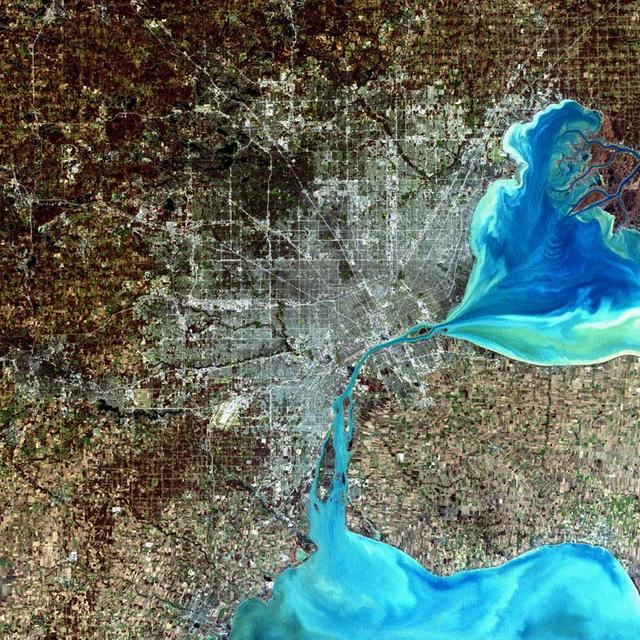
Detroit, Michigan, USA Sensor: L7 ETM+ Acquisition Date: December 11, 2001 Path/Row: 20/30 Lat/Long: 42.330/-83.046 Detroit, Michigan, is commonly referred to as Motor City because of the many automobile manufacturing plants located in the city. It is the largest city in Michigan, with a population approaching one million. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Landsat <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
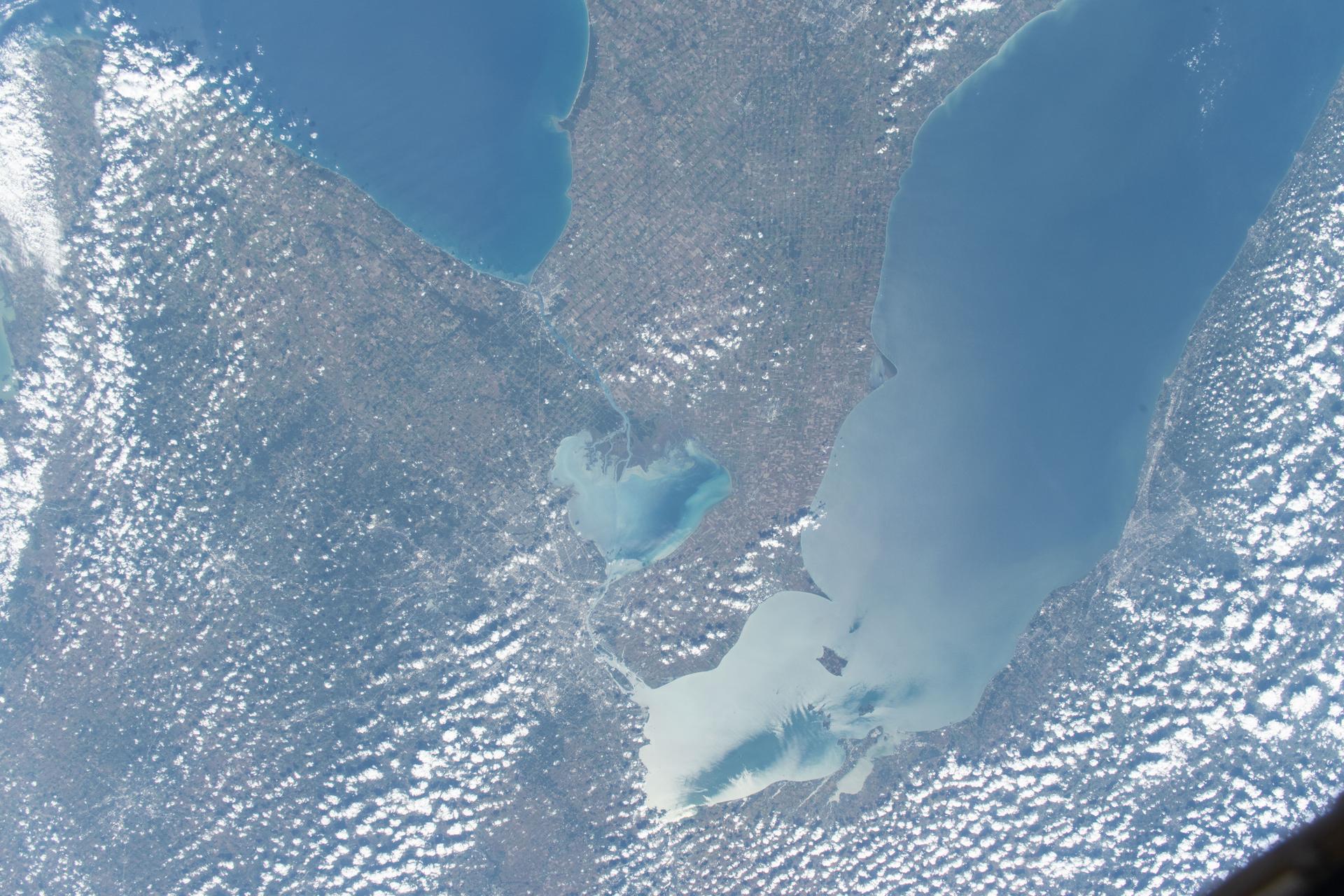

iss073e0814049 (Sept. 26, 2025) --- Detroit, Michigan, sits on the banks of the Detroit River, which connects Lake St. Clair (center) to Lake Erie to the south. To the north, the St. Clair River links Lake St. Clair with Lake Huron. Both rivers serve as natural borders between the United States and Canada. The International Space Station was orbiting 259 miles above Ontario, Canada, at the time of this photograph.
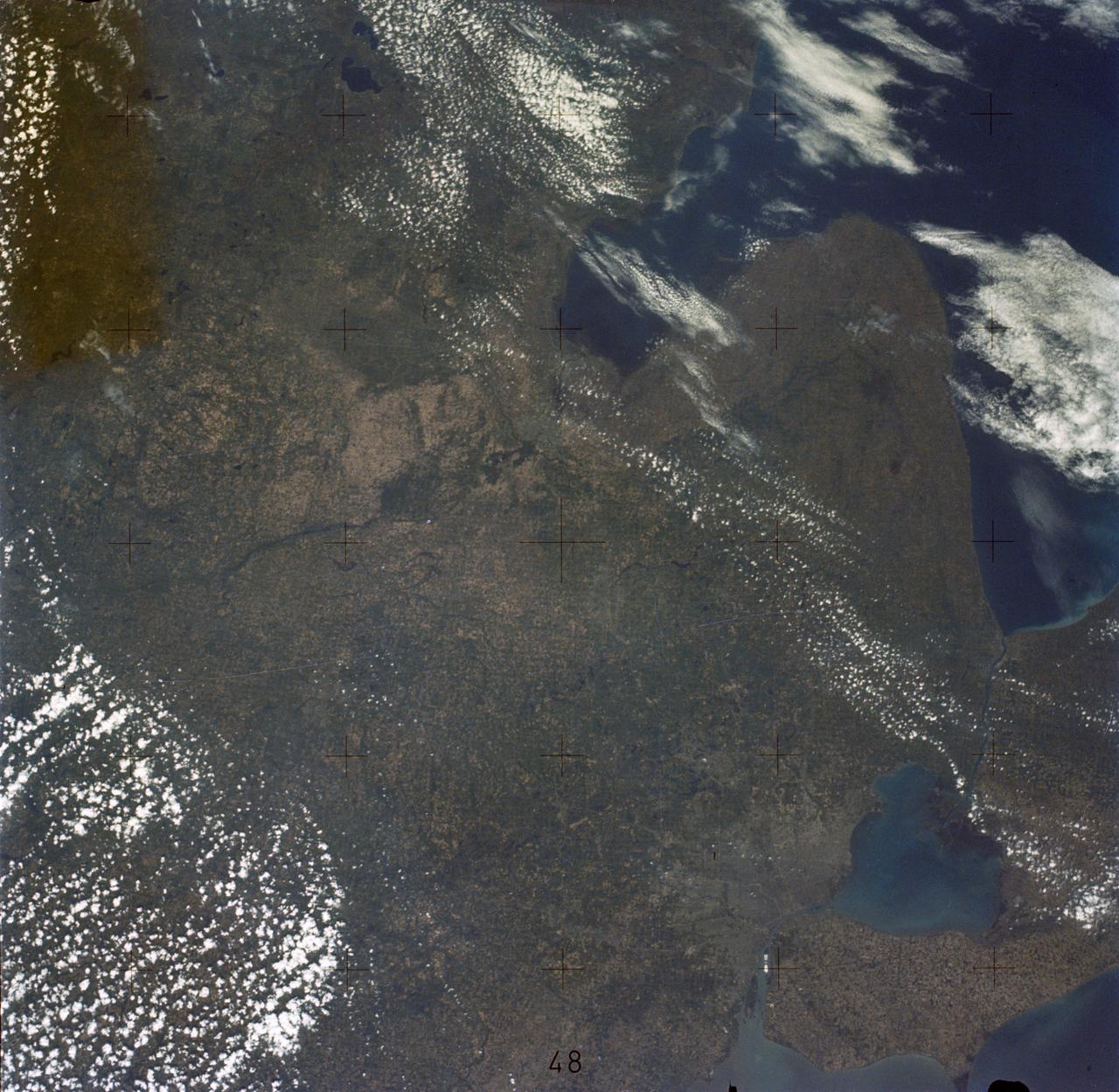

SL2-05-389 (22 June 1973) --- This scene displays the southeastern part of Michigan's Lower Peninsula and adjacent Ontario, Canada (43.0N, 84.0W). Detroit can be recognized by its radial pattern of development and sediment plumes in the rivers from the massive industrial activity. The area pockmarked by lakes northwest of Detroit essentially outlines the limits of the Defiance Moraine caused by the stagnation and melting of Ice Age glaciers. Photo credit: NASA

SL2-05-390 (22 June 1973) --- Greater Detroit (42.0N, 82.5W) is located at the southeastern border of Michigan on the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario, Canada and Lake Huron to the north. The river connecting Lake Erie is a channel left over from the Ice Age Glaciers. The land use pattern in this scene is typical of this part of the upper Midwest. The once extensive forests have been cleared for farmland and pasture, but narrow rows of trees still line farm boundaries. Photo credit: NASA
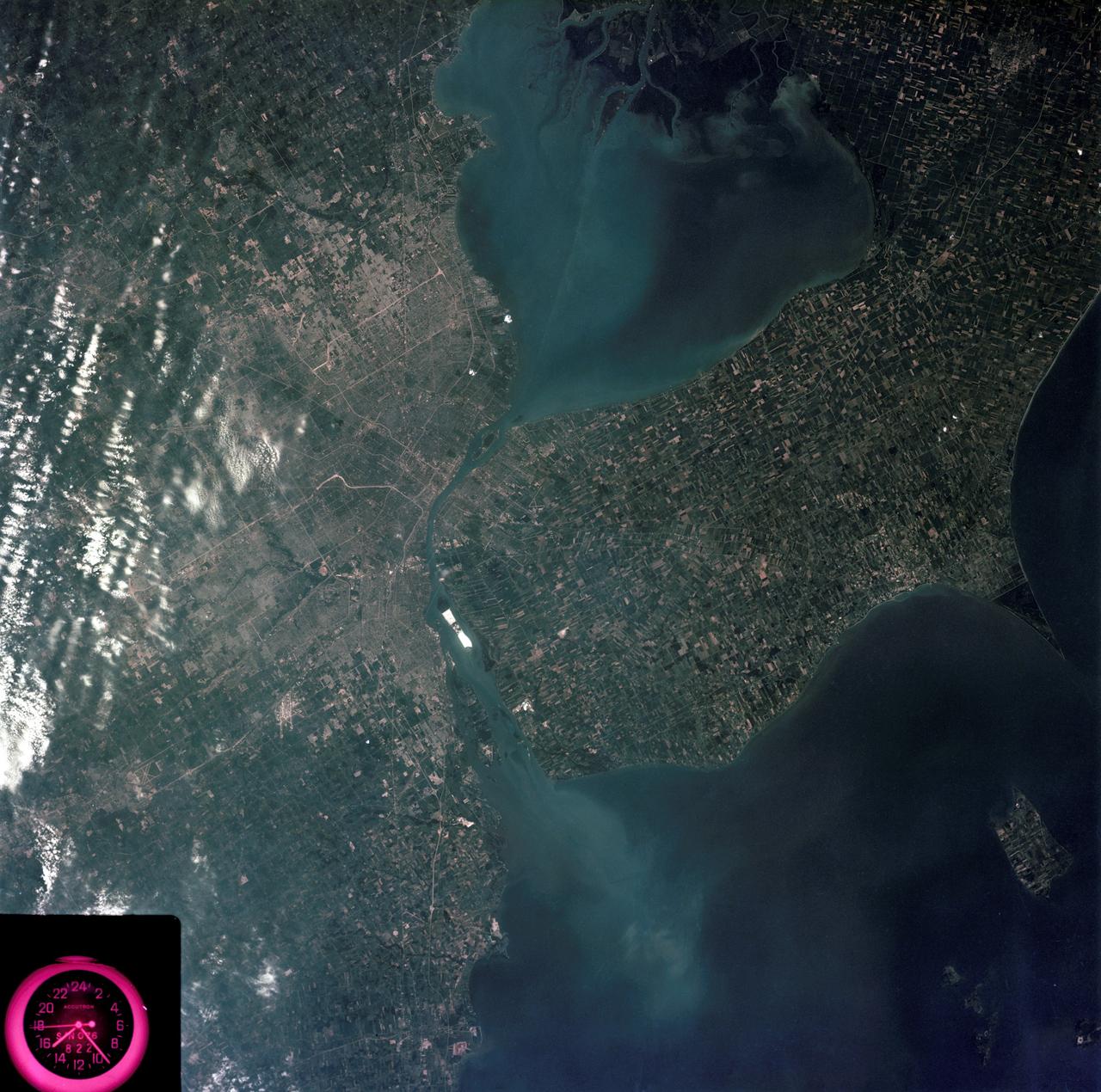

SL3-83-0152 (July-September 1973) --- A near vertical view of the metropolitan Detroit, Michigan area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The 25-mile long Detroit River drains the smaller body of water (Lake St. Clair) and flows southwestward separating Detroit from Windsor, Ontario, and empties into Lake Erie. The Detroit River handles a great deal of Great Lakes barge and ship traffic. Major streets and thoroughfares radiating from the city are clearly visible. Fighting Island is the highly reflective, white area located almost in the center of the picture. This high reflectivity is caused by the functional use of the island-disposal ponds for chemical salts. Sedimentation and/or pollution patterns in the area provide interesting visual phenomena for speculation and analysis. Distinct and rather unique cultivated field patterns can be observed south and east of Windsor, Ontario. This is a direct result of an English survey and land tenure system which was utilized when the area was settled. New areas of residential development are fairly easy to differentiate from older, established residential areas. Vegetation and extent of area coverage can be determined. The Oakland County Planning Commission and the Federal Bureau of Outdoor Recreation working closely with Irv Sattinger of the Environmental Research Institute of Michigan (University of Michigan) are presently processing and analyzing photographic and Multispectral scanner data to determine its usefulness for recreation and open space site studies for this area. Photo credit: NASA
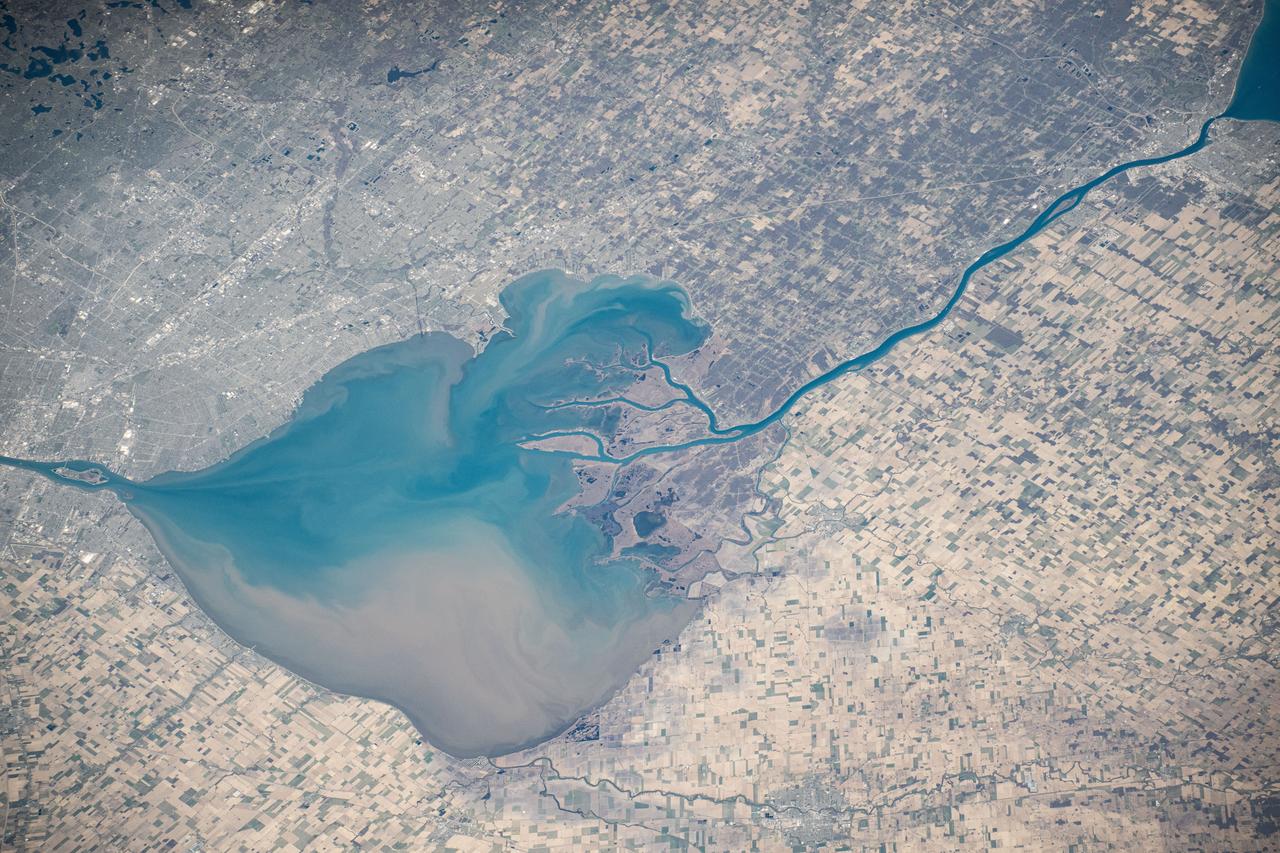

iss073e0000553 (April 22, 2025) --- The freshwater Lake St. Clair rests in between Detroit, Michigan (left), and Ontario, Canada, and connects Lake Huron and Lake Erie in North America in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above.

iss064e051420 (April 2, 2021) --- The Detroit River, pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above, separates Detroit, Michigan, from Windsor in Ontario, Canada. The Detroit River also connects to Lake St. Clair (pictured at top) and Lake Erie (out of frame).
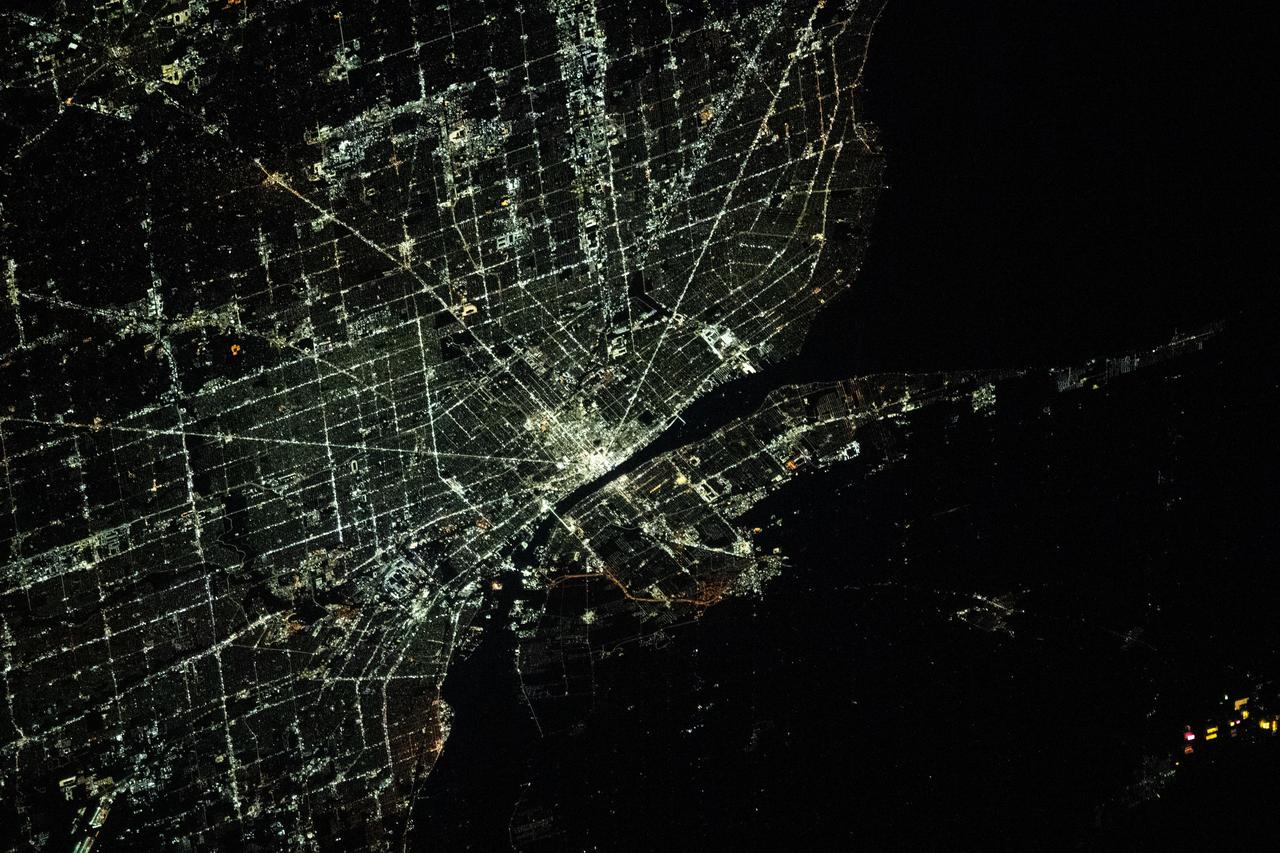

iss070e105102 (March 1, 2024) --- The city lights of Detroit, Michigan, separated from the city of Windsor in Ontario, Canada, by the Detroit River, are pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above.
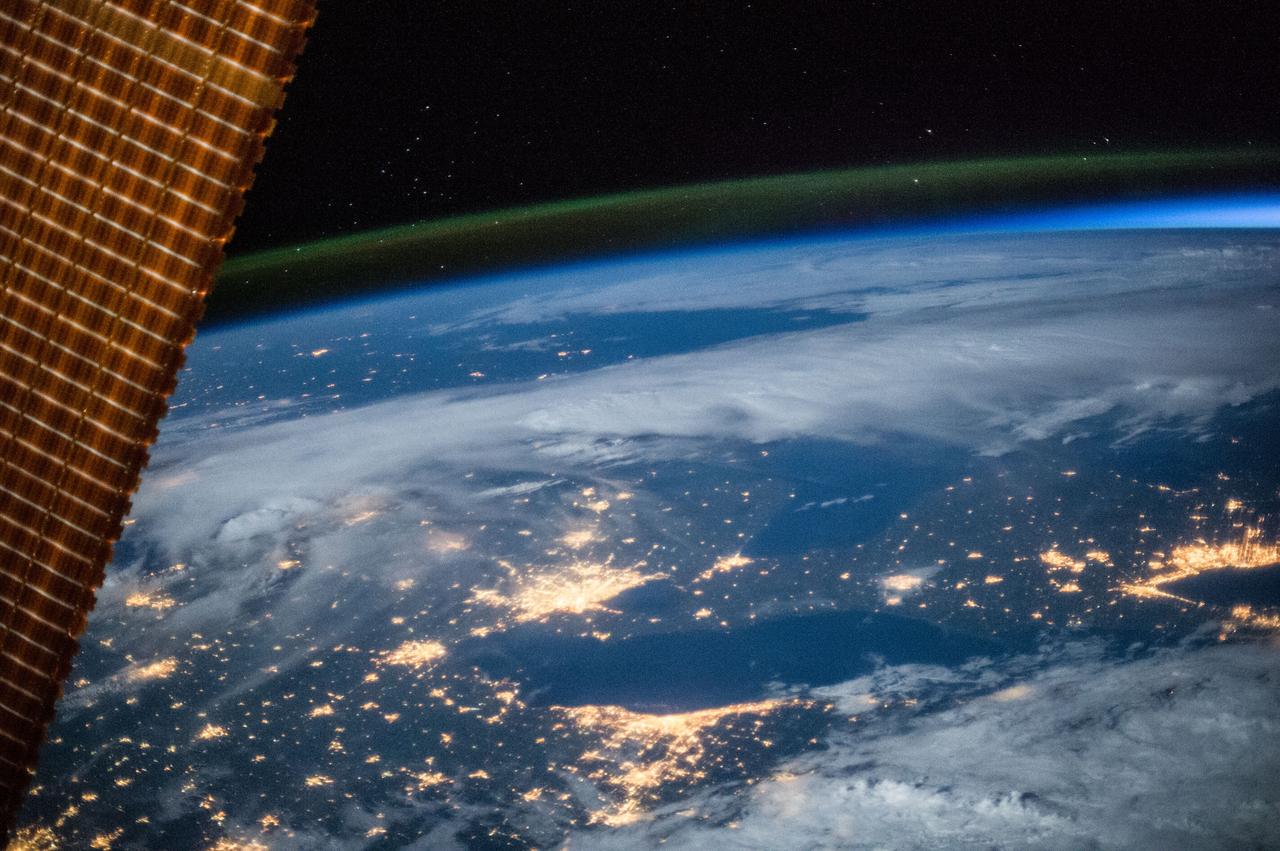

Earth observation taken during a night pass by an Expedition 36 crew member on board the International Space Station (ISS). Per Twitter message this is labeled as: Detroit, Cleveland, Toronto and a blue hint of sunrise.

STS-122 Crew Members visit the Pro Football Hall of Fame in Canton Ohio. STS-122 Astronaut poses by a Detroit Lions display case. He was drafted by the Lions in 1986
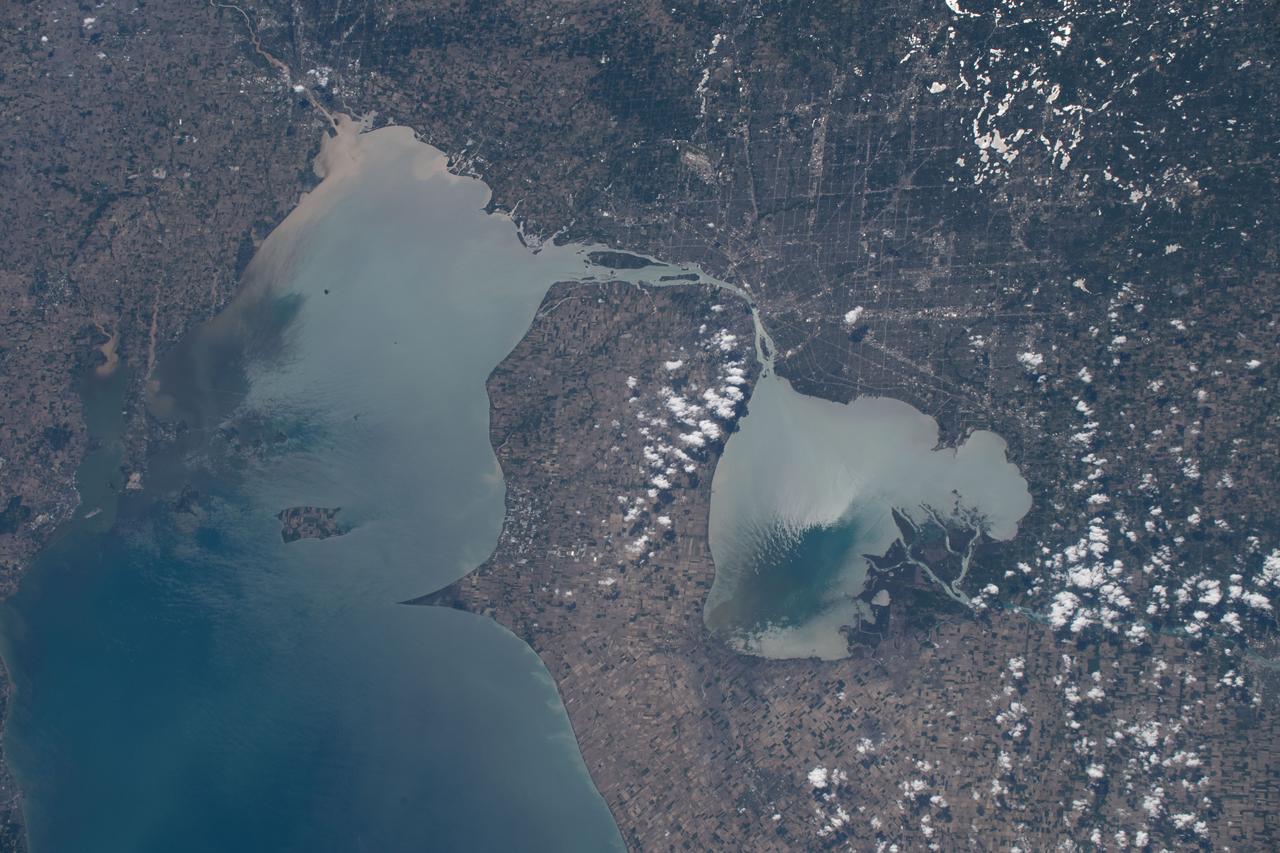

iss059e090279 (June 3, 2019) --- Lakes Erie and St. Clair and the cities of Detroit, Michigan and Toledo, Ohio are pictured as the International Space Station orbited 257 miles over North America.
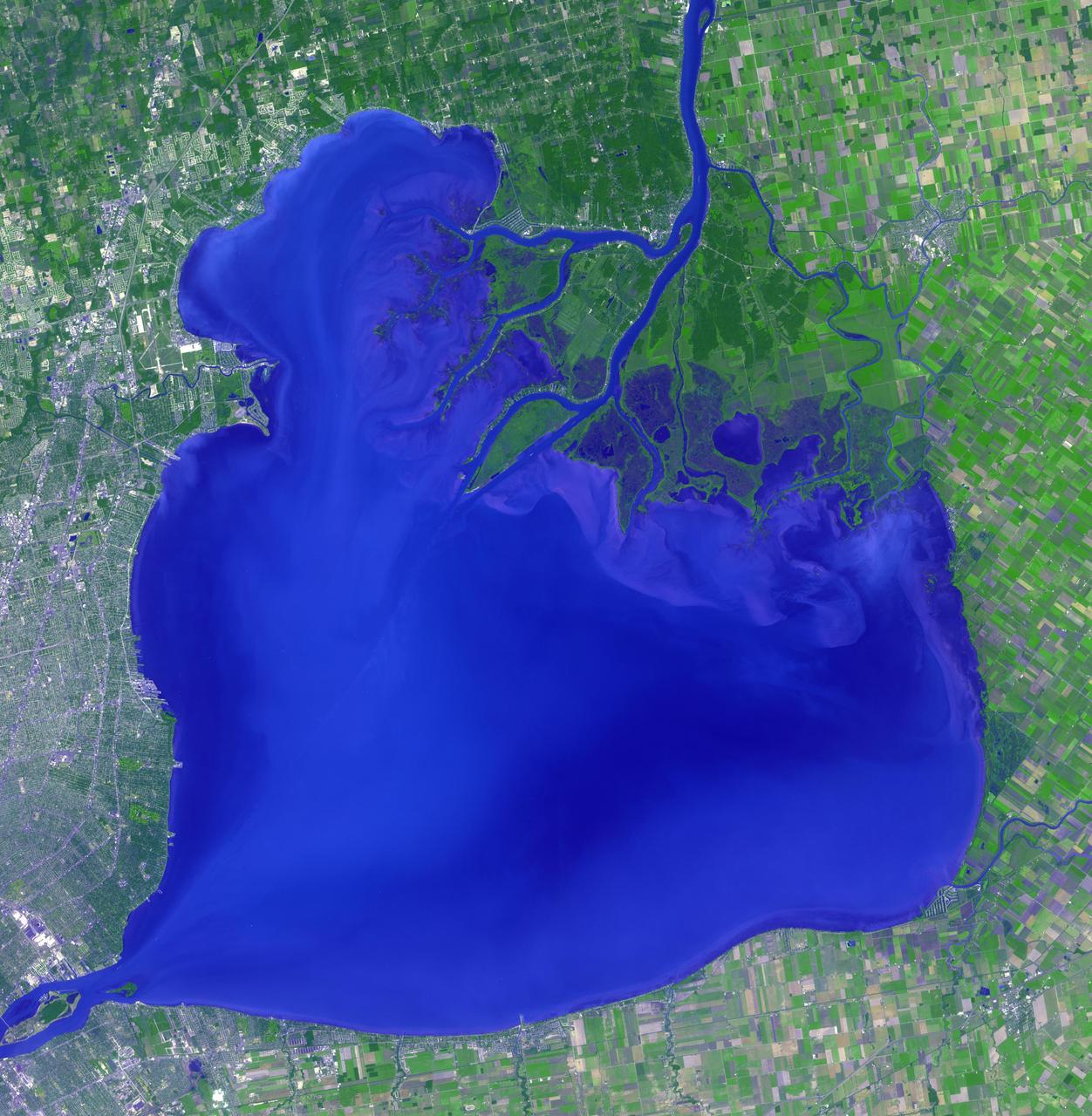

Lake St. Clair connects Lake Huron, via the St. Clair River, to Lake Erie, via the Detroit River. It is named after Claire of Assisi, on whose feast day it was first navigated by French explorers in 1679. The lake covers an area of about 1100 square kilometers, with an average depth of 3.5 meters. Both the U.S. and Canada maintain a deep shipping channel through the lake. The image was acquired September 9, 2002, covers an area of 51.4 by 52.5 kilometers, and is located at 42.5 degrees north, 82.7 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23234
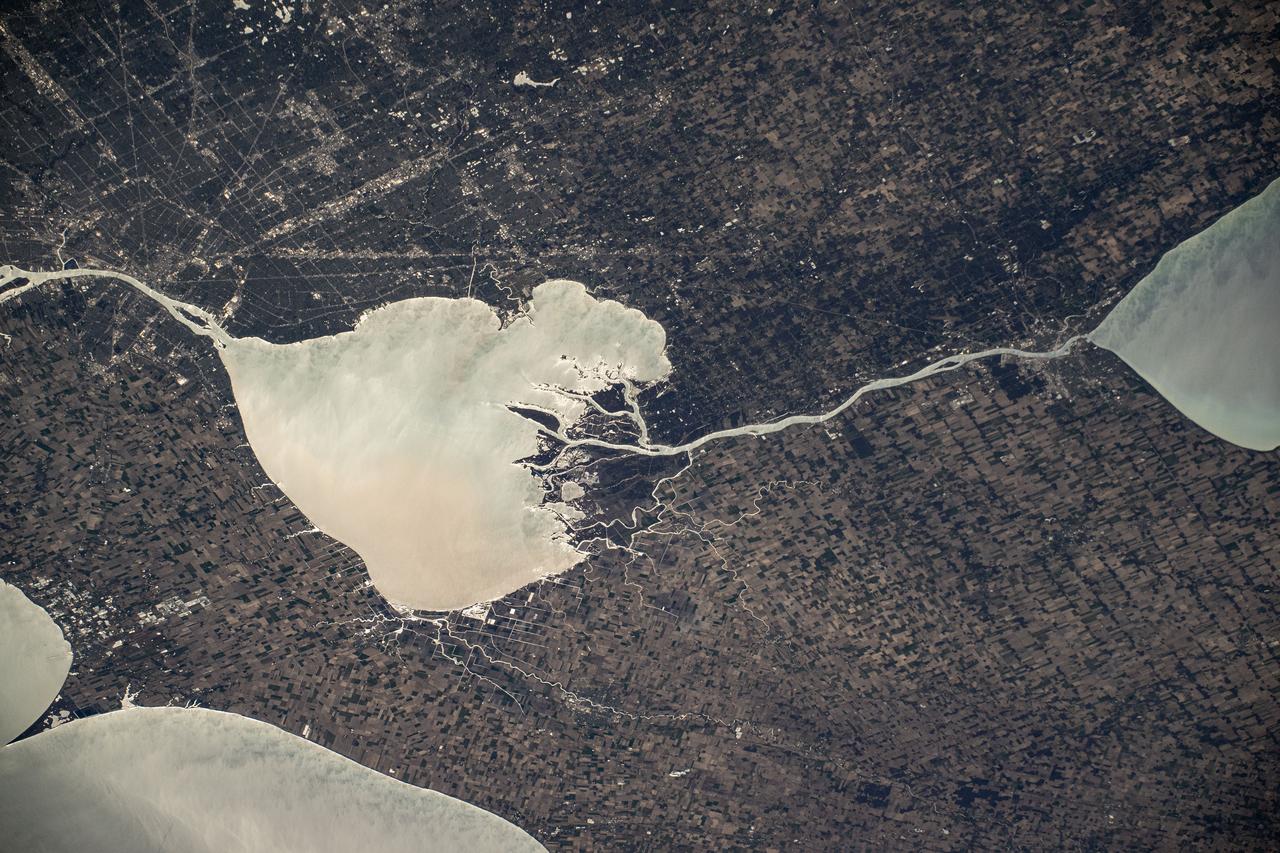

iss073e0000460 (April 22, 2025) --- The sun's glint beams off the freshwater Lake St. Clair, sits in between Lake Huron (right) and Lake Erie (bottom left), and separates Detroit, Michigan (top left) from Ontario, Canada, in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above.
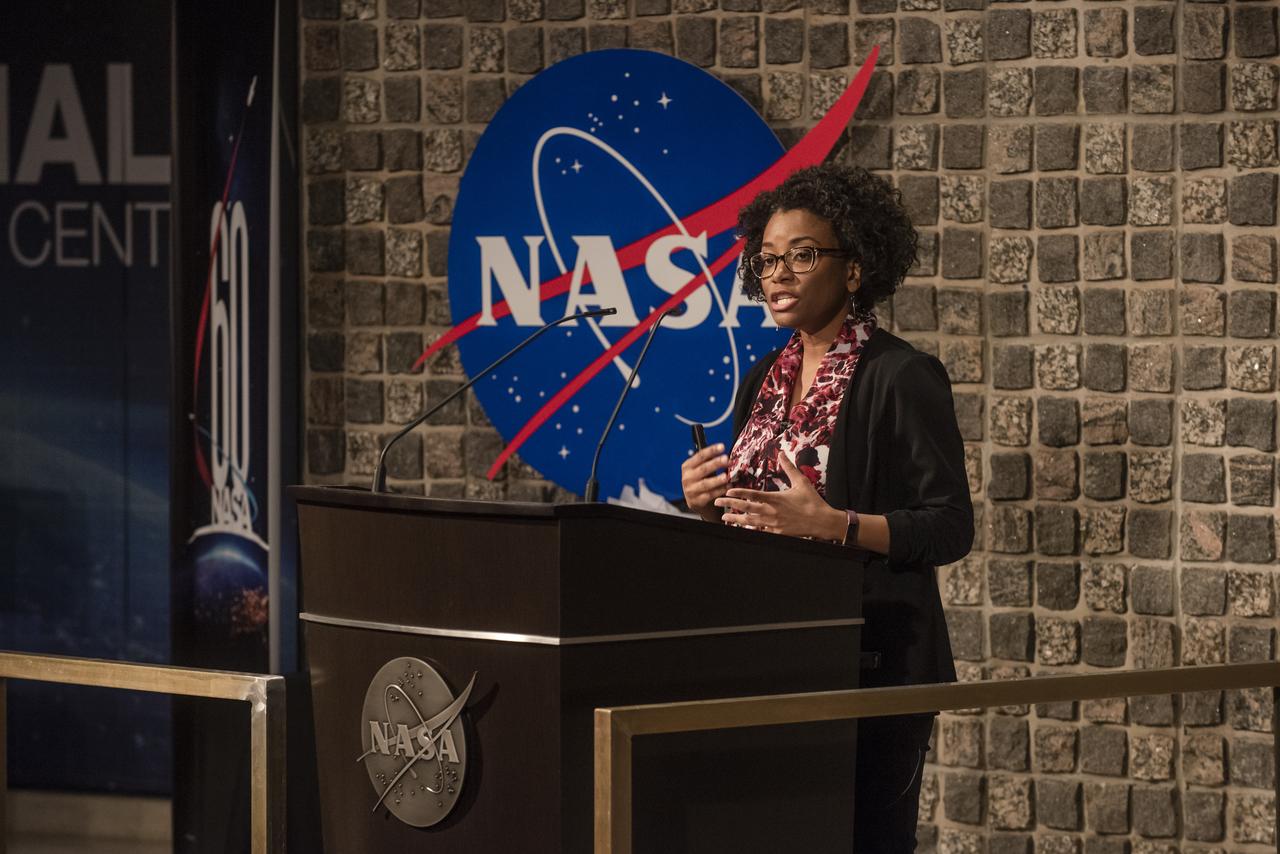

Dr. Shanique Brown, an assistant professor of industrial-organizational psychology at Wayne State University in Detroit, Michigan, delivers the Black History Month keynote address to team members at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center Feb. 28. Participants mingled with Brown and Marshall leaders after the speech and a panel discussion on diversity and inclusion, and sampled a variety of ethnic foods. The 2019 commemoration, themed "Migrations From Here to There," was organized by Marshall's Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity
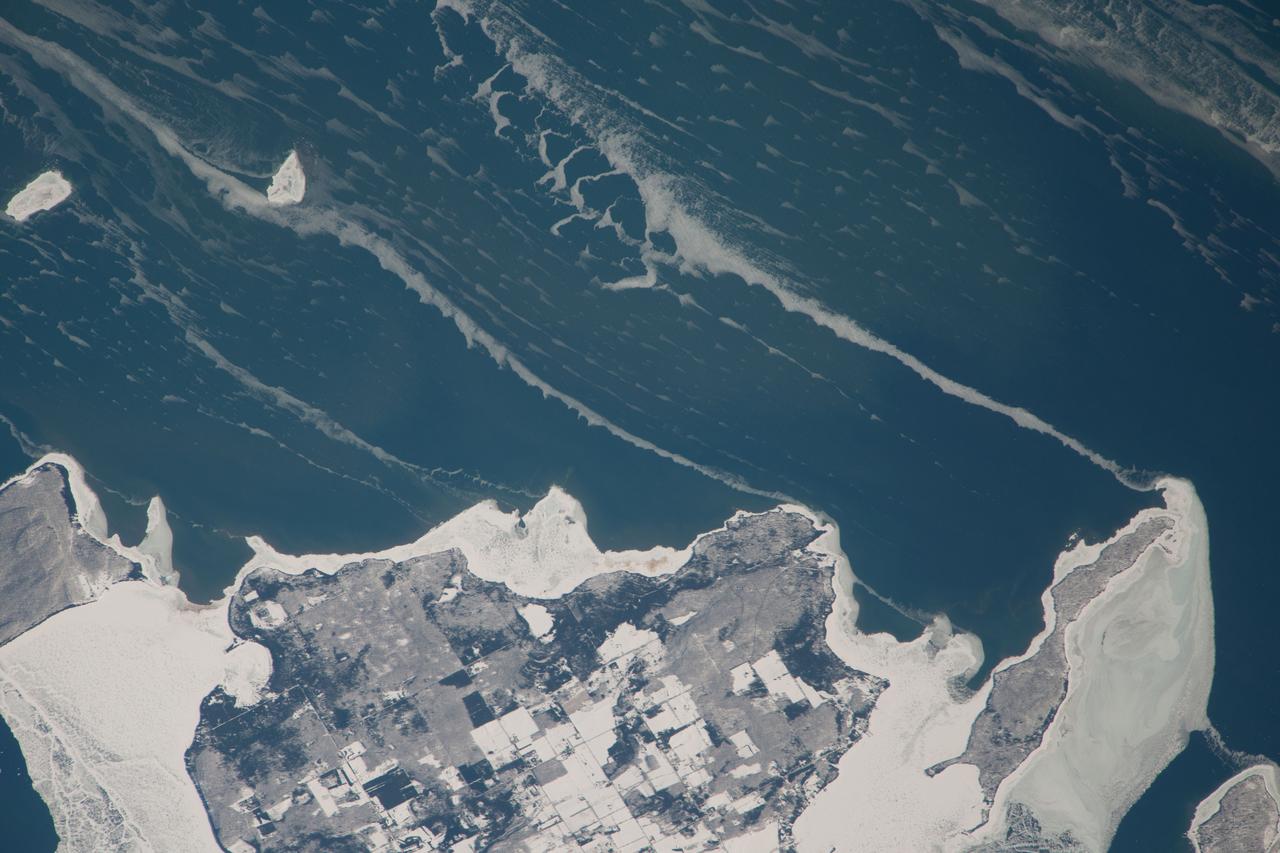

ISS038-E-057977 (22 Feb. 2014) --- Snow-covered fields appear as geometric patterns on Washington Island, on Lake Michigan, in this photograph taken by the Expedition 38 crew of the International Space Station. The island is nine kilometers long (5.6 miles) and lies on the western shore of Lake Michigan, as a continuation of Door Peninsula (Wisconsin). Note that north is to the lower left in the image. White coastal ice hugs the shoreline and connects Washington Island with Detroit Island and Rock Island. Ice typically accumulates first near land, where cooling is more rapid than in deeper lake water. Two other snow-covered islands (image top left) are small enough and far enough from land to evade the collars of ice. On the day this image was taken, southwesterly winds were blowing ice into the lake in the form of long, coherent stringers. The thickness of a stringer is related to the length of coastline that feeds it. The smallest northern stringer (image left) is fed by the shortest section of upwind coastline, and the longest (image right) is supplied by the large amount of shore ice around Detroit Island.
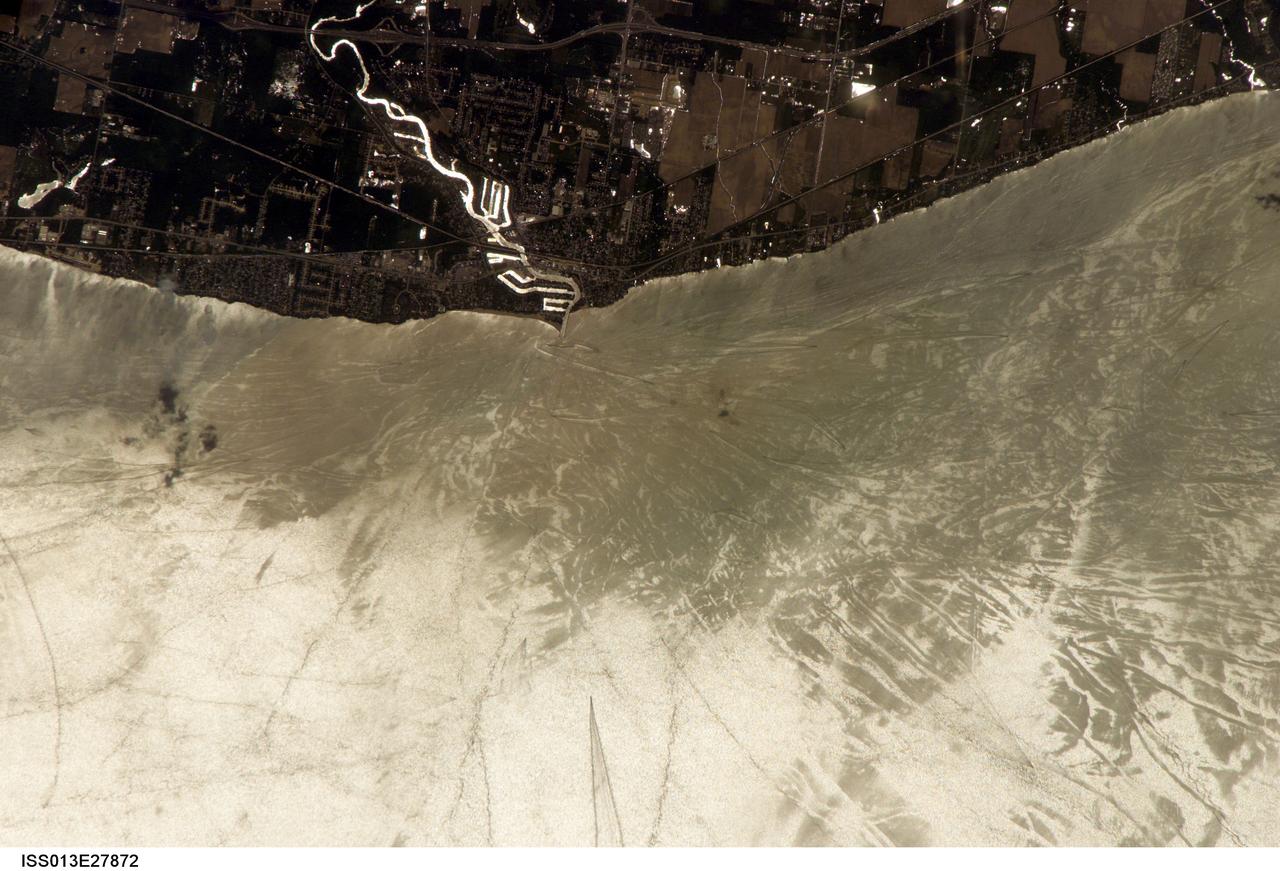

ISS013-E-27872 (28 May 2006) --- Considerable sunglint emphasizes features on Lake Erie in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. This detailed, south-looking image shows features on the surface of Lake Erie, about 30 miles west of Cleveland, Ohio. This view shows the Vermilion River in strong sunglint. The angular water bodies along the river are likely marinas. The main part of the image show numerous ship wakes in the zone of partial glint around the disk of the Sun's reflection point. The wakes radiate from the mouth of the Vermilion River, with many of them heading northwest in the direction of Detroit, Michigan.
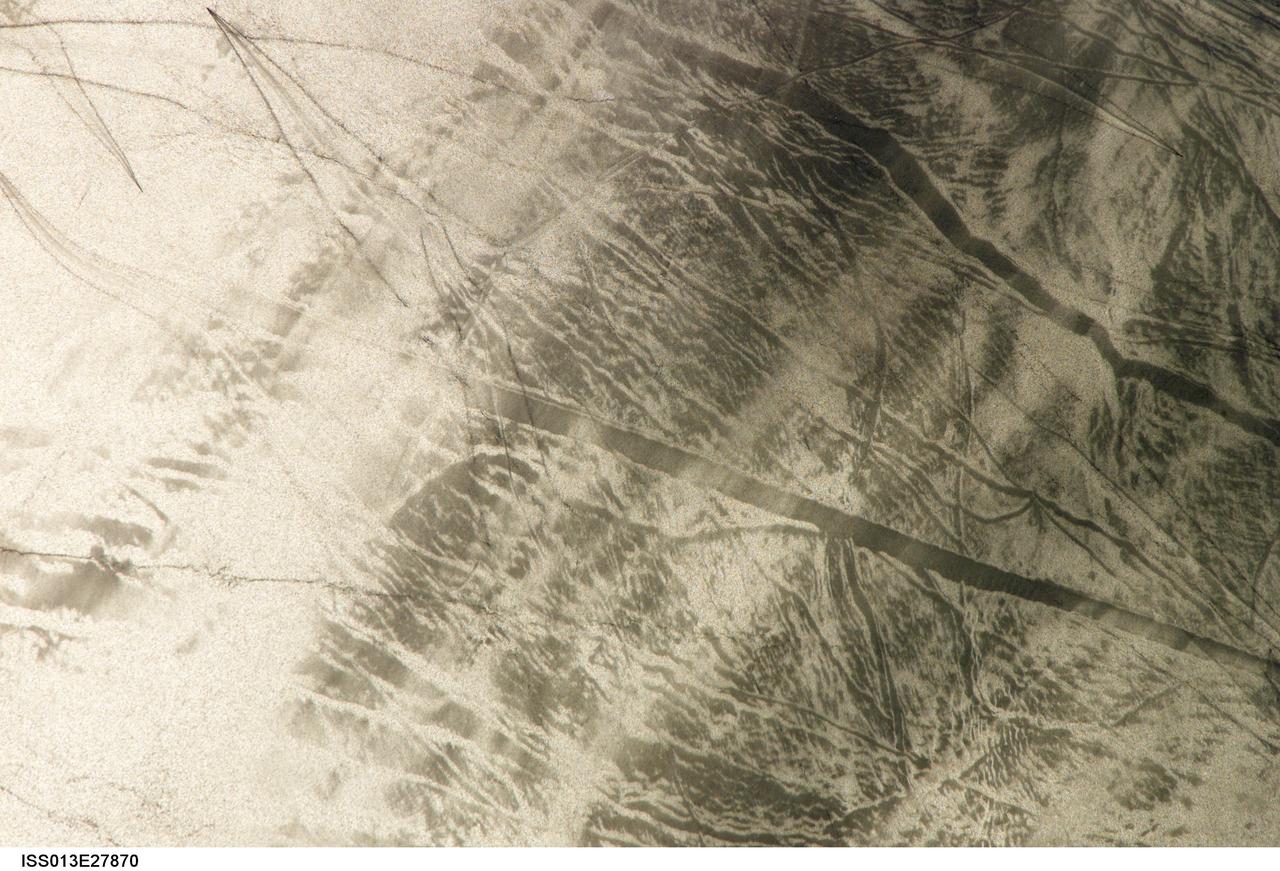
ISS013-E-27870 (28 May 2006) --- Considerable sunglint emphasizes features on Lake Erie in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. This detailed, south-looking image shows features on the surface of Lake Erie, about 30 miles west of Cleveland, Ohio. This view shows tight-V-shaped wakes of small craft. It also shows broad patterns of larger craft, probably large freighters carrying cargo that displace and disturb more water during passage. These larger wakes are aligned with the direct course between Detroit (out of frame) and Cleveland (out of frame). Some of the broad, ill-defined swaths of light and dark are streaks of wind-roughened water, which reflect the Sun differently.

From Space to the Super Bowl Members of the STS-129 shuttle mission present a specially minted silver medallion to National Football League officials on Wednesday, Jan. 27, 2010, at the Pro Football Hall of Fame in Canton, Ohio. The coin, which was flown in space during the November flight of Atlantis, will be used for the official coin toss prior to the kickoff of Super Bowl XLIV on Sunday, Feb. 7, 2010. One member of Atlantis' crew, Leland Melvin, was drafted by the NFL's Detroit Lions in 1986. The crew also flew other NFL-related memorabilia, including jerseys and a football inscribed with the name of every member of the Hall of Fame. From left: Astronauts Bobby Satcher, Randy Bresnik, and Charlie Hobaugh; Joe Horrigan, Vice President of Communications/Exhibits for the Pro Football Hall of Fame, Steve Perry, President/Executive Director of the Pro Football Hall of Fame; astronauts Berry Wilmore, Michael Foreman and Leland Melvin. Photo Credit: NASA/Marv Smith
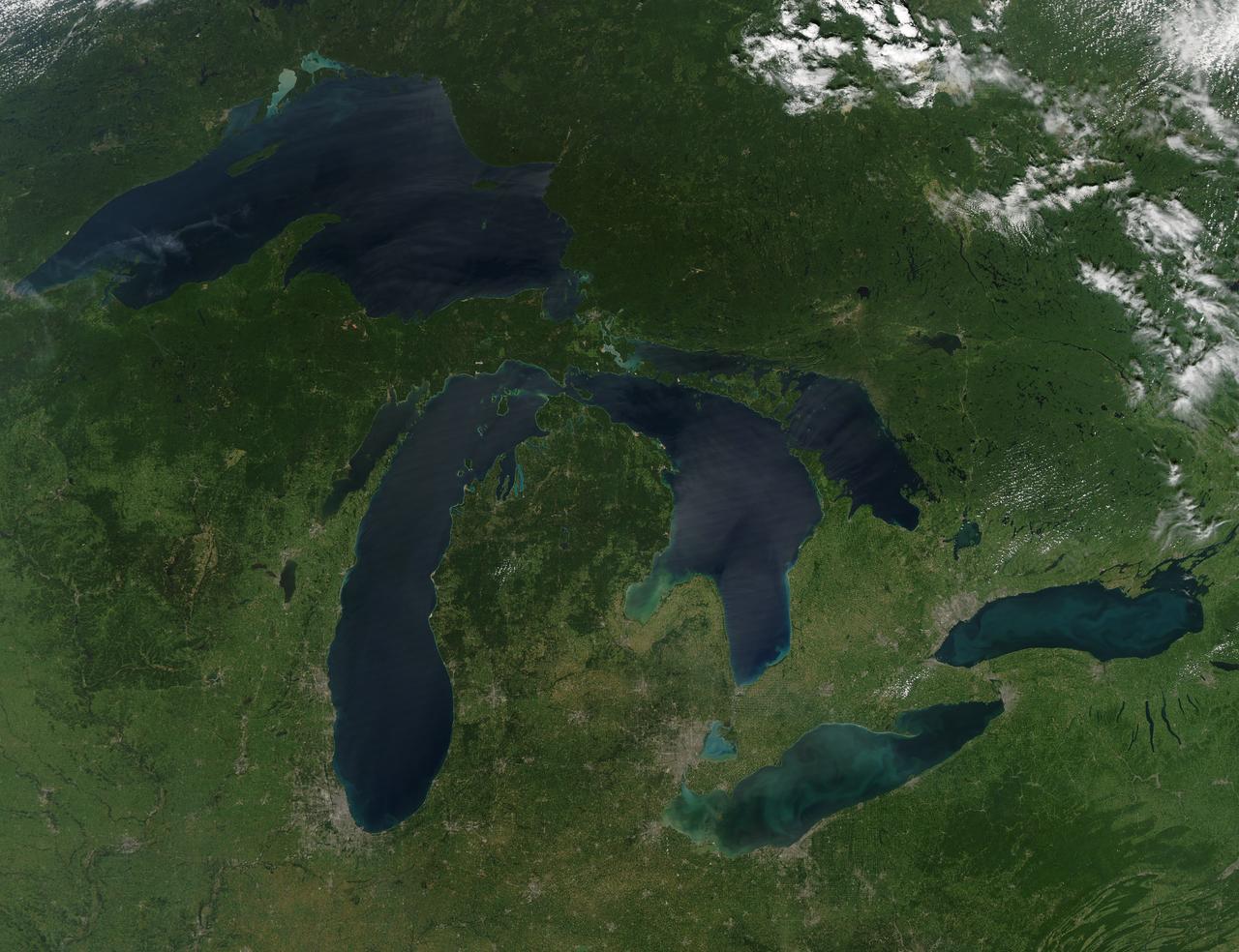
NASA image acquired August 28, 2010 Late August 2010 provided a rare satellite view of a cloudless summer day over the entire Great Lakes region. North Americans trying to sneak in a Labor Day weekend getaway on the lakes were hoping for more of the same. The Great Lakes comprise the largest collective body of fresh water on the planet, containing roughly 18 percent of Earth's supply. Only the polar ice caps contain more fresh water. The region around the Great Lakes basin is home to more than 10 percent of the population of the United States and 25 percent of the population of Canada. Many of those people have tried to escape record heat this summer by visiting the lakes. What they found, according to The Hamilton Spectator, was record-breaking water temperatures fueled by record-breaking air temperatures in the spring and summer. By mid-August, the waters of Lake Superior were 6 to 8°C (11 to 14°F) above normal. Lake Michigan set records at about 4°C (7°F) above normal. The other three Great Lakes – Huron, Erie, and Ontario -- were above normal temperatures, though no records were set. The image was gathered by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite at 1:30 p.m. Central Daylight Time (18:30 UTC) on August 28. Open water appears blue or nearly black. The pale blue and green swirls near the coasts are likely caused by algae or phytoplankton blooms, or by calcium carbonate (chalk) from the lake floor. The sweltering summer temperatures have produced an unprecedented bloom of toxic blue-green algae in western Lake Erie, according to the Cleveland Plain Dealer. NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS Click here to see more images from <b><a href="#//earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Goddard’s Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>