
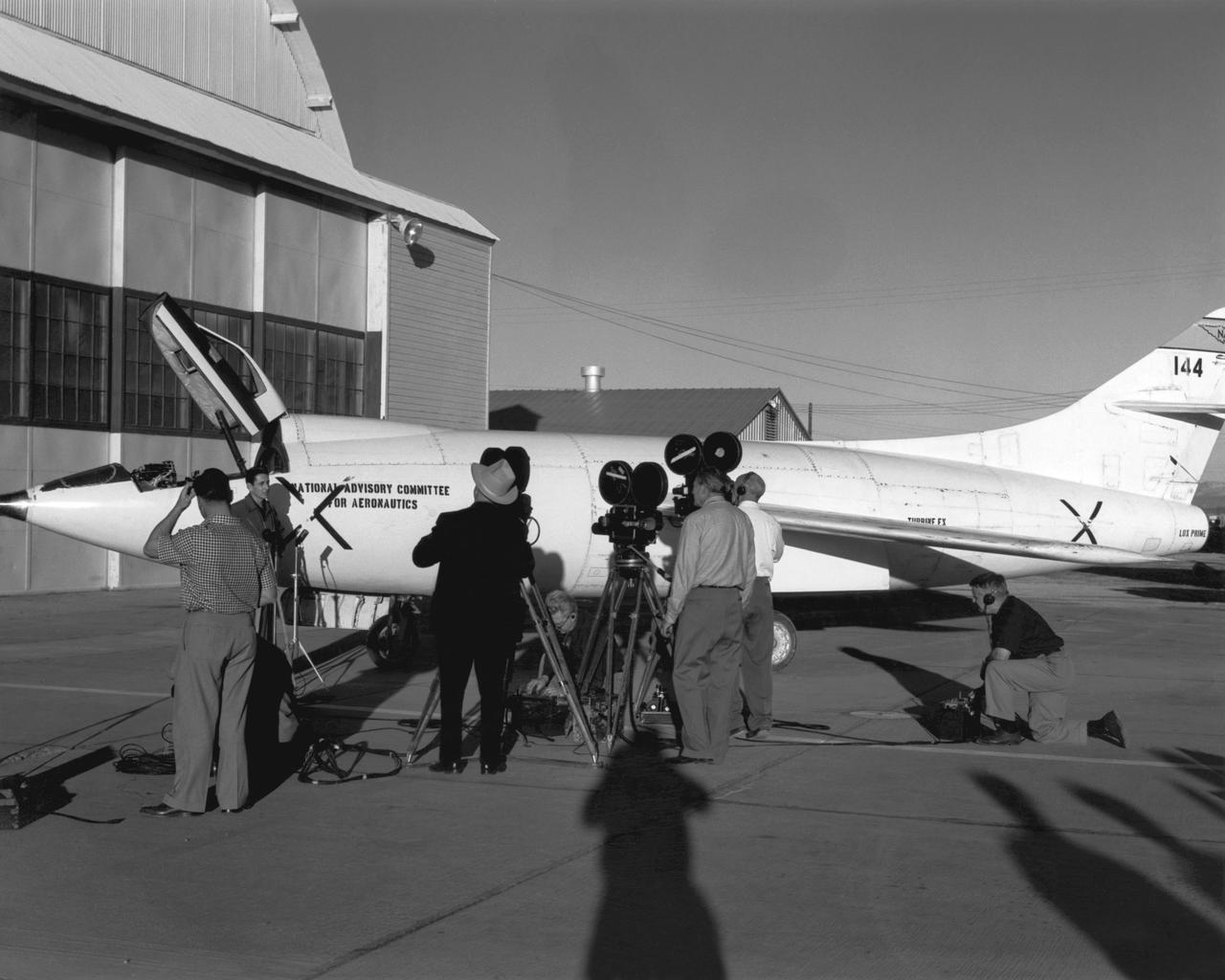
The first X-43A hypersonic research aircraft and its modified Pegasus booster rocket were carried aloft by NASA's NB-52B carrier aircraft from Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 2, 2001 for the first of three high-speed free flight attempts. About an hour and 15 minutes later the Pegasus booster was released from the B-52 to accelerate the X-43A to its intended speed of Mach 7. Before this could be achieved, the combined Pegasus and X-43A "stack" lost control about eight seconds after ignition of the Pegasus rocket motor. The mission was terminated and explosive charges ensured the Pegasus and X-43A fell into the Pacific Ocean in a cleared Navy range area. A NASA investigation board is being assembled to determine the cause of the incident. Work continues on two other X-43A vehicles, the first of which could fly by late 2001. Central to the X-43A program is its integration of an air-breathing "scramjet" engine that could enable a variety of high-speed aerospace craft, and promote cost-effective access to space. The 12-foot, unpiloted research vehicle was developed and built for NASA by MicroCraft Inc., Tullahoma, Tenn. The booster was built by Orbital Sciences Corp. at Chandler, Ariz.
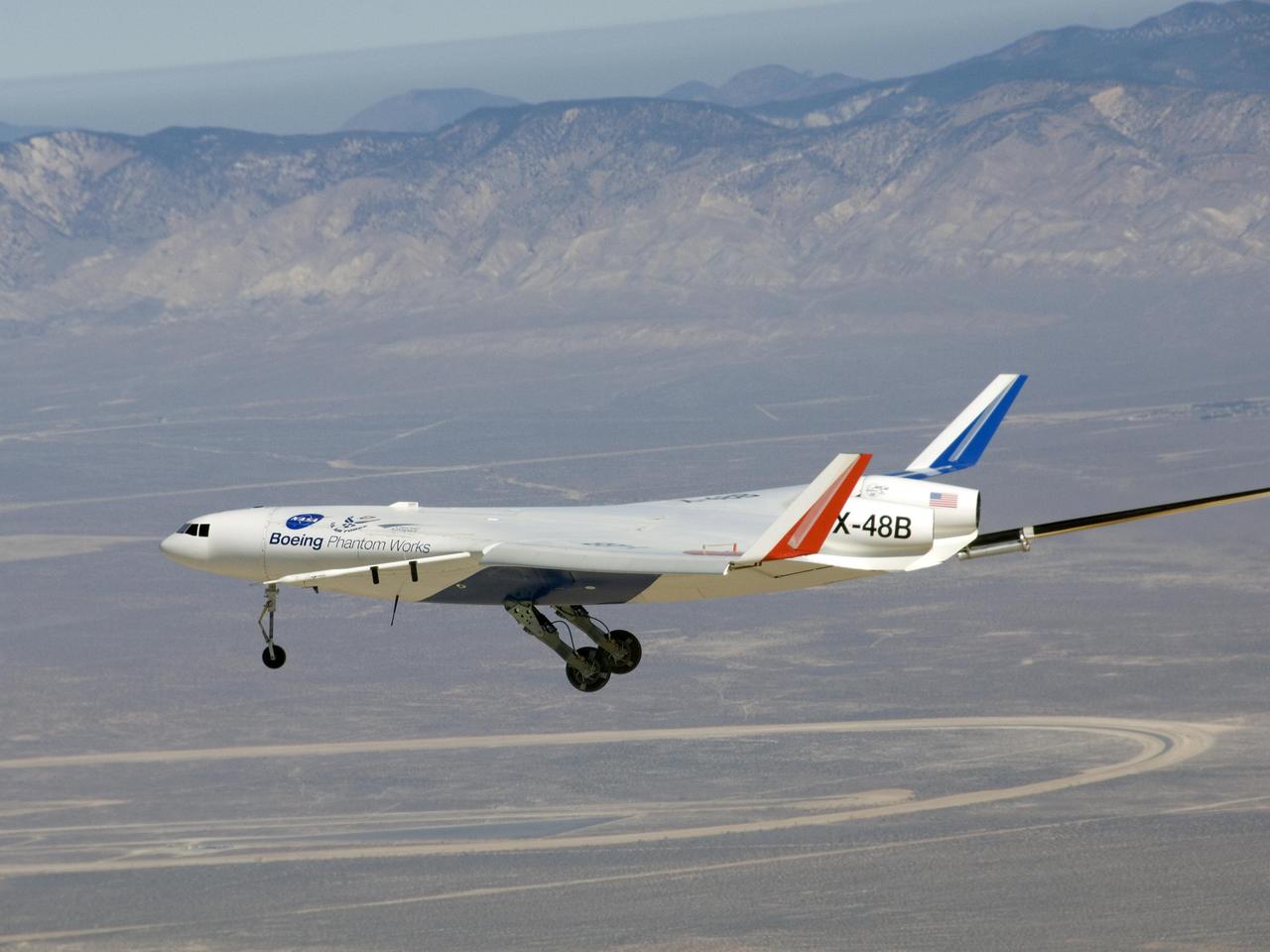

X-48B blended wing body aircraft during first flight on July 20, 2007.
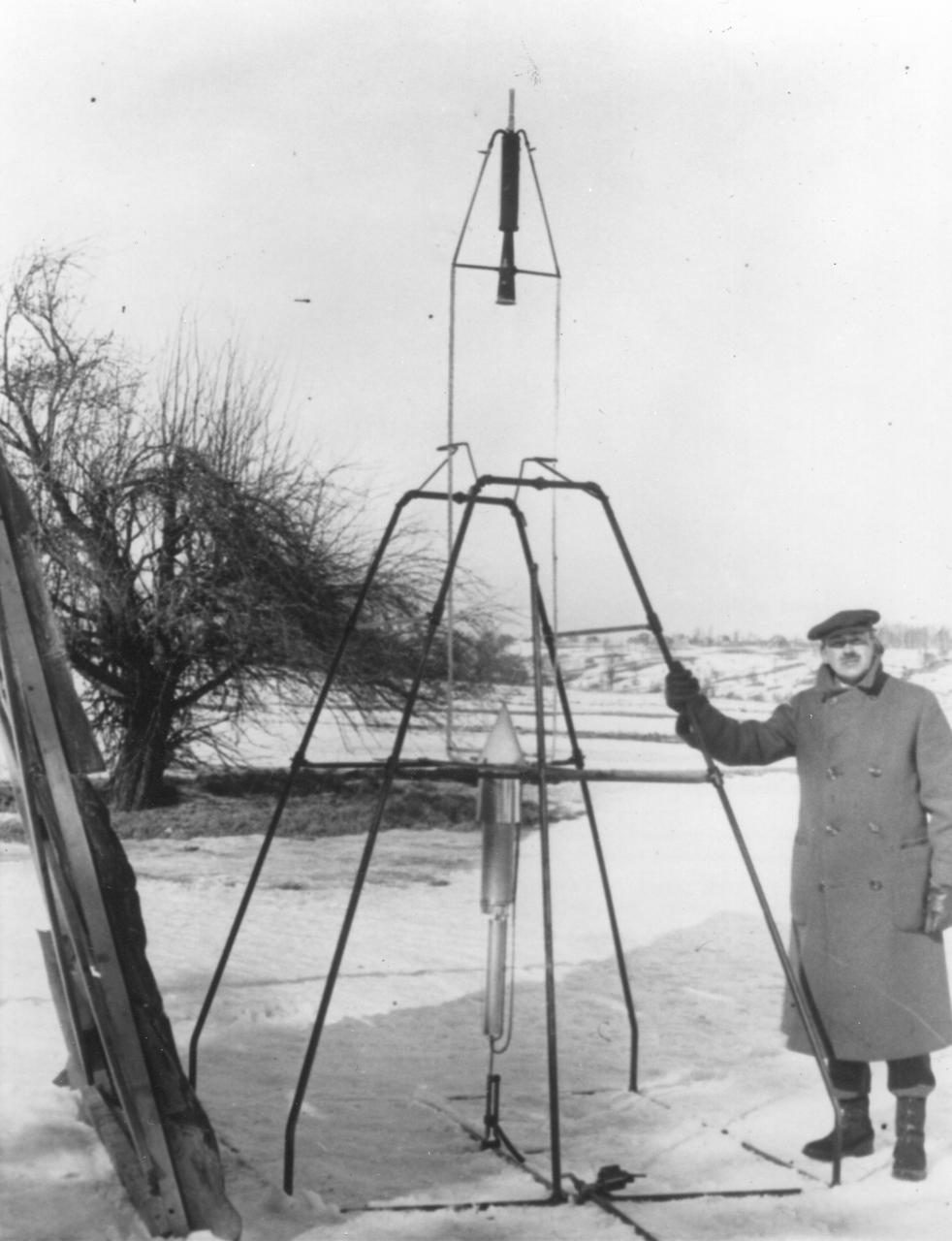

Dr. Robert H. Goddard and a liquid oxygen-gasoline rocket in the frame from which it was fired on March 16, 1926, at Auburn, Massachusetts. From 1930 to 1941, Dr. Goddard made substantial progress in the development of progressively larger rockets, which attained altitudes of 2400 meters, and refined his equipment for guidance and control, his techniques of welding, and his insulation, pumps and other associated equipment. In many respects, Dr. Goddard laid the essential foundations of practical rocket technology. He is considered one of the fathers of rocketry along with Konstantin Tsiolovsky (1857-1935) and Hermann Oberth (1894-1989). <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
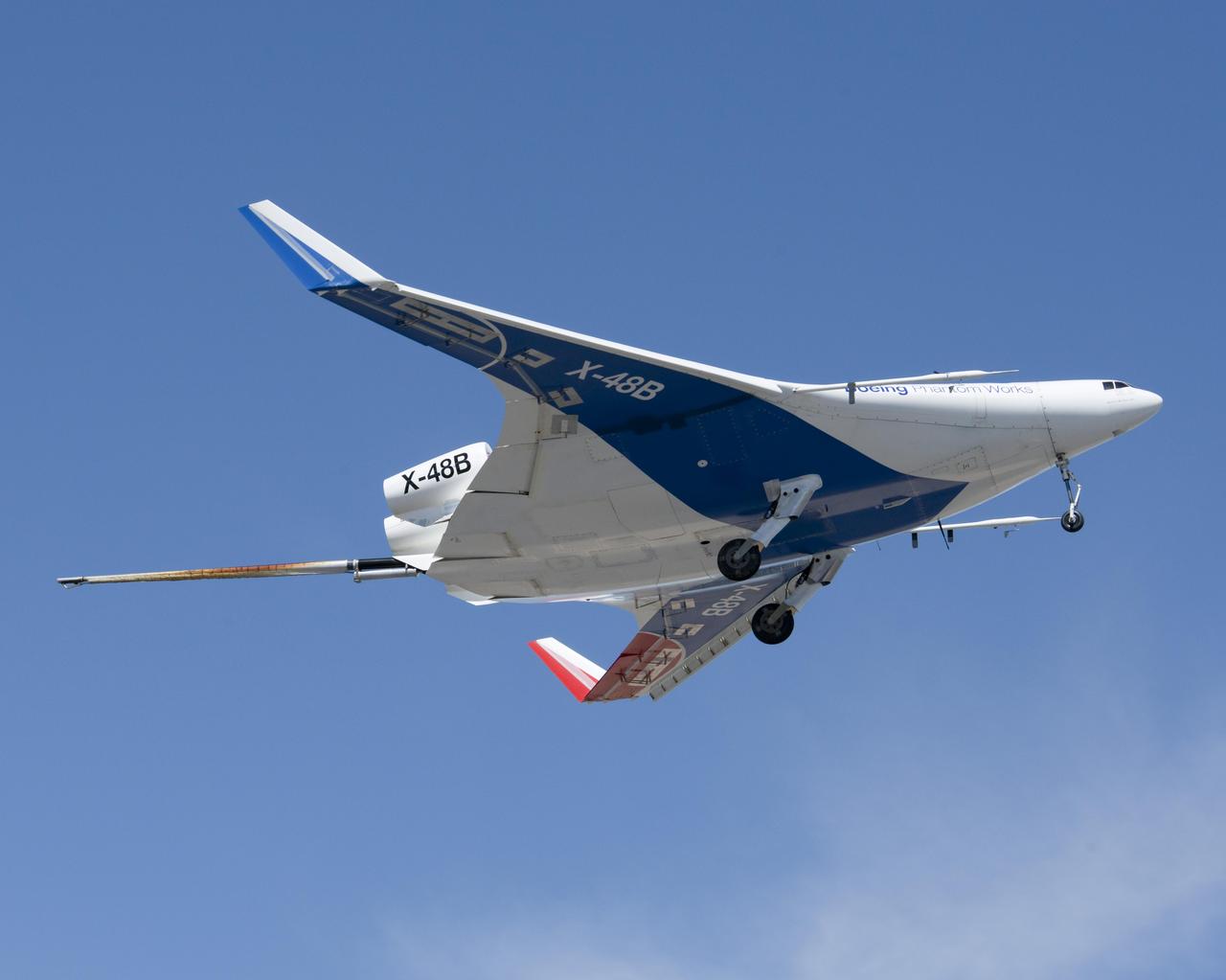

A joint NASA/Boeing team completed the first phase of flight tests on the unique X-48B Blended Wing Body aircraft at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, CA. The team completed the 80th and last flight of the project's first phase on March 19, 2010.

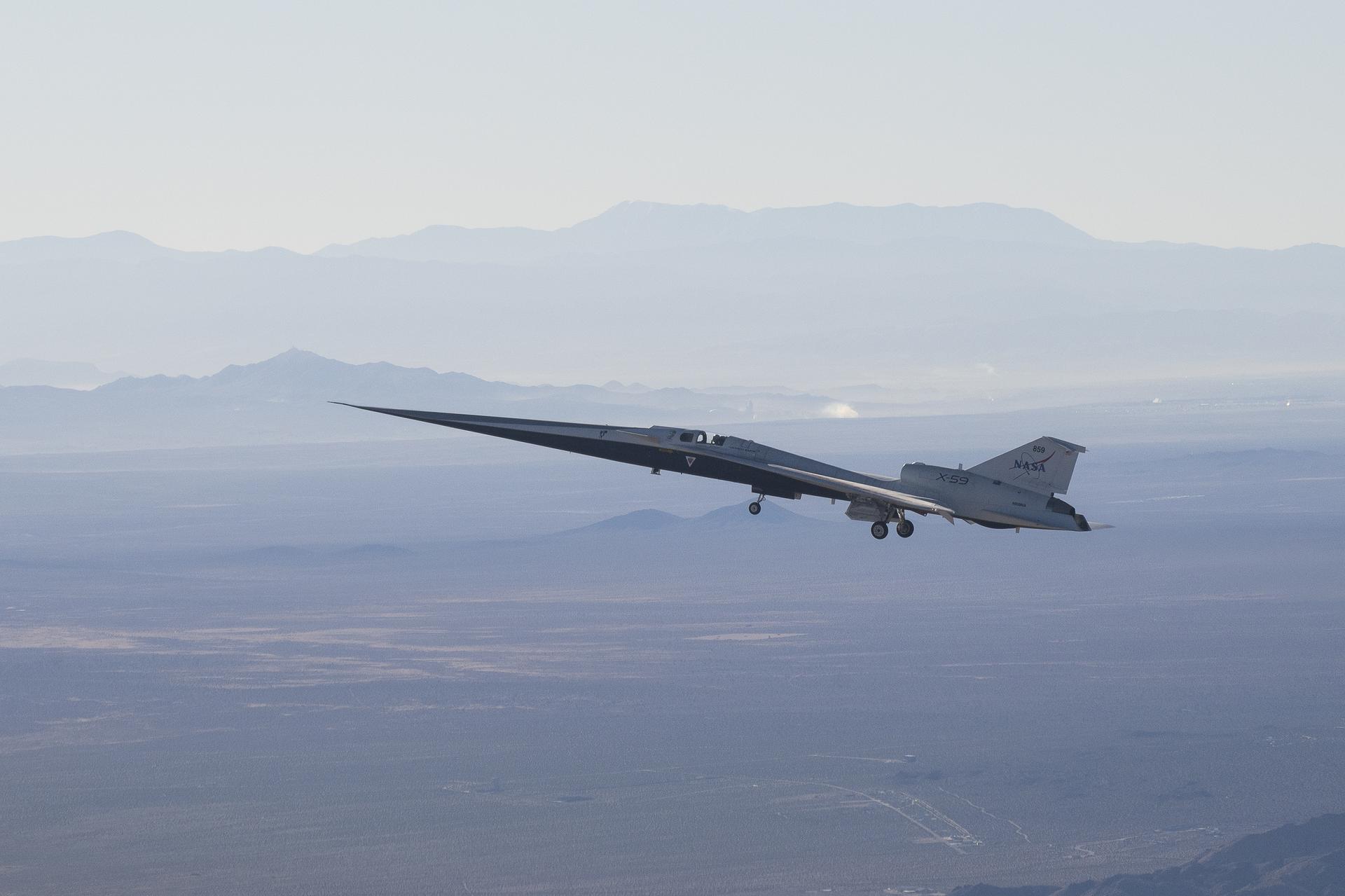
NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft lifts off for its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, from U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California. The aircraft’s first flight marks the start of flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, the result of years of design, integration, and ground testing and begins a new chapter in NASA’s aeronautics research legacy.
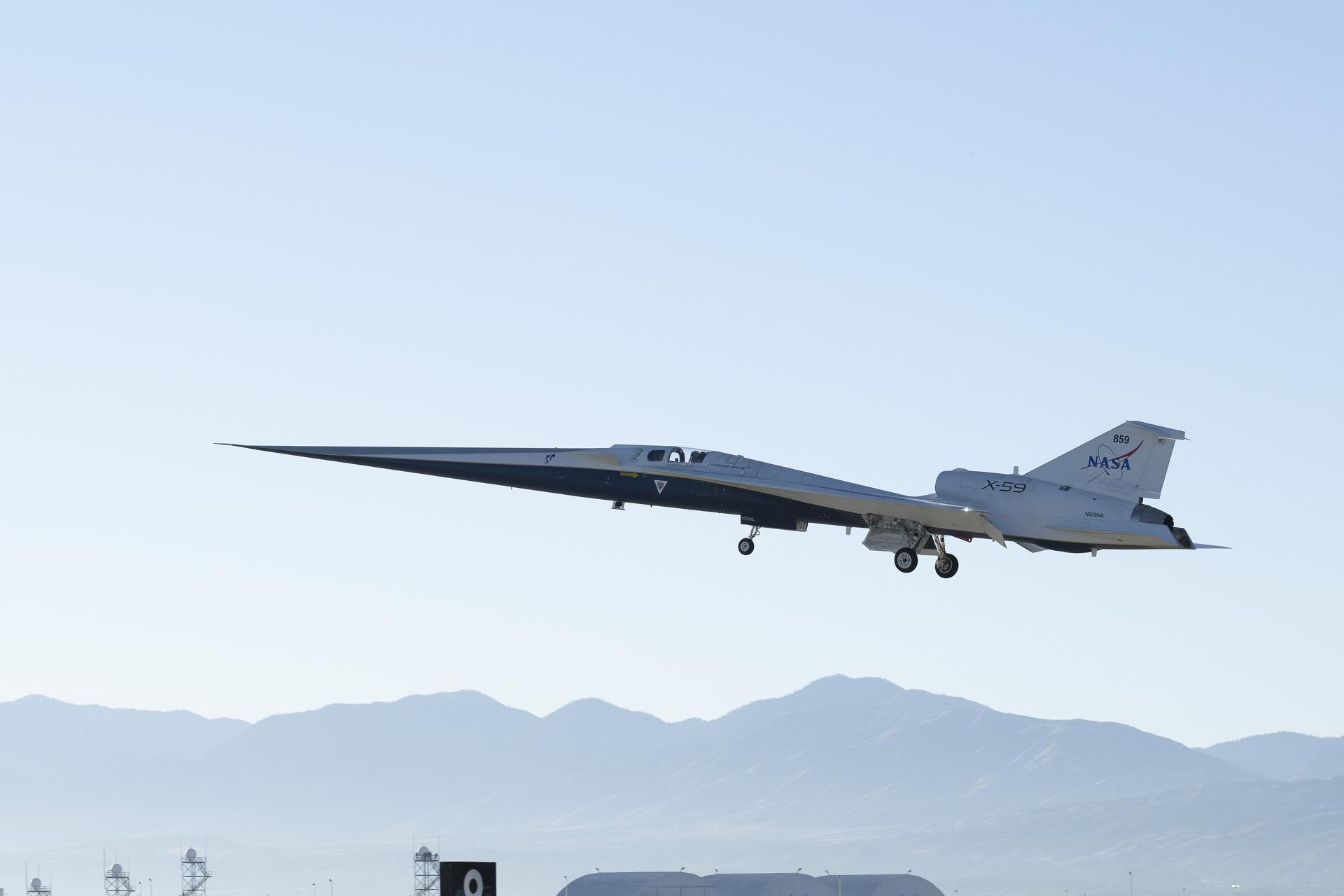

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft lifts off for its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, from U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California. The aircraft’s first flight marks the start of flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, the result of years of design, integration, and ground testing and begins a new chapter in NASA’s aeronautics research legacy.
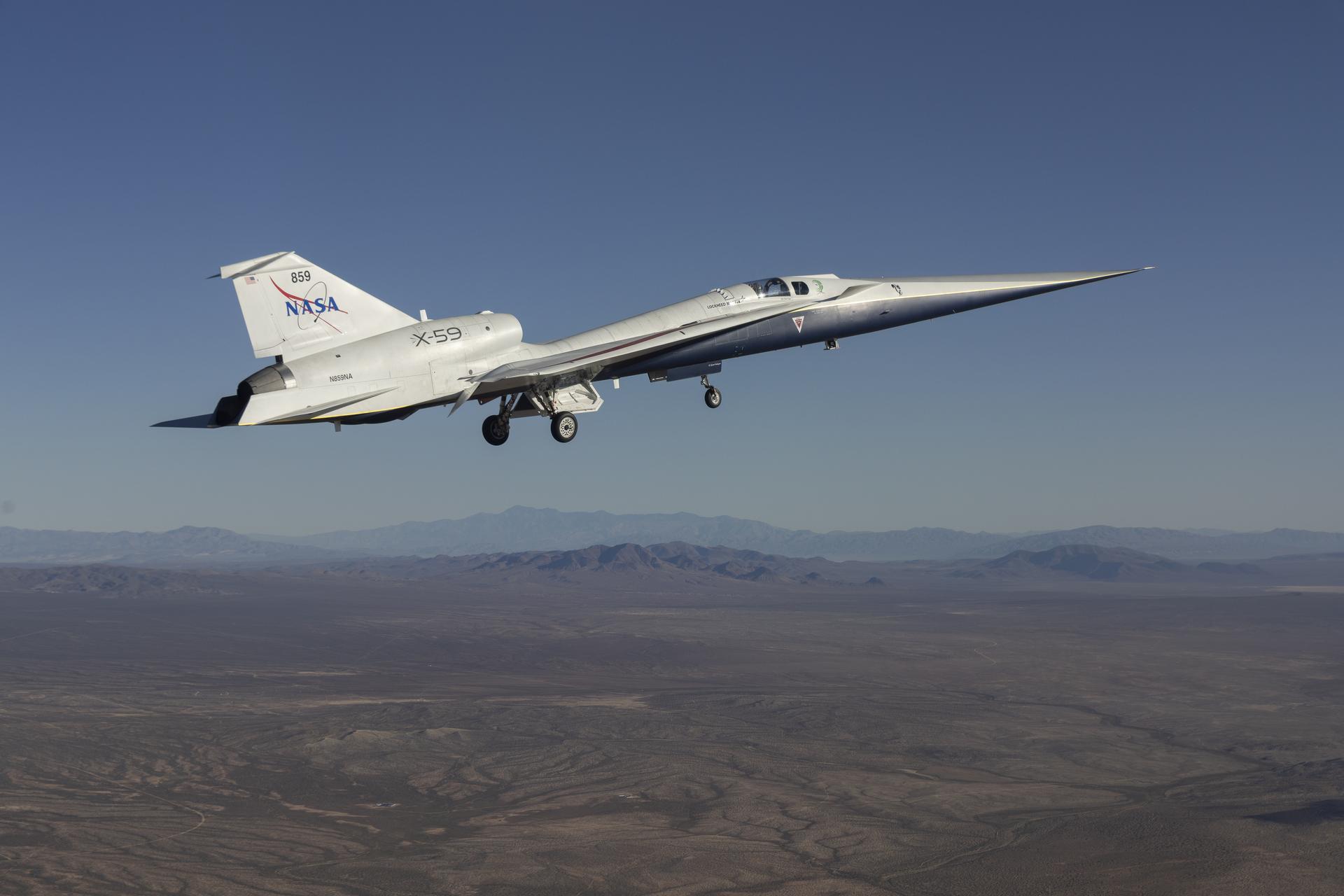

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft lifts off for its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, from U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California. The aircraft’s first flight marks the start of flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, the result of years of design, integration, and ground testing and begins a new chapter in NASA’s aeronautics research legacy.
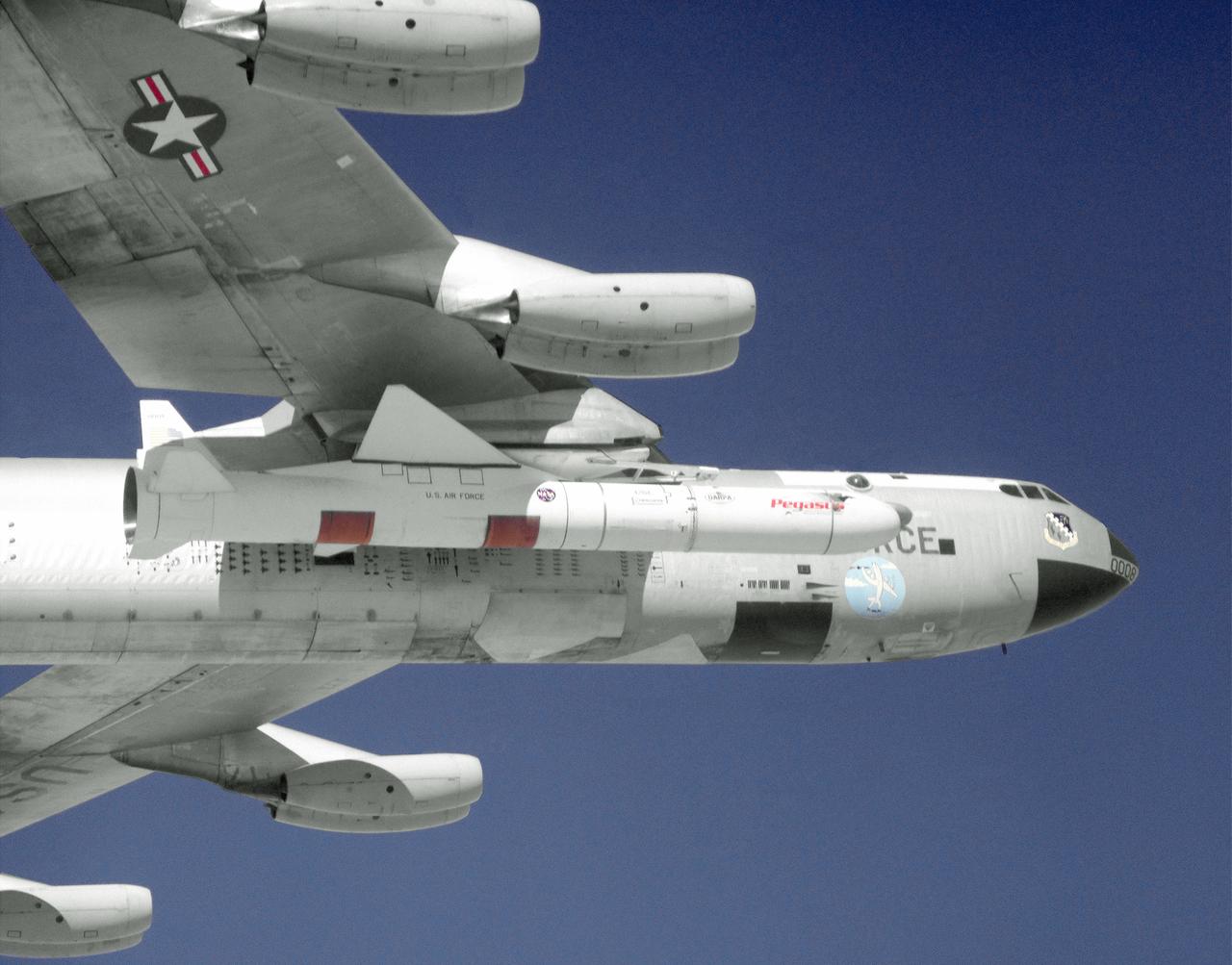

The Pegasus air-launched space booster is carried aloft under the right wing of NASA's B-52 carrier aircraft on its first captive flight from the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The first of two scheduled captive flights was completed on November 9, 1989. Pegasus is used to launch satellites into low-earth orbits cheaply. In 1997, a Pegasus rocket booster was also modified to test a hypersonic experiment (PHYSX). An experimental "glove," installed on a section of its wing, housed hundreds of temperature and pressure sensors that sent hypersonic flight data to ground tracking facilities during the experiment’s flight.
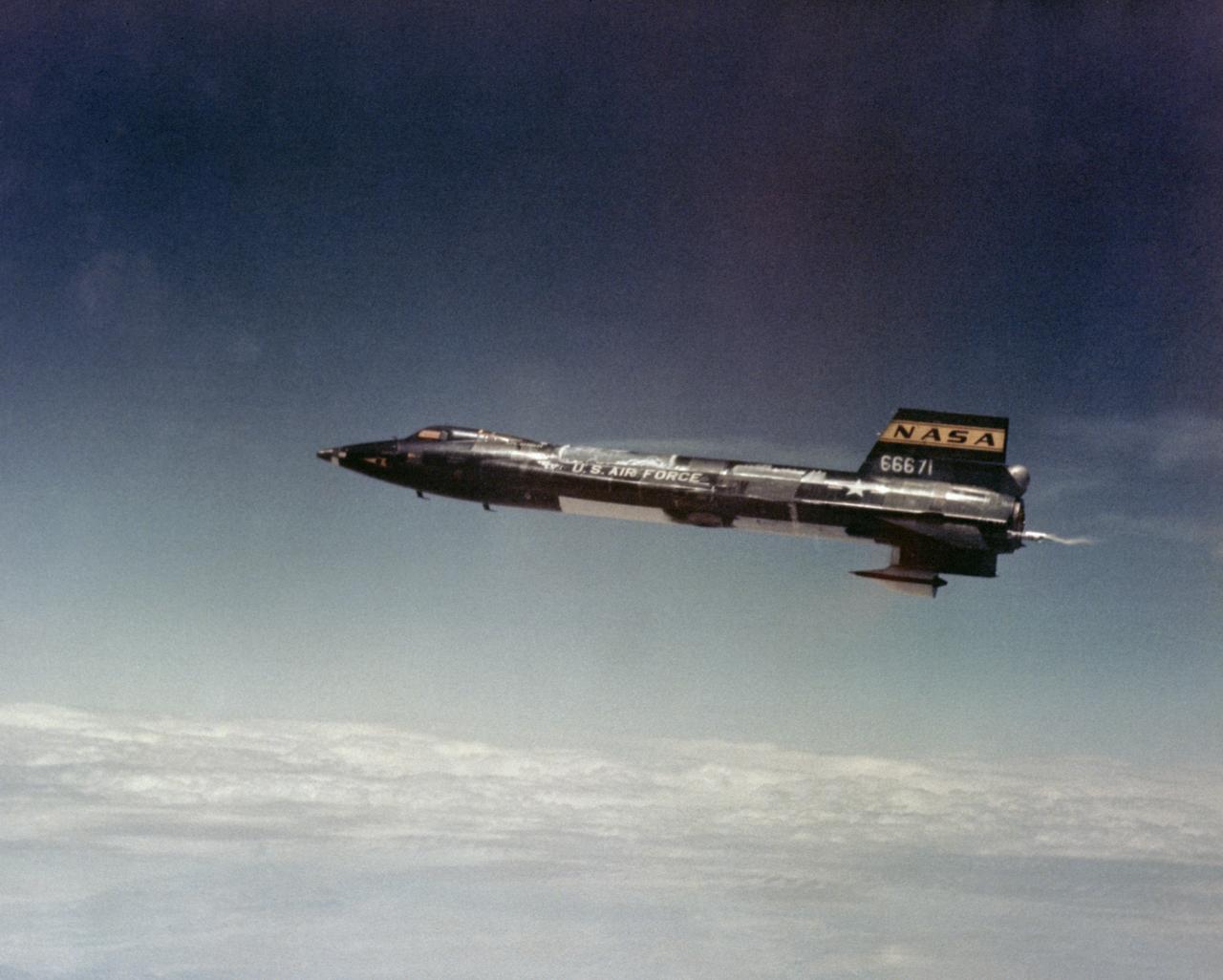

X-15A-2 in flight. First flight wih dummy ramjet attached. Flt. 2-51-92, Pete Knight-pilot. 8 May 67
This altimeter chart shows data from the first flight of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, which occurred on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24587

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft flies above Palmdale and Edwards, California, on its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The aircraft traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, where it will begin flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land.

This video animation made with data from the first flight of NASA's Ingenuity helicopter shows the flight from different angles. The flight occurred on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24588
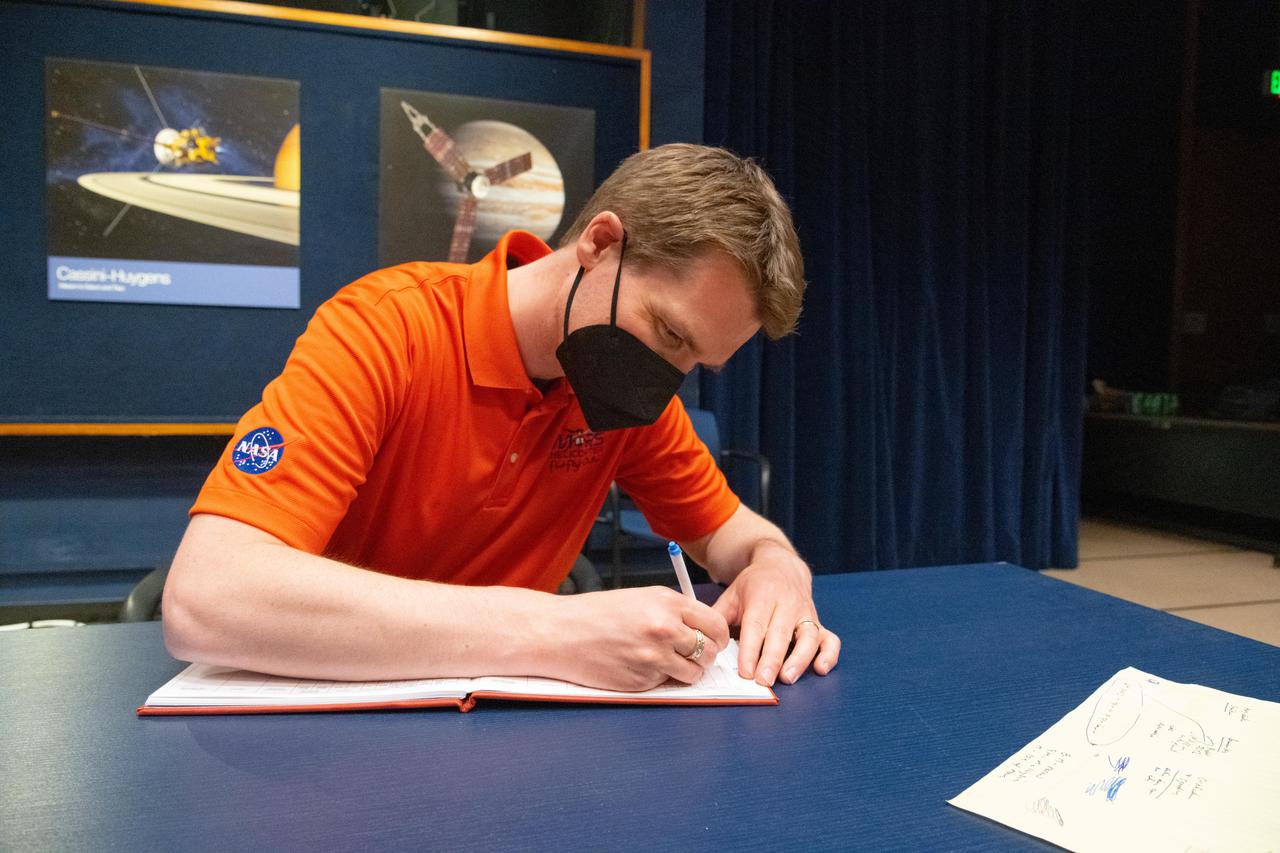

Ingenuity Mars chief pilot Håvard Grip records data of the first flight of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter into the official pilot's logbook for the project — the "Nominal Pilot's Logbook for Planets and Moons." The image was taken at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on April 19, 2021. Pilot logbooks are used by aviators to provide a record of their flights, including current and accumulated flight time, number and locations of takeoffs and landings, as well as unique operating conditions and certifications. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24591
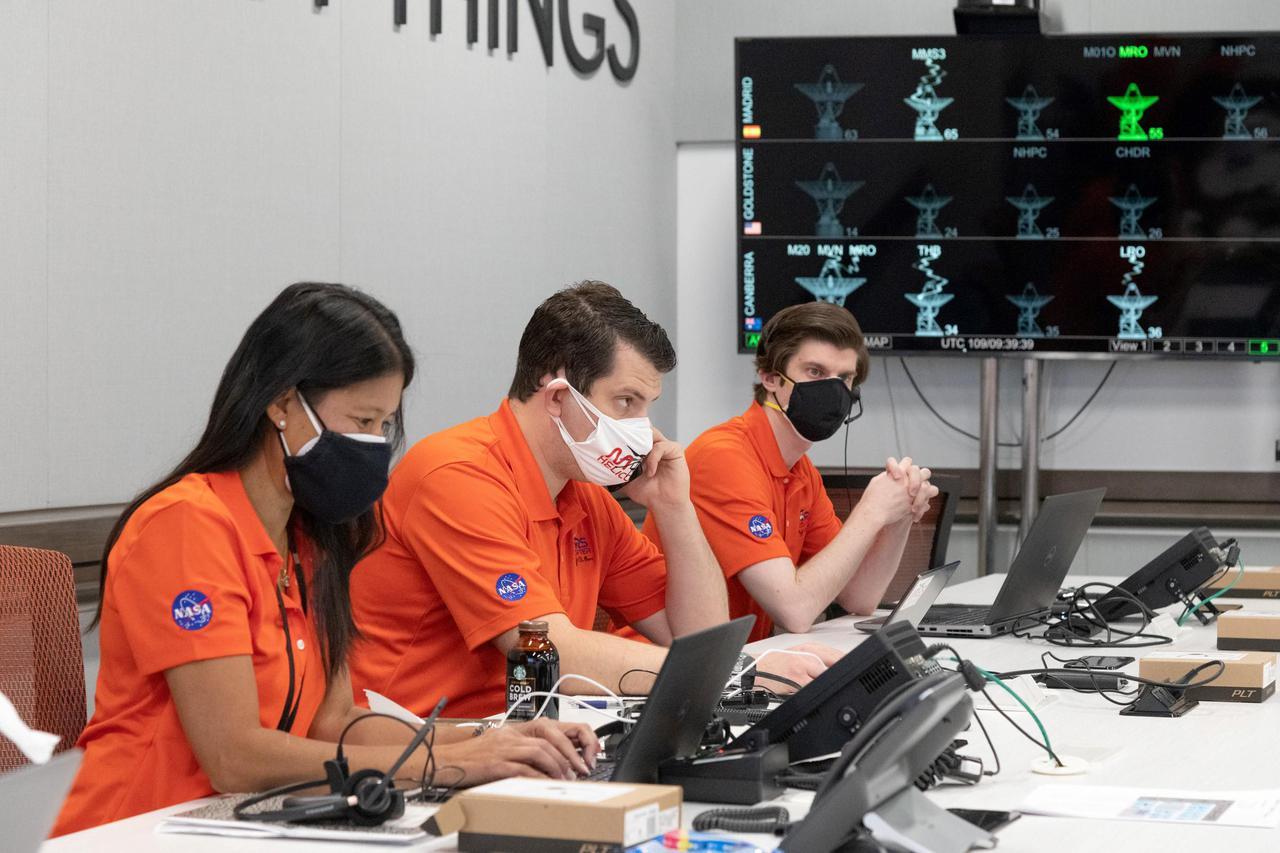

Members of NASA's Ingenuity helicopter team in the Space Flight Operations Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory prepare to receive the data downlink showing whether the helicopter completed its first flight on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24585
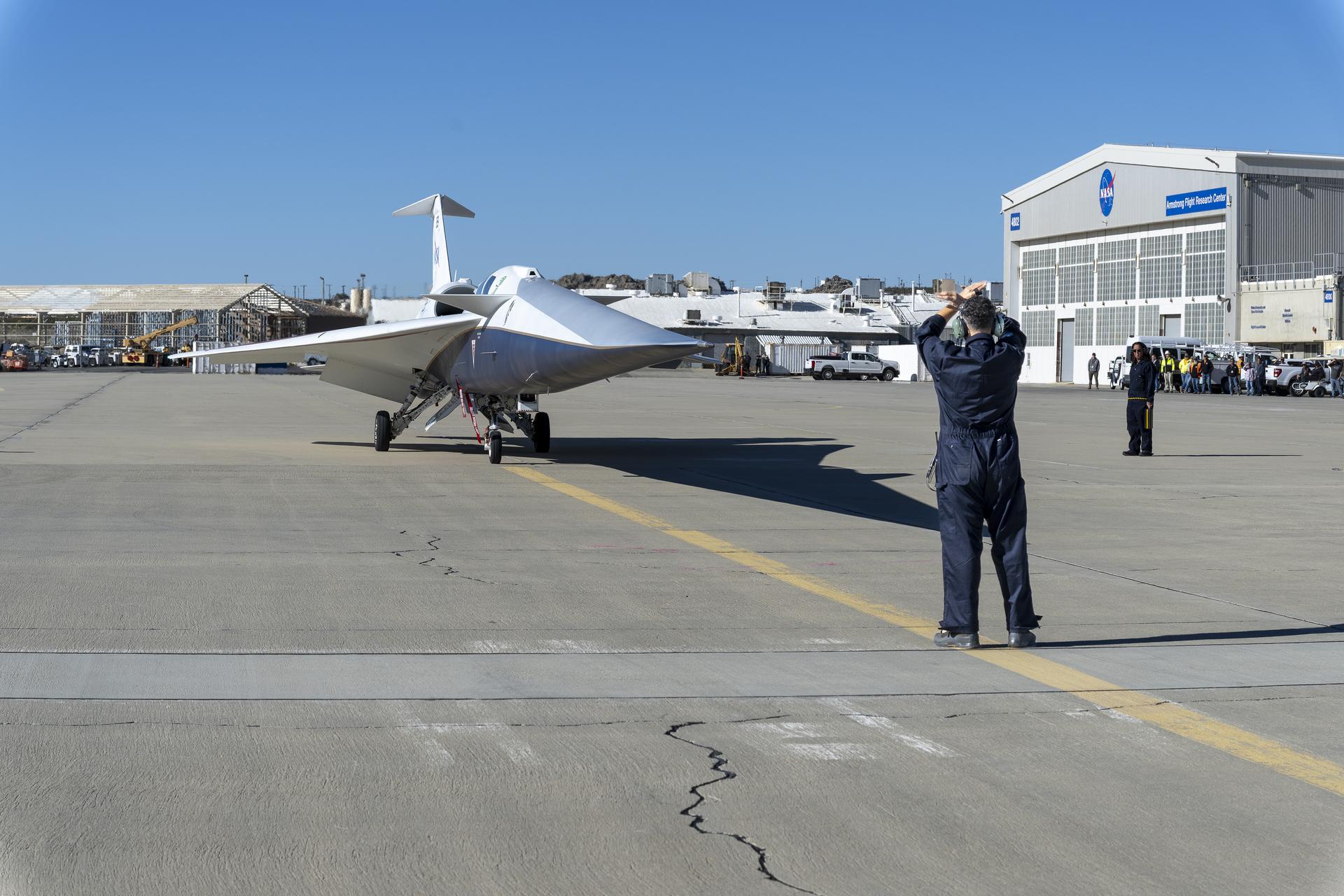

The X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft arrives at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, following its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The arrival marks the aircraft’s transition from ground testing to flight operations. Next, the aircraft will undergo scheduled maintenance followed by a series of additional test flights, gradually building toward its first supersonic flight.
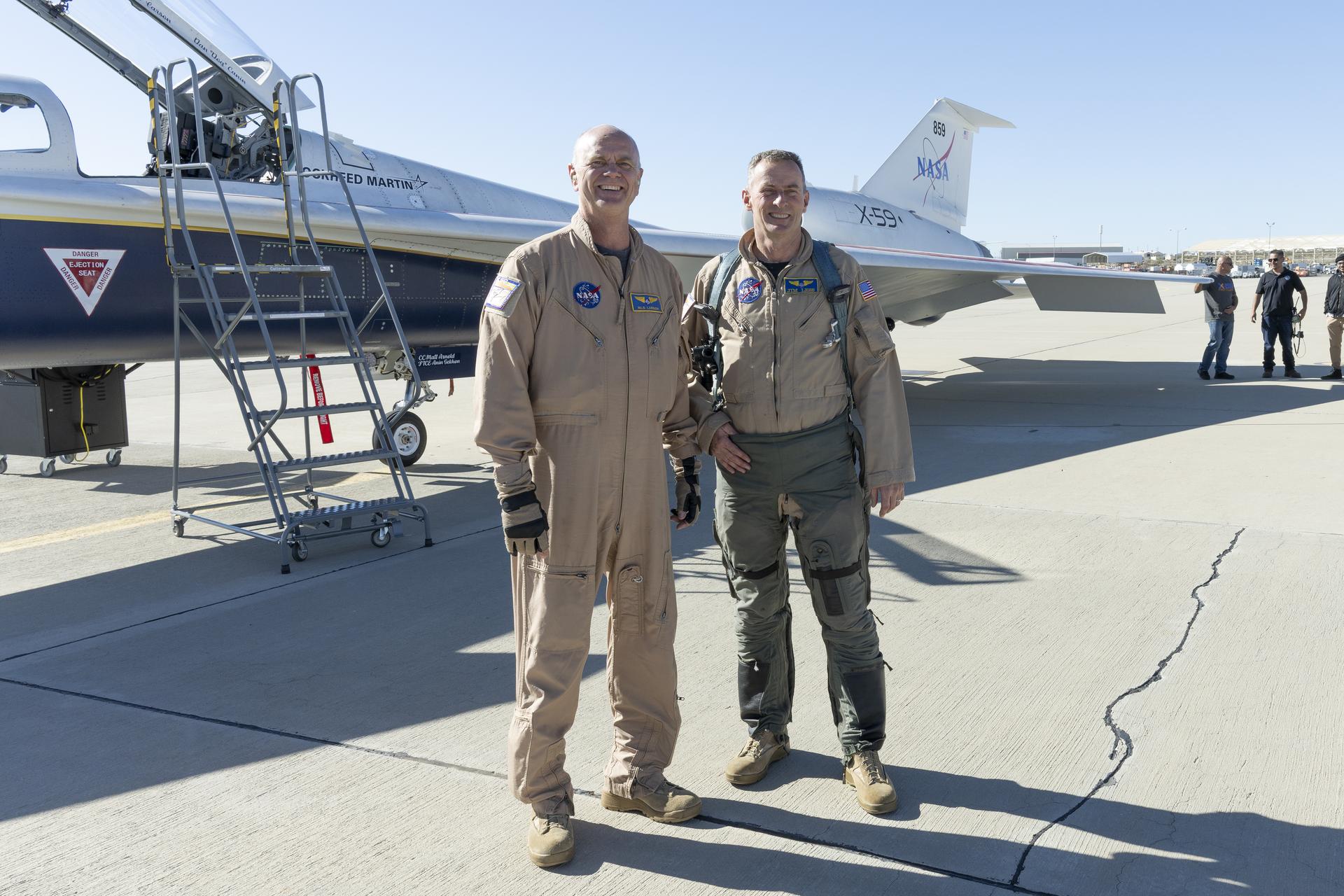

NASA chase pilot Jim “Clue” Less congratulates Nils Larson after completing the X-59’s first flight on Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The milestone marks a major step toward demonstrating quiet supersonic technology that could enable future air travel over land without the disruptive noise of traditional sonic booms.
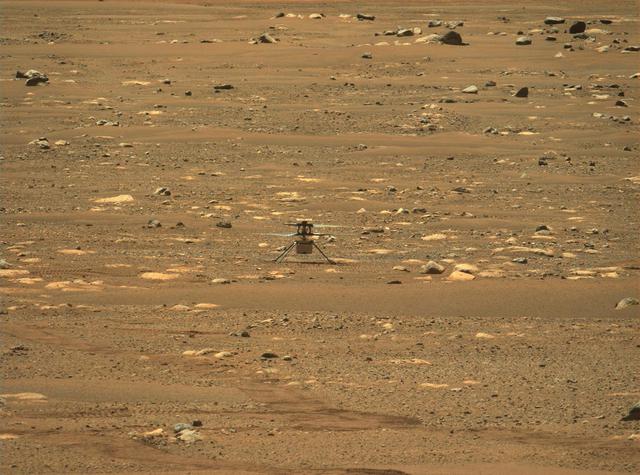

This image was taken after the first flight of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter — and the first powered, controlled flight on another planet. It was captured by Mastcam-Z, a pair of zoomable cameras aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover, on April 19, 2021. Flying in a controlled manner on Mars is far more difficult than flying on Earth. The Red Planet has significant gravity (about one-third that of Earth's), but its atmosphere is just 1% as dense as Earth's at the surface. Stitched together from multiple images, the mosaic is not white balanced; instead, it is displayed in a preliminary calibrated version of a natural color composite, approximately simulating the colors of the scene that we would see if we were there viewing it ourselves. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24550
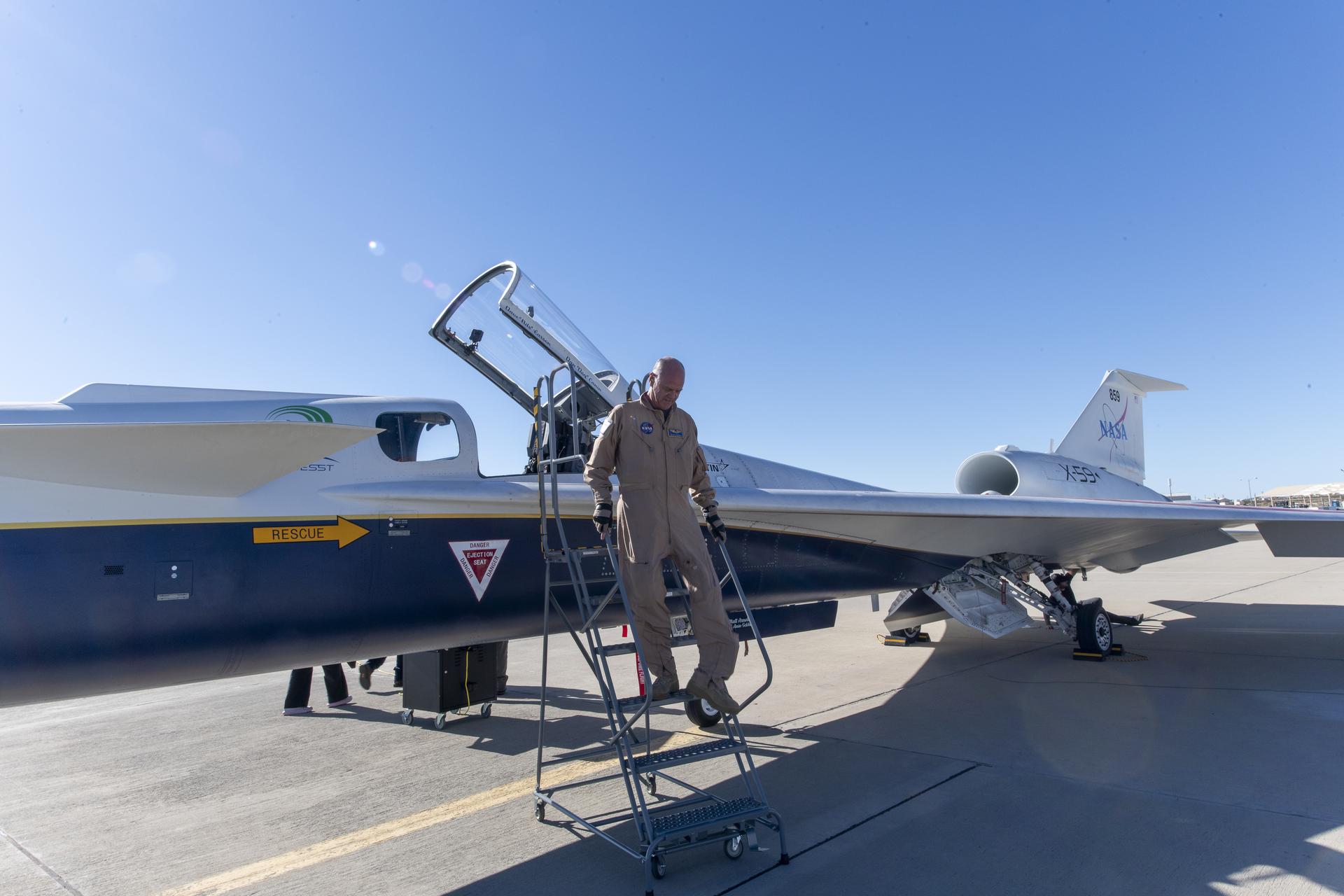

NASA test pilot Nils Larson steps out of the X-59 after successfully completing the aircraft’s first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The mission marked a key milestone in advancing NASA’s Quesst mission to enable quiet supersonic flight over land.

How differential deflection of the inboard and outboard leading-edge flaps affected the handling qualities of this modified F/A-18A was evaluated during the first check flight in the Active Aeroelastic Wing program at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center.
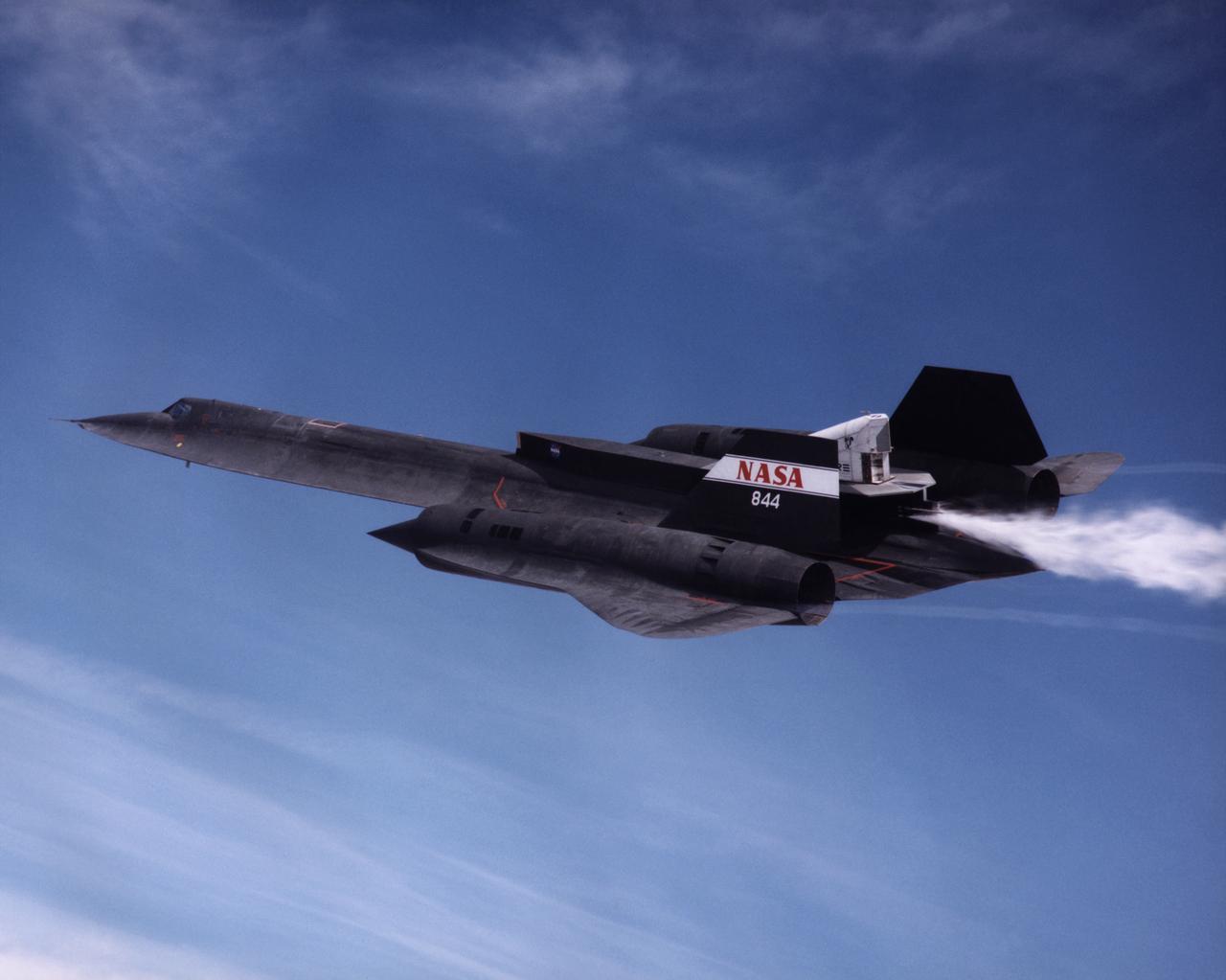

The NASA SR-71A successfully completed its first cold flow flight as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California on March 4, 1998. During a cold flow flight, gaseous helium and liquid nitrogen are cycled through the linear aerospike engine to check the engine's plumbing system for leaks and to check the engine operating characterisitics. Cold-flow tests must be accomplished successfully before firing the rocket engine experiment in flight. The SR-71 took off at 10:16 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty-seven minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.58 before landing at Edwards at 12:13 p.m. PST. "I think all in all we had a good mission today," Dryden LASRE Project Manager Dave Lux said. Flight crew member Bob Meyer agreed, saying the crew "thought it was a really good flight." Dryden Research Pilot Ed Schneider piloted the SR-71 during the mission. Lockheed Martin LASRE Project Manager Carl Meade added, "We are extremely pleased with today's results. This will help pave the way for the first in-flight engine data-collection flight of the LASRE."

Members of NASA's Ingenuity helicopter team in the Space Flight Operations Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory react to data showing that the helicopter completed its first flight on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24499
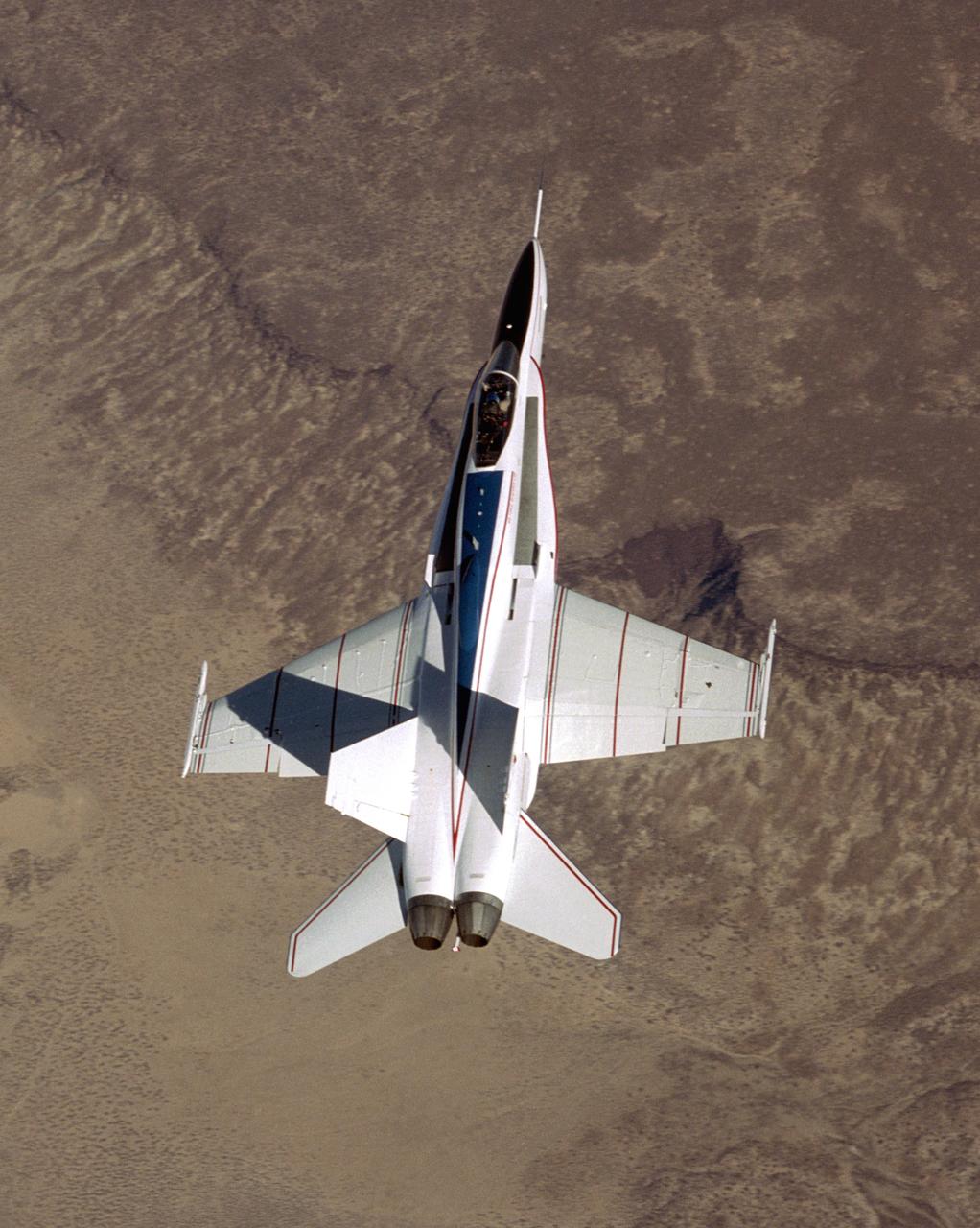

The modified F/A-18 being flown in the joint NASA/Air Force Active Aeroelastic Wing research program shows off its colors during its first checkout flight from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center.
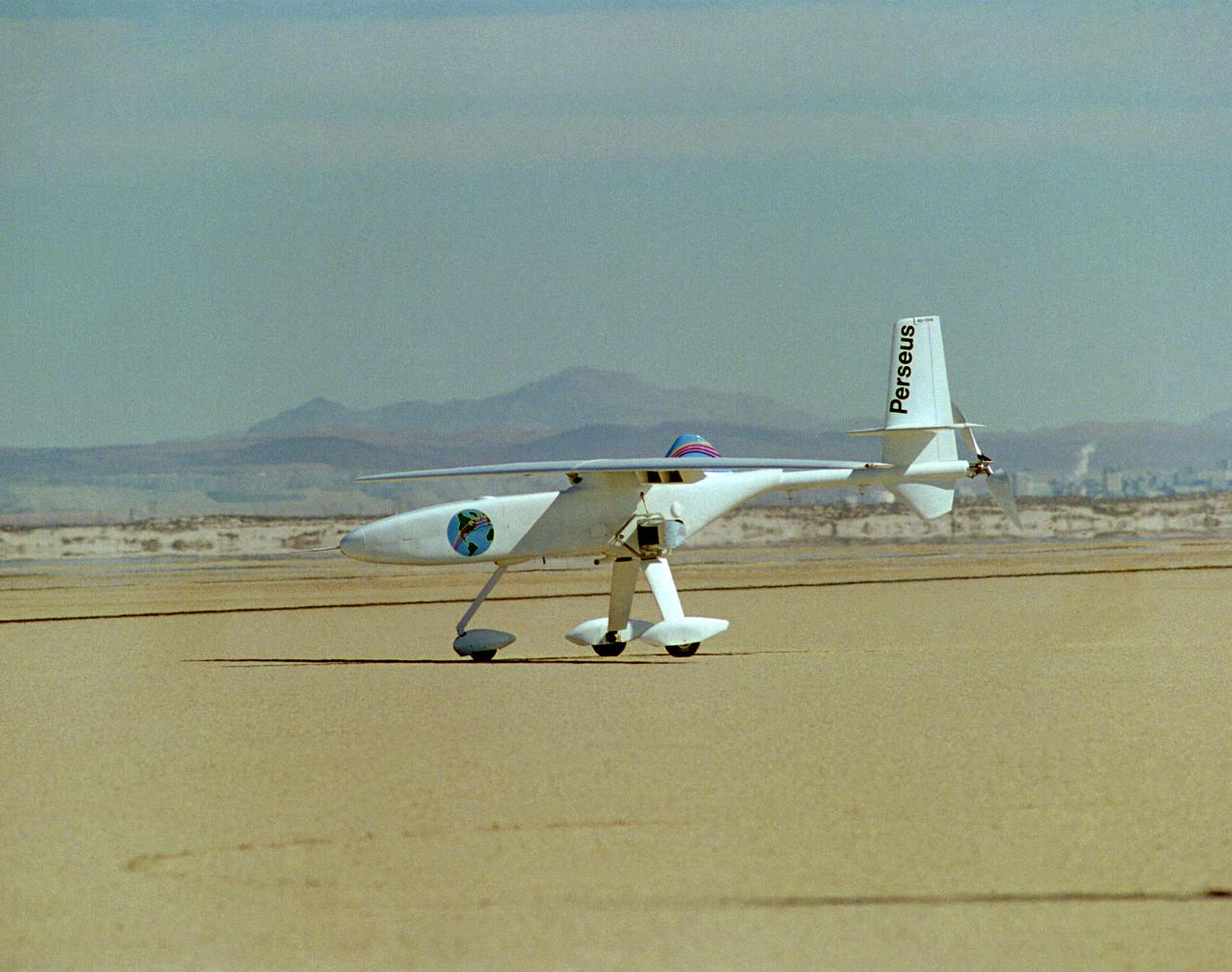

One of NASA's unmanned, remotely controlled aircraft, the Perseus B, is seen here before its first flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
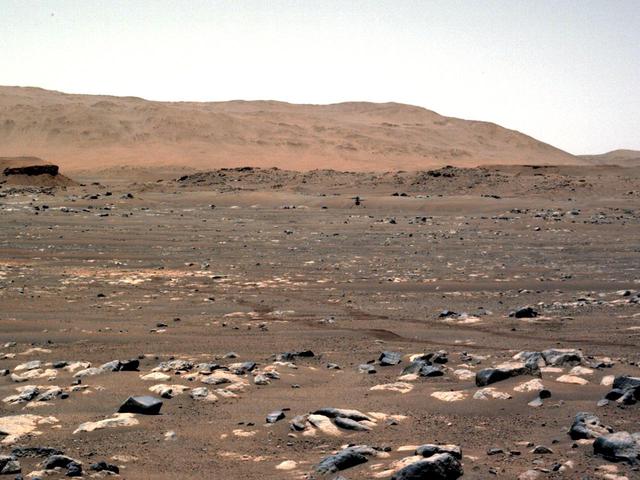

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter achieves powered, controlled flight for the first time on another planet, hovering for several seconds before touching back down on April 19, 2021. The image was taken by the left Navigation Camera, or Navcam, aboard the agency's Perseverance Mars rover from a distance of 210 feet (64 meters). A short movie was also recorded and can be downloaded here as a GIF. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24586
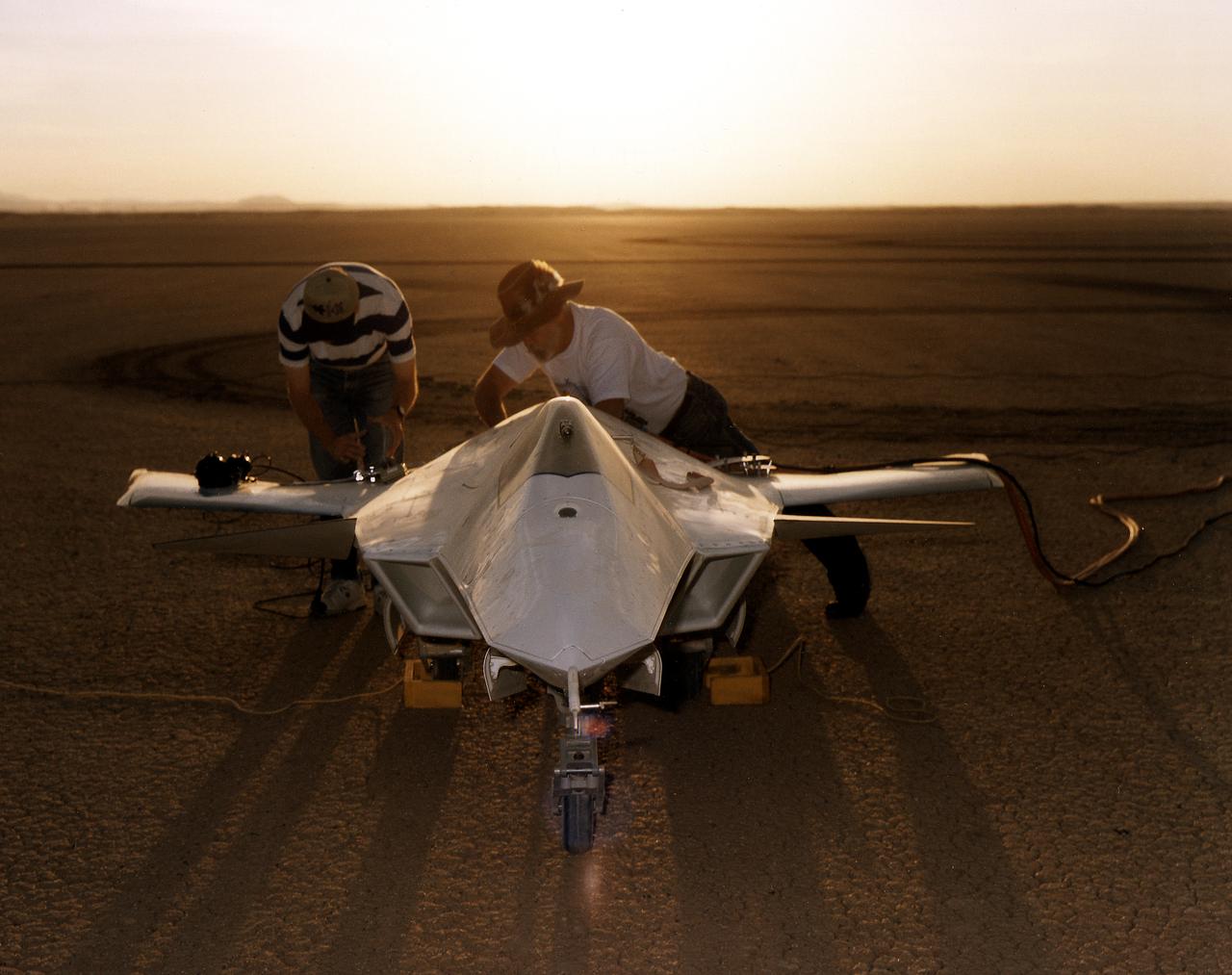

As the sun creeps above the horizon of Rogers Dry Lake at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, technicians make final preparations for the first flight of the X-36 Tailless Fighter Agility Research Aircraft.
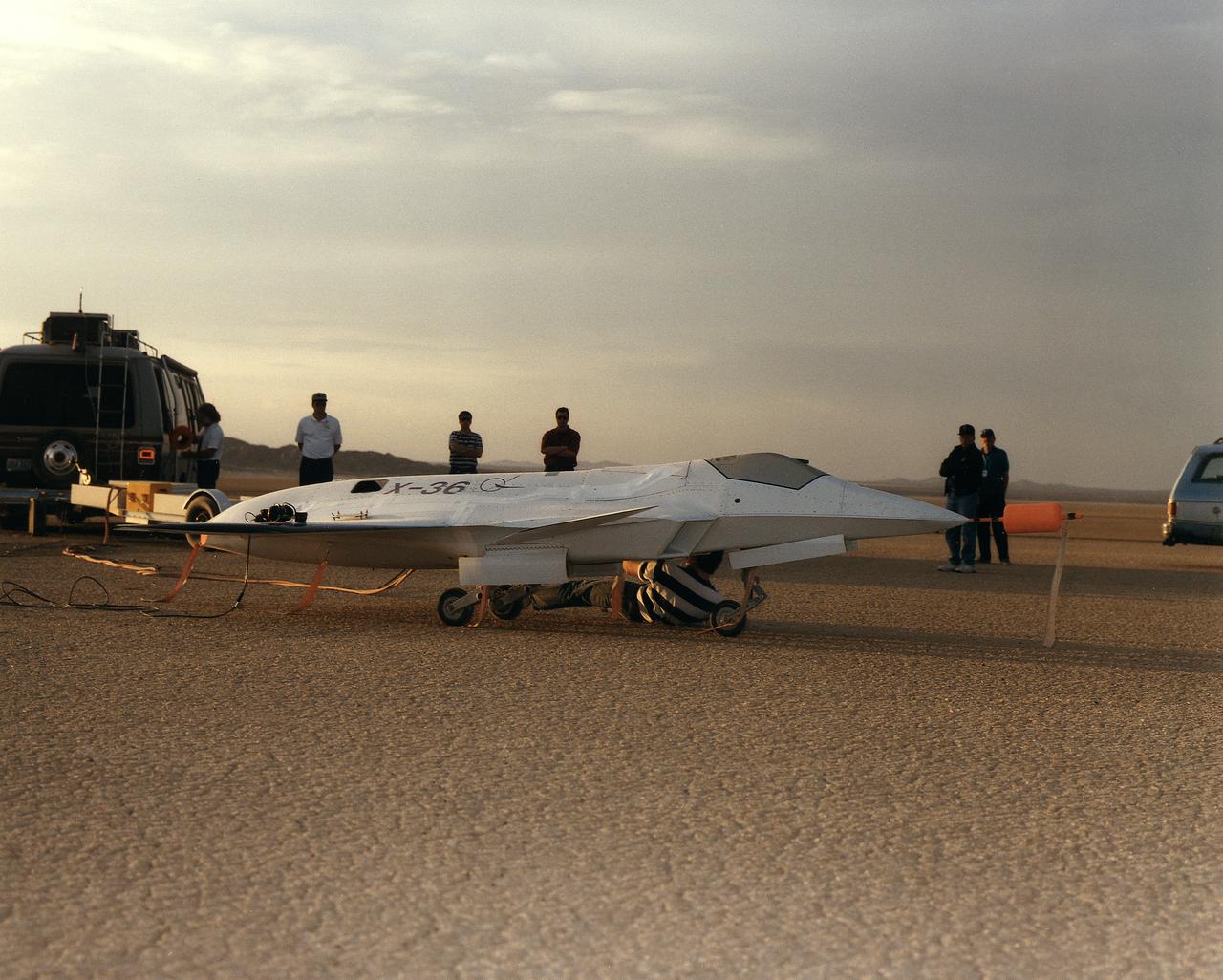

Lit by the rays of the morning sunrise on Rogers Dry Lake, adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, technicians prepares the remotely-piloted X-36 Tailless Fighter Agility Research Aircraft for its first flight on May 17, 1997.
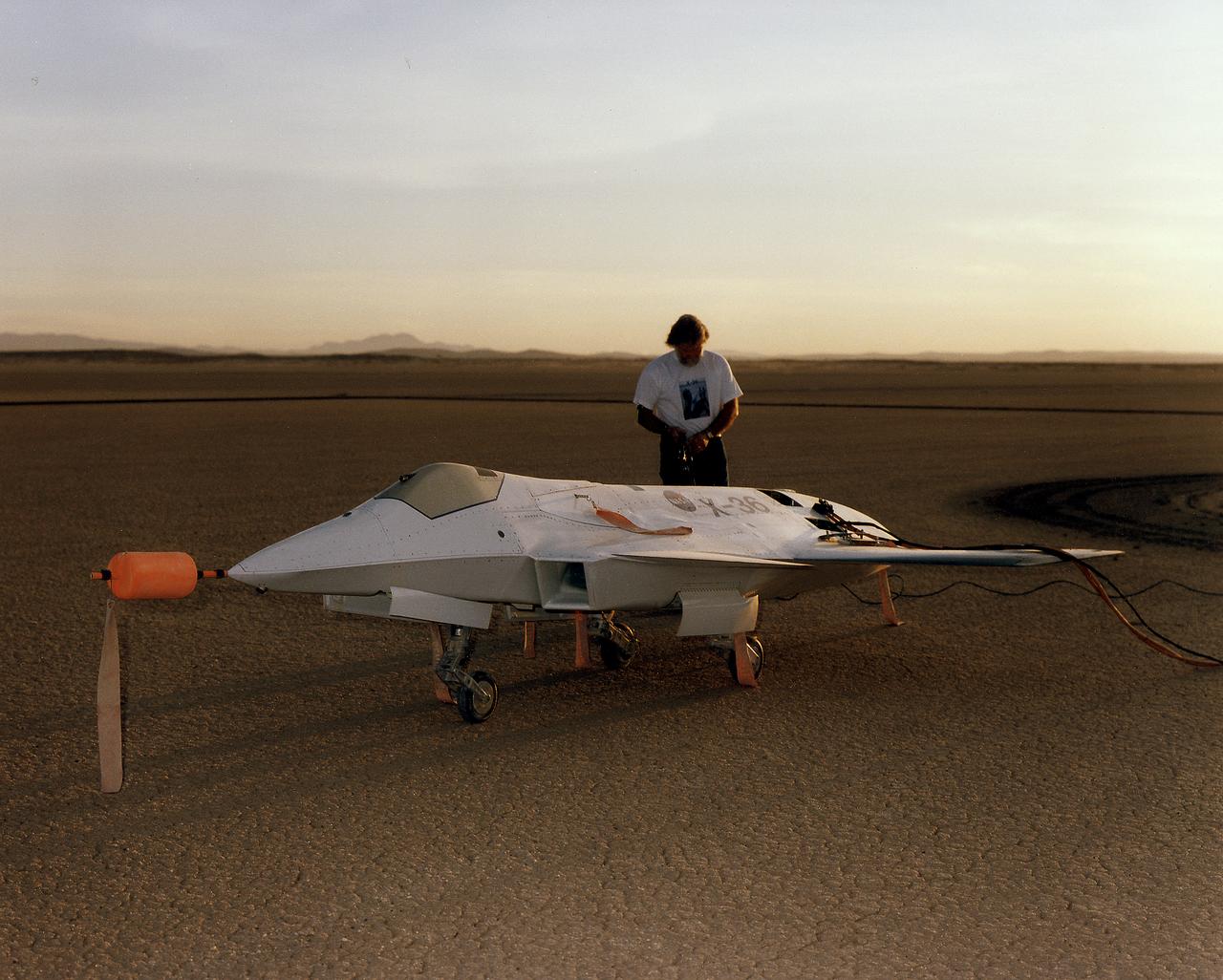

Lit by the rays of the morning sunrise on Rogers Dry Lake, adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, a technician prepares the remotely-piloted X-36 Tailless Fighter Agility Research Aircraft for its first flight on May 17, 1997.
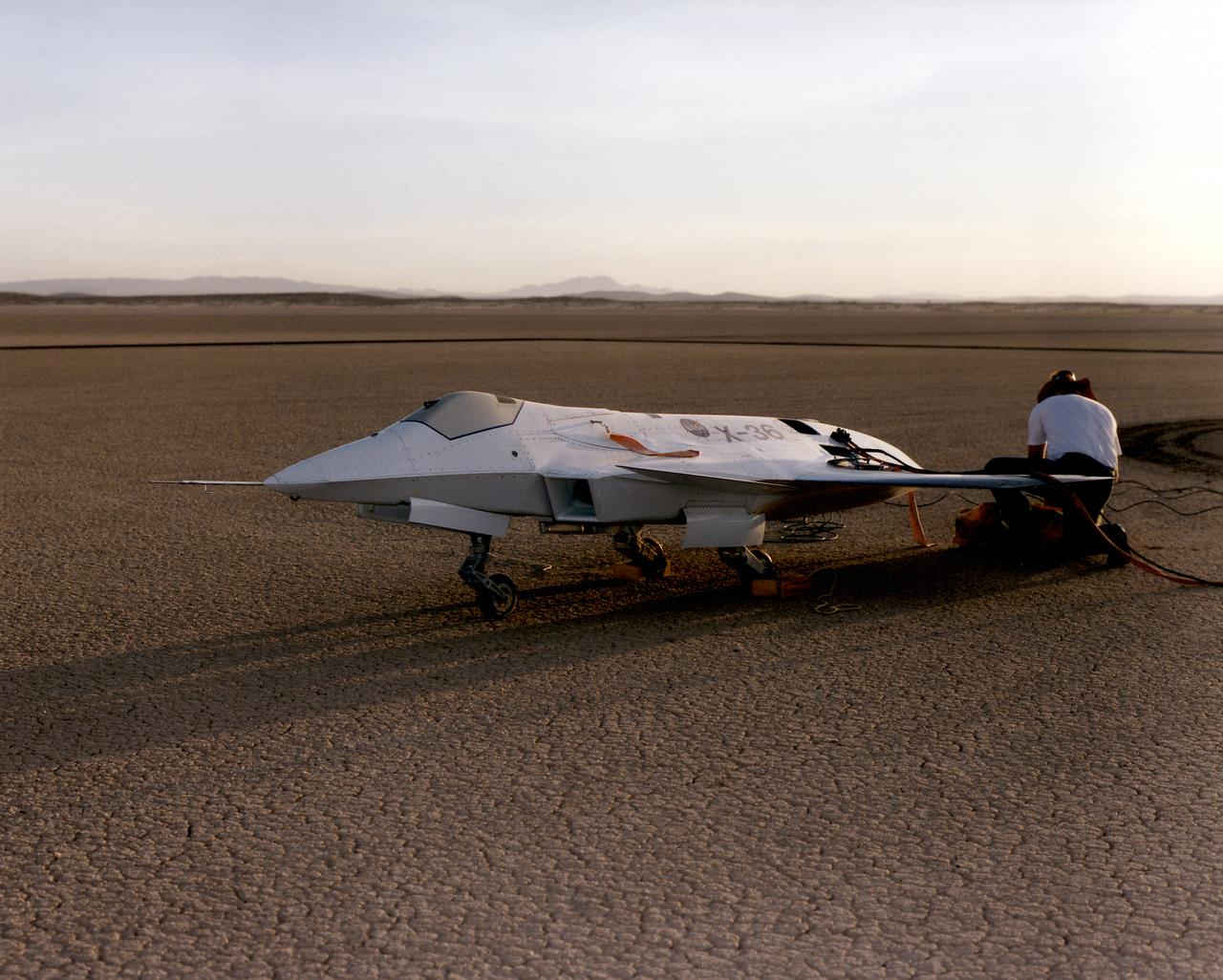

Lit by the rays of the morning sunrise on Rogers Dry Lake, adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, technicians prepare the remotely-piloted X-36 Tailless Fighter Agility Research Aircraft for its first flight in May 1997.
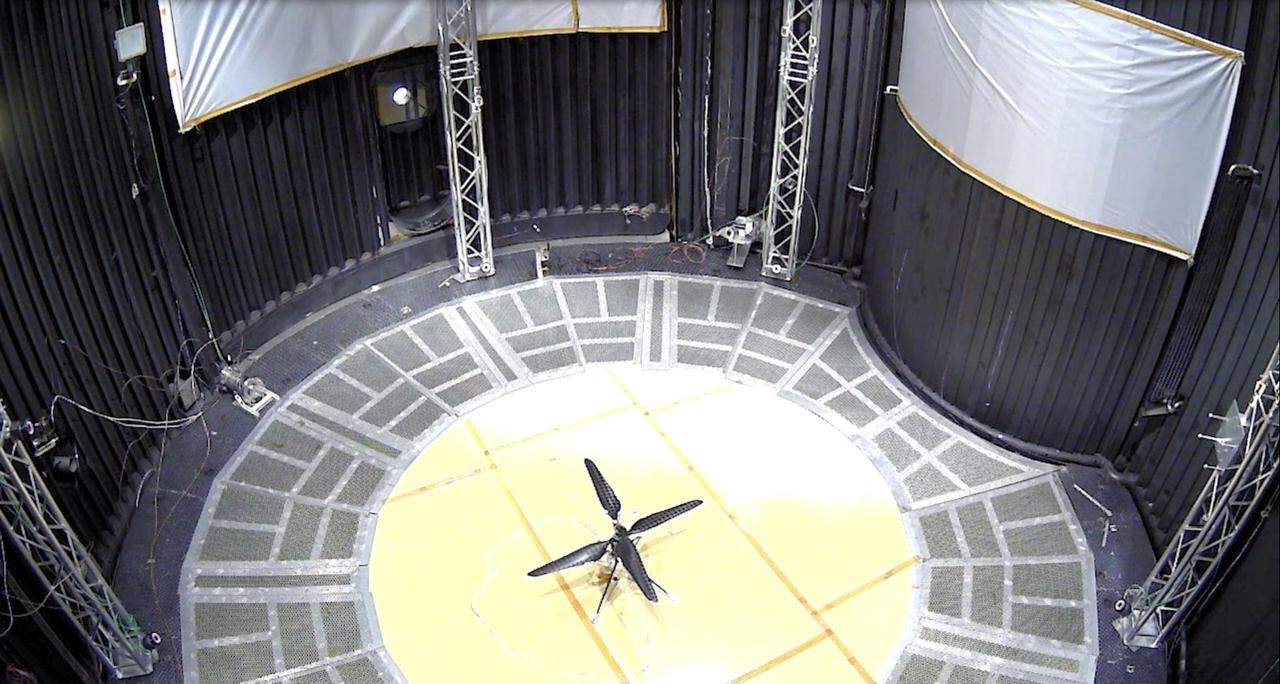

This image shows a test flight of a full-scale prototype of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter. The flight took place on May 31, 2016, in the 25-foot-wide, 85-foot-tall (8-meter-by-26-meter) Space Simulator Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The flight was the first demonstration that powered-controlled flight could be successfully executed in Mars-like conditions. The simulator's vacuum chamber allows engineers to test spacecraft and components in conditions like those they would face on Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26233
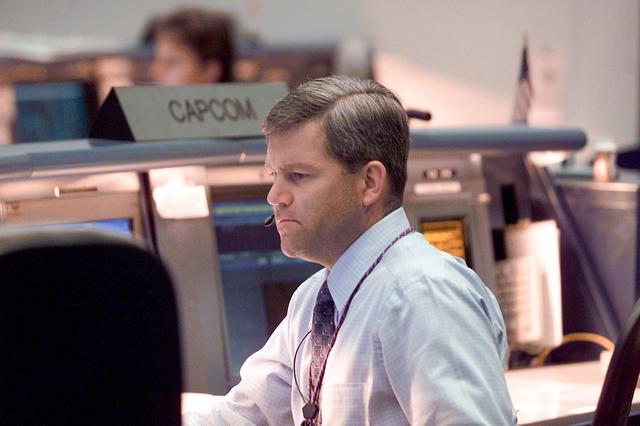

JSC2004-E-45138 (13 October 2004) --- Astronaut Stephen N. Frick monitors communications at the spacecraft communicator (CAPCOM) console in the Shuttle Flight Control Room (WFCR) in Johnson Space Center’s (JSC) Mission Control Center (MCC) with the STS-114 crewmembers during a fully-integrated simulation on October 13. The seven member crew was in a JSC-based simulator during the sims. The dress rehearsal of Discovery's rendezvous and docking with the International Space Station (ISS) was the first flight-specific training for the Space Shuttle's return to flight.
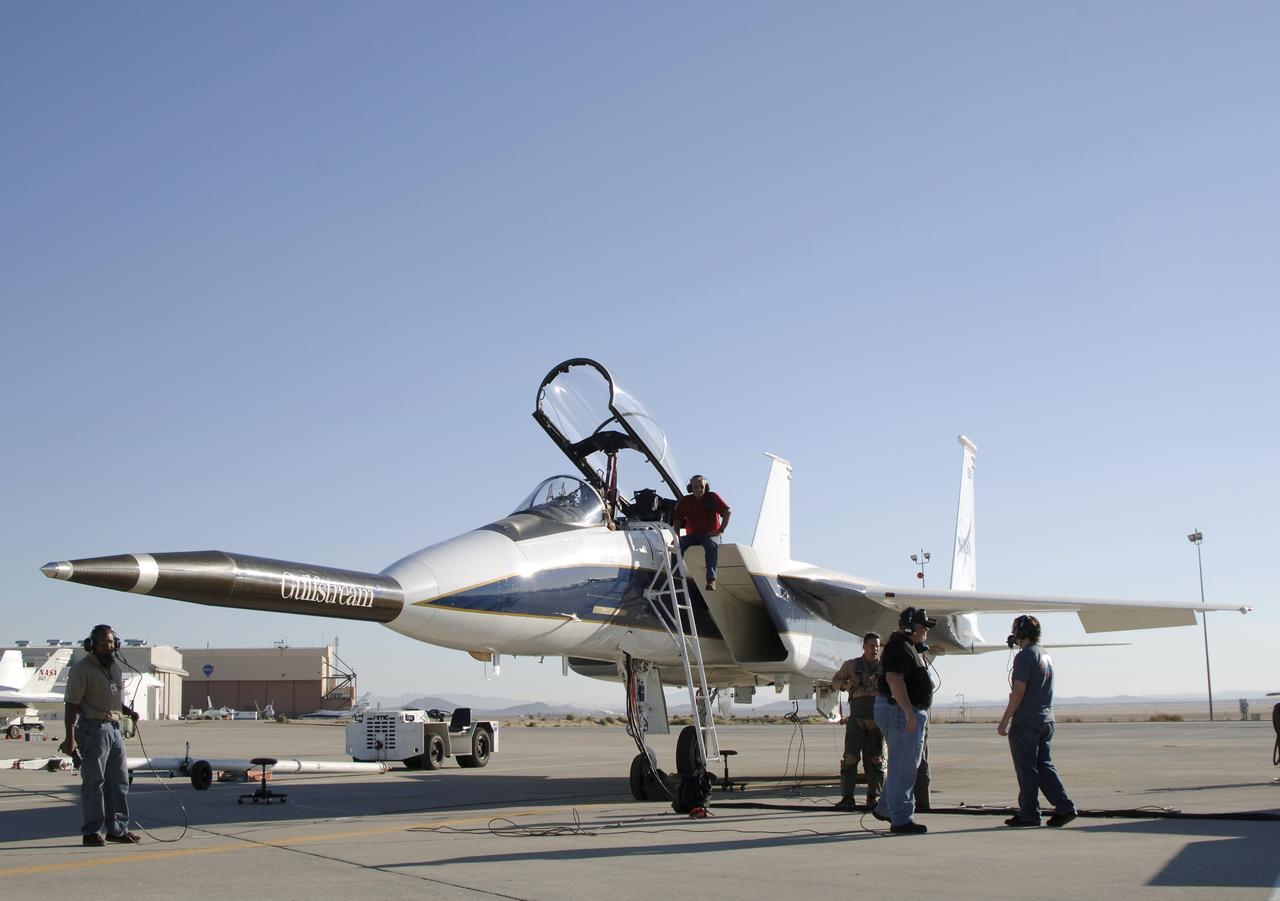

NASA's F-15B testbed aircraft undergoes pre-flight checks before performing the first flight of the Quiet Spike project. The first flight was performed for evaluation purposes, and the spike was not extended. The Quiet Spike was developed as a means of controlling and reducing the sonic boom caused by an aircraft 'breaking' the sound barrier.
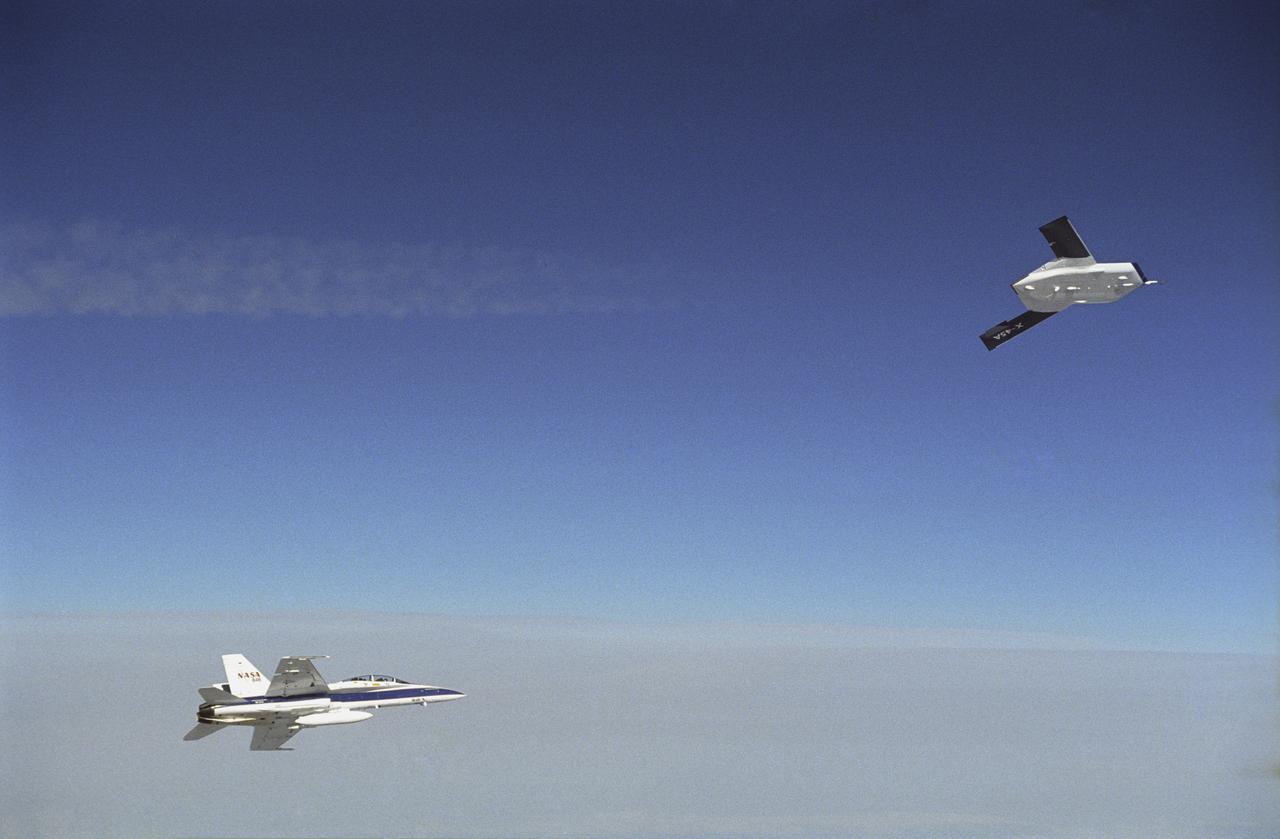

X-45A in flight with F-18 #846 chase aircraft, during first GPS-guided weapon demonstration flight.
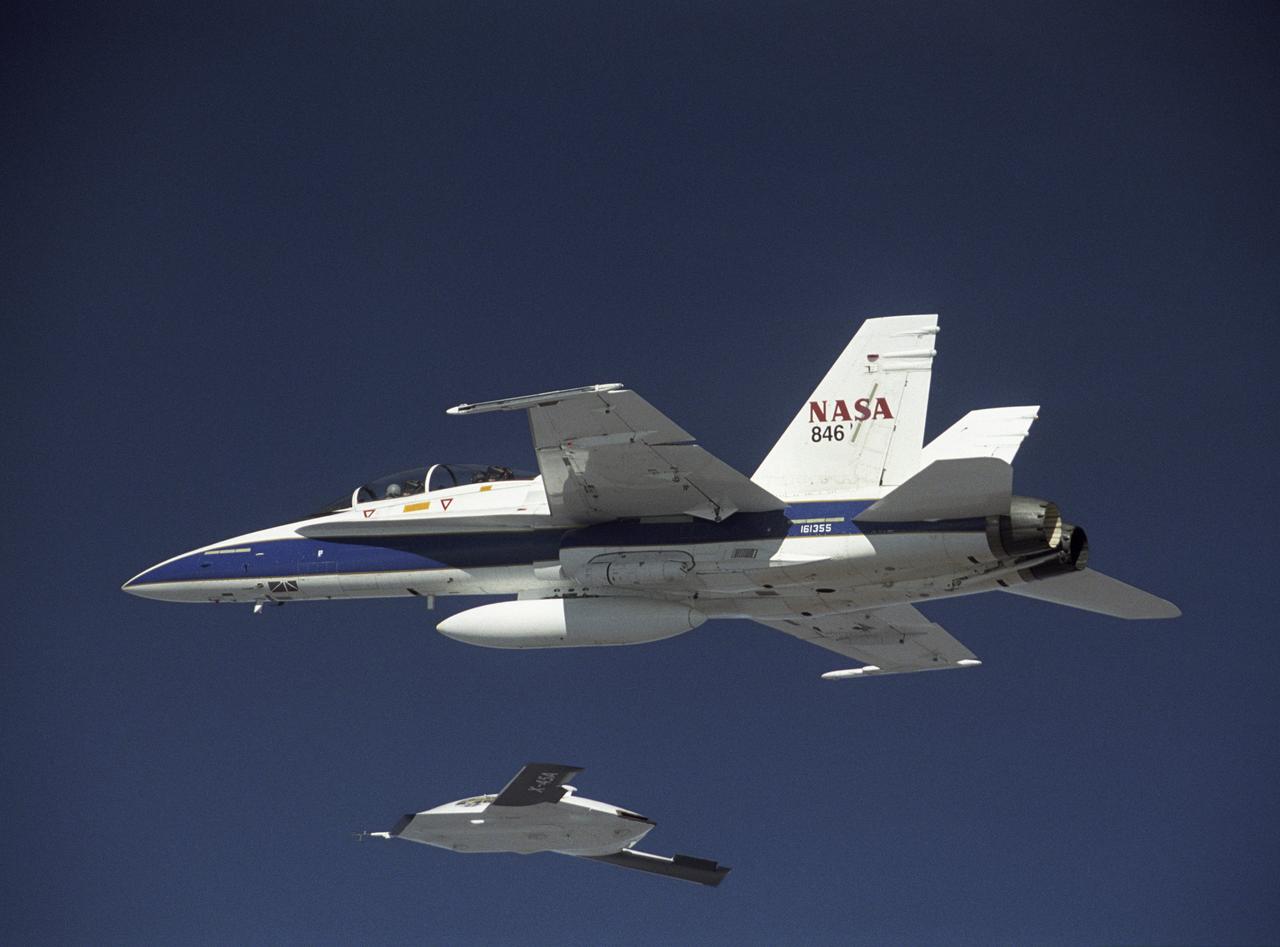

X-45A in flight with F-18 #846 chase aircraft, during first GPS-guided weapon demonstration flight.
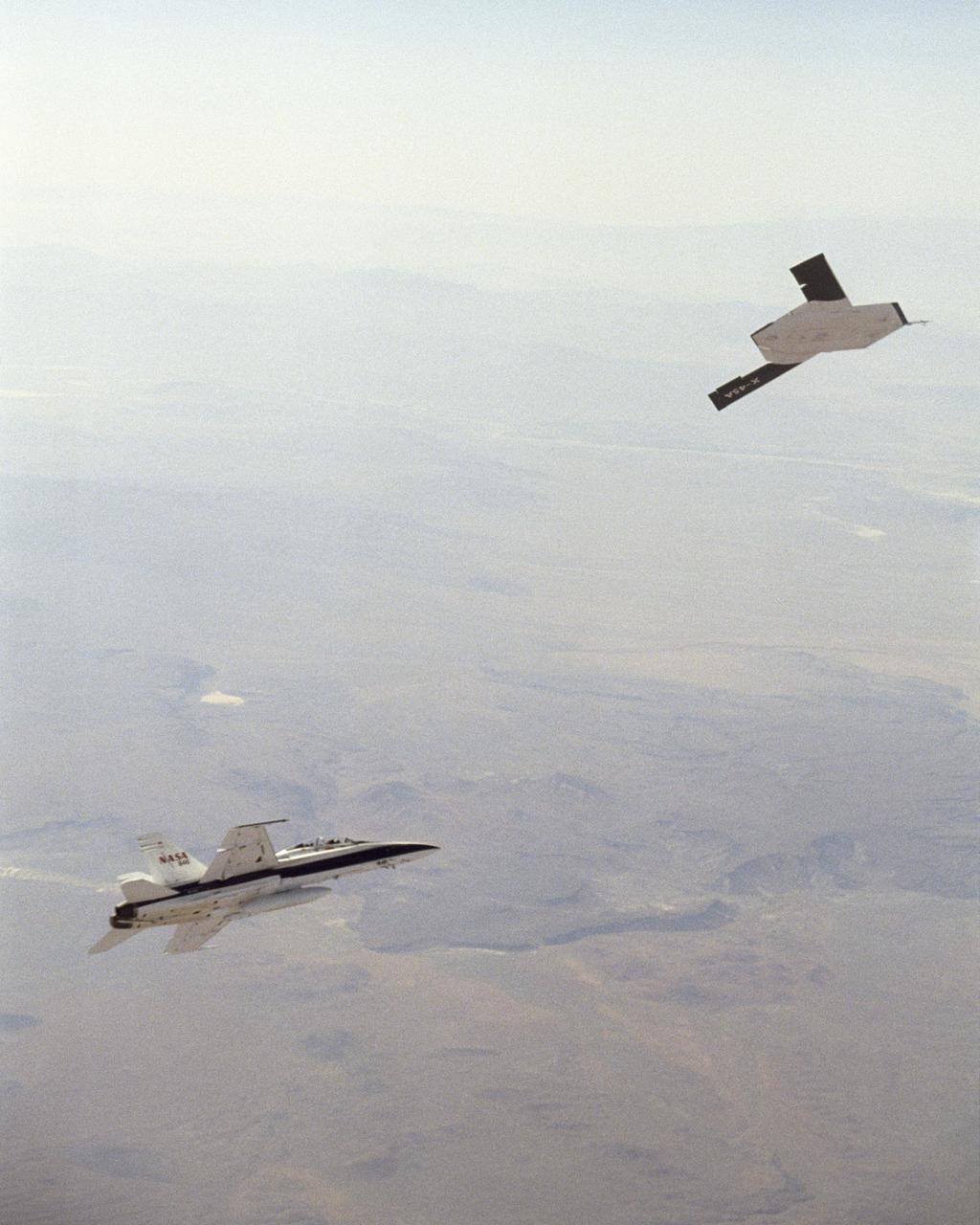

X-45A in flight with F-18 #846 chase aircraft, during first GPS-guided weapon demonstration flight.
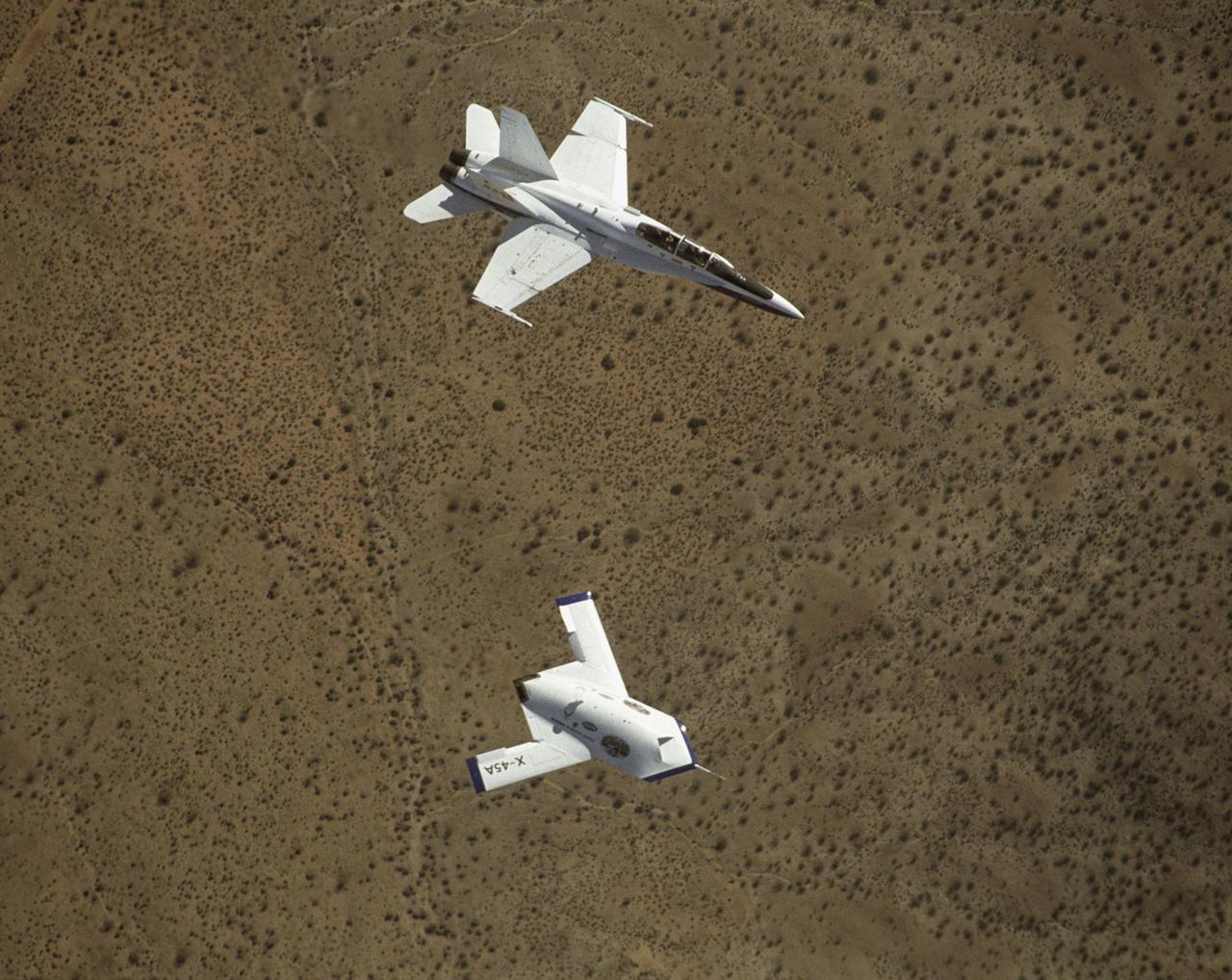

X-45A in flight with F-18 #846 chase aircraft, during first GPS-guided weapon demonstration flight.
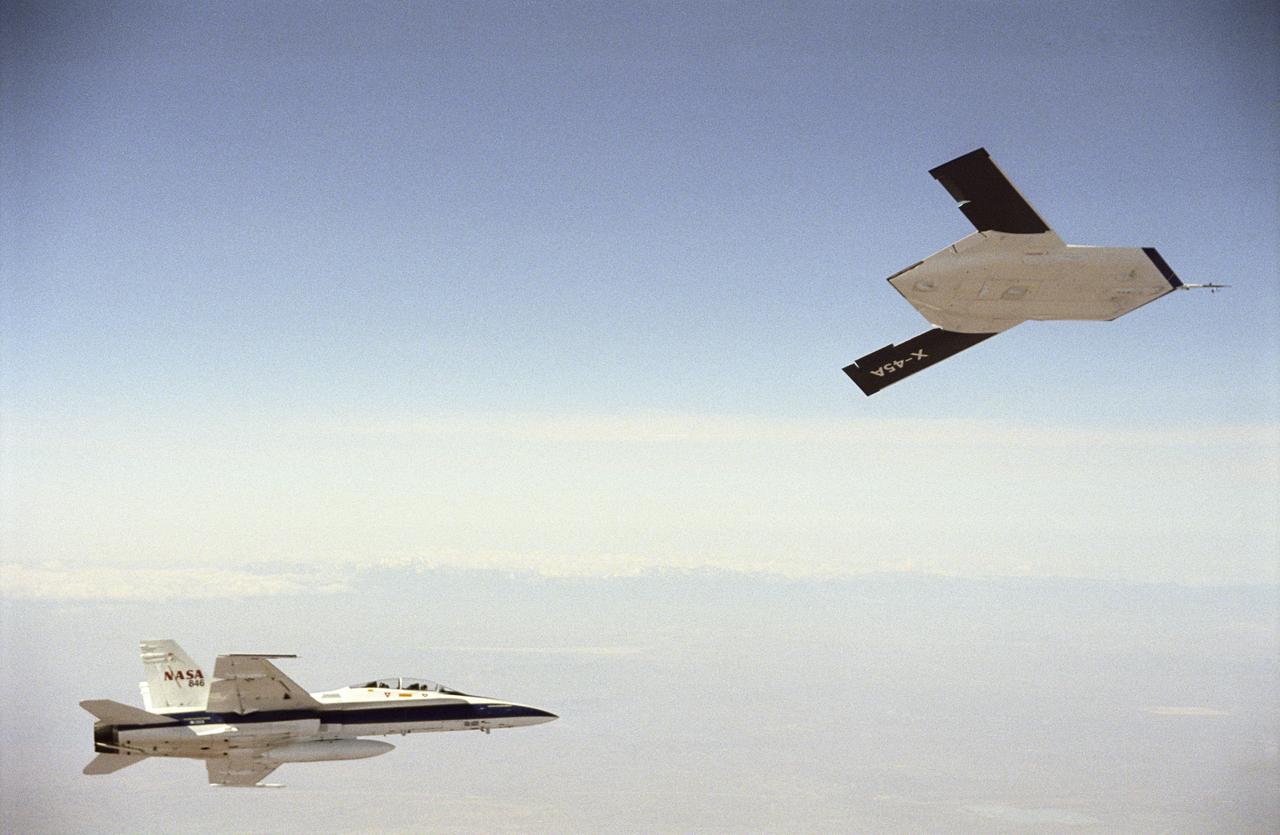

X-45A in flight with F-18 #846 chase aircraft, during first GPS-guided weapon demonstration flight.
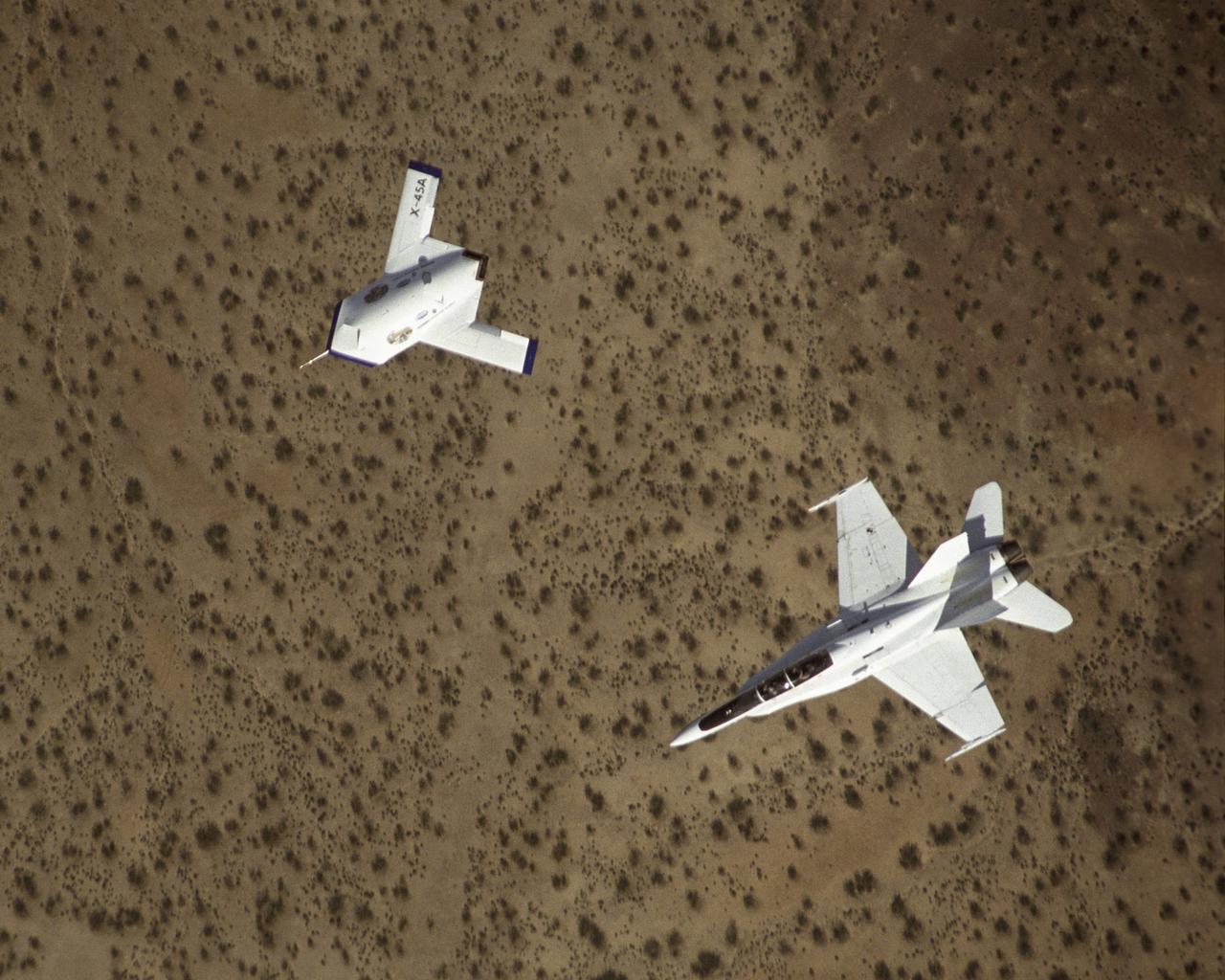

X-45A in flight with F-18 #846 chase aircraft, during first GPS-guided weapon demonstration flight.

The third iteration of the X-38, V-131R, glides down under a giant parafoil towards a landing on Rogers Dry Lake near NASAÕs Dryden Flight Research Center during its first free flight Nov. 2, 2000. The X-38 prototypes are intended to perfect technology for a planned Crew Return Vehicle (CRV) ÒlifeboatÓ to carry a crew to safety in the event of an emergency on the International Space Station. Free-flight tests of X-38 V-131R are evaluating upgraded avionics and control systems and the aerodynamics of the modified upper body, which is more representative of the final design of the CRV than the two earlier X-38 test craft, including a simulated hatch atop the body. The huge 7,500 square-foot parafoil will enable the CRV to land in the length of a football field after returning from space. The first three X-38Õs are air-launched from NASAÕs venerable NB-52B mother ship, while the last version, V-201, will be carried into space by a Space Shuttle and make a fully autonomous re-entry and landing.
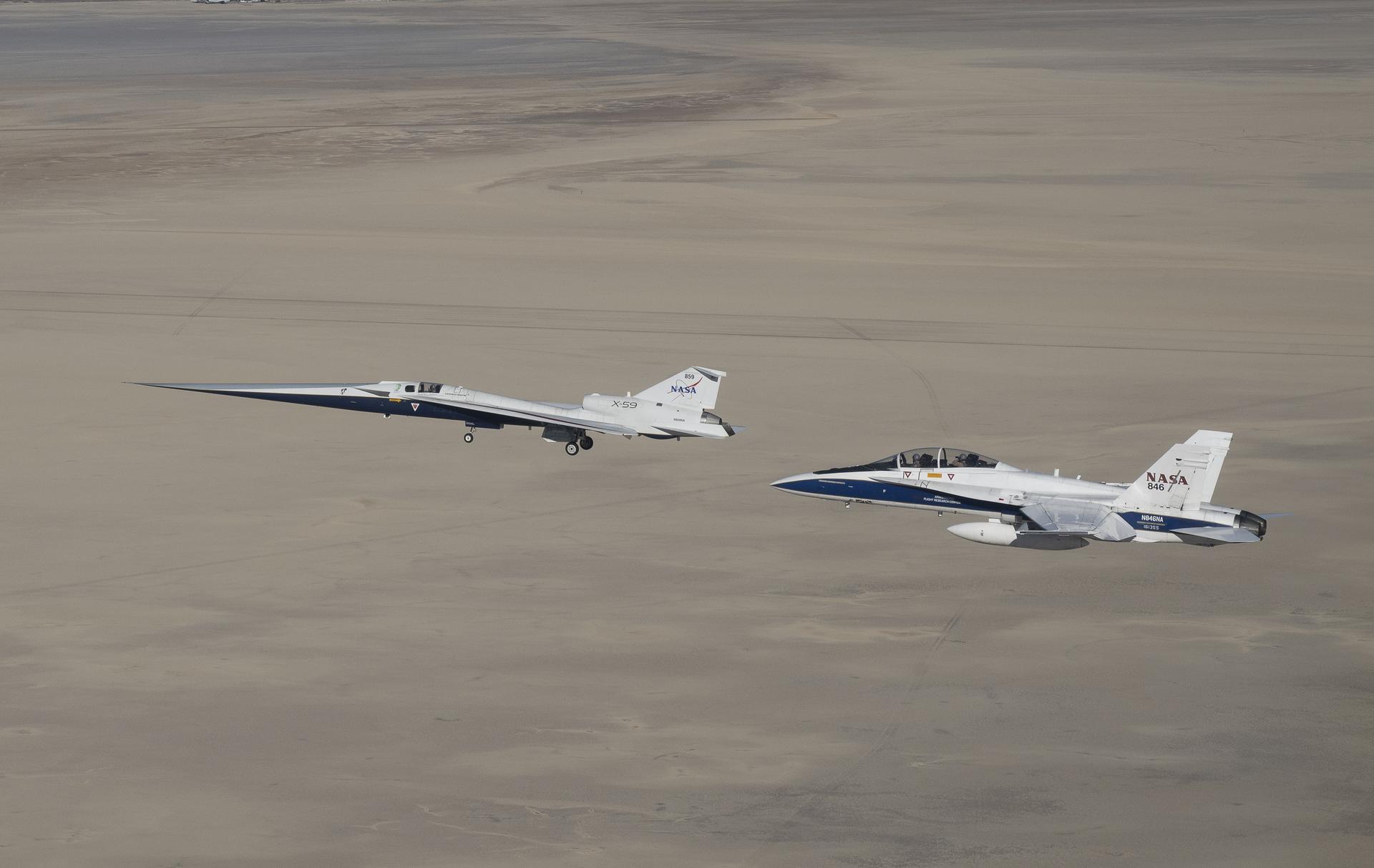

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft flies above Palmdale and Edwards, California, during its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, accompanied by a NASA F/A-18 research aircraft. A NASA F-15 research aircraft (not pictured) captured the image as the X-59 traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, where it will begin flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land.
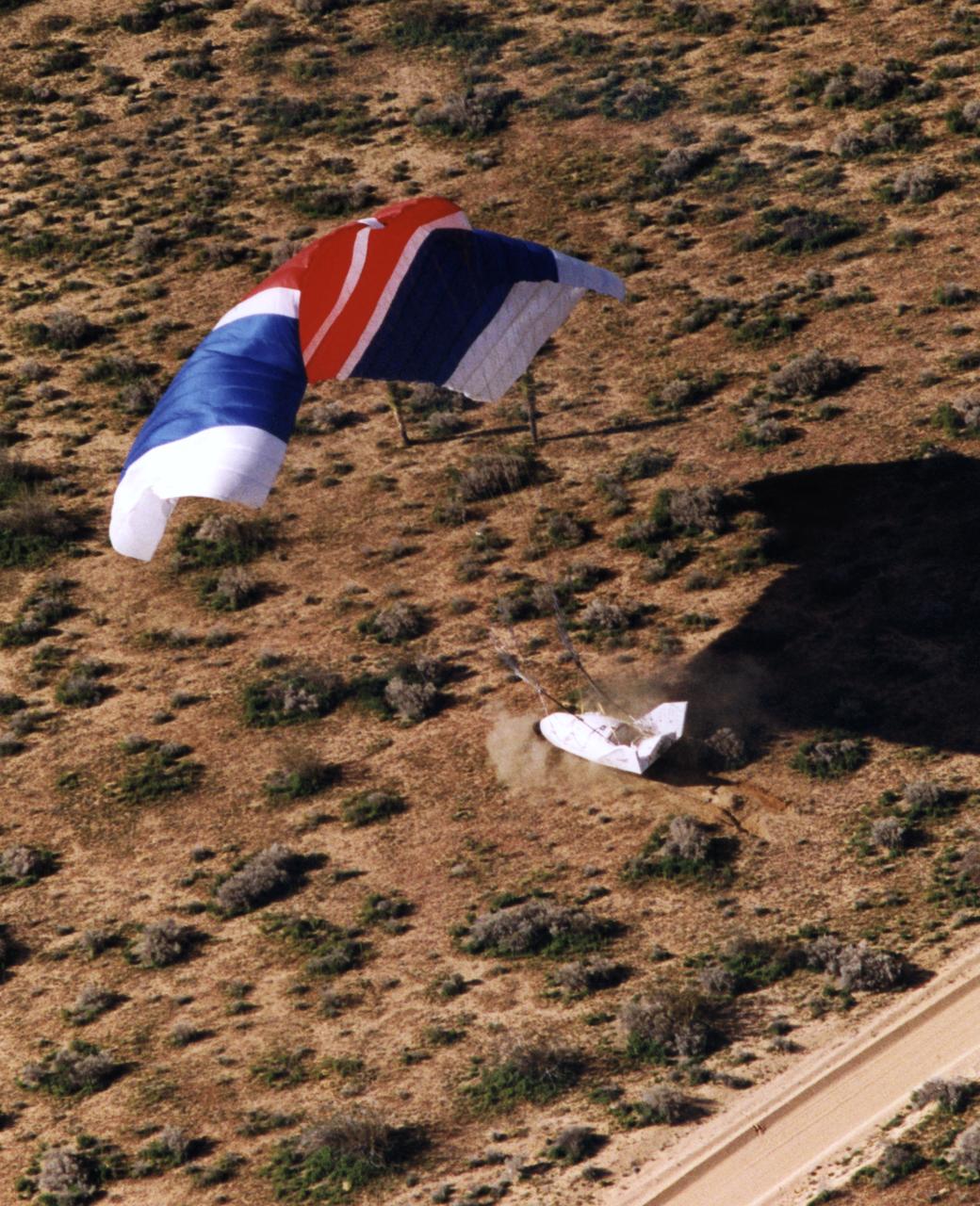

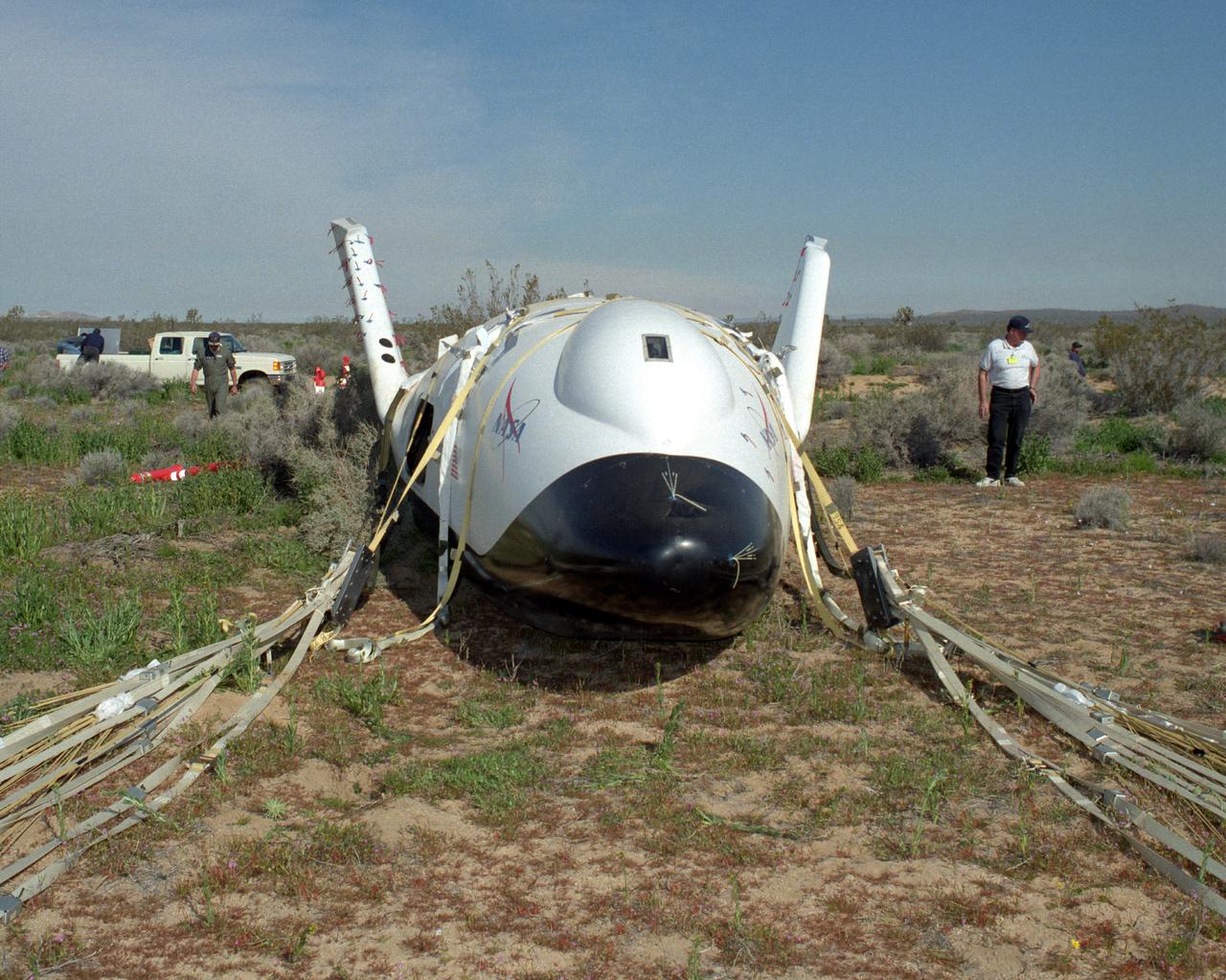
The X-38 Crew Return Vehicle touches down amidst the California desert scrubbrush at the end of its first free flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, in March 1998.
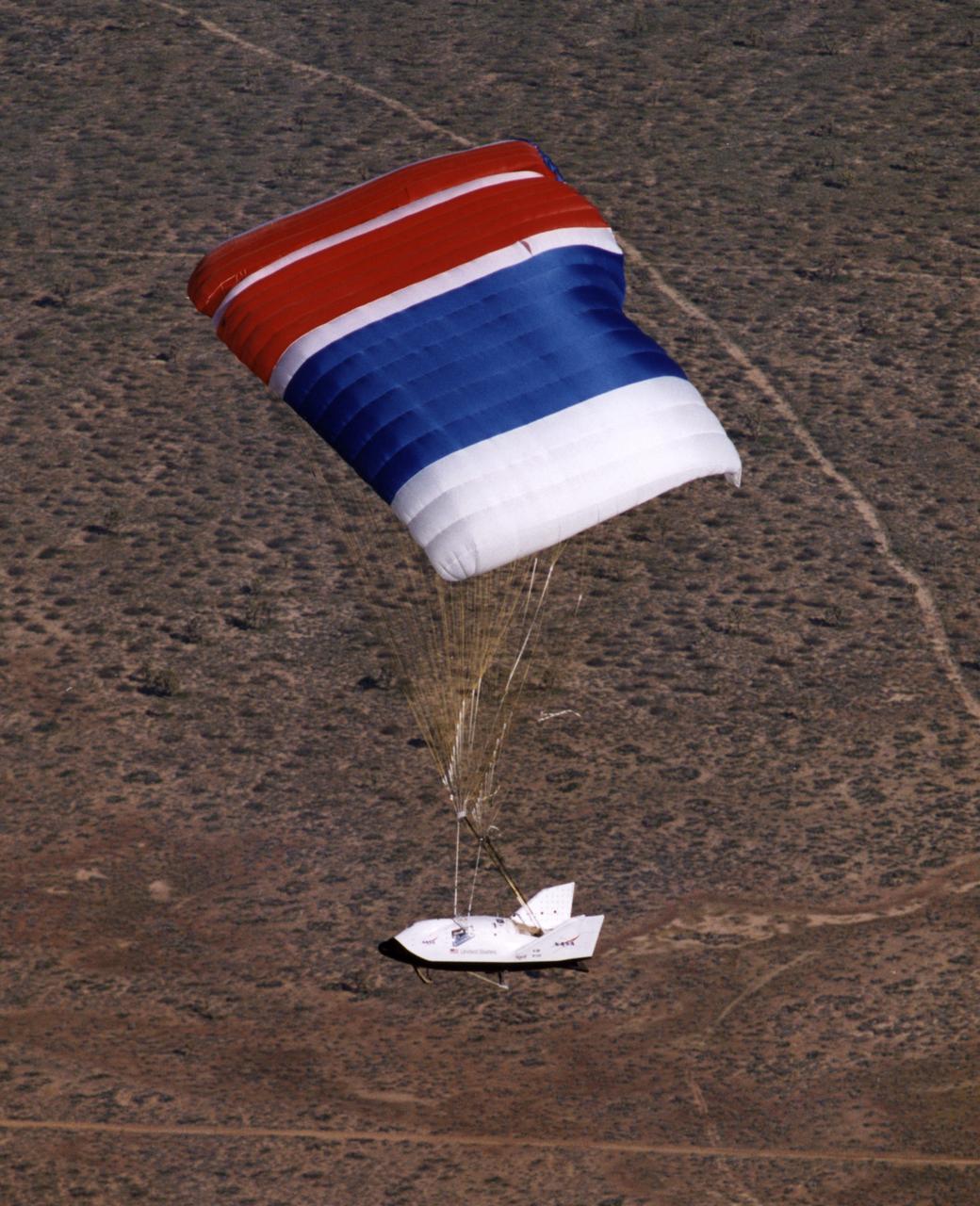

The X-38 Crew Return Vehicle descends under its steerable parafoil over the California desert during its first free flight in March 1998 at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.

Crew members surround the X-38 lifting body research vehicle after a successful test flight and landing in March 1998. The flight was the first free flight for the vehicle and took place at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
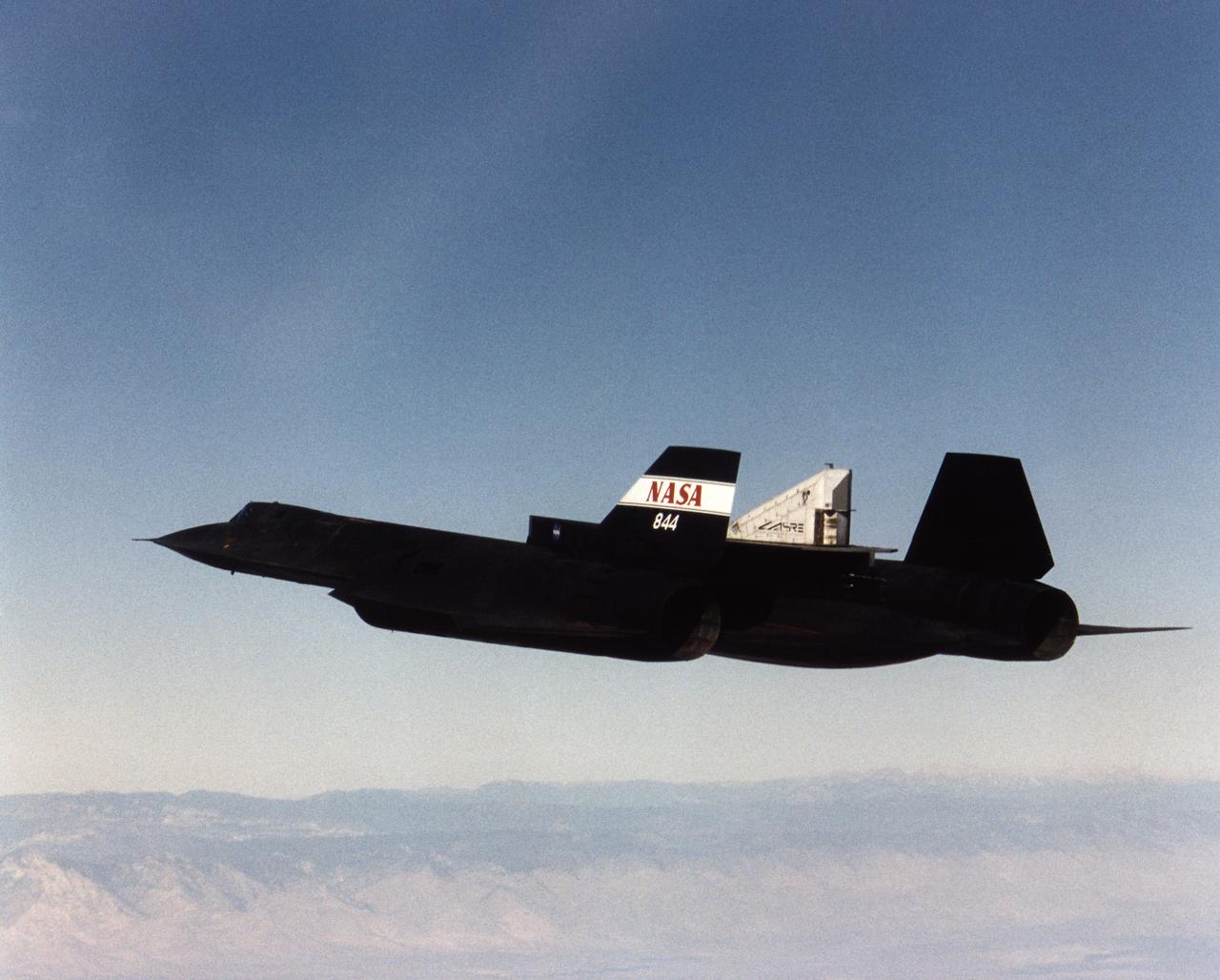

A NASA SR-71 successfully completed its first flight 31 October 1997 as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
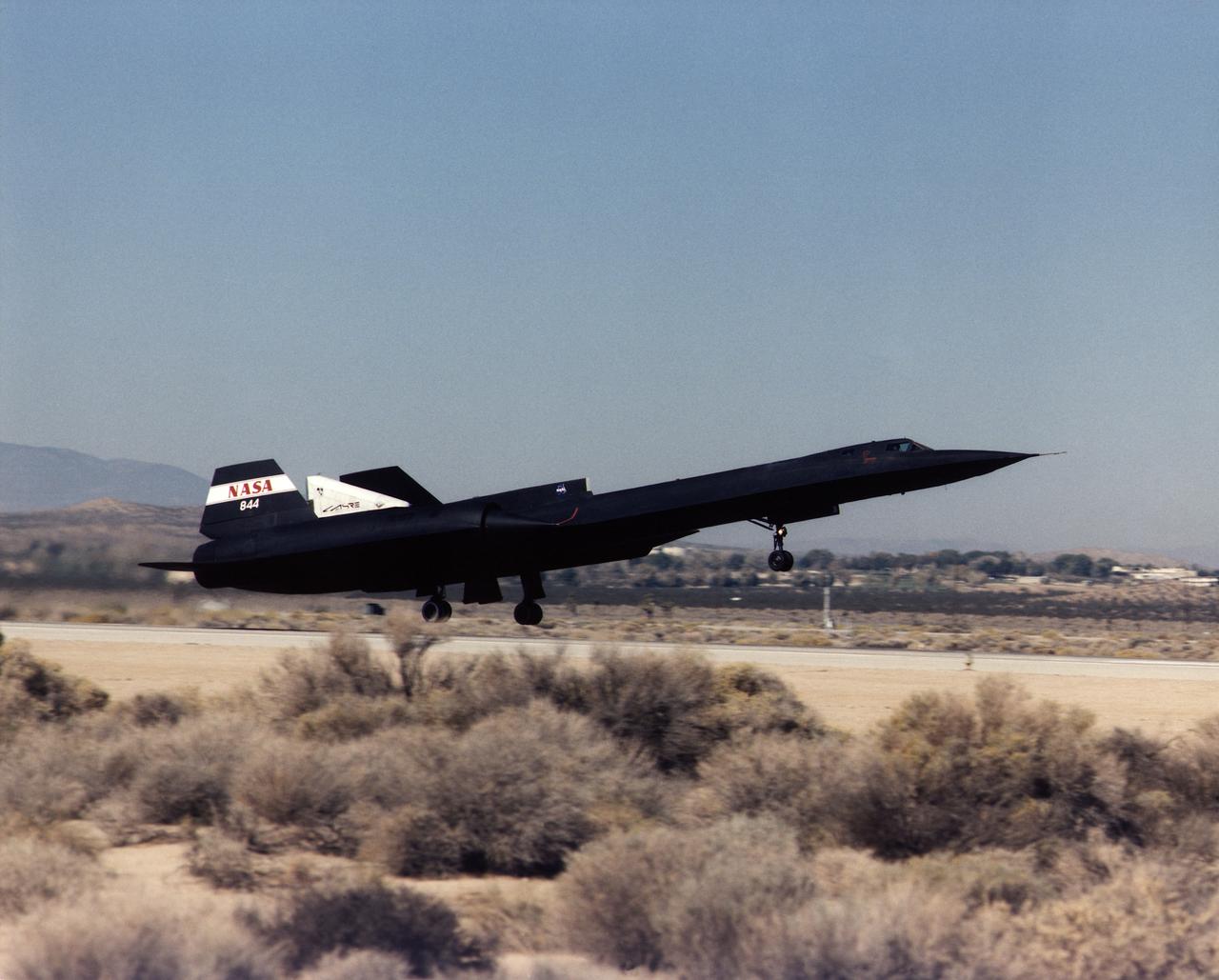

A NASA SR-71 takes off Oct. 31, making its first flight as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
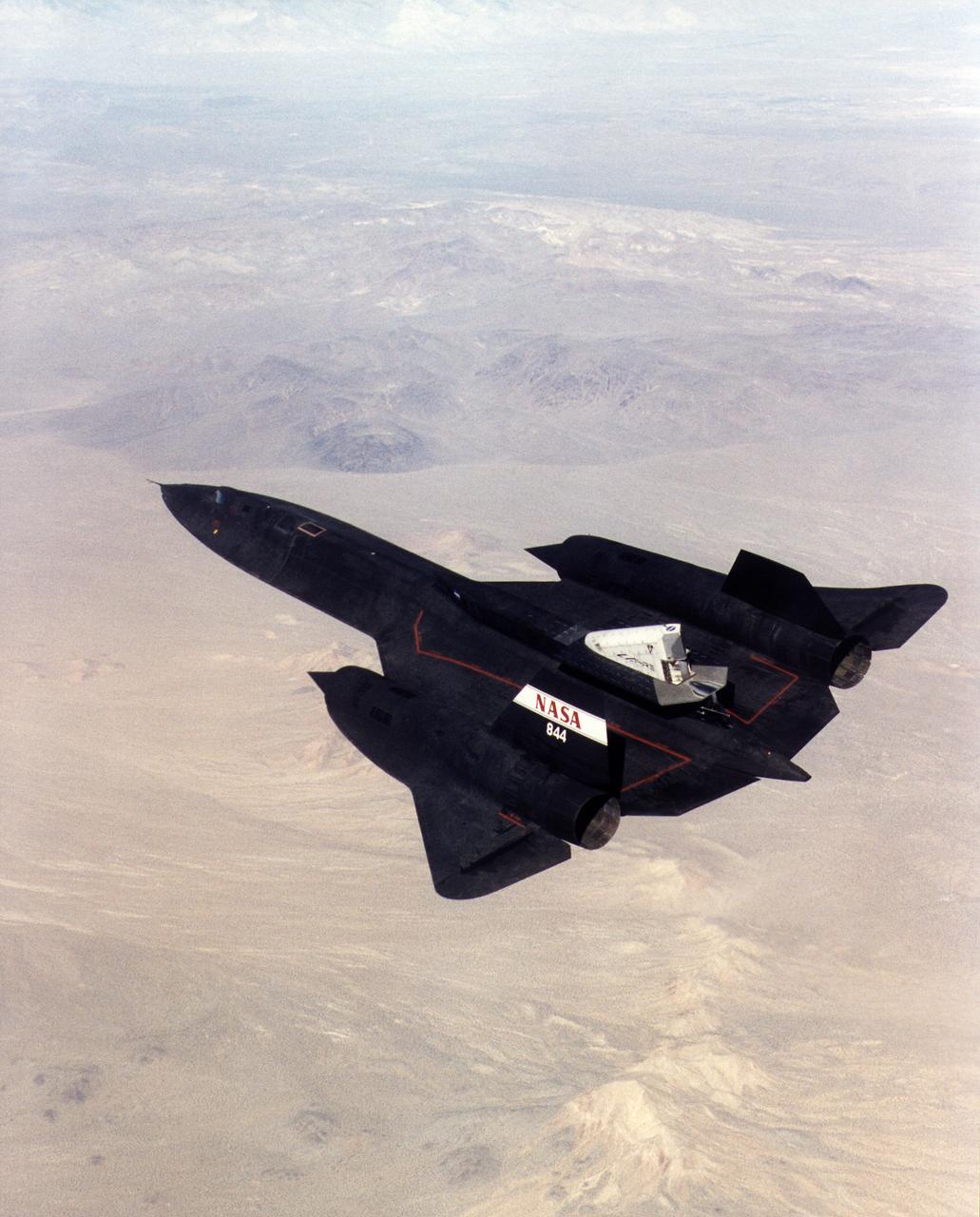

A NASA SR-71 successfully completed its first flight 31 October 1997 as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
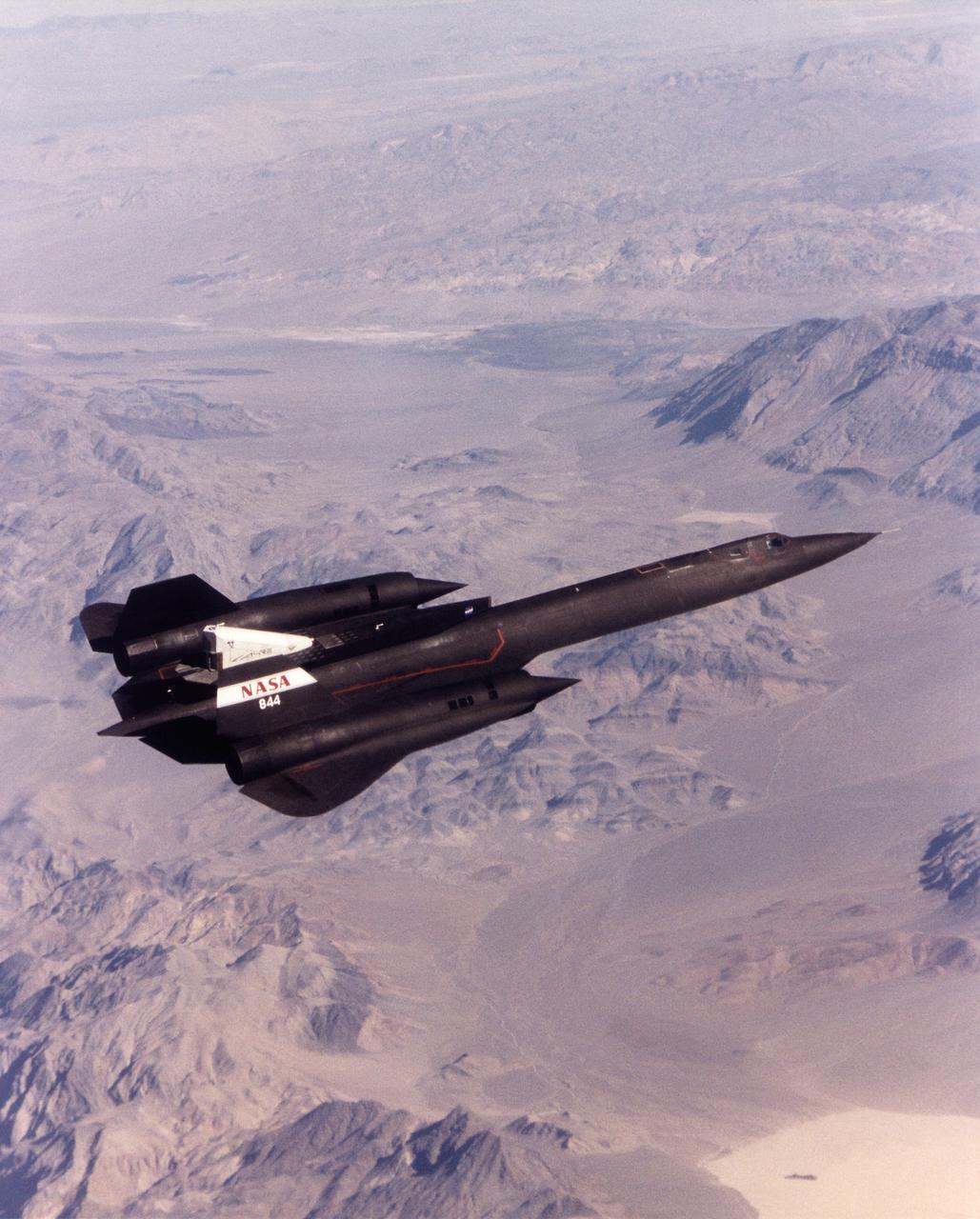

A NASA SR-71 made its successful first flight Oct. 31 as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/ Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
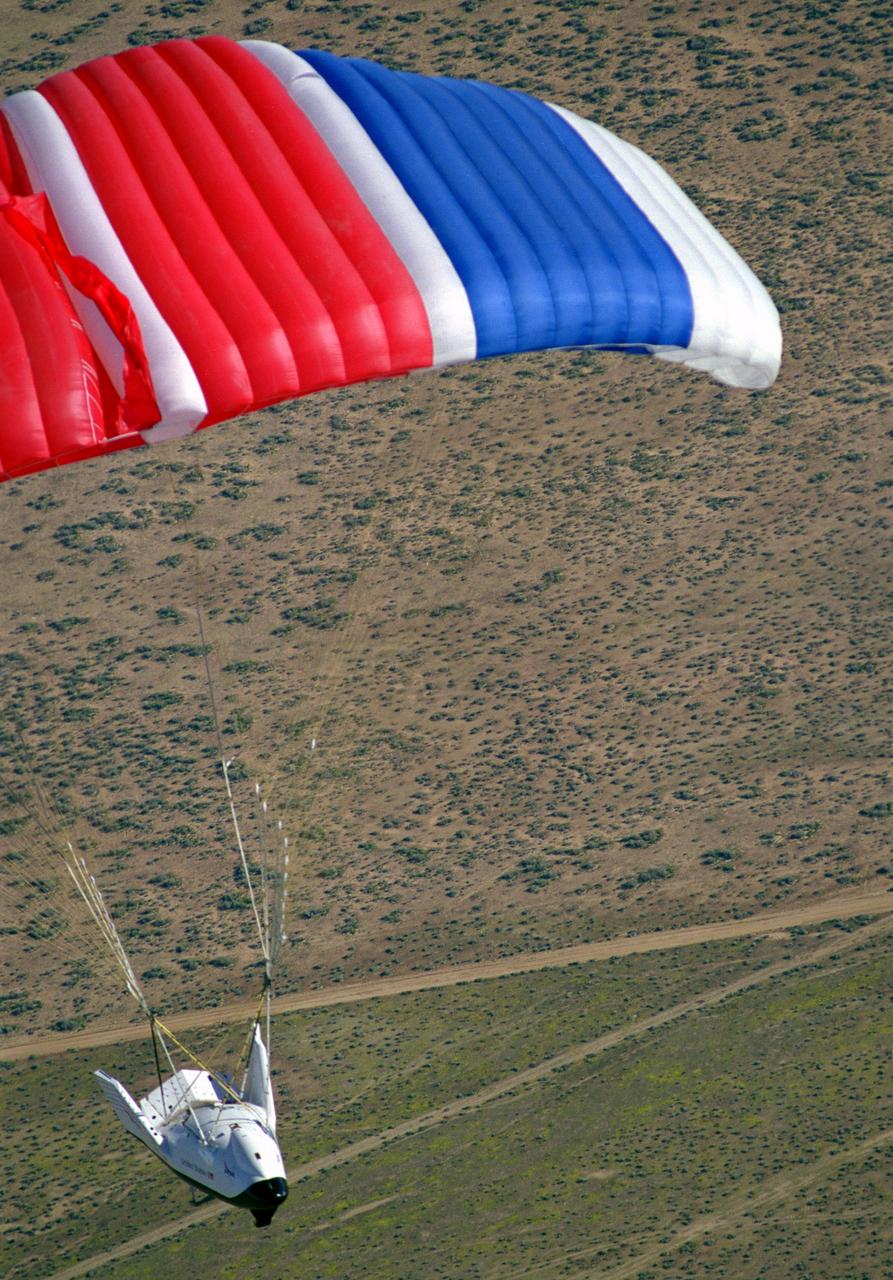

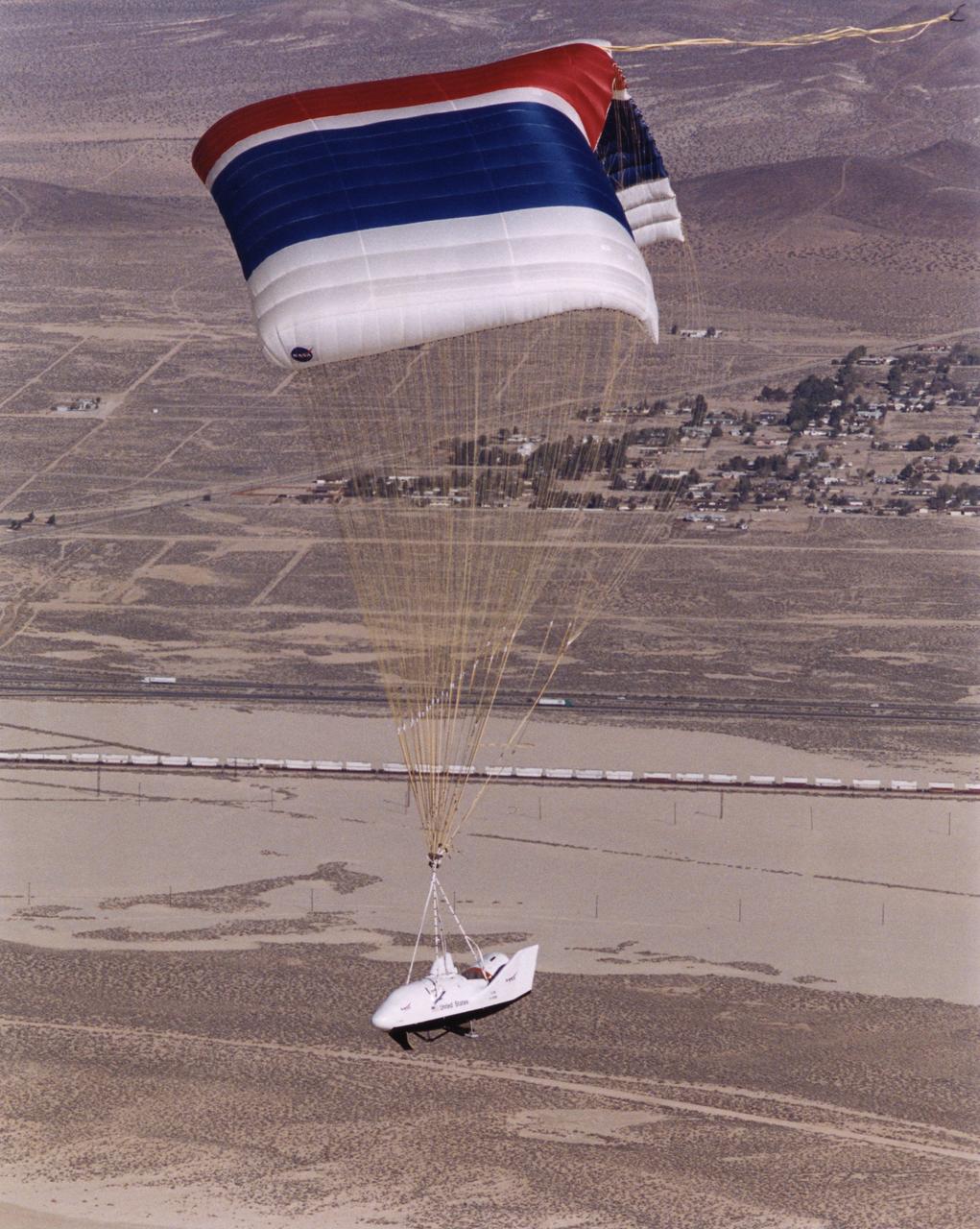
The X-38 Crew Return Vehicle descends under its steerable parafoil over the California desert in its first free flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The flight took place March 12, 1998.
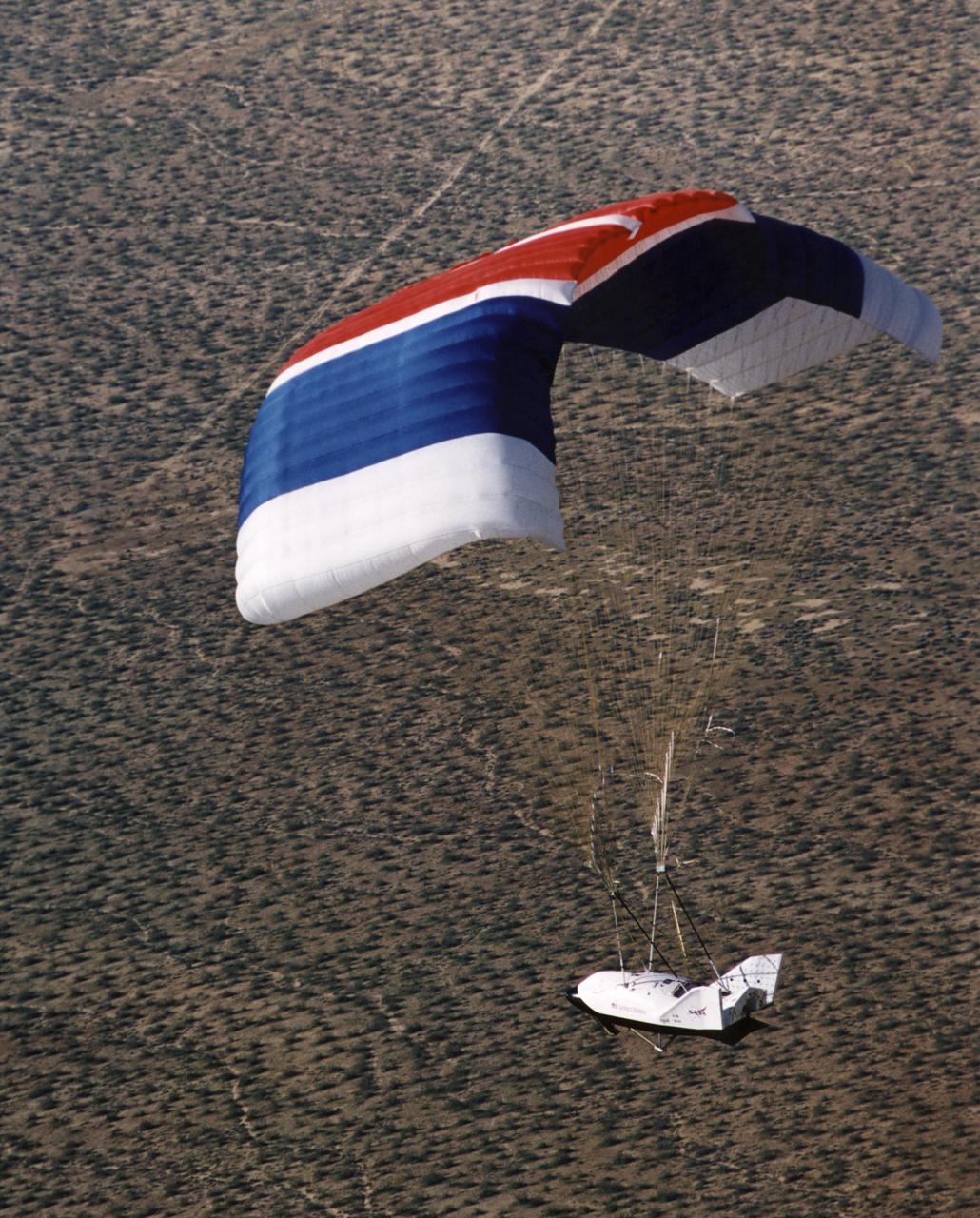

The X-38 Crew Return Vehicle descends under its steerable parafoil over the California desert in its first free flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The flight took place March 12, 1998.
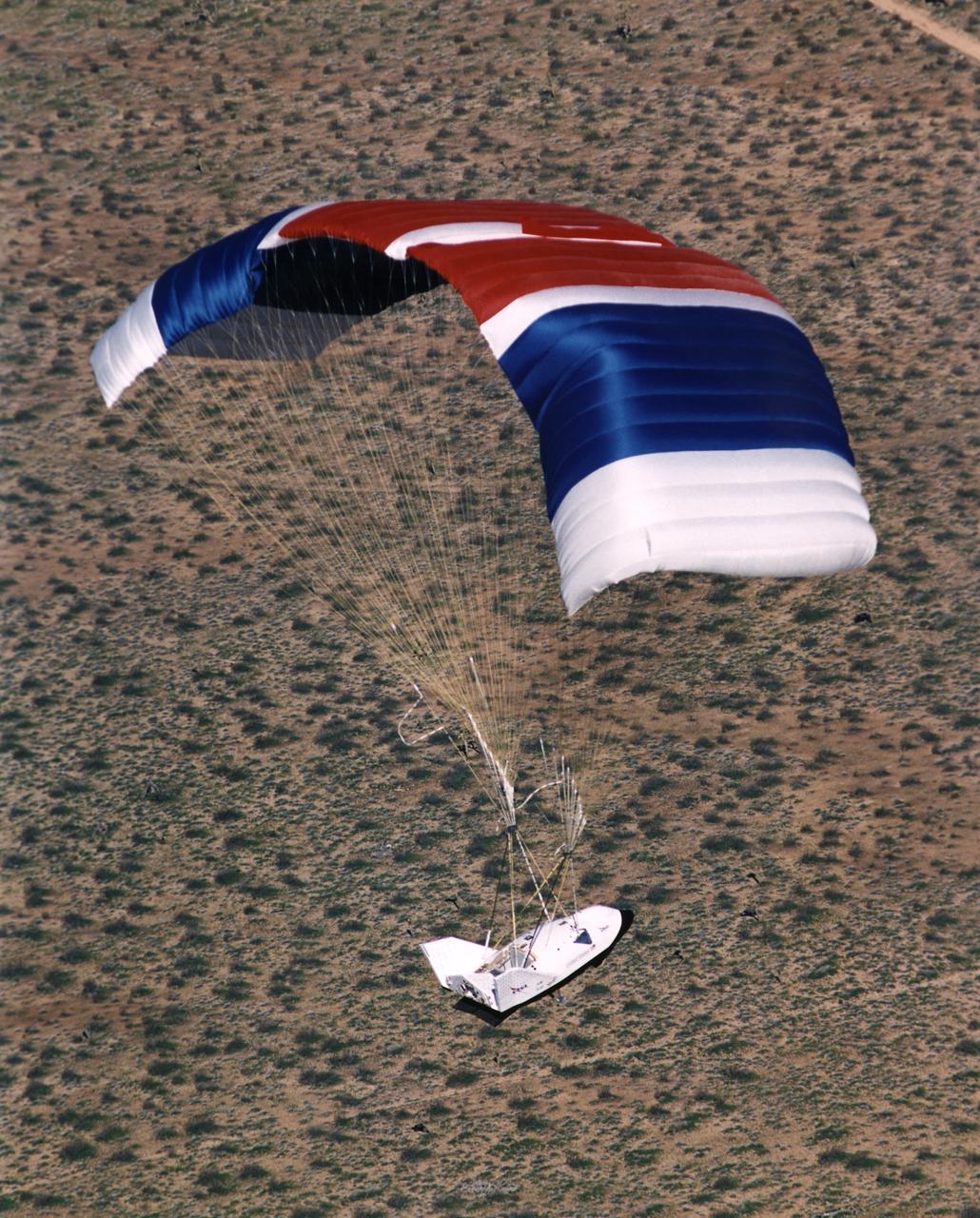

The X-38 Crew Return Vehicle descends under its steerable parafoil over the California desert in its first free flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The flight took place March 12, 1998.
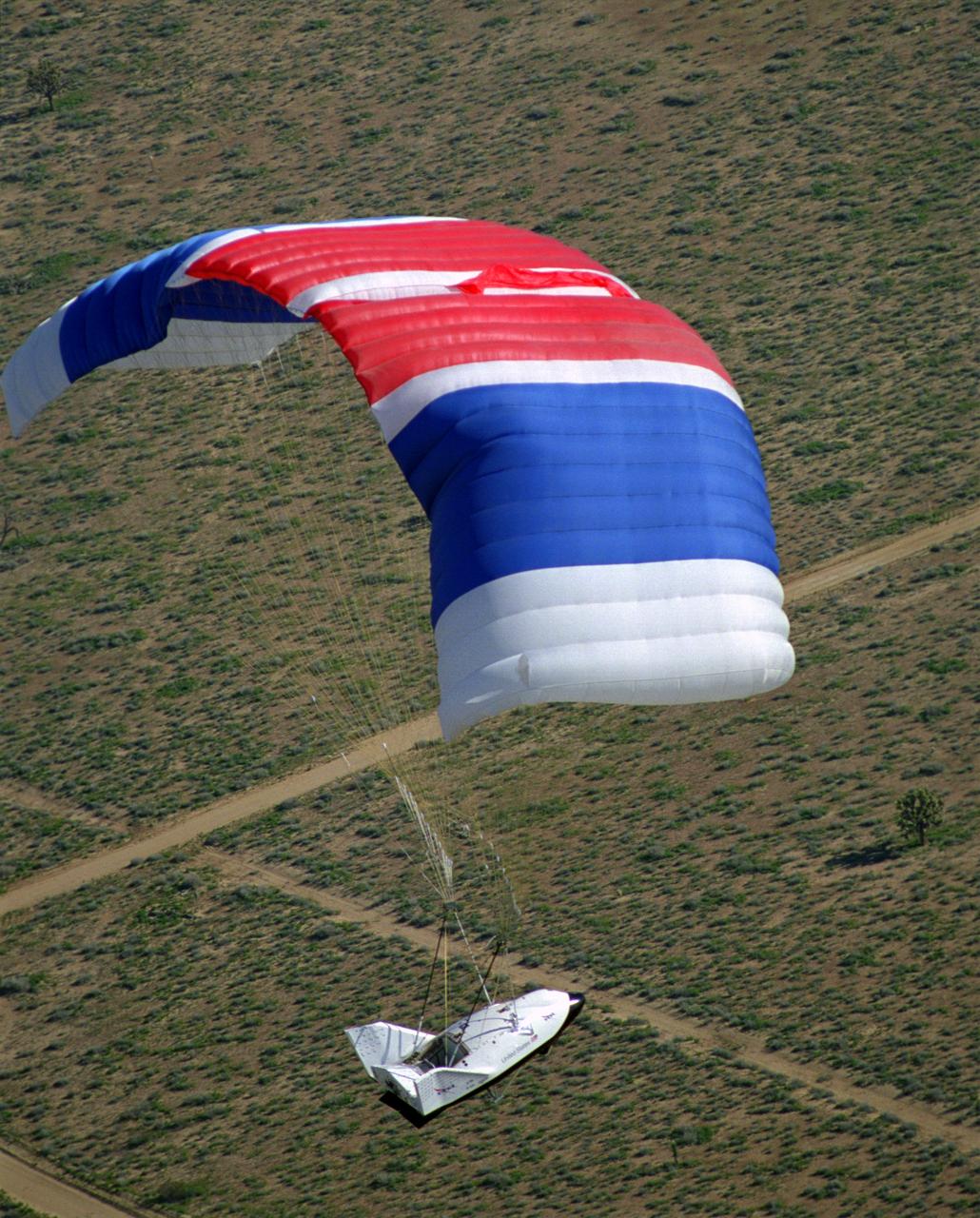

The X-38 Crew Return Vehicle descends under its steerable parafoil over the California desert in its first free flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The flight took place March 12, 1998.

The one-third scale twin-fuselage towed glider glides in for landing on Rogers Dry Lake after its successful first test flight.

NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) was airborne for almost two hours during its first check flight at Waco, Texas on April 26, 2007.

With landing gear extended, the NASA/DLR Stratospheric Observatory for Infared Astronomy (SOFIA) 747SP cruises over central Texas on its first checkout flight.
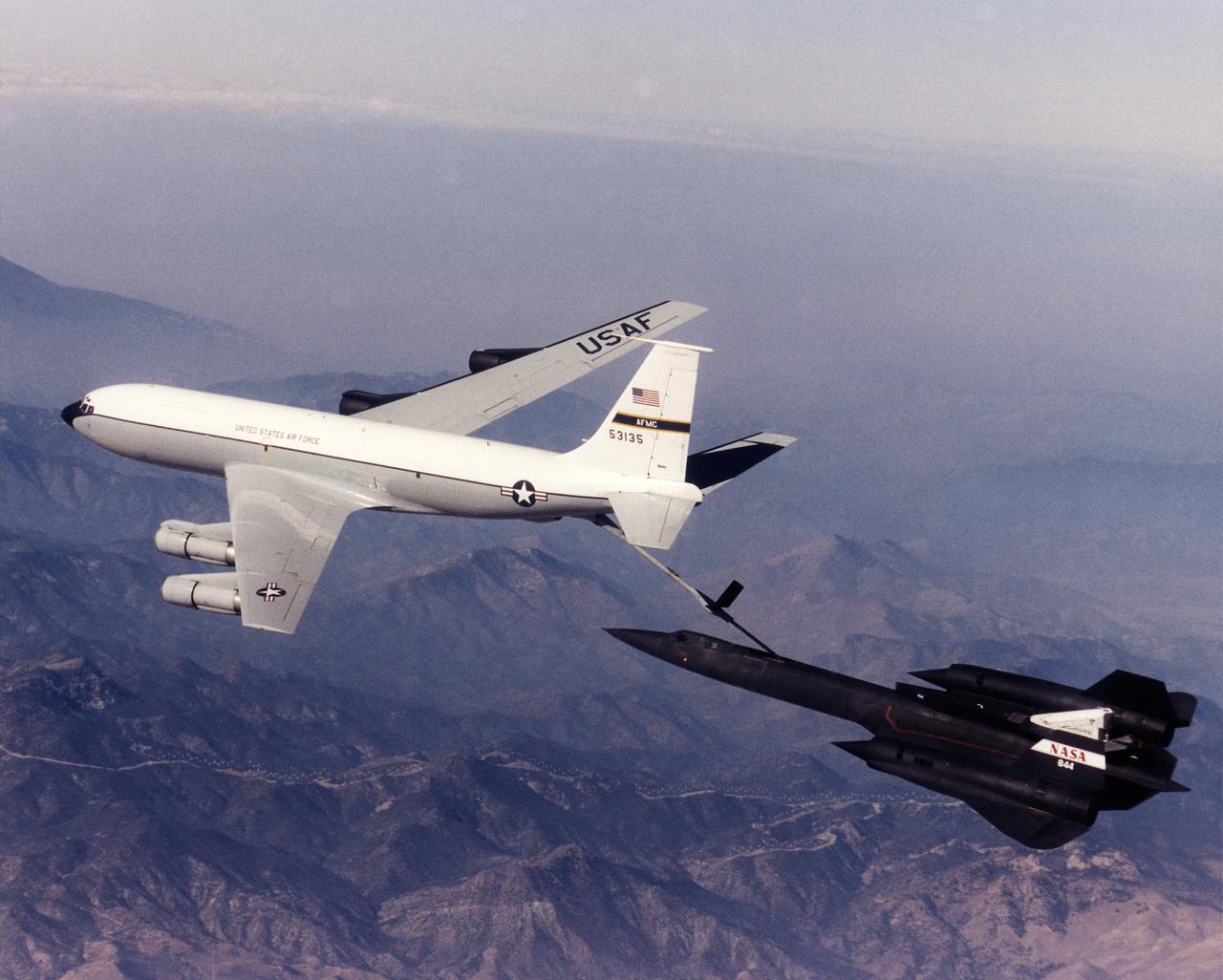

A NASA SR-71 refuels with an Edwards Air Force Base KC-135 during the first flight of the NASA/Rocketdyne/ Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE). The flight took place Oct. 31 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
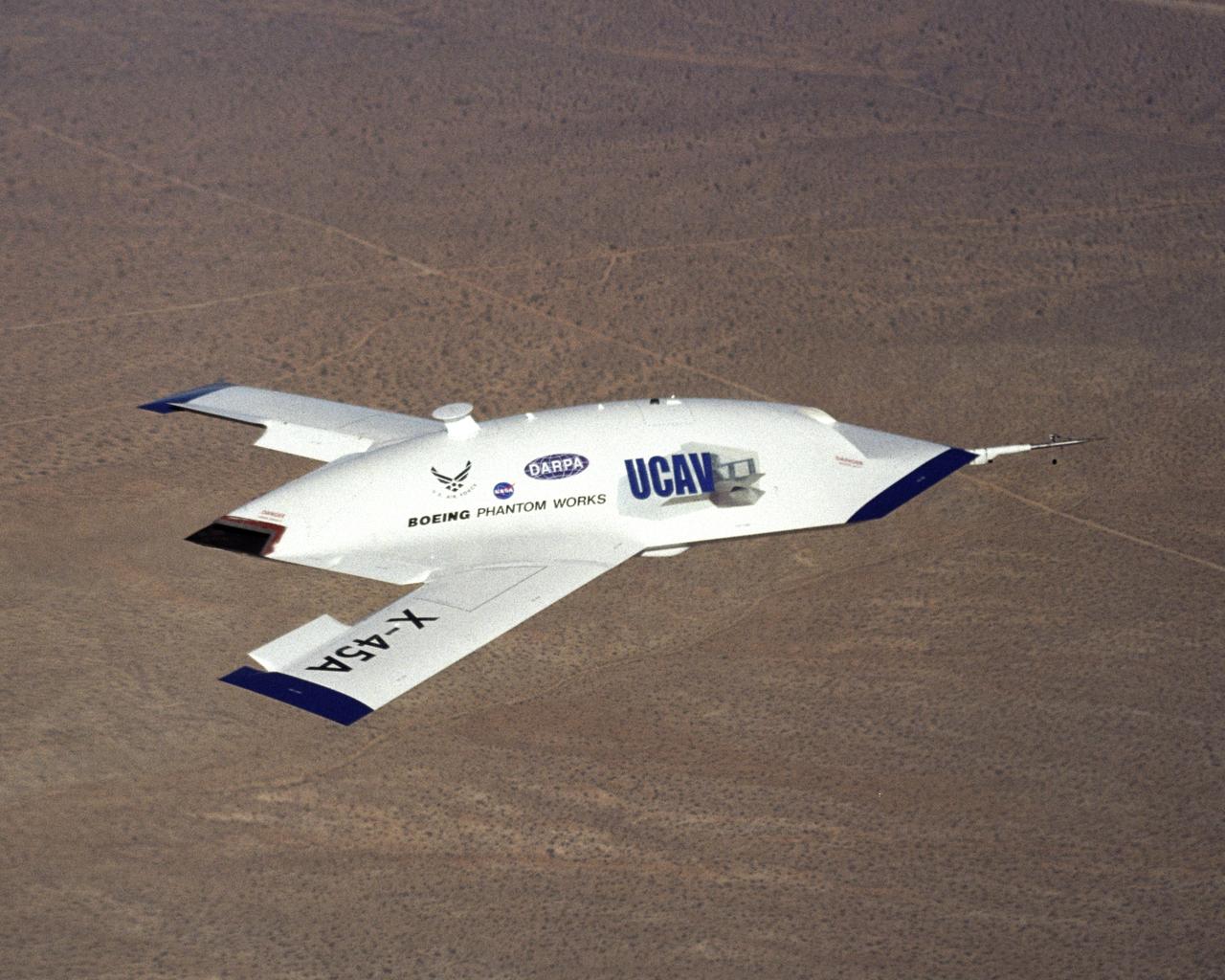

The first X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology demonstrator completed its sixth flight on Dec. 19, 2002, raising its landing gear in flight for the first time. The X-45A flew for 40 minutes and reached an airspeed of 195 knots and an altitude of 7,500 feet. Dryden is supporting the DARPA/Boeing team in the design, development, integration, and demonstration of the critical technologies, processes, and system attributes leading to an operational UCAV system. Dryden support of the X-45A demonstrator system includes analysis, component development, simulations, ground and flight tests.
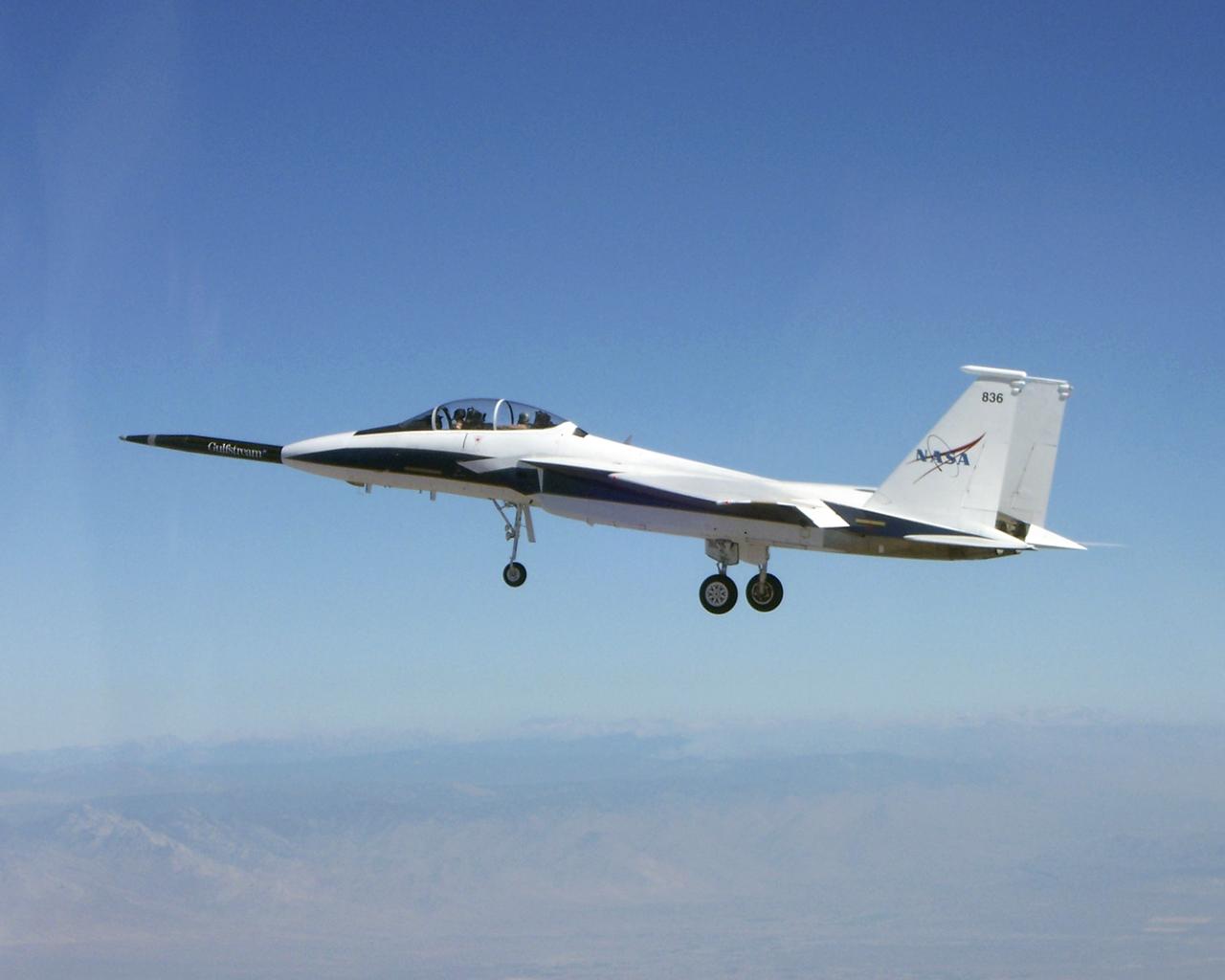

NASA's F-15B testbed aircraft in flight during the first evaluation flight of the joint NASA/Gulfstream Quiet Spike project. The project seeks to verify the structural integrity of the multi-segmented, articulating spike attachment designed to reduce and control a sonic boom.
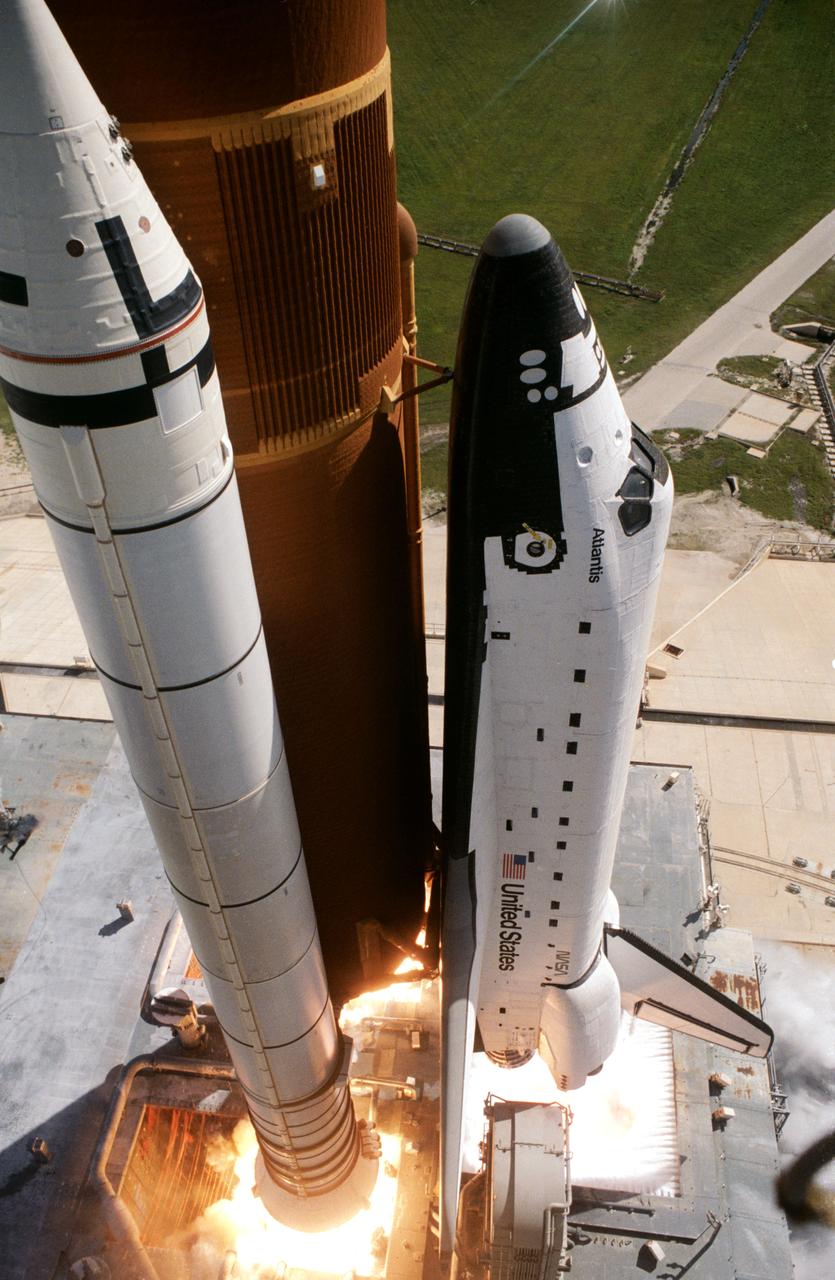

Liftoff of first flight of Atlantis and the STS 51-J mission. Mid-day skies of Florida form the backdrop for this smokey scene of the 51-J launch (001); This photograph, taken from the support structure at Launch Pad 39A, captures the first moments of the initial blastoff of the shuttle Atlantis (002); This frame was taken moments after the Atlantis cleared the launch tower. The view is from the below the orbiter and show its solid rocket boosters firing (003).
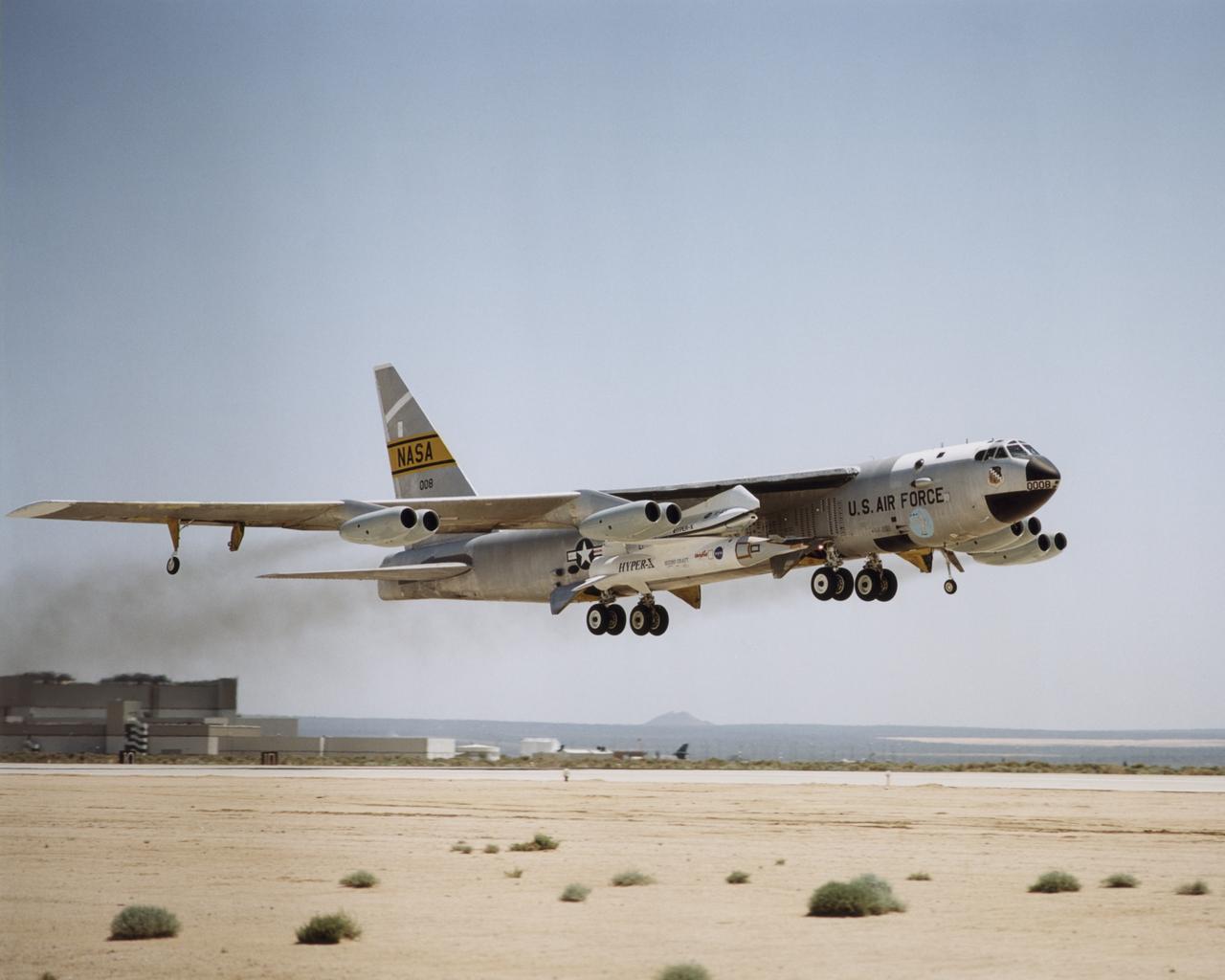

The NASA X-43A hypersonic research vehicle and its Pegasus booster rocket, mounted beneath the wing of their B-52 mothership, had a successful first captive-carry flight on April 28, 2001, Basically a dress rehearsal for a subsequent free flight, the captive-carry flight kept the X-43A-and-Pegasus combination attached to the B-52's wing pylon throughout the almost two-hour mission from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif., over the Pacific Missile Test Range, and back to Dryden.
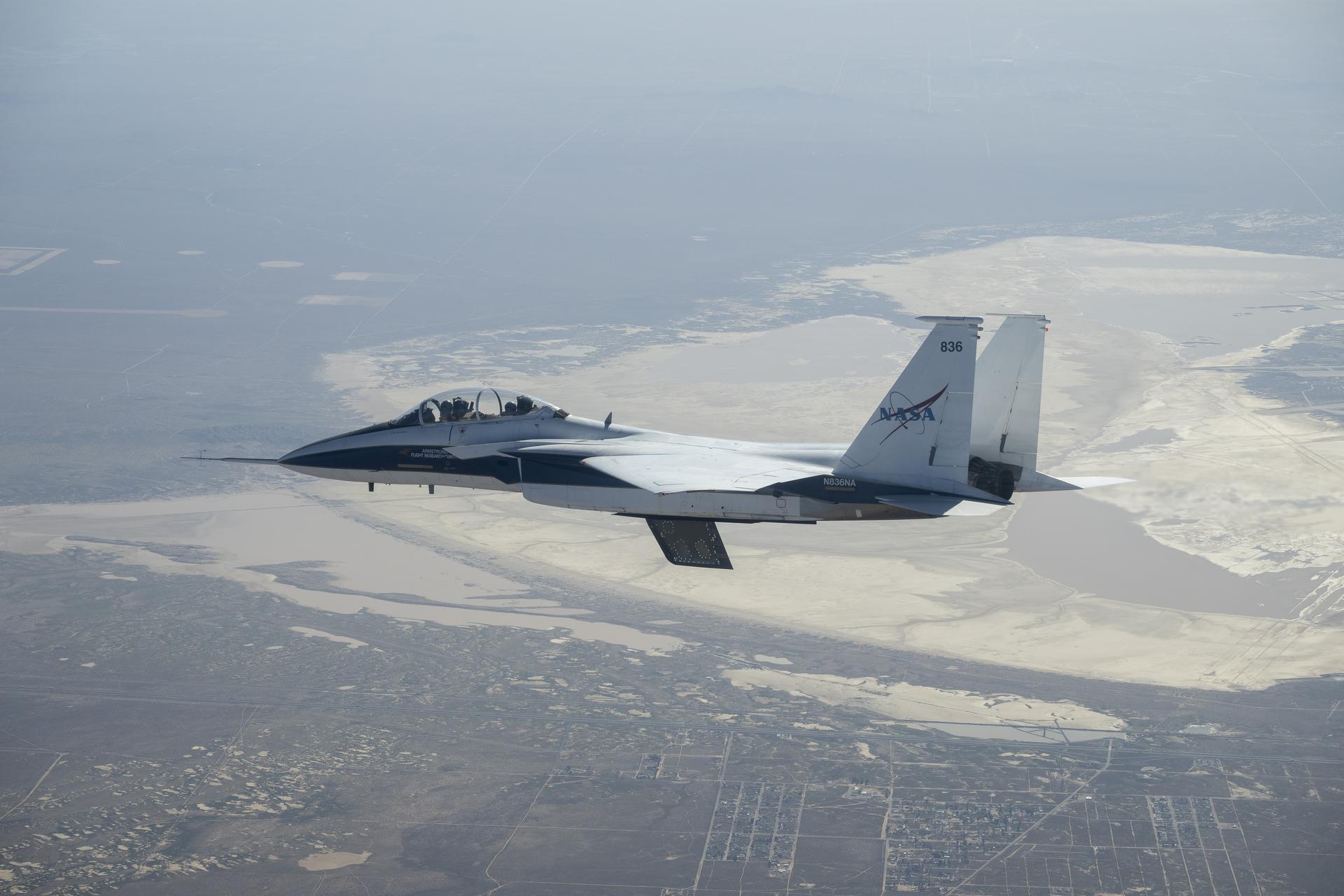

NASA’s Crossflow Attenuated Natural Laminar Flow (CATNLF) scale-model wing flies for the first time on a NASA F-15 research jet during a test flight from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The 75-minute flight confirmed the aircraft could maneuver safely with the approximately 3-foot-tall test article mounted beneath it. NASA will continue flight tests to collect data that validates the CATNLF design and its potential to improve laminar flow, reducing drag and lowering fuel costs for future commercial aircraft.
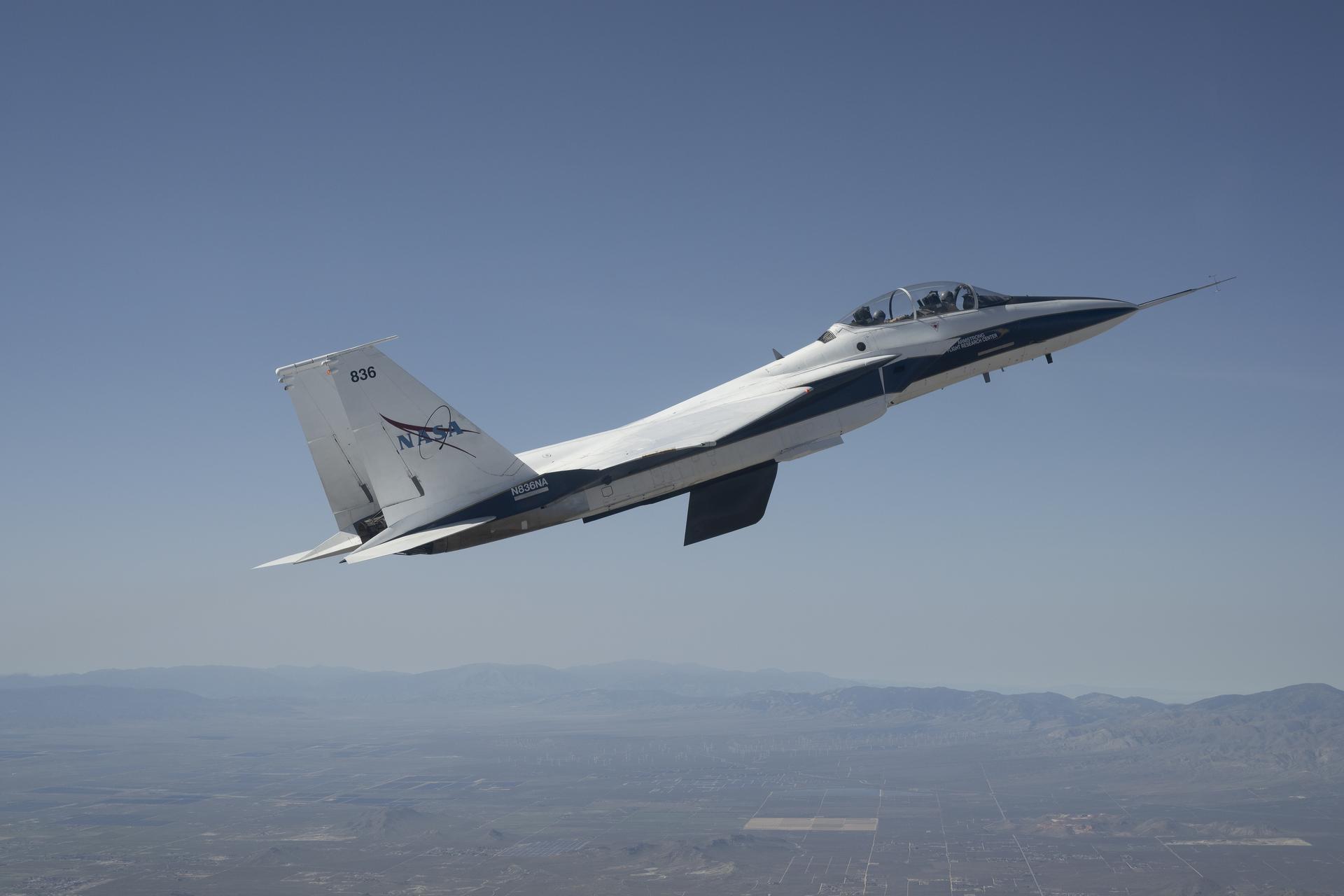

NASA’s Crossflow Attenuated Natural Laminar Flow (CATNLF) scale-model wing flies for the first time on a NASA F-15 research jet during a test flight from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The 75-minute flight confirmed the aircraft could maneuver safely with the approximately 3-foot-tall test article mounted beneath it. NASA will continue flight tests to collect data that validates the CATNLF design and its potential to improve laminar flow, reducing drag and lowering fuel costs for future commercial aircraft.
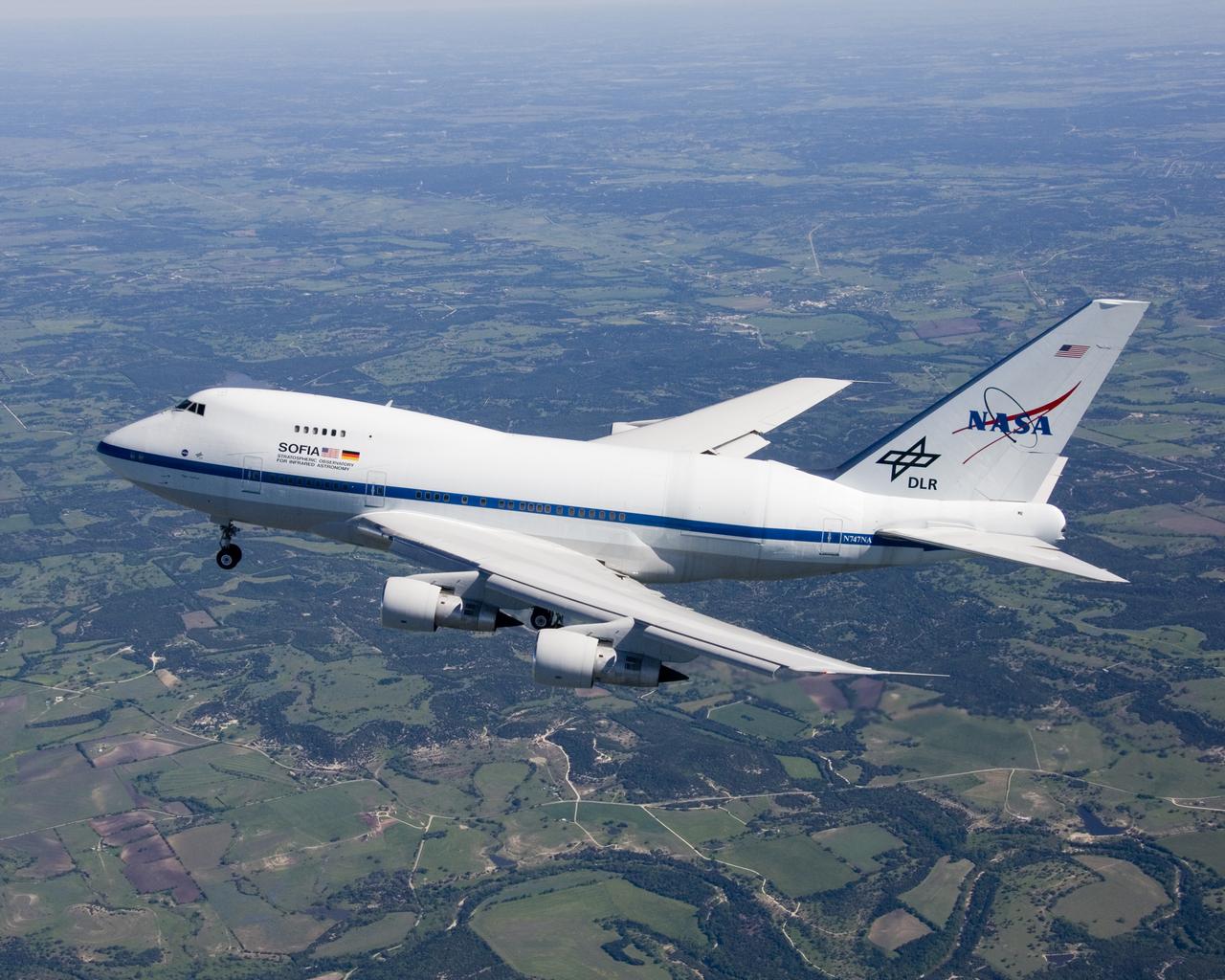

Christened "Clipper Lindbergh" when it flew for Pan American Airways in the 1970s, the SOFIA 747SP shows evidence of modification to its aft fuselage contours to accommodate a 16-foot-tall opening for a 45,000-pound infrared telescope. This inflight photo was taken on SOFIA's first flight since its modification to become an airborne observatory.
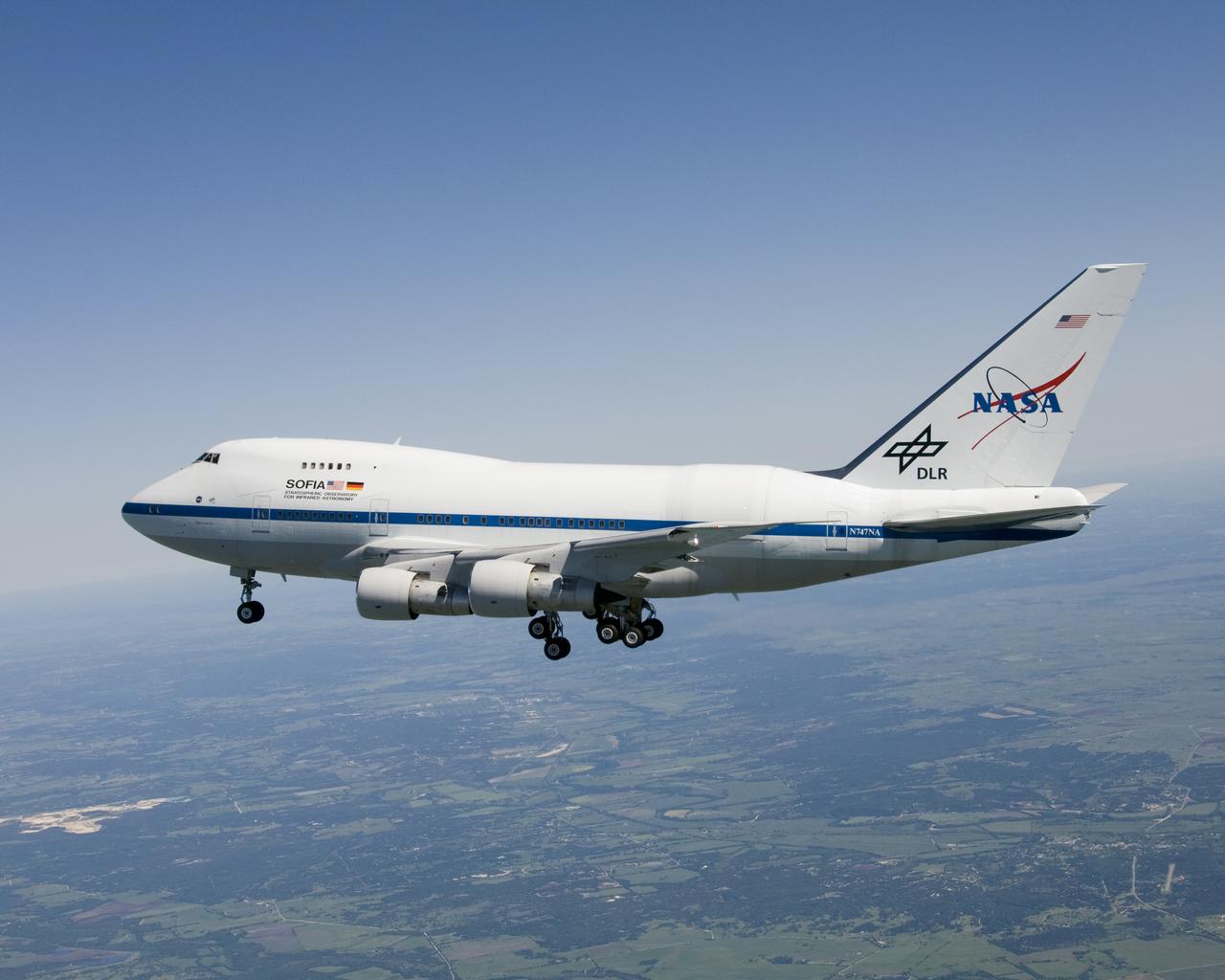

Christened "Clipper Lindbergh" when it flew for Pan American Airways in the 1970s, the SOFIA 747SP shows evidence of modification to its aft fuselage contours to accommodate a 16-foot-tall opening for a 45,000-pound infrared telescope. This inflight photo was taken on SOFIA's first flight since its modification to become an airborne observatory.
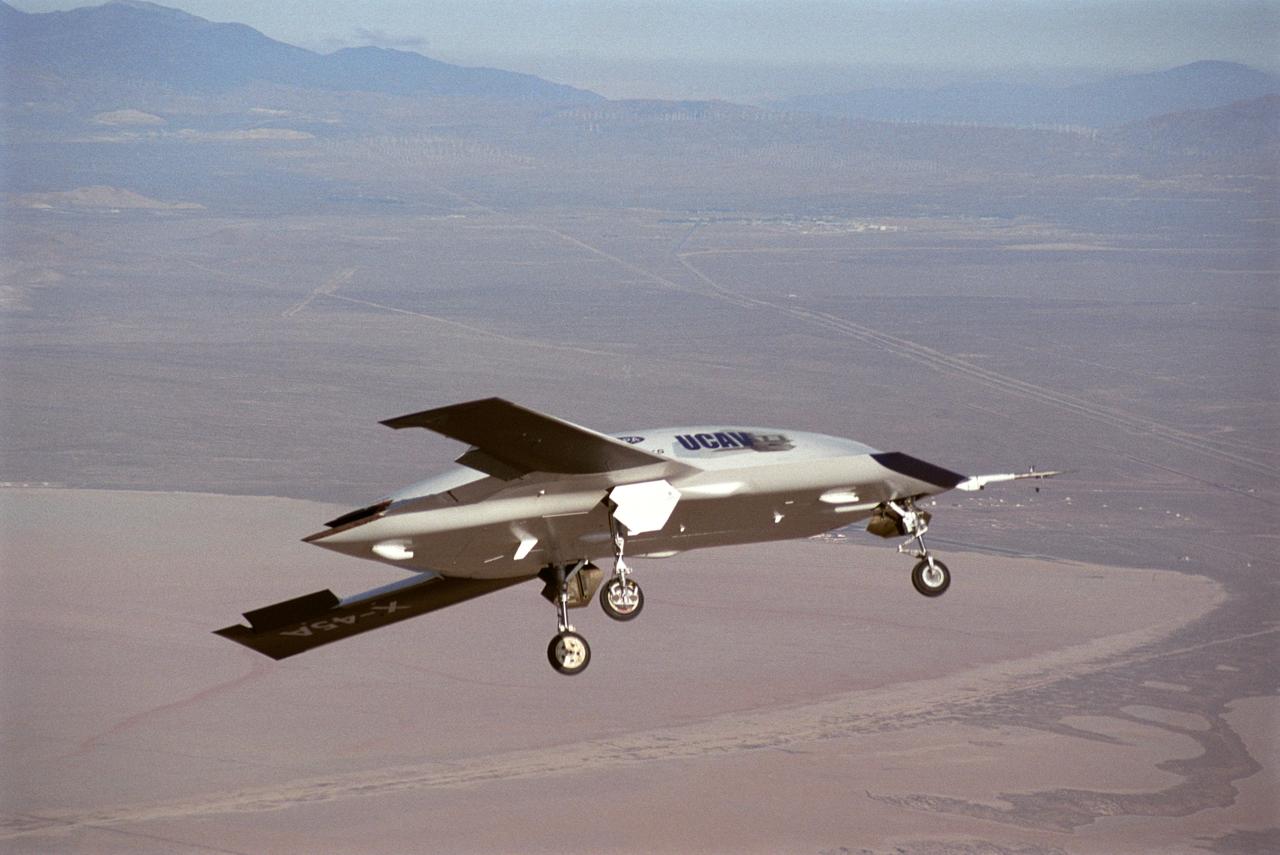

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
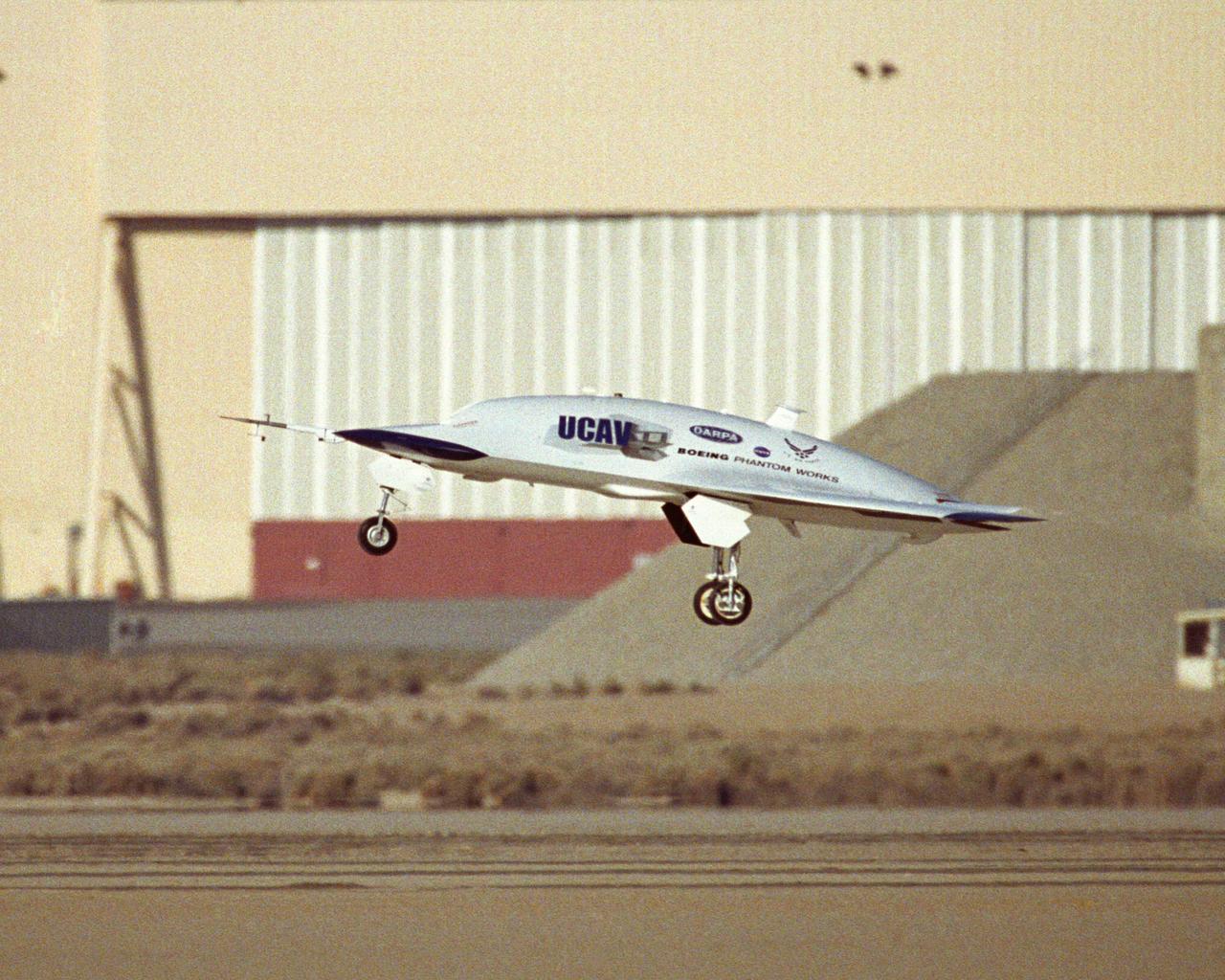

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
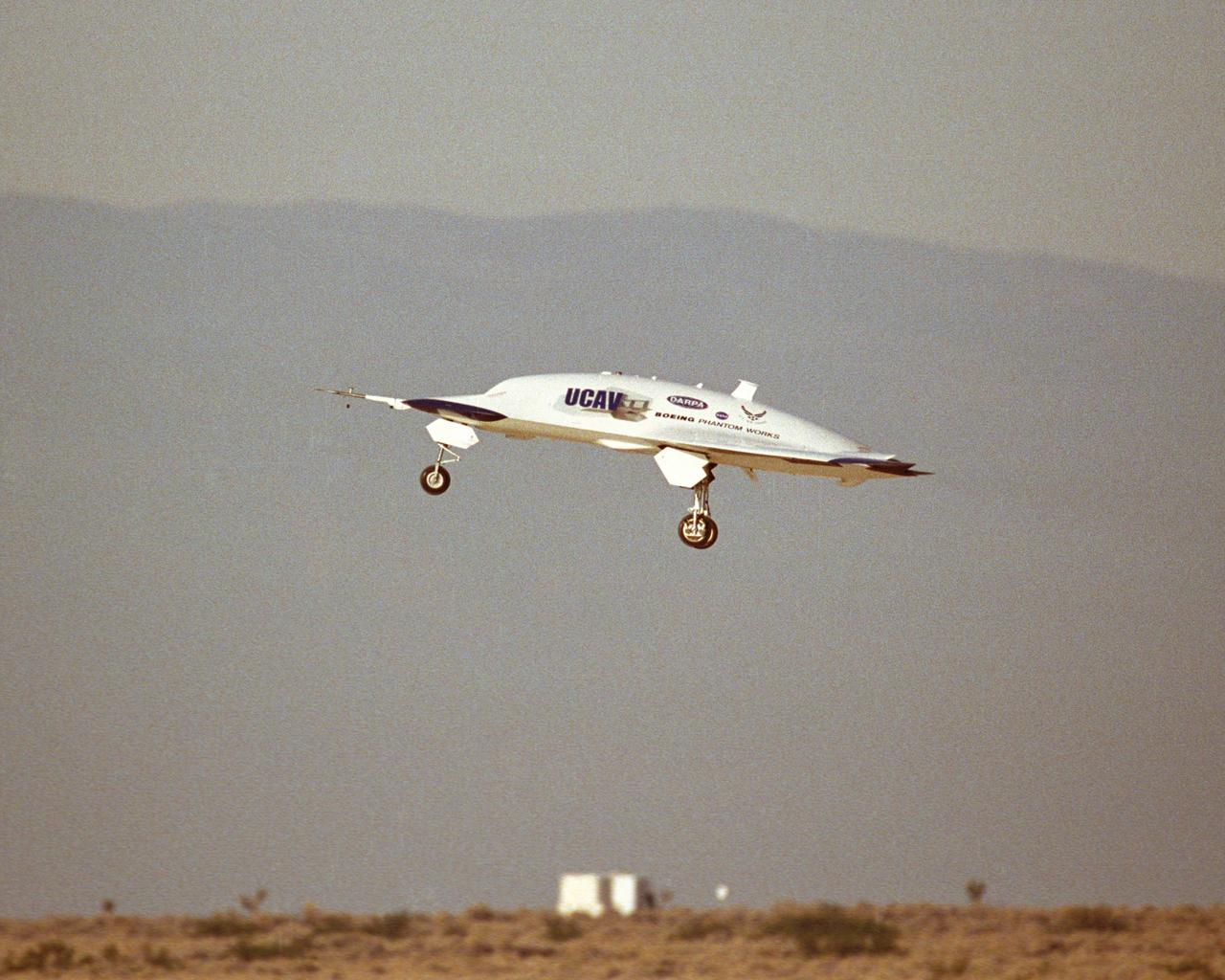

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
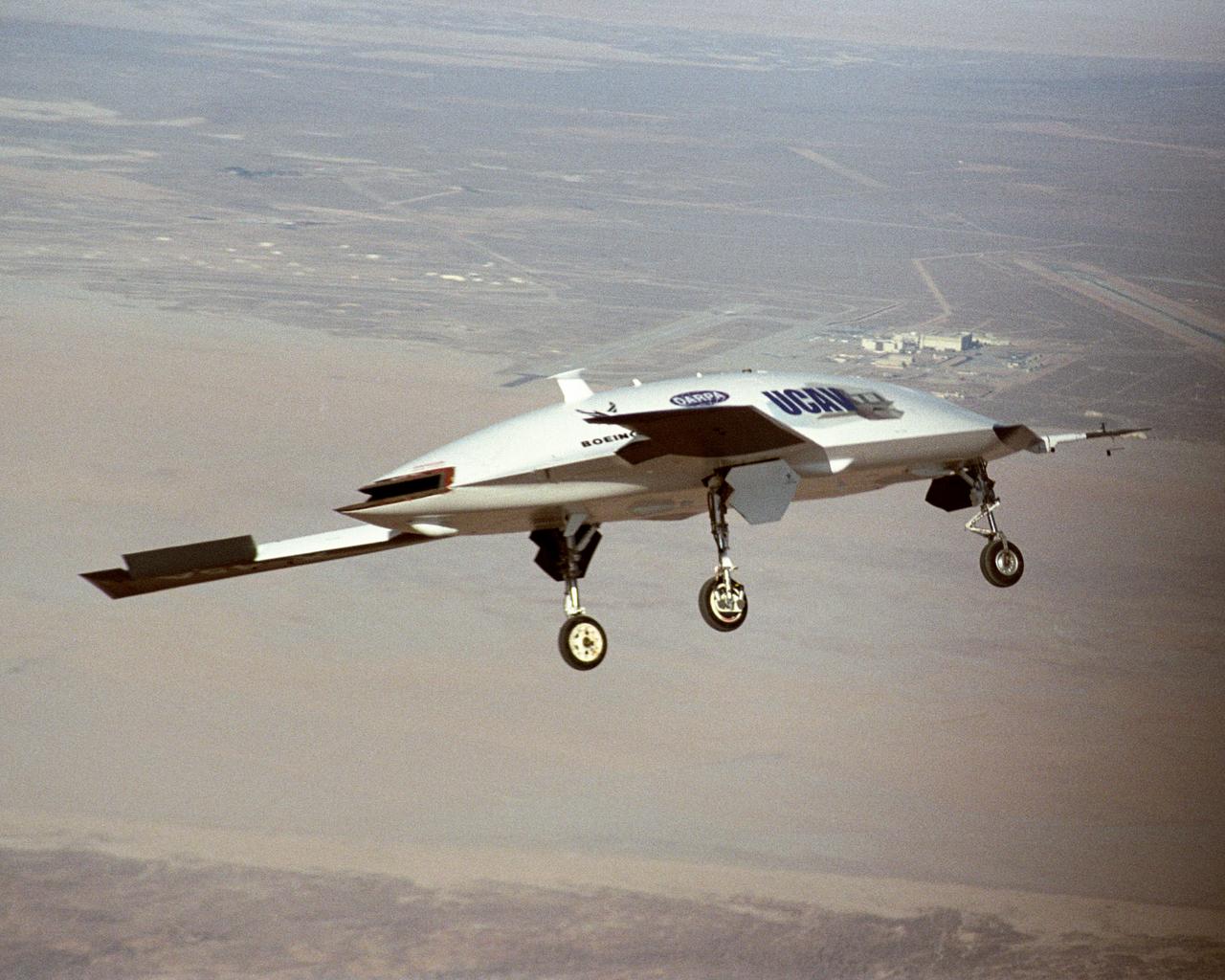

X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle, or UCAV, technology demonstration aircraft in flight during its first flight at Edwards Air Force Base, California.
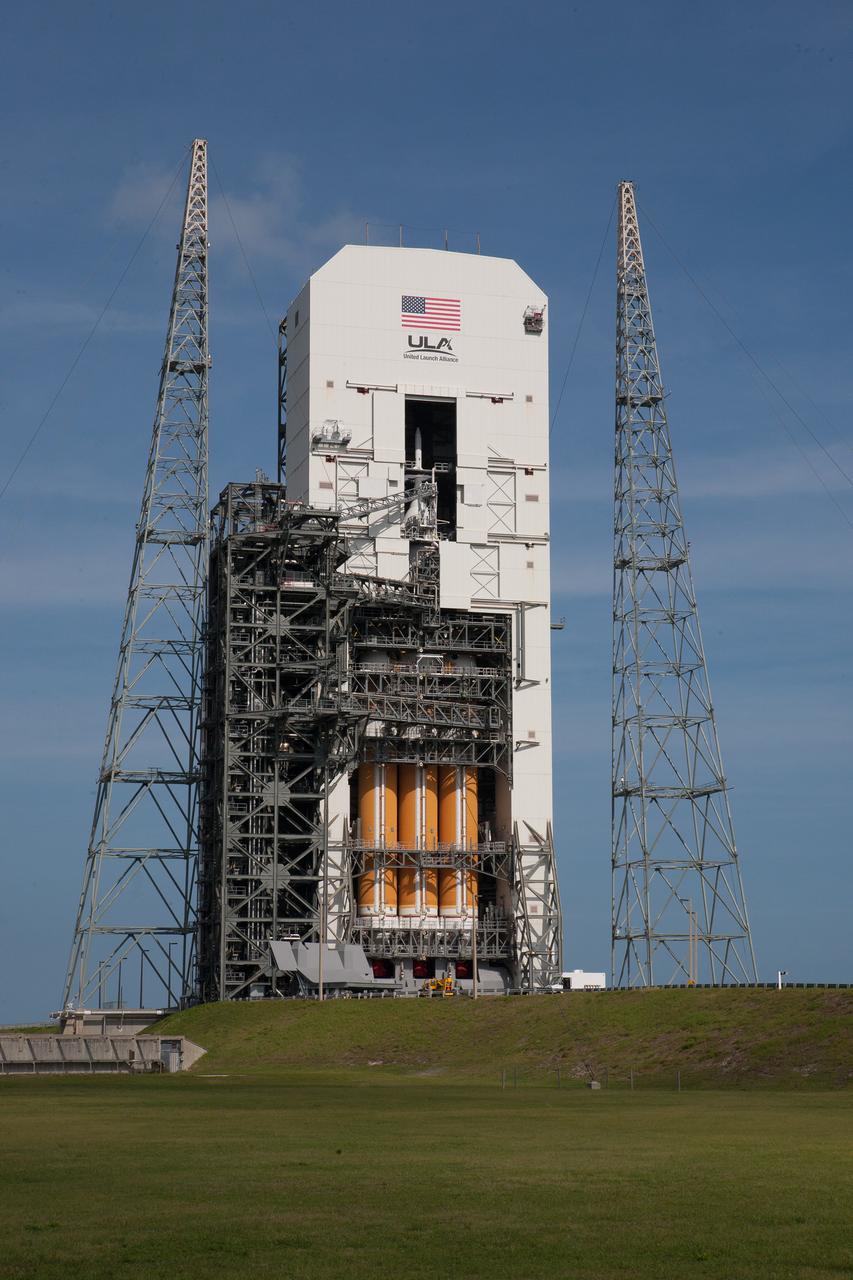

Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion stacked on the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at United Launch Alliance Launch Complex 37B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 24, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
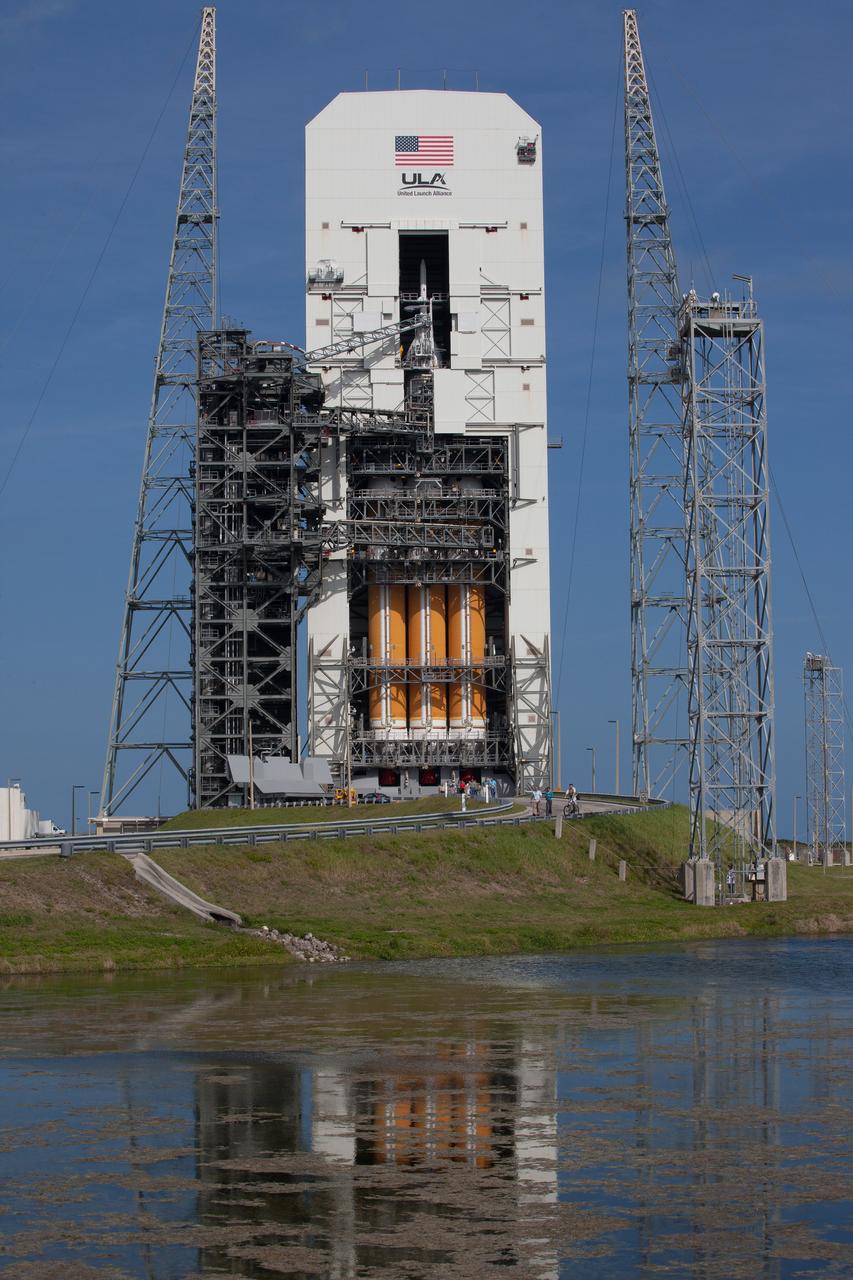

Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion stacked on the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at United Launch Alliance Launch Complex 37B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 24, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
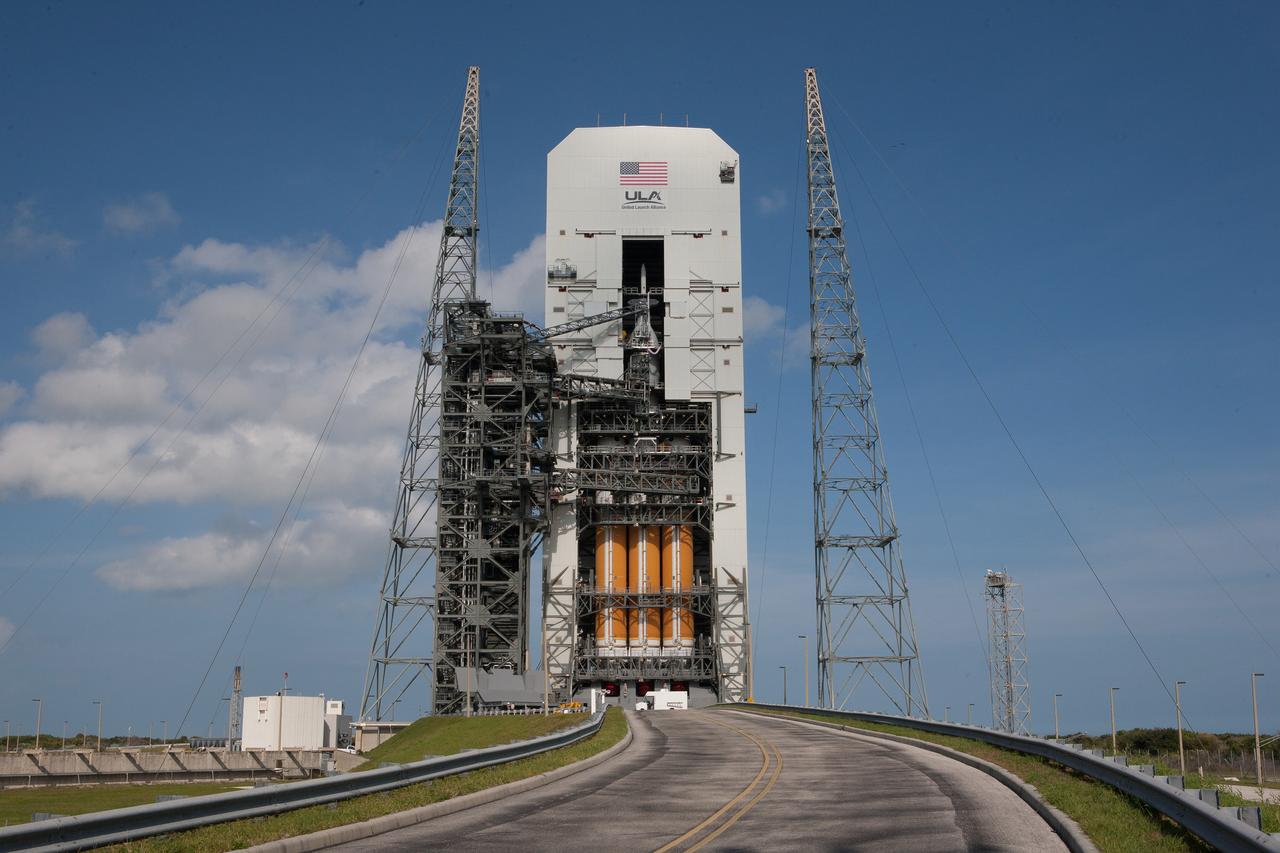

Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion stacked on the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at United Launch Alliance Launch Complex 37B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 24, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
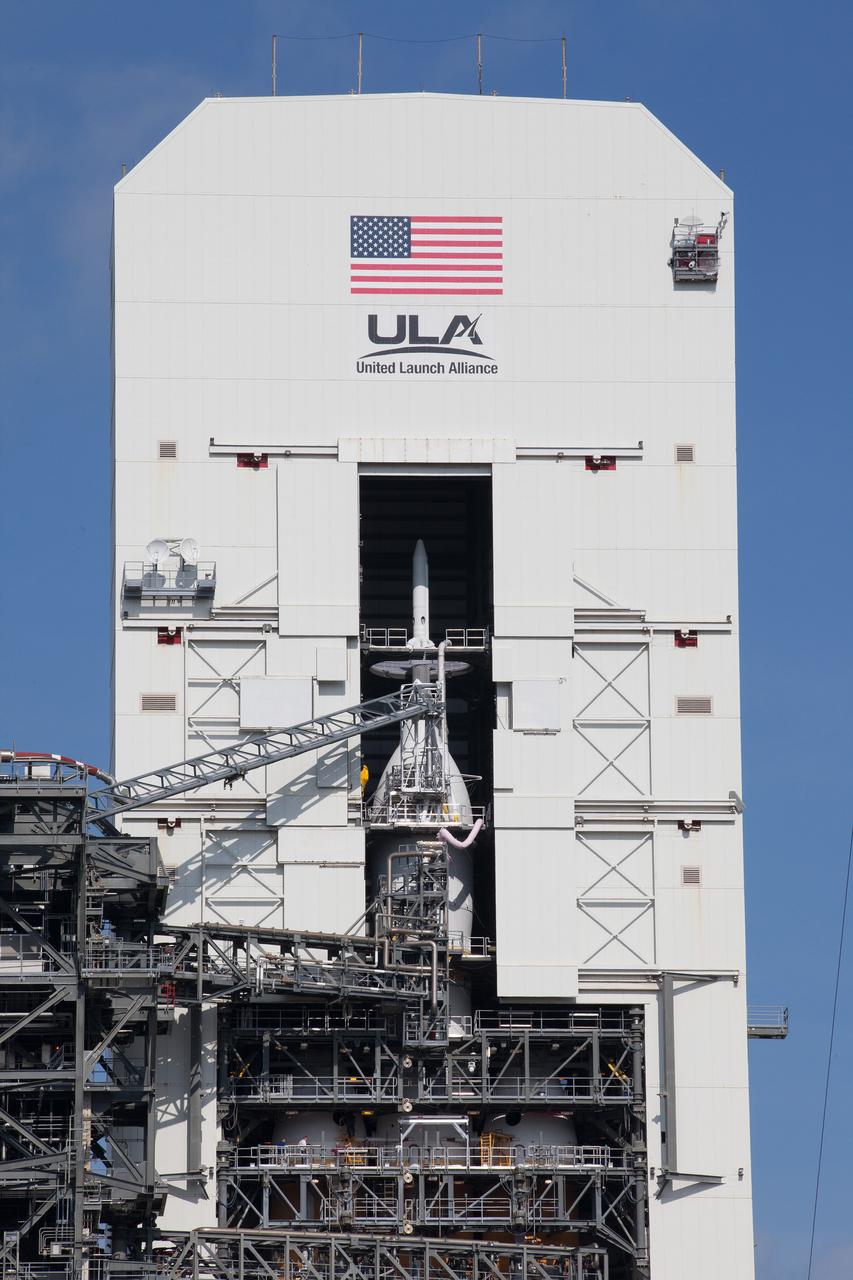

Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion stacked on the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at United Launch Alliance Launch Complex 37B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 24, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
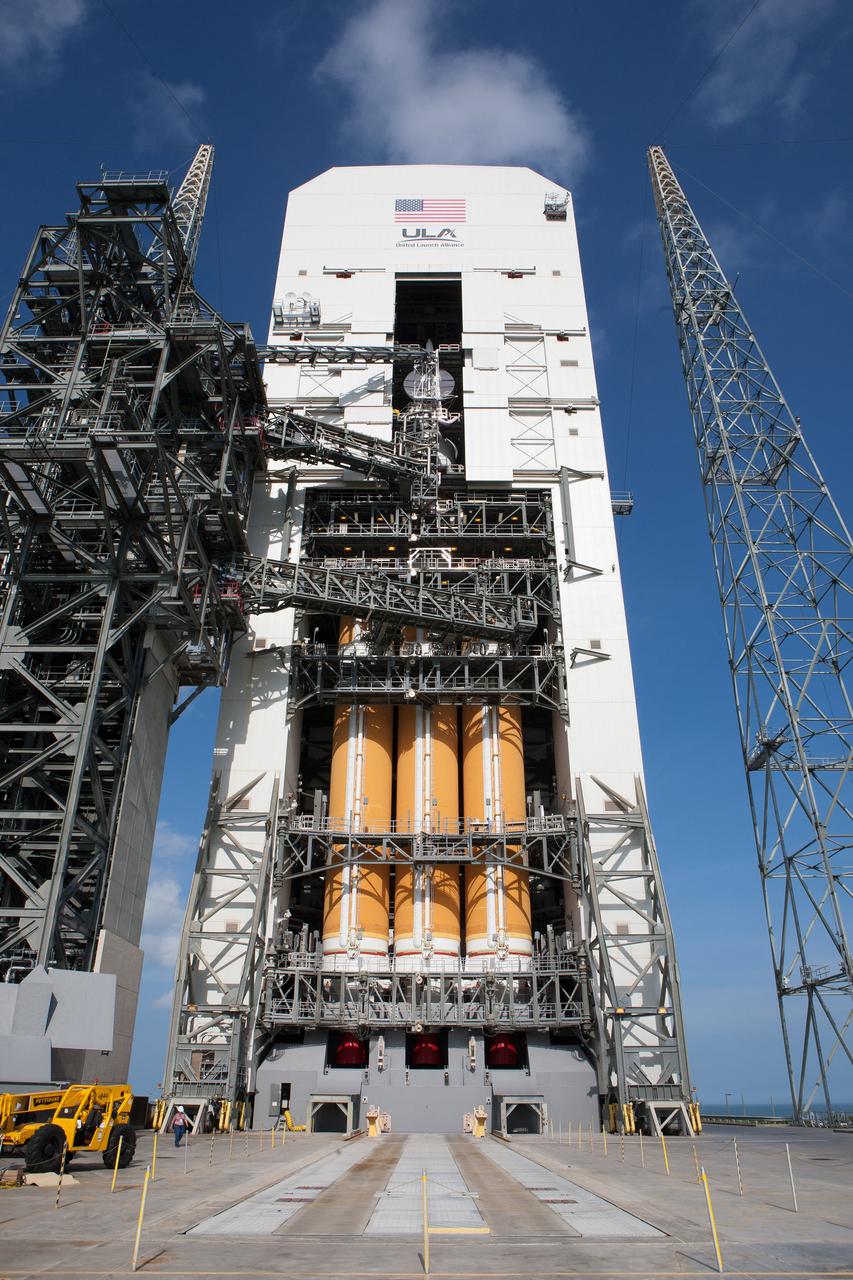

Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion stacked on the Delta IV Heavy launch vehicle at United Launch Alliance Launch Complex 37B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 24, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
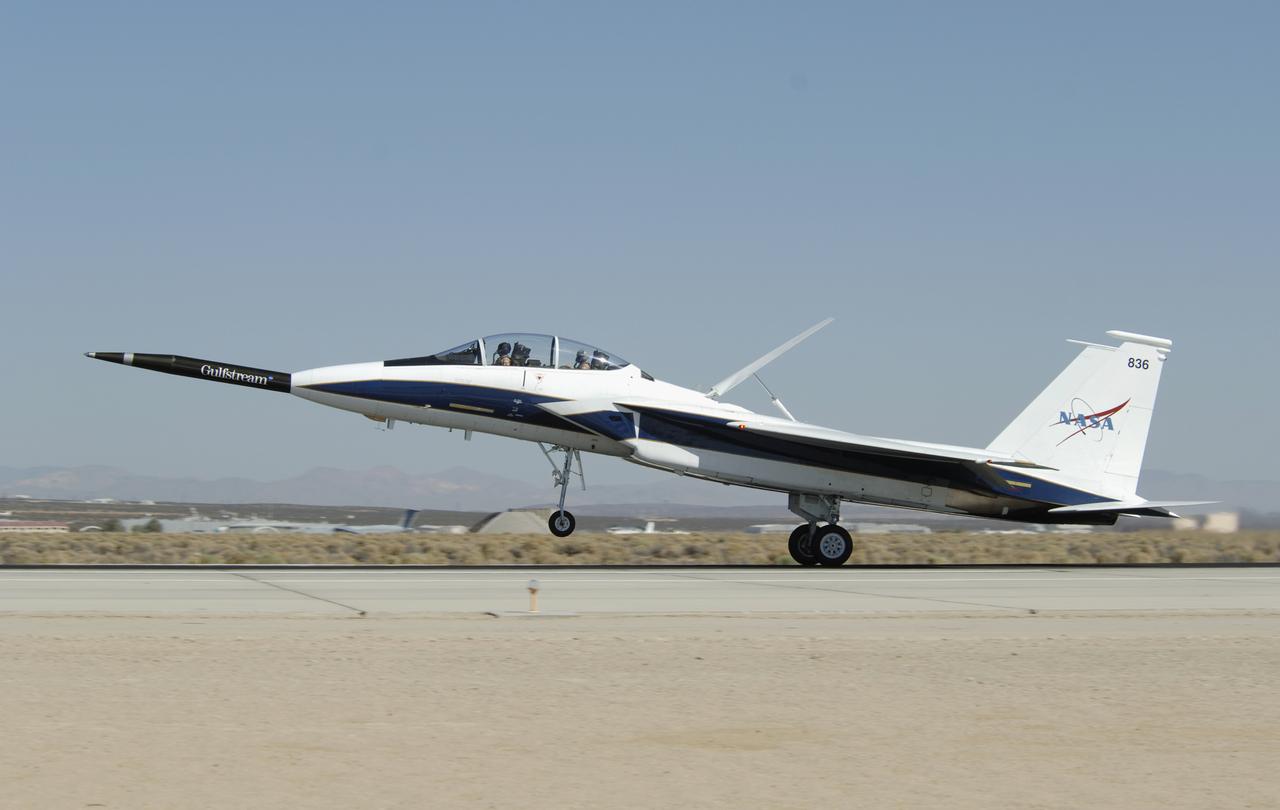

NASA's F-15B testbed aircraft lands after the first flight of the Quiet Spike project. The first flight was performed for evaluation purposes, and the spike was not extended. The Quiet Spike was developed as a means of controlling and reducing the sonic boom caused by an aircraft 'breaking' the sound barrier.

The latest version of the X-38, V-131R, touches down on Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASAÕs Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California, at the end of its first free flight under a giant parafoil on Nov. 2, 2000. The X-38 prototypes are intended to perfect technology for a planned Crew Return Vehicle (CRV) ÒlifeboatÓ to carry a crew to safety in the event of an emergency on the International Space Station. Free-flight tests of X-38 V-131R are evaluating upgraded avionics and control systems and the aerodynamics of the modified upper body, which is more representative of the final design of the CRV than the two earlier X-38 test craft, including a simulated hatch atop the body. The huge 7,500 square-foot parafoil will enable the CRV to land in the length of a football field after returning from space. The first three X-38Õs are air-launched from NASAÕs venerable NB-52B mother ship, while the last version, V-201, will be carried into space by a Space Shuttle and make a fully autonomous re-entry and landing.
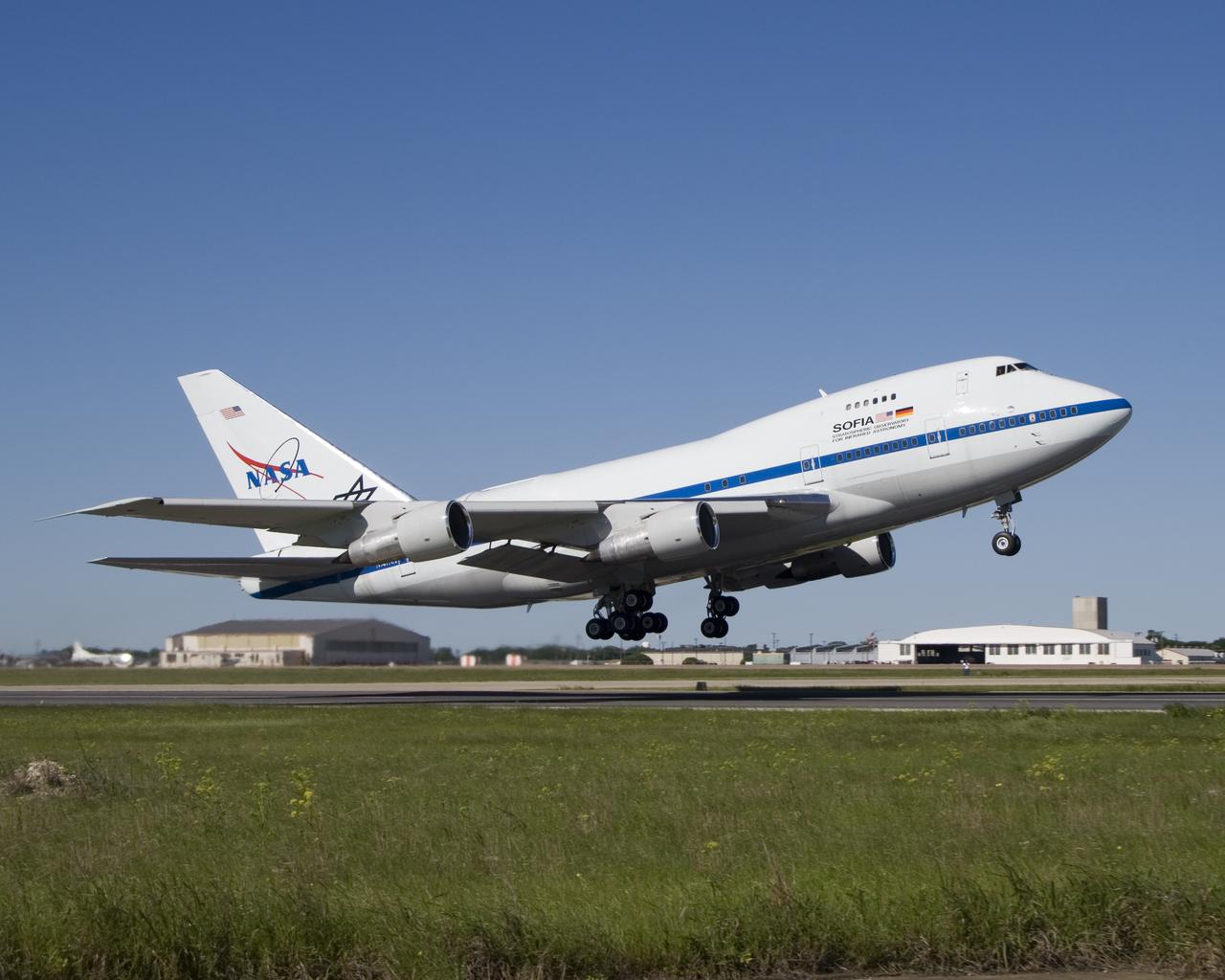

The NASA and German Aerospace Center SOFIA airborne infrared observatory took flight for the first time April 26, 2007, from its modification center in Waco, Texas.
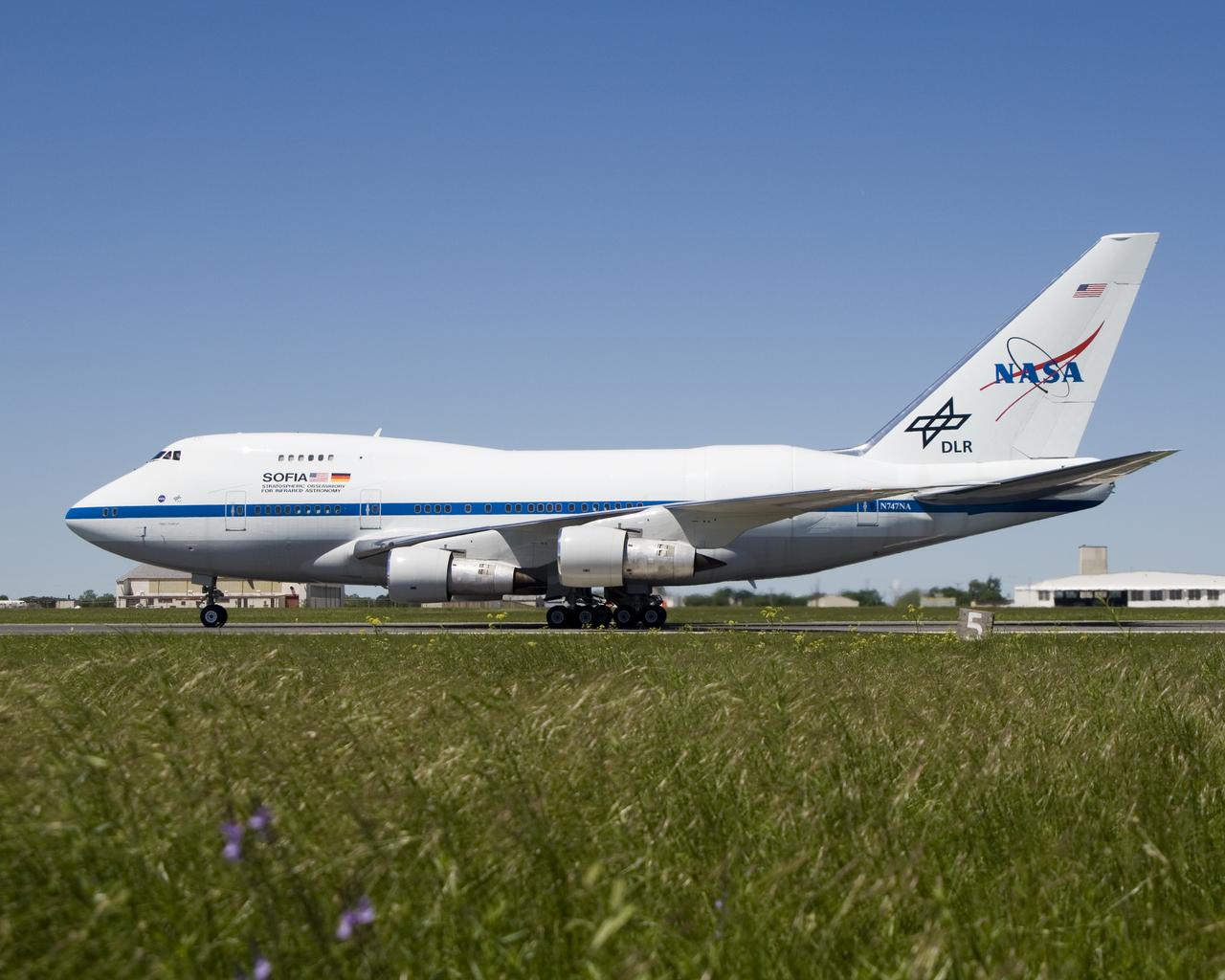

NASA's modified Boeing 747SP SOFIA airborne observatory taxis along the runway at Waco, Texas after completing its first checkout flight on April 26, 2007.
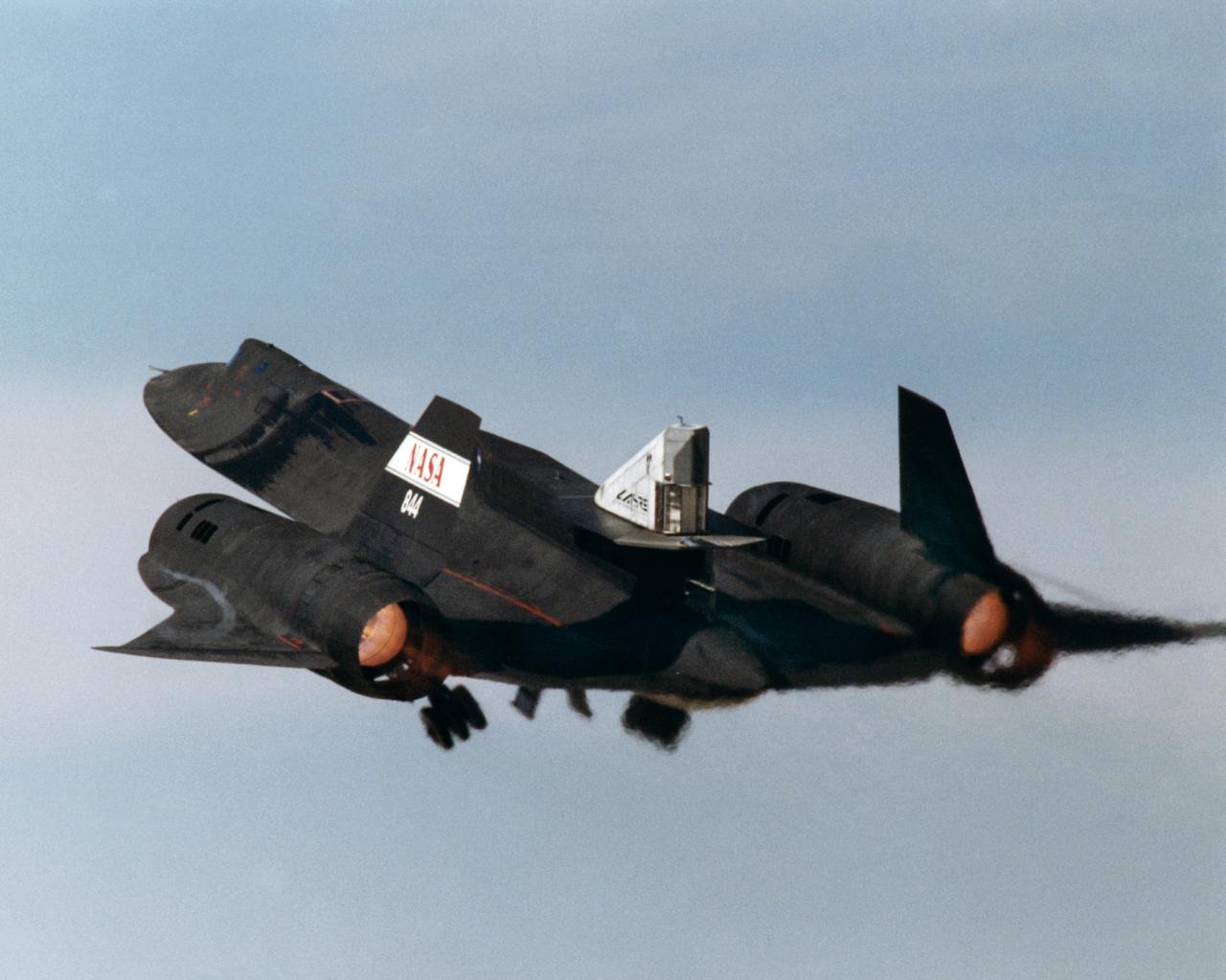

This photograph shows the LASRE pod on the upper rear fuselage of an SR-71 aircraft during take-off of the first flight to experience an in-flight cold flow test. The flight occurred on 4 March 1998.
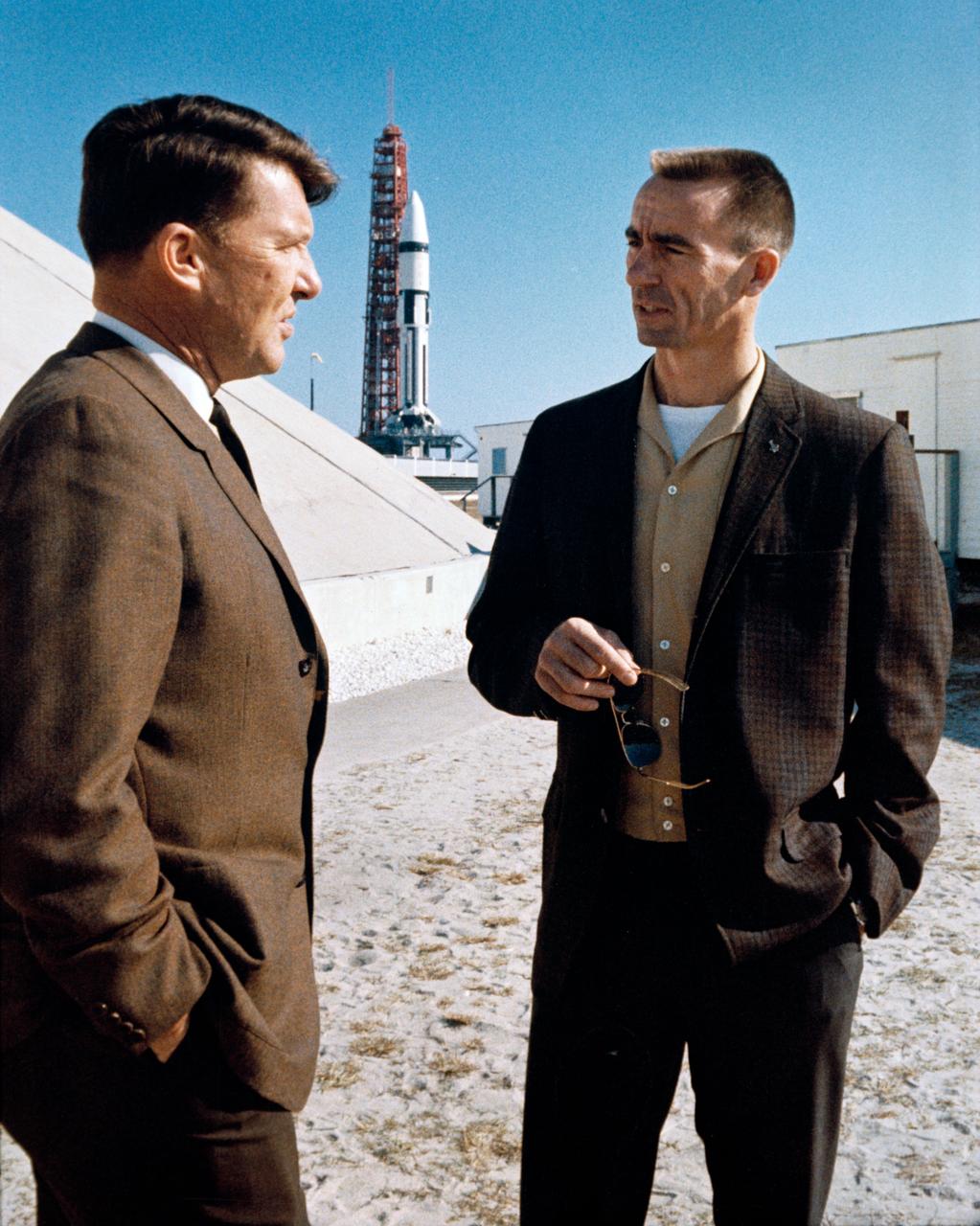

S68-18700 (22 Jan. 1968) --- Two prime crew members of the first manned Apollo space flight were present at Cape Kennedy for the launch of the Apollo V (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission. On left is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr.; and on right is astronaut R. Walter Cunningham. In background is the Apollo V stack at Launch Complex 37 ready for launch.
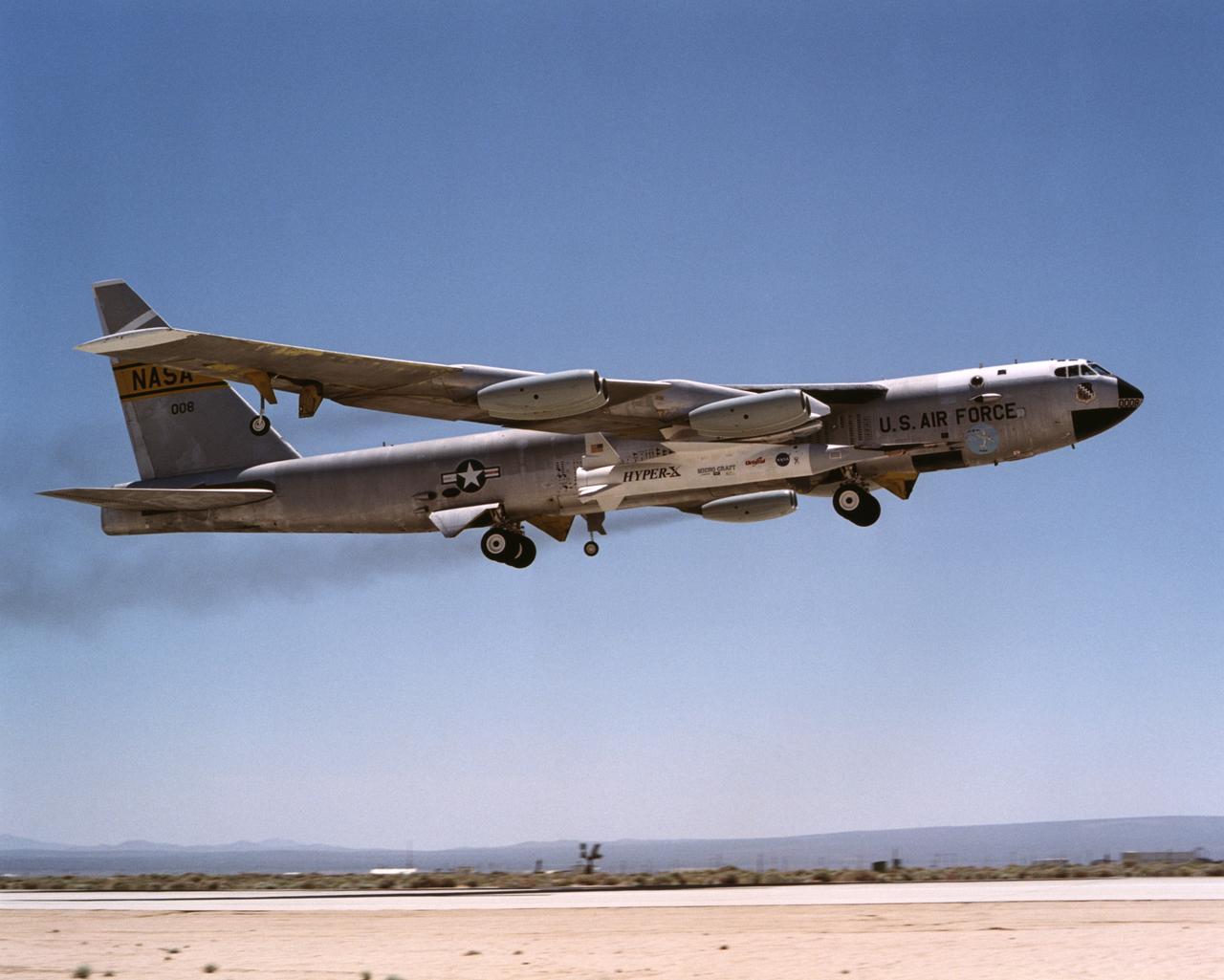

The first X-43A hypersonic research aircraft and its modified Pegasus booster rocket were carried aloft by NASA's NB-52B carrier aircraft from Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 2, 2001 for the first of three high-speed free flight attempts. About an hour and 15 minutes later the Pegasus booster was released from the B-52 to accelerate the X-43A to its intended speed of Mach 7. Before this could be achieved, the combined Pegasus and X-43A "stack" lost control about eight seconds after ignition of the Pegasus rocket motor. The mission was terminated and explosive charges ensured the Pegasus and X-43A fell into the Pacific Ocean in a cleared Navy range area. A NASA investigation board is being assembled to determine the cause of the incident. Work continues on two other X-43A vehicles, the first of which could fly by late 2001. Central to the X-43A program is its integration of an air-breathing "scramjet" engine that could enable a variety of high-speed aerospace craft, and promote cost-effective access to space. The 12-foot, unpiloted research vehicle was developed and built for NASA by MicroCraft Inc., Tullahoma, Tenn. The booster was built by Orbital Sciences Corp. at Chandler, Ariz.
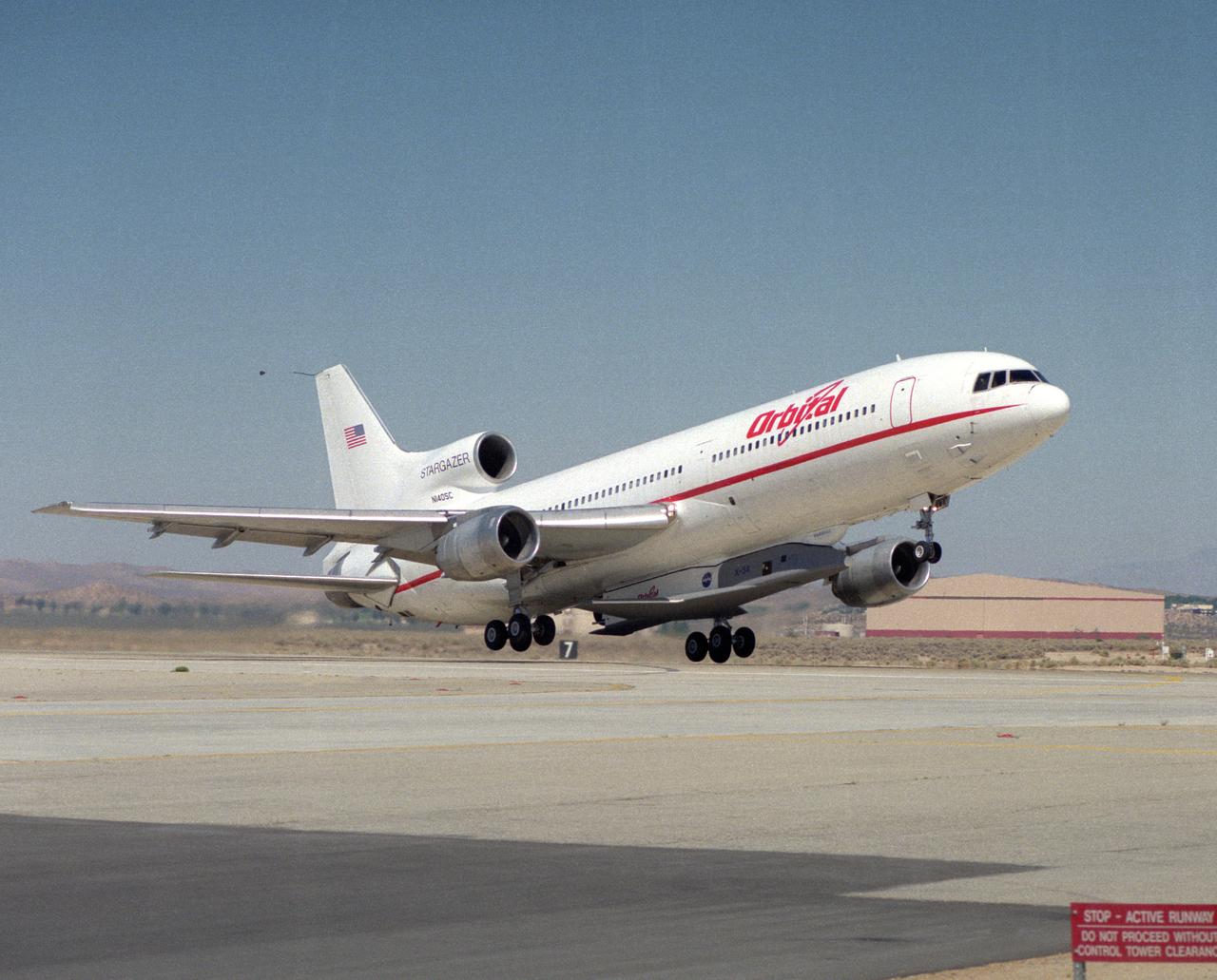

X-34 mated to modified L-1011 during takeoff on first captive carry flight

X-34 mated to modified L-1011 during takeoff on first captive carry flight
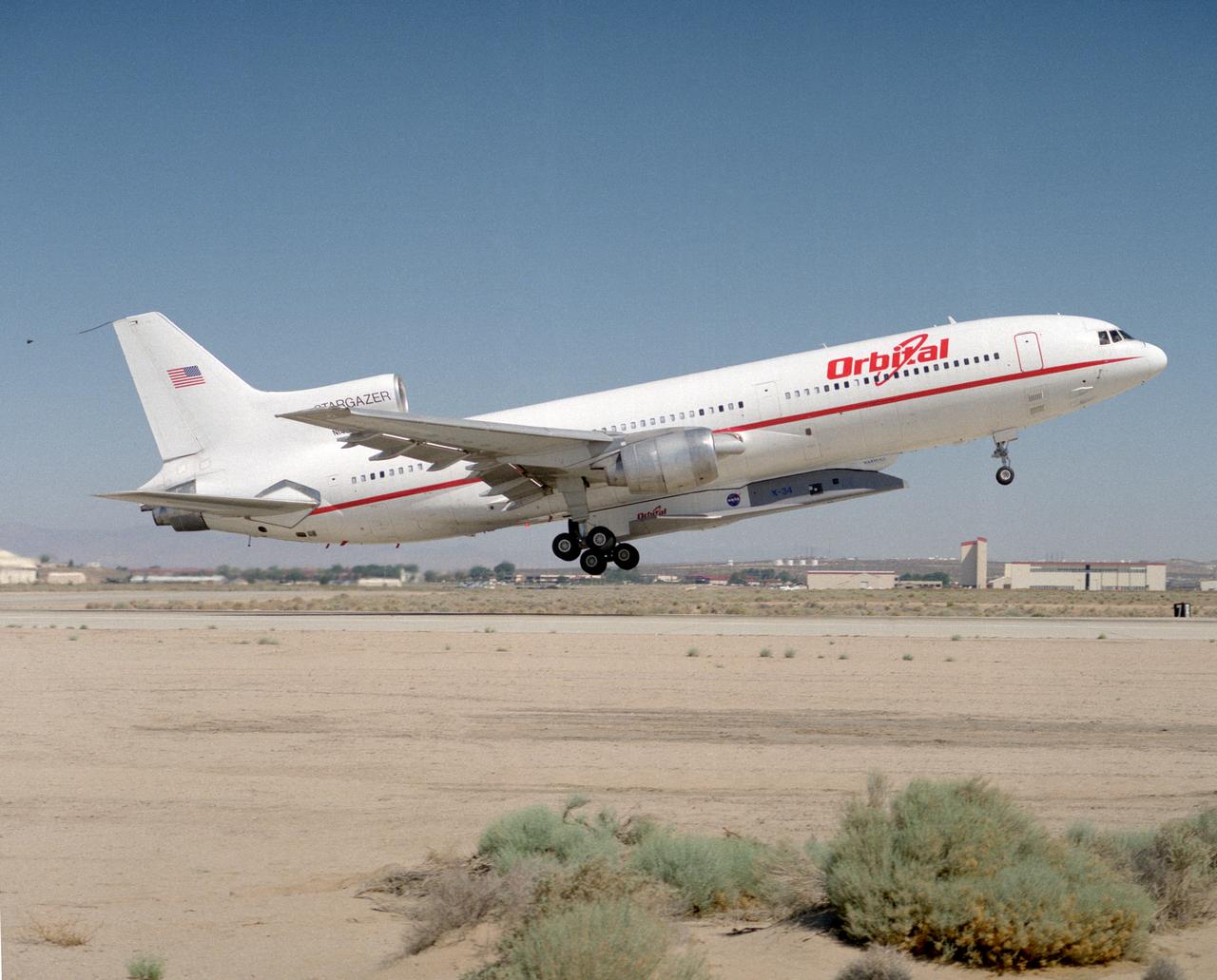

X-34 mated to modified L-1011 during takeoff on first captive carry flight
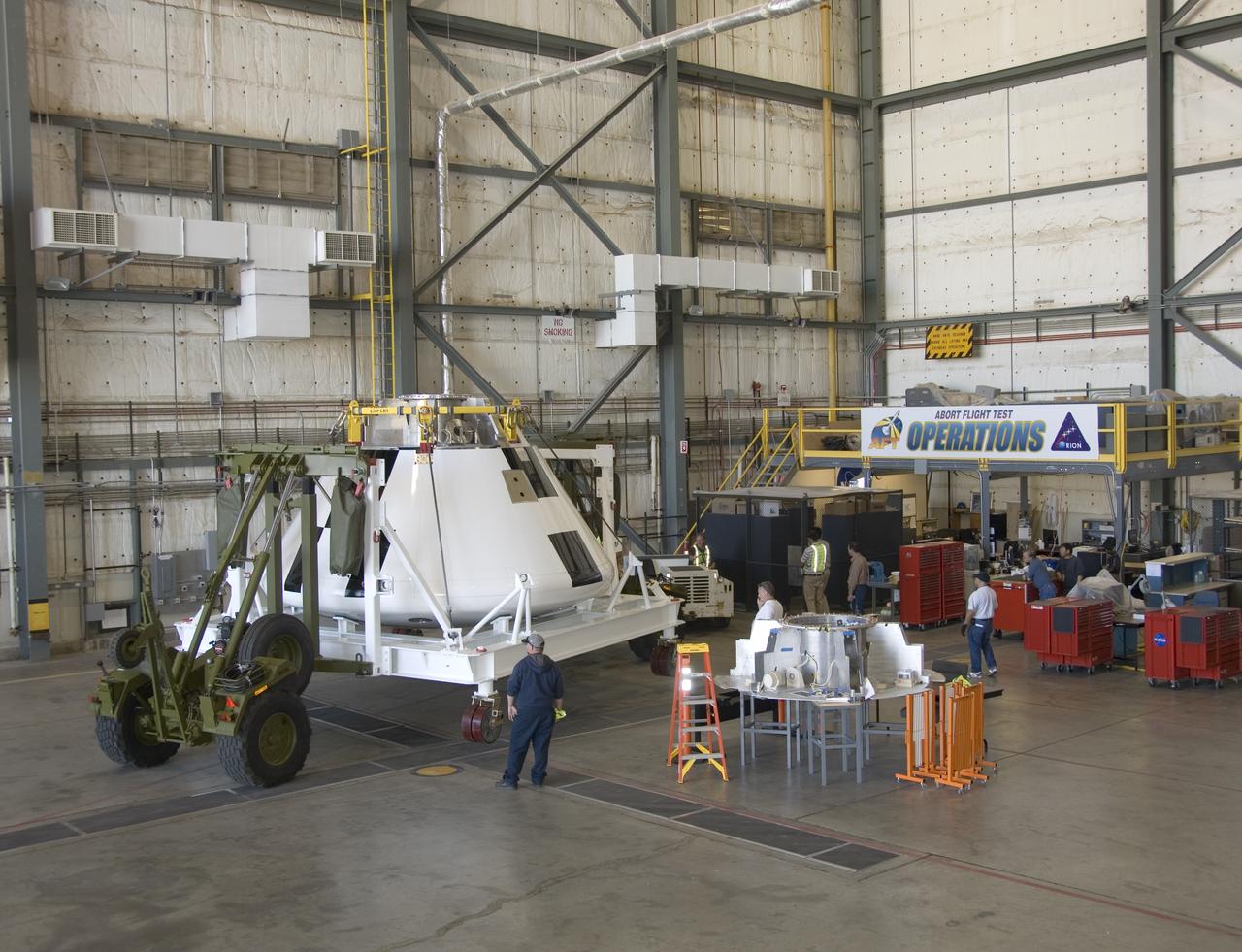

A full-scale flight-test mockup of the Constellation program's Orion crew vehicle arrived at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in late March 2008 to undergo preparations for the first short-range flight test of the spacecraft's astronaut escape system later that year. Engineers and technicians at NASA's Langley Research Center fabricated the structure, which precisely represents the size, outer shape and mass characteristics of the Orion space capsule. The Orion crew module mockup was ferried to NASA Dryden on an Air Force C-17. After painting in the Edwards Air Force Base paint hangar, the conical capsule was taken to Dryden for installation of flight computers, instrumentation and other electronics prior to being sent to the U.S. Army's White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico for integration with the escape system and the first abort flight test in late 2008. The tests were designed to ensure a safe, reliable method of escape for astronauts in case of an emergency.
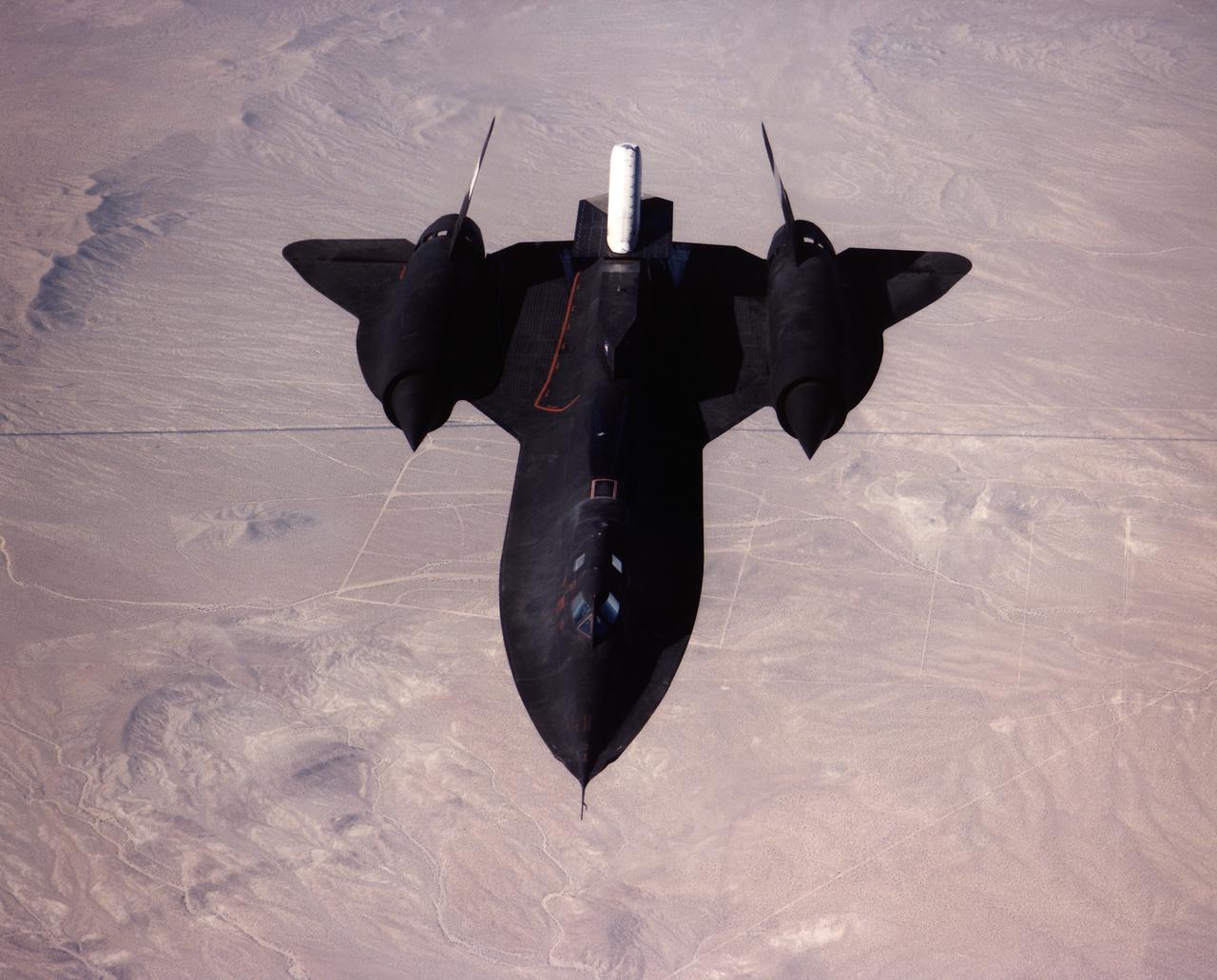

A NASA SR-71 made its successful first flight Oct. 31 as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
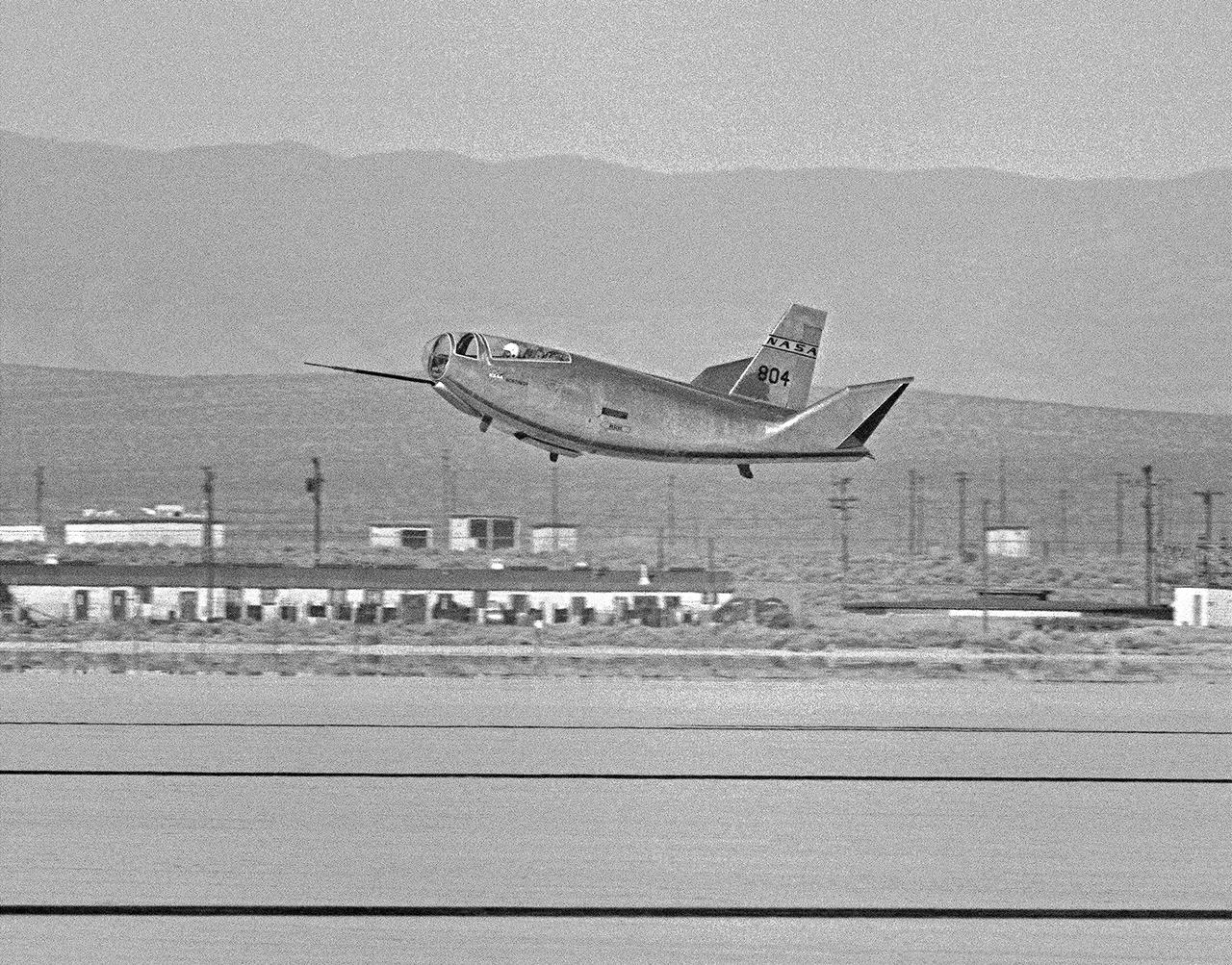

The HL-10 Lifting Body completes its first research flight with a landing on Rogers Dry Lake at Edwards AFB, California, on December 22, 1966. The HL-10 suffered from buffeting and poor control during the flight. Pilot Bruce Peterson was able to make a successful landing despite the severe problems. These were traced to airflow separation from the fins. As a result, the fins were no longer able to stabilize the vehicle. A small reshaping of the fins' leading edges cured the airflow separation, but it was not until March 15, 1968, that the second HL-10 flight occurred.
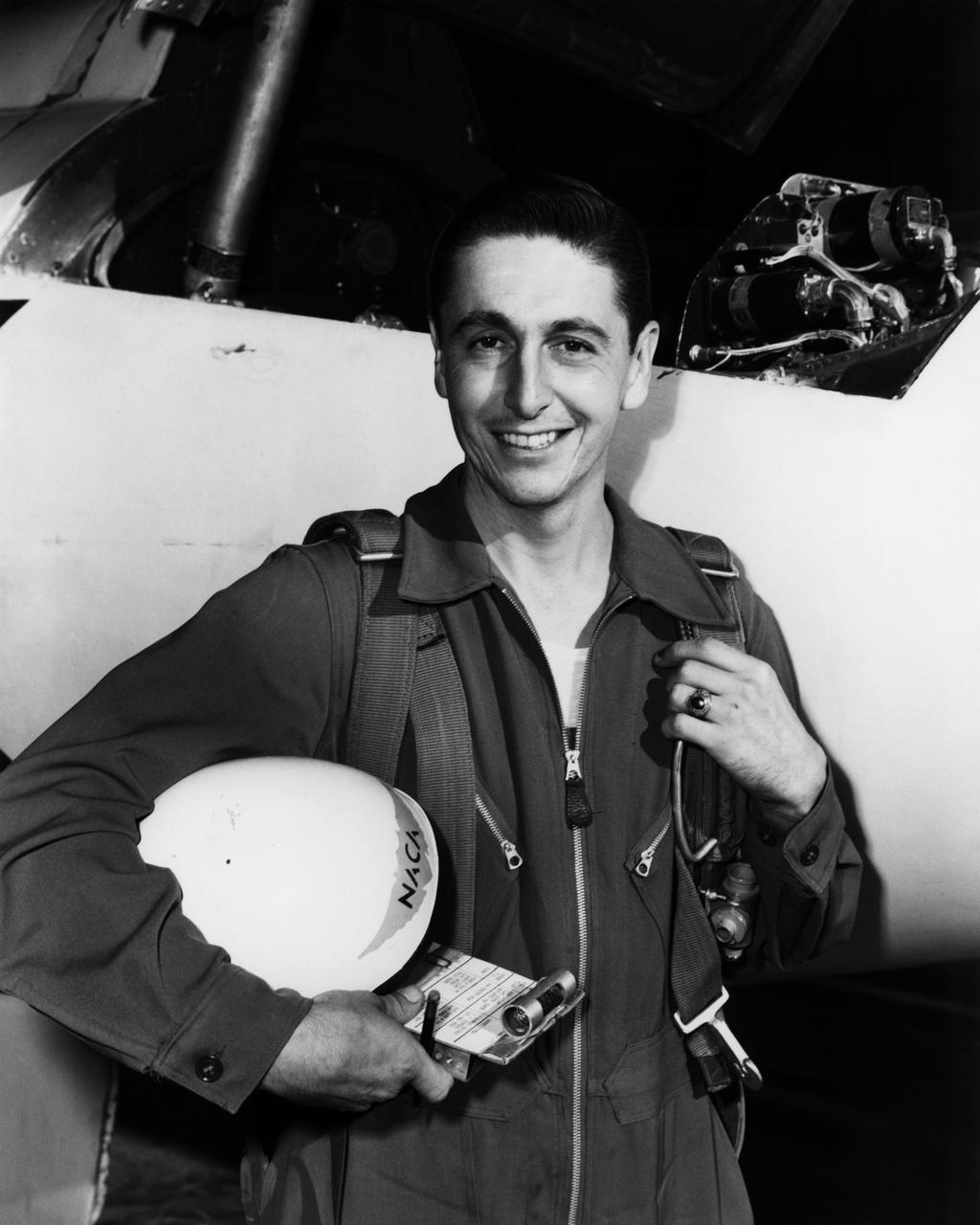

NACA pilot A. Scott Crossfield next to the D-558-2 after first Mach 2 flight.
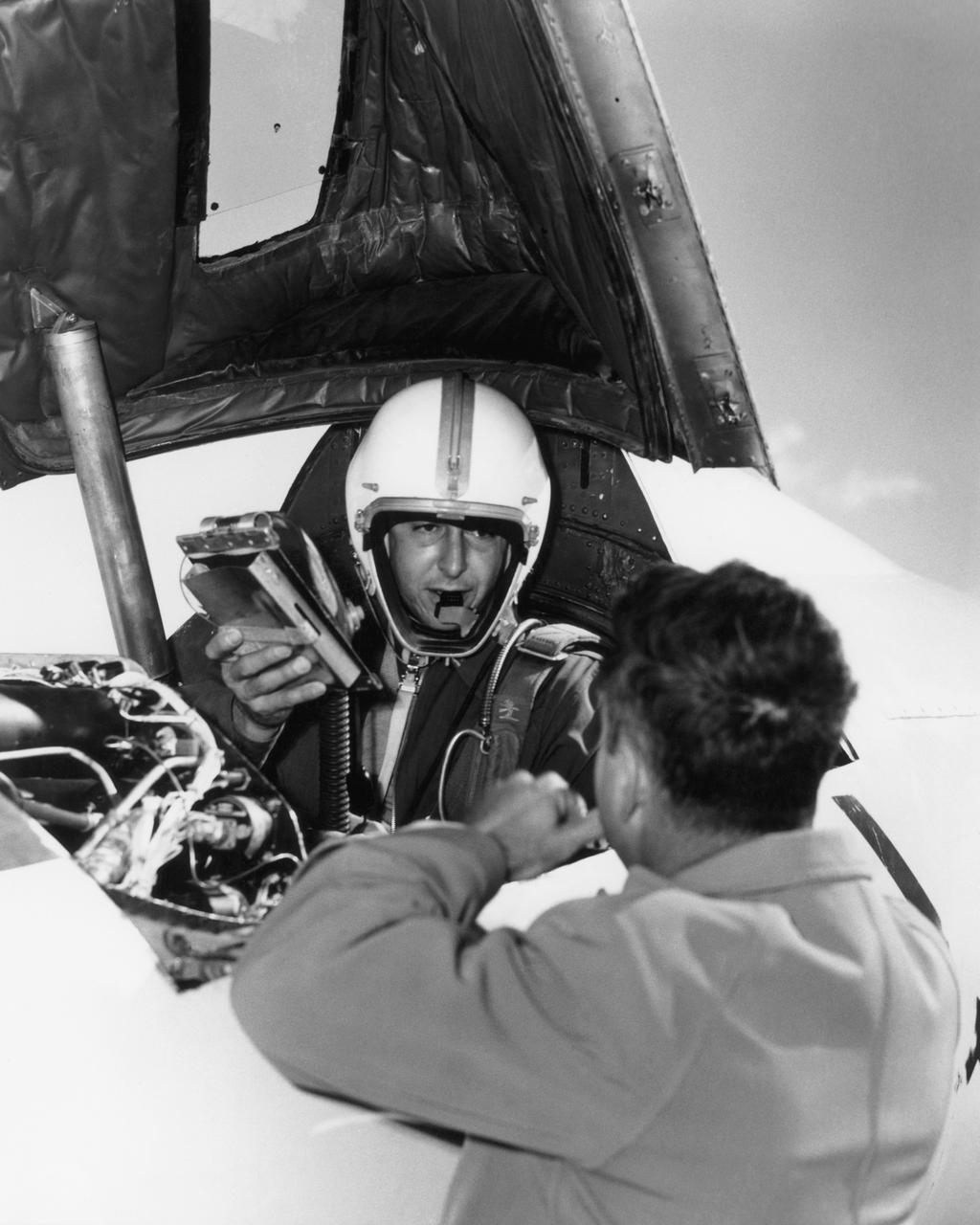

Scott Crossfield in cockpit of the Douglas D-558-2 after first Mach 2 flight.

On June 12, 2018, NASA’s remotely-piloted Ikhana aircraft, based at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, lifted off for its first mission in the National Airspace System without a safety chase aircraft. The June 12 flight successfully demonstrated the first remotely-piloted aircraft to use airborne detect and avoid technology to meet the intent of the FAA’s “see and avoid” rules.

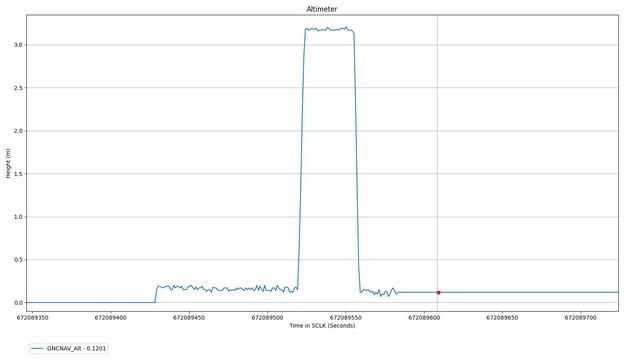
In this footage captured by the Mastcam-Z imager aboard the Perseverance Mars rover on April 19, 2021, the agency's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter lifts of from the Martian surface, hovers for 30 seconds, then touches back down. Lasting a total of 39.1 seconds, the flight marks the first instance of powered, controlled flight on another planet. The solar-powered helicopter first became airborne at 3:34 a.m. EDT (12:34 a.m. PDT) — 12:33 Local Mean Solar Time (Mars time) — a time the Ingenuity team determined would have optimal energy and flight conditions. Altimeter data indicate Ingenuity climbed to its prescribed maximum altitude of 10 feet (3 meters) and maintained a stable hover for 30 seconds. It then descended. Flying in a controlled manner on Mars is far more difficult than flying on Earth. The Red Planet has significant gravity (about one-third that of Earth's), but its atmosphere is just 1% as dense as Earth's at the surface. Stitched together from multiple images, the mosaic is not white balanced; instead, it is displayed in a preliminary calibrated version of a natural-color composite, approximately simulating the colors of the scene as it would appear on Mars. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24521

Surrounded by work platforms, NASA's first full-scale Orion abort flight test (AFT) crew module (center) is undergoing preparations at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center in California for the first flight test of Orion's launch abort system. To the left is a space shuttle orbiter purge vehicle sharing the hangar.
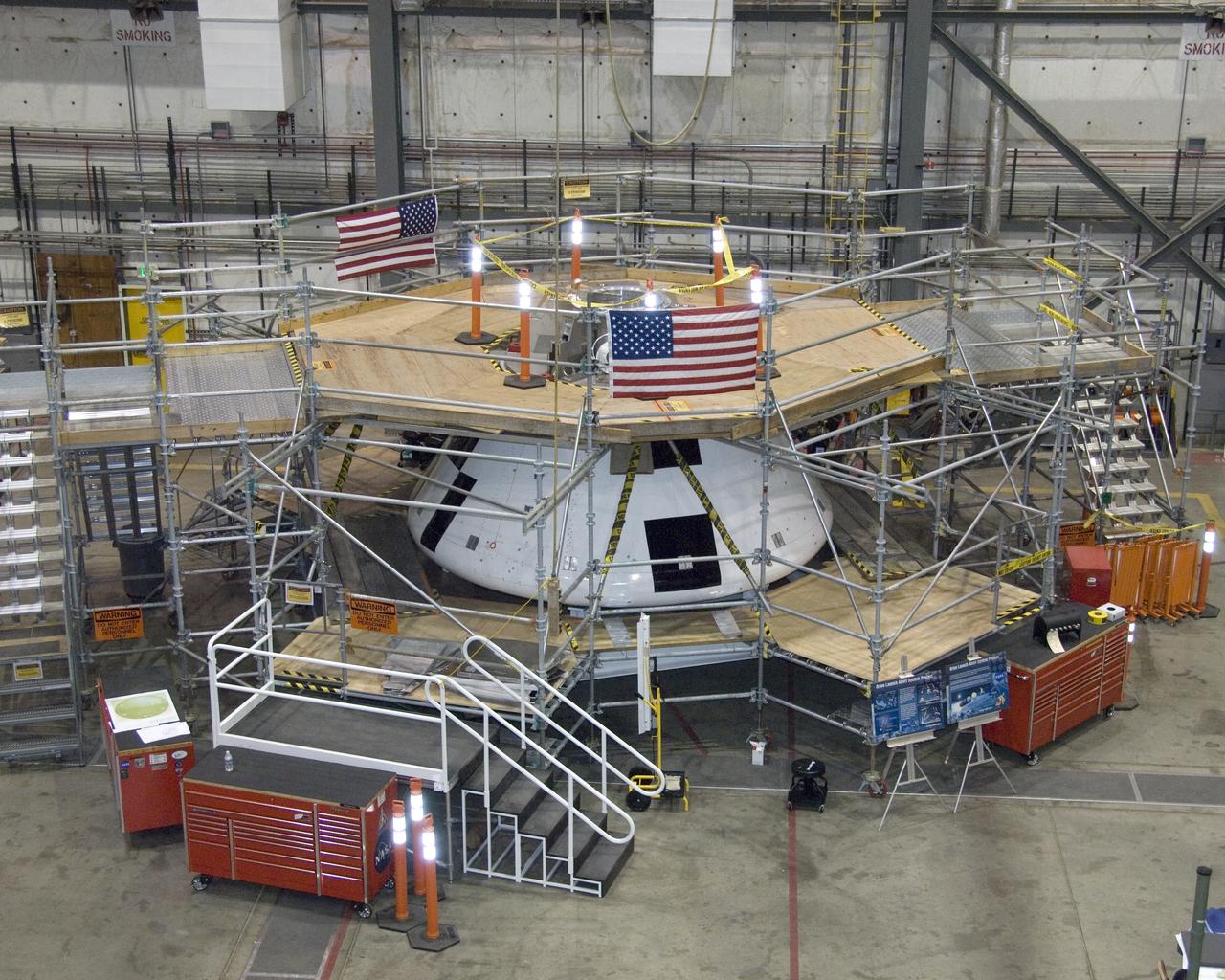

Surrounded by work platforms, NASA's first full-scale Orion abort flight test (AFT) crew module (center) is undergoing preparations at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center in California for the first flight test of Orion's launch abort system.
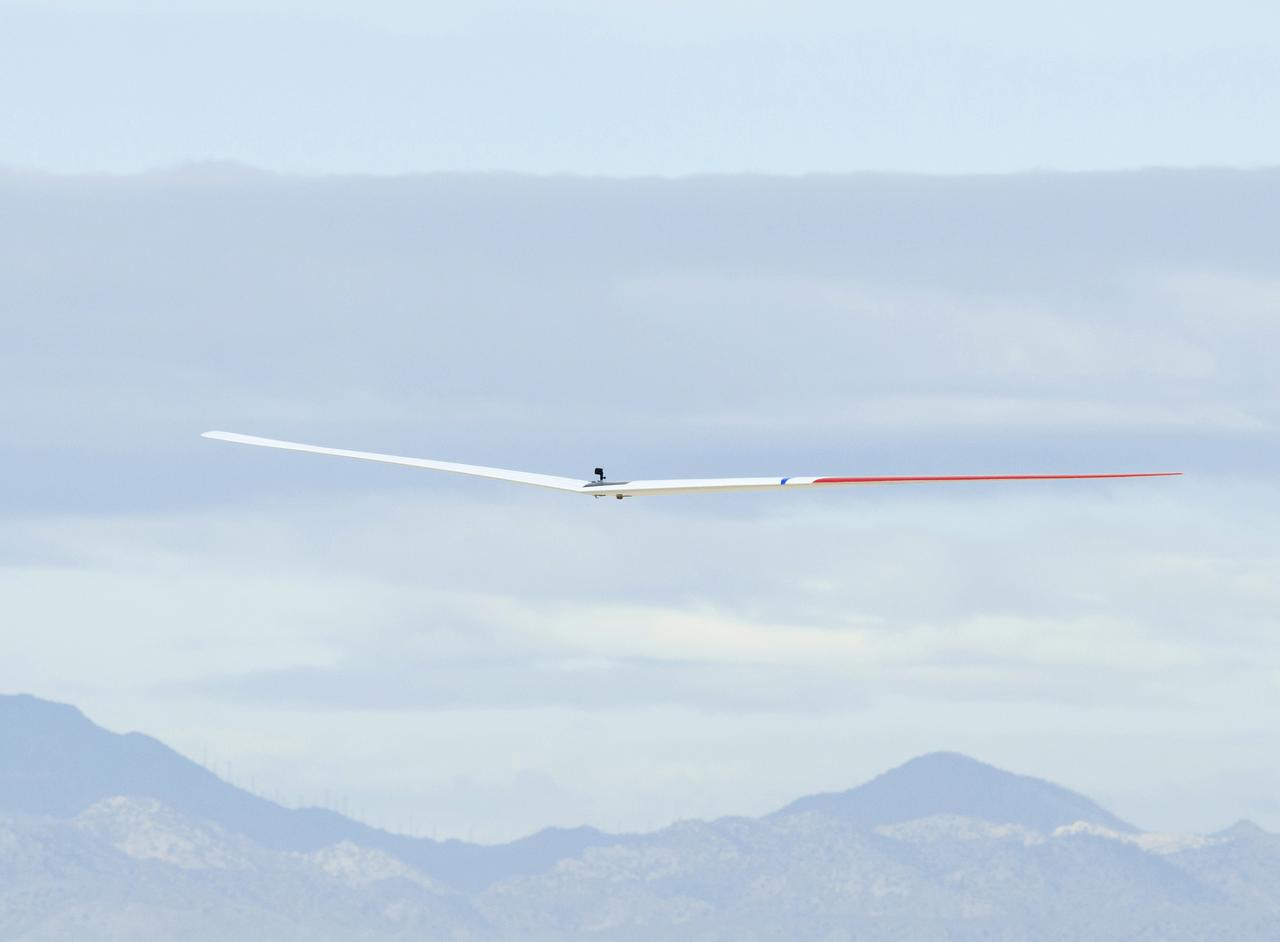

The Prandtl-D No. 3 research aircraft is being readied for new flight tests this summer. It had its first flight on Oct. 28, 2015.

A full-scale flight-test mockup of the Constellation program's Orion crew vehicle arrived at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in late March 2008 to undergo preparations for the first short-range flight test of the spacecraft's astronaut escape system later that year. Engineers and technicians at NASA's Langley Research Center fabricated the structure, which precisely represents the size, outer shape and mass characteristics of the Orion space capsule. The Orion crew module mockup was ferried to NASA Dryden on an Air Force C-17. After painting in the Edwards Air Force Base paint hangar, the conical capsule was taken to Dryden for installation of flight computers, instrumentation and other electronics prior to being sent to the U.S. Army's White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico for integration with the escape system and the first abort flight test in late 2008. The tests were designed to ensure a safe, reliable method of escape for astronauts in case of an emergency.

Scott Crossfield talks to newsmen in front of NACA South Base hangar after his first flight to Mach 2 in the Douglas D-558-2.
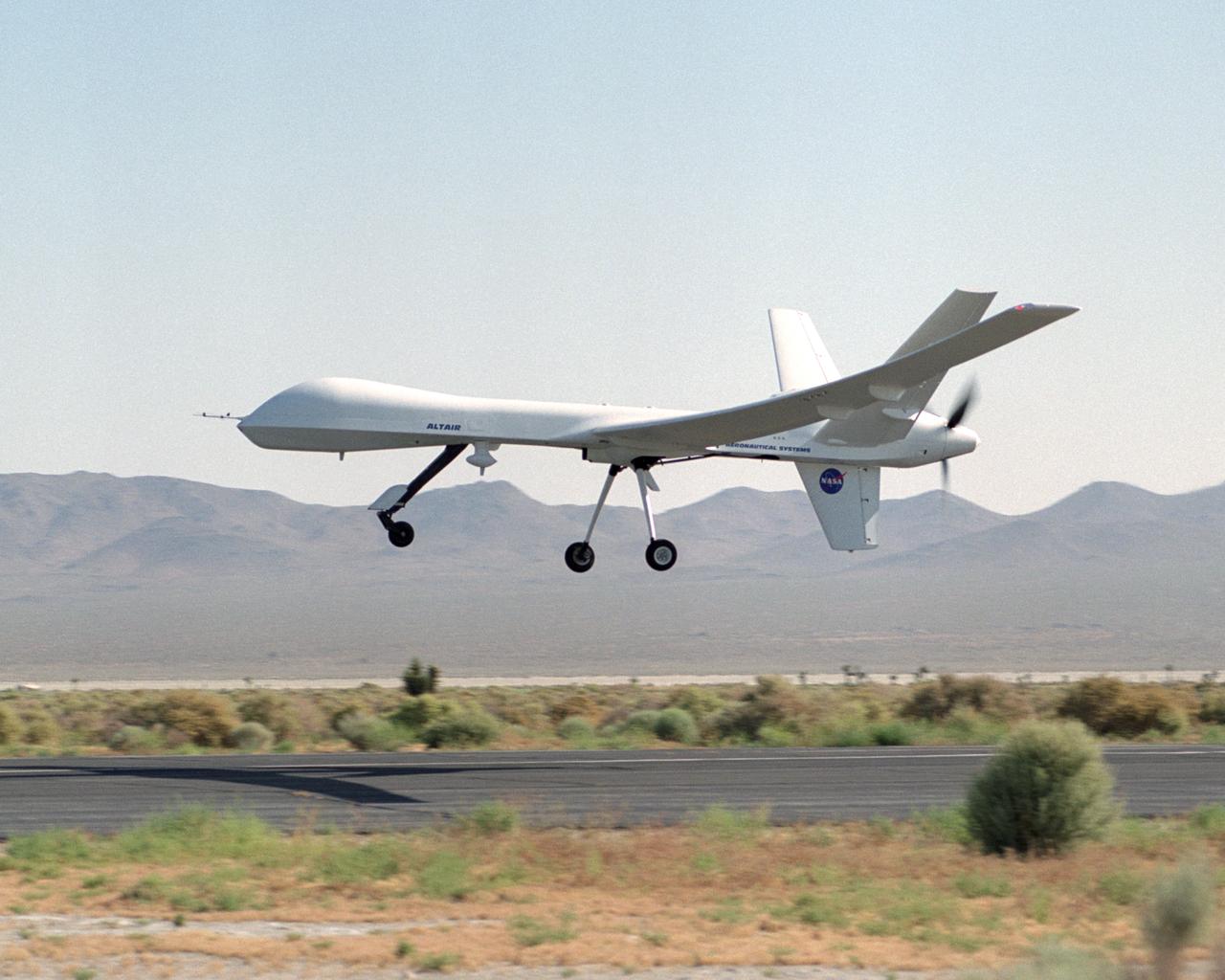

The remotely-piloted Altair unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) took to the air on its first checkout flight on June 9, 2003 at El Mirage, California.

A joint NASA/Boeing team completed the first phase of flight tests on the unique X-48B Blended Wing Body aircraft at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, CA. The team completed the 80th and last flight of the project's first phase on March 19, 2010.
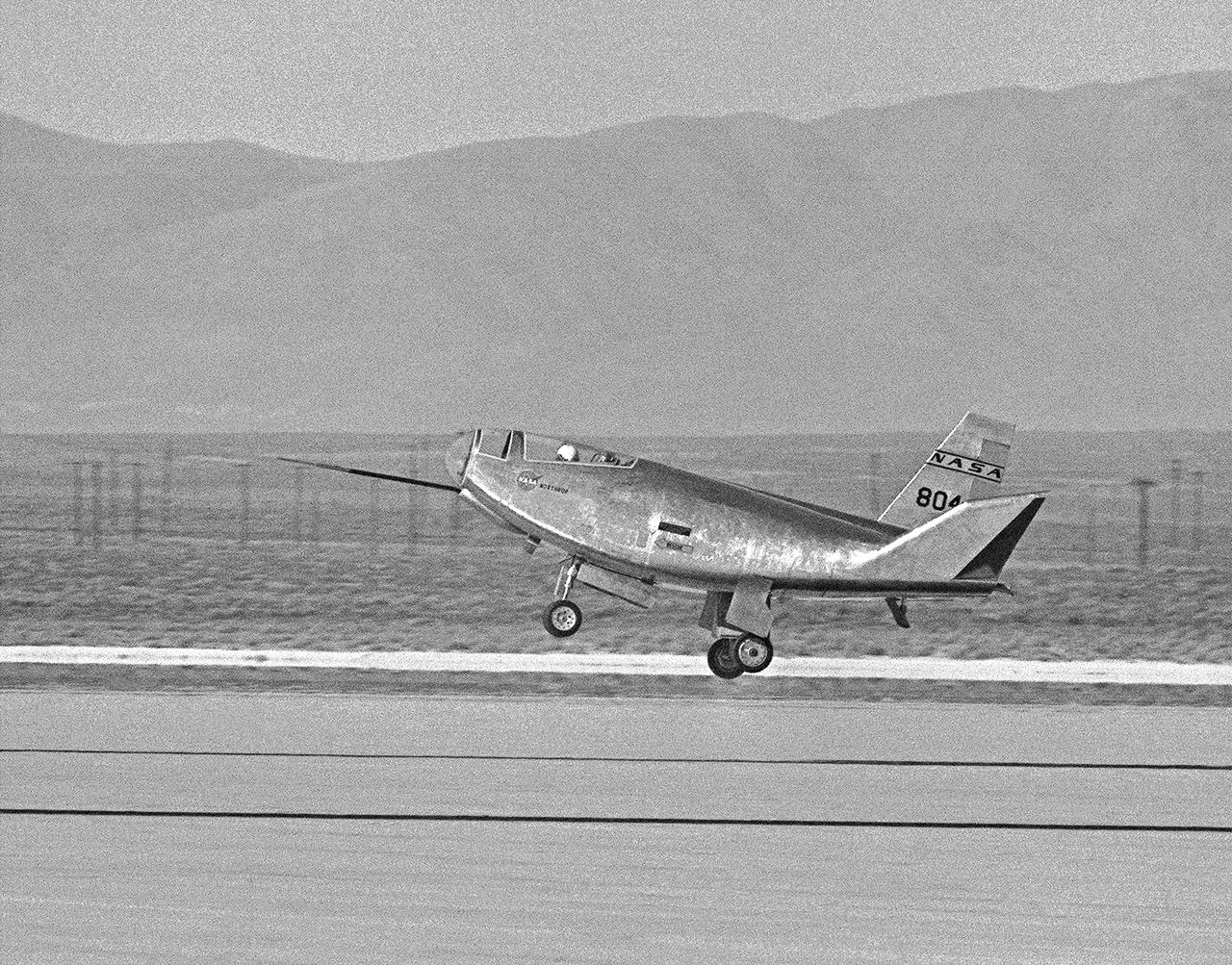

The HL-10 Lifting Body completes its first research flight with a landing on Rogers Dry Lake. Due to control problems, pilot Bruce Peterson had to land at a higher speed than originally planned in order to keep the vehicle under control. The actual touchdown speed was about 280 knots. This was 30 knots above the speed called for in the flight plan. The HL-10's first flight had lasted 3 minutes and 9 seconds.
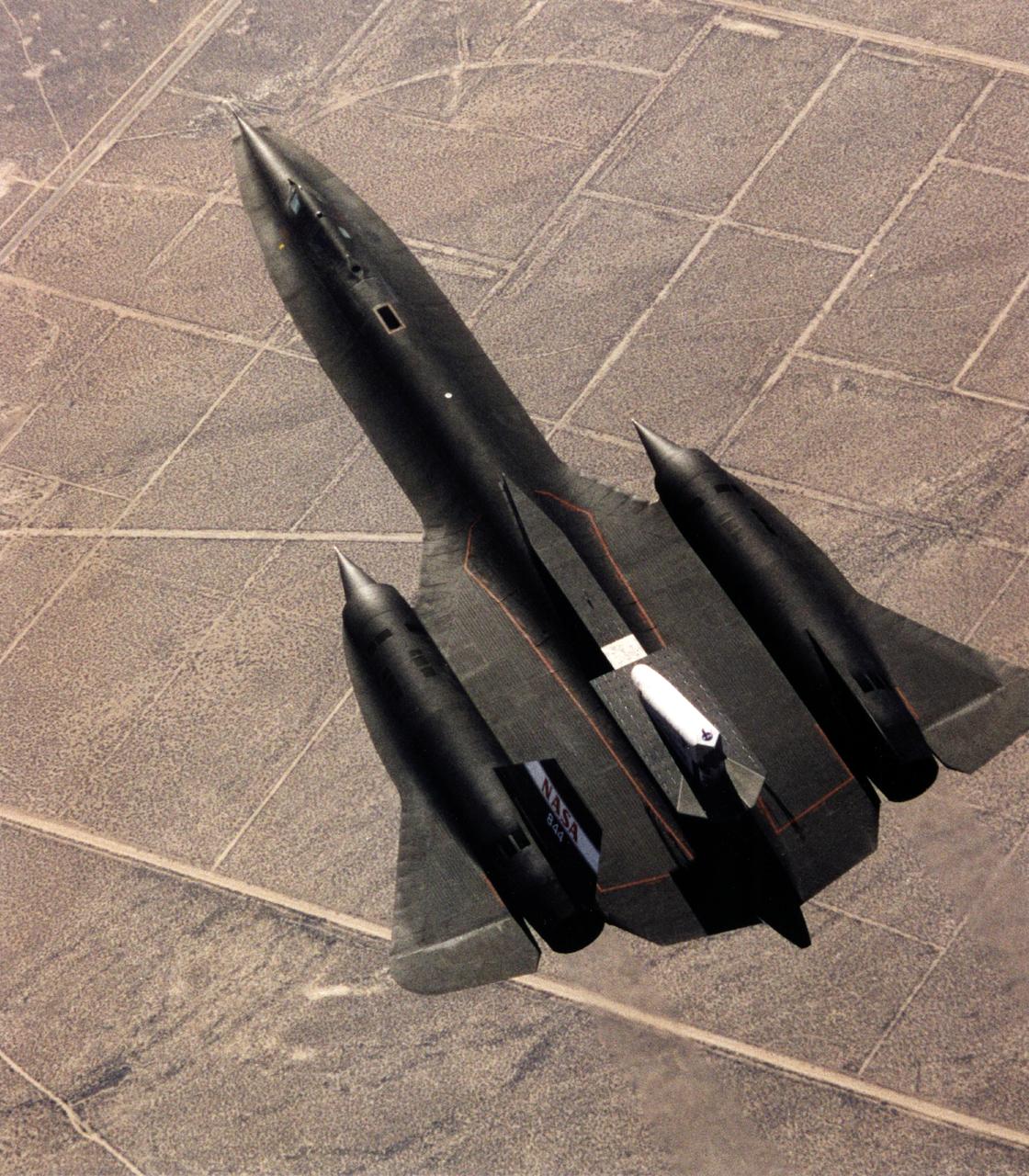

This photograph shows the SR-71 with the Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment on the rear fuselage as seen from above. The photo was taken on the first flight of the aircraft with the experiment aboard, which took place on 31 October 1997.
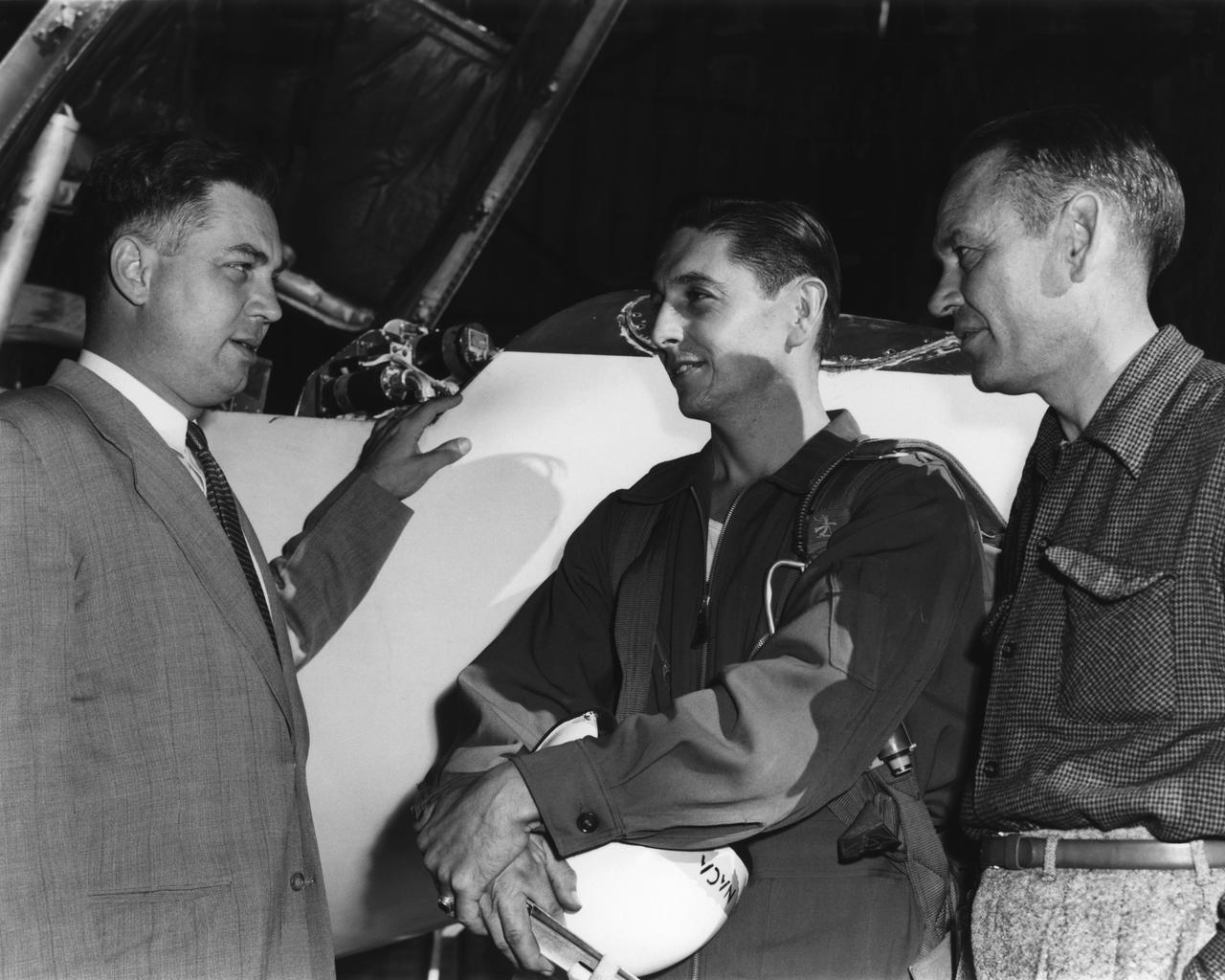

High-Speed Research Station Director Walter C. Williams, NACA pilot A. Scott Crossfield, and Director of Flight Operations Joe Vensel in front of the Douglas D-558-2 after the first Mach 2 flight.

Technicians fill SOFIA’s instrument with liquid nitrogen and helium to keep the detectors cold. The now retired instrument was called the First Light Infrared Test Experiment Camera, or FLITECAM. When SOFIA lands after each flight its instruments can be exchanged, serviced or upgraded to harness new technologies. Left: Chris Koerber, right UCLA's Ken Magnone.

In Rockford, Illinois, Ingersoll Machine Tools builds parts for the Artemis II Orion crew module, shown here on April 13, 2017, which will carry humans beyond Earth orbit.