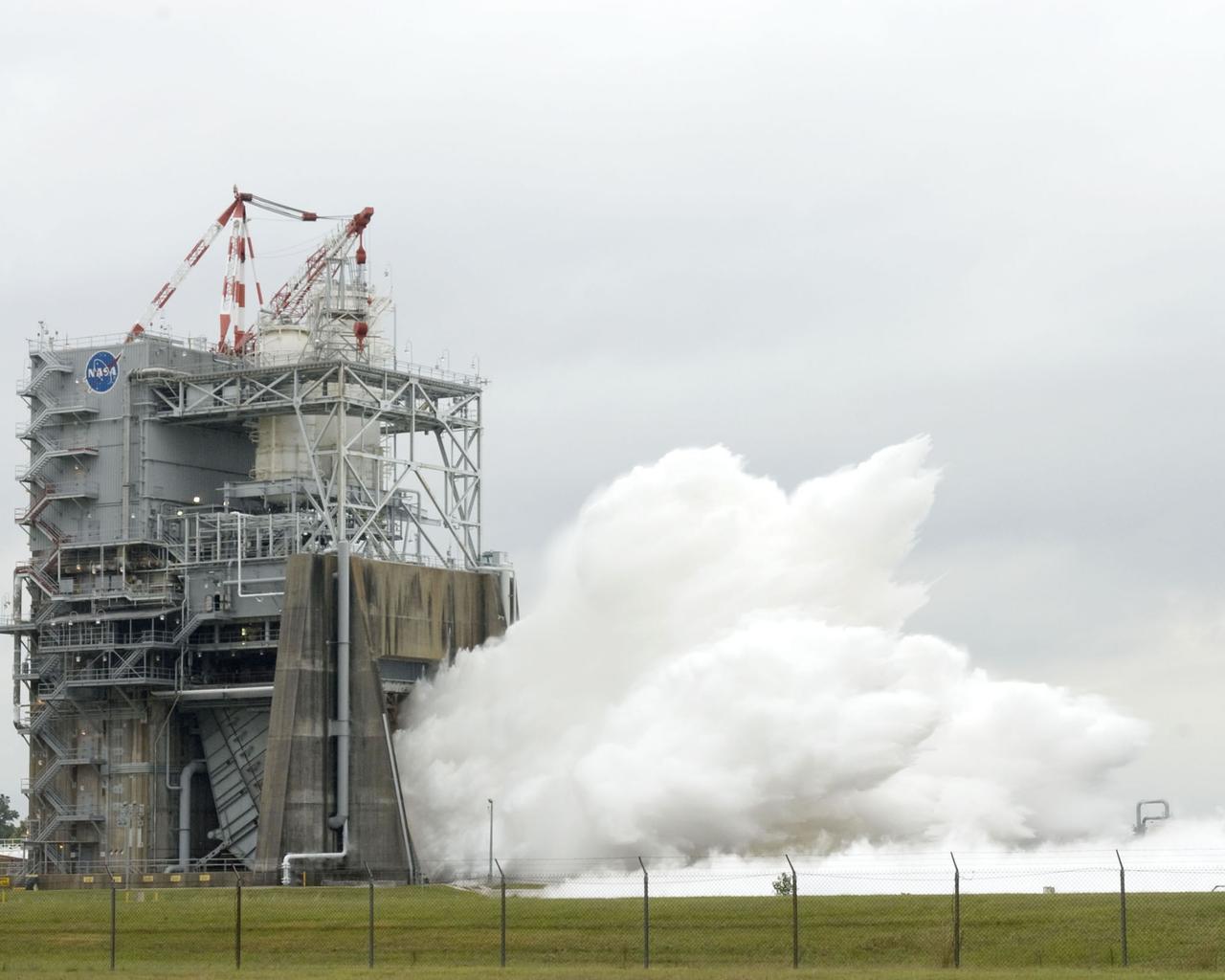

Steam blasts out of the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22 as engineers begin a certification test on engine 2061, the last space shuttle main flight engine scheduled to be built. Since 1975, Stennis has tested every space shuttle main engine used in the program - about 50 engines in all. Those engines have powered more than 120 shuttle missions - and no mission has failed as a result of engine malfunction. For the remainder of 2008 and throughout 2009, Stennis will continue testing of various space shuttle main engine components.
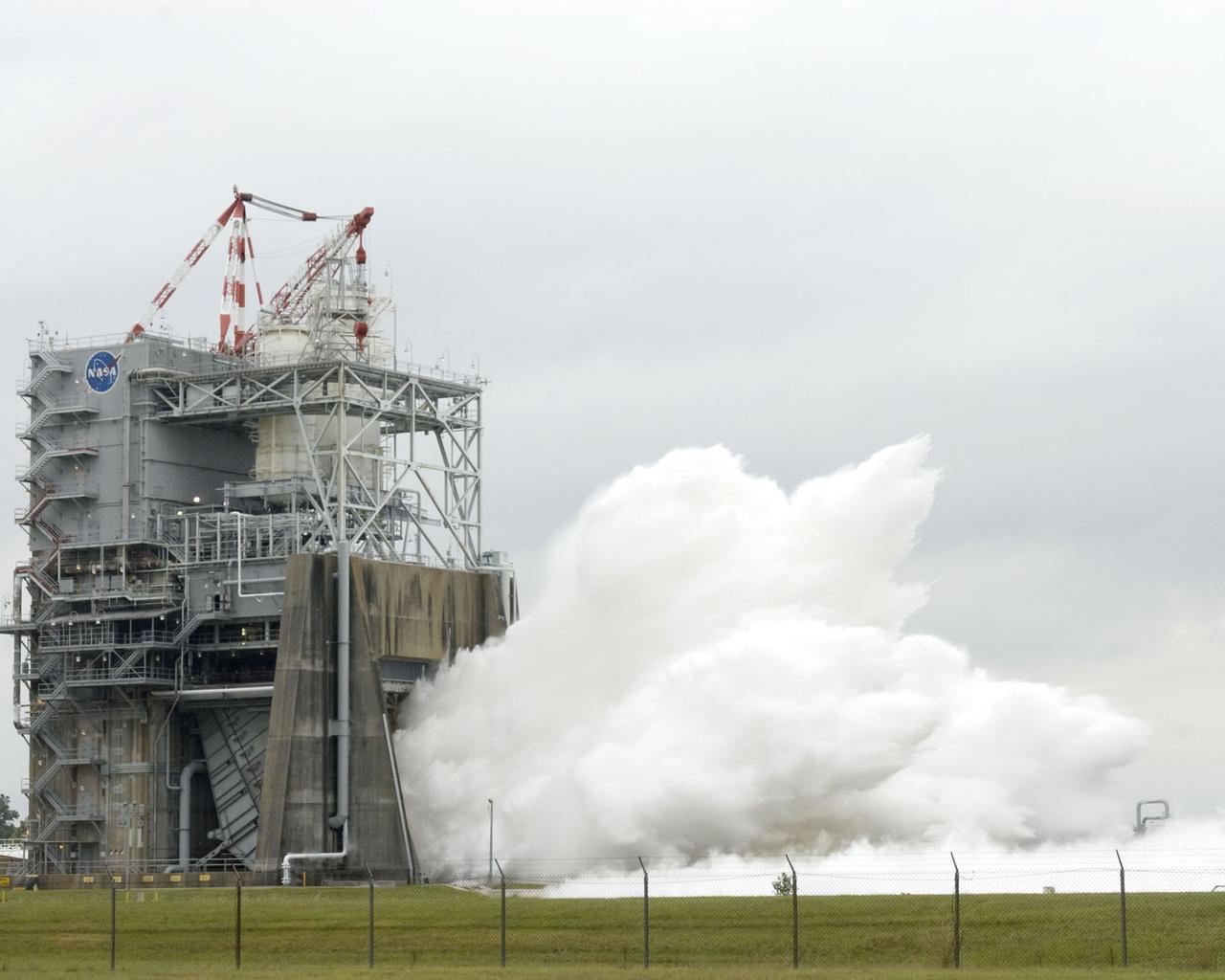

Steam blasts out of the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Oct. 22 as engineers begin a certification test on engine 2061, the last space shuttle main flight engine scheduled to be built. Since 1975, Stennis has tested every space shuttle main engine used in the program - about 50 engines in all. Those engines have powered more than 120 shuttle missions - and no mission has failed as a result of engine malfunction. For the remainder of 2008 and throughout 2009, Stennis will continue testing of various space shuttle main engine components.
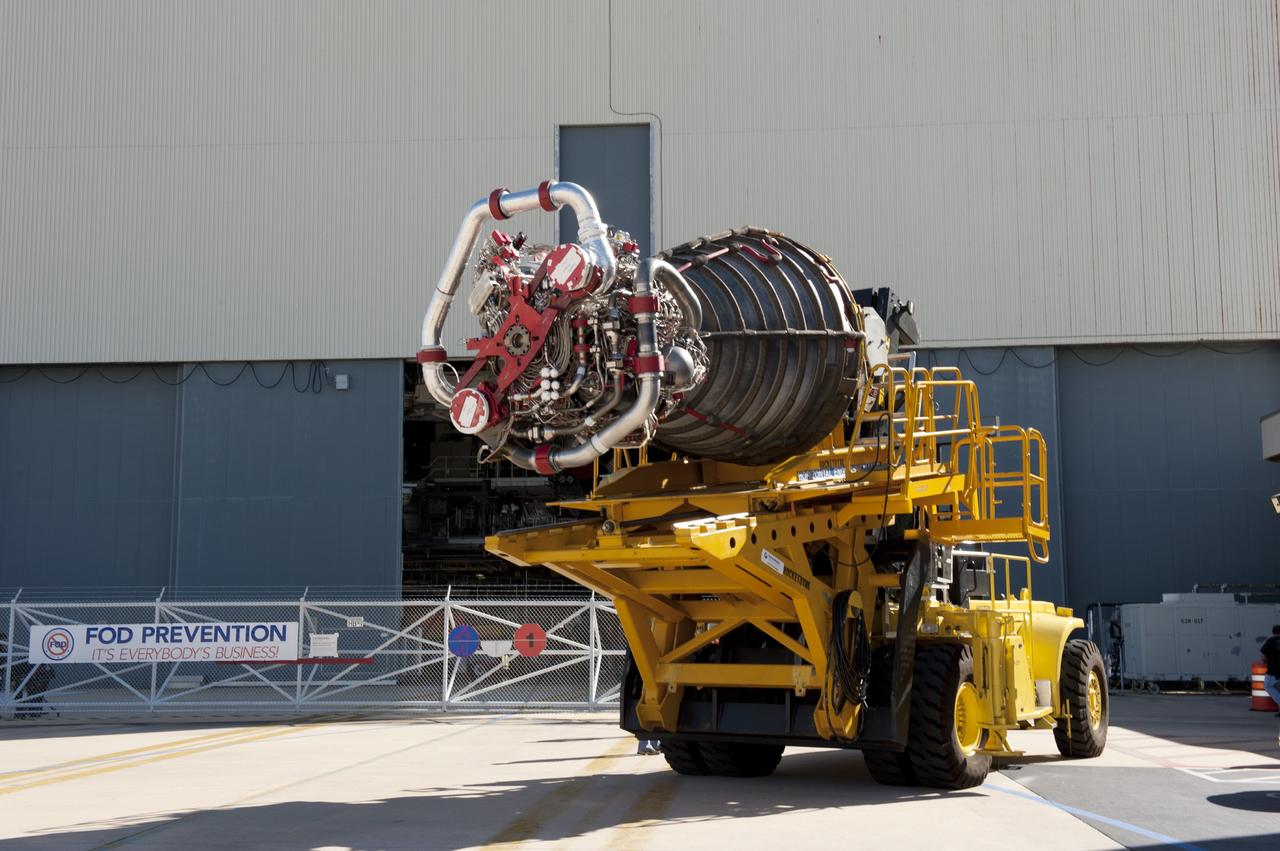

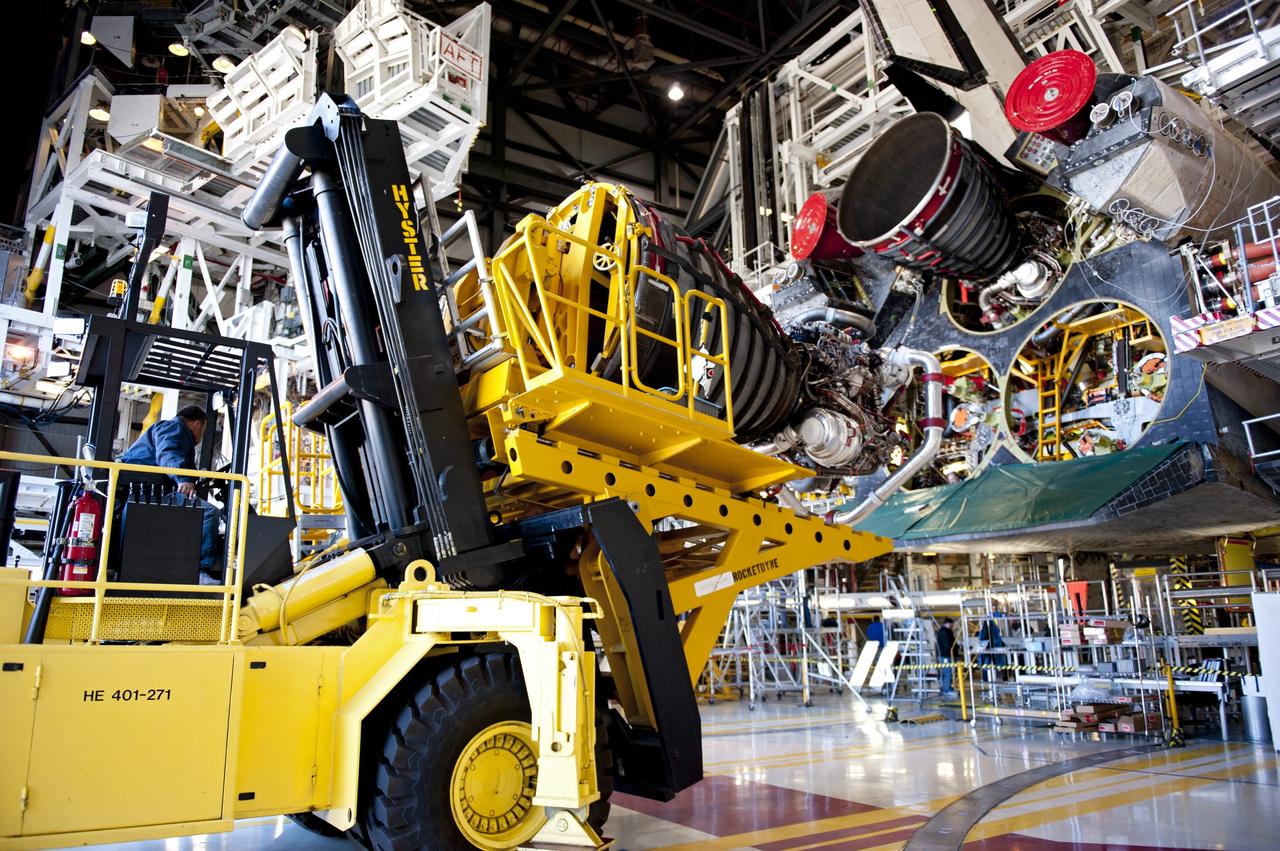
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transports engine #2, the last of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines, from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the processing facility, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
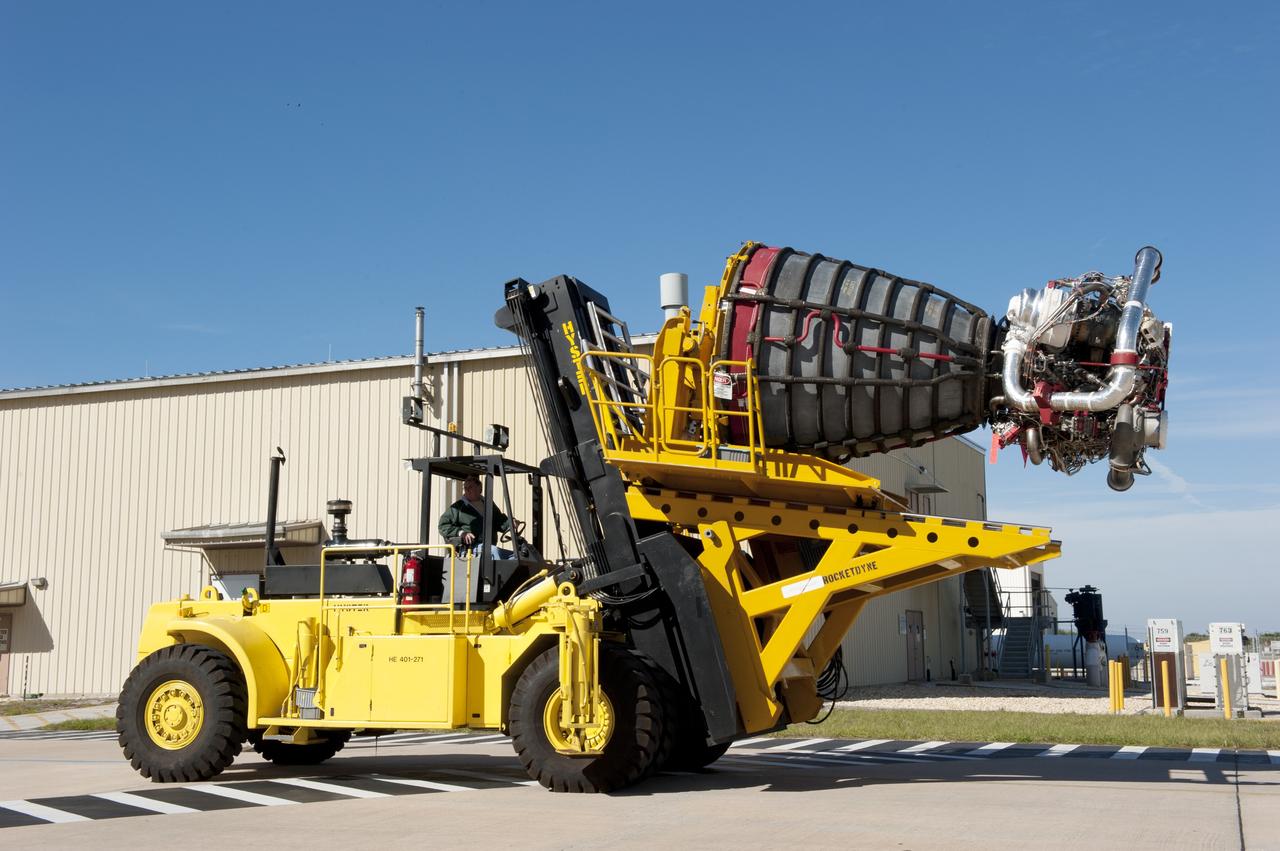

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transports engine #2, the last of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines, from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the processing facility, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
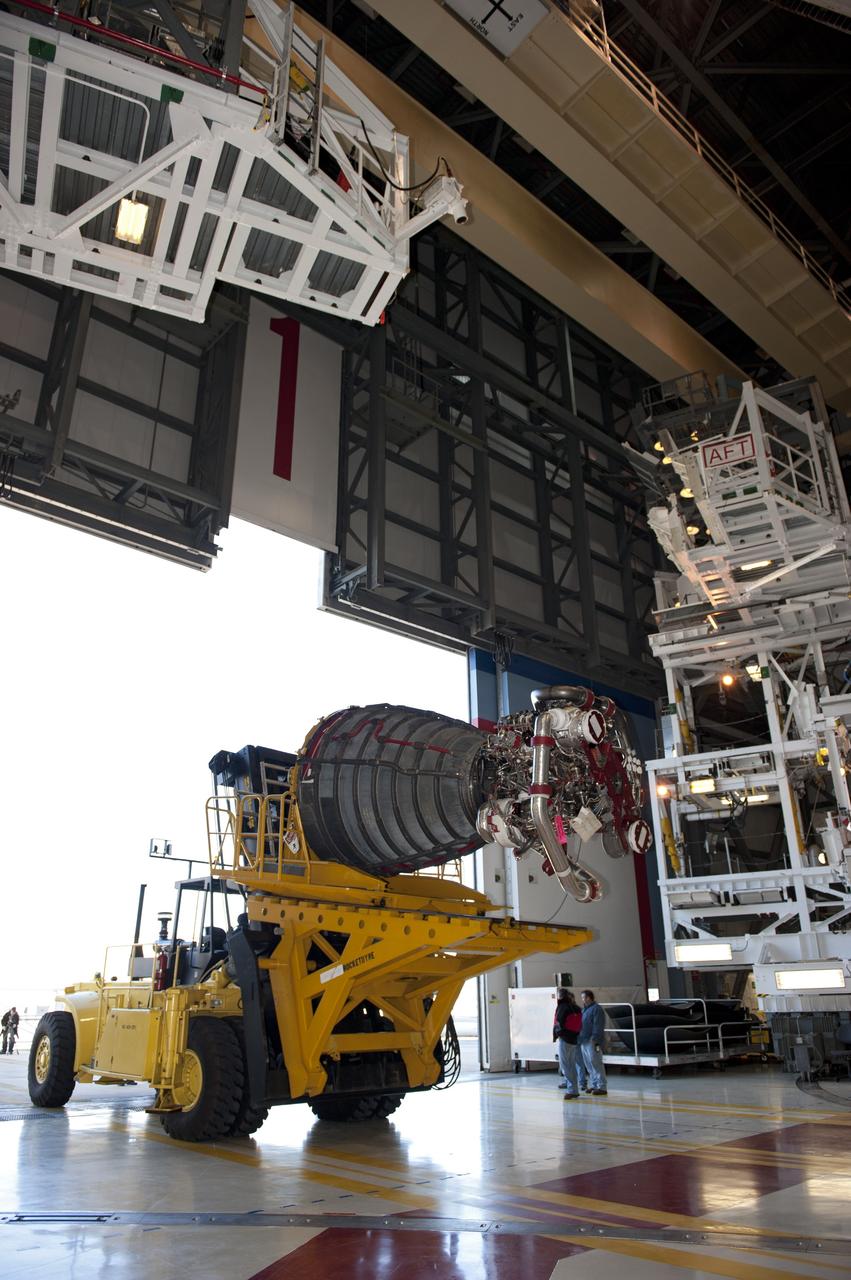

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transporting the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines arrives at Orbiter Processing Facility-1 from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. There, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
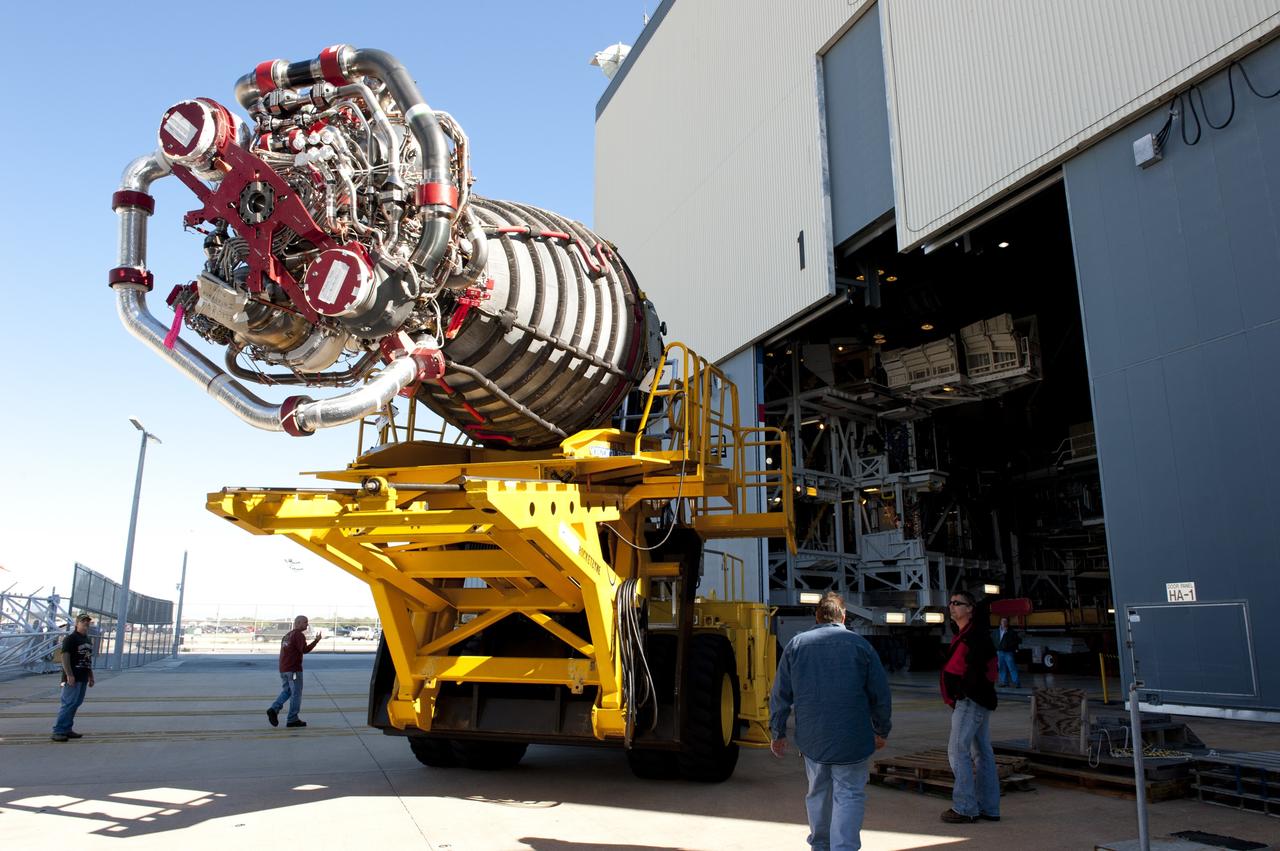

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transports the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once inside the processing facility, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
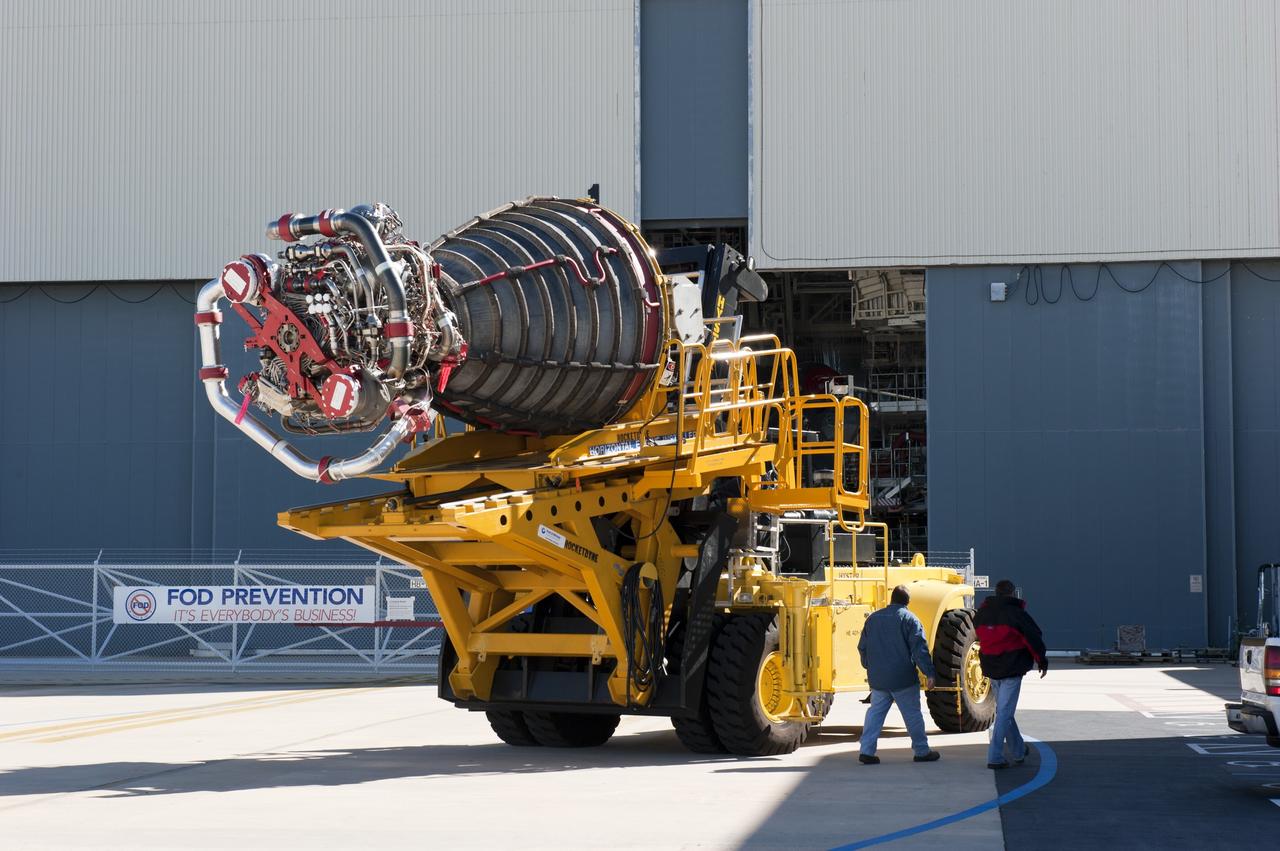

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transports the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once inside the processing facility, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
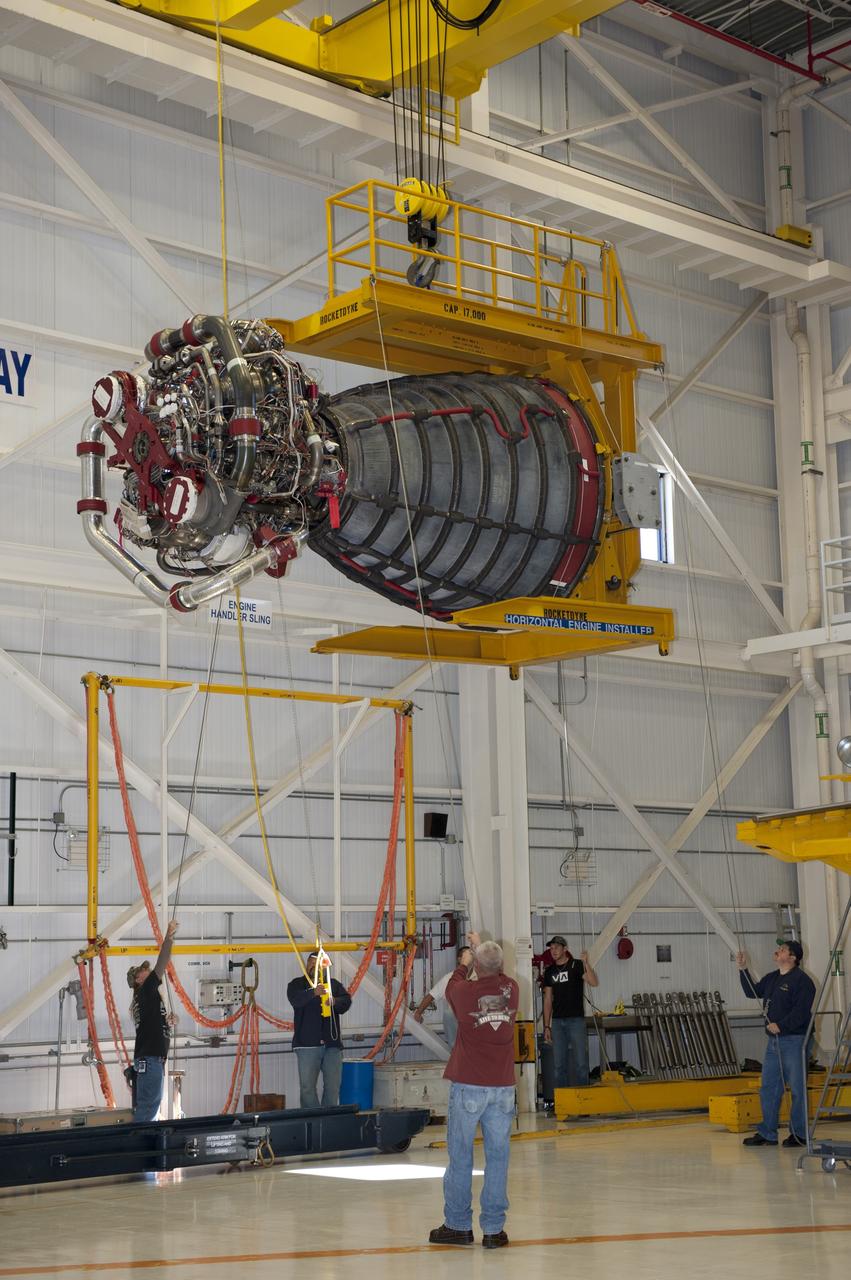

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers in the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida raise the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines so it can be attached to a Hyster forklift. Then, the engine will be transported to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 where it will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
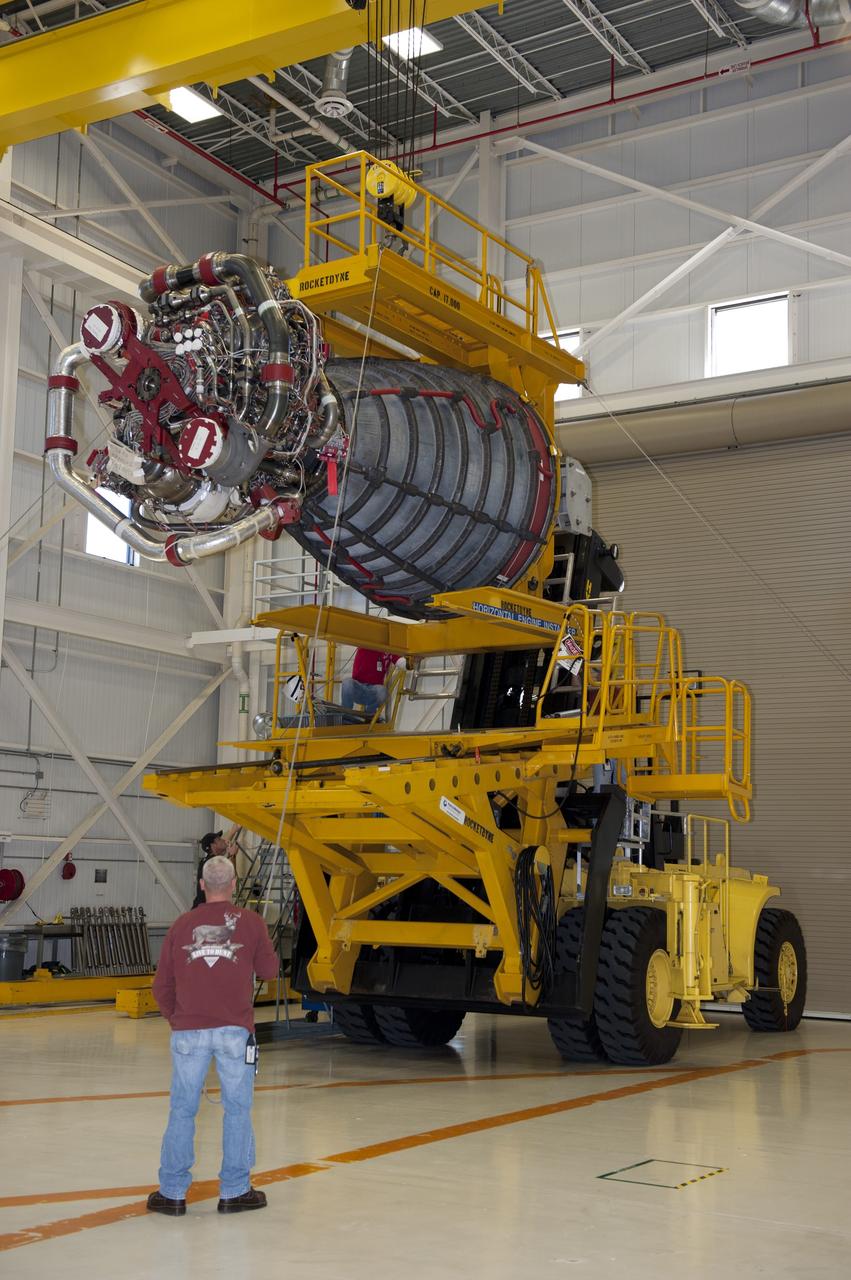

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers in the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida attached the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines to a Hyster forklift. Next, the engine will be transported to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 where it will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
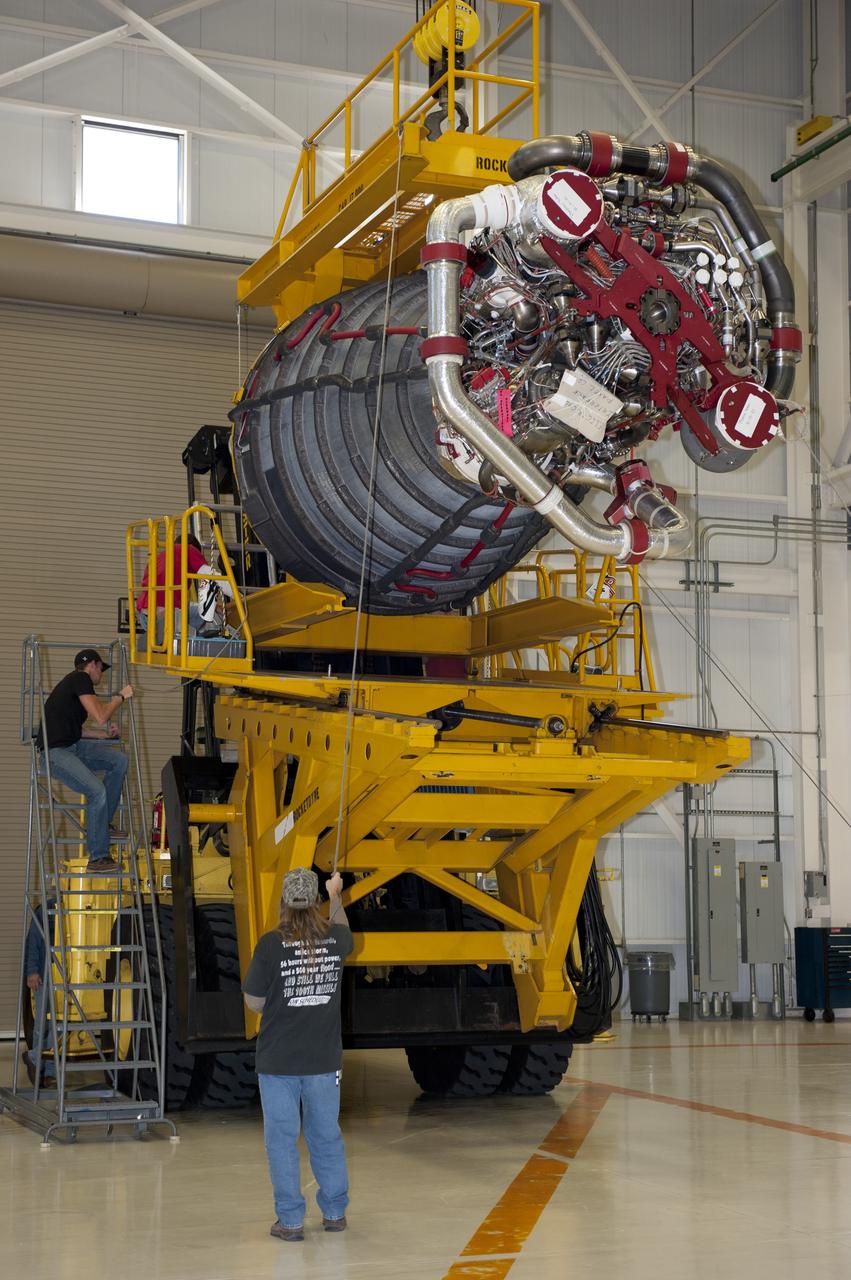

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers in the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida attached the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines to a Hyster forklift. Next, the engine will be transported to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 where it will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
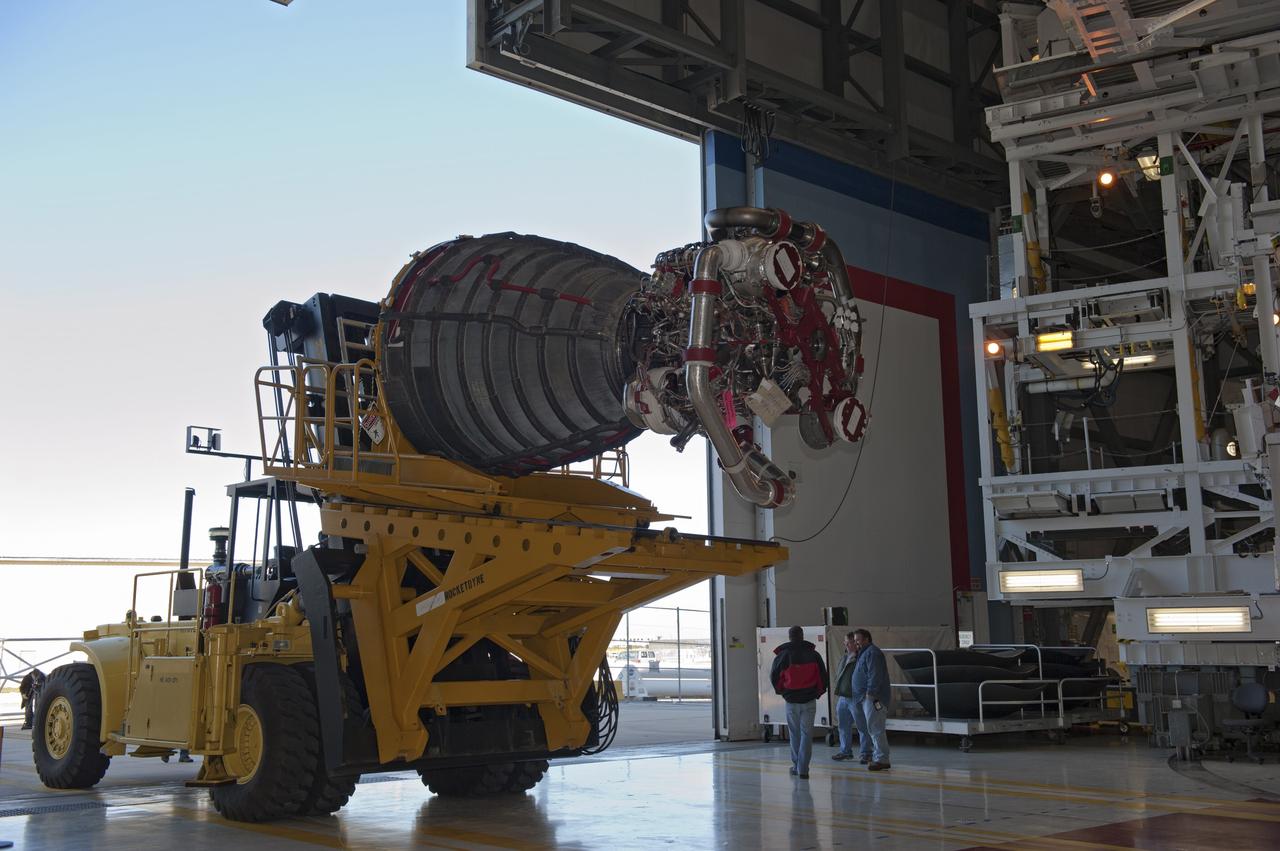

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transporting the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines arrives at Orbiter Processing Facility-1 from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. There, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transporting the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines arrives at Orbiter Processing Facility-1 from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. There, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
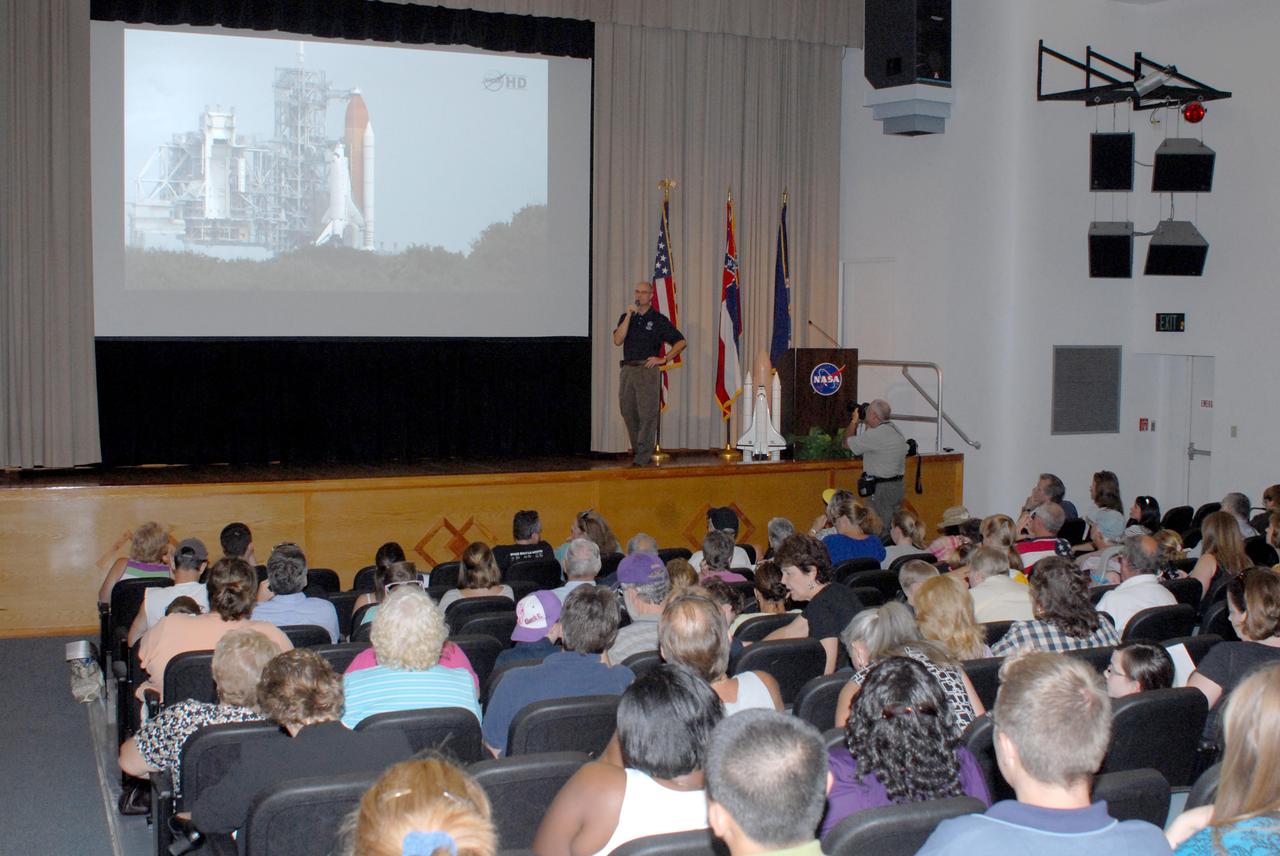

NASA engineer Don Beckmeyer speaks to an audience gathered at StenniSphere auditorium at Stennis Space Center to view the launch of the STS-135 space shuttle mission July 8. The mission marked the final flight for Atlantis and the final flight for the Space Shuttle Program. Viewers applauded and cheered as Atlantis headed to space, powered by a trio of main engines tested at Stennis Space Center.
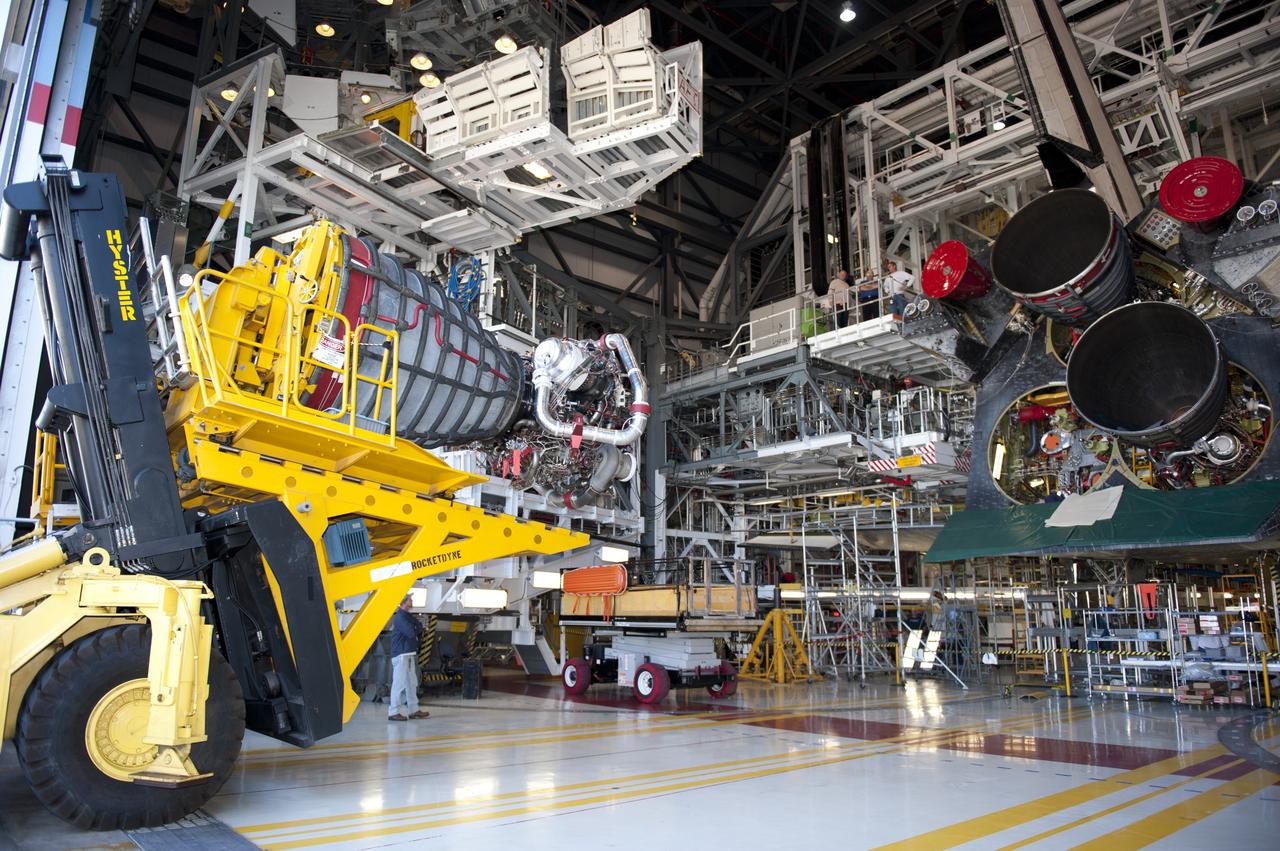

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transporting engine #2, the last of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop, enters Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the processing facility, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
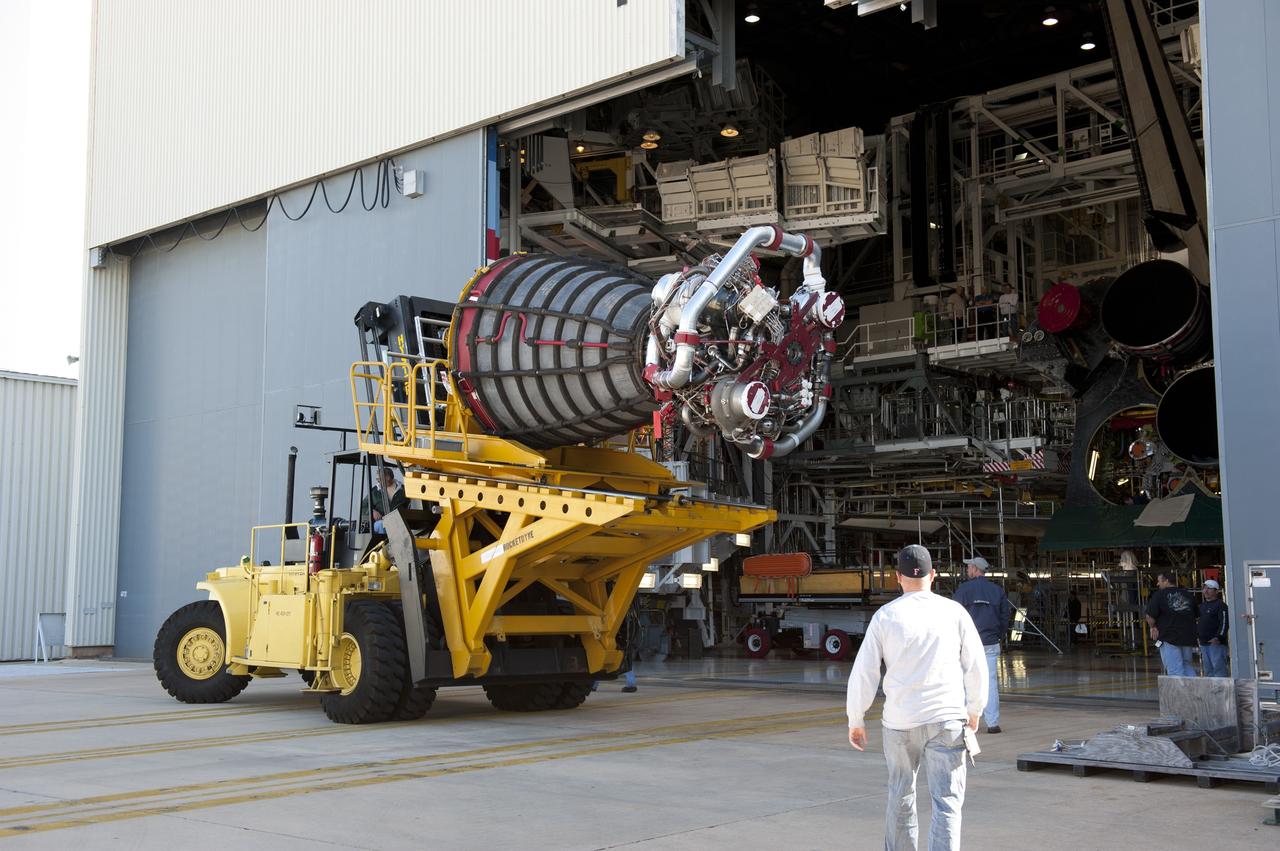

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transporting engine #2, the last of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop, arrives at Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the processing facility, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Hyster forklift transporting engine #2, the last of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines from the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop, enters Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the processing facility, the engine will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
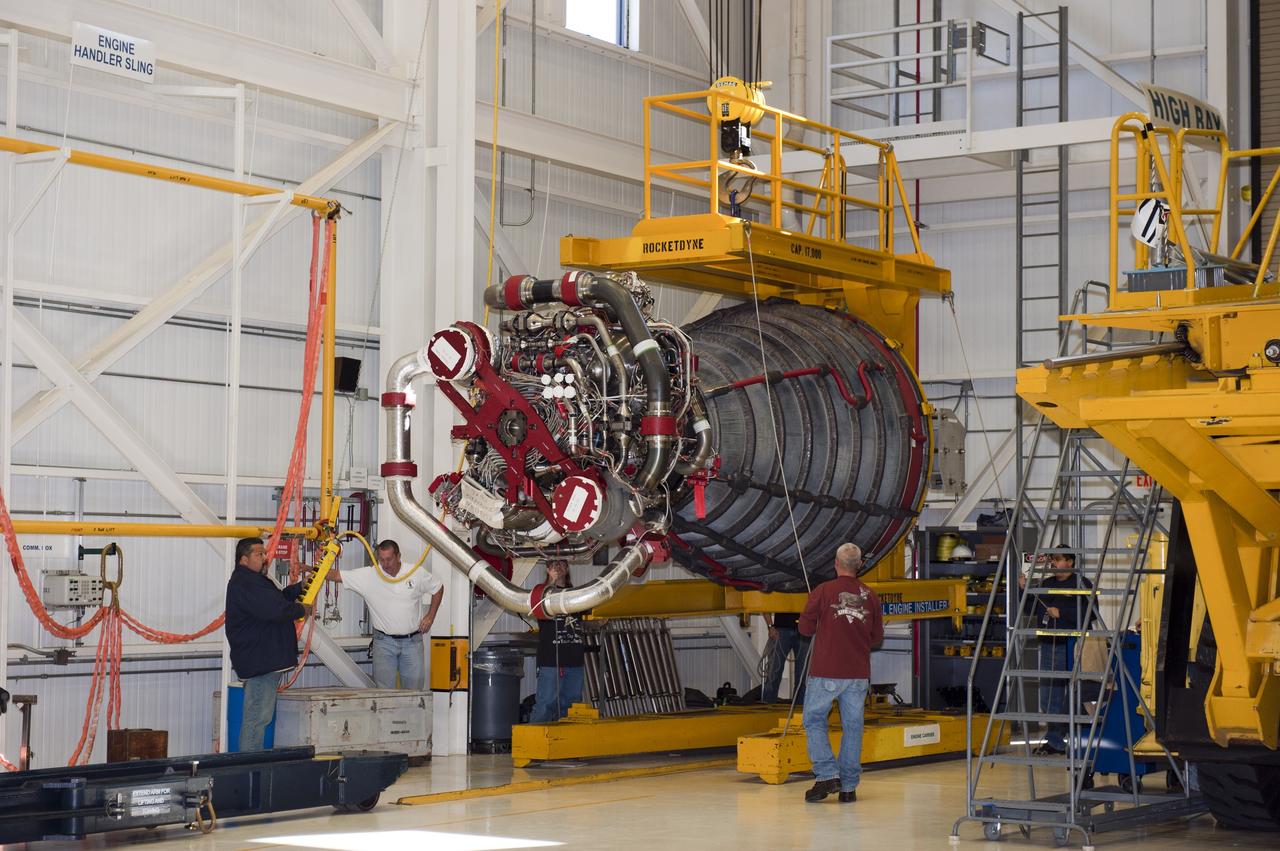

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers in the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Shop at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida get ready to raise the second of shuttle Atlantis' three main engines so it can be attached to a Hyster forklift. Then, the engine will be transported to Orbiter Processing Facility-1 where it will be installed in the shuttle. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
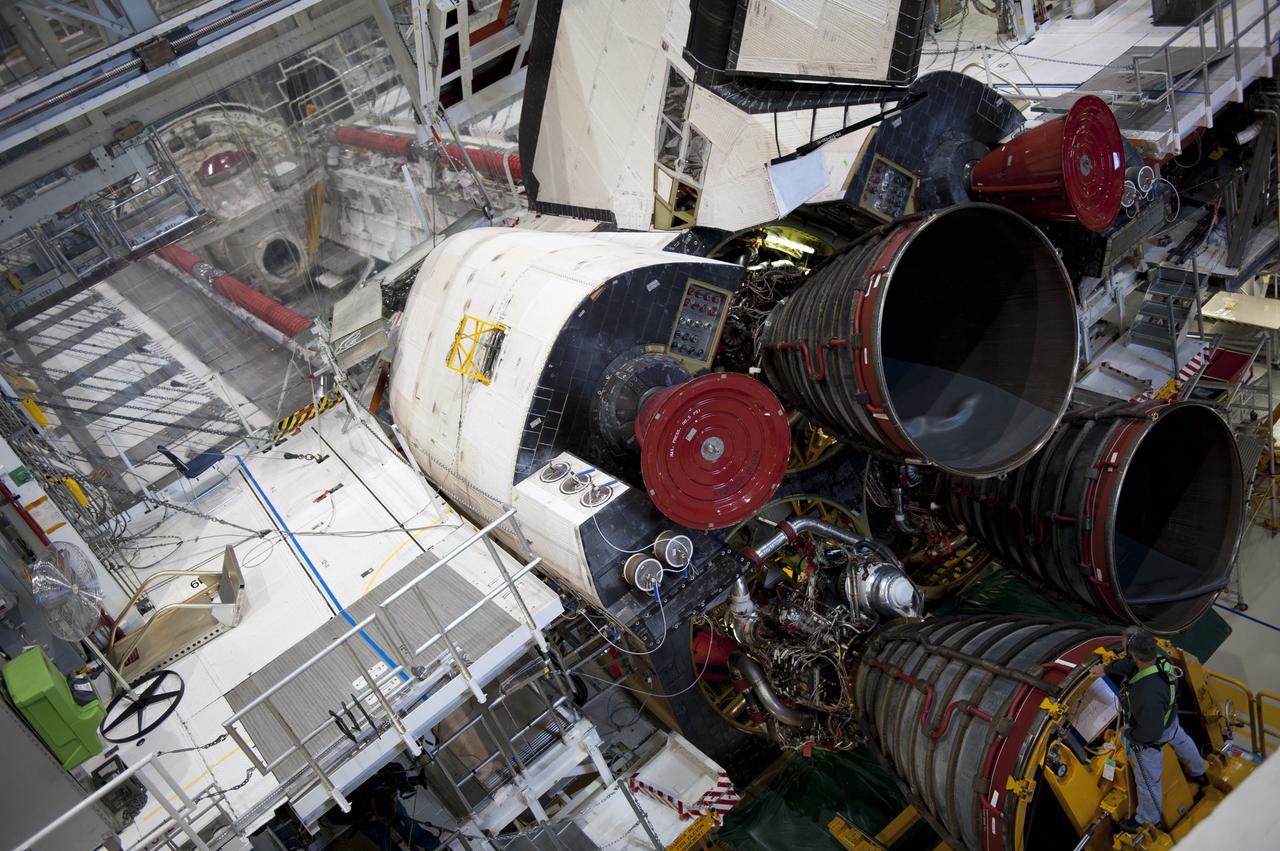

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines is installed in shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
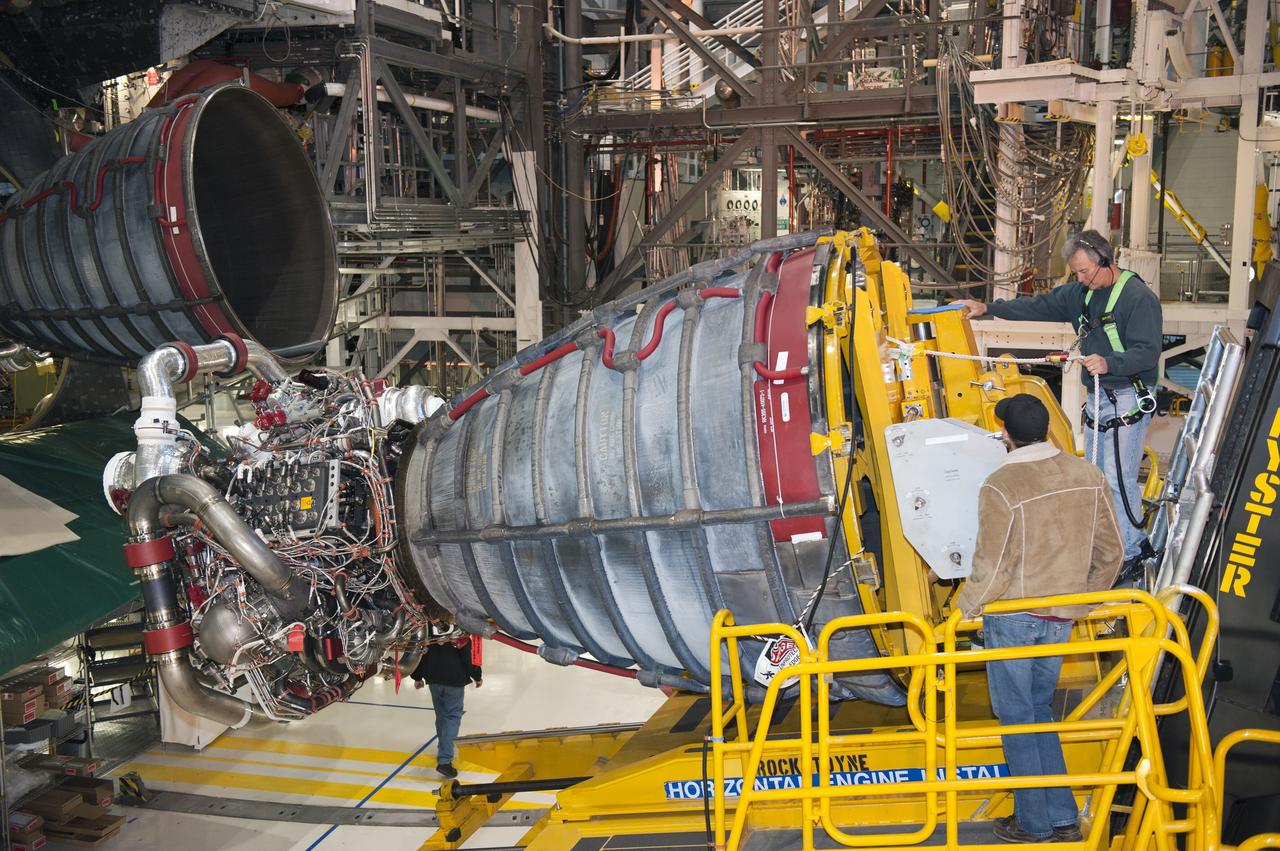

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines, closer to shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
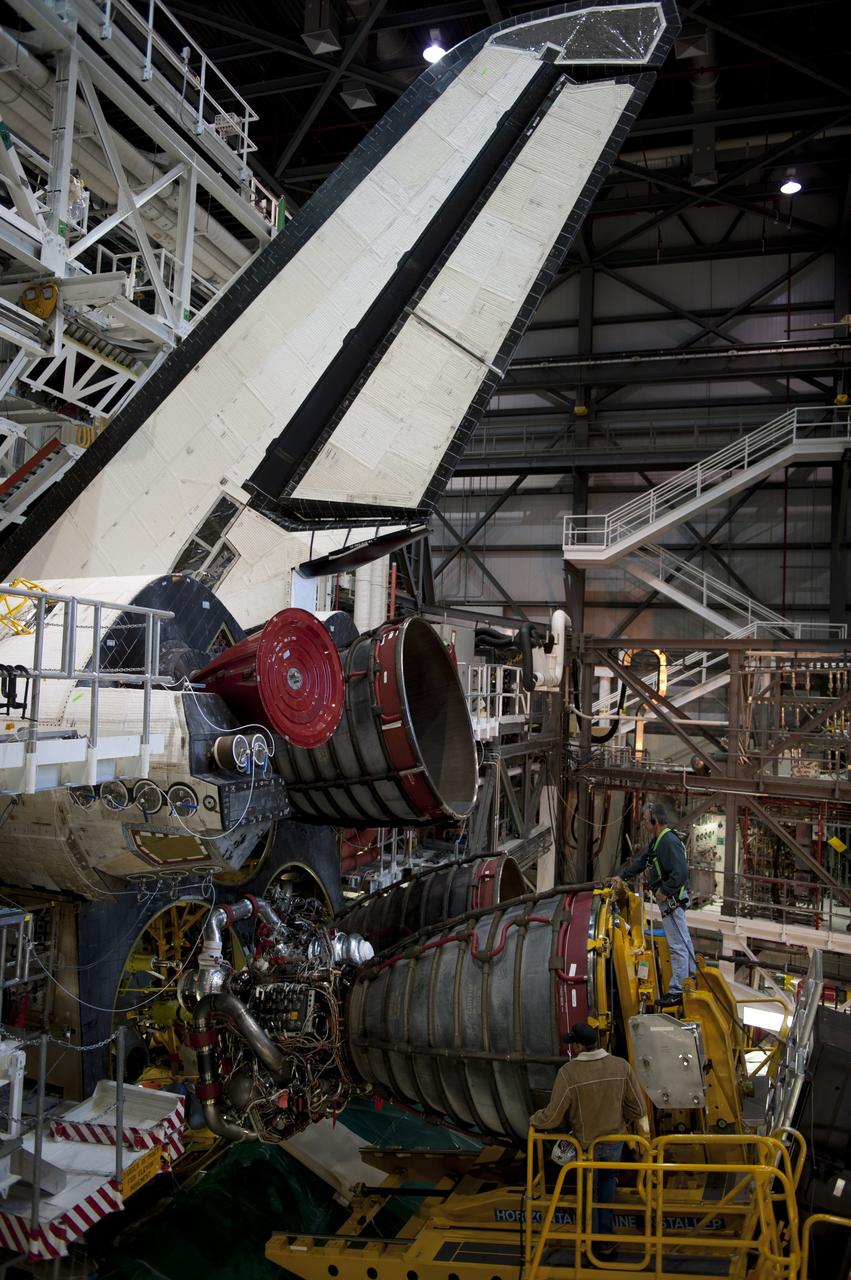

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines, into position for installation on shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
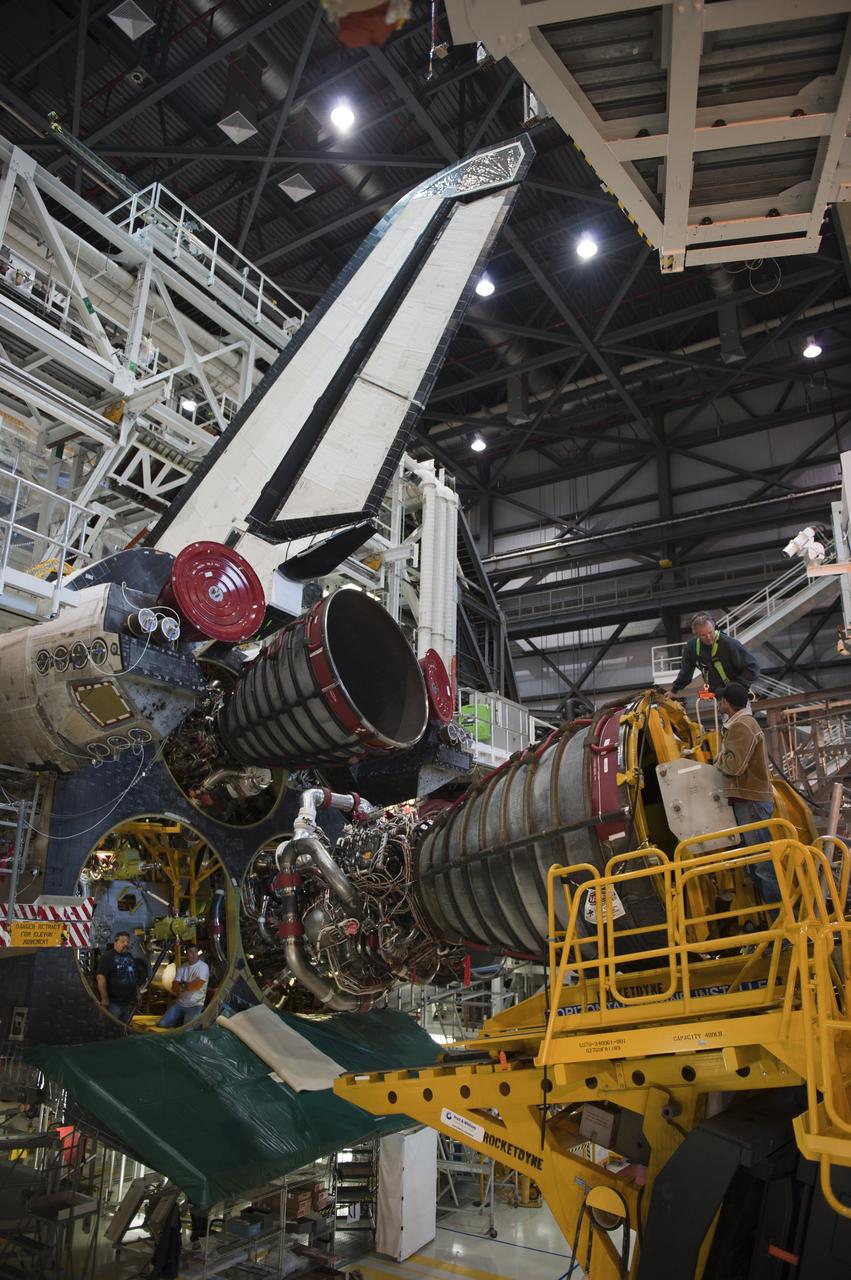

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines, into position for installation on shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
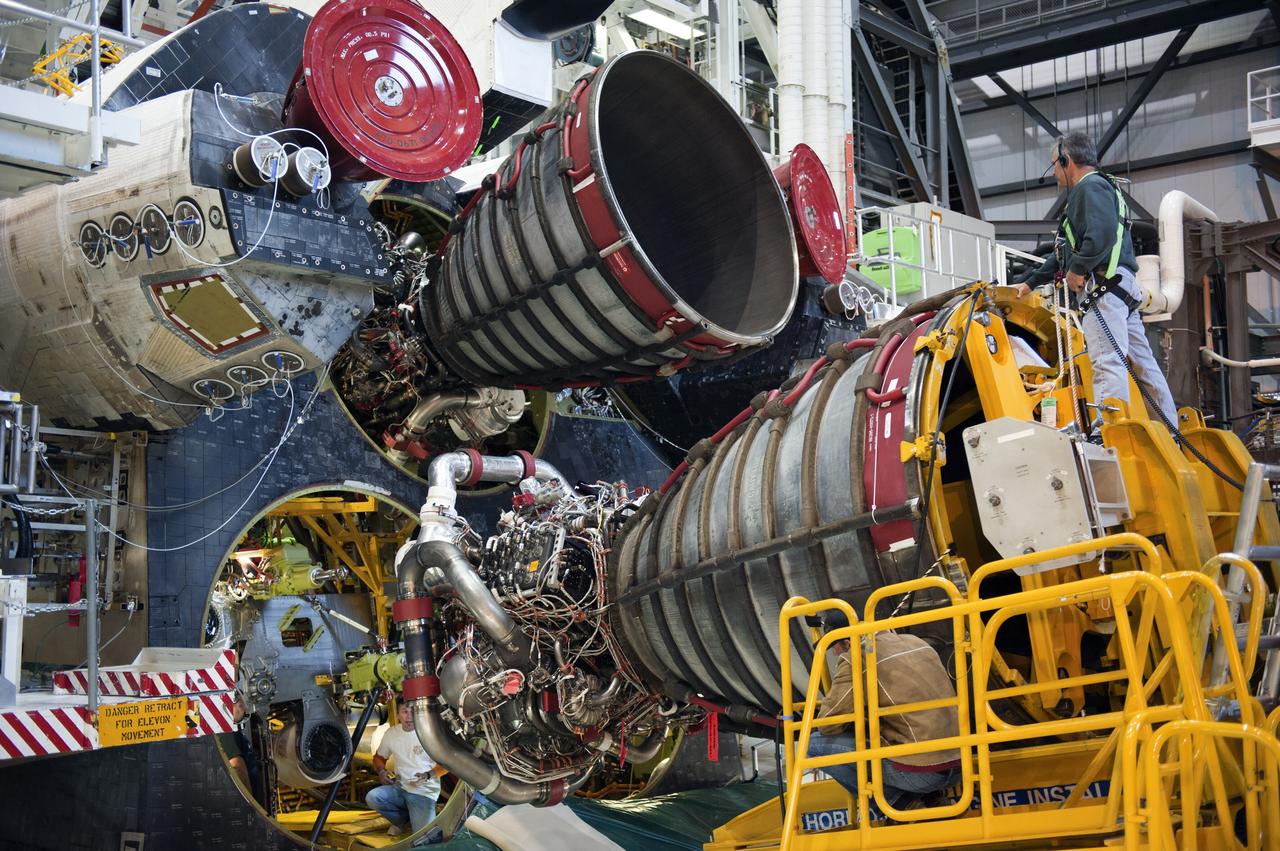

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines, into position for installation on shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
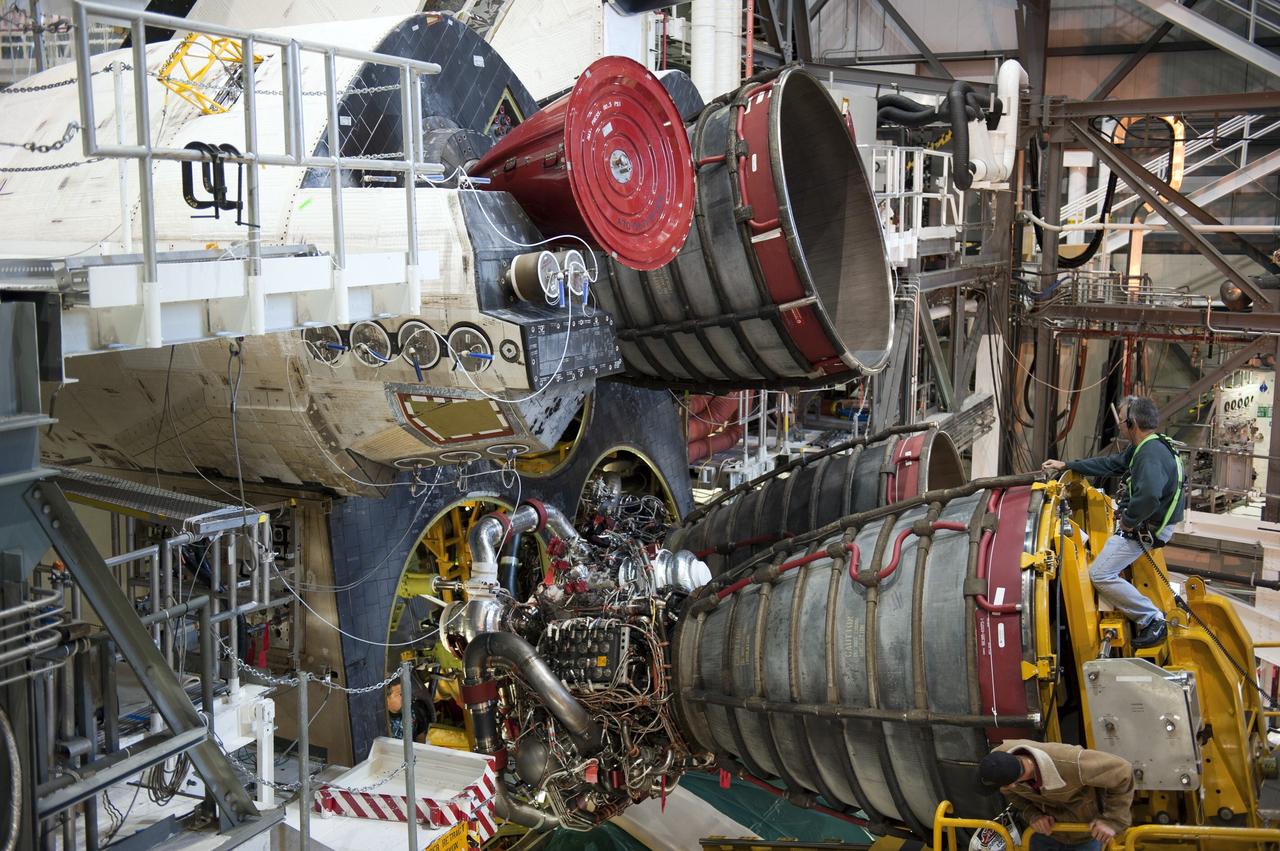

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines is being installed in shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
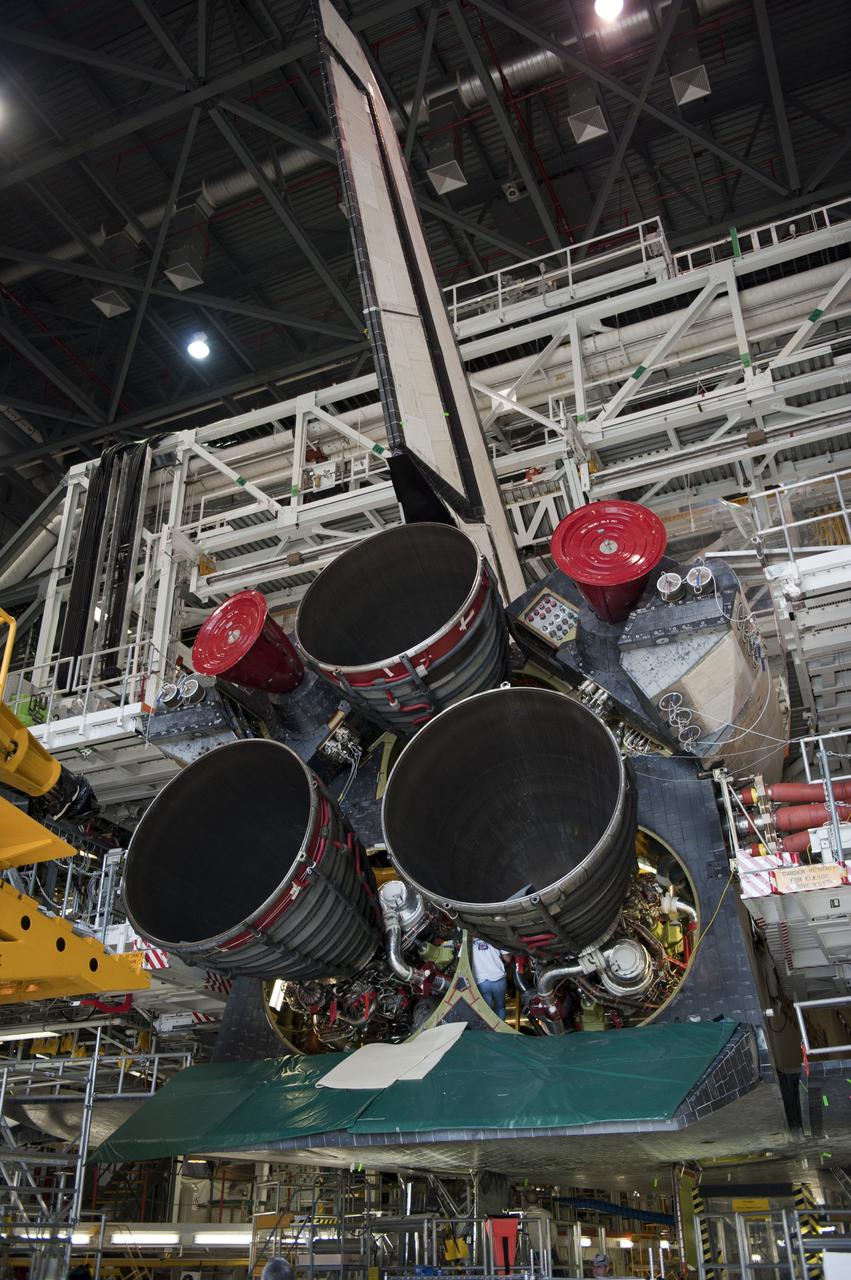

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines is installed in shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
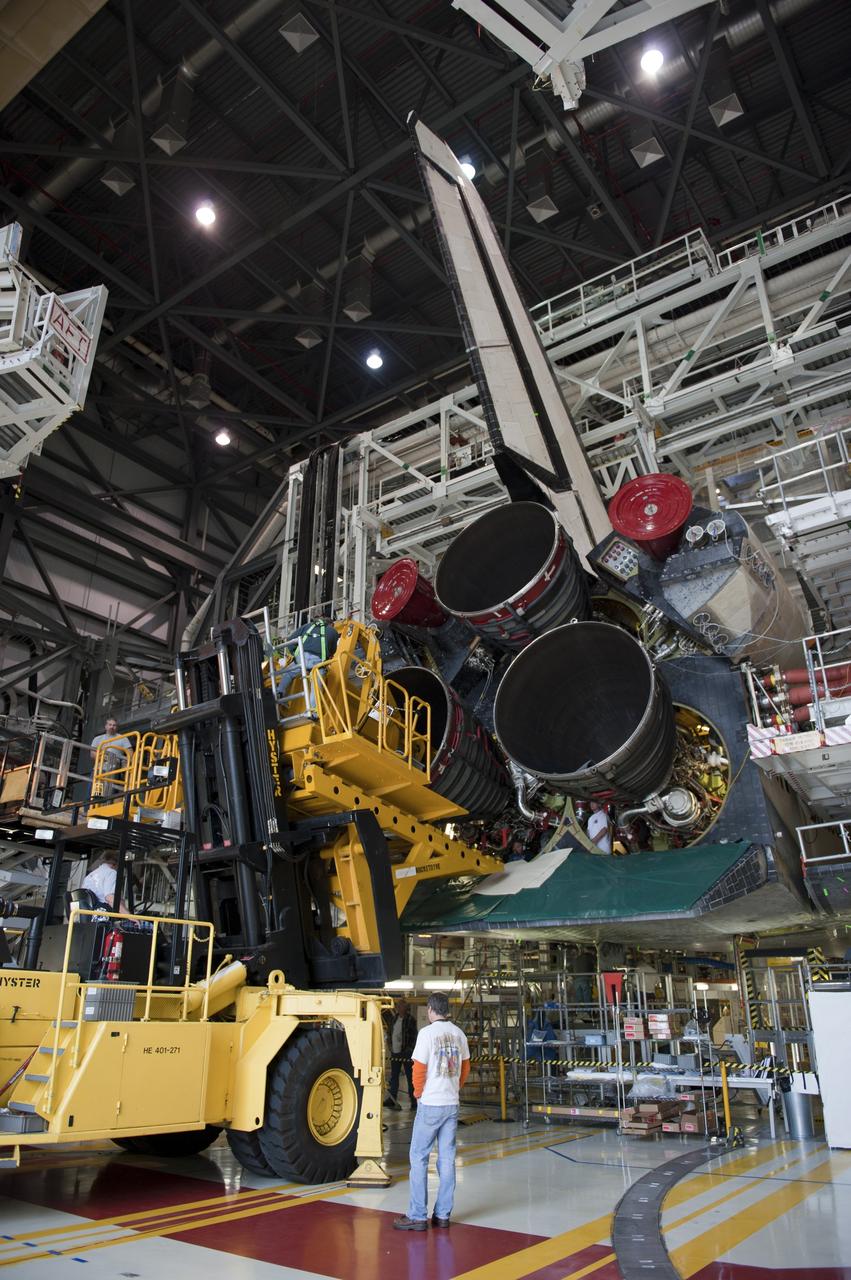

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, engine #2, the last of three space shuttle main engines is being installed in shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
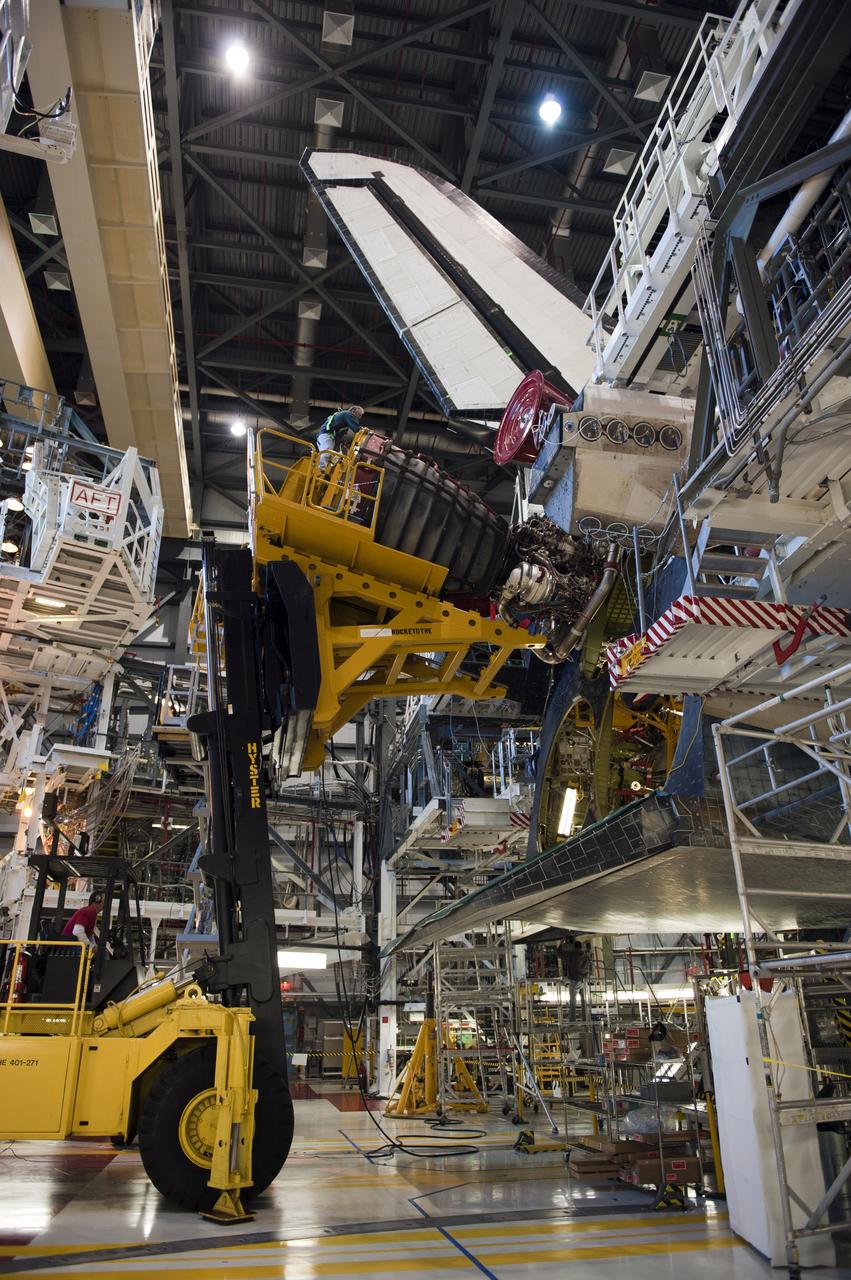

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the first of three space shuttle main engines closer to space shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
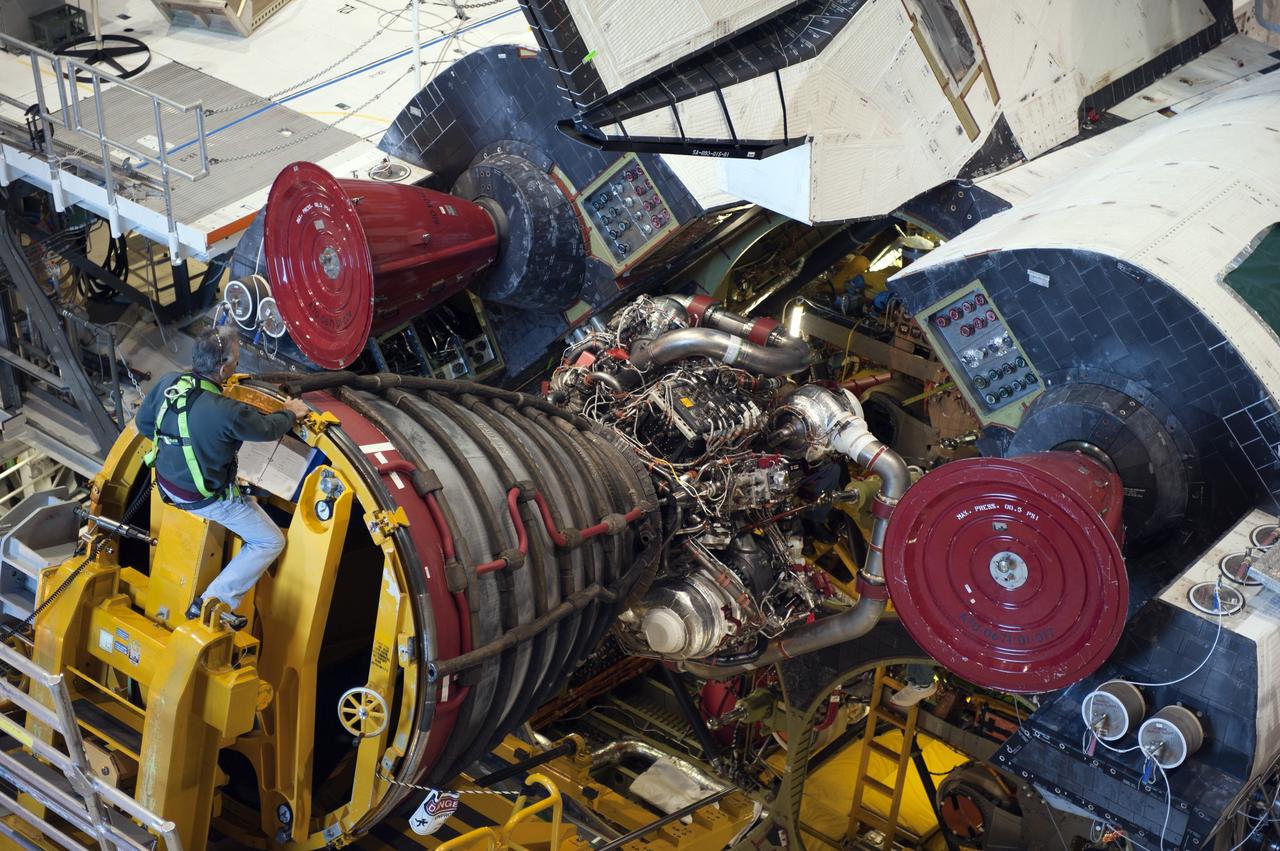

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the first of three space shuttle main engines closer to space shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
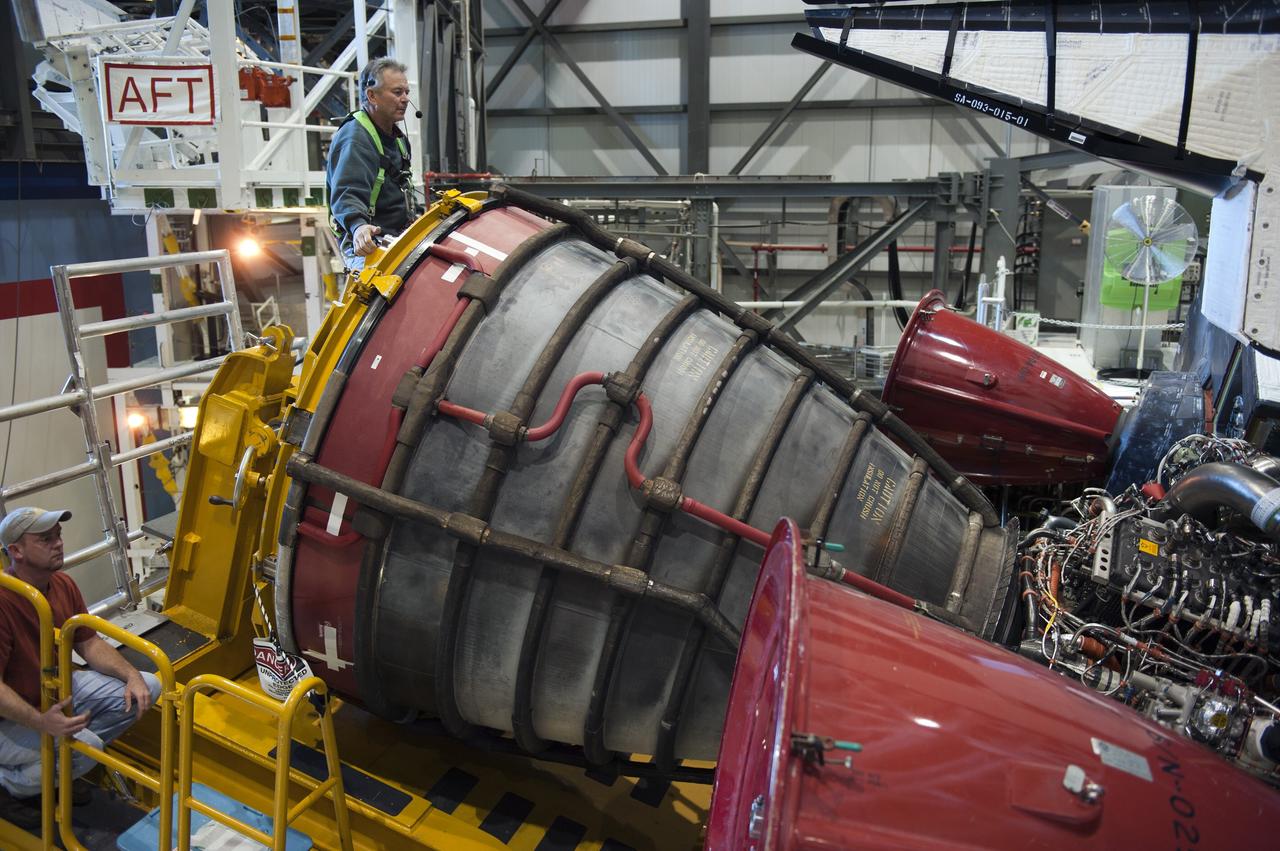

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the first of three space shuttle main engines closer to space shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
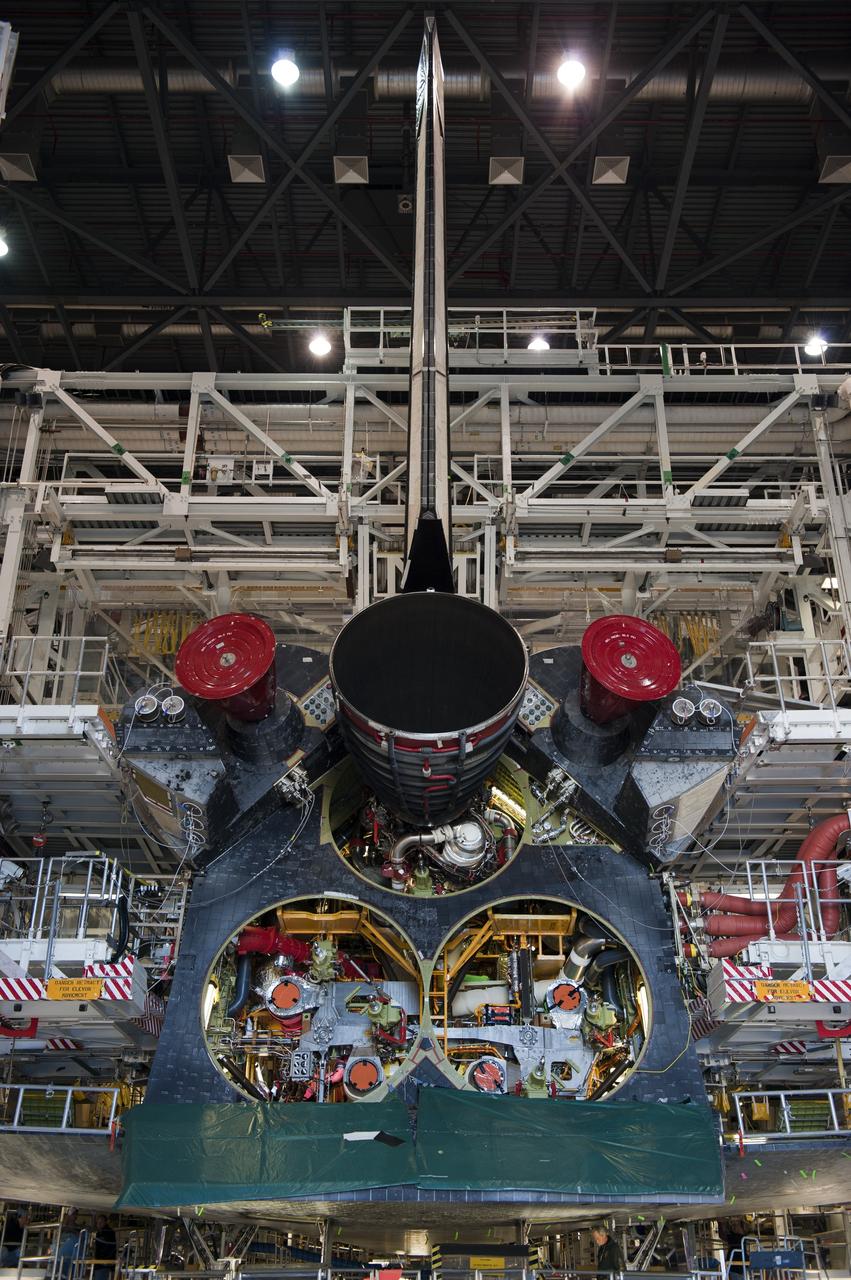

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the first of three space shuttle main engines is installed in space shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
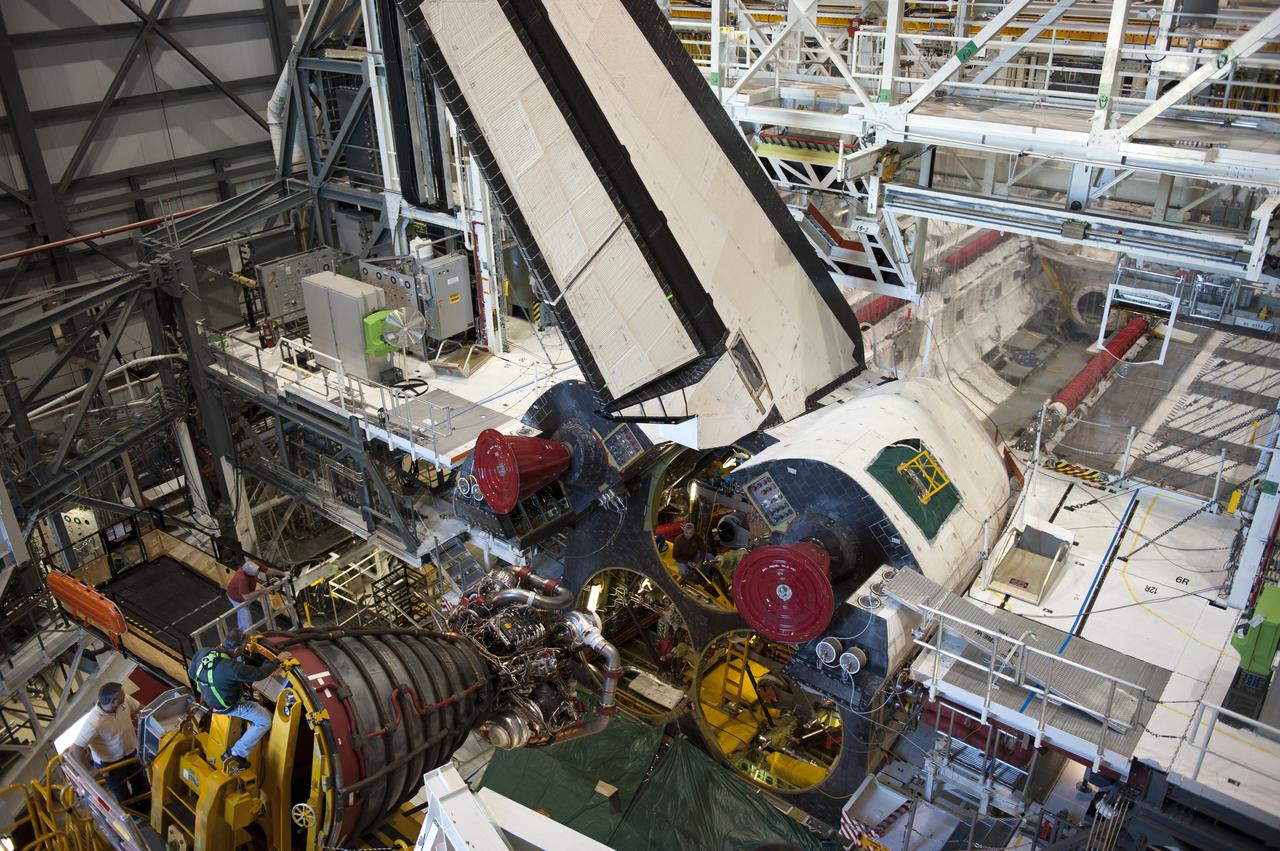

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the first of three space shuttle main engines closer to space shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
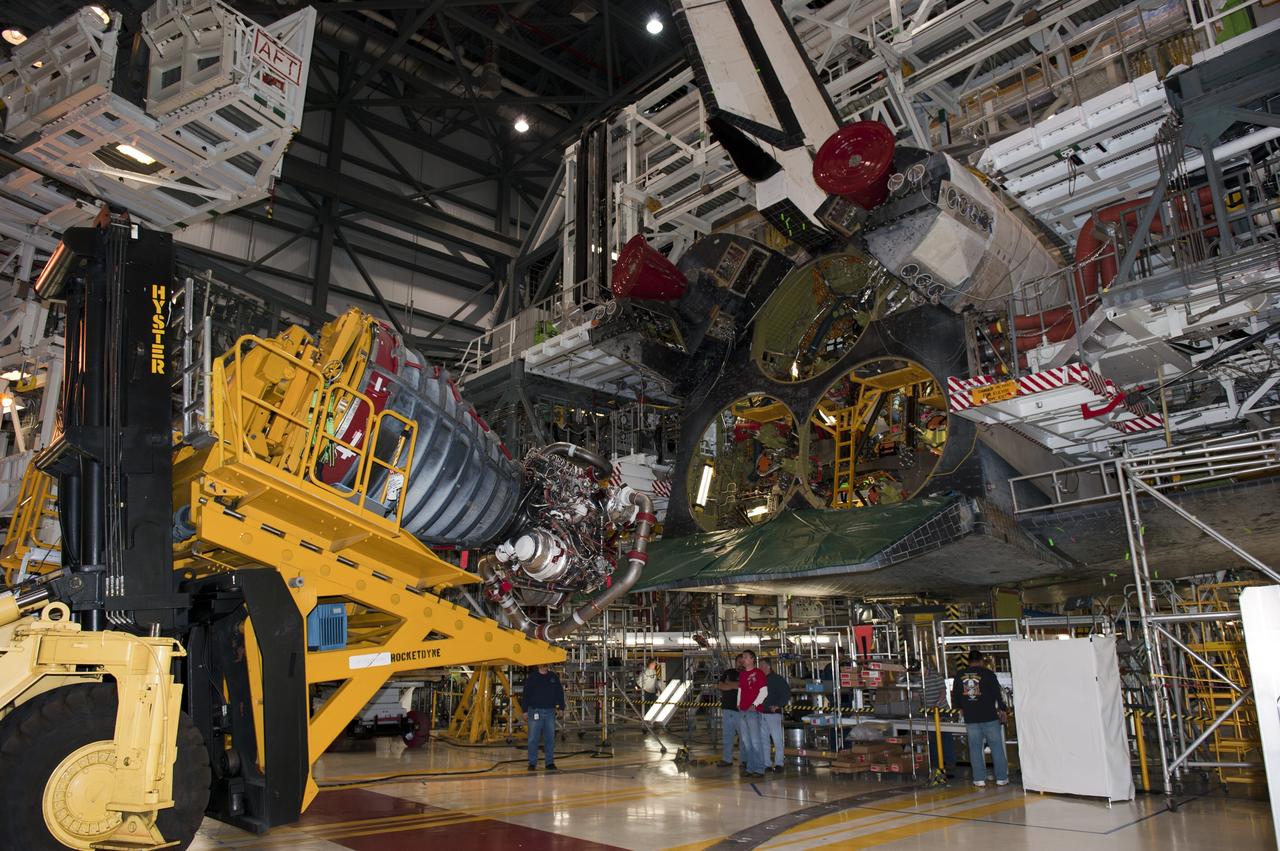

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the first of three space shuttle main engines closer to space shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
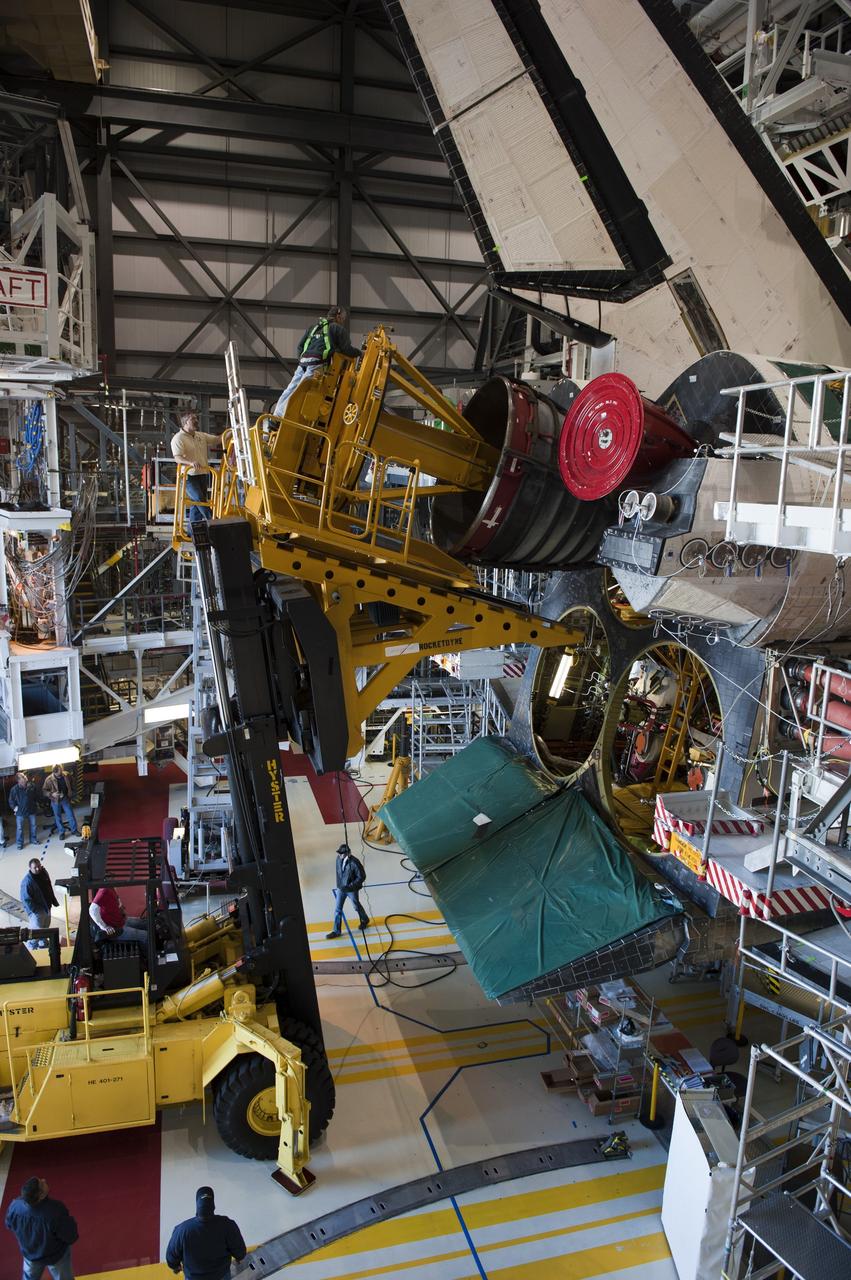

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the first of three space shuttle main engines closer to space shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
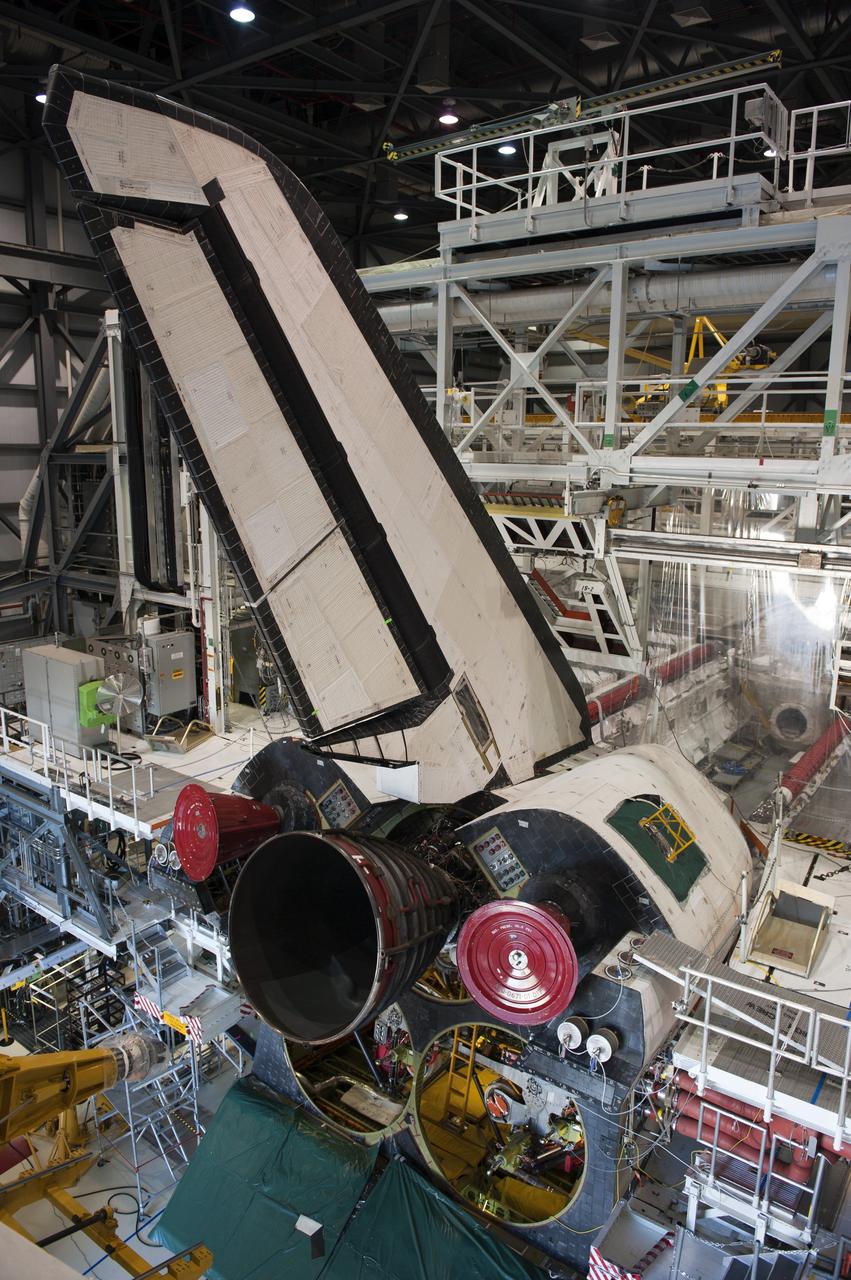

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the first of three space shuttle main engines is installed in space shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the first of three space shuttle main engines closer to space shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

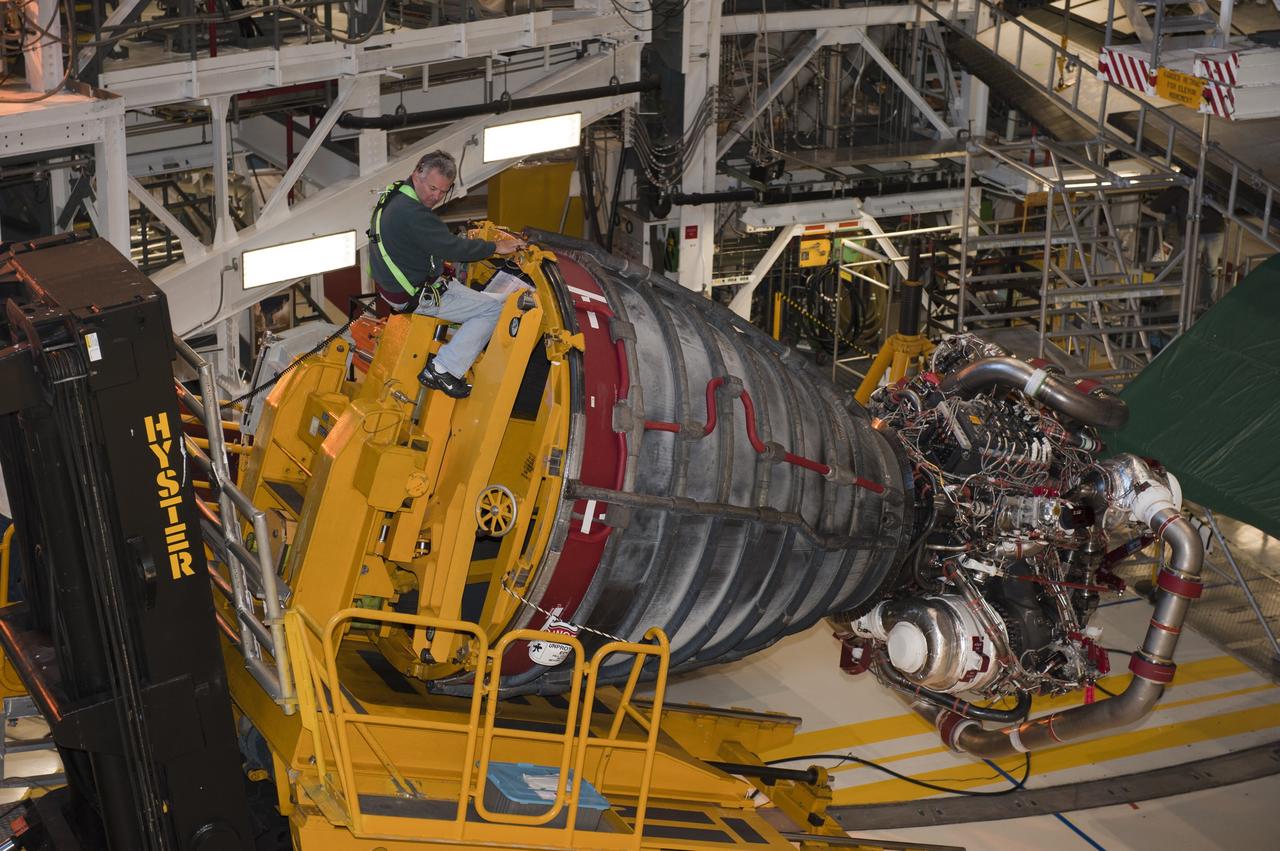
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the second of three space shuttle main engines closer to shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

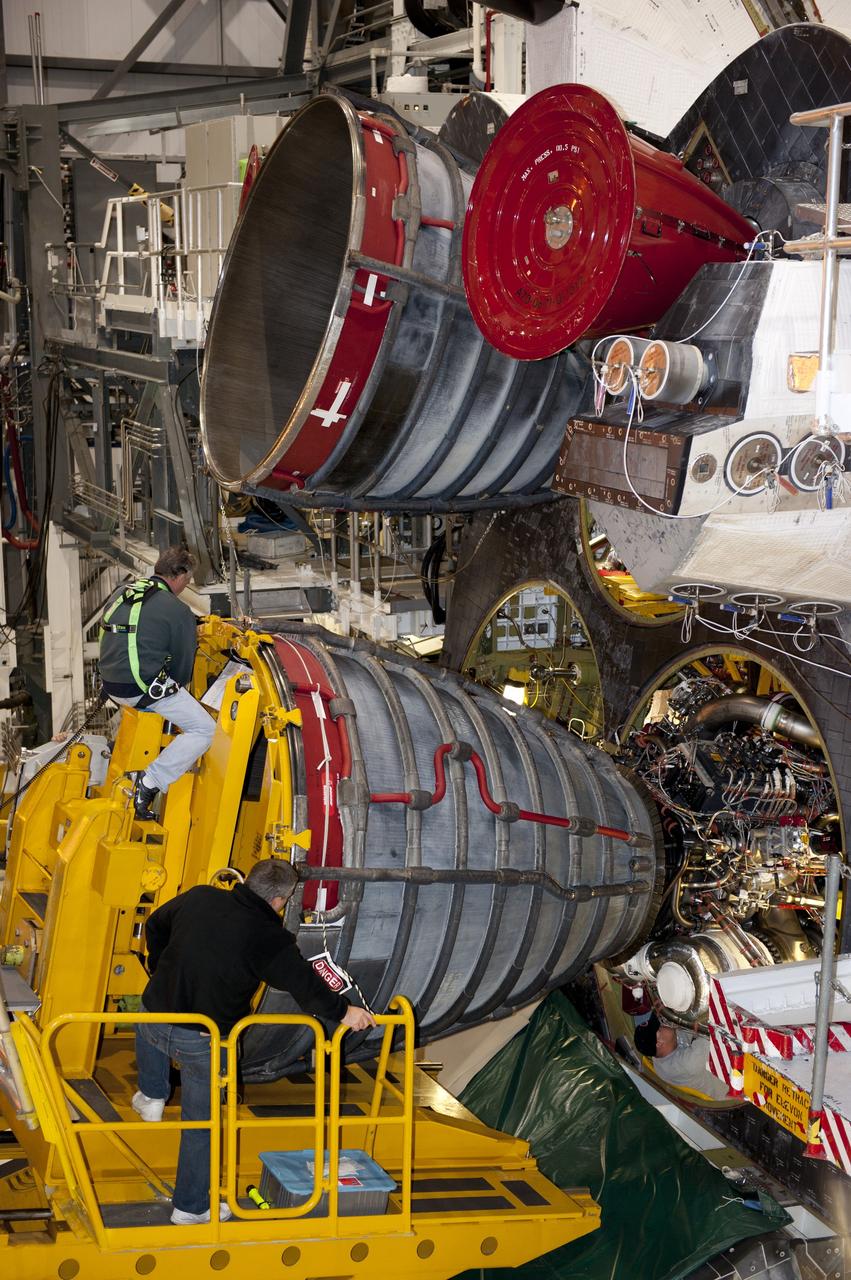
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the second of three space shuttle main engines closer to shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

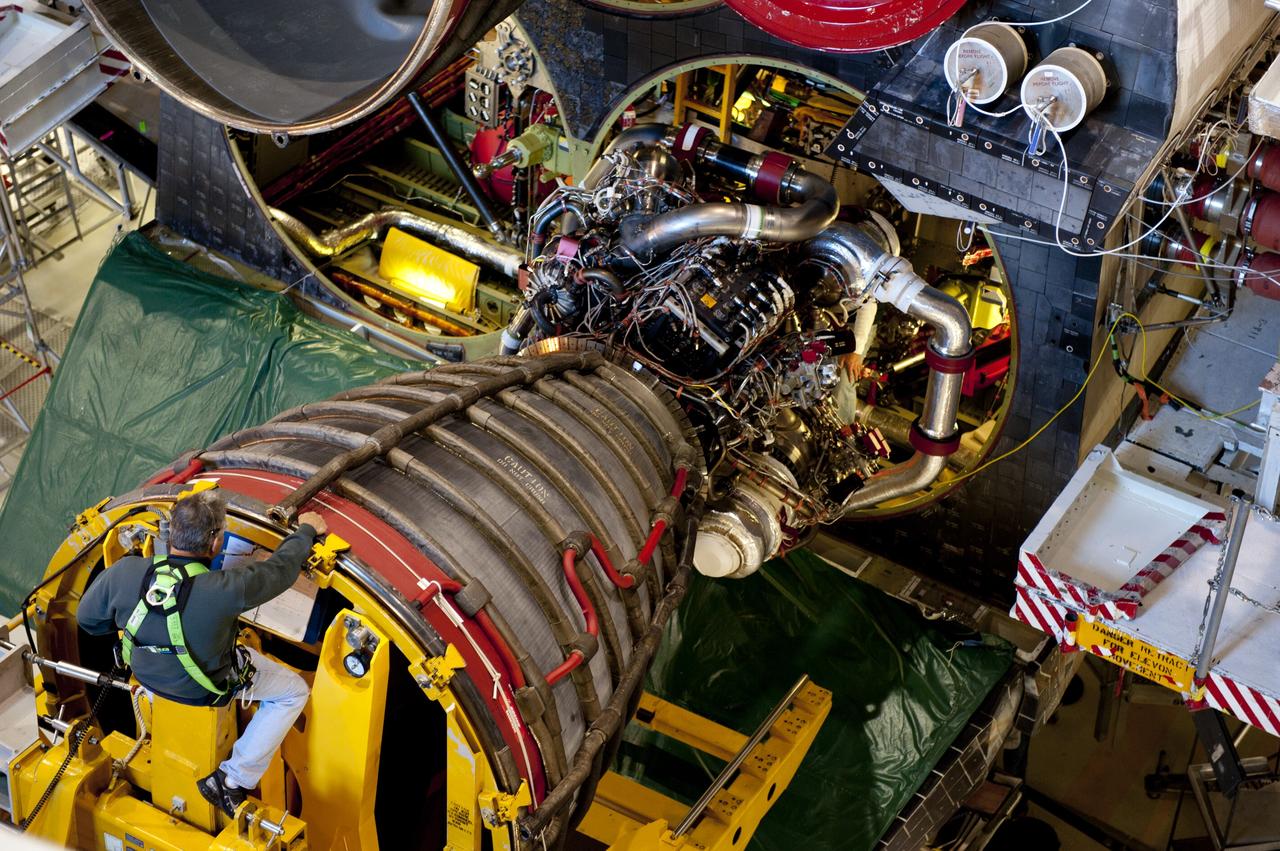
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the second of three space shuttle main engines closer to shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
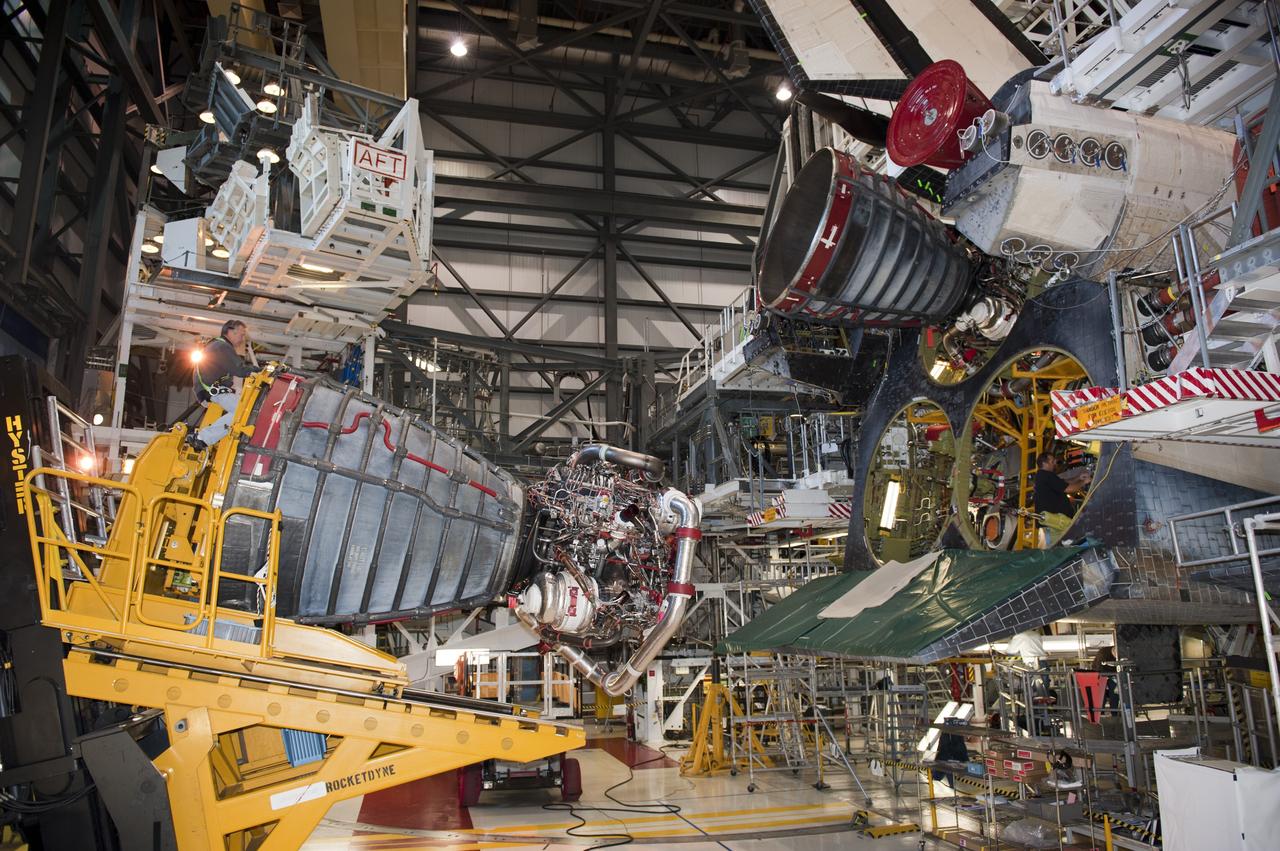

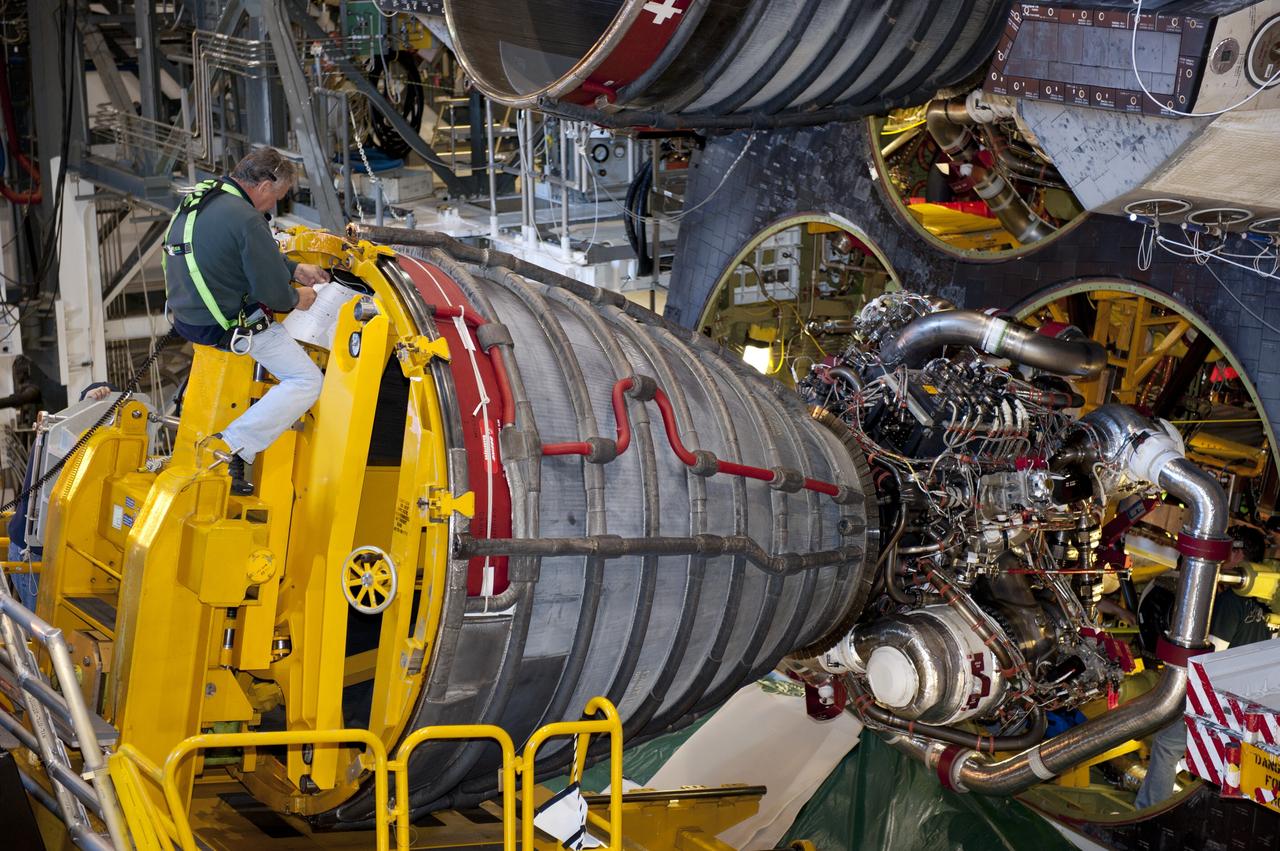
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Hyster forklift moves the second of three space shuttle main engines closer to shuttle Atlantis for installation. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
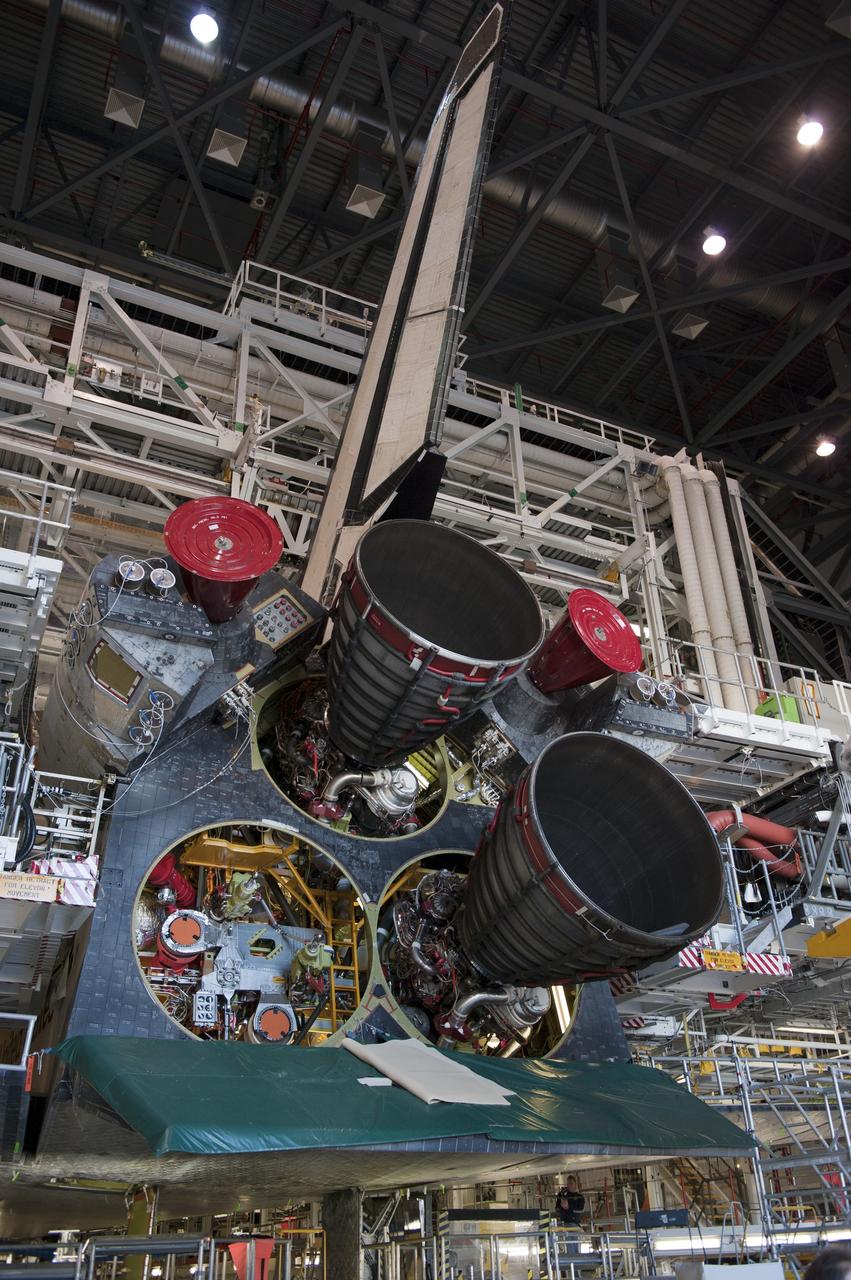

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the second of three space shuttle main engines is installed in shuttle Atlantis. Each engine is 14 feet long, weighs about 6,700 pounds, and is 7.5 feet in diameter at the end of the nozzle. This is the final planned engine installation for the Space Shuttle Program. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
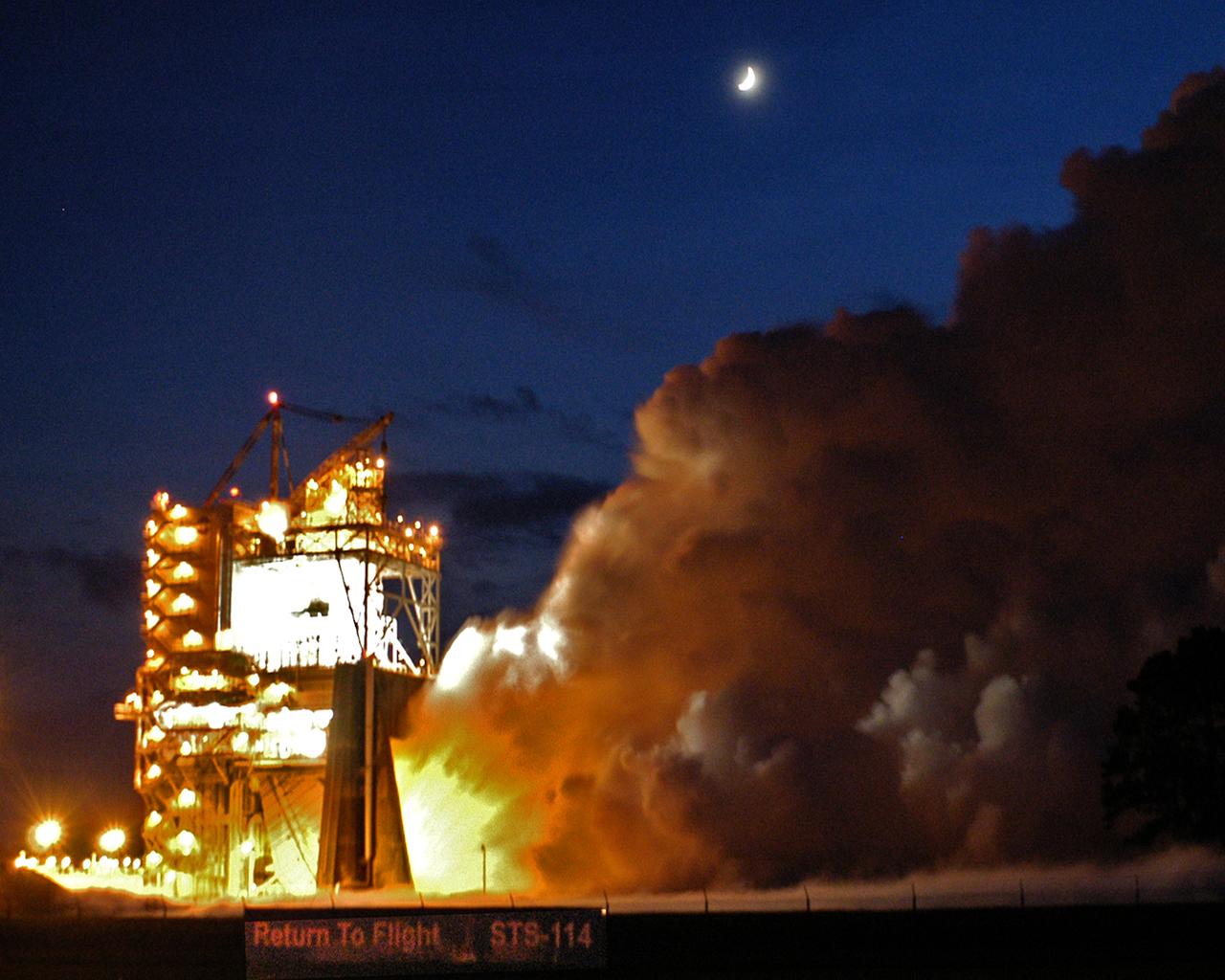

The Space Shuttle's Main Engine (SSME) reached another milestone Aug. 19, 2004, when a successful flight acceptance test was conducted at NASA Stennis Space Center (SSC). The engine tested was the final of three engines that will carry the next Space Shuttle into orbit. The engine will be shipped to NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida for installation on Space Shuttle Discovery for STS-114, NASA's Return to Flight mission. The engine test, which began about 8:10 p.m. CDT, ran for 520 seconds (8 minutes), the length of time it takes for the Space Shuttle to reach orbit.
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians move an aft access platform into place behind shuttle Atlantis, following the installation of the spacecraft's three main engines. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
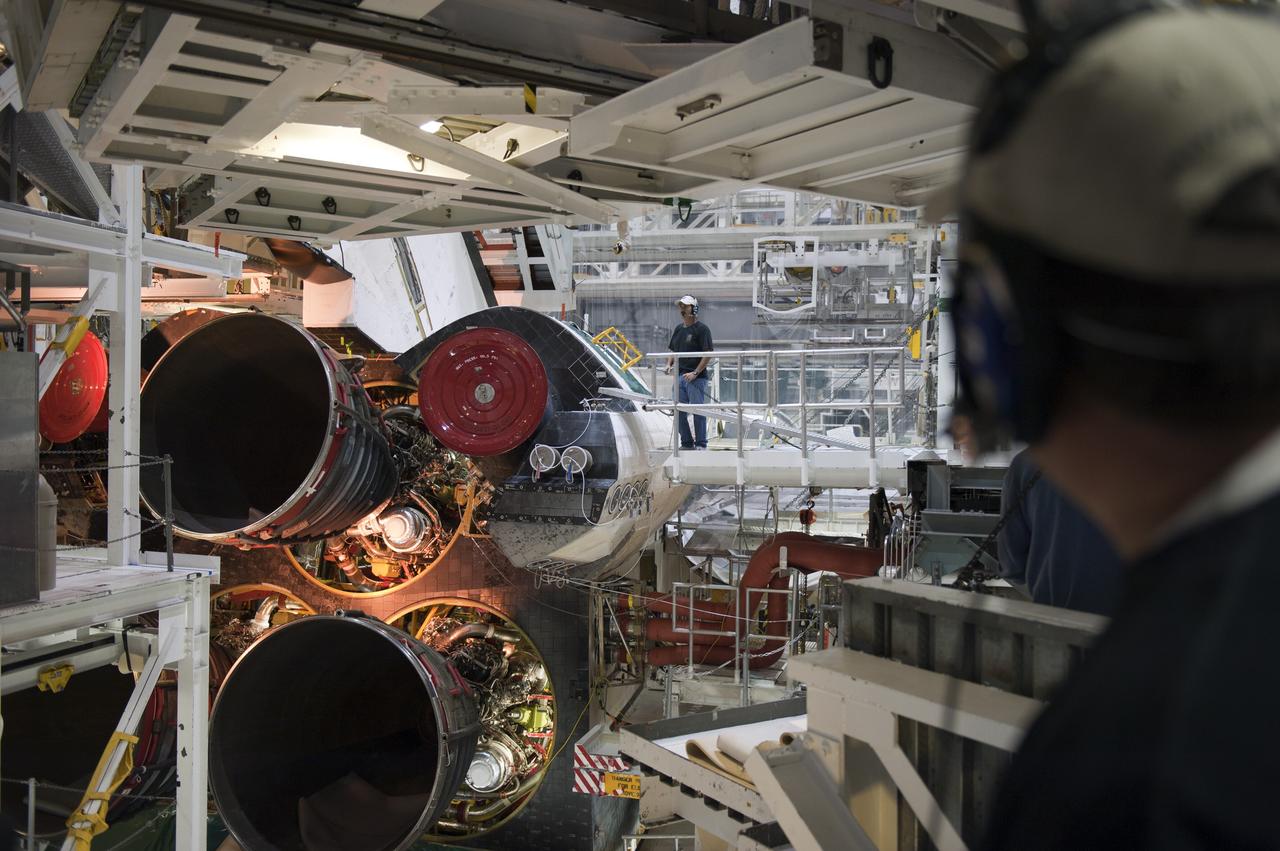

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians move an aft access platform into place behind shuttle Atlantis, following the installation of the spacecraft's three main engines. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
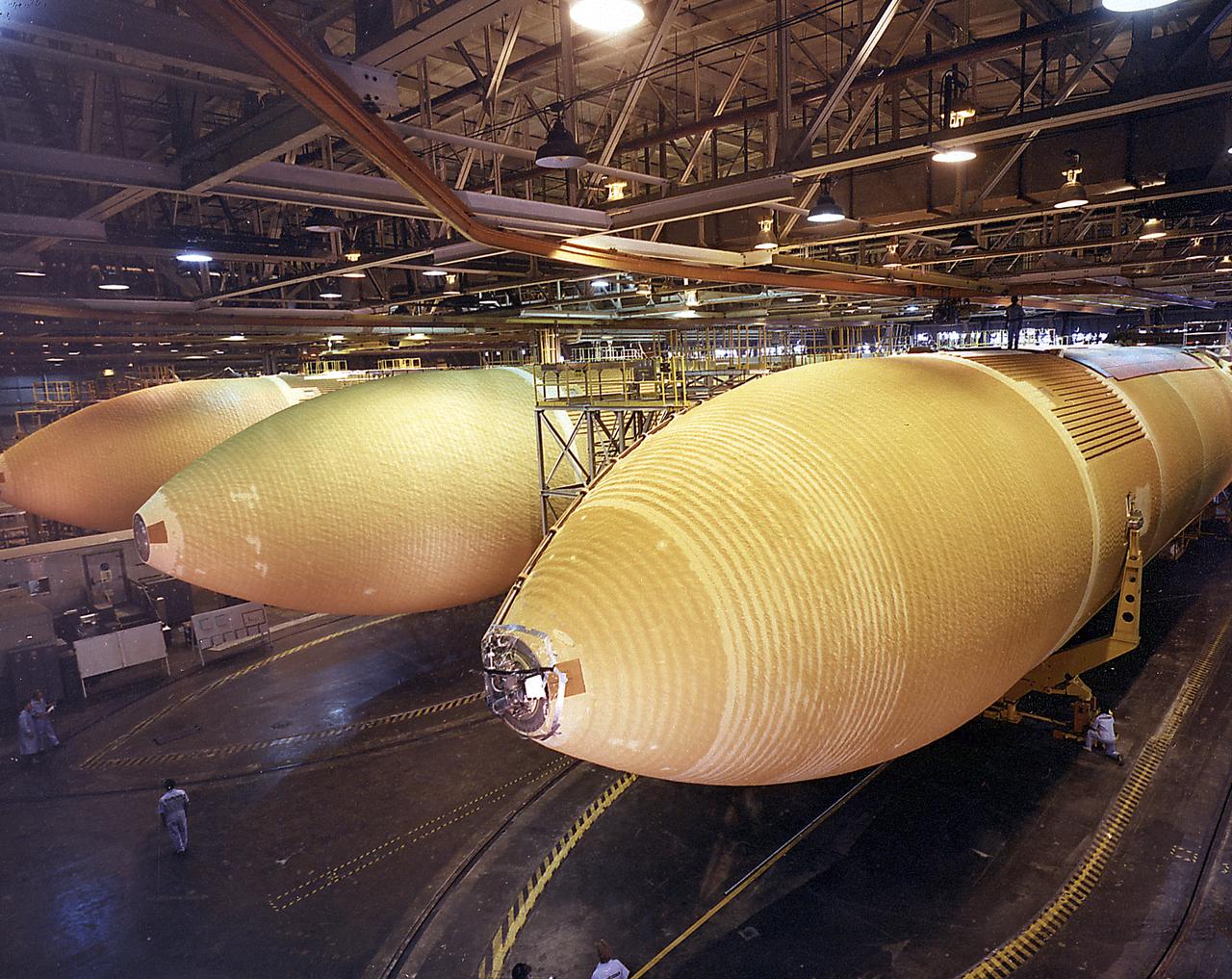

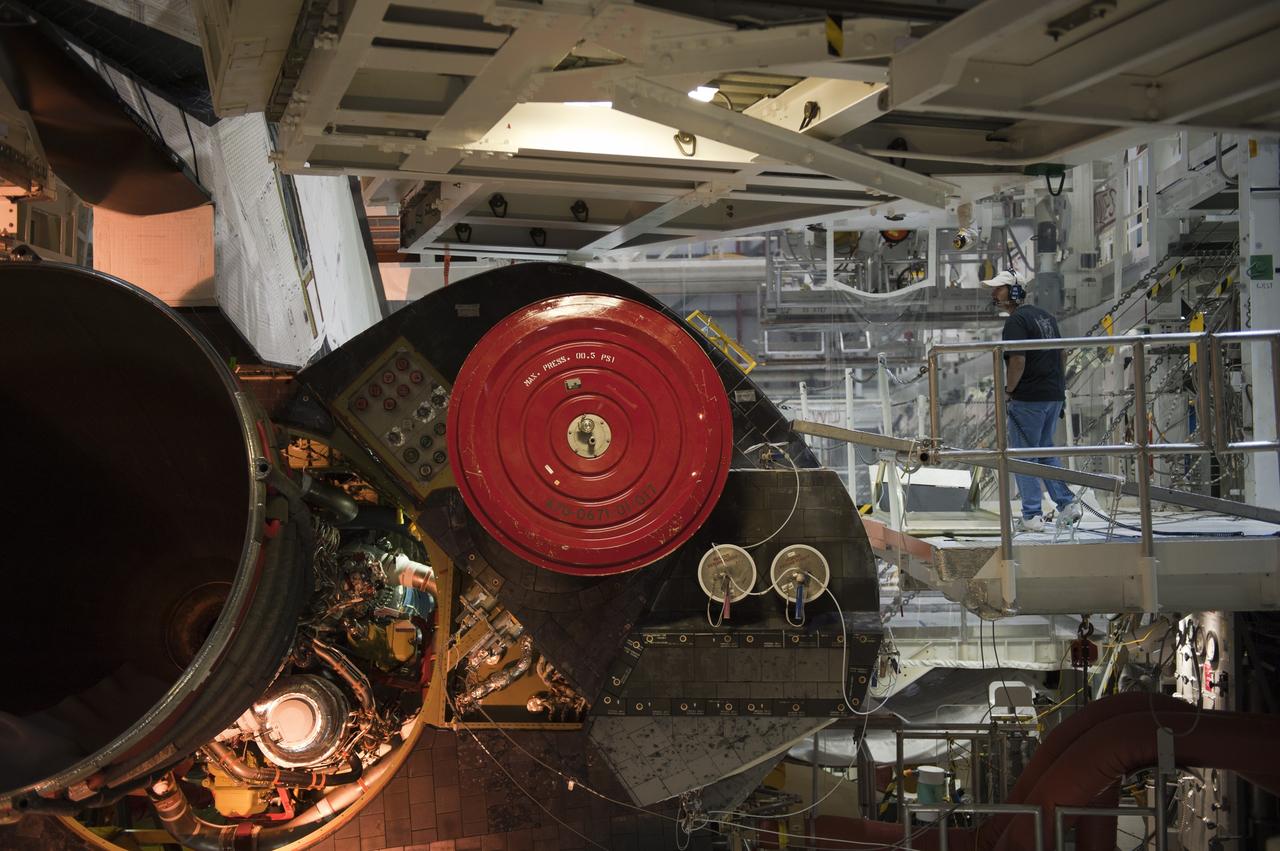
This photograph was taken during the final assembly phase of the Space Shuttle light weight external tanks (LWT) 5, 6, and 7 at the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana. The giant cylinder, higher than a 15-story building, with a length of 154-feet (47-meters) and a diameter of 27.5-feet (8.4-meters), is the largest single piece of the Space Shuttle. During launch, the external tank (ET) acts as a backbone for the orbiter and solid rocket boosters. In separate, internal pressurized tank sections, the ET holds the liquid hydrogen fuel and liquid oxygen oxidizer for the Shuttle's three main engines. During launch, the ET feeds the fuel under pressure through 17-inch (43.2-centimeter) ducts which branch off into smaller lines that feed directly into the main engines. Some 64,000 gallons (242,260 liters) of fuel are consumed by the main engines each minute. Machined from aluminum alloys, the Space Shuttle's ET is the only part of the launch vehicle that currently is not reused. After its 526,000 gallons (1,991,071 liters) of propellants are consumed during the first 8.5 minutes of flight, it is jettisoned from the orbiter and breaks up in the upper atmosphere, its pieces falling into remote ocean waters. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for developing the ET
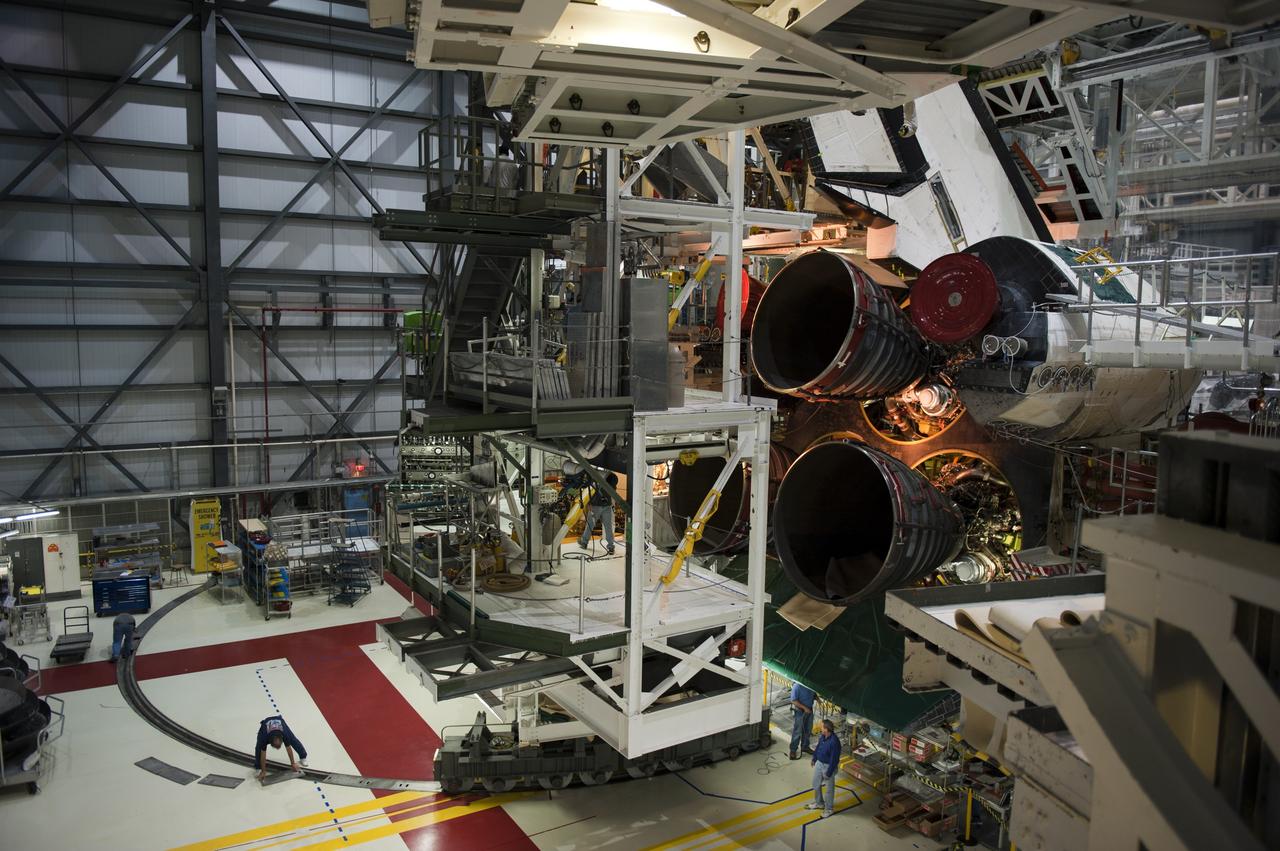

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to move an aft access platform into place behind shuttle Atlantis, following the installation of the spacecraft's three main engines. Shown is the right-hand orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod and engine taken from the right-hand access arm. Atlantis is being prepared for the "launch on need," or potential rescue mission, for the final planned shuttle flight, Endeavour's STS-134 mission. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
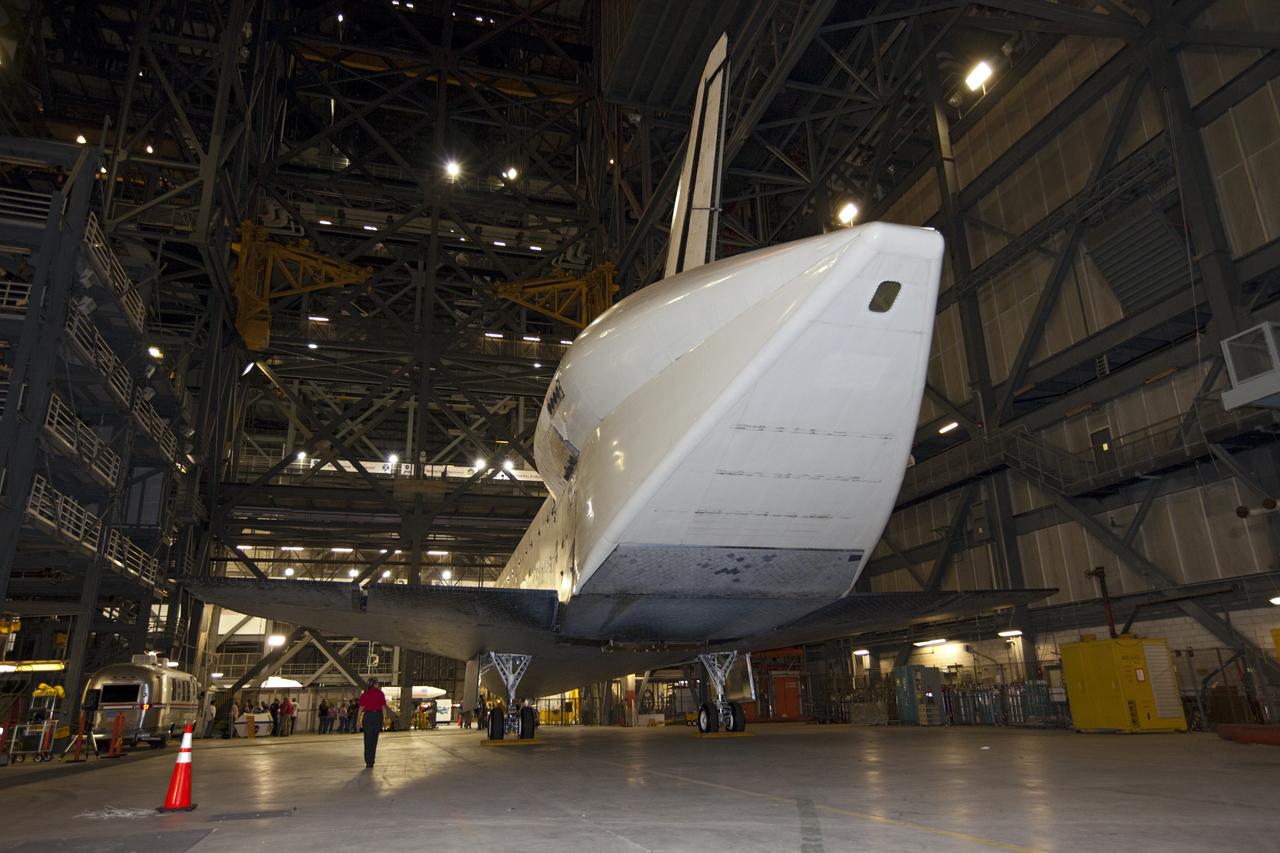

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerodynamic tail cone covers space shuttle Endeavour's trio of replica shuttle main engines as the spacecraft backs out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour moved to the nearby Shuttle Landing Facility, where it will be lifted in the gantry-like Mate-Demate Device and placed atop NASA's modified 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft for the final ferry flight of the Space Shuttle Program. Endeavour will be placed on permanent public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
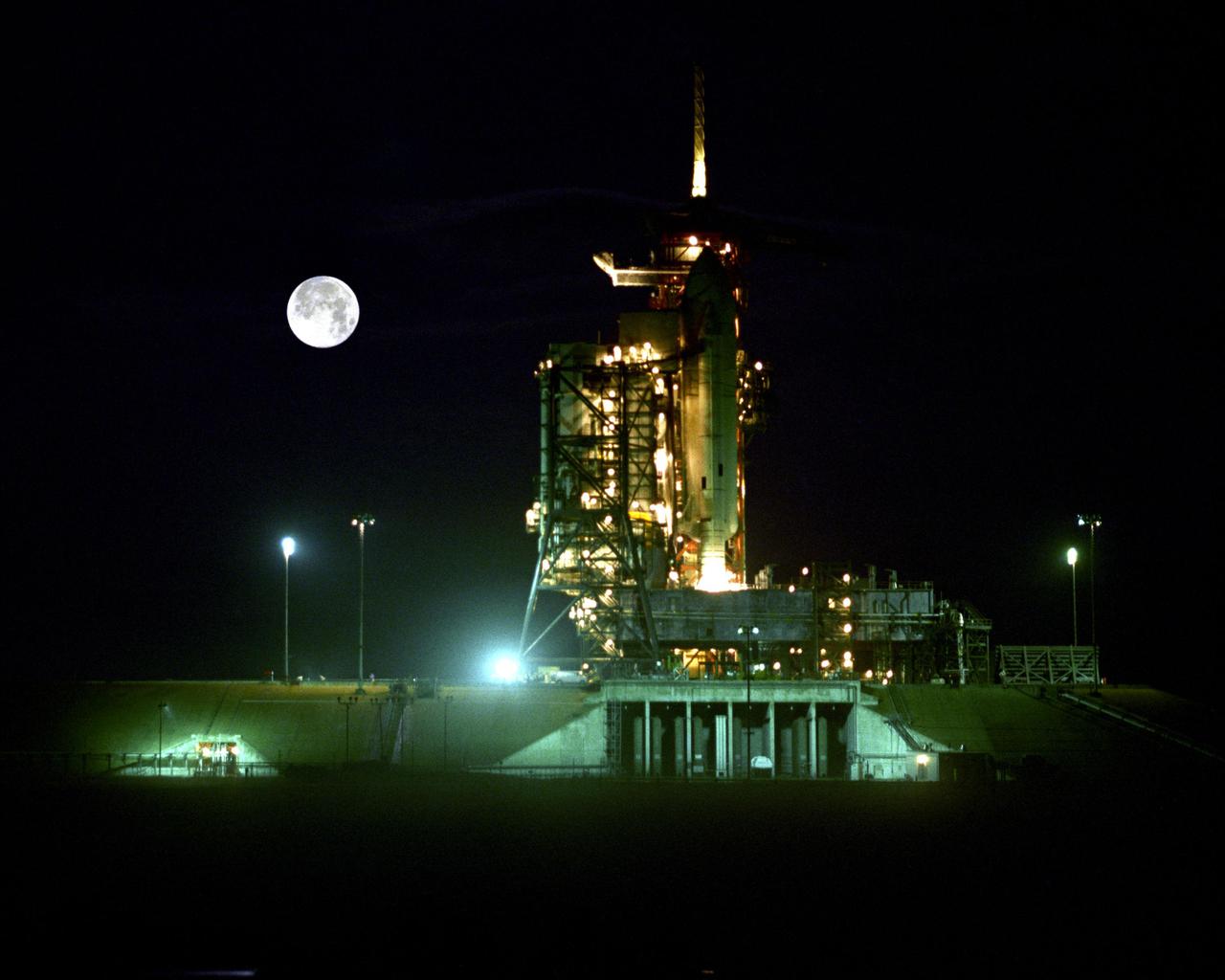

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Looking like the perfect staging for a science fiction movie, STS-1 is a dramatic companion for the Moon 'over its shoulder.' The Space Shuttle, comprised of the orbiter Columbia, the external tank and two solid rocket boosters, is pictured during final preparations for Flight Readiness Firing of the orbiter's main engines, a landmark test during launch preparations.

The STS-110 mission began the third and final phase of construction for the International Space Station (ISS) by delivering and installing the Starboard side S0 (S-zero) truss segment that was carried into orbit in the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The STS-110 crew patch is patterned after the cross section of the S0 truss, and encases the launch of the Shuttle Atlantis and a silhouette of the ISS as it will look following mission completion. The successfully installed S0 segment is highlighted in gold. The three prominent flames blasting from the shuttle emphasizes the first shuttle flight to use three Block II Main Engines.
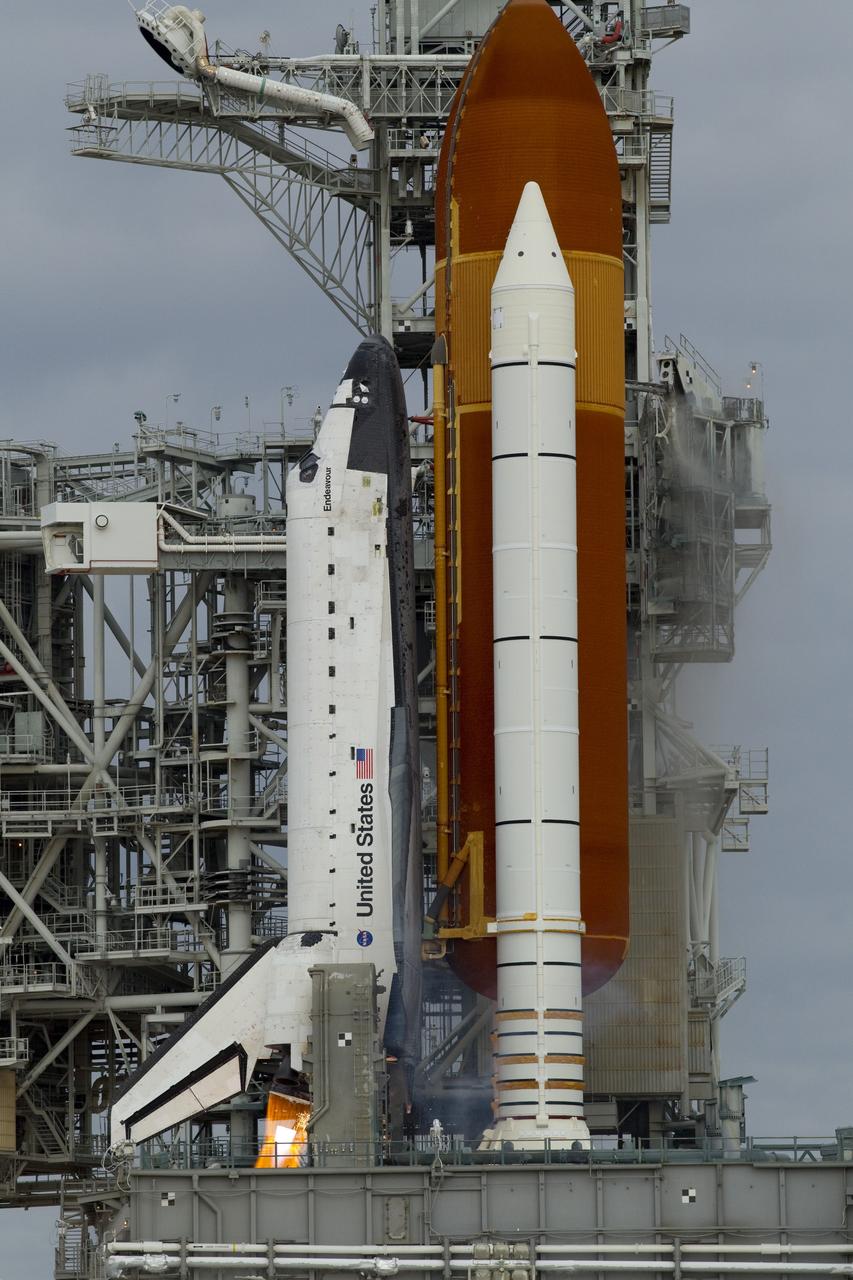

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite to lift the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/George Roberts and Mike Kerley
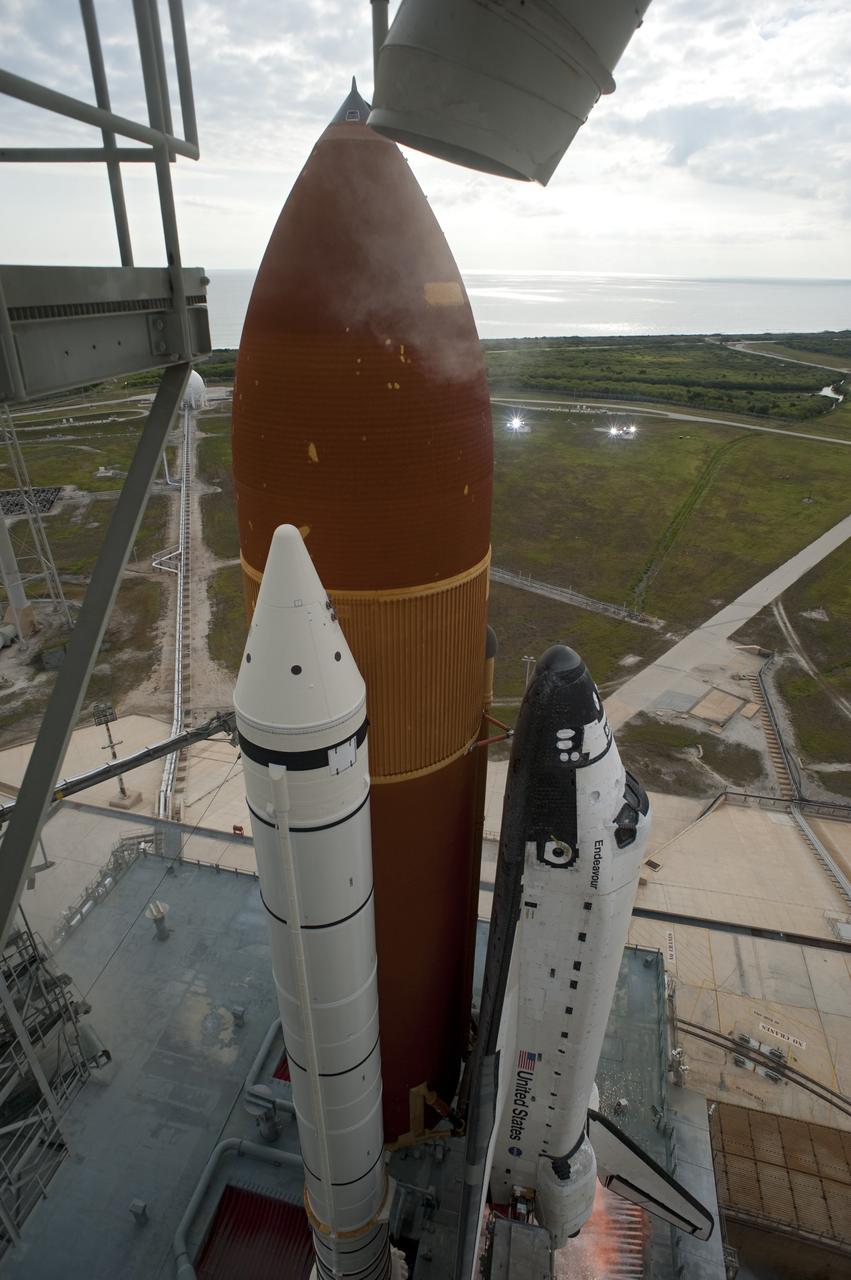

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite to lift the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
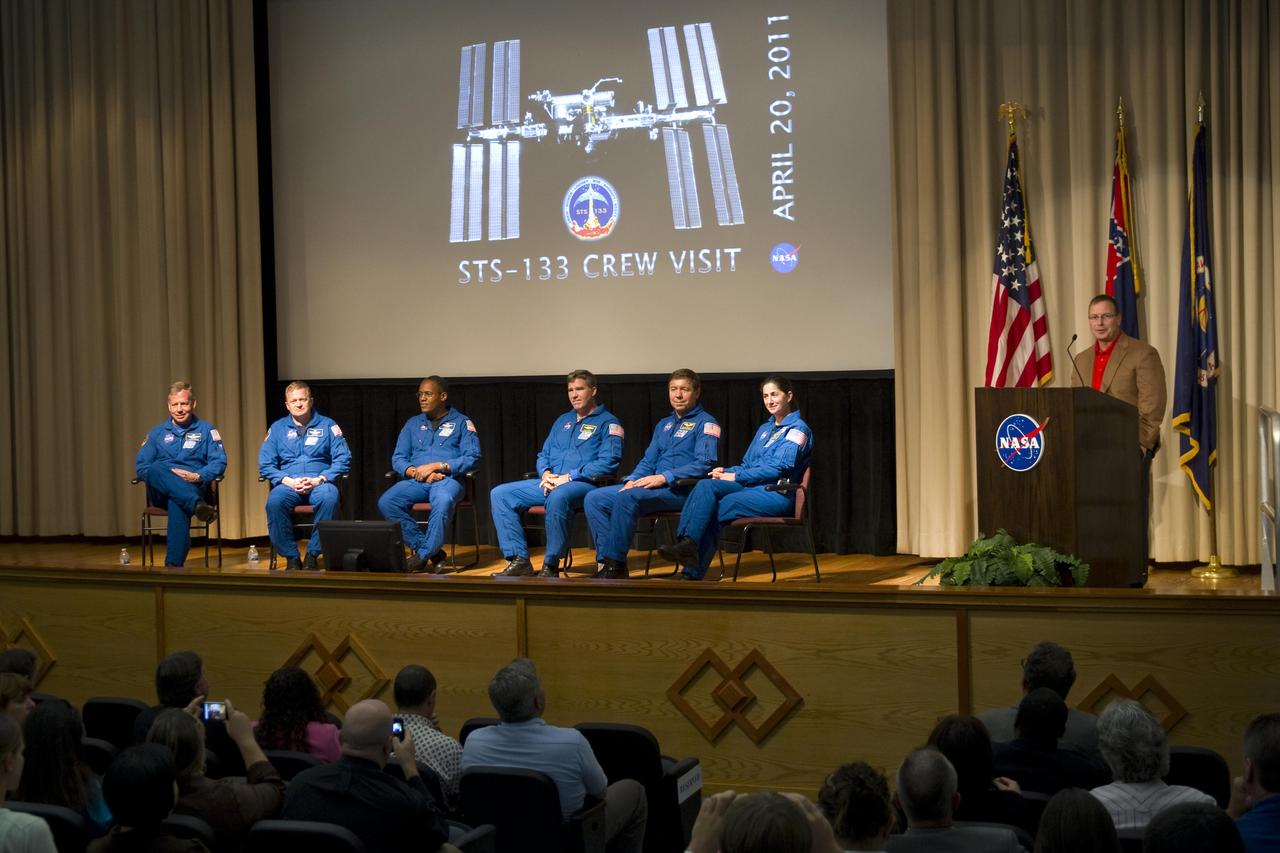

Stennis Space Center Deputy Director Rick Gilbrech (far right) welcomes members of the STS-133 shuttle mission crew during an April 20 visit. The mission was the final flight for the space shuttle Discovery, which now becomes the first of the three-orbiter fleet to be retired. During the visit to Stennis, Mission Commander Steven Lindsey ( l to r), Pilot Eric Boe and mission specialists Alvin Drew, Steven Bowen, Michael Barratt and Nicole Stott recapped their historic flight and thanked site employees for providing main engines that performed 'as advertised.'
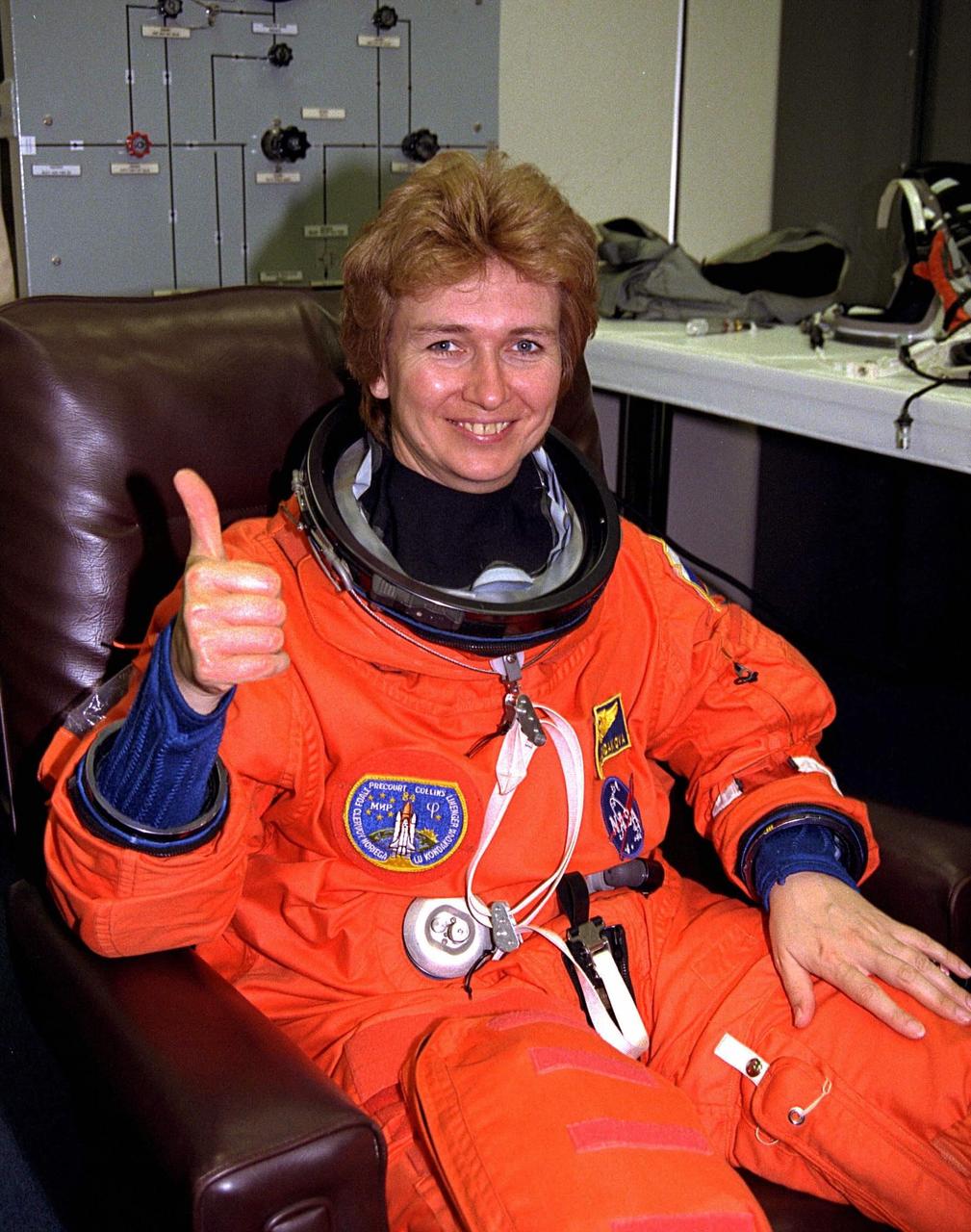

STS-84 Mission Specialist Elena V. Kondakova gives a "thumbs up" as she dons her launch and entry suit during final prelaunch preparations in the Operations and Checkout Building. Kondakova is a cosmonaut with the Russian Space Agency. This is her second trip into space, but her first on the Space Shuttle. She spent 169 days in space as flight engineer of the 17th main mission on the Russian Space Station Mir from Oct. 4, 1994, to March 9, 1995. STS-84 aboard Atlantis will be the sixth docking of the Space Shuttle with the Mir
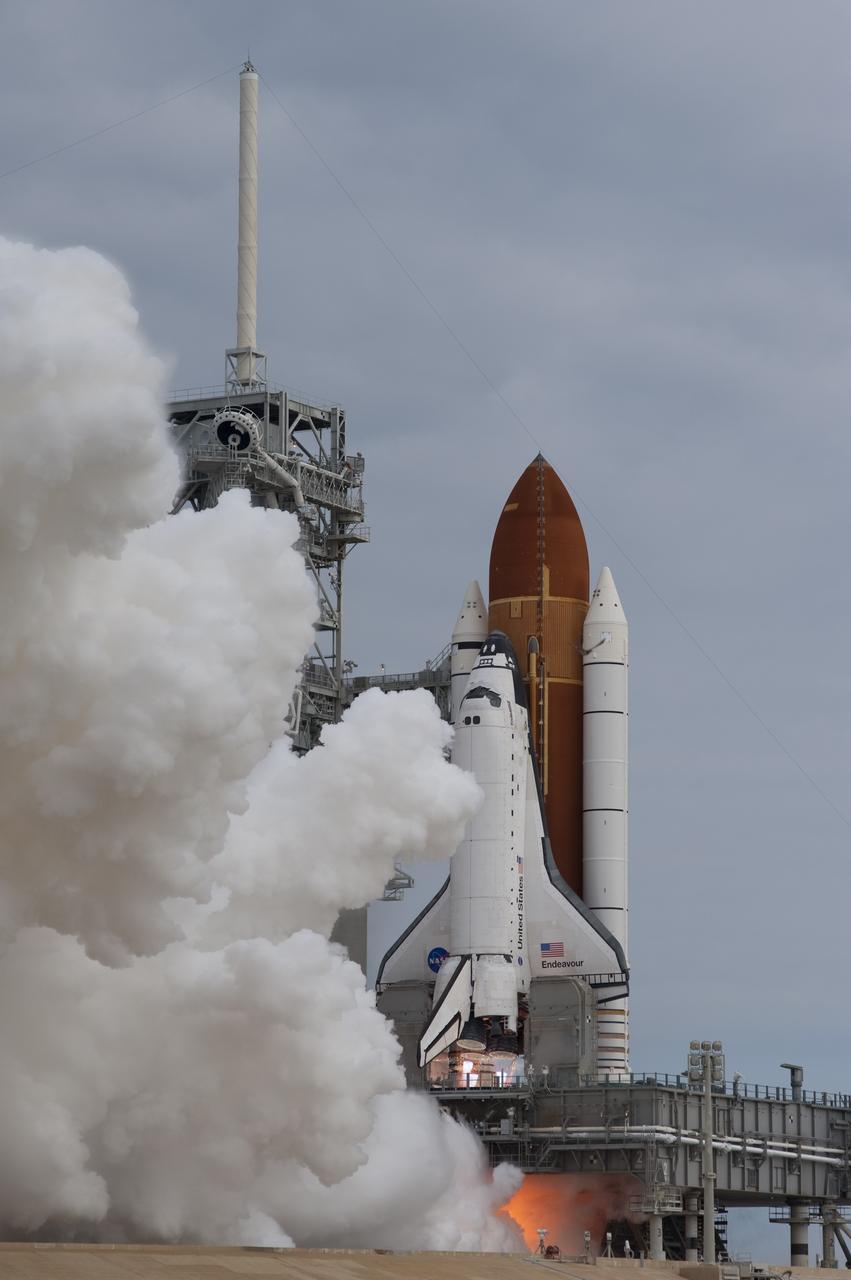

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A cloud of steam and smoke emerge as space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
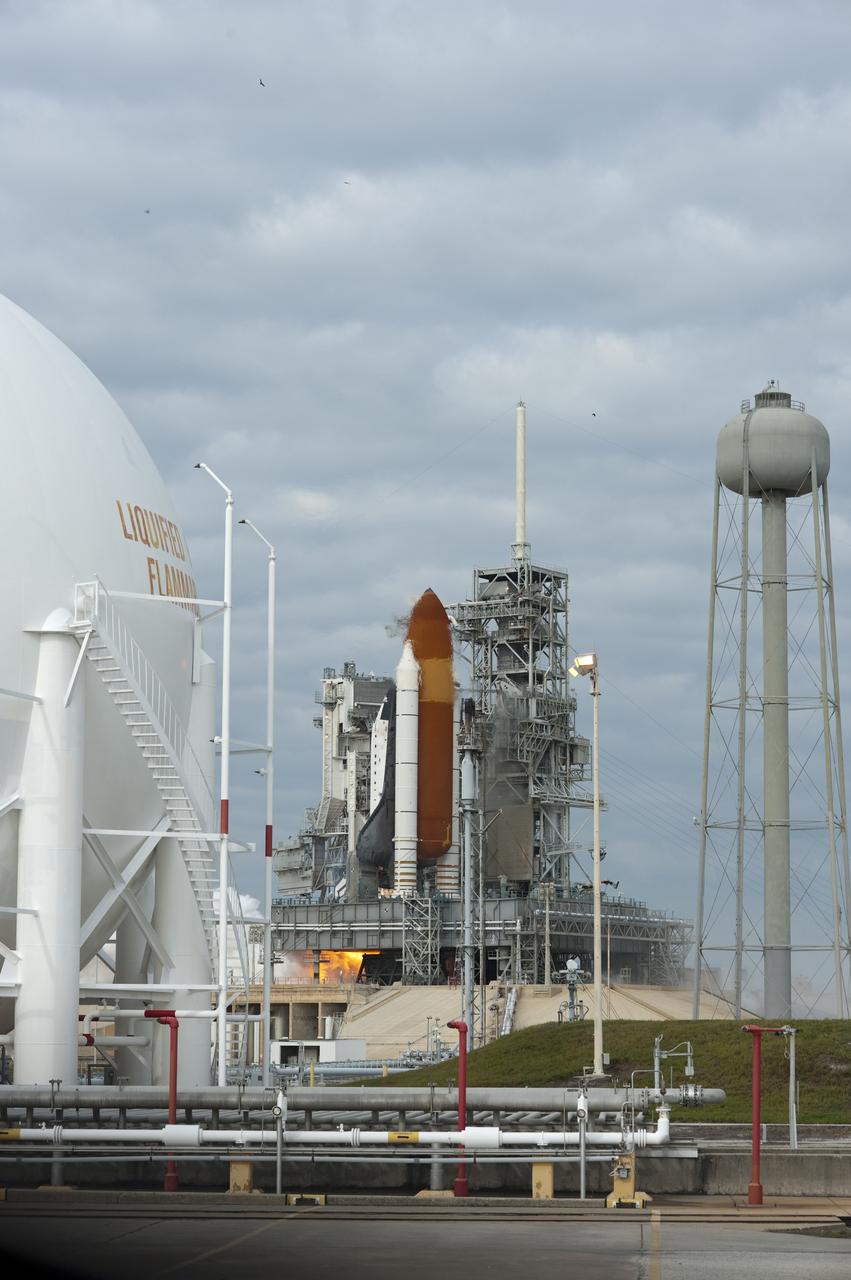

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines are ignited for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
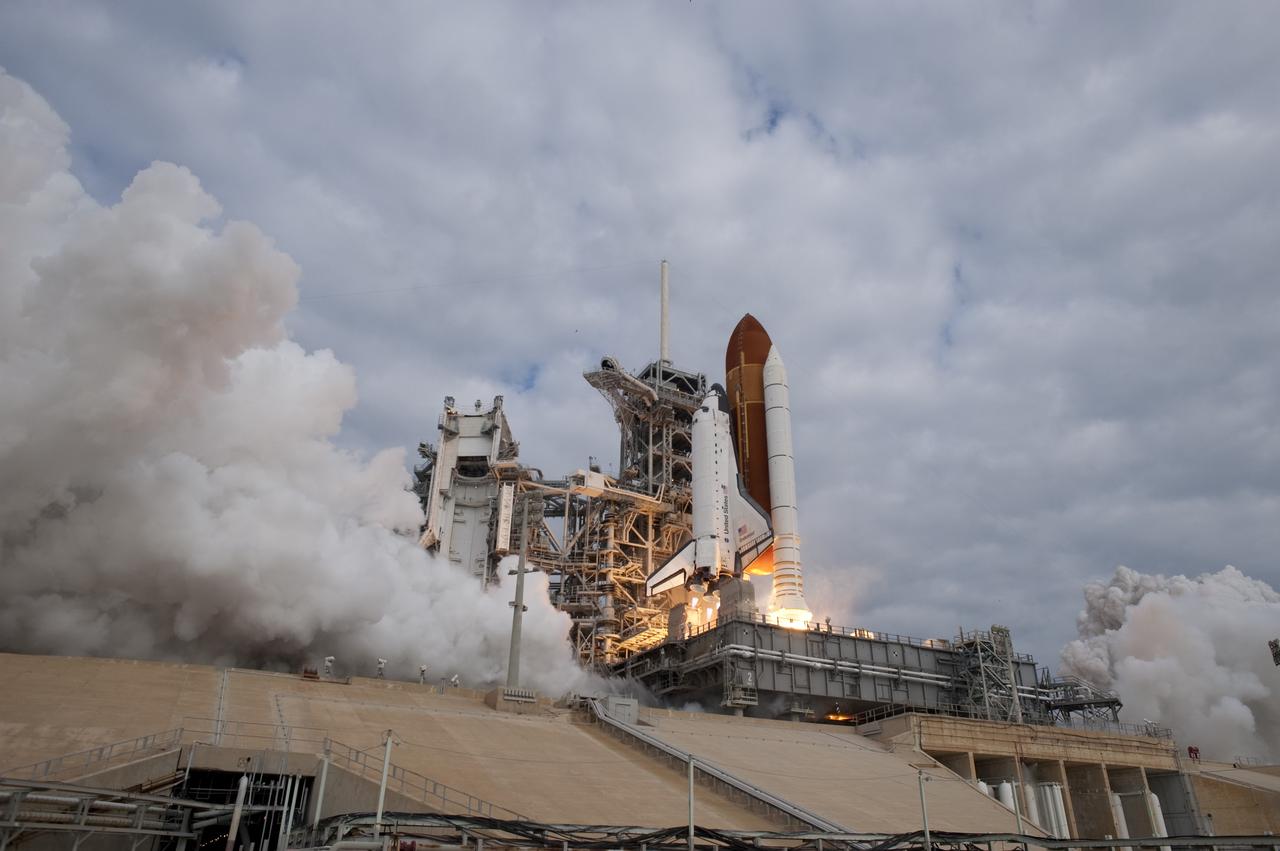

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
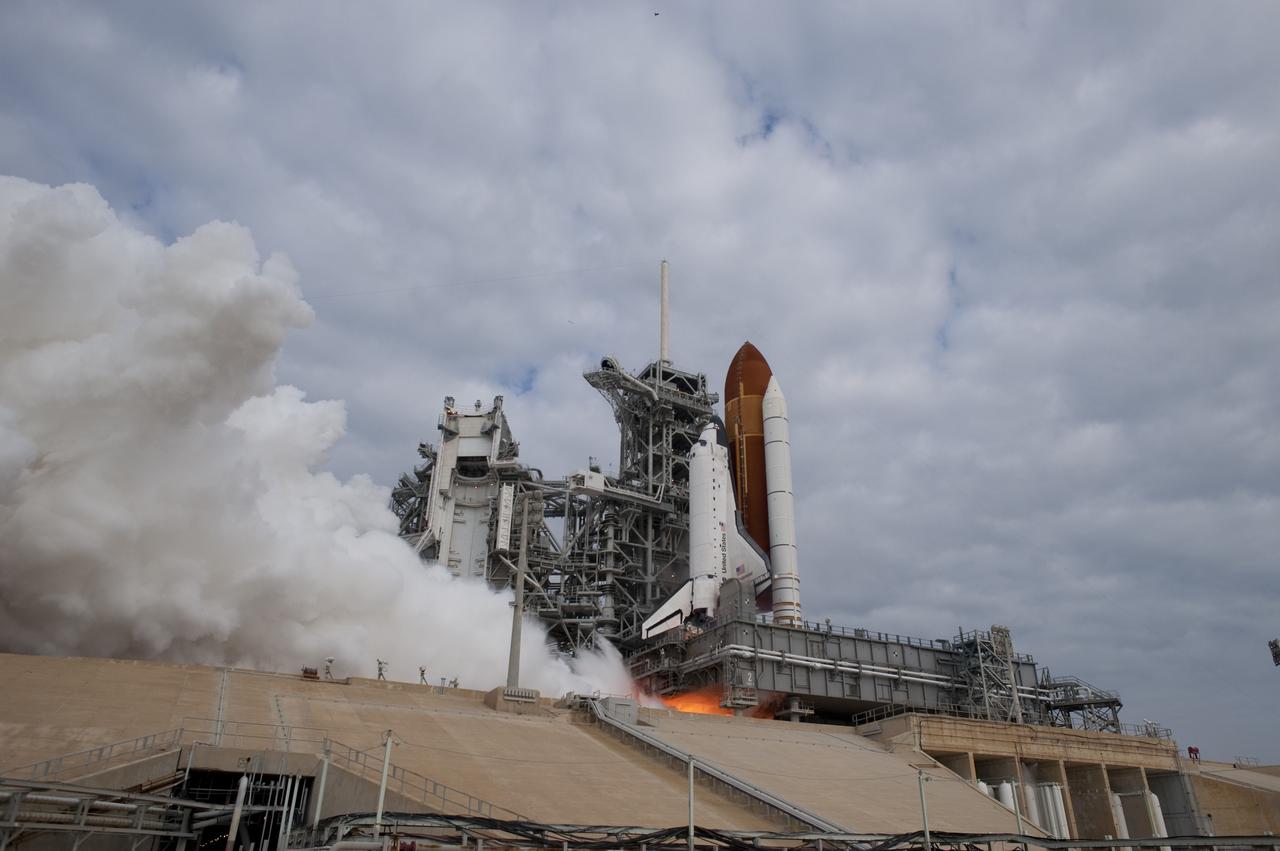

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
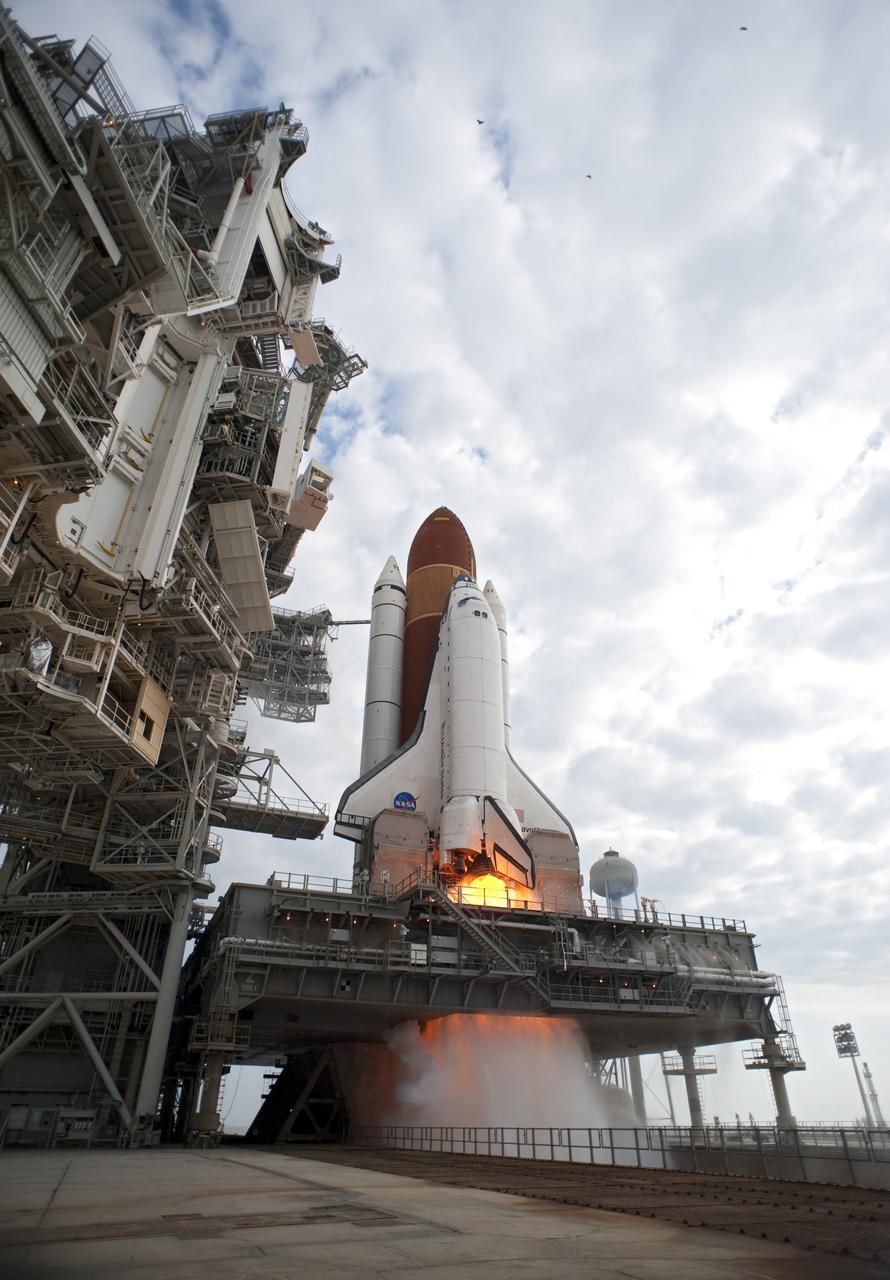

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
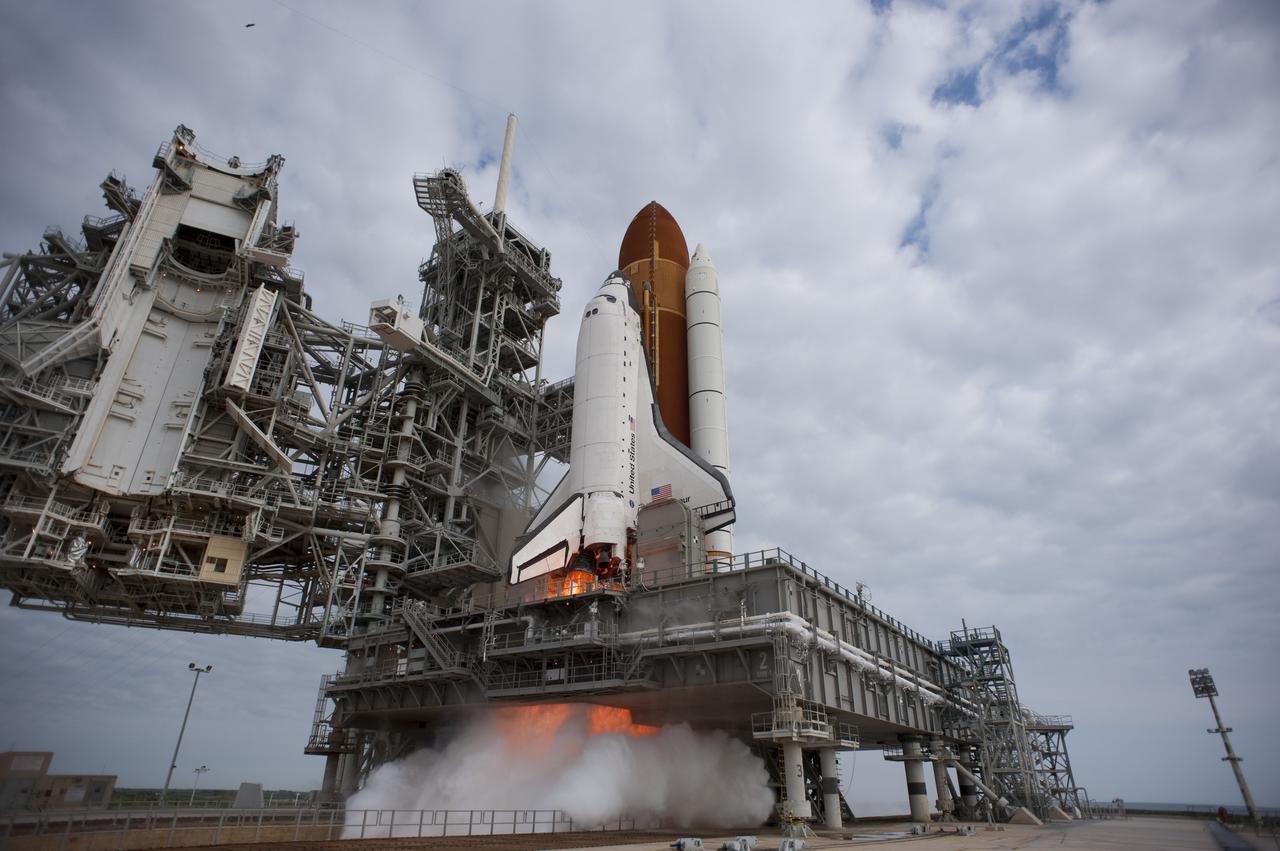

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
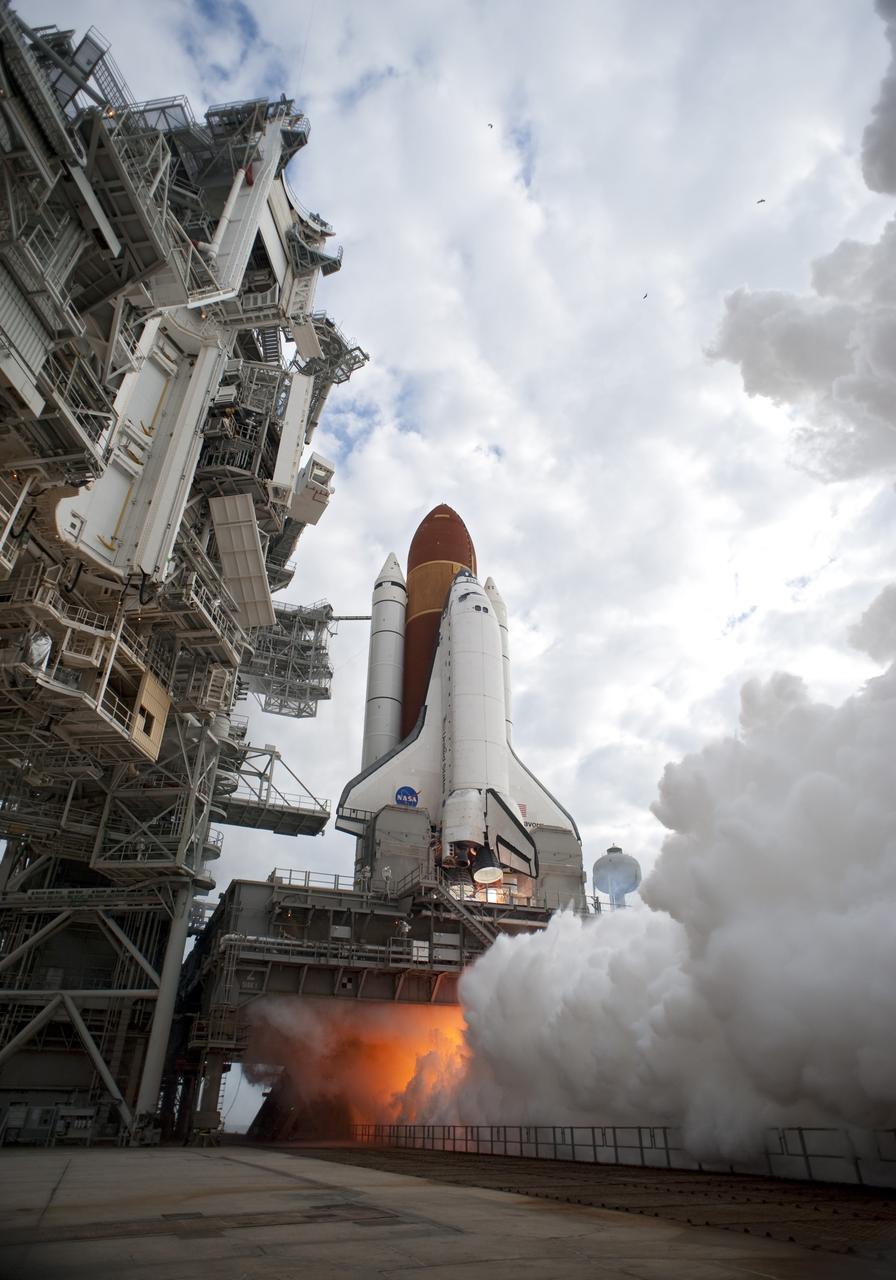

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
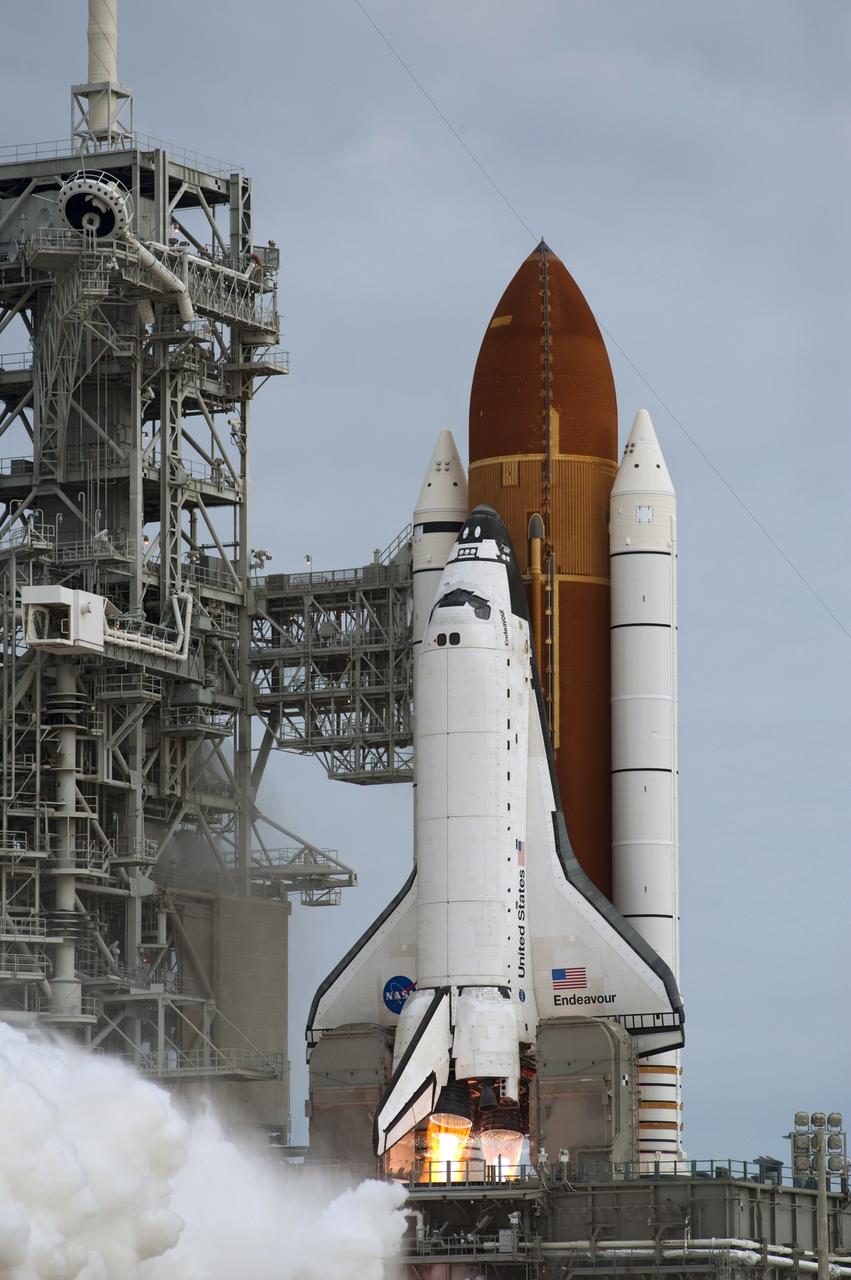

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell

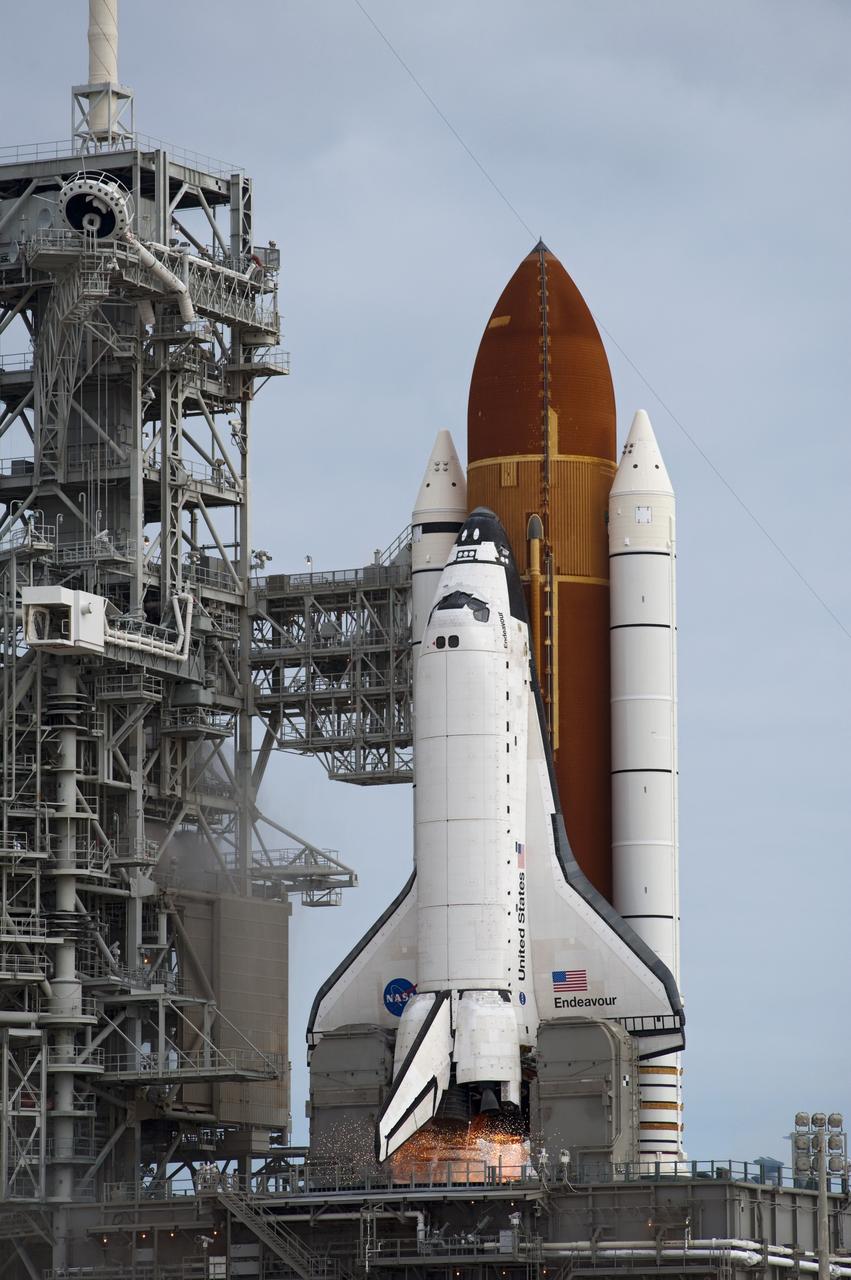
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
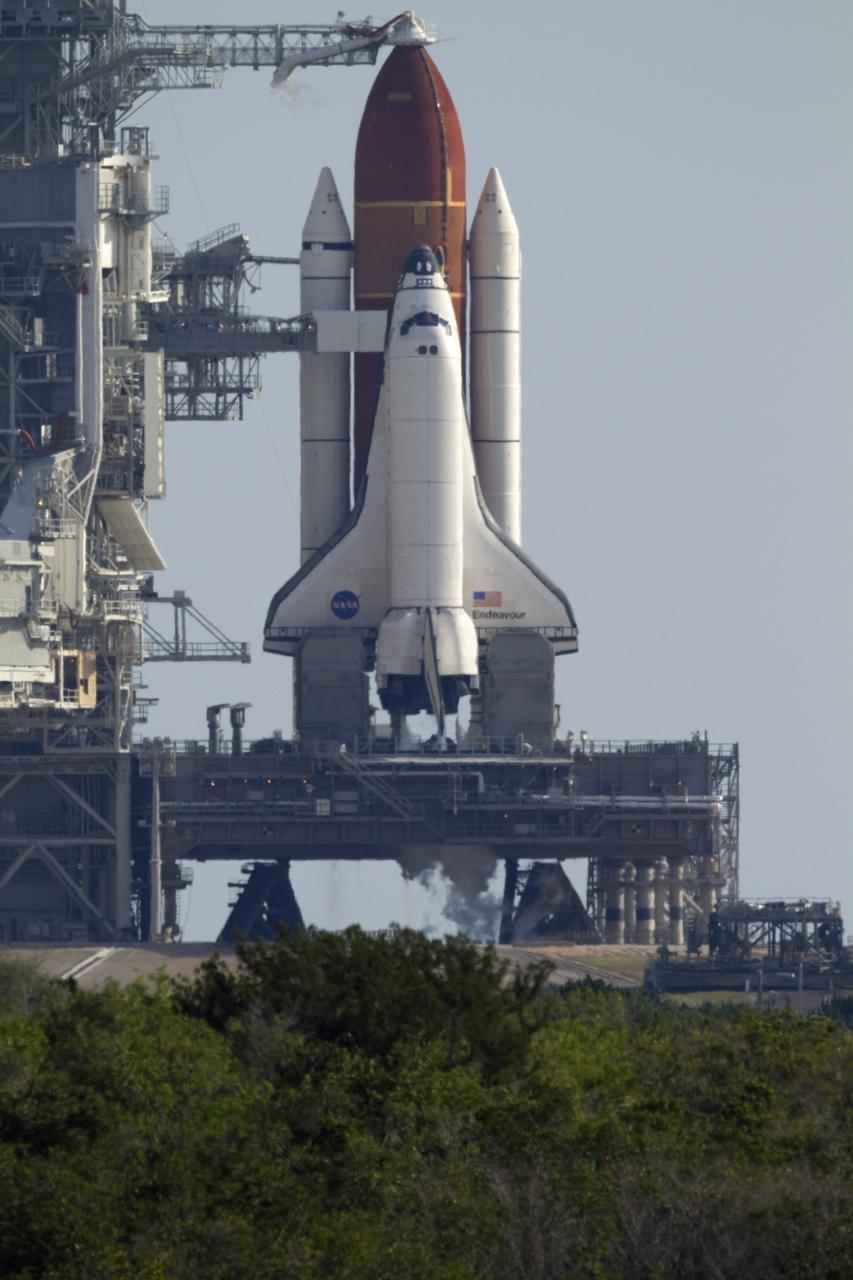

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines are ready to be ignited for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kenny Allen

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
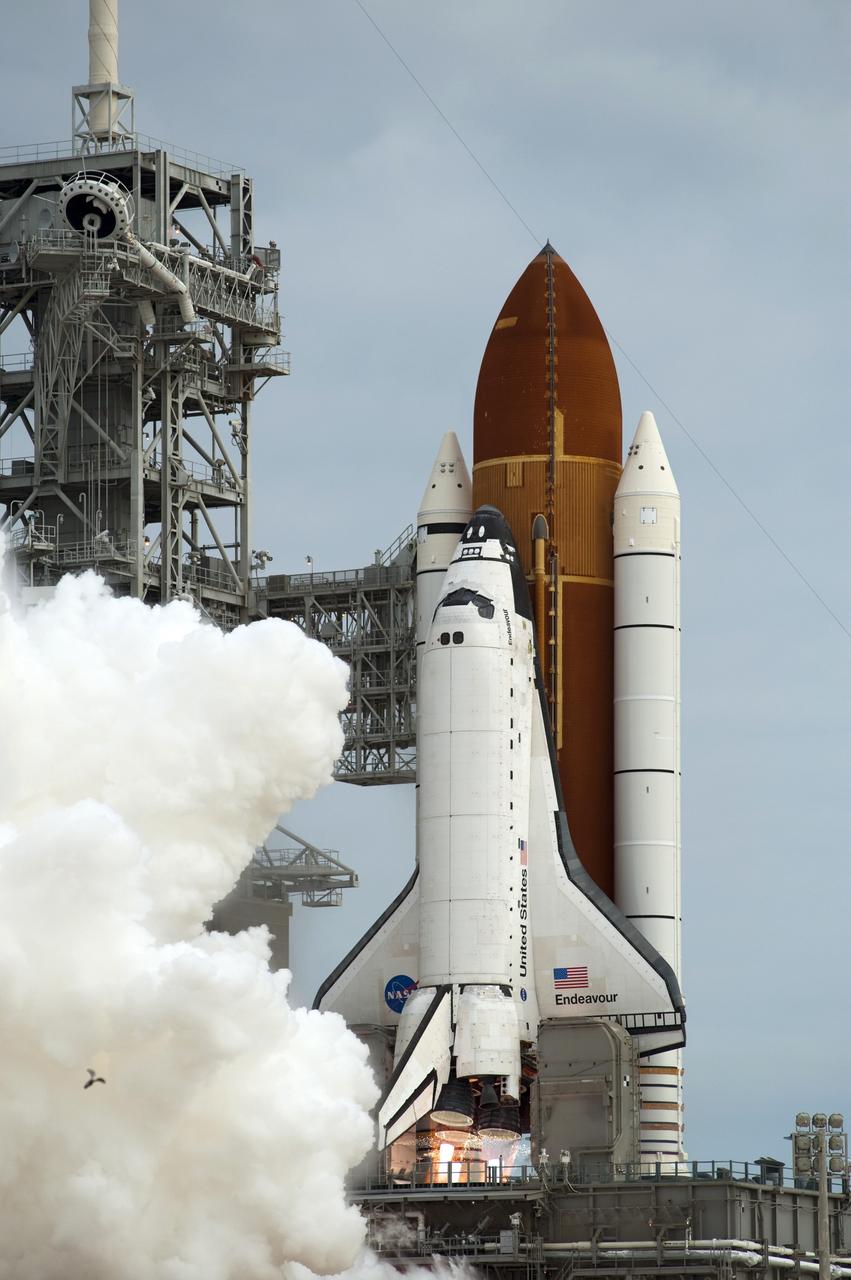

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
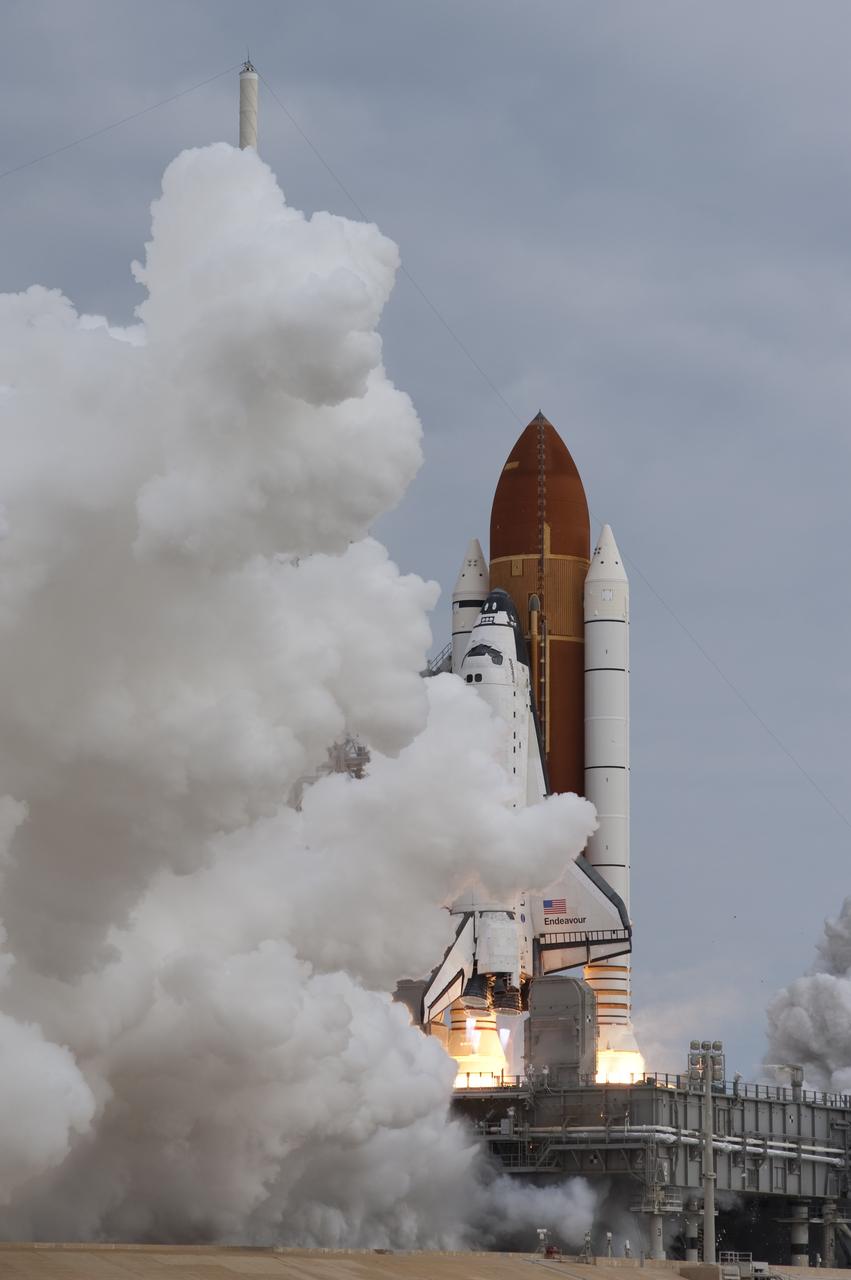

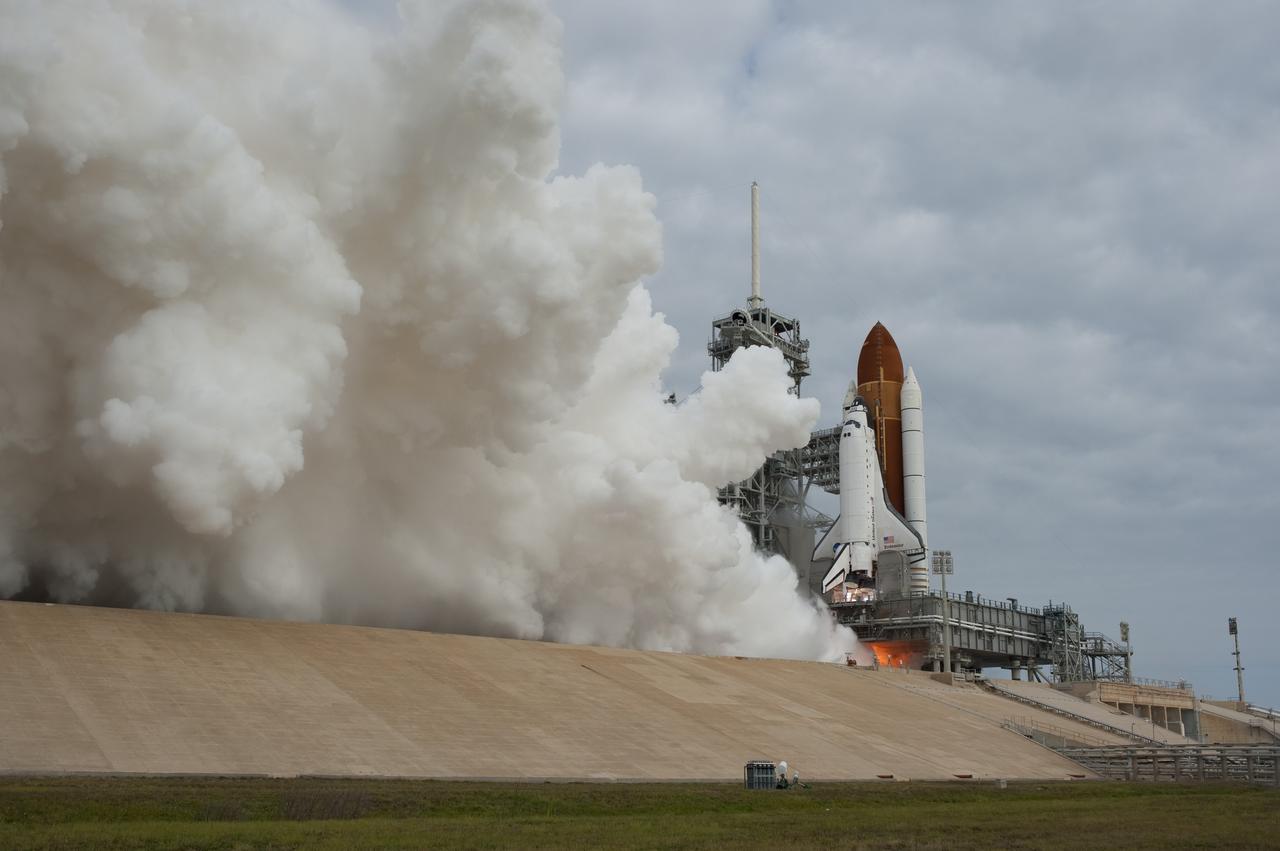
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A cloud of steam and smoke emerge as space shuttle Endeavour's main engines ignite for liftoff at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
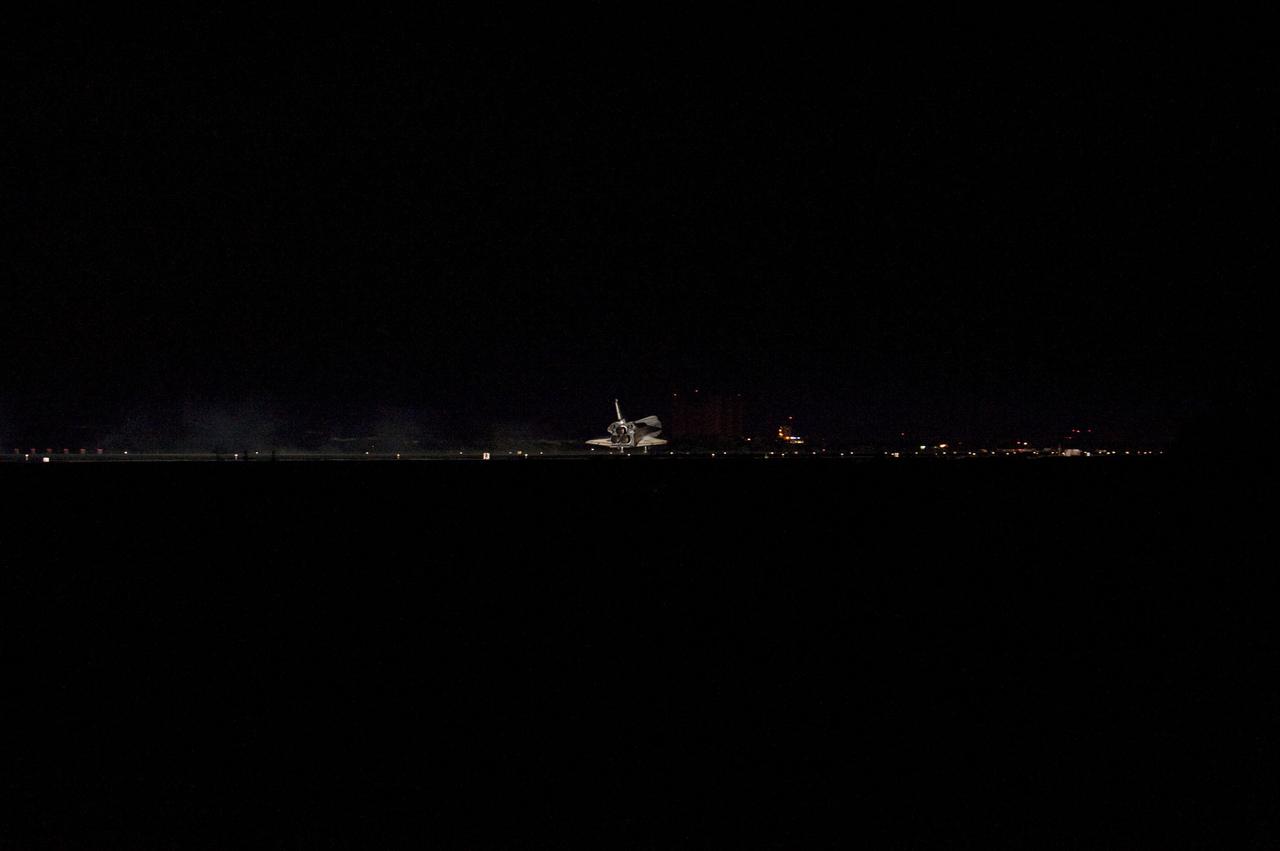

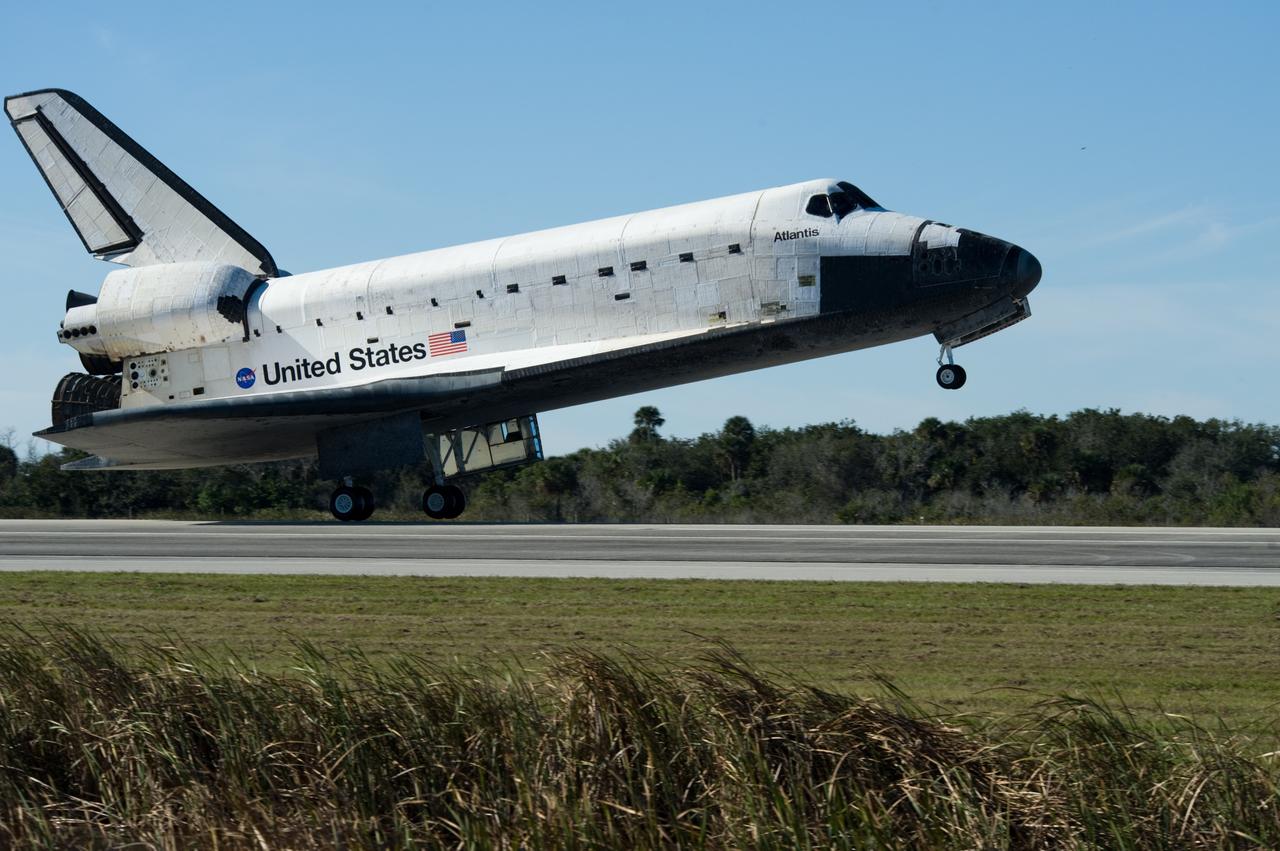
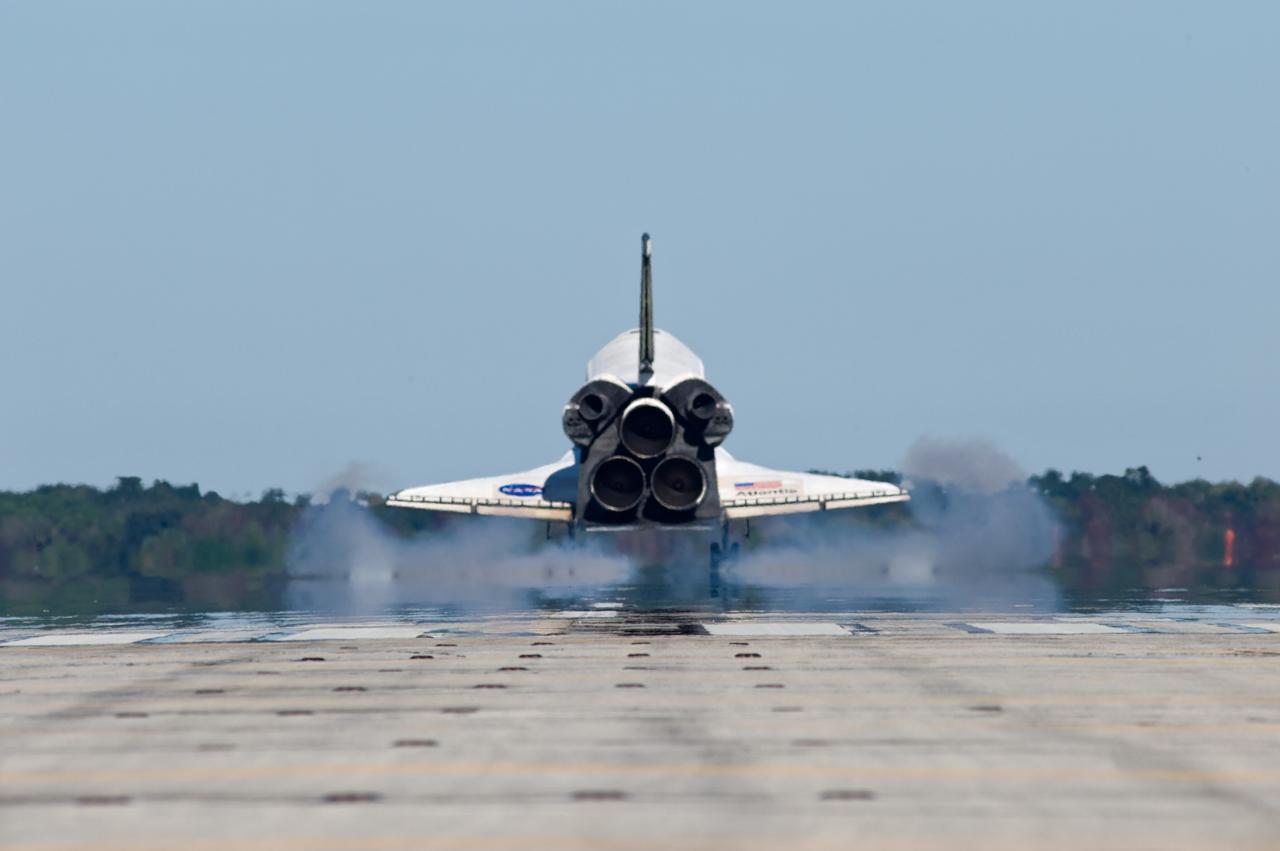
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis' three main engines glow a red hue in the spacecraft's tail end as it touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. On board are STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies in the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Atlantis' three main engines glow a red hue in the spacecraft's tail end as it touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. On board are STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies in the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph
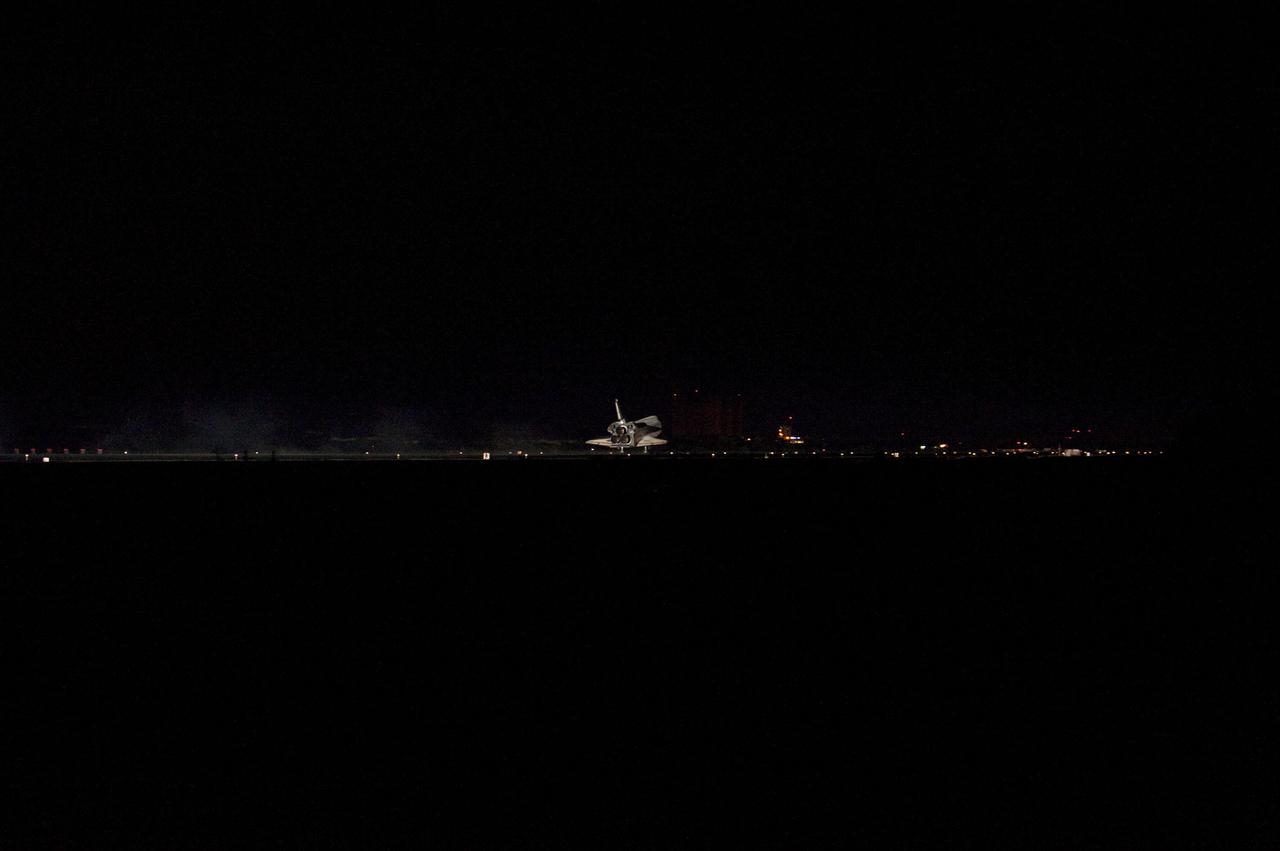

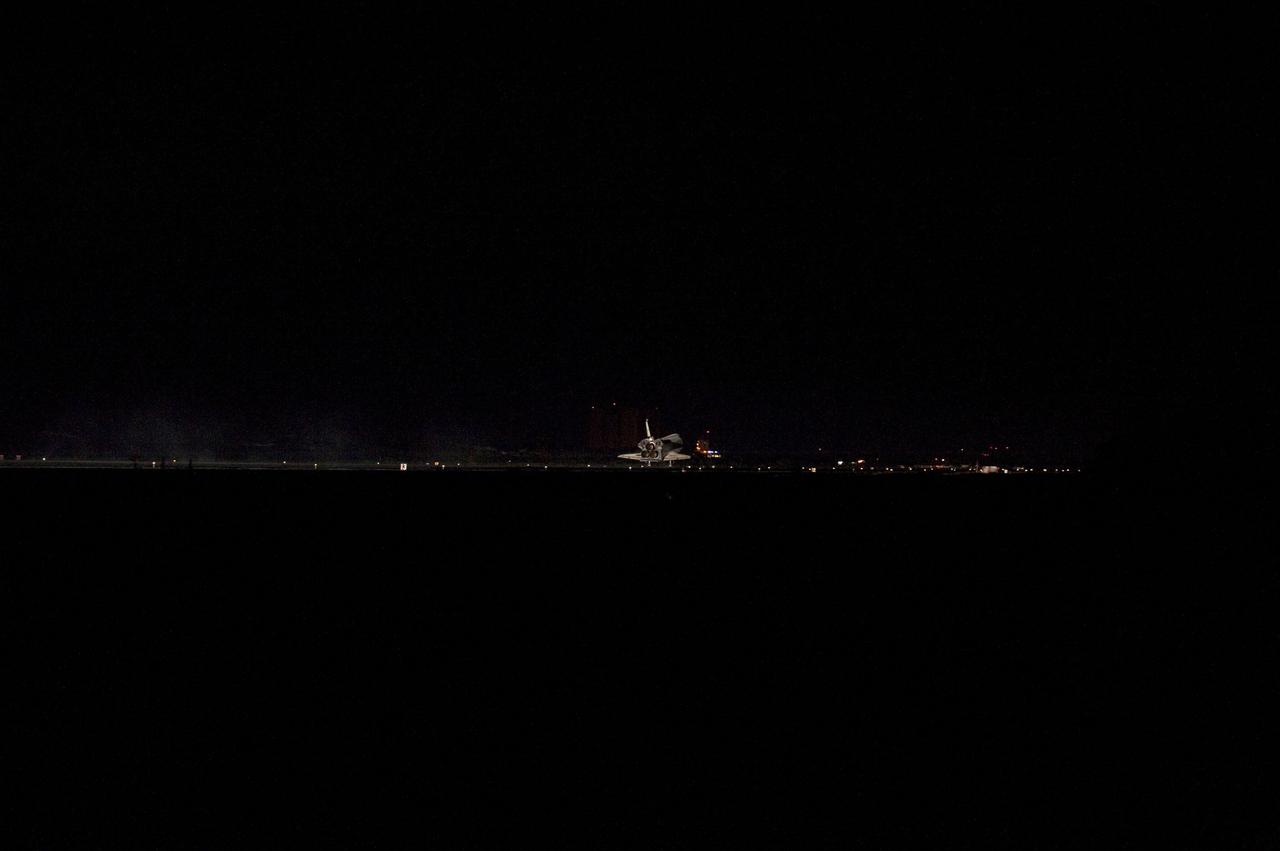
STS135-S-183 (21 July 2011) --- Space shuttle Atlantis' three main engines glow a red hue in the spacecraft's tail end as it touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. (EDT) on July 21, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, STS-135 commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies in the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. Photo credit: NASA
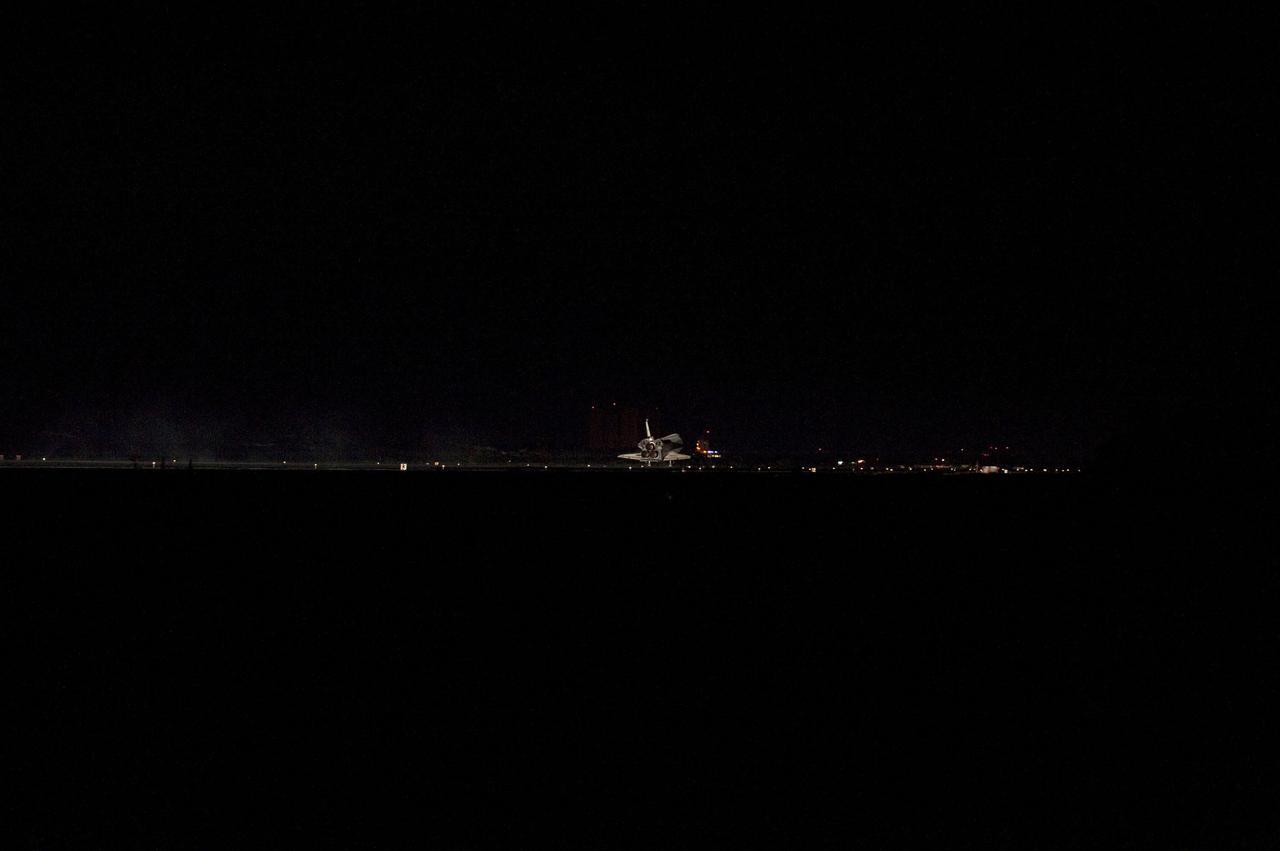

STS135-S-184 (21 July 2011) --- Space shuttle Atlantis' three main engines glow a red hue in the spacecraft's tail end as it touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Securing the space shuttle fleet's place in history, Atlantis marked the 26th nighttime landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program and the 78th landing at Kennedy. Main gear touchdown was at 5:57:00 a.m. (EDT) on July 21, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 5:57:20 a.m., and wheelstop at 5:57:54 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Chris Ferguson, STS-135 commander; Doug Hurley, pilot; Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, both mission specialists. On the 37th shuttle mission to the International Space Station, STS-135 delivered more than 9,400 pounds of spare parts, equipment and supplies in the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module that will sustain station operations for the next year. STS-135 was the 33rd and final flight for Atlantis, which has spent 307 days in space, orbited Earth 4,848 times and traveled 125,935,769 miles. Photo credit: NASA
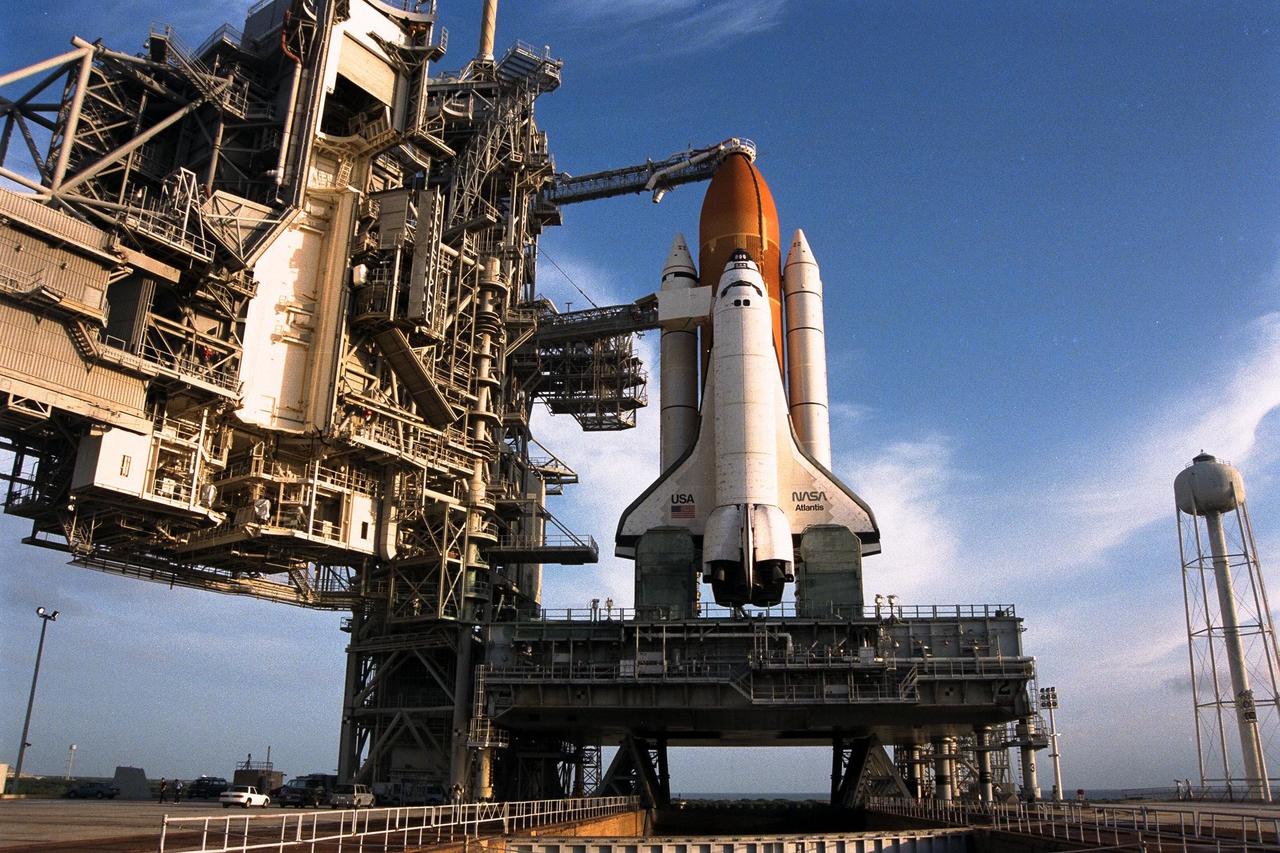

With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, at left, the Space Shuttle Atlantis undergoes final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39A for the STS-86 mission. One of the final steps will be to load the external tank with approximately 500,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen for fueling the orbiter’s three main engines. STS-86 is slated to be the seventh docking of the Space Shuttle with the Russian Space Station Mir. Liftoff is targeted for Sept. 25 at 10:34 p.m. EDT during a preferred launch window which lasts six minutes and 45 seconds. Seven crew members will lift off for the scheduled 10-day flight. One of those crew members, David A. Wolf, will transfer to the Mir for an approximate four-month stay. He will replace U.S. astronaut C. Michael Foale, who will return to Earth with the remainder of the STS86 crew. Foale has been on the Russian space station since mid-May
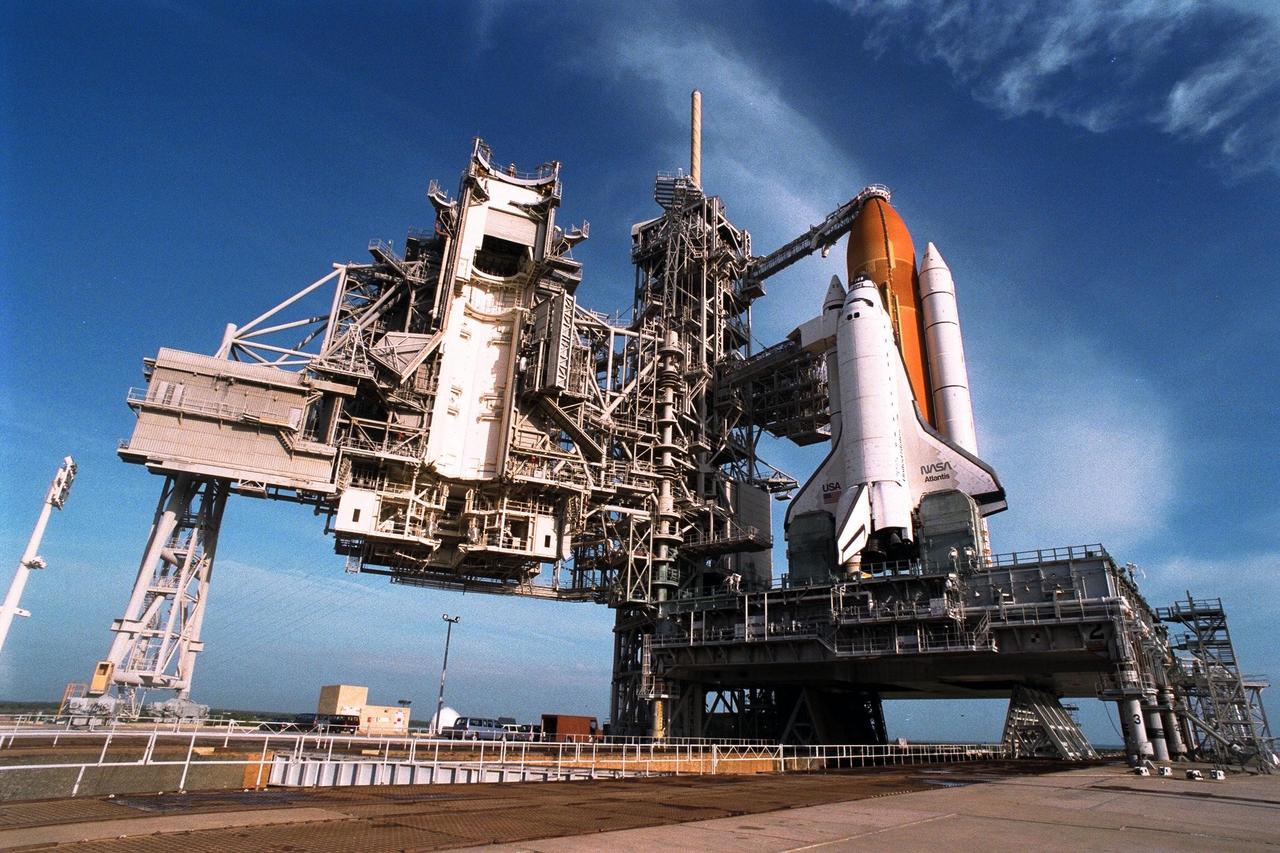

With the Rotating Service Structure rolled back, at left, the Space Shuttle Atlantis undergoes final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39A for the STS-86 mission. One of the final steps will be to load the external tank with approximately 500,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen for fueling the orbiter’s three main engines. STS-86 is slated to be the seventh docking of the Space Shuttle with the Russian Space Station Mir. Liftoff is targeted for Sept. 25 at 10:34 p.m. EDT during a preferred launch window which lasts six minutes and 45 seconds. Seven crew members will lift off for the scheduled 10-day flight. One of those crew members, David A. Wolf, will transfer to the Mir for an approximate four-month stay. He will replace U.S. astronaut C. Michael Foale, who will return to Earth with the remainder of the STS86 crew. Foale has been on the Russian space station since mid-May

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A team of aerospace technicians accompanies space shuttle Discovery as it is towed for the final time from the Launch Complex 39 area to the Shuttle Landing Facility or SLF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A tail cone has been installed over Discovery’s three replica shuttle main engines to reduce aerodynamic drag and turbulence during its upcoming ferry flight. At the SLF, Discovery will be hoisted onto a Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, with the aid of a mate-demate device. The SCA, a modified Boeing 747 jet airliner, is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on permanent public display in the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Smoke and steam billow around space shuttle Discovery and Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, as the shuttle's solid rocket boosters and main engines ignite for lift off, embarking on its final flight, the STS-133 mission. Launch to the International Space Station was at 4:53 p.m. EST. Discovery and its six-member crew will deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. Discovery is flying on its 39th mission and is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This is the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. For more information on the STS-133 mission, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts133/. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
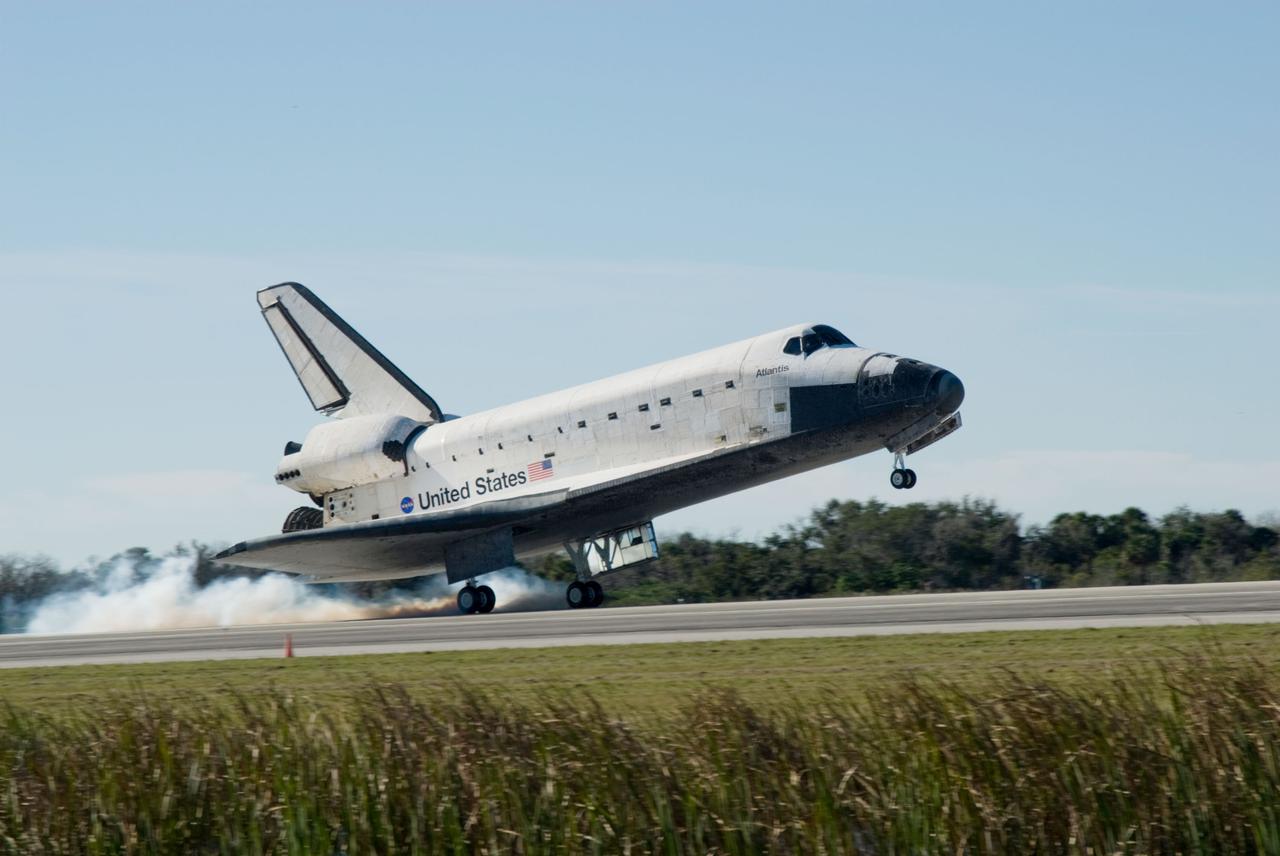

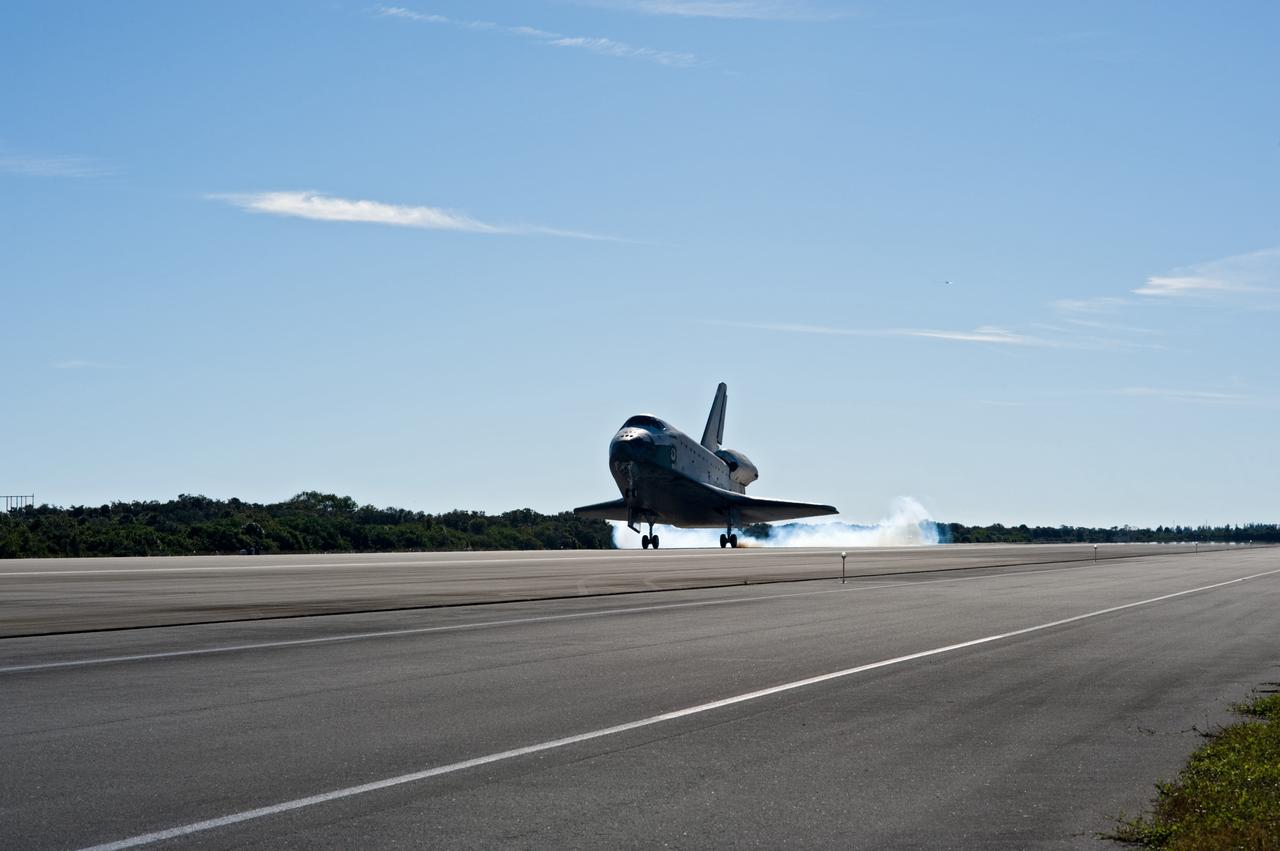
PHOTO CREDIT: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EDT. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Carl Winebarger

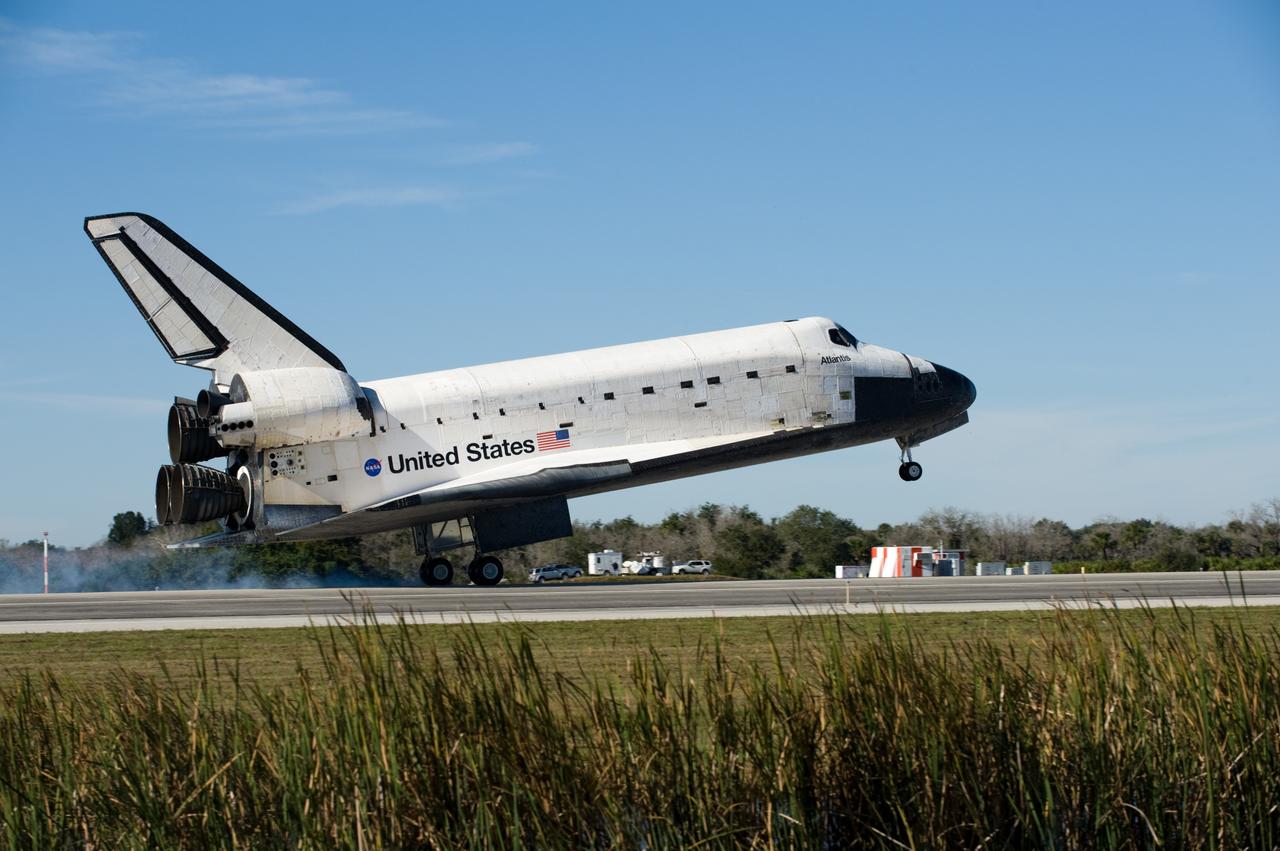
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Atlantis' main landing gear tires near contact with Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Carl Winebarger

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell and Rick Prickett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The tires of space shuttle Atlantis' main landing gear make contact with Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Thomas Farrar Jr.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Touchdown is apparent by the cloud of dust kicked up by space shuttle Atlantis as its main landing gear tires contact Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After 11 days in space, Atlantis' 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission is completed on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell and Rick Prickett
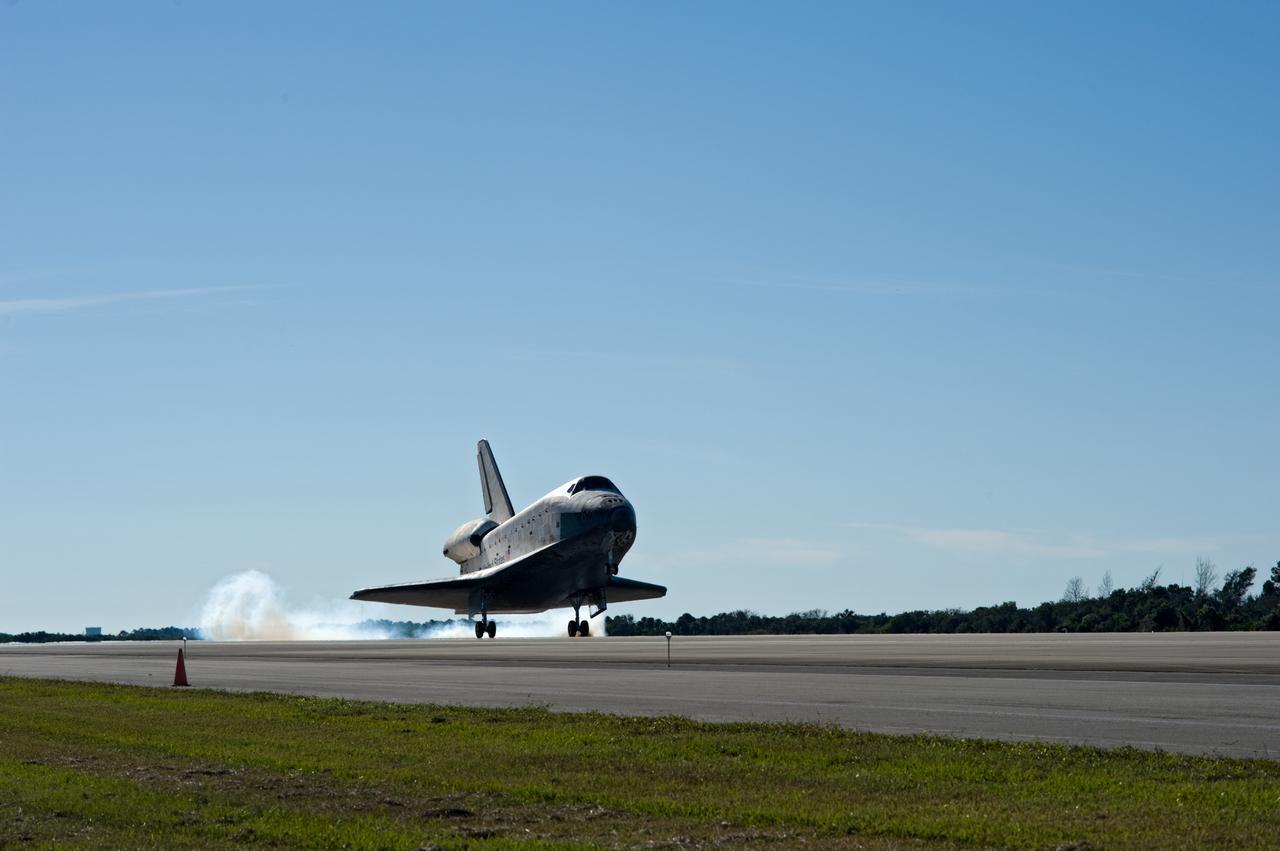

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Touchdown is apparent by the streams of smoke trailing space shuttle Atlantis as its main landing gear tires contact Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After 11 days in space, Atlantis' 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission is completed on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell and Rick Prickett
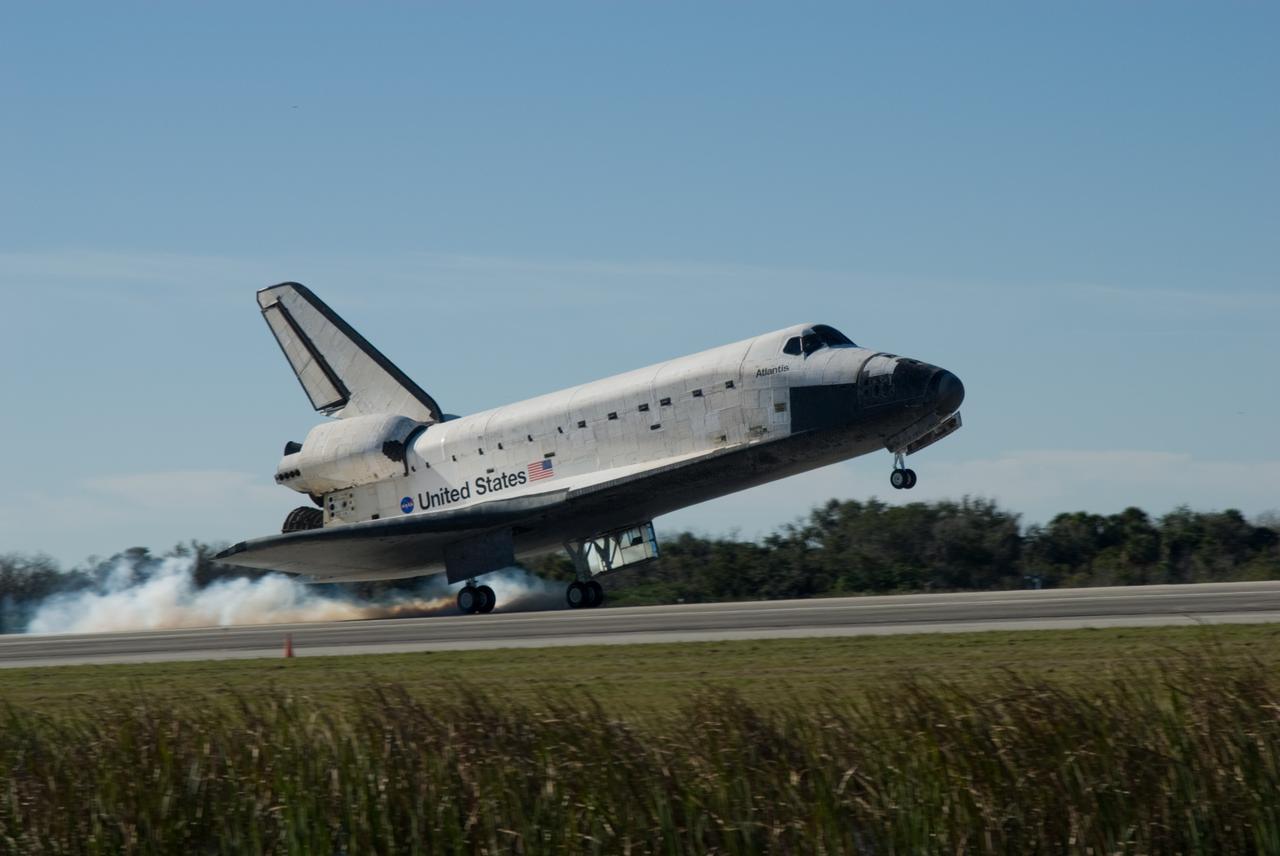

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Atlantis touches down on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after 11 days in space, completing the 4.5-million-mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
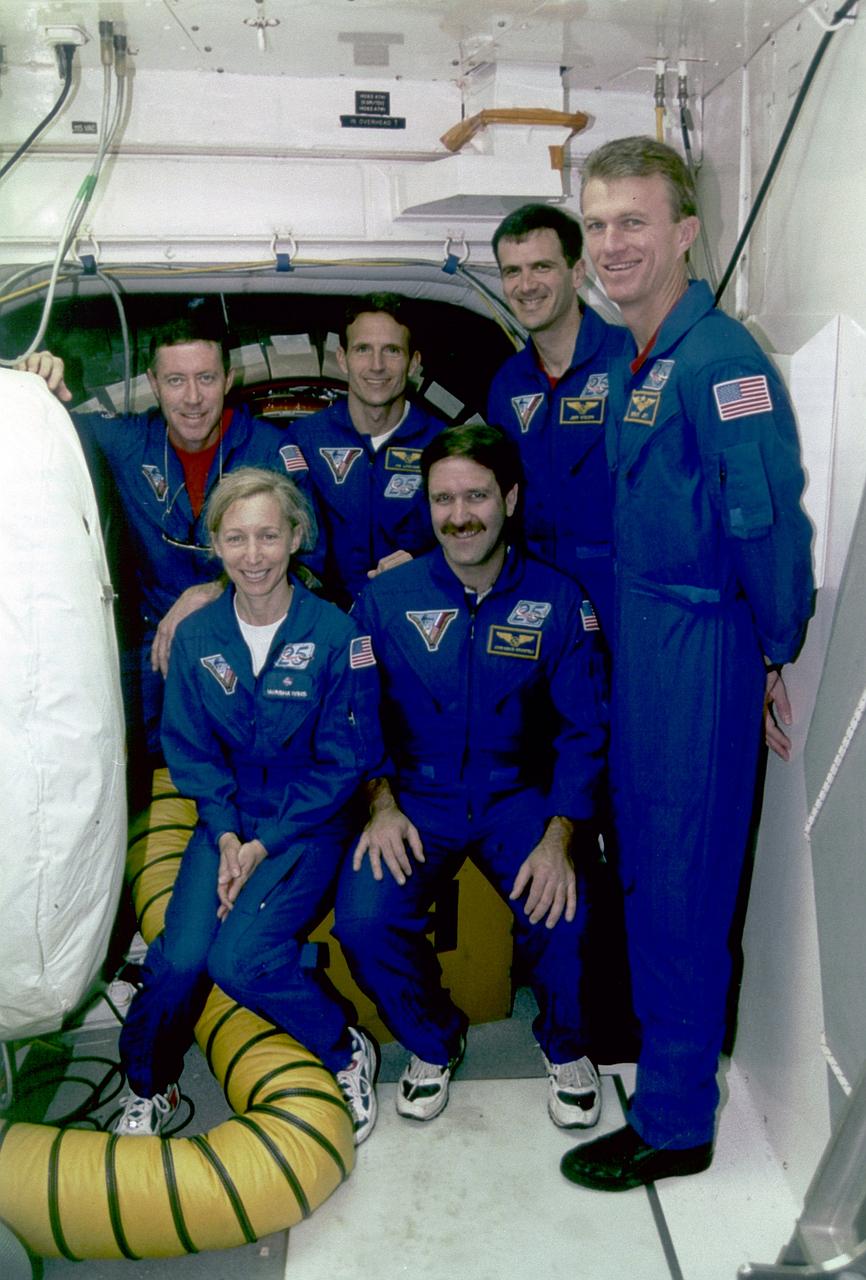

S97-00247 (15 Dec. 1996) --- The STS-81 mission flight crew poses outside the hatch of the space shuttle Atlantis at Launch Pad 39B during a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT represents a simulated final countdown rehearsal that ends just before main engine ignition. The actual launch is now scheduled for Jan. 12, 1997. Pictured (from the left) are astronauts Michael A. Baker, Marsha S. Ivins, Jerry M. Linenger, John M. Grunsfeld, Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff, and Brent W. Jett Jr.
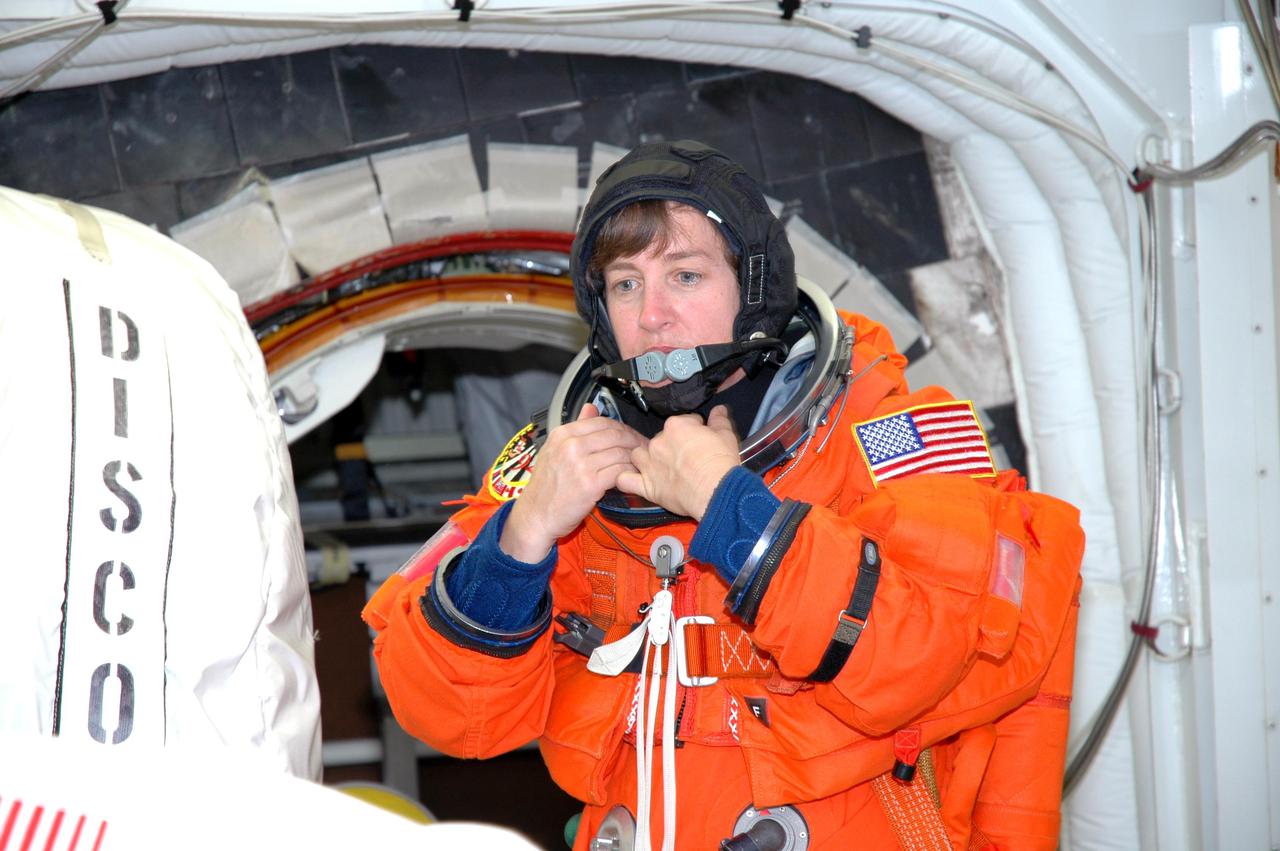

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the White Room on Launch Pad 39B, STS-114 Mission Specialist Wendy Lawrence makes a final adjustment on her launch suit before entering the hatch on Space Shuttle Discovery, behind her. The crew is taking part in a full dress rehearsal for launch, including countdown and culminating in main engine cutoff. The rehearsal is the final part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that the crew has been involved in for three days. TCDT provides the crew of each mission an opportunity to participate in various simulated countdown activities, including equipment familiarization and emergency egress training. STS-114 is the first Return to Flight mission to the International Space Station. The launch window extends July 13 through July 31.
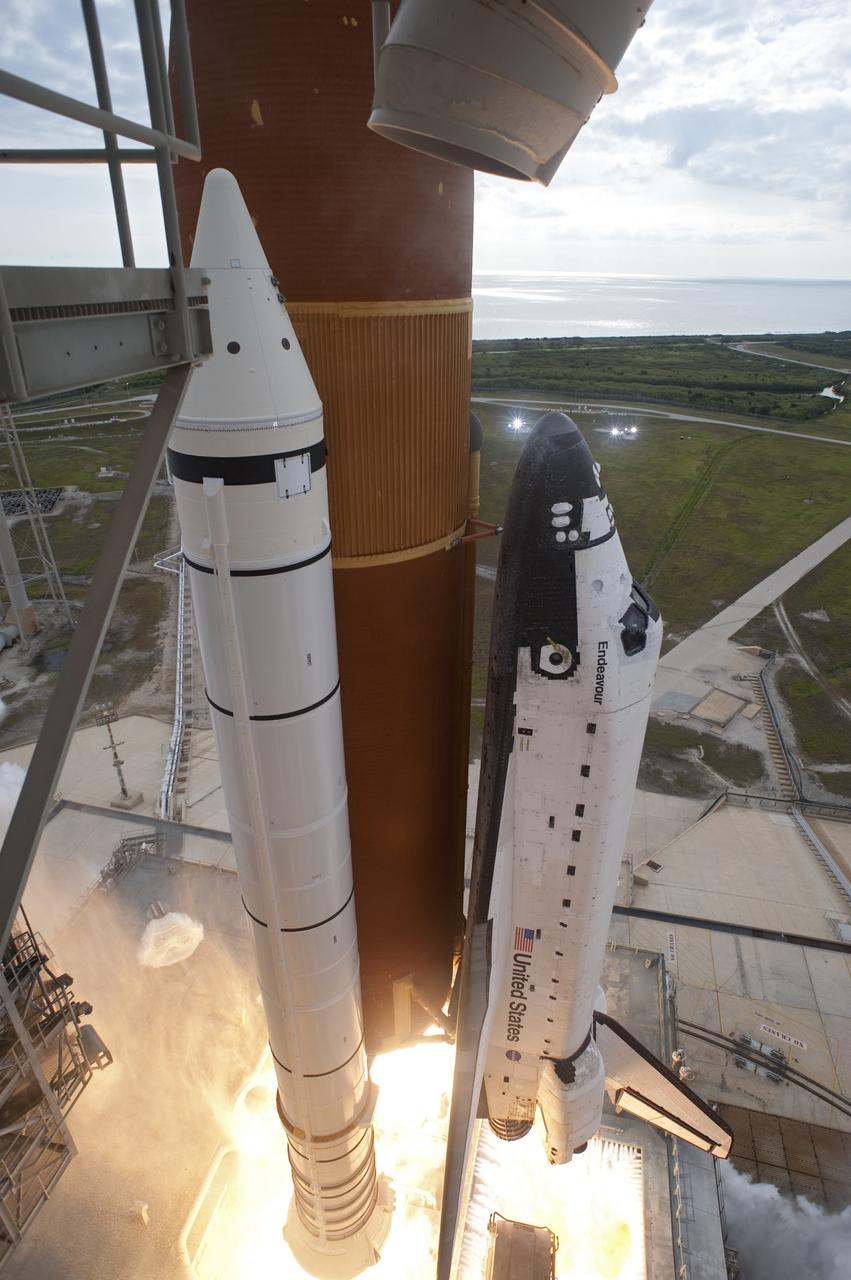

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst to life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
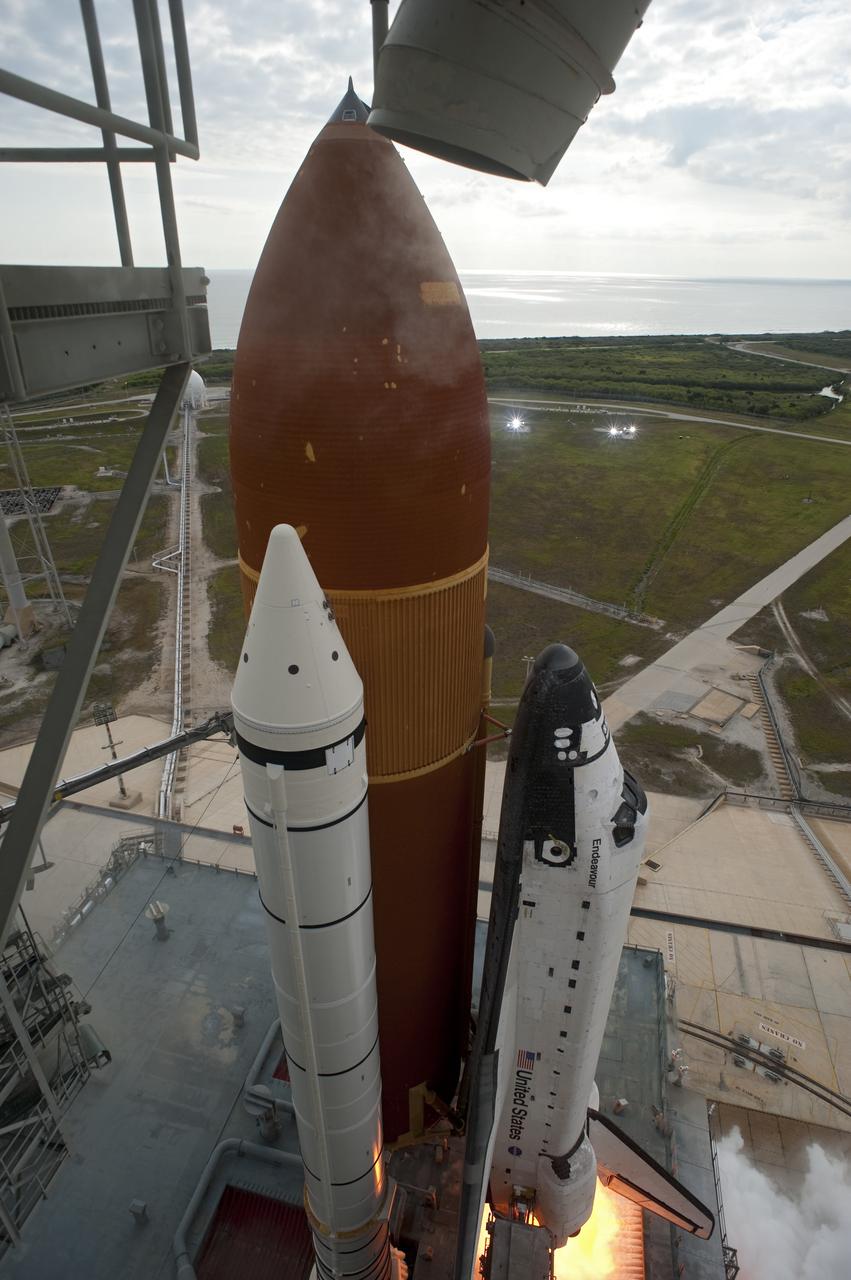

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst to life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
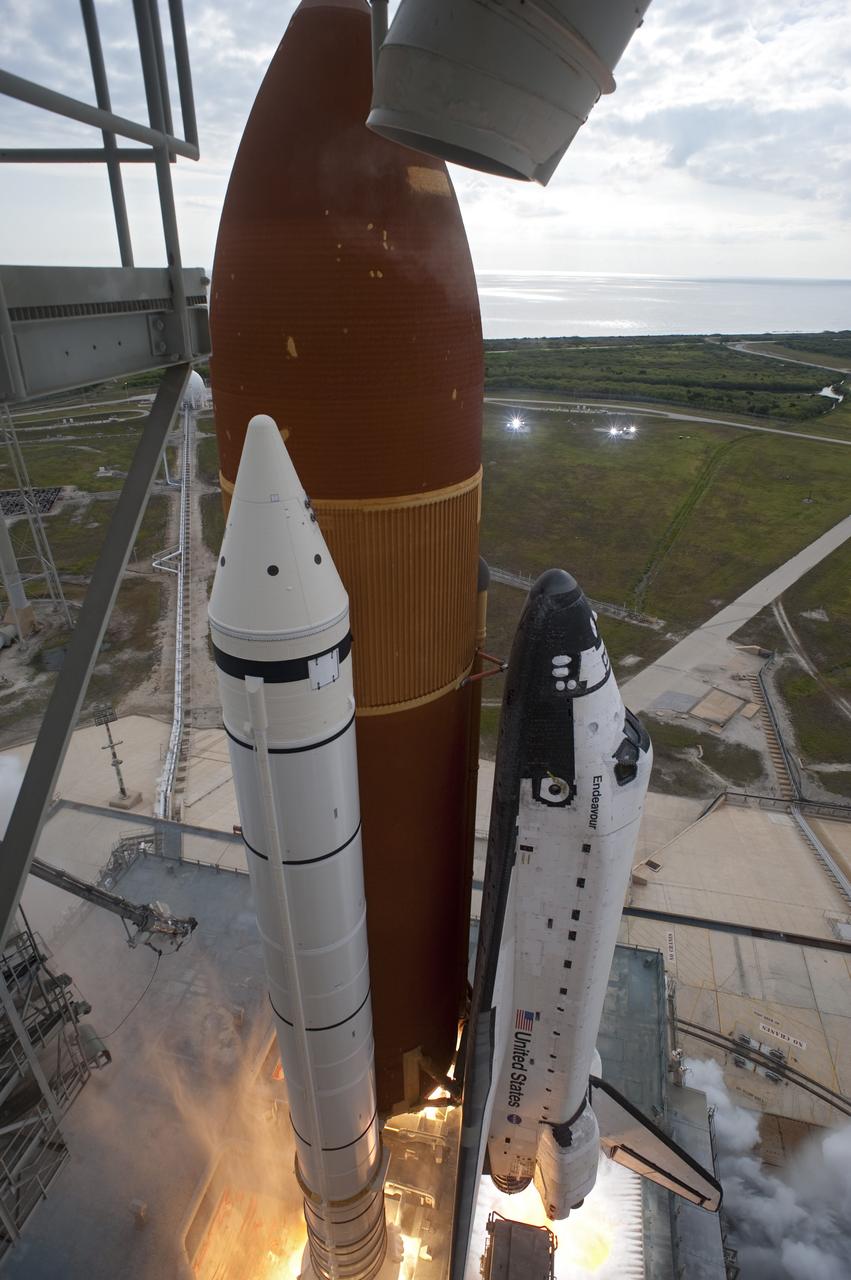

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst to life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
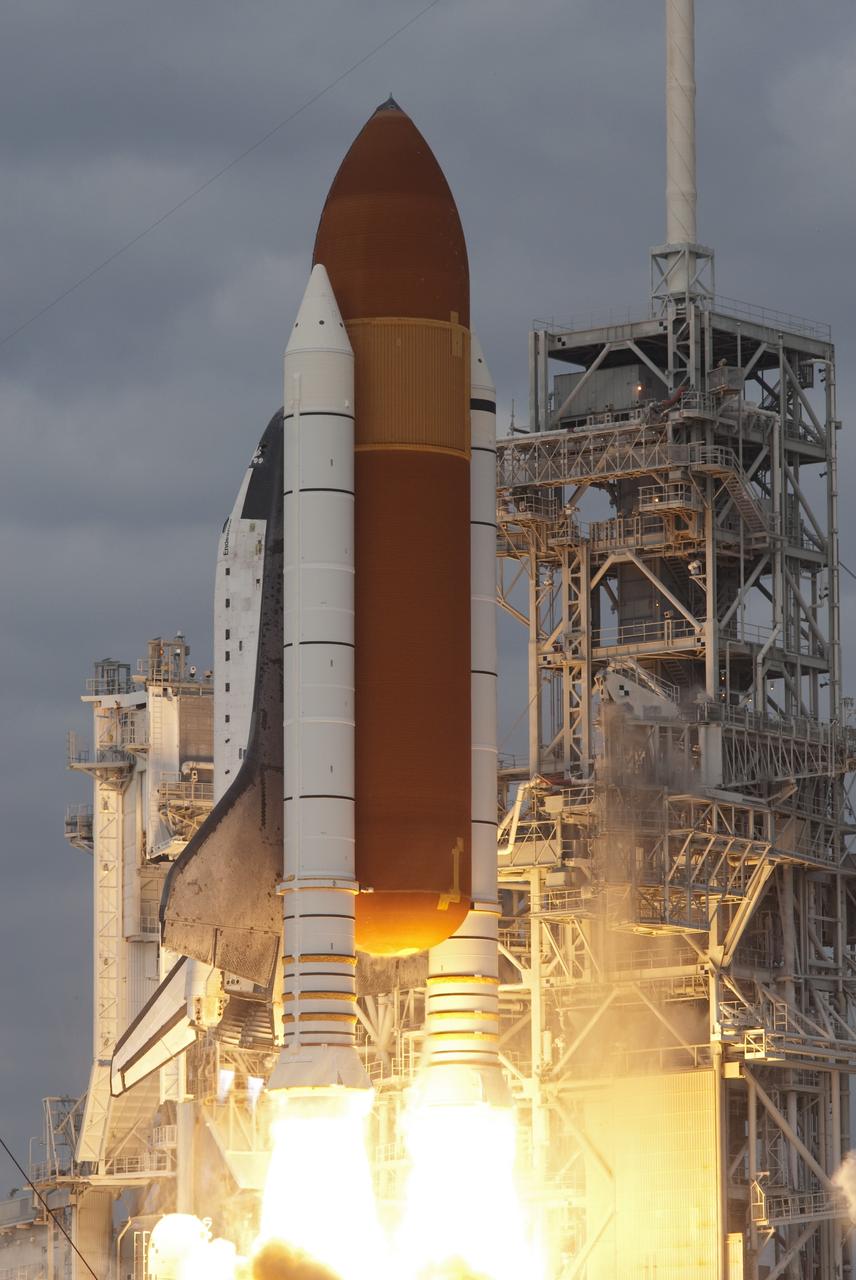

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst to life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer and Mike Gayle
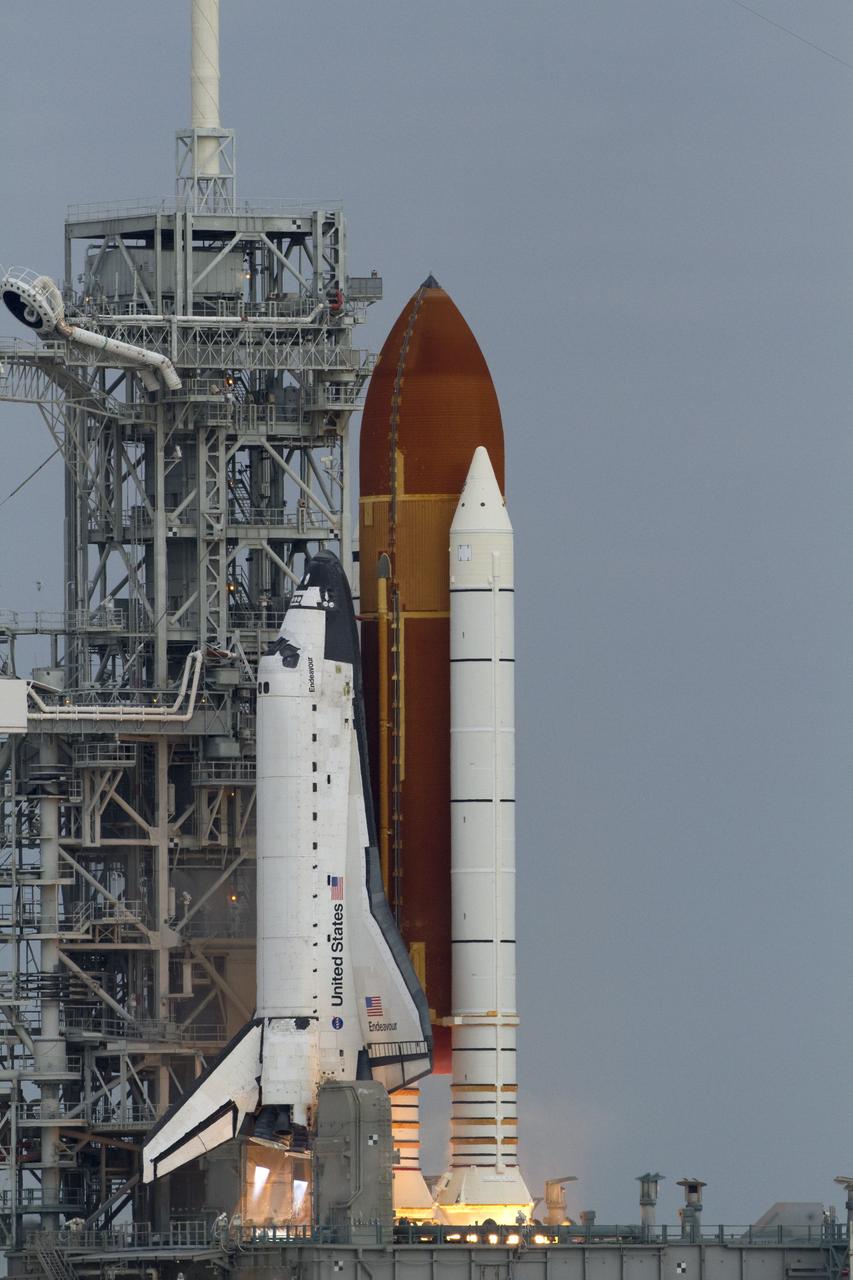

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst into life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kenny Allen and George Roberts
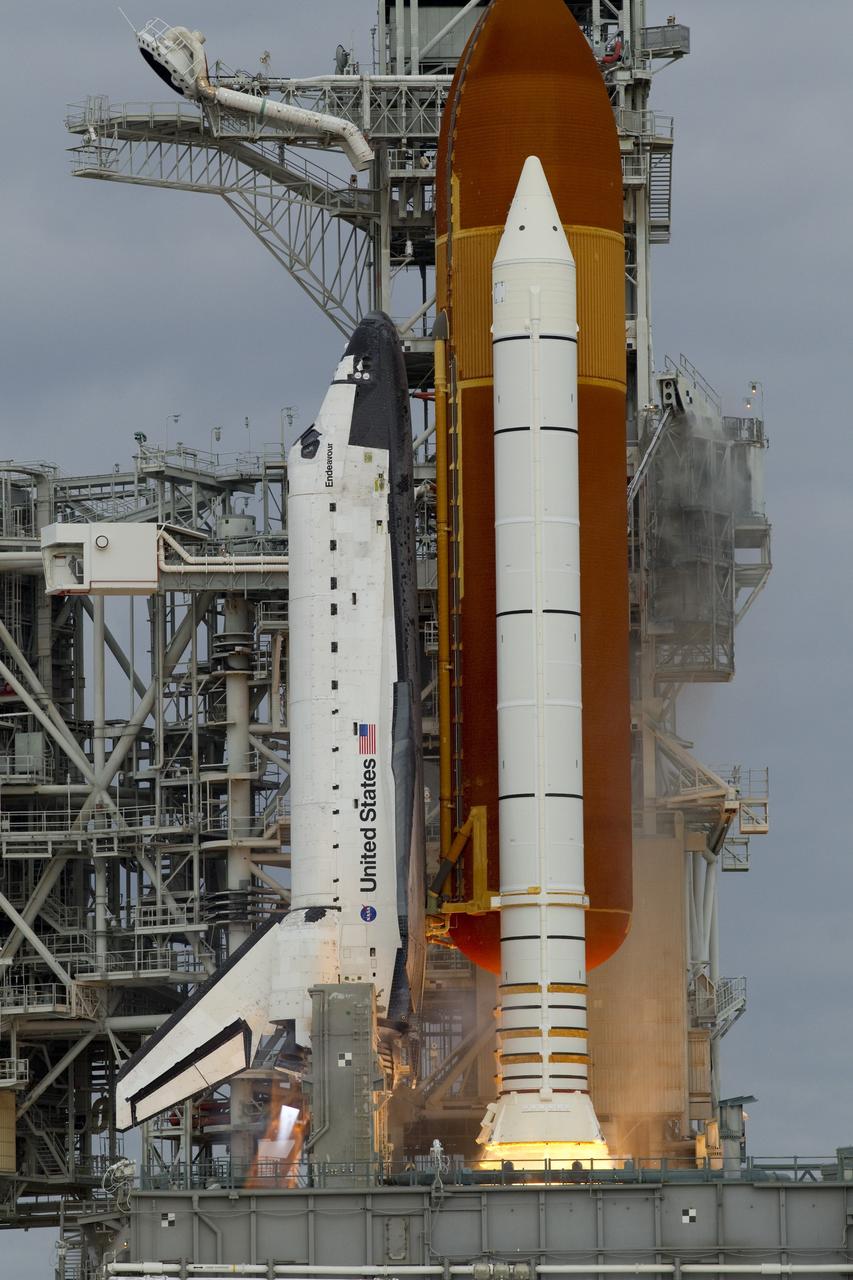

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst into life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/George Roberts and Mike Kerley
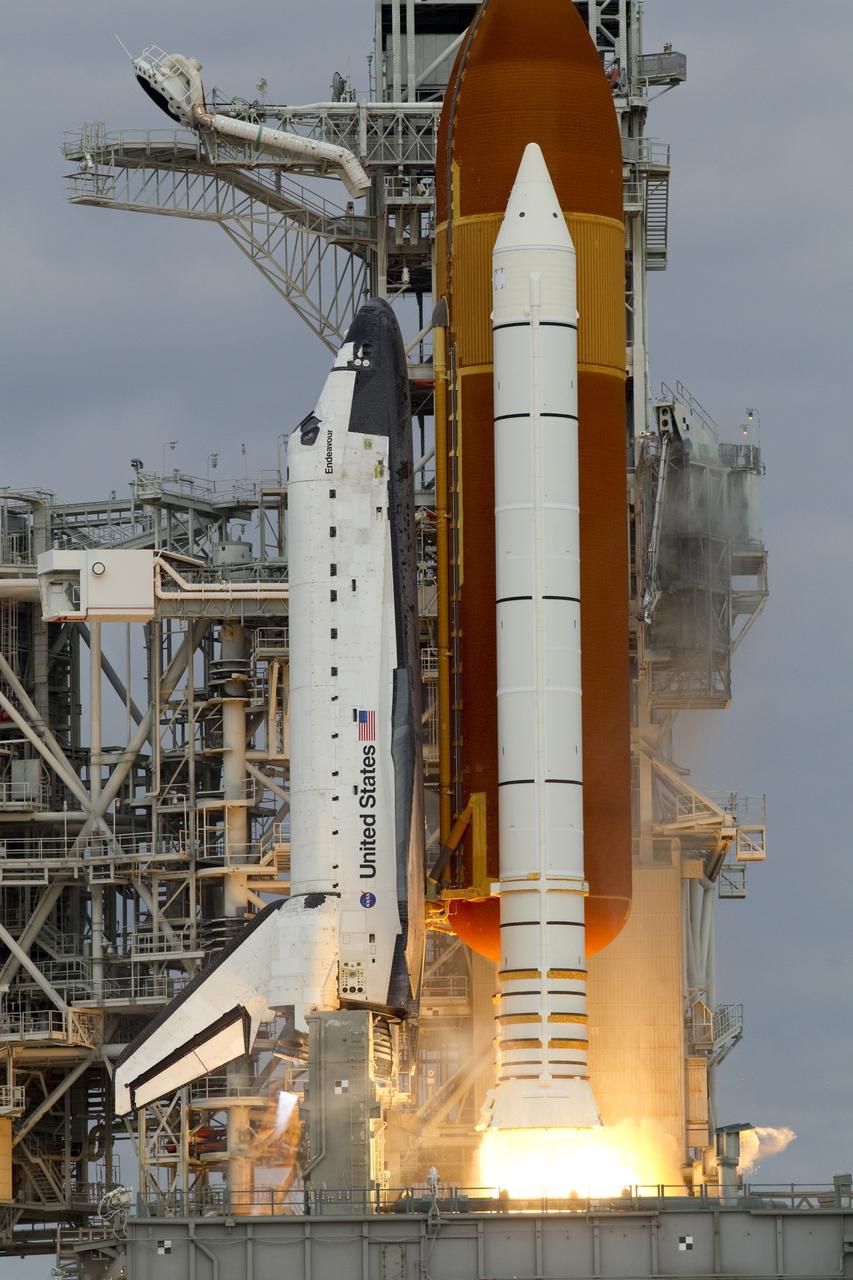

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst into life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/George Roberts and Mike Kerley
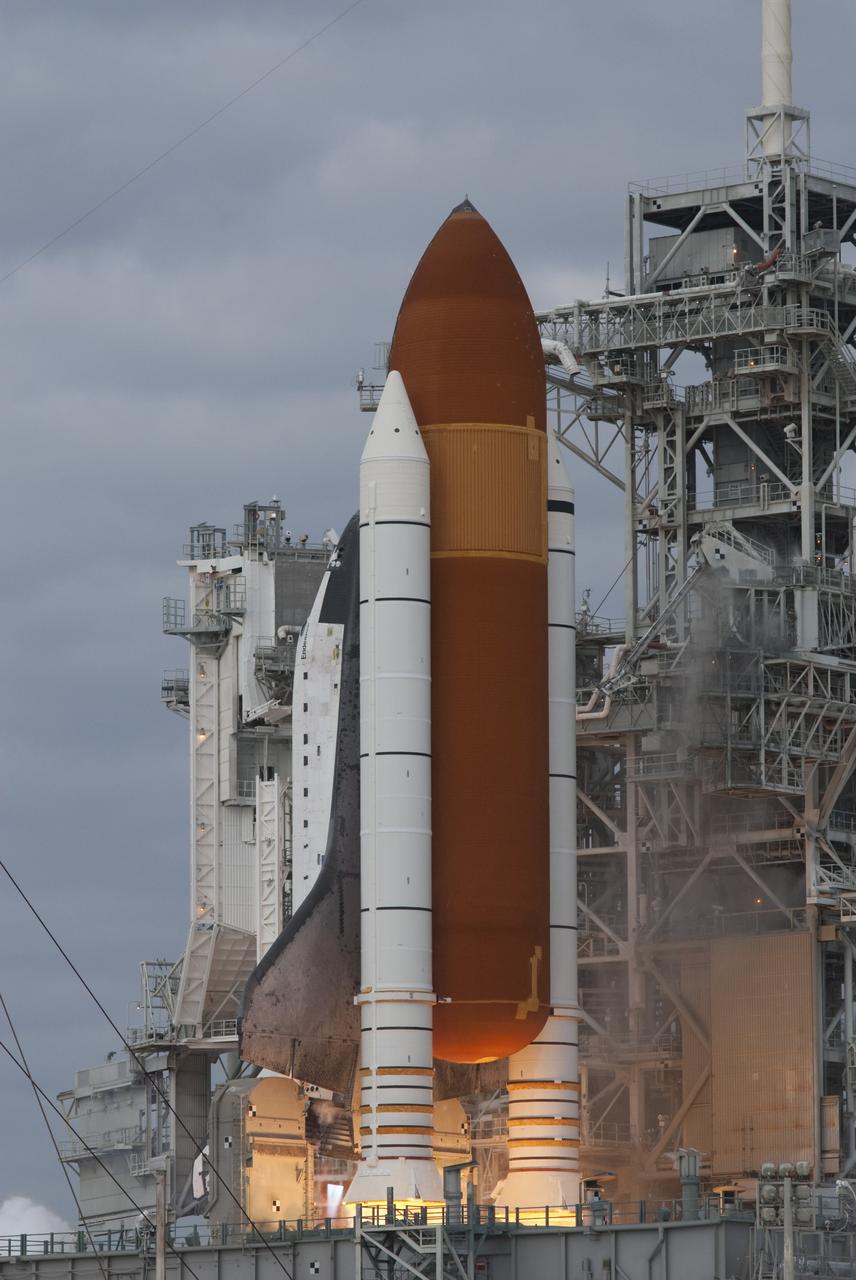

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst to life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer and Mike Gayle
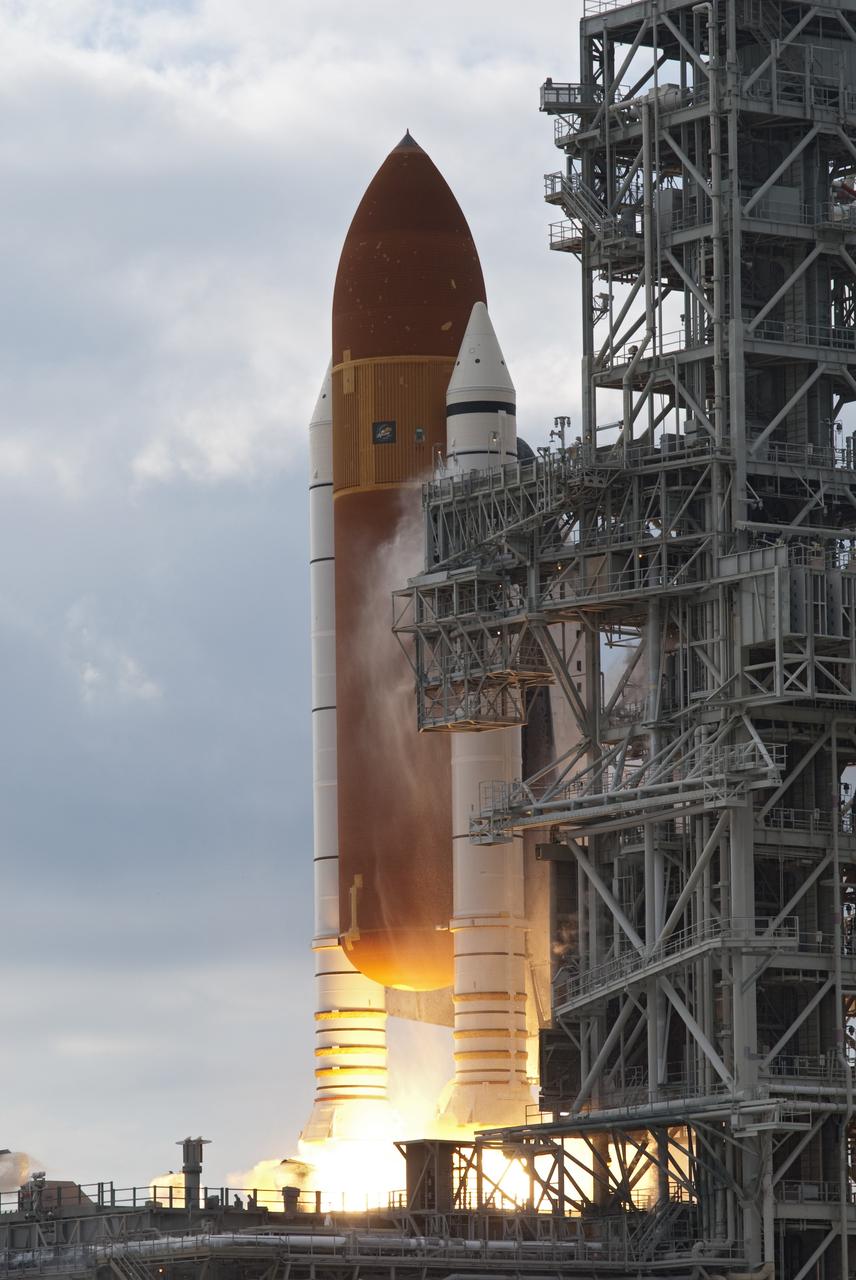

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst to life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/George Roberts and Tom Farrar
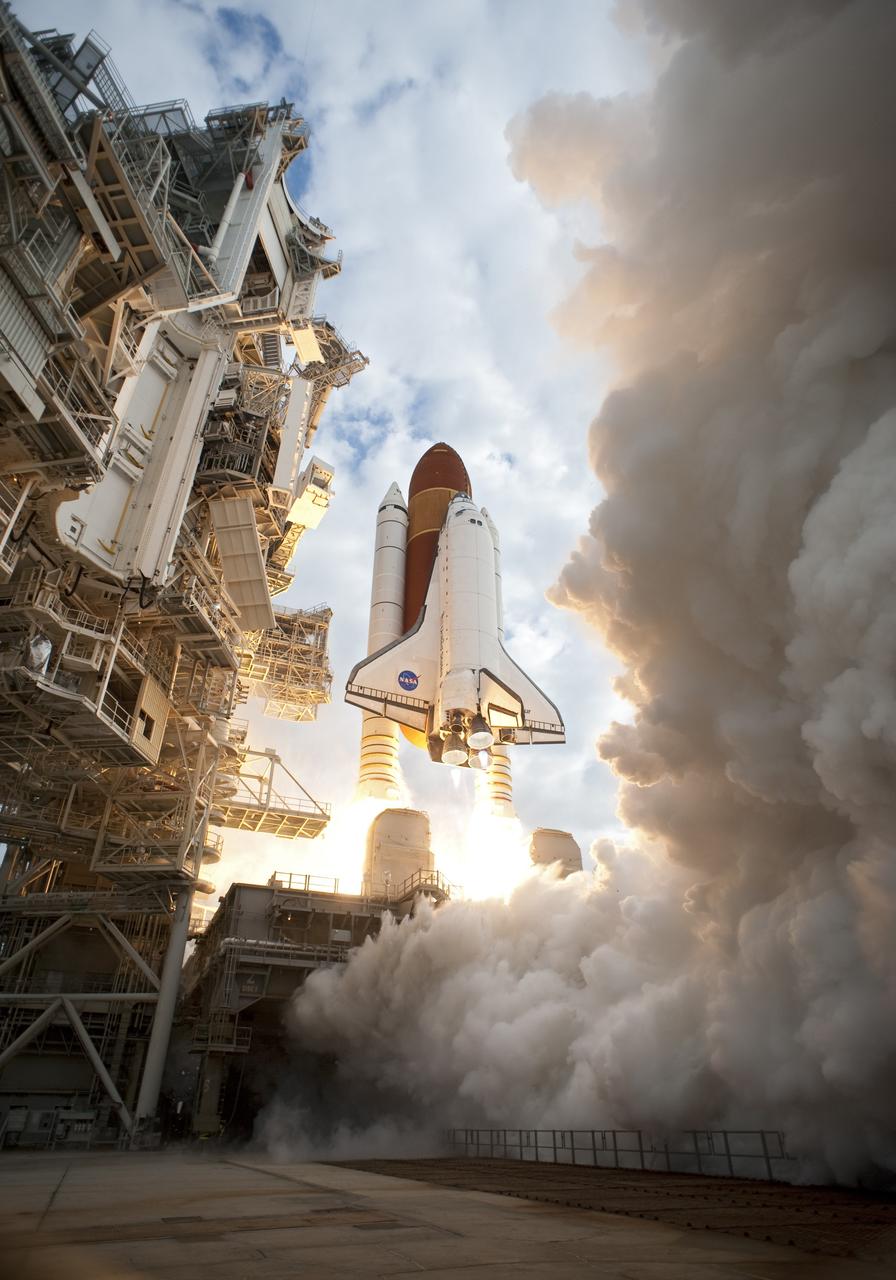

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst to life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
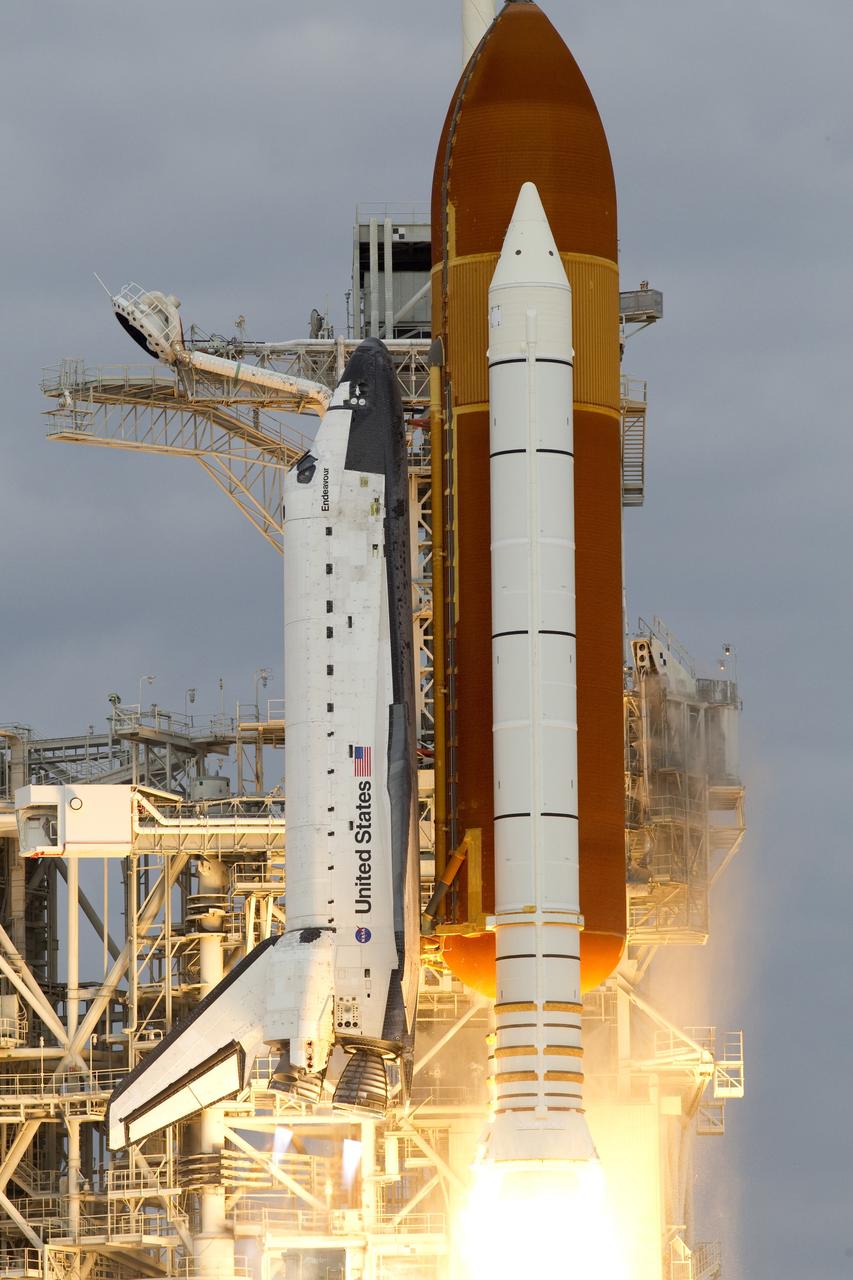

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space shuttle Endeavour's main engines and solid rocket boosters burst into life lifting the shuttle from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/George Roberts and Mike Kerley
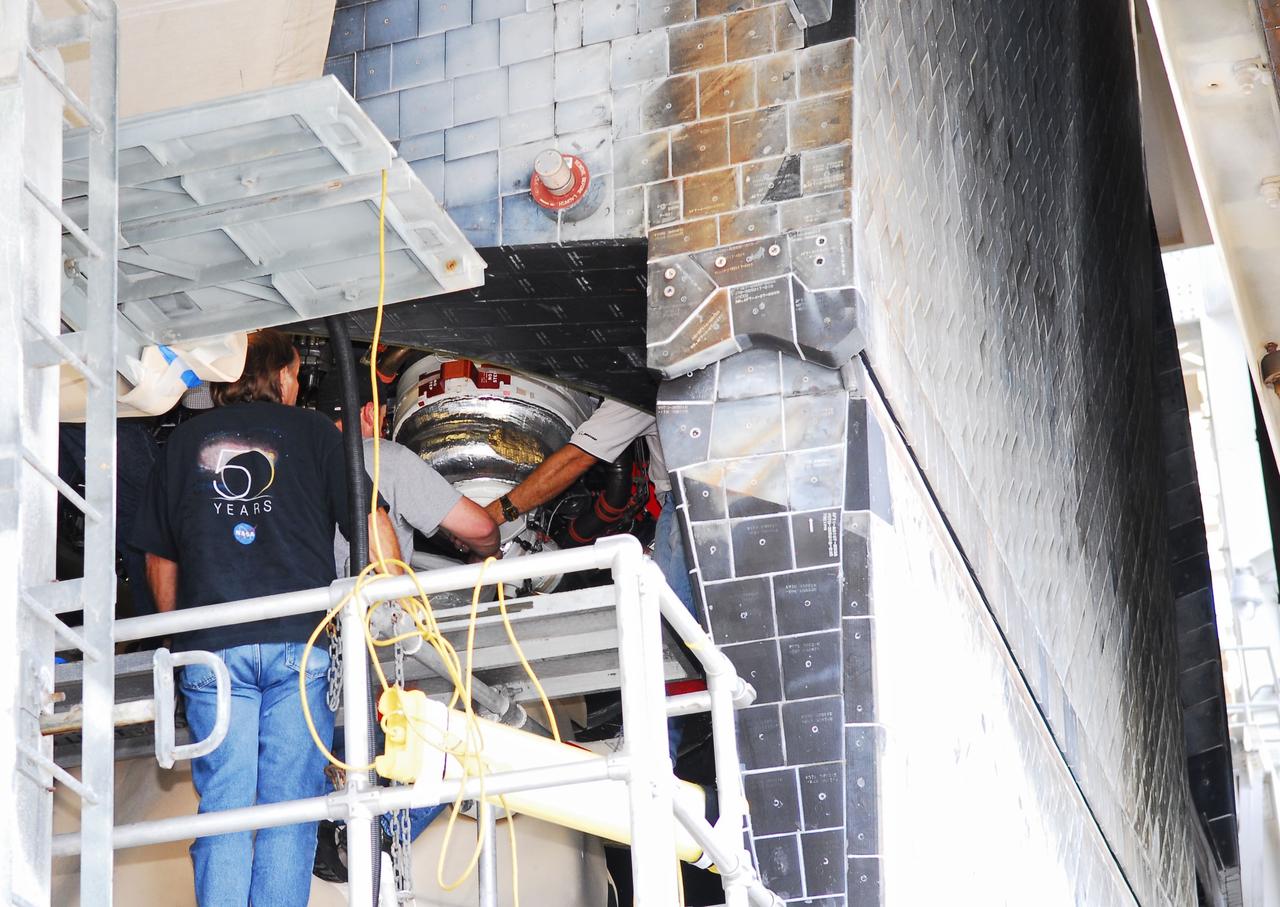

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a tanking test on June 15 at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, there was an apparent liquid hydrogen leak in the main fuel valve in Atlantis' space shuttle main engine No. 3. Technicians now are replacing the suspect valve and a leak check of the valve and associated systems will be conducted. The work is expected to take about a week, which still would support Atlantis' targeted July 8 launch date. STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
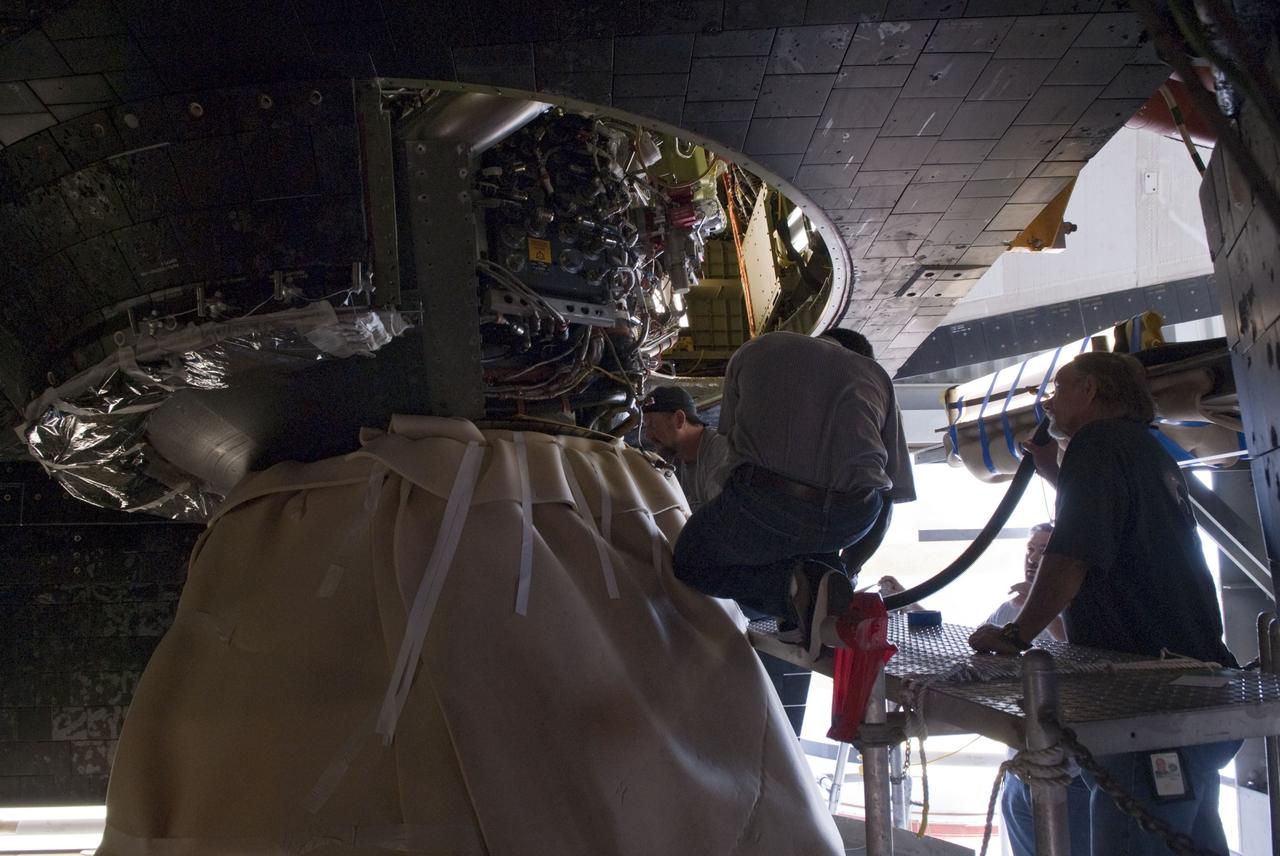

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a tanking test on June 15 at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, there was an apparent liquid hydrogen leak in the main fuel valve in Atlantis' space shuttle main engine No. 3. Technicians now are replacing the suspect valve and a leak check of the valve and associated systems will be conducted. The work is expected to take about a week, which still would support Atlantis' targeted July 8 launch date. STS-135 Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
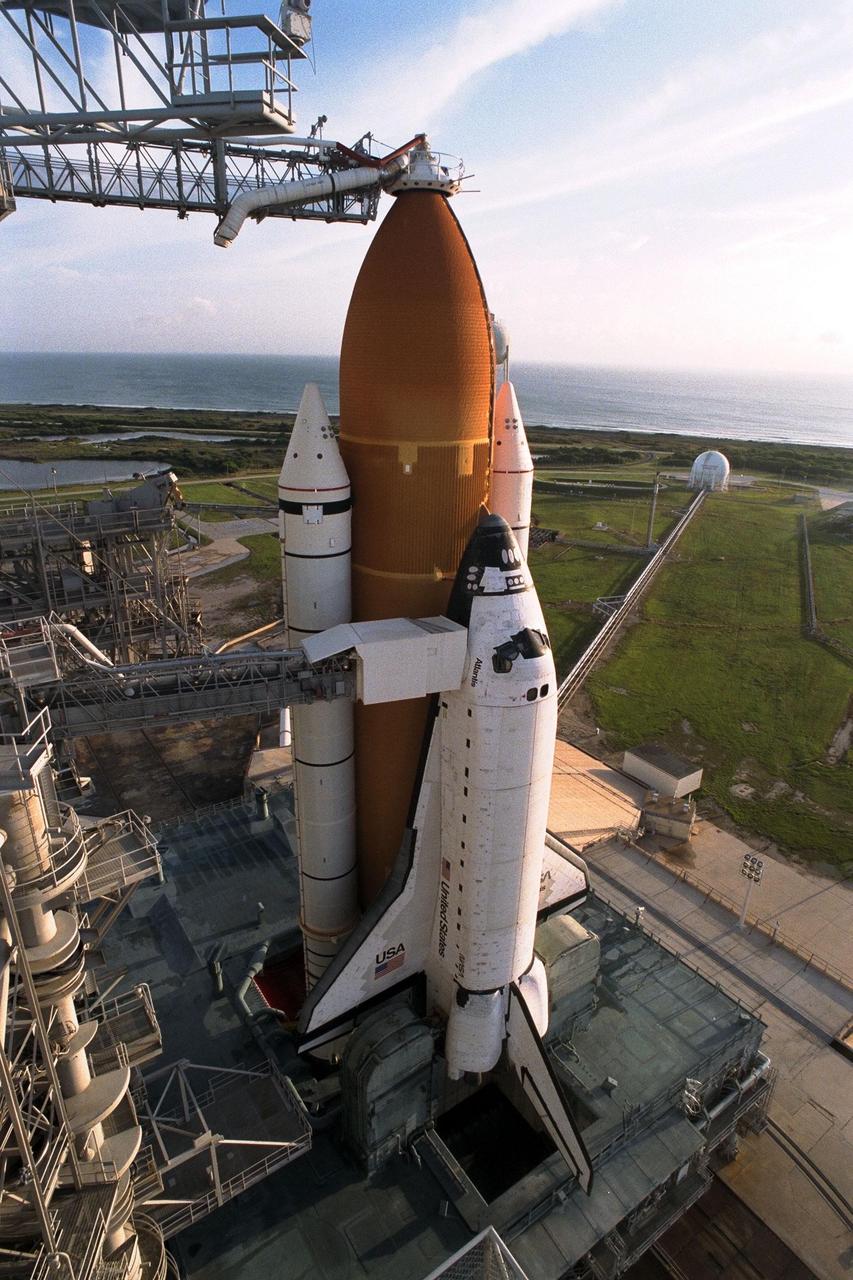

The Space Shuttle Atlantis is poised for liftoff on the STS-86 mission from Launch Pad 39A. Now that the Rotating Service Structure is rolled back, one of the final prelaunch milestones will be the loading of the external tank with approximately 500,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen to fuel the three main engines. STS-86 is slated to be the seventh docking of the Space Shuttle with the Russian Space Station Mir. Liftoff is targeted for Sept. 25 at 10:34 p.m. EDT during a preferred launch window which lasts six minutes and 45 seconds. Seven crew members will lift off for the scheduled 10-day flight. One of those crew members, David A. Wolf, will transfer to the Mir for an approximate four-month stay. He will replace U.S. astronaut C. Michael Foale, who will return to Earth with the remainder of the STS-86 crew. Foale has been on the Russian space station since mid-May
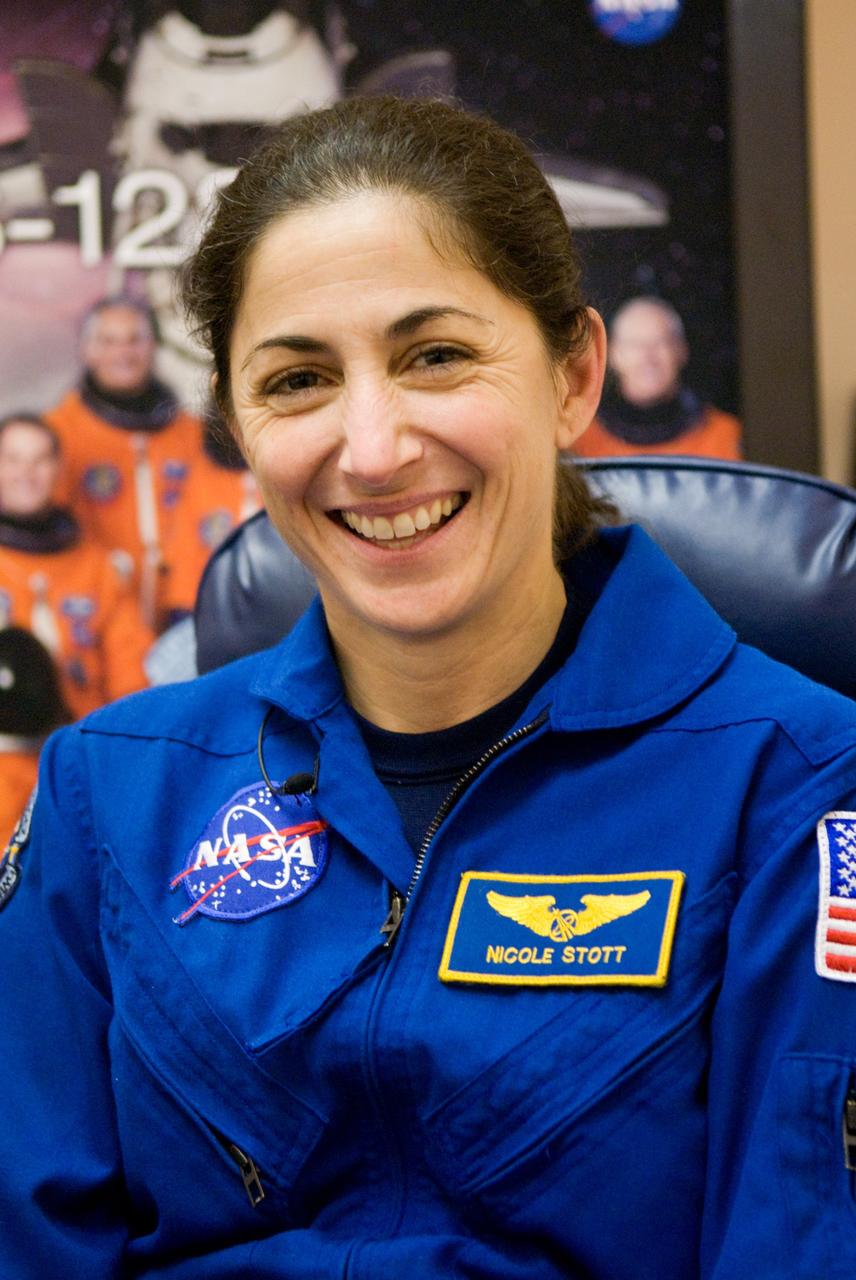

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott, who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station, appears pleased with the success of her mission on the orbiting laboratory. Stott returned to Earth aboard space shuttle Atlantis with the STS-129 crew. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. STS-129 is the final time the shuttle is expected to rotate station crew members. For information on the Expedition crews, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/expeditions/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
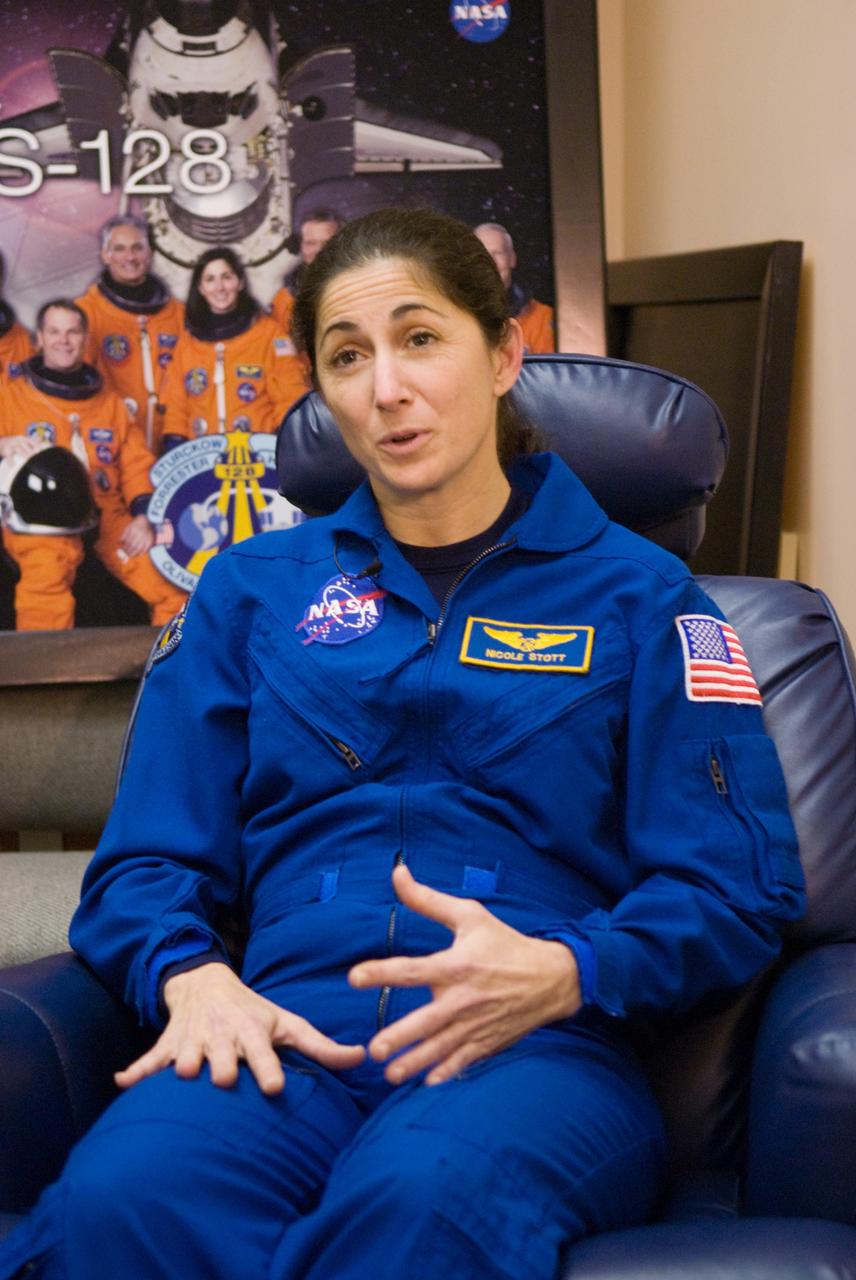

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott, who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station, answers questions regarding her experiences on the orbiting laboratory. Stott returned to Earth aboard space shuttle Atlantis with the STS-129 crew. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. STS-129 is the final time the shuttle is expected to rotate station crew members. For information on the Expedition crews, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/expeditions/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Soichi Noguchi holds the mission patch that will be attached to Space Shuttle Discovery for flight. Noguchi is with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The crew is taking part in a full dress rehearsal for launch, including countdown and culminating in main engine cutoff. The rehearsal is the final part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that the crew has been involved in for three days. TCDT provides the crew of each mission an opportunity to participate in various simulated countdown activities, including equipment familiarization and emergency egress training. STS-114 is the first Return to Flight mission to the International Space Station. The launch window extends July 13 through July 31.
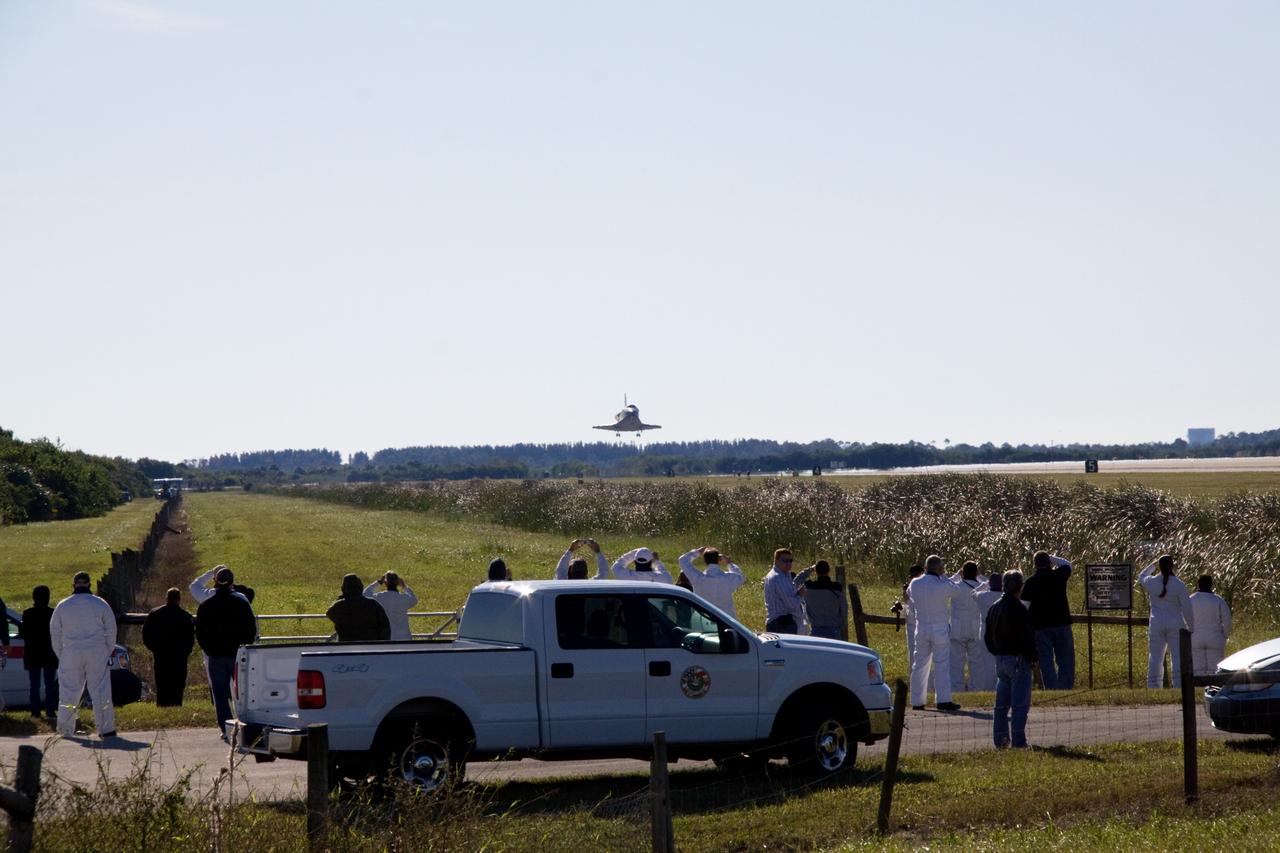

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle workers await landing of shuttle Atlantis on Runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After 11 days in space, Atlantis completed the 4.5-million mile STS-129 mission on orbit 171. Main gear touchdown was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Aboard Atlantis are Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller