
Leading Edge De-Icing Evaluation Test of the General Atomics Predator B Wing Section using Electro-Expulsive De-Icing System (EEDS) Testing conducted in cooperation with Wichita State University
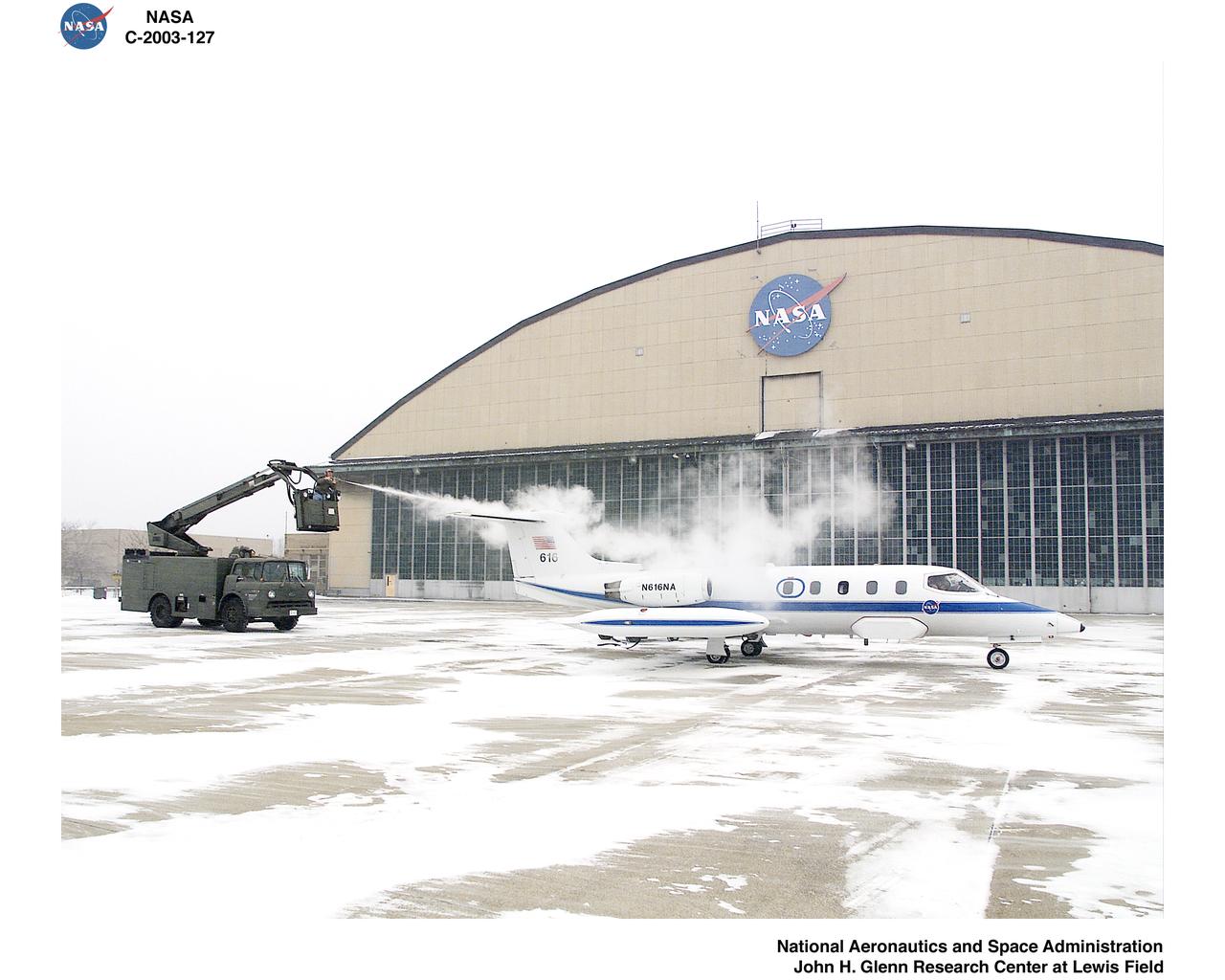

NASA Lear Jet De-Icing
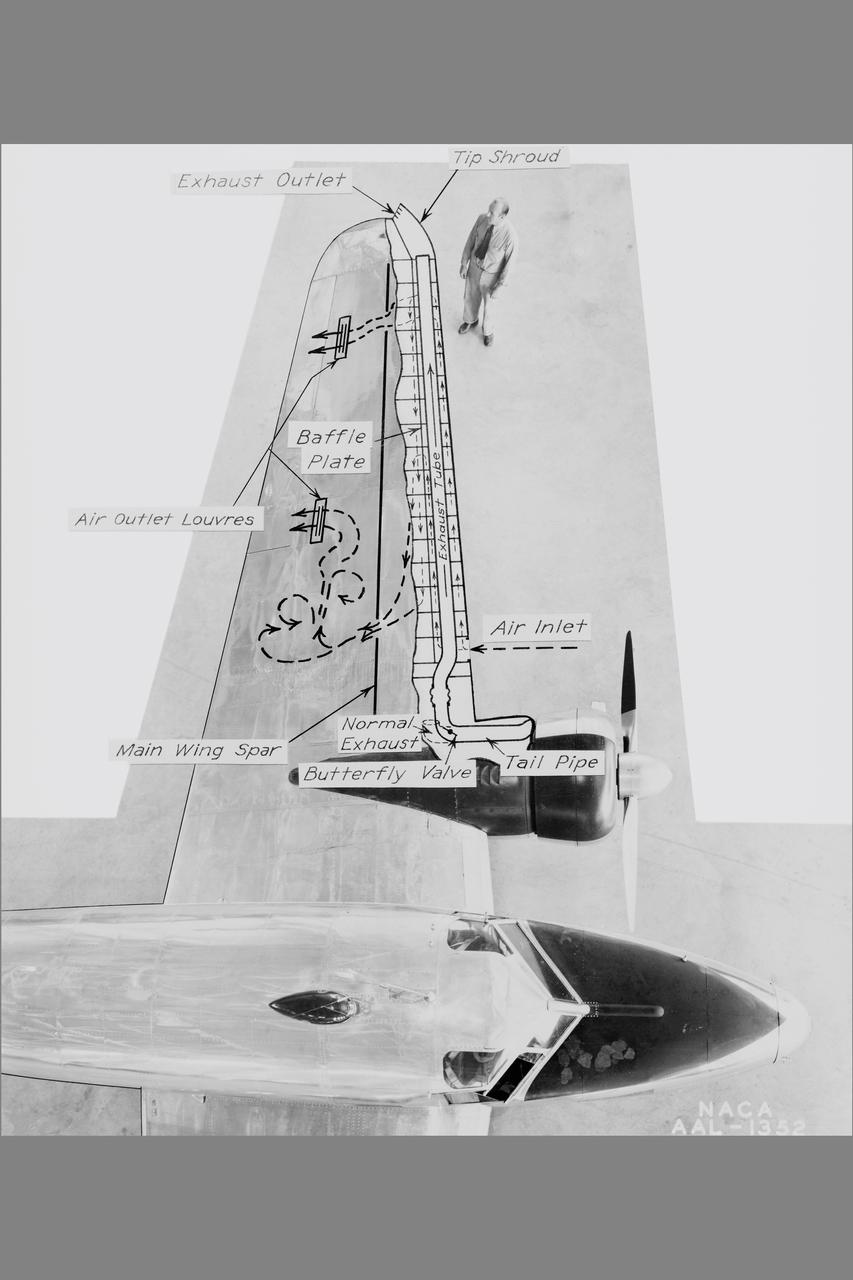
NACA Photographer NASA Ames De-icing project: diagram of the systems using exhaust-heated air to prevent icing on the Lockheed 12A wings Published: Adventures in Research SP-4302
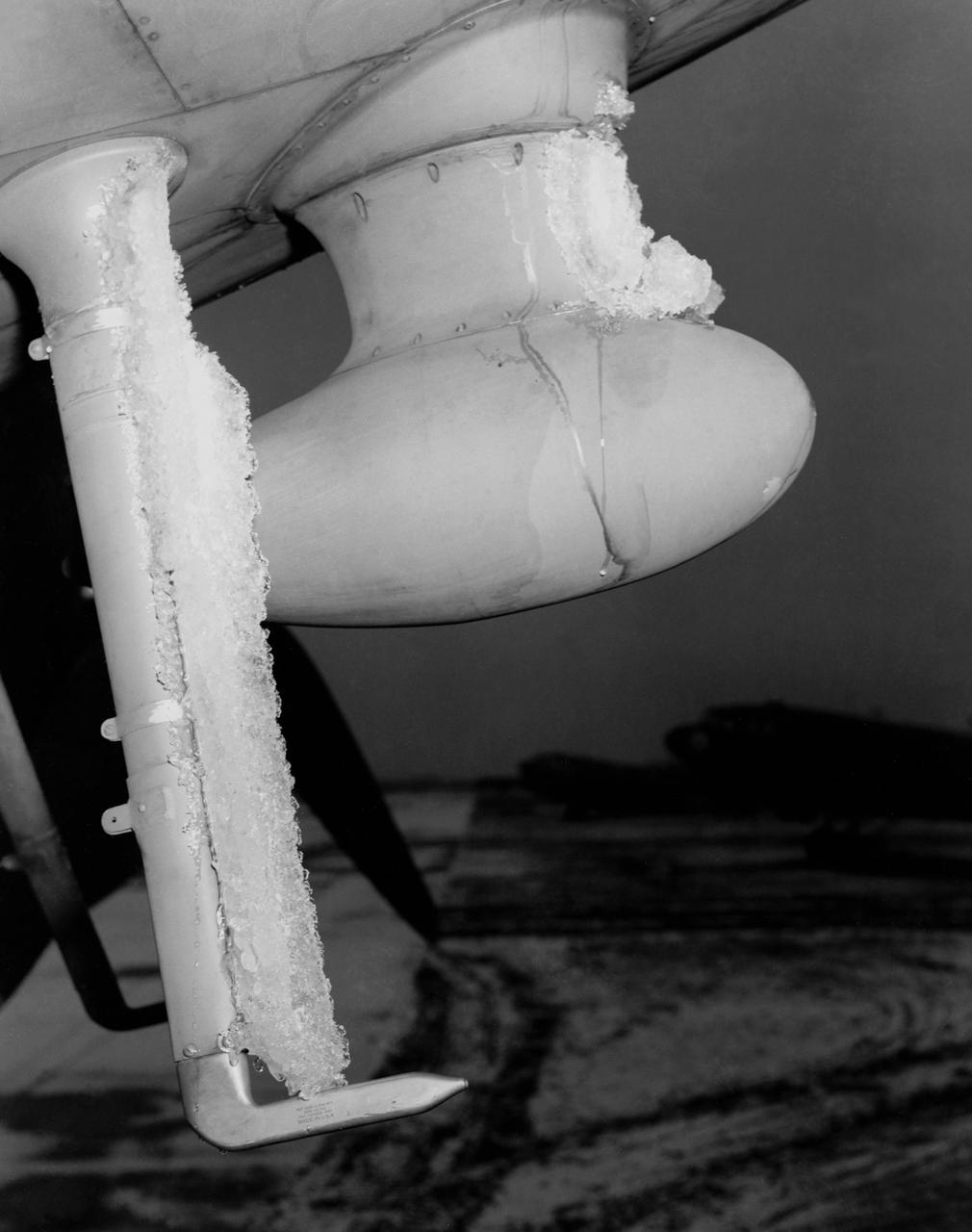

De-icing Research conducted at the NASA Ames Research Center. Icing flight test on C-46 airplane (flight 29 11:25am to 12:50 am) glaze ice on loop antenna co-pilots airspeed mast.
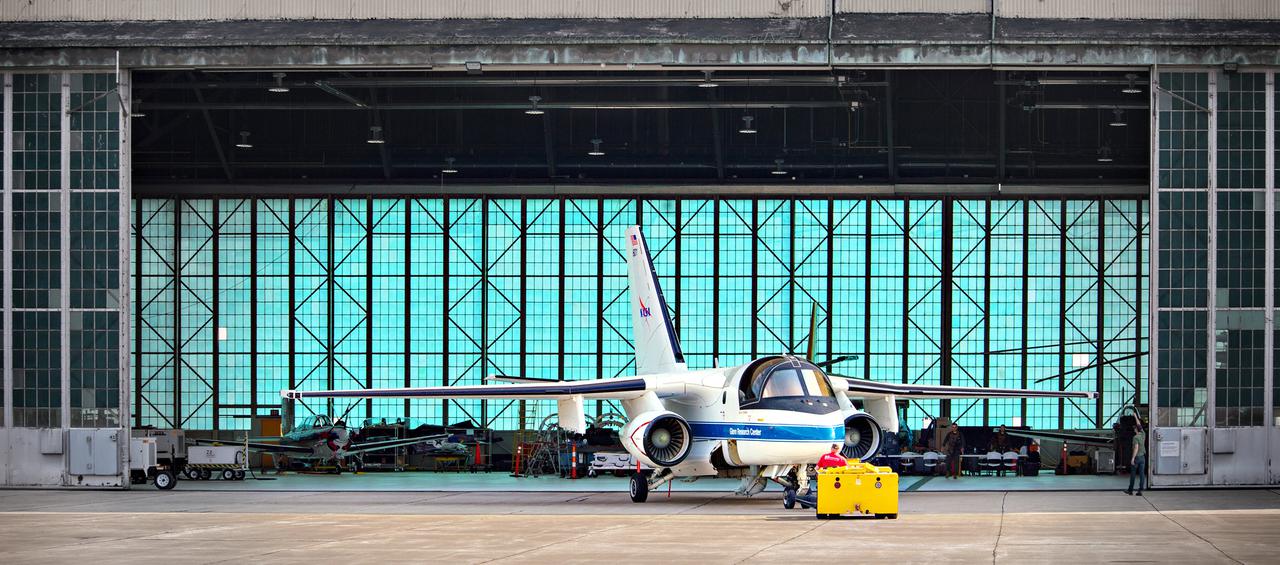

The Lockheed Viking S-3B aircraft is being pulled out of the hangar at Glenn Research Center in preparation for its departure and retirement from service. This former NAVY aircraft was the last such aircraft still flying. It has gone to a museum on the west coast. After leaving service with the NAVY, it came to GRC to be used in aircraft icing experiments. The swept wings made it suitable for such research as opposed to the straight wings on GRG’s other icing research aircraft, the De Havilland Twin Otter.

Test engineers clean the ice cloud detection probe in the Icing Research Tunnel in between test runs. Steam is used to melt the accumulated ice on the detection probe. The test engineers need to wear goggles to protect them from the laser light that the probe emits. The laser detects water content and ice particles in the cloud that the wind tunnel produces. This process is done to calibrate the tunnel for research by characterizing the cloud flow.

ISS026-E-025437 (10 Feb. 2011) --- Pico de Orizaba, Mexico is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member on the International Space Station. The snow and ice-clad peak of Pico de Orizaba (also known as Citlaltepetl) boasts a summit elevation of 5,675 meters (18,619 feet) above sea level, making it the highest peak in Mexico and North America’s highest volcano. It is also one of three volcanic peaks in Mexico—together with Popocatepetl and Iztaccihuatl—that retain summit glaciers. Pico de Orizaba is part of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt that extends roughly east-west across Mexico. The last recorded eruption took place in 1846; while the volcano is considered dormant at present, geologists continue to investigate the potential hazards associated with a renewal of activity. Shadows accentuate several features of the Pico de Orizaba stratovolcano visible in this photograph from the space station. The 300-meter-deep summit crater is clearly visible against surrounding ice and snow cover at center. Several lava flows extend down the flanks of the volcano, made readily visible by prominent cooling ridges along their sides known as flow levees—one of the most clearly visible examples is located on the southwest flank of the cone. The extinct Sierra Negra volcano to the southwest has a summit elevation of 4,640 meters (15,223 feet) above sea level; while not as lofty as Pico de Orizaba, it is also one of Mexico’s highest peaks.

ISS018-E-028898 (7 Feb. 2009) --- The summit of Popocatepetl Volcano in Mexico is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 18 crewmember on the International Space Station. Volcano Popocatepetl, a large stratovolcano located approximately 70 kilometers to the southeast of Mexico City, is considered by many volcanologists to be ?the planet?s riskiest volcano?. The volcano warrants this distinction because of its proximity to one of the most densely populated megacities on Earth (population near 23 million in 2009). The variety of potential volcanic hazards at Popocatepetl is also considerable, including explosive eruptions of ash, pyroclastic flows (hot, fluidized masses of rock and gas that flow rapidly downhill), and debris avalanches. This detailed photograph of the summit crater of Popocatepetl (center) also highlights Ventorillo and Noroccidental Glaciers ? together with ice on nearby Iztaccihuatl Volcano and Pico de Orizaba (Mexico?s highest peak and the highest volcano in North America), these are the only mountain glaciers in tropical North America. The presence of glaciers on Popocatepetl is also connected with another volcanic hazard ? the creation of dangerous mudflows, or lahars, should the ice melt during eruptive activity. At the time this image was taken, steam and ash plumes were observed at the volcano ? a faint white steam plume is visible against gray ash deposits on the eastern and southern flanks of the volcano.
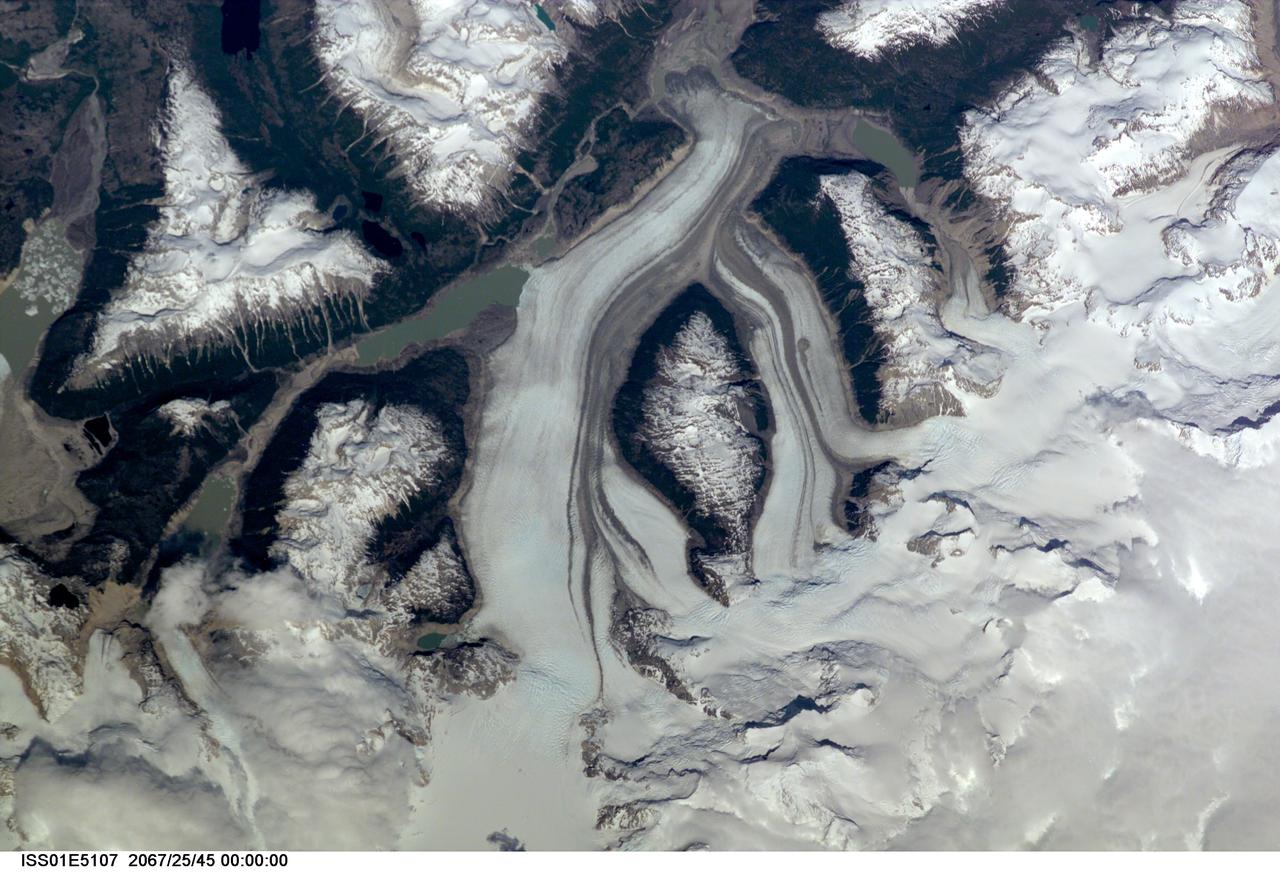

ISS01-E-5107 (December 2000) --- This nadir view of a Chilean glaciated area was provided by one of the early December digital still camera images down linked from the International Space Station (ISS) to ground controllers in Houston. The remote headwaters of the Rio de la Colonia are located on the eastern flank of the Cerro Pared Norte, a high, coastal range of the Andes in southern Chile. This is but a portion of a larger glaciated region of the Chilean coast located at only 47 degrees south latitude. The river actually begins its flow just off the top of this scene at the foot of the two large, converging, valley glaciers near the center. Some of the numerous lakes visible are tinted by the fine glacial sediments suspended in their waters. Note the shards of ice that have calved from the glaciers into the lakes on the left. Also note the shadows of the crest of the over 14,000-foot mountains (lower center). The remote headwaters of the Rio de la Colonia are located on the eastern flank of the Cerro Pared Norte, a high, coastal range of the Andes in southern Chile. This is a but a portion of a larger glaciated region of the Chilean coast located at only 47 degrees south latitude. The river actually begins its flow just off the top of this scene at the foot of the two large, converging, valley glaciers near the center. Some of the numerous lakes visible are tinted by the fine glacial sediments suspended in their waters. Note the shards of ice that have calved from the glaciers into the lakes on the left. Also note the shadows of the crest of the over 14,000-foot mountains (lower center).
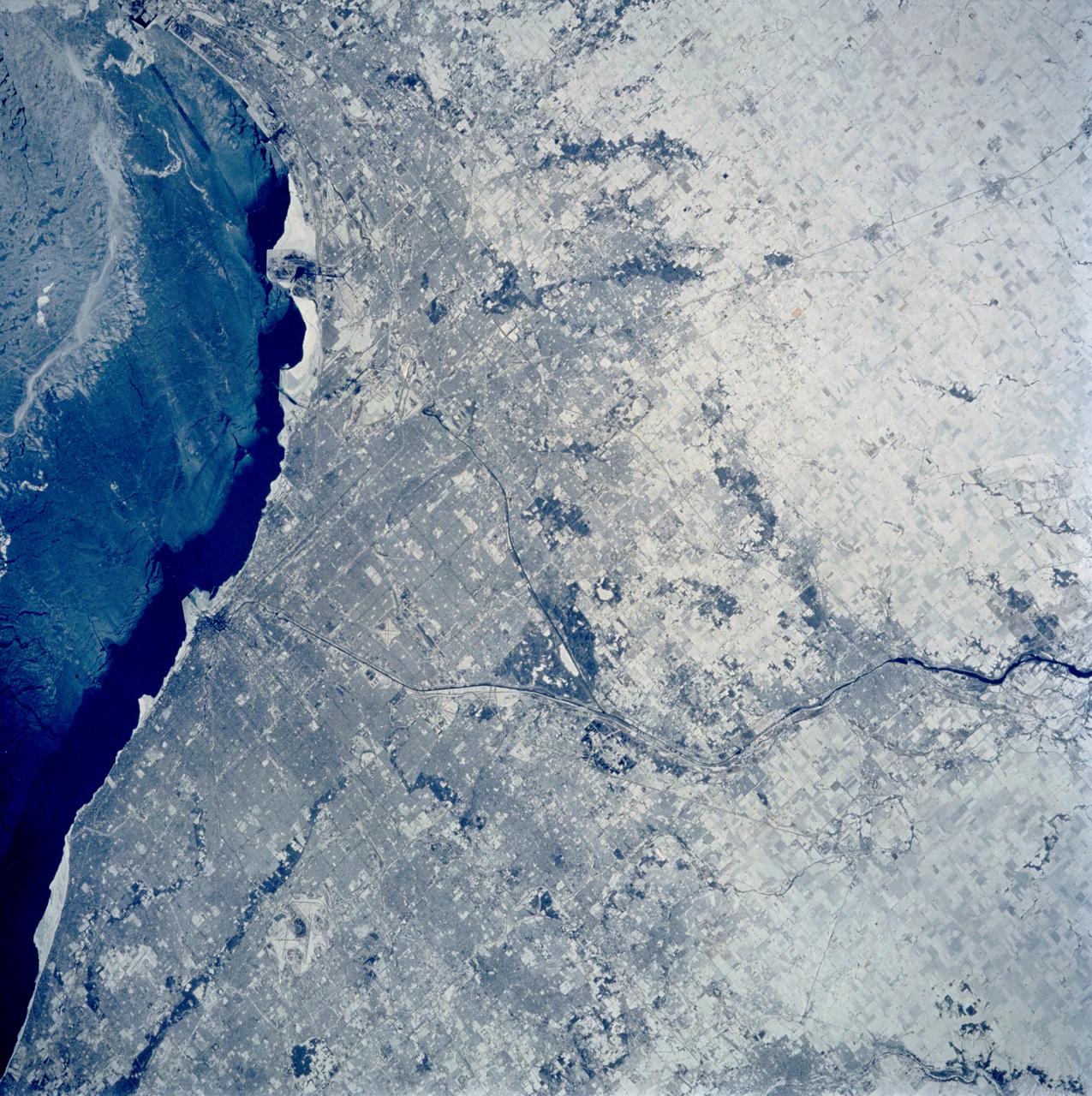

STS060-103-089 (3-11 Feb. 1994) --- The Chicago, Illinois area is in this northeast looking low oblique view obtained in February, 1994. Lake Michigan, a good portion covered with ice due to the very cold winter weather that has plagued this region since early December, 1993, can be seen to the east of the city. The Des Plaines river is visible traversing northeast to southwest through the center of the city. O'Hare International Airport and the Glenview Naval Air Station can be seen to the north of the Des Plaines River. Midway Airport is visible just to the south of the river. Chicago is a port of entry; a major Great Lakes port located at the junction of the St. Lawrence Seaway with the Mississippi River system; the busiest air center in the United States; and an important rail and highway transportation hub. Chicago is known for large grain mills and elevators, iron and steel works, steel fabrication plants, stockyards, meat-packing establishments, and printing and publishing houses. In the early days of settlement, the narrow watershed between Lake Michigan and the Des Plaines River (draining the Mississippi River through the Illinois River), offered an easy portage that led explorers like Father Marquette and Louis Joliet and others to the Great Central Plains. Fort Dearborn, a military post was established in 1803. By 1860, the railroad connected Chicago to the rest of the country and the city became a great mid-continent shipping and receiving center. In 1871, the city built of wood, was almost entirely destroyed by a great fire. After the fire, Chicago was built as a city of steel and stone. During the World's Colombian Exposition held in Chicago in 1893, the city became a leading architectural center. It was here during the Exposition that the skyscraper came into being. Chicago continues to lead the way in this type of architectural structure as is evidenced with the completion of the Sears Tower in 1974.
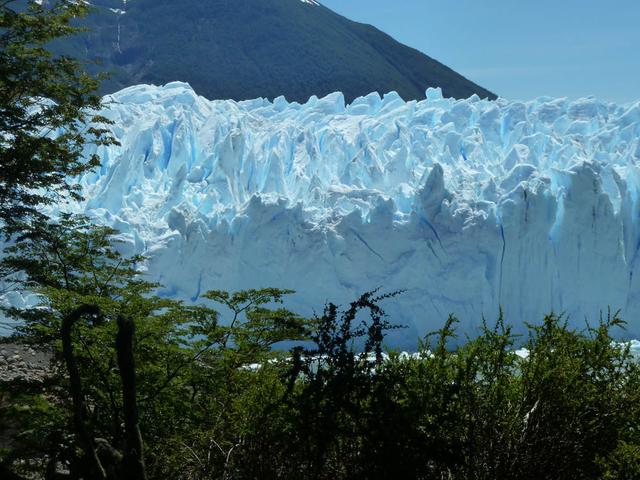

Calving front of the Perito Moreno Glacier (Argentina). Contrary to the majority of the glaciers from the southern Patagonian ice field, the Perito Moreno Glacier is currently stable. It is also one of the most visited glaciers in the world. To learn about the contributions of glaciers to sea level rise, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/glacier-sea-rise.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/glacier-sea-rise.html</a> Credit: Etienne Berthier, Université de Toulouse <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
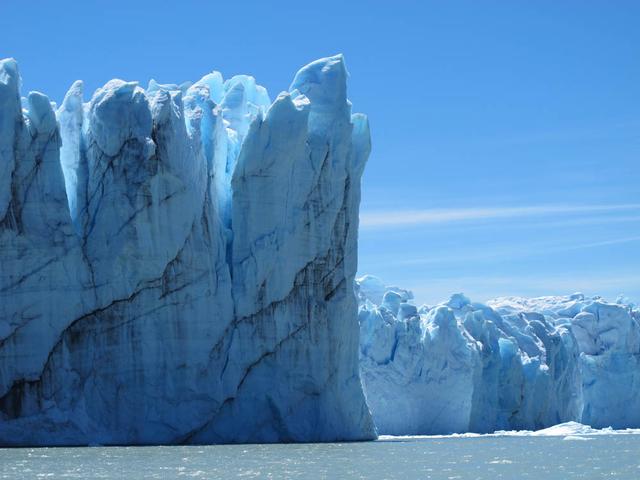

Calving front of the Perito Moreno Glacier (Argentina). Contrary to the majority of the glaciers from the southern Patagonian ice field, the Perito Moreno Glacier is currently stable. It is also one of the most visited glaciers in the world. To learn about the contributions of glaciers to sea level rise, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/glacier-sea-rise.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/glacier-sea-rise.html</a> Credit: Etienne Berthier, Université de Toulouse <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Lying more than 110 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Antlia (The Air Pump) is the spiral galaxy IC 2560, shown here in an image from NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. At this distance it is a relatively nearby spiral galaxy, and is part of the Antlia cluster — a group of over 200 galaxies held together by gravity. This cluster is unusual; unlike most other galaxy clusters, it appears to have no dominant galaxy within it. In this image, it is easy to spot IC 2560's spiral arms and barred structure. This spiral is what astronomers call a Seyfert-2 galaxy, a kind of spiral galaxy characterized by an extremely bright nucleus and very strong emission lines from certain elements — hydrogen, helium, nitrogen, and oxygen. The bright center of the galaxy is thought to be caused by the ejection of huge amounts of super-hot gas from the region around a central black hole. There is a story behind the naming of this quirky constellation — Antlia was originally named antlia pneumatica by French astronomer Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, in honor of the invention of the air pump in the 17th century. Credit: Hubble/European Space Agency and NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This is a composite image of Uranus by Voyager 2 and two different observations made by Hubble — one for the ring and one for the auroras. Ever since Voyager 2 beamed home spectacular images of the planets in the 1980s, planet-lovers have been hooked on auroras on other planets. Auroras are caused by streams of charged particles like electrons that come from various origins such as solar winds, the planetary ionosphere, and moon volcanism. They become caught in powerful magnetic fields and are channeled into the upper atmosphere, where their interactions with gas particles, such as oxygen or nitrogen, set off spectacular bursts of light. The auroras on Jupiter and Saturn are well-studied, but not much is known about the auroras of the giant ice planet Uranus. In 2011, the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope became the first Earth-based telescope to snap an image of the auroras on Uranus. In 2012 and 2014 a team led by an astronomer from Paris Observatory took a second look at the auroras using the ultraviolet capabilities of the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) installed on Hubble. They tracked the interplanetary shocks caused by two powerful bursts of solar wind traveling from the sun to Uranus, then used Hubble to capture their effect on Uranus’ auroras — and found themselves observing the most intense auroras ever seen on the planet. By watching the auroras over time, they collected the first direct evidence that these powerful shimmering regions rotate with the planet. They also re-discovered Uranus’ long-lost magnetic poles, which were lost shortly after their discovery by Voyager 2 in 1986 due to uncertainties in measurements and the featureless planet surface. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, L. Lamy / Observatoire de Paris <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>