
Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians prepare to perform a blacklight test and sampling for contaminants on the two ULA Atlas V rocket payload fairings for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 23, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians perform a blacklight test and sampling for contaminants on one of two ULA Atlas V rocket payload fairings for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 23, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians prepare to perform a blacklight test and sampling for contaminants on the two ULA Atlas V rocket payload fairings for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 23, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

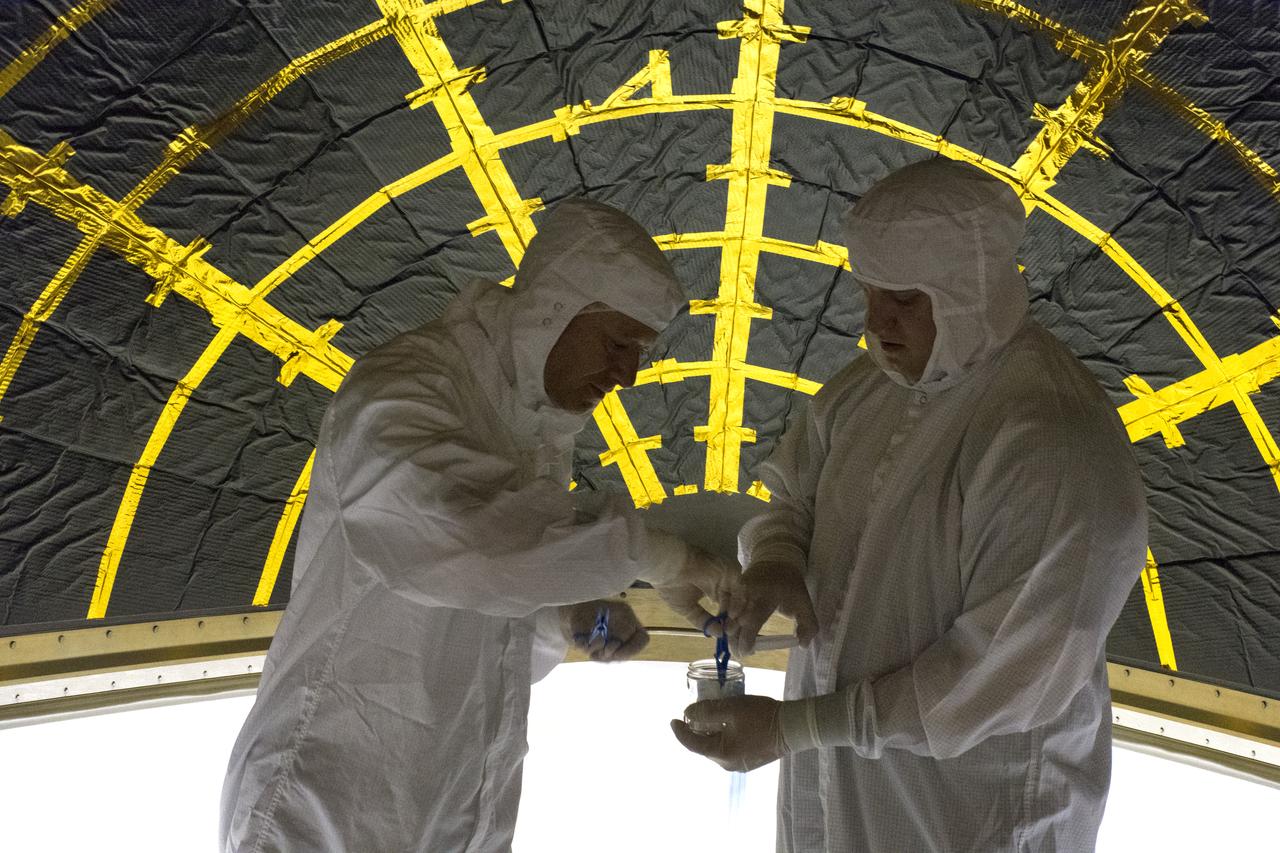
On Friday, April 6, 2018, in NASA’s Building 8337 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers clean and take samples from the payload fairing the will protect NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2, or ICESat-2, satellite during launch. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 12, 2018, from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg. It will be the last for the venerable Delta II rocket. ICESat-2, which is being built and tested by Orbital ATK in Gilbert, Arizona, will carry a single instrument called the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System, or ATLAS. The ATLAS instrument is being built and tested at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland. Once in orbit, the satellite is designed to measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much, Earth’s frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing.

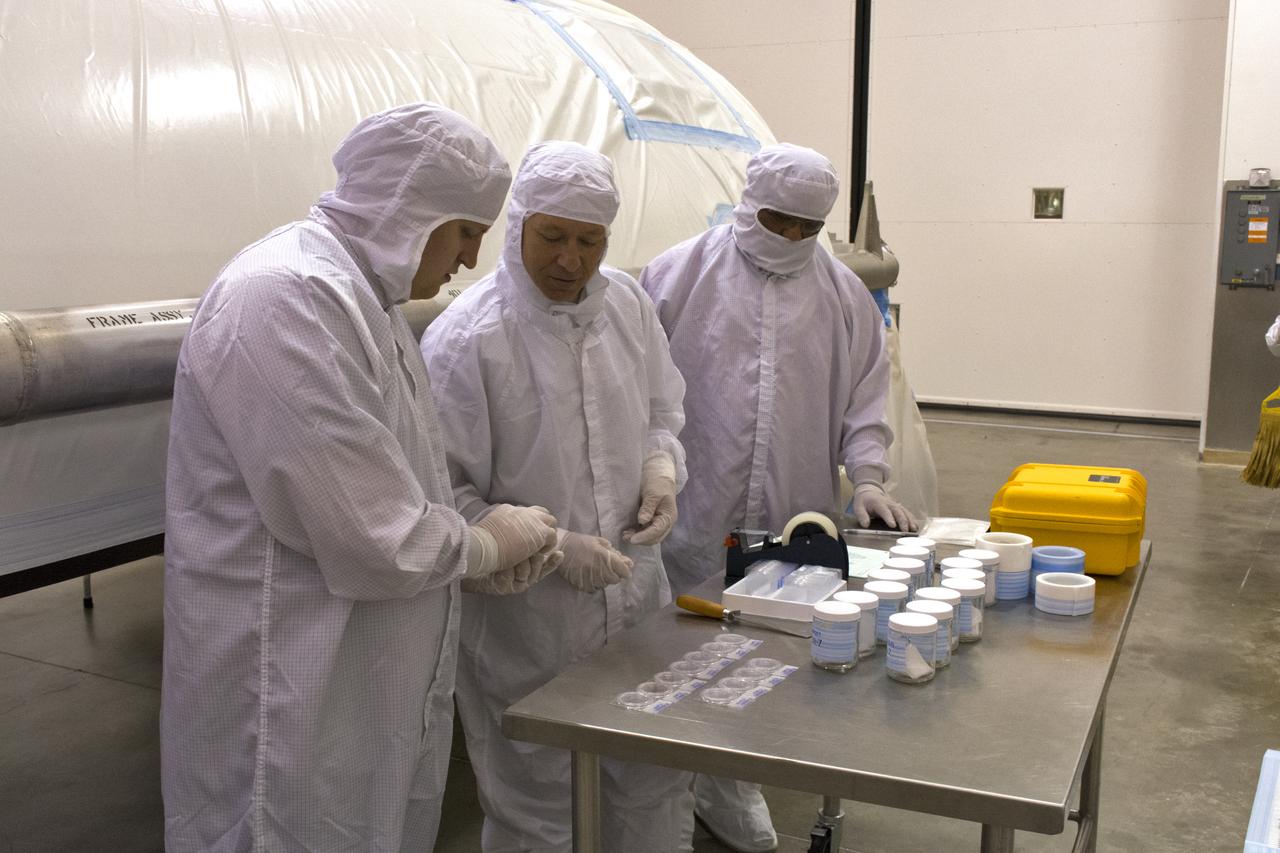
On Friday, April 6, 2018, in NASA’s Building 8337 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers clean and take samples from the payload fairing the will protect NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2, or ICESat-2, satellite during launch. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 12, 2018, from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg. It will be the last for the venerable Delta II rocket. ICESat-2, which is being built and tested by Orbital ATK in Gilbert, Arizona, will carry a single instrument called the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System, or ATLAS. The ATLAS instrument is being built and tested at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland. Once in orbit, the satellite is designed to measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much, Earth’s frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing.

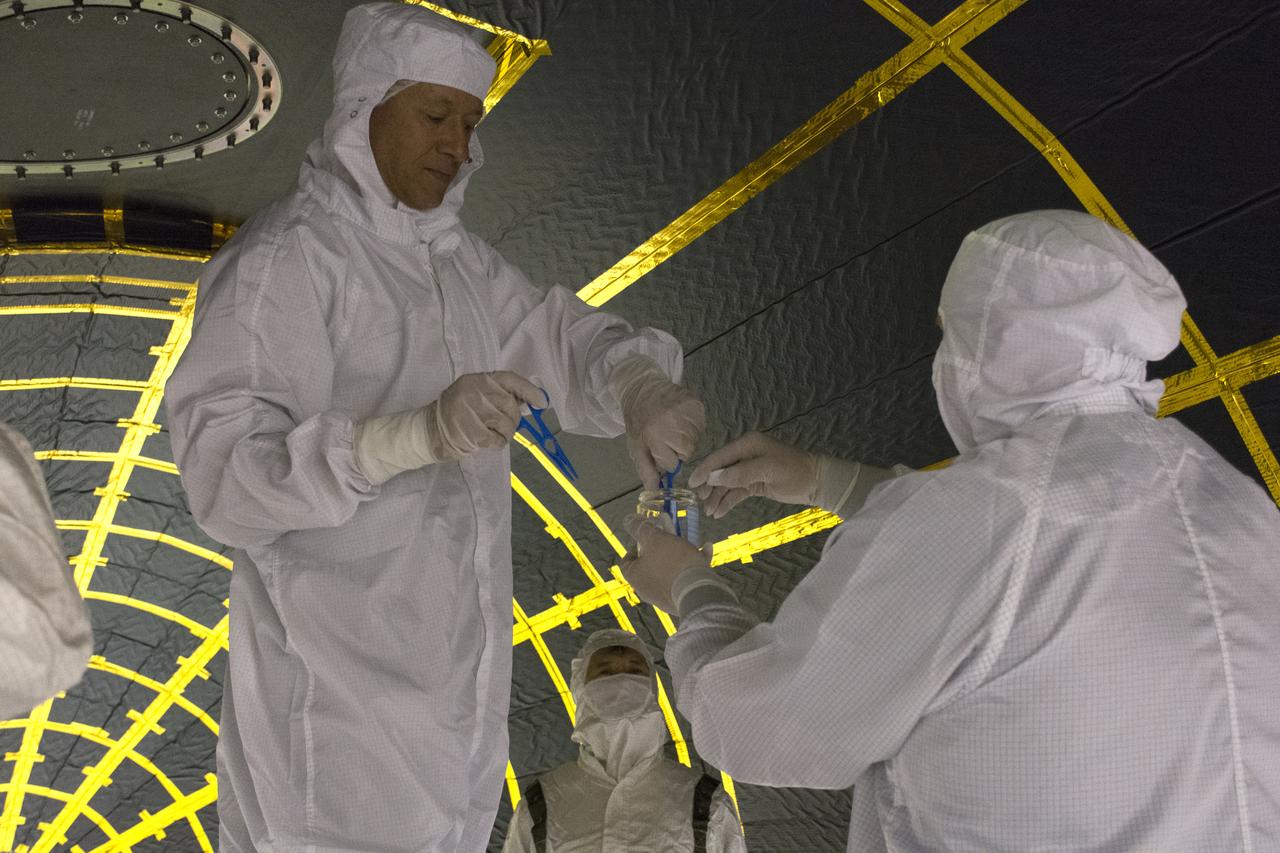
On Friday, April 6, 2018, in NASA’s Building 8337 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers check samples during cleaning of the payload fairing that will protect NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2, or ICESat-2, satellite during launch. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 12, 2018, from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg. It will be the last for the venerable Delta II rocket. ICESat-2, which is being built and tested by Orbital ATK in Gilbert, Arizona, will carry a single instrument called the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System, or ATLAS. The ATLAS instrument is being built and tested at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland. Once in orbit, the satellite is designed to measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much, Earth’s frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing.

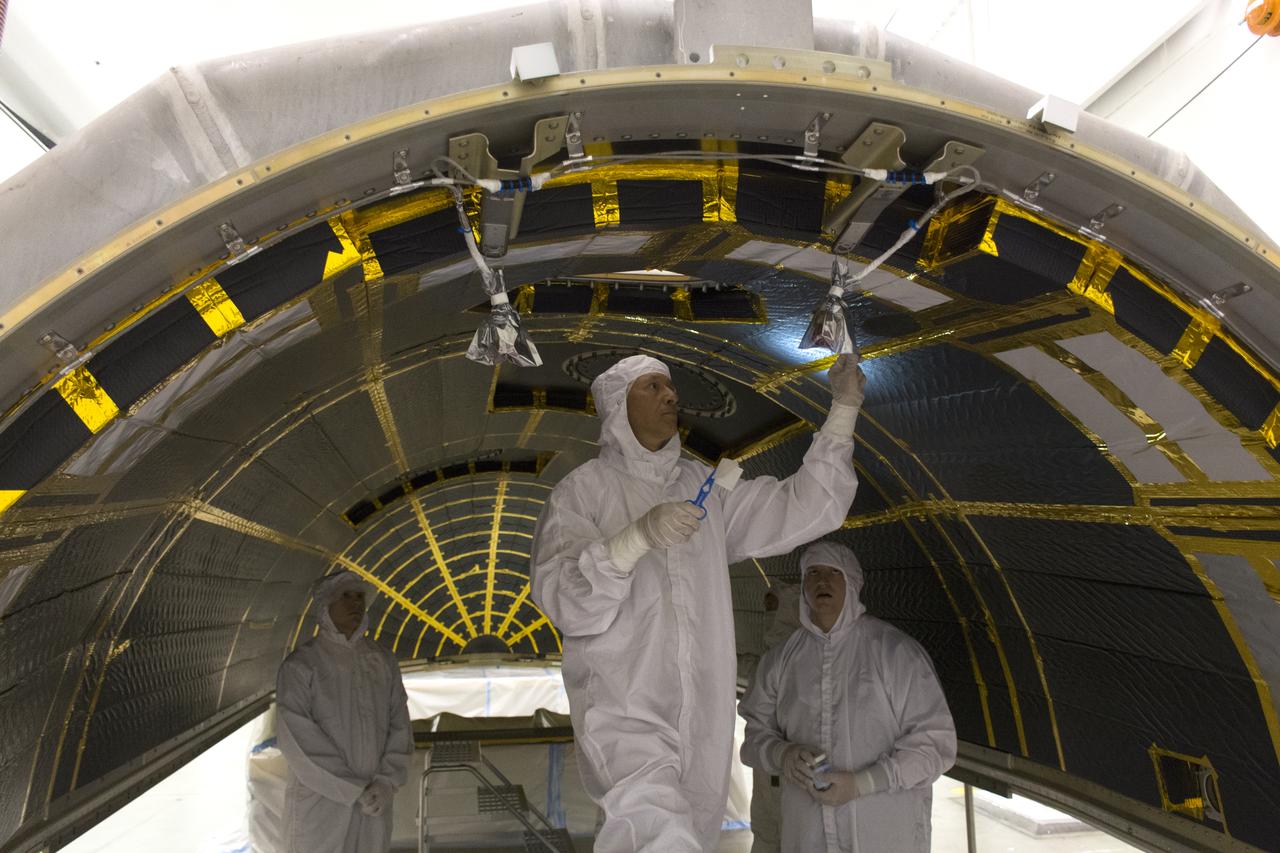
On Friday, April 6, 2018, in NASA’s Building 8337 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers clean and take samples from the payload fairing the will protect NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2, or ICESat-2, satellite during launch. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 12, 2018, from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg. It will be the last for the venerable Delta II rocket. ICESat-2, which is being built and tested by Orbital ATK in Gilbert, Arizona, will carry a single instrument called the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System, or ATLAS. The ATLAS instrument is being built and tested at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland. Once in orbit, the satellite is designed to measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much, Earth’s frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing.
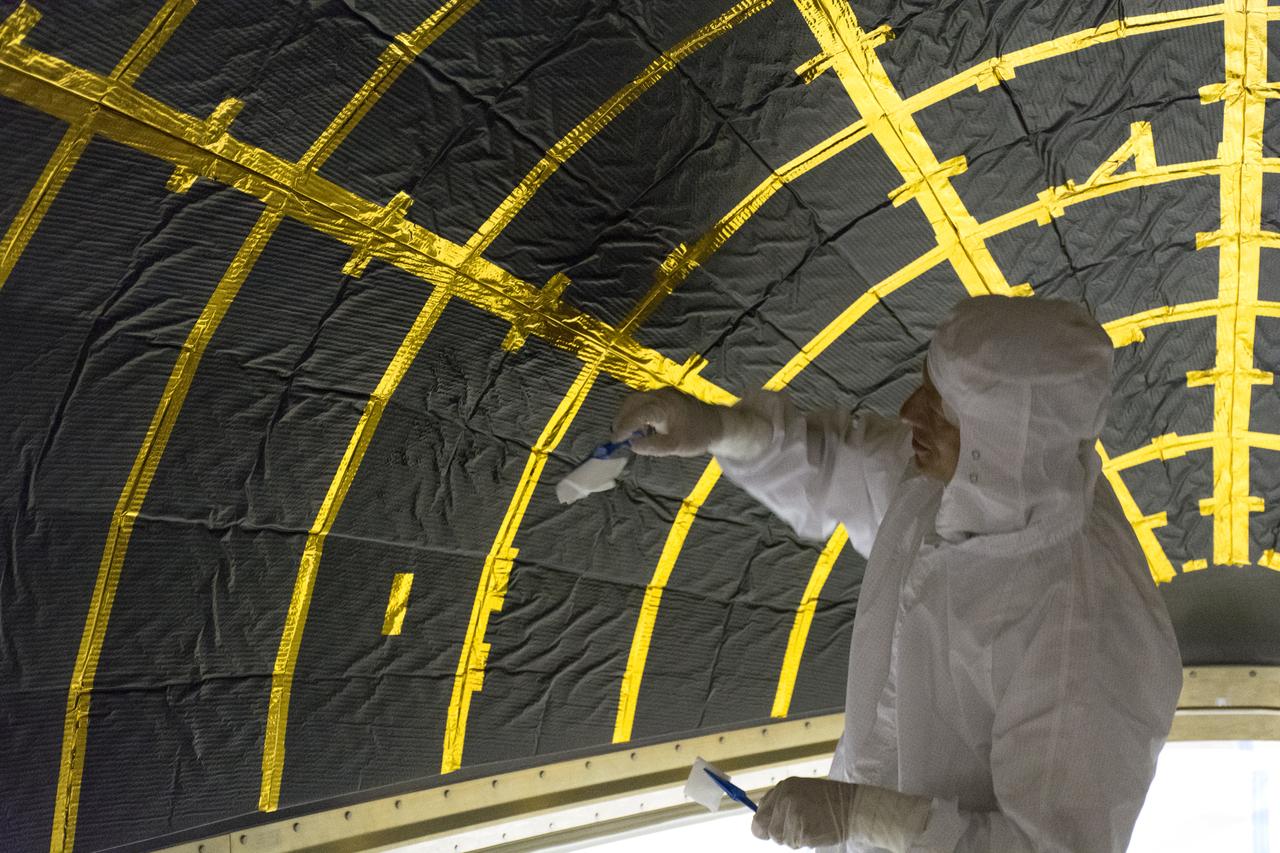

On Friday, April 6, 2018, in NASA’s Building 8337 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician cleans and takes samples from the payload fairing the will protect NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2, or ICESat-2, satellite during launch. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 12, 2018, from Space Launch Complex-2 at Vandenberg. It will be the last for the venerable Delta II rocket. ICESat-2, which is being built and tested by Orbital ATK in Gilbert, Arizona, will carry a single instrument called the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System, or ATLAS. The ATLAS instrument is being built and tested at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland. Once in orbit, the satellite is designed to measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much, Earth’s frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing.
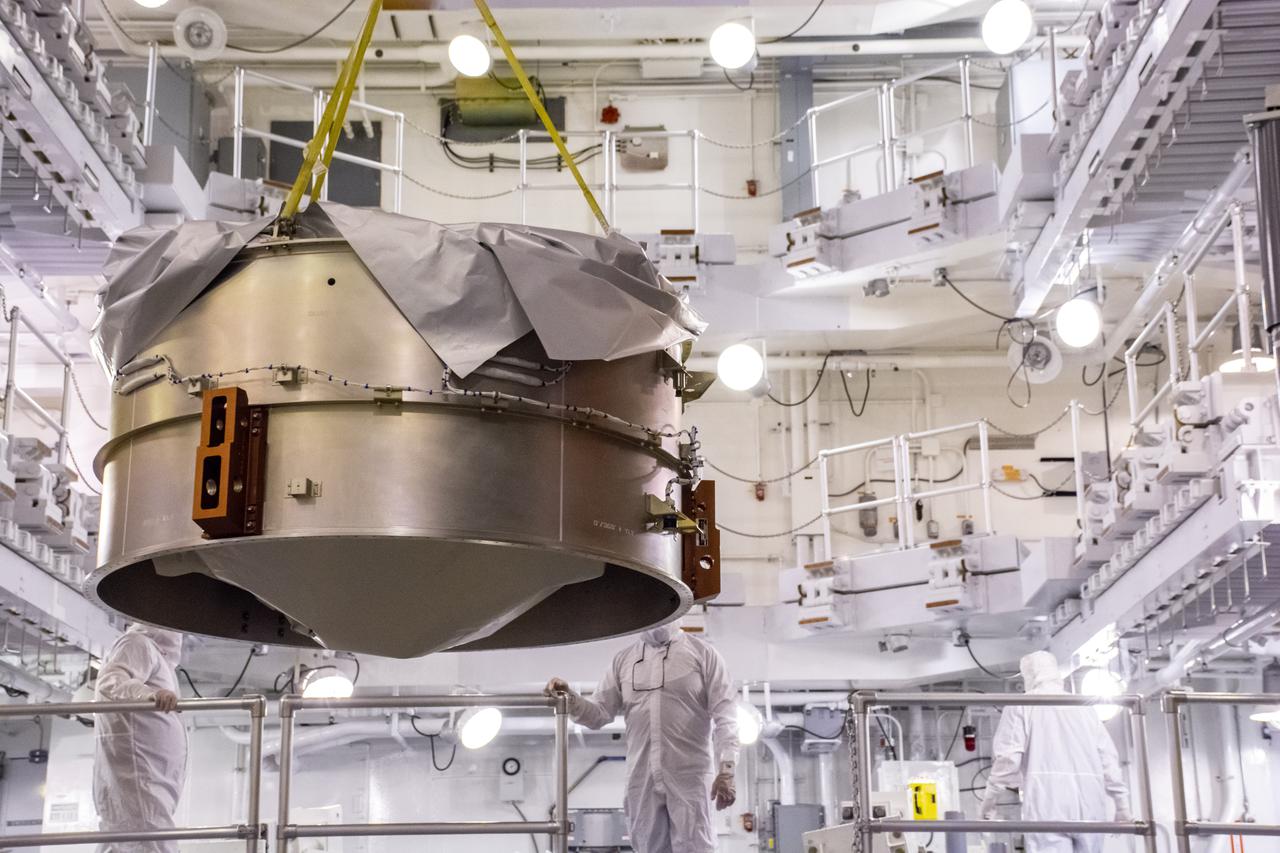

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians lift the launch vehicle adapter for the ULA Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 22, 2021. Landsat 9 is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
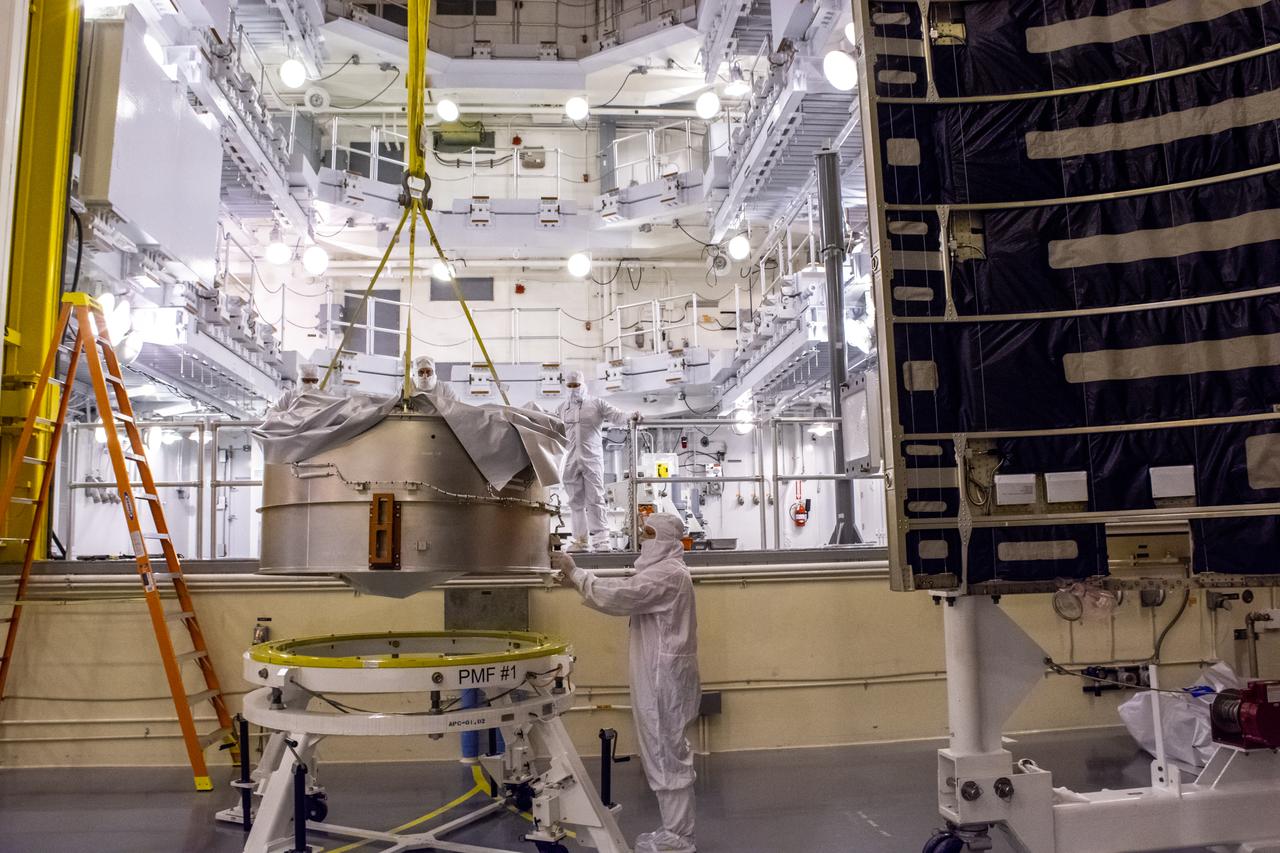

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians move the launch vehicle adapter for the ULA Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 22, 2021. Landsat 9 is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
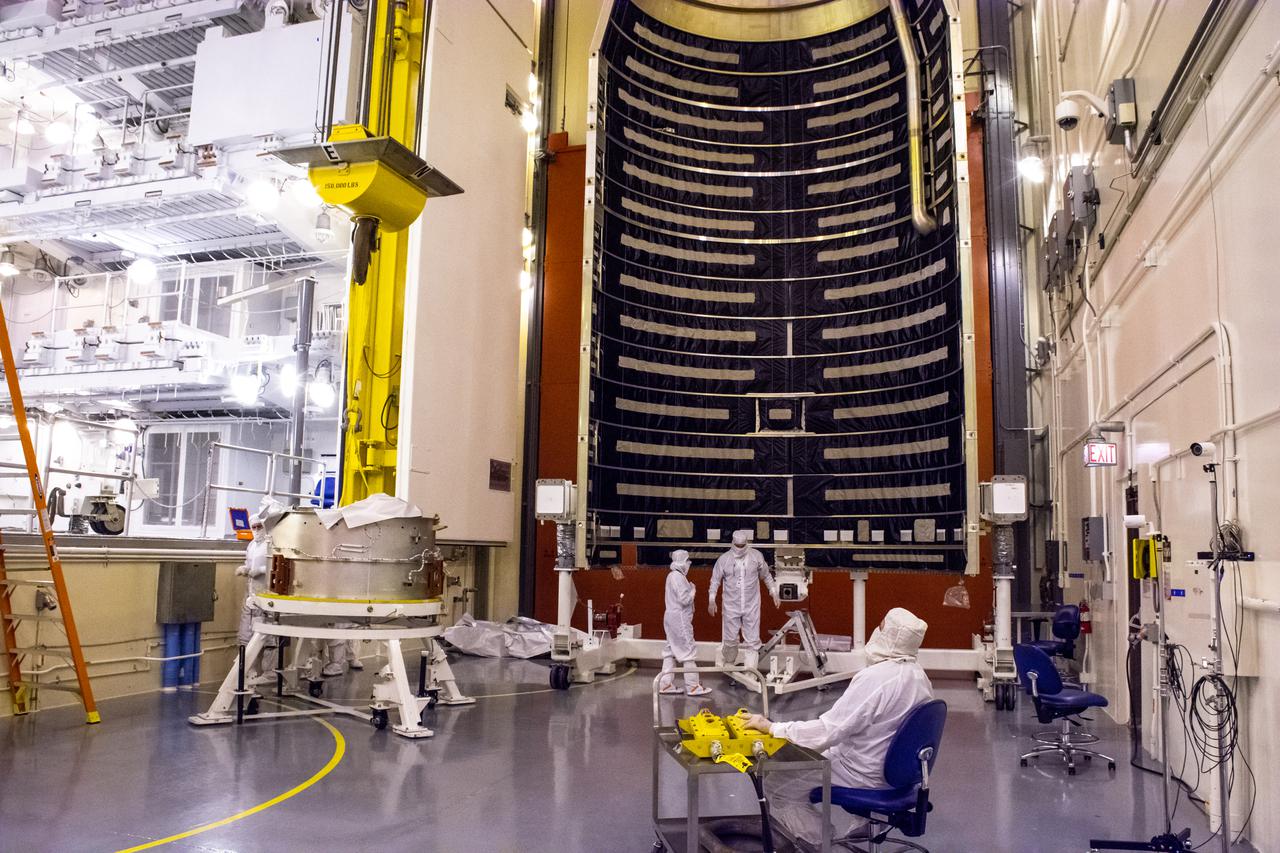

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians prepare to align the two ULA Atlas V rocket payload fairings for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 22, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Inside the Integrated Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians prepare to align the two ULA Atlas V rocket payload fairings for NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite on June 22, 2021. The fairings will encapsulate the satellite for its launch atop the Atlas V from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
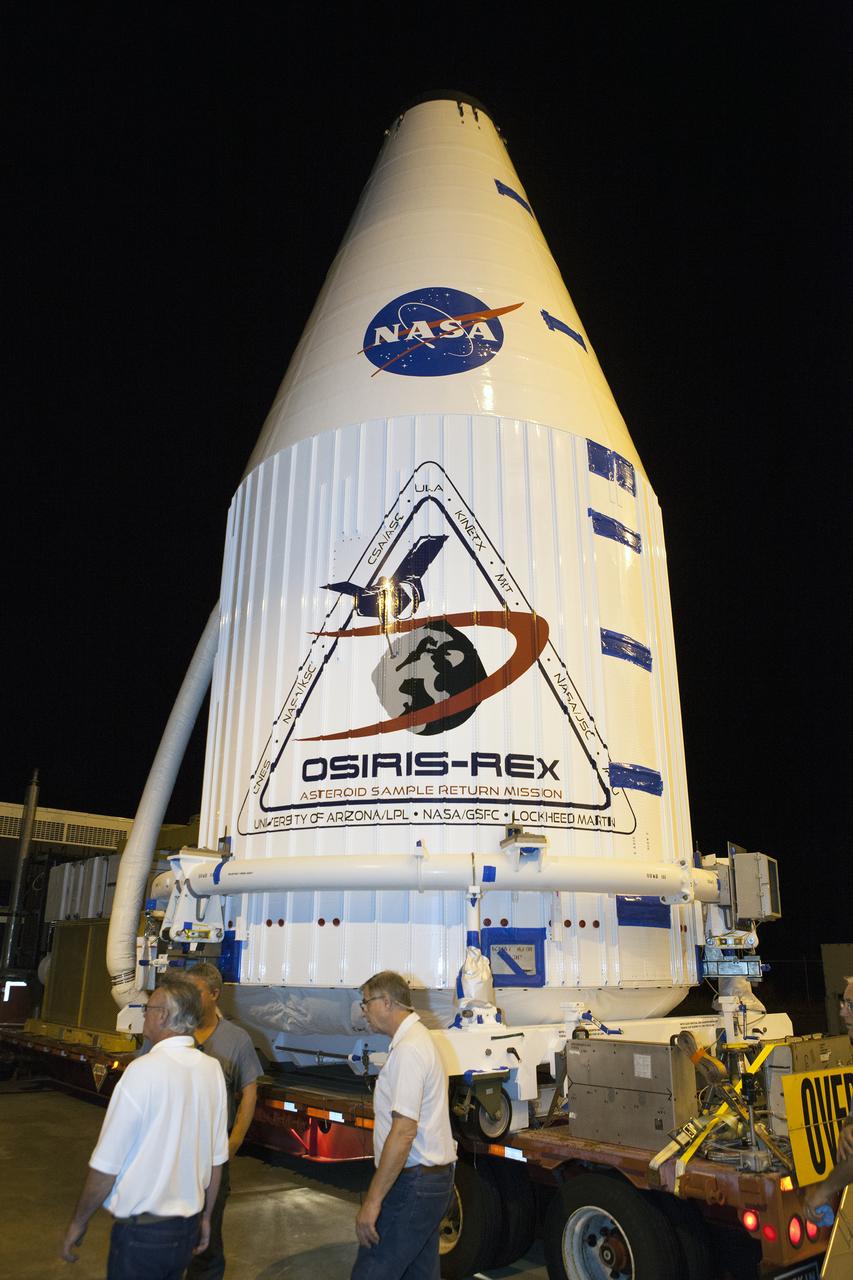

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is towed from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center to begin the trip to Space Launch Complex 41 at the adjacent Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
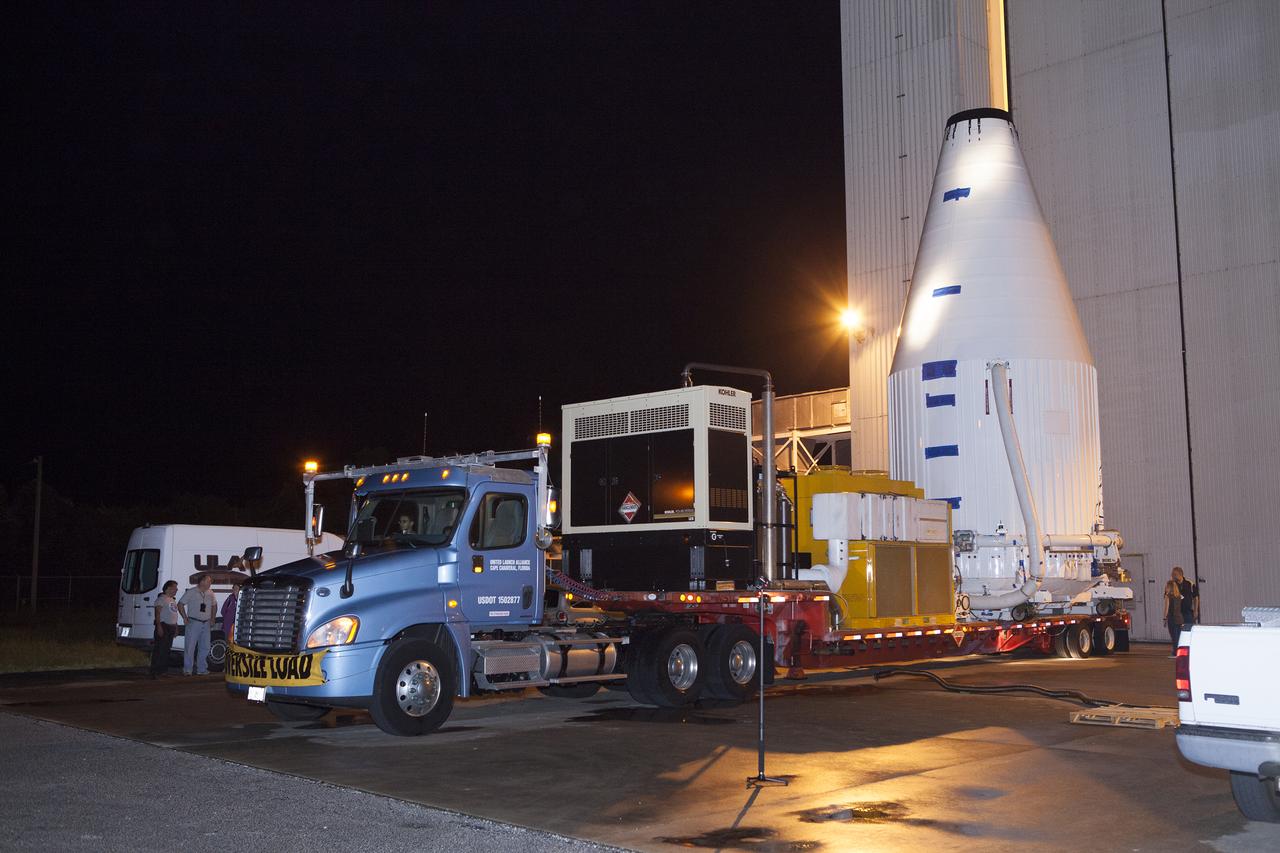

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is towed from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center to begin the trip to Space Launch Complex 41 at the adjacent Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
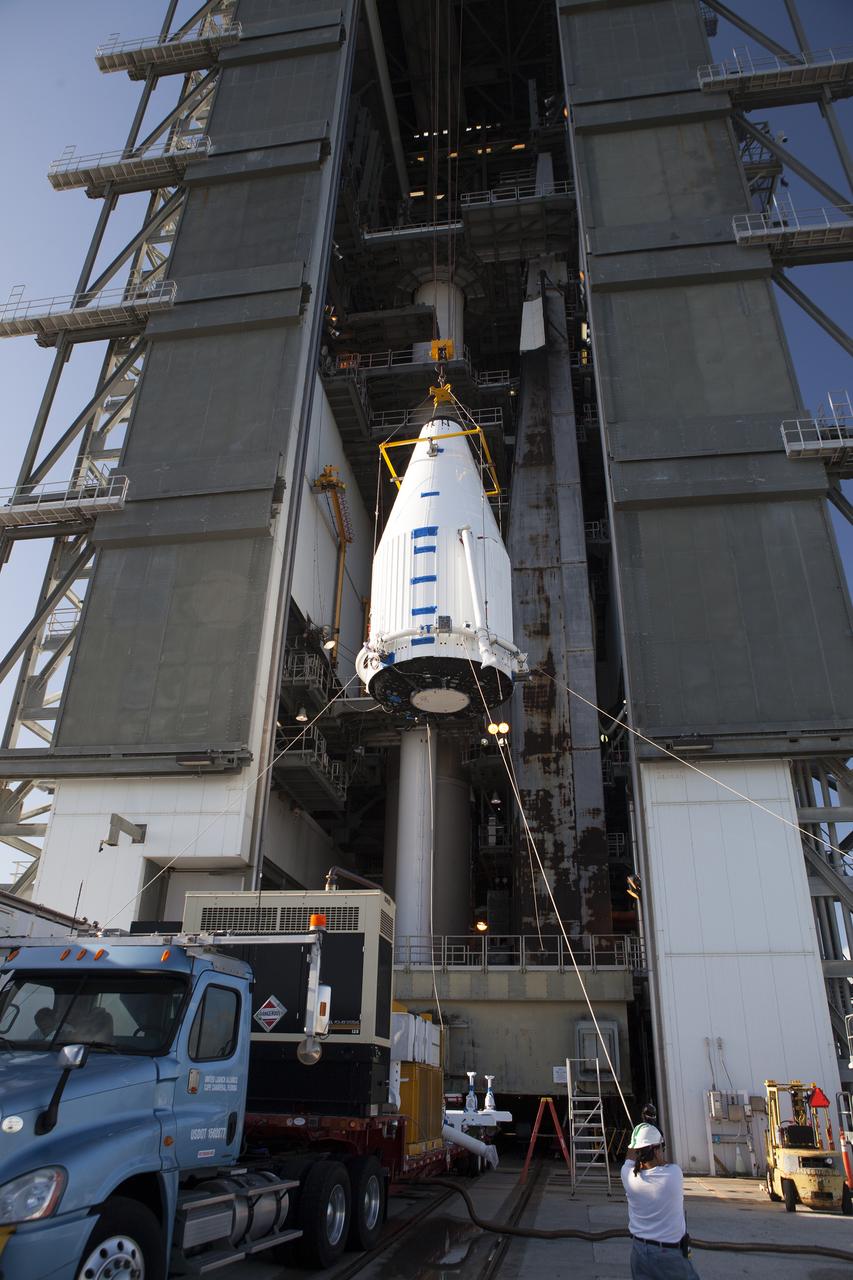

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is lifted at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
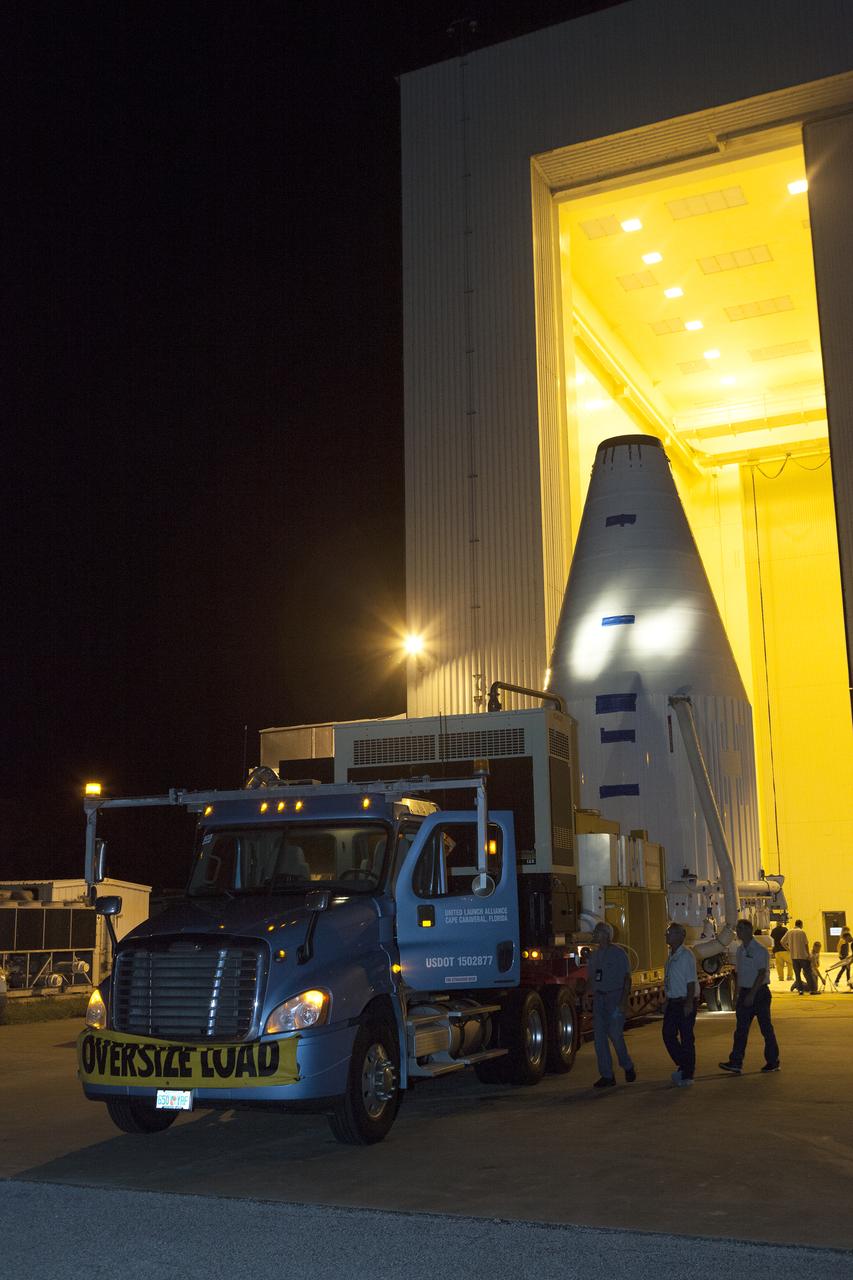

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is towed from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center to begin the trip to Space Launch Complex 41 at the adjacent Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
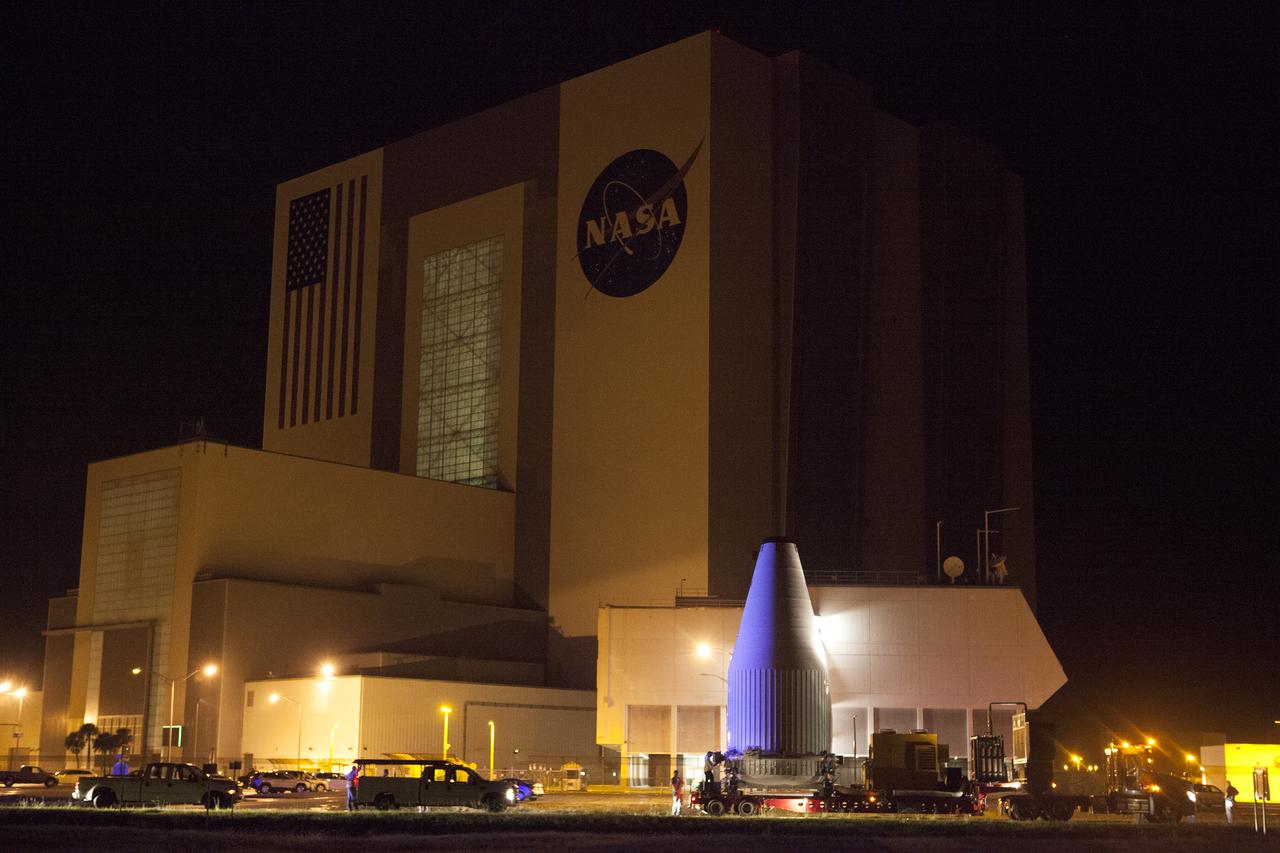

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is towed past the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on its way to Space Launch Complex 41 at the adjacent Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
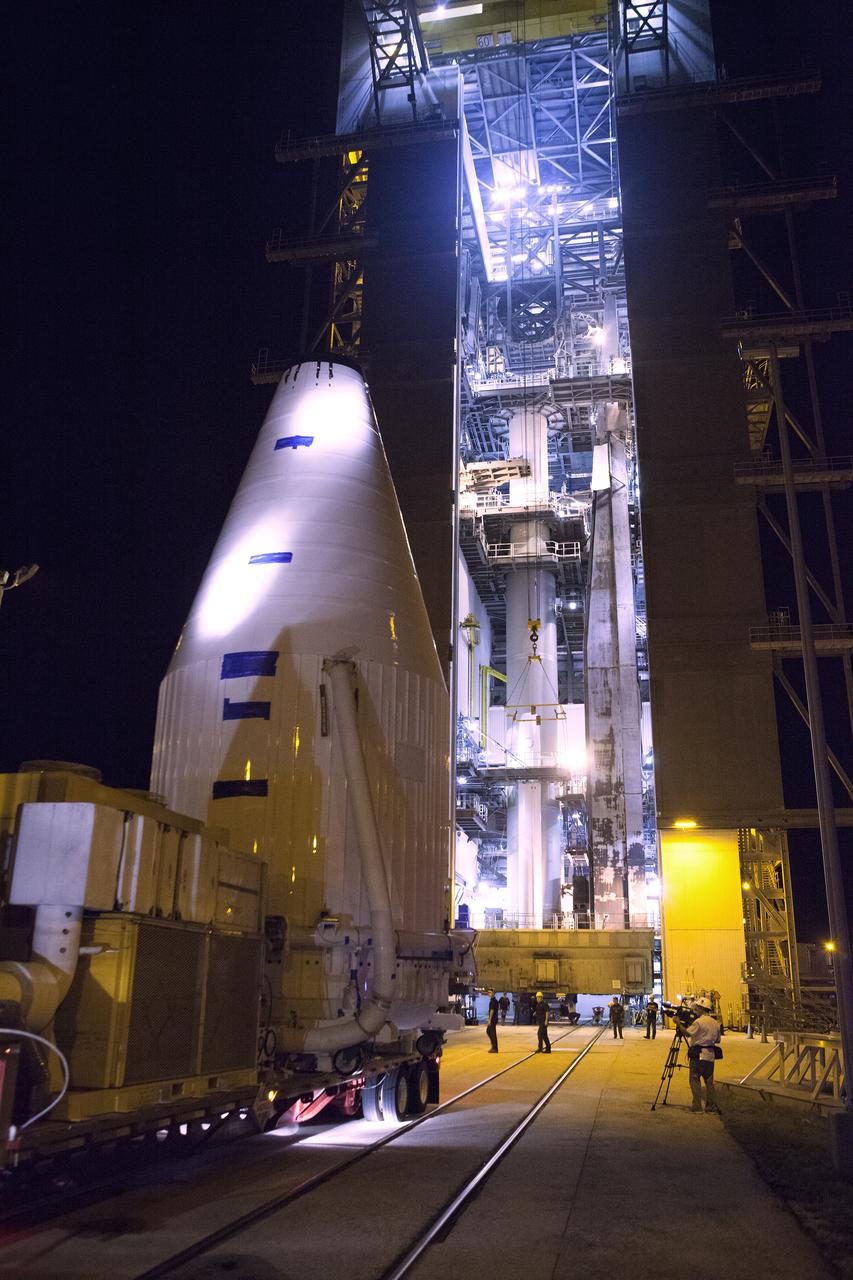

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, arrives at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
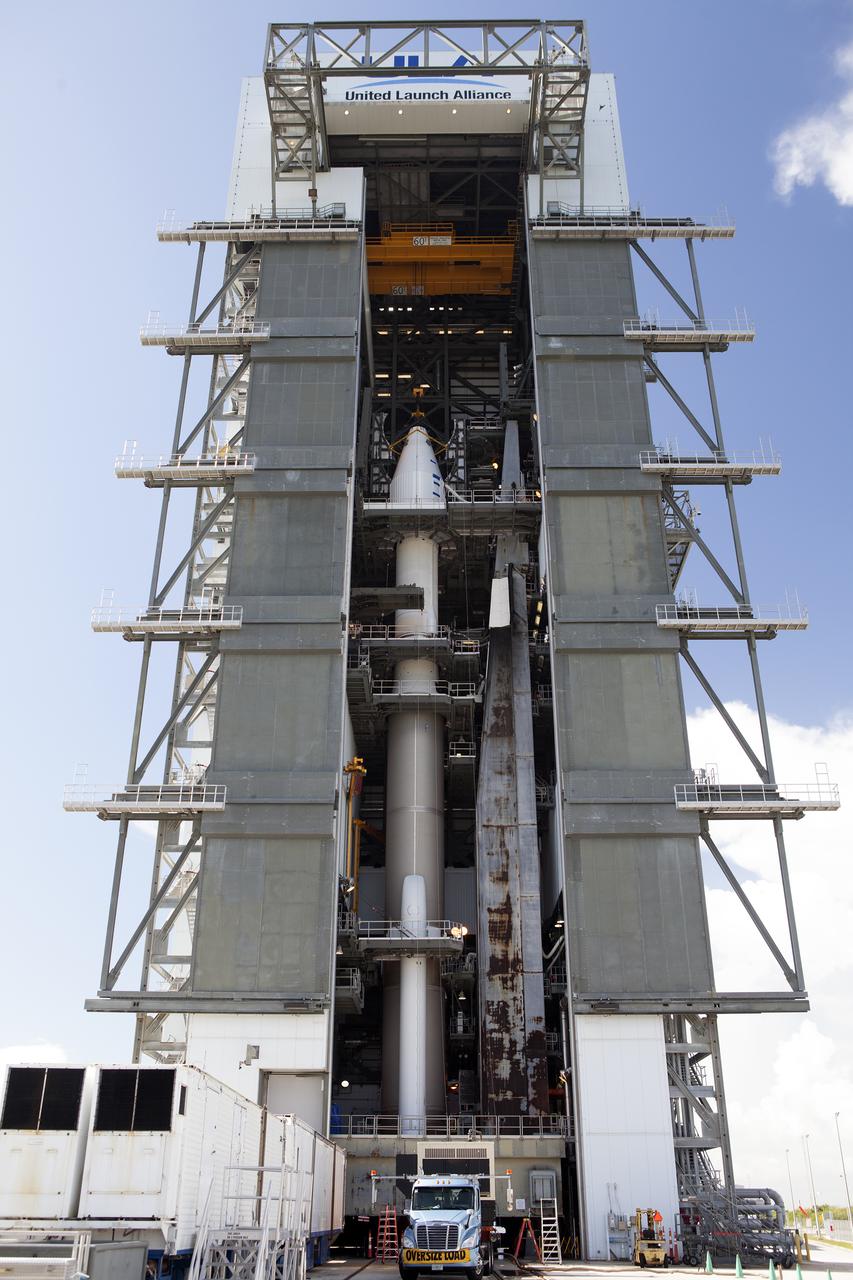

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is positioned atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is positioned for lifting at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
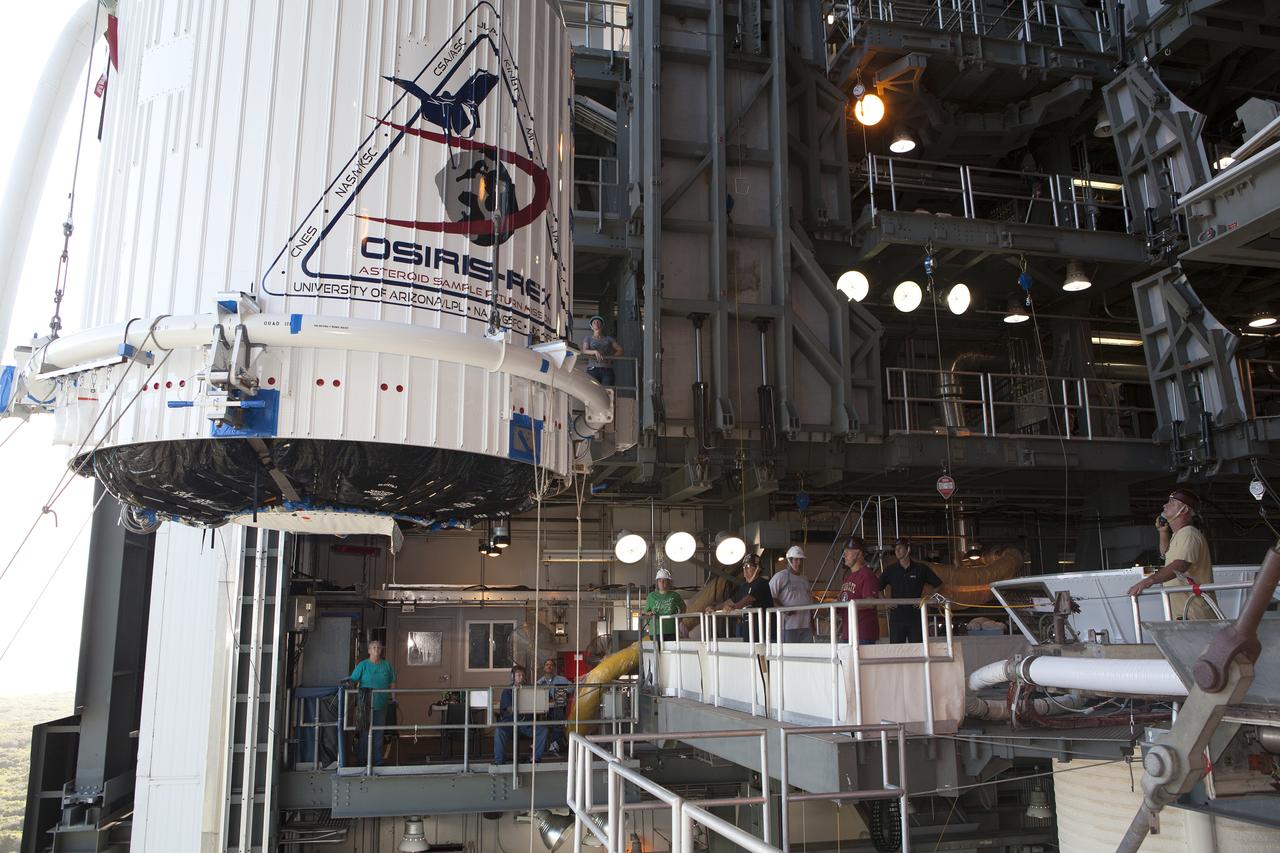

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is lifted at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
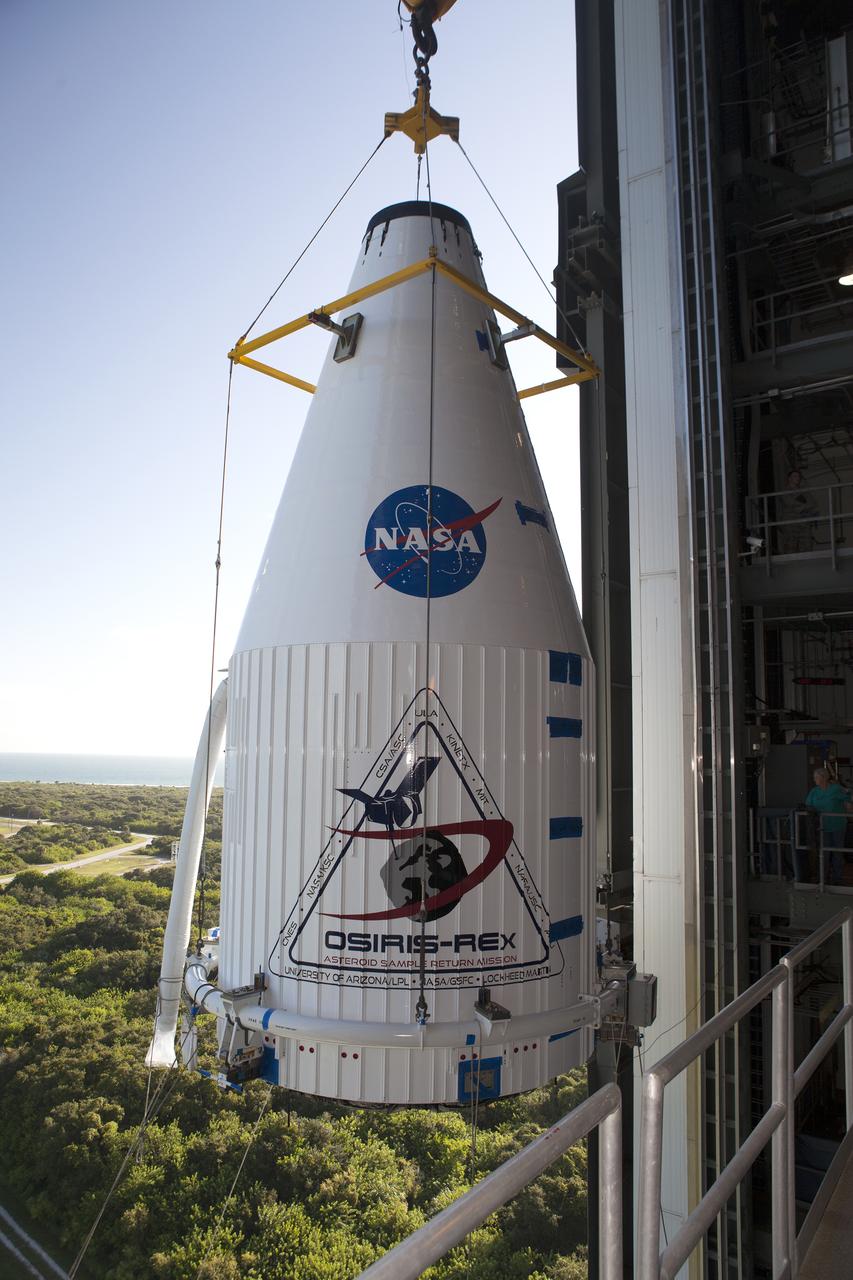

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is lifted at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
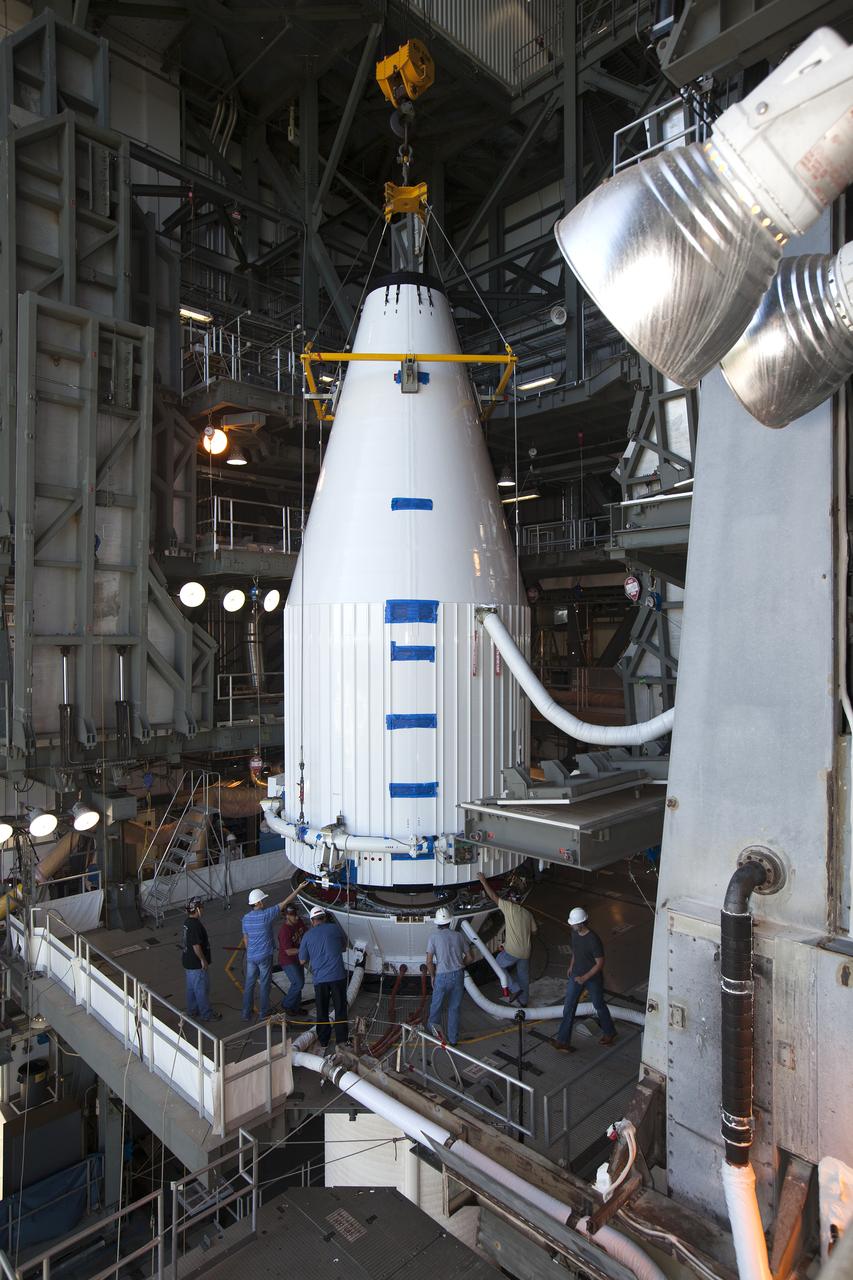

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is positioned atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
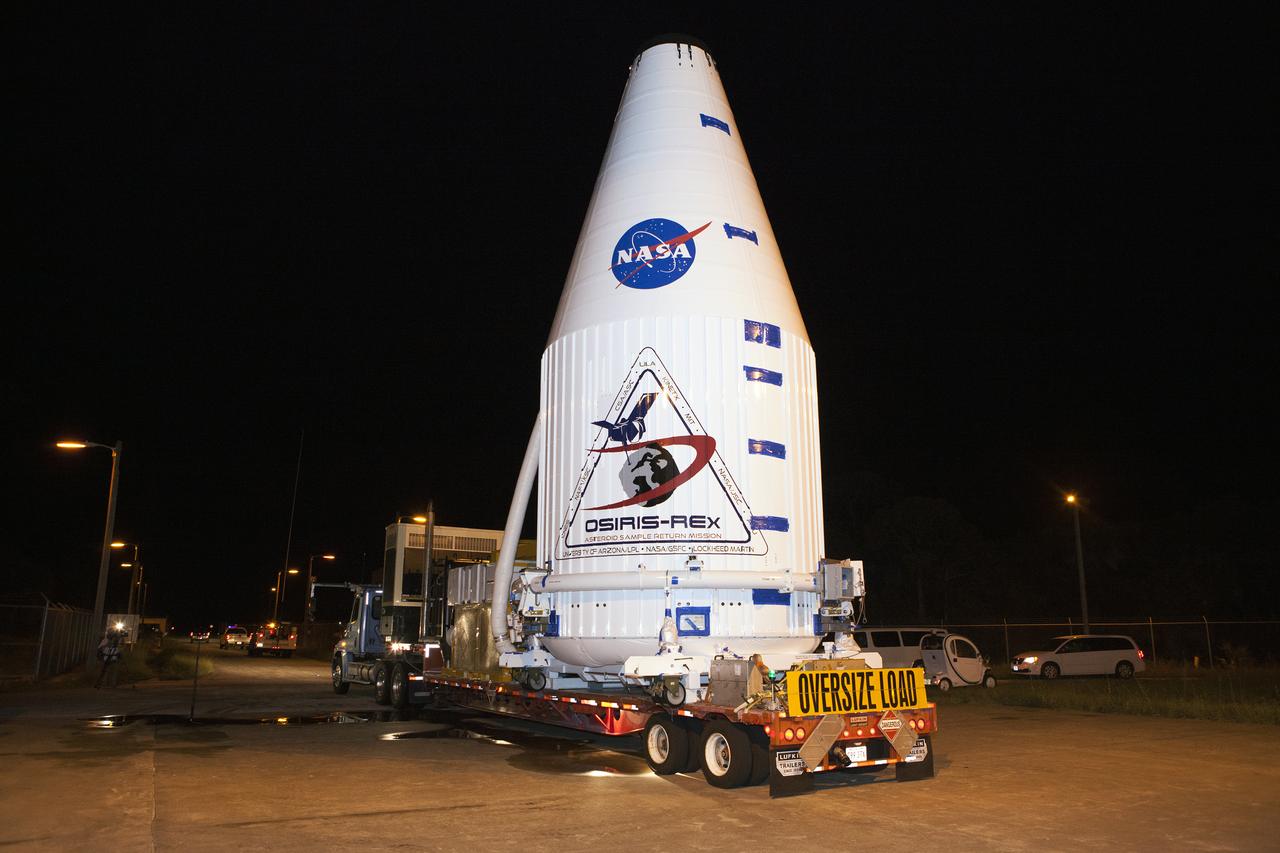

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, enclosed in a payload fairing, is towed from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center to begin the trip to Space Launch Complex 41 at the adjacent Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that is to lift OSIRIS-REx into space was stacked at SLC-41 so the spacecraft and fairing could be hoisted and bolted to the rocket promptly. The spacecraft will be sent to rendezvous with, survey and take a sample from an asteroid called Bennu.
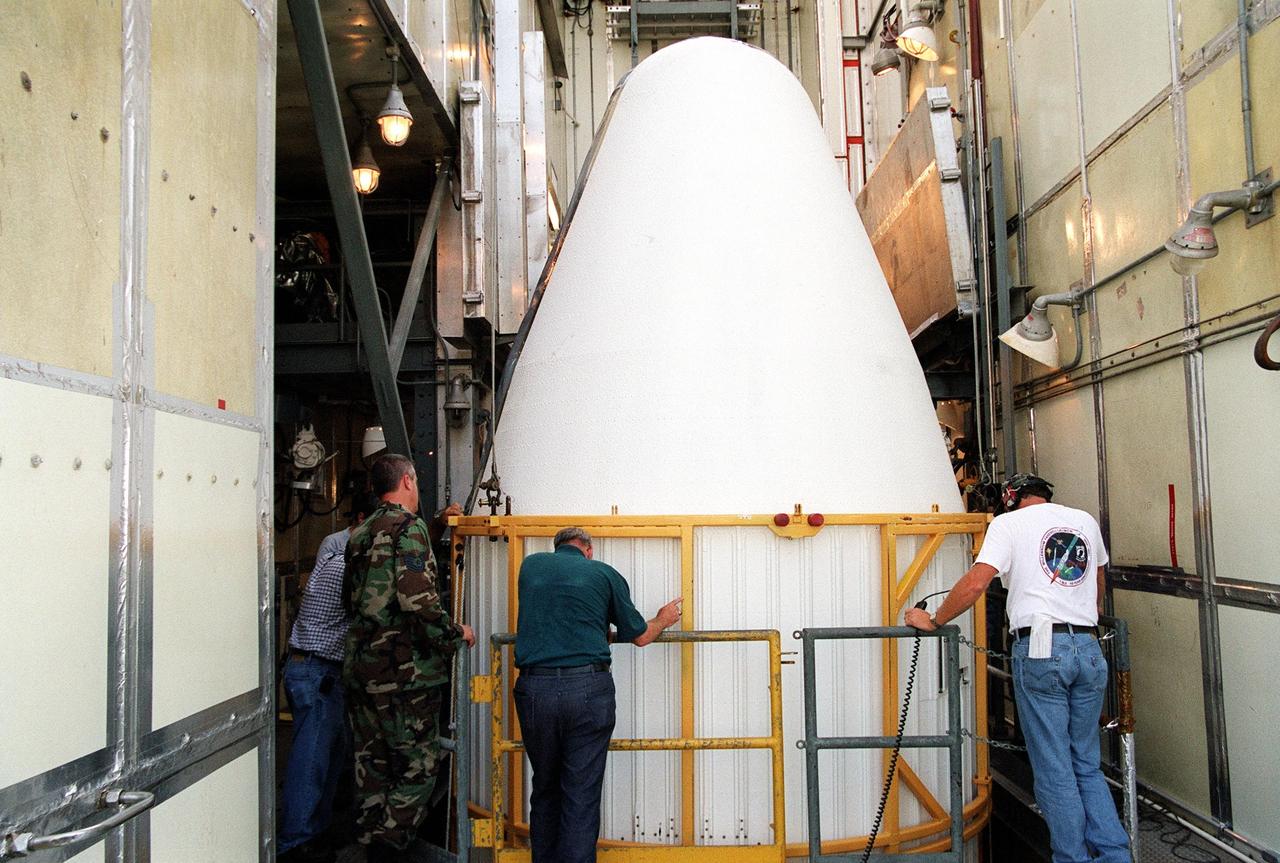

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second part of the fairing for the Genesis spacecraft arrives at the top of the gantry. The fairing will encapsulate the spacecraft to protect it during launch aboard a Delta II rocket. Genesis will be on a journey to capture samples of the ions and elements in the solar wind and return them to Earth for scientists to use to determine the exact composition of the Sun and the solar system’s origin. NASA’s Genesis project in managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics built the Genesis spacecraft for NASA in Denver, Colo. The launch is scheduled for July 30 at 12:36 p.m. EDT
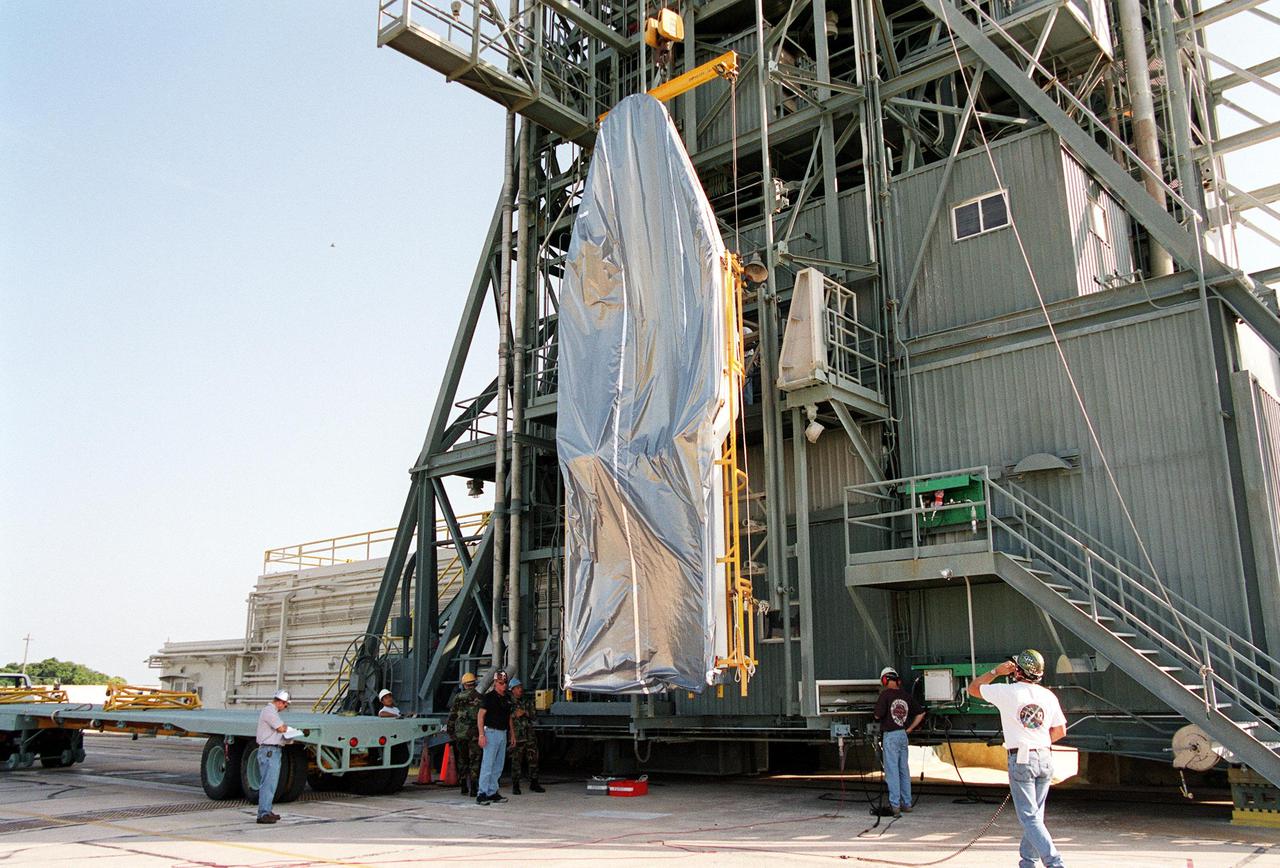

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second part of the fairing for the Genesis spacecraft is lifted up the gantry. The fairing will encapsulate the spacecraft to protect it during launch aboard a Delta II rocket. Genesis will be on a journey to capture samples of the ions and elements in the solar wind and return them to Earth for scientists to use to determine the exact composition of the Sun and the solar system’s origin. NASA’s Genesis project in managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics built the Genesis spacecraft for NASA in Denver, Colo. The launch is scheduled for July 30 at 12:36 p.m. EDT
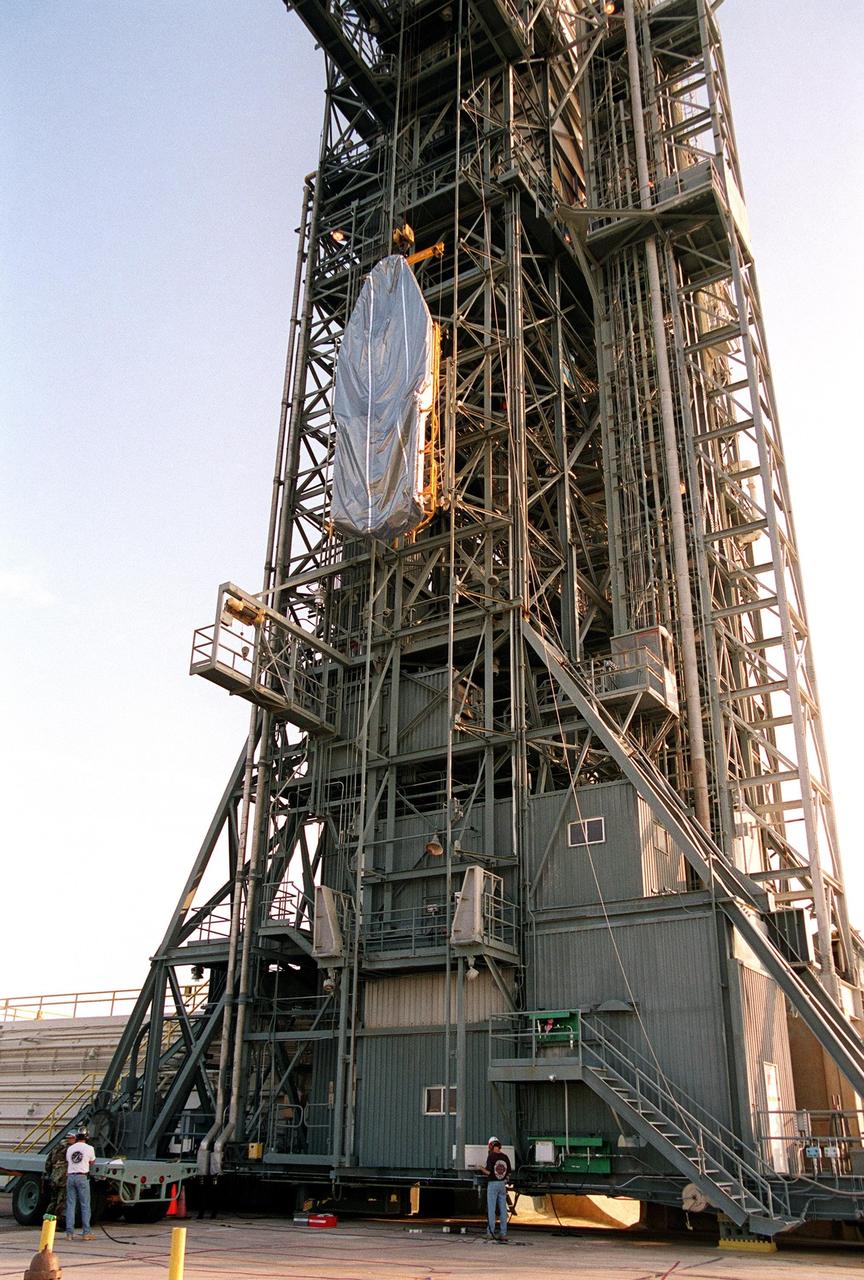

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, part of the fairing for the Genesis spacecraft is lifted up the gantry. The fairing will encapsulate the spacecraft to protect it during launch aboard a Delta II rocket. Genesis will be on a journey to capture samples of the ions and elements in the solar wind and return them to Earth for scientists to use to determine the exact composition of the Sun and the solar system’s origin. NASA’s Genesis project in managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics built the Genesis spacecraft for NASA in Denver, Colo. The launch is scheduled for July 30 at 12:36 p.m. EDT
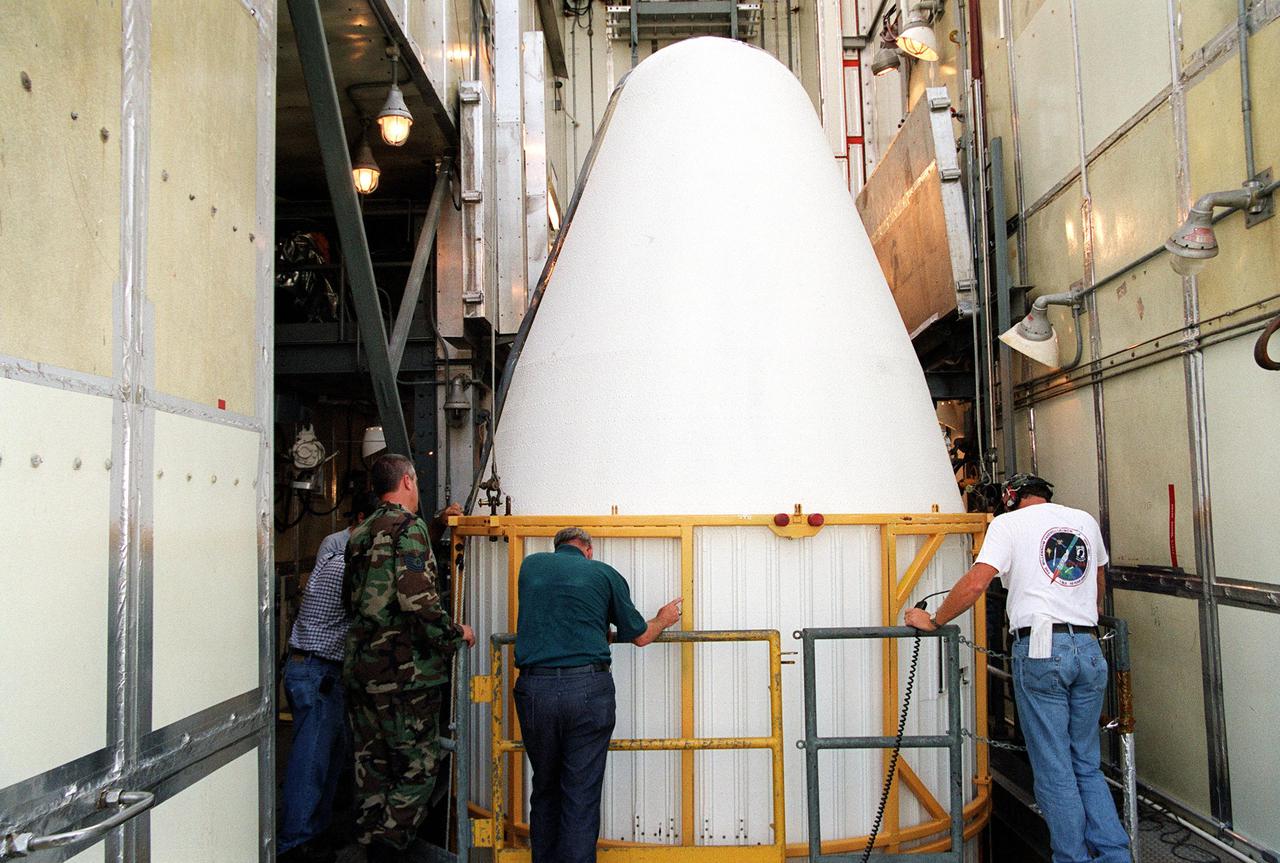

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second part of the fairing for the Genesis spacecraft arrives at the top of the gantry. The fairing will encapsulate the spacecraft to protect it during launch aboard a Delta II rocket. Genesis will be on a journey to capture samples of the ions and elements in the solar wind and return them to Earth for scientists to use to determine the exact composition of the Sun and the solar system’s origin. NASA’s Genesis project in managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics built the Genesis spacecraft for NASA in Denver, Colo. The launch is scheduled for July 30 at 12:36 p.m. EDT
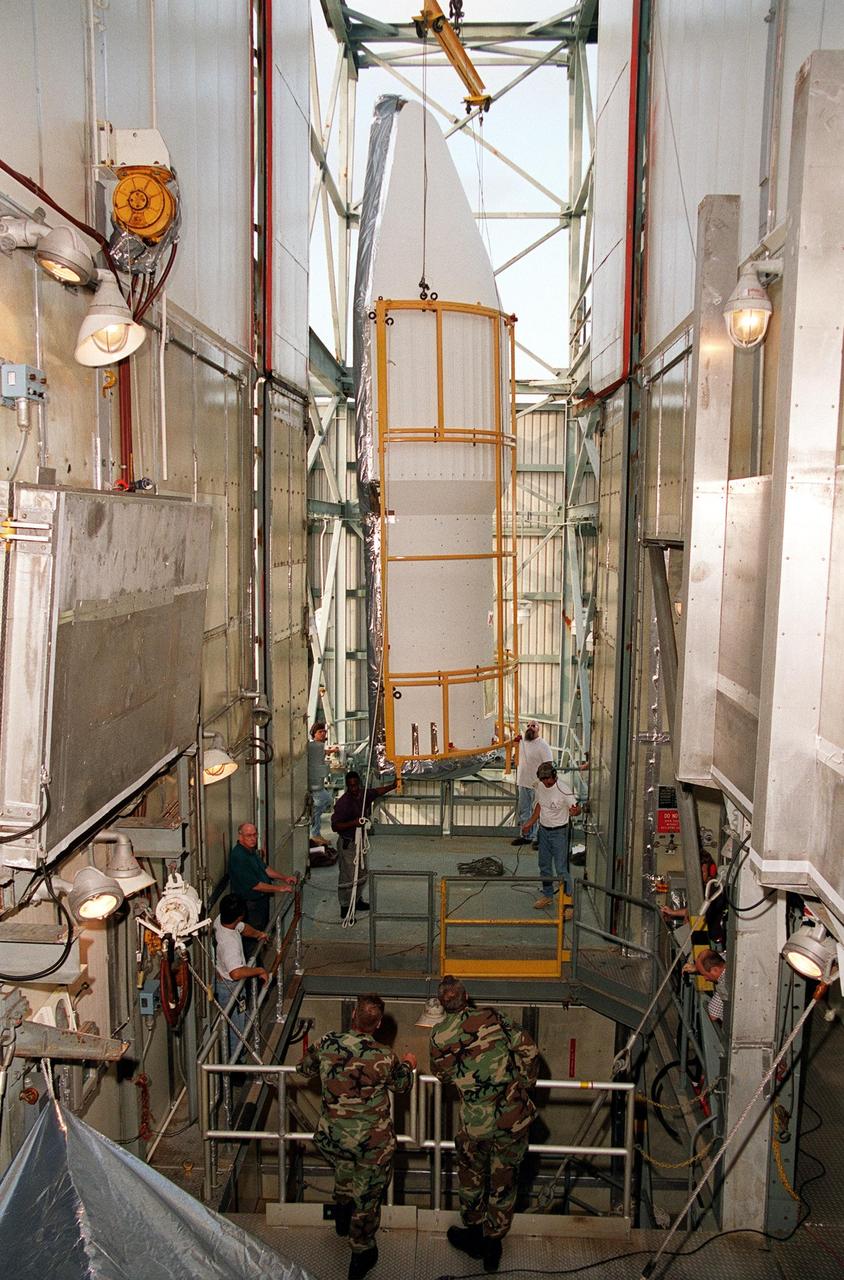

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, one part of the fairing for the Genesis spacecraft is being moved toward the opening in the foreground where the Genesis spacecraft waits for encapsulation. The fairing will protect the spacecraft during launch aboard a Delta II rocket. Genesis will be on a journey to capture samples of the ions and elements in the solar wind and return them to Earth for scientists to use to determine the exact composition of the Sun and the solar system’s origin. NASA’s Genesis project in managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics built the Genesis spacecraft for NASA in Denver, Colo. The launch is scheduled for July 30 at 12:36 p.m. EDT
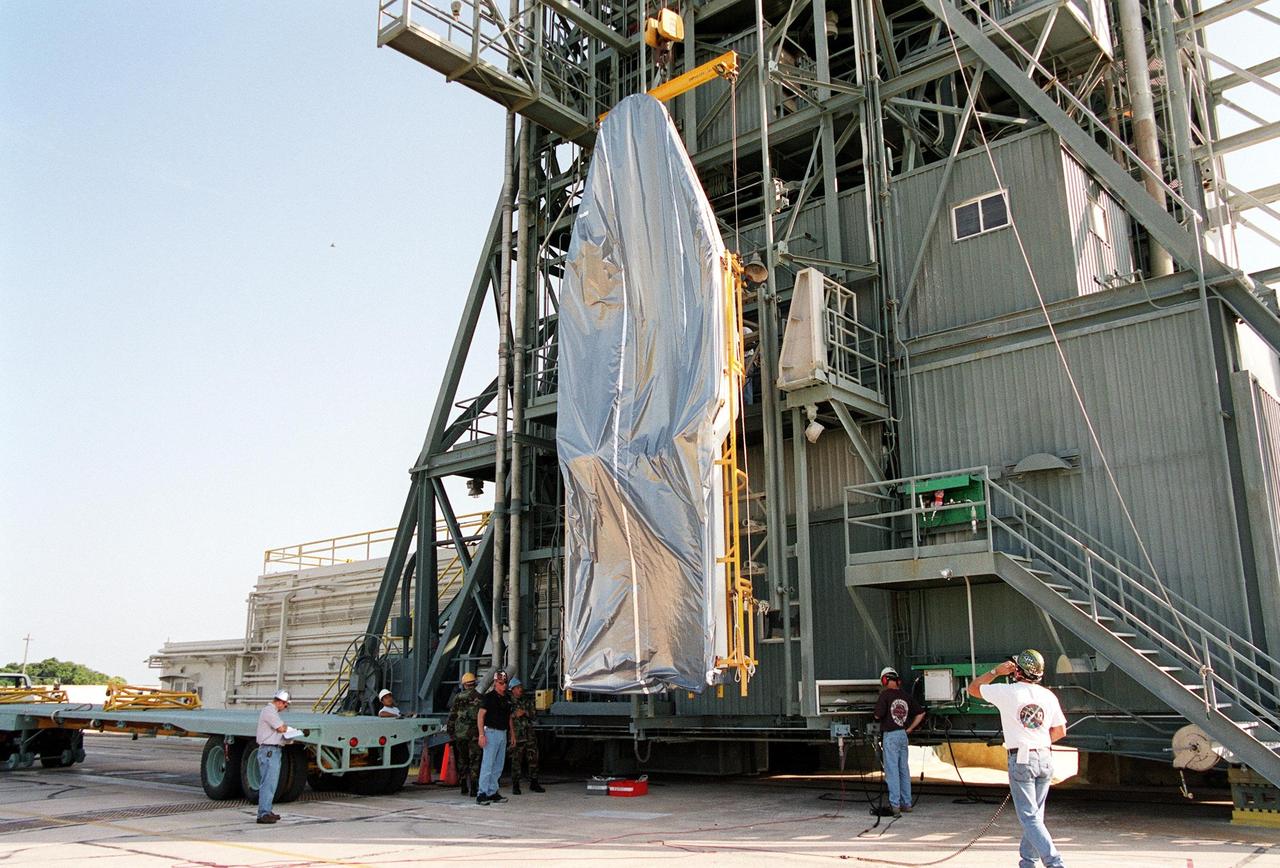

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second part of the fairing for the Genesis spacecraft is lifted up the gantry. The fairing will encapsulate the spacecraft to protect it during launch aboard a Delta II rocket. Genesis will be on a journey to capture samples of the ions and elements in the solar wind and return them to Earth for scientists to use to determine the exact composition of the Sun and the solar system’s origin. NASA’s Genesis project in managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics built the Genesis spacecraft for NASA in Denver, Colo. The launch is scheduled for July 30 at 12:36 p.m. EDT
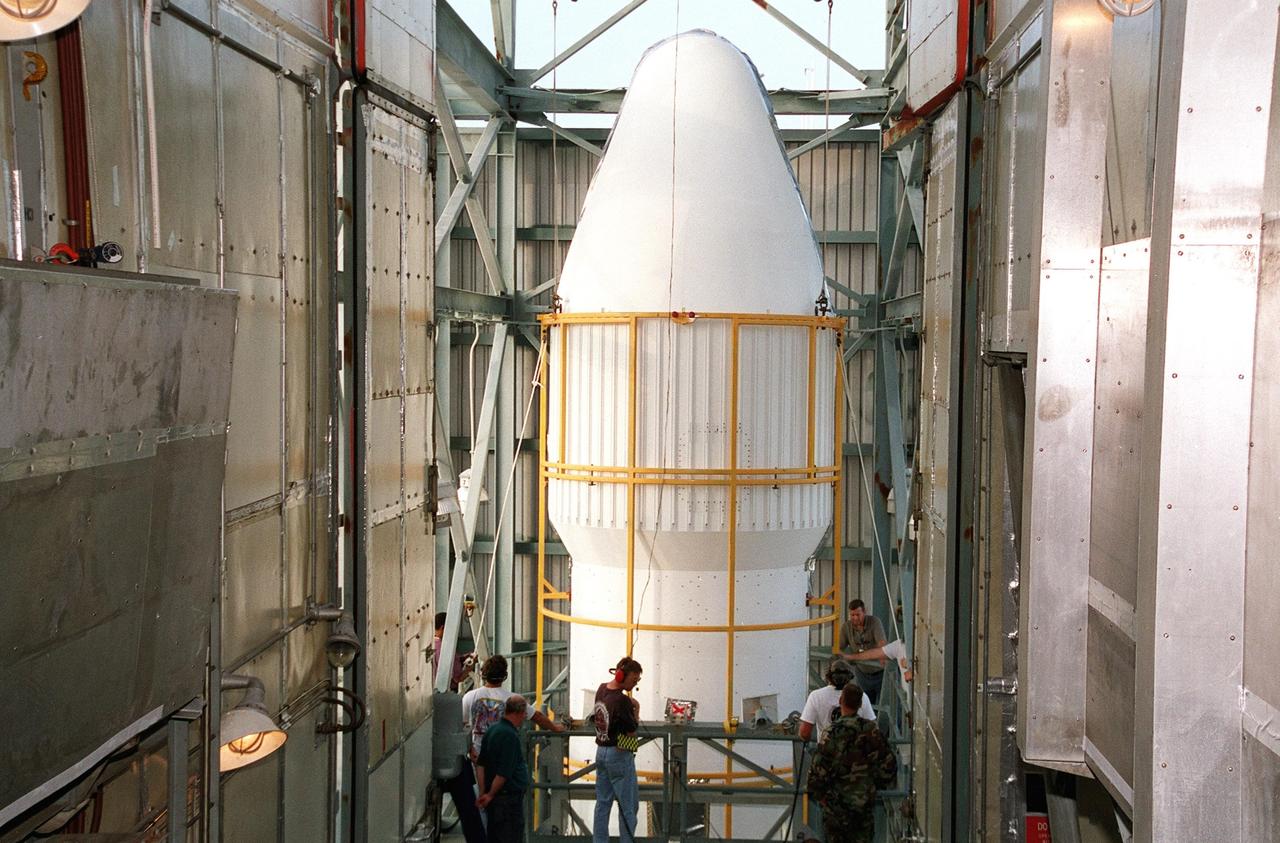

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, one part of the fairing for the Genesis spacecraft arrives at the top of the gantry. The fairing will encapsulate the spacecraft to protect it during launch aboard a Delta II rocket. Genesis will be on a journey to capture samples of the ions and elements in the solar wind and return them to Earth for scientists to use to determine the exact composition of the Sun and the solar system’s origin. NASA’s Genesis project in managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. Lockheed Martin Astronautics built the Genesis spacecraft for NASA in Denver, Colo. The launch is scheduled for July 30 at 12:36 p.m. EDT
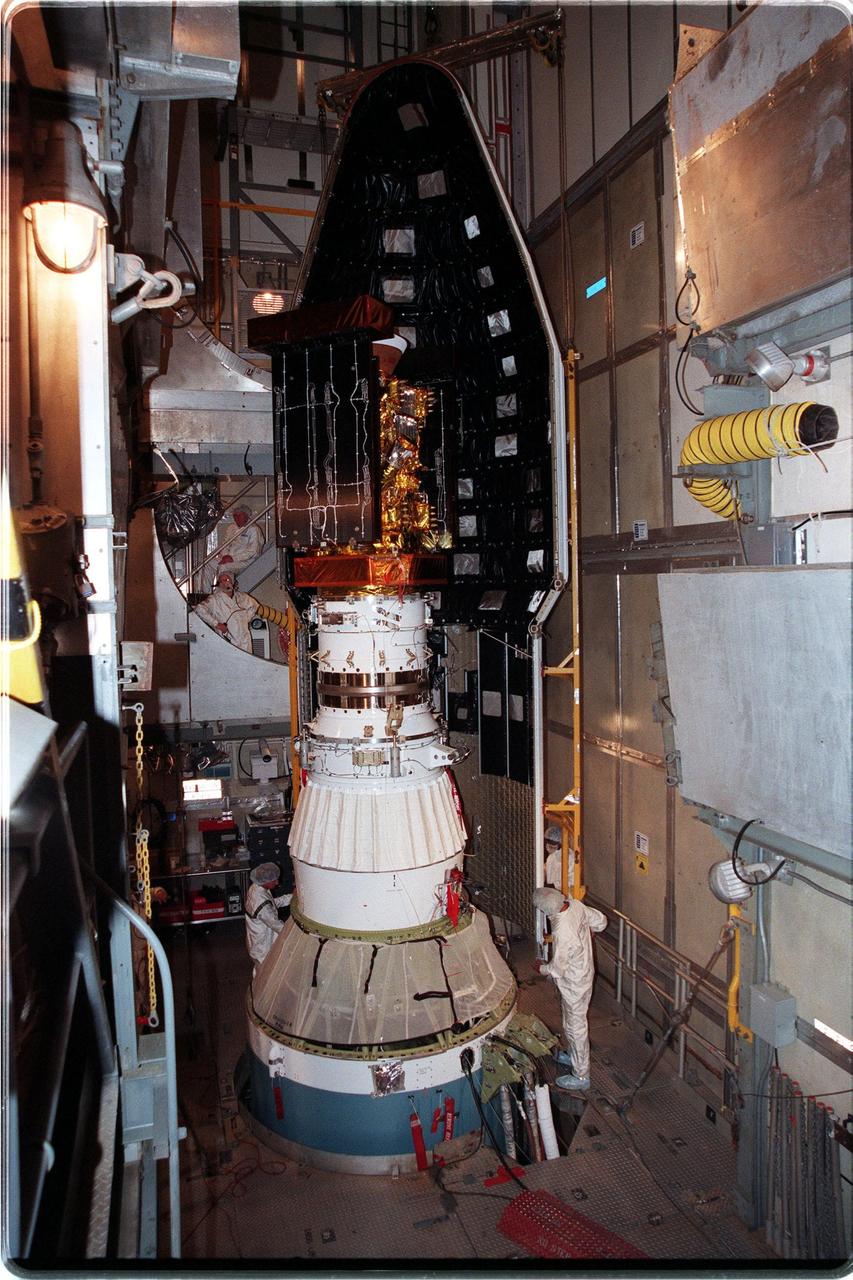
At Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers begin placing the fairing around the Stardust spacecraft and upper stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Targeted for launch at 4:06:42 p.m. on Feb. 6, Stardust is destined for a close encounter with the comet Wild 2 in January 2004. Using a silicon-based substance called aerogel, Stardust will capture comet particles flying off the nucleus of the comet. The spacecraft also will bring back samples of interstellar dust. These materials consist of ancient pre-solar interstellar grains and other remnants left over from the formation of the solar system. Scientists expect their analysis to provide important insights into the evolution of the sun and planets and possibly into the origin of life itself. The collected samples will return to Earth in a sample return capsule to be jettisoned as Stardust swings by Earth in January 2006
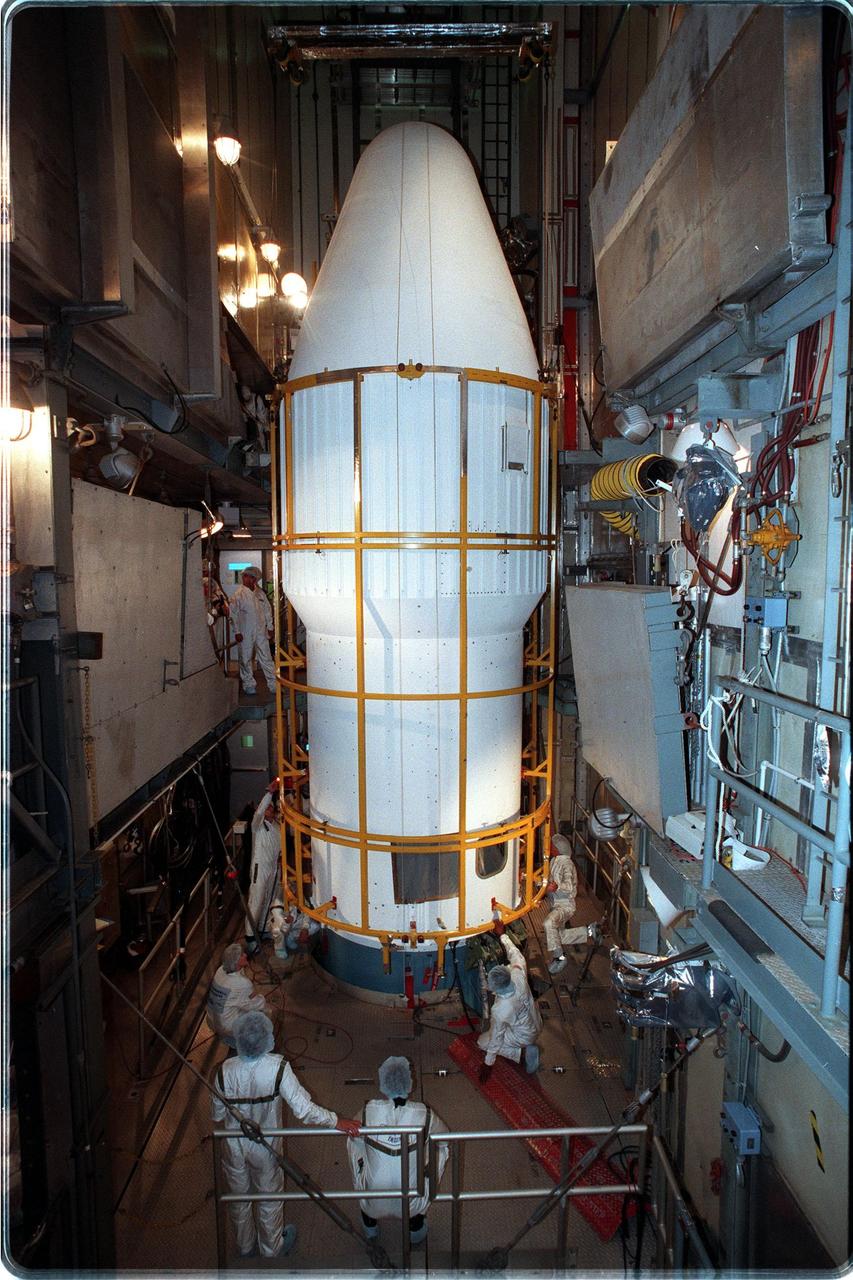

At Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers check the lower fittings of the fairing installed around the Stardust spacecraft and upper stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Targeted for launch at 4:06:42 p.m. on Feb. 6, the spacecraft is destined for a close encounter with the comet Wild 2 in January 2004. Using a silicon-based substance called aerogel, Stardust will capture comet particles flying off the nucleus of the comet. The spacecraft also will bring back samples of interstellar dust. These materials consist of ancient pre-solar interstellar grains and other remnants left over from the formation of the solar system. Scientists expect their analysis to provide important insights into the evolution of the sun and planets and possibly into the origin of life itself. The collected samples will return to Earth in a sample return capsule to be jettisoned as Stardust swings by Earth in January 2006
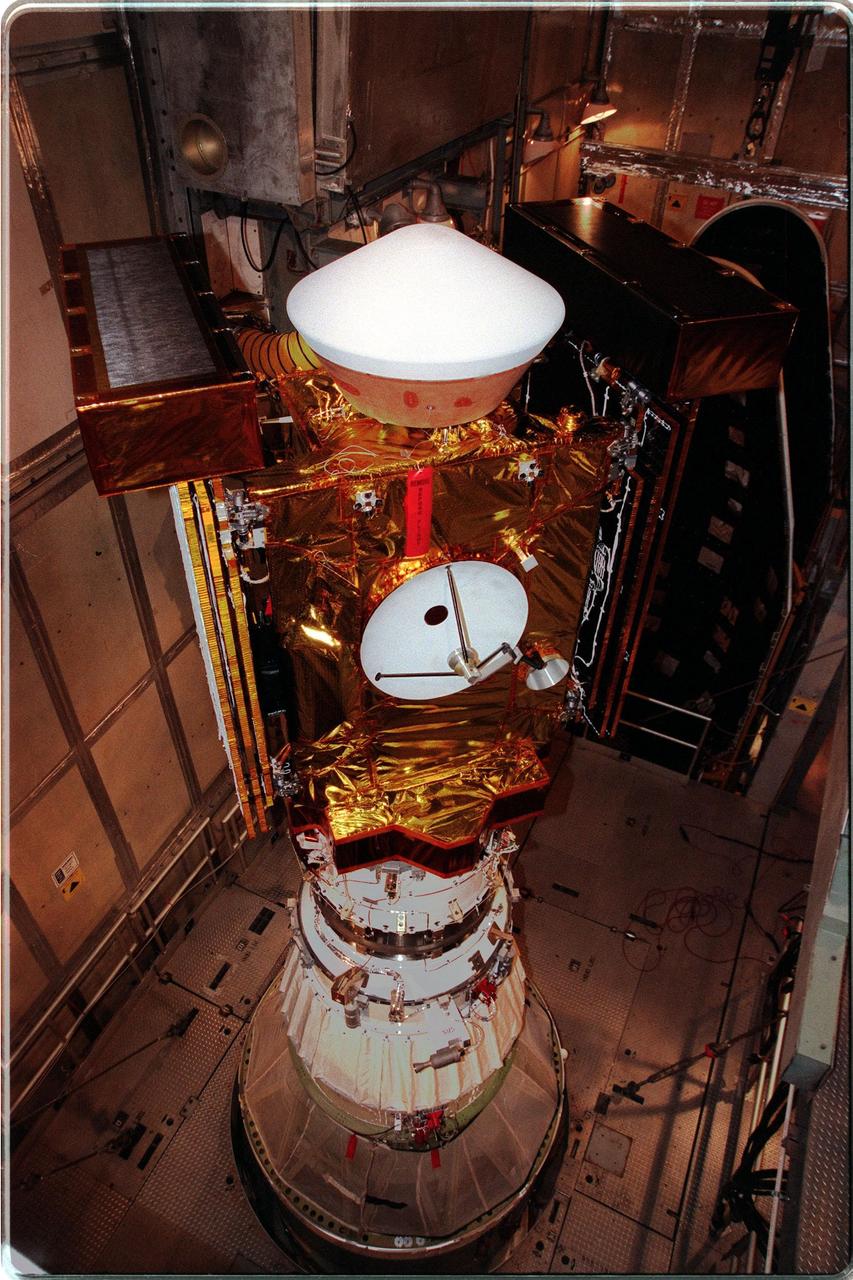

At Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, the Stardust spacecraft waits for installation of the fairing (behind, right) that will enclose the spacecraft and the upper stage of the Boeing Delta II rocket. Targeted for launch at 4:06:42 p.m. on Feb. 6, Stardust is destined for a close encounter with the comet Wild 2 in January 2004. Using a silicon-based substance called aerogel, Stardust will capture comet particles flying off the nucleus of the comet. The spacecraft also will bring back samples of interstellar dust. These materials consist of ancient pre-solar interstellar grains and other remnants left over from the formation of the solar system. Scientists expect their analysis to provide important insights into the evolution of the sun and planets and possibly into the origin of life itself. The collected samples will return to Earth in a sample return capsule to be jettisoned as Stardust swings by Earth in January 2006
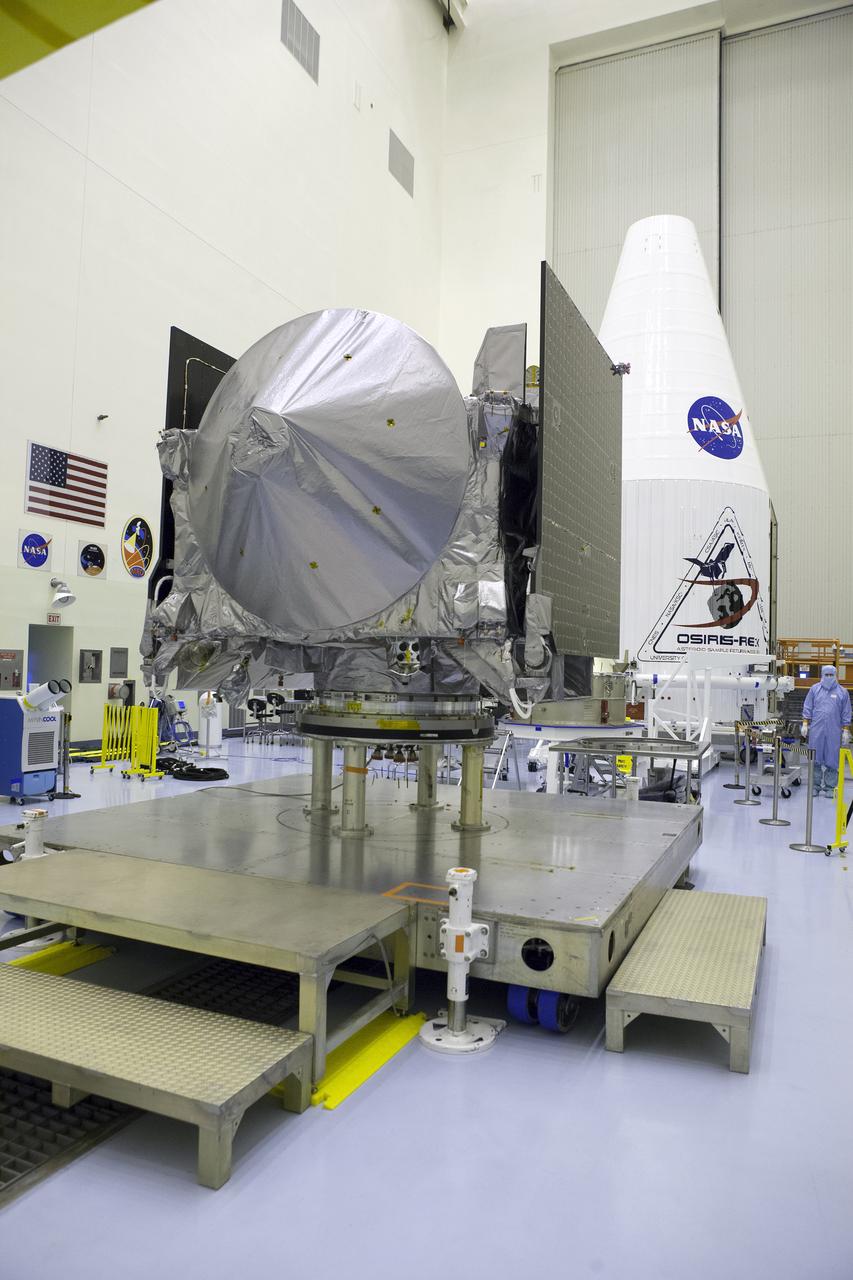

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is prepared for encapsulation in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.
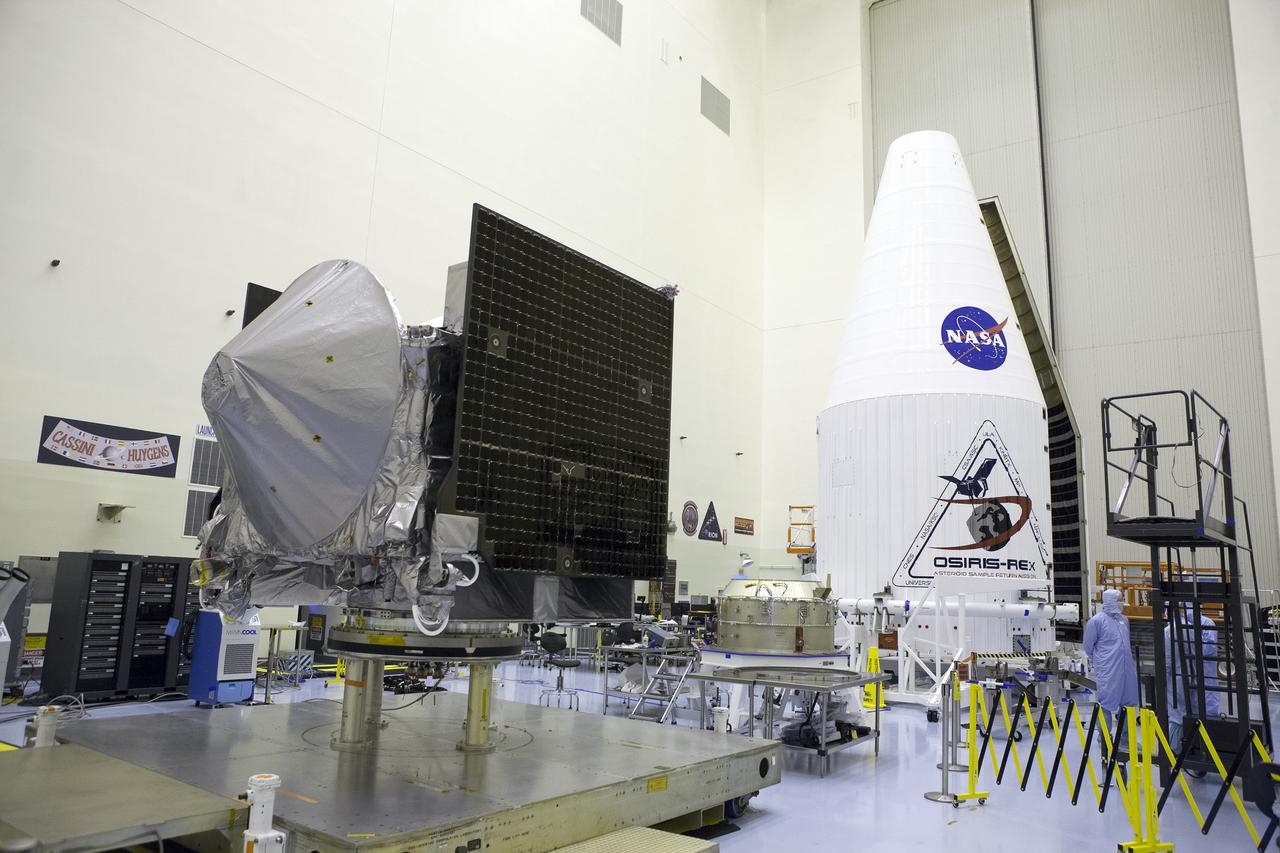

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is prepared for encapsulation in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.
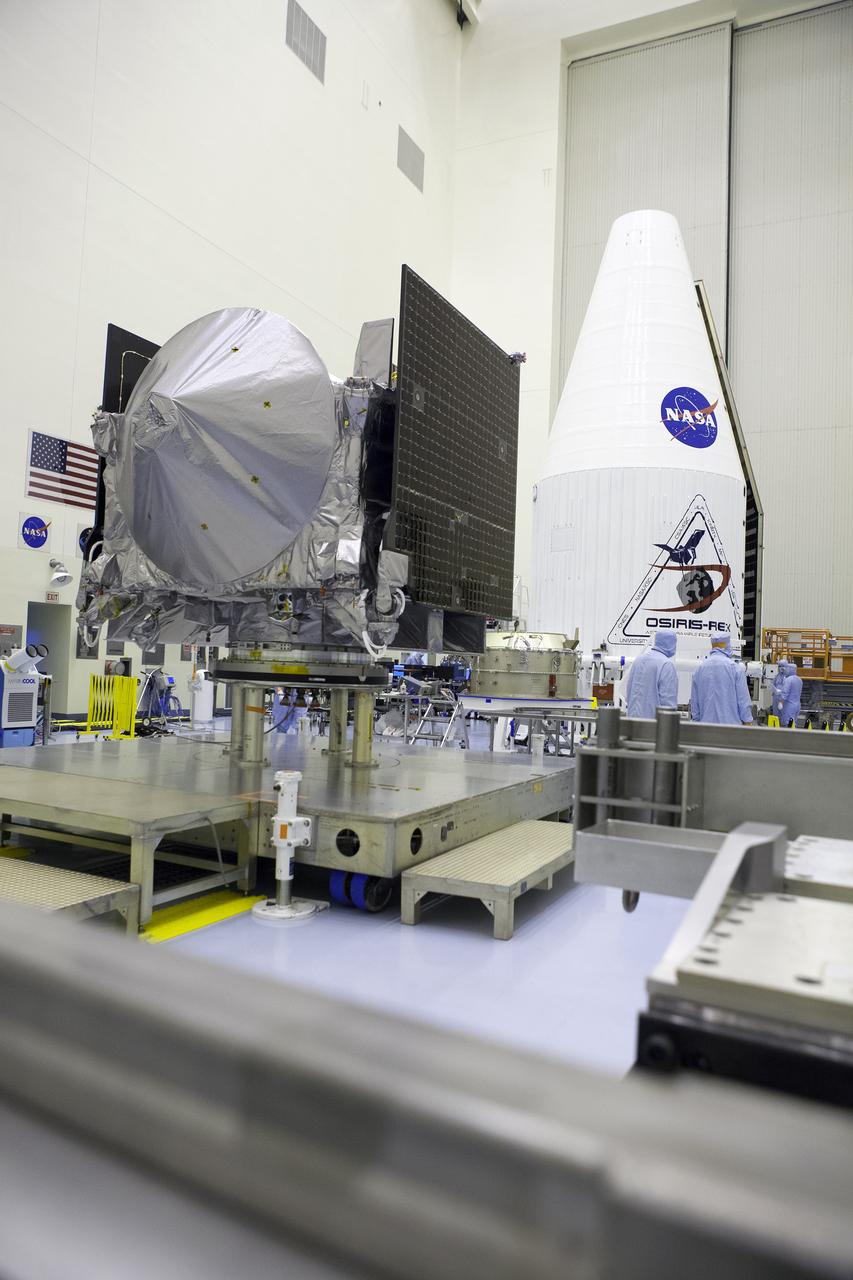

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is prepared for encapsulation in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engineers and technicians encapsulate the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff at 7:05 p.m. EDT Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engineers and technicians encapsulate the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff at 7:05 p.m. EDT Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.
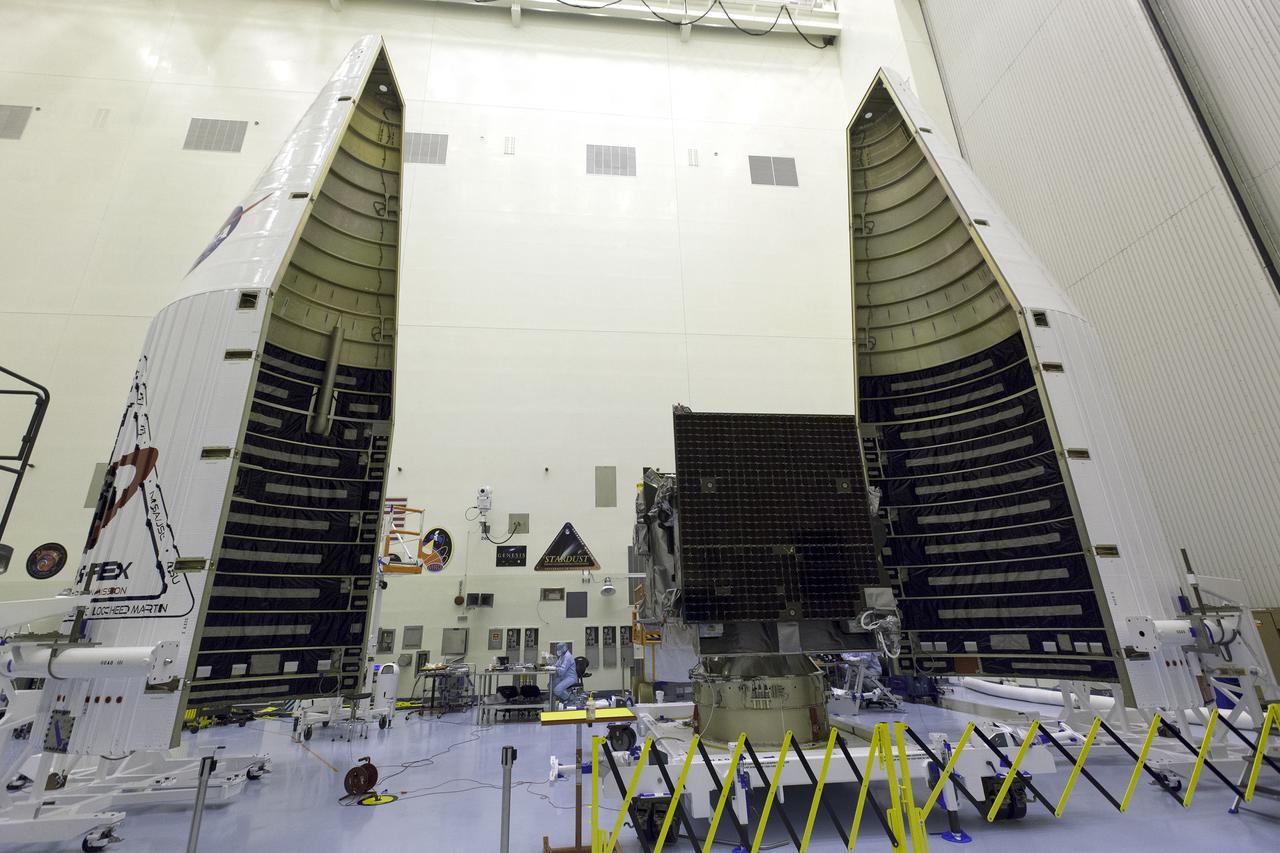

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is encapsulated in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff at 7:05 p.m. EDT Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.
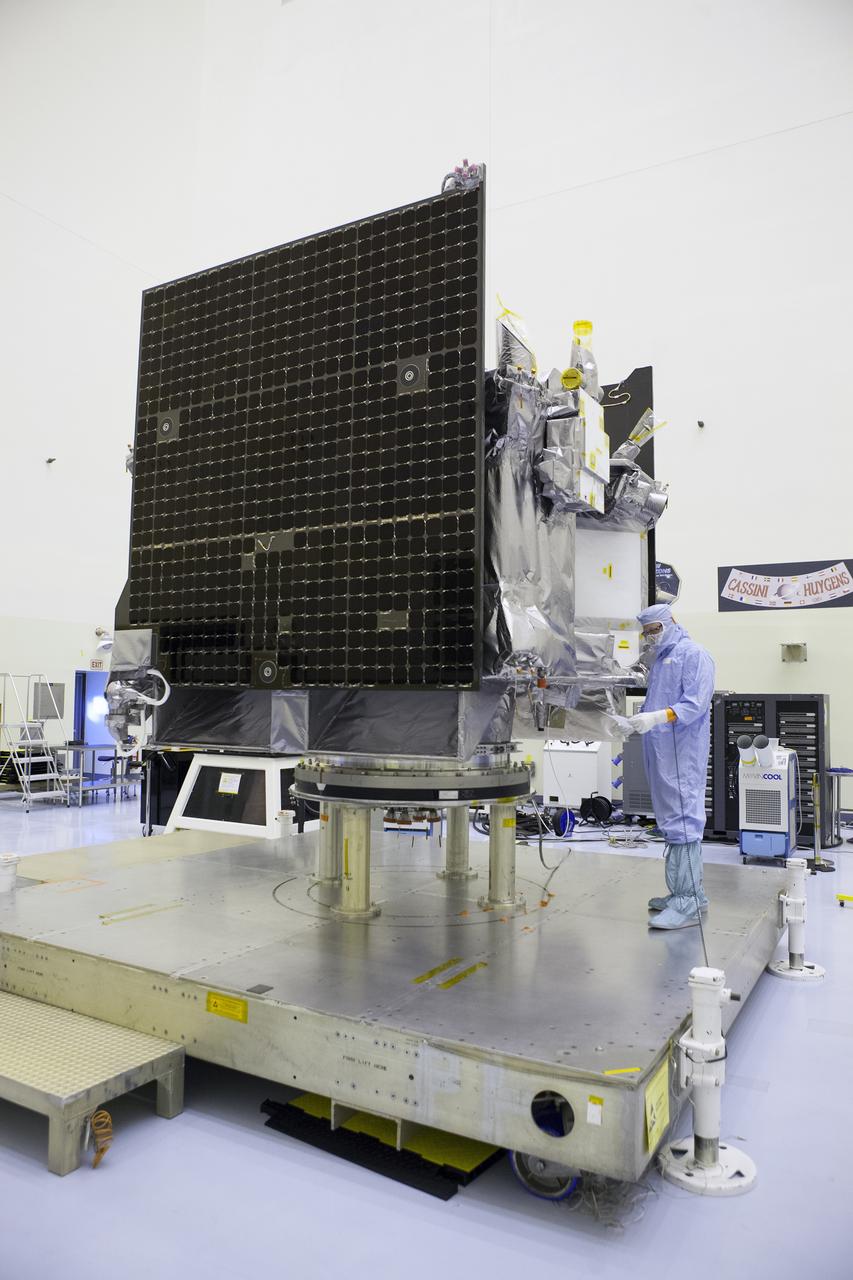

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft undergoes final inspections and checkouts prior to encapsulation in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.
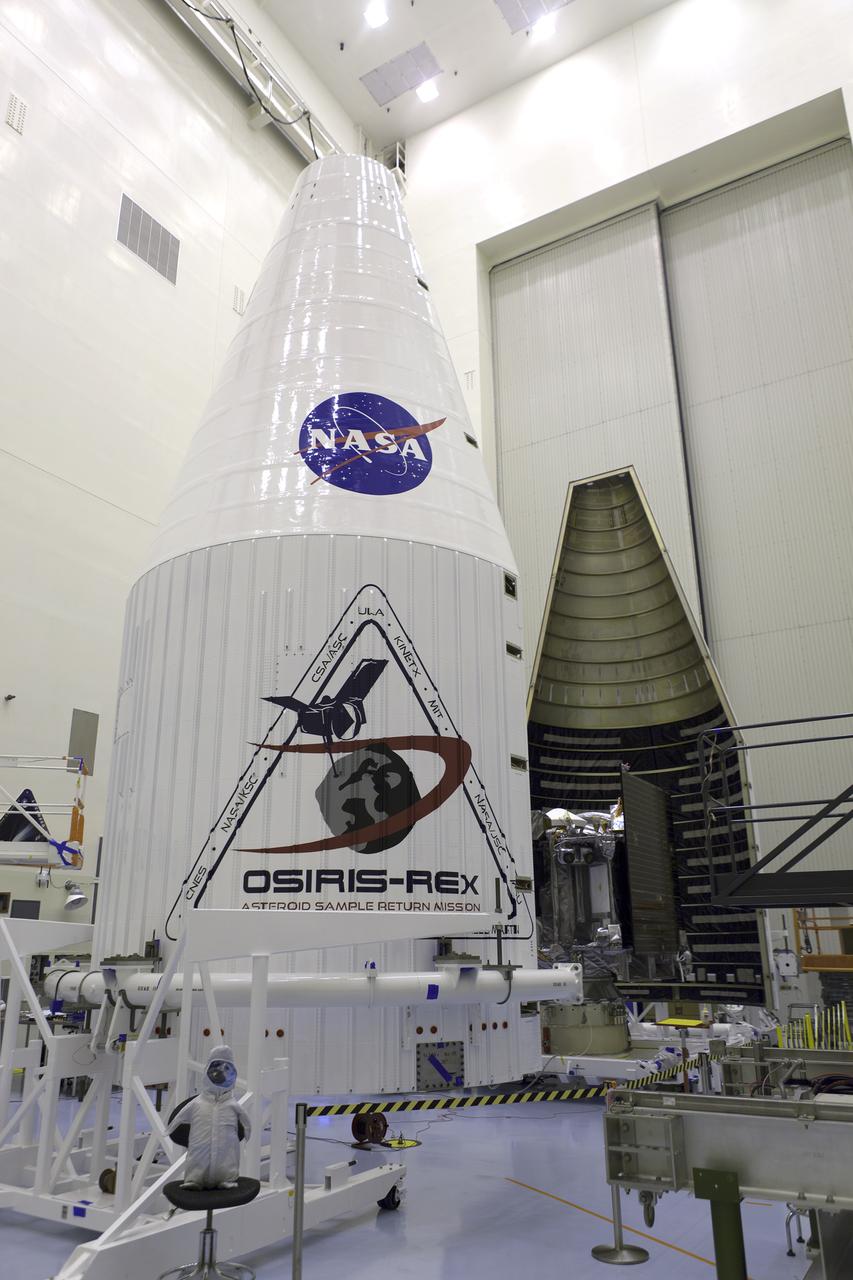

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is encapsulated in its payload fairing. Targeted for liftoff at 7:05 p.m. EDT Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.

After a 24-hour postponement, the Boeing Delta II rocket carrying the Stardust spacecraft waits on Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, for its scheduled launch at 4:04 p.m. EST. Umbilical lines (at top) still attached to the fixed utility tower (at right) feed electricity, air conditioning and coolants for the Stardust spacecraft inside the fairing (enclosing the upper stage) before launch. Stardust is destined for a close encounter with the comet Wild 2 in January 2004. Using a silicon-based substance called aerogel, Stardust will capture comet particles flying off the nucleus of the comet. The spacecraft also will bring back samples of interstellar dust. These materials consist of ancient pre-solar interstellar grains and other remnants left over from the formation of the solar system. Scientists expect their analysis to provide important insights into the evolution of the sun and planets and possibly into the origin of life itself. The collected samples will return to Earth in a sample return capsule to be jettisoned as Stardust swings by Earth in January 2006
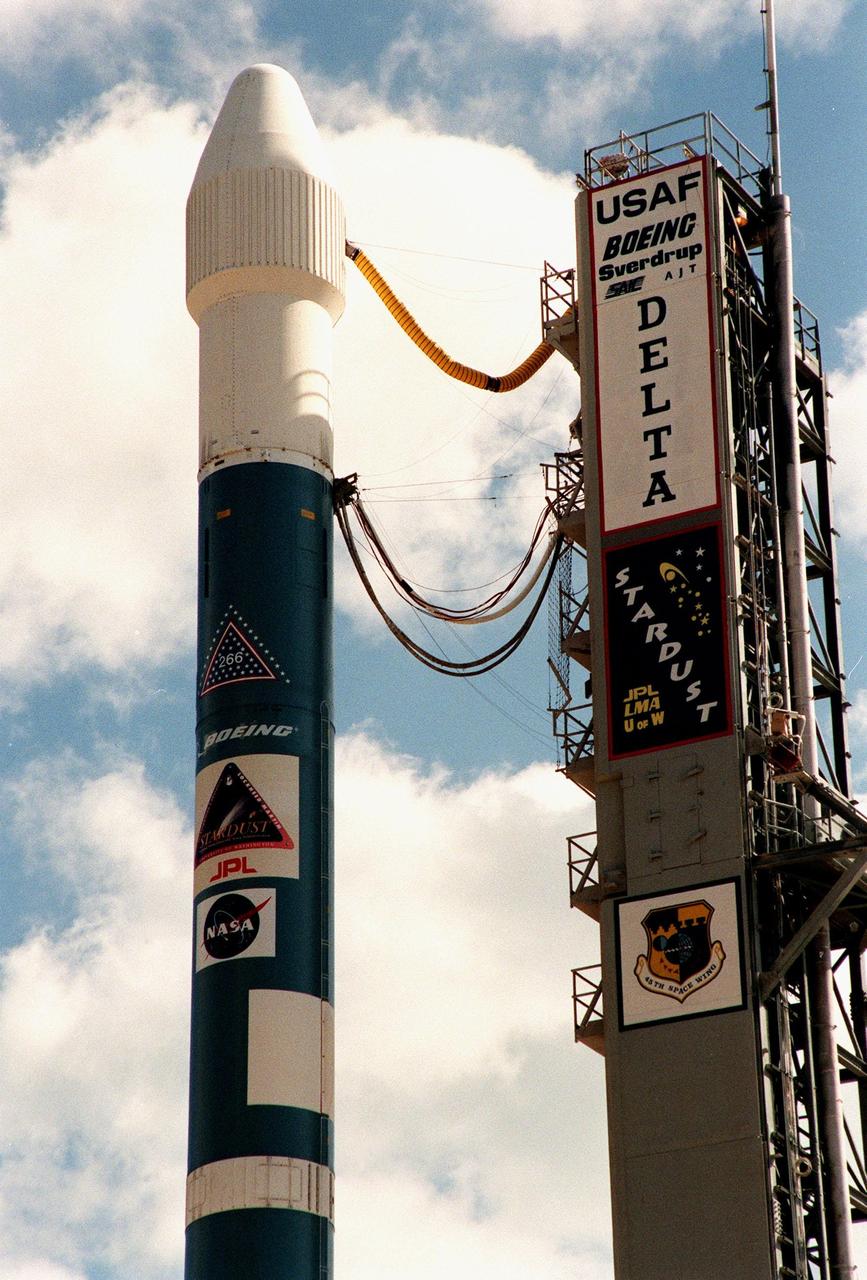

At Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, a Boeing Delta II rocket is poised for liftoff after tower rollback. Umbilical lines (at top) still attached to the fixed utility tower (at right) feed electricity, air conditioning and coolants for the Stardust spacecraft inside the fairing (enclosing the upper stage) before launch. The targeted launch time is 4:06 p.m. EST. Stardust is destined for a close encounter with the comet Wild 2 in January 2004. Using a silicon-based substance called aerogel, Stardust will capture comet particles flying off the nucleus of the comet. The spacecraft also will bring back samples of interstellar dust. These materials consist of ancient pre-solar interstellar grains and other remnants left over from the formation of the solar system. Scientists expect their analysis to provide important insights into the evolution of the sun and planets and possibly into the origin of life itself. The collected samples will return to Earth in a sample return capsule to be jettisoned as Stardust swings by Earth in January 2006
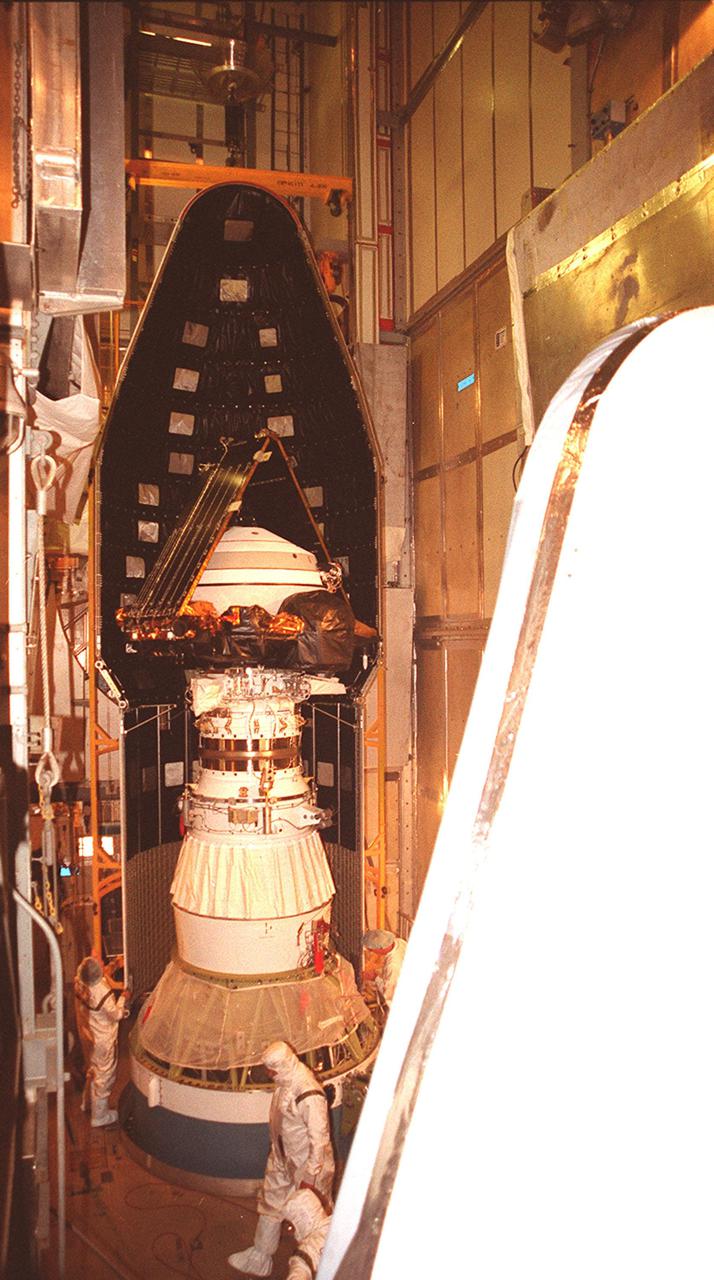
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Genesis spacecraft is being encapsulated inside the fairing. Workers check the fittings on the first half. The second half is in the foreground. Genesis is 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) long and 6.6 feet (2 meters) wide, with a wingspan of solar array 26 feet (7.9 meters) tip to tip. Genesis will be on a robotic NASA space mission to collect and return to Earth just 10 to 20 micrograms -- or the weight of a few grains of salt -- of solar wind, invisible charged particles that flow outward from the Sun. This treasured smidgen of the Sun will be preserved in a special laboratory for study by scientists over the next century in search of answers to fundamental questions about the exact composition of our star and the birth of our solar system. The sample return capsule is 4.9 feet (1.5 meters) in diameter and 52 inches (1.31 meters) tall. The Genesis launch is scheduled for 12:36 p.m. EDT on July 30 from CCAFS
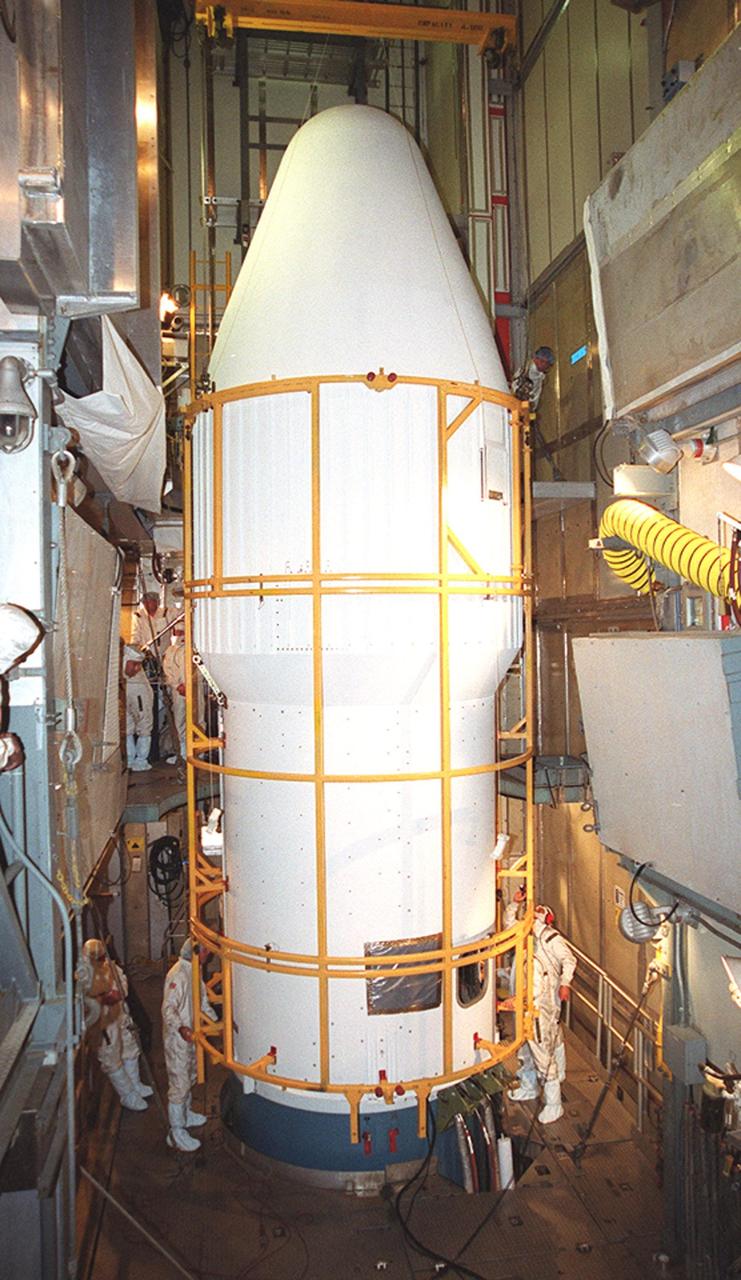

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Fairing installation around the Genesis spacecraft is complete inside the mobile service tower at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Genesis is 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) long and 6.6 feet (2 meters) wide, with a wingspan of solar array 26 feet (7.9 meters) tip to tip. Genesis will be on a robotic NASA space mission to collect and return to Earth just 10 to 20 micrograms -- or the weight of a few grains of salt -- of solar wind, invisible charged particles that flow outward from the Sun. This treasured smidgen of the Sun will be preserved in a special laboratory for study by scientists over the next century in search of answers to fundamental questions about the exact composition of our star and the birth of our solar system. The sample return capsule is 4.9 feet (1.5 meters) in diameter and 52 inches (1.31 meters) tall. The Genesis launch is scheduled for 12:36 p.m. EDT on July 30 from CCAFS
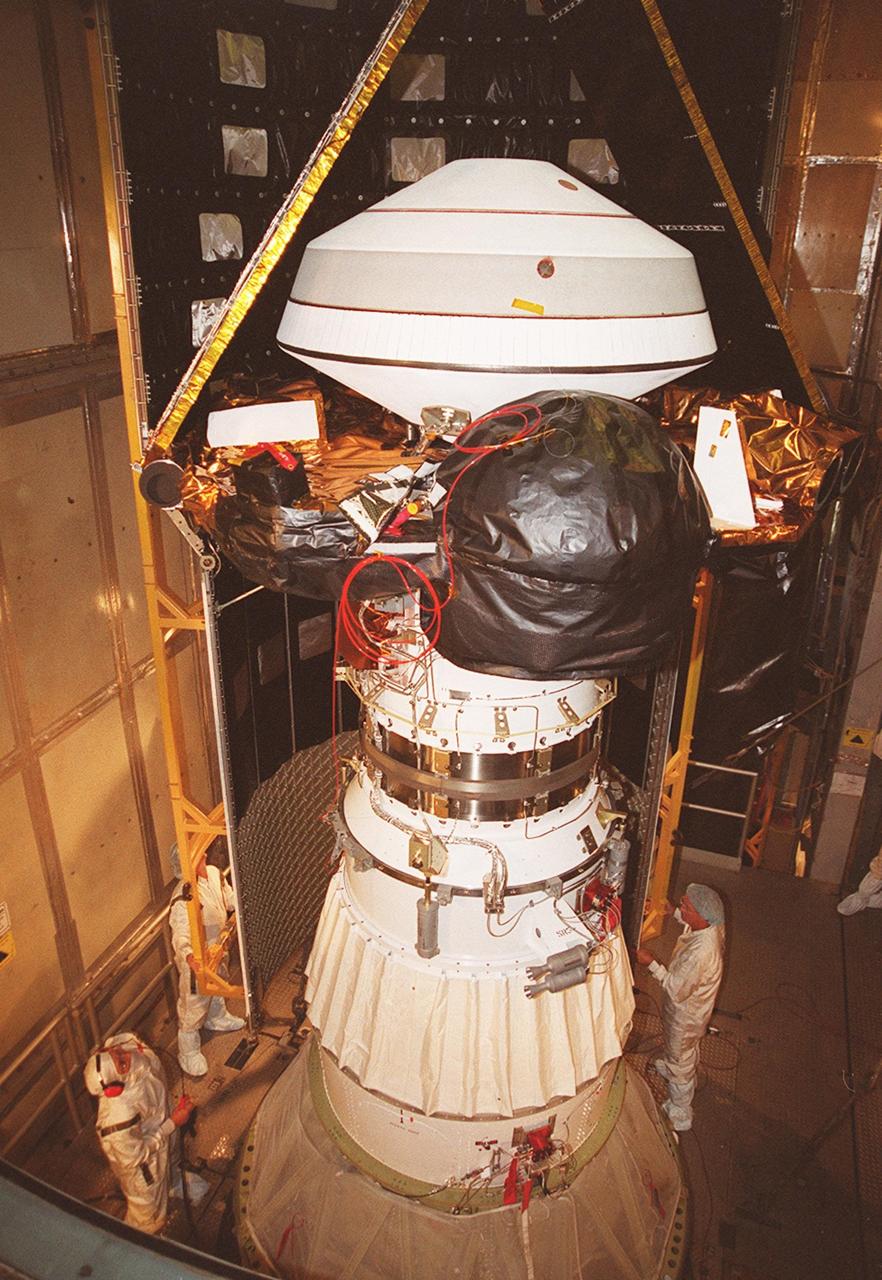

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower at Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Genesis spacecraft waits for the first half of the fairing to be installed (behind it). Genesis is 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) long and 6.6 feet (2 meters) wide, with a wingspan of solar array 26 feet (7.9 meters) tip to tip. Genesis will be on a robotic NASA space mission to collect and return to Earth just 10 to 20 micrograms -- or the weight of a few grains of salt -- of solar wind, invisible charged particles that flow outward from the Sun. This treasured smidgen of the Sun will be preserved in a special laboratory for study by scientists over the next century in search of answers to fundamental questions about the exact composition of our star and the birth of our solar system. The sample return capsule is 4.9 feet (1.5 meters) in diameter and 52 inches (1.31 meters) tall. The Genesis launch is scheduled for 12:36 p.m. EDT on July 30 from CCAFS
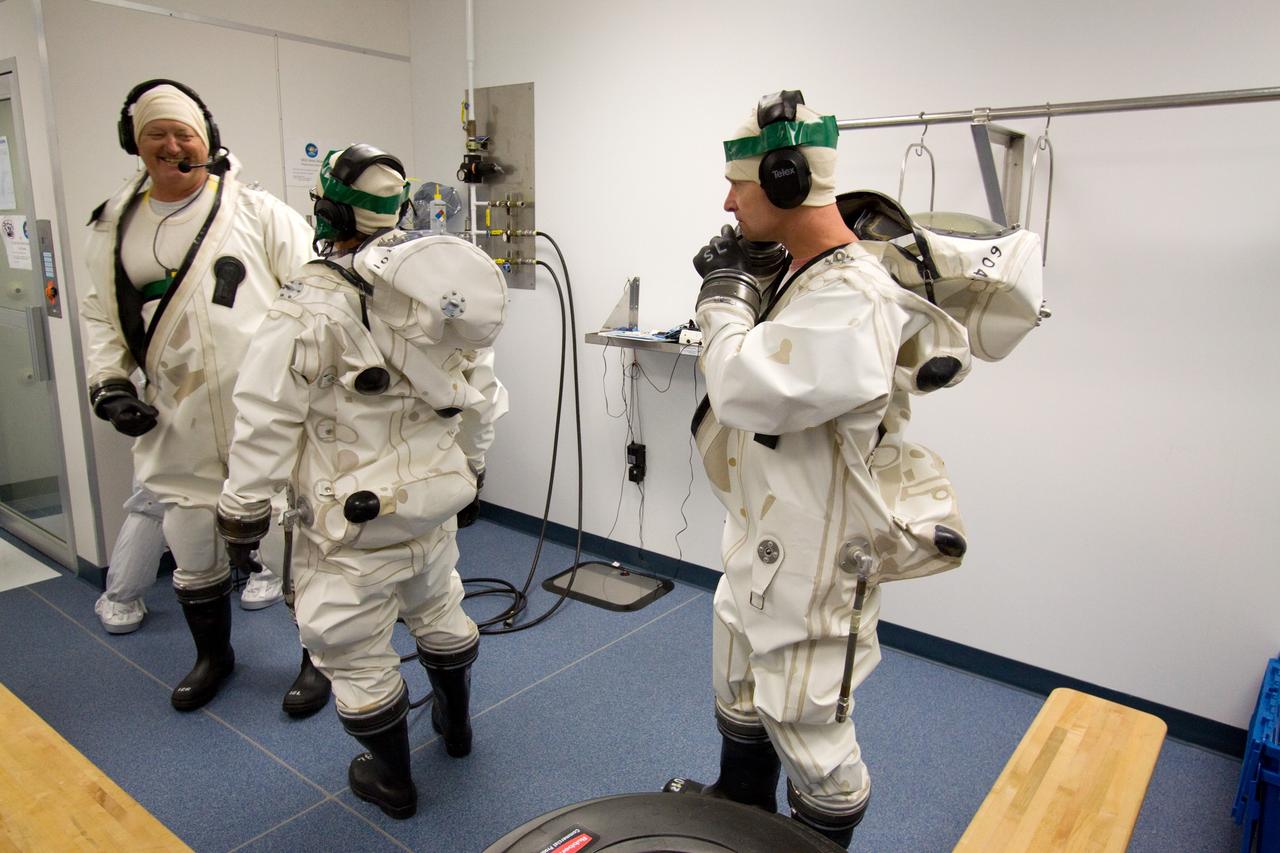

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center prepare to sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. From left are Boeing technicians Richard Gillman and Steve Lay, and SDO technician Brian Kittle. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
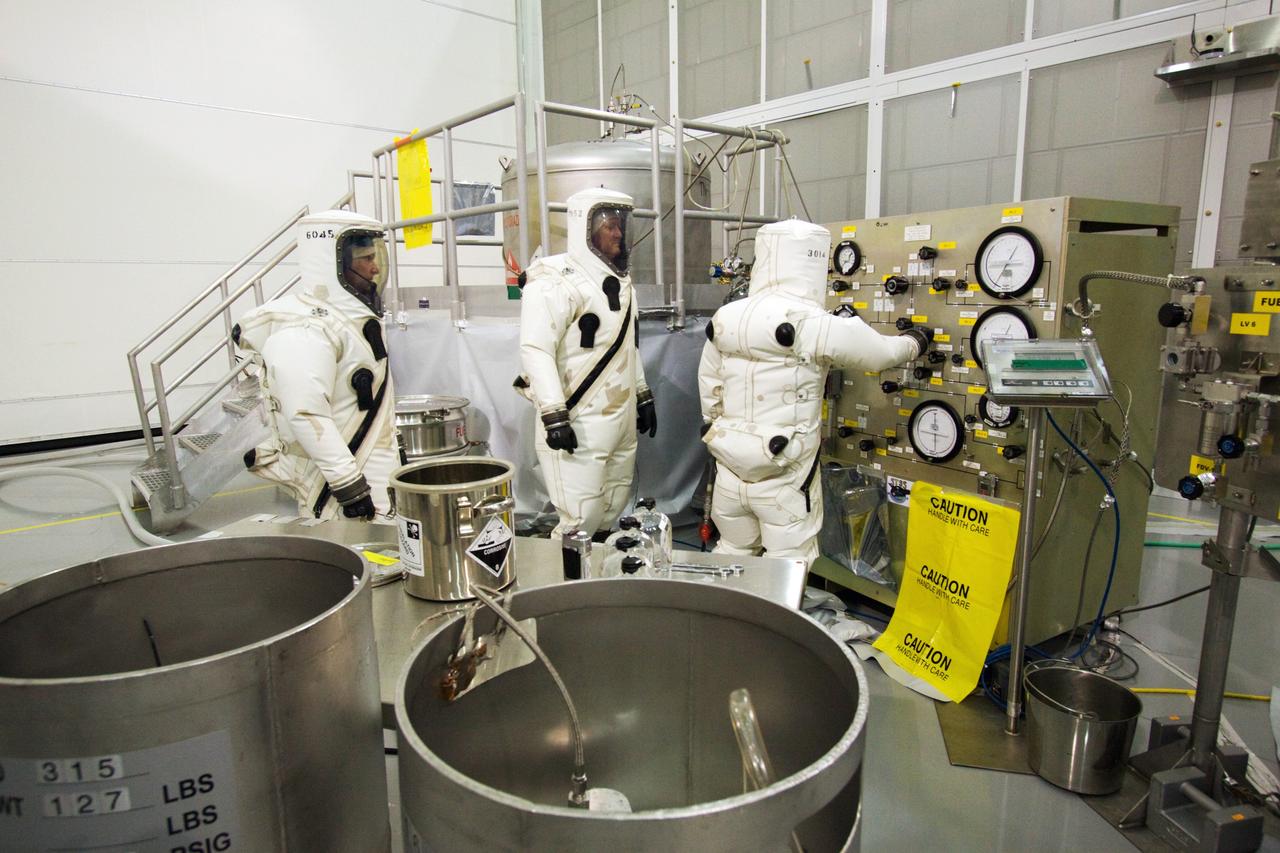

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., Boeing spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center prepare the equipment necessary to sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the control room at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., test conductors from ASTROTECH and Kennedy Space Center monitor data received from the clean room as technicians sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
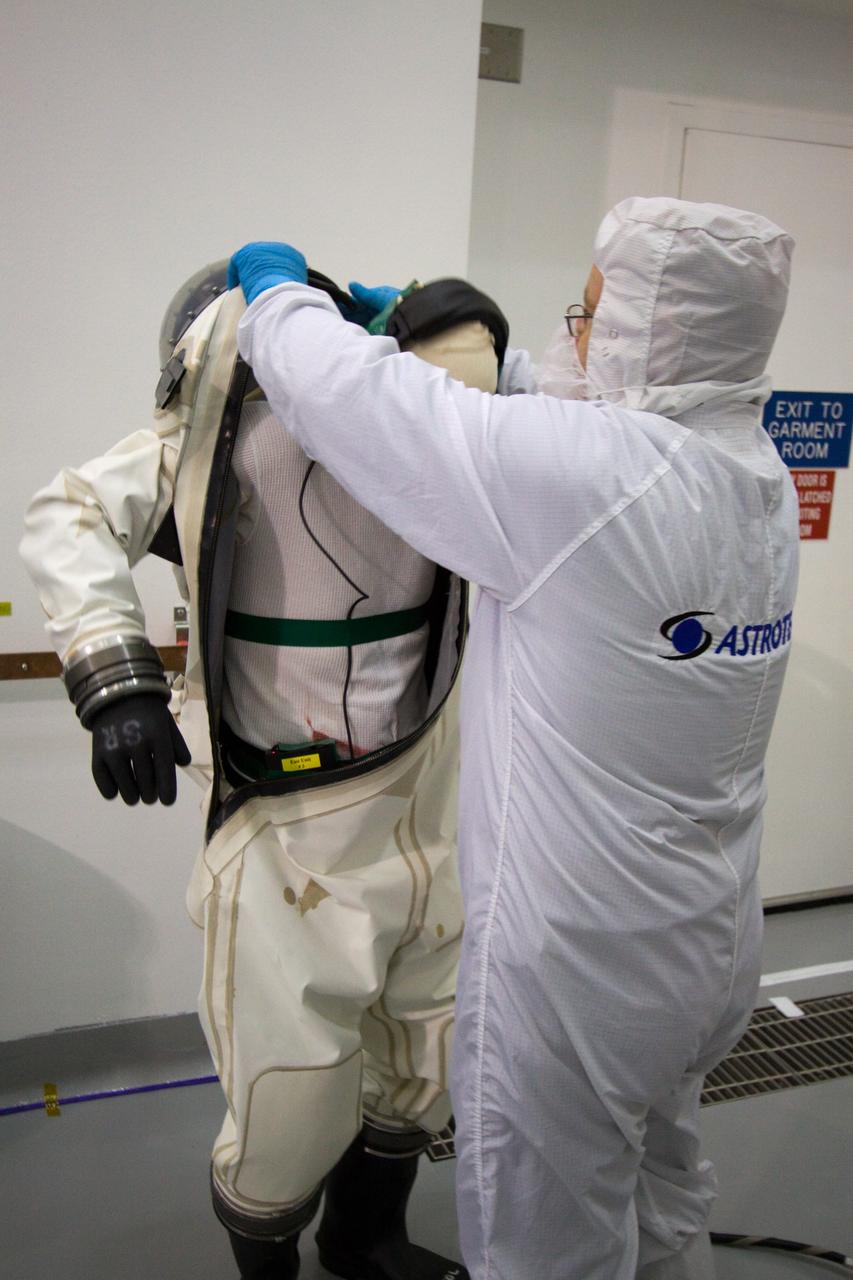

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center prepare to sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. From left are Boeing technician Steve Lay and ASTROTECH mission/facility manager Gerard Gleeson. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
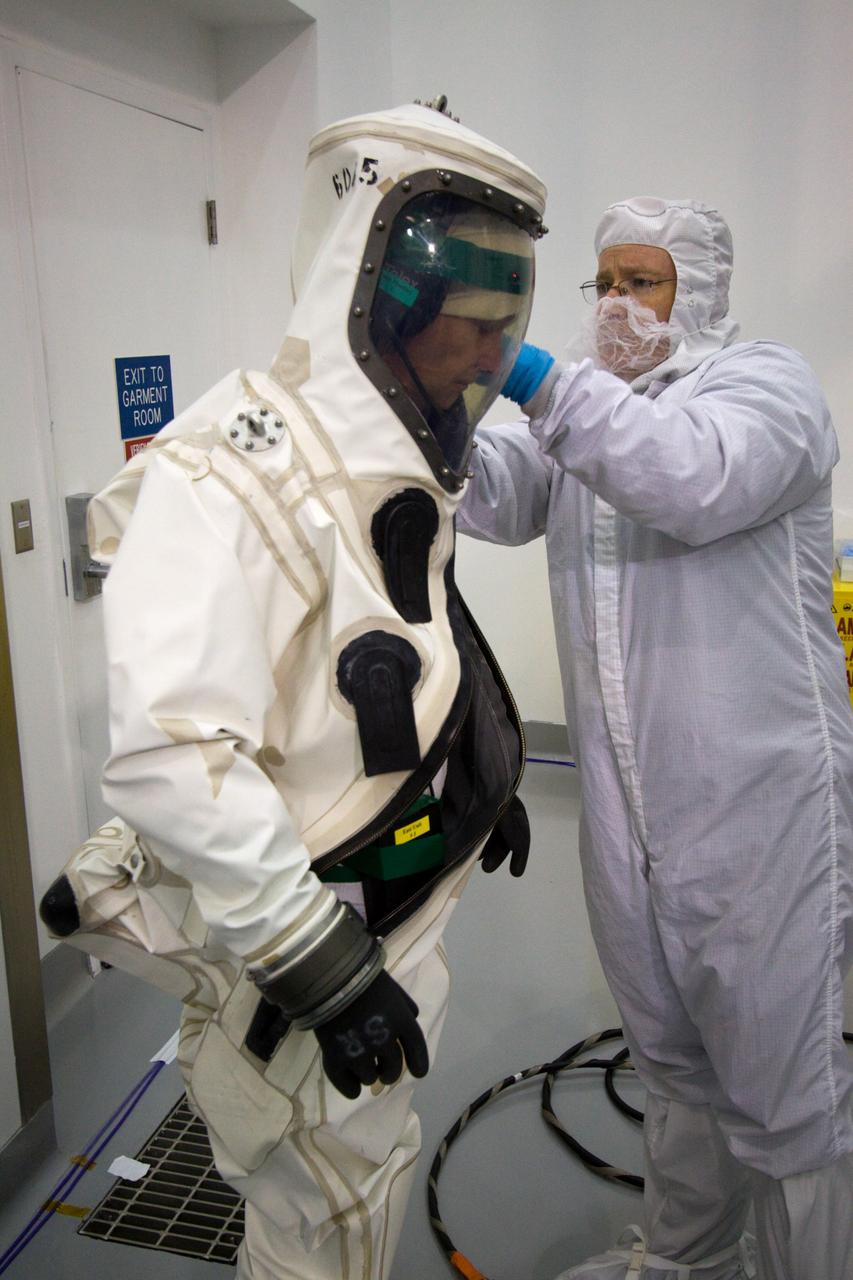

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center prepare to sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. From left are SDO technician Brian Kittle and ASTROTECH mission/facility manager Gerard Gleeson. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
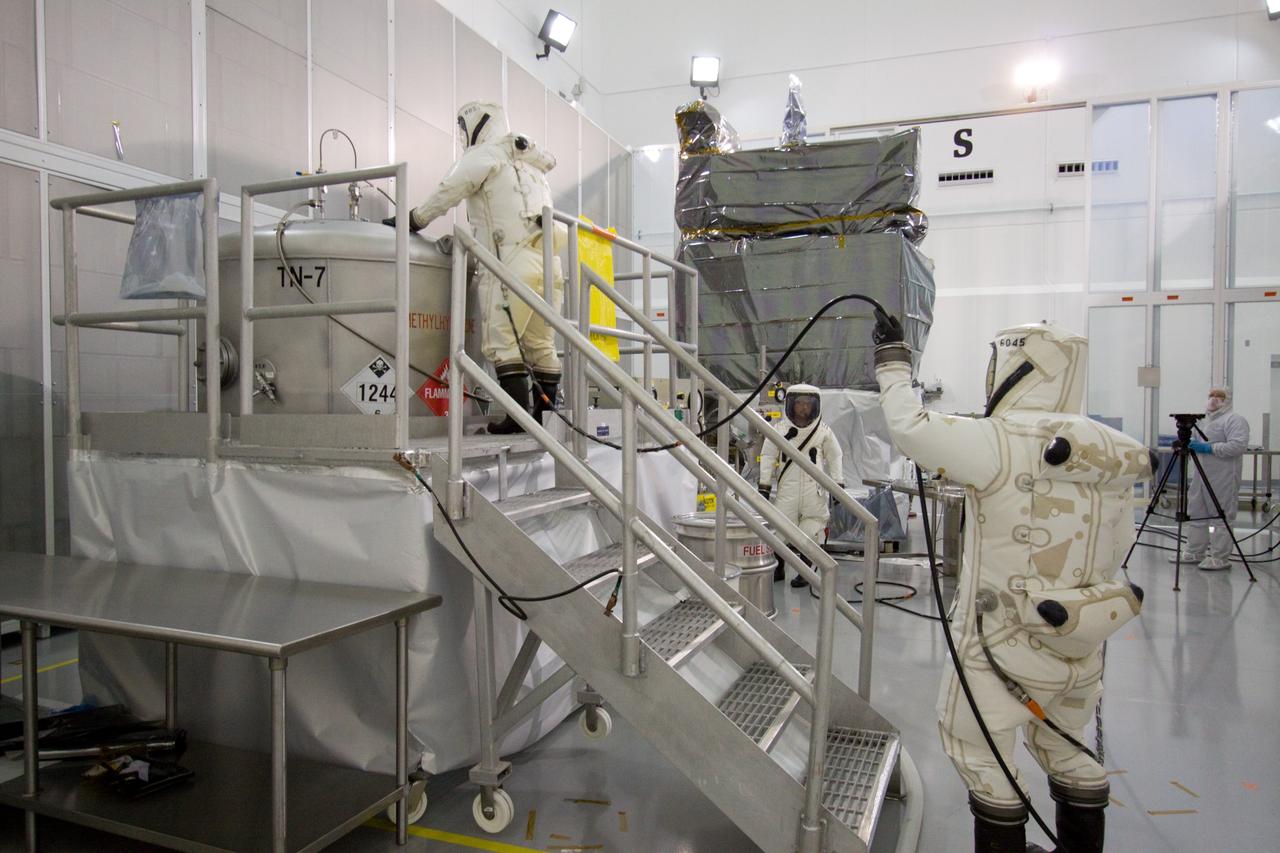

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., Boeing spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center take a sample of the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which is protectively covered. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the control room at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., a team of Kennedy Space Center spacecraft fueling specialists and engineers monitors data received from the clean room as technicians sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
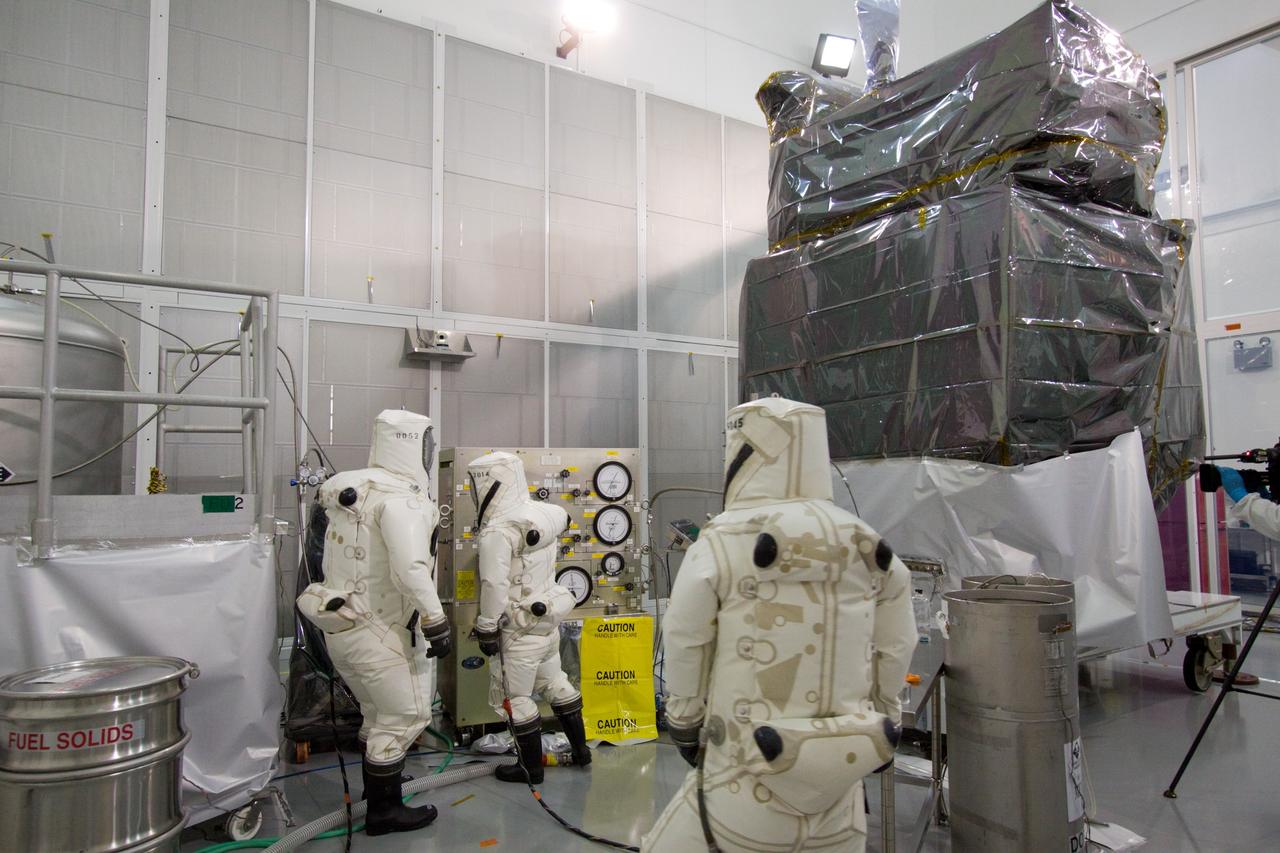

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., Boeing spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center prepare to sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which is protectively covered. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
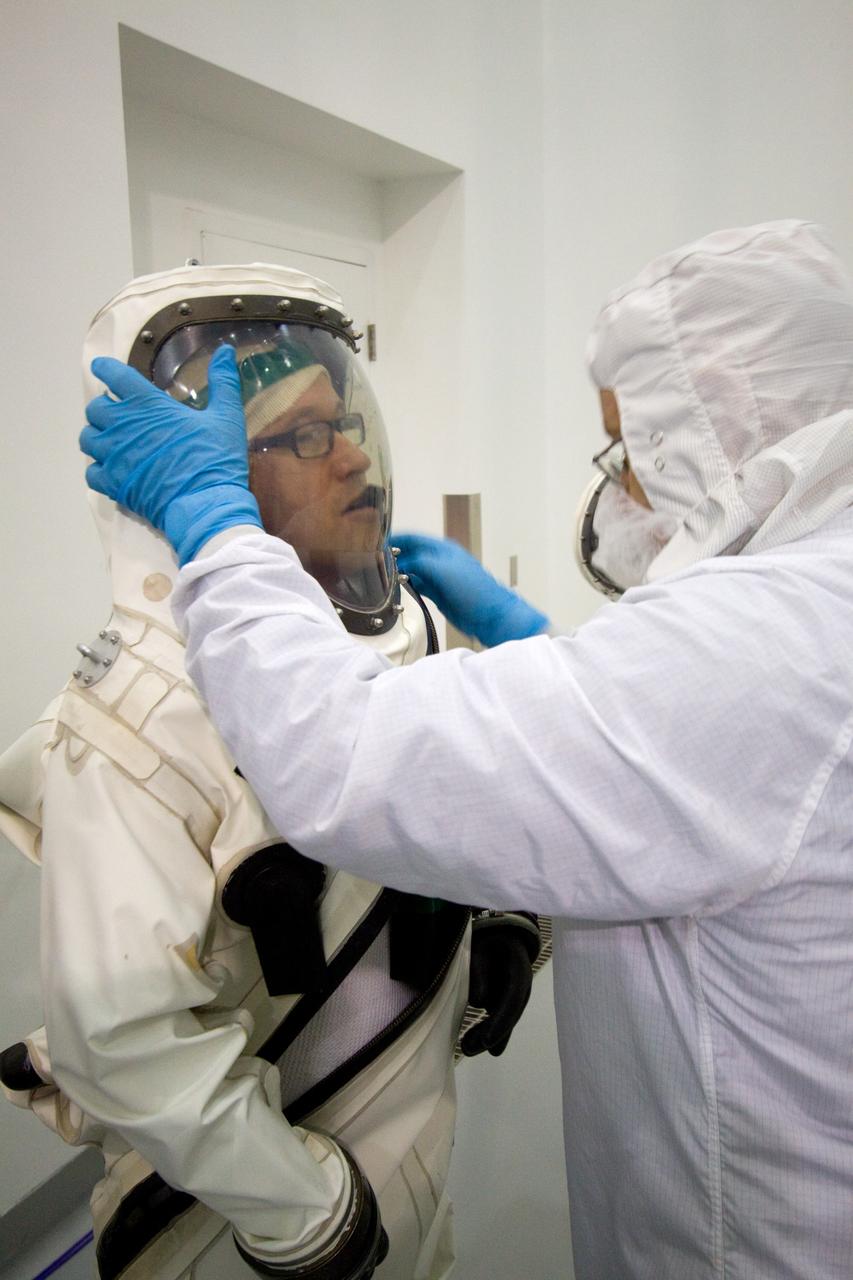

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center prepare to sample the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. From left are Boeing technician Steve Lay and ASTROTECH mission/facility manager Gerard Gleeson. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
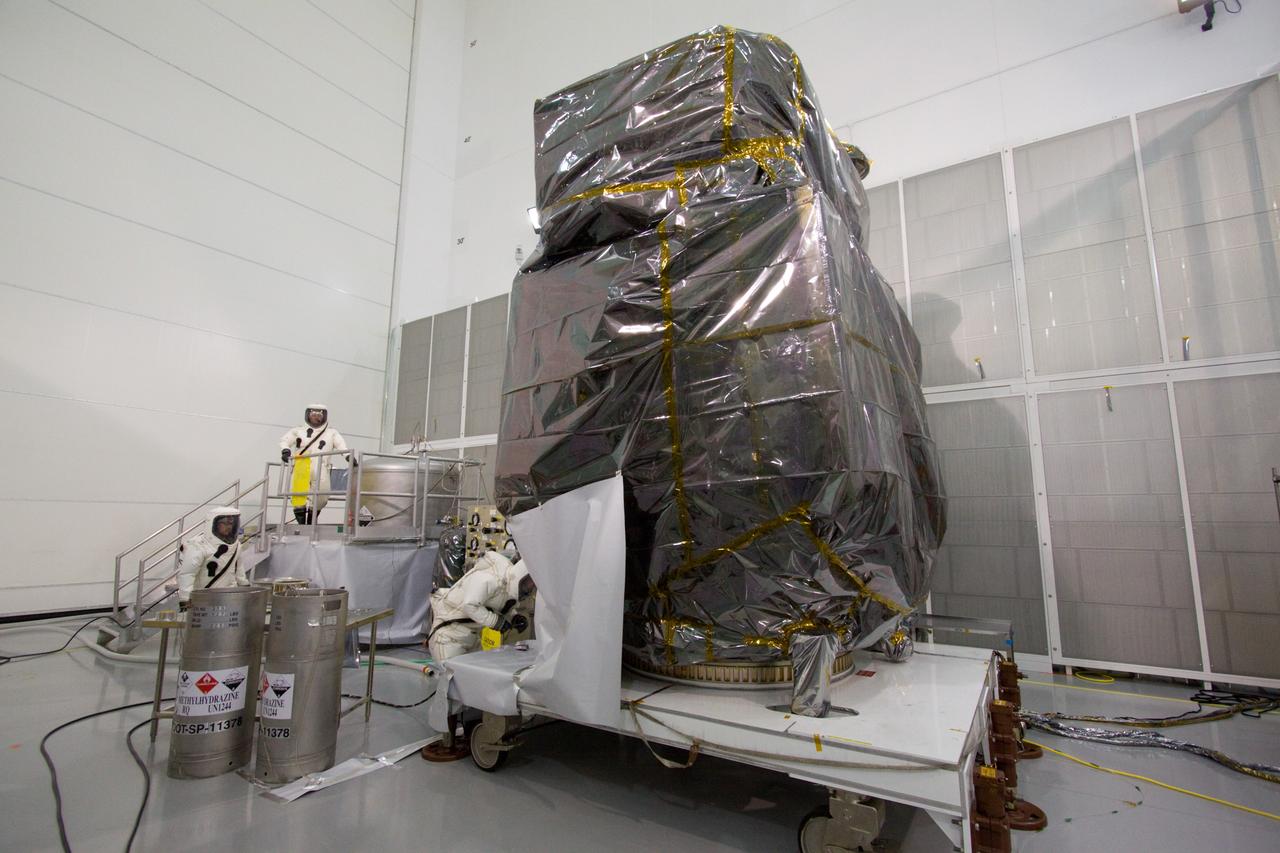

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., Boeing spacecraft fueling technicians from Kennedy Space Center take a sample of the monomethylhydrazine propellant that will be loaded aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which is protectively covered. The hydrazine fuel is being sampled for purity before it is loaded aboard the spacecraft. The technicians are dressed in self-contained atmospheric protective ensemble suits, or SCAPE suits, as a safety precaution in the unlikely event that any of the highly toxic chemical should escape from the storage tank. The nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer was loaded earlier in the week which is customarily followed by loading of the fuel. Propellant loading is one of the final processing milestones before the spacecraft is encapsulated in its fairing for launch. SDO is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. Liftoff aboard an Atlas V rocket is targeted for Feb. 9 from Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller