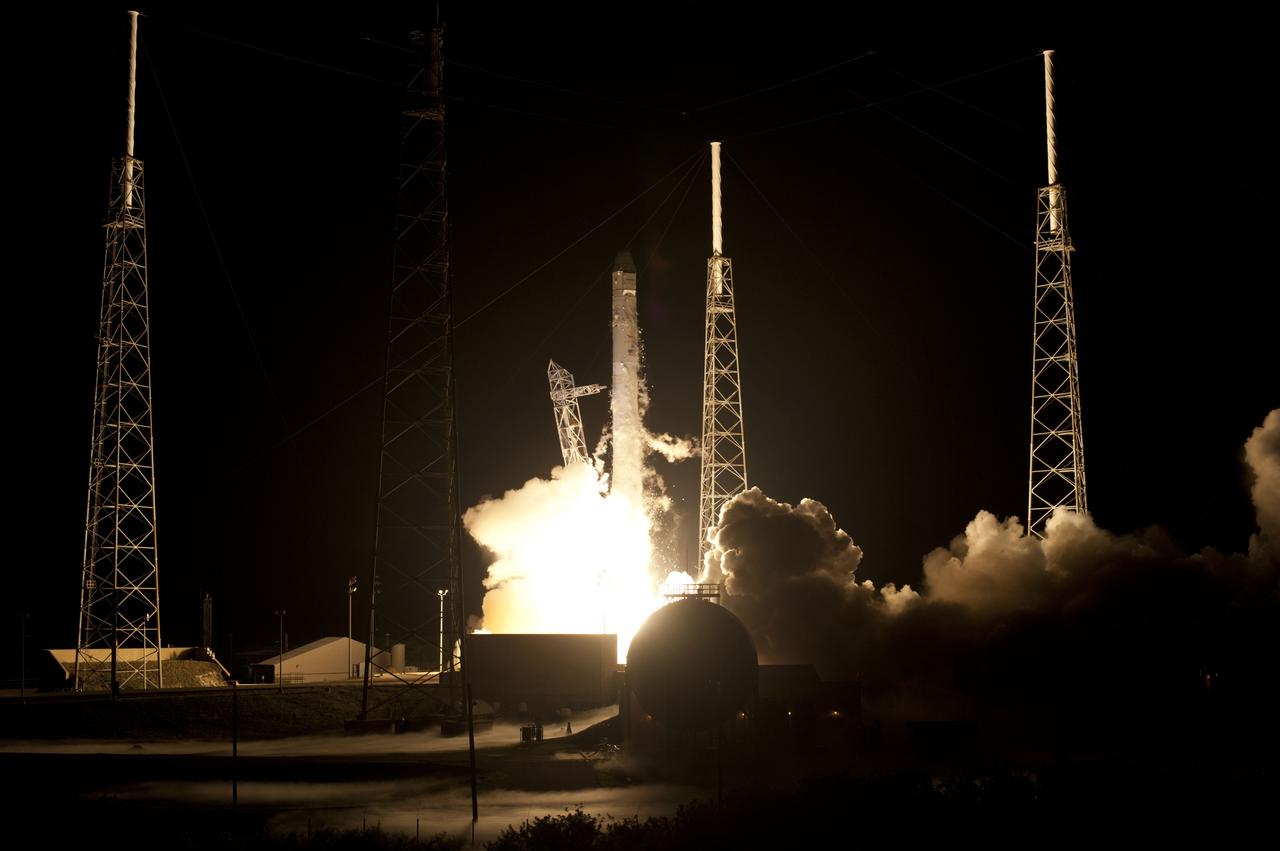
SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch - DD028-203
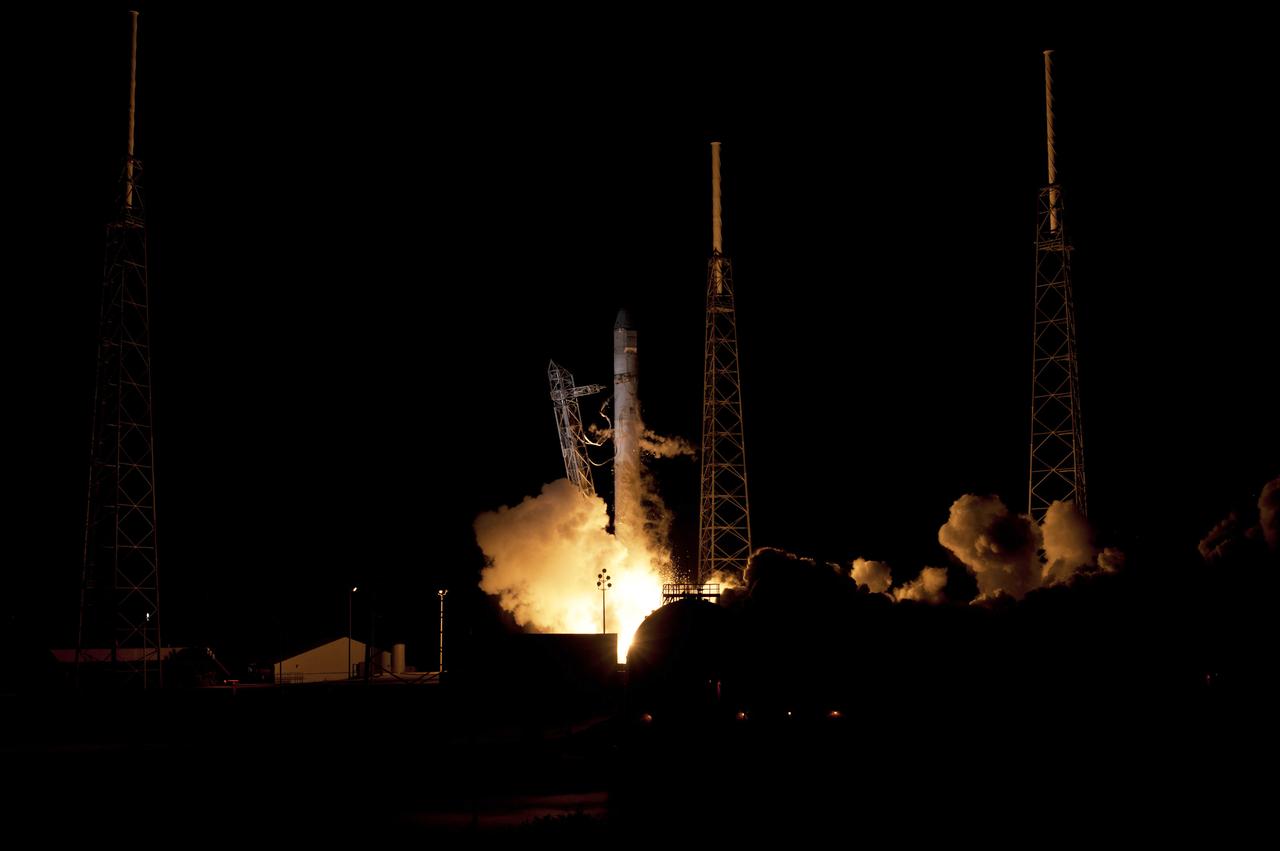

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch - DD028-203
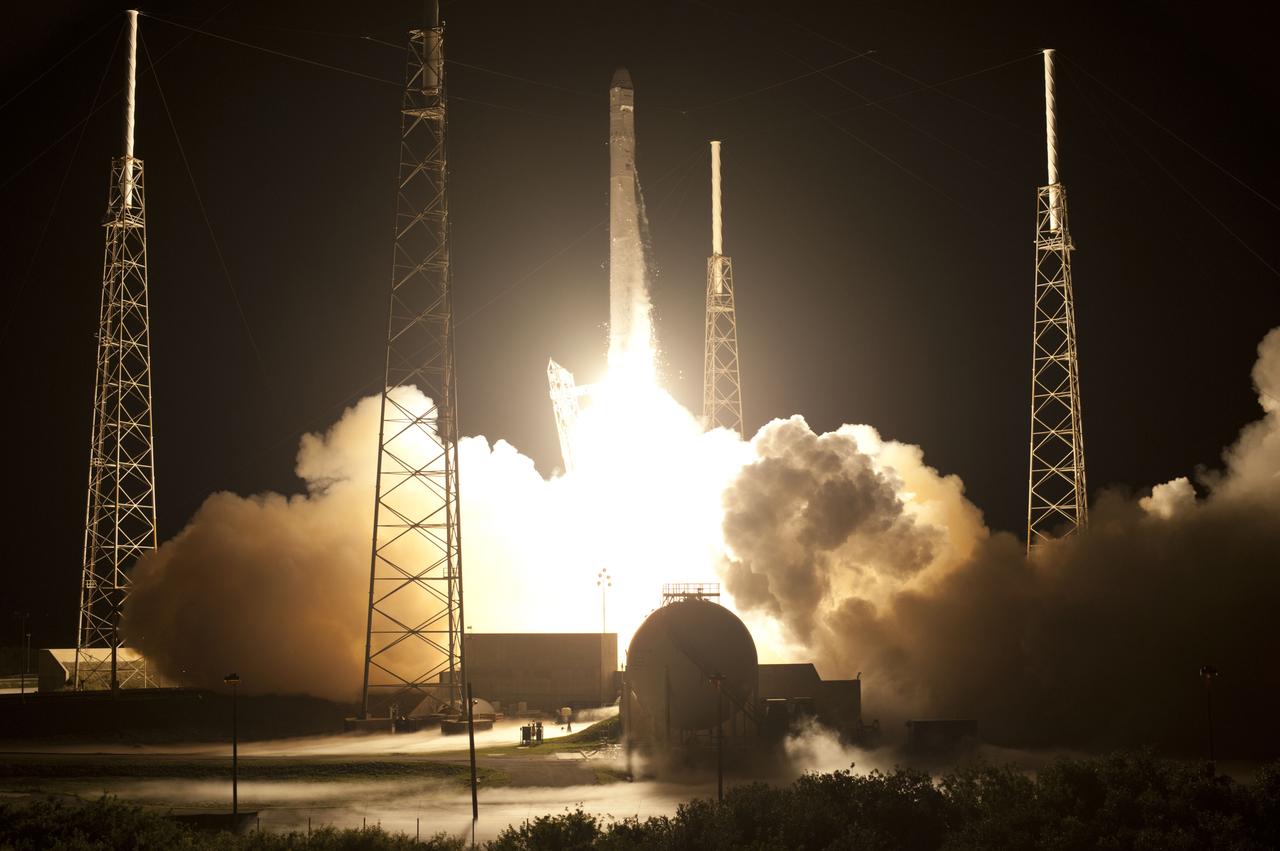

SpaceX Falcon 9/COTS 2 Launch - DD028-203
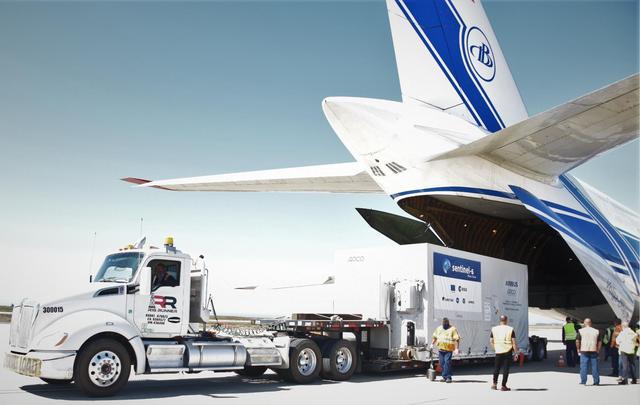

A shipping container containing the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is transported on a truck to the SpaceX payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base after arriving in California on Sept. 24, 2020. An Antonov aircraft carrying the spacecraft arrived at around 10:40 a.m. PDT (1:40 p.m. EDT) after a two-day journey from an IABG engineering facility near Munich, Germany. The ocean-monitoring satellite will undergo prelaunch tests before its scheduled launch on Nov. 10, 2020. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich will begin a five-and-a-half-year mission to collect sea surface height measurements down to the centimeter for 90% of the world's oceans. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. Sentinel-6/Jason-CS is being jointly developed by ESA, the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), NASA, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, with funding support from the European Commission and technical support from France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, is contributing three science instruments for each Sentinel-6 satellite: the Advanced Microwave Radiometer, the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation, and the Laser Retroreflector Array. NASA is also contributing launch services, ground systems supporting operation of the NASA science instruments, the science data processors for two of these instruments, and support for the international Ocean Surface Topography Science Team. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24104

A shipping container containing the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is removed from an Antonov 124 aircraft at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The flight arrived at around 10:40 a.m. PDT (1:40 p.m. EDT) after a two-day journey from an IABG engineering facility near Munich, Germany. The ocean-monitoring satellite will undergo prelaunch tests before its scheduled launch on Nov. 10, 2020. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich will begin a five-and-a-half-year mission to collect sea surface height measurements down to the centimeter for 90% of the world's oceans. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions specifically to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. Sentinel-6/Jason-CS is being jointly developed by ESA, the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), NASA, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, with funding support from the European Commission and technical support from France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). NASA JPL is contributing three science instruments for each Sentinel-6 satellite: the Advanced Microwave Radiometer, the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation, and the Laser Retroreflector Array. NASA is also contributing launch services, ground systems supporting operation of the NASA science instruments, the science data processors for two of these instruments, and support for the international Ocean Surface Topography Science Team. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24103
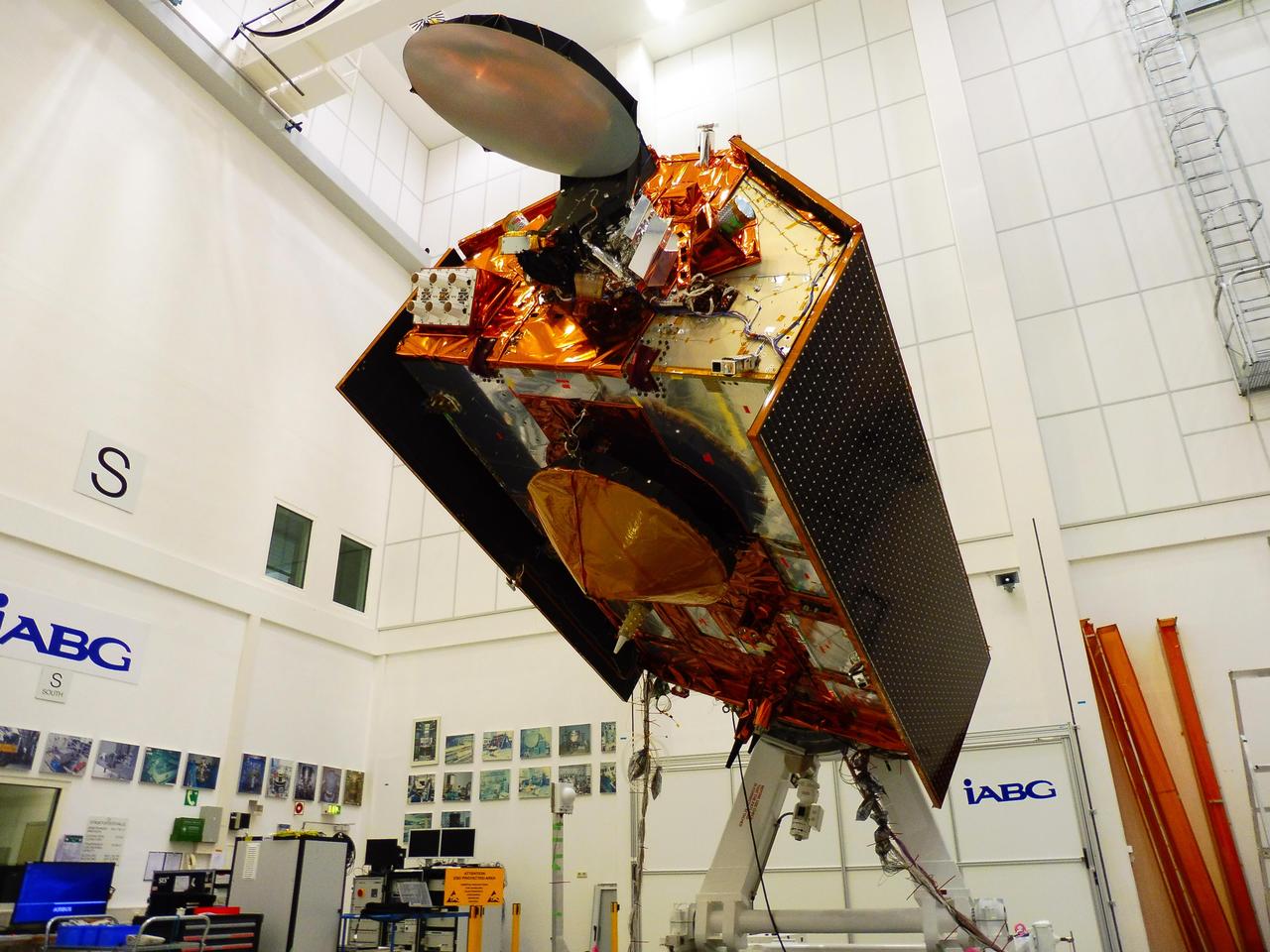

The Sentinel-6A spacecraft sits in its clean room in Germany's IABG space test center. The satellite is being prepared for a scheduled launch in November 2020 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The spacecraft is part of Sentinel-6/Jason-CS, a 10-year mission by U.S and European agencies that will continue to study rising sea levels. The mission consists of two identical satellites, Sentinel-6A and Sentinel-6B, launching five years apart and follows in the footsteps of four other joint U.S.-European satellite missions — TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1, Ocean Surface Topography/Jason-2, and Jason-3 — that over the past three decades have documented Earth's oceans rising by an average of 0.1 inches (3 millimeters) per year. Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will study not just sea level change but also changes in ocean circulation, climate variability such as El Niño and La Niña, and weather patterns, including hurricanes and storms. It is being jointly developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellite (EUMETSAT), NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) with funding support from the European Commission and support from France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). NASA's contributions to the Sentinel-6 mission are science instrument payloads for the two Sentinel-6 satellites, launch services for those satellites, ground systems supporting the science instruments operations and support for the international Ocean Surface Topography Science Team. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23549
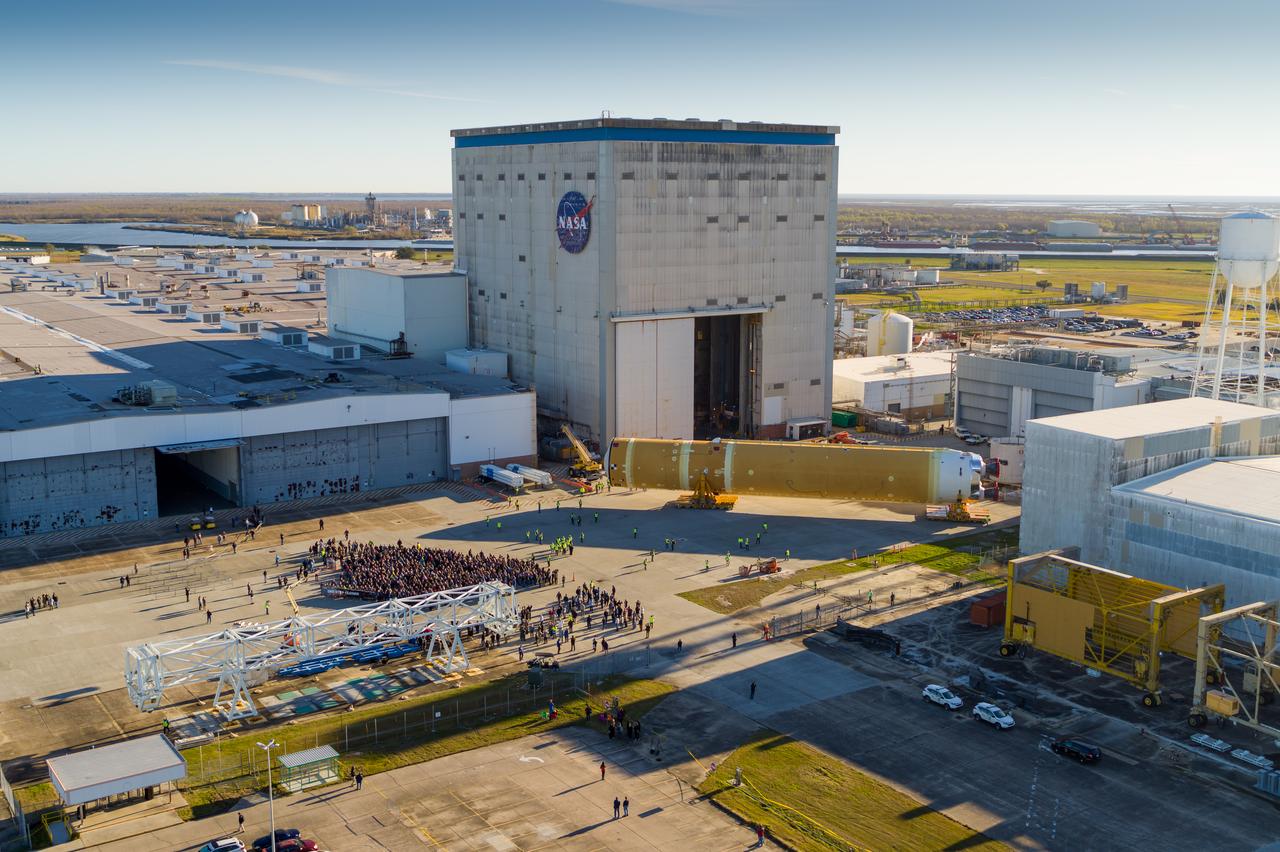

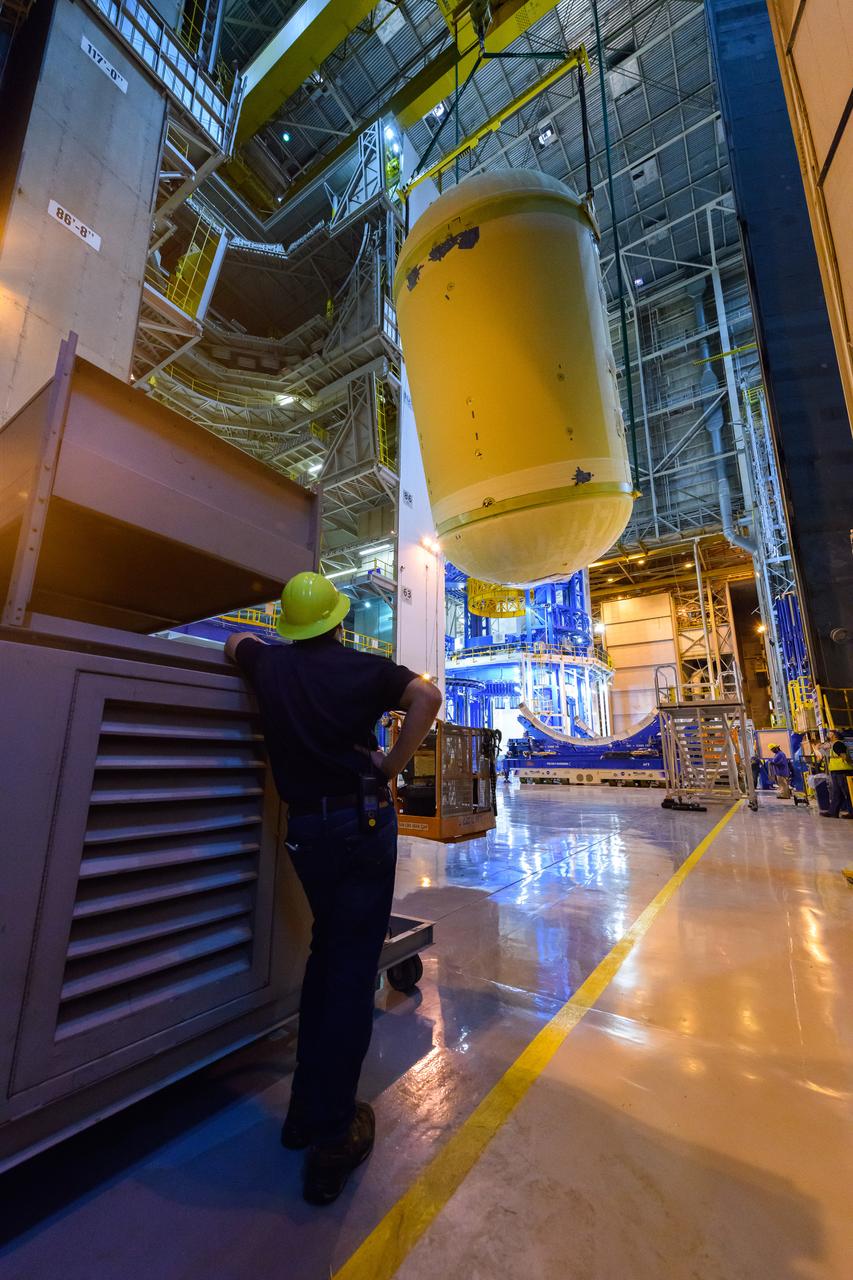
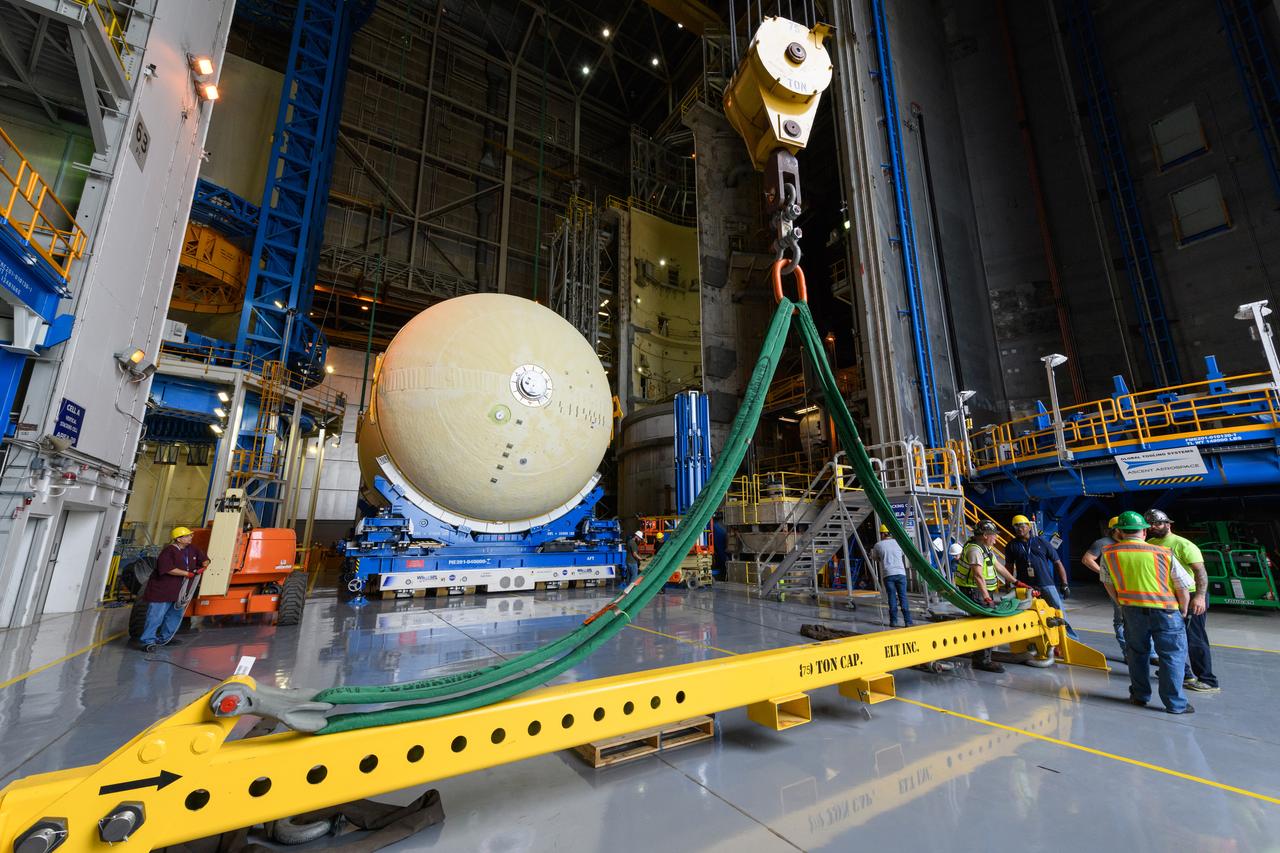
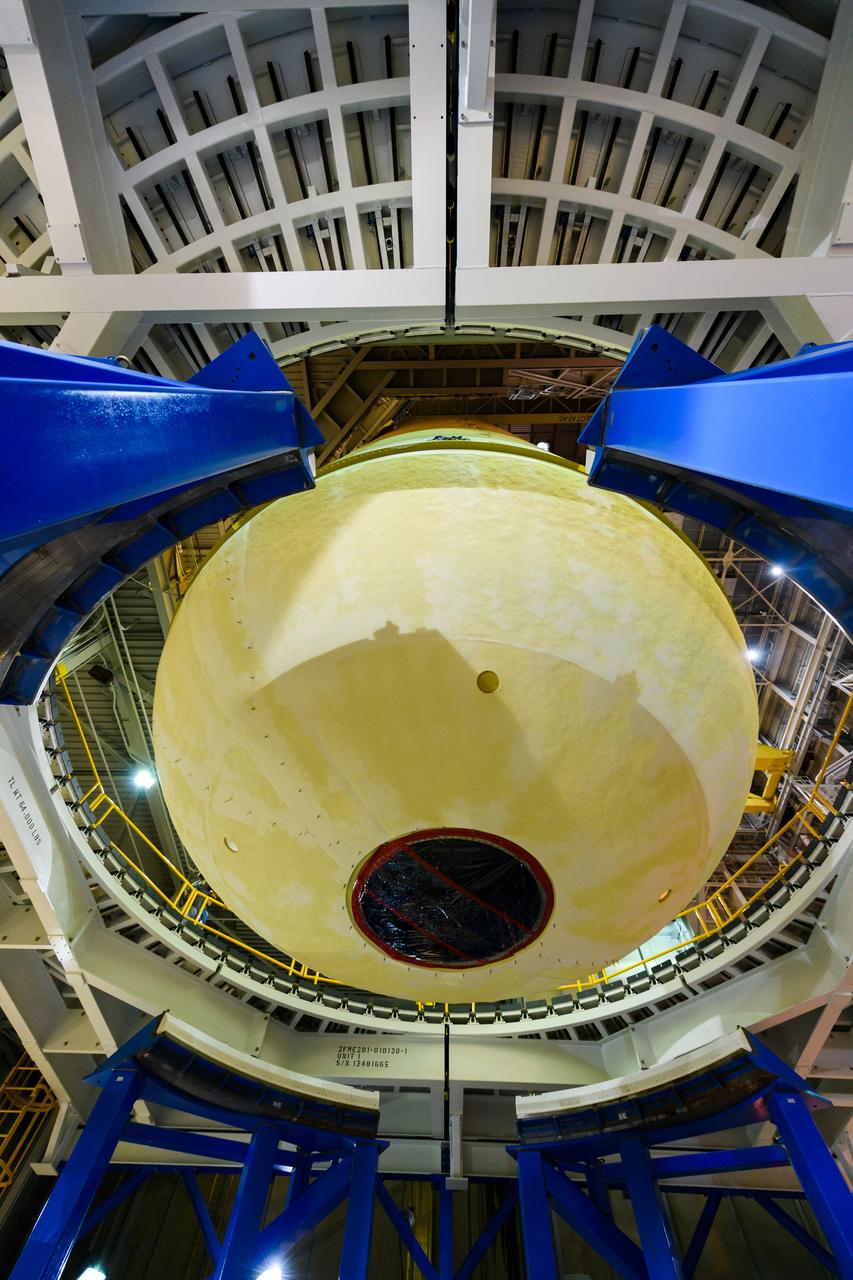
These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
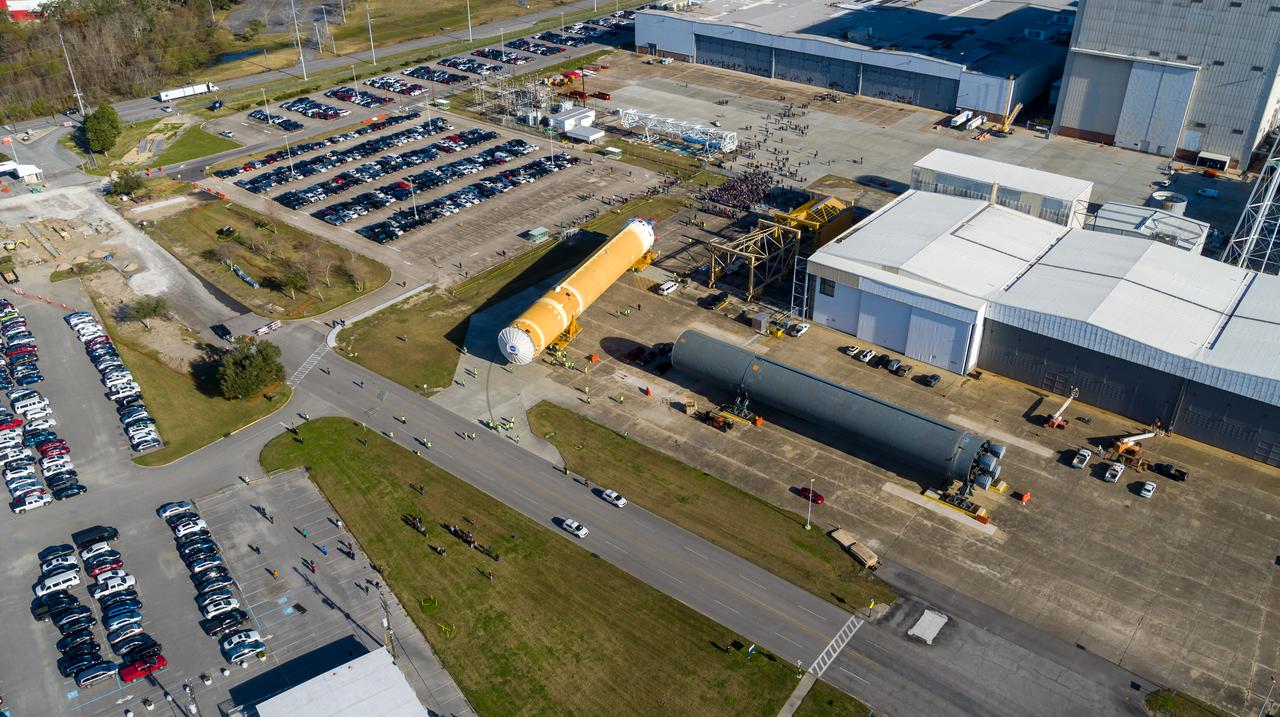

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
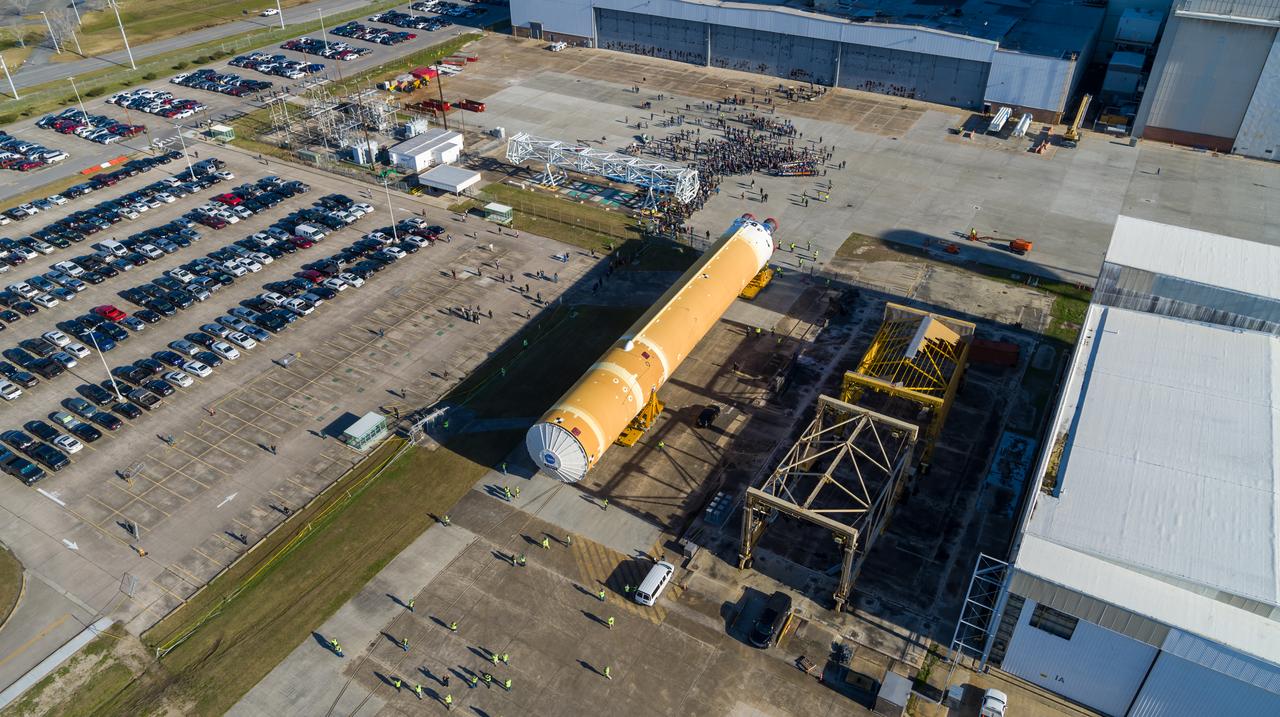

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
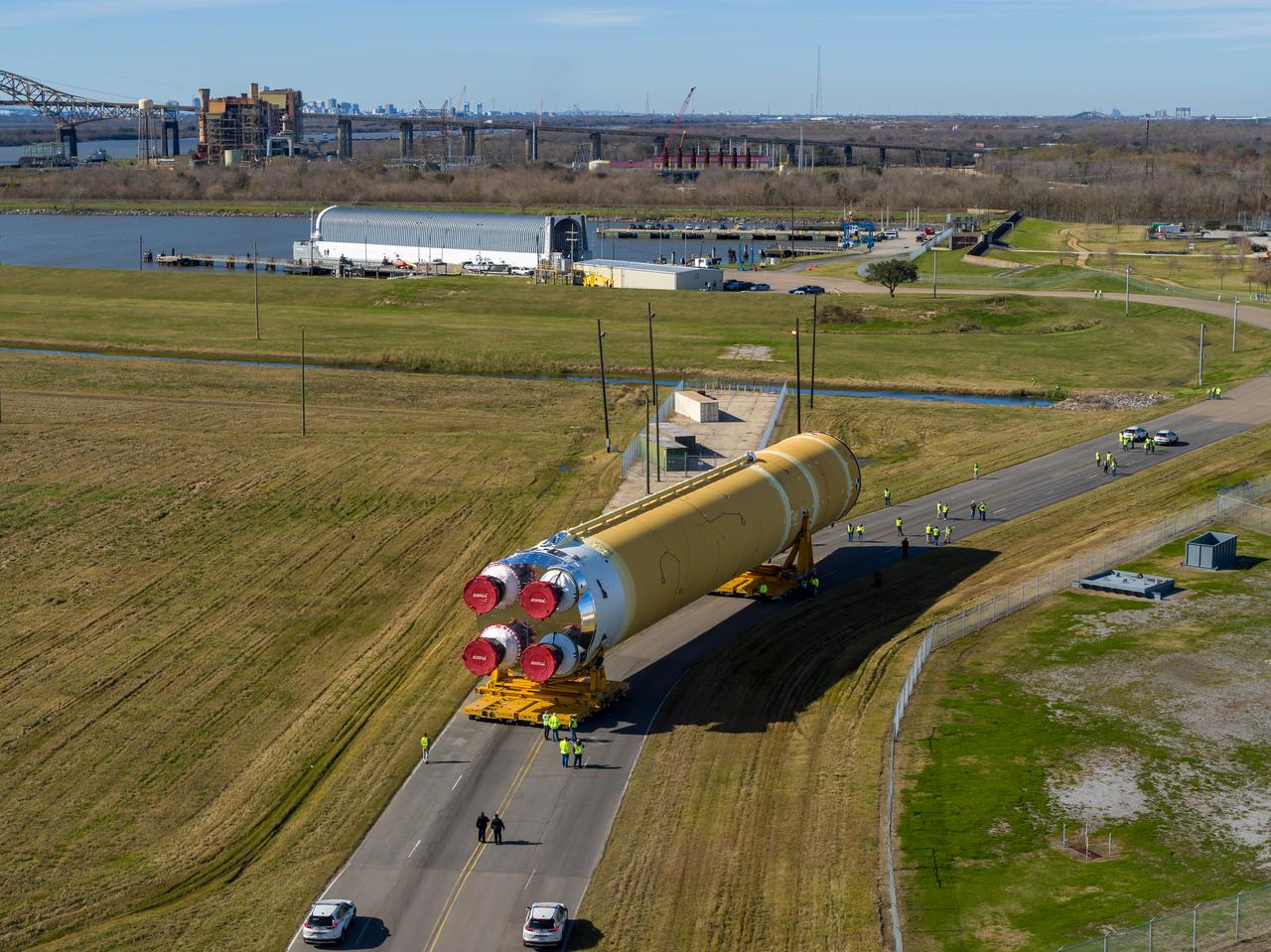

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
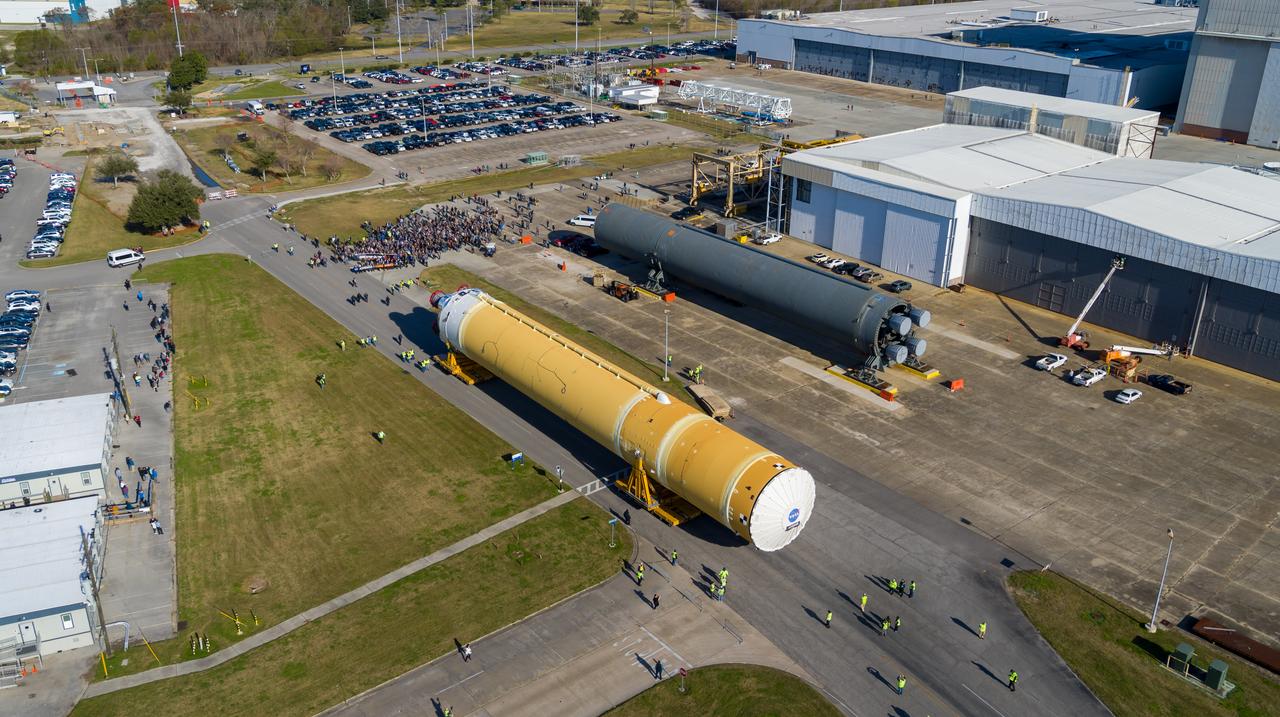

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
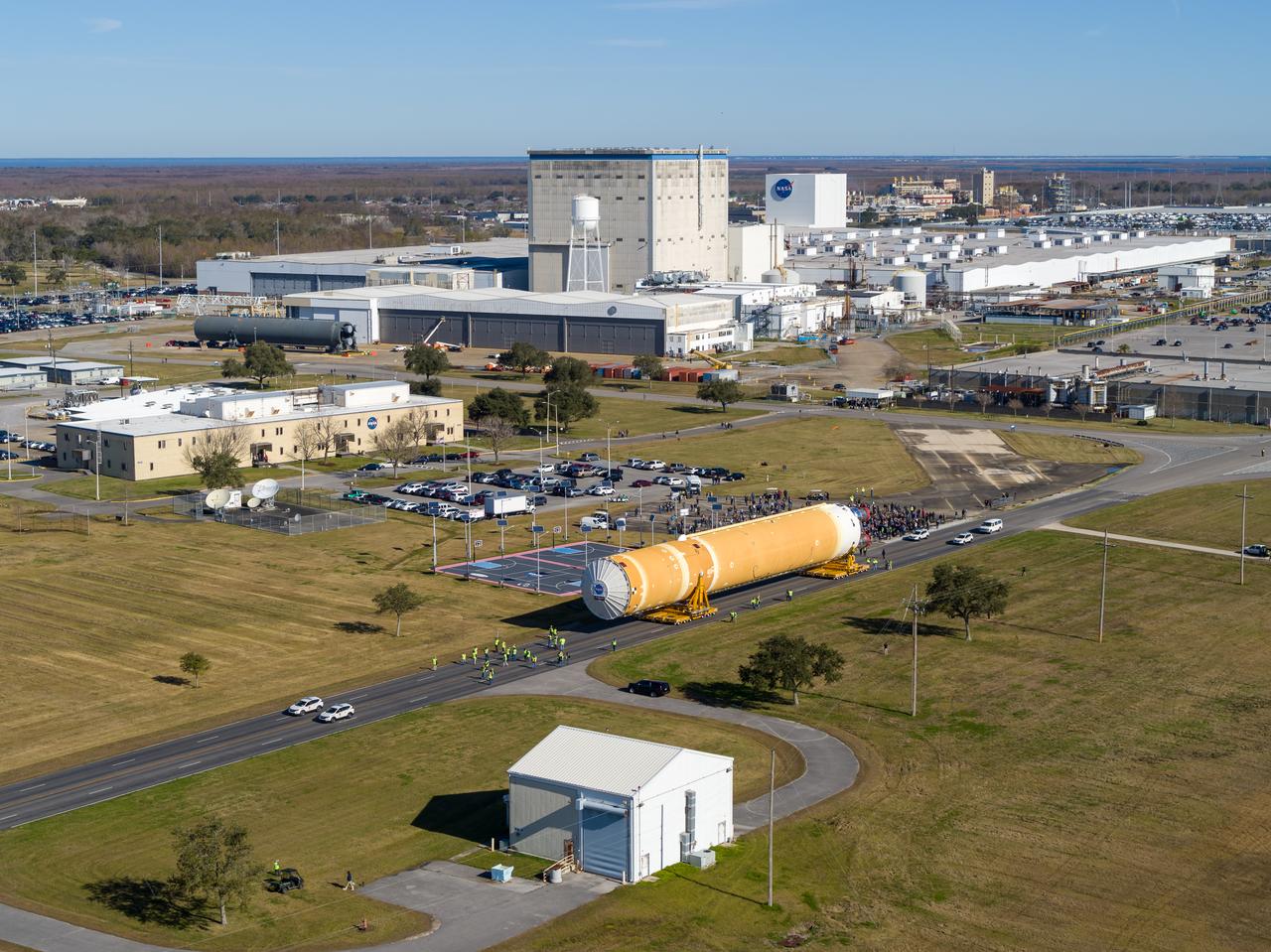

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
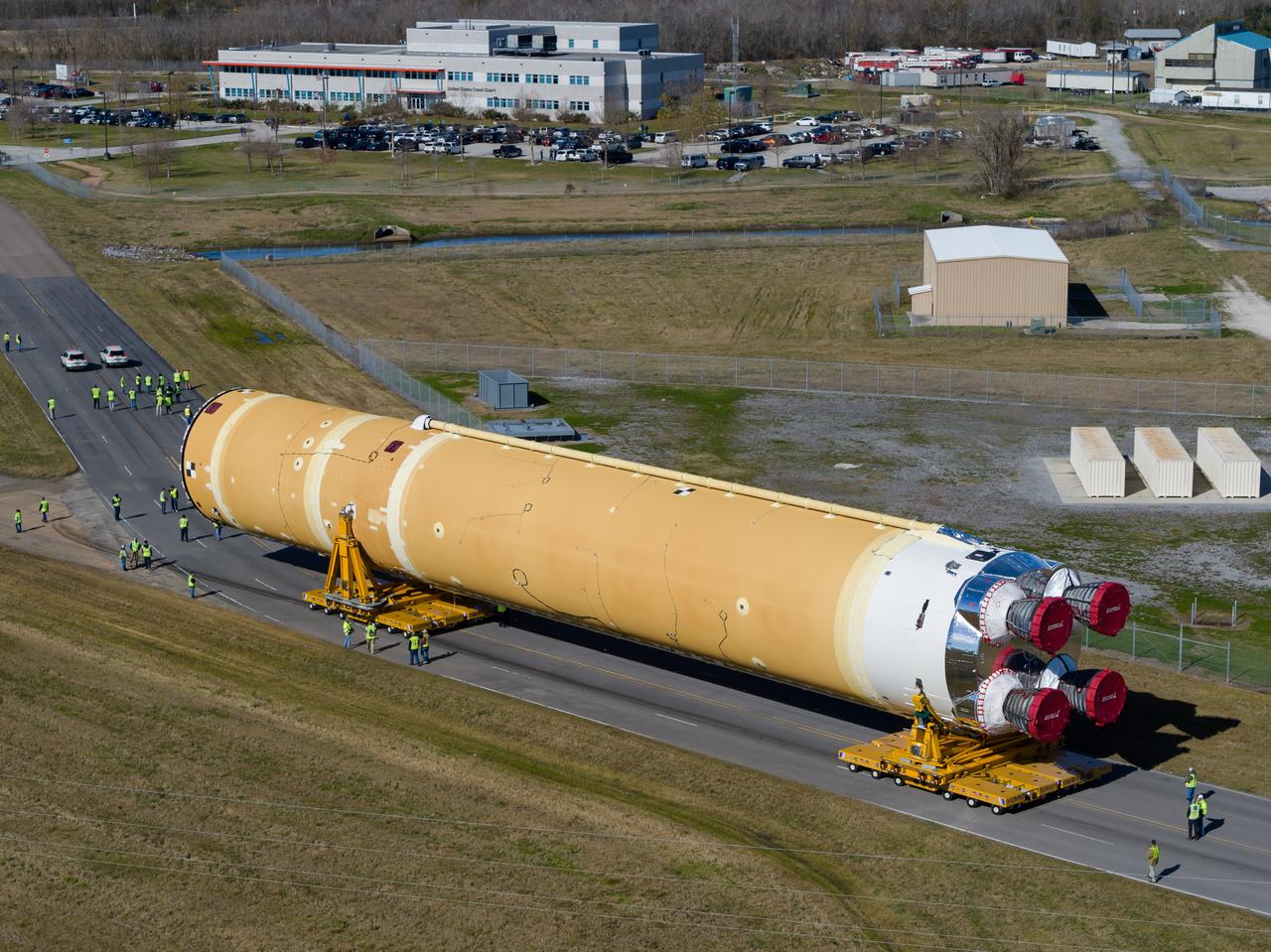

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
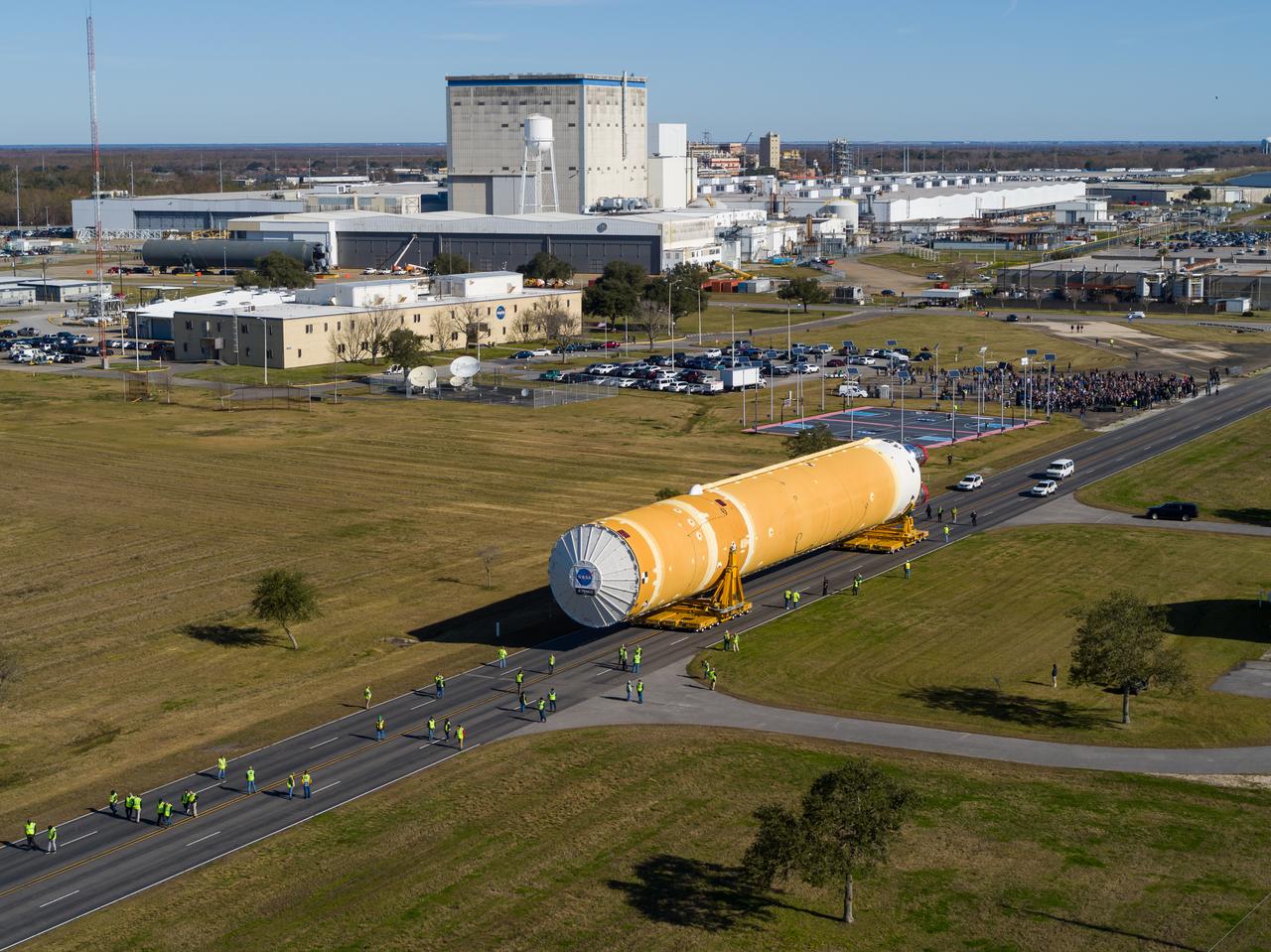

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
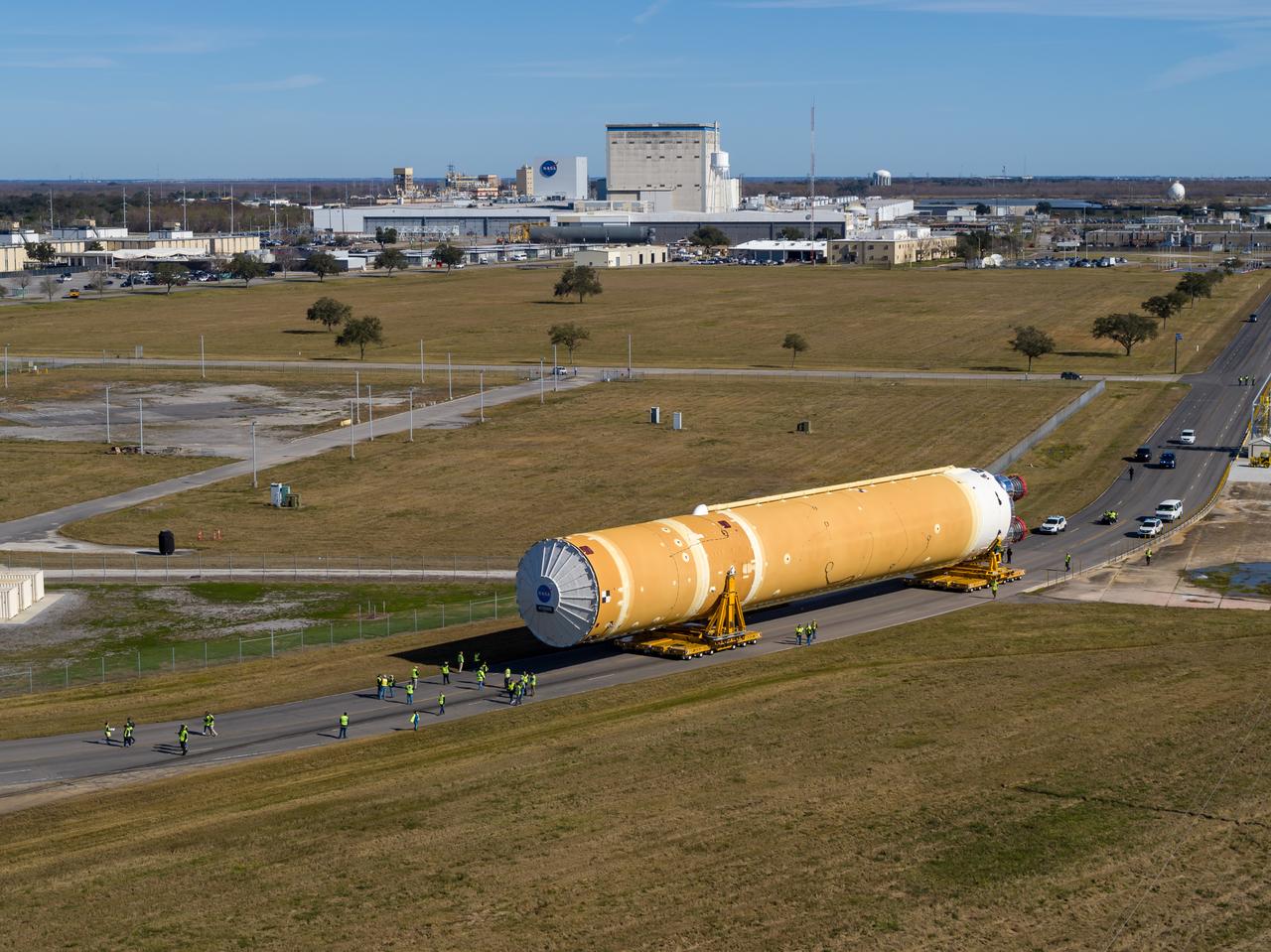

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
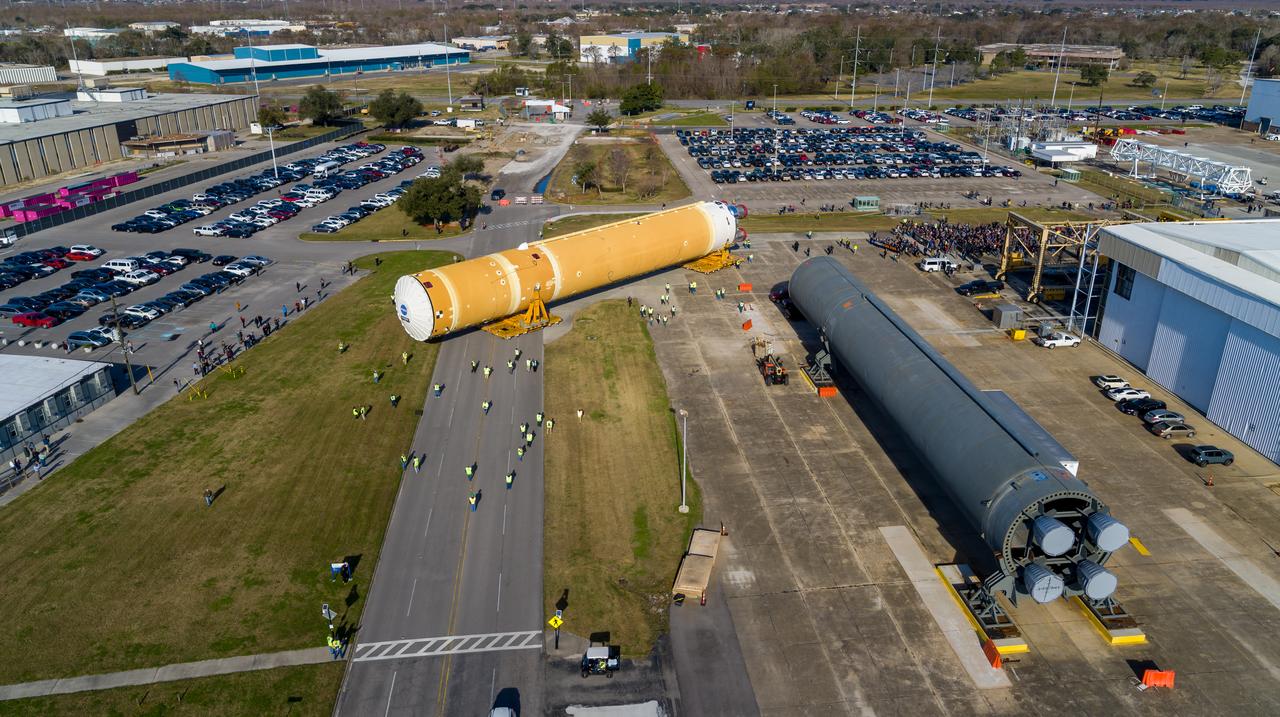

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
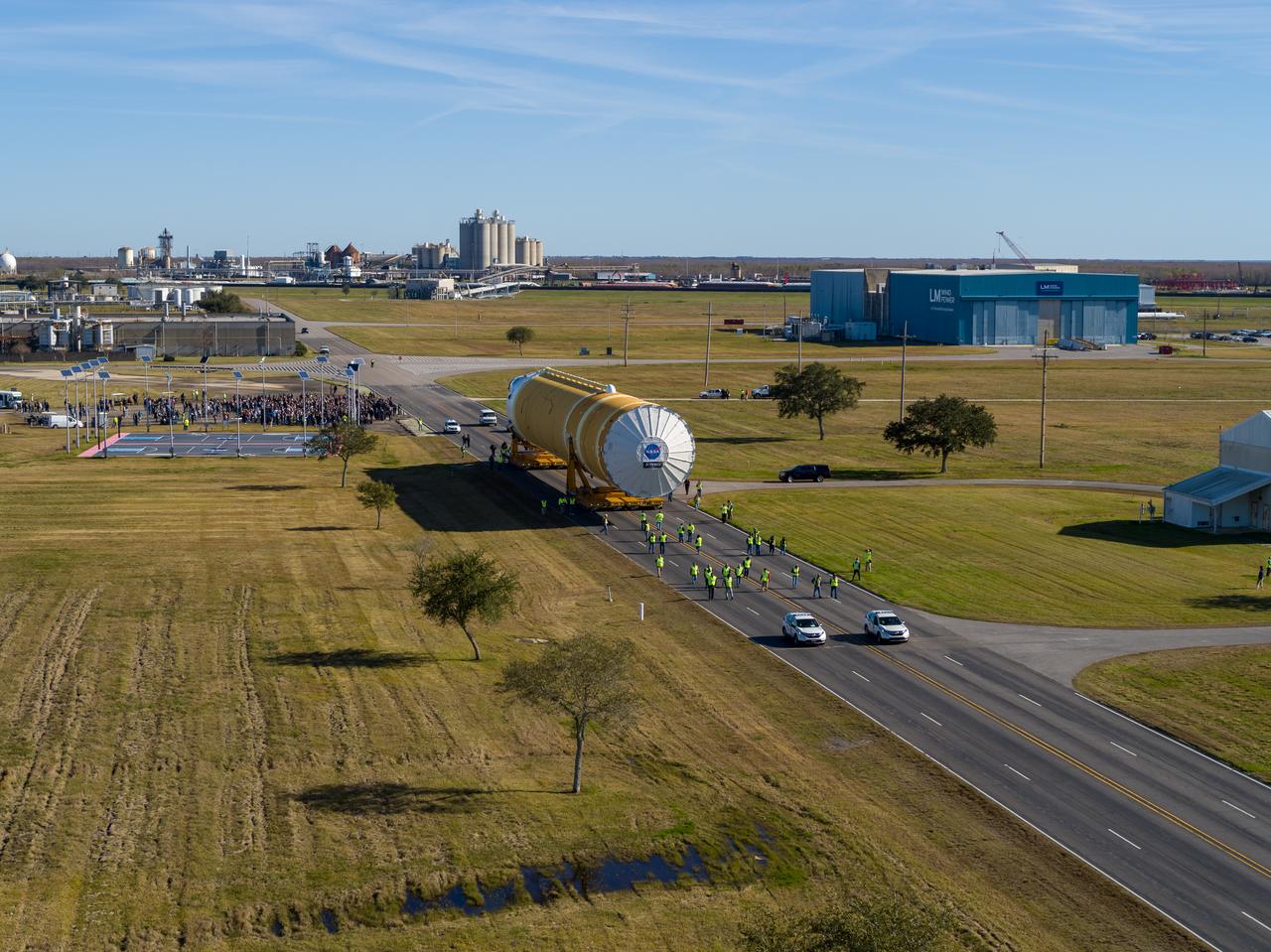

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
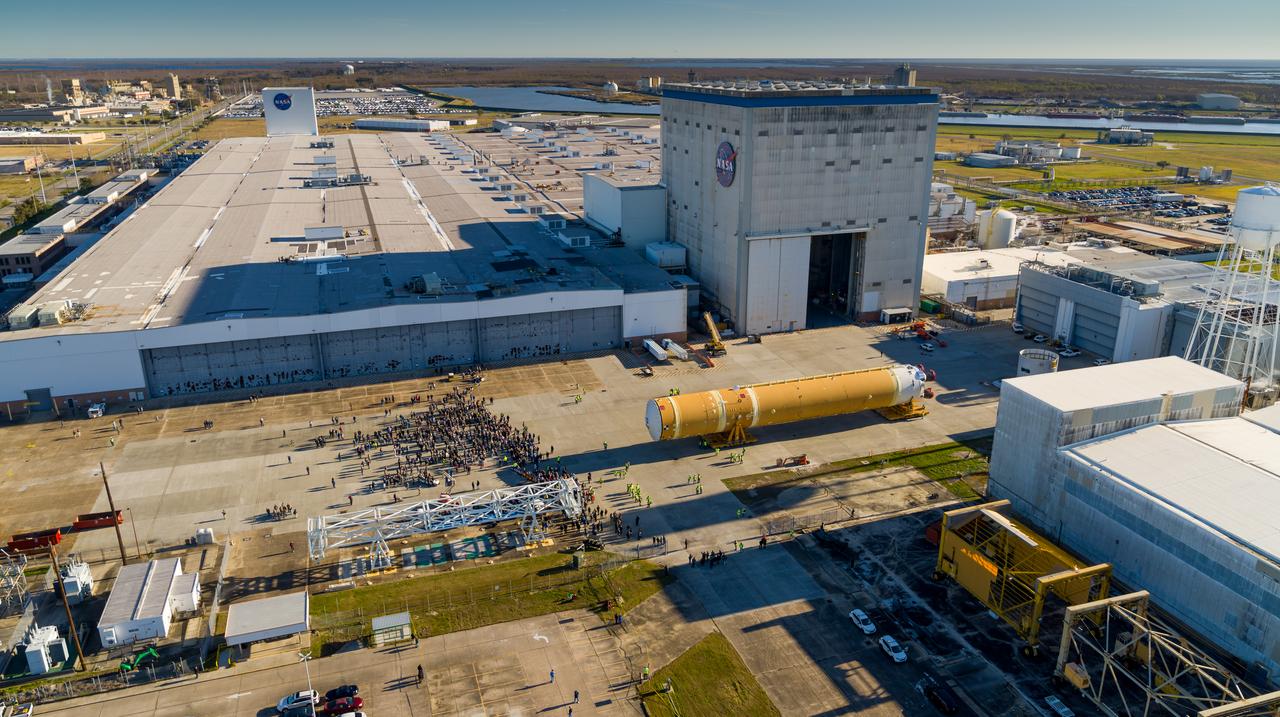

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
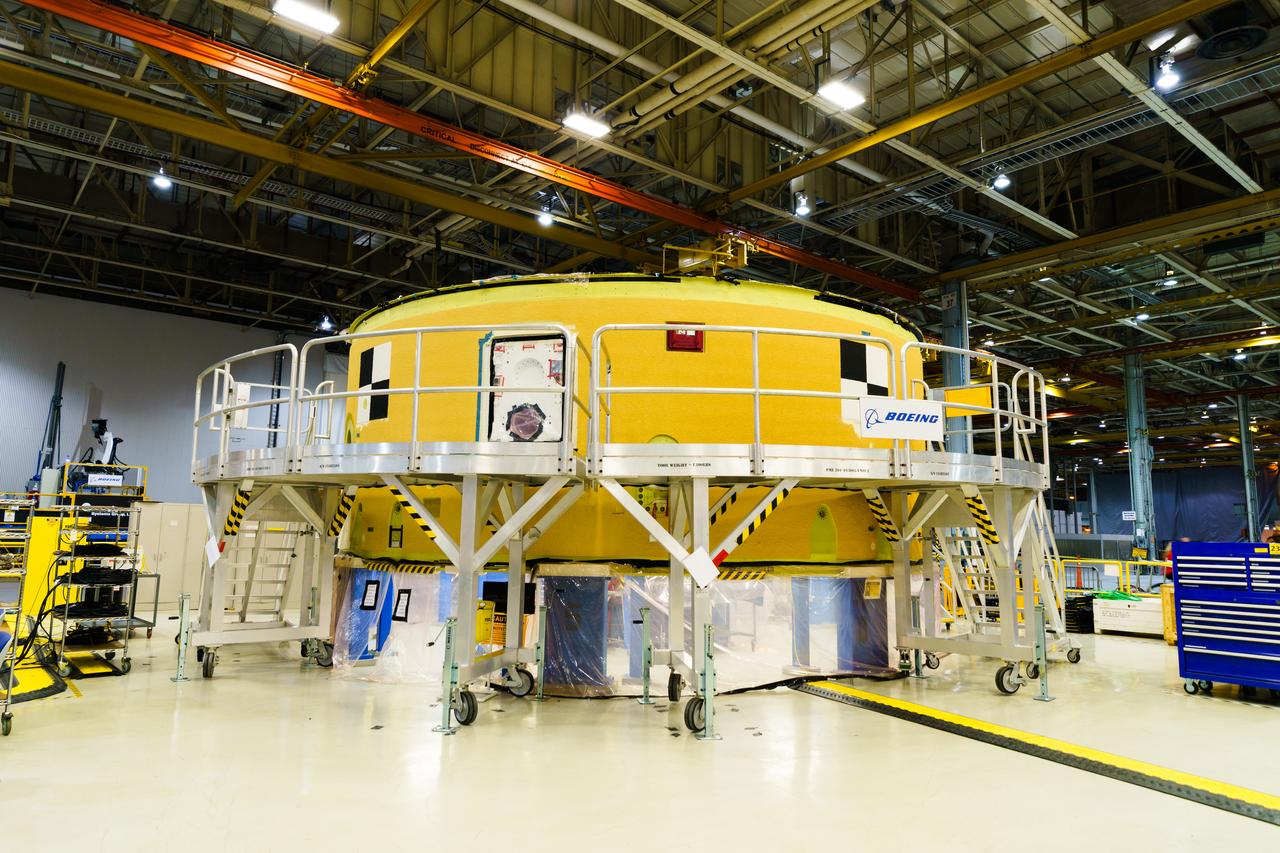

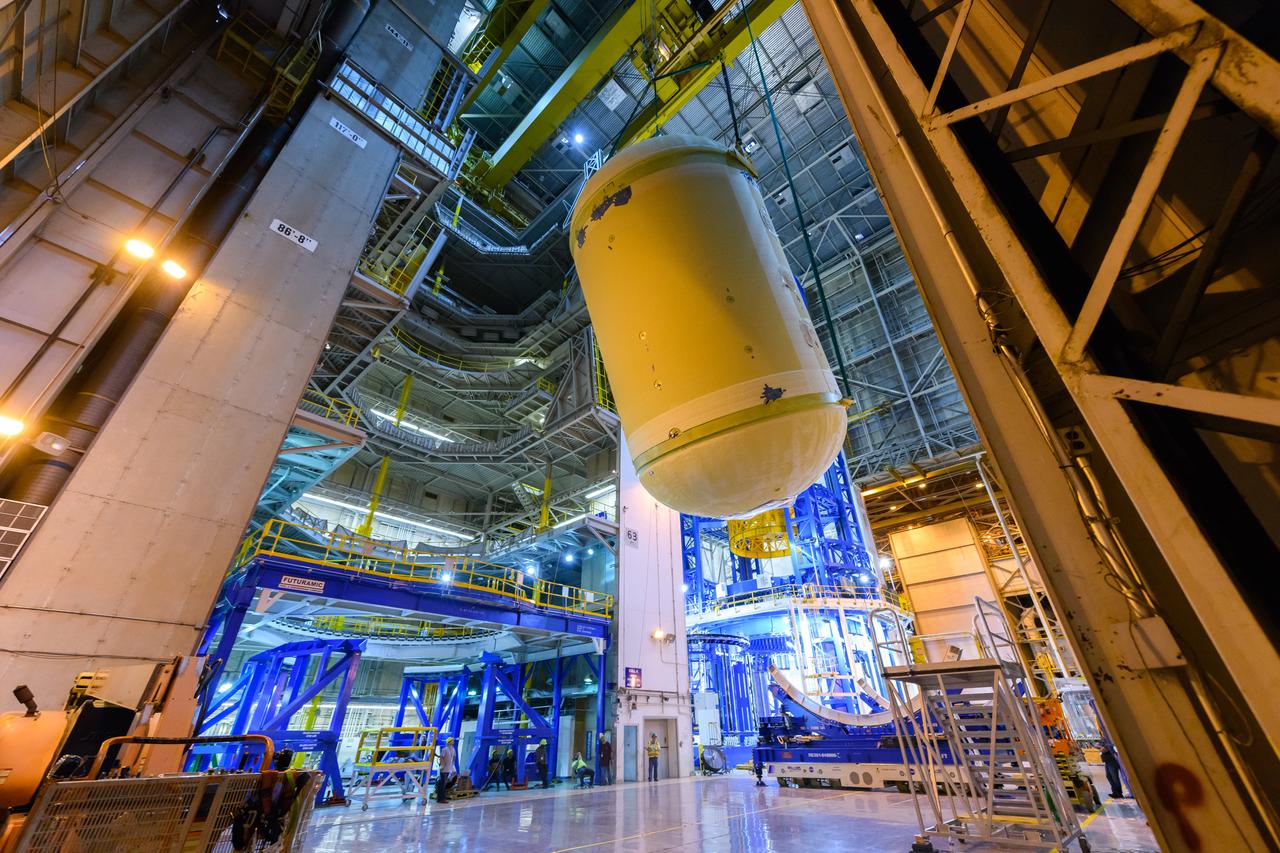
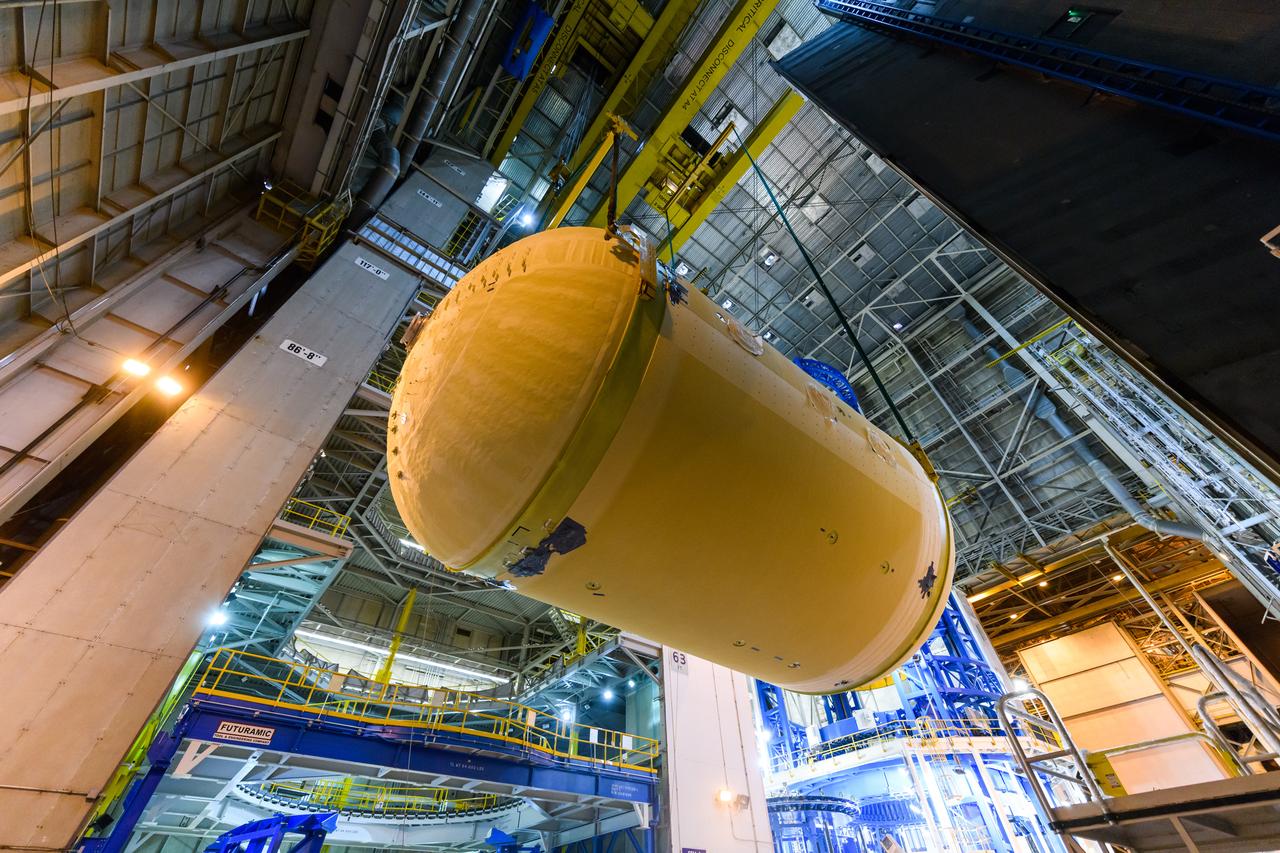
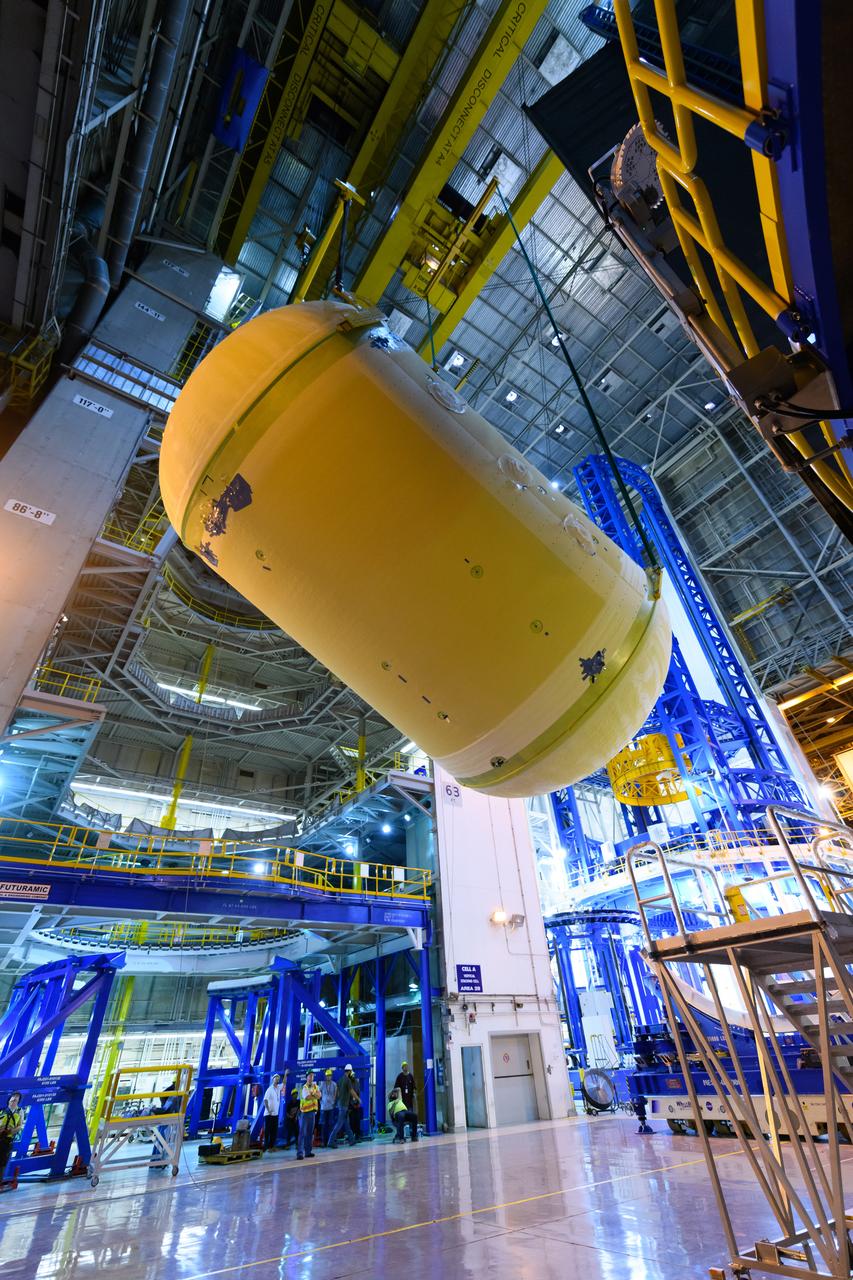
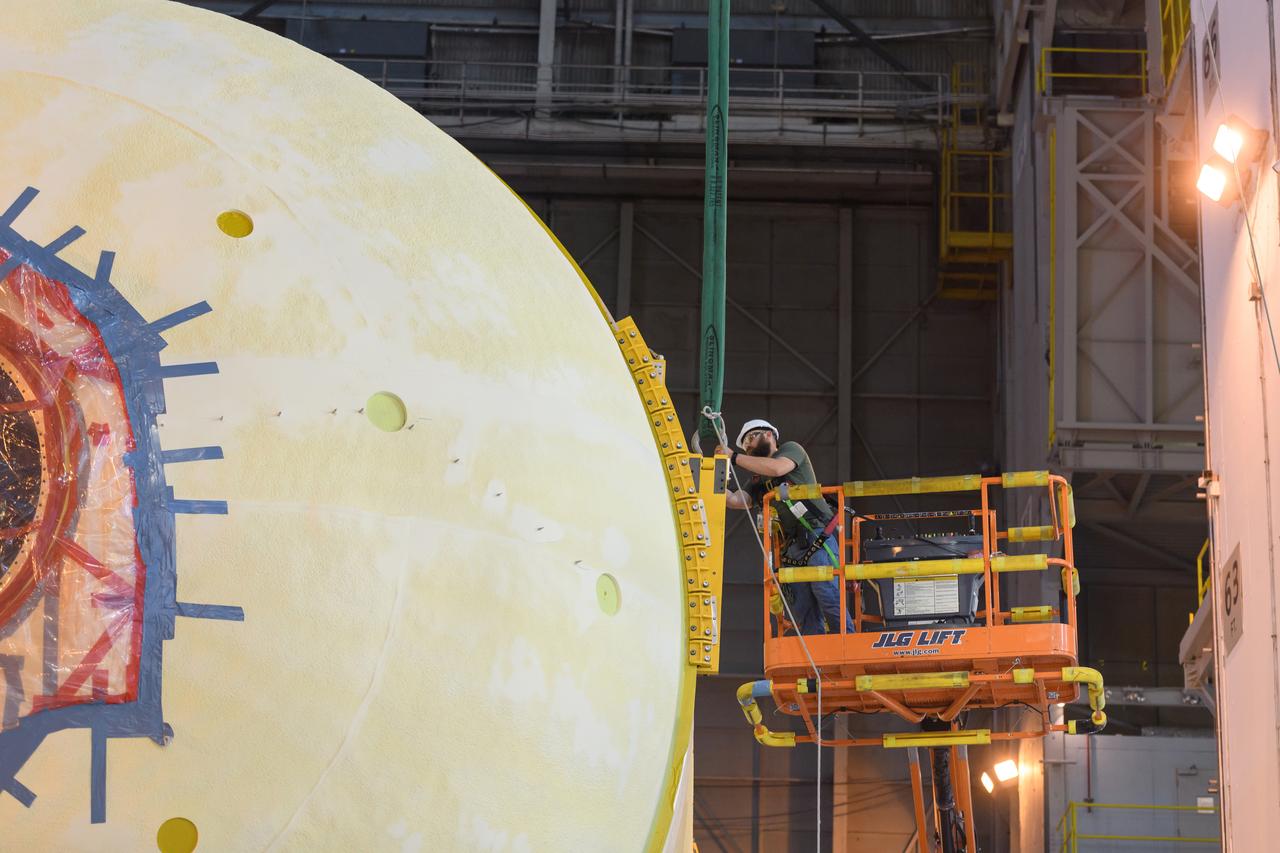
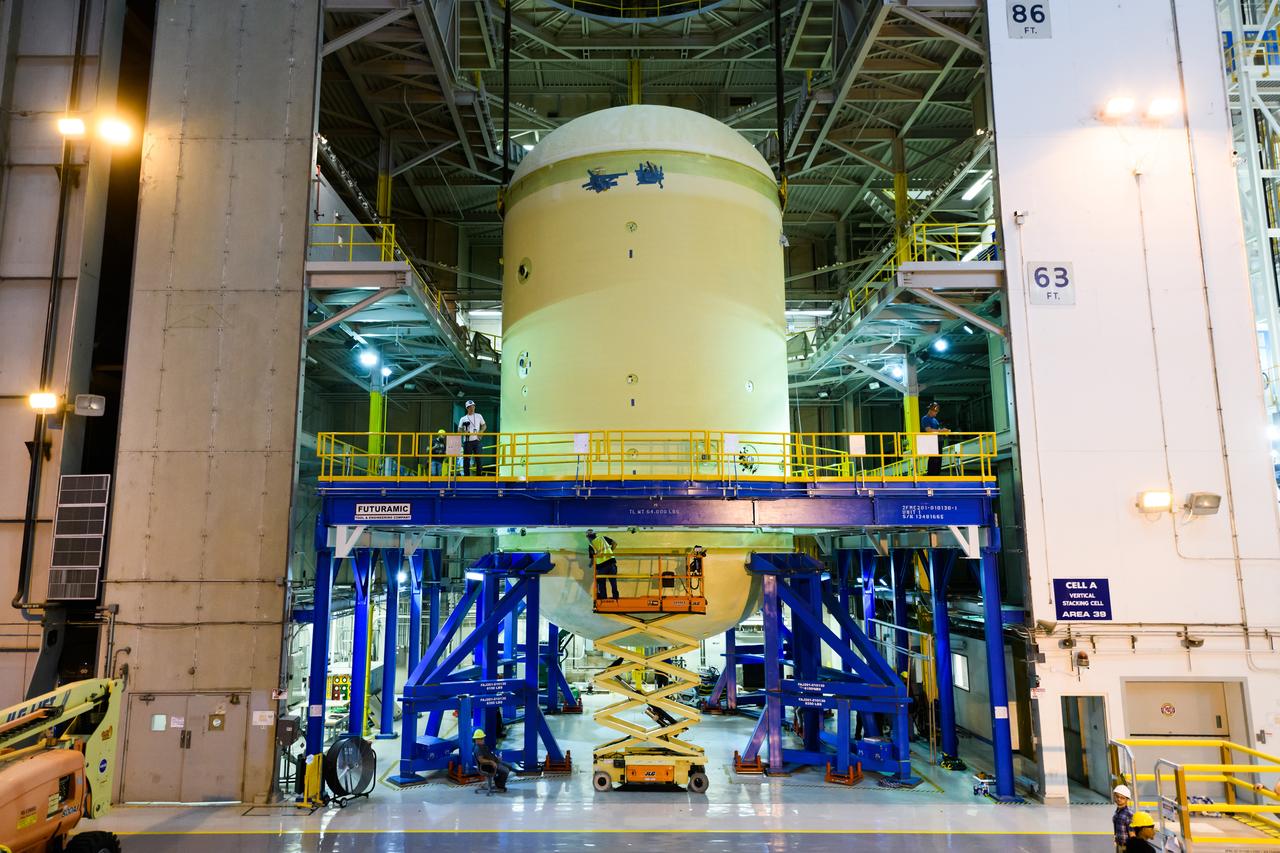
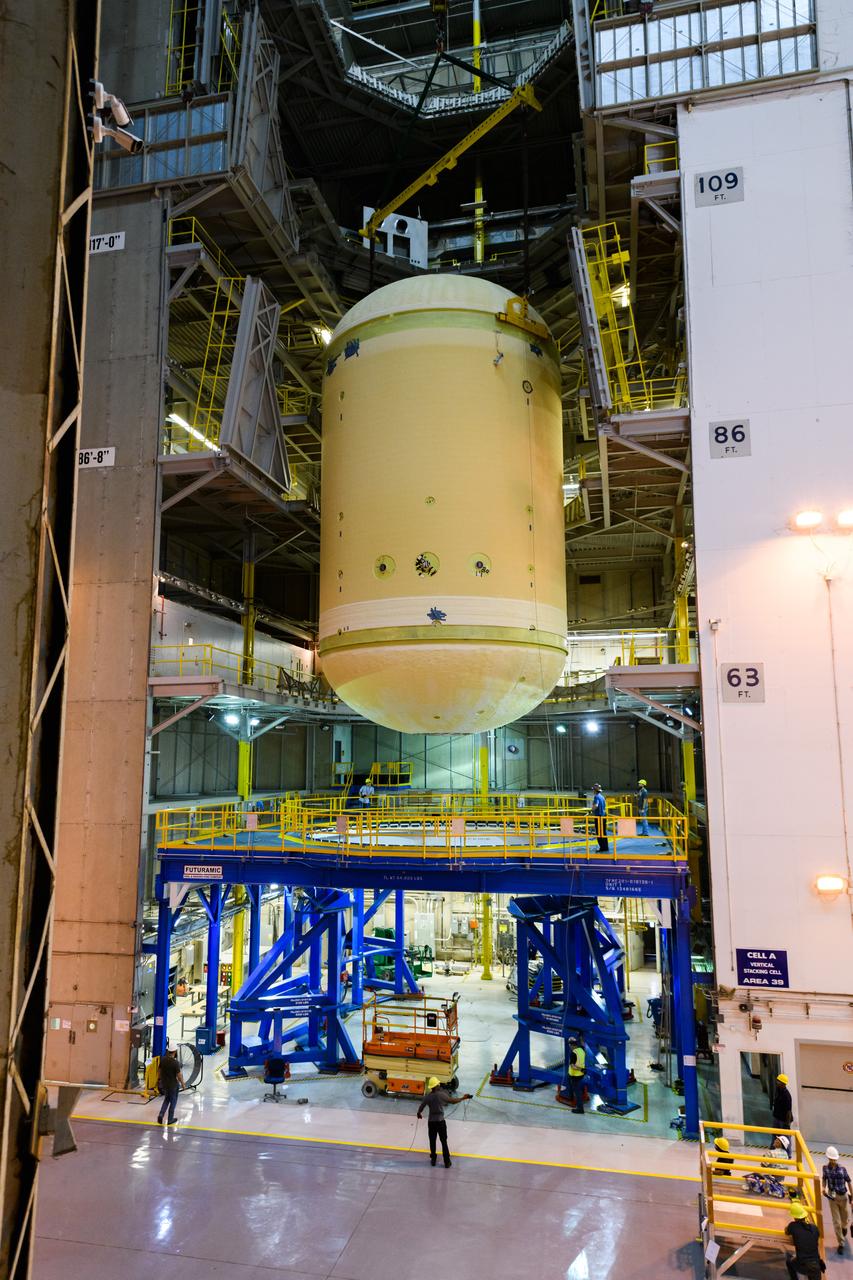
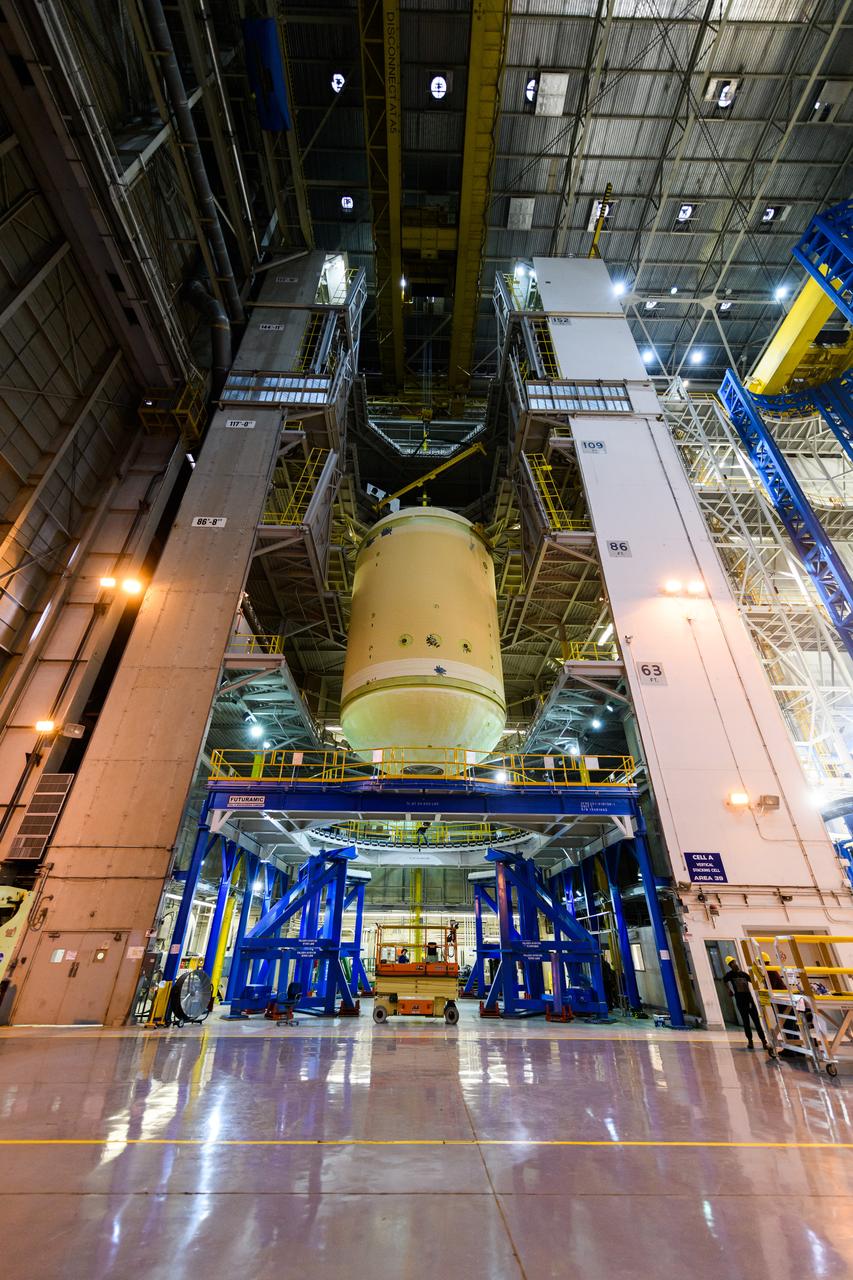
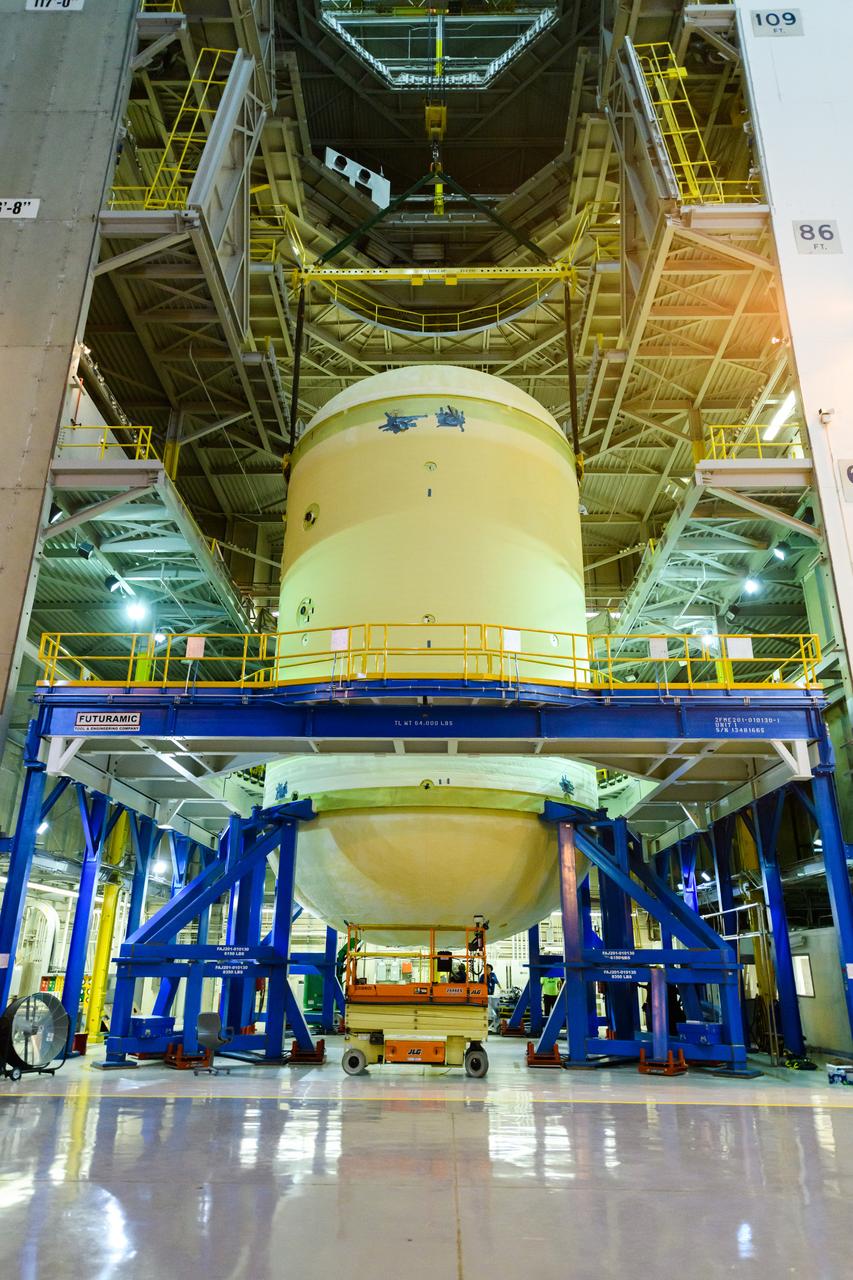
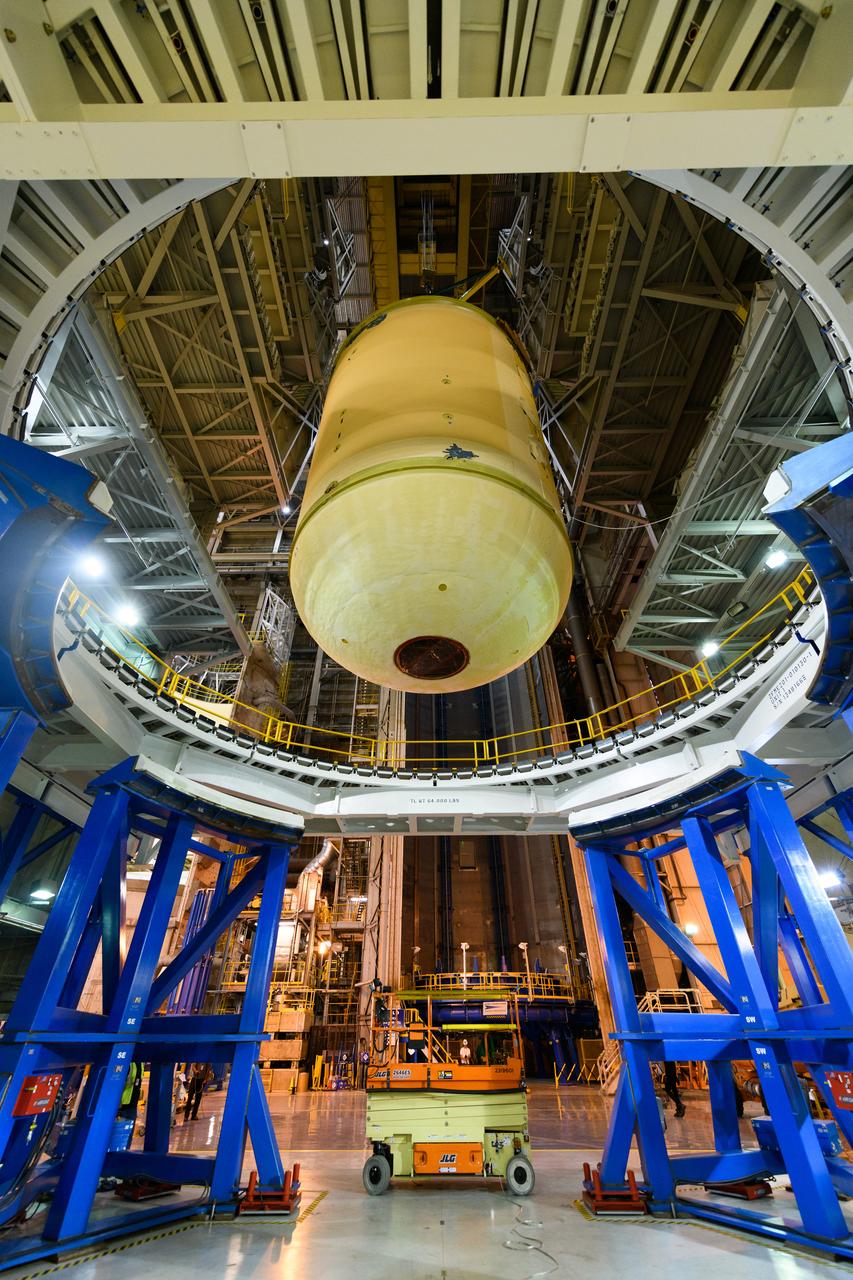
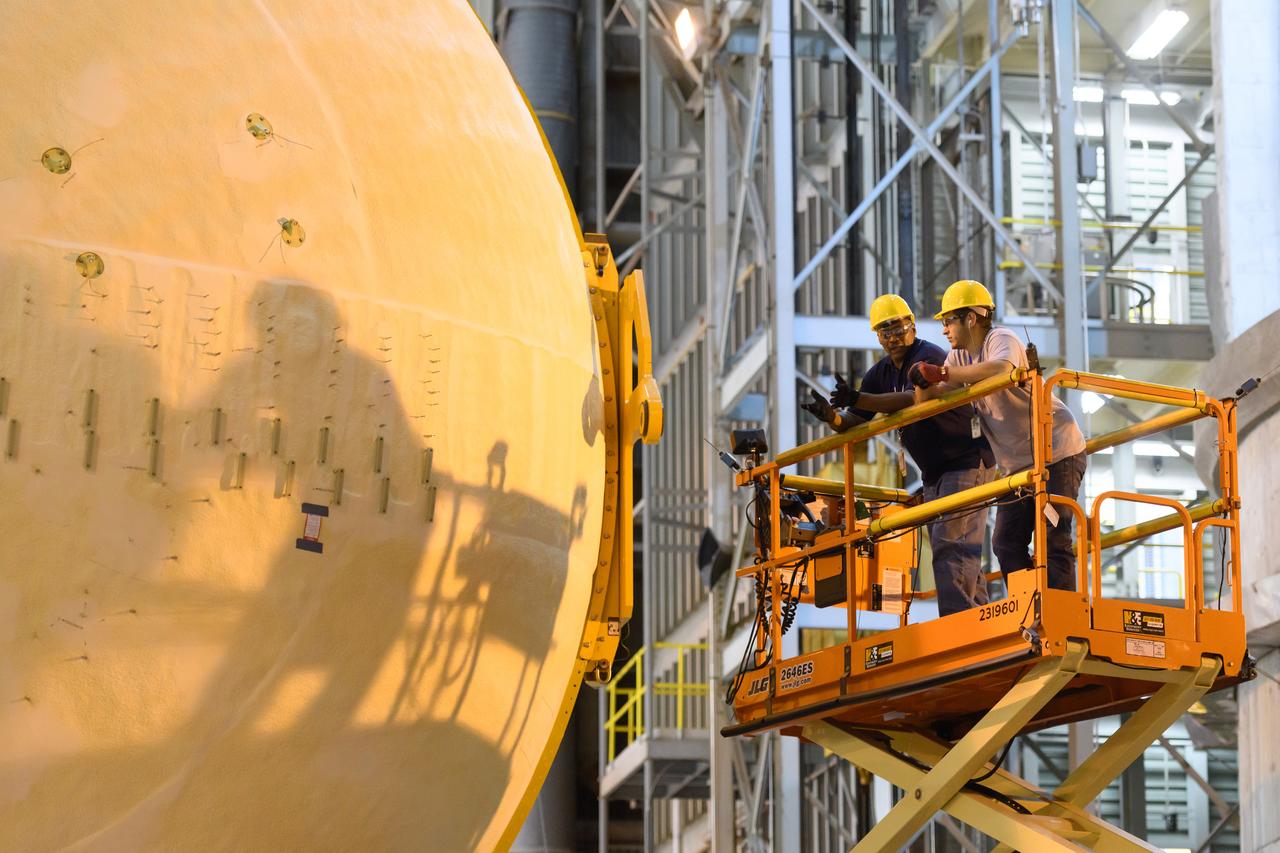
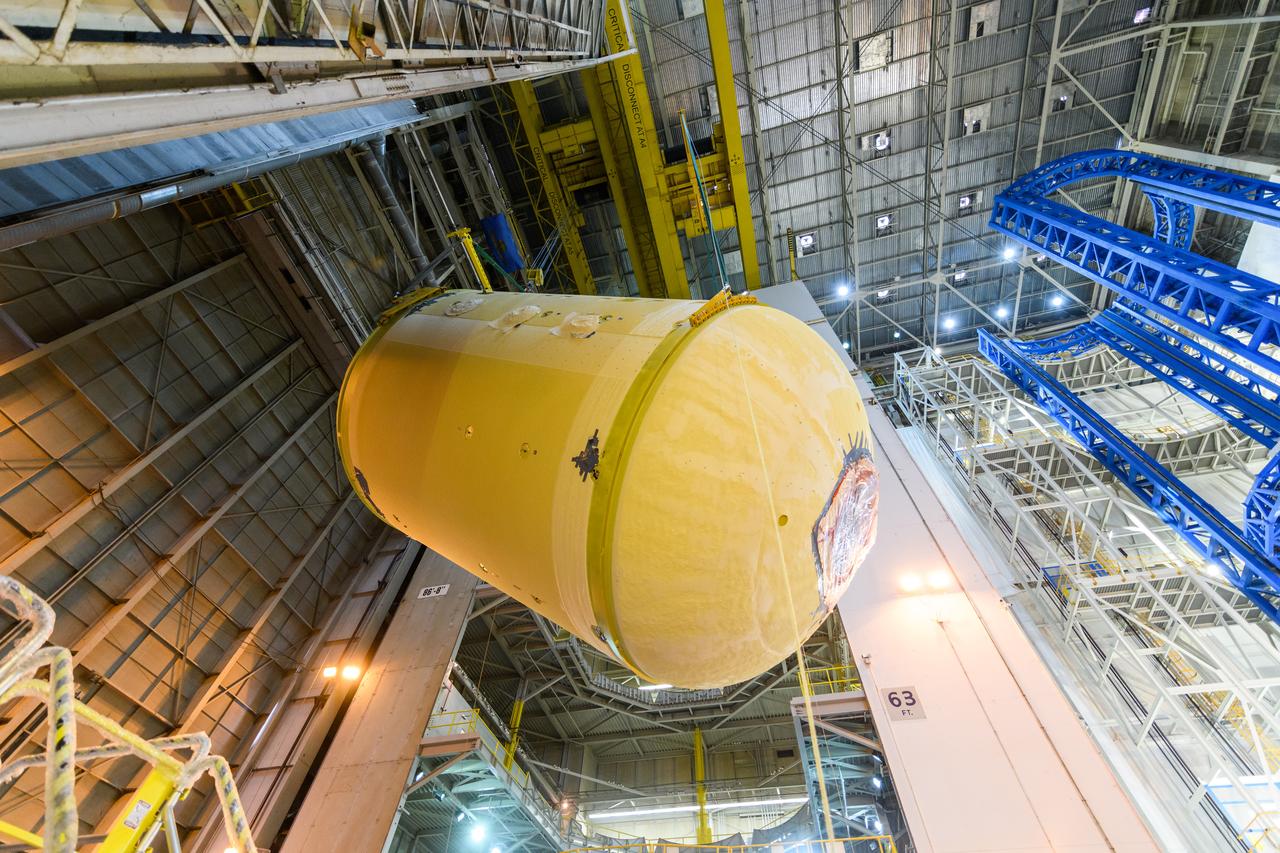
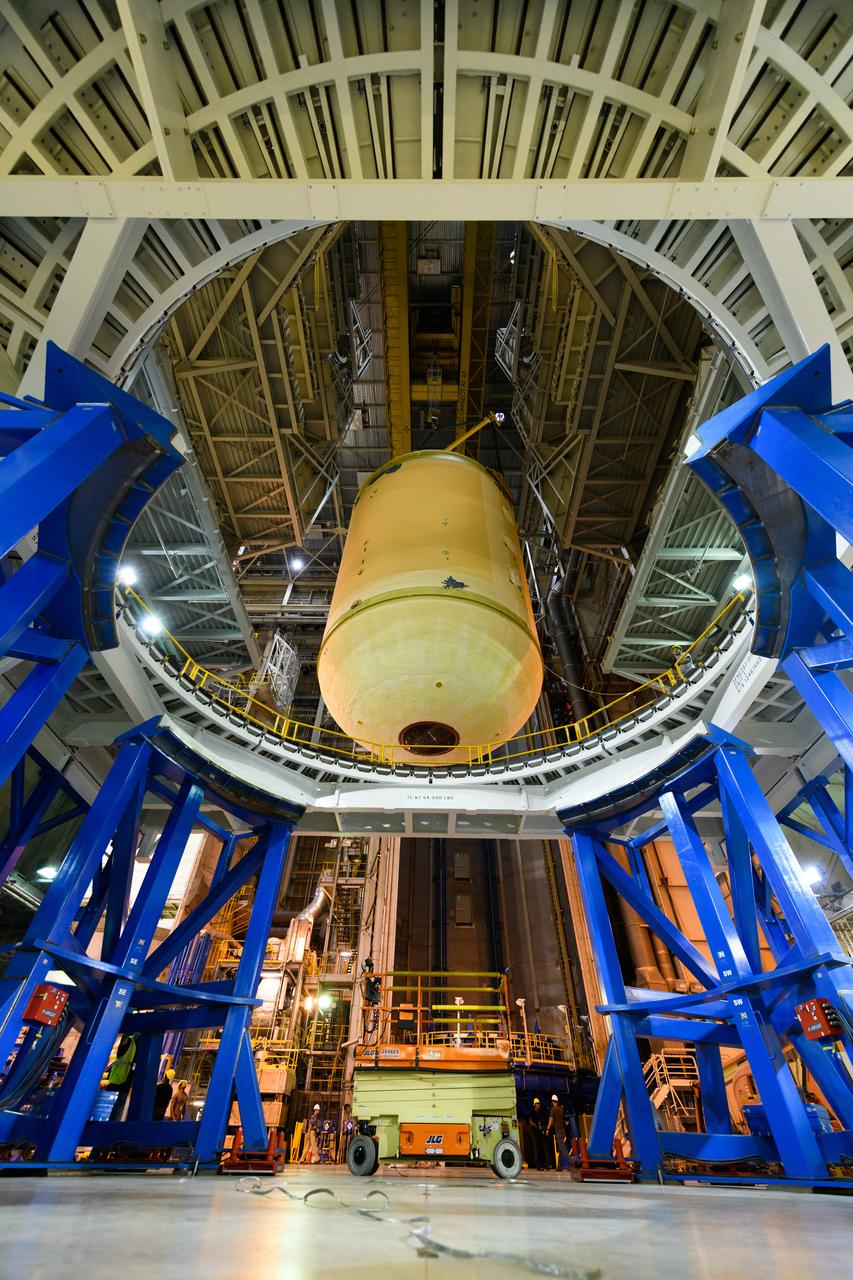
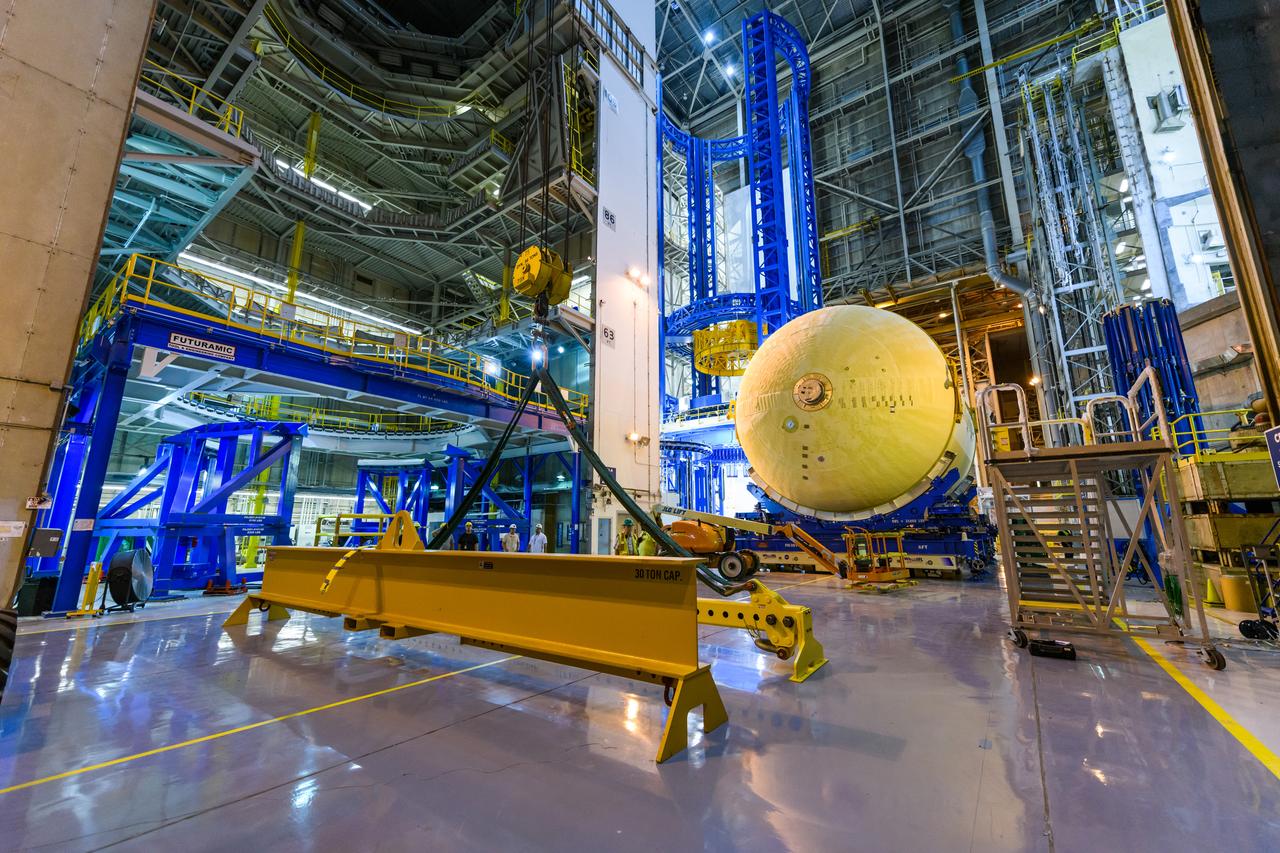
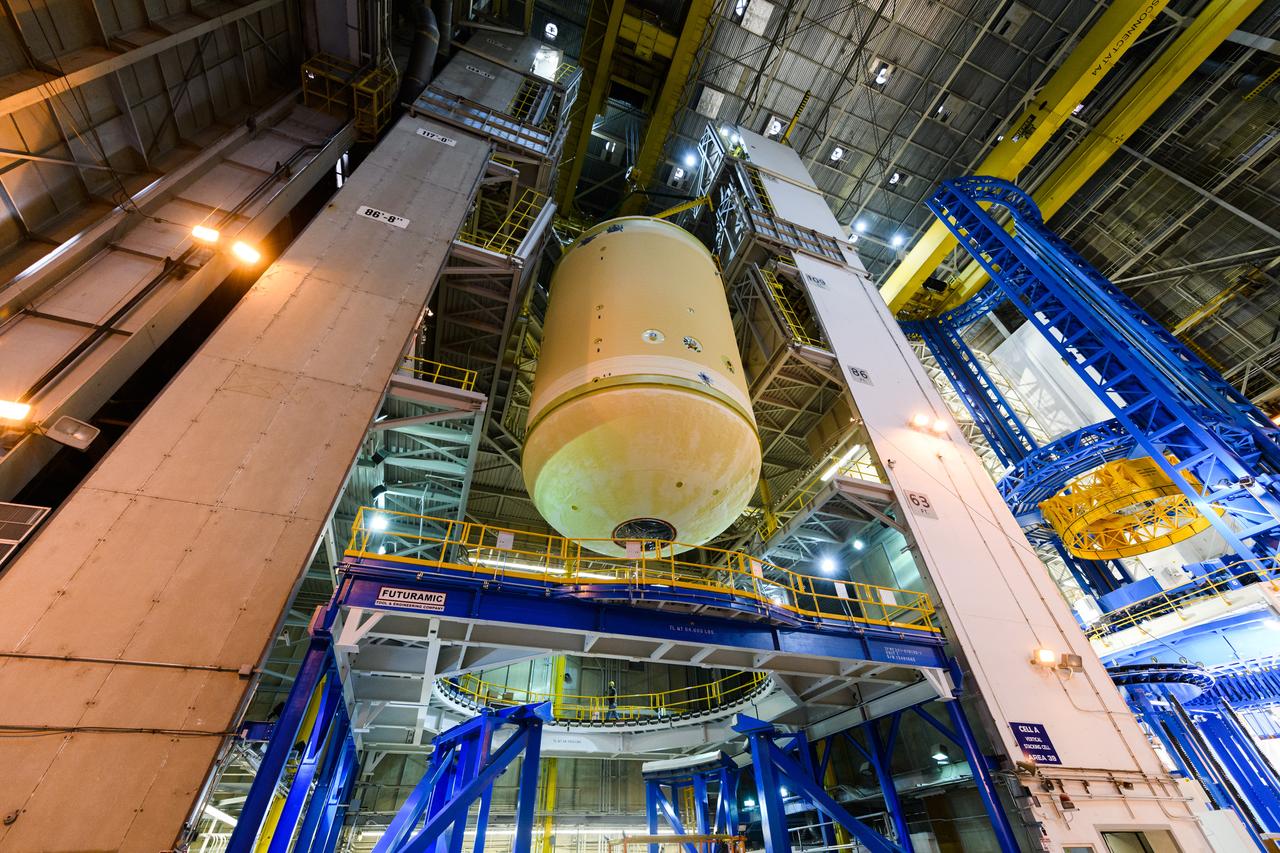
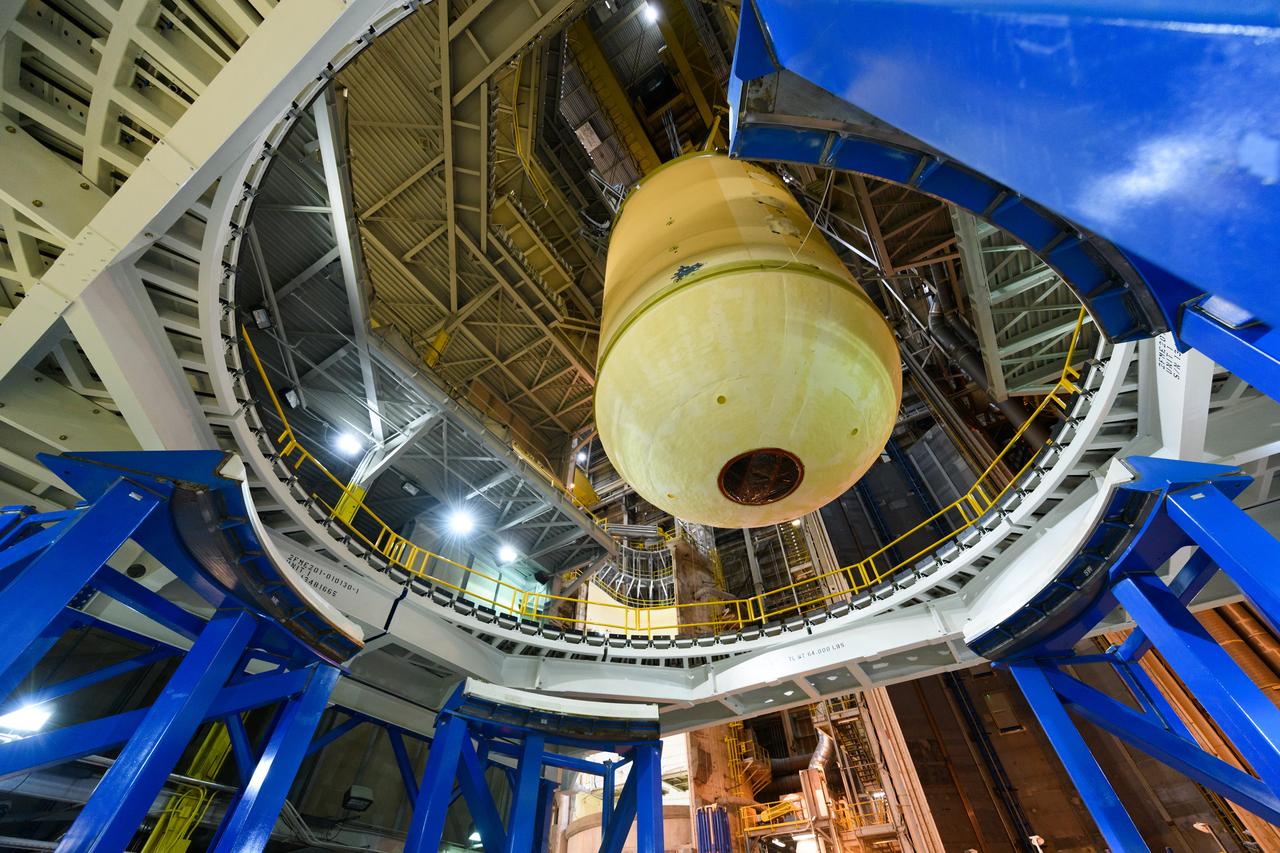
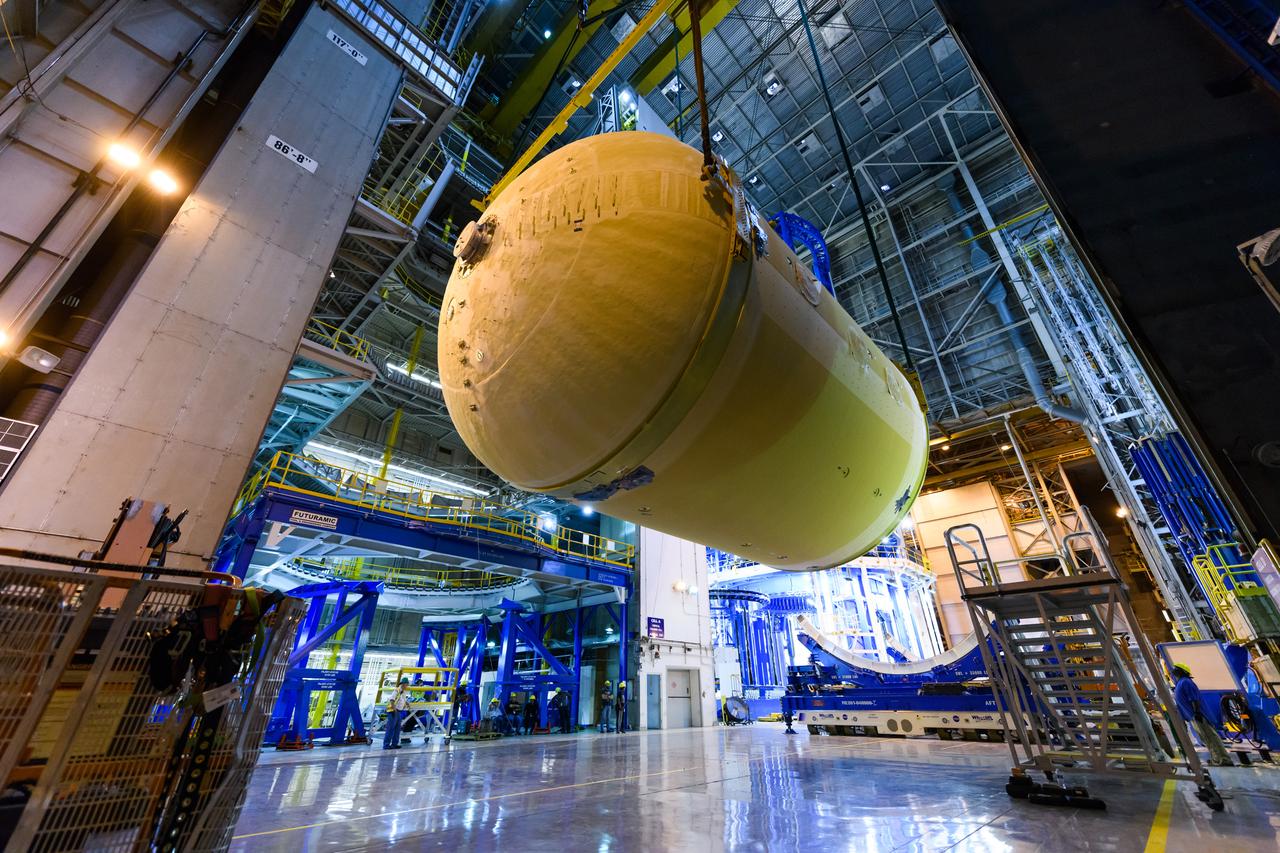
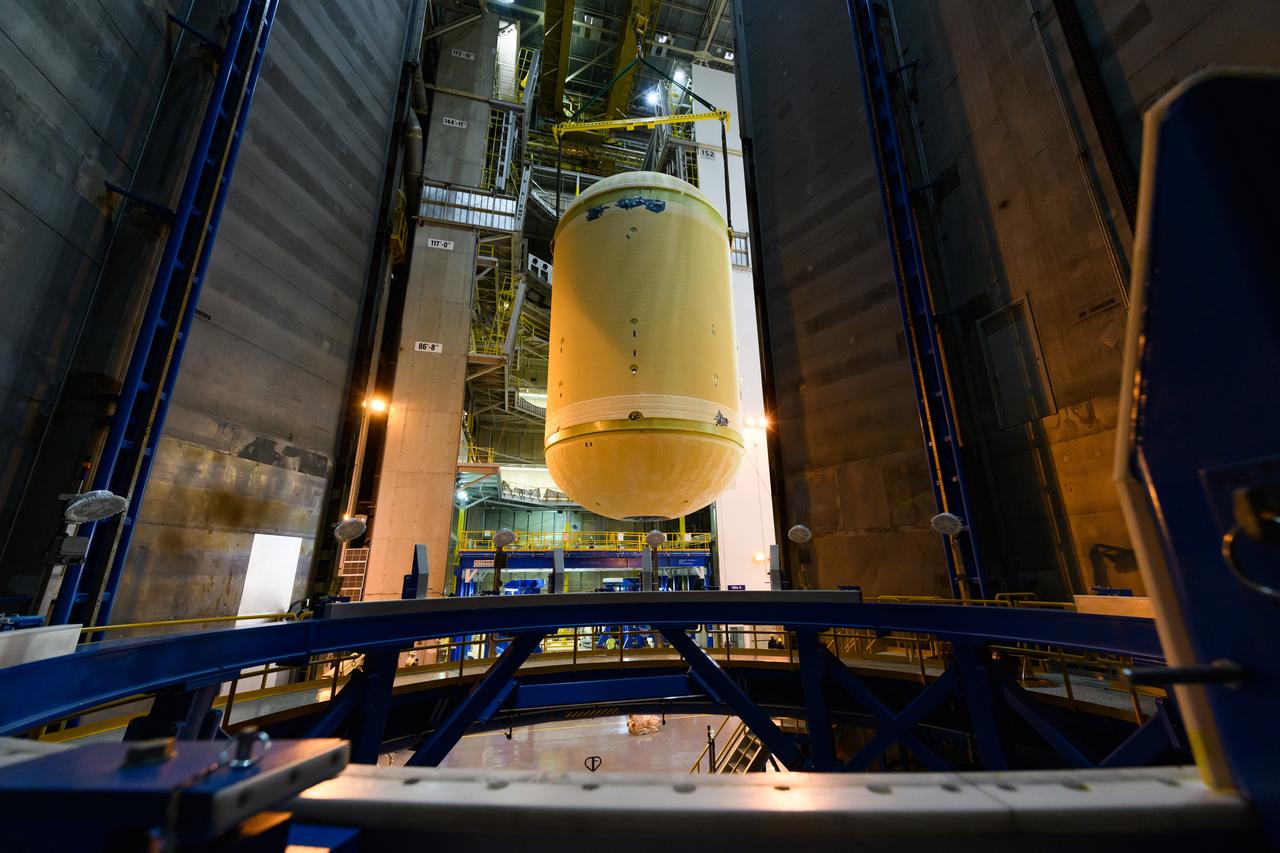
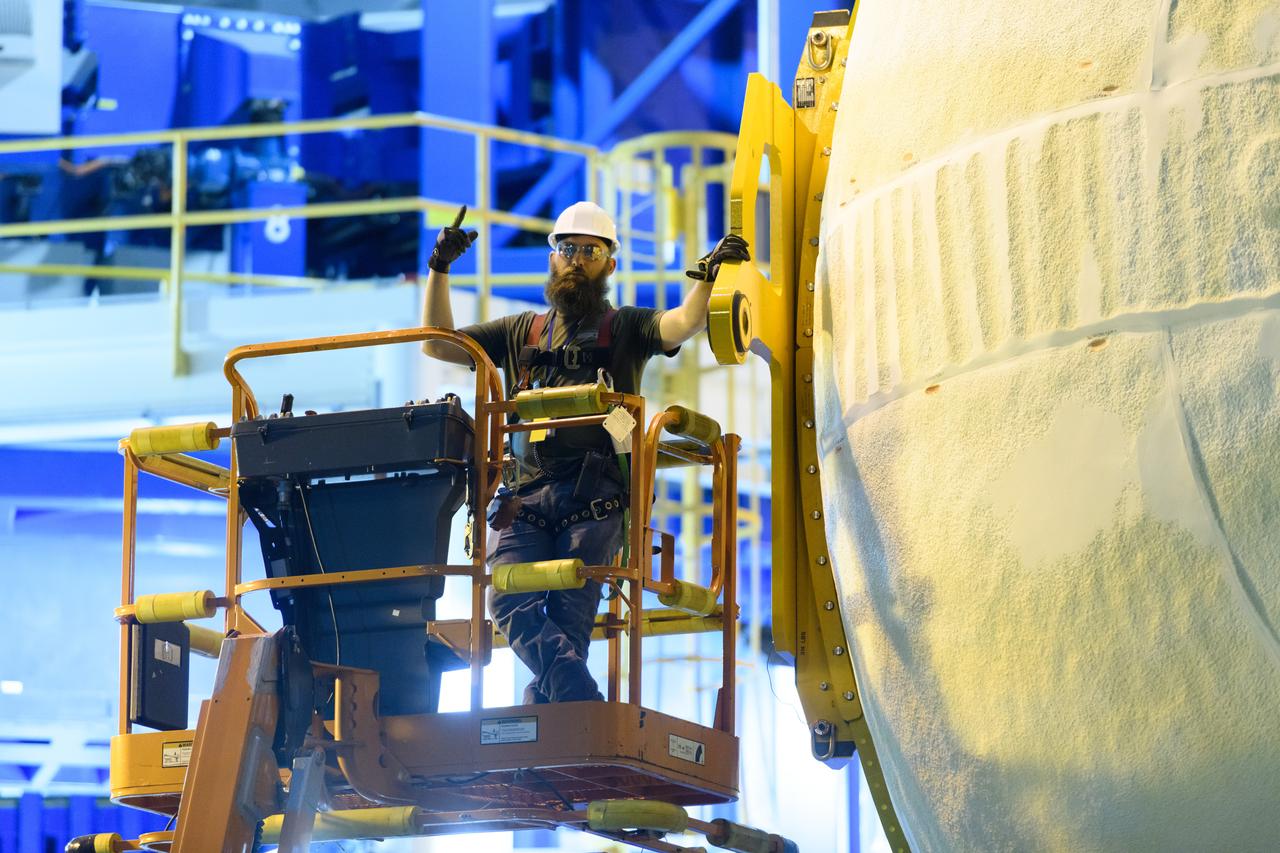
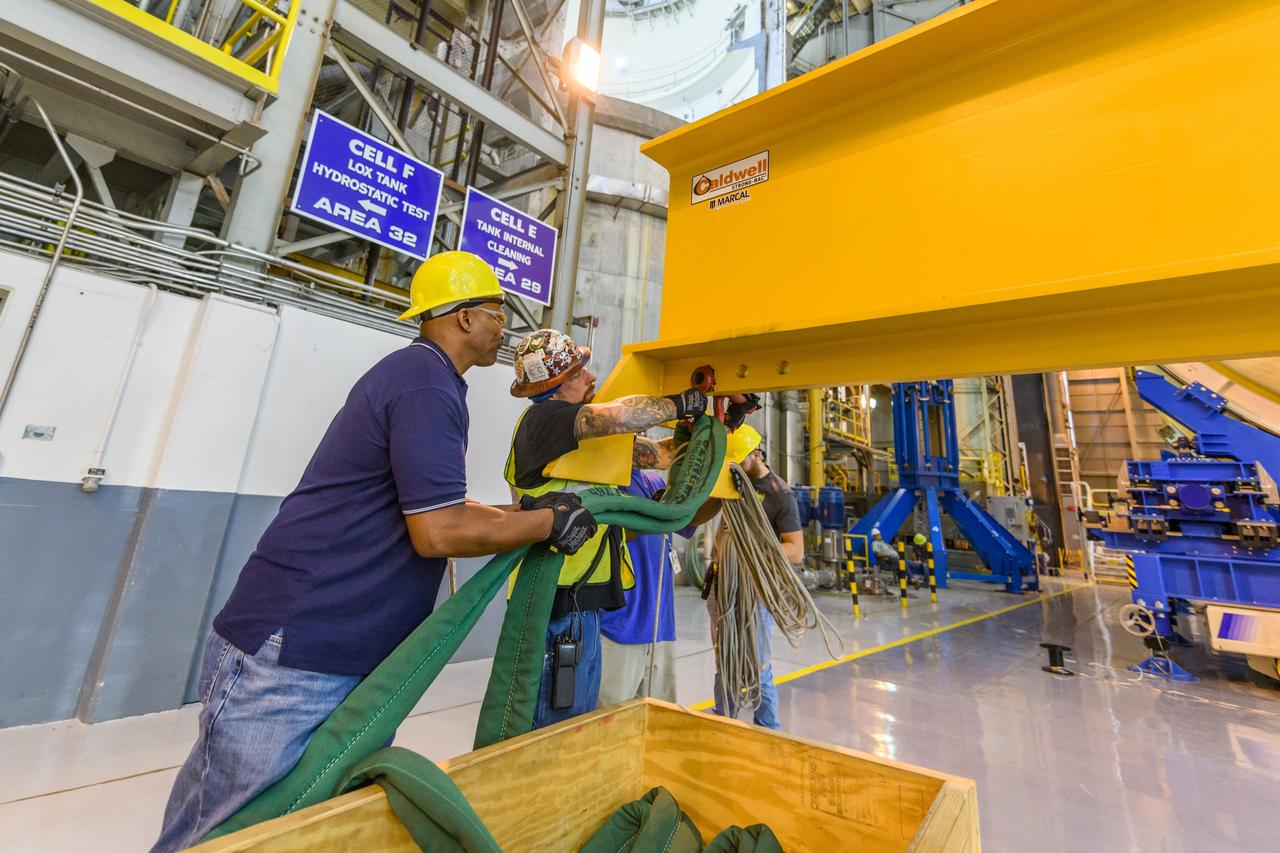
The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
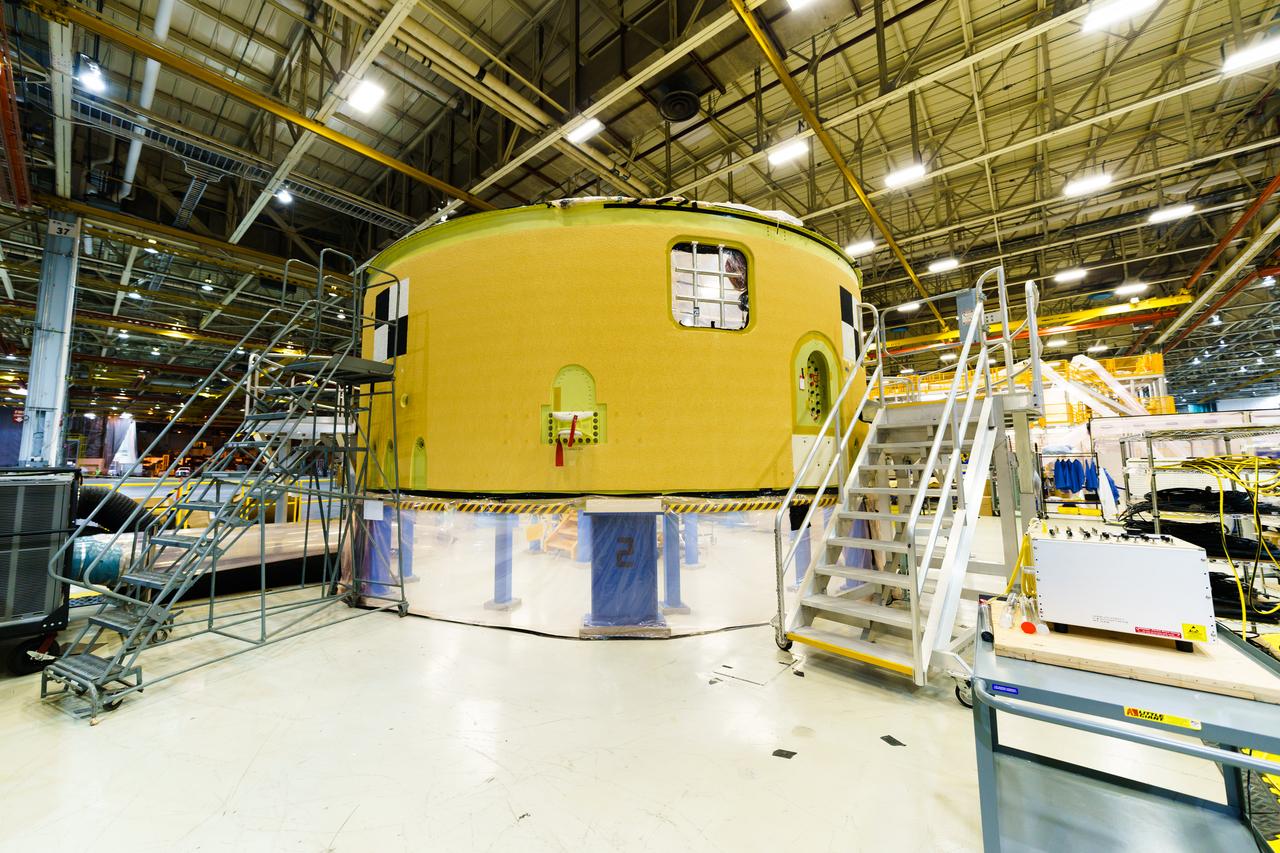

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
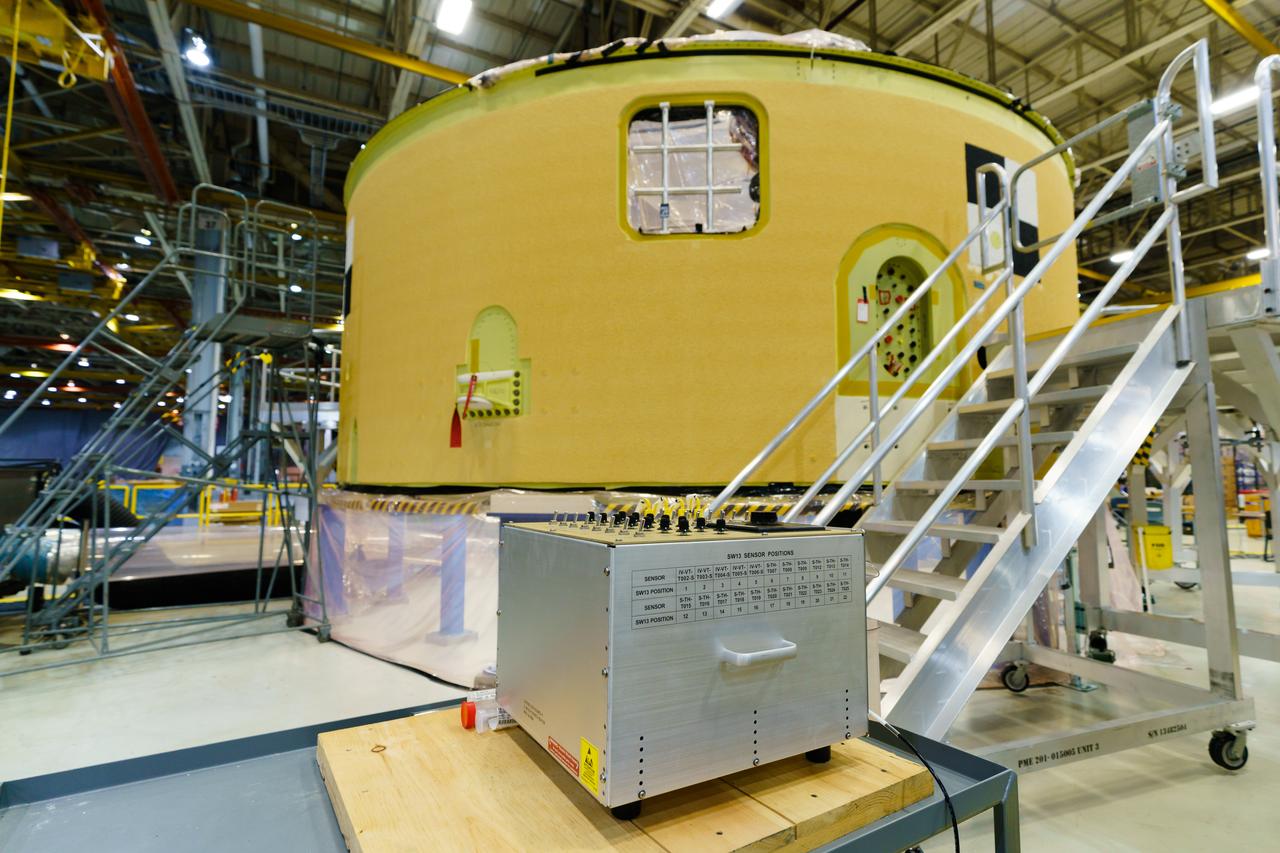

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
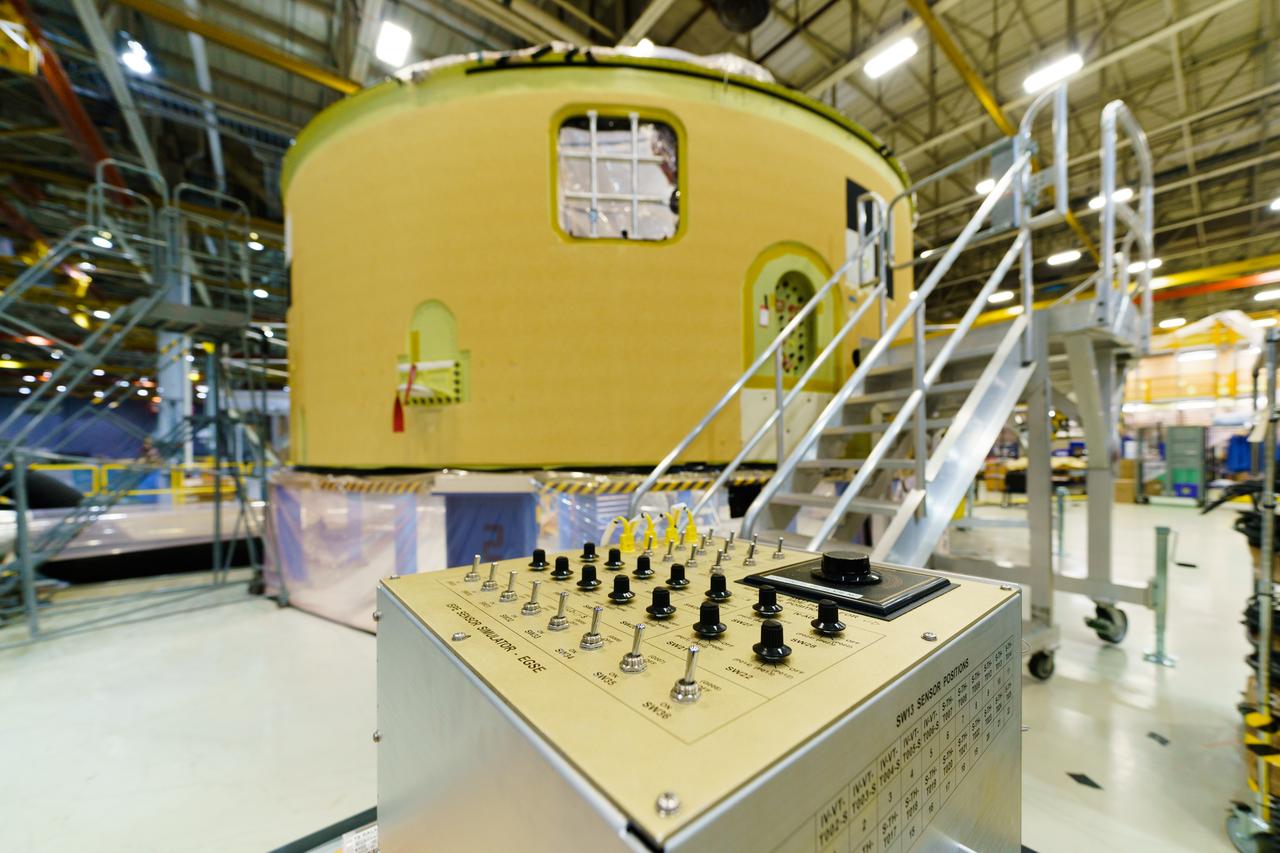

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
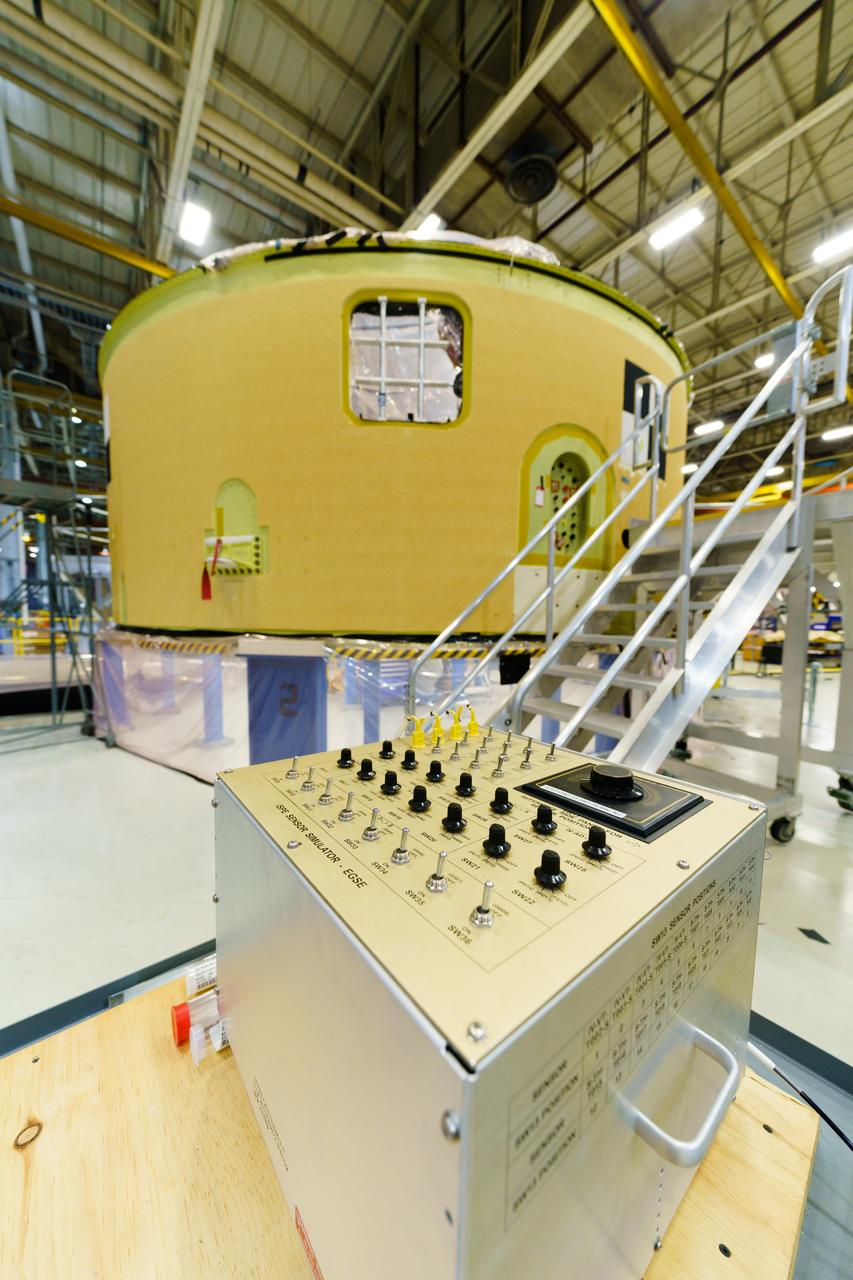

The forward skirt section of NASA's SLS rocket is completed and awaiting stacking for the EM-1 launch.
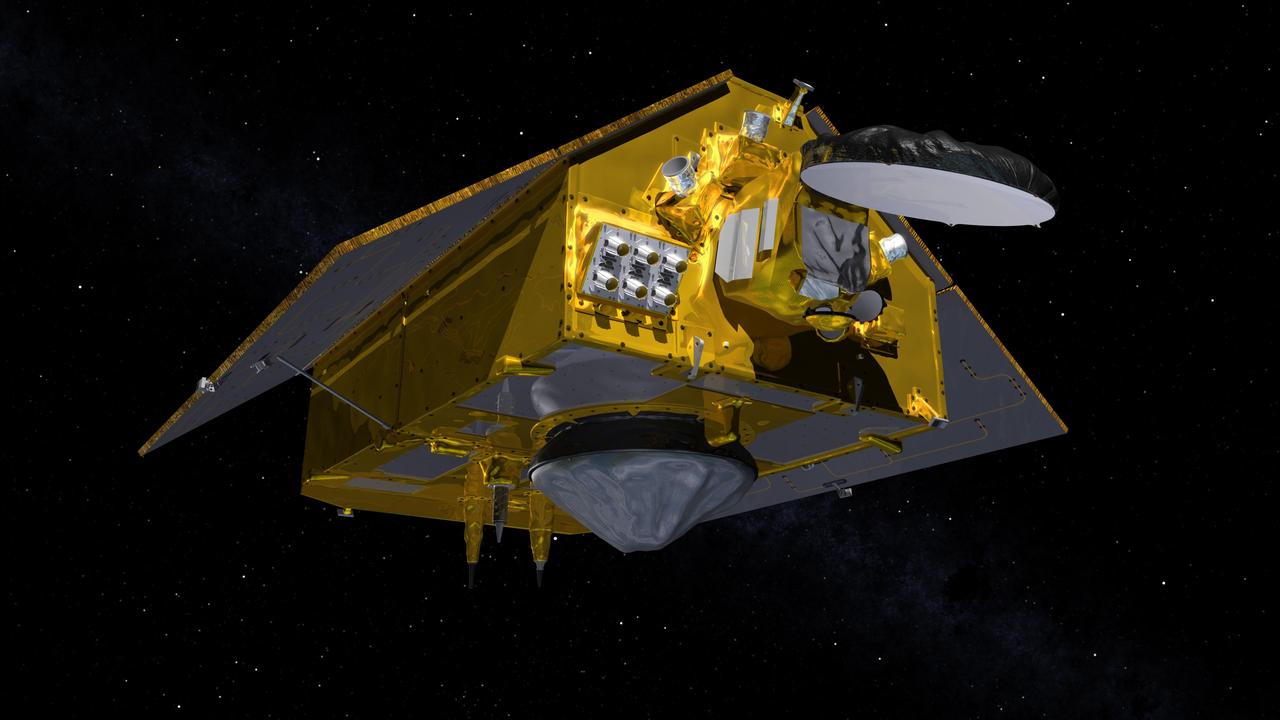

This illustration shows the front of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft in orbit above Earth with its deployable solar panels extended. As the world's latest ocean-monitoring satellite, it is launching on Nov. 10, 2020, to collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. The mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity that will help improve weather forecasts and climate models. The conelike instrument on the bottom (Earth-facing side) of the spacecraft is the satellite's Poseidon-4 radar altimeter. The disklike instrument at the front of the spacecraft is the Advanced Microwave Radiometer (AMR-C). Both instruments will be used together to measure ocean surface height. The gray rectangle with six cones attached at the front-left of the spacecraft is part of the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation (GNSS-RO) instrument. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich extends the near-30-year record of satellite measurements of sea level initiated by the U.S.-European TOPEX/Poseidon mission in 1992 and that continued with the Jason-1, 2, and 3 series of sea level observation satellites. Launched in 2016, Jason-3 is currently providing data. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). Other partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the intergovernmental European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), and France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24106
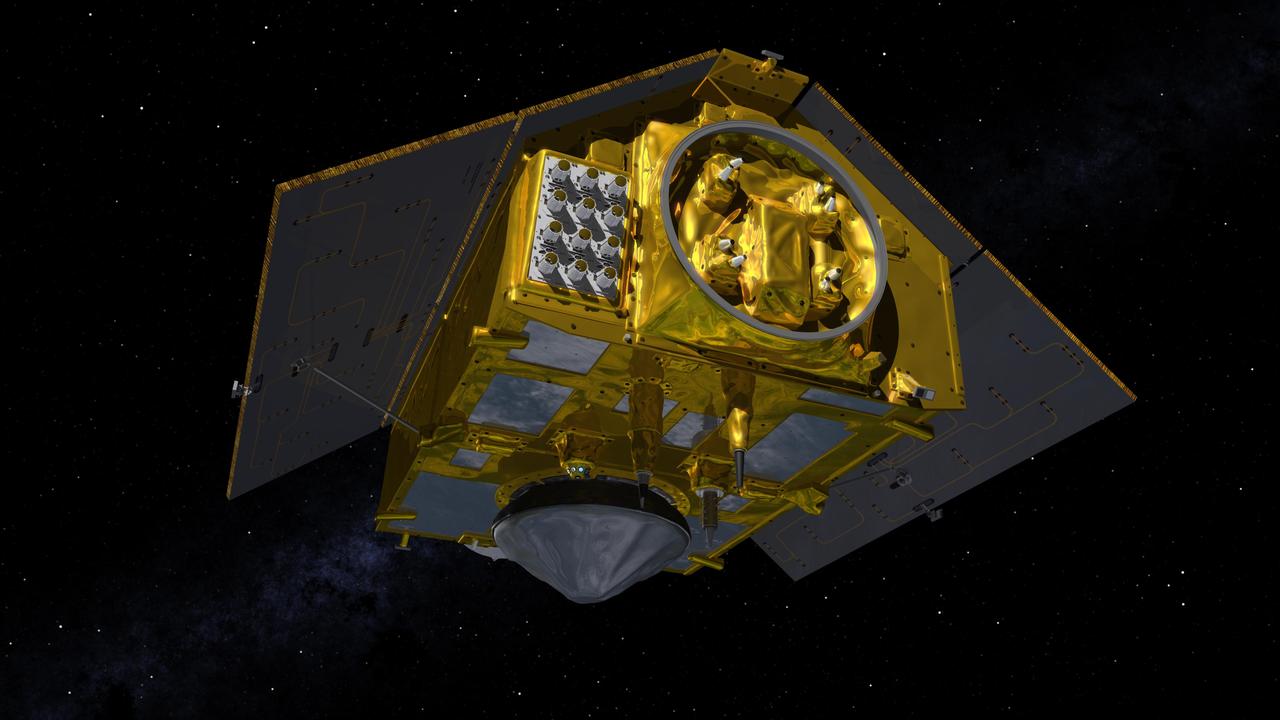

This illustration shows the rear of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft in orbit above Earth with its deployable solar panels extended. As the world's latest ocean-monitoring satellite, it is launching on Nov. 10, 2020, to collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. The mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity that will help improve weather forecasts and climate models. The conelike instrument on the bottom (Earth-facing side) of the spacecraft is the satellite's Poseidon-4 radar altimeter. When used with the Advanced Microwave Radiometer (AMR-C) attached to the front of the spacecraft, both instruments will be used to make precise measurements of sea surface height. The gray rectangle with 12 cones attached at the rear-left of the spacecraft is part of the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation (GNSS-RO) instrument. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich extends the near-30-year record of satellite measurements of sea level initiated by the U.S.-European TOPEX/Poseidon mission in 1992 and that continued with the Jason-1, 2, and 3 series of sea level observation satellites. Launched in 2016, Jason-3 is currently providing data. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). Other partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the intergovernmental European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), and France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24107
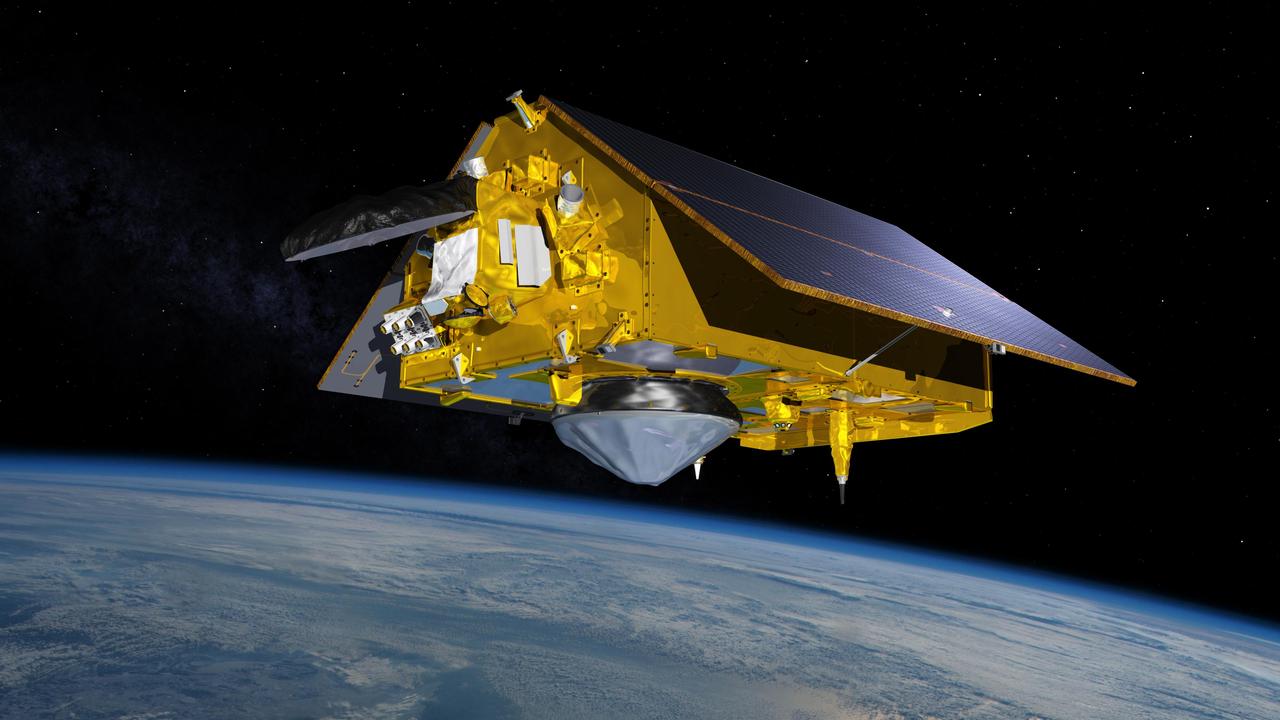

This illustration shows the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft in orbit above Earth with its deployable solar panels extended. As the world's latest ocean-monitoring satellite, it will collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. The mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity that will help improve weather forecasts and climate models. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich extends the near-30-year record of satellite measurements of sea level that was initiated by the U.S.-European TOPEX/Poseidon mission in 1992 and continued with the Jason-1, 2, and 3 series of sea level observation satellites. Launched in 2016, Jason-3 is currently providing data. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). Other partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the intergovernmental European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), and France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24105