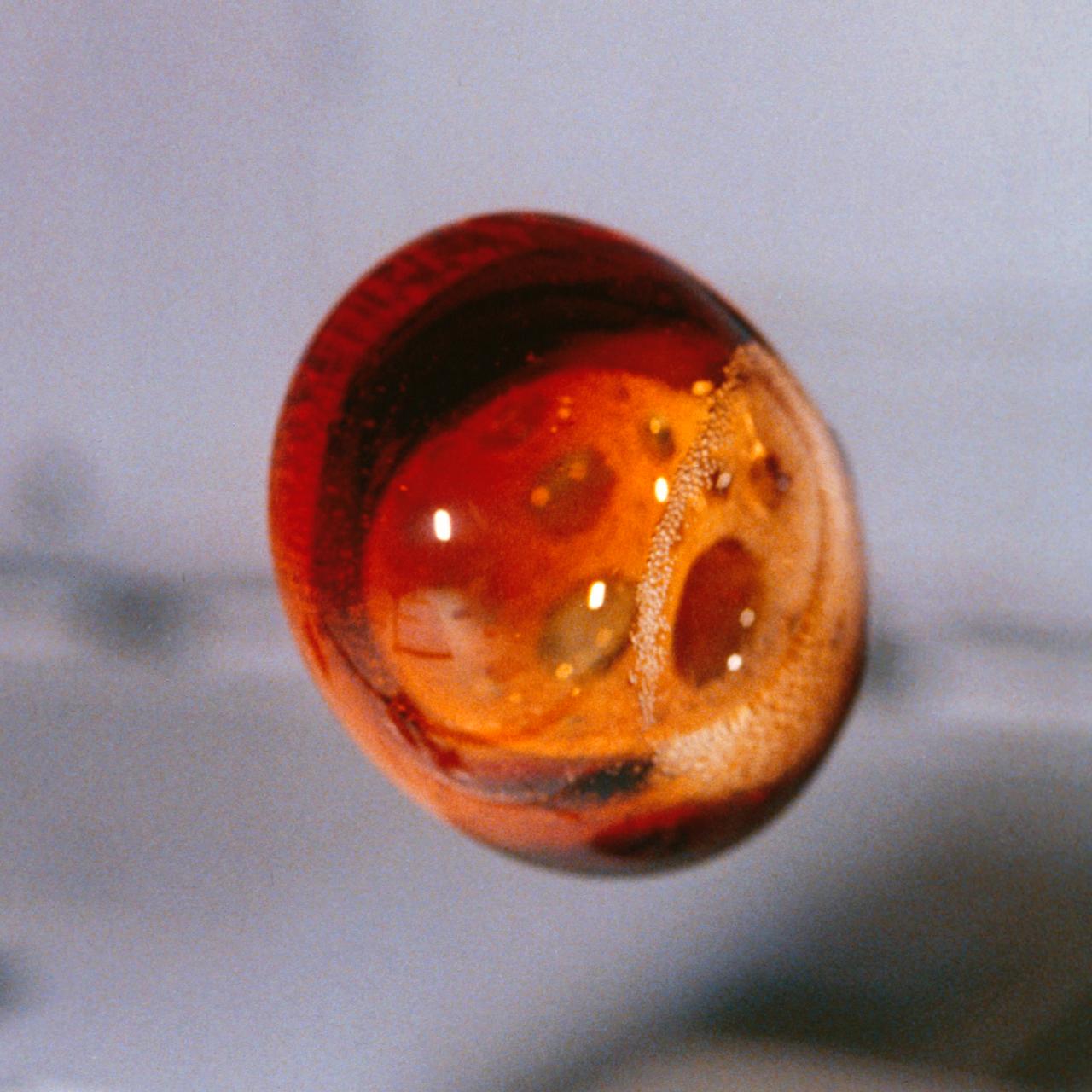
The lack of normal convection in microgravity is demonstrated by a carbonated soft drink floating in the middeck of the Space Shuttle. While the droplet is oscillating slightly and starting to assume a spherical shape, it is filled with carbon dioxide bubbles in a range of sizes. On Earth, the bubbles would quickly foat up to form a head. In space, they are suspended. They may drift with time and eventually the surface tension between individual bubbles breaks, allowing larger bubbles to form. This image was taken during STS-51F mission (Spacelab 2) which carried test models of dispensers from two pupular soft drink manufacturers. Photo credit: NASA/Johnson Space Center (JSC)
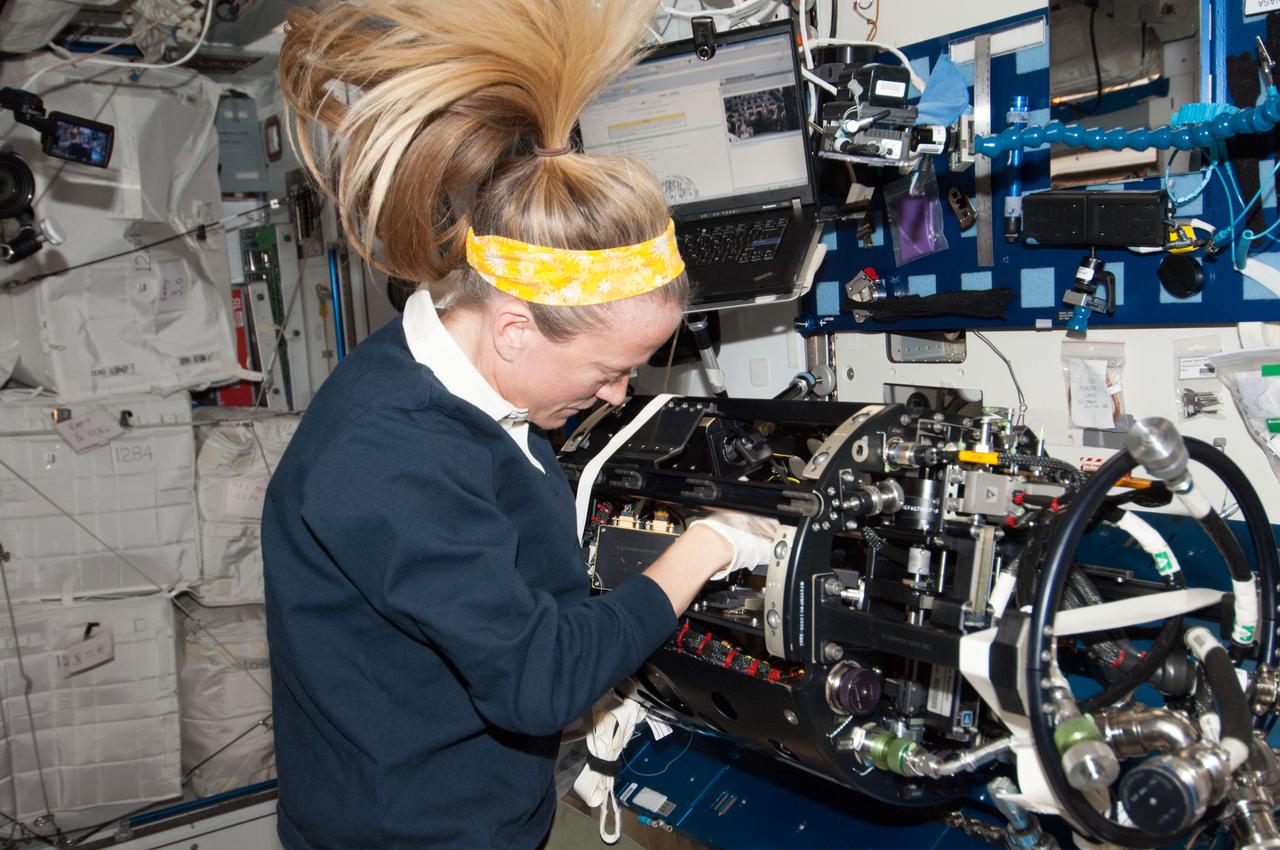
ISS037-E-004959 (2 Oct. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 37 flight engineer, performs the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) hardware replacement in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
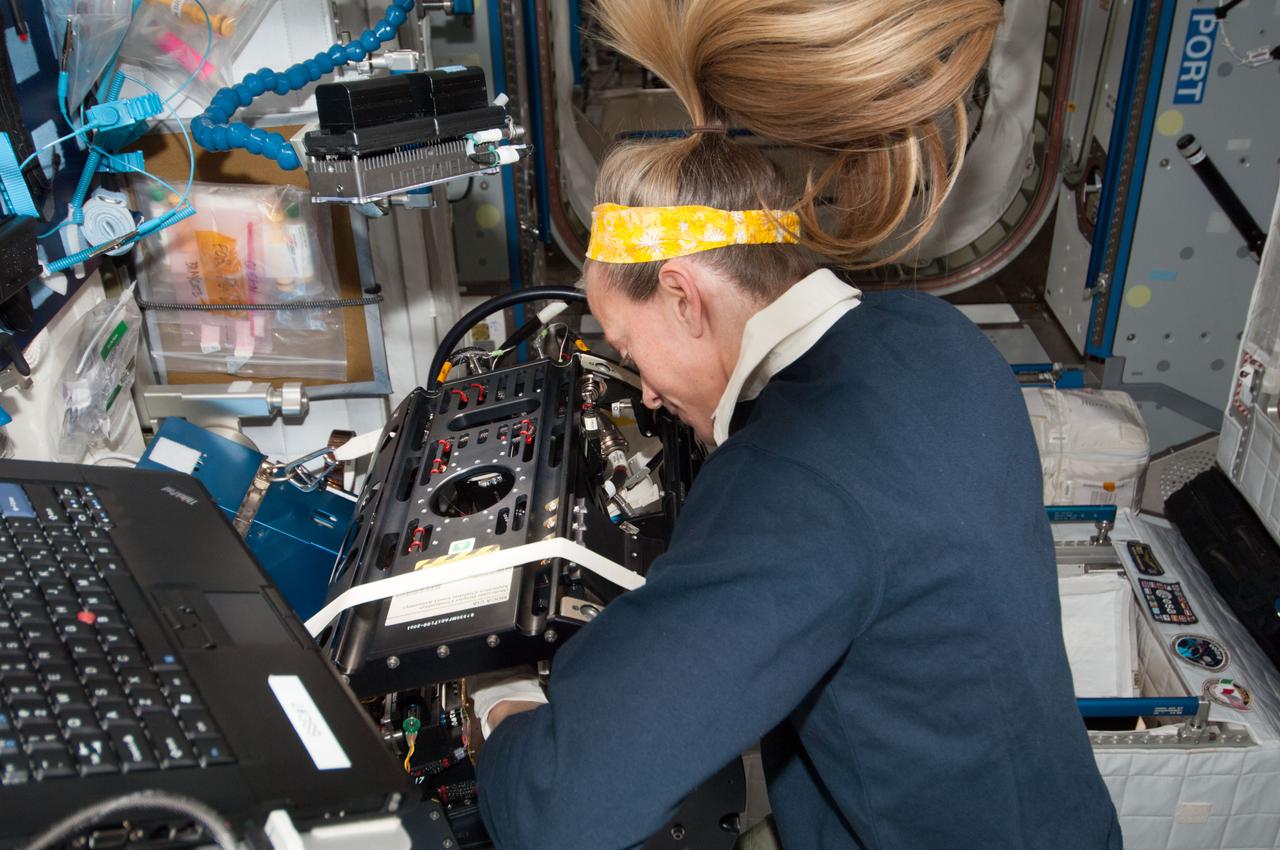

ISS037-E-004956 (2 Oct. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 37 flight engineer, performs the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) hardware replacement in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
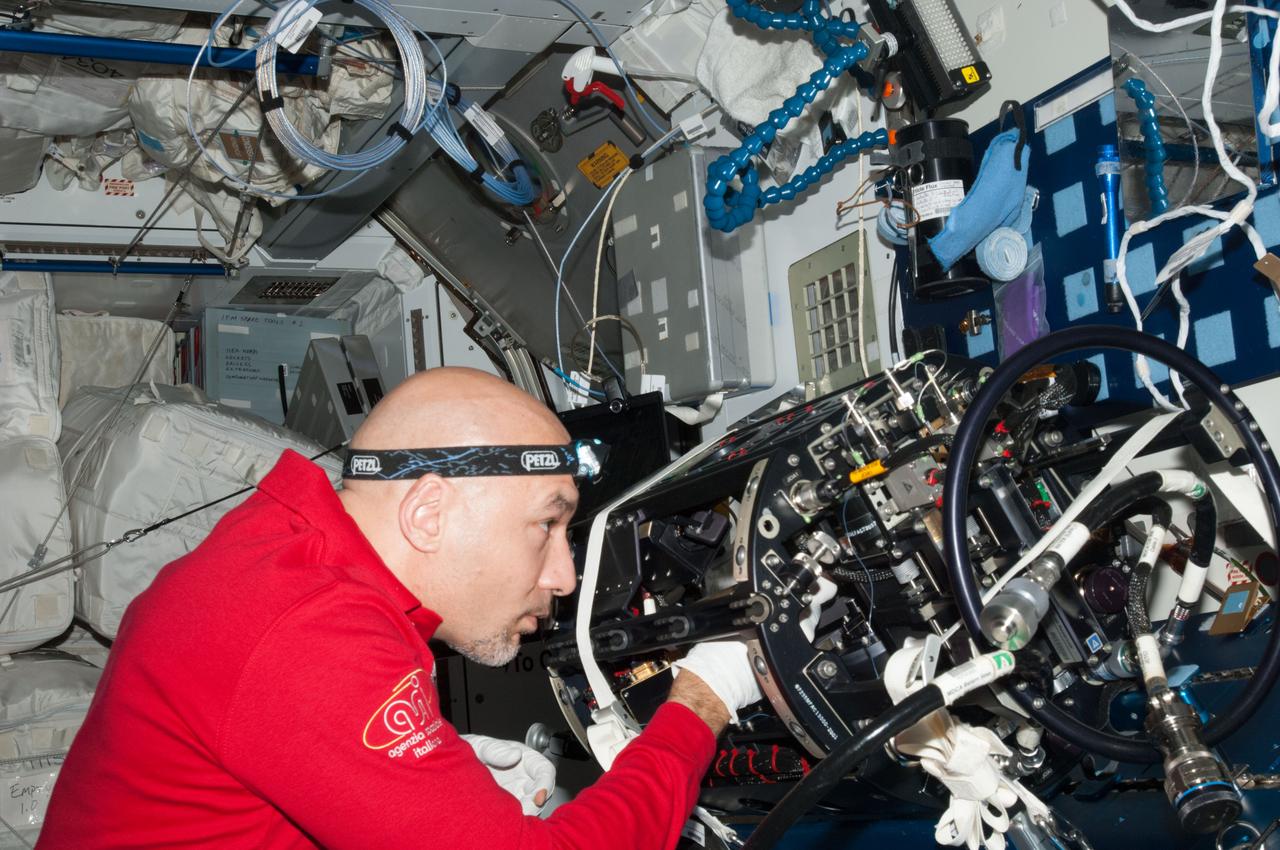

ISS036-E-024605 (24 July 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
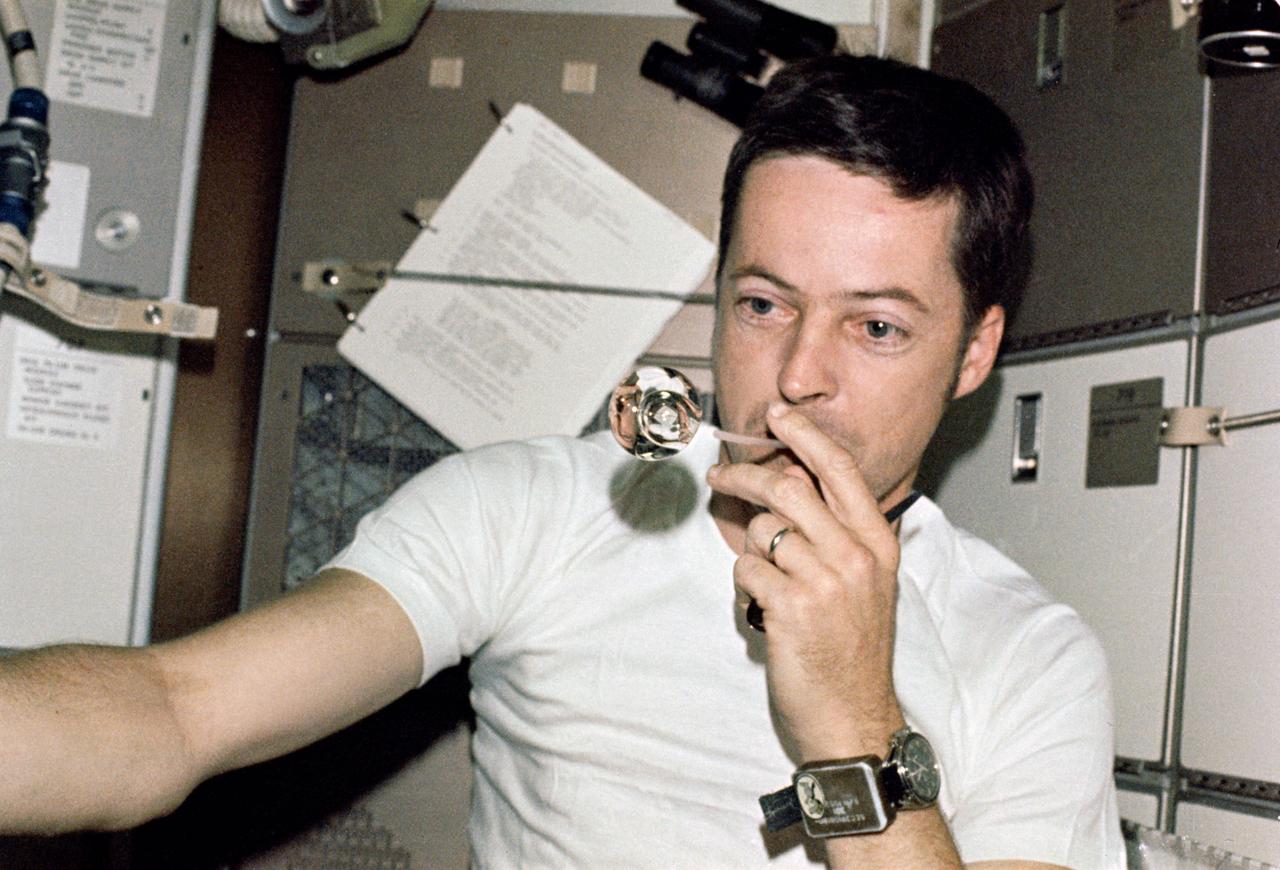

SL2-X9-730 (1 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, forms a perfect sphere by blowing water droplets from a straw in zero-gravity. He is in the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
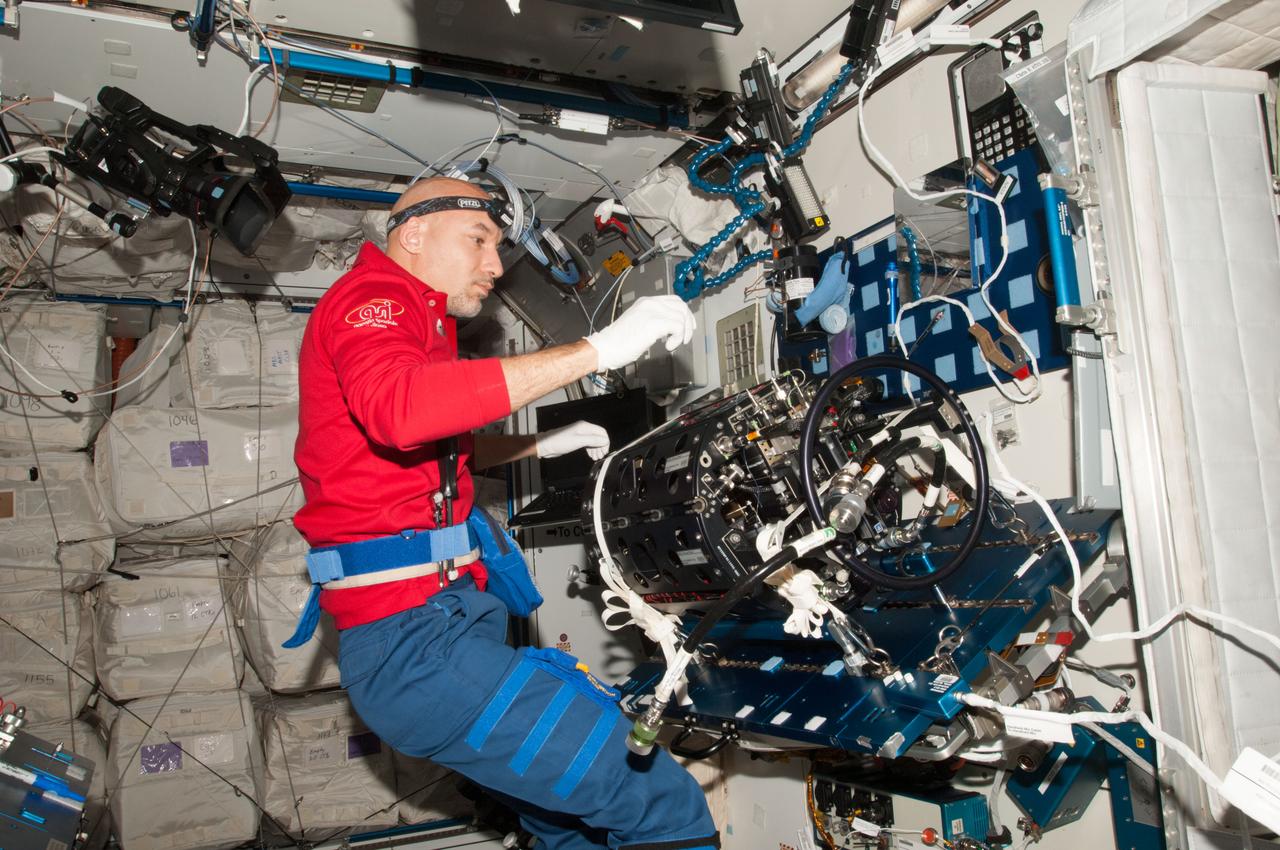

ISS036-E-024569 (24 July 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
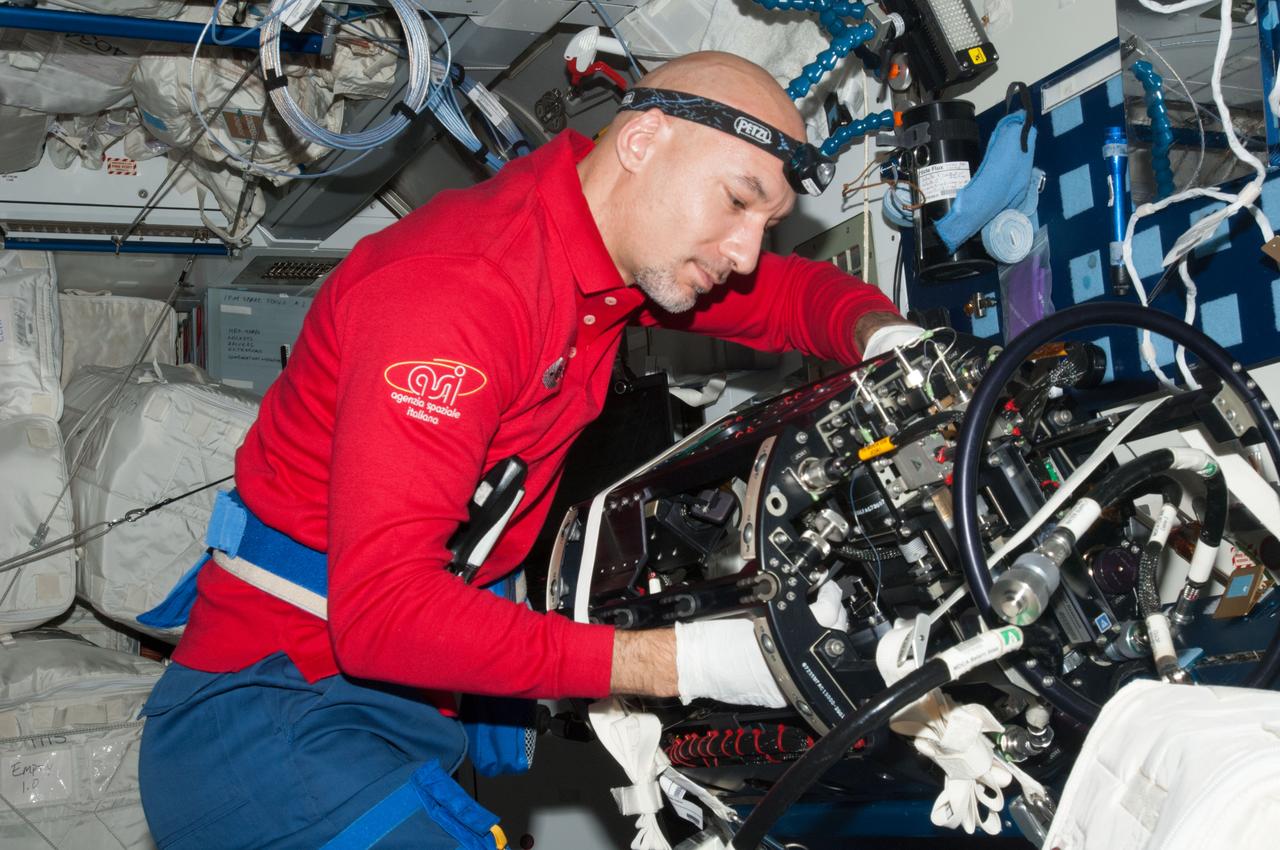

ISS036-E-024637 (24 July 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
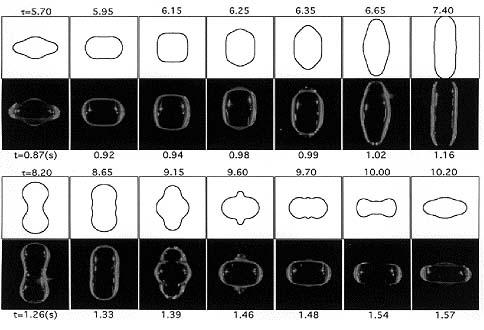
Apfel's excellent match: This series of photos shows a water drop containing a surfactant (Triton-100) as it experiences a complete cycle of superoscillation on U.S. Microgravity Lab-2 (USML-2; October 1995). The time in seconds appears under the photos. The figures above the photos are the oscillation shapes predicted by a numerical model. The time shown with the predictions is nondimensional. Robert Apfel (Yale University) used the Drop Physics Module on USML-2 to explore the effect of surfactants on liquid drops. Apfel's research of surfactants may contribute to improvements in a variety of industrial processes, including oil recovery and environmental cleanup.
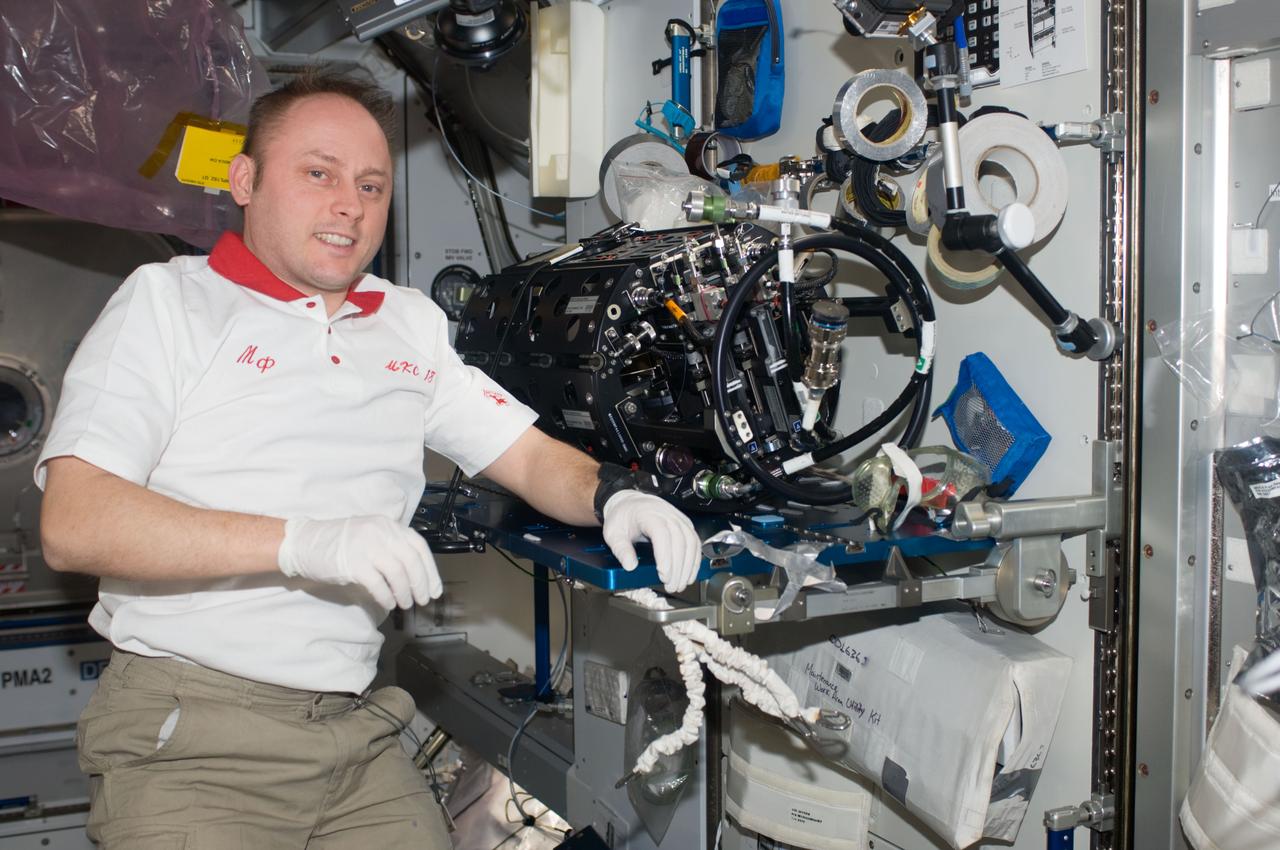

ISS018-E-010645 (6 Dec. 2008) --- Astronaut Michael Fincke, Expedition 18 commander, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
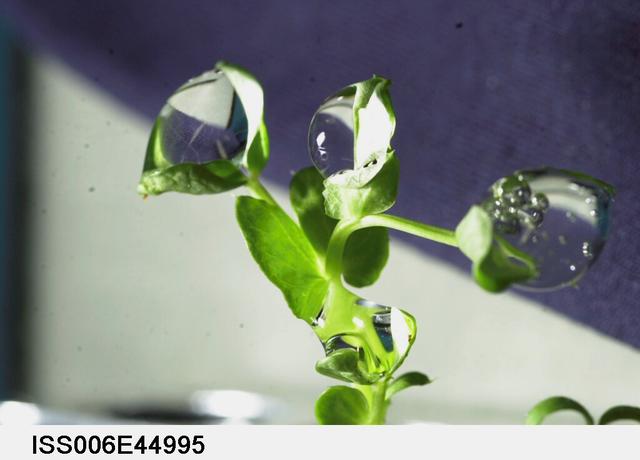

ISS006-E-44995 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of water droplets on leaves on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
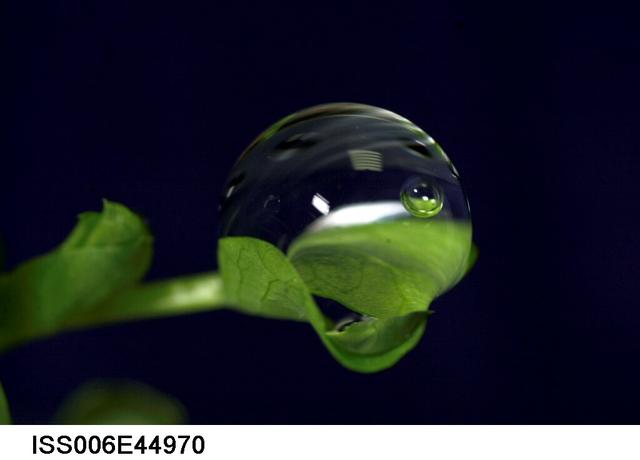

ISS006-E-44970 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
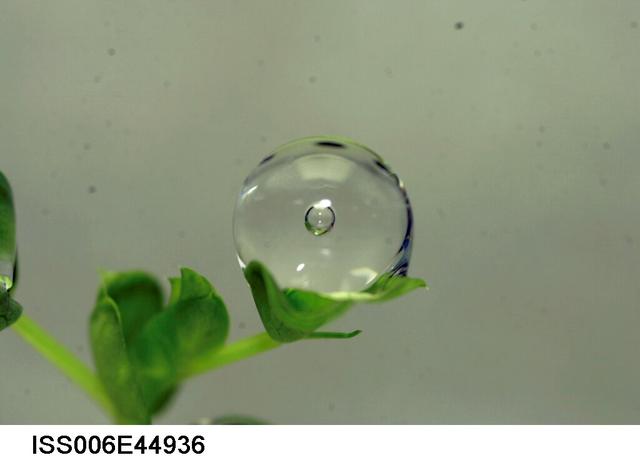

ISS006-E-44936 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
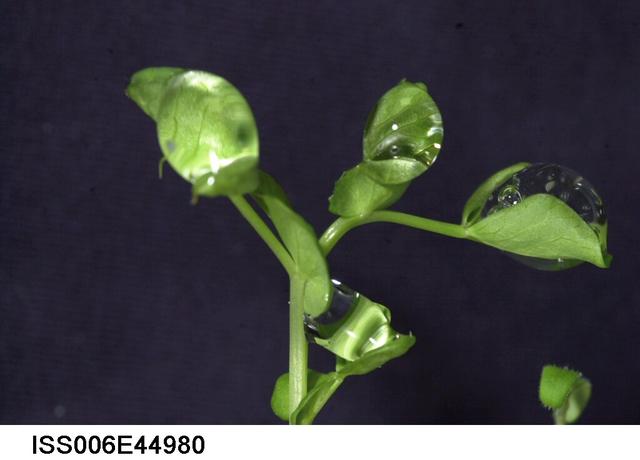

ISS006-E-44980 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of water droplets on leaves on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
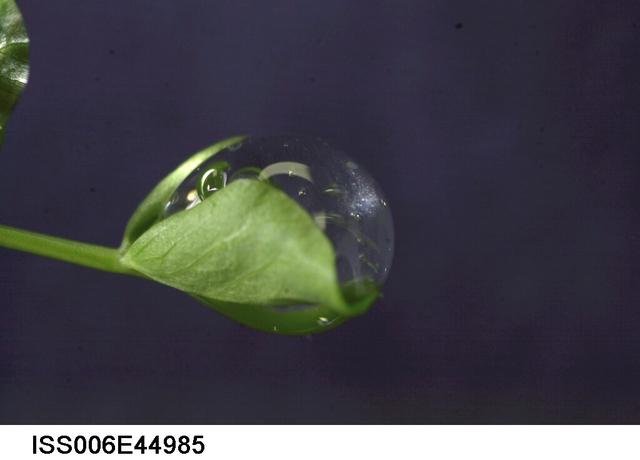

ISS006-E-44985 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
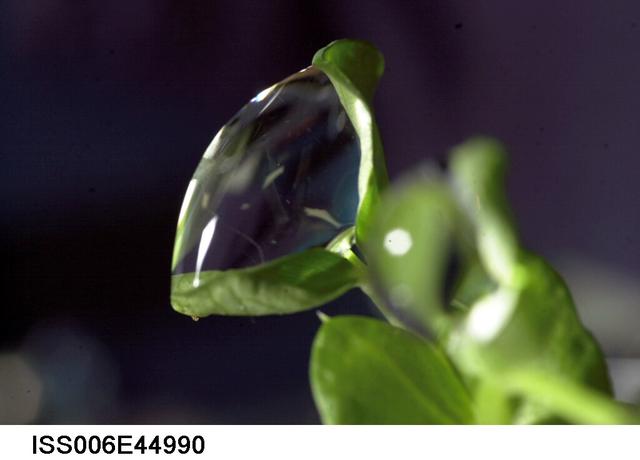

ISS006-E-44990 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
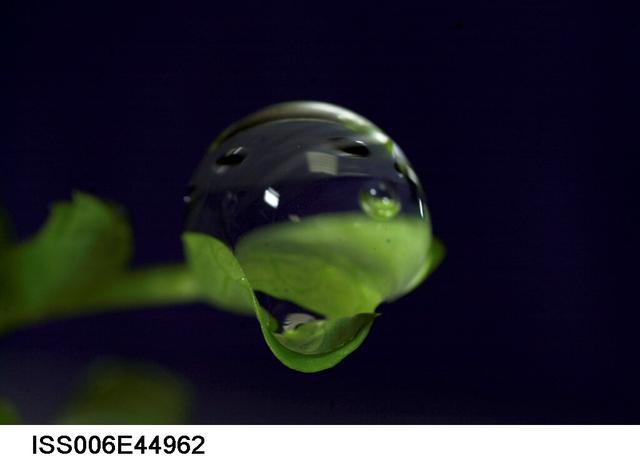

ISS006-E-44962 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).

ISS006-E-44929 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of water droplets on leaves on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
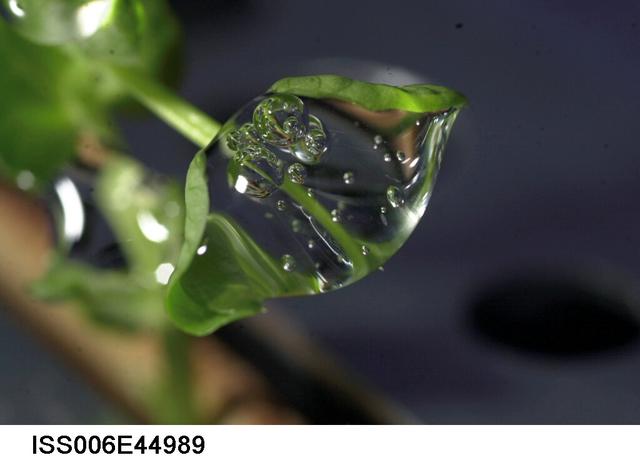

ISS006-E-44989 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
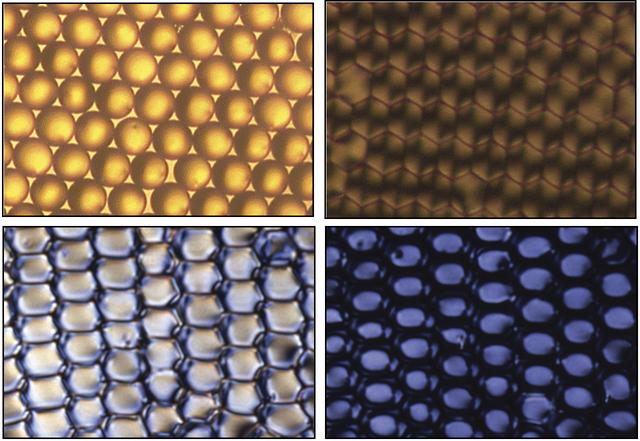
These images, from David Weitz’s liquid crystal research, show ordered uniform sized droplets (upper left) before they are dried from their solution. After the droplets are dried (upper right), they are viewed with crossed polarizers that show the deformation caused by drying, a process that orients the bipolar structure of the liquid crystal within the droplets. When an electric field is applied to the dried droplets (lower left), and then increased (lower right), the liquid crystal within the droplets switches its alignment, thereby reducing the amount of light that can be scattered by the droplets when a beam is shone through them.
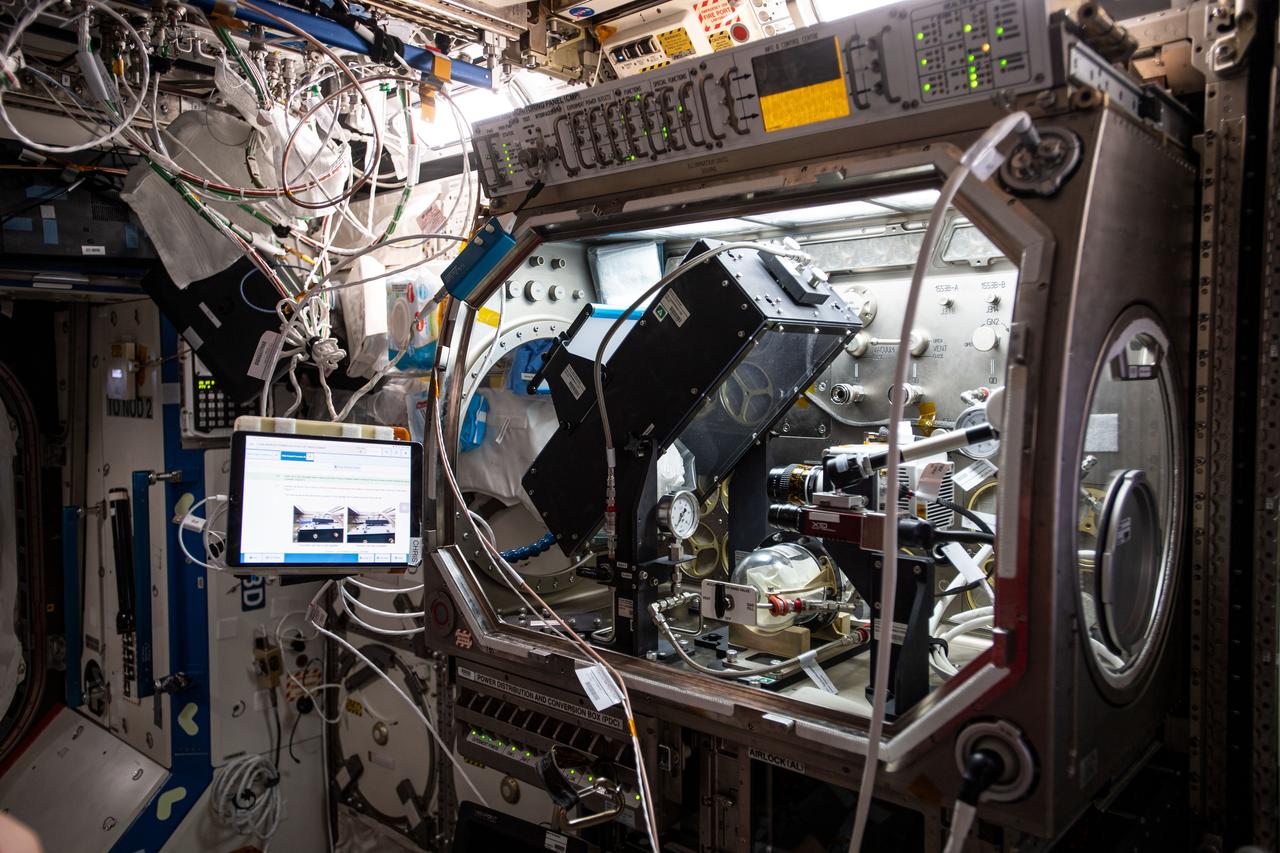

iss063e062018 (7/29/2020) --- Photo documentation of the Droplet Formation Study inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Droplet Formation Study observes how microgravity shapes water droplets, possibly improving water conservation and water pressure techniques on Earth.
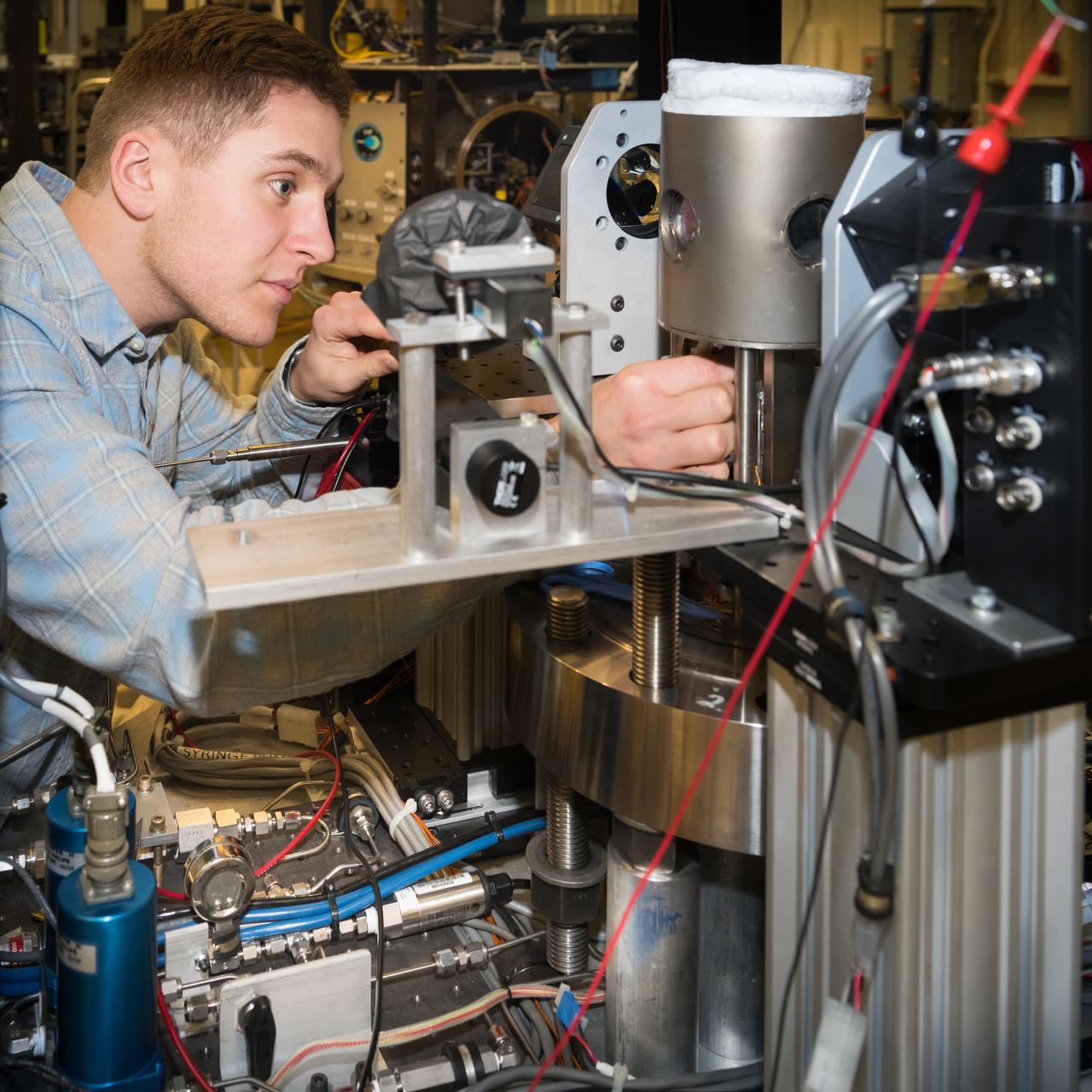
High Pressure Microgravity Combustion Experiment, HPMC, subjects liquid fuel droplets to high pressures and temperatures to study the ignition process in engine conditions, with a goal of improving fuel efficiency. In this configuration, the experiment is capable of testing droplet combustion at up to 100 atm of pressure, testing the droplet deployment system, which inserts the fuel droplet into the experiment.
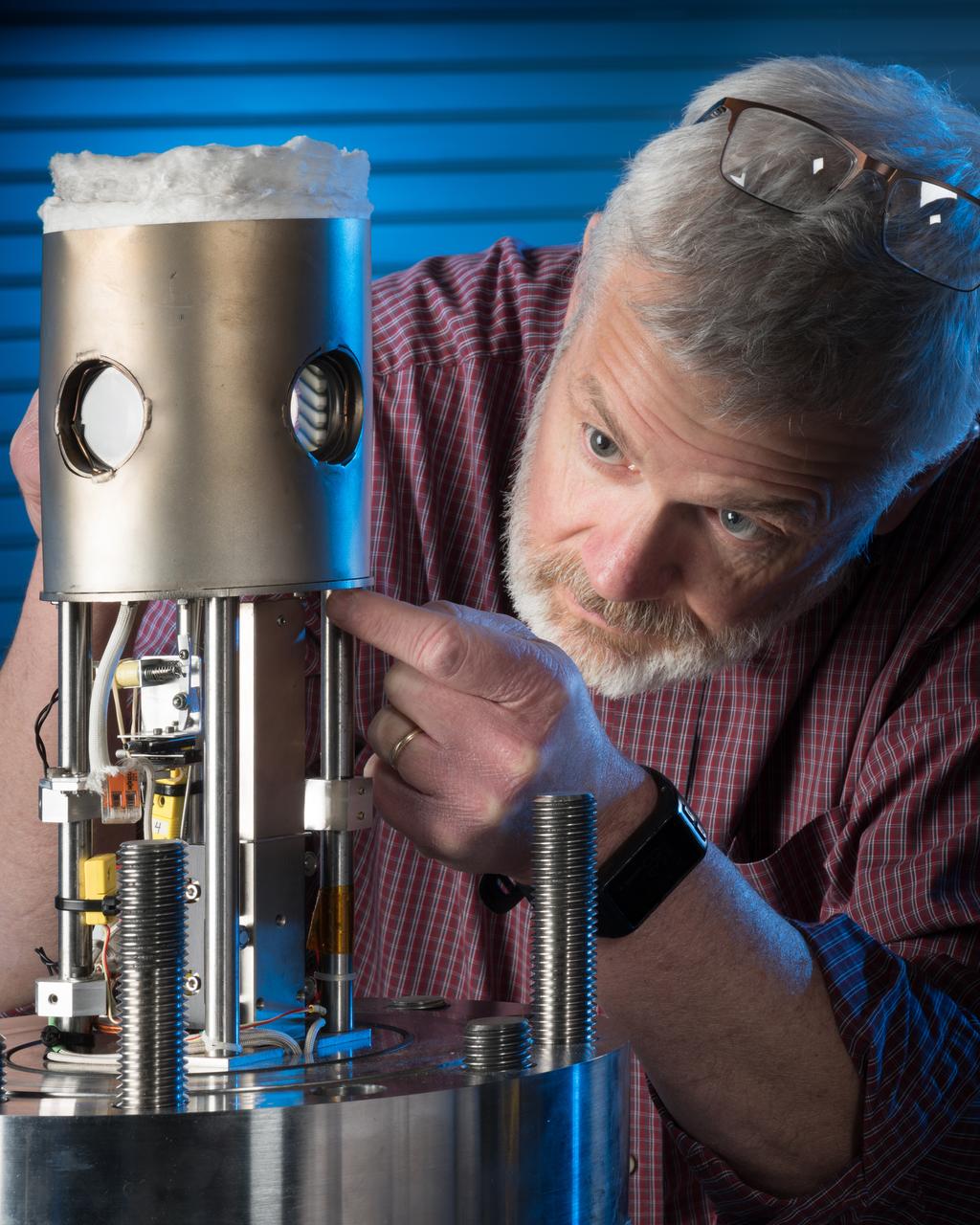
High Pressure Microgravity Combustion Experiment, HPMC, subjects liquid fuel droplets to high pressures and temperatures to study the ignition process in engine conditions, with a goal of improving fuel efficiency. In this configuration, the experiment is capable of testing droplet combustion at up to 100 atm of pressure, testing the droplet deployment system, which inserts the fuel droplet into the experiment.
MOLTEN SOLDER DROPLET RIG
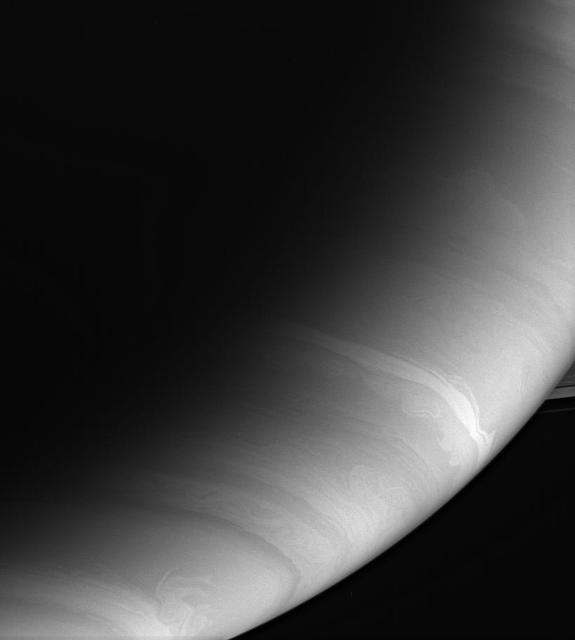

The clouds of Saturn swirl, billow and merge. These bands are layered into stratified cloud decks consisting of droplets of ammonia, ammonium hydrosulfide and water set aloft in a sea of hydrogen and helium
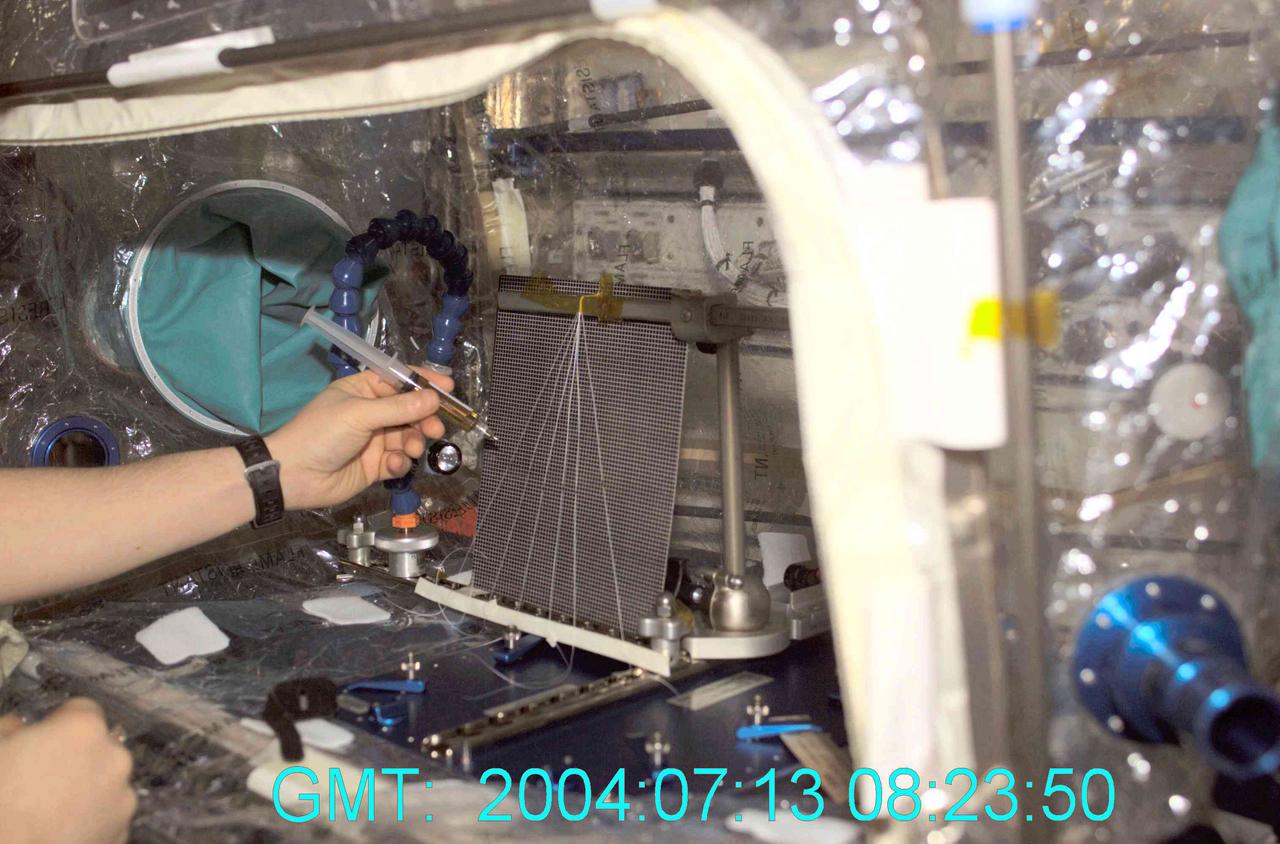

Astronaut Mike Fincke places droplets of honey onto the strings for the Fluid Merging Viscosity Measurement (FMVM) investigation onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The FMVM experiment measures the time it takes for two individual highly viscous fluid droplets to coalesce or merge into one droplet. Different fluids and droplet size combinations were tested in the series of experiments. By using the microgravity environment, researchers can measure the viscosity or "thickness" of fluids without the influence of containers and gravity using this new technique. Understanding viscosity could help scientists understand industrially important materials such as paints, emulsions, polymer melts and even foams used to produce pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic products.

Astronaut Mike Fincke places droplets of honey onto the strings for the Fluid Merging Viscosity Measurement (FMVM) investigation onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The FMVM experiment measures the time it takes for two individual highly viscous fluid droplets to coalesce or merge into one droplet. Different fluids and droplet size combinations were tested in the series of experiments. By using the microgravity environment, researchers can measure the viscosity or "thickness" of fluids without the influence of containers and gravity using this new technique. Understanding viscosity could help scientists understand industrially important materials such as paints, emulsions, polymer melts and even foams used to produce pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic products.
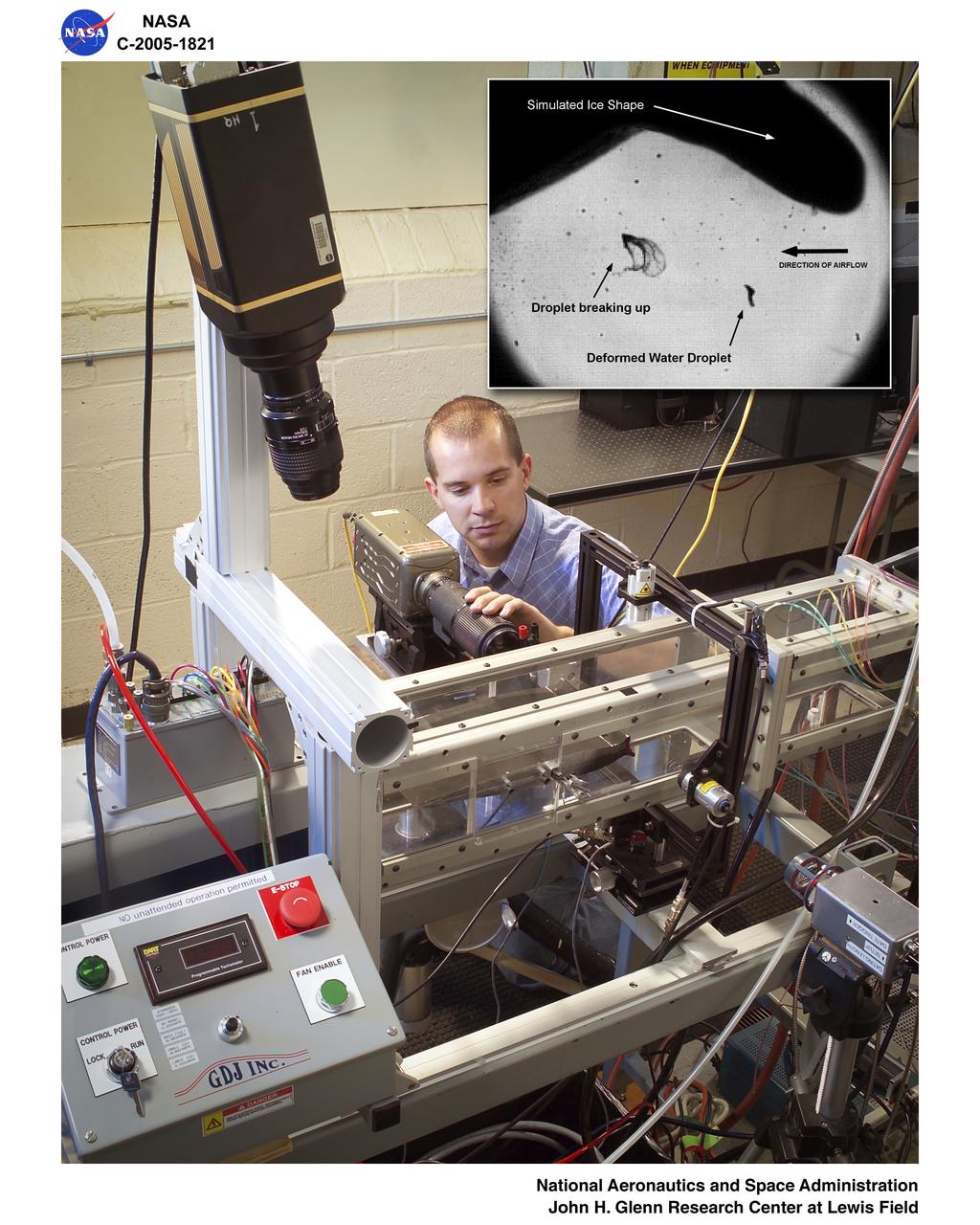
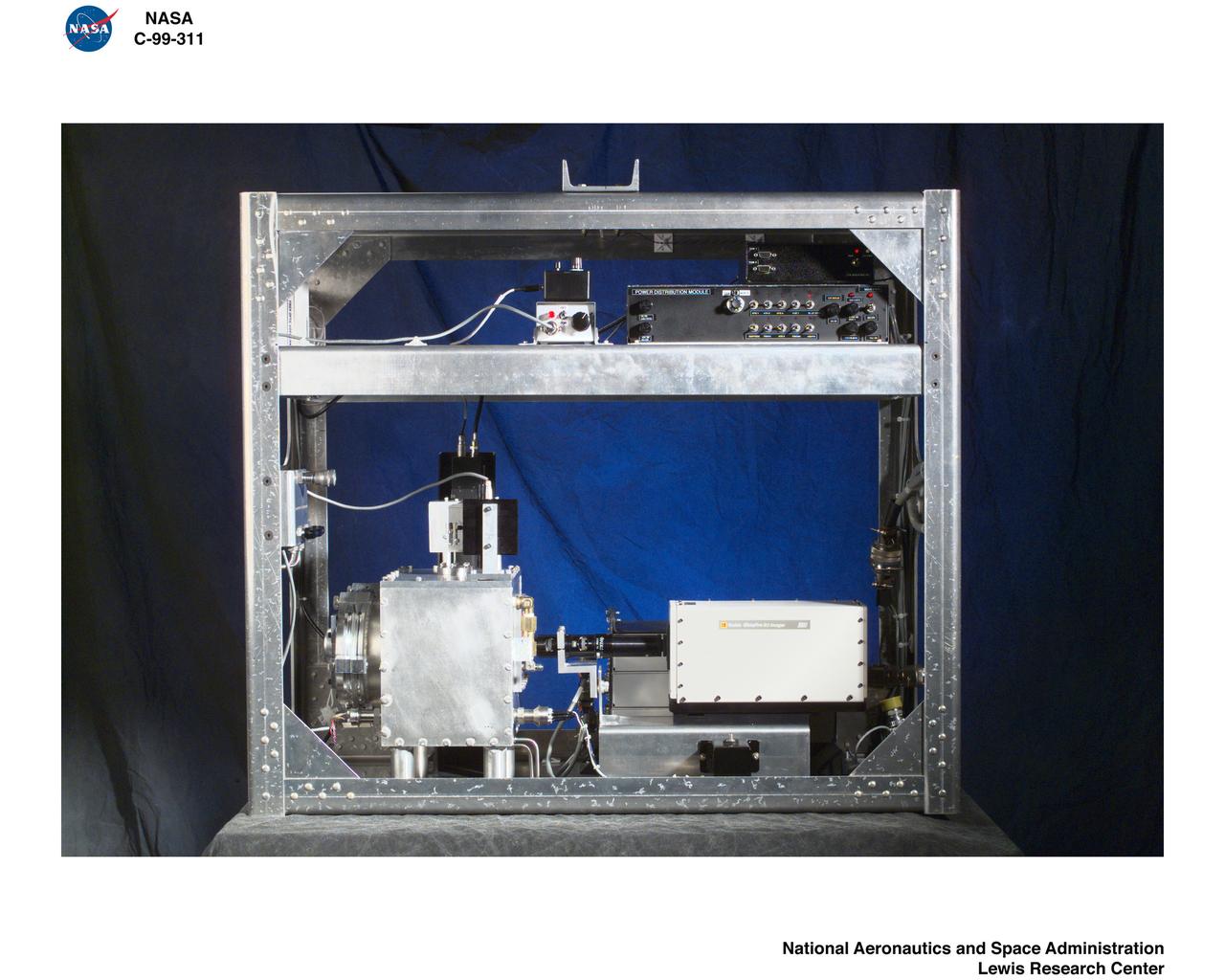
Droplet Imaging Flow Tunnel (D.R.I.F.T.)
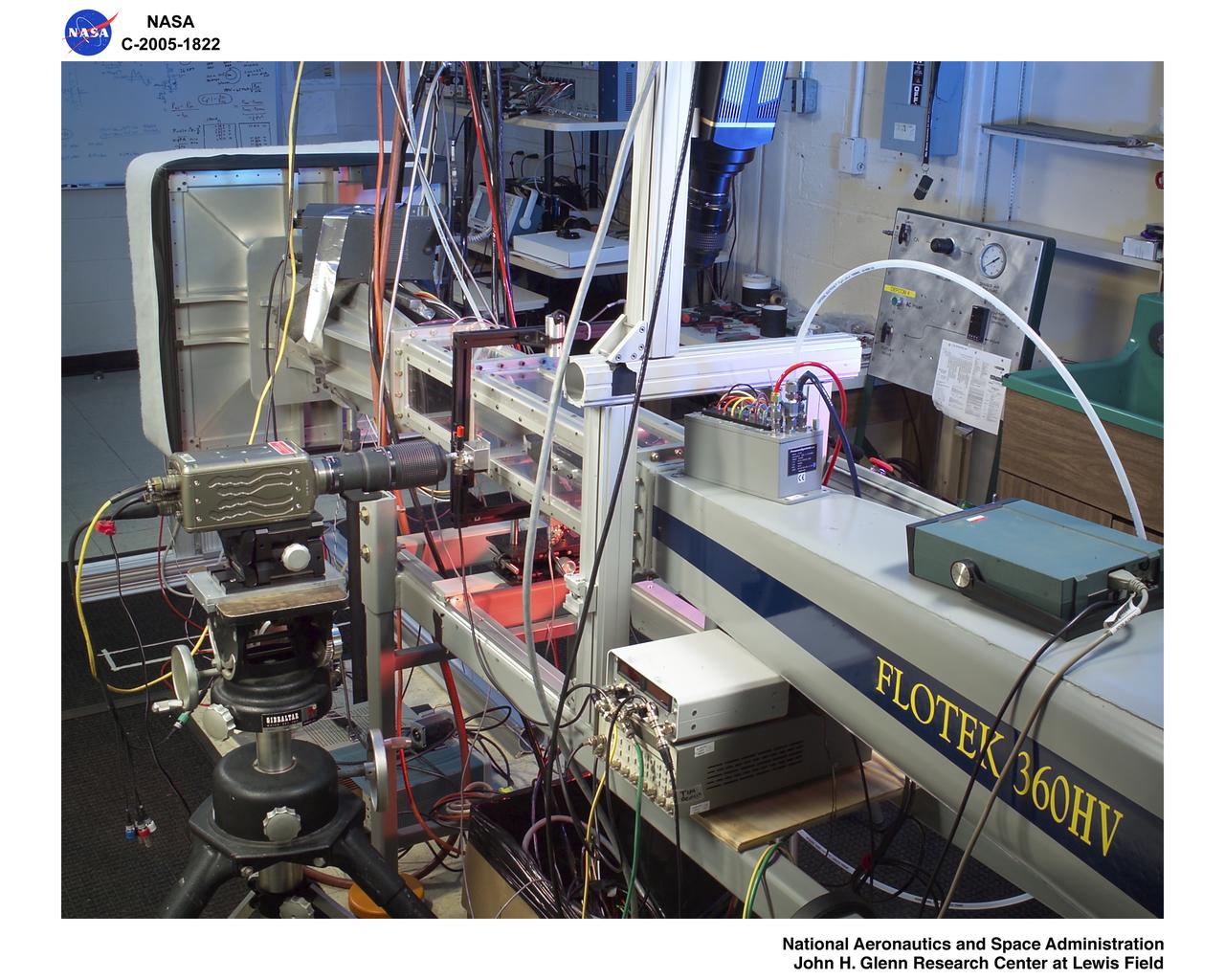
Droplet Imaging Flow Tunnel (D.R.I.F.T.)
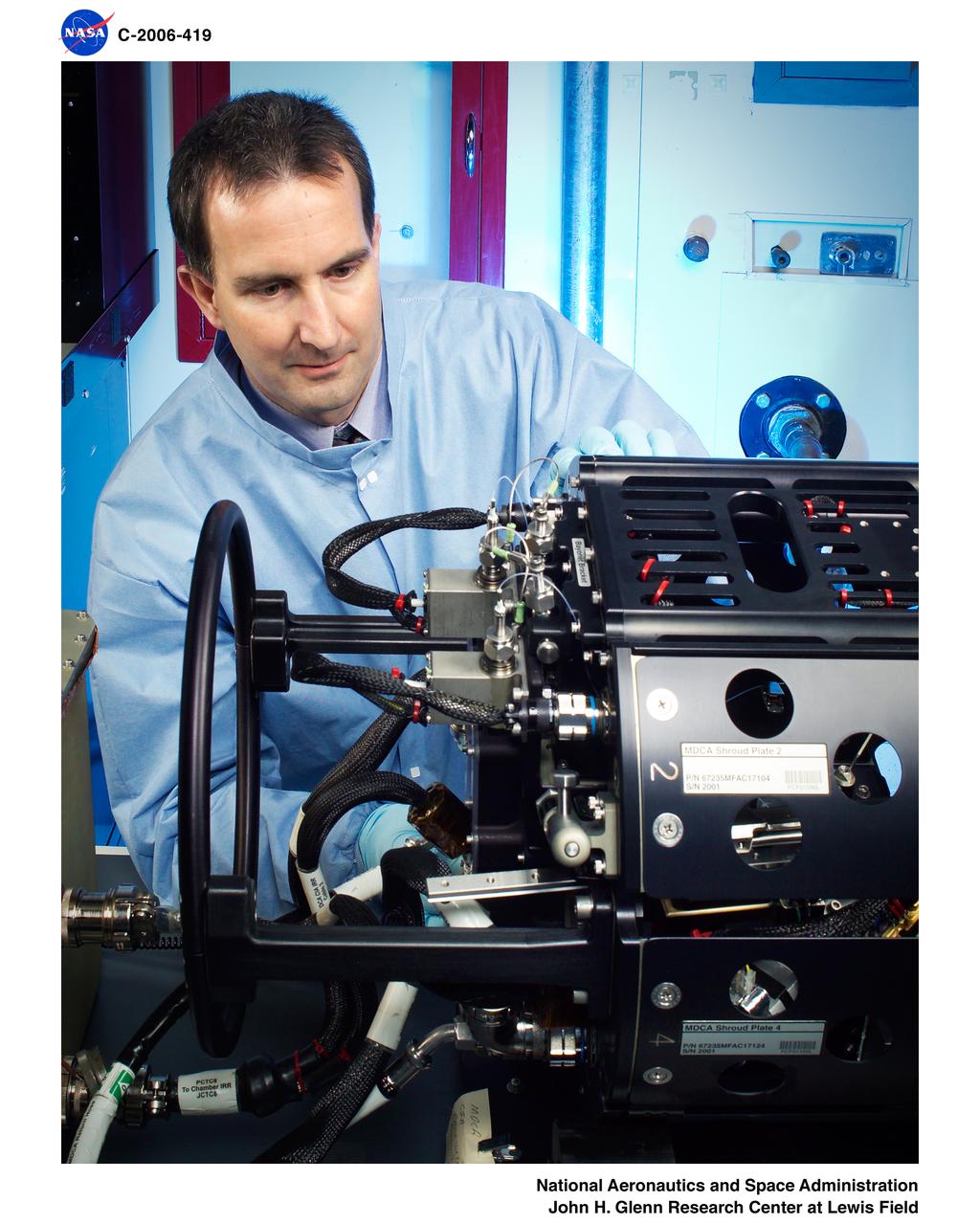

Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA)

MDCA - MULTI USER DROPLET COMBUSTION APPARATUS

INTERNAL FLOWS BI COMPONENT DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT
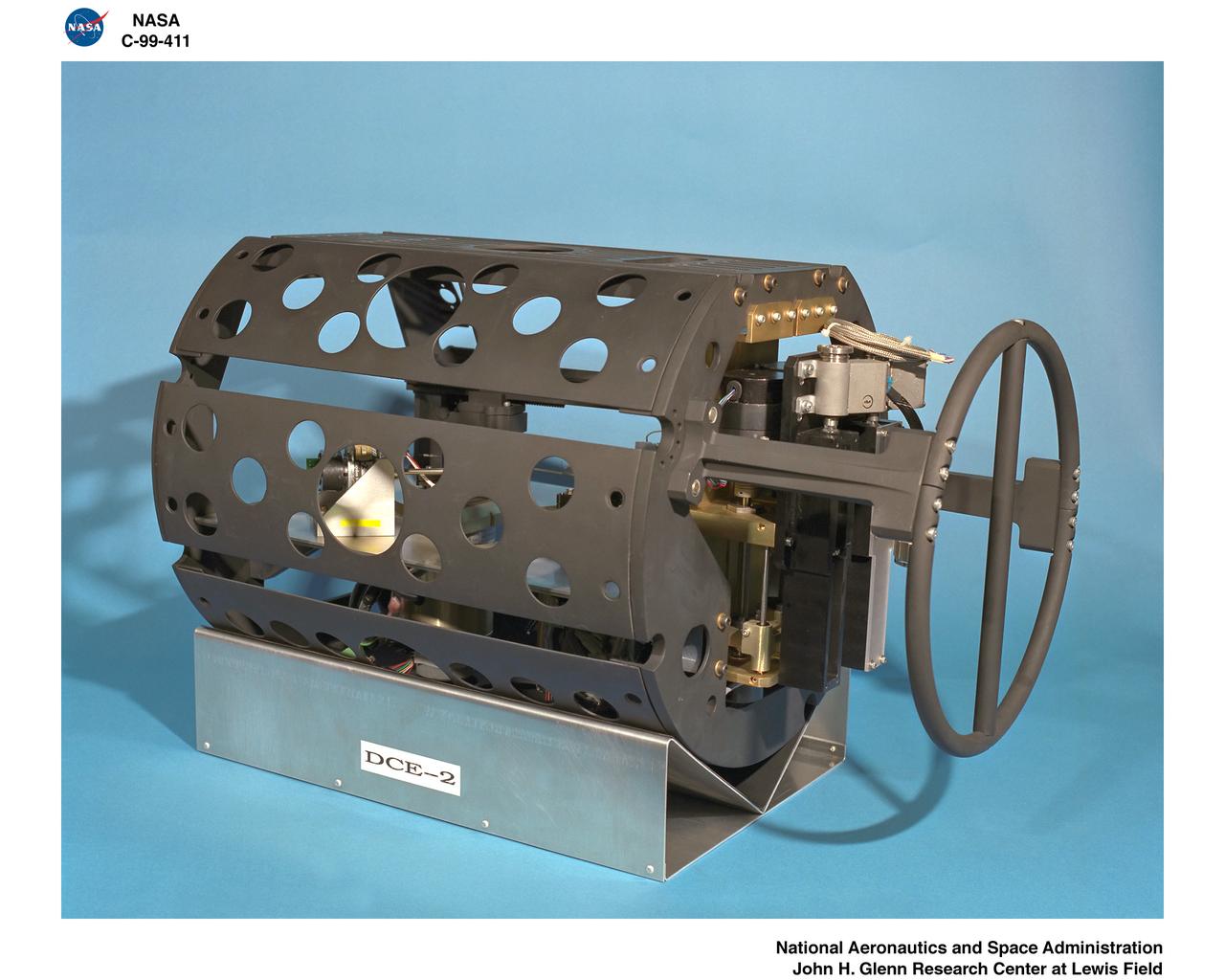
DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT II CHAMBER INSERT ASSEMBLY
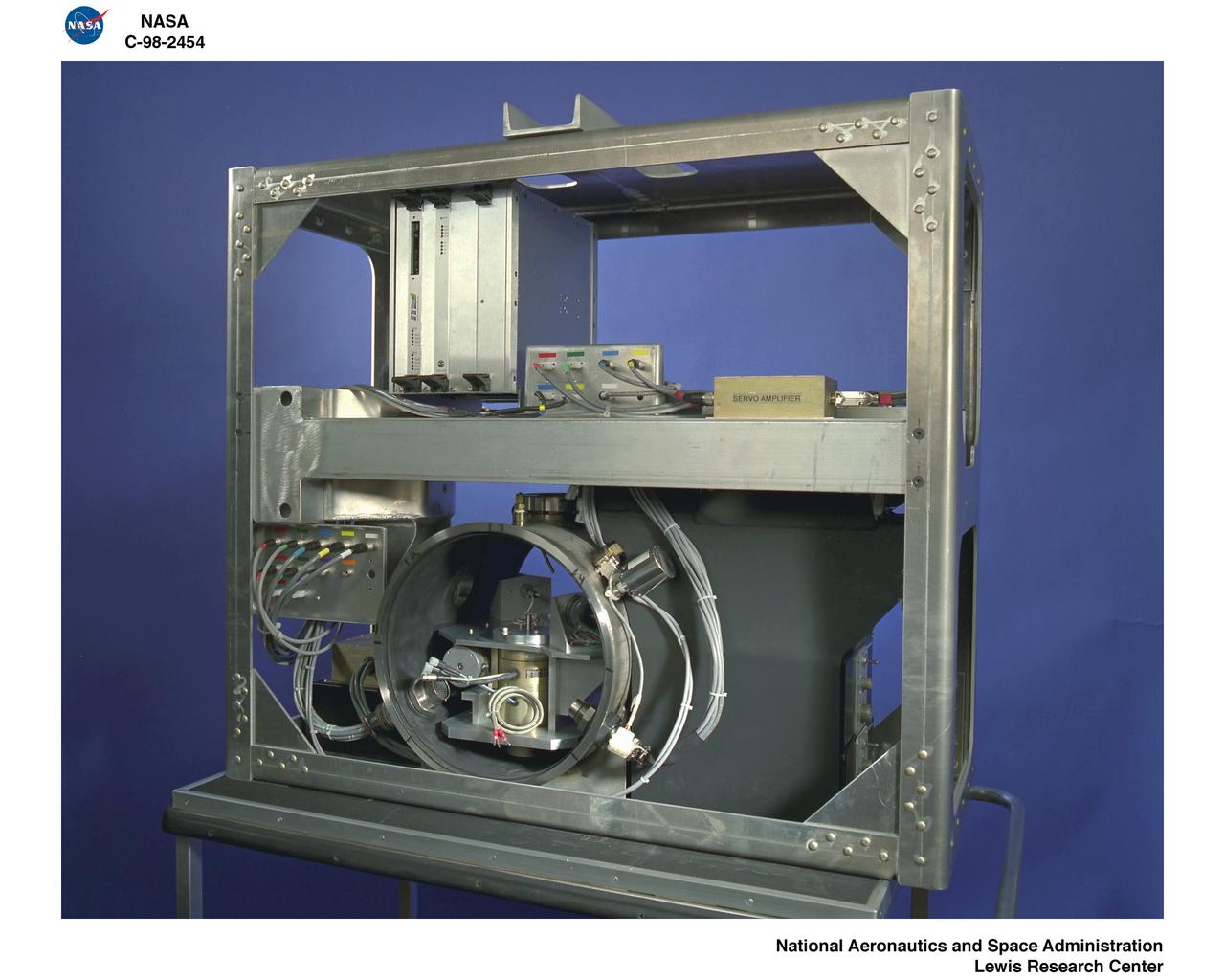
DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT DCE DROP RIG
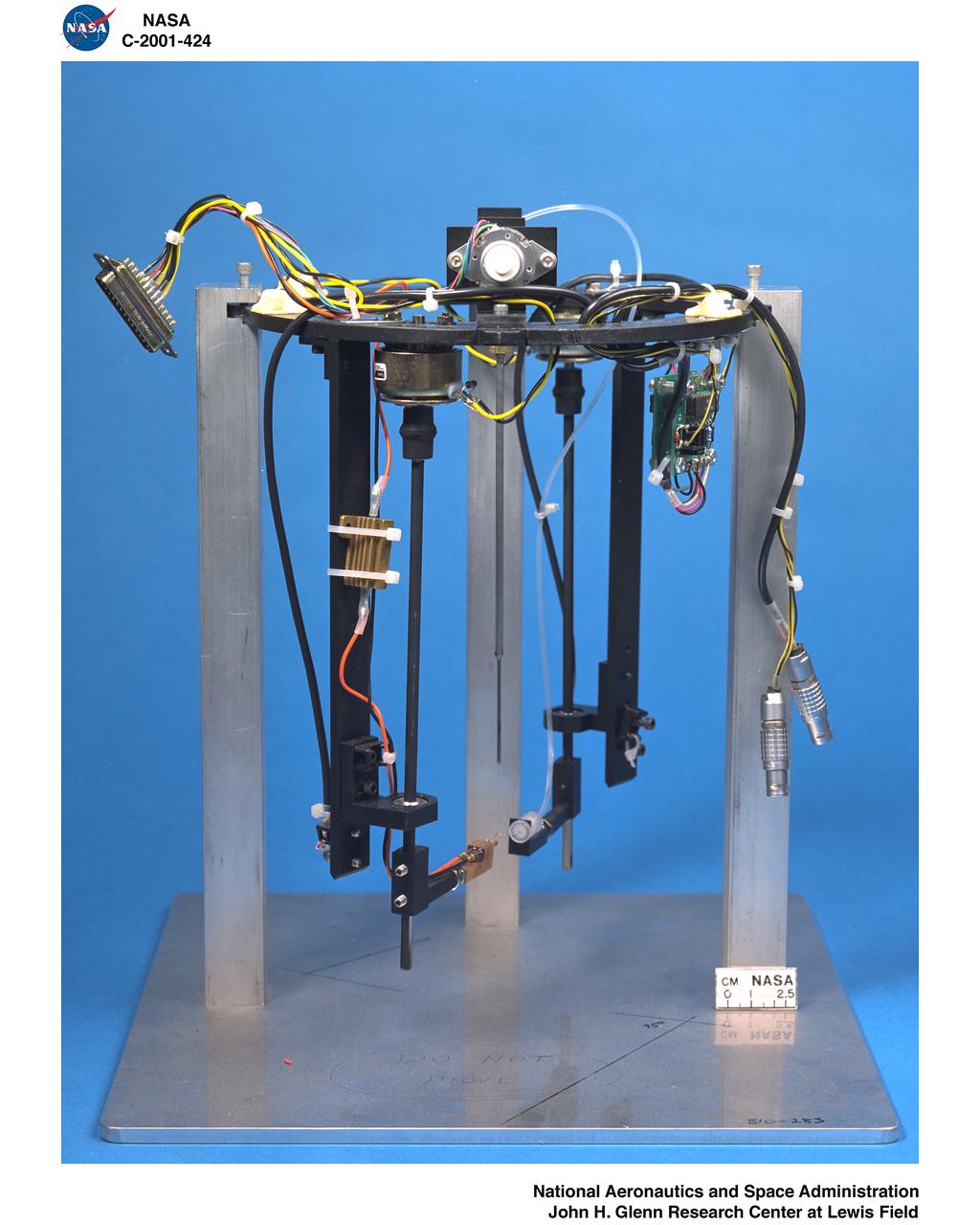
DYNAMICS OF DROPLET COMBUSTION AND EXTINCTION GROUND TEST HARDWARE
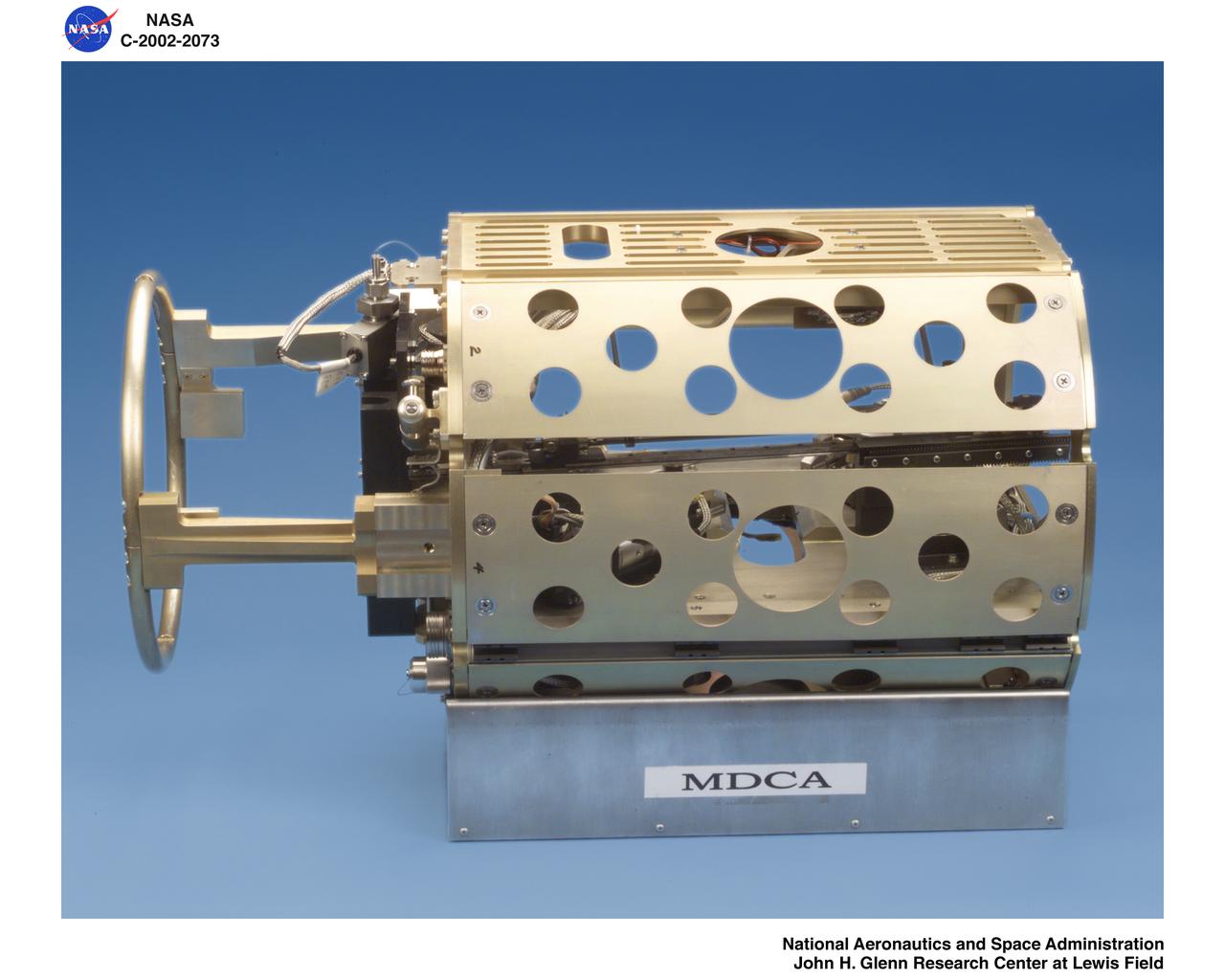

MDCA - MULTI USER DROPLET COMBUSTION APPARATUS
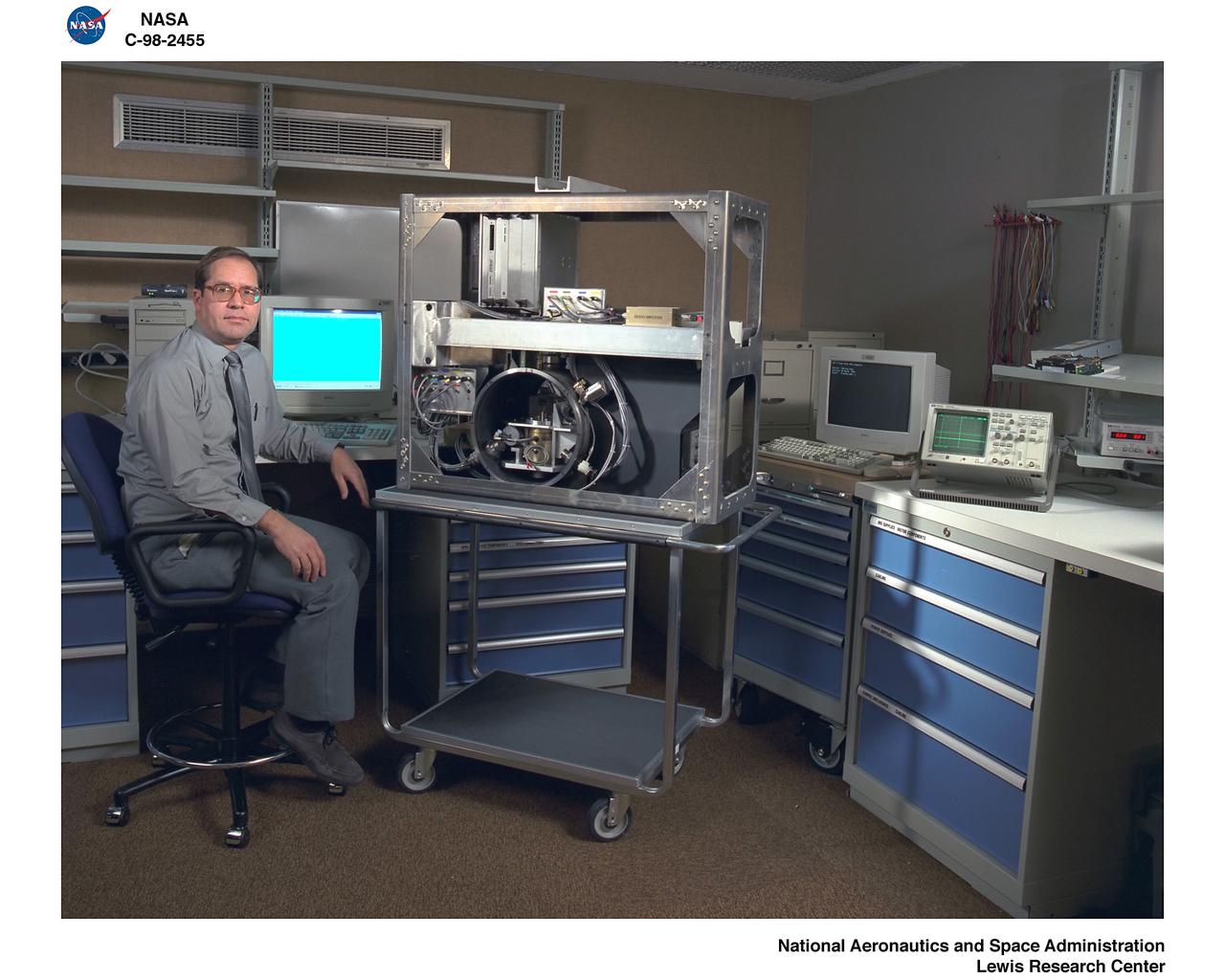

DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT DCE DROP RIG
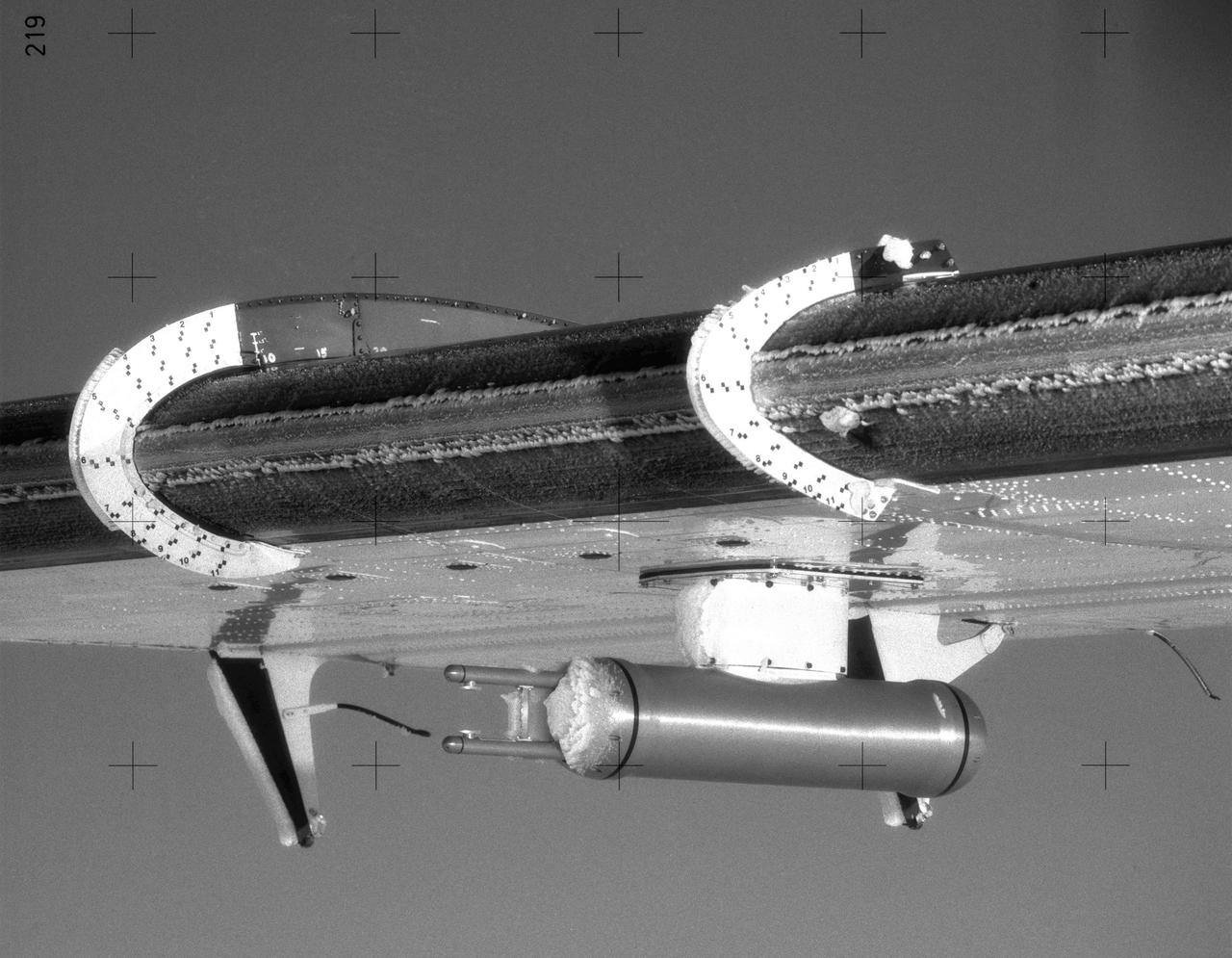
TWIN OTTER AIRPLANE SUPERCOOLED LARGE DROPLETS ICE ACCRETIONS
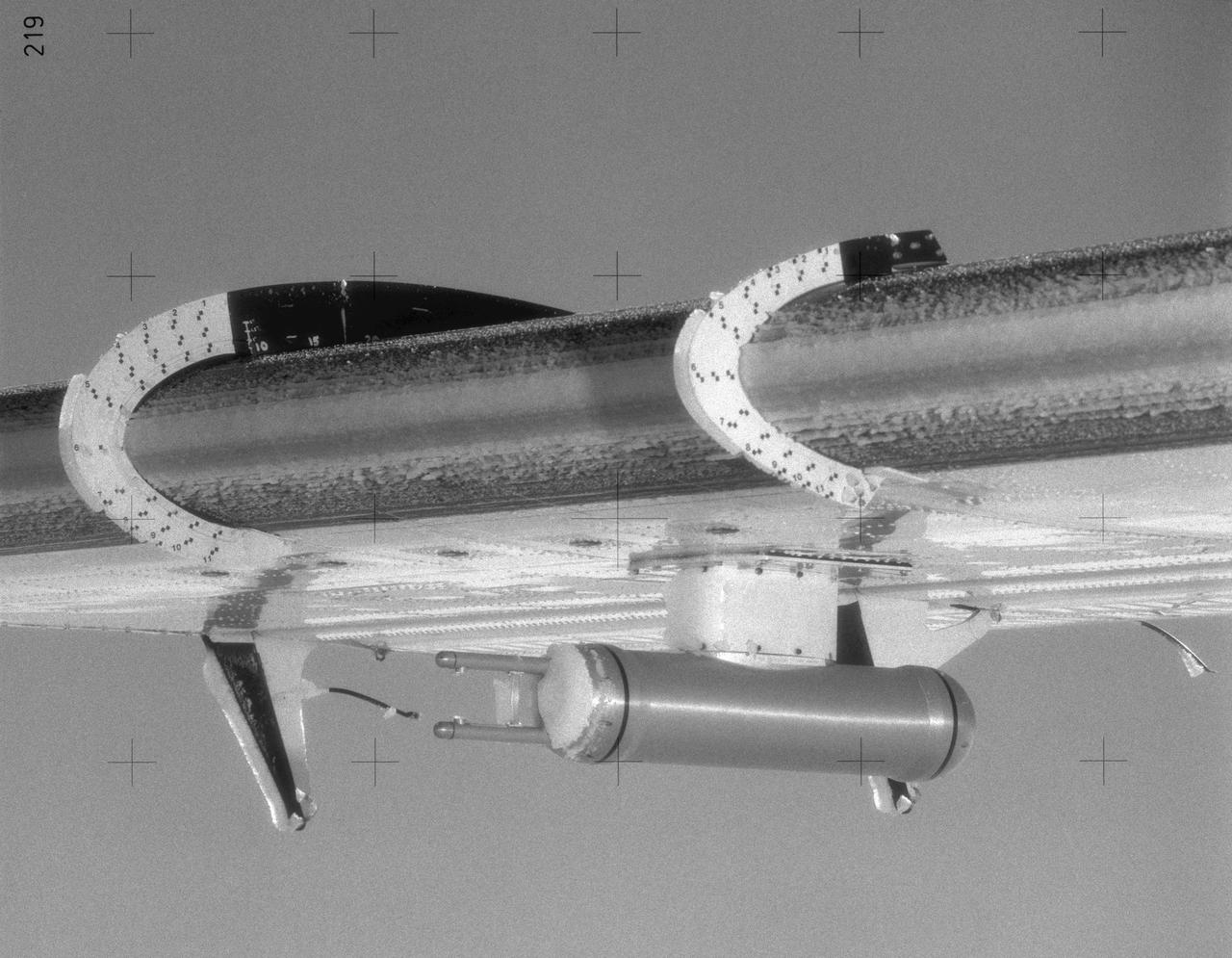
TWIN OTTER AIRPLANE SUPERCOOLED LARGE DROPLETS ICE ACCRETIONS
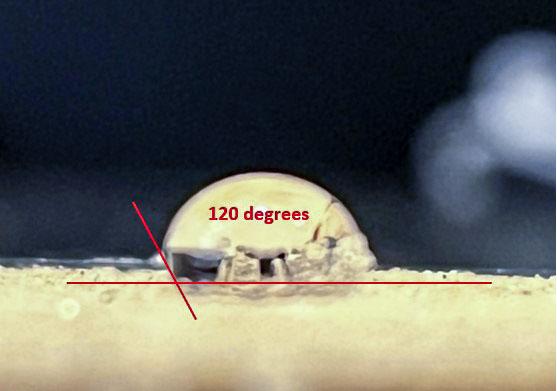
jsc2022e072961 (9/16/2022) --- Researchers drop a water droplet on the flat surface of hydrophobic fine sand. The water droplet has a contact angle of 120 degrees at the three-phase interface. The water droplet stands up and has a more rounded shape than a flattened shape compared to normal hydrophilic sand. Catastrophic Post-Wildfire Mudflows studies the formation and stability of this bubble-sand structure in microgravity. A better understanding of these phenomena could improve the understanding, modeling, and predicting of mudflows and support development of innovative solutions to prevent catastrophic post-fire events. Image courtesy of the UCSD Geo-Micromechanics Research Group.
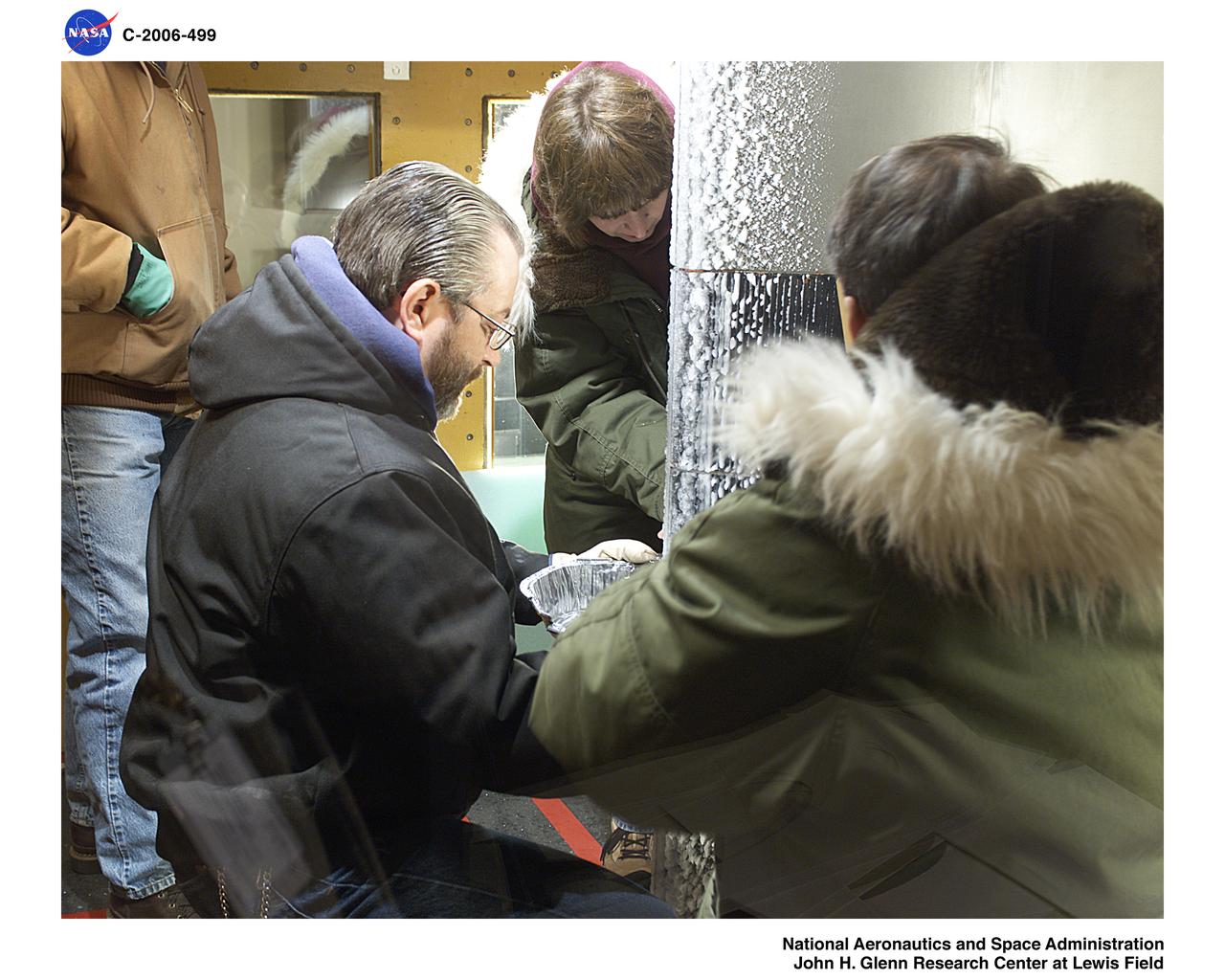

Super Large Droplet (SLD) icing test on a 36 foot cord Natural Laminar Flow wing shape
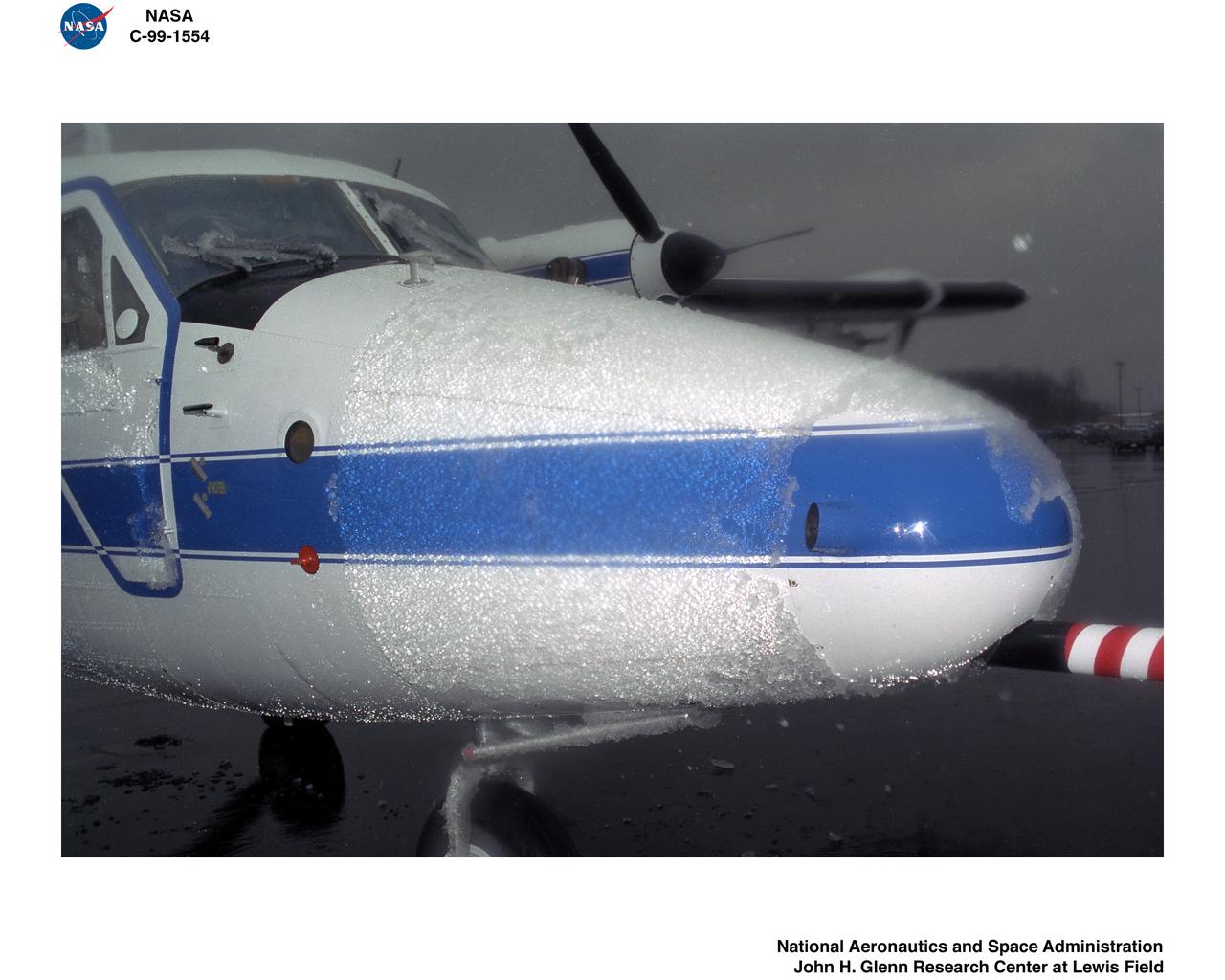

SLD - SUPER COOLED LARGE DROPLET ICING ON TWIN OTTER AIRPLANE 1 - 2 - 3
DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT DCE DROP RIG SUB COMPONENTS IGNITOR FUEL DISPENSER MOTOR 2 PC BOARDS
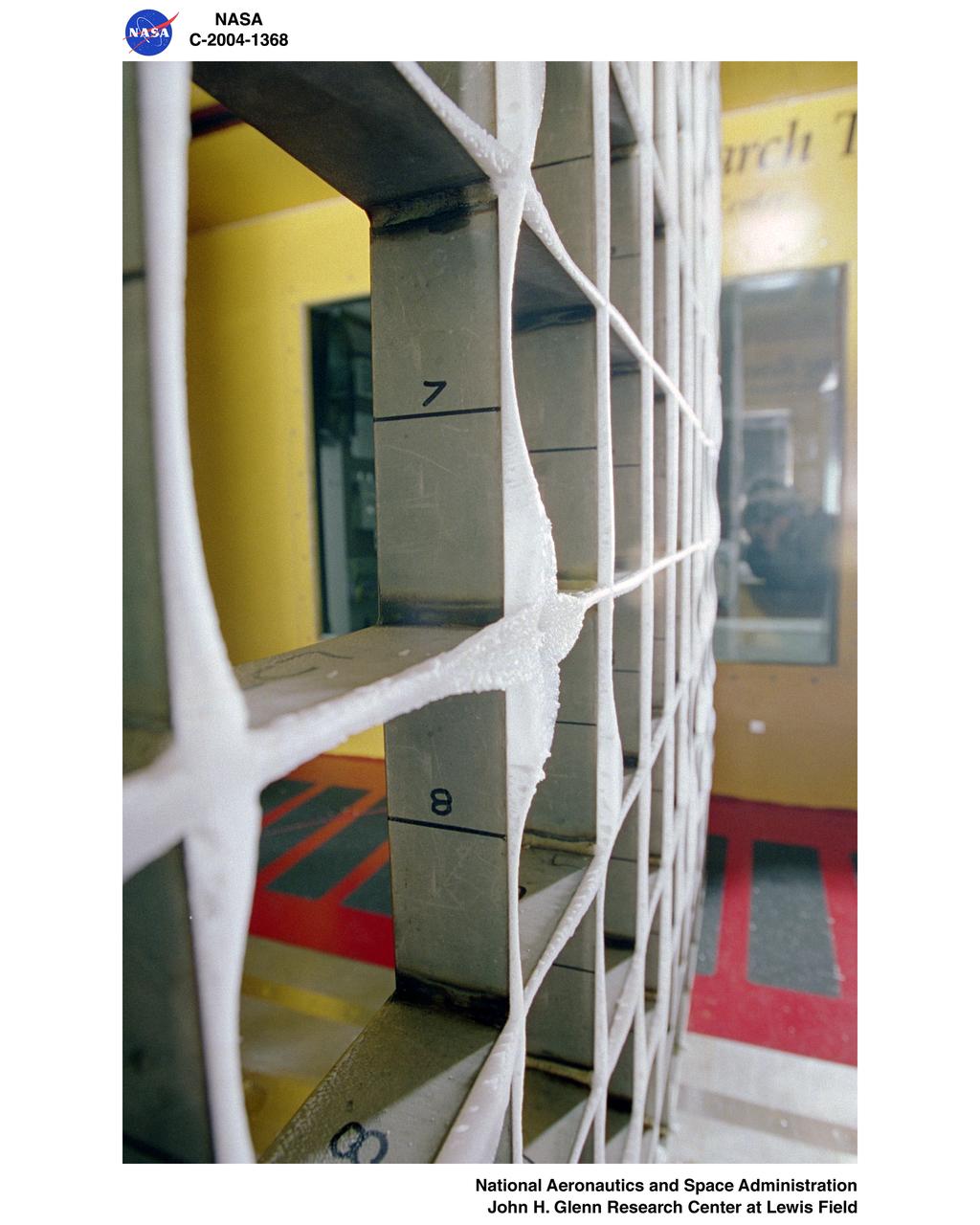

Icing Research Tunnel's icing grid with super-cooled large droplet (SLD) icing conditions
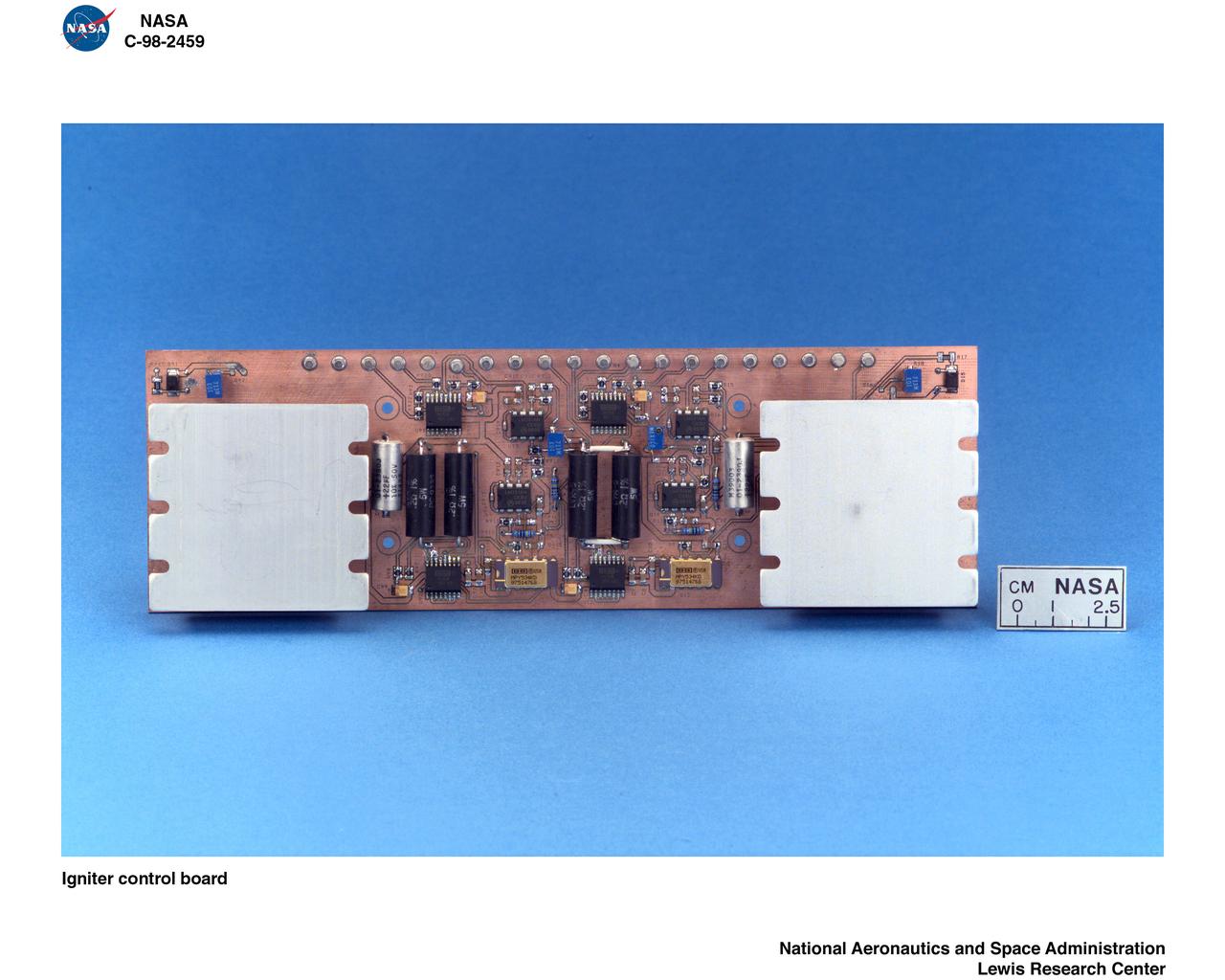
DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT DCE DROP RIG SUB COMPONENTS IGNITOR FUEL DISPENSER MOTOR 2 PC BOARDS
DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT DCE DROP RIG SUB COMPONENTS IGNITOR FUEL DISPENSER MOTOR 2 PC BOARDS

DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT DCE DROP RIG SUB COMPONENTS IGNITOR FUEL DISPENSER MOTOR 2 PC BOARDS

DROPLET COMBUSTION EXPERIMENT DCE DROP RIG SUB COMPONENTS IGNITOR FUEL DISPENSER MOTOR 2 PC BOARDS
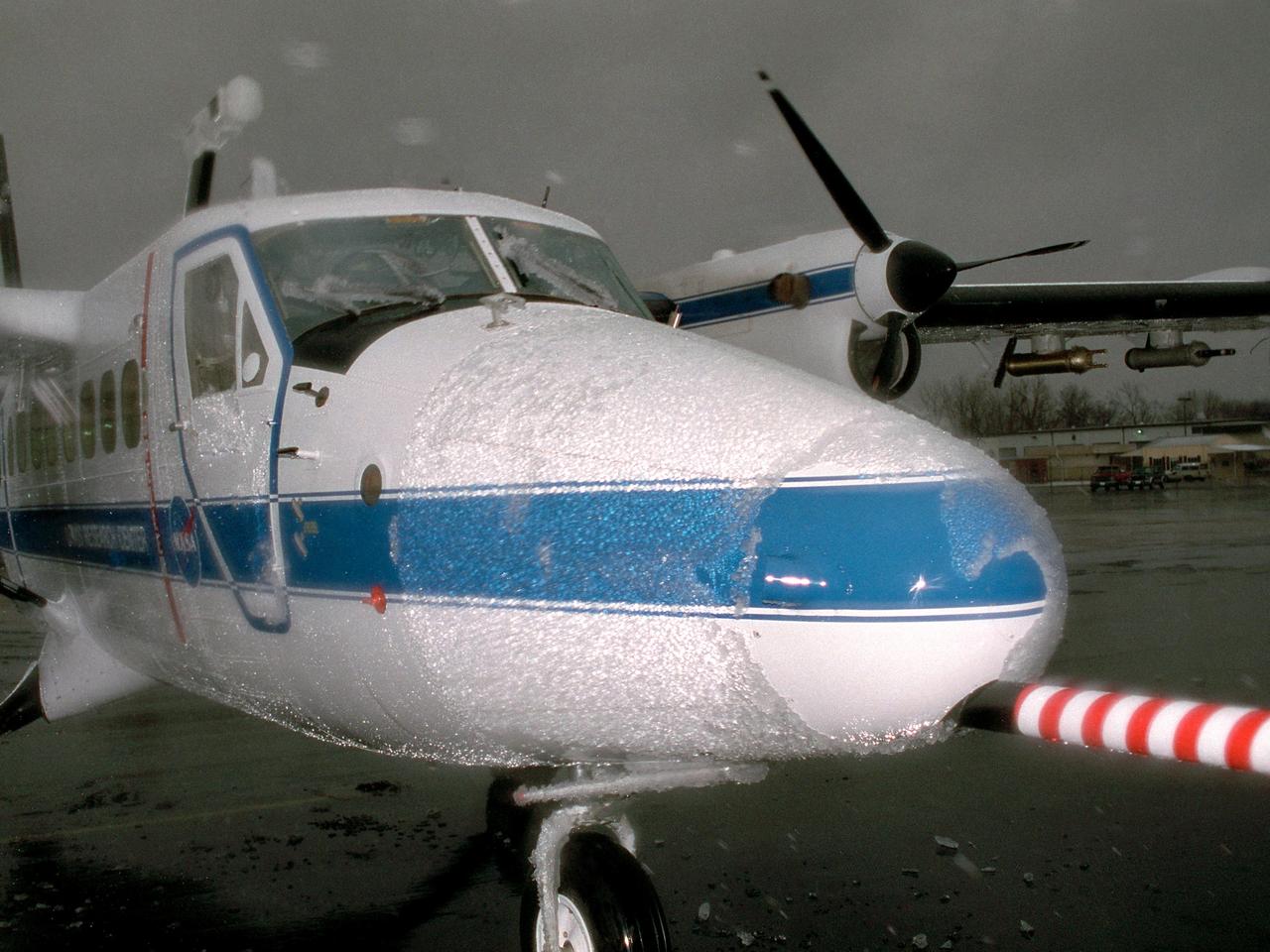

Supercooled Large Droplet (SLD) icing encounter in the Twin Otter icing research aircraft.
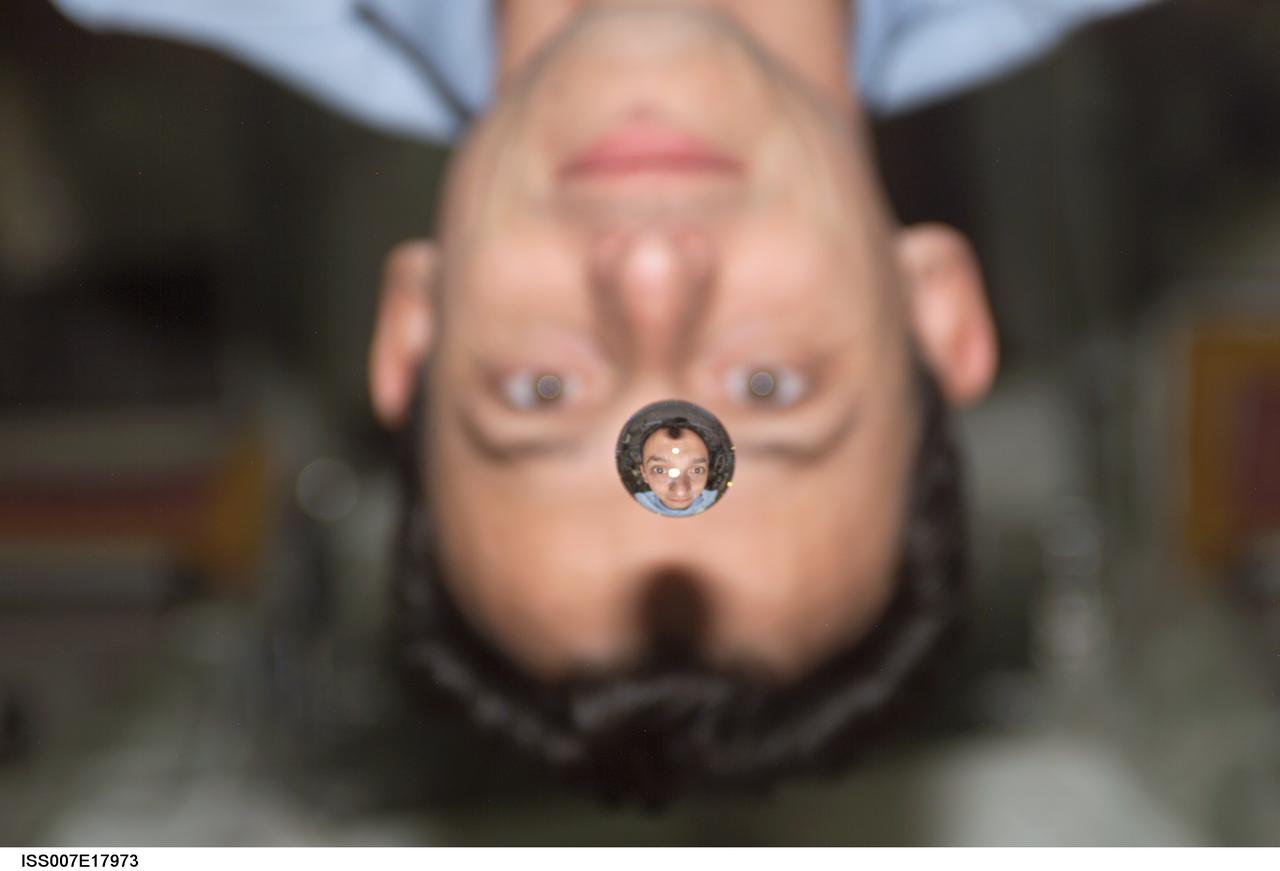

ISS007-E-17973 (25 October 2003) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Pedro Duque of Spain watches a water bubble float between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, on the International Space Station (ISS).
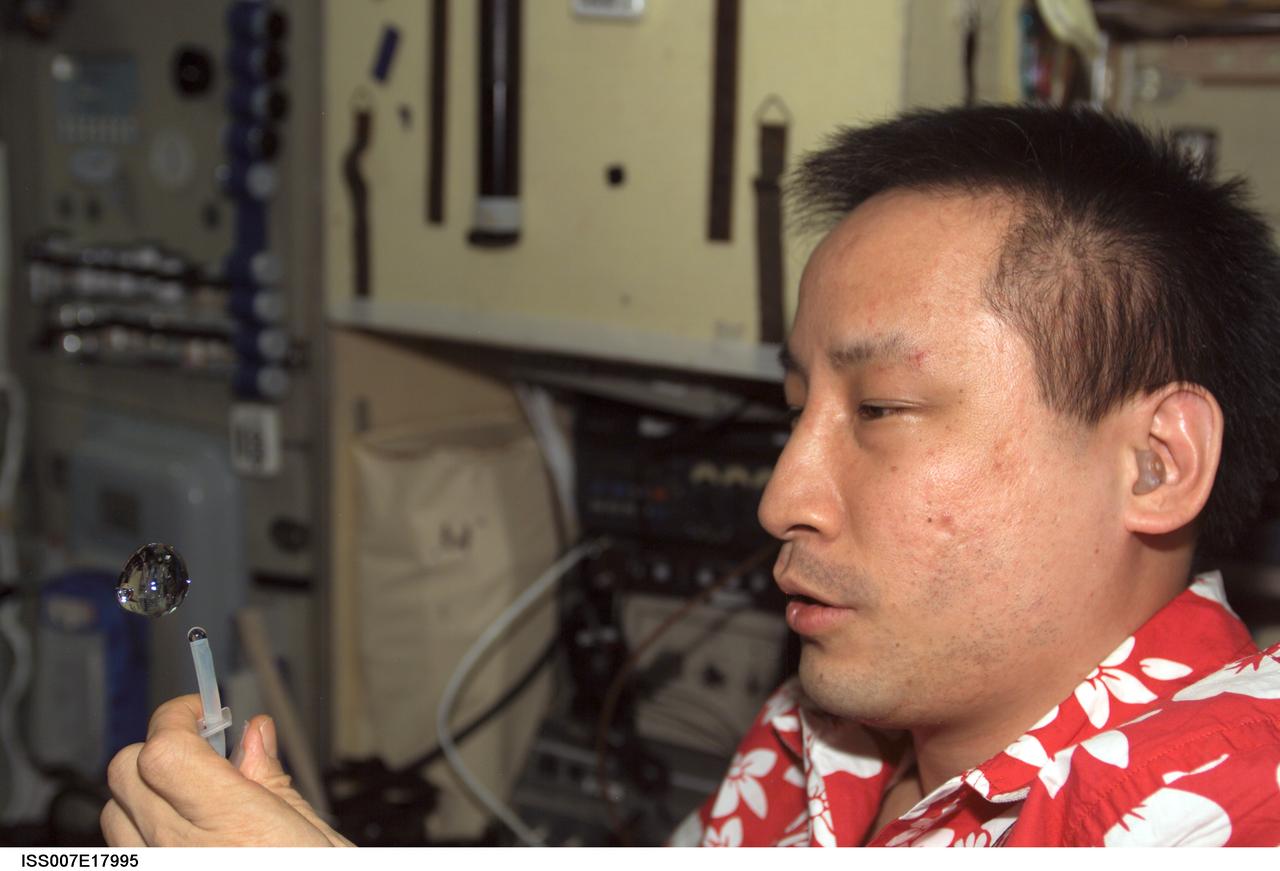
ISS007-E-17995 (25 October 2003) --- Astronaut Edward T. Lu, Expedition 7 NASA ISS science officer and flight engineer, squeezes a bubble out of a tube in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
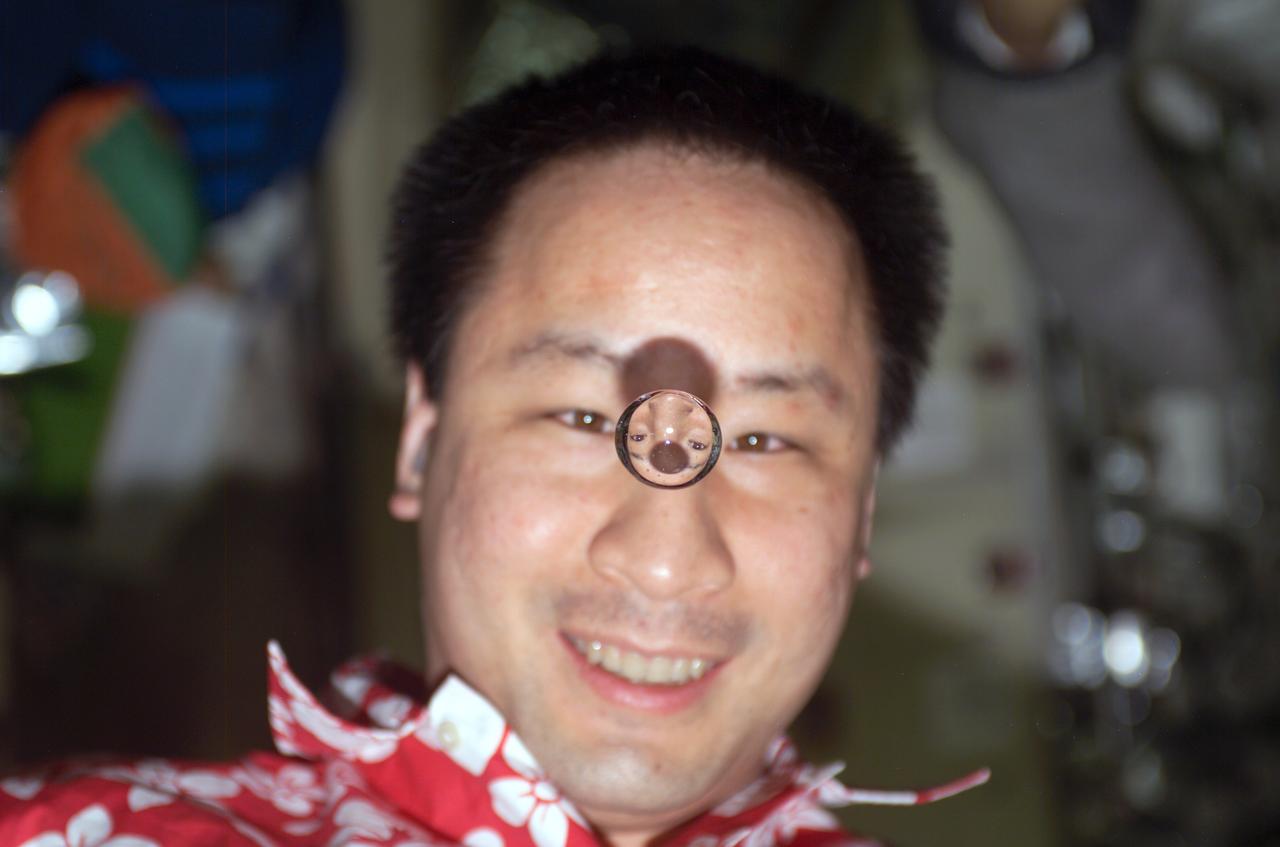

ISS007-E-17985 (2003) --- Astronaut Edward T. Lu, Expedition 7 NASA ISS science officer and flight engineer, watches a water bubble float between him and the camera, showing his image refracted, on the International Space Station (ISS).
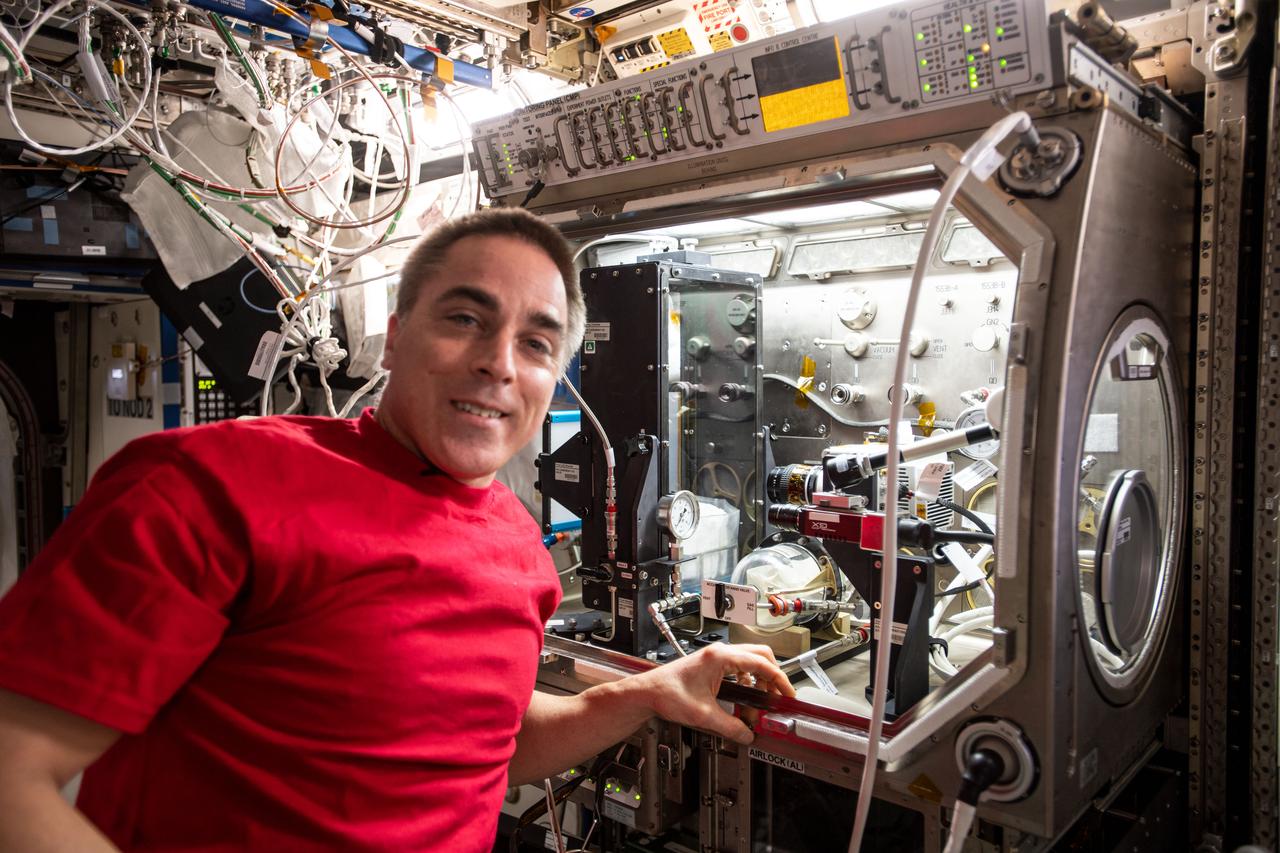

iss063e062021 (July 29, 2020) --- Expedition 63 Commander and NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy installs fluid research hardware inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox. Cassidy was working on the Droplet Formation Study that observes how microgravity shapes water droplets possibly improving water conservation and water pressure techniques on Earth.
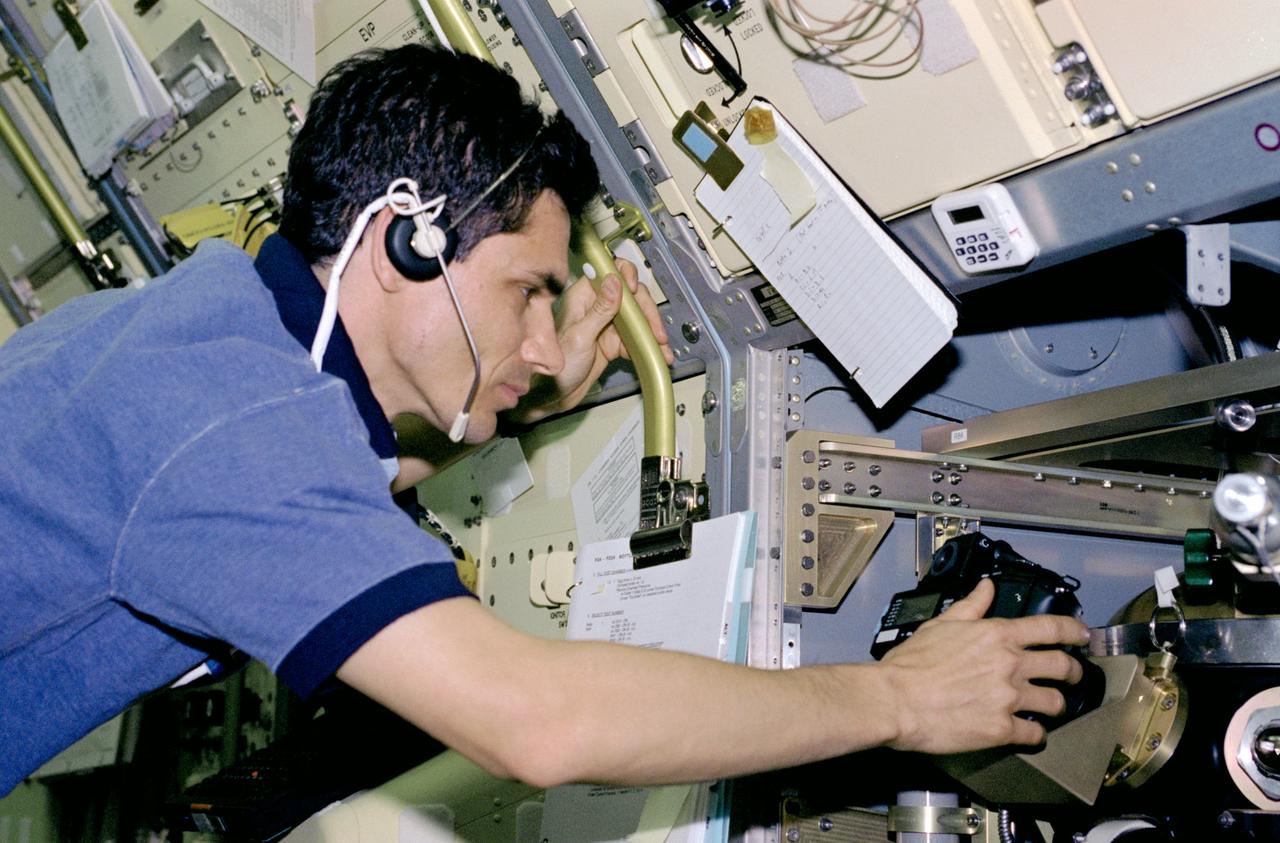

STS083-312-017 (4-8 April 1997) --- Payload specialist Gregory T. Linteris sets up a 35mm camera, one of three photographic/recording systems on the Drop Combustion Experiment (DCE) Apparatus. DCE is an enclosed chamber in which Helium-Oxygen fuel mixtures are injected and burned as single droplets. Combustion of fuel droplets is an important part of many operations, home heating, power production by gas turbines and combustion of gasoline in an automobile engine.
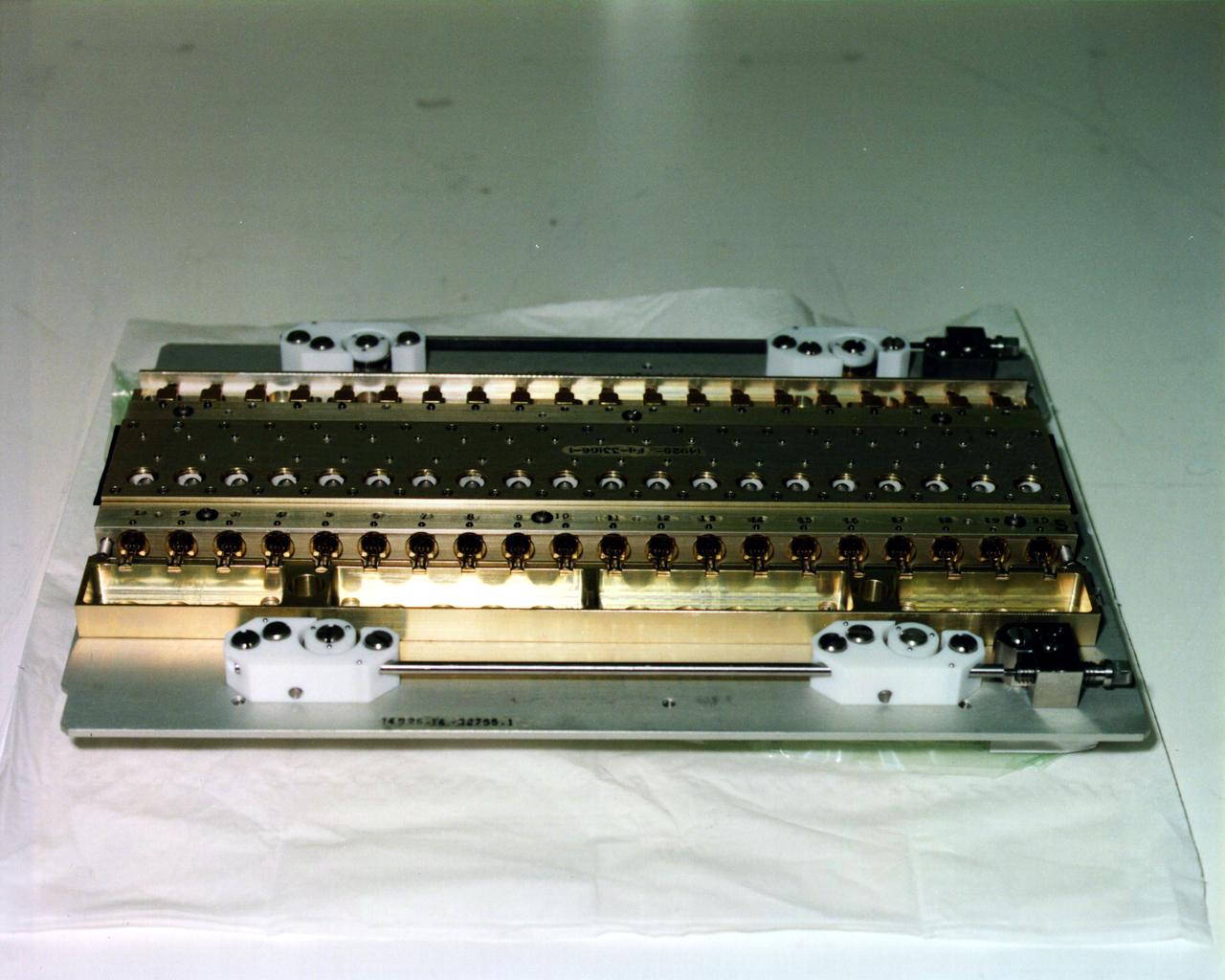
These Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA) trays were first flown in the Thermal Enclosure System (TES) during the USMP-2 (STS-62) mission. Each tray can hold 20 protein crystal growth chambers. Each chamber contains a double-barrel syringe; one barrel holds protein crystal solution and the other holds precipitant agent solution. During the microgravity mission, a torque device is used to simultaneously retract the plugs in all 20 syringes. The two solutions in each chamber are then mixed. After mixing, droplets of the combined solutions are moved onto the syringe tips so vapor diffusion can begin. During the length of the mission, protein crystals are grown in the droplets. Shortly before the Shuttle's return to Earth, the experiment is deactivated by retracting the droplets containing protein crystals, back into the syringes.
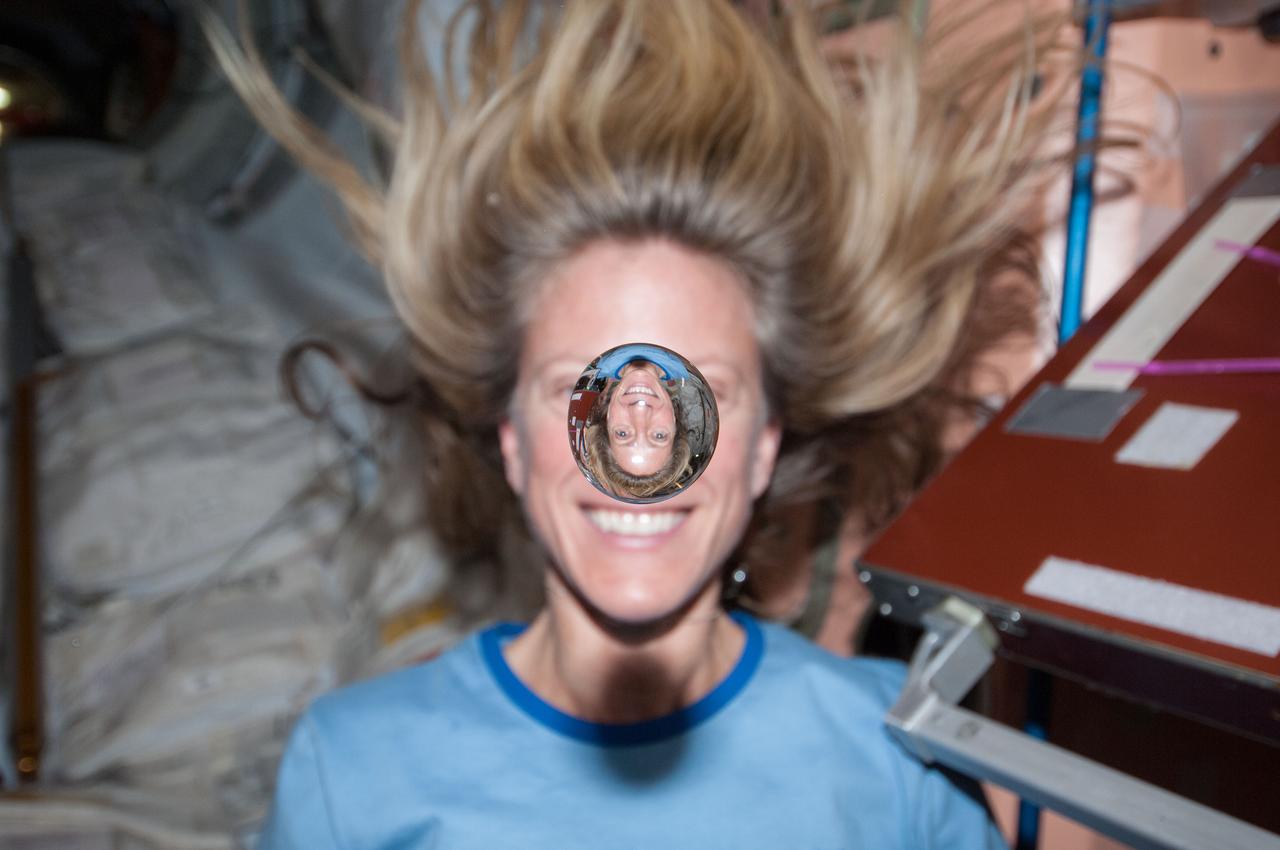

NASA astronaut Karen Nyberger, Expedition 36 flight engineer, watches a water bubble float freely between her and the camera, showing her image refracted in the droplet, while in the Node 1Unity module of the International Space Station.
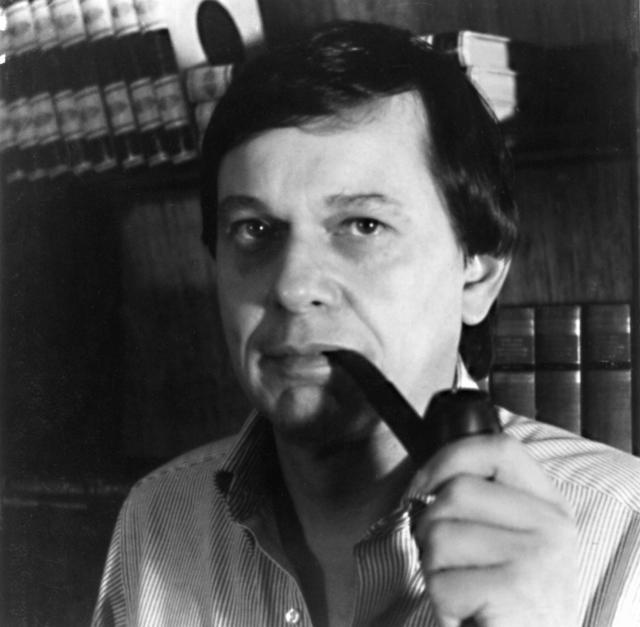

Dr. Forman Williams of the University of California, San Diego. He is principal investigator for Droplet Combustion Experiment (DCE/DCE-2) and High Pressure Combustion of Binary Fuel Sprays experiment.
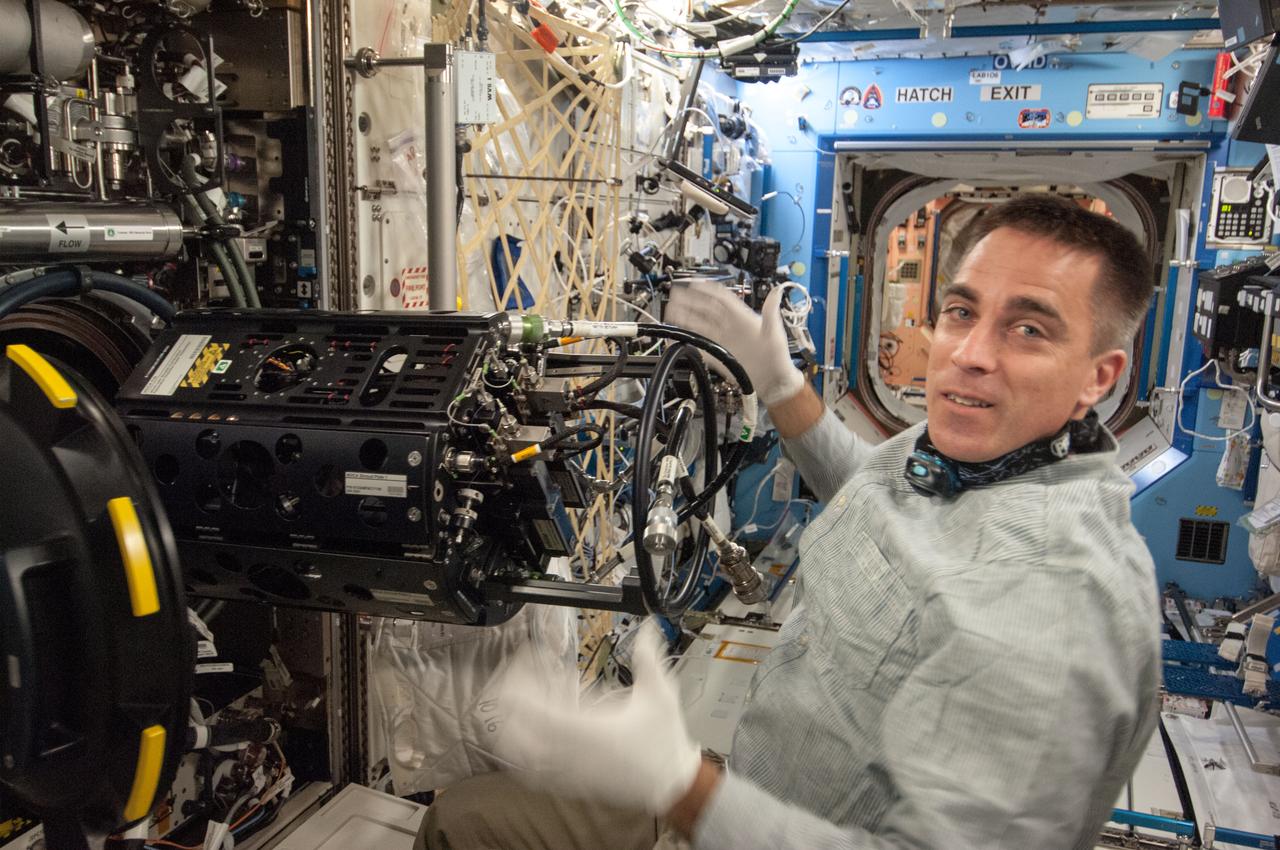

ISS035-E-017699 (10 April 2013) --- This is one of several photos documenting the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Fuel Reservoir replacement. Here, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy removes and replaces one of the Fuel Reservoirs with the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) pulled partially out of the Combustion Chamber. The MDCA Fuel Reservoirs contain the liquid fuel used during droplet combustion experiments. This reservoir change-out was in support of the FLame EXtinguishment (FLEX)-2 experiment, scheduled to be executed by ground controllers.
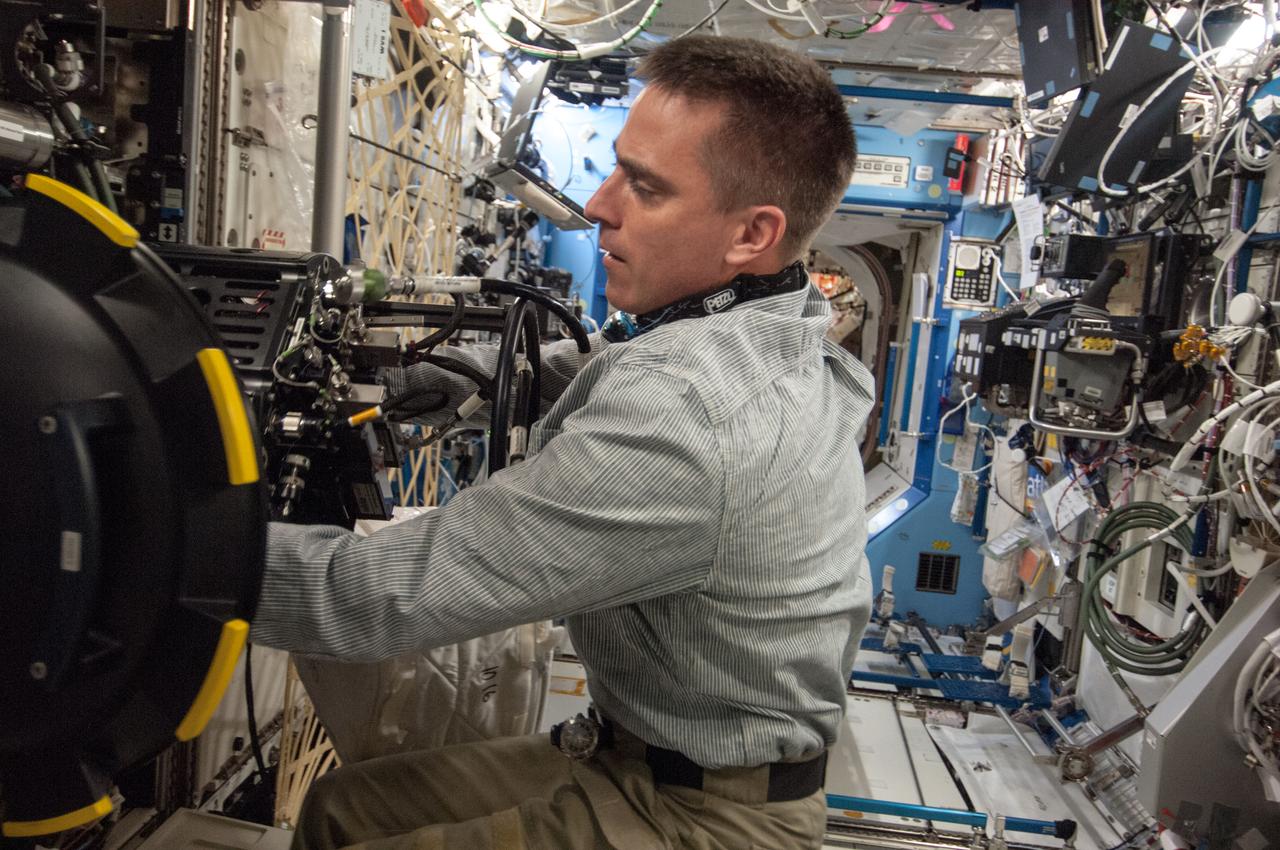

ISS035-E-017699 (10 April 2013) --- This is one of several photos documenting the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Fuel Reservoir replacement. Here, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy removes and replaces one of the Fuel Reservoirs with the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) pulled partially out of the Combustion Chamber. The MDCA Fuel Reservoirs contain the liquid fuel used during droplet combustion experiments. This reservoir change-out was in support of the FLame EXtinguishment (FLEX)-2 experiment, scheduled to be executed by ground controllers.

ISS035-E-017699 (10 April 2013) --- This is one of several photos documenting the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Fuel Reservoir replacement. Here, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy removes and replaces one of the Fuel Reservoirs with the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) pulled partially out of the Combustion Chamber. The MDCA Fuel Reservoirs contain the liquid fuel used during droplet combustion experiments. This reservoir change-out was in support of the FLame EXtinguishment (FLEX)-2 experiment, scheduled to be executed by ground controllers.

ISS035-E-017699 (10 April 2013) --- This is one of several photos documenting the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Fuel Reservoir replacement. Here, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy removes and replaces one of the Fuel Reservoirs with the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) pulled partially out of the Combustion Chamber. The MDCA Fuel Reservoirs contain the liquid fuel used during droplet combustion experiments. This reservoir change-out was in support of the FLame EXtinguishment (FLEX)-2 experiment, scheduled to be executed by ground controllers.

ISS035-E-017699 (10 April 2013) --- This is one of several photos documenting the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Fuel Reservoir replacement. Here, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy removes and replaces one of the Fuel Reservoirs with the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) pulled partially out of the Combustion Chamber. The MDCA Fuel Reservoirs contain the liquid fuel used during droplet combustion experiments. This reservoir change-out was in support of the FLame EXtinguishment (FLEX)-2 experiment, scheduled to be executed by ground controllers.
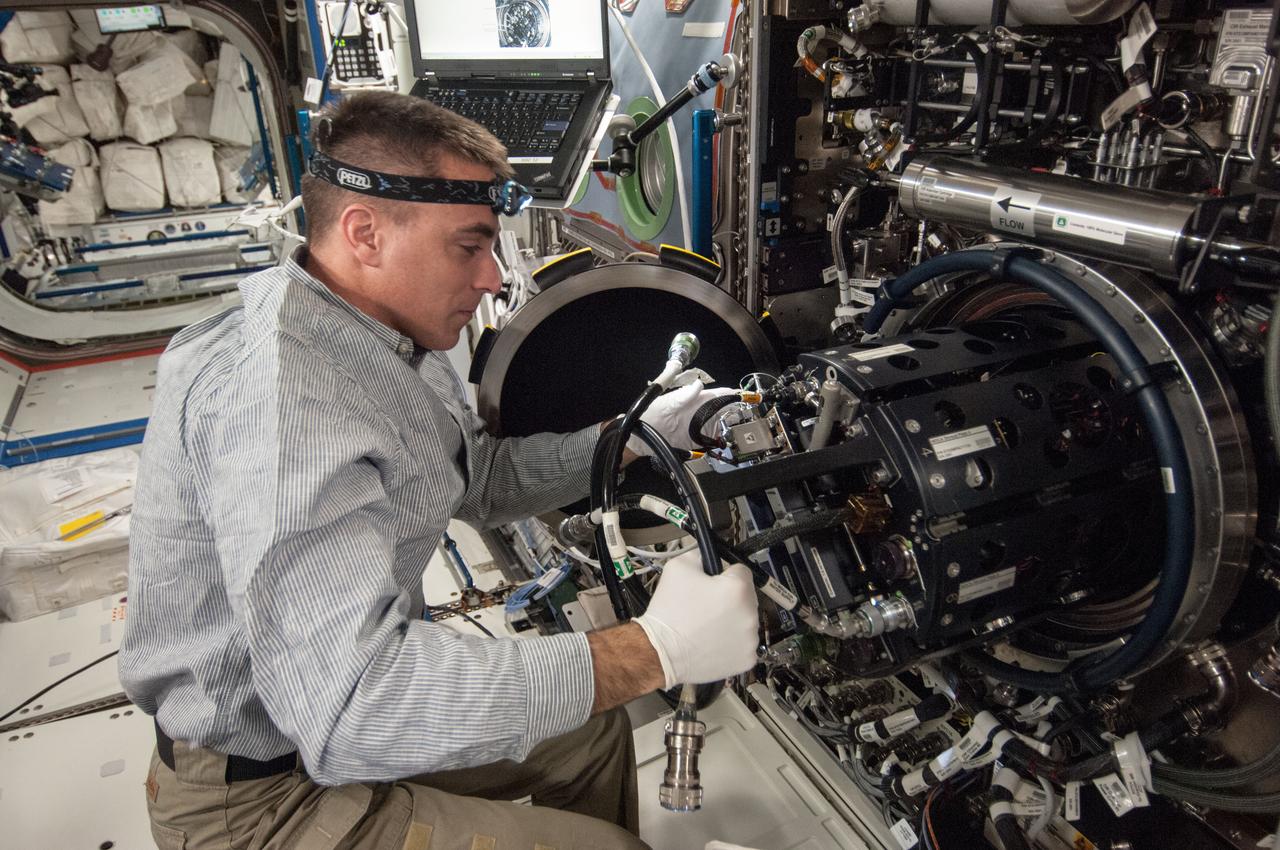

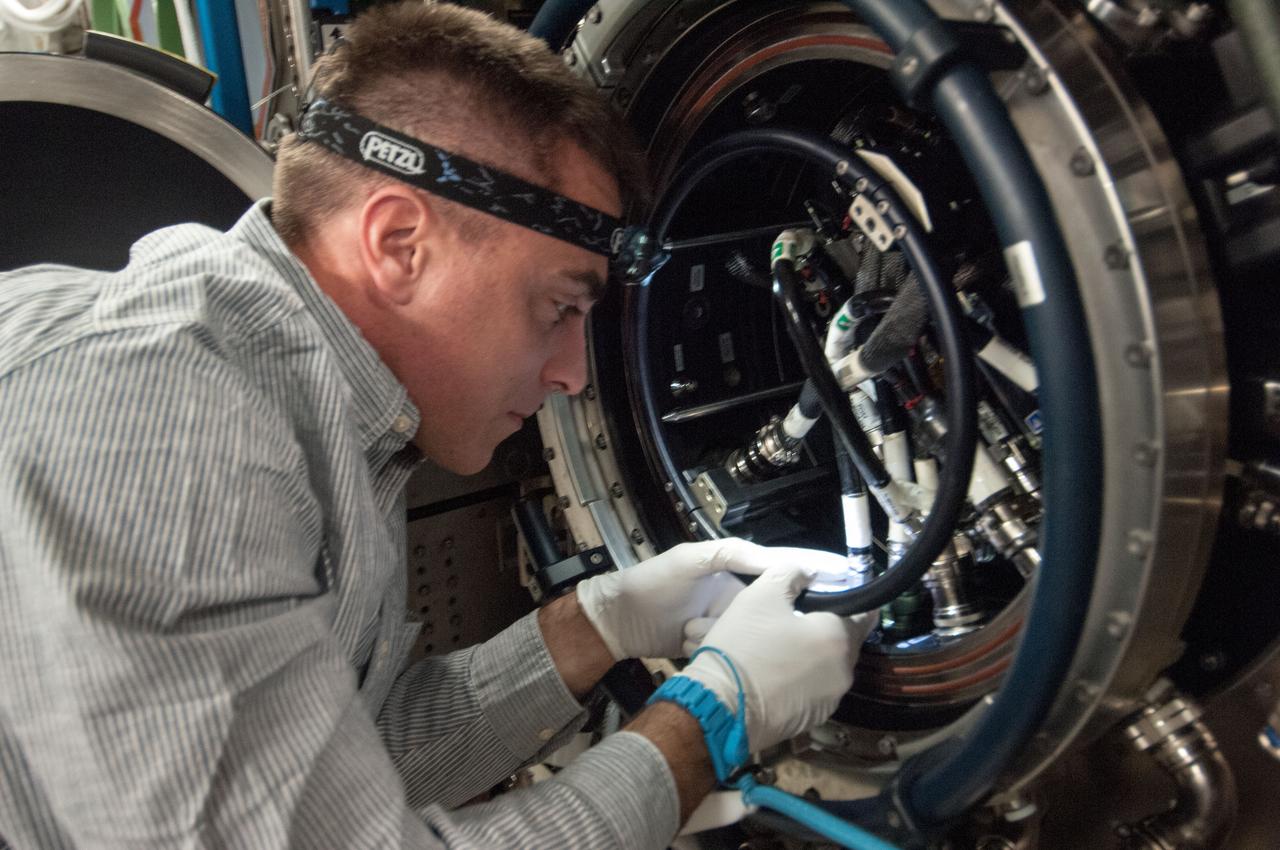
ISS035-E-017712 (10 April 2013)?-- This is one of several photos documenting the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Fuel Reservoir replacement in the U.S. lab Destiny. Here, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy removes and replaces one of the Fuel Reservoirs with the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) pulled partially out of the Combustion Chamber. The MDCA Fuel Reservoirs contain the liquid fuel used during droplet combustion experiments. This reservoir change-out was in support of the FLame EXtinguishment (FLEX)-2 experiment, scheduled to be executed by ground controllers.
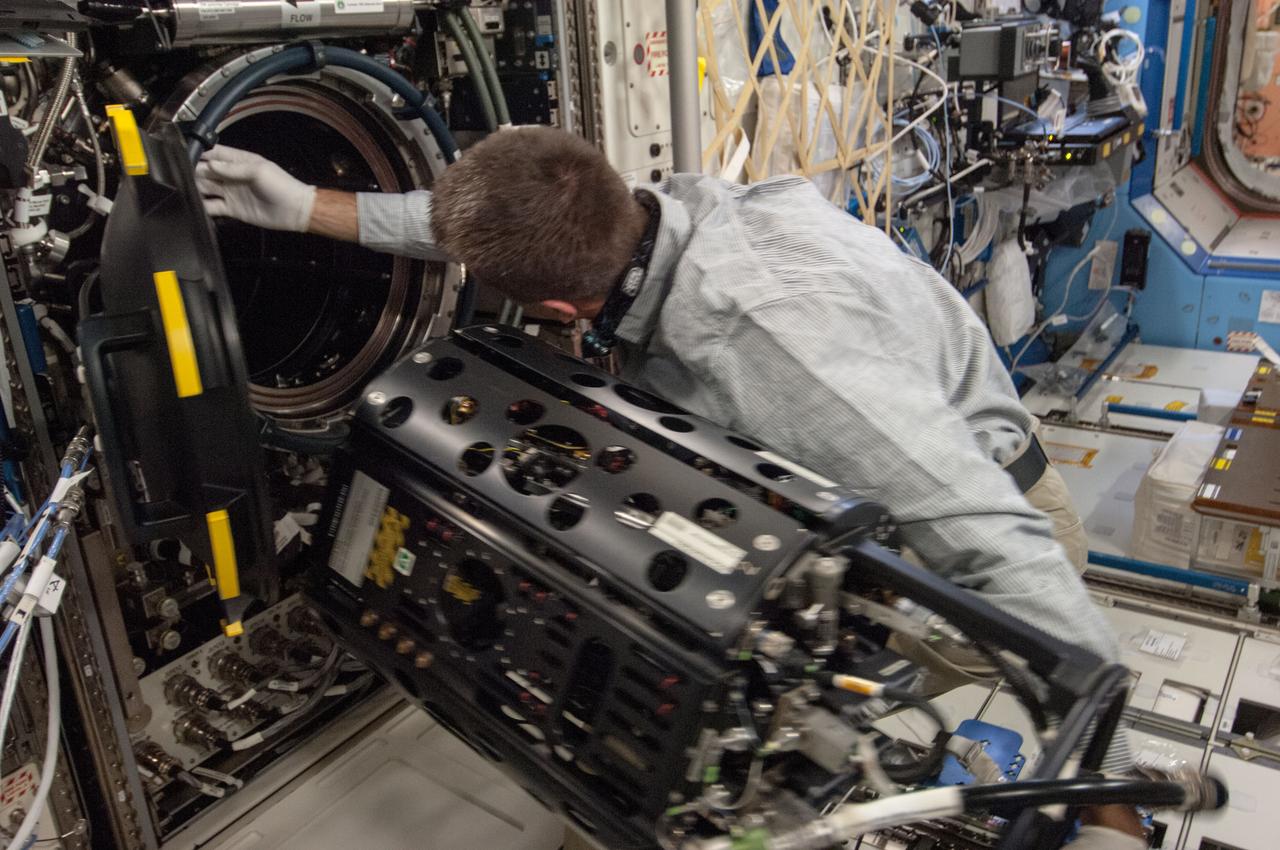
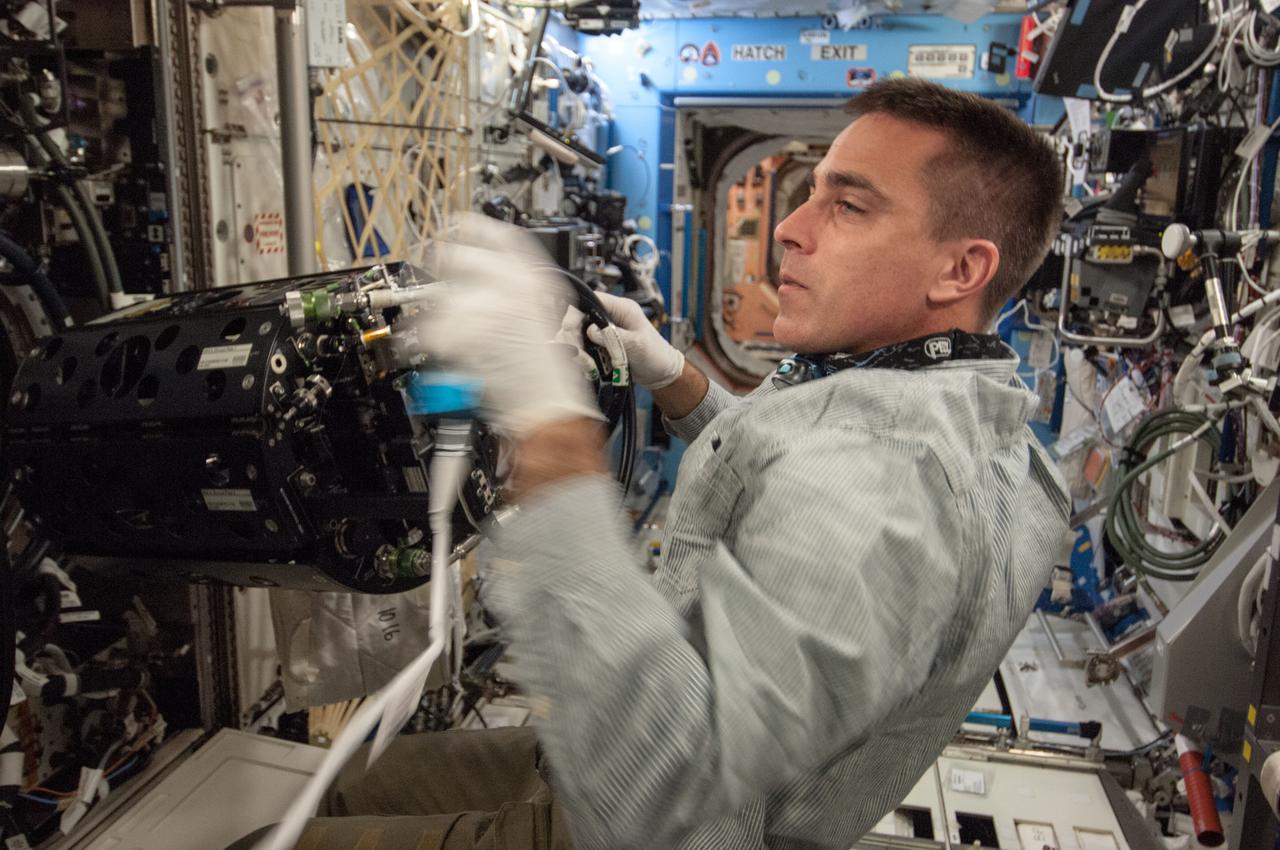
ISS035-E-017699 (10 April 2013) --- This is one of several photos documenting the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Fuel Reservoir replacement. Here, Expedition 35 Flight Engineer Chris Cassidy removes and replaces one of the Fuel Reservoirs with the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) pulled partially out of the Combustion Chamber. The MDCA Fuel Reservoirs contain the liquid fuel used during droplet combustion experiments. This reservoir change-out was in support of the FLame EXtinguishment (FLEX)-2 experiment, scheduled to be executed by ground controllers.
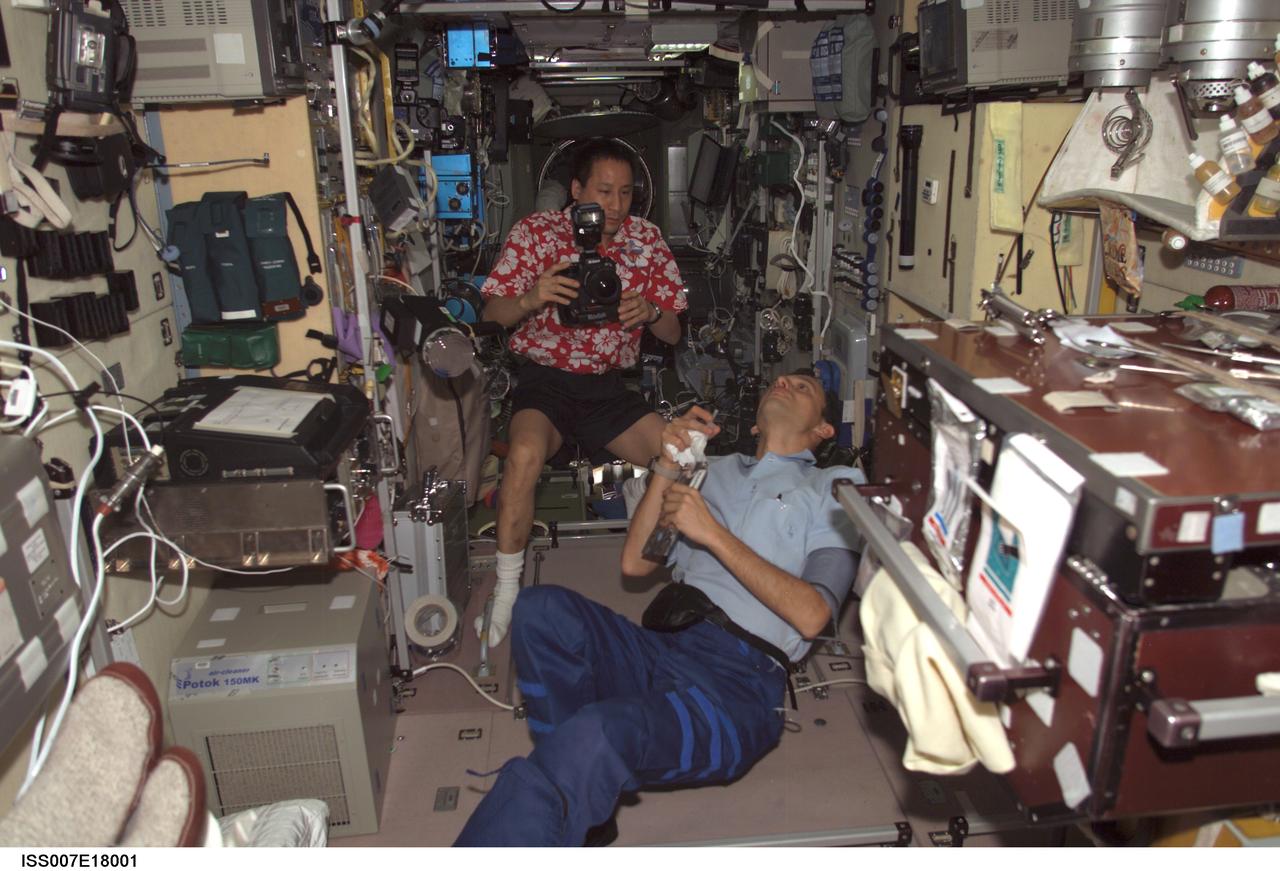
ISS007-E-18001 (25 October 2003) --- Astronaut Edward T. Lu (with camera), Expedition 7 NASA ISS science officer and flight engineer, and European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Pedro Duque of Spain observe a bubble of liquid floating freely in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
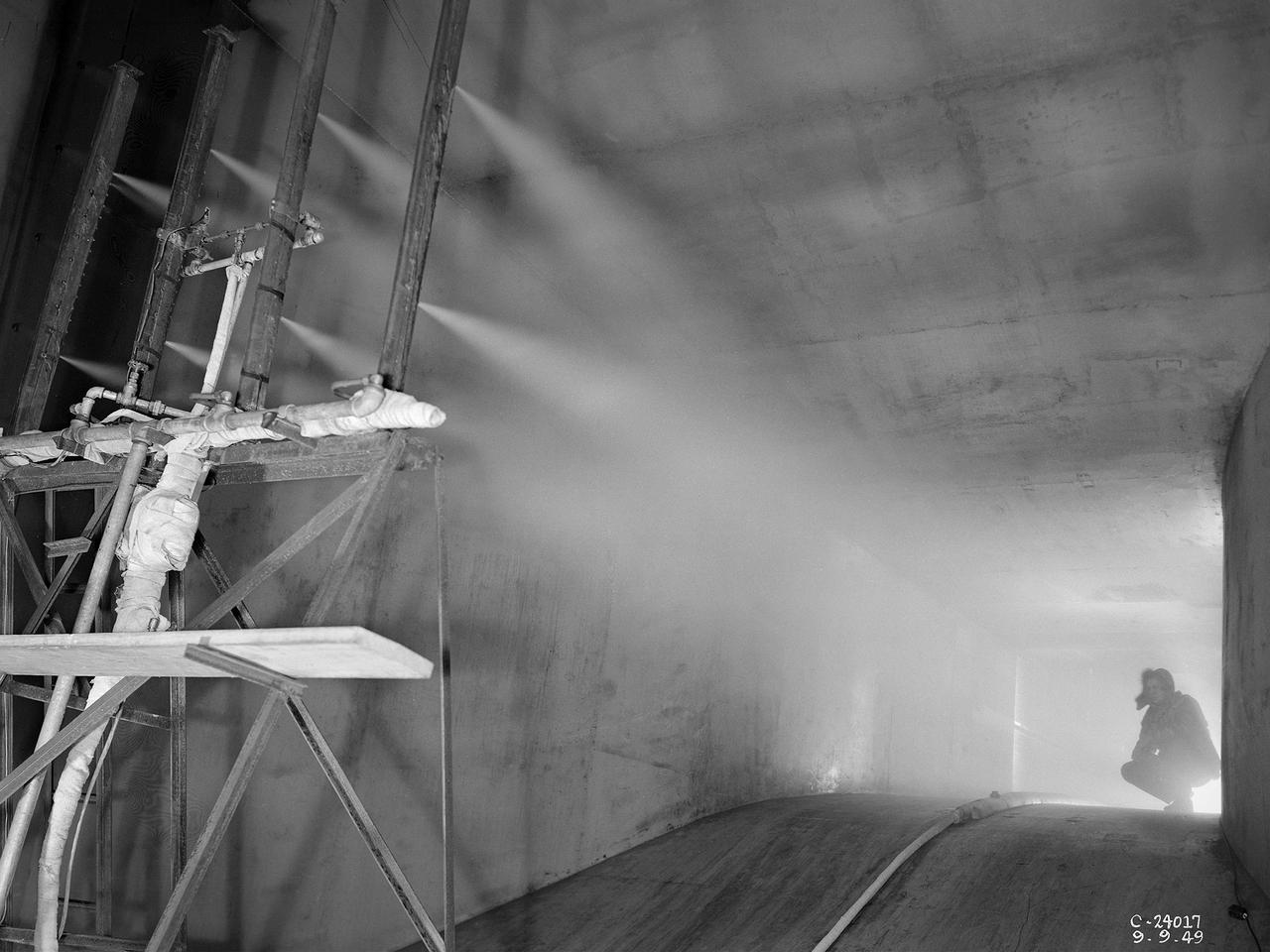

The spray bar system introduces water droplets into the Icing Research Tunnel’s air stream at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The icing tunnel was designed in the early 1940s to study ice accretion on airfoils and models. The Carrier Corporation designed a refrigeration system that reduced temperatures to -45° F. The tunnel’s drive fan generated speeds up to 400 miles per hour. The uniform injection of water droplets to the air was a key element of the facility’s operation. The system had to generate small droplets, distribute them uniformly throughout the airstream, and resist freezing and blockage. The Icing Research Tunnel’s designers struggled to develop a realistic spray system because they did not have access to data on the size of naturally occurring water droplets. For five years a variety of different designs were painstakingly developed and tested before the system was perfected. This photograph shows one of the trials using eight air-atomizing nozzles placed 48 feet upstream from the test section. A multi-cylinder device measured the size, liquid content, and distribution of the water droplets. The final system that was put into operation in 1950 included six horizontal spray bars with 80 nozzles that produced a 4- by 4-foot cloud in the test section. The Icing Research Tunnel produced excellent data throughout the 1950s and provided the basis for a hot air anti-icing system used on many transport aircraft.

Researchers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory conducted an extensive investigation into the composition of clouds and their effect on aircraft icing. The researcher in this photograph is installing cameras on a Beach AT-11 Kansan in order to photograph water droplets during flights through clouds. The twin engine AT-11 was the primary training aircraft for World War II bomber crews. The NACA acquired this aircraft in January 1946, shortly after the end of the war. The NACA Lewis’ icing research during the war focused on the resolution of icing problems for specific military aircraft. In 1947 the laboratory broadened its program and began systematically measuring and categorizing clouds and water droplets. The three main thrusts of the Lewis icing flight research were the development of better instrumentation, the accumulation of data on ice buildup during flight, and the measurement of droplet sizes in clouds. The NACA researchers developed several types of measurement devices for the icing flights, including modified cameras. The National Research Council of Canada experimented with high-speed cameras with a large magnification lens to photograph the droplets suspended in the air. In 1951 NACA Lewis developed and flight tested their own camera with a magnification of 32. The camera, mounted to an external strut, could be used every five seconds as the aircraft reached speeds up to 150 miles per hour. The initial flight tests through cumulus clouds demonstrated that droplet size distribution could be studied.
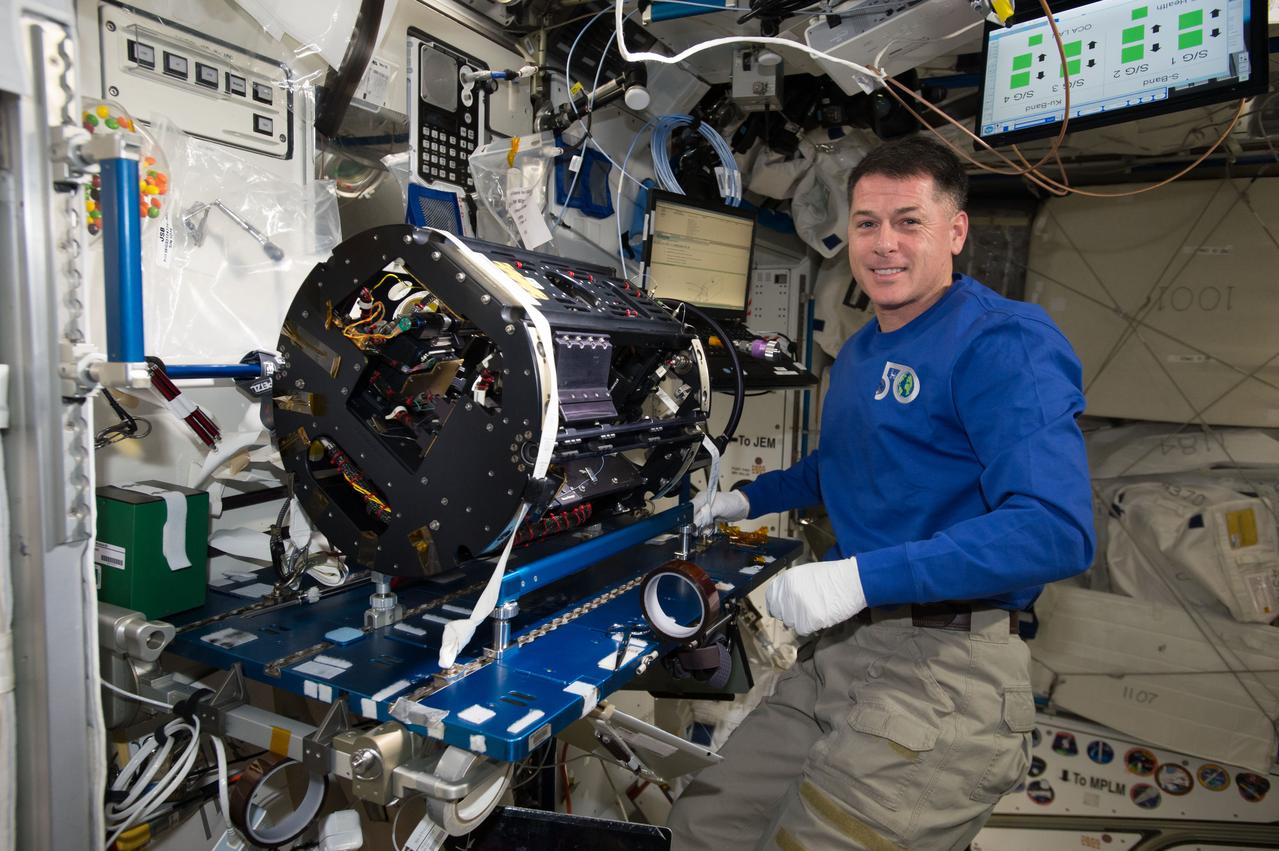

iss050e035112 (1/24/2017) --- NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough completing the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) reconfiguration to the Cool Flames Investigation (CFI) setup. The Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) includes an optics bench, combustion chamber, fuel and oxidizer control, and five different cameras for performing combustion experiments in microgravity.
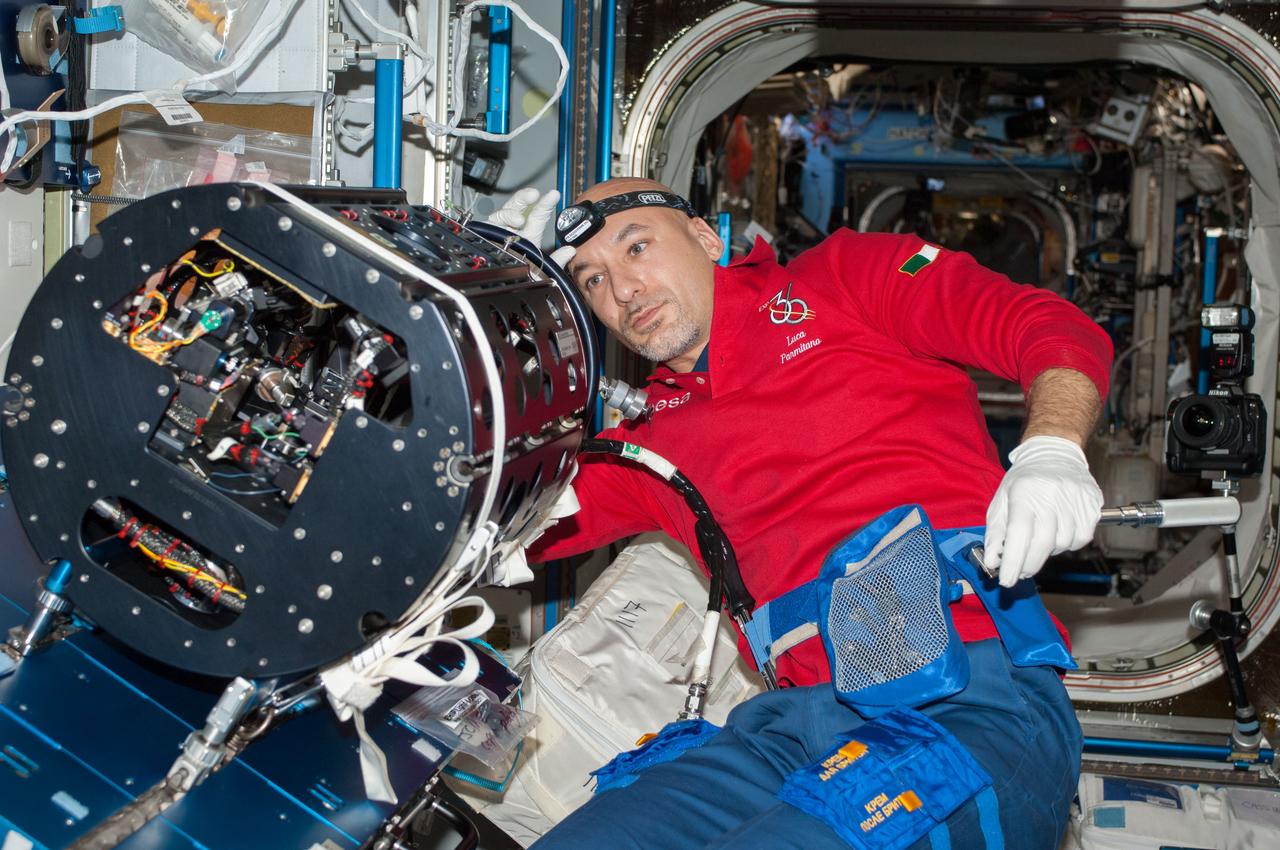

ISS036-E-025481 (24 July 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
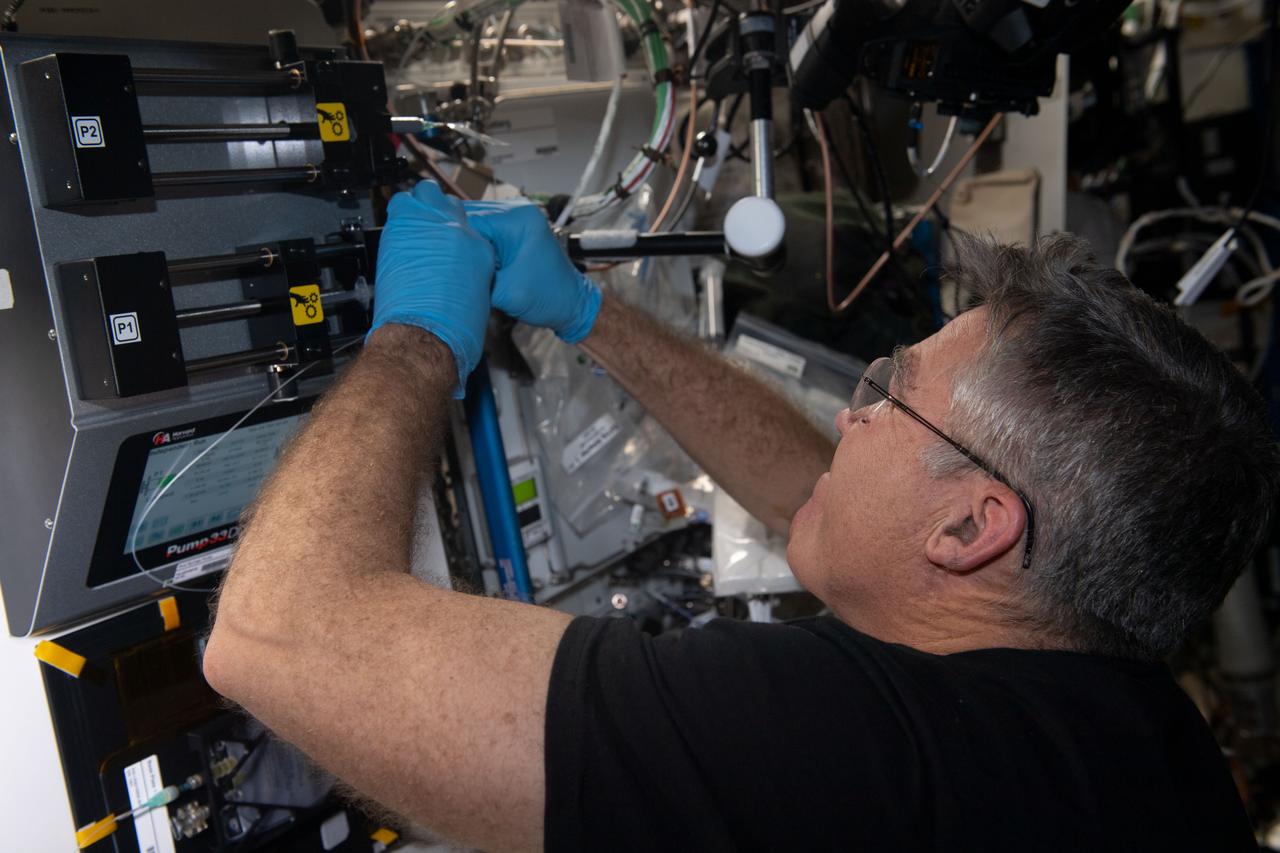

iss069e000660 (April 1, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen conducts research operations for the Foams and Emulsions physics experiment that observes the dispersion of bubbles and droplets in liquids that may lead to newer, more advanced space research and expanded commercial opportunities in space.
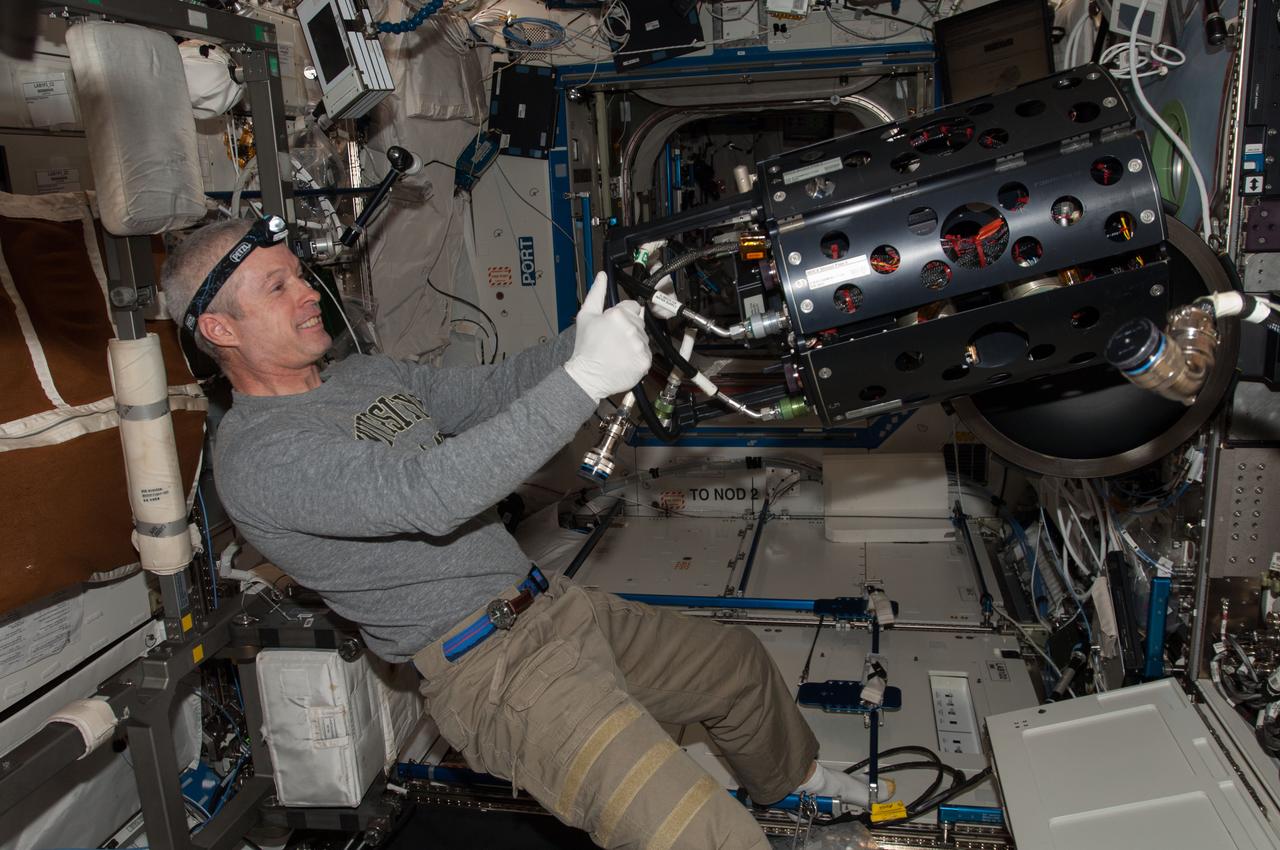

ISS040-E-010502 (11 June 2014) --- NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, works with the Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) inside the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. The MDCA contains hardware and software to conduct unique droplet combustion experiments in space.
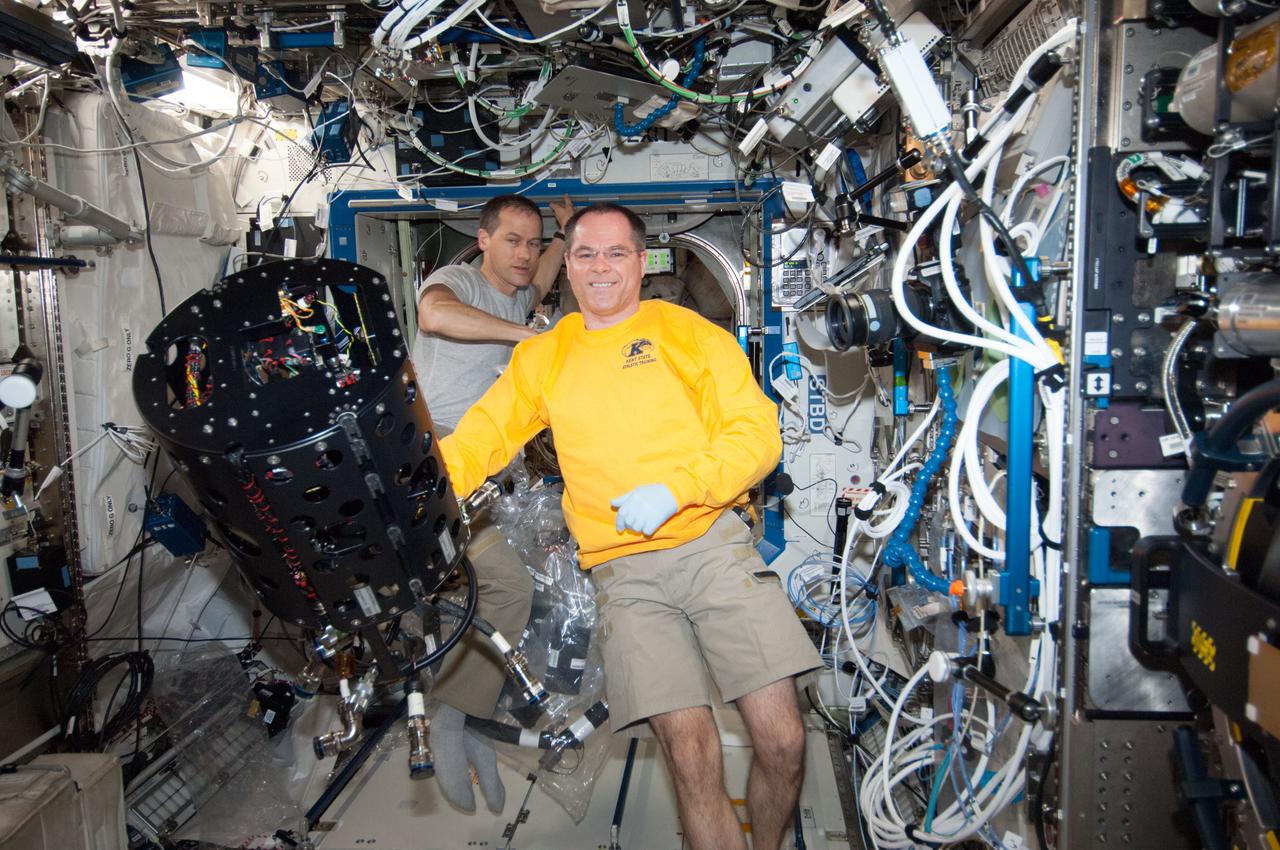

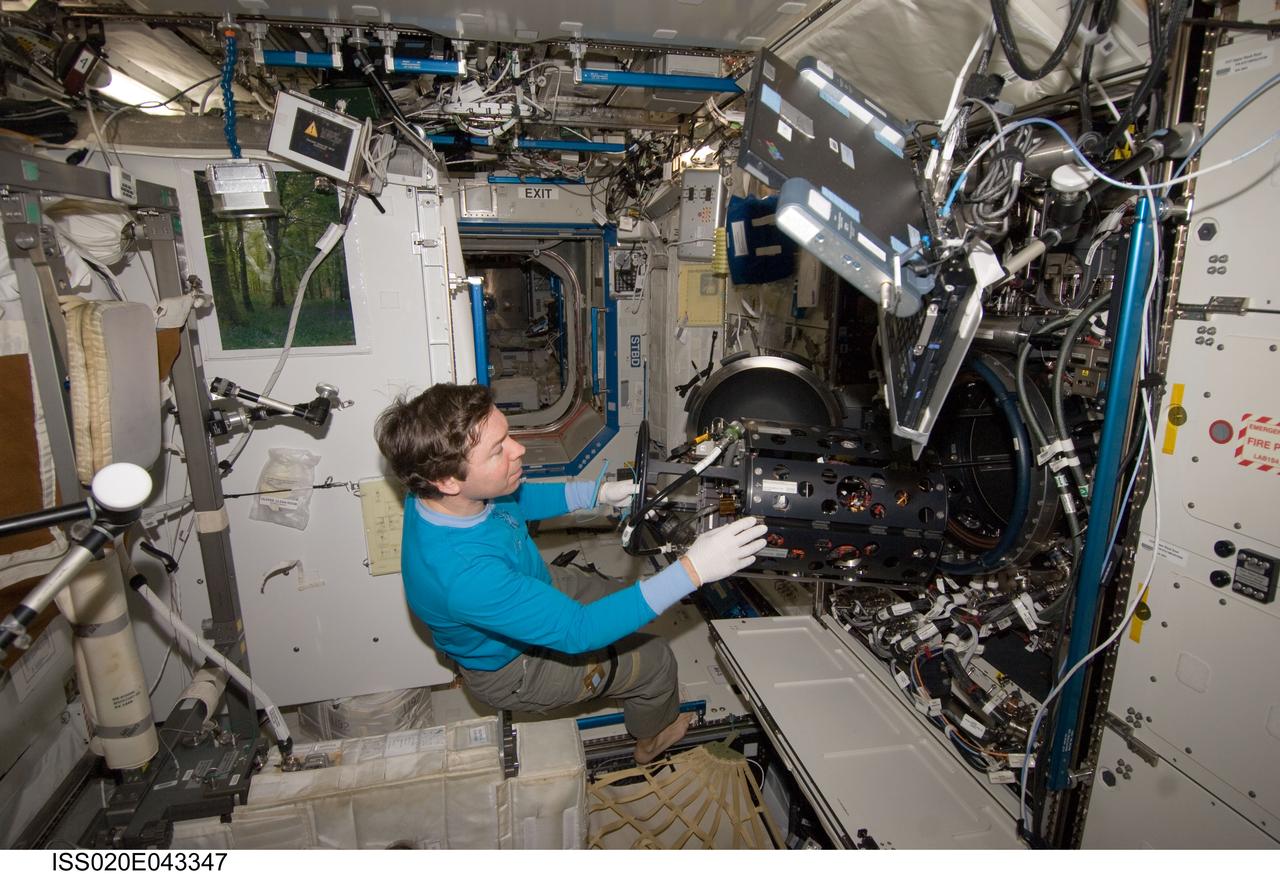
ISS034-E-023541 (9 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronauts Kevin Ford (foreground), Expedition 34 commander; and Tom Marshburn, flight engineer, work with the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory.
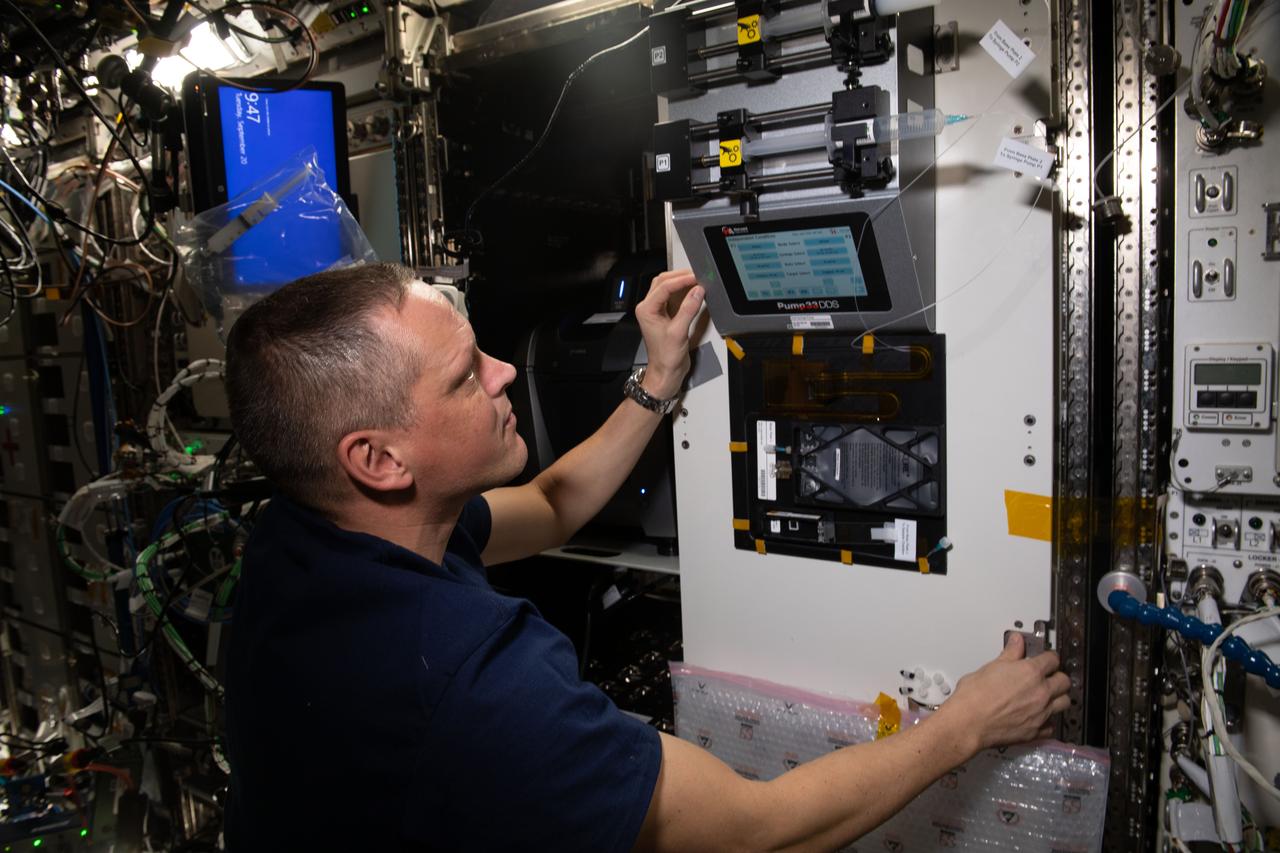

iss067e378832 (9/20/2022) --- NASA astronaut Bob Hines conducts research operations for the Foams and Emulsions physics experiment that observes the dispersion of bubbles and droplets in liquids that may lead to newer, more advanced space research and expanded commercial opportunities in space.

ISS036-E-015521 (5 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, services the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory.

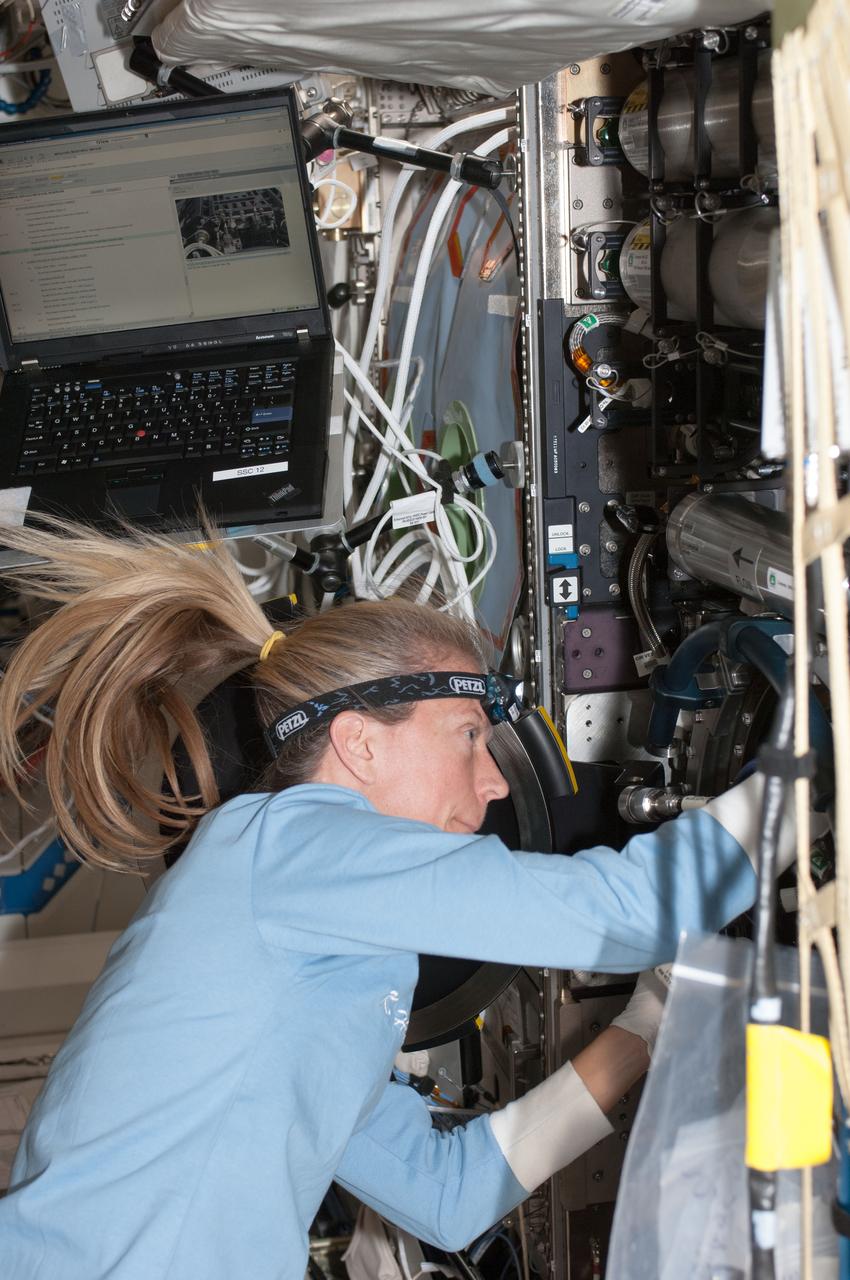
ISS020-E-043347 (26 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 20 flight engineer, works with the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus / Chamber Insert Assembly (MDCA CIA) in the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) located in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
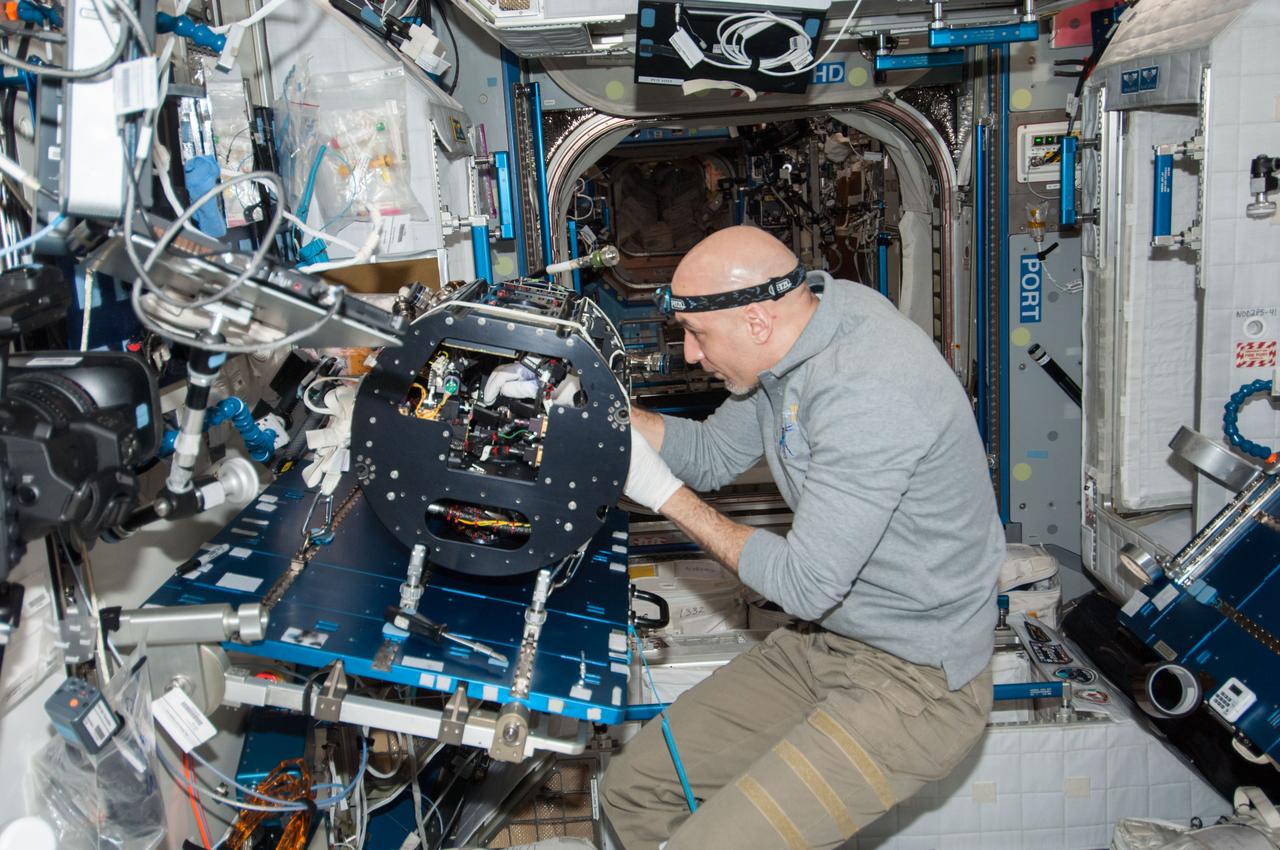

ISS037-E-012586 (10 Oct. 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 37 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
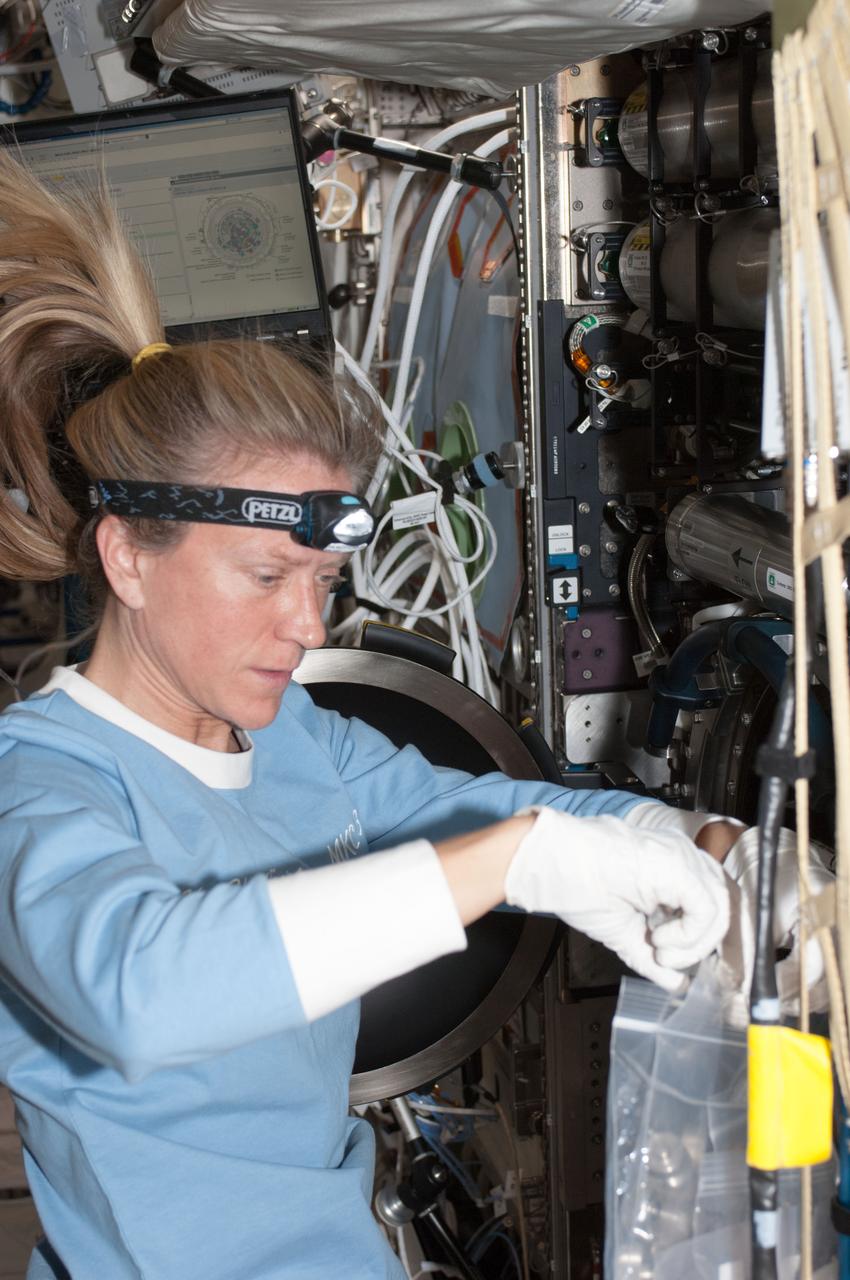

ISS036-E-015530 (5 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, services the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory.
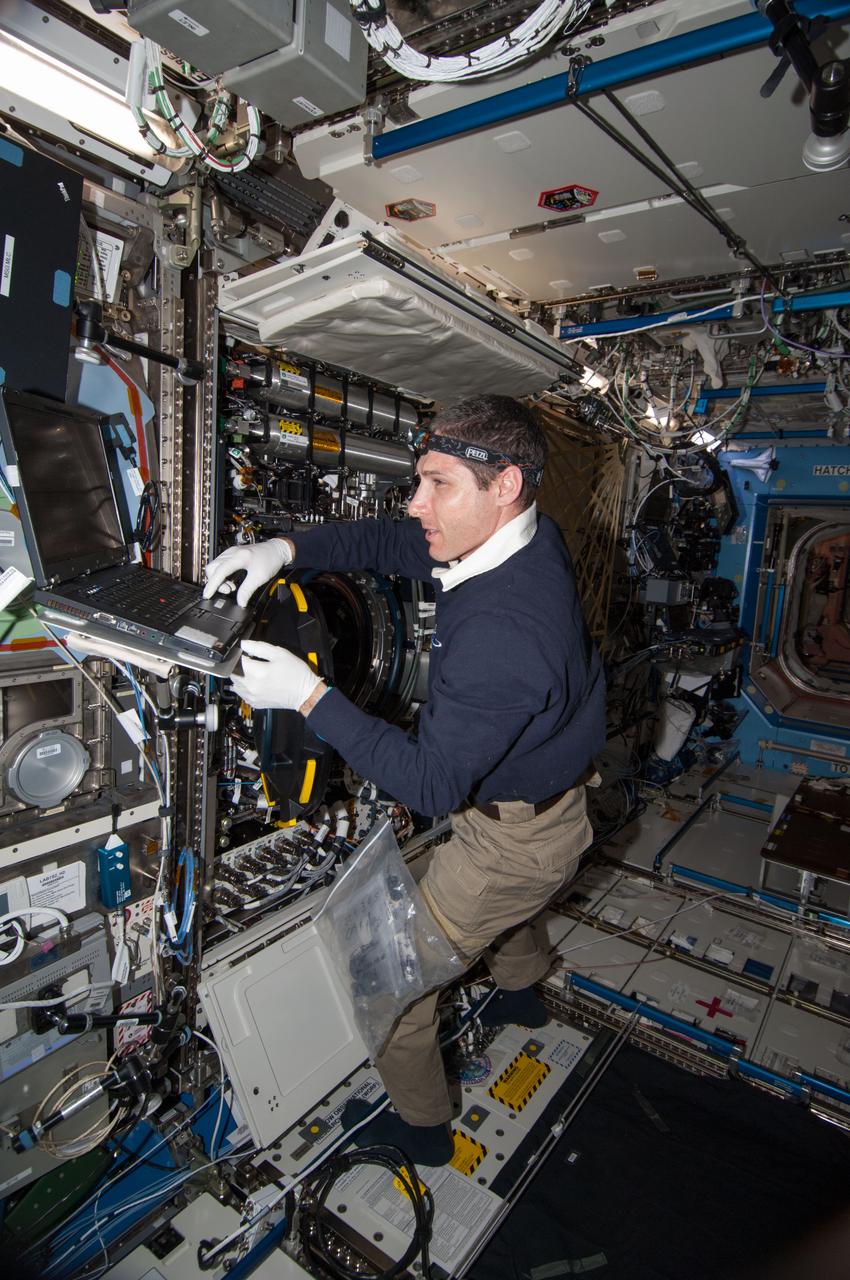

ISS038-E-024145 (30 Dec. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on combustion research hardware in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. Hopkins replaced a Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) fuel reservoir inside the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR).

ISS040-E-010258 (11 June 2014) --- NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, works with the Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) at a workstation in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. The MDCA contains hardware and software to conduct unique droplet combustion experiments in space.
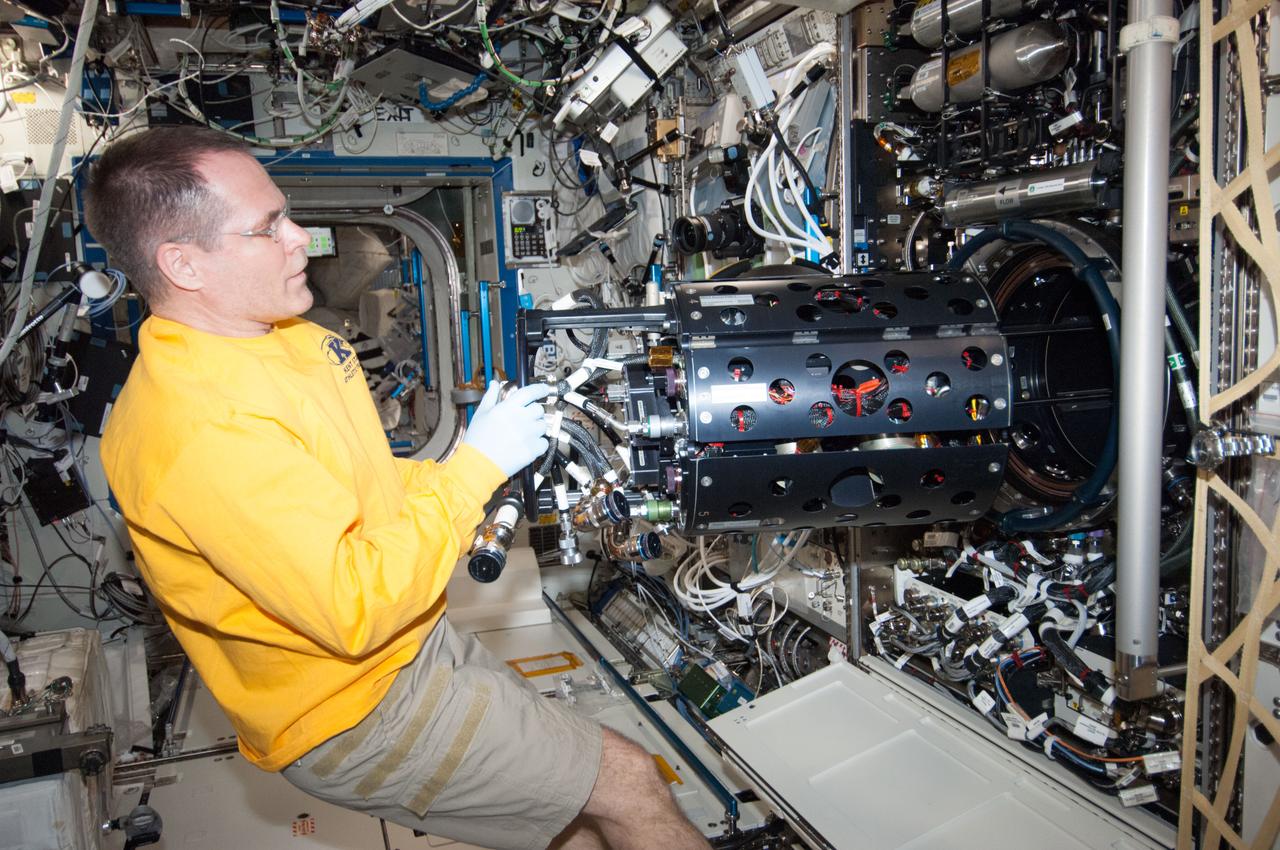

ISS034-E-023546 (9 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Kevin Ford, Expedition 34 commander, works with the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory.
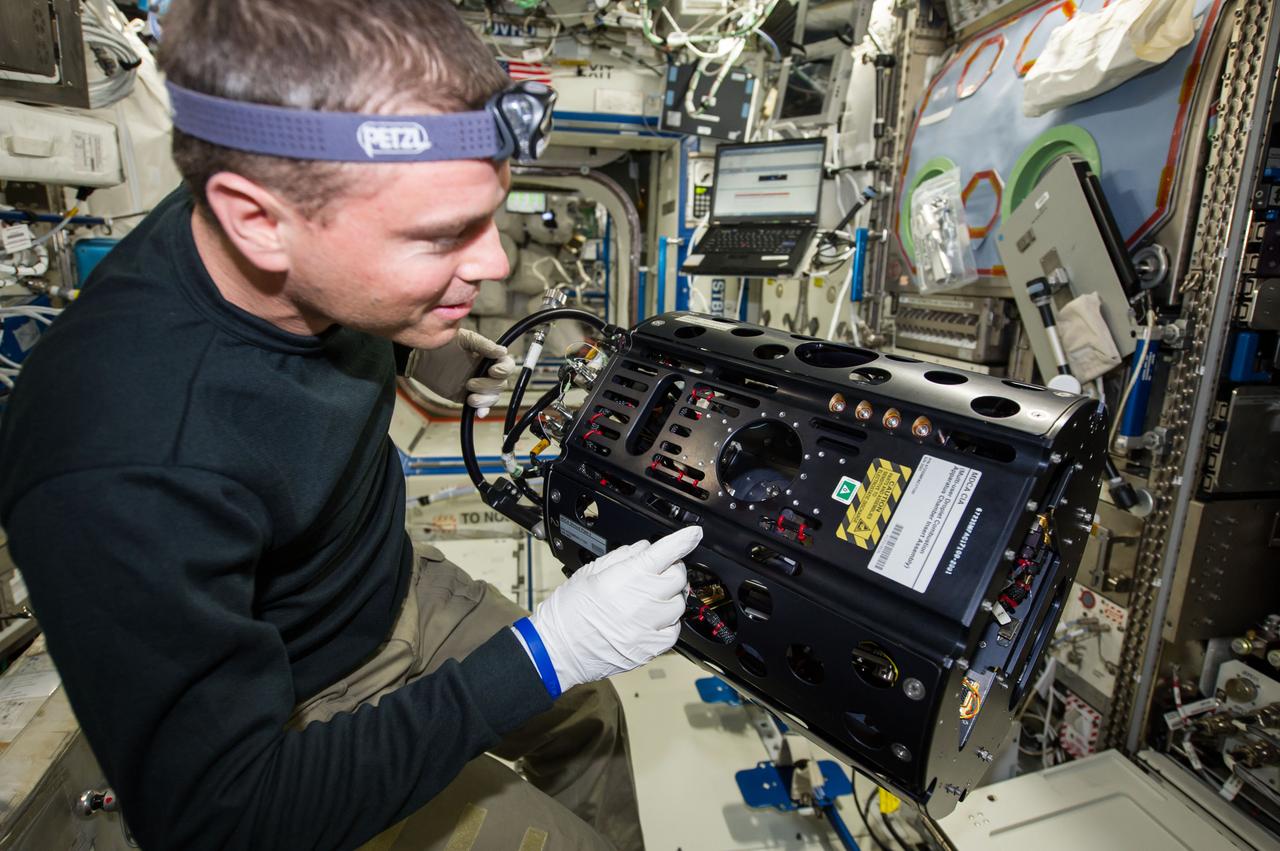

ISS041-E-016781 (18 Sept. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman, Expedition 41 flight engineer, works with the Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. The MDCA contains hardware and software to conduct unique droplet combustion experiments in space.
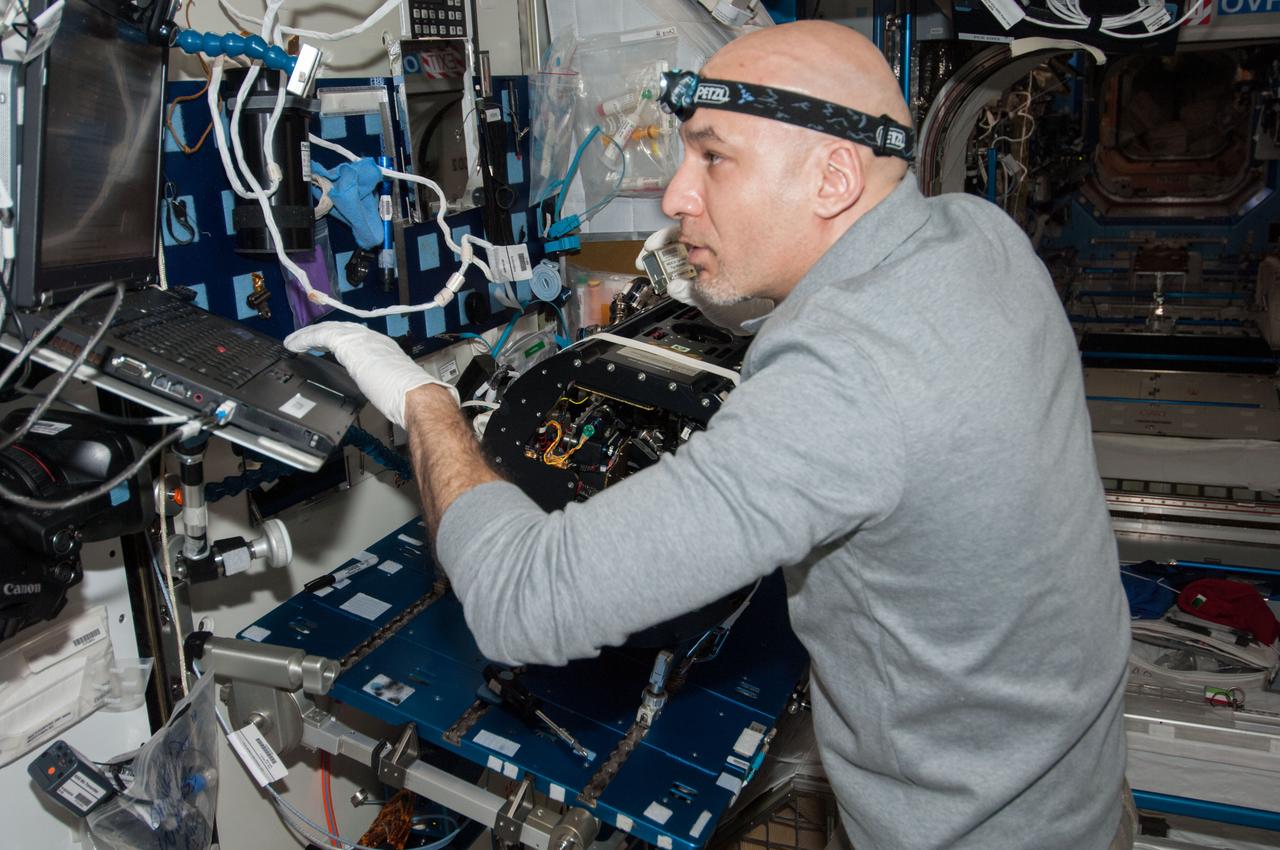

ISS037-E-012579 (10 Oct. 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 37 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
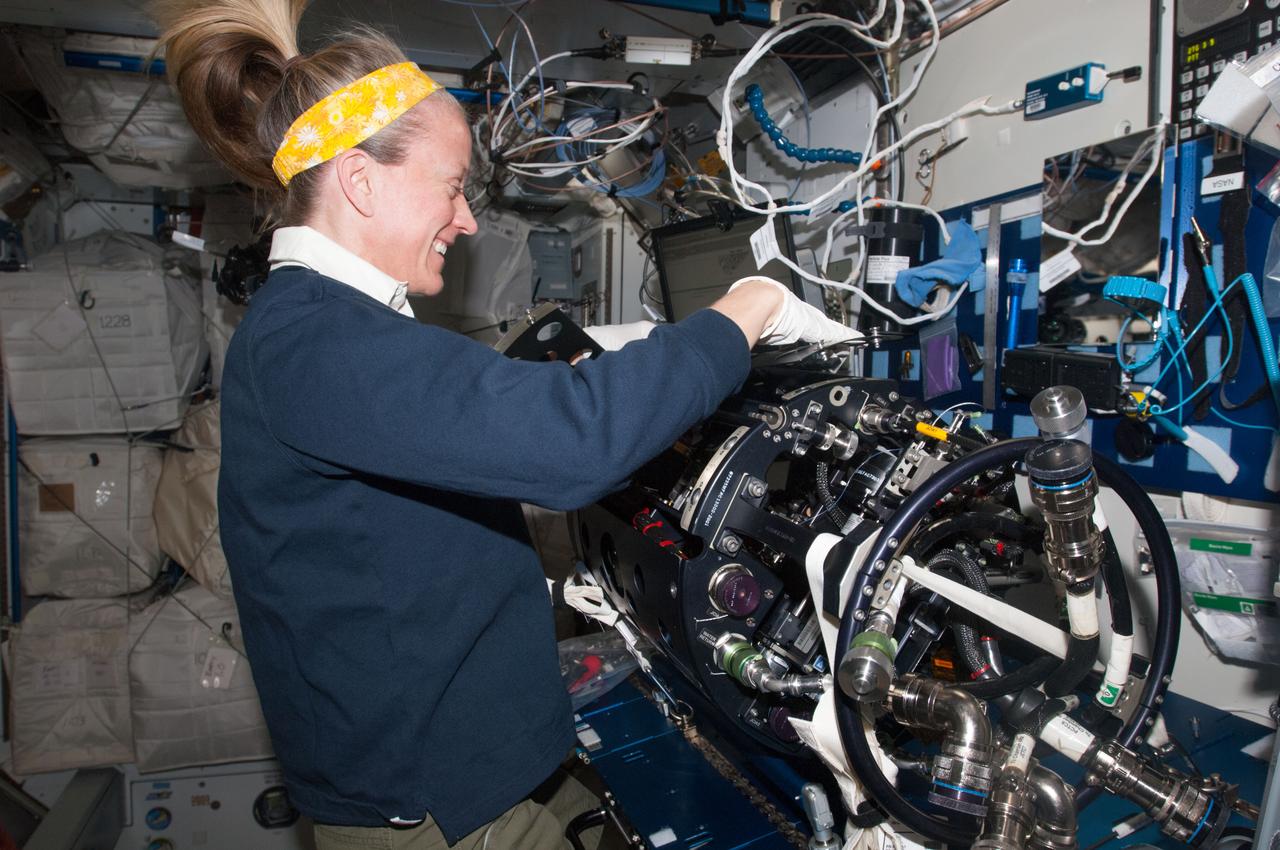

ISS037-E-004881 (1 Oct. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 37 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
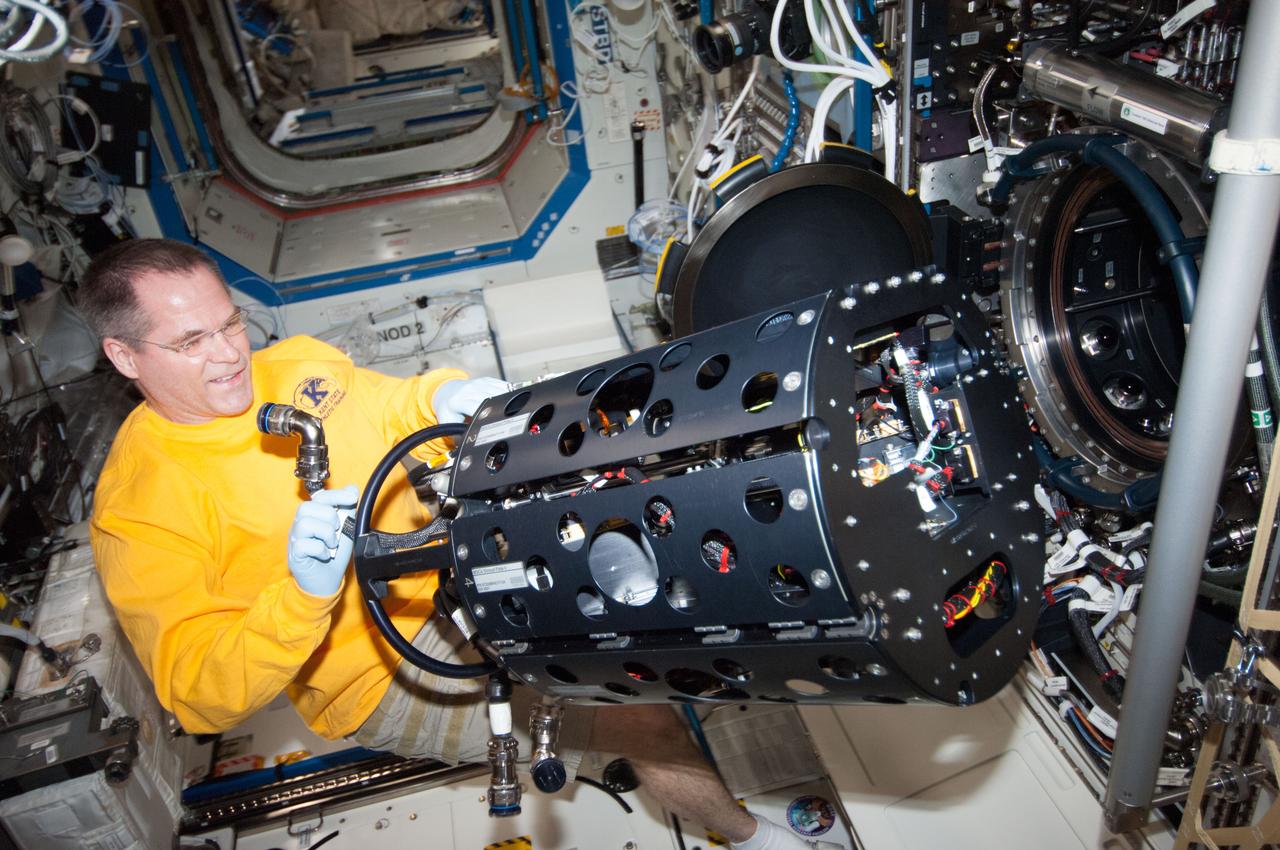

ISS034-E-023544 (9 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Kevin Ford, Expedition 34 commander, works with the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory.
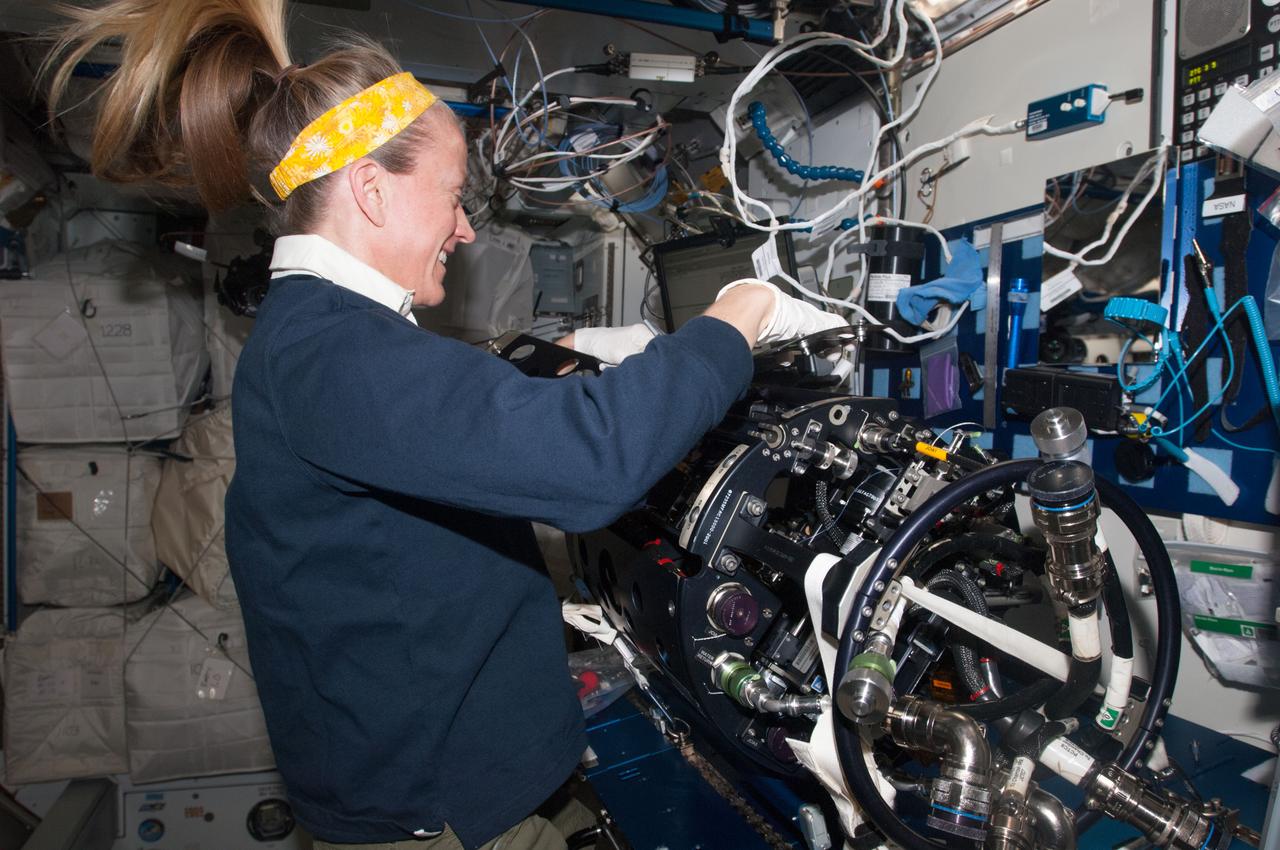

ISS037-E-004882 (1 Oct. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 37 flight engineer, works on the Multi-User Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA) at a maintenance work station in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
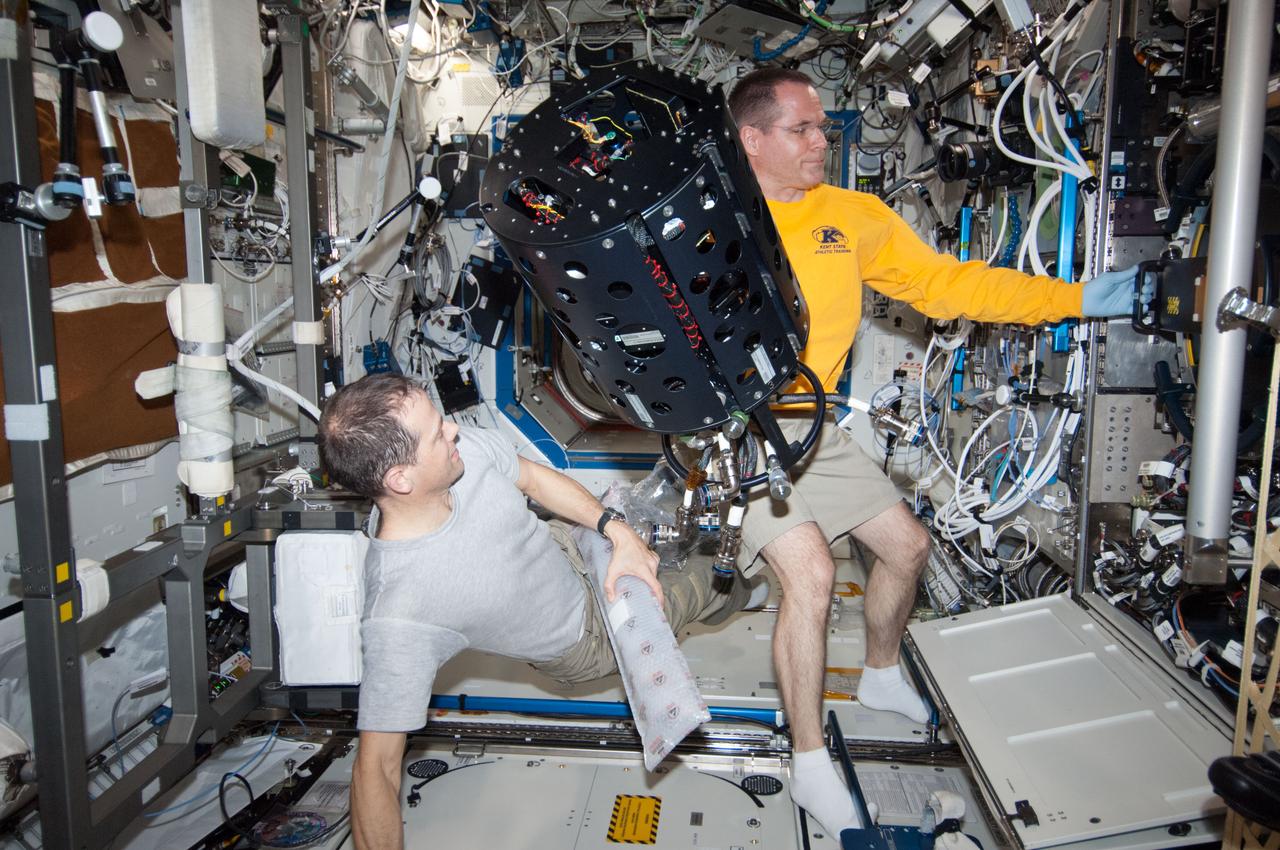

ISS034-E-023543 (9 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronauts Kevin Ford (right), Expedition 34 commander; and Tom Marshburn, flight engineer, work with the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory.
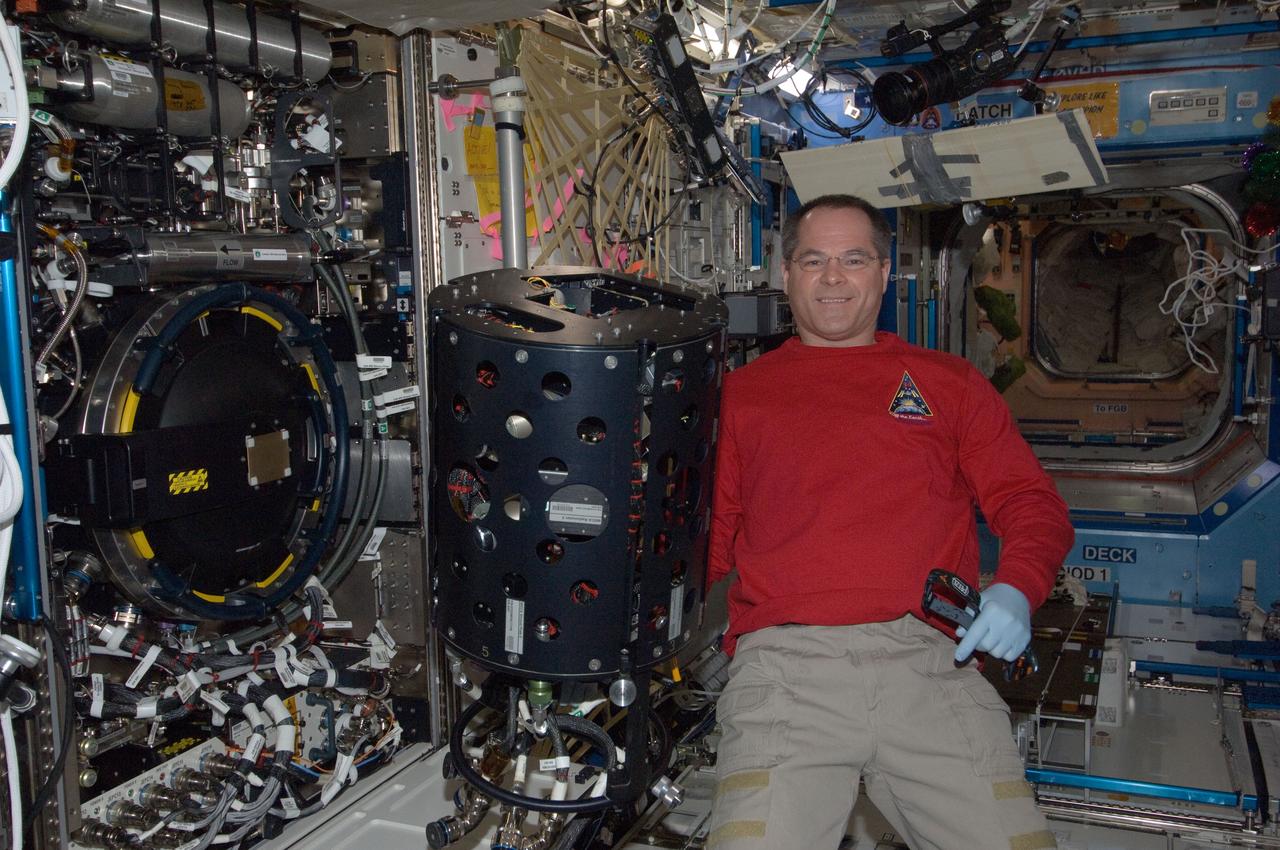

ISS034-E-007409 (12 Dec. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Kevin Ford, Expedition 34 commander, performs in-flight maintenance on the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory.
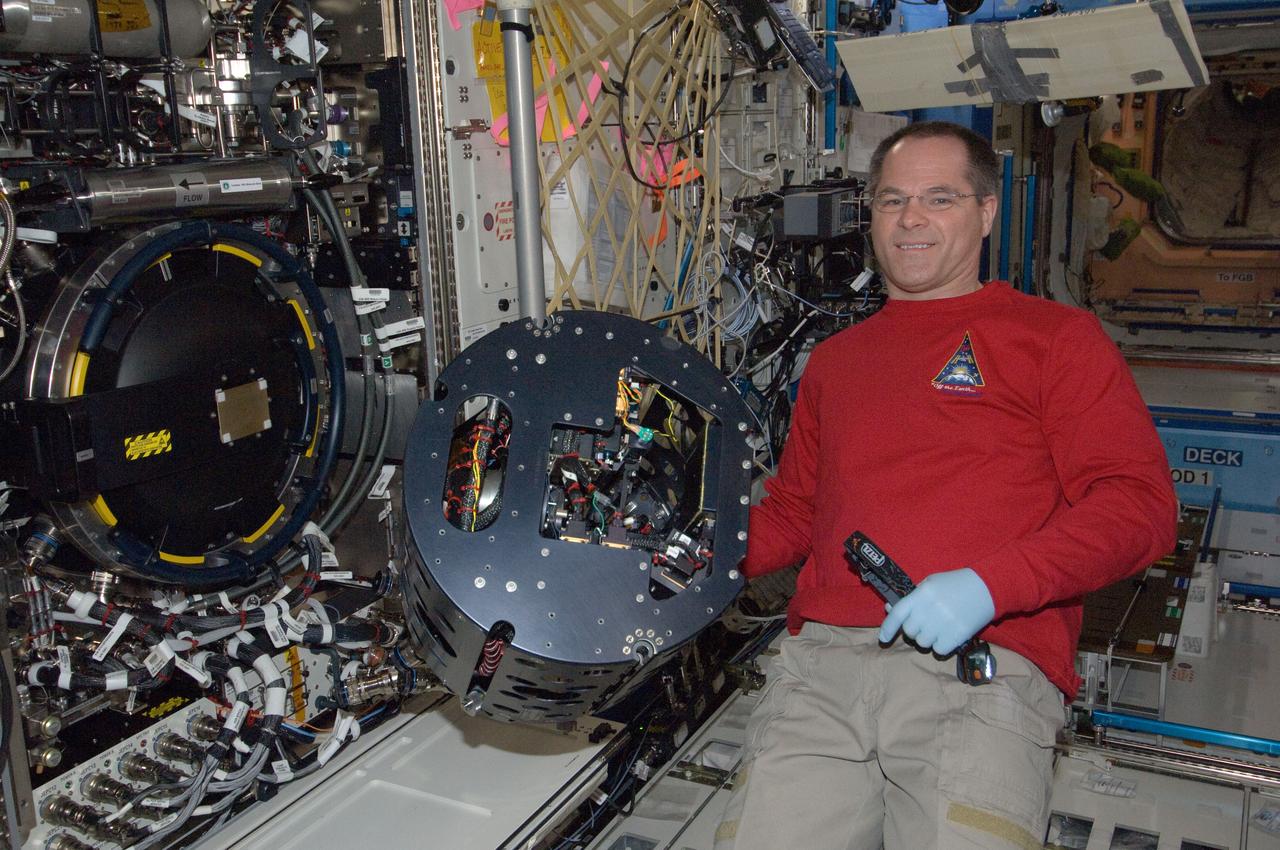

ISS034-E-007411 (12 Dec. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Kevin Ford, Expedition 34 commander, performs in-flight maintenance on the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) in the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory.
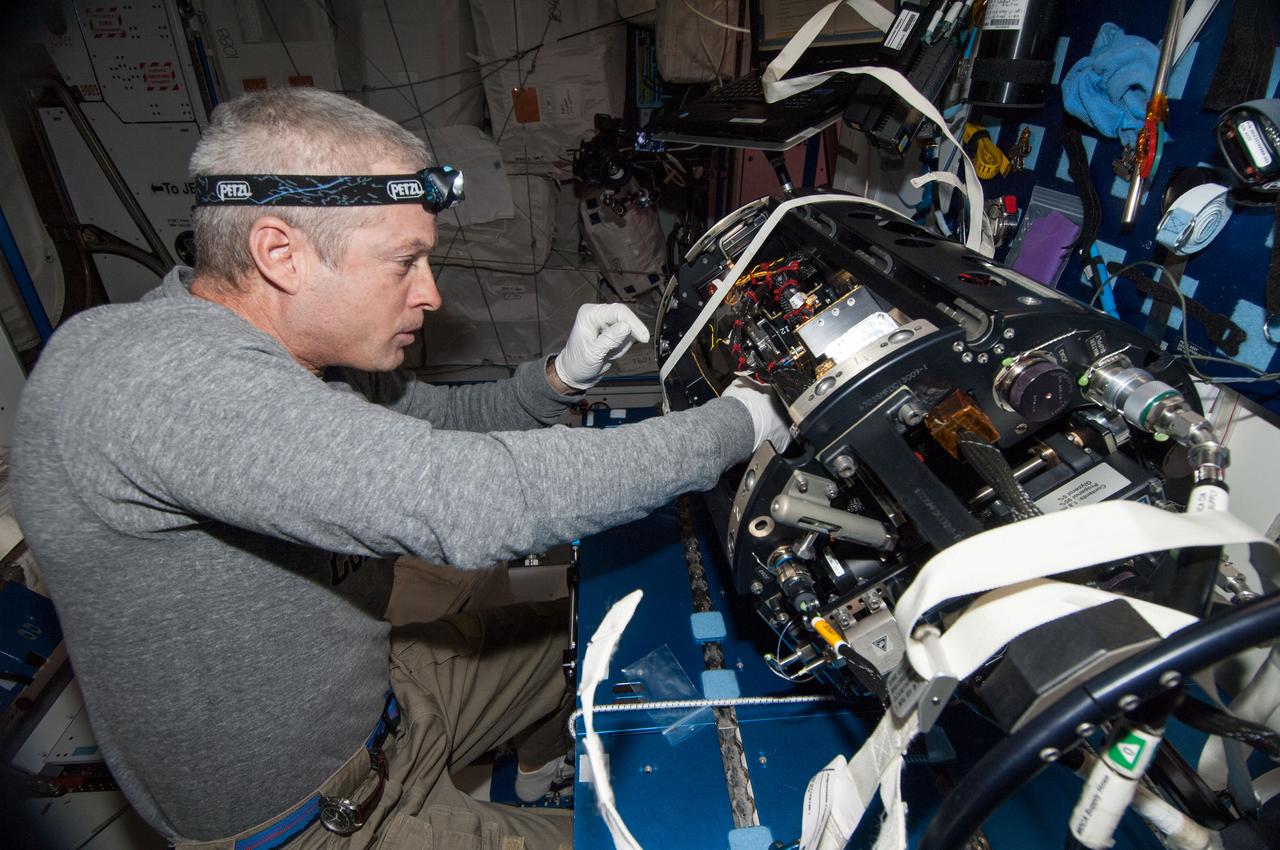

ISS040-E-010261 (11 June 2014) --- NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, works with the Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) at a workstation in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. The MDCA contains hardware and software to conduct unique droplet combustion experiments in space.
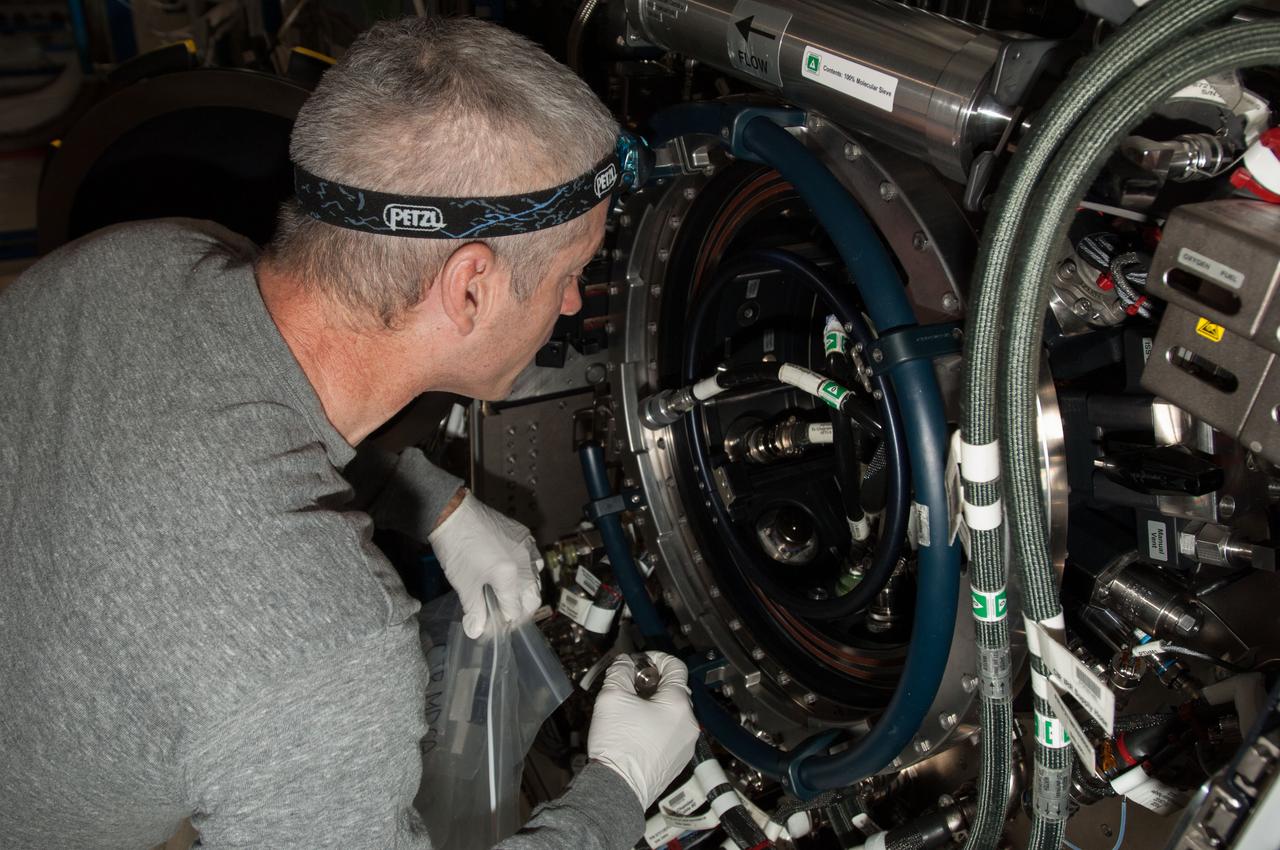

ISS040-E-010496 (11 June 2014) --- NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, works with the Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) inside the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. The MDCA contains hardware and software to conduct unique droplet combustion experiments in space.
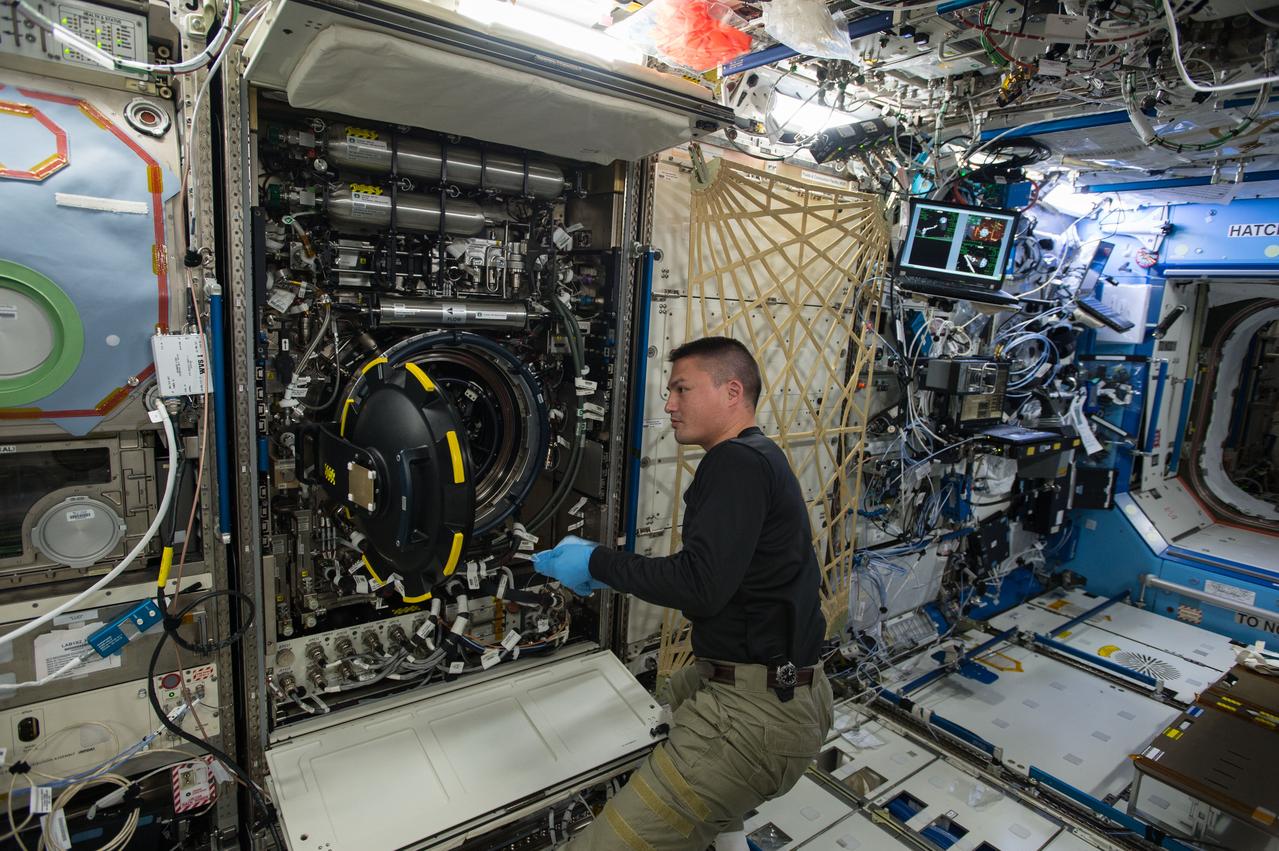

ISS044E064666 (08/20/2015) --- NASA astronaut Kjell Lindgren replaces items inside the Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus found inside the station’s Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR.) The CIR houses hardware capable of performing combustion experiments to further research of combustion in microgravity.

On, Aug. 27, 2019 NASA's CloudSat satellite passed over Dorian, still a tropical storm at the time, near Puerto Rico. CloudSat uses an advanced cloud-profiling radar that "slices" through clouds giving us the ability to see how tall they are, where the different cloud layers are, and where the heavier bands of rain are found within the storm system. The 3D animation shows Dorian when it had maximum sustained winds of 52 mph (84 kph) with some of its cloud tops extending about 9 miles (15 kilometer) into the atmosphere. The colors represent the size of water or ice droplets inside the storm — deep red and pink indicate larger droplets with areas of moderate and heavy rainfall. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23359
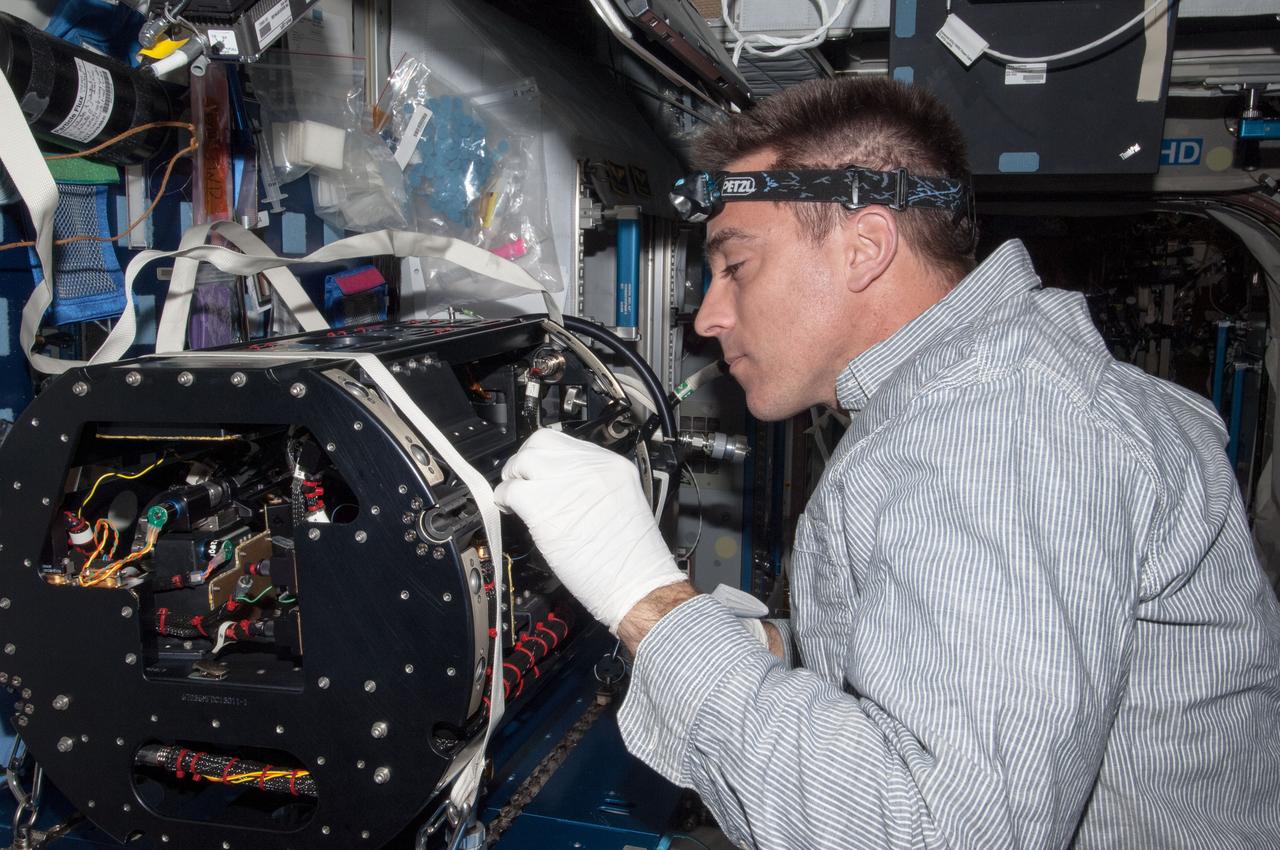

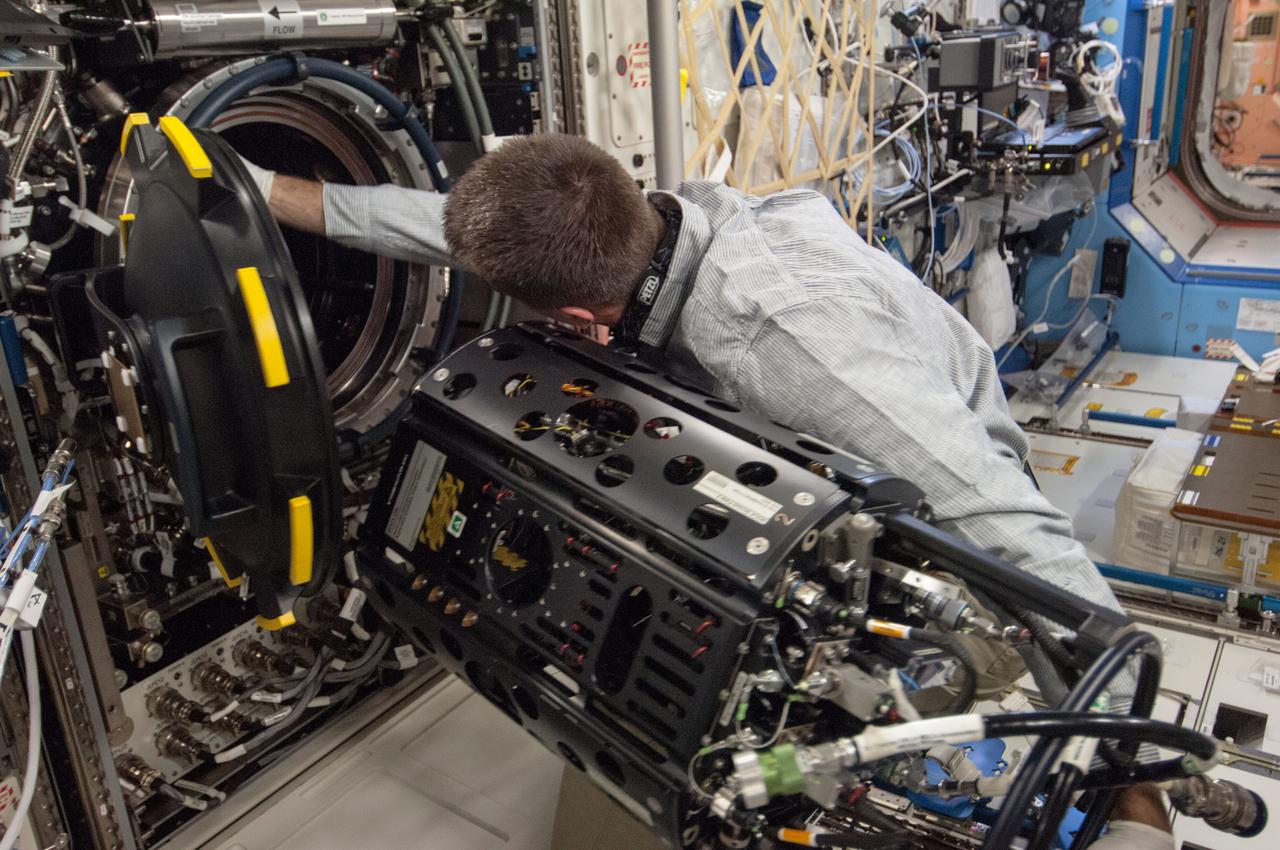
ISS035-E-025557(22 April 2013) ---Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Hardware Replacement: Cassidy accessed the Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) Combustion Chamber and removed the MDCA Chamber Insert Assembly (CIA). He then replaced the MDCA Needle 1 due to a fuel line that was damaged during previous activities when the MDCA CIA was being removed from the Combustion Chamber.

jsc2022e004237 (11/8/2021) --- A Preflight image of the Acoustics to Manipulate Fluids investigation, the acoustic tweezer apparatus is installed inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox Engineering Unit. The sample chamber, shown in the upper the right side, is where fluid droplets are injected via a septum located on the right side and manipulated by an ultrasonic transducer located on the left side. Image courtesy of Dr. Robert Lirette.
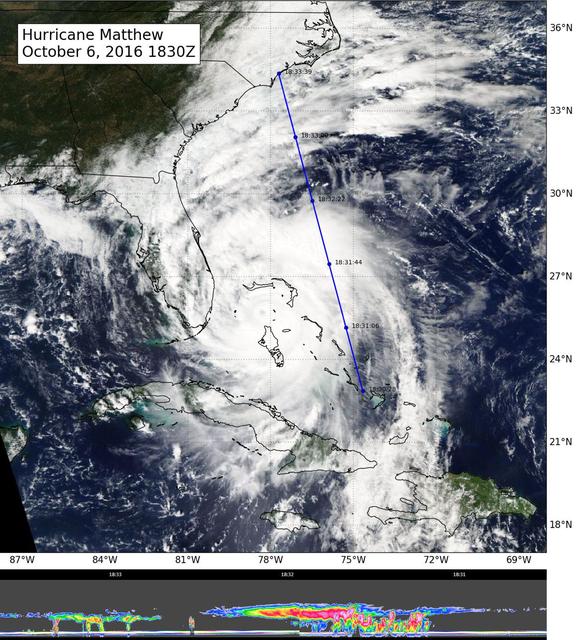
NASA's CloudSat flew east of Hurricane Matthew's center on Oct. 6 at 11:30 a.m. PDT (2:30 p.m. EDT), intersecting parts of Matthew's outer rain bands and revealing Matthew's anvil clouds (thick cirrus cloud cover), with cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds beneath (lower image). Reds/pinks are larger water/ice droplets. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21095
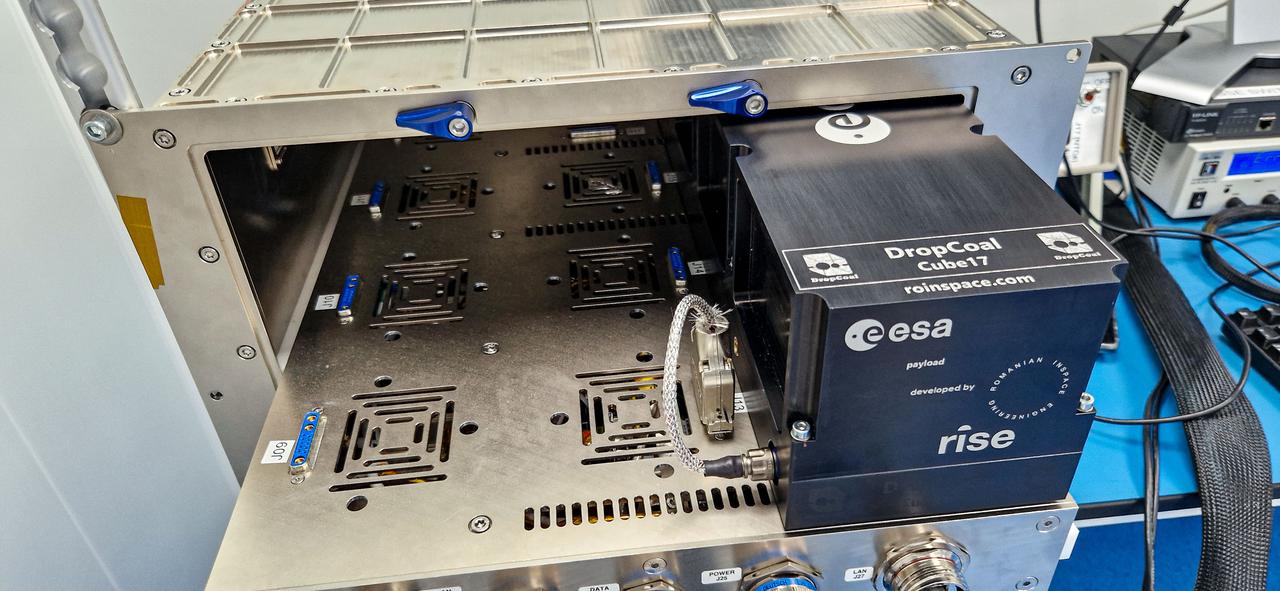

jsc2024e068512 (7/24/2024) --- Setup for Investigation of Drops Coalescence in View of Medical Applications (DropCoal) (ICE Cubes #17 - DropCoal) during the Interface test, integrated into the ICE Cubes Facility engineering model (EM) at Space Application Services (SAS) premises in Brussels. The investigation studies how water and ethanol droplets of various sizes behave when colliding at different velocities. Image courtesy of Romanian InSpace Engineering.
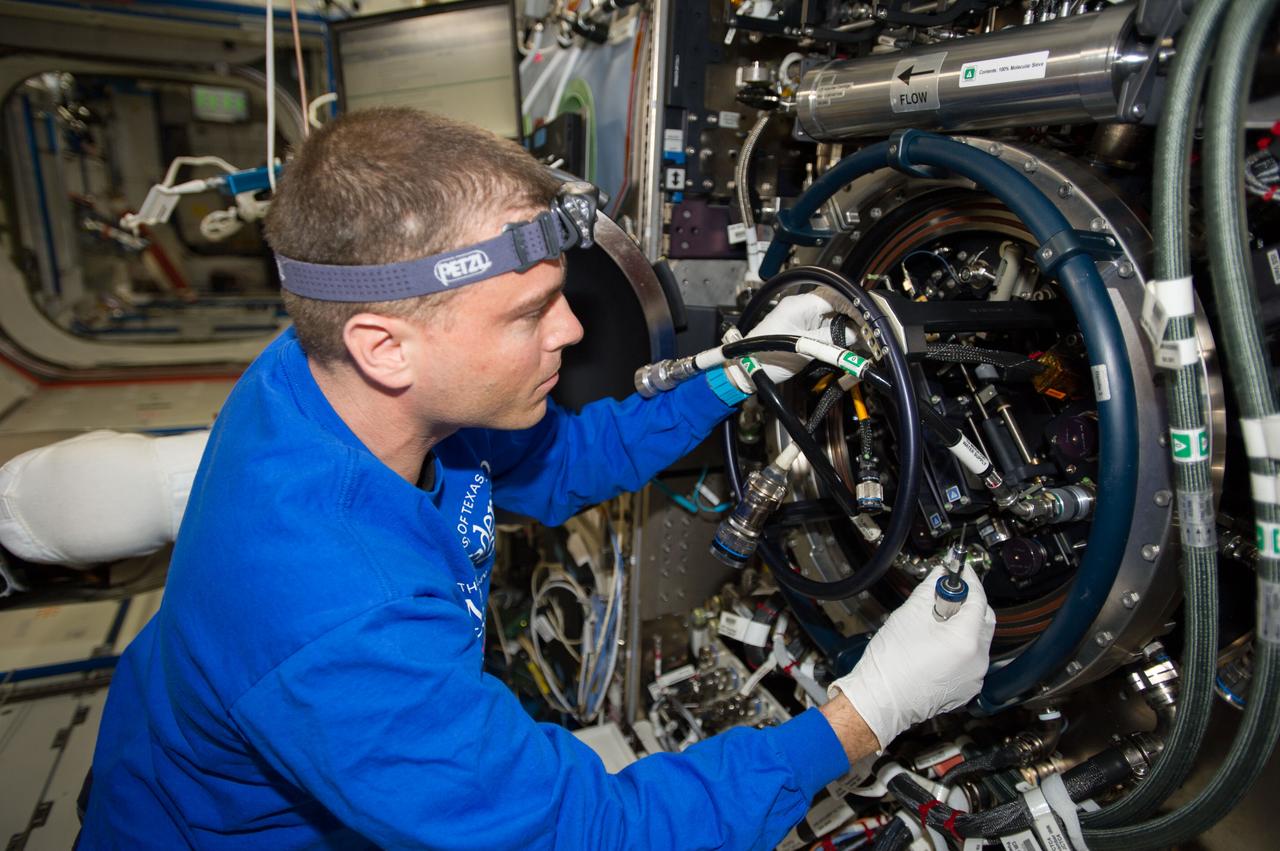

ISS040-E-090484 (11 Aug. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman, Expedition 40 flight engineer, performs routine in-flight maintenance on the Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) inside the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. The MDCA contains hardware and software to conduct unique droplet combustion experiments in space.
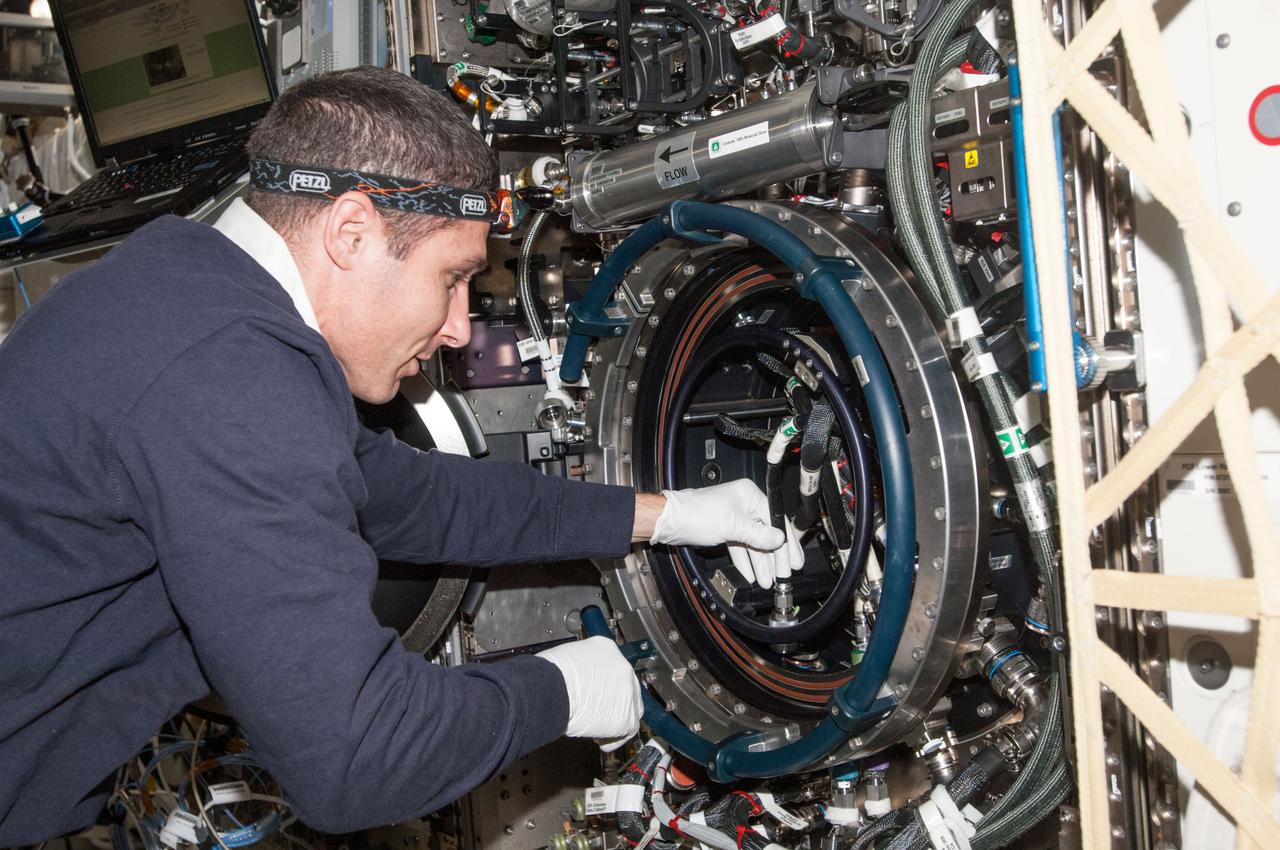

ISS038-E-001298 (12 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, works with the Multi-user Drop Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) inside the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. The MDCA contains hardware and software to conduct unique droplet combustion experiments in space.
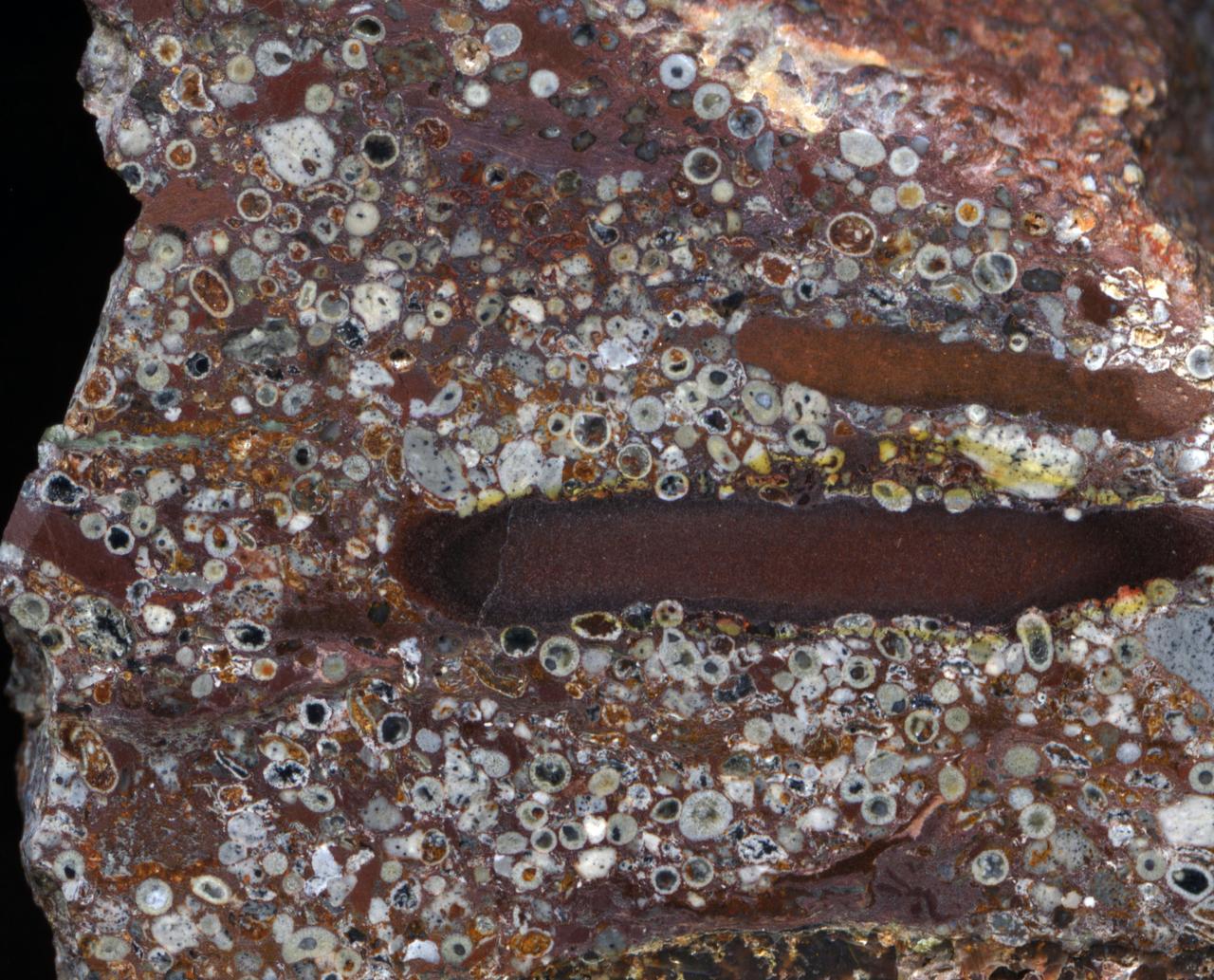

The millimeter-scale circles and irregular gray particles in this sample are formerly molten droplets ejected into space when a asteroid hit the Earth 2.63 billion years ago late in the Archean period. Credit: Bruce Simonson, Oberlin College and Conservatory. The sample was cut and polished in Bruce's lab in Ohio, where the photo was taken, but the sample itself came from a spherule bed in Australia. Copyright released with permission for public distribution.
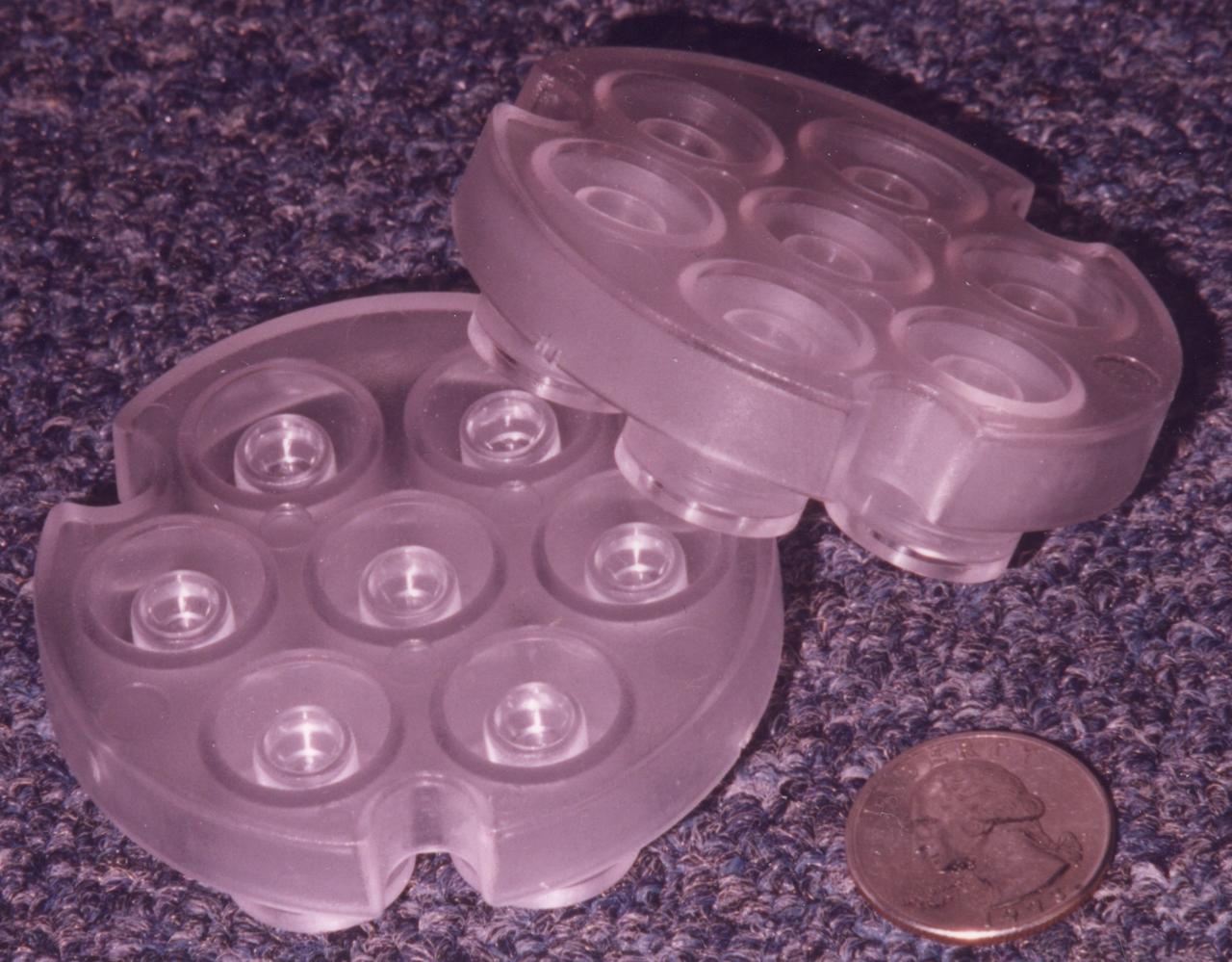

The Protein Crystallization for Microgravity (DCAM) was developed at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. A droplet of solution with protein molecules dissolved in it is isolated in the center of a small well. In orbit, an elastomer seal is lifted so the solution can evaporate and be absorbed by a wick material. This raises the concentration of the solution, thus prompting protein molecules in the solution to form crystals. The principal investigator is Dr. Dan Carter of New Century Pharmaceuticals in Huntsville, AL.
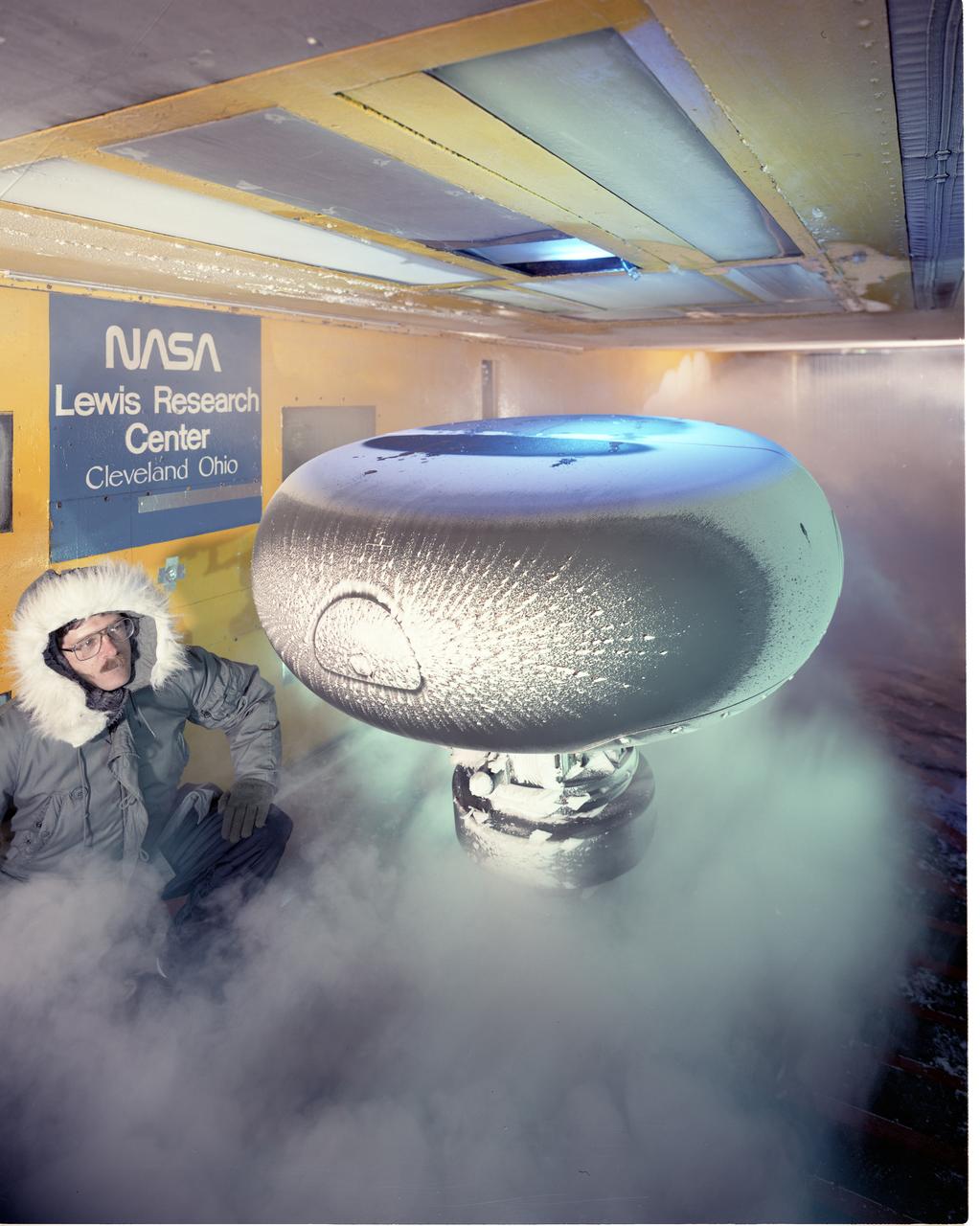

An AH-64 (Apache) Longbow fire control full size radar photographed during icing tests in the Icing Research wind tunnel. Built at the end of World War II, the Icing Research Tunnel is the oldest and largest refrigerated icing wind tunnel in the world. It can produce winds that travel up to 395 miles per hour and reach temperatures as low as -30 degrees Fahrenheit. The facility simulates ice formation during flight by spraying a cloud of super-cooled water droplets onto an aircraft component or model.