/jsc2024e024307 (3)~medium.jpg)
jsc2024e024307 (April 3, 2024) -- Gateway electric field validation tests for the Gateway communication and tracking system antennas. Photo Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
/jsc2024e024308 (2)~medium.jpg)
jsc2024e024308 (April 3, 2024) -- Gateway electric field validation tests for the Gateway communication and tracking system antennas. Photo Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
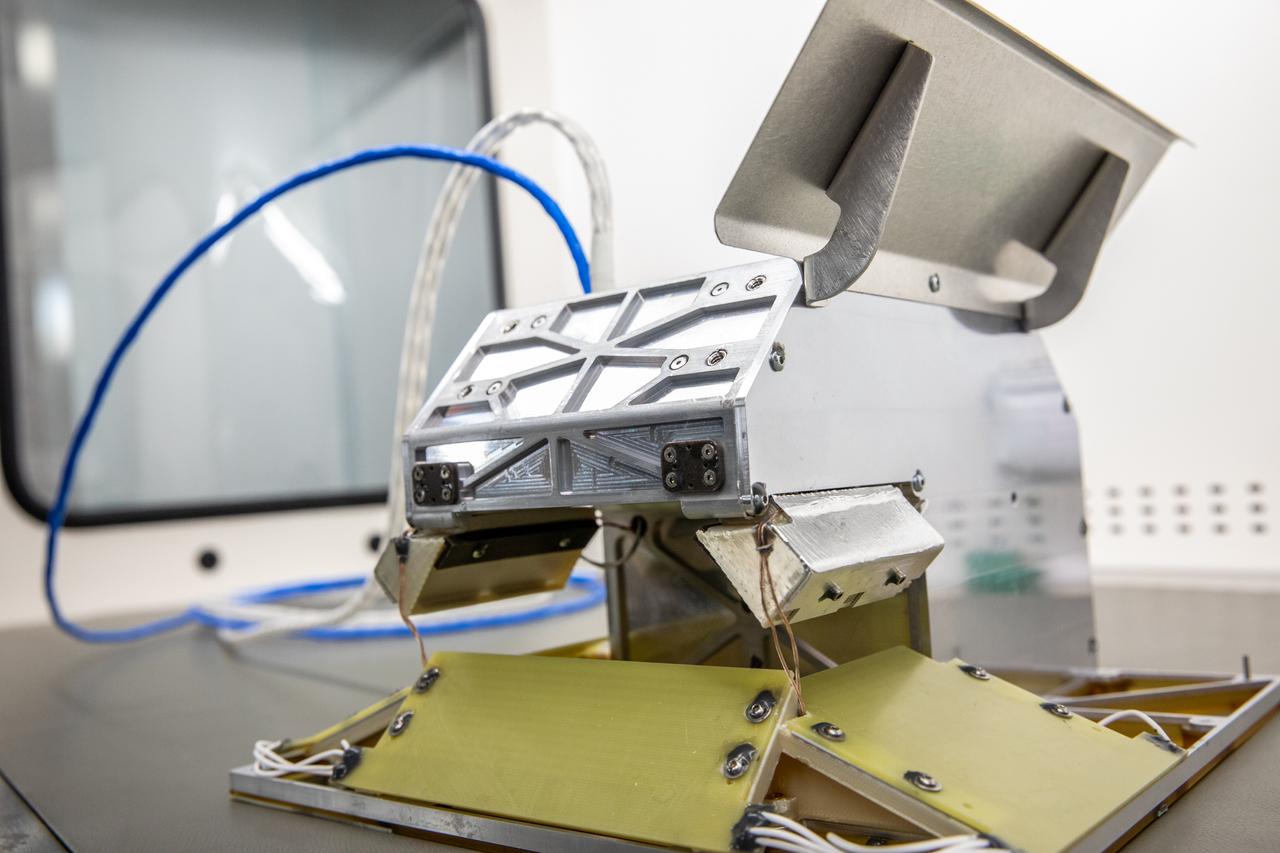
Inside of the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an electrodynamic dust shield (EDS) is in view on Jan. 18, 2023. The dust shield is one of the payloads that will fly aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative. During the mission, EDS will generate a non-uniform electric field using varying high voltage on multiple electrodes. This traveling field, in turn, carries away the particles and has potential applications in thermal radiators, spacesuit fabrics, visors, camera lenses, solar panels, and many other technologies. The CLPS initiative is a key part of NASA’s Artemis lunar exploration efforts. The science and technology payloads sent to the Moon’s surface as part of the initiative will help lay the foundation for human missions and a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
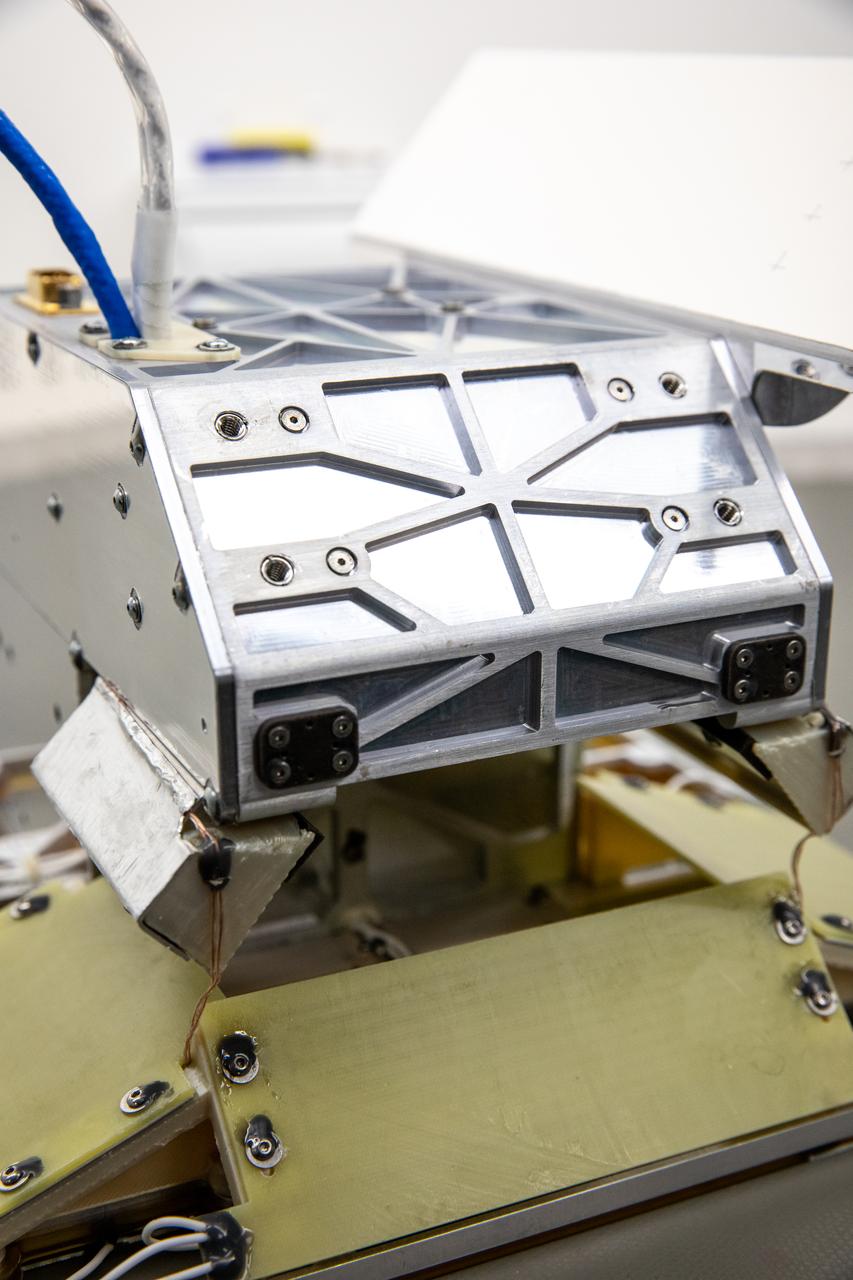
Inside of the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an electrodynamic dust shield (EDS) is in view on Jan. 18, 2023. The dust shield is one of the payloads that will fly aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative. During the mission, EDS will generate a non-uniform electric field using varying high voltage on multiple electrodes. This traveling field, in turn, carries away the particles and has potential applications in thermal radiators, spacesuit fabrics, visors, camera lenses, solar panels, and many other technologies. The CLPS initiative is a key part of NASA’s Artemis lunar exploration efforts. The science and technology payloads sent to the Moon’s surface as part of the initiative will help lay the foundation for human missions and a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
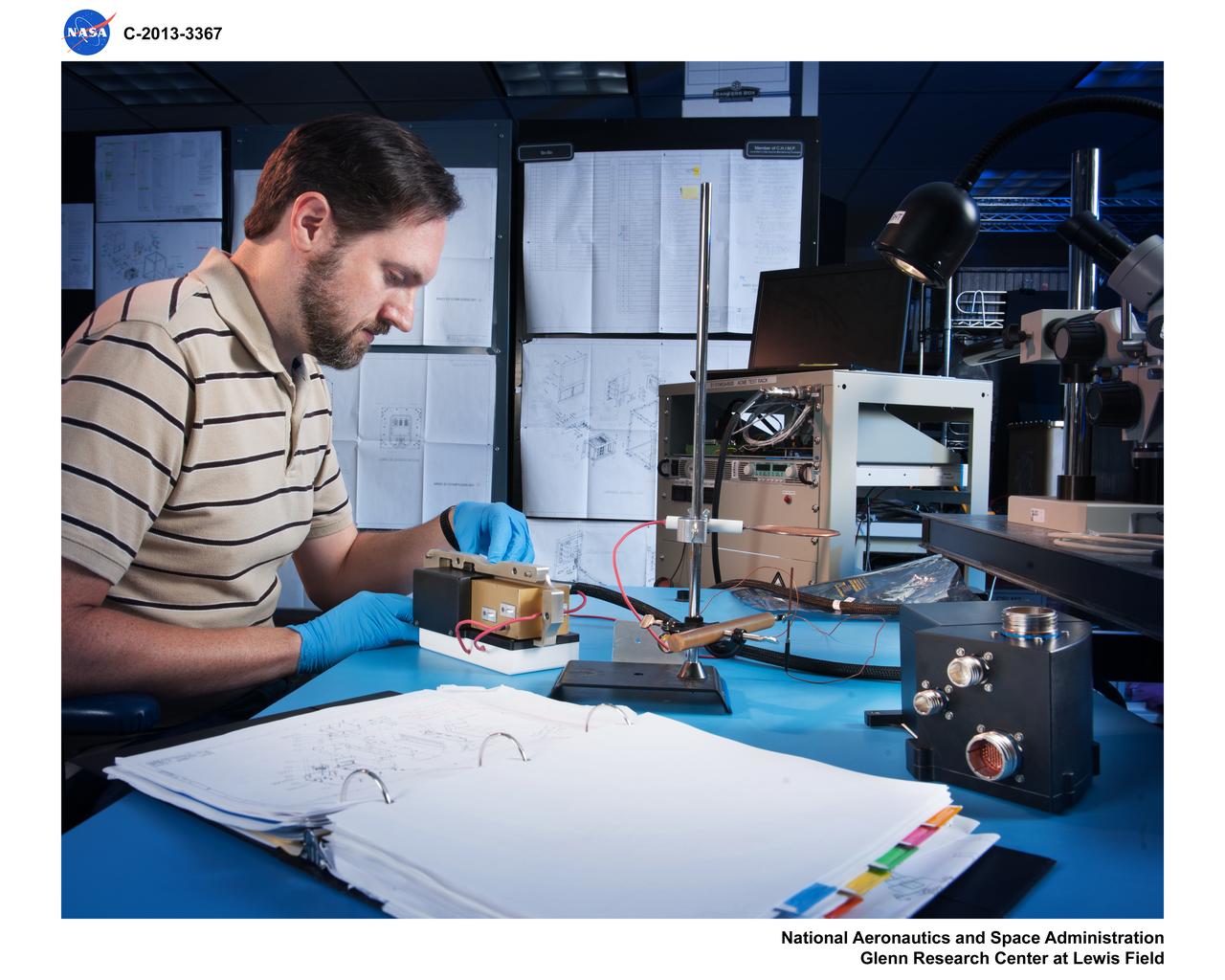

Mechanical Engineer Adrian Drake inspects engineering model hardware built to generate a high-voltage electric field for the Electric-Field Effects on Laminar Diffusion Flames (E-FIELD Flames) experiment of the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME) project. ACME’s small computer (i.e., the Cube) for data acquisition and control within the CIR combustion chamber is seen in the right foreground. The E-FIELD Flames tests were conducted in the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) on the International Space Station (ISS) in 2018.
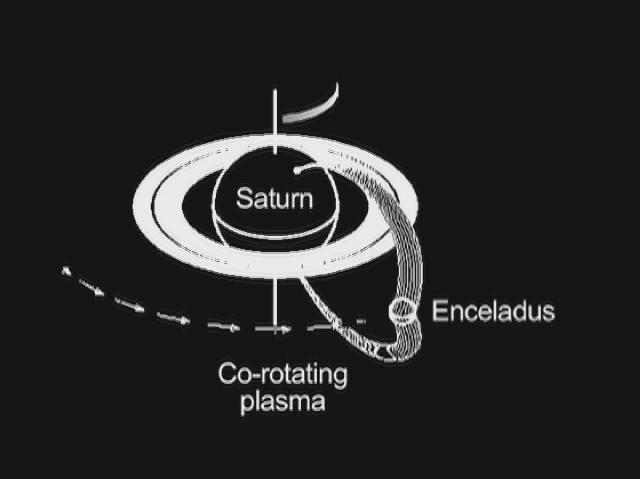
This graphic shows how Saturn and its moon Enceladus are electrically linked. Magnetic field lines, invisible to the human eye but detectable by the fields and particles instruments on NASA's Cassini spacecraft, arc from Saturn's north polar region to south polar region. Enceladus resides in the arc of a set of the field lines and feeds charged particles into the Saturn atmosphere. As Enceladus orbits around Saturn, the "footprint" of its connection to Saturn's north polar region, visible in ultraviolet light, also rotates. A doughnut of plasma, or hot ionized gas, revolves around Saturn at the same pace as the planet turns. The interaction of this plasma cloud with Enceladus shoots electrons along the magnetic field lines into the polar region of Saturn. The rain of electrons into Saturn's atmosphere creates an ultraviolet glow in an aurora-like phenomenon. Cassini's radio and plasma wave science instrument has detected a "hiss-like" radio noise generated by electrons moving along magnetic field lines from Enceladus to the glowing patch of ultraviolet light on Saturn. An animation is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA13897

iss040e108291 (8/26/2014) --- Photographic documentation of final installation of MAGVECTOR hardware in the Columbus module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). MAGVECTOR qualitatively investigates the interaction between a moving magnetic field and an electrical conductor. The set up will provide initial insights regarding the principal feasibility on board the ISS,future improvements and phenomenological trends and dependencies. The expected changes in the magnetic field structure on the Ram and Wake side of the electrical conductor are of interest for technical applications as well as for astrophysical research.
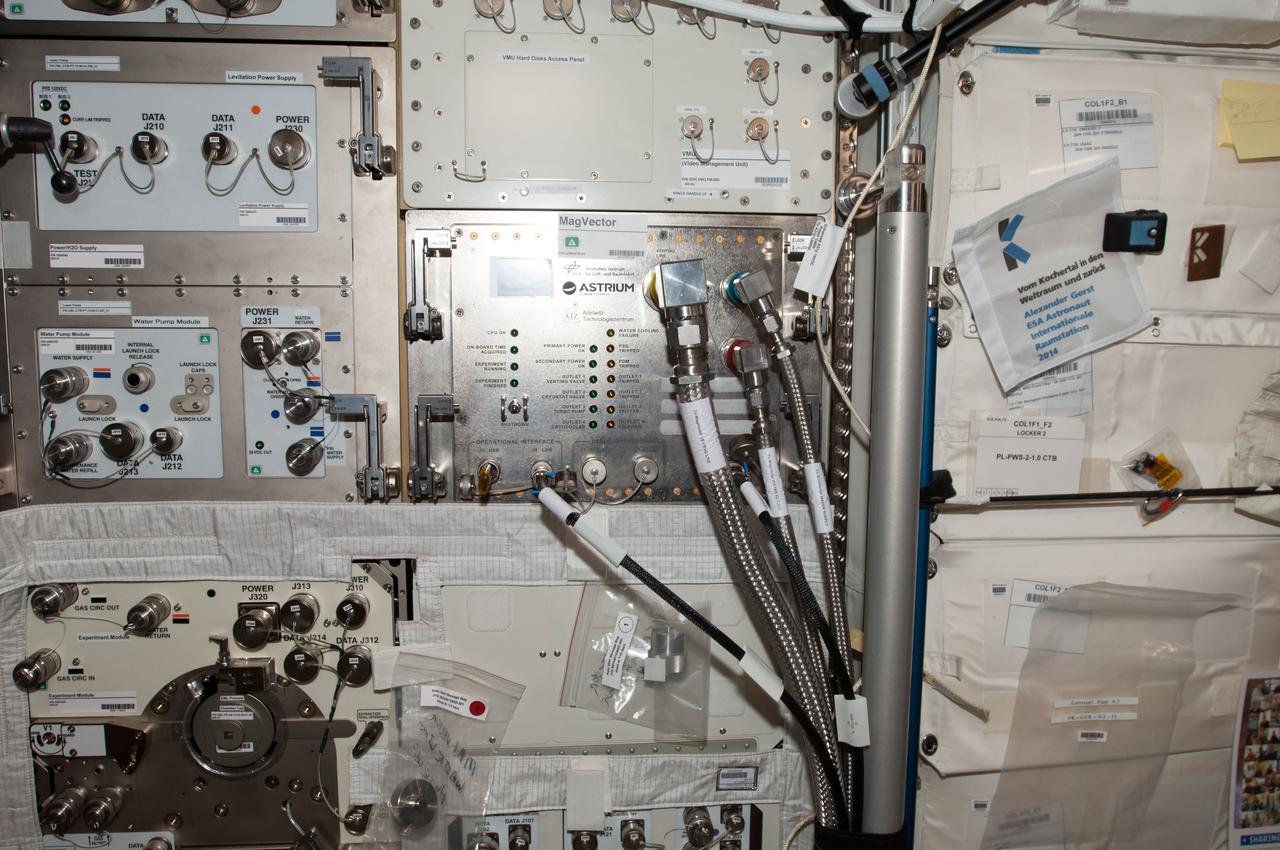

iss040e123621 (9/4/2014) --- Photographic documentation of final installation of MAGVECTOR hardware in the Columbus module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). MAGVECTOR qualitatively investigates the interaction between a moving magnetic field and an electrical conductor. The set up will provide initial insights regarding the principal feasibility on board the ISS,future improvements and phenomenological trends and dependencies. The expected changes in the magnetic field structure on the Ram and Wake side of the electrical conductor are of interest for technical applications as well as for astrophysical research.
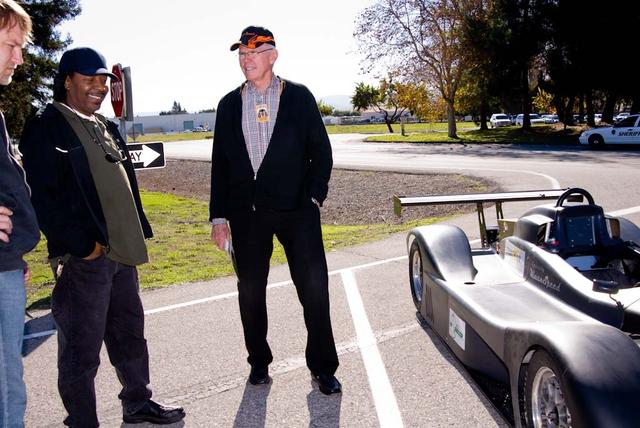

Airship Ventures Zeppelin Dedication during the Moffett Field Diamond Jubilee. New NRP Partner KleenSpeed Chairman Timothy Collins (l) with THRUXAR electric race car at the Nov. 21 Diamond Jubilee exhibits. KleenSpeed is an advanced R&D firm focusing on scalable electric propulsion systems for transportation
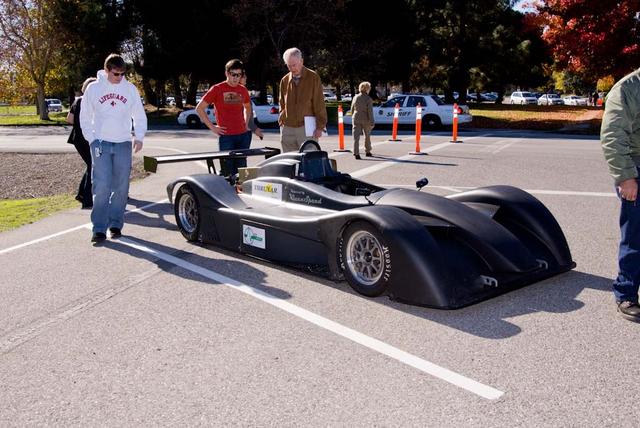

Airship Ventures Zeppelin Dedication during the Moffett Field Diamond Jubilee. The Thruxar electric race car at the Nov. 21 Diamond Jubilee exhibits. KleenSpeed is an advanced R&D firm focusing on scalable electric propulsion systems for transportation
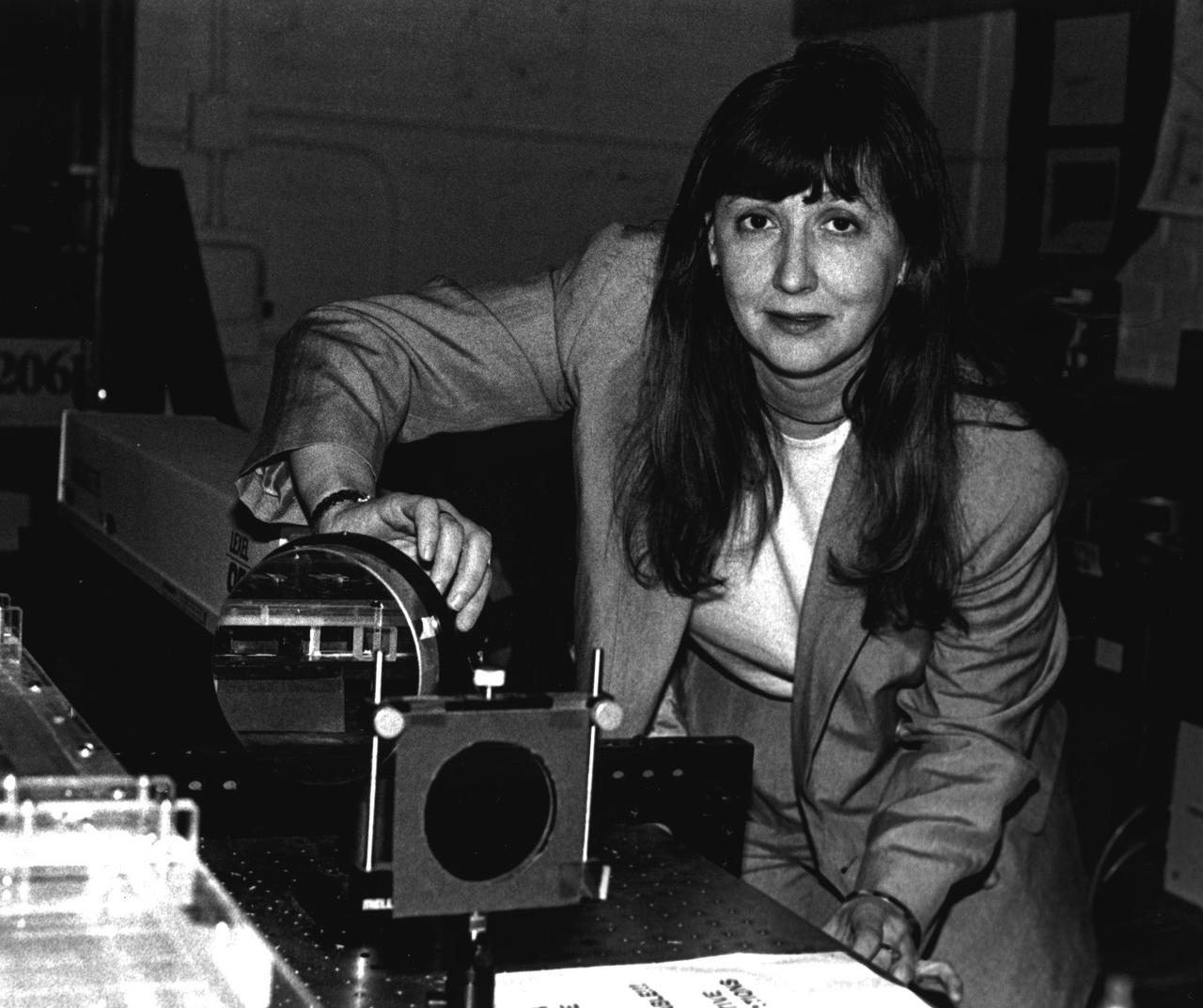

Dr. Cila Herman, G.W.C. Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She is the principal investigator for the Experimental Investigation of Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Enhancement in Microgravity in the Presence of Electric Fields.
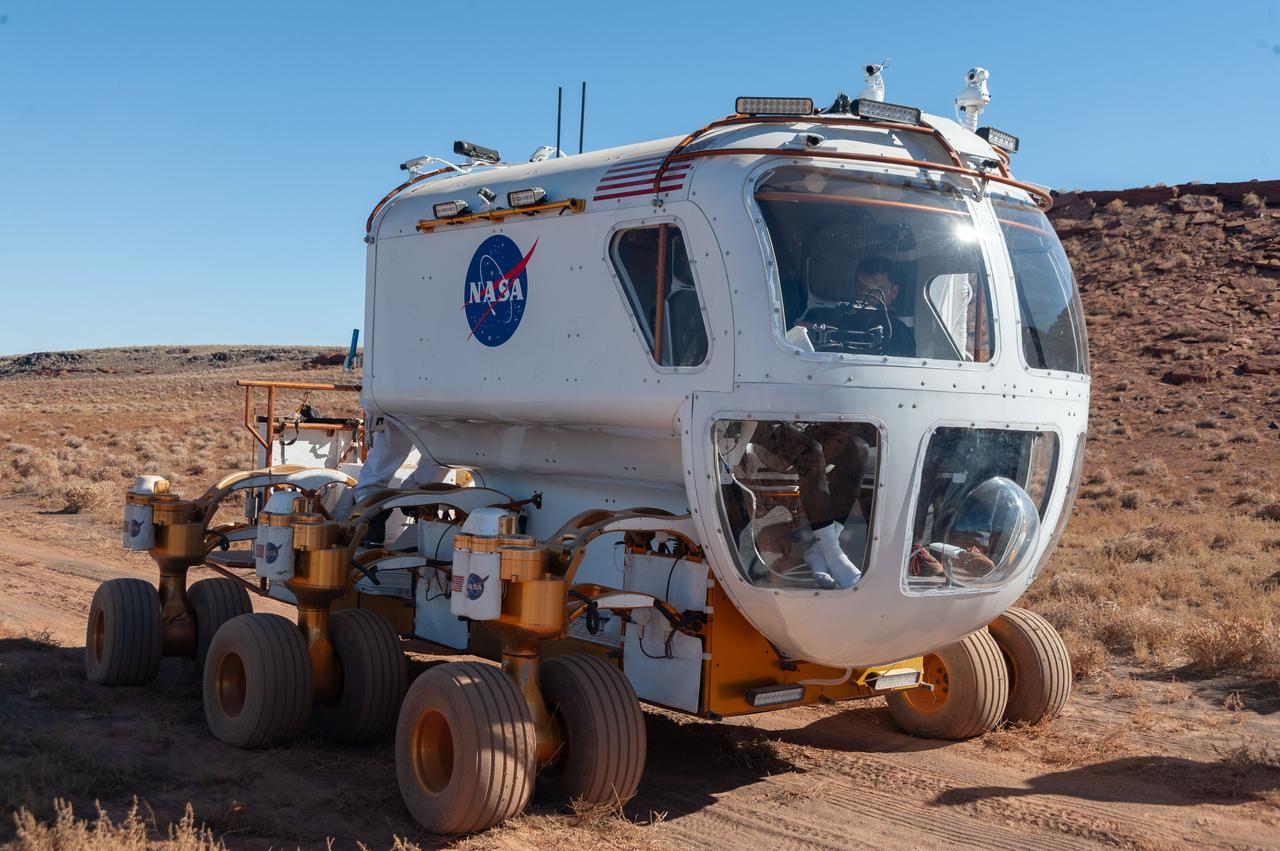

A front view of the Lunar Electric Rover (LER) during the Desert Research and Technology Studies (RATS) remote field test at Black Point Lava Flow, Arizona in 2008.
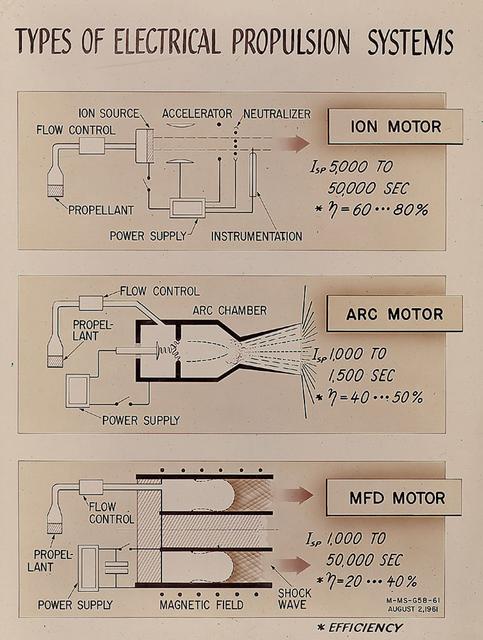
As presented by Gerhard Heller of Marshall Space Flight Center's Research Projects Division in 1961, this chart illustrates three basic types of electric propulsion systems then under consideration by NASA. The ion engine (top) utilized cesium atoms ionized by hot tungsten and accelerated by an electrostatic field to produce thrust. The arc engine (middle) achieved propulsion by heating a propellant with an electric arc and then producing an expansion of the hot gas or plasma in a convergent-divergent duct. The electromagnetic, or MFD engine (bottom) manipulated strong magnetic fields to interact with a plasma and produce acceleration.
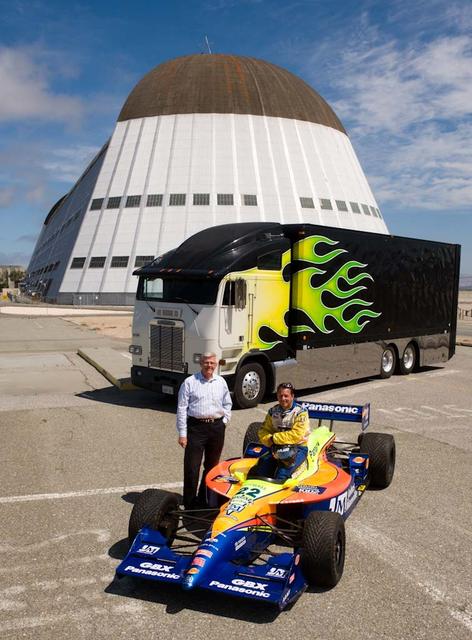

NASA Research Park (NRP) Moffett Field, California: Timothy Collins, President and Chairman, KleenSpeed Technologies, Inc. and Captain Andrew Butte, rescue helicopter pilot and former Army Aviator, with Butte's 1999 SWIFT. ChampCar Butte has given his racecar to KleenSpeed for conversion to electric. KleenSpeed is an advanced R&D firm focusing on scalable electric propulsion systems for transportation.
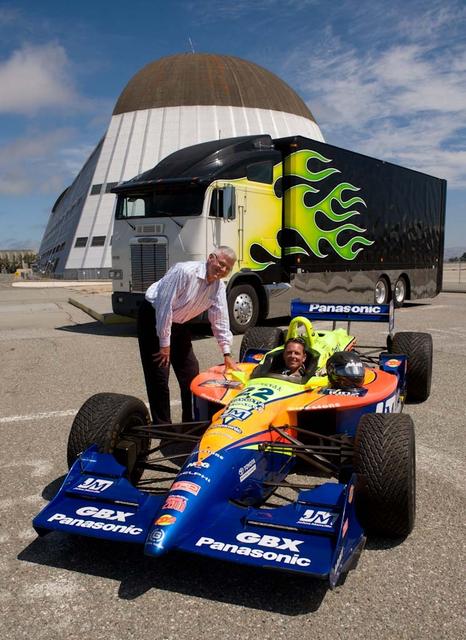

Timothy Collins, President and Chairman, KleenSpeed Technologies, Inc. and Captain Andrew Butte, rescue helicopter pilot and former Army Aviator, with Butte's 1999 SWIFT. ChampCar Butte has given his racecar to KleenSpeed for conversion to electric. KleenSpeed is an advanced R&D firm focusing on scalable electric propulsion systems for transportation. The company is based at the NASA Research Park (NRP) Moffett Field, California as a lease holder.
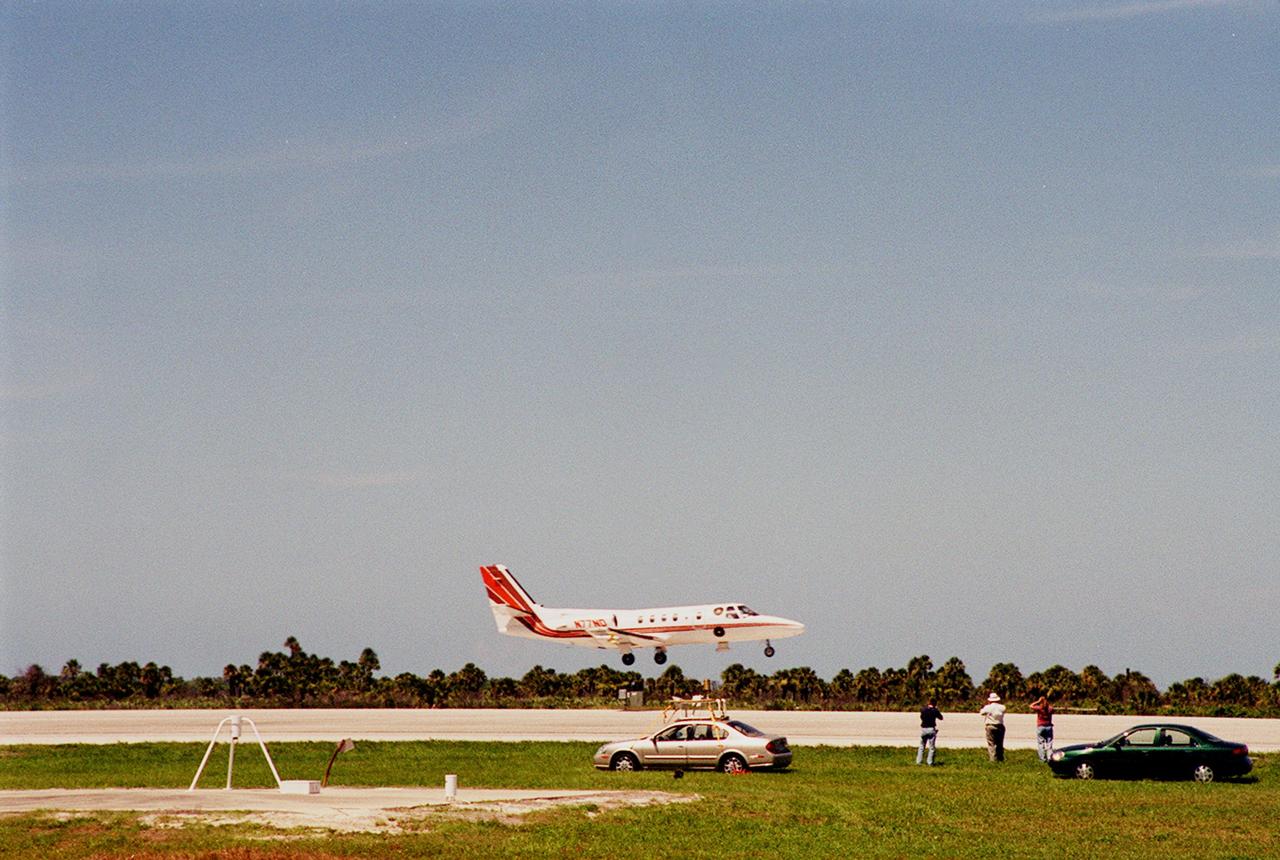

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cesna's field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at center). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.
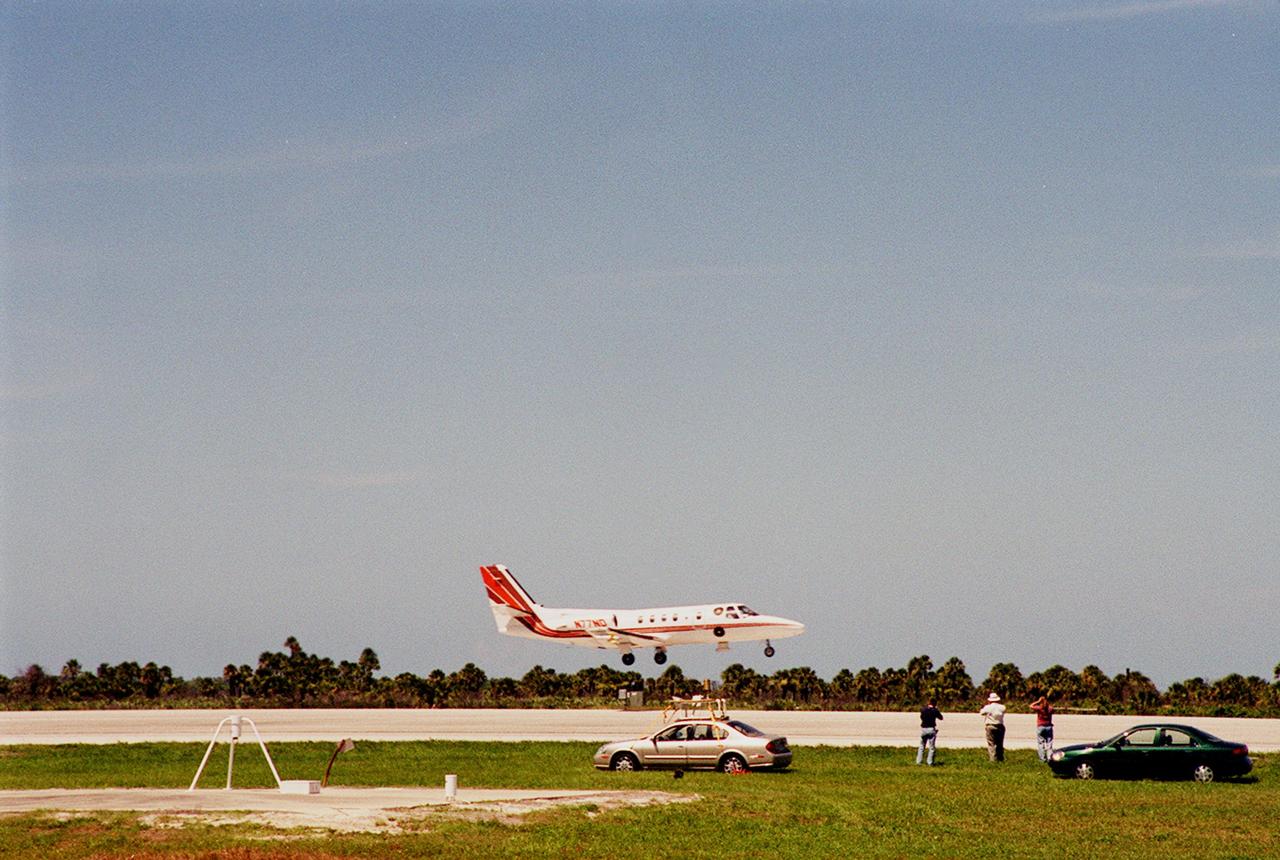

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cesna's field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at center). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.
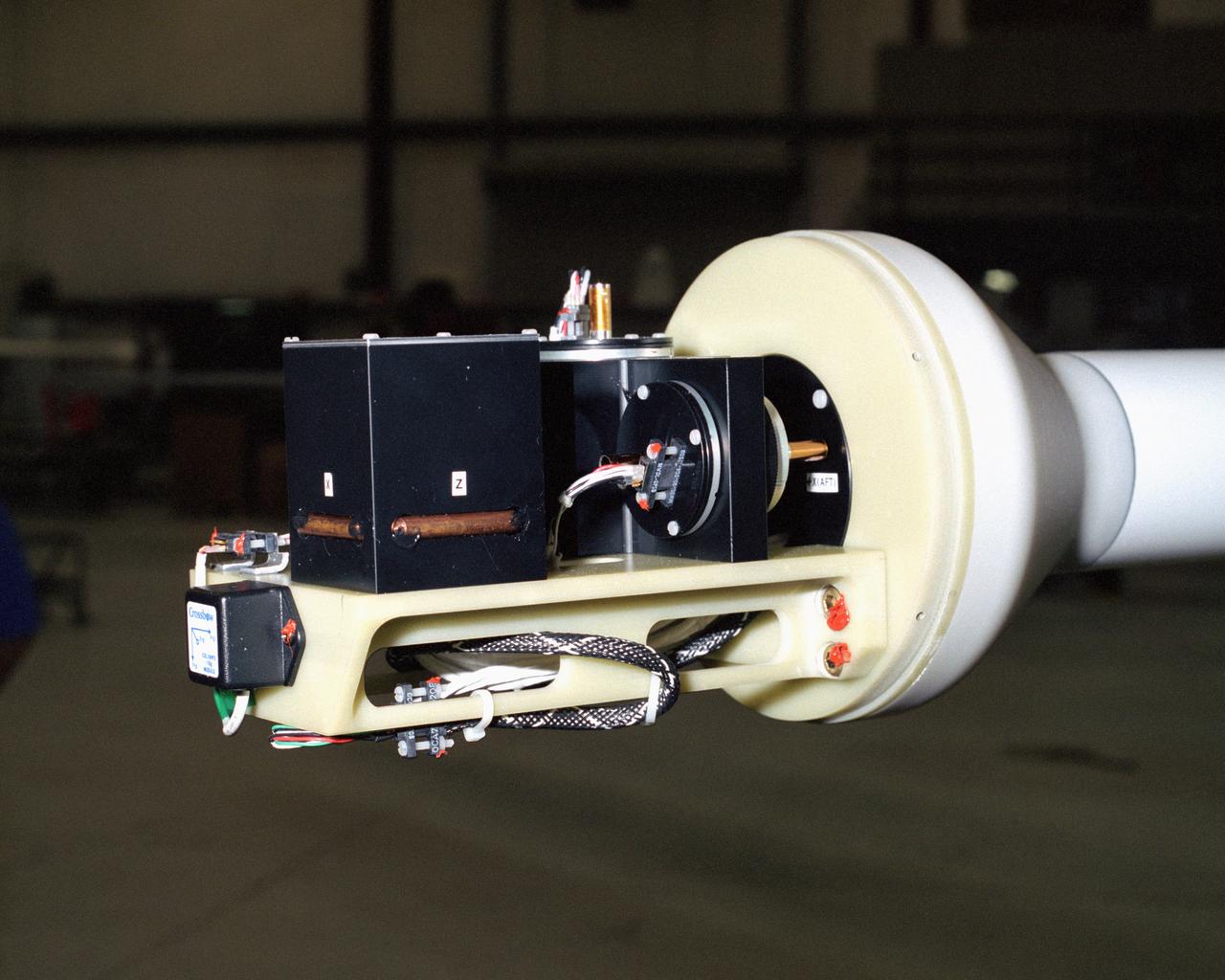
A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely-piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. Data obtained through sensors mounted to the aircraft will allow researchers in ACES to gauge elements such as lightning activity and the electrical environment in and around storms. By learning more about individual storms, scientists hope to better understand the global water and energy cycle, as well as climate variability. Contained in one portion of the aircraft is a three-axis magnetic search coil, which measures the AC magnetic field; a three-axis electric field change sensor; an accelerometer; and a three-axis magnetometer, which measures the DC magnetic field. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
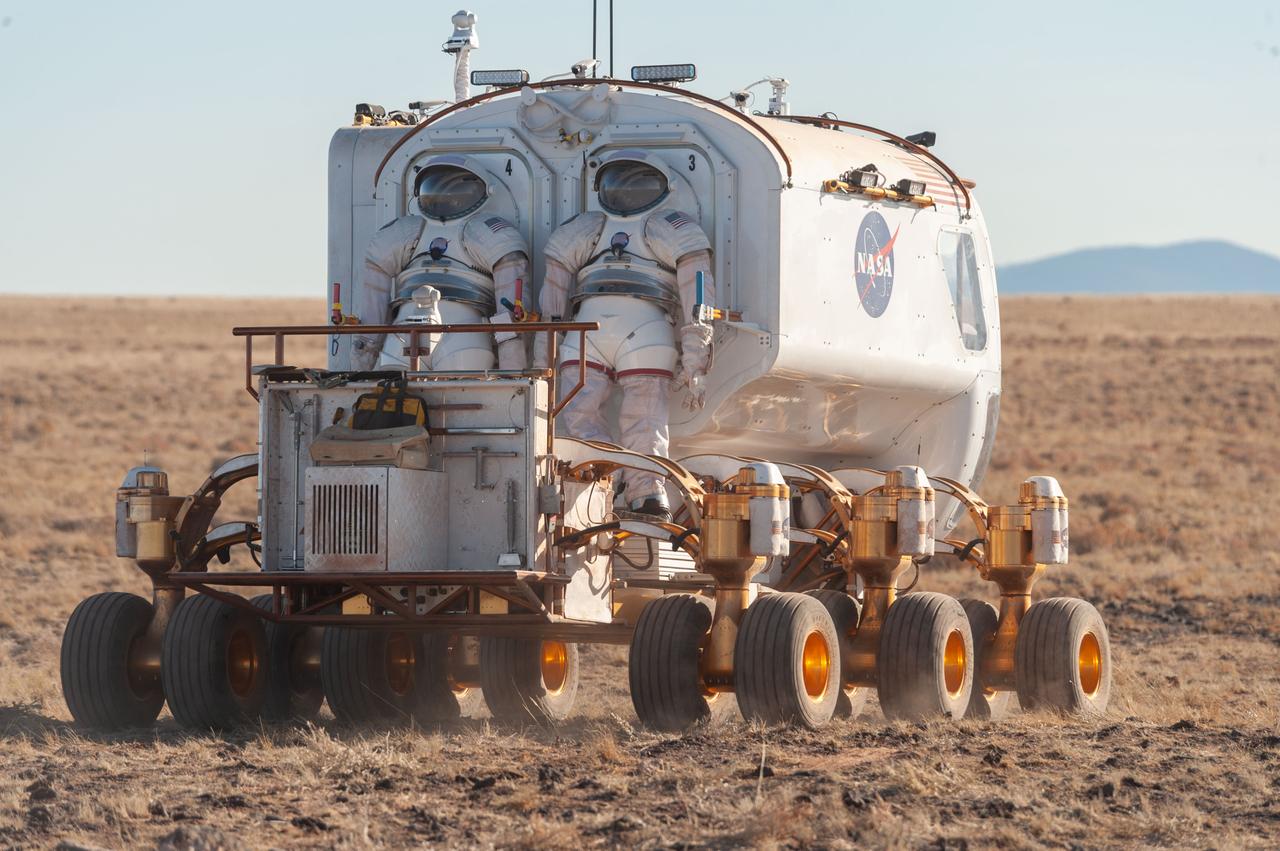

A back view of the Lunar Electric Rover (LER) during the Desert Research and Technology Studies (RATS) remote field test at Black Point Lava Flow, Arizona in 2008. Two Mark III spacesuits are visibly mounted on the LER suit port.
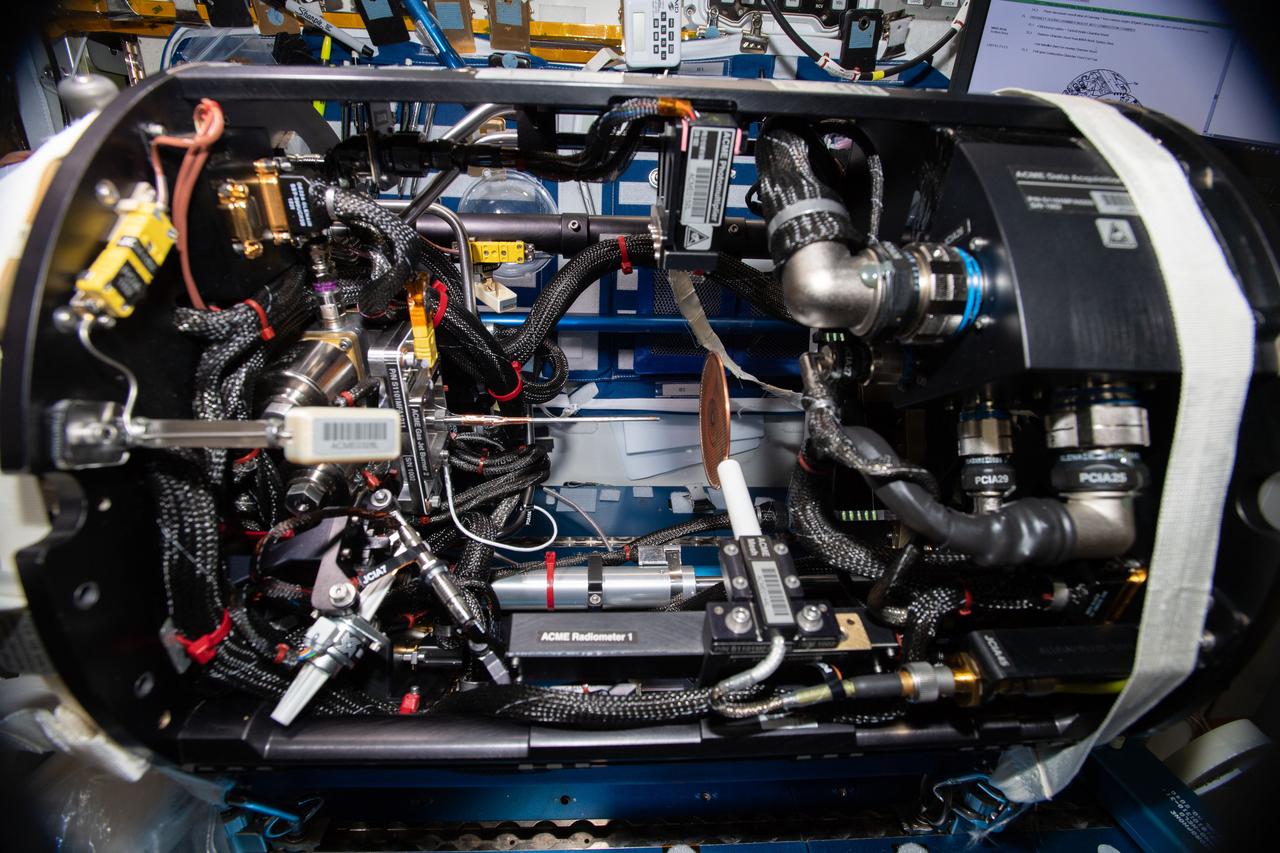
iss057e055269 (10/22/2018) --- Photo documentation of the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Combustion Chamber, with Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME) Mesh installed, during operations (OPS) to reconfigure CIR ACME hardware for the Electric-Field Effects on Laminar Diffusion Flames (E-FIELD Flames) experiment aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
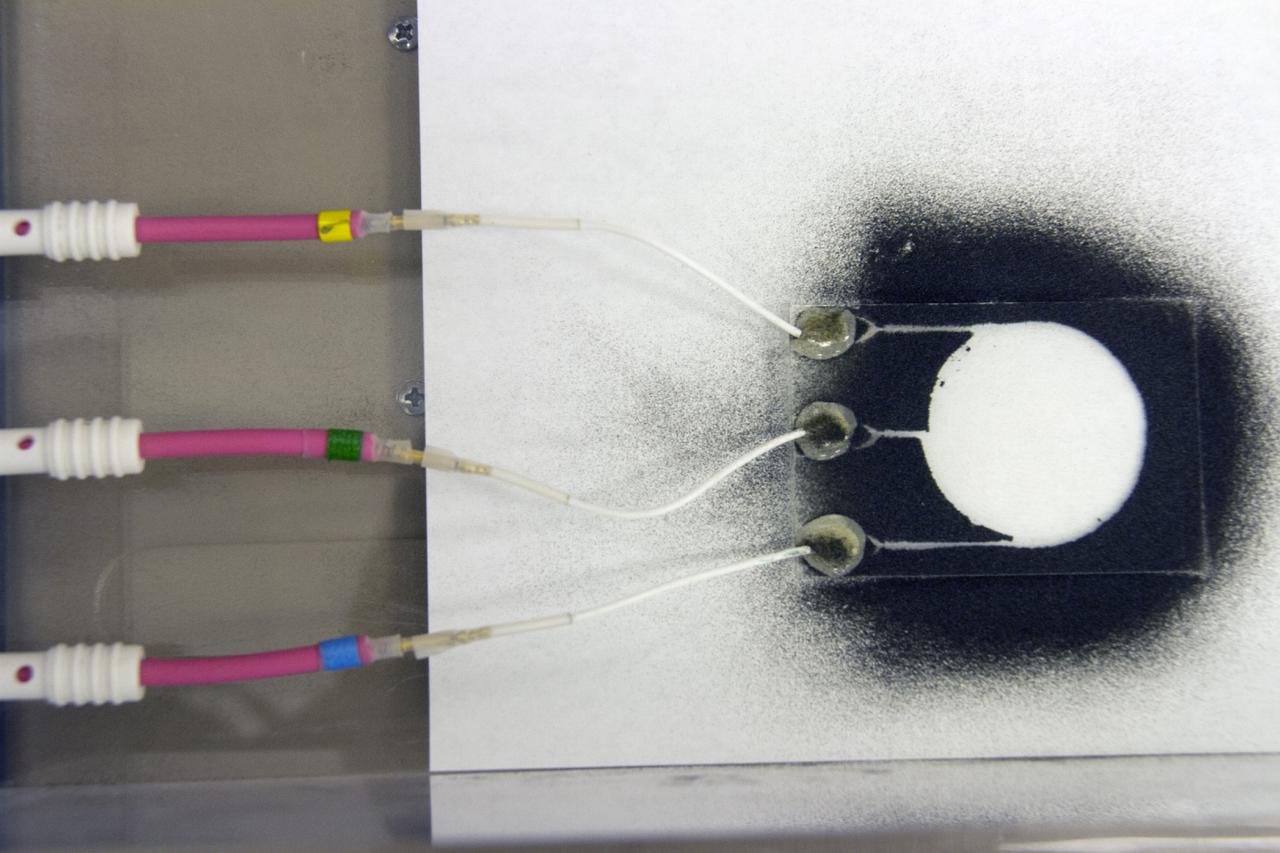
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dust particles scatter during an experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fabricated material is designed to mimic the dust on the lunar surface. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities.
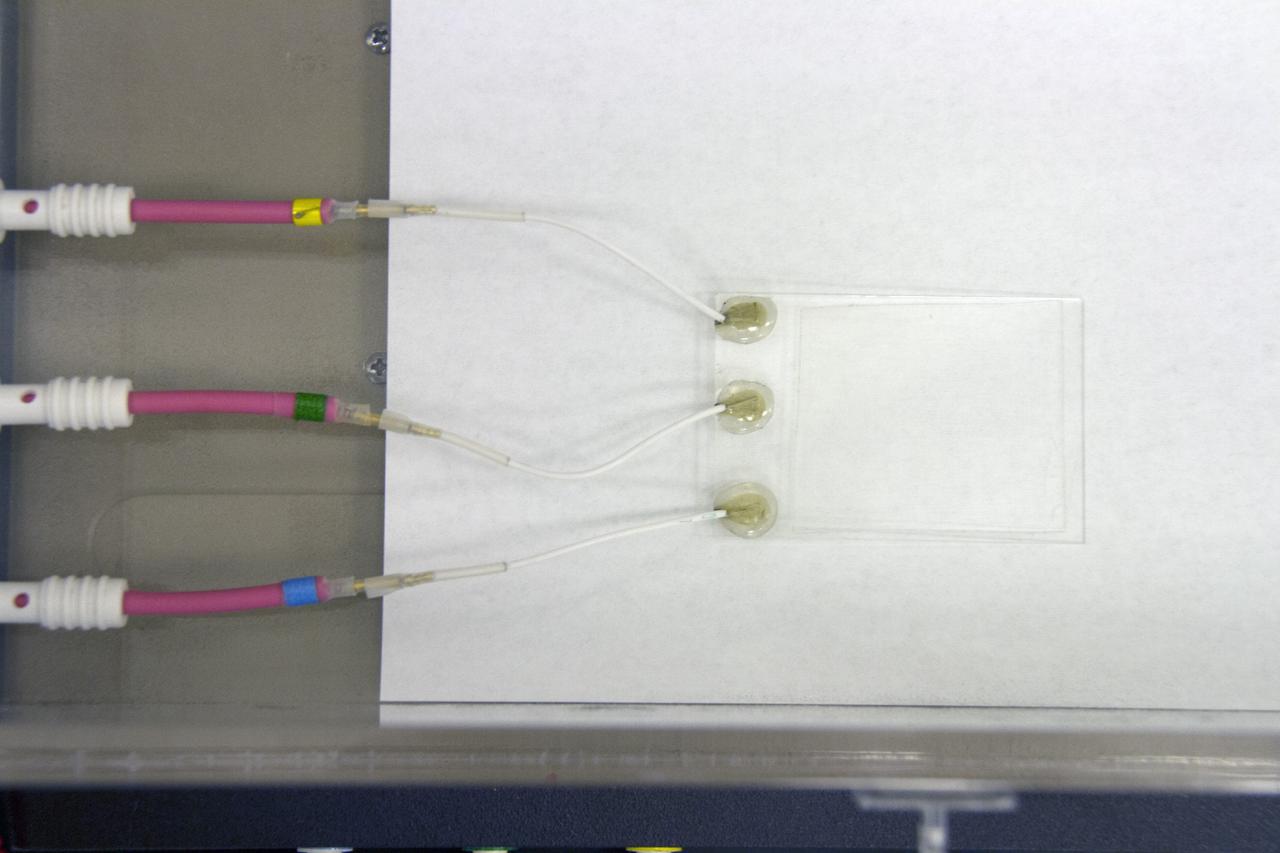
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities.
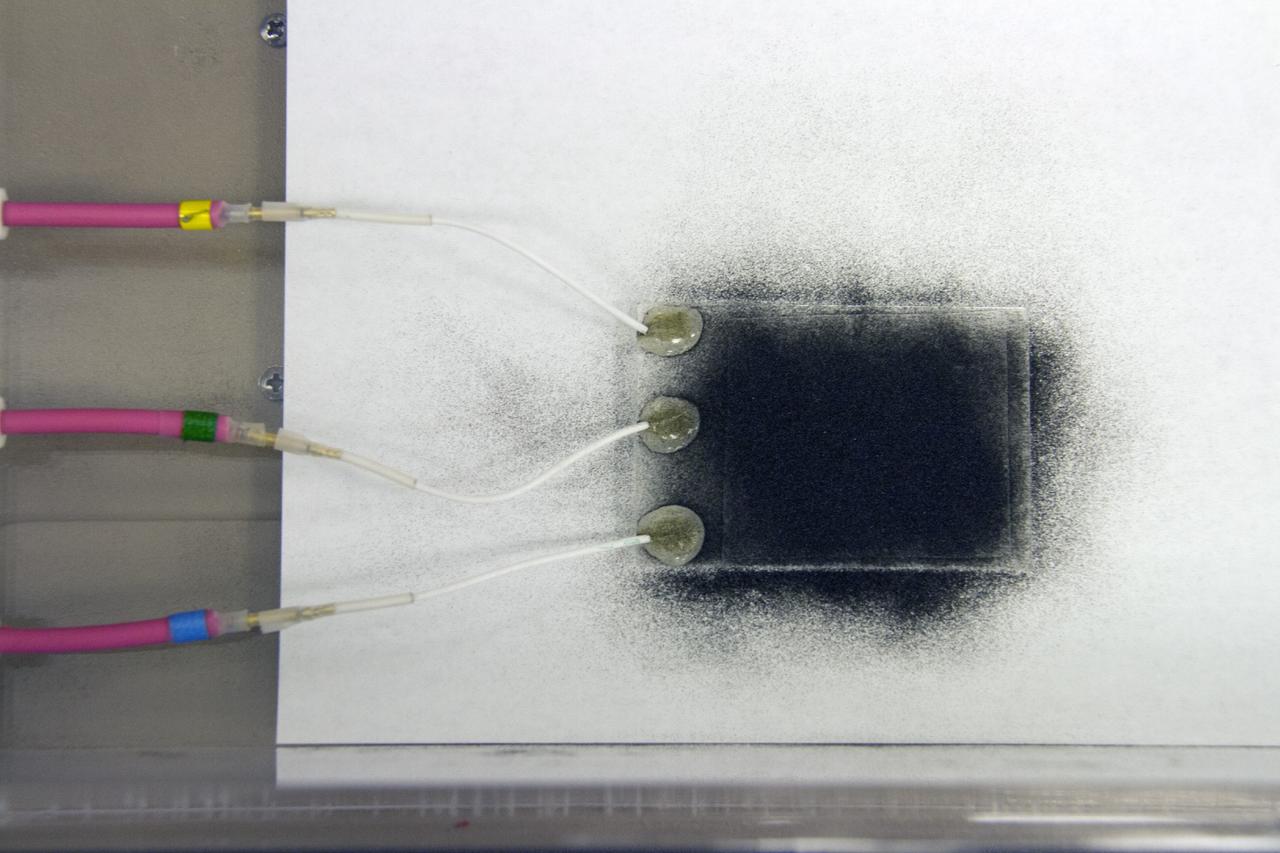
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dust particles are readied for an experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fabricated material is designed to mimic the dust on the lunar surface. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Preparations are underway to conduct a dust particle experiment for the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities.
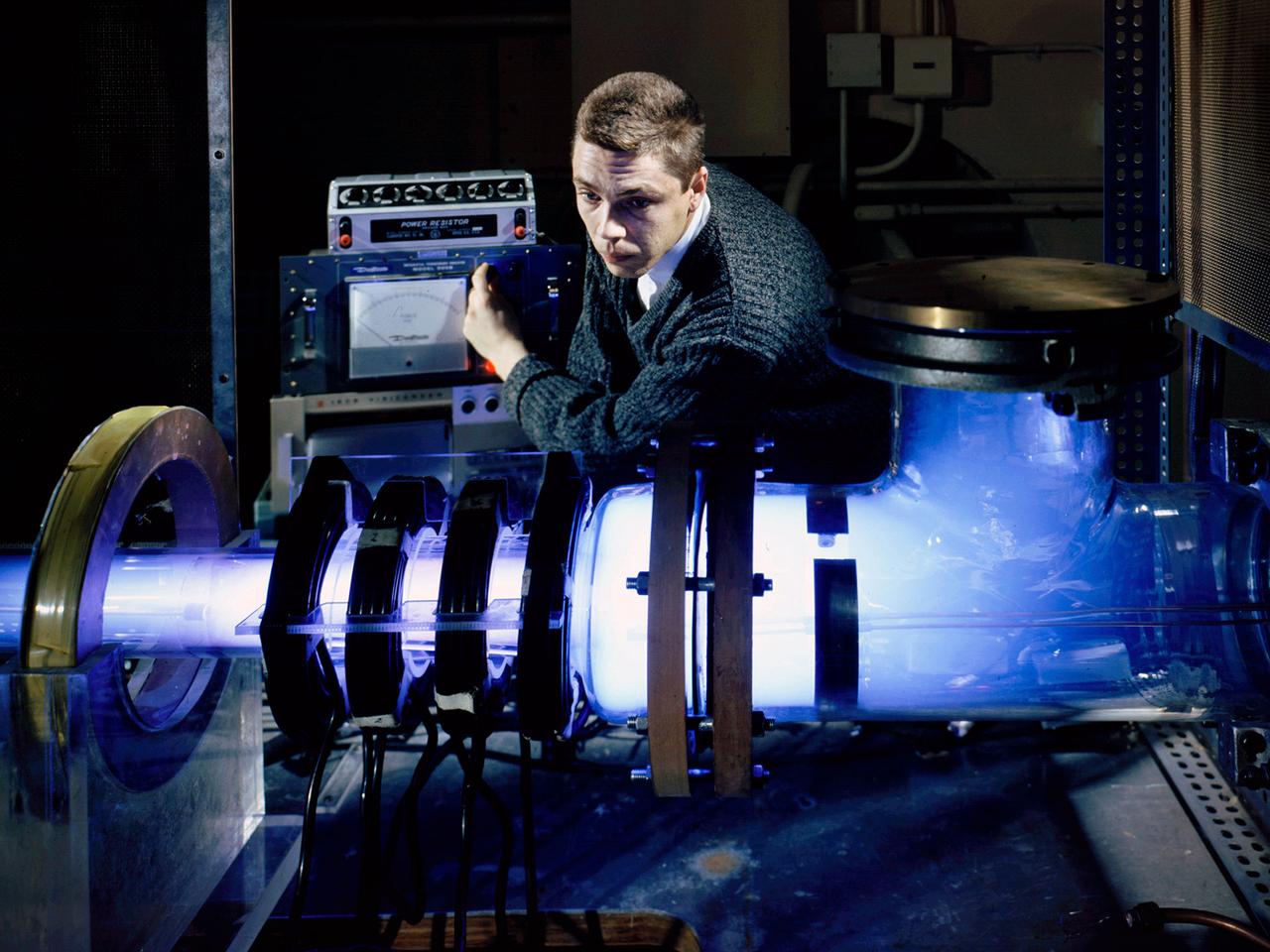

Raymond Palmer, of the Electromagnetic Propulsion Division’s Plasma Flow Section, adjusts the traveling magnetic wave plasma engine being operated in the Electric Power Conversion at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. During the 1960s Lewis researchers were exploring several different methods of creating electric propulsion systems, including the traveling magnetic wave plasma engine. The device operated similarly to alternating-current motors, except that a gas, not a solid, was used to conduct the electricity. A magnetic wave induced a current as it passed through the plasma. The current and magnetic field pushed the plasma in one direction. Palmer and colleague Robert Jones explored a variety of engine configurations in the Electric Propulsion Research Building. The engine is seen here mounted externally on the facility’s 5-foot diameter and 16-foot long vacuum tank. The four magnetic coils are seen on the left end of the engine. The researchers conducted two-minute test runs with varying configurations and used of both argon and xenon as the propellant. The Electric Propulsion Research Building was built in 1942 as the Engine Propeller Research Building, often called the Prop House. It contained four test cells to study large reciprocating engines with their propellers. After World War II, the facility was modified to study turbojet engines. By the 1960s, the facility was modified again for electric propulsion research and given its current name.
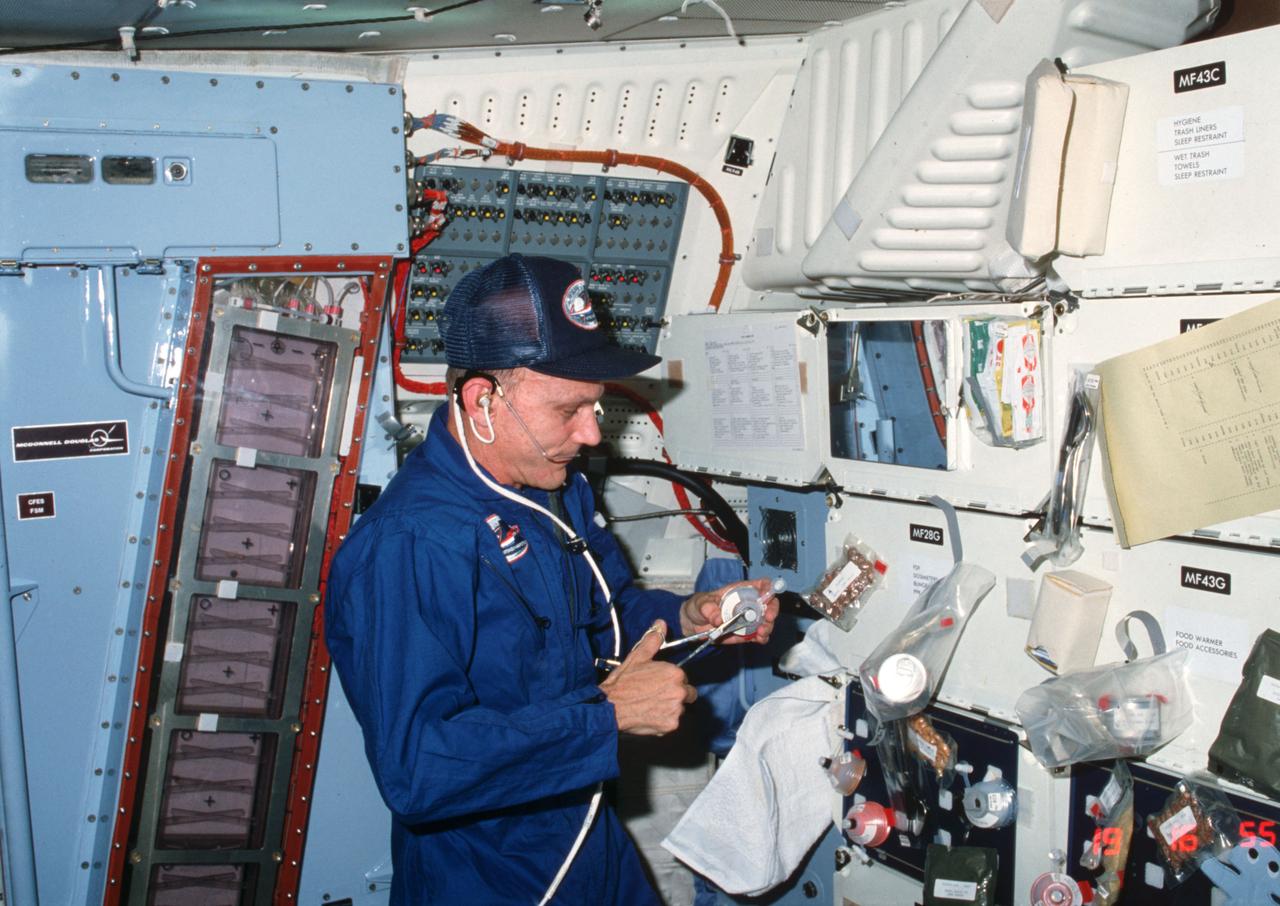

STS004-28-312 (27 June-4 July 1982) --- Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, STS-4 crew commander, prepares a meal in the middeck area of space shuttle Columbia. He uses scissors to open a drink container. Various packages of food and meal accessories are attached to locker doors. At far left edge of the frame is the tall payload called continuous flow electrophoresis experiment (CFES) system-designed to separate biological materials according to their surface electrical charges as they pass through an electrical field. Astronaut Henry W. Hartsfield Jr. exposed this frame with a 35mm camera. Photo credit: NASA
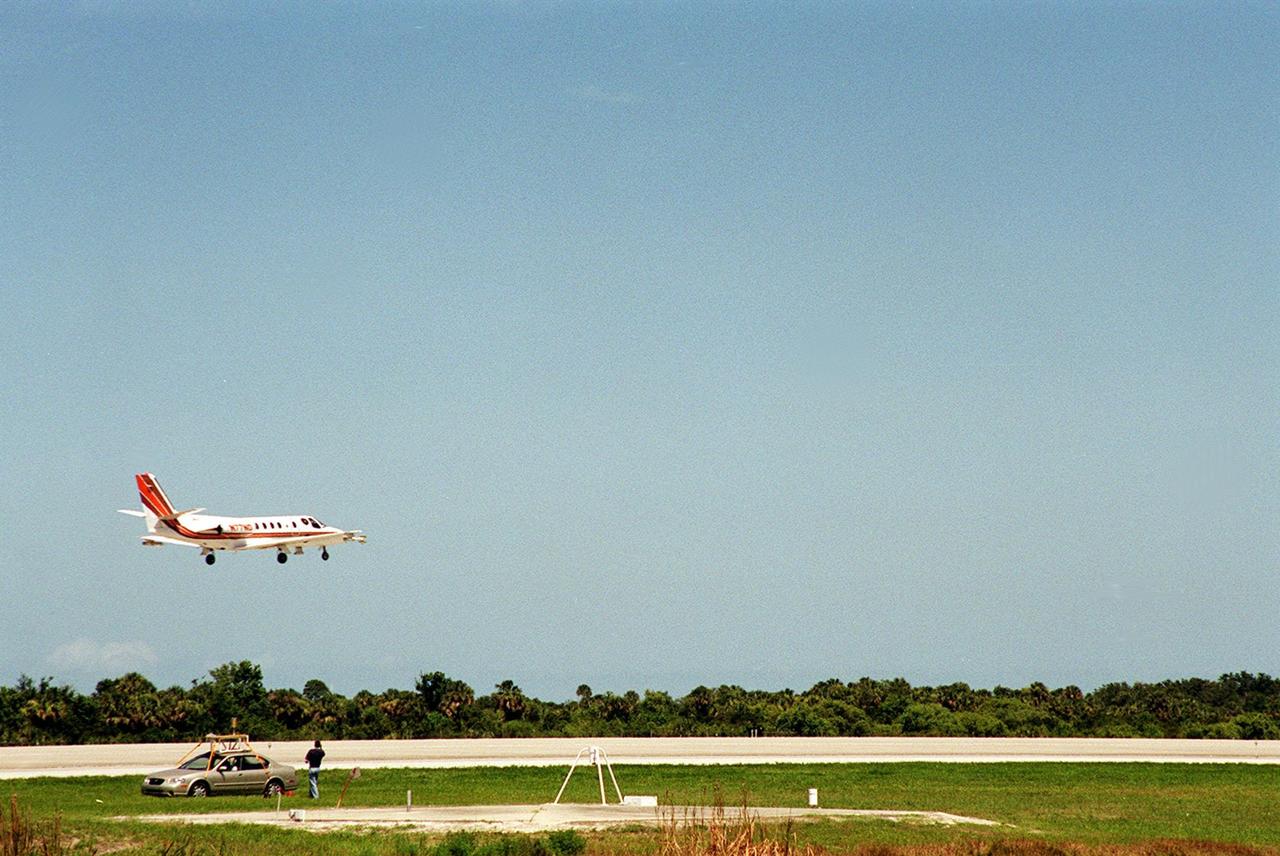

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft approaches the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
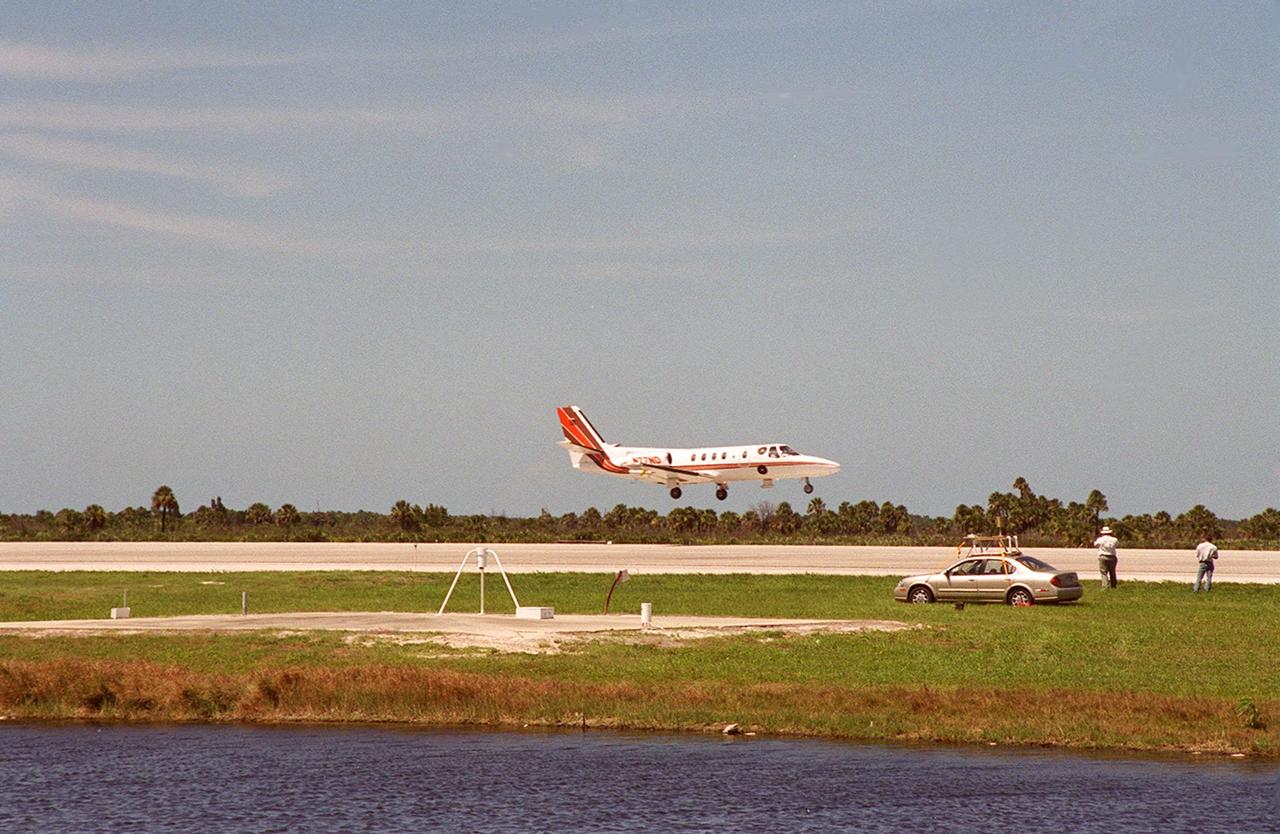

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
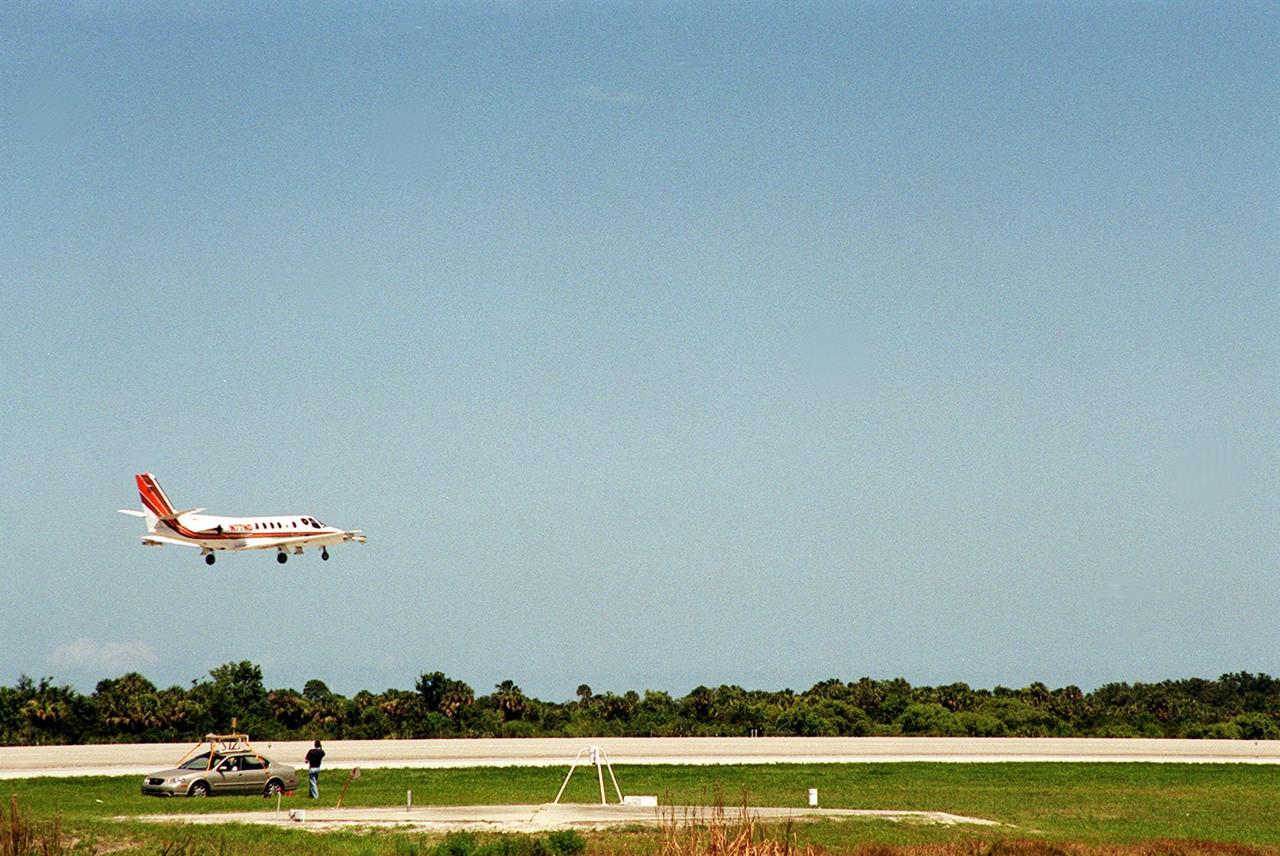

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft approaches the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
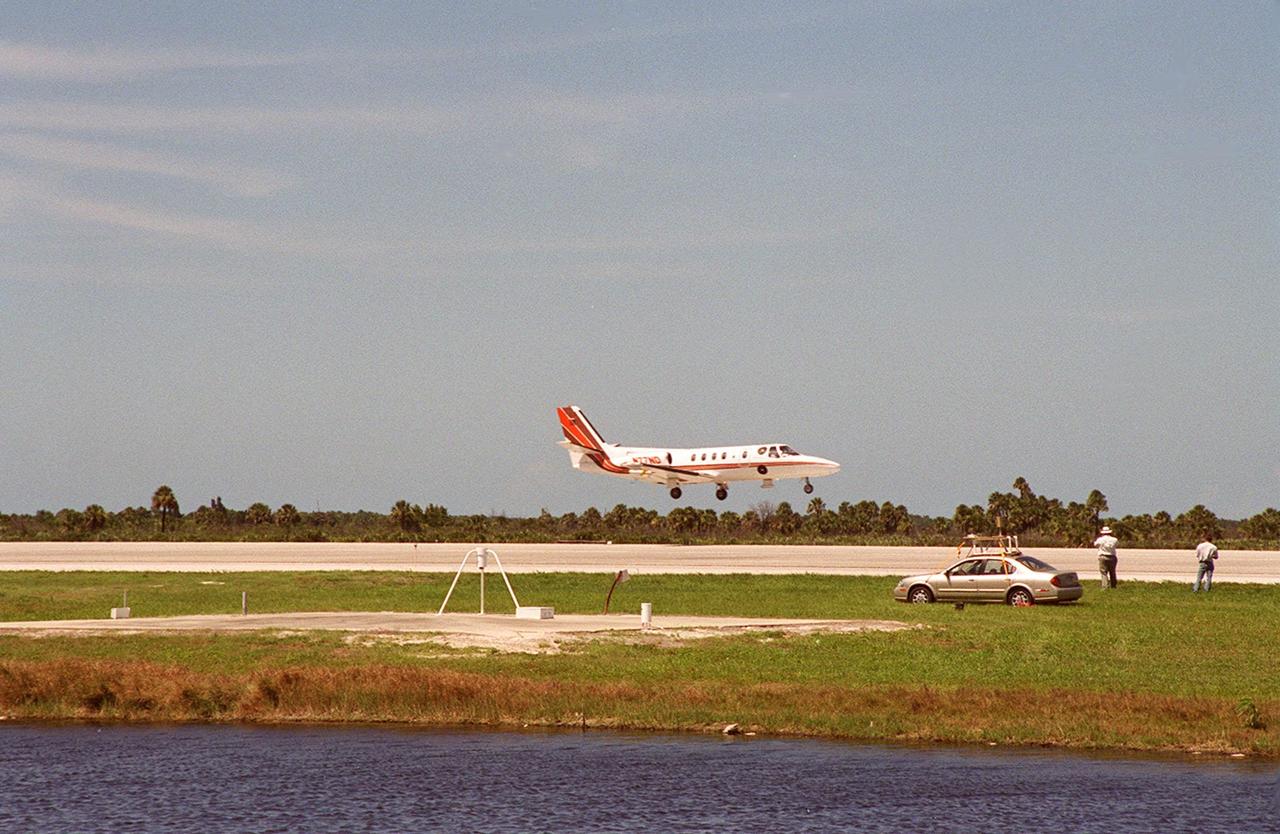

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
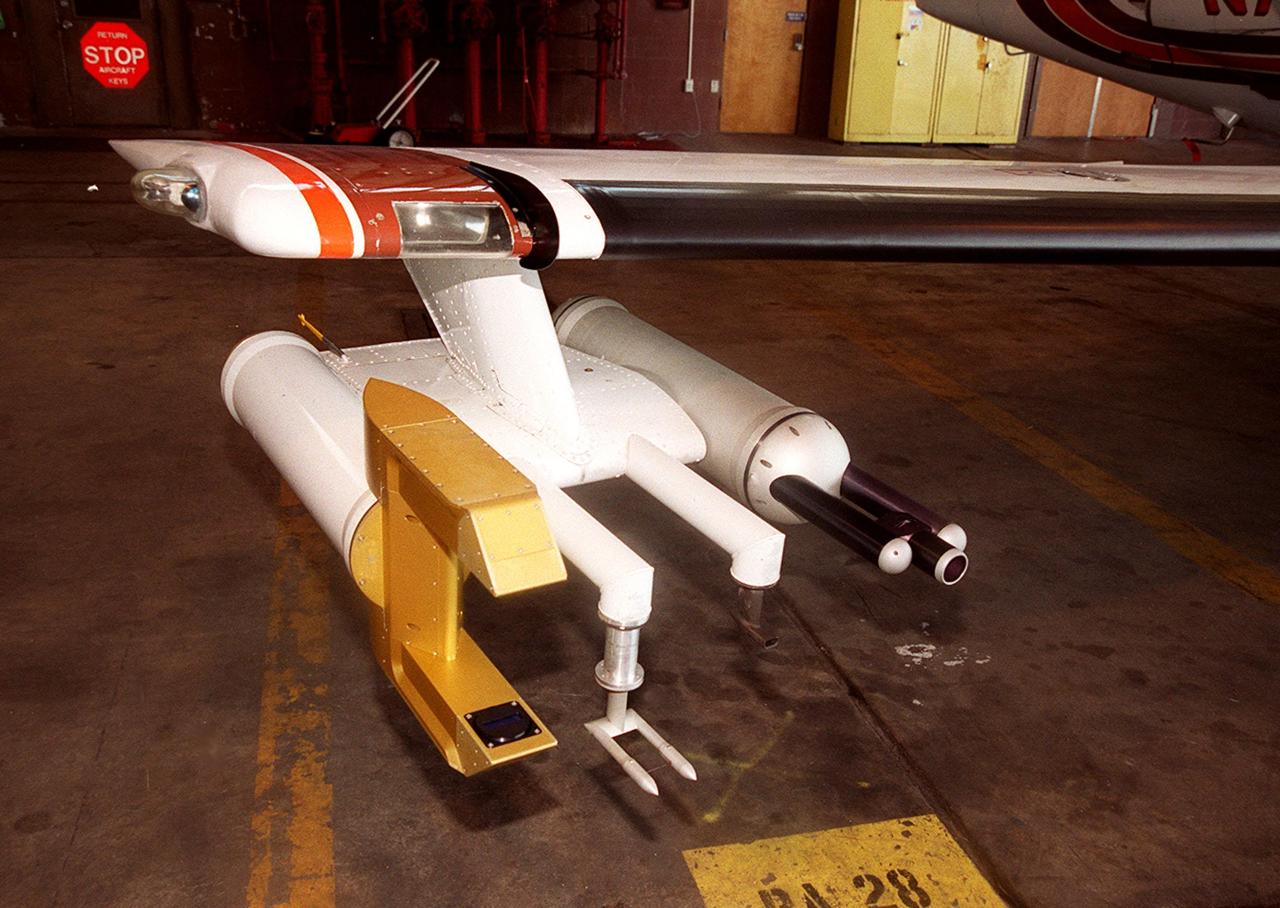

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
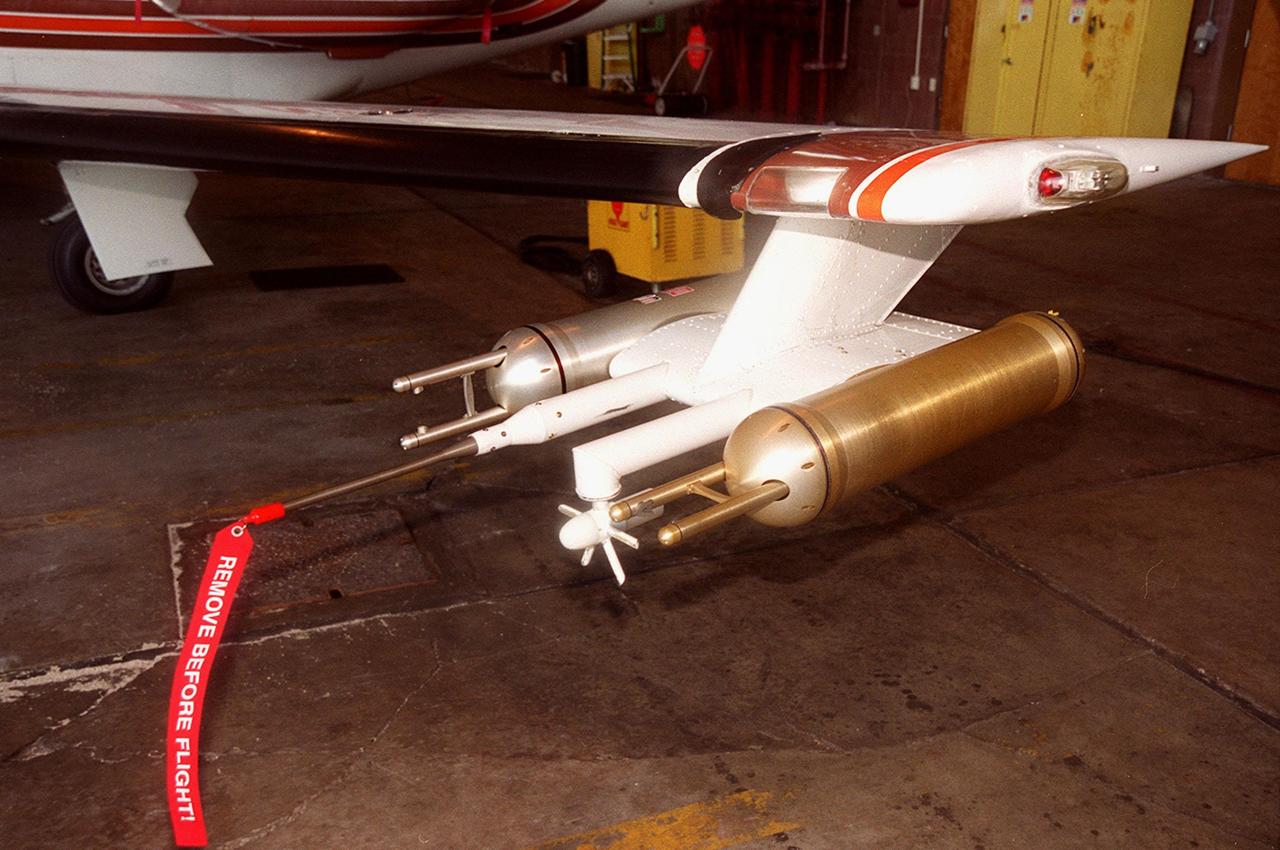

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
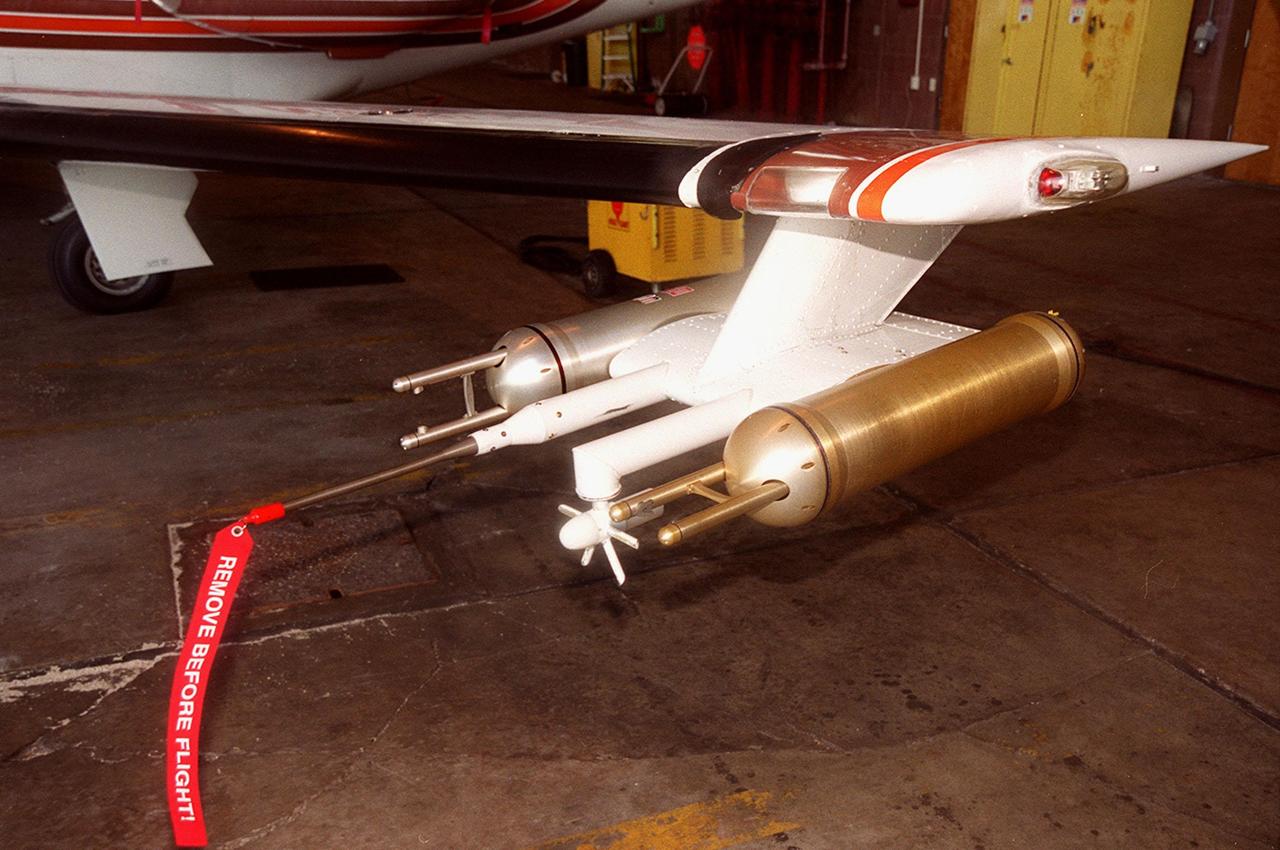

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
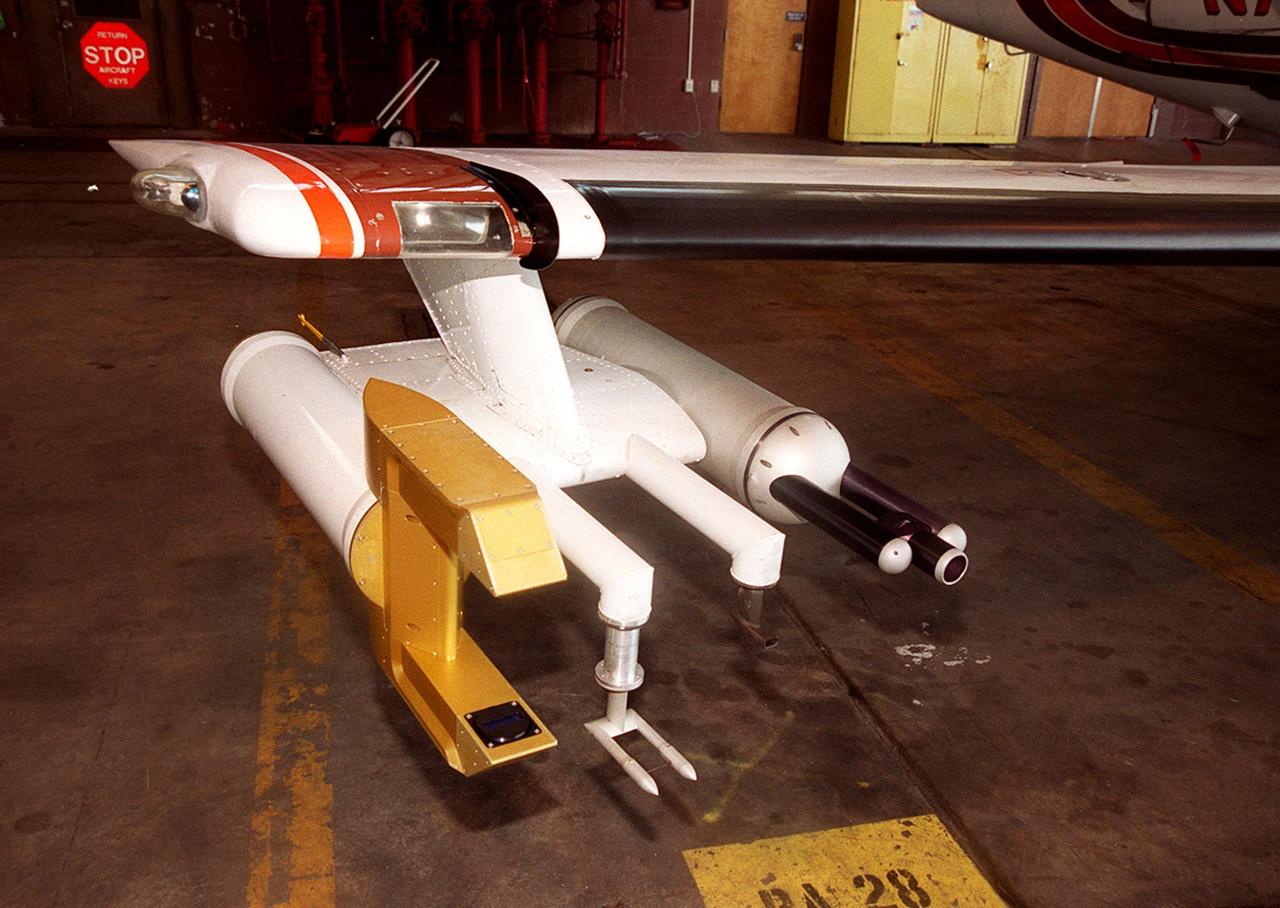

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
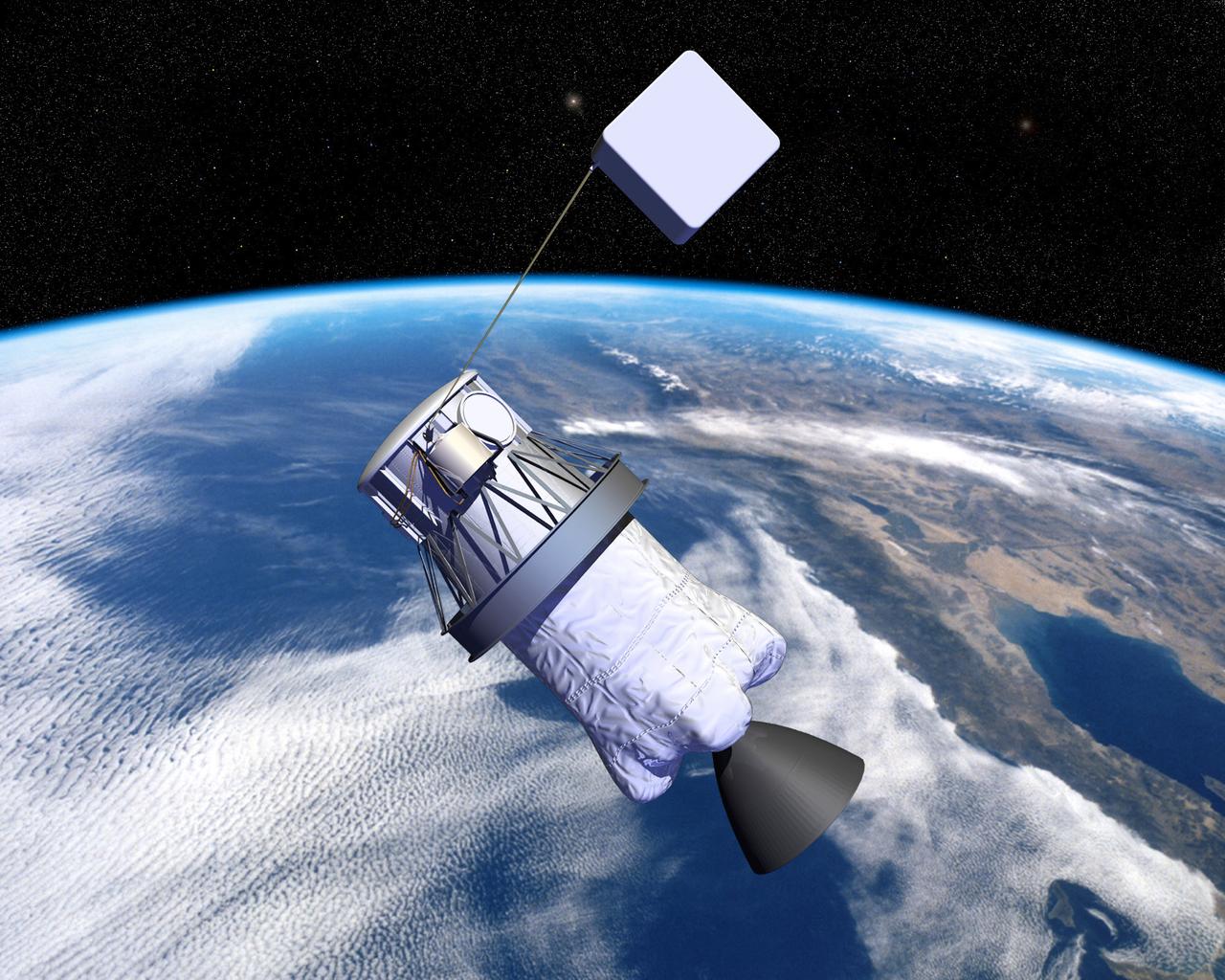

Pictured is an artist's concept of NASA's Propulsive Small Expendable Deployer System experiment (ProSEDS). ProSEDS will demonstrate the use of an electrodynamic tether, basically a long, thin wire, for propulsion. An electrodynamic tether uses the same principles as electric motors in toys, appliances and computer disk drives, and generators in automobiles and power plants. When electrical current is flowing through the tether, a magnetic field is produced that pushes against the magnetic field of the Earth. For ProSEDS, the current in the tether results by virtue of the voltage generated when the tether moves through the Earth's magnetic field at more than 17,000 mph. This approach can produce drag thrust generating useable power. Since electrodynamic tethers require no propellant, they could substantially reduce the weight of the spacecraft and provide a cost-effective method of reboosting spacecraft. The initial flight of ProSEDS is scheduled to fly aboard an Air Force Delta II rocket in summer of 2002. In orbit, ProSEDS will deploy from a Delta II second stage. It will be a 3.1-mile (5 kilometer) long, ultrathin base-wire tether cornected with a 6.2-mile (10 kilometer) long nonconducting tether. The ProSEDS experiment is managed by the Space Transportation Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
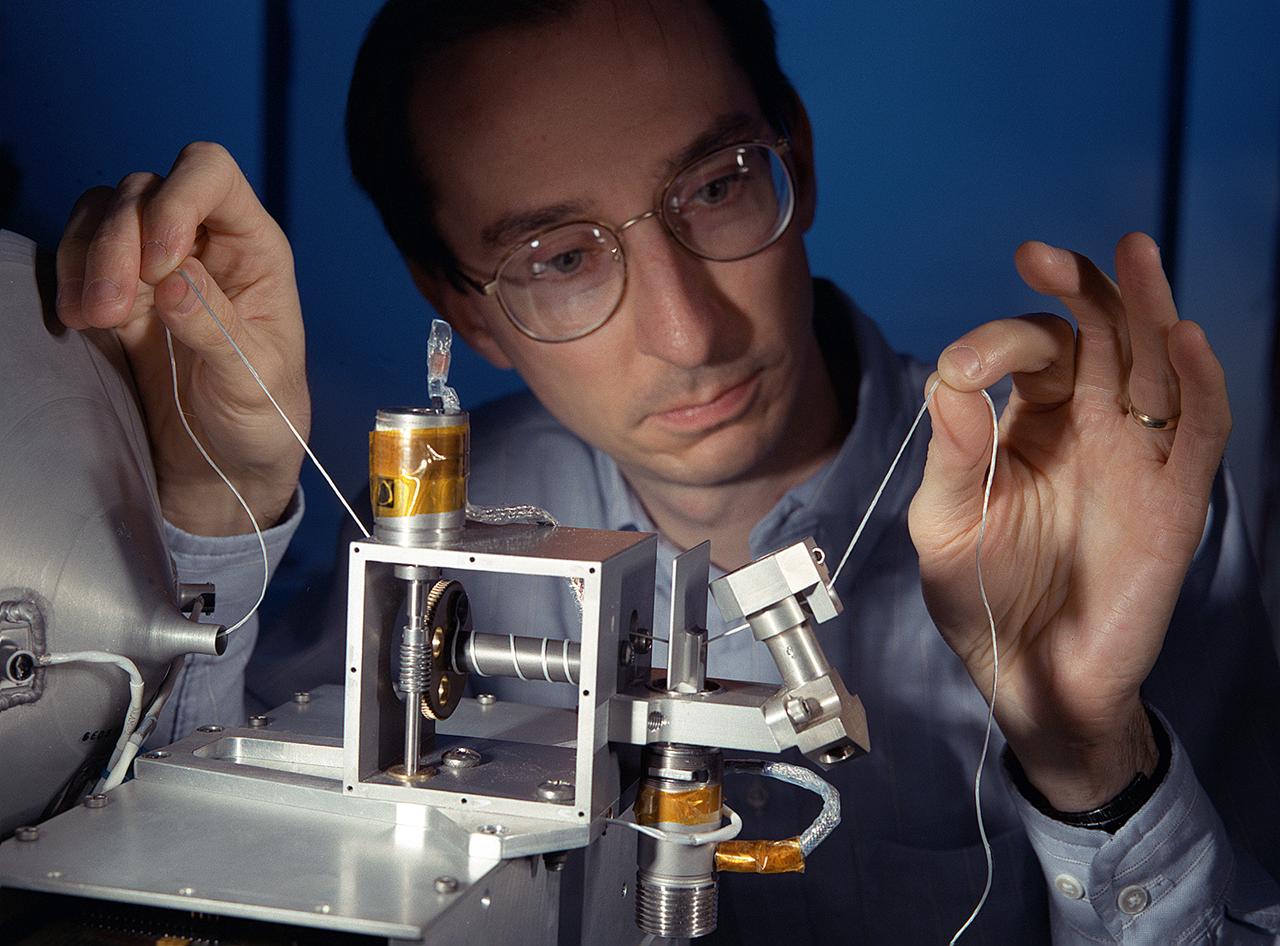

NASA's Propulsive Small Expendable Deployer System experiment (ProSEDS) will demonstrate the use of an electrodynamic tether, basically a long, thin wire, for propulsion. An electrodynamic tether uses the same principles as electric motors in toys, appliances and computer disk drives, and generators in automobiles and power plants. When electrical current is flowing through the tether, a magnetic field is produced that pushes against the magnetic field of the Earth. For ProSEDS, the current in the tether results by virtue of the voltage generated when the tether moves through the Earth's magnetic field at more than 17,000 mph. This approach can produce drag thrust generating useable power. Since electrodynamic tethers require no propellant, they could substantially reduce the weight of the spacecraft and provide a cost-effective method of reboosting spacecraft. The initial flight of ProSEDS is scheduled to fly aboard an Air Force Delta II rocket in the summer of 2002. In orbit, ProSEDS will deploy from a Delta II second stage. It will be a 3.1-mile (5 kilometer) long, ultrathin base-wire cornected with a 6.2-mile (10 kilometer) long nonconducting tether. This photograph shows Less Johnson, a scientist at MSFC inspecting the nonconducting part of a tether as it exits a deployer similar to the one to be used in the ProSEDS experiment. The ProSEDS experiment is managed by the Space Transportation Directorate at MSFC.
Lightning field study devices are visible on a Cessna Citation aircraft during flight over Central Florida. The center of the black circle contains one of six field mills, used to measure electric fields, located on the body of the plane. Below the circle is one of several cloud physics probes attached to the plane that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The Cessna is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
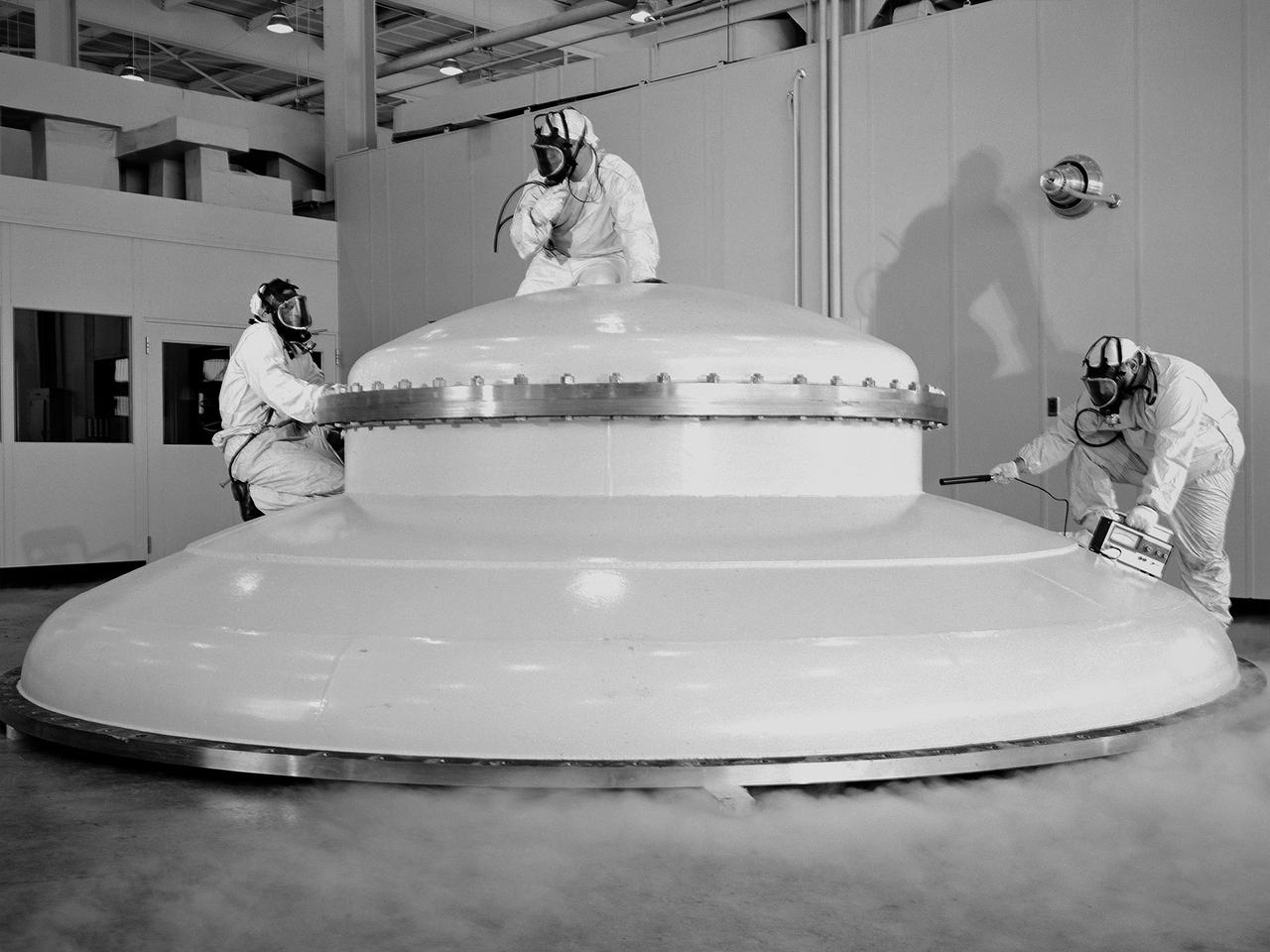

Engineer Paul Reader and his colleagues take environmental measurements during testing of a 20-inch diameter ion engine in a vacuum tank at the Electric Propulsion Laboratory (EPL). Researchers at the Lewis Research Center were investigating the use of a permanent-magnet circuit to create the magnetic field required power electron bombardment ion engines. Typical ion engines use a solenoid coil to create this magnetic field. It was thought that the substitution of a permanent magnet would create a comparable magnetic field with a lower weight. Testing of the magnet system in the EPL vacuum tanks revealed no significant operational problems. Reader found the weight of the two systems was similar, but that the thruster’s efficiency increased with the magnet. The EPL contained a series of large vacuum tanks that could be used to simulate conditions in space. Large vacuum pumps reduced the internal air pressure, and a refrigeration system created the cryogenic temperatures found in space.
Lightning field study devices are visible on a Cessna Citation aircraft during flight over Central Florida. The center of the black circle contains one of six field mills, used to measure electric fields, located on the body of the plane. Below the circle is one of several cloud physics probes attached to the plane that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The Cessna is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
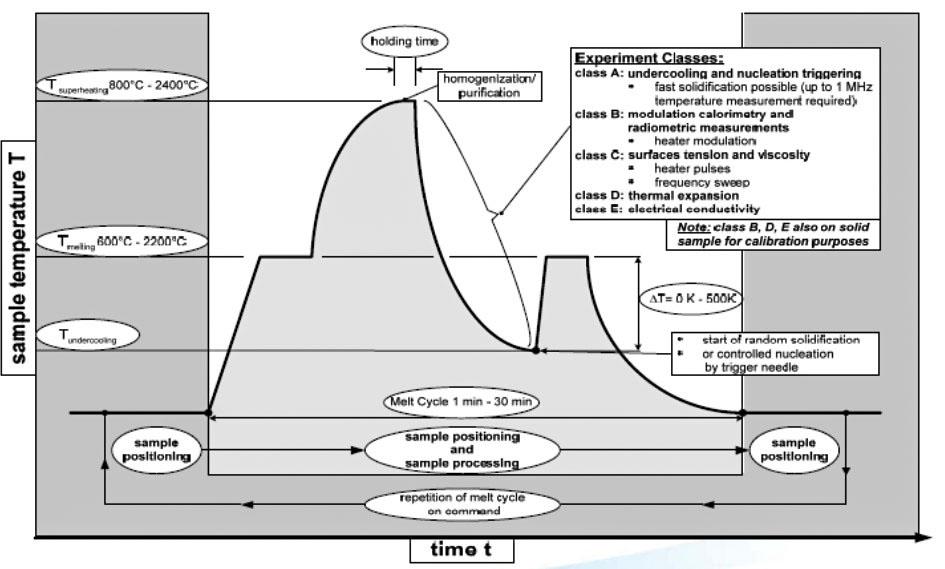
jsc2021e029751 (7/15/2021) --- A diagram showing the the Process cycle of the Electromagnetic Levitator (EML) - Batch 3 of samples. EML is a multi-user facility that provides containerless melting and solidification of electrically conductive, spherical samples, under ultra-high vacuum and/or high gas-purity conditions. Heating and positioning of the sample is achieved by electromagnetic fields generated by a coil system. Batch 3 is a new Sample Chamber to be mounted to the EML process chamber, bringing 18 new samples
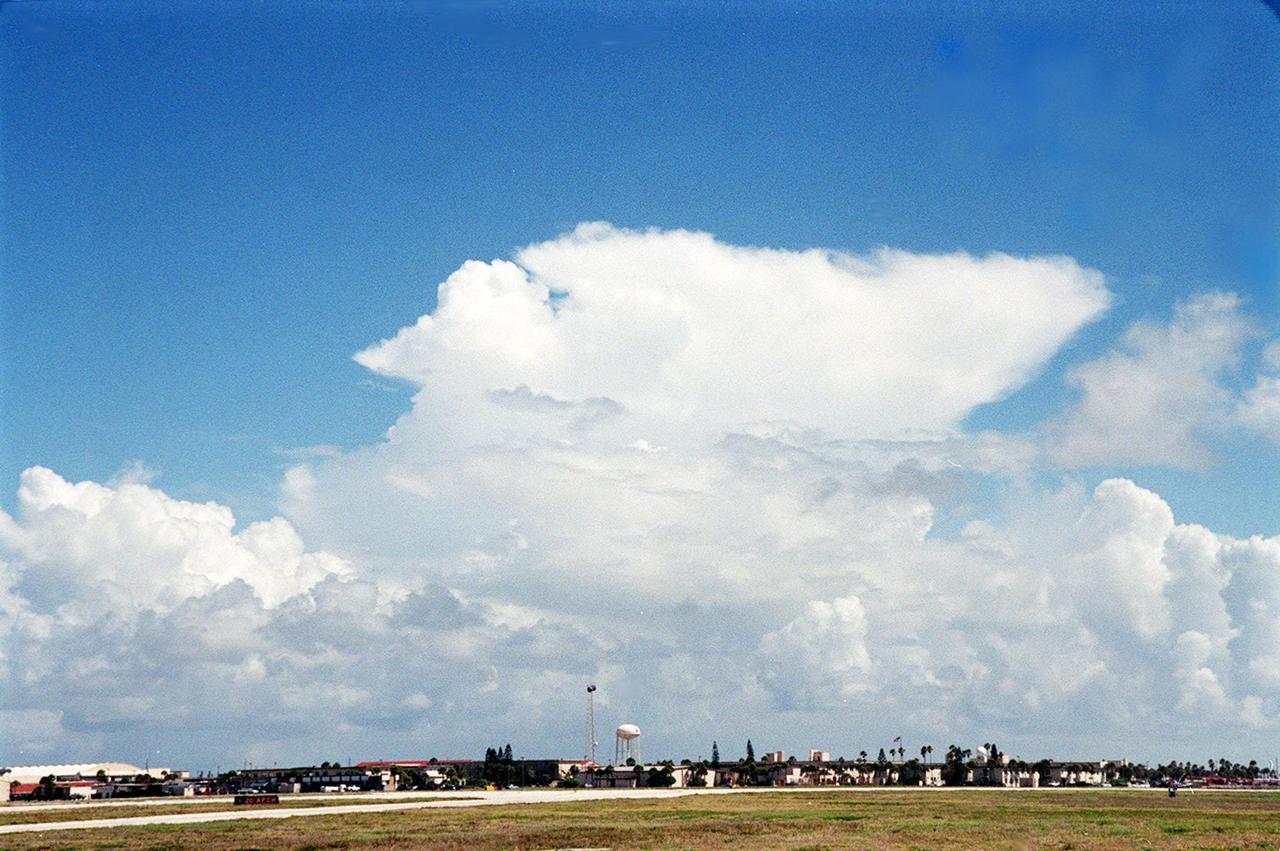

This anvil-shaped cloud over the Central Florida coast is part of a NASA study measuring electric fields in this type of cloud. A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area . The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
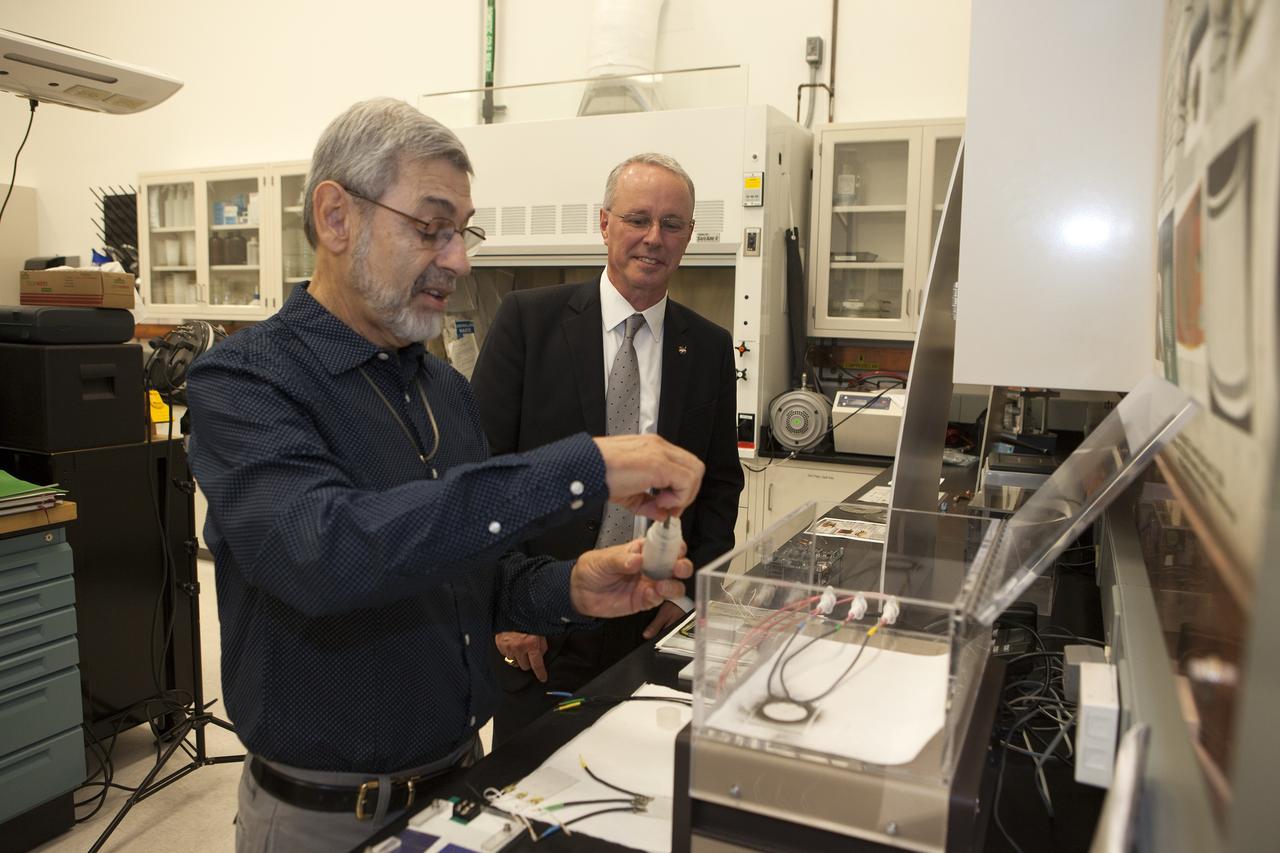

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Chief Technologist David Miller, right, tours laboratories inside the Swamp Works facility. At left, Dr. Carlos Calle, lead in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory, demonstrates a system that uses an electric field wave to move simulated moon dust away from surfaces. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
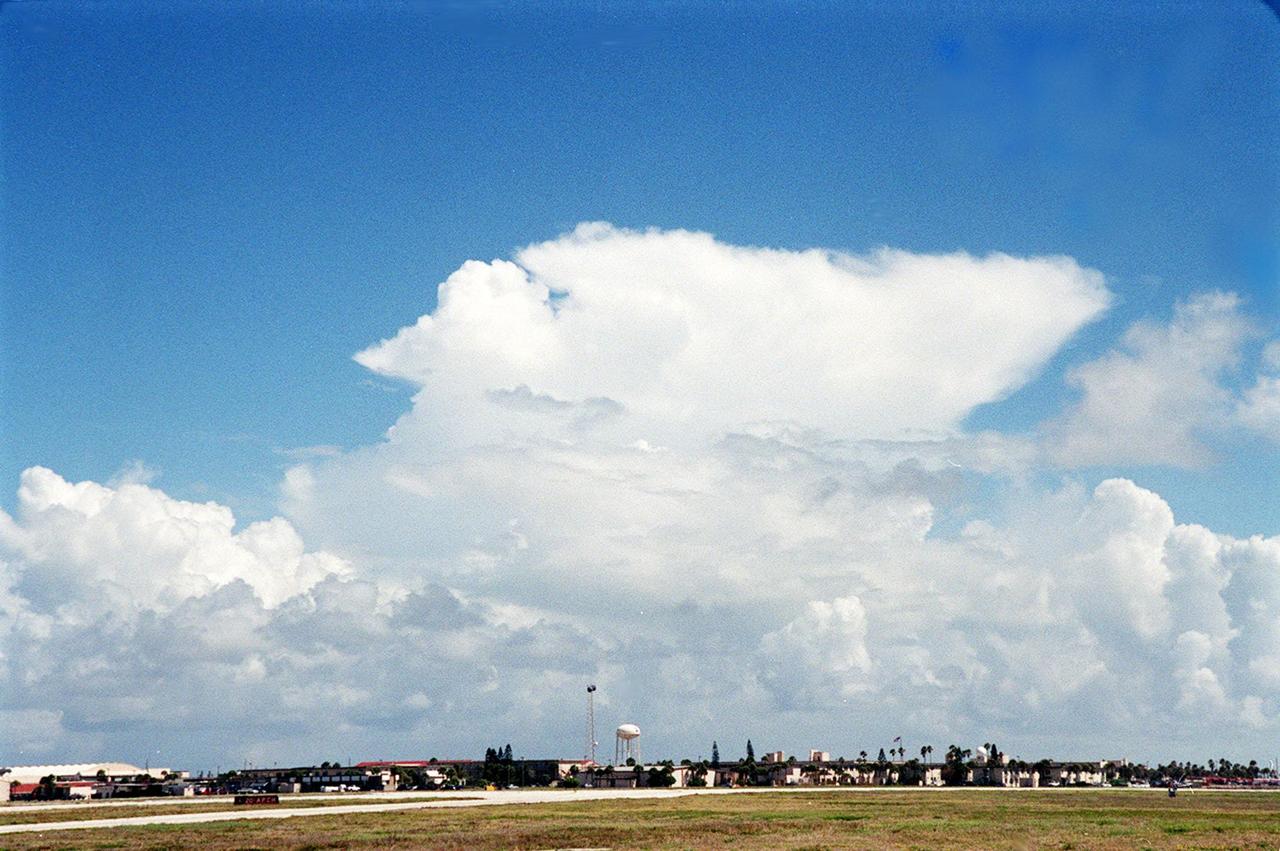

This anvil-shaped cloud over the Central Florida coast is part of a NASA study measuring electric fields in this type of cloud. A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area . The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
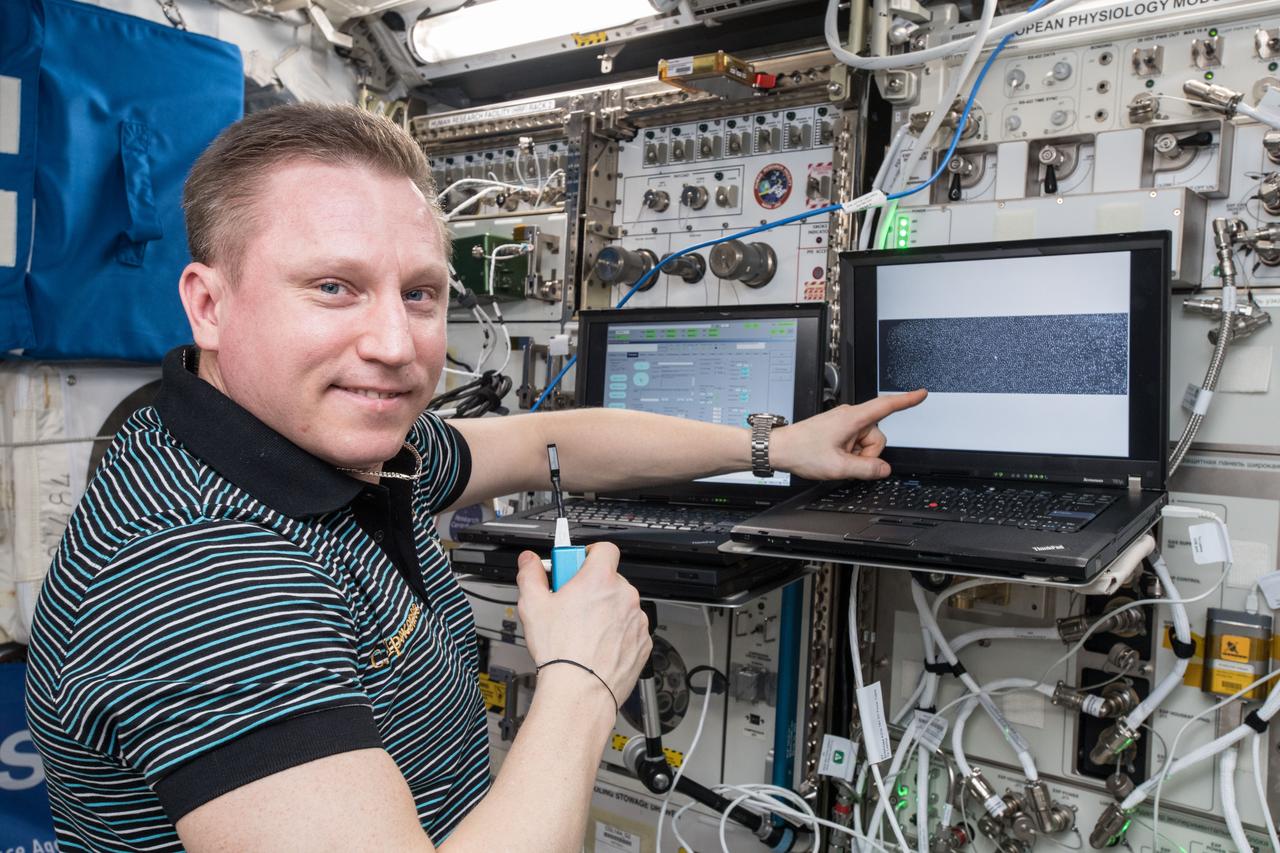

iss057e074494 (Nov. 7, 2018) --- Russian cosmonaut and Expedition 57 Flight Engineer Sergey Prokopyev is pictured inside Europe's Columbus lab module conducting research for the Plasma Krystall-4 experiment that researches how microgravity, electric fields and the Sun impact complex plasmas which are low temperature gaseous mixtures composed of ionized gas, neutral gas, and micron-sized particles..
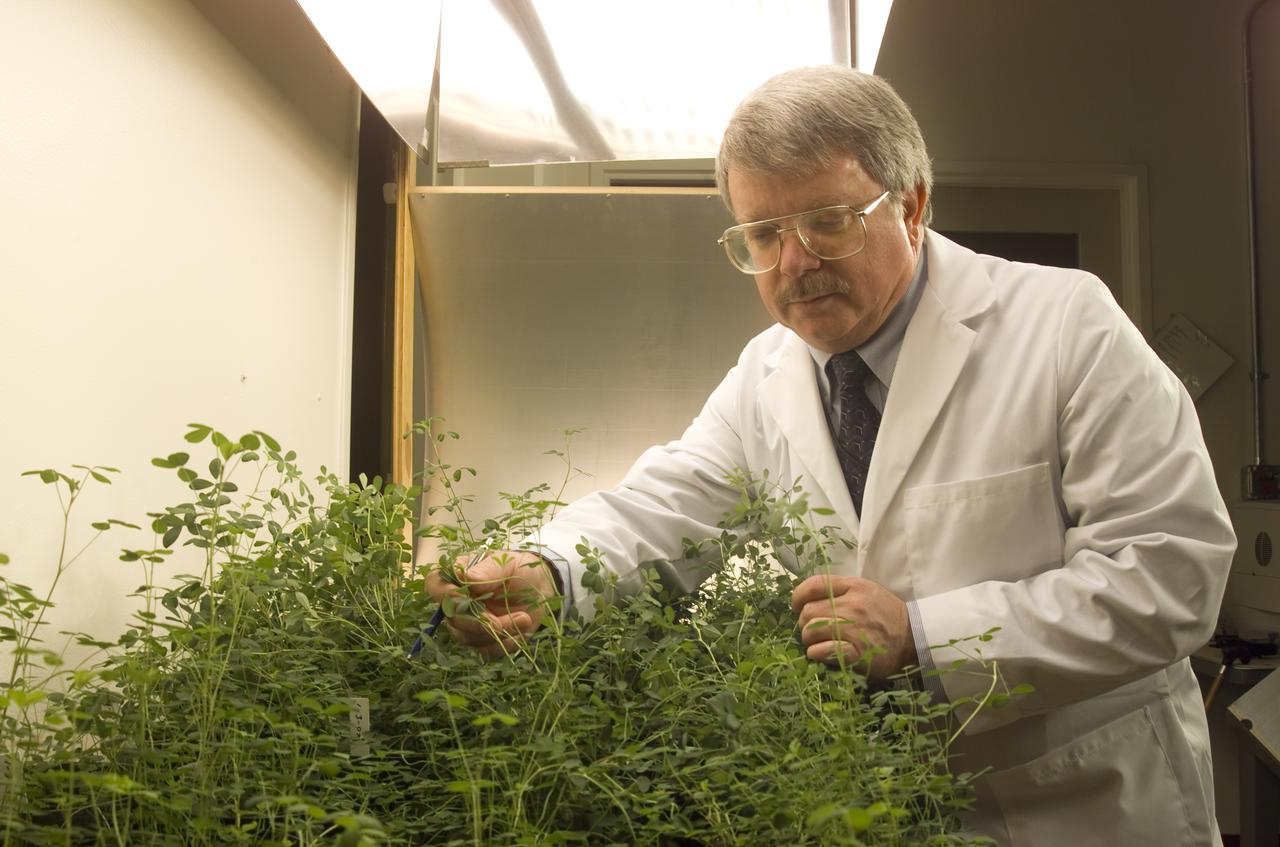

Microvave effects on plant growth (alfalfa), shown here is Dr. Jay Skiles of NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. NASA scientists are about to test that hypothesis by evaluating the effects of continuously beaming weak microwaves on alfalfa plants during laboratory tests. Microwaves derived from solar power and transmitted by orbiting satellites to electric power stations on Earth may someday enable U.S. energy self-sufficiency, but is this method safe for local plant life?
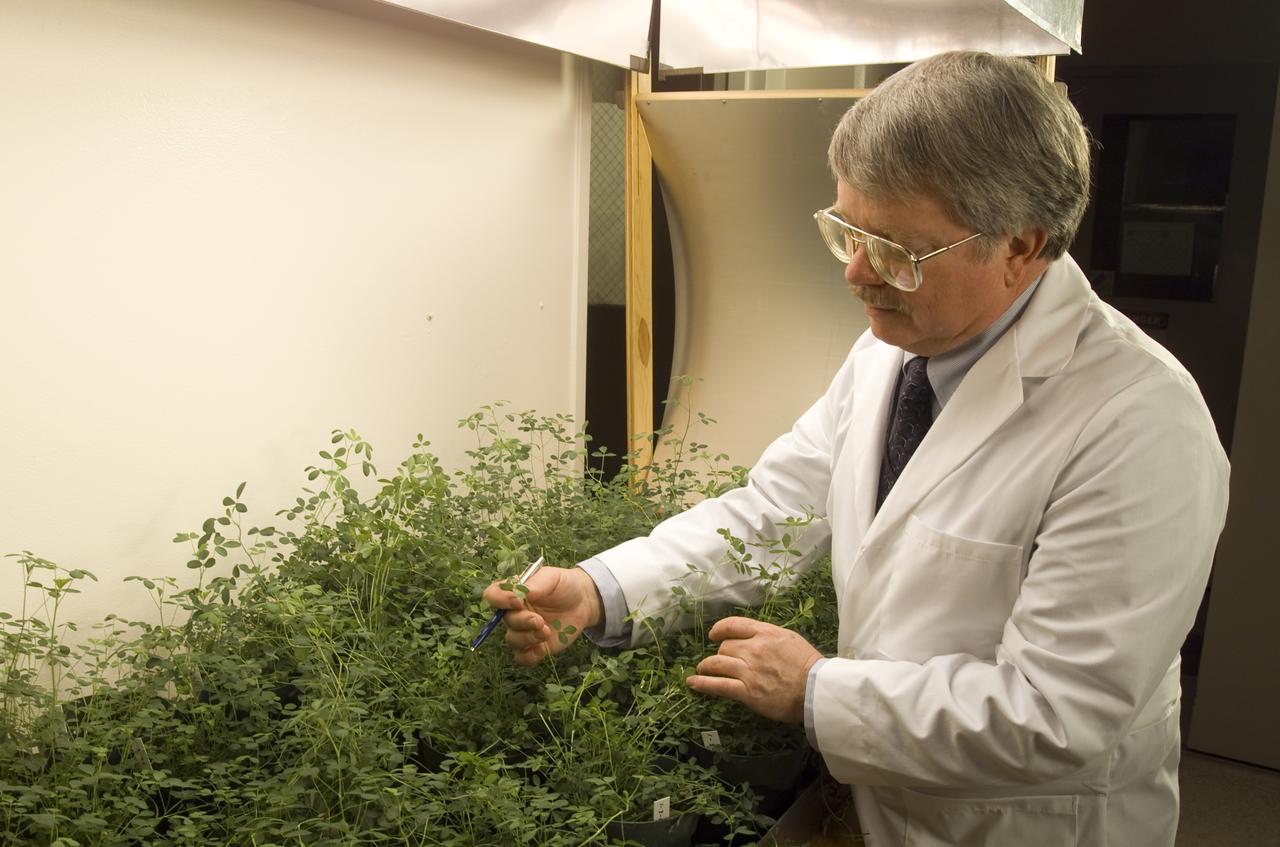

Microvave effects on plant growth (alfalfa), shown here is Dr. Jay Skiles of NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. NASA scientists are about to test that hypothesis by evaluating the effects of continuously beaming weak microwaves on alfalfa plants during laboratory tests. Microwaves derived from solar power and transmitted by orbiting satellites to electric power stations on Earth may someday enable U.S. energy self-sufficiency, but is this method safe for local plant life?
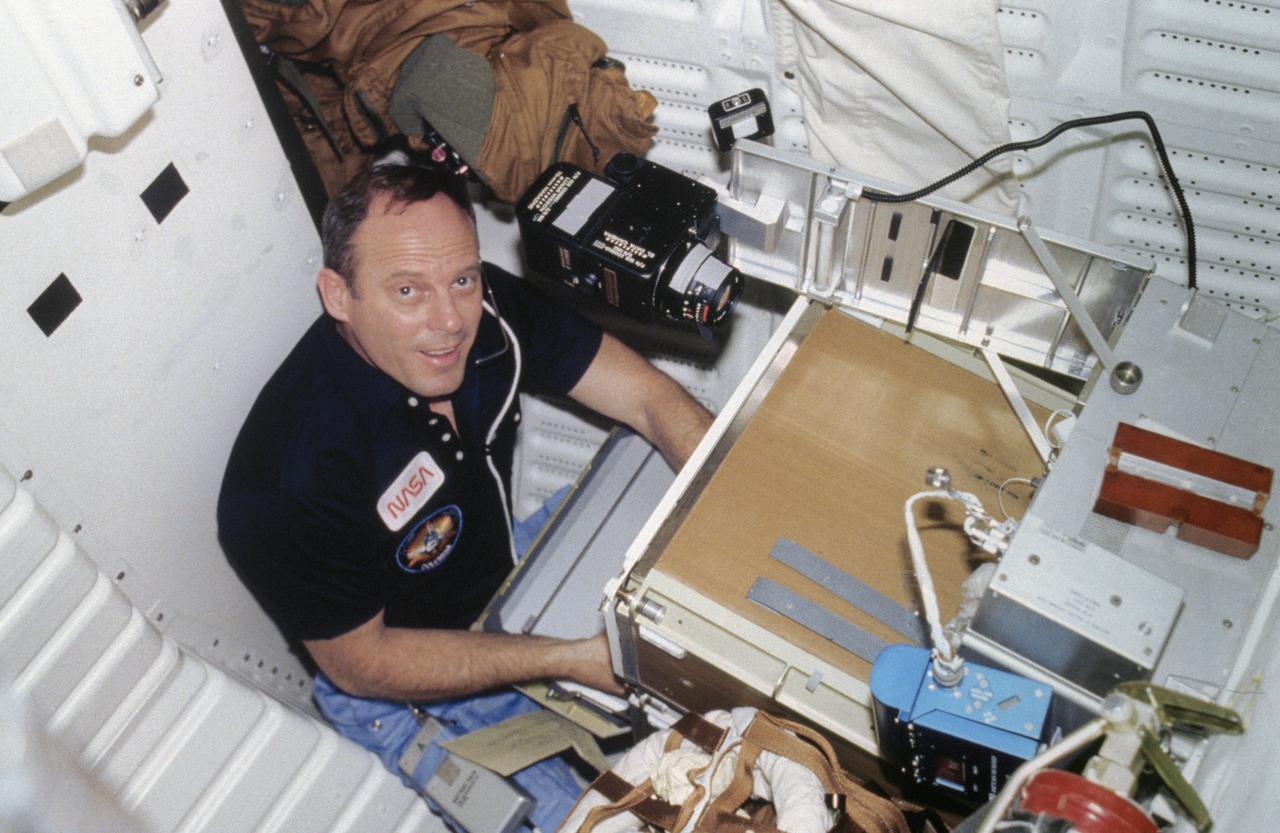

S82-28911 (March 1982) --- The L-shaped experiment in the right half of this photo was one of a number of scientific experiments which made the trip for NASA's third space transportation system (STS-3) mission, along with astronauts Jack R. Lousma, pictured, and C. Gordon Fullerton. The experiment, making encore in space (it also flew on the Apollo Soyuz Test Project in 1985), is designed to evaluate the feasibility of separating cells according to their surface electrical charge. It is a forerunner to planned experiments with other equipment that will purify biological materials in the low gravity environment of space. The process of electrophoresis utilizes an electric field to separate cells, and other biological material in fluids without damaging the cells which can then be used in the study of cell biology, immunology and medical research. This photograph was taken with a 35mm camera by Fullerton. Photo credit: NASA

A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over KSC during a calibration test of field mills used to measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
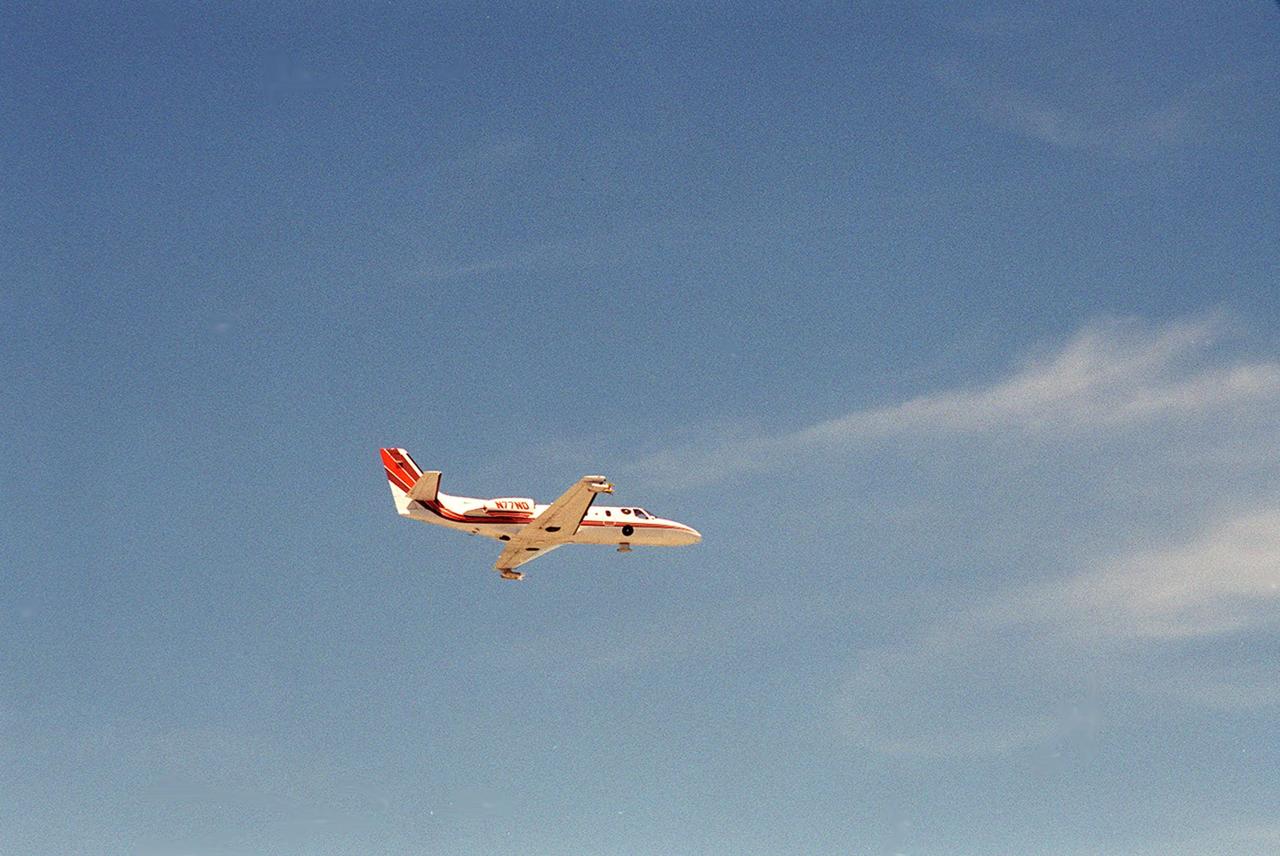

A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over KSC during a calibration test of field mills used to measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
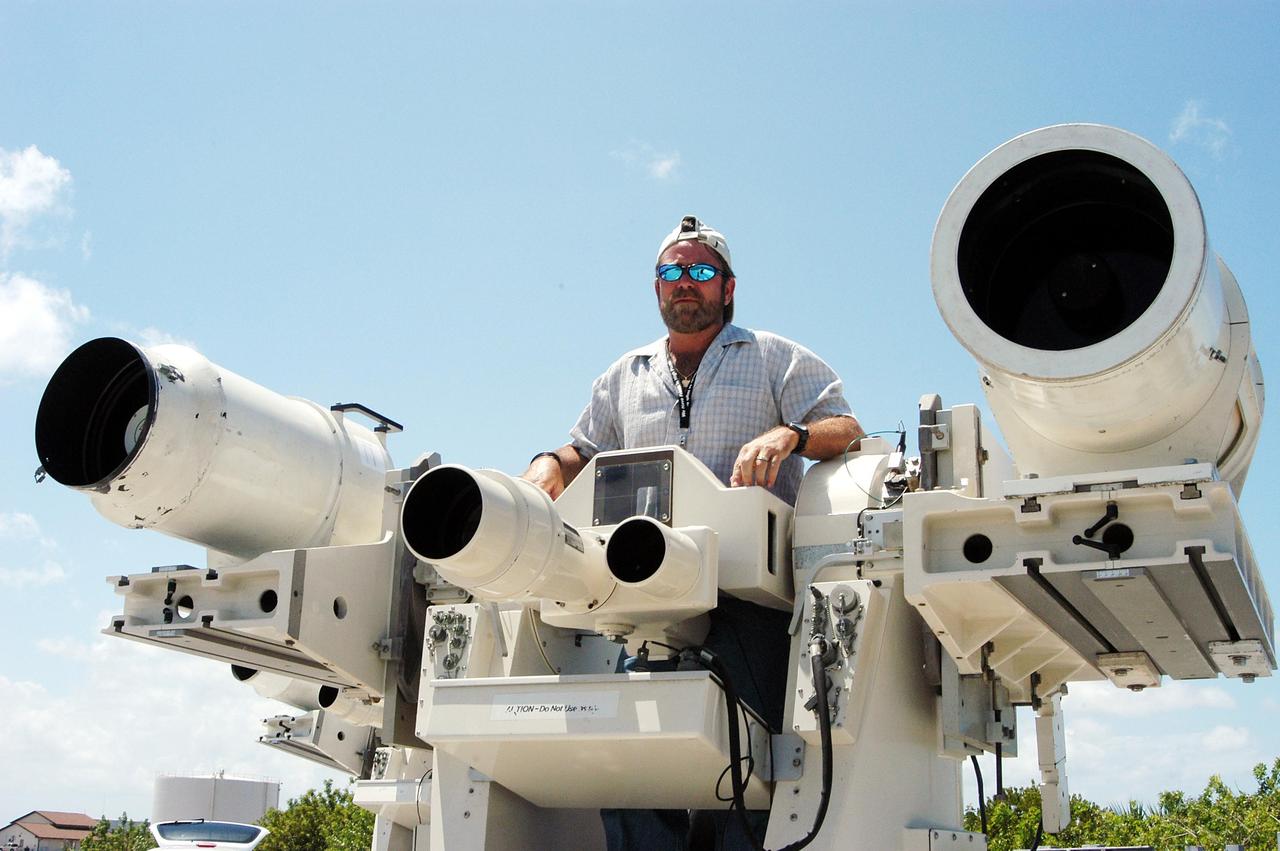

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operator Kenny Allen stands in the center console area of one of the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mounts (KTM). There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range. The KTM, which is trailer-mounted with an electric-drive tracking mount, includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff.
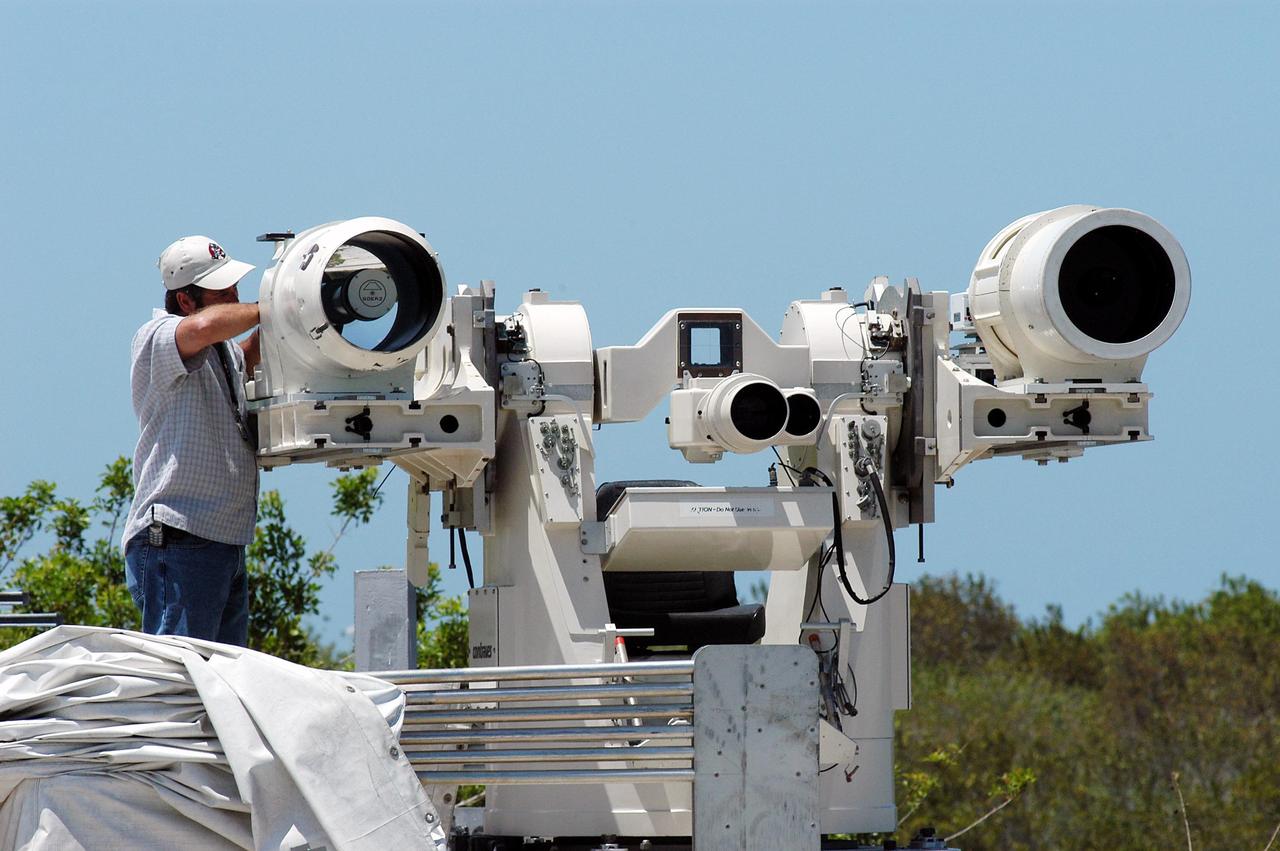

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operator Kenny Allen works on the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mount (KTM). Trailer-mounted with a center console/seat and electric drive tracking mount, the KTM includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff. There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range.
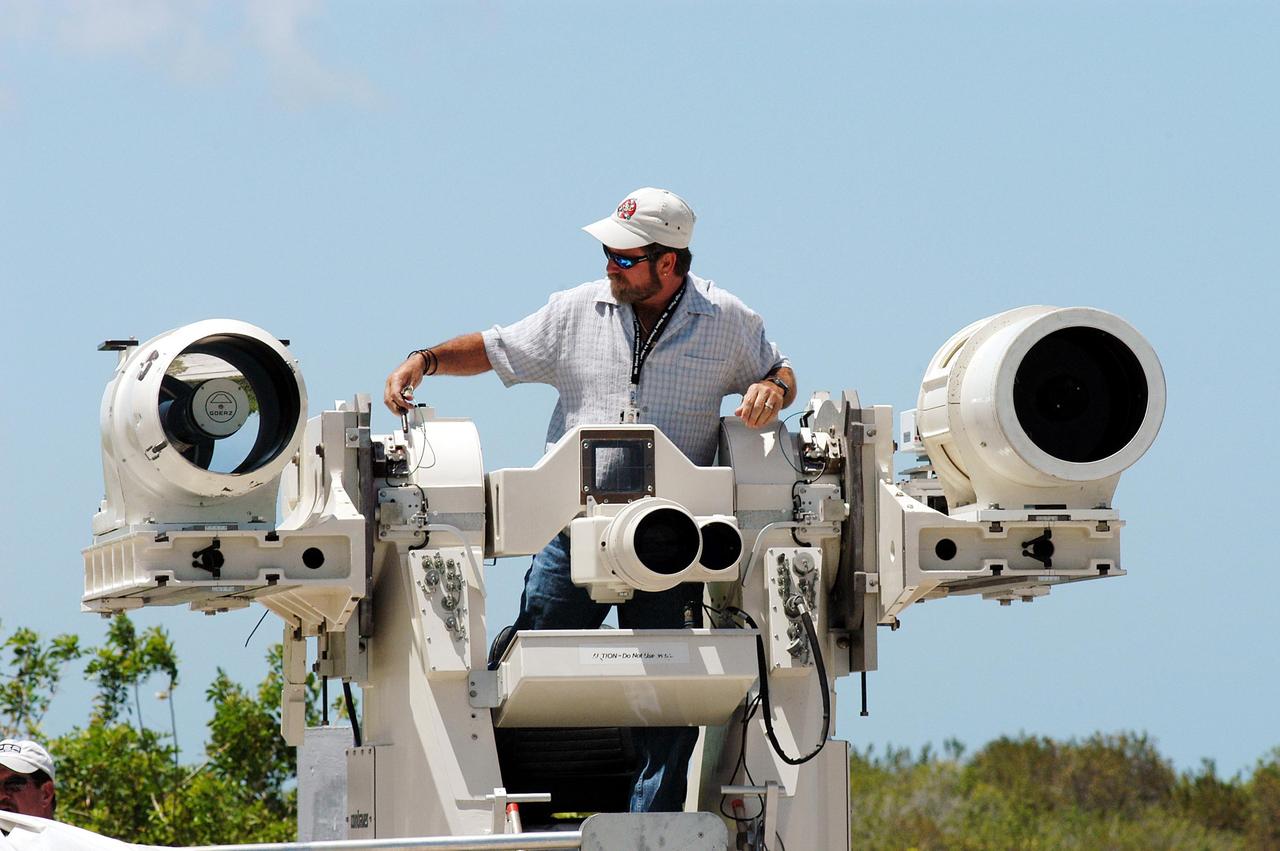

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operator Kenny Allen works on the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mount (KTM). Trailer-mounted with a center console/seat and electric drive tracking mount, the KTM includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff. There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operator Rick Wetherington checks out one of the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mounts (KTM). There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range. The KTM, which is trailer-mounted with an electric drive tracking mount, includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operator Rick Wetherington sits in the center console seat of one of the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mounts (KTM). There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range. The KTM, which is trailer-mounted with an electric drive tracking mount, includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff.
This image, created with data from Juno's Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrometer (UVS), marks the path of Juno's readings of Jupiter's auroras, highlighting the electron measurements that show the discovery of the so-called discrete auroral acceleration processes indicated by the "inverted Vs" in the lower panel (Figure 1). This signature points to powerful magnetic-field-aligned electric potentials that accelerate electrons toward the atmosphere to energies that are far greater than what drive the most intense aurora at Earth. Scientists are looking into why the same processes are not the main factor in Jupiter's most powerful auroras. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21937
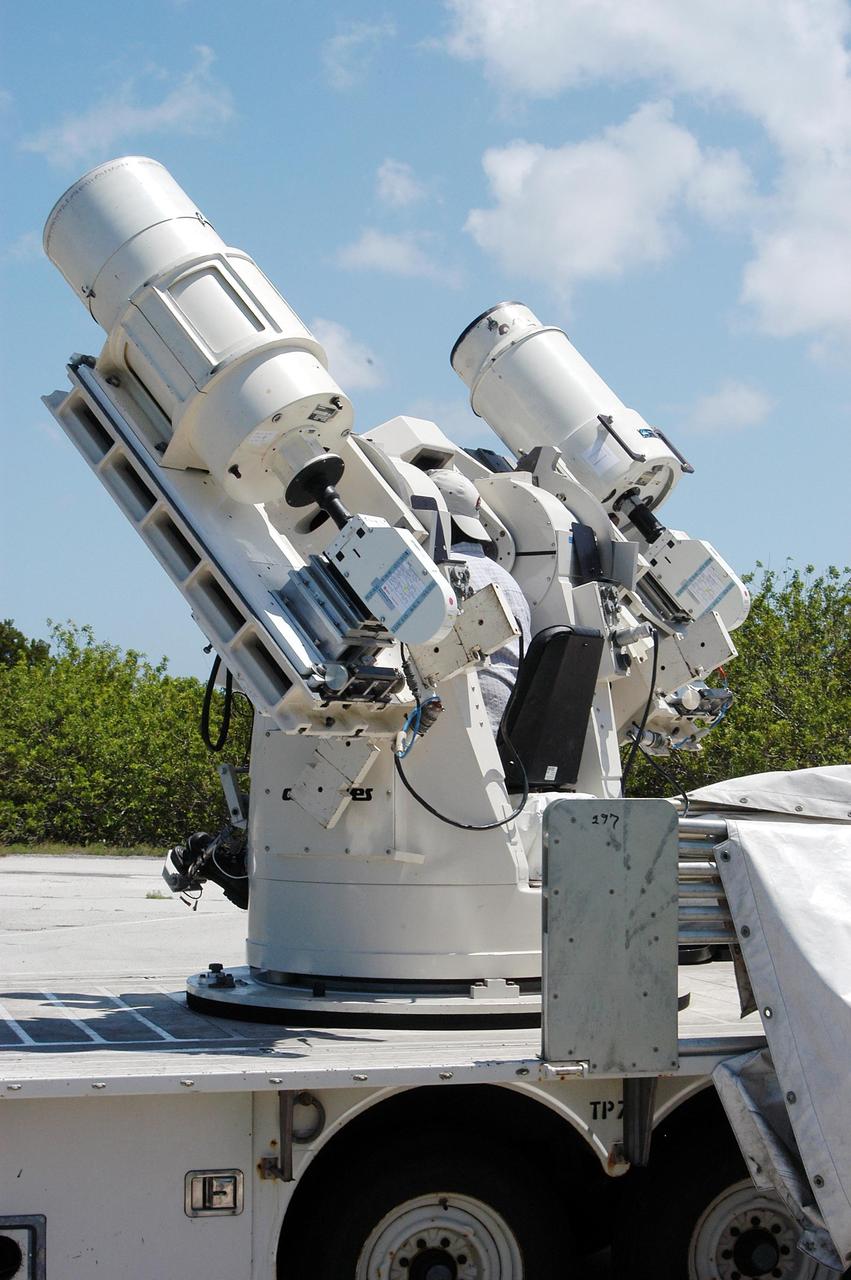

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operator Kenny Allen checks out one of the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mounts (KTM). There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range. The KTM, which is trailer-mounted with an electric drive tracking mount, includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff.
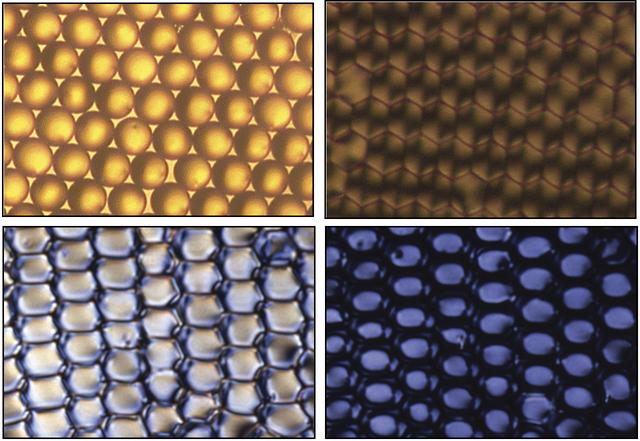
These images, from David Weitz’s liquid crystal research, show ordered uniform sized droplets (upper left) before they are dried from their solution. After the droplets are dried (upper right), they are viewed with crossed polarizers that show the deformation caused by drying, a process that orients the bipolar structure of the liquid crystal within the droplets. When an electric field is applied to the dried droplets (lower left), and then increased (lower right), the liquid crystal within the droplets switches its alignment, thereby reducing the amount of light that can be scattered by the droplets when a beam is shone through them.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operator Kenny Allen makes adjustments on one of the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mounts (KTM). There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range. The KTM, which is trailer-mounted with a center console/seat and electric drive tracking mount, includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff.
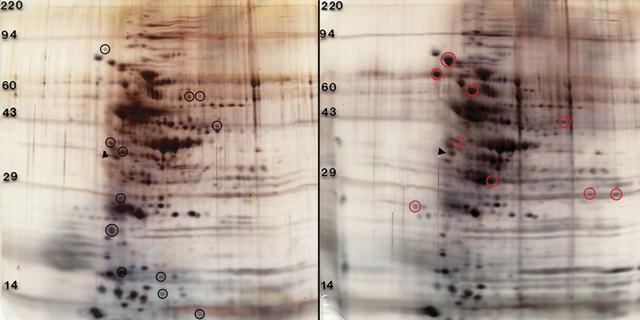
These gels were obtained by two-dimensional (2D) electrophoresis, in which proteins move different substances through a polyacrylamide gel matrix based on their molecular weight and total charge in an electric field. The gels illustrate principal investigator David Niesel’s findings that exposure to modeled microgravity results in some Streptoccoccus Pneumonia’s proteins being upregulated and others being downregulated. In 2D protein profiles of whole cell lysates of Streptoccoccus Pneumonia, 6,304 cultured under normal gravity (left), appear to be expressed at higher levels indicated with black circles. Red circles (right) indicate proteins that were grown under modeled microgravity in a high aspect ratio vessel HARV).
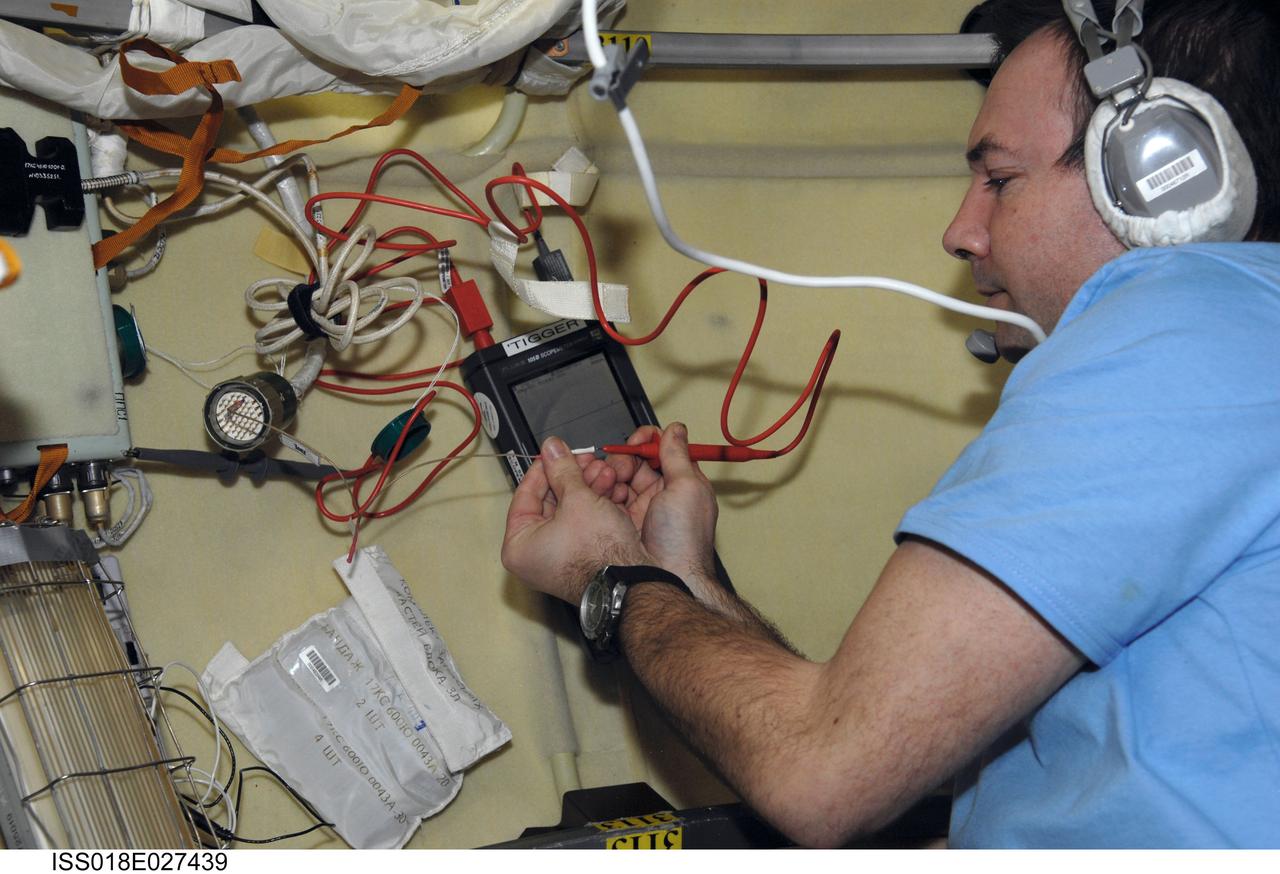

ISS018-E-027439 (6 Feb. 2009) --- Cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, Expedition 18 flight engineer, uses an oscilloscope to measure voltage in the Pirs Docking Compartment of the International Space Station.
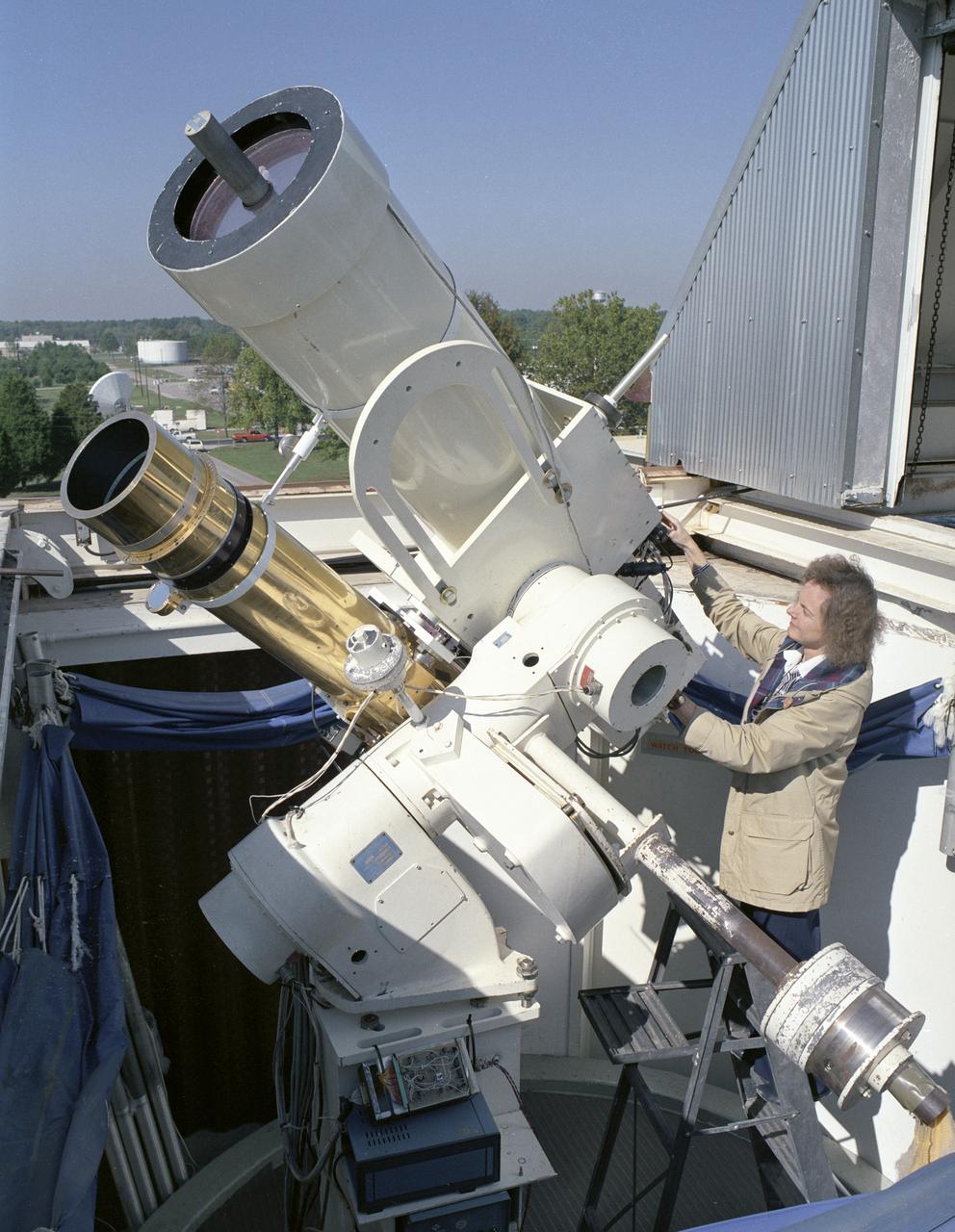

Using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are monitoring the explosive potential of magnetic areas of the Sun. This effort could someday lead to better prediction of severe space weather, a phenomenon that occurs when blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, the magnetic storm wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. The researchers from MSFC and NSSTC's solar physics group develop instruments for measuring magnetic fields on the Sun. With these instruments, the group studies the origin, structure, and evolution of the solar magnetic field and the impact it has on Earth's space environment. This photograph shows the Solar Vector Magnetograph and Dr. Mona Hagyard of MSFC, the director of the observatory who leads the development, operation and research program of the Solar Vector Magnetograph.
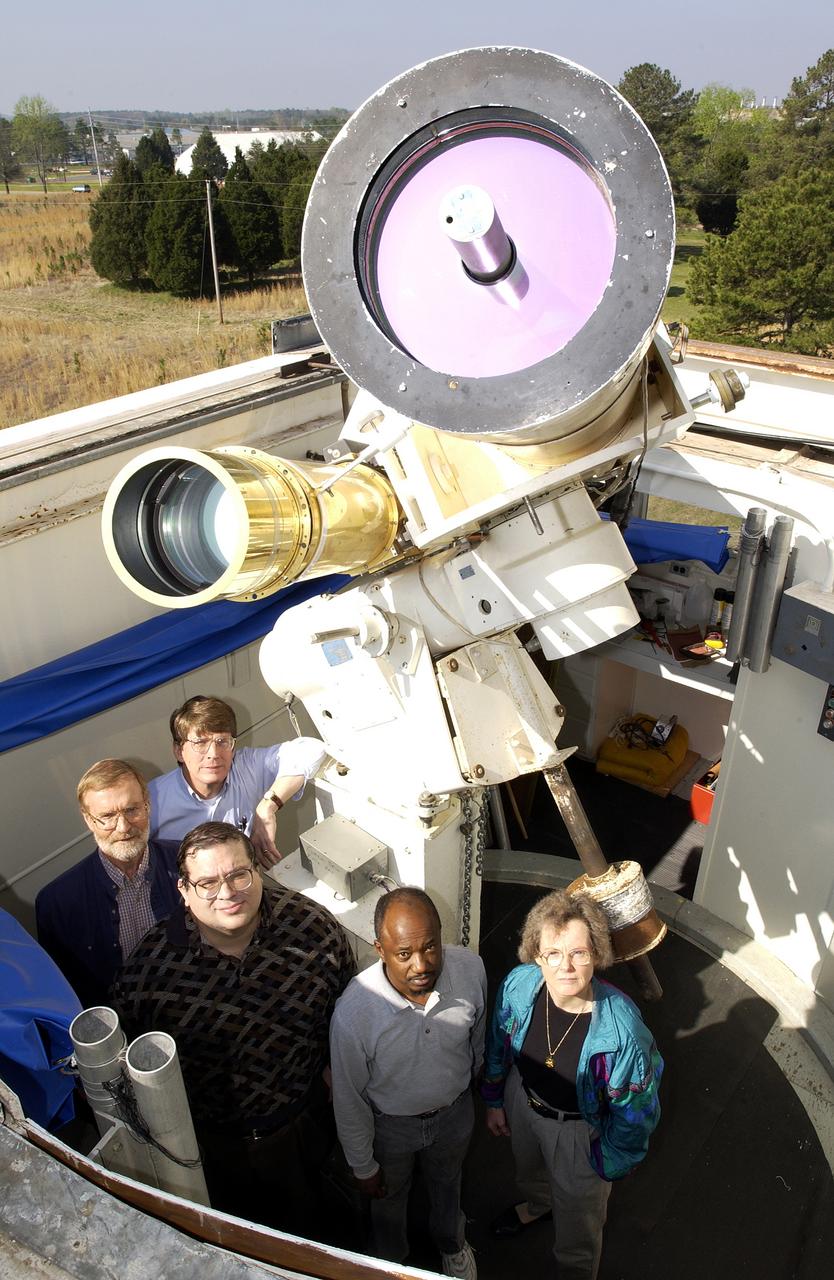

Using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are monitoring the explosive potential of magnetic areas of the Sun. This effort could someday lead to better prediction of severe space weather, a phenomenon that occurs when blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, magnetic storms wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. Photographed are a group of contributing researchers in front of the Solar Vector Magnetograph at MSFC. The researchers are part of NSSTC's solar physics group, which develops instruments for measuring magnetic fields on the Sun. With these instruments, the group studies the origin, structure, and evolution of the solar magnetic fields and the impact they have on Earth's space environment.
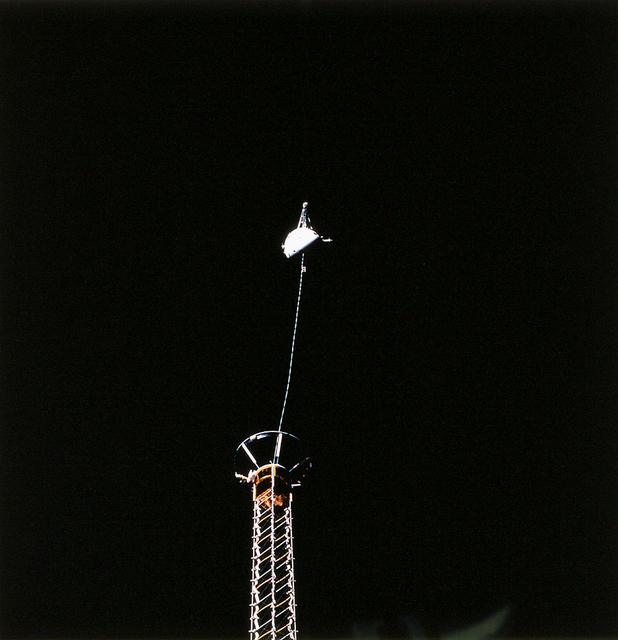

An STS-75 onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System-1 Reflight (TSS-1R) atop its extended boom. The TSS-1R was a reflight of TSS-1, which was flown on the Space Shuttle in July/August, 1992. Building on the knowledge gained on the TSS-1 about tether dynamics, the TSS will circle the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), placing the tether system well within the rarefield, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. The satellite was plarned to be deployed 20.7 kilometers (12.9 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether, generating high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the ionosphere cutting magnetic field lines, would allow scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. In addition, the TSS would increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, such as plasma waves and currents. The tether on the TSS broke as the Satellite was nearing the full extent of its 12.5 mile deployment from the Shuttle. The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA, and was managed by scientists at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
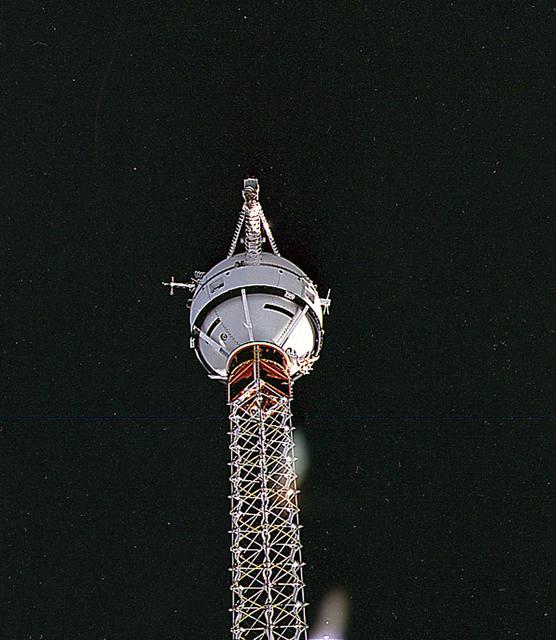

An STS-75 onboard photo of the Tethered Satellite System-1 Reflight (TSS-1R) atop its extended boom. The TSS-1R was a reflight of TSS-1, which was flown on the Space Shuttle in July/August, 1992. Building on the knowledge gained on the TSS-1 about tether dynamics, the TSS will circle the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), placing the tether system well within the rarefield, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. The satellite was plarned to be deployed 20.7 kilometers (12.9 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether, generating high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the ionosphere cutting magnetic field lines, would allow scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. In addition, the TSS would increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, such as plasma waves and currents. The tether on the TSS broke as the Satellite was nearing the full extent of its 12.5 mile deployment from the Shuttle. The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA, and was managed by scientists at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
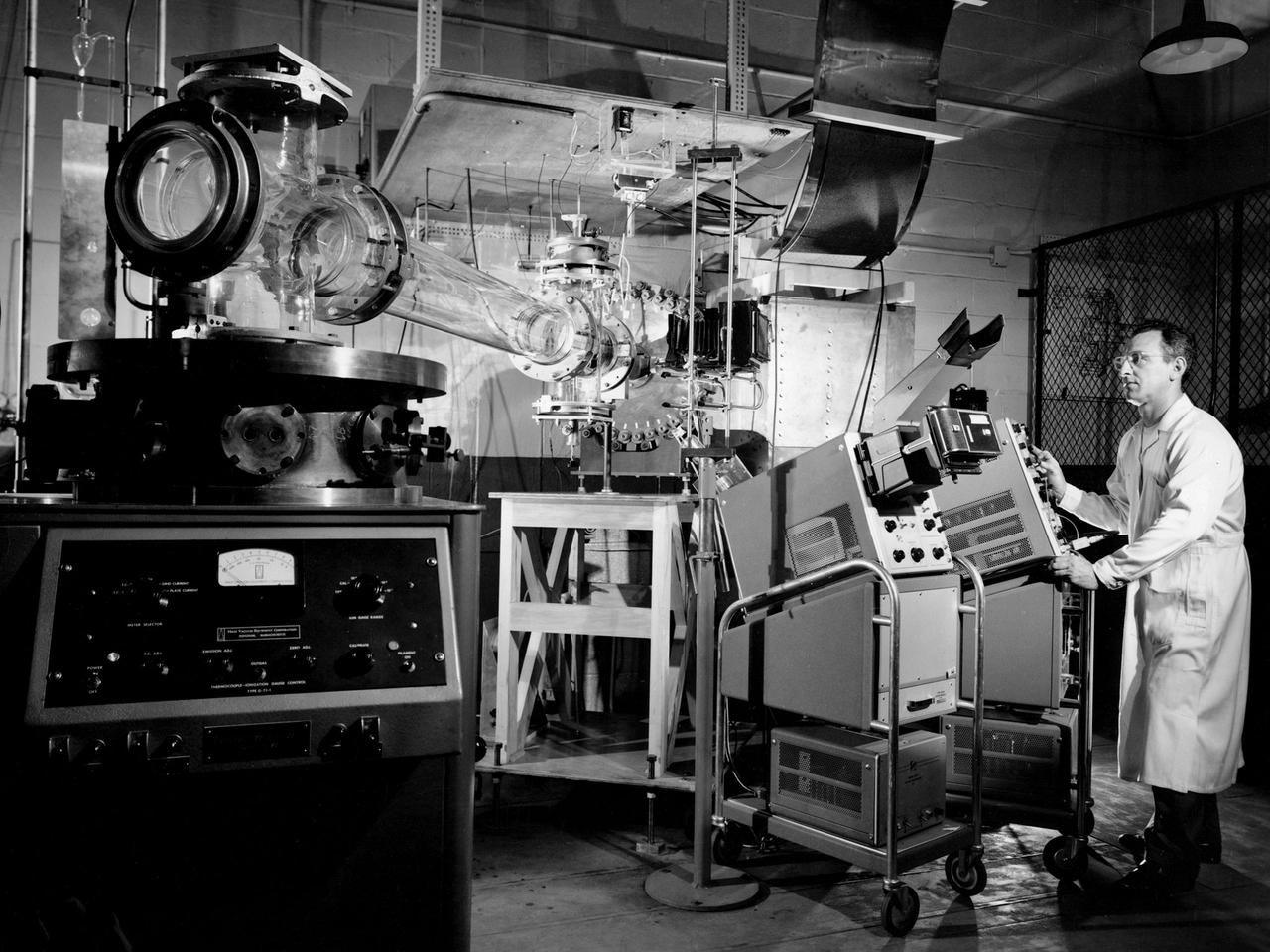

Researcher Charles Michels operates a coaxial plasma gun rig in Cell SW-13 of the Engine Research Building at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. From 1962 to 1967 NASA Lewis investigated coaxial plasma guns powered by conventional capacitor banks. The studies were part of a larger effort to identify electromagnetic accelerators for space propulsion. NASA worked with General Dynamics, General Electric, General Motors, and Republic Aviation on the project. NASA Lewis conducted a research program to determine which factors influenced the coaxial gun’s efficiency and analyze the acceleration process. The system had not previously been used for propulsion applications. The single-shot gun’s fast gas valve and capacitor banks with variable-delay ignition source permitted the evaluation of gun performance under controllable propellant quantity and distribution conditions. The coaxial plasma gun was the most basic type of electromagnetic accelerator. It included a charged capacitor in series with a pair of coaxial electrodes. An electrical breakdown occurred when gas was admitted to the inter-electrode region. The gas instantly became a good conductor and formed a conducting sheet that separated the magnetic field from the open region beyond. The highly-conducting gas was basically expelled by the force of the magnetic pressure. This type of thruster could operate at the high instantaneous power levels without decreasing its average power level.

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Radio news media can talk with Dr. Richard Blakeslee, the project's principal investigator, and Tony Kim, project manager at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), about their results and how their work will help improve future weather forecasting ability. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely- piloted aircraft to study a thunderstorm in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West, two storms at the western edge of the Everglades, and a large storm over the northwestern corner of the Everglades. This photograph shows Tony Kim And Dr. Richard Blakeslee of MSFC testing aircraft sensors that would be used to measure the electric fields produced by thunderstorm as part of NASA's ACES. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the MSFC, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
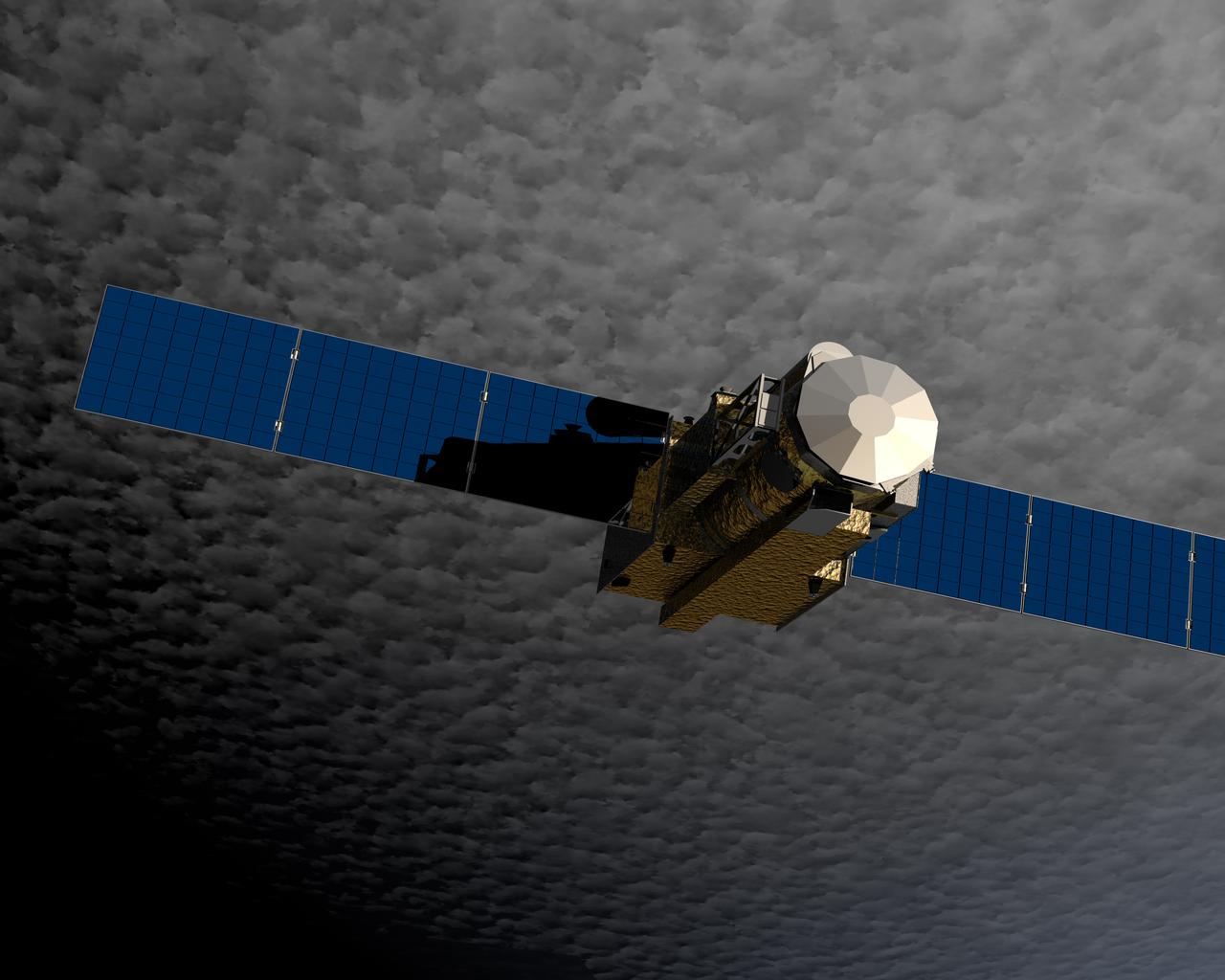

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). Provided by the Multimedia support group at MSFC, this rendering illustrates the Solar-B Spacecraft in earth orbit with its solar panels completely extended.

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). This image of a sunspot, taken by Hinode, is a prime example of what the spacecraft can offer.
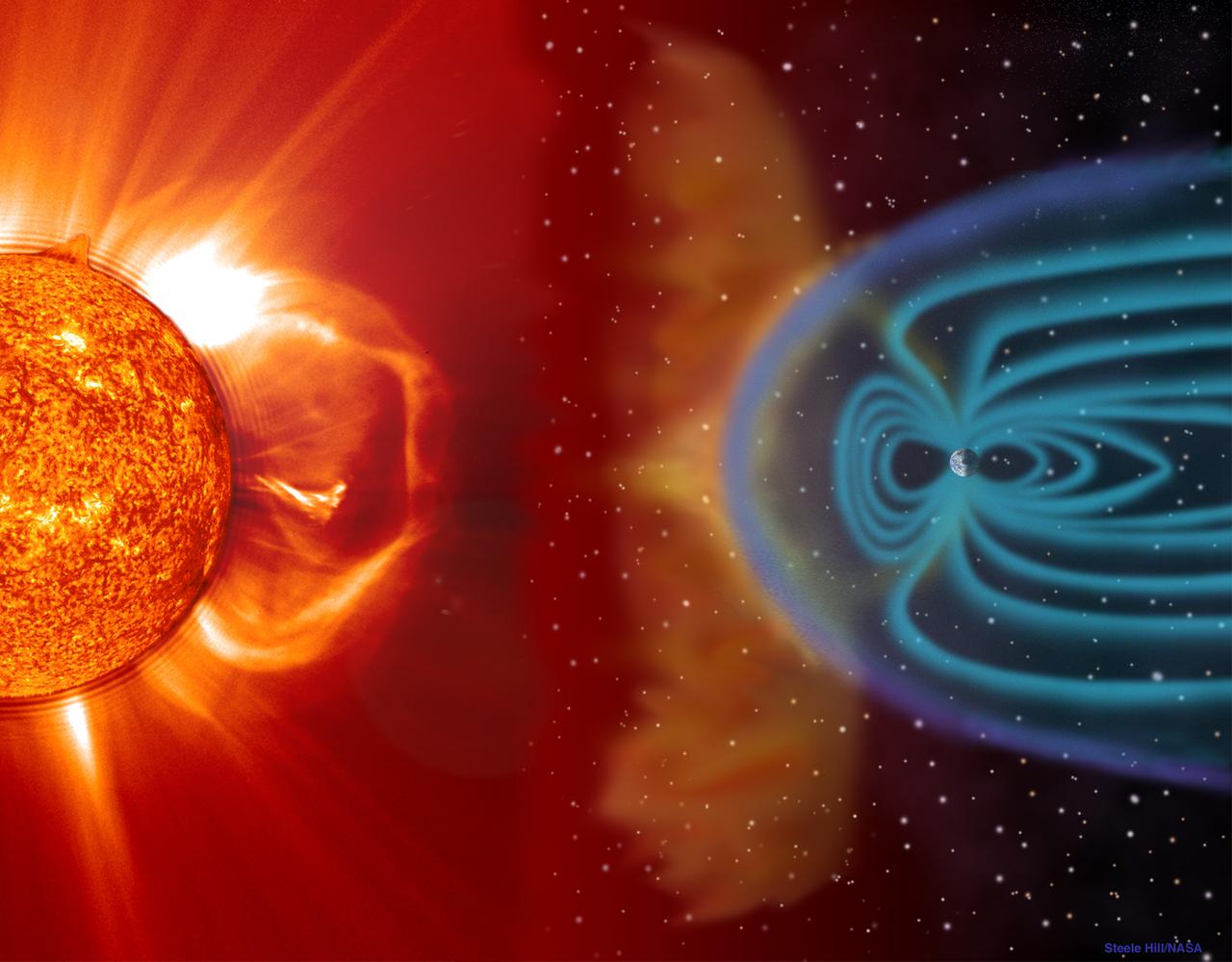
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and university scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are watching the Sun in an effort to better predict space weather - blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun that impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. Filled by charged particles trapped in the Earth's magnetic field, the spherical comet-shaped magnetosphere extends out 40,000 miles from Earth's surface in the sunward direction and more in other directions. This image illustrates the Sun-Earth cornection. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, magnetic storms wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. By using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at MSFC, scientists are learning what signs to look for as indicators of potential severe space weather.
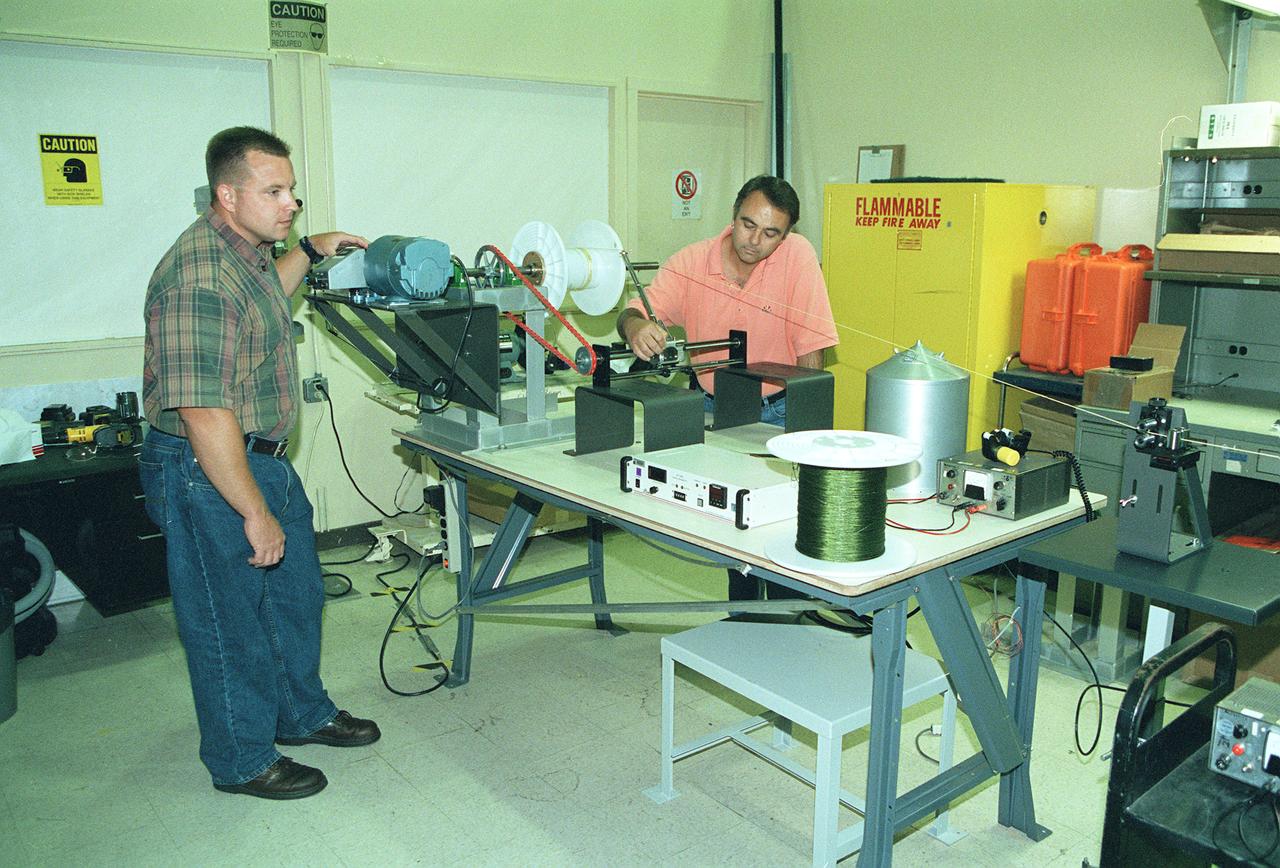

This photograph shows two Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) engineers, Mark Vaccaro (left) and Ken Welzyn, testing electrodynamic tethers in the MSFC Tether Winding and Spark Testing Facility. For 4 years, MSFC and industry partners have been developing the Propulsive Small Expendable Deployer System experiment, called ProSEDS. ProSEDS will test electrodynamic tether propulsion technology. Electrodynamic tethers are long, thin wires that collect electrical current when passing through a magnetic field. The tether works as a thruster as a magnetic field exerts a force on a current-carrying wire. Since electrodynamic tethers require no propellant, they could substantially reduce the weight of the spacecraft and provide a cost-effective method of reboosting spacecraft. The initial flight of ProSEDS is scheduled to fly aboard an Air Force Delta II rocket in the summer of 2002. In orbit, ProSEDS will deploy from a Delta II second stage. It will be a 3.1-mile (5 kilometer) long, ultrathin base-wire tether cornected with a 6.2-mile (10 kilometer) long non-conducting tether. This photograph shows Less Johnson, a scientist at MSFC, inspecting the nonconducting part of a tether as it exits a deployer similar to the one to be used in the ProSEDS experiment. The ProSEDS experiment is managed by the Space Transportation Directorate at MSFC.
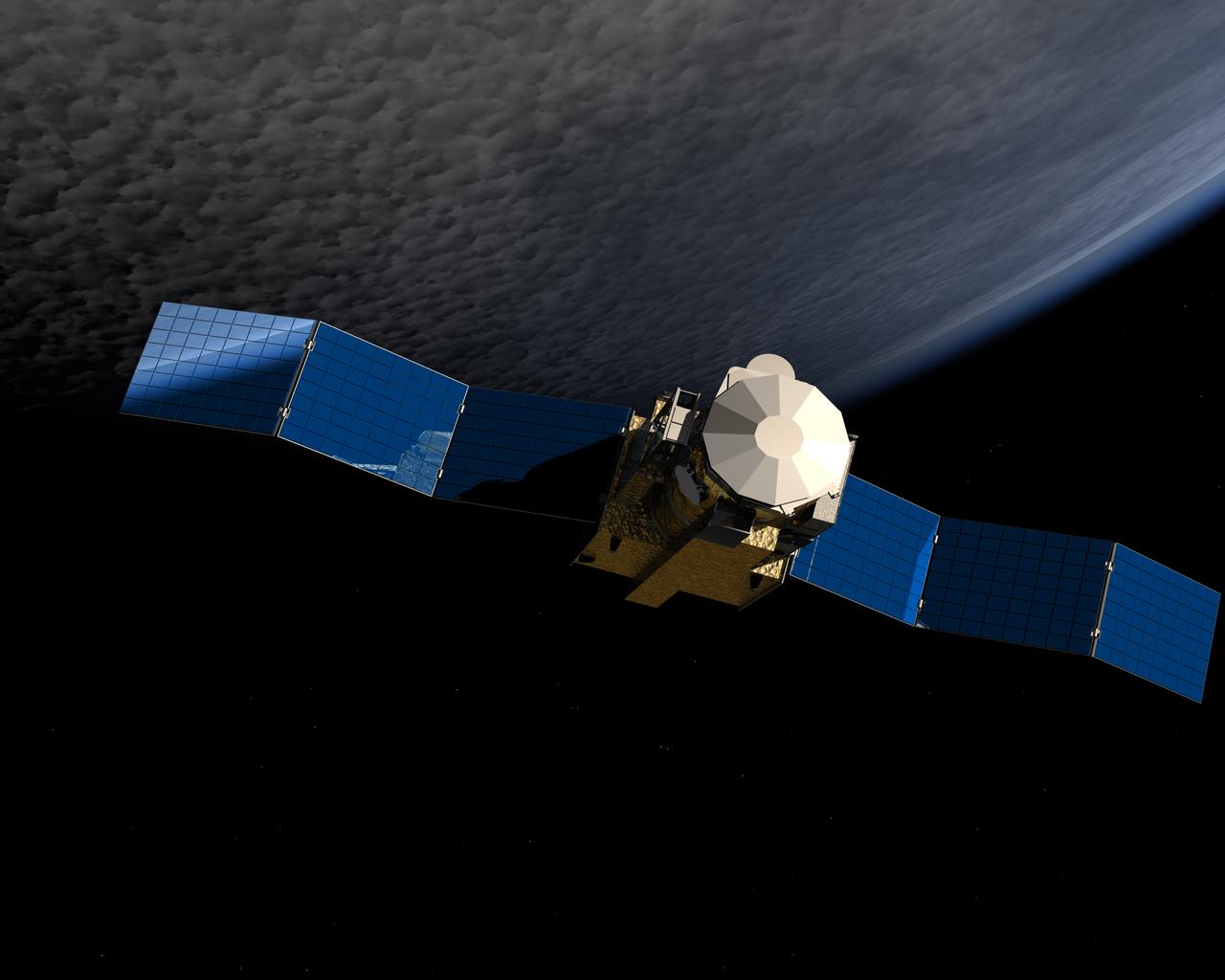

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). Provided by the Multimedia support group at MSFC, this rendering illustrates the Solar-B Spacecraft in earth orbit with its solar panels partially extended.
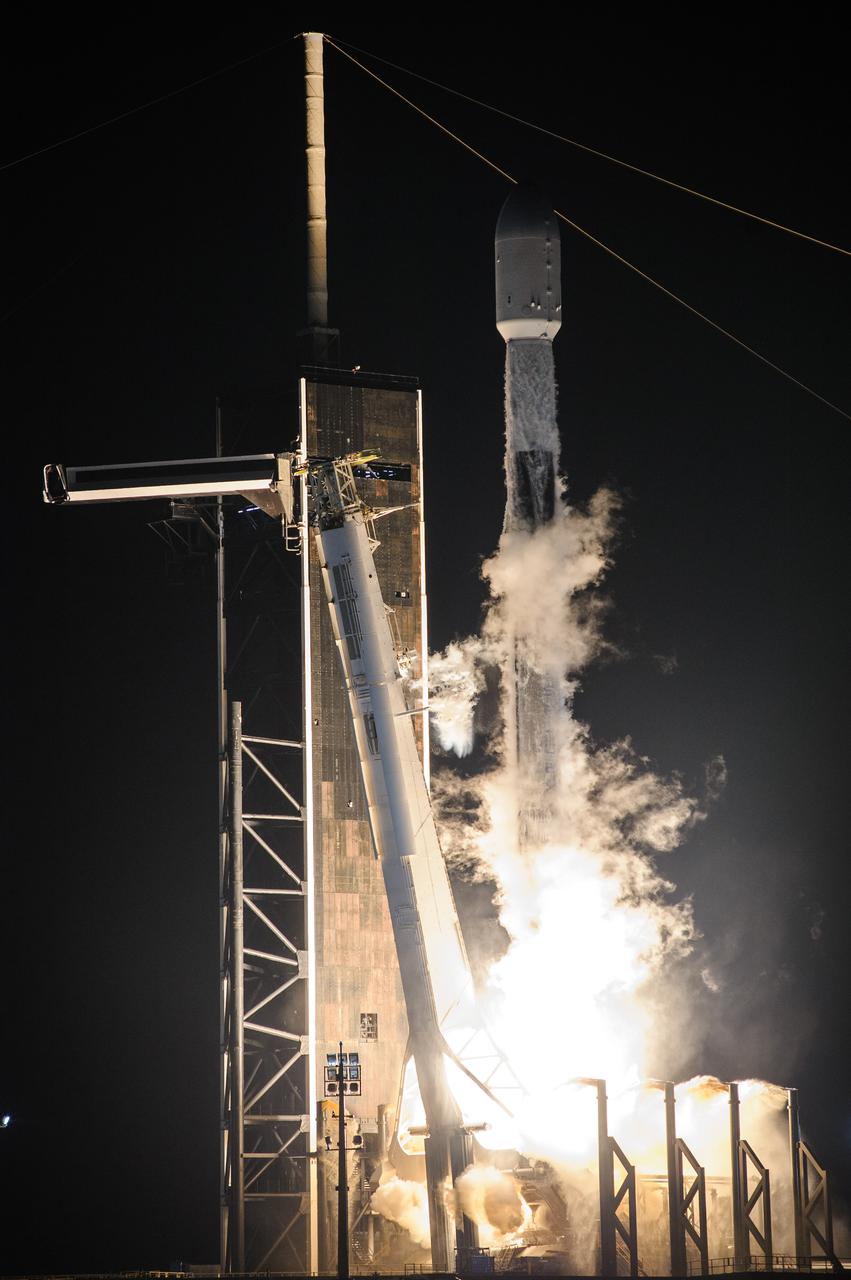

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
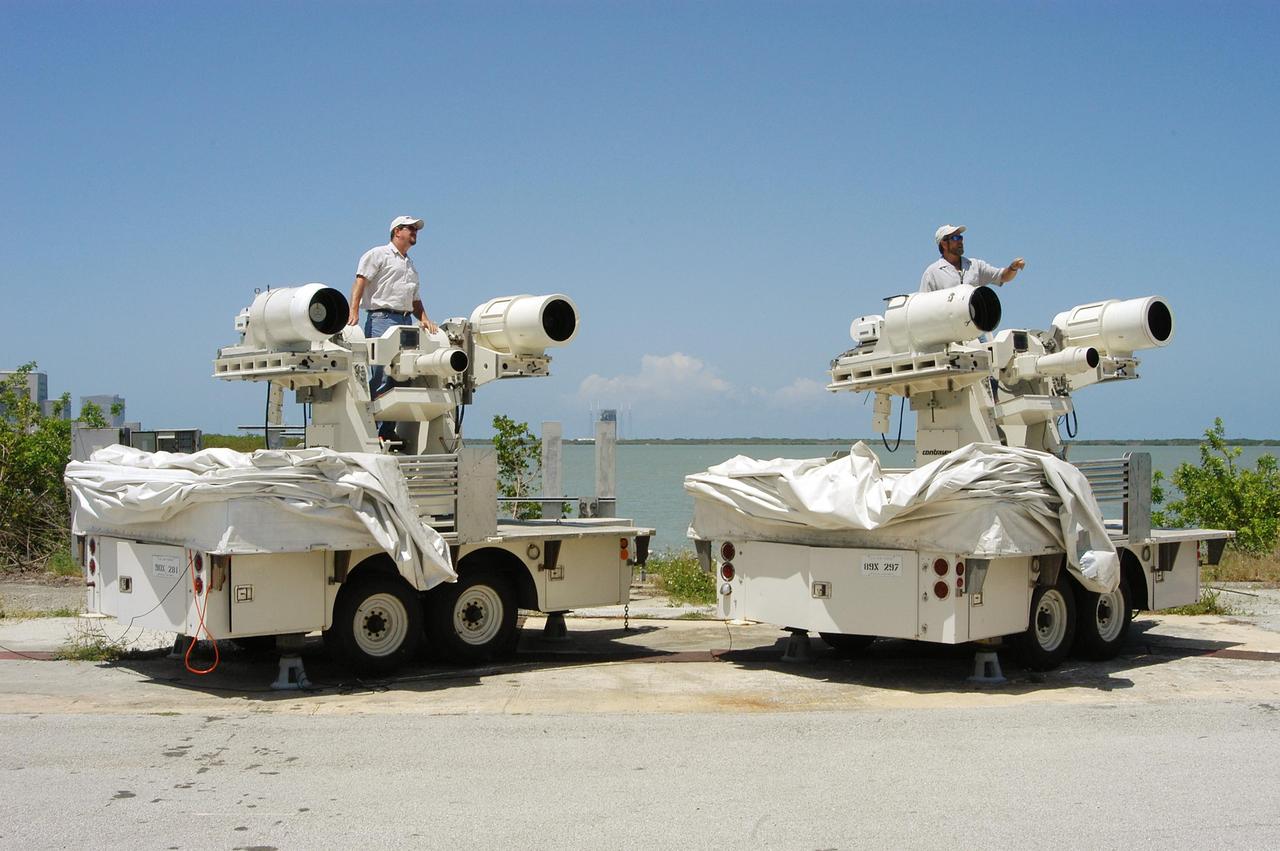

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operators Rick Wetherington (left) and Kenny Allen work on two of the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mounts (KTM). There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range. The KTM, which is trailer-mounted with a center console/seat and electric drive tracking mount, includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff.
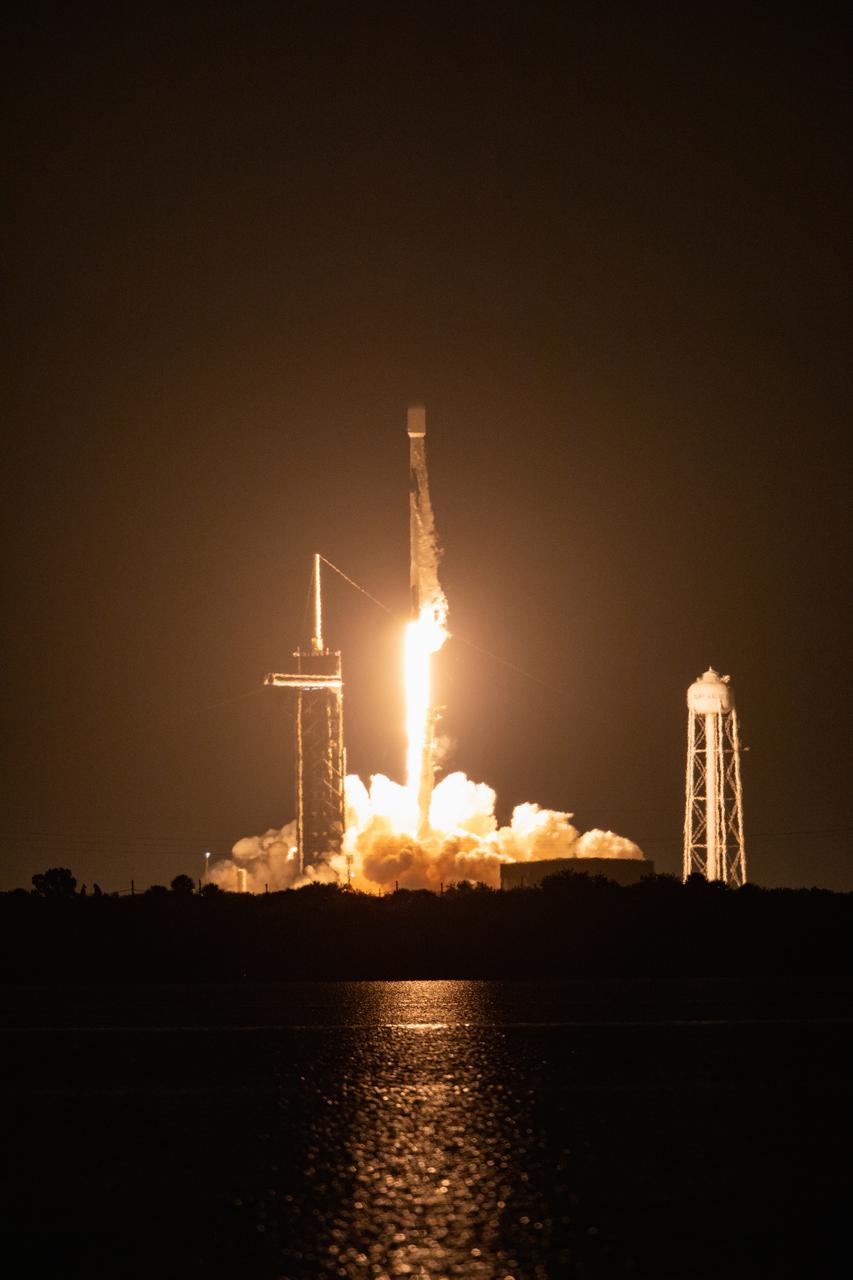

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
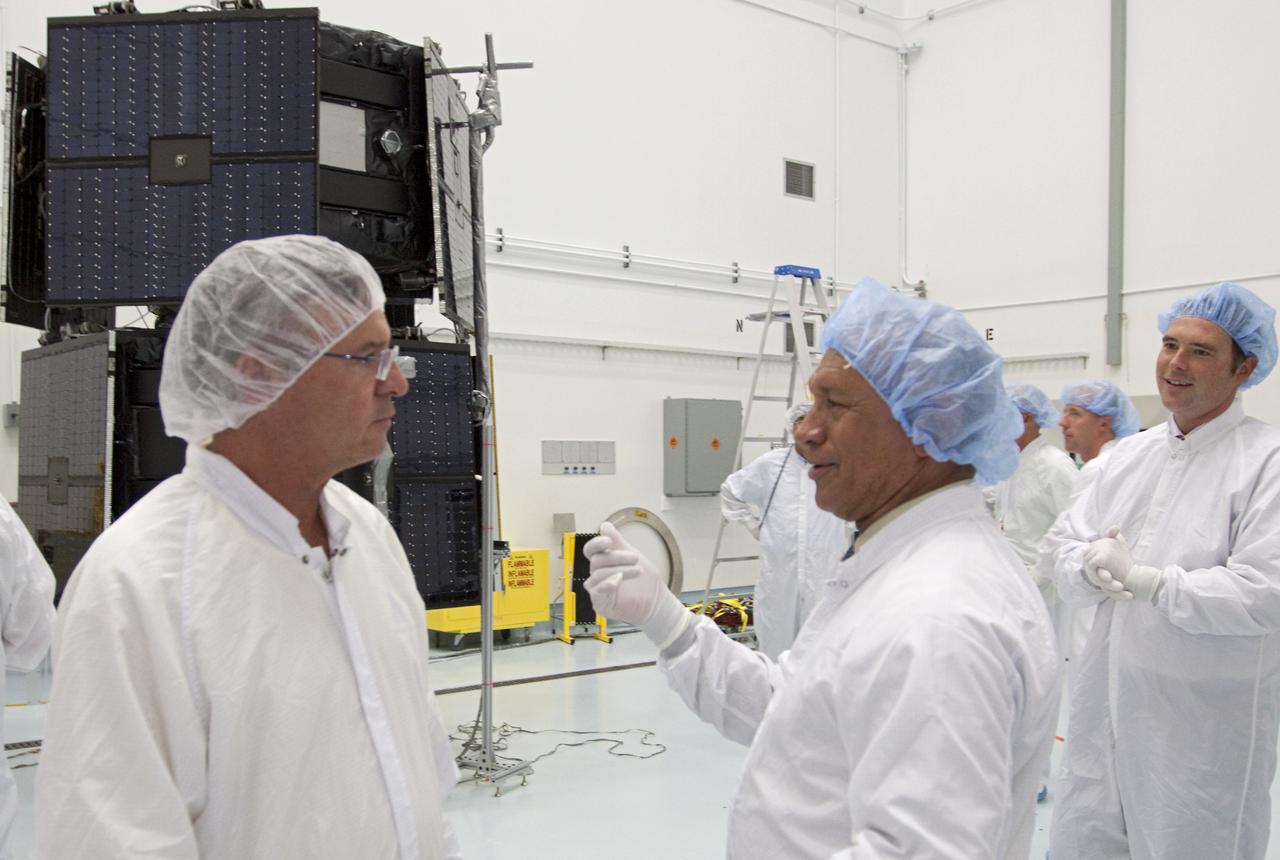

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, center, talks to technicians about the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. As the spacecraft orbits Earth, the four solar panels will continuously face the sun to provide constant power to its instruments. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
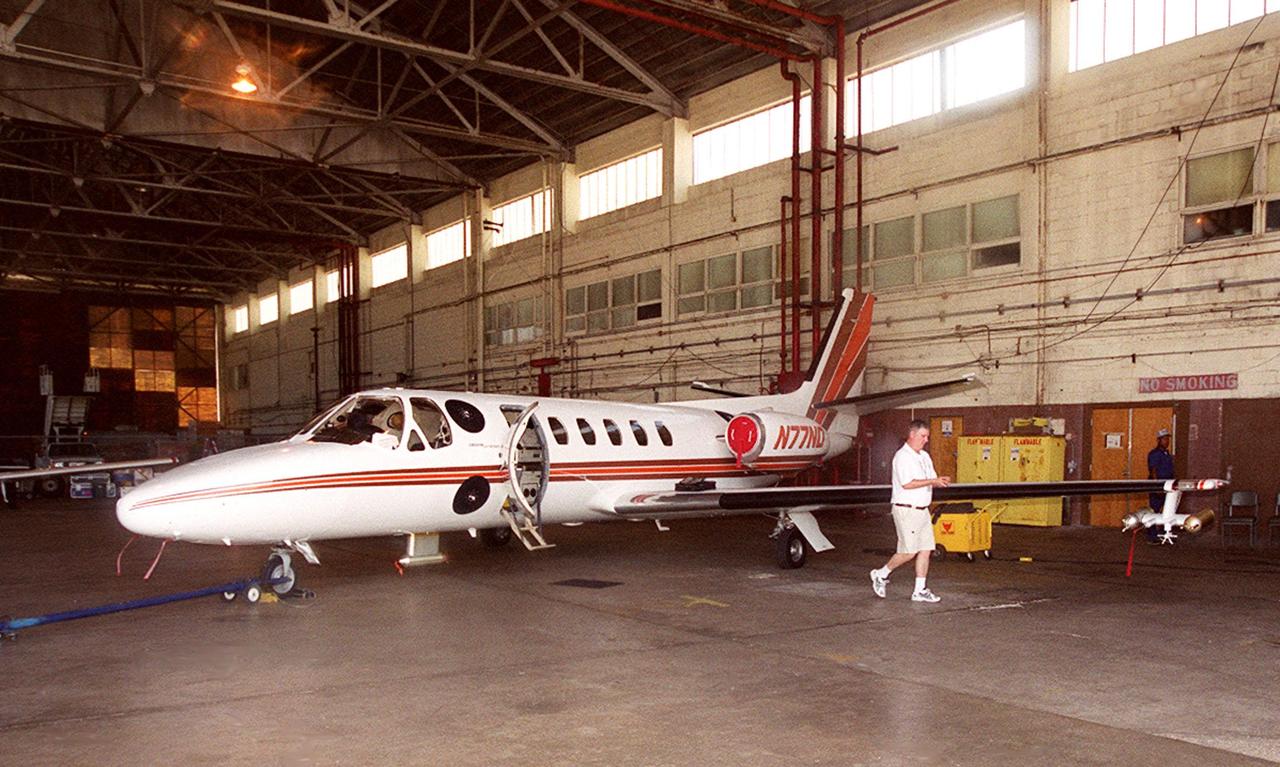

In a hangar at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Cessna Citation aircraft has been fitted on the wings with devices that measure electric fields (black circles shown behind the open door) and with cloud physics probes (under the body and wings) that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
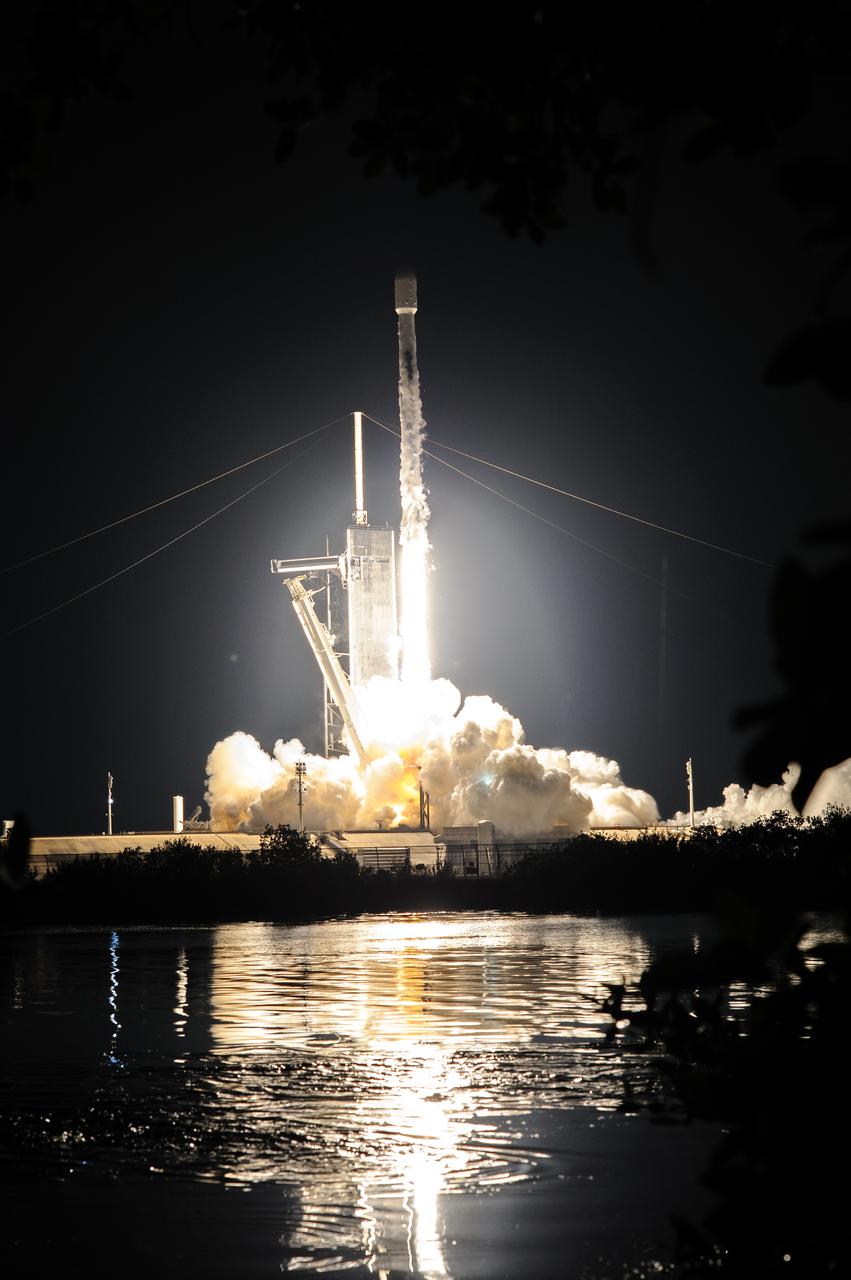

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians work on the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. As the spacecraft orbits Earth, the four solar panels will continuously face the sun to provide constant power to its instruments. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
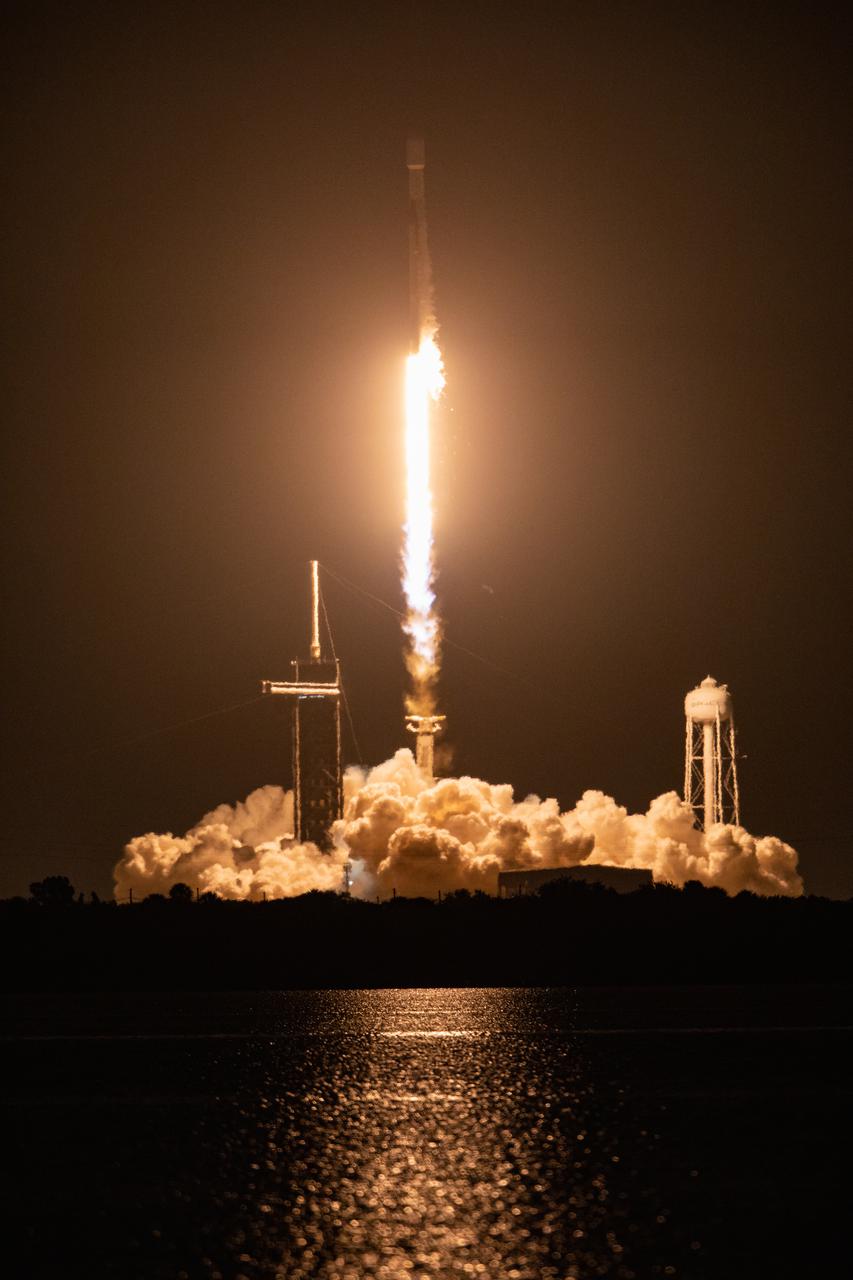

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
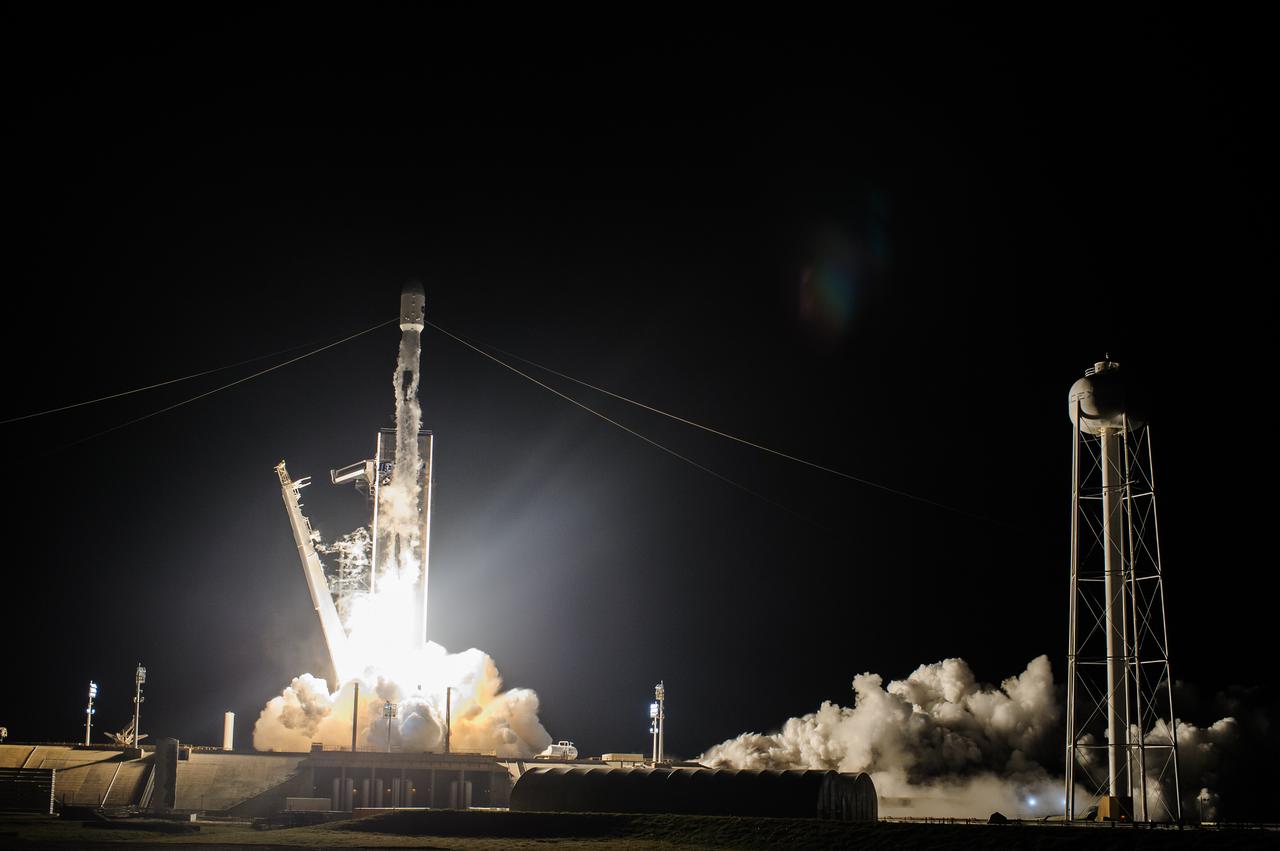

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, at left, talks to technicians about the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. As the spacecraft orbits Earth, the four solar panels will continuously face the sun to provide constant power to its instruments. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
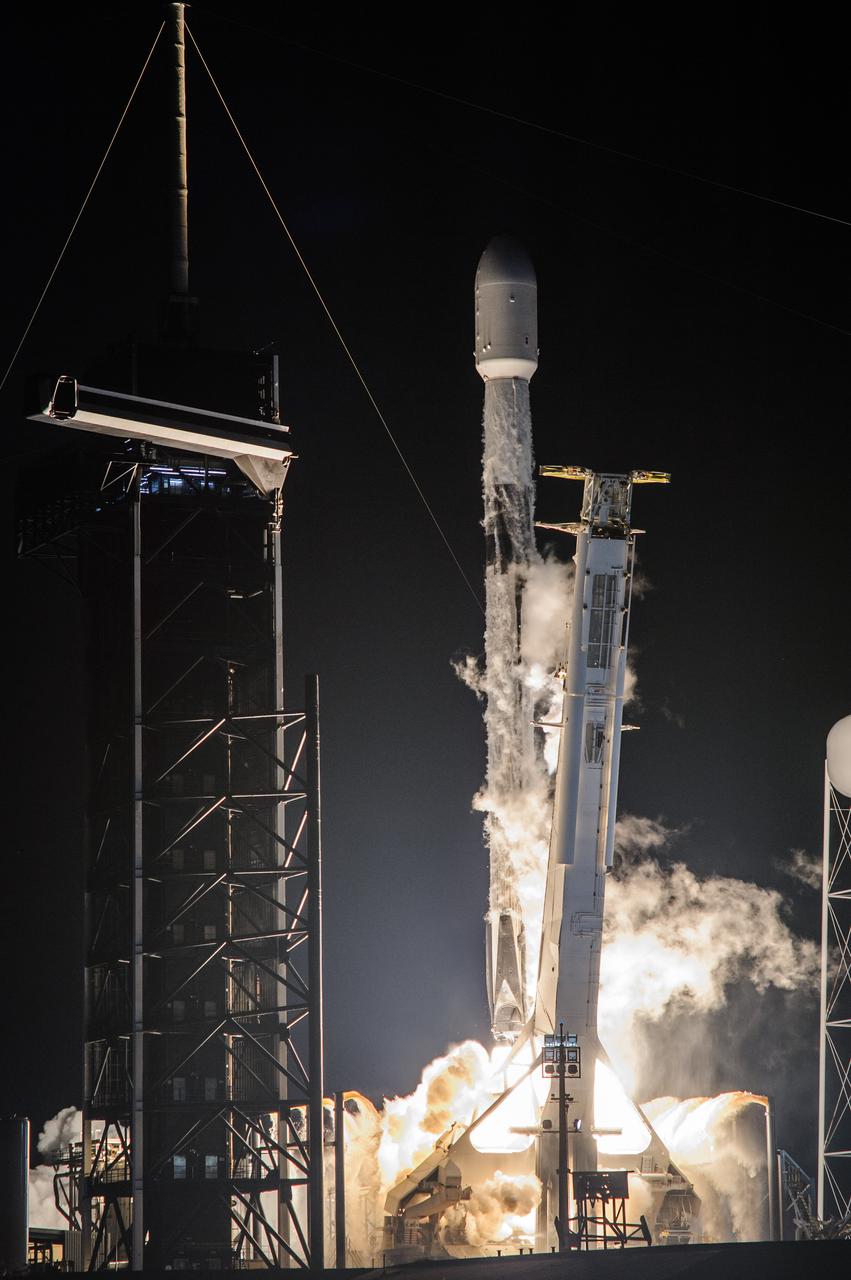

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
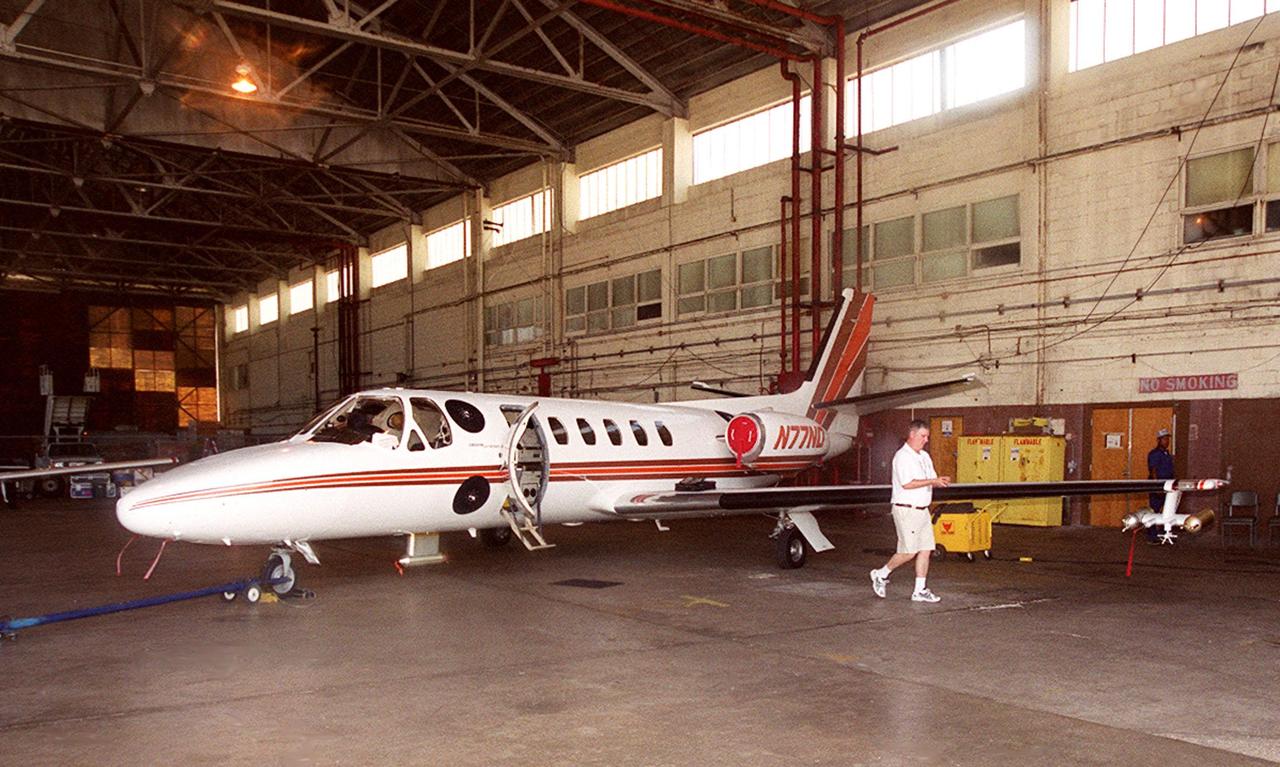

In a hangar at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Cessna Citation aircraft has been fitted on the wings with devices that measure electric fields (black circles shown behind the open door) and with cloud physics probes (under the body and wings) that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
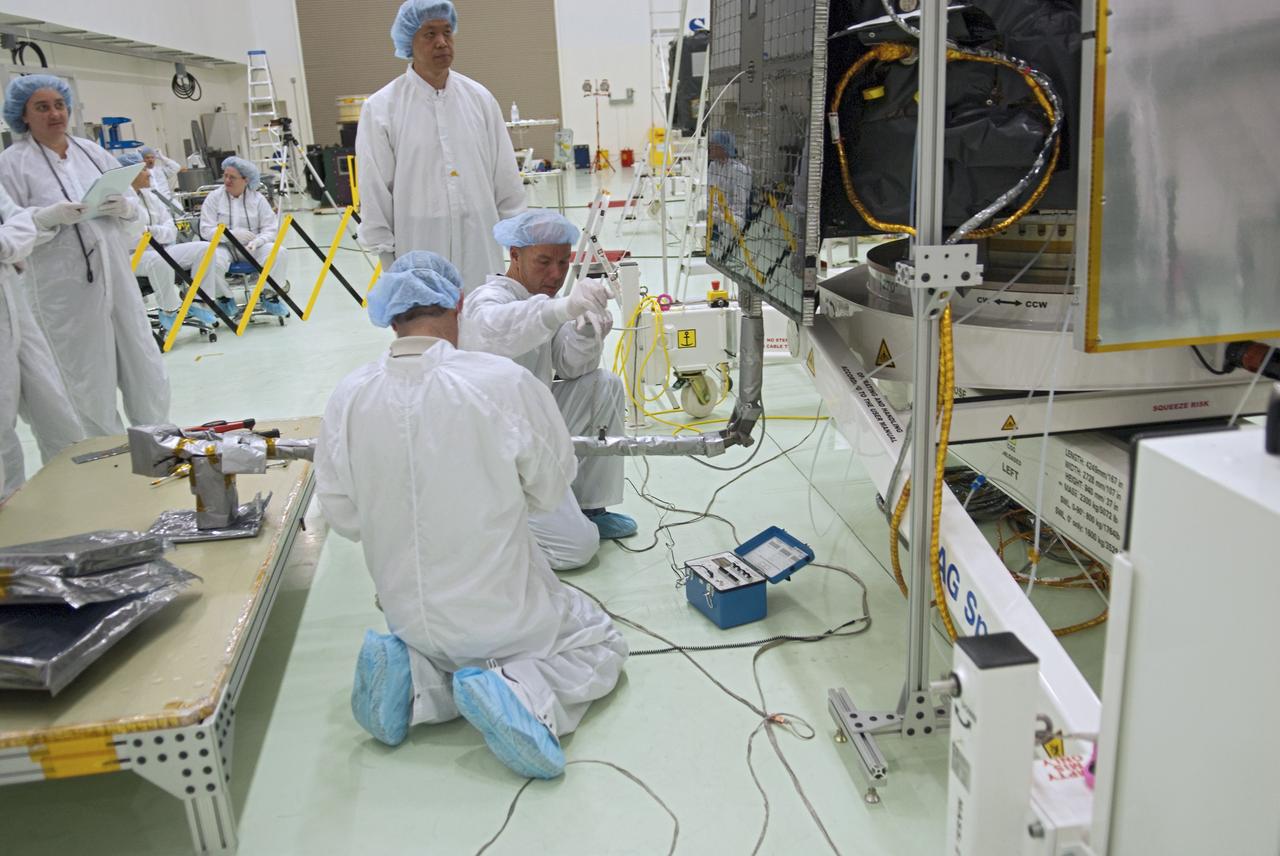

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians deploy the magnetometer boom of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A. Deploying this instrument is standard procedure to ensure it will work properly on Earth before it heads into space. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
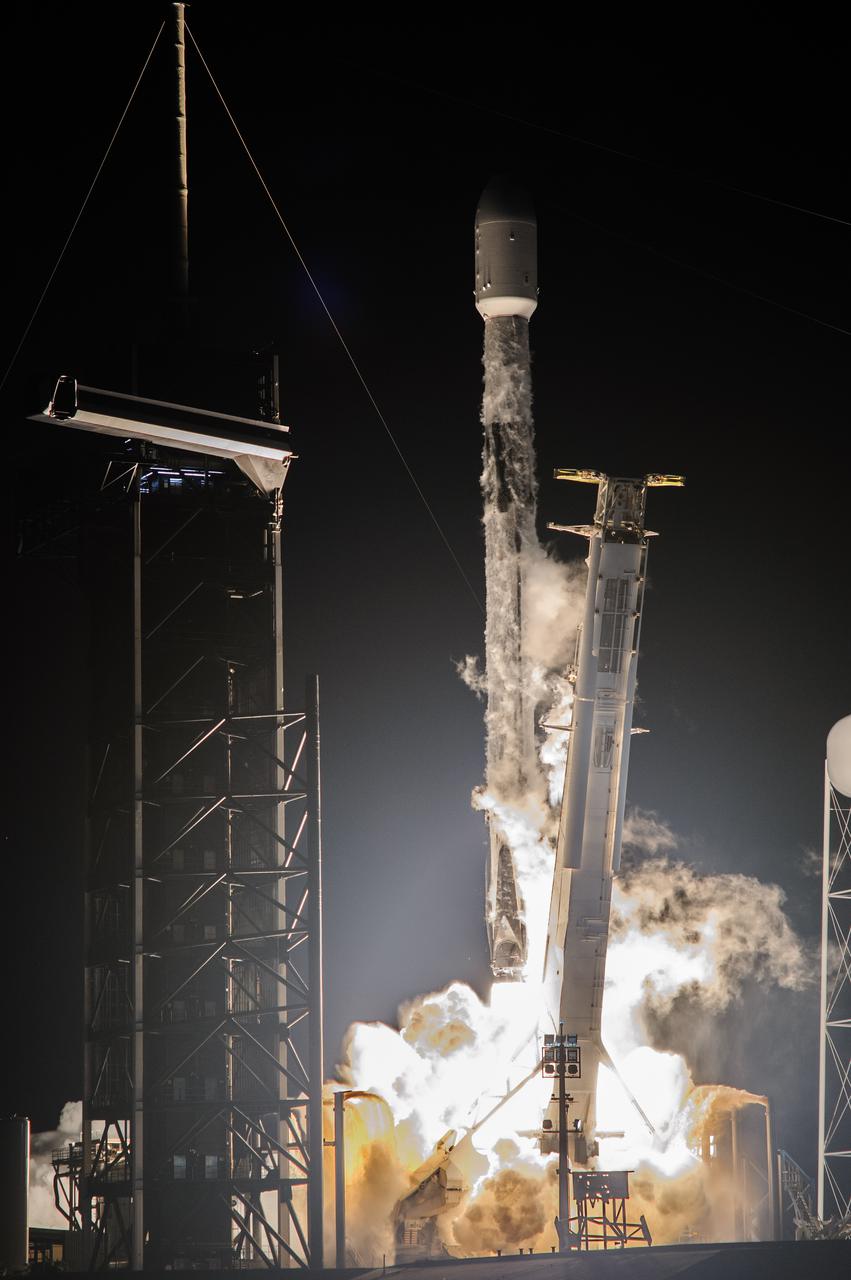

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
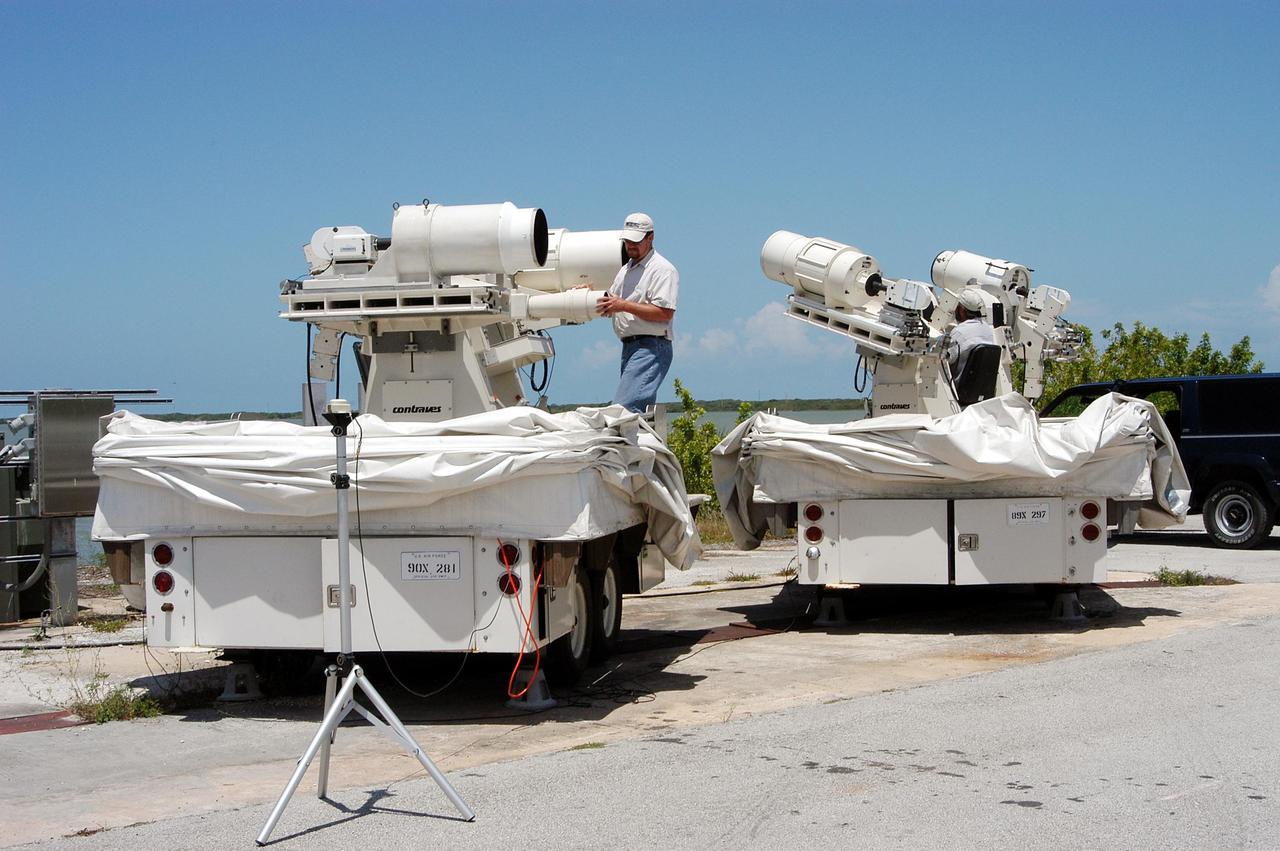

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Johnson Controls operators Rick Worthington (left) and Kenny Allen work on one of the recently acquired Contraves-Goerz Kineto Tracking Mounts (KTM). There are 10 KTMs certified for use on the Eastern Range. The KTM, which is trailer-mounted with a center console/seat and electric drive tracking mount, includes a two-camera, camera control unit that will be used during launches. The KTM is designed for remotely controlled operations and offers a combination of film, shuttered and high-speed digital video, and FLIR cameras configured with 20-inch to 150-inch focal length lenses. The KTMs are generally placed in the field and checked out the day before a launch and manned 3 hours prior to liftoff.
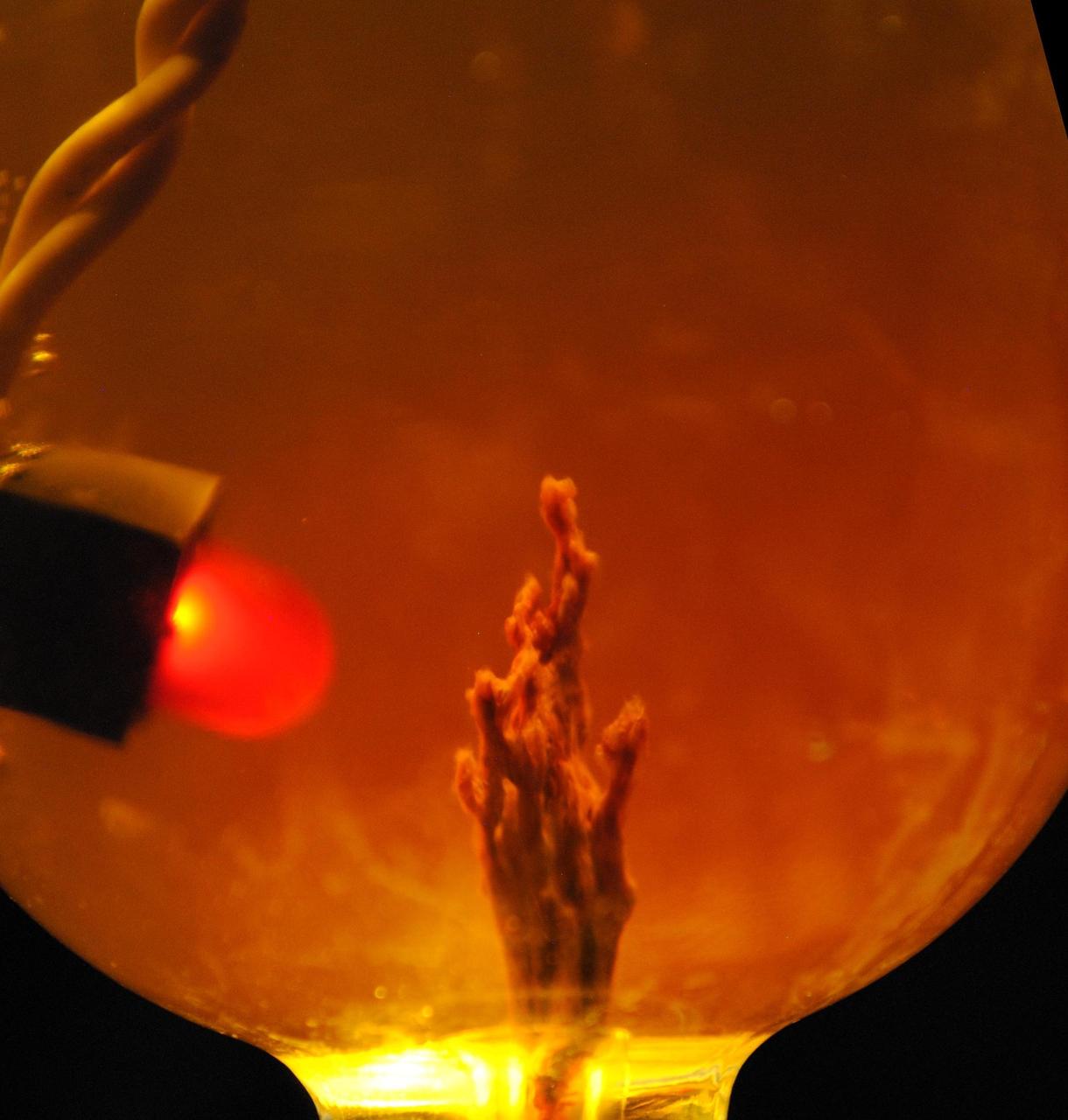

This photo simulation shows a laboratory-created "chemical garden," which is a chimney-like structure found at bubbling vents on the seafloor. Some researchers think life on Earth might have got its start at structures like these billions of years ago, partly due to their ability to transfer electrical currents -- an essential trait of life as we know it. The battery-like property of these chemical gardens was demonstrated by linking several together in series to light an LED (light-emitting diode) bulb. In this photo simulation, the bulb is not really attached to the chimney. The chimney membranes are made of iron sulfides and iron hydroxides, geologic materials that conduct electrons. JPL's research team is part of the Icy Worlds team of the NASA Astrobiology Institute, based at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. JPL is managed by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19834

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket roars off the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1 a.m. EST on Thursday, Dec. 9, 2021, carrying NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft. NASA’s Launch Services Program managed this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The IXPE spacecraft includes three space telescopes with sensitive detectors capable of measuring the polarization of cosmic X-rays, allowing scientists to answer fundamental questions about extremely complex environments in space where gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields are at their limits. The project is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency.
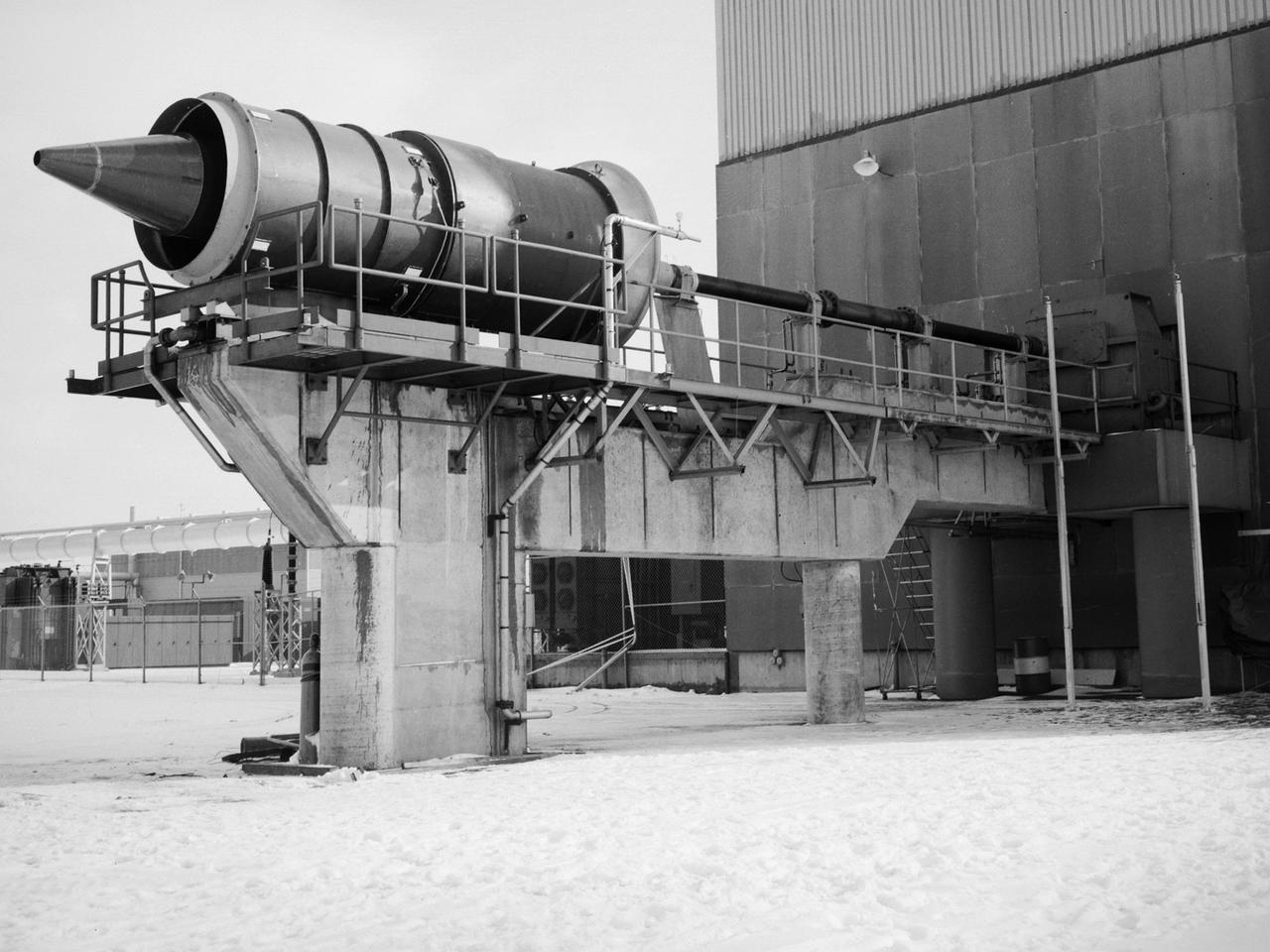

The Fan Noise Test Facility built at the Lewis Research Center to obtain far-field noise data for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and General Electric Quiet Engine Program. The engine incorporated existing noise reduction methods into an engine of similar power to those that propelled the Boeing 707 or McDonnell-Douglas DC-8 airliner. The new the low-bypass ratio turbofan engines of the 1960s were inherently quieter than their turbojet counterparts, researchers had a better grasp of the noise generation problem, and new acoustic technologies had emerged. Lewis contracted General Electric in 1969 to build and aerodynamically test three experimental engines with 72-inch diameter fans. The engines were then brought to Lewis and tested with an acoustically treated nacelle. This Fan Noise Test Facility was built off of the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel’s Main Compressor and Drive Building. Lewis researchers were able to isolate the fan’s noise during these initial tests by removing the core of the engine. The Lewis test rig drove engines to takeoff tip speeds of 1160 feet per second. The facility was later used to test a series of full-scale model fans and fan noise suppressors to be used with the quiet engine. NASA researchers predicted low-speed single-stage fans without inlet guide vanes and with large spacing between rotors and stators would be quieter. General Electric modified a TF39 turbofan engine by removing the the outer protion of the fan and spacing the blade rows of the inner portion. The tests revealed that the untreated version of the engine generated less noise than was anticipated, and the acoustically treated nacelle substantially reduced engine noise.
Data from NASA's Galileo spacecraft were used to produce this false-color composite of Jupiter's northern aurora on the night side of the planet. The height of the aurora, the thickness of the auroral arc, and the small-scale structure are revealed for the first time. Images in Galileo's red, green, and clear filters are displayed in red, green, and blue respectively. The smallest resolved features are tens of kilometers in size, which is a ten-fold improvement over Hubble Space Telescope images and a hundred-fold improvement over ground-based images. The glow is caused by electrically charged particles impinging on the atmosphere from above. The particles travel along Jupiter's magnetic field lines, which are nearly vertical at this latitude. The auroral arc marks the boundary between the "closed" field lines that are attached to the planet at both ends and the "open" field lines that extend out into interplanetary space. At the boundary the particles have been accelerated over the greatest distances, and the glow is especially intense. The latitude-longitude lines refer to altitudes where the pressure is 1 bar. The image shows that the auroral emissions originate about 500 kilometers (about 310 miles) above this surface. The colored background is light scattered from Jupiter's bright crescent, which is out of view to the right. North is at the top. The images are centered at 57 degrees north and 184 degrees west and were taken on April 2, 1997 at a range of 1.7 million kilometers (1.05 million miles) by Galileo's Solid State Imaging (SSI) system. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00603

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS. -- STS-110 INSIGNIA: The STS-110 mission begins the third and final phase of construction for the International Space Station (ISS) by delivering and installing the S0 truss segment that will be carried into orbit in the payload bay of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The Station's robotic arm will remove the S0 segment from the Shuttle's payload bay and place it on top of the United States Laboratory. During several spacewalks, S0 will be mechanically attached to ISS, and then multiple cables will be connected allowing electrical power and communications to flow between S0 and ISS. The STS-110 crew patch is patterned after the cross-section of the S0 truss, and encases the launch of the Shuttle Atlantis and a silhouette of the ISS as it will look following mission completion. The successfully installed S0 segment is highlighted in gold. The S0 truss will serve as the cornerstone for the remaining ISS truss segments, which together will span a distance greater than the length of a football field. This truss holds the Station's massive solar arrays, providing electrical power for the modules of all the International Partners, and enables the ISS to reach its full potential as a world-class research facility. The NASA insignia design for Space Shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved onlly in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced
![This graphic shows a new radiation zone surrounding Jupiter, located just above the atmosphere near the equator, that has been discovered by NASA's Juno mission. The new radiation zone is depicted here as a glowing blue area around the planet's middle. This radiation zone includes energetic hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur ions moving at close to the speed of light (referred to as "relativistic" speeds). It resides inside Jupiter's previously known radiation belts. The zone was identified by the mission's Jupiter Energetic Particle Detector Instrument (JEDI), enabled by Juno's unique close approach to the planet during the spacecraft's science flybys (2,100 miles or 3,400 kilometers from the cloud tops). Juno scientists believe the particles creating this region of intense radiation are derived from energetic neutral atoms -- that is, fast-moving atoms without an electric charge -- coming from the tenuous gas around Jupiter's moons Io and Europa. The neutral atoms then become ions -- atoms with an electric charge -- as their electrons are stripped away by interaction with the planet's upper atmosphere. (This discovery is discussed further in an issue of the journal Geophysical Research Letters [Kollmann et al. (2017), Geophys. Res. Lett., 44, 5259-5268].) Juno also has detected signatures of a population of high-energy, heavy ions in the inner edges of Jupiter's relativistic electron radiation belt. This radiation belt was previously understood to contain mostly electrons moving at near light speed. The signatures of the heavy ions are observed at high latitude locations within the electron belt -- a region not previously explored by spacecraft. The origin and exact species of these heavy ions is not yet understood. Juno's Stellar Reference Unit (SRU-1) star camera detects the signatures of this population as extremely high noise in images collected as part of the mission's radiation monitoring investigation. The locations where the heavy ions were detected are indicated on the graphic by two bright, glowing spots along Juno's flight path past the planet, which is shown as a white line. The invisible lines of Jupiter's magnetic field are also portrayed here for context as faint, bluish lines. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22179](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22179/PIA22179~small.jpg)
This graphic shows a new radiation zone surrounding Jupiter, located just above the atmosphere near the equator, that has been discovered by NASA's Juno mission. The new radiation zone is depicted here as a glowing blue area around the planet's middle. This radiation zone includes energetic hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur ions moving at close to the speed of light (referred to as "relativistic" speeds). It resides inside Jupiter's previously known radiation belts. The zone was identified by the mission's Jupiter Energetic Particle Detector Instrument (JEDI), enabled by Juno's unique close approach to the planet during the spacecraft's science flybys (2,100 miles or 3,400 kilometers from the cloud tops). Juno scientists believe the particles creating this region of intense radiation are derived from energetic neutral atoms -- that is, fast-moving atoms without an electric charge -- coming from the tenuous gas around Jupiter's moons Io and Europa. The neutral atoms then become ions -- atoms with an electric charge -- as their electrons are stripped away by interaction with the planet's upper atmosphere. (This discovery is discussed further in an issue of the journal Geophysical Research Letters [Kollmann et al. (2017), Geophys. Res. Lett., 44, 5259-5268].) Juno also has detected signatures of a population of high-energy, heavy ions in the inner edges of Jupiter's relativistic electron radiation belt. This radiation belt was previously understood to contain mostly electrons moving at near light speed. The signatures of the heavy ions are observed at high latitude locations within the electron belt -- a region not previously explored by spacecraft. The origin and exact species of these heavy ions is not yet understood. Juno's Stellar Reference Unit (SRU-1) star camera detects the signatures of this population as extremely high noise in images collected as part of the mission's radiation monitoring investigation. The locations where the heavy ions were detected are indicated on the graphic by two bright, glowing spots along Juno's flight path past the planet, which is shown as a white line. The invisible lines of Jupiter's magnetic field are also portrayed here for context as faint, bluish lines. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22179
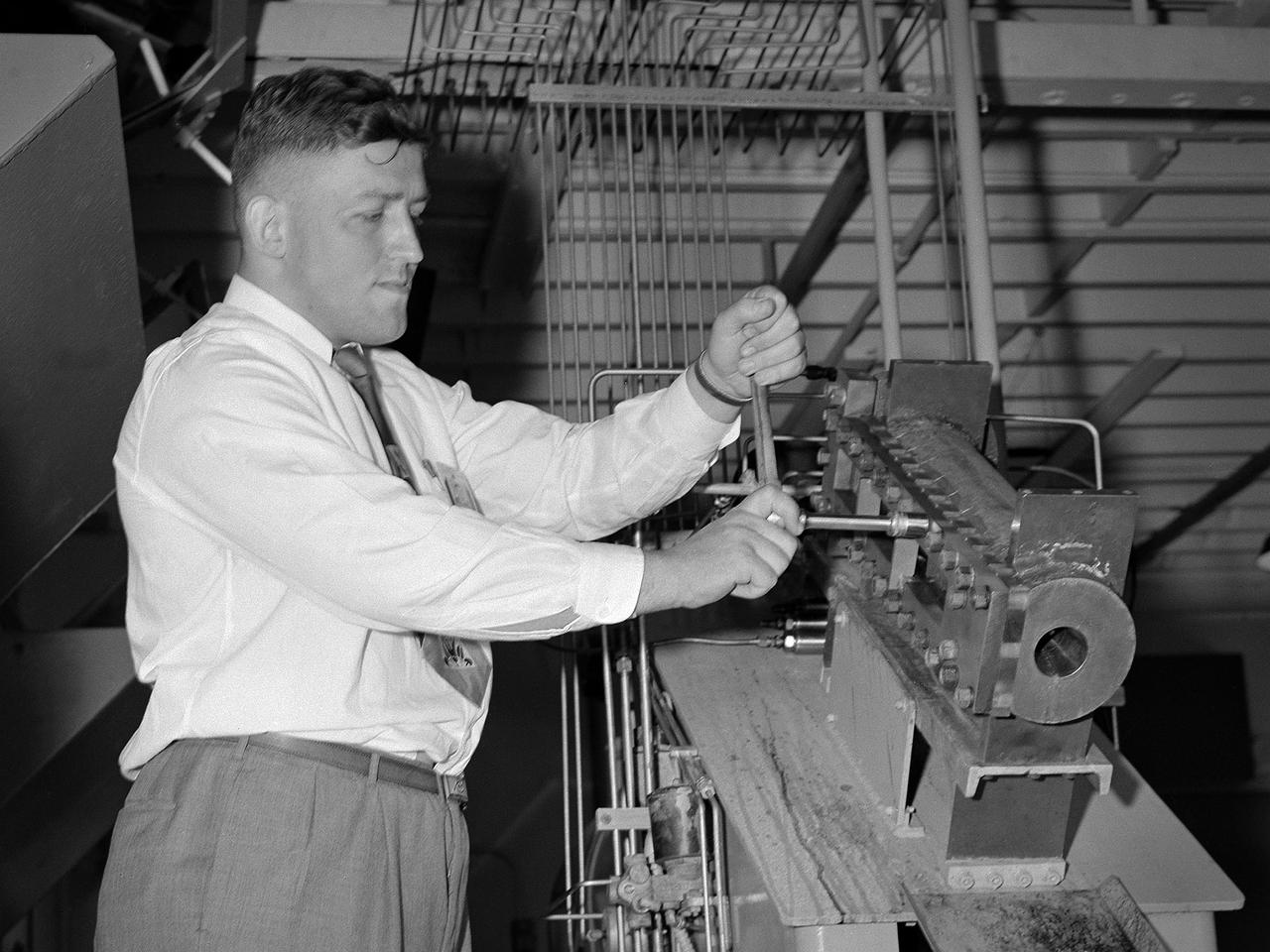

William Kerslake, a combustion researcher at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory, examines the setup of a transparent rocket in a Rocket Laboratory test cell. Kerslake joined NACA Lewis the previous summer after graduating from the Case Institute of Technology with a chemistry degree. His earliest professional research concentrated on combustion instability in small rocket engines. While at Case the quiet, 250-pound Kerslake also demonstrated his athletic prowess on the wrestling team. He continued wrestling for roughly a decade afterwards while conducting his research with the NACA. Kerslake participated in Olympic competitions in Helsinki (1952), Melbourne (1956), and Rome (1960). He won 30 national championships in three different weight classes and captured the gold at the 1955 Pan American Games in Mexico City. Kerslake accomplished all this while maintaining his research career, raising a family, and paying his own expenses. As his wrestling career was winding down in the early 1960s, Kerslake’s professional career changed, as well. He was transferred to Harold Kaufman’s Electrostatic Propulsion Systems Section in the new Electromagnetic Propulsion Division. Kaufman was developing the first successful ion engine at the time, and Kerslake spent the remainder of his career working in the electric propulsion field. He was heavily involved in the two Space Electric Rocket Test (SERT) missions which demonstrated that the ion thrusters could successfully operate in space. Kerslake retired in 1985 with over 30 years of service.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to deploy the solar arrays and magnetometer boom of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A. Deploying these components are standard procedure to ensure they work properly on Earth before they head into space. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. As the spacecraft orbits Earth, the four solar panels will continuously face the sun to provide constant power to its instruments. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
This illustration is an artist’s concept of a Magnetic Launch Assist System, formerly referred as the Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) system, for space launch. Overcoming the grip of Earth’s gravity is a supreme challenge for engineers who design rockets that leave the planet. Engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center have developed and tested Magnetic Launch Assist System technologies that could levitate and accelerate a launch vehicle along a track at high speeds before it leaves the ground. Using electricity and magnetic fields, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would drive a spacecraft along a horizontal track until it reaches desired speeds. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long and capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, landing gear and the wing size, as well as the elimination of propellant weight resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to deploy the solar arrays and magnetometer boom of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A. Deploying these components are standard procedure to ensure they work properly on Earth before they head into space. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. As the spacecraft orbits Earth, the four solar panels will continuously face the sun to provide constant power to its instruments. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to deploy the solar arrays and magnetometer boom of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A. Deploying these components are standard procedure to ensure they work properly on Earth before they head into space. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. As the spacecraft orbits Earth, the four solar panels will continuously face the sun to provide constant power to its instruments. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin technicians in Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare to test the solar arrays on NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A, or GRAIL-A, spacecraft to ensure that they will function as planned during the mission. The electrical power subsystem on each of GRAIL's twin spacecraft includes two solar arrays and a lithium ion battery. Each solar array is capable of producing no less than 700 watts. They will be deployed shortly after separation from the launch vehicle and remain fixed throughout the mission. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
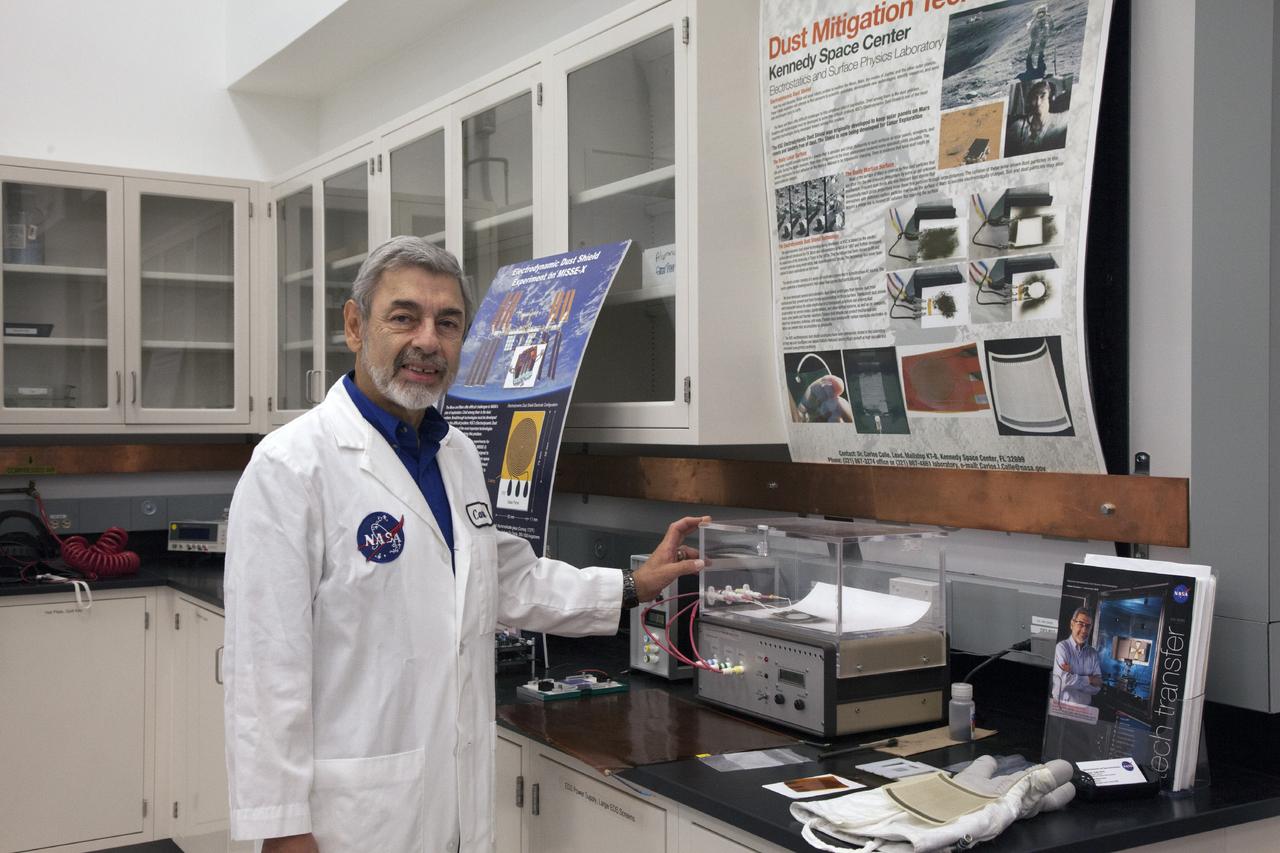

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Dr. Carlos Calle, senior research scientist on the Electrodynamic Dust Shield for Dust Mitigation project, demonstrates a dust particle experiment in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory in the SwampWorks at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The technology works by creating an electric field that propagates out like the ripples on a pond. This could prevent dust accumulation on spacesuits, thermal radiators, solar panels, optical instruments and view ports for future lunar and Mars exploration activities. Electrodynamic dust shield, or EDS, technology is based on concepts originally developed by NASA as early as 1967 and later by the University of Tokyo. In 2003, NASA, in collaboration with the University of Arkansas at Little Rock, started development of the EDS for dust particle removal from solar panels to be used on future missions to the moon, an asteroid or Mars. A flight experiment to expose the dust shields to the space environment currently is under development. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/scientists-developing-ways-to-mitigate-dust-problem-for-explorers/ Photo credit: NASA/Dan Casper