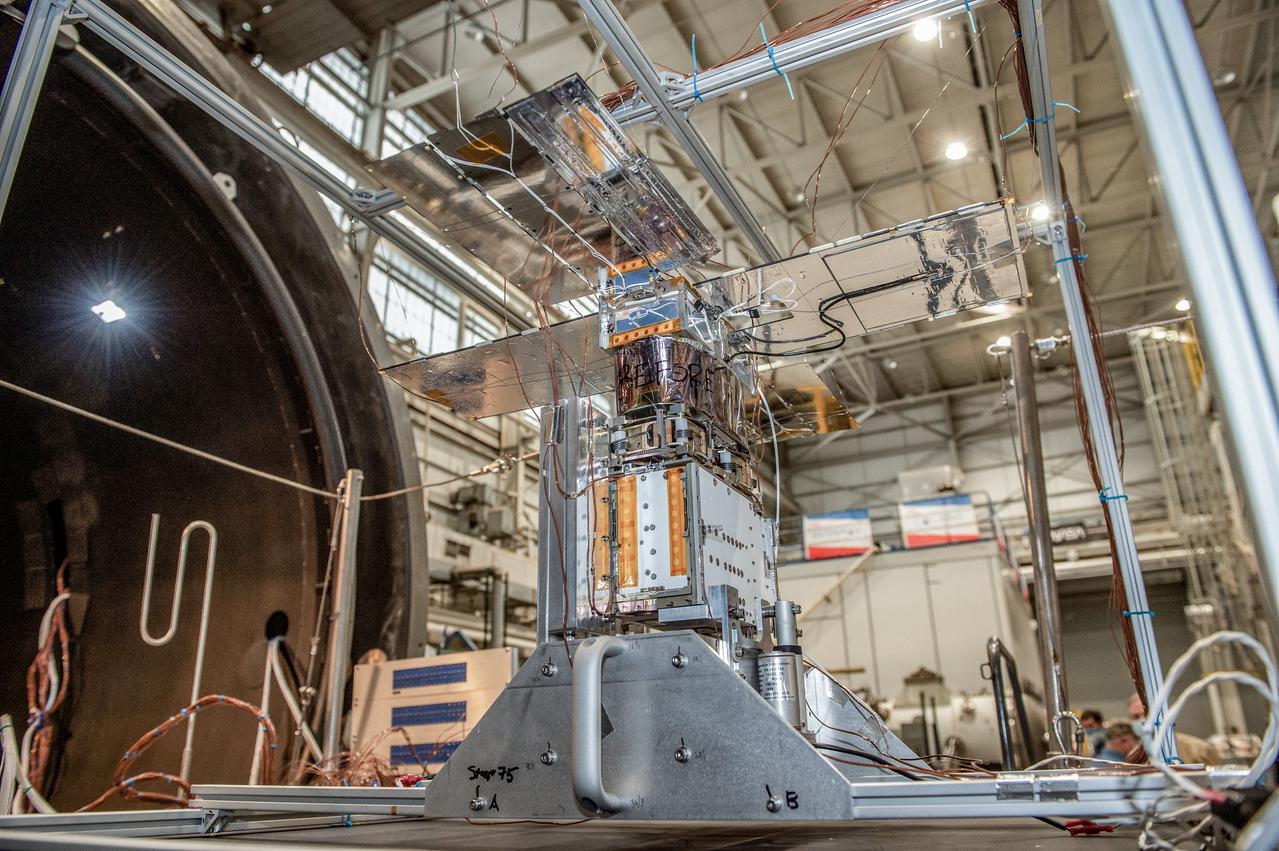
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
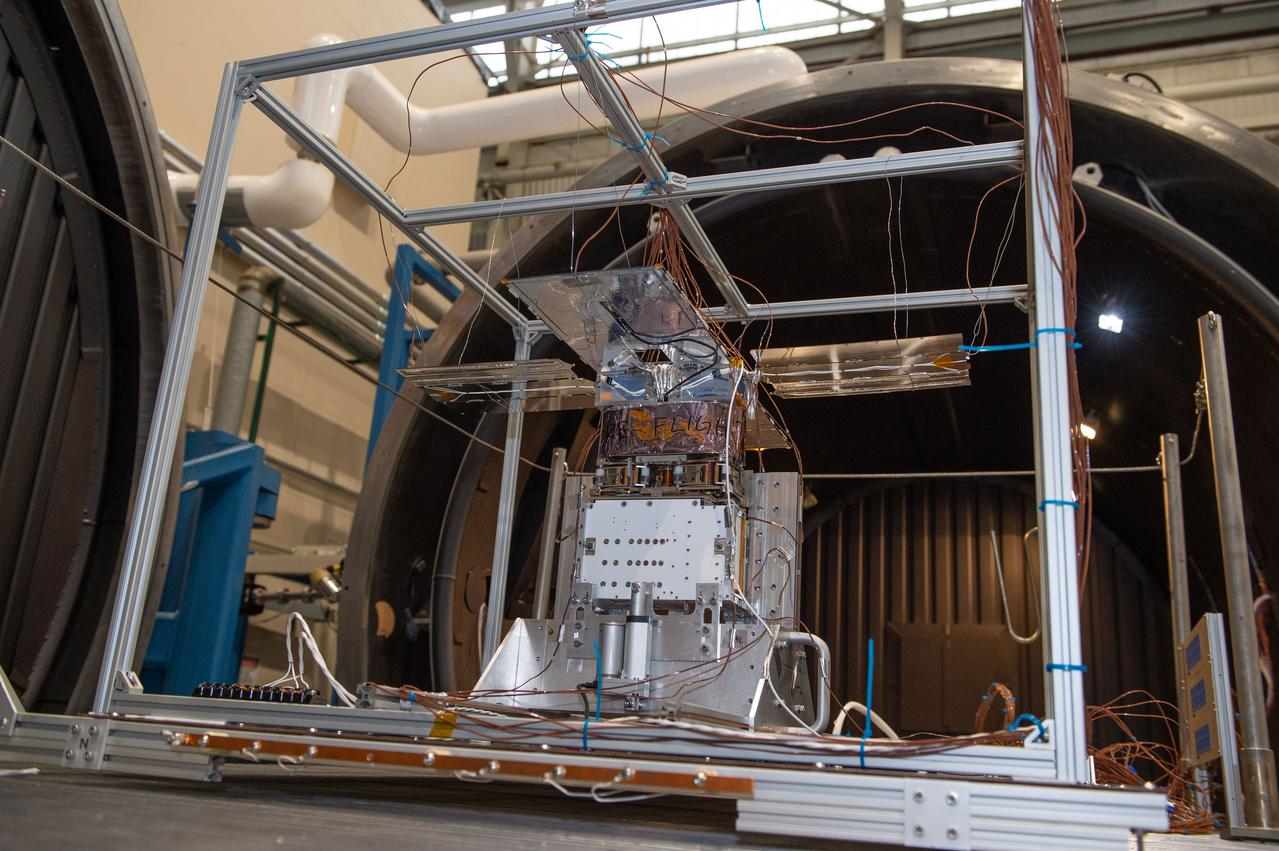
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
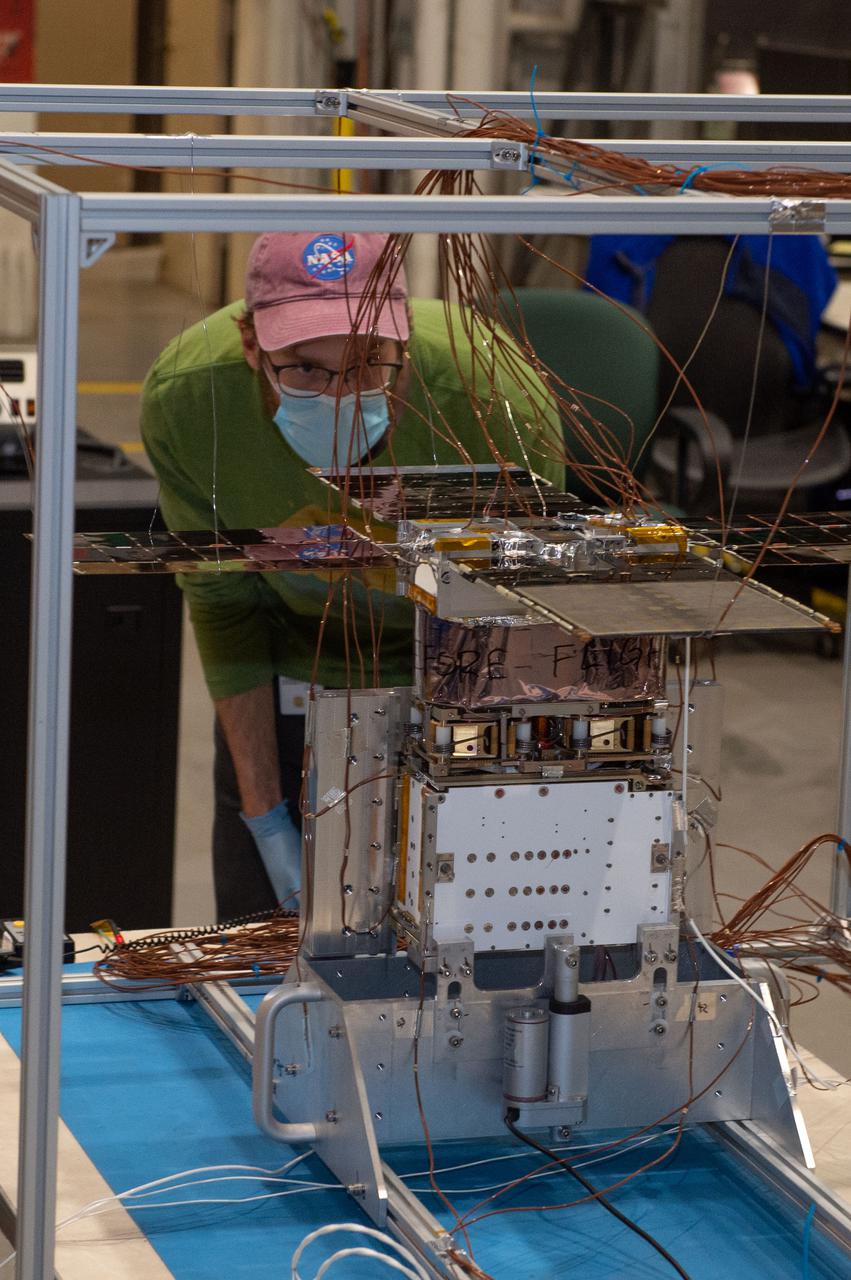
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
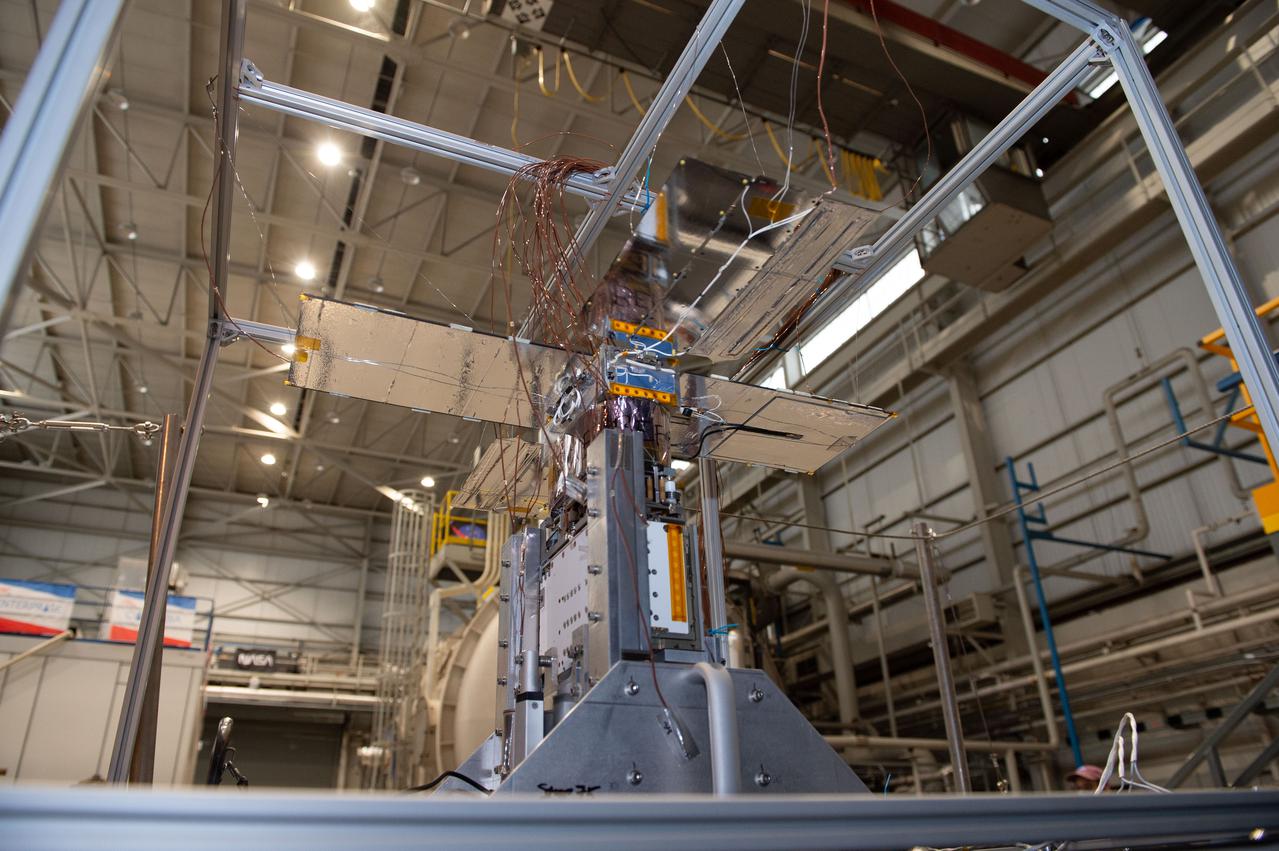

NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
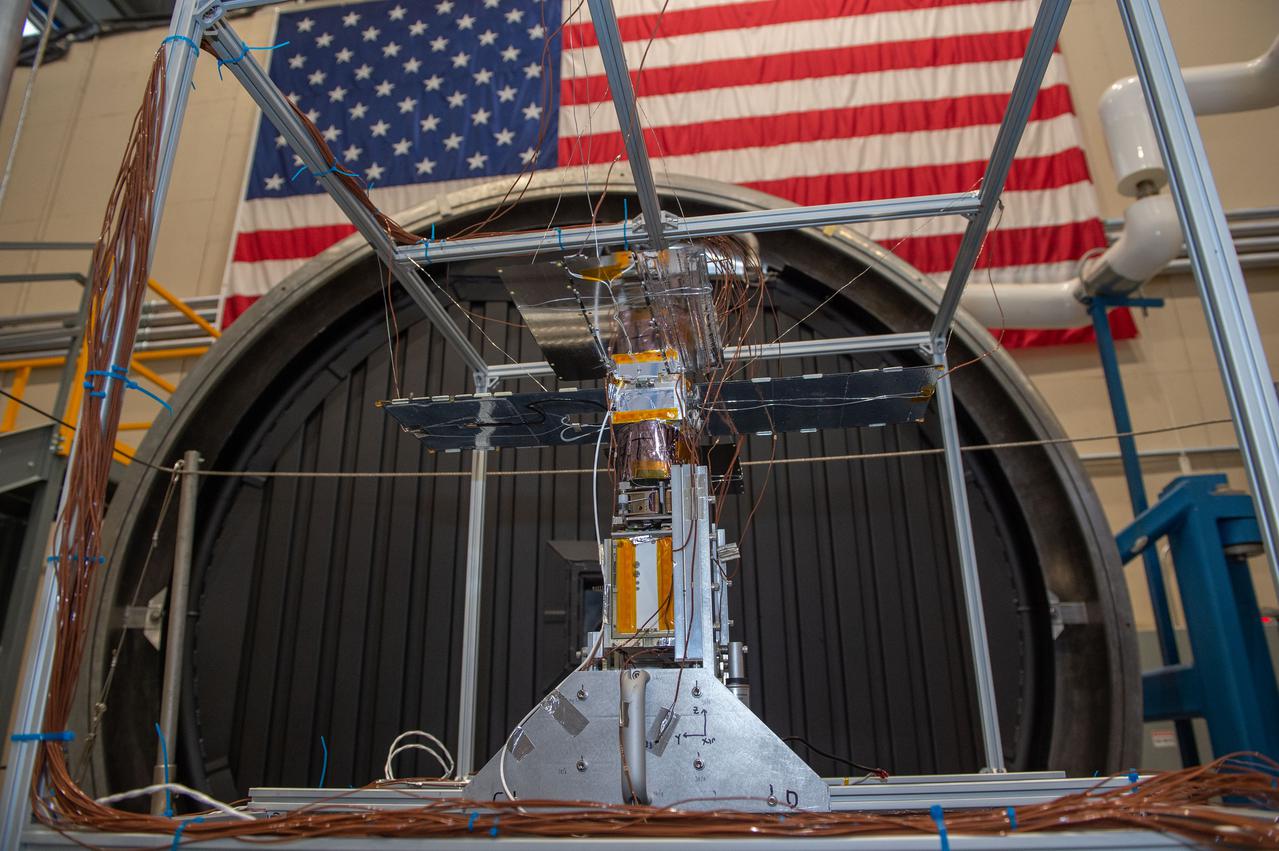
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
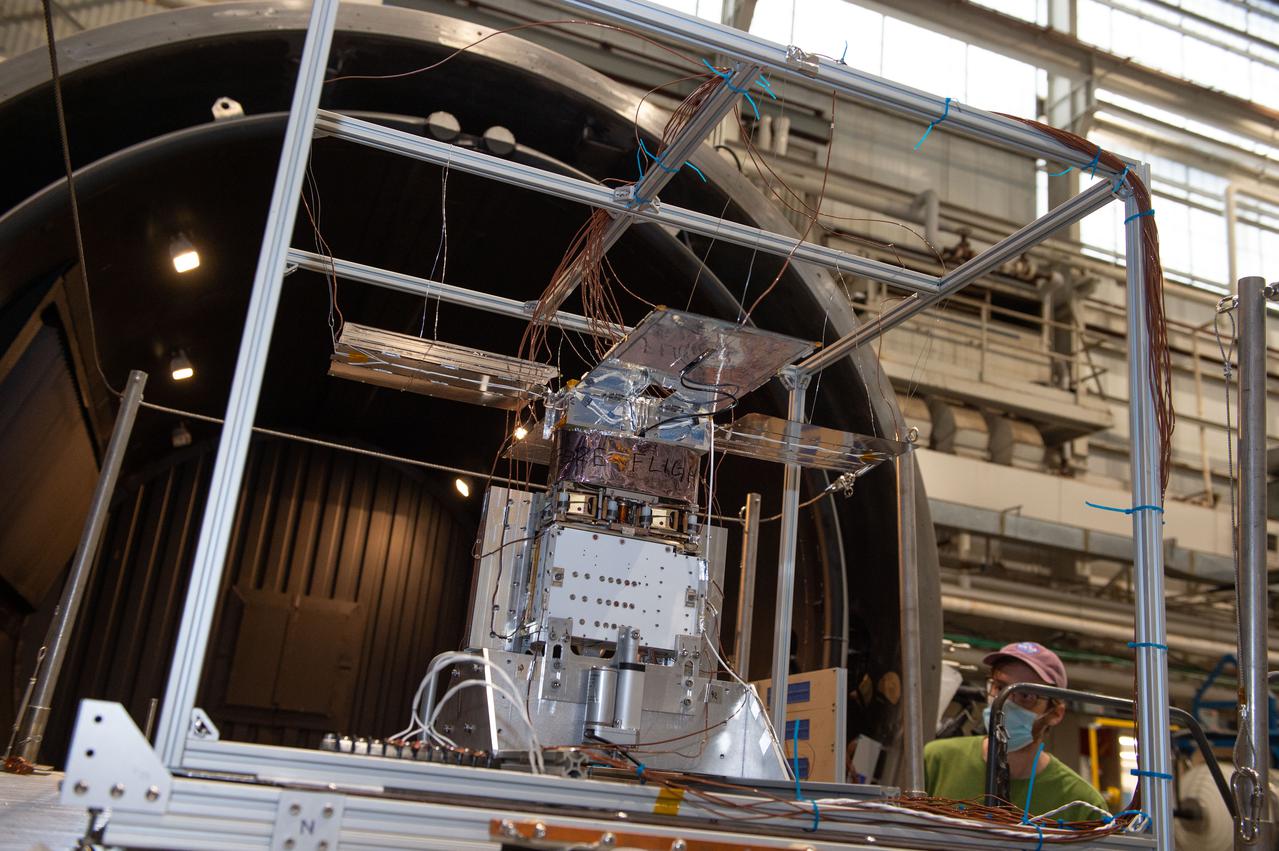
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box

jsc2023e010189 (12/13/2022) --- Lightcube Principal Investigator Jaime Sanchez de la Vega holds the CubeSat prior to integration into the deployer. Image courtesy of Jaime Sanchez de la Vega.
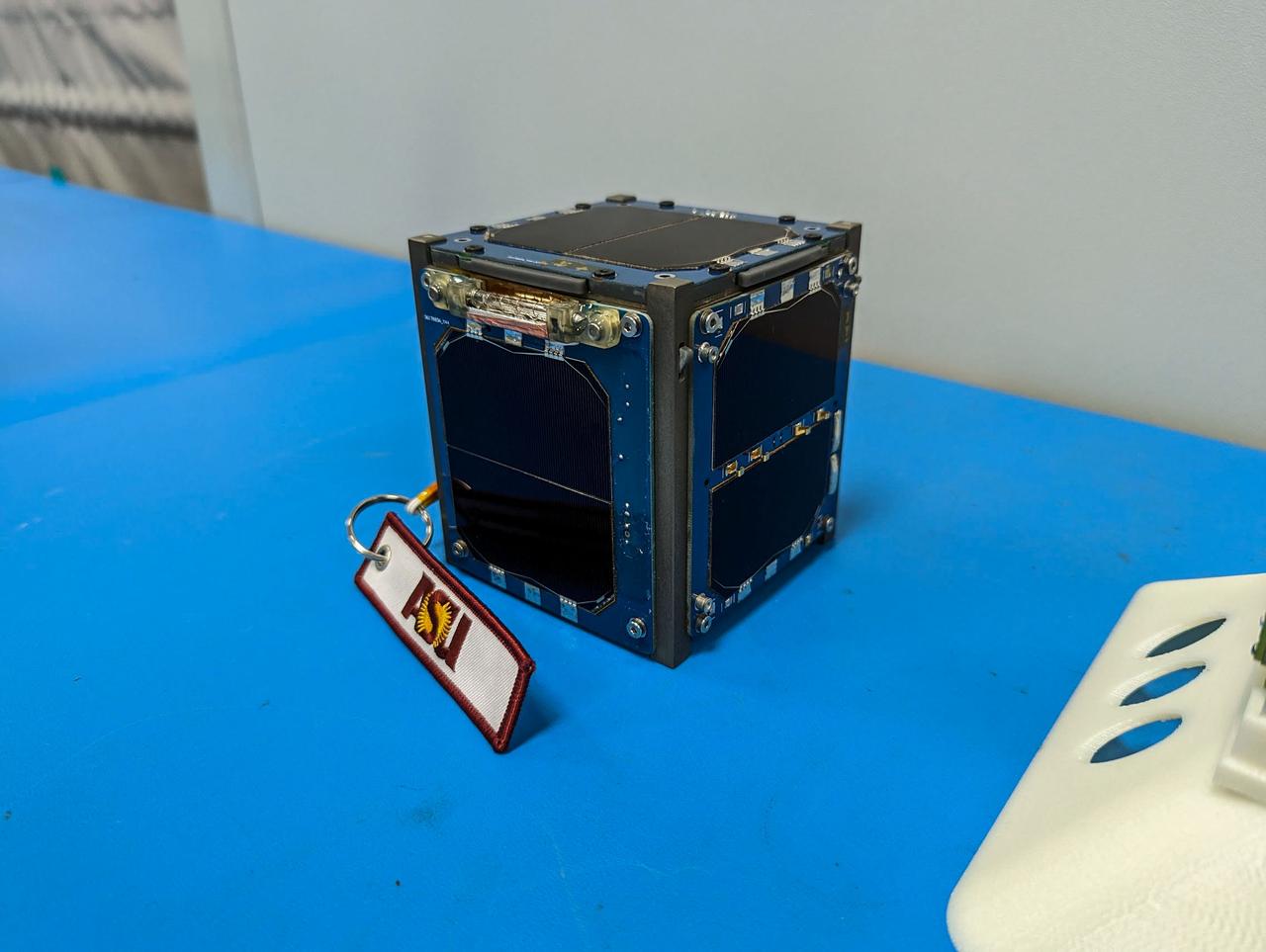

jsc2023e010192 (12/13/2022) --- LightCube CubeSat awaits integration. Image courtesy of Jaime Sanchez de la Vega.
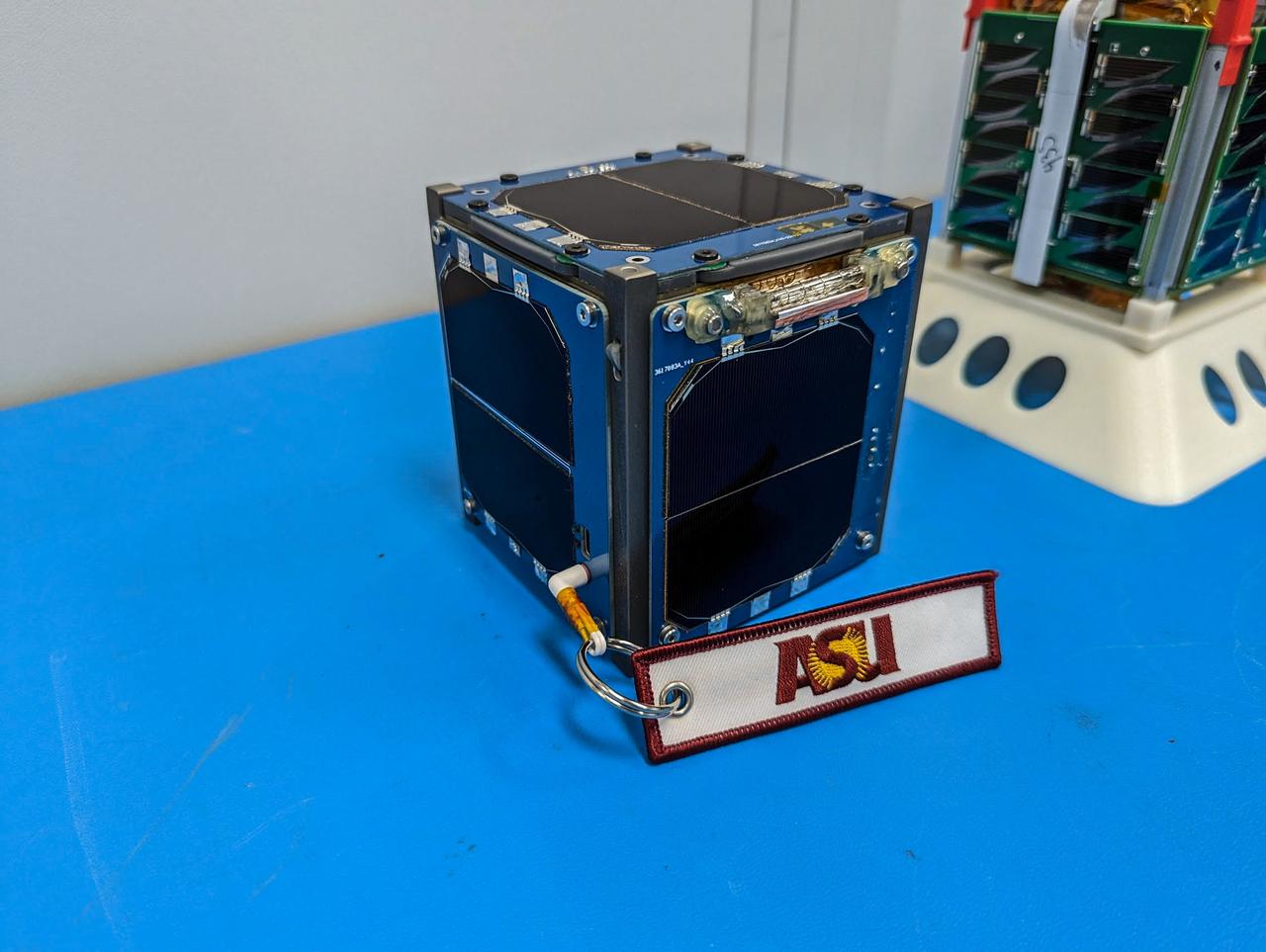

jsc2023e010191 (12/13/2022) --- LightCube CubeSat (foreground) and ARKSat-1 (background) await integration. Image courtesy of Jaime Sanchez de la Vega.
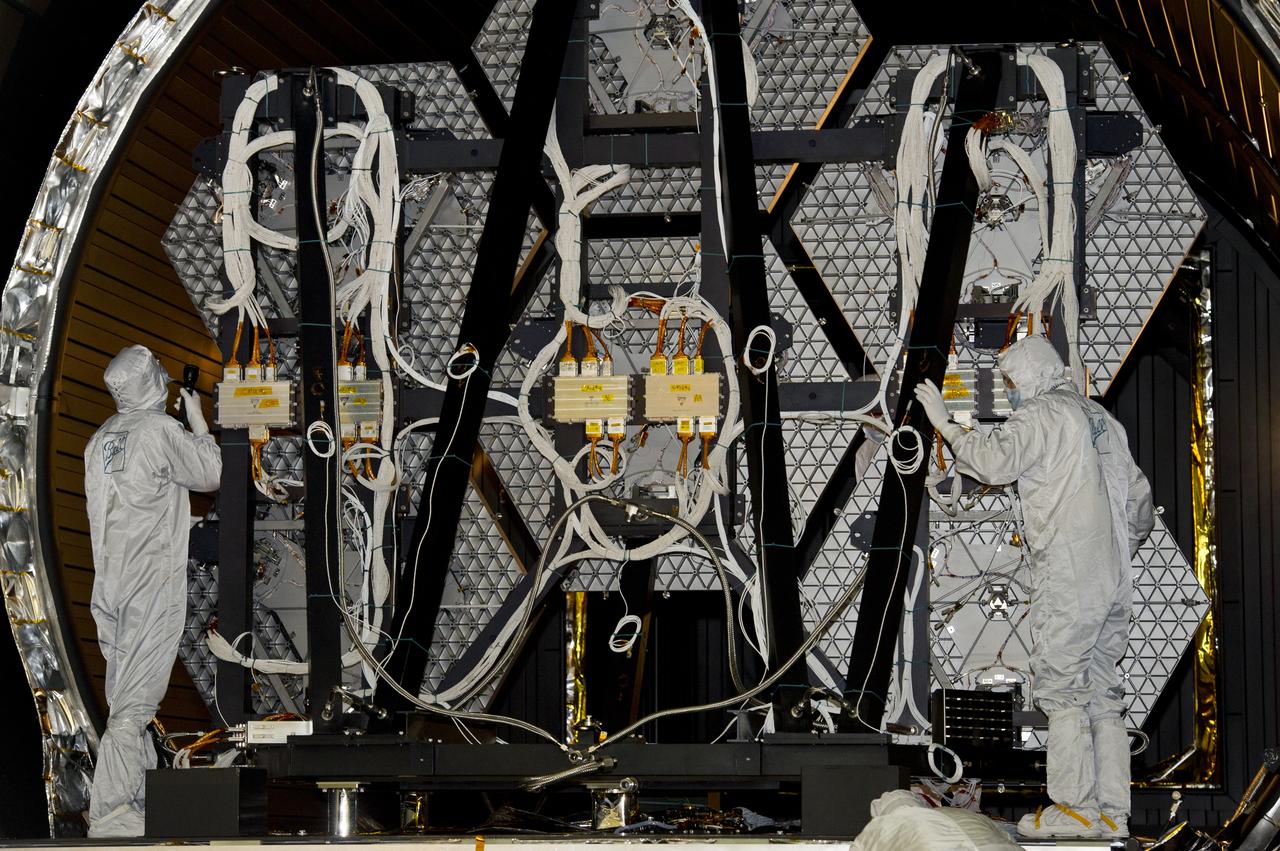
JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
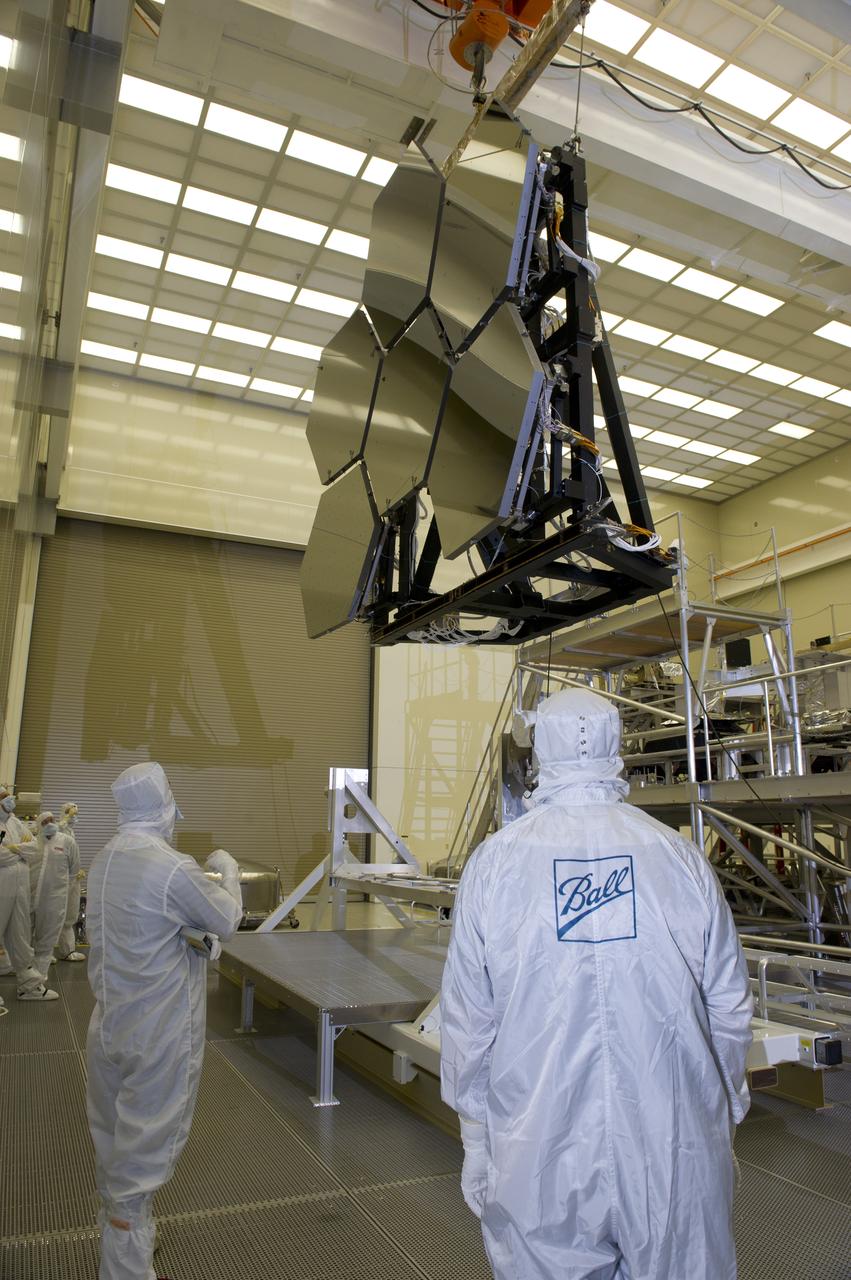

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
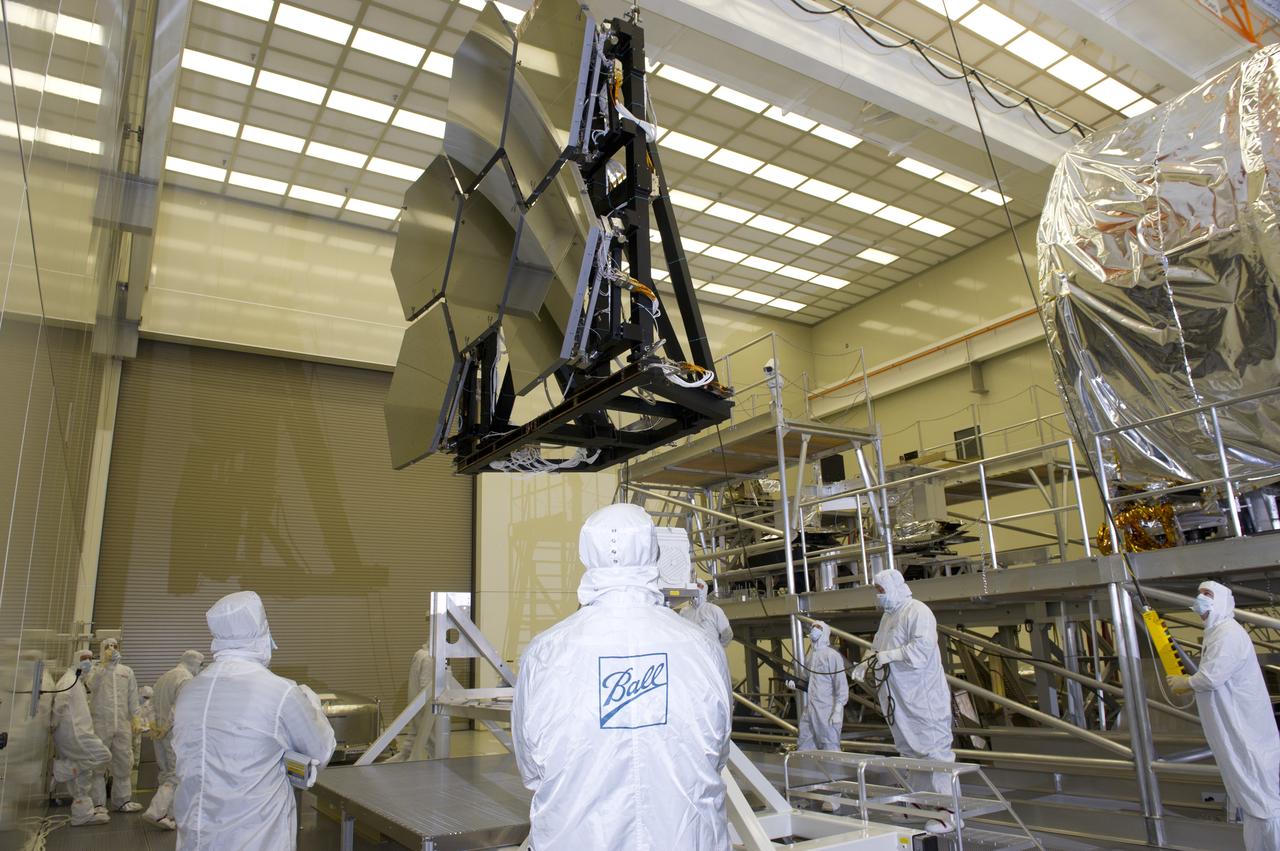

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
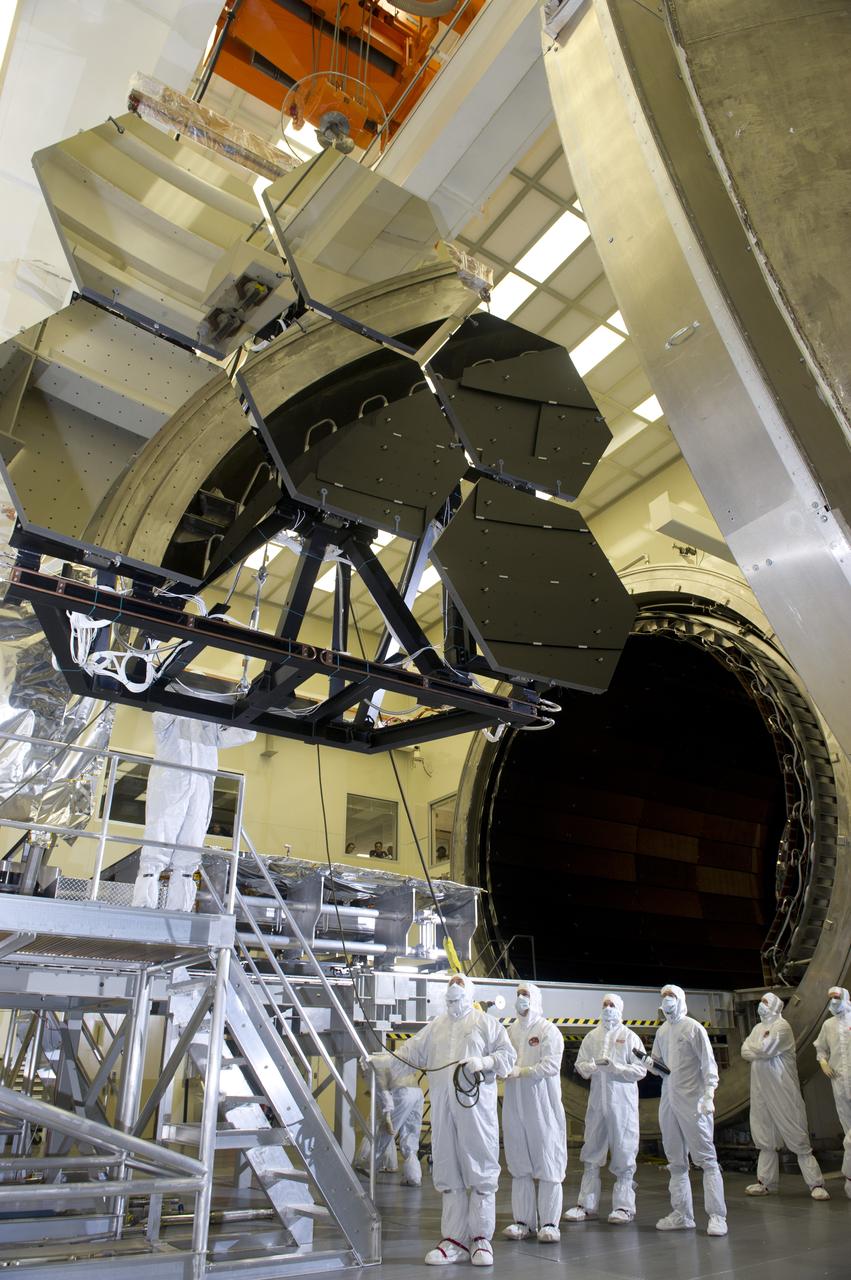

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
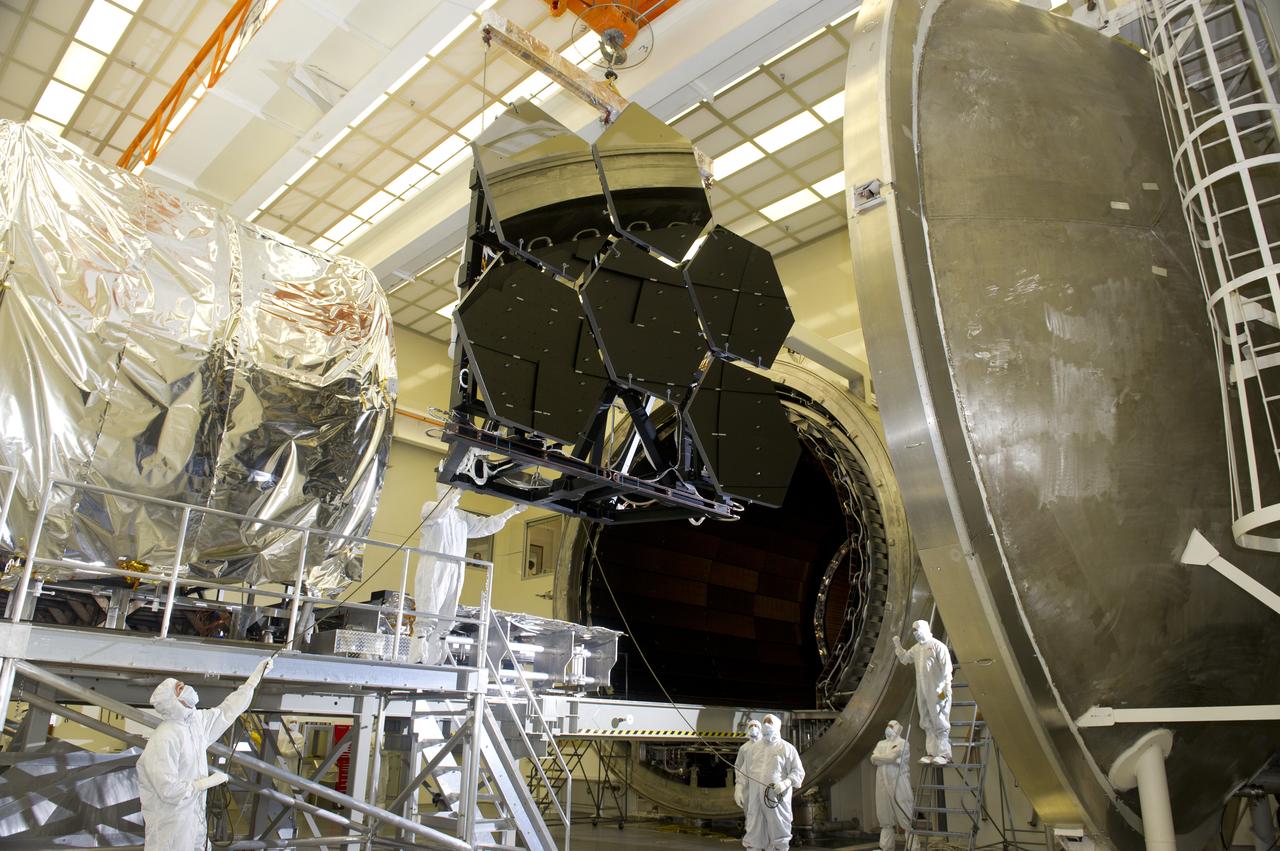

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
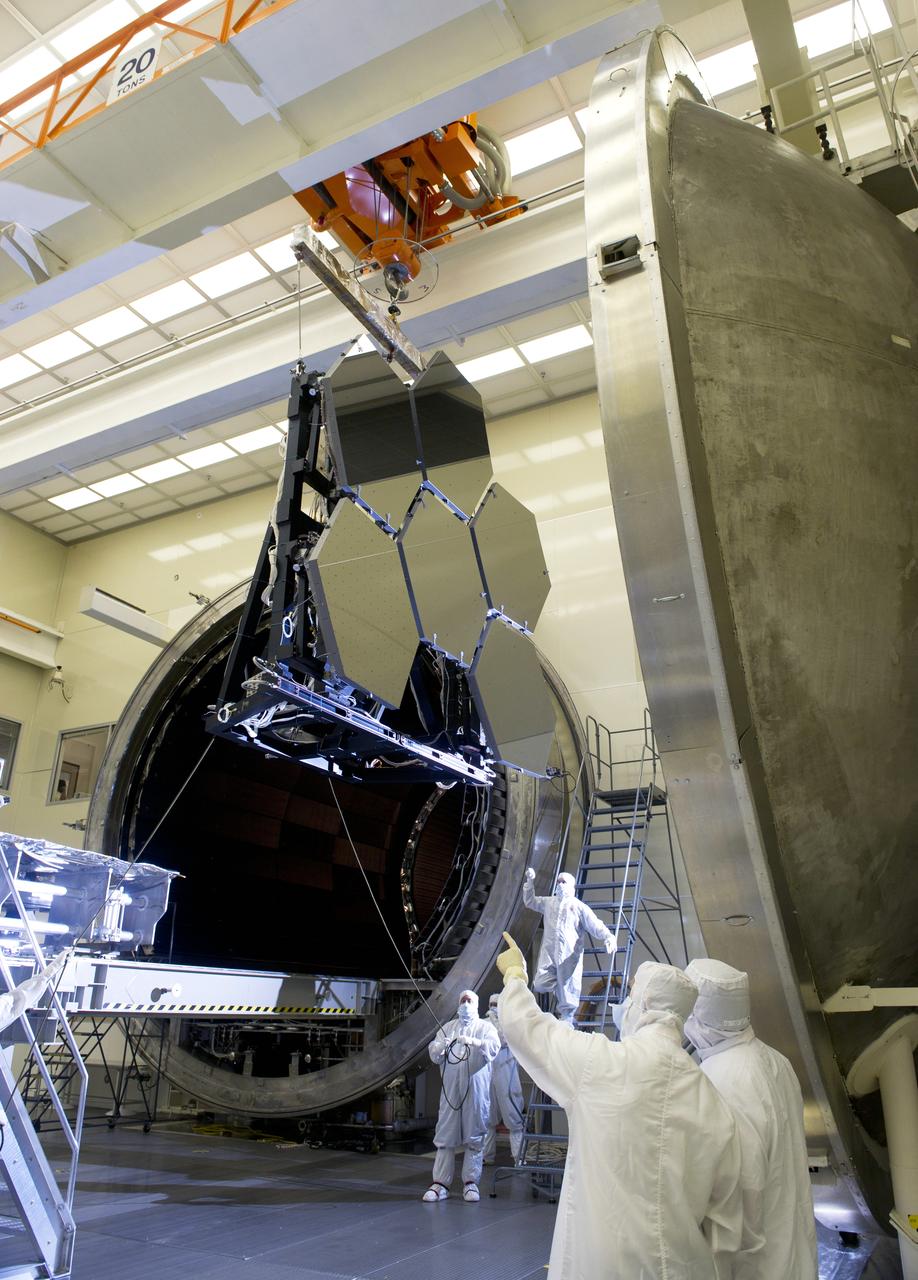

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
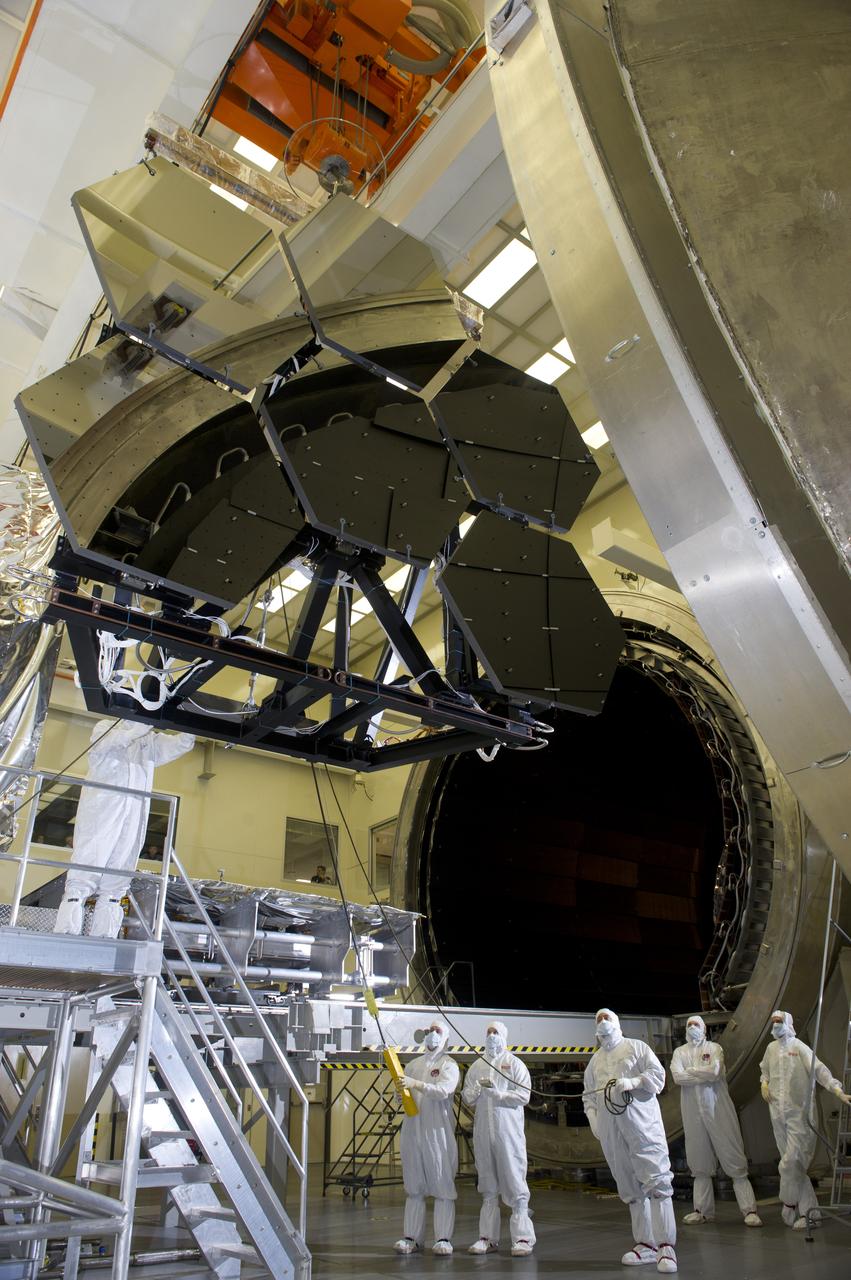

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
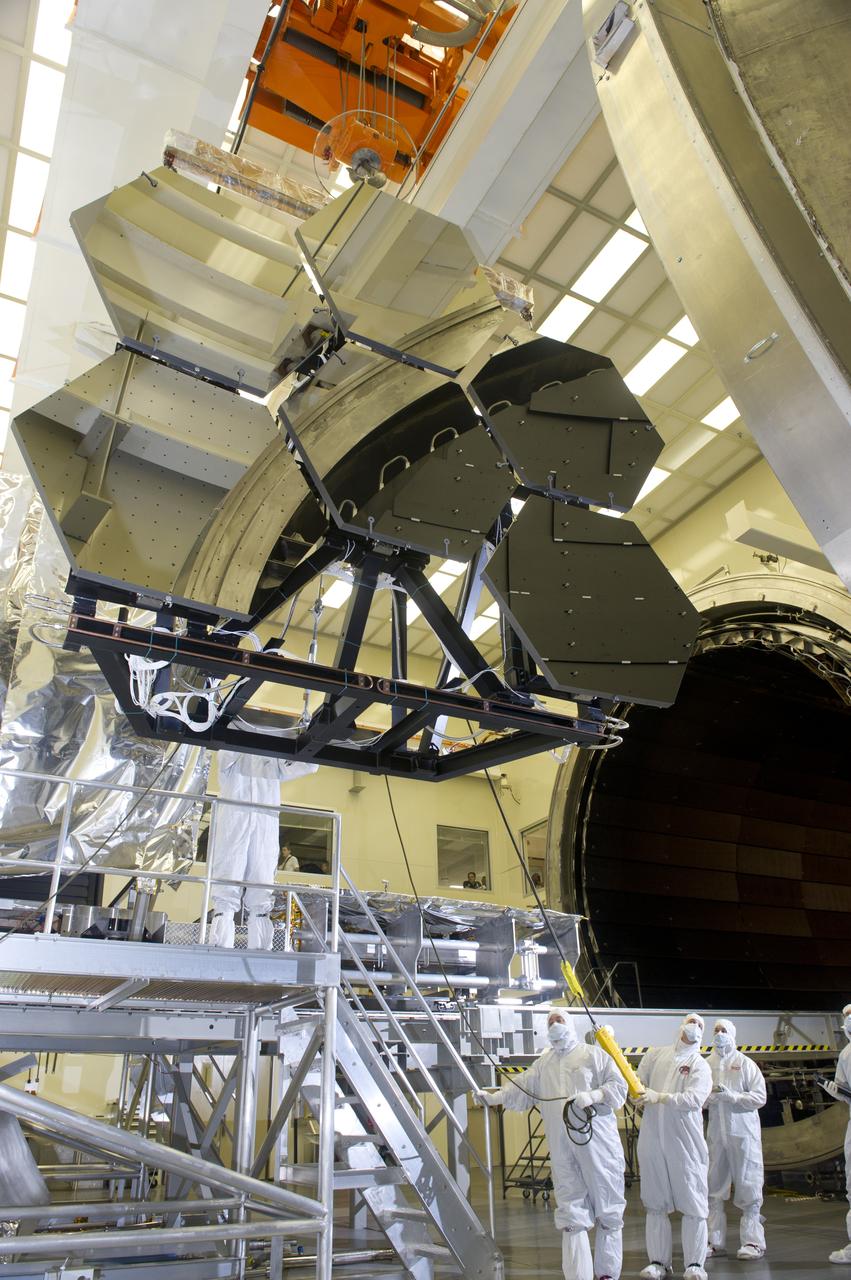

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
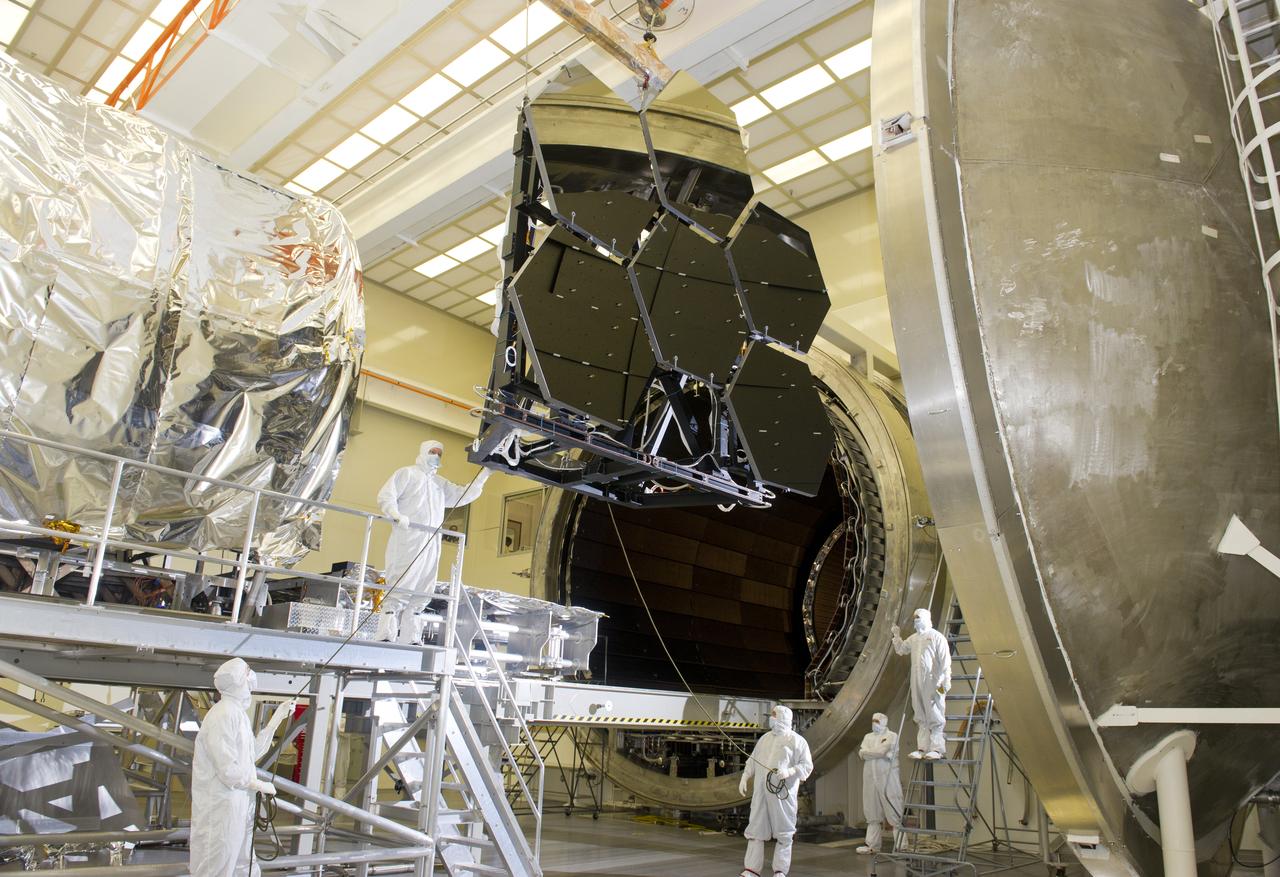

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
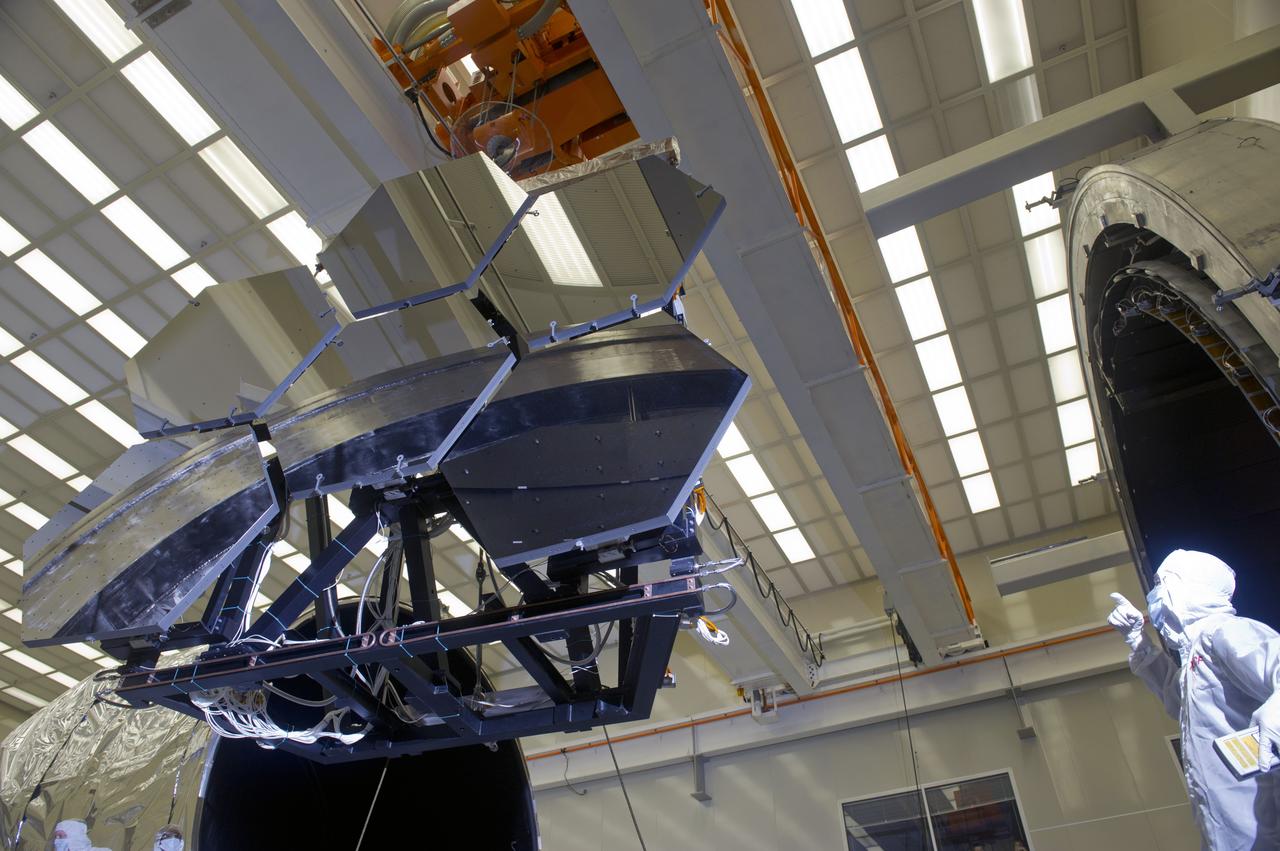

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
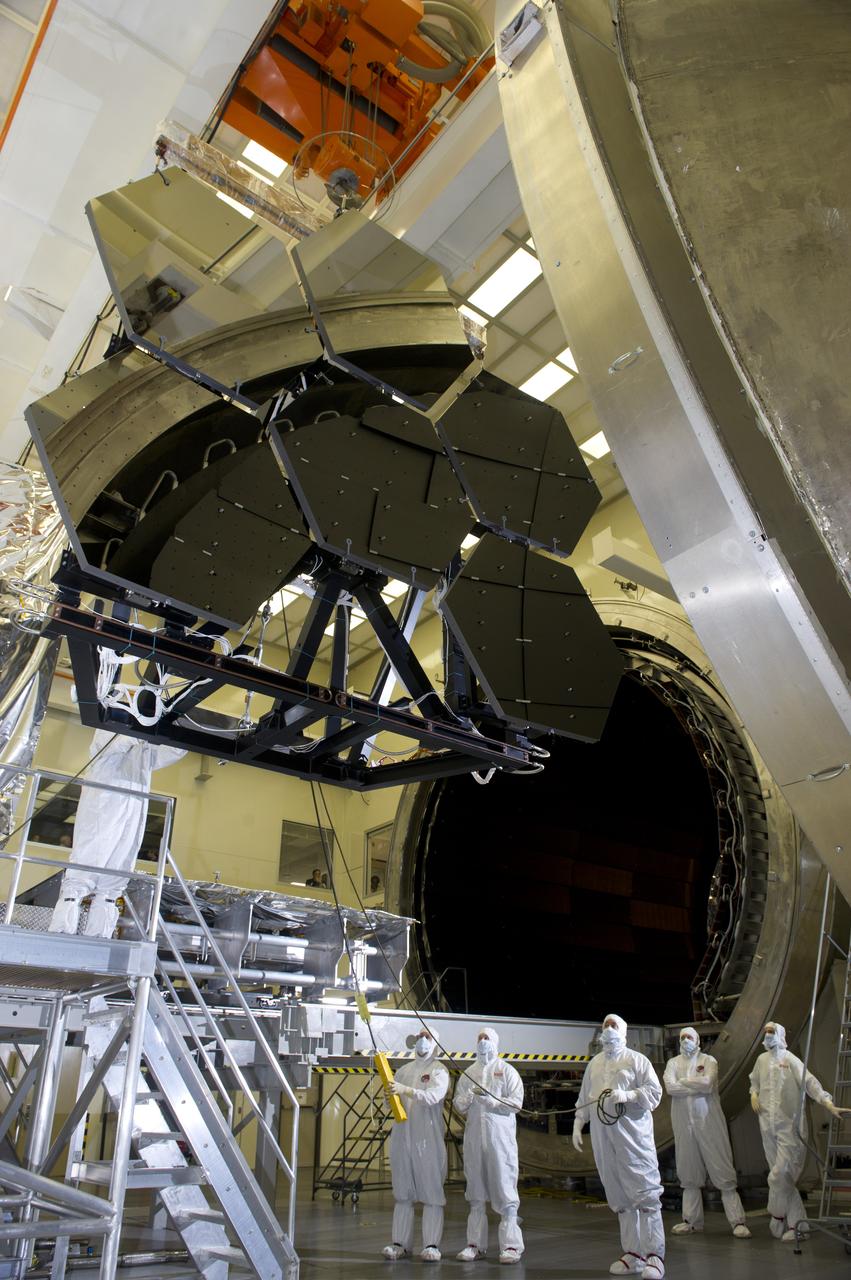

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
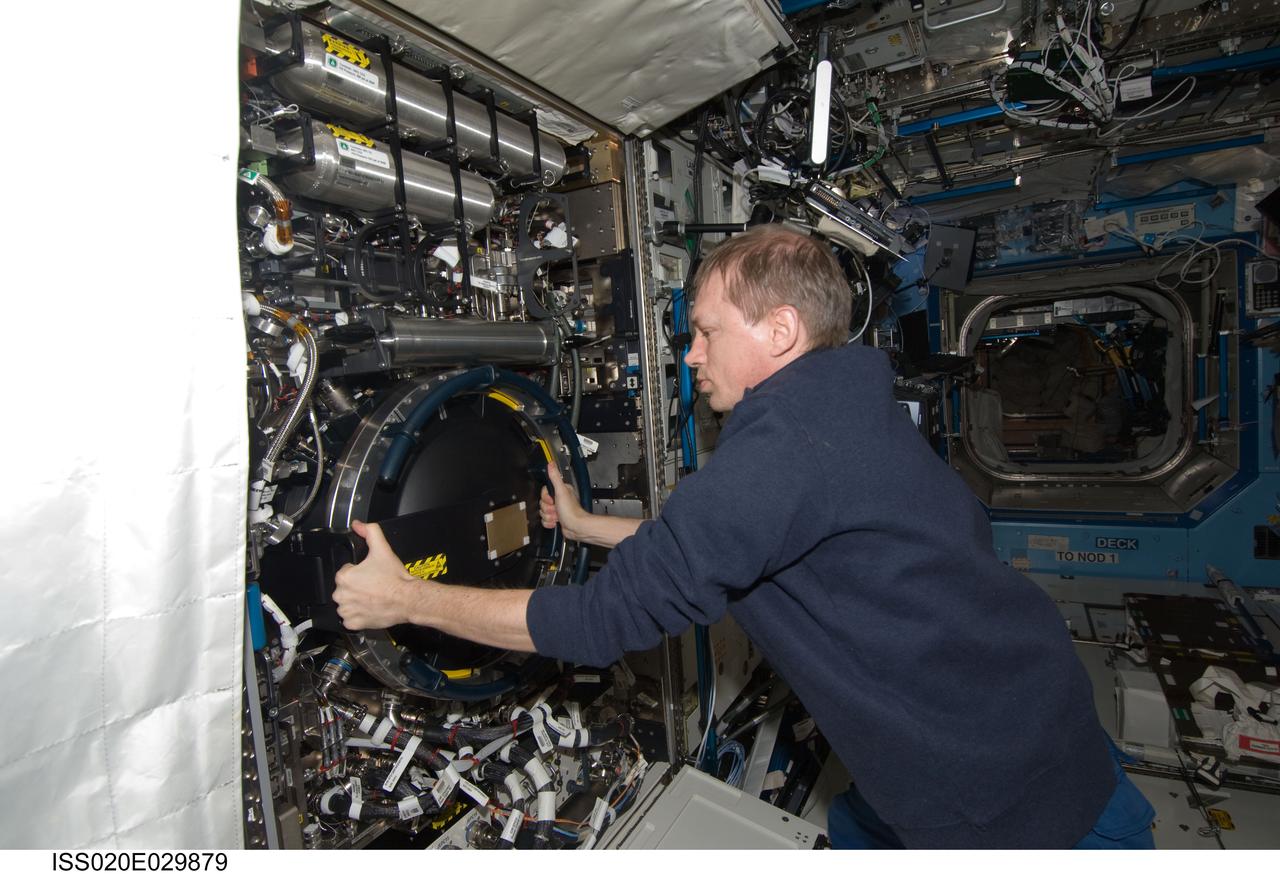

ISS020-E-029879 (12 Aug. 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer, works with the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
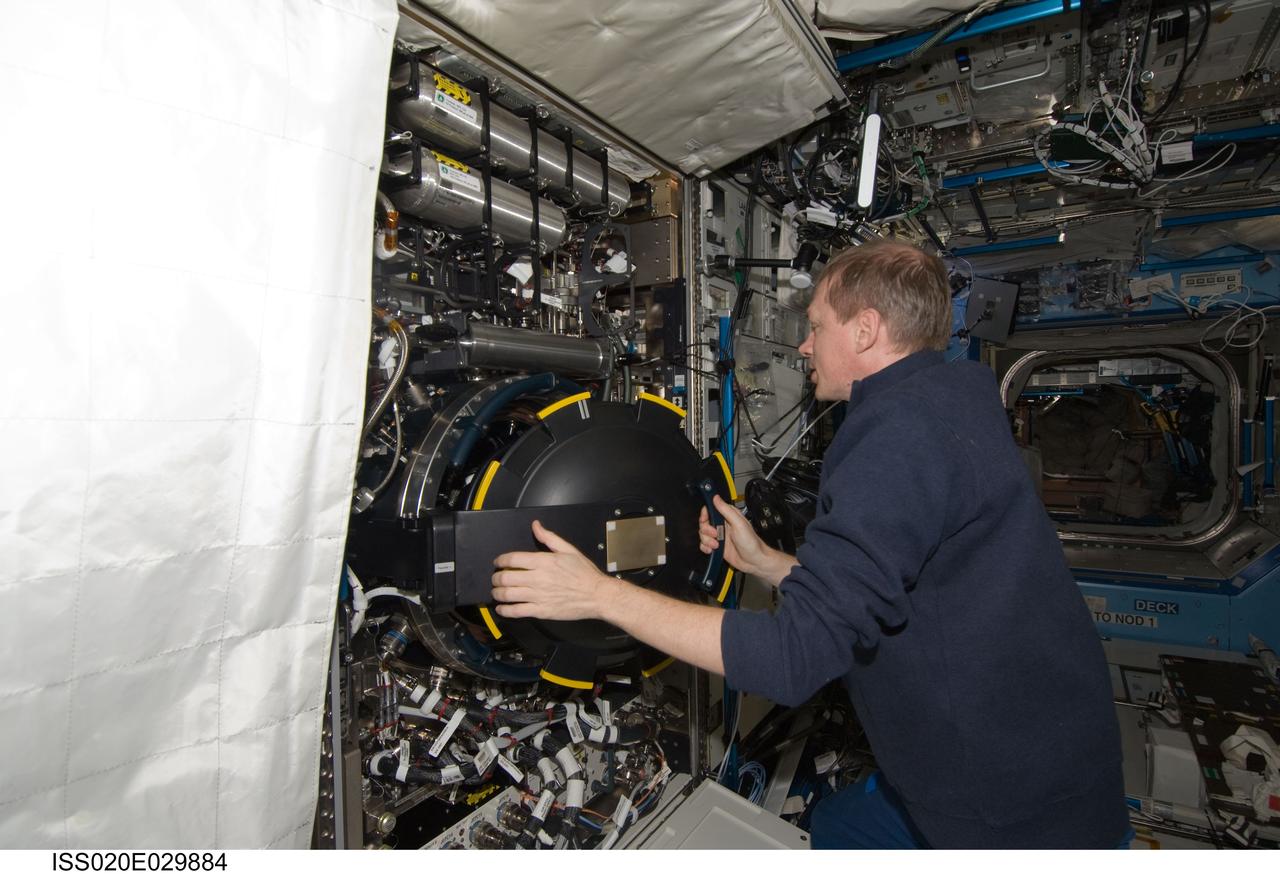

ISS020-E-029884 (12 Aug. 2009) --- European Space Agency astronaut Frank De Winne, Expedition 20 flight engineer, works with the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.

jsc2023e010190 (12/13/2022) --- LightCube team members inspect the CubeSat prior to integration into the deployer. From left to right: David Ordaz Perez, Chandler Hutchens, Sam Cherian, Christopher McCormick, Ashley Lepham, Raymond Barakat. Image courtesy of Jaime Sanchez de la Vega.
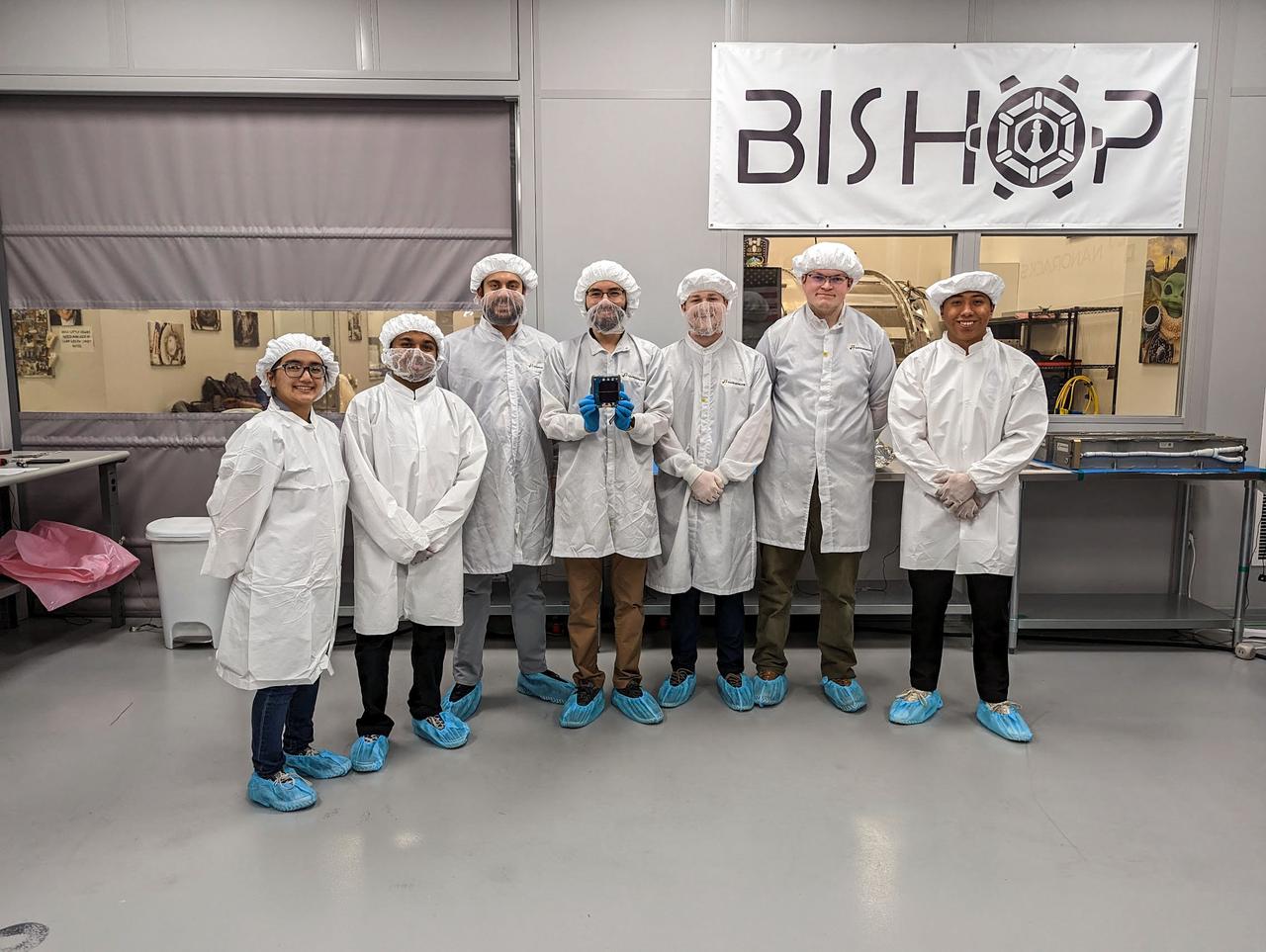

jsc2023e010187 (12/13/2022) --- LightCube team members with their CubeSat on integration day. From back to left to right: Ashley Lepham, Sam Cherian, Raymond Barakat, Jaime Sanchez de la Vega, Chandler Hutchens, Christopher McCormick, David Ordaz Perez. Image courtesy of Sam Cherian.
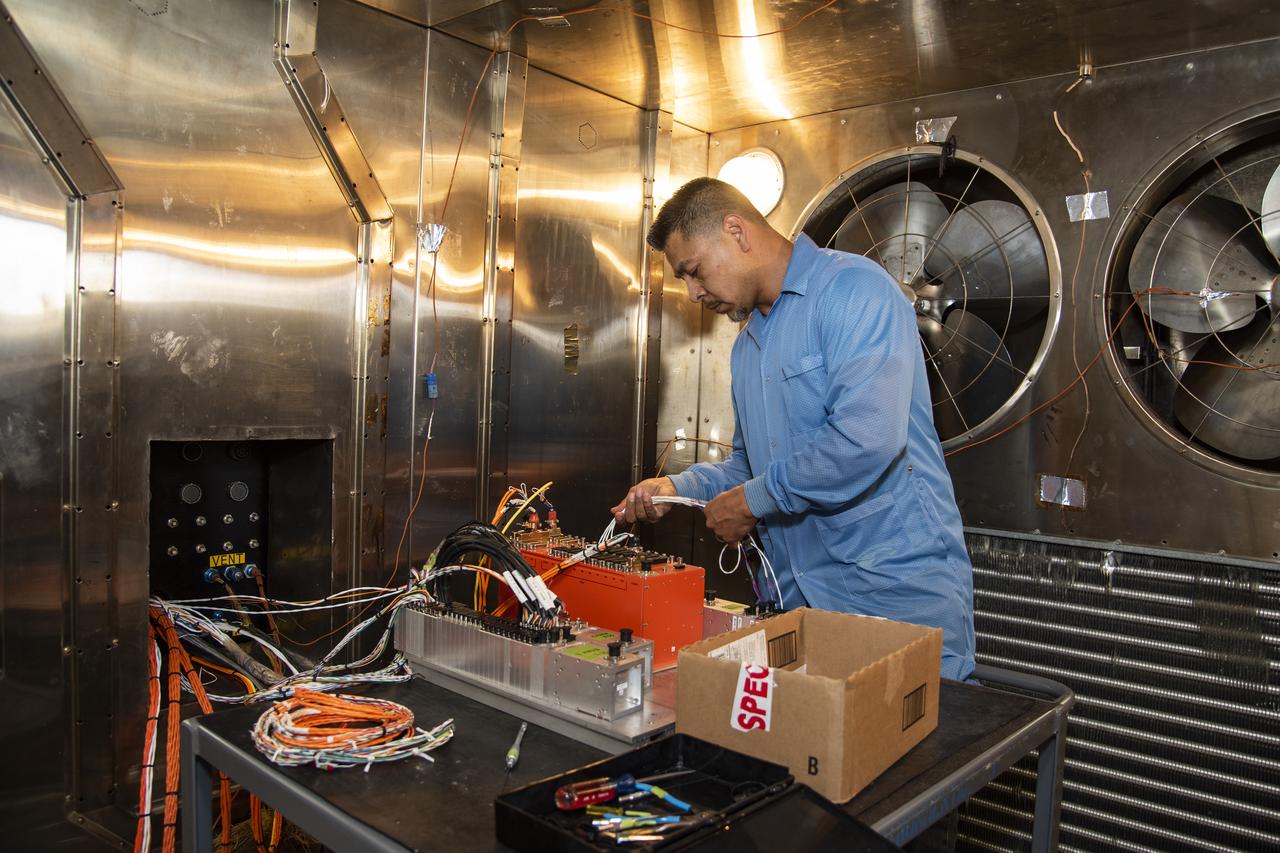

Angelo De La Rosa works inside the Environmental Laboratory’s thermal chamber to attach test articles to the testing architecture at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The center is testing components for integration into the Orion AA-2 test article scheduled for a test flight of the launch abort system in 2019.
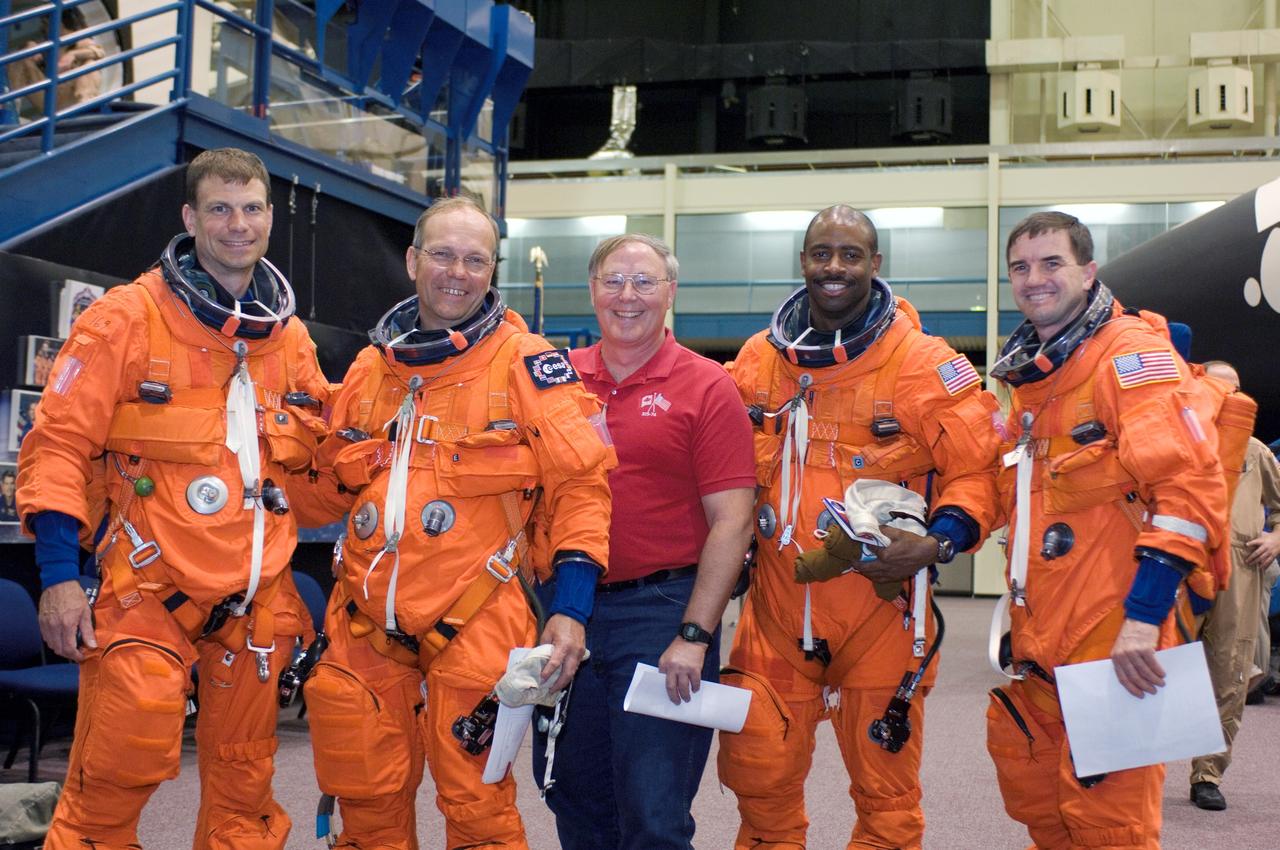

JSC2007-E-14482 (20 March 2007) --- Jerry L. Ross (center), chief, vehicle integration test office, poses for a photo with astronauts Stanley G. Love (left), European Space Agency's (ESA) Hans Schlegel, Leland D. Melvin and Rex J. Walheim, STS-122 mission specialists, as they prepare for a post insertion/de-orbit training session in one of the full-scale trainers (out of frame) in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at Johnson Space Center.
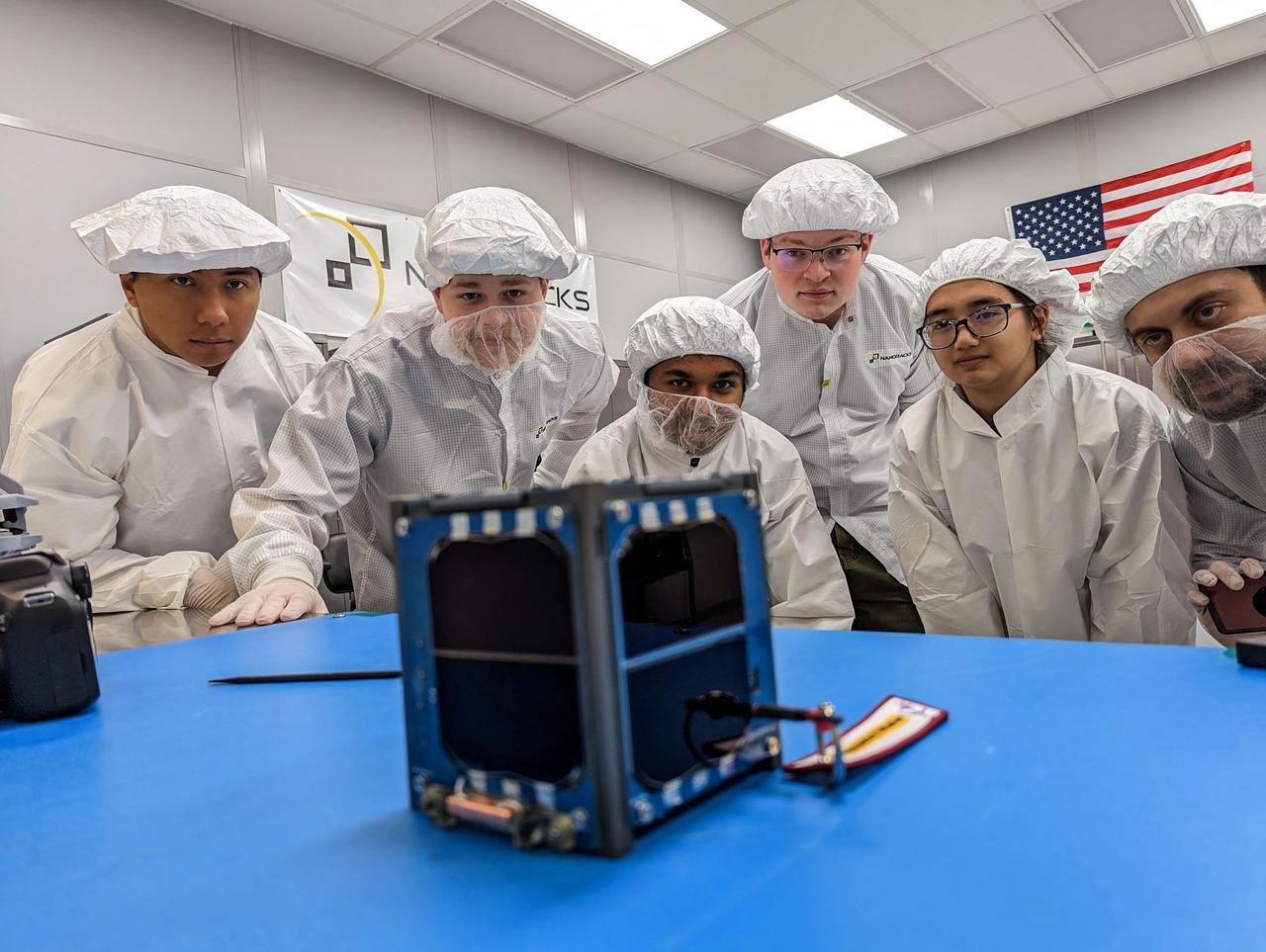
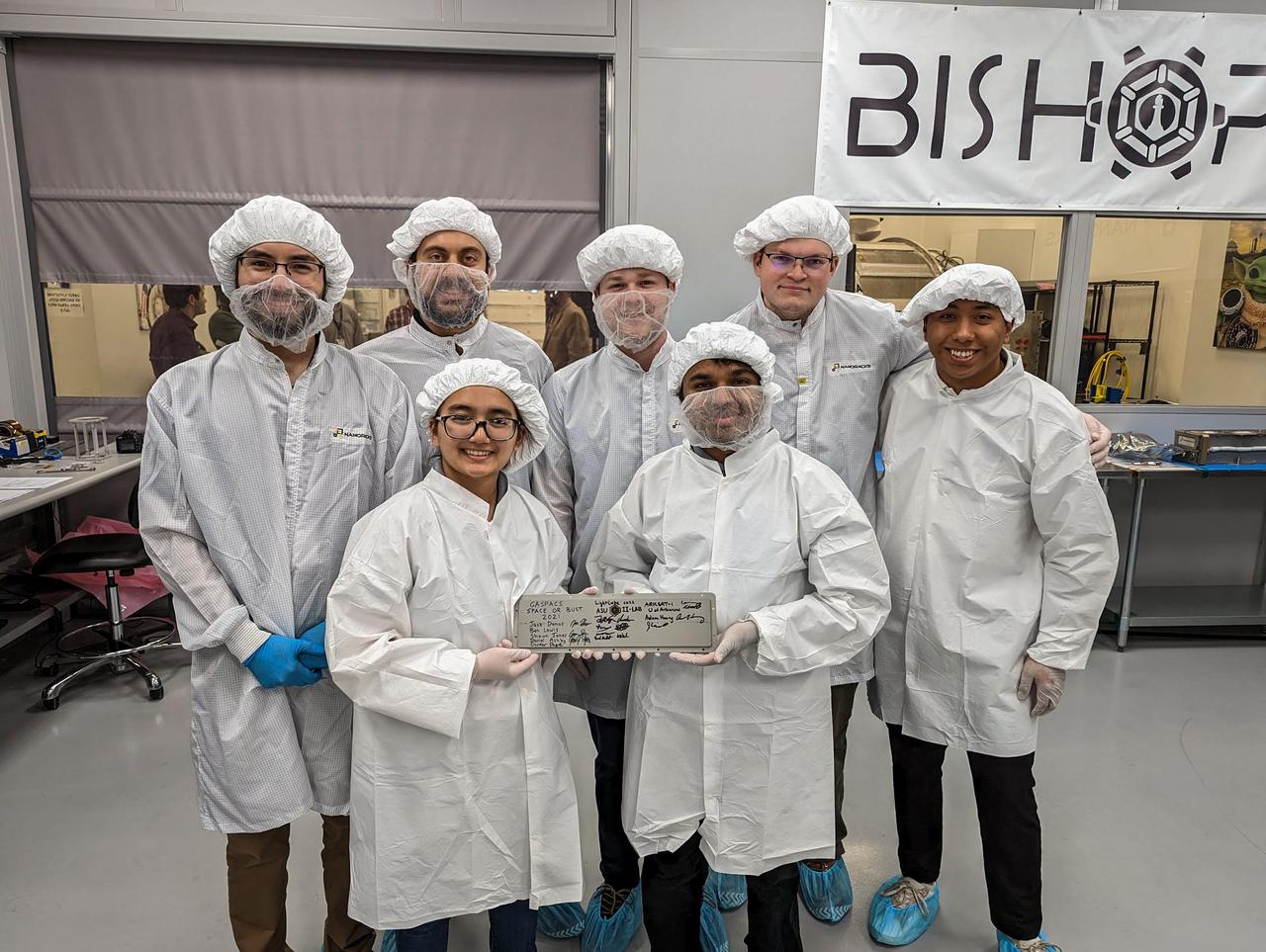
jsc2023e010188 (12/13/2022) --- LightCube team holds a signed Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer panel following integration of the LightCube CubeSat. From back to front and from left to right: Jaime Sanchez de la Vega, Raymond Barakat, Chandler Hutchens, Christopher McCormick, David Ordaz Perez, Ashley Lepham, Sam Cherian. Image courtesy of Sam Cherian.
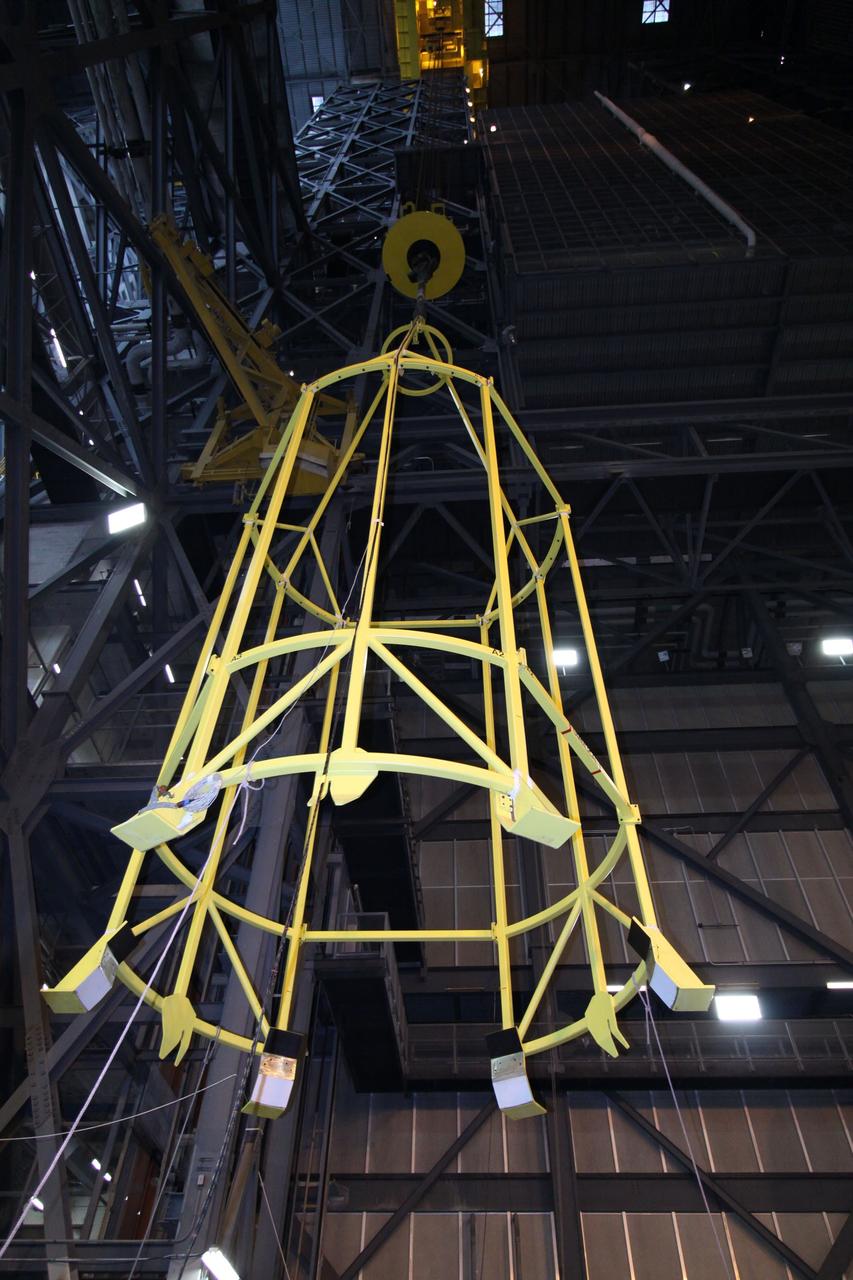

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. The yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered by crane toward Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
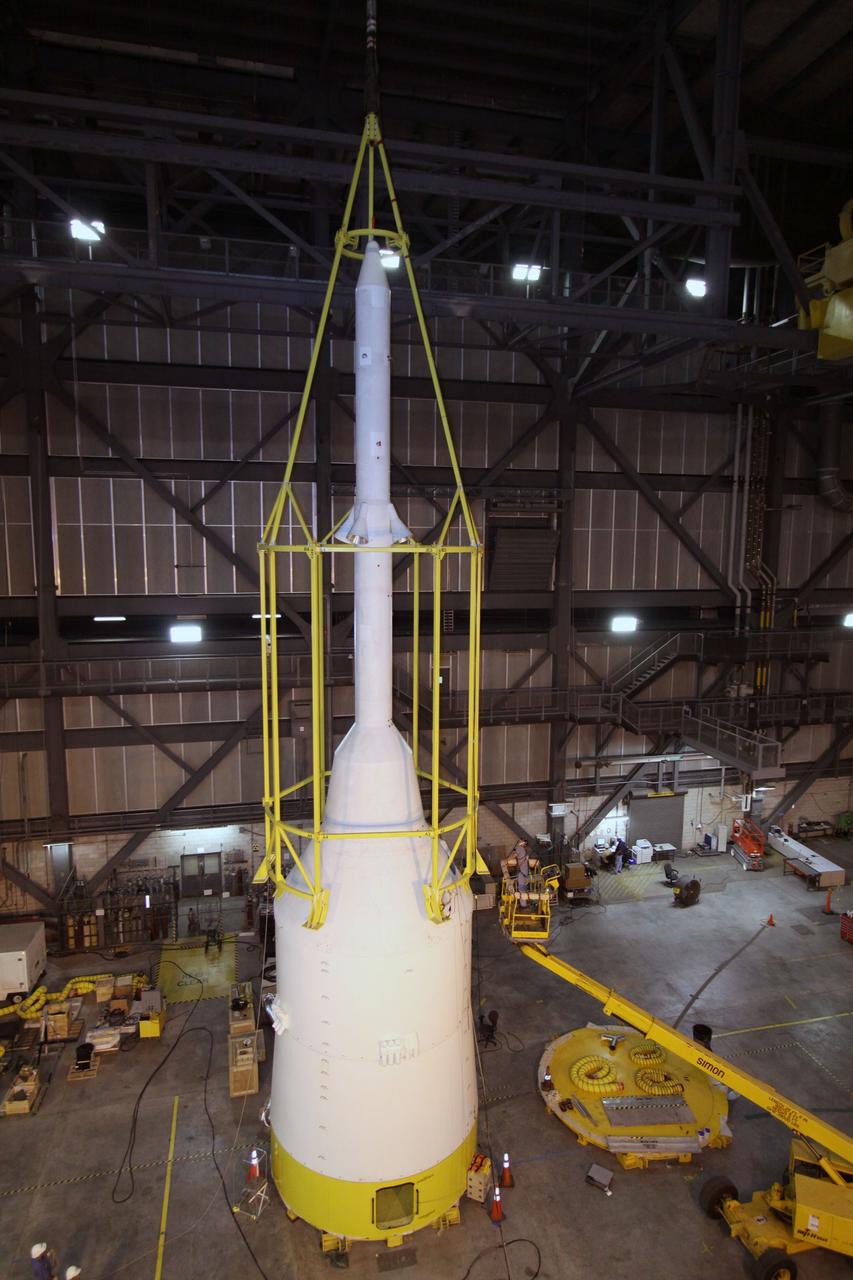

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. The yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered by crane over Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
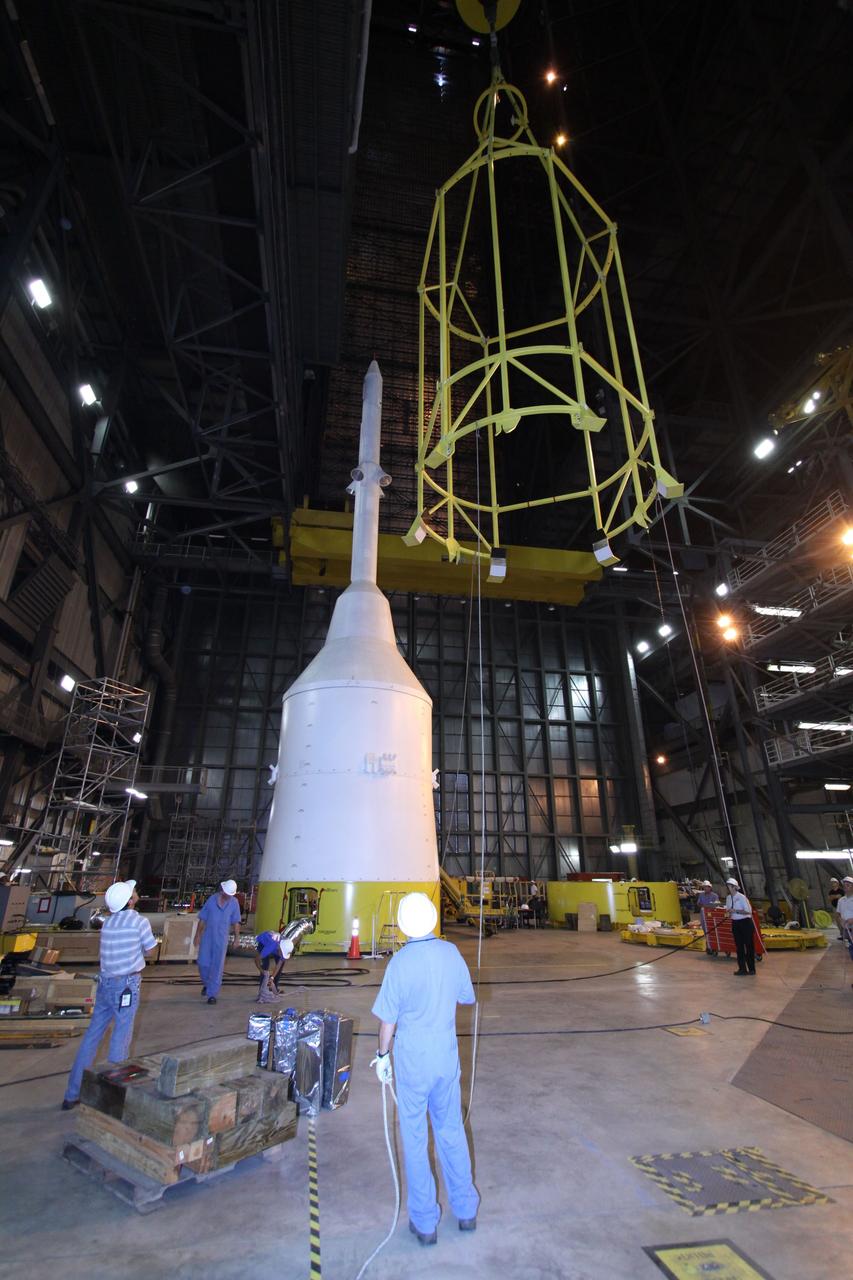

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. Technicians monitor the yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," as it is lowered by crane toward Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
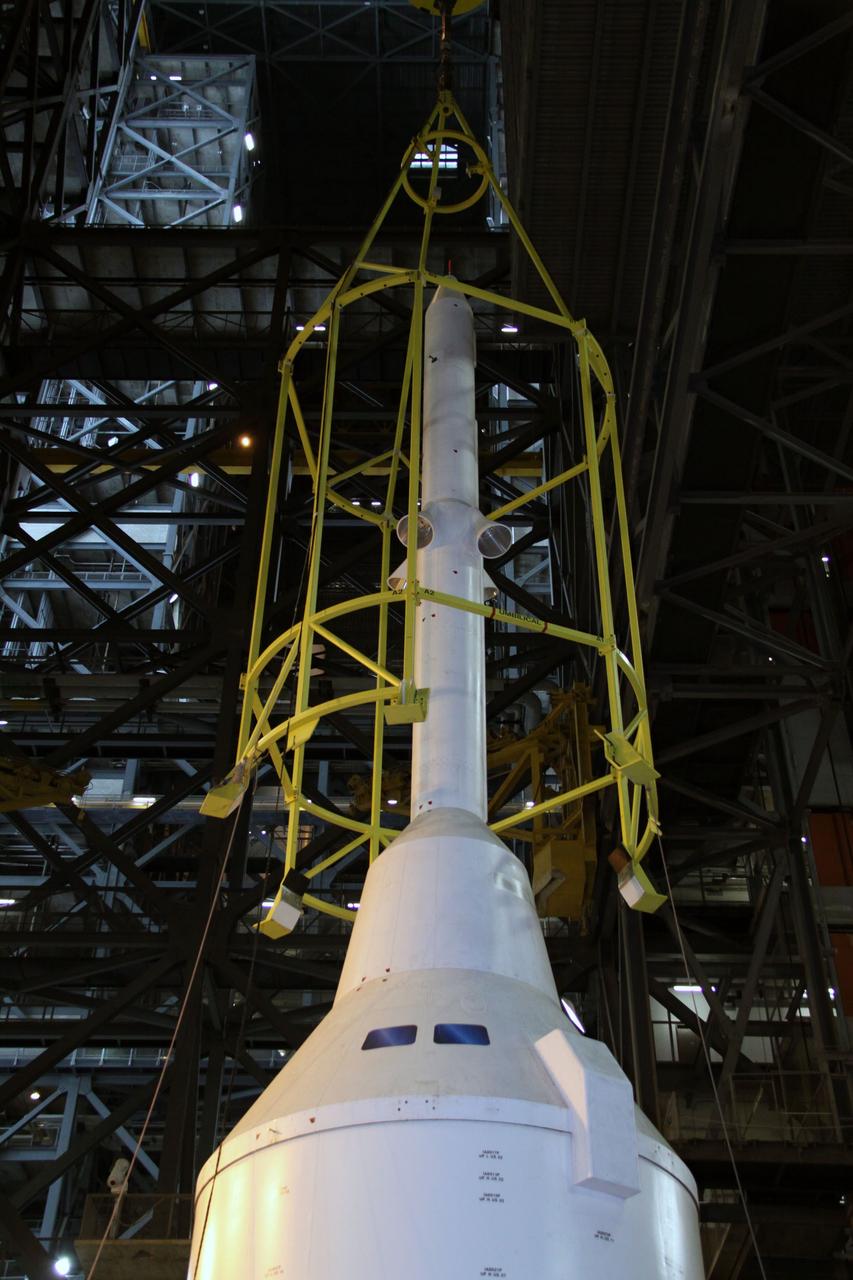

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. The yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered by crane over the Launch Abort System, or LAS, of Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller