
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences technicians check the bottom of the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator as it is raised off its platform. The spacecraft was developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
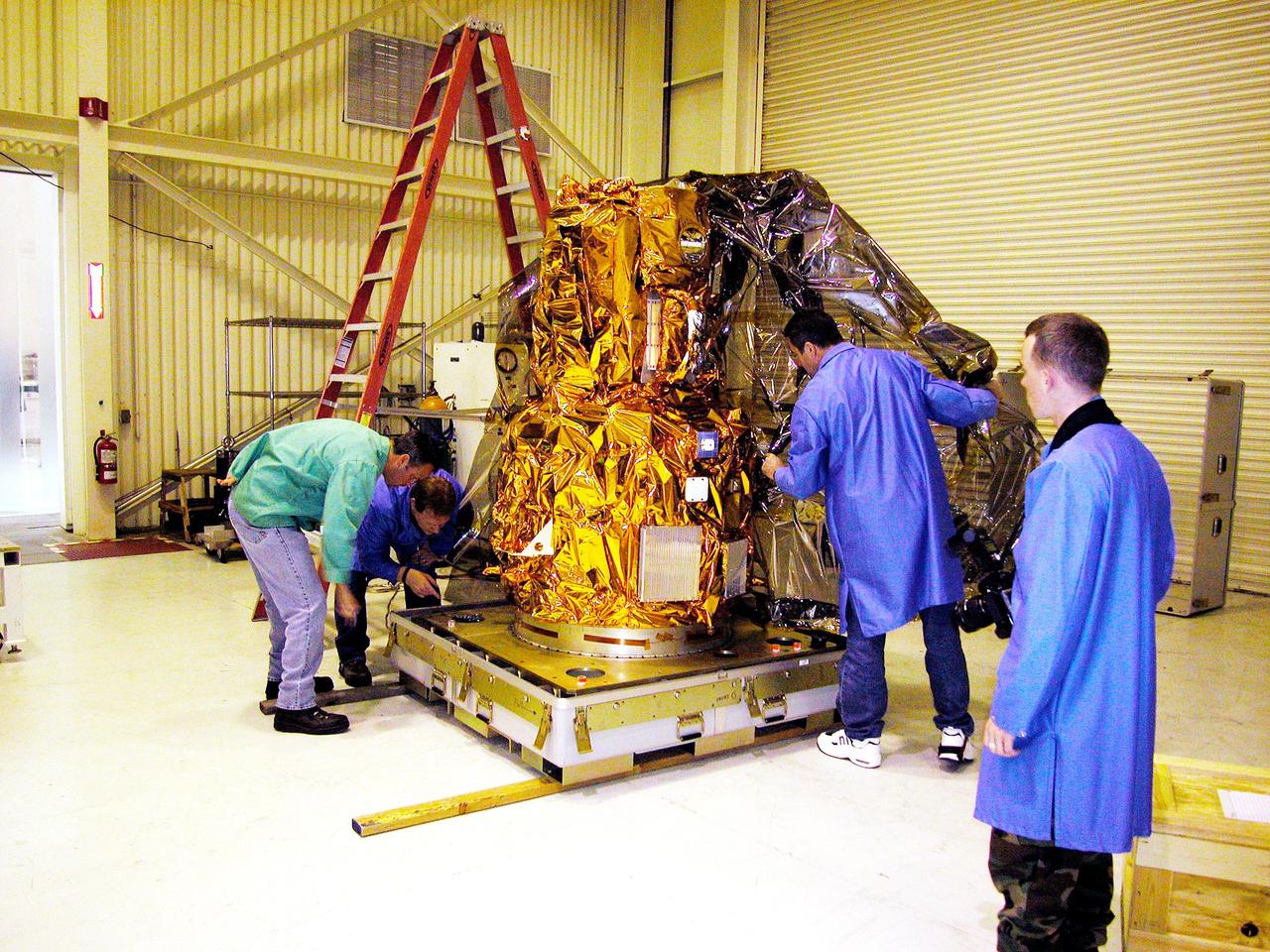

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator is revealed after its protective cover has been removed. The spacecraft was developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
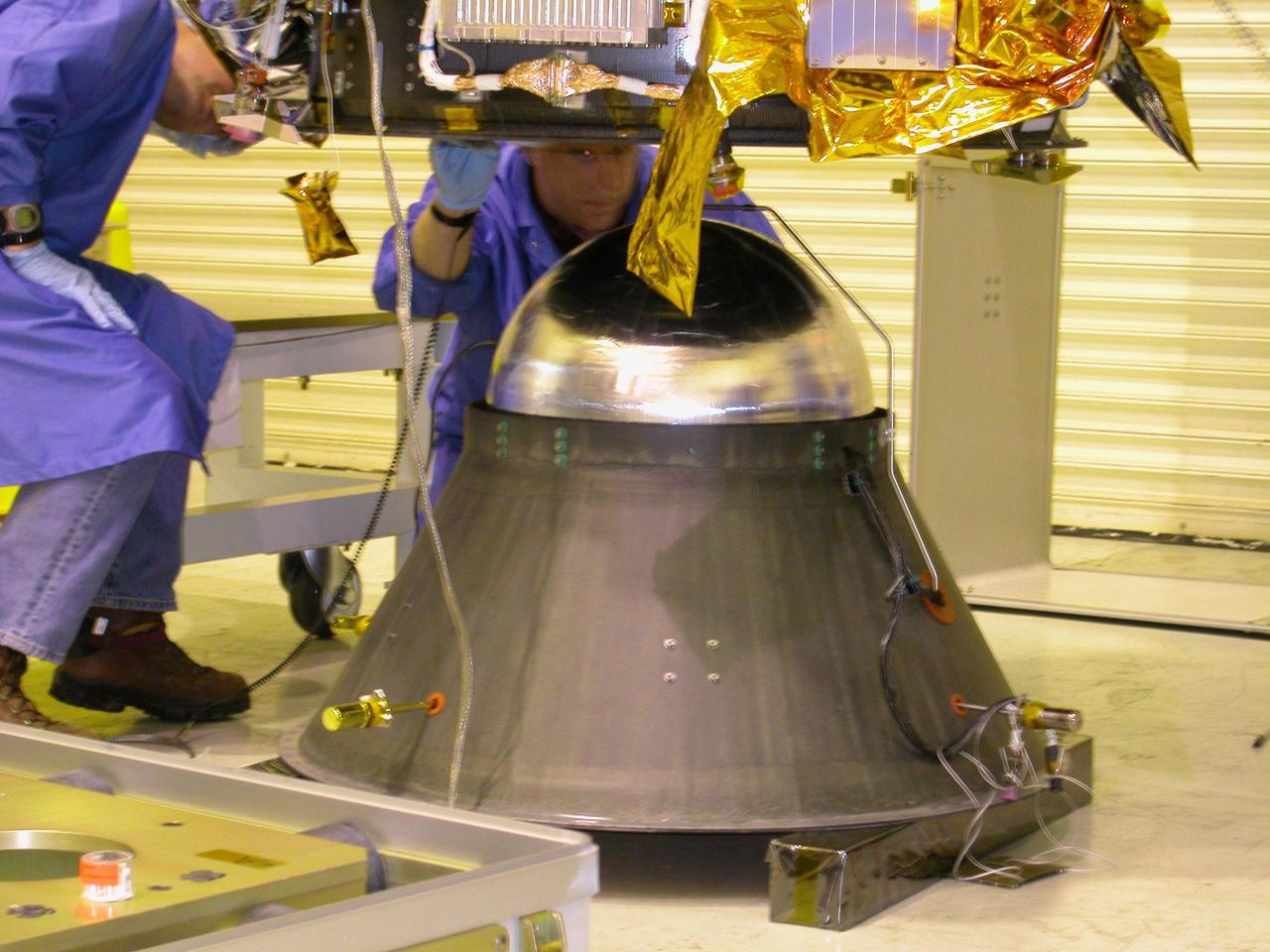

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences technicians watch closely as the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator is lowered onto a stand. The spacecraft was developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences technicians observe closely the movement of the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator as it is lowered onto a stand. The spacecraft was developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences technicians check the bottom of the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator as it is raised of its platform. The spacecraft was developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
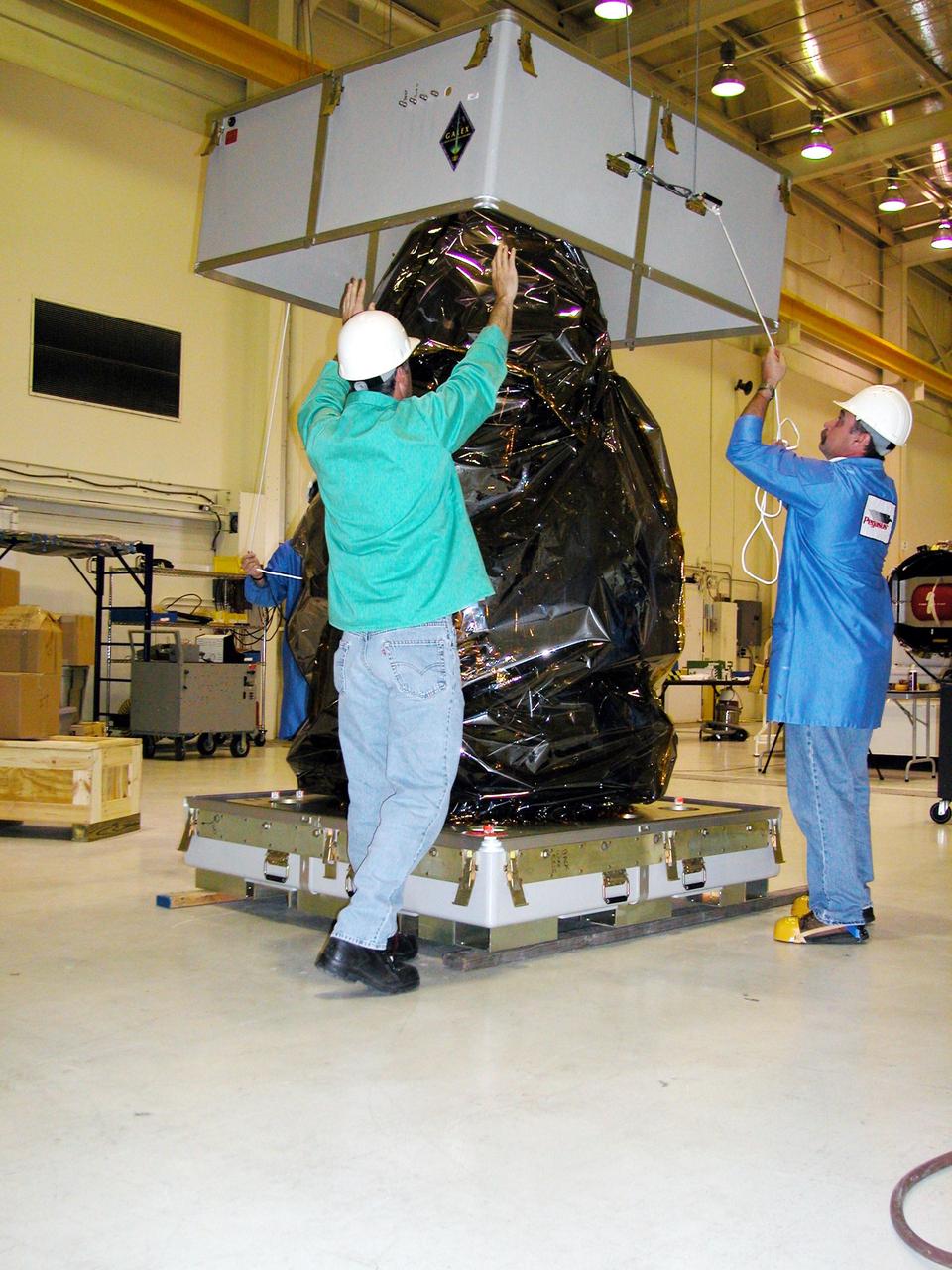

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences workers remove the canister from the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator, a spacecraft developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
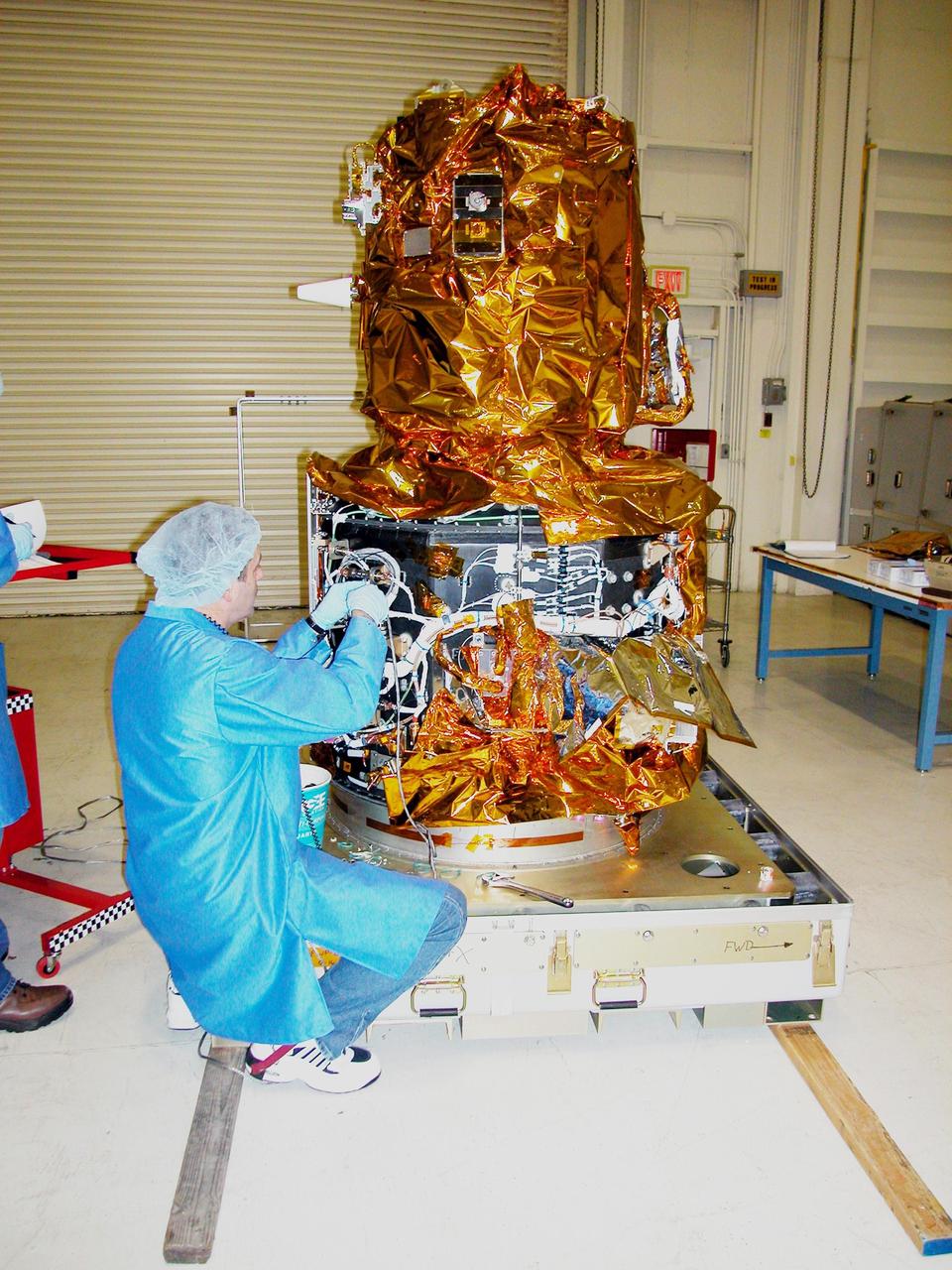

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, an Orbital Sciences technician works with wiring on the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator, a spacecraft developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
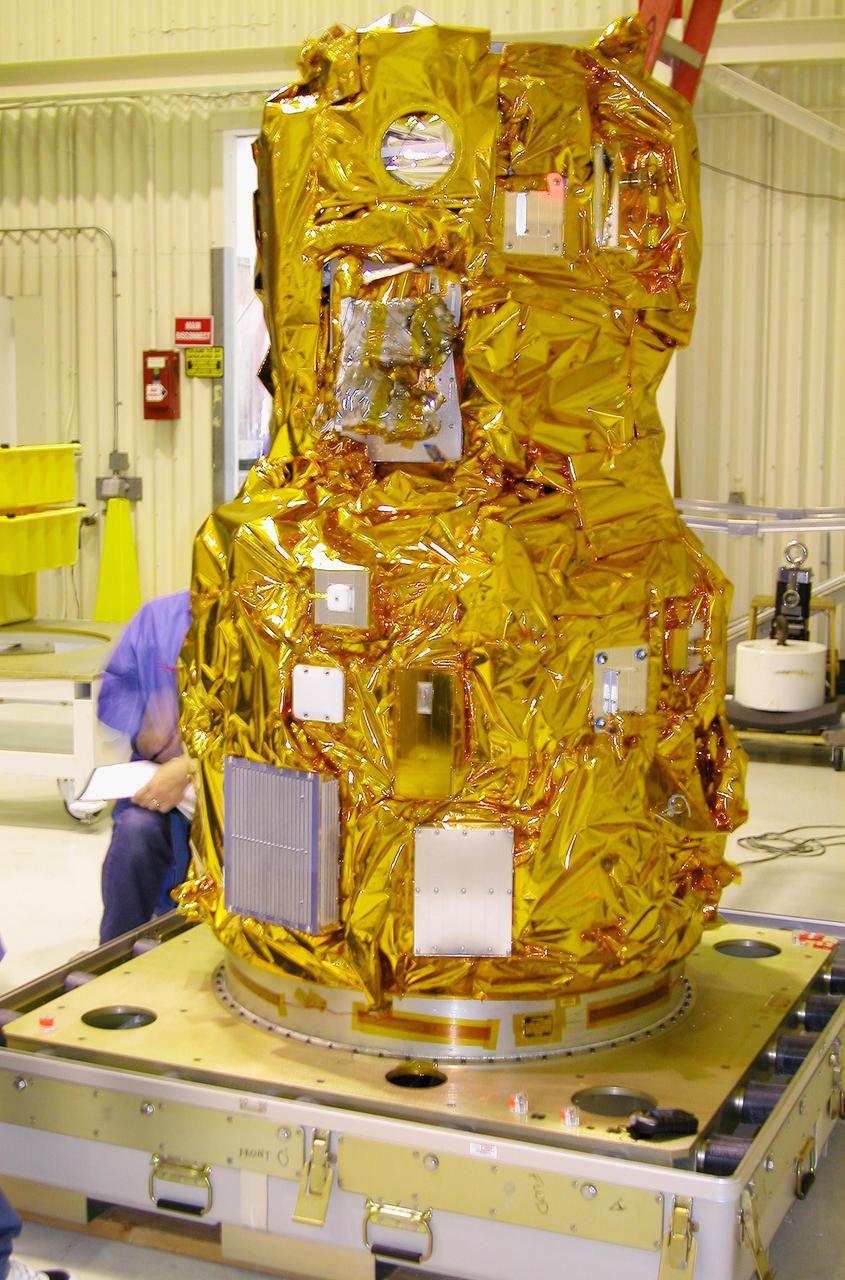

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator is revealed after its protective cover has been removed. The spacecraft was developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
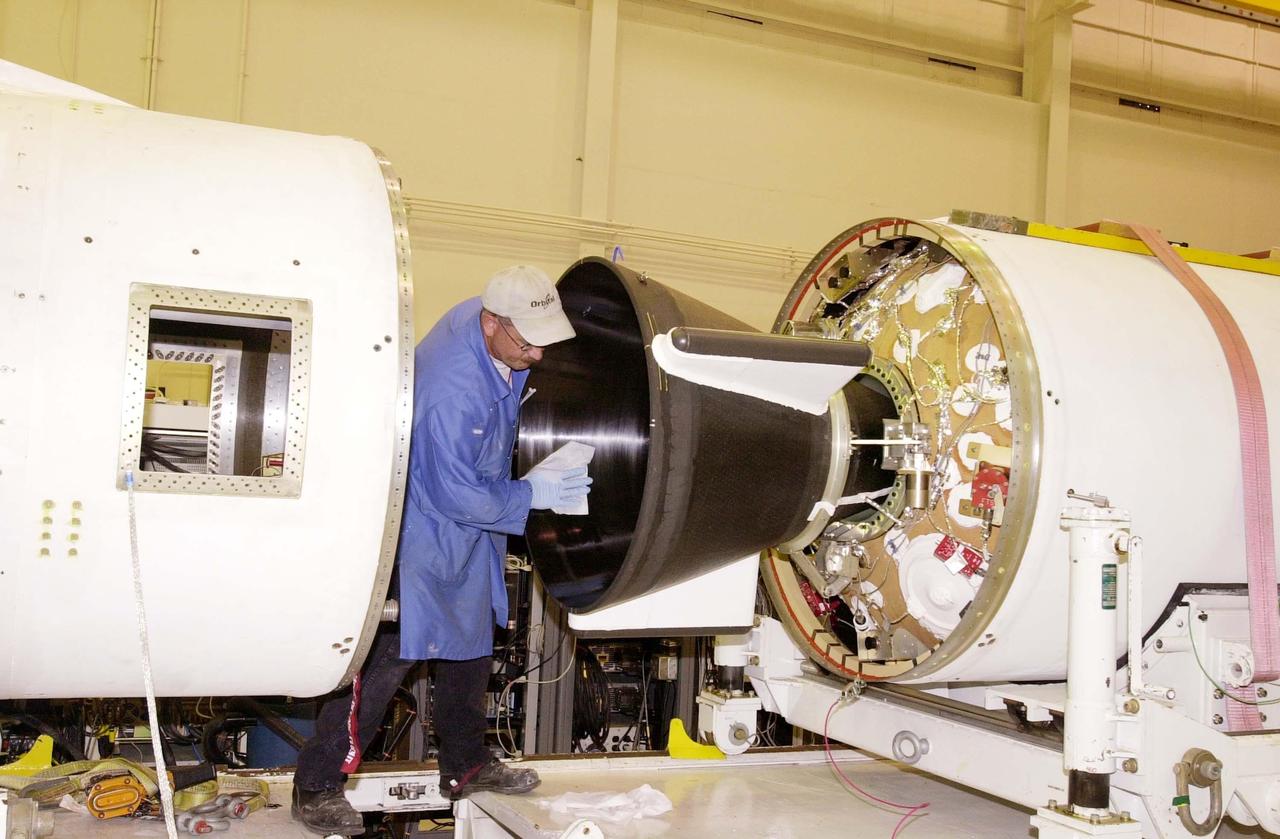
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker prepares the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle for mating. The Pegasus XL will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
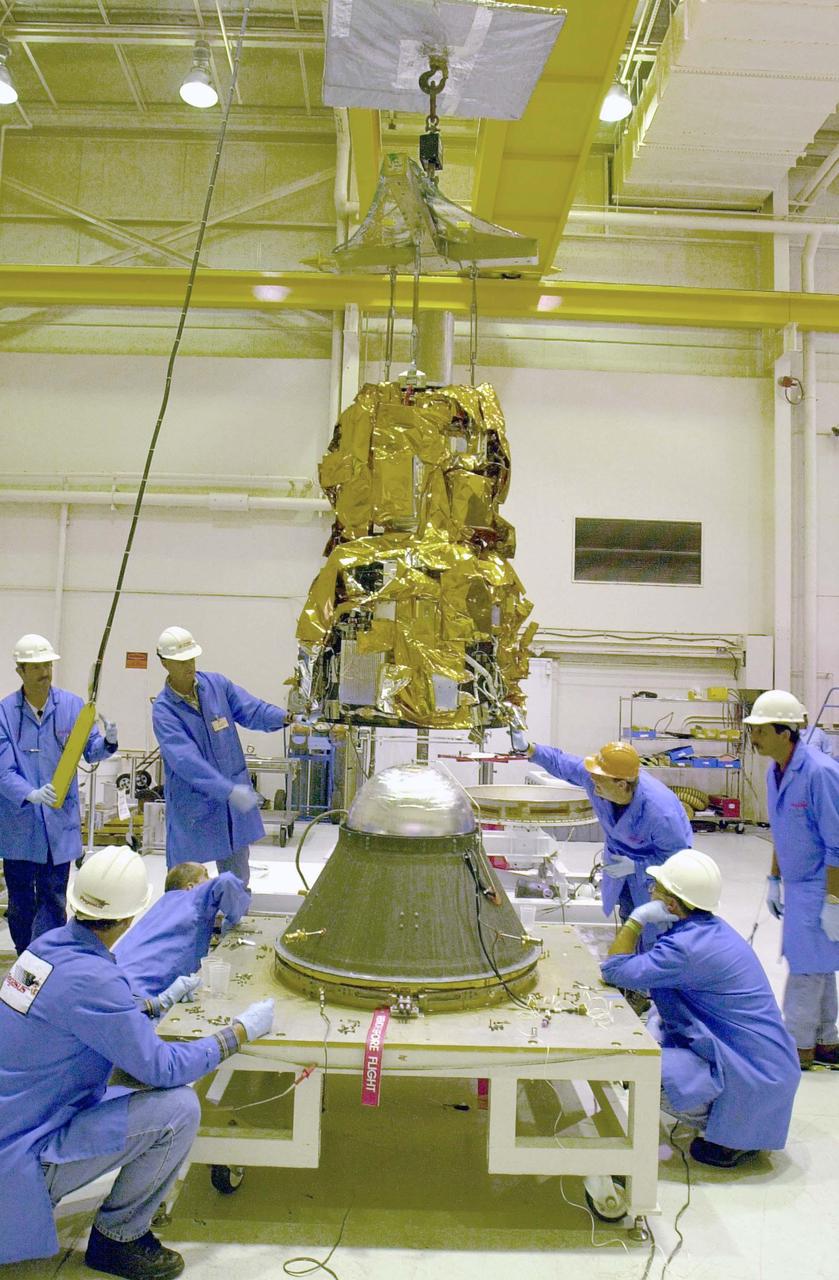

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, suspended by a crane, over the upper stage in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (right) is ready for mating with the upper stage (foreground) in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
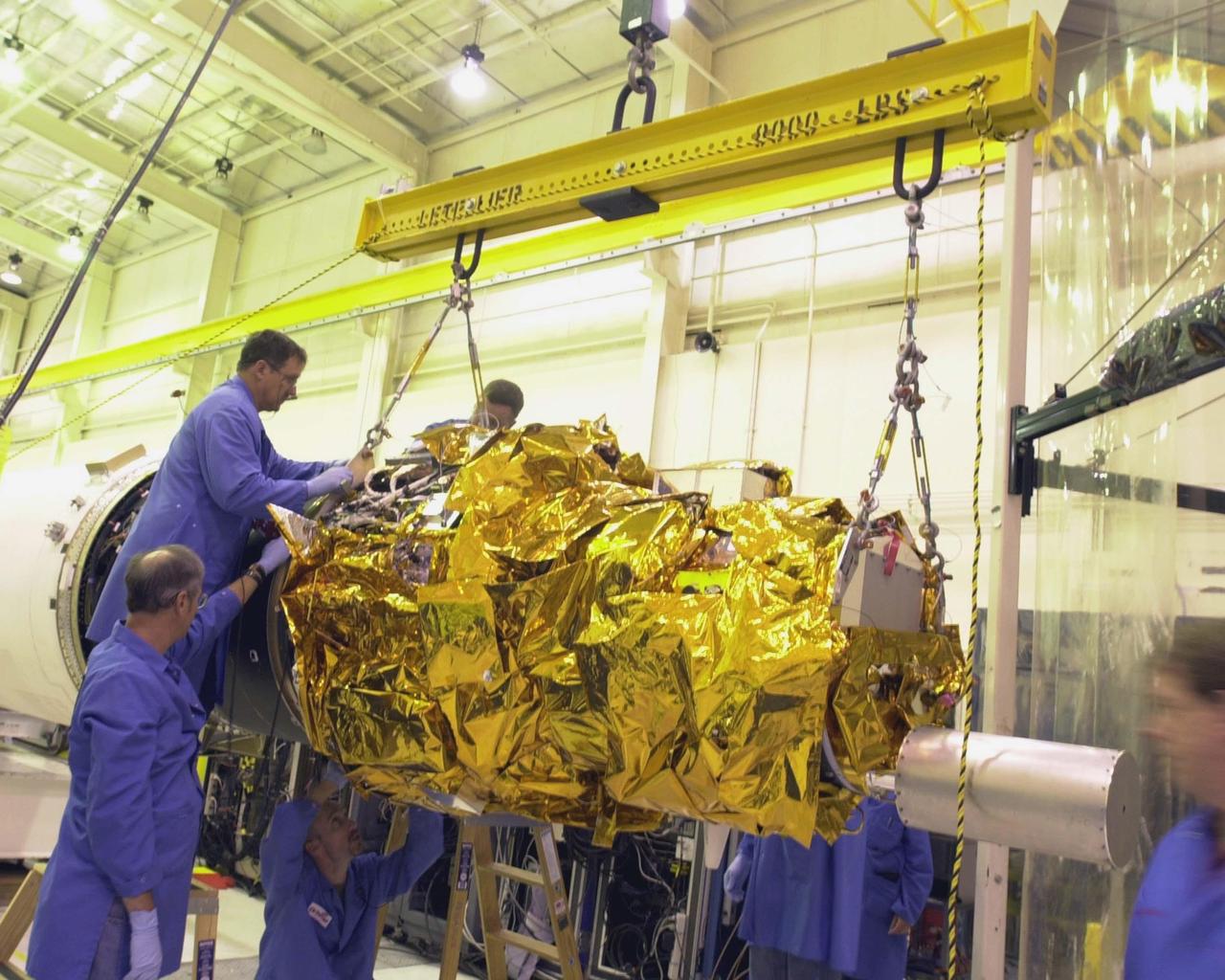

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and mated upper stage toward the second stage behind them in preparation or launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and mated upper stage toward the second stage at right in preparation or launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
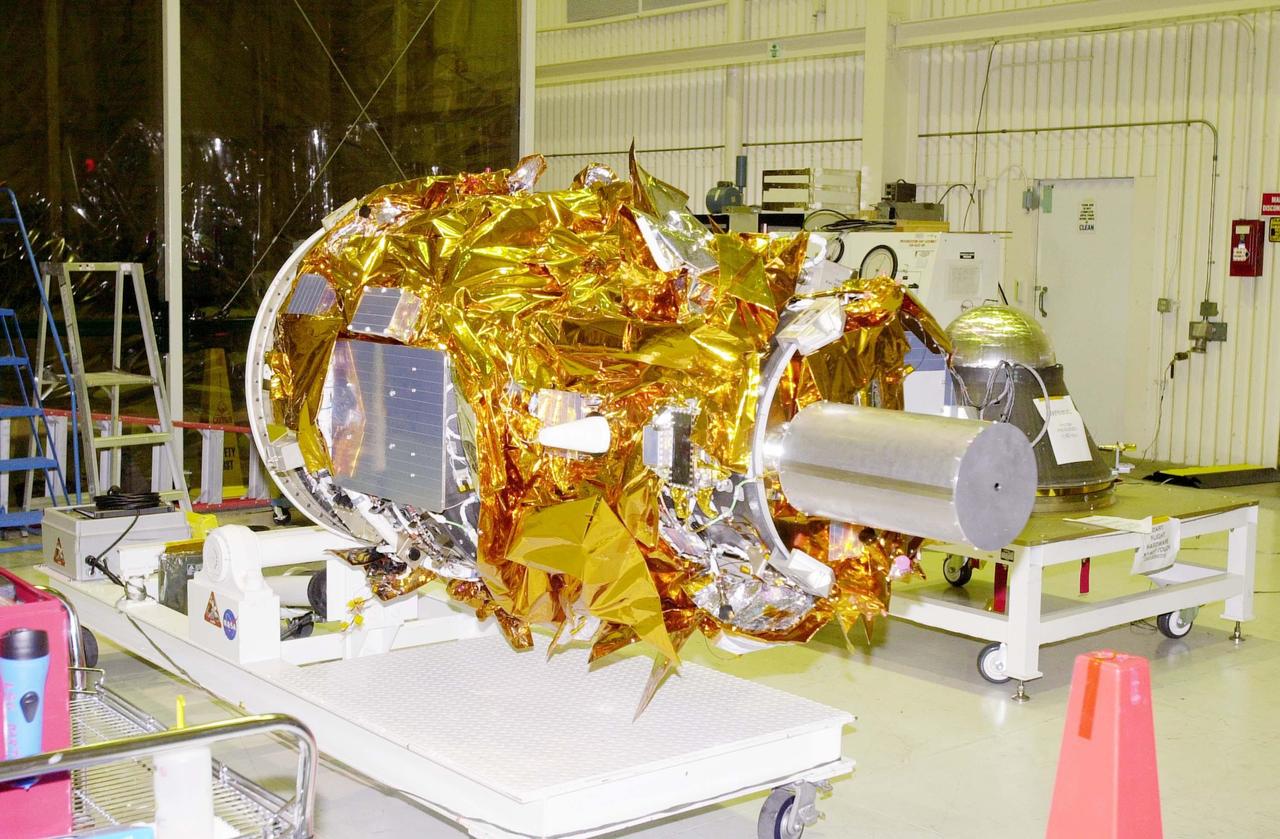

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is ready for mating with the upper stage of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL behind it (right). DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
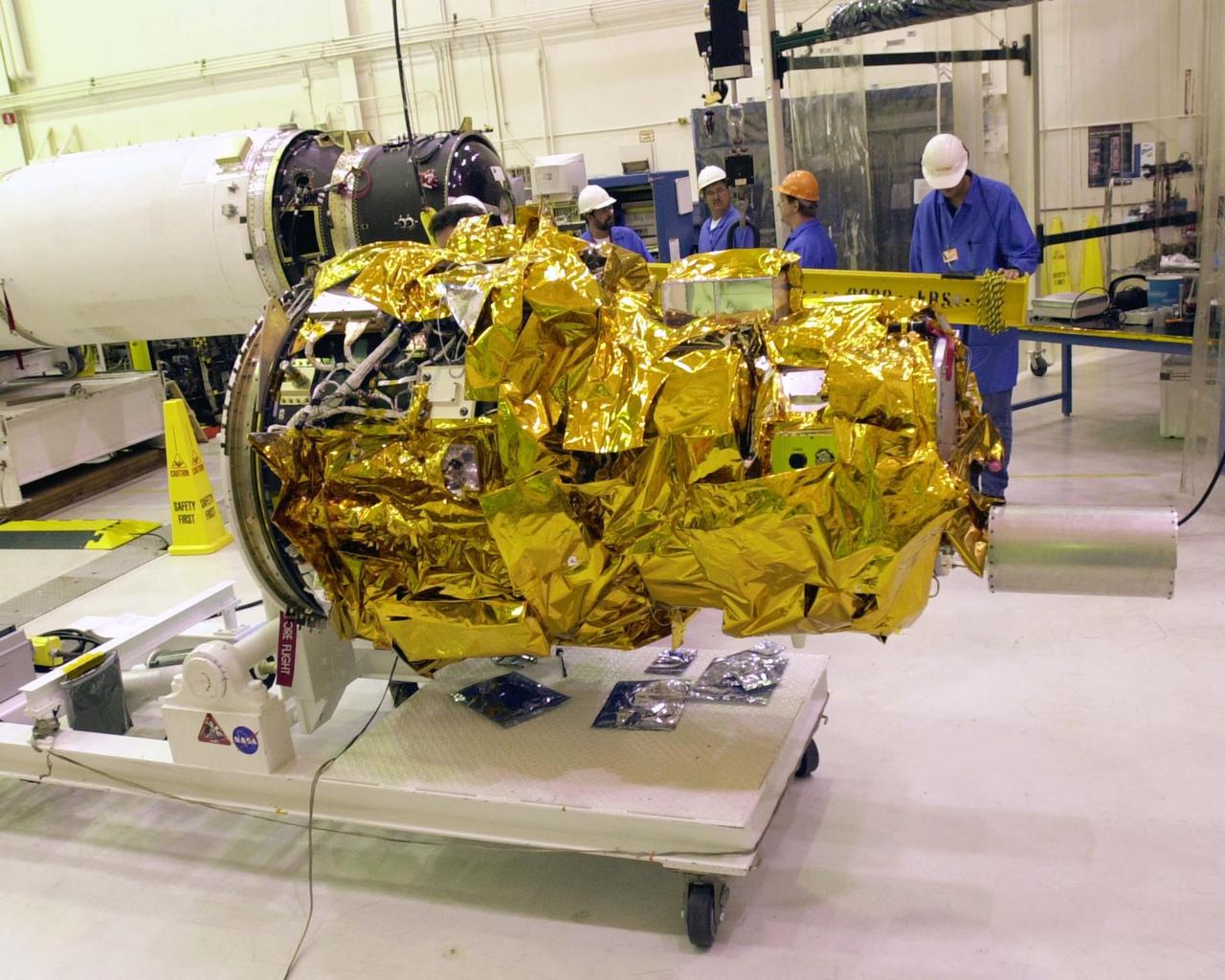

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (foreground) is ready to be mated to second and third stages in preparation for the launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (right) is ready for mating with the upper stage (behind it) in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers begin mating the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
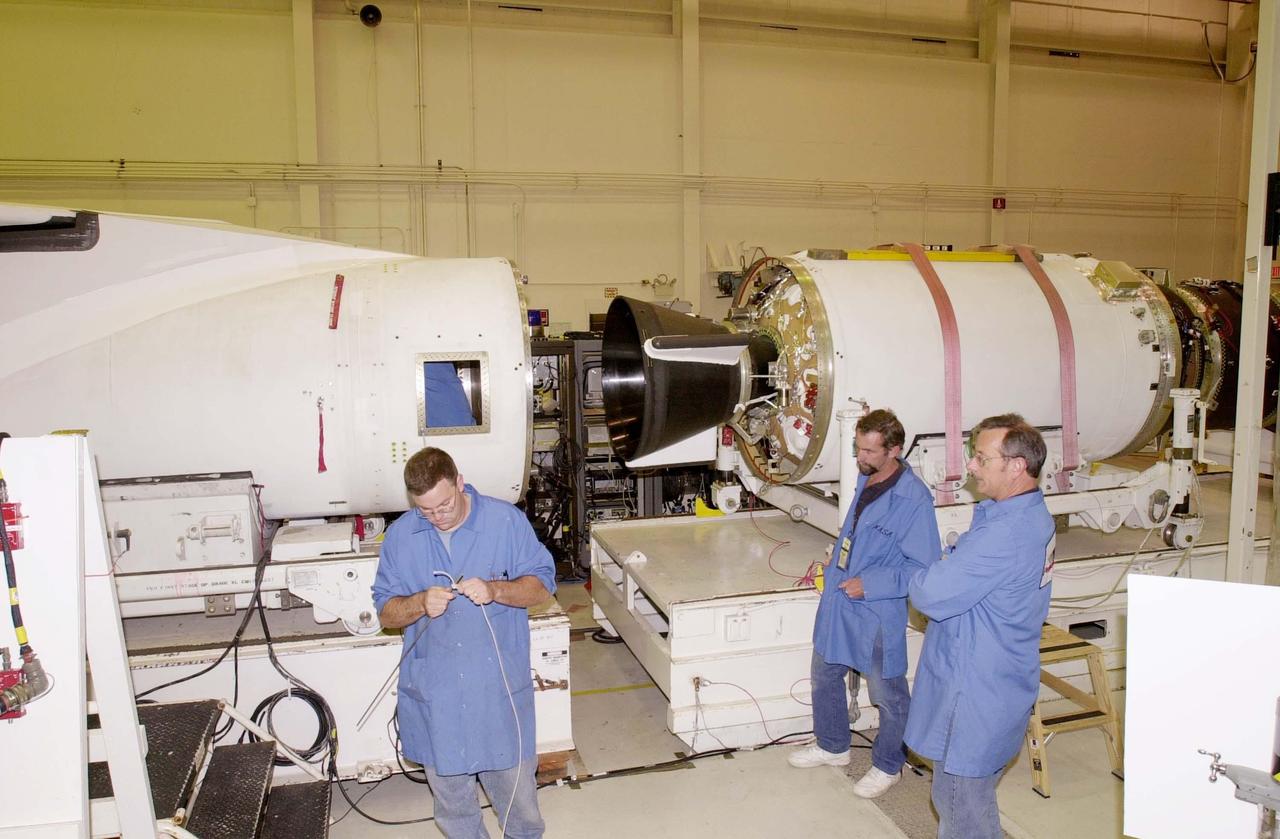

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare to mate the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
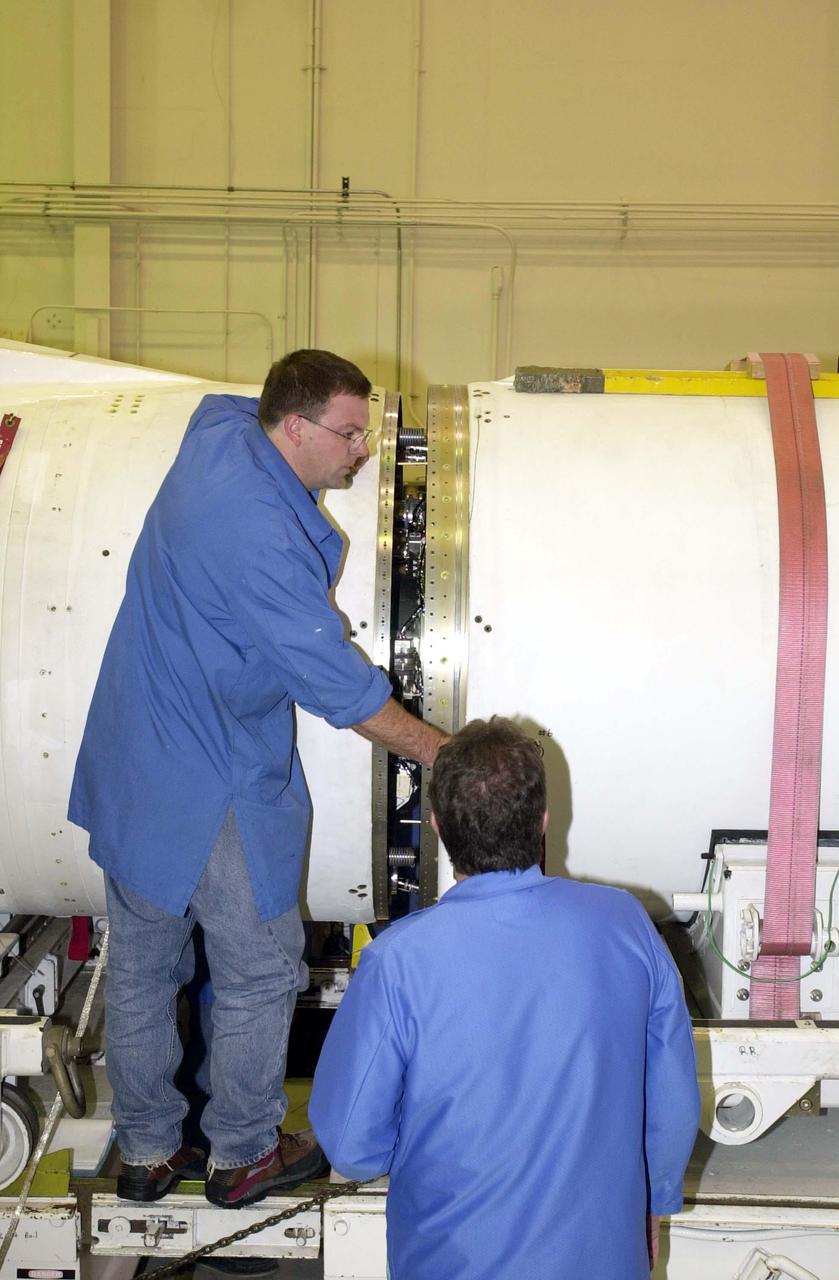

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers begin closing the gap between the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians get ready to attach the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, mated earlier, to the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft above. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
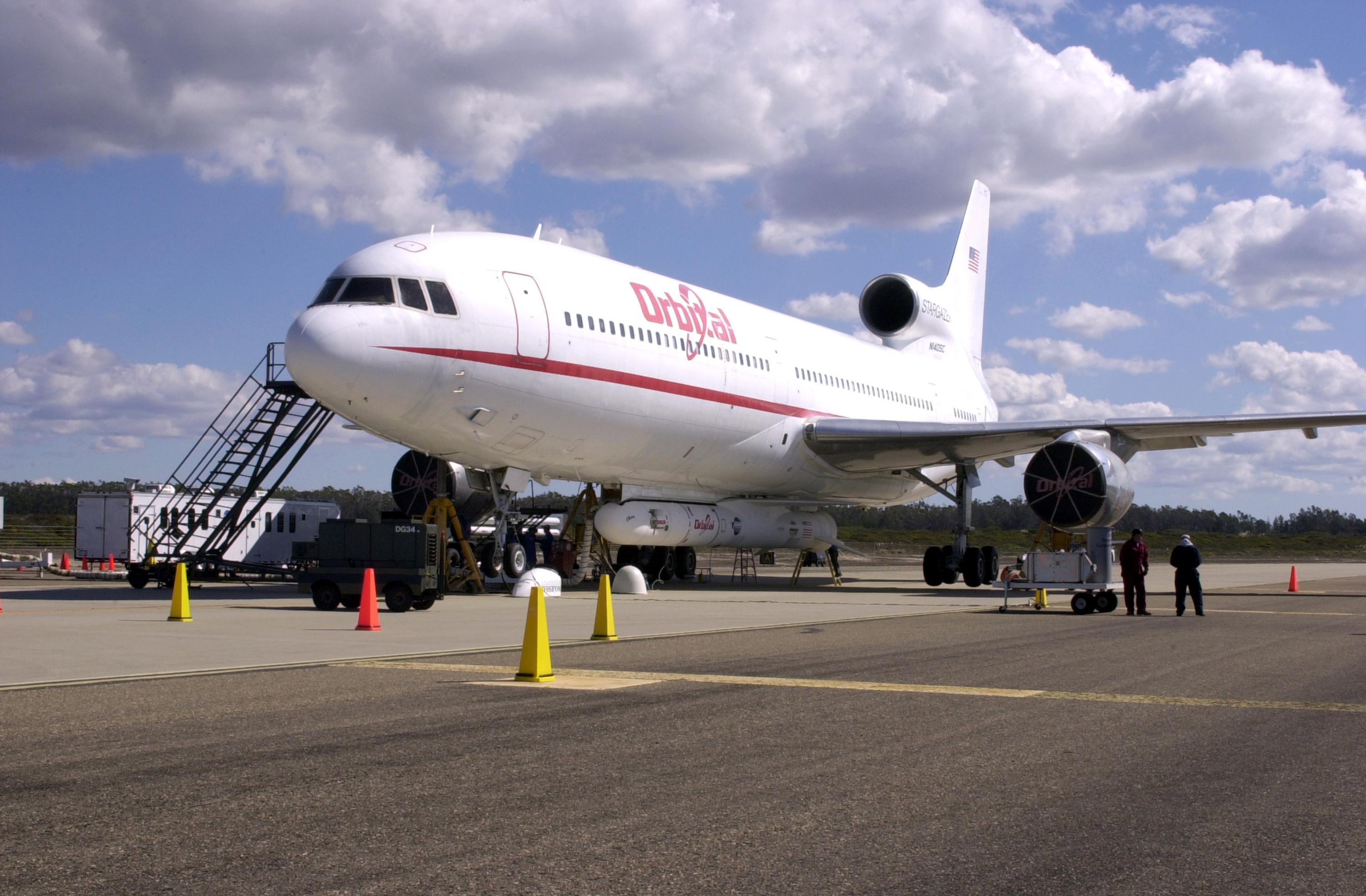

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Corporation’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft is ready for flight with the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle attached underneath. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
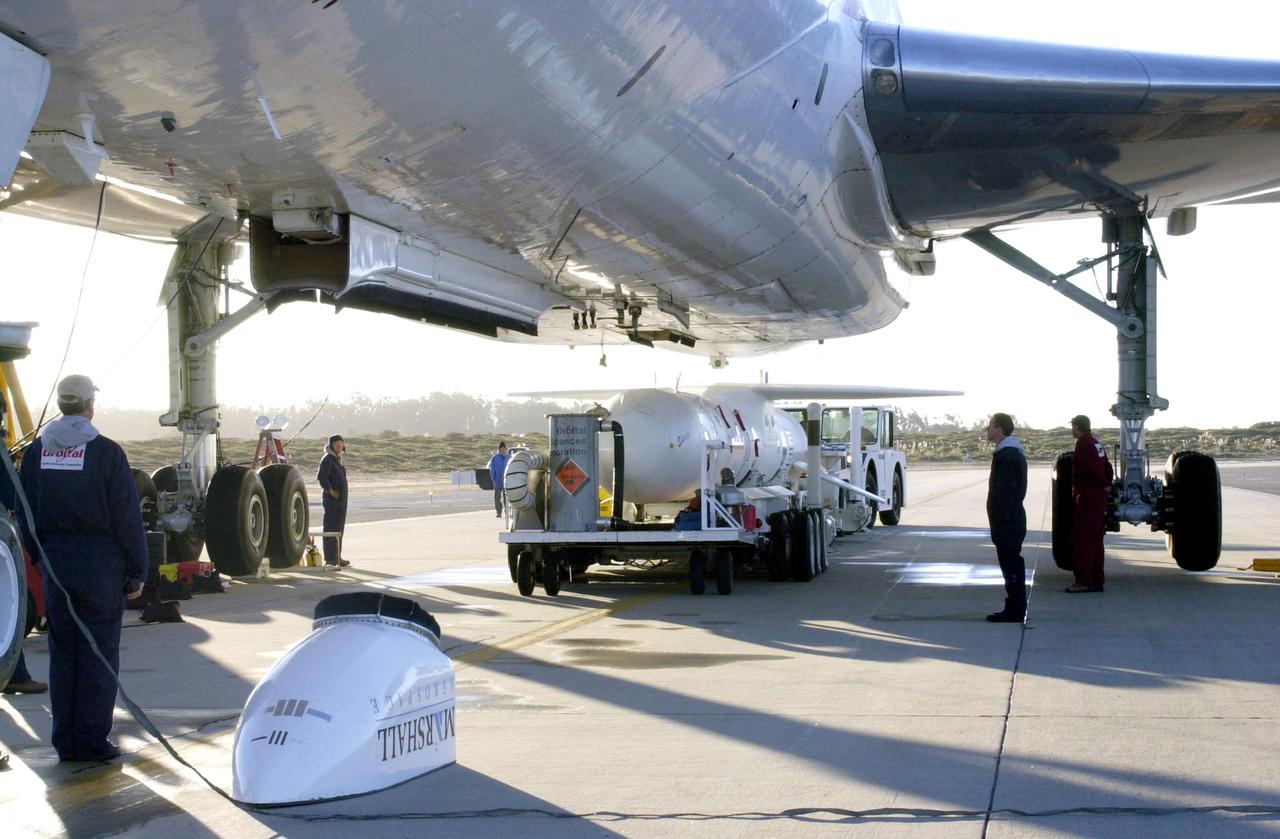

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, mated earlier, arrive at the Vandenberg Air Force Base runway for mating to the belly of the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft (foreground). The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians complete attachment of the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, to the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft above. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
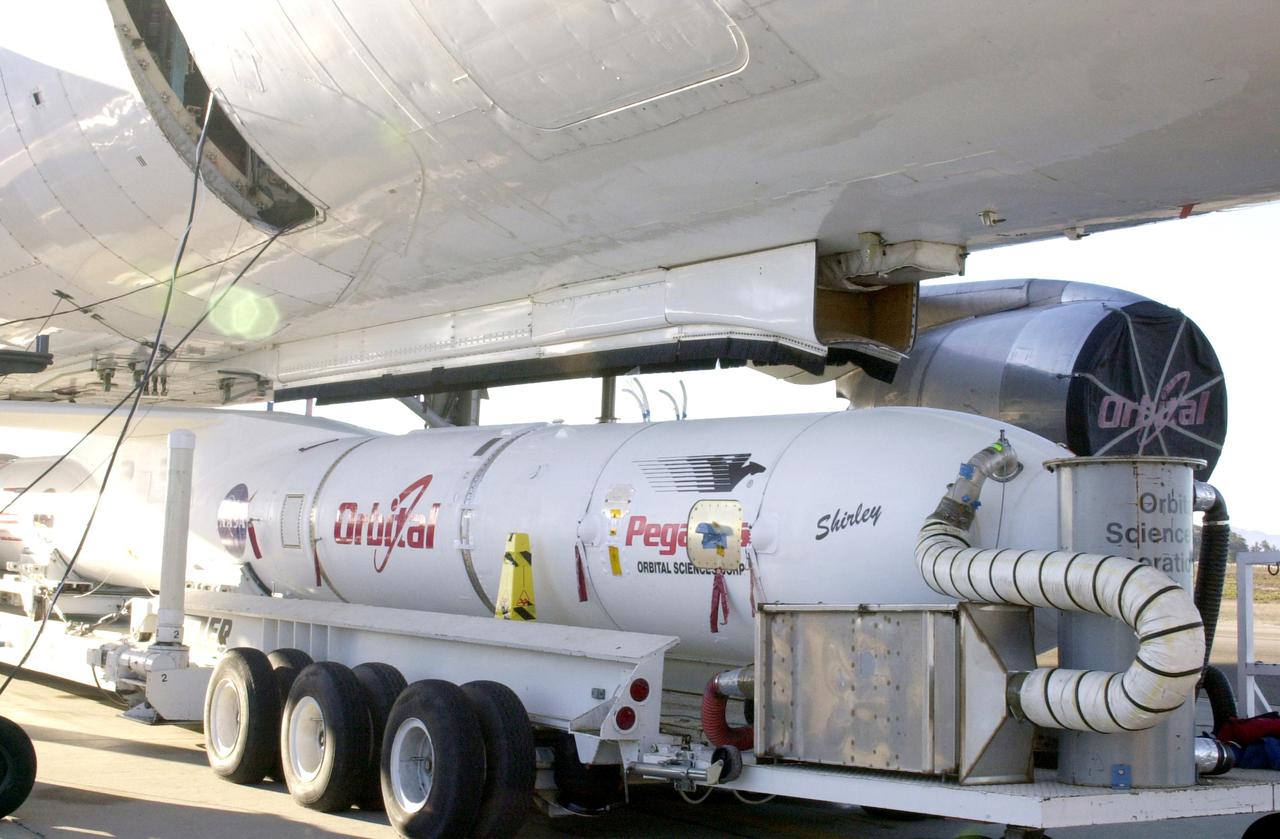

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, mated earlier, are being attached to the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft above. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
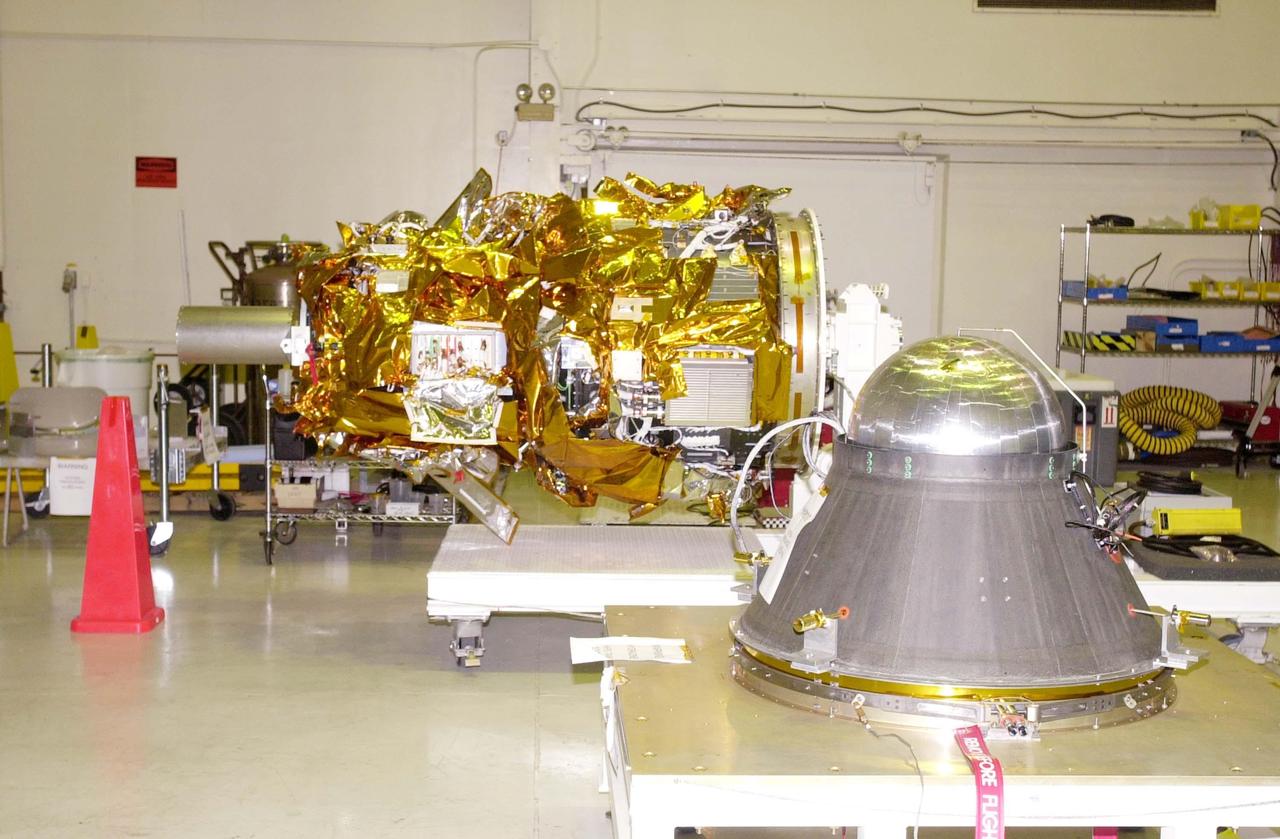

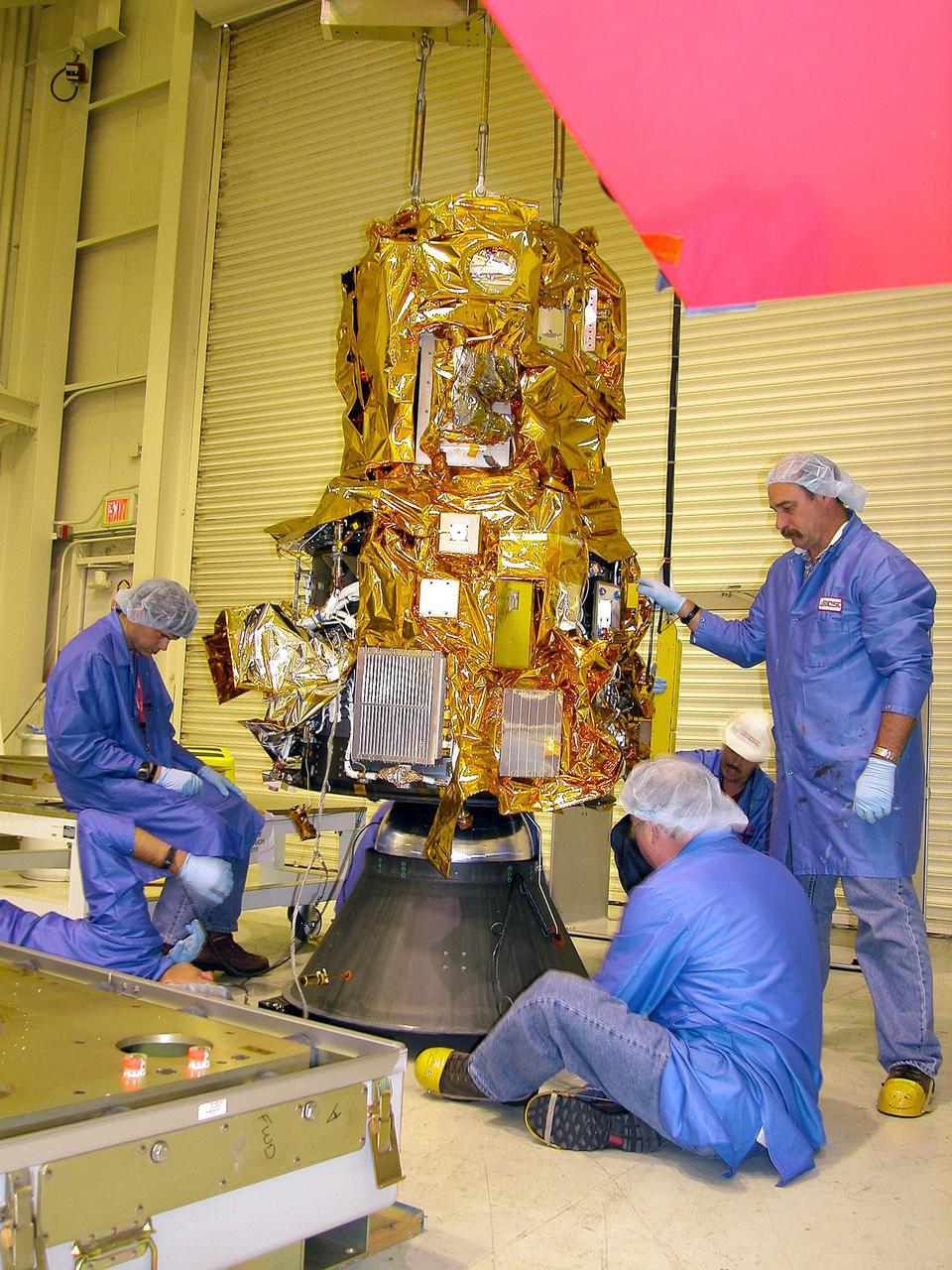
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (in background) has been rotated from vertical to horizontal and is ready for mating with the upper stage (foreground). DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
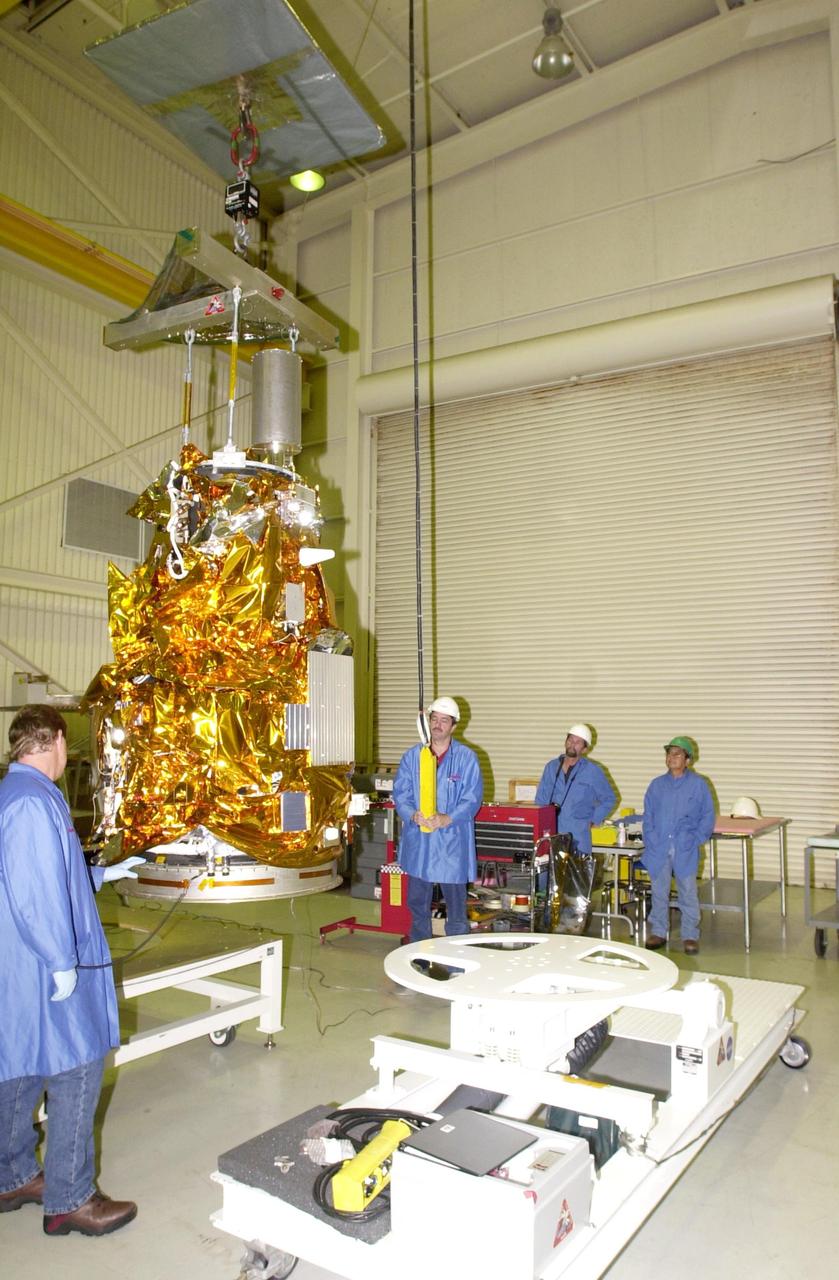

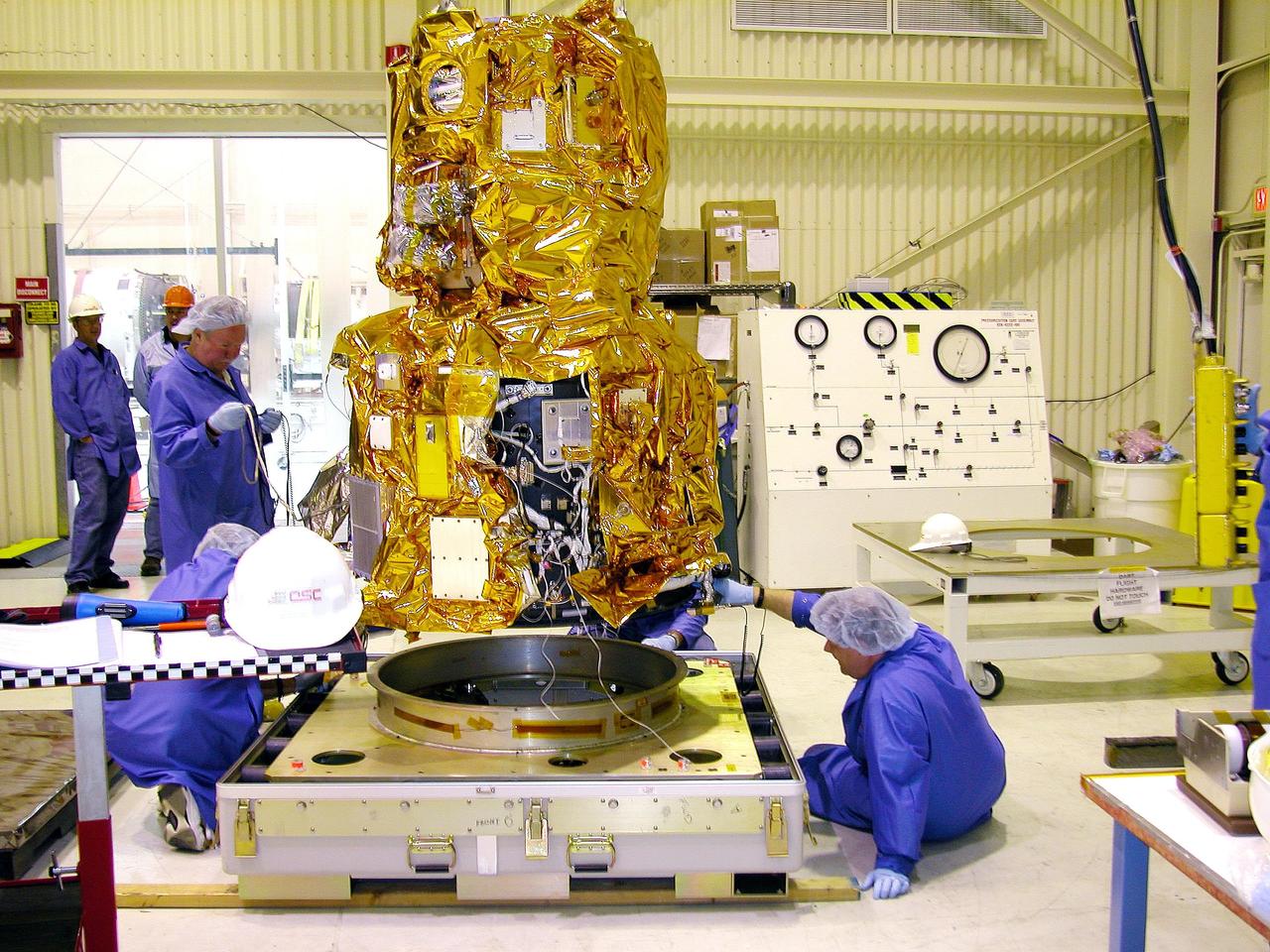
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers stand by while an overhead crane moves the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft onto the mobile stand at right. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
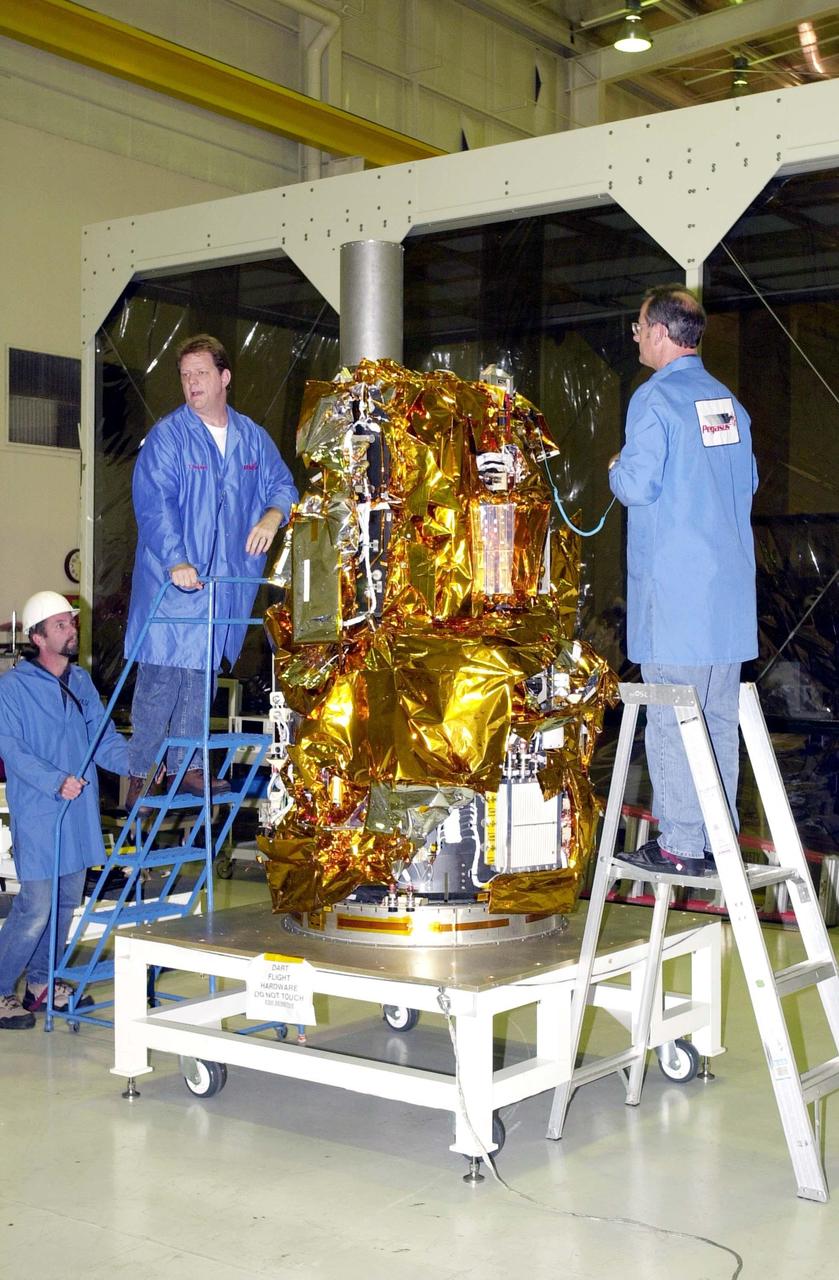

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft for launch. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
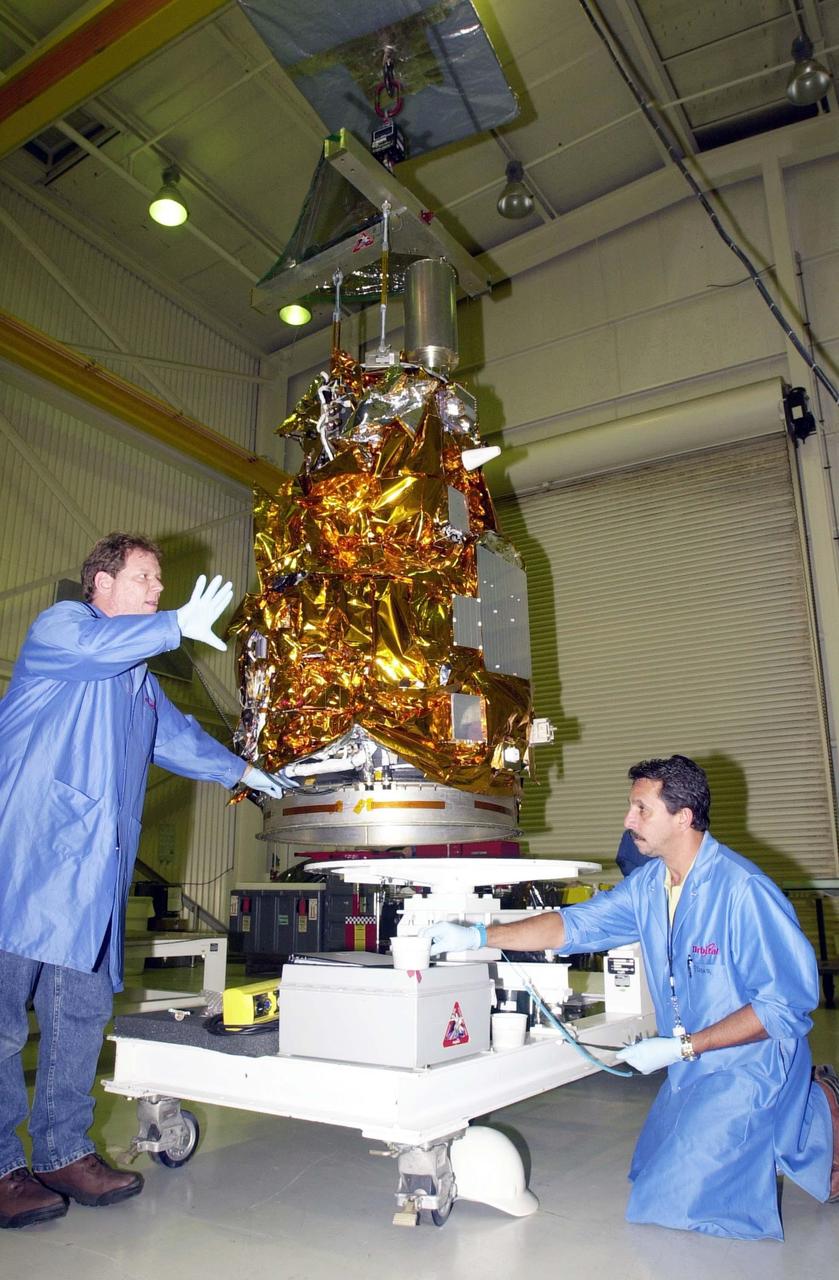

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers help guide the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft onto the mobile stand below. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
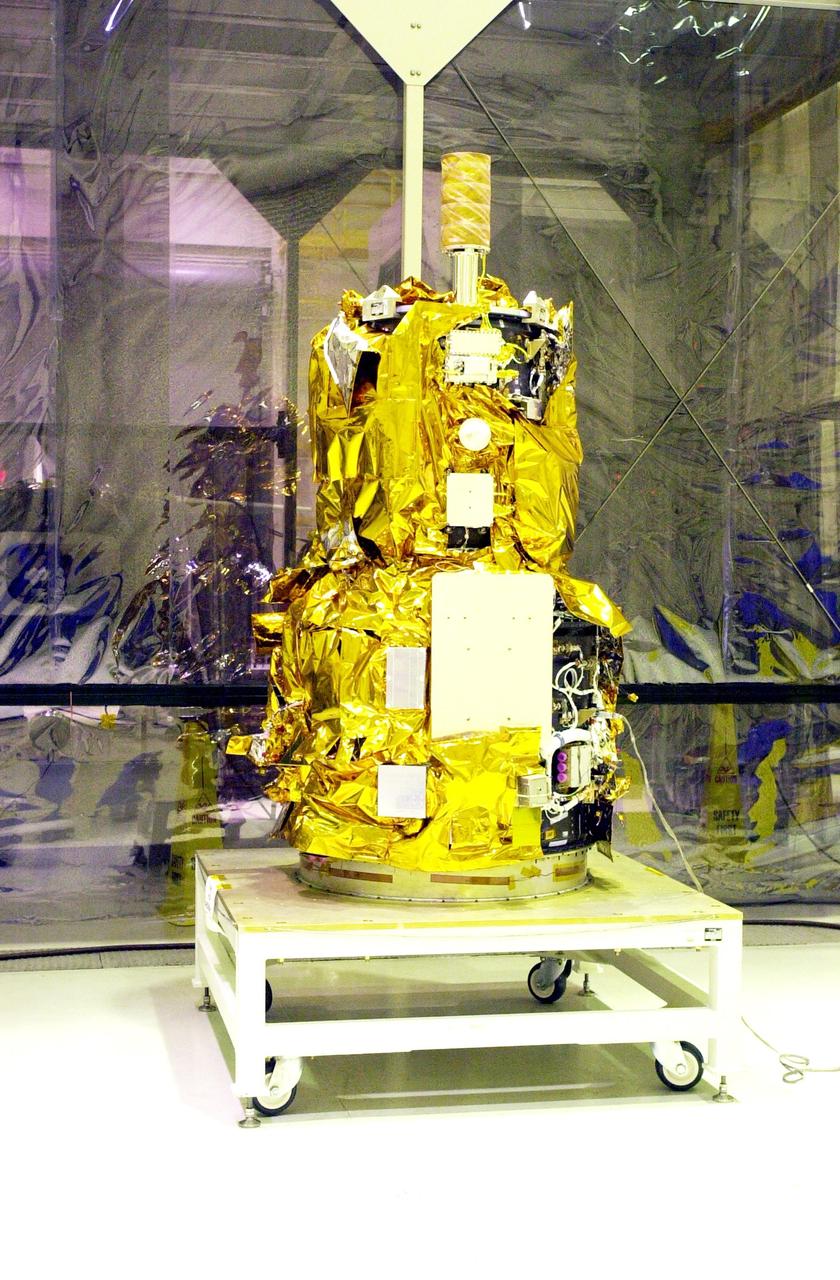

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is on a work stand waiting for processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
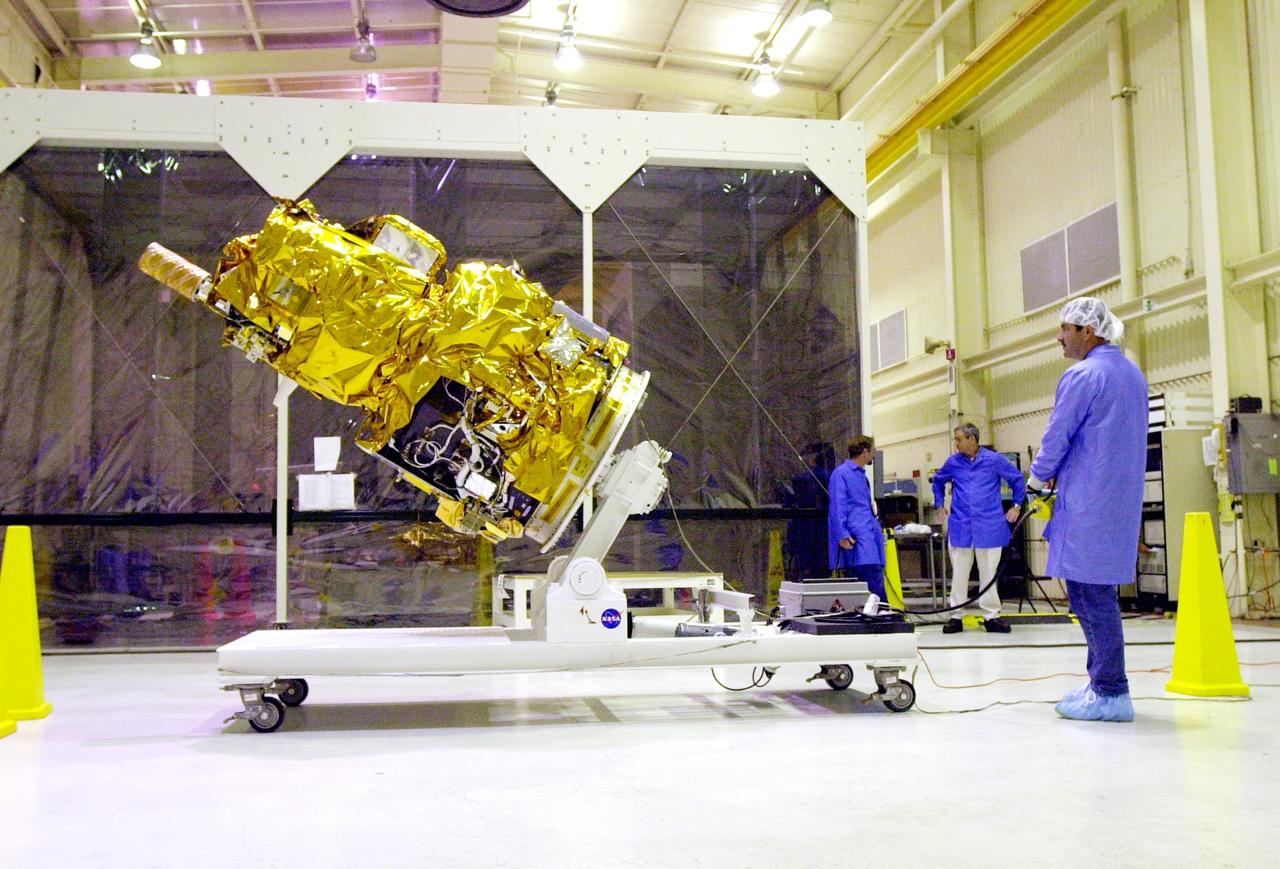

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is raised to a vertical position. It will be lifted onto a test stand for launch processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
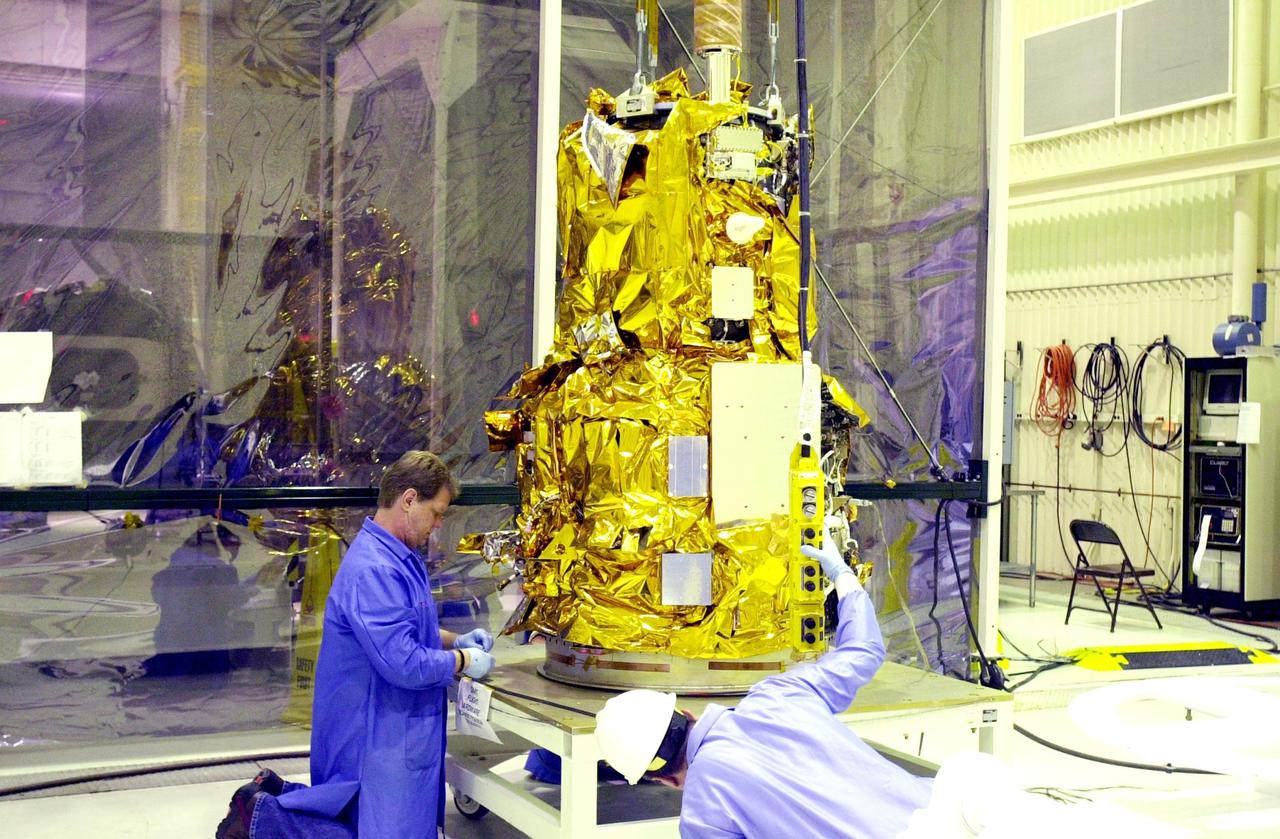

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is placed on a work stand for processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
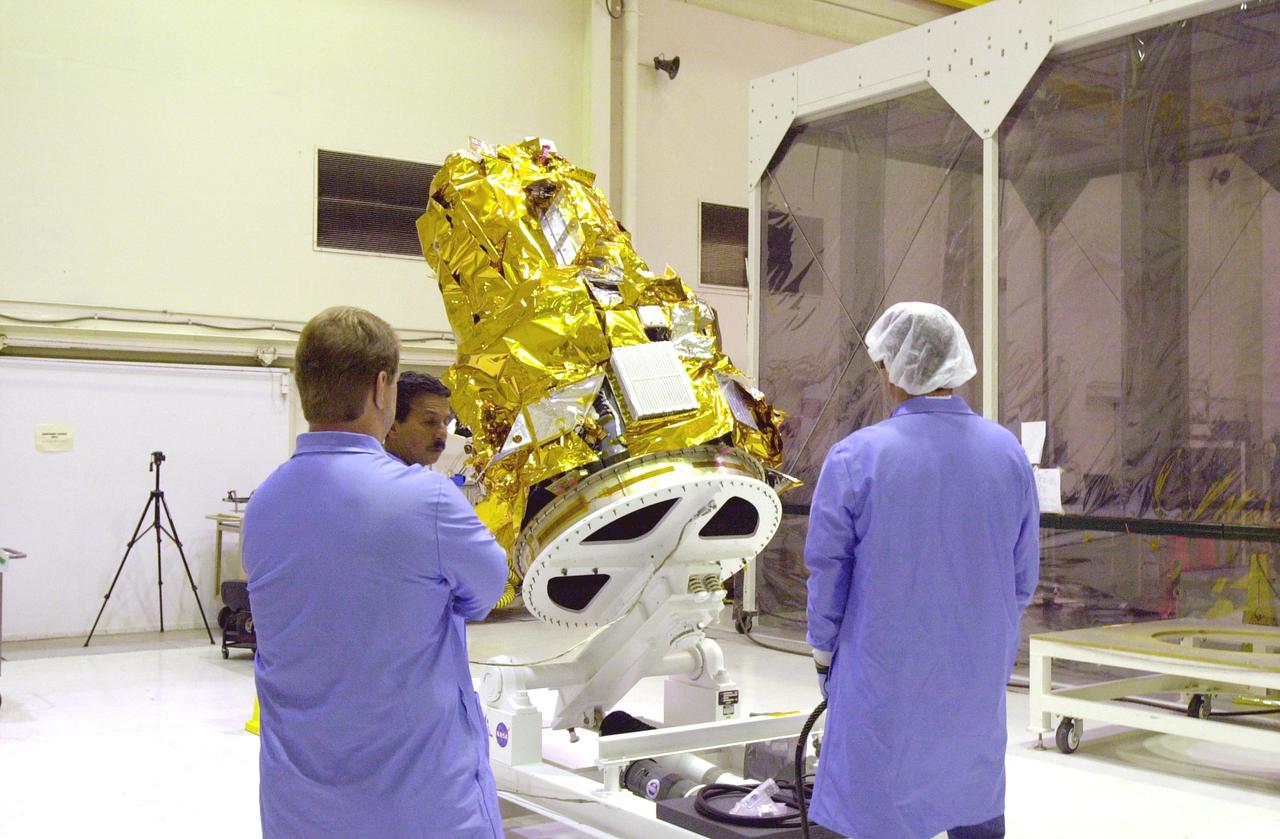

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is raised to a vertical position. It will be lifted onto a test stand for launch processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
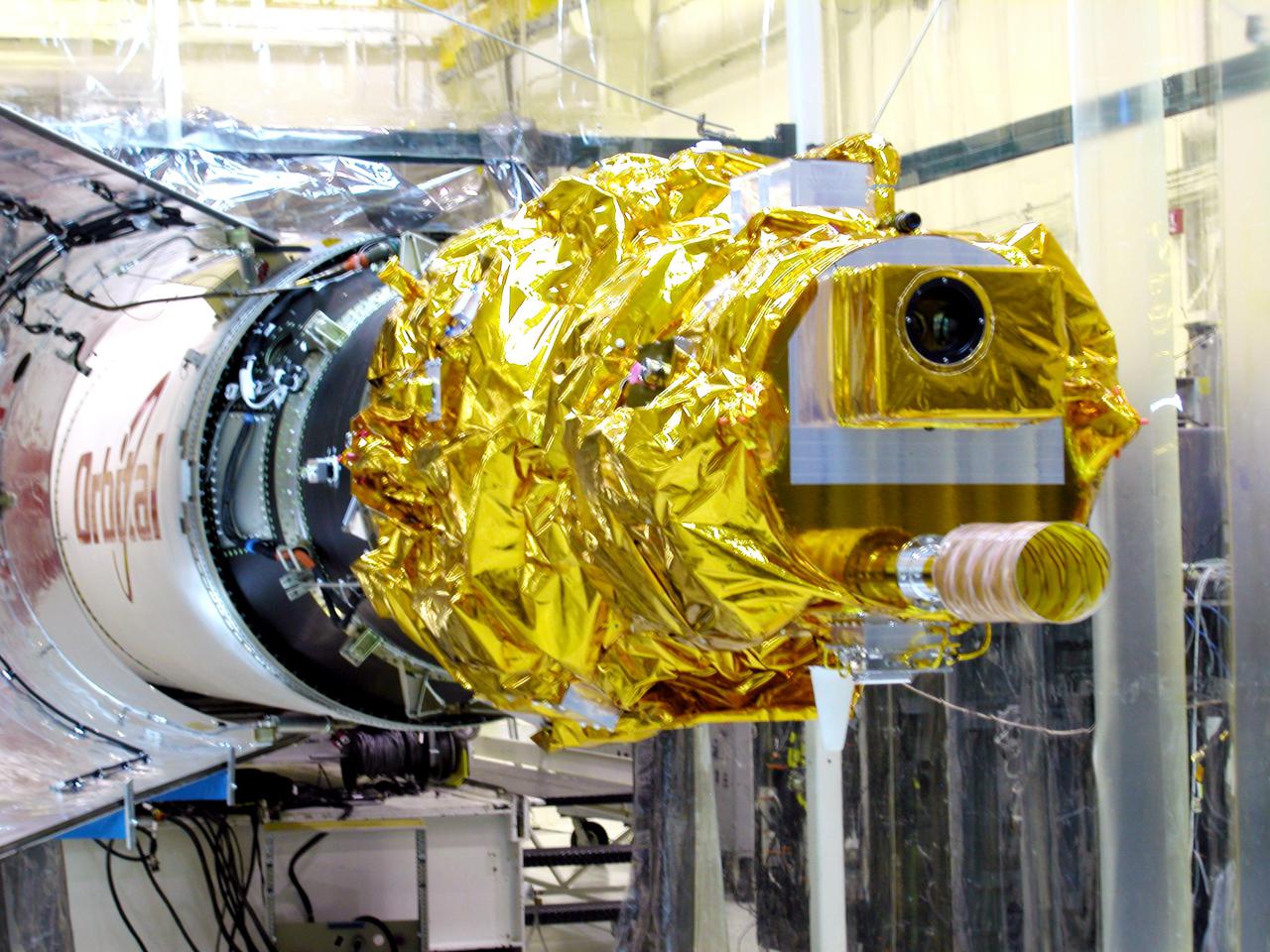
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) waits for fairing installation. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
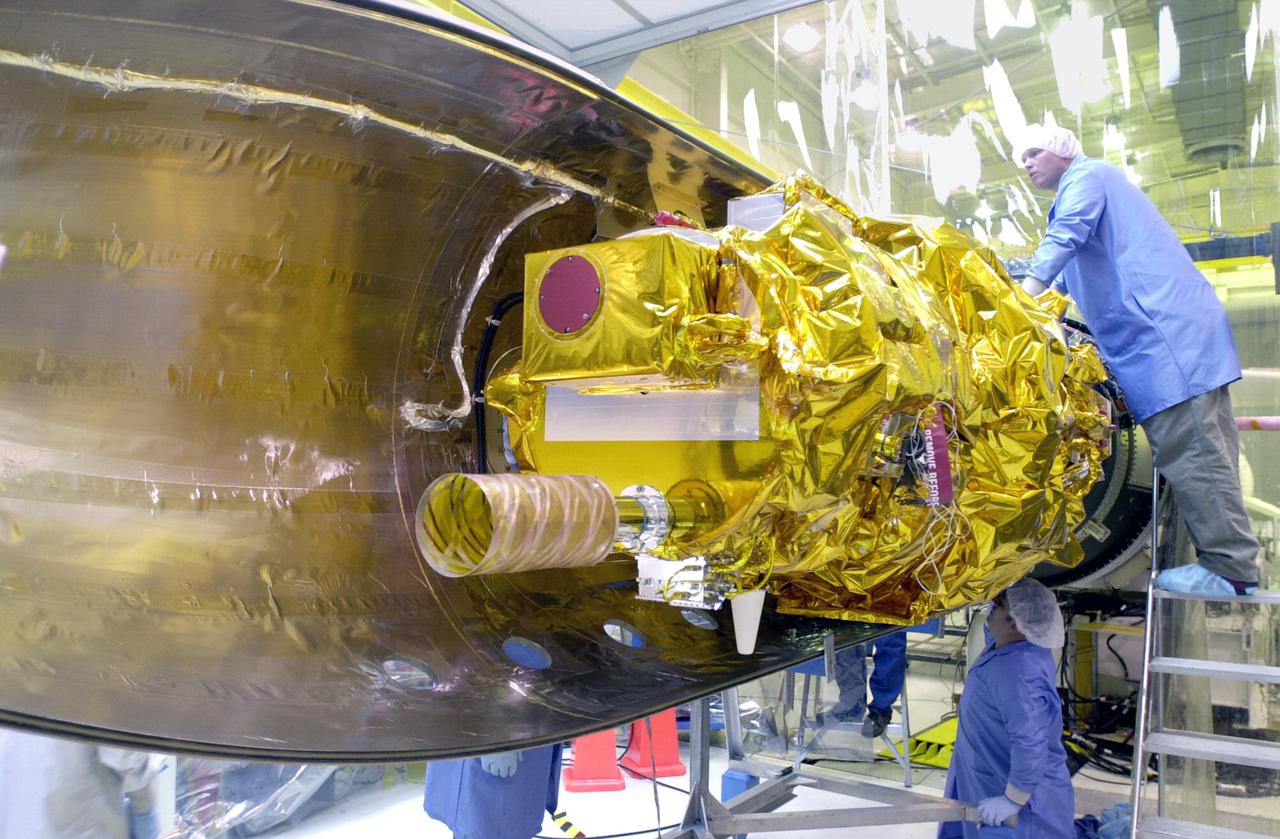

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In preparation for launch, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California check the placement of the first fairing half around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
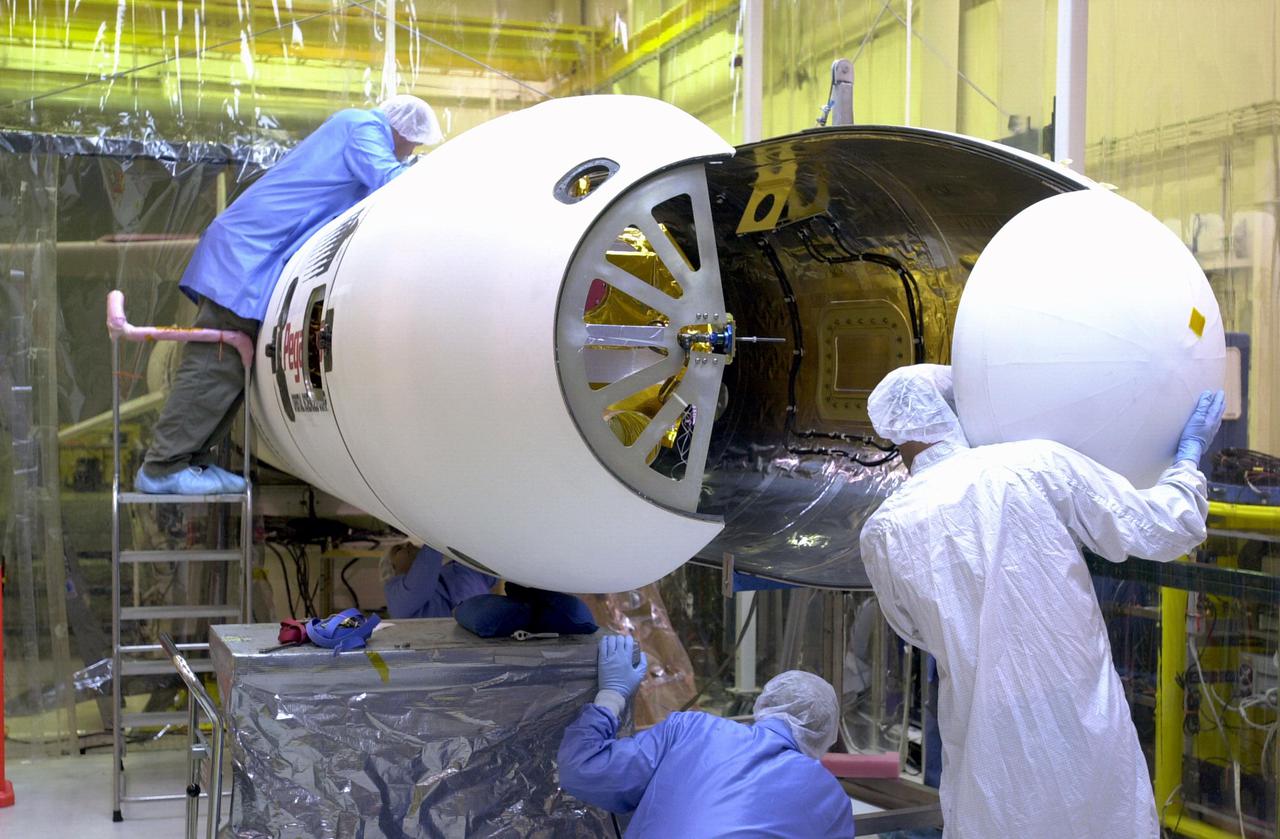

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California maneuver the second fairing half into place around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft in preparation for launch. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
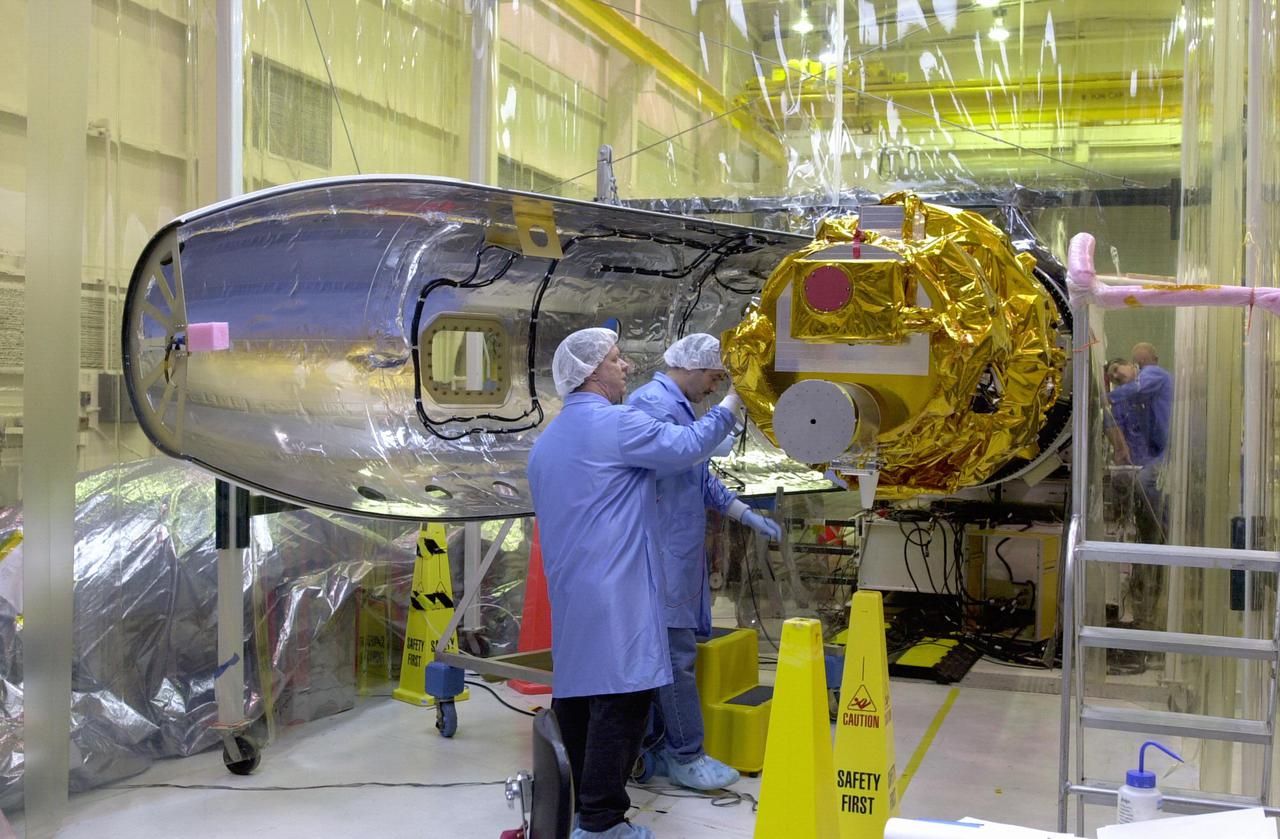

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In preparation for launch, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California get ready to place the first fairing half around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
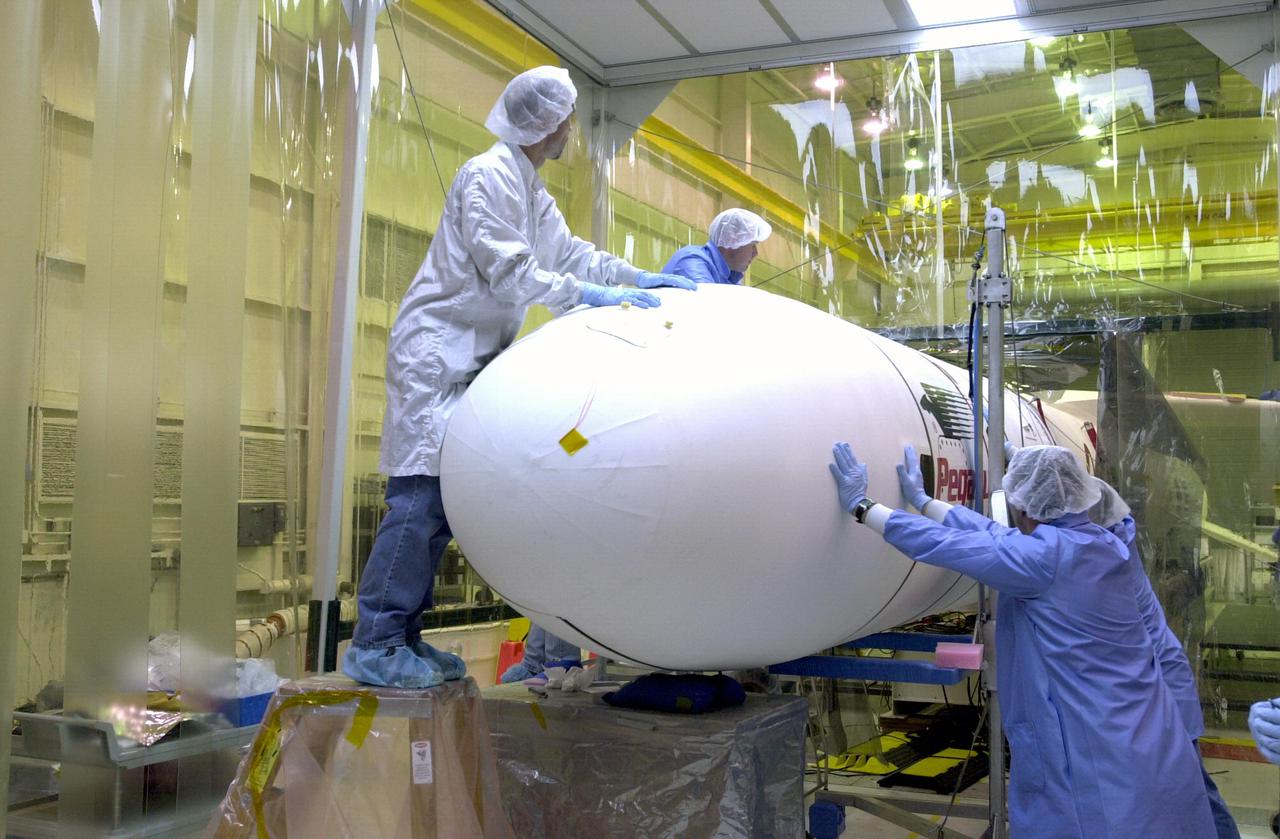

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California finish installation of the fairing around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft in preparation for launch. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
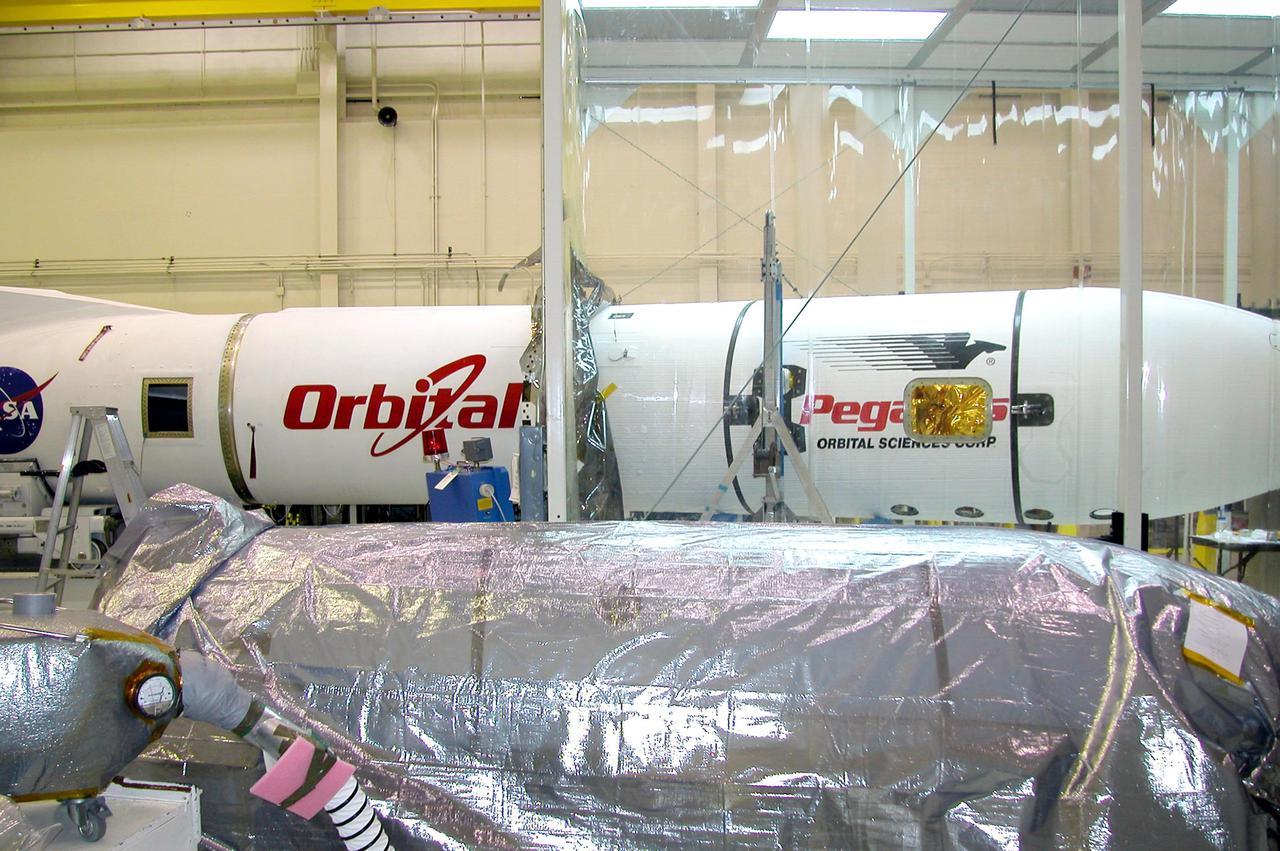

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) is encapsulated and ready to be moved to the runway where it will be attached to the Orbital Sciences Corporation Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) is mated to the belly of the Orbital Sciences Corporation Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After postponement of the launch, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is covered with protective material. DART is mated to Orbital Sciences Corporation’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, which will release its cargo over the Pacific Ocean at 40,000 feet. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) is mated to the belly of the Orbital Sciences Corporation Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California finish attaching the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
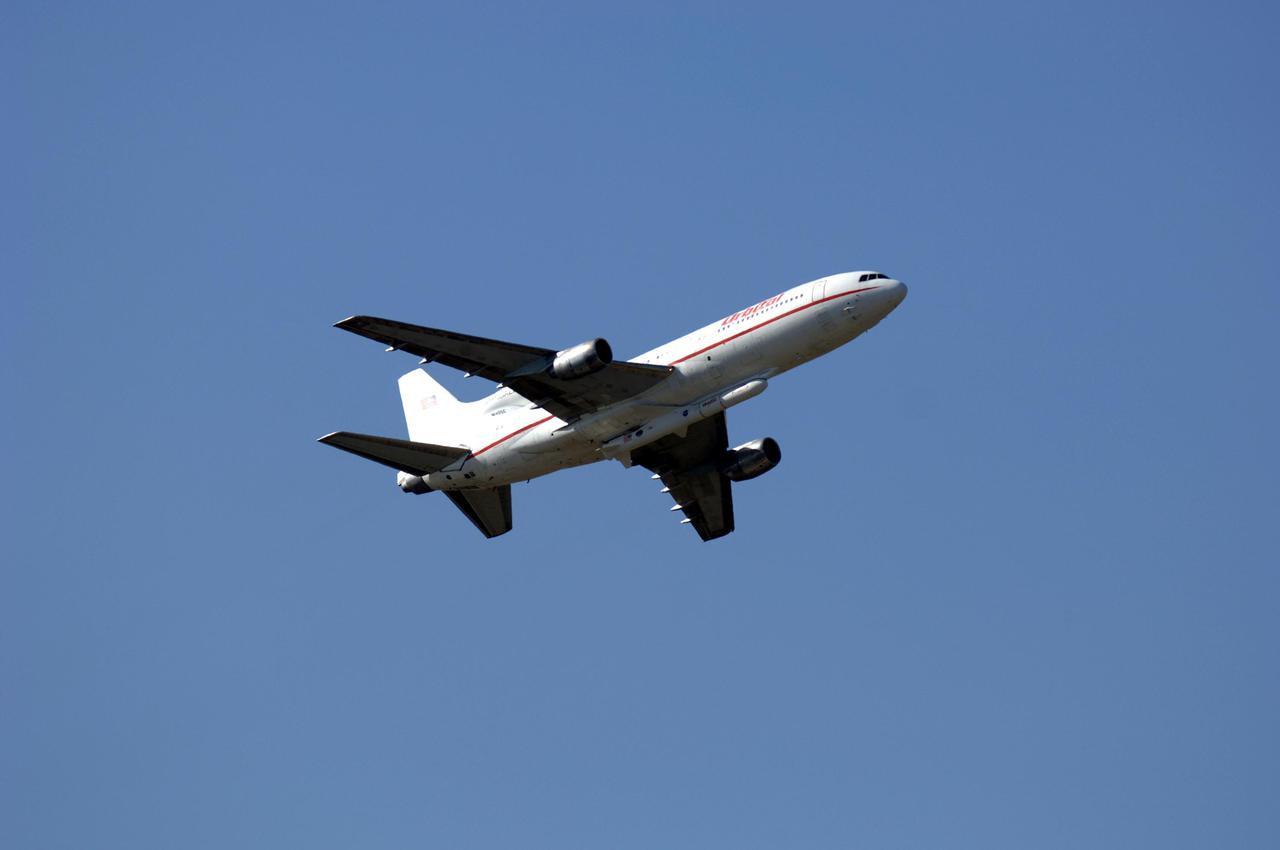

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky to launch the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft attached to its underbelly. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
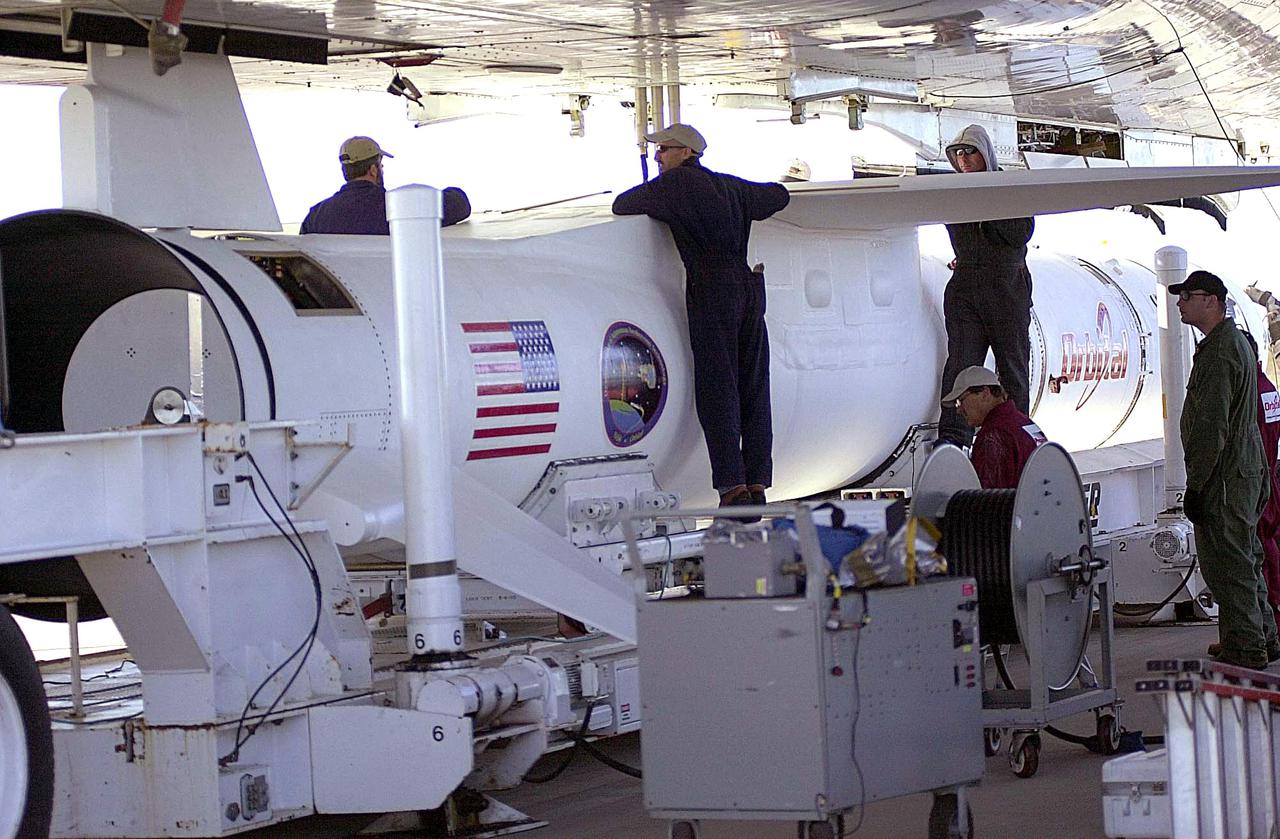

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
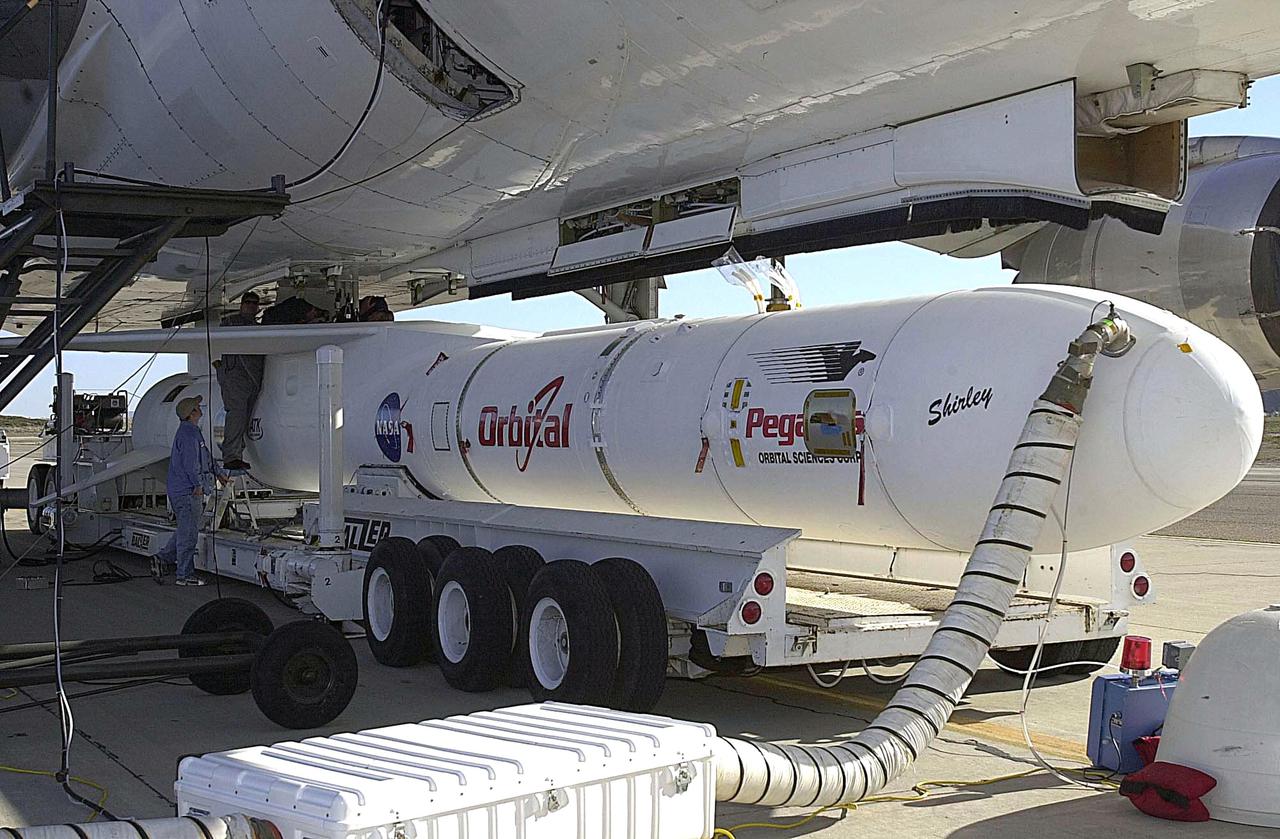

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
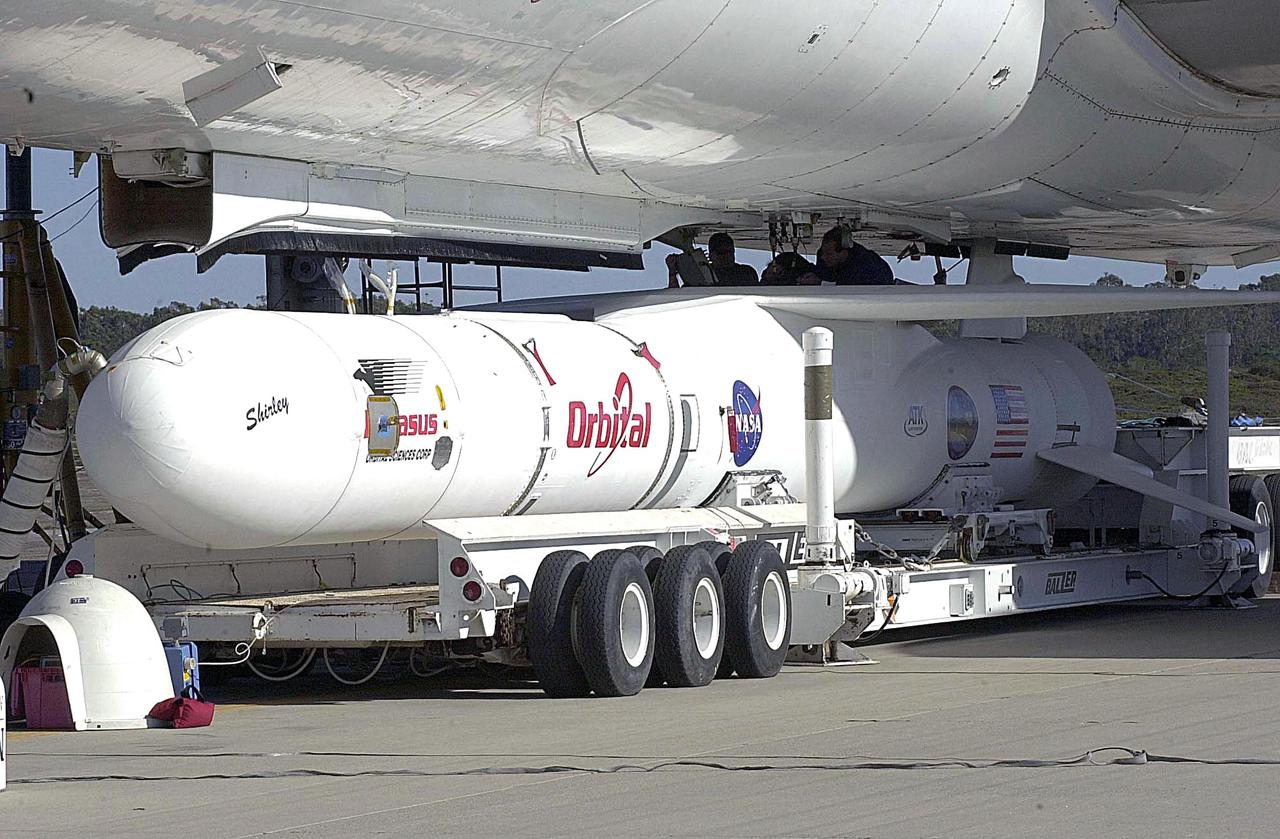

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
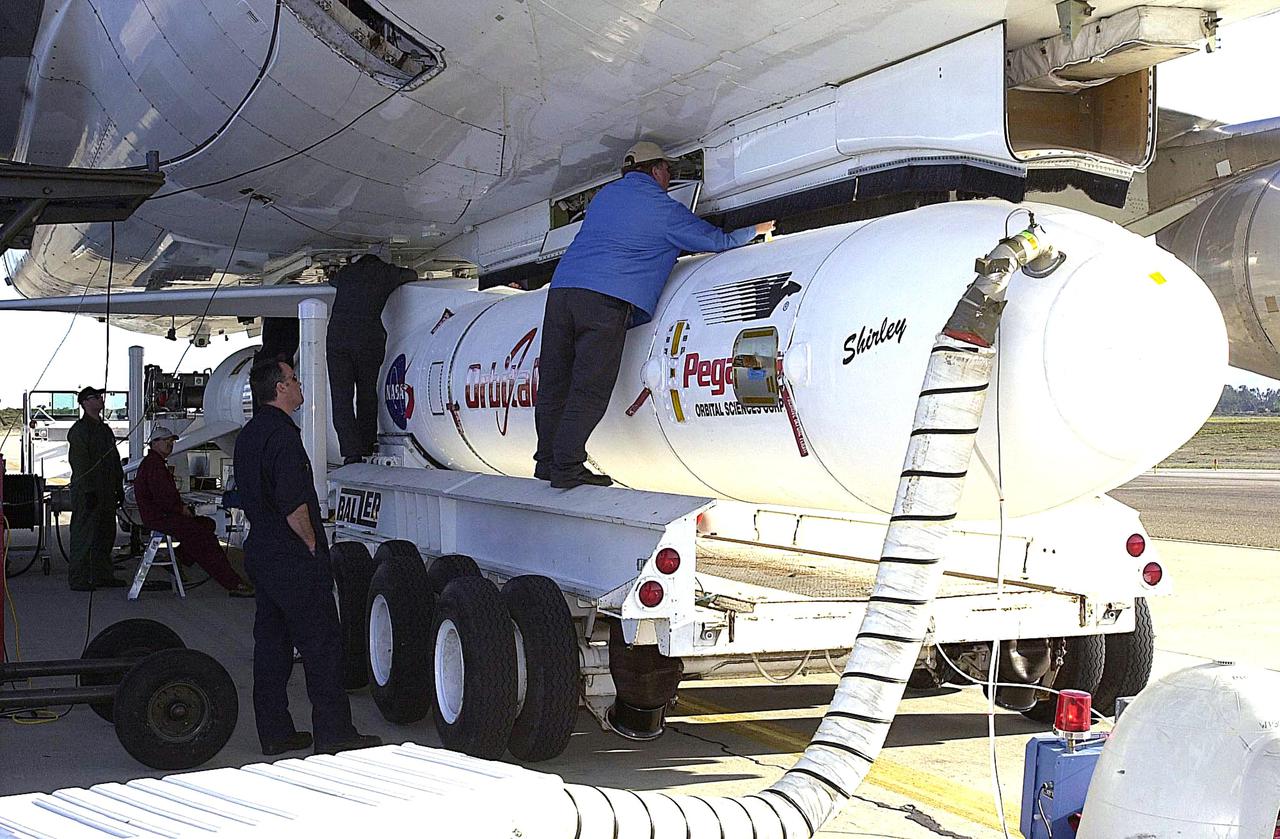

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker stands on the transporter to attach the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky to launch the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft attached to its underbelly. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
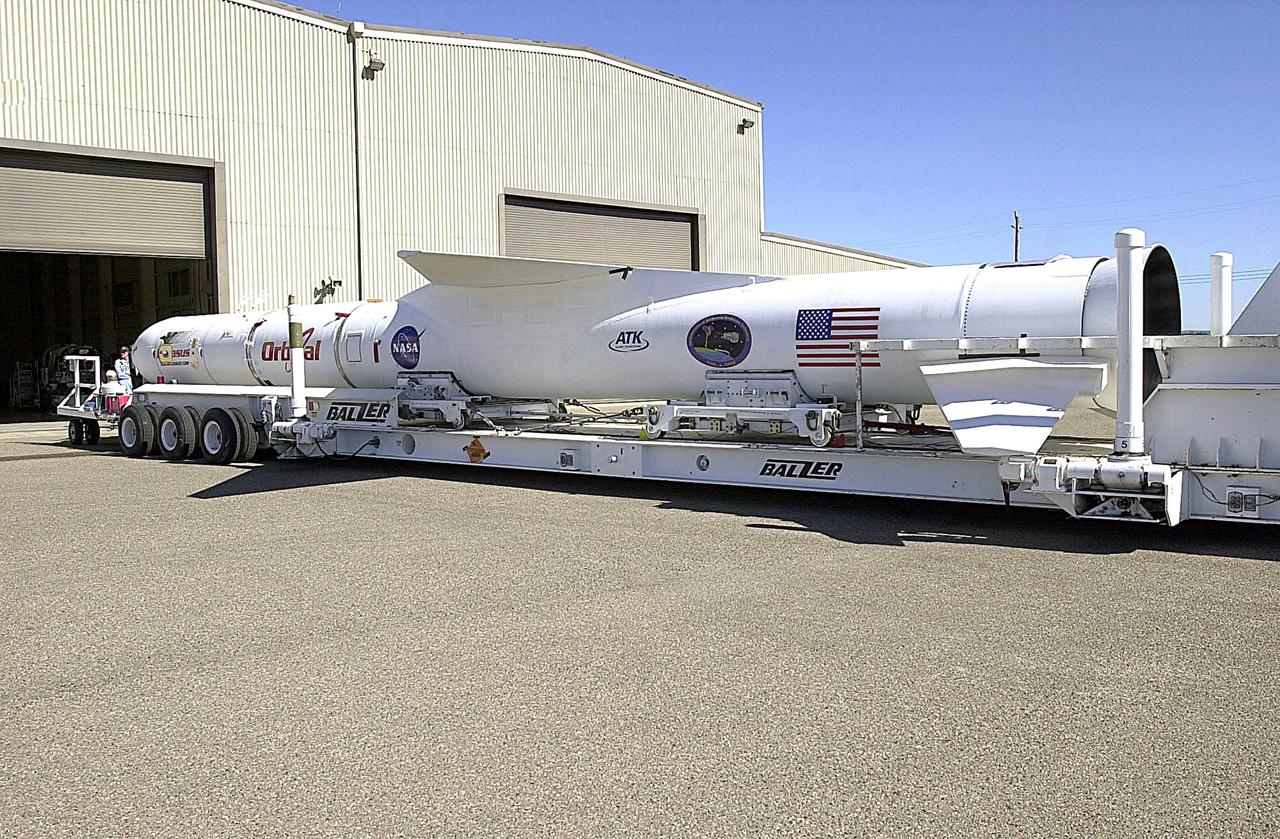

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft roll out of the hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. They will head to the runway and be attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
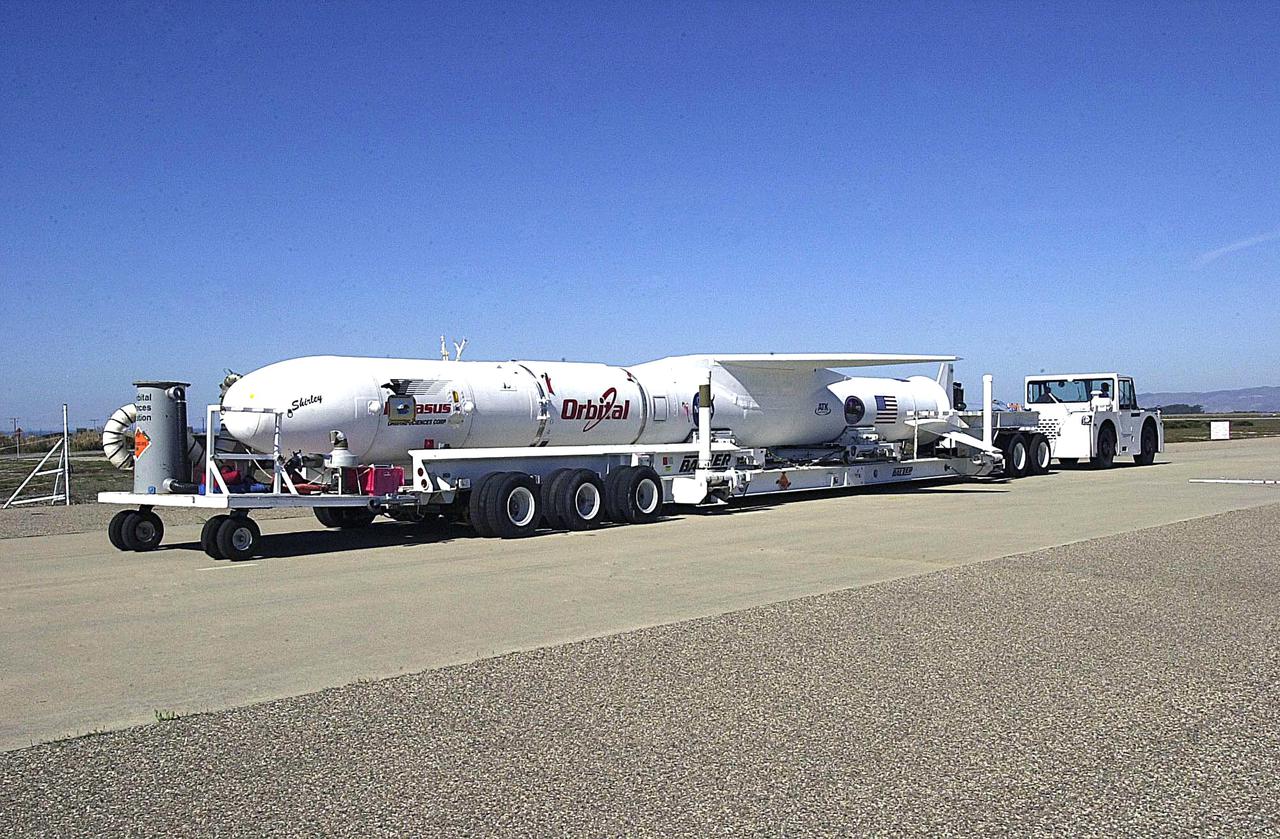

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft head for the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California and the waiting Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft. The Pegasus_DART will be attached to the underbelly of the L-1011 for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
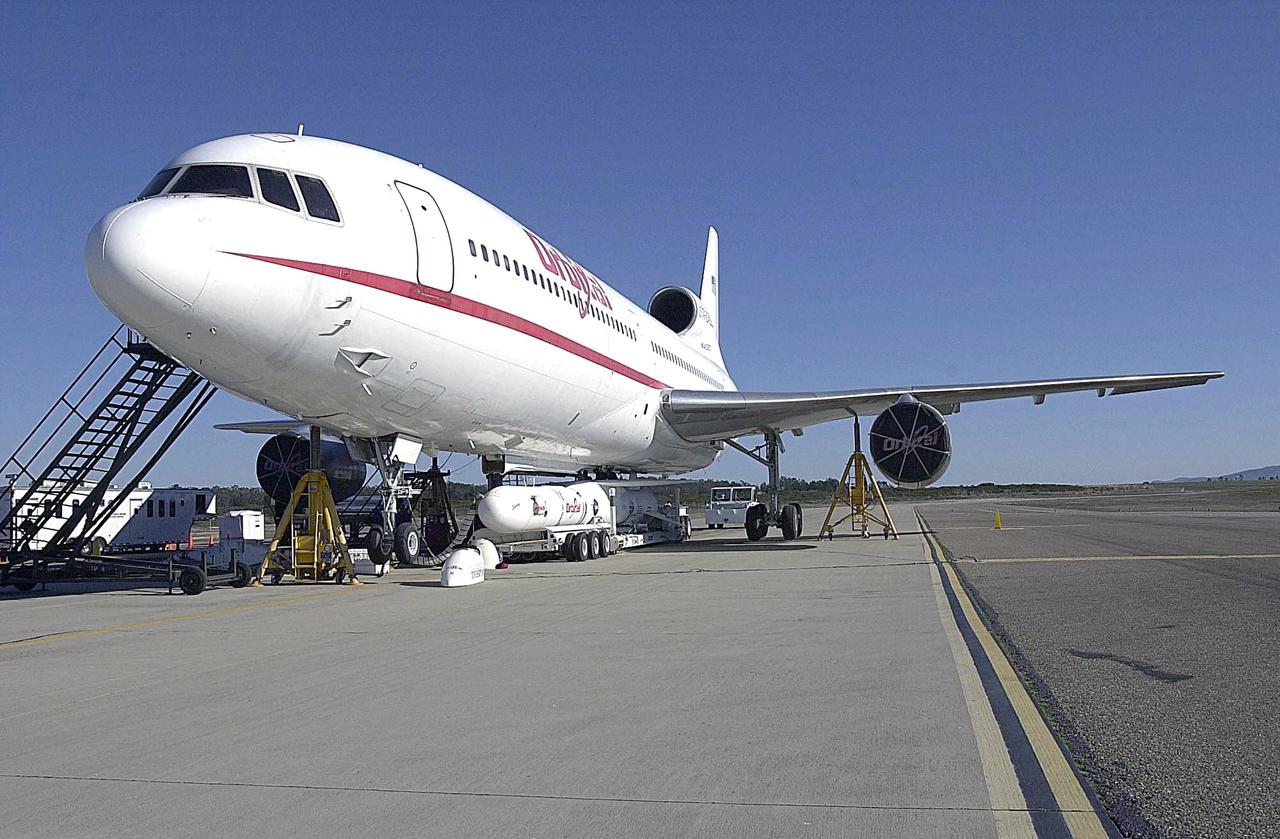

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, which are mated, are being attached to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
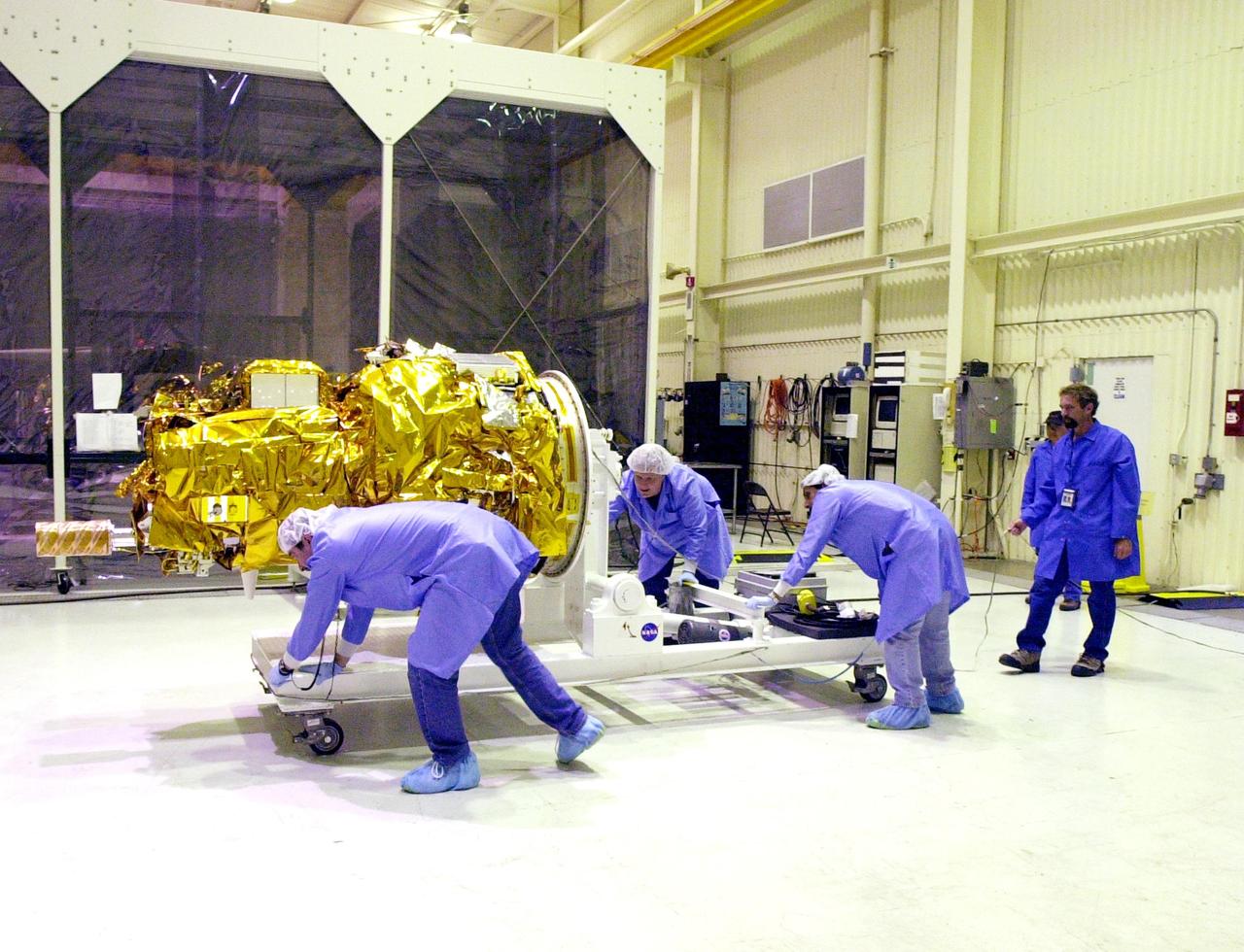

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is prepared for rotation from horizontal to vertical. It will be lifted onto a test stand for launch processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.