
View a video clip zoom in on galaxy ESO 306-17 here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4409589832/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/4409589832/</a> This image from the Advanced Camera for Surveys aboard the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope highlights the large and bright elliptical galaxy called ESO 306-17 in the southern sky. In this image, it appears that ESO 306-17 is surrounded by other galaxies but the bright galaxies at bottom left are thought to be in the foreground, not at the same distance in the sky. In reality, ESO 306-17 lies fairly abandoned in an enormous sea of dark matter and hot gas. Researchers are also using this image to search for nearby ultra-compact dwarf galaxies. Ultra-compact dwarfs are mini versions of dwarf galaxies that have been left with only their core due to interaction with larger, more powerful galaxies. Most ultra-compact dwarfs discovered to date are located near giant elliptical galaxies in large clusters of galaxies, so it will be interesting to see if researchers find similar objects in fossil groups. Credit: NASA, ESA and Michael West (ESO)

NASA image release May 11, 2010 Hubble Catches Heavyweight Runaway Star Speeding from 30 Doradus Image: ESO 2.2-m WFI Image of the Tarantula Nebula A blue-hot star, 90 times more massive than our Sun, is hurtling across space fast enough to make a round trip from Earth to the Moon in merely two hours. Though the speed is not a record-breaker, it is unique to find a homeless star that has traveled so far from its nest. The only way the star could have been ejected from the star cluster where it was born is through a tussle with a rogue star that entered the binary system where the star lived, which ejected the star through a dynamical game of stellar pinball. This is strong circumstantial evidence for stars as massive as 150 times our Sun's mass living in the cluster. Only a very massive star would have the gravitational energy to eject something weighing 90 solar masses. The runaway star is on the outskirts of the 30 Doradus nebula, a raucous stellar breeding ground in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud. The finding bolsters evidence that the most massive stars in the local universe reside in 30 Doradus, making it a unique laboratory for studying heavyweight stars. 30 Doradus, also called the Tarantula Nebula, is roughly 170,000 light-years from Earth. To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/runaway-star.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/runaway-star.html</a> Credit: NASA/ESO, J. Alves (Calar Alto, Spain), and B. Vandame and Y. Beletski (ESO) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

NASA image release May 11, 2010 Hubble Catches Heavyweight Runaway Star Speeding from 30 Doradus Image: Hubble/WFPC2 and ESO/2.2-m Composite Image of 30 Dor Runaway Star A blue-hot star, 90 times more massive than our Sun, is hurtling across space fast enough to make a round trip from Earth to the Moon in merely two hours. Though the speed is not a record-breaker, it is unique to find a homeless star that has traveled so far from its nest. The only way the star could have been ejected from the star cluster where it was born is through a tussle with a rogue star that entered the binary system where the star lived, which ejected the star through a dynamical game of stellar pinball. This is strong circumstantial evidence for stars as massive as 150 times our Sun's mass living in the cluster. Only a very massive star would have the gravitational energy to eject something weighing 90 solar masses. The runaway star is on the outskirts of the 30 Doradus nebula, a raucous stellar breeding ground in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud. The finding bolsters evidence that the most massive stars in the local universe reside in 30 Doradus, making it a unique laboratory for studying heavyweight stars. 30 Doradus, also called the Tarantula Nebula, is roughly 170,000 light-years from Earth. To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/runaway-star.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/runaway-star.html</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, J. Walsh (ST-ECF), and ESO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

This image, taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 on board the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows the globular cluster Terzan 1. Lying around 20 000 light-years from us in the constellation of Scorpius (The Scorpion), it is one of about 150 globular clusters belonging to our galaxy, the Milky Way. Typical globular clusters are collections of around a hundred thousand stars, held together by their mutual gravitational attraction in a spherical shape a few hundred light-years across. It is thought that every galaxy has a population of globular clusters. Some, like the Milky Way, have a few hundred, while giant elliptical galaxies can have several thousand. They contain some of the oldest stars in a galaxy, hence the reddish colours of the stars in this image — the bright blue ones are foreground stars, not part of the cluster. The ages of the stars in the globular cluster tell us that they were formed during the early stages of galaxy formation! Studying them can also help us to understand how galaxies formed. Terzan 1, like many globular clusters, is a source of X-rays. It is likely that these X-rays come from binary star systems that contain a dense neutron star and a normal star. The neutron star drags material from the companion star, causing a burst of X-ray emission. The system then enters a quiescent phase in which the neutron star cools, giving off X-ray emission with different characteristics, before enough material from the companion builds up to trigger another outburst.

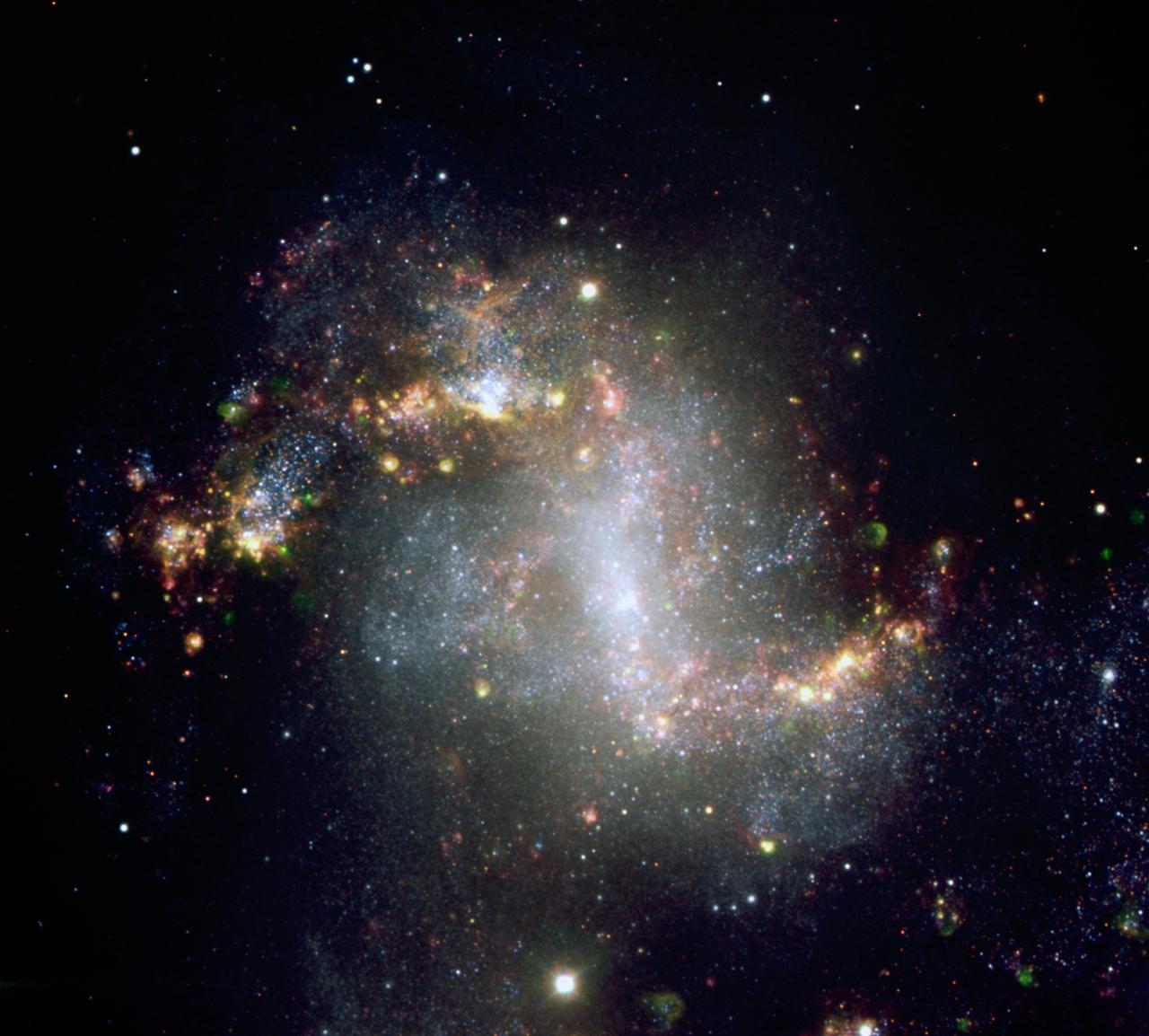
This composite of the giant barred spiral galaxy NGC 6872 is 522,000 light-years across, making it about five times the size of the Milky Way.

NASA Hubble Space Telescope has imaged an unusual edge-on galaxy, revealing remarkable details of its warped dusty disc and showing how colliding galaxies trigger the birth of new stars.

This image displays a galaxy known as ESO 486-21 (with several other background galaxies and foreground stars visible in the field as well). ESO 486-21 is a spiral galaxy — albeit with a somewhat irregular and ill-defined structure — located some 30 million light-years from Earth. The NASA/ESA (European Space Agency) Hubble Space Telescope observed this object while performing a survey — the Legacy ExtraGalactic UV Survey (LEGUS) — of 50 nearby star-forming galaxies. The LEGUS sample was selected to cover a diverse range of galactic morphologies, star formation rates, galaxy masses and more. Astronomers use such data to understand how stars form and evolve within clusters, and how these processes affect both their home galaxy and the wider universe. ESO 486-21 is an ideal candidate for inclusion in such a survey because it is known to be in the process of forming new stars, which are created when large clouds of gas and dust (seen here in pink) within the galaxy crumple inwards upon themselves. Credit: NASA/ESA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release May 20, 2011 <b>To see a really cool video related to this image go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5740451675/in/photostream">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5740451675/in/photostream</a></b> This composite of visible, microwave (orange) and X-ray (blue) data reveals the jets and radio-emitting lobes emanating from Centaurus A's central black hole. Credit: ESO/WFI (visible); MPIfR/ESO/APEX/A.Weiss et al. (microwave); NASA/CXC/CfA/R.Kraft et al. (X-ray) To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/radio-particle-jets.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/radio-particle-jets...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

The central parts of the starburst galaxy NGC 1313. The very active state of this galaxy is evident from the image, showing many star formation regions. A great number of supershell nebulae, that is, cocoons of gas inflated and etched by successive bursts of star formation, are visible. The green nebulosities are regions emitting in the ionised oxygen lines and may harbour clusters with very hot stars. This colour-composite is based on images obtained with the FORS1 instrument on one of the 8.2-m Unit Telescope of ESO's Very Large Telescope, located at Cerro Paranal. The data were obtained in the night of 16 December 2003, through different broad- (R, B, and z) and narrow-band filters (H-alpha, OI, and OIII).
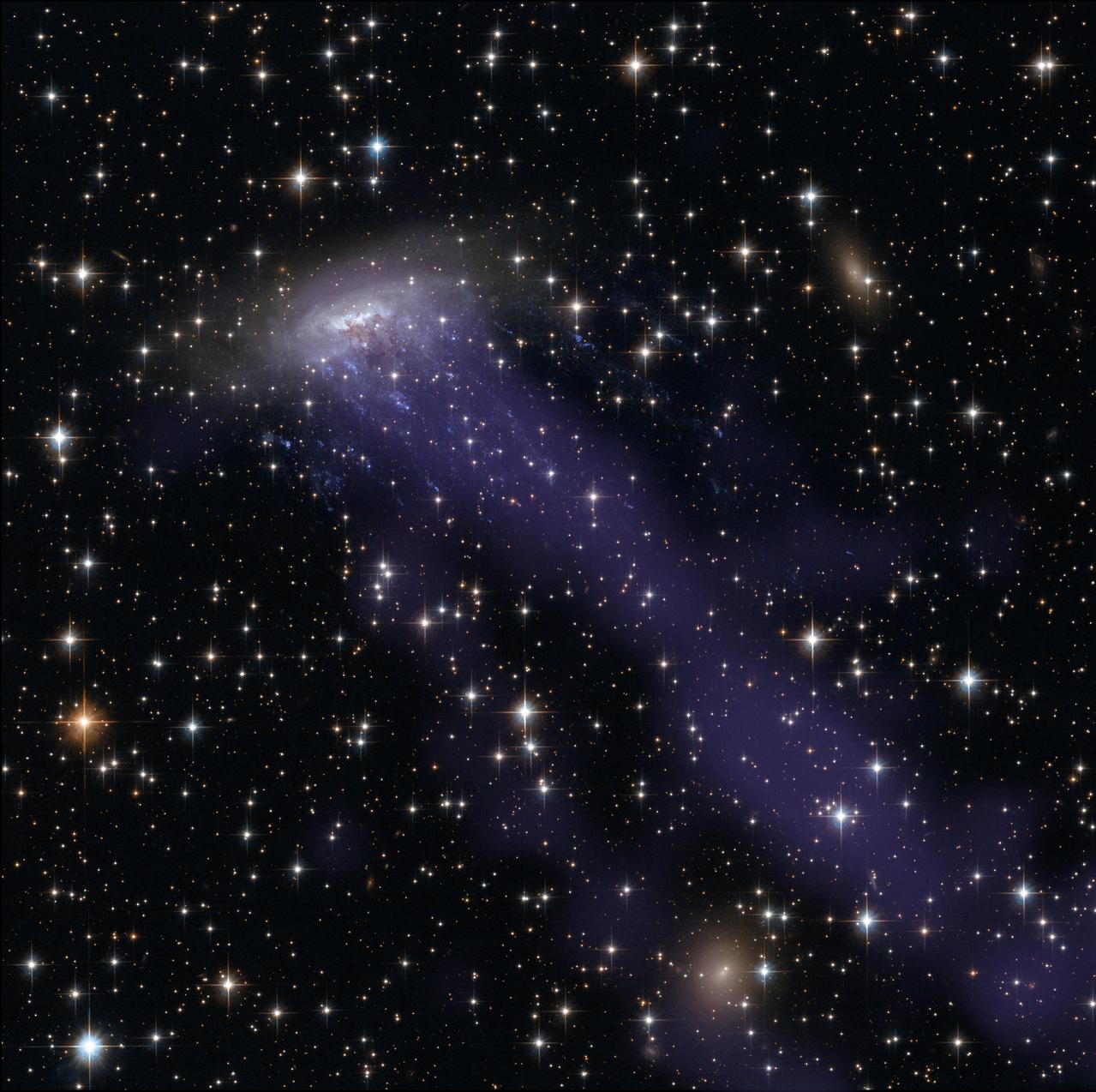

This image combines NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope observations with data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory. As well as the electric blue ram pressure stripping streaks seen emanating from ESO 137-001, a giant gas stream can be seen extending towards the bottom of the frame, only visible in the X-ray part of the spectrum. Credit: NASA, ESA, CXC The spiral galaxy ESO 137-001 looks like a dandelion caught in a breeze in this new Hubble Space Telescope image. The galaxy is zooming toward the upper right of this image, in between other galaxies in the Norma cluster located over 200 million light-years away. The road is harsh: intergalactic gas in the Norma cluster is sparse, but so hot at 180 million degrees Fahrenheit that it glows in X-rays. The spiral plows through the seething intra-cluster gas so rapidly – at nearly 4.5 million miles per hour — that much of its own gas is caught and torn away. Astronomers call this "ram pressure stripping." The galaxy’s stars remain intact due to the binding force of their gravity. Tattered threads of gas, the blue jellyfish-tendrils trailing ESO 137-001 in the image, illustrate the process. Ram pressure has strung this gas away from its home in the spiral galaxy and out over intergalactic space. Once there, these strips of gas have erupted with young, massive stars, which are pumping out light in vivid blues and ultraviolet. The brown, smoky region near the center of the spiral is being pushed in a similar manner, although in this case it is small dust particles, and not gas, that are being dragged backwards by the intra-cluster medium. Read more here: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P0HSFh" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P0HSFh</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
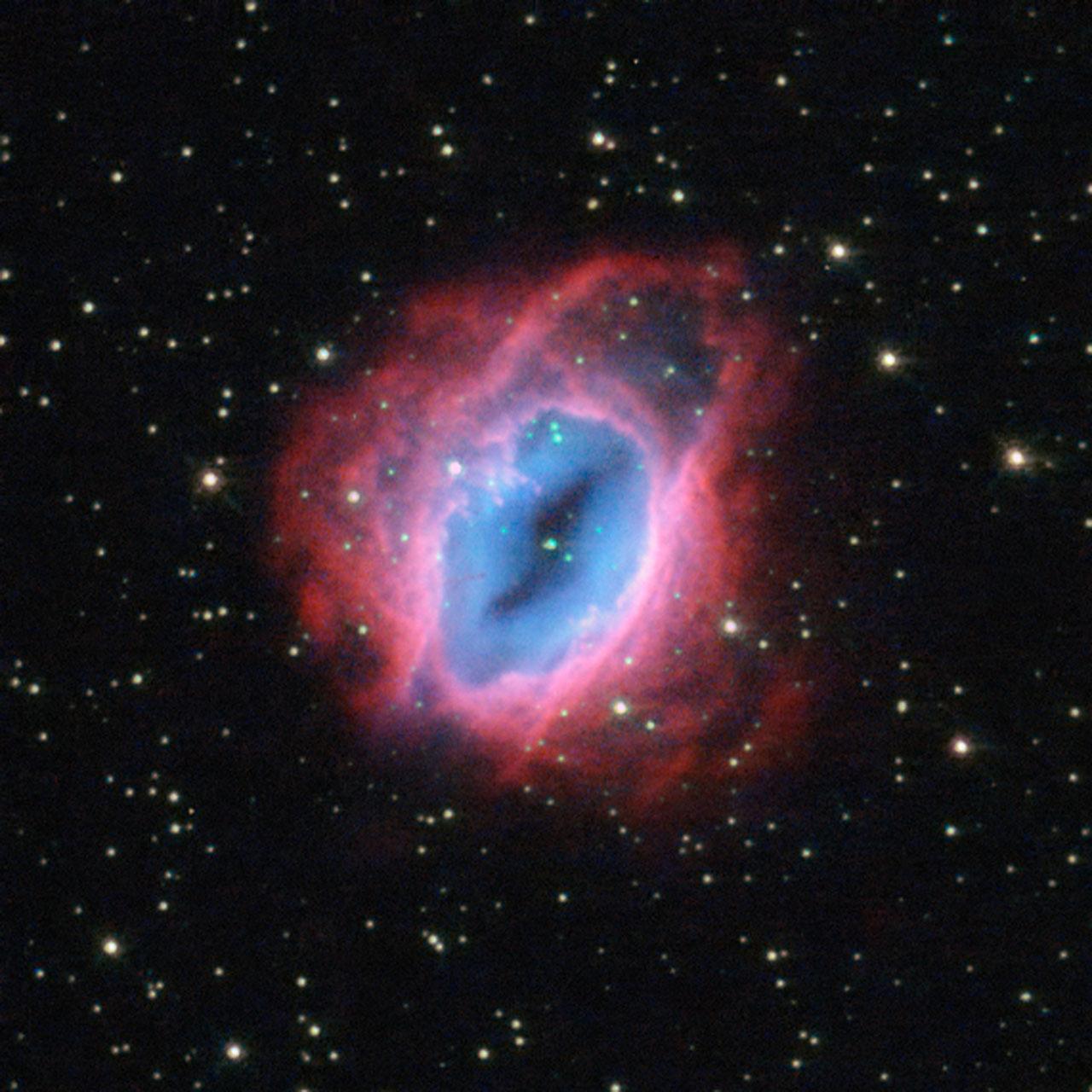

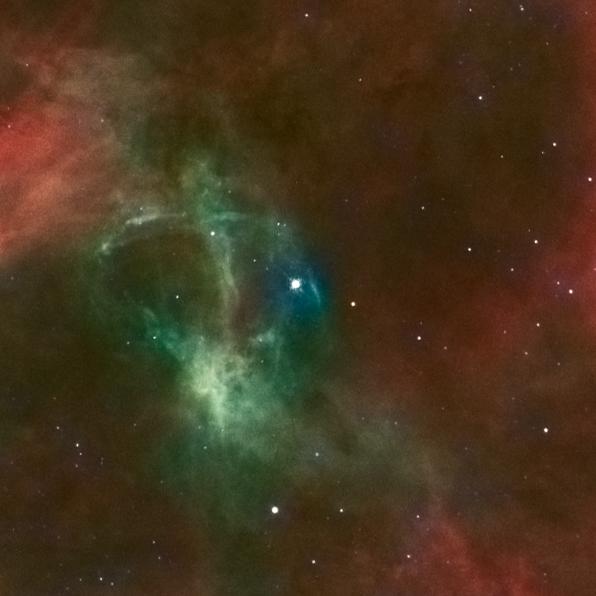
It may look like something from "The Lord of the Rings," but this fiery swirl is actually a planetary nebula known as ESO 456-67. Set against a backdrop of bright stars, the rust-colored object lies in the constellation of Sagittarius (The Archer), in the southern sky. In this image of ESO 456-67, it is possible to see the various layers of material expelled by the central star. Each appears in a different hue - red, orange, yellow, and green-tinted bands of gas are visible, with clear patches of space at the heart of the nebula. It is not fully understood how planetary nebulae form such a wide variety of shapes and structures; some appear to be spherical, some elliptical, others shoot material in waves from their polar regions, some look like hourglasses or figures of eight, and others resemble large, messy stellar explosions - to name but a few. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble and NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This video clip shows a visualisation of the three-dimensional structure of the Pillars of Creation within the star formation region Messier 16 (also called the Eagle Nebula). It is based on new observations of the object using the MUSE instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope in Chile. The pillars actually consist of several distinct pieces on either side of the star cluster NGC 6611. Credit: ESO/M. Kornmesser Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/goddard/pillars-of-creation-revealed-in-3-d" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/image-feature/goddard/pillars-of-creation-re...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
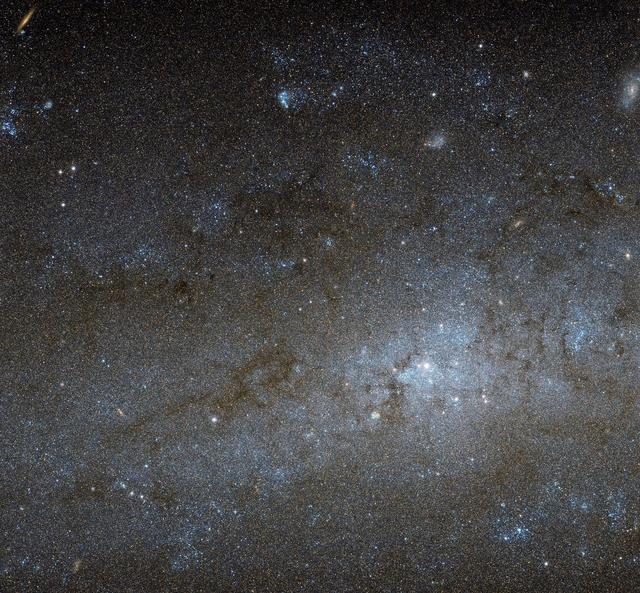

This Hubble image shows the central region of a spiral galaxy known as NGC 247. NGC 247 is a relatively small spiral galaxy in the southern constellation of Cetus (The Whale). Lying at a distance of around 11 million light-years from us, it forms part of the Sculptor Group, a loose collection of galaxies that also contains the more famous NGC 253 (otherwise known as the Sculptor Galaxy). NGC 247’s nucleus is visible here as a bright, whitish patch, surrounded by a mixture of stars, gas and dust. The dust forms dark patches and filaments that are silhouetted against the background of stars, while the gas has formed into bright knots known as H II regions, mostly scattered throughout the galaxy’s arms and outer areas. This galaxy displays one particularly unusual and mysterious feature — it is not visible in this image, but can be seen clearly in wider views of the galaxy, such as a picture from ESO’s MPG/ESO 2.2-meter telescope. The northern part of NGC 247’s disc hosts an apparent void, a gap in the usual swarm of stars and H II regions that spans almost a third of the galaxy’s total length. There are stars within this void, but they are quite different from those around it. They are significantly older, and as a result much fainter and redder. This indicates that the star formation taking place across most of the galaxy’s disk has somehow been arrested in the void region, and has not taken place for around one billion years. Although astronomers are still unsure how the void formed, recent studies suggest it might have been caused by gravitational interactions with part of another galaxy. Image Credit: NASA/ESA
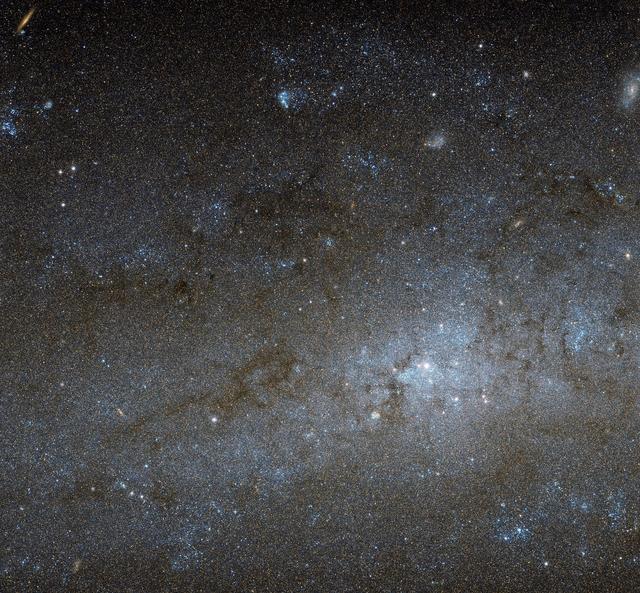

This Hubble image shows the central region of a spiral galaxy known as NGC 247. NGC 247 is a relatively small spiral galaxy in the southern constellation of Cetus (The Whale). Lying at a distance of around 11 million light-years from us, it forms part of the Sculptor Group, a loose collection of galaxies that also contains the more famous NGC 253 (otherwise known as the Sculptor Galaxy). NGC 247’s nucleus is visible here as a bright, whitish patch, surrounded by a mixture of stars, gas and dust. The dust forms dark patches and filaments that are silhouetted against the background of stars, while the gas has formed into bright knots known as H II regions, mostly scattered throughout the galaxy’s arms and outer areas. This galaxy displays one particularly unusual and mysterious feature — it is not visible in this image, but can be seen clearly in wider views of the galaxy, such as this picture from ESO’s MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope. The northern part of NGC 247’s disc hosts an apparent void, a gap in the usual swarm of stars and H II regions that spans almost a third of the galaxy’s total length. There are stars within this void, but they are quite different from those around it. They are significantly older, and as a result much fainter and redder. This indicates that the star formation taking place across most of the galaxy’s disc has somehow been arrested in the void region, and has not taken place for around one billion years. Although astronomers are still unsure how the void formed, recent studies suggest it might have been caused by gravitational interactions with part of another galaxy.

This visualization provides a three-dimensional perspective on Hubble's 25th anniversary image of the nebula Gum 29 with the star cluster Westerlund 2 at its core. The flight traverses the foreground stars and approaches the lower left rim of the nebula Gum 29. Passing through the wispy darker clouds on the near side, the journey reveals bright gas illuminated by the intense radiation of the newly formed stars of cluster Westerlund 2. Within the nebula, several pillars of dark, dense gas are being shaped by the energetic light and strong stellar winds from the brilliant cluster of thousands of stars. Note that the visualization is intended to be a scientifically reasonable interpretation and that distances within the model are significantly compressed. Download here: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2015/12/video/" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2015/12/video/</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, G. Bacon, L. Frattare, Z. Levay, and F. Summers (Viz3D Team, STScI), and J. Anderson (STScI) Acknowledgment: The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), A. Nota (ESA/STScI), the Westerlund 2 Science Team, and ESO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
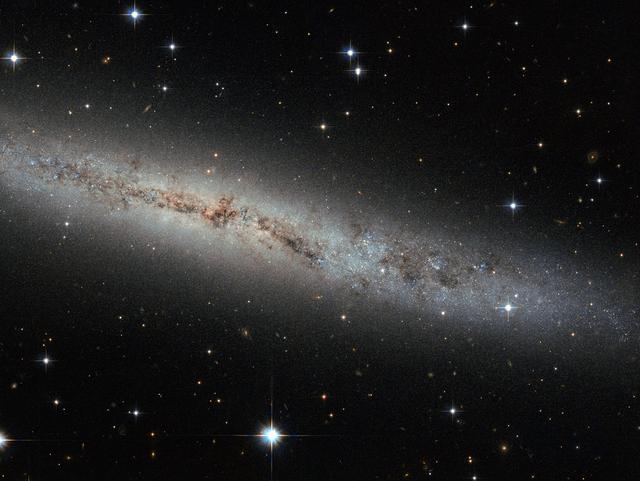

Located some 25 million light-years away, this new Hubble image shows spiral galaxy ESO 373-8. Together with at least seven of its galactic neighbors, this galaxy is a member of the NGC 2997 group. We see it side-on as a thin, glittering streak across the sky, with all its contents neatly aligned in the same plane. We see so many galaxies like this — flat, stretched-out pancakes — that our brains barely process their shape. But let us stop and ask: Why are galaxies stretched out and aligned like this? Try spinning around in your chair with your legs and arms out. Slowly pull your legs and arms inwards, and tuck them in against your body. Notice anything? You should have started spinning faster. This effect is due to conservation of angular momentum, and it’s true for galaxies, too. This galaxy began life as a humungous ball of slowly rotating gas. Collapsing in upon itself, it spun faster and faster until, like pizza dough spinning and stretching in the air, a disc started to form. Anything that bobbed up and down through this disk was pulled back in line with this motion, creating a streamlined shape. Angular momentum is always conserved — from a spinning galactic disk 25 million light-years away from us, to any astronomer, or astronomer-wannabe, spinning in an office chair. Credit: NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This image of galaxy W2246-0526 was created using data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) - a collection of individual radio antennas that work together as a single telescope. The galaxy is syphoning material away from three companion galaxies through trans-galactic streamers. The main galaxy and one of its companions are in the center. To the lower left is another companion and its large tidal tail that connects it to the main galaxy. The upper left concentration is the third companion galaxy. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22359
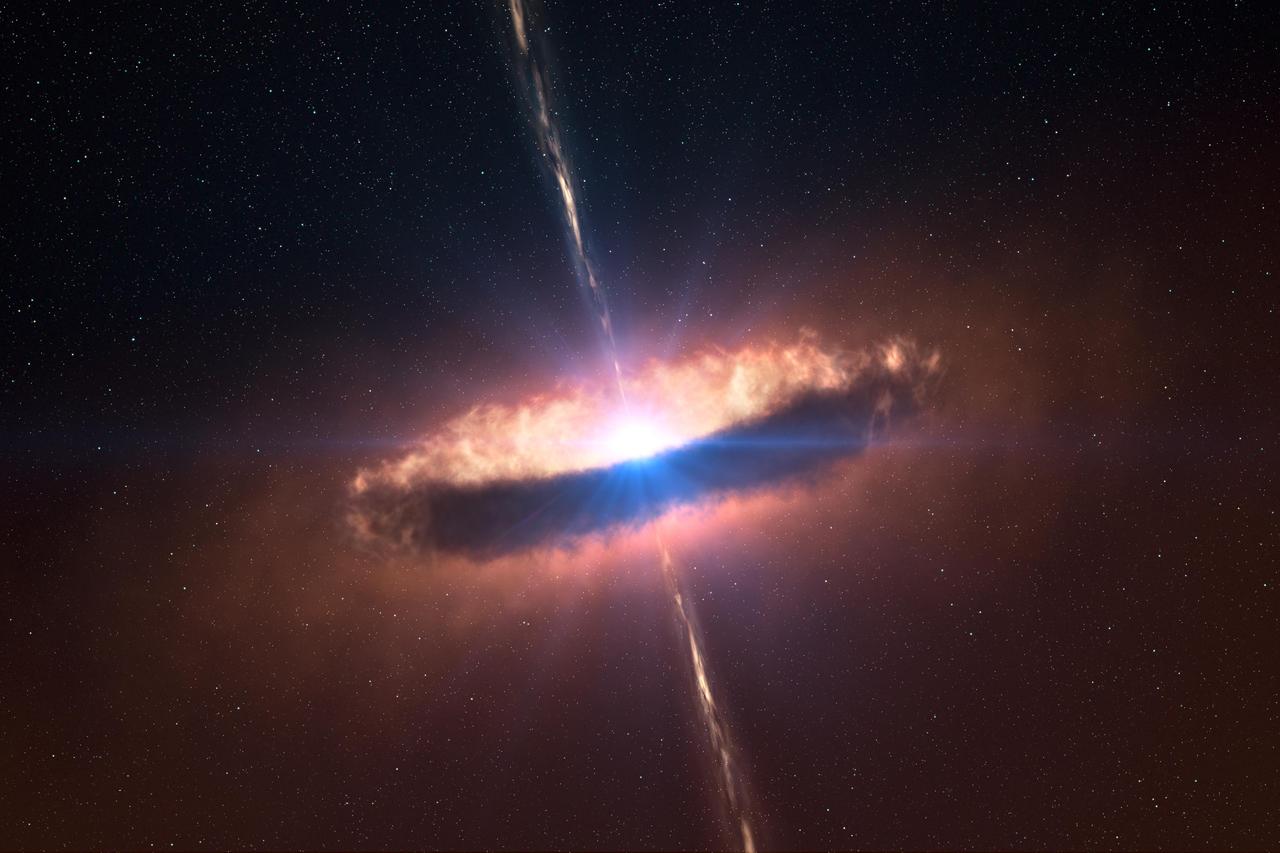

Astronomers have obtained the first clear look at a dusty disk closely encircling a massive baby star; this artist concept shows what such a massive disk might look like.
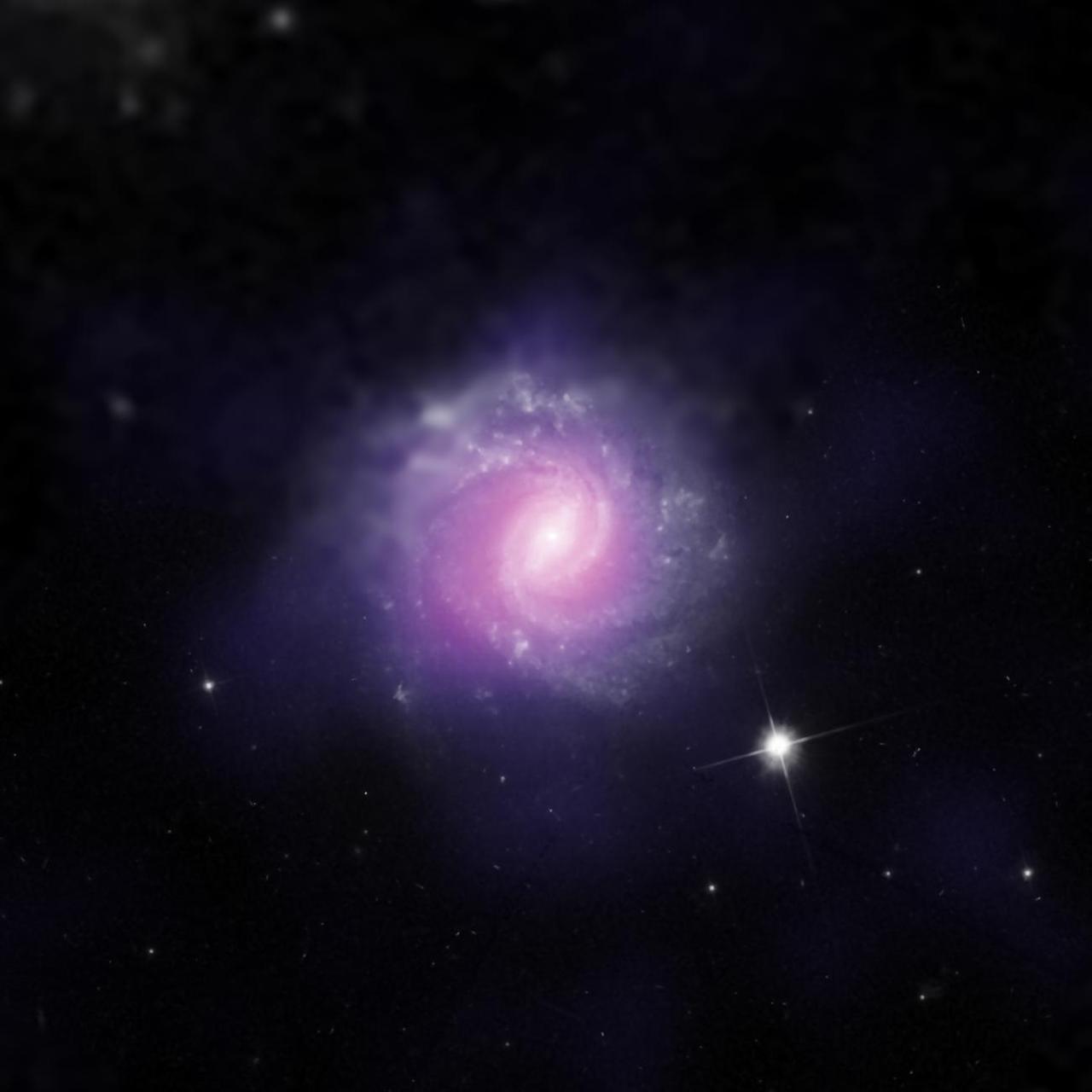

IC 3639, a galaxy with an active galactic nucleus, is seen in this image combining data from the Hubble Space Telescope and the European Southern Observatory. This galaxy contains an example of a supermassive black hole hidden by gas and dust. Researchers analyzed NuSTAR data from this object and compared them with previous observations from NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory and the Japanese-led Suzaku satellite. The findings from NuSTAR, which is more sensitive to higher energy X-rays than these observatories, confirm the nature of IC 3639 as an active galactic nucleus that is heavily obscured, and intrinsically much brighter than observed. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21087

These thermal images show a hot south pole on the planet Neptune. These warmer temperatures provide an avenue for methane to escape out of the deep atmosphere. The images were obtained with the Very Large Telescope in Chile Sept. 1 and 2, 2006.
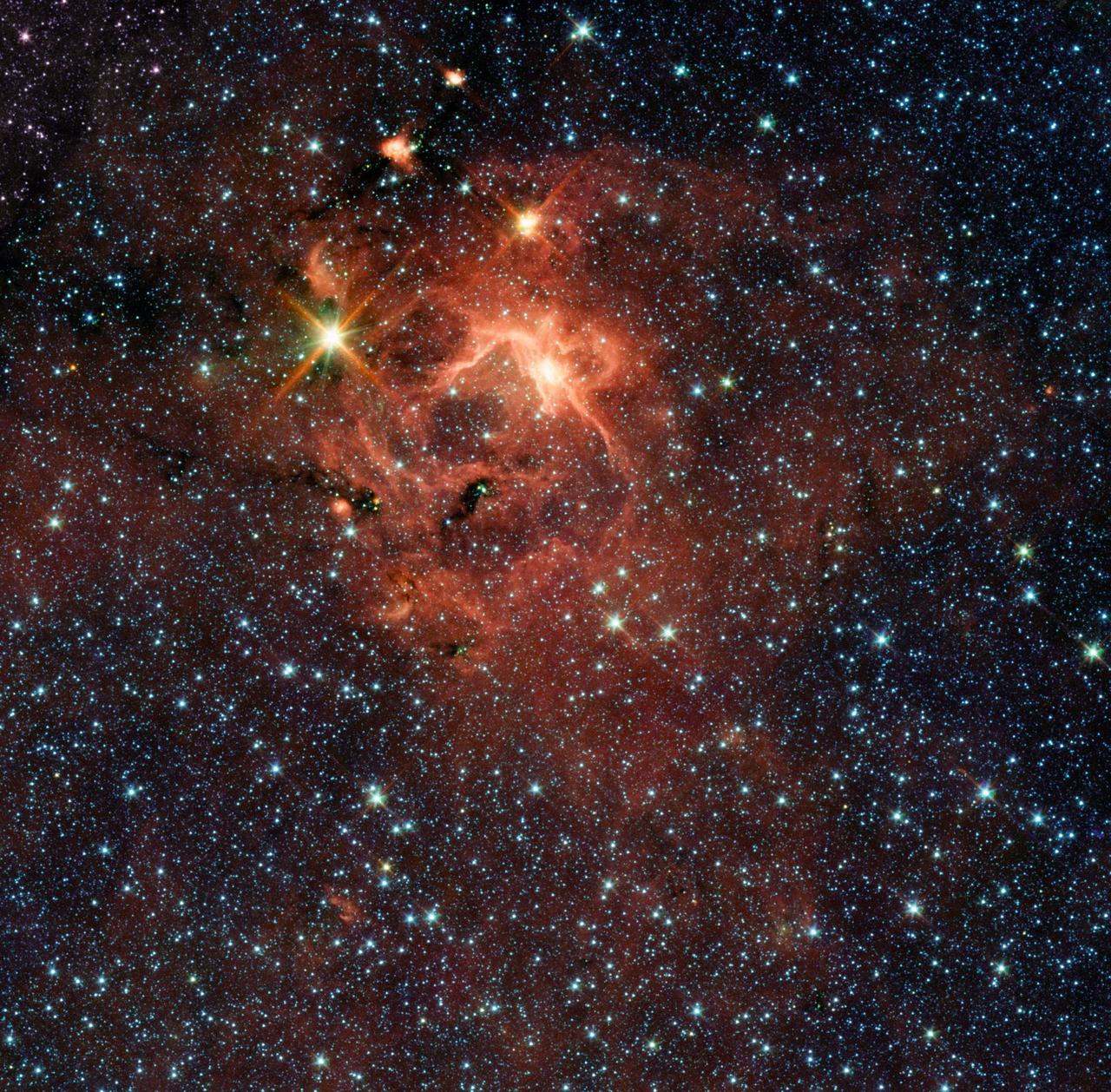

This star-forming region, captured by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, is dominated by the bright, young star IRAS 13481-6124; it is the first massive baby star for which astronomers could obtain a detailed look at the dusty disk closely encircling it.
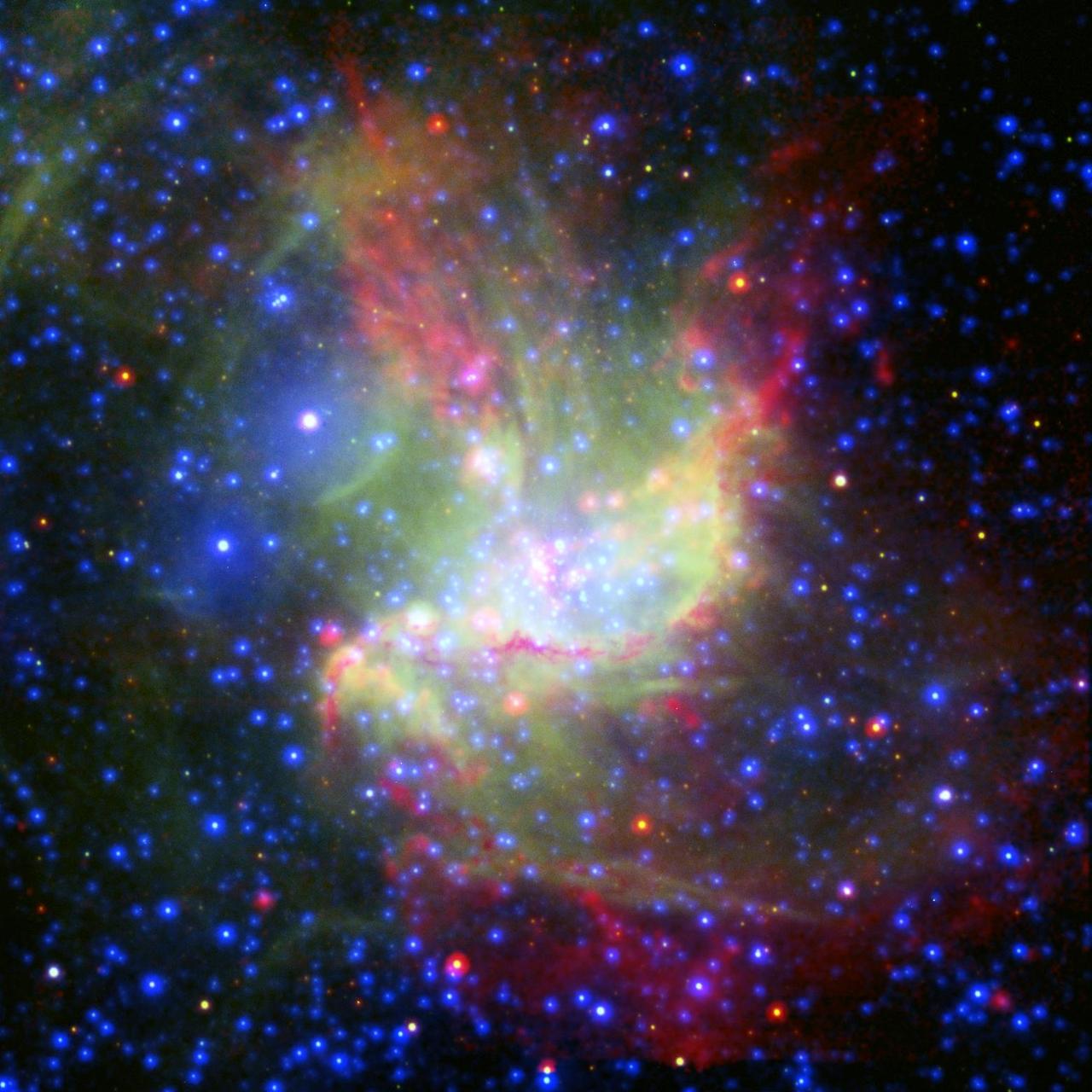

This painterly portrait of a star-forming cloud, called NGC 346, is a combination of multiwavelength light from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, the European Southern Observatory New Technology Telescope, and the European Space Agency.

This image shows the most recent observations of the 2-mile-wide 4-kilometer-wide comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, which is the upcoming target of the European Space Agency Rosetta mission.
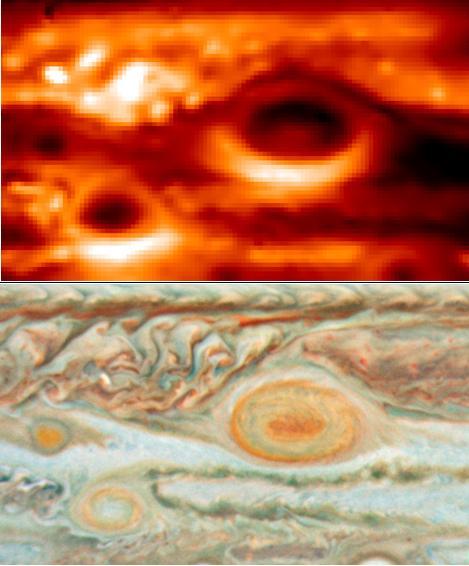
New thermal images from powerful ground-based telescopes show swirls of warmer air and cooler regions never seen before within Jupiter Great Red Spot.

Astronomers have discovered some of the youngest stars ever seen thanks to the Herschel space observatory; dense envelopes of gas and dust surround the fledging stars known as protostars, make their detection difficult until now.

Eight Looks at the Jupiter Impact

This image from an animation shows beacons of hot air seen in the infrared that appeared during a great springtime storm on Saturn from January 2011 to March 2012.
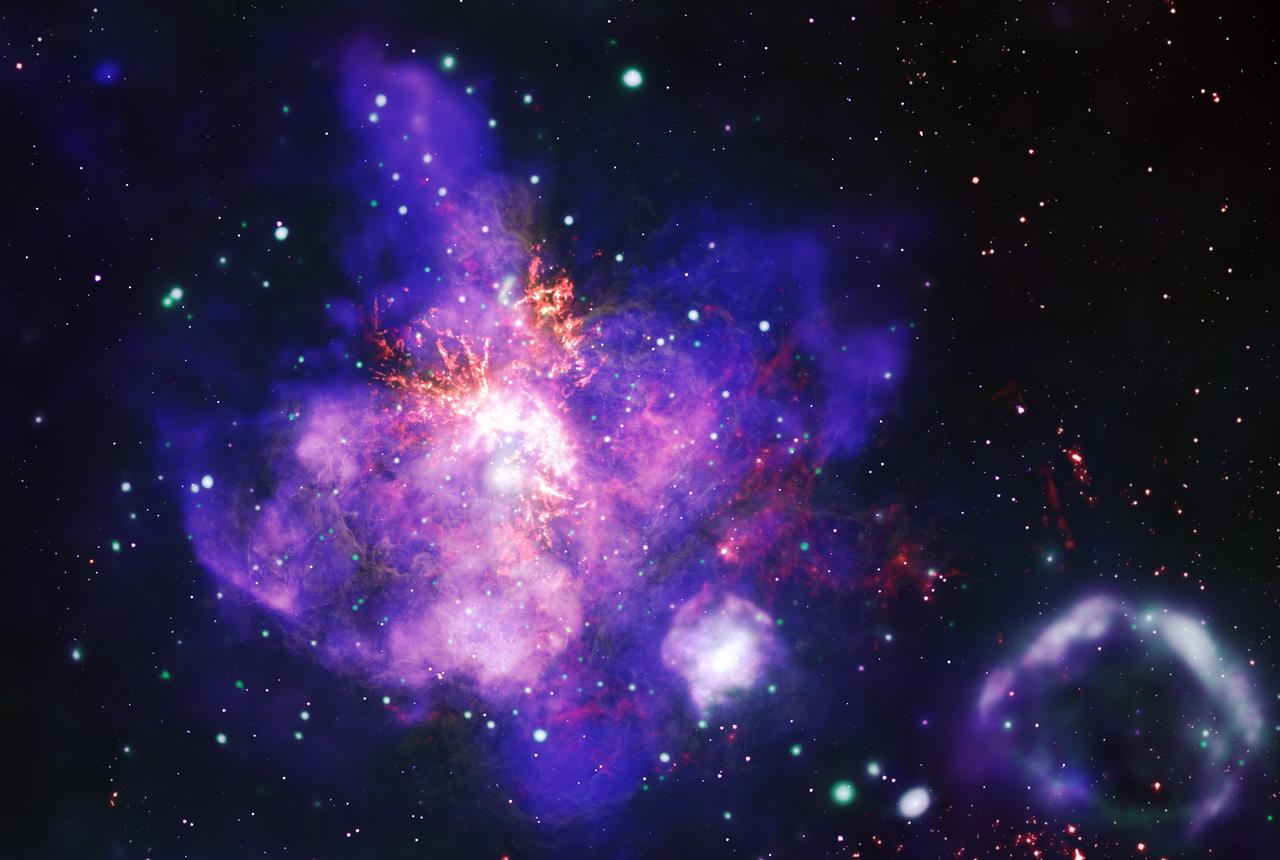

This composite image contains the deepest X-ray image ever made of the spectacular star forming region called 30 Doradus. By combining X-ray data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory (blue and green) with optical data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (yellow) and radio data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (orange), this stellar arrangement comes alive.

This is the clearest view yet of the distant planet Pluto and its moon, Charon, as revealed by NASA Hubble Space Telescope. The image was taken by the European Space Agency Faint Object Camera on February 21, 1994.

The spiral galaxy NGC 3627, located about 30 million light years from Earth as seen by four NASA telescopes; inset shows the central region, which contains a bright X-ray source that is likely powered by material falling onto a supermassive black hole.