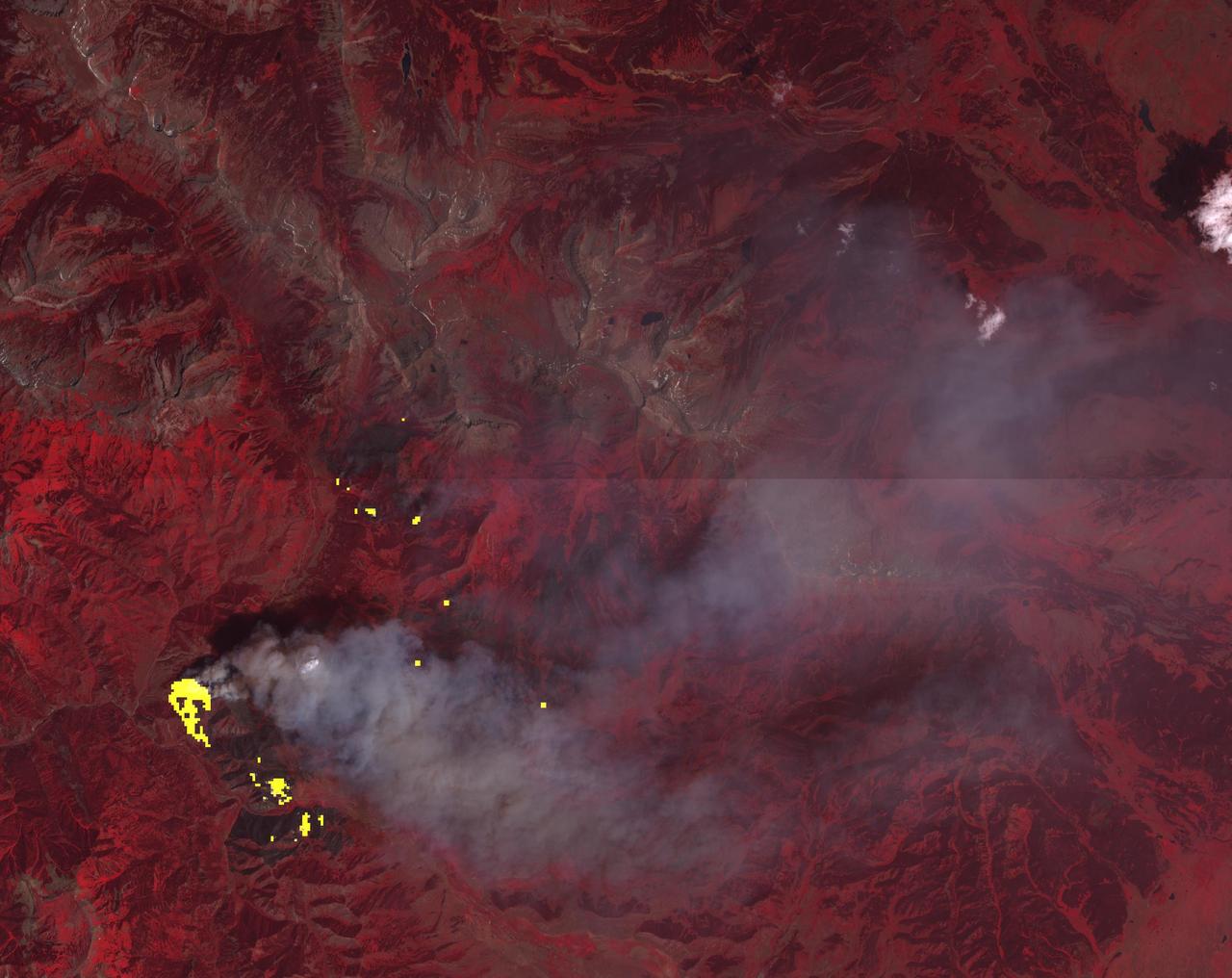

The blue dots in this field of galaxies, known as the COSMOS field, show galaxies that contain supermassive black holes emitting high-energy X-rays. The black holes were detected by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Array, or NuSTAR, which spotted 32 such black holes in this field and has observed hundreds across the whole sky so far. The other colored dots are galaxies that host black holes emitting lower-energy X-rays, and were spotted by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra data show X-rays with energies between 0.5 to 7 kiloelectron volts, while NuSTAR data show X-rays between 8 to 24 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20865
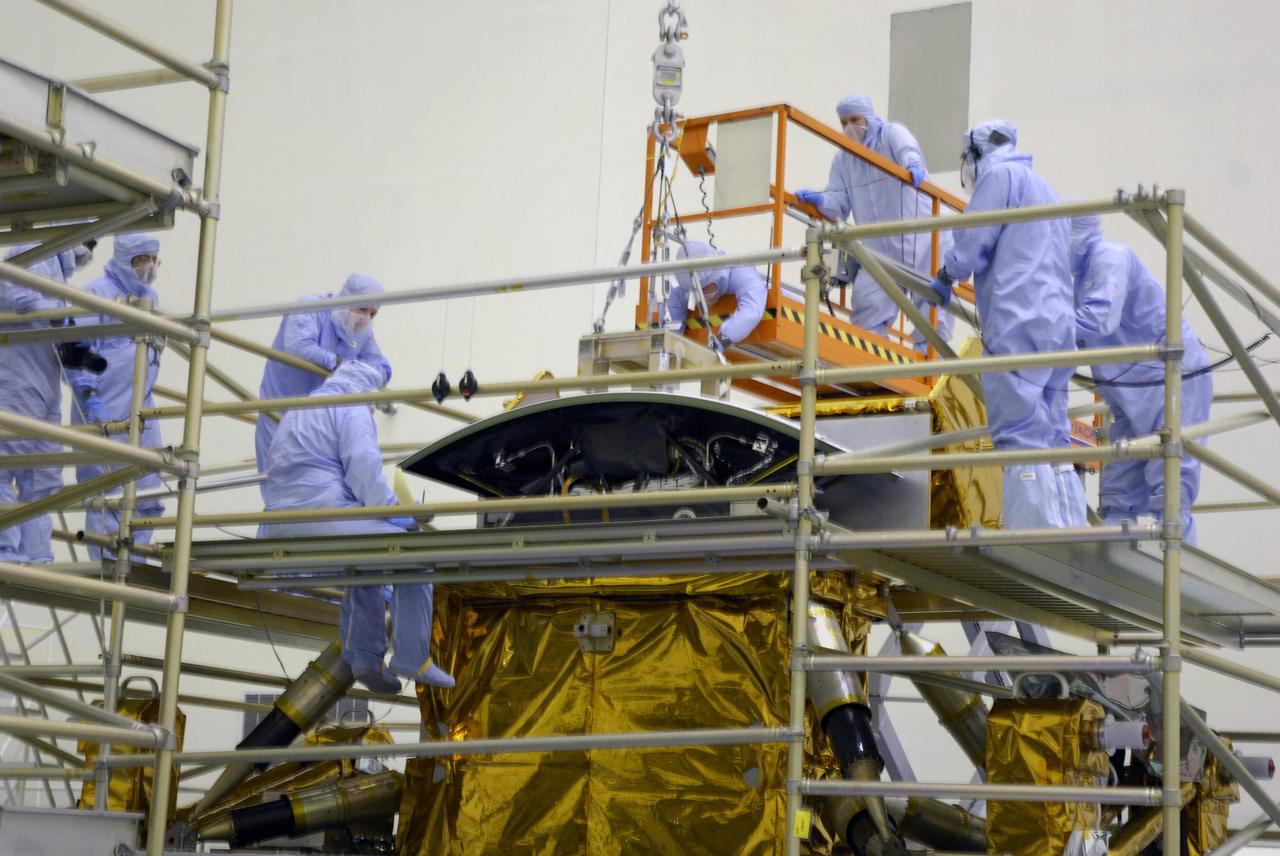

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is lowered onto the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

Composer Henry Dehlinger, right, answers a question alongside Scott Wiessinger, multimedia producer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, left, Wade Sisler, executive producer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, second from left, maestro Piotr Gajewski, second from right, following the world premier performance of Dehlinger’s “Cosmic Cycles,” Thursday, May 11, 2023, at Capital One Hall in Tysons, Va. “Cosmic Cycles: A Space Symphony” is a collaboration between composer Henry Dehlinger, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, and the National Philharmonic that features a fusion of music and video in seven multimedia works on the Sun, Earth, Moon, Planets, and Cosmos. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, rests on a work stand in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility since its arrival Aug. 12. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility remove the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
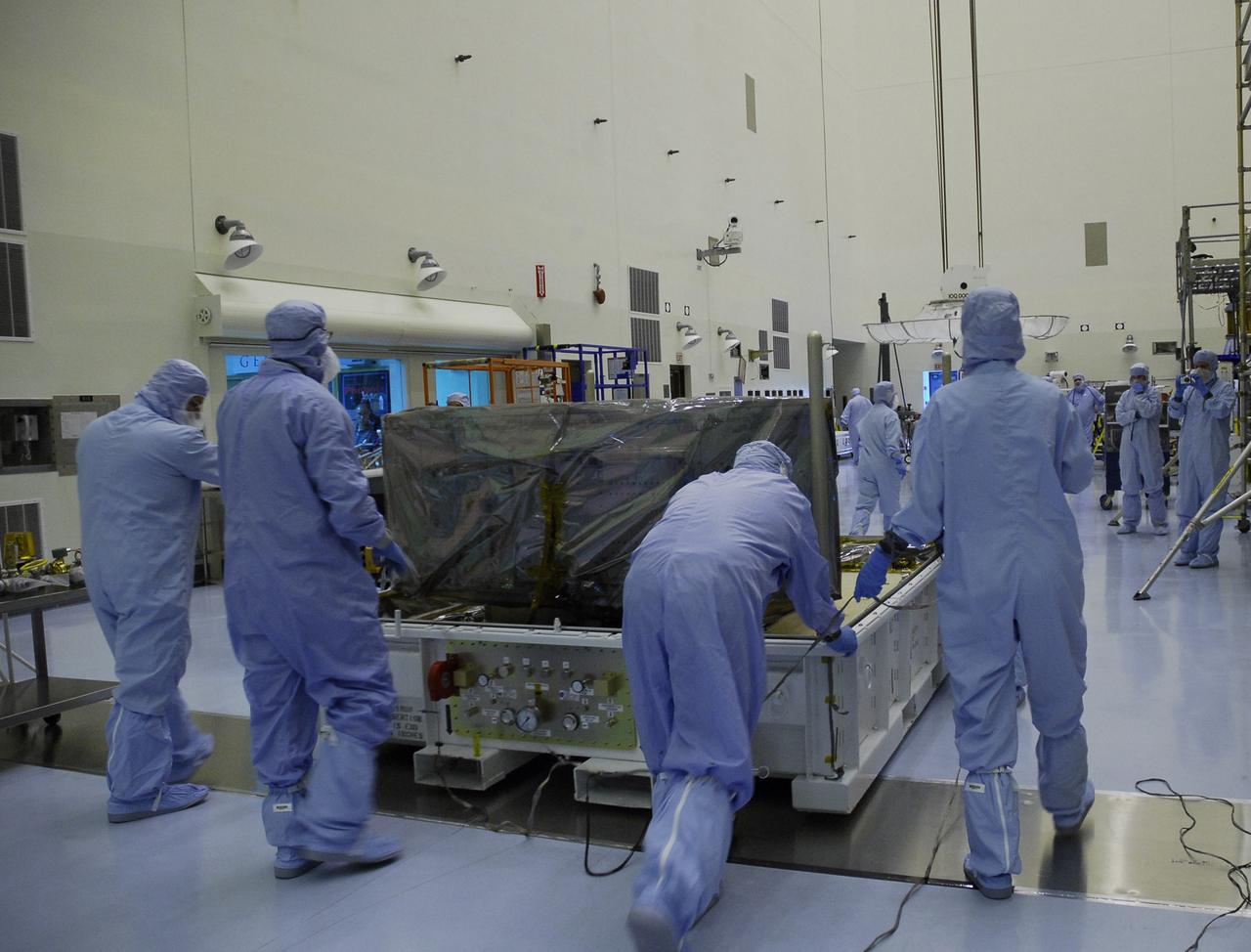

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians move the base of the shipping container holding the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, into the high bay. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
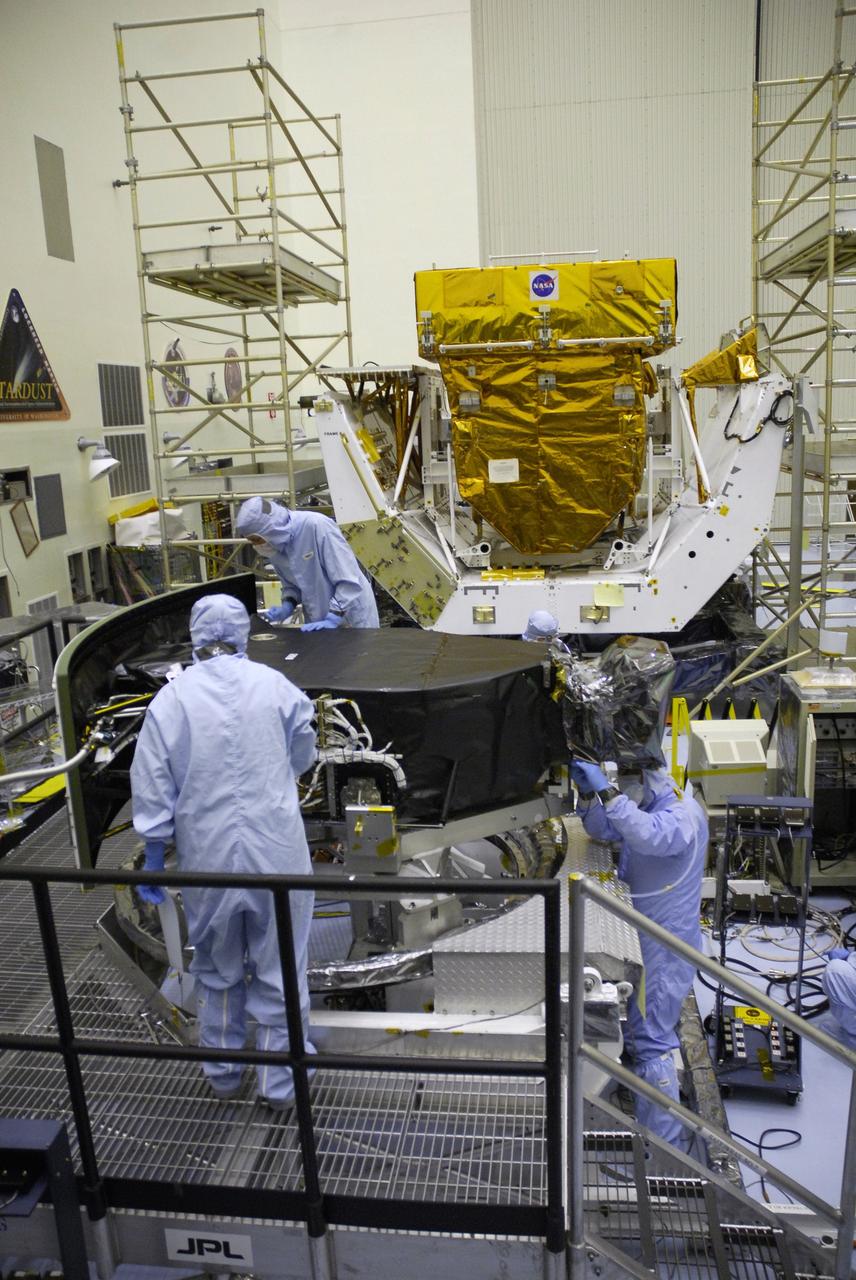

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility complete removal of the protective cover from the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis for the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians move the base of the shipping container holding the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. WFC3 is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller