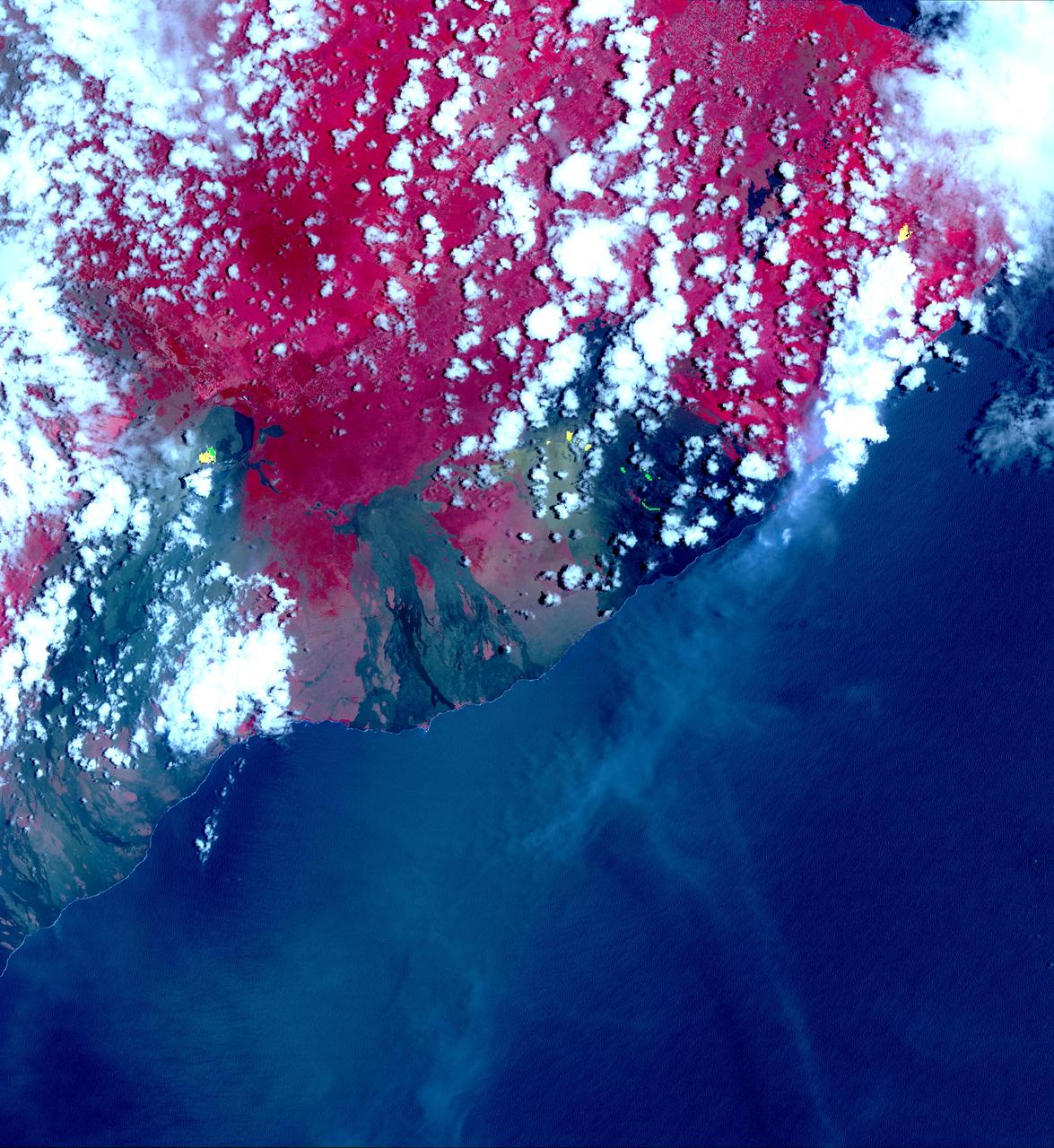

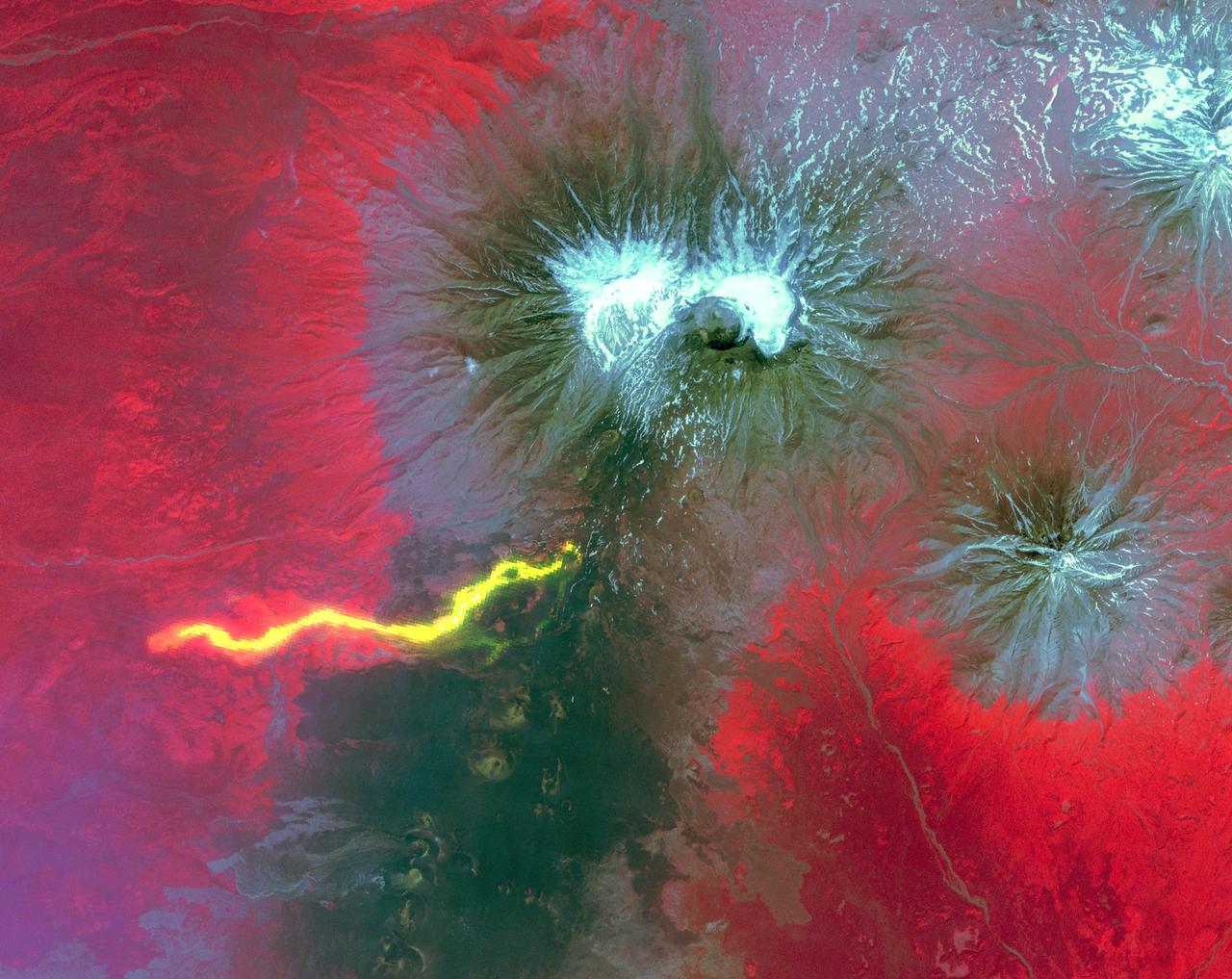
This image from NASA's Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft show recent eruptions of Kilauea volcano on the island of Hawaii (the Big Island). Following days of increased seismic activity, Kilauea erupted May 3, 2018, and triggered a number of additional fissure eruptions along the East Rift Zone. The eruptions and high level of sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) prompted evacuations in the area, including the Leilani Estates subdivision near the town of Pahoa. The ASTER images, acquired on May 6, 2018, show different aspects of the eruption. A color composite depicts vegetation in red, and old lava flows in black and gray. Superimposed on the image in yellow are hotspots detected on the thermal infrared bands. The easternmost hot spots show the newly formed fissures and the lava flow spilling to the northwest. The middle spots are Pu'u O'o crater, and lava flows descending the slopes to the southeast. The westernmost area is the crater and lava lake on Kilauea's summit. The greenish area southwest of Pu'u O'o is ash deposits from its short eruption on Friday. The inset shows the massive sulfur dioxide plume is shown in yellow and yellow-green, extracted from ASTER's multiple thermal bands. A smaller, but thicker, sulfur dioxide gas plume can be seen coming from Kilauea. The prevailing trade winds blow the plumes to the southwest, out over the ocean. The images cover an area of 57.8 by 63 kilometers, and are located at 19.3 degrees North, 155.1 degrees West. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22450
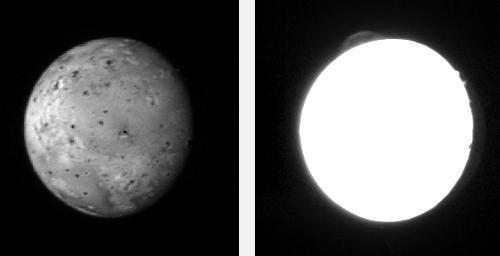
An Eruption on Io
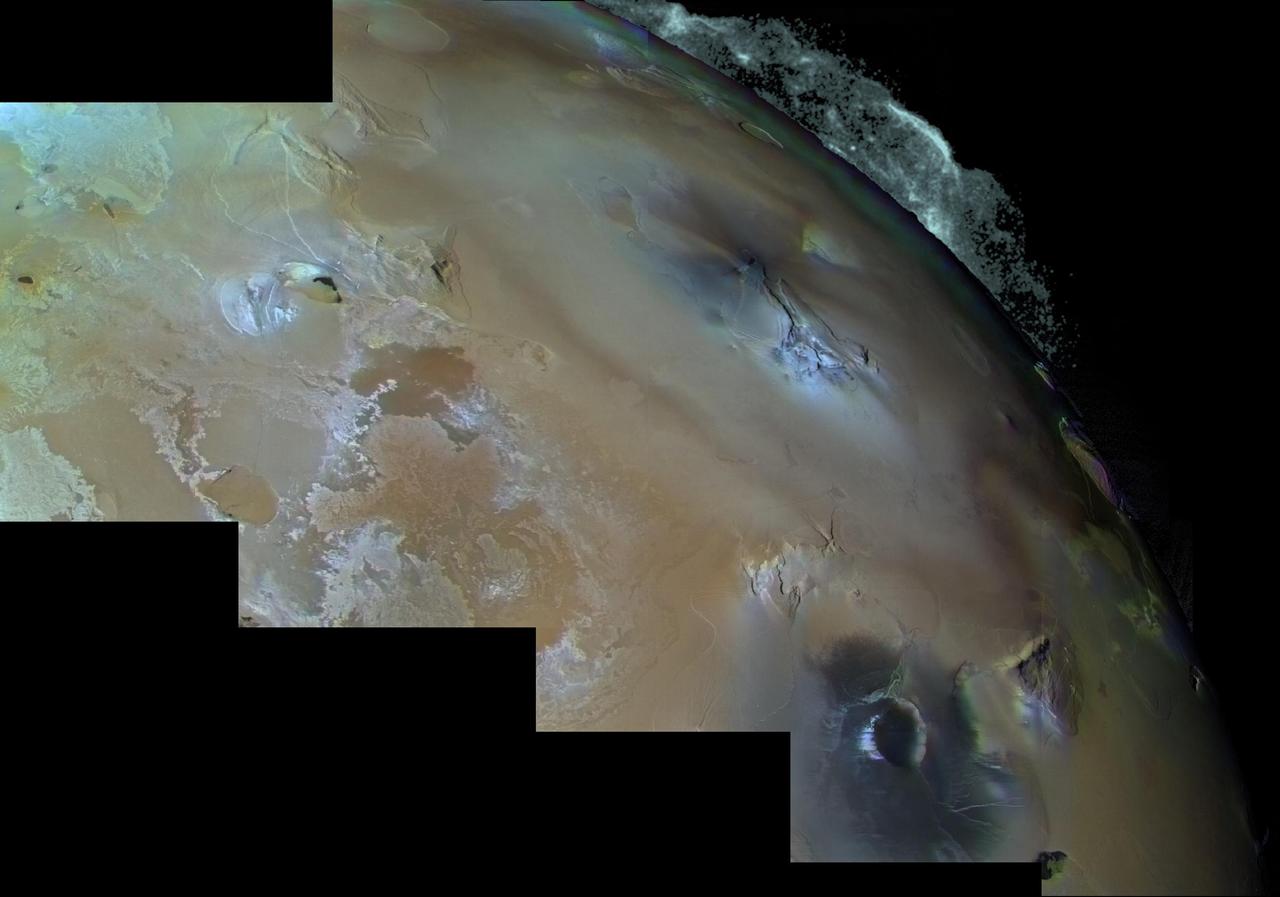

Eruption of Pele http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00323

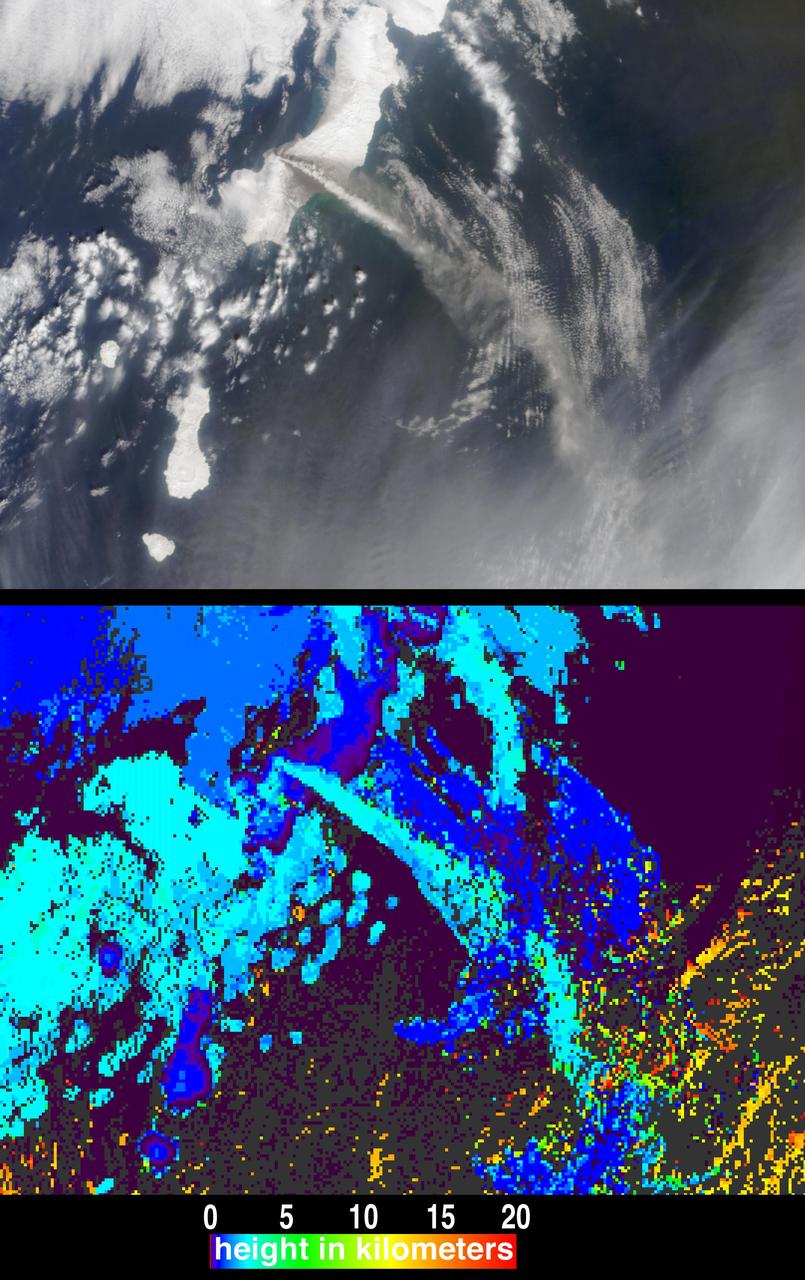
On May 3, 2018, a new eruption began at a fissure of the Kilauea volcano on the Island of Hawaii. Kilauea is the most active volcano in the world, having erupted almost continuously since 1983. Advancing lava and dangerous sulfur dioxide gas have forced thousands of residents in the neighborhood of Leilani Estates to evacuate. A number of homes have been destroyed, and no one can say how soon the eruption will abate and evacuees can return home. On May 6, 2018, at approximately 11 a.m. local time, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured this view of the island as it passed overhead. Much of the island was shrouded by clouds, including the fissure on its eastern point. However, an eruption plume is visible streaming southwest over the ocean. The MISR instrument is unique in that it has nine cameras that view Earth at different angles: one pointing downward, four at various angles in the forward direction, and four in the backward direction. This image shows the view from one of MISR's forward-pointing cameras (60 degrees), which shows the plume more distinctly than the near-vertical views. The information from the images acquired at different view angles is used to calculate the height of the plume, results of which are superimposed on the right-hand image. The top of the plume near the fissure is at approximately 6,500 feet (2,000 meters) altitude, and the height of the plume decreases as it travels south and west. These relatively low altitudes mean that the ash and sulfur dioxide remained near the ground, which can cause health issues for people on the island downwind of the eruption. The "Ocean View" air quality monitor operated by the Clean Air Branch of the State of Hawaii Department of Health recorded a concentration of 18 μg/m3 of airborne particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter at 11 a.m. local time. This amount corresponds to an air quality rating of "moderate" and supports the MISR results indicating that ash was most likely present at ground level on this side of the island. These data were acquired during Terra orbit 97780. An annotated version is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22451
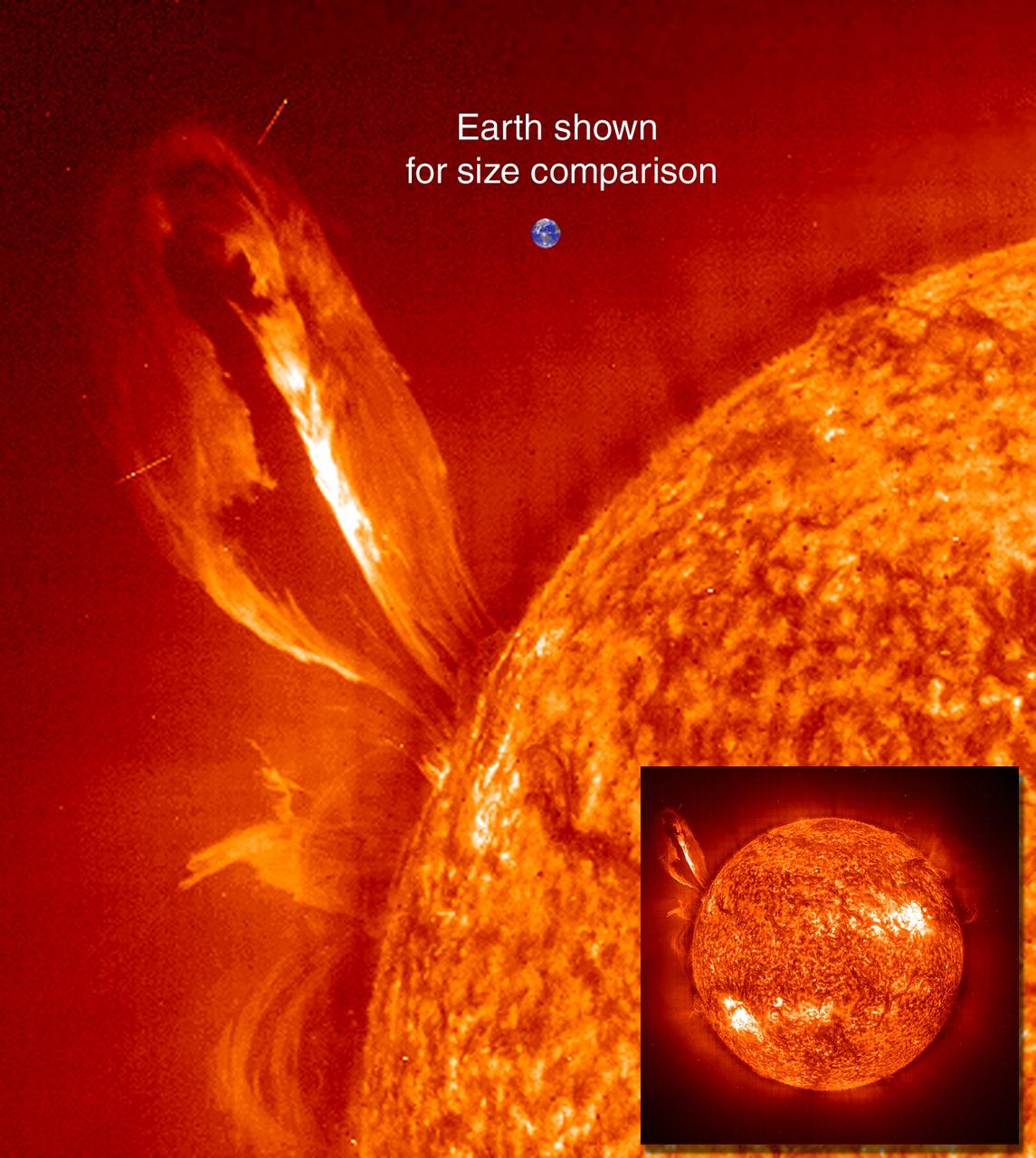

Large, eruptive prominence in He II at 304Å, with an image of the Earth added for size comparison. This prominence from 24 July 1999 is particularly large and looping, extending over 35 Earths out from the Sun. Erupting prominences (when Earthward directed) can affect communications, navigation systems, even power grids, while also producing auroras visible in the night skies. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
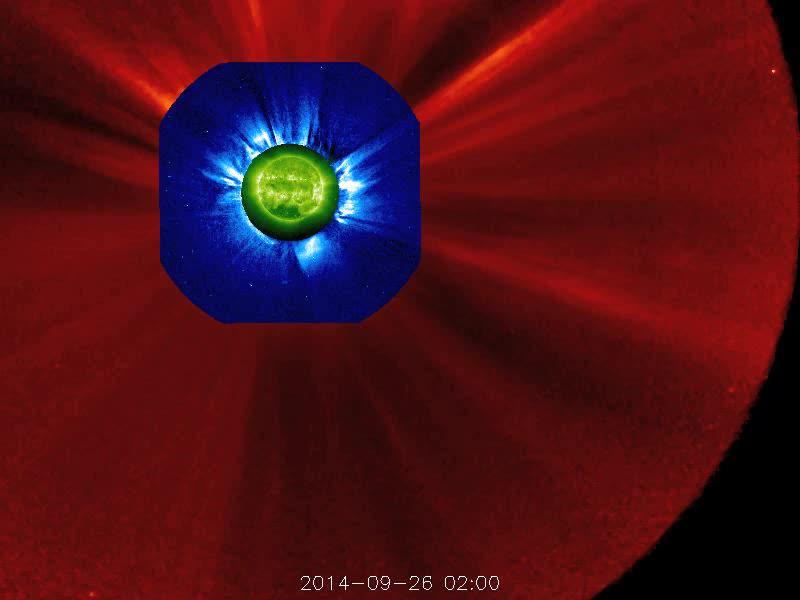
The STEREO (Behind) spacecraft captured this large prominence and corona mass ejection as they erupted into space (Sept. 26, 2014). By combining images from three instruments, scientists can see the eruption itself (in extreme UV light) as well as follow its progression over the period of about 13 hours with its two coronagraphs. Credit: NASA/Goddard/STEREO The STEREO (Behind) spacecraft captured this large prominence and corona mass ejection as they erupted into space (Sept. 26, 2014). By combining images from three instruments, scientists can see the eruption itself (in extreme UV light) as well as follow its progression over the period of about 13 hours with its two coronagraphs.

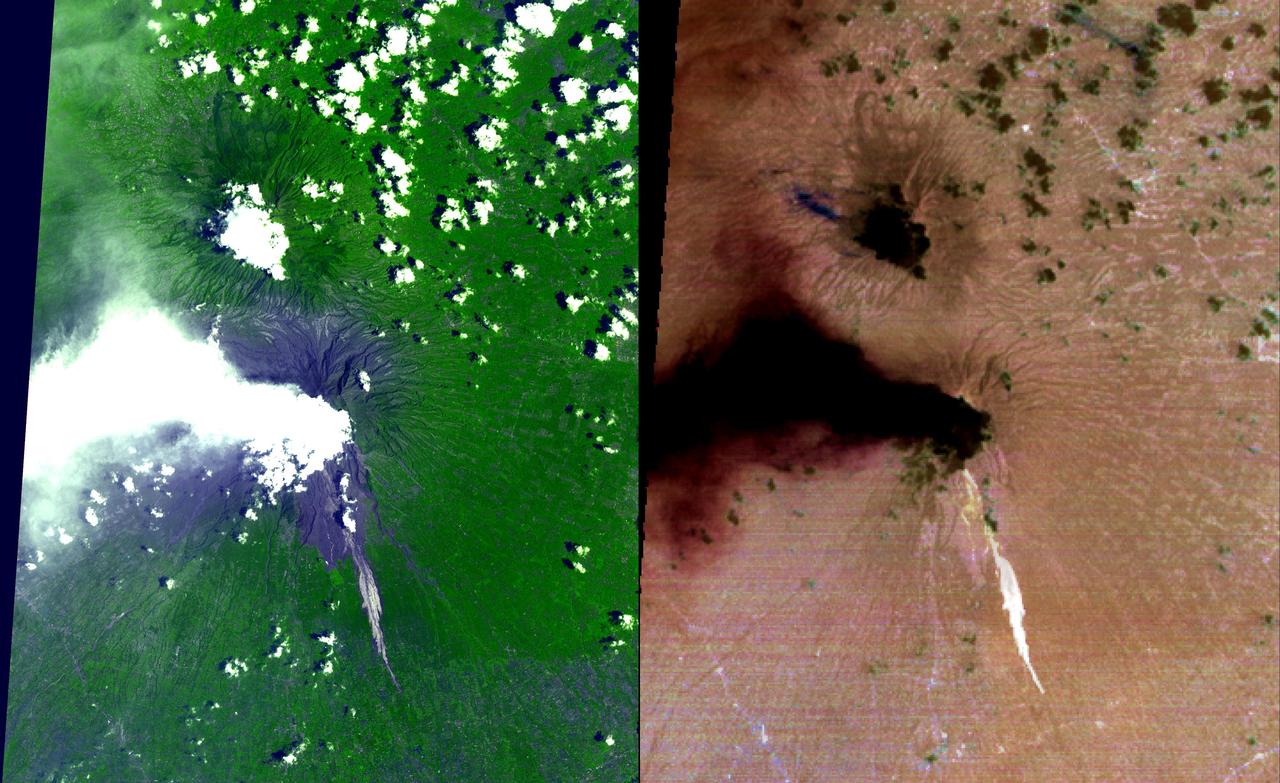
NASA Image acquired March 24, 2010 To learn more and to download a high res version of this image go here: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=43252" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=43252</a> Iceland’s Eyjafjallajökull Volcano burst into life for the first time in 190 years on March 20, 2010. A 500-meter- (2,000-foot) long fissure opened in the Fimmvörduháls pass to the west of the ice-covered summit of Eyjafjallajökull. Lava fountains erupted fluid magma, which quickly built several hills of bubble-filled lava rocks (scoria) along the vent. A lava flow spread northeast, spilling into Hrunagil Gully. This natural-color satellite image shows lava fountains, lava flows, a volcanic plume, and steam from vaporized snow. The image was acquired on March 24, 2010, by the Advanced Land Imager (ALI) aboard NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite. The lava fountains are orange-red, barely visible at the 10-meter (33-foot) resolution of the satellite. The scoria cones surrounding the fissure are black, as is the lava flow extending to the northeast. White volcanic gases escape from the vent and erupting lava, while a steam plume rises where the hot lava meets snow. (The bright green color along the edge of the lava flow is an artifact of the sensor.) The eruption of Eyjafjallajökull was presaged by a series of earthquakes starting in early March. Over time, the earthquakes rose towards the surface, and land near the volcano rose at least 40 millimeters (2 inches)—both indications that magma was moving underneath the volcano. The eruption continued through at least March 26th, and may continue for several more months. Previous eruptions in the area have caused flooding due to the melting of glacial ice (a Jökulhlaup), but the current eruption is in an area covered by winter snow, not permanent ice. Although some past eruptions of Eyjafjallajökull were followed by larger, explosive eruptions at nearby Katla Volcano, there is currently no sign of activity at Katla. NASA image by Robert Simmon, using ALI data from the EO-1 team. Caption by Robert Simmon. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

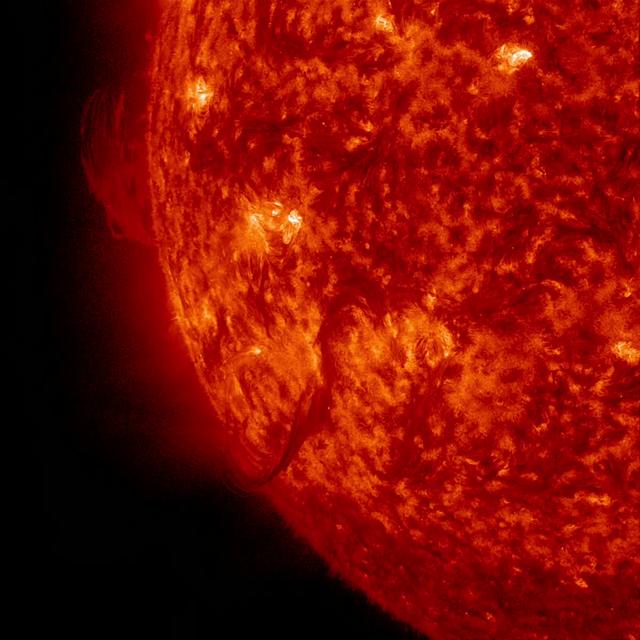
The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 5:40 p.m. EDT on Oct. 24, 2014. The flare erupted from a particularly large active region -- labeled AR 12192 -- on the sun that is the largest in 24 years. This is the fourth substantial flare from this active region since Oct. 19. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/giant-sunspot-erupts-with-4th-substantial-flare" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/giant-sunspot-erupts-with-4t...</a>

Io - One of at Least Four Simultaneous Erupting Volcanic Eruptions http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00374
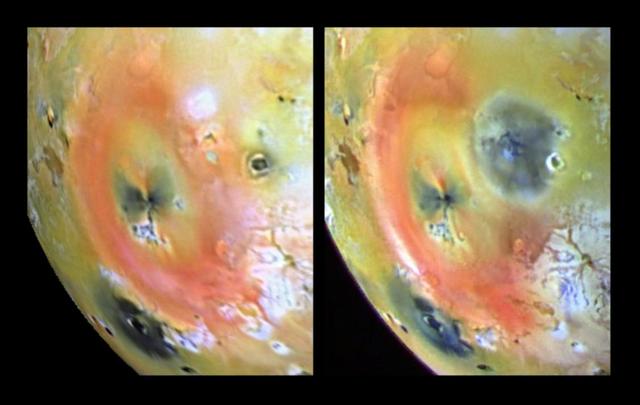
Arizona-sized Io Eruption
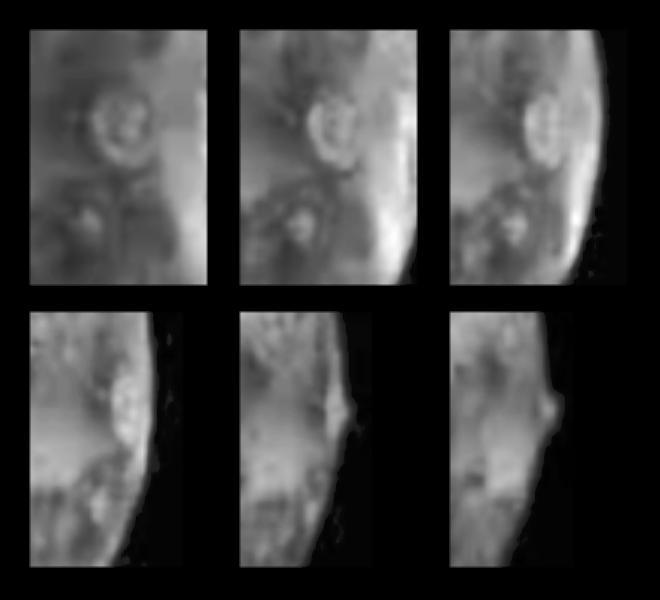
Active Volcanic Eruptions on Io
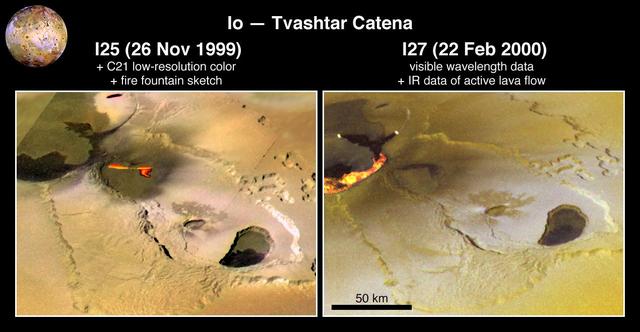
Eruption at Tvashtar Catena on Io

Io - Volcanic Eruption http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00373

Volcanic Eruptions on Io http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00379
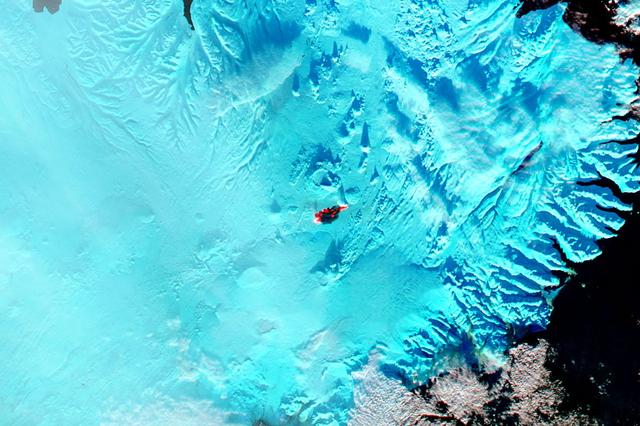
The main caldera of Bardarbunga volcano is tucked beneath Iceland’s largest glacier, Vatnajökull. Beginning in August, 2014, red-hot basaltic lava originating from Bardarbunga has been pouring from fissures just north of Vatnajökull, creating the massive Holuhraun lava field. As of January 6, 2015, the Holuhraun lava field had spread across more than 84 square kilometers (32 square miles), making it larger than the island of Manhattan. Holuhraun is Iceland’s largest basaltic lava flow since the Laki eruption in 1783–84, an event that killed 20 percent of the island’s population. Scientists from the University of Iceland’s Institute of Earth Sciences have estimated the thickness of the lava field based on data from surveillance flights. On average, the eastern part was about 10 meters (33 feet) thick, the center was 12 meters, and the western part was 14 meters. Their preliminary analysis put the volume of lava at 1.1 cubic kilometers, enough for the eruption to be considered a flood basalt. While Holuhraun continues to spew copious amounts of lava and sulfur dioxide, some observations suggest the eruption may be slowing down. As Edinburgh University volcanologist John Stevenson noted on his blog, Icelandic scientists have shown that the sinking (subsidence) of the caldera has declined from 80 centimeters (31 inches) to 25 centimeters per day—a sign that less magma is moving toward the surface. In addition, magnitude 5 or higher earthquakes that used to occur daily are now happening about once a week. Meanwhile, satellite observations of heat flux show a decline from more than 20 gigawatts in early September to fewer than 5 gigawatts by the end of November. As reported by Volcano Discovery, one bold scientist has even suggested that it is reasonable to forecast that the eruption may be over by March, 2015. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite flew over Iceland on January 18, 2015 and captured a false-color image of the lava field. In this image, clouds are bright white, cold snow is electric blue, and the North Atlantic Ocean is inky blue-black. Fresh lava appears bright red, while newly formed basaltic rock in the lava field, cooler than the fresh lava, appears black. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A filament (which at one point had an eerie similarity to a snake) broke away from the sun and out into space (Nov. 1, 2014). The video covers just over three hours of activity. This kind of eruptive event is called a Hyder flare. These are filaments (elongated clouds of gases above the sun's surface) that erupt and cause a brightening at the sun's surface, although no active regions are in that area. It did thrust out a cloud of particles but not towards Earth. The images were taken in the 304 Angstrom wavelength of extreme UV light. Credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A filament (which at one point had an eerie similarity to a snake) broke away from the sun and out into space (Nov. 1, 2014). The video covers just over three hours of activity. This kind of eruptive event is called a Hyder flare. These are filaments (elongated clouds of gases above the sun's surface) that erupt and cause a brightening at the sun's surface, although no active regions are in that area. It did thrust out a cloud of particles but not towards Earth. The images were taken in the 304 Angstrom wavelength of extreme UV light. Credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
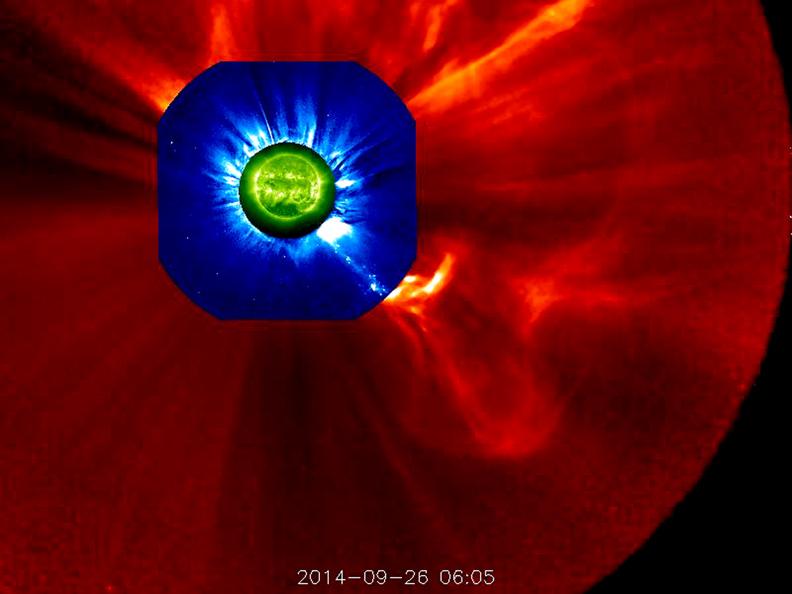
The STEREO (Behind) spacecraft captured this large prominence and corona mass ejection as they erupted into space (Sept. 26, 2014). By combining images from three instruments, scientists can see the eruption itself (in extreme UV light) as well as follow its progression over the period of about 13 hours with its two coronagraphs. Credit: NASA/Goddard/STEREO The STEREO (Behind) spacecraft captured this large prominence and corona mass ejection as they erupted into space (Sept. 26, 2014). By combining images from three instruments, scientists can see the eruption itself (in extreme UV light) as well as follow its progression over the period of about 13 hours with its two coronagraphs.
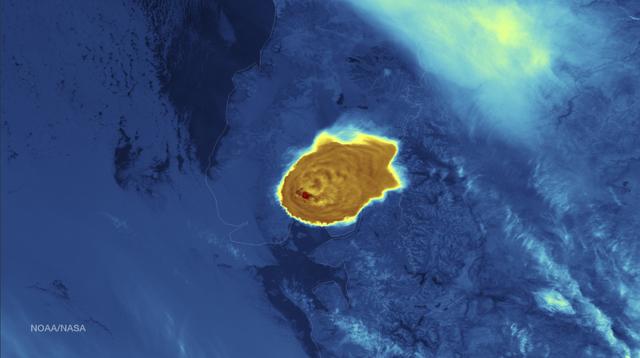
Calbuco Volcano in southern Chile has erupted for the first time since 1972, with the last major eruption occurring in 1961 that sent ash columns 12-15 kilometers high. This image was taken by the Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument in a high resolution infrared channel around 0515Z on April 23, 2015. Credit: NOAA/NASA/NPP/VIIRS

NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory caught this image of an eruption on the side of the sun on June 18, 2015. The eruption ultimately escaped the sun, growing into a substantial coronal mass ejection, or CME — a giant cloud of solar material traveling through space. This imagery is shown in the 304 Angstrom wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, a wavelength that highlights material in the low parts of the sun’s atmosphere and that is typically colorized in red. The video clip covers about four hours of the event. Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO Download: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11908" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11908</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
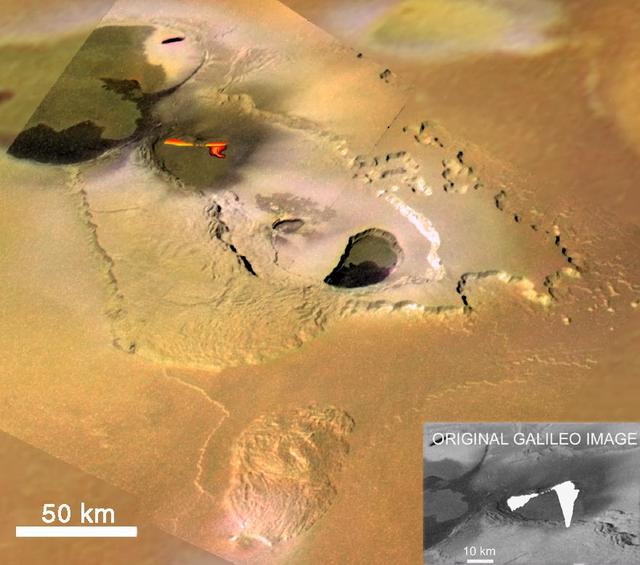
Eruption at Tvashtar Catena, Io, in Color

NASA image captured December 6, 2010 To view a video of this event go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5258354738">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5258354738</a> A very long solar filament that had been snaking around the Sun erupted (Dec. 6, 2010) with a flourish. STEREO (Behind) caught the action in dramatic detail in extreme ultraviolet light of Helium. It had been almost a million km long (about half a solar radius) and a prominent feature on the Sun visible over two weeks earlier before it rotated out of view. Filaments, elongated clouds of cooler gases suspended above the Sun by magnetic forces, are rather unstable and often break away from the Sun. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
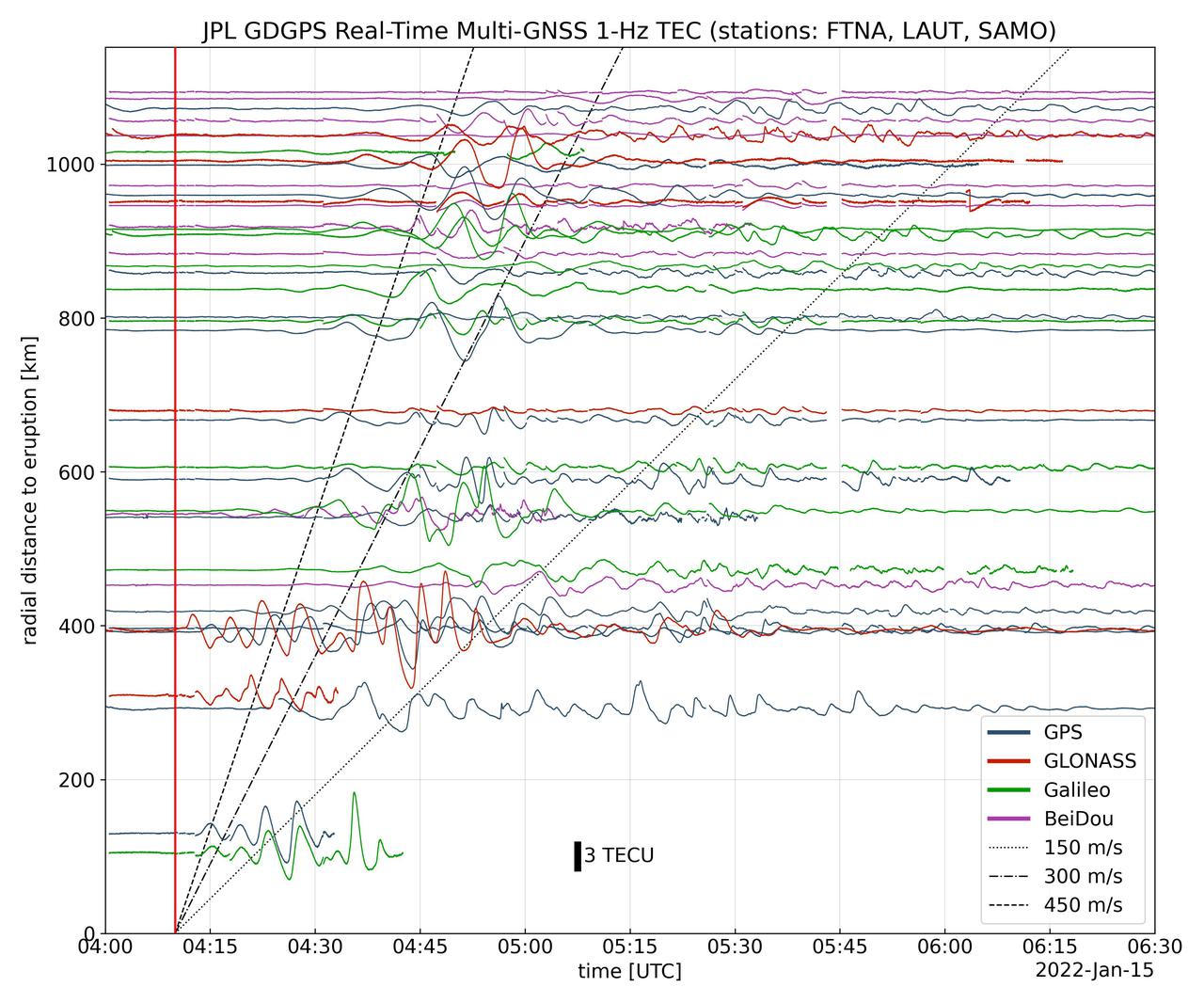
Real-time data collected by the Global Differential Global Positioning System network, operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, shows the atmospheric signature of the Hunga Tonga Hunga Ha'apai volcanic eruption in Tonga on Jan. 15, 2022. The data is a measure of the density of electrons (known as total electron content units, or TECU) in the ionosphere – the outermost layer of the atmosphere, which starts between 50 and 56 miles (80 to 90 kilometers) above Earth's surface. Navigation radio signals, like those received by location sensors on smartphones, are broadcast by global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) and experience delays when passing through the ionosphere. The extent of the delay depends on the density of electrons within the path of the GNSS signal in this atmospheric layer. When an explosive event such as a volcanic eruption or large earthquake injects energy into the atmosphere, the pressure waves from that event change the electron density in the ionosphere. These perturbations show up as tiny changes to the delays that GNSS radio signals usually experience as they pass through the atmosphere. The vertical red line in the data plot indicates the time of the eruption. The horizontal squiggles show electron density profiles picked up in the signals of four GNSS constellations, or groups of satellites: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou. The slanted dashed and dotted lines indicate the velocity of waves. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24905
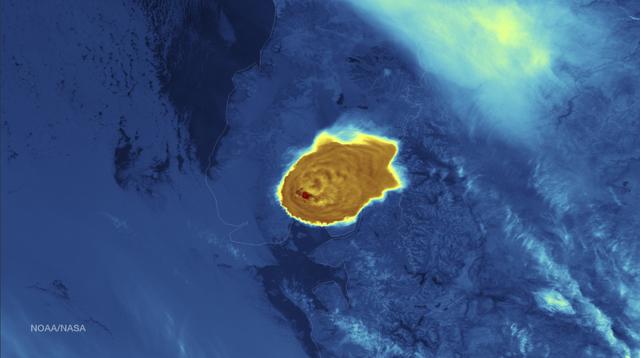
Calbuco Volcano in southern Chile has erupted for the first time since 1972, with the last major eruption occurring in 1961 that sent ash columns 12-15 kilometers high. This image was taken by the Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument in a high resolution infrared channel around 0515Z on April 23, 2015. Credit: NOAA/NASA/NPP/VIIRS <b><a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Hubble Captures Volcanic Eruption Plume From Io

Earth-based images of the Fall 1999 Loki Eruption

Ongoing Volcanic Eruption at Tvashtar Catena, Io
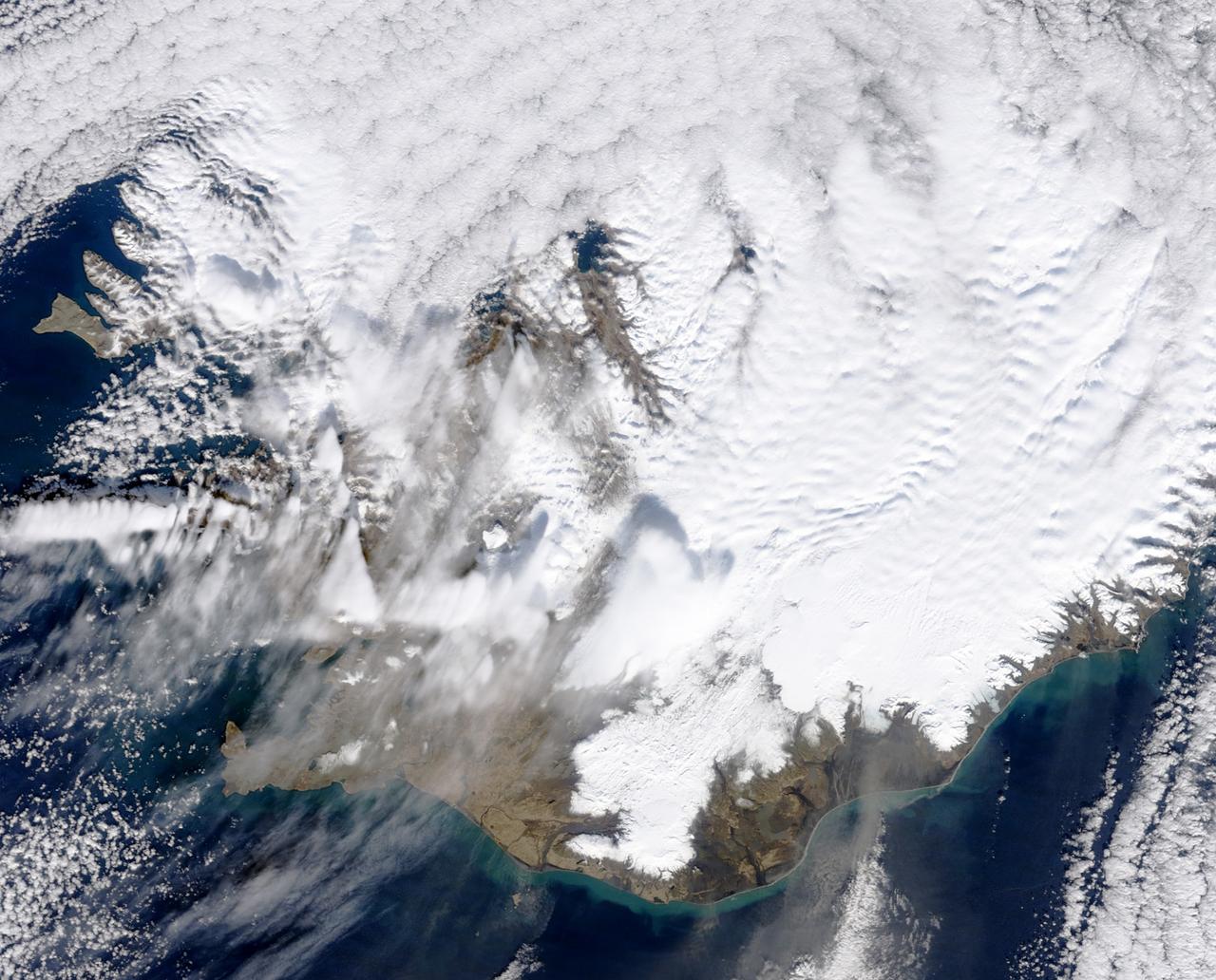
March 31, 2010..The volcanic eruption near Eyjafjallajökull persists into its second week, with continued lava fountaining and lava flows spilling into nearby canyons. The eruption is located at the Fimmvörduháls Pass between the Eyjafjallajökull ice field to the west (left) and the Mýrdalsjökull ice field to the east (right). This natural-color satellite image was acquired on March 26, 2010, by the MODIS aboard NASA’s Terra satellite. Dark ash and scoria cover the northern half of the Fimmvörduháls Pass. White snow covers the rest of the pass, sandwiched between white glaciers. Snow-free land is tan, brown, or dark gray, devoid of vegetation in early spring. To download a high res version of this image go to: <a href="http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2010-03-31" rel="nofollow">modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2010-0...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
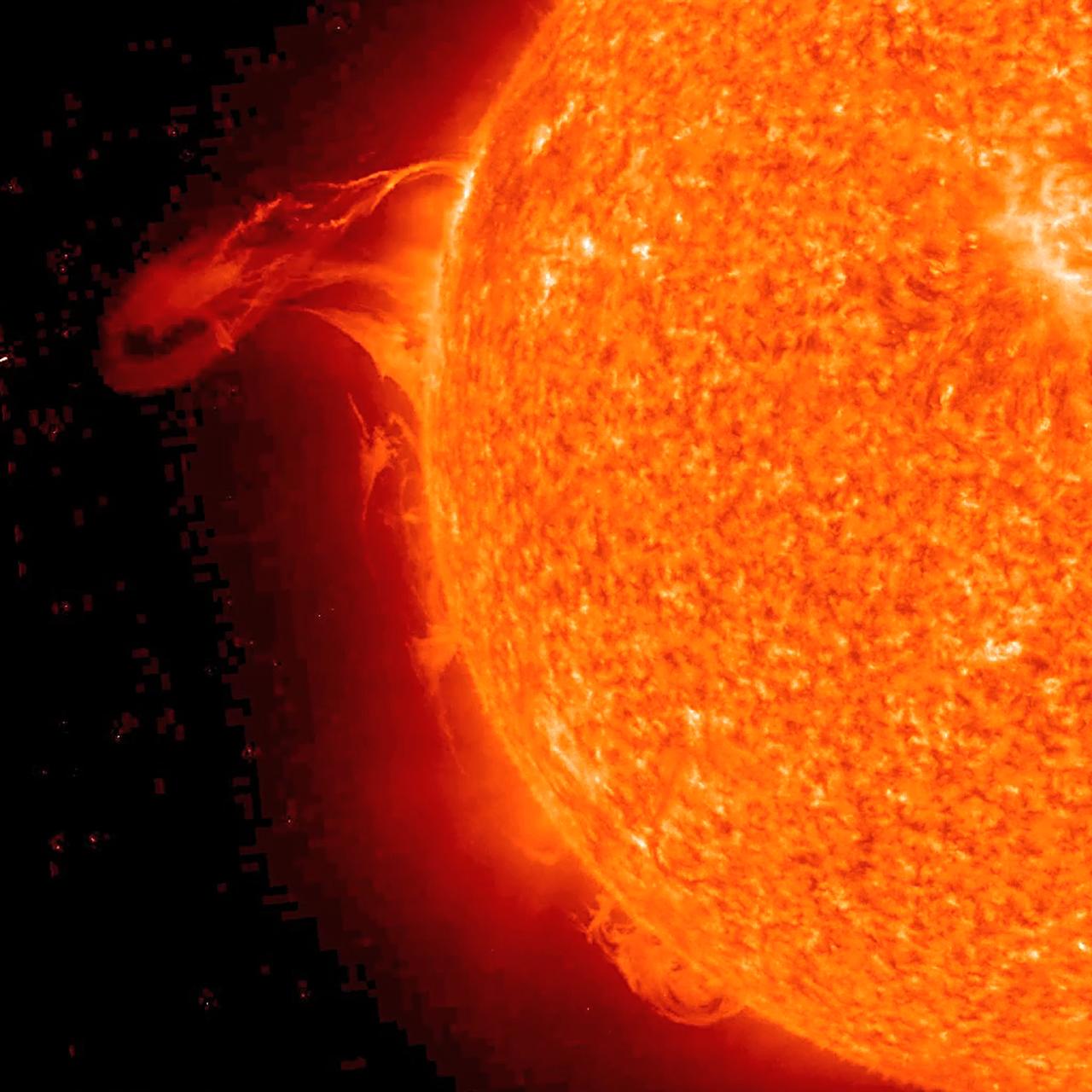

NASA image acquired May 1, 2010. As an active region rotated into view, it blew out three relatively small eruptions over about two days (Apr. 30 - May 2) as STEREO (Ahead) observed in extreme UV light. The first one was the largest and exhibited a pronounced twisting motion (shown in the still from May 1, 2010). The plasma, not far above the Sun's surface in these images, is ionized Helium heated to about 60,000 degrees. Note, too, the movement of plasma flowing along magnetic field lines that extend out beyond and loop back into the Sun's surface. Such activity occurs every day and is part of the dynamism of the changing Sun. Credit: NASA/GSFC/STEREO To learn more about STEREO go to: <a href="http://soho.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">soho.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
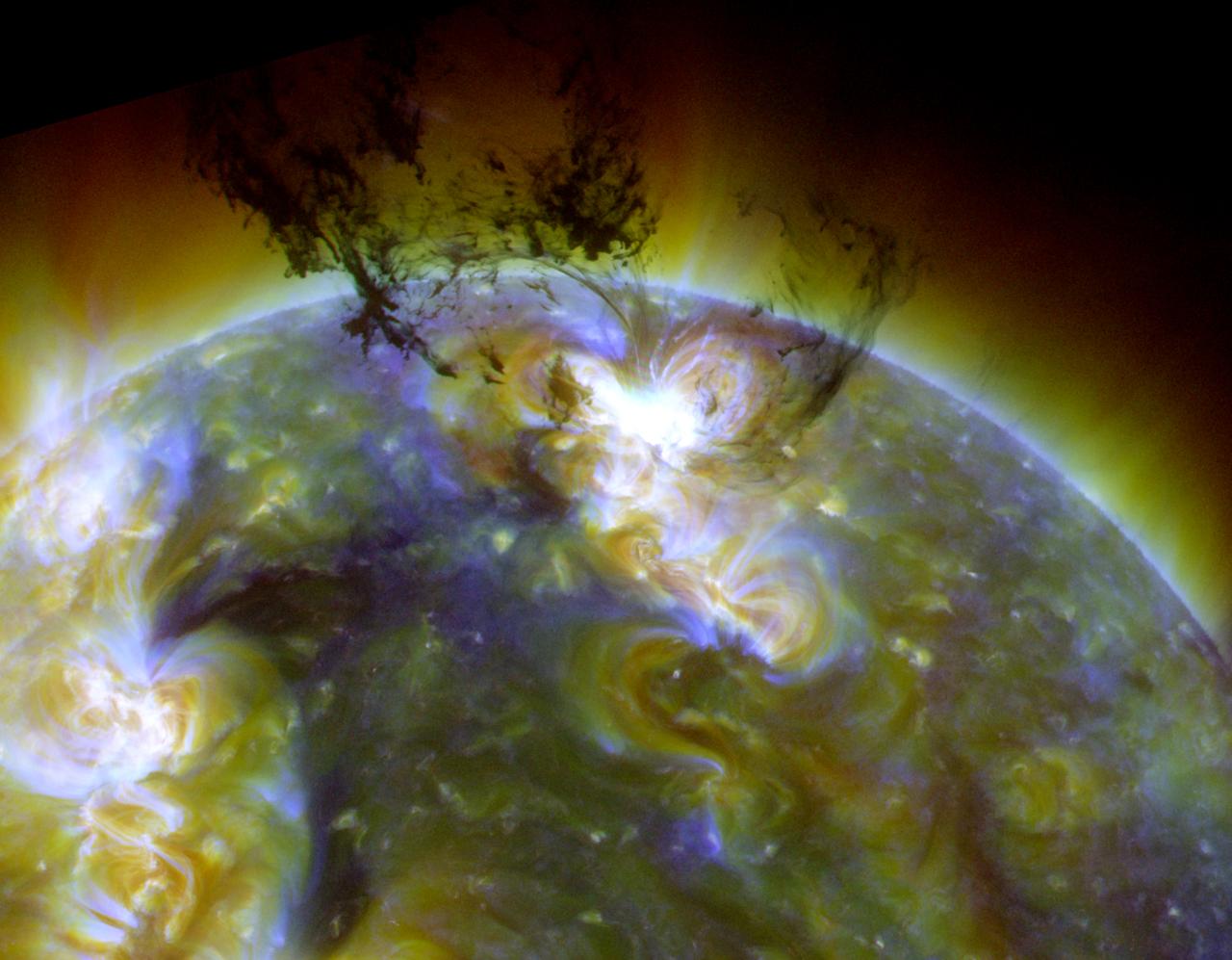
Spectacular eruption: On June 7, 2011, SDO captured this image as a massive eruption lifted an enormous amount of cool, dark material into the corona. Most of that material fell back onto the sun, where the gravitational energy of the fall caused it to heat up to a million degrees and more. Scientists concluded that this event on the sun was a small-scale version of what happens as stars form and collect gases via gravity. Thus, AIA allowed us to study in detail a phenomenon that cannot be observed so closely anywhere else in the universe. Credit: NASA/SDO/AIA/LMSAL Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/sdo-telescope-collects-its-100-millionth-image/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/sdo-telescope-collects-its-1...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
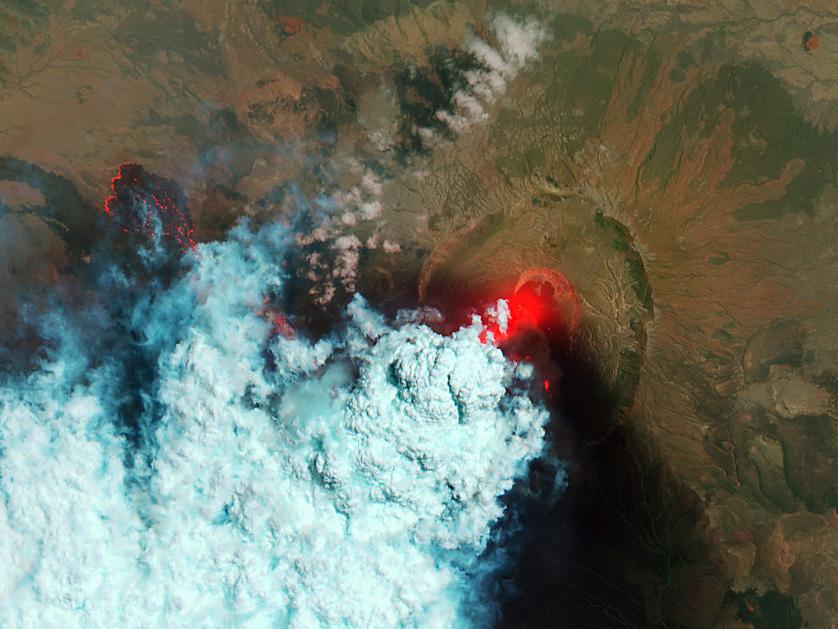

NASA image acquired June 24, 2011 Since it began erupting on June 12, 2011, emissions from Eritrea’s Nabro Volcano have drifted over much of East Africa and the Middle East. Ash has displaced residents living near the volcano and disrupted flights in the region. Despite the volcano’s widespread effects, little is known about the eruption. Nabro is located in an isolated region along the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia, and few English-language reports have been published. Satellite remote sensing is currently the only reliable way to monitor the ongoing eruption. This satellite image is among the first detailed pictures of the erupting vent and lava flows. They were acquired by the Advanced Land Imager (ALI) aboard the Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite on June 24, 2011. The bright red portions of the false-color image (top) indicate hot surfaces. Hot volcanic ash glows above the vent, located in the center of Nabro’s caldera. To the west of the vent, portions of an active lava flow (particularly the front of the flow) are also hot. The speckled pattern on upstream portions of the flow are likely due to the cool, hardened crust splitting and exposing fluid lava as the flow advances. The bulbous blue-white cloud near the vent is likely composed largely of escaping water vapor that condensed as the plume rose and cooled. The whispy, cyan clouds above the lava flow are evidence of degassing from the lava. NASA Earth Observatory image by Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data. Caption by Robert Simmon. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI To download the high res go here: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=51216" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=51216</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
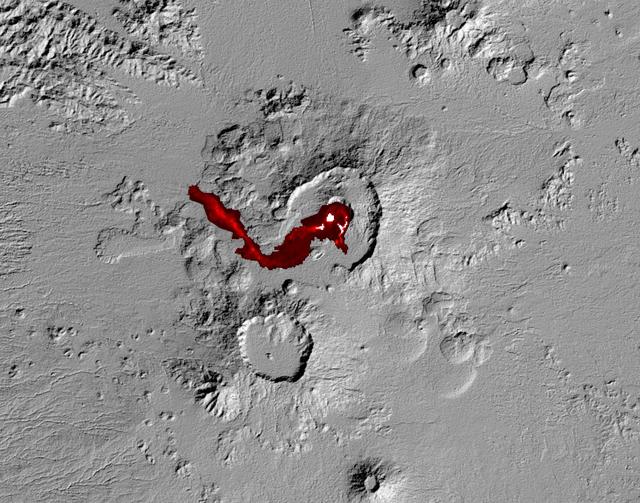

Nabro volcano in the African nation of Eritrea began erupting June 12, 2011, the first-ever recorded eruption of this stratovolcano. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft on July 5, 2011.

NASA Hubble Space Telescope shows detailed analysis of two continent-sized storms that erupted in Jupiter atmosphere in March 2007 shows that Jupiter internal heat plays a significant role in generating atmospheric disturbances .
This thermal infrared image from NASA Terra spacecraft of Merapi continuing eruption has been processed to reveal the dominant presence of volcanic ash in the eruption plume and clouds, displayed in dark red. The warm volcanic flow appears bright.
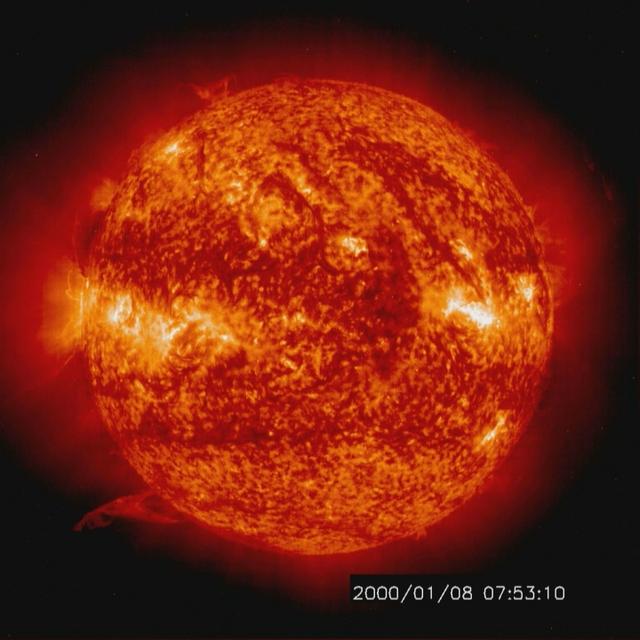

Solar activity and erupting prominences. EIT 304A (Jan. 8-10, 2000) Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>
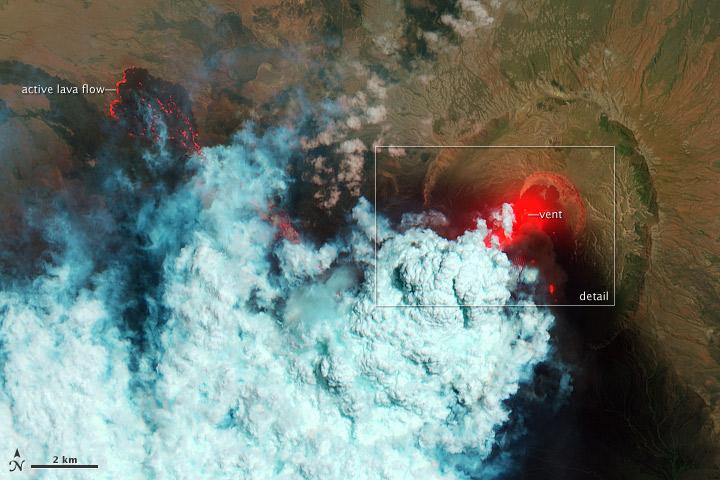
NASA image acquired June 24, 2011 Since it began erupting on June 12, 2011, emissions from Eritrea’s Nabro Volcano have drifted over much of East Africa and the Middle East. Ash has displaced residents living near the volcano and disrupted flights in the region. Despite the volcano’s widespread effects, little is known about the eruption. Nabro is located in an isolated region along the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia, and few English-language reports have been published. Satellite remote sensing is currently the only reliable way to monitor the ongoing eruption. This satellite image is among the first detailed pictures of the erupting vent and lava flows. They were acquired by the Advanced Land Imager (ALI) aboard the Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite on June 24, 2011. The bright red portions of the false-color image (top) indicate hot surfaces. Hot volcanic ash glows above the vent, located in the center of Nabro’s caldera. To the west of the vent, portions of an active lava flow (particularly the front of the flow) are also hot. The speckled pattern on upstream portions of the flow are likely due to the cool, hardened crust splitting and exposing fluid lava as the flow advances. The bulbous blue-white cloud near the vent is likely composed largely of escaping water vapor that condensed as the plume rose and cooled. The whispy, cyan clouds above the lava flow are evidence of degassing from the lava. NASA Earth Observatory image by Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data. Caption by Robert Simmon. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI To download the high res go here: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=51216" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=51216</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
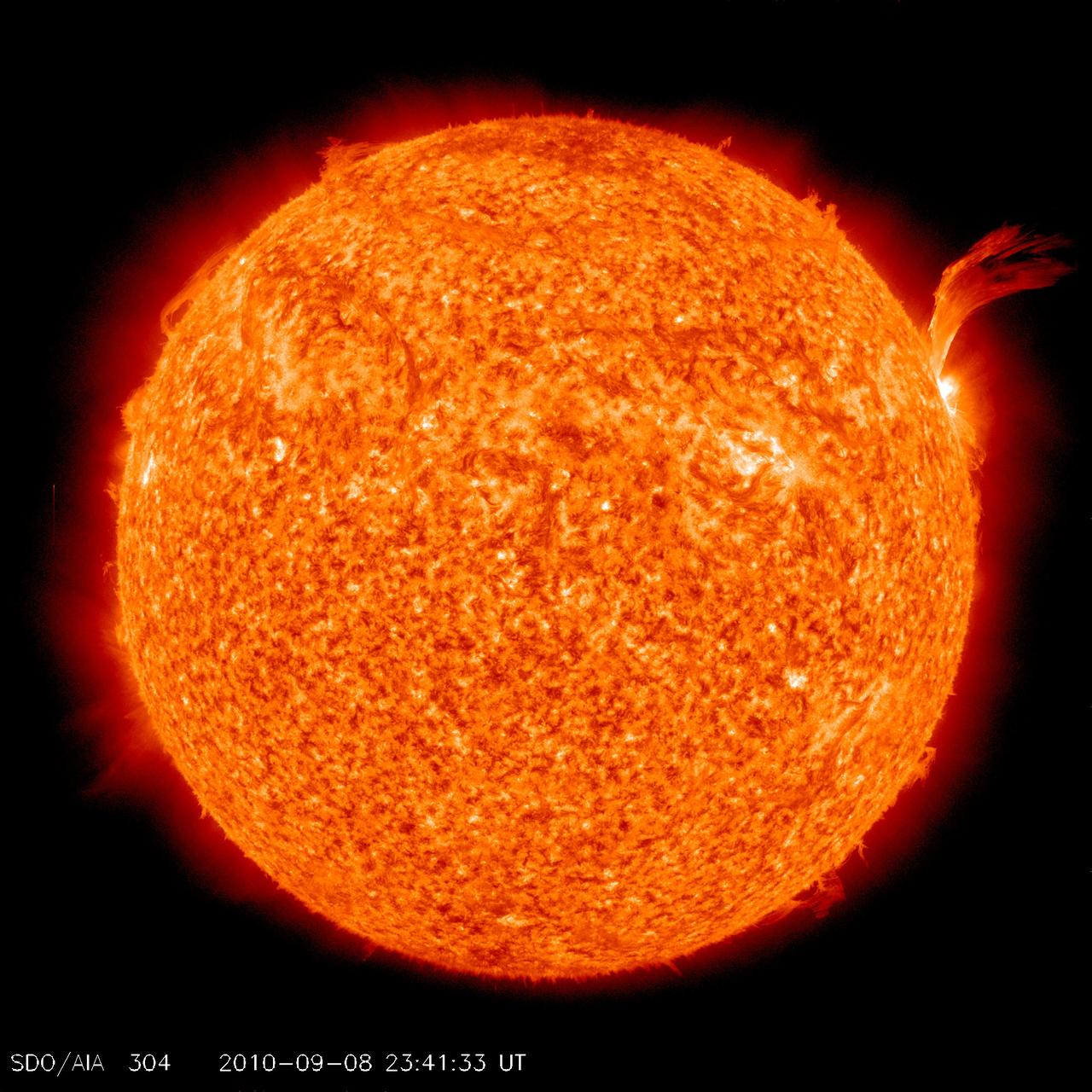

NASA image release Sept 9, 2010 Just as sunspot 1105 was turning away from Earth on Sept. 8, the active region erupted, producing a solar flare and a fantastic prominence. The eruption also hurled a bright coronal mass ejection into space. The eruption was not directed toward any planets. To see a detail go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974263471/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974263471/</a> View the video here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090</a> This is a snapshot of the prominence. Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
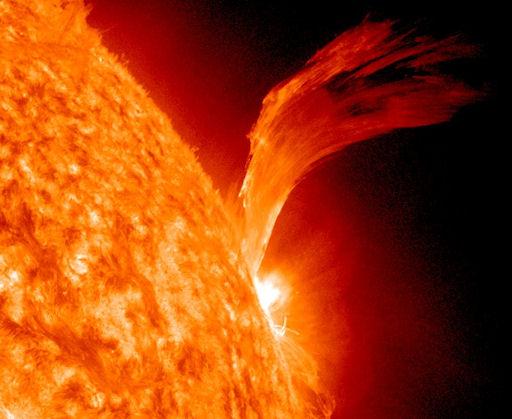

NASA image release Sept 9, 2010 Just as sunspot 1105 was turning away from Earth on Sept. 8, the active region erupted, producing a solar flare and a fantastic prominence. The eruption also hurled a bright coronal mass ejection into space. The eruption was not directed toward any planets. View the video here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4974878090</a> To see a full disk view go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4975115754/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4975115754/</a> This is a snapshot of the prominence. Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A magnetic filament of solar material erupted on the sun in late September, breaking the quiet conditions in a spectacular fashion. The 200,000 mile long filament ripped through the sun's atmosphere, the corona, leaving behind what looks like a canyon of fire. The glowing canyon traces the channel where magnetic fields held the filament aloft before the explosion. Visualizers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. combined two days of satellite data to create a short movie of this gigantic event on the sun: <a href="http://bit.ly/166CncU" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/166CncU</a> In reality, the sun is not made of fire, but of something called plasma: particles so hot that their electrons have boiled off, creating a charged gas that is interwoven with magnetic fields. These images were captured on Sept. 29-30, 2013, by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which constantly observes the sun in a variety of wavelengths. Read more/download video: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1dnrsjF" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1dnrsjF</a> Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
Mt. Etna, a volcano on the island of Sicily, erupted on October 26, 2002, as seen by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounding System AIRS on NASA Aqua. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00355
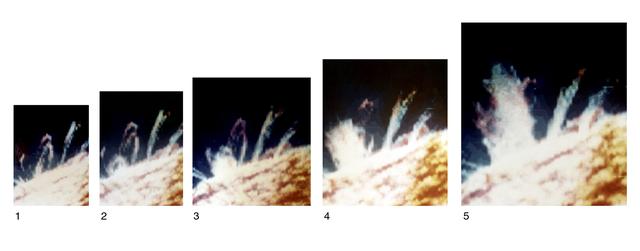
Breaking the grip of the closed magnetic loops that constrain other gases around it, a spray of chromospheric material surges upward, free of the Sun. Views 1 through 5 were recorded about 5 minutes apart by Skylab and comprise a composite of separate images made in chromospheric (red), transition region (green), and coronal (blue) temperatures of an ultraviolet sequence that depicts a solar eruption. Eruption begins (view 2) as material in or near a small, compact loop develops enough energy to overcome the Sun's magnetic bonds.

Nabro volcano, Eritrea, in the Horn of Africa, began erupting June 12, 2011, the first-ever recorded eruption of this stratovolcano. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft on June 19, 2011.
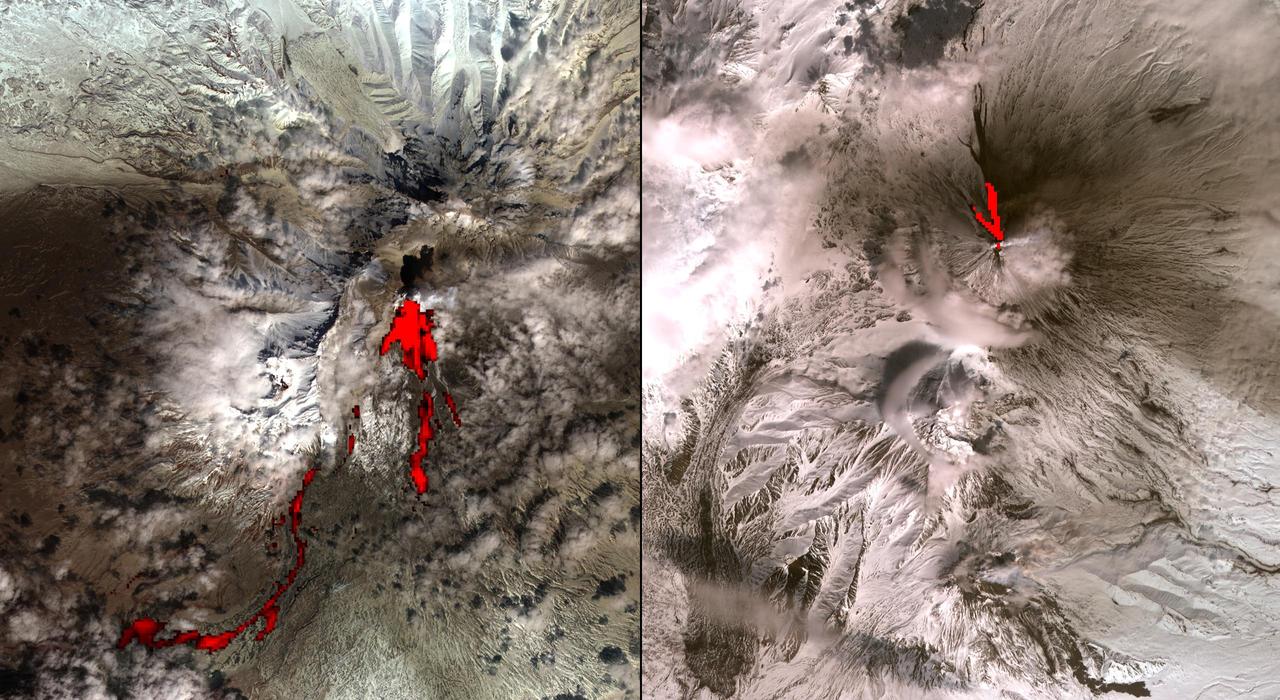
The height and motion of the ash and gas plume from the April 22, 2003, eruption of the Chikurachki volcano is portrayed in these views NASA Terra spacecraft.

This image taken by NASAS Galaxy Evolution Explorer shows one of the largest flares, or star eruptions, ever recorded at ultraviolet wavelengths. This star is called GJ 3685A.
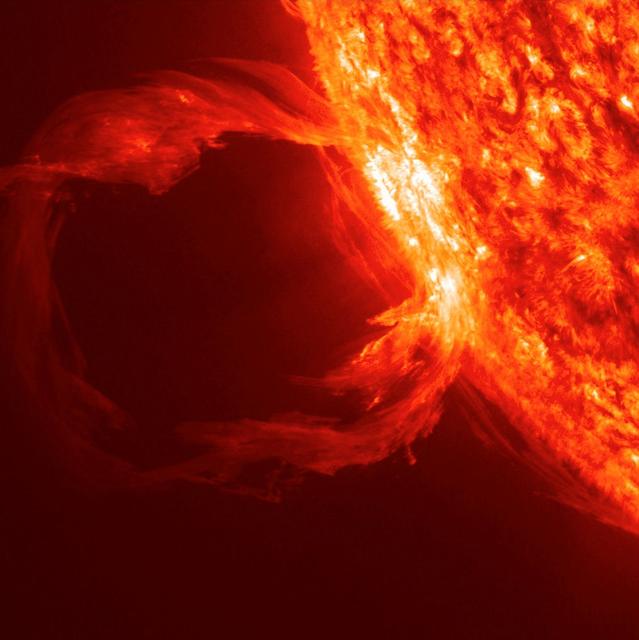

An erupting prominence observed by SDO on March 30, 2010. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO To read more about this image go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/first-light.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/first-light.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
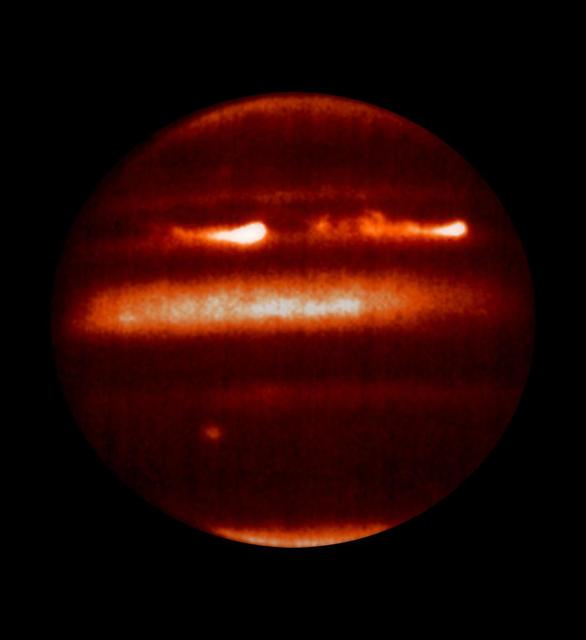

NASA Hubble Space Telescope shows detailed analysis of two continent-sized storms that erupted in Jupiter atmosphere in March 2007 shows that Jupiter internal heat plays a significant role in generating atmospheric disturbances.
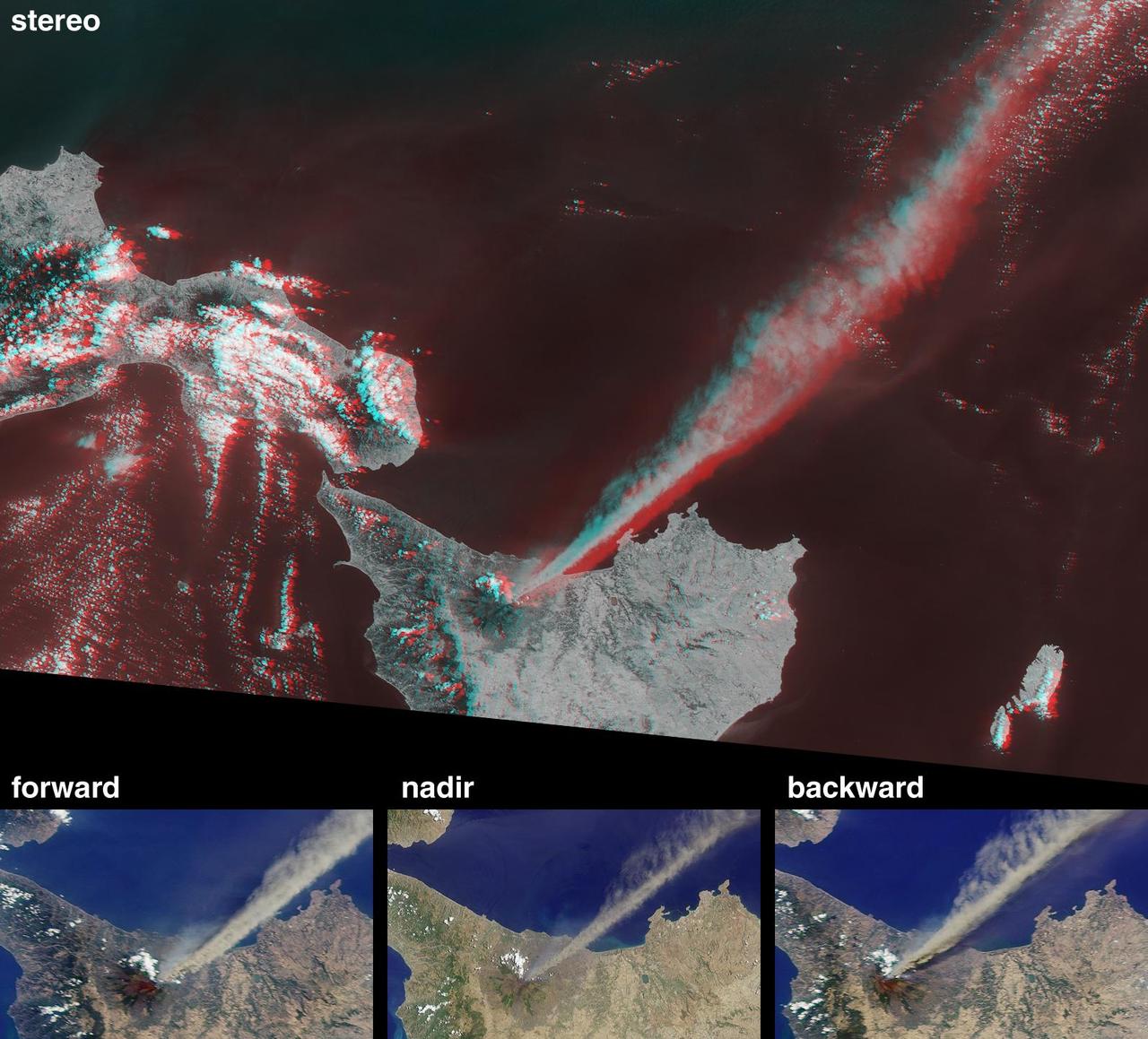
This anaglyph from the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft shows the eruption of Mt. Etna volcano located near the eastern coast of Sicily on July 22, 2001. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
One of the most volcanically active regions of the world is the Kamchatka Peninsula in eastern Siberia, Russia. It is not uncommon for several volcanoes to be erupting at the same time. NASA Terra satellite acquired this image on April 26, 2007
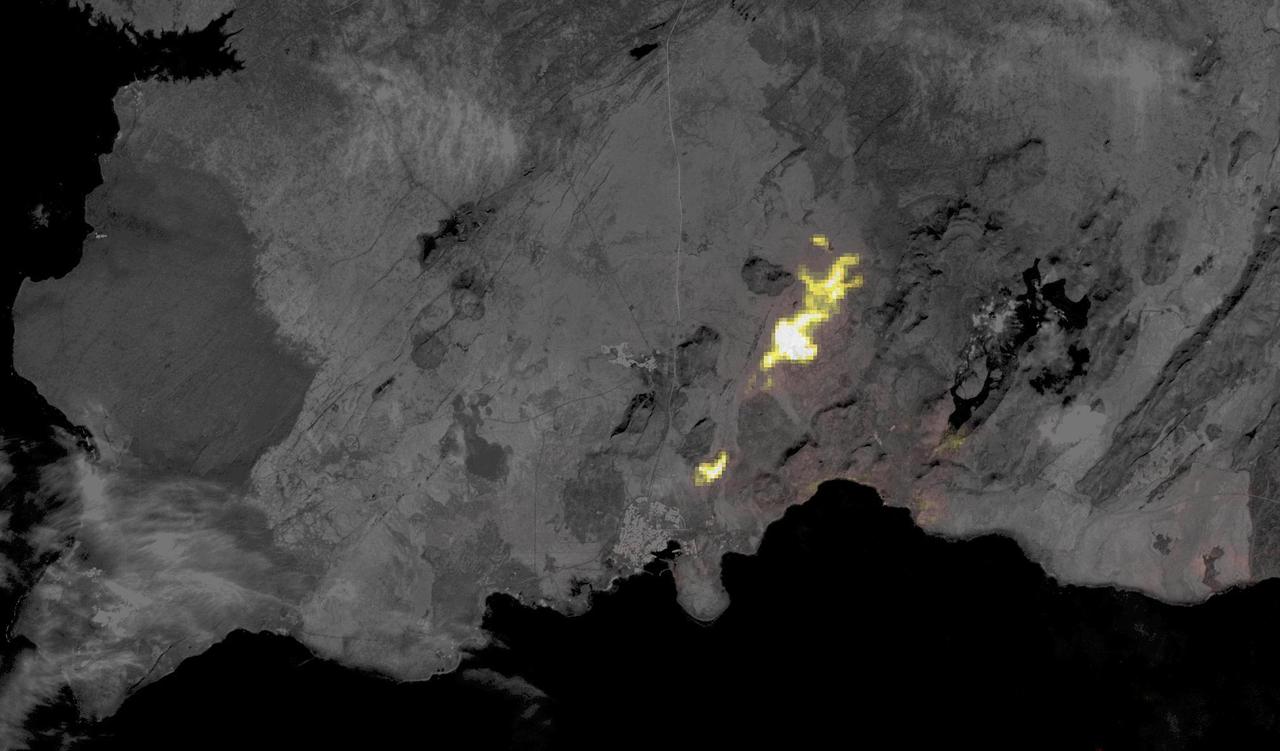

Volcanic activity resumed near the town of Grindavik, Iceland on January 14. A fissure eruption began several kilometers southwest of the 2023 fissure eruptions. This time, several houses were engulfed by lava. When this nighttime thermal image was captured by ASTER on January 24, the eruption had stopped. The background image is an earlier ASTER daytime scene acquired on August 15, 2022. The images cover an area of 17.8 by 30.2 km, and are located at 63.9 degrees north, 22 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26283

On March 3, 2015, Chile's Villarrica volcano erupted, forcing the evacuation of thousands of people. The eruption deposited a layer of ash over the volcano's eastern slope, blanketing and darkening the normal winter snow cover. The eruption and its effects were captured by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft on March 9. Black flows on the other flanks are mud and ash flows. Vegetation is displayed in red colors. The thermal infrared image shows hot spots (white colored) at the summit crater, indicating continuing volcanic activity. The ash blanket is warmer (brighter) than the cold snow (black). The image covers an area of 13.5 by 16.5 kilometers, and is located at 39.4 degrees south, 71.9 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19241
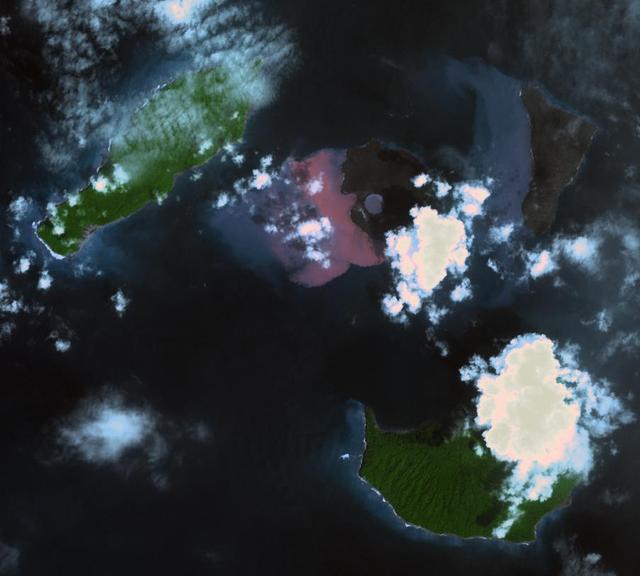

On Dec. 22, 2018, Indonesia's Anak Krakatau volcano erupted and partially collapsed. NASA's Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection (ASTER) instrument imaged the volcano on Jan. 13 -- several weeks after the eruption. This image shows that the crater area has closed to become a lake and the forest on the island has been destroyed by ash falls. The reddish area in the water southwest of the island is likely due to either iron-rich ash in the water or the interaction of seawater with underwater volcanic eruption products. The image covers an area of 7.5 by 8.4 miles (12.2 by 13.5 kilometers), and is located at 6.1 degrees south, 105.4 degrees east. The tsunami that followed the eruption killed more than 400 people in western Indonesia. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22821

Active region AR 12192 on the sun erupted with a strong flare on Oct. 24, 2014, as seen in the bright light of this image captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. This image shows extreme ultraviolet light that highlights the hot solar material in the sun's atmosphere. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO More info: The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 5:40 p.m. EDT on Oct. 24, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This flare is classified as an X3.1-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. The flare erupted from a particularly large active region -- labeled AR 12192 -- on the sun that is the largest in 24 years. This is the fourth substantial flare from this active region since Oct. 19. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
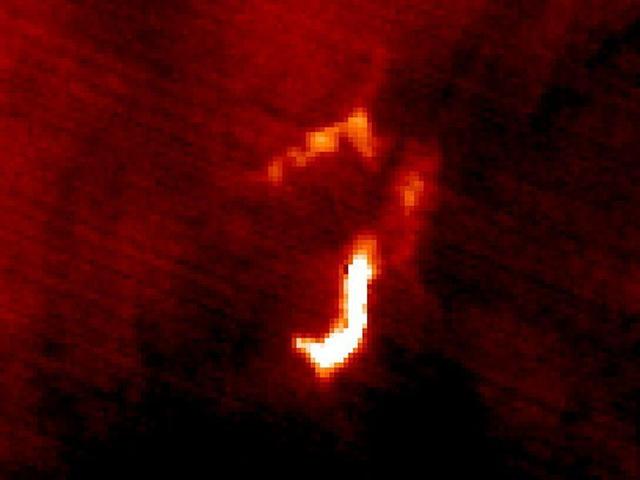
The March 16 volcanic eruption in Iceland's Reykjanes Peninsula was the fourth in many months. On March 22, ASTER's thermal infrared scanner detected the hot lava flow, through a thick cloud cover. The image matched the most recent official map, released March 20. The image covers an area of 7.5 by 10 km, and is located at 63.9 degrees north, 22.3 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26288

The April 18, 2015 eruption of Calbuco Volcano in Chile, as seen by NASA Terra spacecraft, led to the evacuation of thousands of citizens near the summit, blanketed nearby towns with a layer of ash, and disrupted air traffic. One week later, on April 26, the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft acquired this nighttime thermal infrared image of Calbuco. Hot eruptive material at the summit appears in white (hot), with a purple plume streaming to the right, indicating that it is ash-laden. The image covers an area of 3.1 by 4.1 miles (5 by 6.6 kilometers), and is located at 41.3 degrees south, 72.5 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19382
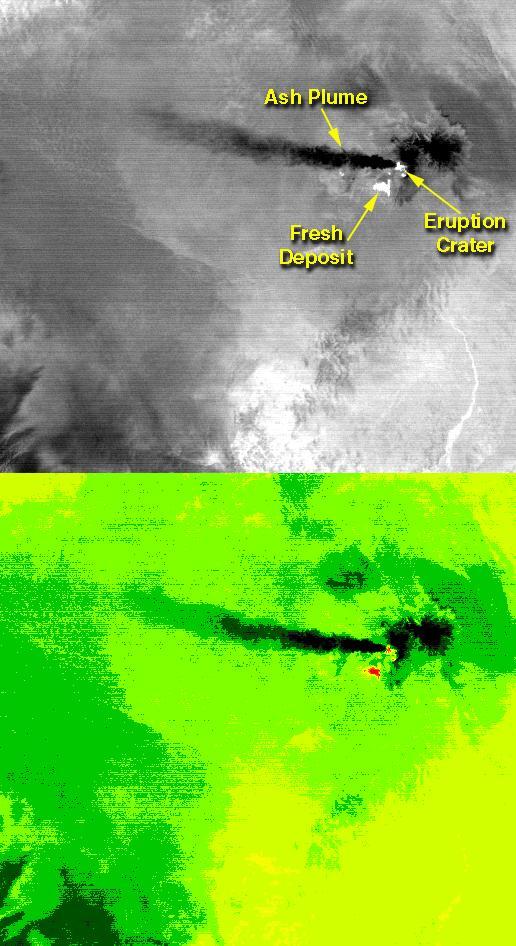

On the night of June 4, 2001 ASTER captured this thermal image of the erupting Shiveluch volcano. Located on Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula, Shiveluch rises to an altitude of 8028'. The active lava dome complex is seen as a bright (hot) area on the summit of the volcano. To the southwest, a second hot area is either a debris avalanche or hot ash deposit. Trailing to the west is a 25 km ash plume, seen as a cold "cloud" streaming from the summit. At least 60 large eruptions have occurred during the last 10,000 years; the largest historical eruptions were in 1854 and 1964. Because Kamchatka is located along the major aircraft routes between North America/Europe and the Far East, this area is constantly monitored for potential ash hazards to aircraft. The lower image is the same as the upper, except it has been color coded: red is hot, light greens to dark green are progressively colder, and gray/black are the coldest areas. The image is located at 56.7 degrees north latitude, 161.3 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02674
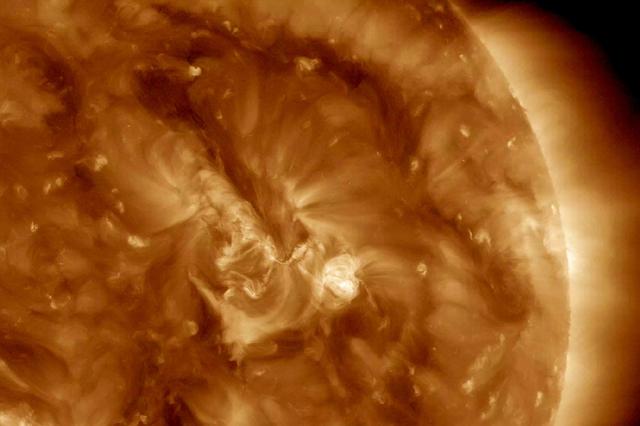
A minor solar eruption triggered a crackling, white flash that sent an expanding wave of plasma below it over about six hours (Nov. 4, 2016). Some of the plasma also appeared to surge along a narrow path above the active region as well. Such occurrences are fairly common, but still interesting to watch up close. The images were taken in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Movies are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21202
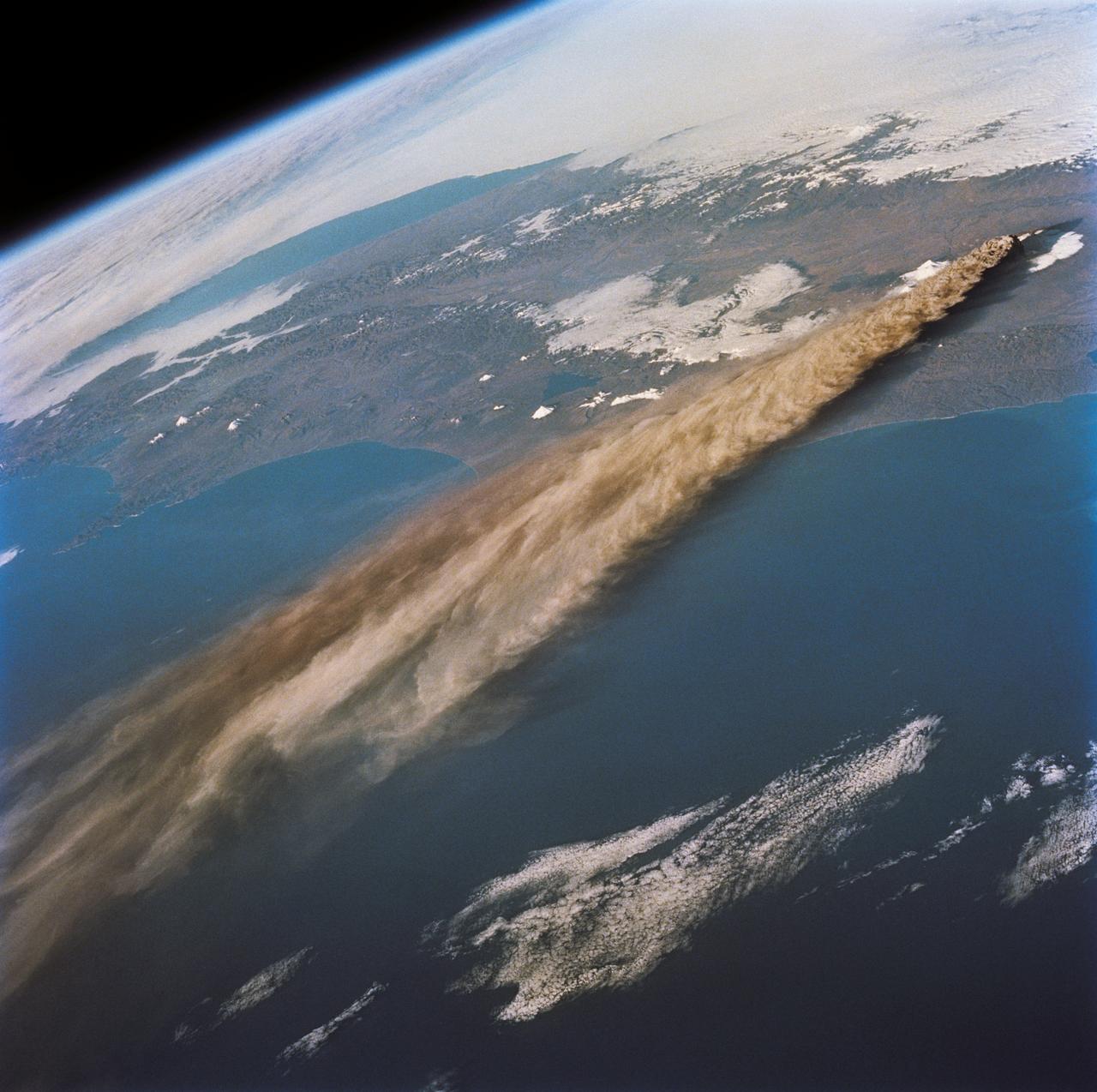

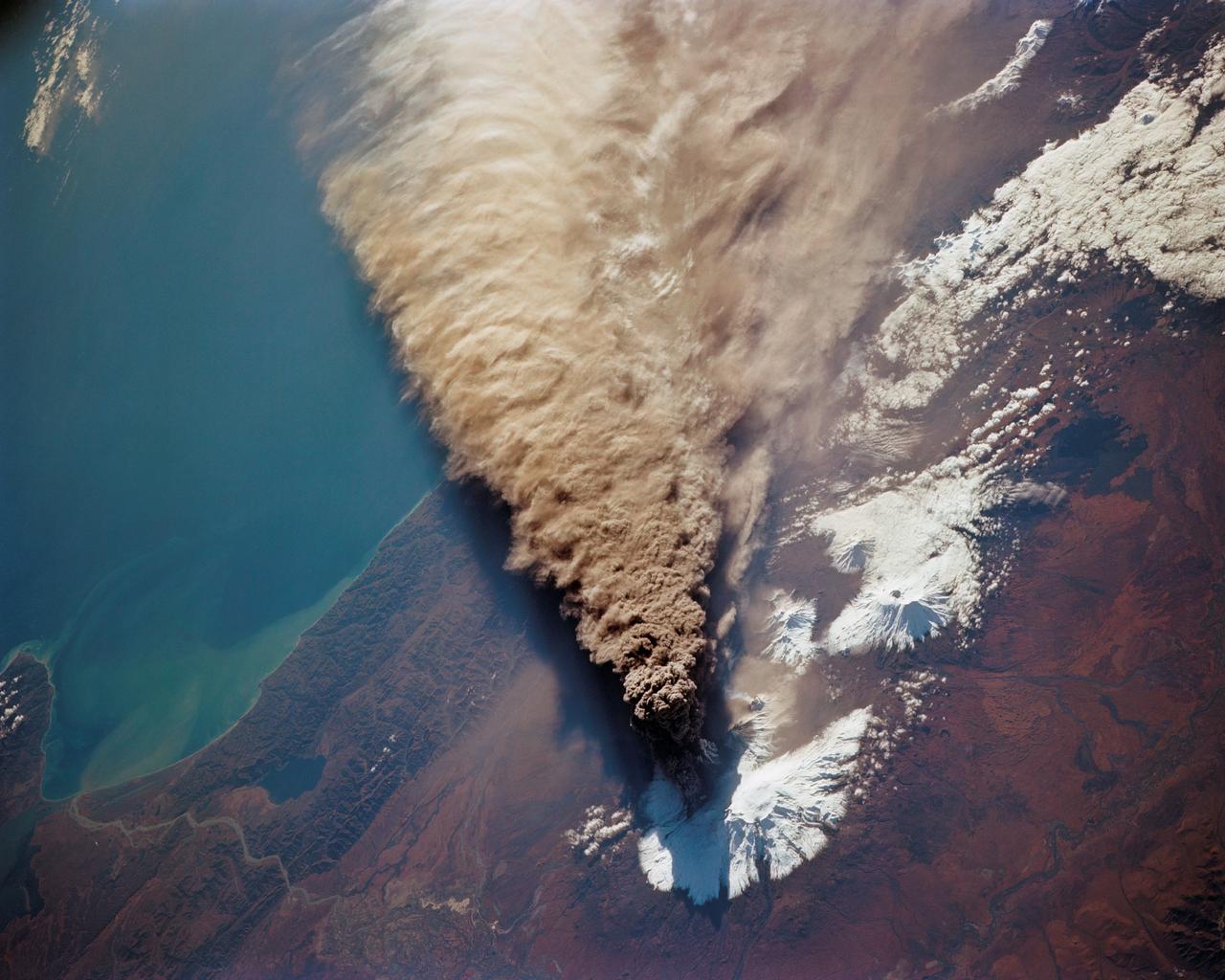
STS068-218-007 (30 September-11 October 1994) --- (Kliuchevskoi Volcano) The crewmembers used a 70mm camera to photograph this northeasterly looking view of the plume from the Kamchatka peninsula's newly erupted volcano. The eruption was photographed from 115 nautical miles above Earth. Six NASA astronauts spent a week and a half aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in support of the Space Radar Laboratory 2 (SRL-2) mission.

Solar Flare Extremely energetic objects permeate the universe. But close to home, the sun produces its own dazzling lightshow, producing the largest explosions in our solar system and driving powerful solar storms.. When solar activity contorts and realigns the sun’s magnetic fields, vast amounts of energy can be driven into space. This phenomenon can create a sudden flash of light—a solar flare. Flares typically last a few minutes and unleash energies equivalent to millions of hydrogen bombs. The above picture features a filament eruption on the sun, accompanied by solar flares. To learn more about solar flares, go to NASA’s SDO mission: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/sdo" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/sdo</a> --------------------------------- Original caption: <b>Click here to view an image showing the size of this CME compared to the size of Earth: <a href="http://bit.ly/RkYr7z" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/RkYr7z</a> </b> On August 31, 2012 a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into space at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The coronal mass ejection, or CME, traveled at over 900 miles per second. The CME did not travel directly toward Earth, but did connect with Earth's magnetic environment, or magnetosphere, causing aurora to appear on the night of Monday, September 3. Pictured here is a lighten blended version of the 304 and 171 angstrom wavelengths. Cropped Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On August 31, 2012 a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into space at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The coronal mass ejection, or CME, traveled at over 900 miles per second. The CME did not travel directly toward Earth, but did connect with Earth's magnetic environment, or magnetosphere, causing aurora to appear on the night of Monday, September 3. This is a a lighten blended version of the 304 and 171 angstrom wavelengths. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
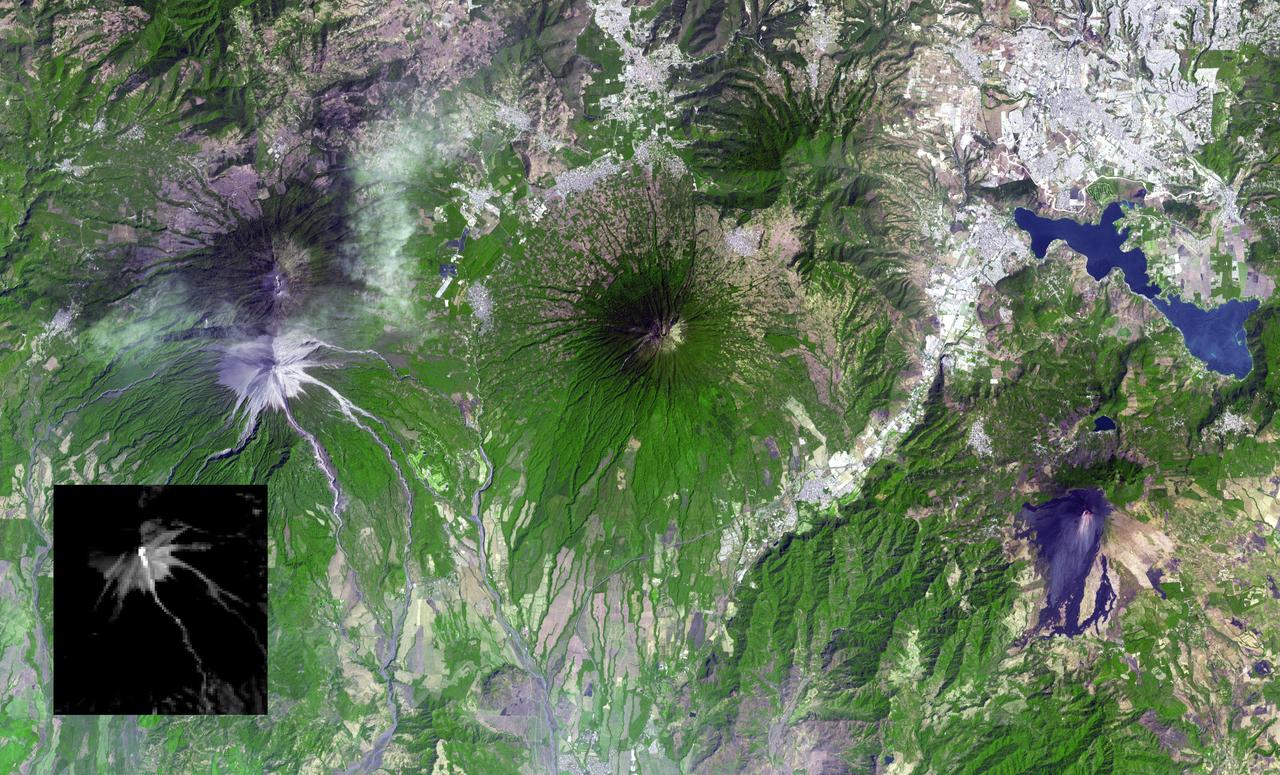

Guatemala's Fuego volcano continued its frequent moderate eruptions in early February 2015. Pyroclastic flows from the eruptions descended multiple drainages, and the eruptions sent ash plumes spewing over Guatemala City 22 miles (35 kilometers) away, and forced closure of the international airport. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument onboard NASA's Terra spacecraft captured a new image of the region on February 17. Fuego is on the left side of the image. The thermal infrared inset image shows the summit crater activity (white equals hot), and remnant heat in the flows on the flank. Other active volcanoes shown in the image are Acatenango close by to the north, Volcano de Agua in the middle of the image, and Pacaya volcano to the east. The image covers an area of 19 by 31 miles (30 by 49.5 kilometers), and is located at 14.5 degrees north, 90.9 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19297
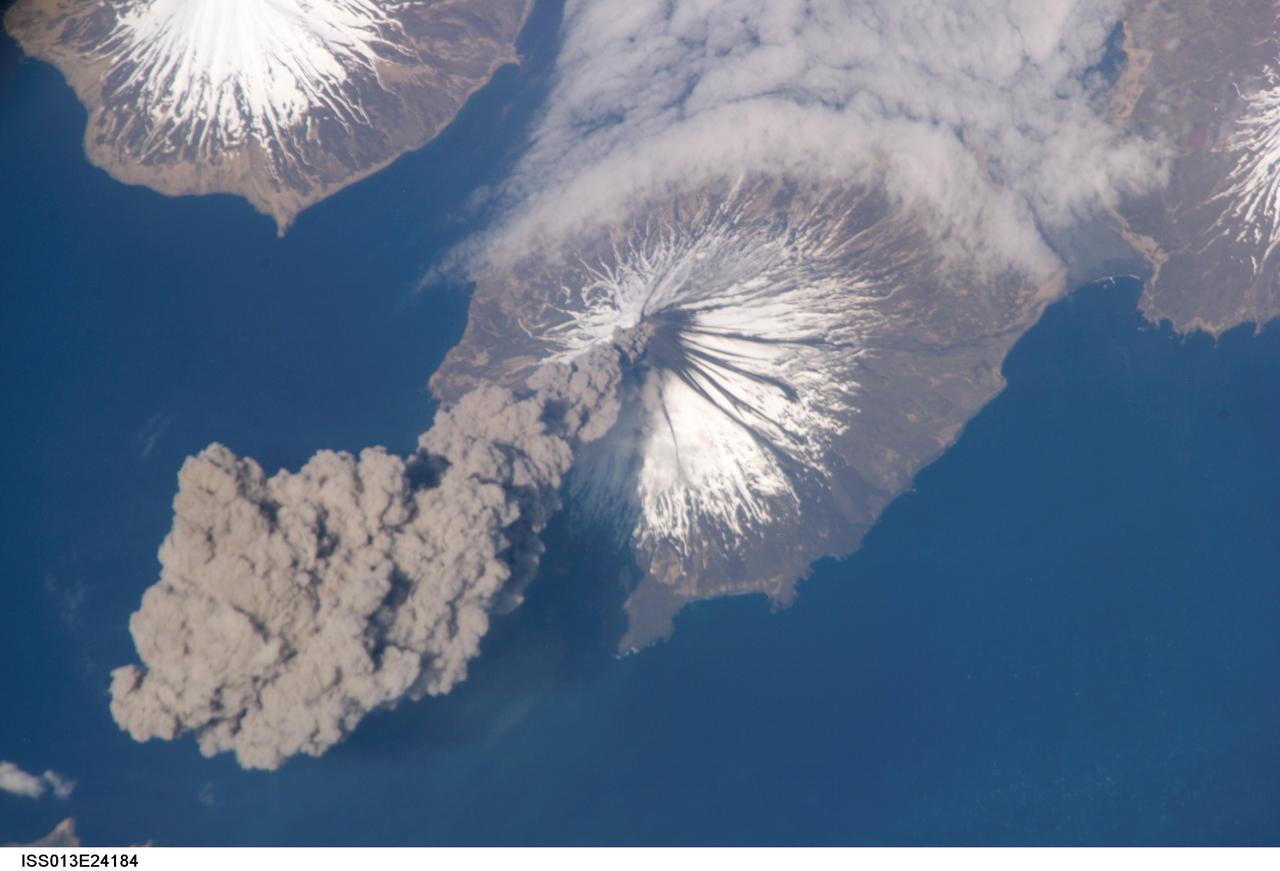

ISS013-E-24184 (23 May 2006) --- Eruption of Cleveland Volcano, Aleutian Islands, Alaska is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. This most recent eruption was first reported to the Alaska Volcano Observatory by astronaut Jeffrey N. Williams, NASA space station science officer and flight engineer, at 3:00 p.m. Alaska Daylight Time (23:00 GMT). This image, acquired shortly after the beginning of the eruption, captures the ash plume moving west-southwest from the summit vent. The eruption was short-lived; the plume had completely detached from the volcano summit two hours later.
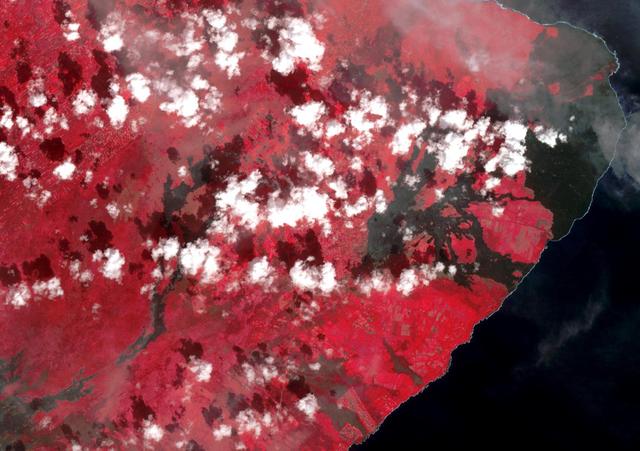

The 2018 Kilauea, Hawaii eruption began in May on Kilauea's East Rift Zone. Lava fountains up to 100 meters high, lava flows, and volcanic gas continued until August. By the time the eruption ended, over 700 houses had been destroyed, and 35 square kilometers of land had been covered by lava flows. About 3.5 square kilometers (875 acres) of new land has been created in the ocean. The before image was acquired by Landsat 8 on September 5, 2013; the ASTER image was acquired November 14, 2018. The images cover an area of 18 by 25.5 kilometers, and are located at 19.5 degrees north, 154.9 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22899
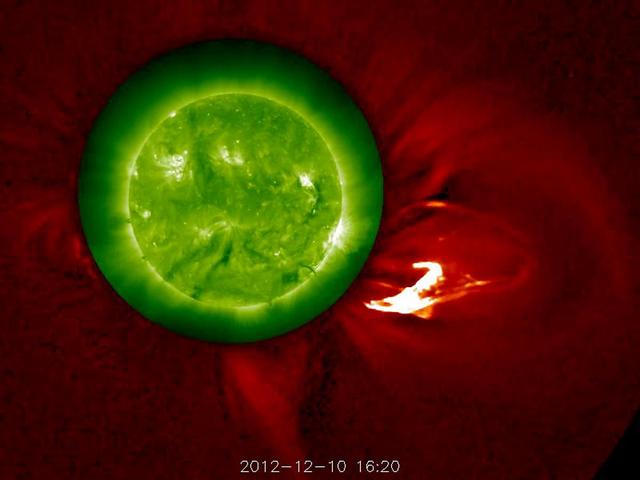

The Sun blows a robust prominence out into space (Dec. 10, 2102). The outer image, from the STEREO-A's COR1 coronagraph, has been changed from green to red to complement the green Sun image, taken in extreme UV light. The movie covers six hours of activity. Kind of Christmassy looking, isn't it? Some of the prominence falls back towards the sun, although the disturbance as a whole continues out into the solar system. Credit: NASA/GSFC/STEREO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
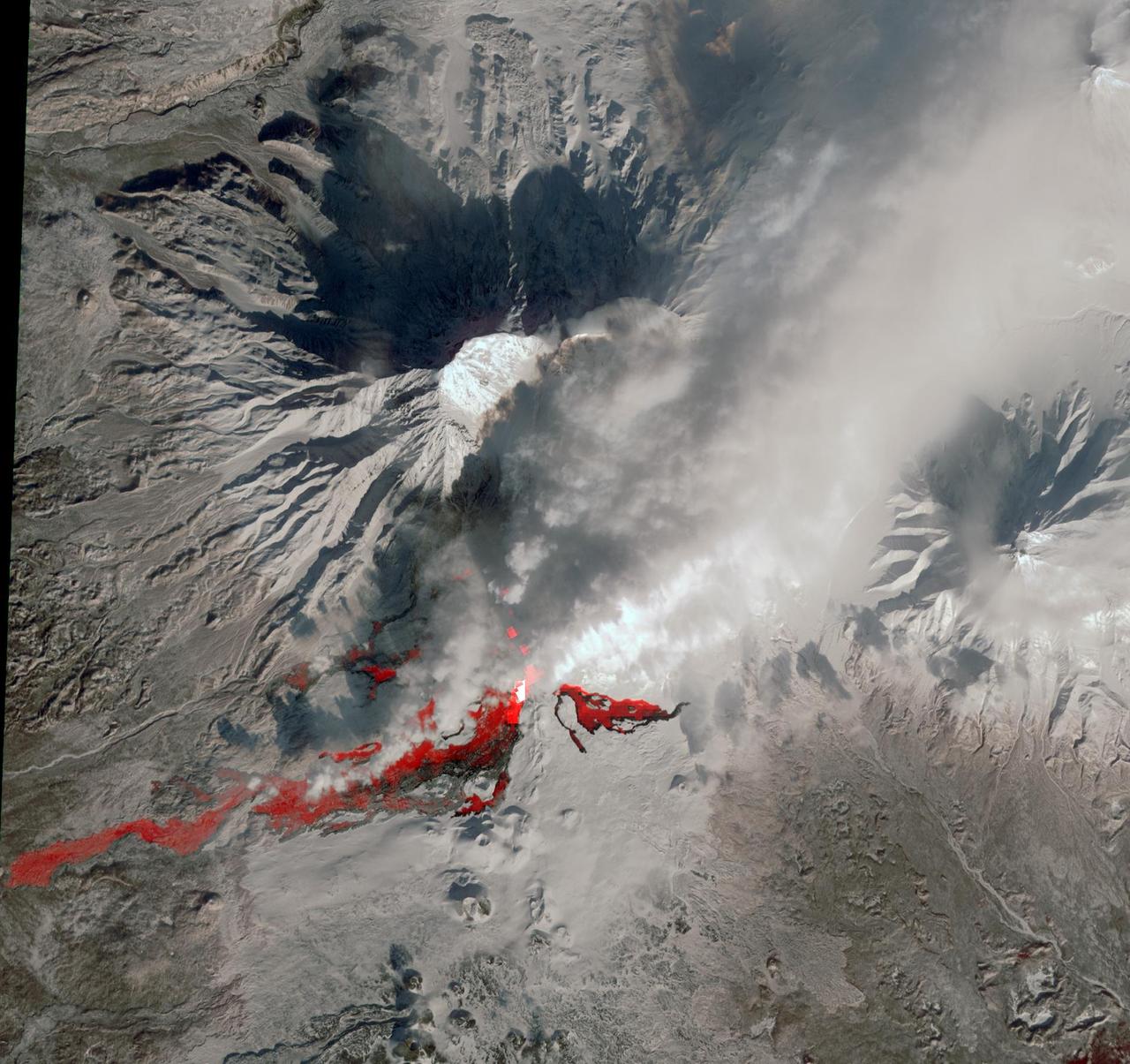
NASA Terra spacecraft reveals the still-active lava flows in the snowy winter landscape of Plosky Tolbachik volcano, which erupted for the first time in 35 years on Nov. 27, 2012, in Russia far eastern Kamchatka Peninsula.
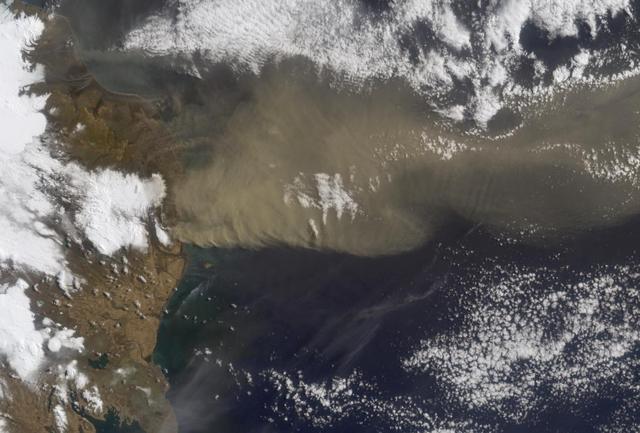

NASA Terra satellite flew directly over Iceland on April 19, 2010 and captured this image of the Eyjafjallajökull volcano and its erupting ash plume. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
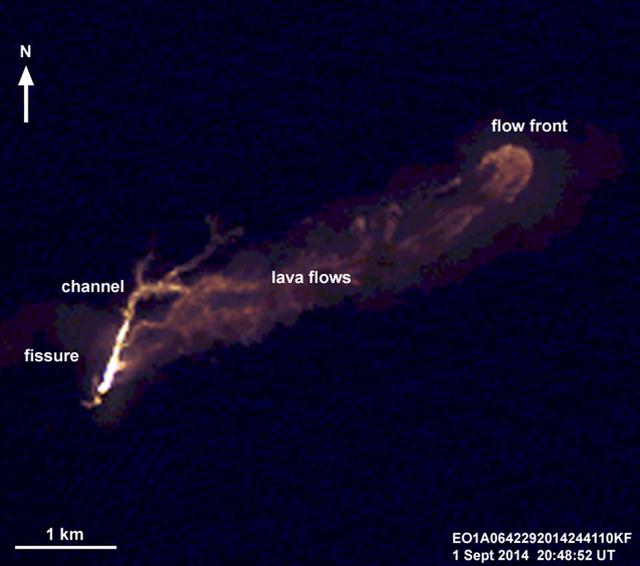

On the night of Sept. 1, 2014, NASA Earth Observing 1 EO-1 spacecraft observed the ongoing eruption at Holuhraun, Iceland. This false-color image that emphasizes the hottest areas of the vent and resulting lava flows.
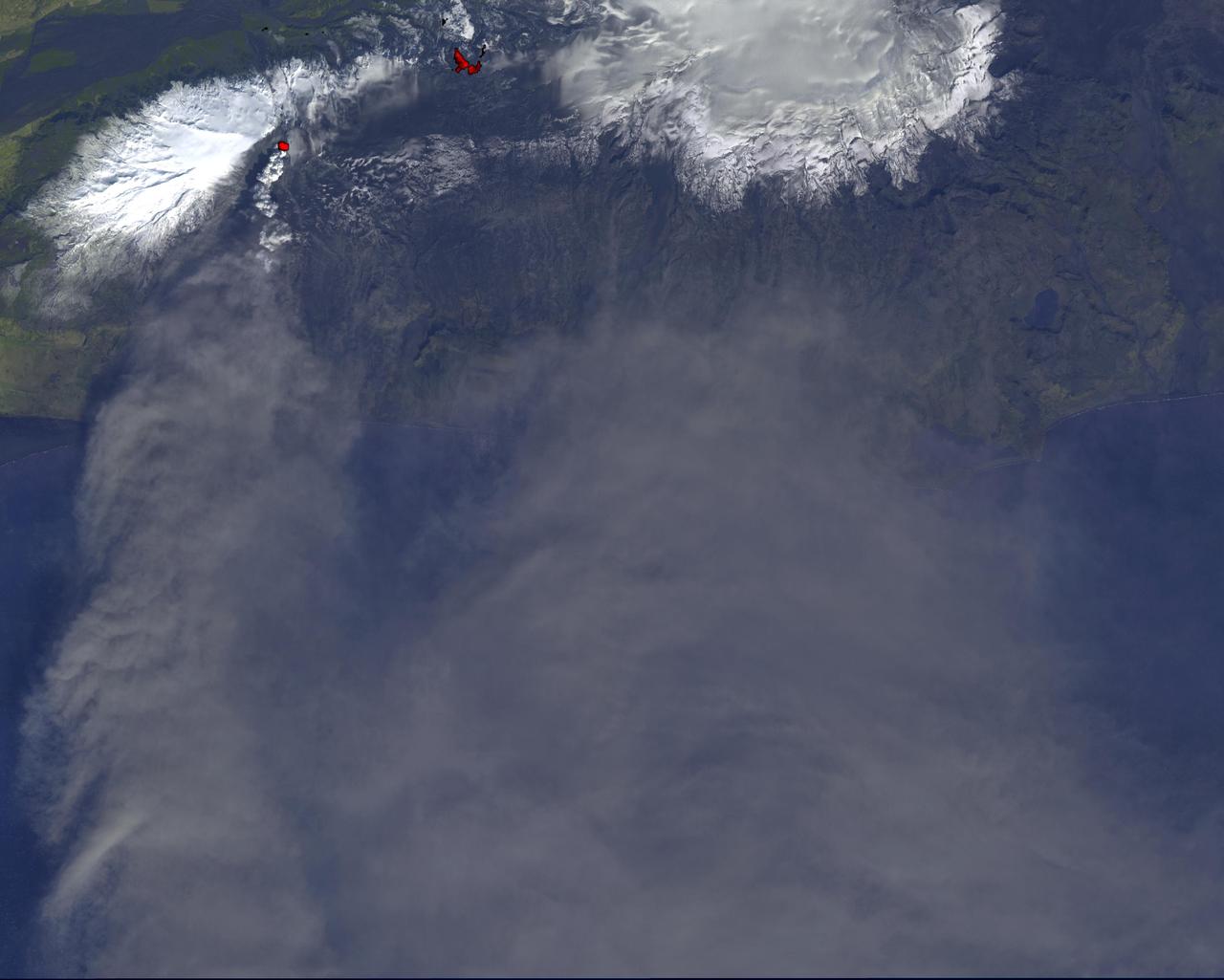
On Monday, April 19, 2010, the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer ASTER instrument onboard NASA Terra spacecraft obtained this image of the continuing eruption of Iceland Eyjafjallajökull volcano.
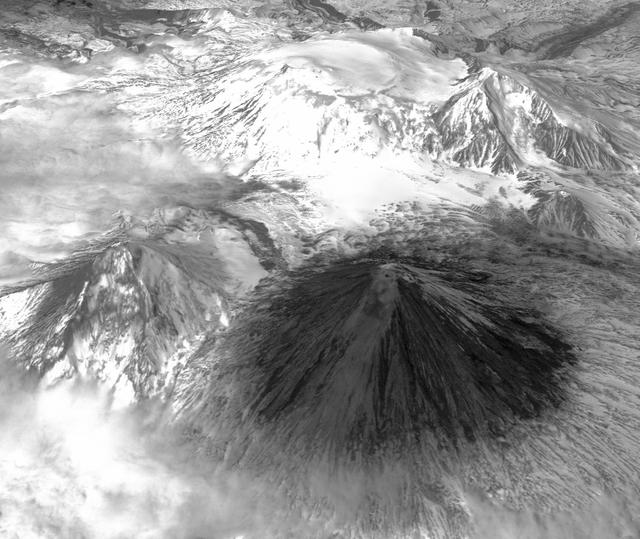

Winter still grips the volcanoes on Russia Kamchatka peninsula. NASA Terra spacecraft acquired this image showing the mantle of white, disturbed by dark ash entirely covering Sheveluch volcano from recent eruptions.

Plosky Tolbachik volcano, in Russia far eastern Kamchatka peninsula, erupted on Nov. 27, 2012 for the first time in 35 years, sending clouds of ash almost 10,000 feet into the sky. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft.

STS068-150-045 (30 September 1994) --- (Kliuchevskoi Volcano) The major eruption that began September 30, 1994 (launch day) got almost immediate coverage by the astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The eruption cloud reached 60,000 feet above sea level, and the winds carried ash as far as 640 miles southeast from the volcano into the North Pacific air routes. This picture was made with a large format Linhof camera. While astronauts used handheld camera's to keep up with the Kamchatka event, instruments in the cargo bay of Endeavour recorded data to support the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL-2) mission.
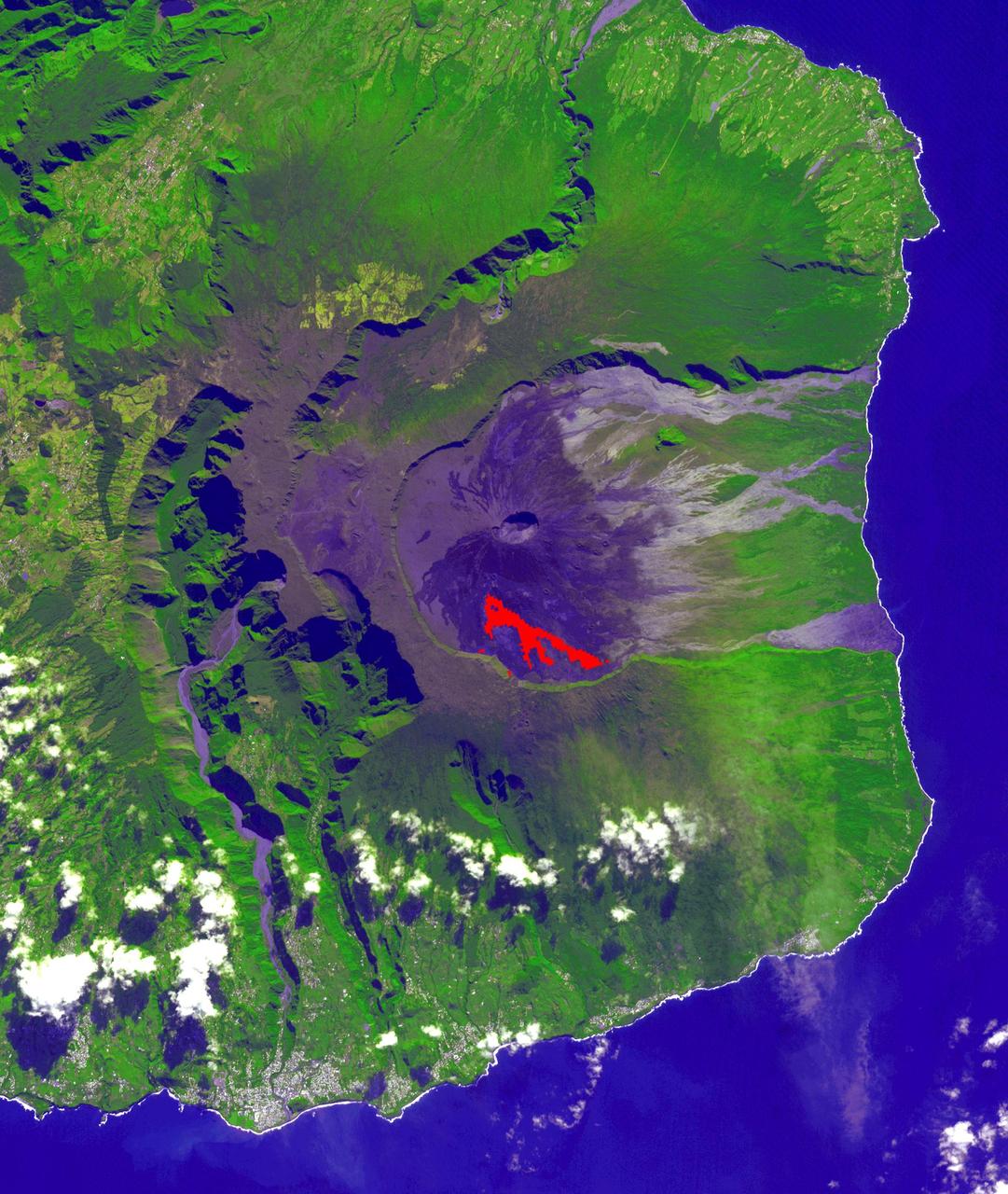
In July, 2018 an eruption began from Piton de la Fournaise volcano on Reunion Island in the western Indian Ocean. Activity continued through November, when these ASTER data were acquired. More than 150 eruptions have occurred since the 17th century. The active flow, derived from the thermal infrared band, is shown in red. The background is a pre-eruption image. The background image was acquired July 16, 2018, and the thermal image on November 1, 2018. The images cover an area of 18 miles by 21 miles (28.9 by 34.2 kilometers), and in the area of 21.3 degrees south, 55.8 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22755

NASA Terra spacecraft shows Popocatepetl, the nearly 18.000-foot-high volcano about 40 miles southeast of Mexico City, continuing to spew water vapor, gas, ashes and glowing rocks from its latest eruption, which started in mid-April 2012.
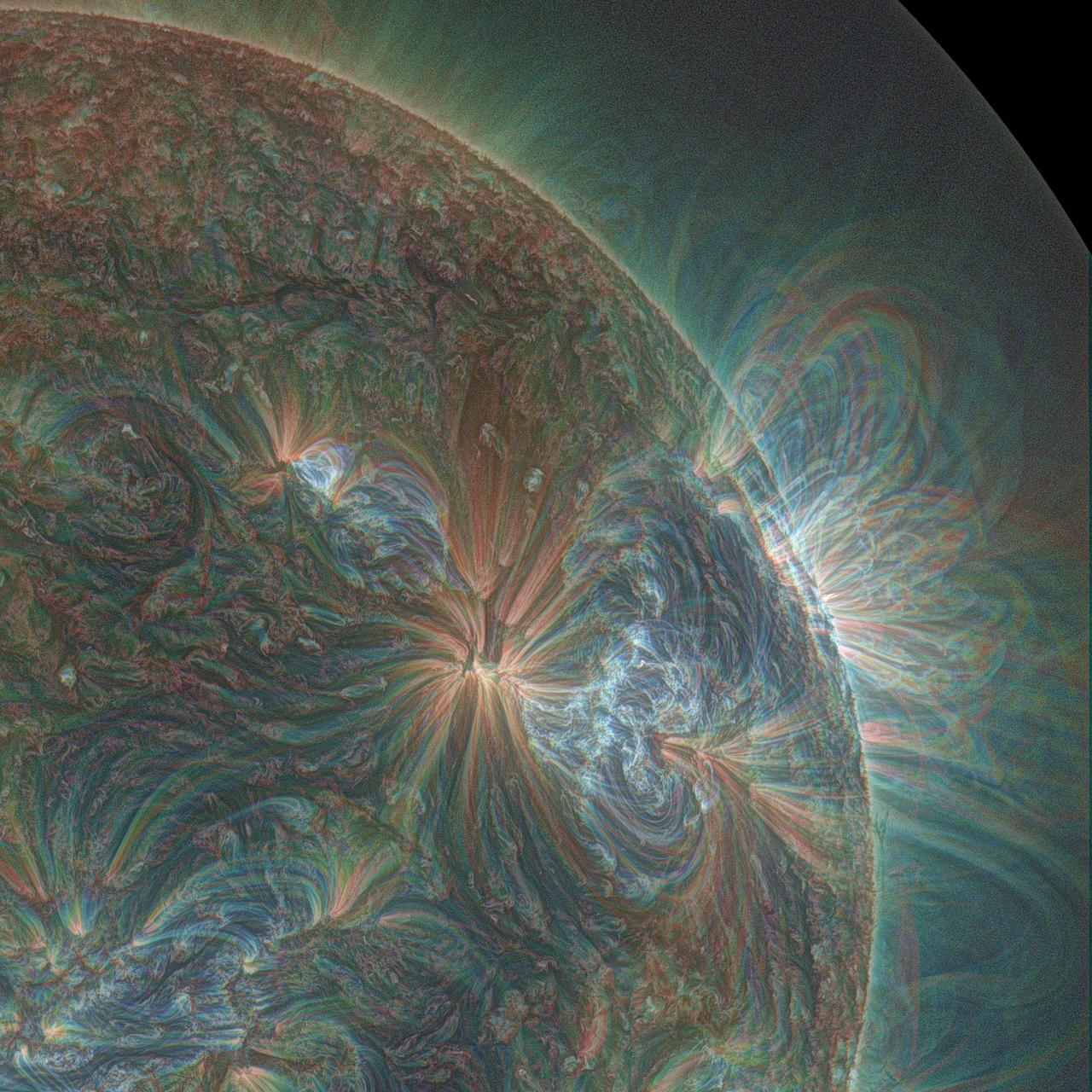

This combination of three wavelengths of light from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory shows one of the multiple jets that led to a series of slow coronal puffs on Jan. 17, 2013. The light has been colorized in red, green and blue. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/UQi41p" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/UQi41p</a> Credit: NASA//SDO/Alzate <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
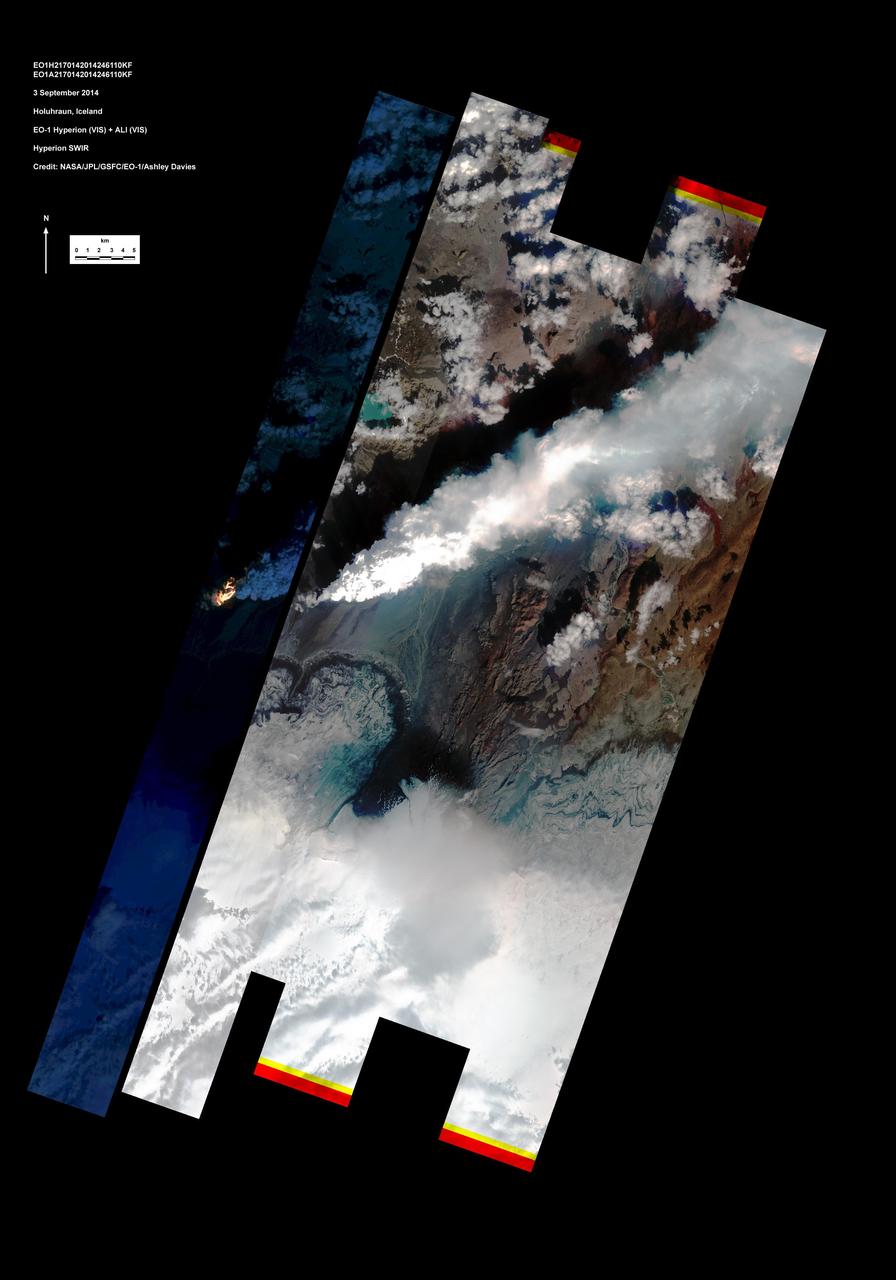
This image shows Iceland volcanic eruption monitored by NASA EO-1 spacecraft. To the south is the edge of Dyngjujökull and to the north is the volcano called Askja.
The Nyiragongo volcano in the Congo erupted on January 17, 2002, and subsequently sent streams of lava into the city of Goma on the north shore of Lake Kivu.
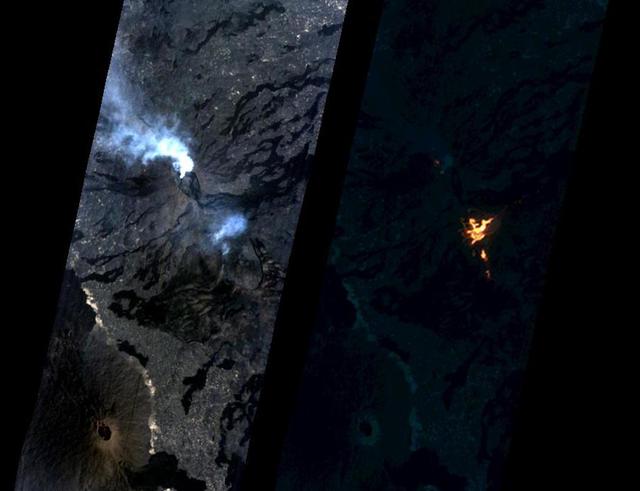

On Jan. 24, 2017, the Hyperion Imager on NASA's Earth Observing 1 (EO-1) spacecraft observed a new eruption at Erta'Ale volcano, Ethiopia, from an altitude of 438 miles (705 kilometers). Data were collected at a resolution of 98 feet (30 meters) per pixel at different visible and infrared wavelengths and were combined to create these images. A visible-wavelength image is on the left. An infrared image is shown on the right. The infrared image emphasizes the hottest areas and reveals a spectacular rift eruption, where a crack opens and lava gushes forth, fountaining into the air. The lava flows spread away from the crack. Erta'Ale is the location of a long-lived lava lake, and it remains to be seen if this survives this new eruption. The observation was scheduled via the Volcano Sensor Web, a network of sensors linked by artificial intelligence software to create an autonomous global monitoring program of satellite observations of volcanoes. The Volcano Sensor Web was alerted to this new activity by data from another spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11239

The eruption of Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai in 2022 produced a plume 58 km high, and produced the biggest atmospheric explosion ever recorded. At least six people lost their lives in the ensuing tsunami. The two small islands are all that is left visible of a huge underwater volcano. The image covers an area of 4.6 by 4.6 km, was acquired September 7, 2022, and is located at 20.5 degrees south, 175.4 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26006

SDO AIA image of the X3.1 flare in 131 angstrom light from 21:43 UT on October 24, 2014. Credit:NASA/SDO More info: The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 5:40 p.m. EDT on Oct. 24, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel. This flare is classified as an X3.1-class flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. The flare erupted from a particularly large active region -- labeled AR 12192 -- on the sun that is the largest in 24 years. This is the fourth substantial flare from this active region since Oct. 19. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
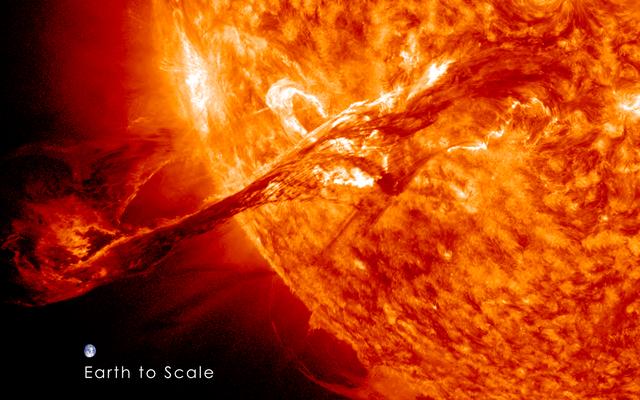

On August 31, 2012 a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into space at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The coronal mass ejection, or CME, traveled at over 900 miles per second. The CME did not travel directly toward Earth, but did connect with Earth's magnetic environment, or magnetosphere, causing aurora to appear on the night of Monday, September 3. The image above includes an image of Earth to show the size of the CME compared to the size of Earth. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA satellite image acquired May 2, 2010 To view a detail of this image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4584266734/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4584266734/</a> Ash and steam continued billowing from Eyjafjallajökull Volcano in early May 2010. The Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite captured this natural-color image on May 2, 2010. The volcano’s summit is near the left edge of this image, capped by a dark plume. The plume is dull gray-brown, indicating that its principal visible component is volcanic ash. Ash from the plume blows toward the east-southeast, passing over a charcoal-colored ash field on the land surface. Just to the north of Eyjafjallajökull’s summit are white puffs of steam, likely from surface lava flows vaporizing snow and glacial ice. On May 4, 2010, the Icelandic Meteorological Office warned that Eyjafjallajökull showed no signs of ending its eruptive activity in the near future. The Met Office reported that ash from the volcano had reached a height of 5.8 to 6.0 kilometers (19,000 to 20,000 feet) above sea level, and had spread 65 to 80 kilometers (40 to 50 miles) east-southeast of the volcano, where it impeded visibility for local residents. The Met Office also reported that lava continued flowing down a steep hill north of the crater. NASA image by Robert Simmon, using ALI data from the EO-1 team. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: EO-1 – ALI To view other images from the Earth Observatory go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
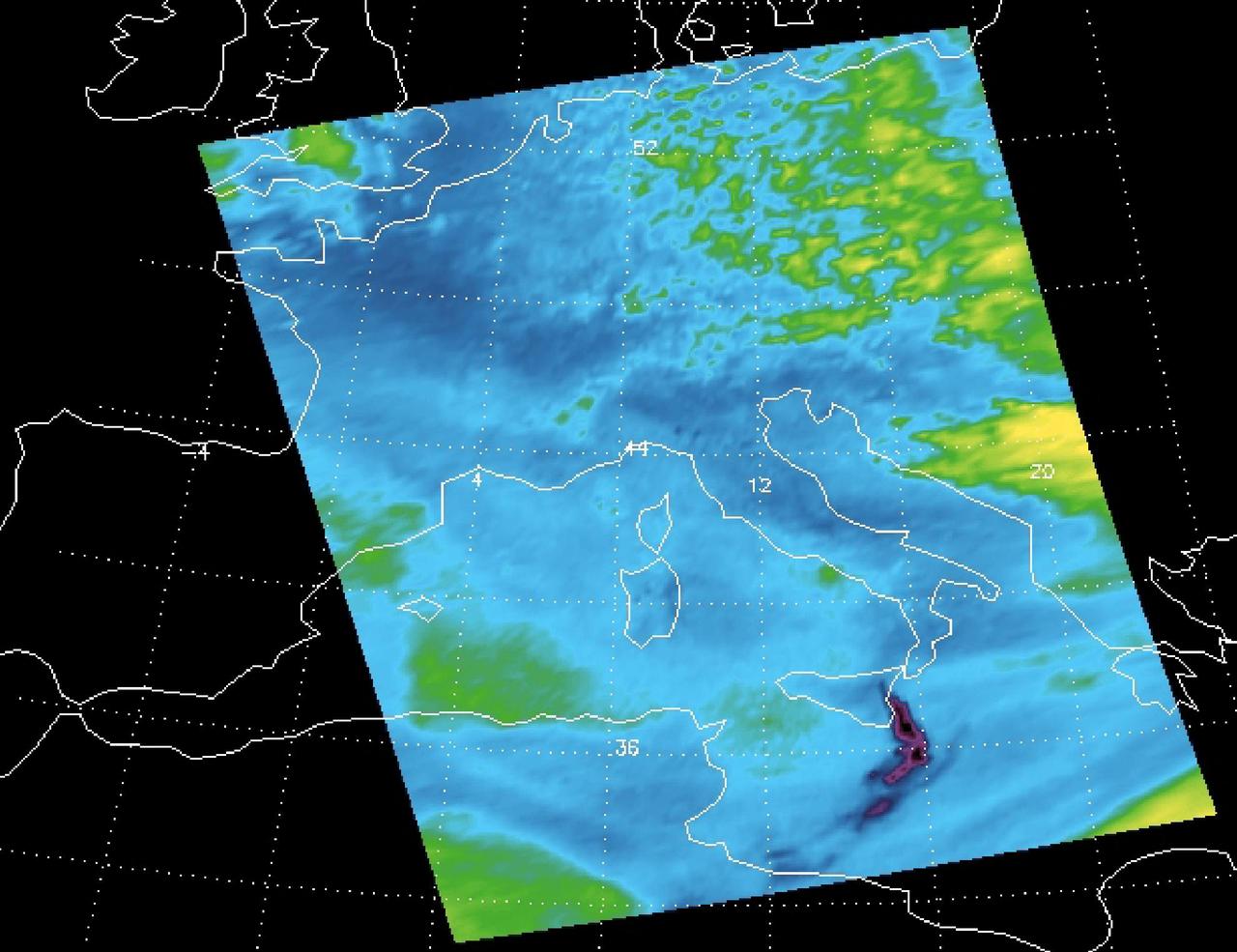
Sulfur dioxide plume from the Mt. Etna Eruption 2002 as seen by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder AIRS on NASA Aqua satellite.

A very active volcano on Jupiter moon Io, probably composed of erupting lava fountains, was seen by NASA Galileo spacecraft.
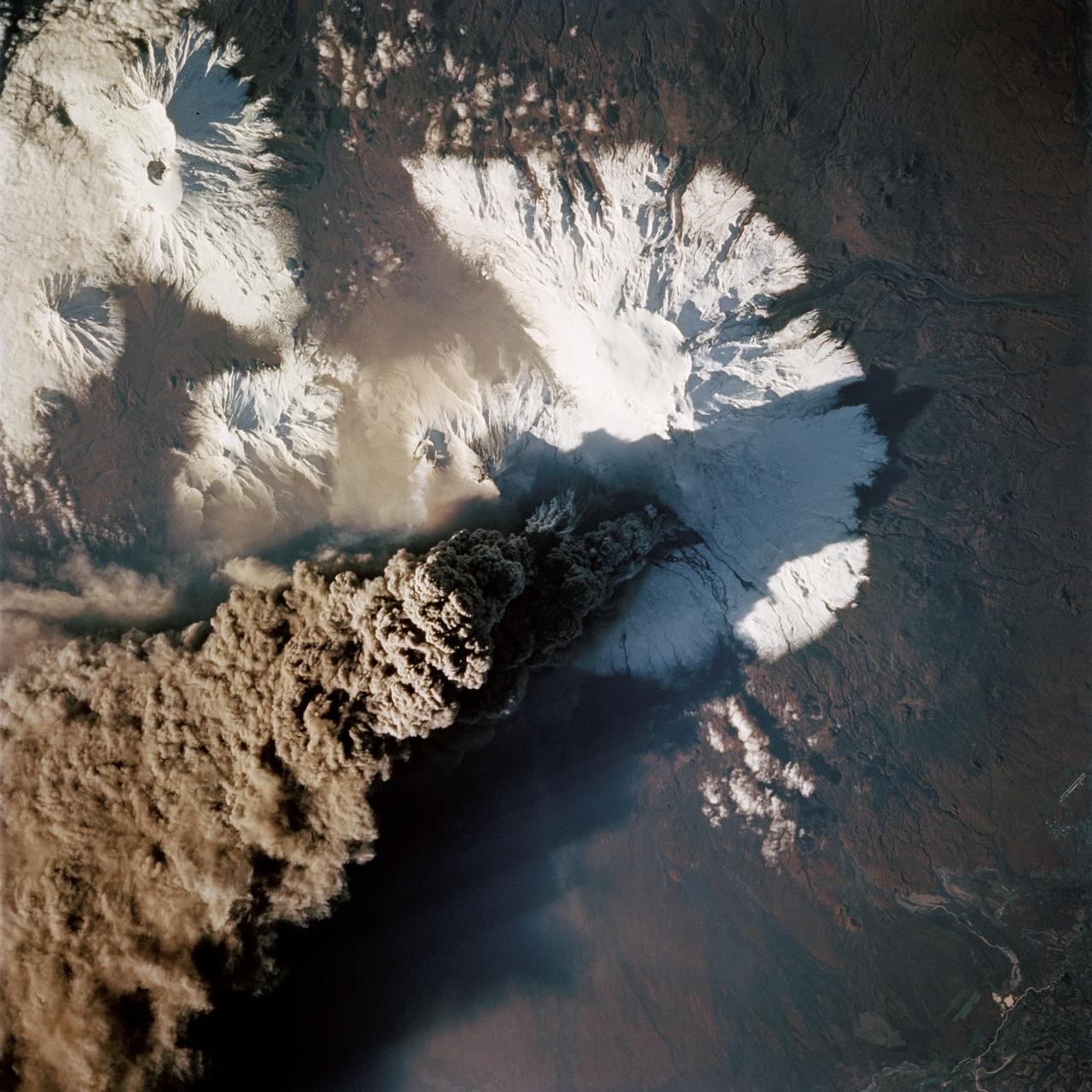

STS068-214-035 (30 September 1994) --- One of the first photos taken by the crewmembers on launch day of the Space Shuttle Endeavour was this 70mm frame of the Kliuchevskoi volcano on the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia. The volcano was near its peak at this time. The large, black eruption plume billows from the summit, as ash is being deposited on the snow-covered region to the east and southeast (north is to upper left). A small steam plume rises from the peak of Bezymianny just south of Kliuchevskoi (or just right of center). As various members of the six-person crew were using handheld cameras to record the eruption, hardware in Endeavour's cargo bay was taking radar data of the event in support of the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL-2) project.
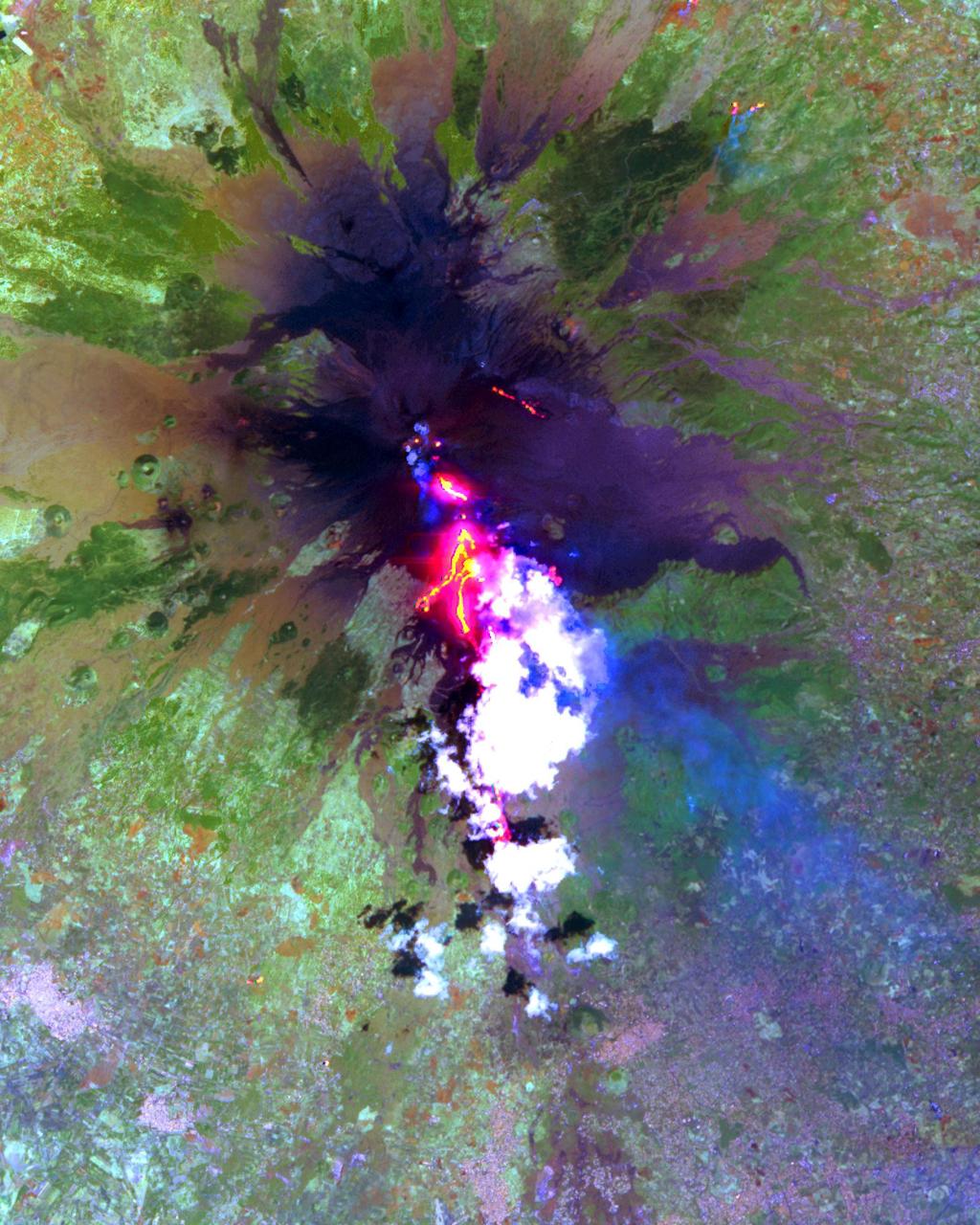

The current eruption of Mt. Etna started on July 17, and has continued to the present. This ASTER image was acquired on Sunday, July 29 and shows advancing lava flows on the southern flank of Mt. Etna above the town of Nicolosi, which is potentially threatened if the eruption increases in magnitude. Also visible are glowing summit craters above the main lava flows, and a small fissure eruption. The bright puffy clouds were formed from water vapor released during the eruption. The image covers an area of 24 x 30 km. The image is centered at 37.7 degrees north latitude, 15 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02677
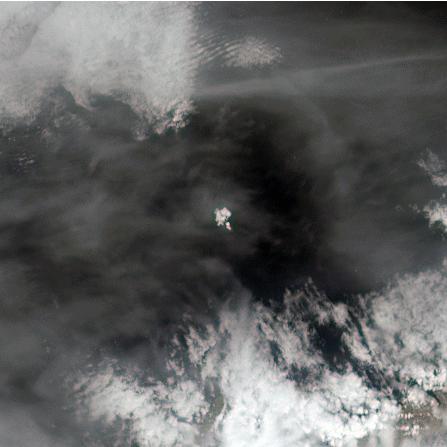

The tiny Aleutian island of Bogoslof in Alaska, erupting regularly since December 2016, produced fresh activity on Sunday, May 28, 2017. Bogoslof is a stratovolcano fueled by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the North American Plate and forms part of the larger Aleutian Arc, which includes more than 60 volcanoes on the Aleutian Islands and the Aleutian Range on the Alaska mainland. Previous to its recent period of activity, Bogoslof had last erupted in 1992, and its above-water surface area was a mere 0.11 square miles (0.29 square kilometers). As of March 11, the most recent data available, the area of the island had tripled to 0.38 square miles (0.98 square kilometers). The event on May 28 produced an ash cloud that reached 40,000 feet (12 km) in altitude, causing the Alaskan Volcano Observatory to issue a red alert for air travel in the area. Volcanic ash can cause major damage to aircraft engines, and the region is close to several major air routes between North America and Asia. On May 28, 2017, at approximately 2:23 p.m. local time, NASA's Terra satellite passed over Bogoslof, less than 10 minutes after the eruption began. MISR has nine cameras that view Earth at different angles. It takes slightly less than seven minutes for all nine cameras to view the same location on Earth. An animation made from the images from the nine MISR cameras, captured between 2:19 and 2:26 p.m., demonstrates how the angled views give a glimpse of the underside of the growing plume of volcanic ash, showing the eruption column widening into the cloud at the top. The animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21655
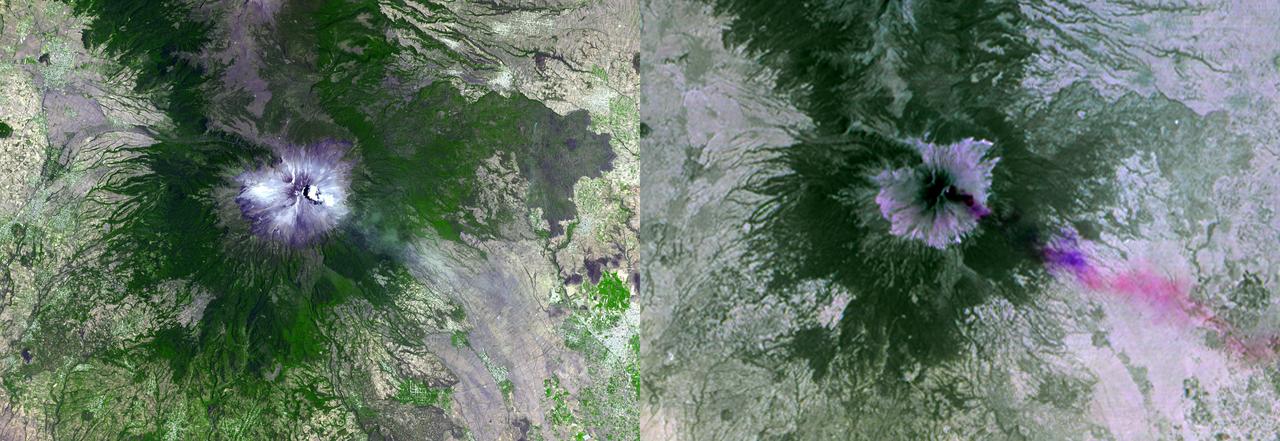

NASA Terra spacecraft shows Mexico active Popocatepetl volcano, located about 40 miles southeast of Mexico City, spewing water vapor, gas, ashes and glowing rocks since its most recent eruption period began in April 2012.
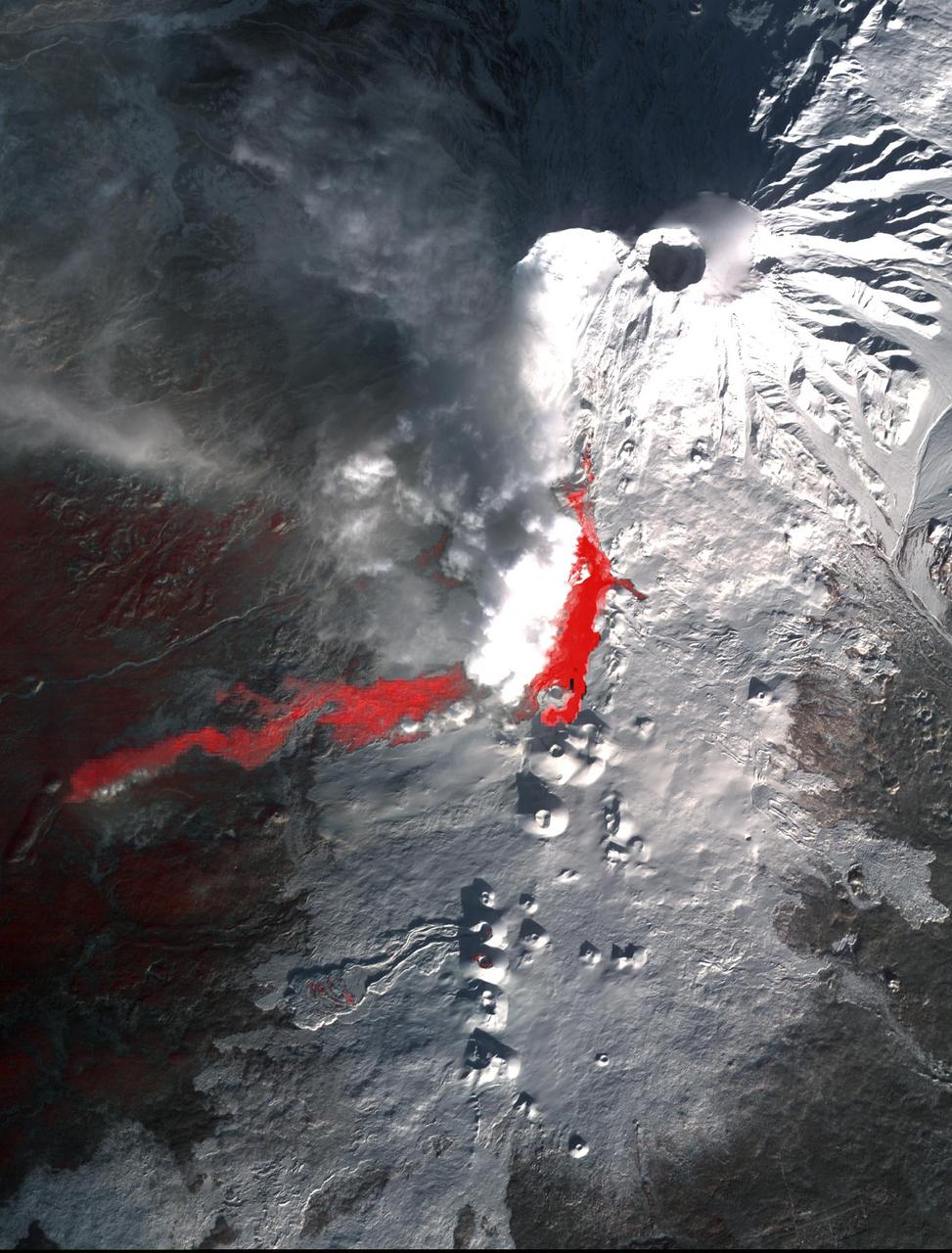
Plosky Tolbachik volcano in Russia far eastern Kamchatka peninsula erupted on Nov. 27, 2012, for the first time in 35 years, sending clouds of ash to the height of more than 9,800 feet 3,000 meters in this image from NASA Terra spacecraft.

This satellite interferometric synthetic aperture radar image-pair shows relative deformation of the Earth surface when nn April 22-23, 2015, significant explosive eruptions occurred at Calbuco volcano, Chile.
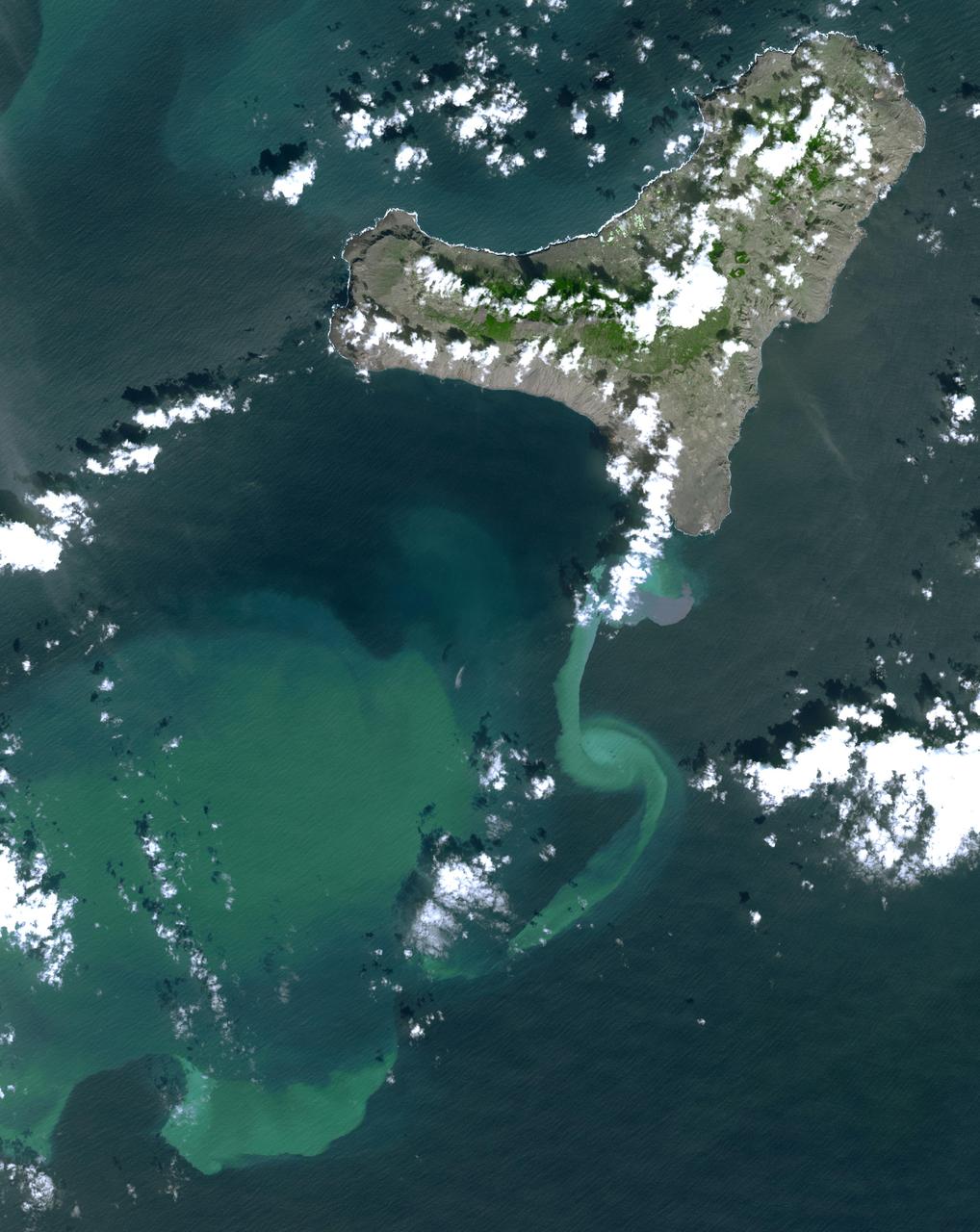

In July 2011, volcanic tremors began on the Island of El Hierro in the Canary Islands; by September, many tourists evacuated the resort island, fearing a volcanic eruption. This image is from NASA Terra spacecraft.
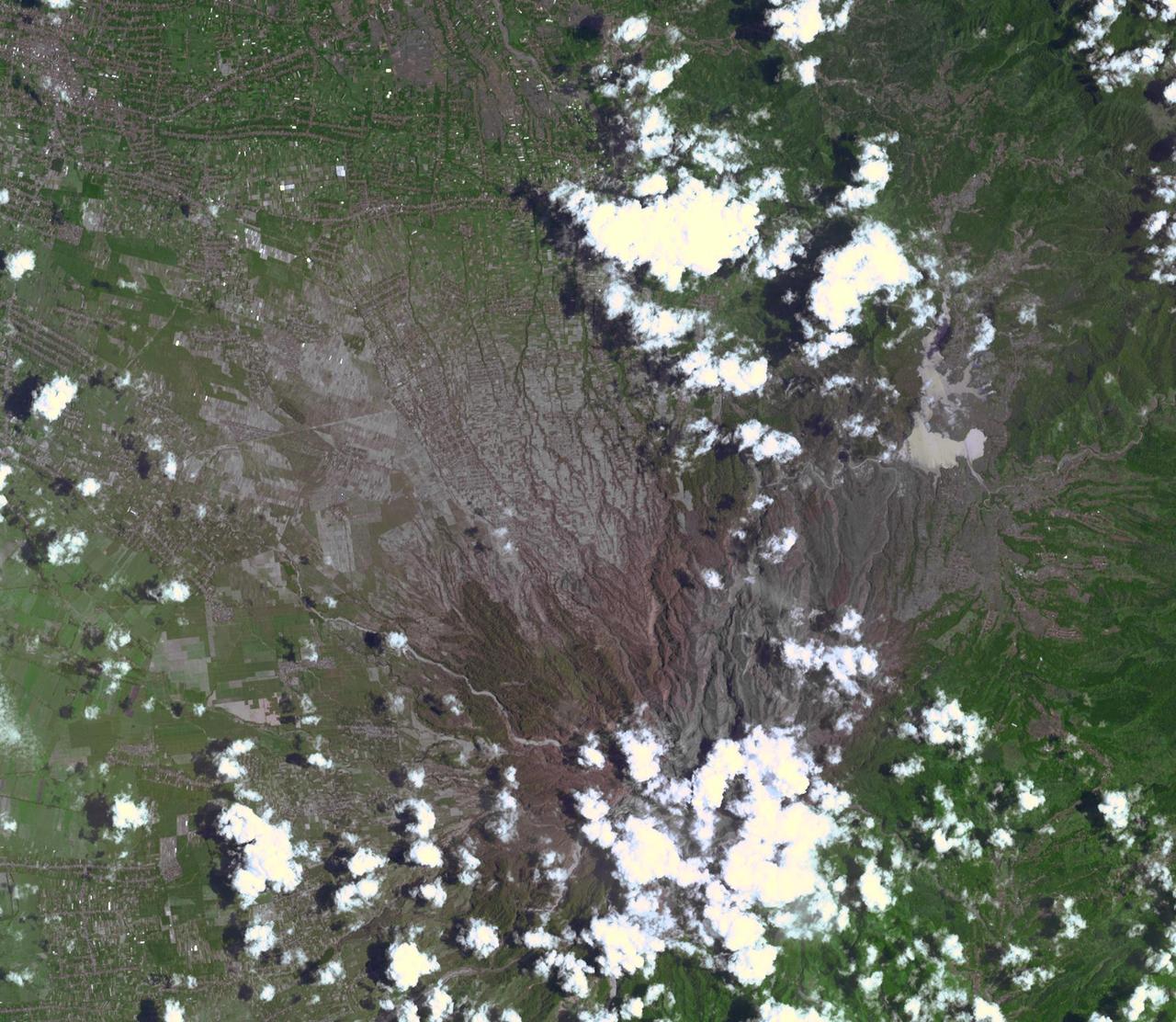

On Feb. 13, 2014, violent eruption of Kelud stratovolcano in Java, Indonesia sent volcanic ash covering an area of 70,000 square miles, prompting the evacuation of tens of thousands of people. This image is from NASA Terra spacecraft.
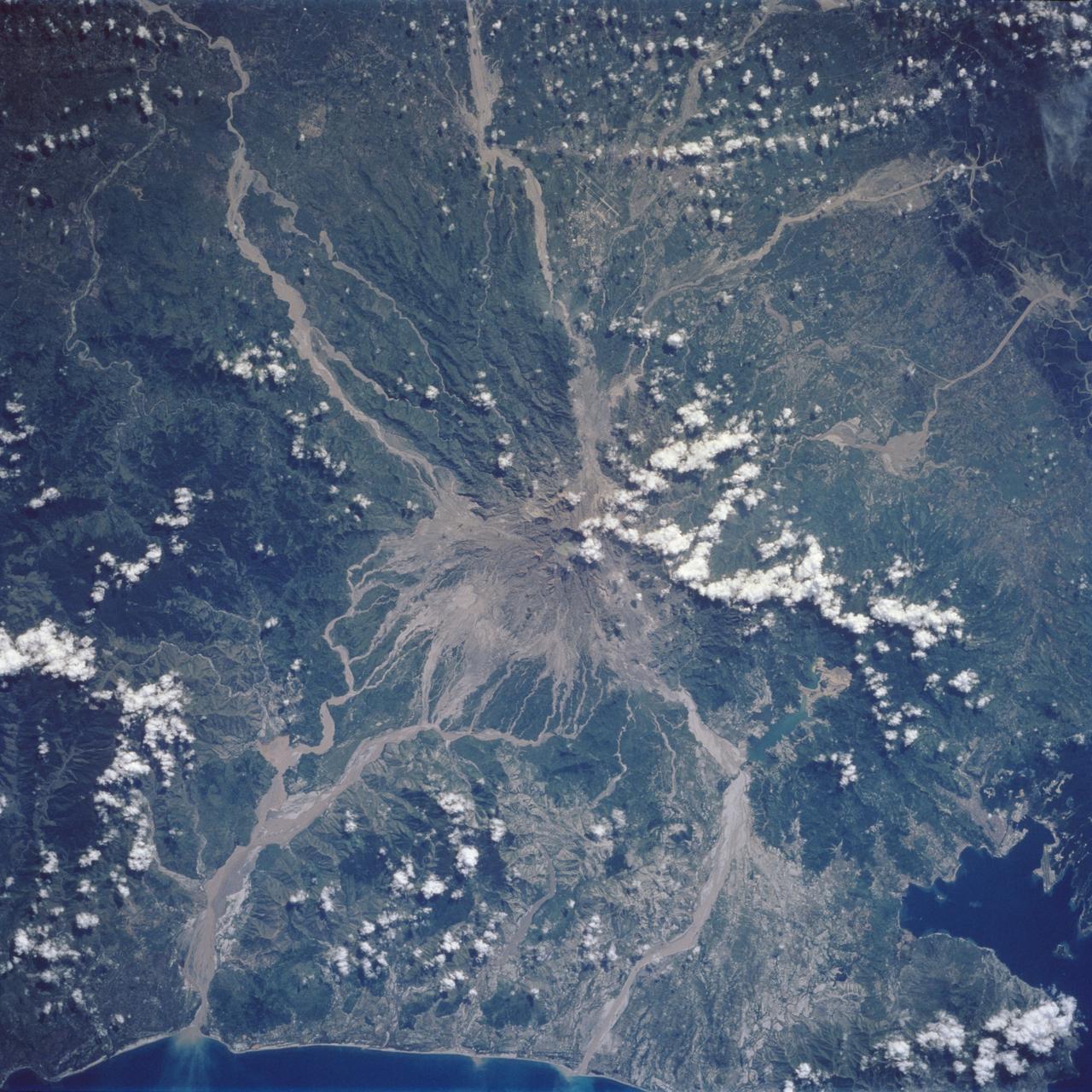

Mt. Pinatubo on the island of Luzon (15.0N, 120.0E) erupted catastrophically in June 1991 after over 600 years of inactivity. In this vertical view, the full extent of the eruption is obvious. Thick layers of ash completely surrounds the crater and the effect of mudflows in this previously heavily forested and agricultural region can be traced as ribbons flowing downhill. Clark AFB, once the crossroads of the SW Pacific can only partially be seen.

This spectacular view is a color-enhanced ultraviolet exposure of a colossal eruption, photographed during the Skylab-4 mission by the Apollo Telescope Mount facility on December 19, 1973. This giant prominence, one of the mightiest in 25 years, sparned a third of a million miles into space, roughly the distance between Earth and the Moon.
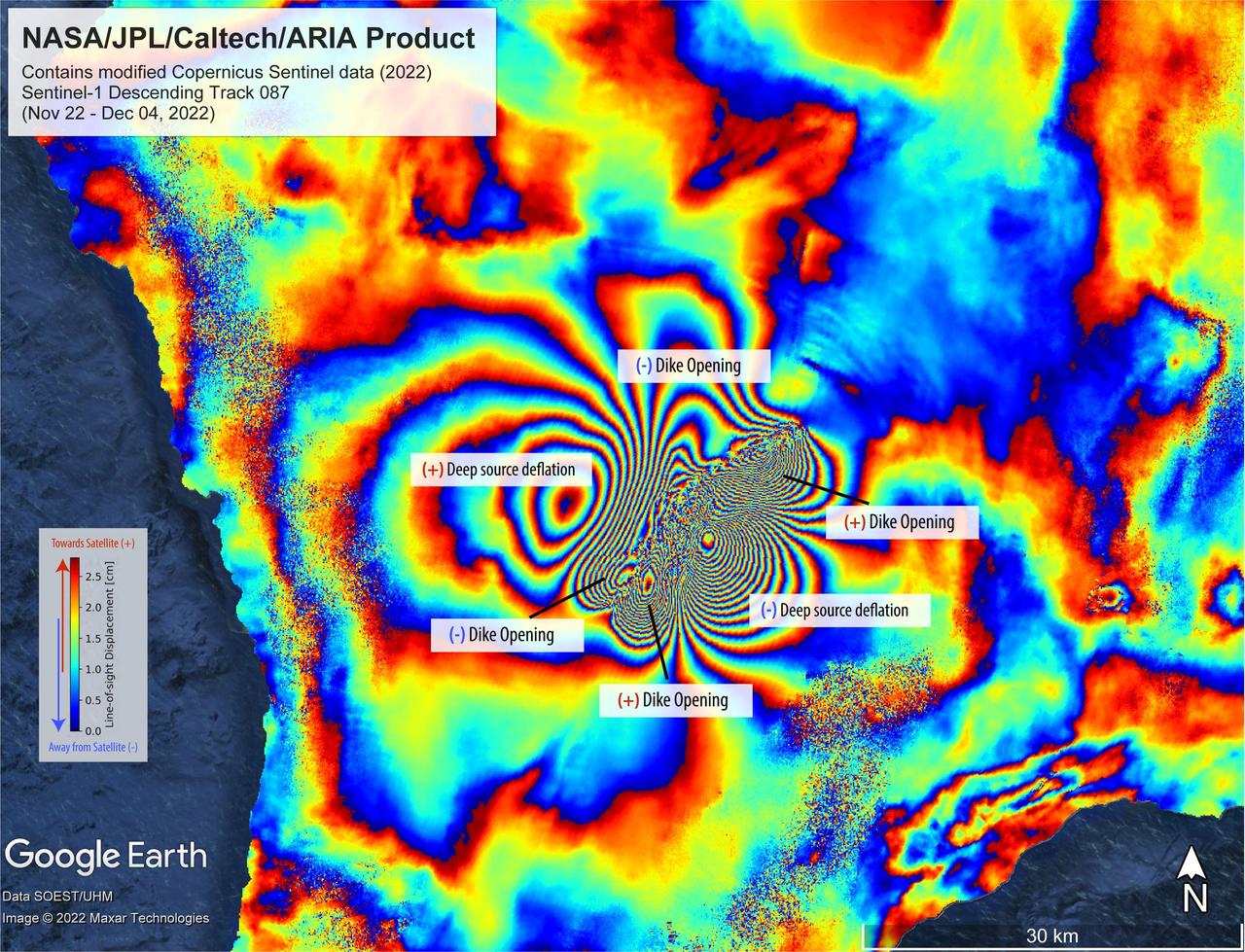
On Nov. 27, 2022, Mauna Loa, Earth's largest active volcano, began erupting from the summit caldera inside Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. Scientists with the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis project (ARIA), a collaboration between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the California Institute of Technology, which manages JPL for the agency, analyzed synthetic aperture radar images from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 satellites operated by ESA (European Space Agency) to calculate a map of the Earth's ground movement as a result of the eruption. Using images acquired before and after the start of the eruption – Nov. 22 and Dec. 4, 2022, respectively – scientists produced this false-color map showing the amount of ground surface movement, or displacement, the eruption caused. In the map, surface displacements are seen as color contours, or "fringes," where each color cycle represents about 2.8 centimeters of surface motion. The direction of the ground movement (whether toward or away from the satellite) is indicated by the color cycle (from outer to inner direction). A positive (+) indication, meaning "ground moved towards satellite," has a color cycle of blue-green-yellow-orange-red. A negative (-) indication, meaning "ground moved away from the satellite," has a color cycle of red-orange-yellow-green-blue. The broader fringes are representative of deep source processes within the volcano. In this case, a broad tabular source of magma deflated and fed the eruption as magma or lava was being supplied, somewhat like a deflating balloon (only tabular in shape) that shrank because pressure was relieved. The dense fringes marked as "dike opening" are a signature of the ground rupturing (or opening) as the magma made its way towards the Earth's surface. Scientists use these maps to build detailed models of subsurface volcanic processes to better forecast and understand the impact of future volcanic activity. The Sentinel-1 data were provided by ESA. The image contains modified Copernicus 2022 data, processed by ESA and analyzed by NASA-JPL. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25525

STS068-155-094 (30 September-11 October 1994) --- (Kliuchevskoi Volcano) The crewmembers used a Linhof large format Earth observation camera to photograph this nadir view of the Kamchatka peninsula's week-old volcano. The eruption and the follow-up environmental activity was photographed from 115 nautical miles above Earth. Six NASA astronauts spent a week and a half aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in support of the Space Radar Laboratory 2 (SRL-2) mission.
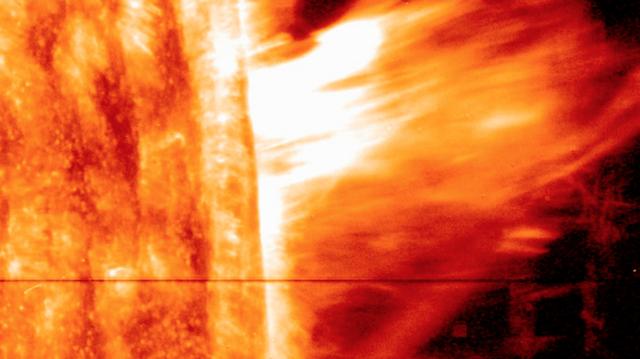
Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
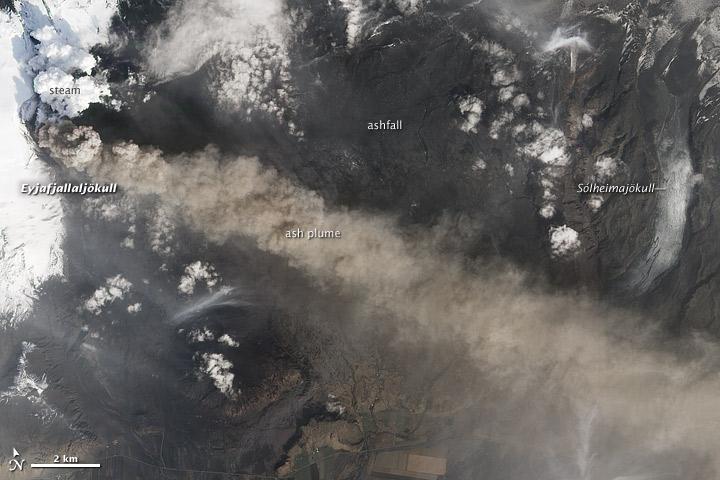

NASA satellite image acquired May 2, 2010 To see the full view of this image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4584266582/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4584266582/</a> Ash and steam continued billowing from Eyjafjallajökull Volcano in early May 2010. The Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite captured this natural-color image on May 2, 2010. The volcano’s summit is near the left edge of this image, capped by a dark plume. The plume is dull gray-brown, indicating that its principal visible component is volcanic ash. Ash from the plume blows toward the east-southeast, passing over a charcoal-colored ash field on the land surface. Just to the north of Eyjafjallajökull’s summit are white puffs of steam, likely from surface lava flows vaporizing snow and glacial ice. On May 4, 2010, the Icelandic Meteorological Office warned that Eyjafjallajökull showed no signs of ending its eruptive activity in the near future. The Met Office reported that ash from the volcano had reached a height of 5.8 to 6.0 kilometers (19,000 to 20,000 feet) above sea level, and had spread 65 to 80 kilometers (40 to 50 miles) east-southeast of the volcano, where it impeded visibility for local residents. The Met Office also reported that lava continued flowing down a steep hill north of the crater. NASA image by Robert Simmon, using ALI data from the EO-1 team. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: EO-1 – ALI To view other images from the Earth Observatory go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Watch a video from this event here: <a href="https://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/14118958800/</a> A coronal mass ejection, or CME, surged off the side of the sun on May 9, 2014, and NASA's newest solar observatory caught it in extraordinary detail. This was the first CME observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, which launched in June 2013 to peer into the lowest levels of the sun's atmosphere with better resolution than ever before. Watch the movie to see how a curtain of solar material erupts outward at speeds of 1.5 million miles per hour. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kp7O4F</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>