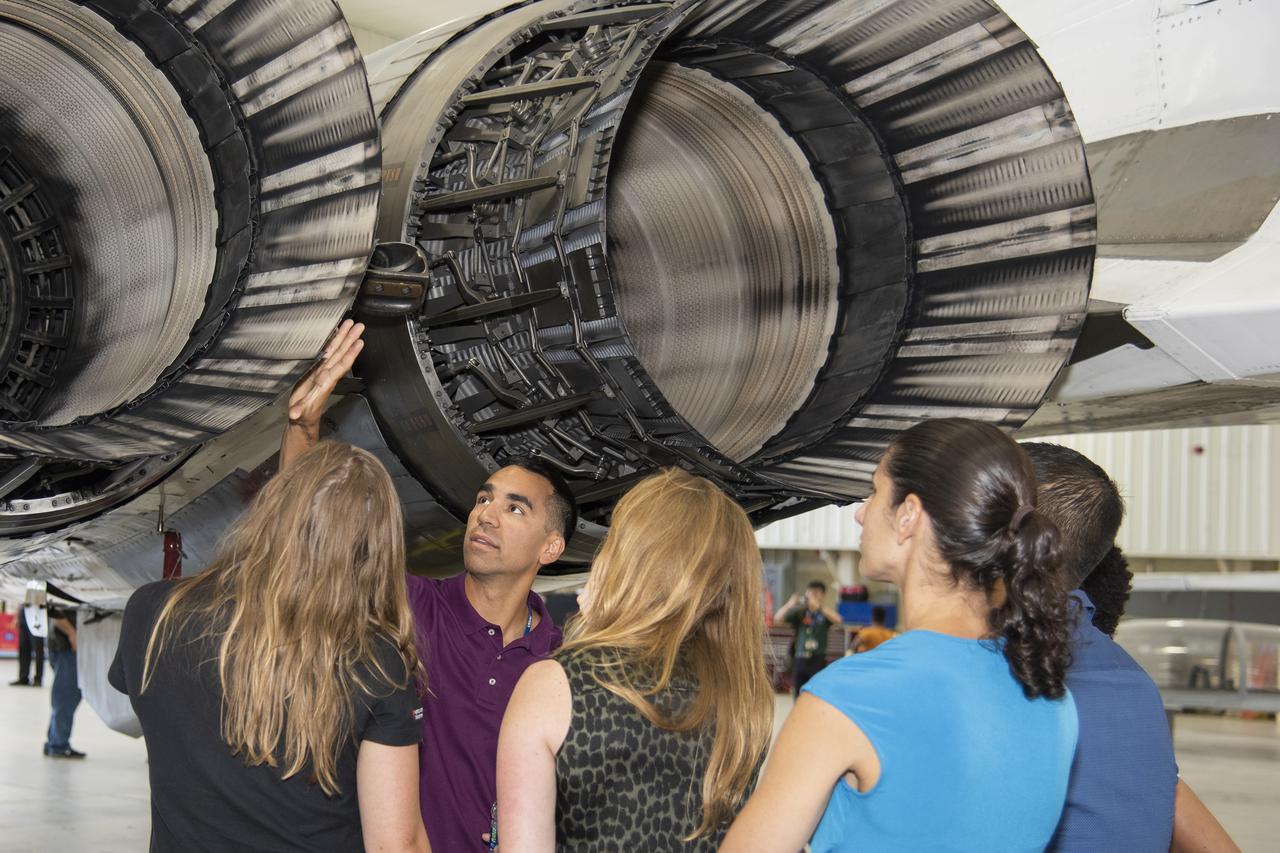

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California (L to R) Jenni Sidey-Gibbons, Raja Chari, Loral O'Hara, Jasmin Moghbeli, Jonny Kim and Jessica Watkins look inside the engine nozzle of an F-15 jet. The F-15 will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages for the X-59 development.
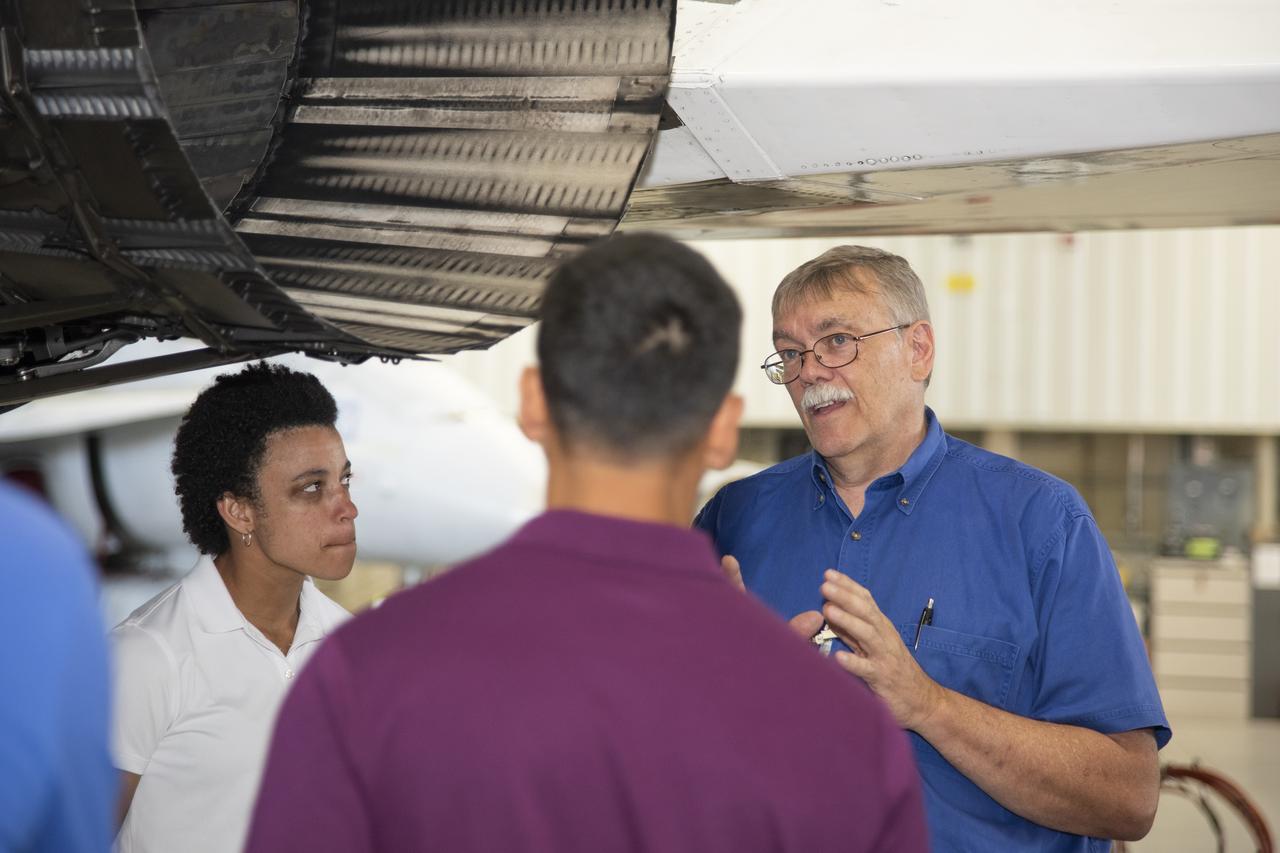

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California where Crew Chief Tom Grindle talks with (L to R) Jessica Watkins and Raja Chari near engine nozzle of F-15 jet. The F-15 will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages for the X-59 development.
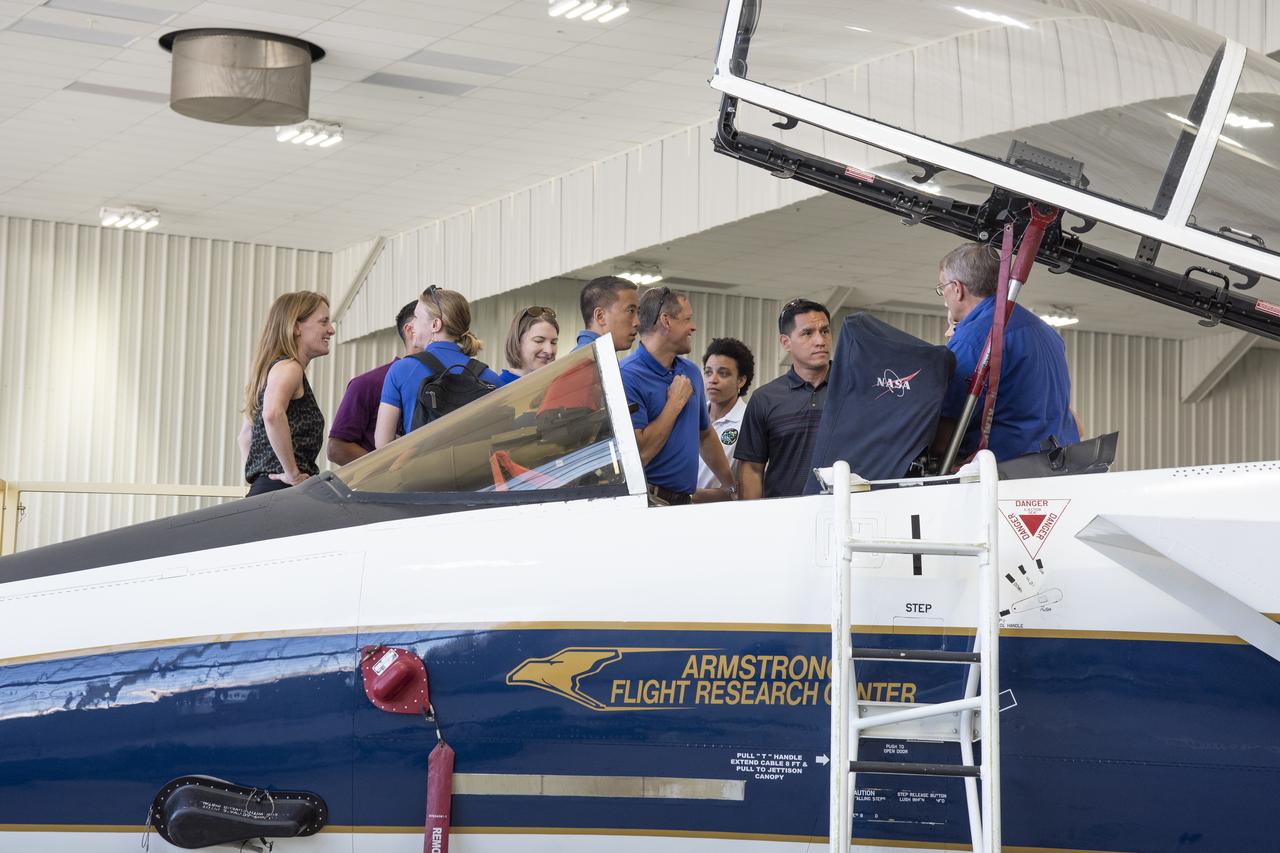

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California where they checked out a F-15 cockpit. The center is using its fleet of supersonic research support aircraft for sonic boom research, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
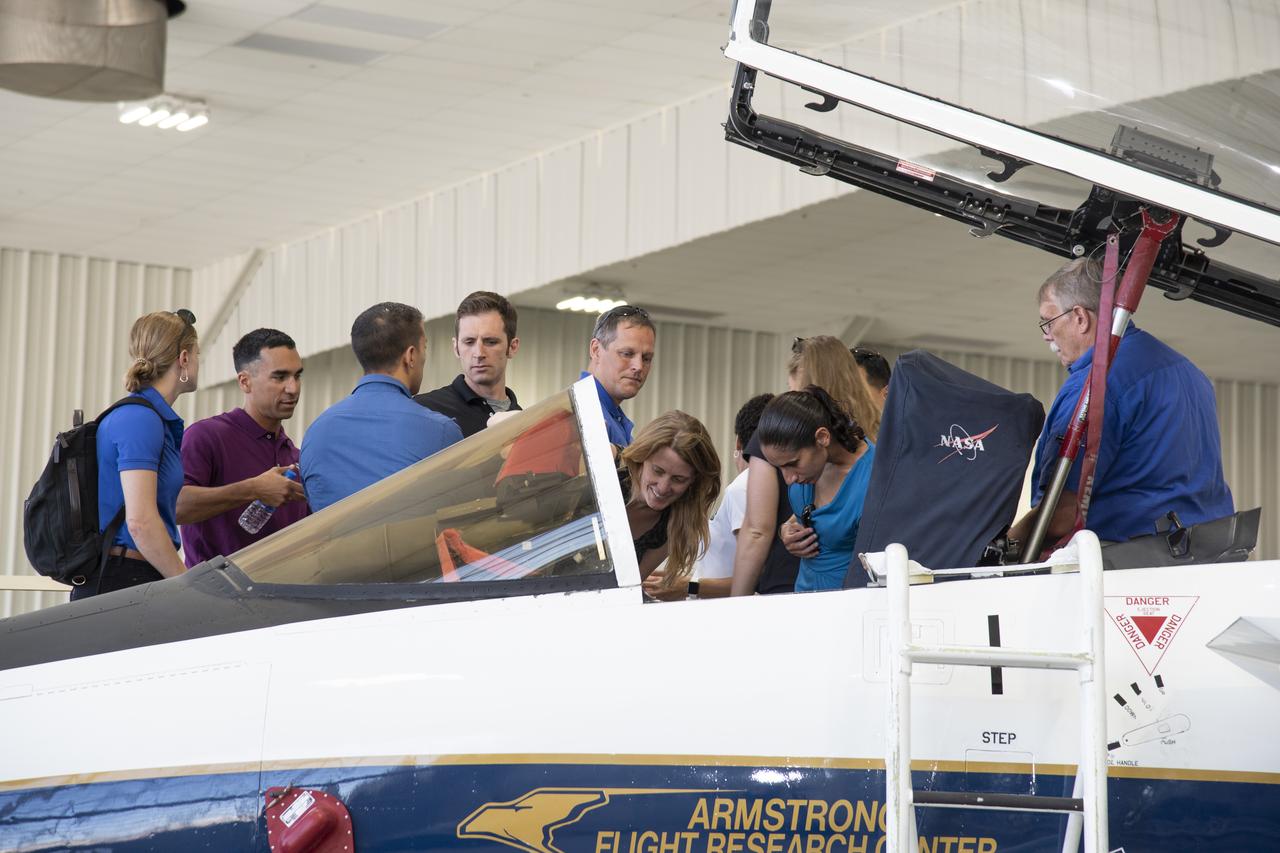

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California where they checked out a F-15 cockpit. The center is using its fleet of supersonic research support aircraft for sonic boom research, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
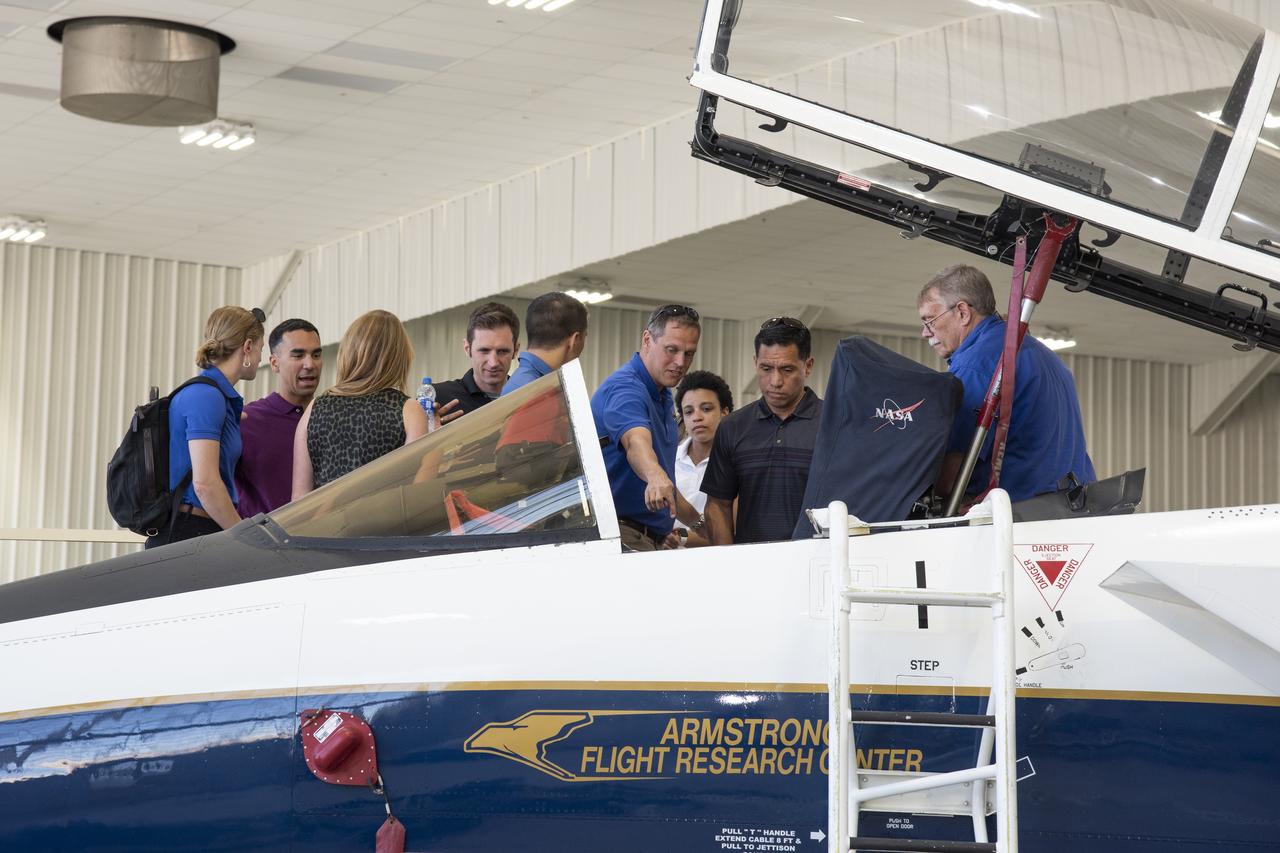

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California where they checked out a F-15 cockpit. The center is using its fleet of supersonic research support aircraft for sonic boom research, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, installs OSCAR to the flight hardware that will carry it on its suborbital flight test. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees have worked on constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Dr. Shawn Domagal-Goldman, Research Space Scientist, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
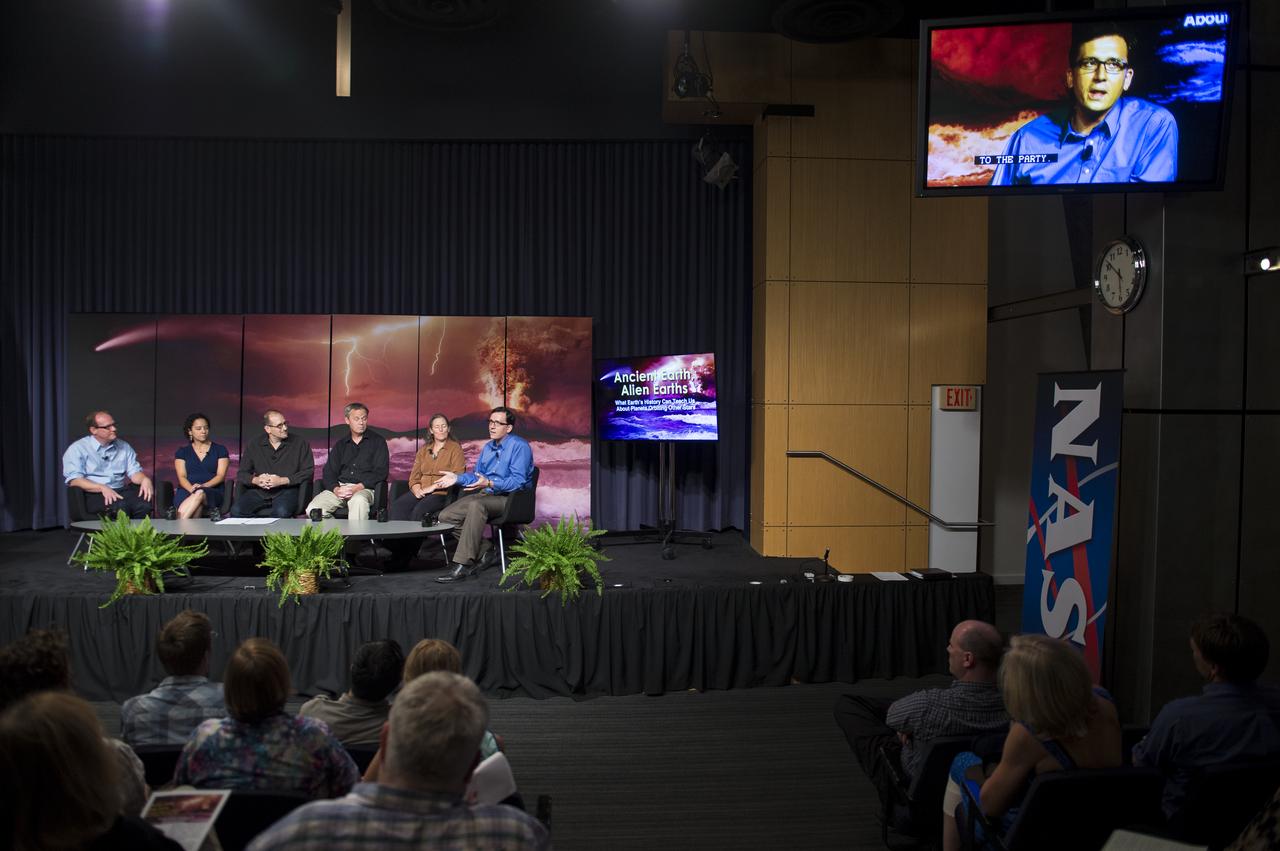

Dr. Shawn Domagal-Goldman, Research Space Scientist, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
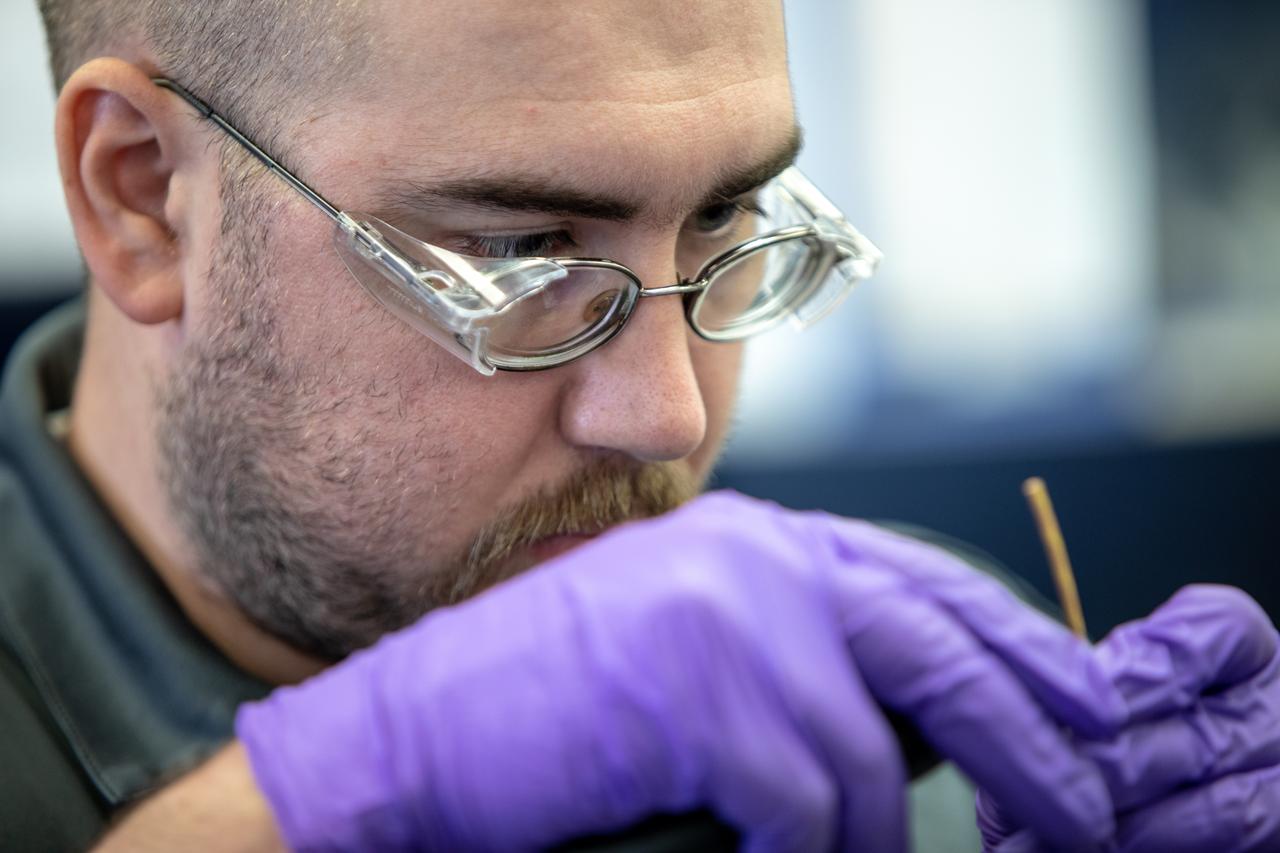

Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
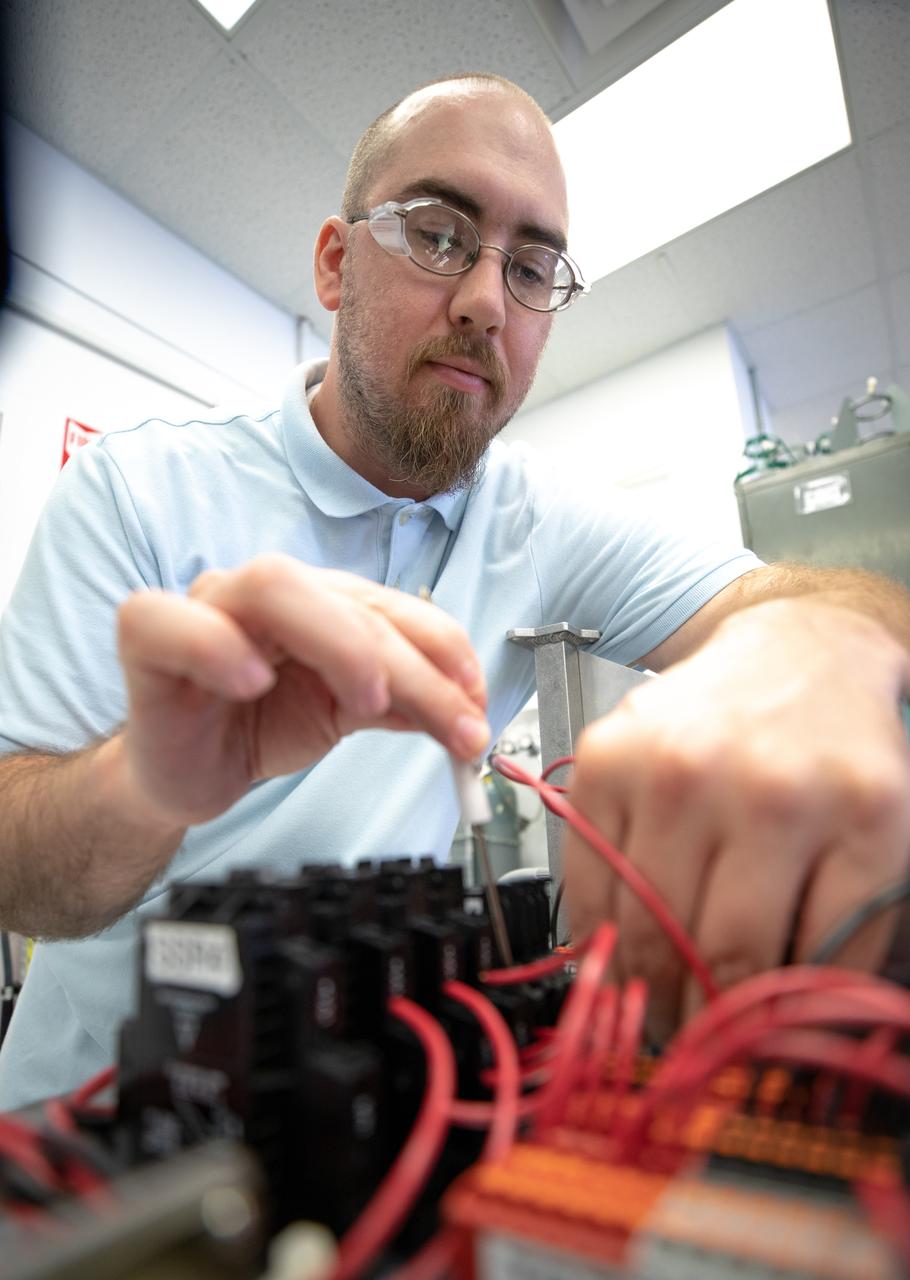
Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
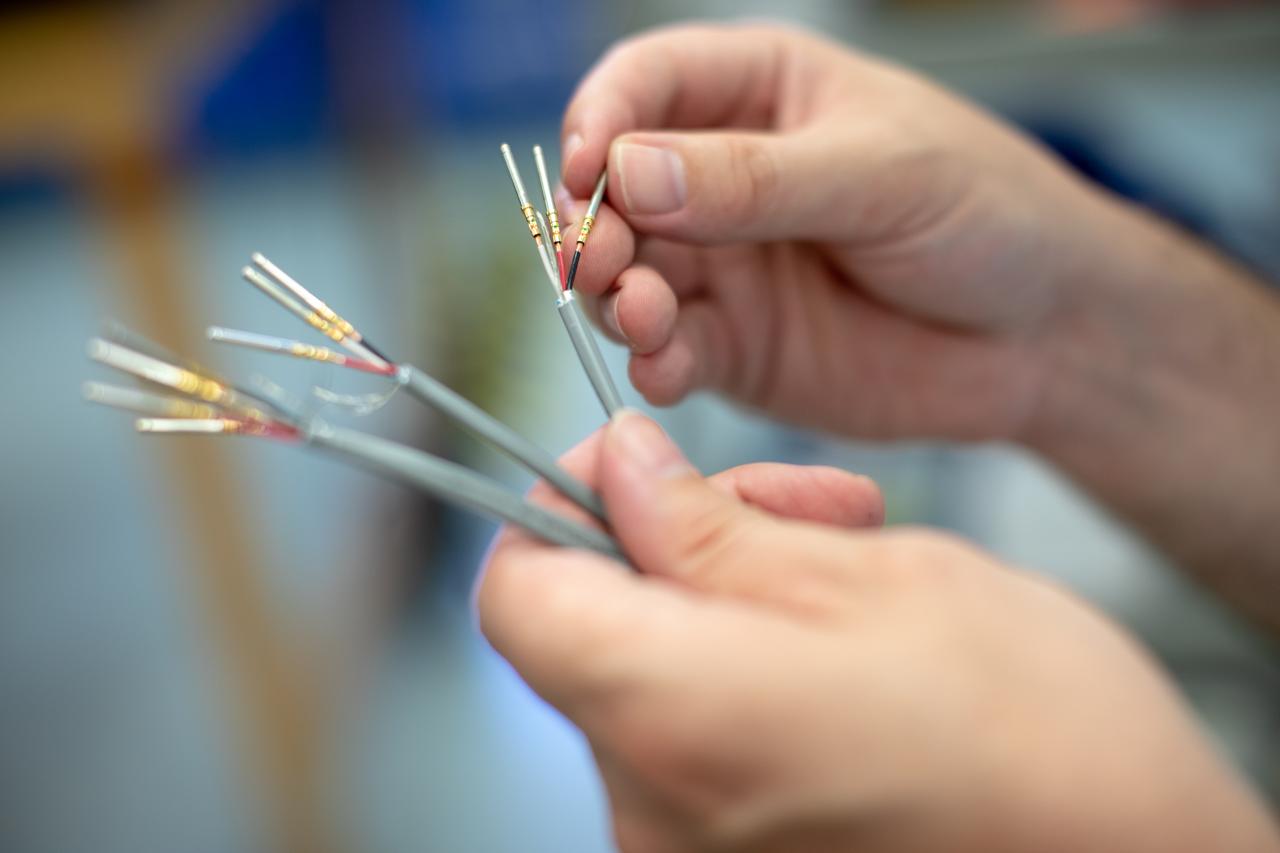
Flight hardware for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Rector, or OSCAR, is photographed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
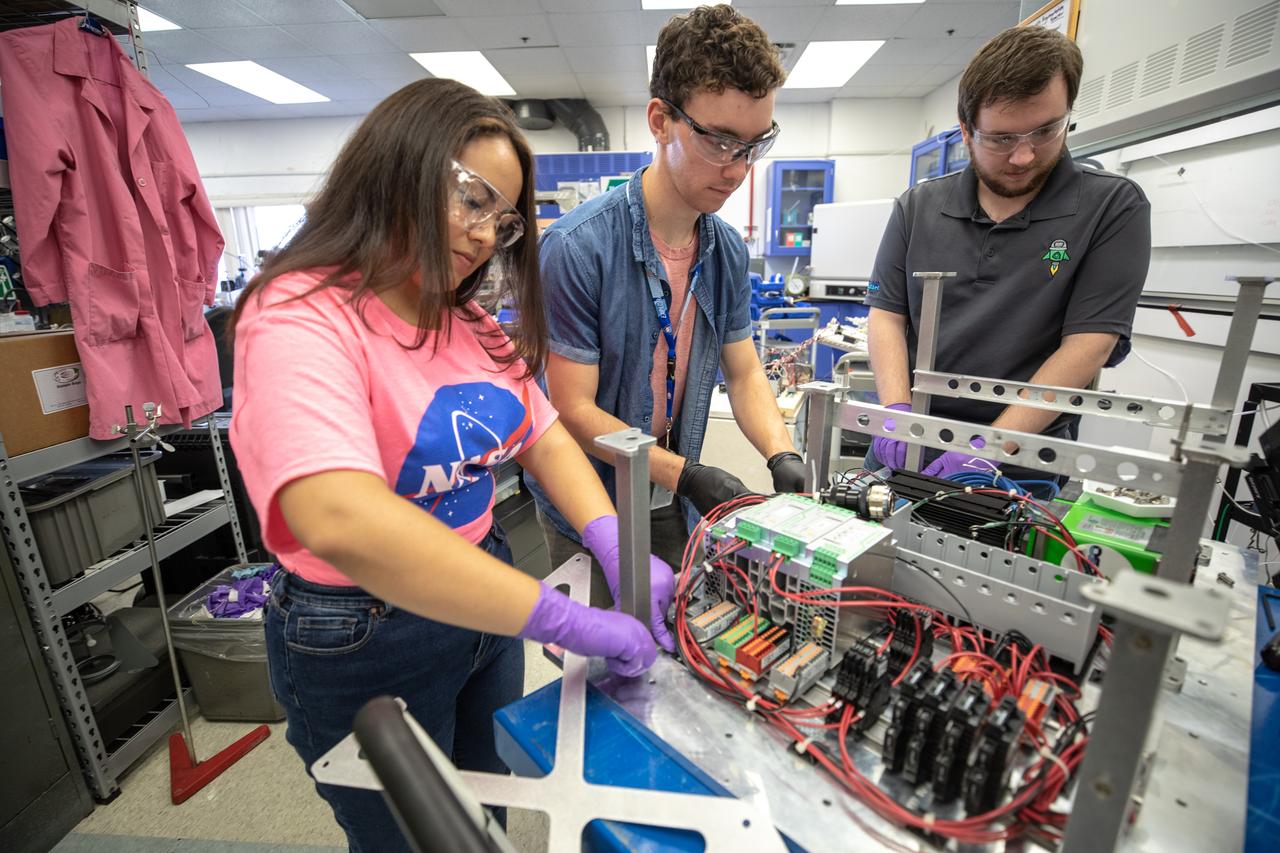

From left, Kennedy Space Center interns Brianna Sandoval and Patrick Follis, and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
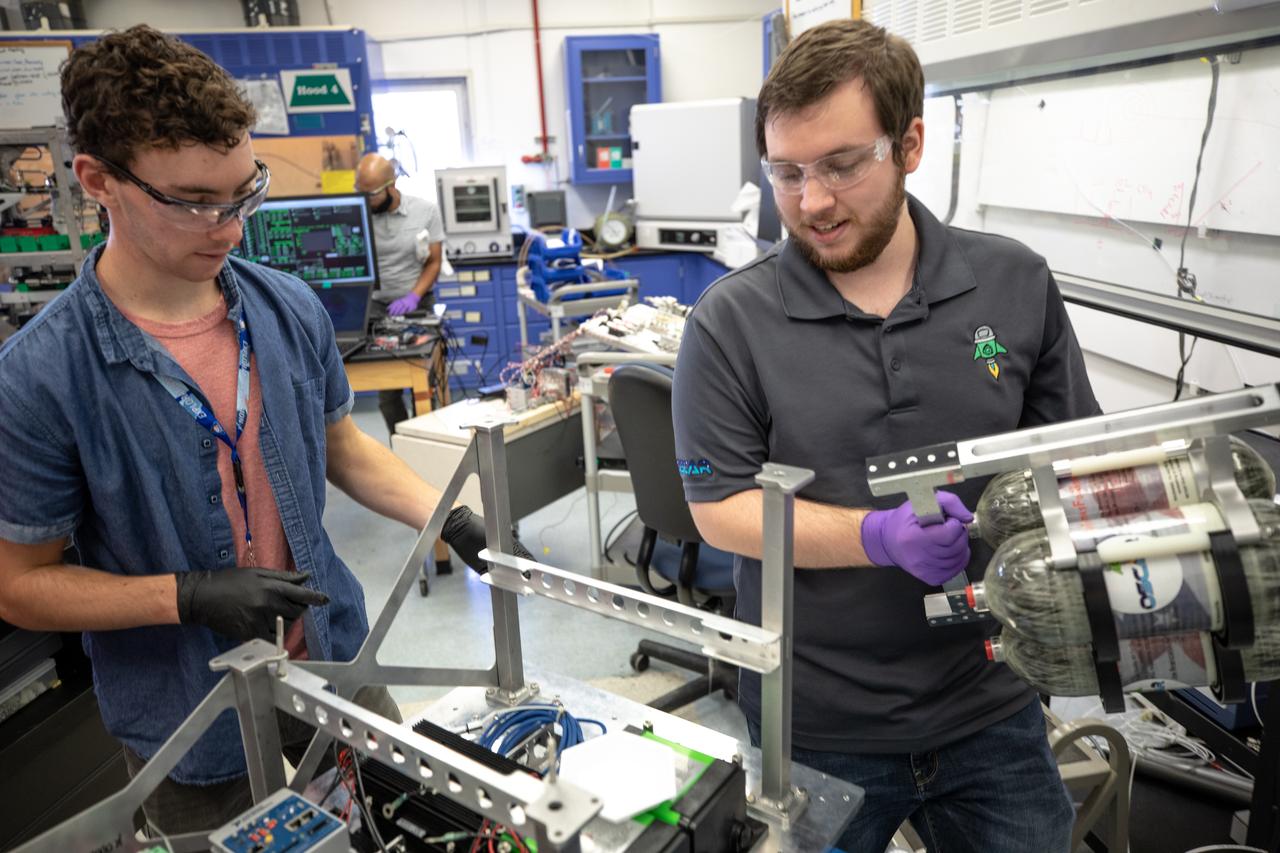
Kennedy Space Center employee Jonathan Gleeson (right) and Kennedy intern Patrick Follis assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
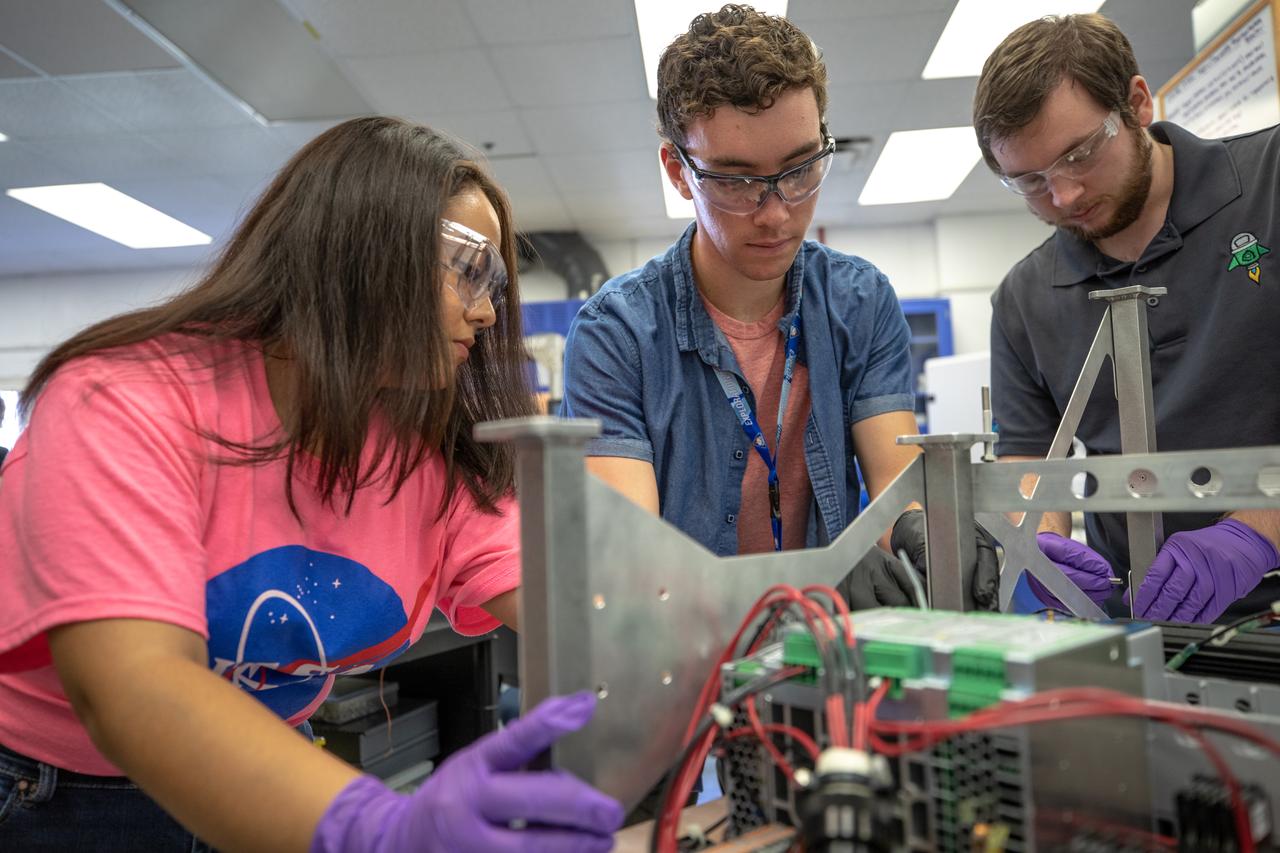

From left, Kennedy Space Center interns Brianna Sandoval and Patrick Follis, and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
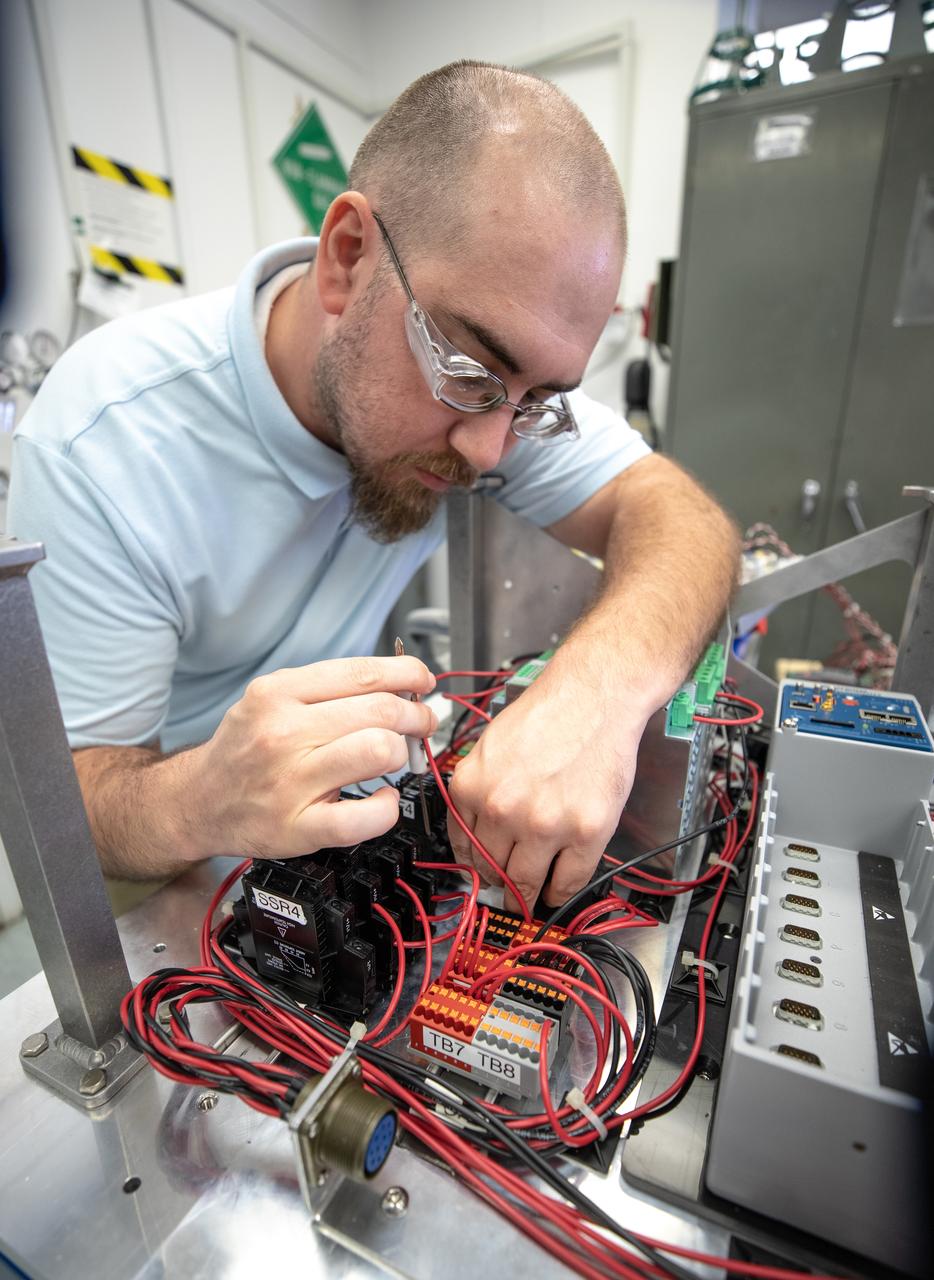

Thomas Cauvel, an intern assisting with software/electrical engineering on NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, at Kennedy Space Center assembles the flight hardware. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
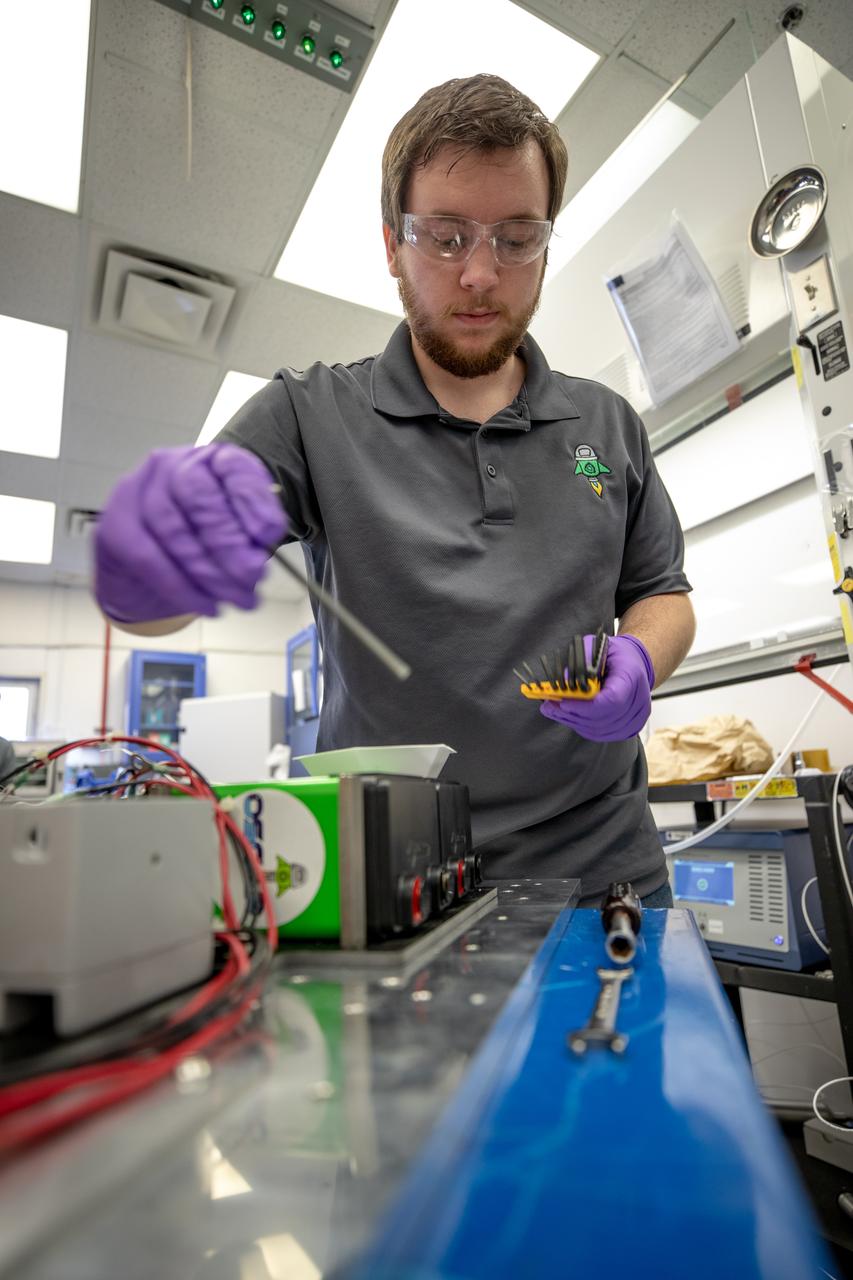

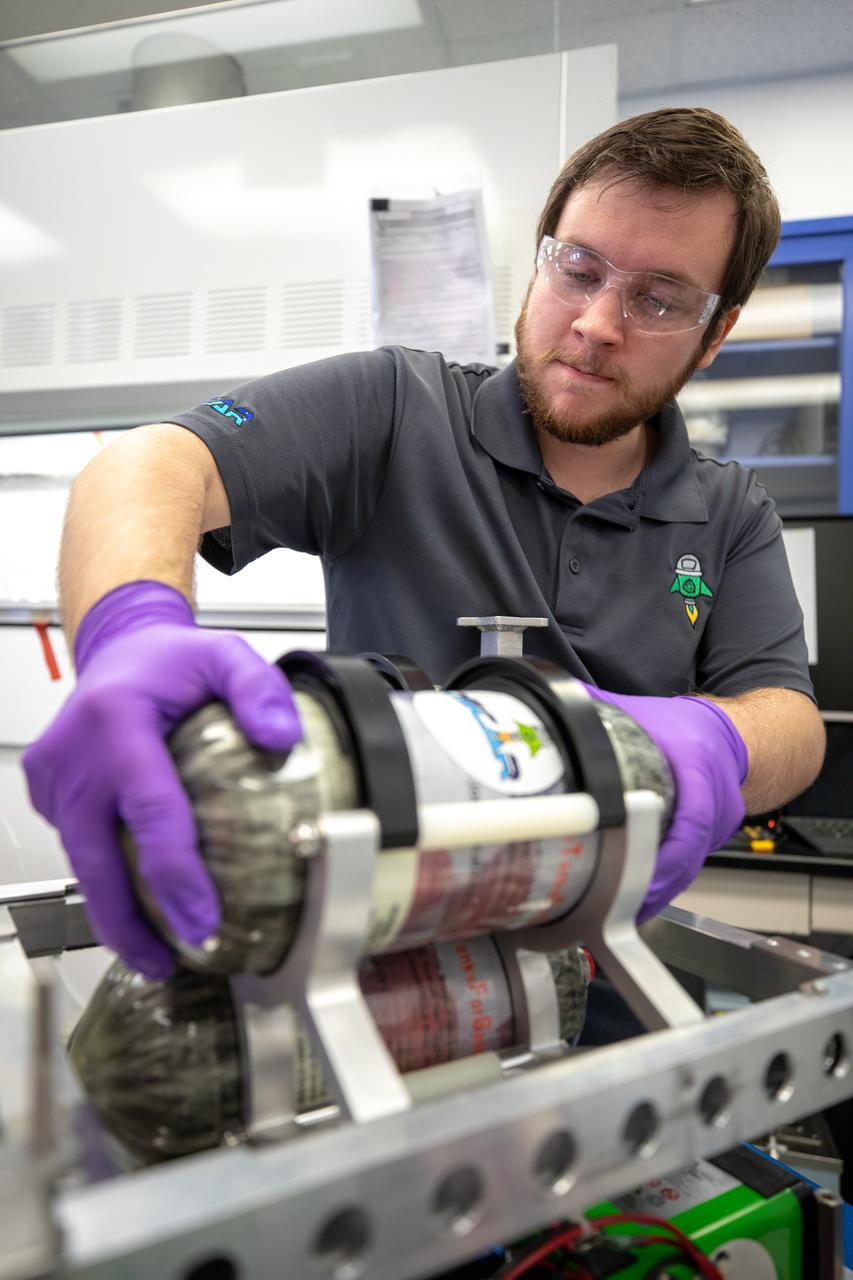
Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
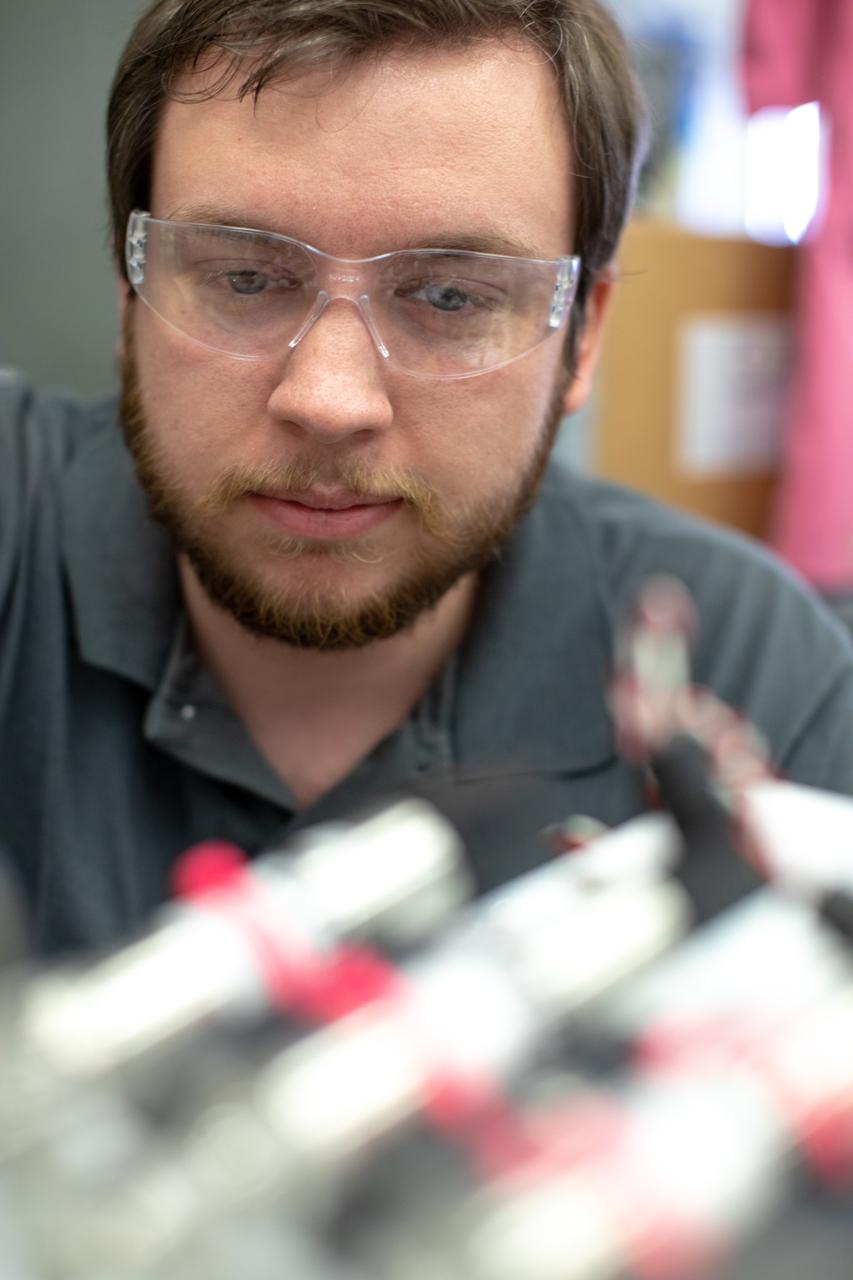

Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy Space Center employee providing support for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assembles the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
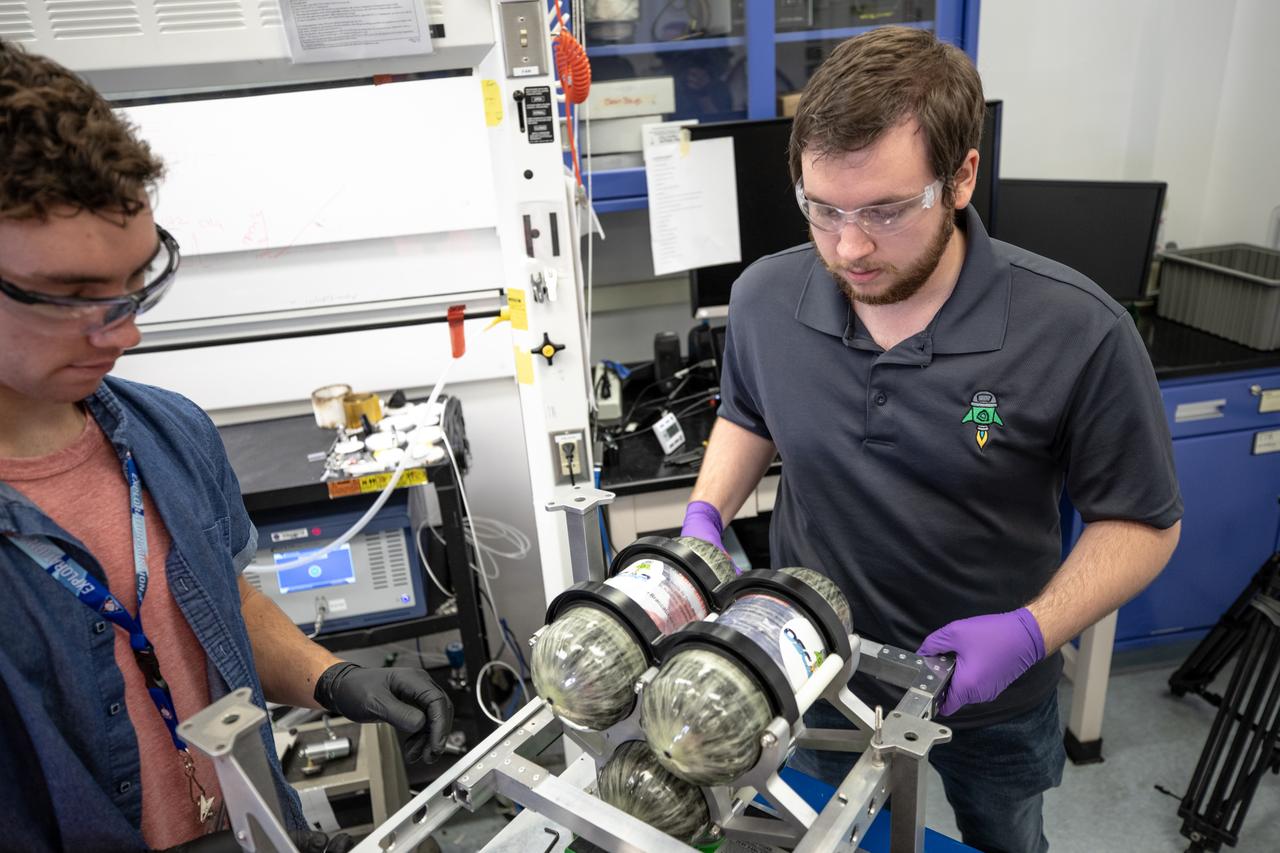

Kennedy Space Center employee Jonathan Gleeson (right) and Kennedy intern Patrick Follis assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Patrick Follis, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, assembles the flight hardware for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, is being prepared for suborbital flight testing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for the suborbital flight test.
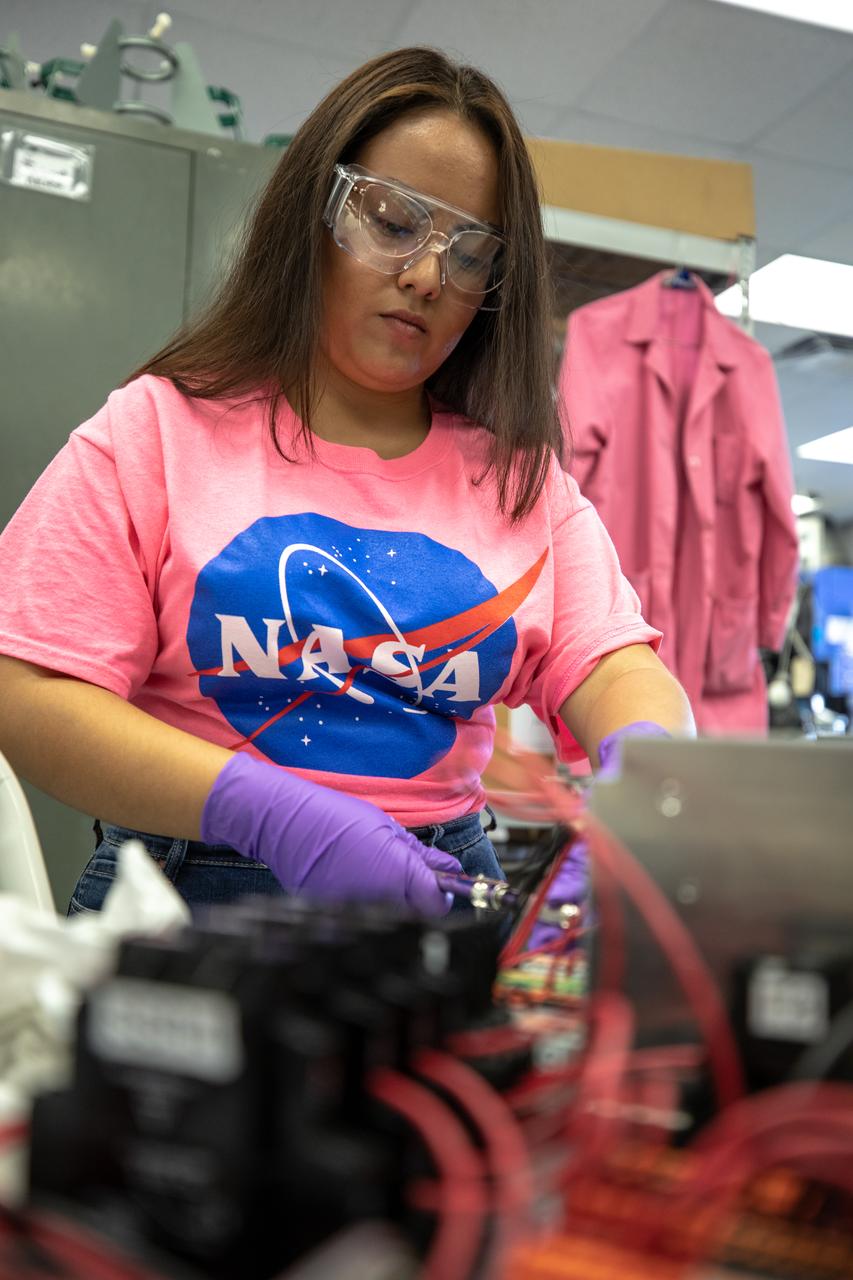

Brianna Sandoval, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, assembles the flight hardware of the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.

Kennedy Space Center intern Patrick Follis (left) and Kennedy employee Jonathan Gleeson assemble the flight hardware of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR – an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
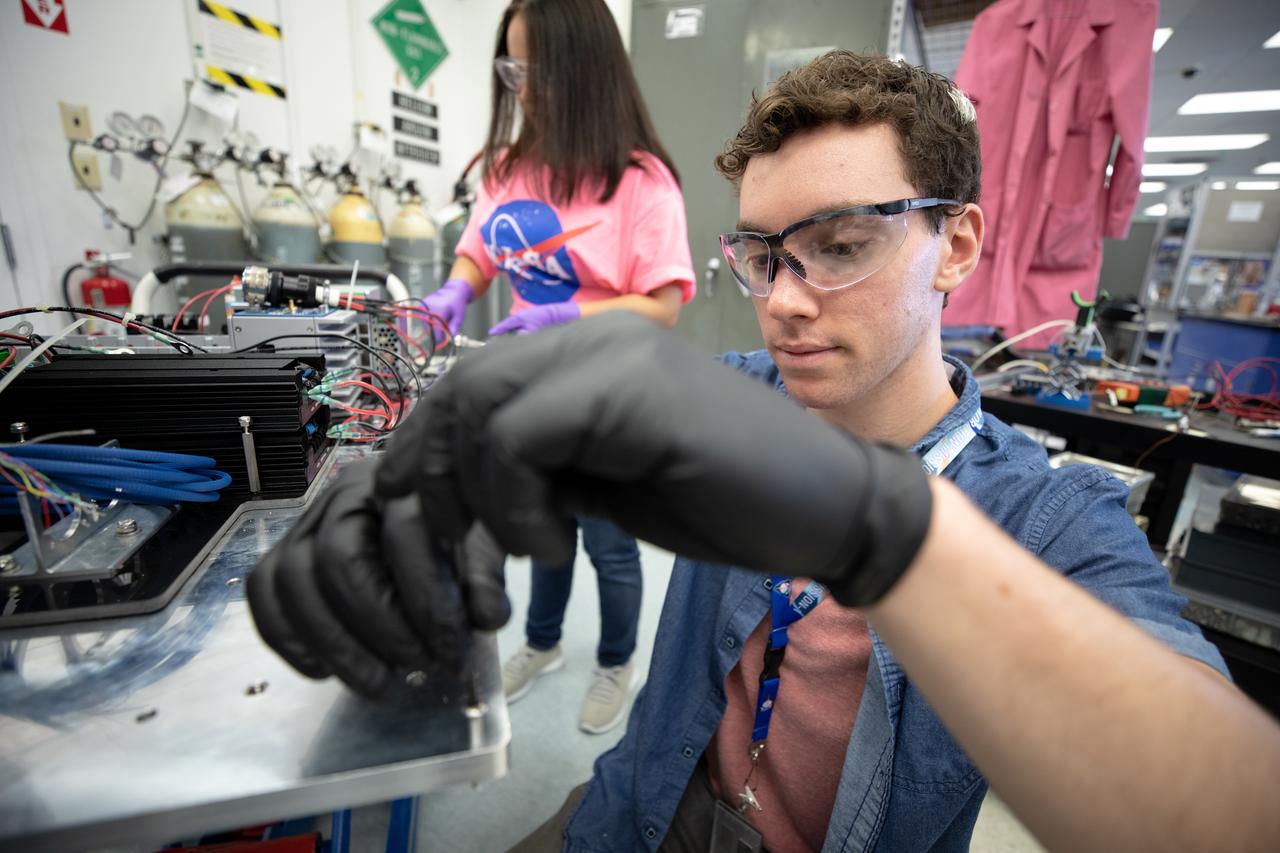

Interns Brianna Sandoval (left) and Patrick Follis at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida assemble the flight hardware for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
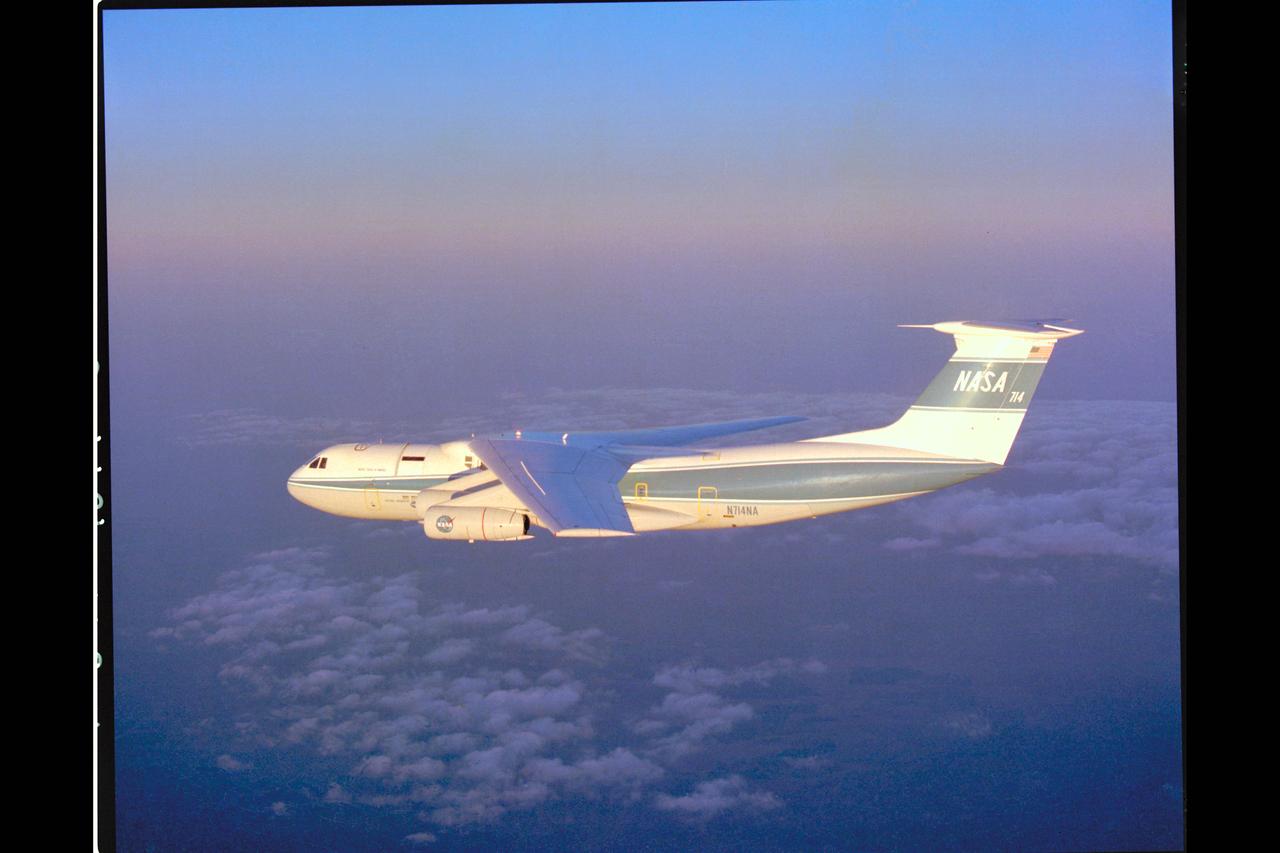

C-141 KAO in early morning flight home to Ames Research Center
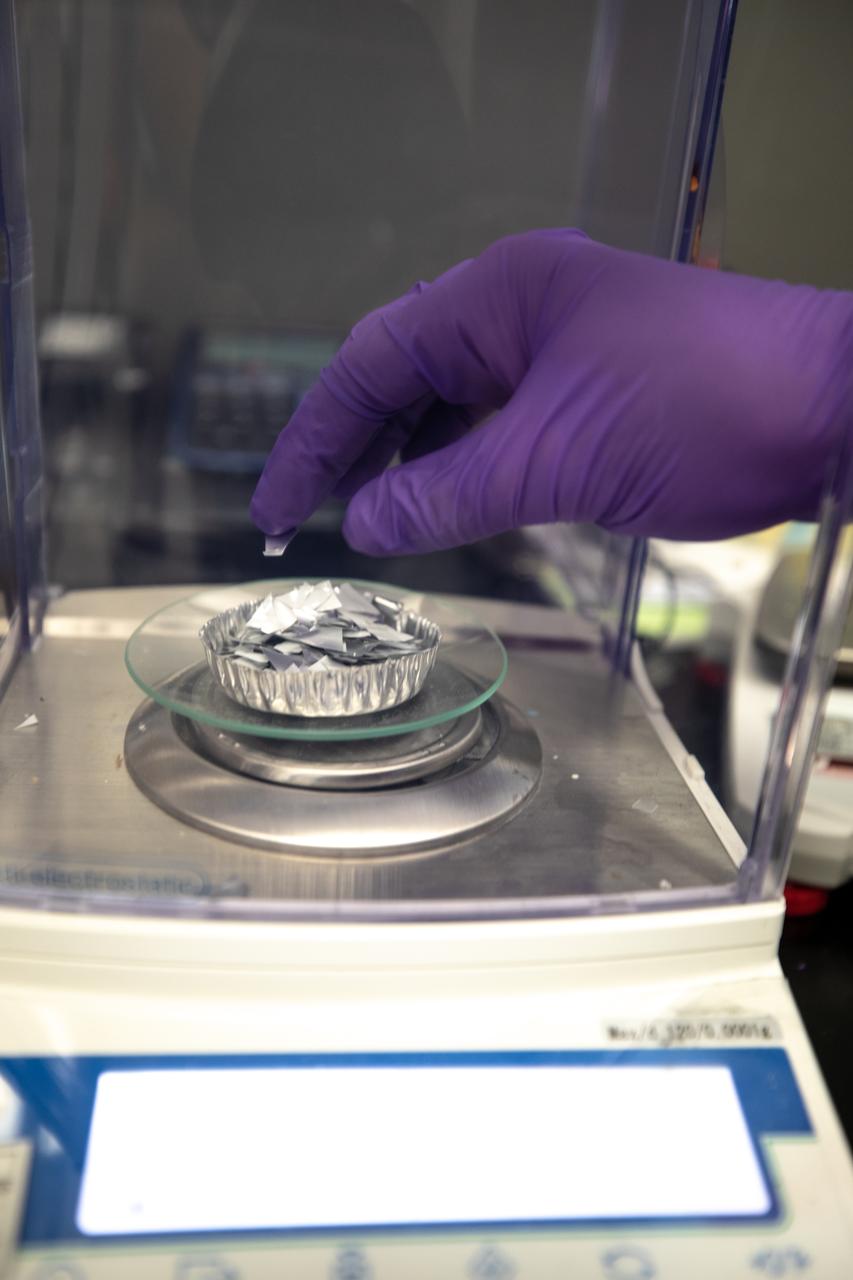
A Kennedy Space Center intern weighs trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
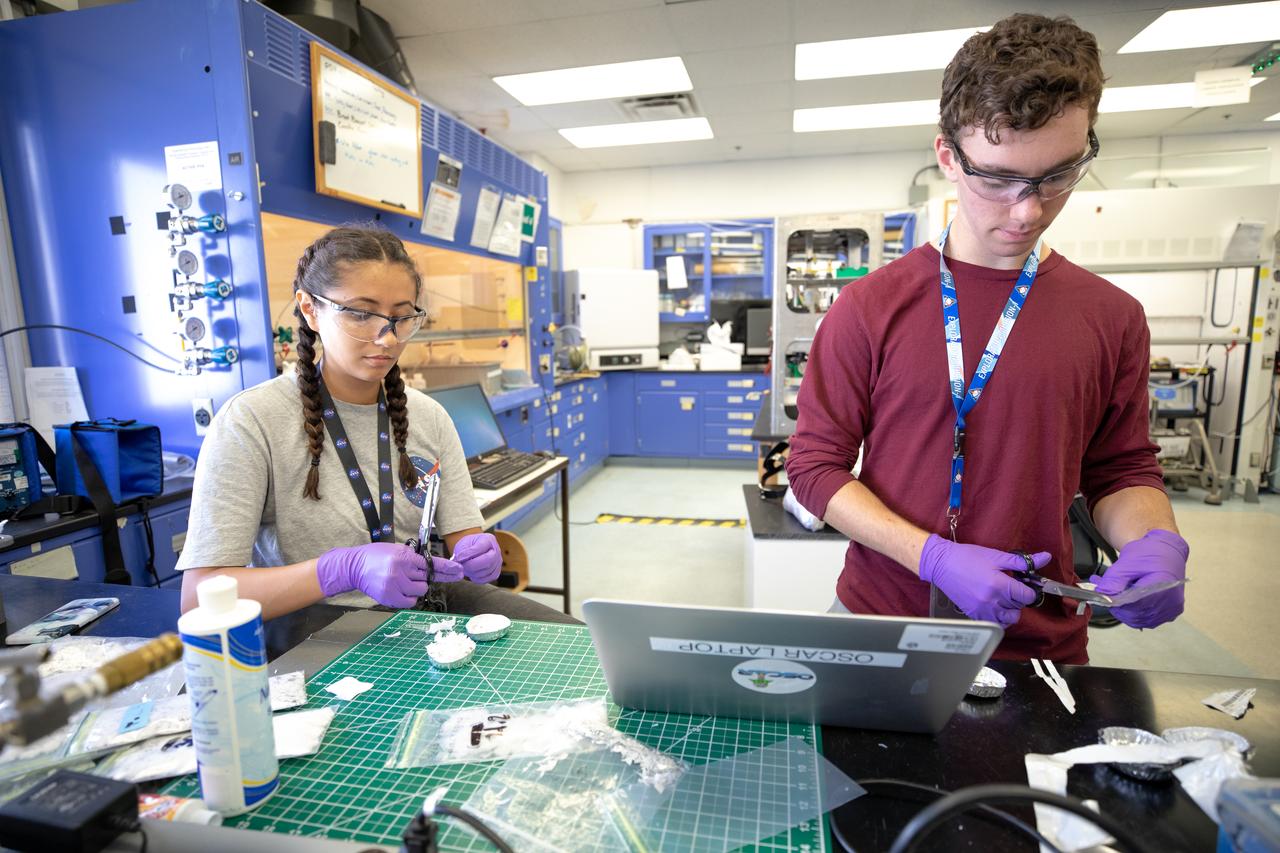

From left, interns Isabella Aviles and Patrick Follis at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cut up different types of material for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, to use as a trash simulant during microgravity testing. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, recover water from trash and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
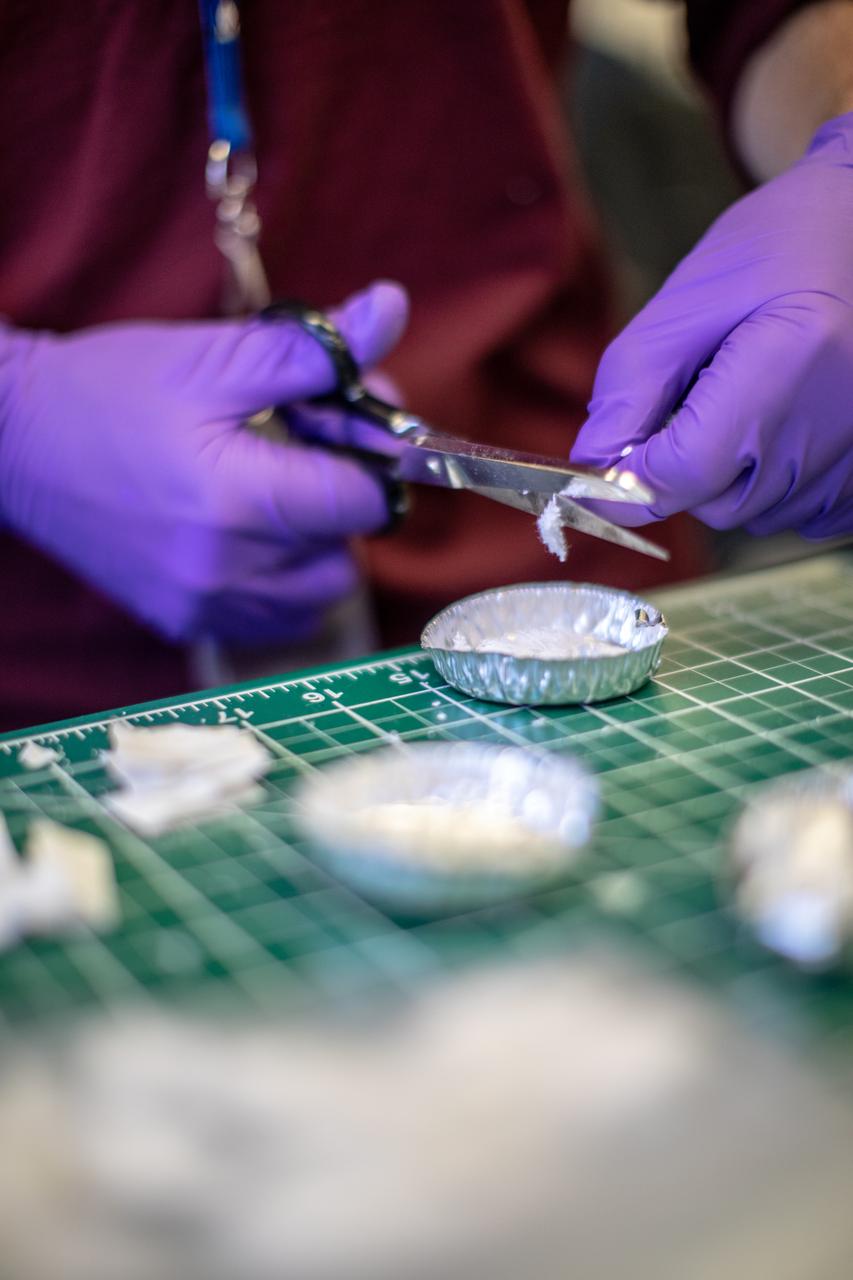

An intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts up different types of material to be utilized as trash simulant for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
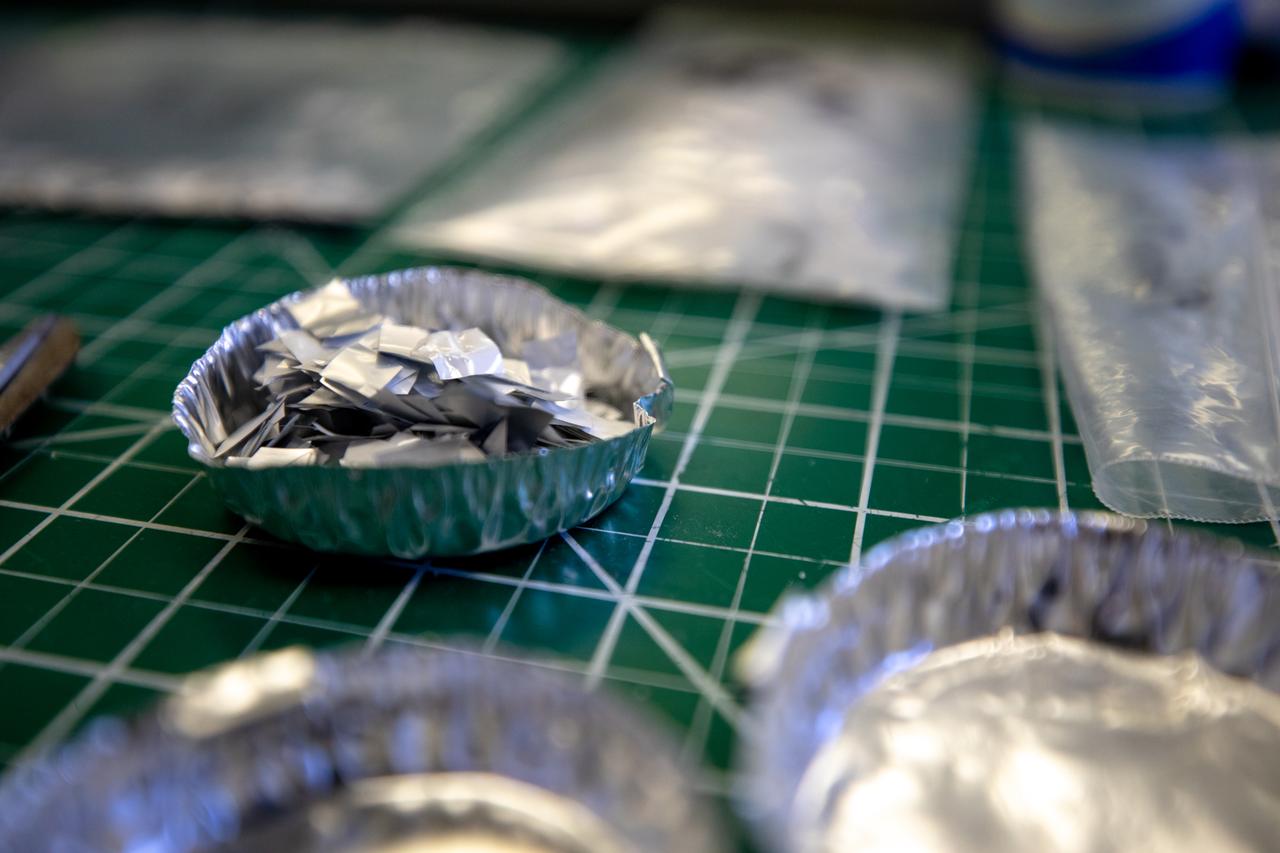

Pictured at Kennedy Space Center is trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
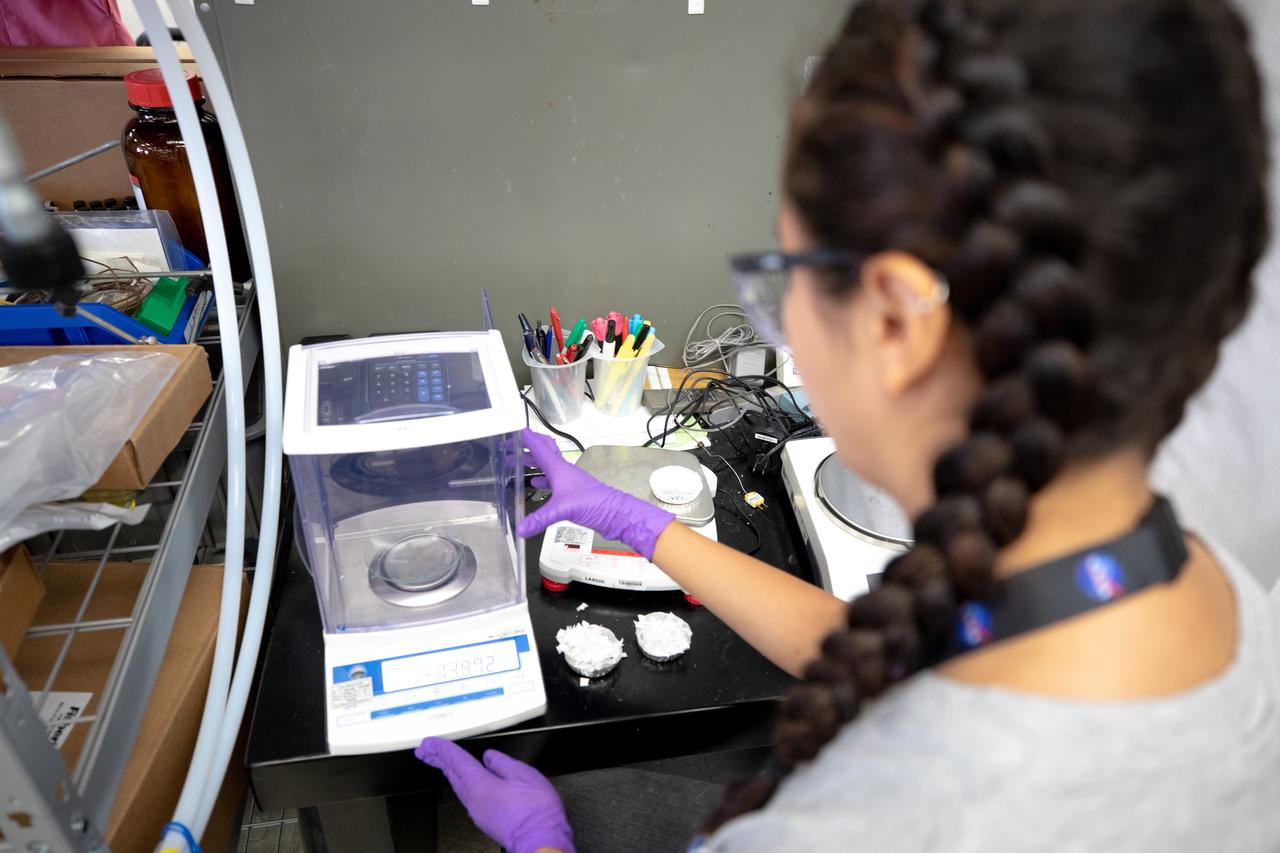
Isabella Aviles, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, weighs trash simulant – comprised of different types of material that have been cut into tiny pieces – that will be utilized for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
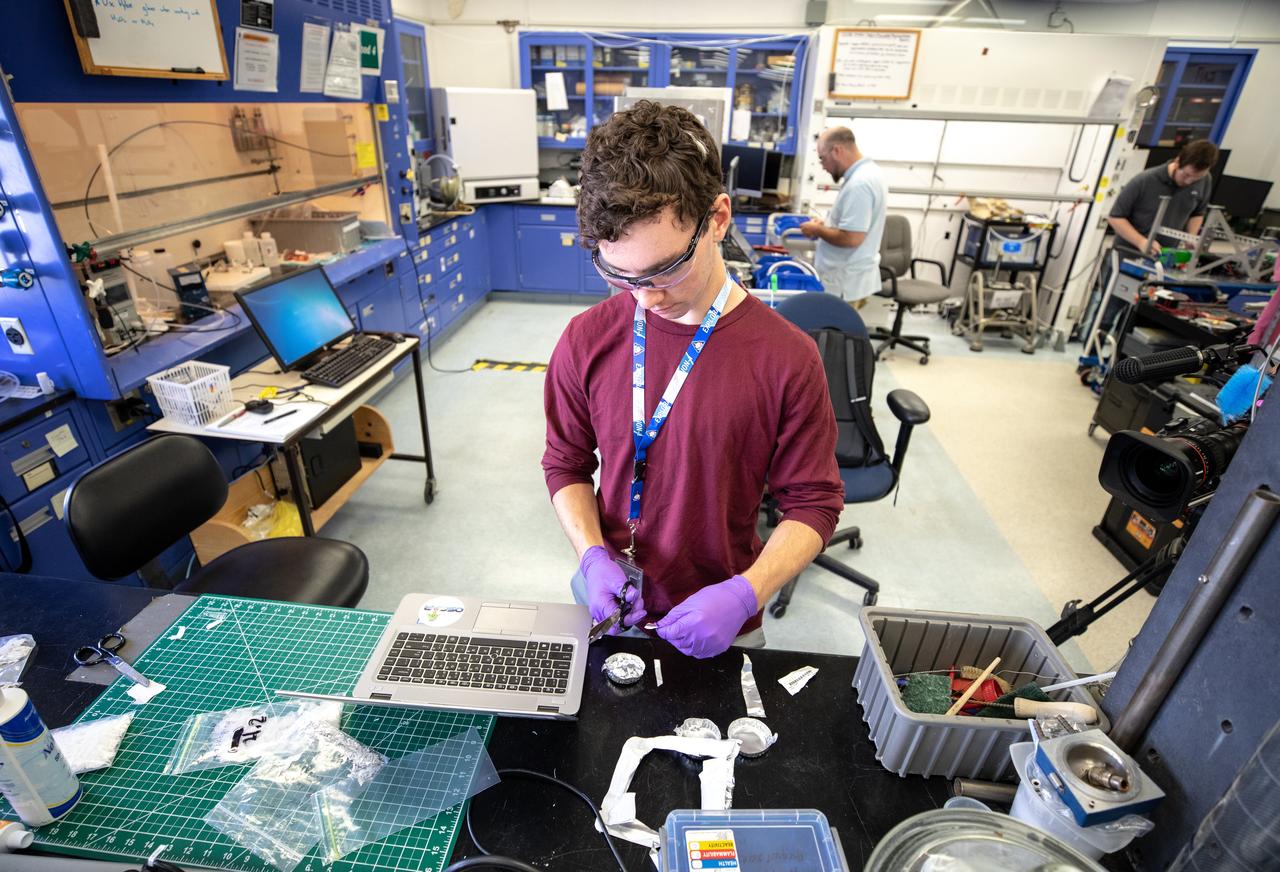

Patrick Follis, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cuts up different types of material for the agency’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, to use as a trash simulant during microgravity testing. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
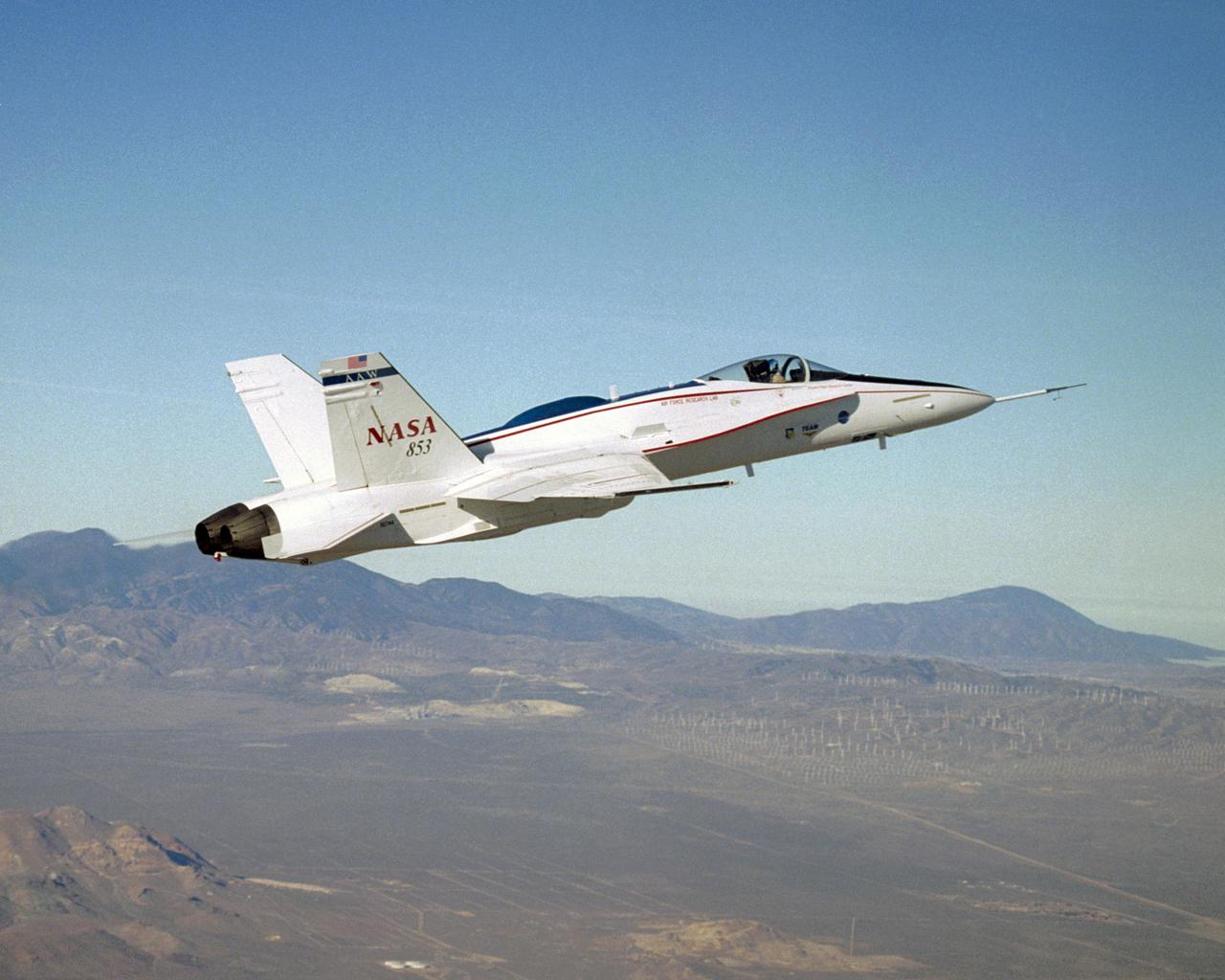

NASA's Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 resumed flight tests in the second phase of the program at the Dryden Flight Research Center in early December 2004.
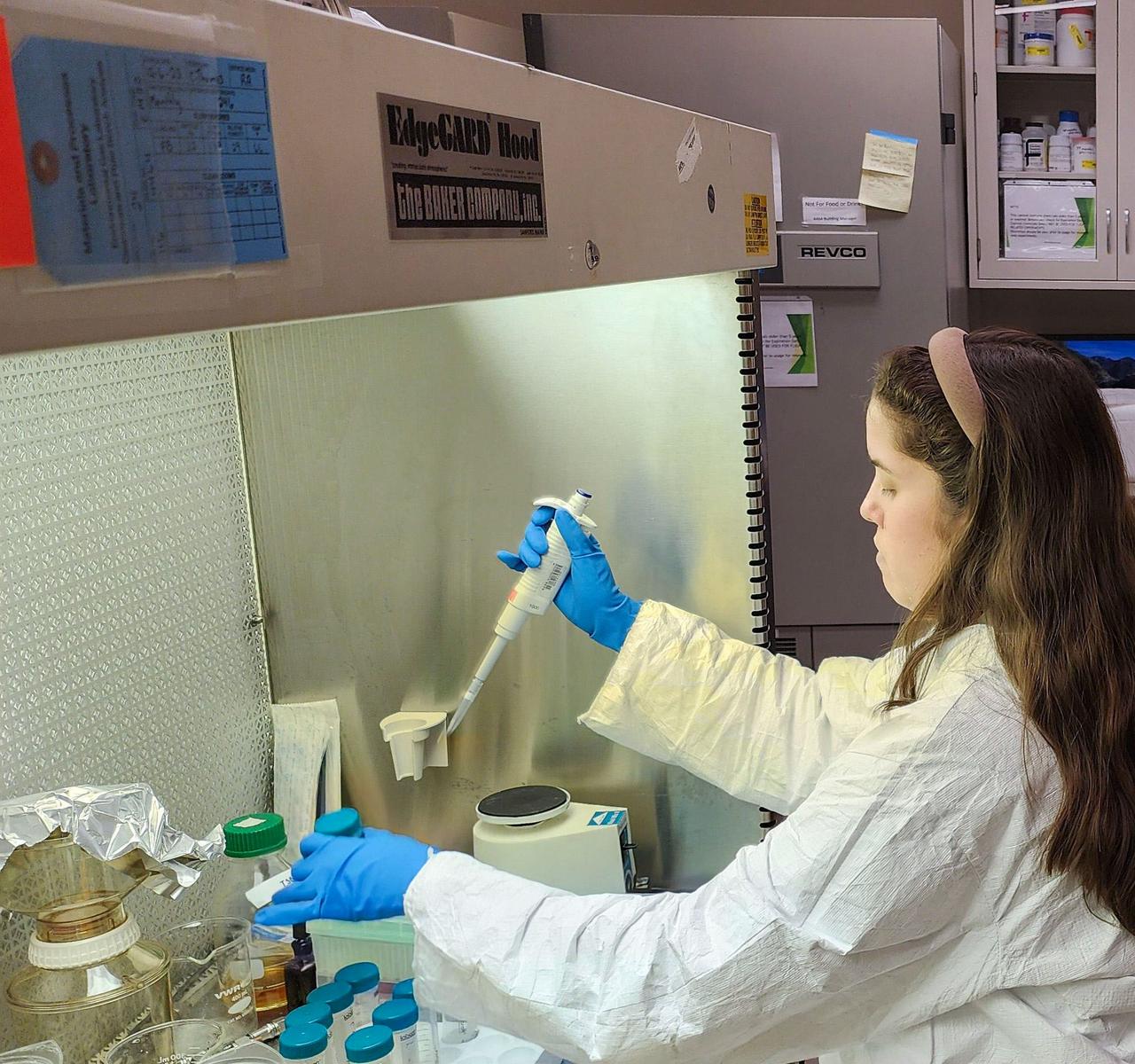

jsc2025e007250 (2/14/2025) --- Early plasmid research in the Biofilm lab at the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
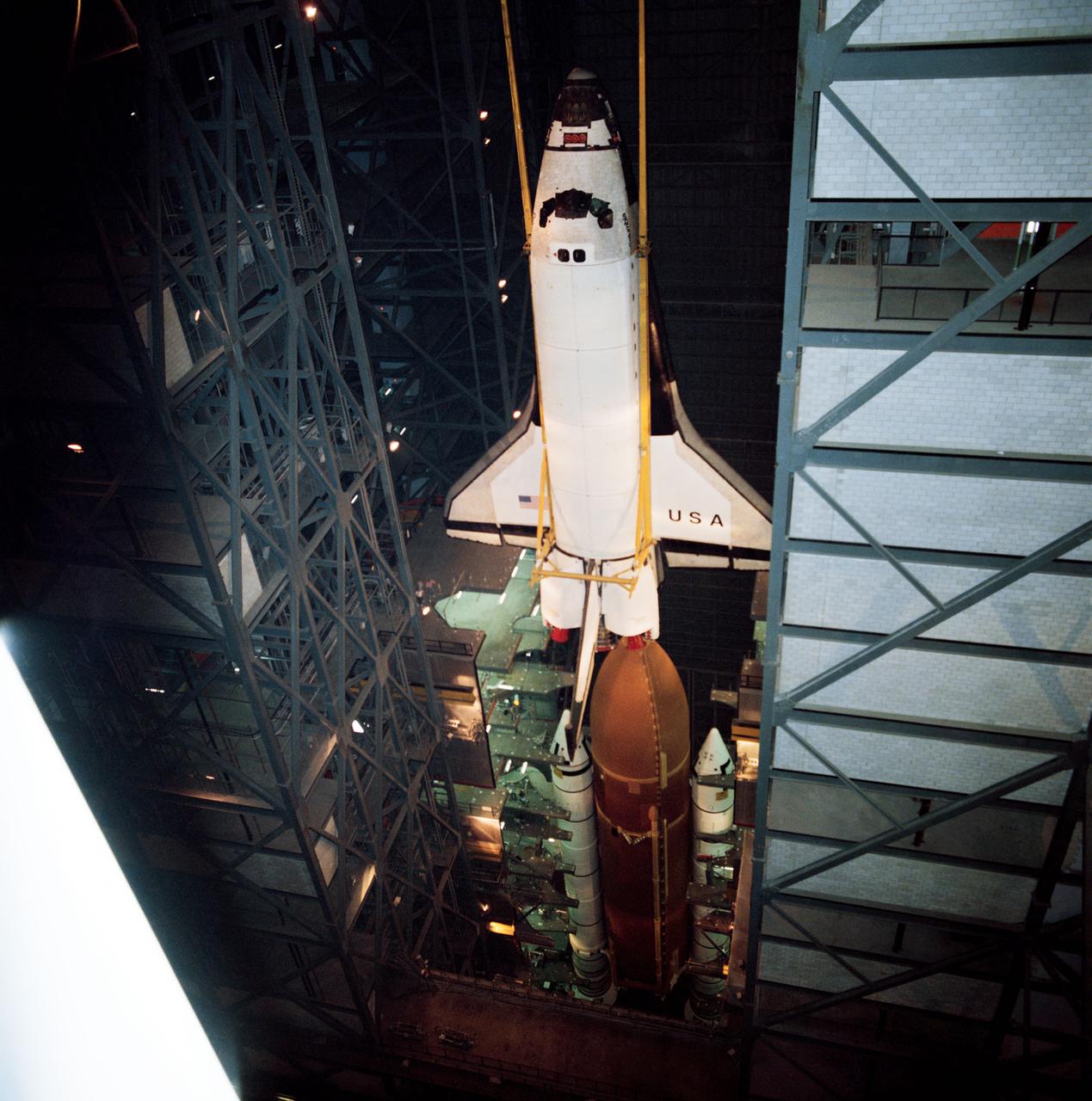

S89-40392 (12 July 1989) --- Inside KSC's giant vehicle assembly building, Space Shuttle Columbia is mated to two solid rocket boosters (SRB) and an external fuel tank as preparations continue for an early September launch. The mission is scheduled as a DOD-devoted flight, set for launch early next month.
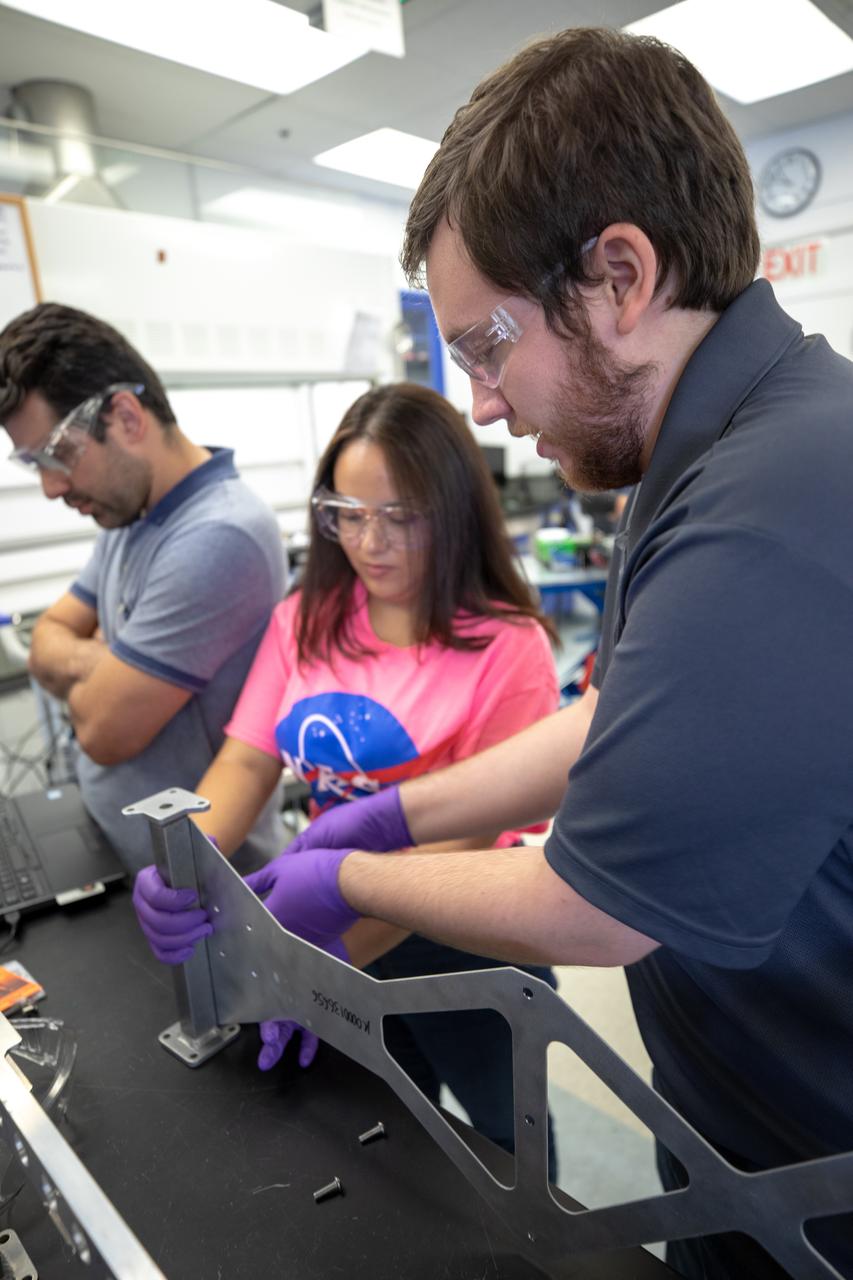

From left, Kennedy Space Center Mechanical Engineer Jaime Toro, NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) data acquisition and testing; Brianna Sandoval, OSCAR intern; and Jonathan Gleeson, Kennedy employee providing support for OSCAR under the center’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations contract, assemble the flight hardware of OSCAR. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the Florida spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. OSCAR would reduce the amount of space needed for waste storage within a spacecraft, turn some waste into gasses that have energy storage and life support applications, and ensure waste is no longer biologically active. A prototype has been developed, and a team of Kennedy employees are in the process of constructing a new rig for suborbital flight testing.
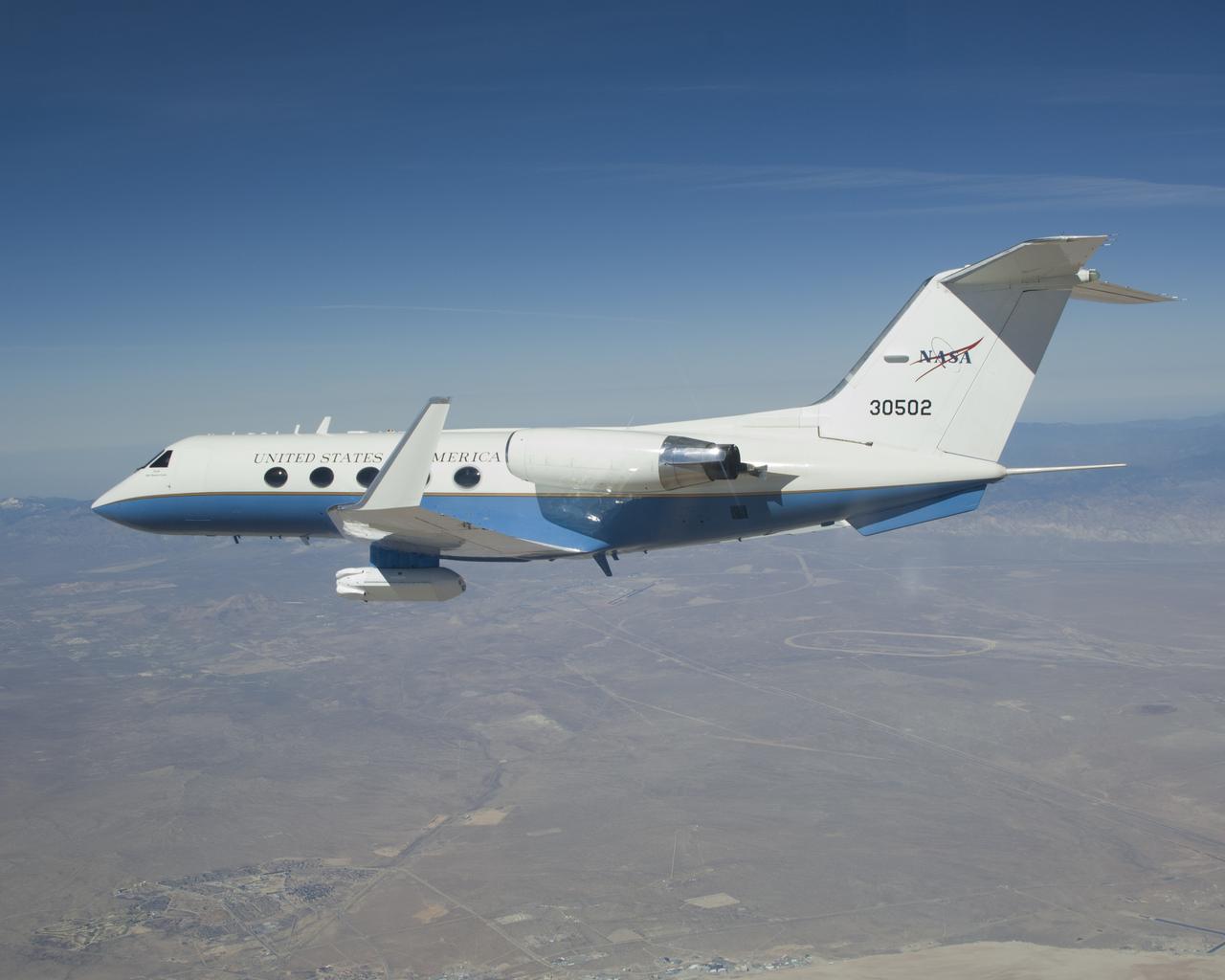

The effect of the underbelly UAVSAR pod on the aerodynamics of NASA's Gulfstream-III research aircraft was evaluated during several check flights in early 2007.

A half-dozen test flights in early 2007 evaluated the aerodynamic effect of the UAVSAR pod on the performance of NASA's Gulfstream-III research testbed.
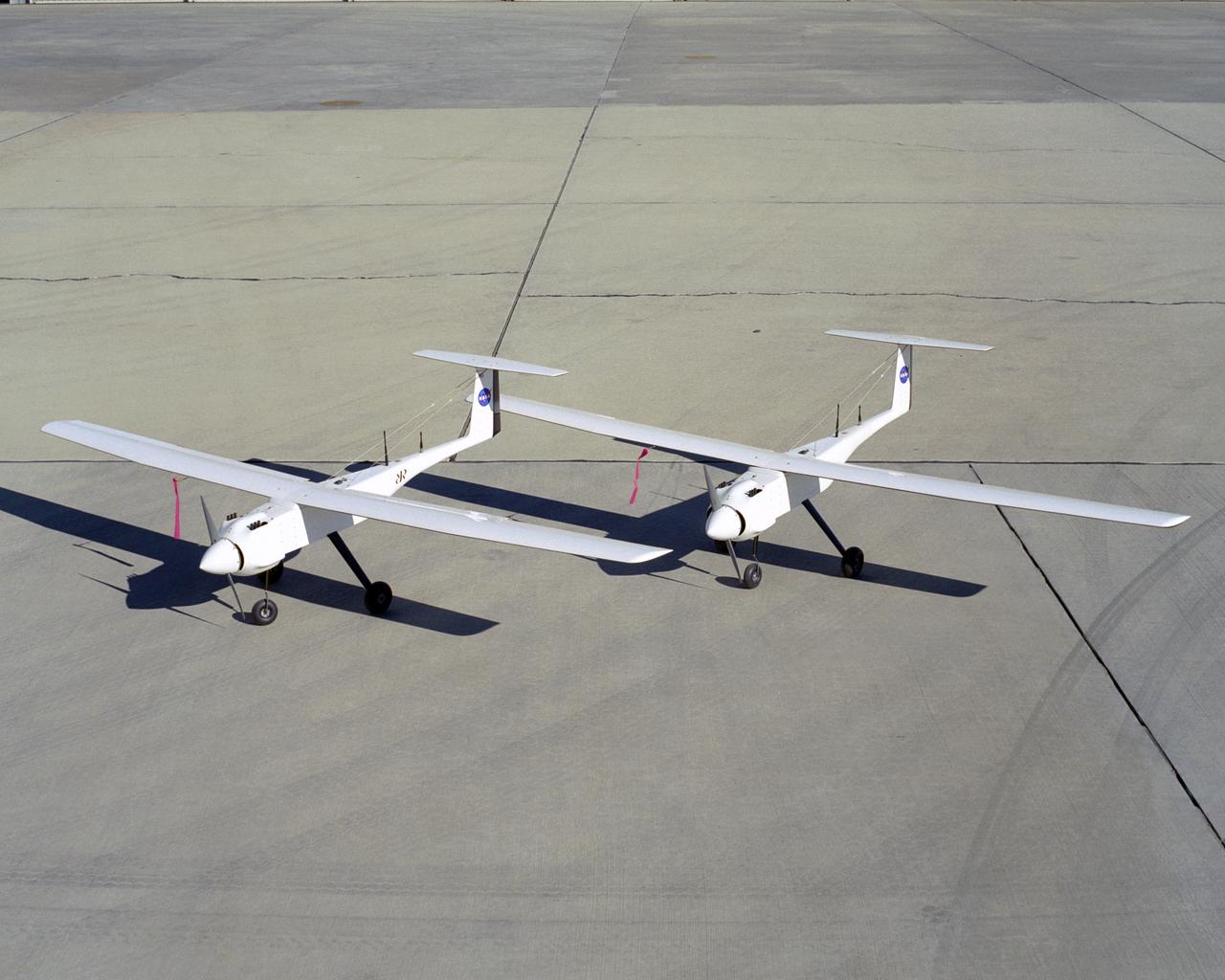

Two identical RnR Products APV-3 aircraft validated cooperative flight control software in the Networked UAV Teaming Experiment at NASA Dryden in early 2005.
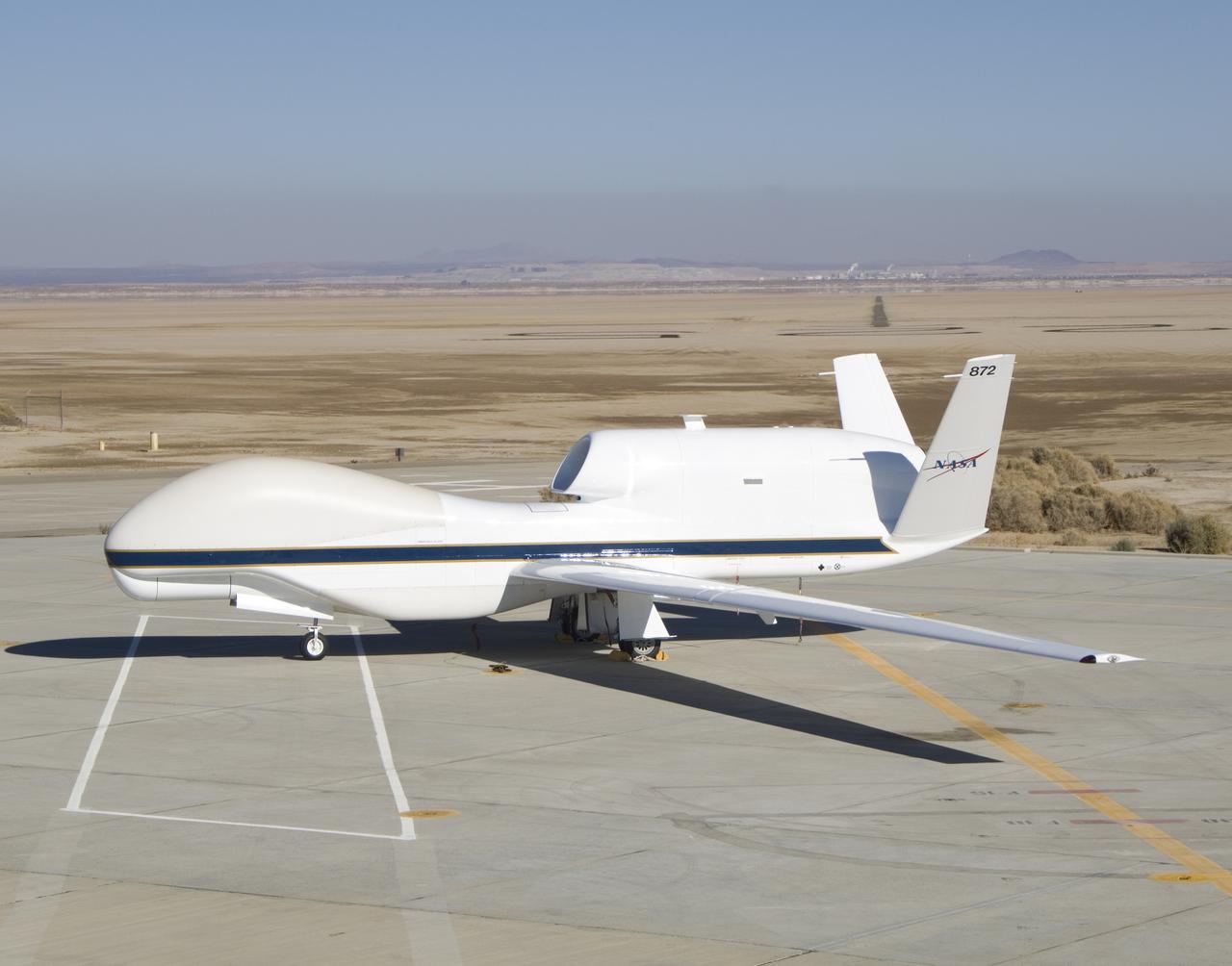

In its new white-and-blue NASA livery, an early development model of the Global Hawk unmanned aircraft rests on the ramp at the Dryden Flight Research Center.
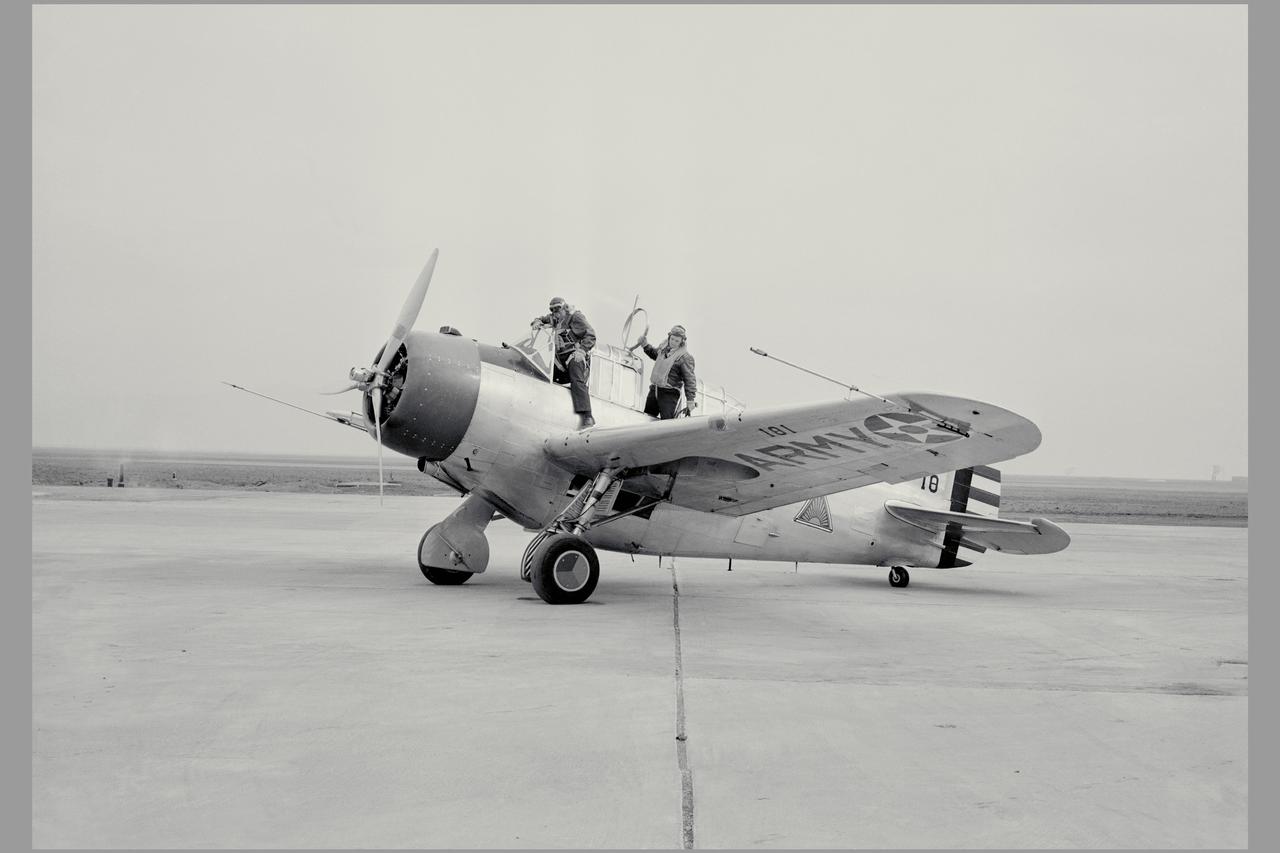

W.H. MCAVOY AMES TEST PILOT RETURNING FROM AN EARLY FLIGHT OF FIRST TEST AIRPLANE AT AMES, A NORTH AMERICAN O-47
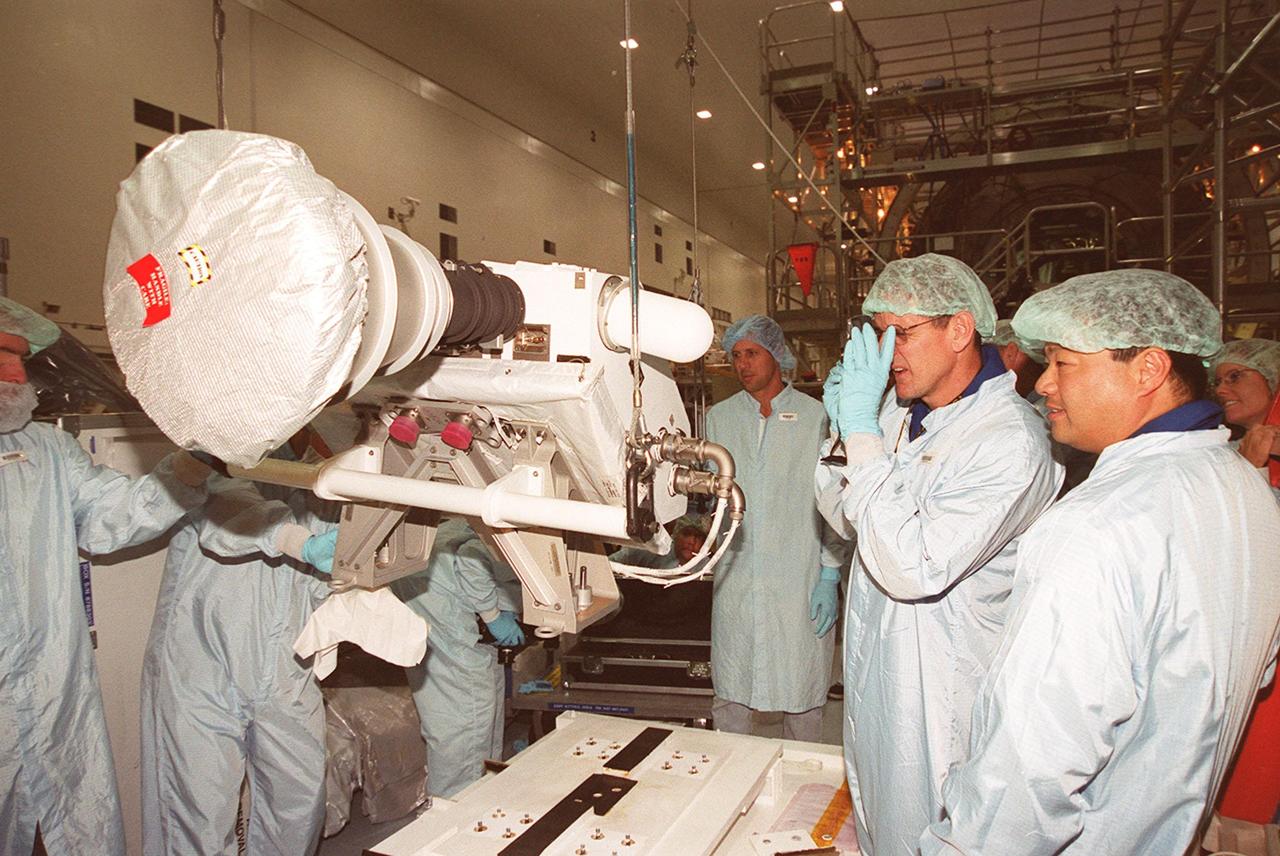

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew examine equipment that will be part of their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, the mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan.
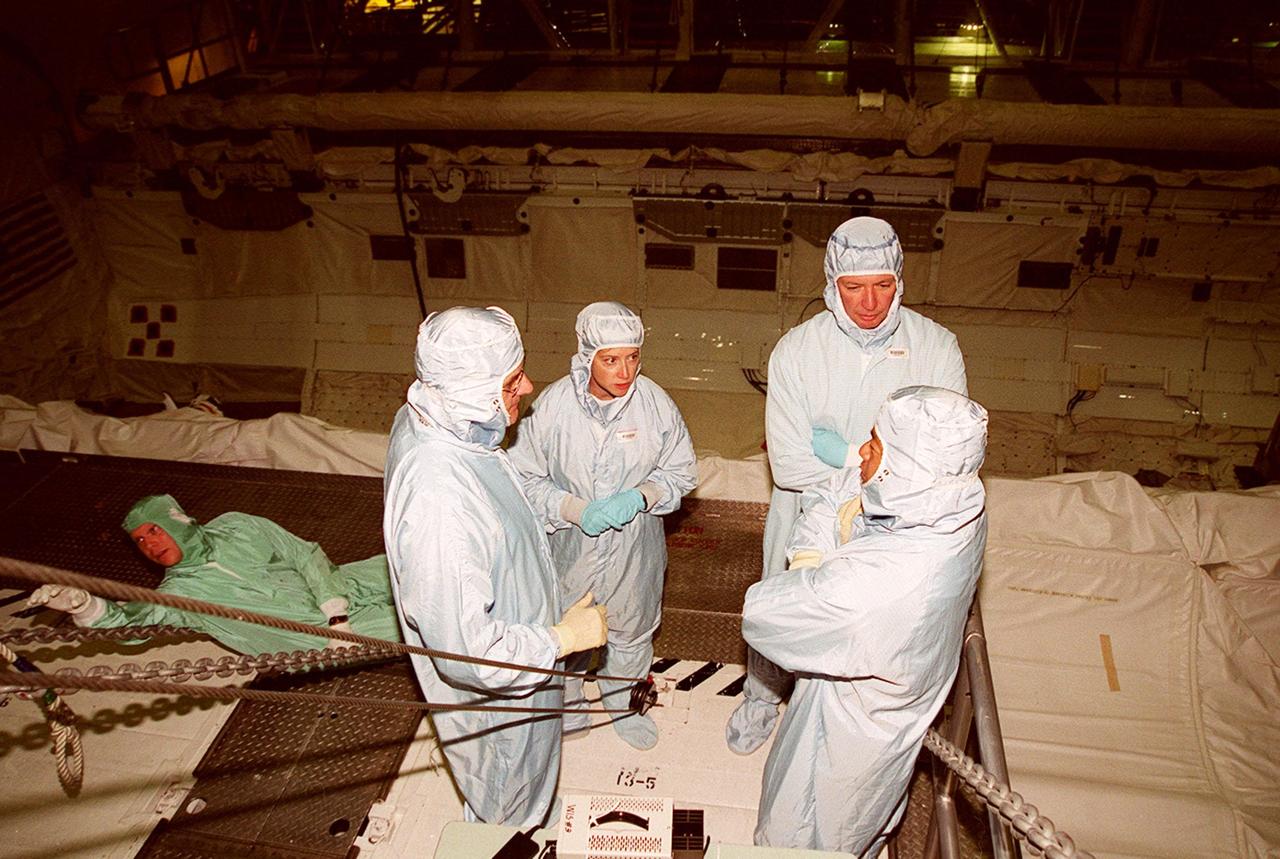

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew take a moment for discussion while checking out the payload bay of the orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. Their mission, the fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, includes as payload the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
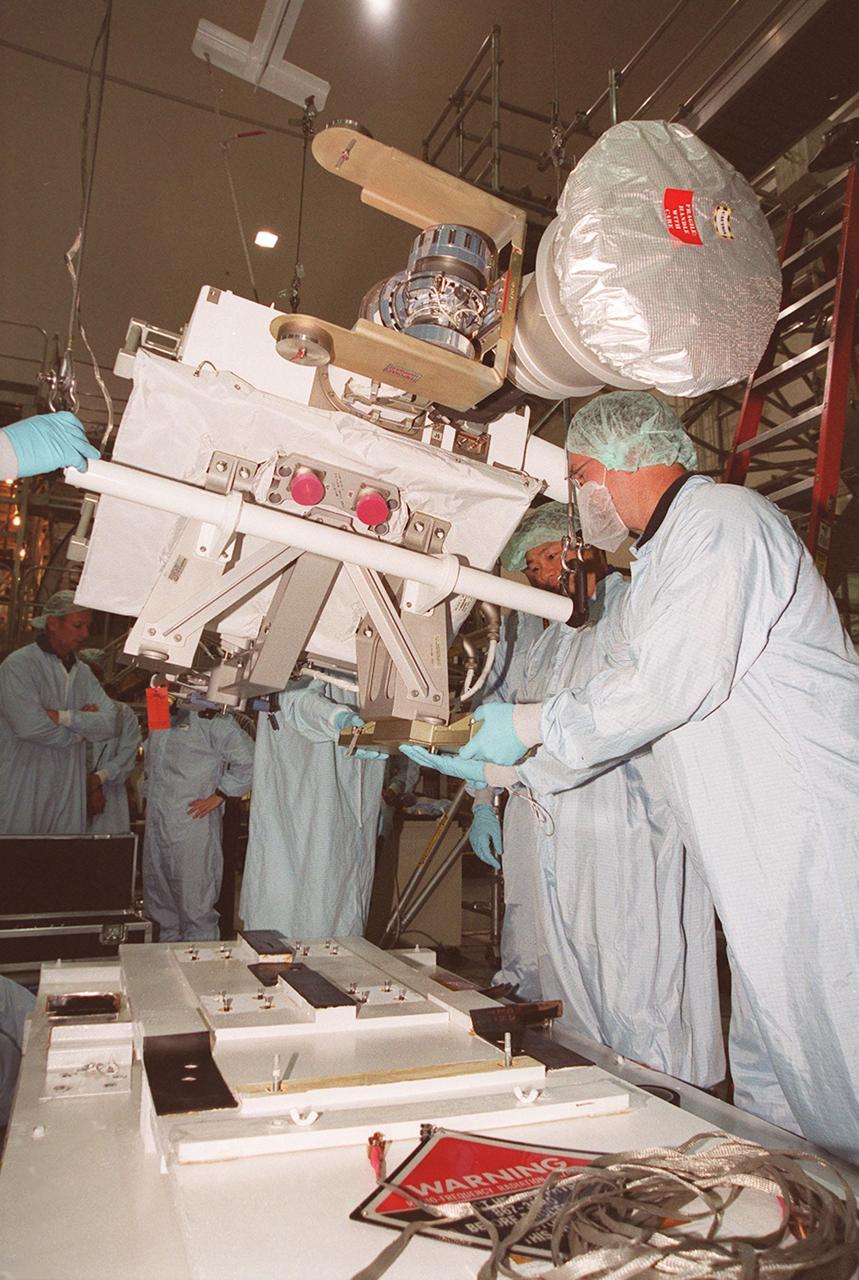

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew examine equipment that will be part of their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, the mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
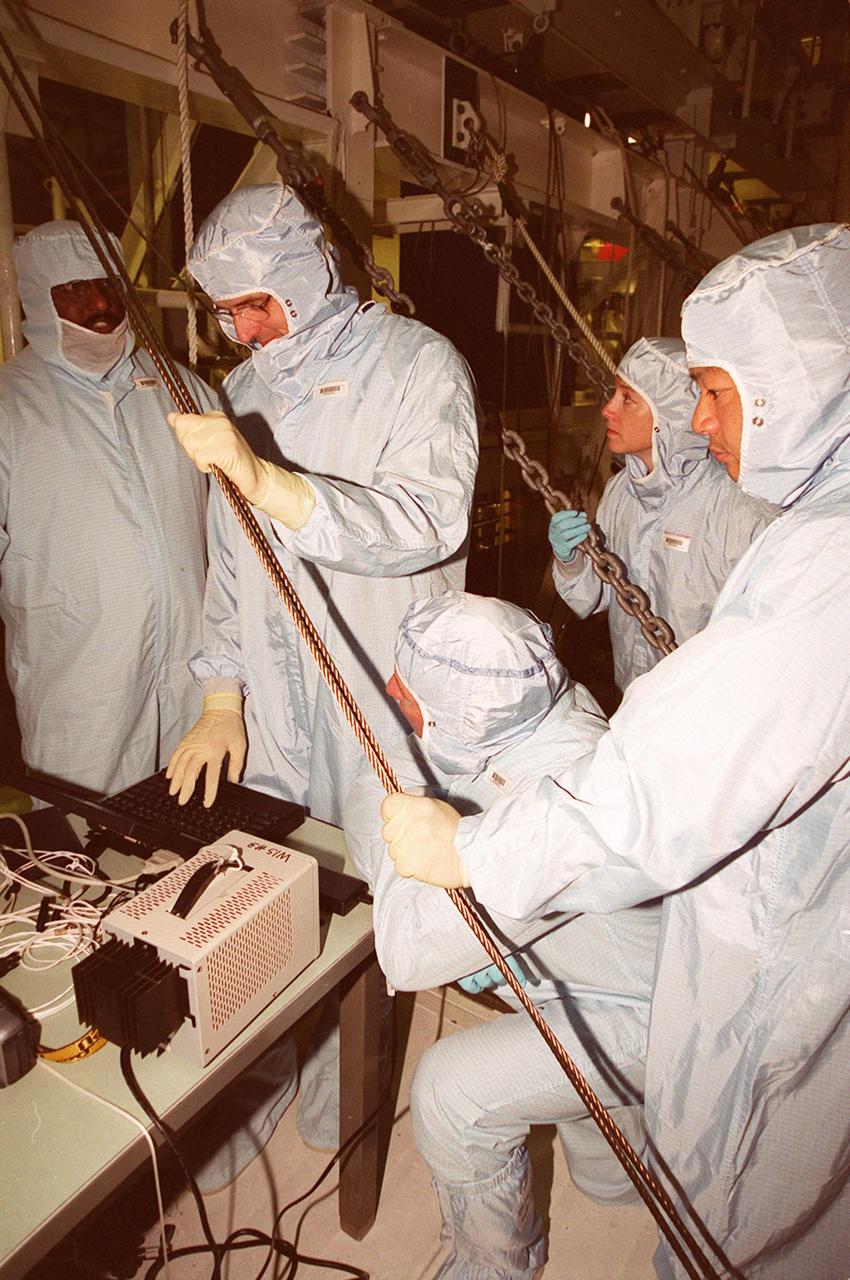
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, members of the STS-92 crew examine equipment that will be part of their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, the mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
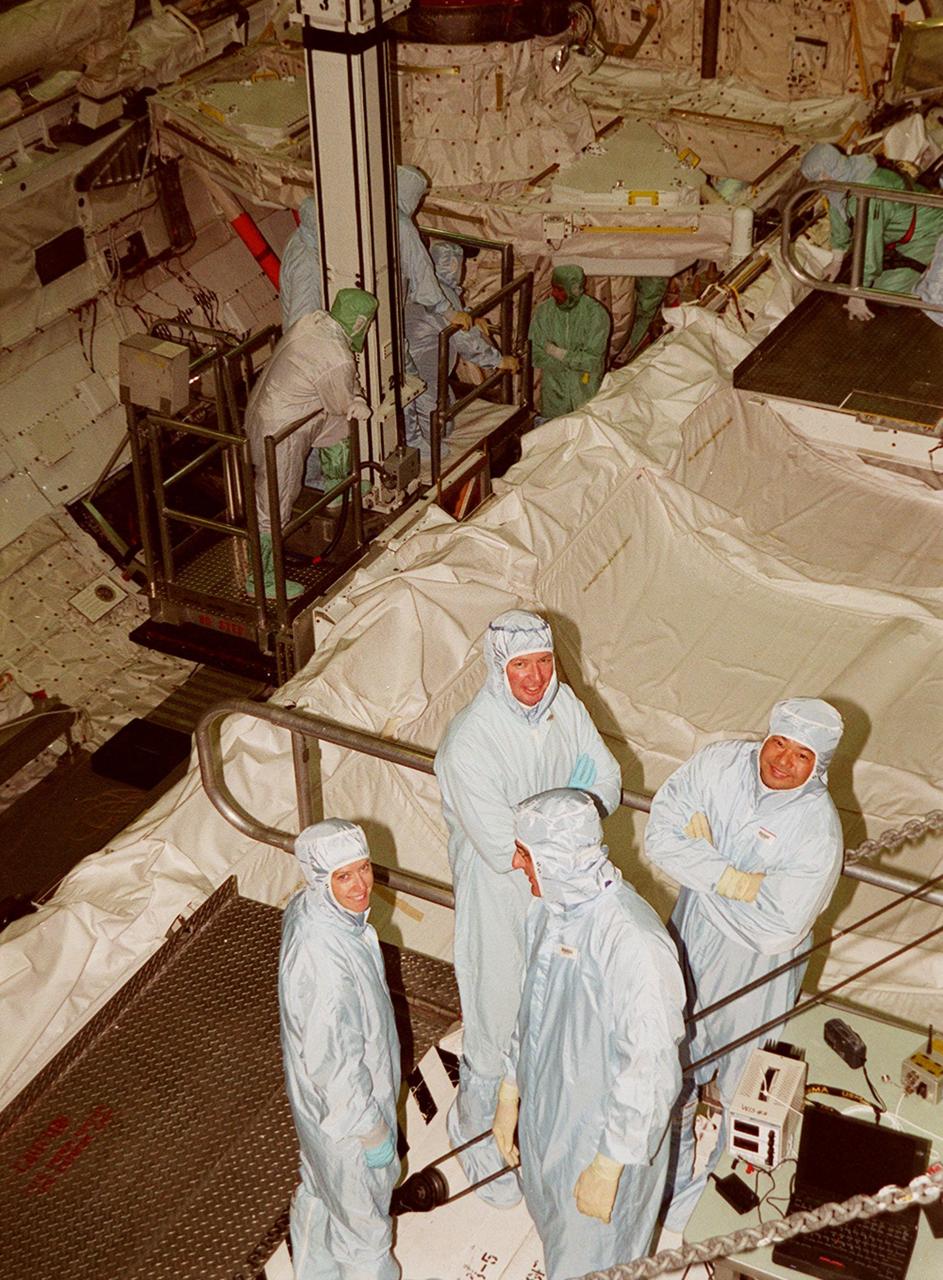

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew pose for the photographer during a break from checking out Discovery's payload bay in the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. Their mission, the fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, includes as payload the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
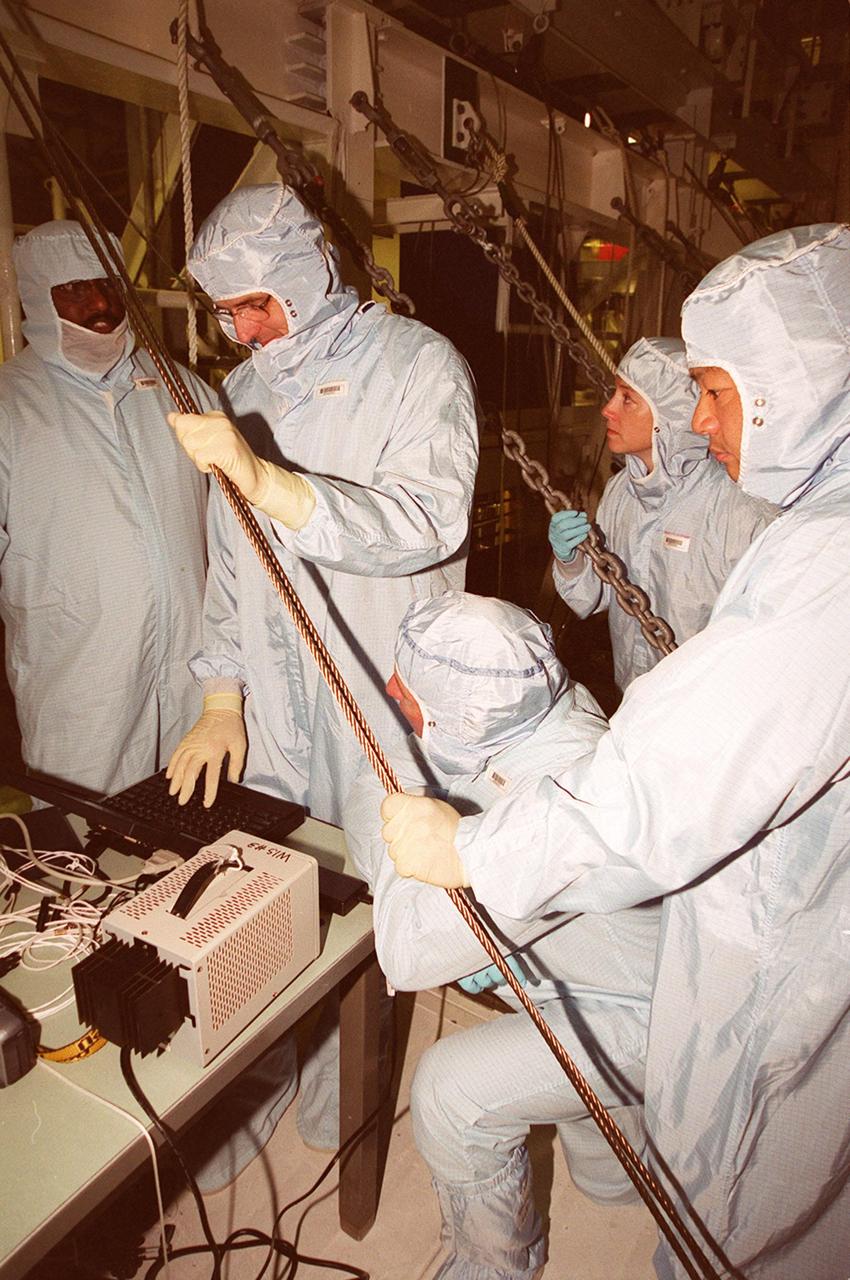
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, members of the STS-92 crew examine equipment that will be part of their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, the mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
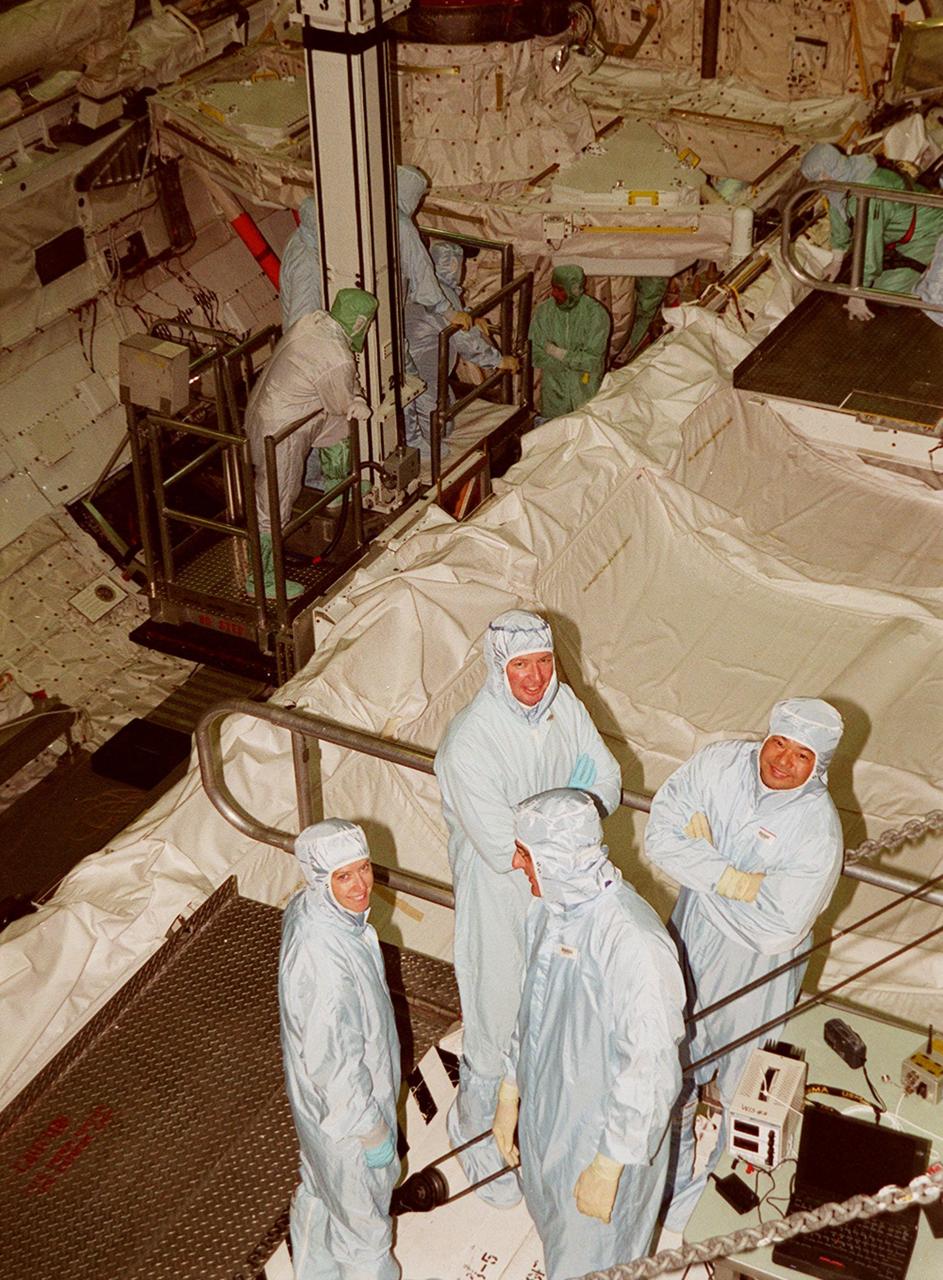

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew pose for the photographer during a break from checking out Discovery's payload bay in the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. Their mission, the fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, includes as payload the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
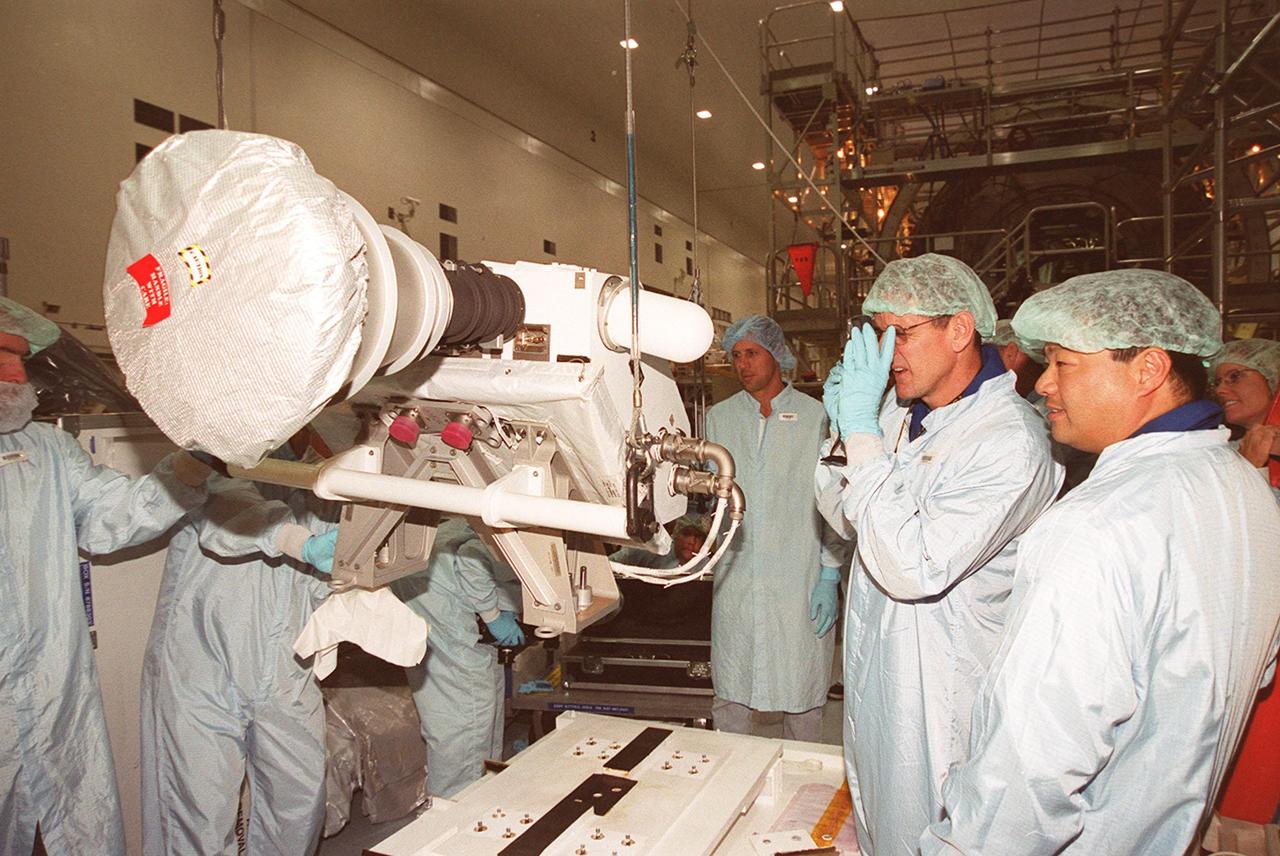

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew examine equipment that will be part of their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, the mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan.
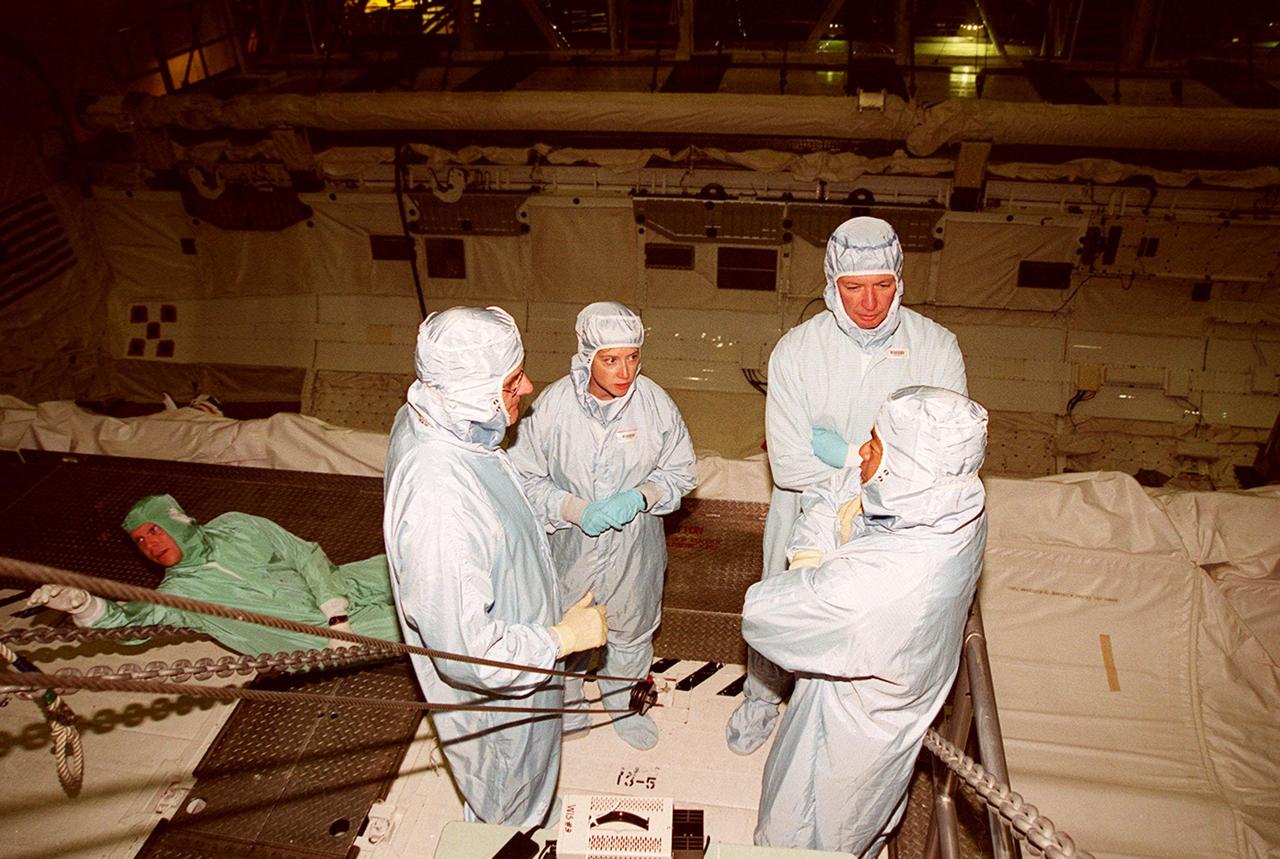

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew take a moment for discussion while checking out the payload bay of the orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. Their mission, the fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, includes as payload the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
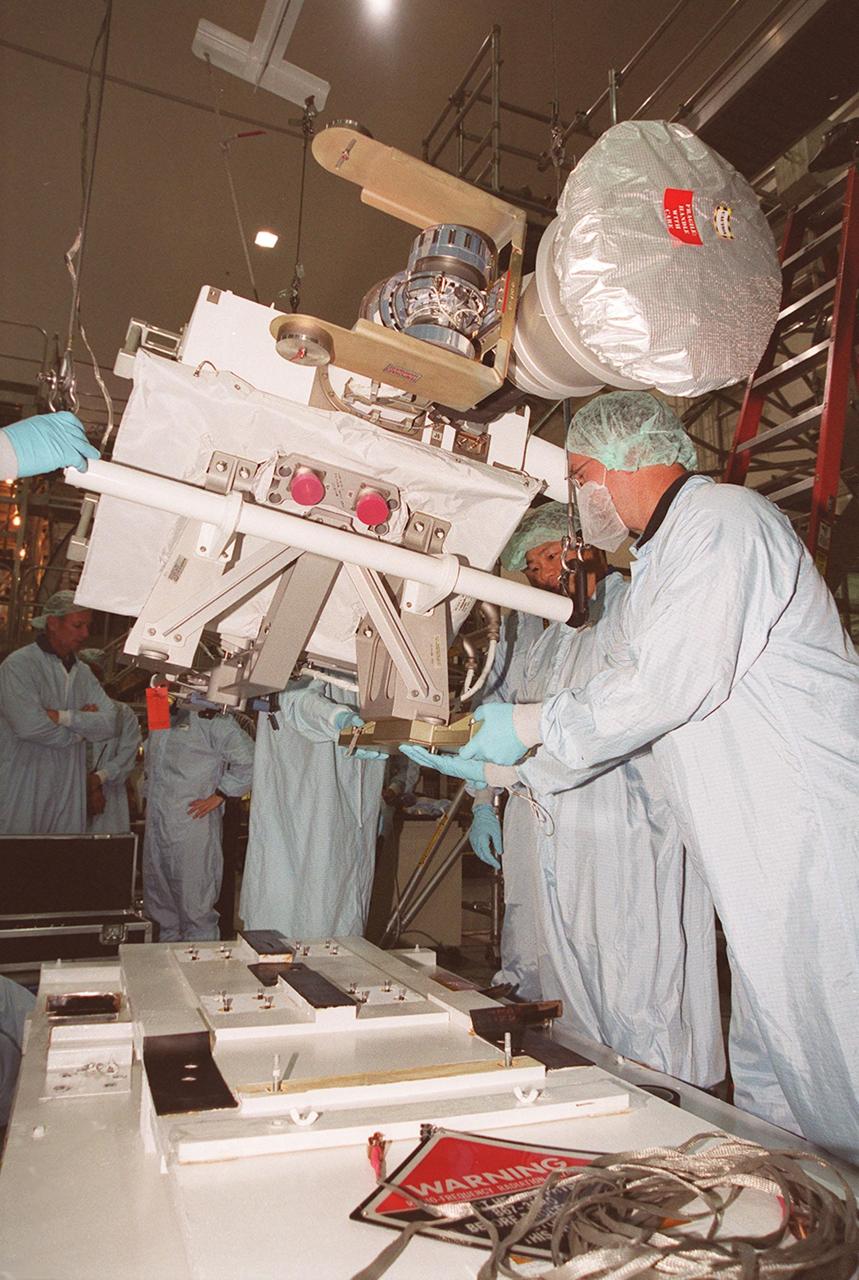

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew examine equipment that will be part of their mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The fourth U.S. flight to the ISS, the mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter "Jeff" Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria, and William McArthur. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan
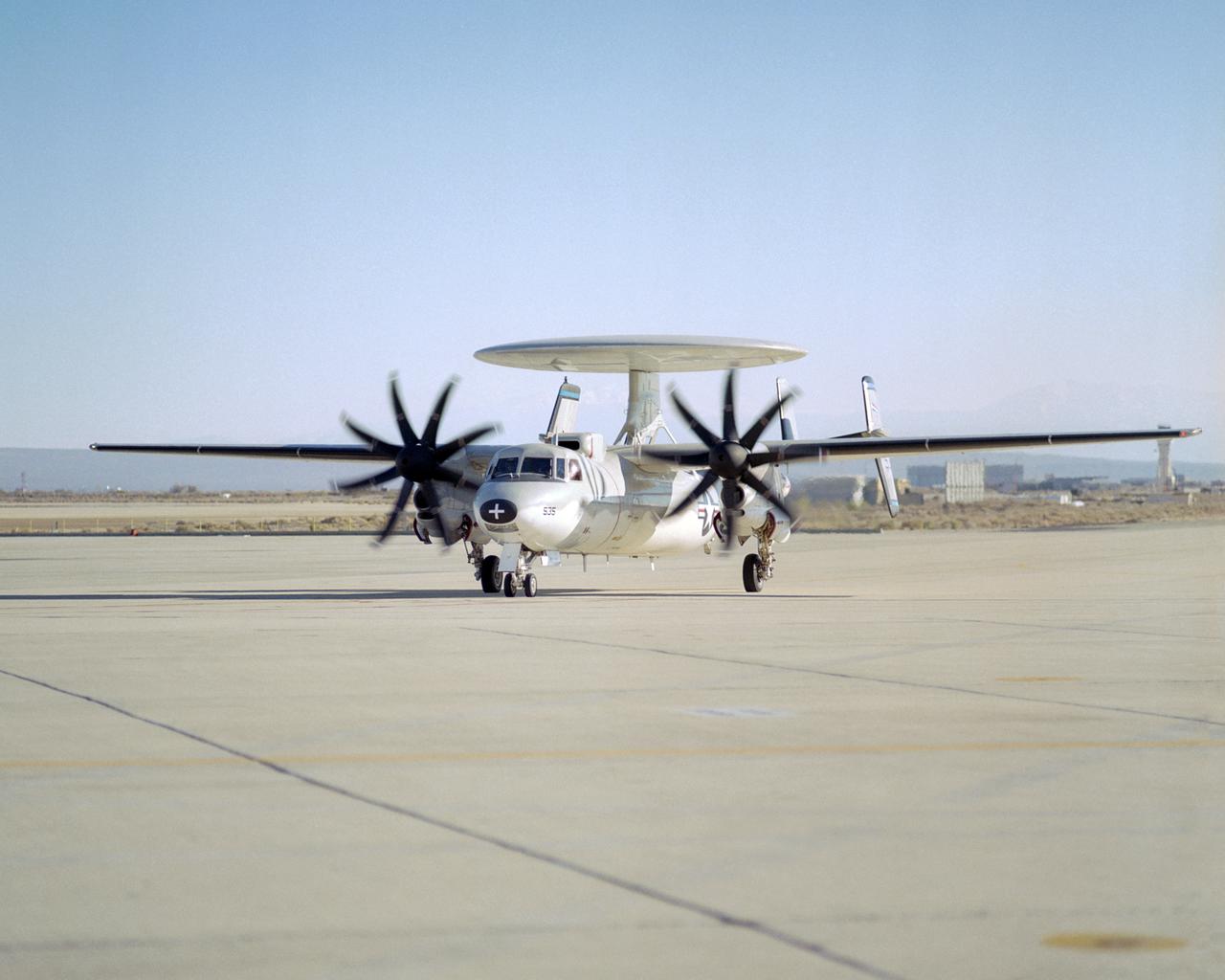

A Navy E-2C Hawkeye early-warning aircraft arrives at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center for extensive structural loads tests in Dryden's flight loads lab.
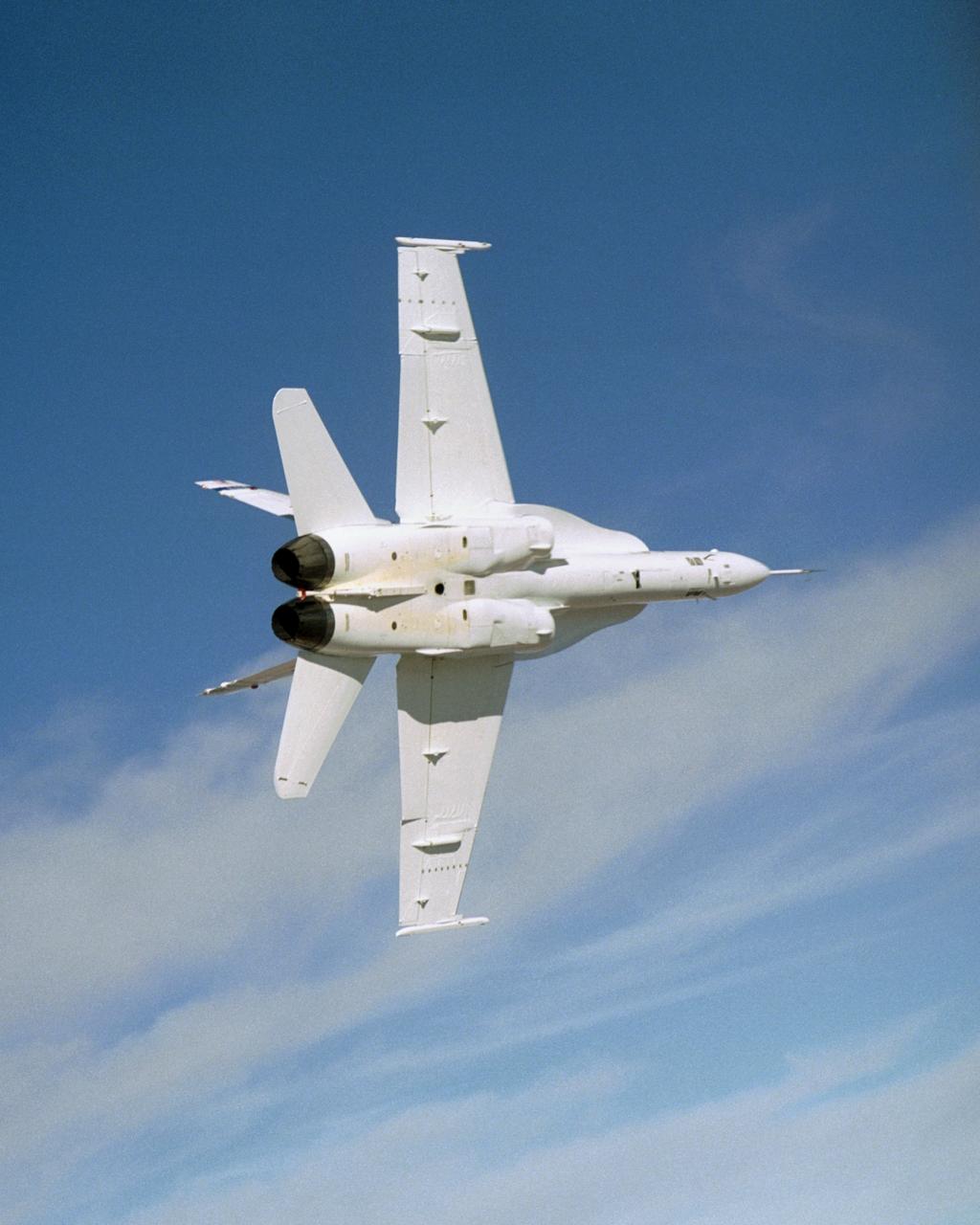

NASA's Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 rolls into a hard left turn during a research flight in early December 2004 from the Dryden Flight Research Center.
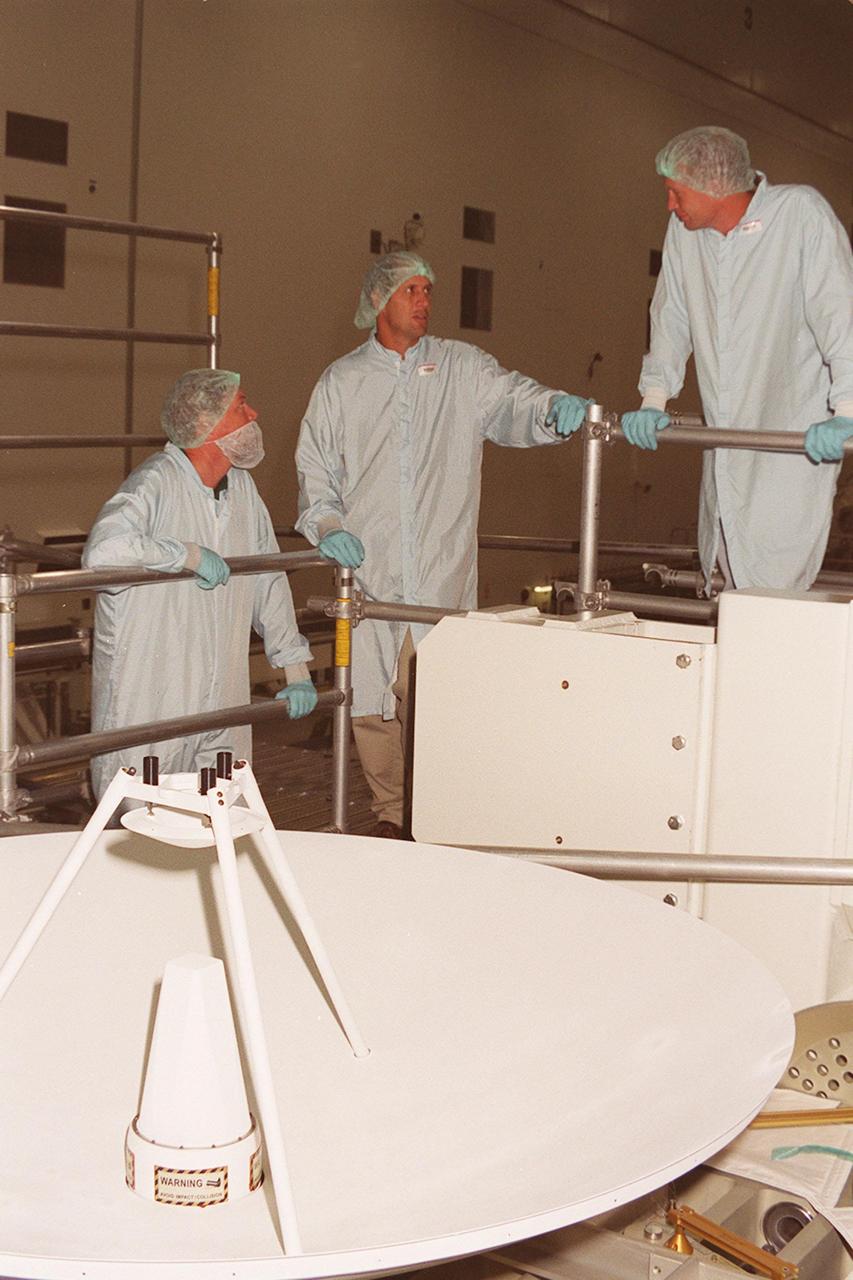

In the Space Shuttle Processing Facility, workers confer about the high-gain antenna in front of them that will be attached to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1. The Z1, part of the payload on mission STS-92 (flight 3A) to be launched in mid-fall, is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station. It will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97 (flight 4A), to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
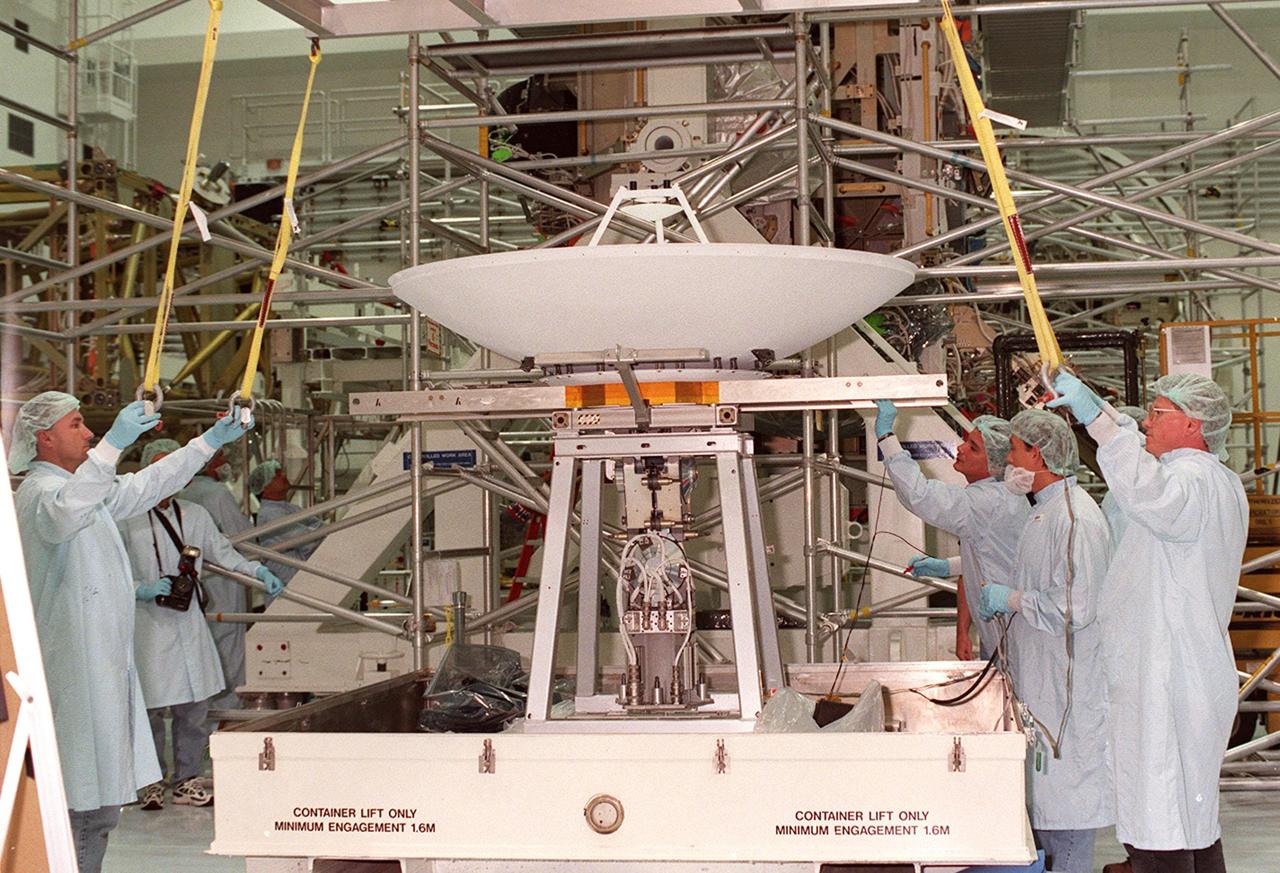

In the Space Shuttle Processing Facility, workers get ready to attach cables to a high-gain antenna that will be lifted and attached to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1. The Z1, part of the payload on mission STS-92 (flight 3A) to be launched in mid-fall, is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station. It will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97 (flight 4A), to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
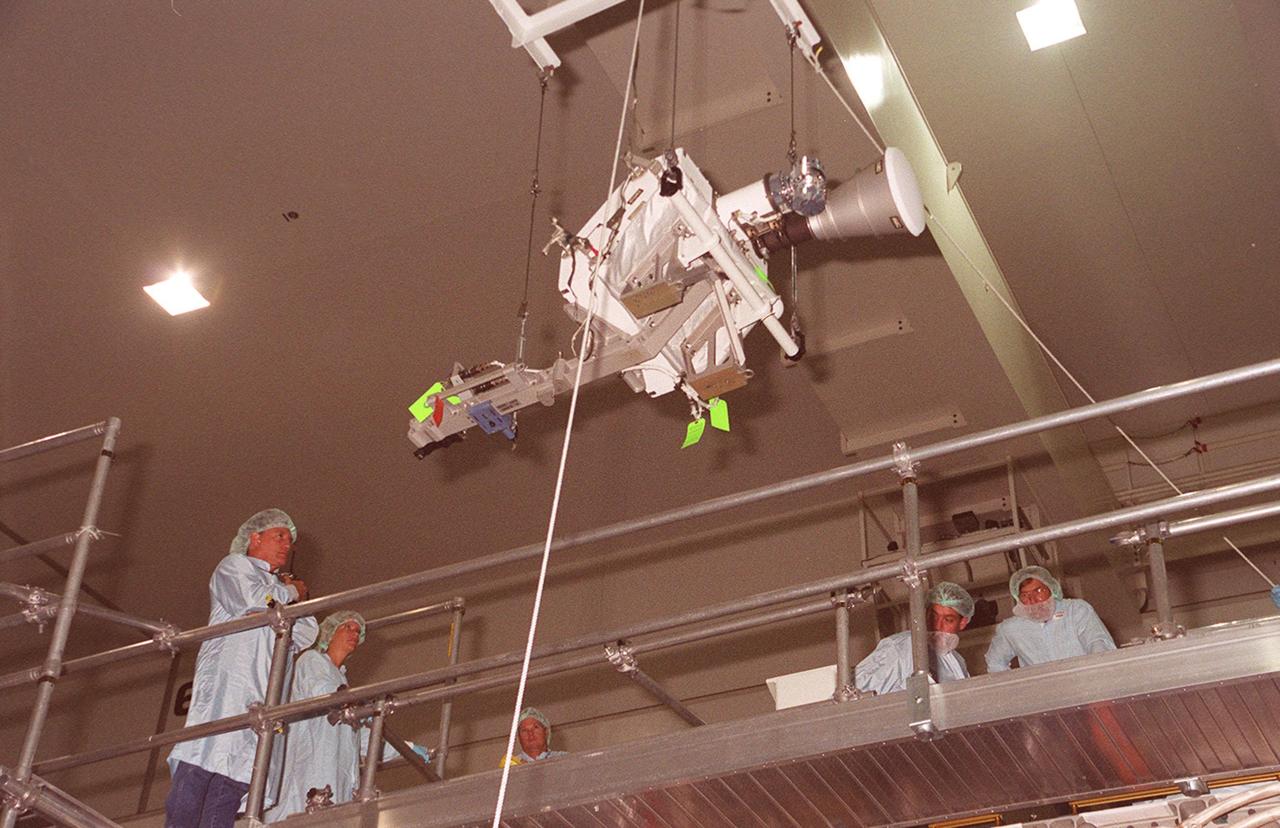

An overhead crane in the Space Station Processing Facility moves an S-band Antenna Support Assembly (SASA) to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, an element of the International Space Station. . The antenna will be attached to the truss. The SASA antenna is primarily for local communications between the orbiter and Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall

STS-92 Mission Specialist Leroy Chiao poses in front of the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1 in the Space Shuttle Processing Facility. Chiao is a member of the crew on the fifth flight to the International Space Station, scheduled for launch in mid-fall. The Z1 is an early exterior framework for the Space Station, and will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
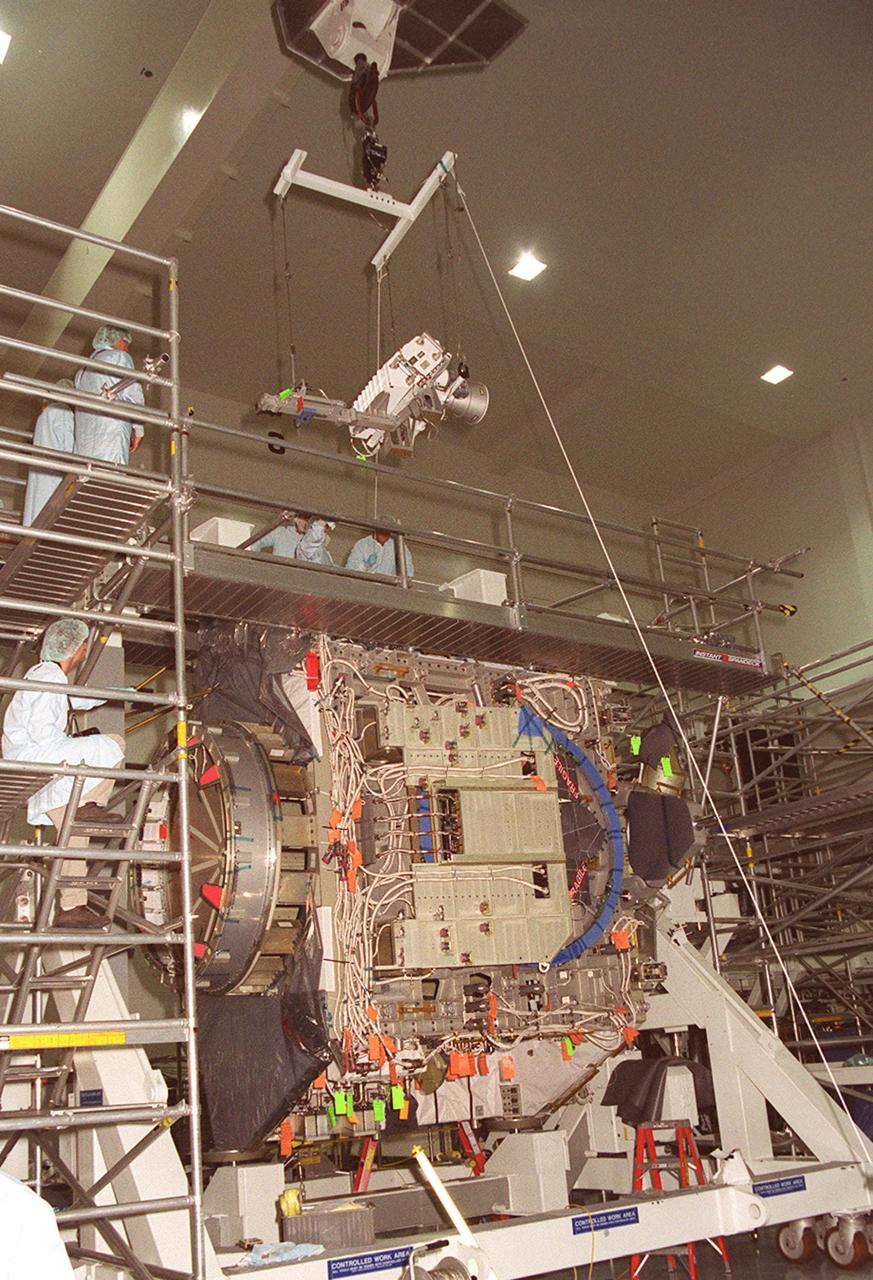

An S-band Antenna Support Assembly (SASA) is suspended from an overhead crane in the Space Station Processing Facility. It will be attached to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, an element of the International Space Station, sitting below. The SASA is primarily for local communications between the orbiter and Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall
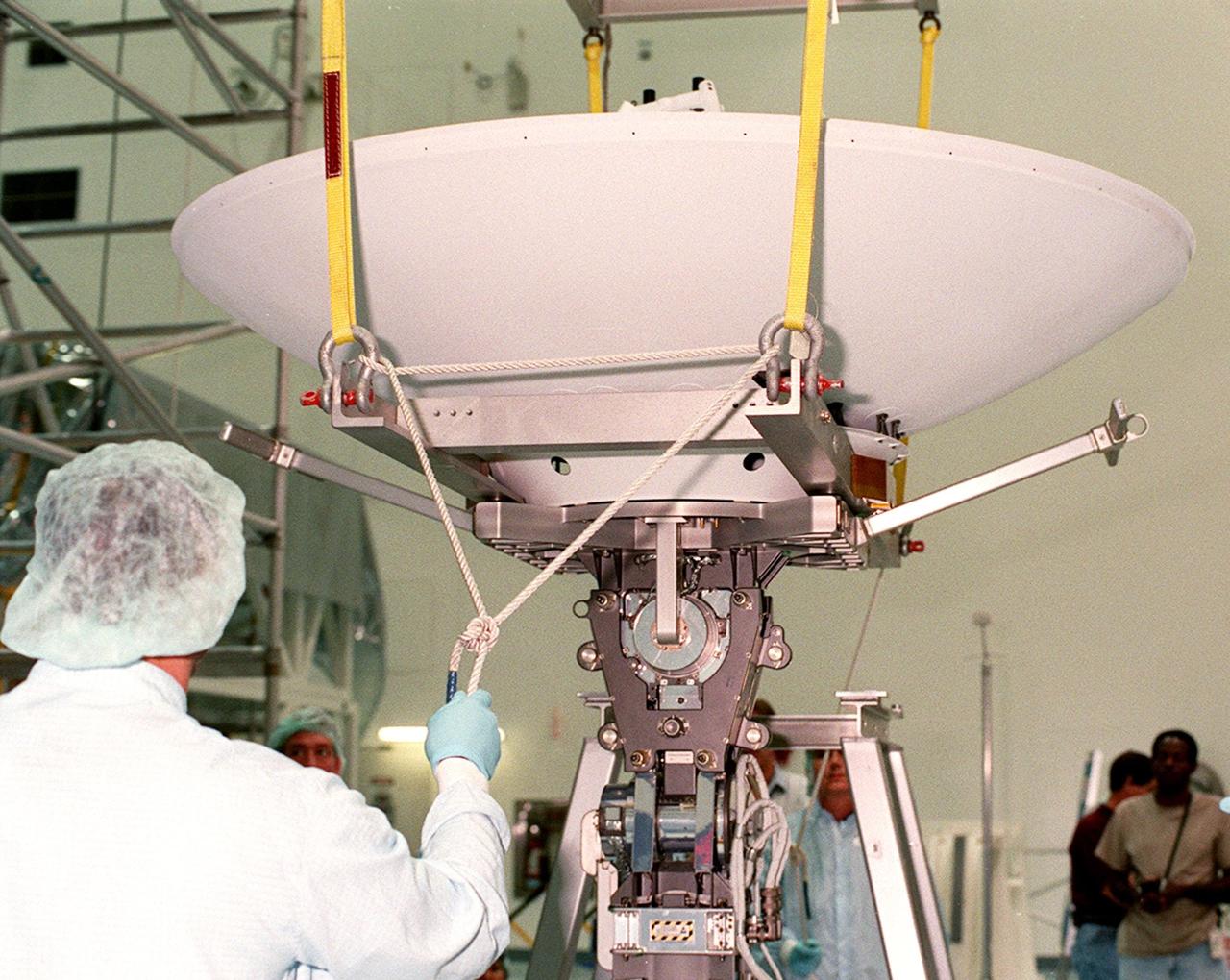

In the Space Shuttle Processing Facility, a worker checks a rope attached to a high-gain antenna before it moves to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, to which it will be attached. The Z1, part of the payload on mission STS-92 (flight 3A) to be launched in mid-fall, is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station. It will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97 (flight 4A), to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
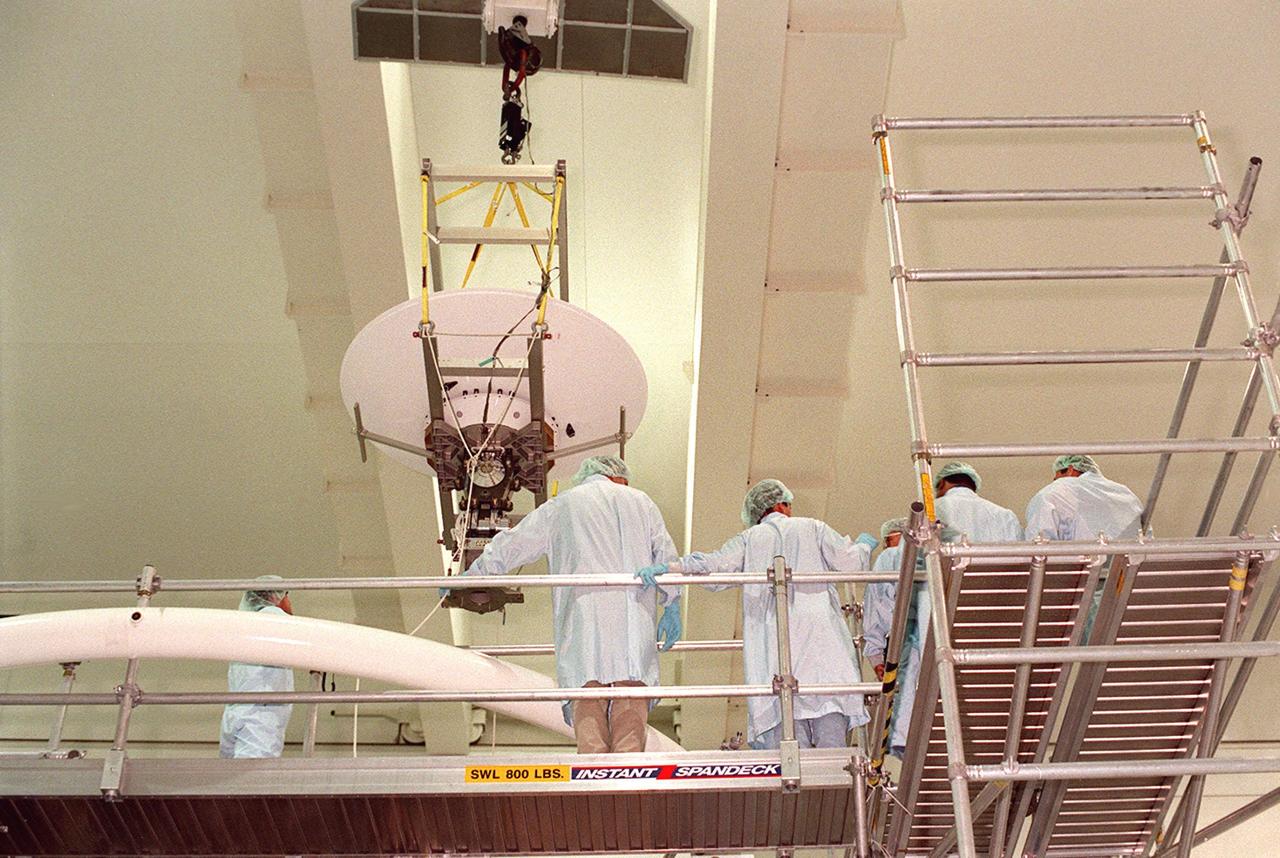

An overhead crane in the Space Shuttle Processing Facility lifts a high-gain antenna over a work platform toward the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, to which it will be attached. The Z1, part of the payload on mission STS-92 (flight 3A) to be launched in mid-fall, is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station. It will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97 (flight 4A), to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
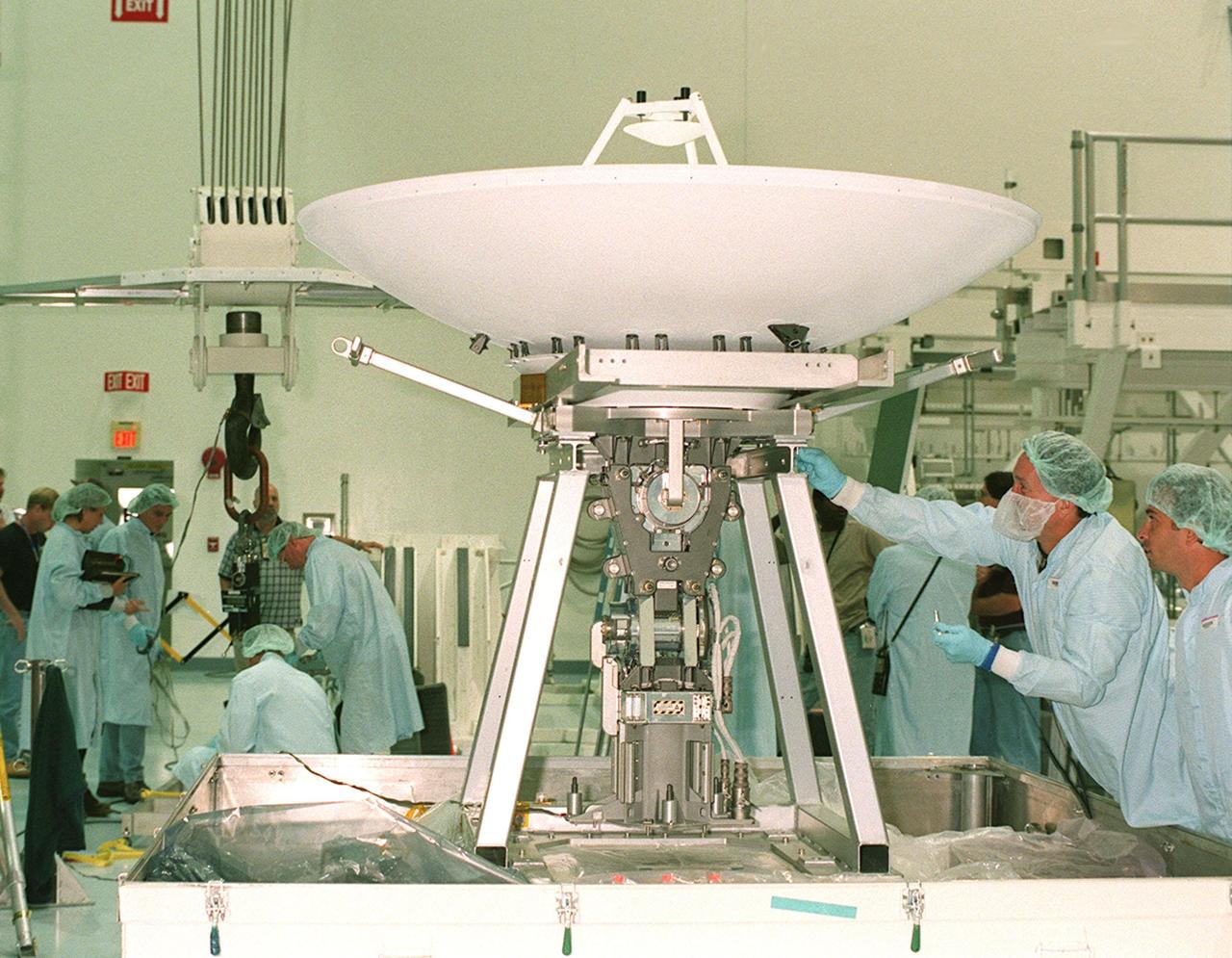
In the Space Shuttle Processing Facility, workers make adjustments on a high-gain antenna that will be attached to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1. The Z1, part of the payload on mission STS-92 (flight 3A) to be launched in mid-fall, is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station. It will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97 (flight 4A), to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
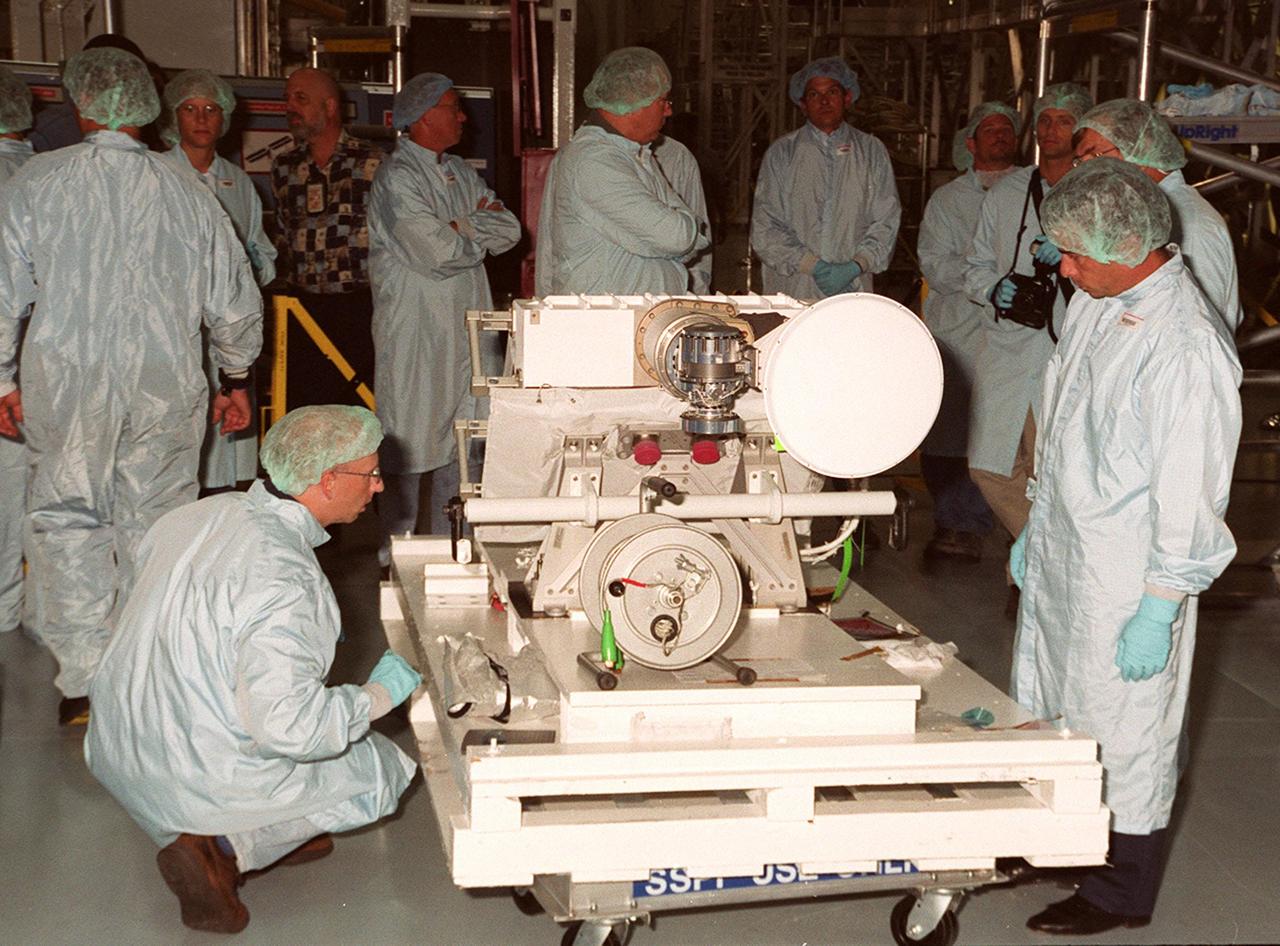

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility look over an S-band Antenna Support Assembly (SASA) that will be attached to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1 on the International Space Station. The SASA antenna is primarily for local communications between the orbiter and Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall
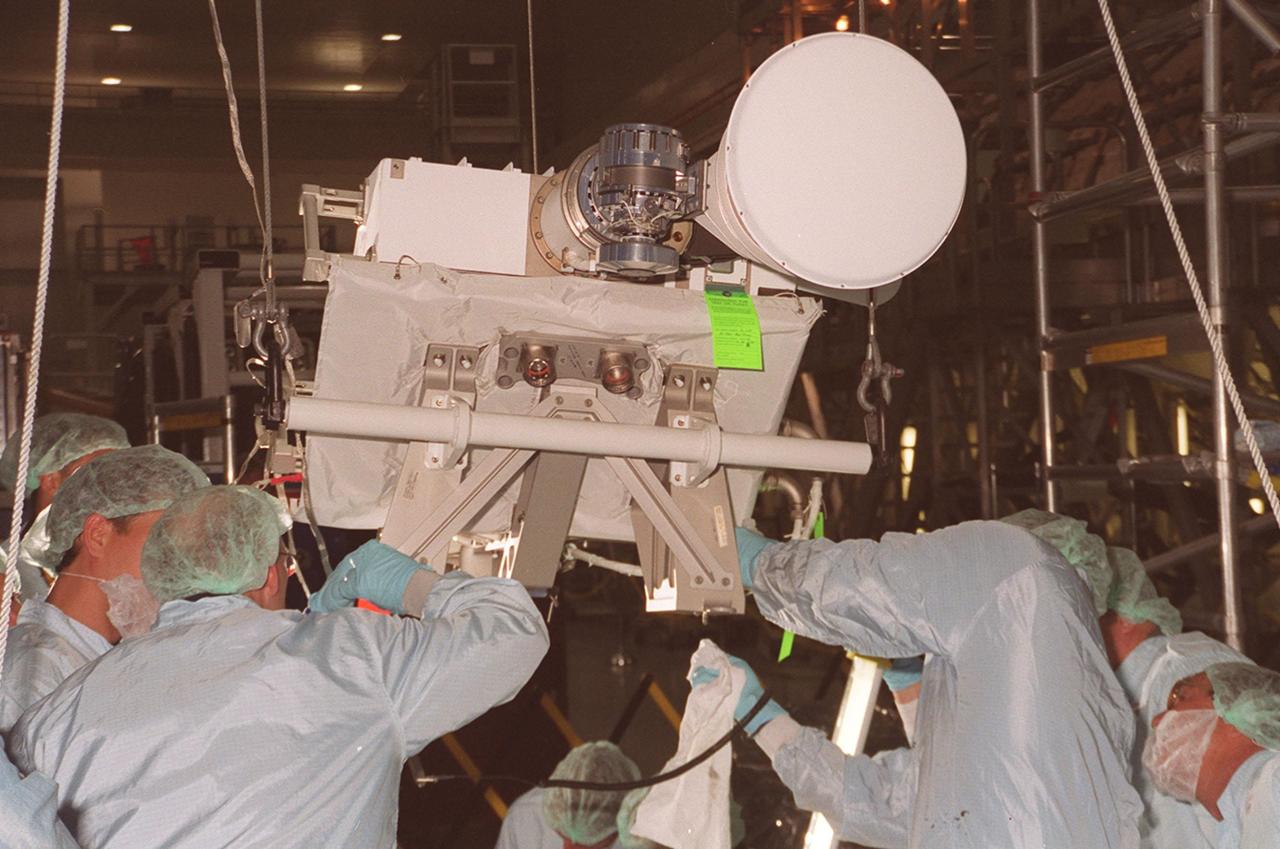

In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers prepare an S-band Antenna Support Assembly (SASA) to be lifted and moved to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, an element of the International Space Station. The antenna will be attached to the truss. The SASA antenna is primarily for local communications between the orbiter and Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall
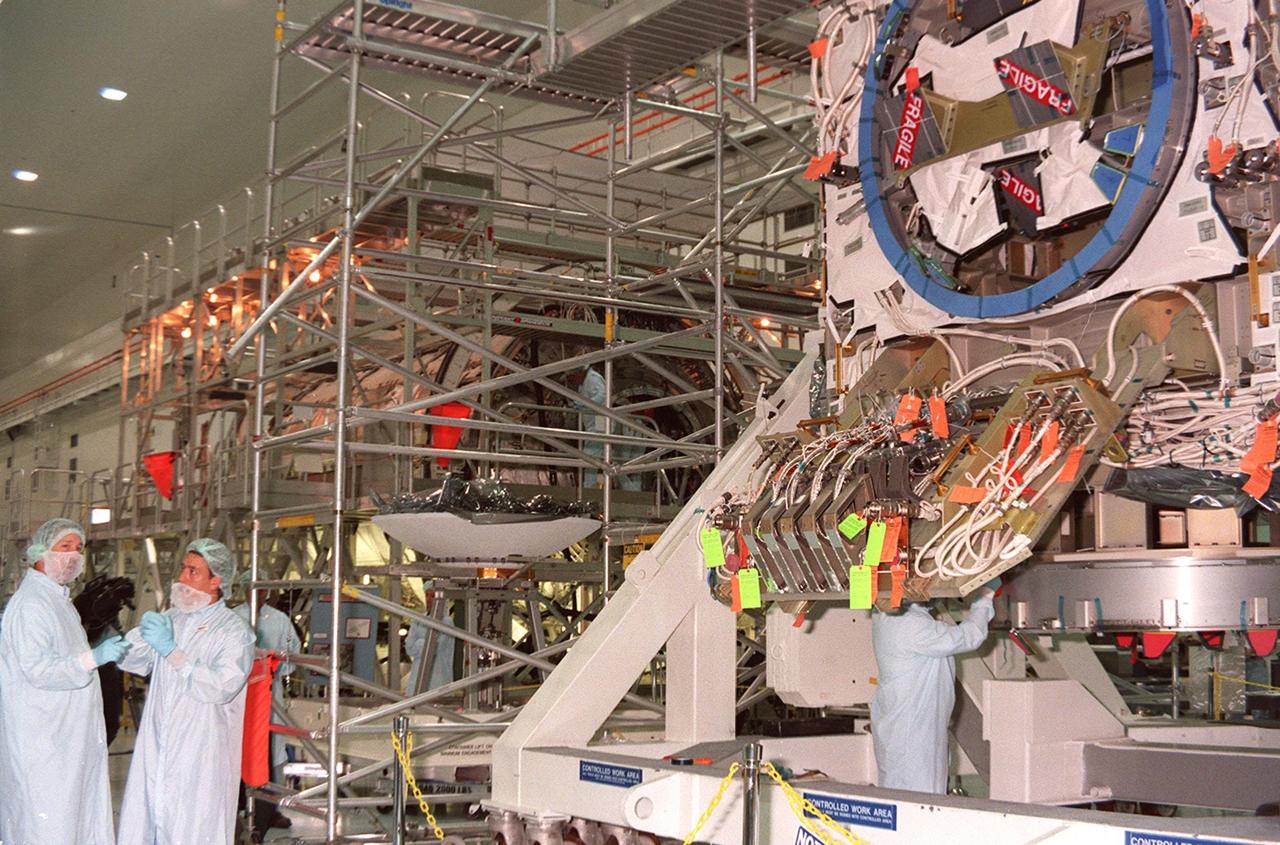
Workers at left stand by while work is done on the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1 at right. To the left of the Z1 is a high-gain antenna that will be installed on the Z1. An early exterior framework for the International Space Station, the Z1 will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is a payload scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall
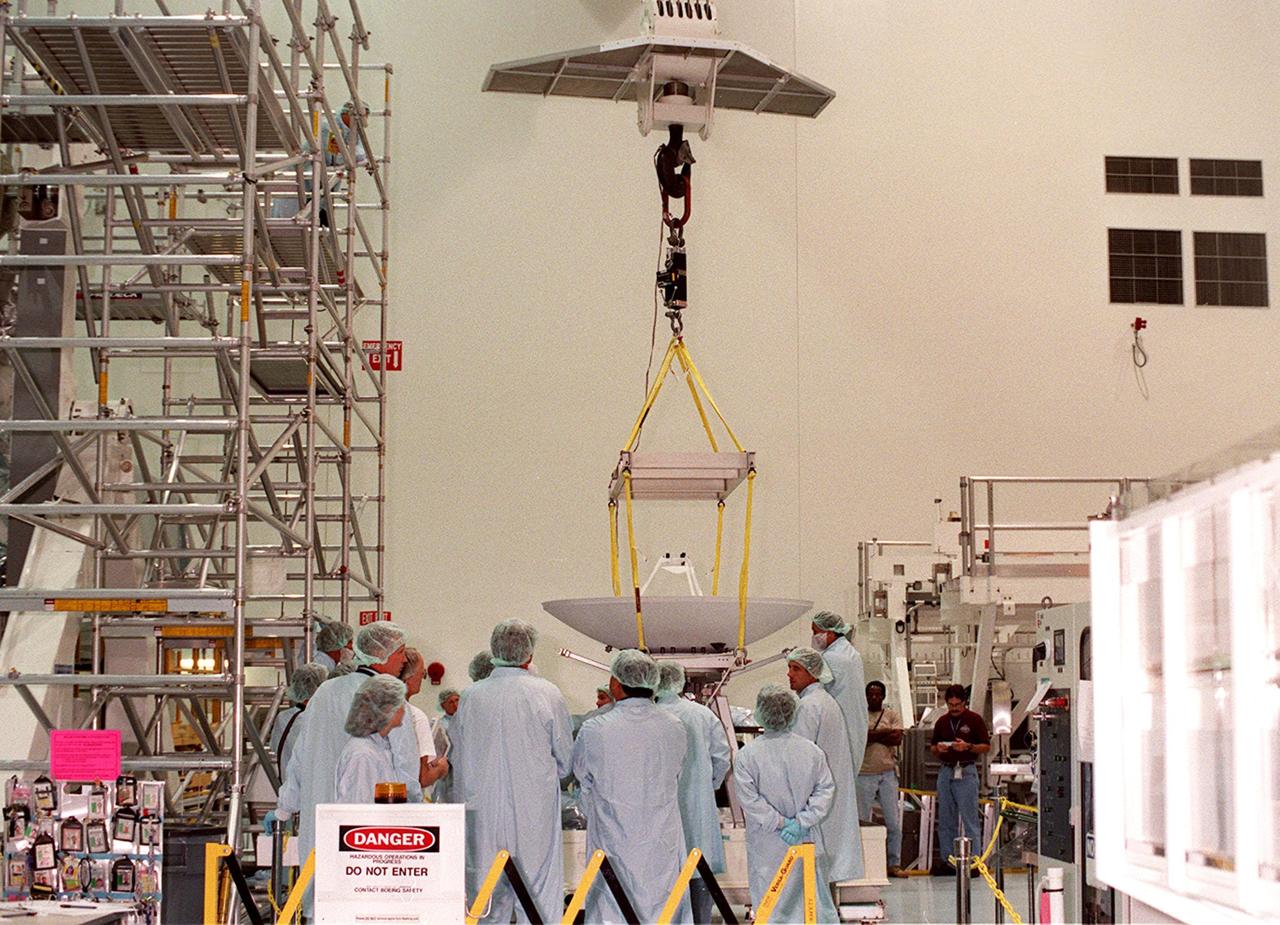

In the Space Shuttle Processing Facility, an overhead crane begins lifting a high-gain antenna to move it to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, to which it will be attached. The Z1, part of the payload on mission STS-92 (flight 3A) to be launched in mid-fall, is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station. It will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97 (flight 4A), to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
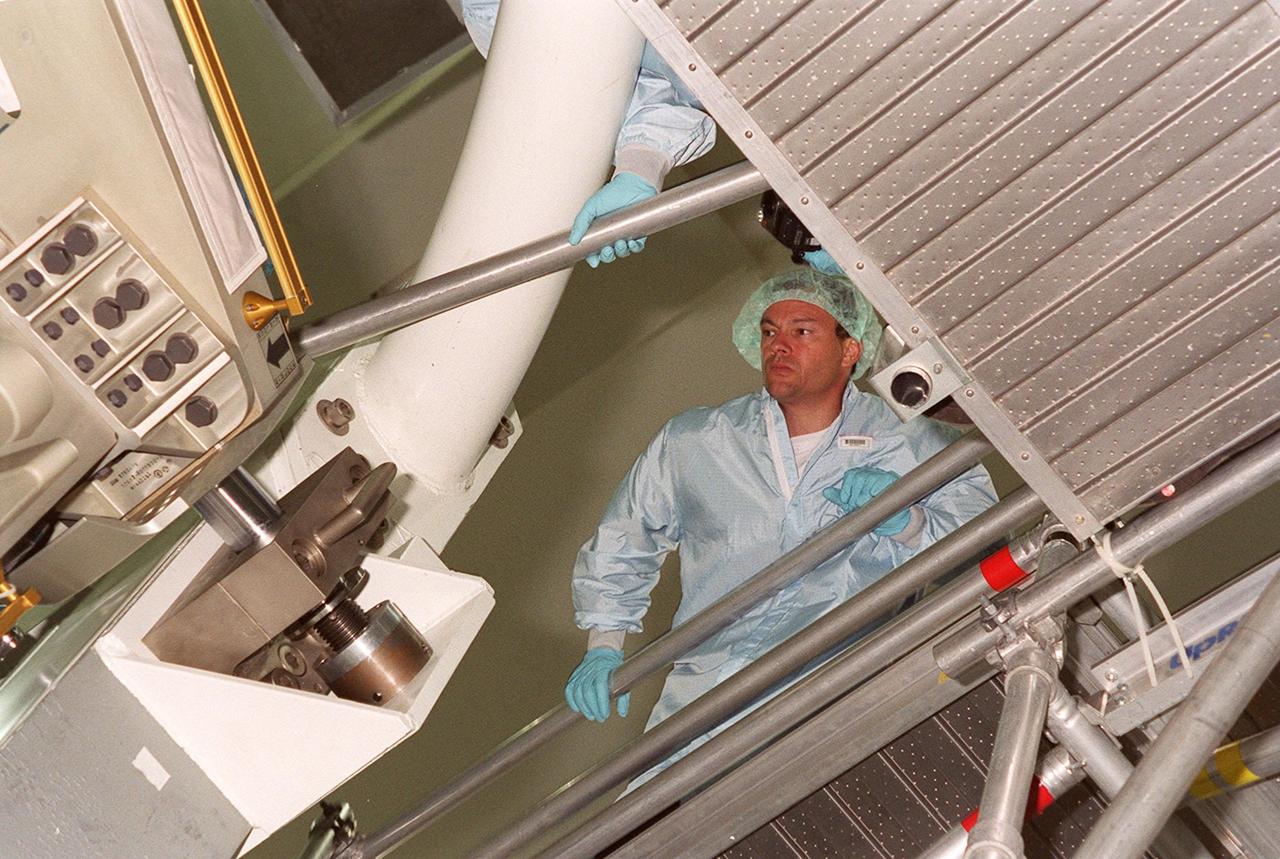

On the scaffolding in the Space Shuttle Processing Facility (SSPF), STS-92 Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria leans over to get a better look at the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1 below. The Z1 is a payload scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall. The Z1 is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station, and will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power
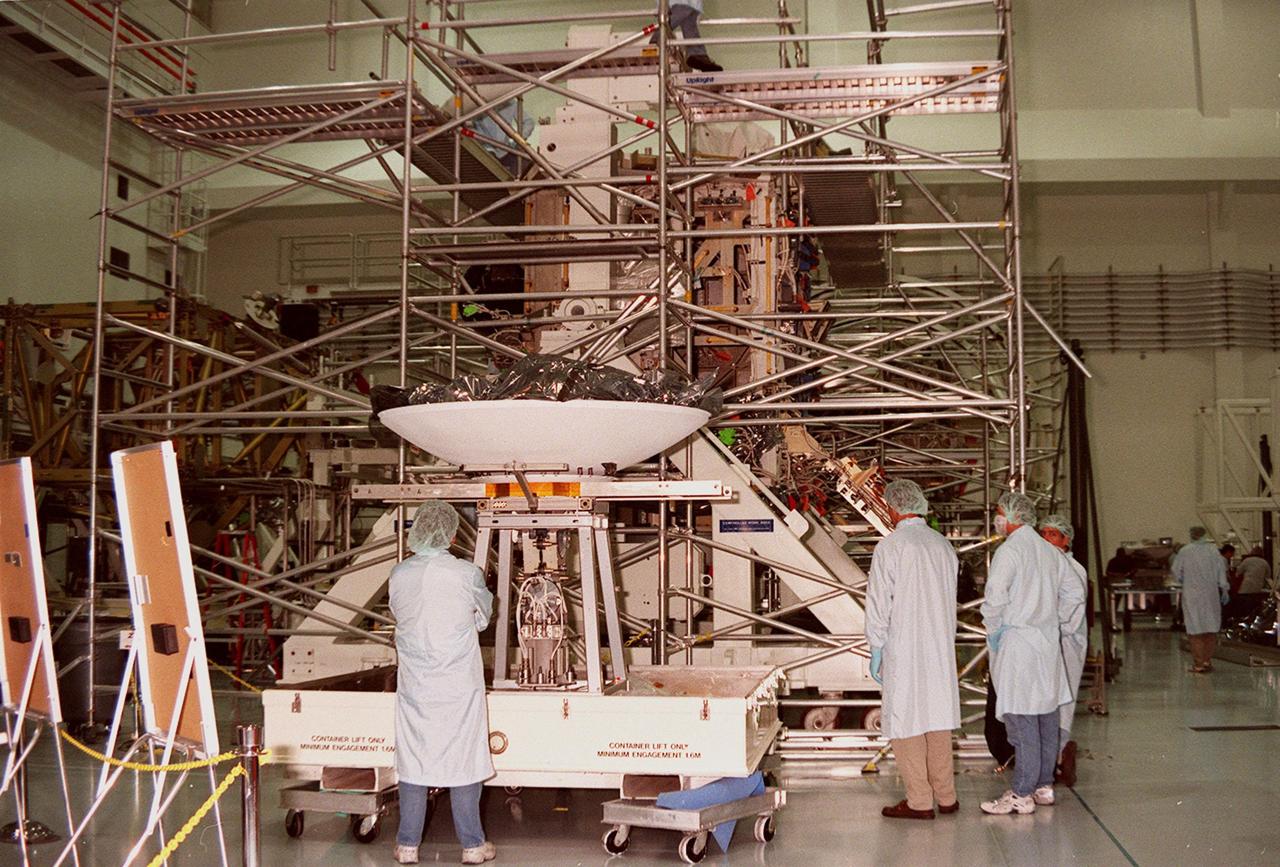
Workers in the Space Shuttle Processing Facility (SSPF) are getting ready to prepare the high-gain antenna beside them on the floor for installation on the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, just beyond the scaffolding. The Z1 is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station to allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is a payload scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall
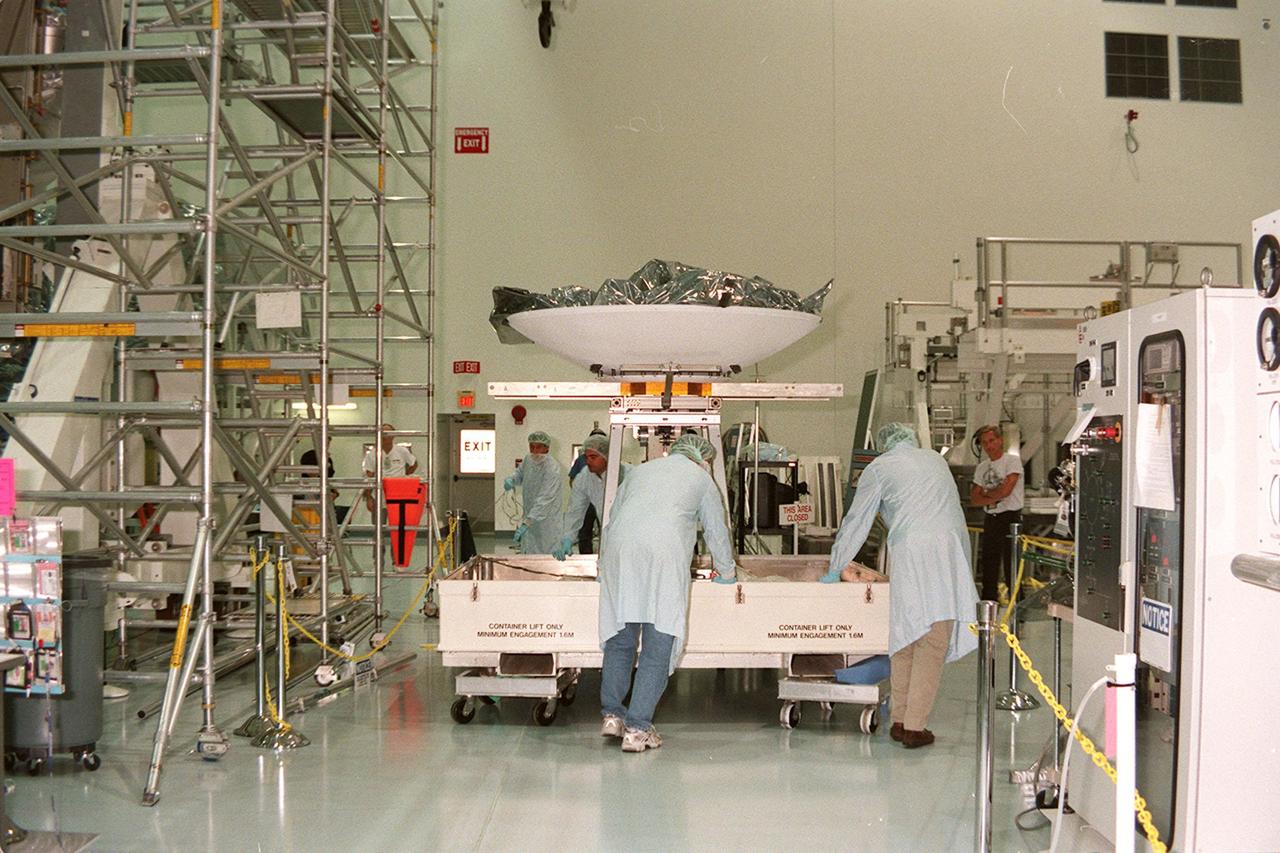

Workers in the Space Shuttle Processing Facility (SSPF) move a high-gain antenna for installation onto the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, already in the SSPF. The Z1 is an early exterior framework for the International Space Station that will allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is a payload scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall
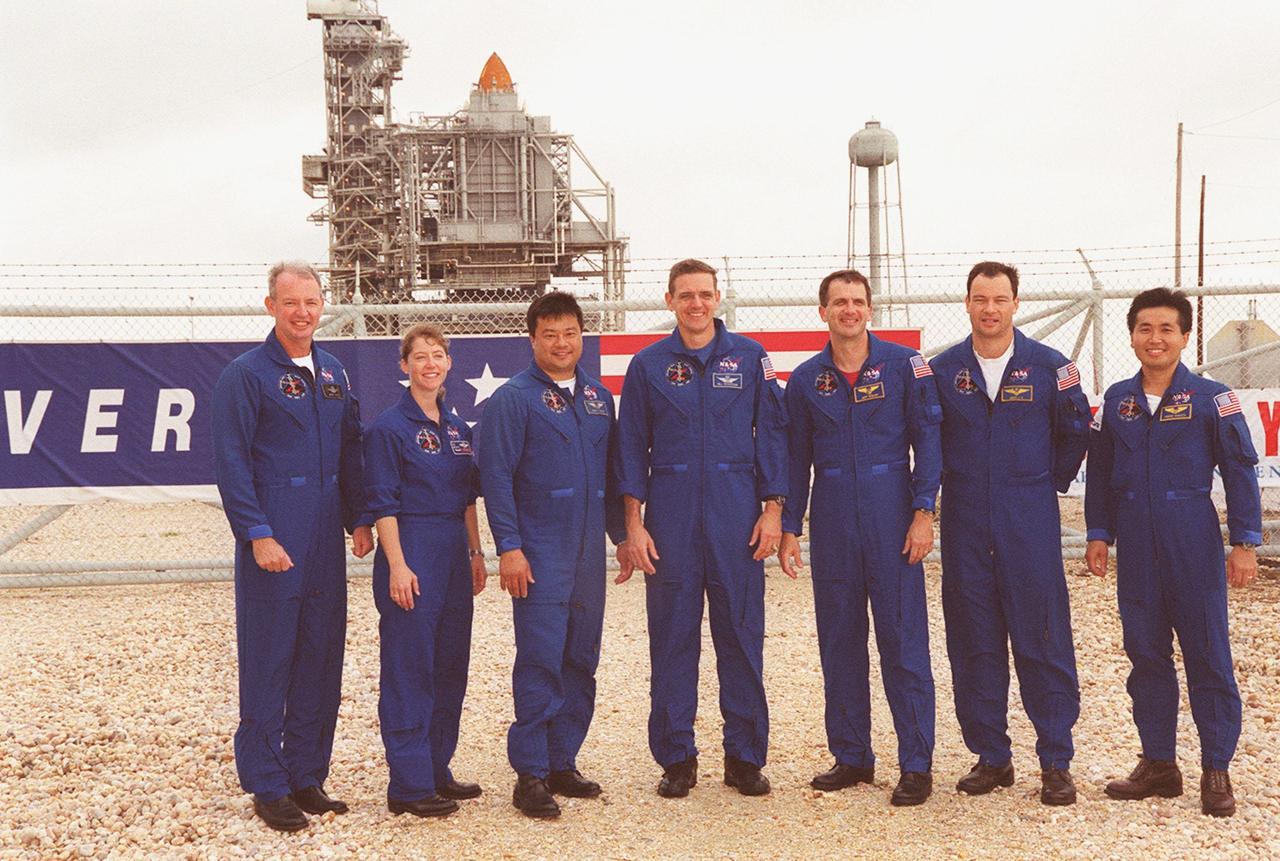

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-92 crew gather outside the gate to Launch Pad 39A where Space Shuttle Discovery waits in the background for liftoff Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT. From left to right are Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy, and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks
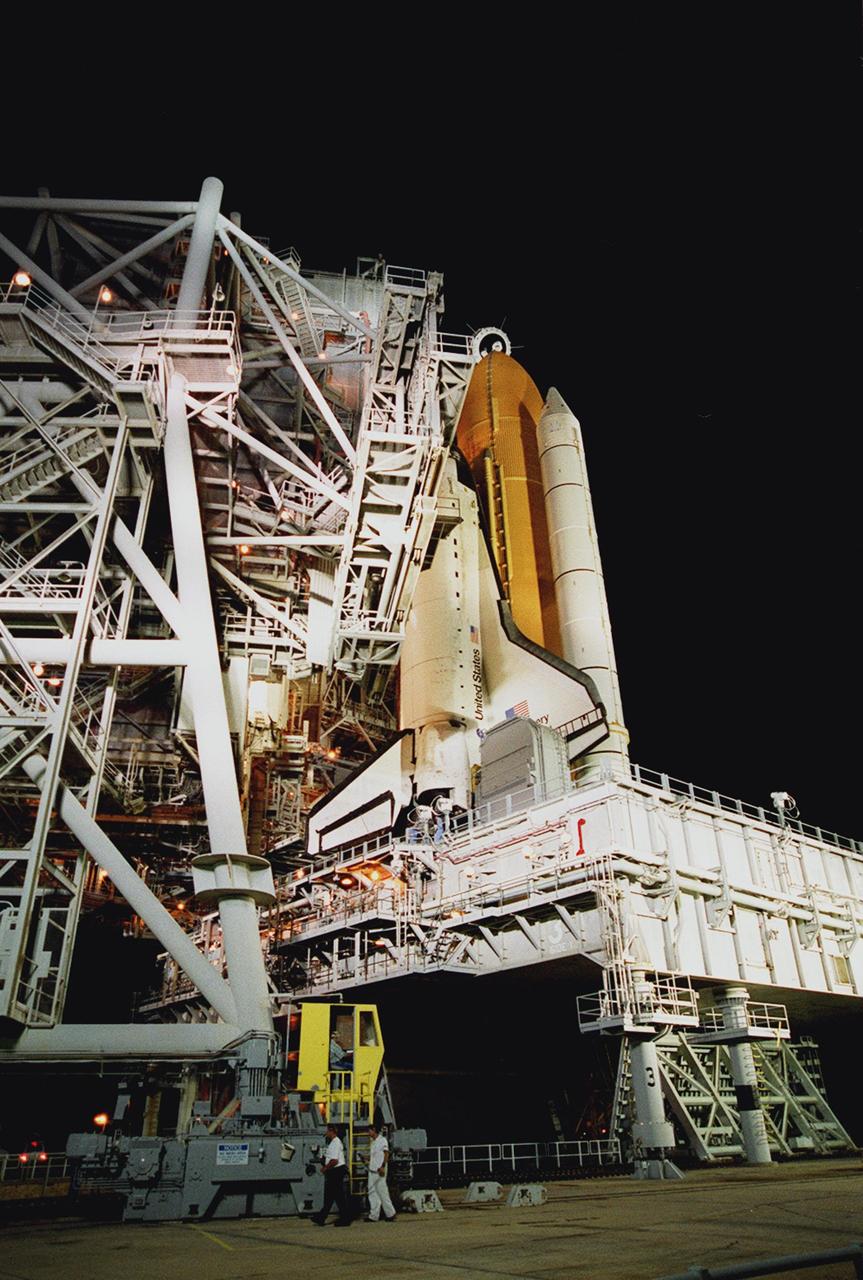

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Rotating Service Structure at Launch Pad 39A rolls back, revealing the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Mobile Launcher Platform. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
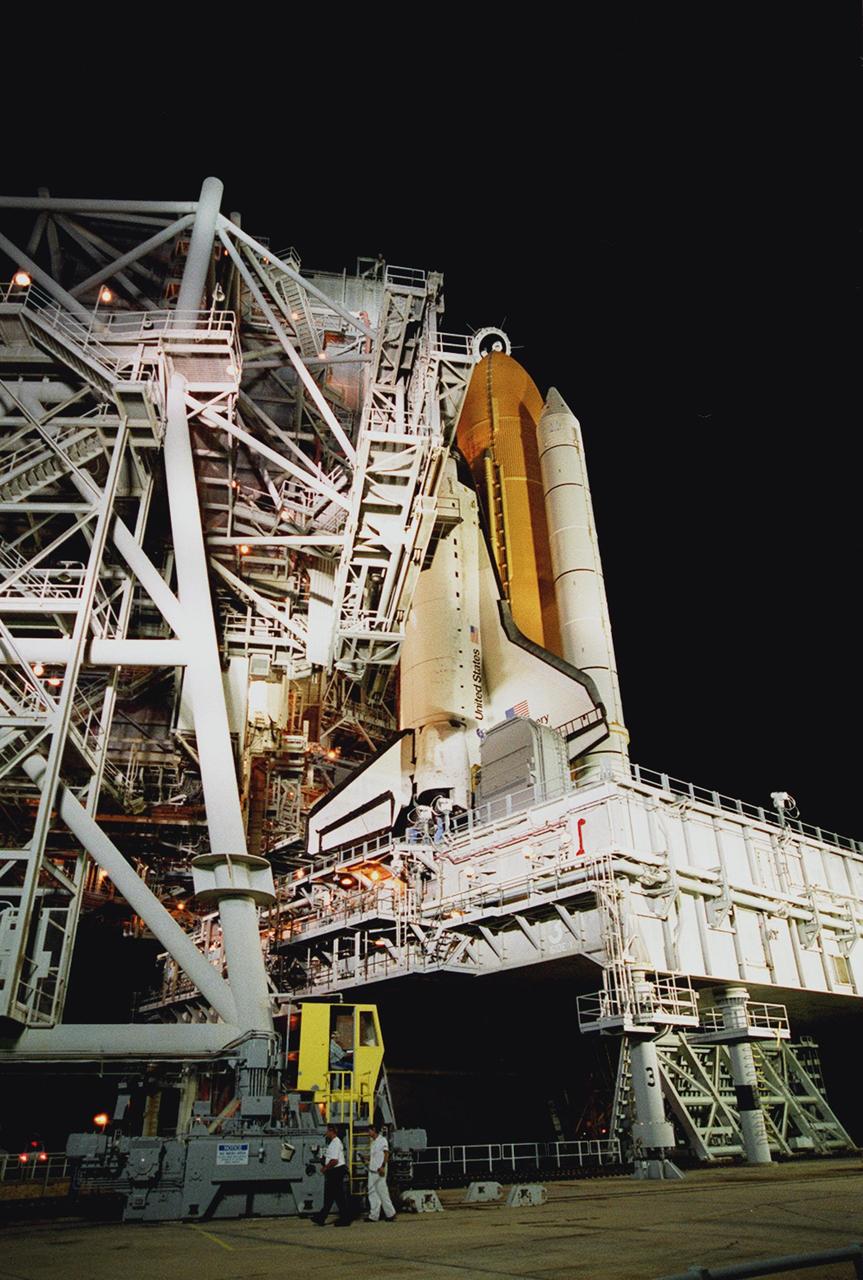

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Rotating Service Structure at Launch Pad 39A rolls back, revealing the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Mobile Launcher Platform. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-92 crew gather outside the gate to Launch Pad 39A where Space Shuttle Discovery waits in the background for liftoff Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT. From left to right are Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy, and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks
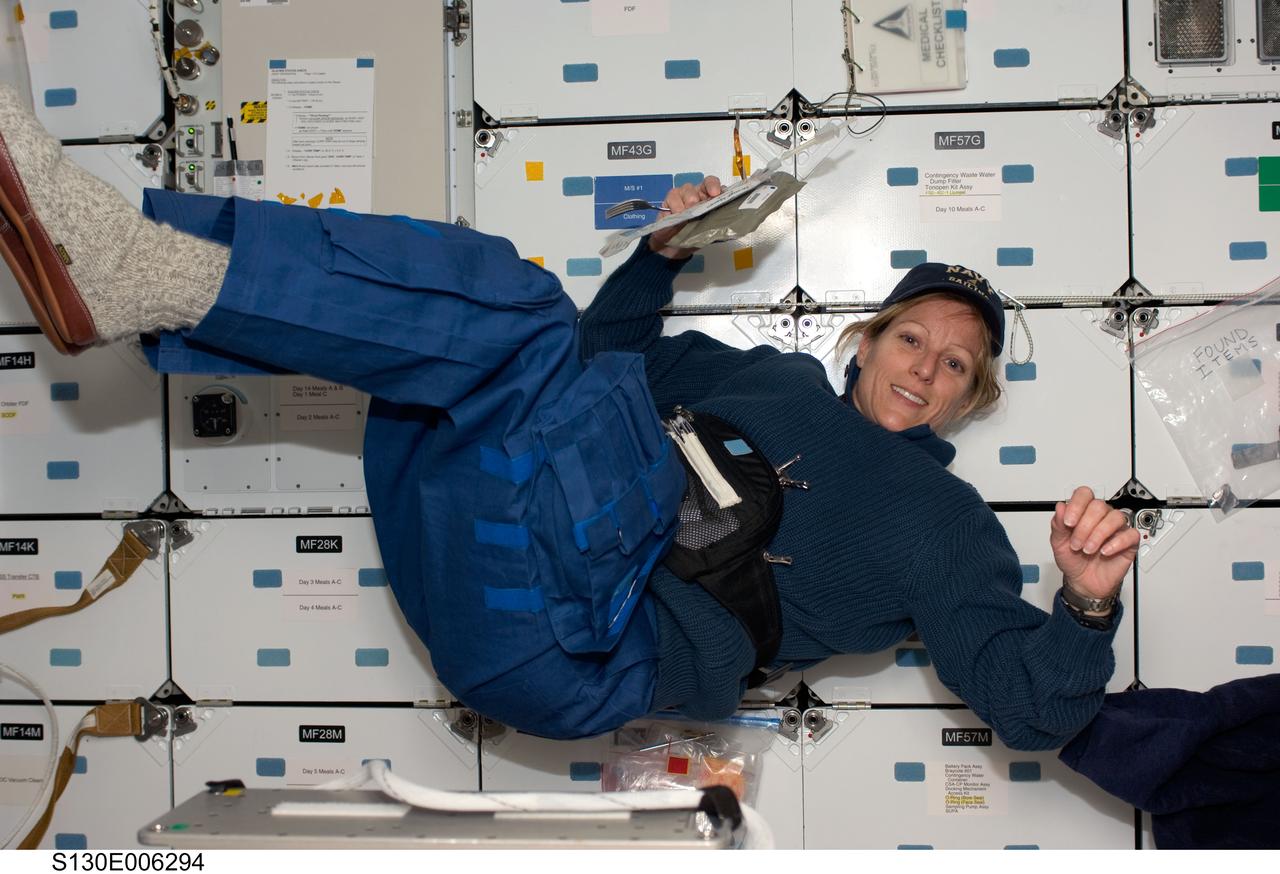

S130-E-006294 (9 Feb. 2010) --- Astronaut Kathryn Hire, STS-130 mission specialist, floats on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Endeavour during the early hours of flight day two.
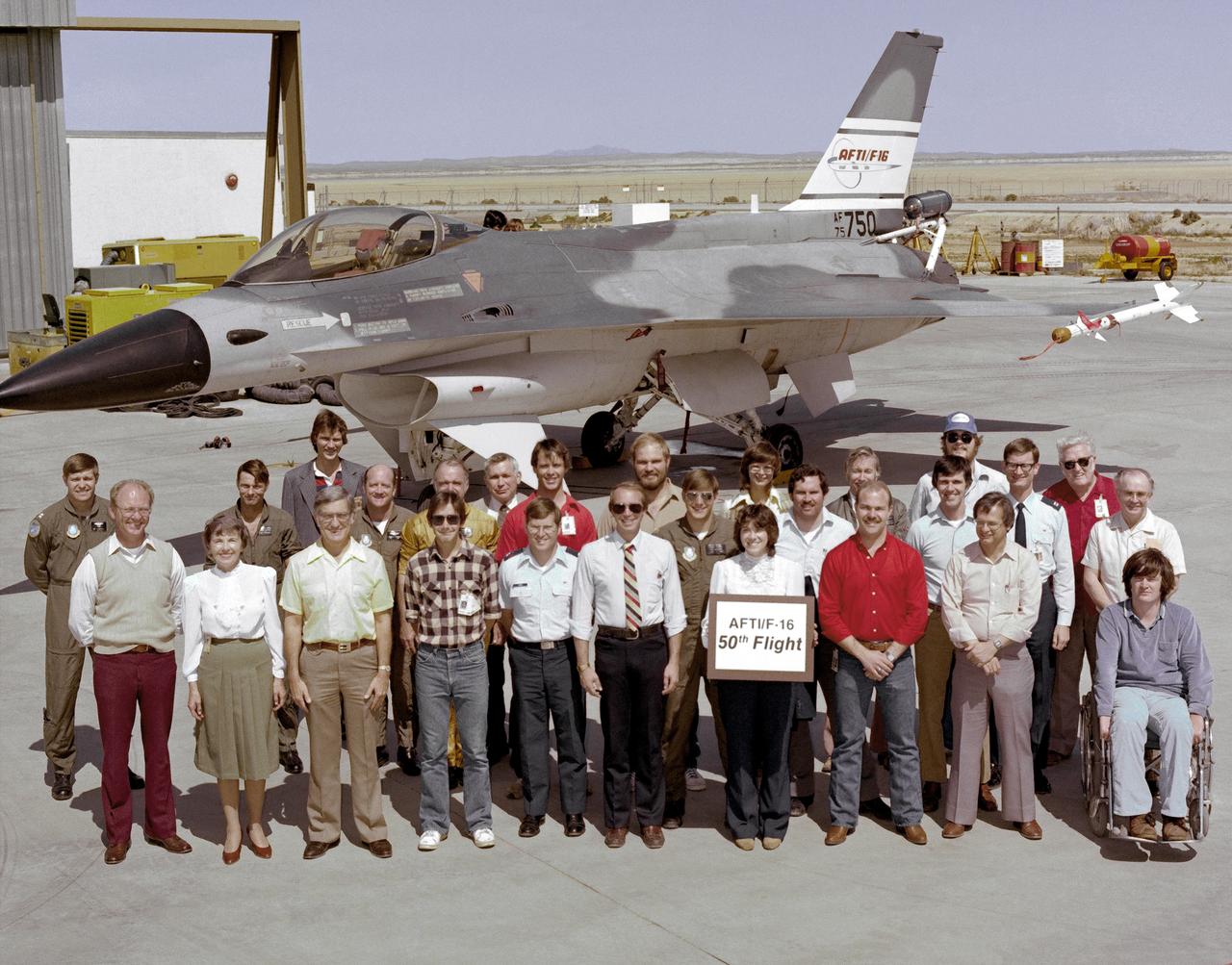

An early (1983) photograph of the AFTI F-16 team, commemorating the aircraft's 50th flight. It shows the initial configuration and paint finish of the AFTI F-16, as well as the forward mounted canards and the spin chute.
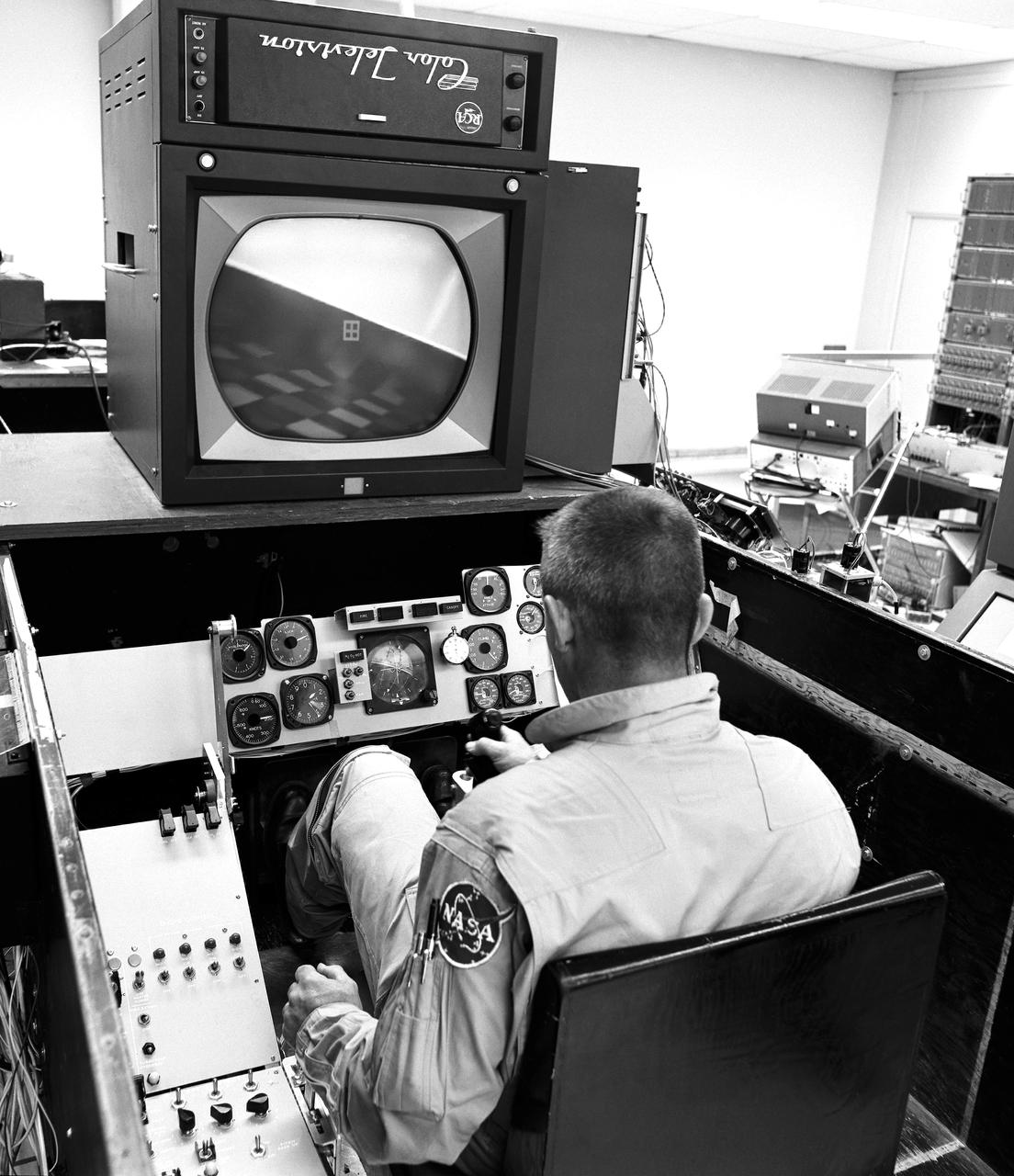

As shown in this photo of the HL-10 flight simulator, the lifting-body pilots and engineers made use of early simulators for both training and the determination of a given vehicle's handling at various speeds, attitudes, and altitudes. This provided warning of possible problems.
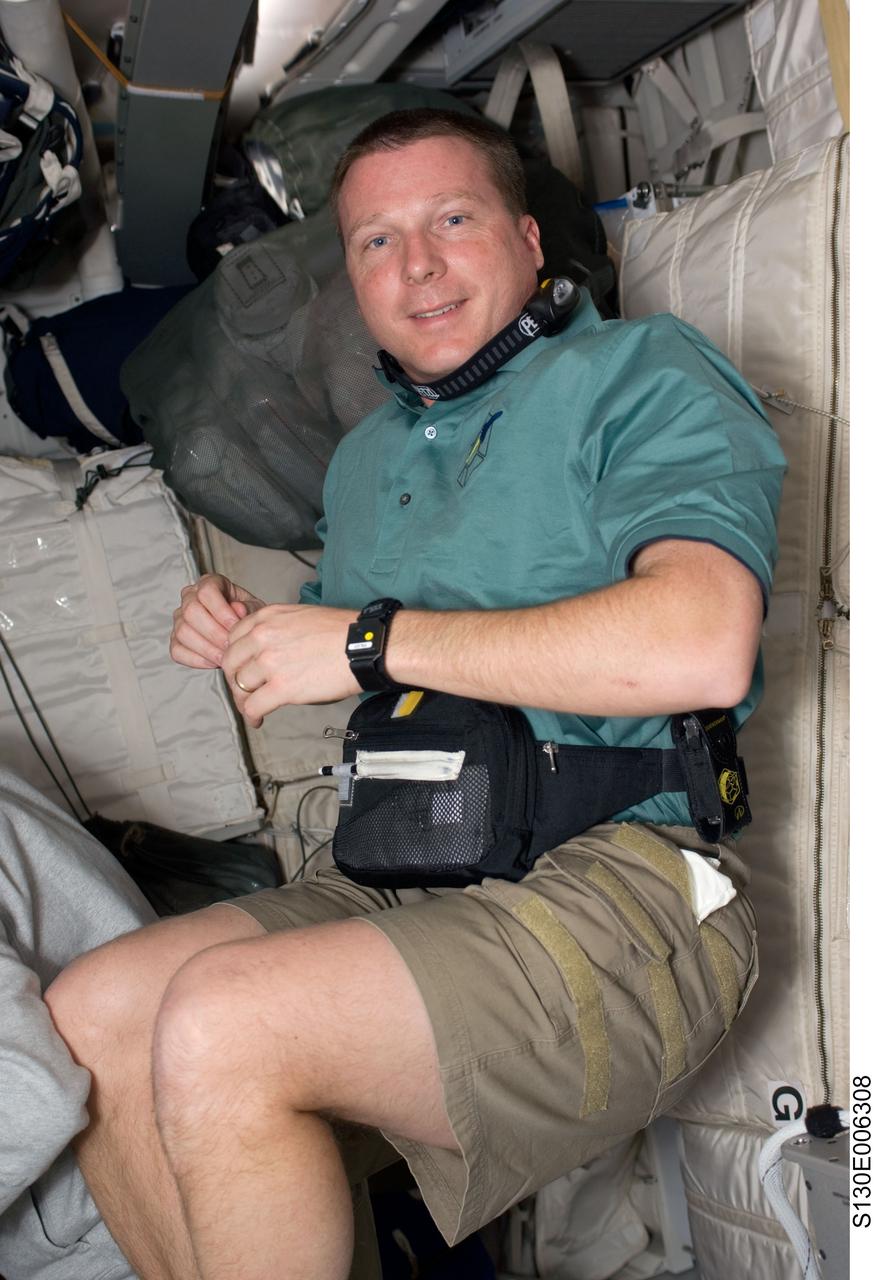

S130-E-006308 (9 Feb. 2010) --- Astronaut Terry Virts, STS-130 pilot, is pictured on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Endeavour during the early hours of flight day two.
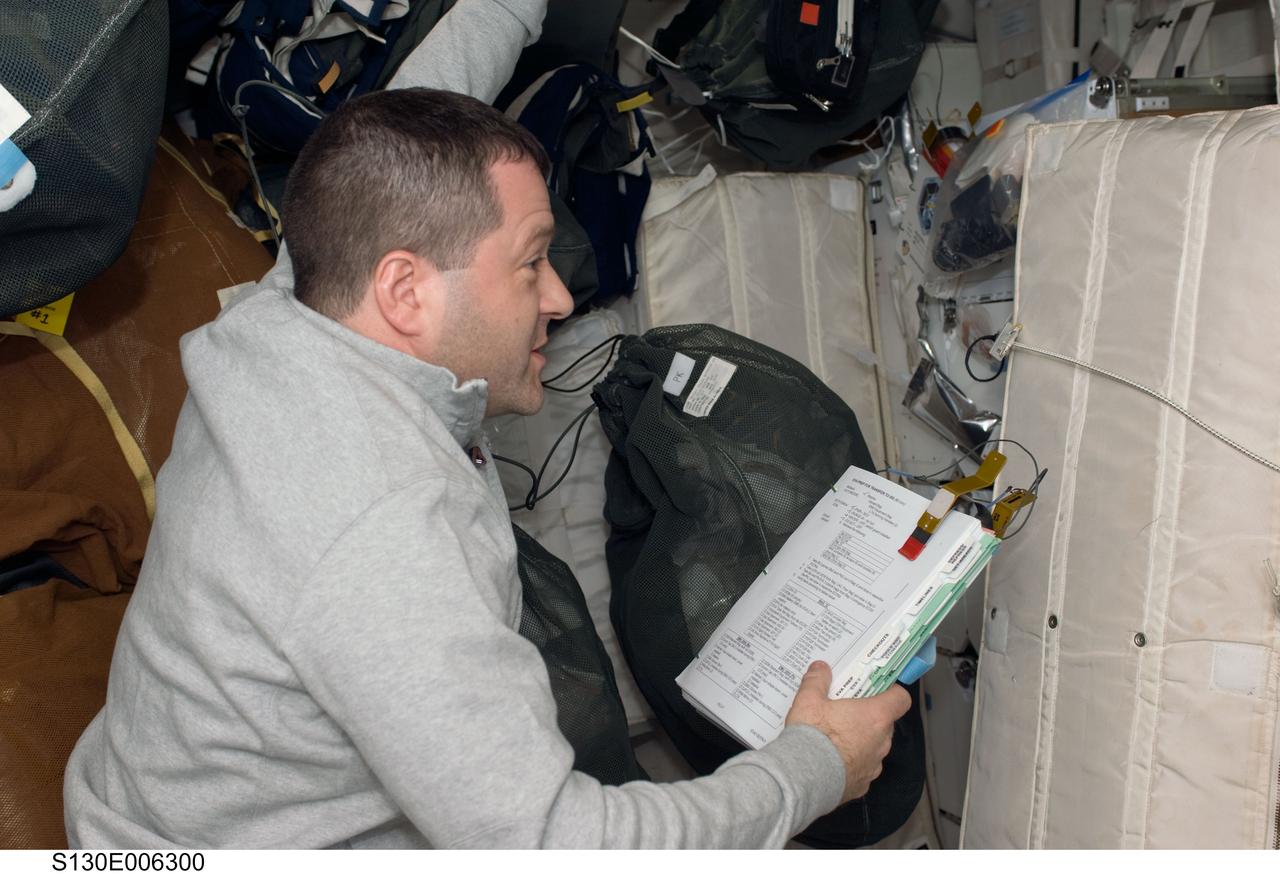

S130-E-006300 (9 Feb. 2010) --- Astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, checks equipment and supplies on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Endeavour during the early hours of flight day two.
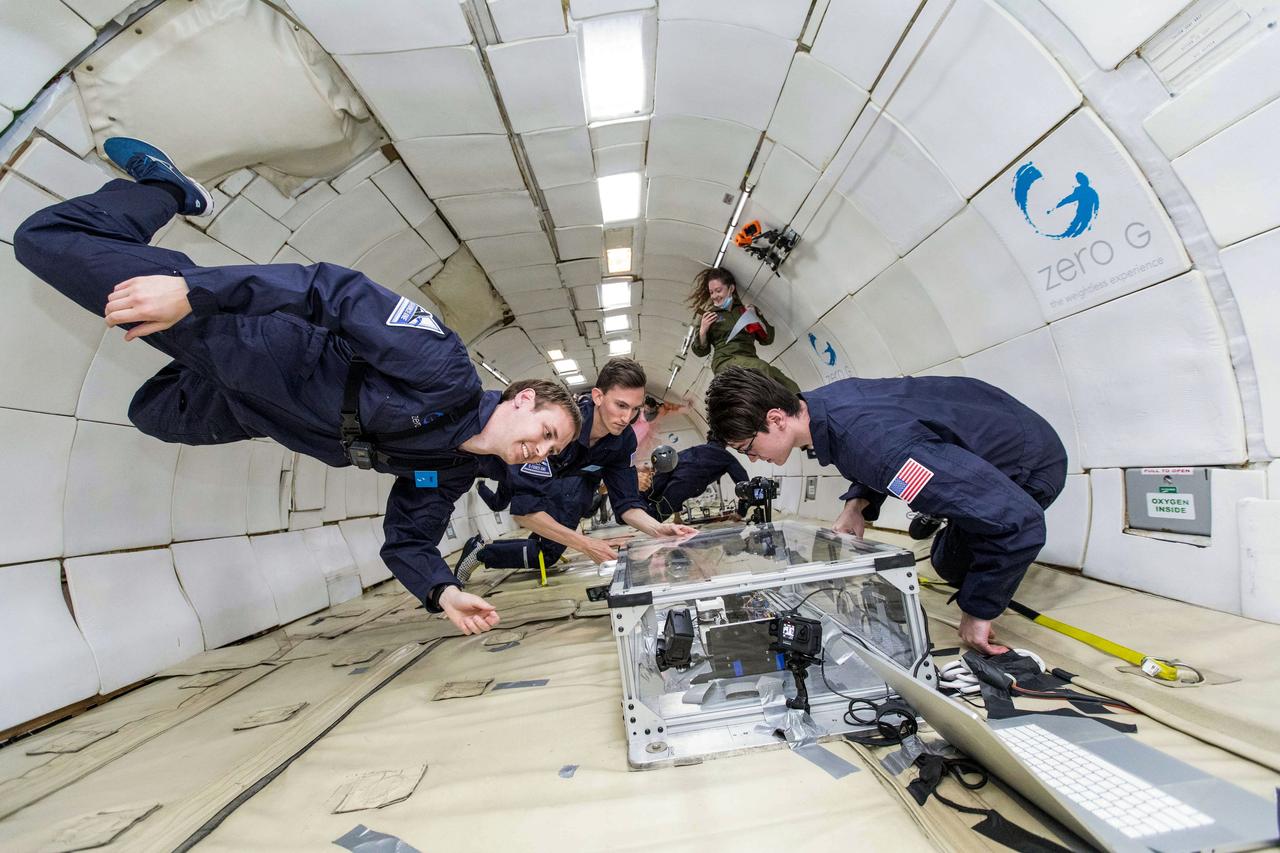

jsc2022e083566 (5/20/2022) --- The MIT Space Exploration Initiative team tests an early Extrusion payload hardware model on a parabolic flight in May 2021. Image courtesy of the MIT Space Exploration Initiative
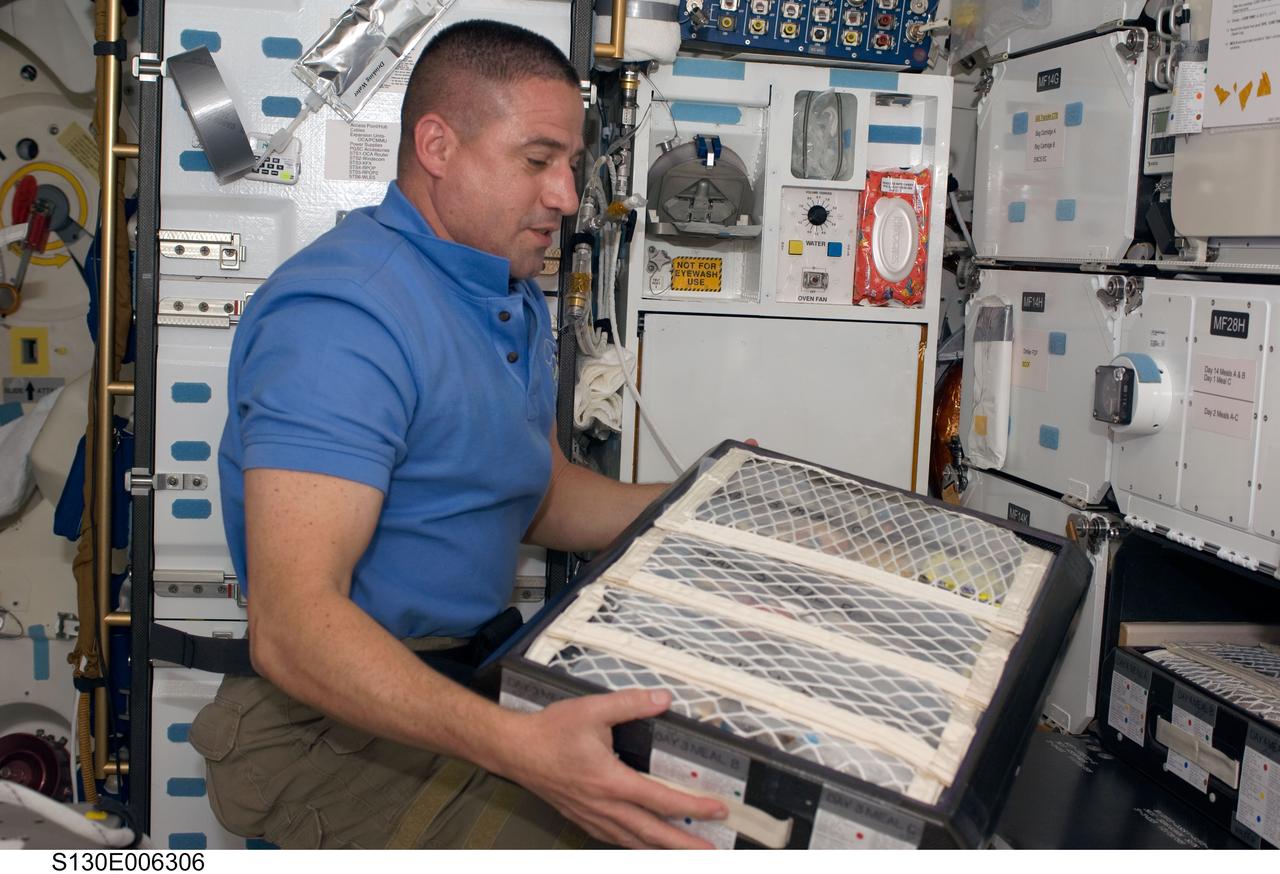

S130-E-006306 (9 Feb. 2010) --- Astronaut George Zamka, STS-130 mission commander, retrieves a drawer of food on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Endeavour during the early hours of flight day two.
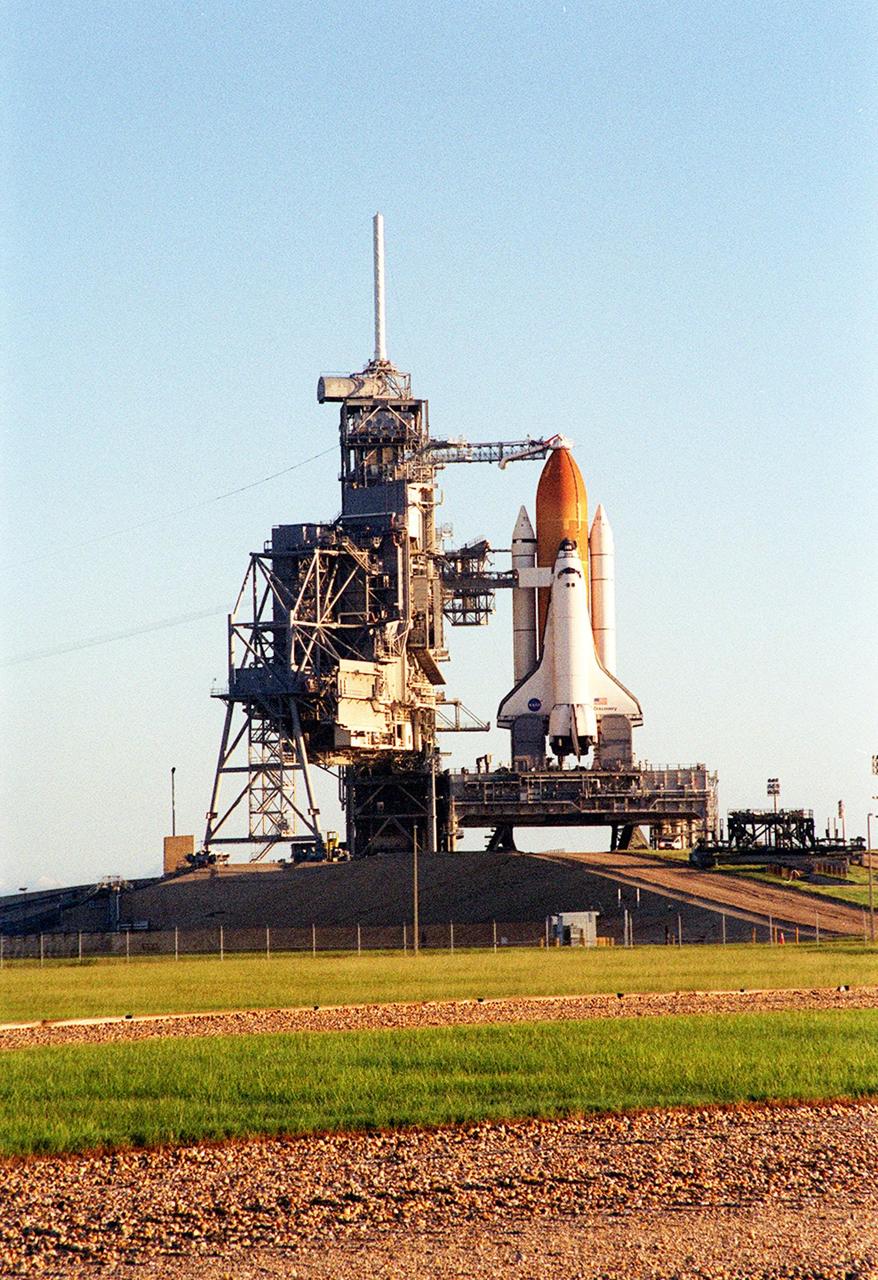
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- An early morning shot of the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Mobile Launcher Platform and Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
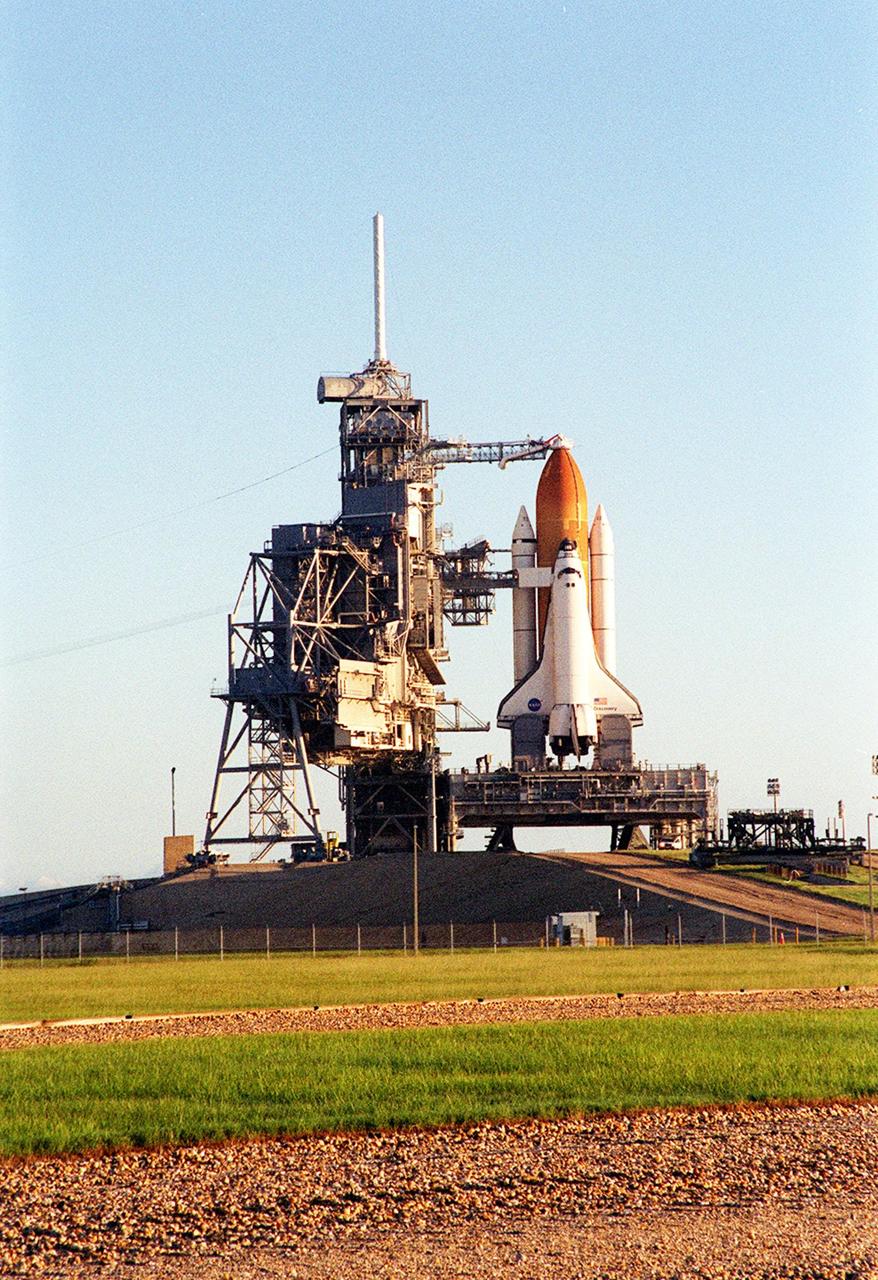
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- An early morning shot of the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Mobile Launcher Platform and Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
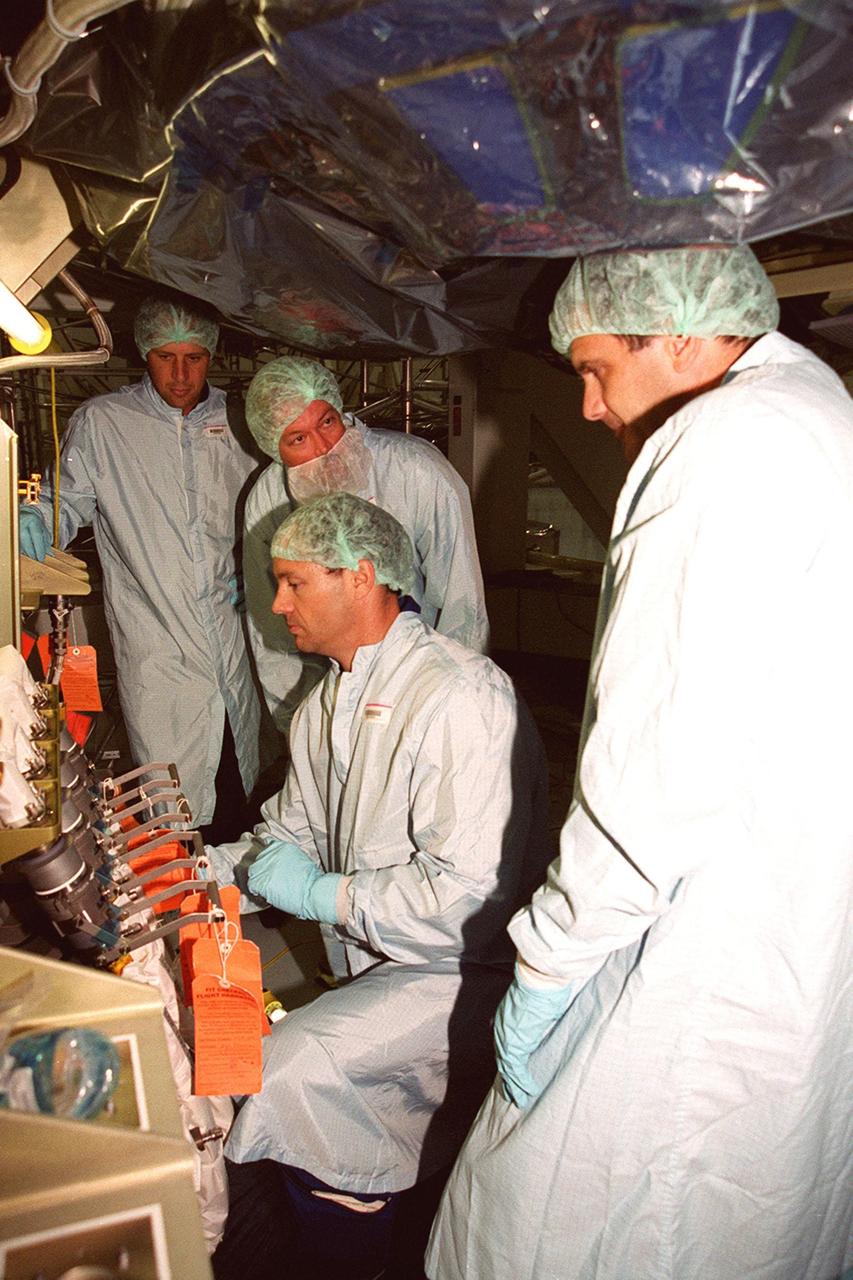

STS-92 Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria (center) and Jeff Wisoff (right) check out the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the International Space Station and payload on their mission. They and other crew members are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities while at KSC. The Z1 truss is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
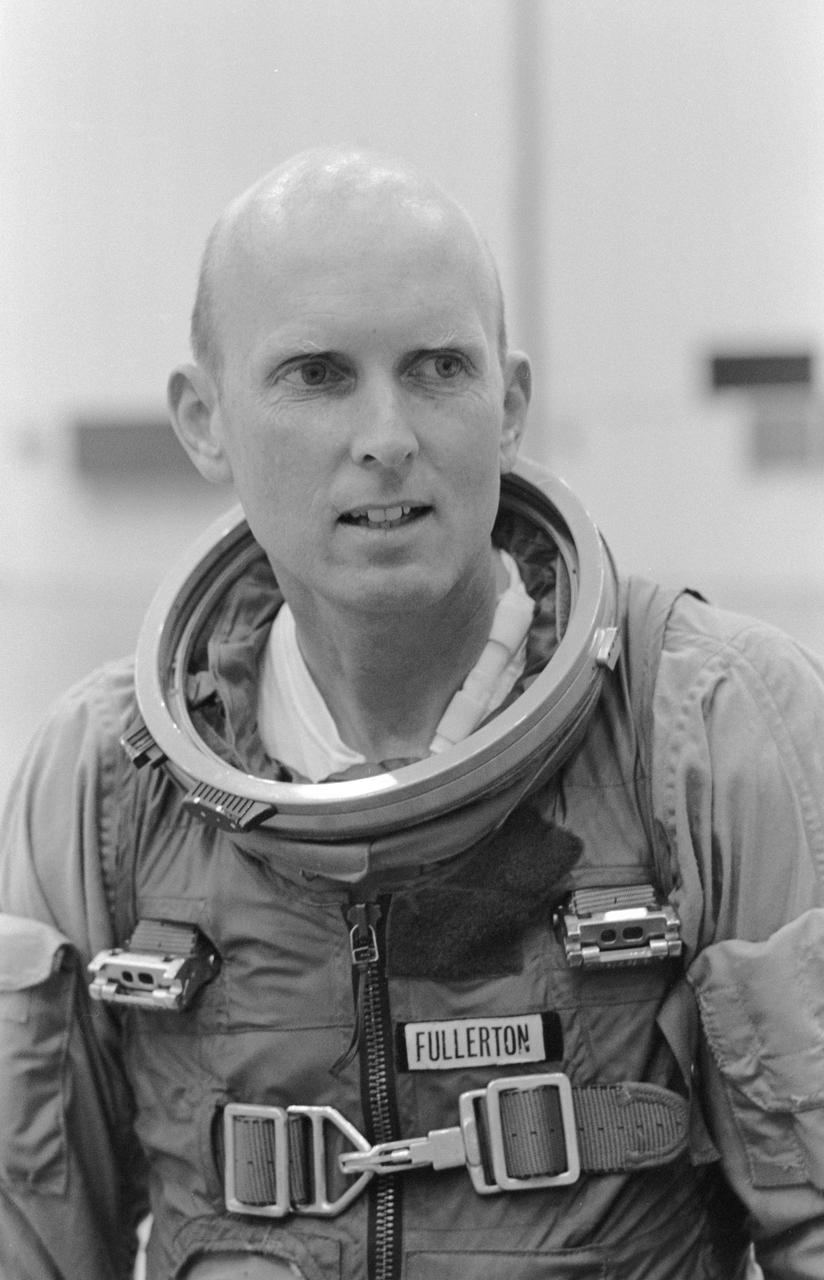

S78-34917 (31 Aug. 1978) --- Just about to don his helmet and enter JSC?s shuttle engineering mock-up/trainer is astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, one of eight NASA astronauts recently named to man the space shuttle Columbia on a series of orbital flight tests in the early 1980s. Photo credit: NASA NOTE: Since this photograph was made, astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton was named pilot for STS-3, scheduled for launch in early spring of 1982.
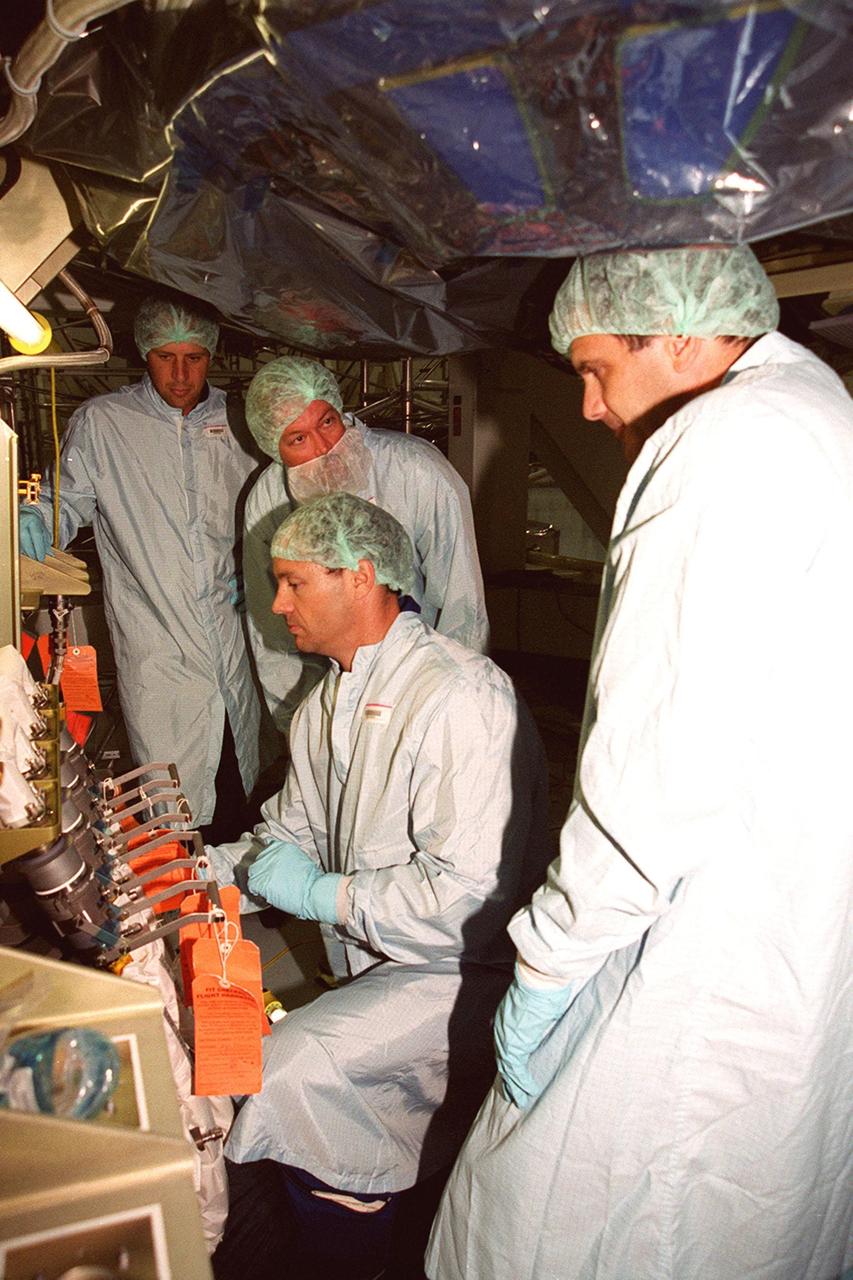

STS-92 Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria (center) and Jeff Wisoff (right) check out the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, a component of the International Space Station and payload on their mission. They and other crew members are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities while at KSC. The Z1 truss is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A

On a workstand in the Space Station Processing Facility, workers release the S-band Antenna Support Assembly (SASA) from an overhead crane. The SASA will be attached to the Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) Z1, an element of the International Space Station, sitting below. The antenna is primarily for local communications between the orbiter and Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays, on mission STS-97, flight 4A, to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. The Z1 is scheduled on mission STS-92, the fifth flight to the Space Station, in the fall
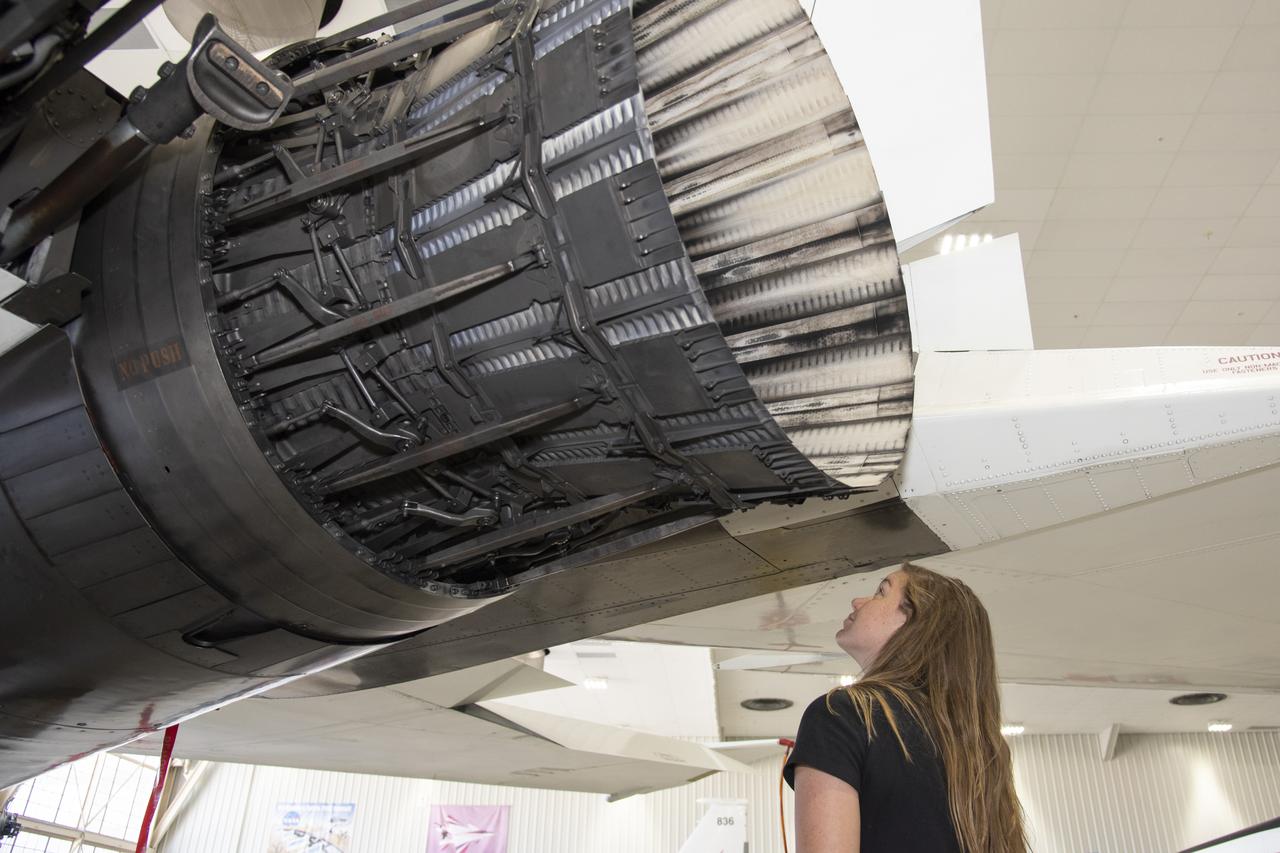

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California where Jenni Sidey-Gibbons looks inside engine nozzle of F-15 jet. The F-15 will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages for the X-59 development.
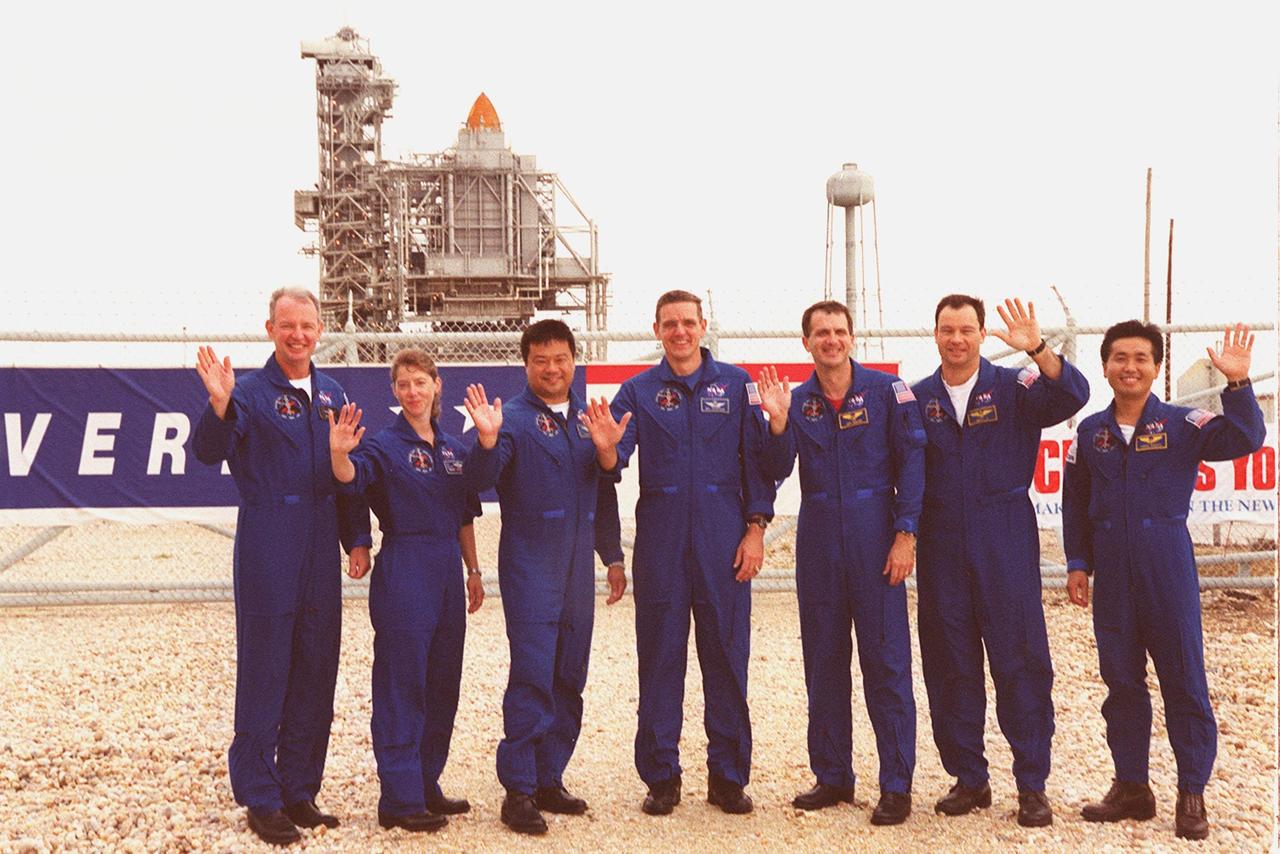

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-92 crew happily wave to onlookers as they gather gather outside the gate to Launch Pad 39A where Space Shuttle Discovery waits in the background for liftoff Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT. From left to right are Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy, and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. stallation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks
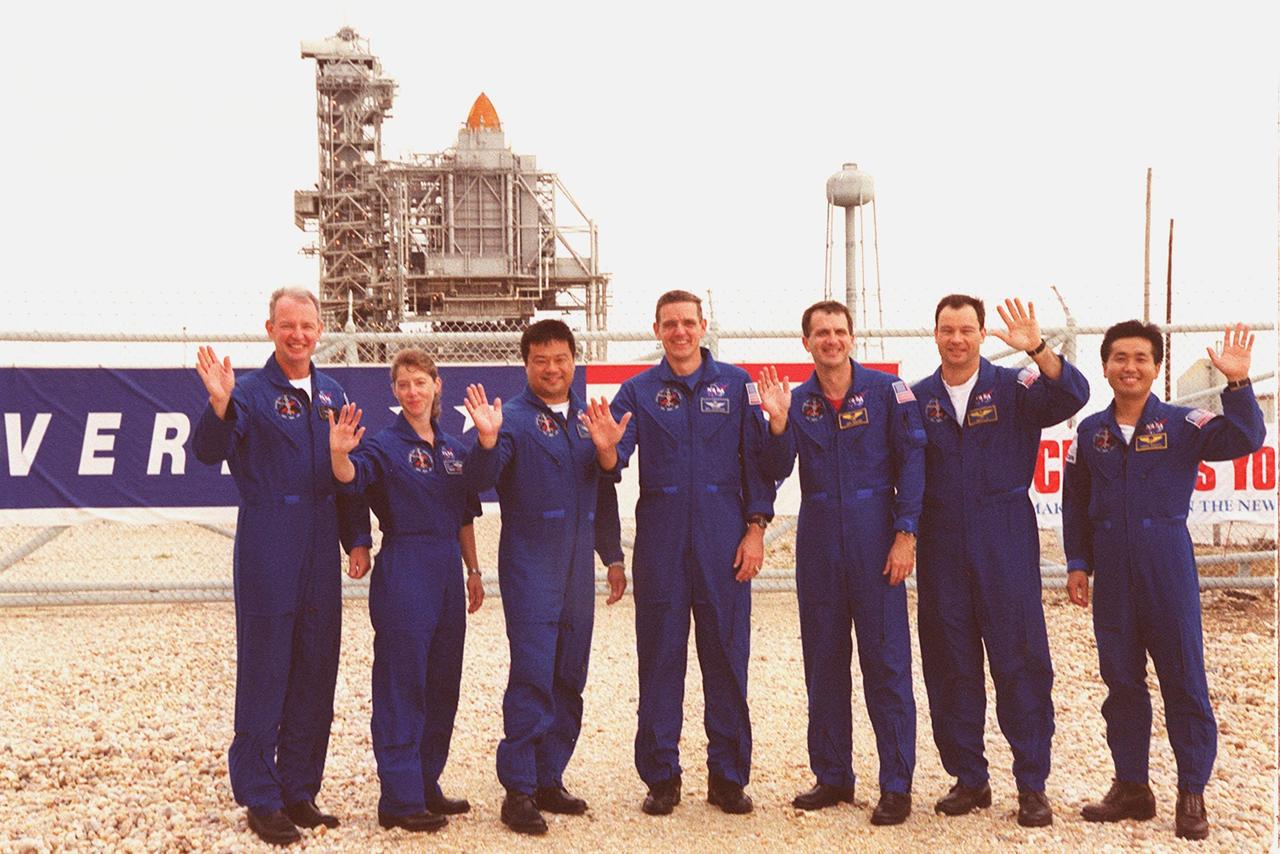

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-92 crew happily wave to onlookers as they gather gather outside the gate to Launch Pad 39A where Space Shuttle Discovery waits in the background for liftoff Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT. From left to right are Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy, and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. stallation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks
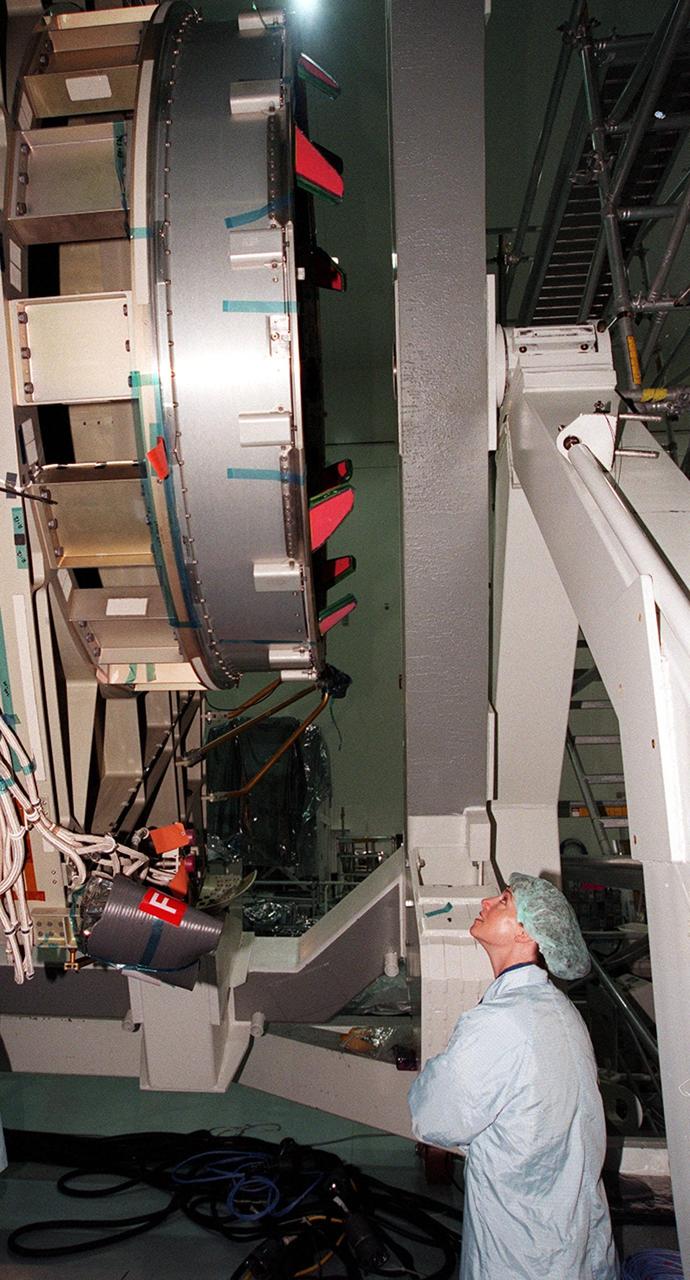

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-92 Pilot Pamela A. Melroy gets a close look at the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 that will fly on the mission, the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. Other crew members are Commander Brian Duffy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chaio, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
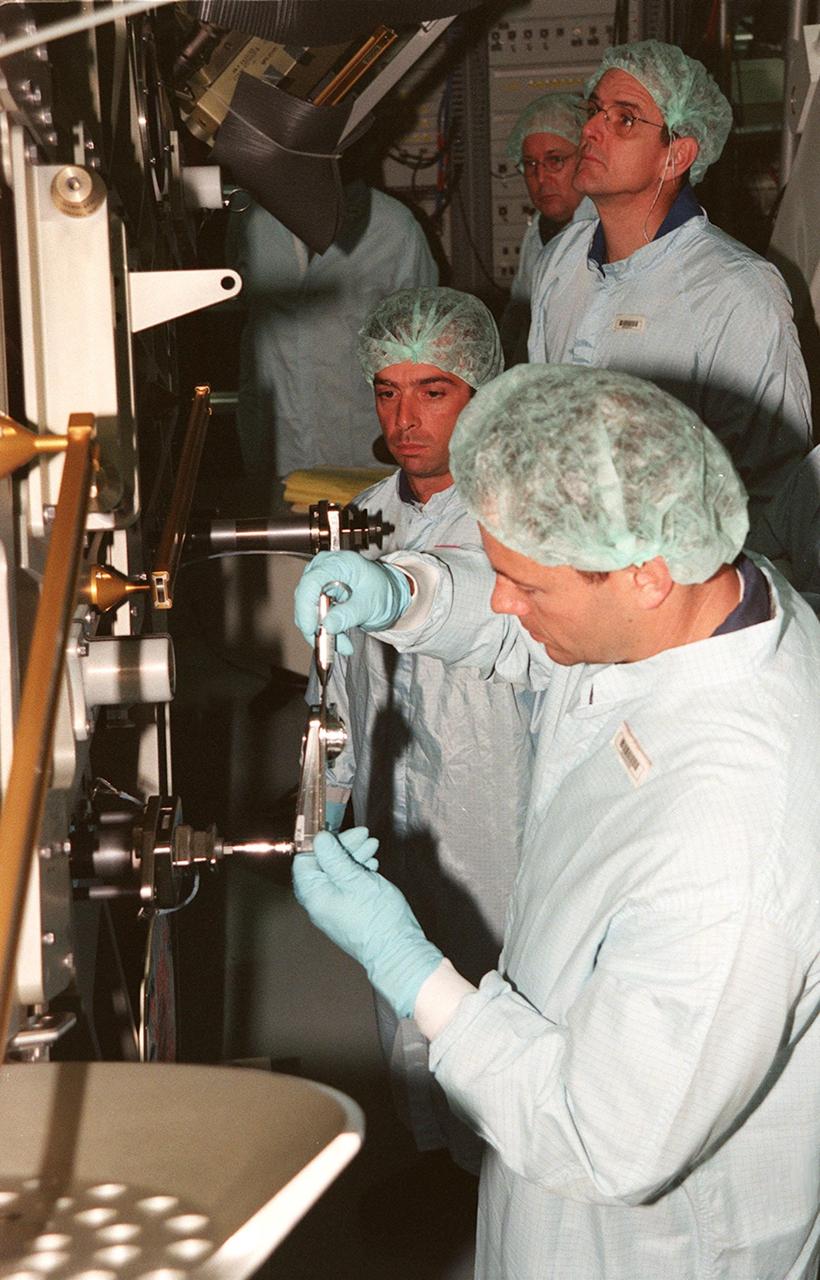

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get hands-on experience with some of the equipment, such as the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, to fly on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
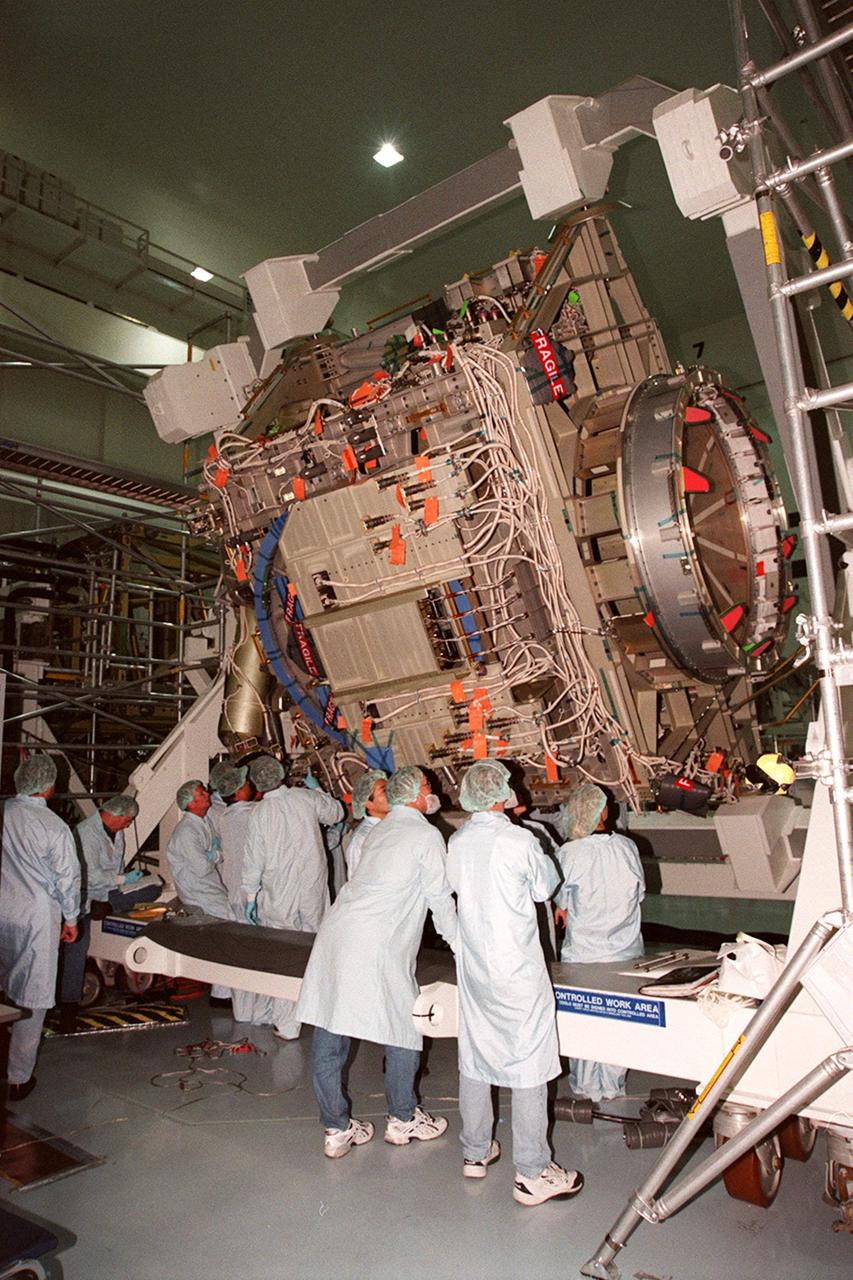

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get a close look at the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, part of the payload on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
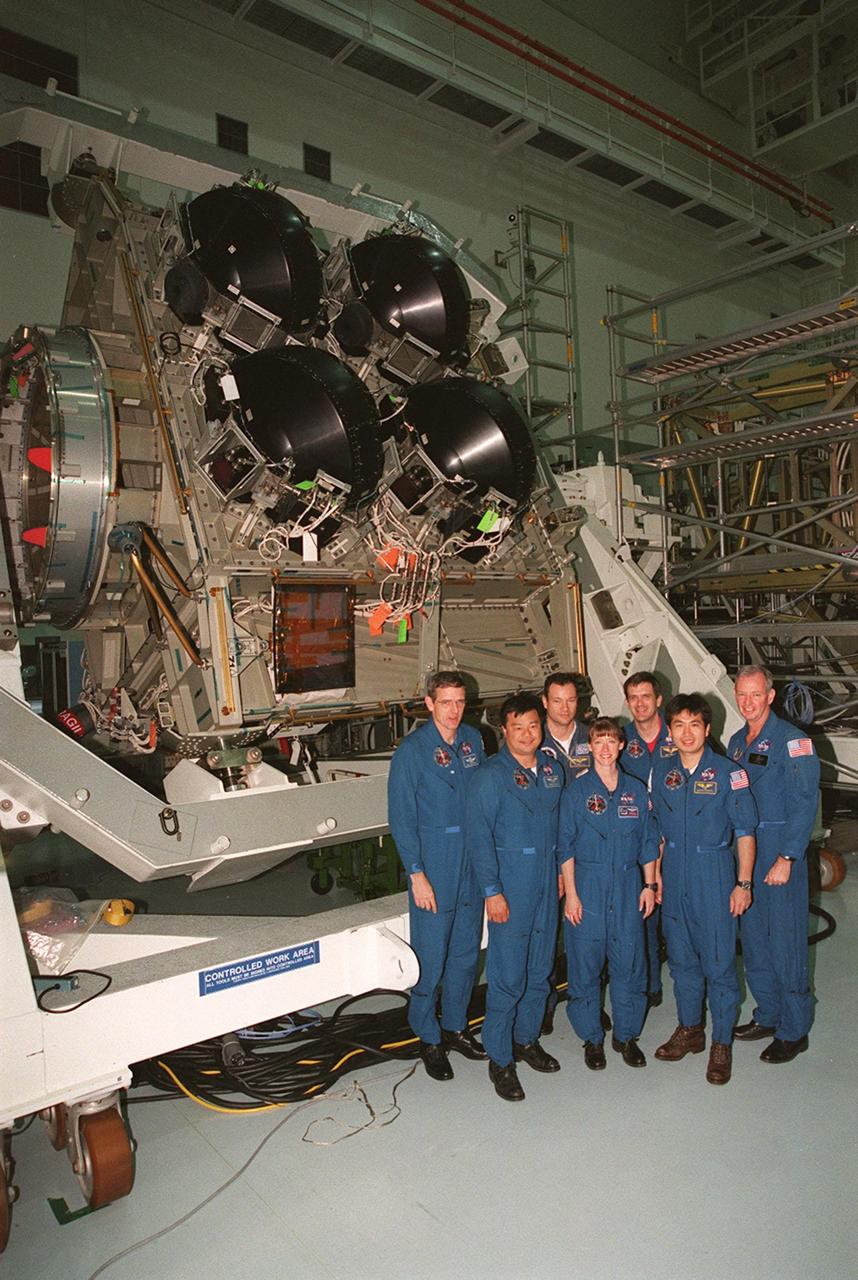

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-92 crew pose in front of the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an element of the International Space Station that will be part of the mission payload. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. Standing left to right are Mission Specialists William S. McArthur Jr., Leroy Chiao, and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria; Pilot Pamela A. Melroy; Mission Specialists Peter J.K. Wisoff and Koichi Wakata; and Commander Brian Duffy. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
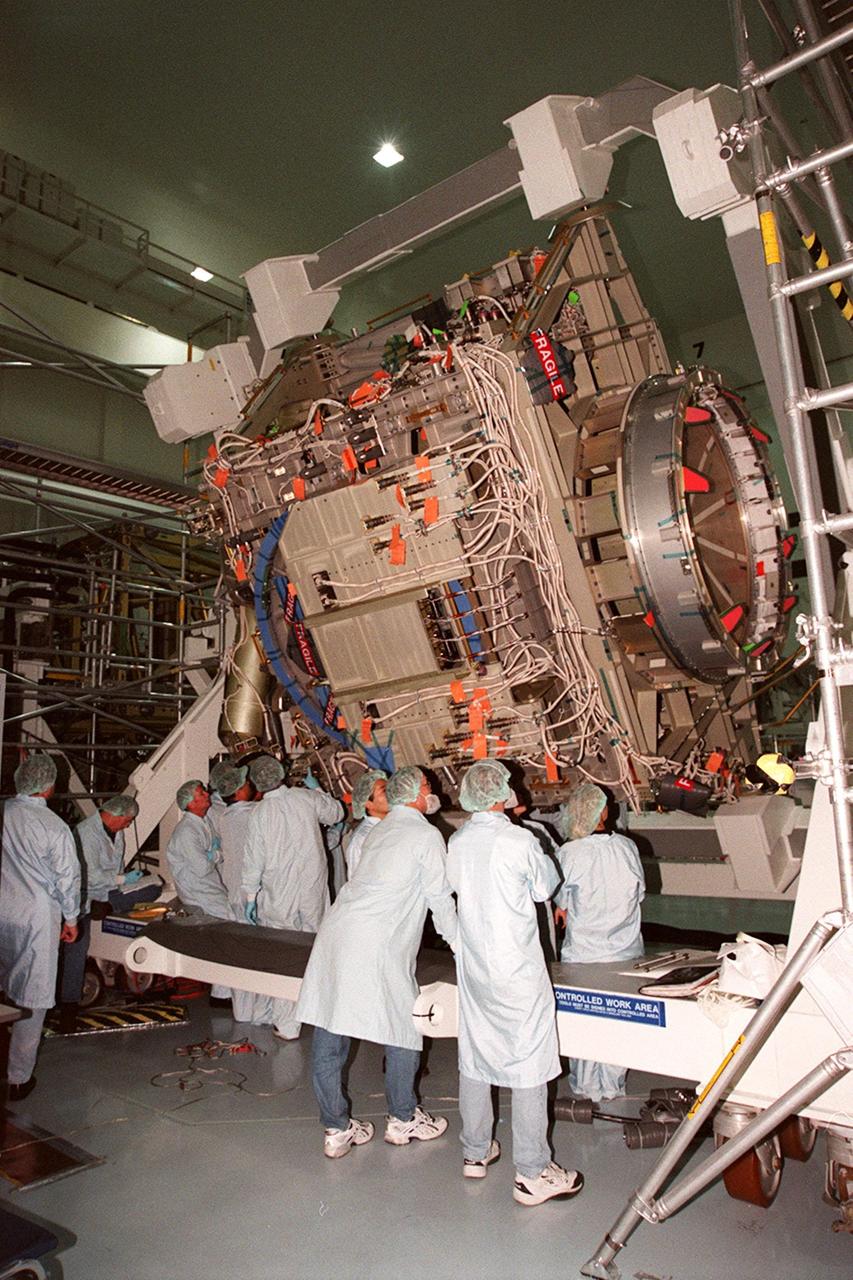

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get a close look at the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, part of the payload on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
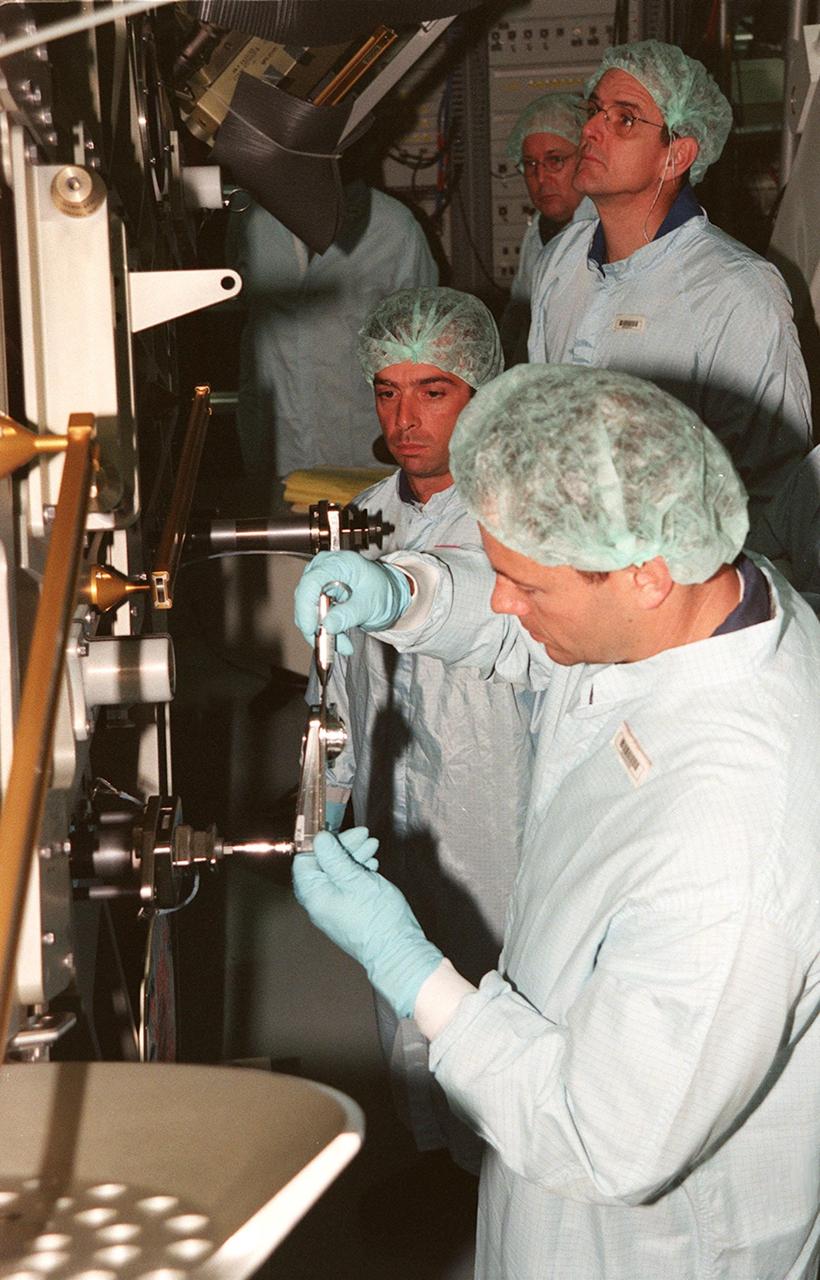

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-92 crew get hands-on experience with some of the equipment, such as the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, to fly on their mission. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The crew comprises Mission Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela A. Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
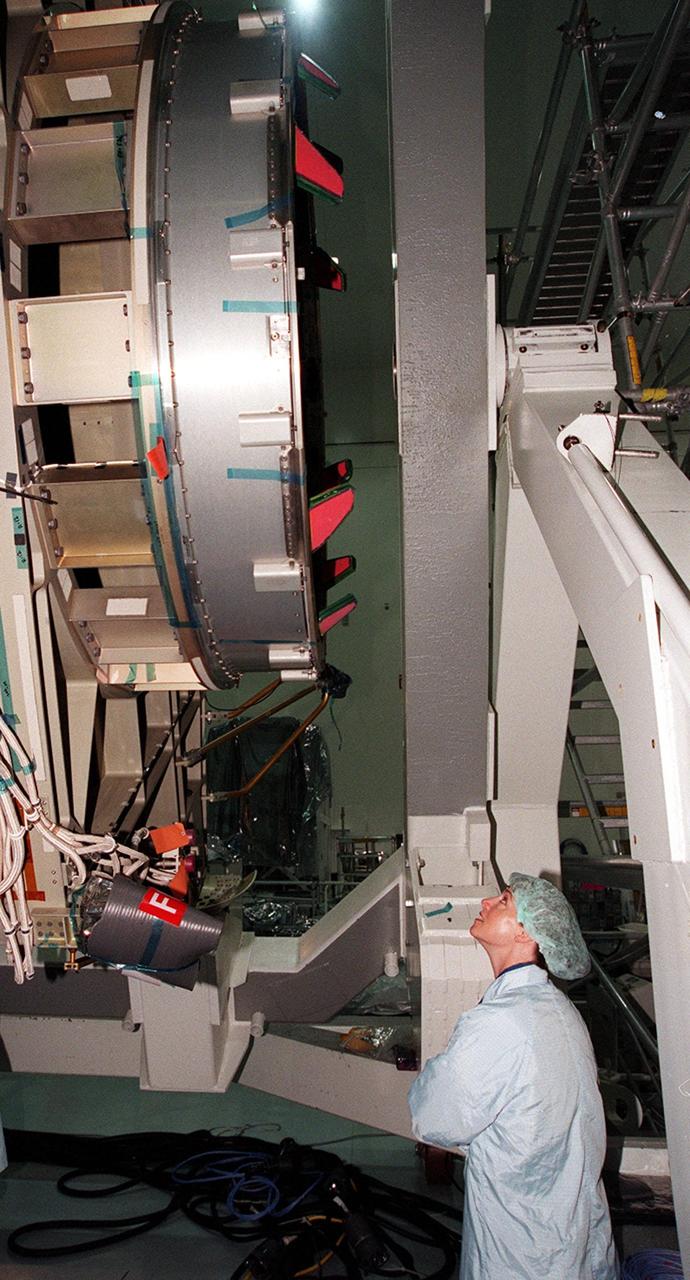

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-92 Pilot Pamela A. Melroy gets a close look at the Integrated Truss Structure Z1 that will fly on the mission, the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. Other crew members are Commander Brian Duffy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chaio, Peter J.K. Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, and William S. McArthur Jr. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
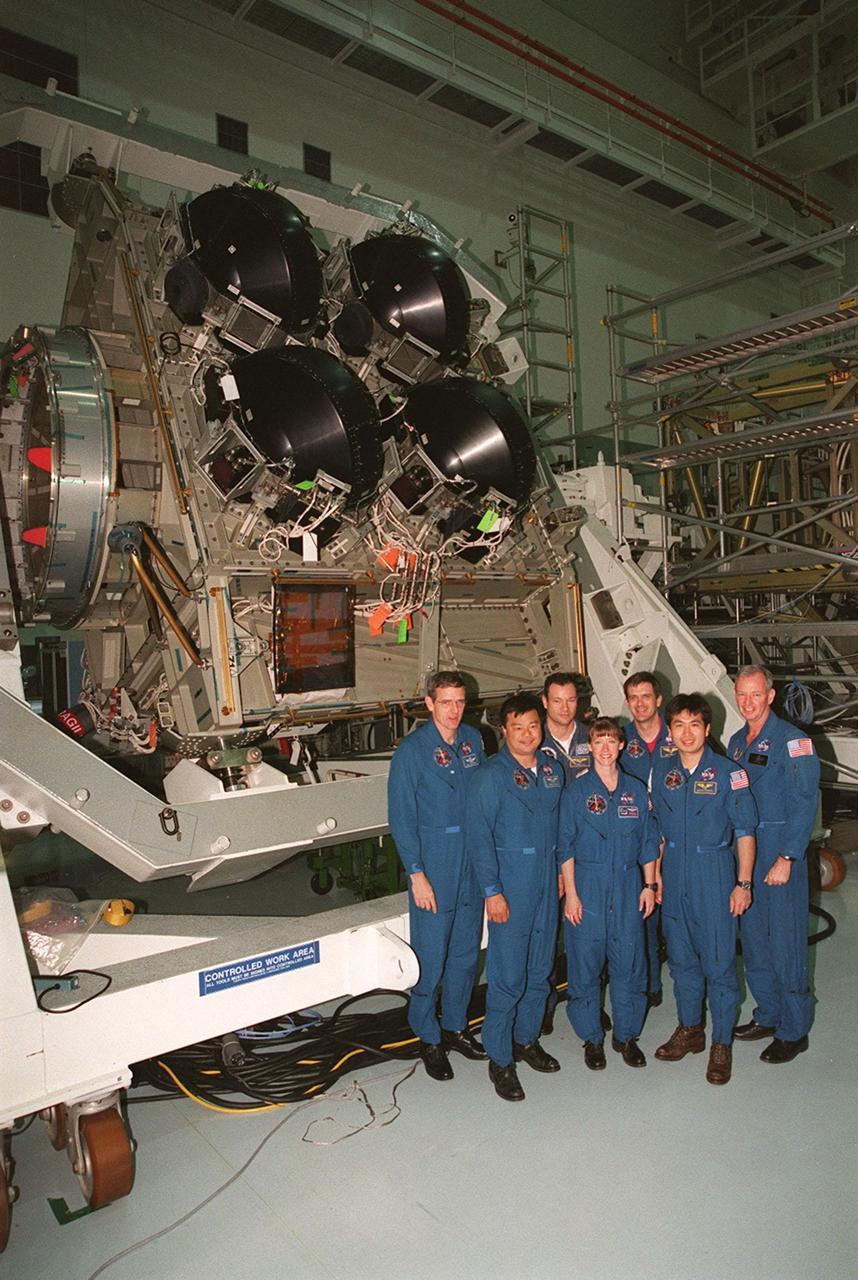

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-92 crew pose in front of the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an element of the International Space Station that will be part of the mission payload. STS-92 is the fifth U.S. flight in the construction of the International Space Station. Standing left to right are Mission Specialists William S. McArthur Jr., Leroy Chiao, and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria; Pilot Pamela A. Melroy; Mission Specialists Peter J.K. Wisoff and Koichi Wakata; and Commander Brian Duffy. Wakata is with the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The Z1 is an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power. Another part of the payload is a pressurized mating adapter, PMA-3, to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. Launch of STS-92 is scheduled for Sept. 21, 2000
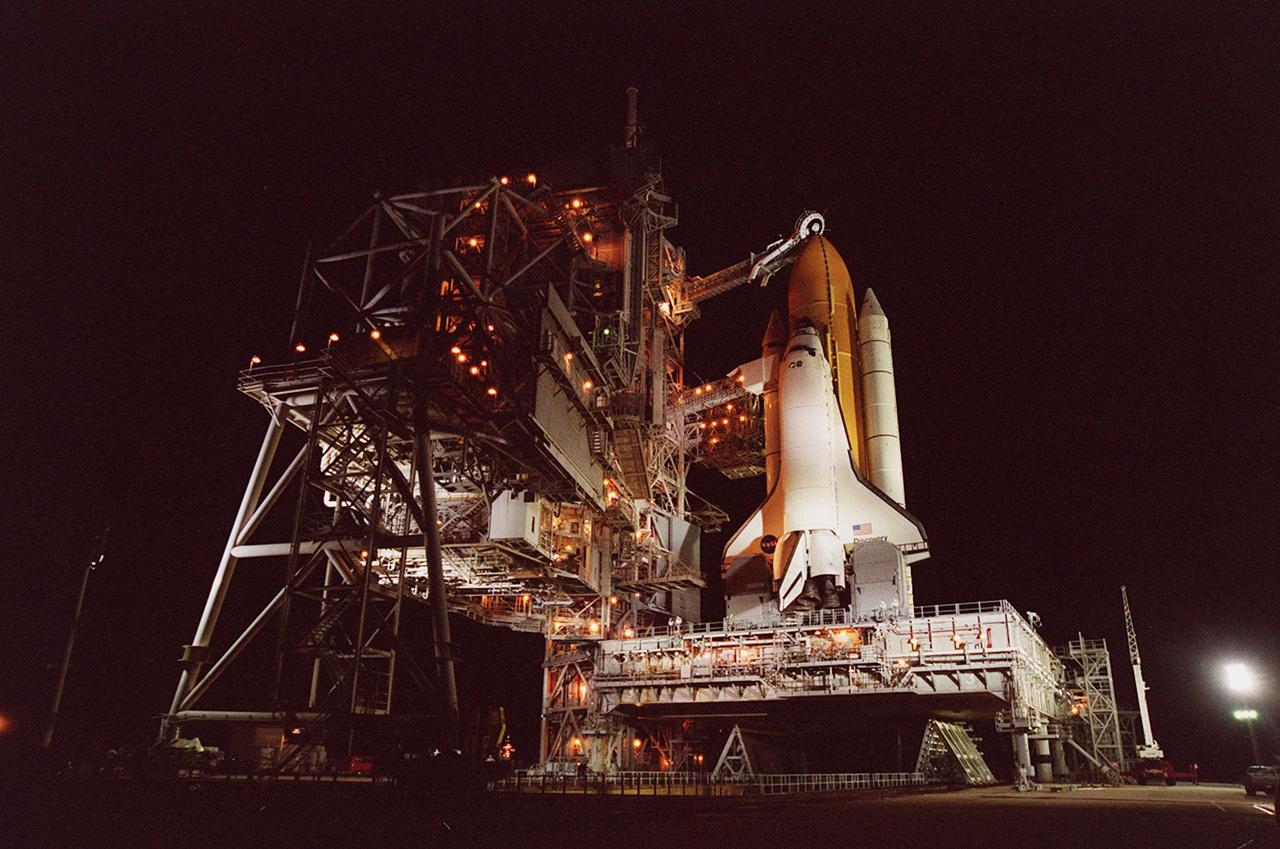

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, Space Shuttle Discovery is revealed on the Mobile Launcher Platform at Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT
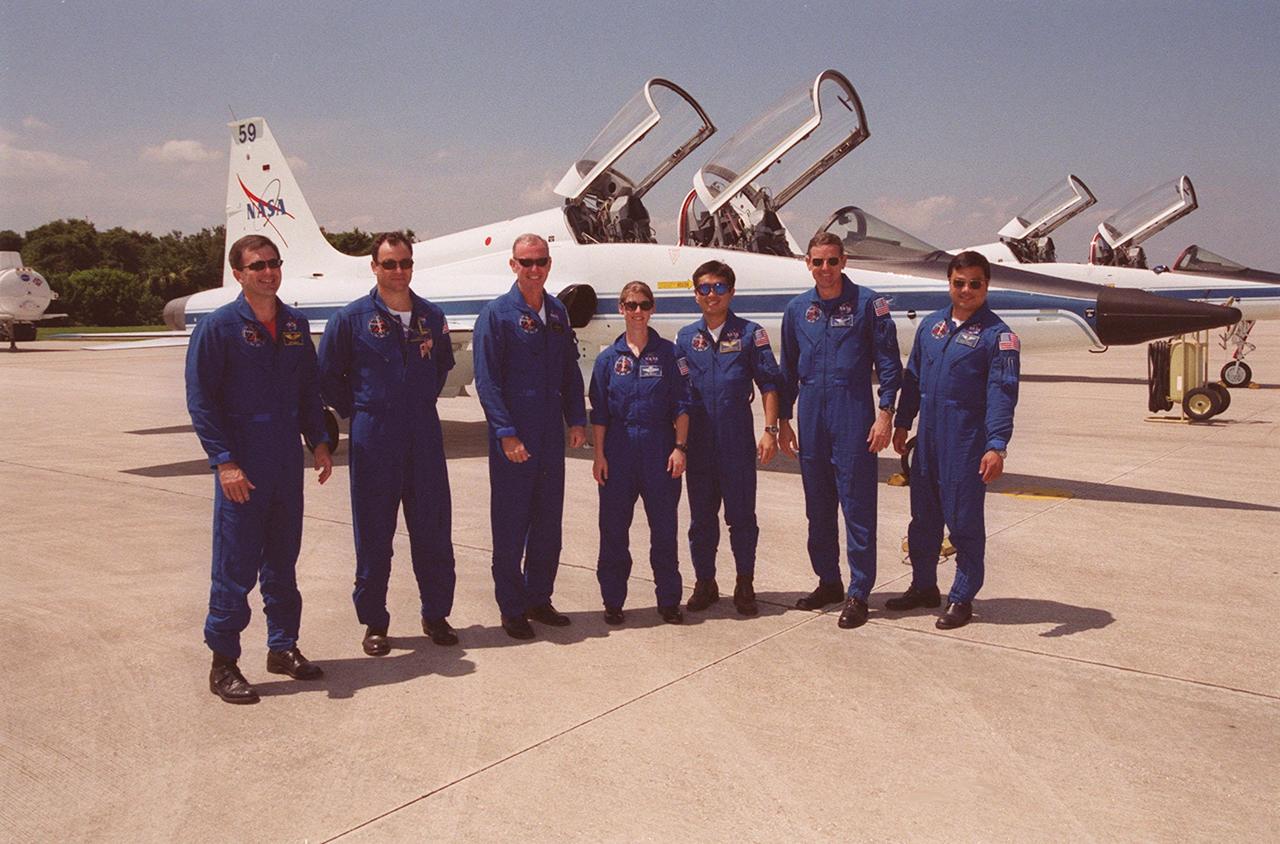

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew line up on the runway at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility after arriving to take part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT). From left are Mission Specialists Jeff Wisoff and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pam Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao. Wakata is with the Japanese space agency. During the CEIT, the crew will spend time at SPACEHAB becoming familiar with the payload and equipment they will use on their mission to the International Space Station. The mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
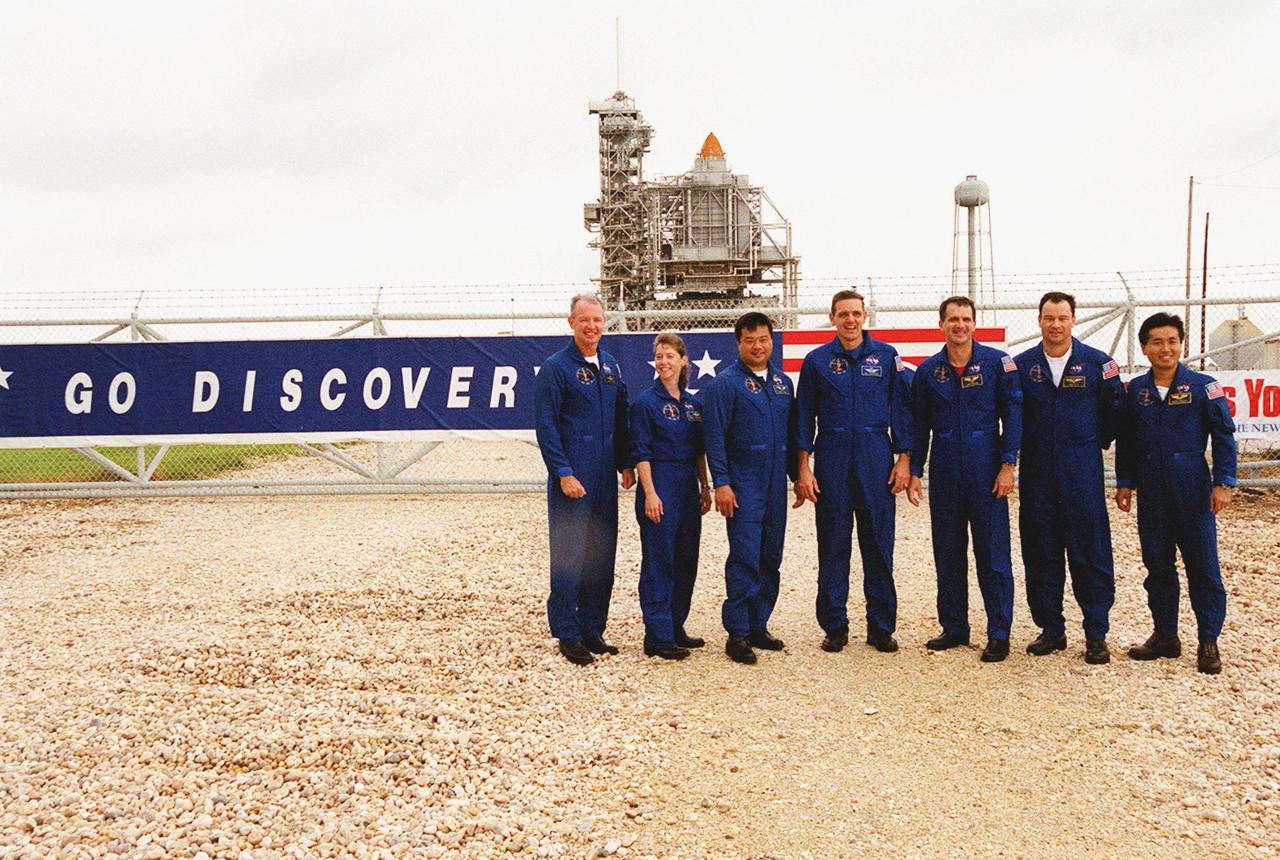

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-92 crew gather outside the gate to Launch Pad 39A where the sign on the gate identifies Space Shuttle Discovery in the background. From left to right are Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy, and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT
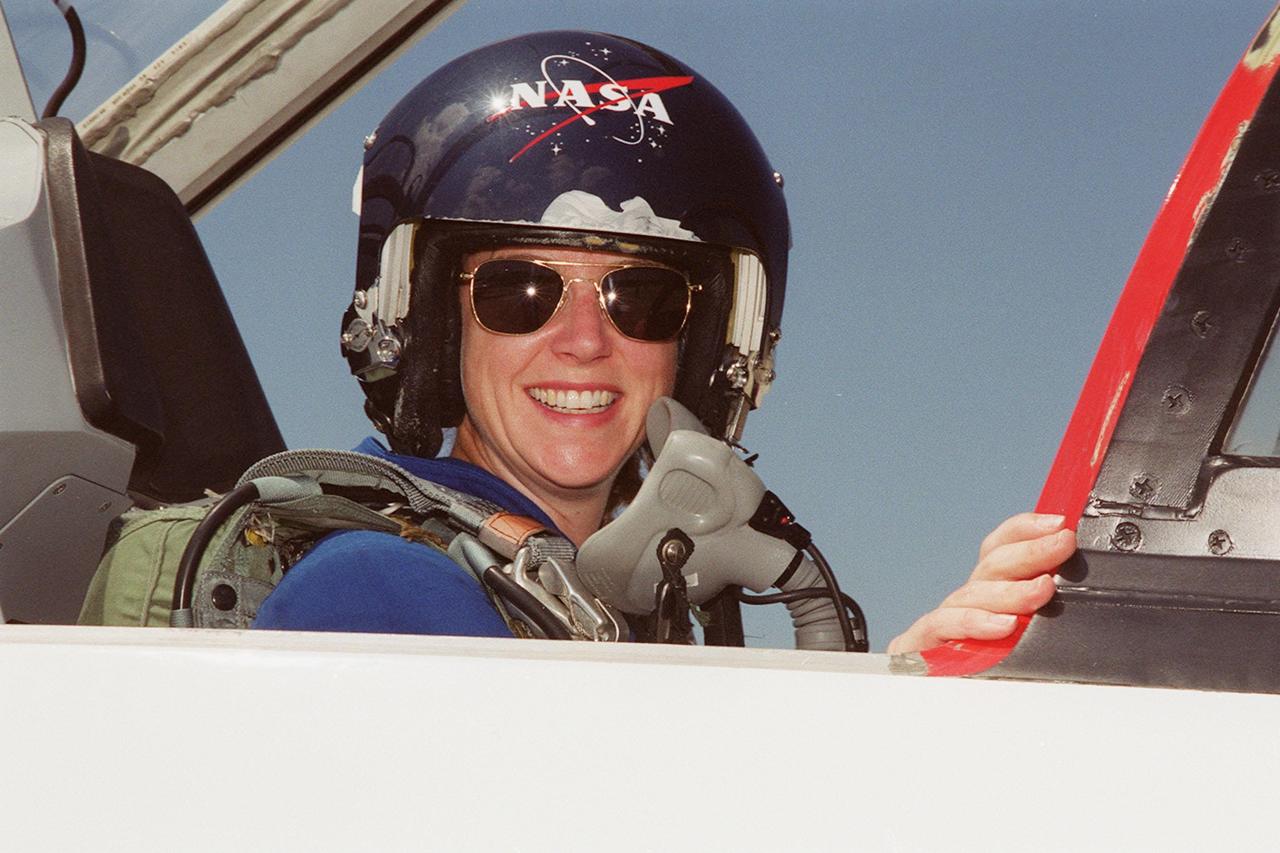

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Pilot Pam Melroy arrives at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility to take part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test. She and other crew members Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Leroy Chiao, Jeff Wisoff, Michael Lopez-Alegria and Bill McArthur will spend time at SPACEHAB becoming familiar with the payload and equipment they will use on their mission to the International Space Station. Wakata is with the Japanese space agency. The mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
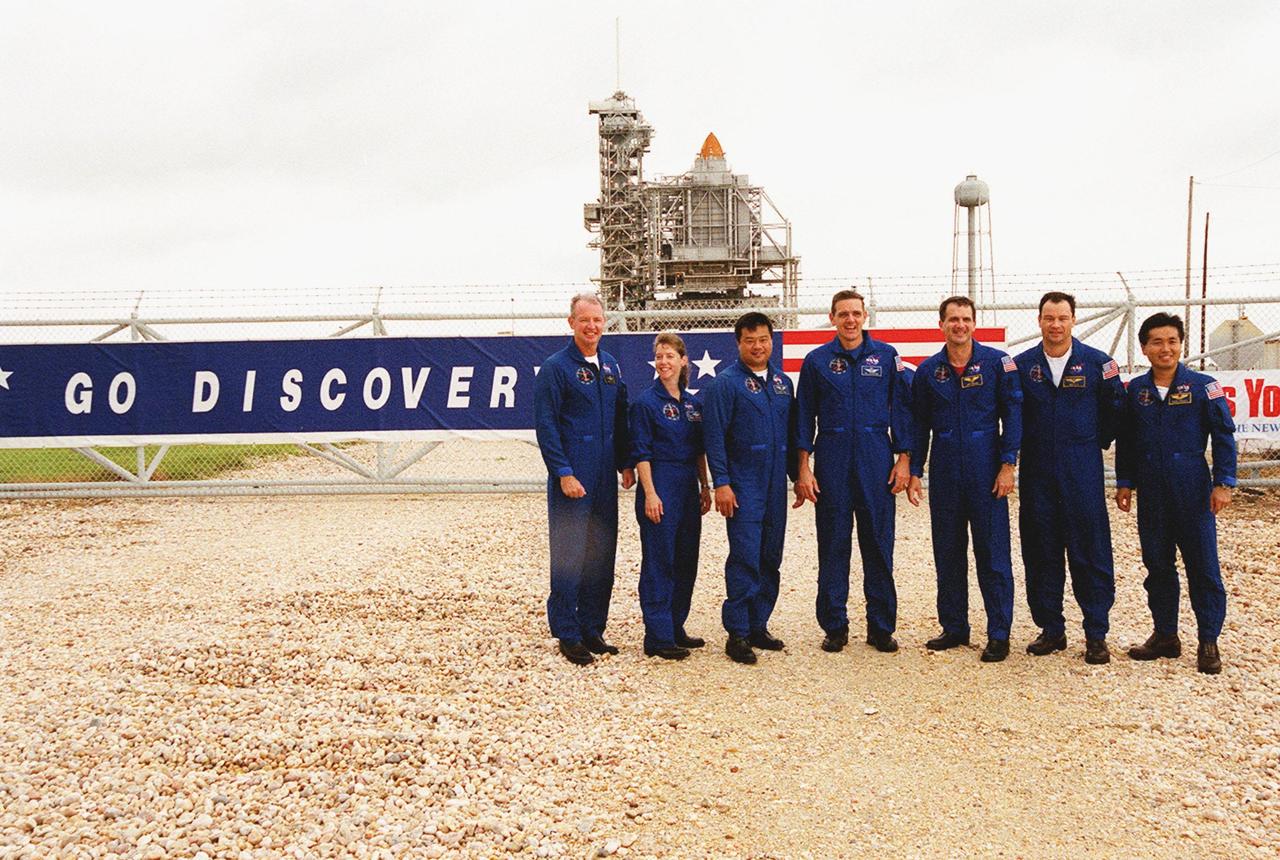

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-92 crew gather outside the gate to Launch Pad 39A where the sign on the gate identifies Space Shuttle Discovery in the background. From left to right are Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy, and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 5 at 9:38 p.m. EDT
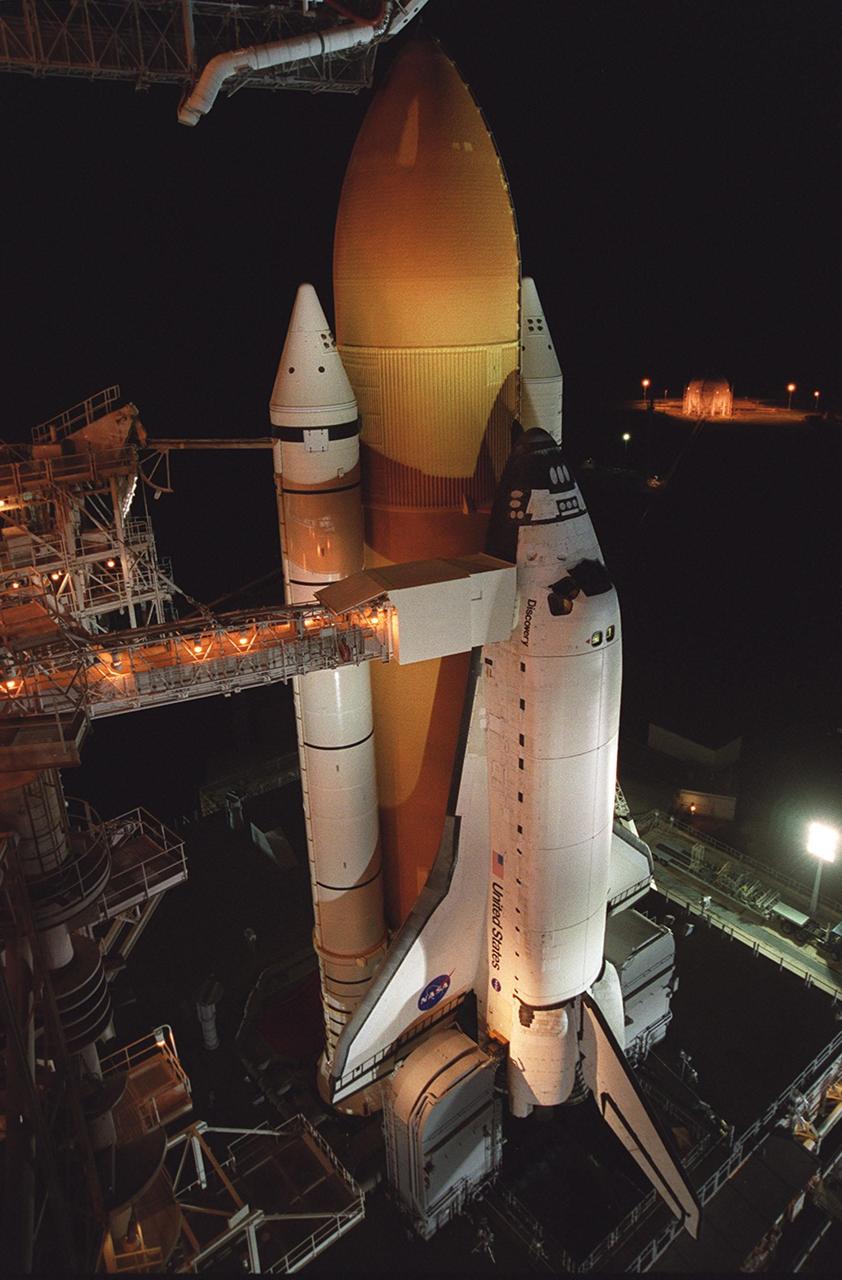

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, Space Shuttle Discovery is revealed on the Mobile Launcher Platform at Launch Pad 39A. Discovery is being readied for the STS-92 mission launch to the International Space Station (ISS). At the top is the 13-foot-wide “beanie cap,” at the end of the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm, designed to vent gaseous oxygen vapors away from the Space Shuttle. Lower is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmental chamber, known as the “white room,” extended to the orbiter. The chamber provides entry for the crew into the orbiter and also serves as emergency egress up to 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. The STS-92 mission payload includes Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. The 11-day mission will include four spacewalks. Liftoff is scheduled for Oct. 6 at 9:16 p.m. EDT